
- Book Solutions
- State Boards

Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Life Processes
Case study questions class 10 science chapter 6 life processes.

At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks.
CBSE Case Based Questions Class 10 Science Chemistry Chapter 6
CASE STUDY : 1
Carbon and energy requirements of the autotrophic organism are fulfilled by photosynthesis. It is the process by which autotrophs take in substances from the outside and convert them into stored forms of energy. This material is taken in the form of carbon dioxide and water which is converted into carbohydrates in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll. Carbohydrates are utilised for providing energy to the plant.
i) Write a chemical reaction which occur during photosynthesis?
Ans: 6CO2 +12H2O + Chlorophyll & sunlight👉 C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O
ii) In which form of carbohydrates does the plant stored in them?
Ans: The carbohydrates are stored in the form of starch as the internal energy.
iii) What is stomata?
Ans: The process present in the surface of a leaf or the stem of a plant to allow the exchange of gases.
iv) What are the functions of stomata?
Ans: i) Exchange of gases i.e oxygen and CO2
ii) Transpiration
v) What is Chloroplast?
Ans: Chloroplast is a cell organelles which contains photosynthetic pigment called as chlorophyll which help in the absorption of sunlight.
CASE STUDY : 2
The alimentary canal is basically a long tube extending from the mouth to the anus. In Fig. 6.6, we can see that the tube has different parts. Various regions are specialised to perform different functions.
We eat various types of food which has to pass through the same digestive tract. Naturally the food has to be processed to generate particles which are small and of the same texture. This is achieved by crushing the food with our teeth
i) Which enzyme is present in our mouth to digest starch?
Ans: Salivary amylase from salivary glands.
ii) What are the types of enzymes released by our stomach?
Ans: Hydrochloric acid, pepsin and a mucus.
iii) Which is the longest part of our alimentary canal in our body?
Ans: Small intestine
iv) What are villi?
Ans: Villi are finger like projection present inside the inner lining of the small intestine which increases the surface area for absorption.
v) What are the enzymes that are released by pancreas?
Ans: Enzyme released by pancreas – • trypsin- Digestion of protein
lipase – breakdown of emulsified fats
CASE STUDY : 3
The food material taken in during the process of nutrition is used in cells to provide energy for various life processes. Diverse organisms do this in different ways – some use oxygen to break-down glucose completely into carbon dioxide and water, some use other pathways that do not involve oxygen (Fig. 6.8). In all cases, the first step is the break-down of glucose, a six-carbon molecule, into a three-carbon molecule called pyruvate. This process takes place in the cytoplasm.
i) What is anaerobic respiration?
Ans: The conversion of pyruvate into ethanol, CO2 & energy take place in the absence of air(oxygen), it is called anaerobic respiration.
ii) Explain the process which happen in our muscle cells?
Ans- The conversion of pyruvate to lactic acid( 3 carbon molecule) and energy due to the lack of oxygen.
iii) In which form our body used the energy?
Ans: It is in the form of ATP molecule i.e Adenosine Triphosphate.
iv) Why there is a faster breathing rate of aquatic animals then the terrestrial animals?
Ans- The amount of O2 dissolved in water is low as compared to amount of O2 present in air. Therefore, aquatic animals have faster breathing rate.
v) Write the name of organ used for respiration by different organism- fish, frog?
Ans- i) fish- gills
ii) frog- skin, lungs
CASE STUDY : 4
The excretory system of human beings includes a pair of kidneys, a pair of ureters, a urinary bladder and a urethra. Kidneys are located in the abdomen, one on either side of the backbone. Urine produced in the kidneys passes through the ureters into the urinary bladder where it is stored until it is released through the urethra.
i) What is the purpose of making urine?
Ans: Urine is to filter out the blood i e to remove waste product from the blood such as urea.
ii) What is Bowman’s capsule?
Ans: A cup shaped end of a coiled tube which is associated with capillaries to collect filterate.
iii) What is dialysis?
Ans: To remove nitrogenous waste from your blood by using machine when kidney does not its function i.e in case of kidney failure.
iv) What is the function of urinary bladder?
Ans: It is used to stored urine until the pressure comes from the brain to pass it out.
v) What are the different parts of nephrons?
Ans: Renal artery, Bowman’s capsule, glomerulus, tubular part of nephron and a collecting duct.
CASE STUDY : 5
The heart is a muscular organ which is as big as our fist. Because both oxygen and carbon dioxide have to be transported by the blood, the heart has different chambers to prevent the oxygen-rich blood from mixing with the blood containing carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide-rich blood has to reach the lungs for the carbon dioxide to be removed, and the oxygenated blood from the lungs has to be brought back to the heart. This oxygen-rich blood is then pumped to the rest of the body.
i) How many chambers are present in the heart of mammals and reptiles?
Ans: Mammals- 4 chamber heart and reptiles- 3 chambered heart
ii) Who carry deoxygenated blood from body to heart?
Ans: Vena cava carries deoxygenated blood from body to heart.
iii) What do you meant by the term double circulation?
Ans: The blood goes through the heart twice during each cycle known as double circulation.
iv) What is hypertension?
Ans: The force that blood experts against the wall of a vessels is called hypertension or high blood pressure.
V) Which device measured blood pressure?
Ans: Sphygmomanometer
CASE STUDY : 6
Plant transport systems will move energy stores from leaves and raw materials from roots. These two pathways are constructed as independently organised conducting tubes. One, the xylem moves water and minerals obtained from the soil. The other, phloem transports products of photosynthesis from the leaves where they are synthesised to other parts of the plant
i) What are the different parts of xylem?
Ans: vessels, tracheids, xylem parenchyma and fibres.
ii) What do you meant by the term transpiration?
Ans: The loss of water in the form of vapour from the aerial parts of the plant.
iii) What are the advantages of transpiration?
Ans: i) help in the absorption and the upward movement of water
ii) temperature regulation
iv) What is translocation?
Ans: The transport of soluble products of photosynthesis is called translocation.
v) How does plant remove their waste product?
Ans: They remove their waste product in the form of fallen leaves, resins and gums.
For more update follow net explanations page
Wonderful..
It’s helpful thank u
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We have a strong team of experienced Teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts
Bse odisha 8th english questions answer solution, odisha board class 8 english the mountain and the squirrel question answers solution, sikkim scert class 5 english chapter 3c let’s plant a tree solution, manipur board class 6 social science chapter 15 the first empire.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
- Bihar Board
SRM University
- NBSE Result 2024
- MP Board 10th Result 2024
- MP Board 12th Result 2024
- TS Board Results 2024
- NBSE Board Result 2024
- UK Board Result 2024
- Karnataka Board Result
- Shiv Khera Special
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- नए भारत का नया उत्तर प्रदेश
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
- CBSE Class 10
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter Wise Important Case Study Questions
Chapter wise important case study questions cbse class 10 science: cbse class 10 science board exam 2024 is just around the corner and students are working hard to score maximum marks. check these case study questions from class 10 science to ace your examination this year also download the solutions from the pdf attached towards the end. .

CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter Wise Important Case Study Questions: While the CBSE Board exam for Class 10 students are ongoing, the CBSE Class 10 Science board exam 2024 is to be held on March 2, 2024. With the exams just a few days away, CBSE Class 10th Board exam candidates are rushing to prepare the remaining syllabus, practising their weak portions, trying to revise the important questions from the past year papers, practise questions, etc.
Why are CBSE Class 10 Science Case Study Questions Important?
- Section A : 20 Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) carrying 1 mark each.
- Section B : 6 Very Short Answer type questions carrying 2 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 30 to 50 words.
- Section C : 7 Short Answer type questions carrying 3 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 50 to 80 words.
- Section D : 3 Long Answer type questions carrying 5 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
- Section E : 3 Case Based/ Source Based units of assessment (4 marks each) with sub-parts.
How to solve case study questions in CBSE Class 10 Science?
- Read the case given and the associated questions carefully.
- Read the questions attentively and analyse what they are asking.
- Apply your subject knowledge and theories in the given case to decide what the correct answers should be.
1.A chemical reaction is a representation of chemical change in terms of symbols and formulae of reactants and products. There are various types of chemical reactions like combination, decomposition, displacement, double displacement, oxidation and reduction reactions. Reactions in which heat is released along with the formation of products are called exothermic chemical reactions. All combustion reactions are exothermic reactions.
(i) The massive force that pushes the rocket forward through space is generated due to the
(a) combination reaction
(b) decomposition reaction
(c) displacement reaction
(d) double displacement reaction
(ii) A white salt on heating decomposes to give brown fumes and yellow residue is left behind. The yellow residue left is of
(a) lead nitrate
(b) nitrogen oxide
(c) lead oxide
(d) oxygen gas
(iii) Which of the following reactions represents a combination reaction?
(a) CaO (s) + H2O (l) → Ca (OH)2 (aq)
(b) CaCO3 (s) → CaO (s) + CO2(g)
(c) Zn(s) + CuSO4 (aq) → ZnSO4 (aq) + Cu(s)
(d) 2FeSO4(s) → Fe2O3 (s) +SO2(g) + SO3(g)
(iv) Complete the following statements by choosing correct type of reaction for X and Y.
Statement 1: The heating of lead nitrate is an example of ‘X’ reaction.
Statement 2: The burning of magnesium is an example of ‘Y’ reaction.
(a)X-Combination,Y-Decomposition
(b)X-Decomposition,Y-Combination
(c)X-Combination,Y-Displacement
(d) X- Displacement, Y-Decomposition
2.The earlier concept of oxidation and reduction is based on the addition or removal of oxygen or hydrogen elements so, in terms of oxygen and hydrogen, oxidation is addition of oxygen to a substance and removal of hydrogen from a substance. On the other hand, reduction is addition of hydrogen to a substance and removal of oxygen from a substance. The substance which gives oxygen to another substance or removes hydrogen from another substance in an oxidation reaction is known as oxidising agent, while the substance which gives hydrogen to another substance or removes oxygen from another substance in a reduction reaction is known as reducing agent. For example,
(i) A redox reaction is one in which
(a) both the substances are reduced
(b) both the substances are oxidised
(c) an acid is neutralised by the base
(d) one substance is oxidised while the other is reduced.
(ii) In the reaction, H2S+Cl2⟶S+2HCl
(a) H2S is the reducing agent.
(b) HCl is the oxidising agent.
(c) H2S is the oxidising agent.
(d) Cl2 is the reducing agent.
(iii) Which of the following processes does not involve either oxidation or reduction?
(a) Formation of slaked lime from quicklime.
(b) Heating mercuric oxide.
(c) Formation of manganese chloride from manganese oxide (MnO2).
(d) Formation of zinc from zinc blende.
(iv) Mg+CuO⟶MgO+Cu
Which of the following is wrong relating to the above reaction?
(a) CuO gets reduced
(b) Mg gets oxidised.
(c) CuO gets oxidised.
(d) It is a redox reaction.
3.A copper vessel gets tarnished due to formation of an oxide layer on its surface. On rubbing lemon on the vessel, the surface is cleaned, and the vessel begins to shine again. This is due to the fact that which reacts with the acid present in lemon to form a salt which is washed away with water. As a result, the layer of copper oxide is removed from the surface of the vessel and the shining surface is exposed.
1.Which of the following acids is present in lemon?
(a) Formic acid
(b) Acetic acid
(c) Citric acid
(d) Hydrochloric acid
2.The nature of copper oxide is
d) amphoteric
3.Name the salt formed in the above reaction
a) copper carbonate
b) copper chloride
c)copper citrate
d) copper citrate
4.The phenomenon of copper getting tarnished is
a) corrosion
b) rancidity
c) displacement
d)none of these
4.Metals as we know, are very useful in all fields, industries in particular. Non-metals are no less in any way. Oxygen present in air is essential for breathing as well as for combustion. Non-metals form a large number of compounds which are extremely useful, e.g., ammonia, nitric acid, sulphuric acid, etc. Non-metals are found to exist in three states of matter. Only solid non-metals are expected to be hard however, they have low density and are brittle. They usually have low melting and boiling points and are poor conductors of electricity.
i.____________ is a non-metal but is lustrous
A.Phosphorus
ii.Which of the following is known as 'King of chemicals'?
C. Sulphuric acid
D. Nitric acid
iii.Which of the following non-metals is a liquid?
iv.Hydrogen is used
A.for the synthesis of ammonia
B. for the synthesis of methyl alcohol
C.nitrogenous fertilizers
D. all of these
5.Nisha observed that the bottoms of cooking utensils were turning black in colour while the flame of her stove was yellow in colour. Her daughter suggested cleaning the air holes of the stove to get a clean, blue flame. She also told her mother that this would prevent the fuel from getting wasted.
a) Identify the reasons behind the sooty flame arising from the stove.
b) Can you distinguish between saturated and unsaturated compounds by burning them? Justify your answer.
c) Why do you think the colour of the flame turns blue once the air holes of the stove are cleaned?
6.Blood transport food, Oxygen and waste materials in our bodies. It consists of plasma as a fluid medium. A pumping organ [heart] is required to push the blood around the body. The blood flows through the chambers of the heart in a specific manner and direction. While flowing throughout the body, blood exerts a pressure against the wall or a vessel.
- Pulmonary artery
- Pulmonary vein
- Very narrow and have high resistance
- Much wide and have low resistance
- Very narrow and have low resistance
- Much wide and have high resistance
- It is a hollow muscular organ
- It is four chambered having three auricles and one ventricle.
- It has different chambers to prevent O2 rich blood from mixing with the blood containing CO2
- Both A & C
- Blood = Plasma + RBC + WBC + Platelets
- Plasma = Blood – RBC
- Lymph = Plasma + RBC
- Serum = Plasma + RBC + WBC
7.A brain is displayed at the Allen Institute for Brain Science. The human brain is a 3-pound (1.4-kilogram) mass of jelly-like fats and tissues—yet it's the most complex of all known living structures The human brain is more complex than any other known structure in the universe. Weighing in at three pounds, on average, this spongy mass of fat and protein is made up of two overarching types of cells—called glia and neurons— and it contains many billions of each. Neurons are notable for their branch-like projections called axons and dendrites, which gather and transmit electrochemical signals. Different types of glial cells provide physical protection to neurons and help keep them, and the brain, healthy. Together, this complex network of cells gives rise to every aspect of our shared humanity. We could not breathe, play, love, or remember without the brain.
1)Animals such as elephants, dolphins, and whales actually have larger brains, but humans have the most developed cerebrum. It's packed to capacity inside our skulls and is highly folded. Why our brain is highly folded?
- b) Learning
3)Which among these protects our brain?
a)Neurotransmitter
b) Cerebrospinal fluid
d) Grey matter
4.Ram was studying in his room. Suddenly he smells something burning and sees smoke in the room. He rushes out of the room immediately. Was Ram’s action voluntary or involuntary? Why?
8.Preeti is very fond of gardening. She has different flowering plants in her garden. One day a few naughty children entered her garden and plucked many leaves of Bryophyllum plant and threw them here and there in the garden. After few days, Preeti observed that new Bryophyllum plants were coming out from the leaves which fell on the ground.
1.What does the incident sited in the paragraph indicate?
(a). Bryophyllum leaves have special buds that germinate to give rise to new plant.
(b). Bryophyllum can propagate vegetatively through leaves.
(c). Bryophyllum is a flowering plant that reproduces only asexually
(d). Both (a) and (b).
2.Which of the following plants can propagate vegetatively through leaves like Bryophyllum?
3.Do you think any other vegetative part of Bryophyllum can help in propagation? If yes, then which part?
(c) Flowers
4.Which of the following plant is artificially propagated (vegetatively) by stem cuttings in horticultural practices?
(b)Snakeplant
(d)Water hyacinth
9.The growing size of the human population is a cause of concern for all people. The rate of birth and death in a given population will determine its size. Reproduction is the process by which organisms increase their population. The process of sexual maturation for reproduction is gradual and takes place while general body growth is still going on. Some degree of sexual maturation does not necessarily mean that the mind or body is ready for sexual acts or for having and bringing up children. Various contraceptive devices are being used by human beings to control the size of the population.
1) What are common signs of sexual maturation in boys?
a) Broadening of shoulders
b) Development of mammary glands
c) Broadening of waist
d) High pitch of voice
2) Common sign of sexual maturation in girls is
a) Low pitch voice
b) Appearance of moustache and beard
c) Development of mammary glands
d) Broadening of shoulders
3) Which contraceptive method changes the hormonal balance of the body?
b) Diaphragms
c) Oral pills
d) Both a) and b)
4) What should be maintained for healthy society?
a) Rate of birth and death rate
b) Male and female sex ratio
c) Child sex ratio
d) None of these
10.Pea plants can have smooth seeds or wrinkled seeds. One of the phenotypes is completely dominant over the other. A farmer decides to pollinate one flower of a plant with smooth seeds using pollen from a plant with wrinkled seeds. The resulting pea pod has all smooth seeds.
i) Which of the following conclusions can be drawn?
(1) The allele for smooth seeds is dominated over that of wrinkled seeds.
(2) The plant with smooth seeds is heterozygous.
(3) The plant with wrinkled seeds is homozygous.
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ii) Which of the following crosses will give smooth and wrinkled seeds in same proportion?
(a) RR X rr
(b) Rr X rr
(d) rr X rr
iii) Which of the following cross can be used to determine the genotype of a plant with dominant phenotype?
(a) RR X RR
(b) Rr X Rr
(c) Rr X RR
(d) RR X rr
iv) On crossing of two heterozygous smooth seeded plants (Rr), a total of 1000 plants were obtained in F1 generation. What will be the respective number of smooth and wrinkled seeds obtained in F1 generation?
(a) 750, 250
(b) 500, 500
(C) 800, 200
(d) 950, 50
11.Food chains are very important for the survival of most species.When only one element is removed from the food chain it can result in extinction of a species in some cases.The foundation of the food chain consists of primary producers.Primary producers or autotrophs,can use either solar energy or chemical energy to create complex organic compounds,whereas species at higher trophic levels cannot and so must consume producers or other life that itself consumes producers. Because the sun’s light is necessary for photosynthesis,most life could not exist if the sun disappeared.Even so,it has recently been discovered that there are some forms of life,chemotrophs,that appear to gain all their metabolic energy from chemosynthesis driven by hydrothermal vents,thus showing that some life may not require solar energy to thrive.
1.If 10,000 J solar energy falls on green plants in a terrestrial ecosystem,what percentage of solar energy will be converted into food energy?
(d)It will depend on the type of the terrestrial plant
2.Matter and energy are two fundamental inputs of an ecosystem. Movement of
(a)Energy is by directional and matter is repeatedly circulating
(b)Energy is repeatedly circulating and matter is unidirectional
(c)Energy is unidirectional and matter is repeatedly circulating
(d)Energy is multidirectional and matter is bidirectional
3.Raj is eating curd/yoghurt. For this food intake in a food chain he should be considered as occupying
(a)First trophic level
(b)Second trophic level
(c)Third trophic level
(d)Fourth trophic level
4.Which of the following, limits the number of trophic levels in a food chain
(a)Decrease in energy at higher trophic levels
(b)Less availability of food
(c)Polluted air
5.The decomposers are not included in the food chain. The correct reason for the same is because decomposers
(a) Act at every trophic level at the food chain
(b) Do not breakdown organic compounds
(c) Convert organic material to inorganic forms
(d) Release enzymes outside their body to convert organic material to inorganic forms
12.Shyam participated in a group discussion in his inter school competition on the practical application of light and was very happy to win an award for his school. That very evening his father gave treat to celebrate Shyam’s win. Shyam while sitting saw an image of a person sitting at his backside in his curved plate and could see that person’s mobile drop in the flower bed. Person was not aware until Shyam went and informed him. He thanked Shyam for his clever move.
a)From which side of his plate Shyam observed the incident –
i)outward curved
ii)inward curved
iii)plane surface
b)Part of plate from which Shyam observed the incident acted like a-
i)concave mirror
ii)convex mirror
iii)plane mirror
c)The nature of the size of the image formed in above situation is –
i)real, inverted and magnified
ii)same size , laterally inverted
iii)virtual, erect and diminished
iv)real , inverted and diminished
d)Magnification of the image formed by convex mirror is –
more than 1
iii)equal to 1
iv)less than 1
- The location of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at infinity is
(a) at focus
(c) at optical center
- When the object is placed at the focus of concave lens, the image formed is
(a)real and smaller
(b) virtual and smaller
(c) virtual and inverted
- The size of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at the focus ofconvex lens is
(a) highly magnified
(b) point in size
- When the object is placed at 2F in front of convex lens, the location of image is
(b) between F and optical center
(c) at infinity
(d) none of the above
14.One of the wires in domestic circuits supply, usually with a red insulation cover, is called live wire. with black insulation is called neutral wire. The earth wire, which has insulation of green colour, is usually connected to a metal plate deep in the earth near the house appliances that has a metallic body. Overloading contact, in such a situation the current in the circuit abruptly increases. circuit prevents damage to the appliances and the circuit due to overloading.
1 When do we say that an electrical appliance
2 Mention the function of earth wire in electrical line
3 How is an electric fuse connected in a domestic circuit?
4 When overloading and short circuiting are said to occur?
5 What is a live wire?
15.Light of all the colours travel at the same speed in vacuum for all wavelengths. But in any transparent medium(glass or water), the light of different colours travels at different speeds for different wavelengths, which means that the refractive index of a particular medium is different for different wavelengths. As there is a difference in their speeds, the light of different colours bend through different angles. The speed of violet colour is maximum and the speed of red colour is minimum in glass so, the red light deviates least and violet colour deviates most. Hence, higher the wavelength of a colour of light, smaller the refractive index and less is the bending of light.
(i)Which of the following statements is correct regarding the propagation of Light of different colours of white light in air?
(a) Red light moves fastest.
(b) Blue light moves faster than green light.
(c) All the colours of the white light move with the same speed.
(d) Yellow light moves with the mean speed as that of the red and the violet light.
(ii)Which of the following is the correct order of wavelength?
(a) Red> Green> Yellow
(b) Red> Violet> Green
(c) Yellow> Green> Violet
(d) Red> Yellow> Orange
(iii)Which of the following is the correct order of speed of light in glass?
(a) Red> Green> Blue
(b) Blue> Green> Red
(c) Violet> Red> Green
(d) Green> Red> Blue
(iv)Which colour has maximum frequency?
16.The region around a magnet where magnetism acts is represented by the magnetic field.The force of magnetism is due to moving charge or some magnetic material. Like stationary charges produce an electric field proportional to the magnitude of charge, moving charges produce magnetic fields proportional to the current. In other words, a current carrying conductor produces a magnetic field around it. The subatomic particles in the conductor, like the electrons moving in atomic orbitals, are responsible for the production of magnetic fields. The magnetic field lines around a straight conductor (straight wire) carrying current are concentric circles whose centres lie on the wire.
1)The magnetic field associated with a current carrying straight conductor is in anti- clockwise direction. If the conductor was held horizontally along east west direction,what is the direction of current through it?
2)Name and state the rule applied to determine the direction of magnetic field in a straight current carrying conductor.
3)Ramus performs an experiment to study the magnetic effect of current around a current carrying straight conductor with the help of a magnetic compass. He reports that
a)The degree of deflection of magnetic compass increases when the compass is moved away from the conductor.
b)The degree of deflection of the magnetic compass increases when the current through the conductor is increased.
Which of the above observations of the student appears to be wrong and why?
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science CBSE Chapter Wise PDF
Related resources to prepare for cbse 10th science board exam 2024.
- CBSE class 10 Science syllabus 2024
- NCERT Book for Class 10th Science 2023-2024 (PDF)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
- CBSE Class 10 Science sample paper
- Previous Year Questions of CBSE Class 10 Science
- CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions and Answers
- CBSE Class 10 Physics Chapter Wise Important Questions and Answers
- CBSE Class 10 Chemistry Chapter Wise Important Questions and Answers
- CBSE Class 10 Biology Chapter Wise Important Questions and Answers
- CBSE Class 10 Science Topper Answer Sheet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Practice Paper 2023 with Answers
- Class 10 CBSE Admit Card 2023-24
- CBSE Class 10 Date Sheet 2023
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus 2023 - 2024
- CBSE Class 10 DELETED Syllabus 2023-24
- CBSE Class 10th Sample Paper 2022-23: Download Sample Question Papers and Marking Scheme
- CBSE Class 10 Previous Year Question Papers for 2022-23
- CBSE Class 10 Important Questions and Answers for 2023-24 of ALL Chapters
- CBSE Class 10 Practice Papers: All Subjects
- CBSE Topper Answer Sheet Class 10: Model Answer Paper Download PDF
- CBSE Class 10 Mock Tests: All Subjects
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari and Sarkari Result . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App . Check Board Result 2024 for Class 10 and Class 12 like CBSE Board Result , UP Board Result , Bihar Board Result , MP Board Result , Rajasthan Board Result and Other States Boards.
- Nagaland Board Result 2024
- Nagaland Board HSLC Result 2024
- NBSE HSLC, HSSLC Result 2024
- Nagaland Board HSSLC Result 2024
- nbsenl.edu.in NBSE Result 2024
- NBSE Toppers List 2024
- एमपी बोर्ड 10 वीं टॉपर लिस्ट 2024
- AP SSC Results 2024 Manabadi by Jagran Josh
- AP SSC Topper List 2024
- CBSE Class 10 QnA
Latest Education News
Lok Sabha Elections 2024: 'आदर्श आचार संहिता', धारा-144 से कैसे है अलग चलिये समझें?
[DIRECT LINK] Nagaland Board Result 2024: Check Class 10th, 12th with NBSE Result School Login, Roll Number, and Name
NBSE Toppers List 2024: Nagaland Board HSLC, HSSLC Subject-wise Toppers Name, Marks, District-wise School Name
[Click Here] NBSE HSLC, HSSLC Result 2024 OUT: Download Nagaland 10th, 12th Class Results and Provisional Marksheet from NBSE Portal
Team-wise Most Consecutive Losses in IPL history till 2024
NBSE Result 2024 Released: Check Nagaland Board Class 10, 12 Results Online at nbsenl.edu.in by Roll Number, DOB and APP
ISC Class 12 Environmental Science Syllabus 2024-25: Download Class 12th Environmental Science Syllabus PDF
Nagaland Board HSSLC Result 2024: NBSE 12th Result at Jagran Josh and nbsenl.edu.in
Lok Sabha Elections 2024: यहां देखें दूसरे फेज के 5 सबसे अमीर उम्मीदवारों की संपत्ति, उड़ जायेंगे होश
Nagaland Board Result 2024: NBSE Result at Jagran Josh and nbsenl.edu.in
ISC Class 11th Maths Syllabus 2024-25: Download Revised PDF for ISC Class 11 Maths
Nagaland Board HSLC Result 2024: NBSE 10th Result at Jagran Josh and nbsenl.edu.in
nbsenl.edu.in 2024 Result: Official Websites to Check Nagaland Board 10th, 12th Results Online and Jagran Josh
[Link Here] Nagaland Board Result 2024 Declared: Check NBSE HSLC, HSSLC Results at nbsenl.edu.in and Download Pass Certificate
BSEB Bihar Sakshamta Pariksha 2 Exam 2024 Notification OUT at bsebsakshamta.com, Apply Here
Class 10th JSP
Result HomePage JSP
Class12thJSP
UP Higher Judicial Service Recruitment 2024: इलाहाबाद हाईकोर्ट में अधिवक्ता के 83 पदों पर निकली भर्ती
ICAR IARI Assistant DV Date 2024 Out at iari.res.in, Download CPT Schedule Here
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Unit 1: Life processes
About this unit.
In this unit, we learn about basic life processes such as photosynthesis, nutrition, transportation and excretion.
What are life processes?
- Intro to life processes (Opens a modal)
Nutrition & types
- Autotrophs & heterotrophs (nutrition modes) (Opens a modal)
- Types of nutrition Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Autotrophic nutrition
- Photosynthesis (Opens a modal)
- Guard cells and stomata Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Photosynthesis and respiration Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Nutrition in human beings
- Digesting Food (Opens a modal)
- Digestion in Intestines Get 5 of 7 questions to level up!
- Human digestion Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Respiration
- Aerobic & anaerobic respiration (Opens a modal)
- Respiration site & ATP (Opens a modal)
- Meet the lungs! (Opens a modal)
- The lungs and pulmonary system (Opens a modal)
- Inhaling and exhaling (Opens a modal)
- How does lung volume change? (Opens a modal)
- The respiratory system review (Opens a modal)
- Types of respiration Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Breathing in animals Get 5 of 7 questions to level up!
Transportation in plants
- Intro to vascular tissues (xylem & phloem) (Opens a modal)
- Xylem & transpiration (Opens a modal)
- Phloem & translocation (Opens a modal)
- Transportation in plants Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Transportation in animals
- Meet the heart! (Opens a modal)
- Flow through the heart (Opens a modal)
- Two circulations in the body (Opens a modal)
- Arteries vs. veins - what's the difference? (Opens a modal)
- Lymph & lymphatic system (Opens a modal)
- The circulatory system review (Opens a modal)
- Transportation in human beings Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Blood vessels and their maintenance Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Meet the kidneys! (Opens a modal)
- Parts of a nephron (Opens a modal)
- Excretion in human beings Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
myCBSEguide
- Case Study Questions Class...
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
Download Case study questions for CBSE class 10 Science in PDF format from the myCBSEguide App . We have the new pattern case study-based questions for free download. Class 10 Science case study questions
This article will guide you through:
What are case study questions?
- Sample Papers with Case Study questions
- Class 10 Science Case Study question examples
- How to get case-based questions for free?
- How to attempt the case-based questions in Science?
Questions based on case studies are some real-life examples. The questions are asked based on a given paragraph i.e. Case Study. Usually, 4-5 questions are asked on the basis of the given passage. In most cases, these are either MCQs or assertion & reason type questions. Let’s take an example to understand. There is one paragraph on how nitrogen is generated in the atmosphere. On the basis of this paragraph, the board asks a few objective-type questions. In other words, it is very similar to the unseen passages given in language papers. But the real cases may be different. So, read this article till the end to understand it thoroughly.
What is CBE?
CBSE stands for competency-based education. The case study questions are part of this CBE. The purpose of CBE is to demonstrate the learning outcomes and attain proficiency in particular competencies.
Questions on Real-life Situations
As discussed the case study questions are based on real-life situations. Especially for grade 10 science, it is very essential to have the practical knowledge to solve such questions. Here on the myCBSEguide app, we have given many such case study paragraphs that are directly related to real-life implications of the knowledge.
Sample Papers with Case Study Questions
Class 10 Science Sample Papers with case study questions are available in the myCBSEguide App . There are 4 such questions (Q.No.17 to 20) in the CBSE model question paper. If you analyze the format, you will find that the MCQs are very easy to answer. So, we suggest you, read the given paragraph carefully and then start answering the questions. In some cases, you will find that the question is not asked directly from the passage but is based on the concept that is discussed there. That’s why it is very much important to understand the background of the case study paragraph.
CBSE Case Study Sample Papers
You can download CBSE case study sample papers from the myCBSEguide App or Student Dashboard. Here is the direct link to access it.
Case Study Question Bank
As we mentioned that case study questions are coming in your exams for the last few years. You can get them in all previous year question papers issued by CBSE for class 1o Science. Here is the direct link to get them too.
Class 10 Science Case Study Question Examples
As you have already gone through the four questions provided in the CBSE model question paper , we are proving you with other examples of the case-based questions in the CBSE class 10 Science. If you wish to get similar questions, you can download the myCBSEguide App and access the Sample question papers with case study-type questions.
Case-based Question -1
Read the following and answer any four questions: Salt of a strong acid and strong base is neutral with a pH value of 7. NaCl common salt is formed by a combination of hydrochloride and sodium hydroxide solution. This is the salt that is used in food. Some salt is called rock salt bed of rack salt was formed when seas of bygone ages dried up. The common salt thus obtained is an important raw material for various materials of daily use, such as sodium hydroxide, baking soda, washing soda, and bleaching powder.
- Phosphoric acid
- Carbonic acid
- Hydrochloric acid
- Sulphuric acid
- Blue vitriol
- Washing soda
- Baking soda
- Bleaching powder
Case-based Question -2
- V 1 + V 2 + V 3
- V 1 – V 2 +V 2
- None of these
- same at every point of the circuit
- different at every point of the circuit
- can not be determined
- 20 3 Ω 203Ω
- 15 2 Ω 152Ω
Case-based Question -3
- pure strips
- impure copper
- refined copper
- none of these
- insoluble impurities
- soluble impurities
- impure metal
- bottom of cathode
- bottom of anode
How to Attempt the Case-Based Questions in Science?
Before answering this question, let’s read the text given in question number 17 of the CBSE Model Question Paper.
All living cells require energy for various activities. This energy is available by the breakdown of simple carbohydrates either using oxygen or without using oxygen.
See, there are only two sentences and CBSE is asking you 5 questions based on these two sentences. Now let’s check the first questions given there.
Energy in the case of higher plants and animals is obtained by a) Breathing b) Tissue respiration c) Organ respiration d) Digestion of food
Now let us know if you can relate the question to the paragraph directly. The two sentences are about energy and how it is obtained. But neither the question nor the options have any similar text in the paragraph.
So the conclusion is, in most cases, you will not get direct answers from the passage. You will get only an idea about the concept. If you know it, you can answer it but reading the paragraph even 100 times is not going to help you.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- CBSE Practice Papers 2023
- Class 10 Science Sample Papers 2024
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
2 thoughts on “Case Study Questions Class 10 Science”
Where is the answer
Class 10 Science MCQ
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- NCERT Exemplar
- Science Exemplar Class 10
- Life Processes
NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Solutions for Chapter 6 - Life Processes
Ncert exemplar solutions class 10 science chapter 6 – free pdf download.
NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes are premier study material required for the students to score good marks in Class 10 CBSE examinations as well as to avoid difficulty in understanding the concepts to be taught in higher secondary and graduation courses. The Class 10 Exemplar provided here consists of MCQs, fill in the blanks, practice questions, value-based questions, and previous years’ questions on Life Processes.
Class 10 Science Chapter 6 mainly deals with the maintenance processes in living organisms. In this chapter, students will learn to identify vital life processes and understand different types of nutrition as well as the respiratory organs and their mechanism, excretion, digestion, etc. To make learning more interesting and easy, we provide NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 – Life Processes in PDF here.
Download the PDF of NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 – Life Processes

Access Answers to NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 – Life Processes
Multiple-choice questions.
1. Which of the following statements about autotrophs is incorrect?
(a) They synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll
(b) They store carbohydrates in the form of starch
(c) They convert carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates in the absence of sunlight
(d) They constitute the first trophic level in food chains
The answer is (c) They convert carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates in the absence of sunlight
Explanation:
They need sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates.
2. In which of the following groups of organisms, food material is broken down outside the body and absorbed?
(a) Mushroom, green plants, Amoeba
(b) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould
(c) Paramecium, Amoeba, Cuscuta
(d) Cuscuta, lice, tapeworm
The answer is (b) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould
Yeast, mushroom and bread moulds are saprophytes, and Saprophytes break the food material outside their body and absorbed it.
3. Select the correct statement
(a) Heterotrophs do not synthesise their own food
(b) Heterotrophs utilise solar energy for photosynthesis
(c) Heterotrophs synthesise their own food
(d) Heterotrophs are capable of converting carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates
The answer is (a) Heterotrophs do not synthesise their own food
Heterotrophs are either dependent on Phototrophs or other organisms for their food.
4. Which is the correct sequence of parts in the human alimentary canal?
(a) Mouth → stomach → small intestine → oesophagus → large intestine
(b) Mouth →oesophagus → stomach → large intestine → small intestine
(c) Mouth → stomach → oesophagus → small intestine → large intestine
(d) Mouth → oesophagus → stomach → small intestine → large intestine
The answer is (d) Mouth → oesophagus → stomach → small intestine → large intestine
5. If salivary amylase is lacking in the saliva, which of the following events in the mouth cavity will be affected?
(a) Proteins breaking down into amino acids
(b) Starch breaking down into sugars
(c) Fats breaking down into fatty acids and glycerol
(d) Absorption of vitamins
The answer is (b) Starch breaking down into sugars
The Salivary Amylase enzyme present in the saliva breaks down Starch into simpler sugar and helps in digesting them. Hence the breakdown of starch will be affected if salivary amylase is lacking in the saliva.
6. The inner lining of the stomach is protected by one of the following from hydrochloric acid. Choose the correct one (a) Pepsin
(c) Salivary amylase
The answer is (b) Mucus
7. Which part of the alimentary canal receives bile from the liver?
(a) Stomach
(b) Small intestine
(c) Large intestine
(d) Oesophagus
The answer is (b) Small intestine
Bile goes to the small intestine from the gall bladder through hepta pancreatic duct.
8. A few drops of iodine solution were added to rice water. The solution turned blue-black in colour. This indicates that rice water contains
(a) complex proteins
(b) simple proteins
The answer is (d) starch
Explanation
Starch is made up of two components Amylose and Amylopectin. When we add iodine to starch-containing water Amylose reacts with iodine to form a blue colour complex. Here solution gives blue-black colour on adding Iodine which confirms the presence of starch in the rice water.
9. In which part of the alimentary canal is food finally digested?
(b) Mouth cavity
(d) Small intestine
The answer is (d) Small intestine
Although the primary digestion process is conducted in mouth and stomach most of the digestion process occurs in the small intestine and large intestine digestion process will not take place.
10. Choose the function of the pancreatic juice from the following
(a) trypsin digests proteins and lipase carbohydrates
(b) trypsin digests emulsified fats and lipase proteins
(c) trypsin and lipase digest fats
(d) trypsin digests proteins and lipase emulsified fats
The answer is (d) trypsin digests proteins and lipase emulsified fats
Trypsin breaks down proteins into polypeptides and Lipase digest emulsified fat molecules into fatty acids and glycerol.
11. When air is blown from the mouth into a test-tube containing lime water, the lime water is turned milky due to the presence of
(b) carbon dioxide
(c) nitrogen
(d) water vapour
The answer is (b) carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide reacts with lime water and turns the lime water milky.
12. The correct sequence of anaerobic reactions in yeast is

The answer is d)
In Yeast cytoplasm, Glucose is breakdown in anaerobic condition to produce Pyruvate which is further breakdown to Ethanol and carbon-di-oxide
13. Which of the following is most appropriate for aerobic respiration?

Soln: Answer is Option (B)
14. Which of the following statement(s) is (are) true about respiration?
(i) During inhalation, ribs move inward and diaphragm is raised
(ii) In the alveoli, exchange of gases takes place i.e., oxygen from alveolar air diffuses into blood and carbon dioxide from the blood into the alveolar air
(iii) Haemoglobin has a greater affinity for carbon dioxide than oxygen
(iv) Alveoli increase surface area for exchange of gases
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
The answer is (d) (ii) and (iv)
Statement i) is wrong because ribs move outward and the diaphragm is lowered during inhalation. Similarly Option iii) is wrong because Hemoglobin has greater affinity for Oxygen than CO 2.
15. Which is the correct sequence of air passage during inhalation?
(a) Nostrils →larynx →pharynx →trachea →lungs
(b) Nasal passage →trachea →pharynx →larynx →alveoli
(c) larynx →nostrils →pharynx →lungs
(d) Nostrils →pharynx →larynx →trachea →alveoli
The answer is (d) Nostrils →pharynx →larynx →trachea→alveoli
Air enter respiratory system through nostrils, passes to pharynx, larynx, trachea and then to alveoli. After inhalation diaphragm and intercoastal muscles contract along with expansion of thoracic muscles which creates enough space for the air to enter into the lungs.
16. During respiration exchange of gases take place in
(a) trachea and larynx
(b) alveoli of lungs
(c) alveoli and throat
(d) throat and larynx
The answer is (b) alveoli of lungs
Trachea, Larynx provide a passage for the movement of air. Gas exchange takes place in Alveoli of lungs. From alveoli, oxygen diffuses into blood and Carbon-di-oxide exhaled out of blood.
17. Which of the following statement (s) is (are) true about the heart?
(i) The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from different parts of the body while the right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from lungs
(ii) Left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to different body parts while right ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs
(iii) Left atrium transfers oxygenated blood to the right ventricle which sends it to different body parts
(iv) The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from different parts of the body while the left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to different parts of the body
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iii)
The answer is (c) (ii) and (iv)
Oxygenated blood circulates through the left part of the heart whereas deoxygenated blood circulates through the right part of the heart. Atrium receives blood and ventricle pumps the blood out of the heart.
18. What prevents backflow of blood inside the heart during contraction?
(a) Valves in heart
(b) Thick muscular walls of ventricles
(c) Thin walls of atria
(d) All of the above
The answer is (a) Valves in the heart
Walls in the heart are responsible for only pumping of the blood and they are not responsible for blocking backflow of blood inside the heart during contraction.
19. Single circulation i.e., blood flows through the heart only once during one cycle of passage through the body, is exhibited by
(a) Labeo, Chameleon, Salamander
(b) Hippocampus, Exocoetus, Anabas
(c) Hyla, Rana, Draco
(d) Whale, Dolphin, Turtle
The answer is (b) Hippocampus, Exocoetus, Anabas
In Option a) Chameleon is a reptile and Salamander is an amphibian which has 3 chambered hearts and shows partial double circulation. In Option c) all are Amphibians and they show partial double circulation. In option d) Whale is a mammal, but a turtle is a reptile hence option d) is wrong.
20. In which of the following vertebrate group/groups, the heart does not pump oxygenated blood to different parts of the body?
(a) Pisces and amphibians
(b) Amphibians and reptiles
(c) Amphibians only
(d) Pisces only
The answer is (d) Pisces only
This is because of the single circulation where deoxygenated blood from all part of the body is pumped into the heart. From the heart, it is pumped to gills where it gets oxygenated and gets transferred to all parts of the body. Hence it proves Pisces will not receive oxygenated blood.
21. Choose the correct statement that describes arteries.
(a) They have thick elastic walls, blood flows under high pressure; collect blood from different organs and bring it back to the heart
(b) They have thin walls with valves inside, blood flows under low pressure and carries blood away from the heart to various organs of the body
(c) They have thick elastic walls, blood flows under low pressure; carry blood from the heart to various organs of the body
(d) They have thick elastic walls without valves inside, blood flows under high pressure and carry blood away from the heart to different parts of the body.
The answer is (d) They have thick elastic walls without valves inside, blood flows under high pressure and carries blood away from the heart to different parts of the body.
22. The filtration units of kidneys are called
(b) urethra
(c) neurons
(d) nephrons
The answer is (d) nephrons
Nephron is called as the functional unit of the kidney. It helps in removing the waste products and excess substances from our body.
23. Oxygen liberated during photosynthesis comes from
(b) chlorophyll
(c) carbon dioxide
(d) glucose
The answer is (a) water
During photosynthesis, water molecule splits to produce Oxygen and Hydrogen Ions. Oxygen is expelled out of plants and Hydrogen is used to reduce Carbon-di-oxide to produce carbohydrates.
24. The blood leaving the tissues becomes richer in
(a) carbon dioxide
(c) haemoglobin
The answer is (a) carbon dioxide
Because of respiration Carbon-di-oxide gets accumulated in tissues. Hence blood leaving the tissues becomes richer in Carbon-di-oxide.
25. Which of the following is an incorrect statement?
(a) Organisms grow with time
(b) Organisms must repair and maintain their structure
(c) Movement of molecules does not take place among cells
(d) Energy is essential for life processes
The answer is (c) Movement of molecules does not take place among cells
Movement of molecule is a vital process. Movement of molecules in cells take place in active and passive modes such as Diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion etc.
26. The internal (cellular) energy reserve in autotrophs is
(a) glycogen
(b) protein
(d) fatty acid
The answer is (c) starch
Glycogen is the stored energy in animals, Plants stores energy in the form of Starch.
27. Which of the following equations is the summary of photosynthesis?
(a) 6CO 2 + 12H2O → C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 + 6H 2 O
(b) 6CO 2 +H 2 O + Sunlight→C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 + 6H 2 O
(c) 6CO 2 + 12H 2 O + Chlorophyll + Sunlight→ C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O2 + 6H 2 O
(d) 6CO 2 + 12H 2 O + Chlorophyll + Sunlight→ C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O
Answer is (c) 6CO 2 + 12H 2 O + Chlorophyll + Sunlight→ C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 + 6H 2 O
Option a does not show the factors responsible for photosynthesis. Option b) is not a balanced equation. Option d) is wrong as it has CO2 in the products.
28. Choose the event that does not occur in photosynthesis
(a) Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll
(b) Reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates
(c) Oxidation of carbon to carbon dioxide
(d) Conversion of light energy to chemical energy
Answer is (c) Oxidation of carbon to carbon dioxide
29. The opening and closing of the stomatal pore depend upon
(b) temperature
(c) water in guard cells
(d) concentration of CO2 in stomata
The answer is (c) water in guard cells
Opening of guard cells is facilitated by the entry of water inside guard cells. This makes the guard cell turgid. The closing of guard cells is facilitated by water coming out of guard cells. This will make the guard cells flaccid.
30. Choose the forms in which most plants absorb nitrogen
(i) Proteins
(ii) Nitrates and Nitrites
(iv) Atmospheric nitrogen
(a) (i) and (ii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
The answer is (b) (ii) and (iii)
Plants cannot absorb atmospheric Nitrogen. They can absorb Nitrogen in the form of Nitrates, Nitrites and Urea present in the soil.
31. Which is the first enzyme to mix with food in the digestive tract?
(b) Cellulase
(c) Amylase
(d) Trypsin
Answer is (c) Amylase
Amylase is secreted in mouth and acts on the starch to convert into simpler molecules. Hence Amylase is the first enzyme to mix with food in the digestive tract.
32. Which of the following statement(s) is (are) correct?
(i) Pyruvate can be converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide by yeast
(ii) Fermentation takes place in aerobic bacteria
(iii) Fermentation takes place in mitochondria
(iv) Fermentation is a form of anaerobic respiration
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
The answer is(c) (i) and (iv)
Fermentation is carried out by anaerobes in the cytoplasm. Hence option ii) and iii) are wrong.
33. Lack of oxygen in muscles often leads to cramps among cricketers. This results due to
(a) conversion of pyruvate to ethanol
(b) conversion of pyruvate to glucose
(c) non-conversion of glucose to pyruvate
(d) conversion of pyruvate to lactic acid
The answer is (d) conversion of pyruvate to lactic acid
The breakdown of Pyruvate in the presence of oxygen takes place in mitochondria leading to the formation of Lactic acid. Due to workout oxygen is used for the production of energy leading to the lack of oxygen and production of lactic acid.
34. Choose the correct path of urine in our body
(a) kidney → ureter → urethra → urinary bladder
(b) kidney → urinary bladder → urethra → ureter
(c) kidney → ureters → urinary bladder → urethra
(d) urinary bladder → kidney → ureter → urethra
Answer is (c) kidney → ureters → urinary bladder → urethra
Urine from nephron is brought to the collecting duct of kidneys where the urine enters the ureters. There are 2 ureters, each opening from one kidney into the urinary bladder. The urinary bladder stores urine and its size increases as the amount of urine collected increases. When the CNS gives a voluntary message the muscles of bladder contract and the bladder sphincter relaxes thus excreting urine out through the urethra.
35. During deficiency of oxygen in tissues of human beings, pyruvic acid is converted into lactic acid in the
(a) cytoplasm
(b) chloroplast
(c) mitochondria
(d) Golgi body
Answer is (a) cytoplasm
When there is lack of oxygen Breakdown of Pyruvate takes place in the cytoplasm of muscle cells leading to the formation of Lactic acid.
Short Answer Questions
36. Name the following
(a) The process in plants that links light energy with chemical energy
(b) Organisms that can prepare their own food
(c) The cell organelle where photosynthesis occurs
(d) Cells that surround a stomatal pore
(e) Organisms that cannot prepare their own food
(f) An enzyme secreted from gastric glands in the stomach that acts on proteins.
- Photosynthesis
- Chloroplasts
- Guard cells
- Heterotrophs
37. “All plants give out oxygen during day and carbon dioxide during the night”. Do you agree with this statement? Give reason.
The statement is wrong because plants respire every time and expel out Carbon-di-oxide every time but they give out oxygen only in the daytime as the photosynthesis process can take place only in the presence of sunlight.
38. How do the guard cells regulate the opening and closing of stomatal pores?
Opening of guard cells is facilitated by the entry of water inside guard cells. This make the guard cell turgid. The closing of guard cells is facilitated by water coming out of guard cells. This will make the guard cells flaccid.
Entry of water inside guard cells will make the cell turgid leading to the opening of stomata. Similarly, the cell becomes flaccid when water comes out of guard cells, this leads to the closing of the stomata.
39. Two green plants are kept separately in oxygen-free containers, one in the dark and the other in continuous light. Which one will live longer? Give reasons.
The plant kept in continuous light live longer because plants release CO 2 during respiration. In the case of the plant kept in the dark, CO 2 resulting in lack of oxygen and the plant will die earlier.
40. If a plant is releasing carbon dioxide and taking in oxygen during the day, does it mean that there is no photosynthesis occurring? Justify your answer.
If a plant is releasing carbon dioxide and taking in oxygen during the day means plant is respiring; it does not mean that there is no photosynthesis occurring in the plant. This is because Photosynthesis and respiration are two independent processes.
41. Why do fishes die when taken out of water?
Fishes can respire only by using dissolved oxygen. When we take fish out of the water it cannot respire due to lack of dissolved oxygen and they die.
42. Differentiate between an autotroph and a heterotroph
43. Is ‘nutrition’ a necessity for an organism? Discuss.
Nutrition is an absolute necessity for the organisms because nutrition provides energy for carrying out metabolic activities.
44. What would happen if green plants disappear from earth?
Green plants are the sources of energy for all the heterotrophs on earth. Plants convert solar and chemical energy into viable food sources. If plants get disappeared from the earth, it leads to an imbalance in the ecosystem and heterotrophs may die without food.
45. Leaves of a healthy potted plant were coated with vaseline. Will this plant remain healthy for long? Give reasons for your answer.
Coating vaseline to the leaves of a healthy plant will clog its stomata pores and stops the respiration of plants and the plants die.
46. How does aerobic respiration differ from anaerobic respiration?
47. Match the words of Column (A) with that of Column (B)
48. Differentiate between an artery and a vein.
Artery has thick walls whereas Veins has thin walls.
Arteries carry blood away from the heart but veins carry blood to the heart.
In arteries valves are absent and in veins they are present
In arteries, blood flows under pressure but in veins, there will be no pressure.
49. What are the adaptations of leaf for photosynthesis?
Adaptation of leaf for photosynthesis are as follows
- The surface of the leaf is flat to allow greater exposure of light.
- Presence of chlorophyll to trap sunlight
- Presence of stomata on the lower surface for easy transpiration
50. Why is small intestine in herbivores longer than in carnivores?
Food of herbivores contains mostly cellulose. To digest cellulose herbivores need help of certain bacteria. To accommodate the microbes and to facilitate digestion of food herbivores has longer small intestine than carnivores.
51. What will happen if the mucus is not secreted by the gastric glands?
Mucus prevent the inner lining of the stomach from HCL. Mucus prevents drying of the inner lining of the stomach. Mucus helps in easy movement of food particles through the digestive system. If the mucus is not secreted food will not easily be moved through the digestive system. HCL will damage the stomach lining and the digestion process will not take place.
52. What is the significance of the emulsification of fats?
Emulsification is a process of breakage of larger fats molecules into digestible fat globules. Emulsification aids action enzymes on fats by breaking larger fat molecules.
53. What causes movement of food inside the alimentary canal?
Peristalsis is the process that cause movement of food inside the alimentary canal.
54. Why does the absorption of digested food occur mainly in the small intestine?
Small intestine has specialized structures that facilitate the absorption of digested food. Small intestine has several folds that increase the area of absorption. Small intestine also has fingerlike projection called microvilli which are richly supplied by blood vessels.
55. Match Group (A) with Group (B)
56. Why is the rate of breathing in aquatic organisms much faster than in terrestrial organisms?
Rate of breathing in aquatic organisms much faster than in terrestrial organisms because the availability of oxygen is less in water than on land, hence to obtain required oxygen aquatic organisms has to work hard.
57. Why is blood circulation in the human heart called double circulation?
In Humans blood flow in two directions simultaneously in one cardiac cycle. Oxygenated blood comes to the heart from the lungs and at the same time, de-oxygenated blood goes from Heart towards the lungs. Because of this double movement is blood circulation in the human heart called double circulation.
58. What is the advantage of having a four-chambered heart?
Four chambered heart has the following advantages
- Clear cut division of labours among different chambers
- Segregation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in the heart.
- Efficiency of the heart will increase.
59. Mention the major events during photosynthesis
Major events of Photosynthesis are
- Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll
- Conversion of light energy into chemical energy
- Splitting of water molecules into Hydrogen and Oxygen
- Reduction of CO2 to form carbohydrates.
60. In each of the following situations what happens to the rate of photosynthesis?
(a) Cloudy days
(b) No rainfall in the area
(c) Good manuring in the area
(d) Stomata get blocked due to dust
- Rate of photosynthesis will reduce due to the availability of sunlight.
- Rainfall will not affect the rate of Photosynthesis
- Manuring will not affect the rate of Photosynthesis
- Blockage of stomata will reduce the rate of photosynthesis because blockage will affect availability pf Carbon-di-oxide.
61. Name the energy currency in the living organisms. When and where is it produced?
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the energy currency in the living organisms. It is produced in Mitochondria during respiration.
62. What is common for Cuscuta, ticks and leeches?
These all are parasite. They live on or inside another body to obtain food from the host. In obtaining food parasites always harm their host.
63. Explain the role of the mouth in digestion of food.
Role of mouth in digestion of food.
- Ingestion of food
- Breakage of food by Mastication
- Saliva aids easy swallowing of food
- Salivary amylase breaks starch into simpler carbohydrates.
64. What are the functions of gastric glands present in the wall of the stomach?
Hydrochloric acid, pepsin and mucus are secreted by gastric gland present in the stomach. They have following functions.
HCL Kills germs present in the food and it decreases P H of the stomach which is essential for the working of digestive enzymes.
Pepsin digests protein.
Mucus protects the stomach’s inner line from HCL.
65. Match the terms in Column (A) with those in Column (B)
66. Name the correct substrates for the following enzymes
(a) Trypsin
(b) Amylase
67. Why do veins have thin walls as compared to arteries?
Blood flow through veins does not exert pressure on walls of veins hence they have thin walls. Blood flow in arteries exerts high pressure on arterial walls hence they need thick walls.
68. What will happen if platelets were absent in the blood?
Platelets are responsible for the clotting of the blood. If platelets are absent blood will not clot. In case of injuries, blood flow cannot be stopped without clotting and this may prove fatal for the person.
69. Plants have low energy needs as compared to animals. Explain.
Most of the transport in plants occurs through passive transport which does not require energy and plants standstill at one place and they will not travel in search of food Hence Plants require low energy compared to animals.
70. Why and how does water enter continuously into the root xylem?
Water should enter the root xylem continuously to assist the various process such as photosynthesis. Continuous flow of water into root xylem is due to transpiration pull.
71. Why is transpiration important for plants?
Transpiration is important for plants because of the following reasons.
(a) It creates transpiration pull to facilitate the ascent of sap.
(b) Ascent of sap is necessary to make water available for photosynthesis.
(c) It helps a plant to get rid of excess water.
72. How do leaves of plants help in excretion?
Leaves plays an important role in excretion in plants because CO 2 is expelled out through pores of stomata present in the leaf. Plants shed leaves to get rid of excretory products deposited on them.
Long Answer Questions
73. Explain the process of nutrition in Amoeba.
Amoeba shows holozoic nutrition which is comprised of Ingestion, Digestion, Absorption, Assimilation and Egestion.
Ameoba traps food particles through fingerlike projections called pseudopodia. Pseudopodia present outside its body and helps in taking food along with water
Food vacuoles are made after ingesting the food. Enzymes are released in the food vacuole for digestion.
Absorption:
After digestion, nutrients enter the cytoplasm through osmosis.
Assimilation:
Nutrients are utilized by the cell for various purposes.
Food vacuole goes near the cell membrane to empty its contents outside the cell. This results in the expulsion of waste materials from the cell.
74. Describe the alimentary canal of man.

Human Alimentary canal has the following parts
Buccal Cavity:
Generally called as mouth and it consists of tongue, teeth and salivary gland. It is the entry site for the food to the digestive system. Food is breakdown into simpler molecules by mastication in the buccal cavity and salivary amylase breaks Starch into simpler carbohydrates in the Buccal cavity.
Oesophagus:
Buccal cavity is connected to the long tube-like structure called as Oesophagus. Oesophagus connects the buccal cavity to the stomach and assists the inflow of food towards the stomach. Oesophagus has a valve to prevent backflow of food particles.
Stomach is a J Shaped organ which has gastric glands in it. Gastric glands secrets Hydrochloric acid, Pepsin and Mucus that helps in the digestion of food.
Small Intestine:
Small intestine is highly coiled long structure. Small intestine performs major of the food absorption. Small intestine has specialized structures that facilitate the absorption of digested food. Small intestine has several folds that increase the area of absorption. Small intestine also has fingerlike projection called microvilli which are richly supplied by blood vessels.
Large Intestine :
This is shorter than the small intestine and its lumen is larger than that of Small intestine. The major function of the large intestine is to absorb water from the remaining indigestible food matter and transmit the useless waste material from the body.
Large Intestine open into rectum. Waste materials and undigested food are stored in the rectum.
It is the opening at the end of the alimentary canal. Solid waste materials leave the body through Anus.
75. Explain the process of breathing in man
Breathing in Humans has two processes 1) Inhalation 2) Exhalation
Inhalation:
Inhalation is the process of taking oxygen. During this process, ribs come out and the diaphragm moves down. This increases the volume of the lungs and decreases the pressure. This will make the air move towards the lungs.
Exhalation:
Exhalation is a process of throwing out carbon-dioxide. During this process, ribs go down and the diaphragm moves up. This decreases the volume of the lungs and increases the pressure. As a result, air moves out of the lungs.
76. Explain the importance of soil for plant growth.
Soil is very important for the growth of the plant for the following reasons.
- Soil provides the base for the growth of the plants and provides a platform for the penetration of roots.
- It acts as a reservoir of the water.
- Soil has different minerals essential for the growth of the plant. Soil is the only medium from which soil obtain nutrients.
- Soil has organic materials essential for the growth of the plants.
- Soil has microorganisms that have a symbiotic relationship with the plant and these microbes assist the plant in their growth and life processes.
77. Draw the diagram of the alimentary canal of man and label the following parts. Mouth, Oesophagus, Stomach, Intestine

78. How do carbohydrates, proteins and fats get digested in human beings?
Carbohydrate Digestion
Digestion of carbohydrates starts with buccal cavity where salivary enzymes break down the starch into simple sugar molecules. Other sugar molecules are breakdown to glucose in the small intestine.
Protein digestion
Proteins are partially digested by pepsin secreted by gastric glands present in the stomach. Then Pancreatic juice secrets trypsin and chymotrypsin enzymes in the small intestine where complete digestion of proteins takes place.
Fat Digestion
Fats are digested in the small intestine. Bile juice present in the liver emulsifies the fat which breaks fats into small globules. These small fat globules are converted into glycerol and fatty acids by Lipase enzyme.
79. Explain the mechanism of photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process by which plants produce their own food by utilizing sunlight, CO2 and water. CO@ and water are converted to carbohydrates with the evolution of oxygen. Photosynthesis reaction can be given by the following reaction.
6CO 2 + 6H 2 O Sunlight energy C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2
Process of Photosynthesis is divided into 4 processes
- Reduction of CO2 to produce carbohydrates
80. Explain the three pathways of breakdown in living organisms.

Glucose is first broken down to 3 carbon molecule called pyruvate. This process takes place in the cytoplasm of all organisms. Pyruvate is further broken down by the flowing steps.
Pyruvate is broken down in the absence of oxygen and the process is called anaerobic respiration. In yeasts, pyruvate is broken down to produce CO 2 and ethanol.
In Muscle Cells:
During rigorous physical activity, the energy demand of our muscles cells increases rapidly. This is compensated by anaerobic respiration in muscle cells. In muscle cells, pyruvate is broken down into lactic acid.
In Mitochondria:
In case of aerobic respiration( in presence of oxygen) pyruvate is broken down in mitochondria. Here Pyruvate is broken down to produce H 2 O and CO 2. Aerobic respiration is most common in most of the organisms.
81. Describe the flow of blood through the heart of human beings

• Deoxygenated blood from different organs comes to the right atrium through the vena cava.
• From the right atrium, blood goes to the right ventricle. The tricuspid valve between the right atrium and right ventricle prevents the backflow of blood.
• From the right ventricle, blood goes to the lungs through the pulmonary artery. Inside the lungs, carbon dioxide is removed from the blood and oxygen enters the blood.
• From the lungs, blood goes to the left atrium through the pulmonary vein.
• From the left atrium, blood goes to the left ventricle.
• From the left ventricle, blood is pumped into the aorta so that it can be supplied to different organs.
82. Describe the process of urine formation in kidneys

The basic filtration unit in the kidneys is a cluster of very thin-walled blood capillaries. Each capillary cluster in the kidney is associated with the cup-shaped end of a coiled tube called Bowman’s capsule that collects the filtrate (Fig. 6.14). Each kidney has large numbers of these filtration units called nephrons packed close together.
Some substances in the initial filtrate, such as glucose, amino acids, salts and a major amount of water, are selectively re-absorbed as the urine flows along the tube. The amount of water re-absorbed depends on how much
excess water is there in the body and on how much of dissolved waste there is to be excreted. The urine forming in each kidney eventually enters a long tube, the ureter, which connects the kidneys with the urinary bladder.
Urine is stored in the urinary bladder until the pressure of the expanded bladder leads to the urge to pass it out through the urethra. The bladder is muscular, so it is under nervous control.
Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes NCERT Exemplar
These Exemplars will help students gain insights into all the important chapter questions as well as develop a better understanding of each topic. Additionally, using these exemplars will enable students to study effectively and be well-prepared to answer any type of question that can be asked in the board exam.
Class 10 Science NCERT Life Process Important Topics
- What Is Life Process?
- Autotrophic Nutrition
- Heterotrophic Nutrition
- How Do Organisms Obtain Their Nutrition?
- Nutrition in Human Beings
- Respiration
- Transportation
- Excretion in Human Beings
- Excretion in Plants
NCERT Exemplar Solutions, provided on BYJU’S website, will boost your exam preparation by providing you with the additional knowledge required to understand the concepts clearly. Students are recommended to study these Exemplar Solutions and NCERT Solutions thoroughly to excel in CBSE Class 10 examination. To score good marks in the Class 10 examinations, students can access and download the study materials provided at BYJU’S in PDFs for free. To access the study material, you can visit BYJU’S website or download BYJU’S – The Learning App.
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6
Why are byju’s ncert exemplar solutions for class 10 science chapter 6 important, what concepts will i learn from the ncert exemplar solutions for class 10 science chapter 6, what are the advantages of using the ncert exemplar solutions for class 10 science chapter 6 from byju’s, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

CBSE Expert
Class 10 Science: Case Study Chapter 6 Life Processes PDF Download
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given.

Here we are providing you with Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes Case Study Questions, by practicing this Case Study and Passage Based Questions will help you in your Class 10th Board Exam.
Case Study Chapter 6 Life Processes
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Question 1:
Transpiration is the evaporative loss of water by plants. It occurs mainly through the stoma in the leaves. Besides the loss of water vapor in transpiration, the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the leaf also occurs through pores called stomata. Normally stomata remain open in the daytime and close during the night
(i) Which of the following will not directly affect transpiration?
Answer: (d) Chlorophyll content of leaves
(ii) Water vapour comes out from the plant leaf through the stomatal opening. Through the same stomatal opening, carbon dioxide diffuses into the plant during photosynthesis. Reason out the above statements . using one of following options. (a) The above processes happen only during night time. (b) One process occurs during day time and the other at night. (c) Both processes cannot happen Simultaneously. (d) Both processes can happen together at day time.
Answer: (d) Both processes can happen together at day time.
(iii) Which of the following statements is not true for stomatal apparatus? (a) Guard cells invariably possess chloroplasts and mitochondria. (b) Guard cells are always surrounded by subsidiary cells. (c) Stomata are involved in gaseous exchange. (d) Inner wall of guard cells are thick.
Answer: (b) Guard cells are always surrounded by subsidiary cells.
(iv) Which of the following is not a purpose of transpiration? (a) Helps in absorption and transport in plants (b) Prevents loss of water (c) Maintains shape and structure of plants by keeping the cells turgid (d) Supplies water for photosynthesis
Answer: (b) Prevents loss of water
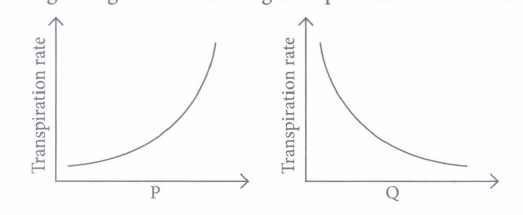
Answer: (a) P-Atmospheric temperature; Q-Atmospheric pressure
Question 2:
Heterotrophic nutrition is a mode of nutrition in which organisms obtain readymade organic food from outside sources. The organisms that depend upon outside sources for obtaining organic nutrients are called heterotrophs. Heterotrophic nutrition is of three types: saprophytic, parasitic, and holozoic nutrition.
(i) In which of the following groups of organisms food material is broken outside the body and absorbed? (a) Mushroom, green plants, Amoeba (b) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould (c) Paramecium, Amoeba, Cuscuta (d) Cuscuta, lice, tapeworm
Answer: (b) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould
(ii) Which of the following is a parasite? (a) Yeast (b) Taenia (c) Amoeba (d) Earthworm
Answer: (b) Taenia
(iii) Which of the following is an example of saprotroph? (a) Grass (b) Mushroom (c) Amoeba (d) Paramecium
Answer: (b) Mushroom
(iv) Heterotrophic nutrition involves (a) production of simple sugar from inorganic compounds (b) utilisation of chemical energy to prepare food (c) utilisation of energy obtained by plants (d) all of these.
Answer: (c) utilisation of energy obtained by plants
(v) In Paramecium, food enters the body through (a) mouth (b) pseudopodia (c) cilia (d) cytostom
Answer: (d) cytostom
You can also practice Class 10 Science MCQ Questions for Board Exams.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!
- New QB365-SLMS
- NEET Materials
- JEE Materials
- Banking first yr Materials
- TNPSC Materials
- DIPLOMA COURSE Materials
- 5th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships


CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Life Processes Chapter Case Study Questions 2021
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 10 , and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Cbse 10th standard science subject life processes case study questions 2021.
10th Standard CBSE
Final Semester - June 2015
Digestion is a catabolic process in which complex and large components of food are broken down into their respective simpler and smaller forms with the help of various hydrolytic enzymes. In human, the process of intake of essential nutrients in the form of food takes place through an entire system known as digestive system. The digestive system in human includes alimentary canal and its associated digestive glands. (i) Identify the cells whose secretion protects the lining of gastro-intestinal tract from various enzymes.
(ii) Digestion of proteins is incomplete in the absence of enterokinase, because (a) trypsinogen is not converted into trypsin (b) pepsinogen is not converted into pepsin (c) prorennin is not converted into rennin (d) chymotrypsinogen is not converted into chymotrypsin (iii) Match the column I with column II and column III. Choose the correct option.
(v) If the inner surface of the ileum in the human small intestine was smooth, rather than being folded and subdivided into villi, which of the following statements would be true? (a) The rate of absorption of digested food molecules would be higher, because the digested food would pass more easily through the digestive tract. (b) Digestion would not be as effective, because there would be fewer cells secreting trypsin (a proteindigesting enzyme). (c) Humans would have needed to evolve a much longer small intestine to absorb sufficient nutrients from their food. (d) Humans would not be able to survive, because the digestive tract would be more susceptible to damage.
Respiration is an energy releasing enzymatically controlled process which involves a stepwise oxidative breakdown of food substances inside living cells. The oxidative breakdown of respiratory substrates with the help of atmospheric oxygen is aerobic respiration. Glucose is completely broken down into CO 2 and H 2 O by this process of oxidation and large amount of energy is produced. (i) Site of Krebs' cycle is
(ii) The pathway of respiration common in all living organisms is X ;it occurs in the Y and the products formed are two molecules of Z . Identify X, Y and Z in the above paragraph and select the correct answer.
(iii) Number of oxygen molecules utilised in glycolysis is ____________.
(iv) How many ATP molecules could maximally be generated from one molecule of glucose, if the complete oxidation of one molecule of glucose to CO 2 and H 2 O yields 686 kcal and the useful chemical energy available in the high energy phosphate bond of one molecule of ATP is 12 kcal?
(v) The end product of aerobic respiration is
Heterotrophic nutrition is a mode of nutrition in which organisms obtain readymade organic food from outside sources. The organisms that depend upon outside sources for obtaining organic nutrients are called heterotrophs. Heterotrophic nutrition is of three types: saprophytic, parasitic and holozoic nutrition. (i) In which of the following groups of organisms food material is broken outside the body and absorbed?
(ii) Which of the following is a parasite?
(iii) Which of the following is an example of saprotroph?
(iv) Heterotrophic nutrition involves (a) production of simple sugar from inorganic compounds (b) utilisation of chemical energy to prepare food (c) utilisation of energy obtained by plants (d) all of these.
(v) In Paramecium, food enters the body through
The food which is prepared by the process of photosynthesis in the leaves of a plant has to be transported to other parts like stem, roots, branches, etc. Therefore this food is transported to other parts of the plant through phloem. (i) A few drops of sap were collected by cutting across a plant stem by a suitable method. The sap was tested chemically. Which one of the following test results indicates that it is phloem sap?
(ii) What is the direction of movement of sugars in phloem?
(iv) A girdled plant (upto bast) may survive for some time but it will eventually die, because (a) water will not move downwards (b) water will not move upwards (c) sugars and other organic materials will not move downwards (d) sugars and other organic materials will not move upwards (v) Phloem sap is mainly made of
*****************************************
Cbse 10th standard science subject life processes case study questions 2021 answer keys.
(i) (c): Goblet cells or mucous cells are present throughout the epithelium of gastric glands and secrete mucus, which protects gastro-intestinallining from enzymatic action. (ii) (a) (iii) (c) (iv) (b): Pepsin and trypsin both are protein digesting enzymes, but they work at different locations and different pH in alimentary canal. Pepsin, which is most active at pH of 1.5 to 2.5, is an important peptic enzyme in stomach. Trypsin, which is a pancreatic protease, acts mostly in upper small intestine (duodenum and jejunum), works at an optimum pH of 7.5 - 8.5. (v) (c): The absorptive surface of small intestinal mucosa have many folds, which increase its surface area. Also located on epithelial surface of small intestine are millions of small villi. Intestinal epithelial cell on each villus is characterised by a brush- border which further increases the surface area. Thus, to compensate for this and to have effective absorption of nutrients, intestine would need to be much longer in length.
(i) Krebs' cycle takes place in mitochondrial matrix. (ii) (b) (iii) (a) : Glycolysis does not utilise any oxygen as it is an anaerobic process. (iv) (d) (v) (d): In aerobic respiration, glucose is completely broken down to CO 2 and H 2 O with the production of a large amount of energy (ATP).
(i) (b): Yeast, mushroom and bread mould have a saprophytic mode of nutrition which is chemoheterotrophic in nature. They breakdown complex organic substances by secreting digestive enzyme outside their body and absorb simple molecules as nutrients. (ii) (b) (iii) (b): Yeast, mushroom and bread mould have a saprophytic mode of nutrition which is chemoheterotrophic in nature. They breakdown complex organic substances by secreting digestive enzyme outside their body and absorb simple molecules as nutrients. (iv) (c): Heterotrophic nutrition is mode of nutrition in which an organism depends on other living organisms for food. (v) (a)
(i) (d) (ii) (c): Baked potatoes consist of starch which is a polysaccharide. In oral cavity, the food is mixed with saliva that contains an enzyme salivary amylase which converts starch into maltose, isomaltose and small dextrins. The pancreatic juice (present in small intestine) contains pancreatic amylase which converts starch into maltose, isomaltose and \(\alpha\) -dextrins. \(\text { Starch } \frac{\text { Pancreatic }}{\alpha \text { -amylase }}>\text { Maltose }+\text { Isomaltose }+\alpha \text { -Dextrins }\) Further, disaccharidases such as maltase (present in intestinal juice in small intestine) break down disaccharides such as maltose into monosaccharides or simpler sugars. (iii) (d): After removal of gall bladder, bile could no longer to be stored and hence fat metabolism would be affected. Therefore, fat intake should be restricted. (iv) (d) (v) (c)
(i) (b) (ii) (a): Food is transported by vascular tissue phloem from source to sink. Source is a part that synthesise food and sink is a part that stores or needs the food. Since source and sink can be reversed depending on plant's need, therefore direction of movement of sugar in phloem can be bidirectional, i.e., both upwards or downwards. (iii) (b) (iv) (c)
Related 10th Standard CBSE Science Materials
10th standard cbse syllabus & materials, cbse 10th maths probability chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths statistics chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths surface areas and volumes chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths areas related to circles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths circles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths some applications of trigonometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths introduction to trigonometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths coordinate geometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths triangles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths arithmetic progressions chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 10th maths quadratic equations chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 10th social science the making of a global world chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science nationalism in india chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science the rise of nationalism in europe chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths pair of linear equation in two variables chapter case study question with answers.

Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

10th Standard CBSE Study Materials

10th Standard CBSE Subjects
Quizizz provides several resources that help CBSE Science teachers to effectively teach the topic Nutrition in chapter Life Processes.

Explore our Quiz Library

Surface Processes

Life processes

20 Questions
Explore other topics.
Respiration
Transportation
Explore other chapters
- Chemical Reactions and Equations
Acids Bases and Salts
Carbon and It's Compounds
Metals and Non-metals
Periodic Classification of Elements
Life Processes
Control and Coordination
- How do Organisms Reproduce?
Heredity and Evolution
Light: Reflection and Refraction
Human Eye and the Colourful World
Electricity
Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- Sources of Energy
- Our Environment
Management of Natural Resources
Any specific topic in mind?
Suggested topics, explore the subjects.
Mathematics
Other topics to explore
CBSE | Science | 10th Grade | Human Eye and the Colourful World - Quizizz
CBSE | Science | 10th Grade | Periodic Classification of Elements - Quizizz
CBSE | Science | 10th Grade | Life Processes - Quizizz
CBSE | Science | 10th Grade | Chemical Reactions and Equations - Quizizz
CBSE | Science | 10th Grade | Heredity and Evolution - Quizizz
CBSE | Science | 10th Grade | Light: Reflection and Refraction - Quizizz
CBSE | Science | 10th Grade | Electricity - Quizizz
CBSE | Science | 10th Grade | Acids Bases and Salts - Quizizz
CBSE | Science | 10th Grade | Management of Natural Resources - Quizizz
CBSE | Science | 10th Grade | Metals and Non-metals - Quizizz
Everything you need for mastery and engagement
Explore our powerful tools.

Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 10th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Case study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 8 are very important to solve for your exam. Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving case study-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Question 1:
The male reproductive system consists of portions that produce the germ cells and other portions that deliver the germ cells to the site of fertilization. Testes are located outside the abdominal cavity in the scrotum because sperm formation requires a lower temperature than normal body temperature. It also has a role of secretion of male sex hormone which brings changes in appearance seen in boys at the time of puberty. Vas deferens unites with a tube coming from the urinary bladder. The urethra is a common passage for sperms and urine. The prostate gland and seminal vesicles add their secretions so that sperms are now in a fluid.

(i) Name the sex hormone associated with males. (a) Testosterone (b) Progesterone (c) Oestrogen (d) None of these
Answer: (a) Testosterone
(ii) Which of the following statements is incorrect ? (a) Sperms are present in a fluid (b) Fluid provides nutrition to sperms (c) Fluid makes easier transportation of sperms (d) Fluid helps to bind the sperms together
(iii) Testes are located outside the abdominal cavity in scrotum because (a) sperms formation requires higher temperature than body temperature (b) sperms formation requires lower temperature than body temperature (c) it is easier to transport sperms from the scrotum (d) None of these
Answer: (b) sperms formation requires lower temperature than body temperature
(iv) Which of the following statement is incorrect? (a) Sperms and urine has a common passage from urethra.
(b) Sperms have long tail that helps them to move forward. (c) Sperms contain genetic material. (d) Sperms formation requires 1–3°C higher temperature than normal body temperature.
Answer: (d) Sperms formation requires 1–3°C higher temperature than normal body temperature.
(v) What is the nature of semen? (a) slightly acidic (b) Neutral (c) Slightly basic (d) Strongly basic
Answer: (c) Slightly basic
Question 2:
Rohit collected some pond water which was dark green in color in a test tube. She took out green-colored mass from it and separated its filaments by using needles. She broke some filaments into small fragments and put them in a Petri dish containing clean water. She observed that after a few days the small fragments gave rise to complete filaments.
2.1) What do you think the mass of green filament was ? (a) It was a mass of Spirogyra filament. (b) It was a colony of Volvox algae. (c) It was large brown algae. (d) It was a mass of fungal filaments
Answer:(a) It was a mass of Spirogyra filament.
2.2) Organisms that reproduces in similar ways as Spirogyra is : (a) yeast (b) hydra (c) Planaria (d) Sea anemone
Answer: (d) Sea anemone
2.3) The small fragment gave rise to new filament. What does it indicate ? (a) Spirogyra reproduces asexually through budding. (b) Spirogyra reproduces asexually through spore formation. (c) Spirogyra reproduces asexually through fragmentation. (d) Spirogyra reproduces asexually through fission
Answer: (c) Spirogyra reproduces asexually through fragmentation.
2.4) Which among the following organisms do not reproduce by fragmentation ? (a) Riccia (b) Selaginella (c) Aurelia (d) Marchantia
Answer: (c) Aurelia.
2.5) Select the correct statement from the following. (a) Only multicellular organisms can undergo fragmentation. (b) Both unicellular and multicellular organisms can undergo fragmentation. (c) Fragmentation is sexual mode of reproduction. (d) Fragmentation is found only in algae
Answer: (a) Only multicellular organisms can undergo fragmentation
Question 3:
In humans, if the egg is not fertilized, it lives for about one day. Since the ovary releases one egg every month, the uterus also prepares itself every month to receive a fertilized egg. Thus its lining becomes thick and spongy. This would be required for nourishing the embryo if fertilization had taken place. Now, however, this lining is not needed any longer. So, the lining slowly breaks and comes out through the vagina as blood and mucous. This cycle takes place roughly every month and is known as menstruation. It usually lasts for about two to eight days.
3.1) What is the sexual cycle in human female that takes place every 28 days and marked by bleeding ? (a) Sexual cycle (b) Reproductive cycle (c) Menstrual cycle (d) Blood cycle
Answer: (c) Menstrual cycle
3.2) If fertilisation takes place, it results in the formation of : (a) an embryo (b) a zygote (c) a foetus (d) a placenta
Answer: (b) a zygote
3.3) Why does vaginal bleeding occur in human females on attaining puberty ? (a) Unfertilised egg along with thick uterus lining come out of vagina in form of bleeding. (b) In human females, ovaries start releasing egg or ovum once every 28 days from the age of puberty. (c) If fertilisation does not occur then menstrual flow occurs at the end of cycle. (d) All of these
Answer: (d) All of these
3.4) In what conditions vaginal bleeding will not occur in a human female who has attained puberty ? (a) If the ovum is fertilised (b) If the ovum is not fertilised (c) If there is some hormonal imbalance in female (d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer: (d) Both (a) and (b)
3.5) Mark one change from the following associated with sexual maturation in boys ? (a) loss of milk teeth (b) weight gain (c) increase in height (d) cracking of voice
Answer: (d) cracking of voice
Question 4: A newly married couple does not want have children for few years. They consulted a doctor who advised them barrier method and chemical method of birth control. Yet another couple who already have two children and are middle aged also consulted doctor for some permanent solution to avoid unwanted pregnancy. Doctor advised them surgical method of birth control.
Another category of contraceptives acts by changing the hormonal balance of the body so that eggs are not released and fertilisation cannot occur. These drugs commonly need to be taken orally as pills. However, since they change hormonal balances, they can cause side-effects too. Other contraceptive devices such as the loop or the copper-T are placed in the uterus to prevent pregnancy. Again, they can cause side effects due to irritation of the uterus.
4.1) What are the barrier methods of birth control ? (a) Condoms (b) Oral pills (c) Surgery (d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer: (a) Condoms
4.2) How physical barrier prevent pregnancy ? (a) They kill the sperms. (b) They kill the ovum. (c) They prevent intercourse. (d) They prevent fertilisation
Answer: (d) They prevent fertilisation.
4.3) How chemical methods prevent pregnancy ? (a) Vaginal pills contain chemical called spermicides which kill the sperms. (b) Oral pills prevent ovulation so there will be no fertilisation. (c) Oral pills stop menstruation in females. (d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer: (d) Both (a) and (b)
4.4) Select the correct statement regarding surgical method of birth control. (a) It involves termination of pregnancies in women particularly after eight weeks of conception. (b) Small portion of sperm duct or vas deferences in males is removed by surgical operation and both cut ends are ligated properly. (c) Small portion of oviducts in females is removed by surgical operation and cut ends are ligated. (d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer: (d) Both (b) and (c)
4.5) Select the correct statement regarding birth control methods. (a) Barrier method of birth control also protects the couple from sexually transmitted diseases. (b) Some women experience unpleasant side effects on taking oral pills because of change in hormonal balance in body. (c) Surgical method in males is called vasectomy and in females is called tubectomy. (d) All of these
Answer: (d) All of these
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries of CBSE Class 10 Science How do Organisms Reproduce Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible. By Team Study Rate
You Might Also Like
Class 10 evergreen self study in social science pdf download, extra questions of class 10 science chapter 1 chemical reactions and equations pdf download, ntse daily practice problems(dpp) of all subjects (mat+sat) with solutions, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes
Get extra questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes with PDF. Our subject expert prepared these solutions as per the latest NCERT textbook. These extra questions will be helpful to revise the important topics and concepts. You can easily download all the questions and answers in PDF format from our app.
Life Processes Class 10 Science Extra Questions with Answers
Question 1: Mention the raw materials required for photosynthesis.
Answer: The following raw materials are required for photosynthesis: (i) Carbon Dioxide: Plants get CO 2 from atmosphere through stomata. (ii)Water: Plants absorb water from soil through roots and transport to leaves. (iii) Sunlight: Sunlight, which is absorbed by the chlorophyll and other green parts of the plant.
Question 2: What would be the consequences of deficiency of haemoglobin in your body?
Answer: The deficiency of haemoglobin in our body is called anaemia. In anaemia, the blood is unable to carry the sufficient amount of oxygen required by the body. So, respiration would be less and less energy will be available to the body. The haemoglobin deficient person will feel weak, pale, lethargic and will be unable to perform heavy physical work.
Question 3: Name the green dot like structures in some cells observed by a student when a leaf peel was viewed under a microscope. What is this green colour due to?
Answer: The green dot-like structures in some cells observed by a student when a leaf peel is viewed under a microscope are chloroplasts. The green colour is due to the presence of green pigment, chlorophyll.
Question 4: State any one difference between autotrophic and heterotrophic modes of nutrition.
Answer: In autotrophic nutrition, organisms obtain their food from inorganic substances. In heterotrophic nutrition, organisms derive their food from organic substances.
Question 5: A Give one reason why multicellular organisms require special organs for exchange of gases between their body and their environment.
Answer: In unicellular organisms the entire body of the organism is in contact with the environment hence exchange of materials can take place but, in multicellular organisms the entire body of the organism is not in contact with the environment and hence simple diffusion is not helpful.
Question 6: Name the process in plants where water is lost as water vapour. :
Answer: Transpiration is the process when plants loose water as vapour.
Question 7: What is translocation in plants?
Answer: Translocation is the movement of soluble materials, products of photosynthesis from leaves to other tissues throughout the plant.
Question 8: State the basic difference between the process of respiration and photosynthesis.
Question 9: In the experiment “Light is essential for photosynthesis”, why does the uncovered part of the leaf turn blue-black after putting iodine solution?
Answer: Starch is produced in the uncovered part of the leaf because it is exposed to sunlight allowing it to photosynthesize, which turns blue-black in presence of iodine solution.
Question 10: Name the component of blood that helps in the formation of blood clot in the event of a cut.
Answer: Platelets help in clotting of blood in the event of a cut.
Question 111: Mention how organisms like bread moulds and mushrooms obtain their food.
Answer: Organisms like bread moulds and mushrooms breakdown the food materials outside the body and then absorb the nutrients of the bread.
Question 12: What will happen to a plant if its xylem is removed?
Answer: Xylem in plant transports water and dissolved mineral nutrients from the roots to all parts of the vascular plant. So, if xylem is removed from the plant, the water and mineral supply to the plant will stop and therefore, the plant will die.
Question 13: Where does digestion of fat take place in our body?
Answer: Digestion of fat takes place in the small intestine of our body.
Question 14: What is the mode of nutrition in human beings?
Answer: Holozoic nutrition.
Question 15: What are enzymes? Name any one enzyme of our digestive system and write its function.
Answer: Enzymes are biological catalysts. Catalysts are proteins that increase the rate of chemical reactions without being used up. For example: Amylase catalyses the breakdown of starch into sugars in the mouth and small intestine
Question 16: (i) Write the balanced chemical equation for the process of photosynthesis,
(ii) When do the desert plants take up carbon dioxide and perform photosynthesis?
Answer: (i) Photosynthesis can be represented using a chemical equation. The overall balanced equation is
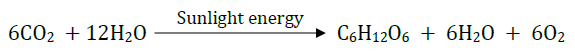
(ii) Desert plants open up their stomata during night and take in CO 2 . Stomata remains close during the day time to prevent the loss of water by i transpiration. They store the CO 2 in their cells until the sun comes out and they can carry on with photosynthesis during the day time.
Question 17: Why do herbivores have longer, small intestine than carnivores?
Answer: Digestion of cellulose takes a longer time. Hence, herbivores eating grass need a longer small intestine to allow complete digestion of cellulose. Carnivorous animals cannot digest cellulose due to the absence of enzyme cellulose hence they have a shorter intestine.
Question 18: Why do the walls of the trachea not collapse when there is less air in it?
Answer: Rings of cartilages are present in trachea. These rings support the trachea and do not allow the trachea to collapse when there is less air in it.
Question 19: What are the final products after digestion of carbohydrates and proteins?
Answer: The final product produced after digestion of carbohydrates is glucose and of proteins is amino acids.
Question 20: What is saliva? State its role in the digestion of food.
Answer: Saliva is a watery fluid secreted by the salivary glands in the mouth. The digestive functions of saliva include moistening food, and helping to create a food bolus, so it can be swallowed easily. Saliva contains the enzyme amylase that breaks some starches down into maltose and dextrin.
Question 21: Explain the process of nutrition in Amoeba.
Answer: Amoeba is a protozoan found in fresh water. It feeds on microscopic plants and animals present in water. The mode of nutrition in amoeba is Holozoic. And the process of obtaining food by amoeba is called phagocytosis. The different processes involved in the nutrition of amoeba are:
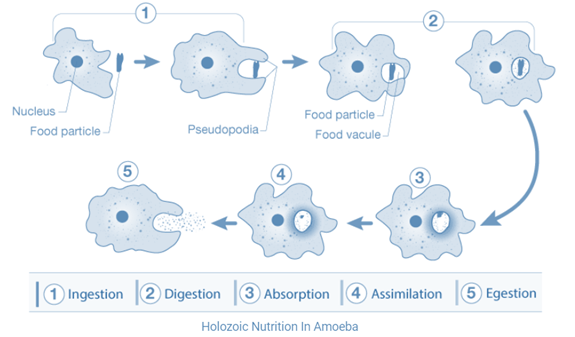
Ingestion: Ingestion is the process of taking food in the body. Amoeba is a unicellular animal, so it doesn’t have a mouth for ingestion of food. Amoeba ingests the food by encircling it by forming pseudopodia. When the food is completely encircled, the food is engulfed in the form of a bag called food vacuole.
Digestion: Digestion is the process of breaking the large and insoluble molecules in small and water soluble molecules. In amoeba, several digestive enzymes react on the food present in the food vacuoles and break it down into simple and soluble molecules.
Absorption: The food digested by digestive enzymes is then absorbed in the cytoplasm by the process of diffusion. While the undigested food remains in the food vacuole. If a large amount of food is absorbed by amoeba, the excess food is stored in the cytoplasm in the form of glycogen and lipids.
Assimilation: During this step the food absorbed by the cytoplasm is used to obtain energy, growth and repair. This process of utilizing absorbed food for obtaining energy, repair and growth is called assimilation.
Egestion: When a sufficient amount of undigested food gets collected in the food vacuole, it is thrown out of the body by rupturing cell membrane. The process of removal of undigested food from the body is called egestion.
Question 22: State differences between arteries and veins.
Question 23: How are the alveoli designed to maximise the exchange of gases?
Answer: Alveoli are small pouches or sacs like structure. They are surrounded by blood capillaries. Thus a large amount of air is brought in contact with the air in the lungs. More than millions of alveoli are present in the lungs. The presence of millions of alveoli in the lungs provides a very large surface area for the exchange of gases. The availability of large surface area maximises the exchange of gases.
Question 24: Name two excretory products other than O 2 and CO 2 in plants.
Answer: The two excretory products other than O 2 and CO 2 in plants are resins and gums.
Question 25: In single celled organisms diffusion is sufficient to meet all their requirements of food, exchange of gases or removal of wastes but it is not in case of multicellular organisms. Explain the reason for this difference.
Answer: Unicellular organisms can absorb sufficient oxygen because of its complete
contact with the atmosphere, but in multicellular organisms the rate of absorption and diffusion becomes very less because all cells are not in direct contact with the atmosphere. Multicellular organisms require greater amount of oxygen to sustain life processes which cannot be fulfilled by the process of diffusion.
Question 26: Draw a diagram of human excretory system and label kidneys, ureters on it.
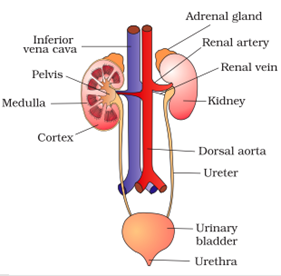
Question 27: Name the acid presents in the following:
(i) Tomato (ii) Vinegar (iii) Tamarind
Answer: (i) Oxalic acid (ii) citric acid (iii) Tartaric acid.
Question 28: State the role of the following in human digestive system:
(i) Digestive enzymes (ii) Hydrochloric acid (iii) Villi
Answer: (i) Digestive enzymes – Foods need to be broken into their small or simpler molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. However, the physical breakdown of food is not enough. Enzymes are hence needed for the chemical breakdown of food and speeding up the digestive process. The products of digestion can hence be small enough to be absorbed.
(ii) Hydrochloric acid – Hydro chloric acid helps to kill the germs which might have entered in to the system through food. It creates acidic medium for the pepsin to act on food to breakdown proteins.
(iii) Villi – Villi are finger like projections in the small intestine. They help to increase the surface area for absorption of the digested food. Villi are richly supplied with blood vessel which help to absorb digested food in to the blood stream.
Question 29: In mammals and birds why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and de-oxygenated blood?
Answer: Mammals and birds are warm blooded animals. This means they can control their body temperature and do not have to depend on environment for their body temperature regulation. Because of this birds and mammals require optimum oxidization of glucose which would be possible with good supply of oxygen. So it is required to have separate oxygenated and de-oxygenated blood to supply the required amount of oxygen.
Question 30: Draw a diagram of human respiratory system and label it.
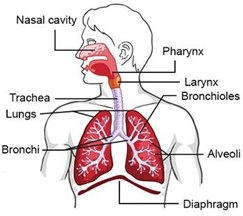
Question 31: (a) Name the site of exchange of material between the blood and surrounding cells.
(b) Draw a schematic representation of transport and exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in human body.
Answer: (a) Capillaries
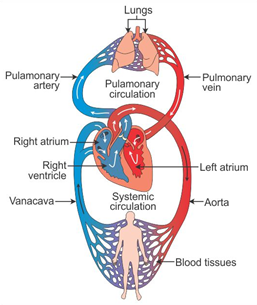
Question 32: List three characteristics of lungs which make it an efficient respiratory surface.
Answer: These features which particularly make our lungs efficient for gas exchange.
- Thin: the air sac walls are very thin so that gases can quickly diffuse through them. Oxygen is absorbed in to the blood and carbon dioxide is given out in to the lungs to be exhaled out.
- Moist: the air sacs are moist with mucus so that gases can dissolve before diffusing.
- Large surface area: the surface area for gases to diffuse through in human lungs is roughly the same as a tennis court. The alveoli help to increase the surface area for absorption of oxygen.
- Good blood supply: the air sacs or the alveoli have a large capillary network so that large volumes of gases can be exchanged. More the flow of blood more exchange.
Question 33: (a) What is the role of HCl in our stomach? (b) What is emulsification of fats? (c) Which protein digesting enzyme is present in pancreatic juice?
Answer: (a)(i) It sterilises food by killing pathogens and other microbes.
(ii) It has a pH of 2, which is perfect for entyaus such as pepsin to break down proteins as effectively as possible.
(iii) Helps emulsify food (digestion of protein and stimulates the pancreas to produce digestive enzymes and bile) and protects against harmful bacteria.
(b) Breakdown of large globule fats into smaller fats droplets is known as emulsification.
(c) Trypsin is the enzyme secreted by the pancreas which aids in digestion of proteins.
Question 34: In human alimentary canal, name the site of complete digestion of various components of food. Explain the process of digestion.
Answer: In small intestine, complete digestion of various components of food take place. The process of digestion of food in mouth, stomach and small intestine in human body are as follows:
Mouth: Digestion of food begins in the mouth. Saliva present in mouth contains a digestive enzyme, called salivary amylase, maltose and dextrin, which breaks down starch into sugar.
Stomach: Stomach stores and mixes the food received from the oesophagus with gastric juices. The main components of gastric juice are hydrochloric acid, mucus and pepsinogen. Hydrochloric acid dissolves bits of food and creates an acidic medium. In this medium, pepsinogen is converted to pepsin which is a protein-digesting enzyme. Mucus protects the inner lining of the stomach from the action of HCl.
Small Intestine: Small intestine is the site of complete digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Small intestine produces intestinal juice from the glands present in its wall. The intestinal juice helps in further digestion of food. Small intestine also obtains digestive juices from liver and pancreas. The liver produces bile juice that causes emulsification of fats and the pancreas produces pancreatic juice for digesting proteins and emulsified fats. This digested food is finally absorbed through the intestinal walls.
Question 35: (a) “The breathing cycle is rhythmic whereas exchange of gases is a continuous process”. Justify this statement.
(b) What happens if conducting tubes of circulatory system develops a leak? State in brief, how could this be avoided?
(c) How opening and closing of stomata takes place?
Answer: (a) The breathing cycle involves inhalation and exhalation of air due to alternate expansion and contraction of thoracic cavity. Thus, it is a rhythmic process. But exchange of gases is a continuous process as it takes place between the blood and each and every cell, by diffusion.
(b) The circulatory system will become inefficient if it develops a leak. This could be avoided by maintaining a normal blood pressure.
(c) When water flows into the guard cells, the guard cells swell and the stomatal pore opens up. When water moves out the guard cells shrinks and the stomatal pore closes.
Question 36: Describe in brief the function of kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra.
Answer: The Kidneys filter the blood and concentrate the filtrate to make urine. They also help regulate blood pressure. Ureters transport the urine to the urinary bladder. Urinary bladder is like a holding tank for the urine until it’s ready to be excreted. Urethra is the tube that connects the urinary bladder to the outside of the body for excretion.
Question 37: Explain the process of breakdown of glucose in a cell (ii) in the absence of oxygen.
Answer: The process of breakdown of glucose in a cell are as follows:
The first step in the breakdown of glucose both in presence of O 2 and in absence of O 2 is same. In this step, glucose is broken down into pyruvate.
Second step which involves further breakdown of private into simple compounds can take place in two different ways:
(i) In presence of O 2 : In the presence of O 2 , private is converted into CO 2 and water. Energy released during aerobic respiration is much greater than that released during an anaerobic respiration.
(ii) In absence of O 2 : In the absence of O 2 in yeast, pyruvate is converted into ethanol and CO 2 and the process is called fermentation. In absence of O 2 , in our muscle cells, pyruvate is converted into lactic acid. The build up of lactic acid in muscle cells causes cramps.
Question 38: (a)Explain how does the exchange of gases occur in plants across the surface of stems, roots and leaves. (b) How are water and minerals transported in plants?
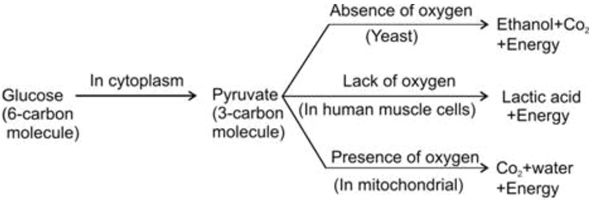
(a) In plants there are tiny pores called stomata on leaves and lenticels in stem which facilitate the exchange of gases. Carbon dioxide is taken in and oxygen given out {during photosynthesis} and vice versa during respiration.
(b) Water and minerals are transported within the plant by the Xylem vessels (mainly in an upward direction); these are part of the vascular system which also includes Phloem vessels. Phloem transports the products of photosynthesis within the plant, to all parts like the stem, roots, fruits etc. in all directions.
Question 39: State in brief the function of: 1. renal artery 2. kidney 3. ureter 4. urinary bladder
Answer: Renal artery: The renal artery carries blood to the kidneys from the abdominal aorta. This blood comes directly from the heart and is sent to the-kidneys to be filtered before it passes through the rest of the body. Up to one-third of the total cardiac output per heartbeat is sent to the renal arteries to be filtered by the kidneys. Each kidney has one renal artery that supplies it with blood. The filtered blood then can exit the renal vein.
Kidney: The kidneys perform the essential function of removing waste products from the blood and regulating the water fluid levels. The kidneys regulate the body’s fluid volume, mineral composition and acidity by excreting and reabsorbing water and inorganic electrolytes.
Ureter: The ureter is a tube that carries urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder.’ There are two ureters, one attached to each kidney.
Urinary bladder: The urinary bladder is an expandable muscular sac that stores urine before it is excreted out of the body through the urethra.
Question 40: How is urine produced and eliminated?
Answer: Blood from the heart comes into the kidneys afferent and efferent arteriole from the renal arteries where it enters about 2-3 million nephrons per kidney. Then, it goes through the glomerulus a tuft or bunch of blood capillaries and get rid of some of the unwanted substances like urea, uric acid, creatinine in the blood and then continues through the renal tubules. The loop of Henley, reabsorb certain substances such as water (actually if body is dehydrated, body will send antidiuretic hormone (ADH) to kidneys to prevent extra water from going into urine and thus saving water for body and get rid of anything else that isn’t wanted, then the urine goes through ureters to bladder and then to urethra where it is excreted out of body as urine.
Question 41: (a) Draw a diagram to show open stomatal pore and label on it: (i) guard cells (ii) chloroplast (b) State two functions of stomata. (c) How do guard cells regulate the opening and closing of stomatal pore?
Answer: (a)
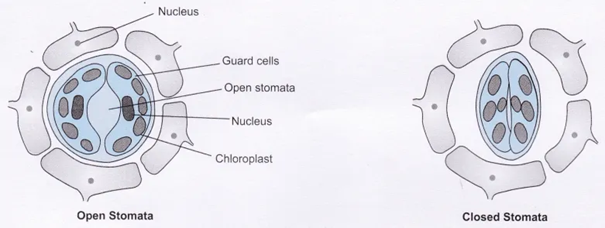
(b) Two functions of stomata are: (i) Exchange of gases between the plant and the atmosphere takes place through stomata. (ii)Transpiration in plants takes place through stomata.
(c) Opening and Closing of Stomatal Pore: The opening and closing of the pore is a function of the guard cells. The guard cells swell when water flows into them causing the stomatal pore to open. Similarly, the pore closes if the guard cells shrink. As large amount of water is lost through these stomata, the plant closes these pores when it does not require carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
Question 42: Why is the rate of breathing in aquatic organisms much faster than in terrestrial organisms?
Answer: Quantity of dissolved oxygen is fairly low in water as compared to the amount of oxygen in air. Aquatic organisms therefore have to breath faster than terrestrial organisms to absorb the required amount of oxygen from the water.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 6 - Life Processes 2024-25

CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter-6 Important Questions with Answers - Free PDF Download
Class 10 examination is the most crucial and significant exam in a student’s life. The marks secured in Class 10th Board exams are an essential attribute that decides their future study course. It is during this year in school that a student chooses his/her career. Losing marks is not an option for a student in 10th Board exams. Science is one of the most important subjects of Class 10 CBSE exam . In this subject, the students learn about various activities that occur in our surroundings. It also teaches the students about human beings, plants and animals. Science can be pretty tough for the students to understand. A brief comprehension of the chapters and important questions and answers can help you get a complete knowledge of the subject. Vedantu brings you the Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6, which are compressed in a PDF format. The students can refer to these questions during the preparation of exams. Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials for students. Maths Students who are looking for the better solutions, they can download Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Download CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions 2024-25 PDF
Also, check CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions for other chapters:

Related Chapters
Study Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 – Life Processes
Very Short Answer Questions (1 Mark)
1. Amoeba shows following kind of nutrition –
autotrophic
saprotrophic
Ans: (b) holozoic
2. The process by which blood is cleared of metabolic wastes in case of kidney failure is called
artificial kidney
transplantation
Ans: b) dialysis
3. Woody plants carry gaseous exchange through
epidermal cells.
Ans: (c) Lenticels.
4. Where does digestion of starch begin in human body?
Ans: The digestion of starch begins in the human body in the mouth.
5. Give one example of each of saprophytic and parasitic nutrition.
Ans: One example each of saprophytic and parasitic nutrition is as follows:
Parasitic Nutrition – Plasmodium (Protozoa)
Saprophytic Nutrition – fungi.
6. Which of the following statements about the autographs is incorrect?
They store carbohydrates in the form of starch.
They constitute the first trophy level in food chains.
They convert $\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ and water into carbohydrates in the absence of sunlight
They synthesize carbohydrates from $\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ and water in the presence of sunlight & chlorophyll.
Ans: c) They convert $C{{O}_{2}}$ and water into carbohydrates in the absence of sunlight.
7. Which of these is not a part of the small intestine?
Rectum
Ans: d) Rectum is not a part of the small intestine.
8. During contraction of the heart, what prevents backflow of blood?
Thin walls of atria
Thick muscular walls of ventricles
Valves in heart
All of the above
Ans: c) Valves in heart
9. Name excretory organs in amoeba and earthworm.
Ans: The excretory organ in amoeba and earthworms are as follows:
Amoeba – Cell membrane, Earthworm – Outer covering (skin)
10. Name the plant tissue through which water and minerals are transported in plants.
Ans: The plant tissue through which water and minerals are transported in plants is Xylem.
11. Trachea do not collapse when there is not much air because they are –
thick and muscular
having cartilaginous rings
have valves
supported by the larynx.
Ans: b) having cartilaginous rings.
12. Which one of the following blood vessels contains only deoxygenated blood?
pulmonary vein
pulmonary artery
capillaries
Ans: b) Pulmonary artery
13. The autotrophic mode of nutrition requires –
Chlorophyll
Carbon – dioxide & water
Ans: d) All of the above
14. Name the red pigment carrying oxygen in the blood.
Ans: The red pigment carrying oxygen in blood Haemoglobin.
15. Name the hormone which is responsible for the reabsorption of water in nephrons.
Ans: The hormone which is responsible for reabsorption of water in nephrons Antidiuretic – hormone (ADH) or vasopressin.
16. When air is blown from the mouth into a test tube containing lime water, the lime water turned milky due to the presence of –
b) nitrogen
c) water vapours
d) carbon – dioxide
Ans: d) carbon – dioxide
17. In which of the following group/ groups of animals, heart does not pump oxygenated blood to different parts of the body?
Pisces only
Amphibians only
Amphibians and reptiles only
Pisces and amphibians
Ans: The following group/ groups of animals, in which the heart does not pump oxygenated blood to different parts of the body a) Pisces only.
18. The filtration units of kidneys are called –
Ans: d) nephrons
19. What is the mode of nutrition in fungi and plasmodium?
Ans: The mode of nutrition in fungi and plasmodium are as following:
Fungi – Saprophytic
Plasmodium – parasitic.
20. Which of them contain less nitrogenous waste – renal vein or the renal artery?
Ans: Renal veins contain less nitrogenous waste.
21. Amoeba captures food with the help of –
pseudopodia
Ans: c) pseudopodia.
22. Which of the following is most appropriate for aerobic respiration?
$\text{Glucose}\xrightarrow{\text{mitochondria}}\text{pyruvate}\xrightarrow{\text{cytoplasm}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O+Energy}$
$\text{Glucose}\xrightarrow{\text{cytoplasm}}\text{pyruvate}\xrightarrow{\text{mitochondria}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O+Energy}$
$\text{Glucose}\xrightarrow{\text{cytoplasm}}\text{pyruvate+Energy}\xrightarrow{\text{mitochondria}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}$
$\text{Glucose}\xrightarrow{\text{cytoplasm}}\text{pyruvate+Energy}\xrightarrow{\text{mitochondria}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O+Energy}$
Ans: (b) $\text{Glucose}\xrightarrow{cytoplasm}pyruvate\xrightarrow{mitochondria}C{{O}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O+Energy$.
23. Name the part of the alimentary canal that receives bile from the liver.
Small intestine
Large intestine
Ans: The part of the alimentary canal that receives bile from the liver c) Small Intestine.
24. What is glycolysis?
Ans: Breakdown of Glucose into pyruvate is known as glycolysis.
25. Name the largest artery of the body.
Ans: The largest artery of the body is Aorta.
26. The kidneys in human beings are parts of the system for
respiration
transpiration
Ans: The kidneys in human beings are parts of the system for (c) excretion.
27. The xylem in plants are responsible for
transport of water
transport of food
transport of amino acids
transport of oxygen
Ans: (a) transport of water.
28. The autotrophic mode of nutrition requires
carbon dioxide and water
chlorophyll
all of the above
Ans: The autotrophic mode of nutrition requires (d) all of the above.
29. The breakdown of pyruvate to give carbon dioxide, water and energy takes place in
mitochondria
chloroplast
Ans: The breakdown of pyruvate to give carbon dioxide, water and energy takes place in (b) mitochondria.
30. Food moves down the gut by peristalsis. Which region of the brain controls peristalsis.
Ans: Food moves down the gut by peristalsis and the region of brain which controls peristalsis is the Medulla of the hindbrain.
31. Name the pigment present in plants, which can absorb solar energy.
Ans: The pigment present in plants, which can absorb solar energy is Chlorophyll.
32. Which of the four chambers of the human heart has the thickest muscular walls?
Ans: Right ventricle has the thickest muscular walls.
33. Which part of the visible spectrum is absorbed by chlorophyll pigments?
Ans: Blue and Red light are absorbed by chlorophyll pigments.
34. Name the cartilaginous flap which closes the glottis to check the entry of food into it during swallowing.
Ans: The cartilaginous flap which closes the glottis to check the entry of food into it during swallowing is Epiglottis.
35. Which equipment is used to facilitate breathing during serious breathing problems?
Ans: The equipment that is used to facilitate breathing during serious breathing problems is Ventilator.
36. What do you mean by double circulation of blood?
Ans: Double circulation of blood means that blood passes through the heart twice for each cycle of the body.
Short Answer Questions (2 Marks)
1. What is common for cuscuta, ticks and leeches?
Ans: Cuscuta, ticks, and leeches all feed in a parasitic manner, harming their hosts in the process.
2. What advantage over an aquatic organism does a terrestrial organism have with regard to obtaining oxygen for respiration?
Ans: Terrestrial organisms have evolved to be more efficient at absorbing oxygen from the air than watery organisms. –
Increased respiratory surface area.
Very fine and delicate surface for easy exchange of oxygen and carbon – dioxide.
Placement of respiratory surface within the body for protection.
The mechanism for transporting air into and out of the respiratory surface, which absorbs oxygen.
3. Differentiate between single and double circulation found in vertebrates.
Ans: The differences between single and double circulation found in vertebrates are:
4. Name the substrates for the following enzymes.
Ans: The substrates for the following enzymes are as shown below
5. What are the two stages in photosynthesis?
Ans: Two stages in photosynthesis are–
Light reaction – Photolysis of water is the process of breaking down water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen using light energy.
Dark reaction – Carbon dioxide ($C{{O}_{2}}$) is fixed and converted into glucose, a simple carbohydrate.
6. What is the difference between arteries & veins?
Ans: The differences between arteries & veins are:
7. What is villi? What are its functions?
Ans: Villi are projections in the small intestine's inner lining that resemble fingers. They enhance the surface area available for digested meal absorption in the small intestine.
8. What type of respiration takes place in human muscles during vigorous exercise and why?
Ans: Anaerobic respiration occurs in human muscles during severe exercise. During exercise, our energy requirement increases, so our striated muscles start respiring anaerobically in the lack of oxygen and produce ATP molecules.
9. How is opening and closing of stomata regulated?
Ans: Guard cells control the closure and opening of the stomata. The stomata open when the guard cells enlarge or become turgid owing to water ingress. Because of the loss of water, the guard cells shrink and the stomata close.
10. State two vital functions of the kidney.
Ans: Function of the kidney are –
It keeps the body's water balance in check.
It regulates calcium levels in the blood to keep bones healthy.
11. Differentiate between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Ans: The differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration are:
12. Meat is easier to digest as compared to grass. Why?
Ans: Meat is easier to digest because our digestive juices contain enzymes that can break down meat, but our bodies cannot break down cellulose, which is a major component of grass.
13. Differentiate between transport of materials in xylem & phloem.
Ans: The differences between transport of materials in xylem & phloem are:
14. What is the role of the glomerulus in the kidney?
Ans: Glomerulus, like Bowman's Capsule, is a collection of capillaries found in the cup. It gets blood from the renal artery, which is responsible for transporting excretory wastes from the body to the kidney. It removes from the liver water, salts, glucose, urea, nitrogen-containing protein end products, and yellow bile components.
15. Why is it essential to match the blood groups of donors and receiver person before arranging transfusion of blood?
Ans: Blood RBCs carry both antigen and antibodies. If the blood is not matched before transfusion, the recipient's blood produces antibodies against the donor blood and destroys blood cells, resulting in a blood shortage and death.
16. Why is it necessary to separate oxygenated & deoxygenated blood in mammals & birds?
Ans: The separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood allows the organism to receive adequate oxygen. This mechanism is beneficial to creatures who demand a lot of energy. Mammals and birds use oxygen to obtain energy in order to maintain a consistent body temperature.
17. Why are the walls of the trachea supported by cartilaginous rings?
Ans: The trachea is held together by cartilaginous rings that keep it from collapsing even when there isn't much air in it.
18. What are the raw materials for photosynthesis?
Ans: Raw materials for photosynthesis are –
Carbon – dioxide
Chlorophyll and Sunlight
19. What is the role of the diaphragm during inhalation and exhalation?
Ans: During inhalation and exhalation, the diaphragm changes form, increasing and decreasing the capacity of the thoracic cavity. This causes air to enter and exit the lungs.
20. What is the advantage of four chambers of heart?
Ans: A septum separates the right and left halves of the heart, preventing oxygenated and deoxygenated blood from mingling. This satisfies their constant need for energy to keep their body temperature steady. Their energy requirements are substantial, which are met effectively due to the non-mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
21. Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans?
Ans: As all cells in multicellular animals are not in direct contact with the environment, simple diffusion is insufficient to supply the needs of all body cells.
22. What criteria do we use to decide whether something is alive?
Ans: To be considered alive, all living organisms must have movement at the molecular level, as well as respiration and other life processes such as nutrition, respiration, transportation, and excretion.
23. What is the function of digestive enzymes?
Ans: Enzymes break down food's different complicated components into simple, soluble components that can be easily absorbed.
24. How are the lungs designed in human beings to maximize the area for exchange of gases?
Ans: Bronchioles end in alveoli, which are balloon-like structures in the lungs. Alveoli have a network of blood capillaries that increase the surface area available for gas exchange.
25. What is the role of saliva in the digestion of food?
Ans: Salivary amylase is an enzyme found in the mouth that breaks down starch, a complicated molecule, into glucose.
26. While eating you are advised not to talk. Why are you advised to do so?
Ans: We are urged to do so because food particles may enter the windpipe when eating, causing choking.
27. We say that movement is a characteristic of living organisms but we always don’t see visible movements in plants. Comment.
Ans: Plants do not always show obvious movement. It doesn't necessarily imply that they aren't living. In their bodies, molecular movements take place.
28. If a person is working on a treadmill in a gymnasium, will it affect his rate of breathing? How?
Ans: Yes, it will have an impact on his breathing rate. To satisfy the increased demand for energy, the rate of breathing will increase in order to supply more oxygen.
29. If you compare your rate of breathing by feeling your chest movement with the number of times a fish opens and closes its mouth. Which will be higher and way?
Ans: As the amount of dissolved oxygen in water is relatively low compared to the amount of oxygen in the air, the number of times a fish opens and closes its mouth will be higher. As a result, aquatic organisms breathe at a significantly higher rate than terrestrial organisms.
30. Mucus is not used for churning the food or digesting it. Then why is it secreted in the stomach?
Ans: In order to protect the stomach's inner lining from being harmed by HCI, mucus is released. Excessive HCI secretion can harm the lining of the stomach and cause a peptic ulcer.
31. In the process of Photosynthesis food A is prepared which gets converted into food B. What are A and B? Why is A converted to B?
Ans: Glucose is food A, whereas starch is food B. As B is an insoluble carbohydrate, it is transformed to A. It is more compact, making it better for storage.
32. When we are asleep we are not performing any activity while our life processes are going on. Why?
Ans: “The maintenance functions of living organisms must go on even when they are not doing anything particular.” That is why the life processes are going on even while we are asleep or not performing any activity.
33. What will be the outcome if a farmer floods his field every day?
Ans: The oxygen contained in the interspaces of the soil will be replaced by water, affecting plant respiration.
34. Name the respiratory organs of:
(i) fish
Ans: The respiratory organs of fish are gills.
(ii) mosquito
Ans: The respiratory organs of mosquitoes are Trachea (air tubes).
(iii) earthworm.
Ans: The respiratory organs of earthworms are moist skin.
35. Due to the availability of less water, how does the plant cope with the lack of water in desert conditions?
Ans: To preserve moisture, they open their stomata at night and close them during the day.
36. After a vigorous exercise, you may experience cramps in your leg muscles. Why does this happen?
Ans: Leg muscle cramps are produced by a sudden build-up of lactic acid in our muscles following strenuous exercise.
37. What will happen if carbon monoxide combines with hemoglobin?
Ans: If haemoglobin binds firmly to carbon monoxide, oxygen will not be transported by blood, resulting in the organism's death.
38. Chloroplasts are called energy convertors. Explain.
Ans: As chloroplasts catch solar energy and convert it to chemical energy, they are known as energy converters.
39. Why is the rate of breathing much faster in aquatic organisms than those in terrestrial organisms?
Ans: Aquatic species get their oxygen from dissolved oxygen in the water. Water has a relatively low oxygen availability as compared to air. As a result, aquatic organisms must breathe more quickly than terrestrial organisms.
40. Why are glomeruli considered as dialysis bags?
Ans: The glomeruli's major filtering function is selective filtration. Small molecules comprising glucose, salts, urea, and liquid senim are filtered. Etc. Proteins and other big molecules remain in the blood. As a result, the glomeruli of the kidneys serve as dialysis bags.
41. Autotrophs synthesize food for the living world. Justify this statement in one sentence only by interconnecting autotrophs and heterotrophs.
Ans: The food producers are autotrophs, and all heterotrophs directly or indirectly consume the food produced by the autotrophs.
42. Veins and arteries carry blood. Which of these carry blood?
Away from the heart?
Ans: Arteries carry blood away from the heart.
Back to the heart?
Ans: Veins carry blood back to the heart.
43. Which of the organs perform the following functions in humans?
Absorption of food.
Ans: Absorption of food takes place in the small intestine.
Absorption of water
Ans: Large intestine
44. Name the areas in a woody stem through which respiratory exchange of gases take place.
Ans: In a woody stem, the bark has lenticels for gaseous exchange.
45. Why doesn’t the lungs collapse even after forceful expiration?
Ans: Even after forced expiration to maximum capacity, residual volume refers to the amount of air that remains in the lungs following forceful expiration. As a result, even after a strong expiration, the lungs do not collapse.
46. “If there were no algae there would be no fish in the sea”. Comment.
Ans: Photosynthesis results in the production of ${{O}_{2}}$ by algae. The oxygen used by fish in the sea is used for breathing. There would have been no oxygen created if algae had not existed. As a result, fish may have died.
47. Why is the process of diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirement of human beings?
Ans: For bigger multicellular creatures like humans, the diffusion method is insufficient to transport ${{O}_{2}}$ to all areas of the body. As a result, the respiratory pigment haemoglobin absorbs oxygen from the air and transports it throughout our bodies via blood.
Long Answer Questions (3 Marks)
1. What are the functions of lymph in our body?
Ans: Functions of lymph are-
a) It removes tissue fluid from the interstitial region and restores it to the bloodstream.
b) Through tissue fluid, it gathers carbon dioxide, waste products, and metabolites from tissues.
c) Lymph contains lymphocytes (WBCs), which aid in the body's immunity and fight against invading invaders.
2. How is haemoglobin associated with respiration explained?
Ans: The respiratory pigment haemoglobin is responsible for transporting oxygen and carbon dioxide. Haemoglobin is a crimson pigment with a strong oxygen affinity. Oxyhemoglobin transports oxygen from the lungs to the cells of the body. Carbon dioxide is carried to the lungs by carbamino – haemoglobin from the bodily cells.
3. What are the modes of excretion in plants?
Ans: Modes of excretion in plants are –
The plants get rid of excess water by transpiration.
Plants' only primary gas excretory product is oxygen. Plants emit it into the environment by diffusion. Organic wastes of plants are stored within dead permanent tissues such as wood or within leaves or bark which are periodically removed.
The plants also excrete some waste substances into the soil around them.
Plant waste products are accumulated in cellular vacuoles in large quantities.
4. Give an experiment to prove the essentiality of light for photosynthesis.
Ans: An experiment to prove the essentiality of light for photosynthesis is as shown below:
a) Destarched the plant by leaving it in dart for 48 – 72 hours.
b) Now place strips of black paper or metal foil over destarched leaves and expose them to light for several hours.
5. What is “translocation”? Why it is essential for plants.
Ans: The term "translocation" refers to the movement of organic solutes within plants. It is required since all cells require sustenance to perform their essential tasks. It affects the storage organs of roots, fruits, seeds, and developing organs in both upward and downward directions.
6. How respiration takes place in plants?
Ans: There are three modes for the exchange of gases in plants –
a) Some little plants can exchange gaseous matter by simply diffusing it throughout their entire surface.
b) Stomata on the leaves and green stems of large flowering plants exchange gases.
c) Exchange occurs in woody stems through fractures in the bark or lenticels.
7. How is transpiration pull responsible for upward movement of water?
Ans: Transpiration is the process through which leaves lose water in the form of water vapours through stomata. Continuous transpiration causes a suction in the xylem elements' water column, which reaches the roots. This is known as transpiration pull. The water column of the plant is drawn up from the bottom to the top due to transpiration.
8. Discuss the major steps involved in the process of nutrition in human beings.
Ans: Major steps involved in human nutrition are –
a) Ingestion – Food is taken in through the mouth. Humans have a holozoic feeding mode. Solid particles are swallowed by them.
b) Digestion – In the alimentary canal, mechanical and chemical processes are used to break down complex dietary materials into simpler ones.
c) Absorption – The little finger-like projections, or villi, of the small intestine absorb digested food.
d) Assimilation – Food is absorbed and transported to all cells via blood, where it is used for energy, growth, and development.
e) Excretion – Food from the small intestine passes through to the big intestine, where it is ejected out by Anus.
9. Discuss the mode of nutrition in amoeba.
Ans: The steps of Nutrition in amoeba are–
a) Formation of pseudopodia – When an amoeba comes into contact with a food particle, it creates pseudopodia that encase the food particle.
b) Ingestion – Ingestion occurs when the terminals of pseudopodia merge with one other, forming a food vacuole with a variable amount of food particles and water.
c) Digestion – The vacuoles are encircled by lysosomes, which fuse with the vacuole and consume the food particles inside.
d) Exocytosis – The food vacuole passes the soluble products of digestion into the appropriate cytoplasm. Exocytosis is the process through which the remaining undigested items are passed out of the body.
10. With the help of a labelled diagram, discuss the structure of the cross–section of leaf.
Ans: Leaf has two parts:
Epidermis – The epidermis is the cell's outermost layer. Stomata are tiny pores that connect cells in the lower epidermis.
Mesophyll – Mesophyll refers to the chloroplast-containing parenchyma cells. Palisade and spongy parenchyma are the two types.
11. What do you mean by ‘lymph’? Mention its function.
Ans: Lymph- Tissue fluid, or lymph, is the fluid that fills the gaps between the cells in the tissues.
Functions of lymph:
It returns tissue fluid from the interstitial spaces into the blood.
Lacteals, which are lymph capillaries found in intestinal villi, aid in fat absorption.
Through tissue fluid, it gathers carbon dioxide, waste products, and metabolites from tissues.
12. How are lungs designed in human beings to maximize the area of exchange of gases?
Ans: Lungs have evolved various characteristics to allow for effective gas exchange. The modifications are as follows:
Increased surface area
Very fine and delicate surface for easy exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide
13. Dark reactions of photosynthesis do not need light. Do plants undergo dark reactions at night?
Ans: The term "dark reaction" does not refer to a reaction that occurs in the absence of light, such as at night. In fact, these reactions are independent of light energy and occur at the same time as light reactions.
14. Differentiate inhalation and exhalation.
Ans: The differences between inhalation and exhalation are:
15. With the help of a diagram, show pulmonary circulation in man.
Ans: With the help of a diagram, pulmonary circulation in man can be represented as shown below:
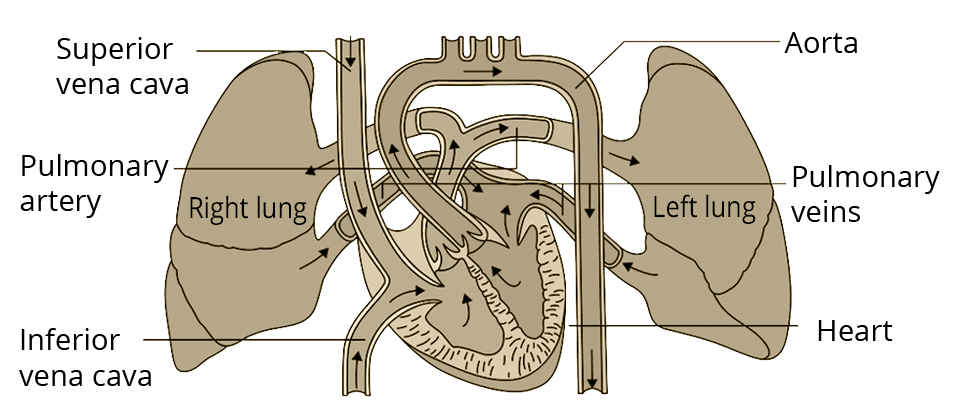
16. What are the functions of the human respiratory system?
Ans: The functions of the human respiratory system are:
(i). The cellular respiration function requires gaseous exchange.
(ii). The vocal cords produce sound.
(iii). Abdominal compression assists with urination, face passing, and birthing.
(iv). Laughing and sneezing to clean the respiratory surface on their own.
17. What is the role of skin, lungs and intestine in the process of excretion in man?
Ans: The role of skin, lungs and intestine in the process of excretion in man are:
Skin – Skin excrete excess salts and water in the form of sweat.
Lungs – Exhalation causes carbon dioxide to be expelled from the lungs.
Intestine – Intestine throw out undigested food in the form of faeces through the anus
18. Explain the structure of chloroplast.
Ans: The structure of chloroplast can be explained using the diagram as shown below:
(Image will be uploaded soon)
19. Why and how does water enter continuously into the root xylem of plants?
Ans: Water and minerals are transported to the plant body via xylem. Root hairs are hairs that grow on a plant's roots. The root hairs come into close touch with the water film that forms between soil particles. Diffusion allows water and minerals to penetrate the root hair. The water and minerals are taken by the root hair from the soil move via the epidermis, root cortex, endodermis, and root xylem by osmosis from cell to cell. The plant's xylem vessels in the root are connected to the xylem vessels in the stem. As a result, dissolved mineral-containing water passes through the root xylem vessels and into the stem xylem vessels. The stem's xylem vessels branch out into the plant's leaves. As a result, the water and minerals supplied by the xylem vessels in the stem reach the leaves via the branched xylem vessels that enter each area of the leaf from the petiole. As a result, water and minerals from the earth reach the plants' leaves via the root and stem. The suction created by the evaporation of water molecules from the cells of a leaf pulls water from the xylem cells of roots. Transpiration is the loss of water from the aerial portions of plants in the form of vapour.
20. What is the role of following in human digestive system –
Ans: Mucus – It shields the stomach's inner life from HCl.
Bicarbonate
Ans: Bicarbonate – It alkalizes the acidic meal so that pancreatic enzymes may work on it.
Ans: Trypsin – It digest proteins into amino acids.
21. What are outside raw materials used for by an organism?
Ans: The following are examples of external raw materials used by an organism:
22. What processes would you consider essential for maintaining life?
Ans: The processes essential for maintaining life are:
Respiration
Transportation
23. What is the difference between autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition?
Ans: The difference between autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition is:
24. Where do plants get each of the raw materials required for photosynthesis?
Ans: Plants do get each of the raw materials required for photosynthesis from:
a) Carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
b) Light from Sun
c) Water from Soil
d) Chlorophyll from chloroplast of green plants.
25. What is the role of acids in our stomach?
Ans: HCl plays the following role in our stomach:
Make the medium acidic to allow the pepsin enzyme to work.
Kills the harmful bacteria present in food
Prevents fermentation of food
26. How is small intestine designed to absorb digested?
Ans: The villi, which are finger-like projections on the inner lining of the small intestine, enhance the surface area available for absorption. The villi are densely packed with blood arteries that convey the absorbed food to all of the body's cells. It is used to obtain energy and repair damaged tissues.
27. What advantage over an aquatic organism does a terrestrial organism have with regard to obtaining oxygen for respiration?
Ans: In comparison to aquatic organisms, terrestrial organisms breathe at a slower rate. This is owing to the fact that there is less oxygen in water than there is in air, thus aquatic species breathe at a faster rate.
28. What are different ways in which glucose is oxidized to provide energy in various organisms?
Ans: The pathways of break-down of glucose in various organisms are as below:
29. How is oxygen and carbon dioxide transported in human beings?
Ans: In humans, the pigment haemoglobin is found in RBC and has a high affinity for oxygen. It absorbs oxygen from the air in the lungs and transports it to tissues that are oxygen-deficient. In blood plasma, some oxygen is carried in a dissolved condition. Because carbon dioxide is more soluble in water than oxygen, it is usually carried through human blood as a dissolved form.
30. What are the components of the transport system in human beings? What are the functions of these components?
Ans: The components of the human transport system include:
Heart- receives and pumps the blood.
Arteries- carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to various organs:
Veins- Bring back blood to the heart.
Capillaries- exchange of various materials and gases between blood and tissues.
31. Why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds?
Ans: The right and left sides of the heart are separated to prevent oxygenated and deoxygenated blood from mingling. This separation allows for a very effective oxygen supply to the organism. This is important in creatures with high energy needs, such as birds and mammals, that use energy to maintain their body temperature all of the time.
32. What are the components of the transport system in highly organized plants?
Ans: The xylem and phloem transport systems are found in higher plants. Water and minerals are transported from the root to different parts of the plant via vessels and tracheids in xylems. Food is transported from leaves to storage organs and other sections of the plant by phloem, which is made up of sieve tubes and companion cells.
33. How are water and minerals transported in plants?
Ans: Plants transport water and minerals through the xylem, which is made up of tracheids and vessels. Osmosis transports water and minerals received by root hairs to the xylem tissues of the root. Water travels from the root xylem to the stem xylem and then to the leaves.
34. How is food transported in plants?
Ans: Plants carry food via the phloem, which is made up of sieve tubes, sieve cells, and companion cells. Food is prepared in leaves and transferred to the phloem of the leaves in a soluble form. Food is actively transported to all other areas of the plant.
35. What are the methods used by plants to get rid of excretory products?
Ans: The methods used by plants to get rid of excretory products are:
(i) During respiration, plants produce carbon dioxide as a waste product, and photosynthesis produces oxygen as a waste product.
Excess water is removed through transpiration.
Some waste products like gums and resins are stored in older xylem tissue.
36. How is the amount of urine produced regulated?
Ans: The amount of urine produced is determined by the amount of excess water in the body and the amount of water-soluble waste to be expelled. When the amount of water and dissolved waste in a boy is high, the amount of urine generated is high, and when the amount of wastes is low, the amount of urine produced is low.
37. How are fats digested in our bodies? Where does this process take place?
Ans: The small intestine is where lipids are digested. The fats that enter the intestine take the form of big globules. These huge globules are broken down into smaller globules by bile juice. Following that, the fat-digesting enzyme lipase, which is found in pancreatic and intestinal juice, turns it into fatty acids and glycerol.
38. What are the necessary conditions for autotrophic nutrition and what are its by-products?
Ans: Conditions necessary for autotrophic nutrition are:
Carbon dioxide
By-products are:
39. What are the differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration? Name some organisms that use anaerobic mode of respiration.
Yeast, bacteria, and some internal parasites, such as tapeworms, use anaerobic respiration.
40. How are the alveoli designed to maximize the exchange of gases?
Ans: The nostril, larynx, nasal chamber, pharynx, trachea, epiglottis, alveoli, bronchioles, bronchi, and lungs make up the human respiratory tract. Through millions of small sacs known as alveoli, oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide waste within the lungs. Inhaled oxygen diffuses into the lungs' capillaries, binds to haemoglobin, and is pumped into the bloodstream. Exhalation allows the carbon dioxide from the blood to diffuse through the alveoli and be evacuated. To promote the exchange of gases between blood and the air-filled alveoli, the alveoli have thin walls and are richly supplied with a network of blood veins. They have a balloon-like shape to maximise gas exchange surface area. The alveolar walls are folded and have a significant surface area. It has a large network of blood arteries that serve as a surface for gas exchange.
41. What would be the consequence of a deficiency of haemoglobin in our bodies?
Ans: Haemoglobin is a pigment found in red blood cells. It has a strong preference for oxygen. It transports oxygen from the lungs to other tissues that are oxygen-deficient. The presence of less haemoglobin reduces the oxygen supply to tissues. A person with low haemoglobin levels will become exhausted quickly and seem pale.
42. What are the differences between the transport of materials in xylem and phloem?
Ans: The differences between the transport of materials in xylem and phloem are:
43. Compare the functioning of alveoli in the lungs and nephron in the kidneys with respect to their structure and functioning.
Ans: Comparison between alveoli and nephron:
44. Leaves of a healthy potted plant were coated with petroleum jelly. How will it affect the plant? State two reasons.
Ans: The plant will not remain healthy for long due to the following reasons:
There will be no transpiration.
There will be no exchange of gases which will affect the rate of photosynthesis.
45. How does respiration in plants differ from that in animals?
Ans: In plants, all portions such as the root, stem, and leaves do individual respiration, but in animals, either the general body surface or particular organs such as the skin, gills, and lungs perform respiration. Plants have a significantly slower rate of respiration than animals. Gases are not transported from one section of the plant to another way they are in animals.
46. How does respiration in plants differ from that in animals?
Ans: After eating sugary food (chocolates and sweets), acid is generated in the mouth. The pH of the mouth is lowered by this acid. When the pH of the acid generated in the mouth falls below, tooth decay begins. This is because the acid develops strong enough to attack and damage the enamel of our teeth.
47. Name the cartilaginous flap which closes the glottis to check the entry of food into it during swallowing.
Ans: It's possible that the tissue that became clogged was the xylem. Water and minerals taken by roots from the soil are carried to the leaves and other parts of the plant via the xylem. As a result, if the xylem is obstructed, the leaves will be deprived of nutrients and will wilt.
48. How does respiration in plants differ from that in animals?
49. Write one feature which is common to each of the following pairs of the term/organs.
glycogen and starch
Ans: The feature that is common to the following pair is Carbohydrate (food).
chlorophyll and haemoglobin
Ans: The feature that is common to the following pair is Pigments.
gills and lungs
Ans: The feature that is common to the following pair is Respiratory organs.
arteries and veins.
Ans: The feature that is common to the following pair is Blood vessels.
50. A certain tissue in a green plant somehow gets blocked and the leaves wilted. What was the tissue that got blocked?
51. Write the functions of the following in the digestive process:
Ans: Bile: It is secreted by the gallbladder and it emulsifies & it into the smaller droplets for their easy digestion.
Bicarbonate secreted by the duodenal wall.
Ans: It provides an alkaline medium in the duodenum which is needed for the action of pancreatic enzymes of different food components for their digestion.
Pancreatic amylase.
Ans: Pancreatic amylase enzyme digests starch and changes it into maltose.
52. The two openings of the pharynx, one leading to the trachea and the other leading to oesophagus, lie very close to each other. Yet food we swallow normally does not enter into our trachea. Why?
Ans: The food does not enter the trachea because the aperture leading to the trachea (glottis) is covered by a cartilaginous flap termed the epiglottis during swallowing, leaving the food with no other option except to go down the oesophagus.
53. How would it affect the digestion of proteins and carbohydrates in the duodenum of man if there is a blockade in the pancreatic duct?
Ans: The pancreatic juice is secreted by the pancreas and enters the duodenum. Pancreatic amylase and trypsin are enzymes that aid in the digestion of carbohydrates and proteins. As a result, if there is a blockade, carbohydrate and protein digestion is impaired.
Long Answer Questions (5 Marks)
1. What is ‘clotting of blood?’ Write a flow chart showing major events taking place in clotting of blood?
Ans: Formation of a clot at the site of injury to stop bleeding is known as ‘clotting of blood.’ Steps for clotting of blood
2. With the help of a labelled diagram of the human excretory system, Mention its important part and explain them.
Ans: A labelled diagram of the human excretory system mentioning its important part with a proper explanation is as displayed below:
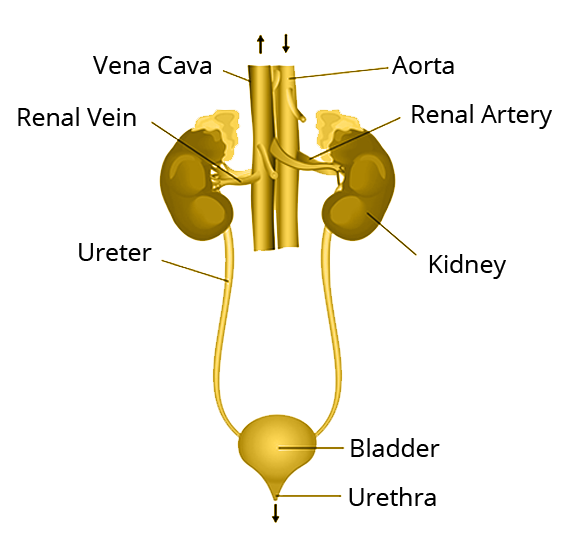
1) Kidney – It is the excretory system's functional unit. About a million small coiled channels called nephrons make up each kidney. The basic filtration unit in the kidneys is the nephron. The glomerulus, Bowman's capsule, and convoluted tubule are the components.
2) Ureter – Wastes come out of the kidney into the ureter.
3) Urinary Bladder – The ureter pours its contents into a muscular sac called the urinary bladder.
4) Urethra – Urine flows from the bladder to the outside through the urethra.
(i) Draw a well-labelled diagram of the human digestive system
Ans: A well labelled diagram of the human digestive system is as shown below:
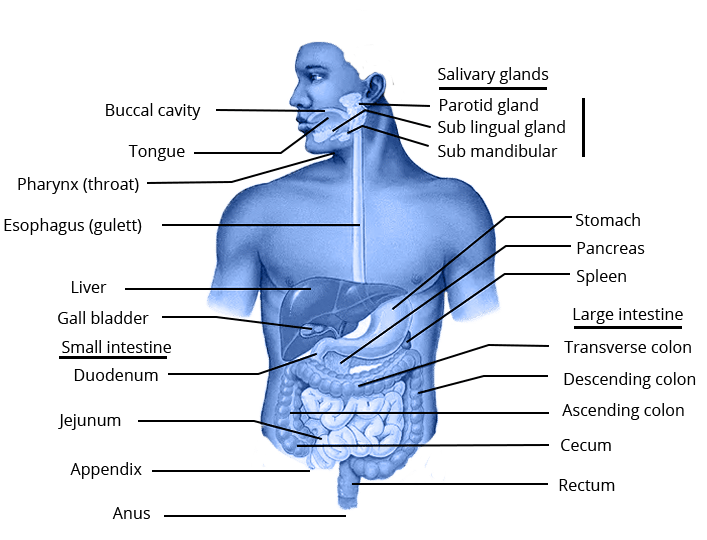
(ii) Describe the role of following in digestion.
Ans: Bile – emulsification of fats
Salivary amylase
Ans: Salivary amylase – digest starch in the mouth
Ans: HCl – Activate pepsinogen by making medium acidic in stomata.
4. With the help of a labelled diagram, Discuss the mechanism of respiration in human beings.
Ans: Mechanism of Respiration – It occurs in the following steps
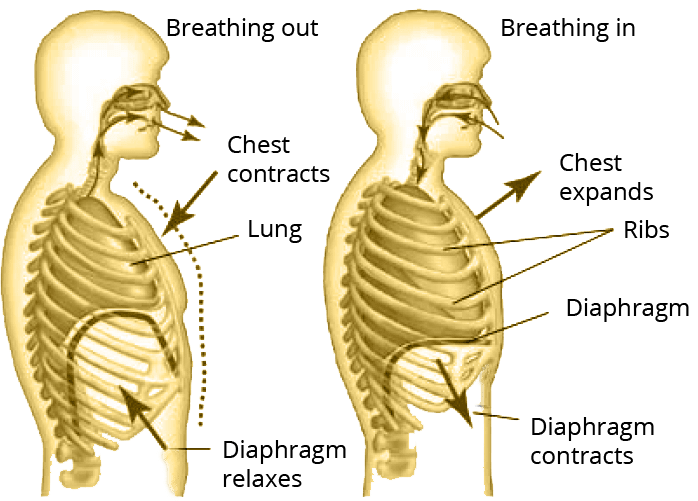
Breathing – Taking in oxygen and expelling carbon – dioxide out is called breathing. It involves the following steps –
Inhalation – It is consuming oxygen. It happens when the muscles linked to the ribcage contract. The ribs are lifted and the diaphragm is flattened, increasing the volume of the thoracic cavity. As a result, the pressure inside the thoracic cavity drops, allowing air to flow into the lungs.
Exhalation – It is the process of releasing carbon dioxide. It happens when the muscles linked to the ribs relax and the diaphragm is formed. This reduces the volume of the thoracic cavity, lowers air pressure, and expels air from the lungs.
b) Exchange of Gases – It takes place between the alveoli of the lungs and surrounding blood capillaries.
c) Transport of Gases in Blood – Haemoglobin is a protein that transports oxygen throughout the body. In the form of any haemoglobin, oxygen is transported from the lungs to the bodily cells.
d) Oxidation of Food – Break down of glucose molecules that produce energy. It occurs in chondria.
5. Describe an experiment to prove that carbon – dioxide is essential for the process of photosynthesis.
Ans: Experiment showing that carbon dioxide is essential for photosynthesis.
Take a potted plant with elongated leaves
Take an empty bottle and put a little amount of potassium hydroxide ($KOH$) in it.
Now cut the cork of the bottle into two parts and place it on one of the leaves of the potted plant in between the two parts of the cork.
Now put the bottle in the presence of sunlight for 72 – 96 hours.
Now test the leaf for the presence of starch.
6. Describe the structure and functioning of nephron.
Ans: Each nephron is a collection of blood capillaries with very thin walls. Each glomerulus (capillary cluster) in the kidney is linked to the cup-shaped Bowman's capsule, which collects the filtered urine. The blood is filtered by the nephron to eliminate nitrogenous waste.
They also absorb some vital substances from the filtrate, including glucose, amino acids, minerals, and a significant amount of water.
7. Describe double circulation in human beings. Why is it necessary?
Ans: During each cycle, blood passes through the heart twice in mammals and birds. Double circulation is the term for this situation.
Blood that has been deoxygenated enters the right auricle and then enters the right ventricle, where it is pushed to the lungs for oxygenation. It travels from the lungs to the left auricle, where it is oxygenated, and then to the left ventricle, where it is pumped to various regions of the body.
Such a circulatory system prevents the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, allowing for an effective supply of oxygen to the body
Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Important Questions - Free PDF Download
The Class 10 Science Ch 6 Important Questions PDF are the best guide for the students. The questions will help you have a good grip over the chapter. Chapter 6 Science Class 10 Important Questions are designed solely for providing the students with a proper understanding of the chapter. With these questions’ correct practice, you can achieve a better score and increase your overall percentage. Chapter 6 is based on the life processes inside the human body and the plant body. And it can be confusing to remember the different organs and their functions. To make the learning more comfortable, we have designed the Important Questions of Ch 6 Science Class 10 . The PDF of the important questions are available on Vedantu website for free.
Students of all calibre can refer to the Important Questions of Chapter 6 Science Class 10 . These questions are prepared as per the latest guidelines of CBSE board. It will clarify the doubts of the students and will also help them understand the pattern of examination.
Further if you want to brush up on the topics of CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 6 - Life Processes , read the table below, as it contains all the important topics and subtopics included in the chapter.
Important Questions For Class 10 Science Chapter 6, Life Processes
In chapter 6 of science, students will learn about the different set of life processes in the human body. The chapter also explains the different parts of the human organ system and its functions. By practising the important questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 , students can learn new things as well as get a detailed overview of the chapter. Some of the topics covered under the chapter are as follows:
Life Processes
Earth is the only planet in the solar system that supports life. We can distinguish between living organisms and other inanimate objects based on different parameters of life processes.
Life processes refer to those processes that help in the maintenance of life. The processes are responsible for keeping the body in a well and healthy manner. These processes help in the development of living organisms. The important life processes are nutrition, respiration, excretion and circulation. These processes work in a coordinated manner to assist in the sustenance of life. In unicellular organisms, the life processes are carried out by a single cell, whereas, in multicellular organisms, these processes are carried out by different organ systems.
Nutrition can be defined as the process of acquiring food and other minerals that are required for the nourishment and maintenance of living organisms. The modes through with a living organism can obtain nutrition are: Autotrophic and Heterotrophic.
Autotrophic Nutrition - It is a type of nutrition in which a living organism can nurture itself by preparing its food. This type of nutrition is generally found in green plants as they can prepare their food in the presence of sunlight and other chemicals.
Heterotrophic Nutrition - It is a type of nutrition in which a living organism derives its nourishment from other organisms. This mode of nutrition can be subdivided into three categories, Holozoic Nutrition, Saprophytic Nutrition, and Parasitic Nutrition.
Digestive System in Humans
Human beings can consume both plant products as well as animal products. And to digest the complex food particles, humans have a complex digestive system. The digestive system in humans consists of an alimentary canal along with other digestive organs that function together to provide proper nourishment to the body. The human digestive system performs four main functions: ingestion, digestion, absorption and assimilation.
The digestive system has various organs that function together to help in the digestion of food. Some of the important organs of the digestive system are: Alimentary canal, Mouth, Oesophagus, Stomach, Small intestine, Large Intestine, and there are sever digestive glands that produce digestive juices for the proper digestion of food, they are Salivary gland, Gastric glands, Liver, Gallbladder, and Pancreas.
Respiration System in Humans
Respiration can be defined as the exchange of gases that takes place in the human body. The process of respiration takes place differently in different organisms.
Respiration in cellular level in an organism means the burning of food for the generation of energy to support the life processes. At cellular level respiration can be divided into two subtypes: Aerobic respiration and Anaerobic respiration.
The human respiratory system is complex and consists of various organs. It consists of the nose, nasal cavities, pharynx, larynx, windpipe or trachea, then comes the lungs which enclose the bronchi, bronchioles and alveoli. The human respiratory system is complex as it processes breathing, exchange of gases, and cellular respiration.
Circulation System in Humans
For their survival, every living organism requires certain components such as oxygen, water and food. All these components are needed by every living cell in the human body. So, they need to be transported to various parts of the body. Transportation in humans occurs with the help of the circulatory system.
The circulatory system is a complex system consisting of the blood, blood vessels and heart. The circulatory system is mainly responsible for the effective transmission of food, nutrients, oxygen. It helps in the effective removal of carbon dioxide and other waste materials from the body.
The circulatory system in plants involves the transportation of food, water and necessary nutrients to different parts of the plant. The transportation in plants is done by two tissues, namely xylem and phloem.
Xylem is responsible for the effective transmission of water, and it transports water in an upward direction only. Phloem is responsible for the transmission of food and other nutrients in the plants. The food and nutrients move in both upward and downward direction in the phloem.
Excretory System in Humans
Excretion is an essential function performed by the human body. Excretion means the effective removal of waste materials and other unuseful substances from the human body.
The excretory system in humans is the most complex and well-developed. It consists of a pair of kidneys, a pair of ureters, an urinary bladder and a urethra. All the organs of the excretory system work in unison to remove all the unwanted waste and other unuseful substances from the human body.
The excretion in plants takes place through the stomatal opening. The excretion in plants is mostly in the form of gases. The excess water is removed from the plants through transpiration.
Chapter 6 Class 10 Science Important Questions
To provide you with a proper understanding of the questions, we at Vedantu have provided some Important Questions on Chapter 6 in this article. These Life Processes Class 10 Important Questions will help you understand the exam pattern as well as the type of questions you will face in the exams.
What is the meaning of Life Processes?
What is Nutrition? Explain its types.
What is the meaning of Photosynthesis?
How does amoeba obtain nutrition?
Explain the digestive system in brief.
What are the different types of teeth? Explain their functions.
Explain small intestine along with its function.
Explain the role of HCL in Digestion.
What is Respiration?
Explain the Physiology of respiration.
Explain the Circulatory system in humans.
How does the excretion of waste material take place in the human body?
Benefits of Class 10th Science Chapter 6 Important Questions
Here are some points that explain the benefits of these important questions.
The Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Important Questions will provide the students with a brief comprehension of the chapter and clear all sorts of doubts.
The Class 10 Science Ch 6 Important Questions are designed by experts at Vedantu, after thorough research. These questions have the highest probability of coming in the exams.
The questions come with proper answers and cover all the topics under the chapter.
These questions are prepared to keep in mind the latest guidelines of CBSE Board .
Chapter 6 Science Class 10 Important Questions are simplified and the most suitable study material for the students. The students can refer to these study materials for revisions and preparation of exams. The materials will provide them with a competitive edge and help them secure better grades.
Important Related Links for CBSE Class 10 Science

FAQs on Important Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 6 - Life Processes 2024-25
1. How many chapters are there in CBSE Class 10 science book?
Ans: There are a total of 7 units in CBSE Class 10 science solutions book. Below is the list of units:
Unit 1: Chemical Substances - Nature and Behaviour
Chemical reactions
Acids, bases and salts
Metals and non-metals
Carbon and compounds
Periodic classification of elements
Unit 2: World of Living
Life processes
Control and coordination in animals and plants
How do organisms reproduce
Control and coordination in animals
Reproduction
Heredity and evolution
Unit 3: Natural Phenomenon
Refraction of light
Reflection of light
The functioning of the human eye
Unit 4: Effects of Current
Effects of current
Magnetic effects of current
Unit 5: Natural Resources
Sources of Energy
Our environment
management of natural resources
Unit 6: How things work
Unit 7: Moving Things, People and Idea
2. Give a brief description of evolution.
Ans: Evolution:
In this part of Class 10 Science Chapter 9, you will not only learn about the evolution of humans but also the evolution of animals and birds.
Homologous and Analogous organs are the ones which are used in the evolutionary relationships of animals.
There are various stages of evolution. You shall read about the artificial selection, in which one particular species will evolve into various species.
Phylogeny is considered for the evolutionary relationship of biological species.
Humans from primates evolution is still a big mystery and here, you will learn some more details about it.
Here, you will also understand what is somatic variation and Gametic variation and they occur in somatic cells and germ cells of the body. You will also read about the importance of variations and what are the causes of variations.
3. Explain about magnetic field and field lines.
Ans: Here, the topic discusses field and field lines where magnetics play a major role. Attraction or repulsion of objects can be seen in magnetic fields. Nickel, Iron and Cobalt are the best examples of magnetic fields. You will also read about:
North and south poles
Like poles repel and unlike poles attract
Magnetic field
Magnetic field lines
Iron filings test around a bar magnet
No two magnetic field lines intersect
The relative strength of magnetic field inferred from magnetic field lines
Magnetic field lines form a closed-loop.
Here, the concept also educates you on the concentric circles which are used to represent at every point over a conductor. This will be explained to you with various experiments such as Oersted’s experiment, electromagnetism and electromagnet, magnetic field due to a straight current-carrying conductor, right-hand thumb rule, magnetic field due to current through a circular loop and magnetic field due to current in a solenoid.
4. Benefits of NCERT solutions with Vedantu?
Ans: These solutions are drafted by our Science experts with utmost care to make you’re learning more fun and interactive. You can score well if you have secured 100% confidence to answer any question asked from this chapter. They made sure that CBSE and NCERT guidelines are strictly followed while drafting these solutions.
Our NCERT solutions will help you in developing a strong conceptual foundation with all the important concepts in a very simple language. Solutions provided to the questions are crisp and concise with 100% accuracy in the exercises. They have been designed in such a way that through which you can expand your knowledge base, improve your learning skills and it clears all your doubts instantly.
5. What are the important topics in life processes according to Chapter 6 of Class 10 Science
Ans: Chapter 6 of Class 10 Science will help students to understand the different life processes. In this chapter, students will study the type of nutrition in different organisms. They will also study the concept of photosynthesis in detail. They will even study the process of digestion in human beings in detail and will learn about the different organs of the digestive system and how different organs help in the digestion of food. The process of excretion and how waste products are excreted out of the body is also a part of life processes.
6. Why are life processes important?
Ans: Life processes are important for healthy living. Life processes such as respiration, digestion, absorption, assimilation, and excretion are vital for all living organisms. The processes may differ from one organism to another. Students of Class 10 science will learn about the different life processes in Chapter 6. It is an interesting chapter and an essential one if the student wants to pursue a career in Biology.
7. If there is less air in the trachea, its walls do not collapse. Give a reason.
Ans: The trachea is a tube through which we breathe in air and give out carbon dioxide. The trachea is made up of small rings arranged in the form of C. The rings are muscular and made of connective tissue. Thus, the rings present in the trachea help prevent it from collapsing when there is no air in it. The muscular rings expand when air enters into it and contracts when air moves out of our lungs. For Important Questions of Chapter 6 of Class 10 Science, visit Vedantu website or mobile app and download the PDF free of cost.
8. What is the process of digestion and where does the complete digestion of various components of food take place?
Ans: Digestion of food takes place in different organs. In the mouth, the process starts by chewing food. Then it passes to the stomach for further digestion. The small intestine is the part where complete digestion of food takes place. Different juices and enzymes present in the different parts of the digestive system help in the complete digestion of the food. The digestion starts in the mouth and breaks into small molecules that are digested quickly in the stomach and other parts of the digestive system.
9. Explain how urine is produced?
Ans: Urine is the waste product excreted out of the body. Urine is produced in the kidneys. It consists of harmful substances. Therefore, it is necessary to pass out the waste products in the form of urine. Kidneys filter the blood and important substances such as glucose, amino acids, and salts are reabsorbed. Excess amounts of water present in the blood and other waste substances are converted into the urine and it is excreted out through the urinary system.
CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions
Cbse study materials.
Use Case Studies to Bring Life Into Your Nutrition Course
NutritionCalc Case studies are a helpful way for students to bring life to the information in their textbook and Connect offers a variety of different topics to be used in your class.
Case Studies are great as a stand-alone project but they can also be built into assignments or even expanded upon in a variety of ways. No matter how you use the case studies your students will gain a deeper understanding of the topic while increasing their critical thinking skills.
Here are a couple of ways you can use the auto-graded Case Study assignment in your classroom, whether virtual or in seated class.
Alternative to a personal 3-day record
A case study can be an alternative assignment for students who feel uncomfortable analyzing their diet and/or have a history of an eating disorder. The case study takes the focus off analyzing a personal record.
If needed, you can adjust the questions to focus more on the quality of the diet versus analyzing numbers like calories or grams of protein etc. You could also add more open-ended questions that include students looking for recipes that are suitable for that case study scenario.
Delve deeper to spark conversation into the topic
Use the case studies as an opportunity to have your students delve deeper into the topic with a discussion. If your students are in person, you can have them work in small groups and then discuss the case study. Alternatively, an online class may use discussion boards.
For example, the case study “Staying Energized When Stressed” could be a great case study to have at the beginning of the semester. This case study is a good starting point for students to bring self-awareness and begin to make connections with how college life can impact their eating habits.
Combine with another assignment
Each case study has 10 auto-graded questions that can be an excellent addition to an assignment you already have.
A nutrition article review assignment where students analyze the credibility of the article’s information can be a nice complement to many of the different case studies in Connect. By having an article review at the start of the assignment and then ending with a case study students can better demonstrate understanding and comprehension of the topic.
Add an AI menu planning feature
Take the case study one step further by incorporating a meal plan that is created using AI. Artificial intelligence will not always be accurate but one of the cool things about it is that it can create sample meal plans.
AI platforms can quickly create meal plans for various concerns or medical conditions; the accuracy of these plans is another story. Use an AI meal plan as a learning moment for students.
For example, assign the Polycystic Ovary Syndrome case study and then add an open-ended question where you instruct students to create an AI-generated meal plan. You can have the students write in their thoughts on the accuracy and feasibility of the meal plan. For your in-seat classes, you could have them bring their laptops and discuss in a small group.
Available Case Studies in NutritionCalc Plus: Nutrient Density, Keto Diet, Dietary Guidelines, Whole vs. Refined Grains, Diabetes, Mediterranean Diet, High Protein Diet, Vegan Dietary Pattern, DASH Diet, Weight Management, 5,000-calorie Diet, Breastfeeding Diet, School-Age Dietary Pattern, Okinawan Diet, WIC, Bone Health, Female Athlete Triad RED-S, Constipation.
New Cases coming Summer 2024: Celiac Disease, Elderly, Irritable Bowel Syndrome, Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, Fermented/Probiotic Foods, Heart Health, Anemia, Supporting Detox, Staying Energized when Stressed, Metabolic Support.
Attending a conference?
Checkout if mcgraw hill will be in attendance:.

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Assertion and Reason Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes
- Last modified on: 6 days ago
- Reading Time: 12 Minutes

Table of Contents
Following questions consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below: (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. (b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A. (c) A is true but R is false. (d) A is false but R is true.
Q.1. Assertion (A) : Plants lack excretory organs. Reason (R) : Plants usually absorb essential nutrients.
Q.2. Assertion (A) : In anaerobic respiration, one of the end product is alcohol. Reason (R) : There is an incomplete breakdown of glucose.
Q.3. Assertion (A) : In plants there is no need of specialised respiratory organs. Reason (R) : Plants do not have great demands of gaseous exchange.
Q.4. Assertion (A) : Bile is essential for digestion of lipids. Reason (R) : Bile juice contains enzymes.
Q.5. Assertion (A) : Carbohydrate digestion mainly takes place in small intestine. Reason (R) : Pancreatic juice contains the enzyme lactase.
Also read: Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes
Q.6. Assertion (A) : Aerobic respiration requires less energy as compared to anaerobic respiration. Reason (R) : Mitochondria is the powerhouse of the cell.
Q.7. Assertion (A): Arteries are thick-walled and elastic in nature. Reason (R) : Arteries have to transport blood away from the heart.
Q.8. Assertion (A) : Human heart is four-chambered. Reason (R) : Vena cava is the only artery that supplies deoxygenated blood to the heart.
Q.9. Assertion (A): Energy is required to carry out different life processes. Reason (R) : Energy is obtained in the form of ATP in the mitochondria.
Q.10. Assertion (A): Rings of cartilage are present in the throat, Reason (R) : These ensure that the air-passage does not collapse
Q.11. Assertion (A): Pyruvate is a six-carbon molecule Reason (R) : It is prepared in the cytoplasm as the first step to cellular respiration
Q.12. Assertion (A): Molecular movements are needed for life. Reason (R): Body structures made up of these molecules need continuous repair and maintenance
Also read: MCQ Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes
Q.13. Assertion (A): Diffusion does not meet high energy requirements of multi-cellular organisms Reason (R) : Diffusion is a fast process but occurs at the surface of the body.
Q.14. Assertion (A): The opening and closing of the pore is a function of the guard cells. Reason (R) : Stomatal pores are the site for exchange of gases by diffusion.
Q.15. Assertion (A): The purpose of making urine is to filter out undigested food from intestine Reason (R): Kidneys filter the waste and produce urine,
Q.16. Assertion (A): The inner lining of the small intestine has numerous finger-like projections called villi. Reason (R) : The villi increase the surface area for absorption.
Q.17. Assertion (A): In human beings, the respiratory pigment is haemoglobin Reason (R) : It is a type of protein which has high-affinity carbon dioxide.
Q.18. Assertion : The plants store some of the waste products in their body parts. Reason: Raphides are the solid waste products of plants.
Q.19. Assertion : The movement of water and dissolved salts in xylem is always upwards. Reason: ‘The upward movement of water is due to low pressure created by transpiration.
Q.20. Assertion : Photosynthesis takes place in green parts of the plants. Reason: Photosynthesis always takes place in leaves.
Q.21. Assertion: The average number of heart beat of a person at rest is about 80 per minute. Reason: One contraction and relaxation of the heart constitutes a complete heart beat.
Q.22. Assertion : Ureters are the tubes which carry urine from kidneys to the bladder. Reason: Urine is stored in the urethra.
Also read: Extra Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes
Q.23. Assertion : Ventricles have thicker walls than auricles. Reason: Ventricles have to pump blood into various organs with great pressure
Q.24. Assertion : Capillaries are the thinnest blood vessels. Reason: Capillaries connect the branches of arteries and veins.
Q.25. Assertion : Blood takes up oxygen from the alveolar air and release CO2 during exchange. Reason: ‘The concentration of O, is more in alveolar air.
Q.26. Assertion: The large intestine is the largest part of the alimentary canal. Reason: Tiger has a shorter small intestine, than herbivores.
Q.27. Assertion : Most of the living organisms carry out aerobic respiration. Reason: Mitochondria is the site of aerobic respiration in the cell.
Q.28. Assertion : The Bowman’s capsule and the tubule together make a nephron. Reason : The function of tubule is to allow the selective reabsorption of substances like glucose, amino acids, urea, salts and water into the blood capillaries.
Q.29. Assertion : Pancreatic juice digests starch, proteins and fats. Reason: Pancreatic juice contains digestive enzymes like pancreatic amylase, trypsin and lipase.
Q.30. Assertion: The accumulation of lactic acid in the muscles causes muscle cramps. Reason: During vigorous physical exercise leg muscles respire anaerobically.
Also read: CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes Notes
Q.31. Assertion : Phloem helps in translocation of food from the leaves. Reason: Phloem provides mechanical support to plant.
Q.32. Assertion : Trachea does not collapse, when there is no air in it. Reason : Trachea is supported by cartilage.
Related Posts
Category lists (all posts).
All categories of this website are listed below with number of posts in each category for better navigation. Visitors can click on a particular category to see all posts related to that category.
- Full Form (1)
- Biography of Scientists (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions in Biology (37)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Biology (14)
- DPP Biology for NEET (12)
- Blog Posts (35)
- Career Guidance (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths (15)
- Extra Questions for Class 10 Maths (12)
- Maths Formulas for Class 10 (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Maths (15)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths (4)
- Quick Revision Notes for Class 10 Maths (14)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science (14)
- Evergreen Science Book Solutions for Class 10 (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 10 Science (23)
- HOTS for Class 10 Science (17)
- Important Questions for Class 10 Science (10)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Biology Solutions (4)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Chemistry Solutions (5)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Physics Solutions (5)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science (20)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science (16)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science (15)
- Quick Revision Notes for Class 10 Science (4)
- Study Notes for Class 10 Science (17)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Social Science (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Social Science (24)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Social Science (3)
- Topicwise Notes for Class 10 Social Science (4)
- CBSE CLASS 11 (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (11)
- Free Assignments for Class 11 Chemistry (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (8)
- Very Short Answer Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Entrepreneurship (8)
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Entrepreneurship (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Geography (24)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Geography (24)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 History (12)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 History (12)
- Assertion and Reason Questions for Class 11 Maths (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Maths (16)
- Formulas for Class 11 Maths (6)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Maths (17)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths (8)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Physical Education (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Physics (15)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Physics (12)
- Class 11 Physics Study Notes (5)
- Concept Based Notes for Class 11 Physics (2)
- Conceptual Questions for Class 11 Physics (10)
- Derivations for Class 11 Physics (3)
- Extra Questions for Class 11 Physics (13)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Physics (16)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics (16)
- Numerical Problems for Class 11 Physics (4)
- Physics Formulas for Class 11 (7)
- Revision Notes for Class 11 Physics (11)
- Very Short Answer Questions for Class 11 Physics (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Political Science (20)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Political Science (20)
- CBSE CLASS 12 (8)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Biology (14)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Biology (13)
- Case Studies for CBSE Class 12 Business Studies (13)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Business Studies (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Business Studies (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (15)
- Case Study Based Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (14)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (5)
- Important Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (15)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (8)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry (16)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Chemistry (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Economics (9)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Economics (9)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Economics (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 English (2)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Geography (18)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 History (8)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 History (13)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (13)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (11)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (5)
- Assertion and Reason Questions for Class 12 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Maths (13)
- Maths Formulas for Class 12 (5)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Maths (14)
- Problems Based on Class 12 Maths (1)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 12 Maths (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (11)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (11)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Physics (16)
- Case Study Based Questions for Class 12 Physics (14)
- Class 12 Physics Conceptual Questions (16)
- Class 12 Physics Discussion Questions (1)
- Class 12 Physics Latest Updates (2)
- Derivations for Class 12 Physics (8)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Physics (4)
- Important Questions for Class 12 Physics (8)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physics (14)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics (18)
- Numerical Problems Based on Class 12 Physics (16)
- Physics Class 12 Viva Questions (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Physics (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Political Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Political Science (16)
- Notes for Class 12 Political Science (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Maths (13)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Maths (13)
- Extra Questions for Class 6 Maths (1)
- Worksheets for Class 6 Maths (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science (16)
- Extra Questions for Class 6 Science (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science (9)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Social Science (1)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Social Science (26)
- NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Maths (13)
- NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Science (19)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Maths (12)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science (18)
- NCERT Notes for Class 7 Science (18)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Maths (14)
- Extra Questions for Class 7 Maths (5)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Science (18)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Science (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 7 Science (19)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Social Science (1)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Social Science (30)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Maths (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Maths (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 8 Maths (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 8 Maths (6)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Science (11)
- Extra Questions for Class 8 Science (2)
- MCQ Questions for Class 8 Science (4)
- Numerical Problems for Class 8 Science (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 8 Science (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Social Science (27)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Social Science (23)
- CBSE Class 9 English Beehive Notes and Summary (2)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths (14)
- MCQ Questions for Class 9 Maths (11)
- NCERT Notes for Class 9 Maths (6)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths (12)
- Revision Notes for Class 9 Maths (3)
- Study Notes for Class 9 Maths (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science (15)
- Evergreen Science Book Solutions for Class 9 (15)
- Extra Questions for Class 9 Science (22)
- MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science (11)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science (15)
- Revision Notes for Class 9 Science (1)
- Study Notes for Class 9 Science (15)
- Topic wise MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science (2)
- Topicwise Questions and Answers for Class 9 Science (15)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Social Science (15)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Social Science (19)
- CHEMISTRY (8)
- Chemistry Articles (2)
- Daily Practice Problems (DPP) (3)
- Books for CBSE Class 9 (1)
- Books for ICSE Class 10 (3)
- Editable Study Materials (8)
- Exam Special for CBSE Class 10 (3)
- H. C. Verma (Concepts of Physics) (13)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Biology (14)
- Extra Questions for ICSE Class 10 Chemistry (1)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Chemistry (5)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Maths (16)
- Important Questions for ICSE Class 10 Physics (13)
- MCQ Questions for ICSE Class 10 Physics (4)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Physics (8)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 9 Maths (7)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 9 Physics (10)
- Topicwise Problems for IIT Foundation Mathematics (4)
- Challenging Physics Problems for JEE Advanced (2)
- Topicwise Problems for JEE Physics (1)
- DPP for JEE Main (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Main (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Chemistry (6)
- Chapterwise Questions for JEE Main Physics (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Main Physics (8)
- Physics Revision Notes for JEE Main (4)
- JEE Mock Test Physics (1)
- JEE Study Material (1)
- JEE/NEET Physics (6)
- CBSE Syllabus (1)
- Maths Articles (2)
- NCERT Books for Class 12 Physics (1)
- NEET Chemistry (13)
- Important Questions for NEET Physics (17)
- Topicwise DPP for NEET Physics (5)
- Topicwise MCQs for NEET Physics (32)
- NTSE MAT Questions (1)
- Physics (1)
- Alternating Current (1)
- Electrostatics (6)
- Fluid Mechanics (2)
- PowerPoint Presentations (13)
- Previous Years Question Paper (3)
- Products for CBSE Class 10 (15)
- Products for CBSE Class 11 (10)
- Products for CBSE Class 12 (6)
- Products for CBSE Class 6 (2)
- Products for CBSE Class 7 (5)
- Products for CBSE Class 8 (1)
- Products for CBSE Class 9 (3)
- Products for Commerce (3)
- Products for Foundation Courses (2)
- Products for JEE Main & Advanced (10)
- Products for NEET (6)
- Products for ICSE Class 6 (1)
- Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance (1)
- Topic Wise Study Notes (Physics) (2)
- Topicwise MCQs for Physics (2)
- Uncategorized (138)
Test series for students preparing for Engineering & Medical Entrance Exams are available. We also provide test series for School Level Exams. Tests for students studying in CBSE, ICSE or any state board are available here. Just click on the link and start test.
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
4 thoughts on “ Assertion and Reason Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes ”
thank you so much! it was very helpful.
ya…I have the same feedback for it. It was absolutely helpful.
Really helpful! The question and answers are good enough. It really helped in my holiday homework 📚….. Thanks a bunch 😃
Thankyou. So much pls give many questions and answers
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
CBSE Papers, Questions, Answers, MCQ ...
Blog provides NCERT solutions, CBSE, NTSE, Olympiad study material, model test papers, important Questions and Answers asked in CBSE examinations. References to Educational Sites and resources.
- CareerAfter12
- Syllabus 2017-18
- Entrance Exams
Friday 7 April 2017
Cbse class 10 - biology - life processes (nutrition) - q and a (#cbsenotes), life processes (nutrition) .

No comments:
Post a comment.
We love to hear your thoughts about this post!
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.
Ad-Blocker Detected!
Please turn off the ad blocker. This is only way that we can earn some penny. Please support us by trun off the ad blocker. Thank you!!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
CBSE Case Based Questions Class 10 Science Chemistry Chapter 6. CASE STUDY : 1. Carbon and energy requirements of the autotrophic organism are fulfilled by photosynthesis. It is the process by which autotrophs take in substances from the outside and convert them into stored forms of energy. This material is taken in the form of carbon dioxide ...
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. Here, we have provided case … Continue reading Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 ...
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Life Processes Case Study Questions With Solution 2021 Answer Keys. (i) (c): In the test tube full of mercury (figure A) there is no air and, therefore, the introduced soaked seeds do not get air for aerobic respiration. But they are capable of respiration in the absence of oxygen as is indicated by the ...
Life Processes Case Study Questions With Answers. Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes. Case Study/Passage-Based Questions. Question 1: Transpiration is the evaporative loss of water by plants. It occurs mainly through the stoma in the leaves. Besides the loss of water vapor in ...
entities. These processes are vital for sustaining life. Holozoic nutrition is the process of nutrition that takes place in organisms which take solid or liquid food inside their body. Amoeba follows holozoic nutrition. Holozoic nutrition in amoeba takes place in the following steps: 1. Ingestion 2. Digestion 3. Absorption 4. Assimilation 5 ...
The nutrition that involves the taking in of solid or liquid (in case of fluid feeders) particles of food which have to be further broken down into simpler particles inside the organism. These particles may be big or small. ... Class 10 Nutrition Important questions; Class 10 Respiration Important questions; Class 10 Excretion Important questions;
The Chapter wise Important case study based questions with their solved answers in CBSE Class 10 Science can be accessed from the table below: CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions ...
In this unit, we learn about basic life processes such as photosynthesis, nutrition, transportation and excretion. ... Class 10 Biology (India) 4 units · 36 skills. Unit 1. Life processes. Unit 2. Control & Coordination. ... Types of nutrition Get 3 of 4 questions to level up! Autotrophic nutrition. Learn. Photosynthesis (Opens a modal)
Class 10 Science Sample Papers with case study questions are available in the myCBSEguide App. There are 4 such questions (Q.No.17 to 20) in the CBSE model question paper. If you analyze the format, you will find that the MCQs are very easy to answer. So, we suggest you, read the given paragraph carefully and then start answering the questions.
Solution: The factors which affect photosynthesis, are light, water, temperature, humidity, age of the leaf and carbon dioxide. Question-6. Define a herbivore and a carnivore. Solution: The animals that feed only on plants are called herbivores. The animals that feed only on flesh are called carnivores. Question-7.
Class 10 Science Chapter 6 mainly deals with the maintenance processes in living organisms. In this chapter, students will learn to identify vital life processes and understand different types of nutrition as well as the respiratory organs and their mechanism, excretion, digestion, etc. To make learning more interesting and easy, we provide ...
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions. Question 1: Transpiration is the evaporative loss of water by plants. It occurs mainly through the stoma in the leaves. Besides the loss of water vapor in transpiration, the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the leaf also occurs through pores called stomata. Normally stomata remain open in the daytime ...
Answer: (a) small intestine. Question 2. Mention the raw materials required for photosynthesis. (Board Term I, 2016) Answer: Raw materials required for photosynthesis are carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), water, light and chloroplast. Question 3. State the location and function of gastric glands.
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Life Processes Case Study Questions 2021. 10th Standard CBSE. Reg.No. : Science. Time : 00:30:00 Hrs. Total Marks : 20. Digestion is a catabolic process in which complex and large components of food are broken down into their respective simpler and smaller forms with the help of various hydrolytic enzymes.
Quizizz provides several resources that help CBSE Science teachers to effectively teach the topic Nutrition in chapter Life Processes. ... 11th - 12th grade 386. Plays. 3. Likes. Daniel Miller 1 year ago. quiz Surface Processes 20. Questions. 9th - 12th grade ... Asynchronous concept checks and study tools ...
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce. Case Study/Passage-Based Questions. Question 1: The male reproductive system consists of portions that produce the germ cells and other portions that deliver the germ cells to the site of fertilization.
Life Processes Class 10 Science Extra Questions with Answers. Question 1: Mention the raw materials required for photosynthesis. Answer: The following raw materials are required for photosynthesis: (i) Carbon Dioxide: Plants get CO 2 from atmosphere through stomata. (ii)Water: Plants absorb water from soil through roots and transport to leaves.
Ans: Life processes are important for healthy living. Life processes such as respiration, digestion, absorption, assimilation, and excretion are vital for all living organisms. The processes may differ from one organism to another. Students of Class 10 science will learn about the different life processes in Chapter 6.
AI platforms can quickly create meal plans for various concerns or medical conditions; the accuracy of these plans is another story. Use an AI meal plan as a learning moment for students. For example, assign the Polycystic Ovary Syndrome case study and then add an open-ended question where you instruct students to create an AI-generated meal plan.
Also read: Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes. Q.6. Assertion (A) : Aerobic respiration requires less energy as compared to anaerobic respiration. Reason (R) : Mitochondria is the powerhouse of the cell. Answer. (d) Q.7.Assertion (A): Arteries are thick-walled and elastic in nature.
① Saprotrophic nutrition ② Parasitic nutrition ③ Holozoic nutrition Q14: Give examples of heterotrophs. Answer: Animals and Fungi Q15: What is the mode of nutrition of plasmodium. Answer: Parasitic nutrition. Q16: What is the mode of nutrition in fungi. Answer: Saprophytic or Parasitic nutrition. Q17: Give an example of plant parasite.