113 Gender Roles Essay Topics & Examples
Looking for gender roles essay topics? This field is hot, controversial, and really worth exploring!
- 🔝 Top 10 Gender Topics
- 📝 Gender Essay: Writing Tips
- 🏆 Gender Essay Examples & Topic Ideas

✍️ Gender Argumentative Essay Topics
❓ research questions about gender roles.
In your gender role essay, you might want to focus on the issues of gender equality in the workplace. Another exciting option is to write about gender stereotypes in education. Finally, you can elaborate on how traditional gender roles are changing.
In this article, you’ll find a list of gender argumentative essay topics, ideas for papers on gender and society, as well as top gender roles essay examples.
🔝 Top 10 Gender Roles Topics
- Gender stereotypes and the way they affect people
- Fighting gender stereotypes and sexism
- Gender equality in the workplace
- Gender stereotypes in education
- Gender schema theory
- Is gender socially constructed?
- Social learning theory and gender
- Gender roles and sexual orientation
- Body image and gender
- Social gender construction in the media
📝 Gender Roles Essay: Writing Tips
Essays on gender roles present students’ understanding of the similarities, differences, and aspects of gender roles in society.
Writing gender roles essays helps learners to understand the significance of topics related to gender roles and the changes in societal norms. Students should be highly aware of the problems associated with traditional gender roles. For example, there are many periods in world history, in which people did not have equal rights.
Moreover, some aspects of gender roles may be associated with discrimination. To make an essay on this problem outstanding, you should discuss the problem in detail and present your points clearly. A useful tip is to develop a good structure for your paper.
Before starting to work on the paper, you should select the problem that is most interesting or relevant to you.
Gender roles essay topics and titles may include:
- The history of gender roles and their shifts throughout the time
- Male and female roles in society
- Gender roles in literature and media
- How a man and a woman is perceived in current society
- The causes and outcomes of gender discrimination
- The problem of ‘glass ceiling’
- The problem of social stratification and its outcomes
- The revolution in the concept of gender
After selecting the issue for discussion, you can start working on the essay’s structure. Here are some useful tips on how to structure your paper:
- Select the topic you want to discuss (you can choose one from the list above). Remember to pay attention to the type of essay you should write. If it is an argumentative essay, reflect on what problem you would want to analyze from opposing perspectives.
- Gender roles essay titles are important because they can help you to get the reader’s attention. Think of something simple but self-explanatory.
- An introductory paragraph is necessary, as it will present the questions you want to discuss in the paper. Remember to state the thesis of your essay in this section.
- Think of your gender roles essay prompts. Which aspects of the selected problem do you want to focus on? Dedicate a separate section for each of the problems.
- Remember to include a refutation section if you are writing an argumentative essay. In this section, you should discuss an alternative perspective on the topic in 1-2 paragraphs. Do not forget to outline why your opinion is more credible than the alternative one.
- Avoid making the paragraphs and sentences too long. You can stick to a 190 words maximum limit for one paragraph. At the same time, make sure that the paragraphs are longer than 65 words. Try to make all sections of the body paragraphs of similar length.
- Check out examples online to see how you can structure your paper and organize the information. Pay attention to the number of paragraphs other students include.
- Remember to include a gender roles essay conclusion. In this paragraph, you will discuss the most important claims of your paper.
- Do not forget to add a reference page in which you will include the sources used in the paper. Ask your professor in advance about the types of literature you can utilize for the essay.
Do not forget that there are free samples on our website that can help you to get the best ideas for your essay!
🏆 Gender Roles Essay Examples & Topic Ideas
- Gender Roles in Antigone Essay This will be seen through an analysis of the other characters in the play and the values of ancient Greeks. Indeed this central character appears to be at odds with the inclinations of the other […]
- Gender Roles Set in Stone: Prehistoric and Ancient Work of Arts In the prehistoric and ancient works of art, the representation of women and men reveals a massive imbalance in gender equity that favors men over women.
- Gender Roles in “The Glass Menagerie” by Tennessee Williams In the play The Glass Menagerie, Tennessee Williams has written the story of the Wingfield family that lived in St Louis during the 1940s.
- Conflict of Gender Roles in Munro’s “Boys and Girls” Munro’s “Boys and Girls” is a story about a puzzled girl who struggles to find the balance between the battles of her inner female-housewife side, like her mother, and a boyish character who likes to […]
- Gender Roles in The Yellow Wallpaper & Trifles The two texts; the short story ‘The Yellow Wallpaper’ by Charlotte Perkins and the play ‘Trifles’ by Susan Glaspell strategically illustrate this claim since they both aim at attracting the reader’s attention to the poor […]
- Gender Roles: Changes From the Late 1800’s to Today The definition of who is a male or a female depends on the types of gender roles one was exposed to during the early ages. In today’s society, we have a greater number of women […]
- Gender Roles in “Bridge to Terabithia” by Paterson The theme of gender roles is consistently present in the novel, starting with character origins and becoming the central concept as they mature to defy archetypal perceptions of feminine and masculine expectations in order to […]
- Gender Roles in Society One might think that a child is born with the idea of how to behave in relation to gender while in the real sense; it is the cultivation of the society that moulds people to […]
- Gender Roles and Family Systems in Hispanic Culture In the Hispanic culture, amarianismo’ and amachismo’ are the terms used to determine the various behavioral expectations among the family members.
- Athena and Gender Roles in Greek Mythology According to Eicher and Roach-Higgins, the elements of her dress were important because they immediately communicated specific ideas about her character that was as contradictory as the physical gender of the birthing parent.”In appropriating the […]
- Gender Roles in Brady’s “Why I Want a Wife” and Sacks’ “Stay-at-Home Dads” Yet, there are some distinctions Judy Brady believes that women are often viewed as unpaid house servants who have to take care of husbands’ needs, whereas Glenn Sacks argues that gender roles begin to transform […]
- Gender Roles in the 19th Century Society: Charlotte Gilman’s The Yellow Wallpaper However, the narrator’s developing madness can also act as the symbolical depiction of the effects of the men’s dominance on women and the female suppression in the 19th-century society.”The Yellow Wallpaper” was first published in […]
- Gender Roles Inversion: The Madonna Phenomenon At the same time partial narrowing of the gender gap in the context of economic participation did not lead to the equality of men and women in the field of their occupations.
- Gender Roles and Stereotyping in Education Teachers should be trained to give clear and useful instruction to students on the issue of gender roles in modern society.
- Gender roles in the Wind in the Willows For instance, in the case where both the mole and the rat make comments to the toad that are full of women critics.
- Gender Roles and Body Image in Disney Movies In this research, attention will be paid to gender roles and body images of Disney princesses to understand the popularity of the franchise and its impact on child development.
- Changing Gender Roles in Families Over Time The division of labor and traditional gender roles in the family usually consists of men doing the work while women take care of the children, other relatives, and housekeeping.
- China’s Gender Roles in Mo Yan’s and Shen Fu’s Works Six Records of a Floating Life is a multi-faceted chronicle which helps to comprehend the difficulties and the features of Shen Fu’s life and the romance between him and his beloved Chen Yun.
- Gender Roles by Margaret Mead Once the a rift defining men and women develops this way, it goes further and defines the positions, which men and women occupy in the society, basing on these physical and biological differences, which form […]
- Gender Roles in South Korean Laws and Society At the same time, all custody is traditionally granted to husbands and fathers in a case of a divorce” though the anxiety about the high divorce rate and the nasty endings of relationships is more […]
- Cohabitation and Division of Gender Roles in a Couple Cohabitation is perceived in the society as the form of relationships which is an effective alternative to the traditional marriage because of focusing on the principles of flexibility, freedom, and equality, but few couples can […]
- The Concepts of Gender Roles and Sexuality by John Money and Judith Butler These categories of feminists are united in the belief of existence of many children and little sex. This paper explains the concepts and ideologies relating to gender roles and sexuality.as advocated by John Money and […]
- Gender Roles: From Prehistoric Era to Modern Society Since each gender was assigned a particular role in the past due to the differences in the biological makeup between a man and a woman in the prehistoric era, the modern process of communication between […]
- Gender Roles in Brady’s and Theroux’s Works In the satire “Being a Man” by Paul Theroux, the author demonstrates to readers the essence of how a particular manifestation of masculinity is extolled in American society.
- Evaluating Gender Roles in Nursing The purpose of this study was to explore perspectives on the experience and gender roles of male and female students, as well as how they think about their future professional roles.
- Women’s Gender Roles in American Literature The stories written by Constance Woolson Fenimore, Mary Wilkins Freeman, and Jaqueline Bishop highlight the harmful gender roles and discrimination that still remains a major topic for disputes and illustrate the fate of oppressed women.
- Aspects of Gender Roles and Identity The breadth of her practice in transgender issues suggests that every choice Bowers makes is ethical, requiring her to be respectful and highly responsible.
- Gender Roles, Expectations, and Discrimination Despite Isaac being the calmest boy in the school, he had a crush on Grace, a beautiful girl in the school who was from a wealthy family.
- Gender Roles in Social Constructionism The reality, in the view of sociologists, is a social attitude in connection with which a personality is formed that adapts to the requirements of the world.
- Gender Roles and Stereotypes in Straightlaced Film One might conclude that gender neutrality and abstraction in offices are only a cover to maintain the basis of gender injustice.
- Gender Roles and Body Images The media has one of the most widespread and significant effects on how we perceive men and women. It is incorrectly assumed that men are the cultural norm, while women stay invisible and underrepresented by […]
- Biology and Gender Roles in Society Thus, it may be more convenient for society to justify the imposition of certain gender roles on men and women using biology-related arguments, which, in reality, are more related to culture and social development.
- Children’s Views of Gender Roles Today, both parents and teachers see the positive impact of the attempts to integrate anti-biased gender-related education on young children as they get more freedom to express themselves and grow up less aggressive.
- The Construction of Gender Roles However, it is wrong to consider women exposed to the domestic work powerless, as they have the opportunity to informally or implicitly influence men and the decisions they make.
- Sociology of the Family: Gender Roles Thus, the societal predisposition and notion that women are lesser in the community should be abandoned, and greater emphasis should be placed on the critical functions they perform in the household. These assertions, equivocations, and […]
- Femininity and Masculinity: Understanding Gender Roles The understanding of how gender roles are portrayed in the media and the general perception of the expected behavior for men and women communicated non-verbally in the society is the basis on which children build […]
- Injustice Within Strict Gender Roles There is still no clear answer to how a person can find his or her destiny and place in the world, and understand the opportunities and prospects, considering the opinion of the dominant number of […]
- Gender Roles and How People Perceive Them However, all of the survey participants indicated that their families would be inclined to differentiate between the toys for a child based on the latter’s sex and the corresponding perceived gender role.
- Gender Roles in TV Commercials and Values in the Society Each of them will watch, code, and analyze the TV commercials separately; at the end of the procedure, their results will be compared in order to ensure the inter-observer reliability of the chosen research method.
- Toxic Masculinity and Gender Roles: New Aspects in Discussions Between Men and Women It is believed that men have to be silent and invincible warriors who exercise power due to their status of a man.
- Gender Roles in Contemporary Society The conditions of life are tough and it is presumed that only men are able to carry out such hardships and limitations of a soldier life.
- Gender Roles in ‘Mr. Green’ by Robert Olen Butler Green Butler uses the character of the grandfather to develop the theme of gender roles within the culture. The character of the grandfather is extremely sound for the cultural beliefs the author conveyed through all […]
- Culture and History: Gender Roles Over the Past 50 or So Years It is not that there were no women in the workforce; it was just that she had to choose one over the other, juggling the two was quite rare and unheard of.
- Gender Roles and Sexuality in Media: Cosmopolitan & Maxim The woman portrayed in these sites is supposed to look ‘hot’ and sexy in order to be attractive to a man.
- The Problem of Gender Roles in Society Based on Plays by Glaspell and Ibsen The men in the play are constantly showing their self-importance, they are trying to act like real detectives, and they do not even realize that Mrs. But, all of a sudden, the moment of repaying […]
- Social Element in Gender Roles I learned of the origins of gay and lesbian studies, as well that of the confining of such studies in earlier times to specific institutions.
- Equality: The Use of TV to Develop Our Gender Roles In this sense, when it is the men who predominantly work outside of the home, they will usually see the home as a place of leisure and so use the TV as a source of […]
- Family Unit and Gender Roles in Society and Market The role of molding the infant into an adult belonged to the family in the ancient society. In the past, the father was expected to be the breadwinner of the family.
- Gender Roles and Social Classes in Wartime The message is as simple as “The women of Britain say ‘Go.’” It points to the role of both men and women in wartime.
- The Necessity for Gender Roles The potential change from the elimination of the differences in gender may affect every perceived part of one’s life. Such factors as one’s occupation, status, and appearance may also contribute to the creation of stereotypes.
- Changing Gender Roles Between Boys and Girls In the twenty-first Century, girls have greatly stepped up and assumed some of the roles that were considered to be boy’s while boys have done the same leading to an interchange of roles.
- Nomadic Society’s Gender Roles and Warrior Culture On the one hand, it was clear that the 1100s and the 1200s included the period of male power. It was wrong to assume that all women were similar and treat them in the same […]
- “Beside Oneself” by Judith Butler: Gender Roles Following the views of the author, who states that choice in the formation of gender and sexuality is not transparent, and a key role is still played by others in the form of expectations and […]
- Gender Roles in Couples and Sex Stereotypes Altogether, the last reconsiderations of the nature of relations promoted the appearance of numerous debates related to the role of partners and their right to be the leader.
- Understanding the Social Element in Gender Roles When saying that gender is a binary construction, one implies that there are two genders, namely, the masculine and the feminine one, and two corresponding types of social behaviour, which are predetermined by the existing […]
- Gender Roles in Tango: Cultural Aspects However, one should not assume that the role of women in tango is inferior because they create the most aesthetic aspects of this dance.
- Gender Roles in Toy Stores According to Fisher-Thompson et al, two of the major differentiating factors in toys for girls and boys are color and nature.
- Discussing Gender Roles in the Interaction Perspective It is the purpose of this issue to discuss the concept of gender roles using the sociological perspective of symbolic interaction.
- Women in Hip-Hop Music: A Provocative and Objectified Gender Roles It is one thing that men want women to be in music videos and play a particular role, but women are willing to participate in the videos.
- Content Analysis of Gender Roles in Media In the critical analysis of the article, the point of disagreement is that of under-representation of women in the media. How do the media subordinate and relegate roles of women in society?
- Effects of Media Messages about Gender Roles Media articles, such as the Maxim Magazine and the Cosmopolitan Magazine, socialize individuals to believe that women are very different from men as regards to dressing, behaving, and eating.
- The Change of Gender Roles This similarity is one of the most important to focus on the structure of the narrative. In both plays, the main actions of the characters are not directly described by the authors.
- Gender Equality: Male Dominance The simple reason is that gender inequality exists in affluent societies wherein women are free to do what they want, have access to education, and have the capacity to create wealth.
- “The Odd Women” and “Women in Love”: Evolving Views of Gender Roles An effort is also made to track the changes of the roles of women in the social fabric in the Victorian era by considering The Odd Women by George Gissing written in 1893.
- Gender Roles: Constructing Gender Identity In the course of the twentieth century and at the threshold of the twenty-first century, the images and roles of gender have constantly been changing.
- Analysis of the Peculiarities of Gender Roles Within Education, Families and Student Communities Peculiarities of gender aspect within the education system and labour market Attitude for marriage of men and women as one of the major aspects within the analysis of gender roles Family relations as a significant […]
- Ideology of Gender Roles In the world of literature, ideology has played a vital role in depicting the condition of the society. In this scenario, Kingston reveals that the men out-live their roles in the society, and they are […]
- Concepts of Gender Roles As a result of these, the war on gender inequality and sexism has failed, because of the failure of these agents of change to promote gender equality and eliminate discriminative notions held by the society.
- Gender Roles in the United States Over the Last Century The men’s perception towards this idea was negative, and this consequently resulted to a conflict with the men claiming that the roles of the women were in the kitchen.
- Fashions, gender roles and social views of the 1950s and 1960s Fashion was highly valued and this can be seen in the way the clothes worn by the wives of the presidential candidates in America hit the headlines. In the 1950s, the role of housekeeping and […]
- Cheating, Gender Roles, and the Nineteenth-Century Croquet Craze The author’s main thesis is, “Yet was this, in fact, how the game was played on the croquet lawns of the nineteenth century?” Whereas authors of croquet manuals and magazines emphasize so much on the […]
- Gender Roles in Cartoons Though the males are portrayed to be logical, but it is shown that the females are more successful because of simple blunders or miscalculations which males fail to understand, females are able to beat males […]
- The Industrial Revolution Impact on the Gender Roles The population growth combined with the increased productivity of small parts of the country and the migration of the now landless people in search of work opportunities led to the phenomena of urbanization.
- How Does Aristophanes Represent Gender Roles in Lysistrata?
- Are Gender Roles and Relationships More Equal in Modern Family Life?
- How Do Children Develop Gender Roles?
- Does Men’s Fashion Reflect Changes in Male Gender Roles?
- How Did Colonialism Resonate With Gender Roles and Oppression?
- Are Gender Roles Damaging Society?
- How Did Revolutions Affect Gender Roles?
- Are Gender Roles Defined by Society or by Genetics?
- How Have Family Structure and Gender Roles Changed?
- Are Gender Roles Fluid When Dealing With Death and Tragedy?
- How Do Gender Roles Affect Communication?
- Are Gender Roles Natural?
- How Do Gender Roles Affect Immigrants?
- Are Gender Stereotyped Roles Correct?
- How Do Gender Roles Affect the Physical and Emotional Health?
- Have Gender Roles Played a Big Part in the History?
- How Do Gender Roles and Extroversion Effects How Much People Talk?
- What Are Gender Roles? How Are They Defined?
- How Are Gender Roles Predetermined by the Environment?
- What Drives the Gender Wage Gap?
- How Has Gender Roles Changed Over the Last Centuries?
- What Factors Influence Gender Roles?
- How Have Gender Roles in Japanese Theatre Influenced and Affected Societal View on Homosexuality and Masculinity?
- What Society Norms for Gender Roles Should Be Conceived?
- How Have Traditional Gender Roles Been Stressful?
- What Was Distinctive About Gender Roles in the Nineteenth Century?
- How Has Hegemonic Masculinity Set Ideas of Gender Roles?
- How Do Media and Politics Influence Gender Roles?
- Where Does the Truth on Gender Roles Lie in Nahua and Mayan Civilizations?
- How Radical Are the Changes to the Gender Roles in Carter’s “The Company of Wolves”?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 26). 113 Gender Roles Essay Topics & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/gender-roles-essay-examples/
"113 Gender Roles Essay Topics & Examples." IvyPanda , 26 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/gender-roles-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '113 Gender Roles Essay Topics & Examples'. 26 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "113 Gender Roles Essay Topics & Examples." February 26, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/gender-roles-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "113 Gender Roles Essay Topics & Examples." February 26, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/gender-roles-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "113 Gender Roles Essay Topics & Examples." February 26, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/gender-roles-essay-examples/.
- Masculinity Topics
- Social Stratification Essay Titles
- Sexism Essay Ideas
- Women’s Movement Questions
- Feminism Questions
- Cultural Relativism Questions
- Domestic Violence Paper Topics
- Sociological Perspectives Titles

5 Powerful Essays Advocating for Gender Equality
Gender equality – which becomes reality when all genders are treated fairly and allowed equal opportunities – is a complicated human rights issue for every country in the world. Recent statistics are sobering. According to the World Economic Forum, it will take 108 years to achieve gender parity . The biggest gaps are found in political empowerment and economics. Also, there are currently just six countries that give women and men equal legal work rights. Generally, women are only given ¾ of the rights given to men. To learn more about how gender equality is measured, how it affects both women and men, and what can be done, here are five essays making a fair point.
Take a free course on Gender Equality offered by top universities!
“Countries With Less Gender Equity Have More Women In STEM — Huh?” – Adam Mastroianni and Dakota McCoy
This essay from two Harvard PhD candidates (Mastroianni in psychology and McCoy in biology) takes a closer look at a recent study that showed that in countries with lower gender equity, more women are in STEM. The study’s researchers suggested that this is because women are actually especially interested in STEM fields, and because they are given more choice in Western countries, they go with different careers. Mastroianni and McCoy disagree.
They argue the research actually shows that cultural attitudes and discrimination are impacting women’s interests, and that bias and discrimination is present even in countries with better gender equality. The problem may lie in the Gender Gap Index (GGI), which tracks factors like wage disparity and government representation. To learn why there’s more women in STEM from countries with less gender equality, a more nuanced and complex approach is needed.
“Men’s health is better, too, in countries with more gender equality” – Liz Plank
When it comes to discussions about gender equality, it isn’t uncommon for someone in the room to say, “What about the men?” Achieving gender equality has been difficult because of the underlying belief that giving women more rights and freedom somehow takes rights away from men. The reality, however, is that gender equality is good for everyone. In Liz Plank’s essay, which is an adaption from her book For the Love of Men: A Vision for Mindful Masculinity, she explores how in Iceland, the #1 ranked country for gender equality, men live longer. Plank lays out the research for why this is, revealing that men who hold “traditional” ideas about masculinity are more likely to die by suicide and suffer worse health. Anxiety about being the only financial provider plays a big role in this, so in countries where women are allowed education and equal earning power, men don’t shoulder the burden alone.
Liz Plank is an author and award-winning journalist with Vox, where she works as a senior producer and political correspondent. In 2015, Forbes named her one of their “30 Under 30” in the Media category. She’s focused on feminist issues throughout her career.
“China’s #MeToo Moment” – Jiayang Fan
Some of the most visible examples of gender inequality and discrimination comes from “Me Too” stories. Women are coming forward in huge numbers relating how they’ve been harassed and abused by men who have power over them. Most of the time, established systems protect these men from accountability. In this article from Jiayang Fan, a New Yorker staff writer, we get a look at what’s happening in China.
The essay opens with a story from a PhD student inspired by the United States’ Me Too movement to open up about her experience with an academic adviser. Her story led to more accusations against the adviser, and he was eventually dismissed. This is a rare victory, because as Fan says, China employs a more rigid system of patriarchy and hierarchy. There aren’t clear definitions or laws surrounding sexual harassment. Activists are charting unfamiliar territory, which this essay explores.
“Men built this system. No wonder gender equality remains as far off as ever.” – Ellie Mae O’Hagan
Freelance journalist Ellie Mae O’Hagan (whose book The New Normal is scheduled for a May 2020 release) is discouraged that gender equality is so many years away. She argues that it’s because the global system of power at its core is broken. Even when women are in power, which is proportionally rare on a global scale, they deal with a system built by the patriarchy. O’Hagan’s essay lays out ideas for how to fix what’s fundamentally flawed, so gender equality can become a reality.
Ideas include investing in welfare; reducing gender-based violence (which is mostly men committing violence against women); and strengthening trade unions and improving work conditions. With a system that’s not designed to put women down, the world can finally achieve gender equality.
“Invisibility of Race in Gender Pay Gap Discussions” – Bonnie Chu
The gender pay gap has been a pressing issue for many years in the United States, but most discussions miss the factor of race. In this concise essay, Senior Contributor Bonnie Chu examines the reality, writing that within the gender pay gap, there’s other gaps when it comes to black, Native American, and Latina women. Asian-American women, on the other hand, are paid 85 cents for every dollar. This data is extremely important and should be present in discussions about the gender pay gap. It reminds us that when it comes to gender equality, there’s other factors at play, like racism.
Bonnie Chu is a gender equality advocate and a Forbes 30 Under 30 social entrepreneur. She’s the founder and CEO of Lensational, which empowers women through photography, and the Managing Director of The Social Investment Consultancy.
You may also like

16 Inspiring Civil Rights Leaders You Should Know

15 Trusted Charities Fighting for Housing Rights

15 Examples of Gender Inequality in Everyday Life

11 Approaches to Alleviate World Hunger

15 Facts About Malala Yousafzai

12 Ways Poverty Affects Society

15 Great Charities to Donate to in 2024

15 Quotes Exposing Injustice in Society

14 Trusted Charities Helping Civilians in Palestine

The Great Migration: History, Causes and Facts

Social Change 101: Meaning, Examples, Learning Opportunities

Rosa Parks: Biography, Quotes, Impact
About the author, emmaline soken-huberty.
Emmaline Soken-Huberty is a freelance writer based in Portland, Oregon. She started to become interested in human rights while attending college, eventually getting a concentration in human rights and humanitarianism. LGBTQ+ rights, women’s rights, and climate change are of special concern to her. In her spare time, she can be found reading or enjoying Oregon’s natural beauty with her husband and dog.
Gender Studies: Foundations and Key Concepts
Gender studies developed alongside and emerged out of Women’s Studies. This non-exhaustive list introduces readers to scholarship in the field.

Gender studies asks what it means to make gender salient, bringing a critical eye to everything from labor conditions to healthcare access to popular culture. Gender is never isolated from other factors that determine someone’s position in the world, such as sexuality, race, class, ability, religion, region of origin, citizenship status, life experiences, and access to resources. Beyond studying gender as an identity category, the field is invested in illuminating the structures that naturalize, normalize, and discipline gender across historical and cultural contexts.

At a college or university, you’d be hard pressed to find a department that brands itself as simply Gender Studies. You’d be more likely to find different arrangements of the letters G, W, S, and perhaps Q and F, signifying gender, women, sexuality, queer, and feminist studies. These various letter configurations aren’t just semantic idiosyncrasies. They illustrate the ways the field has grown and expanded since its institutionalization in the 1970s.
This non-exhaustive list aims to introduce readers to gender studies in a broad sense. It shows how the field has developed over the last several decades, as well as how its interdisciplinary nature offers a range of tools for understanding and critiquing our world.
Catharine R. Stimpson, Joan N. Burstyn, Domna C. Stanton, and Sandra M. Whisler, “Editorial.” Signs , 1975; “Editorial,” off our backs , 1970
The editorial from the inaugural issue of Signs , founded in 1975 by Catharine Stimpson, explains that the founders hoped that the journal’s title captured what women’s studies is capable of doing: to “represent or point to something.” Women’s studies was conceptualized as an interdisciplinary field that could represent issues of gender and sexuality in new ways, with the possibility of shaping “scholarship, thought, and policy.”
The editorial in the first issue of off our backs , a feminist periodical founded in 1970, explains how their collective wanted to explore the “dual nature of the women’s movement:” that “women need to be free of men’s domination” and “must strive to get off our backs.” The content that follows includes reports on the Equal Rights Amendment, protests, birth control, and International Women’s Day.
Robyn Wiegman, “Academic Feminism against Itself.” NWSA Journal , 2002
Gender studies developed alongside and emerged out of Women’s Studies, which consolidated as an academic field of inquiry in the 1970s. Wiegman tracks some of the anxieties that emerged with the shift from women’s to gender studies, such as concerns it would decenter women and erase the feminist activism that gave rise to the field. She considers these anxieties as part of a larger concern over the future of the field, as well as fear that academic work on gender and sexuality has become too divorced from its activist roots.
Jack Halberstam, “Gender.” Keywords for American Cultural Studies, Second Edition (2014)
Halberstam’s entry in this volume provides a useful overview for debates and concepts that have dominated the field of gender studies: Is gender purely a social construct? What is the relationship between sex and gender? How does the gendering of bodies shift across disciplinary and cultural contexts? How did the theorizing of gender performativity in the 1990s by Judith Butler open up intellectual trajectories for queer and transgender studies? What is the future of gender as an organizing rubric for social life and as a mode of intellectual inquiry? Halberstam’s synthesis of the field makes a compelling case for why the study of gender persists and remains relevant for humanists, social scientists, and scientists alike.
Miqqi Alicia Gilbert, “Defeating Bigenderism: Changing Gender Assumptions in the Twenty-First Century.” Hypatia , 2009
Scholar and transgender activist Miqqi Alicia Gilbert considers the production and maintenance of the gender binary—that is, the idea that there are only two genders and that gender is a natural fact that remains stable across the course of one’s life. Gilbert’s view extends across institutional, legal, and cultural contexts, imagining what a frameworks that gets one out of the gender binary and gender valuation would have to look like to eliminate sexism, transphobia, and discrimination.
Judith Lorber, “Shifting Paradigms and Challenging Categories.” Social Problems , 2006
Judith Lorber identifies the key paradigm shifts in sociology around the question of gender: 1) acknowledging gender as an “organizing principle of the overall social order in modern societies;” 2) stipulating that gender is socially constructed, meaning that while gender is assigned at birth based on visible genitalia, it isn’t a natural, immutable category but one that is socially determined; 3) analyzing power in modern western societies reveals the dominance of men and promotion of a limited version of heterosexual masculinity; 4) emerging methods in sociology are helping disrupt the production of ostensibly universal knowledge from a narrow perspective of privileged subjects. Lorber concludes that feminist sociologists’ work on gender has provided the tools for sociology to reconsider how it analyzes structures of power and produces knowledge.
bell hooks, “Sisterhood: Political Solidarity between Women.” Feminist Review , 1986
bell hooks argues that the feminist movement has privileged the voices, experiences, and concerns of white women at the expense of women of color. Instead of acknowledging who the movement has centered, white women have continually invoked the “common oppression” of all women, a move they think demonstrates solidarity but actually erases and marginalizes women who fall outside of the categories of white, straight, educated, and middle-class. Instead of appealing to “common oppression,” meaningful solidarity requires that women acknowledge their differences, committing to a feminism that “aims to end sexist oppression.” For hooks, this necessitates a feminism that is anti-racist. Solidarity doesn’t have to mean sameness; collective action can emerge from difference.
Jennifer C. Nash, “re-thinking intersectionality.” Feminist Review , 2008
Chances are you’ve come across the phrase “intersectional feminism.” For many, this term is redundant: If feminism isn’t attentive to issues impacting a range of women, then it’s not actually feminism. While the term “intersectional” now circulates colloquially to signify a feminism that is inclusive, its usage has become divorced from its academic origins. The legal scholar Kimberlé Crenshaw created the term “intersectionality” in the 1980s based on Black women’s experiences with the law in cases of discrimination and violence. Intersectionality is not an adjective or a way to describe identity, but a tool for analyzing structures of power. It aims to disrupt universal categories of and claims about identity. Jennifer Nash provides an overview of intersectionality’s power, including guidance on how to deploy it in the service of coalition-building and collective action.
Treva B. Lindsey, “Post-Ferguson: A ‘Herstorical’ Approach to Black Violability.” Feminist Studies , 2015
Treva Lindsey considers the erasure of Black women’s labor in anti-racist activism , as well as the erasure of their experiences with violence and harm. From the Civil Rights Movement to #BlackLivesMatter, Black women’s contributions and leadership have not been acknowledged to the same extent as their male counterparts. Furthermore, their experiences with state-sanctioned racial violence don’t garner as much attention. Lindsey argues that we must make visible the experiences and labor of Black women and queer persons of color in activist settings in order to strengthen activist struggles for racial justice.
Renya Ramirez, “Race, Tribal Nation, and Gender: A Native Feminist Approach to Belonging.” Meridians , 2007
Renya Ramirez (Winnebago) argues that indigenous activist struggles for sovereignty, liberation, and survival must account for gender. A range of issues impact Native American women, such as domestic abuse, forced sterilization , and sexual violence. Furthermore, the settler state has been invested in disciplining indigenous concepts and practices of gender, sexuality, and kinship, reorienting them to fit into white settler understandings of property and inheritance. A Native American feminist consciousness centers gender and envisions decolonization without sexism.
Hester Eisenstein, “A Dangerous Liaison? Feminism and Corporate Globalization.” Science & Society , 2005
Hester Eisenstein argues that some of contemporary U.S. feminism’s work in a global context has been informed by and strengthened capitalism in a way that ultimately increases harms against marginalized women. For example, some have suggested offering poor rural women in non-U.S. contexts microcredit as a path to economic liberation. In reality, these debt transactions hinder economic development and “continue the policies that have created the poverty in the first place.” Eisenstein acknowledges that feminism has the power to challenge capitalist interests in a global context, but she cautions us to consider how aspects of the feminist movement have been coopted by corporations.
Afsaneh Najmabadi, “Transing and Transpassing Across Sex-Gender Walls in Iran.” Women’s Studies Quarterly , 2008
Afsaneh Najmabadi remarks on the existence of sex-reassignment surgeries in Iran since the 1970s and the increase in these surgeries in the twenty-first century. She explains that these surgeries are a response to perceived sexual deviance; they’re offered to cure persons who express same-sex desire. Sex-reassignment surgeries ostensibly “heteronormaliz[e]” people who are pressured to pursue this medical intervention for legal and religious reasons. While a repressive practice, Najmabadi also argues that this practice has paradoxically provided “ relatively safer semipublic gay and lesbian social space” in Iran. Najmabadi’s scholarship illustrates how gender and sexual categories, practices, and understandings are influenced by geographical and cultural contexts.
Susan Stryker, Paisley Currah, and Lisa Jean Moore’s “Introduction: Trans-, Trans, or Transgender?” Women’s Studies Quarterly , 2008
Susan Stryker, Paisley Currah, and Lisa Jean Moore map the ways that transgender studies can expand feminist and gender studies. “Transgender” does not need to exclusively signify individuals and communities, but can provide a lens for interrogating all bodies’ relationships to gendered spaces, disrupting the bounds of seemingly strict identity categories, and redefining gender. The “trans-” in transgender is a conceptual tool for interrogating the relationship between bodies and the institutions that discipline them.
David A. Rubin, “‘An Unnamed Blank That Craved a Name’: A Genealogy of Intersex as Gender.” Signs , 2012
David Rubin considers the fact that intersex persons have been subject to medicalization, pathologization, and “regulation of embodied difference through biopolitical discourses, practices, and technologies” that rely on normative cultural understandings of gender and sexuality. Rubin considers the impact intersexuality had on conceptualizations of gender in mid-twentieth century sexology studies, and how the very concept of gender that emerged in that moment has been used to regulate the lives of intersex individuals.
Rosemarie Garland-Thomson, “Feminist Disability Studies.” Signs , 2005
Rosemarie Garland-Thomson provides a thorough overview of the field of feminist disability studies. Both feminist and disability studies contend that those things which seem most natural to bodies are actually produced by a range of political, legal, medical, and social institutions. Gendered and disabled bodies are marked by these institutions. Feminist disability studies asks: How are meaning and value assigned to disabled bodies? How is this meaning and value determined by other social markers, such as gender, sexuality, race, class, religion, national origin, and citizenship status?
The field asks under what conditions disabled bodies are denied or granted sexual, reproductive, and bodily autonomy and how disability impacts the exploration of gender and sexual expression in childhood, adolescence, and adulthood historical and contemporary pathologization of genders and sexualities. It explores how disabled activists, artists, and writers respond to social, cultural, medical, and political forces that deny them access, equity, and representation
Karin A. Martin, “William Wants a Doll. Can He Have One? Feminists, Child Care Advisors, and Gender-Neutral Child Rearing.” Gender and Society , 2005
Karin Martin examines the gender socialization of children through an analysis of a range of parenting materials. Materials that claim to be (or have been claimed as) gender-neutral actually have a deep investment in training children in gender and sexual norms. Martin invites us to think about how adult reactions to children’s gender nonconformity pivots on a fear that gender expression in childhood is indicative of present or future non-normative sexuality. In other words, U.S. culture is unable to separate gender from sexuality. We imagine gender identity and expression maps predictably onto sexual desire. When children’s gender identity and expression exceeds culturally-determined permissible bounds in a family or community, adults project onto the child and discipline accordingly.
Sarah Pemberton, “Enforcing Gender: The Constitution of Sex and Gender in Prison Regimes.” Signs , 2013
Sarah Pemberton’s considers how sex-segregated prisons in the U.S. and England discipline their populations differently according to gender and sexual norms. This contributes to the policing, punishment, and vulnerability of incarcerated gender-nonconforming, transgender, and intersex persons. Issues ranging from healthcare access to increased rates of violence and harassment suggest that policies impacting incarcerated persons should center gender.
Dean Spade, “Some Very Basic Tips for Making High Education More Accessible to Trans Students and Rethinking How We Talk about Gendered Bodies.” The Radical Teacher , 2011
Lawyer and trans activist Dean Spade offers a pedagogical perspective on how to make classrooms accessible and inclusive for students. Spade also offers guidance on how to have classroom conversations about gender and bodies that don’t reassert a biological understanding of gender or equate certain body parts and functions with particular genders. While the discourse around these issues is constantly shifting, Spade provides useful ways to think about small changes in language that can have a powerful impact on students.
Sarah S. Richardson, “Feminist Philosophy of Science: History, Contributions, and Challenges.” Synthese , 2010
Feminist philosophy of science is a field comprised of scholars studying gender and science that has its origins in the work of feminist scientists in the 1960s. Richardson considers the contributions made by these scholars, such as increased opportunities for and representation of women in STEM fields , pointing out biases in seemingly neutral fields of scientific inquiry. Richardson also considers the role of gender in knowledge production, looking at the difficulties women have faced in institutional and professional contexts. The field of feminist philosophy of science and its practitioners are marginalized and delegitimized because of the ways they challenge dominant modes of knowledge production and disciplinary inquiry.
Bryce Traister’s “Academic Viagra: The Rise of American Masculinity Studies.” American Quarterly , 2000
Bryce Traister considers the emergence of masculinity studies out of gender studies and its development in American cultural studies. He argues that the field has remained largely invested in centering heterosexuality, asserting the centrality and dominance of men in critical thought. He offers ways for thinking about how to study masculinity without reinstituting gendered hierarchies or erasing the contributions of feminist and queer scholarship.

JSTOR is a digital library for scholars, researchers, and students. JSTOR Daily readers can access the original research behind our articles for free on JSTOR.
Get Our Newsletter
Get your fix of JSTOR Daily’s best stories in your inbox each Thursday.
Privacy Policy Contact Us You may unsubscribe at any time by clicking on the provided link on any marketing message.
More Stories

Building Classroom Discussions around JSTOR Daily Syllabi

The Power of the Veil for Spanish Women

Elephant Executions

Scaffolding a Research Project with JSTOR
Recent posts.
- Tramping Across the USSR (On One Leg)
- How Government Helped Birth the Advertising Industry
- Harvey Houses: Serving the West
- MeerKAT: The South African Radio Telescope That’s Transformed Our Understanding of the Cosmos
- Pakistan’s Ambiguous Islamic Identity
Support JSTOR Daily
Sign up for our weekly newsletter.
Closing the equity gap
Jeni Klugman
Caren Grown and Odera Onyechi
Why addressing gender inequality is central to tackling today’s polycrises
Nonresident Senior Fellow, Africa Growth Initiative, Global Economy and Development, Brookings Institution
As we enter 2023, the term “ polycrisis ” is an increasingly apt way to describe today’s challenges. 1 Major wars, high inflation, and climate events are creating hardship all around the world, which is still grappling with a pandemic death toll approaching 7 million people.
Faced with such daunting challenges, one might well ask why we should be thinking about the gender dimensions of recovery and resilience for future shocks. The answer is simple: We can no longer afford to think in silos. Today’s interlocking challenges demand that sharp inequalities, including gender disparities, must be addressed as part and parcel of efforts to tackle Africa’s pressing issues and ensure the continent’s future success.
“We can no longer afford to think in silos. … Gender disparities, must be addressed as part and parcel of efforts to tackle Africa’s pressing issues and ensure the continent’s future success.”
The burdens of the pandemic have been unequally borne across regions and countries, and between the poor and better off. Inequalities exist around gender—which can be defined as the “socially constructed roles, behaviors, activities, attributes and opportunities that any society considers appropriate for men and women, boys and girls” and people with non-binary identities. 2 As Raewyn Connell laid out more than two decades ago, existing systems typically distribute greater power, resources, and status to men and behaviors considered masculine . 3 As a result, gender intersects with other sources of disadvantage, most notably income, age, race, and ethnicity.
This understanding is now mainstream. As recently observed by the IMF, “The gender inequalities exposed by the COVID-19 pandemic follow different paths but almost always end up the same: Women have suffered disproportionate economic harm from the crisis.” 4 Among the important nuances revealed by micro-surveys is that rural women working informally continued to work through the pandemic , but with sharply reduced earnings in Nigeria and elsewhere. 5 And as the burden of child care and home schooling soared, rural households headed by women were far less likely than urban households to have children engaged in learning activities during school closures.
Important insights emerge from IFPRI’s longitudinal panel study (which included Ghana, Kenya, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, and Uganda) covering income loss, coping strategies, labor and time use, food and water insecurity, and child education outcomes. 6
Among the especially adverse impacts for women were greater food and water insecurity compared to men, including worrying about insufficient food and eating less than usual, while a large proportion of women also did not have adequately diverse diets. Moreover, many women had to add hours to their workday caring for sick family members, and their economic opportunities shrank, cutting their earnings and widening gender income gaps.
While today’s problems seem daunting, there remain huge causes for optimism, especially in Africa. Over the past three decades, many African countries have achieved enormous gains in levels of education, health, and poverty reduction. Indeed, the pace of change has been staggering and commendable. As captured in the Women Peace and Security Index , which measures performance in inclusion, justice, and security, 6 of the top 10 score improvers during the period 2017-2021 were in sub-Saharan Africa. [GIWPS.2022. “Women Peace and Security Index” Georgetown Institute for Women, Peace and Security.] The Democratic Republic of Congo was among top score improvers since 2017, as the share of women with financial accounts almost tripled, to 24 percent; and increases exceeding 5 percentage points were registered in cell phone use and parliamentary representation. In the Central African Republic, improvements were experienced in the security dimension, where organized violence fell significantly, and women’s perceptions of community safety rose 6 percentage points up to 49 percent.
Looking ahead, efforts to mitigate gender inequalities must clearly be multi-pronged, and as highlighted above—we need to think outside silos. That said, two major policy fronts emerge to the fore.
Ensure cash transfers that protect against poverty , are built and designed to promote women’s opportunities, with a focus on digital payments. 7 Ways to address gender inequalities as part of social protection program responses 8 include deliberate efforts to overcome gender gaps in cell phone access by distributing phones to those women who need them, as well as private sector partnerships to subsidize airtime for the poorest, and to make key information services and apps freely available . 9 Programs could also make women the default recipient of cash transfer schemes, instead of the head of household. Furthermore, capacity-building initiatives can be built into program design to give women the skills and capabilities needed to successfully manage accounts and financial decisionmaking. 10
Reducing the risk of violence against women. Women who are not safe at home are denied the freedom from violence needed to pursue opportunities that should be afforded to all. In 2018, 10 of the 15 countries with the worst rates of intimate partner violence were in sub-Saharan Africa—in descending order of average intimate partner violence these were, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Madagascar, Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Zambia, Ethiopia, Liberia, South Sudan, Djibouti, and Uganda.
“As the burden of child care and home schooling soared, rural households headed by women were far less likely than urban households to have children engaged in learning activities.”
Conflicts and crises multiply women’s risk of physical, emotional, and sexual violence . During the pandemic, risk factors like economic stress were compounded by service closures and stay-at-home orders, which increased exposure to potential perpetrators. 11 Several governments responded by strengthening existing help services , including police and justice, supporting hotlines, ensuring the provision of psychological support, and health sector responses. 12 Examples of good practice included an NGO in North-Eastern Nigeria, which equipped existing safe spaces with phone booths to enable survivors to contact caseworkers.
However, given the high levels of prevalence and often low levels of reporting, prevention of gender-based violence is key. Targeted programs with promising results in prevention include community dialogues and efforts to change harmful norms, safe spaces, as well as possibilities to reduce the risk of violence through cash plus social protection programs. These efforts should be accompanied by more systematic monitoring and evaluation to build evidence about what works in diverse settings.
Finally, but certainly not least, women should have space and voices in decisionmaking. This case was powerfully put by former President Sirleaf Johnson in her 2021 Foresight essay, which underlined that “ economic, political, institutional, and social barriers persist throughout the continent, limiting women’s abilities to reach high-level leadership positions .” 13 Persistent gender gaps in power and decision-making, not only limits innovative thinking and solutions, but also the consideration of more basic measures to avoid the worsening of gender inequalities. Overcoming these gaps in power and decision-making requires safeguarding legal protections and rights, investing in women and girls financially, and opening space for women in political parties so that women have the platforms to access high-level appointed and competitive positions across national, regional, and international institutions. 14
Strengthening fiscal policy for gender equality
Senior Fellow, Center for Sustainable Development, Global Economy and Development, Brookings Institution
Research Analyst, Center for Sustainable Development, Global Economy and Development, Brookings Institution
It is often said that women act as “shock absorbers” during times of crisis; this is even more so in the current context of climate change, the COVID-19 pandemic, and increased geopolitical conflict. These three global crises have simultaneously stretched women’s ability to earn income and intensified their unpaid work. Well-designed fiscal policy can help cushion the effects of these shocks and enable women and their households to recover more quickly.
Over 60 percent of employed women in Africa work in agriculture, including in small-scale food production; women are the primary sellers in food markets, and they work in other sectors such as informal trading. At the same time, women are an increasing share of entrepreneurs in countries such as Ghana and Uganda, even as they face financial and other constraints to start and grow their firms. [Africa Gender Innovation Lab (GIL). 2020. “Supporting Women Throughout the Coronavirus Emergency Response and Economic Recovery.” World Bank Group. ] In addition to earning income for their households, women bear the major responsibility for unpaid domestic activities such as cooking; collecting water and fuelwood; caring for children, elderly, and other dependents—so women are more time-poor than are men.
African women and entrepreneurs have been impacted disproportionately more than men by the triple shocks mentioned earlier. Extreme weather events disrupt food production and agricultural employment, making it harder for women to earn income . 15 16 17 The pandemic and conflict in Ukraine further intensified women’s paid and unpaid activities . 18 19 Beyond climate change and the war in Ukraine, localized conflicts and insecurity in East and West Africa exposes women and girls to gender-based violence and other risks as they seek to support their families and develop new coping strategies. 20 21 22
“Responding to these shocks necessitates a large infusion of resources. In this context, fiscal policy can be deployed more smartly to advance gender equality and create an enabling environment for women to play a greater role in building their economies’ recovery and resilience.”
Responding to these shocks necessitates a large infusion of resources. In this context, fiscal policy can be deployed more smartly to advance gender equality and create an enabling environment for women to play a greater role in building their economies’ recovery and resilience. Public expenditure supports critical sectors such as education, health, agriculture, social protection, and physical and social infrastructure, while well-designed tax policy is essential to fund the public goods, services, and infrastructure on which both women and men rely.
Gender-responsive budgets, which exist in over 30 countries across the continent, can be strengthened. Rwanda provides a good model for other countries. After an early unsuccessful attempt, Rwanda invested seriously in gender budgeting beginning in 2011. 23 24 The budget is focused on closing gaps and strengthening women’s roles in key sectors—agriculture, education, health, and infrastructure—which are all critical for short- and medium-term economic growth and productivity. The process has been sustained by strong political will among parliamentarians. Led by the Ministry of Finance, the process has financed and been complemented by important institutional and policy reforms. A constitutional regulatory body monitors results, with additional accountability by civil society organizations.
However, raising adequate fiscal revenue to support a gender budget is a challenge in the current macro environment of high public debt levels, increased borrowing costs, and low levels of public savings. Yet, observers note there is scope to increase revenues through taxation reforms, debt relief, cutting wasteful public expenditure, and other means. 25 26 We focus here on taxation.
Many countries are reforming their tax systems to strengthen revenue collection. Overall tax collection is currently low; the average tax-to-GDP ratio in Africa in 2020 was 14.8 percent and fell sharply during the pandemic, although it may be rebounding. 27 Very few Africans pay personal income tax or other central government taxes, 28 29 and statutory corporate tax rates (which range from 25-35 percent), are higher than even the recent OECD proposal for a global minimum tax 30 so scope for raising them further is limited. Efforts should be made to close loopholes and reduce tax evasion.
As countries reform their tax policies, they should be intentional about avoiding implicit and explicit gender biases. 31 32 33 34 Most African countries rely more on indirect taxes than direct taxes, given the structure of their economies, but indirect taxes can be regressive as their incidence falls primarily on the poor. Presumptive or turnover taxes, for example, which are uniform or fixed amounts of tax based on the “presumed” incomes of different occupations such as hairdressers, can hit women particularly hard, since the burden often falls heavily on sectors where women predominate. 35 36
Property taxes are also becoming an increasingly popular way to raise revenue for local governments. The impact of these efforts on male and female property owners has not been systematically evaluated, but a recent study of land use fees and agricultural income taxes in Ethiopia finds that female-headed and female adult-only households bear a larger tax burden than male-headed and dual-adult households of property taxes. This is likely a result of unequal land ownership patterns, gender norms restricting women’s engagement in agriculture, and the gender gap in agricultural productivity. 37
“Indirect taxes can be regressive as their incidence falls primarily on the poor. Presumptive or turnover taxes … can hit women particularly hard, since the burden often falls heavily on sectors where women predominate.”
Going forward, two key ingredients for gender budgeting on the continent need to be strengthened. The first is having sufficient, regularly collected, sex-disaggregated administrative data related to households, the labor force, and other survey data. Investment in the robust technical capacity for ministries and academia to be able to access, analyze, and use it is also necessary. For instance, the World Bank, UN Women, and the Economic Commission for Africa are all working with National Statistical Offices across the continent to strengthen statistical capacity in the areas of asset ownership and control, work and employment, and entrepreneurship which can be used in a gender budget.
The second ingredient is stronger diagnostic tools. One promising new tool, pioneered by Tulane University, is the Commitment to Equity methodology, designed to assess the impact of taxes and transfers on income inequality and poverty within countries. 38 It was recently extended to examine the impact of government transfers and taxes on women and men by income level and other dimensions. The methodology requires standard household-level data but for maximum effect should be supplemented with time use data, which are becoming more common in several African countries. As African countries seek to expand revenue from direct taxes, lessons from higher income economies are instructive. Although there is no one size fits all approach, key principles to keep in mind for designing personal income taxes include building in strong progressivity, taxing individuals as opposed to families, ensuring that the allocation of shared income (e.g., property or non-labor income) does not penalize women, and building in allowances for care of children and dependents. 39 As noted, corporate income taxes need to eliminate the many breaks, loopholes, and exemptions that currently exist, 40 and countries might consider experimenting with wealth taxes.
In terms of indirect taxes, most African countries do not have single-rate VAT systems and already have zero or reduced rates for basic necessities, including foodstuffs and other necessities. While it is important to minimize exempted sectors and products, estimates show that goods essential for women’s and children’s health (e.g., menstrual health products, diapers, cooking fuel) should be considered part of the basket of basic goods that have reduced or zero rates. 41 And while African governments are being advised to bring informal workers and entrepreneurs into the formal tax system, 42 it should be noted that this massive sector earns well below income tax thresholds and already pays multiple informal fees and levies, for instance in fees to market associations. 43 44
Lastly, leveraging data and digital technologies to improve tax administration (i.e., taxpayer registration, e-filing, and e-payment of taxes) may help minimize costs and processing time, and reduce the incidence of corruption and evasion.32 Digitalization can also be important for bringing more female taxpayers into the net, especially if digital systems are interoperable; for instance, digital taxpayer registries linked to national identification or to property registration at the local level. However, digitalization can be a double-edged sword if privacy and security concerns are not built-in from the outset. Women particularly may need targeted digital financial literacy and other measures to ensure their trust in the system. Recent shocks have worsened gender inequality in Africa. It is therefore important now, more than ever, to invest in strengthening fiscal systems to help women and men recover, withstand future shocks, and reduce gender inequalities. While fiscal policy is not the only tool, it is an important part of government action. To be effective and improve both budgeting and revenue collection, more and better data, new diagnostic tools, and digitalization will all be necessary.
- 1. Martin Wolf. 2022.“How to think about policy in a policy crisis”. Financial Times.
- 2. WTO. 2022. “Gender and Health”. World Health Organization.
- 3. Connell RW. 1995. “Masculinities”. Cambridge, UK. Polity Press.
- 4. Aoyagi, Chie.2021.“Africa’s Unequal Pandemic”. Finance and Development. International Monetary Fund.
- 5. WB.2022. “LSMS-Supported High-Frequency Phone Surveys”. World Bank.
- 6. Muzna Alvi, Shweta Gupta, Prapti Barooah, Claudia Ringler, Elizabeth Bryan and Ruth Meinzen-Dick.2022.“Gendered Impacts of COVID-19: Insights from 7 countries in Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia”. International Food Policy Research Institute.
- 7. Klugman, Jeni, Zimmerman, Jamie M., Maria A. May, and Elizabeth Kellison. 2020. “Digital Cash Transfers in the Time of COVID 19: Opportunities and Considerations for Women’s Inclusion and Empowerment”. World Bank Group.
- 8. IFPRI.2020. “Why gender-sensitive social protection is critical to the COVID-19 response in low-and middle-income countries”. International Food Policy Research Institute.
- 9. IDFR.2020. “Kenya: Mobile-money as a public-health tool”. International Day of Family Remittances.
- 10. Jaclyn Berfond Franz Gómez S. Juan Navarrete Ryan Newton Ana Pantelic. 2019. “Capacity Building for Government-to-Person Payments A Path to Women’s Economic Empowerment”. Women’s World Banking.
- 11. Peterman, A. et al.2020. “Pandemics and Violence Against Women and Children”.Center for Global Development Working Paper.
- 12. UNDP/ UN Women Tracker.2022. “United Nations Development Programme. COVID-19 Global Gender Response Tracker”. United Nations Development Programme. New York.
- 13. McKinsey Global Institute .2019. “The power of parity: Advancing women’s equality in Africa”.
- 14. Foresight Africa. 2022. “African Women and Girls: Leading a continent.” The Brookings Institution.
- 15. One recent study in West, Central Africa, East and Southern Africa found that women represented a larger share of agricultural employment in areas affected by heat waves and droughts, and a lower share in areas unaffected by extreme weather events. Nico, G. et al. 2022. “How Weather Variability and Extreme Shocks Affect Women’s Participation in African Agriculture.” Gender, Climate Change, and Nutrition Integration Initiative Policy Note 14.
- 16. Carleton, E. 2022. “Climate Change in Africa: What Will It Mean for Agriculture and Food Security?” International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI).
- 17. Nebie, E.K. et al. 2021. “Food Security and Climate Shocks in Senegal: Who and Where Are the Most Vulnerable Households?” Global Food Security, 29.
- 18. Sen, A.K. 2022. “Russia’s War in Ukraine Is Taking a Toll on Africa.” United States Institute of Peace.
- 19. Thomas, A. 2020. “Power Structures over Gender Make Women More Vulnerable to Climate Change.” Climate Change News.
- 21. Kalbarczyk, A. et al. 2022. “COVID-19, Nutrition, and Gender: An Evidence-Informed Approach to Gender Responsive Policies and Programs.” Social Science & Medicine, 312.
- 22. Epstein, A. 2020. “Drought and Intimate Partner Violence Towards Women in 19 Countries in Sub-Saharan Africa During 2011-2018: A Population-Based Study.” PLoS Med, 17(3).
- 23. Stotsky, J. et al. 2016. “Sub-Saharan Africa: A Survey of Gender Budgeting Efforts. IMF Working Paper 2016/512.
- 24. Kadama, C. et al. 2018. Sub-Saharan Africa.” In Kolovich, L. (Ed.), Fiscal Policies and Gender Equality (pp. 9-32). International Monetary Fund (IMF).
- 25. Ortiz, I. and Cummins, M. 2021. “Abandoning Austerity: Fiscal Policies for Inclusive Development.” In Gallagher, K. and Gao, H. (Eds.), Building Back a Better Global Financial Safety Net (pp. 11-22). Global Development Policy Center.
- 26. Roy, R. et al. 2006. “Fiscal Space for Public Investment: Towards a Human Development Approach.”
- 27. ATAF, 2021.
- 28. Moore, M. et al. 2018. “Taxing Africa: Coercion, Reform and Development. Bloomsbury Publishing.
- 29. Rogan, M. 2019. Tax Justice and the Informal Economy: A Review of the Debates.” Women in Informal Employment: Globalizing and Organizing Working Paper 14.
- 30. African Tax Administrative Forum (ATAF). 2021. African Tax Outlook 2021.
- 31. Stotsky, J. et al. 2016. “Sub-Saharan Africa: A Survey of Gender Budgeting Efforts.” IMF Working Paper 2016/512.
- 32. Coelho, M. et al. 2022. “Gendered Taxes: The Interaction of Tax Policy with Gender Equality.” IMF Working Paper 2022/26.
- 33. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). 2021. Gender and Capital Budgeting.
- 34. Grown, C. and Valodia, I. 2010. Taxation and Gender Equity: A Comparative Analysis of Direct and Indirect Taxes in Developing and Developed Countries. Routledge.
- 35. Joshi, Anuradha et al. 2020. “Gender and Tax Policies in the Global South.” International Centre for Tax and Development.
- 36. Komatsu, H. et al. 2021. “Gender and Tax Incidence of Rural Land Use Fee and Agricultural In¬come Tax in Ethiopia.” Policy Research Working Papers.
- 38. Lustig, N. 2018. “Commitment to Equity Handbook: Estimating the Impact of Fiscal Policy on Inequality and Poverty.” Brookings Institution Press.
- 39. Grown, C. and Valodia, I. 2010. “Taxation and Gender Equity: A Comparative Analysis of Direct and Indirect Taxes in Developing and Developed Countries.” Routledge.
- 40. Cesar, C. et al. 2022. “Africa’s Pulse: An Analysis of Issues Shaping Africa’s Economic Future.” World Bank.
- 41. Woolard, I. 2018. Recommendations on Zero Ratings in the Value-Added Tax System. Independent Panel of Experts for the Review of Zero Rating in South Africa.
- 42. It is important to distinguish between firms and individuals that are large enough to pay taxes but do not (which include icebergs, e.g., which are registered and therefore partially visible to tax authorities but do not pay their full obligations) and ghosts, e.g., those which should register to pay but do not and there invisible to tax authorities) and firms and individuals that are small and potentially but not necessarily taxable such as street vendors and waste pickers. Rogan, M. (2019). “Tax Justice and the Informal Economy: A Review of the Debates.” Women in Informal Employment: Globalizing and Organizing Working Paper 14.
- 44. Ligomeka, W. 2019. “Expensive to be a Female Trader: The Reality of Taxation of Flea Market Trad¬ers in Zimbabwe.” International Center for Tax and Development Working Paper 93.

By Mavis Owusu-Gyamfi
Mavis Owusu-Gyamfi explores the role of gender equality in Africa’s economic development.

By Cina Lawson
Cina Lawson describes Togolese initiatives to expand the reach of social protection.

By Malado Kaba
Malado Kaba identifies four priorities for governments to transform the informal sector and economic prospects for African women.

By J. Jarpa Duwuni
J. Jarpa Dawuni identifies priority areas to expand access to justice for women and girls in Africa.
Next Chapter
06 | Climate Change Adapting to a new normal
Foresight Africa: Top Priorities for the Continent in 2023
On January 30, AGI hosted a Foresight Africa launch featuring a high-level panel of leading Africa experts to offer insights on regional trends along with recommendations for national governments, regional organizations, multilateral institutions, the private sector, and civil society actors as they forge ahead in 2022.
Africa in Focus
What should be the top priority for Africa in 2023?
BY ALOYSIUS UCHE ORDU
Aloysius Uche Ordu introduces Foresight Africa 2023, which outlines top priorities for the year ahead and offers recommendations for supporting Africa at a time of heightened global turbulence.
Foresight Africa Podcast
The Foresight Africa podcast celebrates Africa’s dynamism and explores strategies for broadening the benefits of growth to all people of Africa.
- Media Relations
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy

- Table of Contents
- Random Entry
- Chronological
- Editorial Information
- About the SEP
- Editorial Board
- How to Cite the SEP
- Special Characters
- Advanced Tools
- Support the SEP
- PDFs for SEP Friends
- Make a Donation
- SEPIA for Libraries
- Entry Contents
Bibliography
Academic tools.
- Friends PDF Preview
- Author and Citation Info
- Back to Top
Feminist Perspectives on Sex and Gender
Feminism is said to be the movement to end women’s oppression (hooks 2000, 26). One possible way to understand ‘woman’ in this claim is to take it as a sex term: ‘woman’ picks out human females and being a human female depends on various biological and anatomical features (like genitalia). Historically many feminists have understood ‘woman’ differently: not as a sex term, but as a gender term that depends on social and cultural factors (like social position). In so doing, they distinguished sex (being female or male) from gender (being a woman or a man), although most ordinary language users appear to treat the two interchangeably. In feminist philosophy, this distinction has generated a lively debate. Central questions include: What does it mean for gender to be distinct from sex, if anything at all? How should we understand the claim that gender depends on social and/or cultural factors? What does it mean to be gendered woman, man, or genderqueer? This entry outlines and discusses distinctly feminist debates on sex and gender considering both historical and more contemporary positions.
1.1 Biological determinism
1.2 gender terminology, 2.1 gender socialisation, 2.2 gender as feminine and masculine personality, 2.3 gender as feminine and masculine sexuality, 3.1.1 particularity argument, 3.1.2 normativity argument, 3.2 is sex classification solely a matter of biology, 3.3 are sex and gender distinct, 3.4 is the sex/gender distinction useful, 4.1.1 gendered social series, 4.1.2 resemblance nominalism, 4.2.1 social subordination and gender, 4.2.2 gender uniessentialism, 4.2.3 gender as positionality, 5. beyond the binary, 6. conclusion, other internet resources, related entries, 1. the sex/gender distinction..
The terms ‘sex’ and ‘gender’ mean different things to different feminist theorists and neither are easy or straightforward to characterise. Sketching out some feminist history of the terms provides a helpful starting point.
Most people ordinarily seem to think that sex and gender are coextensive: women are human females, men are human males. Many feminists have historically disagreed and have endorsed the sex/ gender distinction. Provisionally: ‘sex’ denotes human females and males depending on biological features (chromosomes, sex organs, hormones and other physical features); ‘gender’ denotes women and men depending on social factors (social role, position, behaviour or identity). The main feminist motivation for making this distinction was to counter biological determinism or the view that biology is destiny.
A typical example of a biological determinist view is that of Geddes and Thompson who, in 1889, argued that social, psychological and behavioural traits were caused by metabolic state. Women supposedly conserve energy (being ‘anabolic’) and this makes them passive, conservative, sluggish, stable and uninterested in politics. Men expend their surplus energy (being ‘katabolic’) and this makes them eager, energetic, passionate, variable and, thereby, interested in political and social matters. These biological ‘facts’ about metabolic states were used not only to explain behavioural differences between women and men but also to justify what our social and political arrangements ought to be. More specifically, they were used to argue for withholding from women political rights accorded to men because (according to Geddes and Thompson) “what was decided among the prehistoric Protozoa cannot be annulled by Act of Parliament” (quoted from Moi 1999, 18). It would be inappropriate to grant women political rights, as they are simply not suited to have those rights; it would also be futile since women (due to their biology) would simply not be interested in exercising their political rights. To counter this kind of biological determinism, feminists have argued that behavioural and psychological differences have social, rather than biological, causes. For instance, Simone de Beauvoir famously claimed that one is not born, but rather becomes a woman, and that “social discrimination produces in women moral and intellectual effects so profound that they appear to be caused by nature” (Beauvoir 1972 [original 1949], 18; for more, see the entry on Simone de Beauvoir ). Commonly observed behavioural traits associated with women and men, then, are not caused by anatomy or chromosomes. Rather, they are culturally learned or acquired.
Although biological determinism of the kind endorsed by Geddes and Thompson is nowadays uncommon, the idea that behavioural and psychological differences between women and men have biological causes has not disappeared. In the 1970s, sex differences were used to argue that women should not become airline pilots since they will be hormonally unstable once a month and, therefore, unable to perform their duties as well as men (Rogers 1999, 11). More recently, differences in male and female brains have been said to explain behavioural differences; in particular, the anatomy of corpus callosum, a bundle of nerves that connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres, is thought to be responsible for various psychological and behavioural differences. For instance, in 1992, a Time magazine article surveyed then prominent biological explanations of differences between women and men claiming that women’s thicker corpus callosums could explain what ‘women’s intuition’ is based on and impair women’s ability to perform some specialised visual-spatial skills, like reading maps (Gorman 1992). Anne Fausto-Sterling has questioned the idea that differences in corpus callosums cause behavioural and psychological differences. First, the corpus callosum is a highly variable piece of anatomy; as a result, generalisations about its size, shape and thickness that hold for women and men in general should be viewed with caution. Second, differences in adult human corpus callosums are not found in infants; this may suggest that physical brain differences actually develop as responses to differential treatment. Third, given that visual-spatial skills (like map reading) can be improved by practice, even if women and men’s corpus callosums differ, this does not make the resulting behavioural differences immutable. (Fausto-Sterling 2000b, chapter 5).
In order to distinguish biological differences from social/psychological ones and to talk about the latter, feminists appropriated the term ‘gender’. Psychologists writing on transsexuality were the first to employ gender terminology in this sense. Until the 1960s, ‘gender’ was often used to refer to masculine and feminine words, like le and la in French. However, in order to explain why some people felt that they were ‘trapped in the wrong bodies’, the psychologist Robert Stoller (1968) began using the terms ‘sex’ to pick out biological traits and ‘gender’ to pick out the amount of femininity and masculinity a person exhibited. Although (by and large) a person’s sex and gender complemented each other, separating out these terms seemed to make theoretical sense allowing Stoller to explain the phenomenon of transsexuality: transsexuals’ sex and gender simply don’t match.
Along with psychologists like Stoller, feminists found it useful to distinguish sex and gender. This enabled them to argue that many differences between women and men were socially produced and, therefore, changeable. Gayle Rubin (for instance) uses the phrase ‘sex/gender system’ in order to describe “a set of arrangements by which the biological raw material of human sex and procreation is shaped by human, social intervention” (1975, 165). Rubin employed this system to articulate that “part of social life which is the locus of the oppression of women” (1975, 159) describing gender as the “socially imposed division of the sexes” (1975, 179). Rubin’s thought was that although biological differences are fixed, gender differences are the oppressive results of social interventions that dictate how women and men should behave. Women are oppressed as women and “by having to be women” (Rubin 1975, 204). However, since gender is social, it is thought to be mutable and alterable by political and social reform that would ultimately bring an end to women’s subordination. Feminism should aim to create a “genderless (though not sexless) society, in which one’s sexual anatomy is irrelevant to who one is, what one does, and with whom one makes love” (Rubin 1975, 204).
In some earlier interpretations, like Rubin’s, sex and gender were thought to complement one another. The slogan ‘Gender is the social interpretation of sex’ captures this view. Nicholson calls this ‘the coat-rack view’ of gender: our sexed bodies are like coat racks and “provide the site upon which gender [is] constructed” (1994, 81). Gender conceived of as masculinity and femininity is superimposed upon the ‘coat-rack’ of sex as each society imposes on sexed bodies their cultural conceptions of how males and females should behave. This socially constructs gender differences – or the amount of femininity/masculinity of a person – upon our sexed bodies. That is, according to this interpretation, all humans are either male or female; their sex is fixed. But cultures interpret sexed bodies differently and project different norms on those bodies thereby creating feminine and masculine persons. Distinguishing sex and gender, however, also enables the two to come apart: they are separable in that one can be sexed male and yet be gendered a woman, or vice versa (Haslanger 2000b; Stoljar 1995).
So, this group of feminist arguments against biological determinism suggested that gender differences result from cultural practices and social expectations. Nowadays it is more common to denote this by saying that gender is socially constructed. This means that genders (women and men) and gendered traits (like being nurturing or ambitious) are the “intended or unintended product[s] of a social practice” (Haslanger 1995, 97). But which social practices construct gender, what social construction is and what being of a certain gender amounts to are major feminist controversies. There is no consensus on these issues. (See the entry on intersections between analytic and continental feminism for more on different ways to understand gender.)
2. Gender as socially constructed
One way to interpret Beauvoir’s claim that one is not born but rather becomes a woman is to take it as a claim about gender socialisation: females become women through a process whereby they acquire feminine traits and learn feminine behaviour. Masculinity and femininity are thought to be products of nurture or how individuals are brought up. They are causally constructed (Haslanger 1995, 98): social forces either have a causal role in bringing gendered individuals into existence or (to some substantial sense) shape the way we are qua women and men. And the mechanism of construction is social learning. For instance, Kate Millett takes gender differences to have “essentially cultural, rather than biological bases” that result from differential treatment (1971, 28–9). For her, gender is “the sum total of the parents’, the peers’, and the culture’s notions of what is appropriate to each gender by way of temperament, character, interests, status, worth, gesture, and expression” (Millett 1971, 31). Feminine and masculine gender-norms, however, are problematic in that gendered behaviour conveniently fits with and reinforces women’s subordination so that women are socialised into subordinate social roles: they learn to be passive, ignorant, docile, emotional helpmeets for men (Millett 1971, 26). However, since these roles are simply learned, we can create more equal societies by ‘unlearning’ social roles. That is, feminists should aim to diminish the influence of socialisation.
Social learning theorists hold that a huge array of different influences socialise us as women and men. This being the case, it is extremely difficult to counter gender socialisation. For instance, parents often unconsciously treat their female and male children differently. When parents have been asked to describe their 24- hour old infants, they have done so using gender-stereotypic language: boys are describes as strong, alert and coordinated and girls as tiny, soft and delicate. Parents’ treatment of their infants further reflects these descriptions whether they are aware of this or not (Renzetti & Curran 1992, 32). Some socialisation is more overt: children are often dressed in gender stereotypical clothes and colours (boys are dressed in blue, girls in pink) and parents tend to buy their children gender stereotypical toys. They also (intentionally or not) tend to reinforce certain ‘appropriate’ behaviours. While the precise form of gender socialization has changed since the onset of second-wave feminism, even today girls are discouraged from playing sports like football or from playing ‘rough and tumble’ games and are more likely than boys to be given dolls or cooking toys to play with; boys are told not to ‘cry like a baby’ and are more likely to be given masculine toys like trucks and guns (for more, see Kimmel 2000, 122–126). [ 1 ]
According to social learning theorists, children are also influenced by what they observe in the world around them. This, again, makes countering gender socialisation difficult. For one, children’s books have portrayed males and females in blatantly stereotypical ways: for instance, males as adventurers and leaders, and females as helpers and followers. One way to address gender stereotyping in children’s books has been to portray females in independent roles and males as non-aggressive and nurturing (Renzetti & Curran 1992, 35). Some publishers have attempted an alternative approach by making their characters, for instance, gender-neutral animals or genderless imaginary creatures (like TV’s Teletubbies). However, parents reading books with gender-neutral or genderless characters often undermine the publishers’ efforts by reading them to their children in ways that depict the characters as either feminine or masculine. According to Renzetti and Curran, parents labelled the overwhelming majority of gender-neutral characters masculine whereas those characters that fit feminine gender stereotypes (for instance, by being helpful and caring) were labelled feminine (1992, 35). Socialising influences like these are still thought to send implicit messages regarding how females and males should act and are expected to act shaping us into feminine and masculine persons.
Nancy Chodorow (1978; 1995) has criticised social learning theory as too simplistic to explain gender differences (see also Deaux & Major 1990; Gatens 1996). Instead, she holds that gender is a matter of having feminine and masculine personalities that develop in early infancy as responses to prevalent parenting practices. In particular, gendered personalities develop because women tend to be the primary caretakers of small children. Chodorow holds that because mothers (or other prominent females) tend to care for infants, infant male and female psychic development differs. Crudely put: the mother-daughter relationship differs from the mother-son relationship because mothers are more likely to identify with their daughters than their sons. This unconsciously prompts the mother to encourage her son to psychologically individuate himself from her thereby prompting him to develop well defined and rigid ego boundaries. However, the mother unconsciously discourages the daughter from individuating herself thereby prompting the daughter to develop flexible and blurry ego boundaries. Childhood gender socialisation further builds on and reinforces these unconsciously developed ego boundaries finally producing feminine and masculine persons (1995, 202–206). This perspective has its roots in Freudian psychoanalytic theory, although Chodorow’s approach differs in many ways from Freud’s.
Gendered personalities are supposedly manifested in common gender stereotypical behaviour. Take emotional dependency. Women are stereotypically more emotional and emotionally dependent upon others around them, supposedly finding it difficult to distinguish their own interests and wellbeing from the interests and wellbeing of their children and partners. This is said to be because of their blurry and (somewhat) confused ego boundaries: women find it hard to distinguish their own needs from the needs of those around them because they cannot sufficiently individuate themselves from those close to them. By contrast, men are stereotypically emotionally detached, preferring a career where dispassionate and distanced thinking are virtues. These traits are said to result from men’s well-defined ego boundaries that enable them to prioritise their own needs and interests sometimes at the expense of others’ needs and interests.
Chodorow thinks that these gender differences should and can be changed. Feminine and masculine personalities play a crucial role in women’s oppression since they make females overly attentive to the needs of others and males emotionally deficient. In order to correct the situation, both male and female parents should be equally involved in parenting (Chodorow 1995, 214). This would help in ensuring that children develop sufficiently individuated senses of selves without becoming overly detached, which in turn helps to eradicate common gender stereotypical behaviours.
Catharine MacKinnon develops her theory of gender as a theory of sexuality. Very roughly: the social meaning of sex (gender) is created by sexual objectification of women whereby women are viewed and treated as objects for satisfying men’s desires (MacKinnon 1989). Masculinity is defined as sexual dominance, femininity as sexual submissiveness: genders are “created through the eroticization of dominance and submission. The man/woman difference and the dominance/submission dynamic define each other. This is the social meaning of sex” (MacKinnon 1989, 113). For MacKinnon, gender is constitutively constructed : in defining genders (or masculinity and femininity) we must make reference to social factors (see Haslanger 1995, 98). In particular, we must make reference to the position one occupies in the sexualised dominance/submission dynamic: men occupy the sexually dominant position, women the sexually submissive one. As a result, genders are by definition hierarchical and this hierarchy is fundamentally tied to sexualised power relations. The notion of ‘gender equality’, then, does not make sense to MacKinnon. If sexuality ceased to be a manifestation of dominance, hierarchical genders (that are defined in terms of sexuality) would cease to exist.
So, gender difference for MacKinnon is not a matter of having a particular psychological orientation or behavioural pattern; rather, it is a function of sexuality that is hierarchal in patriarchal societies. This is not to say that men are naturally disposed to sexually objectify women or that women are naturally submissive. Instead, male and female sexualities are socially conditioned: men have been conditioned to find women’s subordination sexy and women have been conditioned to find a particular male version of female sexuality as erotic – one in which it is erotic to be sexually submissive. For MacKinnon, both female and male sexual desires are defined from a male point of view that is conditioned by pornography (MacKinnon 1989, chapter 7). Bluntly put: pornography portrays a false picture of ‘what women want’ suggesting that women in actual fact are and want to be submissive. This conditions men’s sexuality so that they view women’s submission as sexy. And male dominance enforces this male version of sexuality onto women, sometimes by force. MacKinnon’s thought is not that male dominance is a result of social learning (see 2.1.); rather, socialization is an expression of power. That is, socialized differences in masculine and feminine traits, behaviour, and roles are not responsible for power inequalities. Females and males (roughly put) are socialised differently because there are underlying power inequalities. As MacKinnon puts it, ‘dominance’ (power relations) is prior to ‘difference’ (traits, behaviour and roles) (see, MacKinnon 1989, chapter 12). MacKinnon, then, sees legal restrictions on pornography as paramount to ending women’s subordinate status that stems from their gender.
3. Problems with the sex/gender distinction
3.1 is gender uniform.
The positions outlined above share an underlying metaphysical perspective on gender: gender realism . [ 2 ] That is, women as a group are assumed to share some characteristic feature, experience, common condition or criterion that defines their gender and the possession of which makes some individuals women (as opposed to, say, men). All women are thought to differ from all men in this respect (or respects). For example, MacKinnon thought that being treated in sexually objectifying ways is the common condition that defines women’s gender and what women as women share. All women differ from all men in this respect. Further, pointing out females who are not sexually objectified does not provide a counterexample to MacKinnon’s view. Being sexually objectified is constitutive of being a woman; a female who escapes sexual objectification, then, would not count as a woman.
One may want to critique the three accounts outlined by rejecting the particular details of each account. (For instance, see Spelman [1988, chapter 4] for a critique of the details of Chodorow’s view.) A more thoroughgoing critique has been levelled at the general metaphysical perspective of gender realism that underlies these positions. It has come under sustained attack on two grounds: first, that it fails to take into account racial, cultural and class differences between women (particularity argument); second, that it posits a normative ideal of womanhood (normativity argument).
Elizabeth Spelman (1988) has influentially argued against gender realism with her particularity argument. Roughly: gender realists mistakenly assume that gender is constructed independently of race, class, ethnicity and nationality. If gender were separable from, for example, race and class in this manner, all women would experience womanhood in the same way. And this is clearly false. For instance, Harris (1993) and Stone (2007) criticise MacKinnon’s view, that sexual objectification is the common condition that defines women’s gender, for failing to take into account differences in women’s backgrounds that shape their sexuality. The history of racist oppression illustrates that during slavery black women were ‘hypersexualised’ and thought to be always sexually available whereas white women were thought to be pure and sexually virtuous. In fact, the rape of a black woman was thought to be impossible (Harris 1993). So, (the argument goes) sexual objectification cannot serve as the common condition for womanhood since it varies considerably depending on one’s race and class. [ 3 ]
For Spelman, the perspective of ‘white solipsism’ underlies gender realists’ mistake. They assumed that all women share some “golden nugget of womanness” (Spelman 1988, 159) and that the features constitutive of such a nugget are the same for all women regardless of their particular cultural backgrounds. Next, white Western middle-class feminists accounted for the shared features simply by reflecting on the cultural features that condition their gender as women thus supposing that “the womanness underneath the Black woman’s skin is a white woman’s, and deep down inside the Latina woman is an Anglo woman waiting to burst through an obscuring cultural shroud” (Spelman 1988, 13). In so doing, Spelman claims, white middle-class Western feminists passed off their particular view of gender as “a metaphysical truth” (1988, 180) thereby privileging some women while marginalising others. In failing to see the importance of race and class in gender construction, white middle-class Western feminists conflated “the condition of one group of women with the condition of all” (Spelman 1988, 3).
Betty Friedan’s (1963) well-known work is a case in point of white solipsism. [ 4 ] Friedan saw domesticity as the main vehicle of gender oppression and called upon women in general to find jobs outside the home. But she failed to realize that women from less privileged backgrounds, often poor and non-white, already worked outside the home to support their families. Friedan’s suggestion, then, was applicable only to a particular sub-group of women (white middle-class Western housewives). But it was mistakenly taken to apply to all women’s lives — a mistake that was generated by Friedan’s failure to take women’s racial and class differences into account (hooks 2000, 1–3).
Spelman further holds that since social conditioning creates femininity and societies (and sub-groups) that condition it differ from one another, femininity must be differently conditioned in different societies. For her, “females become not simply women but particular kinds of women” (Spelman 1988, 113): white working-class women, black middle-class women, poor Jewish women, wealthy aristocratic European women, and so on.
This line of thought has been extremely influential in feminist philosophy. For instance, Young holds that Spelman has definitively shown that gender realism is untenable (1997, 13). Mikkola (2006) argues that this isn’t so. The arguments Spelman makes do not undermine the idea that there is some characteristic feature, experience, common condition or criterion that defines women’s gender; they simply point out that some particular ways of cashing out what defines womanhood are misguided. So, although Spelman is right to reject those accounts that falsely take the feature that conditions white middle-class Western feminists’ gender to condition women’s gender in general, this leaves open the possibility that women qua women do share something that defines their gender. (See also Haslanger [2000a] for a discussion of why gender realism is not necessarily untenable, and Stoljar [2011] for a discussion of Mikkola’s critique of Spelman.)
Judith Butler critiques the sex/gender distinction on two grounds. They critique gender realism with their normativity argument (1999 [original 1990], chapter 1); they also hold that the sex/gender distinction is unintelligible (this will be discussed in section 3.3.). Butler’s normativity argument is not straightforwardly directed at the metaphysical perspective of gender realism, but rather at its political counterpart: identity politics. This is a form of political mobilization based on membership in some group (e.g. racial, ethnic, cultural, gender) and group membership is thought to be delimited by some common experiences, conditions or features that define the group (Heyes 2000, 58; see also the entry on Identity Politics ). Feminist identity politics, then, presupposes gender realism in that feminist politics is said to be mobilized around women as a group (or category) where membership in this group is fixed by some condition, experience or feature that women supposedly share and that defines their gender.
Butler’s normativity argument makes two claims. The first is akin to Spelman’s particularity argument: unitary gender notions fail to take differences amongst women into account thus failing to recognise “the multiplicity of cultural, social, and political intersections in which the concrete array of ‘women’ are constructed” (Butler 1999, 19–20). In their attempt to undercut biologically deterministic ways of defining what it means to be a woman, feminists inadvertently created new socially constructed accounts of supposedly shared femininity. Butler’s second claim is that such false gender realist accounts are normative. That is, in their attempt to fix feminism’s subject matter, feminists unwittingly defined the term ‘woman’ in a way that implies there is some correct way to be gendered a woman (Butler 1999, 5). That the definition of the term ‘woman’ is fixed supposedly “operates as a policing force which generates and legitimizes certain practices, experiences, etc., and curtails and delegitimizes others” (Nicholson 1998, 293). Following this line of thought, one could say that, for instance, Chodorow’s view of gender suggests that ‘real’ women have feminine personalities and that these are the women feminism should be concerned about. If one does not exhibit a distinctly feminine personality, the implication is that one is not ‘really’ a member of women’s category nor does one properly qualify for feminist political representation.
Butler’s second claim is based on their view that“[i]dentity categories [like that of women] are never merely descriptive, but always normative, and as such, exclusionary” (Butler 1991, 160). That is, the mistake of those feminists Butler critiques was not that they provided the incorrect definition of ‘woman’. Rather, (the argument goes) their mistake was to attempt to define the term ‘woman’ at all. Butler’s view is that ‘woman’ can never be defined in a way that does not prescribe some “unspoken normative requirements” (like having a feminine personality) that women should conform to (Butler 1999, 9). Butler takes this to be a feature of terms like ‘woman’ that purport to pick out (what they call) ‘identity categories’. They seem to assume that ‘woman’ can never be used in a non-ideological way (Moi 1999, 43) and that it will always encode conditions that are not satisfied by everyone we think of as women. Some explanation for this comes from Butler’s view that all processes of drawing categorical distinctions involve evaluative and normative commitments; these in turn involve the exercise of power and reflect the conditions of those who are socially powerful (Witt 1995).
In order to better understand Butler’s critique, consider their account of gender performativity. For them, standard feminist accounts take gendered individuals to have some essential properties qua gendered individuals or a gender core by virtue of which one is either a man or a woman. This view assumes that women and men, qua women and men, are bearers of various essential and accidental attributes where the former secure gendered persons’ persistence through time as so gendered. But according to Butler this view is false: (i) there are no such essential properties, and (ii) gender is an illusion maintained by prevalent power structures. First, feminists are said to think that genders are socially constructed in that they have the following essential attributes (Butler 1999, 24): women are females with feminine behavioural traits, being heterosexuals whose desire is directed at men; men are males with masculine behavioural traits, being heterosexuals whose desire is directed at women. These are the attributes necessary for gendered individuals and those that enable women and men to persist through time as women and men. Individuals have “intelligible genders” (Butler 1999, 23) if they exhibit this sequence of traits in a coherent manner (where sexual desire follows from sexual orientation that in turn follows from feminine/ masculine behaviours thought to follow from biological sex). Social forces in general deem individuals who exhibit in coherent gender sequences (like lesbians) to be doing their gender ‘wrong’ and they actively discourage such sequencing of traits, for instance, via name-calling and overt homophobic discrimination. Think back to what was said above: having a certain conception of what women are like that mirrors the conditions of socially powerful (white, middle-class, heterosexual, Western) women functions to marginalize and police those who do not fit this conception.
These gender cores, supposedly encoding the above traits, however, are nothing more than illusions created by ideals and practices that seek to render gender uniform through heterosexism, the view that heterosexuality is natural and homosexuality is deviant (Butler 1999, 42). Gender cores are constructed as if they somehow naturally belong to women and men thereby creating gender dimorphism or the belief that one must be either a masculine male or a feminine female. But gender dimorphism only serves a heterosexist social order by implying that since women and men are sharply opposed, it is natural to sexually desire the opposite sex or gender.
Further, being feminine and desiring men (for instance) are standardly assumed to be expressions of one’s gender as a woman. Butler denies this and holds that gender is really performative. It is not “a stable identity or locus of agency from which various acts follow; rather, gender is … instituted … through a stylized repetition of [habitual] acts ” (Butler 1999, 179): through wearing certain gender-coded clothing, walking and sitting in certain gender-coded ways, styling one’s hair in gender-coded manner and so on. Gender is not something one is, it is something one does; it is a sequence of acts, a doing rather than a being. And repeatedly engaging in ‘feminising’ and ‘masculinising’ acts congeals gender thereby making people falsely think of gender as something they naturally are . Gender only comes into being through these gendering acts: a female who has sex with men does not express her gender as a woman. This activity (amongst others) makes her gendered a woman.
The constitutive acts that gender individuals create genders as “compelling illusion[s]” (Butler 1990, 271). Our gendered classification scheme is a strong pragmatic construction : social factors wholly determine our use of the scheme and the scheme fails to represent accurately any ‘facts of the matter’ (Haslanger 1995, 100). People think that there are true and real genders, and those deemed to be doing their gender ‘wrong’ are not socially sanctioned. But, genders are true and real only to the extent that they are performed (Butler 1990, 278–9). It does not make sense, then, to say of a male-to-female trans person that s/he is really a man who only appears to be a woman. Instead, males dressing up and acting in ways that are associated with femininity “show that [as Butler suggests] ‘being’ feminine is just a matter of doing certain activities” (Stone 2007, 64). As a result, the trans person’s gender is just as real or true as anyone else’s who is a ‘traditionally’ feminine female or masculine male (Butler 1990, 278). [ 5 ] Without heterosexism that compels people to engage in certain gendering acts, there would not be any genders at all. And ultimately the aim should be to abolish norms that compel people to act in these gendering ways.
For Butler, given that gender is performative, the appropriate response to feminist identity politics involves two things. First, feminists should understand ‘woman’ as open-ended and “a term in process, a becoming, a constructing that cannot rightfully be said to originate or end … it is open to intervention and resignification” (Butler 1999, 43). That is, feminists should not try to define ‘woman’ at all. Second, the category of women “ought not to be the foundation of feminist politics” (Butler 1999, 9). Rather, feminists should focus on providing an account of how power functions and shapes our understandings of womanhood not only in the society at large but also within the feminist movement.
Many people, including many feminists, have ordinarily taken sex ascriptions to be solely a matter of biology with no social or cultural dimension. It is commonplace to think that there are only two sexes and that biological sex classifications are utterly unproblematic. By contrast, some feminists have argued that sex classifications are not unproblematic and that they are not solely a matter of biology. In order to make sense of this, it is helpful to distinguish object- and idea-construction (see Haslanger 2003b for more): social forces can be said to construct certain kinds of objects (e.g. sexed bodies or gendered individuals) and certain kinds of ideas (e.g. sex or gender concepts). First, take the object-construction of sexed bodies. Secondary sex characteristics, or the physiological and biological features commonly associated with males and females, are affected by social practices. In some societies, females’ lower social status has meant that they have been fed less and so, the lack of nutrition has had the effect of making them smaller in size (Jaggar 1983, 37). Uniformity in muscular shape, size and strength within sex categories is not caused entirely by biological factors, but depends heavily on exercise opportunities: if males and females were allowed the same exercise opportunities and equal encouragement to exercise, it is thought that bodily dimorphism would diminish (Fausto-Sterling 1993a, 218). A number of medical phenomena involving bones (like osteoporosis) have social causes directly related to expectations about gender, women’s diet and their exercise opportunities (Fausto-Sterling 2005). These examples suggest that physiological features thought to be sex-specific traits not affected by social and cultural factors are, after all, to some extent products of social conditioning. Social conditioning, then, shapes our biology.
Second, take the idea-construction of sex concepts. Our concept of sex is said to be a product of social forces in the sense that what counts as sex is shaped by social meanings. Standardly, those with XX-chromosomes, ovaries that produce large egg cells, female genitalia, a relatively high proportion of ‘female’ hormones, and other secondary sex characteristics (relatively small body size, less body hair) count as biologically female. Those with XY-chromosomes, testes that produce small sperm cells, male genitalia, a relatively high proportion of ‘male’ hormones and other secondary sex traits (relatively large body size, significant amounts of body hair) count as male. This understanding is fairly recent. The prevalent scientific view from Ancient Greeks until the late 18 th century, did not consider female and male sexes to be distinct categories with specific traits; instead, a ‘one-sex model’ held that males and females were members of the same sex category. Females’ genitals were thought to be the same as males’ but simply directed inside the body; ovaries and testes (for instance) were referred to by the same term and whether the term referred to the former or the latter was made clear by the context (Laqueur 1990, 4). It was not until the late 1700s that scientists began to think of female and male anatomies as radically different moving away from the ‘one-sex model’ of a single sex spectrum to the (nowadays prevalent) ‘two-sex model’ of sexual dimorphism. (For an alternative view, see King 2013.)
Fausto-Sterling has argued that this ‘two-sex model’ isn’t straightforward either (1993b; 2000a; 2000b). Based on a meta-study of empirical medical research, she estimates that 1.7% of population fail to neatly fall within the usual sex classifications possessing various combinations of different sex characteristics (Fausto-Sterling 2000a, 20). In her earlier work, she claimed that intersex individuals make up (at least) three further sex classes: ‘herms’ who possess one testis and one ovary; ‘merms’ who possess testes, some aspects of female genitalia but no ovaries; and ‘ferms’ who have ovaries, some aspects of male genitalia but no testes (Fausto-Sterling 1993b, 21). (In her [2000a], Fausto-Sterling notes that these labels were put forward tongue–in–cheek.) Recognition of intersex people suggests that feminists (and society at large) are wrong to think that humans are either female or male.
To illustrate further the idea-construction of sex, consider the case of the athlete Maria Patiño. Patiño has female genitalia, has always considered herself to be female and was considered so by others. However, she was discovered to have XY chromosomes and was barred from competing in women’s sports (Fausto-Sterling 2000b, 1–3). Patiño’s genitalia were at odds with her chromosomes and the latter were taken to determine her sex. Patiño successfully fought to be recognised as a female athlete arguing that her chromosomes alone were not sufficient to not make her female. Intersex people, like Patiño, illustrate that our understandings of sex differ and suggest that there is no immediately obvious way to settle what sex amounts to purely biologically or scientifically. Deciding what sex is involves evaluative judgements that are influenced by social factors.
Insofar as our cultural conceptions affect our understandings of sex, feminists must be much more careful about sex classifications and rethink what sex amounts to (Stone 2007, chapter 1). More specifically, intersex people illustrate that sex traits associated with females and males need not always go together and that individuals can have some mixture of these traits. This suggests to Stone that sex is a cluster concept: it is sufficient to satisfy enough of the sex features that tend to cluster together in order to count as being of a particular sex. But, one need not satisfy all of those features or some arbitrarily chosen supposedly necessary sex feature, like chromosomes (Stone 2007, 44). This makes sex a matter of degree and sex classifications should take place on a spectrum: one can be more or less female/male but there is no sharp distinction between the two. Further, intersex people (along with trans people) are located at the centre of the sex spectrum and in many cases their sex will be indeterminate (Stone 2007).
More recently, Ayala and Vasilyeva (2015) have argued for an inclusive and extended conception of sex: just as certain tools can be seen to extend our minds beyond the limits of our brains (e.g. white canes), other tools (like dildos) can extend our sex beyond our bodily boundaries. This view aims to motivate the idea that what counts as sex should not be determined by looking inwards at genitalia or other anatomical features. In a different vein, Ásta (2018) argues that sex is a conferred social property. This follows her more general conferralist framework to analyse all social properties: properties that are conferred by others thereby generating a social status that consists in contextually specific constraints and enablements on individual behaviour. The general schema for conferred properties is as follows (Ásta 2018, 8):
Conferred property: what property is conferred. Who: who the subjects are. What: what attitude, state, or action of the subjects matter. When: under what conditions the conferral takes place. Base property: what the subjects are attempting to track (consciously or not), if anything.
With being of a certain sex (e.g. male, female) in mind, Ásta holds that it is a conferred property that merely aims to track physical features. Hence sex is a social – or in fact, an institutional – property rather than a natural one. The schema for sex goes as follows (72):
Conferred property: being female, male. Who: legal authorities, drawing on the expert opinion of doctors, other medical personnel. What: “the recording of a sex in official documents ... The judgment of the doctors (and others) as to what sex role might be the most fitting, given the biological characteristics present.” When: at birth or after surgery/ hormonal treatment. Base property: “the aim is to track as many sex-stereotypical characteristics as possible, and doctors perform surgery in cases where that might help bring the physical characteristics more in line with the stereotype of male and female.”
This (among other things) offers a debunking analysis of sex: it may appear to be a natural property, but on the conferralist analysis is better understood as a conferred legal status. Ásta holds that gender too is a conferred property, but contra the discussion in the following section, she does not think that this collapses the distinction between sex and gender: sex and gender are differently conferred albeit both satisfying the general schema noted above. Nonetheless, on the conferralist framework what underlies both sex and gender is the idea of social construction as social significance: sex-stereotypical characteristics are taken to be socially significant context specifically, whereby they become the basis for conferring sex onto individuals and this brings with it various constraints and enablements on individuals and their behaviour. This fits object- and idea-constructions introduced above, although offers a different general framework to analyse the matter at hand.
In addition to arguing against identity politics and for gender performativity, Butler holds that distinguishing biological sex from social gender is unintelligible. For them, both are socially constructed:
If the immutable character of sex is contested, perhaps this construct called ‘sex’ is as culturally constructed as gender; indeed, perhaps it was always already gender, with the consequence that the distinction between sex and gender turns out to be no distinction at all. (Butler 1999, 10–11)
(Butler is not alone in claiming that there are no tenable distinctions between nature/culture, biology/construction and sex/gender. See also: Antony 1998; Gatens 1996; Grosz 1994; Prokhovnik 1999.) Butler makes two different claims in the passage cited: that sex is a social construction, and that sex is gender. To unpack their view, consider the two claims in turn. First, the idea that sex is a social construct, for Butler, boils down to the view that our sexed bodies are also performative and, so, they have “no ontological status apart from the various acts which constitute [their] reality” (1999, 173). Prima facie , this implausibly implies that female and male bodies do not have independent existence and that if gendering activities ceased, so would physical bodies. This is not Butler’s claim; rather, their position is that bodies viewed as the material foundations on which gender is constructed, are themselves constructed as if they provide such material foundations (Butler 1993). Cultural conceptions about gender figure in “the very apparatus of production whereby sexes themselves are established” (Butler 1999, 11).
For Butler, sexed bodies never exist outside social meanings and how we understand gender shapes how we understand sex (1999, 139). Sexed bodies are not empty matter on which gender is constructed and sex categories are not picked out on the basis of objective features of the world. Instead, our sexed bodies are themselves discursively constructed : they are the way they are, at least to a substantial extent, because of what is attributed to sexed bodies and how they are classified (for discursive construction, see Haslanger 1995, 99). Sex assignment (calling someone female or male) is normative (Butler 1993, 1). [ 6 ] When the doctor calls a newly born infant a girl or a boy, s/he is not making a descriptive claim, but a normative one. In fact, the doctor is performing an illocutionary speech act (see the entry on Speech Acts ). In effect, the doctor’s utterance makes infants into girls or boys. We, then, engage in activities that make it seem as if sexes naturally come in two and that being female or male is an objective feature of the world, rather than being a consequence of certain constitutive acts (that is, rather than being performative). And this is what Butler means in saying that physical bodies never exist outside cultural and social meanings, and that sex is as socially constructed as gender. They do not deny that physical bodies exist. But, they take our understanding of this existence to be a product of social conditioning: social conditioning makes the existence of physical bodies intelligible to us by discursively constructing sexed bodies through certain constitutive acts. (For a helpful introduction to Butler’s views, see Salih 2002.)
For Butler, sex assignment is always in some sense oppressive. Again, this appears to be because of Butler’s general suspicion of classification: sex classification can never be merely descriptive but always has a normative element reflecting evaluative claims of those who are powerful. Conducting a feminist genealogy of the body (or examining why sexed bodies are thought to come naturally as female and male), then, should ground feminist practice (Butler 1993, 28–9). Feminists should examine and uncover ways in which social construction and certain acts that constitute sex shape our understandings of sexed bodies, what kinds of meanings bodies acquire and which practices and illocutionary speech acts ‘make’ our bodies into sexes. Doing so enables feminists to identity how sexed bodies are socially constructed in order to resist such construction.
However, given what was said above, it is far from obvious what we should make of Butler’s claim that sex “was always already gender” (1999, 11). Stone (2007) takes this to mean that sex is gender but goes on to question it arguing that the social construction of both sex and gender does not make sex identical to gender. According to Stone, it would be more accurate for Butler to say that claims about sex imply gender norms. That is, many claims about sex traits (like ‘females are physically weaker than males’) actually carry implications about how women and men are expected to behave. To some extent the claim describes certain facts. But, it also implies that females are not expected to do much heavy lifting and that they would probably not be good at it. So, claims about sex are not identical to claims about gender; rather, they imply claims about gender norms (Stone 2007, 70).
Some feminists hold that the sex/gender distinction is not useful. For a start, it is thought to reflect politically problematic dualistic thinking that undercuts feminist aims: the distinction is taken to reflect and replicate androcentric oppositions between (for instance) mind/body, culture/nature and reason/emotion that have been used to justify women’s oppression (e.g. Grosz 1994; Prokhovnik 1999). The thought is that in oppositions like these, one term is always superior to the other and that the devalued term is usually associated with women (Lloyd 1993). For instance, human subjectivity and agency are identified with the mind but since women are usually identified with their bodies, they are devalued as human subjects and agents. The opposition between mind and body is said to further map on to other distinctions, like reason/emotion, culture/nature, rational/irrational, where one side of each distinction is devalued (one’s bodily features are usually valued less that one’s mind, rationality is usually valued more than irrationality) and women are associated with the devalued terms: they are thought to be closer to bodily features and nature than men, to be irrational, emotional and so on. This is said to be evident (for instance) in job interviews. Men are treated as gender-neutral persons and not asked whether they are planning to take time off to have a family. By contrast, that women face such queries illustrates that they are associated more closely than men with bodily features to do with procreation (Prokhovnik 1999, 126). The opposition between mind and body, then, is thought to map onto the opposition between men and women.
Now, the mind/body dualism is also said to map onto the sex/gender distinction (Grosz 1994; Prokhovnik 1999). The idea is that gender maps onto mind, sex onto body. Although not used by those endorsing this view, the basic idea can be summed by the slogan ‘Gender is between the ears, sex is between the legs’: the implication is that, while sex is immutable, gender is something individuals have control over – it is something we can alter and change through individual choices. However, since women are said to be more closely associated with biological features (and so, to map onto the body side of the mind/body distinction) and men are treated as gender-neutral persons (mapping onto the mind side), the implication is that “man equals gender, which is associated with mind and choice, freedom from body, autonomy, and with the public real; while woman equals sex, associated with the body, reproduction, ‘natural’ rhythms and the private realm” (Prokhovnik 1999, 103). This is said to render the sex/gender distinction inherently repressive and to drain it of any potential for emancipation: rather than facilitating gender role choice for women, it “actually functions to reinforce their association with body, sex, and involuntary ‘natural’ rhythms” (Prokhovnik 1999, 103). Contrary to what feminists like Rubin argued, the sex/gender distinction cannot be used as a theoretical tool that dissociates conceptions of womanhood from biological and reproductive features.
Moi has further argued that the sex/gender distinction is useless given certain theoretical goals (1999, chapter 1). This is not to say that it is utterly worthless; according to Moi, the sex/gender distinction worked well to show that the historically prevalent biological determinism was false. However, for her, the distinction does no useful work “when it comes to producing a good theory of subjectivity” (1999, 6) and “a concrete, historical understanding of what it means to be a woman (or a man) in a given society” (1999, 4–5). That is, the 1960s distinction understood sex as fixed by biology without any cultural or historical dimensions. This understanding, however, ignores lived experiences and embodiment as aspects of womanhood (and manhood) by separating sex from gender and insisting that womanhood is to do with the latter. Rather, embodiment must be included in one’s theory that tries to figure out what it is to be a woman (or a man).
Mikkola (2011) argues that the sex/gender distinction, which underlies views like Rubin’s and MacKinnon’s, has certain unintuitive and undesirable ontological commitments that render the distinction politically unhelpful. First, claiming that gender is socially constructed implies that the existence of women and men is a mind-dependent matter. This suggests that we can do away with women and men simply by altering some social practices, conventions or conditions on which gender depends (whatever those are). However, ordinary social agents find this unintuitive given that (ordinarily) sex and gender are not distinguished. Second, claiming that gender is a product of oppressive social forces suggests that doing away with women and men should be feminism’s political goal. But this harbours ontologically undesirable commitments since many ordinary social agents view their gender to be a source of positive value. So, feminism seems to want to do away with something that should not be done away with, which is unlikely to motivate social agents to act in ways that aim at gender justice. Given these problems, Mikkola argues that feminists should give up the distinction on practical political grounds.
Tomas Bogardus (2020) has argued in an even more radical sense against the sex/gender distinction: as things stand, he holds, feminist philosophers have merely assumed and asserted that the distinction exists, instead of having offered good arguments for the distinction. In other words, feminist philosophers allegedly have yet to offer good reasons to think that ‘woman’ does not simply pick out adult human females. Alex Byrne (2020) argues in a similar vein: the term ‘woman’ does not pick out a social kind as feminist philosophers have “assumed”. Instead, “women are adult human females–nothing more, and nothing less” (2020, 3801). Byrne offers six considerations to ground this AHF (adult, human, female) conception.
- It reproduces the dictionary definition of ‘woman’.
- One would expect English to have a word that picks out the category adult human female, and ‘woman’ is the only candidate.
- AHF explains how we sometimes know that an individual is a woman, despite knowing nothing else relevant about her other than the fact that she is an adult human female.
- AHF stands or falls with the analogous thesis for girls, which can be supported independently.
- AHF predicts the correct verdict in cases of gender role reversal.
- AHF is supported by the fact that ‘woman’ and ‘female’ are often appropriately used as stylistic variants of each other, even in hyperintensional contexts.
Robin Dembroff (2021) responds to Byrne and highlights various problems with Byrne’s argument. First, framing: Byrne assumes from the start that gender terms like ‘woman’ have a single invariant meaning thereby failing to discuss the possibility of terms like ‘woman’ having multiple meanings – something that is a familiar claim made by feminist theorists from various disciplines. Moreover, Byrne (according to Dembroff) assumes without argument that there is a single, universal category of woman – again, something that has been extensively discussed and critiqued by feminist philosophers and theorists. Second, Byrne’s conception of the ‘dominant’ meaning of woman is said to be cherry-picked and it ignores a wealth of contexts outside of philosophy (like the media and the law) where ‘woman’ has a meaning other than AHF . Third, Byrne’s own distinction between biological and social categories fails to establish what he intended to establish: namely, that ‘woman’ picks out a biological rather than a social kind. Hence, Dembroff holds, Byrne’s case fails by its own lights. Byrne (2021) responds to Dembroff’s critique.
Others such as ‘gender critical feminists’ also hold views about the sex/gender distinction in a spirit similar to Bogardus and Byrne. For example, Holly Lawford-Smith (2021) takes the prevalent sex/gender distinction, where ‘female’/‘male’ are used as sex terms and ‘woman’/’man’ as gender terms, not to be helpful. Instead, she takes all of these to be sex terms and holds that (the norms of) femininity/masculinity refer to gender normativity. Because much of the gender critical feminists’ discussion that philosophers have engaged in has taken place in social media, public fora, and other sources outside academic philosophy, this entry will not focus on these discussions.
4. Women as a group
The various critiques of the sex/gender distinction have called into question the viability of the category women . Feminism is the movement to end the oppression women as a group face. But, how should the category of women be understood if feminists accept the above arguments that gender construction is not uniform, that a sharp distinction between biological sex and social gender is false or (at least) not useful, and that various features associated with women play a role in what it is to be a woman, none of which are individually necessary and jointly sufficient (like a variety of social roles, positions, behaviours, traits, bodily features and experiences)? Feminists must be able to address cultural and social differences in gender construction if feminism is to be a genuinely inclusive movement and be careful not to posit commonalities that mask important ways in which women qua women differ. These concerns (among others) have generated a situation where (as Linda Alcoff puts it) feminists aim to speak and make political demands in the name of women, at the same time rejecting the idea that there is a unified category of women (2006, 152). If feminist critiques of the category women are successful, then what (if anything) binds women together, what is it to be a woman, and what kinds of demands can feminists make on behalf of women?
Many have found the fragmentation of the category of women problematic for political reasons (e.g. Alcoff 2006; Bach 2012; Benhabib 1992; Frye 1996; Haslanger 2000b; Heyes 2000; Martin 1994; Mikkola 2007; Stoljar 1995; Stone 2004; Tanesini 1996; Young 1997; Zack 2005). For instance, Young holds that accounts like Spelman’s reduce the category of women to a gerrymandered collection of individuals with nothing to bind them together (1997, 20). Black women differ from white women but members of both groups also differ from one another with respect to nationality, ethnicity, class, sexual orientation and economic position; that is, wealthy white women differ from working-class white women due to their economic and class positions. These sub-groups are themselves diverse: for instance, some working-class white women in Northern Ireland are starkly divided along religious lines. So if we accept Spelman’s position, we risk ending up with individual women and nothing to bind them together. And this is problematic: in order to respond to oppression of women in general, feminists must understand them as a category in some sense. Young writes that without doing so “it is not possible to conceptualize oppression as a systematic, structured, institutional process” (1997, 17). Some, then, take the articulation of an inclusive category of women to be the prerequisite for effective feminist politics and a rich literature has emerged that aims to conceptualise women as a group or a collective (e.g. Alcoff 2006; Ásta 2011; Frye 1996; 2011; Haslanger 2000b; Heyes 2000; Stoljar 1995, 2011; Young 1997; Zack 2005). Articulations of this category can be divided into those that are: (a) gender nominalist — positions that deny there is something women qua women share and that seek to unify women’s social kind by appealing to something external to women; and (b) gender realist — positions that take there to be something women qua women share (although these realist positions differ significantly from those outlined in Section 2). Below we will review some influential gender nominalist and gender realist positions. Before doing so, it is worth noting that not everyone is convinced that attempts to articulate an inclusive category of women can succeed or that worries about what it is to be a woman are in need of being resolved. Mikkola (2016) argues that feminist politics need not rely on overcoming (what she calls) the ‘gender controversy’: that feminists must settle the meaning of gender concepts and articulate a way to ground women’s social kind membership. As she sees it, disputes about ‘what it is to be a woman’ have become theoretically bankrupt and intractable, which has generated an analytical impasse that looks unsurpassable. Instead, Mikkola argues for giving up the quest, which in any case in her view poses no serious political obstacles.
Elizabeth Barnes (2020) responds to the need to offer an inclusive conception of gender somewhat differently, although she endorses the need for feminism to be inclusive particularly of trans people. Barnes holds that typically philosophical theories of gender aim to offer an account of what it is to be a woman (or man, genderqueer, etc.), where such an account is presumed to provide necessary and sufficient conditions for being a woman or an account of our gender terms’ extensions. But, she holds, it is a mistake to expect our theories of gender to do so. For Barnes, a project that offers a metaphysics of gender “should be understood as the project of theorizing what it is —if anything— about the social world that ultimately explains gender” (2020, 706). This project is not equivalent to one that aims to define gender terms or elucidate the application conditions for natural language gender terms though.
4.1 Gender nominalism
Iris Young argues that unless there is “some sense in which ‘woman’ is the name of a social collective [that feminism represents], there is nothing specific to feminist politics” (1997, 13). In order to make the category women intelligible, she argues that women make up a series: a particular kind of social collective “whose members are unified passively by the objects their actions are oriented around and/or by the objectified results of the material effects of the actions of the other” (Young 1997, 23). A series is distinct from a group in that, whereas members of groups are thought to self-consciously share certain goals, projects, traits and/ or self-conceptions, members of series pursue their own individual ends without necessarily having anything at all in common. Young holds that women are not bound together by a shared feature or experience (or set of features and experiences) since she takes Spelman’s particularity argument to have established definitely that no such feature exists (1997, 13; see also: Frye 1996; Heyes 2000). Instead, women’s category is unified by certain practico-inert realities or the ways in which women’s lives and their actions are oriented around certain objects and everyday realities (Young 1997, 23–4). For example, bus commuters make up a series unified through their individual actions being organised around the same practico-inert objects of the bus and the practice of public transport. Women make up a series unified through women’s lives and actions being organised around certain practico-inert objects and realities that position them as women .
Young identifies two broad groups of such practico-inert objects and realities. First, phenomena associated with female bodies (physical facts), biological processes that take place in female bodies (menstruation, pregnancy, childbirth) and social rules associated with these biological processes (social rules of menstruation, for instance). Second, gender-coded objects and practices: pronouns, verbal and visual representations of gender, gender-coded artefacts and social spaces, clothes, cosmetics, tools and furniture. So, women make up a series since their lives and actions are organised around female bodies and certain gender-coded objects. Their series is bound together passively and the unity is “not one that arises from the individuals called women” (Young 1997, 32).
Although Young’s proposal purports to be a response to Spelman’s worries, Stone has questioned whether it is, after all, susceptible to the particularity argument: ultimately, on Young’s view, something women as women share (their practico-inert realities) binds them together (Stone 2004).
Natalie Stoljar holds that unless the category of women is unified, feminist action on behalf of women cannot be justified (1995, 282). Stoljar too is persuaded by the thought that women qua women do not share anything unitary. This prompts her to argue for resemblance nominalism. This is the view that a certain kind of resemblance relation holds between entities of a particular type (for more on resemblance nominalism, see Armstrong 1989, 39–58). Stoljar is not alone in arguing for resemblance relations to make sense of women as a category; others have also done so, usually appealing to Wittgenstein’s ‘family resemblance’ relations (Alcoff 1988; Green & Radford Curry 1991; Heyes 2000; Munro 2006). Stoljar relies more on Price’s resemblance nominalism whereby x is a member of some type F only if x resembles some paradigm or exemplar of F sufficiently closely (Price 1953, 20). For instance, the type of red entities is unified by some chosen red paradigms so that only those entities that sufficiently resemble the paradigms count as red. The type (or category) of women, then, is unified by some chosen woman paradigms so that those who sufficiently resemble the woman paradigms count as women (Stoljar 1995, 284).
Semantic considerations about the concept woman suggest to Stoljar that resemblance nominalism should be endorsed (Stoljar 2000, 28). It seems unlikely that the concept is applied on the basis of some single social feature all and only women possess. By contrast, woman is a cluster concept and our attributions of womanhood pick out “different arrangements of features in different individuals” (Stoljar 2000, 27). More specifically, they pick out the following clusters of features: (a) Female sex; (b) Phenomenological features: menstruation, female sexual experience, child-birth, breast-feeding, fear of walking on the streets at night or fear of rape; (c) Certain roles: wearing typically female clothing, being oppressed on the basis of one’s sex or undertaking care-work; (d) Gender attribution: “calling oneself a woman, being called a woman” (Stoljar 1995, 283–4). For Stoljar, attributions of womanhood are to do with a variety of traits and experiences: those that feminists have historically termed ‘gender traits’ (like social, behavioural, psychological traits) and those termed ‘sex traits’. Nonetheless, she holds that since the concept woman applies to (at least some) trans persons, one can be a woman without being female (Stoljar 1995, 282).
The cluster concept woman does not, however, straightforwardly provide the criterion for picking out the category of women. Rather, the four clusters of features that the concept picks out help single out woman paradigms that in turn help single out the category of women. First, any individual who possesses a feature from at least three of the four clusters mentioned will count as an exemplar of the category. For instance, an African-American with primary and secondary female sex characteristics, who describes herself as a woman and is oppressed on the basis of her sex, along with a white European hermaphrodite brought up ‘as a girl’, who engages in female roles and has female phenomenological features despite lacking female sex characteristics, will count as woman paradigms (Stoljar 1995, 284). [ 7 ] Second, any individual who resembles “any of the paradigms sufficiently closely (on Price’s account, as closely as [the paradigms] resemble each other) will be a member of the resemblance class ‘woman’” (Stoljar 1995, 284). That is, what delimits membership in the category of women is that one resembles sufficiently a woman paradigm.
4.2 Neo-gender realism
In a series of articles collected in her 2012 book, Sally Haslanger argues for a way to define the concept woman that is politically useful, serving as a tool in feminist fights against sexism, and that shows woman to be a social (not a biological) notion. More specifically, Haslanger argues that gender is a matter of occupying either a subordinate or a privileged social position. In some articles, Haslanger is arguing for a revisionary analysis of the concept woman (2000b; 2003a; 2003b). Elsewhere she suggests that her analysis may not be that revisionary after all (2005; 2006). Consider the former argument first. Haslanger’s analysis is, in her terms, ameliorative: it aims to elucidate which gender concepts best help feminists achieve their legitimate purposes thereby elucidating those concepts feminists should be using (Haslanger 2000b, 33). [ 8 ] Now, feminists need gender terminology in order to fight sexist injustices (Haslanger 2000b, 36). In particular, they need gender terms to identify, explain and talk about persistent social inequalities between males and females. Haslanger’s analysis of gender begins with the recognition that females and males differ in two respects: physically and in their social positions. Societies in general tend to “privilege individuals with male bodies” (Haslanger 2000b, 38) so that the social positions they subsequently occupy are better than the social positions of those with female bodies. And this generates persistent sexist injustices. With this in mind, Haslanger specifies how she understands genders:
S is a woman iff [by definition] S is systematically subordinated along some dimension (economic, political, legal, social, etc.), and S is ‘marked’ as a target for this treatment by observed or imagined bodily features presumed to be evidence of a female’s biological role in reproduction.
S is a man iff [by definition] S is systematically privileged along some dimension (economic, political, legal, social, etc.), and S is ‘marked’ as a target for this treatment by observed or imagined bodily features presumed to be evidence of a male’s biological role in reproduction. (2003a, 6–7)
These are constitutive of being a woman and a man: what makes calling S a woman apt, is that S is oppressed on sex-marked grounds; what makes calling S a man apt, is that S is privileged on sex-marked grounds.
Haslanger’s ameliorative analysis is counterintuitive in that females who are not sex-marked for oppression, do not count as women. At least arguably, the Queen of England is not oppressed on sex-marked grounds and so, would not count as a woman on Haslanger’s definition. And, similarly, all males who are not privileged would not count as men. This might suggest that Haslanger’s analysis should be rejected in that it does not capture what language users have in mind when applying gender terms. However, Haslanger argues that this is not a reason to reject the definitions, which she takes to be revisionary: they are not meant to capture our intuitive gender terms. In response, Mikkola (2009) has argued that revisionary analyses of gender concepts, like Haslanger’s, are both politically unhelpful and philosophically unnecessary.
Note also that Haslanger’s proposal is eliminativist: gender justice would eradicate gender, since it would abolish those sexist social structures responsible for sex-marked oppression and privilege. If sexist oppression were to cease, women and men would no longer exist (although there would still be males and females). Not all feminists endorse such an eliminativist view though. Stone holds that Haslanger does not leave any room for positively revaluing what it is to be a woman: since Haslanger defines woman in terms of subordination,
any woman who challenges her subordinate status must by definition be challenging her status as a woman, even if she does not intend to … positive change to our gender norms would involve getting rid of the (necessarily subordinate) feminine gender. (Stone 2007, 160)
But according to Stone this is not only undesirable – one should be able to challenge subordination without having to challenge one’s status as a woman. It is also false: “because norms of femininity can be and constantly are being revised, women can be women without thereby being subordinate” (Stone 2007, 162; Mikkola [2016] too argues that Haslanger’s eliminativism is troublesome).
Theodore Bach holds that Haslanger’s eliminativism is undesirable on other grounds, and that Haslanger’s position faces another more serious problem. Feminism faces the following worries (among others):
Representation problem : “if there is no real group of ‘women’, then it is incoherent to make moral claims and advance political policies on behalf of women” (Bach 2012, 234). Commonality problems : (1) There is no feature that all women cross-culturally and transhistorically share. (2) Delimiting women’s social kind with the help of some essential property privileges those who possess it, and marginalizes those who do not (Bach 2012, 235).
According to Bach, Haslanger’s strategy to resolve these problems appeals to ‘social objectivism’. First, we define women “according to a suitably abstract relational property” (Bach 2012, 236), which avoids the commonality problems. Second, Haslanger employs “an ontologically thin notion of ‘objectivity’” (Bach 2012, 236) that answers the representation problem. Haslanger’s solution (Bach holds) is specifically to argue that women make up an objective type because women are objectively similar to one another, and not simply classified together given our background conceptual schemes. Bach claims though that Haslanger’s account is not objective enough, and we should on political grounds “provide a stronger ontological characterization of the genders men and women according to which they are natural kinds with explanatory essences” (Bach 2012, 238). He thus proposes that women make up a natural kind with a historical essence:
The essential property of women, in virtue of which an individual is a member of the kind ‘women,’ is participation in a lineage of women. In order to exemplify this relational property, an individual must be a reproduction of ancestral women, in which case she must have undergone the ontogenetic processes through which a historical gender system replicates women. (Bach 2012, 271)
In short, one is not a woman due to shared surface properties with other women (like occupying a subordinate social position). Rather, one is a woman because one has the right history: one has undergone the ubiquitous ontogenetic process of gender socialization. Thinking about gender in this way supposedly provides a stronger kind unity than Haslanger’s that simply appeals to shared surface properties.
Not everyone agrees; Mikkola (2020) argues that Bach’s metaphysical picture has internal tensions that render it puzzling and that Bach’s metaphysics does not provide good responses to the commonality and presentation problems. The historically essentialist view also has anti-trans implications. After all, trans women who have not undergone female gender socialization won’t count as women on his view (Mikkola [2016, 2020] develops this line of critique in more detail). More worryingly, trans women will count as men contrary to their self-identification. Both Bettcher (2013) and Jenkins (2016) consider the importance of gender self-identification. Bettcher argues that there is more than one ‘correct’ way to understand womanhood: at the very least, the dominant (mainstream), and the resistant (trans) conceptions. Dominant views like that of Bach’s tend to erase trans people’s experiences and to marginalize trans women within feminist movements. Rather than trans women having to defend their self-identifying claims, these claims should be taken at face value right from the start. And so, Bettcher holds, “in analyzing the meaning of terms such as ‘woman,’ it is inappropriate to dismiss alternative ways in which those terms are actually used in trans subcultures; such usage needs to be taken into consideration as part of the analysis” (2013, 235).
Specifically with Haslanger in mind and in a similar vein, Jenkins (2016) discusses how Haslanger’s revisionary approach unduly excludes some trans women from women’s social kind. On Jenkins’s view, Haslanger’s ameliorative methodology in fact yields more than one satisfying target concept: one that “corresponds to Haslanger’s proposed concept and captures the sense of gender as an imposed social class”; another that “captures the sense of gender as a lived identity” (Jenkins 2016, 397). The latter of these allows us to include trans women into women’s social kind, who on Haslanger’s social class approach to gender would inappropriately have been excluded. (See Andler 2017 for the view that Jenkins’s purportedly inclusive conception of gender is still not fully inclusive. Jenkins 2018 responds to this charge and develops the notion of gender identity still further.)
In addition to her revisionary argument, Haslanger has suggested that her ameliorative analysis of woman may not be as revisionary as it first seems (2005, 2006). Although successful in their reference fixing, ordinary language users do not always know precisely what they are talking about. Our language use may be skewed by oppressive ideologies that can “mislead us about the content of our own thoughts” (Haslanger 2005, 12). Although her gender terminology is not intuitive, this could simply be because oppressive ideologies mislead us about the meanings of our gender terms. Our everyday gender terminology might mean something utterly different from what we think it means; and we could be entirely ignorant of this. Perhaps Haslanger’s analysis, then, has captured our everyday gender vocabulary revealing to us the terms that we actually employ: we may be applying ‘woman’ in our everyday language on the basis of sex-marked subordination whether we take ourselves to be doing so or not. If this is so, Haslanger’s gender terminology is not radically revisionist.
Saul (2006) argues that, despite it being possible that we unknowingly apply ‘woman’ on the basis of social subordination, it is extremely difficult to show that this is the case. This would require showing that the gender terminology we in fact employ is Haslanger’s proposed gender terminology. But discovering the grounds on which we apply everyday gender terms is extremely difficult precisely because they are applied in various and idiosyncratic ways (Saul 2006, 129). Haslanger, then, needs to do more in order to show that her analysis is non-revisionary.
Charlotte Witt (2011a; 2011b) argues for a particular sort of gender essentialism, which Witt terms ‘uniessentialism’. Her motivation and starting point is the following: many ordinary social agents report gender being essential to them and claim that they would be a different person were they of a different sex/gender. Uniessentialism attempts to understand and articulate this. However, Witt’s work departs in important respects from the earlier (so-called) essentialist or gender realist positions discussed in Section 2: Witt does not posit some essential property of womanhood of the kind discussed above, which failed to take women’s differences into account. Further, uniessentialism differs significantly from those position developed in response to the problem of how we should conceive of women’s social kind. It is not about solving the standard dispute between gender nominalists and gender realists, or about articulating some supposedly shared property that binds women together and provides a theoretical ground for feminist political solidarity. Rather, uniessentialism aims to make good the widely held belief that gender is constitutive of who we are. [ 9 ]
Uniessentialism is a sort of individual essentialism. Traditionally philosophers distinguish between kind and individual essentialisms: the former examines what binds members of a kind together and what do all members of some kind have in common qua members of that kind. The latter asks: what makes an individual the individual it is. We can further distinguish two sorts of individual essentialisms: Kripkean identity essentialism and Aristotelian uniessentialism. The former asks: what makes an individual that individual? The latter, however, asks a slightly different question: what explains the unity of individuals? What explains that an individual entity exists over and above the sum total of its constituent parts? (The standard feminist debate over gender nominalism and gender realism has largely been about kind essentialism. Being about individual essentialism, Witt’s uniessentialism departs in an important way from the standard debate.) From the two individual essentialisms, Witt endorses the Aristotelian one. On this view, certain functional essences have a unifying role: these essences are responsible for the fact that material parts constitute a new individual, rather than just a lump of stuff or a collection of particles. Witt’s example is of a house: the essential house-functional property (what the entity is for, what its purpose is) unifies the different material parts of a house so that there is a house, and not just a collection of house-constituting particles (2011a, 6). Gender (being a woman/a man) functions in a similar fashion and provides “the principle of normative unity” that organizes, unifies and determines the roles of social individuals (Witt 2011a, 73). Due to this, gender is a uniessential property of social individuals.
It is important to clarify the notions of gender and social individuality that Witt employs. First, gender is a social position that “cluster[s] around the engendering function … women conceive and bear … men beget” (Witt 2011a, 40). These are women and men’s socially mediated reproductive functions (Witt 2011a, 29) and they differ from the biological function of reproduction, which roughly corresponds to sex on the standard sex/gender distinction. Witt writes: “to be a woman is to be recognized to have a particular function in engendering, to be a man is to be recognized to have a different function in engendering” (2011a, 39). Second, Witt distinguishes persons (those who possess self-consciousness), human beings (those who are biologically human) and social individuals (those who occupy social positions synchronically and diachronically). These ontological categories are not equivalent in that they possess different persistence and identity conditions. Social individuals are bound by social normativity, human beings by biological normativity. These normativities differ in two respects: first, social norms differ from one culture to the next whereas biological norms do not; second, unlike biological normativity, social normativity requires “the recognition by others that an agent is both responsive to and evaluable under a social norm” (Witt 2011a, 19). Thus, being a social individual is not equivalent to being a human being. Further, Witt takes personhood to be defined in terms of intrinsic psychological states of self-awareness and self-consciousness. However, social individuality is defined in terms of the extrinsic feature of occupying a social position, which depends for its existence on a social world. So, the two are not equivalent: personhood is essentially about intrinsic features and could exist without a social world, whereas social individuality is essentially about extrinsic features that could not exist without a social world.
Witt’s gender essentialist argument crucially pertains to social individuals , not to persons or human beings: saying that persons or human beings are gendered would be a category mistake. But why is gender essential to social individuals? For Witt, social individuals are those who occupy positions in social reality. Further, “social positions have norms or social roles associated with them; a social role is what an individual who occupies a given social position is responsive to and evaluable under” (Witt 2011a, 59). However, qua social individuals, we occupy multiple social positions at once and over time: we can be women, mothers, immigrants, sisters, academics, wives, community organisers and team-sport coaches synchronically and diachronically. Now, the issue for Witt is what unifies these positions so that a social individual is constituted. After all, a bundle of social position occupancies does not make for an individual (just as a bundle of properties like being white , cube-shaped and sweet do not make for a sugar cube). For Witt, this unifying role is undertaken by gender (being a woman or a man): it is
a pervasive and fundamental social position that unifies and determines all other social positions both synchronically and diachronically. It unifies them not physically, but by providing a principle of normative unity. (2011a, 19–20)
By ‘normative unity’, Witt means the following: given our social roles and social position occupancies, we are responsive to various sets of social norms. These norms are “complex patterns of behaviour and practices that constitute what one ought to do in a situation given one’s social position(s) and one’s social context” (Witt 2011a, 82). The sets of norms can conflict: the norms of motherhood can (and do) conflict with the norms of being an academic philosopher. However, in order for this conflict to exist, the norms must be binding on a single social individual. Witt, then, asks: what explains the existence and unity of the social individual who is subject to conflicting social norms? The answer is gender.
Gender is not just a social role that unifies social individuals. Witt takes it to be the social role — as she puts it, it is the mega social role that unifies social agents. First, gender is a mega social role if it satisfies two conditions (and Witt claims that it does): (1) if it provides the principle of synchronic and diachronic unity of social individuals, and (2) if it inflects and defines a broad range of other social roles. Gender satisfies the first in usually being a life-long social position: a social individual persists just as long as their gendered social position persists. Further, Witt maintains, trans people are not counterexamples to this claim: transitioning entails that the old social individual has ceased to exist and a new one has come into being. And this is consistent with the same person persisting and undergoing social individual change via transitioning. Gender satisfies the second condition too. It inflects other social roles, like being a parent or a professional. The expectations attached to these social roles differ depending on the agent’s gender, since gender imposes different social norms to govern the execution of the further social roles. Now, gender — as opposed to some other social category, like race — is not just a mega social role; it is the unifying mega social role. Cross-cultural and trans-historical considerations support this view. Witt claims that patriarchy is a social universal (2011a, 98). By contrast, racial categorisation varies historically and cross-culturally, and racial oppression is not a universal feature of human cultures. Thus, gender has a better claim to being the social role that is uniessential to social individuals. This account of gender essentialism not only explains social agents’ connectedness to their gender, but it also provides a helpful way to conceive of women’s agency — something that is central to feminist politics.
Linda Alcoff holds that feminism faces an identity crisis: the category of women is feminism’s starting point, but various critiques about gender have fragmented the category and it is not clear how feminists should understand what it is to be a woman (2006, chapter 5). In response, Alcoff develops an account of gender as positionality whereby “gender is, among other things, a position one occupies and from which one can act politically” (2006, 148). In particular, she takes one’s social position to foster the development of specifically gendered identities (or self-conceptions): “The very subjectivity (or subjective experience of being a woman) and the very identity of women are constituted by women’s position” (Alcoff 2006, 148). Alcoff holds that there is an objective basis for distinguishing individuals on the grounds of (actual or expected) reproductive roles:
Women and men are differentiated by virtue of their different relationship of possibility to biological reproduction, with biological reproduction referring to conceiving, giving birth, and breast-feeding, involving one’s body . (Alcoff 2006, 172, italics in original)
The thought is that those standardly classified as biologically female, although they may not actually be able to reproduce, will encounter “a different set of practices, expectations, and feelings in regard to reproduction” than those standardly classified as male (Alcoff 2006, 172). Further, this differential relation to the possibility of reproduction is used as the basis for many cultural and social phenomena that position women and men: it can be
the basis of a variety of social segregations, it can engender the development of differential forms of embodiment experienced throughout life, and it can generate a wide variety of affective responses, from pride, delight, shame, guilt, regret, or great relief from having successfully avoided reproduction. (Alcoff 2006, 172)
Reproduction, then, is an objective basis for distinguishing individuals that takes on a cultural dimension in that it positions women and men differently: depending on the kind of body one has, one’s lived experience will differ. And this fosters the construction of gendered social identities: one’s role in reproduction helps configure how one is socially positioned and this conditions the development of specifically gendered social identities.
Since women are socially positioned in various different contexts, “there is no gender essence all women share” (Alcoff 2006, 147–8). Nonetheless, Alcoff acknowledges that her account is akin to the original 1960s sex/gender distinction insofar as sex difference (understood in terms of the objective division of reproductive labour) provides the foundation for certain cultural arrangements (the development of a gendered social identity). But, with the benefit of hindsight
we can see that maintaining a distinction between the objective category of sexed identity and the varied and culturally contingent practices of gender does not presume an absolute distinction of the old-fashioned sort between culture and a reified nature. (Alcoff 2006, 175)
That is, her view avoids the implausible claim that sex is exclusively to do with nature and gender with culture. Rather, the distinction on the basis of reproductive possibilities shapes and is shaped by the sorts of cultural and social phenomena (like varieties of social segregation) these possibilities gives rise to. For instance, technological interventions can alter sex differences illustrating that this is the case (Alcoff 2006, 175). Women’s specifically gendered social identities that are constituted by their context dependent positions, then, provide the starting point for feminist politics.
Recently Robin Dembroff (2020) has argued that existing metaphysical accounts of gender fail to address non-binary gender identities. This generates two concerns. First, metaphysical accounts of gender (like the ones outlined in previous sections) are insufficient for capturing those who reject binary gender categorisation where people are either men or women. In so doing, these accounts are not satisfying as explanations of gender understood in a more expansive sense that goes beyond the binary. Second, the failure to understand non-binary gender identities contributes to a form of epistemic injustice called ‘hermeneutical injustice’: it feeds into a collective failure to comprehend and analyse concepts and practices that undergird non-binary classification schemes, thereby impeding on one’s ability to fully understand themselves. To overcome these problems, Dembroff suggests an account of genderqueer that they call ‘critical gender kind’:
a kind whose members collectively destabilize one or more elements of dominant gender ideology. Genderqueer, on my proposed model, is a category whose members collectively destabilize the binary axis, or the idea that the only possible genders are the exclusive and exhaustive kinds men and women. (2020, 2)
Note that Dembroff’s position is not to be confused with ‘gender critical feminist’ positions like those noted above, which are critical of the prevalent feminist focus on gender, as opposed to sex, kinds. Dembroff understands genderqueer as a gender kind, but one that is critical of dominant binary understandings of gender.
Dembroff identifies two modes of destabilising the gender binary: principled and existential. Principled destabilising “stems from or otherwise expresses individuals’ social or political commitments regarding gender norms, practices, and structures”, while existential destabilising “stems from or otherwise expresses individuals’ felt or desired gender roles, embodiment, and/or categorization” (2020, 13). These modes are not mutually exclusive, and they can help us understand the difference between allies and members of genderqueer kinds: “While both resist dominant gender ideology, members of [genderqueer] kinds resist (at least in part) due to felt or desired gender categorization that deviates from dominant expectations, norms, and assumptions” (2020, 14). These modes of destabilisation also enable us to formulate an understanding of non-critical gender kinds that binary understandings of women and men’s kinds exemplify. Dembroff defines these kinds as follows:
For a given kind X , X is a non-critical gender kind relative to a given society iff X ’s members collectively restabilize one or more elements of the dominant gender ideology in that society. (2020, 14)
Dembroff’s understanding of critical and non-critical gender kinds importantly makes gender kind membership something more and other than a mere psychological phenomenon. To engage in collectively destabilising or restabilising dominant gender normativity and ideology, we need more than mere attitudes or mental states – resisting or maintaining such normativity requires action as well. In so doing, Dembroff puts their position forward as an alternative to two existing internalist positions about gender. First, to Jennifer McKitrick’s (2015) view whereby gender is dispositional: in a context where someone is disposed to behave in ways that would be taken by others to be indicative of (e.g.) womanhood, the person has a woman’s gender identity. Second, to Jenkin’s (2016, 2018) position that takes an individual’s gender identity to be dependent on which gender-specific norms the person experiences as being relevant to them. On this view, someone is a woman if the person experiences norms associated with women to be relevant to the person in the particular social context that they are in. Neither of these positions well-captures non-binary identities, Dembroff argues, which motivates the account of genderqueer identities as critical gender kinds.
As Dembroff acknowledges, substantive philosophical work on non-binary gender identities is still developing. However, it is important to note that analytic philosophers are beginning to engage in gender metaphysics that goes beyond the binary.
This entry first looked at feminist objections to biological determinism and the claim that gender is socially constructed. Next, it examined feminist critiques of prevalent understandings of gender and sex, and the distinction itself. In response to these concerns, the entry looked at how a unified women’s category could be articulated for feminist political purposes. This illustrated that gender metaphysics — or what it is to be a woman or a man or a genderqueer person — is still very much a live issue. And although contemporary feminist philosophical debates have questioned some of the tenets and details of the original 1960s sex/gender distinction, most still hold onto the view that gender is about social factors and that it is (in some sense) distinct from biological sex. The jury is still out on what the best, the most useful, or (even) the correct definition of gender is.
- Alcoff, L., 1988, “Cultural Feminism Versus Post-Structuralism: The Identity Crisis in Feminist Theory”, Signs , 13: 405–436.
- –––, 2006, Visible Identities , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Andler, M., 2017, “Gender Identity and Exclusion: A Reply to Jenkins”, Ethics , 127: 883–895.
- Ásta (Sveinsdóttir), 2011, “The Metaphysics of Sex and Gender”, in Feminist Metaphysics , C. Witt (ed.), Dordrecht: Springer, pp. 47–65.
- –––, 2018, Categories We Live By: The Construction of Sex, Gender, Race, and Other Social Categories, New York: Oxford University Press.
- Ayala, S. and Vasilyeva, N., 2015, “Extended Sex: An Account of Sex for a More Just Society”, Hypatia , 30: 725–742.
- Antony, L., 1998, “‘Human Nature’ and Its Role in Feminist Theory”, in Philosophy in a Feminist Voice , J. Kourany (ed.), New Haven: Princeton University Press, pp. 63–91.
- Armstrong, D., 1989, Universals: An Opinionated Introduction , Boulder, CO: Westview.
- Bach, T., 2012, “Gender is a Natural Kind with a Historical Essence”, Ethics , 122: 231–272.
- Barnes, E., 2020, “Gender and Gender Terms”, Noûs , 54: 704–730.
- de Beauvoir, S., 1972, The Second Sex , Harmondsworth: Penguin.
- Benhabib, S., 1992, Situating the Self , New York: Routledge.
- Bettcher, T.M., 2013, “Trans Women and the Meaning of ‘Woman’”, in The Philosophy of Sex , N. Power, R. Halwani, and A. Soble (eds.), Lanham, MD: Rowman and Littlefield Publishers, Inc, pp. 233–250.
- Bogardus, T., 2020, “Evaluating Arguments for the Sex/Gender Distinction”, Philosophia , 48: 873–892.
- Butler, J., 1990, “Performative Acts and Gender Constitution”, in Performing Feminisms , S-E. Case (ed.), Baltimore: John Hopkins University, pp. 270–282.
- –––, 1991, “Contingent Foundations: Feminism and the Question of ‘Postmodernism’”, Praxis International , 11: 150–165.
- –––, 1993, Bodies that Matter , London: Routledge.
- –––, 1997, The Psychic Life of Power , Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
- –––, 1999, Gender Trouble , London: Routledge, 2 nd edition.
- Byrne, A., 2020, “Are Women Adult Human Females?”, Philosophical Studies , 177: 3783–3803.
- –––, 2021, “Gender Muddle: Reply to Dembroff”, Journal of Controversial Ideas , 1: 1–24.
- Campbell, A., 2002, A Mind of One’s Own: The Evolutionary Psychology of Women , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Chodorow, N., 1978, Reproducing Mothering , Berkeley: University of California Press.
- –––, 1995, “Family Structure and Feminine Personality”, in Feminism and Philosophy , N. Tuana, and R. Tong (eds.), Boulder, CO: Westview, pp. 43–66.
- Deaux, K. and B. Major, 1990, “A Social-Psychological Model of Gender”, in Theoretical Perspectives on Sexual Difference , D. Rhode (ed.), New Haven: Yale University Press, pp. 89-99.
- Dembroff, R., 2020, “Beyond Binary: Genderqueer as Critical Gender Kind”, Philosopher’s Imprint , 20: 1–23.
- –––, 2021, “Escaping the Natural Attitude about Gender”, Philosophical Studies , 178: 983–1003.
- Fausto-Sterling, A., 1993a, Myths of Gender: Biological Theories about Women and Men , New York: Basic Books, 2 nd edition.
- –––, 1993b, “The Five Sexes: Why Male and Female are Not Enough”, The Sciences , 33: 20–24.
- –––, 2000a, “The Five Sexes: Revisited”, The Sciences , July/August: 18–23.
- –––, 2000b, Sexing the Body , New York: Basic Books.
- –––, 2003, “The Problem with Sex/Gender and Nature/Nurture”, in Debating Biology: Sociological Reflections on Health, Medicine and Society , S. J. Williams, L. Birke, and G. A. Bendelow (eds.), London & New York: Routledge, pp. 133–142.
- –––, 2005, “The Bare Bones of Sex: Part 1 – Sex and Gender”, Signs , 30: 1491–1527.
- Friedan, B., 1963, Feminine Mystique , Harmondsworth: Penguin Books Ltd.
- Frye, M., 1996, “The Necessity of Differences: Constructing a Positive Category of Women”, Signs, 21: 991–1010.
- –––, 2011, “Metaphors of Being a φ”, in Feminist Metaphysics , C. Witt (ed.), Dordrecht: Springer, pp. 85–95.
- Gatens, M., 1996, Imaginary Bodies , London: Routledge.
- Gorman, C. 1992, “Sizing up the Sexes”, Time , January 20: 42–51.
- Green, J. M. and B. Radford Curry, 1991, “Recognizing Each Other Amidst Diversity: Beyond Essentialism in Collaborative Multi-Cultural Feminist Theory”, Sage , 8: 39–49.
- Grosz, E., 1994, Volatile Bodies: Toward a Corporeal Feminism , Bloomington, IN: Indiana University Press.
- Harris, A., 1993, “Race and Essentialism in Feminist Legal Theory”, in Feminist Legal Theory: Foundations , D. K. Weisberg (ed.), Philadelphia: Temple University Press, pp. 248–258.
- Haslanger, S., 1995, “Ontology and Social Construction”, Philosophical Topics , 23: 95–125.
- –––, 2000a, “Feminism in Metaphysics: Negotiating the Natural”, in Feminism in Philosophy , M. Fricker, and J. Hornsby (eds.), Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 107–126.
- –––, 2000b, “Gender and Race: (What) are They? (What) Do We Want Them To Be?”, Noûs , 34: 31–55.
- –––, 2003a, “Future Genders? Future Races?”, Philosophic Exchange , 34: 4–27.
- –––, 2003b, “Social Construction: The ‘Debunking’ Project”, in Socializing Metaphysics: The Nature of Social Reality, F. Schmitt (ed.), Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield Publishers Inc, pp. 301–325.
- –––, 2005, “What Are We Talking About? The Semantics and Politics of Social Kinds”, Hypatia , 20: 10–26.
- –––, 2006, “What Good are Our Intuitions?”, Proceedings of the Aristotelian Society , Supplementary Volume 80: 89–118.
- –––, 2012, Resisting Reality , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Heyes, C., 2000, Line Drawings , Ithaca & London: Cornell University Press.
- hooks, b., 2000, Feminist Theory: From Margins to Center , London: Pluto, 2 nd edition.
- Jaggar, A., 1983, “Human Biology in Feminist Theory: Sexual Equality Reconsidered”, in Beyond Domination: New Perspectives on Women and Philosophy , C. Gould (ed.), Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, Inc, pp. 21–42.
- Jenkins, K., 2016, “Amelioration and Inclusion: Gender Identity and the Concept of Woman”, Ethics , 126: 394–421.
- –––, 2018, “Toward an Account of Gender Identity”, Ergo , 5: 713–744.
- Kimmel, M., 2000, The Gendered Society , New York: Oxford University Press.
- King, H., 2013, The One-Sex Body on Trial: The Classical and Early Modern Evidence , Farnham: Ashgate Publishing, Ltd.
- Laqueur, T., 1990, Making Sex: Body and Gender from the Greeks to Freud , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Lawford-Smith, H., 2021, “Ending Sex-Based Oppression: Transitional Pathways”, Philosophia , 49: 1021–1041.
- Lloyd, G., 1993, The Man of Reason: ‘Male’ and ‘Female’ in Western Philosophy , London: Routledge, 2 nd edition.
- MacKinnon, C., 1989, Toward a Feminist Theory of State , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Martin, J. R. 1994, “Methodological Essentialism, False Difference, and Other Dangerous Traps”, Signs , 19: 630–655.
- McKitrick, J., 2015, “A Dispositional Account of Gender”, Philosophical Studies , 172: 2575–2589.
- Mikkola, M. 2006, “Elizabeth Spelman, Gender Realism, and Women”, Hypatia , 21: 77–96.
- –––, 2007, “Gender Sceptics and Feminist Politics”, Res Publica , 13: 361–380.
- –––, 2009, “Gender Concepts and Intuitions”, Canadian Journal of Philosophy , 9: 559–583.
- –––, 2011, “Ontological Commitments, Sex and Gender”, in Feminist Metaphysics , C. Witt (ed.), Dordrecht: Springer, pp. 67–84.
- –––, 2016, The Wrong of Injustice: Dehumanization and its Role in Feminist Philosophy , New York: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 2020, “The Function of Gender as a Historical Kind”, in Social Functions in Philosophy: Metaphysical, Normative, and Methodological Perspectives , R. Hufendiek, D. James, and R. van Riel (eds.), London: Routledge, pp. 159–182.
- Millett, K., 1971, Sexual Politics , London: Granada Publishing Ltd.
- Moi, T., 1999, What is a Woman? , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Munro, V., 2006, “Resemblances of Identity: Ludwig Wittgenstein and Contemporary Feminist Legal Theory”, Res Publica , 12: 137–162.
- Nicholson, L., 1994, “Interpreting Gender”, Signs , 20: 79–105.
- –––, 1998, “Gender”, in A Companion to Feminist Philosophy , A. Jaggar, and I. M. Young (eds.), Malden, MA: Blackwell, pp. 289–297.
- Price, H. H., 1953, Thinking and Experience , London: Hutchinson’s University Library.
- Prokhovnik, R., 1999, Rational Woman , London: Routledge.
- Rapaport, E. 2002, “Generalizing Gender: Reason and Essence in the Legal Thought of Catharine MacKinnon”, in A Mind of One’s Own: Feminist Essays on Reason and Objectivity , L. M. Antony and C. E. Witt (eds.), Boulder, CO: Westview, 2 nd edition, pp. 254–272.
- Renzetti, C. and D. Curran, 1992, “Sex-Role Socialization”, in Feminist Philosophies , J. Kourany, J. Sterba, and R. Tong (eds.), New Jersey: Prentice Hall, pp. 31–47.
- Rogers, L., 1999, Sexing the Brain , London: Phoenix.
- Rubin, G., 1975, “The Traffic in Women: Notes on the ‘Political Economy’ of Sex”, in Toward an Anthropology of Women , R. Reiter (ed.), New York: Monthly Review Press, pp. 157–210.
- Salih, S., 2002, Judith Butler , London: Routledge.
- Saul, J., 2006, “Gender and Race”, Proceedings of the Aristotelian Society (Supplementary Volume), 80: 119–143.
- Spelman, E., 1988, Inessential Woman , Boston: Beacon Press.
- Stoljar, N., 1995, “Essence, Identity and the Concept of Woman”, Philosophical Topics , 23: 261–293.
- –––, 2000, “The Politics of Identity and the Metaphysics of Diversity”, in Proceedings of the 20 th World Congress of Philosophy , D. Dahlstrom (ed.), Bowling Green: Bowling Green State University, pp. 21–30.
- –––, 2011, “Different Women. Gender and the Realism-Nominalism Debate”, in Feminist Metaphysics , C. Witt (ed.), Dordrecht: Springer, pp. 27–46.
- Stoller, R. J., 1968, Sex and Gender: On The Development of Masculinity and Femininity , New York: Science House.
- Stone, A., 2004, “Essentialism and Anti-Essentialism in Feminist Philosophy”, Journal of Moral Philosophy , 1: 135–153.
- –––, 2007, An Introduction to Feminist Philosophy , Cambridge: Polity.
- Tanesini, A., 1996, “Whose Language?”, in Women, Knowledge and Reality , A. Garry and M. Pearsall (eds.), London: Routledge, pp. 353–365.
- Witt, C., 1995, “Anti-Essentialism in Feminist Theory”, Philosophical Topics , 23: 321–344.
- –––, 2011a, The Metaphysics of Gender , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 2011b, “What is Gender Essentialism?”, in Feminist Metaphysics , C. Witt (ed.), Dordrecht: Springer, pp. 11–25.
- Wittig, M., 1992, The Straight Mind and Other Essays , Boston: Beacon Press.
- Young, I. M., 1997, “Gender as Seriality: Thinking about Women as a Social Collective”, in Intersecting Voices , I. M. Young, Princeton: Princeton University Press, pp. 12–37.
- Zack, N., 2005, Inclusive Feminism , Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield.
How to cite this entry . Preview the PDF version of this entry at the Friends of the SEP Society . Look up topics and thinkers related to this entry at the Internet Philosophy Ontology Project (InPhO). Enhanced bibliography for this entry at PhilPapers , with links to its database.
- The Feminist Philosophers Blog
- QueerTheory.com , from the Internet Archive
- World Wide Web Review: Webs of Transgender
- What is Judith Butler’s Theory of Gender Performativity? (Perlego, open access study guide/ introduction)
Beauvoir, Simone de | feminist philosophy, approaches: intersections between analytic and continental philosophy | feminist philosophy, topics: perspectives on reproduction and the family | feminist philosophy, topics: perspectives on the self | homosexuality | identity politics | speech acts
Acknowledgments
I am very grateful to Tuukka Asplund, Jenny Saul, Alison Stone and Nancy Tuana for their extremely helpful and detailed comments when writing this entry.
Copyright © 2022 by Mari Mikkola < m . mikkola @ uva . nl >
- Accessibility
Support SEP
Mirror sites.
View this site from another server:
- Info about mirror sites
The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy is copyright © 2024 by The Metaphysics Research Lab , Department of Philosophy, Stanford University
Library of Congress Catalog Data: ISSN 1095-5054
Quick links
- Make a Gift
- Directories

- News Feed
- Newsletter
Gender Equality Essay: How to Inspire Action and Awareness

Writing about the importance of gender equality is crucial in shedding light on the inequalities and disparities that persist between men and women. These essays are like windows into our society, showing us the good and the bad. They're not just for school – they're about real people's lives. When we read and write about gender parity, we're shining a light on issues like discrimination and stereotypes, and we're saying, "Hey, this isn't right!" In this article, we will show you how to write an essay about gender equality to encourage your peers to think about making things more fair for everyone and standing up for what's right, making the world a better place for everyone.
Tips for Writing an Argumentative Essay About Gender Equality
First, let’s answer the question of what is gender equality essay? By definition, it is a written composition that investigates and discusses the concept of gender fairness, aiming to highlight the importance of fair treatment and opportunities for individuals regardless of gender. These essays typically explore historical contexts, societal norms, and contemporary disparities-related challenges, offering insights into how stereotypes, discrimination, and cultural expectations affect people based on gender. Moreover, such assignments seek to raise awareness and foster understanding, prompting readers to critically examine the necessity of creating a society where everyone, regardless of gender, enjoys equal rights, opportunities, and dignity.
At this point, we should write a gender equality essay thesis statement that will serve as the anchor, encapsulating the core argument and purpose of the essay. The thesis is a concise declaration that outlines the writer's stance on the topic and provides a roadmap for the essay's content. An effective thesis statement for a gender parity essay might assert the fundamental principle of equal rights and opportunities for all genders, emphasizing the need to challenge and dismantle societal norms perpetuating discrimination. For instance, a thesis statement could assert that achieving true balance requires dismantling stereotypes, promoting equal access to education and employment, and fostering a cultural shift toward recognizing the inherent value of every individual, irrespective of gender. The thesis statement acts as a guiding beacon, steering the essay in the direction of a comprehensive exploration of the chosen perspective on evenness. Suddenly forgot your task is due tomorrow? Don’t strain yourself, and use our argumentative essay service to achieve the best outcome fast.
Brainstorming Gender Equality Essay Topics
When looking for argumentative essay topics about gender equality, you can find inspiration in various places. Keep an eye on the news, social media discussions, and academic research to see what issues are currently being debated. Personal stories from people who've faced gender-related challenges or your own experiences can be powerful starting points. Understand how past events shaped gender dynamics or analyze how it is portrayed in literature and media. For your gender roles essay, you can analyze global perspectives, legal frameworks, and social movements for additional insights. By drawing from these diverse sources, you can brainstorm compelling arguments that not only tackle the complexities of gender equality but also connect with your audience on a personal and societal level. For your inspiration, we’ve prepared some peculiar ideas for gender equality in society essay, so check them out!
.webp)
- Workplace fairness for men and women.
- Breaking boys and girls stereotypes in children's books.
- The impact of inequality on mental health stigma.
- Challenges faced by women entrepreneurs.
- Addressing gender bias in healthcare.
- The role of men in feminist movements.
- Promoting inclusivity in sports teams.
- Gender-neutral language in education.
- Breaking the glass ceiling in corporate leadership.
- Tackling gender-based violence in schools.

Gender Equality Essay Outline
Choosing a good title for a gender equality essay involves capturing the essay's main ideas and sparking interest. You can include keywords like "equality" or "empowerment" and use phrasing that makes readers think. For the gender equality essay thesis statement, keep it concise and clear. An example could be: "To achieve real fairness, we need to challenge stereotypes, ensure equal opportunities in education and work, and transform our culture to value everyone's contribution. Only through these comprehensive efforts can we create a society where everyone has a fair shot." Before we proceed to the essay’s outline, revise how many paragraphs in an argumentative essay and its length.
.webp)
Gender Equality Essay Introduction
To kick off your gender equality introduction essay effectively, start with something that grabs your reader's attention, like a quote, a surprising fact, or a relatable scenario. Next, give a quick background on what gender equality means today or historically, keeping it concise. Then, smoothly transition to your thesis statement – the main point you will argue in your essay. For example, you might say that real parity requires us to challenge stereotypes, make sure everyone has equal chances in education and work, and change our culture to value everyone's contributions. This approach helps your reader understand why the topic is important and what your essay is all about.
For the main body of a future gender equality essay, think about what could be coming up. Consider how new technology, like artificial intelligence, might affect how we see male and female roles. Talk about whether it might help break stereotypes or create new challenges. Give real examples or discuss policies that encourage women to take on roles in fields like technology.
Then, look into how work is changing and what that means for equality. Explore the idea of remote work, flexible schedules, and gig jobs and how they might create more equal opportunities. Discuss how companies or governments are making policies to support work-life balance and equal chances for leadership roles. Use examples to show where these progressive work practices are already happening and how they could impact equivalence in the future. Keep it real and forward-thinking, looking at the positives and potential challenges.
Gender Equality Essay Conclusion
To wrap up your essay, start by briefly restating your main point or thesis. Summarize the key ideas discussed in the essay's body, highlighting their importance in the context of gender equality. Don't bring in new information; instead, emphasize the connections between your arguments and the main point. Finish your gender equality conclusion essay on a strong note by inspiring your reader to consider the broader implications and take action toward achieving genuine parity in society. Keep it clear, concise, and impactful, leaving a lasting impression on your audience.
Essay Revision
To edit and proofread your gender equality essay introduction body and conclusion, start by reviewing the introduction to ensure clarity and conciseness. Verify that your thesis statement is strong and effectively communicates the main argument. Check the hook for its impact on grabbing the reader's attention. Moving to the body, focus on the logical flow of ideas between paragraphs. Confirm that each paragraph has a clear topic sentence, supporting evidence, and a smooth transition to the next. Pay attention to the coherence of your arguments and ensure they align with the overall thesis. Lastly, in the conclusion, restate the thesis, summarize key points, and end with a compelling call to action. Throughout the essay, check for grammar, punctuation, and spelling errors with the help of our paper writer , ensuring a polished and error-free final draft.
Gender Equality Essay Example
Please review our example of argumentative essay about gender equality to get inspired to produce your own brilliant essay. Remember that these two gender equality essay examples are not for submission because this will be considered plagarism. If you want equally engaging and insightful work, please say, ‘ write my essay ,’ so our experts can procure a new essay for you from scratch to avoid affecting your academic integrity.
Empowering Equality: Breaking Barriers and Building Bridges
Gender equality stands as a fundamental principle for building a just and inclusive society. In recent years, progress has been made, but challenges persist. This essay delves into the multifaceted landscape of fairness, examining the importance of dismantling stereotypes, promoting equal opportunities, and fostering a cultural shift. As we navigate the complexities of the 21st century, the pursuit of genuine equality emerges not only as a moral imperative but also as a critical driver of social and economic progress.
To achieve true equality, the first step involves challenging ingrained stereotypes that limit individuals based on their gender. Stereotypes perpetuate biased expectations, restricting both men and women to predefined roles. For instance, the persistent notion that certain professions are exclusively suited for one gender perpetuates inequality in the workplace. Initiatives promoting diverse role models, debunking myths, and redefining societal norms contribute to dismantling these stereotypes.
Ensuring equal opportunities in education and employment forms the cornerstone of equality. Educational institutions and workplaces must adopt policies that eliminate barriers and provide a level playing field. This involves addressing disparities in STEM education, encouraging girls to pursue careers in traditionally male-dominated fields, and advocating for fair hiring practices. Achieving balance in educational and professional spheres fosters an environment where talent and capability, rather than gender, determine success.
A genuine cultural shift is imperative for achieving lasting equality. Cultural norms often perpetuate inequality, shaping attitudes and behaviors. Encouraging open conversations about gender, challenging discriminatory practices, and promoting inclusivity in all aspects of life contribute to this transformation. It requires collective efforts from communities, media, and policymakers to create a culture that respects and values individuals irrespective of their gender.
In conclusion, the journey toward gender fairness is a dynamic process that involves dismantling stereotypes, ensuring equal opportunities, and fostering cultural transformation. By challenging societal norms and advocating for inclusive policies, we can pave the way for a future where every individual has the opportunity to thrive, unbound by gender-based constraints. Empowering equality not only aligns with the principles of justice and fairness but also propels societies toward greater prosperity and harmony.
Breaking Chains: The Unfinished Journey Towards Gender Equality"
Gender equality, a beacon of progress in contemporary societies, still faces significant challenges, with deeply rooted stereotypes and systemic barriers hindering its realization. This essay embarks on an exploration of the persistent issues surrounding evenness, emphasizing the imperative to dismantle stereotypes, advocate for equal opportunities, and drive transformative change. As we confront the complexities of the 21st century, the pursuit of authentic equality emerges as not only a societal responsibility but also as an essential catalyst for fostering diversity, inclusivity, and social prosperity.
The journey toward true gender parity necessitates a concerted effort to challenge and dismantle age-old stereotypes that confine individuals within rigid male and female roles. These stereotypes perpetuate harmful biases, limiting opportunities for personal and professional growth. A critical focus should be on dispelling myths surrounding gendered expectations, such as the notion that certain professions are exclusively for one gender. Initiatives promoting diverse role models and challenging societal norms are pivotal in dismantling these restrictive stereotypes.
An indispensable component of achieving gender equality lies in advocating for equal opportunities in education. Educational institutions should implement policies that eradicate barriers and promote inclusivity. This involves addressing gender disparities in STEM fields, encouraging girls to pursue careers in traditionally male-dominated sectors, and ensuring fair and unbiased educational environments. By cultivating an educational landscape that values competence over gender, societies can lay the foundation for a more equitable future.
Achieving genuine gender equality requires a holistic approach that includes systemic change at various levels of society. This involves not only addressing individual attitudes but also transforming institutional practices. Policies promoting equal pay, parental leave, and unbiased hiring practices contribute to dismantling systemic barriers. Additionally, fostering workplace cultures that prioritize diversity and inclusivity plays a crucial role in creating environments where all individuals, regardless of gender, can thrive.
In conclusion, the journey toward gender equality is an ongoing struggle that demands persistent efforts to dismantle stereotypes, advocate for equal opportunities, and drive systemic change. By challenging societal norms and fostering inclusive policies, societies can move closer to realizing the promise of a future where gender does not dictate one's opportunities or potential. Breaking the chains of ingrained biases is not just a societal obligation; it is a transformative endeavor that paves the way for a more just, inclusive, and harmonious world.
When students are assigned to write about gender equality, it isn't just about getting a grade. It's a valuable way to get young minds thinking and talking about how fairness and evenness play out in our world. By putting their thoughts into words, students not only practice expressing themselves but also become part of a bigger conversation about treating everyone fairly. Use this opportunity to challenge stereotypes, call for equal rights, and be a voice for positive change. To succeed, you can buy essay online from our competent writers, who will make sure your teacher will be pleased.
Frequently asked questions
Why is gender equality essay important, how to promote gender equality essay, how to choose the best gender equality essay title.
She was flawless! first time using a website like this, I've ordered article review and i totally adored it! grammar punctuation, content - everything was on point
This writer is my go to, because whenever I need someone who I can trust my task to - I hire Joy. She wrote almost every paper for me for the last 2 years
Term paper done up to a highest standard, no revisions, perfect communication. 10s across the board!!!!!!!
I send him instructions and that's it. my paper was done 10 hours later, no stupid questions, he nailed it.
Sometimes I wonder if Michael is secretly a professor because he literally knows everything. HE DID SO WELL THAT MY PROF SHOWED MY PAPER AS AN EXAMPLE. unbelievable, many thanks

You Might Also Like

New Posts to Your Inbox!
Stay in touch
Home — Essay Samples — Sociology — Gender Roles — Gender Roles In Society
Gender Roles in Society
- Categories: Gender Roles Society
About this sample

Words: 534 |
Published: Mar 13, 2024
Words: 534 | Page: 1 | 3 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof. Kifaru
Verified writer
- Expert in: Sociology

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 971 words
1 pages / 512 words
3 pages / 1325 words
5 pages / 2303 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Gender Roles
John Steinbeck's short story "The Chrysanthemums" is a poignant exploration of gender roles, isolation, and the longing for fulfillment. Through the character of Elisa Allen, Steinbeck delves into the complexities of a woman's [...]
Edith Wharton, a famous American novelist, and playwright, is known for her works that depict the life of the upper class of New York during the early 1900s. Her writing style often highlights the themes of love, marriage, and [...]
The main character, Desiree, represents the qualities and characteristics typical of 19th-century women, reflecting their expectations, values, and morals. The central thesis of the story revolves around Armand’s inability to [...]
Gender stereotypes have long influenced career choices, particularly in Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) fields. This qualitative essay undertakes an in-depth analysis of the impact of gender stereotypes [...]
Domestic violence, or intimate partner violence, is a widespread problem that affects people of all genders, ages, and socio-economic backgrounds. It encompasses various forms of abuse, including physical, emotional, sexual, and [...]
The ancient Greek city-states of Athens and Sparta were powerful and influential societies in the classical world, each with its own unique customs and traditions. While both city-states valued the contributions of women to [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Gender Inequality Essay
500+ words essay on gender inequality.
For many years, the dominant gender has been men while women were the minority. It was mostly because men earned the money and women looked after the house and children. Similarly, they didn’t have any rights as well. However, as time passed by, things started changing slowly. Nonetheless, they are far from perfect. Gender inequality remains a serious issue in today’s time. Thus, this gender inequality essay will highlight its impact and how we can fight against it.

About Gender Inequality Essay
Gender inequality refers to the unequal and biased treatment of individuals on the basis of their gender. This inequality happens because of socially constructed gender roles. It happens when an individual of a specific gender is given different or disadvantageous treatment in comparison to a person of the other gender in the same circumstance.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Impact of Gender Inequality
The biggest problem we’re facing is that a lot of people still see gender inequality as a women’s issue. However, by gender, we refer to all genders including male, female, transgender and others.
When we empower all genders especially the marginalized ones, they can lead their lives freely. Moreover, gender inequality results in not letting people speak their minds. Ultimately, it hampers their future and compromises it.
History is proof that fighting gender inequality has resulted in stable and safe societies. Due to gender inequality, we have a gender pay gap. Similarly, it also exposes certain genders to violence and discrimination.
In addition, they also get objectified and receive socioeconomic inequality. All of this ultimately results in severe anxiety, depression and even low self-esteem. Therefore, we must all recognize that gender inequality harms genders of all kinds. We must work collectively to stop these long-lasting consequences and this gender inequality essay will tell you how.
How to Fight Gender Inequality
Gender inequality is an old-age issue that won’t resolve within a few days. Similarly, achieving the goal of equality is also not going to be an easy one. We must start by breaking it down and allow it time to go away.
Firstly, we must focus on eradicating this problem through education. In other words, we must teach our young ones to counter gender stereotypes from their childhood.
Similarly, it is essential to ensure that they hold on to the very same beliefs till they turn old. We must show them how sports are not gender-biased.
Further, we must promote equality in the fields of labour. For instance, some people believe that women cannot do certain jobs like men. However, that is not the case. We can also get celebrities on board to promote and implant the idea of equality in people’s brains.
All in all, humanity needs men and women to continue. Thus, inequality will get us nowhere. To conclude the gender inequality essay, we need to get rid of the old-age traditions and mentality. We must teach everyone, especially the boys all about equality and respect. It requires quite a lot of work but it is possible. We can work together and achieve equal respect and opportunities for all genders alike.
FAQ of Gender Inequality Essay
Question 1: What is gender inequality?
Answer 1: Gender inequality refers to the unequal and biased treatment of individuals on the basis of their gender. This inequality happens because of socially constructed gender roles. It happens when an individual of a specific gender is given different or disadvantageous treatment in comparison to a person of the other gender in the same circumstance.
Question 2: How does gender inequality impact us?
Answer 2: The gender inequality essay tells us that gender inequality impacts us badly. It takes away opportunities from deserving people. Moreover, it results in discriminatory behaviour towards people of a certain gender. Finally, it also puts people of a certain gender in dangerous situations.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Transphobia Makes Chest Binding More Dangerous

C hest binding, or wearing anything to flatten the chest in order to appear masculine or androgynous, is one of many ways that transmasculine and nonbinary people can affirm their gender identity and harmonize their physical presentation with their sense of self. Some people bind in order to “pass” as male at times when being visibly transgender could be dangerous. Others bind for the mental health benefits, documented across multiple studies , of being able to move through the world feeling at home in an authentic identity. But despite these life-changing benefits, anti-trans activists focus on the risks of binding, such as shortness of breath, skin abrasions, or shoulder pain, and seek to restrict the practice.
Binding scares anti-trans activists because of its accessibility. Unlike hormones, binding requires no prescription; unlike state-ID changes, it requires no paperwork. Binding is often one of the first ways that trans and nonbinary youth who are assigned female at birth can flexibly, reversibly—sometimes quietly under their clothes and unbeknownst to anyone else—“try on” a new gender identity to see how it feels. This accessibility makes binding terrifying to those who want to eradicate trans people from public life. Their usual tricks are powerless to stop binding: there is no teacher they can gag, no librarian they can defund, no doctor they can criminalize to stop people from binding. Unless anti-trans zealots are willing to ban sports bras, bandages, tape, shapewear, or even swimsuits and tight shirts, there is no way to render binding completely inaccessible.
It is no surprise then that anti-trans activists hyperfocus on the health risks of binding, often misrepresenting studies on binding to inflate the physical risks of binding and ignoring the sometimes life-saving mental health benefits. We know because one of us (Sarah Peitzmeier) conducted most of those studies. Tired of seeing statistics from these research studies ripped out of context and weaponized against the very communities who participated in and supported the research, we began to discuss turning the findings from these studies into a book. Breathe: Journeys To Healthy Binding , is a resource for those who have questions and concerns about binding, and for those who already bind and want to do so in ways that maximize the mental health benefits and minimize the physical risk. We want to help people bind in ways that are affirming, yet gentle on the body.
Read More: Elliot Page: Embracing My Trans Identity Saved Me
Anti-trans activists who claim to be “protecting” people from the harms of binding by trying to restrict binding specifically and trans people more generally are in fact making binding more dangerous. In our research and lived experience, here are six ways we have seen transphobia make binding far more dangerous than it should be for trans and gender diverse people.
Legislative attacks on medically necessary healthcare
Binding is the only option left to mitigate chest dysphoria in states where best-practice medical care has been banned. Anti-trans bills blocking medical or surgical affirming care for trans youth have been passed in 24 states , with politicians inserting themselves between patients, families, and their doctors. Trans youth who go through puberty early without access to puberty blockers may have to manage severe chest dysphoria for a decade before they are even legally allowed to pursue top surgery, assuming they have the financial resources to access it. We know that receiving puberty blockers, compared to wanting puberty blockers but being unable to access them, is associated with 70% lower lifetime odds of suicidal ideation – so this is lifesaving care. It seems particularly cruel, then, for the same people who advocated for these laws denying healthcare to also attack binding. If anti-trans activists truly cared about the potential risks of binding for trans youth, they would not simultaneously advocate for bans on medically necessary care.
Marginalization in healthcare
Trans patients who do experience injuries or health issues from binding often don’t have access to knowledgeable and compassionate treatment. Even trans-affirming providers generally receive no training in how to counsel patients to reduce their risk around binding, as medical and nursing schools typically see trans-specific topics like binding as “specialty” topics. At worst, providers may be actively prejudiced against trans people. Laws against providing gender-affirming care in 24 states can be interpreted broadly and scare providers from offering any kind of care to trans adolescents or even adults. Binding-related medical issues are thus left to worsen without quality clinical care.
Binding can be necessary to navigate transphobic spaces
Being visibly trans can expose people to discrimination, and binding is sometimes the only way to safely move through a hostile world. It is still legal to discriminate against trans people in employment or housing in 30 states, and trans people are banned from using the restroom that matches their gender in 10 states. Some trans people may present as otherwise masculine but for the appearance of their unbound chest, which would “out” them as transgender. Until we live in a world where people can safely express a range of gender presentations without living in fear of assault or discrimination, binding is essentially the only option for many transmasculine people who need to “pass” for their own safety. These people may also have to keep binding for safety reasons regardless of any symptoms they may develop.
Concealing binding due to stigma increases the risks
The health risks from binding are increased by the need to conceal it. For instance, teens who are trying to conceal their binder from their parents often have trouble washing their binder regularly without their parents seeing it in the laundry. As a result, the dirt and sweat buildup on their unwashed binder predisposes them to skin complications. Without parental support, many teens cannot purchase a binder, which is typically ordered online with a credit card. Some of these teens resort to using ACE bandages, which are more readily available but far more dangerous because they are designed to compress inflammation. One 2020 study by researchers and clinicians at the Children’s Hospital of Los Angeles found that teens with parents who opposed binding were almost twice as likely to have used ACE bandages to bind their chests. Teens with supportive parents had access to safer options.
Restricted access to information on safer binding that does exist
Because discussing gender identity is banned or restricted in schools in 14 states, trans and nonbinary people often struggle to access information about trans-specific issues such as binding. We have a growing evidence base and clinical expertise around how to reduce risk associated with binding—including taking one day off from binding each week, avoiding use of ACE bandages, and stretching muscles and ligaments that may be constricted by binding—but in an era of book bans and gag rules, many trans people have no way to learn these important tips. Instead, they may assume that binding is inherently painful and this is just the price they have to pay, which is unequivocally not true. We now know there are so many ways to make binding safer.
Unmet need for gender affirmation
When there is a gap between how people fundamentally see themselves and how the world sees them, they are more likely to engage in risky (but identity-affirming) behaviors to help close that gap. When trans people are chronically misgendered at work or school and are banned from medically affirming their gender, binding may be one of the only tools they have to affirm their gender. They will be more likely to ignore signs that their body is struggling with the side effects of binding, as they have nothing else to affirm them. Combine this with lack of information about how to bind more safely and lack of healthcare to address problems that emerge, and people can end up with serious binding-related symptoms.
Forty percent of trans adults in the U.S. have attempted suicide at some point in their lives. Binding can help people imagine a future for themselves that feels worth living. As one of our research participants said, “Binding gave me the freedom to exist.”
Many people successfully bind with minimal physical side effects even in today’s world. If every trans person who wanted to bind could do so with a properly fitting binder, while living day to day without fear violence for being visibly trans, all while having access to knowledgeable and affirming medical care (including puberty blockers or top surgery as desired and appropriate), binding could become safer for everyone.
It’s on all of us to create that world. We call on everyone to fight back against anti-trans legislation, disrupt anti-trans hostility, and to support the trans youth and adults in our communities as they become their most authentic selves.
More Must-Reads from TIME
- The New Face of Doctor Who
- Putin’s Enemies Are Struggling to Unite
- Women Say They Were Pressured Into Long-Term Birth Control
- Scientists Are Finding Out Just How Toxic Your Stuff Is
- Boredom Makes Us Human
- John Mulaney Has What Late Night Needs
- The 100 Most Influential People of 2024
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Contact us at [email protected]
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Gender Equality Essay

Introduction to Gender Equality
In a society, everyone has the right to lead his/her life accordingly without any discrimination. When this state is achieved where all individuals are considered to be equal irrespective of their caste, gender, colour, profession, and status, we call it equality. Equality can also be defined as the situation where every individual has the same rights and equal opportunity to grow and prosper.
Every individual of society dreams for equal rights and access to resources available at their disposal, but there is a lot of discrimination. This discrimination can be due to cultural differences, geographical differences, the colour of the individual, social status and even gender. The most prevalent discrimination is gender inequality. It is not a localised issue and is limited to only certain spheres of life but is prevalent across the globe. Even in progressive societies and top organisations, we can see many examples of gender bias.
Gender equality can only be achieved when both male and female individuals are treated similarly. But discrimination is a social menace that creates division. We stop being together and stand together to tackle our problems. This social stigma has been creeping into the underbelly of all of society for many centuries. This has also been witnessed in gender-based cases. Gender inequality is the thing of the past as both men and women are creating history in all segments together.
Gender Equality builds a Nation
In this century, women and men enjoy the same privileges. The perception is changing slowly but steadily. People are now becoming more aware of their rights and what they can do in a free society. It has been found that when women and men hold the same position and participate equally, society progresses exclusively and creates a landmark. When a community reaches gender equality, everyone enjoys the same privileges and gets similar scopes in education, health, occupation, and political aspect. Even in the family, when both male and female members are treated in the same way, it is the best place to grow, learn, and add great value.
A nation needs to value every gender equally to progress at the right place. A society attains better development in all aspects when both genders are entitled to similar opportunities. Equal rights in decision making, health, politics, infrastructure, profession, etc will surely advance our society to a new level. The social stigma of women staying inside the house has changed. Nowadays, girls are equally competing with boys in school. They are also creating landmark development in their respective profession. Women are now seeking economic independence before they get married. It gives them the confidence to stand against oppression and make better decisions for themselves.
The age-old social structure dictated that women need to stay inside the home taking care of all when men go out to earn bread and butter. This has been practised for ages when the world outside was not safe. Now that the time has changed and we have successfully made our environment quite safer, women can step forward, get educated, pursue their passion, bring economic balance in their families, and share the weight of a family with men. This, in a cumulative way, will also make a country’s economy progress faster and better.
Methods to measure Gender Equality
Gender equality can be measured and a country’s growth can be traced by using the following methods.
Gender Development Index (GDI) is a gender-based calculation done similar to the Human Development Index.
Gender Empowerment Measure (GEM) is a detailed calculation method of the percentage of female members in decision-making roles.
Gender Equity Index (GEI) considers economic participation, education, and empowerment.
Global Gender Gap Index assesses the level of gender inequality present on the basis of four criteria: economic participation and opportunity, educational attainment, political empowerment, health and survival .
According to the Gender Gap Index (GGI), India ranks 140 among 156 participating countries. This denotes that the performance of India has fallen from the previous years, denoting negative growth in terms of closing the gender gap. In the current environment where equality and equal opportunities are considered supreme, this makes India be at a significant disadvantage.
Roadblocks to Gender Equality
Indian society is still wrecked by such stigmas that dictate that women are meant to manage the home and stay indoors. This is being done for ages, leading to neglect of women in areas like education, health, wealth, and socio-economic fields.
In addition to that, the dowry system is further crippling society. This ill practice had led to numerous female feticides. It has created a notion that girls are a burden on a family, which is one of the primary reasons a girl child cannot continue her education. Even if they excel in education and become independent, most of them are forced to quit their job as their income is considered a backup source, which is not fair. New-age women are not only independent, but they are confident too. The only thing they demand from society is support, which we should provide them.
Along with dowry, there is one more burning issue that has a profound impact on women's growth. It is prevalent in all kinds of society and is known as violence. Violence against women is present in one or another form in public and private spaces. Sometimes, violence is accompanied by other burning issues such as exploitation, harassment, and trafficking, making the world unsafe for women. We must take steps to stop this and ensure a safe and healthy place for women.
Poverty is also one of the major roadblocks towards gender equality. It has led to other malpractices such as child marriage, sale of children, trafficking and child labour, to name a few. Providing equal job opportunities and upliftment of people below the poverty line can help bring some checks onto this.
Initiative Towards Gender Equality
Any kind of discrimination acts as a roadblock in any nation’s growth, and a nation can only prosper when all its citizens have equal rights. Most of the developed countries has comparatively less gender discrimination and provide equal opportunity to both genders. Even the Indian government is taking multiple initiatives to cut down gender discrimination.
They have initiated a social campaign called “Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao Yojana” to encourage the education of girl children. Besides this, the government runs multiple other schemes, such as the Women Helpline Scheme, UJJAWALA, National Mission for Empowerment of Women, etc., to generate awareness among the people. Moreover, as responsible citizens, it is our responsibility to spread knowledge on gender discrimination to create a beautiful world for wome n [1] [2] .

FAQs on Gender Equality Essay
1. What Makes Women Unequal to Men?
The social stigmas and beliefs that have been running deeply in the veins of all families make women unequal to men. Women are considered to be a burden by many families and are not provided with the same rights men enjoy in society. We are ill-informed regarding women’s rights and tend to continue age-old practices. This is made worse with social menaces such as the dowry system, child labor, child marriage, etc. Women can gather knowledge, get educated, and compete with men. This is sometimes quite threatening to the false patriarchal society.
2. How can We Promote Gender Equality?
Education is the prime measure to be taken to make society free from such menaces. When we teach our new generation regarding the best social practices and gender equal rights, we can eradicate such menaces aptly. Our society is ill-informed regarding gender equality and rights. Many policies have been designed and implemented by the government. As our country holds the second position in terms of population, it is hard to tackle these gender-based problems. It can only be erased from the deepest point by using education as the prime weapon.
3. Why should Women be Equal to Men?
Women might not be similar to men in terms of physical strength and physiological traits. Both are differently built biologically but they have the same brain and organs to function. Women these days are creating milestones that are changing society. They have traveled to space, running companies, creating history, and making everyone proud. Women are showing their capabilities in every phase and hence, they should be equal to men in all aspects.
4. Mention a few initiatives started by the Indian Government to enable gender equality.
The Indian government has initiated a social campaign called “Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao Yojana” to encourage girls’ education. Besides this, the government runs multiple other schemes, such as the Women Helpline Scheme, UJJAWALA, National Mission for Empowerment of Women, etc., to generate awareness among the people.
(Stanford users can avoid this Captcha by logging in.)
- Send to text email RefWorks EndNote printer
The female gaze : essays on gender, society and media
Available online, at the library.

Green Library
More options.
- Find it at other libraries via WorldCat
- Contributors
Description
Creators/contributors, contents/summary.
- The home. Same work no gains ; Economic evaluation of housework ; On HIV, marriages and happily ever afters ; Caged and abandoned ; The culture of invisible violence ; Barely alive: widows of dead farmers ; Are we refugees? ; The deafening sound of silence ; Of lipsticks and masks ; Domestic trafficking ; Monetary compensation for rape victims ; Family planning and gender bias ; Should men take responsibility to stop violence against women? ; Ageing: a positive approach ; Journey of a woman priestess ; Is the prostitute not a 'worker'?
- The world. Women and parliament ; Women and regional journalism ; Women, war and conflict journalism ; On gender, media and human rights ; The gender revolution in film posters: from Mother India to Kahaani ; My choice or no choice? ; When reel meets real: Gulab gang vs Gulabi gang ; Saankal: a bizarre tale of a social custom ; Mai Ghat: crime number 103/2005 ; The housewife as a prostitute ; How brutal is patriarchy? ; Films in which women dominate ; Daughters of clay ; Sex or gender? ; Run Kalyani ; Ajji: a mirror to system ; Thappad: a slap on society
Bibliographic information
Browse related items.
- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
We will keep fighting for all libraries - stand with us!
Internet Archive Audio

- This Just In
- Grateful Dead
- Old Time Radio
- 78 RPMs and Cylinder Recordings
- Audio Books & Poetry
- Computers, Technology and Science
- Music, Arts & Culture
- News & Public Affairs
- Spirituality & Religion
- Radio News Archive

- Flickr Commons
- Occupy Wall Street Flickr
- NASA Images
- Solar System Collection
- Ames Research Center

- All Software
- Old School Emulation
- MS-DOS Games
- Historical Software
- Classic PC Games
- Software Library
- Kodi Archive and Support File
- Vintage Software
- CD-ROM Software
- CD-ROM Software Library
- Software Sites
- Tucows Software Library
- Shareware CD-ROMs
- Software Capsules Compilation
- CD-ROM Images
- ZX Spectrum
- DOOM Level CD

- Smithsonian Libraries
- FEDLINK (US)
- Lincoln Collection
- American Libraries
- Canadian Libraries
- Universal Library
- Project Gutenberg
- Children's Library
- Biodiversity Heritage Library
- Books by Language
- Additional Collections

- Prelinger Archives
- Democracy Now!
- Occupy Wall Street
- TV NSA Clip Library
- Animation & Cartoons
- Arts & Music
- Computers & Technology
- Cultural & Academic Films
- Ephemeral Films
- Sports Videos
- Videogame Videos
- Youth Media
Search the history of over 866 billion web pages on the Internet.
Mobile Apps
- Wayback Machine (iOS)
- Wayback Machine (Android)
Browser Extensions
Archive-it subscription.
- Explore the Collections
- Build Collections
Save Page Now
Capture a web page as it appears now for use as a trusted citation in the future.
Please enter a valid web address
- Donate Donate icon An illustration of a heart shape
Caribbean portraits : essays on gender ideologies and identities
Bookreader item preview, share or embed this item, flag this item for.
- Graphic Violence
- Explicit Sexual Content
- Hate Speech
- Misinformation/Disinformation
- Marketing/Phishing/Advertising
- Misleading/Inaccurate/Missing Metadata
inherent obscured text on back cover
![[WorldCat (this item)] [WorldCat (this item)]](https://archive.org/images/worldcat-small.png)
plus-circle Add Review comment Reviews
33 Previews
2 Favorites
DOWNLOAD OPTIONS
No suitable files to display here.
PDF access not available for this item.
IN COLLECTIONS
Uploaded by station53.cebu on December 2, 2022
SIMILAR ITEMS (based on metadata)

Confusion over how pregnancy dates are measured is widespread – and makes for uninformed debate over abortion limits
Professor of Political Science, Hartwick College
Professor of political science, Augusta University
Professor of Political Science, North Carolina State University
Disclosure statement
The funding for the survey discussed in this article was funded by the NC State School of Public and International Affairs.
Mary-Kate Lizotte and Steven Greene do not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and have disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
View all partners
Most Americans don’t know two key facts about pregnancy, including how they are dated and how long a trimester is – and this could matter, as a growing number of states place restrictions on abortion.
Florida enacted a new law on May 1, 2024, that bans abortions after six weeks of pregnancy, with a few exceptions – including documented rape, incest and to save the life of the mother.
Florida joins the majority of Southern states that now have complete bans or highly restrictive abortion laws, enacted since the Supreme Court overturned the federal right to get an abortion in June 2022. Many of the restrictive laws ban abortion after a set number of weeks.
Florida Republicans supporting the bill have labeled it a reasonable compromise between a full abortion ban and few abortion restrictions.
Some OB-GYNs have explained that many women do not even know they are pregnant at six weeks . Research shows that women on average find out they are pregnant at five and a half weeks. About 23% do not know until seven weeks of pregnancy or later.
So, do Americans, including those enacting six-week bans, actually understand how the timing or dating of pregnancy works?
We are scholars of political science , gender and public opinion and are writing a book about public opinion on abortion after the Supreme Court’s reversal of the federal right to get an abortion in June 2022.
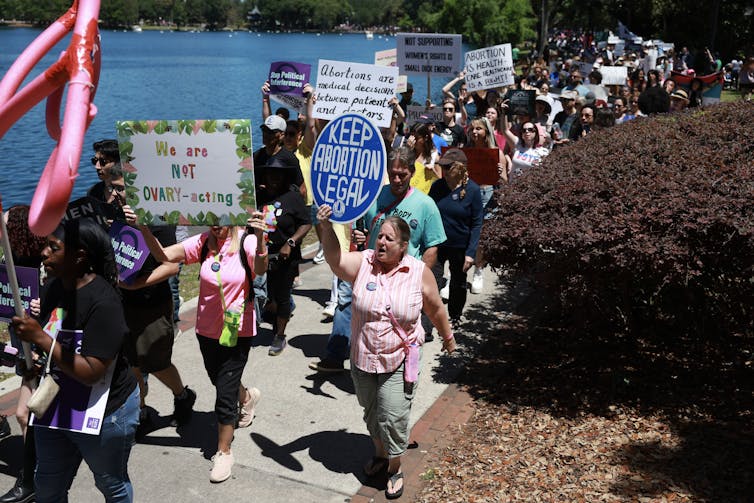
How does pregnancy work?
To gain insights into this issue, we developed a few pregnancy questions and included them in a research survey in late September 2023. The survey had 1,356 respondents, who were broadly representative of the U.S. population. The respondents’ median age was 46. Approximately 49% of these people were men, while 70% were white and 29% were college graduates. Meanwhile, 43% of them were Democrats, and 38% were Republicans.
The first question asked respondents how pregnancies are dated. The correct answer is that pregnancies are dated using the first day of the woman’s last menstrual period, which is often two to three weeks before conception.
The second question asked about trimesters. Many Americans are familiar with the term trimester, and polling consistently shows that Americans find abortion most acceptable during the first trimester. We asked Americans if they knew approximately how many weeks a trimester was. The correct answer is 13.
Americans’ pregnancy knowledge
We found that only one-third of respondents knew how pregnancy is dated. A majority – approximately 60% – falsely thought that pregnancy is dated from conception or in the weeks since the woman last had sex. Less than one-fourth of the respondents answered both pregnancy knowledge questions correctly.
In our survey, we also asked respondents whether they support a six-week abortion ban. Similar to other national surveys , we find that most Americans oppose strict abortion restrictions – only 35% support six-week bans.
Importantly, we find that those who support six-week abortion bans are significantly less likely than others to correctly understand the timing of pregnancy. The statistically significant relationship between having low levels of pregnancy timing knowledge and support for a six-week abortion ban holds in analyses controlling for potentially confounding variables.
Some anti-abortion lawmakers have demonstrated their ignorance about pregnancy before.
There is, for example, a long history of some anti-abortion politicians saying, incorrectly, that it is extremely rare for a person who is raped to get pregnant. Our survey shows that a large swath of those opposing abortion lack knowledge about the basics of pregnancy.

A gender disparity
Perhaps not surprisingly, women in this survey knew more about pregnancy than men. The question about how pregnancies are dated, for example, was answered correctly by 43% of women compared with only 23% of men. As mentioned above, a majority of Americans incorrectly believe pregnancy is dated from conception, but significantly more men than women think this is true.
This finding is particularly important when considering the gender breakdown of the Florida state lawmakers who approved the six-week ban. Although we do not have data on the pregnancy knowledge of those legislators, we do know that those who voted for the ban were overwhelmingly men .
Florida’s six-week ban will make it much harder for anyone to get abortions there – and it will also affect people in neighboring states who want or need an abortion. In 2023, Florida was home to the closest abortion clinic for 6.4 million women living in the South. In 2023, around 7,700 women from other Southern states, where abortion is now largely banned , traveled to Florida to get abortions.
Overall, our findings raise serious questions about whether Americans without medical training – much like those in our state legislatures – have the necessary knowledge needed to regulate abortion access.
This story has been updated to remove an incorrect reference to the Susan B. Anthony Pro-Life America group’s position on an abortion ban after six weeks.
- Abortion law
- US Supreme Court
- Abortion rights
- Heartbeat bills
- Abortion bans
- Abortion restrictions
- Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization
- anti-abortion rights
- Early pregnancy
- Southern states
- Abortion policy

Case Management Specialist

Lecturer / Senior Lecturer - Marketing

Assistant Editor - 1 year cadetship

Executive Dean, Faculty of Health

Lecturer/Senior Lecturer, Earth System Science (School of Science)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Gender roles essay topics and titles may include: The history of gender roles and their shifts throughout the time. Male and female roles in society. Gender roles in literature and media. How a man and a woman is perceived in current society. The causes and outcomes of gender discrimination.
Activists are charting unfamiliar territory, which this essay explores. "Men built this system. No wonder gender equality remains as far off as ever.". - Ellie Mae O'Hagan. Freelance journalist Ellie Mae O'Hagan (whose book The New Normal is scheduled for a May 2020 release) is discouraged that gender equality is so many years away.
Gender studies developed alongside and emerged out of Women's Studies. This non-exhaustive list introduces readers to scholarship in the field. The icon indicates free access to the linked research on JSTOR. Gender studies asks what it means to make gender salient, bringing a critical eye to everything from labor conditions to healthcare ...
After an early unsuccessful attempt, Rwanda invested seriously in gender budgeting beginning in 2011. 23 24 The budget is focused on closing gaps and strengthening women's roles in key sectors ...
Feminist Perspectives on Sex and Gender. First published Mon May 12, 2008; substantive revision Tue Jan 18, 2022. Feminism is said to be the movement to end women's oppression (hooks 2000, 26). One possible way to understand 'woman' in this claim is to take it as a sex term: 'woman' picks out human females and being a human female ...
Gender essay topics offer a wide range of options for exploration, from gender roles in society to gender and power dynamics. By incorporating relevant keywords and phrases into essays on these topics, writers can improve their search engine visibility and attract more readers to their work. Whether you are interested in exploring the social ...
Though she doesn't use exactly these terms, Angela McRobbie's Feminism and the Politics of Resilience: Essays on Gender, Media, and the End of Welfare is about how early twenty-first-century British neoliberalism transforms the classic virgin/whore dichotomy into one between so-called "mom bosses" and "welfare queens." A focused complement to Melinda Cooper's Family Values: Between ...
Transgender Studies Quarterly 9.2: 143-159. Publications, Essays. Gender, Transgender Studies. Jiwoon Yulee. "A Feminist Critique of Labor Precarity and Neoliberal Forgetting: Life Stories of Feminized Laboring Subjects in South Korea," Feminist Studies, Special Issue: Feminism & Capitalism, 2021, 47:3.
Summary. This chapter features the contributions of influential and lesser-known essayists who have written persuasively and engagingly on gender and sexuality in the twentieth and twenty-first centuries. Issues of identity and difference have had a profound effect on the writing of our age, and certainly on the essay, the most elusive of genres.
Gender Equality Essay Outline. Choosing a good title for a gender equality essay involves capturing the essay's main ideas and sparking interest. You can include keywords like "equality" or "empowerment" and use phrasing that makes readers think. For the gender equality essay thesis statement, keep it concise and clear.
Gender roles in society have been a topic of much discussion and debate for years. From the traditional expectations of men as breadwinners and women as homemakers to the evolving understanding of gender as a spectrum, the concept of gender roles has shaped the way individuals navigate their lives. This essay will explore the complexities of ...
What is gender? A deconstruction of the concept. Defining gender is both highly important and complex. Hegarty (Citation 2001) suggests that the quantitative researcher should address this definition from a performative perspective to de-construct the gender concept.In this way, gender is a non-essential category which instead is repeatedly performed based on societal norms (Morgenroth & Ryan ...
Discourses of gender unfold not only in explicit talk about gender, but in talk about things (like burnt toast) that may be grafted on to gender. If enough people joke together continually about men's ineptness in the kitchen, women's role as cooks takes center stage, along with men's incompetence in the kitchen.
Essays published so far: Vic Valentine: " Self-declaration would bring Britain into line with international best practice ". Debbie Hayton: " Gender identity needs to be based on objective ...
500+ Words Essay on Gender Equality Essay. Equality or non-discrimination is that state where every individual gets equal opportunities and rights. Every individual of the society yearns for equal status, opportunity, and rights. However, it is a general observation that there exists lots of discrimination between humans.
This essay argues that gender roles are socially constructed and not biologically based. Within every society, gender is a socially constructed term with gender identity expectations. In society; development of gender roles beginning as early as infancy, adopting gender identity later on in life through influence of peers and media. ...
Answer 2: The gender inequality essay tells us that gender inequality impacts us badly. It takes away opportunities from deserving people. Moreover, it results in discriminatory behaviour towards people of a certain gender. Finally, it also puts people of a certain gender in dangerous situations. Share with friends.
Kobabe (e/eir/em) is author of the award-winning and bestselling memoir Gender Queer, the most challenged book in America for the last three years. Peitzmeier Ph.D., MSPH (she/her) is a social ...
Introduction to Gender Equality. In a society, everyone has the right to lead his/her life accordingly without any discrimination. When this state is achieved where all individuals are considered to be equal irrespective of their caste, gender, colour, profession, and status, we call it equality. Equality can also be defined as the situation ...
Summary. "Shoma A. Chatterji's The Female gaze: essays on gender, society and media explores the complex journey of Indian women in the era of globalizaion and its resultant impact on cultural values and the lives of Indian women in the twenty-first century." -- Book jacket.
Caribbean portraits : essays on gender ideologies and identities ... "In association with the Centre for Gender and Development Studies, University of the West Indies." Includes bibliographical references (p. [457]-492) Notes. inherent obscured text on back cover. Access-restricted-item
A gender disparity Perhaps not surprisingly, women in this survey knew more about pregnancy than men. The question about how pregnancies are dated, for example, was answered correctly by 43% of ...