

BI Case Studies With Examples
Bi case study—overview.

- Enhancing business productivity
- Improving access to critical information
- Identifying hidden opportunities
- Improving competitive standing
- Driving strategic, data-based decision making
- Increasing customer satisfaction
What’s Included in BI Case Studies?
- Client profile —company type, industry, and brief history and description of the company
- The situation —the circumstances that initially caused the company to become interested in a new BI solution
- The challenges —the problems and issues the company was facing that a BI solution could solve
- The process —the heart of the case study, as it shows how the BI vendor or service provider, or TEC, performed its services in a way that met or exceeded the client’s goals and expectations
- The results —the benefits to the client at the end of the day
- Vendor/service provider profile —brief description of the vendor or service provider including contact information
The Benefits of a BI Case Study in the Selection Process
Companies facing a BI selection project will often turn to many different kinds of resources to assist them in the process. Case studies are seen by many to be of particular value because they provide insights into how other companies approached their BI selection, how the project unfolded, and how the vendor or service provider, or an impartial third party such as TEC, approached its role. With so many BI case studies available, you will likely be able to find BI case studies that highlight companies like yours that were in a similar situation.
How TEC's BI Case Studies Can Help You to Find the Best-Fit Software
TEC is an impartial software advisory firm. We specialize in software selection and evaluation, implementation oversight, and contract negotiations, so naturally these are the areas that our case studies focus on. By reading TEC’s case studies , you can learn how other companies were able to achieve success in these key areas with the assistance of TEC’s advisory services.
TEC’s BI Software Selection Process
- Assess : Assess the client’s business processes and goals, gaps in key processes, and discover their functional requirements
- Review : Review BI solutions and vendor capabilities to meet the client’s business needs
- Identify : Identify the shortlist of BI vendors and their partner(s)
- Demonstration : Assess BI solution demonstrations scripted to the client’s business processes
- Proposal : Create and distribute BI request for proposal (RFP) to vendors to clarify deliverables and project total cost of ownership (TCO)
- Reference : Evaluate BI vendor and their partner(s) through reference checks from real-world clients on previous projects
- Contract : Perform contract review and price negotiations on behalf of the client for cost savings
- Implementation : Perform oversight and monitor the implementation of the BI application(s) to enable successful transformation and business growth
Check Out Our Free Library of Case Studies Below
Refine results.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) 536
- Discrete Manufacturing ERP 127
- Process Manufacturing ERP 122
- Mixed-Mode ERP 112
- ERP for Small Manufacturing Business 100
- Distribution ERP 83
- ERP for Service Industry 35
- ERP for Small Business 33
- Engineer-to-Order (ETO) 121
- Supply Chain & Logistics 299
- Inventory Management 87
- Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) 57
- Merchandising Software 18
- Supply Relationship Management (SRM) 29
- Transportation Management Systems (TMS) 25
- Demand Management Software 27
- RFID Software 5
- Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) 97
- Supply Chain Management (SCM) 158
- Business Intelligence & Data Analytics 247
- Business Intelligence (BI) and Data Management 181
- Spreadsheet 1
- Business Process Management (BPM) 100
- Enterprise Performance Management 60
- Customer Relationship Management & Support 219
- Call Center 6
- Event Management 1
- Proposal Management 10
- Contract Management 2
- Sales Force Automation Software 21
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) 185
- Field Service Management (FSM) 80
- Configure Price Quote (CPQ) 33
- Benefits Administration 12
- Compensation Management 6
- Human Resources 24
- Performance Management 14
- Time & Attendance 11
- Workforce Management 15
- Learning Management Systems (LMS) 75
- Talent Acquisition Software 14
- Talent Management Systems 43
- Human Capital Management (HCM) 83
- Financial 130
- Billing & Invoicing 17
- Point of Sale (POS) 2
- Accounting and Financial Software 85
- Asset Management 122
- Facility Management 6
- Computerized Maintenance Management System 109
- Asset Management (EAM) 97
- Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) 115
- Process PLM 15
- Discrete PLM 16
- Regulatory and Compliance PLM 26
- Fashion PLM 22
- Retail PLM 48
- Information & Document Management 69
- Document Management Systems (DMS) 58
- Enterprise Content Management (ECM) 52
- Content Management System (CMS) 17
- IT & IT Security 57
- Help Desk 6
- Virtual Private Network (VPN) 1
- Remote Access 3
- Network Security 16
- E-commerce 31
- Web Content Management (WCM) 6
- Communication & Collaboration 31
- Collaboration 2
- Project Management 8
- Project and Process Management (PPM) 23
- Marketing 23
- Marketing Automation 23
- Design/Creative 9
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD) 9
- Industry-Specific 3
- Property Management 3
- Manufacturing 24
- Wholesale and Retail Trade 22
- Finance and Banking 10
- Publishing and Media 10
- Education 9
- Food and Beverage Products 5
- Industry Independent 4
- Public Administration and Defense 4
- Recreational, Cultural, and Sporting Activities 4
- Chemical Products 3
- Health Care and Social Work 3
- Pharmaceutical and Botanical Products 3
- Real Estate 3
- Telecommunications 3
- Agriculture and Forestry 2
- Computer, IT, and Software 2
- Insurance 2
- Mining & Quarrying 2
- Construction 1
- Electronics and High-tech Components 1
- Hotels and Restaurants 1
- Motor Vehicles and Other Transport Equipment 1
- Non Profit Organization 1
- Textile and Apparel 1
- Transportation 1
- Utilities 1
Publication Types
- White Papers 1,575
- Blog Posts 612
- Case Studies 181
- Brochures 119
- Industry Reports 58
- Software Reviews 22
- Datasheets 18
- Buyer's Guides 11
- Accreditation Reports 4
- Microsoft 8
- Nucleus Research 6
- OutlookSoft 5
- Panorama Software 5
- Strategy Companion 5
- Board International 4
- Pronto Software 4
- AnyDoc Software, Inc. 3
- Habanero Consulting Group 3
- Halo Business Intelligence 3
- ProjectLocker 3
- TECTURA Corporation 3
- BQE Software 2
- Logi Analytics 2
- Polymita Technologies 2
- Sage Intacct 2
- The Access Group 2
- Wellesley Information Services 2
- Active Strategy 1
- Know the option you’re looking for? Type in the search field.

Top Publications

23 Case Studies and Real-World Examples of How Business Intelligence Keeps Top Companies Competitive

Business intelligence (BI) provides data that helps companies make timely and informed decisions. We explain how implementing BI software can give companies of any size a competitive edge. Plus, we share examples of how some of the most tech savvy companies are using BI.
What Is Business Intelligence (BI)?
Business intelligence refers to the technology that enables businesses to organize, analyze and contextualize business data from around the company. BI includes multiple tools and techniques to transform raw data into meaningful and actionable information.
BI systems have four main parts:
- A data warehouse stores company information from a variety of sources in a centralized and accessible location.
- Business analytics or data management tools mine and analyze data in the data warehouse.
- Business performance management (BPM) tools monitor and analyze progress towards business goals.
- A user interface (usually an interactive dashboard with data visualization reporting tools) provides quick access the information.
German market research firm Statista estimates the volume of data created worldwide by 2024 will be 149 zettabytes. This vast amount of data, or "big data," has made business intelligence systems relevant for companies that want to harness its power for a competitive advantage. Many BI systems use artificial intelligence (AI) and other capabilities as a part of business analytics.
Key Takeaways:
- Business intelligence offers a wide variety of tools and techniques to support reliable and accurate decision-making.
- The most successful companies use BI to make sense of ever-increasing amounts of data in a fast and economical way.
- BI-based, data-driven decision-making helps companies stay relevant and competitive.
Where Is BI Used?
Sales, marketing, finance and operations departments use business intelligence. Tasks include quantitative analysis, measuring performance against business goals, gleaning customer insights and sharing data to identify new opportunities.
Here are examples of how various teams and departments use business intelligence.
Data scientists and analysts:
Analysts are BI power users, and they use centralized company data paired with powerful analytics tools to understand where opportunities for improvement exist and what strategic recommendations to propose to company leadership.
By blending financial data with operations, marketing and sales data, users can pull insights from which decisions can be acted upon and understand factors that impact profit and loss.
Business intelligence tools help marketers track campaign metrics from a central digital space. BI systems can provide real-time campaign tracking, measure each effort’s performance and plan for future campaigns. This data gives marketing teams more visibility into overall performance and provides contextual visuals for sharing with the company.
Sales data analysts and operation managers often use BI dashboards and key performance indicators (KPIs) for quick access to complex information like discount analysis, customer profitability and customer lifetime value. Sales managers monitor revenue targets, sales rep performance along with the status of the sales pipeline using dashboards with reports and data visualizations.
Operations:
To save time and resources, managers can access and analyze data like supply chain metrics to find ways to optimize processes. Business intelligence can also ensure that service level agreements are met and help improve distribution routes.
In a genuinely data-driven company, every department and employee can take advantage of BI-generated insights.
What Is the Value of Business Intelligence?
Business intelligence's highest value is its ability to support data-driven decisions. BI transforms pools of raw data into useful information that informs decisions and leads to actions that yield positive bottom-line impact.
BI systems drive decisions based on historical, current and potential future data.
Descriptive analytics:
These analytics reveal what has happened or is happening and are part of dashboards, business reporting, data warehousing and scorecards. When managed well, you’ll have a better understanding of problem areas in your business and can find opportunities to improve.
Predictive analytics:
These advanced analytics use data mining, predictive modeling, and machine learning to help make projections of future events and assess the likelihood that something will happen.
Prescriptive analytics:
These analytics reveal why you should take a particular action. Prescriptive analytics enable optimization, simulation, decision modeling and provide the best possible analysis for business decisions and actions.
BI software gathers sales, production, financial and many other business data sources. Many companies use industry data to benchmark performance against competitors.
The Benefits of Business Intelligence
Business intelligence has many benefits and can be a useful tool to achieve positive outcomes for your business.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Business Intelligence at Work
Fast, data-informed decision-making can drive success. High customer expectations, global competition and narrow profit margins mean many organizations, regardless of size or sector, look to BI for a competitive advantage.
What is an example of business intelligence? Using data to serve up personalized ads based on browsing history, providing contextual KPI data access for all employees and centralizing data from across the business into one digital ecosystem so processes can be more thoroughly reviewed are all examples of business intelligence. Here are some case studies that show some ways BI is making a difference for companies around the world:
Lotte.com: BI Increases Company Revenue
Lotte.com is the leading internet shopping mall in Korea with 13 million customers.
- Challenge: With more than 1 million site visitors daily, company executives wanted to understand why customers abandon shopping carts.
- Solution: The assistant general manager of the marketing planning team implemented customer experience analytics, the first online behavioral analysis system applied in Korea. The manager used the information to understand customer behavior and implement targeted marketing and transform the website.
- Results: With the insights from the new BI analytics program, there was an increase in customer loyalty after one year and an increase of $10 million in sales. The changes came from identifying the causes of shopping cart abandonment, such as a long checkout process and unexpected delivery times and remedying the situation.
Cementos Argos: BI Improves Financial Efficiency
Cementos Argos is a cement company with operations in the U.S., Central and South America and the Caribbean.
- Challenge: The company looked for an overall competitive advantage and a way to support better decision-making.
- Solution: Cementos Argos created a dedicated business analytics center. The company invested in experienced business analysts and data science teams and used BI to leverage data.
- Results: The company standardized the finance process and applied big data to gain more in-depth insight into customer behavior which yielded a higher profitability level.
Baylis & Harding: BI Provides Decision Making Process Support
Baylis & Harding is a wholesale distributor specializing in world-class toiletries and gift sets found in major and independent resellers.
- Challenge: The company needed to give managers and executives greater visibility into financial, customer and sales data to make better decisions and expand the business.
- Solution: Managers and executives used business intelligence tools to create standard and ad hoc reports.
- Results: Company executives and managers now have instant access to the business data they need to act proactively. They can create custom dashboards with KPIs relevant to their areas of focus and share the goals and performance details with their teams without having to request a custom report from IT.
Sabre Airline Solutions: BI Accelerates Business Insights
Sabre Airline Solutions provides booking tools, revenue management, web and mobile itinerary tools, as well as other technology, for airlines, hotels and other companies in the travel industry.
- Challenge: The travel industry is remarkably fast paced. And Sabre's clients needed advanced tools that could provide real-time data on customer behavior and actions.
- Solution: Sabre developed an enterprise travel data warehouse (ETDW) to hold its enormous amounts of data. Sabre executive dashboards provide near real-time insights in user-friendly environments with a 360-degree overview of business health, reservations, operational performance and ticketing.
- Results: The scalable infrastructure, graphic user interface, data aggregation and ability to work collaboratively have led to more revenue and increased client satisfaction.
Spear Education: BI Streamlines Internal Processes and Workflow
Spear Education is a leader in continuing education for dentists.
- Challenges: Spear's phone system was lacking functionality that could make its customer service reps work more efficiently and provide better customer service. For example, their phone system didn’t record calls and wasn’t connected to a customer relationship management (CRM) tool.
- Solution: After some research, Spear connected its call center software with its BI solution to maintain more thorough customer interaction records and provide a complete view of customer interactions.
- Results: After implementing a new solution for their contact center, Spear increased agent efficiency and saved the company 35 hours of rep time per week. Spear's agents now reinvest that time by placing 4,000 more outbound calls every week.
Univision: BI Increases Market Spend Efficiency
Univision is an American Spanish-language, free-to-air television network. It’s the largest provider of Spanish-language content in the country.
- Challenge: Univision wanted more visibility into its data to unify and focus on targeted ad campaigns.
- Solution: Programmatic TV is an automated and data-driven approach to buying and delivering ads against video content on television, including ads served across the web, mobile devices and connected TVs, as well as linear TV ads served across set-top boxes. With BI powered with information from applications like Facebook, Google Analytics and Adobe Analytics, the company can obtain more value from its programmatic advertising.
- Results: Univision achieved an 80% growth in yield during the first quarter after implementing business intelligence.
New York Shipping Exchange: BI Reduces IT Dependency
New York Shipping Exchange (NYSHEX) is a shipping-technology company working to improve the process of shipping overseas.
- Challenge: To make sense of overall company performance, NYSHEX would manually extract data from its proprietary application and various cloud apps and then import it into Excel. This was a laborious process and few people had access to the data, and most of the requests for reports fell on the engineering team to execute.
- Solution: NYSHEX invested in BI, centralized its data into one system and gave the entire company access empowering those with no coding knowledge to dive deep into analysis.
- Results: Thanks to business intelligence and other efforts, in 2019, the company more than tripled its volume shipping between Asia and U.S.
Stitch Fix: BI Connects Departments, Data and Processes
Stitch Fix provides online personal clothing and accessory styling services. The company uses recommendation algorithms and data science to personalize clothing items based on size, budget and style.
- Challenge: The company wants to reduce returns, keep repeat customers and generate word-of-mouth business with recommendations from customers to their friends and family.
- Solution: Stitch Fix collects data within BI throughout the buying process, meaning the more a customer shops with Stitch Fix, the better the styling team comprehends their taste in clothing. The company hired astrophysicists to decode the different personal style components—intricate work that would be impossible without the powerful analytics of BI.
- Results: Using business intelligence to profile buyers and their preferences, the company, which started in 2011, reported a customer base of 3.4 million in 2020 and revenues of $1.7 billion in fiscal year 2020.
SKF: BI Streamlines Manufacturing Processes
SKF is a Sweden-based global manufacturer and supplier of bearings, seals, mechatronics and lubrication systems with 17,000 distributor locations.
- Challenge: SKF's broad geographic coverage and product diversity required consistent market size and product demand forecasting to adjust its manufacturing. The company needed to simplify the complex Excel files used to produce a demand forecast.
- Solution: Management realized it needed to implement a business intelligence to serve as a single source of reliable information. Maintaining the system is easier than trying to manage everything with Excel, and now employees don’t have to rely on outdated spreadsheets and can access simple-to-understand reports and dashboards.
- Results: By centralizing data assets into a single system, SFK was quickly able to share data and analyses between several departments — including sales, manufacturing planning, application engineering, business development and management. SKF now combines demand forecasts between departments and has improved the planning process.
Expedia: BI Builds Customer Satisfaction
Expedia is the parent company of some top-tier travel companies, including Expedia, Hotwire and TripAdvisor.
- Challenge: Customer satisfaction is essential to the company's mission, strategy and success. The online experience should mirror a good trip experience, but the company had no visibility into the voice of the customer.
- Solution: The company had mountains of data they were manually aggregating, leaving little time for analysis. Using business intelligence, the customer satisfaction group was able to analyze customer data from across the company and link results with 10 objectives related directly to corporate initiatives. Owners of those KPIs build, manage and analyze data to discover trends or patterns.
- Results: The customer service team can see how well it is doing against KPIs in real-time and take corrective steps if necessary. Plus, other departments can use the data. For example, a travel manager can use BI to discover high volumes of unused tickets or offline booking and create strategies to adjust behavior and increase overall savings.
Use Cases: Examples of Business Intelligence Strategies Prominent Companies Use
The most successful companies use BI to drive revenue, customer loyalty, operational effectiveness, ad delivery, drive shareholder value, predict customer behavior and develop new business opportunities.
Examples of How Leading Companies Use BI to Propel Their Success
What companies use business intelligence? From financial institutions like American Express to social media giant Facebook and outdoor retailer REI, the most advanced and successful companies in the world leverage BI. Here’s how some are using BI to power their prosperity.
American Express:
Business intelligence is instrumental in the finance industry. American Express has been using the technology to develop new payment service products and market offers to customers. The company's experiments in the Australian market have rendered it capable of identifying up to 24% of all Australian users who will close their accounts within four months. Using that information, American Express takes steps to retain customers. BI also helps the company accurately detect fraud and protect customers whose card data may be compromised.
Chipotle Mexican Grill:
The restaurant chain has more than 2,400 restaurants worldwide. It implemented BI to track operational effectiveness. Chipotle can now monitor every restaurant's operational efficiency and serve up detailed information in dashboards. By standardizing the reporting and working from the same data ecosystem, Chipotle was able to make uniform KPIs for benchmarking and sharing improvement and success stories. That solution saves thousands of hours for the company.
With 35 million Twitter followers and a whopping 105 million Facebook fans, Coca-Cola benefits from its social media data. Using AI-powered image-recognition technology, the company can tell when photographs of its drinks post online. This data, paired with the power of BI, gives the company important insights into who is drinking their beverages, where they are and why they mention the brand online. The information helps serve consumers more targeted advertising, which is four times more likely than a general ad to result in a click.
Delta Airlines:
Big data and BI support customer service and differentiate the Delta experience. Flight attendants now have the tools to personally thank and recognize valued corporate travelers. Positive customer experience coupled with thoughtful programs help position Delta as a leader in the business travel space. While any Delta customer can receive personal recognition, the airline goes the extra mile to serve corporate travelers and its medallion members. This enhancement provides more opportunities to thank flyers and build customer loyalty.
The company processes 35% of U.S. mortgage applications. Record low-interest rates created a high demand for loan processing. To make data more accessible for lenders, Ellie Mae developed a hosted data warehouse model that allows lenders to analyze data by connecting a BI application directly to their systems without replicating the data to a local data warehouse. Capital market teammates can use that data to navigate volatile markets, allowing them to provide excellent service and process loans for their customers.
The home improvement company uses business intelligence to merge what the customer tells them with actual behavior occurring online and in the store. They use this data to discover deeper insights that lead to better product assortment and staffing at specific store locations. The process of data analysis drives sales and also serves the customer. For instance, Lowe's uses predictive analytics to load trucks specific to individual zip codes, so the right store gets the right type and amount of product.
The online entertainment company's 148 million subscribers give it a massive BI advantage. How does Netflix use business intelligence? Netflix uses data in multiple ways. One example is how the company formulates and validates original programming ideas based on previously viewed programs. Netflix also uses business intelligence to get people to engage with its content. The service is so good at targeted content promotion that its recommendation system drives over 80% of streamed content.
REI uses its business intelligence platform for customer segmentation analysis, which helps inform decisions like member lifecycle management, shipping methods and product category assortments. BI-based decisions also inform member acquisition initiatives with detailed demographics on factors such as gender to personalize ads. The insights from BI help determine everything from how to display content on the website and how to segment email campaigns.
Through its popular loyalty card program and mobile application, Starbucks owns individual purchase data from millions of customers. Using this information and BI tools, the company predicts purchases and sends individual offers of what customers will likely prefer via their app and email. This system draws existing customers into its stores more frequently and increases sales volumes.
The innovative automotive company uses BI to connect their cars wirelessly to their corporate offices to collect data for analysis. This approach links the carmaker to the customer and anticipates and corrects problems such as component damage, traffic or road hazard data. The result is a high customer satisfaction score and better-informed decisions on future upgrades and products.
The social media company deploys BI with AI to fight inappropriate and potentially dangerous content on its platform. Algorithms rather than human users identify 95% of suspended terrorism-related accounts.
BI and AI also support fine-tuning to improve the overall user experience. Twitter personnel and its business intelligence tools monitor live video feeds and categorize them based on subject matter. They use this data to enhance search capabilities, and help algorithms identify videos users might be interested in viewing.
The company uses business intelligence to determine multiple core aspects of its business. An example is surge pricing. Algorithms monitor traffic conditions, journey times, driver availability and customer demand in real-time, meaning prices adjust as demand rises and traffic conditions change. Dynamic pricing in real-time action is akin to what airlines and hotel chains use to adjust cost based on need.
The retail behemoth uses BI to understand how online behavior influences online and in-store activity. By analyzing simulations, Walmart can understand customer purchasing patterns, for example, how many eyeglass exams and glasses are sold in a single day, and pinpoint the busiest times during each day or month.
How to Improve Your Business Intelligence to Make Your Company a Leader
BI and tools like AI may seem complicated. However, current user interfaces are straightforward and easy to use. So even smaller companies can take advantage of data to make profitable and positive decisions.
Examples of Business Intelligence Tools and Techniques
What are examples of business intelligence tools? Predictive modeling, data mining and contextual dashboards or KPIs are just some of the most common BI tools. Here are more tools and how they’re used.
A BI technique that probes data to extract trends and insights from historical and current findings to drive valuable data-driven decisions.
Dashboards:
Interactive collections of role-relevant data are typically stocked with intuitive data visualizations, KPIs, analytics metrics and other data points that play a role in decision-making.
Data mining:
This practice uses statistics, database systems and machine learning to uncover patterns in large datasets. Data mining also requires pre-processing of data. End-users use data mining to create models that reveal patterns.
Extract Transfer Load (ETL):
This tool extracts data from data-sources, transforms it, cleans it in preparation for reports and analysis and loads it into a data warehouse.
Model visualization:
The model visualization technique transforms facts into charts, histograms and other visuals to support correct insight interpretation.
Online Analytical Processing (OLAP):
OLAP is a technique for solving analytical problems with multiple dimensions from various perspectives. OLAP is useful for completing tasks such as performing CRM data analysis, financial forecasting and budgets.
Predictive modeling:
A BI technique that utilizes statistical methods to generate probabilities and trend models. With this technique, predicting a value for specific data sets and attributes using many statistical models is possible.
Reporting involves gathering data using various tools and software to mine insights. This tool provides observations and suggestions about trends to simplify decision-making.
Scorecards:
Visual tools, such as BI dashboards and scorecards, provide a quick and concise way to measure KPIs and indicate how a company is progressing to meet its goals.
Examples of Business Intelligence Trends
BI is continually evolving and improving, but four trends – artificial intelligence, cloud analytics, collaborative BI and embedded BI – are changing how companies are using expansive data sets and making decisions far easier.
Artificial intelligence:
AI and machine learning emulate complex tasks executed by human brains. This capability drives real-time data analysis and dashboard reporting.
Cloud analytics:
BI applications in the cloud are replacing on-site installations. More businesses are shifting to this technology to analyze data on demand and enrich decision-making.
Embedded BI:
When BI software is integrated into another business application, it’s called embedded BI or embedded analytics . Some of the benefits of embedded BI include enhanced reporting functionalities, and it’s been shown to improve sales and increase customer retention.
Many companies look to cloud-based or software-as-a-service (SaaS) instead of on-premise software to keep up with growing warehousing requirements and faster implementations. A growing trend is the use of mobile BI to take advantage of the proliferation of mobile devices.
Examples of Business Intelligence Software and Systems
BI software and systems provide options suited to specific business needs. They include comprehensive platforms, data visualization, embedded software applications, location intelligence software and self-service software built for non-tech users.
Here are some examples of the latest BI software and systems:
Business intelligence platforms:
These are comprehensive analytics tools that data analysts use to connect to data warehouses or databases. The platforms require a certain level of coding or data preparation knowledge. These solutions offer analysts the ability to manipulate data to discover insights. Some options provide predictive analytics, big data analytics and the ability to ingest unstructured data.
Data visualization software:
Suited to track KPIs and other vital metrics, data visualization software allow users to build dashboards to track company goals and metrics in real-time to see where to make changes to achieve goals. Data visualization software accommodates multiple KPI dashboards so that each team can set up their own.
Embedded business intelligence software:
This software allows BI solutions to integrate within business process portals or applications or portals. Embedded BI provides capabilities such as reporting, interactive dashboards, data analysis, predictive analytics and more.
Location intelligence software:
This BI software allows for insights based on spatial data and maps. Similarly, a user can find patterns in sales or financial data with a BI platform; analysts can use this software to determine the ideal location to open their next retail store, warehouse or restaurant.
Self-service business intelligence software:
Self-service business intelligence tools require no coding knowledge to take advantage of business end-users. These solutions often provide prebuilt templates for data queries and drag-and-drop functionality to build dashboards. Users like HR managers, sales representatives and marketers use this product to make data-driven decisions.
#1 Cloud ERP Software
How NetSuite Improves and Increases the Value of BI for Your Organization
BI tools can have an enormous impact on your business. They can help you improve your inventory control, better manage your supply chain, identify and remove bottlenecks in your operations and automate routine tasks. But for BI tools to be most effective, you first have to centralize data that’s stored in multiple disparate systems.
NetSuite business intelligence tools take the data stored in your enterprise resource planning (ERP) software and provides built-in, real-time dashboards with powerful reporting and analysis features. By centralizing data from your supply chain, warehouse, CRM and other areas with an ERP, NetSuite business intelligence tools can help you identify issues, trends and opportunities, along with the ability to then drill down to the underlying data for even further insight.
It’s likely your business has large amounts of data that could be used to boost your profitability. The challenge is organizing and structuring your data in such a way that you can then glean insights. From there, you need to create clear, concise and actionable reports and data visualizations and distributing them to key stakeholders on your team. None of this can be done without advanced software, such as ERP products that collect and manage all your data.

How Business Intelligence Is Used in Accounting Today
An accounting team that’s both data-driven and proactive can be downright transformative. And CFOs get that: Brainyard’s Winter 2021 Survey of about 150 finance and business leaders from a range of industries shows…

Trending Articles

Learn How NetSuite Can Streamline Your Business
NetSuite has packaged the experience gained from tens of thousands of worldwide deployments over two decades into a set of leading practices that pave a clear path to success and are proven to deliver rapid business value. With NetSuite, you go live in a predictable timeframe — smart, stepped implementations begin with sales and span the entire customer lifecycle, so there’s continuity from sales to services to support.
Before you go...
Discover the products that 37,000+ customers depend on to fuel their growth.
Before you go. Talk with our team or check out these resources.
Want to set up a chat later? Let us do the lifting.
NetSuite ERP
Explore what NetSuite ERP can do for you.
Business Guide
Complete Guide to Cloud ERP Implementation
- Terms and Conditions
Privacy Policy
- Free Giveaway: How To Start A Freelance Business
7 Business Intelligence Success Stories and Examples (Case Studies)
Team Kolleqtive
Welcome to the intriguing Business Intelligence (BI) world, where data is more than just numbers; it’s the key to informed decisions and remarkable success stories through real-world examples. Picture it as a toolbox that transforms raw data into valuable insights, enabling companies like Facebook, Airbnb, Netflix, Amazon, Spotify, and Google to provide personalized experiences for their users.
In our journey through the landscape of BI, we’ll explore its fundamental components, understand how it enriches your daily life, and see how it empowers aspiring entrepreneurs, much like we ( Kolleqtive ) also do. Business Intelligence is a world where data isn’t just information; it’s the driving force behind extraordinary achievements and business intelligence success stories.
Let’s examine real-world examples of Business Intelligence and learn how companies use data to discover numerous opportunities.
Table of Contents
What is business intelligence.
Business Intelligence (BI) is the technology-driven process for analyzing and presenting data to help business leaders, managers, and other stakeholders make informed decisions. BI in companies involves a set of tools, processes, and methodologies that gather, process, and transform raw data into meaningful insights. These insights support business decision-making, optimize operations, and improve overall performance.
Key components of Business Intelligence in Companies include:
1- Data Collection: BI starts with collecting data from various sources, such as databases and spreadsheets , and external sources like social media or market data.
2- Data Transformation: Once data is collected, it’s transformed into a format suitable for analysis. This might involve cleaning, structuring, and organizing the data.
3- Data Analysis: Analyzing the data involves using various techniques and tools to discover patterns, trends, and insights. This often includes data visualization to present findings in a more understandable format.
4- Reporting: Reporting is a critical aspect of BI, as it involves presenting the results of data analysis in a clear and digestible way. Reports can take the form of dashboards, charts, graphs, and written summaries.
5- Data Mining: Data mining is the process of discovering patterns and trends in large datasets. It’s a critical element of BI, as it helps uncover hidden insights that might not be apparent through standard analysis.
6- Predictive Analytics: Predictive analytics uses historical data and statistical algorithms to forecast future trends and events. It helps businesses make proactive decisions.
7- Data Warehousing: Data warehousing involves storing data from multiple sources in a central repository, making it more accessible for analysis.
8- KPIs and Metrics: Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and metrics are used to measure the success of business operations. Business intelligence case study examples often track and display these metrics.
Business Intelligence is widely used across various industries to improve decision-making, identify opportunities, and solve complex problems. It gives organizations a competitive advantage by allowing them to make data-driven decisions based on accurate, real-time information. BI examples can be tailored to an organization’s specific needs, whether improving sales, optimizing supply chains, enhancing customer service, or any other aspect of business management.

7 Real-World Examples of Business Intelligence
To truly grasp the power of business intelligence, let’s dive into some inspiring business intelligence case studies. These case studies showcase how BI in companies has transformed ordinary businesses into extraordinary ones. Let’s see what entrepreneurs can learn from them.
Example 1: Facebook – A Marvel of Business Intelligence
Imagine Facebook as a magical place where you connect with friends and discover content tailored just for you. It feels so perfect because of the powerful use of business intelligence.
When you open your Facebook feed, you’re greeted with posts from friends and pages you care about. This isn’t by chance. Facebook uses data to determine who you interact with the most and what content you enjoy. It then shows you posts from those connections at the top. This personalized approach makes you feel more connected to the people and things you love.
Have you noticed that the ads you see on Facebook are often related to your interests? This is thanks to BI in companies. Facebook analyzes your behaviour and interests to show you advertisements that are more likely to be interesting. If you’re a foodie, you might see ads for kitchen gadgets. It’s like having ads that cater to your hobbies.
Ever found old friends or colleagues on Facebook? BI makes it happen. Facebook suggests people you may know based on your existing connections, work history, and other data points. It helps you reconnect with old pals and make new friends.
When you react to posts with likes, comments, or shares, you provide valuable feedback. Facebook uses this information to fine-tune your feed, ensuring you see more of what makes you happy and engaged.
In a nutshell, Facebook is a shining example of business intelligence that can make your online experience wonderful. It’s like having a personal assistant who ensures your Facebook world is full of friends and content you adore.
Example 2: Airbnb
If you’ve ever booked a place to stay on Airbnb , you’ve experienced an example of business intelligence.
Imagine you’re planning a vacation and want to find the perfect place to stay within your budget. That’s where Airbnb’s smart pricing comes in. Airbnb uses data to check when and where you want to stay. They analyze all this information to suggest the best price for hosts. This means you can often find great deals, and hosts can make more money. It’s like Airbnb’s saying, “Hey, look at these amazing places. You can afford them!”
They look at your preferences and your host’s details to make a perfect match. This personal touch is why you feel comfortable and relaxed during your stay. It’s like having a travel buddy that knows exactly what you like.
Airbnb used data to understand that some travellers want more than a place to sleep. So, they added things like Experiences, where you can do fun activities. They saw that people needed long-term stays, and they adapted their platform for that. Airbnb is like your personalized travel assistant, making your trips unforgettable.
Example 3: Netflix
Imagine you’re watching a show on Netflix, and it recommends another series you might like. That’s business intelligence at work.
Netflix gathers information about what shows people watch and what they like. They use this data to create their own unique series and movies that they think people will enjoy. For example, “Stranger Things” was made because Netflix noticed many viewers loved ’80s nostalgia and spooky stories.
When you see recommendations on Netflix, it’s because they’ve looked at what you watched before and suggested something similar. This keeps you engaged and watching more.
Netflix also expanded to different countries based on data about what people in those places enjoy watching. This way, they can offer something for everyone around the world.
Example 4: Amazon
Picture this: you’re on Amazon , and it knows precisely what you want before you do. It’s like having a mind-reading shopping assistant. Amazon uses data to forecast what products will be super popular. This means they always have the stuff you want ready to ship. Fast delivery, great prices, and a wide selection – that’s the Amazon promise.
When Amazon suggests products you might like, it’s not a coincidence. They’ve studied your past purchases and browsing history. Their recommendations make shopping more accessible and more enjoyable. It’s as if Amazon is saying, “Hey, we found these cool things that you’ll love!”
Amazon’s recommendation system is a testament to BI’s power in companies. Examining your browsing and purchase history suggests products that align with your interests. This not only increases sales but also enhances the overall shopping experience.
Example 5: Spotify
Have you ever wondered how Spotify knows which songs to recommend? It’s all about business intelligence. They use data to make sure you hear songs you’ll enjoy.
Spotify keeps track of what songs you listen to and what you like. They use this information to create playlists just for you. These playlists have songs they think you’ll love, and they keep you coming back for more music.
They analyze your listening history to find new songs you might like. It’s a fun way to discover fresh music without any effort.
If you’re a musician, Spotify helps you, too. They provide data about your listeners and where they’re from. It’s like having a map of your fanbase. This information helps artists understand their audience and make better music. It is a perfect example of business intelligence.
Example 6: Google
Ever wondered how Google knows what you’re searching for? Business Intelligence is at the heart of it.
When you start typing a question into Google, it suggests search terms. It’s like having a psychic search engine. Google uses data to predict what you’re looking for, making searching faster and easier.
Do the ads you see online often match your interests? Google tailors ads based on your online activity. It’s like window shopping for things you actually want. This personalization keeps the internet experience more relevant to you.
Google Maps helps you avoid traffic jams, right? It’s like a traffic wizard. They use data from other drivers to predict real-time traffic conditions and suggest the fastest routes.
Example 7: Kolleqtive
Kolleqtive is a platform committed to nurturing the entrepreneurial spirit, and at its core is the power of business intelligence . We use data to understand our members’ unique challenges and goals, tailoring our resources and community support for their success.
Our dynamic community is a hub for knowledge and connections, similar to how business intelligence examples like Facebook and Google use data to personalize experiences.
We’re also driven by data analytics, tracking your progress and outcomes to keep refining and improving our offerings, ensuring you’re always ahead in your entrepreneurial journey.
A positive mindset is fundamental to your success, and at Kolleqtive, we foster it. We encourage a supportive network, gratitude, and embracing failure as a learning opportunity.
In entrepreneurship, Kolleqtive is a prime example of how business intelligence can be harnessed to empower and guide aspiring business owners toward success. Kolleqtive serves as a beacon for entrepreneurs seeking knowledge , a positive environment, and a supportive community to help them.
Join us at Kolleqtive and let the magic of business intelligence drive your entrepreneurial success. Your journey starts here.
In these case studies, businesses such as Spotify, Starbucks, Google, Airbnb, Netflix, and Amazon demonstrate the indispensable role of business intelligence in companies creating a personalized and enriching experience for consumers. They employ data-driven insights to offer tailored content, services, and products, ensuring that your music playlists, search results, and travel experiences are finely tuned to your interests and needs. These examples vividly illustrate the transformative power of BI in companies in enhancing our daily lives and making them more enjoyable and convenient. The magic of business intelligence enables these companies to provide experiences that feel uniquely tailored to each individual.

Leveraging Data Analytics for Growth
One of the pillars of business intelligence is data analytics . Let’s explore how to harness the power of data to drive the businesses forward.
Data analytics involves examining data to discover useful insights. It enables businesses to make data-driven decisions, identify patterns, and gain a competitive edge. It’s like having a magnifying glass for your business data.
Imagine having the ability to predict what your customers want. Data analytics can help you do just that. By analyzing customer behaviour and purchasing patterns, you can tailor your products and marketing strategies to boost sales.
Data analytics also plays a crucial role in streamlining business operations. By examining data related to processes and workflows, we can identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies, allowing for smoother and more efficient operations.

Key Takeaways
In this journey through the world of business intelligence and case studies, we’ve covered key points. Let’s recap what we’ve learned:
- Business intelligence is the key to informed decision-making.
- Success stories like Netflix, Airbnb, and Amazon showcase the power of BI.
- Failure is a stepping stone to success.
- Data analytics can boost sales and streamline business operations.
- Nurturing a positive mindset is crucial for overcoming challenges.
You have the world at your feet. You can achieve remarkable success with the right mindset and the power of business intelligence. Remember, success often arises from learning, adapting, and staying positive in facing challenges. So, embark on your journey confidently because you have the tools to succeed.
Embark on a journey to business success with Kolleqtive . Our platform provides you with the keys to unlock valuable insights and expert guidance that will accelerate your path to success. Whether your focus is on business growth, mastering marketing strategies, or building resilience, our resources are thoughtfully designed to be your guiding light. Join us today to harness the tools, knowledge, and connections that are essential for instilling confidence and driving positive change in both your personal and professional life.
Share this Article!
Liked This Article? Sign up today to receive our newsletter
Join thousands of subscribers who get our newsletter with insider tips, tricks, eBooks and offers!
Other posts you may like

Business , Resilience
50 Positive Affirmations to Tell Yourself Daily to Stay Motivated
By Team Kolleqtive
Published, 1 week ago

5 Tips for Time Management for Professionals and Entrepreneurs at Work

Business , Lifestyle
Top 10 Ways to Boost Your Productivity at Work
Published, 2 weeks ago

The Power of Positive Thinking in Business: How Positivity Pays Off in Business

7 Mindsets for Success: Understanding the Standards That Lead to Achievement
Published, 3 weeks ago

Business , Fashion & Beauty , Lifestyle
Why is it Important to Dress Appropriately at Work
Published, 1 month ago
Motivation, Productivity, & Self-Empowerment
The most important thing in creating a successful business is the mindset of the business owner!
Stay in loop
Insights, content, news, and events.
By submitting, you agree to receive Kolleqtive marketing emails and that you have read the Privacy Policy and Terms of Usage.
© 2024, Kolleqtive |
Terms of Usage

Get a FREE copy of How To Start A Freelance Business
The only guide you need to get started as a freelancer.
- We respect your privacy and would never sell, rent or share your data with any third party. You can chose to opt out from our emails anytime.
Sign Up For the Newsletter Today.
And join thousands of others who enjoy our newsletter.
Please check your inbox for your free ebook!
7 real-world examples of business intelligence in use
Posted by: matt david.
While the core definition of business intelligence (BI) has remained relatively the same over the past 155 years — using data to make good business decisions — how businesses use BI has changed quite a bit.
Examples of business intelligence in use vary widely because, over the past two decades, BI technology transitioned from highly technical tools that expert teams use to more user-friendly, cloud-based software. This has made it more agile and accessible than ever before, leading to a proliferation of different BI use cases.
Even so, the common trait among the most effective BI tools is that they are built with the business user in mind, allowing anyone across the company to access, analyze, and act on data without coding knowledge.
There are a lot of benefits to this widespread “culture of data,” like removing bottlenecks in company-wide workflows; reducing grunt work, so you can tackle more important tasks; and, ultimately, proving the validity of your business through growth.
But the best way to explore these benefits is through specific examples of business intelligence in use. Below are seven companies using business intelligence to not only make good business decisions but also to shape the future of their respective industries.
First, let’s set the stage.
How is business intelligence used?
Companies can use business intelligence to make a company’s raw data usable. The goal is to make better decisions about your business by utilizing your data in more efficient and effective ways.
Because BI has improved so much in the past decade, it’s much easier for more employees across the company to benefit from it. That’s because much of what makes up a business intelligence system is now streamlined or automated.
What is a business intelligence system?
According to Solomon Nash and Paul Gray , professors at Kennesaw State University and Claremont Graduate University, a business intelligence system consists of data gathering, data storage, knowledge management, and analysis.
- Data gathering collects information from every source and funnels it into one place. An example of technology that powers this is a customer data platform like Segment .
- Data storage safely hosts all of that data in a data warehouse, like Amazon Redshift .
- Knowledge management is how all this data gets disseminated throughout an organization.
Analysis is, well, the analysis of this data to aid in decision-making.
What companies use business intelligence?
Most organizations do some form of business intelligence, but it’s not uncommon for a lot of it to be manual work. For instance, a small startup’s “data gathering” may be manually exporting CSVs from each data source. If they store all those spreadsheets on Google Drive, that’s essentially their data warehouse.
This kind of process works OK up to a point, but it’s not sustainable for most businesses.
BI tools (especially self-service BI tools) manage your business’s data in a way that’s more secure, easier to manage, and simpler to use. And the best BI tools automate much of the system we outlined above, allowing employees to focus their efforts on analysis and taking action.
The companies that benefit most from using business intelligence tend to be those that require their employees to make independent decisions quickly. This makes it a good fit for startups, data-centric companies, and companies looking to grow rapidly.
Let’s dive into seven examples of business intelligence used by these types of companies.
1. Koodos proves their concept
Koodos is a new startup from Harvard Business School’s Rock Center for Entrepreneurship that builds content curation technology for Gen Z based on user-generated data. One venture capitalist called them “the competitive messaging-based Pinterest for music.”
Where they started
Koodos’ business model is dependent on understanding relationships between different sets of data. Their first experiment matched emojis with music— if you texted an emoji to 566-367 , you got a song recommendation from another person.
We just tried it and found that 👴 recommends “Legend” by Twenty One Pilots , which is a song celebrating the life of the lead singer’s grandfather.
It works well, but before a BI tool, they had no easy way of truly analyzing product performance to understand how their experiments were going.
They would have to download product logs as CSVs and upload them to Google Sheets. From there, they sometimes used SQL to run queries, but because their data wasn’t centralized, they found it difficult and time-consuming to prove whether their experiments were running as intended.
How BI helped
With a business intelligence tool, Koodos is able to unify their data to gain an understanding of how their experiments are performing and then use those insights to build a better product.
First, they set up their business intelligence tool as a “central repository” for all product log data. With all that data collected, they could then run queries, no matter how clean the dataset was . With those queries, they could build out dashboards that compared sets of data directly in real time, making it a cinch to identify trends and relationships.
For instance, in the emoji experiment, Koodos found that the 🥺 emoji received the most song suggestions. They now know that Gen Z has more songs to recommend to people who are feeling sad than, say, people who feel like 🕺.
Using these insights helps Koodos not only build a better content curation product but also prove their product works well.
Use business intelligence to unite all your data to understand what’s happening in your product, when it’s happening, and what to do about it.
2. New York Shipping Exchange moves faster
New York Shipping Exchange (NYSHEX) is a shipping-technology company working to improve the process of shipping overseas. They’ve been doing very well, doubling enrollment in 2019 , thanks in no small part to business intelligence.
To make sense of overall company performance, NYSHEX used to manually extract data from their proprietary application and their various cloud apps and then import it all into Excel. Because this was such a laborious process, few people had access to this data, and most of the requests for reports fell on the engineering team to execute.
Gordon Downes, CEO at NYSHEX, explains his thoughts during that time: “There had to be a better way to make information more readily available and save time for our engineering team. We needed a solution so that I, along with the rest of the team, could explore data on the fly.”
NYSHEX decided to give the entire company access to the data using their business intelligence tool, Chartio. This has been possible not only because all that data is centralized into one system, but also because it’s easy for someone with no coding knowledge to dive deep into analysis.
With Chartio’s drag-and-drop Visual SQL builder, any NYSHEX employee can run queries, set up dashboards, and create reports. Even if they have no idea what SQL stands for (structured query language), they can still get exactly what they need, when they need it.
NYSHEX is now an incredibly efficient operation because every employee can access and act on real-time data. Gordon says: “Chartio gets information to the people who need it so they can make decisions without taking loads of time.”
A low-code or no-code BI solution is vital for any company looking to provide the ability to understand and act on data to every employee.
3. CareLinx personalizes care
CareLinx is a nationwide, in-home care network connecting families to over 300,000 in-home caregivers. In recent years, they’ve increased their profile by establishing partnerships with the likes of AARP and Aetna . Taking their next step toward growth required them to adopt a compliant business intelligence solution so they could better serve their customers.
To serve the families that use their product, CareLinx deals with protected health information (PHI). Because PHI is sensitive, they need a BI solution that’s compliant with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) .
Before they established a HIPAA-compliant solution, they had two systems: a BI for non-PHI data and a separate manual system for PHI data. Anytime they wanted to do any sort of business analysis, they’d have to filter out all PHI data in order to remain compliant, leading to an incomplete picture of the people they serve. This dual-system approach wasn’t feasible as CareLinx prepared to scale the business nationwide.
CareLinx already used Chartio as their business intelligence tool for non-PHI data, so their engineering and product teams already realized the benefits of good BI. Once Chartio became HIPAA-compliant, a whole new world of opportunities opened up for them.
Now, every team in the company is able to safely query any data, PHI or otherwise, to understand their users on a deeper level. Customer success, for example, utilizes Chartio to analyze data in real time and use those insights to better serve their users.
No matter how big CareLinx gets, they can still provide personal attention to each family that uses their product by using a HIPAA-compliant BI tool.
Look for a BI solution that addresses all your specific needs so it can grow with you.
4. Bugcrowd reduces churn
Bugcrowd is a cybersecurity platform that connects its customers to security researchers to identify vulnerabilities in products and applications. Just recently, they closed Series D funding for $30 million , and they’ve helped many Fortune 500 companies shore up their security. And the ways Bugcrowd uses BI have helped them establish their place at the forefront of their industry.
Bugcrowd’s goal is to successfully connect companies with security researchers. In an effort to keep both groups happy, they needed to dive into the mountains of data involved in each interaction. It was too much data to handle with spreadsheets and SQL, so they turned to business intelligence.
Their requirements were strict: airtight security and the ability to handle many data sources—and it had to be easy to use. They were having trouble finding a BI tool that fit those parameters, so they considered building their own analytics system. They had the know-how to do so, but it would’ve been costly and time-consuming. Fortunately, they found a ready-made solution.
Quite a few BI tools meet the first two requirements (security and number of sources), but, too often, they sacrifice usability to reach that point. Bugcrowd found their solution in Chartio, and with those three requirements satisfied, they were able to surpass their goal of retaining customers by keeping them happy.
To retain your customers, you need to deeply understand them and learn how they use your product. Bugcrowd used Chartio to centralize all their interaction data in one place. From there, they could dive into each interaction individually or zoom out to see them all in aggregate.
This made it much easier to identify trends and insights, and it improved the work of all teams, from “customer support for proactive problem solving” to “engineering for feature release activity.”
At first, Bugcrowd’s goal was to just understand these interactions. But their business intelligence tool made this so easy that they moved seamlessly to improving each interaction. The result was a high-touch customer service approach that helped Bugcrowd acquire new business and retain existing business.
Jonathan Cran, VP of product at Bugcrowd, says: “We are able to drive negative churn because everyone from Sales to Customer Success uses Chartio to look at how customers are interacting and ask the right questions to improve an account’s health or find an opportunity to upsell.”
Start with a concrete and attainable business intelligence goal (e.g., understand user interactions), and then set stretch goals based on achieving that objective (e.g., improving those interactions).
5. DataRobot democratizes data
DataRobot is an enterprise-level artificial intelligence platform that invented the automated machine-learning category. They’re used by a third of the Fortune 50 companies and recently announced Series E funding, amounting to $206 million. What would a company of this caliber need a business intelligence tool for? Quite a bit, it turns out.
As a data-centric company, DataRobot knows its way around analyzing, modeling, and presenting data. Early on, they created an ad hoc business intelligence solution, in which they created a few custom reports using Python and sent them via email. It worked pretty well for their purposes—for a while.
But after growing 60% in 2018 , they realized this solution couldn’t scale with them. It wasn’t enough for DataRobot to have a data-centric culture—they needed a culture of data democracy.
DataRobot made the choice to onboard new employees with a seat on their BI tool, Chartio. Their goal was to give every team the power to understand and act on data without the need to go through the engineering or analytics team.
The result was an 83% adoption rate of Chartio throughout the company. By incorporating their BI tool into the onboarding process, DataRobot cemented a culture of data democratization, where every employee had the power to analyze and act on data.
This culture turned out to be vital to their recent success. Daniil Bratchenko, VP of business operations and analytics at DataRobot, said, “Democratization of access to data is super important when you see how it works, and if we didn’t have it, we would be much less effective as a company.”
Entrench your business intelligence into the day-to-day functions of your employees from day one to establish a culture of data democracy.
6. Reddit eliminates a data bottleneck
Reddit is a social media website with a focus on aggregating news and community discussion. It currently ranks seventh in Alexa’s list of Top Sites in the United States , and its ability to monetize that traffic relies on their business intelligence.
With over 430 monthly visitors around the globe, Reddit has a lot of data to deal with. Previously, the data team was tasked with completing one-off requests that not only took time away from their own projects but also made it harder for other teams to access data.
This bottleneck obscured promising insights and made it nearly impossible to fully leverage the monetization opportunities available to the seventh-most-visited site in the United States.
Reddit didn’t originally plan on everyone using their business intelligence tool, but because Chartio was so easy to use, they kept getting requests from employees to query data on their own. The end result was a culture of data democracy like DataRobot, but through a “grassroots” progression.
Once they gave access to the rest of the company, the sales team became some of the biggest BI enthusiasts, using it to analyze Reddit’s huge data set in real time to identify when brands or products got mentioned among the 2-million-plus communities . They use Chartio and Google BigQuery to create graphs and visualizations showing how brands can naturally enter the discussions happening every day on Reddit.
This kind of insight never would have happened if the bottleneck stayed in place. It also wouldn’t have happened without a culture of data democracy. As Justin Bassett, data scientist at Reddit, says: “More people are making discoveries and uncovering answers they couldn’t have found on their own before,” later adding, “Sales have increased dramatically.”
Leverage the culture of data democracy that business intelligence naturally develops to surface opportunities you never could’ve foreseen otherwise.
7. Clever surfaces insights collaboratively
Clever is a portal for digital learning used in 60% of K-12 schools in the United States. Its near-ubiquitous role in the modern classroom is due to the culture of collaboration made possible with their business intelligence.
Clever grew very fast and had to deal with a massive influx of data using MongoDB, a database; Amazon Redshift, a data warehouse; and SQL to make sense of it all. To keep things running smoothly, they needed a way to filter through all that data faster. Specifically, they sought to understand how educators used their technology.
Like a few of our other examples of business intelligence, Clever took a page out of DataRobot’s book and sought to establish a culture of data democracy using Chartio, their BI tool. By giving every employee data source access to Chartio, they quickly took data democracy to a new level and now have a 90% adoption rate among all employees.
To help each other use BI more effectively, Clever created an internal group called the “ Number Munchers ” (named after the classic video game) , who interact through a dedicated Slack channel. In this channel, they share their reports, insights, and advice with each other.
Out of this collaboration comes greater insight into how their users interact with Clever’s product. For instance, the customer success team can independently identify trends in support-ticket data from educators that the product team can then use to inform prioritization of future features.
With 90% of the company functioning like this, thanks to business intelligence, Clever is able to identify and act on insights faster. Colin DuRant, product manager at Clever, says, “In democratizing data, [we] ensured that no one would make a decision in the absence of data. When you give people access to data, you are automatically enabling them to make better decisions.”
Use business intelligence to combine a culture of data democracy with a culture of collaboration to make better decisions faster.
Leverage these examples of business intelligence to democratize data
Most of the benefits of using BI we’ve covered so far are due to one factor: more people having easy access to data.
This establishes a culture of data democracy, which has helped countless businesses improve their product, build better relationships with their customers, and ultimately grow in smart ways. The right BI tool will solve for your immediate need, like keeping teams aligned, optimizing your tech stack, or reducing time spent on reporting.
But what you gain in the process of solving these specific issues with BI will shape the future of your business and your industry.
Chartio is built to democratize data so you can reap the rewards of good BI. And the good news is that you don’t have to wait.
Business Intelligence Case Studies
Business Intelligence case studies are real life examples of a successful implementation of a Business Intelligence solution.
Often quoting several comments made by the client, they will highlight what solutions have been implemented, the issues faced, and the benefits received by the customers user base following its implementation.
While these can be useful, it should be borne in mind that they are effectively marketing materials, developed by the software vendor and normally only available on the vendors website. However, they can give the reader some confidence if a particular product under consideration has been implemented successfully at a similar company.
All the major Business Intelligence vendors will provide case studies from their websites. A few links have been provided below to some of the better case studies available:
Microsoft Case Studies Panorama Case Studies Business Objects Case Studies
Other case studies are written by research analysts, and are often sponsored by the software house. Where not sponsored, they are available for a fee.
Bear in mind when reading these case studies that they will ALL paint a very rosy picture of the software product or service. They will not dicsuss any of the problems, issues and pains experienced during its implementation.
Above all, you will find that the best references are those given by word of mouth. Speak to your colleagues in other organisations and hear what they are doing in the field of Business Intelligence. Also search the internet for the technology you are considering. Do the articles, forums, etc. speak positively about the product? Are they issues you were previously not aware of? Are users happy with the product? By doing this, you will be able to make a good decision on the Business Intellilgence product to buy.
Business Intelligence Strategy
Privacy Overview
10 Case Studies On The Benefits of Business Intelligence And Analytics

Table of Contents
1) Why Is Business Intelligence So Important?
2) What Are The Benefits of Business Intelligence?
3) 10 Real-World BI & Analytics Use Cases
4) BI & Analytics Practical Examples
Using business intelligence and analytics effectively is the crucial difference between companies that succeed and companies that fail in the modern environment. Why? Because things are changing and becoming more competitive in every business sector, the benefits of using business intelligence and proper use of data analytics are key to outperforming the competition.
For example, in marketing, traditional advertising methods of spending large amounts of money on TV, radio, and print ads without measuring ROI aren’t working like they used to. Consumers have grown increasingly immune to ads that aren’t targeted directly at them.
The companies that are most successful at marketing in both B2C and B2B are using data and online BI tools to craft hyper-specific campaigns that reach out to targeted prospects with a curated message. Everything is being tested, and the successful campaigns get more money put into them, while the others aren’t repeated.
But what is the true value of BI? In this post, we will explore ten advantages of business intelligence supported by real-world BI case studies. By the end, you’ll need to double down on creating a data-driven culture at your company, and you’ll have some hard evidence you can use to persuade skeptical teammates.
Let’s get started!
Why Is Business Intelligence So Important?
The main use of business intelligence is to help business units, managers, top executives, and other operational workers make better-informed decisions backed up with accurate data. It will help them spot new business opportunities, cut costs, or identify inefficient processes needing reengineering.
BI software uses algorithms to extract actionable insights from a company’s data and guide its strategic decisions. BI users analyze and present data in the form of dashboards and various types of reports to visualize complex information in an easier, more approachable way. Business intelligence can also be called “descriptive analytics,” as it only shows past and current state: it doesn’t say what to do, but what is or was. The responsibility to take action still lies in the hands of the executives.
This “test, look at the data, adjust” methodology is at the heart and soul of business intelligence. It’s all about using data to understand reality better so that your company can make more strategically sound decisions (instead of relying on gut instinct or corporate inertia).
Ultimately, business intelligence and analytics are about much more than the technology used to gather and analyze data. They’re about having the mindset of an experimenter and being willing to let data guide a company’s decision-making process.
What Are The Benefits of Business Intelligence?
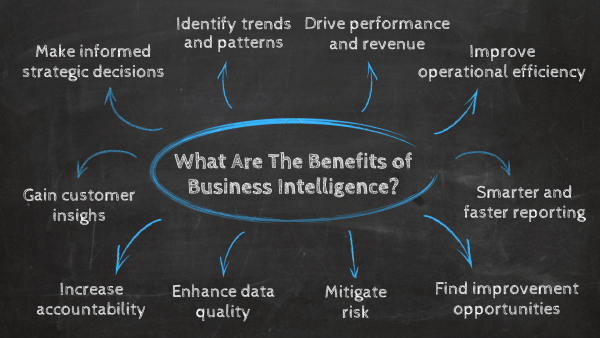
The benefits of business intelligence and analytics are plentiful and varied, but they all have one thing in common: they bring power. The power of knowledge. Whichever unit they impact, they can deeply transform your organization and how you do business. Here is an overview of 10 main business intelligence benefits:
- Make informed strategic decisions: Business intelligence and analytics provide valuable data insights, empowering decision-makers to make more informed choices.
- Identify trends and patterns: By analyzing data from multiple sources, companies can delve into customer behaviors, business performance, and the industry landscape. This deep dive allows them to hone their competitive advantages and identify areas for improvement.
- Drive performance and revenue: Using targeted strategies, businesses can identify new revenue opportunities, optimize pricing, and maximize profitability.
- Improve operational efficiency: BI tools offer a bird' s-eye view of all operations, allowing companies to identify bottlenecks, streamline processes, and optimize performance.
- Find improvement opportunities through predictions: Businesses are better positioned to anticipate market changes and project needs and proactively adjust their marketing and operational strategies using predictive analytics.
- Smarter and faster reporting: With data and analytics in a single place, users can quickly and easily report on performance and progress, share with stakeholders, and choose their next best actions.
- Mitigate risk: Analyzing trends and historical data can better understand risks and potential threats.
- Enhance data quality: BI initiatives often require data cleansing and standardization exercises, both of which can ensure you’re collecting accurate and usable data.
- Increase accountability: BI provides transparency into key performance metrics and business processes, which can foster accountability within organizations.
- Gain essential customer insights for ongoing growth: Learning more about customer preferences, behaviors, and needs can lead to more targeted marketing and positioning and greater customer satisfaction.
Benefits Of Business Intelligence: 10 Real-World Valuable Use Cases
Here are ten use cases that illustrate the different benefits of business intelligence.
1) Informed Strategic Decisions
As the first and most impactful of all benefits of analytics, we can make informed strategic decisions backed by factual information. Experts say that BI and data analytics make the decision-making process 5x times faster for businesses. Let's look at our first use case.
Renowned author Bernard Marr wrote an insightful article about Shell’s journey to become a fully data-driven company. Although the oil company has been producing massive amounts of data for a long time, with the rise of new cloud-based technologies and data becoming increasingly relevant in business contexts, they needed a way to manage their information at an enterprise level and keep up with the new skills in the data industry.
In order to do this, they first defined what data was the most relevant for the company. As Dan Jeavons, Data Science Manager at Shell, stated: “What we try to do is to think about minimal viable products that are going to have a significant business impact immediately and use that to inform the KPIs that really matter to the business”. With this information in hand, the company started thinking about how to invest in data quality standards, and the required technology to support it.
Skills were a big challenge for Shell. However, the company developed tailored training programs for its employees so that they could learn to use data to solve problems. Additionally, it invested in professionalizing the core work of data scientists for more complex operations.
Shell’s initiatives were successful because they implemented a data-driven culture in their entire organization. Empowering all levels of employees to use data for their decision-making process means extracting relevant insights at every level of the company. Undoubtedly, one of the big benefits of data analytics and professional self-service BI tools is the democratization of data.
2) Identify Trends and Patterns
As mentioned above, one of the great benefits of business intelligence and analytics is the ability to make informed, data-based decisions. This benefit goes hand in hand with the fact that analytics provide businesses with technologies to spot trends and patterns that will optimize resources and processes. Business intelligence and analytics allow users to know their businesses more deeply. Let’s see it with a real-world example.
The famous Boston Celtics basketball club hopped on the analytics bandwagon , too, so as to understand how their market evolves and also so as to evaluate their players.
Thanks to the data they collected on their customers, they have been able to analyze who they are, where they sit, and how much they pay. That is precious insight for the sales team, who can look into the data in real time and understand its leverages. It helped them quickly create promotions to sell more tickets and conduct revenue analyses based on these trends.
Moreover, visualizing their data helped them see how much revenue a given seat is producing during a season and compare the different areas of the stadium. Given that the Celtics have a very complex ticket pricing structure (over a hundred different prices depending on the package, section, individuals, students, competitive games, etc.), it is all the more important to understand at a glance which seat brings what, to make decisions on the fly for promotions.
A simple example is: If many low-cost seats are still available for an upcoming game, the sales team can send a customized email offer to local students.
The results?
Regular “five-figure” returns from promotions are based on analytics, according to Morey, senior VP of operations at the Boston Celtics. But it is just the beginning. After analyzing the fans’ seating plan, the sales team can redraw the lines for price breaks for the next season.
Of course, the purpose is to make more money, but it is not just for money’s sake. The money they get from these analytics will be reinvested in the players and their training, which means that players will get better, and so will the games.
3) Drive Performance And Revenue
Driving performance and revenue is one of the relevant benefits of business analytics for companies. McKinsey realized a business intelligence case study on a fast-food chain restaurant company with thousands of outlets worldwide. That company wanted to focus on its personnel and analyze deeper any data concerning its staff to understand what drives them and what they could do to improve business performance.
After exhausting most of its traditional methods, the company was looking for other ways to improve customer experience while tackling its high annual employee turnover, which was above the average of its competitors. The top management believed that tackling this turnover would be key to improving the customer experience and that this would lead to higher revenues.
To do so, the company started by defining the goals and finding a way to translate employees’ behaviors and experiences into data to model against actual outcomes. The goals were multiple: revenue growth, customer satisfaction, and speed of service. They then analyzed three areas: employee selection and onboarding, daily staff management, and employees’ behaviors and interactions in the restaurants.
The restaurant used the data collected to build regression and unsupervised learning models to determine the potential relationship between drivers and outcomes. They then started to test over a hundred hypotheses, many of which had been championed by senior managers who strongly believed in these methods after their experience. That was a powerful experience as it confronted senior managers with evidence against what they believed was true and practiced for years.
All the insights they gleaned challenged their beliefs and experience, but the results after implementing new measures, according to their findings, were indisputable: customer satisfaction scores had increased by more than 100% in four months, the speed of service improved by 30 seconds, attrition of new hires had decreased considerably, and sales went up by 5%.
4) Improve Operational Efficiency
Technology giant Microsoft was looking for a way to improve productivity and collaboration in the workplace. For this purpose, a senior researcher from the company conducted a study to understand the common problems faced by remote work on Microsoft. The findings showed that the main challenges included “communication in planned meetings, ad-hoc conversations, awareness of teammates and their work, and building trust relationships between teammates.”
These findings validated the theory that team members' awareness degrades with physical distance. The study even showed that employees who are situated in the same building but on different floors are less likely to collaborate. With this issue in mind, Microsoft came up with the idea of moving 1,200 people from 5 buildings to 4 to improve collaboration.
As a result of the relocation, the analytics team analyzed metadata attached to employee calendars and found a 46% decrease in meeting travel time, translating into estimated savings of $520,000 per year in employee time. As seen in the chart below, the team found out that “minutes saved for each employee equates to hundreds of thousands of dollars in cost-savings for an organization over time.”
** Source : hbr.org**
The analysis also showed that the number of weekly meetings per person increased from 14 to 18. Overall, data analysis in this use case showed a significant increase in employee collaboration and operational efficiency for the company. Chantrelle Nielsen, director of research and strategy for Workplace Analytics, said, “Companies must take these metrics and direct them thoughtfully towards the design of office spaces that maximize face time over screen time.” This is a great way to illustrate the operational benefits of business intelligence.
5) Find Improvement Opportunities Through Predictions
The fifth benefit of implementing business intelligence and data analytics into your company is using predictive analytics. A great use case of this benefit is Uber. This company was originally founded in 2009 as a black car-hailing service in San Francisco. Although the service costed more money than a regular taxi ride, customers were attracted to the experience of ordering a car from their smartphones.
Now, you might be wondering how this small San Francisco start-up turned into the successful global company it is today. The answer is data analytics and business intelligence.
Uber has an algorithm that takes valuable data from every driver and passenger and uses it to predict supply and demand. The gathered data includes everything from customers’ waiting times, peak demand hours, traffic for each city, a driver’s speed during a trip, and much more. All this data is then used to set pricing fees, meet demand, and ensure an excellent service for both their drivers and clients. For example, by using prediction models, they can generate a heatmap to tell drivers where they should place themselves to take advantage of the best demand areas.
According to this case study on business analytics, one of the most interesting uses of data from Uber is its surge pricing method. The algorithm makes Uber more expensive during peak traffic hours, holidays, rainy days, etc. Uber has made this system using real-time predictions based on traffic patterns, supply, and demand. While this is a successful pricing system that other enterprises praise, the higher fares have brought the company a lot of backlash for trips that are twice as expensive. To avoid this issue, Uber has recently announced that they will use machine learning technologies to predict future demand and ensure that more drivers are redirected to the high-demand areas to avoid surge pricing and offer their clients a fair fee.
This is a clear example of the advantages of business analytics and how predictive analytics can help businesses spot improvement opportunities, optimize their processes, and ensure higher customer satisfaction levels.
6) Smart and Faster Reporting
Next, in our rundown of the top benefits of BI and analytics, we discuss data management and visualization. One of the powers of BI tools is that they open the door to a more efficient reporting process, which also makes data analytics accessible for everyone without the need for prior technical knowledge. Let’s put this into perspective with a success story from datapine.
Lieferando is a European online food-ordering service acquired by Just Eat Take Away in 2014. The brand, which operates mainly in Germany, the UK, and Sweden, has a clear mission of providing a fast and easy way for its 98 million customers to get food from their favorite restaurants. With millions of consumers and more than 580,000 partner restaurants within 25 countries, the company faced issues related to data management and access to massive amounts of enterprise-level information.
Their main challenges were combining different data sources in real-time in one central location, optimizing their marketing campaigns with data-based insights, and getting a comprehensive view of their entire customer lifecycle. Additionally, they needed a tool that allowed all employees in the company to deal with data without involving the IT department.
With the implementation of datapine's BI reporting tool into their system, the company was able to manage large amounts of data in real-time while significantly cutting the time they spent on report generation. This allowed for a faster decision-making process, streamlining of their marketing and sales activities, and the overall optimization of several processes at an internal and external level.
Team members at Lieferando said that “our new real-time dashboards allow us to monitor all major business operations through customized Key Performance Indicators. We can instantly act on changes and can now better adapt to new business challenges right when they occur, not weeks or even months later.”
7) Risk Mitigation
Businesses like to see risks coming a mile away, or at least in enough time to devise a defense strategy. That’s why companies are increasingly interested in applying BI to their risk mitigation efforts. Data can tell a number of compelling stories, including those that are on the brink of coming to life.
To better understand how it works, we can review a case study on business intelligence based on using BI in agricultural insurance. BI tools are essential for effective risk management, leveraging organizational data to minimize uncertainties and improve decision-making. They play a role in developing early warning systems, which are common tools in industries that regularly deal with crises.
Gaining a heads-up about potential risks was essential to the Iran Agricultural Insurance Fund, the only active insurance company in the country's agriculture sector. The fund aims to protect farmers and ranchers whose crops become damaged by pests, weather, drought, disease, and other disasters. It’s essential to understand the capacity of this fund, paid compensations each year, and the need to increase and improve existing agriculture insurance products based on risk, all of which can be solved with BI.
Model development involved creating a multidimensional online analytical processing (MOLAP) architecture using SQL server analysis services (SSAS) and BI tools. MOLAP for risk management identified financial risks and predicted trends in premium earnings and paid compensation, aiding decision-making for agricultural insurance branches. Predictive analyses based on historical data offered insights into future trends, enabling insurers to manage their risk management strategies proactively.
8) Enhanced Data Quality
Companies are increasingly dependent on their data and need to be able to trust that data in a moment of need rather than spending time fact-checking it. When you have good data, you can make good decisions that ultimately lead to good outcomes. The opposite is also true: when you have bad data, it can lead to a catastrophic series of events.
This was the unfortunate case for Unity Technologies, which experienced a data quality issue that cost them $110 million and a 37% drop in share price. The 3D content platform attempted to use its Audience Pinpoint tool to help game developers target and acquire players. However, after ingesting bad data from a large customer, the effectiveness of its tool eroded significantly. They targeted the wrong audiences because the machine learning algorithms were trained on inaccurate data, which yielded poor results.
CEO John Riccitello said the blunder cost them a combined $110 million in revenue losses, model rebuilding and retraining, and delayed launches of new revenue drivers. Investors also lost faith in the company, causing share prices to tumble.
It was an eye-opening experience for Unity, prompting them to focus more on data quality as the costs of not doing so became glaringly evident. A well-implemented BI system and software can ensure a level of data quality that will drive accurate and successful decision-making.
9) Increased Accountability
Data transparency can create a sense of belonging and ownership. Employees no longer work in the dark, pushing buttons and pulling levers to make things happen. With data, they can understand how their actions create subsequent events and the overall impact they make.
To see this in action, we look to Customer Alliance , a long-time datapine customer. The company provides a rating system for hotels to review and analyze customer data. By learning more about customers’ experiences, they can better attract website visitors and drive bookings. CEO Moritz Klussman said this visibility has made all the difference in their sales teams’ efforts.
They now have an easy way to provide management teams with access to all data and dashboards. They can filter to their level of interest and drill into reports for more details. Reviewing relevant customer data is faster, and data can be combined from multiple sources to generate new insights for the sales team. In Klussman’s words, it “has increased the number of closed deals significantly.”
10) Gain Essential Customer Insights
The more you know about your customers, the better you can adjust your messaging, products, and acquisition techniques to attract and retain them. Ideally, you can look at your existing customers to find common denominators: What industry are they in? How did they find you? How much are they spending with you? What do they buy from you? What makes them choose you vs. a competitor? What makes them stop doing business with you?
These are all essential questions with answers that directly impact your growth potential. To answer them, we can use BI to find patterns, trends, and other connections between data that would be too time-consuming or complex for humans to identify alone.
Deloitte shares this case study about how they helped a major media company develop a customer insights platform to turn data into business value. The organization knew it had valuable data but lacked an efficient way to utilize it. The company built a platform using Amazon Web Services to improve customer segmentation, predict churn, and quantify total customer value for millions of global subscribers. The platform aggregates data from disparate legacy systems and uses AI to analyze the data and develop insights.
The new models and dashboards accelerated growth by identifying customer trends. Improved segmenting led to hyper-targeted campaigns and better content delivery, increasing customer satisfaction. Clean and accessible customer data, coupled with AI utilization, enables the client to extract actionable insights and drive real business value—in this case, that value turned out to be worth millions of dollars.
Now that you understand the value that BI and analytics can bring to your organization, let’s examine some practical examples of how it would look in practice.
Business Intelligence and Analytics Benefits: Practical Examples
Business intelligence is key to monitoring business trends, detecting significant events, and, thanks to data, getting the full picture of what is happening inside your organization. It is important to optimize processes, increase operational efficiency, drive new revenue, and improve the company's decision-making.
We’re living in the most competitive business market in history. Technological advances and a global economy have created a pressure cooker of competition, with weaker companies being swallowed or broken down. Luckily, business intelligence tools have developed the necessary technology for companies to manage their data efficiently. BI dashboards like the ones presented below provide a centralized view of the most important metrics businesses need to stay ahead of their competitors. Not only that but getting a visual overview of the performance of several areas also empowers employees to use data for their decision-making process.
Let’s review a few examples of this:
1. Sales KPI Dashboard
With the essential sales dashboard at your fingertips, you can understand the current state of incoming funds and see whether you’re on target to meet company goals.
**click to enlarge**
Comparison data helps you see trends and patterns, allowing you to understand where to adjust to stay on track. For example, if customer churn suddenly spikes, you can start looking at other areas to figure out why and find creative ways to plug the holes. Having these insights at a glance is useful in mitigating risk, making informed decisions, and gaining essential customer insights that directly impact your top line.
2. Financial KPI Dashboard
Our financial dashboard answers your most pressing questions about invoicing, budgeting, and overall financial stability. Get a glimpse of your working capital, assets, and liabilities in a single snapshot to gauge your financial health at any given moment.
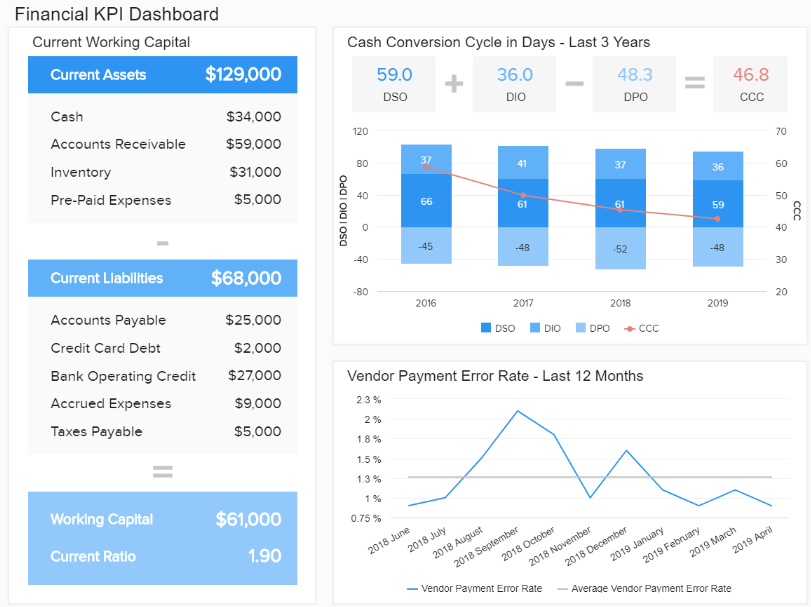
Having these insights is a key piece of risk mitigation. For instance, if your cash conversion cycle is upward trending, your risk of running into a cash flow issue is higher. We can also see use cases for improving operational efficiency and accountability. Take the vendor payment error rate, for example. Things like duplicate payments, wrong addresses, and incorrect amounts can all affect vendor payment error rates, and these spikes may show where the accounts payable department can improve its processes.
3. Marketing KPI Dashboard
Lastly, we have a marketing dashboard , which ultimately ties back to your bottom line. Here we see some important figures showing us how marketing efforts are paying off, which can provide jumping-off points to dive deeper into other data.
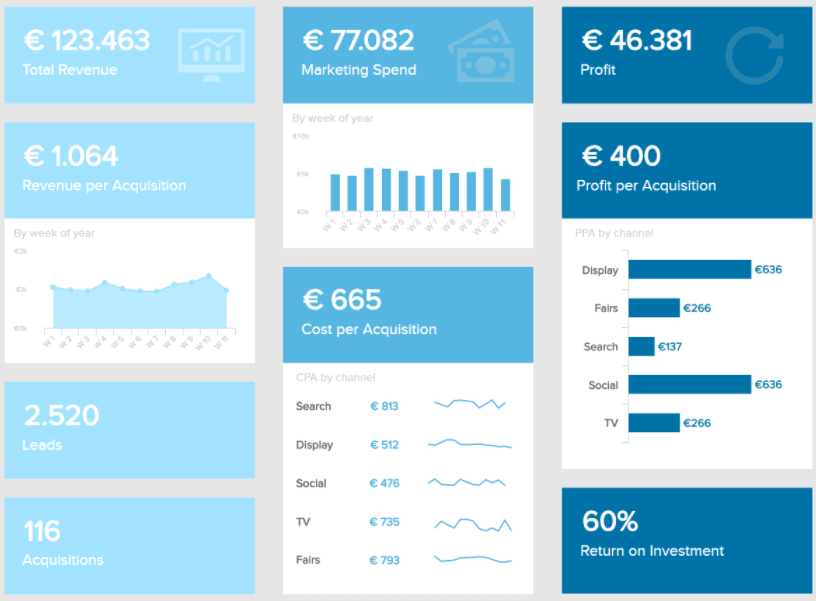
Helpful use cases include strategic decision-making, increased accountability, and gaining essential customer information. Marketers can see how small tweaks and whole campaigns are acquiring customers and generating revenue and the most effective channels to reach customers.
BI Benefits: Final Thoughts
Given the current state of affairs, your company can’t afford not to use BI tools, especially after we examined ten business intelligence case studies that showed the incredible ROI possible from using them and the many benefits of business analytics. Such business intelligence ROI can come in many forms. You need to know what’s going on in the minds of your customers, who your next best customers will be, and how to serve them most effectively. These areas can be answered with data – which you need BI and analytics tools to process. However, be aware of any faux pas, and remember that there are some business intelligence best practices to know and some worst practices to avoid!
When your company has to rely on internal or external IT staff to generate data reports, it creates a huge barrier to what is most needed: a data-driven corporate culture where decisions are validated by clearly seeing reality.
If you’d like to take your first step towards using an intuitive self-service business analytics tool, try our 14-day free trial and test what datapine can do for you.

Business intelligence (BI) is a set of technological processes for collecting, managing and analyzing organizational data to yield insights that inform business strategies and operations.
Business intelligence analysts transform raw data into meaningful insights that drive strategic decision-making within an organization. BI tools enable business users to access different types of data—historical and current, third-party and in-house, as well as semistructured data and unstructured data such as social media. Users can analyze this information to gain insights into how the business is performing and what it should do next.
According to CIO magazine : “Although business intelligence does not tell business users what to do or what will happen if they take a certain course, neither is BI only about generating reports. Rather, BI offers a way for people to examine data to understand trends and derive insights.” 1
Organizations can use the insights gained from BI and data analysis to improve business decisions, identify problems or issues, spot market trends and find new revenue or business opportunities.
IBM Planning Analytics benefits businesses with more accurate reporting, analysis and planning.
Report from Ventana Research: Debunking myths about data and analytics
Business intelligence (BI) is descriptive, enabling better business decisions that are based on a foundation of current business data. Business analytics (BA) is then a subset of BI, with business analytics providing the prescriptive , forward-looking analysis. It is the umbrella of BI infrastructure that includes the tools for the identification and storage of the data for decision-making.
BI might tell an organization how many new customers were acquired last month and whether order size was up or down for the month. As opposed to this, business analytics might predict which strategies, based on that data, would most benefit the organization. For example: What happens if we increase advertising spending to give new customers a special offer?
BI platforms traditionally rely on data warehouses for their baseline information. The strength of a data warehouse is that it aggregates data from multiple data sources into one central system to support business data analytics and reporting. BI presents the results to the user in the form of reports, charts and maps, which might be displayed through a dashboard.
Data warehouses can include an online analytical processing (OLAP) engine to support multidimensional queries. For example: “What are the sales for our eastern region versus our western region this year, compared to last year?”
OLAP provides powerful technology for data discovery, facilitating BI, complex analytic calculations and predictive analytics . One of the main benefits of OLAP is the consistency of its calculations that can improve product quality, customer interactions and business process.
Data lakehouses are now also being used for BI. The benefit of a data lakehouse is that it seeks to resolve the core challenges across both data warehouses and data lakes to yield a more ideal data management solution for organizations. A lakehouse represents the next evolution of data management solutions.
The steps taken in BI usually flow in this order:
- Data sources : Identify the data to be reviewed and analyzed, such as from a data warehouse or data lake , cloud , Hadoop , industry statistics, supply chain, CRM , inventory, pricing, sales, marketing or social media.
- Data collection : Gather and clean data from various sources. This data preparation might be manually gathering information in a spreadsheet or an automatic extract, transform and load (ETL) program.
- Analysis : Look for trends or unexpected results in the data. This might use data mining , data discovery or data modeling tools.
- Visualization : Create data visualizations, graphs and dashboards that use business intelligence tools such as Tableau , Cognos Analytics , Microsoft Excel or SAP . Ideally this visualization includes drill-down, drill-through, drill-up features to enable users to investigate various data levels.
- Action plan : Develop actionable insights based on analysis of historical data versus key performance indicators (KPIs) . Actions might include more efficient processes, changes in marketing , fixing supply chain issues or adapting customer experience issues.
Some newer BI products can extract and load raw data directly by using technology such as Hadoop, but data warehouses often remain the data source of choice.
Get fast answers with AI-powered business intelligence across the enterprise
The term “business intelligence” was first used in 1865 by author Richard Millar Devens, when he cited a banker who collected intelligence on the market before his competitors did. In 1958, an IBM computer scientist named Hans Peter Luhn explored the potential of using technology to gather BI. His research helped establish methods for creating some of IBM’s early analytics platforms.
In the 1960s and 70s, the first data management systems and decision support systems (DSS) began to store and organize the growing volumes of data. “Many historians suggest the modern version of BI evolved from the DSS database,” says the IT education site Dataversity. “An assortment of tools was developed during this time, to access and organize data in simpler ways. OLAP, executive information systems and data warehouses were some of the tools developed to work with DSS.” 2
By the 1990s, BI grew increasingly popular, but the technology was still complex. It usually required IT support—which often led to backlogs and delayed reports. Even without IT, BI analysts and users needed extensive training to be able to successfully query and analyze their data. 3
Business intelligence is as much a way of thinking as it is composed of hardware and software. By adopting a data-driven culture—based on a complete set of approaches, processes, digital technology and data analysis—an organization can find new insights to make better business decisions and gain new advantages. Installing a new BI software package alone does not bring about this culture shift.
Benefits of BI :
- Clearer reporting : BI gives organizations the ability to ask questions in plain language and get answers they can understand. Dashboards can prioritize the most important insights, saving time for both data experts and nontechnical team members. Instead of using best guesses, staff can base decisions on what their business data is telling them—whether it relates to production, supply chain, customers or market trends. The data can help answer an organization’s pressing questions: Why are sales dropping in this region? Where do we have excess inventory? What are customers saying on social media?
- Consolidated data : BI delivers business insights by pulling in and consolidating data from multiple sources—internal and external—for complete analysis. By providing an accurate picture of the business and market, BI provides an organization with the means to design a business strategy.
- Create new efficiencies : Organizations can monitor business operations against benchmarks and fix or make improvements on an ongoing basis—all fueled by data insights. Analytics can discover and help eliminate manufacturing or supply chain bottlenecks. Managers can monitor staff performance to help pinpoint where organizational changes can be made. Supply chain management can be improved by monitoring activity up and down the line and communicating results with partners and suppliers.
- Deeper data insights : BI helps organizations become more data-driven, to continually improve business performance, gain competitive advantage, and locate new customers and new opportunities. They can improve ROI by understanding their business and market, and intelligently allocating resources to meet strategic objectives. New data insights can reveal customer behavior, preferences and market trends. Those insights enable marketers to better target prospects or tailor products to changing market needs.
- Faster decision making : As progress is monitored and analyzed digitally, better informed decisions can be made more quickly for faster adjustments in the marketplace.
- Increase customer satisfaction : When customer service staff have access to customer data and insights, they can provide requested information and resolve issues more quickly.
- Increase employee satisfaction : Self-help access to important business data can optimize workflows so that staff can do their jobs faster, with fewer added or repetitive steps.
Challenges of BI
- Contradictory conclusions : Self-service BI empowers multiple teams to search for the insights they need, but can also lead to divergent conclusions, which can create more friction instead of a unified plan of action. This can be especially true if human bias creeps into the analysis.
- Skills shortfall : The need for data integration might be difficult, given a wide variety of sources, and integration might exceed current capabilities. Expertise in data science, engineering and architecture is required to help ensure that analysis yields insights that reflect reality.
- Up-front costs : The initial costs to develop a powerful, modern BI system might appear large—but the cost savings generated by analysis will offset the investment.
Data is the lifeblood of successful organizations. Beyond the traditional data roles—data engineers, data scientists, analysts and architects—decision-makers across an organization need flexible, self-service access to data-driven insights accelerated by artificial intelligence (AI) . From marketing to HR, finance to supply chain and more, decision-makers can use these insights to improve decision-making and productivity enterprise-wide.
Organizations benefit when they can fully assess operations and processes, understand their customers, gauge the market, and drive improvement. They need the right tools to aggregate business information from anywhere, analyze it, discover patterns and find solutions. To deliver a BI system that can make all of this possible, organizations should:
- Set clear business objectives : Determining the most valuable and actionable information enables an organization to determine the data that needs to be collected or sourced and help select the BI system features needed to deliver that information.
- Comprehensive user training : The culture change to becoming a data-driven organization is most achievable when all users are given clear and compelling lessons on the new tools. Perfunctory training or self-guided hacking might discourage team buy-in or produce inaccurate results.
- Monitor data quality and relevance : Constant data monitoring is needed to help ensure that results are consistent and trustworthy. As market conditions change, new measures might need to be added or different reporting formats developed to add clarity. The input data sets must be sound and unbiased , and managed according to clear governance standards that ensure it is secure, private, accurate and usable. Any AI models that inform decision-making and forecasting must be explainable and transparent . And the BI system should connect to a wide variety of data systems across business functions and be usable by those who are not professional data analysts.
- Ensure data access to decision-makers : Many businesses are behind. Essential data is not sufficiently captured or analyzed, according to an IDC report 4 that estimates up to 68% of business data goes unleveraged. Companies with a modern data architecture and robust BI adoption enjoy competitive advantage: They are positioned to move even further ahead by adopting real-time decisioning practices and predictive analytics.
Business intelligence adds value across multiple functions in almost any industry. For example: Customer service : With both customer information and product details available through a unified data source, customer service agents are able to quickly answer customer questions or begin to solve customer concerns.
Finance and banking : Financial firms can determine current organizational health and risks, and predict future success by viewing combined customer histories and market conditions. Data can be reviewed branch-by-branch with a single interface to identify opportunities for improvement or further investment.
Healthcare : Patients can quickly get answers to many pressing healthcare questions without asking time-consuming questions of staff or medical personnel. Internal operations, including inventories, are easier to track, minute-by-minute.
Retail : Retailers can boost cost savings by comparing performance and benchmarks across stores, channels and regions. And, with visibility into the claims process, insurers can see where they are missing service targets and use that information to improve outcomes.
Sales and marketing : By unifying data on promotions, pricing, sales, customer actions and market conditions, marketers and sales teams are better able to plan future promotions and campaigns. Detailed targeting or segmentation can help boost sales.
Security and compliance : Centralized data and a unified dashboard can improve accuracy and help determine the root causes of security problems. Compliance with regulations can be simplified with a single system to gather reporting data.
Statistical analytics : Using descriptive analytics , organizations can review statistics to spot new trends and uncover why those trends are developing. Supply chain : Worldwide data on a single pane of glass (SPOG) can speed the movement of goods and the identification of supply chain inefficiencies and bottlenecks.
Recent developments in business intelligence are focused on self-service BI applications that enable non-tech-savvy users to use automatic analysis and reporting. The IT team remains responsible for managing corporate data—including accuracy and security—but multiple teams can now have direct access to data and be responsible for their own analysis, rather than having the job wait in a queue for IT to run.
The ongoing advances in modern business intelligence and analytics systems are expected to integrate machine learning algorithms and AI to streamline complicated tasks. With the new emphasis on self-service, these capabilities can also accelerate the enterprise’s ability to analyze data and gain insights at a deeper level. AI-based systems can read from multiple sources automatically while grabbing the most relevant information to lead decision-making.
As an example, consider how IBM Cognos® Analytics brings together data analysis and visual tools to support map-creation for reports. The system uses AI to automatically identify geographical information. It can then refine visualizations by adding geospatial mapping of the entire globe, an individual neighborhood or anything in between.
Modern BI solutions live on cloud-based platforms to extend the reach of BI worldwide. Consumer insights can be drawn from big data , producing information that ranges from descriptive to predictive. Many BI solutions now include real-time processing, enabling immediate decision-making.
Further advances in enterprise-grade BI systems include natural language queries, which are easier for users who are not SQL experts. Low-code or no-code development capabilities are available in some BI systems so users can create their own tools, apps and reporting interfaces to further speed the answers and time-to-market.
Your AI-powered business analyst and advisor will answer your business questions in seconds, guiding you toward the most impactful decisions.
Automate planning, budgeting, forecasting and analysis processes. Go beyond spreadsheets to create efficiency and remove manual steps. Echoing the benefits, Mick Ferguson, Finance Manager, Hunter Industries, states: "We're delighted with IBM Planning Analytics on Cloud; it’s become the one-stop shop for all of our finance and accounting needs."
Take advantage of this single analytics solution across your entire organization to confidently monitor, explore and share insights from data. Stefanie Nicholson, Head of Operations, Go Health Clubs, underscores this impact: "We're much more confident in our metrics—in fact, there’s now an attitude in the business that 'it doesn’t count if it doesn’t come from Cognos."
Use predictive analytics to help you uncover data patterns, gain accurate insights and improve decision making. Mark Lack, Strategy Analytics and Business Intelligence Manager, Mueller, Inc., confirms this benefit: "Deep analytics. Just add data."
Read why companies that thrive will be those that make fast, data-driven decisions using augmented analytics.
Find out how businesses use artificial intelligence, learn about its benefits and advantages, and more.
Find out about the importance of a responsive supply chain plan and how to achieve it.
Discover how this customer is helping to ensure the quality of care by calculating daily performance metrics, identifying trends and fine-tuning its processes.
Predict outcomes with flexible AI-infused forecasting and analyze what-if scenarios in real-time. IBM Planning Analytics is an integrated business planning solution that turns raw data into actionable insights. Deploy as you need, on-premises or on cloud.
All links reside outside ibm.com
1 CIO magazine: https://www.cio.com/article/272364/business-intelligence-definition-and-solutions.html
2 Dataversity Digital: https://www.dataversity.net/brief-history-business-intelligence/
3 Better Buys: https://www.betterbuys.com/bi/history-of-business-intelligence/
4 Report by Seagage and IDC: https://www.seagate.com/files/www-content/our-story/rethink-data/files/Rethink_Data_Report_2020.pdf

Business Intelligence Case Studies

Process Insights – Complex Cross-Border Cloud Data Warehouse with Azure SQL and Power BI Case Study

Brookshire Brothers – Data Warehouse Consulting and Analytics for retailer

Boyd – Data warehouse delivers unified view and decision-making
Be for beauty – sales data warehouse for consumer market.

ACI Learning: Data Warehouse for Unified View of Company Performance
Mass mutual: power bi for survey data, to discuss your project requirements, send us a message, for a free assessment, quick quote or training information, send us a message, to book this course, please fill in your details and submit the form., to discuss your training requirements or book a class, drop us a line.
- Our Customers
Some of Our Representative Clients Include:

- Solutions by Industry
- BI Analytics
- Business Intelligence
- Cloud Data Management
- Data Governance
- Data Integration
- Data Migration
- Data Science
- Data Warehouse
- Machine Learning
- Master Data Management
- Predictive Analytics
- Regulatory Compliance
- IBM Infosphere
- Informatica
- Microsoft Power BI
- Microsoft SQL Server
- MicroStrategy
- SAP BusinessObjects
About Exist BI
- Technology Expertise
- Case Studies
U.S. Headquarters Century Plaza Towers, 2029 Century Park E Suite 400, Los Angeles, CA 90067 (866) 965-6332 (Toll-Free) (310) 683-0115
UK Office Hamilton House, Mabledon Place, London WC1H 9BB, UK +44 (0)207 554 8568
Other Locations
Jersey City Office 101 Hudson Street, 21st Floor, Jersey City, NJ 07302 (866) 965-6332 (Toll-Free) (347) 229-9507
Washington DC Office 1050 Connecticut Ave NW, Suite 500, Washington, DC 20036 (202) 301-4679
German Office Europaplatz 2, 8th Floor, Berlin, 10557, Germany +49 302 204 3994
Cleveland Office 600 Superior Ave, 3rd Floor, Cleveland, OH 44114 (216) 242-4125
Denver Office 1600 Broadway Suite 1600, Denver, CO 80202 (720) 399-4525
Croatia Office Bencekovićeva 33, 10000 Zagreb, Croatia +44 (0)207 554 8568

Business Intelligence
Many new clients were echoing the same message; they were embarrassed they were unable to quickly and easily report to their cpo or cmo exactly how much money they were spending with their marketing agencies..
Yes, each brand team knew their budget, and the finance organization had the rolled-up budgets, but there was no single source of truth, or centralized database, capturing agency spend and performance information at a more detailed level. This is a common challenge for large, multinational companies. Their ERP system doesn’t provide the appropriate level of agency activity to be able to perform business analytics on agency performance, production and creative spend, and project tracking so most companies rely on spreadsheets and lots of emails.
Decideware helps large advertisers not only centralize and streamline their agency data, (to create that single source of truth), we also develop custom, easy-to-understand dashboards and reports. Our business intelligence team creates data visualizations that can quickly highlight key, actionable insights. Decideware’s Business Intelligence team specializes in taking large data sets and making it easier for clients to identify trends, patterns, and outliers.
Below is a simple illustration of how data visualization helps present a clearer picture.
Count the numbers of 1’s in the original presentation vs. the 2nd presentation.
Original presentation of data:
Presentation with data visualization:
The number of 1’s is the same in both images, but when presented with data visualization, you can easily identify the 1’s, count them, and see a pattern emerge. This is the power of business intelligence.
Below are a couple of examples where clients have benefited from Decideware’s Business Intelligence expertise.
Case Study 1
Major advertiser uses business intelligence to inform and improve how they manage their agency management program and relationships.
Simply automating processes and centralizing data without a solid understanding of how the foundational data structure impacts the ability to perform business analytics will result in lackluster Business Intelligence. A major US advertiser came to Decideware because of our in-depth experience and understanding of how to structure data to provide powerful and actionable Business Intelligence. A large US advertiser moved to Decideware because they were not getting the level of Business Intelligence they needed from an alternative software provider. They had all of their data captured in a database, but because it wasn’t structured appropriately, they were unable to pull meaningful and actionable analytics from the data.
The advertiser wanted analytics that would enable them to gain a better understanding of the types of deliverables they were buying, how deliverables and costs were broken down by business unit, which agencies were performing well relative to cost, and much more. Decideware worked with the client to understand the end goals as part of the software implementation due diligence—it is a fundamental and critical first step to setting up agency management software to perform powerful data analytics. With the right data structure in place the business intelligence team worked with the marketing operations and procurement teams to create data visualizations to help them understand their data in a way that enabled them to make faster, more informed decisions. Custom dashboards were created based on scope of work, performance evaluation, production, and diversity, equity & inclusion data. The result was the client was able to quickly and easily interpret the data, filter and drill down into details that helped inform business decisions.
Example of Business Intelligence:
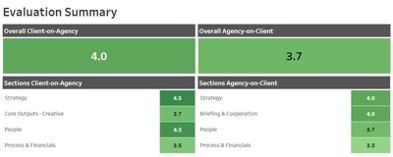
Case Study 2
Travel industry client thankful they had decideware when the pandemic hit.
Expect the unexpected. Yes, companies can get by with spreadsheets and limited business intelligence, but when something unexpected happens, quick decisions are critical, and financial sustainability is at stake, having access to timely, accurate data can save an organization millions of dollars and help them utilize limited resources in an efficient way.
A client in the travel industry was hit extremely hard by the recent pandemic. They needed to act urgently to review all of their scopes of work, with every agency, to identify what work could be halted immediately and which agencies could address essential marketing needs during the pandemic. Informed with good data from Decideware, the advertiser made business critical decisions and partnered closely with their selected agencies in a transparent manner to minimize the negative impact to both themselves and their agencies.
Needing to re-arrange global spend in a hurry, and with the help of Decideware Business Intelligence the client knew within minutes the following information:
- Number and spend details of Scopes of Work in the workflow approval process, not yet approved
- Details of projects within an approved Scope of Work that had not yet started
- The financial impact of halting all work not yet started
- The financial impact of pausing projects that were already in progress
With access to good data, tough decisions were able to be made at the senior level of the organization in order to protect their brands under obvious considerable market stress. Scopes of Work were able to be updated and thanks to business intelligence, the CMO and CFO were able to see the financial impact of their decisions in a timely manner. The feedback from the client’s marketing operations team was that they didn’t know how they would have managed the process with the agencies without having the Decideware tool in place.
With access to good data, tough decisions were able to be made at the senior level of the organization in order to protect their brands under obvious considerable market stress. Scopes of Work were able to be updated and thanks to business intelligence, the CMO and CFO were able to see the financial impact of their decisions in a timely manner.
The feedback from the client’s marketing operations team was that they didn’t know how they would have managed the process with the agencies without having the Decideware tool in place.

Get The eBook
How to apply business intelligence to agency management, learn what decideware can do for you..
Request a demo of our industry-leading agency relationship management solutions today.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
HBS Case Selections
OpenAI: Idealism Meets Capitalism
- Shikhar Ghosh
- Shweta Bagai
Generative AI and the Future of Work
- Christopher Stanton
- Matt Higgins
Copilot(s): Generative AI at Microsoft and GitHub
- Frank Nagle
- Shane Greenstein
- Maria P. Roche
- Nataliya Langburd Wright
- Sarah Mehta
Innovation at Moog Inc.
- Brian J. Hall
- Ashley V. Whillans
- Davis Heniford
- Dominika Randle
- Caroline Witten
Innovation at Google Ads: The Sales Acceleration and Innovation Labs (SAIL) (A)
- Linda A. Hill
- Emily Tedards
Juan Valdez: Innovation in Caffeination
- Michael I. Norton
- Jeremy Dann
UGG Steps into the Metaverse
- Shunyuan Zhang
- Sharon Joseph
- Sunil Gupta
- Julia Kelley
Metaverse Wars
- David B. Yoffie

Roblox: Virtual Commerce in the Metaverse
- Ayelet Israeli
- Nicole Tempest Keller
Timnit Gebru: "SILENCED No More" on AI Bias and The Harms of Large Language Models
- Tsedal Neeley
- Stefani Ruper
Hugging Face: Serving AI on a Platform
- Kerry Herman
- Sarah Gulick
SmartOne: Building an AI Data Business
- Karim R. Lakhani
- Pippa Tubman Armerding
- Gamze Yucaoglu
- Fares Khrais
Honeywell and the Great Recession (A)
- Sandra J. Sucher
- Susan Winterberg
Target: Responding to the Recession
- Ranjay Gulati
- Catherine Ross
- Richard S. Ruback
- Royce Yudkoff
Hometown Foods: Changing Price Amid Inflation
- Julian De Freitas
- Jeremy Yang
- Das Narayandas
Elon Musk's Big Bets
- Eric Baldwin
Elon Musk: Balancing Purpose and Risk
Tesla's ceo compensation plan.
- Krishna G. Palepu
- John R. Wells
- Gabriel Ellsworth
China Rapid Finance: The Collapse of China's P2P Lending Industry
- William C. Kirby
- Bonnie Yining Cao
- John P. McHugh
Forbidden City: Launching a Craft Beer in China
- Christopher A. Bartlett
- Carole Carlson
Booking.com
- Stefan Thomke
- Daniela Beyersdorfer
Innovation at Uber: The Launch of Express POOL
- Chiara Farronato
- Alan MacCormack
Racial Discrimination on Airbnb (A)
- Michael Luca
- Scott Stern
- Hyunjin Kim
Unilever's Response to the Future of Work
- William R. Kerr
- Emilie Billaud
- Mette Fuglsang Hjortshoej
AT&T, Retraining, and the Workforce of Tomorrow
- Joseph B. Fuller
- Carl Kreitzberg
Leading Change in Talent at L'Oreal
- Lakshmi Ramarajan
- Vincent Dessain
- Emer Moloney
- William W. George
- Andrew N. McLean
Eve Hall: The African American Investment Fund in Milwaukee
- Steven S. Rogers
- Alterrell Mills
United Housing - Otis Gates
- Mercer Cook
The Home Depot: Leadership in Crisis Management
- Herman B. Leonard
- Marc J. Epstein
- Melissa Tritter
The Great East Japan Earthquake (B): Fast Retailing Group's Response
- Hirotaka Takeuchi
- Kenichi Nonomura
- Dena Neuenschwander
- Meghan Ricci
- Kate Schoch
- Sergey Vartanov
Insurer of Last Resort?: The Federal Financial Response to September 11
- David A. Moss
- Sarah Brennan
Under Armour
- Rory McDonald
- Clayton M. Christensen
- Daniel West
- Jonathan E. Palmer
- Tonia Junker
Hunley, Inc.: Casting for Growth
- John A. Quelch
- James T. Kindley
Bitfury: Blockchain for Government
- Mitchell B. Weiss
- Elena Corsi
Deutsche Bank: Pursuing Blockchain Opportunities (A)
- Lynda M. Applegate
- Christoph Muller-Bloch
Maersk: Betting on Blockchain
- Scott Johnson
Yum! Brands
- Jordan Siegel
- Christopher Poliquin
Bharti Airtel in Africa
- Tanya Bijlani
Li & Fung 2012
- F. Warren McFarlan
- Michael Shih-ta Chen
- Keith Chi-ho Wong
Sony and the JK Wedding Dance
- John Deighton
- Leora Kornfeld
United Breaks Guitars
David dao on united airlines.
- Benjamin Edelman
- Jenny Sanford
Marketing Reading: Digital Marketing
- Joseph Davin
Social Strategy at Nike
- Mikolaj Jan Piskorski
- Ryan Johnson
The Tate's Digital Transformation
Social strategy at american express, mellon financial and the bank of new york.
- Carliss Y. Baldwin
- Ryan D. Taliaferro
The Walt Disney Company and Pixar, Inc.: To Acquire or Not to Acquire?
- Juan Alcacer
- David J. Collis
Dow's Bid for Rohm and Haas
- Benjamin C. Esty
Finance Reading: The Mergers and Acquisitions Process
- John Coates
Apple: Privacy vs. Safety? (A)
- Henry W. McGee
- Nien-he Hsieh
- Sarah McAra
Sidewalk Labs: Privacy in a City Built from the Internet Up
- Leslie K. John
Data Breach at Equifax
- Suraj Srinivasan
- Quinn Pitcher
- Jonah S. Goldberg
Apple's Core
- Noam Wasserman
Design Thinking and Innovation at Apple
- Barbara Feinberg
Apple Inc. in 2012
- Penelope Rossano
Iz-Lynn Chan at Far East Organization (Abridged)
- Anthony J. Mayo
- Dana M. Teppert
Barbara Norris: Leading Change in the General Surgery Unit
- Boris Groysberg
- Nitin Nohria
- Deborah Bell
Adobe Systems: Working Towards a "Suite" Release (A)
- David A. Thomas
- Lauren Barley
Home Nursing of North Carolina
Castronics, llc, gemini investors, angie's list: ratings pioneer turns 20.
- Robert J. Dolan
Basecamp: Pricing
- Frank V. Cespedes
- Robb Fitzsimmons
J.C. Penney's "Fair and Square" Pricing Strategy
J.c. penney's 'fair and square' strategy (c): back to the future.
- Jose B. Alvarez
Osaro: Picking the best path
- James Palano
- Bastiane Huang
HubSpot and Motion AI: Chatbot-Enabled CRM
- Thomas Steenburgh
GROW: Using Artificial Intelligence to Screen Human Intelligence
- Ethan S. Bernstein
- Paul D. McKinnon
- Paul Yarabe
Arup: Building the Water Cube
- Robert G. Eccles
- Amy C. Edmondson
- Dilyana Karadzhova
(Re)Building a Global Team: Tariq Khan at Tek
Managing a global team: greg james at sun microsystems, inc. (a).
- Thomas J. DeLong
Organizational Behavior Reading: Leading Global Teams
Ron ventura at mitchell memorial hospital.
- Heide Abelli
Anthony Starks at InSiL Therapeutics (A)
- Gary P. Pisano
- Vicki L. Sato
Wolfgang Keller at Konigsbrau-TAK (A)
- John J. Gabarro
Midland Energy Resources, Inc.: Cost of Capital
- Timothy A. Luehrman
- Joel L. Heilprin
Globalizing the Cost of Capital and Capital Budgeting at AES
- Mihir A. Desai
- Doug Schillinger
Cost of Capital at Ameritrade
- Mark Mitchell
- Erik Stafford
Finance Reading: Cost of Capital
David Neeleman: Flight Path of a Servant Leader (A)
- Matthew D. Breitfelder
Coach Hurley at St. Anthony High School
- Scott A. Snook
- Bradley C. Lawrence
Shapiro Global
- Michael Brookshire
- Monica Haugen
- Michelle Kravetz
- Sarah Sommer
Kathryn McNeil (A)
- Joseph L. Badaracco Jr.
- Jerry Useem
Carol Fishman Cohen: Professional Career Reentry (A)
- Myra M. Hart
- Robin J. Ely
- Susan Wojewoda
Alex Montana at ESH Manufacturing Co.
- Michael Kernish
Michelle Levene (A)
- Tiziana Casciaro
- Victoria W. Winston
John and Andrea Rice: Entrepreneurship and Life
- Howard H. Stevenson
- Janet Kraus
- Shirley M. Spence
Partner Center

Top 10 Business Intelligence Case Studies and Solutions
Business intelligence case studies are generally scenario-based questions that ask you to work through a solution to a proposed business problem.
For example, in a business intelligence case interview, you might be asked: How would you de-duplicate product listings that don’t have the same title, SKU, or description?
Your job is to ask the interviewer for more information, make assumptions about the case, propose a solution, and finally, consider the trade-offs of your solution. For business intelligence engineering roles, business case studies tend to fall into two broad categories:
Analytics - Analytics questions test your understanding of metrics and how they relate to business goals. Your job is to ask the interviewer for more information, make assumptions about the case, propose a solution, and finally, consider the trade-offs of your solution.
Database Design - Database/ technology questions ask you to design or discuss a tech solution to a given business problem.
Generally, business intelligence case studies are the most difficult part of business intelligence interviews, but using frameworks and understanding how they are graded can help you to prepare for your next BI case study interview.
What Does a Business Intelligence Engineer Do?
Business intelligence (BI) engineers are technology specialists who ensure that analysts and data scientists have access to the right data and technologies. A key responsibility is ensuring that the company’s data is organized and accessible. BI engineer case interviews mirror the type of work that candidates will perform on the job.
Specific tasks business intelligence engineers do include:
Creating reports, developing dashboards, and implementing analytics applications such as DataMiner or Tableau Desktop
Designing, developing, and maintaining data warehouses to store large volumes of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data
Selecting hardware, software, and database management systems for data warehousing projects in line with organizational goals
Training and onboarding users to use business intelligence software
What Is a Business Intelligence Case Study?
Case studies are a common business intelligence interview question that present the interviewee with a specific business problem. The interviewee must then talk the interviewer through a potential solution for that problem.
Most business intelligence case studies cover designing dashboards or creating databases to function for business needs. Therefore, most problems are general business case studies or technical SQL case studies, and the interviewee must solve a problem relating to how data is being presented or stored.
A typical framework for solving business intelligence case questions includes four steps:
1. Clarify - Your first step should be to gather more information from the interviewer. Case studies tend to be vague and lack information. You’re responsible for digging in and finding out exactly what the question is asking.
2. Make Assumptions - Start forming a hypothesis and talk through your reasoning. Your goal should be to land on one hypothesis/solution for the problem, which you will analyze further.
3. Propose a Solution - State your solution, and talk the interviewer through your processes for building the solution.
4. Conduct Further Analysis - For analytics case studies, you’ll want to narrow your investigation to one key metric and support your hypothesis with data. For database design case studies, you’ll walk the interviewer through the schema for a database.
How Are Business Intelligence Case Interviews Graded?

There is not a set grading rubric for business intelligence case studies, as it’s often at the discretion of the interviewer. However, there are some areas you should focus on that will make your response stronger:
Curiosity- Clarifying questions helps you narrow your response. An Amazon business intelligence engineer told us: “If you don’t ask questions, the interviewer could fail you, because they wanted to give you some information to steer the discussion down a particular path.”
Ability to take direction - Our source said: “The interviewer decides where the candidate needs to end up in their solution.” Therefore, it’s important to take hints and coaching during the interview.
Thoroughness - Case questions assess the depth of your problem-solving approach. You can show this by asking clarifying questions, providing multiple data points for analysis, and making assumptions (and checking that those assumptions are correct).
Ability to adapt - Inevitably, something unexpected will come up in a case study question, like your preferred method isn’t feasible, and you will have to adapt. Take the cues the interviewer provides, and always be willing to change courses if needed.
Communication - BI cases assess your ability to summarize your solution and clearly explain your thought processes and assumptions. One tip: Ask the interviewer if they have any questions throughout your response. This can help you clarify your answer at the moment.
There’s no right or wrong answer to case study questions. Rather, candidates are graded on the quality of their responses. Using a framework will help you structure your response more clearly.
Business Intelligence Case Study: Mock Interview
Let’s take a look at an in-depth mock interview solution to a business intelligence case question asked at Amazon:
1. You want to de-duplicate products from multiple sellers in a large eCommerce database. How would you approach this?
More context. Products are listed under different seller names. So for the same product, we might see many variations, e.g., iPhone X and Apple iPhone 10. However, let’s say this example shows up for a lot of different products in various categories.
See a full mock interview solution to this question on YouTube .
Example Solution:
Here’s an edited solution from the mock interview:
Interviewee: “If it’s an established e-commerce company, I would assume that they would have some kind of an ID for every product in their inventory. So something like an SKU or an ID. And if it’s Amazon, then that’s pretty unique, and you know that even if the description is different under different sellers, I would assume that they would have the same SKU.”
“So if you just look at the list of all the SKUs and different sellers and then do a distinct GROUP BY on SKU across all sellers, you’ll find out which SKUs are replicated. And then, once you have that, you can go to the business team saying what you want to do with them.”
Follow-Up Question 1: Let’s say you don’t have an SKU. People create their product titles, along with an image and descriptions.
How would we then do the mapping to the SKU, or would you think of a different approach towards solving the problem?
Identifying Similar Images
“If we have images for these products that we think may be duplicated, we could try to use an algorithm to identify similar images. Then once you have that list of similar images, you look at the descriptions and build a string similarity algorithm that outputs which descriptions sound similar or are close to each other. Now you would have at least two data points that you know these two products are similar. Then it’s probably going to be a little bit of manual intervention to identify if they really are similar or not.”
Similar Product Reviews
“The other thing that I can think of is maybe reviews on different products. So imagine that there are two different products just named differently, but both of them are the Apple iPhone 10. You would assume that the reviews are pretty much talking about a phone and that it’s manufactured by Apple. They probably have the same kinds of experiences and reviews, so you could see if the reviews are very similar to each other, and that would give a good indication that the product is probably the same. ”
Follow-Up Question 2: We’re looking at similarities across images, descriptions, and reviews, and we’re getting this score for each one of them. Now how do we go about deciding if we can de-duplicate them or not?
Would we have a human review every single one? Do we do some sort of scaling process? Because let’s say we have to do this for thousands and thousands of products, right? What’s the next step?
“Well, from the beginning, we don’t really know which products are the same or not, so we can’t do a supervised learning method. It needs to be an unsupervised technique that first tries to identify what products are similar to each other. I probably would do a clustering technique based on just descriptions and reviews.”
“We’ll definitely need to do some cleaning and tokenization for the text data to bring it to a structured format. Then we can run a TF IDF on different descriptions and reviews to find out which documents are similar. We’ll get some scores depending on how many documents end up in a particular cluster, and we will definitely have to do a manual step to see if they’re actually the same or not.”
“ I’m unaware of a clustering technique that works on images, but we would probably have to build out features from the image, bring it to a structured format, and then do clustering on top. So we might identify ten different clusters if there are ten items that are duplicated and then look at the clusters’ descriptive statistics to see if the customer in reviews is really talking about a phone, a tablet, or a computer. And then try to go about in a manual investigation from that point.”
Follow-Up Question 3: Let’s say we do that. We’re going through these clusters, and we find that the algorithm clustered just phones together instead of doing a specific enough cluster for the same product. Or maybe we’re getting thousands of different clusters that may or may not be duplicated.
Is there any way that we can optimize our manual intervention or scale this problem out so that we use the least amount of manual oversight while also figuring out a way to deduplicate efficiently?
“I guess it would depend on the features that we actually extract, as the more granular the features in our dataset, the better the clusters could be. If we are creating clusters just on the type of device, then you’re right. I think all phones and all computers will just end up together.”
“But if we are given that these are also duplicate listings, we would definitely want to look at more information in the listing itself; like the price of the product, the different types of colors that are available, and then the features in iPhones and Androids that are similar to each other. The features need to be as close to the product itself so that our clusters are more identifiable amongst each other and not as generic as phones and computers.”
“Finally, we could look at customers to see purchasing behavior. iPhones typically tend to sell out as soon as they are launched, so we can try to use the information around when a particular product was launched and then look at the purchase pattern during that time and then try to integrate these features into the dataset.”
Mock Interview Feedback
The example response provided some solid jumping-off points to solve the problem. However, there were missing factors that could have made the response stronger:
Consider the Scope
The response focused primarily on the example provided in the problem statement, e.g., iPhone X vs. Apple iPhone 10. However, in business case studies, it’s important to consider the broader context and incorporate that into your answer. In this case, considering a wider variety of products would have made the response stronger.
Having Multiple Data Points
In the example, there was just one type of product proposed. Having more data points to explain these concepts would have made the response more thorough and would have provided more examples to illustrate the proposed solution.
Considering Limitations
This particular response would have benefited from considering trade-offs to the proposed solution. In particular, the response didn’t address limitations like threshold error rates and automation. How accurate can we get with an automated word-matching solution, and would we be satisfied with the threshold?
Ultimately, the response could have benefited from a dialogue about implementation and business impact, as well as the technical details.
Additional BI Case Study Questions
Practice for the business intelligence interview with these sample database design and analytics case study questions:
2. Your company is launching a software product. Would you hire a customer success manager or use a free trial to grow the product?
The hypothesis you want to test is: Does a free trial result in cheaper engagement and acquisition costs, compared to using a CS manager?
Since this is a business intelligence role, you’ll want to frame the question in terms of metrics. Some of the metrics to consider include:
- Costs of hiring the CSM (continuous) vs cost of free trial implementation (fixed)
- Conversion rate from free to paid
- Total revenue gained
- Future product value
Each one of these metrics can be segmented additionally into new vs existing users. And if we apply weighting to each of these metrics we can ultimately come up with an equation that can maximize our goals.
3. What do you think are the most important metrics for WhatsApp?
An easy BI case study question like this assesses your data sense and the depth of your analytics knowledge. You might start with a clarifying question: Are we interested in revenue statistics (e.g. WhatsApp for Business) or more general user metrics?
For more general user engagement metrics, you could propose something like:
- Daily active users (how would you define this?)
- Average time spent on the platform by DAU
- Average number of messages sent per user
- Year-over-year or month-over-month increase in the average number of messages by users in different percentiles
- Churn rate and retention curve
As you propose metrics, be sure to tie them back to the business. Answer this question: Why does this metric matter to WhatsApp?
4. What metrics would you look at to determine the demand for rides on a ride-sharing app? What metrics would tell you there is high demand and low supply?
First, define some of the metrics. Demand would be the number of ride requests, while supply would be the number of available drivers. How would you further analyze ride requests to measure demand?
See a full mock interview solution for this question on YouTube:

5. In an insurance database, the marriage attribute column is marked TRUE for all customers. How would you debug what happened?
Follow-up question: What data would you look into and how would you find out who is actually married and who is not?
With this question, you’d want to start with some clarifying questions like:
- What’s the table structure like?
- How long has the bug existed?
- Where is the insurance company located?
One first step would be to look at what went wrong. You could look at UPDATE and INSERT queries to identify what might have caused the problem initially.
Next, you might look for an easy solution. Are there dimensions or columns related to marriage? If there was a column spouse.name, for example, this would provide insights into whether a client is married or not. You could also look to see if reverting the data would show the correct marriage status before the bug existed.
A more complex approach might be to GROUP clients by the last name and then see if entries with the same last name share an address, insurance plan ID, etc.
6. You work for a SAAS business. To catch up to end-of-quarter revenue goals, would you send an email blast to your entire customer list?
Broadly speaking, sending a mass email blast to a list of customers is generally not a good idea, especially when the objective of the email is to increase sales.
A better solution is to segment the audience and personalize the messaging by the audience. For example, if a customer was about to reach their licensing limit, we could send a personalized offer to add more licenses, while a win-back campaign could be used for recently churned users.
7. You work for a 14-month-old SAAS company. You’re asked to calculate the average customer lifetime value. How would you do it?
More context: We know that the product costs $100, an average 10% monthly churn, and the average customer sticks around for 3.5 months.
Average lifetime value is defined by the prediction of the net revenue attributed to the entire future relationship with all customers averaged. Given that we don’t know the future net revenue, we can estimate it by taking the total amount of revenue generated divided by the total number of customers acquired over the same period of time.
However, there’s a catch: it’s only a 14-month-old company. As a result, the average customer length is biased , because the company hasn’t existed long enough to correctly measure a sample average that is indicative of the mean.
How would you calculate this? Try to find the expected value of the customer at each month as a multiplier of retention times the product cost.
More Business Intelligence Resources
Prepare with these business intelligence interview questions , which are 29 commonly asked BI questions in areas like SQL, generic scenario-based cases, Python, and database design. Also, see our guide to Amazon business intelligence interviews and Google business intelligence interviews for more BI interview prep help.
- Explore AI by Industry PLUS
- Consumer goods
- Heavy industry
- Natural resources
- Professional services
- Transportation
- AI Best Practice Guides PLUS
- AI White Paper Library PLUS
- AI Business Process Explorer PLUS
- Enterprise AI Newsletter
- Emerj Plus Research
- AI in Business Podcast
- The AI Consulting Podcast
- AI in Financial Services Podcast
- Precisely – Building Trust in Data
- Shift Technology – How Insurers are Using AI
- Uniphore – The Future of Banking CX in APAC
- Uniphore – The Economic Impact of Conversational AI and Automation
- Uniphore – The Future of Complaints Management
- Uniphore – Conversational AI in Banking
5 Business Intelligence & Analytics Case Studies Across Industry

Daniel Faggella is Head of Research at Emerj. Called upon by the United Nations, World Bank, INTERPOL, and leading enterprises, Daniel is a globally sought-after expert on the competitive strategy implications of AI for business and government leaders.

When businesses make investments in new technologies, they usually do so with the intention of creating value for customers and stakeholders and making smart long-term investments. This is not always an easy thing to do when implementing cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. Business intelligence case studies that show how these technologies have been leveraged with results are still scarce, and many companies wonder where to apply machine learning first (a question at the core of one of Emerj’s most recent expert consensuses.)
Artificial intelligence and machine learning have certainly increased in capability over the past few years. Predictive analytics can help glean meaningful business insights using both sensor-based and structured data, as well as unstructured data, like unlabeled text and video, for mining customer sentiment. In the last few years, a shift toward “cognitive cloud” analytics has also increased data access, allowing for advances in real-time learning and reduced company costs. This recent shift has made an array of advanced analytics and AI-powered business intelligence services more accessible to mid-sized and small companies.
In this article, we provide five case studies that illustrate how AI and machine learning technologies are being used across industries to help drive more intelligent business decisions. While not meant to be exhaustive, the examples offer a taste for how real companies are reaping real benefits from technologies like advanced analytics and intelligent image recognition.
1 – Global Tech LED :Google Analytics Instant Activation of Remarketing
Company description: Headquartered in Bonita Springs, Florida, Global Tech LED is a LED lighting design and supplier to U.S. and international markets, specializing in LED retrofit kits and fixtures for commercial spaces.
How Google Analytics is being used:
- Google Analytics’ Smart Lists were used to automatically identify Global Tech LED prospects who were “most likely to engage”, and to then remarket to those users with more targeted product pages.
- Google’s Conversion Optimizer was used to automatically adjust potential customer bids for increased conversions.
Value proposition:
- Remarketing campaigns triggered by Smart Lists drove 5 times more clicks than all other display campaigns.
- The click-through rate of Global Tech LED’s remarketing campaigns was more than two times the remarketing average of other campaigns.
- Traffic to the company’s website grew by more than 100%, and was able to re-engage users in markets in which it was trying to make a dent, including South Asia, Latin America, and Western Europe.
- Use of the Conversion Optimizer allowed Global Tech LED to better allocate marketing costs based on bid potential.
2 – Under Armour : IBM Watson Cognitive Computing
Company description: Under Armour, Inc. is an American manufacturer of sports footwear and apparel, with global headquarters in Baltimore, Maryland.
How IBM Watson is being used:
- Under Armour’s UA Record™ app was built using the IBM Watson Cognitive Computing platform. The “Cognitive Coaching System” was designed to serve as a personal health assistant by providing users with real-time, data-based coaching based on sensor and manually input data for sleep, fitness, activity and nutrition. The app also draws on other data sources, such as geospatial data, to determine how weather and environment may affect training. Users are also able to view shared health insights based on other registered people in the UA Record database who share similar age, fitness, health, and other attributes.
- The UA Record app has a rating of 4.5 stars by users; based on sensor functionality, users are encouraged (via the company’s website and the mobile app) to purchase UA HealthBox devices (like the UA Band and Headphones) that synchronize with the app.
- According to Under Armour’s 2016 year-end results , revenue for Connected Fitness accessories grew 51 percent to $80 million.
3 – Plexure (VMob) : IoT and Azure Stream Analytics
Company description: Formerly known as VMob, Plexure is a New Zealand-based media company that uses real-time data analytics to help companies tailor marketing messages to individual customers and optimize the transaction process.
How Azure Stream Analytics is being used:
- Plexure used Azure Stream to help McDonald’s increase customer engagement in the Netherlands, Sweden and Japan, regions that make up 60 percent of the food service retailer’s locations worldwide.
- Azure Stream Analytics was used to analyze the company’s stored big data (40 million+ endpoints) in the cloud, honing in on customer behavior patterns and responses to offers to ensure that targeted ads were reaching the right groups and individuals.
- Plexure combined Azure Analytics technology with McDonald’s mobile app, analyzing with contextual information and social engagement further customize the user experience. App users receive individualized content based on weather, location, time of day, as well as purchasing a and ad response habits. For example, a customer located near a McDonald’s location on a hot afternoon might receive a pushed ad for a free ice cream sundae.
- McDonald’s in the Netherlands yielded a 700% increase in customer redemptions of targeted offers.
- Customers using the app returned to stores twice as often and on average spent 47% more than non-app users.
4 – Coca-Cola Amatil : Trax Retail Execution

Company description: Coca-Cola Amatil is the largest bottler and distributor of non-alcoholic, bottled beverages in the Asia Pacific, and one of the largest bottlers of Coca-Cola products in the region.
How Trax Image Recognition for Retail is being used:
- Prior to using Trax’s imaging technology, Coca-Cola Amatil was relying on limited and manual measurements of products in store, as well as delayed data sourced from phone conversations.
- Coca-Cola Amatil sales reps used Trax Retail Execution image-based technology to take pictures of stores shelves with their mobile devices; these images were sent to the Trax Cloud and analyzed, returning actionable reports within minutes to sales reps and providing more detailed online assessments to management.
- Real-time images of stock allowed sales reps to quickly identify performance gaps and apply corrective actions in store. Reports on shelf share and competitive insights also allowed reps to strategize on opportunities in store and over the phone with store managers.
- Coca-Cola Amatil gained 1.3% market share in the Asia Pacific region within five months.
5 – Peter Glenn : AgilOne Advanced Analytics
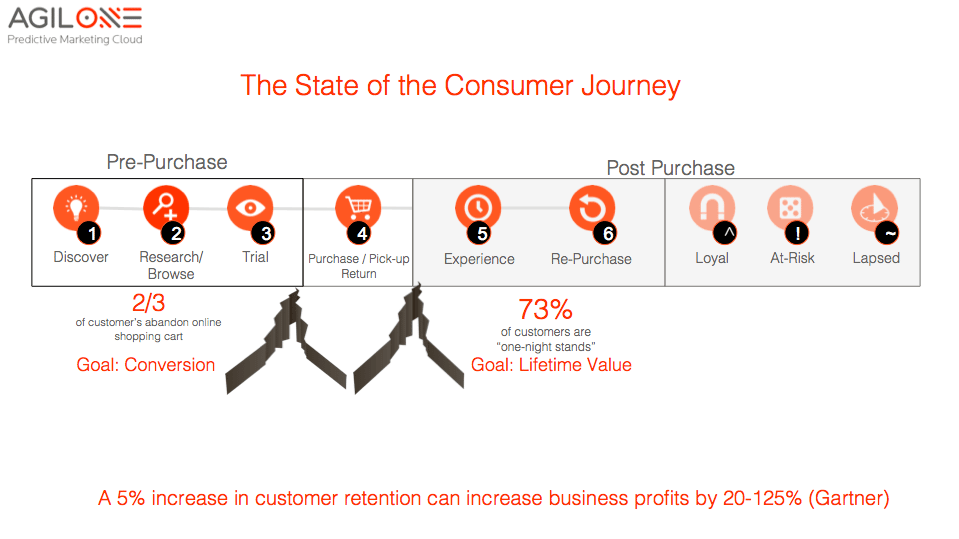
Company description: Peter Glenn has provided outdoor apparel and gear to individual and wholesale customers for over 50 years, with brick-and-mortar locations along the east coast, Alaska, and South Beach.
How AgilOne Analytics is being used:
- AgilOne Analytics’ Dashboard provides a consolidated view across online and offline channels, which allowed Peter Glenn to view trends between buyer groups and make better segmentation decisions.
- Advanced segmentation abilities included data on customer household, their value segment, and proximity to any brick-and-mortar locations.
- Peter Glenn used this information to launch integrated promotional, triggered, and lifecycle campaigns across channels, with the goal of increasing sales during non-peak months and increasing in-store traffic.
- Once AgilOne’s data quality engine had combed through Peter Glenn’s customer database, the company learned that more than 80% of its customer base had lapsed; they were able to use that information to re-target and re-engage stagnant customers.
- Peter Glenn saw a 30% increase in Average Order Value (AOV) as a result of its automated marketing campaigns.
- Access to data points, such as customer proximity to a store, allowed Peter Glenn to target customers for store events using advanced segmentation and more aligned channel marketing strategies.
Image credit: DSCallards
Related Posts
Digitally-native eCommerce businesses are used to working with their customer data in order to write…
Reuters referenced a Stratistics MRC figure estimating the size of the business intelligence industry around $15.64…
In the past few decades, insurance companies have collected vast amounts of data relevant to…
In 2017, Emerj conducted research into the applications of machine learning in marketing with 51…
Decision-makers in the banking sector have a unique set of business intelligence needs, and artificial…
Related posts (5)

Business Intelligence in Insurance – Current Applications
In the past few decades, insurance companies have collected vast amounts of data relevant to their business processes, customers, claims, and so on. This data can be unstructured in the form of PDFs, text documents, images, and videos, or structured, organized and curated for big data analytics.

Business Intelligence in Retail – Current Applications
In 2017, Emerj conducted research into the applications of machine learning in marketing with 51 different AI-focused marketing executives. The AI marketing vendors we spoke to named retail and eCommerce as the top sectors ripe for applying marketing AI software. Below is a graphic from our research showing the sectors that AI marketing vendors sell into most:

Business Intelligence in Finance – Current Applications
Reuters referenced a Stratistics MRC figure estimating the size of the business intelligence industry around $15.64 billion in 2016. It follows that AI would find its way into the business intelligence world. In our previous report, we covered 6 use-cases for AI in business intelligence. As of now, numerous companies claim to assist business leaders in the finance domain, specifically, in aspects of their roles using AI.

6 Examples of AI in Business Intelligence Applications
Enterprise seems to be entering a new era ruled by data. What was once the realm of science fiction, AI in business intelligence is evolving into everyday business as we know it. Companies can now use machines algorithms to identify trends and insights in vast reams of data and make faster decisions that potentially position them to be competitive in real-time.

Business Intelligence in Healthcare – Current Applications
According to Deloitte, global healthcare spending is expected to grow annually by 4.1% from 2017-2021, up from just 1.3% in 2012-2016. The report suggests this growth will be fuelled by aging, rising populations, the growth of developing markets, advances in medical treatments, and rising labor costs.
- Market Reasearch and Advisory
- AI Presentations and Keynotes
- Emerj Plus Membership
- AI In Business Podcast
- AI In Finance Services Podcast
- Subscribe to our AI Newsletter
- Advertise with us
- Terms and Conditions
- Refund and Cancellation Policy
- Privacy Policy

Gartner Insights for FP&A leaders
Download now here
By Olga Rudakova , Finance Professional and Data Skills Trainer, the International FP&A Board Ambassador
In an era marked by rapid technological advancements, the intersection of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Financial Planning and Analysis (FP&A) is redefining how we work. The recent FP&A Trends webinar, “Human & AI Synergy in FP&A”, shed light on how it would be best to combine AI insights with human expertise. As AI continues to evolve, its integration into FP&A is not only enhancing analytical capabilities but also setting the stage for more innovative and efficient financial practices.
This article dives into the practical applications of AI in FP&A, exploring the opportunities and challenges of adopting this cutting-edge technology in corporate finance.
VMware Case Study: Practical AI Application in FP&A
In his presentation, Alex Erasso , Former Sr. Director, Global Business Unit FP&A Finance at Broadcom (VMware), provided an extensive overview of AI applications within FP&A. Initially, Alex discussed different AI techniques, highlighting supervised and unsupervised learning. Supervised learning utilises known data labels to identify patterns, which can be beneficial in tasks like invoice processing. Unsupervised learning, on the other hand, detects patterns without predefined labels, which are useful for tasks such as customer segmentation.
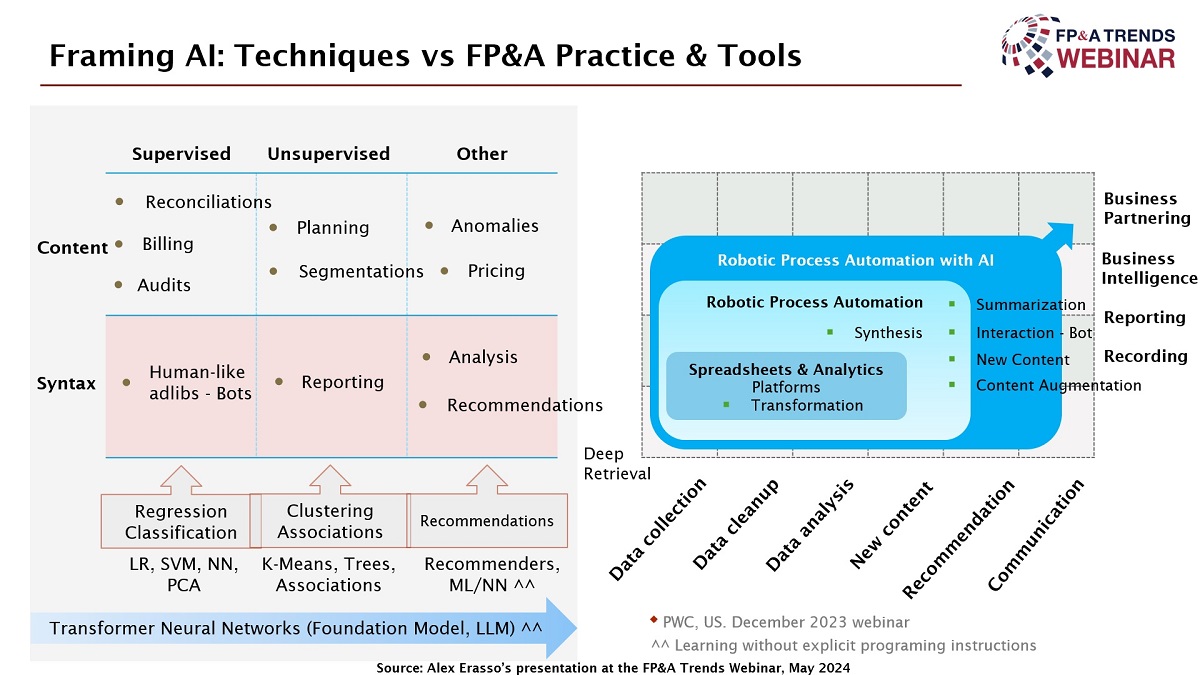
Alex then introduced transformational networks, a cutting-edge AI technique that learns without explicitly programmed rules, demonstrating significant advancements in how AI autonomously processes and analyses data. The practical application of these technologies in FP&A encompasses everything from data collection and analysis to generating actionable business insights.
Throughout the session, Alex emphasised the integration of robotic process automation (RPA) with AI to enhance various aspects of FP&A, including automating data collection and improving the granularity and relevance of financial advice. By leveraging AI, FP&A can now perform more sophisticated data analysis, leading to better strategic decisions and more effective Business Partnering .
Alex has demonstrated multiple practical cases of AI usage in VMware, including but not limited to:
- Pattern Recognition (market basket analysis),
- Segmentation (customer and partner behaviours: buying preferences and pricing),
- Deal simulations (price x volume scenarios ),
- Deal discounting (line item, total deal),
- Monitoring anomalies (sales audits).
Moreover, Alex touched on the importance of regulatory and business practice adjustments needed to harness AI effectively, addressing potential risks and the need for standardised protocols to manage and protect data securely. His session concluded with a nod to the ongoing evolution and potential of AI technologies. He mentioned the example of Tesla Autopilot, underscoring the balance between technological hype and practical implementation.
What Do We Expect from Merging AI and Human Expertise in FP&A?
Most of the webinar audience (41%) sees shifting the FP&A role towards more creative and strategic tasks as a main expected outcome. Meanwhile, another large chunk of the audience (35%) believes that the integration will lead to increased analytical capabilities and deeper insights. Another 18% hope for improved speed and quality of existing financial processes, and 7% of the audience fear that millions of FTEs in FP&A will be displaced by automation.
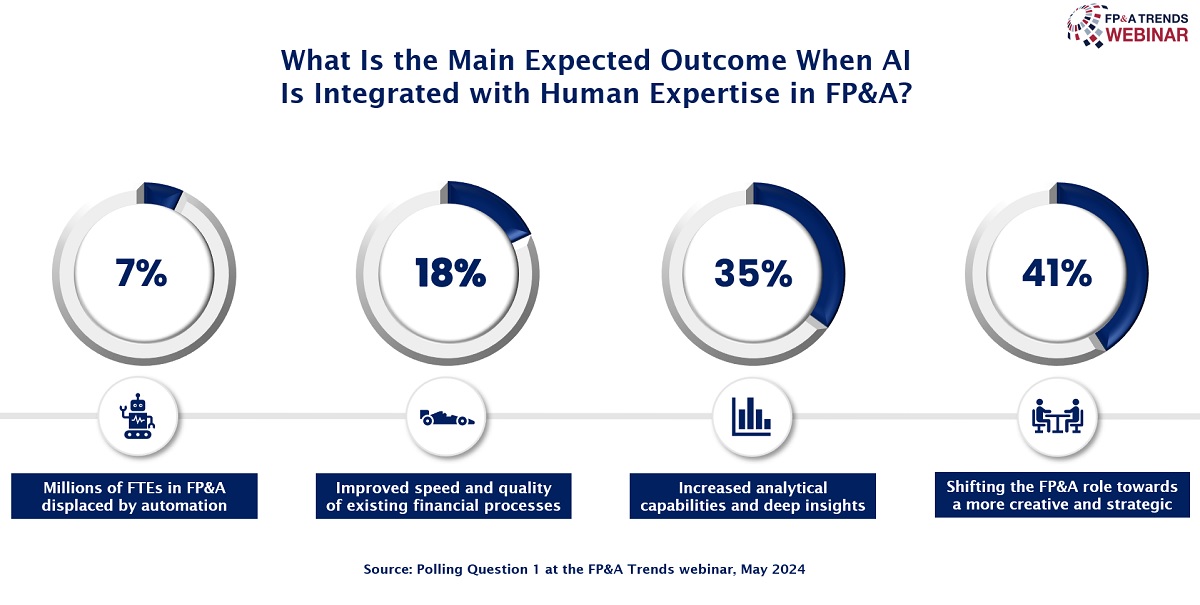
ETH Zurich Case Study: Leveraging AI for Business Steering
In his compelling presentation, Stefan Spiegel , CFO at ETH Zurich, highlighted practical applications of AI in Financial Planning and Analysis, focusing on business steering and administration. Stefan demonstrated how large language models (LLMs) can streamline the management of internal guidelines and regulations within organisations. By integrating these AI tools, companies can maintain all critical information securely in-house, ensuring it remains confidential.
Stefan pointed out a significant challenge with language models – dealing with inaccuracies or "hallucinations." To address this, he underscored the importance of linking AI-generated answers to the reference documents for verification, enhancing reliability and transparency.
The primary example Stefan shared revolved around simplifying corporate procedures. He explained a scenario where employees could query a language model about permissible expenses, such as dining costs , during business trips. This AI application provides immediate, specific answers, potentially including conditions under which expenses might exceed standard limits.

Moreover, Stefan outlined how this technology can handle complex, dynamic regulations across different countries, updating responses as rules change without the need for manual reprogramming. This approach significantly reduces the time and effort traditionally required to navigate corporate documentation.
Stefan's presentation illustrated the transformative potential of AI for optimising business operations and decision-making processes within FP&A, improving its efficiency.
Which Area of FP&A Can Benefit the Most from AI Integration?
Most of the audience (36%) believes that AI can be most helpful in automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks. 28% see the biggest benefit coming to the area of Predictive Forecasting and Scenario Planning . The last two options, anomaly and pattern detection and dynamic insights generation and Storytelling gained 18% of responses each.
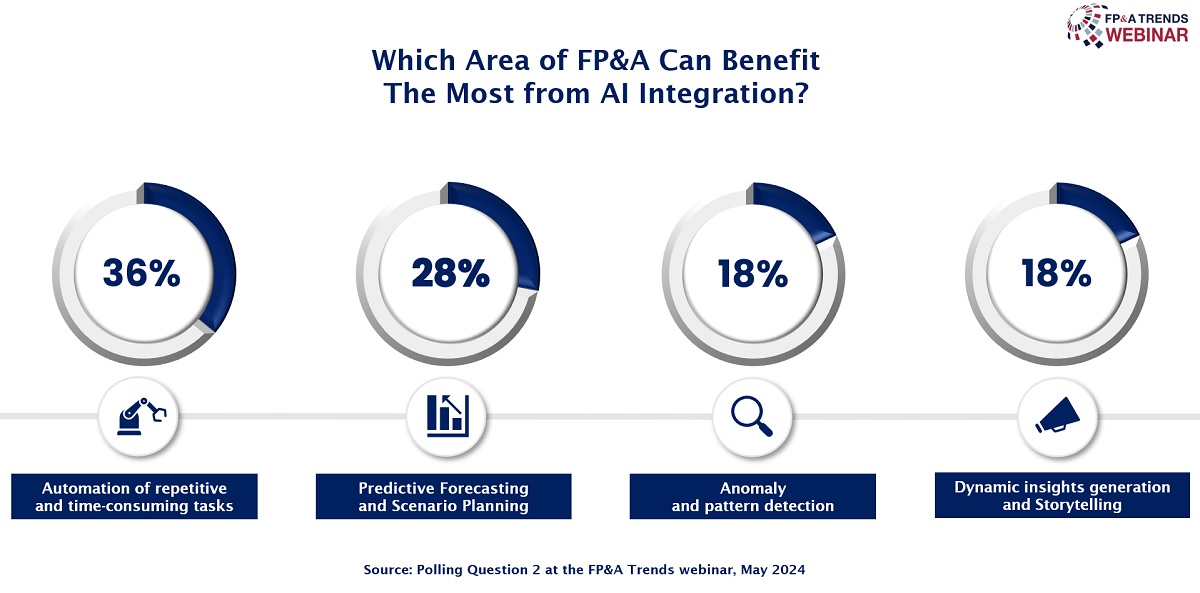
Technology’s Role in Enhancing AI
During his presentation, Greg Volpe , Solution Marketing Director at Workday, discussed the evolving role of FP&A driven by advancements in AI. He emphasised how AI is transforming FP&A from traditional number crunching to a more strategic advisory role within businesses. This shift means FP&A professionals will need to adapt to new technologies, moving away from manual tasks to more automated, efficient processes.
Greg outlined how AI enhances the FP&A function by automating tasks like report generation, variance analysis, and forecasting. It speeds up operations and enables FP&A teams to focus on more value-added activities, such as strategic decision-making and Scenario Planning. He highlighted the trend towards data-driven and exception-based planning , where AI tools play a crucial role in Predictive Forecasting and anomaly detection.
He also touched on broader AI applications, such as data anomaly detection and analysis, Predictive Forecasting and Generative AI, which can significantly impact future FP&A activities by enabling more interactive and dynamic planning processes. For instance, conversational AI can facilitate quick access to data insights through simple text queries within planning applications, enhancing the user experience and decision-making.
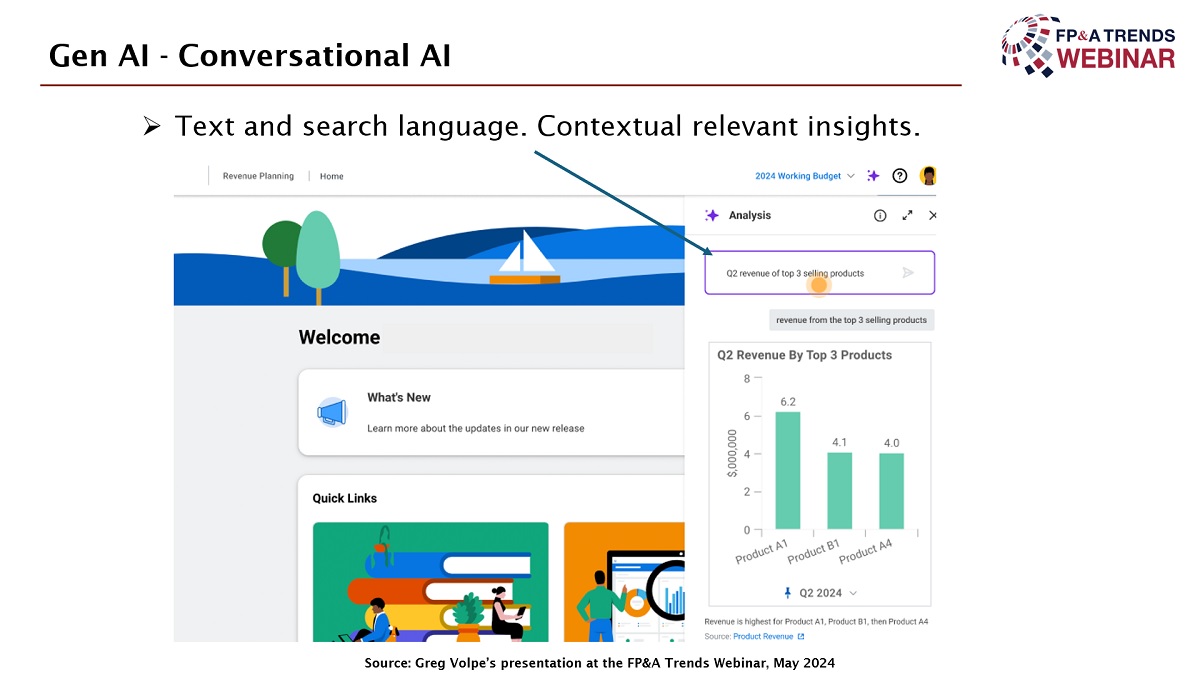
Overall, Greg portrayed AI as a tool for augmenting the FP&A role, making it more strategic while ensuring the technology remains responsible and trustworthy. This adaptation aims to fundamentally improve business operations and the nature of work in FP&A.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the integration of AI into FP&A processes promises a significant transformation in how finance teams operate. As seen in the insightful discussions from VMware and ETH Zurich case studies and further reinforced by technology expert Greg Volpe, AI is not poised to replace human roles but to enhance them. This technological evolution allows finance professionals to transition from traditional tasks to roles that require more strategic thinking and creativity. However, as AI reshapes the landscape, there is a crucial need for upskilling . Professionals must become adept at working alongside AI, understanding its capabilities, and leveraging its insights effectively.
As we forge ahead, the key to success will be continuous learning and adaptation. We will have to ensure that teams are equipped to meet the demands of an increasingly automated and data-driven world.
To watch the full webinar recording, please check out this link .
This webinar was proudly sponsored by Workday .
Related articles

In this article, the author explains how Artificial Intelligence (AI) can help FP&A professionals become invaluable...

In this article, the author outlines how AI transformation may impact the finance domain and explains...

In this article, the author emphasises the need for more value creation from FP&A professionals and...

This article explores how Large Language Models (LLMs) could improve FP&A productivity and redefine finance Business...

This article provides an overview of the topics and cases presented and discussed by the expert...

In this article, the author talks about two of the most prominent applications of AI in...
Subscribe to FP&A Trends Digest

We will regularly update you on the latest trends and developments in FP&A. Take the opportunity to have articles written by finance thought leaders delivered directly to your inbox; watch compelling webinars; connect with like-minded professionals; and become a part of our global community.
Create new account
The Business of Fashion
Agenda-setting intelligence, analysis and advice for the global fashion community.
News & Analysis
- Professional Exclusives
- The News in Brief
- Sustainability
- Direct-to-Consumer
- Global Markets
- Fashion Week
- Workplace & Talent
- Entrepreneurship
- Financial Markets
- Newsletters
- Case Studies
- Masterclasses
- Special Editions
- The State of Fashion
- Read Careers Advice
- BoF Professional
- BoF Careers
- BoF Insights
- Our Journalism
- Work With Us
- Read daily fashion news
- Download special reports
- Sign up for essential email briefings
- Follow topics of interest
- Receive event invitations
- Create job alerts
Indie Beauty Brand Fara Homidi Launches in Sephora

Fara Homidi, the cult “cool girl” cosmetics label endorsed by models Paloma Elsesser, Adwoa Aboah and Hailey Bieber, is going wide thanks to a tie-up with Sephora.
Starting June 1, consumers will be able to shop the brand’s lip and complexion compacts on the retailer’s e-commerce channel with a brick-and-mortar entrance slated for next year, the company announced Wednesday.
Sephora will be the brand’s largest retailer in terms of distribution after having also inked partnerships with Goop, Violet Grey, Dover Street Parfums Market and Moda Operandi since the business’ launch in March 2023.
The label’s founder, makeup artist Fara Homidi, describes the brand as “slow beauty” — her team plans to establish a cadence of one or two launches a year. She added that the label is uniquely positioned to enter Sephora at this time, following her participation in the retailer’s Accelerate programme in 2022.
ADVERTISEMENT
”We wanted to start small with retailers that live in a fashion adjacent world,” said Homidi. “Launching in Sephora means we’re more established, we’ve proven ourselves, the brand has legs and we can bring it out into the world in a bigger way.”
Homidi said the brand’s light blue and red refillable packaging and a focus on “simple and utilitarian beauty routines” that are centred on complexion products will help it stand out among Sephora’s crowded marketplace. The label’s products are priced between $36 and $298. The company is projected to grow its sales at a rate of 400 percent in this year and expects to reach $15 million in sales in 2025.
Despite launching in the prestige retailer, Homidi still wants to make the brand’s consumers feel part of the inner circle. Last year, the label launched a loyalty programme, FH Friends, in which returning shoppers are automatically enrolled and are eligible for discounts, offered sneak previews and can attend the brand’s launch parties alongside its muses, including Elsesser.
The self-funded beauty brand has plans to expand internationally to markets in the Middle East as well as the UK and Australia in the next few years and is open to raising capital or a possible acquisition in the near future.
”As a brand, we’re focused on making beauty feel more personalised,” said Homidi. “I’m not putting out products that are frivolous or trendy but products that are meant to last the test of time.”

Yola Mzizi is the Editorial Apprentice at The Business of Fashion (BoF). She is based in New York and provides operational support to the New York team and writes features for BoF and The Business of Beauty.
- Beauty : Cosmetics
- Paloma Elsesser
© 2024 The Business of Fashion. All rights reserved. For more information read our Terms & Conditions

Why Australia Is the Next Step in Glossier’s Global Ambitions
After expanding to US and UK brick-and-mortar retail, the former DTC darling will be available in 70 Mecca stores beginning July 16.

How to Make Beauty Merch That Matters
Beauty is in the midst of “merch” madness, with brands rushing to debut branded sweatshirts, stickers and more in hopes of securing viral hits like Rhode’s lipgloss phone case. But as more brands focus on merch, making products that stand out takes a sharper strategy.

Case Study | Building an Effective Loyalty Programme
Serving as the 'heartbeat' for brands and retailers that deploy them with the right rewards, loyalty programmes incentivise repeat purchases, boost customer lifetime value and provide businesses with invaluable data for personalised marketing. But brands need to balance costs and benefits while creating a programme that supports their goals, maintains brand equity and keeps users engaged.

Putting the Performance into Wellness
As customer engagement with wellness practices matures, performance-based science and activities are increasingly popular and distinguishing providers in the market. BoF meets the VP of wellbeing at Auberge Resorts Collection, to discuss emerging trends in wellness and health and discover more about Auberge luxury resort Stanly Ranch’s best-in-class performance-suite and products.
Subscribe to the BoF Daily Digest
The essential daily round-up of fashion news, analysis, and breaking news alerts.
Our newsletters may include 3rd-party advertising, by subscribing you agree to the Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
Our Products
- BoF Insights Opens in new window

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here is a selected TEC case study that showcases how TEC can help clients in various industries select the best-fit BI system for their business needs: Arysta LifeScience: BI/BPM Success Story Arysta LifeScience, a global agricultural leader, sought a business intelligence (BI) and performance management (BPM) system to tackle their data ...
Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Business Intelligence at Work Fast, data-informed decision-making can drive success. High customer expectations, global competition and narrow profit margins mean many organizations, regardless of size or sector, look to BI for a competitive advantage.
Business intelligence case study examples often track and display these metrics. Business Intelligence is widely used across various industries to improve decision-making, identify opportunities, and solve complex problems. It gives organizations a competitive advantage by allowing them to make data-driven decisions based on accurate, real-time ...
Let's dive into seven examples of business intelligence used by these types of companies. 1. Koodos proves their concept. Koodos is a new startup from Harvard Business School's Rock Center for Entrepreneurship that builds content curation technology for Gen Z based on user-generated data.
5. Starbucks Keeps You Sippin'. Starbucks is one of the most interesting businesses to study in the modern era. Of course, Starbucks' stranglehold over the coffee-on-the-go market is impressive in and of itself, but what's even more interesting in the case of Starbucks is how they've embraced the digital frontier.
Case study: Hershey's chocolate and business intelligence. Hershey pivoted its marketing and inventory to embrace new trends. As it turns out, one popular pandemic activity for people all over the United States was making s'mores. Hershey realized this when it discovered that the demand for s'mores ingredients skyrocketed in areas with a high ...
All the major Business Intelligence vendors will provide case studies from their websites. A few links have been provided below to some of the better case studies available: Microsoft Case Studies. Panorama Case Studies. Business Objects Case Studies. Other case studies are written by research analysts, and are often sponsored by the software ...
3) Drive Performance And Revenue. Driving performance and revenue is one of the relevant benefits of business analytics for companies. McKinsey realized a business intelligence case study on a fast-food chain restaurant company with thousands of outlets worldwide. That company wanted to focus on its personnel and analyze deeper any data ...
Business intelligence is as much a way of thinking as it is composed of hardware and software. By adopting a data-driven culture—based on a complete set of approaches, processes, digital technology and data analysis—an organization can find new insights to make better business decisions and gain new advantages. ... Case study North York ...
ScienceSoft shares prominent use cases on the successful implementation of business intelligence solutions for diverse businesses. Careers. For Journalists. ... ScienceSoft's experts will study your case and get back to you with the details within 24 hours. Close 5900 S. Lake Forest Drive Suite 300, McKinney, Dallas area, TX 75070
Recent Case Studies, BI Analytics Case Studies, Business Intelligence Case Studies, CRM Case Studies, Data Integration Case Studies, Data Quality Case Studies, Data Warehouse Case Studies, ERP Case Studies, Industry: Retail, Microsoft Azure Case Studies, Microsoft Case Studies, Microsoft Power BI Case Studies
In this special issue, we asked researchers to submit works that concentrate on conducting analytics to address business initiatives. The papers in this issue represent various analytical methods applied in a case study approach to illustrate the value of analytics to producing information to enhance organizational processes and strategies.
Expect the unexpected. Yes, companies can get by with spreadsheets and limited business intelligence, but when something unexpected happens, quick decisions are critical, and financial sustainability is at stake, having access to timely, accurate data can save an organization millions of dollars and help them utilize limited resources in an efficient way.
This study uses the case study methodology which is used to examine a phenomenon in its natural setting to collect information from people, groups, or organizations. Case studies offer in-depth understanding of contemporary phenomenon within their organizational context (Aberdeen, 2013; Yin, 2003, 2012).
HBS Case Selections. Get the perspectives and context you need to solve your toughest work problems with these immersive sets of real-world scenarios from Harvard Business School.
These data can provide vital strategic value to firms across industry sectors by providing actionable information for decision support or Business Intelligence (BI) through the application of analytics techniques. These analytics can range from the more basic BI methods of report generation, on-line analytical processing (OLAP), and dashboards ...
Irvine Company Case Study 11. Collaborating closely with Web Neighbor, SVP of Strategic Initiatives, Competitive Analytics recently completed a myriad of BI projects that assisted Irvine Company with evolving their internal data (cleaning, wrangling, organizing), advanced analytics, and business intelligence solutions).
Most business intelligence case studies cover designing dashboards or creating databases to function for business needs. Therefore, most problems are general business case studies or technical SQL case studies, and the interviewee must solve a problem relating to how data is being presented or stored.
2. Accelerate and improve business decision-making. BI brings together data mining, data analysis and data visualization to give executives and other business users a comprehensive view of enterprise data, which they can then use to make business decisions in a more informed way. Using BI tools to support decision-making is one of the primary ...
This recent shift has made an array of advanced analytics and AI-powered business intelligence services more accessible to mid-sized and small companies. In this article, we provide five case studies that illustrate how AI and machine learning technologies are being used across industries to help drive more intelligent business decisions.
Business Intelligence Solution for an SME: A Case Study. 45. deals with un-normalised tables for extracting summarised and aggregated data. The main building blocks of building a dimensional model are: facts and dimensions. We have followed Kimball s four steps to dimensional modelling (Kimball and Ross, 2013): 1.
framework as a basis for case study analysis. Keywords: Business Intelligence, Project Success, Case Studies, Work System Framework, Business Students. 1. INTRODUCTION. Gartner defines business intelligence (BI) as: An umbrella term that includes the applications, infrastructure and tools, and best practices that enable access to and
VMware Case Study: Practical AI Application in FP&A. In his presentation, Alex Erasso, Former Sr. Director, Global Business Unit FP&A Finance at Broadcom (VMware), provided an extensive overview of AI applications within FP&A. Initially, Alex discussed different AI techniques, highlighting supervised and unsupervised learning.
30 May 2024. BoF PROFESSIONAL. Fara Homidi, the cult "cool girl" cosmetics label endorsed by models Paloma Elsesser, Adwoa Aboah and Hailey Bieber, is going wide thanks to a tie-up with Sephora. Starting June 1, consumers will be able to shop the brand's lip and complexion compacts on the retailer's e-commerce channel with a brick-and ...