Advertisement

Electric Vehicles Charging Technology Review and Optimal Size Estimation
- Original Article
- Open access
- Published: 02 October 2020
- Volume 15 , pages 2539–2552, ( 2020 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Morris Brenna 1 ,
- Federica Foiadelli 1 ,
- Carola Leone ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4399-3052 1 &
- Michela Longo 1
78k Accesses
136 Citations
3 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Many different types of electric vehicle (EV) charging technologies are described in literature and implemented in practical applications. This paper presents an overview of the existing and proposed EV charging technologies in terms of converter topologies, power levels, power flow directions and charging control strategies. An overview of the main charging methods is presented as well, particularly the goal is to highlight an effective and fast charging technique for lithium ions batteries concerning prolonging cell cycle life and retaining high charging efficiency. Once presented the main important aspects of charging technologies and strategies, in the last part of this paper, through the use of genetic algorithm, the optimal size of the charging systems is estimated and, on the base of a sensitive analysis, the possible future trends in this field are finally valued.
Similar content being viewed by others
A comprehensive review on hybrid electric vehicles: architectures and components

Review and Development of Electric Motor Systems and Electric Powertrains for New Energy Vehicles
Automotive Li-Ion Batteries: Current Status and Future Perspectives
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Growing concern of carbon dioxide emissions, greenhouse effects and rapid depletion of fossil fuels raise the necessity to produce and adopt new eco-friendly sustainable alternatives to the internal combustion engine (ICE) driven vehicles. For this reason, in the last decade, EVs have become in some way widespread, principally because of their negligible flue gas emissions and lesser reliance on oil. It is estimated that by 2022, EVs will be over 35 million in the World. However, a critical problem associated with EVs is that their high penetration causes significant issues on the power distribution grid such as: power quality deterioration, enhanced damaged of line, downturn of distribution transformers, increased distortion and higher fault current [ 1 , 2 ]. One efficient approach to relieve the effect is to integrate local power generation such as renewable energy sources (RESs) into the EV charging infrastructure [ 3 , 4 , 5 ].
Batteries can be charged through conductive or inductive methods [ 6 ]. Inductive charger are wireless charging systems (WCS). WCS can be stationary, which means that they can only be utilized when the car is parked or in stationary modes, such as in car parks, garages, or at traffic signals, or they can be dynamic. This latter method allows battery charging while the vehicle is in motion. In general, WCS can bring some advantages in the form of aesthetic quality, reliability, durability and user friendliness. Anyway, due to some challenges such as electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) issues, limited power transfer, bulky and expensive structures, shorter range, and lower efficiency [ 7 , 8 ], inductive chargers are not largely commercialized and employed as the conductive ones. In this paper only conductive charging strategies are analyzed.
Based on their power ratings EV battery chargers can be divided into level 1, level 2 and level 3. Table 1 summarize the characteristics of the three different power levels [ 9 , 10 ].
A battery charger can allow a unidirectional or bidirectional power flow at all power levels. The bidirectional power flow adds to the grid-to-vehicle interaction (G2V) also the vehicle-to-grid (V2G) mode [ 11 ]. This latter technology can bring significant improvement in the overall reliability of the distribution grid, since in case of system failure, peak load demand or other unexpected scenarios, with a bidirectional power flow, the EVs can be used as back up generation, supplying the energy back to the grid when needed [ 12 ]. With V2G, as all the energy storage systems, EVs battery can be used not only as back up resource but also to improve the power quality, the stability and the operating cost of distribution network. Moreover, in the long run, V2G could reduce investment in new power generation infrastructure [ 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 ]. All the just listed reasons are increasing researchers’ interest in this technology.
Not only the choice of the charging technology, but also the selection of the correct charging method is a feature that has to be considered during the charging procedure. The most popular charging strategies to recharge Li-ion batteries are constant-current/constant-voltage (CC/CV) and pulse current charging methods [ 17 , 18 ]. However these methods do not take into account the several internal process of the battery which influence its charging capability and aging. As a result, some promising charging strategies which are based on more complete models of lithium-ion batteries are now under research [ 19 ].
EV battery and power electronic devices costs are steadily falling [ 20 , 21 ]. This rapid decline is mostly due to a growing manufacturing industry, which is constantly increasing the knowledge, the number of applications and the improvements of both these technologies. As the costs are falling, the trends of EV battery energy density, gross weight and semiconductor devices performances are following exactly the opposite direction; in fact, with equal capacities, batteries are becoming ever smaller and lighter and the power electronic devices ever more performing [ 22 ]. All this impacts the choice and the size of the charging systems. The sizing procedure of a suitable charging system is made even more difficult by the presence of many different technologies of the onboard and off-board chargers and also different cost, dimensions, weights, power rating; and so on.
This the paper is organized as follow. In Sects. 2 and 3 , respectively, on-board and off-board charger most common architectures are presented and their operating principles are explained. In Sect. 4 , the concept of fast charging stations is introduced. The available and most suitable charging methods are listed in Sect. 5 with particular attention to the charging methods most suitable for direct-current (DC) fast charging. Finally, a genetic algorithm is used in Sect. 6 to estimate the optimal charging system size and its possible future trends.
2 Onboard Charger
Battery chargers can be implemented inside (on-board) or outside (off-board) the vehicle. Onboard battery chargers (OBC) are limited by size, weight and volume [ 23 ] for this reason they are usually compatible with level 1 and level 2 chargers. They usually have unidirectional power transfer capability; nevertheless in some case the configuration, a bidirectional power transfer can be achieved. Figure 1 shows the typical architecture of an electric vehicle charging system, in such figure both the on-board charger and the off-board one are represented.
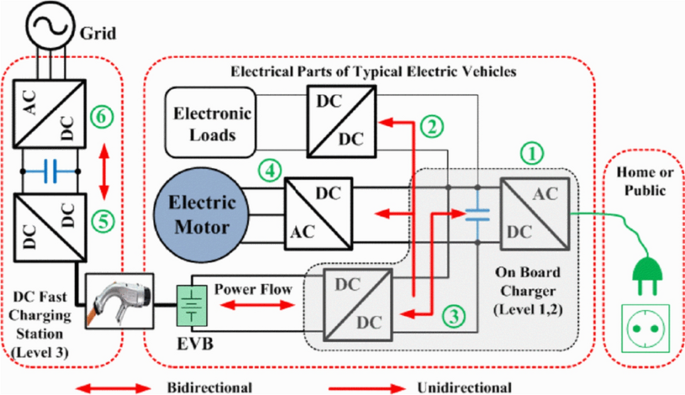
Charging system configuration for electric vehicle
2.1 Two Stage
Onboard chargers are typically composed by two stages: a front-end AC–DC stage and a back-end DC-DC stage. Very different topologies are proposed in literature for both the converters.
The front-end rectifier usually contains a boost power factor correction (PFC) converter to achieve high power factor and low harmonic distortion. The rectifier stage can be performed by a half-bridge, full-bridge or multilevel diode bridge. Half-bridge rectifier is less expensive since it contains less number of diodes/switches, full-bridge rectifier is more complex but the components are subjected to lower stresses. If instead higher power ratings should be achieved a good choice for the ac–dc converter is a multilevel configuration. Figure 2 shows a full-bridge diode rectifier with a conventional PFC boost converter [ 24 , 25 ]. By substituting all the diodes with active switches, a bidirectional power flow can be obtained.
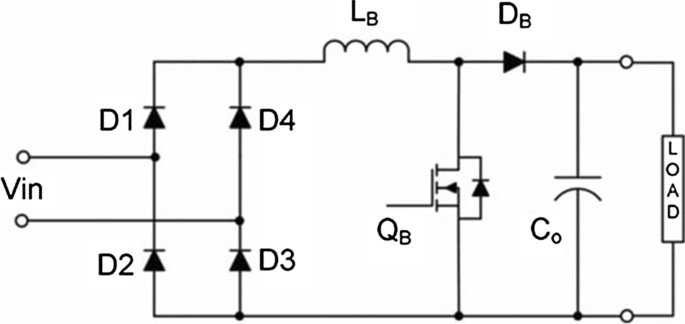
Full-bridge rectifier with conventional PFC boost converter
In PFC converter the interleaved boost converter is becoming more and more popular. As shown in Fig. 3 , an interleaved boost converter simply consists in two boost converters in parallel, operating 180° out of phase [ 26 ]. The main aim of this interleaving is to increase the output current by reducing the input current ripple and hence by reducing the overall volume of the input ElectroMagnetic Interference (EMI) filter and of the boost inductor [ 23 , 27 , 28 , 29 ]. On the other hand, interleaving means increasing the cost and the complexity of the design.

Full-bridge rectifier with interleaved PFC boost converter
The front-end converter is followed by a second dc-dc converter. Resonant power converters are very common to perform this second stage, because of the potential to achieve at the same time both higher switching frequency and lower switching losses [ 29 ]. Among all the resonant converter, LLC configuration, shown in Fig. 4 , is achieving resounding interest, thanks to its several advantages over other resonant topologies, such as: (1) the ability to operate at zero-voltage switching (ZVS) or zero-current switching (ZCS), (2) containing a high frequency transformer it performs the galvanic isolation between the grid and the EV, (3) a wide output voltage regulation is possible, (4) the output filter consists only in a capacitor and not in an LC filter [ 29 , 30 , 31 ].
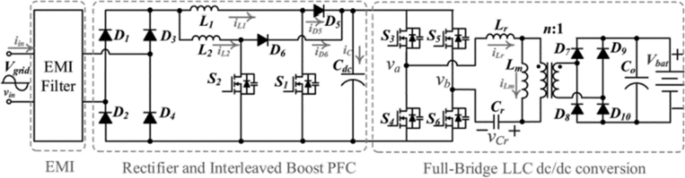
Example of two-stage onboard charger with LLC converter
However in literature other types of dc–dc converter have been proposed. In [ 32 ] a bidirectional buck-boost non-isolated dc/dc converter is proposed whose principal aim is to allow a reduction of the dc-link capacitor. In [ 33 ] is proposed for the dc–dc stage a cascade structure of a high-frequency LLC converter followed by a buck converter. The advantage of this configuration consists in a constant switching frequency operation of the active switches of the LLC converter while the charge control is performed by the buck converter. On the other and by adding an additional stage to the dc–dc converter, the complexity and the cost of the converter increases. Finally, in [ 34 ] a dc–dc non-isolated buck converter is employed. This latter topology is easy to implement but it works only if the dc-link voltage is higher than the battery pack voltage.
2.2 Single Stage
If the ac–dc rectifier is combined with the dc-dc converter, a single stage battery charger is obtained. This topology of battery charger is used if lower cost and size are required [ 23 , 34 ], in fact single stage battery charger allows the elimination of some bulky and expensive components such as inductors and dc-link capacitors [ 35 , 36 ] which instead are required in two-stage charger. However, the drawback is that single stage battery chargers with non-isolated converter suffer from a limited conversion ratio, which limits their application for the wide range of output voltage. If instead a high frequency isolation is present, as in the OCB configuration proposed in [ 35 ], the low frequency component generated by the rectification stage pass through the high frequency transformer leading to large magnetizing current. Moreover to achieve power factor correction, a large number of diodes and active switches could be necessary [ 36 ], increasing in this way the complexity of the configuration and hence decreasing the reliability of the overall charger.
2.3 Integrated
To maximize the reduction of components number and hence to further reduce the size, weight and cost of the battery charger several integrated topologies have been proposed and studied in literature [ 23 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 ]. The concept of integration consists of reusing some of the drivetrain components (inverter and motor windings) to implement the onboard charging system. However, some problems may born from this combination: the configurations proposed in [ 37 , 38 ] required access to inaccessible points of the motor windings, in [ 39 ] a rearrangement of the motor windings is necessary during the transition between different operation modes. Finally, by using the charger configuration proposed in [ 40 ], even if neither access to the neutral point of the motor windings nor their rearrangement are required, the control of the active switches becomes more difficult.
2.4 Multifunctional
The last type of proposed OBC are the so called multifunctional OBCs. In this type of battery charger some components are shared to accomplish different aims. In this way higher fuel efficiency can be reached by smaller and lighter design. In [ 41 ], the proposed multifunctional battery charger can charge the auxiliary battery via the propulsion battery when the vehicle is in a driving state, acting in this way as an OBC and as low-voltage dc-to-dc converter (LDC) jointly. In [ 42 ], a similar configuration, shown in Fig. 5 , with the same duties is presented.
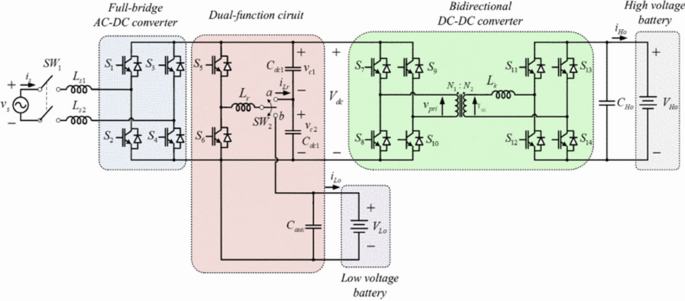
Multifunctional OBC proposed in [ 42 ]
3 Off-Board Charger
Level 3 charger, because of their rating powers, are usually installed outside the vehicle (off-board). Also for level 3 off-board charger a large amount of different solutions is studied in literature [ 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 62 ]. Since it is mandatory to guarantee galvanic isolation between the AC supply circuit and the DC output circuit according to the IEC EN 61,851–23 standard, in this paragraph only isolated off-board charger have been presented.
The off-board charging system is most commonly composed of two stages: a grid-facing AC/DC converter followed by a DC/DC converter providing an interface to EV battery. Based on the converter topology, both these stages can allow unidirectional or bidirectional power flow.
3.1 Bidirectional AC/DC Converter
One of the most widely used bidirectional AC/DC converter is the three-phase LCL active rectifier [ 43 , 44 , 45 ], whose scheme is reported in Fig. 6 .
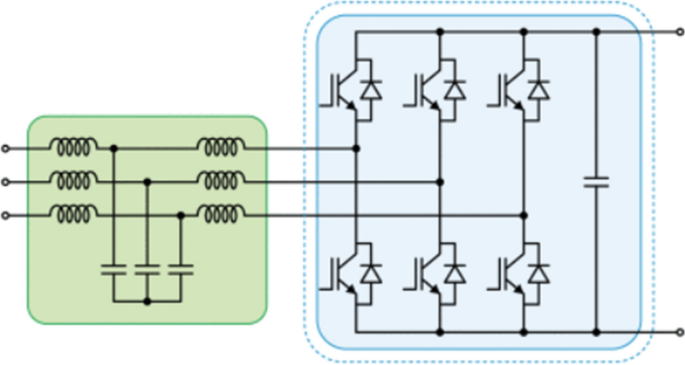
Three-phase LCL active rectifier [ 44 ]
The advantages of this type of converter are low harmonic input currents, bidirectional power flow and power factor (PF) regulation.
In [ 46 ] and [ 47 ] the front end ac–dc conversion is performed by a neutral-point-clamped (NPC) three-phase three-level converter. This converter has been used to increase the power density and to achieve low current harmonics distortion. Another advantage is that it allows the creation of a bipolar dc bus which can be used for the implementation of partial-power converters. However, the NPC causes imbalance of power and, as a result, voltage balancing problem across the DC bus capacitors.
3.2 Unidirectional AC/DC Converter
The most common unidirectional AC/DC converter used in off-board charging system is the Vienna rectifier [ 48 , 49 , 50 ]. It has advantages such as low voltage stress on each switch and high efficiency. However, the main limitations are the restricted reactive power control and the need of a dc-link capacitor voltage balancing. In [ 48 ] the authors propose a 25 kW off-board charger prototype composed by a single-switch Vienna rectifier, as depicted in Fig. 7 , and four three level dc/dc modules parallel connected.
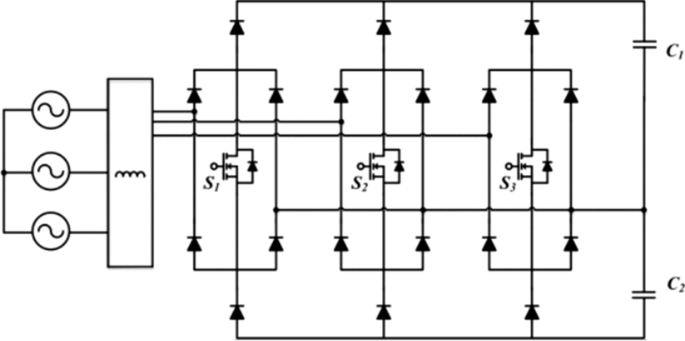
Vienna rectifier scheme proposed in [ 48 ]
3.3 Bidirectional DC/DC Converter
The main isolated DC/DC converter used in case of bidirectional power flow is the dual active bridge (DAB) [ 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 ], reported in Fig. 8 , and its variants (resonant DAB [ 53 ], multilevel DAB [ 54 ]). In particular, this topology is gaining interest thanks to the capabilities of the new wide-bandgap semiconductor (Gan/SiC) devices which enabled the converter efficiency and power density improvements [ 55 ].
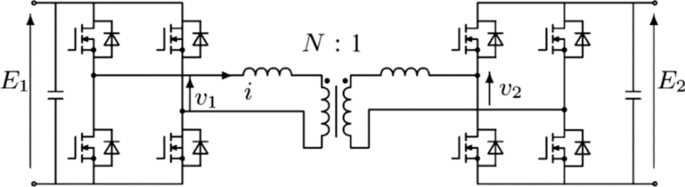
Dual active bridge scheme
3.4 Unidirectional DC/DC Converter
If unidirectional power flow is required, a LLC resonant converter is chosen, in most cases, as power interface between the dc bus of the AC/DC converter and the EV battery because of to its advantages over other resonant topologies [ 56 , 57 ], such as: the ability to operate at zero-voltage switching (ZVS) or zero-current switching (ZCS), it allows a wide output voltage regulation, the output filter consists only of a capacitor and not of an inductor and capacitor (LC) filter [ 58 ].
Another unidirectional DC/DC converter used in case of unidirectional off-board charger is the phase shifted full bridge converter [ 59 , 60 ], whose scheme is reported in Fig. 9 . This type of converter has different advantages such as high power density, low magnetic interference and high efficiency which make it well suitable for the implementation in battery chargers [ 61 ].
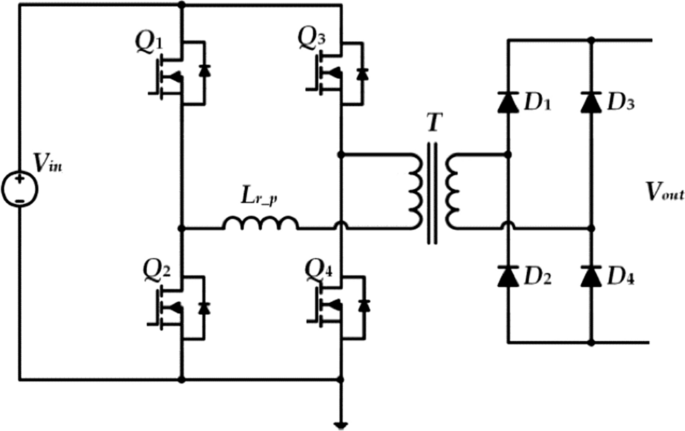
Phase shift full bridge converter
4 Fast Charging Stations
To reduce the driving range anxiety and hence to support a stronger increase of the penetration of EVs worldwide there is the need of a charging system which is able to replace the current existing oil station. A fast charging station (FCS) can allow the charging of an EV at 80% within a half of hour from its depletion, but to reduce the charging time from 7–8 h to 30 min, FCS requires high power from the grid and for this reason they are usually connected to the MV network [ 63 , 64 , 65 ], even if some FCS connected to the LV grid are proposed too [ 66 ]. The connection of such charging stations requires a huge capital investment and it could easily overload the distribution network. Another critical aspect to be considered consists in the voltage drop that the connection of FCS can cause along the lines of the distribution networks, which according to the standard EN50160 has to remain lower than 10%.
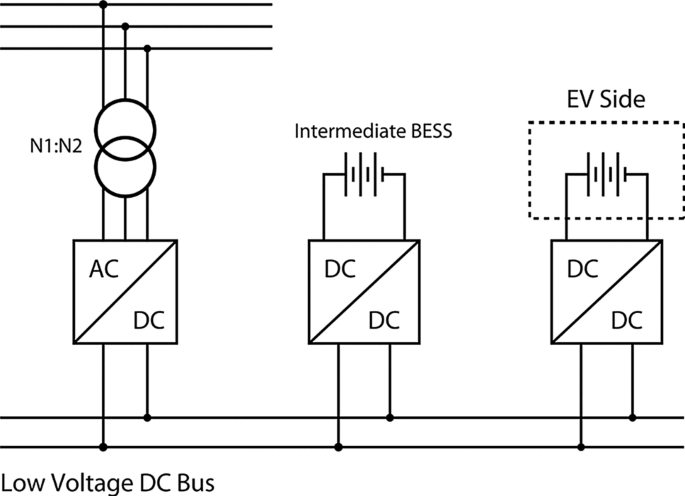
According to [ 67 ] the impact of fast charging stations on distribution MV grid can be mitigated with the use of energy storage systems (ESSs) which can shave peak power demand and provide additional network services. Moreover, ESS can also increase the voltage level in case of too high voltage drop along the lines, this service requires the implementation of a voltage control.
In order to further minimize the impact of the FCS on the grid, renewable energy resources can integrated within the FCS too [ 68 ]. In fact, in normal operation, during daytime, the EV batteries can be charged from the solar PV by reducing in this way the possibility of overloading the MV network. In night-time, instead, when solar energy is not available the EV batteries can be charged from the grid. EVs also can support to the grid at the peak load demand if needed. By this way, the grid will never become unstable with a high pulse power of charging from EVs.
4.1 Architecture
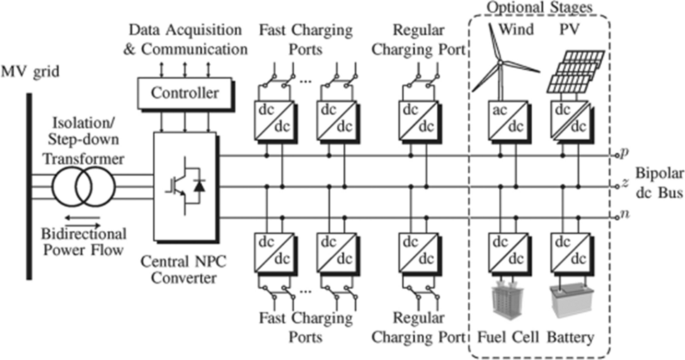
The configuration chosen in [ 63 ] for the ultra-fast charging station is shown in Fig. 10 . The isolation between the AC side and the DC side is performed by the line-frequency transformer. The ac–dc stage is common to all the EV, in fact the output of the Cascade H Bridge (CHB) multilevel converter creates a unipolar common DC voltage bus at which all dc–dc converters are connected. The power interface between the dc bus and the integrated storage or the EV battery is performed by a LLC resonant converter.
Fast charging station with unipolar dc voltage bus proposed in [ 63 ]
In [ 64 ] a bipolar dc bus architecture is proposed. The charging station here adopted is shown in Fig. 11 . The bipolar dc bus is necessary to feed the three-level dc–dc converter. On one side, this architecture increase the capability of the FC station and reduce the THD; on the other hand, this system requires a DC power balance management mechanism [ 65 ].
Fast charging station with bipolar dc voltage bus proposed in [ 64 ]
4.2 Power Control Strategies
A number of studies have been carried out also on the control strategy of EV charging station [ 69 , 70 , 71 , 72 ]. The first difference among them concerns the choice of uncoordinated charging or coordinated charging. In uncoordinated charging scheme the EV battery starts charging immediately when it is plugged in or after a fixed start delay chosen by the user. If the EVs are charged according to this scheme, their impact on the grid will result in very high peak demand and hence in huge grid issues such as: feeders and transformers overloading, high losses, high voltage drops, and more cost [ 69 ]. For all the aforementioned reasons, the research has focused on EV coordinated charging strategies, in particular. Authors in [ 70 ] propose a coordinated control strategy for an FCS with an ESS, their principal aim is that of reducing the electricity purchase cost and flatten the peak load. In [ 71 ] the FCS contains both ESSs and RESs, the coordinated energy management proposed here is obtained by using a Fuzzy Logic based control defined by three inputs and two outputs. Other control strategies based on very different and numerous algorithms have been proposed in literature. Authors in [ 72 ] investigate and compare three different control strategies for a charging station. The charging strategies coordinate in different ways the energy flow of the ESS and PV panels. The results prove that the control strategy which uses the energy of the ESS with in response to the number of EVs plugged in and takes into account also the amount of generated renewable energy has the best performance. Furthermore according to this control method the SoC of the ESS is restored during night and during excess of solar energy.
5 Charging Methods
The advantages of a lithium-ion battery over other types of energy storage devices such as high energy and power density, low memory effect and resulting capacity loss, make this type of battery the best candidate for the field of electric vehicles [ 73 ]. However, li-ion battery charging must be carried out very carefully, since the charging method greatly affects how actively electrochemical side reactions occur inside the battery, and hence the cycle life of the battery itself [ 74 ]. For this reason, finding the optimal technique to charge a battery in the shortest period of time with high efficiency and without damaging the cells, has become a new challenge for many researchers [ 75 ].
In this paragraph the main charging methods for Li-ion batteries are discussed.
5.1 Constant Current-Constant Voltage (CC–CV)
In this method, represented in Fig. 12 , both an initial constant current and a final constant voltage are used. The charging process start with a constant current until a certain voltage value, known as cut-off voltage, is reached. For Li-ion with the traditional cathode materials of cobalt, nickel, manganese and aluminium typically the cut-off voltage value is around 4.20 V/cell. The tolerance is ± 50 mV/cell. Battery charging continues with a constant voltage just equal to the cut-off value. Full charge is reached when the current decreases to between 3 and 5% of the rated current. Trickle or float charge at full charge is not suitable for a Li-ion battery; since it would cause plating of metallic lithium and compromise safety. Instead of trickle charge, a topping charge can be applied when the voltage drops below a set value.
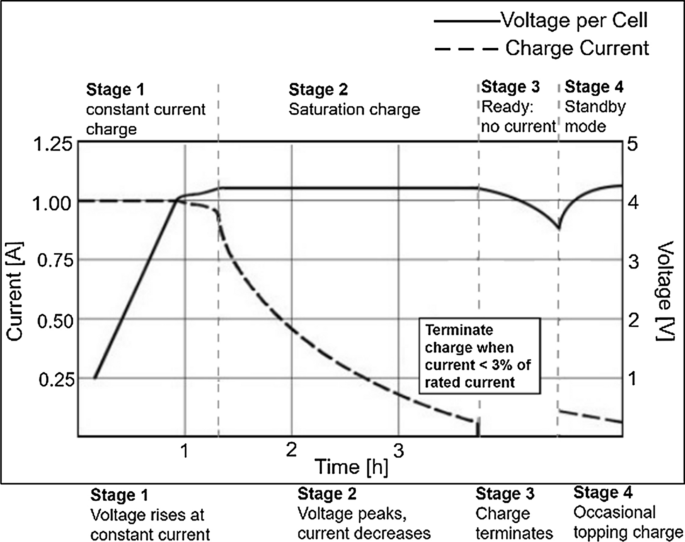
CC–CV charge stages for a Li-ion battery
In [ 77 ], a little bit different variant is proposed, in fact the first stage consists now in a trickle charge. This stage is activated only if the battery is deeply discharged, i.e. the cell voltage is below 3.0 V and after it the CC–CV method keeps place with the aforementioned way.
5.2 Five-Step Charging Pattern
An alternative method is here described in order to obtain faster and safer charging and longer battery cycle life [ 77 , 78 ]. The five-step charging pattern consists in a multistage (five stages) constant-current charging method, in which the charging time is divided into five steps. In each stage, the charging current is set to a constant threshold value. During charging, the voltage of the battery will increase and when it reaches the pre-set limit voltage, the stage number will increase and a new charging current set value will be applied accordingly. This process will continue until the stage number reaches 5. Figure 13 illustrates the concept of the five-step constant current charging pattern.
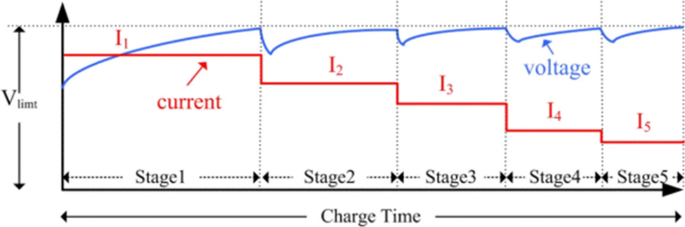
Five-step charging pattern for a Li-ion battery
To find the charging current in each steps different algorithms can be used, however it could be difficult and time ineffective find the optimal charging pattern.
5.3 Pulse Charging Method
With this charging strategy the charging current is injected into the battery in form of pulses, so that a rest period is provided for the ions to diffuse and neutralize. The charging rate, which depends on the average current, can be controlled by varying the width of the pulses. It is claimed [ 77 , 79 ] that this method can really speed up the charging process, slow down the polarization effect and increase life cycles. As shown in Fig. 14 , every pulse charge current that is applied to the battery is characterized by the following factors: peak amplitude I pk , a duty cycle D = t on /T p , and frequency f .
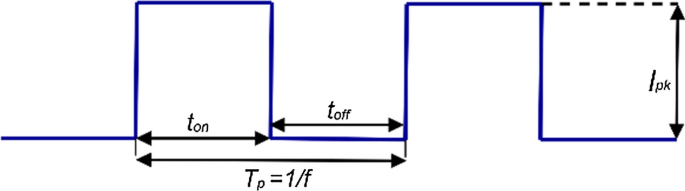
Pulse charge current parameters
Two different pulse charging methods exist: duty-fixed and duty-varied pulse-charge strategy. According to [ 79 ], the duty-varied strategy can increase the charging speed and the charging efficiency with respect to the conventional duty-fixed method.
5.4 Charging Strategies Based on Battery Physical-Based Models
In all the charging methods reported so far, only current and voltage limits are considered. Anyway, these limits do not take into consideration the aging process and the side reactions occurring inside the battery; and hence they might result too conservative for new batteries and possibly dangerous for aged batteries due to the altered behavior and characteristics. This, hence, motivates the development and the research of innovative charging algorithms which tackle the issue of the charging impact on battery state-of-health (SoH) and aging [ 76 , 80 ]. In fact, recently, many researches are focusing on develop new charging methods which minimize the charging time and extend the battery life at the same time [ 75 , 80 , 81 , 82 , 83 ].
This new category of charging strategies employs the electrochemical lithium-ion battery models to calculate quantitatively and almost precisely the amount of battery aging and to directly minimize the aging in a given charge time. The electrochemical battery model estimates the internal states of a battery in a more accurate way since it is built starting from the internal microstructure of the lithium-ion battery. However, it is very arduous to precisely estimate the parameters because the electrochemical model is composed of complicated coupled partial differential equations (PDEs), and involving a large number of parameters and boundary conditions it requires a large computation burden [ 82 ]. Therefore the complexity of these models often leads to the necessity for more memory and computational effort and thus they may not be practically implemented in the fast and real-time computations of EV BMS [ 86 ].
In recent years, many works focus on identifying simplified internal electrochemical models of the battery for efficiently determining the battery operation and hence finding the optimal charging profile.
For example, in [ 75 ] Klein et al. aim at achieving a fast charging rate while not excessively aging the cell, using nonlinear model predictive control (NMPC) techniques founded on a single particle model (SPM) of the lithium ion battery. In the single particle model (SPM) the electrodes are represented by two single spherical porous particles in which intercalation and de-intercalation phenomena take place. However, the variations in the electrolyte con-centration and in the potential are ignored. This electrochemical model is exhaustively explained in [ 83 , 84 ].
In [ 81 ], a method to optimize the charging current for Li-ion batteries using a soft actor-critic (SAC) reinforcement learning algorithm is proposed. As battery aging model Kim et al. use the single particle model augmented by electrolyte and thermal dynamics (SPMeT). Anyway, even if this model is more exhaustive than the SPM one, it is subject to a complicated mathematical structure including PDEs, ordinary-differential equations and algebraic equations. Therefore the corresponding model based algorithms can be computationally too arduous to be implemented in typical battery management systems (BMSs) [ 80 ]. In light of this, in [ 80 ], Zou et al. propose and validate a simplified ODE-based SPMeT model to achieve fast charging control. Once validated the reduced model, the authors present a charging strategy based on model predictive control (MPC) techniques which aims to charge the battery in the fastest possible manner, without excessively degrading the battery’s SOH.
Another widely employed electrochemical battery model is the pseudo two-dimensional model (P2D). This model is constructed based on the assumption that electrodes are seen as an aggregation of spherical particles (2D representation) in which the Li + ions are inserted. The first spatial dimension of this model, represented by variable x, is the horizontal axis. The second spatial dimension is the particle radius r. The cell is comprised of three regions that imply four distinct boundaries. The full description of this model can be found in [ 85 ]. Finally, in [ 82 ], the authors present an effective method to estimate the parameters of the P2D model using a neural network-based estimation scheme.
6 Genetic Algorithm for Optimal Charging Technology Size and Forecasting of Future Trends
Concerning the onboard charger, as seen in paragraph II, different technologies exist in literature and in industrial applications. The cost, dimension and weight of this product is strongly influenced by its power rating; nowadays many sizes are proposed such as: 0.75, 3.3, 6.6, 11 and 22 kW. Many different power ratings are described also for off-board charger and consequently the cost varies as a function of the power and quality.
Generally, the wide range of power ratings, the fast improvements and the lack of standardization in e-mobility technologies make quite difficult estimating the actual optimal power rate of charging technology and forecasting future tendencies for large interval of time.
In this paragraph, initially, using a genetic algorithm (GA) single-objective model, the best size of both the onboard and off-board charging technology is estimated; then, through a sensitive analysis, we try to evaluate the possible future trends in the e-mobility as the costs of the battery and of the charging technology vary.
GA is an heuristic search algorithm, which mimics the natural selection process and it is used to solve optimization problems. GAs are being used to solve a wide variety of optimization problems in the field of EVs such as: charging scheduling [ 87 , 88 , 89 ], charging station planning and location [ 90 , 91 ] and drive train control strategy implementation [92–93].
6.1 Objective Function
For managing the EV charging technology, a single-objective optimization is used to determine the optimal size of the charging technology both on-board and off-board and to determine a suitable battery capacity. The proposed optimization allows to find the optimal trade-off between the onboard and off-board charger power rate.
The aim of the sizing procedure is to minimize the overall costs coming from the charging of electric vehicles. Therefore, the optimization problem is modeled in the expressions ( 1 ), ( 2 ) and ( 3 ).
First of all, the objective function representing the cost of the charging system is computed in ( 1 )
The coefficients \({k}_{i}\) represent the cost of the i-th component allocated to the vehicle, while coefficients \({\beta }_{i}\) embody the benefits. The coefficient \({k}_{bat}\) represents the cost of the battery per kWh, more precisely it also includes an amount which consider the costs arising from the space occupied by the battery inside the vehicle, its positioning and all the other aspects which are influenced by the battery capacity. Therefore, the first factor of the function describes the cost trend as a function of the battery size. This behaviour is not perfectly linear since we assume the fact that as the battery capacity increases the payload available inside the vehicle decreases. Coefficient \({k}_{on}\) includes the costs in € per kW of all the components influenced by the rated power of the onboard charger: the cost of power electronics, cost of space, cost of control and so on. Also for the cost trend of the onboard battery charger a non-linear behaviour has been assumed for the same reasons explained for the battery. In particular for this component, it can be seen that a minimum level of 6.5 kW is taken, since we assume that a smaller battery charger will not be used anymore. The computation of the cost coming from the off-board charger power rating follows the same concept used for the onboard charger, with the difference that a minimum value has not been imposed.
Once the cost of each single technology has been estimated, the next passage consists in weighing its benefits, which will be added in the cost function with a negative sign and two coefficients: \({\beta }_{on}\) and \({\beta }_{bat-off}\) , which respectively represent the benefit in terms of €/kW for the on-board battery charger and the benefits in terms of €/(kW kWh). The coefficient related to the capacity of the battery and to the power rating of the off-board charger is expected to assume high values, since it concerns the reduction of the driving range anxiety, which we know to be one of the major cause limiting the penetration of the EV worldwide. Starting from the onboard charger, for this parameter a logarithm behaviour has been assumed, since we suppose that an increasing of the \({P}_{on}\) specially takes advantage passing from 6.5 kW to values such as 22 kW, an additional increase doesn’t weigh so much on the overall system. Finally, the benefits of the off-board charger power rating \({P}_{off}\) and of the battery capacity \({C}_{bat}\) are introduced. The advantages brought by these two variable are linked together and considered in the last term of the function. An increase in the capacity of the battery should be compensated by an increase in the rating of the off-board charger, otherwise it is not fully appreciated, and vice versa if the off-board charger becomes more powerful, the capacity of the battery has to limit the stresses to which the battery is exposed.
6.2 Optimal Size of the Charging Technology
As aforementioned, finding the minimum of the function \({f}_{c}\) ( 2 ) means find those values of \({C}_{bat}, {P}_{on}\) and \({P}_{off}\) which are such as to minimise as much as possible the cost of the overall charging system. In particular, the minimum of the cost function has been performed through the use of genetic algorithms coded in Matlab. The bounds listed in ( 3 ) have been used.
Figures 15 , 16 and 17 given below report the minimum of the function once the value of the coefficients changes. The starting condition considers the actual prices and benefits reported in Table 2 . By using these values for the coefficients, a battery capacity of 60 kWh, an off-board charger of 170 kW and an onboard one of 14 kW are obtained from the optimization of the cost function.
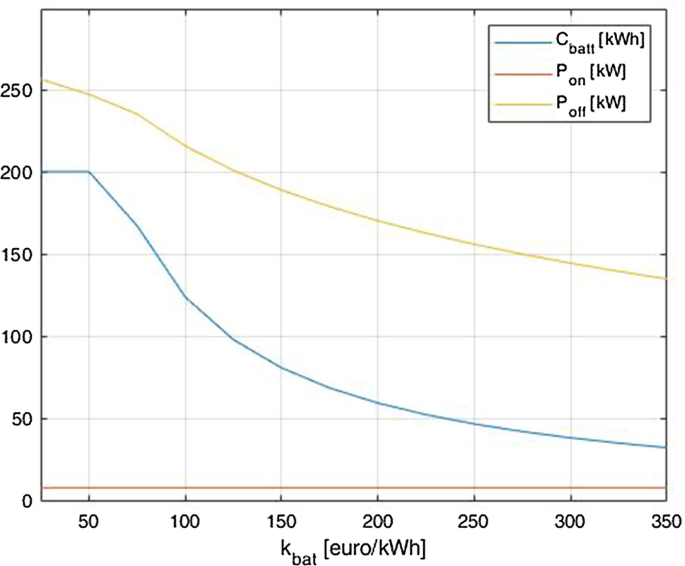
\({C}_{bat},{P}_{on}\) \({\mathrm{C}}_{\mathrm{bat}},{\mathrm{P}}_{\mathrm{on}}\) \({\mathrm{C}}_{\mathrm{bat}},{\mathrm{P}}_{\mathrm{on}}\) \({\mathrm{C}}_{\mathrm{bat}},{\mathrm{P}}_{\mathrm{on}}\) and \({P}_{off}\) trends as the coefficient \({k}_{bat}\) varies
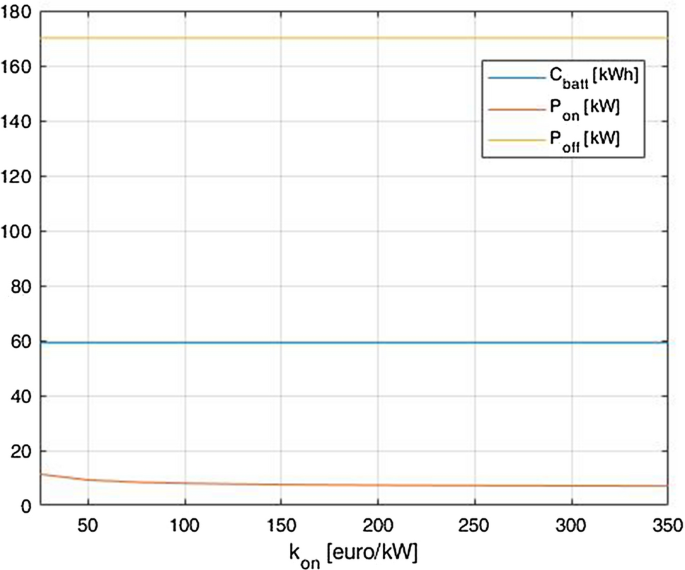
\({C}_{bat},{P}_{on}\) and \({P}_{off}\) trends as the coefficient \({k}_{on}\) varies
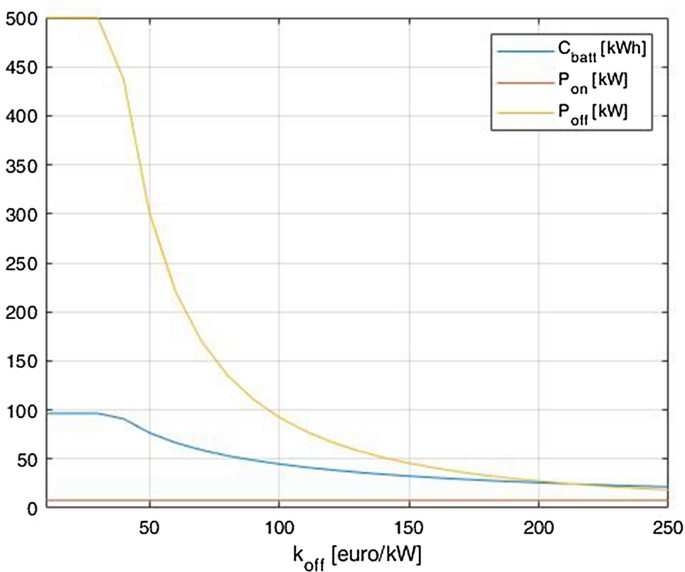
\({C}_{bat},{P}_{on}\) and \({P}_{off}\) trends as the coefficient \({k}_{off}\) varies
6.3 Forecast of Future Trends
In the following second step of the study, the values of coefficients are varied, one at a time, to perform a sensitivity analysis.
It is possible to notice that the capacity of the battery and the power rating of the off-board charger are not influenced by the variation of the cost of the onboard charger per kW. The power rating of the onboard charger seems to stay quite constant around values of 14 kW, however if the cost fell below 100 € each kW, \({P}_{on}\) would start to increase until it reaches 18 kW at 25 €/kW.
As expected, the value of the power of the onboard charger does not change as \({k}_{bat}\) changes since the benefits and the costs of this parameter has not be tied to the cost of the battery technology.
The coefficient \({k}_{off}\) , represented in Fig. 17 , includes all the costs related to the off-board charger weighed from the point of view of the owner. The real cost per kW of this technology is currently around 2500 €, by considering all the aspects such as: power electronics, control, connection to MV grid, connection and communication with the vehicle, installation and maintenance.
Finally, a forecast is done about the semiconductor devices. In this field, two wide bandgap materials are showing great promise for the future: Gallium Nitride (GaN) and Silicon Carbide (SiC). Thanks to all their characteristics, compared in Table 3 , wide bandgap semiconductors allow for greater power efficiency, smaller size, lighter weight and lower overall cost. In particular, by comparing SiC and GaN properties, it can be concluded that GaN is the most suitable for low power, high frequency application while SiC material is more appropriate for high power high frequency applications [ 92 ].
7 Conclusion
The first part of this paper reviews the current conditions of EV battery charging technologies. The most common topologies which are suitable candidates for each level of an EV charger have been presented. Level 1 and level 2 charger topologies are usually mounted inside the vehicle forming in this way the so called onboard charger. On the other side level 3 chargers are installed off board the vehicles, in this way their collection leads to the creation of the so called FCSs which are promising candidates for future EV high penetration. The most common technologies used in a FCS are multilevel converters which have a high power density and a lower current harmonic distortion. To reduce the impact on the grid, almost all the FCSs are integrated with RESs and ESSs.
Li-ion batteries can be recharged according many different charging techniques which can more or less complicate the charger architecture and control. In particular, the standard charging strategy are simplest since they don’t require model information to charge the battery. Furthermore, they can be realized with very basic circuits, keeping the costs of the charger to a minimum. On the other hand, the charging strategies based on electrochemical models, taking into account the internal dynamics of the battery, consider also the aging of the battery and other constraints, hence resulting in greater accuracy and. All this is at the expense of cost and computational difficulty.
A long-term forecasting of future trends in the field of EV charging systems is a very tough task for different many reasons including the lack of standards and the continuous improvements. In the last section of this paper a possible forecasting and estimation based on GA is described. According to the results, with the actual costs, the capacity of the battery of an electric vehicle should be around 60 kWh, the power rating of the onboard charger around 14 kW and that of the off-board fast charger around 170 kW.
Finally, the silicon switching devices are expected to be replaced by wide bandgap silicon carbide (SiC) devices in order to allow a remarkable reduction in charger’s weight and volume.
Rizvi SAA, Xin A, Masood A, Iqbal S, Ullah Jan M, Rehman H (2018) Electric vehicles and their impacts on integration into power grid: a review. In: Presented at the 2nd IEEE Conference on Energy Internet and Energy System Integration (EI2), BeiJing, China, Oct. 20–22, 2018
Papadopoulos P, Cipcigan LM, Jenkins N (2009) Distribution networks with electric vehicles. In: Presented at the 44th International Universities Power Engineering Conference (UPEC), Glasgow, UK, Sept. 1–4, 2009
Longo M, Foiadelli F, Yaïci W (2019) Electric vehicles integrated with renewable energy sources for sustainable mobility. In: Martinez LR (ed) New trends in electrical vehicle powertrains. IntechOpen, UK
Google Scholar
Ces T (2009) Transportation options in a carbon constrained world: hybrids, plug-in hybrids, biofuels, fuel cell electric vehicles, and battery electric vehicles. Int J Hydrogen Energy 34(23):9279–9296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2009.09.058
Article Google Scholar
Liu L, Kong F, Liu X, Peng Y, Wang Q (2015) A review on electric vehicles interacting with renewable energy in smart grid. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 51:648–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.06.036
Pellitteri F, Caruso M, Castiglia V, Di Tommaso AO, Miceli R, Schirone L (2016) An inductive charger for automotive applications. In: Presented at the 42nd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society IECON, Florence, Italy, Oct. 23–26, 2016
Panchal C, Stegen S, Lu J (2018) Review of static and dynamic wireless electric vehicle charging system. Eng Sci Technol Intern J 21(5):922–937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2018.06.015
Sunab L, Maa D, Tanga H (2018) A review of recent trends in wireless power transfer technology and its applications in electric vehicle wireless charging. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 91:490–503
Yilmaz M, Krein PT (2012) Review of charging power levels and infrastructure for plug-in electric and hybrid vehicles. In: Presented at the IEEE International Electric Vehicle Conference, Greenville, SC, USA, Mar. 4–8, 2012
Tran VT, Sutanto D, Muttaqi KM (2017) The state of the art of battery charging infrastructure for electrical vehicles: topologies, power control strategies, and future trend. In: Presented at the Australasian Universities Power Engineering Conference (AUPEC), Melbourne, VIC, Australia, Nov. 19–22, 2017
A novel low cost integrated on-board charger topology for electric vehicles and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. In: Presented at 2012 27th Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Orlando, FL, USA, Feb. 5–9, 2012
Ammous M, Khater M, AlMuhaini M (2017) impact of vehicle-to-grid technology on the reliability of distribution systems. In: Presented at the 9th IEEE-GCC Conference and Exhibition (GCCCE), Manama, Bahrain, May 8–11, 2017
Zhou X, Zou L, Ma Y, Gao Z (2017) Research on impacts of the electric vehicles charging and discharging on power grid. In: Presented at the 29th Chinese Control And Decision Conference (CCDC), Chongqing, China, May 28–30, 2017
Jiang Z, Tian H, Beshir MJ, Sibagatullin R, Mazloomzadeh A (2016) Statistical analysis of electric vehicles charging, station usage and impact on the grid. In: Presented at the IEEE Power & Energy Society Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference (ISGT), Minneapolis, MN, USA, Sept. 6–9, 2016
Yilmaz M, Krein PT (2013) Review of the impact of vehicle-to-grid technologies on distribution systems and utility interfaces. IEEE Trans Power Electron 28(12):5673–5689. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2012.2227500
Tan KM, Ramachandaramurthy VK, Yong JY (2016) Integration of electric vehicles in smart grid: a review on vehicle to grid technologies and optimization techniques. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 53:720–732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.09.012
Abousleiman R, Al-Refai A, Rawashdeh O (2013) Charge capacity versus charge time in CC–CV and pulse charging of Li-ion batteries. SAE Tech Pap. https://doi.org/10.4271/2013-01-1546
Majid N, Hafiz S, Arianto S, Yuono R, Astuti ET, Prihandoko B (2017) Analysis of effective pulse current charging method for lithium ion battery. J Phys Conf Ser 817:012008. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/817/1/012008
Smith KA, Rahn CD, Wang C (2008) Model-based electrochemical estimation of lithium-ion batteries. In:2008 IEEE International Conference on Control Applications, San Antonio, TX, pp. 714–719. https://doi.org/10.1109/CCA.2008.4629589 .
Byrne DM, Oliner SD, Sichel DE (2017) How fast are semiconductor prices falling? Finance and Economics Discussion Series. Washington: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. 2017(005). https://doi.org/10.17016/FEDS.2017.005 .
Goldie-Scot L (2020) A behind the scenes take on lithium-ion battery prices. BloombergNEF, 2019. Accessed 30 June 2020. [Online]. Available https://about.bnef.com/blog/behind-scenes-take-lithium-ion-battery-prices/
Zhuang W, Lu S, Lu H (2014) Progress in materials for lithium-ion power batteries. In: 2014 International Conference on Intelligent Green Building and Smart Grid (IGBSG), Taipei, 2014, pp. 1–2, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/IGBSG.2014.6835262
K. Fahem, D. E. Chariag, L. Sbita, “On-board bidirectional battery chargers topologies for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles”, presented at the International Conference on Green Energy Conversion Systems (GECS), Hammamet, Tunisia, Mar. 23–25, 2017.
L. Cao ; H. Li ; H. Zhang, “Model-free power control of front-end PFC AC/DC converter for on-board charger”, presented at the IEEE 8th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (IPEMC-ECCE Asia), Hefei, China, May 22–26, 2016.
F. Musavi; M. Edington; W. Eberle ; W. G. Dunford, “Energy efficiency in plug-in hybrid electric vehicle chargers: Evaluation and comparison of front end AC–DC topologies”, presented at the IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, Phoenix, AZ, USA, Sept. 17–22, 2011.
Lee PW, Lee YS, Cheng DKW, Liu XC (2000) Steady-state analysis of an interleaved boost converter with coupled inductors. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 47(4):787–795. https://doi.org/10.1109/41.857959
Kanimozhi G, Kumar SS, Likhitha K (2016) Battery charger for automotive applications. In: Presented at the 10th International Conference on Intelligent Systems and Control (ISCO), Coimbatore, India, Jan. 7–8, 2016
Gautam D, Musavi F, Edington M, Eberle W, Dunford WG (2011) An automotive on-board 3.3 kW battery charger for PHEV application. In: Presented at the IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, Sept. 6–9, 2011
Wang H, Dusmez S, Khaligh A (2014) Design and analysis of a full-bridge LLC-based PEV charger optimized for wide battery voltage range. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 63(4):1603–1613. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2013.2288772
Yan X, Li L, Gao Y, Tao Z (2017) Design methodology of LLC converters based on mode analysis for battery charging applications. In: Presented at the 43rd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON), Beijing, China, 29 Oct–1 Nov 2017
Hu S, Deng J, Mi C, Zhang M (2013) LLC resonant converters for PHEV battery chargers. In: Presented at the 28th Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Long Beach, CA, USA, Mar 17–21, 2013
Singh AK, Pathak MK, Rao YS (2017) A new two-stage converter with reduction of DC-link capacitor for plug-in electric vehicle battery charger.In: Presented at the 3rd International Conference on Computational Intelligence & Communication Technology (CICT), Ghaziabad, India, Feb 9–10, 2017
Lee JY, Chae HJ (2014) 6.6-kW onboard charger design using DCM PFC converter with harmonic modulation technique and two-stage DC/DC converter. IEEE Trans Indus Electron 61(3):1243–1252. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2013.2262749
Kurokawa F, Hattori S (2015) Single stage AD–DC full-bridge converter for battery charger. In: Presented at the IEEE International Telecommunications Energy Conference (INTELEC), Osaka, Japan, Oct. 18–22, 2015
Kim B, Kim M, Choi S (2016) Single-stage electrolytic capacitor-less AC–DC converter with high frequency isolation for EV charger. In: Presented at the IEEE 8th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (IPEMC-ECCE Asia), Hefei, China, May 22–26, 2016
Li S, Deng J, Mi CC (2013) Single-stage resonant battery charger with inherent power factor correction for electric vehicles. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 62(9):4336–4344. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2013.2265704
Woo D, Joo D, Lee B (2015) On the feasibility of integrated battery charger utilizing traction motor and inverter in plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. IEEE Trans Power Electron 30(12):7270–7281. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPTEL.2015.2396200
Wang L, Liang J, Xu G, Xu K, Song Z (2012) A novel battery charger for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. In: Presented at the IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation, Shenyang, 2012, pp. 168–173. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICInfA.2012.6246802
Haghbin S, Carlson O (2014) Integrated motor drive and non-isolated battery charger based on the split-phase PM motors for plug-in vehicles. J Eng 2014(6):275–283. https://doi.org/10.1049/joe.2014.0126
Shi C, Tang Y, Khaligh A (2017) A single-phase integrated onboard battery charger using propulsion system for plug-in electric vehicles. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 66(12):10899–10910. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2017.2729345
Kim S, Kang F (2015) Multifunctional onboard battery charger for plug-in electric vehicles. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 62(6):3460–3472. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2014.237687
Nguyen HV, Lee D (2018) Single-phase multifunctional onboard battery chargers with active power decoupling capability. In: Presented at the IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), San Antonio, TX, 2018, pp. 3434–3439
Aggeler D, Canales F, Zelaya-De La Parra H, Coccia A, Butcher N, Apeldoorn O (2010) Ultra-fast DC-charge infrastructures for EV-mobility and future smart grids. In: Presented at the IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference Europe (ISGT Europe), Gothenberg, 2010, pp. 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISGTEUROPE.2010.5638899
Tu H, Feng H, Srdic S, Lukic S (2019) Extreme fast charging of electric vehicles: a technology overview. IEEE Trans Transport Electrific 5(4):861–878. https://doi.org/10.1109/TTE.2019.2958709
Verma A, Singh B (2017) Three phase off-board bi-directional charger for EV with V2G functionality. In: 2017 7th International Conference on Power Systems (ICPS), Pune, 2017, pp. 145–150. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICPES.2017.8387283
Fang Y, Cao S, Xie Y, Wheeler P (2016) Study on bidirectional-charger for electric vehicle applied to power dispatching in smart grid. In: Presented at the IEEE 8th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (IPEMC-ECCE Asia), Hefei, 2016, pp. 2709–2713
Mortezaei A, Abdul-Hak M, Simoes MG (2018) A Bidirectional NPC-based level 3 EV charging system with added active filter functionality in smart grid applications. In: 2018 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC), Long Beach, CA, 2018, pp. 201–206. https://doi.org/10.1109/ITEC.2018.8450196
Kim J, Lee J, Eom T, Bae K, Shin M, Won C (2018) Design and control method of 25 kW high efficient EV fast charger. In: Presented at the 21st International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Jeju, 2018, pp. 2603–2607
Rajendran G, Vaithilingam C, Prakash O (2019) Modeling of Vienna rectifier with PFC controller for electric vehicle charging stations. In: AIP Conference Proceedings. 2137(1). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5120996
Chen S, Yu W, Meyer D (2019) Design and implementation of forced air-cooled, 140 kHz, 20 kW SiC MOSFET based Vienna PFC. In: Proc. IEEE Appl. Power Electron. Conf. Expo. (APEC), Mar 2019, pp. 1196–1203
Taghizadeh S, Hossain MJ, Lu J (2015) Bidirectional isolated vehice to grid (V2G) system: an optimized implementation and approach. In: 2015 IEEE PES Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference (APPEEC), Brisbane, QLD, 2015, pp. 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/APPEEC.2015.7380912
Xue L, Shen Z, Boroyevich D, Mattavelli P, Diaz D (2015) Dual active bridge-based battery charger for plug-in hybrid electric vehicle with charging current containing low frequency ripple. IEEE Trans Power Electron 30(12):7299–7307. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2015.2413815
Zahid ZU, Dalala ZM, Chen R, Chen B, Lai J (2015) Design of bidirectional DC–DC resonant converter for vehicle-to-grid (V2G) applications. IEEE Trans Transport Electrifi 1(3):232–244. https://doi.org/10.1109/TTE.2015.2476035
Moonem MA, Krishnaswami H (2012) Analysis and control of multi-level dual active bridge DC–DC converter. In: 2012 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Raleigh, NC, 2012, pp. 1556–1561. https://doi.org/10.1109/ECCE.2012.6342628
Akagi H, Yamagishi T, Tan NML, Kinouchi S, Miyazaki Y, Koyama M (2015) Power-loss breakdown of a 750-V 100-kW 20-kHz bidirectional isolated DC–DC converter using SiC-MOSFET/SBD dual modules. IEEE Trans Indus Appl 51(1):420–428. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2014.2331426
Tan L, Wu B, Rivera S (2015) A bipolar-DC-bus EV fast charging station with intrinsic DC-bus voltages equalization and minimized voltage ripples. In: IECON 2015-41st Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Yokohama, 2015, pp. 002190–002195. https://doi.org/10.1109/IECON.2015.7392426
Haritha AS, Jithin KJ (2019) An efficient resonant converter based charging scheme for electric vehicle. In: 2019 5th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems (ICACCS), Coimbatore, India, 2019, pp. 599–603
Zhao H, Wang L, Chen Z, He X (2019) Challenges of fast charging for electric vehicles and the role of red phosphorus as anode material: review. Energies 12:3897. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12203897
Dusmez S, Cook A, Khaligh A (2011) Comprehensive analysis of high quality power converters for level 3 off-board chargers. In: 2011 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference, Chicago, IL, 2011, pp. 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1109/VPPC.2011.6043096
Feizi M, Beiranvand R (2020) An improved phase-shifted full-bridge converter with extended ZVS operation range for EV battery charger applications. In: 2020 11th Power Electronics, Drive Systems, and Technologies Conference (PEDSTC), Tehran, Iran, 2020, pp. 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/PEDSTC49159.2020.9088444
Feizi M, Beiranvand R (2020) Simulation of a high power self-equalized battery charger using voltage multiplier and phase-shifted full bridge converter for lithium-ion batteries. In: 2020 11th Power Electronics, Drive Systems, and Technologies Conference (PEDSTC), Tehran, Iran, 2020, pp. 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/PEDSTC49159.2020.9088454
Ota Y, Taniguchi H, Suzuki H, Nakajima T, Baba J, Yokoyama A (2012) Implementation of grid-friendly charging scheme to electric vehicle off-board charger for V2G. In: 2012 3rd IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Europe (ISGT Europe), Berlin, 2012, pp. 1–6
Vasiladiotis M, Rufer A, Béguin A (2012) Modular converter architecture for medium voltage ultra fast EV charging stations: global system considerations. In: Presented a the IEEE International Electric Vehicle Conference, Greenville, SC, 2012, pp. 1–7
Rivera S, Wu B, Kouro S, Yaramasu V, Wang J (2015) Electric vehicle charging station using a neutral point clamped converter with bipolar DC bus. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 62(4):1999–2009
Tan L, Wu B, Rivera S, Yaramasu V (2016) Comprehensive DC power balance management in high-power three-level DC–DC converter for electric vehicle fast charging. IEEE Trans Power Electron 31(1):89–100
Gjelaj M, Træholt C, Hashemi S, Andersen PB (2017) Optimal design of DC fast-charging stations for EVs in low voltage grids. In: Presented at the IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC), Chicago, IL, USA, Jun. 22–24, 2017
Mauri G, Bertini D, Fasciolo E, Fratti S (2013) The impact of EV’s fast charging stations on the MV distribution grids of the Milan metropolitan area. In: Presented at the 22nd International Conference and Exhibition on Electricity Distribution (CIRED 2013), Stockholm, Sweden, Jun. 10–13, 2013
Shiramagond T, Lee W (2018) Integration of renewable energy into electric vehicle charging infrastructure. In: Presented at the 2018 IEEE International Smart Cities Conference (ISC2), Kansas City, MO, USA, Sept. 16–19, 2018, pp. 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISC2.2018.8656981
Abul’Wafa AR, El’Garably A, Mohamed WAF (2017) Uncoordinated vs coordinated charging of electric vehicles in distribution systems performance. Intern J Eng Inform Syst (IJEAIS) 1(6):54–65
Huajie D, Zechun H, Yonghua S, Xiaorui H, Yongxiang L (2014) Coordinated control strategy of energy storage system with electric vehicle charging station. In: Presented at the IEEE Conference and Expo Transportation Electrification Asia-Pacific (ITEC Asia-Pacific), Beijing, China, 31 Aug–3 Sept 2014
García-Triviño P, Fernández-Ramírez LM, Torreglosa JP, Jurado F (2016) Fuzzy logic control for an electric vehicles fast charging station. In: Presented at the International Symposium on Power Electronics, Electrical Drives, Automation and Motion (SPEEDAM), Anacapri, Italy, Jun 22–24, 2016
Castello CC, LaClair TJ, Maxey LC (2014) Control strategies for electric vehicle (EV) charging using renewables and local storage. In: Presented at the IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC), Dearborn, MI, USA, Jun 18–15, 2014
Ayoub E, Karami N (2015) Review on the charging techniques of a Li-ion Battery. In: Presented at the Third Annual International Conference on Technological Advances in Electrical, Electronic, and Computer Engineering (TAEECE2015), Beirut, 2015, pp. 50–55
Gao Y, Jiang J, Zhang C, Zhang W, Ma Z, Jiang Y (2017) Lithium-ion battery aging mechanisms and life model under different charging stresses. J Power Sour 356:103–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.04.084
Klein R, Chaturvedi NA, Christensen J, Ahmed J, Findeisen R, Kojic A (2011) Optimal charging strategies in lithium-ion battery. In: Proceedings of the 2011 American Control Conference, San Francisco, CA, 2011, pp. 382–387. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACC.2011.5991497
Zhang SS (2006) The effect of the charging protocol on the cycle life of a Li-ion battery. J Power Sour 161(2):1385–1391
Ayoub E, Karami N (2015) Review on the charging techniques of a Li-Ion battery. In: Presented at the Third International Conference on Technological Advances in Electrical, Electronics and Computer Engineering (TAEECE), Beirut, 2015, pp. 50–55
Liu Y, Hsieh C, Luo Y (2011) Search for an optimal five-step charging pattern for Li-ion batteries using consecutive orthogonal arrays. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 26(2):654–661
Chen L (2009) Design of duty-varied voltage pulse charger for improving Li-ion battery-charging response. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 56(2):480–487
Zou C, Hu X, Wei Z, Wik T, Egardt B (2018) Electrochemical estimation and control for lithium-ion battery health-aware fast charging. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 65(8):6635–6645. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2017.2772154
Kim M, Baek J, Han S (2020) Optimal charging method for effective Li-ion battery life extension based on reinforcement learning. arXiv e-prints
Chun H, Kim J, Yu J, Han S (2020) Real-time parameter estimation of an electrochemical lithium-ion battery model using a long short-term memory network. IEEE Access 8:81789–81799. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2991124
Santhanagopalan S, Guo Q, Ramadass P, White RE (2006) Review of models for predicting the cycling performance of lithium ion batteries. J Power Sour 156(2):620–628
Perez H, Dey S, Hu X, Moura S (2017) Optimal charging of Li-ion batteries via a single particle model with electrolyte and thermal dynamics. J Electrochem Soc 164(7):A1679. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.1301707jes
Jokar A, Rajabloo B, Désilets M, Lacroix M (2016) Review of simplified pseudo-two-dimensional models of lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sour 327:44–55
Du H, Cao D, Zhang H (2017) Modeling, dynamics, and control of electrified vehicles. Woodhead Publishing, UK
Elmehdi M, Abdelilah M (2019) Genetic algorithm for optimal charge scheduling of electric vehicle fleet. In: Presented at NISS19: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Networking, Information Systems and Security,Rabat (Morocco), Mar. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1145/3320326.3320329
Korotunov S, Tabunshchyk G, Okhmak V (2020) Genetic algorithms as an optimization approach for managing electric vehicles charging in the smart grid. CMIS
Alonso M, Amaris H, Germain JG, Galan JM (2014) Optimal charging scheduling of electric vehicles in smart grids by heuristic algorithms. Energies 7(4):2449. https://doi.org/10.3390/en7042449
Yan X, Duan C, Chen X, Duan Z (2014) Planning of Electric Vehicle charging station based on hierarchic genetic algorithm. In: 2014 IEEE Conference and Expo Transportation Electrification Asia-Pacific (ITEC Asia-Pacific), Beijing, 2014, pp. 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/ITEC-AP.2014.6941087
Chen S, Shi Y, Chen X, Qi F (2015) Optimal location of electric vehicle charging stations using genetic algorithm. In: 2015 17th Asia-Pacific Network Operations and Management Symposium (APNOMS), Busan, 2015, pp. 372–375. https://doi.org/10.1109/APNOMS.2015.7275344
Gallium nitride (GaN) versus silicon carbide (SiC) in the high frequency (RF) and power switching applications. Microsemi Corporation, Aliso Viejo, California, USA. Accessed 17 Apr 2019. [Online]. Available: https://www.richardsonrfpd.com/resources/RellDocuments/SYS26/Microsemi-A-Comparison-of-Gallium-Nitride-Versus-Silicon-Carbide.pdf
Download references
Acknowledgements
This research is part of the Energy for Motion project of the Department of Energy of Politecnico di Milano, funded by the Italian Ministry of University and Research (MIUR) through the Department of Excellence Grant 2018-2022.
Open access funding provided by Politecnico di Milano within the CRUI-CARE Agreement.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Energy, Politecnico Di Milano, Milan, Italy
Morris Brenna, Federica Foiadelli, Carola Leone & Michela Longo
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Carola Leone .
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Brenna, M., Foiadelli, F., Leone, C. et al. Electric Vehicles Charging Technology Review and Optimal Size Estimation. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 15 , 2539–2552 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42835-020-00547-x
Download citation
Received : 08 April 2020
Revised : 07 July 2020
Accepted : 17 September 2020
Published : 02 October 2020
Issue Date : November 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s42835-020-00547-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Electric vehicle
- Plug-in electric vehicles
- Battery charger
- Charging infrastructure
- Vehicle-to-grid
- Grid-to-vehicle
- Charging methods
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- 12V 100Ah Group 24
- Orion 1000- 12V 100Ah with Battery Monitor
- UPS 1000VA/800W

Grandly Promotes:UP TO 40% OFF

10% Off New User Benefits
- Flash Sale 50%OFF
Golf Cart Battery
- RV Trailer Battery
- Ham Radio Battery
Fish Finder Battery
Trolling motor battery.
- Off Grid Solar Battery
- Mobility Scooter Battery

RV Trailer Deep Cycle Battery
- Warranty Policy
Battery Certificate
- What Is Goldenmate Rated?

- Bulk Orders
- Video & Article
- Consumer reviews
- Share Your Experience
- Join Our Affiliate Program

Join the GoldenMate Community

Earn up to 10% commission
- Help Center
- Refund Policy
- Track your order
- How to Charge?

Support Center
How to Charge LiFePO4 Batteries?
12-volt battery charging guide - what voltages mean for charge level.

Do you have a 12-volt battery? Maybe in your car, boat, RV, or something else that runs on a 12-volt battery? If so, you probably wonder - what should my battery read when it's charged up? Knowing the voltage for a full battery can help you take good care of it.
In this article, we'll talk about 12-volt batteries. We'll look at what their voltage should be after a full charge. We'll also share tips on how to measure and maintain your battery. Let's get started!
Understanding 12-Volt Batteries
Basic components and chemistry of a 12-volt battery.
A 12-volt battery has a plastic case with metal plates inside. The plates are positive or negative. It also contains an electrolyte liquid, which usually is a sulfuric acid and water mix.
How A 12-Volt Battery Works And What Constitutes A Full Charge
When the battery charges, electrons collect on the negative plate. When it discharges to power devices, the electrons flow out. Charging pushes in electrons using the charger's voltage. Discharging takes electrons out to make power flow. When all plates are covered in electrons, the battery has a full charge.
What Constitutes A Full Charge?
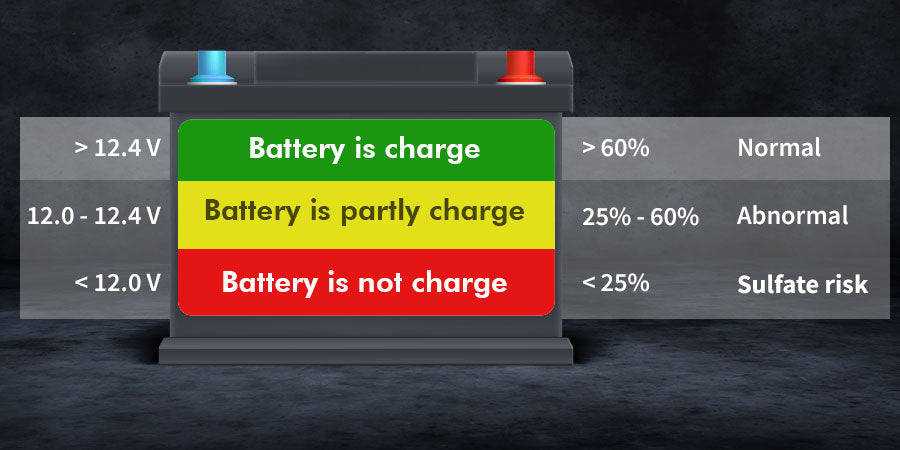
A full charge is when all the battery's plates are covered with electrons and ready to release them to provide power. This happens when the voltage reads around 12.6-12.8 volts. At this level, the battery has its maximum energy stored for powering devices.
The Role Of Voltage In Determining Battery Charge State
Voltage measures how strongly the electrons are pushed from the battery. More voltage = more power available. Less voltage = low battery charge. Checking the voltage reading shows if the battery is fully charged. Around 12.6-12.8 volts means all the electrons are replenished and ready to flow.
Voltage Levels And Battery Charge
Voltage as an indicator of charge level.
Voltage measures the electrical pressure that pushes electrons out of the battery. Think of voltage as the strength of a water hose. Higher voltage gives electrons more pushing force to create power.
Lower voltage means the electrical pressure is weaker, so less power can flow out. Checking voltage shows the charge level.
The Ideal Voltage Reading For a Fully Charged 12-Volt Battery
For a 12-volt battery to have a full charge, the ideal voltage is between 12.6-12.8 volts. At this voltage level, the electrical pressure is strong enough that the battery can provide its maximum power capacity.
Variations In Fully Charged Voltage Readings Across Different Battery Types
The target full voltage may vary slightly between battery types:
- Flooded batteries: Around 12.7 volts fully charged.
- AGM batteries: 12.8-13.2 volts is 100% charged.
- Gel batteries: 13.5-13.8 volts fully charged.
So, check what battery type you use, and its ideal voltage range when fully charged. But for most 12-volt batteries, 12.6-12.8 volts is considered fully charged.
How To Measure Battery Voltage
Tools required for measuring battery voltage.
To measure battery voltage, you need a multimeter. The multimeter measures voltage, current, and other electrical values. Multimeters have leads you connect to the battery terminals.
Step-By-Step Guide On How To Safely Measure The Voltage Of A 12-Volt Battery
Follow these safe steps:
- Turn off anything running on the battery, like lights or engines.
- Connect the red multimeter lead to the positive (+) terminal.
- Connect the black lead to the negative (-) terminal.
- Set the multimeter to measure "DC Volts".
- Read the voltage number on the multimeter screen.
- Disconnect the leads when done.
Tips For Ensuring Accurate Voltage Readings
To get accurate readings:
- Ensure the multimeter leads have a solid connection to the terminals.
- Check the voltage several times and write down the numbers.
- Let the battery rest for 5-10 minutes between voltage checks.
- Test voltage again after charging or using the battery.
- Compare readings over time to see any discharge trends.
Consistent testing gives a clear picture of the battery's charge level and condition.
Interpreting Voltage Readings
What a voltage reading above 12.6 volts indicates about a battery's charge level.
A voltage reading over 12.6 volts means the battery is fully charged. The electrical pressure is strong enough to push maximum power. The battery is ready to deliver at full capacity.
Understanding Voltage Readings Between 12.4 Volts To 12.6 Volts
Readings from 12.4-12.6 volts indicate the battery is charged at 75-100%. It may need a brief recharge to reach full capacity. The lower the voltage, the lower the charge level.
Signs Of Undercharging And Overcharging Based On Voltage Readings
Readings under 12.2 volts show the battery is under 50% charged and needs charging. Over 12.8 volts indicates possible overcharging.
Factors Affecting Voltage Readings
Temperature impacts on battery voltage and charge level.
Colder temperatures make the battery chemistry work slower. This causes lower voltage readings when cold. Hot temperatures speed up the chemical reactions so voltage reads higher when it's hot out.

How Age And Usage Affect Battery Voltage Over Time
As batteries age with normal use, they lose some of their power capacity over the years. So an older battery will often read lower voltages than a brand-new battery, even when fully charged. Heavy use without recharging also discharges batteries faster, dropping the voltage.
The Influence Of The Charging System On Voltage Readings
Faulty alternators or chargers may fail to charge batteries adequately. This will lead to lower voltage readings than expected because the charging system did not restore the battery to a full charge. Checking the charging equipment is important to ensure batteries reach full voltage.
Maintaining A 12-volt Battery
Best practices for charging and maintaining a 12-volt battery.
Use a high-quality 12-volt battery charger to keep your battery properly charged. Choose a charger with an amperage rating between 3-10 amps. Lower amperages are better for slow, gentle charging.
When possible, charge the battery overnight which allows time to fully reach maximum voltage. Use an automatic shut-off charger to avoid overcharging. Always disconnect the charger in the morning before using the battery.
Keep the battery posts and terminals clean of dirt, salt, and corrosion. They impede charging and voltage readings. Check that connections are tight so electricity can flow easily.
The Importance Of Regular Voltage Checks To Extend Battery Life
Checking the battery voltage regularly, about 1-2 times per month, allows you to monitor its charge level and catch any problems early. Look for drops in the readings over time. This can reveal if a battery is wearing down or discharging too quickly. Catching issues early means you can correct them to extend the battery's overall life.
Recommendations For Chargers And Charging Routines
Use a smart battery charger that automatically shuts off when the battery is fully charged. This avoids overcharging. Allow time for a full charge - batteries may need 4-12 hours. Check that charger connections are clean. Store batteries properly when not in use. Fully recharging monthly extends battery life vs. letting them sit in a partial state of charge. Proper charging and care will get the years of service a quality 12-volt battery can deliver.

Troubleshooting Common Issues
What to do if your battery does not reach the ideal fully charged voltage.
If your battery won't charge fully to 12.6-12.8 volts, try charging it for an extended period. Older batteries may need more charging time. Also, check that the charger connections are clean and tight. Consider testing your alternator and charging system to make sure they are working.

How To Address Fluctuations In Voltage Readings
Fluctuations in readings could mean a loose connection when testing voltage. Make sure your multimeter leads are securely attached to the battery terminals. Consistent fluctuations may indicate it's time for a new battery if yours is over three years old.
When To Consider Battery Replacement
Think about replacing a battery that is more than three years old. Older batteries gradually lose power capacity. If the battery won't charge fully or hold a charge for long, it could be time for a new one. Also, replace the battery if the terminals are corroded or cracked. Replacing older batteries before failure avoids being stranded with a dead battery.
Keeping your 12-volt battery well charged is super important. Checking the voltage regularly shows if the charge is dropping. Fully recharging the battery once a month keeps it in top condition. This helps avoid being stuck with a dead battery.
Visit our site today to learn more about batteries and find helpful maintenance tips. With the right knowledge, you can keep your battery running strong for years!
How Many Watts Does a Coffee Maker Use?

GoldenMate is a green new energy enterprise that specializes in LiFePO4 lithium batteries and is committed to creating better, more durable, and more environmentally friendly lithium batteries.
Email: [email protected]
Wholesale Inquiry: [email protected]
- 12V LiFePO4 Series
- Bluetooth LiFePO4 Lithium Battery
- Track My Order
- Become An Affiliate
- Shipping policy
- Refund policy
- Privacy policy
- Payment policy
- Terms & Condition
- Intellectual Property Rights
© 2024 Goldenmate Battery, All rights reserved. Powered by Shopify
Your cart is currently empty.

Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

CHAPTER TWO LITERATURE REVIEW

Related Papers
2005 International Conference on Power Electronics and Drives Systems
Khalid Mohamed Nor
International Journal of Power Electronics and Drive Systems (IJPEDS)
tarik bouragba
In this paper, an implementation of a DC/DC buck converter for electric vehicles charging station and a DSP based closed-loop digital controller design are presented and analyzed. The aim of this work is to achieve an improved control strategy for a Li-ion battery charger implemented on a Real-time test platform. The test platform consists of a popular power pole board (MPCA75136) dedicated to studying the DC/DC converters, and a DSP development kit (TMS320F28379D) that is used to drive the DC/DC buck converter. The control strategy is based on a digital control system containing the closed-loop current controller followed by a pulse width modulation block, and on a real time state of charge estimation technique for a Li-ion battery. However, the overall control design is modeled on Simulink via block diagrams, and automatically generated code that is targeted into the DSP processor. Simulation and experimental results have shown the effectiveness of the proposed test bench and its ...
IRJET Journal
Proceedings of WESCON '93
David Heacock
pranay dattani
in demand, and nowadays a wireless communication or wireless system in BMS.<br> CAN communication system is a very popular and more useful system compare<br> to the other wireless system. In this paper various wireless battery management<br> systems discuss and also a BMS system discuss. As EVs are becoming popular,<br> the use of Lithium-ion (Li-Ion) batteries is exponentially increasing due to their<br> good charge/discharge performance, high energy, and current density, and optimum<br> power support. For safe operation of the battery, precise estimation of the State of<br> Charge (SOC) is necessary. In Evs, various type of chargers is available AC, DC,<br> CCS, DC fast charger, etc. in Gujarat regain CCS charger are very common to use<br> in a private or commercial charging station. ultimately the EVS charging system<br> is dependent on a BMS of the system, when the BMS system is very advance the<br> charging of th...
International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology (IJERT)
IJERT Journal
https://www.ijert.org/design-and-implementation-of-a-battery-charger-with-soft-switching-technique https://www.ijert.org/research/design-and-implementation-of-a-battery-charger-with-soft-switching-technique-IJERTV3IS070538.pdf A new soft switching technique with zero current switching is developed for a battery charger circuit with buck converter.The proposed new circuit is obtained by placing an auxillary circuit in series with the resonant capacitor which significantly decrease the switching losses in the power switches.the new battery charger with a buck converter has many advantages like simple structure,simple control,low cost,light weight,high efficiency etc.The operating principle and the design aspects of the charger circuit are analysed.The required values of the resonant inductance nad resonant capacitance are calculated from the characteristic curve and functions derived from the required circuit.A charger circuit is designed for a 3.7-V 1020mAh lithium ion battery and the simulation is done in matlab.
sunil Abeyratne
Proliferation of portable electronic equipment, that uses secondary battery types with different capacities & cell chemistries, has become a threat to the environment. The number of batteries disposed per day is on the rise; the associated-dedicated-battery-charges naturally get discarded with the equipment, adding much to the pollution. The improper charging patterns that reduce the life cycle of batteries are also contributing to the problem. This paper introduces a concept and a methodology which can be used to reduce the environmental impact due to different batteries and their chargers. The proposed charger is adapting itself to, any battery type (Lead Acid, NiMH, Li-Ion) with any cell number. This finds the charger still useful, though the equipment is wasted and no longer useable. The proposed methodology identifies the battery type using its terminal electrical-characteristics. The method reveals the battery capacity, with no restrictions imposed by the charging state. Having identified the battery type, the proposed quantum table identifies the number of cells in the battery. Therefore, the battery can be properly maintained to get maximum cycles before being disposed. The operation and the control method of the charger are also explained.
PROJECTSLIB P R O J E C T T O P I C S materials
CHAPTER ONE INTRODUCTION 1.1 Background of the study A battery is a device consisting of one or more electrochemical cells that converts stored chemical energy into electrical energy for later use. Each cell contains a positive terminal (cathode) and a negative terminal (anode). Electrolytes allow ions to move between the electrodes and terminals, which allows current to flow out of the battery to perform work. A lead acid battery consists of a number of 2V nominal cells that are connected in series. Each 2V cell consists of an independent enclosed compartment with positive and negative plates dipped in electrolyte composed of diluted sulphuric acid solution of 33.5% v/v sulphuric acid and water [7]. The sealed lead acid batteries find applications in emergency lightning system, inverters, power electric motors in submarines, generators, etc. There are two types of batteries: Primary Batteries (disposable batteries), which are designed to be used once and discarded, and Secondary Batteries (rechargeable batteries), which are designed to be recharged and used multiple times. Battery comes in many size, from miniature cells used to power hearing aids and wristwatches to battery banks the size of rooms that provide standby power for telephone exchanges and computer data centers and inverters. Battery charging is an aspect of engineering technology in which a full-wave rectified filtered output of a transformer is fed to a battery in order to restore it to its fully charged state. The battery charger is used to put energy into a secondary cell by forcing electric current through it. An efficient battery charger requires a charge controller whose main function is to keep the batteries properly charged and safe for the long term and prevent it from deep discharging (Jaya, 2012).
New Advances in Vehicular Technology and Automotive Engineering
Henrique Gonçalves
Rabinder Henry
This paper presents the preliminary development of efficient control module for battery charging and monitoring. While designing a charging system for battery some parameters must be considered such as the state of charge, lifecycle of battery and charging time. These parameters are monitored and controlled with the help of Atmega microcontroller. This embedded module is interfaced with charging module for the battery. The battery used in this work is a lead acid battery. A two stage charging technique, includes combination of constant current and constant voltage source which is used to charge lead acid battery. Index Terms Batteries, Constant Current Mode, Constant Voltage Mode, Lead Acid Battery, Microcontroller, Thermal Management
RELATED PAPERS
George Yannis
Ilias Chantziaras
Dwi Nur Azizah
Journal of Marine Systems
B. Greg Mitchell
Natural product research
Alejandro Inostroza
Journal of Elasticity
Adair Aguiar
rizki wahyu p
Methodi et praxis
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications
Ariela Gross
Lecture Notes in Computer Science
Erika Abraham
Mazowsze Studia Regionalne
Krzysztof Waśniewski
Microorganisms
Fabiola Avelino Flores
Richard Winn
Cost Effectiveness and Resource Allocation
Jean-Marie Lafortune
Ioannis Ivrissimtzis
Sulfikar Muhaemin
Journal of Environmental Quality
Jim Ippolito
Poultry Science
The Medicus
Branislava Milenkovic
The New phytologist
Ben P Miller
Alexander de Resende
Anais de XXXIV Simpósio Brasileiro de Telecomunicações
Elany Farias
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- What's My Car Worth?
- Buyer's Guide
Our car experts choose every product we feature. We may earn money from the links on this page.
Tested: The Best Car Battery Chargers and Maintainers
These car battery chargers and maintainers are the antidote to the dreaded click of a lifeless ignition.
In addition to routine battery upkeep, leaving a car to sit for an extended stretch practically guarantees you a lifeless battery. So, whether your goal is to dodge a towing hassle or ensure your summer ride fires up without a hitch after hibernation, it's important to take proactive steps toward caring for your battery. Why not start by investing a little effort and money into a car battery charger and maintainer, potentially saving you from financial strain down the line?
Our Top Picks

Best Overall
Noco genius 1.

Fast Charging
Schumacher sc1280.

Easiest to Use
Battery tender 3-amp battery charger.

Best for Powersports
Battery tender junior.

Best for Off-the-Grid Charging
Sun energise 10w 12v solar battery charger & maintainer, things to consider.
Not all battery chargers and maintainers are created equal. Before you decide which one to buy, here are some important factors to keep in mind.
Charging vs. Maintaining Your Car Battery
While most chargers on the market are also maintainers, you should know the difference in the modes.
Charging a battery refers to the process of charging a partially discharged battery to regain the battery's voltage. Charging is usually done with higher amperage and is meant to charge the battery quickly and to full health.
Maintaining a battery refers to a low and steady trickle of electrical current to an already charged battery. Batteries, especially over time, lose their charge due to their natural chemical processes. The maintainer function detects and counteracts the loss with a small amount of amperage to top up the battery without overcharging.
We recommend you purchase a product that both charges and maintains. Most products on the market (including all that we tested) will detect the voltage and switch to maintenance mode on their own. But if you purchase a different product than we tested, ensure they will automatically switch to maintenance mode. Otherwise, you risk overcharging.
Battery Type
You'll encounter various battery types in the current market, such as lead-acid, AGM, and gel. It's important to ensure your charger is compatible with your battery type. To confirm your battery type, you may have to look at the side or top of the battery.
Amperage and Charging Rate
Amperage refers to the strength of an electric current and is often used to gauge the charging capacity. A higher current leads to faster charging. So if speed is a major consideration, opt for a higher amperage.
Cord Length
You'll need an external power source to charge your battery. When making your choice for purchase, note your available power sources to confirm the cord can reach from your intended 120-volt wall outlet to the battery terminals. For our testing, we measured the length from the ends of the alligator clamps to the 120-volt plug.
How We Tested Car Battery Chargers and Maintainers
Determining the effectiveness of a charger can be clear as mud, given the sheer amount of variables—from amperage to battery type, battery health, and state of charge. For our test, we steered toward a more subjective test of user experience and evaluated the following parameters:
- Battery compatibility
- Cord length
- Notes on charging behavior while plugged in
Here are the results of our test of some of the top battery chargers and maintainers on the market.
The NOCO Genius 1 belongs to a broader NOCO Genius line of products. The Genius 1 employs a lower 1.0-amp setting to begin a slow, steady charge. It's designed to work with the gamut of battery options—regular lead-acid, AGM, and lithium. Navigating the mode selection button provided a satisfying tactile feel when cycling through options. The bright white LED display made setup a breeze. And once the battery began charging, the pulsing red light indicating charging was underway added a hypnotic quality.
NOCO is a reputable company known for its smart charging features, such as integrated thermal sensors and desulfation modes, designed to prolong your battery's life. It's worth noting, however, that while these modes are reportedly integrated, their activation was not visible during our tests. So, sure, the charger doesn't display the intricate processes at play, but we don't think that's a problem. NOCO seems focused on delivering an effective, user-friendly charger, and to that end, the company nailed it with the Genius 1.
The Schumacher SC1280 is a beefy, cutting-edge battery charger. Blowing all the competitors out of the water with 15.0-amp rapid charging, this massive current will quickly bring your battery back to usable health—if you can wait patiently for the initial desulfation mode.
Of all the chargers we tested, the Schumacher distinguishes itself from the others with its LED display, rather than just indicator lights. The display provides an array of information we were not given with other chargers, including voltage, state of charge, and SULF (desulfation) mode. One thing we couldn't look away from was the sound level. Do you know the sound your computer makes when it gets too hot and the fans roar? That's the sound the Schumacher makes all the time. An editor passed by during testing without seeing the charger and asked, "Is that a Schumacher? My dad has one. They're loud." Despite this, we reckon the charger's operational sound does not pose a huge inconvenience, given you don't tend to linger around your chargers for too long.
If you're looking for a reliable and foolproof charger, Battery Tender is well established in the charging game. For its 3.0-amp model, we struggled to find any flaws other than some users may find the LED lights a little dim.
Otherwise, in terms of its operation, the Battery Tender uses a single button to toggle between 6- and 12-volt. Once a selection is made, you set it and forget it. It's that straightforward. This model doesn't offer extravagant features, but we commend Battery Tender for adhering to the essentials, especially in a market where products can become overly complex. Frankly, most folks are looking for a dependable, easy-to-operate battery charger, and we think the 3.0-amp Battery Tender has that down pat.
To include those in the realm of powersports, we tested the Battery Tender Junior . The Junior model caters to 12-volt battery types, including lead-acid, AGM, and gel batteries. Its 0.75-amp charging capability is most compatible with charging and maintaining motorsport batteries like ATVs, boats, motorcycles, and even lawnmowers.
We hooked the Junior up to senior testing editor David Beard's 12-volt gel ATV battery, which took no setup beyond clamping the alligator clips to the battery posts. After connection, a simple dual-color LED indicator uses red and green hues to convey the operational state of the Junior.
This is where the Battery Tender products shine the greatest: the simplicity of their setup process. The ease of use for both products is a notable advantage, particularly for those who may harbor reservations about electrical systems.
Sun Energise 10W 12V Solar Battery Charger & Maintainer
If your vehicle will be parked away from a conventional power source, consider harnessing the sun instead with the Sun Energise 10-wa tt solar panel . The Sun Energise is a mobile charging solution compatible with 6- and 12-volt vehicle and powersports batteries. Maintenance mode is run through a Maximum Power Point Tracking (MMPT) charge controller. The MMPT boosts efficiency and ensures a sustained charge without the chance of committing the cardinal sin of overcharging the battery.
Designed to be used inside or outside of your car, the Sun Energise features four suction cups for windshield application, which can be mounted to either side of the panel for various configurations. A notable highlight is its ability to charge your battery via the 12-volt port within your vehicle. However, not all vehicle models' 12-volt adaptors function when the ignition is off. For those vehicles, you'll have to use the supplied alligator clips or, alternatively, you can opt to hardwire the panel using the additional set of power and ground cables provided.
Naturally, the prime limitation of Sun Energise is its reliance on sunlight. While our testing left us impressed with the power capabilities of the charger, we recommend using it as a reliable backup rather than your sole charging provider.

The amount of time it takes to charge a car battery depends on many factors—so many that we couldn't realistically measure charging times and get fair, objective results to compare. Instead, we assessed each charger's features and ease of use over two days. Unboxing and taking notes along the way, we were curious about how each product differed in its setup, complexities, and behavior.
However, no matter how you cut it, you can't test chargers without a couple of batteries. For the testing batteries, we visited our friends at Town and Country Auto Parts , where they graciously allowed us to raid their core charge batteries, searching for batteries over 10 volts and at least 50 percent health. After pulling six batteries, we returned them to Gear Team HQ, cleaned and serviced each battery, and prepared for the test.
We unboxed the unit for each product, reading through their user manuals to note features, modes of operation, and battery compatibility . Next, we attached our batteries to charge, assessing the ease of use and setup. Lastly, we observed each charger's behavior , taking note of sounds, displays, and any information communicated by each device in the charging process.
How to Connect Battery Chargers

Always read the instruction manual before setting up any battery charger or maintainer. Here are some basic guidelines to follow:
Prioritize Safety Always ensure you're in a well-ventilated area, and consider wearing protective eyewear. Prepare the Battery If your battery displays signs of corrosion, clean and service it before hooking up any charger or maintainer. This means cleaning the terminals and filling the battery cells with distilled water (if applicable). Set Up the Charger Once you've plugged in the charger, it's time to configure the appropriate settings for your battery. Select battery type and appropriate voltage. Connect the Leads to the Battery This applies to all battery-power procedures, whether using a battery charger, a jump pack, jumper cables, or simply removing your battery from your vehicle. To CONNECT: Positive (red) FIRST, Negative (black) SECOND
To DISCONNECT: Negative (black) FIRST, Positive (red) SECOND

What is the difference between charging and maintaining a battery?
A car battery charger is designed to recharge a vehicle's battery back to a healthy state, whereas a maintainer detects and optimizes a battery's state of charge.
Are battery chargers/maintainers the same as trickle chargers?
No, but they are very similar. The main difference is that a trickle charger will continue to charge even after the battery is fully healthy, which can result in overcharging. If you use a trickle charger, you must monitor and disconnect the battery at the correct time.
How long will it take to charge my battery?
How long it takes to charge your battery depends on many factors, such as the initial level of charge, battery capacity, and the amperage of your charger. However, if your battery is at a decent level of health, you can expect a full charge between four and 18 hours.
Are all battery chargers compatible with AGM, gel, and lead-acid batteries?
No, compatibility varies. Determine your battery type (lead-acid, AGM, or gel) and then select a suitable battery charger for that specific type.
Can I use my charger/maintainer to jump-start my car?
Yes, there are chargers that cost more and feature jump-starting functions, but we didn't test any of those this time around. Need a quick jump? Try one of these jump packs .
What is the correct order of connection when charging my battery?
To begin charging, start by attaching the positive side of your battery to the positive lead (red). Next, connect the negative side to the negative lead (black). For disconnection, follows the same steps in reverse.
Can a battery charger charge the auxiliary 12-volt battery on my hybrid?
You can, but exercise extreme caution. Before proceeding, thoroughly research the auxiliary battery. Be particularly cautious around components with bright orange cables as they indicate high voltage, which can be deadly. In short, prioritize safety.
Why Trust Us?
Hearst Autos combines the talent, resources, and expertise of three of the largest, most influential automotive publications in the world. The Gear Team has tested a wide variety of automotive products, parts, accessories, and gear, such as garage flooring , catalytic converter anti-theft devices , garage heaters , and foam cannons . We get our hands on each and every product we test. Most are purchased; some are supplied by manufacturers.
Hearst Autos doesn't need to game algorithms for traffic or promote lousy products to earn a buck. Instead, we're more concerned with our legacy, our reputation, and the trust that our readers have in Autoweek , Car and Driver , and Road & Track to deliver honest opinions and expert evaluations.
Visit our Tested & Trusted page to see the very best in automotive gear. Read more about our product testing and evaluation process here .
Katherine Keeler is Associate Testing Editor at Hearst Autos. By day she evaluates tools for your enjoyment; by night, she Frankensteins her ever-changing fleet of rustbucket oddities back to repair. Her dream is to open a roadside attraction where the public can view, drive, and learn repairs at her emporium of curious cars.
Gannon Burgett loves cameras, cars, and coffee: a perfect combination for his Hearst Autos work. His byline has appeared in USA Today , Gizmodo , TechCrunch , Digital Trends , the Detroit Free Press , and more.
Collin Morgan is a Commerce Editor at Hearst Autos, where the former Rust Belt mechanic and gadget enthusiast presents the best gear for your automotive endeavors.
.css-1updq97:before{background-color:#000000;color:#fff;left:0;width:50%;border:0 solid transparent;bottom:48%;height:0.125rem;content:'';position:absolute;z-index:-2000000;} The Auto Enthusiast's Shopping Guide .css-1e2ieb7:after{background-color:#000000;color:#fff;right:0;width:50%;border:0 solid transparent;bottom:48%;height:0.125rem;content:'';position:absolute;z-index:-2000000;}

Best Motorcycle Phone Mounts

The Best Motorcycle Jackets You Can Buy

Which Motorcycle Helmet Is the Best You Can Buy?
Tested: Best Dog Car Seat Covers

Best Dog and Pet Car Seats Picked by Experts
Tested: Best Car Wax
Tested: Best Carwash Soaps

Best Car Cleaning Products for 2024
Tested: Best Automotive Glass Cleaners for 2024
Best Shop Vacs for 2024, Tested

Get Amazing Deals on Watches Right Now at Amazon
Ad-free. Influence-free. Powered by consumers.
The payment for your account couldn't be processed or you've canceled your account with us.
We don’t recognize that sign in. Your username maybe be your email address. Passwords are 6-20 characters with at least one number and letter.
We still don’t recognize that sign in. Retrieve your username. Reset your password.
Forgot your username or password ?
Don’t have an account?
- Account Settings
- My Benefits
- My Products
- Donate Donate
Save products you love, products you own and much more!
Other Membership Benefits:
Suggested Searches
- Become a Member
Car Ratings & Reviews
2024 Top Picks
Car Buying & Pricing
Which Car Brands Make the Best Vehicles?
Tires, Maintenance & Repair
Car Reliability Guide
Key Topics & News
Listen to the Talking Cars Podcast
Home & Garden
Bed & Bath
Top Picks From CR
Best Mattresses
Lawn & Garden
TOP PICKS FROM CR
Best Lawn Mowers and Tractors
Home Improvement
Home Improvement Essential
Best Wood Stains
Home Safety & Security
HOME SAFETY
Best DIY Home Security Systems
REPAIR OR REPLACE?
What to Do With a Broken Appliance
Small Appliances
Best Small Kitchen Appliances
Laundry & Cleaning
Best Washing Machines
Heating, Cooling & Air
Most Reliable Central Air-Conditioning Systems
Electronics
Home Entertainment
FIND YOUR NEW TV
Home Office
Cheapest Printers for Ink Costs
Smartphones & Wearables
BEST SMARTPHONES
Find the Right Phone for You
Digital Security & Privacy
MEMBER BENEFIT
CR Security Planner
Take Action
How a Car Battery Charger Can Keep Your Vehicle Ready to Go
The right one can preserve the charge and protect the battery when your car is parked for an extended period

All car batteries lose power over time. This isn’t a factor when the car is driven regularly, allowing the alternator to replenish the battery. But if the car is parked for an extended period, such as for winter storage or while working at home, it is wise to trickle energy into the battery so that it is ready to start the car when you need it. This can be done without removing the battery.
Many modern cars have significant draws on the battery, meaning that parking them even for just a week or two can drain the battery. (The owner’s manual may indicate how long the car can park without losing significant starting power. In some cases, draining the battery may void warranty coverage.) A chief concern is that draining a battery completely can shorten its life span. Plus, if you jump-start a vehicle , there is a risk of damaging electronic components or requiring assistance from a technician. (These days, it is best to leave the jump-starting to professionals, rather than good Samaritans.)
There are two main types of chargers: trickle and maintainer. Basic trickle chargers slowly replenish the battery, but they need to be monitored and manually disconnected when the battery is topped off. A maintainer may be all most people need. True to their name, these affordable chargers are meant to preserve the charge level, not resurrect a dead battery. Unlike trickle chargers, maintainers turn on and off as needed.
A battery maintainer will charge as needed, automatically. Advanced maintainers, often called “smart” chargers, typically have modes to address the needs of absorbed glass mat (AGM) batteries, ensuring that they are charged fully and properly. And there is often a feature to de-sulfate the lead in traditional flooded batteries; that reverses some crystallization that occurs when batteries go unused, extending the battery’s life. These full-featured chargers typically have modes for maintaining a lawn tractor or motorcycle battery, adding to their value.
For those who park outdoors, away from a power source, there are solar-powered battery maintainers. These connect to the car battery, and some cars can be charged via the 12-volt power point inside. Because of their low amperage, a solar unit is used to offset any natural battery discharge, rather than recharge a weak battery. Most solar chargers come with a reverse charge blocking diode to prevent it from draining the car battery at night. Verify that the model you are considering has this feature.
“My preference is a smart battery maintainer,” says John Ibbotson, Consumer Reports’ chief mechanic. “These chargers address a wide range of needs, and they work automatically.”
Ibbotson suggests using quick connectors, often called pigtails. These go onto the battery terminals and allow the charger to quickly plug in and disconnect. Further, they can be safer than clips because they reduce the chance of causing an underhood spark. These eyelet-style connectors often come with smart chargers, or they can be purchased separately.
Before buying, be sure to read the specs for the charger to ensure that it has the features you want. There are many products to choose from, and it can be easy to select one meant for other purposes.
See our car battery ratings and buying guide .
Tips for Using a Car Battery Charger
Connect the charger per the instructions. Then run the cable into the engine compartment, leaving the hood ajar. Make sure not to close the hood on the wires. You also don’t want to leave the hood completely open because that risks leaving a hood light on if your car has one.
Resist the urge to route the wire through the grille or down along the engine. This hides that the car is plugged in, creating a risk that a driver in the household might hop into the car and drive away without disconnecting the wires.
Check the car’s owner’s manual before charging because some cars have specific guidance. This is especially important for models with the battery mounted in the trunk or tucked under the windshield. With those, including some BMWs, there are jump-start points under the hood that could be used for charging.
Charge the battery in a well-ventilated area. Batteries can emit harmful and/or explosive gases. Wear safety glasses or goggles when handling a battery.
Finally, remember that red is positive and black is negative. It does matter. Always confirm with the instructions before connecting anything to the battery.
Jeff S. Bartlett
Jeff S. Bartlett is the managing editor for the autos team at Consumer Reports. He has been with CR since 2005. Previously, Jeff served as the online editorial director of Motor Trend for 11 years. Throughout his career, Jeff has driven thousands of cars, many on racetracks around the globe. Follow him on Twitter @JeffSBartlett .
Sharing is Nice
We respect your privacy . All email addresses you provide will be used just for sending this story.
X2Power SLI24FAGMDP
Econocraft 24f-e, econocraft h6-e, valucraft h6-vl, valucraft 35-vl, napa the legend premium agm bat983585, diehard silver 35, duralast platinum 51r efb, duralast agm h8-agm, acdelco gold 48 agm, napa the legend premium agm bat9824f, aaa premium bat8448aaa.
See All Ratings
Trending in Car Batteries
Best Car Batteries of 2024
Best Car Batteries for the Money
How to Jump-Start a Car With a Dead Battery
More Than 1.8 Million Toyota RAV4 SUVs Recalled Due to Battery Concerns

The Best Car Battery Chargers of 2024
Recommendations are independently chosen by Reviewed's editors. Purchases made through the links below may earn us and our publishing partners a commission.
Why trust Reviewed?
Reviewed's mission is to help you buy the best stuff and get the most out of what you already own. Our team of product experts thoroughly vet every product we recommend to help you cut through the clutter and find what you need.

Schumacher SC1281
Integrated jump starter
Diagnostic tools
Reports of auto-shutoff failure

Ctek MXS 5.0
Safe for unattended use
8-stage charging with monitoring
Not for dead batteries

Ford Performance M-10300-FP 5.0 Smart Battery Charger and Maintainer
Wide compatibility with Ford vehicles
Plug-and-play automatic operation
Only made for charging 12V batteries

Ampeak 2/8/15A 12V Smart Charger
Dedicated winter mode
Numerous charging rates
LCD display
Only for lead-acid batteries

Nexpeak NC201
Supports 12- and 24-volt batteries
Summer and winter modes
Reports of early unit failure

Updated October 13, 2023
A car-battery charger is an excellent tool to have on hand. Unlike a jumpstarter, a car-battery charger keeps the power source for your lawn mower, boat, car, SUV, or truck charged after sitting for long periods of time. (Who wants to get stranded in the middle of nowhere with a dead battery?) These tools come in handy if you’re garaging a car in the winter, putting a snowmobile away for the season, or keeping your boat’s trolling batteries at full charge between fishing trips.
There are a few things to consider before making your purchase. First is to make sure the charger is compatible with your vehicle’s specific battery type. Not all chargers work with lithium-ion technology, for example. You should also make sure that the charger can handle your battery’s voltage. While most car chargers will handle 12 volts, some also work with six- or 24-volt batteries. Finally, check to see whether your charger has all the safety features you need—improper charging can lead to your battery overheating and breaking or, worse, catching fire. At a minimum, any charger should be equipped with temperature sensors as well as trickle-charging technology.
If you’re looking for the best car-battery charger to make sure that your machine stays fully charged, you’ve come to the right place. Here are our top picks among high-quality chargers you can get online now.
The recommendations in this guide are based on thorough product and market research by our team of expert product reviewers. The picks are based on examining user reviews, product specifications, and, in some limited cases, our experience with the specific products named.

The Schumacher SC1281 is a versatile charger, capable of both charging batteries over time and jumpstarting large car batteries in SUVs and trucks. The charger can handle both six-volt and 12-volt batteries, making it perfect for charging everything from motorcycles and small watercraft to boats and trucks. The charger is fully automatic, adjusting the amperage as needed, with integrated diagnostics to ensure your batteries get charging safely and with maximum efficiency.
Unlike most car-battery chargers, the Schumacher SC1281 gives you the emergency support you need. The integrated jumpstart feature has two modes, depending on your situation. The first is a 30-amp quick boost to get your battery over the hump. If the battery is committed to not starting, however, then the 100-amp jumpstart is powerful enough to start your car, such as an SUV or truck, or boat.

The CTEK 40-206 automatic battery charger is one of the highest-rated chargers on the market for 12-volt batteries. This charger features built-in temperature compensation, to adjust the charge rate to match the ambient temperature; a desulphation and reconditioning mode to restore battery life and power to aging batteries; and safe, convenient “set it and forget it” features to prevent overcharging when your battery is left unattended for extended periods.
The 40-206 also has a dedicated AGM mode, making it perfect for charging absorbent glass mat batteries. If you’re looking to charge a 12-volt battery for your vehicle or equipment, then it’s hard to go wrong with the CTEK.

If you own a Ford, this automatic “plug-and-play” charger and maintainer can extend the lifespan of your car or truck’s battery or get you safely back on the road in a hurry. The manufacturer calls it “one of the fastest, most efficient consumer chargers available,” and it’s versatile enough to handle any 12-volt lead-acid battery.
Specifically, it’s known to work great with the Ford Bronco (1970–77), F-150 (2009–21), Fiesta (2014–19), Focus (2013–19), Ford Mustang (2005–21), Ford Ranger (2019–20), and Super Duty (2005–20). There’s no special warranty included, but Ford offers a 30-day return policy if you hang on to your receipt.

The Ampeak smart battery charger is a great option for charging all kinds of 12-volt lead-acid batteries. This unit automatically selects the proper charging rate for your battery—from eight, 12, or 15 amps—allowing you to charge GEL, AGM, and STD lead-acid batteries. With its multi-stage precision and ongoing monitoring, there’s no worry about overcharging or undercharging the battery, regardless of the temperature.
The advanced LCD display sets this unit apart from similar chargers, giving you an easier and more immediate view of your battery’s status. Whether you’re charging a car, motorcycle, boat, ATV, or RV lead-acid battery, the Ampeak charger can handle it.

The NexPeak 10-amp car-battery charger is a go-to solution for charging both 12- and 24-volt lead-acid batteries. The NexPeak offers a seven-stage quick-charge feature for a faster charging speed. The unit also offers eight levels of protection for your batteries, including smart controls, temperature controls, reverse protection to prevent damage to the charger, a cooling system, fireproof materials, and overvoltage protection. In addition, the unit automatically attempts to repair the function of your battery, restoring life and power.
The LCD screen and simple installation make this charger an easy-to-use option for anyone looking to charge their car, motorcycle, or boat battery.

The Noco Genius 5 is a five-amp automatic smart charger, designed for five- and 12-volt batteries. Beyond simply charging your batteries, this product is a full-battery maintenance station. It features a charger maintainer to keep the battery at optimum power without overcharging. It also includes a desulfator to recover some of the battery performance that is inevitably lost over time. Finally, the Noco Genius 5 includes thermal sensors to adapt the charging rate to the ambient temperature, preventing overcharging in hot climates and undercharging in cold.
Genius 5 is universal. It works as a trickle charger, float charger, and more, making it compatible with numerous types of batteries—deep-cycle, lithium-ion, and more. This means that it can work with a wide variety of vehicles, from lawnmowers to ATVs and motorcycles to cars, SUVs, and trucks.
Charges 6- and 12-volt batteries
Several safety features
Charges dead batteries
Reports of faulty equipment

This Battery Tender 4-Amp Automatic Battery Charger and Maintainer is made to fully charge your vehicle before automatically switching to float mode in order to sustain correct levels of voltage. It’s easy to use, and makes it simple to transition battery types, such as from flooded to lithium-ion batteries. Overall, this portable and lightweight charger will keep your vehicles performing well.
Spark-proof
Compact and lightweight
Not very durable
More Articles You Might Enjoy
Prices were accurate at the time this article was published but may change over time.
Meet the testers

Jean Levasseur
Contributor
Jean Levasseur became a professional writer over a decade-long career in marketing, public relations, and technical writing. After leaving that career to stay home to care for his twin boys, Jean has continued to write in a variety of freelance roles, as well as teaching academic writing at a local university. When he's not reviewing tools or chasing toddlers around the house, he's also an avid fiction writer and a growing woodworker.

Lily Hartman
Staff Writer, Search
Lily Hartman is a staff writer who also enjoys writing magazine articles about health and outdoor recreation. In her free time, she likes to hike, camp, run, and lift weights.
Checking our work.
Our team is here for one purpose: to help you buy the best stuff and love what you own. Our writers, editors, and lab technicians obsess over the products we cover to make sure you're confident and satisfied. Have a different opinion about something we recommend? Email us and we'll compare notes.
Sign up for our newsletter.
Enter your email:
Thanks for signing up.
Review on Electric Two Wheeler Chargers and International Standards
Ieee account.
- Change Username/Password
- Update Address
Purchase Details
- Payment Options
- Order History
- View Purchased Documents
Profile Information
- Communications Preferences
- Profession and Education
- Technical Interests
- US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333
- Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060
- Contact & Support
- About IEEE Xplore
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Privacy & Opting Out of Cookies
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. © Copyright 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.

Expert Advice On Improving Your Home
We recommend the best products through an independent review process, and advertisers do not influence our picks. We may receive compensation if you visit partners we recommend. Read our advertiser disclosure for more info.
The Best 12V Solar Battery Chargers And Maintainers
Solar panels typically cost between $12,500–$24,000. Use the form below for custom quotes from local installers.

Alora Bopray
Staff Writer
Alora Bopray is a digital content producer for the home warranty, HVAC, and plumbing categories at Today's Homeowner. She earned her bachelor's degree in psychology from the University of St. Scholastica and her master's degree from the University of Denver. Before becoming a writer for Today's Homeowner, Alora wrote as a freelance writer for dozens of home improvement clients and informed homeowners about the solar industry as a writer for EcoWatch. When she's not writing, Alora can be found planning her next DIY home improvement project or plotting her next novel.
April 24, 2024
Why You Can Trust Us
Today’s Homeowner exists to help you maintain or improve your home safely and effectively. We uphold strict editorial standards and carefully vet the advice and resources referenced in our articles. Click below to learn more about our review process and how we earn money.

Charge and maintain your batteries with these solar-powered maintainers to avoid extra costs.
Solar battery chargers are quick and efficient devices to charge up batteries of your everyday electronics. Whether it’s your vehicle’s battery or a solo portable battery for camping purposes, these chargers allow you to conveniently charge them up anywhere. These chargers not only charge the batteries but also maintain them constantly, thus saving you the effort.
A lot of brands offer various models of battery chargers at different prices. We have done extensive market research to save you from the hassle and compiled a list of the 10 best battery chargers currently available in the market. You can go through their brief descriptions below and choose the right product for yourself.
Editor’s Picks
Following are our top picks from their respective categories. Take a look.
Best Overall: SOLPERK Solar Panel Kit 30W Solar Battery Trickle Charger

SOLPERK Solar kit is the best product on our list thanks to the high value-for-money it provides to its customers. It’s strong, durable, weather-resistant, and comes with a 12-month warranty. It also comes in a reasonable price range. Regarding its usage, this solar charger can be used will multiple battery types and provides reverse charge protection to increase its shelf life.
Best Experience: Topsolar Solar Kit 20W Monocrystalline 10A Solar Charger

Portability is one of the highly demanded features of any solar product. While most solar chargers need to be installed in a fixed place, Topsolar is designed to be used anywhere. This is a perfect charging product for your camping experience. Apart from portability, it all the perks and features that are offered by other top-quality solar chargers. Durability, performance, and excellent customer service are some of the things you can expect once you buy this solar car battery charger.
Best Value: SOLPERK Solar Kit 20W Volt Solar Battery Trickle Charger

SOLPERK provides solar chargers in various wattage options to let a wide range of customers utilize their products at different prices. This solar car battery charger is specifically designed keeping in mind the customers who can’t afford the more expensive battery chargers. You’ll get a 12-month warranty along with a solar panel, two alligator clips, one SAE extension cable, and one set of mounting pieces.
How do 12V Solar Battery Chargers Work?
12V solar battery chargers are best used for maintaining or trickle charging larger batteries such as that of your car, boat, motorcycle, ATV or RV (which mostly use 12V batteries). Unlike standard car battery chargers though, the solar alternative relies solely on the sun’s rays to power up by converting solar power into usable electricity via PV cell solar panels.
This obviously brings a wealth of advantages as no other source of energy is required, which makes them perfect for charging your battery when you’re off the grid but this also brings some limitations. First off, 12V solar battery chargers cannot compete in charging times and effectiveness with standard battery chargers.
You will also be hard pressed to revive a completely dead battery but what they can do is maintain an existing charge or be employed as a trickle charger, supplying a low but constant amount of usable current. Hooking up multiple chargers is sometimes done, but by experts who know the technology well. Be wary of doing this unless you have the appropriate know-how, as you may just fry both the battery and solar charger.
12V solar battery chargers are typically made of two main components: A waterproof and durable solar panel and charge controller. 12V solar battery chargers allow for up to 48V and 4000 Ah of capacity Lead-Acid or Ni-Cd battery charging. A third vital component is the wires that attach the charge controller to the battery via clamps or the vehicles cigarette lighter.
Check out: Top 5 Most Efficient Solar Panels
The charge controller regulates the solar panel’s output voltage. This will change depending on the position and angle of the panel and various atmospheric conditions, mainly the intensity of the sun and the presence of clouds. The charge controller is needed to modulate the voltage to the 12V battery but also to protect the battery from voltage overload.
In short, using a 12V solar battery charges is an effective, lightweight and versatile method of maintaining your battery’s charge. All batteries of a vehicle continually use power due to various electronic devices present (onboard computer, radio, other dashboard components etc). So keeping your battery charged or even stable is of vital importance when outdoors and to be able to so without the use of grid electricity is a huge advantage.
Pros and Cons of Solar 12V Solar Battery Chargers?
We’ve already seen some of the major advantage of 12V solar battery chargers namely versatility, eco-friendliness and durability as most models are intended for prolonged use. Both the charge controller and panel (and wires for that matter) are often long-lasting, highly durable, water and debris proof. As with any device (especially in the solar sphere) they do also have their limitations.
The Best Solar Battery Chargers Reviewed
These are the top 10 solar battery chargers currently available in the market. Let’s take a look at their descriptions along with their pros and cons.

#1 SOLPERK Solar Panel Kit 30W Solar Battery Trickle Charger
- Brand: SOLPERK
- Outstanding Quality
- Waterproof controller
- Wide Application
SOLPERK solar kit is the all-in-one kit to charge up all sorts of 12V batteries with the highest efficiency. The 24% conversion efficiency rate is enough to provide you a fast charging experience. SOLPERK has put in a tremendous effort at providing you the highest build quality. With a tempered glass cover and aluminum frame, this solar charger can easily last for at least 10 years. An advanced PWM technology ensures that your battery doesn’t overcharge. You can connect this battery charger to a number of battery types including Wet, Gel, MF, EFB, and AGM. Lastly, you get a 12-month warranty along with the complete charging kit.
#2 SOLPERK Solar Kit 20W Solar Battery Trickle Charger
- High Efficient Cells
- Adjustable Bracket
- Waterproof Structure
The second most popular car battery charger on our list is also manufactured by SOLPERK. This is an equally brilliant product as the above car charger. This, however, is a 20W option for customers who want to buy a high-quality product at a relatively lower price. This is also protected by a tempered glass cover and aluminum frame to make it weather-resistant. A 24% conversion efficiency ensures quick charging and a PWM algorithm prevents overcharging. Along with the complete kit, you also get a 12-month warranty.
#3 Topsolar Solar Kit 20W Monocrystalline 10A Solar Charger
- Brand: Topsolar
- Color: White
- 20 Watt Monocrystalline Solar Panel
- High efficiency monocrystalline cells
- 10A 12V/24V Auto Charge Controller
Topsolar has produced the highest-rated solar car battery trickle charger to serve you in case of a sudden power breakdown. Whether you are at your home or on a camping trip, this 12-volt portable solar-powered charger not just charges your car battery but all other types of off-grid batteries as well. It is an easy-to-use product that you can set in just a few minutes to charge your electrical devices. It comes with a 10A charge controller to provide reverse polarity protection to your batteries. A strong tempered glass and aluminum frame is used to make this battery charger weather-resistant and last much longer than its 1-year warranty.
#4 POWOXI 7.5W 12 Volt Solar Battery Trickle Charger

- Brand: POWOXI
- Ultra-High Conversion
- Reverse Protection
- Blue LED Indicator
- Back current protection
POWOXI solar battery chargers provide a 20% conversion rate which is lower than the top solar car battery chargers on our list, but it is still one of the highest conversion rates you can get from any car charger in an economic price range. When it comes to both durability and ease of use, this solar battery charger provides the best value for money. Also, this battery charger comes with a charge blocking diode to prevent reverse charging and overheating. To provide you the best customer experience, POWOXI provides a 12-month warranty and excellent customer service.
#5 SUNER POWER 12W Solar Car Battery Charger And Maintainer

- Brand: SUNER POWER
- Charge Anywhere
- Charger & Maintainer
- Durable & Strong
SUNER POWER solar battery chargers are built to provide you a highly user-friendly camping experience. This charger can charge all types of vehicle batteries including cars, bikes, and boat batteries. Once you buy this solar battery charger and maintainer, you’ll not have to worry about discharging battery power as well as its maintenance. This solar battery charger comes with a charge blocking diode to prevent excess solar energy from reducing your battery life. SUNER POWER provides a 12-month warranty on this product along with lifetime technical support.
#6 Topsolar Solar Kit 30W Monocrystalline Battery Charger And Maintainer

- 30 Watt Monocrystalline Solar Panel
Say goodbye to extensive charging methods and charge your off-grid batteries using this 12-volt solar battery charger. Topsolar provides a complete kit that contains a solar panel, two 6.5 feet cables with alligator clips, and an O-ring terminal for a convenient setup experience. It is a highly durable solar battery charger as the panel is protected with a tempered glass cover and an aluminum frame. However, unlike various other solar battery chargers on our list, this one comes without a warranty.
#7 SUNER POWER 10W Waterproof Solar Battery Trickle Charger And Maintainer

- Intelligent Charge & Maintain
- Full Protections
- Adjustable Mount Bracket
- Visual Monitor
SUNER POWER has designed this solar battery charger to charge and maintain fixed batteries that are not moved around after installation. Therefore this solar battery charger is not a great product for your camping trips. The mounting bracket is however adjustable so you can move the position of the solar panel to constantly face the sun. When it comes to performance and energy efficiency, this one works differently than traditional battery chargers. It has a smart 3-stage charging algorithm that carefully controls the charging of batteries and their maintenance. You can monitor this performance via an LED light indicator. The kit contains all the necessary nuts, bolts, and cables to help you in your DIY installation. Lastly, it is IP65 waterproof and comes with a 12-month warranty so you can replace it in case of a malfunction.
#8 SUNER POWER 6W 12 Volt Solar Battery Charger And Maintainer

- Renewable Battery Charger & Maintainer
- Solar Charge Anywhere
- One-way Quick Connector
- Cigarette Lighter Scoket
- Battery Clamps
As the earlier SUNER POWER product was for static battery charging, this one is a portable product. This product can be used as a solar car battery charger. It is offered in a complete kit to provide you a user-friendly experience during its utilization. The blocking diode prevents overcharging and overheating. Also, this one comes with a 12-month warranty. However, one thing that is not great about this product is that while most other solar car battery chargers have tempered glass and aluminum frames for protection, this one is offered in plastic.
#9 Sun Energise Waterproof 20W 12 Volt Solar Battery Charger Pro

- Brand: Sun Energise
- Intelligent Charge
- Mount Brackets
There are a lot of solar chargers on our list that are mentioned as car battery chargers because of their portability. This product is not a car battery charger as it can only be used for fixed purposes. Sun Energise, being a manufacturer and seller, has targeted a customer range that is interested in buying solar chargers and maintainers for their houses. This product has an IP65 rating so that you install it in humid (rain and snow) conditions.
#10 SOLPERK 10W Solar Panel 12V Solar Panel Charger

- High-efficiency solar panel
- Charger and Maintenance Device
- Full-automatic intelligent charging and maintenance Controller
- More durable
SOLPERK has produced many portable solar car battery chargers with different wattage options. This product is yet another great product that isn’t designed primarily for cars, though it can be used as a car charger. This one is designed for more rugged vehicle categories such as boats, snowmobiles, and mountain bikes. This is possible thanks to its ability to connect with multiple battery types. Though it can be used with vehicles, this solar charger is not portable. Once installed, only the angle of the solar panels can be adjusted.
Buyer’s Guide
Solar chargers generally look alike due to the solar panels and all the installation parts, but, in reality, they are quite unique. You might not be able to spot these differences at the first look and might buy the wrong product for your usage. Therefore, we have prepared this buying guide to help you out with the same.
Solar chargers are offered in packs and have different wattage capabilities. This is one of the main reasons behind their price variations. When you decide to buy a solar charger check out all the features that explain the reduced prices.
Warranty is a common feature in most solar chargers. It is very rare to find a product that doesn’t offer you a warranty. Nonetheless, make sure that the solar charger you are buying has at least a 12-month warranty.
The energy production of a solar charger is represented in wattage and most products have different wattages to serve the particular needs of their customers. If you are looking for fast charging, you should invest in the one with higher wattage.
You have to ensure that your solar car battery charger is protected with tempered glass and an aluminum frame which is a standard market practice to increase durability. Other materials will not be as durable as these ones.
Applications
Solar chargers generally have the capability to charge multiple battery types so you don’t have to buy a new charger for each battery type. Although this is a common feature, you must still make sure that the charger you buy has this feature.
Portability
Some solar chargers are lightweight and specifically designed to be hand-carried while others are large and heavy and can only be installed in a fixed place. If you are looking to buy a solar charger for camping purposes make sure you choose the former option.
Charge protection
This is yet another option that is common in most solar chargers where they have a built-in charge blocking diode to prevent overcharging and overheating. This is the reason why they are known as battery maintainers. Before you buy a solar charger, make sure that the customer reviews are positive regarding this particular feature.
Final Verdict
As for our final verdict, SOLPERK solar kit is the best product on our list because it is loaded with plenty of specs and features at a very affordable price. It has a conversion efficiency of 24% which is the highest that can you can get from any solar charger currently listed in the market. Both tempered glass and aluminum framing are used to make it extremely durable. When it comes to user experience, it saves you from the effort of manual management as it comes with an intelligent PWM algorithm for controlled charging. Wide application capabilities allow this solar charger to be connected with various battery types. For your further satisfaction, this product is offered with a 12-month warranty and high-quality customer service.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the materials that make a solar charger more durable.
While some solar chargers are protected with tempered glass and aluminum frames, others are protected with plastic, which is of course less durable. However, one advantage of plastic is that it makes the solar charger a lightweight product which is crucial for your camping experience.
Can you use all solar chargers for camping purposes?
No, all solar chargers can’t be used for camping purposes. Some are installed at a fixed place while others can be used as a portable charging device and hence for camping purposes.
How to make sure if a solar charger is waterproof?
Solar panels are usually water-resistant as they are designed to be used outdoors and in extreme weather conditions. However, if you want to make sure that your solar charger is waterproof, you can look for an IP65 rating.
How can you charge a boat battery with a solar car battery charger?
A boat battery would be charged by a solar charger that can be installed permanently on the boat. General portable chargers will not be effective for this application.
Disclosure: HouseMethod participates in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program. This affiliate advertising program is designed to provide a means for publishers to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites.
Other Solar Product Reviews
- The Best 200 Watt Solar Panels
- The Best Solar Generators
- The Best Solar Gate Openers
- The Best Solar Tubes
- The Best Solar Powered Electric Fence
- The Best Solar Pool Heaters
- The Top Solar Light for Flagpole

Freedom Forever Review
March 16, 2024

SunPower Vs. Tesla Solar: Who Is the Better Solar Installer?
April 1, 2024

Top 7 Best Solar Companies in North Carolina
March 6, 2024

Trinity Solar Review
March 17, 2024

Top 7 Best Solar Companies in Massachusetts
April 29, 2024

Top 6 Best Solar Companies in Illinois
April 30, 2024

Sunrun vs. SunPower: Which Solar Company is Better?
April 28, 2024

Vivint Solar Review

Top 7 Best Solar Companies in Florida

12-Volt Battery Chargers – A Complete Buyer’s Guide
A 12-volt battery charger is of the most important pieces of equipment you’ll be handling with your RV. Not only will it recharge a battery, but a 12v battery charger will provide a huge amount of electricity that can power your vehicle, as well as all sorts of appliances you keep in your caravan, too.
What you'll find...
Battery maintenance is undoubtedly important, and that often means keeping your battery pack charged consistently as well, but of course they're not all made equally.
You really need to research 12v Battery Chargers before buying, but not every option is going to give you what you need to maintain a perfect charge or charge as efficiently as you need.
The 12-volt chargers below in the review are what we believe to be the best on the market, so take a close look at each one.
After the 12v Battery Charger review there's a buyer's guide with more information to help you in your research, such as what things you need to consider before buying one. We also look at and compare the different price entries and what you should expect from the price you're willing to pay.
There's also a step-by-step guide and video on how to use a 12v battery charger, so you'll know exactly what to do with one. Of course, there's an FAQ section where we cover all the main question we get regarding 12 volt battery chargers.
If you prefer, you can jump straight to the 12V Battery Charger Buyer's Guide by clicking the link...

Best Overall 12v Battery Charger: Battery Tender Plus Battery Charger

- Able to combat drainage effectively
- Has an intuitive design and promises high quality
- Features fast charging time and comes with an integrated timer
- Slightly difficult to use on a dead battery
- Would’ve been better if the clamps were larger
What makes the 12v Battery Tender Plus Charger the best overall is how cleverly designed and efficient it is. It can quickly charge up a battery and also keep it at the optimum voltage without causing any of the damage trickle chargers are usually known for. You can also use it to alternate between the float charging mode and full charge mode.
Of course, when buying a battery , charging time is one of the primary factors to look out for. So, if you’re worried about this, know that this is a 1.25-amp charger which charges the battery quicker than a three-amp model.
Another major factor to look for when buying a 12v battery charger is safety. That too comes standard on this unit with the reverse polarity protection and spark protection features. It also comes with a reliable ten-year warranty!
For all to know, this is the plus version of the Tender battery, which makes it 50% more powerful than the previous junior model. This also means that this is much faster. This is quite important considering the increasing dependency on electronics of many modern cars.
It's already a very efficient battery, but the manufacturer has also added numerous upgrades in both software and design to keep it ahead of competitors.
Bottom Line
To put it simply, this is a 12v battery charger you can definitely rely on. It promises excellent quality and has all the common functions anyone would need from a battery. Plus, it also has safety features necessary to keep the unit protected. Lastly, the long warranty it comes with is a sign of how high-quality it is considering its price.
Runner-up: Ampeak 12V Smart Battery Charger

- Sturdily-built design makes the product last Long
- Extremely convenient and easy to use
- The instruction manual is short and easy to follow
- Cannot charge a completely drained battery
Certainly one of the best 12-volt battery chargers available, the Ampeak Smart Battery Charger ranks as the runner-up on our list. Thanks to its fully automatic, high-frequency charging, the battery charger can be used for all types of 12V lead-acid batteries, including AGM, STD, and GEL.
Equipped with a winter charging mode, the unit is innovatively designed for safely charging batteries in cold weather conditions, ensuring perfect charging and longer battery life. It's also microprocessor-controlled, while the multi-stage charging feature further adds safety and precision. With this 12 v battery charger, you don’t need to worry about short circuits, reverse polarity, over-voltage, over-charging, or overheating of the battery!
Moreover, the advanced LED display also keeps track of the charging current, battery type, charging status, voltage, and any error information. Due to its alligator clip and power cord, the model is also easy to use.
The Ampeak 12V Smart Battery Charger is a durable model, ranking second on our list of top picks. Compatible with all 12V lead-acid batteries, this unit is designed with an MCU-controlled program and a winter charging mode. However, the unit’s inability to charge a drained battery might prove to be a hindrance for some.
Best Solar-Powered 12V Battery Charger: POWOXI Solar Battery Charger

- Conserves energy and is environmentally-friendly
- High-quality construction ensures reliability and longevity
- Easy to use and can be used with any 12V cigar lighter
- A bit heavy and might be difficult to carry
- The included suction cups might deteriorate over time
The POWOXI solar battery charger ranks as the best solar powered option on our list of top picks. It's a solid model which gets the job done, even in harsh weather. The unit also works as a trickle charger , which means it can be used for maintaining a charge over time.
Although the model is 7.5 watts, it is still unable to charge a fully drained battery quickly. A solar charge controller is not included, so it is important to monitor your charge carefully.
Thanks to its durable design and medium size, the unit is highly portable as well. However, it weighs more than two pounds, which is a bit heavy. Don't let that put you off, though, because it's easy to install and can be connected to the battery using the alligator clip.
Constructed with a highly transparent and lowly iron-tempered glass, this 12v battery charger ensures durability and is extremely resistant to wind and snow.
The POWOXI Solar Battery Charger deserves a place on our list because of its durability, ease of use, and innovative design. It can also be used as a trickle charger, but the model’s heavy weight might prove to be a no go for some.
Best 12v Battery Charger from Black and Decker: Black & Decker 12V Battery Charger

- Quite sturdy and reliable
- Capable of nearly charging an almost dead battery
- Since it can work as a cigarette lighter adapter , it adds to user convenience
- Makes a clicking noise when it’s in reconditioning mode, which can be annoying
Black and Decker has made a name for themselves in the market given the innovative features their products have and the efficiency they promise. This 12V battery charger from Black and Decker is no different.
It's a six-amp charger which is particularly designed for maximum efficiency, fast charging, and greater performance. What makes it one of the best from this brand is its sealed protection that protects it from being affected by corrosion, moisture, and dust.
As a result, the 12v battery charger can provide maximum efficiency at all times. The outer case is also fully sealed to keep it safe from moisture, oil, dirt, dust, or any other weather elements it may come into contact with.
The charger can detect, as well as maintain, the maximum power in the battery and since it's automatic, you won’t need to monitor it at all times, nor will you have to worry about overcharging or maintaining it. Similarly, you won’t have to deal with a low battery either, as it comes with a long cord that allows you to charge the battery out of the car if you want.
In terms of safety, the 12 volt battery charger comes with built-in circuit protections which provide protection against reverse polarity, short-circuiting, and overcharging. It is also ETL-certified for both safety and performance.
Black and Decker understands the hassle of a dead battery, which is why it has created this completely waterproof 12v battery maintainer and charger. And, since it is fully automatic, it takes out all the guesswork of charging the batteries.
Most Portable 12v Model: BMK 12V 5A Smart Battery Charger

- Plug and play ensures ease of operation
- LED light indicates the different charging modes
- Reduces energy consumption when full power is not needed
- Stabilizes internal battery chemistry for longevity and increased performance
- Absence of a meter makes it difficult to read the charging process
The BMK 12V Smart Battery Charger not only helps charge a battery fully but also maintains a proper storage voltage without causing any damage to the battery. Its stable performance, high reliable efficiency, and longer service life give this product an edge above the other products available.
It's capable of charging a variety of rechargeable batteries from boats, cars, and lawnmowers. This smart charger boosts battery charging, getting it back to functionality, quickly. Its four-stage smart charging modes are controlled by MCU, which helps to keep tabs on the charging process and shuts off after the battery is fully charged.
The BMK Smart Battery Charger features various safety features that include over-discharge protection, overcharging, short circuit protection, reverse polarity protection, and overheat protection. It will also stop charging automatically once the battery is fully charged.
And, it can be used as a trickle battery charger for boats, as well. And if that's not enough, the manufacturer offers considerate and timely after-sale service, lifetime quality warranty, which should eliminate all your worries.
The BMK Smart 12v Battery Charger is a versatile product suitable for lawn mowers, cars, electric vehicles, motorcycles, and electric vehicles. It's lightweight, so you to take it anywhere, and if safety is your main concern the four-stage charging by the MCU controller makes it a very safe product.
Best 12V Deep Cycle Battery Charger: Schumacher Fully Automatic Smart Battery Charger

- Extremely easy to use
- Able to charge fully drained batteries
- Protects your battery from short-circuits, open-circuits, reverse polarity, overcharging, and overheating
- Warranty process is quite lengthy
- Instruction manual is a bit difficult to follow
The most affordable and budget-friendly model available, the NOCO Genius 12V Battery Charger deserves a place on our list. It can be used for year-round battery maintenance of your RV , boat, lawnmower, truck, car, or any other vehicle. It can also recharge smaller capacity batteries on snowmobiles, scooters, personal watercraft, motorcycles, and Power Wheels.
The battery charger is compatible with all types of 12-volt and 6-volt lead-acid batteries, including Gel, Wet, and AGM batteries. With this product, you don’t have to worry about overcharging your battery, simply plug it in and the advanced charging technology will automatically maintain and monitor your battery.
What's more, this product is equipped with reverse polarity protection and spark-proof technology , making it one of the safest chargers available today. The only downside to this product seems to be the instruction manual, which several people have complained about.
The NOCO Genius 12V Battery Charger is one of the most budget-friendly models available. It's suitable for all 12-volt and 6-volt lead-acid batteries, while its spark-proof technology and optimized charge mode ensure durability and longevity. However, the instruction manual might be a bit difficult to follow for some.
Buyer’s Guide
Here we go into greater detail on all things 12v Battery Chargers, such as what things you need to consider before buying one. We also look at and compare the different price entries and what you should expect from the price you're willing to pay.
There's also a step-by-step guide on how to use a 12v battery charger, and a video detailing it, so you'll be a pro by the end. Of course, there's an FAQ section where we cover all the main question we get regarding 12 volt battery chargers.
Aspects to Consider Before Buying a 12v Battery Charger
Whether you want a simple jump-starter or a full-on 12V battery charger, the following are critical to consider before buying one.
What Purpose Will You be Using the Battery For?
Before you buy a unit, ask yourself if you want to maintain the battery's charging capability or if you will be needing the battery for fast charging most of the times. If you only want to maintain the charging, it's better to go for a charger that charges with lower amperes and features active charging monitoring.
Meanwhile, if you’ll be charging car batteries quickly numerous times, you will need higher amperes. And in such cases, you'll need a jump-start function, as well.
Charging Power
You must ensure that you pick out the right amperage depending on your needs. While most 12v battery chargers are capable of charging with various ampere rates, you must take your needs into account. For instance, when maintaining the charge of the battery, you'll need five amps, while for fast charging, ten amps are recommended.
Charging Monitoring
Charging monitoring is essential to have in a 12-volt battery charger. This is particularly important if you're going to be maintaining the charge of your battery as opposed to fast charging. The charging monitoring feature helps not to damage your vehicle’s battery in the long run.
Are All 12-Volt Battery Chargers The Same?
While all of the products we chose are car battery chargers, some of them are slightly more specialized in function. There are essentially three different kinds of 12V battery chargers.
This type doesn’t recharge a completely drained out battery like a standard one. Similarly, it won't restore the batteries cells back to their former state. However, its main purpose is to keep a battery that has a little juice left in it functional and to provide some degree of cell maintenance.
This is the standard battery charger which comes with various permutations such as different amperages or voltages. Its main purpose is to recharge a completely drained battery.

People Also Ask - 12V Battery Charger FAQs
Batteries are essential for our everyday life, but they have a common problem that cannot be avoided – they run down and need to be charged. Typically, batteries use the same process to charge, but there might be minimal adjustments required to ensure optimal performance.
When it comes to charging batteries answers to the following FAQs will help your battery deliver excellent performance:
Can You Use a 12V Battery Charger as a Power Supply?
Essentially yes, but you likely need a battery charger that’s specifically designed to be used as a power supply. Using a standard charger can often be unsafe or ineffective, providing either too much electricity to your appliances and overloading them or too little electricity to effectively power them.
What is the Output of a 12V Battery Charger?
Broadly speaking, a full battery will provide about 12.9 volts when fully charged. If it’s fully depleted, it provides a much lower 11.4 volts instead. These numbers might seem like a small difference, but the change in voltage essentially means the battery can't provide enough energy to power a given vehicle or device.
How Long Does it Take to Charge a 12 Volt Battery at 10 Amps?
With most chargers at 10 amps, you should be able to charge a 12-volt battery in about four and a half hours. That said, this varies based on the type of charger you use. Ensure you read the instructions of your charger carefully to see if it is known to take a longer or shorter amount of time.
How Long Does it Take to Charge a Car Battery With a 12-Volt Charger?
The length of time that a battery needs to charge depends on how drained it is, its size, and the amperage of the charger.
A 12v battery charger with high amps takes less time to charge your battery than one with low amps. However, if you want to keep your battery level fully charged, use a low amp charger instead of a high amp one.
For example, a 40-ampere charger is an excellent option for effectively and quickly charging your battery.

Hello, fellow wanderers! I’m Alyssia. Since 2008, my husband and I have called an RV our home, journeying through life one mile at a time. Our nomadic lifestyle has led us to over 70 countries, each with their unique tales that have shaped our own.
I share our stories and insights right here, hoping to inspire and guide you in your own adventures. Expect tips on RV living, our favorite camping spots, breathtaking hiking trails, and the joys and challenges of an ever-changing view from our window. Alongside, you’ll also find practical advice on outdoorsy stuff, designed to equip you for any journey. Join us as we continue to explore the vast, beautiful world on wheels!

10 Best Car Battery Chargers for 2023
- Updated: March 21, 2024
Mechanic Base is supported by its audience. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission.
Best Overall

Ampeak Smart
A great mix of affordability and performance. Three charging Amp options.
Premium Choice

NOCO Genius10
Works with all types of 6 and 12-volt batteries. High quality with many functions.
Best Budget

12 to 24-volt budget-friendly battery charger with an easy-to-read monitor.
The last thing you want to deal with when you head out to your car is a dead battery, and while a jump start is nice, that usually doesn’t get your vehicle’s battery back to a full charge.
Taking your battery to a shop can leave you stranded for hours, while a top-notch battery charger at home can bail you out. But while an excellent battery charger will get your battery charged and working like new, the wrong one is just a giant waste of time and money.
We’re tired of people wasting their time and money on car chargers that don’t work. That’s why we took the time to track down and review 10 of the best car battery chargers . Any of these car chargers will get your vehicle back on the road in no time.
The Best Car Battery Chargers

- Ampeak Smart – Best Car Battery Charger Overall
- NOCO GENIUS10 Charger – Premium Choice
- NEXPEAK 10-Amp Battery Charger – Best Budget
- Tower Top Smart Charger
- BILT HARD Wheeled Battery Charger
- NOCO GENIUS5 6- & 12-Volt Charger
- Optima Digital 400 AGM Charger
- Outerman 12- & 24-Volt Charger
- SUHU Car Battery Charger
- Amazon Basics Battery Charger
1. Ampeak Smart – Best Car Battery Charger Overall

- Charging Amps – 2, 10, and 25
- Charging Volts – 12
If you’re looking for a top-notch battery charger for your garage, the Ampeak Smart Battery Charger is a great choice. Sure, it only has a 12-volt charging option, but if you’re just looking for a battery charger for your car, that’s all you need.
Even better, with three different charging amps you can cycle through, you charge your battery as fast as you need to. You can set up a trickle charge overnight, or you can quickly charge the battery at 25-amps if you need to get on the road quickly.
This charger works on AGM, lead-acid, and gel batteries, all while offering diagnostic tests and jump-start assists. If you opt to leave your battery on the charger overnight, you don’t need to worry about accidentally overcharging it because of the overcharging protection system.
Additionally, it has a smart detection system that helps you pick the perfect amperage for charging will keep your battery fully charged without overcharging it.
As another perk, this charger comes with an impressive 18-month warranty, if you have any problems with their charger for any reason, they’ll make it right.
And if you’re new to batteries or working in the dark, the reverse polarity protection will keep you from frying both your charged and battery if you hook it up backward.
Finally, this smart charger also can act as a jump starter for your car! With a simple to use start aid button using this charger as a jump starter is just as simple as charging the battery. No matter what you need a 12-volt car charger for, this Ampeak Smart Battery Charger can get the job done.
- Great mix of price and performance
- Three charging amps give you more options
- 18-month warranty
- Smart detection charging system
- Reverse polarity and overcharging protection
- Only works on 12-volt batteries
2. NOCO GENIUS10 Charger

- Charging Amps – 10
- Charging Volts – 6 and 12
The NOCO GENIUS10 might not look like much, but don’t let its small size fool you. This small charger packs a punch and has plenty of versatility. It can charge both 6-volt and 12-volt batteries, and it doesn’t matter if they’re AGM, lead-acid, marine, lithium-ion, or something else.
This small little charger automatically detects the type of battery you’re charging and adjusts the output accordingly. Not only that, but it runs a diagnostic check on the battery to check for excessive sulfation and acid stratification and enter a different charge mode to try and repair damage.
Additionally, this is a charger you can set up and leave. With overcharge protection, you don’t need to worry about blowing up batteries by leaving them on too long. This system accounts for different weather conditions and other environmental concerns, giving you more peace of mind.
While we wish that it had more amperage options than just a 10-amp, with all the extra feature NOCO built-in, that’s not a huge deal. Just don’t expect to charge a completely dead battery in an hour.
This charger will do more than just charge your battery – it can extend the overall service life. After a few batteries, this charger will pay for itself, so look at it as an investment instead of a purchase, which is something you need to keep in mind when you look at the higher price tag.
Finally, NOCO includes a 3-year warranty for this charger, which gives you even more protection. But while the warranty might only last three years, the charger should last far longer.
- Small and portable
- Works on both 6-volt and 12-volt batteries
- It has overcharge protection
- Works with all types of batteries – AGM, lead-acid, marine, etc…
- 3-year warranty
- Detects and attempts to repair sulfation and acid stratification
- More expensive option
- Only one charging amperage
3. NEXPEAK 10-Amp Battery Charger

- Charging Amps – 5 and 10
- Charging Volts – 12 and 24
Just because you don’t have a ton of money to spend on a battery charger doesn’t mean you can’t get one that gets the job one. The NEXPEAK 10-amp charger is an extremely affordable option that you can use to get your battery back on track.
But the price isn’t the only thing that this charger has going its way. It also can charge both 12-volt and 24-volt batteries. However, while there are two amperage options, you truly only get one choice.
That’s because the 10-amp option charges 12-volt batteries, while the 5-amp option charges 24-volt batteries. There’s no way to change it between the battery types.
Still, there are seven different charging steps with this charger, and the charger detects and swaps to each mode automatically throughout the charging process. This helps repair your battery and get it back to running like new.
Moreover, there are plenty of protective circuits throughout this charger, including overcurrent/overcharging protection, reverse polarity protection, short circuit protection, temperature compensation, and more.
Finally, it has an easy-to-read monitor that lets you know the current state of your battery and when you can take it off the charger.
But with all the perks this charger offers, it still is a budget charger. Nothing highlights this more than the fact that it won’t charge completely dead batteries – it won’t even try. It uses a voltage detection system to start charging, and there’s no way to override it.
Not only that, but this charger doesn’t work with lithium-ion batteries. While it works for different battery types besides lead-acid, you must manually cycle through each battery option to get to the right one. It’s not a huge deal, but there is the risk of making a mistake.
- Affordably priced
- Reverse polarity protection
- Overcurrent/overcharging protection
- Easy to read monitor
- Will not charge completely dead batteries fast
- Does not work with lithium-ion batteries
4. Tower Top Smart Charger

- Charging Volts – 12
We understand that garages can be messy and cluttered, and things happen. That’s why the Tower Top Smart Charger is such an excellent choice for those that don’t have a track record of keeping everything right where it belongs.
Whether it’s sliding around your trunk or clanging into things in your garage, the extra protective casing around the Tower Top Smart Charger helps protect it from damage. In addition to the rugged protective casing, this charger offers three different charging amperages for different situations.
You can use the 2-amp option for a slow trickle charge, while the 25-amp option gives you the ability to quickly recharge a dead battery in just a few hours.
And when you’re really in a hurry, it has an engine start aid to help jump-start your car on cold mornings. Additionally, there are tons of protective circuits that include over-voltage protection, overheating prevention, and reverse polarity protection.
With this charger, the chances of damaging your battery, the charger, or yourself are extremely slim. This charger works with GEL, AGM, and lead-acid batteries, which is a huge perk if you have multiple vehicles with different batteries.
Moreover, the auto-detection feature ensures your battery gets an optimal charge without the need to put in a ton of different inputs. Even better, the easy-to-see and read LCD screen lets you know your battery’s current status and what’s going on.
So, while this might be a slightly more expensive option, when you factor in everything you’re getting and the extra protective casing, you’re really getting a great deal.
- It has an engine start aid for busy mornings
- Overvoltage, overheat, and reverse polarity protection circuits
- Works for GEL, AGM, and lead-acid batteries
- Auto-detection features give your battery an optimal charge
- Extremely durable casing
- Slightly more expensive option
5. BILT HARD Wheeled Battery Charger

- Charging Amps – 2, 10, 40, and 200
If you own a maintenance shop or do work out of your garage, you need a charger that offers you tons of versatility, and that’s precisely what you get with this BILT HARD battery charger. There are three different charging options at 2, 10, and 40 amps, and it even has a 200-amp jump-starting option.
The entire setup is fully automatic, so all you need to do is connect the battery and turn it on to get a fully charged battery. And since BILT HARD knows you’re busy in the shop, this charger has overheating and overcharging protection.
With this charger there’s no more forgetting to taking a battery off the charger and damaging a perfectly good battery. Another perk to this charger is that it reconditions the battery you’re charging, which means it can actually extend the remaining battery life!
This battery also has reverse polarity protection, so if you’re in a hurry and hook things back backward on accident, you won’t damage the battery or the charger. Even better for maintenance setups is the fact that this charger works for all types of batteries.
Not only does it work on typical 12-volt batteries, but if you’re working on bikes or something with a smaller six-volt battery, this charger can handle that too.
Whether the customer has an AGM, GEL, or regular lead-acid battery, this charger can handle it. However, there are two drawbacks to this charger. First, it’s a more expensive option. While it’s an acceptable cost for a repair shop, it is something you need to budget for.
Second, it’s a much larger option compared to the other chargers on our list. While it’s a standard size for a shop battery charger, there are much smaller portable options out there now.
- Plenty of charging options
- Fully automatic setup is easy to use
- Reverse polarity, overheating, and overcharging protection circuits
- It works with all kinds of batteries
- Reconditions battery
- Pretty large to lug around
6. NOCO GENIUS5 6- & 12-Volt Charger

- Charging Amps – 5
If you’re looking for a battery charger that works for both your automotive battery and the batteries on your smaller vehicles like ATV, motorcycles, and even lawnmowers, the NOCO GENISU5 is an outstanding choice.
The NOCO GENIUS5 is similar to the GENIUS10 in every way but one, the charging amperage. The GENIUS5 puts out 5-amps, while the GENIUS10 puts out 10-amps. Neither is a lightning-fast charging option, but 5-amps will take twice as long to charge a battery compared to a 10-amp charger.
Of course, a slower trickle charge is better for your battery, so there really is no wrong choice here, it’s just about how much time you have. This charger has overcharge protection to prevent accidentally damaging your batteries and automatically detects battery sulfation and stratification.
If the charger detects either of those conditions, it automatically enters a regen mode where it works to revive and repair the battery. No matter the type of battery you need to charge, the NOCO GENIUS5 can handle it.
It also comes with a 3-year warranty, so you don’t need to worry about replacing it anytime soon. However, considering it only has a 5-amp charging option, it’s a bit expensive for what you get. It’s a good choice and does a great job, but you’re paying for quality and performance.
However, this charger is a bit cheaper than the GENIUS10, so if you’re looking at that as a price point, this one is more affordable.
- No quick charging options
- More expensive for what you get
7. Optima Digital 400 AGM Charger

- Charging Amps – 4
Optima is known for making some of the best automotive batteries in the world, and they take a swing at making an automotive battery charger with the Optima Digital 400. It’s the lower model of their Optima 1200, but that doesn’t make it cheap or low-quality.
However, it does only put out 4 charging amps, which makes it nothing more than a high-quality trickle charger. It can bring batteries back, but it might take a full day or two. Still, it has easy to hang and store hooks, which means you can set it up and forget about it.
That’s also in large part to the overcharge protection that Optima built into the charger. All you need to do is hook up the charger and wait; there’s no reason to worry about overcharging the battery with the Optima Digital 400.
It also has reverse polarity protection and an easy-to-read and use LCD screen, which makes this charger great for beginners.
One of the best perks for this charger is that Optima specifically made it for their AGM batteries. While it can charge lead-acid batteries too, AGM batteries are where it excels.
Of course, just about everything Optima makes is expensive, and their Optima Digital 400 is no exception. It’s one of the more expensive options on our list, but it’s a bargain compared to the Optima 1200.
- Great for AGM batteries
- Spark free connection technology
- Recovers batteries with as little as 1.5 volts
- Easy to read and use LCD screen
- Hook and hang connections make it easy to store and use
- Very slow charging option
8. Outerman 12- & 24-Volt Charger

- Charging Amps – 7.5 and 10
If you own an automotive repair shop, you need a charger that can handle both 12- and 24-volt batteries and the Outerman Battery Charger makes a great choice. It’s easy to set up and use, and the best part is that it automatically switches between 12- and 24-volts.
You don’t need to worry about a new mechanic setting up the charger wrong, all they need to do is install the clamps, and the charger takes care of the rest! Not only that, but this charger has an overcharging protection feature, so you can set it up and forget about it.
Furthermore, the LCD screen gives you the current voltage of the battery and the output charging amps, so you know exactly what’s going on at each stage in the process.
Like all the best chargers, this one works in phases that help revive and regenerate the battery, which means it actually extends the battery’s service life. If you can bring back a single battery with this charger you’ve already offset the charger’s cost!
This is an extremely affordable charger, but it still comes with a one-year warranty, so you don’t have to worry about getting a dud that slipped through the cracks.
However, keep in mind that it only works with lead-acid and lithium batteries, so if you’re looking to charge a different kind of battery, you’re out of luck with this charger.
- Automatically switches between 12 and 24 volts
- Automatic charging option
- Overcharging protection features
- It has a 1-year warranty
- Only works for lead-acid and lithium batteries
9. SUHU Car Battery Charger

- Charging Amps – 4 and 8
If you’re on a budget and need a charger, the SUHU Car Battery Charger is an outstanding choice. It utilizes plenty of top-notch features like automatic charging and voltage detection, all at a reasonable price.
However, keep in mind that it only has an 8-amp charging option for 12-volt batteries and a 4-amp charging option for 24-volt batteries. While this isn’t a big deal if you have time, charging your batteries will take some time.
However, not only can it auto-detect 12- or 24 volts, but it also has advanced safety features like overcharging, short circuit, and reverse polarity protection. This makes it an extremely beginner-friendly device since there are tons of protective features built right in.
Another perk is the fact that it has an easy-to-see and use LCD screen that shows the vehicle’s current voltage and charging status. This gives you a better idea of how much more time your battery will need to stay on the charger and let you keep track of the battery’s health over time.
However, this is a budget charger, and a big part of that is that it’s only a 3-stage battery charger. That’s better than chargers of the past, but most chargers today have five to seven phases. This helps them rejuvenate and restore the life of the battery.
While the SUHU Car Battery Charger can do that some, it’s not nearly as effective as some of the other chargers out there. Still, at this price, it’s hard to complain.
- Works on both 12-volt and 24-volt batteries
- Automatic charging features
- Reverse polarity, short circuit, and overcharging safety features
- LCD shows you current voltage and charging status
- Works on all kinds of batteries
- Only a 3-stage battery charger – not as great at bringing batteries back
10. Amazon Basics Battery Charger

- Charging Amps – 2
In recent years Amazon Basics has come out with tons of products in just about every industry, so it’s no surprise that they have a battery charger. And if you’re looking for a true trickle charger at a great price, this isn’t a terrible choice.
Sure, it’s not the longest-lasting option out there, but it does come with a one-year warranty. And since it’s an Amazon product, redeeming the warranty is far easier than with most other products.
Moreover, storing this charger is easy due to its compact size, and it’s extremely affordable. And while it might not be the longest-lasting option, it does have plenty of technological features built-in to keep you from screwing anything up.
Chief among these features are the overcharge and reverse polarity protection and a spark-proof connection setup. You can use it for both lead-acid and AGM batteries, and it works with both 6- and 12-volt batteries.
Just keep in mind that with a 2-amp battery charger, it can easily take a full day or two for it to recharge a single battery. Not only that, but if the battery has significant sulfation, then 2-amps isn’t enough power to break it up and restore your battery.
But whether you need to charge the batteries in your car, motorcycle, or lawnmower, this Amazon Basics battery charger can get the job done.
- Very affordable
- Low amperage is the best way to charge a battery
- One year warranty from a company you can trust
- Works on both 6- and 12-volt batteries
- Compact size
- Overcharge, reverse polarity, and spark proof protection
- Works with lead-acid and AGM batteries
- Only has one very low trickle charge option
- Not the longest lasting option
Many people only know that when they turn the key in their car, it should turn on. But while it all might seem like magic while it’s running, there’s nothing magical about what’s going on underneath the hood.
But if you don’t know how it works, it can be hard to figure out what you need. That’s why we took the time to address some of the most common questions here.
How Many Amps Do You Need?
As a general guide, the fewer amps you use to recharge your battery, the better. However, there are a few exceptions to this rule. First, if your battery has a ton of sulfation, a jolt of high amperage can help break this up. Second, if you need to charge the battery in a short amount of time, more amps are better. While more amps can damage your battery, they do the job far quicker.
How Long Does It Take To Charge a Battery?
It really depends on how depleted your battery is, but it will typically take anywhere from 4 to 24 hours. The average car battery has about 48 amps, and the amperage of a charger tells you how many amps it will restore in one hour. So, with a 2-amp charger, it will take a full 24 hours to recharge a completely dead battery, while a 10-amp charger can do the same job in just under 5 hours.
How Long Should a Battery Charger Last?
If you store your battery charger properly and take care of it, there’s no reason your battery charger can’t last ten to fifteen years. Of course, it all depends on the battery charger you choose. Low-quality battery chargers won’t last nearly as long.
How Much Should You Spend on a Battery Charger?
For most car chargers, you can expect to spend anywhere from $30 to $100. If you’re shopping for a charger for a commercial application, expect to spend a little more, anything between $100 and $200 is typical.
How Many Volts Is in a Battery?
Despite the common name of a 12-volt battery, there are actually 12.6 volts in a battery. While that might not sound like a big difference, a battery with only 12 volts only has a 25 percent charge! So, when you’re looking at the up-to-date specs on your battery charger, wait until the voltage is at a full 12.6 volts before putting it back in your vehicle.
4 Tips for Charging Your Battery
While you might think that charging your car battery is as simple as hooking up the leads and letting it work its magic, there are a few things you should be aware of. Below we’ve highlighted five crucial tips for charging your car battery.
1. Always Take the Battery Out of Your Vehicle
Modern vehicles have a ton of electronics and sensors throughout, and the last thing you want to do is pulse electricity through all of them while you’re charging your vehicle. But if you leave your battery connected while you’re charging it, that’s exactly what you’re doing.
While all you need to do is disconnect the battery terminals, we recommend removing the battery completely to prevent any accidents. It also makes it far easier to follow our next tip.
2. Charge at Room Temperature
This isn’t always a possibility, but when you can help it, try to charge your vehicle’s battery in a location with a temperature between 60 and 80 degrees. Too much heat can lead to the battery overheating, while too little makes it hard for the battery to accept a charge.
But if you’re thinking of bringing the battery and charger into your home, you should think again because…
3. Vent, Vent, Vent!
When you’re charging batteries, they put off hydrogen gas, which can lead to dangerous conditions. If you’re charging batteries in an indoor setting, you need to have adequate ventilation. This can be fans pushing the air out a window or a more complete setup.
4. Use the Lowest Possible Amperage
If you have a charger that allows you to change the amperage, always start with the lowest amperage first. If you’re on a time crunch, you can up the amps, but the more amps you use, the more you’ll damage the battery. Lower amps are always better – even if it does take more time.
5. Monitor the Progress
We know that all the chargers here have overcharge protection, but we like to play things safe. We’ve had batteries start to bubble because of internal damage and a litany of other alarming conditions. Always check on your battery periodically to ensure that everything is working as it should.
Categories: Car Battery , Maintenance , Reviews
Related Posts

Latest Posts
- The Best & Worst Years Of Ford Explorer
- Best & Worst Years Of Toyota Corolla
- Best & Worst Years of Toyota RAV4
- When Should Your Child Switch To A Forward-Facing Car Seat?
- The Best & Worst Years Of Toyota Camry
- I Accidentally Put Premium Gas In My Car, What To Do?
NEW ON YOUTUBE: Supercharged NA Miata
Best Trickle Chargers: Keep Your Batteries Always Ready
Make dead batteries a thing of the past with these reliable and durable trickle chargers.

We may earn revenue from the products available on this page and participate in affiliate programs. Learn more ›
There are few things that are more frustrating than coming out to your garage to take your car, ATV, snowmobile, dirt bike, or UTV out for a spin only to find out you’ve got a dead battery. This is when you wish you had just bit the bullet and bought that trickle charger you’ve been eyeing. Trust us, it's worth it as a trickle charger hooks up to your idle battery and keeps it properly juiced up even sitting for a long time. It's perfect for any sort of storage situation and to help you find the trickle charger to suit your needs, I sorted through the plethora of options. Take a gander below.

Deltran 12-Volt Junior Automatic Battery Charger
- Reverse-polarity protected
- Can be used on any automobile
Backed by a five-year warranty
Not suitable for AWG batteries
- Not wear resistant
Not for fast charging

Beikalone Sealed Lead Acid Battery Charger
Short-circuit protection
Overcharge protection
Super affordable
- Takes too long to charge larger batteries
- Not as durably constructed as some other options
- No warranty

Noco Genius10 10-Amp Fully Automatic Smart Charger
Can detect and repair battery damage
Extends battery life
Can recharge batteries from as low as one volt
Lengthy warranty process
- Not for use on lithium-ion batteries
Summary List
- Best Overall: Deltran 12-Volt Junior Automatic Battery Charger
- Best Value: Beikalone 12V Sealed Lead Acid Battery Charger
- Best Premium: Noco Genius10 10-Amp Fully Automatic Smart Charger
- Best For ATVs: Battery Tender Plus Charger and Maintainer
- Best Dual-Use: Noco Genius GENM2 Battery Charger
- Best Heavy Duty: CTek Battery Charger MUS 4.3 Polar
- Most User Friendly: Black and Decker 6V, 12V Battery Charger/Maintainer
Our Methodology
When it comes to choosing a reliable and high-quality trickle charger, the options are vast and varied. In order to narrow the playing field, I look at name brands that most people are already familiar with. These companies have a solid track record of providing reliable, comfortable, and high-quality products. I wanted to provide a variety of prices so that there would be a good option to suit any budget. I also tried to include only those options that are super straightforward and easy to use, thus minimizing your chance for error and damage to your battery or yourself. For more about our selection criteria and methodology, check out The Drive’s Gear About page .
Best Trickle Chargers: Reviews & Recommendations
Best Overall

- Brand: Battery Tender
- Model: 22-0351
- Weight: 1.8 pounds
Reversed polarity protection
Can be used on almost any vehicle
Not wear-resistant

- Brand: Beikalone
- Model: QC18070501
- Weight: 5.6 ounces
May interfere with your radio
Takes too long to charge large batteries
Best Premium
- Brand: Noco
- Model: Genius10
- Weight: 3.99 pounds
Doesn’t work on a fully discharged battery
Best For ATVs
Battery Tender Plus Charger and Maintainer

- Model: Plus
- Weight: 2.29 pounds
Four charging modes keep your battery at peak power
Automatic float mode prevents overcharging
10-year warranty
Won’t charge batteries below three volts
Not suitable for all vehicles
Can take a long time to charge
Best Dual Use
Noco Genius GenM2 Battery Charger

- Model: GEN5X2
- Weight: 5.26 pounds
IP68 Waterproof
Easy and straightforward to use
Use for lead-acid, gel, AGM, and deep-cycle batteries
Requires hard-wire
Short cables
Best Heavy Duty
CTek Battery Charger

- Brand: CTek
- Model: 56-958
- Weight: 2 pounds
Heavy-duty waterproof housing
Can function in extreme temperatures
Somewhat pricey
Can’t charge batteries that are fully drained
Known to overheat occasionally
Most User Friendly
Black and Decker 6- and 12-Volt Battery Charger

- Brand: Black and Decker
- Model: BM3B
- Weight: 1.25 pounds
Fully automatic and ETL certified for safety
Easily switch between 6- or 12-volt mode
Not as durable as some other options
Not suitable for lithium-ion batteries
Our Verdict on the Best Trickle Chargers
If you’re looking for the ideal combination between reliability, durability, and price, consider the Battery Tender 12-Volt Junior Automatic Battery Charger . For a great budget-friendly pick, check out the Beikalone 12V Sealed Lead Acid (SLA) Battery Charger .
What to Consider When Buying a Trickle Charger
Not all trickle chargers are created equally as they come in a wide variety of sizes, capacities, and price points. The best one for you will have several key features that ensure proper function, reliability, and limited safety issues. The following buying guide will have you making your choice with confidence.
Types of Trickle Chargers
Traditional charger.
Dumb chargers are traditional chargers that come with more cables that are plugged into a wall socket. They are powerful, cheap, and can charge any battery size. Dumb refers to the fact that these chargers can’t monitor the charging status and often lead to overcharging of the battery if left unsupervised.
Smart Charger
Smart battery chargers sport a modern design and can track the progress of the charging system to prevent overcharging. They are priced high due to their advanced safety features that prevent any battery damage. The chargers can be left unsupervised and can automatically adjust the settings to suit the charging needs of the battery. However, they can’t charge all battery sizes like a traditional charger.
Trickle Charger Key Features
The capacity of the battery and chargers is marked in amp-hours. You need to ensure that your trickle charger has a higher amp-hour value than your vehicle’s battery. Most chargers have adjustable ampere rates, but ideally, a maintenance charger needs to be under 5 amps while a fast charger should be at least 10.
Charging Monitoring
If you are going to maintain your battery throughout the winter season, go for a charger with an automatic battery-charge monitoring feature. This will ensure that your battery isn’t overcharged and that it’s topped off every time the battery level goes down. It will buy you time by keeping your battery in good condition before you get to use your car.
The trickle charger needs to have some safety features that prevent damage to the battery. That might include reverse polarity connection safety, which ensures that you don’t damage your car’s electrical system in case you connect the charger to the wrong terminals. Other safety features include spark-proof technology, short-circuit protection, overload, and overheating protection.
Many good-quality trickle chargers will be offered for sale at or less than $50. At this price point, you should be able to find reliable options that feature smart auto charging technology that can safely charge your battery for prolonged periods with minimal supervision. Once you get above $50, that’s where warranties and safety ratings are more common. You’ll also find chargers suitable for charging larger batteries in this price range as well.
You’ve got questions. The Drive has answers.
Q: Is a trickle charger the same as a battery charger?
A: No, they are different. A battery charger delivers a high-amp electrical current to the battery by converting AC power to DC at a low voltage. Also, battery chargers can neither be left connected for a long time nor left unsupervised. Trickle chargers, on the other hand, can be left unsupervised and connected for days as they deliver power safely at low amps.
Q: After how long should I hook up the trickle charger?
A: Generally, a car’s battery discharges 20 hours after a full charge. It can take longer if you have a larger battery. You should hook up the trickle charger 10 to 15 hours after a full charge. However, if you plan to leave your car idle for weeks or months unsupervised, you can leave the trickle charger on. It will safely charge the battery whenever the battery level drops.
Q: Could I damage my battery if I leave the trickle charger on for too long?
A: It depends on the type of charger you have. Some trickle chargers have an automatic control system that stops charging the battery when it’s at capacity. Others might not have that feature and might end up overcharging and damaging your battery. The trickle charger may take half a day to a full day to fully charge a dead battery.
Q: How do I connect the trickle charger to the car battery?
A: Trickle chargers typically come with red and black clamps. Locate the positive terminal of the battery (often red) and connect the red clamp on the terminal. Then connect the black clamp to the negative terminal (often black) of the battery. Then adjust the setting of the charger to your liking: charging or maintenance mode.
Why Trust Us
Our reviews are driven by a combination of hands-on testing, expert input, “wisdom of the crowd” assessments from actual buyers, and our own expertise. We always aim to offer genuine, accurate guides to help you find the best picks.

Other ‘ Electronics ’ Reviews You Might Like:
Our car experts choose every product we feature. We may earn money from the links on this page.
9 Best Battery Chargers for Any Vehicle
Protect yourself against being stranded with a dead battery for as little as $30.

When your battery goes dead—whether it’s because you left the headlights on or it’s just old—not having to call for a tow truck can save you a few hours and a huge headache, even if the tow is technically free. These jump starters and battery maintainers will give you peace of mind any time of the year. And if you have a car that sits for long stretches in the winter months, these will also keep it charged and ready for a cruise at a moment’s notice.
10 Fully Automatic Smart Charger

The 10 from Noco Genius is smaller and more powerful than the previous model from the company. It has a thermal sensor and can charge batteries as low as 1 volt.
NOCO Car Battery Starter

The NOCO unit has 1000 amps of peak current and can start SUVs, cars, or trucks many times on a full charge. It also has a USB port to top off your devices.
Smart Battery Charger/Maintainer

This highly rated charger from Ampeak has automatic charging for all types of 12V lead-acid batteries. It won’t overcharge or overheat.
Stanley 15-Amp 12V Battery Charger/Maintainer

This charger from Stanley is of the 15-amp variety but can muster 40 amps to start a vehicle in 90 seconds. It can also recondition your batteries, reversing sulfate buildup on plates.
Battery Charger and Maintainer

This compact charger is compatible with various types of vehicles including motorcycles, cars, lawnmowers, ATVs, and more. It has an easy-to-read LED screen denoting the charging mode.
Fully Automatic Battery Charger

This polarity-protected charger from CTEK has built-in temperature sensing and a five-year warranty. Thick cables will last a lifetime, and the minimum battery voltage required is 2 volts.
Battery Saver and Charger

The set-it-and-forget-it TecMate OptiMate charger turns off automatically if it senses a problem. It can recover batteries as low as 0.5 volts and features a fully sealed case to protect against spillage and light rain.
Automatic Smart Battery Charger

This charger from WarmCare automatically adjusts the charge current and maintainability according to the temperature and is suitable for both 12V and 24V batteries.
6V/12V Smart Battery Charger/Maintainer

This small charger has 10-stage, fully automatic charging for 6- and 12-volt batteries. The LCD screen keeps you abreast of the state of charge, and it has a memory function to stay in your chosen mode.
The Hearst Autos Gear Team is dedicated to bringing you the very best in automotive tools, parts, and accessories, based on the expertise of the editors of Car and Driver , Road & Track , and Autoweek .
.css-1u92ux6:before{background-color:#ffffff;border:0 solid transparent;bottom:38%;color:#000;content:'';display:none;height:0.3125rem;position:absolute;right:0;width:100%;z-index:under;}@media(min-width: 40.625rem){.css-1u92ux6:before{height:0.625rem;}}@media(min-width: 64rem){.css-1u92ux6:before{bottom:25%;}} Gear

Best Dog and Pet Car Seats Picked by Experts
Tested: Best Carwash Soaps

Best Deals at Amazon's Spring Sale
Tested: Best Ice Scrapers and Snow Brushes
Best Dash Cams of 2024

Casio Launches Land Cruiser–Inspired G-Shock

Get Geared Up for the Daytona 500

5 Trickle Chargers to Keep Your Battery Healthy

Best Tonneau Covers

Best Portable Jump Starters

Last-Minute Gifts for the Car Enthusiast

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This paper reviews the current status and implementation of battery chargers, charging power levels, and infrastructure for plug-in electric vehicles and hybrids. Charger systems are categorized into off-board and on-board types with unidirectional or bidirectional power flow. Unidirectional charging limits hardware requirements and simplifies interconnection issues. Bidirectional charging ...
levels, battery current ripple, bandwidths of the sensors and control loops, accuracy of. the sensors and microcontroller, and maximum power of the battery charger. The stated. technical ...
A battery charger can allow a unidirectional or bidirectional power flow at all power levels. The bidirectional power flow adds to the grid-to-vehicle interaction (G2V) also the vehicle-to-grid (V2G) mode [].This latter technology can bring significant improvement in the overall reliability of the distribution grid, since in case of system failure, peak load demand or other unexpected ...
voltage is reached, after which the charging process is termi-nated [18]. This way, every charging system has a BMS that coordinates all charging operations. In other words, the battery, charger, and load communicate through the BMS as shown in Figure 1. 2.1 Battery charger circuit topologies Circuit topologies for lithium-ion battery charging ...
A Solar Battery Charger circuit is designed, built and tested. It acts as a control circuit to monitor and regulate the process of charging several batteries ranging from 4 volts to 12 volts, using a photovoltaic (PV) solar panel as the input source for the battery charging process.
There are three primary methods of EV battery charging : battery swapping stations , conductive charging , and wireless charging. Wireless charging, specifically, allows EV batteries to be charged remotely without the need for physical connections [4, 5]. Three techniques are employed for wireless charging: stationary charging, dynamic or in ...
The Ideal Voltage Reading For a Fully Charged 12-Volt Battery. For a 12-volt battery to have a full charge, the ideal voltage is between 12.6-12.8 volts. At this voltage level, the electrical pressure is strong enough that the battery can provide its maximum power capacity. Variations In Fully Charged Voltage Readings Across Different Battery ...
However, this project is based on the construction of a 12volts simple battery charger with local materials to reduce cost. 1.4 Purpose of the study The purpose of this project work is to design, construct and demonstrate how a simple 12volts battery charger works. 1.5 Significance of the study A simple 12-volt battery charger is a simple ...
The auto turn-off battery charger for Ni-Cd rechargeable batter ies automatically disconnects from the. mains to stop charging when the batteries are fully charged. It can be used to charge ...
The power demands of a DC fast-charging station require a significant amount of power, which can easily exceed megawatts. Thus, recently, modular multilevel converters (MMCs) have become more ...
Download Free PDF. View PDF. CHAPTER TWO LITERATURE REVIEW A smart battery charger is mainly a switch mode power supply (also known as high frequency charger) that has the ability to communicate with a smart battery pack's battery management system (BMS) in order to control and monitor the charging process.
NOCO seems focused on delivering an effective, user-friendly charger, and to that end, the company nailed it with the Genius 1. Amperage. 1.0A. Cord Length (Clamps to Outlet) 112.0 in. Battery ...
Tips for Using a Car Battery Charger. Connect the charger per the instructions. Then run the cable into the engine compartment, leaving the hood ajar. Make sure not to close the hood on the wires ...
Voltage (V) x Battery Type x Charger Size (Ah) = Amps Needed. For example: 12V lead-acid x 5Ah = 60 amps. 24V lithium-ion x 2Ah = 48 amps. Read more about amp usage at PowerClues.com. By considering charger compatibility and charging speed, you can select the right amperage charger for your 12-Volt battery.
Peak Sudden voltage drop of the battery measured by DMM 𝛥 𝑖 O Total electric charged going out from battery measured by DMM ∆ 𝐶 changes in SOC because of charging, discharging process
The CTEK 40-206 automatic battery charger is one of the highest-rated chargers on the market for 12-volt batteries. This charger features built-in temperature compensation, to adjust the charge rate to match the ambient temperature; a desulphation and reconditioning mode to restore battery life and power to aging batteries; and safe, convenient "set it and forget it" features to prevent ...
Because of increasing environmental issues caused by greenhouse gas emission of Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) driven vehicles, there is a need to move towards eco-friendly mobility with zero emission. Vehicles driven by electric power caters the need. This paper discusses the different types of chargers and charging methods for electric two wheelers. Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV) and Plug ...
Best Overall. NOCO Genius5 Fully-Automatic Smart Charger. SEE IT. Summary. This unit combines power, reliability, longevity, cutting-edge technology, and price point to outshine most other battery ...
Take a look. Best Overall: SOLPERK Solar Panel Kit 30W Solar Battery Trickle Charger. SOLPERK Solar kit is the best product on our list thanks to the high value-for-money it provides to its customers. It's strong, durable, weather-resistant, and comes with a 12-month warranty. It also comes in a reasonable price range.
The NOCO Genius 12V Battery Charger is one of the most budget-friendly models available. It's suitable for all 12-volt and 6-volt lead-acid batteries, while its spark-proof technology and optimized charge mode ensure durability and longevity. However, the instruction manual might be a bit difficult to follow for some.
Outerman 12- & 24-Volt Charger. SUHU Car Battery Charger. Amazon Basics Battery Charger. 1. Ampeak Smart - Best Car Battery Charger Overall. Charging Amps - 2, 10, and 25. Charging Volts - 12. If you're looking for a top-notch battery charger for your garage, the Ampeak Smart Battery Charger is a great choice.
Best Premium. Noco Genius10 10-Amp Fully Automatic Smart Charger. See It. Summary. A 12-volt battery trickle charger with an onboard mini-computer that monitors the condition of the battery and an ...
6V/12V Smart Battery Charger/Maintainer. $34 at Amazon. Credit: Jane Choi. This small charger has 10-stage, fully automatic charging for 6- and 12-volt batteries. The LCD screen keeps you abreast ...