

Press ESC to close

Mastering Effective Speech Delivery: From Practice to Performance

Start this journey! Dive into the amazing world of effective speech delivery. Find out the secrets of how to engage an audience. Transform practice into incredible performances!
Connect with the audience from the start. Get their attention with interesting opening lines and stories. This sets the stage for a remarkable speech.
Understand body language and vocal projection. Use facial expressions, gestures, and tone to emphasize your message. Show confidence and be authoritative.
Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech is a shining example of great communication. King inspired millions with his passion and words. It’s proof of the potential of effective speech.
To be a masterful speaker, practice storytelling, connecting with an audience, and using body language. Draw inspiration from great orators. Embrace your inner orator! Make a lasting impact with your words.
Importance of Effective Speech Delivery
Delivering a speech effectively is essential for capturing the audience’s attention and getting your message across. Here are 4 key reasons why:
- Engagement: Deliver your speech in an engaging way and your listeners will stay hooked until the end. This ensures that your message resonates with them.
- Clarity: Delivery makes your speech clearer. This helps people understand your words and the main points of your message.
- Persuasion: Good delivery has a persuasive effect. Use the right tone, gestures, and body language to establish a connection with the audience and sway them towards your viewpoint.
- Rapport-building: Effective delivery builds a rapport between you and the audience. Your confident demeanor builds trust and engagement.
It is also important to remember that delivery requires practice and preparation. Pay attention to vocal variety, pacing, enunciation, body posture, and gestures.
Take Tony Robbins as an example – he once gave an inspiring speech that changed the lives of many. His passion filled every word and the crowd was entranced. By delivering the speech with such passion and conviction, Tony Robbins inspired and empowered the audience, leaving a lasting impact on their lives.
Preparing for Speech Delivery
Maximize potential as a speaker and successfully convey your message with this 6-step guide on prepared speech delivery . Follow these steps:
- Determine the purpose and select the topic .
- Research for relevant information and supportive evidence .
- Create an outline, using headings and subheadings .
- Craft an attention-grabbing intro and clearly state the purpose .
- Follow with a coherent presentation of main points and examples .
- Incorporate visuals like slides or props to enhance understanding .
- Lastly, practice delivery techniques like pacing, modulation, body language, and eye contact . Get feedback from others to refine further.
Don’t forget to refine language for the target audience. Look to Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech for inspiration – a powerful, passionate, and compelling speech that captivated the audience and started a movement.
Practicing Speech Delivery
Learn the art of speech delivery with this 6-step guide !
- Prep : Research & gather info. Organize thoughts and make an outline.
- Warm-up : Do vocal exercises like breathing, tongue twisters & scales.
- Memorize : Get key points down. Practice without notes or prompts.
- Body Language : Check your facial expressions, gestures & posture in a mirror.
- Rehearse : Keep increasing the speed & emphasize important words.
- Feedback : Get constructive criticism from trusted people. Join a club to practice.
Remember, each individual has a unique style. Embrace it & stay open to learning opportunities.
True History: Winston Churchill was a master of speech delivery . His powerful speeches during WWII motivated & inspired the UK. He was meticulous in his prep & used rhetorical devices to great effect. His speech delivery had a major impact on history.
Techniques for Effective Speech Delivery
Speech delivery is key to captivating your audience and getting your message across. To master the skill, here are three techniques to enhance it:
- Body Language: Move and gesture purposefully to engage the audience. Use hand and facial expressions to emphasize points and convey emotions. Stand tall and keep an open posture.
- Vocal Range and Tone: Vary your pitch, volume, and tone. Pause for emphasis and modulate your voice for a dynamic flow.
- Eye Contact: Establish eye contact with your audience to build trust. Look at individuals or small groups. Make your speech personal and persuasive.
Remember, successful speech delivery goes beyond words. To perfect it, rehearse in front of a mirror or record yourself. Practice makes perfect!
Also Read: Find Your Passion: A Path to Self-Discovery and Fulfillment
Overcoming Nervousness
Nerves can trip up even the most eloquent speakers, but with a few effective strategies, you can conquer them. Preparing is key. Invest time in practicing your speech and knowing it backwards and forwards. This will build confidence and reduce nervousness.
Visualize success too. Imagine you’re delivering an awesome speech to a captivated audience. This exercise helps create positive thoughts and boosts your assurance.
Controlled breathing is invaluable for fighting nerves. Slow, deep breaths can soothe the mind and relax the body. Taking care of yourself – like getting enough sleep, eating well and exercising – also helps reduce anxiety.
Let me share an inspiring story. A young executive was set to give a presentation to lots of industry experts. Despite feeling jittery beforehand, she practiced and rehearsed her speech. On the day, she focused on visualizing success and took deep breaths for inner calmness. As she spoke confidently and connected with the audience, her nerves vanished. By using these strategies, she conquered her nerves and gave an outstanding performance.
As this tale shows, conquering nervousness isn’t impossible. With dedication, visualization exercises, controlled breathing and self-care – anyone can beat their anxiety and speak confidently. Remember everyone gets nervous sometimes – how we manage it makes us stand out as confident speakers.
Tips for Captivating the Audience
To captivate your listeners , you need effective speech delivery! Here are some tips to try:
- Be personal: Relate to the audience with anecdotes or experiences.
- Use body language: Use gestures, facial expressions, and posture to make your message more impactful.
- Tell stories: Storytelling adds emotion and helps the audience understand your message better.
- Use visual aids: Slides or props can add visual interest and comprehension to your speech.
- Pause for emphasis: Pauses give time to reflect, create suspense, and highlight important points.
Adapt your speech to meet the needs of your listeners. And don’t forget the power of humor! Incorporate tasteful humor at appropriate moments to keep engagement high.
Did you know? Visuals can increase information retention in the audience by a whopping 400%!
Also Read: Top 100 Commonly Used A to Z Phrasal Verbs for English Fluency
For great speech delivery, it’s important to practice and plan. Engage the audience with body language, vocal variation, and clear pronunciation . Incorporate visuals and tech to boost the impact of the speech. Adapt to the audience’s needs and interests to keep their attention. Remember that practice makes perfect!
To make it unique, include storytelling techniques to engage the audience emotionally. Use rhetorical devices like similes and metaphors . Also, adjust pacing and rhythm for emphasis.
We recall an inspiring incident involving Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. His “I Have a Dream” speech in 1963, inspired millions. His voice and powerful message advocating for racial equality captivated the audience. His ability to connect emotionally, through vivid language and imagery, showcases the power of effective speech delivery. Know More – The Fluent Life
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What are some tips for effective speech delivery? A: Some tips for effective speech delivery include practicing beforehand, using body language and gestures, speaking clearly and confidently, and engaging the audience through eye contact.
Q2: How can I improve my speaking voice for better speech delivery? A: To improve your speaking voice, you can try exercises like breathing techniques, vocal warm-ups, and speaking with proper posture. It is also helpful to listen to and mimic good speakers to develop your own style.
Q3: How do I overcome nervousness when delivering a speech?| A: To overcome nervousness when delivering a speech , you can prepare well in advance, practice in front of a mirror or with a supportive audience, focus on your message rather than your fear, and use relaxation techniques such as deep breathing.
Q4: What are some common mistakes to avoid during speech delivery? A: Some common mistakes to avoid during speech delivery include speaking too fast or too slow, using excessive filler words like um or uh, reading directly from notes instead of engaging with the audience, and lacking enthusiasm or energy in delivery.
Q5: How can I keep the audience engaged during my speech? A: To keep the audience engaged during your speech, you can use storytelling, humor, visual aids, rhetorical questions, and interactive elements like asking for volunteers or involving the audience in small activities. It is also important to maintain a confident and enthusiastic delivery.
Q6: What are effective ways to conclude a speech for a strong impact?
A: Effective ways to conclude a speech for a strong impact include summarizing key points, providing a memorable closing statement or call-to-action, using inspirational quotes or stories, and leaving the audience with a thought-provoking question or idea to ponder upon.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Share Article:
You might also like

Public Speaking for Social Impact: A Strong Tool

Public Speaking in Digital Age: Webinars and Online Conferences

Public Speaking Ethics: Principles of Responsible Communication
Other stories, building confidence in public speaking: be successful speaker, effective audience engagement techniques: keep them interested.

Speak Like a Pro: The Ultimate Guide to Flawless Speech Delivery Techniques Revealed!
Eloquence Everly

As an affiliate, we may earn a commission from qualifying purchases. We get commissions for purchases made through links on this website from Amazon and other third parties.
Implementing effective speech delivery techniques is essential to captivate and engage your audience. By following these techniques, you can improve your public speaking skills and deliver persuasive and engaging presentations.
Key Takeaways:
- Thoroughly prepare and practice your speech before delivering it.
- Create a distraction-free presentation environment with proper lighting and visibility.
- Pay attention to your personal appearance and maintain good body language during the speech.
- Focus on vocal delivery strategies such as clear enunciation , appropriate loudness and speed , and variations in speed and force .
- Utilize effective body language by maintaining eye contact , using gestures and movement naturally, and avoiding distracting mannerisms.
Preparation for Speech Delivery
Before delivering a speech, thorough preparation is essential. By taking the time to prepare, you can ensure a smooth and confident delivery that captivates your audience . Here are some key aspects to consider:
- Create a Well-Organized Set of Notes: To guide you during your presentation, create a clear and concise set of notes. This will help you stay on track and ensure you cover all your key points. Structure your notes in a logical manner, using headings and bullet points for easy reference.
- Engage in Ample Practice: Practice makes perfect, so dedicate time to rehearse your speech. Familiarize yourself with the content, flow, and timing of your presentation. Practice in front of a mirror, friends, or colleagues to receive feedback and make necessary improvements.
- Prepare the Presentation Environment : The environment in which you deliver your speech can greatly impact its effectiveness. Consider factors such as lighting, visibility, and distractions. Ensure that the room is well-lit and that your audience can see and hear you clearly. Eliminate any distractions or potential interruptions.
- Test and Have a Backup Plan for Audiovisual Equipment : If you will be using audiovisual equipment , such as a microphone or projector, it is crucial to test them beforehand. Check for any technical issues and have a backup plan in case of equipment failure. This will help you avoid any disruptions and allow for a seamless delivery.
By adequately preparing your speech, notes, and the presentation environment , you can set yourself up for success and deliver a confident and impactful presentation to your audience.
Personal Appearance and Body Language
When delivering a speech, your personal appearance and body language significantly impact the impression you make on your audience. Here are some key tips to ensure you project confidence and professionalism:
Dress Appropriately
Choose attire that is suitable for the occasion and reflects your respect for the audience and the topic. Ensure your outfit is clean, well-fitted, and comfortable. Avoid wearing hats or caps that can obstruct your face and hinder your nonverbal communication.
Maintain Good Posture
Stand or sit up straight, with your shoulders back and chin parallel to the ground. This posture exudes confidence and engages your audience . Remember to distribute your weight evenly and avoid excessive shifting or fidgeting.
Eye Contact
Maintaining eye contact is crucial for establishing connection and credibility with your audience. Look directly at individuals while speaking, making an effort to engage different parts of the room. Avoid constantly referring to notes or reading from a script, as this can diminish the impact of your message.
Avoid Distracting Mannerisms
Be mindful of your body language throughout your speech. Minimize excessive hand movements, pacing, or other distracting mannerisms that can detract from your message. Focus on conveying confidence and clarity through calm and composed gestures .
By paying attention to your personal appearance and body language, you can enhance your speech delivery and effectively engage your audience .
Vocal Delivery Strategies
Your vocal delivery plays a crucial role in how your speech is received by the audience. By implementing effective vocal techniques, you can enhance the impact of your message and maintain audience attention. Let’s explore some strategies to improve your vocal delivery :
Enunciation and Clarity
Clear enunciation is vital for effective communication. Ensure that you pronounce your words distinctly and avoid mumbling or garbling. By articulating each word clearly, you enhance the audience’s understanding and engagement with your speech.
Appropriate Loudness and Speed
Adjusting your volume and speed based on the audience, venue, and topic is crucial for effective vocal delivery. Speak loudly enough to be heard, but avoid being overly loud or shouting. Similarly, vary your speed to maintain audience interest and emphasize key points, but avoid speaking too quickly or too slowly.
Variations in Speed, Inflections, and Force
Utilizing variations in speed, inflections, and force adds depth and meaning to your speech. By emphasizing certain words or phrases, you can convey the significance and emotion behind them. Adjusting the pace of your speech can create anticipation or highlight important information. Use this technique strategically to enhance your message and keep your audience engaged.
Minimize Filler Words
Filler words such as “um,” “uh,” and “like” can detract from the impact and clarity of your delivery. Minimize their use to ensure a smooth and impactful presentation. Pausing briefly instead of using filler words can also add emphasis and facilitate better understanding.
“Clear and confident vocal delivery is essential for engaging your audience. Enunciate your words with clarity, speak at an appropriate loudness and speed , utilize variations in speed and force , and minimize the use of filler words. These strategies will help you captivate your audience and effectively convey your message.”
Now that you have learned about effective vocal delivery strategies, let’s move on to exploring the importance of body language in speech delivery.
Effective Use of Body Language
When delivering a speech, your body language can greatly impact how your message is received by the audience. By mastering the art of body language , you can effectively communicate your ideas and captivate your listeners.
Maintaining Eye Contact
One of the most important aspects of body language is maintaining eye contact with your audience. This establishes a connection between you and your listeners, making them feel engaged and involved in your speech. Avoid excessively reading from notes, as this can hinder eye contact and create a barrier between you and your audience. Instead, glance at your notes discreetly when necessary and focus on making eye contact with individuals throughout the room.
Using Gestures and Movement
“Gestures, in my opinion, are the most powerful tool we have in becoming an effective communicator.” – Andrea Foy
Gestures and movement can add depth and emphasis to your speech. Use them naturally to illustrate concepts, reinforce transitions between ideas, and highlight key points. However, it’s important to be mindful of using gestures in a controlled and purposeful manner. Avoid excessive or distracting movements that can draw attention away from your message. Instead, use gestures and movement to enhance your delivery and engage your audience.
Show Enthusiasm and Commitment
When delivering a speech, it’s vital to demonstrate interest and passion in your topic. Show enthusiasm through your body language, such as by smiling, using facial expressions that reflect your emotions, and maintaining an open and confident posture. This not only captures the audience’s attention but also conveys your commitment to the subject matter, making your speech more compelling and memorable.
Avoiding Distracting Mannerisms
While gestures and movement are important, it’s crucial to avoid distracting or aimless mannerisms that can detract from your message. Be aware of any nervous habits, such as fidgeting, excessive hand movements, or aimless shifting of weight. These mannerisms can undermine your credibility and divert the audience’s attention from your speech. Practice self-awareness and aim for body language that is purposeful, controlled, and complementary to your message.
Improving Verbal Delivery
When delivering a speech, your verbal delivery plays a crucial role in engaging your audience. To ensure your message reaches every corner of the room, focus on the following aspects:
- Projection : Speak with enough volume to reach people in the back of the room. This will ensure clear communication and prevent your words from getting lost in the space.
- Comfortable Rate : Speak at a pace that allows your audience to comprehend and absorb your message. Pausing occasionally not only helps you catch your breath but also gives the listeners time to process the information.
- Clear Articulation : Enunciate your words clearly to facilitate understanding. Avoid mumbling or rushing through your sentences, as this can make it difficult for your audience to follow along.
- Vocal Habits : Pay attention to any vocal habits that may distract your listeners. Eliminate vocalized pauses like “um” or “uh” and work on maintaining a steady volume throughout your speech. Avoid speaking more softly at the end of sentences, as it can diminish the impact of your message.
Sample Table: Comparing Verbal Delivery Techniques
By focusing on projection , comfortable rate , clear articulation , and eliminating distracting vocal habits , you can deliver a speech that captivates your audience and ensures effective communication.
Enhancing Nonverbal Delivery
Nonverbal delivery plays a crucial role in enhancing your overall speech delivery and making a lasting impact on your audience. By utilizing effective eye contact, movement , gestures, and an unobtrusive use of notes , you can captivate and engage your listeners. These nonverbal elements add depth and authenticity to your speech, helping to convey your message effectively.
Eye Contact: Making eye contact with individuals in your audience establishes a connection and shows that you are genuinely interested in their presence. Avoid excessive reading from notes, as it can break the eye contact and lessen your impact. Instead, actively engage with your audience, scanning the room and making meaningful eye contact with different individuals throughout your speech.
Movement: Movement on stage or in front of your audience can help you control nervousness and create visual interest. Utilize the space around you, taking purposeful steps and making slight changes in position to capture the attention of your listeners. Movement should be natural and deliberate, enhancing your message rather than distracting from it.
Gestures: Gestures and arm movements can add emphasis and clarify your spoken words. Use them to reinforce key points, illustrate concepts, and enhance the overall impact of your speech. Effective gestures appear natural and are synchronized with the rhythm and flow of your speech, engaging your audience on a visual level and reinforcing the meaning of your words.
Unobtrusive Use of Notes: While it is common to use notes during a speech to stay on track and remember important points, it is essential to use them unobtrusively. Ensure that your notes are legible and well-organized, allowing you to find the information you need without causing distractions. Place your notes discreetly or use a small podium or lectern to hold them, allowing for seamless transitions and maintaining the focus on your delivery.
Avoid any distracting mannerisms or gestures that detract from your communication. Practice incorporating these nonverbal elements into your delivery to create a powerful and engaging speech that leaves a lasting impression on your audience.
Managing Nervousness and Overcoming Challenges
Nervousness is a common experience when delivering a speech. However, it’s important to remember that you are not alone in feeling this way. Chances are, many members of your audience are also experiencing nerves. The good news is that most signs of nervousness are invisible to the audience, so you can stay calm and composed even if you’re feeling a bit jittery.
Embrace nervousness as it can actually be a valuable tool in enhancing your speech delivery. It can make you more alert, animated, and enthusiastic about your topic. Instead of trying to suppress it, harness that nervous energy and channel it into your presentation. When you embrace your nerves, you can turn them into a positive force that adds authenticity and passion to your speech.
Handling mistakes is another important aspect of managing nervousness . It’s natural to feel flustered if you make a mistake or lose your place during your speech. However, it’s crucial to remember that these slip-ups happen to everyone at some point. Instead of panicking, take a moment to collect yourself, take a deep breath, and calmly continue from where you left off. Most importantly, don’t dwell on the mistake or draw attention to it. Keep your focus on delivering your message effectively.
By embracing and managing nervousness , you can transform it from a potential obstacle into a catalyst for a powerful and engaging presentation. Embrace the nerves, handle mistakes gracefully, and let your genuine enthusiasm shine through.
Mastering effective speech delivery techniques is essential for becoming a confident and persuasive speaker. By implementing these techniques, such as thorough preparation, proper personal appearance, and effective vocal and nonverbal delivery strategies, you can captivate your audience and deliver impactful presentations.
Preparing well before your speech, organizing your notes, and creating a suitable environment are all crucial steps in ensuring an effective delivery. Your personal appearance and body language contribute greatly to the overall impression you make on your audience. Maintaining eye contact, using gestures and movement, and speaking with clear articulation and appropriate variations in speed and force all enhance your communication.
While it is natural to feel nervous before delivering a speech, embracing this nervousness can actually help enhance your delivery. Remember, you are not alone in experiencing nerves, and most signs of nervousness are invisible to the audience. Embrace the energy that nerves bring and use it to your advantage, channeling it into a more animated and enthusiastic performance.
By following these effective speech delivery techniques, you can confidently communicate your ideas and engage your audience in a persuasive and impactful manner. Remember to always strive for clear and effective communication, and never hesitate to seek further opportunities for growth and improvement in your public speaking skills .
What are some effective speech delivery techniques?
Implementing effective speech delivery techniques involves thorough preparation, proper personal appearance, vocal and nonverbal delivery strategies, and managing nervousness .
How important is speech preparation for effective delivery?
Speech preparation is crucial for effective delivery. Creating well-organized notes, practicing, and preparing the presentation environment and audiovisual equipment are essential steps.
How does personal appearance and body language impact speech delivery?
Personal appearance, such as appropriate dressing and tidy hair, and positive body language help to engage the audience. Standing or sitting up straight, making eye contact, and avoiding distracting mannerisms are key aspects.
What are some vocal delivery strategies for effective speech delivery?
Enunciating clearly, speaking with appropriate loudness and speed, using variations in speed and inflections, and minimizing filler words are important strategies for vocal delivery.
How can body language enhance speech delivery?
Maintaining eye contact, using gestures and movement naturally, and displaying enthusiasm through body language can enhance the impact of your speech.
What are some tips for improving verbal delivery in a speech?
Projecting your voice, speaking at a comfortable rate, articulating words clearly, and eliminating vocal habits are key tips to improve verbal delivery.
How can nonverbal delivery support speech delivery?
Making eye contact with the audience, using movement and gestures, and using notes unobtrusively can make your speech more engaging and effective.
How can one manage nervousness during speech delivery?
Managing nervousness can be achieved by realizing that it’s common, remaining calm and composed, using nervous energy to enhance your delivery, and embracing mistakes as learning opportunities.
What are the key takeaways for effective speech delivery?
By implementing effective speech delivery techniques , one can become a confident and persuasive speaker. Thorough preparation, proper personal appearance, vocal and nonverbal delivery strategies, and managing nervousness are key components.
About the author

Latest Posts

Understanding the 5 R’s of Communication
Effective communication is key for our personal and work lives to grow. Even though digital tools are common, talking face-to-face brings a special touch. Knowing how the human voice works helps make our talks better. It’s also important to spot […]
What are the 6 rules of effective communication?
Being a good communicator is key to both personal and professional success. James Humes, who wrote speeches for presidents, called communication the “language of leadership.” It’s not just about being a good talker, but also about sharing the “what,” “why,” […]

7 Principles of Effective Communication
Good communication depends on several important principles. Although they are not set in stone, they help us talk better. These principles aim at being well-spoken, thorough, clear, interesting, logical, open to feedback, and aiming to achieve something. Key Takeaways: Effective […]
- Delivery Techniques →
How to Give a Speech: 10 Tips for Powerful Public Speaking

When we start preparing to give a speech, it can be a nerve-wracking experience. It’s completely normal—most of us feel a combination of excitement and nerves when we’re about to take the stage.
However, with some strategic planning and practical advice, you can make sure your speech is powerful and effective. In this blog post, we’ll explore how to give a speech that will leave your audience engaged and inspired.
We’ll examine 10 tips to help you build a powerful speech, from outlining your points methodically to crafting captivating introductions . Whether you’re a beginner or experienced public speaker, these nuggets of wisdom will help you take your next speech to the next level. Let’s get started!
Quick Review of Key Points
Preparing ahead of time is the key to giving an effective speech. Make sure to structure your speaking points, rehearse your delivery, and be aware of the needs of your audience for maximum impact.
How to Prepare for a Speech
Preparing for a speech is an essential step to public speaking success. It can help to build your confidence, create content that reaches the audience, and reduce performance anxiety.
Although it can be time-consuming in the beginning, preparation will ensure less stress and more comfort during delivery. Here are some tips to consider when preparing for a speech:
Practice : Before delivering a speech, practice it out loud several times. This will allow you to gain experience in speaking without an audience and increase your confidence when you do have one.
Practicing also helps to identify awkward moments in the speech or any difficult phrases which then can be changed or removed altogether. Additionally, it helps you determine where to pause for effect. Research : Depending on the topic of the speech , research should be done beforehand to gather information that is relevant and interesting for the audience. It is important to get acquainted with the language typically used by audiences to ensure a clear understanding of what is being said.
Additionally, relevant statistics and stories concerning the topic are a great way to draw in listeners and make the presentation more engaging .
Know Your Audience : When preparing your speech, be sure to consider who will be listening. For instance, if giving a presentation at work, include industry jargon that members would understand and include relevant topics from publications that might be familiar to the employees.
On the other hand, if consulting business professionals in their field then technical language may be easier for them to comprehend than laypeople or students.
By gathering valuable information about the topic and getting comfortable with a speech’s content and delivery through practice, speakers will gain more assurance during their talk as well as respect from their audience.
Preparing beforehand not only gives insight into how to engage listeners but also encourages more meaningful conversations after the event. Now that we have discussed how to prepare for a speech let us move on to creating an outline which will provide structure during delivery.
Create an Outline
After determining the audience and purpose of your speech, the next step to effective public speaking is to create an outline .
An outline serves as a roadmap to ensure that your speech has a logical flow and contains all important points. It also can help keep you on track during the speech itself, allowing you to stay focused and organized.
When constructing an outline, consider drawing up both a main point and sub-points for each portion of the speech. Both should be relevant to the goal of the presentation and backed up by facts and research.
Brainstorming can help in this process; try grouping your ideas together in clusters to make sure you cover all possible angles.
Furthermore, writing out exact quotations or figures can prove beneficial in forming a cohesive argument. At this stage, it is also wise to decide where transitions, humor, stories, or other engaging techniques will be included.
While there are differing opinions as to whether outlines should be memorized or simply used as a reference while speaking, many agree that they should serve their purpose – not only articulate the main thoughts of the speech but also assist the speaker with maintaining focus and preventing distractions.
The debate between those who advocate for memorization versus casual consulting touches upon issues such as rehearsal time, risk of errors in delivery, ease of practice versus actual performance and more.
Each side has valid arguments that should be weighed prior to deciding what type of approach best suits your needs.
Having a firmly constructed outline acts as a valuable tool when it comes time to deliver a powerful public speech. By actively utilizing this tactic, speakers may not only enhance their clarity and coherence, but also add structure and vibrance to their presentations.
Now that we have explored what goes into crafting an effective outline, let’s dive deeper into how we can best collect resources and research our topics for maximum impact.
Collect Sources and Research
Collecting sources and research is a crucial step for any public speaking engagement. It ensures that you have the necessary information to make strong points and back up your statements.
Before writing your speech, take time to research your topic to gain familiarity with different perspectives, facts, and counterpoints. This will help you to craft an argument that can stand up to scrutiny while also adding a breadth of knowledge to your speech.
Interviews can be a powerful source of evidence and anecdotes, so try to include one or two relevant interviews in your research process. Relying solely on secondary sources such as books and articles can lead to a narrow scope of understanding.
Interviews provide an opportunity to hear directly from an expert and create an interesting dynamic in your speech by adding personal experiences as well as commentary from a professional.
In research it is important to stay objective. Gather a variety of perspectives and be open-minded about their merits. Don’t forget to consider both sides of the argument when researching for your speech.
Doing this allows you to understand the opposing perspective and enables you to anticipate potential counter arguments from your audience.
By acknowledging them beforehand, you may increase the persuasive power of your speech by showing confidence in the points you make.
Once you have collected all sources, review them carefully and separate the most pertinent information from the less useful material.
Synthesising this information into concise yet impactful points is a critical part in delivering powerful talks without overloading your audience with too much data or going off track during your speech delivery.
Organizing Your Speech
Before you start putting your words together, it’s important to consider how the different parts of a speech fit together. By taking the time to organize the ideas in your speech , you’ll be able to deliver a presentation that is well-constructed and easy to understand.
One way to help with organizing your speech is to write an outline . An outline is like a map or plan that will provide you with a framework for each section of your speech.
Start by writing out your main points and then include additional details underneath each one. This will help keep your speech focused and provide direction for where you are going next.
Another approach for organizing your speech is known as the “inverted pyramid” method. This structure starts with your conclusion at the beginning of the speech, and then works backward by providing more explanation and detail as it moves toward the introduction.
This method can be helpful when speaking about topics that are unfamiliar to the audience since it doesn’t require them to wait until near the end of the presentation to learn what you’ve been talking about.
No matter which organization approach you choose, make sure to practice it before giving your speech so that you are comfortable with its flow. Lastly, remember that it’s ok to adjust things while you speak if they don’t seem or feel quite right.
Now let’s take a look at how we can use these organizing techniques to actually put our speeches together – starting with structuring our speech.
Structure Your Speech
Creating a strong structure for your speech will ensure that the audience stays engaged and understands your main points. As you are developing an outline, map out how you want to begin and end your speech.
Break up the information into smaller sections with either verbal or visual cues so that your audience can clearly see how you are transitioning between topics . Consider adding humor judiciously throughout your presentation as this could help engage the audience and lighten any tension.
The length of your presentation is also important. You will want to make sure that you include all of the necessary information without going over time.
Oftentimes less is more; if you can say it in five minutes why use ten? Make sure that you practice timed rehearsals so that you can gauge how long you’re actually speaking.
In contrast, avoid trying to pack too much content into one presentation as this could overwhelm both you and the audience. If needed, offer supplemental reading materials for those who may be interested in delving further into the subject matter.
Paragraphs can also be helpful when organizing large amounts of content within the body of your presentation. Utilizing paragraph breaks gives your audience a break and helps to highlight key ideas or summaries before moving onto a new topic area.
Finally, it is crucial to remember what your desired outcome is from the presentation; plan accordingly by ensuring that the beginning, middle, and end serve their respective purposes and adhere to that goal.
With careful deliberations, structuring a successful presentation can be achieved with relative ease.
Having established a solid structure for your speech, it’s important to focus on another key element: rehearsal. The next section will discuss the benefits of practicing before delivering a powerful public speaking performance.
Rehearse Your Speech
Rehearsing is integral to giving a successful speech. When you rehearse your presentation, you give your mind an opportunity to become familiar with the notes and concepts that you are presenting. It also increases your confidence and reduces anxiety or self-doubt.
In fact, studies have found that those who rehearsed their presentation had higher scores in public speaking performance and language proficiency evaluations.
When it comes to how much rehearsal is enough, opinions are divided. Some people believe that over-rehearsing can lead to a more robotic speech with less natural emotion and connection with the audience .
On the other hand, others argue that no matter how well-versed someone is on the topic, additional rehearsal time improves both the delivery of the speech and memorization of key points and facts.
Ultimately, it’s important to practice until you personally find the most comfortable level for yourself, as this will ultimately result in a more engaging delivery.
Finally, if at all possible, try to practice in front of a friend or colleague for honest feedback on any elements that need improvement before the big day. Rehearsal dedication may be tedious, but it results in big rewards on stage–enabling you to deliver your content with clarity, confidence, and poise.
With thoughtful preparation complete, it’s now time to step into the spotlight and give your speech!
Giving Your Speech
The key to success when giving a speech is to be well prepared and confident. Every individual’s preparation process will vary, but the basics should stay the same.
Start by studying your content, understanding the material and being able to repeat it in your own words. Clarify any potentially difficult points. Create visual aids like PowerPoint slides or handouts that supplement the key ideas in your speech.
Practice your public speaking skills with informal conversations with friends and family or rehearse it alone in front of a mirror. Use visualization; imagine yourself confidently delivering your speech. Consider addressing a practice audience if possible to become more accustomed to a live size group.
On the day of the event, arrive early and plan for any potential obstacles: What if my computer doesn’t work? What if I forget something? Allow sufficient time for setup and check-in.
When you are ready to give your speech, take some deep breaths, focus on the positives, and distract yourself from any anxious thoughts with positive affirmations. Remember you have prepared diligently for this moment, you are well prepared and you will succeed!
Start strong by engaging the audience immediately with an attention grabbing opening statement. Speak clearly and make sure that everyone can hear and understand your message.
Slow down and emphasize points as needed throughout your presentation. Be aware of pace, volume, and tone of voice: too fast/monotone can confuse/bore listeners while pauses add a dramatic effect that keeps their interest piqued.
Ultimately, giving a successful speech will depend on knowing your material well enough to speak confidently in front of your audience without hesitation or missteps.
When you do make a mistake (and they happen!) don’t panic – know that mistakes are inevitable but don’t be discouraged; get back on track as soon as possible and continue at the same energy level you had before the mistake occurred.
Having successfully given your speech, take a moment to reflect on what went well and what could be improved upon for next time before transitioning into the next step: mastering delivery.
Master Your Delivery
Mastering your delivery is the key to an effective speech. Without purposeful body language and careful emphasis on certain words , your speech may lack wow-factor and prevent listeners from tuning in. Following these simple tips can help you get started with delivering an engaging and memorable speech:
The most important part of delivery is practice. Rehearse and perfect your speech ahead of time – this allows for more natural flow and confidence during your presentation. It also helps to create pauses between sentences for clarity, emphasize key points, and not be too casual or stiff.
Practicing inflections and varying tones adds interest to your speech by keeping listeners’ attention.
Additionally, it’s important to project your voic e so everyone in the room can hear you; make sure you’re speaking loud enough but don’t feel pressure to shout or yell at any point unless that’s part of the atmosphere of the event.
It’s also crucial to maintain good posture while speaking – stand tall with both feet on the ground, keep your back straight, hold yourself up without gesturing too much or leaning against a podium if applicable.
To further engage listeners, use purposeful hand gestures as they help emphasize certain points and add visual interest – however, avoid overusing them as it can hinders communication.
Make meaningful eye contact with audience members throughout the presentation – otherwise you might come across as unenthusiastic or bored with what you’re saying which deters attention away from the content itself.
By mastering your delivery, you can boost the impact of your presentation considerably – providing a memorable experience for your audience that stands out from others’. As such, it’s worth investing time into practicing ahead of time until delivery feels comfortable and second nature.
Having said this, making use of visual aids such as PowerPoint slides can greatly improve the impact of a speech once delivery has been mastered – let’s look into that next.
Use Visual Aids
Using visual aids can help presenters express concepts more clearly and engage the audience.
Visuals are particularly useful when conveying complex information, such as data, trends, or statistics — they impart meaning at a glance. But some public speakers may wonder if visual aids can be distracting or unnecessary.
Even though visuals can attract attention away from a presenter’s verbal delivery, carefully designed visuals can actually support the speech and help provide clarity. If done well, visuals are effective for capturing an audience’s interest and helping them to better understand the content being presented.
For example, a graph or chart should relate to the points made in the speech and should be discussed in more detail during its appearance onscreen. The presentation can also include larger images that effectively reinforce the ideas conveyed in the speech.
Videos and sound clips are other powerful forms of multimedia that could be employed to make the speech more meaningful.
To ensure that visuals enhance the message of the presentation, key factors to consider include relevancy to topic, good graphic design or aesthetics, accurate size to prevent distortion or blurriness, and seamless integration into the keynote slides or printed handouts .
In this way, visuals offer an opportunity for presenters to demonstrate their creativity and keep their audiences interested in what is being said. Thus, used wisely and aptly, visuals can add tremendous value to speeches by presenting arguments more efficiently and driving home important points. Now let’s explore effective techniques for speech giving that will allow you to craft and deliver your speeches with confidence.
Effective Techniques for Speech Giving
There are a number of effective techniques for giving a speech that will help you deliver it with confidence and poise.
First, practice your delivery in advance. You should practice both in front of a mirror or recording device to check for any distracting habits such as talking too quickly or mispronouncing words.
Second, use simple, clear language and short, concise sentences. Avoid overly technical terms and jargon that may leave your audience confused.
Third, work to establish a connection with your audience by using appropriate facial expressions and hand gestures while speaking.
Fourth, utilize effective persuasive techniques such as presenting evidence, strong arguments supported by facts, personal anecdotes and vivid metaphors.
Finally, articulate an organized structure for your speech. Your speech should have an introduction, body and conclusion to clearly communicate the main point and provide the audience with the necessary context to understand it better.
While these techniques may sound intimidating at first, they can be learned over time with practice and will make all the difference in how successful your speech delivery is received by your audience.
To build on these skills further , the next section will provide tips on how to build confidence when giving a speech.
Building Confidence
Building confidence is key when giving a powerful speech, as it will enable you to deliver the speech in a more poised and credible manner.
To create this confidence , start by understanding that any hesitation or butterflies prior to your speech are completely normal and should not be feared. Instead, view them as natural states of anticipation for something exciting, knowing that you are about to give an amazing speech.
Next, understanding who your audience is and tailoring your speech to meet their expectations will help build your confidence.
Familiarizing yourself with their interests and knowledge on the subject matter ahead of time can equip you with the understanding needed to respond appropriately if questions arise or objections surface during the speech.
Further, practice is key when building confidence for a public speaking engagement . Rehearsing with friends or colleagues before hand will give you an opportunity to learn where problem areas are within the content of your speech, as well as help solidify your delivery by becoming more comfortable with each step.
Checking sound levels in the room you’re presenting in coupled with learning where exits/emergency locations are located within that space can also help alleviate stress levels and boost self-assurance while delivering the speech.
Finally, wearing comfortable clothing and dressing professionally adds an extra layer of confidence when speaking in public.
If possible, bring an additional outfit on hand during the presentation in case of spills or accidents that would require a quick change between sections of the talk. Having this back-up plan in place can aid in keeping peace of mind at ease throughout the speech.
In conclusion, building confidence prior to a public speaking event can mean the difference between a good and great delivery of your message.
By taking into account each of these tips you can ensure that this part of your preparation runs smoothly and sets you up for success when delivering powerful speeches.
With a well-crafted note card of talking points and strong sense of self-assurance, it’s time to start speaking with passion!
Speaking with Passion
As a public speaker, your audience expects you to engage not only with your words but also with your emotions. To share the most impactful message, it is important to speak passionately about your subject.
Doing so will make your speech more memorable and thereby more effective in convincing your audience of its legitimacy.
The power of speaking authentically with emotion lies in its relatability and connection. Showing feelings allows people to connect with you as a person rather than just a speaker. It opens the door to understanding through empathy and active listening .
Examples might include adding personal stories , telling jokes, or displaying your feelings openly during the delivery of your message.
However, not all topics lend themselves easily to expressing emotion. If the subject matter is overly complex or technical there may be less opportunity for emotional expression—but this doesn’t mean those conversations can’t incorporate emotion.
Even if faced with a difficult situation such as death or financial turmoil, emotions can still be conveyed in a respectful way that keeps audiences engaged.
Remember that how much emotion you show depends on the type of audience you’re sharing it with—using sensitivity when delivering passionate speeches helps avoid awkwardness or embarrassment for any attendees who may find opinionated language uncomfortable for whatever reason.
Striking the right balance between being straightforward and showing compassion takes practice, so take the time to develop a style that works best for you and improves upon each performance.
Finally, incorporating passion into a speech gives it life and makes it relatable and engaging—which are essential elements to speaking effectively.
Having passion means giving ourselves permission to take ownership over our stories, making them deeply personal in order to reach our goals and touch people’s hearts in meaningful ways. With that said, let’s move on to discussing how we should tackle dealing with challenges while giving a speech.
Dealing with Challenges
The process of delivering a speech can be challenging, but it is also rewarding. Difficulties can arise during the process that may threaten to derail your success. To ensure you are adequately prepared for these possible pitfalls it is important to consider strategies for proactively mitigating the risk of encountering these challenges. 1. Public Speaking Anxiety: Many people experience some form of anxiety when asked to speak in public. There are a number of techniques available to combat this fear and increase confidence, such as deep breathing exercises, mental rehearsal, positive self-talk and visualization of success.
Learning about the audience, creating an engaging presentation and using props or visual aids can also help reduce anxiety levels and create a better overall experience for both the speaker and the audience. 2. Unfamiliar Topics or Audiences: When presenting on unfamiliar topics or to an unknown audience it can be difficult to prepare effectively.
In this situation it is important to conduct research on the topic and familiarize yourself with the needs of your audience so that the content is tailored accordingly. It is also helpful to use humor or stories related to the topic in order to engage your audience and make them more receptive to your message. 3. Lack of Support: If you lack support from family, friends, colleagues or mentors, it can be difficult to push through difficult conversations or speeches without any additional motivation.
To overcome this challenge, seek out peer mentorship opportunities or find compatible online communities where people discuss similar topics or objectives. Here you can share ideas, provide feedback and learn from others who have experienced similar issues. 4. Time Constraints: One of the biggest challenges when giving a speech is managing your time effectively in order to deliver an effective message without going over allotted timeslots and boring your audience .
To successfully address this challenge try setting manageable goals for each section of your speech and practice regularly. Replicating real-time conditions as closely as possible will help you stay within time constraints when delivering your speech on the day itself. In conclusion, there are many potential challenges you may face when giving a speech or taking part in a public speaking event – but with proper preparation and practice they are easily managed if approached correctly.
With knowledge of techniques for dealing with such scenarios comes increased confidence when stepping up to the podium – further improving your chances of delivering an effective speech that resonates with your audience members.
Responses to Frequently Asked Questions
How should i end my speech to leave a lasting impression.
The best way to end your speech is by reinforcing your main point and summarizing the key takeaways. You should also encourage the audience to take action, whether it be to sign up for a newsletter, make a donation, or visit your website for more information. This final call to action will not only leave a lasting impression on the audience but will also help you achieve any goals you might have had when making your speech in the first place.
What techniques can I use to keep my audience engaged during my speech?
One of the best techniques for keeping an audience engaged during a speech is to keep it interactive . Ask questions throughout the presentation, as well as allowing for audience input and discussion. This can help to keep people’s attention and create a more engaging experience.
Another great tip is to use humor. Even if you don’t consider yourself a natural comedian, sprinkling in a few jokes here and there can break up the monotony of long speeches and keep people interested. Humor can also help to make points stick in people’s minds, making them easier to remember.
Finally, try to be enthusiastic about the content of your speech. If you show too much indifference or lethargic behavior, it will discourage your audience from paying attention and taking your message seriously.
Instead, be passionate about what you are saying so that the energy of your words carries into the room and engages your audience with excitement.
How can I use storytelling to make my speech more interesting?
Storytelling is a powerful tool that can be used to make any speech more interesting. Telling stories in your speech will help engage the audience and make your message stick. Here are some tips for using storytelling in your speech:
1. Choose stories that are relevant to your message and audience. Think about stories that will best illustrate the point you are trying to convey, or evoke emotions in your listeners. 2. Use vivid descriptions and visuals when telling your story. Be sure to include details such as setting, character descriptions, dialogue and plot points. This will help to bring the story to life for your audience. 3. Make sure the story you are telling has a strong conclusion or moral at the end. This will help add emphasis to your message and make it memorable. 4. Practice telling stories out loud before delivering a speech with them. Rehearsing will help you deliver your story more effectively and with more confidence in front of an audience. By using these tips, storytelling can be an effective tool to make any speech more interesting, engaging, and persuasive!
How can I prepare for my speech effectively?
Preparing for a speech effectively is essential to delivering an impactful and memorable presentation. Here are some tips: 1. Have a clear goal in mind. Before starting to prepare, ask yourself what the purpose of giving the speech is: what message do you want to convey? Defining this will help to structure your content and focus your research. 2. Research thoroughly. Make sure you understand the subject matter well, so that your delivery sounds confident and inspiring. Using facts and data will strengthen your arguments and make your talk more convincing. 3. Outline your speech. Make a rough outline of how you want it to go – from beginning to end – well in advance of the actual presentation. This will give you a strong foundation upon which you can craft an engaging talk with an effective narrative arc that keeps audiences interested and engaged. 4. Practice regularly. Rehearsing your speech out loud several times is key to ensuring that you know it well enough to feel comfortable when delivering it live in front of an audience.
5. Time yourself. Record how long it takes for you to go through your entire speech, so that you can adjust the length as needed before delivering it live – remember that most speeches should last no more than 10-15 minutes. 6. Identify potential questions from the audience and prepare answers before hand. Knowing ahead of time what kind of questions people may ask can help reduce the anxiety of not knowing what comes next, enabling you to stay confident when speaking in public. 7. Work on building up confidence levels before delivering a speech. Visualize yourself succeeding in delivering a great presentation; practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or positive self-talk; or use props during practice sessions such as water bottles or stress balls if needed to remain calm during the real thing!
What strategies can I use to reduce my anxiety when giving a speech?
1. Plan Ahead: Create an outline of your speech beforehand and practice it multiple times to become familiar with the content. Doing a trial run with the audience can also help you get used to speaking in front of people.
2. Visualize Success: Positive visualization is a great way to reduce anxiety before giving a speech. Imagine yourself confidently delivering the speech while feeling relaxed and composed.
3. Get Organized: Make sure you have all the materials necessary for your presentation, including notes, slides, etc., to reduce any additional stress that may come from not having what you need when you speak.
4. Take Deep Breaths: Before and during the speech, take a few deep breaths as this will help calm nerves and make sure your breathing is regulated throughout the duration of your presentation.
5. Speak Slowly: It is common to feel anxious while giving a speech and try to rush through it too quickly. Speaking slowly helps maintain composure while delivering your message effectively and clearly.
6. Pay Attention to Your Body: Your posture, stance, movements , facial expressions can all influence how confident you appear to your audience and how nervous you may be feeling inside. Check in with yourself frequently throughout the presentation and correct any tense body language or physical actions if needed.
7. Focus on the Audience: If you notice that your anxiety levels are growing as you present, shift your focus onto the audience instead of yourself as this will help refocus your attention away from negative thoughts that may arise from fear or insecurity.
8. Make Eye Contact: Establishing eye contact with your audience is a key confidence-builder for public speakers—it shows that you’re strong, engaged with them, and receptive to feedback or questions they might have regarding your speech topic .
9. Practice Positive Affirmations: Positive thoughts will boost your self-confidence as well as your mood which can help increase performance quality significantly during speeches or presentations in general—so don’t forget to tell yourself “you can do it!” several times throughout the day leading up to the event!
10. Seek Support of Friends & Family: Many experienced public speakers suggest seeking support of close friends & family members prior and during their speeches—not only does it allow helpful critique regarding content but it also creates a more comfortable atmosphere while speaking which can reduce pre-speech jitters drastically.
10 Tips for Improving Your Public Speaking Skills
Few are immune to the fear of public speaking. Marjorie North offers 10 tips for speakers to calm the nerves and deliverable memorable orations.
Marjorie North
Snakes? Fine. Flying? No problem. Public speaking? Yikes! Just thinking about public speaking — routinely described as one of the greatest (and most common) fears — can make your palms sweat. But there are many ways to tackle this anxiety and learn to deliver a memorable speech.
In part one of this series, Mastering the Basics of Communication , I shared strategies to improve how you communicate. In part two, How to Communicate More Effectively in the Workplace , I examined how to apply these techniques as you interact with colleagues and supervisors in the workplace. For the third and final part of this series, I’m providing you with public speaking tips that will help reduce your anxiety, dispel myths, and improve your performance.
Here Are My 10 Tips for Public Speaking:
1. nervousness is normal. practice and prepare.
All people feel some physiological reactions like pounding hearts and trembling hands. Do not associate these feelings with the sense that you will perform poorly or make a fool of yourself. Some nerves are good. The adrenaline rush that makes you sweat also makes you more alert and ready to give your best performance.
The best way to overcome anxiety is to prepare, prepare, and prepare some more. Take the time to go over your notes several times. Once you have become comfortable with the material, practice — a lot. Videotape yourself, or get a friend to critique your performance.
Communication Strategies: Presenting with Impact
Search all Communication programs.
2. Know Your Audience. Your Speech Is About Them, Not You.
Before you begin to craft your message, consider who the message is intended for. Learn as much about your listeners as you can. This will help you determine your choice of words, level of information, organization pattern, and motivational statement.
3. Organize Your Material in the Most Effective Manner to Attain Your Purpose.
Create the framework for your speech. Write down the topic, general purpose, specific purpose, central idea, and main points. Make sure to grab the audience’s attention in the first 30 seconds.
4. Watch for Feedback and Adapt to It.
Keep the focus on the audience. Gauge their reactions, adjust your message, and stay flexible. Delivering a canned speech will guarantee that you lose the attention of or confuse even the most devoted listeners.
5. Let Your Personality Come Through.
Be yourself, don’t become a talking head — in any type of communication. You will establish better credibility if your personality shines through, and your audience will trust what you have to say if they can see you as a real person.
6. Use Humor, Tell Stories, and Use Effective Language.
Inject a funny anecdote in your presentation, and you will certainly grab your audience’s attention. Audiences generally like a personal touch in a speech. A story can provide that.
7. Don’t Read Unless You Have to. Work from an Outline.
Reading from a script or slide fractures the interpersonal connection. By maintaining eye contact with the audience, you keep the focus on yourself and your message. A brief outline can serve to jog your memory and keep you on task.
8. Use Your Voice and Hands Effectively. Omit Nervous Gestures.
Nonverbal communication carries most of the message. Good delivery does not call attention to itself, but instead conveys the speaker’s ideas clearly and without distraction.
9. Grab Attention at the Beginning, and Close with a Dynamic End.
Do you enjoy hearing a speech start with “Today I’m going to talk to you about X”? Most people don’t. Instead, use a startling statistic, an interesting anecdote, or concise quotation. Conclude your speech with a summary and a strong statement that your audience is sure to remember.
10. Use Audiovisual Aids Wisely.
Too many can break the direct connection to the audience, so use them sparingly. They should enhance or clarify your content, or capture and maintain your audience’s attention.
Practice Does Not Make Perfect
Good communication is never perfect, and nobody expects you to be perfect. However, putting in the requisite time to prepare will help you deliver a better speech. You may not be able to shake your nerves entirely, but you can learn to minimize them.
Find related Communication programs.
Browse all Professional & Executive Development programs.
About the Author
North is a consultant for political candidates, physicians, and lawyers, and runs a private practice specializing in public speaking, and executive communication skills. Previously, she was the clinical director in the department of speech and language pathology and audiology at Northeastern University.
Why Gender Equity in the Workplace is Good for Business
Research indicates a correlation between gender equity and organizational success, yet it also points to obstacles for women in leadership.
Harvard Division of Continuing Education
The Division of Continuing Education (DCE) at Harvard University is dedicated to bringing rigorous academics and innovative teaching capabilities to those seeking to improve their lives through education. We make Harvard education accessible to lifelong learners from high school to retirement.


How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
A demo is the first step to transforming your business. Meet with us to develop a plan for attaining your goals.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals
How to write a speech that your audience remembers

Whether in a work meeting or at an investor panel, you might give a speech at some point. And no matter how excited you are about the opportunity, the experience can be nerve-wracking .
But feeling butterflies doesn’t mean you can’t give a great speech. With the proper preparation and a clear outline, apprehensive public speakers and natural wordsmiths alike can write and present a compelling message. Here’s how to write a good speech you’ll be proud to deliver.
What is good speech writing?
Good speech writing is the art of crafting words and ideas into a compelling, coherent, and memorable message that resonates with the audience. Here are some key elements of great speech writing:
- It begins with clearly understanding the speech's purpose and the audience it seeks to engage.
- A well-written speech clearly conveys its central message, ensuring that the audience understands and retains the key points.
- It is structured thoughtfully, with a captivating opening, a well-organized body, and a conclusion that reinforces the main message.
- Good speech writing embraces the power of engaging content, weaving in stories, examples, and relatable anecdotes to connect with the audience on both intellectual and emotional levels.
Ultimately, it is the combination of these elements, along with the authenticity and delivery of the speaker , that transforms words on a page into a powerful and impactful spoken narrative.
What makes a good speech?
A great speech includes several key qualities, but three fundamental elements make a speech truly effective:
Clarity and purpose
Remembering the audience, cohesive structure.
While other important factors make a speech a home run, these three elements are essential for writing an effective speech.
The main elements of a good speech
The main elements of a speech typically include:
- Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your speech and grabs the audience's attention. It should include a hook or attention-grabbing opening, introduce the topic, and provide an overview of what will be covered.
- Opening/captivating statement: This is a strong statement that immediately engages the audience and creates curiosity about the speech topics.
- Thesis statement/central idea: The thesis statement or central idea is a concise statement that summarizes the main point or argument of your speech. It serves as a roadmap for the audience to understand what your speech is about.
- Body: The body of the speech is where you elaborate on your main points or arguments. Each point is typically supported by evidence, examples, statistics, or anecdotes. The body should be organized logically and coherently, with smooth transitions between the main points.
- Supporting evidence: This includes facts, data, research findings, expert opinions, or personal stories that support and strengthen your main points. Well-chosen and credible evidence enhances the persuasive power of your speech.
- Transitions: Transitions are phrases or statements that connect different parts of your speech, guiding the audience from one idea to the next. Effective transitions signal the shifts in topics or ideas and help maintain a smooth flow throughout the speech.
- Counterarguments and rebuttals (if applicable): If your speech involves addressing opposing viewpoints or counterarguments, you should acknowledge and address them. Presenting counterarguments makes your speech more persuasive and demonstrates critical thinking.
- Conclusion: The conclusion is the final part of your speech and should bring your message to a satisfying close. Summarize your main points, restate your thesis statement, and leave the audience with a memorable closing thought or call to action.
- Closing statement: This is the final statement that leaves a lasting impression and reinforces the main message of your speech. It can be a call to action, a thought-provoking question, a powerful quote, or a memorable anecdote.
- Delivery and presentation: How you deliver your speech is also an essential element to consider. Pay attention to your tone, body language, eye contact , voice modulation, and timing. Practice and rehearse your speech, and try using the 7-38-55 rule to ensure confident and effective delivery.
While the order and emphasis of these elements may vary depending on the type of speech and audience, these elements provide a framework for organizing and delivering a successful speech.

How to structure a good speech
You know what message you want to transmit, who you’re delivering it to, and even how you want to say it. But you need to know how to start, develop, and close a speech before writing it.
Think of a speech like an essay. It should have an introduction, conclusion, and body sections in between. This places ideas in a logical order that the audience can better understand and follow them. Learning how to make a speech with an outline gives your storytelling the scaffolding it needs to get its point across.
Here’s a general speech structure to guide your writing process:
- Explanation 1
- Explanation 2
- Explanation 3
How to write a compelling speech opener
Some research shows that engaged audiences pay attention for only 15 to 20 minutes at a time. Other estimates are even lower, citing that people stop listening intently in fewer than 10 minutes . If you make a good first impression at the beginning of your speech, you have a better chance of interesting your audience through the middle when attention spans fade.
Implementing the INTRO model can help grab and keep your audience’s attention as soon as you start speaking. This acronym stands for interest, need, timing, roadmap, and objectives, and it represents the key points you should hit in an opening.
Here’s what to include for each of these points:
- Interest : Introduce yourself or your topic concisely and speak with confidence . Write a compelling opening statement using relevant data or an anecdote that the audience can relate to.
- Needs : The audience is listening to you because they have something to learn. If you’re pitching a new app idea to a panel of investors, those potential partners want to discover more about your product and what they can earn from it. Read the room and gently remind them of the purpose of your speech.
- Timing : When appropriate, let your audience know how long you’ll speak. This lets listeners set expectations and keep tabs on their own attention span. If a weary audience member knows you’ll talk for 40 minutes, they can better manage their energy as that time goes on.
- Routemap : Give a brief overview of the three main points you’ll cover in your speech. If an audience member’s attention starts to drop off and they miss a few sentences, they can more easily get their bearings if they know the general outline of the presentation.
- Objectives : Tell the audience what you hope to achieve, encouraging them to listen to the end for the payout.
Writing the middle of a speech
The body of your speech is the most information-dense section. Facts, visual aids, PowerPoints — all this information meets an audience with a waning attention span. Sticking to the speech structure gives your message focus and keeps you from going off track, making everything you say as useful as possible.
Limit the middle of your speech to three points, and support them with no more than three explanations. Following this model organizes your thoughts and prevents you from offering more information than the audience can retain.
Using this section of the speech to make your presentation interactive can add interest and engage your audience. Try including a video or demonstration to break the monotony. A quick poll or survey also keeps the audience on their toes.
Wrapping the speech up
To you, restating your points at the end can feel repetitive and dull. You’ve practiced countless times and heard it all before. But repetition aids memory and learning , helping your audience retain what you’ve told them. Use your speech’s conclusion to summarize the main points with a few short sentences.
Try to end on a memorable note, like posing a motivational quote or a thoughtful question the audience can contemplate once they leave. In proposal or pitch-style speeches, consider landing on a call to action (CTA) that invites your audience to take the next step.

How to write a good speech
If public speaking gives you the jitters, you’re not alone. Roughly 80% of the population feels nervous before giving a speech, and another 10% percent experiences intense anxiety and sometimes even panic.
The fear of failure can cause procrastination and can cause you to put off your speechwriting process until the last minute. Finding the right words takes time and preparation, and if you’re already feeling nervous, starting from a blank page might seem even harder.
But putting in the effort despite your stress is worth it. Presenting a speech you worked hard on fosters authenticity and connects you to the subject matter, which can help your audience understand your points better. Human connection is all about honesty and vulnerability, and if you want to connect to the people you’re speaking to, they should see that in you.
1. Identify your objectives and target audience
Before diving into the writing process, find healthy coping strategies to help you stop worrying . Then you can define your speech’s purpose, think about your target audience, and start identifying your objectives. Here are some questions to ask yourself and ground your thinking :
- What purpose do I want my speech to achieve?
- What would it mean to me if I achieved the speech’s purpose?
- What audience am I writing for?
- What do I know about my audience?
- What values do I want to transmit?
- If the audience remembers one take-home message, what should it be?
- What do I want my audience to feel, think, or do after I finish speaking?
- What parts of my message could be confusing and require further explanation?
2. Know your audience
Understanding your audience is crucial for tailoring your speech effectively. Consider the demographics of your audience, their interests, and their expectations. For instance, if you're addressing a group of healthcare professionals, you'll want to use medical terminology and data that resonate with them. Conversely, if your audience is a group of young students, you'd adjust your content to be more relatable to their experiences and interests.
3. Choose a clear message
Your message should be the central idea that you want your audience to take away from your speech. Let's say you're giving a speech on climate change. Your clear message might be something like, "Individual actions can make a significant impact on mitigating climate change." Throughout your speech, all your points and examples should support this central message, reinforcing it for your audience.
4. Structure your speech
Organizing your speech properly keeps your audience engaged and helps them follow your ideas. The introduction should grab your audience's attention and introduce the topic. For example, if you're discussing space exploration, you could start with a fascinating fact about a recent space mission. In the body, you'd present your main points logically, such as the history of space exploration, its scientific significance, and future prospects. Finally, in the conclusion, you'd summarize your key points and reiterate the importance of space exploration in advancing human knowledge.
5. Use engaging content for clarity
Engaging content includes stories, anecdotes, statistics, and examples that illustrate your main points. For instance, if you're giving a speech about the importance of reading, you might share a personal story about how a particular book changed your perspective. You could also include statistics on the benefits of reading, such as improved cognitive abilities and empathy.
6. Maintain clarity and simplicity
It's essential to communicate your ideas clearly. Avoid using overly technical jargon or complex language that might confuse your audience. For example, if you're discussing a medical breakthrough with a non-medical audience, explain complex terms in simple, understandable language.
7. Practice and rehearse
Practice is key to delivering a great speech. Rehearse multiple times to refine your delivery, timing, and tone. Consider using a mirror or recording yourself to observe your body language and gestures. For instance, if you're giving a motivational speech, practice your gestures and expressions to convey enthusiasm and confidence.
8. Consider nonverbal communication
Your body language, tone of voice, and gestures should align with your message . If you're delivering a speech on leadership, maintain strong eye contact to convey authority and connection with your audience. A steady pace and varied tone can also enhance your speech's impact.
9. Engage your audience
Engaging your audience keeps them interested and attentive. Encourage interaction by asking thought-provoking questions or sharing relatable anecdotes. If you're giving a speech on teamwork, ask the audience to recall a time when teamwork led to a successful outcome, fostering engagement and connection.
10. Prepare for Q&A
Anticipate potential questions or objections your audience might have and prepare concise, well-informed responses. If you're delivering a speech on a controversial topic, such as healthcare reform, be ready to address common concerns, like the impact on healthcare costs or access to services, during the Q&A session.
By following these steps and incorporating examples that align with your specific speech topic and purpose, you can craft and deliver a compelling and impactful speech that resonates with your audience.

Tools for writing a great speech
There are several helpful tools available for speechwriting, both technological and communication-related. Here are a few examples:
- Word processing software: Tools like Microsoft Word, Google Docs, or other word processors provide a user-friendly environment for writing and editing speeches. They offer features like spell-checking, grammar correction, formatting options, and easy revision tracking.
- Presentation software: Software such as Microsoft PowerPoint or Google Slides is useful when creating visual aids to accompany your speech. These tools allow you to create engaging slideshows with text, images, charts, and videos to enhance your presentation.
- Speechwriting Templates: Online platforms or software offer pre-designed templates specifically for speechwriting. These templates provide guidance on structuring your speech and may include prompts for different sections like introductions, main points, and conclusions.
- Rhetorical devices and figures of speech: Rhetorical tools such as metaphors, similes, alliteration, and parallelism can add impact and persuasion to your speech. Resources like books, websites, or academic papers detailing various rhetorical devices can help you incorporate them effectively.
- Speechwriting apps: Mobile apps designed specifically for speechwriting can be helpful in organizing your thoughts, creating outlines, and composing a speech. These apps often provide features like voice recording, note-taking, and virtual prompts to keep you on track.
- Grammar and style checkers: Online tools or plugins like Grammarly or Hemingway Editor help improve the clarity and readability of your speech by checking for grammar, spelling, and style errors. They provide suggestions for sentence structure, word choice, and overall tone.
- Thesaurus and dictionary: Online or offline resources such as thesauruses and dictionaries help expand your vocabulary and find alternative words or phrases to express your ideas more effectively. They can also clarify meanings or provide context for unfamiliar terms.
- Online speechwriting communities: Joining online forums or communities focused on speechwriting can be beneficial for getting feedback, sharing ideas, and learning from experienced speechwriters. It's an opportunity to connect with like-minded individuals and improve your public speaking skills through collaboration.
Remember, while these tools can assist in the speechwriting process, it's essential to use them thoughtfully and adapt them to your specific needs and style. The most important aspect of speechwriting remains the creativity, authenticity, and connection with your audience that you bring to your speech.

5 tips for writing a speech
Behind every great speech is an excellent idea and a speaker who refined it. But a successful speech is about more than the initial words on the page, and there are a few more things you can do to help it land.
Here are five more tips for writing and practicing your speech:
1. Structure first, write second
If you start the writing process before organizing your thoughts, you may have to re-order, cut, and scrap the sentences you worked hard on. Save yourself some time by using a speech structure, like the one above, to order your talking points first. This can also help you identify unclear points or moments that disrupt your flow.
2. Do your homework
Data strengthens your argument with a scientific edge. Research your topic with an eye for attention-grabbing statistics, or look for findings you can use to support each point. If you’re pitching a product or service, pull information from company metrics that demonstrate past or potential successes.
Audience members will likely have questions, so learn all talking points inside and out. If you tell investors that your product will provide 12% returns, for example, come prepared with projections that support that statement.
3. Sound like yourself
Memorable speakers have distinct voices. Think of Martin Luther King Jr’s urgent, inspiring timbre or Oprah’s empathetic, personal tone . Establish your voice — one that aligns with your personality and values — and stick with it. If you’re a motivational speaker, keep your tone upbeat to inspire your audience . If you’re the CEO of a startup, try sounding assured but approachable.
4. Practice
As you practice a speech, you become more confident , gain a better handle on the material, and learn the outline so well that unexpected questions are less likely to trip you up. Practice in front of a colleague or friend for honest feedback about what you could change, and speak in front of the mirror to tweak your nonverbal communication and body language .
5. Remember to breathe
When you’re stressed, you breathe more rapidly . It can be challenging to talk normally when you can’t regulate your breath. Before your presentation, try some mindful breathing exercises so that when the day comes, you already have strategies that will calm you down and remain present . This can also help you control your voice and avoid speaking too quickly.
How to ghostwrite a great speech for someone else
Ghostwriting a speech requires a unique set of skills, as you're essentially writing a piece that will be delivered by someone else. Here are some tips on how to effectively ghostwrite a speech:
- Understand the speaker's voice and style : Begin by thoroughly understanding the speaker's personality, speaking style, and preferences. This includes their tone, humor, and any personal anecdotes they may want to include.
- Interview the speaker : Have a detailed conversation with the speaker to gather information about their speech's purpose, target audience, key messages, and any specific points they want to emphasize. Ask for personal stories or examples they may want to include.
- Research thoroughly : Research the topic to ensure you have a strong foundation of knowledge. This helps you craft a well-informed and credible speech.
- Create an outline : Develop a clear outline that includes the introduction, main points, supporting evidence, and a conclusion. Share this outline with the speaker for their input and approval.
- Write in the speaker's voice : While crafting the speech, maintain the speaker's voice and style. Use language and phrasing that feel natural to them. If they have a particular way of expressing ideas, incorporate that into the speech.
- Craft a captivating opening : Begin the speech with a compelling opening that grabs the audience's attention. This could be a relevant quote, an interesting fact, a personal anecdote, or a thought-provoking question.
- Organize content logically : Ensure the speech flows logically, with each point building on the previous one. Use transitions to guide the audience from one idea to the next smoothly.
- Incorporate engaging stories and examples : Include anecdotes, stories, and real-life examples that illustrate key points and make the speech relatable and memorable.
- Edit and revise : Edit the speech carefully for clarity, grammar, and coherence. Ensure the speech is the right length and aligns with the speaker's time constraints.
- Seek feedback : Share drafts of the speech with the speaker for their feedback and revisions. They may have specific changes or additions they'd like to make.
- Practice delivery : If possible, work with the speaker on their delivery. Practice the speech together, allowing the speaker to become familiar with the content and your writing style.
- Maintain confidentiality : As a ghostwriter, it's essential to respect the confidentiality and anonymity of the work. Do not disclose that you wrote the speech unless you have the speaker's permission to do so.
- Be flexible : Be open to making changes and revisions as per the speaker's preferences. Your goal is to make them look good and effectively convey their message.
- Meet deadlines : Stick to agreed-upon deadlines for drafts and revisions. Punctuality and reliability are essential in ghostwriting.
- Provide support : Support the speaker during their preparation and rehearsal process. This can include helping with cue cards, speech notes, or any other materials they need.
Remember that successful ghostwriting is about capturing the essence of the speaker while delivering a well-structured and engaging speech. Collaboration, communication, and adaptability are key to achieving this.
Give your best speech yet
Learn how to make a speech that’ll hold an audience’s attention by structuring your thoughts and practicing frequently. Put the effort into writing and preparing your content, and aim to improve your breathing, eye contact , and body language as you practice. The more you work on your speech, the more confident you’ll become.
The energy you invest in writing an effective speech will help your audience remember and connect to every concept. Remember: some life-changing philosophies have come from good speeches, so give your words a chance to resonate with others. You might even change their thinking.
Boost your speech skills
Enhance your public speaking with personalized coaching tailored to your needs
Elizabeth Perry, ACC
Elizabeth Perry is a Coach Community Manager at BetterUp. She uses strategic engagement strategies to cultivate a learning community across a global network of Coaches through in-person and virtual experiences, technology-enabled platforms, and strategic coaching industry partnerships. With over 3 years of coaching experience and a certification in transformative leadership and life coaching from Sofia University, Elizabeth leverages transpersonal psychology expertise to help coaches and clients gain awareness of their behavioral and thought patterns, discover their purpose and passions, and elevate their potential. She is a lifelong student of psychology, personal growth, and human potential as well as an ICF-certified ACC transpersonal life and leadership Coach.
How to write an impactful cover letter for a career change
6 presentation skills and how to improve them, how to be more persuasive: 6 tips for convincing others, the 11 tips that will improve your public speaking skills, what is a career statement, and should you write one, asking for a raise: tips to get what you’re worth, self-management skills for a messy world, a guide on how to find the right mentor for your career, want a leg up in your career master these 11 key listening skills, similar articles, how to write an executive summary in 10 steps, 18 effective strategies to improve your communication skills, how to pitch ideas: 8 tips to captivate any audience, your guide to what storytelling is and how to be a good storyteller, how to give a good presentation that captivates any audience, writing an elevator pitch about yourself: a how-to plus tips, how to make a presentation interactive and exciting, how to write a memo: 8 steps with examples, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead™
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care®
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Life Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences

Speech Delivery Tactics To Win Your Audience And Make Your Point

Speech delivery is how you present what you have to say in your speech. There are four main kinds of speech delivery: impromptu, extemporaneous, manuscript, and memorized. What also counts in any speech delivery is how you use your voice and how you present yourself.
No matter what you have to say to an audience, the way you say it is what drives the point home. Speech delivery is the compounded effect of verbal and non-verbal messaging.
The words you share are the core of your speech, but body language, facial expressions, and tone of voice are what listeners often relate to.
Table of Contents
What Are The 4 Types Of Speech Delivery?
How you deliver your speech depends on the circumstances surrounding the speech.
1. Impromptu Speech Delivery:
Impromptu speaking is done without planning and often without notice. You might be asked to say a few words on a topic at a meeting or upon accepting an award you weren’t expecting to win. When in a new group, the leader might call upon you to introduce yourself as part of an icebreaker exercise.
For an impromptu speech, you are unlikely to have visual aids on hand to accompany the words, but you can still be poised and confident, use eye contact, and accent your words with meaningful gestures.
If you are in the public eye, you might expect to be interviewed on the spot at any time. You should have some pre-planned responses to questions about policy so you get your message across even in impromptu opportunities.

2. Extemporaneous Speaking Delivery:
An extemporaneous speech is well-planned but not memorized and given from notes. You follow the note cards as you cover the main points, but the specific lines are ad-libbed.
Speaking extemporaneously from note cards allows you to maintain better eye contact, add anecdotal stories, and be flexible with the presentation.

3. Manuscript Speech Delivery:
If a speech needs to be delivered in very measured and precise terms, manuscript speaking might be the perfect solution. The s peaker reads a manuscript speech from paper or a teleprompter . Having the words written down so they can be read word-for-word ensures it is done accurately when a precise message matters.
Speeches such as the President’s State of the Union are manuscript speeches. To make them flow correctly and not sound like the speaker is reading disconnected words, they should be formatted for easy reading.

4. Memorized Speech Delivery:
Sometimes there are situations where a person needs or wants to memorize a speech, just like actors do. Speeches at weddings or funeral eulogies are examples of times when the message should be given from memory.
Without looking down at notes or a paper, people sometimes try so hard to remember their words that they fail to connect with the audience. They don’t maintain eye contact or use voice inflection or vocal variety, and their speech can sound monotone.

Is there a preferred type of delivery? The type of speech delivery depends on the occasion, but extemporaneous speeches are the most natural sounding to the audience. If the speaker has practiced the speeches, including when to use any prepared visual aids or props, the speech delivery should be smooth.
What Are The 7 Cs Of Speech Delivery?
Public speaking is communication. The quality of your speech depends on putting the 7 Cs of communication into practice.
- Clear: Public speaking needs to be clear in its structure and presentation. A good speech makes it points to audience members with apparent logic . Avoid excessive jargon or technical terms, slang, idioms, confusing vocabulary, and remoted-sound passive voice makes the verbiage relatable . The speaker’s articulation should be crisp to easily understand every word.
- Concise: Everything you say should be relevant . Interesting stories or irrelevant material that fills time but lacks value are just fluff that dilutes the strength of your speech.
- Concrete: Concrete details are tangible things that add to the main point of your speech. Use language and examples that show your expertise and knowledge on the topic. Even if the speech is based on opinion, you should back up your position with facts.
- Correct: Speech content should be accurate and based on thorough research. The words and grammar you use and your pronunciation should be correct to prevent the audience from fixating on errors.
- Coherent and Cohesive: All the points in a speech should come together into a main speech topic. Transitions that link thoughts are helpful for this purpose.
- Complete: Though you have a limited time to present your speech, it should include c omplete thoughts about the important points you are trying to make.
- Courteous: Your audience has taken time out of their day to listen to your speech. You should make your presentation engaging and relatable , with language appropriate to your audience and tone appropriate to the occasion.
What Is The Difference Between Speech Delivery And Voice?
Vocal delivery includes different components of speech. This includes the rate at which you speak, your volume, pitch, pronunciation, articulation, and fluency. Do you enunciate words carefully? Are you speaking too loudly or softly? Do you use voice inflection to make points and prevent monotony? Can you correctly pronounce the words you are using?
Speech delivery includes not just your voice but facial expressions, eye contact, gesture, use of props and visual aids, etc. Nonverbal communication elements such as body language can help make an effective speech even more powerful.

What Is The Difference Between A Speech And A Presentation?
Speeches are the words you deliver. When you add visual aids, you make it a presentation.
Visual aids can vary from a PowerPoint or Google slide show to a trifold board to a prop you can display or hold. Using them correctly is valuable presentation skill.
If you are giving a presentation to convince a client that your company is the best to represent it, you might use PowerPoint. However, if you are giving a demonstration speech on how to fly fish, you might have a fly fishing rod in your hand when speaking.
There is a difference between a speech and a presentation, but many people use the two terms interchangeably.
What Is The Importance Of A Good Delivery In Speech?
Good delivery can make all the difference in giving a powerful speech. The delivery phase starts as soon as you step in front of an audience. First, get the audience’s attention by introducing who you are and perhaps jumping right into an exciting opening to hook them.
Whether your speech is impromptu, extemporaneous, memorized, or manuscript, you can wow the audience with your delivery.
Determining which is best for your speech depends on your intent and the situation.
What Is Good Delivery In Speech?
Unless you are called upon to give an impromptu speech that catches you by surprise, you should come to the podium ready to go with a well-structured speech honed to perfection through practice.
When giving a speech, there are specific aspects to delivering a powerful speech.
- Dress Appropriately: You may wear a suit or business casual, but your dress should be a notch above what the audience is wearing
- Posture: Stand tall with good posture. Don’t bend over or lean on the lectern or podium.
- Establish Credibility : The speaker’s credibility goes a long way to convincing people you know what you are talking about. Be certain to establish that with the audience.
- Notes: Consider using notecards instead of a transcript of your speech. This encourages natural pauses for eye contact. Make sure your note cards are formatted to be useful to you with large type and critical concepts you need to mention.
- Eye Contact : Looking up at the audience is very important to giving a good speech.
- Gestures : Gestures do not come naturally to every speaker, so use gestures if you can do so comfortably and without looking awkward. Practice what you will do with your hands as you rehearse your speech.
- Getting Started: Start with an attention grabber that may be a story, joke, or relevant statistic. You want to generate audience interest early on.
- Avoid Weak Words: Practice enough that you have eliminated the “umms” and “okays” from your vocabulary.
- Speed: Make sure you are not speaking too quickly or too slowly. Find balance.
- Voice Inflection: Work on varying your voice inflection so you do not sound monotone.

What Is The Difference Between Slow And Fast Delivery?
A good speaker controls both speed and inflection to keep the speech from becoming monotonous.
Sometimes it is appropriate to speed up your speaking to prove a point. Fast speaking can convey excitement or urgency .
If your timing gets off track, you may need to alter your delivery speed. When practicing your speech, you should develop a Plan B so you can cut your text down if you need to without compromising the speech. If you have extra time, you can add some additional prepared material.
What Is The Best Way To Improve Your Speech Delivery?
The best way to improve your speech delivery is to practice. Remember, the first time you give the speech will likely be rocky, which is why practicing is so important. You can practice for friends, in front of a mirror, or by recording yourself. When you watch the recording, it is a great opportunity to find ways you can improve your speech.
Another tactic is to watch strong speakers to find tips you might implement. Google great public speakers and see what comes up.
Recent Posts
Active Listening Absorbs The Whole Message, Not Just The Words
Active listening goes beyond hearing the words someone is saying to you and understanding the message they are conveying. Many only hear a small percentage of what is being said as they are...
Counteracting Fear Of Public Speaking With Coaching And Therapy
Nearly 75% of people experience the social phobia of fear of public speaking. The result may be nervousness before speaking or a full-blown panic attack. Practicing public speaking may lessen the...

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9 Delivering a Speech
Introduction
9.1 Managing Public Speaking Anxiety
Sources of speaking anxiety.
Aside from the self-reported data in national surveys that rank the fear of public speaking high for Americans, decades of research conducted by communication scholars shows that communication apprehension is common among college students (Priem & Solomon, 2009). Communication apprehension (CA) is fear or anxiety experienced by a person due to real or perceived communication with another person or persons. CA is a more general term that includes multiple forms of communication, not just public speaking. Seventy percent of college students experience some CA, which means that addressing communication anxiety in a class like the one you are taking now stands to benefit the majority of students (Priem & Solomon, 2009). Think about the jitters you get before a first date, a job interview, or the first day of school. The novelty or uncertainty of some situations is a common trigger for communication anxiety, and public speaking is a situation that is novel and uncertain for many.
Public speaking anxiety is a type of CA that produces physiological, cognitive, and behavioral reactions in people when faced with a real or imagined presentation (Bodie, 2010). Physiological responses to public speaking anxiety include increased heart rate, flushing of the skin or face, and sweaty palms, among other things. These reactions are the result of natural chemical processes in the human body. The fight or flight instinct helped early humans survive threatening situations. When faced with a ferocious saber-toothed tiger, for example, the body released adrenaline, cortisol, and other hormones that increased heart rate and blood pressure to get more energy to the brain, organs, and muscles in order to respond to the threat. We can be thankful for this evolutionary advantage, but our physiology has not caught up with our new ways of life. Our body does not distinguish between the causes of stressful situations, so facing down an audience releases the same hormones as facing down a wild beast.
Cognitive reactions to public speaking anxiety often include intrusive thoughts that can increase anxiety: “People are judging me,” “I’m not going to do well,” and “I’m going to forget what to say.” These thoughts are reactions to the physiological changes in the body but also bring in the social/public aspect of public speaking in which speakers fear being negatively judged or evaluated because of their anxiety. The physiological and cognitive responses to anxiety lead to behavioral changes. All these thoughts may lead someone to stop their speech and return to their seat or leave the classroom. Anticipating these reactions can also lead to avoidance behavior where people intentionally avoid situations where they will have to speak in public.
Addressing Public Speaking Anxiety

While we cannot stop the innate physiological reactions related to anxiety from occurring, we do have some control over how we cognitively process them and the behaviors that result. Research on public speaking anxiety has focused on three key ways to address this common issue: systematic desensitization, cognitive restructuring, and skills training (Bodie,2010).
Although systematic desensitization may sound like something done to you while strapped down in the basement of a scary hospital, it actually refers to the fact that we become less anxious about something when we are exposed to it more often (Bodie, 2010). As was mentioned earlier, the novelty and uncertainty of public speaking is a source for many people’s anxiety. So becoming more familiar with public speaking by speaking more often can logically reduce the novelty and uncertainty of it.
Systematic desensitization can result from imagined or real exposure to anxiety-inducing scenarios. In some cases, an instructor leads a person through a series of relaxation techniques. Once relaxed, the person is asked to imagine a series of scenarios including speech preparation and speech delivery. This is something you could also try to do on your own before giving a speech. Imagine yourself going through the process of preparing and practicing a speech, then delivering the speech, then returning to your seat, which concludes the scenario. Aside from this imagined exposure to speaking situations, taking a communication course like this one is a great way to engage directly in systematic desensitization. Almost all students report that they have less speaking anxiety at the end of a semester than when they started, which is at least partially due to the fact they engaged with speaking more than they would have done if they were not taking the class.
Cognitive Restructuring
Cognitive restructuring entails changing the way we think about something. A first step in restructuring how we deal with public speaking anxiety is to cognitively process through our fears to realize that many of the thoughts associated with public speaking anxiety are irrational (Allen, Hunter & Donohue, 2009). For example, people report a fear of public speaking over a fear of snakes, heights, financial ruin, or even death. It’s irrational to think that the consequences of giving a speech in public are more dire than getting bit by a rattlesnake, falling off a building, or dying. People also fear being embarrassed because they mess up. Well, you cannot literally die from embarrassment, and in reality, audiences are very forgiving and overlook or do not even notice many errors that we, as speakers, may dwell on. Once we realize that the potential negative consequences of giving a speech are not as dire as we think they are, we can move on to other cognitive restructuring strategies.
Communication-orientation modification therapy (COM therapy) is a type of cognitive restructuring that encourages people to think of public speaking as a conversation rather than a performance (Motley, 2009). Many people have a performance-based view of public speaking. This can easily be seen in the language that some students use to discuss public speaking. They say that they “rehearse” their speech, deal with “stage fright,” then “perform” their speech on a “stage.” There is no stage at the front of the classroom; it is a normal floor. To get away from a performance orientation, we can reword the previous statements to say that they “practice” their speech, deal with “public speaking anxiety,” then “deliver” their speech from the front of the room. Viewing public speaking as a conversation also helps with confidence. After all, you obviously have some conversation skills, or you would not have made it to college. We engage in conversations every day. We do not have to write everything we are going to say out on a note card, we do not usually get nervous or anxious in regular conversations, and we are usually successful when we try. Even though we do not engage in public speaking as much, we speak to others in public all the time. Thinking of public speaking as a type of conversation helps you realize that you already have accumulated experiences and skills that you can draw from, so you are not starting from scratch.
Last, positive visualization is another way to engage in cognitive restructuring. Speaking anxiety often leads people to view public speaking negatively. They are more likely to judge a speech they gave negatively, even if it was good. They are also likely to set up negative self-fulfilling prophecies that will hinder their performance in future speeches. To use positive visualization, it is best to engage first in some relaxation exercises such as deep breathing or stretching, and then play through vivid images in your mind of giving a successful speech. Do this a few times before giving the actual speech. Students sometimes question the power of positive visualization, thinking that it sounds corny. Ask an Olympic diver what his or her coach says to do before jumping off the diving board and the answer will probably be “Coach says to image completing a perfect 10 dive.” Likewise a Marine sharpshooter would likely say his commanding officer says to imagine hitting the target before pulling the trigger. In both instances, positive visualization is being used in high-stakes situations. If it is good enough for Olympic athletes and snipers, it is good enough for public speakers.
Skills training is a strategy for managing public speaking anxiety that focuses on learning skills that will improve specific speaking behaviors. These skills may relate to any part of the speech-making process, including topic selection, research and organization, delivery, and self-evaluation. Skills training, like systematic desensitization, makes the public speaking process more familiar for a speaker, which lessens uncertainty. In addition, targeting specific areas and then improving on them builds more confidence, which can in turn lead to more improvement. Feedback is important to initiate and maintain this positive cycle of improvement. You can use the constructive criticism that you get from your instructor and peers in this class to target specific areas of improvement.
Self-evaluation is also an important part of skills training. Make sure to evaluate yourself within the context of your assignment or job and the expectations for the speech. Do not get sidetracked by a small delivery error if the expectations for content far outweigh the expectations for delivery. Combine your self-evaluation with the feedback from your instructor, boss, and/or peers to set specific and measurable goals and then assess whether or not you meet them in subsequent speeches. Once you achieve a goal, mark it off your list and use it as a confidence booster. If you do not achieve a goal, figure out why and adjust your strategies to try to meet it in the future.
Physical Relaxation Exercises
Suggestions for managing speaking anxiety typically address its cognitive and behavioral components, while the physical components are left unattended. While we cannot block these natural and instinctual responses, we can engage in physical relaxation exercises to counteract the general physical signs of anxiety caused by cortisol and adrenaline release, which include increased heart rate, trembling, flushing, high blood pressure, and speech disfluency.
Some breathing and stretching exercises release endorphins, which are your body’s natural antidote to stress hormones. Deep breathing is a proven way to release endorphins. It also provides a general sense of relaxation and can be done discretely, even while waiting to speak. In order to get the benefits of deep breathing, you must breathe into your diaphragm. The diaphragm is the muscle below your lungs that helps you breathe and stand up straight, which makes it a good muscle for a speaker to exercise. To start, breathe in slowly through your nose, filling the bottom parts of your lungs up with air. While doing this, your belly should pooch out. Hold the breath for three to five full seconds and then let it out slowly through your mouth. After doing this only a few times, many students report that they can actually feel a flooding of endorphins, which creates a brief “light-headed” feeling. Once you practice and are comfortable with the technique, you can do this before you start your speech, and no one sitting around you will even notice. You might also want to try this technique during other stressful situations. Deep breathing before dealing with an angry customer or loved one, or before taking a test, can help you relax and focus.
Stretching is another way to release endorphins. Very old exercise traditions like yoga, tai chi, and Pilates teach the idea that stretching is a key component of having a healthy mind and spirit. Exercise in general is a good stress reliever, but many of us do not have the time or willpower to do it. However, we can take time to do some stretching. Obviously, it would be distracting for the surrounding audience if a speaker broke into some planking or Pilates just before his or her speech. Simple and discrete stretches can help get the body’s energy moving around, which can make a speaker feel more balanced and relaxed. Our blood and our energy/ stress have a tendency to pool in our legs, especially when we are sitting.
Vocal Warm-Up Exercises

Vocal warm-up exercises are a good way to warm up your face and mouth muscles, which can help prevent some of the fluency issues that occur when speaking. Newscasters, singers, and other professional speakers use vocal warm-ups. I lead my students in vocal exercises before speeches, which also helps lighten the mood. We all stand in a circle and look at each other while we go through our warm-up list. For the first warm-up, we all make a motorboat sound, which makes everybody laugh. The full list of warm-ups follows and contains specific words and exercises designed to warm up different muscles and different aspects of your voice. After going through just a few, you should be able to feel the blood circulating in your face muscles more. It is a surprisingly good workout!
Top Ten Ways to Reduce Speaking Anxiety
Many factors contribute to speaking anxiety. There are also many ways to address it. The following is a list of the top ten ways to reduce speaking anxiety that I developed with my colleagues, which helps review what we have learned.
- Remember, you are not alone. Public speaking anxiety is common, so do not ignore it—confront it.
- Remember, you cannot literally “die of embarrassment.” Audiences are forgiving and understanding.
- Remember, it always feels worse than it looks.
- Take deep breaths. It releases endorphins, which naturally fight the adrenaline that causes anxiety.
- Look the part. Dress professionally to enhance confidence.
- Channel your nervousness into positive energy and motivation.
- Start your outline and research early. Better information = higher confidence.
- Practice and get feedback from a trusted source. (Do not just practice for your cat.)
- Visualize success through positive thinking.
- Prepare, prepare, prepare! Practice is a speaker’s best friend.
9.2 Delivery Methods and Practice Sessions
There are many decisions to make during the speech-making process. Making informed decisions about delivery can help boost your confidence and manage speaking anxiety. In this section, we will learn about the strengths and weaknesses of various delivery methods. We will also learn how to make the most of your practice sessions.
Delivery Methods
Different speaking occasions call for different delivery methods. While it may be acceptable to speak from memory in some situations, lengthy notes may be required in others. The four most common delivery methods are impromptu, manuscript, memorized, and extemporaneous.
Impromptu Delivery
When using impromptu delivery , a speaker has little to no time to prepare for a speech (LibreTexts, 2021). This means there is little time for research, audience analysis, organizing, and practice. For this reason, impromptu speaking often evokes higher degrees of speaking anxiety than other delivery types. Although impromptu speaking arouses anxiety, it is also a good way to build public speaking skills. Using some of the exercises for managing speaking anxiety discussed earlier in this chapter can help a speaker manage the challenges of impromptu speaking (LibreTexts, 2021). Only skilled public speakers with much experience are usually able to “pull off” an impromptu delivery without looking unprepared. Otherwise, a speaker who is very familiar with the subject matter can sometimes be a competent impromptu speaker, because their expertise can compensate for the lack of research and organizing time.
When Mark Twain famously said, “It usually takes me more than three weeks to prepare a good impromptu speech,” he was jokingly pointing out the difficulties of giving a good impromptu speech, essentially saying that there is no such thing as a good impromptu speech, as good speeches take time to prepare. We do not always have the luxury of preparation, though. So when speaking impromptu, be brief, stick to what you know, and avoid rambling. Quickly organize your thoughts into an introduction, body, and conclusion. Try to determine three key ideas that will serve as the basis of your main points.
When would impromptu speaking be used? Since we have already started thinking of the similarities between public speaking and conversations, we can clearly see that most of our day-to-day interactions involve impromptu speaking. When your roommate asks you what your plans for the weekend are, you do not pull a few note cards out of your back pocket to prompt your response. This type of conversational impromptu speaking is not anxiety inducing because we are talking about our lives, experiences, or something with which we are familiar. This is also usually the case when we are asked to speak publicly with little to no advance warning.
For example, if you are at a meeting for work and you are representing the public relations department, a colleague may ask you to say a few words about a recent news story involving a public relations misstep of a competing company. In this case, you are being asked to speak on the spot because of your expertise. A competent communicator should anticipate instances like this when they might be asked to speak. Of course, being caught completely off guard or being asked to comment on something unfamiliar to you creates more anxiety. In such cases, do not pretend to know something you do not, as that may come back to hurt you later. You can usually mention that you do not have the necessary background information at that time but will follow up later with your comments.
Manuscript Delivery
Speaking from a written or printed document that contains the entirety of a speech is known as manuscript delivery . Manuscript delivery can be the best choice when a speech has complicated information and/or the contents of the speech are going to be quoted or published (LibreTexts, 2021). Despite the fact that most novice speakers are not going to find themselves in that situation, many are drawn to this delivery method because of the security they feel with having everything they are going to say in front of them. Unfortunately, the security of having every word you want to say at your disposal translates to a poorly delivered and unengaging speech (LibreTexts, 2021). Even with every word written out, speakers can still have fluency hiccups and verbal fillers as they lose their place in the manuscript or trip over their words. The alternative, of course, is that a speaker reads the manuscript the whole time, effectively cutting himself or herself off from the audience. One way to make a manuscript delivery more engaging is to use a teleprompter. Almost all politicians who give televised addresses use them.
To make the delivery seem more natural, print the speech out in a larger-than-typical font, triple-space between lines so you can easily find your place, use heavier-than-normal paper so it is easy to pick up and turn the pages as needed, and use a portfolio so you can carry the manuscript securely.
Memorized Delivery
Completely memorizing a speech and delivering it without notes is known as memorized delivery (LibreTexts, 2021). Some students attempt to memorize their speech because they think it will make them feel more confident if they do not have to look at their notes; however, when their anxiety level spikes at the beginning of their speech and their mind goes blank for a minute, many admit they should have chosen a different delivery method. When using any of the other delivery methods, speakers still need to rely on their memory. An impromptu speaker must recall facts or experiences related to their topic, and speakers using a manuscript want to have some of their content memorized so they do not read their entire speech to their audience. The problem with memorized delivery overall is that it puts too much responsibility on our memory, which we all know from experience is fallible (LibreTexts, 2021).
Even with much practice, our memories can fail. If you do opt to use memorized delivery, make sure you have several “entry points” determined, so you can pick up at spots other than the very beginning of a speech if you lose your place and have to start again. Memorized delivery is very useful for speakers who are going to be moving around during a speech when carrying notes would be burdensome. I only recommend memorized delivery in cases where the speech is short (only one to two minutes), the speech is personal (like a brief toast), or the speech will be repeated numerous times (like a tour guide’s story), and even in these cases, it may be perfectly fine to have notes. Many students think that their anxiety and/or delivery challenges will vanish if they just memorize their speech only to find that they are more anxious and have more problems.
Extemporaneous Delivery
Extemporaneous delivery entails memorizing the overall structure and main points of a speech and then speaking from keyword/key-phrase notes (LibreTexts, 2021). This delivery mode brings together many of the strengths of the previous three methods. Since you only internalize and memorize the main structure of a speech, you do not have to worry as much about the content and delivery seeming stale. Extemporaneous delivery brings in some of the spontaneity of impromptu delivery but still allows a speaker to carefully plan the overall structure of a speech and incorporate supporting materials that include key facts, quotations, and paraphrased information (LibreTexts, 2021). You can also more freely adapt your speech to fit various audiences and occasions, since not every word and sentence is predetermined. This can be especially beneficial when you deliver a speech multiple times.
When preparing a speech that you will deliver extemporaneously, you will want to start practicing your speech early and then continue to practice as you revise your content. Investing quality time and effort into the speech-outlining process helps with extemporaneous delivery. As you put together your outline, you are already doing the work of internalizing the key structure of your speech. Read parts of your outline aloud as you draft them to help ensure they are written in a way that makes sense and is easy for you to deliver.
By the time you complete the formal, full-sentence outline, you should have already internalized much of the key information in your speech. Now, you can begin practicing with the full outline. As you become more comfortable with the content of your full outline, start to convert it into your speaking outline. Take out information that you know well and replace it with a keyword or key phrase that prompts your memory. You will probably want to leave key quotes, facts, and other paraphrased information, including your verbal source citation information, on your delivery outline so you make sure to include it in your speech. Once you’ve converted your full outline into your speaking outline, practice it a few more times, making sure to take some time between each practice session so you don’t inadvertently start to memorize the speech word for word. The final product should be a confident delivery of a well-organized and structured speech that is conversational and adaptable to various audiences and occasions.
Practicing Your Speech

Practicing a speech is essential, and practice sessions can be more or less useful depending on how you approach them (Dlugan, 2008). There are three primary phases to the practice process. In the first phase, you practice as you are working through your ideas and drafting your outline. In the second, you practice for someone and get feedback (Dlugan, 2008). In the third, you put the final changes on the speech.
Start practicing your speech early, as you are working through your ideas, by reading sections aloud as you draft them into your working outline. This will help ensure your speech is fluent and sounds good for the audience. Start to envision the audience while you practice and continue to think about them throughout the practicing process. This will help minimize anxiety when you actually have them sitting in front of you. Once you have completed your research and finished a draft of your outline, you will have already practiced your speech several times, as you were putting it together. Now, you can get feedback on the speech as a whole.
You begin to solicit feedback from a trusted source in the second phase of practicing your speech (Dlugan, 2008). This is the most important phase of practicing, and the one that most speakers do not complete. Beginning speakers may be nervous to practice in front of someone. That is normal. However, review the strategies for managing anxiety discussed earlier in this chapter and try to face that anxiety. After all, you will have to face a full audience when you deliver the speech, so getting used to speaking in front of someone can only help you at this point. Choose someone who will give you constructive feedback on your speech. Before you practice for them, explain the assignment or purpose of the speech. When practicing for a classroom speech, you may even want to give the person the assignment guidelines or a feedback sheet that has some key things for them to look for. Ask them for feedback on content and delivery. Almost anyone is good at evaluating delivery, but it is more difficult to evaluate content. In addition, in most cases, the content of your speech will be account for more of your grade. Also, begin to time your speech at this point, so you can determine if it meets any time limits that you have.
In addition to practicing for a trusted source for feedback, you may want to audio or video record your speech (Dlugan, 2008). This can be useful because it provides an objective record that you can then compare with the feedback you got from your friend and to your own evaluation of your speech. The most important part of this phase is incorporating the feedback you receive into your speech. If you practice for someone, get feedback, and then do not do anything with the feedback, then you have wasted your time and theirs. Use the feedback to assess whether or not you met your speaking goals. Was your thesis supported? Was your specific purpose met? Did your speech conform to any time limits that were set? Based on your answers to these questions, you may need to make some changes to your content or delivery, so do not put this part of practicing off to the last minute. Once the content has been revised as needed, draft your speaking outline and move on to the next phase of practice.
During the third and final phase of practice, you are putting the final changes on your speech. You should be familiar with the content based on your early practice sessions. You have also gotten feedback and incorporated that feedback into the speech. Your practice sessions at this point should pre-create, as much as possible, the conditions in which you will be giving your speech. You should have your speaking outline completed so you can practice with it. It is important to be familiar with the content on your note cards or speaking outline so you will not need to rely on it so much during the actual delivery. You may also want to practice in the type of clothing you will be wearing on speech day. This can be useful if you are wearing something you do not typically wear—a suit for example—so you can see how it might affect your posture, gestures, and overall comfort level.
If possible, at least one practice session in the place you will be giving the speech can be very helpful; especially if it is a room you are not familiar with. Make sure you are practicing with any visual aids or technology you will use so you can be familiar with it and it does not affect your speech fluency. (Dlugan, 2008).Continue to time each practice round. If you are too short or too long, you will need to go back and adjust your content some more. Always adjust your content to fit the time limit; do not try to adjust your delivery. Trying to speed talk or stretch things out to make a speech faster or longer is a mistake that will ultimately hurt your delivery, which will hurt your credibility. The overall purpose of this phase of practicing is to minimize surprises that might throw you off on speech day.
Vocal Delivery
Vocal delivery includes components of speech delivery that relate to your voice. These include rate, volume, pitch, articulation, pronunciation, and fluency. Our voice is important to consider when delivering our speech for two main reasons. First, vocal delivery can help us engage and interest the audience. Second, vocal delivery helps ensure we communicate our ideas clearly.
Speaking for Engagement
We have all had the displeasure of listening to an unengaging speaker. Even though the person may care about his or her topic, an unengaging delivery that does not communicate enthusiasm will translate into a lack of interest for most audience members (Davis, 2021). Although a speaker can be visually engaging by incorporating movement and gestures, a flat or monotone vocal delivery can be sedating or even annoying. Incorporating vocal variety in terms of rate, volume, and pitch is key to being a successful speaker.
Rate of speaking refers to how fast or slow you speak (Barnard, 2018). If you speak too fast, your audience will not be able to absorb the information you present. If you speak too slowly, the audience may lose interest. The key is to vary your rate of speaking in a middle range, staying away from either extreme, in order to keep your audience engaged. In general, a higher rate of speaking signals that a speaker is enthusiastic about his or her topic. Speaking slowly may lead the audience to infer that the speaker is uninterested, uninformed, or unprepared to present his or her own topic. These negative assumptions, whether they are true or not, are likely to hurt the credibility of the speaker (Barnard, 2018). The goal is to speak at a rate that will interest the audience and will effectively convey your information. Speaking at a slow rate throughout a speech would likely bore an audience, but that is not a common occurrence.
Volume refers to how loud or soft your voice is. As with speaking rate, you want to avoid the extremes of being too loud or too soft, but still vary your volume within an acceptable middle range (Packard, 2020). When speaking in a typically sized classroom or office setting that seats about twenty-five people, using a volume a few steps above a typical conversational volume is usually sufficient. When speaking in larger rooms, you will need to project your voice. You may want to look for nonverbal cues from people in the back rows or corners, like leaning forward or straining to hear, to see if you need to adjust your volume more. Obviously, in some settings, a microphone will be necessary so the entire audience can hear you. Like rate, audiences use volume to make a variety of judgments about a speaker. Sometimes, softer speakers are judged as meek (Packard, 2020). This may lead to lowered expectations for the speech or less perceived credibility. Loud speakers may be seen as overbearing or annoying, which can lead audience members to disengage from the speaker and message. Be aware of the volume of your voice and, when in doubt, increase your volume a notch, since beginning speakers are more likely to have an issue of speaking too softly rather than too loudly.
Pitch refers to how high or low a speaker’s voice is. As with other vocal qualities, there are natural variations among people’s vocal pitch. Unlike rate and volume, we have less control over pitch. For example, males generally have lower pitched voices than females. Despite these limitations, each person still has the capability to change their pitch across a range large enough to engage an audience. Changing pitch is a good way to communicate enthusiasm and indicate emphasis or closure (Scotti, 2015). In general, our pitch goes up when we are discussing something exciting. Our pitch goes down slightly when we emphasize a serious or important point. Lowering pitch is also an effective way to signal transitions between sections of your speech or the end of your speech, which cues your audience to applaud and avoids an awkward ending.
Of the vocal components of delivery discussed so far, pitch seems to give beginning speakers the most difficulty. It is as if giving a speech temporarily numbs their ability to vary their pitch. Record yourself practicing your speech to help determine if the amount of pitch variety and enthusiasm you think you convey while speaking actually comes through. Speakers often assume that their pitch is more varied and their delivery more enthusiastic than the audience actually perceives it to be (Scotti, 2015). Many students note this on the self-evaluations they write after viewing their recorded speech.
Vocal Variety
Overall, the lesson to take away from this section on vocal delivery is that variety is key. Vocal variety includes changes in your rate, volume, and pitch that can make you look more prepared, seem more credible, and be able to engage your audience better (Moore, 2015). Employing vocal variety is not something that takes natural ability or advanced skills training. It is something that beginning speakers can start working on immediately and everyone can accomplish. The key is to become aware of how you use your voice when you speak, and the best way to do this is to record yourself (Moore, 2015). We all use vocal variety naturally without thinking about it during our regular conversations, and many of us think that this tendency will translate over to our speaking voices. This is definitely not the case for most beginning speakers. Unlike in your regular conversations, it will take some awareness and practice to use vocal variety in speeches. I encourage students to make this a delivery priority early on. Since it is something anyone can do, improving in this area will add to your speaking confidence, which usually translates into better speeches and better grades further on.
Speaking for Clarity
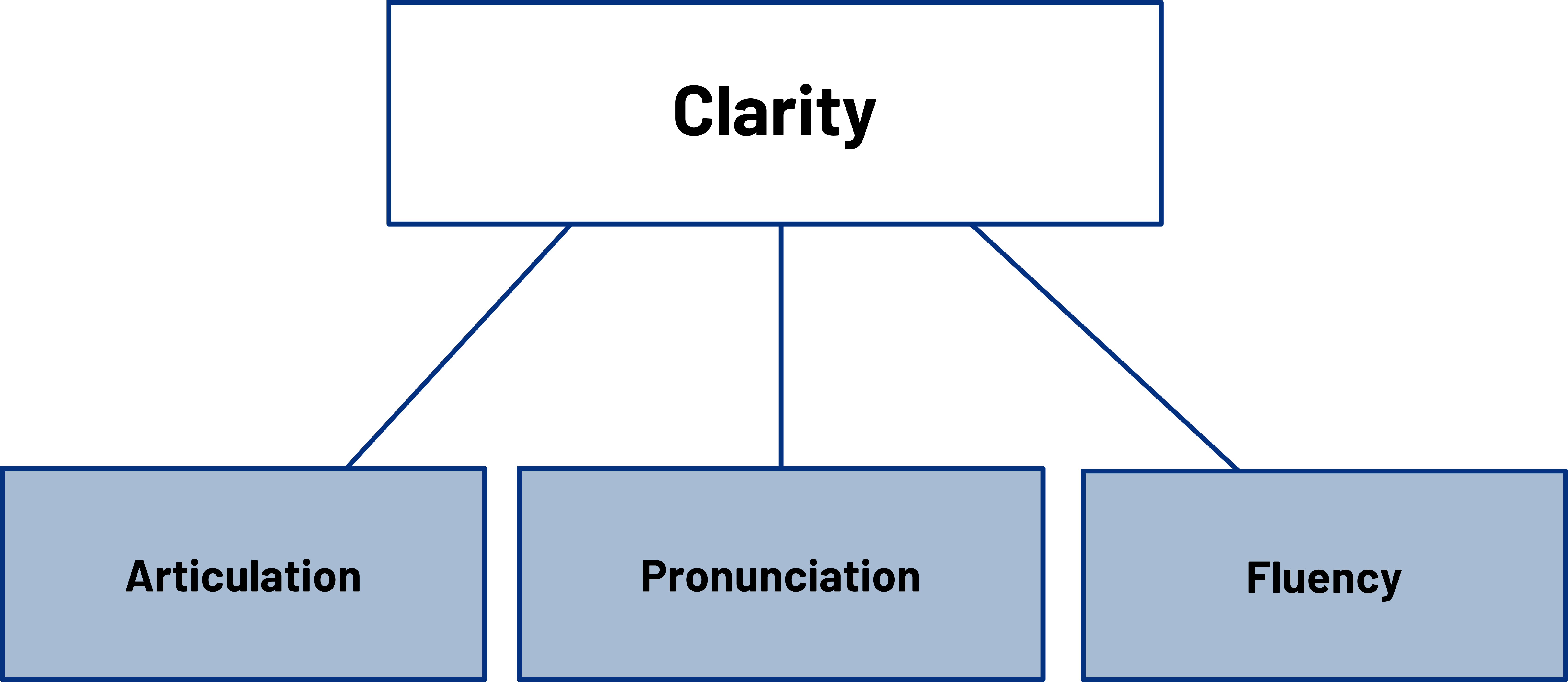
In order to be an effective speaker, your audience should be able to understand your message and digest the information you present (Rampton, 2021). Audience members will make assumptions about our competence and credibility based on how we speak. As with other aspects of speech delivery, many people are not aware that they have habits of speech that interfere with their message clarity. Since most of our conversations are informal and take place with people we know, many people do not make a concerted effort to articulate every word clearly and pronounce every word correctly (Rampton, 2021). Most of the people we talk to either do not notice our errors or do not correct us if they do notice. Since public speaking is generally more formal than our conversations, we should be more concerned with the clarity of our speech.
Articulation
Articulation refers to the clarity of sounds and words we produce. If someone is articulate, they speak words clearly, and speakers should strive to speak clearly. Poor articulation results when speakers do not speak clearly (Ward, 2020). For example, a person may say dinnt instead of didn’t , gonna instead of going to , wanna instead of want to , or hunnerd instead of hundred . Unawareness and laziness are two common challenges to articulation. As with other aspects of our voice, many people are unaware that they regularly have errors in articulation. Recording yourself speak and then becoming a higher self-monitor are effective ways to improve your articulation. Laziness, on the other hand, requires a little more motivation to address. Some people just get in the habit of not articulating their words well. Both mumbling and slurring are examples of poor articulation. In informal settings, this type of speaking may be acceptable, but in formal settings, it will be evaluated negatively. It will hurt a speaker’s credibility. Perhaps the promise of being judged more favorably is enough to motivate a mumbler to speak more clearly.
When combined with a low volume, poor articulation becomes an even greater problem. Doing vocal warm-ups like the ones listed in Section 10.1 “Managing Public Speaking Anxiety” or tongue twisters can help prime your mouth, lips, and tongue to articulate words more clearly. When you notice that you have trouble articulating a particular word, you can either choose a different word to include in your speech or you can repeat it a few times in a row in the days leading up to your speech to get used to saying it.
Pronunciation
Unlike articulation, which focuses on the clarity of words, pronunciation refers to speaking words correctly, including the proper sounds of the letters and the proper emphasis (Shtern, 2017). Mispronouncing words can damage a speaker’s credibility, especially when the correct pronunciation of a word is commonly known. We all commonly run into words that we are unfamiliar with and therefore may not know how to pronounce. Here are three suggestions when faced with this problem. First, look the word up in an online dictionary. Many dictionaries have a speaker icon with their definitions, and when you click on it, you can hear the correct pronunciation of a word. Some words have more than one pronunciation—for example, Caribbean —so choosing either of the accepted pronunciations is fine. Just remember to use consistently that pronunciation to avoid confusing your audience. If a word does not include an audio pronunciation, you can usually find the phonetic spelling of a word, which is the word spelled out the way it sounds.
Second, there will occasionally be words that you cannot locate in a dictionary. These are typically proper nouns or foreign words. In this case, use the “phone-a-friend” strategy. Call up the people you know who have large vocabularies or are generally smart when it comes to words, and ask them if they know how to pronounce it. If they do, and you find them credible, you are probably safe to take their suggestion.
Third, “fake it ‘til you make it” should only be used as a last resort. If you cannot find the word in a dictionary and your smart friends do not know how to pronounce it, it is likely that your audience will also be unfamiliar with the word. In that case, using your knowledge of how things are typically pronounced, decide on a pronunciation that makes sense and confidently use it during your speech. Most people will not question it. In the event that someone does correct you on your pronunciation, thank him or her for correcting you and adjust your pronunciation.
Fluency refers to the flow of your speaking. To speak with fluency means that your speech flows well and that there are not many interruptions to that flow. Two main disfluencies or problems affect the flow of a speech. Fluency hiccups are unintended pauses in a speech that usually result from forgetting what you were saying, being distracted, or losing your place in your speaking notes. Fluency hiccups are not the same as intended pauses, which are useful for adding emphasis or transitioning between parts of a speech. While speakers should try to minimize fluency hiccups, even experienced speakers need to take an unintended pause sometimes to get their bearings or to recover from an unexpected distraction. Fluency hiccups become a problem when they happen regularly enough to detract from the speaker’s message.
Verbal fillers are words that speakers use to fill in a gap between what they were saying and what they are saying next (Hennessy, 2019). Common verbal fillers include um , uh , ah , er , you know , and like . The best way to minimize verbal fillers is to become a higher self-monitor and realize that you use them. Many students are surprised when they watch the video of their first speech and realize they said “um” thirty times in three minutes. Gaining that awareness is the first step in eliminating verbal fillers, and students make noticeable progress with this between their first and second speeches (Hennessy, 2019). If you do lose your train of thought, having a brief fluency hiccup is better than injecting a verbal filler, because the audience may not even notice the pause or may think it was intentional.
9.3 Physical Delivery
Physical delivery.
Many speakers are more nervous about physical delivery than vocal delivery. Putting our bodies on the line in front of an audience often makes us feel more vulnerable than putting our voice out there. Yet most audiences are not as fixated on our physical delivery as we think they are. Knowing this can help relieve some anxiety, but it does not give us a free pass when it comes to physical delivery. We should still practice for physical delivery that enhances our verbal message. Physical delivery of a speech involves nonverbal communication through the face and eyes, gestures, and body movements.
Physical Delivery and the Face
We tend to look at a person’s face when we are listening to them (Hoffler, 2016). Again, this often makes people feel uncomfortable and contributes to their overall speaking anxiety. Many speakers do not like the feeling of having “all eyes” on them, even though having a room full of people avoiding making eye contact with you would be much more awkward. Remember, it is a good thing for audience members to look at you, because it means they are paying attention and interested. Audiences look toward the face of the speaker for cues about the tone and content of the speech.

Facial Expressions

Facial expressions can help bring a speech to life when used by a speaker to communicate emotions and demonstrate enthusiasm for the speech (Hoffler, 2016). As with vocal variety, we tend to use facial expressions naturally and without conscious effort when engaging in day-to-day conversations. Yet many speakers’ expressive faces turn “deadpan” when they stand in front of an audience. Some people naturally have more expressive faces than others do have—think about the actor Jim Carey’s ability to contort his face as an example. However, we can also consciously control and improve on our facial expressions to be speakers that are more effective. As with other components of speech delivery, becoming a higher self-monitor and increasing your awareness of your typical delivery habits can help you understand, control, and improve your delivery. Although you should not only practice your speech in front of a mirror, doing so can help you get an idea of how expressive or unexpressive your face is while delivering your speech.
Facial expressions help set the emotional tone for a speech, and it is important that your facial expressions stay consistent with your message (Hoffler, 2016). In order to set a positive tone before you start speaking, briefly look at the audience and smile. A smile is a simple but powerful facial expression that can communicate friendliness, openness, and confidence. Facial expressions communicate a range of emotions and are associated with various moods or personality traits.
For example, combinations of facial expressions can communicate that a speaker is tired, excited, angry, confused, frustrated, sad, confident, smug, shy, or bored, among other things. Even if you are not bored, for example, a slack face with little animation may lead an audience to think that you are bored with your own speech, which is not likely to motivate them to be interested. So make sure your facial expressions are communicating an emotion, mood, or personality trait that you think your audience will view favorably. Also, make sure your facial expressions match with the content of your speech. When delivering something lighthearted or humorous, a smile, bright eyes, and slightly raised eyebrows will nonverbally enhance your verbal message. When delivering something serious or somber, a furrowed brow, a tighter mouth, and even a slight head nod can enhance that message. If your facial expressions and speech content are not consistent, your audience could become confused by the conflicting messages, which could lead them to question your honesty and credibility.
Eye Contact
Eye contact is an important element of nonverbal communication in all communication settings. Eye contact can also be used to establish credibility and hold your audience’s attention (Barnard, 2017). We often interpret a lack of eye contact to mean that someone is not credible or not competent, and as a public speaker, you do not want your audience thinking either of those things. Eye contact holds attention because an audience member who knows the speaker is making regular eye contact will want to reciprocate that eye contact to show that they are paying attention. This will also help your audience remember the content of your speech better, because acting as if we are paying attention actually leads us to pay attention and better retain information.
Norms for eye contact vary among cultures (Barnard, 2017). Therefore, it may be difficult for speakers from countries that have higher power distances or are more collectivistic to get used to the idea of making direct and sustained eye contact during a speech. In these cases, it is important for the speaker to challenge himself or herself to integrate some of the host culture’s expectations and for the audience to be accommodating and understanding of the cultural differences.
Physical Delivery and the Body
Have you ever gotten dizzy as an audience member because the speaker paced back and forth? Anxiety can lead us to do some strange things with our bodies, like pacing, that we do not normally do, so it is important to consider the important role that your body plays during your speech. We call extra movements caused by anxiety nonverbal adaptors . Most of them manifest as distracting movements or gestures. These nonverbal adaptors, like tapping a foot, wringing hands, playing with a paper clip, twirling hair, jingling change in a pocket, scratching, and many more, can definitely detract from a speaker’s message and credibility. Conversely, a confident posture and purposeful gestures and movement can enhance both.
Posture is the position we assume with our bodies, either intentionally or out of habit. Although people, especially young women, used to be trained in posture, often by having them walk around with books stacked on their heads, you should use a posture that is appropriate for the occasion while still positioning yourself in a way that feels natural. In a formal speaking situation, it is important to have an erect posture that communicates professionalism and credibility (Clayton, 2018). However, a military posture of standing at attention may feel and look unnatural in a typical school or business speech. In informal settings, it may be appropriate to lean on a table or lectern, or even sit among your audience members (Clayton, 2018). Head position is also part of posture. In most speaking situations, it is best to keep your head up, facing your audience. A droopy head does not communicate confidence. Consider the occasion important, as an inappropriate posture can hurt your credibility.
Gestures include arm and hand movements. We all go through a process of internalizing our native culture from childhood. An obvious part of this process is becoming fluent in a language. Perhaps less obvious is the fact that we also become fluent in nonverbal communication, gestures in particular. We all use hand gestures while we speak, but we didn’t ever take a class in matching verbal communication with the appropriate gestures; we just internalized these norms over time based on observation and put them into practice. By this point in your life, you have a whole vocabulary of hand movements and gestures that spontaneously come out while you are speaking. Some of these gestures are emphatic and some are descriptive (Koch, 2007).
Emphatic gestures are the most common hand gestures we use, and they function to emphasize our verbal communication and often relate to the emotions we verbally communicate (Toastmasters International, 2011). Pointing with one finger or all the fingers straight out is an emphatic gesture. We can even bounce that gesture up and down to provide more emphasis. Moving the hand in a circular motion in front of our chest with the fingers spread apart is a common emphatic gesture that shows excitement and often accompanies an increased rate of verbal speaking. We make this gesture more emphatic by using both hands. Descriptive gestures function to illustrate or refer to objects rather than emotions (Toastmasters International, 2011). We use descriptive gestures to indicate the number of something by counting with our fingers or the size, shape, or speed of something. Our hands and arms are often the most reliable and easy-to-use visual aids a speaker can have.
While the best beginning strategy is to gesture naturally, you also want to remain a high self-monitor and take note of your typical patterns of gesturing. If you notice that you naturally gravitate toward one particular gesture, make an effort to vary your gestures more. You also want your gestures to be purposeful, not limp or lifeless.

Sometimes movement of the whole body, instead of just gesturing with hands, is appropriate in a speech. When students are given the freedom to move around, it often ends up becoming floating or pacing, which are both movements that comfort a speaker by expending nervous energy but only serve to distract the audience (Toastmasters International, 2011). Floating refers to speakers who wander aimlessly around, and pacing refers to speakers who walk back and forth in the same path. To prevent floating or pacing, make sure that your movements are purposeful. Many speakers employ the triangle method of body movement where they start in the middle, take a couple steps forward and to the right, then take a couple steps to the left, then return to the center. Obviously, you do not need to do this multiple times in a five- to ten-minute speech, as doing so, just like floating or pacing, tends to make an audience dizzy.
To make your movements appear more natural, time them to coincide with a key point you want to emphasize or a transition between key points. Minimize other movements from the waist down when you are not purposefully moving for emphasis. Speakers sometimes tap or shuffle their feet, rock, or shift their weight back and forth from one leg to the other. Keeping both feet flat on the floor, and still, will help avoid these distracting movements (Toastmasters International, 2011).
Credibility and Physical Delivery
Audience members primarily take in information through visual and auditory channels. Just as the information you present verbally in your speech can add to or subtract from your credibility, nonverbal communication that accompanies your verbal messages affects your credibility.
Professional Dress and Appearance
No matter what professional field you go into, you will need to consider the importance of personal appearance (Caffrey, 2020). Although it may seem petty or shallow to put so much emphasis on dress and appearance, impressions matter, and people make judgments about our personality, competence, and credibility based on how we look. In some cases, you may work somewhere with a clearly laid out policy for personal dress and appearance. In many cases, the suggestion is to follow guidelines for “business casual.”
Despite the increasing popularity of this notion over the past twenty years, people’s understanding of what business casual means is not consistent (Caffrey, 2020). The formal dress codes of the mid-1900s, which required employees to wear suits and dresses, gave way to the trend of business casual dress, which seeks to allow employees to work comfortably while still appearing professional. While most people still dress more formally for job interviews or high-stakes presentations, the day-to-day dress of working professionals varies.
Visual Aids and Delivery
Visual aids play an important role in conveying supporting material to your audience. They also tie to delivery, since using visual aids during a speech usually requires some physical movements. It is important not to let your use of visual aids detract from your credibility (Beqiri, 2018). Many good speeches are derailed by posters that fall over, videos with no sound, and uncooperative PowerPoint presentations.
Figure 9.1: Systematic desensitization can include giving more public speeches, taking communication courses, or imagining public speaking scenarios. William Moreland. 2019. Unsplash license . https://unsplash.com/photos/GkWP64truqg
Figure 9.2: Vocal warm-up exercises. Andrea Piacquadio. 2020. Pexels license . https://www.pexels.com/photo/man-in-red-polo-shirt-3779453/
Figure 9.3: Primary phases to the practice process. Kindred Grey. 2022. CC BY 4.0 .
Figure 9.4: Three facets of speaking for clarity. Kindred Grey. 2022. CC BY 4.0 .
Figure 9.5: Facial expressions set the tone for a speech, and should be consistent with your message. Afif Kusuma. 2021. Unsplash license . https://unsplash.com/photos/F3dFVKj6q8I
Figure 9.6: To make your movements appear natural, time them to coincide with a key point. Product School. 2019. Unsplash license . https://unsplash.com/photos/S3hhrqLrgYM
Section 9.1
Allen, M., Hunter, J. E., & Donohue, W. A. (1989). Meta-analysis of self-report data on the effectiveness of public speaking anxiety treatment techniques. Communication Education, 38 (1), 54–76. https://doi.org/10.1080/03634528909378740
Bodie, G. D. (2010). A racing heart, rattling knees, and ruminative thoughts: Defining, explaining, and treating public speaking anxiety. Communication Education, 59 (1), 70–105. https://doi.org/10.1080/03634520903443849
Motley, M. T. (2009). COM therapy. In J. A. Daly, J. C. McCroskey, J. Ayres, T. Hopf, and D. M. Ayers Sonandré (Eds.), Avoiding communication: Shyness, reticence, and communication apprehension (pp. 379-400) (3rd ed.). Hampton Press.
Priem, J. S., & Haunani Solomon, D. (2009). Comforting apprehensive communicators: The effects of reappraisal and distraction on cortisol levels among students in a public speaking class. Communication Quarterly, 57 (3), 259-281.
Section 9.2
Barnard, D. (2018, January 20). Average speaking rate and words per minute . https://virtualspeech.com/blog/average-speaking-rate-words-per-minute
Davis, B. (2021, June 1). Why is audience engagement important? https://www.mvorganizing.org/why-is-audience-engagement-important/
Hennessy, C. (2019, March 27). Verbal filler: How to slow the flow . https://www.throughlinegroup.com/2019/03/27/verbal-filler-how-to-slow-the-flow/
LibreTexts. (2021, February 20). Methods of speech delivery . https://socialsci.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Communication/Public_Speaking/Exploring_Public_Speaking_(Barton_and_Tucker)/11%3A_Delivery/11.02%3A_Methods_of_Speech_Delivery
Moore, K. (2015, January 13). Public speaking tips: Use vocal variety like a pro! https://coachkiomi.com/best-public-speaking-tips-use-vocal-variety/
Packard, D. (2020, July 13). Speaking up: How to increase the volume of your voice . https://packardcommunications.com/speaking-up-how-to-increase-the-volume-of-your-voice/
Rampton, J. (2021, July 27). Learning to speak with clarity . https://www.calendar.com/blog/learning-to-speak-with-clarity/
Scotti, S. (2015, December 1). Vocal delivery: Take command of your voice . https://professionallyspeaking.net/vocal-delivery-take-command-of-your-voice-part-one/
Shtern, A. (2017, April 17). The importance of good pronunciation . https://shaneschools.com/en/the-importance-of-good-pronunciation/
Section 9.3
Barnard, D. (2017, October 24). The importance of eye contact during a presentation . https://virtualspeech.com/blog/importance-of-eye-contact-during-a-presentation
Beqiri, G. (2018, June 21). Using visual aids during a presentation or training session . https://virtualspeech.com/blog/visual-aids-presentation
Caffrey, A. (2020, February 25). The importance of personal appearance . http://www.publicspeakingexpert.co.uk/importanceofpersonalappearance.html
Clayton, D. (2018, October 31). The importance of good posture in public speaking . https://simplyamazingtraining.co.uk/blog/good-posture-public-speaking
Hoffler, A. (2016, June 7). Why facial expressions are important in public speaking . https://www.millswyck.com/2016/06/07/the-importance-of-facial-expression/
Koch, A. (2007). Speaking with a purpose (7th ed.). Pearson, 2007.
Toastmasters International. (2011). Gestures: Your body speaks . https://web.mst.edu/~toast/docs/Gestures.pdf
Fear or anxiety experience by a person due to real or perceived communication with another person or persons. This is a fear or anxiety that involves several types of communication not limited to public speaking.
Type of communication apprehension that produces physiological, cognitive, and behavioral reactions in people when faced with a real or imagined presentation
A type of cognitive restructuring that encourages people to think of public speaking as conversation rather than a performance
When a speaker has little or no time to prepare a speech
Speaking from a well written or printed document that contains the entirety of a speech
Completely memorizing a speech and delivering it without notes
Memorizing the overall structure and main points of a speech and then speaking from keyword/key-phrase notes
Refers to how fast or slow you speak
Refers to how loud or soft you speak
Refers to how high or low a speaker’s voice is
Changes in your rate, volume, and pitch that make you sound more prepared and credible
Refers to the clarity of sounds and words you pronounce
Whether you say the words correctly
Refers to the flow of your speaking
Unintended pauses in a speech that usually result from forgetting what you were saying, being distracted, or losing your place in speaking
The umms, uhhs, and other linguistic pauses of conversation
The feelings expressed on a person’s face
The act of looking directly into one another’s eyes
Extra movements caused by anxiety (i.e., tapping your foot, wringing your hands, playing with a paperclip, twirling hair, or scratching)
The position in which someone holds their body when standing or sitting
A movement of part of the body, especially a hand or the head, to express an idea or meaning
Communication in the Real World Copyright © by Faculty members in the School of Communication Studies, James Madison University is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Module 6: Organizing and Outlining Your Speech
Methods of speech delivery, learning objectives.
Identify the four types of speech delivery methods and when to use them.
There are four basic methods of speech delivery: manuscript, memorized, impromptu, and extemporaneous. We’ll look at each method and discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each.

A manuscript page from President George W. Bush’s address to the nation on the day of the 9/11 attacks in 2001.
A manuscript speech is when the speaker writes down every word they will speak during the speech. When they deliver the speech, they have each word planned and in front of them on the page, much like a newscaster who reads from a teleprompter.
The advantage of using a manuscript is that the speaker has access to every word they’ve prepared in advance. There is no guesswork or memorization needed. This method comforts some speakers’ nerves as they don’t have to worry about that moment where they might freeze and forget what they’ve planned to say. They also are able to make exact quotes from their source material.
When the exact wording of an idea is crucial, speakers often read from a manuscript, for instance in communicating public statements from a company.
However, the disadvantage with a manuscript is that the speakers have MANY words in front of them on the page. This prohibits one of the most important aspects of delivery, eye contact. When many words are on the page, the speakers will find themselves looking down at those words more frequently because they will need the help. If they do look up at the audience, they often cannot find their place when the eye returns to the page. Also, when nerves come into play, speakers with manuscripts often default to reading from the page and forget that they are not making eye contact or engaging their audience. Therefore, manuscript is a very difficult delivery method and not ideal. Above all, the speakers should remember to rehearse with the script so that they practice looking up often.
Public Speaking in History
The fall of the Berlin Wall on November 9, 1989, owed in large part to a momentary error made by an East German government spokesperson. At a live press conference, Günter Schabowski tried to explain new rules relaxing East Germany’s severe travel restrictions. A reporter asked, “when do these new rules go into effect?” Visibly flustered, Schabowski said, “As far as I know, it takes effect immediately, without delay.” In fact, the new visa application procedure was supposed to begin the following day, and with a lot of bureaucracy and red tape. Instead, thousands of East Berliners arrived within minutes at the border crossings, demanding to pass through immediately. The rest is history.
The outcome of this particular public-relations blunder was welcomed by the vast majority of East and West German citizens, and hastened the collapse of communism in Eastern and Central Europe. It’s probably good, then, that Schabowski ran this particular press conference extemporaneously, rather than reading from a manuscript.
You can view the transcript for “The mistake that toppled the Berlin Wall” here (opens in new window) .
A memorized speech is also fully prepared in advance and one in which the speaker does not use any notes. In the case of an occasion speech like a quick toast, a brief dedication, or a short eulogy, word-for-word memorization might make sense. Usually, though, it doesn’t involve committing each and every word to memory, Memorizing a speech isn’t like memorizing a poem where you need to remember every word exactly as written. Don’t memorize a manuscript! Work with your outline instead. Practice with the outline until you can recall the content and order of your main points without effort. Then it’s just a matter of practicing until you’re able to elaborate on your key points in a natural and seamless manner. Ideally, a memorized speech will sound like an off-the-cuff statement by someone who is a really eloquent speaker and an exceptionally organized thinker!
The advantage of a memorized speech is that the speaker can fully face their audience and make lots of eye contact. The problem with a memorized speech is that speakers may get nervous and forget the parts they’ve memorized. Without any notes to lean on, the speaker may hesitate and leave lots of dead air in the room while trying to recall what was planned. Sometimes, the speaker can’t remember or find his or her place in the speech and are forced to go get the notes or go back to the PowerPoint in some capacity to try to trigger his or her memory. This can be an embarrassing and uncomfortable moment for the speaker and the audience, and is a moment which could be easily avoided by using a different speaking method.
How to: memorize a speech
There are lots of tips out there about how to memorize speeches. Here’s one that loosely follows an ancient memorization strategy called the method of loci or “memory palace,” which uses visualizations of familiar spatial environments in order to enhance the recall of information.
You can view the transcript for “How to Memorize a Speech” here (opens in new window) .
An impromptu speech is one for which there is little to no preparation. There is often not a warning even that the person may be asked to speak. For example, your speech teacher may ask you to deliver a speech on your worst pet peeve. You may or may not be given a few minutes to organize your thoughts. What should you do? DO NOT PANIC. Even under pressure, you can create a basic speech that follows the formula of an introduction, body, and conclusion. If you have a few minutes, jot down some notes that fit into each part of the speech. (In fact, the phrase “speaking off the cuff,” which means speaking without preparation, probably refers to the idea that one would jot a few notes on one’s shirt cuff before speaking impromptu.) [1] ) An introduction should include an attention getter, introduction of the topic, speaker credibility, and forecasting of main points. The body should have two or three main points. The conclusion should have a summary, call to action, and final thought. If you can organize your thoughts into those three parts, you will sound like a polished speaker. Even if you only hit two of them, it will still help you to think about the speech in those parts. For example, if a speech is being given on a pet peeve of chewed gum being left under desks in classrooms, it might be organized like this.
- Introduction : Speaker chews gum loudly and then puts it under a desk (attention getter, demonstration). Speaker introduces themselves and the topic and why they’re qualified to speak on it (topic introduction and credibility). “I’m Katie Smith and I’ve been a student at this school for three years and witnessed this gum problem the entire time.”
- Body : Speaker states three main points of why we shouldn’t leave gum on desks: it’s rude, it makes custodians have to work harder, it affects the next student who gets nastiness on their seat (forecast of order). Speaker then discusses those three points
- Conclusion : Speaker summarizes those three points (summary, part 1 of conclusion), calls on the audience to pledge to never do this again (call to action), and gives a quote from Michael Jordan about respecting property (final thought).
While an impromptu speech can be challenging, the advantage is that it can also be thrilling as the speaker thinks off the cuff and says what they’re most passionate about in the moment. A speaker should not be afraid to use notes during an impromptu speech if they were given any time to organize their thoughts.
The disadvantage is that there is no time for preparation, so finding research to support claims such as quotes or facts cannot be included. The lack of preparation makes some speakers more nervous and they may struggle to engage the audience due to their nerves.
Extemporaneous
The last method of delivery we’ll look at is extemporaneous. When speaking extemporaneously, speakers prepare some notes in advance that help trigger their memory of what they planned to say. These notes are often placed on notecards. A 4”x6” notecard or 5”x7” size card works well. This size of notecards can be purchased at any office supply store. Speakers should determine what needs to go on each card by reading through their speech notes and giving themselves phrases to say out loud. These notes are not full sentences, but help the speakers, who turn them into a full sentence when spoken aloud. Note that if a quote is being used, listing that quote verbatim is fine.
The advantage of extemporaneous speaking is that the speakers are able to speak in a more conversational tone by letting the cards guide them, but not dictate every word they say. This method allows for the speakers to make more eye contact with the audience. The shorter note forms also prevent speakers from getting lost in their words. Numbering these cards also helps if one gets out of order. Also, these notes are not ones the teacher sees or collects. While you may be required to turn in your speech outline, your extemporaneous notecards are not seen by anyone but you. Therefore, you can also write yourself notes to speak up, slow down, emphasize a point, go to the next slide, etc.
The disadvantage to extemporaneous is the speakers may forget what else was planned to say or find a card to be out of order. This problem can be avoided through rehearsal and double-checking the note order before speaking.
Many speakers consider the extemporaneous method to be the ideal speaking method because it allows them to be prepared, keeps the audience engaged, and makes the speakers more natural in their delivery. In your public speaking class, most of your speeches will probably be delivered extemporaneously.
- As per the Oxford English Dictionary' s entry for "Off the Cuff." See an extensive discussion at Mark Liberman's Language Log here: https://languagelog.ldc.upenn.edu/nll/?p=4130 ↵
- Method of loci definition. Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Method_of_loci . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- The mistake that toppled the Berlin Wall. Provided by : Vox. Located at : https://youtu.be/Mn4VDwaV-oo . License : Other . License Terms : Standard YouTube License
- How to Memorize a Speech. Authored by : Memorize Academy. Located at : https://youtu.be/rvBw__VNrsc . License : Other . License Terms : Standard YouTube License
- Address to the Nation. Provided by : U.S. National Archives. Located at : https://prologue.blogs.archives.gov/2011/09/06/911-an-address-to-the-nation/ . License : Public Domain: No Known Copyright
- Methods of Speech Delivery. Authored by : Misti Wills with Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution


41 Final Touches for Successful Speech Delivery
Learning Objectives
- Finish the speech making process by engaging in practice, editing, and delivery.
- Work through public speaking anxiety and deliver a successful speech.
You have made it! You worked through the steps of the speech making process and now you are ready to finish up your practice and delivery. This section will provide you with reminders as you are rehearsing and finishing up your speech preparation for a successful delivery!
Finishing Touches
You have all of the tools you need to be successful. Be sure to refer back to these tools to help you deliver a successful speech.
- Review the assignment description to ensure you have completed all necessary elements.
- Review the assignment rubric for a clear understanding of speech expectations and point distribution.
- Refer to the readings for each part of the speech making process for ideas, tips, and strategies for success.
- Practice, edit, change, and improve! Revise your outline and speaking notes as you practice, engage in peer feedback, and rehearse.
- PRACTICE and PRACTICE and PRACTICE more! You are presenting NOT reading your speech. You will only be able to do this with practice.
- Be sure to practice in the environment you will be presenting your speech at least once. Know how to upload and use your presentation aids. Know what your camera angle looks like. Refer to the delivery module for more tips on success!
- ASK questions if you have them!
Practice and Rehearsal Guidelines
The following guidelines are best practices on how to practice and rehearse an extemporaneous speech:
- Create speaking notes and practice with them! You should not be using your preparation outline or a manuscript to practice.
- Speak in a conversational style by pretending you are with your audience.
- Rehearse with your graphics/visuals and coordinate them with your talk.
- Display your graphics/visuals only when you are talking about them.
- Rehearse in front of others and solicit feedback.
- Record and listen to your timed practice speech.
- Prepare for interruptions and questions at the end.
Extemporaneous speaking is not memorization or manuscript speaking and requires you to organize and prepare your content and notes ahead of time to deliver a speech that will engage your audience.
Delivery Reminders
Revisit module 3 for details on vocal and physical delivery. Below is a short review about delivery elements you should be focusing on during your practice sessions.
Volume Speak loudly enough so that we can hear you. Good volume also makes you sound confident
Clarity Enunciate your words, and avoid mumbling, so the audience can easily understand what you’re saying
Tone Match your tone to the content. Typically, tone goes higher when we are unsure or are asking a question, and goes lower when we are stating a fact or being authoritative
Pace Speak slowly enough to be understood, and vary your pace to add interest
- Choppiness – Speak as fluidly as possible, avoid hesitations and unusual pacing
- Speed – Speak smoothly and confidently, but a little slower than in normal conversation. In multicultural situations (where we might not be familiar with each others’ accents) speak even slower, and watch your audience to make sure they understand you.
- Pauses – Listening can be tiring. Brief pauses let your audience absorb information. You can also use pauses to add emphasis or anticipation.
Vocal variety Vary your tone, pace and volume to add interest, emphasis and clarity. For example, speak a little faster to add excitement or anticipation, or speak a little louder to show emphasis. Some cultures and languages tend to be more monotone, so some students may have to work a little bit harder to ensure they vary their tone.
Body language
Professional posture Good posture supports your voice, and makes you look professional and confident (when we’re nervous we tend to hunch and cross our arms). Face the audience most of the time, and avoid turning your back on them to look at your slides.
Manage your movement Repetitive body movements, such as tapping your foot or swaying, can also distract the audience. If you’re presenting in person, slowly move around the physical space, such as moving towards the audience, or from one part of the room to another.
Use gestures Use gestures to add interest, emphasis, and help explain what you’re saying, such as indicating part of a slide or demonstrating an action.
Eyes & face
Make eye contact most of the time Eye contact shows confidence and helps everyone in the audience feel included. Look at all parts of the room. Secret tip for shy presenters: look at people’s foreheads – it has the same effect as eye contact. If you’re presenting online, this means looking at the camera. If you’re using notes should be point form – not full sentences – that you can quickly glance at, not read.
Manage your facial expressions You can show passion and emotion through facial expressions. But be careful, sometimes presenters show how nervous they are by having a look of worry on their face.
Your passion will engage the audience. Show your enthusiasm, energy, and interest through the appropriate use of tone, pace, volume, facial expressions, gestures, and body language.
Your level of energy can be infectious, and inspire the audience. Even if your topic is serious, like mental health or a tragedy, you can still convey conviction and interest in the subject matter. Conversely, without passion, you can make even the most fascinating content boring, and cause your audience to disengage. Storytelling is very powerful. Do not begin your speech with “Today, I am going to talk to you about ____”. Hook your audience with a story.
Filler words Fillers distract the audience and make you seem nervous, unprepared or professional. These include uhh , umm , like, you know, and any other words or noises that are not actual content. Real words like and and so can also be used as filler words.
Vocabulary Use words and phrases your audience understands; language that is appropriate for them. Will they understand abbreviations, acronyms, slang and jargon?
Transitions Use transitions to connect sentences to each other, indicate that you’re moving to the next major point, or in group presentations, that you’re moving to the next speaker.
Tip: Words we are saying wrong
Make sure the length of your presentation matches your audience’s expectations (or the time limit set by the assignment).
If you have a speech impediment
If you stutter, you’re not alone. Many famous people have found ways to become great presenters while managing their stutter, including President Joe Biden, James Earl Jones (the voice of Darth Vader), and Nicole Kidman. Some basic coping strategies include speaking slowly, managing stress, and thoroughly knowing your material. Additional resources are available from The Canadian Stuttering Association .
Got Nerves?
Finally, remember that nerves are common! The following video offers practical suggestions to work through the jitters and confidently deliver a speech.
Watch this video to recall important aspects of informative speaking, organizing your speech, and delivering your final speech. These tips will help you polish your speech and demonstrate a well-developed outline and impressive delivery.
Key Takeaways
- Extemporaneous speaking requires extensive preparation and practice.
- Effective delivery takes time and work. Working through the speech making process is the best method for successful speech delivery.
- You can work through your nerves and deliver a strong speech!
Public Speaking Copyright © by Dr. Layne Goodman; Amber Green, M.A.; and Various is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

5 Ways of Delivering Speeches
Understanding Delivery Modes
In this chapter . . .
In this chapter, we will explore the three modes of speech delivery: impromptu, manuscript, and extemporaneous. Each offers unique advantages and potential challenges. An effective public speaker needs to be familiar with each style so they can use the most appropriate mode for any speech occasion.
In writing, there’s only one way of delivering the text: the printed word on a page. Public Speaking, however, gives you different ways to present your text. These are called the delivery modes , or simply, ways of delivering speeches. The three modes are impromptu delivery , manuscript delivery , and extemporaneous delivery . Each of these involves a different relationship between a speech text, on the one hand, and the spoken word, on the other. These are described in detail below.

Impromptu Delivery
Impromptu speaking is a short form speech given with little to no preparation. While being asked to stand in front of an audience and deliver an impromptu speech can be anxiety-producing, it’s important to remember that impromptu speaking is something most people do without thinking in their daily lives . If you introduce yourself to a group, answer an open-ended question, express an opinion, or tell a story, you’re using impromptu speaking skills. While impromptus can be stressful, the more you do it the easier it becomes.
Preparation for Impromptu Delivery
The difficulty of impromptu speaking is that there is no way to prepare, specifically, for that moment of public speaking. There are, however, some things you can do to stay ready in case you’re called upon to speak unrehearsed.
For one, make sure your speaking instruments (your voice and body) are warmed up, energized, and focused. It could be helpful to employ some of the actor warm-up techniques mentioned earlier as part of an everyday routine. If appropriate to the impromptu speaking situation, you could even ask to briefly step aside and warm yourself up so that you feel relaxed and prepared.
Furthermore, a good rule when brainstorming for an impromptu speech is that your first idea is your best. You can think about impromptu speaking like improvisation: use the “yes, and” rule and trust your instincts. You’ll likely not have time to fully map out the speech, so don’t be too hard on yourself to find the “perfect” thing to say. You should let your opinions and honest thoughts guide your speaking. While it’s easy to look back later and think of approaches you should have used, try to avoid this line of thinking and trust whatever you come up with in the moment.
Finally, as you prepare to speak, remind yourself what your purpose is for your speech. What is it that you hope to achieve by speaking? How do you hope your audience feels by the end? What information is most important to convey? Consider how you’ll end your speech. If you let your purpose guide you, and stay on topic throughout your speech, you’ll often find success.
Delivery of Impromptu Speeches
Here is a step-by-step guide that may be useful if you’re called upon to give an impromptu speech:
- Thank the person for inviting you to speak. Don’t make comments about being unprepared, called upon at the last moment, on the spot, or uneasy.
- Deliver your message, making your main point as briefly as you can while still covering it adequately and at a pace your listeners can follow.
- Stay on track. If you can, use a structure, using numbers if possible: “Two main reasons . . .” or “Three parts of our plan. . .” or “Two side effects of this drug. . .” Past, present, and future or East Coast, Midwest, and West Coast are common structures.
- Thank the person again for the opportunity to speak.
- Stop talking when you are finished (it’s easy to “ramble on” when you don’t have something prepared). If in front of an audience, don’t keep talking as you move back to your seat. Finish clearly and strong.
Impromptu speeches are most successful when they are brief and focus on a single point.
Another helpful framing technique for impromptus is to negate the premise. This is the deliberate reframing of a given prompt in a way that acknowledges the original but transitions into talking about the topic in a different way than expected. Negating the premise can be an effective rhetorical technique if used carefully and can help you focus your response on a topic that you’re interested in talking about.
If you suddenly run out of things to say in the middle of your speech, be open to pivoting . Giving another example or story is the easiest way to do this. What’s important is to not panic or allow yourself to ramble aimlessly. No matter what, remember to keep breathing.
Finally, the greatest key to success for improving impromptu speaking is practice. Practice speaking without rehearsal in low-stakes environments if you can (giving a toast at a family dinner, for example). But remember this: no one is expecting the “perfect” speech if you’re called upon to speak impromptu. It’s okay to mess up. As Steven Tyler of the rock band Aerosmith would say: dare to suck. Take a risk and make a bold choice. What is most important is to stay sure of yourself and your knowledge.
Manuscript Delivery
The opposite of an impromptu speech is the manuscript speech. This involves having the complete text of your speech written out on paper or on notecards. You may be reading the speech from a computer or a teleprompter. In some cases, the speaker memorizes this manuscript.
Manuscript delivery is the word-for-word iteration of a written message. In a manuscript speech, the speaker maintains their attention on the printed page except when using visual aids. The advantage of reading from a manuscript is the exact repetition of original words. In some circumstances, this can be extremely important.
Advantages & Disadvantages to Manuscript Delivery
There are many advantages in speaking from a manuscript. Some people find they are less nervous when they have the whole text in front of them. If you get lost or flustered during the speech you can glance down and get back on track. For speakers who struggle with vocalized pauses, it can be easier to know exactly what you want to say so that you’re not searching for the right word. Some people prefer to carefully craft the language of their speech instead of just having a sense of the main point and expounding upon it. Particularly if there are a lot of statistics or quotations, it can be helpful to have the whole passage written out to make sure you not only convey it correctly but frame it in the right context. It’s also easier to rehearse and time a manuscript speech, thus making sure it stays within time limits and isn’t unexpectedly too short or long. For some formal occasions or events that may be emotional for the speaker, such as a funeral, using a manuscript may be the best approach.
There are some disadvantages in delivering a speech from a manuscript. Having a manuscript in front of you often encourages looking down and reading the speech instead of performing it. A lack of eye contact makes the audience feel less engaged. The speech can feel stilted and lacking energy. Some speakers may feel constrained and that they can’t deviate from their script. Furthermore, while some find it easier to find their place with a quick glance down having the full manuscript, others find it difficult to avoid losing their place. If you go off script it can be harder to recover.
Successful Manuscript Delivery
A successful manuscript delivery requires a dynamic performance that includes lots of eye contact, animated vocals, and gestures. This can only be accomplished if you’re very familiar with the manuscript. Delivering a manuscript that you have written but only spoken aloud once before delivery will most often result in stumbling over words and eyes locked to the page. You’ll be reading aloud at your audience, instead of speaking to them. Remember what it’s like in school when a teacher asks a student to stand up and read something aloud? If the student isn’t familiar with the text, it can be a struggle both for the reader and the audience.
The key to avoiding this problem is to practice your written speech as much as you can, at least five or six times. You want to get so familiar with your speech that you can take your eyes off the page and make frequent eye contact with your audience. When you’re very familiar with your speech, your tone of speaking becomes more conversational. The text flows more smoothly and you begin to sound like a speaker, not a reader. You can enjoy the presentation and your audiences will enjoy it as well.
To improve your skills at manuscript delivery, practice reading written content aloud. This allows you to focus exclusively on delivery instead of worrying about writing a speech first. In particular, reading dialogue or passages from theatre plays, film/television scripts, or books provides material that is intended to be expressive and emotive. The goal is to deliver the content in a way that is accessible, interesting, alive, and engaging for the audience.
To Memorize or Not to Memorize
One way to overcome the problem of reading from the page is to memorize your word-for-word speech. When we see TED Talks, for example, they are usually memorized.
Memorized speaking is the delivery of a written message that the speaker has committed to memory. Actors, of course, recite from memory whenever they perform from a script. When it comes to speeches, memorization can be useful when the message needs to be exact, and the speaker doesn’t want to be confined by notes.
The advantage to memorization is that it enables the speaker to maintain eye contact with the audience throughout the speech. However, there are some real and potential costs. Obviously, memorizing a seven-minute speech takes a great deal of time and effort, and if you’re not used to memorizing, it’s difficult to pull off.
For strategies on how to successfully memorize a speech, refer to the “Memorization” section in the chapter “ From Page to Stage .”
Extemporaneous Delivery
Remember the fairy tale about Goldilocks and the Three Bears? One bed is too soft, the other bed is too hard, and finally one is just right? Extemporaneous delivery combines the best of impromptu and manuscript delivery. Like a manuscript speech, the content is very carefully prepared. However, instead of a word-for-word manuscript, the speaker delivers from a carefully crafted outline. Therefore, it has elements of impromptu delivery to it. We call this type of speaking extemporaneous ( the word comes from the Latin ex tempore, literally “out of time”).
Extemporaneous delivery is the presentation of a carefully planned and rehearsed speech, spoken in a conversational manner using brief notes. By using notes rather than a full manuscript, the extemporaneous speaker can establish and maintain eye contact with the audience and assess how well they understand the speech as it progresses. Without all the words on the page to read, you have little choice but to look up and make eye contact with your audience.
For an extemporaneous speech, the speaker uses a carefully prepared outline. We will discuss how to create an effective outline in the chapters on speechwriting.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Extemporaneous Delivery
Speaking extemporaneously has some major advantages. As mentioned above, without having a text to be beholden to it’s much easier to make eye contact and engage with your audience. Extemporaneous speaking also allows flexibility; you’re working from the solid foundation of an outline, but if you need to delete, add, or rephrase something at the last minute or to adapt to your audience, you can do so. Therefore, the audience is more likely to pay better attention to the message. Furthermore, it promotes the likelihood that you, the speaker, will be perceived as knowledgeable and credible since you know the speech well enough that you don’t need to read it. The outline also helps you be aware of main ideas vs. subordinate ones. For many speakers, an extemporaneous approach encourages them to feel more relaxed and to have more fun while speaking. If you’re enjoying presenting your speech the audience will sense that and consequently, they will enjoy it more.
A disadvantage of extemporaneous speaking is that it requires substantial rehearsal to achieve the verbal and nonverbal engagement that is required for a good speech. Adequate preparation can’t be achieved the day before you’re scheduled to speak. Be aware that if you want to present an engaging and credible extemporaneous speech, you’ll need to practice many times. Your practice will need to include both the performative elements as well as having a clear sense of the content you’ll cover. As mentioned previously, an extemporaneous speech can also be harder to have consistent and predictable timing. While delivering the speech it’s more likely you’ll wander off on a tangent, struggle to find the words you want, or forget to mention crucial details. Furthermore, if you get lost it may be harder to get yourself back on track.
Successful Extemporaneous Delivery
Like other delivery modes, a dynamic performance on an extemporaneous delivery is one that includes lots of eye contact, animated vocals, and gestures. At the same time, you want a speech that is structured and focused, not disorganized and wandering.
One strategy to succeed in extemporaneous speaking is to begin by writing out a full manuscript of your speech. This allows you to map out all the information that will be covered in each main point and sub-point. This method also gives you a better sense of your timing and flow than starting from just an outline. Another approach is to write out an outline that is less complete than a manuscript but still detailed. This will be used only for preparation; once you have a clear sense of the content you can reduce it down to a streamlined performance outline which you’ll use when delivering the actual speech.
By the time of presentation, an extemporaneous speech becomes a mixture of memorization and improvisation. You’ll need to be familiar enough with your content and structure that you cover everything, and it flows with logical transitions. Simultaneously, you must be willing to make changes and adapt in the moment. Hence, thorough rehearsal is critical. While this approach takes more time, the benefits are worth the extra effort required.
When you’re asked to prepare a speech for almost any occasion except last-minute speeches, you must choose either a manuscript or extemporaneous approach. As you experiment with assorted styles of public speaking, you’ll find you prefer one style of delivery over the other. Extemporaneous speaking can be challenging, especially for beginners, but it’s the preferred method of most experienced public speakers. However, the speaking occasion may dictate which method will be most effective.
Online Delivery
Impromptu, manuscript, and extemporaneous speaking are delivery modes . They describe the relationship between the speaker and the script according to the level of preparation (minutes or weeks) and type of preparation (manuscript or outline). Until now, we have assumed that the medium for the speech is in-person before an audience. Medium means the means or channel through which something is communicated. The written word is a medium. In art, sculpture is a medium. For in-person public speaking, the medium is the stage. For online public speaking, the medium is the camera.
The Online Medium
Public speakers very often communicate via live presentation. However, we also use the medium of recordings, shared through online technology. We see online or recorded speaking in many situations. A potential employer might ask for a short video self-presentation. Perhaps you’re recording a “How-To” video for YouTube. A professor asks you to create a presentation to post to the course website. Or perhaps an organization has solicited proposals via video. Maybe a friend who lives far away is getting married and those who can’t attend send a video toast. While this textbook can’t address all these situations, below are three important elements to executing recorded speeches.
Creating Your Delivery Document
As with an in-person speech, it’s important to consider all the given circumstances of the speech occasion. Why are you speaking? What is the topic? How much time do you have to prepare? How long is this speech? In online speeches, having a sense of your audience is critical. Not only who are they, but where are they? You may be speaking live to people across the country or around the world. If they are in a different time zone it may influence their ability to listen and respond, particularly if it’s early, late, or mealtime. If you’re recording a speech for a later audience, do you know who that audience will be?
As with in-person speeches, different speech circumstances suggest one of three delivery modes: impromptu, extemporaneous, or manuscript. Whether your medium is live or camera, to prepare you must know which of the three delivery modes you’ll be using. Just because a speech is online does not mean it doesn’t need preparation and a delivery text.
Technical Preparation
To prepare for online speaking, you’ll want to practice using your online tools. To begin, record yourself speaking so you have a sense of the way your voice sounds when mediated. Consider practicing making eye contact with your camera so that you feel comfortable with your desired focal point. In addition, consider how to best set up your speaking space. It may take some experimenting to find the best camera angle and position. Consider lighting when deciding your recording place. Make the lighting as bright as possible and ensure that the light is coming from behind the camera.
You should put some thought into what you’ll be wearing. You’ll want to look appropriate for the occasion. Make sure your outfit looks good on camera and doesn’t clash with your background. In general, keep in mind what your background will look like on-screen. You’ll want a background that isn’t overly distracting to viewers. Furthermore, ensure that there is a place just off-screen where you can have notes and anything else you may need readily at hand. Your recording location should be somewhere quiet and distraction-free.
You should test your camera and microphone to make sure they are working properly, and make sure you have a stable internet connection. But, even when you complete pre-checks of equipment, sometimes technology fails. Therefore, it’s helpful to know how to troubleshoot on the spot. Anticipate potential hiccups and have a plan for how to either fix issues that arise or continue with your presentation.
Vibrant Delivery
The tools for successful public speaking discussed in the rest of this textbook still apply to online speaking, but there are some key differences to consider before entering the virtual space. Online speaking, for example, will not have the same energy of a back-and-forth dialogue between speaker and live audience. If you’re recording without an audience, it might feel like you’re speaking into a void. You must use your power of imagination to keep in mind the audience who will eventually be watching your speech.
It’s important to utilize all your vocal tools, such as projection, enunciation, and vocal variety. Most important is having a high level of energy and enthusiasm reflected in your voice. If your voice communicates your passion for your speech topic, the audience will feel that and be more engaged. Use humor to keep your speech engaging and to raise your own energy level. Some experts recommend standing while giving an online speech because it helps raise your energy level and can better approximate the feeling of presenting in public.
If you’re presenting online to an audience, be sure to start the presentation on time. However, be aware that some participants may sign in late. Likewise, be cognizant about finishing your speech and answering any questions by the scheduled end time. If there are still questions you can direct the audience to reach out to you by your preferred means of communication. You may be able to provide the audience with a recording of the talk in case they want to go back and rewatch something.
Finally, consider ways you can enhance your performance by sharing images on the screen. Be sure you have that technology ready.
Other suggestions from experts include:
- Your anxiety does not go away just because you can’t see everyone in your “web audience.” Be aware of the likelihood of anxiety; it might not hit until you’re “on air.”
- During the question-and-answer period, some participants will question orally through the webcam set-up, while others will use the chat feature. It takes time to type in the chat. Be prepared for pauses.
- Remember the power of transitions. The speaker needs to tie the messages of their slides together.
- Verbal pauses can be helpful. Since one of the things that put audiences to sleep is the continual, non-stop flow of words, a pause can get attention.
As you begin delivering more public speeches you will likely find a preference for one or more of these delivery modes. If you are given a choice, it’s often best to lean into your strengths and to utilize the method you feel most comfortable with. However, the speech occasion may dictate your presentation style. Therefore, it’s important to practice and become comfortable with each mode. In an increasingly technological world online speaking in particular is likely going to be a required method of communication.
Media Attributions
- Delivery Modes and Delivery Document © Mechele Leon is licensed under a CC BY-NC-SA (Attribution NonCommercial ShareAlike) license
Public Speaking as Performance Copyright © 2023 by Mechele Leon is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Speech delivery practice
A speech is not an assignment that can be done the night before; practice is essential. Practicing a speech will boost your confidence as a speaker and ease potential anxiety.
Podium/lectern practice
Using or not using a podium does not make or break a speech. If using a podium, it should not be used to hide from the audience.
- Stand tall—do not hold or lean on the podium
- Makes an impact especially at the conclusion of the speech
- Allows audience to see you as a person, not just a face behind the podium
- Be sure gestures can be seen
- It is easy with a podium to look down especially if you have notes or outlines
- Maintain eye contact with the audience
Notes can be helpful. Know your instructor’s preference as some allow notes and some don’t.
- Make sure to look at the audience
- Know your notes well enough to find what you need
- Know at what point(s) in your speech you may need to look down at your notes
- Notes should be simple enough to keep the speech on track
A gesture is the movement of your hands to express an idea. When practicing your speech, do not practice gestures, let them occur naturally.
- Use natural gestures. Gestures should be relaxed and enhance your speech
- If the topic is exciting, then be excited
- Make gestures visible, even if using a podium/lectern
- Use gestures sparingly. Gestures should not be what the audience remembers about your speech
Vocal delivery
Your voice should be loud enough to be heard and have variation (not monotone). This occurs naturally in conversation with friends—so your speech should sound the same.
Try practicing the following to work on vocal variations and delivery.
- Tongue twisters
- Funny voices
These will help you transition to a natural variation in volume and tone.
Adapt to length of the speech
In extemporaneous speaking, there are no ties to a manuscript, so there is flexibility in structure.
- Move to conclusion of the speech
- The audience doesn’t know what was planned—they just experience the speech as it is delivered
- Understands your topic
- Remembers your thesis and key points
Be direct in speaking
For clarity and time constraints, watch for places where phrases can be more concise. Practicing your speech will allow you to hear where phrases can be shortened and made more concise. For example, instead of “due to the fact” say “because”.
Beebe, S. A., & Beebe, S. J. (2012). A concise public speaking handbook . Boston: Allyn & Bacon.
Lucas, S. (2012). The art of public speaking . New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Sprague, J. & Stuart, D. (2013). The speaker's compact handbook, 4th ed . Portland: Ringgold, Inc.
Vrooman, S. S. (2013). The zombie guide to public speaking: Why most presentations fail, and what you can do to avoid joining the horde . Place of publication not identified: CreateSpace.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
14.1 Four Methods of Delivery
Learning objectives.
- Differentiate among the four methods of speech delivery.
- Understand when to use each of the four methods of speech delivery.

Maryland GovPics – House of Ruth Luncheon – CC BY 2.0.
The easiest approach to speech delivery is not always the best. Substantial work goes into the careful preparation of an interesting and ethical message, so it is understandable that students may have the impulse to avoid “messing it up” by simply reading it word for word. But students who do this miss out on one of the major reasons for studying public speaking: to learn ways to “connect” with one’s audience and to increase one’s confidence in doing so. You already know how to read, and you already know how to talk. But public speaking is neither reading nor talking.
Speaking in public has more formality than talking. During a speech, you should present yourself professionally. This doesn’t mean you must wear a suit or “dress up” (unless your instructor asks you to), but it does mean making yourself presentable by being well groomed and wearing clean, appropriate clothes. It also means being prepared to use language correctly and appropriately for the audience and the topic, to make eye contact with your audience, and to look like you know your topic very well.
While speaking has more formality than talking, it has less formality than reading. Speaking allows for meaningful pauses, eye contact, small changes in word order, and vocal emphasis. Reading is a more or less exact replication of words on paper without the use of any nonverbal interpretation. Speaking, as you will realize if you think about excellent speakers you have seen and heard, provides a more animated message.
The next sections introduce four methods of delivery that can help you balance between too much and too little formality when giving a public speech.
Impromptu Speaking
Impromptu speaking is the presentation of a short message without advance preparation. Impromptu speeches often occur when someone is asked to “say a few words” or give a toast on a special occasion. You have probably done impromptu speaking many times in informal, conversational settings. Self-introductions in group settings are examples of impromptu speaking: “Hi, my name is Steve, and I’m a volunteer with the Homes for the Brave program.” Another example of impromptu speaking occurs when you answer a question such as, “What did you think of the documentary?”
The advantage of this kind of speaking is that it’s spontaneous and responsive in an animated group context. The disadvantage is that the speaker is given little or no time to contemplate the central theme of his or her message. As a result, the message may be disorganized and difficult for listeners to follow.
Here is a step-by-step guide that may be useful if you are called upon to give an impromptu speech in public.
- Take a moment to collect your thoughts and plan the main point you want to make.
- Thank the person for inviting you to speak.
- Deliver your message, making your main point as briefly as you can while still covering it adequately and at a pace your listeners can follow.
- Thank the person again for the opportunity to speak.
- Stop talking.
As you can see, impromptu speeches are generally most successful when they are brief and focus on a single point.
Extemporaneous Speaking
Extemporaneous speaking is the presentation of a carefully planned and rehearsed speech, spoken in a conversational manner using brief notes. By using notes rather than a full manuscript, the extemporaneous speaker can establish and maintain eye contact with the audience and assess how well they are understanding the speech as it progresses. The opportunity to assess is also an opportunity to restate more clearly any idea or concept that the audience seems to have trouble grasping.
For instance, suppose you are speaking about workplace safety and you use the term “sleep deprivation.” If you notice your audience’s eyes glazing over, this might not be a result of their own sleep deprivation, but rather an indication of their uncertainty about what you mean. If this happens, you can add a short explanation; for example, “sleep deprivation is sleep loss serious enough to threaten one’s cognition, hand-to-eye coordination, judgment, and emotional health.” You might also (or instead) provide a concrete example to illustrate the idea. Then you can resume your message, having clarified an important concept.
Speaking extemporaneously has some advantages. It promotes the likelihood that you, the speaker, will be perceived as knowledgeable and credible. In addition, your audience is likely to pay better attention to the message because it is engaging both verbally and nonverbally. The disadvantage of extemporaneous speaking is that it requires a great deal of preparation for both the verbal and the nonverbal components of the speech. Adequate preparation cannot be achieved the day before you’re scheduled to speak.
Because extemporaneous speaking is the style used in the great majority of public speaking situations, most of the information in this chapter is targeted to this kind of speaking.
Speaking from a Manuscript
Manuscript speaking is the word-for-word iteration of a written message. In a manuscript speech, the speaker maintains his or her attention on the printed page except when using visual aids.
The advantage to reading from a manuscript is the exact repetition of original words. As we mentioned at the beginning of this chapter, in some circumstances this can be extremely important. For example, reading a statement about your organization’s legal responsibilities to customers may require that the original words be exact. In reading one word at a time, in order, the only errors would typically be mispronunciation of a word or stumbling over complex sentence structure.
However, there are costs involved in manuscript speaking. First, it’s typically an uninteresting way to present. Unless the speaker has rehearsed the reading as a complete performance animated with vocal expression and gestures (as poets do in a poetry slam and actors do in a reader’s theater), the presentation tends to be dull. Keeping one’s eyes glued to the script precludes eye contact with the audience. For this kind of “straight” manuscript speech to hold audience attention, the audience must be already interested in the message before the delivery begins.
It is worth noting that professional speakers, actors, news reporters, and politicians often read from an autocue device, such as a TelePrompTer, especially when appearing on television, where eye contact with the camera is crucial. With practice, a speaker can achieve a conversational tone and give the impression of speaking extemporaneously while using an autocue device. However, success in this medium depends on two factors: (1) the speaker is already an accomplished public speaker who has learned to use a conversational tone while delivering a prepared script, and (2) the speech is written in a style that sounds conversational.
Speaking from Memory
Memorized speaking is the rote recitation of a written message that the speaker has committed to memory. Actors, of course, recite from memory whenever they perform from a script in a stage play, television program, or movie scene. When it comes to speeches, memorization can be useful when the message needs to be exact and the speaker doesn’t want to be confined by notes.
The advantage to memorization is that it enables the speaker to maintain eye contact with the audience throughout the speech. Being free of notes means that you can move freely around the stage and use your hands to make gestures. If your speech uses visual aids, this freedom is even more of an advantage. However, there are some real and potential costs. First, unless you also plan and memorize every vocal cue (the subtle but meaningful variations in speech delivery, which can include the use of pitch, tone, volume, and pace), gesture, and facial expression, your presentation will be flat and uninteresting, and even the most fascinating topic will suffer. You might end up speaking in a monotone or a sing-song repetitive delivery pattern. You might also present your speech in a rapid “machine-gun” style that fails to emphasize the most important points. Second, if you lose your place and start trying to ad lib, the contrast in your style of delivery will alert your audience that something is wrong. More frighteningly, if you go completely blank during the presentation, it will be extremely difficult to find your place and keep going.
Key Takeaways
- There are four main kinds of speech delivery: impromptu, extemporaneous, manuscript, and memorized.
- Impromptu speaking involves delivering a message on the spur of the moment, as when someone is asked to “say a few words.”
- Extemporaneous speaking consists of delivering a speech in a conversational fashion using notes. This is the style most speeches call for.
- Manuscript speaking consists of reading a fully scripted speech. It is useful when a message needs to be delivered in precise words.
- Memorized speaking consists of reciting a scripted speech from memory. Memorization allows the speaker to be free of notes.
- Find a short newspaper story. Read it out loud to a classroom partner. Then, using only one notecard, tell the classroom partner in your own words what the story said. Listen to your partner’s observations about the differences in your delivery.
- In a group of four or five students, ask each student to give a one-minute impromptu speech answering the question, “What is the most important personal quality for academic success?”
- Watch the evening news. Observe the differences between news anchors using a TelePrompTer and interviewees who are using no notes of any kind. What differences do you observe?
Stand up, Speak out Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Games, topic printables & more
- The 4 main speech types
- Example speeches
- Commemorative
- Declamation
- Demonstration
- Informative
- Introduction
- Student Council
- Speech topics
- Poems to read aloud
- How to write a speech
- Using props/visual aids
- Acute anxiety help
- Breathing exercises
- Letting go - free e-course
- Using self-hypnosis
- Delivery overview
- 4 modes of delivery
- How to make cue cards
- How to read a speech
- 9 vocal aspects
- Vocal variety
- Diction/articulation
- Pronunciation
- Speaking rate
- How to use pauses
- Eye contact
- Body language
- Voice image
- Voice health
- Public speaking activities and games
- About me/contact
- Speech delivery
What is delivery in speech?
The 2 basic principles of effective speech delivery and how to excel in both of them.
By: Susan Dugdale
Speech delivery is not WHAT you say, but HOW you say it. It's a catch-all term covering all the elements that make up giving a speech.
These include:
- the style or method you select to use to give your speech
- vocal aspects: how you use your voice
- personal presentation aspects: how you dress for the occasion, how you move and gesture, how you make eye contact, and how you use visual aids
Use the index below to find out more about how to deliver a good speech.
What's on this page
2 basic principles of effective speech delivery
The two basic principles underlying effective speech delivery are simple.
- that the speaker uses the most appropriate delivery style or method for the speech content, its purpose and its audience
- that audience engagement is highest when a speaker has thoroughly prepared and practiced
A speech is successful when the speaker fulfills both of them.
Return to top
Speech delivery for different situations
There are four basic styles or methods of speech delivery: manuscript, memorized, extemporaneous, and impromptu.
Each has its place. Which one you choose to use depends on the type of information you have to deliver, your speech purpose, the context or setting for it, your audience's expectations and needs, the time you have available to prepare the speech, and your own capabilities as a speaker.
Manuscript speeches
A manuscript speech is one that has been completely scripted: word for word, sentence by sentence, from beginning to end. It is read by the speaker, either from notes on paper or from a teleprompter.
Manuscript speeches are used by anybody whose words are going to be closely scrutinized and need to be 100% accurate, for example: newscasters, government and public service officials.
And they're also used by people who don't have the time available to thoroughly practice giving their speech any other way, and those who are speaking at an emotional occasion (for example a wedding or funeral) and don't want to run the risk of finding themselves overcome and literally at a loss for words.
Memorized speeches
A memorized speech is entirely committed to memory and delivered verbatim - word for word as written. To be successful you must have plenty of time to do the work required. Knowing a speech so thoroughly that you don't need to think about what comes next gives a speaker complete freedom to specifically tailor the delivery for the audience. That's a great experience!
Extemporaneous speeches
An extemporaneous speech is one combining the use of speaking notes (an outline or cue cards ) with key words and phrases for reference, and unscripted speech. It is the most common delivery style.
Although it may appear impromptu, it is not. To be effective the speaker will have rehearsed the speech carefully, particularly the transitions or links between points.
Impromptu speeches
An impromptu speech is one that is 'made up on the spot', generally without planning. These are mostly short and although they are often social speeches: for example, a welcome to an event, a toast, or a few words of thanks, they are also asked for in our workplaces. Examples are being requested at a meeting to quickly summarize current team issues, to give an overview of the state of the latest project etc.
For more information about each style please see: 4 modes of speech delivery .
Tools for effective speech delivery
Use the links to find out more about the techniques and tools needed for developing good speech delivery.
The 9 vocal aspects of speech delivery This is a very long page covering the impact of voice quality on our lives, ( how what we sound like in the ears of others affects what happens in our lives), the nine vocal aspects of speech delivery, (pitch, tone, articulation, pronunciation, volume, rate, fluency, pausing, and breath), and how to work with each of them. (Plus scholarly references.)
Specific vocal aspects of delivery with exercises
Voice image : how the quality of our voices is a major influence on what happens in our lives and the character traits we attribute to a person because of how their voice sounds. With links to scholarly research articles.
Vocal variety : pitch (how high or low our voice is and its range), tone (the emotional content conveyed by how the words are spoken eg. lovingly, angrily, shyly ...) and volume (how loud or soft our voice is).
Speech rate : how speech rate (talking too fast or too slowly) affects listeners, how to develop a flexible speaking rate to fit the needs of your content and those listening to you, six exercises.
How to calculate your own habitual speech rate : two ways to find out how fast you speak, speech rate guidelines, plus a standard test passage printable.
How many words per minute in a speech : a quick reference guide for the number of words needed for 1 - 10 minute speeches delivered at a slow, medium or fast speech rate.
Diction exercises : 35 articulation drills using tongue twisters, with audio examples.
Mrs Tongue Does Her Housework : a sequence of tongue stretches for improving agility and accuracy set to a simple story. An evergreen exercise that's been used by speech therapists and drama teachers for years!
Proper pronunciation : an overview of the possible consequences of mispronouncing common words and phrases. With links to truly excellent resources to assist with pronunciation issues.
How to use silence effectively : harnessing the power of the pause - the benefits of using pauses for both the speaker and the audience. An easily learned 'counting' method for working where pauses should be used, and how long to make them. With audio examples.
Voice health : how to look after your voice and keep it healthy. Very important for teachers, salespeople, call center workers - anybody who uses their voice in order to work.
The physical aspects of speech delivery
Breath : to deliver a speech well we need to breathe well which in turn will also help to control nervousness or anxiety about speaking in front of others. These exercises are easy to do and very effective.
Body language : how stance, gesture, facial expressions, eye contact, movement around the stage etc., influences how an audience responds to a speaker.
Eye contact : 5 exercises for teaching and practicing eye contact, the importance and meaning of eye contact, cultural differences - plus references.
Characterization for storytelling : an introduction to taking on physical and vocal characteristics to enhance telling a story as part of a speech.
Personal grooming : a checklist for speakers because how you present yourself matters.
How to practice a speech : step by step guidelines on how to thoroughly rehearse a speech. Preparing what you are going to say is the first half of the task. Presenting it is the second, and to do that well, you need to practice.
How to practice public speaking : 9 key ways to effectively prepare for a presentation. (This page is an excellent supplement to what's covered in how to practice a speech .)
Managing public speaking anxiety
Feeling nervous prior to giving a speech is absolutely normal. Most people feel like that and then, as they get into their presentation, the anxiety disappears. But sometimes it sticks around and it takes a little more effort to send it on its way.
These pages will help.
- 14 ways to calm public speaking fear
- Breathing exercises (especially recommended!)
- Letting go of public speaking fear - a free 7 part e-course
- How to manage public speaking anxiety using self-hypnosis
speaking out loud
Subscribe for FREE weekly alerts about what's new For more see speaking out loud

Top 10 popular pages
- Welcome speech
- Demonstration speech topics
- Impromptu speech topic cards
- Thank you quotes
- Impromptu public speaking topics
- Farewell speeches
- Phrases for welcome speeches
- Student council speeches
- Free sample eulogies
From fear to fun in 28 ways
A complete one stop resource to scuttle fear in the best of all possible ways - with laughter.

Useful pages
- Search this site
- About me & Contact
- Blogging Aloud
- Free e-course
- Privacy policy
©Copyright 2006-24 www.write-out-loud.com
Designed and built by Clickstream Designs
How to make a great presentation
Stressed about an upcoming presentation? These talks are full of helpful tips on how to get up in front of an audience and make a lasting impression.

The secret structure of great talks

The beauty of data visualization

TED's secret to great public speaking

How to speak so that people want to listen

How great leaders inspire action

Shortform Books
The World's Best Book Summaries
Speech Delivery: The Art of Public Speaking
This article is an excerpt from the Shortform book guide to "Talk Like TED" by Carmine Gallo. Shortform has the world's best summaries and analyses of books you should be reading.
Like this article? Sign up for a free trial here .
What makes a good speech delivery? What can you do to deliver your speech in the most impactful and persuasive way possible?
Speech delivery is how you say the words you’ve prepared. It involves many factors, such as how loudly you speak, the pitch of your speech, and how often you pause between points.
Here is how to improve your speech delivery, according to Carmine Gallo.
What Is Speech Delivery?
As the name suggests, speech delivery is how you deliver your speech: your tone, your pace, your body language, your demeanor. However, Gallo focuses on the one element of speech delivery that he believes is crucial to success: the speed of your speech. Speak too quickly, and people will struggle to understand what you’re saying. Speak too slowly, and your audience will swiftly become bored.
So, what speed is “just right”? After analyzing many TED talks, Gallo has concluded that the optimal rate of speech when giving a talk is around 190 words per minute. He argues that this is a conversational speed—for instance, the speed of speech you’d adopt if you were talking to a friend about your favorite TV show. Therefore, it’s a rate of speech that seems both natural and authentic.
An Exception to the Rule
There are some exceptions to this 190-words-per-minute rule. For instance, it’s acceptable to vary the speed of your speech to reflect the tone or content of what you’re saying. For example, when photographer Lisa Kristine gave a TED talk on modern slavery in 2012, she slowed down her rate of speech when she made the important point that despite slavery being illegal worldwide, it still exists almost everywhere. Making this point slowly added emphasis and gravitas to Kristine’s words.
Meanwhile, when Dr. Jill Bolte Taylor gave a 2013 TEDxYouth talk on how the brain changes throughout puberty, the rate of her speech delivery increase to 220 words per minute. She decided to speak this quickly to emphasize the swift nature of the brain’s transformation at this time of life.
Confident Body Language
Rehearse holding your body in a way that suggests you’re sure of yourself and your opinions. If you fail to appear confident in your convictions, your audience will trust you and your opinions less. After all, why would they believe or agree with what you’re saying if you don’t seem certain of it yourself?
There are a number of things you can do to exude confidence through body language:
- Stand up straight—don’t slouch.
- Hold your head up high, rather than looking downwards.
- Make frequent eye contact with the audience.
- Resist the urge to fidget—for instance, play with your hair or scratch your nose.
If you’re not sure which of these confident actions you’re taking already and which you aren’t, video yourself making a speech. Then, watch the video and identify where your problem areas lie.
Fake It ‘Till You Make It
If you’re already feeling confident about your speech delivery, confident body language will likely come naturally. However, if you’re feeling nervous or insecure, you may doubt your ability to hold your body in a way that’s contradictory to your emotions.
If you’re in the latter situation, don’t be afraid to “fake it ‘till you make it.” In other words, keep practicing confident body language no matter how insecure you actually feel. Studies have shown that doing so can actually make you feel more confident. Standing in a confident position increases your levels of testosterone —a hormone which, amongst other functions, increases your confidence—while simultaneously reducing levels of the stress hormone cortisol.
Researchers claim the so-called “power pose” is particularly effective at boosting confidence levels. This involves stretching your arms as wide as possible for two minutes.
Don’t Be Boring
As well as ensuring that your body language is confident, you also need to make sure that it’s not too boring. A common mistake that speakers make is staying still and rooted to the same spot for the entirety of their presentation. Such rigidity will make you seem dull and unenthusiastic about your topic. Instead, continually walk around your presentation space or stage, moving from one end to the other. Your constant movement will keep your audience engaged and make you seem more dynamic.
Hand Gestures
As you speak, don’t simply hide your hands in your pockets. Instead, use gestures to add emphasis to what you’re saying. For example, if you’re talking about how much a problem has grown in size, create a small circle with your hands and expand it. If you want to emphasize that you’ve personally experienced this problem, point at yourself.
Using hand gestures has a number of benefits:
- It prevents you from using your hands to fidget, thus helping you to exude confidence.
- Movement of any kind—including hand movement—makes you more interesting to watch, and therefore grips your audience’s attention.
- Studies have shown that making hand gestures will increase the audience’s confidence in you and what you’re saying.
Four Tips for Using Hand Gestures
Tip #1: Don’t use gestures too often. They’ll lose their impact and may become overly distracting. Only use gestures to punctuate crucial points of your presentation—for example, your main argument, or the conclusion of a story you’re telling.
Tip #2: Only use gestures that feel comfortable and natural to you. In particular, don’t try to mimic another person’s gesturing style—for example, that of a politician or famous speaker—if it’s out of your comfort zone. The gestures will seem forced and you’ll seem inauthentic.
Tip 3: Don’t overthink which gestures to use. Settle on those that feel the most natural and appropriate to the situation.
Tip #4: Keep your gestures within the “power sphere.” This is the area of the body from the eyes down to the navel. Placing your hands any lower than the navel suggests a lack of confidence and energy.
The ‘Eager Nonverbal’ Strategy
If you’re struggling to come up with appropriate hand gestures to use in your speech or presentation, consider applying the ‘eager nonverbal’ strategy. This is a three-pronged strategy that involves:
- Using hand movements that are expansive and animated: for example, opening your arms wide with your palms open.
- Using hand movements that project outward, towards the audience: for example, pointing in their direction.
- Leaning your body forward, again towards the audience.
Research has shown that using the eager nonverbal strategy can persuade others to act in the way you desire. For example, in one study, shoppers were more likely to buy candy from salespeople who implemented this strategy than from those who didn’t. In the case of a presentation, using the eager nonverbal strategy may help you to persuade your audience to adopt your idea or agree with your point of view.
Remember: As noted in the tips above, you should only implement someone else’s gesturing strategy—including the eager nonverbal strategy—if it feels natural and comfortable for you.
———End of Preview———
Like what you just read read the rest of the world's best book summary and analysis of carmine gallo's "talk like ted" at shortform ..
Here's what you'll find in our full Talk Like TED summary :
- The 9 key principles to good public speaking
- How to apply the public speaking strategies of popular TED talks
- How storytelling enhances your appeal to audiences
- ← Get Rid of Fear and Stop Playing It Safe
- James Clear: What Does It Take to Form a Habit? →

Darya Sinusoid
Darya’s love for reading started with fantasy novels (The LOTR trilogy is still her all-time-favorite). Growing up, however, she found herself transitioning to non-fiction, psychological, and self-help books. She has a degree in Psychology and a deep passion for the subject. She likes reading research-informed books that distill the workings of the human brain/mind/consciousness and thinking of ways to apply the insights to her own life. Some of her favorites include Thinking, Fast and Slow, How We Decide, and The Wisdom of the Enneagram.
You May Also Like

How to Deal With Change in a Relationship’s Phases

How to Build a Good Relationship With Your Boss

How to Define Your Message in Public Speaking

Mark Manson on Dating With Honesty

How to Improve Your Oral Communication Skills

The 10 Best Books About Friendship: Expand Your Circle
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Places on our 2024 summer school are filling fast. Don’t miss out. Enrol now to avoid disappointment
- 11 Tips for Giving a Great Speech
You might also enjoy…
- How to Survive Your First Academic Conference: 10 Vital Tips
- 6 Ways to Overcome Writer’s Block
Chances are you’ll be asked to give speeches or presentations in classes at school. If you get involved in volunteer groups, brief speeches to open events or thank participants are a must. Then there are the speeches at events such as weddings, as well as speeches that you might have to give in the workplace. That amounts to the average person being required to give quite a lot of speeches, even if they don’t get involved in an area such as politics where the ability to give a good speech becomes even more important. You might also have suffered through quite a number of bad speeches from other people – whether that’s at family events where the microphone squeaks the whole way through or a school presentation where the headteacher can’t quite make the jokes work. If you don’t want to inflict the same sort of experience on others, here are our top tips for giving a great speech.
1. Practise your microphone technique

2. Keep it short

Particularly at something like a party or a wedding, no one will be unhappy if your speech runs a little short; it’ll just give them more time to investigate the canapés. If you are giving a speech for a class in school, and it’ll be assessed, you need to prioritise keeping it within the required time limits. But even under these circumstances, if you’ve been tasked – say – with giving a 10-15 minute speech, it’s usually better to come in nearer the 10 than the 15 minute mark. Put simply, even if your speech is terrible, your audience can probably tolerate it for 10 minutes. Much longer, and they’ll be struggling. This shouldn’t limit what you can cover; in the film Up , the whole of Carl and Ellie’s heartbreaking love story is told in under 12 minutes. Do you really need longer to make your points? Achieve brevity by writing out the speech you would give if you had all the time in the world, and then cut anything that seems extraneous or boring.
3. Consider what your audience wants to hear
If you are giving a speech in class because it’s your assignment, what your audience wants to hear is likely to be “the bell ringing for lunch”; you can’t help them there. But under other circumstances, consider what your audience wants to hear and what you want to say, and strive for there to be as much overlap as possible. In the context of a political speech, for instance, what you want to say might be why your party should receive votes; what your audience wants to hear is what your party would do for them, if they won power. Hopefully it should be possible to write a speech that meets both sets of needs, rather than focusing solely on whatever it is that you want to say and leaving your audience disappointed.
4. Pick a theme and stick to it

Here’s a goal for giving a speech: someone sitting near the back, who’s messing around on their phone for at least two-thirds of it and focusing mainly on how long it will be until lunch, should nonetheless be able to give a reasonably accurate answer to the question, “what was it about?” If you’re supposed to be giving a speech in defence of the nuclear deterrent, for example, both the topic and your position on it should be clearly identifiable. This means – to stick with the nuclear deterrent example – not talking for a while about jobs, and then the wider economy, and then the North-South divide, and then Scottish independence, and then Ukraine with a brief digression into South Ossetia before rounding off by squeaking out “and that’s why we should renew Trident!” seconds before you run out of time – no matter how relevant that cornucopia of topics may feel (and they are all relevant, albeit tenuously). It means that even if you do have to take a while to explain a more complex idea, you need to be concise, and bring it back to your theme as quickly as you can.
5. Speak slowly
Most people speak more quickly than they realise when they’re on stage, especially if they’re nervous. But no one will be able to follow your speech if you’re jabbering it out. Thankfully, this one is easy to fix with a little effort and practise. First of all, figure out how quickly you’re actually speaking: do a word count for your speech and then time yourself saying it. A fast speaker will speak at maybe 160 words per minute, a slow speaker at 100 wpm and an average speaker at 130 wpm. For a formal speech, you want to be speaking on the slow side. While this will vary by culture and environment, 120 wpm is a reasonable target to aim for; slow enough that everyone should be able to understand you, and fast enough that you hopefully won’t be sending them to sleep.
6. Tell a couple of jokes

This is a tricky tip because there are lots of pitfalls in the world of telling jokes. For instance, there’s the temptation to include an in-joke that three of your friends will understand and find hilarious, that is utterly baffling to everyone else in the room. Avoid this – if you include any jokes, witty references or anything along those lines, make sure they are accessible to everyone present. All the same, if you can manage a joke or two, it can be a useful way to break up a speech and retain the audience’s interest. A little self-deprecation (not too much!) or the use of classic joke formats such as “the scene was chaotic; it looked as if a bomb had hit and we didn’t know where to start on repairs – but that’s enough about the hen party…” work nicely even if you’re not very confident. Don’t turn it into a stand-up comedy sketch if you’re not a comedian, don’t wait for ages for laughter that’s not showing up, and don’t make jokes at the expense of anyone who you don’t know for sure can take it.
7. Don’t be afraid to repeat yourself if you need to
If you follow US or UK politics at all, you’ve probably heard some of these phrases recently: take back control, make America great again, long-term economic plan, son of a bus driver. Three of these have already led the party or people they’re associated with to electoral victory; the fourth remains to be seen. To take the ‘son of a bus driver’ as an example, this refers to Sadiq Khan, now Mayor of London. There can be hardly anyone in London who doesn’t know what their Mayor’s dad did for a living. Meanwhile, many of them probably can’t remember his rival Zac Goldsmith’s name, let alone anything he said during the campaign. The point is that repetition works. In pursuit of point 4, if you want people to remember your key theme, you’re going to have to say it more than once. Don’t assume that everyone will have paid attention to everything you’ve said, unless you’re in a classroom setting where they’ll get told off if they don’t.
8. Only use the visual aids you need

This tip applies to two things: PowerPoints and notes. If you can do without either (and your assignment allows it), then do. Every time you’re glancing over your notes or up at the screen, fiddling with the laptop to get the slide to move on, fighting with a video that isn’t working or struggling to read your own handwriting, is time that you’re not spending engaging with your audience. A well-written, clear speech delivered without notes is always going to be better than someone awkwardly reading aloud the bullet points on their PowerPoint slides. If you must do a presentation – for instance, because there are photos that need to be included – have as little text on it as possible, preferably none. That way, if there are people at the back who can’t really see the screen through the sea of heads in front of them, they’ll still be able to follow what you’re saying.
9. Get a friend to check for awkward mannerisms
Mannerisms that are entirely fine in normal life become awkward and strange when you’re speaking in public. Perhaps you’re inclined to fiddle with your hair or your cuffs, you rock back and forth on the balls of your feet, or you have a habit of reaching your hand to your cheek when you’re talking. No one would notice in everyday conversation, but when you’re on a stage, it’ll become all they’ll see. Some of this is easily avoidable – for instance, if you have long hair that you’re inclined to twirl or otherwise fiddle with, tie it up. For other mannerisms, get the critical friend who helped you sort out your microphone technique to tell you what they are, and do your best to suppress the more annoying ones.
10. Look around the room

Talking about eye contact usually has the effect of making normal eye contact a lot harder, and so does giving a speech. All of a sudden, you’re up on stage, and you have no idea what a normal way to look at a group of people is. Some speakers deal with this by picking a point in the middle distance and speaking to it; others by picking a particular person near to the back and addressing their entire speech at them. This is obviously no fun for that person, who probably spends the whole thing feeling extremely uncomfortable, but it’s not too weird for everyone else. Better still, though, if you can manage it, is to look slowly and steadily around the room, trying to make eye contact with a decent range of people, before returning to the middle distance for a while, rinse and repeat. This needs to be slow and steady, or you give the impression that you’ve just smelled smoke and are casting about for a fire exit before the stampede beings.
11. Don’t be scared of a good reaction
If your speech is genuinely engaging, funny, inspiring or any of the other things you might hope it would be, your audience will react to it. There might be laughter, or applause, or even a bit of cheering depending on the setting. This can be daunting because when you’re practising your speech in front of your bedroom mirror, there’s no way to prepare for it. And it’s where even the best speakers can go wrong, by launching straight into what they were going to say next without waiting for the laughter or applause to stop, or by looking painfully awkward while it’s going on. It’s a pitfall that’s mostly solved by being aware it might happen. If your audience is applauding you or otherwise reacting well, it’s OK to smile, look up, wait for them to stop and then keep going with your speech – it’s as simple as that. You could even throw in a “thank you” before you continue in the knowledge that it’s all going well. Image credits: microphones ; audience ; boy with microphone ; clock ; winding road ; enjoy a joke ; sticky notes ;

The 8 Key Elements of Highly Effective Speech
…and why your words barely matter.
Posted July 10, 2012 | Reviewed by Ekua Hagan
I’d like you to take a moment to experience the following sentence, taken from a recent article exploring the nature of human consciousness: “Neuroplastic mechanisms relevant to the growing number of empirical studies of the capacity of directed attention and mental effort systematically alter brain function.”
Exciting? Hardly! In fact, most of the words you read barely register in your brain, and most of the words you speak barely register in the listener’s brain. In fact, research shows that words are the least important part of communication when you have face-to-face conversations with others. So before you utter another word to another person, memorize this list of the 8 key elements of highly effective speech:
- Gentle eye contact
- Kind facial expression
- Warm tone of voice
- Expressive hand and body gestures
- Relaxed disposition
- Slow speech rate
- The words themselves
Effective communication is based on trust, and if we don’t trust the speaker, we’re not going to listen to their words. Trust begins with eye contact because we need to see the person’s face to evaluate if they are being deceitful or not. In fact, when we are being watched, cooperation increases. [1] When we are not being watched, people tend to act more selfishly, with greater dishonesty. [2]
Gentle eye contact increases trustworthiness and encourages future cooperation, [3] and a happy gaze will increase emotional trust. [4] However, if we see the slightest bit of anger or fear on the speaker’s face, our trust will rapidly decrease. [5] But you can’t fake trustworthiness because the muscles around your mouth and eyes that reflect contentment and sincerity are involuntary. Solution: if you think about someone you love, or an event that brought you deep joy and satisfaction, a "Mona Lisa" smile will appear on your face and the muscles around your eyes will soften.
The tone of your voice is equally important when it comes to understanding what a person is really trying to say. If the facial expression expresses one emotion , but if the tone conveys a different one, neural dissonance takes place in the brain, causing the person confusion. [6] The result: trust erodes, suspicion increases, and cooperation decreases.
Researchers at the University of Amsterdam found that expressions of anger, contempt, disgust, fear, sadness, and surprise were better communicated through vocal tone than facial expression, whereas the face was more accurate for communicating expressions of joy, pride, and embarrassment . [7] And in business, a warm supportive voice is the sign of transformational leadership , generating more satisfaction, commitment, and cooperation between other members of the team. [8]
You can easily train your voice to convey more trust to others, and all you have to do is slow down and drop your pitch. This was tested at the University of Houston: when doctors reduced their speaking rate and pitch, especially when delivering bad news, the listener perceived them “as more caring and sympathetic.” [9] Harvard's Ted Kaptchuk also discovered that using a warm voice would double the healing power of a therapeutic treatment. [10]
If you want to express joy, your voice needs to become increasingly melodic, whereas sadness is spoken with a flat and monotonic voice. When we are angry, excited, or frightened, we raise the pitch and intensity of our voice, and there’s a lot of variability in both the speed and the tone. However, if the emotion is incongruent with the words you are using, it will create confusion for the listener. [11]
Gestures, and especially hand movements, are also important because they help orchestrate the language comprehension centers of your brain. [12] In fact, your brain needs to integrate both the sounds and body movements of the person who is speaking in order to accurately perceive what is meant. [13] From an evolutionary perspective, speech emerged from hand gestures and they both originate the same language area of the brain. [14] If our words and gestures are incongruent, it will create confusion in the listener’s brain. [15] Our suggestion: practice speaking in front of a mirror, consciously using your hands to “describe” the words you are speaking.

Your degree of relaxation is also reflected in your body language , facial expressions, and tone of voice, and any form of stress will convey a message of distrust . Why? Your stress tells the observer’s brain that there may be something wrong, and that stimulates defensive posturing in the listener. Research shows that even a one-minute relaxation exercise will increase activity in those parts of the brain that control language, communication, social awareness, mood-regulation, and decision-making . [16] Thus, a relaxed conversation allows for increased intimacy and empathy. Stress, however, causes us to talk too much because it hinders our ability to speak with clarity.
When you speak, slow down! Slow speech rates will increase the ability for the listener to comprehend what you are saying, and this is true for both young and older adults. [17] Slower speaking will also deepen that person’s respect for you, [18] Speaking slowly is not as natural as it may seem, and as children we automatically speak fast. But you can teach yourself, and your children to slow down by consciously cutting your speech rate in half. A slow voice has a calming effect on a person who is feeling anxious , whereas a loud fast voice will stimulate excitement, anger, or fear. [19]
Try this experiment: pair up with a partner and speak so slowly that … you … leave … 5 … seconds … of … silence … between … each … word. You’ll become aware of your negative inner speech that tells you that you should babble on endlessly and as fast as possible. It’s a trap, because the listener’s brain can only recall about 10 seconds of content! That’s why, when we train people in Compassionate Communication, we ask participants to speak only one sentence at a time, slowly, and then listen deeply as the other person speaks for ten seconds or less. This exercise will increase your overall consciousness about the importance of the first 7 elements of highly effective communication. Then, and only then, will you truly grasp the deeper meaning that is imparted by each word spoken by others.
But what about written communication, where you only have access to the words? When it comes to mutual comprehension, the written word pales in comparison to speech. To compensate, your brain imposes arbitrary meanings onto the words. You, the reader, give the words emotional impact that often differs from what the writer intended, which is why so many email correspondences get misinterpreted. And unless the writer fills in the blanks with specific emotional words and descriptive speech – storytelling – the reader will experience your writing as being flat, boring , dry, and probably more negative than you intended.
The solution: help the reader “paint a picture” in their mind with your words. Use concrete nouns and action verbs because they are easier for the reader’s brain to visualize. Words like “sunset” or “eat” are easy to see in the mind's eye, but words like “freedom” or “identify” force the brain to sort through too many conceptual frameworks. Instead, our lazy brain will skip over as many words as possible, especially the abstract ones. When this happens the deeper levels of meaning and feeling will be lost.
For more information on how to improve your speaking and listening skills, along with additional exercises to practice, see Words Can Change Your Brain: 12 Conversation Strategies for Building Trust, Reducing Conflict, and Increasing Intimacy (Newberg & Waldman, 2012, Hudson Street Press).
[1] Cues of being watched enhance cooperation in a real-world setting. Bateson M, Nettle D, Roberts G. Biol Lett. 2006 Sep 22;2(3):412-4.
[2] Effects of anonymity on antisocial behavior committed by individuals. Nogami T, Takai J. Psychol Rep. 2008 Feb;102(1):119-30.
[3] Eyes are on us, but nobody cares: are eye cues relevant for strong reciprocity? Fehr E, Schneider F. Proc Biol Sci. 2010 May 7;277(1686):1315-23.
[4] Evaluating faces on trustworthiness: an extension of systems for recognition of emotions signaling approach/avoidance behaviors. Todorov A. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008 Mar;1124:208-24.
[5] Common neural mechanisms for the evaluation of facial trustworthiness and emotional expressions as revealed by behavioral adaptation. Engell AD, Todorov A, Haxby JV. Perception. 2010;39(7):931-41.
[6] Use of affective prosody by young and older adults. Dupuis K, Pichora-Fuller MK. Psychol Aging. 2010 Mar;25(1):16-29.
[7] "Worth a thousand words": absolute and relative decoding of nonlinguistic affect vocalizations. Hawk ST, van Kleef GA, Fischer AH, van der Schalk J. Emotion. 2009 Jun;9(3):293-305.
[8] Leadership = Communication? The Relations of Leaders' Communication Styles with Leadership Styles, Knowledge Sharing and Leadership Outcomes. de Vries RE, Bakker-Pieper A, Oostenveld W. J Bus Psychol. 2010 Sep;25(3):367-380.
[9] Voice analysis during bad news discussion in oncology: reduced pitch, decreased speaking rate, and nonverbal communication of empathy. McHenry M, Parker PA, Baile WF, Lenzi R. Support Care Cancer. 2011 May 15.
[10] Components of placebo effect: randomised controlled trial in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Kaptchuk TJ, Kelley JM, Conboy LA, Davis RB, Kerr CE, Jacobson EE, Kirsch I, Schyner RN, Nam BH, Nguyen LT, Park M, Rivers AL, McManus C, Kokkotou E, Drossman DA, Goldman P, Lembo AJ. BMJ. 2008 May 3;336(7651):999-1003.
[11] Use of affective prosody by young and older adults. Dupuis K, Pichora-Fuller MK. Psychol Aging. 2010 Mar;25(1):16-29.
[12] Gestures orchestrate brain networks for language understanding. Skipper JI, Goldin-Meadow S, Nusbaum HC, Small SL. Curr Biol. 2009 Apr 28;19(8):661-7.
[13] When language meets action: the neural integration of gesture and speech. Willems RM, Ozyürek A, Hagoort P. Cereb Cortex. 2007 Oct;17(10):2322-33.
[14] When the hands speak. Gentilucci M, Dalla Volta R, Gianelli C. J Physiol Paris. 2008 Jan-May;102(1-3):21-30. Epub 2008 Mar 18.
[15] How symbolic gestures and words interact with each other. Barbieri F, Buonocore A,Volta RD, Gentilucci M. Brain Lang. 2009 Jul;110(1):1-11.
[16i] Short-term meditation training improves attention and self-regulation. Tang YY, Ma Y, Wang J, Fan Y, Feng S, Lu Q, Yu Q, Sui D, Rothbart MK, Fan M, Posner MI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Oct 23;104(43):17152-6.
[17] Comprehension of speeded discourse by younger and older listeners. Gordon MS, Daneman M, Schneider BA. Exp Aging Res. 2009 Jul-Sep;35(3):277-96.
[18] Celerity and cajolery: rapid speech may promote or inhibit persuasion through its impact on message elaboration. Smith SM, Shaffer, DR. Pers Soc Psychol Bull. 1991 Dec;17(6):663-669.
[19] Voices of fear and anxiety and sadness and depression: the effects of speech rate and loudness on fear and anxiety and sadness and depression. Siegman AW, Boyle S. J Abnorm Psychol. 1993 Aug;102(3):430-7. The angry voice: its effects on the experience of anger and cardiovascular reactivity. Siegman AW, Anderson RA, Berger T. Psychosom Med. 1990 Nov-Dec;52(6):631-43.

Andrew Newberg, M.D ., and Mark Robert Waldman are the authors of Words Can Change Your Brain .
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that threatens to derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face our triggers with less reactivity so that we can get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

Ace the Presentation

3 KEY Things For Delivering a Successful Speech
Speeches are moments that are part of our routine, whether it’s graduation, weddings, anniversaries, and company gatherings, meetings with co-workers, social events, and manifestations.
What is a Good Speech Delivery?
A good speech does not use sophisticated words; the words may even seem the most critical factor in speeches, but the great speakers are those who focus less on each word and more on the idea they want to convey.
Good speech delivery can persuade or transmit a message in a convincing way by adapting to the public to whom it will be presented.
Primary Purposes of a Speech
- To Persuade
- To Instruct
- To Entertain
- To Appreciate
Highly Recommended Article: 7 Elements of Public Speaking

1. The Message We Want to Deliver
Nick Morgan, author of the book “Power Cues: The Subtle Science of Leading Groups, Persuading Others, and Maximizing Your Personal Impact.” (Signs of Power: The Subtle Science of Group Leadership, Persuasion, and Maximization of Its Impact”), argues that a great speaker should have regard for the public and should be prepared to talk to particular types of audience.
“A speech is not ours entirely, and it is partly ours, the audience and the occasion, the circumstances.”
As the speakers, we must ask ourselves:
- Who is the audience?
- What do you want?
- What do we fear?
- For what purpose have you invited me to speak?
- What aspect of my speech will be most relevant.
We have to consider the current situation, something that the majority of the audience knows, topics and points that should not speak, and think about what the audience needs to hear.
2. The overall Structure and Sequence of Events
To elaborate on an attractive speech, we must devote time to write a script detailing everything we would like to say during our speech.
- Define the theme and focus of our speech;
- Then seek information and references on this subject to support our talking.
With all the information in hand, we begin to structure our speech, dividing it into three central moments :
- Introduction
Remember that the introduction is when you will gain (or not) the attention of people, giving importance to the beginning of our speech, thinking of forms interesting to start your speech.
- Content Developing
According to Scottish philosopher and educator George Campbell, speeches serves four main objectives:
- Stir up the imagination;
- Foster understanding;
- Arouse passion;
- Influence determination.
So our content development should be guided following the points above, create a background for the task: write down the theme, the general and specific objectives, the main topics, and, finally, the conclusion. In this way, you will have a coherent flow, with less chance of getting lost in ideas and a greater probability of making ourselves understood by the audience.
The conclusion of a speech is also a crucial step. Generally, the most significant and inspirational communicators of history destined their speeches’ final moments to increase the burden of emotion to awaken people’s feelings about what was said.
3. Practice your Speech
With the script in hand, it’s time that we practice our speech, read it aloud until we get familiarized with the text, use this step to identify:
- Errors, cacophony, over-repeated words, among other things, improved.
- During our rehearsals aloud, we should take the opportunity to calculate the duration of our speech, ensuring that it is not too long or too short;
- With practice, start speaking our speech without reading everything we have written, and eventually, we’ll have the essentials.
Some situations, such as graduations, still allow the speaker to read his speech. In others, the ideal is for us to give our speech without the need to read the full text, so it’s good to be prepared for whichever scenarios.
Golden Tip : Practice your speech in front of other people and ask for the point of view. An outside view helps a lot in our speech improvement, ensuring it’s perfect on the event’s day.
Importance of Delivery in a Speech
Speech delivery techniques, using relatable quotes.
When making the quote, we need to remember two essential things:
- Quote the source of the statement;
- Relate the citation to the central theme of the presentation.
For example, the president of a company can talk about significant changes happening within the organization, citing the famous phrase of Franklin Roosevelt, spoken during the Great Depression, to calm the nation:
“The only thing we have to fear is fear itself.”
Present-Future Technique
A good speech inspires, regardless of context, and a graduation speech can be inspiring, a wedding toast, too. It will all depend on the content and, most importantly, how we present the speech.
The Present-Future technique is to make the public visualize a real future because of an attitude we take today.
For example, “Today, we are newly graduated doctors because we follow our vocation, tomorrow, we will be happy professionals who will take care of people’s lives.”
In the summary form, we mean that by listening to our intuition and graduating from what we love – medicine; to dedicate ourselves and today becomes a tomorrow rewarding.
Using Humor in your speech.
A touch of humor (tasteful, of course) is a great way to break the ice with the audience, relieve tension and connect with everyone. As the example given above quote, the key to success is to make the joke stand linked to the topic to be discussed.
Otherwise, it will serve as a distraction and could divert the public’s attention, regardless of the joke’s tone.
Golden Tip: If that’s not your style, you can address the other tips in this article.
Tell a Story with Emotion
During the presentation, telling a story is another very clever way to start a speech. After all, stories connect people in a compelling way .
As in the case of jokes, our story needs:
- Bridge or contain a message that can link the introduction to the content of the presentation.
An excellent way to use storytelling is to use an “imaginary” scenario, but that is the history of life that people can relate to; this will leave interested participants and be able to identify themselves better with us.
Examples of Great Leaders who are well known for their Speeches
Sir winston churchill.
The former prime minister of England was characterized by his consistently accurate comparisons, which facilitated the understanding of different audiences on complex topics.
As Churchill himself defined in one of his many speeches in the British parliament:
“A proper analogy connects the most distant spheres.”
When someone can bring elements that bring people closer to reality, it is possible to draw parallels with subjects, sometimes little known by them.
Nelson Mandela
Ex-President of South Africa and prominent leader against the known segregation regime known as Apartheid, Mandela had at the pace the highest quality for his excellent conversation.
Through dramatic pauses, he could capture everyone’s attention and give due importance to what was being said.
The appeal could be easily noted in Mandela’s inaugural speech as President of Africa South in 1994 – mainly by listing with adjectives the government’s objectives.
If you search your lines on YouTube, you will notice that the African leader also has the custom to always cite examples in the group of three. It’s not a pure coincidence.
The three is a powerful number and can be easily remembered by people; in one of their demonstrations against apartheid, Mandela spoke:
“For a complete, just, and lasting peace.”
Barack Obama
Another leader who has made a name for his great speeches while in charge of his was the United States president, Barack Obama.
Obama, in turn, had as its main feature the emphasis used on certain words during a sentence, those taken as the most important, which represented the central idea of everything.
An example of this is the slogan for his 2008 presidential campaign entitled “Yes, we can.”
The strategy was a way of valuing the American people’s importance in their search for solutions to overcome difficulties, but not only that. The feature was also a way found by Obama not to pose as just more, among others, trying to make a difference.
The creator of Apple trained eight hours before presenting any of their products; the training was also a way for Jobs to improve his performance as a speaker. Each word of his speech was meticulously tested to assess the impacts it could cause.
The care with the speech was practically the same adopted with his inventions, highlighting the importance that the entrepreneur gave to communication.
Discourse is any situation that involves a set of ideas organized through language to influence the reasoning, or at least the feelings of the listener or reader. Discourse is a form of communication within a particular context and concerns the speaker, the speaker, and the speaker.
Reference and Further Reading
Hamilton.EDU Tips for Effective Delivery
OpenLib.EDU Practicing for Successful Speech Delivery
AMADEBAI, Emídio. 8 Awesome Persuasive Speech Techniques. AcethePresentation.
AMADEBAI, Emídio. 9 Basic Elements of a Great Persuasive Speech. AcethePresentation.
AMADEBAI, Emídio. 11 Best Body Language Tips for Engaging Presentations. AcethePresentation.
Similar Posts

Diction – A Key Rhetorical Device and Staple for Speakers
Language is quite a peculiar thing, don’t you feel? We all use it every single day for one thing or the other, but we’re pretty sure few of you stop and ponder about what kind of words you use, how you use them, and whether they’re having any impact on your audience. This is where…

80+ Impromptu Speech Topics & 7 Ways to Nail One
What is an impromptu speech? An impromptu speech is one delivered without prior notification and preparation. For certain persons who may not be easily open to giving public speeches, an impromptu speech may be a total scare in general. However, there are ways to make sure that impromptu speeches are not as scary as it…

Formal Speech Style Examples
Formal speech is used in professional settings, such as business meetings, presentations and job interviews; it’s important to stay aware of your audience when using a formal style of speaking. This article will explain the various types of formal speech style examples available and how they should be used. Formal speech style examples include using…

15 Ideas To Make A Speech Unique, Memorable & Inspiring
Are you often called to speak in front of others? If yes, then the art of making your speech unique, memorable, and inspiring is something you should be able to do with little or no effort. This is important because listening to a yawn-inducing and lifeless speech is one of the worst things your audience…

17 Ways to Help Your Child Develop Public Speaking Skills (Public Speaking Tips for Kids)
Speaking in public can be nerve-wracking for a lot of people, and is one area many people shy away from a lot. But if this important skill can be learned at a very early age, kids stand to gain a lot of benefits from it that can serve them well into adulthood. Therefore, today we…

15 Solid Public Speaking Tips for Women
Women differ from men in a number of ways. One of such ways is the manner each of them makes speeches and conveys information. We will be discussing below, a couple of public speaking tips for women, so that more women can harness and polish their public speaking skills. Men are more of natural orators…

How Do You Deliver a Successful Speech?
April 1, 2022
College News
Share Options
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Linkedin

The McKinney Prize is offered to students in each class year for a persuasive speech. Abbie Wolff ’22 was the senior winner with the topic “ Apathy and Access: Accessibility at Hamilton College .” The underclass winner was Tinashe Dylan Manguwa ’25 with his speech, “ Here is Holy .”
The Clark Prize requires students to respond to a specific prompt in a persuasive speech. This year's prompt was “What lesson(s) should we learn from the COVID-19 pandemic?” Cherry Zhang ’23 was the winner with her speech. “ How Productive Should I Be? Reflections on the Meanings of Work .”
Wolff also won the Warren E. Wright Prize , which is reserved for students who have taken a public speaking course and present an informative speech on the topic of their choosing. Her speech was “ Reimagining Time and Space with Walkable Communities .”
We asked the winners to share three suggestions or pieces of advice.

Tinashe Dylan Manguwa ’25
- Be personal . No one can tell your story for you, which makes it that much more powerful. So, speak out about that which tugs at your heartstrings because others can then find themselves within your story.
- Be impartial . It is tempting to believe everything is great about your speech and you can do no wrong, but acknowledge your limitations. Reach out and seek help. Study past winning speeches to gauge what made them unique and compelling.
- Be patient . The process takes time, from writing the speech, to memorization to presentation. One should give themselves grace and leverage all parts of the process.

Abbie Wolff ’22
- Writing a speech is different from writing an essay. Your speech should use more casual language and shorter sentences. As you write, be sure to read your speech aloud to see how it sounds.
- Move around the stage, but remember to plant your feet! Movement is a powerful tool to emphasize points and indicate transitions. Plan these movements out ahead of time. Constant movement can distract from your message.
- Utilize hooks, anecdotes, and analogies to keep your audience engaged. Small stories, or explaining a point in a new way can help you be memorable. Try drawing upon your own life to find stories that can help you relate with your audience.

Hamilton’s annual Public Speaking Competition gives students an opportunity to demonstrate their abilities while competing for more than $15,000 in prizes.
Cherry Zhang ’23
- Practice, practice, and practice. Practice everything from your tonality to your facial expression.
- Always remember why you are giving the speech in the first place: it’s because you have something valuable to share with others.
- If you forget anything on the spot, no one would know. Just carry on!
At Hamilton, we believe written and oral communication skills are critical for successful lives and careers. Students hone these with support from the College’s writing and oral communication centers so they can present their ideas clearly and persuasively.
Photo Gallery

Help us provide an accessible education, offer innovative resources and programs, and foster intellectual exploration.
Site Search

- Find a Club
- Start a Club
- Toggle Search
- / Resources
- / Public Speaking Tips
- / Successful Speeches
Successful Speeches

- Be prepared. Your audience is giving you their time and consideration, so rehearse enough to be confident you'll leave a good impression.
- Start strong. Begin your speech with a powerful opening that will grab your audience's attention, such as a startling fact or statistic, an interesting story or a funny joke.
- Be conversational. Avoid reading your speech word for word. Instead, refer to notes or points from an outline to help your speech have a more free-flowing, conversational tone.
- Speak with passion. If you're truly invested in what you're saying, you'll be better able to keep your audience's attention.
- Be patient. It's easy to get frustrated if you make a mistake. But remember that public speaking is not easy and it takes time to hone your skills. Keep practicing and you will reach your goals.
Back to previous page
Helpful Resources
Scared of public speaking.
You’re not alone. Learn why giving speeches can be terrifying—and how to tame the fear.
How to Rock Your Presentation
Avoid these top 10 mistakes.
A Word About the Word of the Day
Knowing why you care is key, especially in workplace communication.
Ditch the Notecards
Step-by-step methods for helping you internalize your speech.
Present With Executive Presence Online
Learn how to convey confidence in a virtual setting with these five key elements.
Quick Links
Tips for success.
Enjoy helpful resources that will aid you in improving your communication and help you build leadership skills.
Hybrid Meeting Tips
Learn how to run a successful hybrid meeting.
Come to Learn!
Don't miss the inspiring, insightful education sessions.
Connect With Us
Follow us on Facebook, X, LinkedIn, Instagram, TikTok, and YouTube for exciting updates, inspiration, and more.
10 steps for delivering a great speech
by Carole Bozkurt | Sep 19, 2012 | Blog | 4 comments

Many people dread the thought of public speaking, myself included. However, if you are an entrepreneur, solo operator or running a small company there will come a time when you are going to have to step out onto the stage and perform. Yes, it’s called making a speech. One of the most nerve racking experiences apart from doing a bungee jump – somehow that just scares me more! To deliver a good speech, let alone a great speech, you need to view what you are doing as a performance rather than making a presentation. You need to see yourself as the prima ballerina of your company and you need to practice your craft until it becomes effortless so that you alone are seen as the expert in the room.
Follow the steps listed below and you will soon be giving a first-class performance.
- Watch the experts in action and notice their style and habits – what can you learn from them? Look at people both in and outside of your industry. Great examples of good public speakers are: Oprah Winfrey, Bill Gates, Cheryl Sandberg, Martin Luther King Jr, Margaret Thatcher, HRH Prince of Wales and President Barak Obama. Watch how they deliver those important speeches and ask yourself what are their key messages, how quickly do they speak, how often do they pause, how much eye contact do they make with their audiences?
- Regardless of how many times you’ve made a speech there is always room for improvement. It’s great if you got public speaking experience but don’t become over confident and think that you can just turn up and present without doing your homework! You might get away with it a couple of times but eventually you will be caught out.
- Your opening statement needs to ‘pack a punch’ – tell a joke – probably one of the hardest things to do unless you are a stand-up comedian, or share a shocking statistic, ask a question and get the audience to participate by a show of hands or by using an interactive voting system. Julie Hall, CEO and founder of Women Unlimited, always creates an uplifting energy in the room by sharing a funny video.
- Arrange your presentation into digestible chunks but remember that you want your audience to walk away with at least three points from your talk that remain at the forefront of their mind.
- Preparation includes taking care of yourself so makes sure that you run through your speech the day before with a friend, get a good night’s sleep and don’t drink alcohol to the point where you wake up with a hangover. And when presenting make sure you have room temperature water at hands. Cold water makes the throat constrict.
- On the day of your speech make sure you arrive with enough time to settle yourself. Take time to visit the room you will presenting in and run through your speech. Becoming familiar with the room and how it’s set up technically will help settle any nerves and you should always remember to test the equipment.
- One of the most common errors people make when giving a speech, especially if they are new to public speaking, is they rush through their presentation. You need to slow down so that people can actually take on board what you are saying. If in doubt record yourself and play it back, if you are speaking faster than the anchor person on the news you know it’s too fast.
- Even the best of speakers use notes/q-cards as a guide for their speech but they are not used as a crutch. Notes help the speaker keep on track and therefore they should be bullet points with no more than 3-4 words per point – if you can use one then that’s all the better but remember your notes should not be a script.
- When you stand up to speak walk slowly to the podium and wait a few seconds, suddenly an eerie silence will descend on the room, you then know you have everyone’s attention and you can start your presentation.
- Be authentic –people can hear it in your voice when you are authentic and they will love you for it.
Getting up and talking in public takes a lot of courage and like most things in life the more you do it the better you become. So what are you waiting for?
Recent Posts
- How to improve engagement with your blog
- Standing out in a crowded market
- New Year, New Goals
Follow Me Here
- GROW YOUR BUSINESS AND ATTRACT YOUR IDEAL CLIENTS
- GET CLARITY AND DIRECTION
- STAND OUT IN YOUR MARKETPLACE

Powered by OptinMonster

The Top Characteristics Of A Good Speech
“I tell my story, not because it is unique, but because it is not. It is the story of many…

“I tell my story, not because it is unique, but because it is not. It is the story of many girls… Though I appear as one girl, one person, who is 5ft 2in tall, if you include my high heels, I am not a lone voice, I am many. I am Shazia. I am Kainat Riaz. I am Kainat Somro. I am Mezon. I am Amina. I am those 66 million girls who are out of school.”
The youngest-ever Nobel Prize winner, Malala Yousafzai, then 17, uttered these evocative words at her acceptance speech in 2014.
A good speech such as this one is provocative, inspiring and personal. It is structured to present a clearly defined message and convey the speaker’s ideas and thoughts.
At work, you may be asked to speak at meetings, seminars and conferences. These are important events in your professional career that will help you establish your credibility, and build your personal brand and professional network.
Learning how to deliver a good speech will equip you for career success. Let’s look at the characteristics of a good speech to push you in the right direction.
Characteristics Of A Good Speech
If you want to make a good speech that leaves a lasting impression, focus on what you’re going to speak and how. A good speech isn’t only about your words but also how you present yourself. Body language and gestures play a critical role in transforming an average speech into a memorable one.
If you’re wondering what a good speech is, here are some of its qualities:
Clear Message And Key Ideas
A good speech always starts with a key idea and a well-defined message. Many people make the mistake of burying their ideas in the middle or at the end. That’s a mistake. The audience may get distracted halfway into your speech, and leave without even knowing what you’re talking about. If you want people to understand your big idea, present it right at the start. That will set the context for the rest of the speech.
Impactful Oral Delivery
Remember to consider every aspect of the speech. Your oral delivery—pitch, pause and pace—also influences the audience’s response. ( klonopin ) Modulate your voice and pace to keep your listeners interested in your words. You should be also prepared to make impromptu adjustments to your delivery if you sense the audience drifting away. For instance, if you’re talking about statistical data, make it interesting by asking questions or engaging in a dialogue with the audience. This way, you keep them involved.
Sprinkled With Personal Anecdotes
Don’t rely only on facts and figures. If you can support your claims with personal experiences, it’ll make it more interesting. Start with a personal anecdote that’s linked to your big idea and that your audience can relate to. Humor is also a fun way to break the ice and put everyone at ease.
Informative, But Not Repetitive
Your speech needs to be informative and packed with fresh and new information to have an impact. Be careful not to recycle old ideas packaged in fancy words. . Being original and sharing relevant, critical and helpful information will make your speech memorable. Edit your speech carefully to ensure there are no repetitions or data gaps. You can also add inspiring quotes for a good speech.
Powerful Nonverbal Cues
One of the most important qualities of a good speech is nonverbal communication . You may believe that your words do all the work. But your posture, facial expressions and gestures are equally, if not more, important. Imagine someone making a speech with a blank expression on their face or just reading their words off a page without emotion. That doesn’t make for a good speech. It’s about building tension, asking provoking questions and engaging with the audience. There’s power in using nonverbal cues, like making eye contact with someone in the audience. Using these cues well can greatly improve the quality of your speech.
There are many more characteristics of a good speech that you can incorporate. Harappa Education’s Speaking Effectively course is designed for professionals who want to improve their communication skills. You can use these skills for public speaking or formal workplace conversations, to connect and empathize with others. Build meaningful connections, share ideas effectively, and deliver memorable speeches with our high-impact online course.
Explore topics & skills such as Public Speaking , Verbal Communication , Oral Communication , Speaking Skills & Oratory Skills from Harappa Diaries and learn to express your ideas with confidence.

Bronx cheers: Donald Trump promises to make New York great again with spending
NEW YORK — Upon exiting the closest subway station to former President Donald Trump's campaign rally in the Bronx Thursday evening, the only signs of anything unusual were the NYPD officers at the turnstile with bomb-sniffing dogs and a helicopter buzzing overhead. There wasn't a single piece of Trump paraphernalia on the New Yorkers filing out of the station.
But upon arriving at Crotona Park, a sprawling green expanse in the impoverished borough, red "Make America Great Again" hats and all manner of Trump-emblazoned apparel covered the bodies of thousands — even "Team Trump" cowboy hats. And in his address to the mostly non-white audience, Trump showed that he will readily depart rhetorically from Republican orthodoxy to find common ground.
Across the street, vendors hawked shirts with slogans such as "Women for Trump," "Latinos for Trump," "God, Guns & Trump," and a few that insulted prominent Democrats.
Outside the park, a small band of protesters sporting Palestinian and Puerto Rican flags chanted "All the people from the Bronx say, 'F--- Trump!'" But their signs also proclaimed "F--- Biden!"
They refused to answer who, if anyone, they were supporting.
Prep for the polls: See who is running for president and compare where they stand on key issues in our Voter Guide
The snaking line to enter the area cordoned off for the rally by police barricades was filled with enthusiastic Trump supporters, who cheered and gaped when they spotted his motorcade. Once he took the stage, the crowd went up on their tippy toes, arms upright with cellphone cameras aloft, hoping to catch just a glimpse of him.
"Hello to all the strong, hard-working American patriots right here in the Bronx," Trump said, after bragging about the long lines to get in. "Who would think?"
A pitch for New York's votes, with Democratic talking points
New York City itself was a major focus of Trump's remarks, which included extended reminiscence about his renovations of a local skating rink and a golf course.
Trump frequently depicts New York as suffering from criminality unleashed by progressive governance. But he combined those talking points with an olive branch, of sorts, to the city he so frequently bashes.
If he retakes the White House, he promised: "I am going to pick up the phone and I'm going to call your mayor and your governor, and I'm going to say, 'this is President Trump and I want to come back and help.'"
New York City's murder rate dropped by 11.9% last year when its 386 homicides were roughly one-seventh of its 1990 peak . And its astronomical cost of living indicates robust demand to live there.
But one wouldn't know it from Trump's remarks, which repeatedly cast the city as beset by an unprecedented crime wave and general deterioration.
"Sadly, this is a city in decline," he declared. "I've never seen it like this. We have filthy encampments of drugged-out homeless people living in our places where we spent so much time with our children that they used to play, lunatics killing innocent bystanders by pushing them on the railroad tracks."
To address that, he promised to deliver results that could just as easily have been offered by a Democrat.
"We are going to turn New York City around," Trump said. "We're going to bring safety back to our streets, we're going to bring success back to our schools. We're going to bring prosperity back to every neighborhood in every borough of the greatest city of our land."
"We're going to make New York bigger, better and more beautiful than ever before, and that includes right here in the Bronx and it's going to be done and funded, starting on Jan. 20, directly from our great and beautiful White House," he added.
Later, Trump lamented that "our subways are squalid and unsafe," and pledged to "make it beautiful again." He also added: "We're going to do what it takes to fix our roads and bridges."
The Biden administration, which enacted a $1.2 billion infrastructure law that included money for the subway system, clapped back on X , saying that Biden is already doing what Trump proposes.
But the audience, many of whom said that Biden has done nothing in office, cheered Trump's lines with enthusiasm.
More typical Republican positions were left mostly undiscussed. There was no mention of abortion, just one passing reference to tax cuts, and no discussion of Trump's openness to cutting Social Security and Medicare .
An unlikely location for a Republican rally
The Bronx would not seem like hospitable territory for Trump, who won just 14% of its votes in 2020. It is 28% Black and 56% Latino — two groups that have historically favored Democrats by wide margins.
Nor is it in a swing state. New York favored President Joe Biden over Trump 61% to 38% in the last election.
But Trump is trying to squeeze in campaigning during his criminal hush money trial in neighboring Manhattan, so he has been making campaign appearances in his former hometown, such as stopping at a Harlem bodega to attack Manhattan District Attorney Alvin Bragg over crime last month.
There are signs that Trump has some potential to improve his standing. His 2020 performance was an improvement from 2016, when he won just 10% in the Bronx. That was similar to shifts nationally that showed movement toward Trump among voters of color, particularly Latinos and especially Latino men . This year, polling has shown Trump with a greater share of Latinos and young voters than he had in previous elections, although there are also signs that support is slipping .
The crowd seemed to reflect those demographic changes: It skewed young and heavily male, and while it was much more white and less Black than the Bronx, Hispanics were very well-represented.
Pedro and Gina Dominguez, Dominican immigrants who live in New Jersey, came to show their support for Trump. Like every other attendee interviewed, their reasons for backing Trump were based more on personality than policy.
"The United States needs a strong man to command our country and I believe Trump is the person," Pedro Dominguez said. Gina Dominguez added that many of her friends who criticized her for supporting Trump in 2020 are leaning towards voting for him now because of inflation.
How it fits into Trump’s campaign strategy
Throughout his remarks, Trump tied his typical talking points to his appeal to the local market. When inveighing against migrants, for example, Trump argued that the groups hurt most by immigration are Blacks and Hispanics.
Trump also sharply criticized the Iraq invasion, which he falsely claimed to have opposed before it began.
And he predicted that he would successfully win over New Yorkers.
"Who said we're not gonna win New York?" Trump asked rhetorically. "We're gonna win New York City. If we win New York, we win the whole thing."
But while Trump's advisors might know better than to think he can win the Empire State or Black and Latino voters outright, the image of him campaigning there could still help him among swing voters.
In what pundits sometimes refer to as a “ricochet pander,” reaching out to inner-city voters of color could benefit Trump among white suburban moderates by softening his image as racially divisive. According to National Review’s Ramesh Ponnuru , the classic example of this tactic is "when Republicans put a lot of black people on stage at their conventions in the expectation not that many black voters will join the GOP as a result but that some white voters will vote GOP because they see an effort being made."
Election 2024: Trump, Biden spar over whether Trump's 30-second pause was intentional or a 'glitch'
Local elected officials react negatively
Rep. Ritchie Torres, D-N.Y., represents the congressional district in which Trump’s rally was held, the poorest in the country . Young, gay, Afro-Latino, and a self-identified progressive, he is seemingly Trump’s polar opposite.
On Thursday morning, Torres held a news conference in which he assailed Trump as a "fraud."
"The South Bronx has no greater enemy than Donald Trump, who is on a mission to dismantle the social safety net on which Bronx families depend for their survival," Torres said in a statement. "The South Bronx—the most Democratic area in the nation—will not buy the snake oil that he is selling."
A counterrally was held at the same time in the same park, organized by Bronx Democratic state Assembly Member Amanda Septimo, civil rights activist Kirsten John Foy, and labor unions.
"I'm trying to talk some sense into these idiots," said Rick Caballero, a Bronx resident and counter-protester. "Donald Trump is only for white people."
Limited local support
The only elected official to share the stage with Trump was Rep. Byron Donalds , a Florida Republican who grew up in Brooklyn.
But Ruben Diaz, Sr., a conservative Democrat from the Bronx who represented the borough on the City Council and in the state Senate, came up onstage to laud Trump after his speech. Diaz has stirred controversy in New York with homophobic remarks and by welcoming Sen. Ted Cruz to the borough in 2016.
"As a Puerto Rican, as a Hispanic, I want to apologize to you for the conduct of Judge Juan Merchan," Diaz told Trump, referring to the judge in Trump's trial for allegedly falsifying business records to cover up payments to porn star Stormy Daniels. (Trump attacked Merchan as "crooked" and "conflicted" during his speech, although he didn't specify what was "crooked" and the New York State Advisory Committee on Judicial Ethics found Merchan has no conflict of interest.)
Diaz concluded his remarks with an endorsement, which Trump said was unexpected.
"This Democrat, this Black Puerto Rican, with kinky hair and broken English: please accept my endorsement for president," Diaz declared.
"He can't even speak right, and he's got millions and we're broke," joked Joe Walsh, a middle-aged attendee, in response to Diaz.
But, Walsh later added, "He's probably the smartest Democrat because he's for Trump."

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
As such, excessive or nonexistent physical manipulation can detract from a speaker's speech. Good delivery is a habit that is built through effective practice. Exercises. Find a speech online and examine the speaker's overall presentation. How good was the speaker's delivery? Make a list of the aspects of delivery in this chapter and ...
Here are 4 key reasons why: Engagement: Deliver your speech in an engaging way and your listeners will stay hooked until the end. This ensures that your message resonates with them. Clarity: Delivery makes your speech clearer. This helps people understand your words and the main points of your message.
The good news is that most signs of nervousness are invisible to the audience, so you can stay calm and composed even if you're feeling a bit jittery. Embrace nervousness as it can actually be a valuable tool in enhancing your speech delivery. It can make you more alert, animated, and enthusiastic about your topic. Instead of trying to ...
4. Take Deep Breaths: Before and during the speech, take a few deep breaths as this will help calm nerves and make sure your breathing is regulated throughout the duration of your presentation. 5. Speak Slowly: It is common to feel anxious while giving a speech and try to rush through it too quickly.
Nonverbal communication carries most of the message. Good delivery does not call attention to itself, but instead conveys the speaker's ideas clearly and without distraction. 9. Grab Attention at the Beginning, and Close with a Dynamic End. Do you enjoy hearing a speech start with "Today I'm going to talk to you about X"? Most people ...
Create an outline: Develop a clear outline that includes the introduction, main points, supporting evidence, and a conclusion. Share this outline with the speaker for their input and approval. Write in the speaker's voice: While crafting the speech, maintain the speaker's voice and style.
Good delivery can make all the difference in giving a powerful speech. The delivery phase starts as soon as you step in front of an audience. First, get the audience's attention by introducing who you are and perhaps jumping right into an exciting opening to hook them.
Although speaking anxiety is natural and normal, it can interfere with verbal and nonverbal delivery, which makes a speech less effective. In this chapter, we will explore causes of speaking anxiety, ways to address it, and best practices of vocal and physical delivery. ... which makes it a good muscle for a speaker to exercise. To start ...
Learning Objectives. Identify the four types of speech delivery methods and when to use them. There are four basic methods of speech delivery: manuscript, memorized, impromptu, and extemporaneous. We'll look at each method and discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each.
41. Final Touches for Successful Speech Delivery. Finish the speech making process by engaging in practice, editing, and delivery. Work through public speaking anxiety and deliver a successful speech. You have made it! You worked through the steps of the speech making process and now you are ready to finish up your practice and delivery. This ...
These are called the delivery modes, or simply, ways of delivering speeches. The three modes are impromptu delivery, manuscript delivery, and extemporaneous delivery. Each of these involves a different relationship between a speech text, on the one hand, and the spoken word, on the other. These are described in detail below.
A speech is not an assignment that can be done the night before; practice is essential. Practicing a speech will boost your confidence as a speaker and ease potential anxiety. Using or not using a podium does not make or break a speech. If using a podium, it should not be used to hide from the ...
Key Takeaways. There are four main kinds of speech delivery: impromptu, extemporaneous, manuscript, and memorized. Impromptu speaking involves delivering a message on the spur of the moment, as when someone is asked to "say a few words.". Extemporaneous speaking consists of delivering a speech in a conversational fashion using notes.
The two basic principles underlying effective speech delivery are simple. that the speaker uses the most appropriate delivery style or method for the speech content, its purpose and its audience. that audience engagement is highest when a speaker has thoroughly prepared and practiced. A speech is successful when the speaker fulfills both of them.
The secret structure of great talks. From the "I have a dream" speech to Steve Jobs' iPhone launch, many great talks have a common structure that helps their message resonate with listeners. In this talk, presentation expert Nancy Duarte shares practical lessons on how to make a powerful call-to-action. 18:00.
As the name suggests, speech delivery is how you deliver your speech: your tone, your pace, your body language, your demeanor. However, Gallo focuses on the one element of speech delivery that he believes is crucial to success: the speed of your speech. Speak too quickly, and people will struggle to understand what you're saying.
11. Don't be scared of a good reaction. If your speech is genuinely engaging, funny, inspiring or any of the other things you might hope it would be, your audience will react to it. There might be laughter, or applause, or even a bit of cheering depending on the setting.
So before you utter another word to another person, memorize this list of the 8 key elements of highly effective speech: Gentle eye contact. Kind facial expression. Warm tone of voice. Expressive ...
Importance of Delivery in a Speech. A Speech is important because it is a way to communicate, establish connections, and can in many ways motivate several people to take productive attitudes toward themselves and the World. Therefore Speech Delivery is paramount for succeeding in selling ideas. Speech Delivery Techniques Using Relatable Quotes
Reach out and seek help. Study past winning speeches to gauge what made them unique and compelling. Be patient. The process takes time, from writing the speech, to memorization to presentation. One should give themselves grace and leverage all parts of the process. Abbie Wolff '22. Photo: Yassine Dhouib.
Successful Speeches. Whether you're talking to a small group of people or speaking to a large audience, you want to be sure your speech is memorable and enjoyable. Follow these five easy tips to help ensure your speech delivers: Be prepared. Your audience is giving you their time and consideration, so rehearse enough to be confident you'll ...
Cold water makes the throat constrict. On the day of your speech make sure you arrive with enough time to settle yourself. Take time to visit the room you will presenting in and run through your speech. Becoming familiar with the room and how it's set up technically will help settle any nerves and you should always remember to test the ...
One of the most important qualities of a good speech is nonverbal communication. You may believe that your words do all the work. But your posture, facial expressions and gestures are equally, if not more, important. Imagine someone making a speech with a blank expression on their face or just reading their words off a page without emotion.
Bronx cheers: Donald Trump promises to make New York great again with spending. NEW YORK — Upon exiting the closest subway station to former President Donald Trump's campaign rally in the Bronx ...
Former President Donald Trump was loudly and consistently booed throughout his speech Saturday at the Libertarian Party's national convention, particularly when he asked attendees to "nominate ...
The return of National Service could boost Britain's resilience, a retired senior RAF officer has said. Air Marshal Edward Stringer, who served as Director General of Joint Force Development and ...