- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to footer
Enchanting Marketing
Writing advice for small business

11 Creative Writing Techniques
Learn how to add pizzazz to any type of writing.
The articles below show you how to use creative writing tools in fiction or non-fiction. Each article features a series of examples so it becomes easier to apply the technique.
List of creative writing techniques
Click the links below to go to a specific section:
Personification
Show don’t tell
Repetition in writing
Contrast in writing
The rule of three in writing
Parallelism
1. Metaphors

Learn how to use metaphors and get inspired by these examples …
Learn how to use metaphors >>
Metaphor examples >>

Get inspired by over 10 simile examples by various authors …
Simile examples >>
3. Analogies

Get inspired by these analogy examples …
Analogy examples >>

Improve your writing style
Learn how to write better and find your voice. Get free writing tips in your inbox.
Get free writing tips >>

Get inspired by these imagery examples …
Imagery examples >>
5. Personification

Learn how to use personification to make your writing sparkle …
Personification examples >>
6. Show don’t tell

Get inspired by these examples of “show, don’t tell” …
Show don’t tell examples >>
7. Repetition in writing

Get inspired by these examples of word repetition …
Examples of repetition in writing >>
8. Contrast in writing

Discover how to use contrast in your writing …
Examples of contrast in writing >>
9. The rule of 3 in writing

Get inspired by these examples of the rule of 3 …
The rule of 3 in writing >>
10. Parallelism in writing

Get inspired by these examples of the parallelism …
Parallelism examples >>
11. Switch the point of view (POV)

Discover how to switch the point of view …
Point of view examples >>
You may also like …

Creative writing examples
Learn how to inject creativity in any writing.

Creative writing exercises
Try these exercises to add a touch of creativity to your writing.
Share this page:

Books and courses
Follow proven templates for specific writing tasks, practice your skills, and get professional feedback so you become a confident business writer. Take on any writing project with gusto. Learn more about books and courses

About Henneke
I never saw myself as a writer, but in my early forties, I learned how to write and discovered the joy of writing. Now, I’d like to empower you to find your voice, share your ideas and inspire your audience. Learn how I can help you
Popular topics
Sales copywriting
Blog writing for business
Your writing voice
Tips for beginning writers
The writing process
Improve your writing skills
Writing examples
Popular blog posts
Recent blog posts
Free Snackable Writing Course
Get 16 concise emails and learn how to write more persuasive content.
Success! Now check your email to confirm your subscription.
There was an error submitting your subscription. Please try again.

What Is Creative Writing? (Ultimate Guide + 20 Examples)
Creative writing begins with a blank page and the courage to fill it with the stories only you can tell.
I face this intimidating blank page daily–and I have for the better part of 20+ years.
In this guide, you’ll learn all the ins and outs of creative writing with tons of examples.
What Is Creative Writing (Long Description)?
Creative Writing is the art of using words to express ideas and emotions in imaginative ways. It encompasses various forms including novels, poetry, and plays, focusing on narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes.

Table of Contents
Let’s expand on that definition a bit.
Creative writing is an art form that transcends traditional literature boundaries.
It includes professional, journalistic, academic, and technical writing. This type of writing emphasizes narrative craft, character development, and literary tropes. It also explores poetry and poetics traditions.
In essence, creative writing lets you express ideas and emotions uniquely and imaginatively.
It’s about the freedom to invent worlds, characters, and stories. These creations evoke a spectrum of emotions in readers.
Creative writing covers fiction, poetry, and everything in between.
It allows writers to express inner thoughts and feelings. Often, it reflects human experiences through a fabricated lens.
Types of Creative Writing
There are many types of creative writing that we need to explain.
Some of the most common types:
- Short stories
- Screenplays
- Flash fiction
- Creative Nonfiction
Short Stories (The Brief Escape)
Short stories are like narrative treasures.
They are compact but impactful, telling a full story within a limited word count. These tales often focus on a single character or a crucial moment.
Short stories are known for their brevity.
They deliver emotion and insight in a concise yet powerful package. This format is ideal for exploring diverse genres, themes, and characters. It leaves a lasting impression on readers.
Example: Emma discovers an old photo of her smiling grandmother. It’s a rarity. Through flashbacks, Emma learns about her grandmother’s wartime love story. She comes to understand her grandmother’s resilience and the value of joy.
Novels (The Long Journey)
Novels are extensive explorations of character, plot, and setting.
They span thousands of words, giving writers the space to create entire worlds. Novels can weave complex stories across various themes and timelines.
The length of a novel allows for deep narrative and character development.
Readers get an immersive experience.
Example: Across the Divide tells of two siblings separated in childhood. They grow up in different cultures. Their reunion highlights the strength of family bonds, despite distance and differences.
Poetry (The Soul’s Language)
Poetry expresses ideas and emotions through rhythm, sound, and word beauty.
It distills emotions and thoughts into verses. Poetry often uses metaphors, similes, and figurative language to reach the reader’s heart and mind.
Poetry ranges from structured forms, like sonnets, to free verse.
The latter breaks away from traditional formats for more expressive thought.
Example: Whispers of Dawn is a poem collection capturing morning’s quiet moments. “First Light” personifies dawn as a painter. It brings colors of hope and renewal to the world.
Plays (The Dramatic Dialogue)
Plays are meant for performance. They bring characters and conflicts to life through dialogue and action.
This format uniquely explores human relationships and societal issues.
Playwrights face the challenge of conveying setting, emotion, and plot through dialogue and directions.
Example: Echoes of Tomorrow is set in a dystopian future. Memories can be bought and sold. It follows siblings on a quest to retrieve their stolen memories. They learn the cost of living in a world where the past has a price.
Screenplays (Cinema’s Blueprint)
Screenplays outline narratives for films and TV shows.
They require an understanding of visual storytelling, pacing, and dialogue. Screenplays must fit film production constraints.
Example: The Last Light is a screenplay for a sci-fi film. Humanity’s survivors on a dying Earth seek a new planet. The story focuses on spacecraft Argo’s crew as they face mission challenges and internal dynamics.
Memoirs (The Personal Journey)
Memoirs provide insight into an author’s life, focusing on personal experiences and emotional journeys.
They differ from autobiographies by concentrating on specific themes or events.
Memoirs invite readers into the author’s world.
They share lessons learned and hardships overcome.
Example: Under the Mango Tree is a memoir by Maria Gomez. It shares her childhood memories in rural Colombia. The mango tree in their yard symbolizes home, growth, and nostalgia. Maria reflects on her journey to a new life in America.
Flash Fiction (The Quick Twist)
Flash fiction tells stories in under 1,000 words.
It’s about crafting compelling narratives concisely. Each word in flash fiction must count, often leading to a twist.
This format captures life’s vivid moments, delivering quick, impactful insights.
Example: The Last Message features an astronaut’s final Earth message as her spacecraft drifts away. In 500 words, it explores isolation, hope, and the desire to connect against all odds.
Creative Nonfiction (The Factual Tale)
Creative nonfiction combines factual accuracy with creative storytelling.
This genre covers real events, people, and places with a twist. It uses descriptive language and narrative arcs to make true stories engaging.
Creative nonfiction includes biographies, essays, and travelogues.
Example: Echoes of Everest follows the author’s Mount Everest climb. It mixes factual details with personal reflections and the history of past climbers. The narrative captures the climb’s beauty and challenges, offering an immersive experience.
Fantasy (The World Beyond)
Fantasy transports readers to magical and mythical worlds.
It explores themes like good vs. evil and heroism in unreal settings. Fantasy requires careful world-building to create believable yet fantastic realms.
Example: The Crystal of Azmar tells of a young girl destined to save her world from darkness. She learns she’s the last sorceress in a forgotten lineage. Her journey involves mastering powers, forming alliances, and uncovering ancient kingdom myths.
Science Fiction (The Future Imagined)
Science fiction delves into futuristic and scientific themes.
It questions the impact of advancements on society and individuals.
Science fiction ranges from speculative to hard sci-fi, focusing on plausible futures.
Example: When the Stars Whisper is set in a future where humanity communicates with distant galaxies. It centers on a scientist who finds an alien message. This discovery prompts a deep look at humanity’s universe role and interstellar communication.
Watch this great video that explores the question, “What is creative writing?” and “How to get started?”:
What Are the 5 Cs of Creative Writing?
The 5 Cs of creative writing are fundamental pillars.
They guide writers to produce compelling and impactful work. These principles—Clarity, Coherence, Conciseness, Creativity, and Consistency—help craft stories that engage and entertain.
They also resonate deeply with readers. Let’s explore each of these critical components.
Clarity makes your writing understandable and accessible.
It involves choosing the right words and constructing clear sentences. Your narrative should be easy to follow.
In creative writing, clarity means conveying complex ideas in a digestible and enjoyable way.
Coherence ensures your writing flows logically.
It’s crucial for maintaining the reader’s interest. Characters should develop believably, and plots should progress logically. This makes the narrative feel cohesive.
Conciseness
Conciseness is about expressing ideas succinctly.
It’s being economical with words and avoiding redundancy. This principle helps maintain pace and tension, engaging readers throughout the story.
Creativity is the heart of creative writing.
It allows writers to invent new worlds and create memorable characters. Creativity involves originality and imagination. It’s seeing the world in unique ways and sharing that vision.
Consistency
Consistency maintains a uniform tone, style, and voice.
It means being faithful to the world you’ve created. Characters should act true to their development. This builds trust with readers, making your story immersive and believable.
Is Creative Writing Easy?
Creative writing is both rewarding and challenging.
Crafting stories from your imagination involves more than just words on a page. It requires discipline and a deep understanding of language and narrative structure.
Exploring complex characters and themes is also key.
Refining and revising your work is crucial for developing your voice.
The ease of creative writing varies. Some find the freedom of expression liberating.
Others struggle with writer’s block or plot development challenges. However, practice and feedback make creative writing more fulfilling.
What Does a Creative Writer Do?
A creative writer weaves narratives that entertain, enlighten, and inspire.
Writers explore both the world they create and the emotions they wish to evoke. Their tasks are diverse, involving more than just writing.
Creative writers develop ideas, research, and plan their stories.
They create characters and outline plots with attention to detail. Drafting and revising their work is a significant part of their process. They strive for the 5 Cs of compelling writing.
Writers engage with the literary community, seeking feedback and participating in workshops.
They may navigate the publishing world with agents and editors.
Creative writers are storytellers, craftsmen, and artists. They bring narratives to life, enriching our lives and expanding our imaginations.
How to Get Started With Creative Writing?
Embarking on a creative writing journey can feel like standing at the edge of a vast and mysterious forest.
The path is not always clear, but the adventure is calling.
Here’s how to take your first steps into the world of creative writing:
- Find a time of day when your mind is most alert and creative.
- Create a comfortable writing space free from distractions.
- Use prompts to spark your imagination. They can be as simple as a word, a phrase, or an image.
- Try writing for 15-20 minutes on a prompt without editing yourself. Let the ideas flow freely.
- Reading is fuel for your writing. Explore various genres and styles.
- Pay attention to how your favorite authors construct their sentences, develop characters, and build their worlds.
- Don’t pressure yourself to write a novel right away. Begin with short stories or poems.
- Small projects can help you hone your skills and boost your confidence.
- Look for writing groups in your area or online. These communities offer support, feedback, and motivation.
- Participating in workshops or classes can also provide valuable insights into your writing.
- Understand that your first draft is just the beginning. Revising your work is where the real magic happens.
- Be open to feedback and willing to rework your pieces.
- Carry a notebook or digital recorder to jot down ideas, observations, and snippets of conversations.
- These notes can be gold mines for future writing projects.
Final Thoughts: What Is Creative Writing?
Creative writing is an invitation to explore the unknown, to give voice to the silenced, and to celebrate the human spirit in all its forms.
Check out these creative writing tools (that I highly recommend):
Read This Next:
- What Is a Prompt in Writing? (Ultimate Guide + 200 Examples)
- What Is A Personal Account In Writing? (47 Examples)
- How To Write A Fantasy Short Story (Ultimate Guide + Examples)
- How To Write A Fantasy Romance Novel [21 Tips + Examples)
TRY OUR FREE APP
Write your book in Reedsy Studio. Try the beloved writing app for free today.
Craft your masterpiece in Reedsy Studio
Plan, write, edit, and format your book in our free app made for authors.

Blog • Perfecting your Craft , Book Design
Last updated on May 01, 2024
60 Literary Devices With Examples: The Master List
Literary devices are perhaps the greatest tools that writers have in literature. Just think — Shakespeare could have written: Everyone has a role in life.
Instead, he used a literary device and penned what is likely the most famous metaphor in literature:
All the world’s a stage
And all the men and women merely players
And the rest is history.

What are literary devices?
A literary device is a writing technique that writers use to express ideas, convey meaning, and highlight important themes in a piece of text. A metaphor, like we mentioned earlier, is a famous example of a literary device.
These devices serve a wide range of purposes in literature. Some might work on an intellectual level, while others have a more emotional effect. They may also work subtly to improve the flow and pacing of your writing. No matter what, if you're looking to inject something special into your prose, literary devices are a great place to start.
How to identify literary devices
A writer using a literary device is quite different from a reader identifying it. Often, an author’s use of a literary device is subtle by design —you only feel its effect, and not its presence.
Therefore, we’ve structured this post for both purposes:
- If you’re a reader, we’ve included examples for each literary device to make it easier for you to identify them in the wild.
- If you’re a writer, we’ve included exercises for the literary devices, so that you can practice using them in your works.
Let’s get to it.
60 common literary devices, with examples
1. alliteration.
Alliteration describes a series of words in quick succession that all start with the same letter or sound. It lends a pleasing cadence to prose and Hamlet and the dollar as currency in Macbeth .
Example: “ One short sleepe past, wee wake eternally,
And death shall be no more; death, thou shalt die.” — “Death, Be Not Proud” by John Donne
Exercise: Pick a letter and write a sentence where every word starts with that letter or one that sounds similar.
2. Anaphora
Anaphora is the repetition of a word or phrase at the beginning of a series of clauses or sentences. It’s often seen in poetry and speeches, intended to provoke an emotional response in its audience.
Example: Martin Luther King’s 1963 “I Have A Dream” speech.
“I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up and live out the true meaning of its creed.
"… and I have a dream that one day on the red hills of Georgia the sons of former slaves and the sons of former slave owners will be able to sit together at the table of brotherhood.
"… I have a dream that little children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin, but by the content of their character.”
Exercise: Pick a famous phrase and write a paragraph elaborating on an idea, beginning each sentence with that phrase.
Similar term: repetition
3. Anastrophe
Anastrophe is a figure of speech wherein the traditional sentence structure is reversed. So a typical verb-subject-adjective sentence such as “Are you ready?” becomes a Yoda-esque adjective-verb-subject question: “Ready, are you?” Or a standard adjective-noun pairing like “tall mountain” becomes “mountain tall.”
Example: “Deep into that darkness peering, long I stood there wondering, fearing.” — “The Raven” by Edgar Allan Poe
Exercise: Write a standard verb-subject-adjective sentence or adjective-noun pairing then flip the order to create an anastrophe. How does it change the meaning or feeling of the sentence?
4. Chiasmus
Chiasmus is when two or more parallel clauses are inverted. “Why would I do that?” you may be wondering. Well, a chiasmus might sound confusing and unnecessary in theory, but it's much more convincing in practice — and in fact, you've likely already come across it before.
Example: “Ask not what your country can do for you; ask what you can do for your country.” — John F. Kennedy
5. Congeries
Congeries is a fancy literary term for creating a list. The items in your list can be words, ideas, or phrases, and by displaying them this way helps prove or emphasize a point — or even create a sense of irony. Occasionally, it’s also called piling as the words are “piling up.”
Example: "Apart from better sanitation and medicine and education and irrigation and public health and roads and a freshwater system and baths and public order, what have the Romans done for us?" — Monty Python’s Life of Brian
6. Cumulative sentence
A cumulative sentence (or “loose sentence”) is one that starts with an independent clause, but then has additional or modifying clauses. They’re often used for contextual or clarifying details. This may sound complex, but even, “I ran to the store to buy milk, bread, and toilet paper” is a cumulative sentence, because the first clause, “I ran to the store,” is a complete sentence, while the rest tells us extra information about your run to the store.
Example: “It was a large bottle of gin Albert Cousins had brought to the party, yes, but it was in no way large enough to fill all the cups, and in certain cases to fill them many times over, for the more than one hundred guests, some of whom were dancing not four feet in front of him.” – Commonwealth by Ann Patchett
Example: Write three sentences that are related to each other. Can you combine the information into a cumulative sentence?

FREE RESOURCE
Literary Devices Cheatsheet
Master these 40+ devices to level up your writing skills.
7. Epistrophe
Epistrophe is the opposite of anaphora, with this time a word or phrase being repeated at the end of a sentence. Though its placement in a sentence is different it serves the same purpose—creating emphasis—as an anaphora does.
Example: “I’ll be ever’where – wherever you look. Wherever they’s a fight so hungry people can eat, I’ll be there. Wherever they’s a cop beatin’ up a guy, I’ll be there . If Casy knowed, why, I’ll be in the way guys yell when they’re mad an’ – I’ll be in the way kids laugh when they’re hungry an’ they know supper’s ready. An’ when our folks eat the stuff they raise an’ live in the houses they build, why, I’ll be there .” — The Grapes of Wrath by John Steinbeck
Similar terms: repetition, anaphora
Exercise: Write a paragraph where a phrase or a word is repeated at the end of every sentence, emphasizing the point you’re trying to make.
8. Erotesis
Erotesis is a close cousin of the rhetorical question. Rather than a question asked without expectation of an answer, this is when the question (and the asker) confidently expects a response that is either negative or affirmative.
Example: “ Do you then really think that you have committed your follies in order to spare your son them?” — Siddhartha by Herman Hesse
Similar term: rhetorical question
9. Hyperbaton
Hyperbaton is the inversion of words, phrases, or clauses in a sentence that differs from how they would normally be arranged. It comes from the Greek hyperbatos, which means “transposed” or “inverted.” While it is similar to anastrophe, it doesn’t have the same specific structure and allows you to rearrange your sentences in whatever order you want.
Example: “Object there was none. Passion there was none. I loved the old man. He had never wronged me. He had never given me insult. For his gold I had no desire.” — “The Tell-Tale Heart” by Edgar Allan Poe
Similar terms: anastrophe, epistrophe
10. Isocolon
If you’re a neat freak who likes things just so , isocolon is the literary device for you. This is when two or more phrases or clauses have similar structure, rhythm, and even length — such that, when stacked up on top of each other, they would line up perfectly. Isocolon often crops up in brand slogans and famous sayings; the quick, balanced rhythm makes the phrase catchier and more memorable.
Example: Veni, vidi, vici (“I came, I saw, I conquered”)
11. Litotes
Litotes (pronounced lie-toe-teez ) is the signature literary device of the double negative. Writers use litotes to express certain sentiments through their opposites, by saying that that opposite is not the case. Don’t worry, it makes more sense with the examples. 😉
Examples: “You won’t be sorry” (meaning you’ll be happy); “you’re not wrong” (meaning you’re right); “I didn’t not like it” (meaning I did)
12. Malapropism
If Shakespeare is the king of metaphors, Michael Scott is the king of malapropisms . A malapropism is when similar-sounding words replace their appropriate counterparts, typically to comic effect — one of the most commonly cited is “dance a flamingo,” rather than a “flamenco.” Malapropisms are often employed in dialogue when a character flubs up their speech.
Example: “I am not to be truffled with.”
Exercise: Choose a famous or common phrase and see if you can replace a word with a similar sounding one that changes the meaning.

13. Onomatopoeia
Amusingly, onomatopoeia (itself a difficult-to-pronounce word) refers to words that sound like the thing they’re referring to. Well-known instances of onomatopoeia include whiz, buzz, snap, grunt, etc.
Example: The excellent children's book Click, Clack, Moo: Cows That Type . “Farmer Brown has a problem. His cows like to type. All day long he hears: Click, clack, moo. Click, clack, moo. Clickety, clack, moo. ”
Exercise: Take some time to listen to the sounds around you and write down what you hear. Now try to use those sounds in a short paragraph or story.
14. Oxymoron
An oxymoron comes from two contradictory words that describe one thing. While juxtaposition contrasts two story elements, oxymorons are about the actual words you are using.
Example: "Parting is such sweet sorrow.” — Romeo and Juliet by William Shakespeare. (Find 100 more examples of oxymorons here .)
Similar terms: juxtaposition, paradox
Exercise: Choose two words with opposite meanings and see if you can use them in a sentence to create a coherent oxymoron.

15. Parallelism
Parallelism is all about your sentence structure. It’s when similar ideas, sounds, phrases, or words are arranged in a way that is harmonious or creates a parallel, hence the name. It can add rhythm and meter to any piece of writing and can often be found in poetry.
Example: “ That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind.” — Neil Armstrong
Which famous author do you write like?
Find out which literary luminary is your stylistic soulmate. Takes one minute!
16. Polysyndeton
Instead of using a single conjunction in lengthy statements, polysyndeton uses several in succession for a dramatic effect. This one is definitely for authors looking to add a bit of artistic flair to their writing, or who are hoping to portray a particular (usually naïve) sort of voice.
Example: “Luster came away from the flower tree and we went along the fence and they stopped and we stopped and I looked through the fence while Luster was hunting in the grass.” — The Sound and the Fury by William Faulkner
Exercise: Write three or four independent sentences. Try combining them using conjunctions. What kind of effect does this have on the overall meaning and tone of the piece?
17. Portmanteau
A portmanteau is when two words are combined to form a new word which refers to a single concept that retains the meanings of both the original words. Modern language is full of portmanteaus. In fact, the portmanteau is itself a portmanteau. It’s a combination of the French porter (to carry) and manteau (cloak).
Example: Brunch (breakfast and lunch); cosplay (costume and roleplay); listicle (list and article); romcom (romance and comedy)
Exercise: Pick two words that are often used together to describe a single concept. See if there’s a way to combine them and create a single word that encompasses the meaning of both.
18. Repetition
Repetition , repetition, repetition… where would we be without it? Though too much repetition is rarely a good thing, occasional repetition can be used quite effectively to drill home a point, or to create a certain atmosphere. For example, horror writers often use repetition to make the reader feel trapped and scared.
Example: In The Shining , Jack Torrance types over and over again on his pages, “All work and no play makes Jack a dull boy.” In this case, obsessive repetition demonstrates the character’s unraveling mind.
Similar term: anaphora
Exercise: Repetition can be used to call attention to an idea or phrase. Pick an idea you want to emphasize and write a few sentences about it. Are there any places where you can add repetition to make it more impactful?

19. Tautology
A tautology is when a sentence or short paragraph repeats a word or phrase, expressing the same idea twice. Often, this is a sign that you should trim your work to remove the redundancy (such as “frozen ice”) but can also be used for poetic emphasis.
Example: "But the fact is I was napping, and so gently you came rapping, And so faintly you came tapping, tapping at my chamber door" – “The Raven” by Edgar Allan Poe
20. Tmesis
Tmesis is when a word or phrase is broken up by an interjecting word, such as abso-freaking-lutely. It’s used to draw out and emphasize the idea, often with a humorous or sarcastic slant.
Example: "This is not Romeo, he's some-other-where." – Romeo and Juliet by William Shakespeare
21. Allegory
An allegory is a type of narrative that uses characters and plot to depict abstract ideas and themes . In an allegorical story, things represent more than they appear to on the surface. Many children's fables, such as The Tortoise and the Hare , are simple allegories about morality — but allegories can also be dark, complex, and controversial.
Example: Animal Farm by George Orwell. This dystopian novella is one of modern literature’s best-known allegories. A commentary on the events leading up to Stalin's rise and the formation of the Soviet Union, the pigs at the heart of the novel represent figures such as Stalin, Trotsky, and Molotov.
Exercise: Pick a major trend or problem in the world and consider what defines it. Try and create a story where that trend plays out on a smaller scale.
22. Anecdote
An anecdote is like a short story within a story. Sometimes, they are incredibly short—only a line or two—and their purpose is to add a character’s perspective, knowledge, or experience to a situation. They can be inspirational, humorous, or be used to inspire actions in others. Since anecdotes are so short, don’t expect them to be part of a main story. They’re usually told by a character and part of the dialogue.
Example: Marcel Proust’s Swann’s Way , part of his series of novels, In Search of Lost Time, deals with the themes of remembrance and memory. In one section of this book, to illustrate these ideas, the main character recalls an important memory of eating a madeleine cookie. “Many years had elapsed during which nothing of Combray, save what was comprised in the theatre and the drama of my going to bed there, had any existence for me, when one day in winter, as I came home, my mother, seeing that I was cold, offered me some tea, a thing I did not ordinarily take. I declined at first, and then, for no particular reason, changed my mind. She sent out for one of those short, plump little cakes called ‘petites madeleines,’ which look as though they had been moulded in the fluted scallop of a pilgrim’s shell.”
23. Deus Ex Machina
Literally meaning “god in the machine” in Greek, deus ex machina is a plot device where an impossible situation is solved by the appearance of an unexpected or unheard of character, action, object, or event. This brings about a quick and usually happy resolution for a story and can be used to surprise an audience, provide comic relief, or provide a fix for a complicated plot. However, deus ex machinas aren’t always looked upon favorably and can sometimes be seen as lazy writing, so they should be used sparingly and with great thought.
Example: William Golding’s famous novel of a group of British boys marooned on a desert island is resolved with a deus ex machina. At the climax of The Lord of the Flies, just as Ralph is about to be killed by Jack, a naval officer arrives to rescue the boys and bring them back to civilization. It’s an altogether unexpected and bloodless ending for a story about the boys’ descent into savagery.
Exercise: Consider the ending of your favorite book or movie and then write an alternate ending that uses a deus ex machina to resolve the main conflict. How does this affect the overall story in terms of theme and tone?
If you struggle to write consistently, sign up for our How to Write a Novel course to finish a novel in just 3 months.

NEW REEDSY COURSE
How to Write a Novel
Enroll in our course and become an author in three months.
24. Dramatic irony
Dramatic irony is when the readers know more about the situation going on than at least one of the characters involved. This creates a difference between the ways the audience and the characters perceive unfolding events. For instance, if we know that one character is having an affair, when that character speaks to their spouse, we will pick up on the lies and double-meanings of their words, while the spouse may take them at face value.
Example: In Titanic , the audience knows from the beginning of the movie that the boat will sink. This creates wry humor when characters remark on the safety of the ship.
25. Exposition
Exposition is when the narrative provides background information in order to help the reader understand what’s going on. When used in conjunction with description and dialogue, this literary device provides a richer understanding of the characters, setting, and events. Be careful, though — too much exposition will quickly become boring, thus undercutting the emotional impact of your work.
Example: “The Dursley’s had everything they wanted, but they also had a secret, and their greatest fear was that somebody would discover it.” – Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone by J.K. Rowling
Exercise: Pick your favorite story and write a short paragraph introducing it to someone who knows nothing about it.
26. Flashback
Flashbacks to previous events split up present-day scenes in a story, usually to build suspense toward a big reveal. Flashbacks are also an interesting way to present exposition for your story, gradually revealing to the reader what happened in the past.
Example: Every other chapter in the first part of Gone Girl is a flashback, with Amy’s old diary entries describing her relationship with her husband before she disappeared.
Similar term: foreshadowing
27. Foreshadowing
Foreshadowing is when the author hints at events yet to come in a story. Similar to flashbacks (and often used in conjunction with them), this technique is also used to create tension or suspense — giving readers just enough breadcrumbs to keep them hungry for more.
Example: One popular method of foreshadowing is through partial reveals — the narrator leaves out key facts to prompt readers’ curiosity. Jeffrey Eugenides does this in The Virgin Suicides : “On the morning the last Lisbon daughter took her turn at suicide — it was Mary this time, and sleeping pills, like Therese, the two paramedics arrived at the house knowing exactly where the knife drawer was, and the gas oven, and the beam in the basement from which it was possible to tie a rope.”
Similar term: flashback
Exercise: Go back to your favorite book or movie. Can you identify any instances of foreshadowing in the early portions of the story for events that happen in the future?
28. Frame story
A frame story is any part of the story that "frames" another part of it, such as one character telling another about their past, or someone uncovering a diary or a series of news articles that then tell the readers what happened. Since the frame story supports the rest of the plot, it is mainly used at the beginning and the end of the narrative, or in small interludes between chapters or short stories.
Example: In The Name of the Wind by Patrick Rothfuss, Kvothe is telling Chronicler the story of his life over the span of three days. Most of the novel is the story he is telling, while the frame is any part that takes place in the inn.
29. In Medias Res
In medias res is a Latin term that means "in the midst of things" and is a way of starting a narrative without exposition or contextual information. It launches straight into a scene or action that is already unfolding.
Example: “Many years later, as he faced the firing squad, Colonel Aureliano Buendía was to remember that distant afternoon when his father took him to discover ice.” — The opening line of One Hundred Years of Solitude by Gabriel García Márquez
Exercise: Pick a story you enjoy and rewrite the opening scene so that it starts in the middle of the story.
30. Point of view
Point of view is, of course, the mode of narration in a story. There are many POVs an author can choose, and each one will have a different impact on the reading experience.
Example: Second person POV is uncommon because it directly addresses the reader — not an easy narrative style to pull off. One popular novel that manages to employ this perspective successfully is Bright Lights, Big City by Jay McInerney: “You are not the kind of guy who would be at a place like this at this time of the morning. But here you are, and you cannot say that the terrain is entirely unfamiliar, although the details are fuzzy.”
Exercise: Write a short passage in either first, second, or third person. Then rewrite that passage in the other two points of view, only changing the pronouns. How does the change in POV affect the tone and feel of the story?

FREE COURSE
Understanding Point of View
Learn to master different POVs and choose the best for your story.
31. Soliloquy
Soliloquy involves a character speaking their thoughts aloud, usually at length (and often in a Shakespeare play). The character in question may be alone or in the company of others, but they’re not speaking for the benefit of other people; the purpose of a soliloquy is for a character to reflect independently.
Example: Hamlet’s “to be or not to be” speech, in which he ruminates on the nature of life and death, is a classic dramatic soliloquy.
Exercise: Pick a character from your favorite book or movie and write a soliloquy from their point of view where they consider their thoughts and feelings on an important part of their story or character arc.
Which writing app is right for you?
Find out here! Takes 30 seconds
Tone refers to the overall mood and message of your book. It’s established through a variety of means, including voice, characterization, symbolism, and themes. Tone sets the feelings you want your readers to take away from the story.
Example: No matter how serious things get in The Good Place , there is always a chance for a character to redeem themselves by improving their behavior. The tone remains hopeful for the future of humanity in the face of overwhelming odds.
Exercise: Write a short paragraph in an upbeat tone. Now using the same situation you came up with, rewrite that passage in a darker or sadder tone.
33. Tragicomedy
Tragicomedy is just what it sounds like: a blend of tragedy and comedy. Tragicomedy helps an audience process darker themes by allowing them to laugh at the situation even when circumstances are bleak.
Example: Lemony Snicket’s A Series of Unfortunate Events uses wordplay, absurd situations, and over-the-top characters to provide humor in an otherwise tragic story.
34. Allusion
An allusion is a reference to a person, place, thing, concept, or other literary work that a reader is likely to recognize. A lot of meaning can be packed into an allusion and it’s often used to add depth to a story. Many works of classic Western literature will use allusions to the Bible to expand on or criticize the morals of their time.
Example: “The two knitting women increase his anxiety by gazing at him and all the other sailors with knowing unconcern. Their eerie looks suggest that they know what will happen (the men dying), yet don’t care.” The two women knitting in this passage from Joseph Conrad’s Heart of Darkness are a reference to the Fates from Greek mythology, who decide the fate of humanity by spinning and cutting the threads of life.
Exercise: In a relatively simple piece of writing, see how many times you can use allusions. Go completely crazy. Once you’re finished, try to cut it down to a more reasonable amount and watch for how it creates deeper meaning in your piece.
35. Analogy
An analogy connects two seemingly unrelated concepts to show their similarities and expand on a thought or idea. They are similar to metaphors and similes, but usually take the comparison much further than either of these literary devices as they are used to support a claim rather than provide imagery.
Example: “ It has been well said that an author who expects results from a first novel is in a position similar to that of a man who drops a rose petal down the Grand Canyon of Arizona and listens for the echo.” — P.G. Wodehouse
Exercise: Pick two seemingly unrelated nouns and try to connect them with a verb to create an analogy.
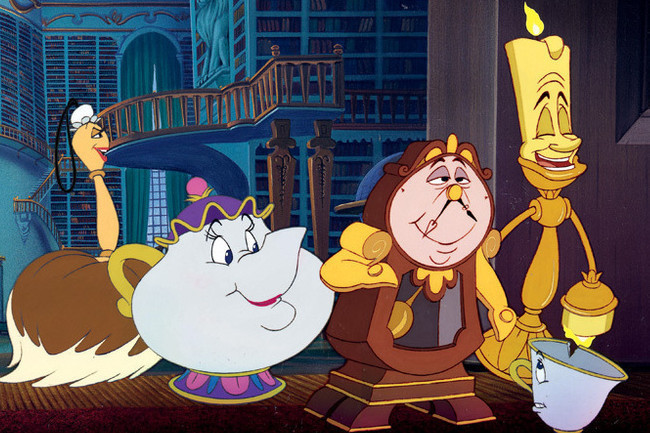
36. Anthropomorphism
To anthropomorphize is to apply human traits or qualities to a non-human thing such as objects, animals, or the weather. But unlike personification, in which this is done through figurative description, anthropomorphism is literal: a sun with a smiling face, for example, or talking dogs in a cartoon.
Examples: In Disney’s Beauty and the Beast , Mrs. Potts the teapot, Cogsworth the clock, and Lumière the candlestick are all household objects that act and behave like humans (which, of course, they were when they weren’t under a spell).
Similar term: personification
Exercise: Pick a non-human object and describe it as if it was human, literally ascribing human thoughts, feelings, and senses to it.

37. Aphorism
An aphorism is a universally accepted truth stated in a concise, to-the-point way. Aphorisms are typically witty and memorable, often becoming adages or proverbs as people repeat them over and over.
Example: “To err is human, to forgive divine.” — Alexander Pope
38. Archetype
An archetype is a “universal symbol” that brings familiarity and context to a story. It can be a character, a setting, a theme, or an action. Archetypes represent feelings and situations that are shared across cultures and time periods, and are therefore instantly recognizable to any audience — for instance, the innocent child character, or the theme of the inevitability of death.
Example: Superman is a heroic archetype: noble, self-sacrificing, and drawn to righting injustice whenever he sees it.
Exercise: Pick an archetype — either a character or a theme — and use it to write a short piece centered around that idea.
A cliché is a saying or idea that is used so often it becomes seen as unoriginal. These phrases might become so universal that, despite their once intriguing nature, they're now looked down upon as uninteresting and overused.
Examples: Some common cliches you might have encountered are phrases like “easy as pie” and “light as a feather.” Some lines from famous books and movies have become so popular that they are now in and of themselves cliches such as Darth Vader’s stunning revelation from The Empire Strikes Back, “Luke, I am your father.” Also, many classic lines of Shakespeare are now considered cliches like, “All that glitters is not gold” from The Merchant of Venice.
Exercise: Write a short passage using as many cliches as possible. Now try to cut them out and replace them with more original phrasing. See how the two passages compare.
40. Colloquialism
Colloquialism is the use of casual and informal language in writing, which can also include slang. Writers use colloquialisms to provide context to settings and characters, and to make their writing sound more authentic. Imagine reading a YA novel that takes place in modern America, and the characters speak to each other like this:
“Good morning, Sue. I hope that you slept well and are prepared for this morning’s science exam.”
It’s not realistic. Colloquialisms help create believable dialogue :
“Hey Sue, what’d you get up to last night? This science test is gonna suck.”
Example: Trainspotting by Irvine Welsh takes place in Scotland, a fact made undeniably obvious by the dialect: “Thing is, as ye git aulder, this character-deficiency gig becomes mair sapping. Thir wis a time ah used tae say tae aw the teachers, bosses, dole punters, poll-tax guys, magistrates, when they telt me ah was deficient: ’Hi, cool it, gadge, ah’m jist me, jist intae a different sort ay gig fae youse but, ken?’”
Exercise: Write a dialogue between two characters as formally as possible. Now take that conversation and make it more colloquial. Imagine that you’re having this conversation with a friend. Mimic your own speech patterns as you write.
41. Euphemism
A euphemism is an indirect, “polite” way of describing something too inappropriate or awkward to address directly. However, most people will still understand the truth about what's happening.
Example: When an elderly person is forced to retire, some might say they’re being “put out to pasture.”
Exercise: Write a paragraph where you say things very directly. Now rewrite that paragraph using only euphemisms.
42. Hyperbole
Hyperbole is an exaggerated statement that emphasizes the significance of the statement’s actual meaning. When a friend says, "Oh my god, I haven't seen you in a million years," that's hyperbole.
Example: “At that time Bogotá was a remote, lugubrious city where an insomniac rain had been falling since the beginning of the 16th century.” — Living to Tell the Tale by Gabriel García Márquez
Exercise: Tall tales often make use of hyperbole to tell an exaggerated story. Use hyperbole to relate a completely mundane event or experience to turn it into a tall tale.
43. Hypophora
Hypophora is much like a rhetorical question, wherein someone asks a question that doesn't require an answer. However, in hypophora, the person raises a question and answers it immediately themselves (hence the prefix hypo, meaning 'under' or 'before'). It’s often used when characters are reasoning something aloud.
Example: “Do you always watch for the longest day of the year and then miss it? I always watch for the longest day in the year and then miss it.” — Daisy in The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald

An idiom is a saying that uses figurative language whose meaning differs from what it literally says. These phrases originate from common cultural experiences, even if that experience has long ago been forgotten. Without cultural context, idioms don’t often make sense and can be the toughest part for non-native speakers to understand.
Example: In everyday use, idioms are fairly common. We say things like, “It’s raining cats and dogs” to say that it’s downpouring.
Exercise: Idioms are often used in dialogue. Write a conversation between two people where idioms are used to express their main points.
45. Imagery
Imagery appeals to readers’ senses through highly descriptive language. It’s crucial for any writer hoping to follow the rule of "show, don’t tell," as strong imagery truly paints a picture of the scene at hand.
Example: “In the hard-packed dirt of the midway, after the glaring lights are out and the people have gone to bed, you will find a veritable treasure of popcorn fragments, frozen custard dribblings, candied apples abandoned by tired children, sugar fluff crystals, salted almonds, popsicles, partially gnawed ice cream cones and wooden sticks of lollipops.” — Charlotte's Web by E.B. White
Exercise: Choose an object, image, or idea and use the five senses to describe it.

Show, Don't Tell
Master the golden rule of writing in 10 five-minute lessons.
Irony creates a contrast between how things seem and how they really are. There are three types of literary irony : dramatic (when readers know what will happen before characters do), situational (when readers expect a certain outcome, only to be surprised by a turn of events), and verbal (when the intended meaning of a statement is the opposite of what was said).
Example: This opening scene from Orson Welles’ A Touch of Evil is a great example of how dramatic irony can create tension.
47. Juxtaposition
Juxtaposition places two or more dissimilar characters, themes, concepts, etc. side by side, and the profound contrast highlights their differences. Why is juxtaposition such an effective literary device? Well, because sometimes the best way for us to understand something is by understanding what it’s not .
Example: In the opening lines of A Tale of Two Cities , Charles Dickens uses juxtaposition to emphasize the societal disparity that led to the French Revolution: “It was the best of times, it was the worst of times, it was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness, it was the epoch of belief, it was the epoch of incredulity, it was the season of Light, it was the season of Darkness…”
Similar terms: oxymoron, paradox
Exercise: Pick two ideas, objects, places, or people that seem like complete opposites. Introduce them side by side in the beginning of your piece and highlight their similarities and differences throughout.
48. Metaphor
A metaphor compares two similar things by saying that one of them is the other. As you'd likely expect, when it comes to literary devices, this one is a heavy hitter. And if a standard metaphor doesn't do the trick, a writer can always try an extended metaphor : a metaphor that expands on the initial comparison through more elaborate parallels.
Example: Metaphors are literature’s bread and butter (metaphor intended) — good luck finding a novel that is free of them. Here’s one from Frances Hardinge’s A Face Like Glass : “Wishes are thorns, he told himself sharply. They do us no good, just stick into our skin and hurt us.”
Similar term: simile
Exercise: Write two lists: one with tangible objects and the other concepts. Mixing and matching, try to create metaphors where you describe the concepts using physical objects.
One metaphor example not enough? Check out this post , which has 97 of ‘em!
49. Metonymy
Metonymy is like symbolism, but even more so. A metonym doesn’t just symbolize something else, it comes to serve as a synonym for that thing or things — typically, a single object embodies an entire institution.
Examples: “The crown” representing the monarchy, “Washington” representing the U.S. government.
Similar term: synecdoche
Exercise: Create a list of ten common metonymies you might encounter in everyday life and speech.
Whatever form a motif takes, it recurs throughout the novel and helps develop the theme of the narrative. This might be a symbol, concept, or image.
Example: In Anna Karenina by Leo Tolstoy, trains are an omnipresent motif that symbolize transition, derailment, and ultimately violent death and destruction.
Similar term: symbol
Exercise: Pick a famous book or movie and see if you can identify any common motifs within it.
51. Non sequitur
Non sequiturs are statements that don't logically follow what precedes them. They’ll often be quite absurd and can lend humor to a story. But they’re just not good for making jokes. They can highlight missing information or a miscommunication between characters and even be used for dramatic effect.
Example: “It was a spring day, the sort that gives people hope: all soft winds and delicate smells of warm earth. Suicide weather.” — Girl, Interrupted by Susanna Kaysen
Exercise: Write a conversation that gets entirely derailed by seemingly unrelated non sequiturs.
52. Paradox
Paradox derives from the Greek word paradoxon , which means “beyond belief.” It’s a statement that asks people to think outside the box by providing seemingly illogical — and yet actually true — premises.
Example: In George Orwell’s 1984 , the slogan of the totalitarian government is built on paradoxes: “War is Peace, Freedom is Slavery, Ignorance is Strength.” While we might read these statements as obviously contradictory, in the context of Orwell’s novel, these blatantly corrupt sentiments have become an accepted truth.
Similar terms: oxymoron, juxtaposition
Exercise: Try writing your own paradox. First, think of two opposing ideas that can be juxtaposed against each other. Then, create a situation where these contradictions coexist with each other. What can you gather from this unique perspective?
53. Personification
Personification uses human traits to describe non-human things. Again, while the aforementioned anthropomorphism actually applies these traits to non-human things, personification means the behavior of the thing does not actually change. It's personhood in figurative language only.
Example: “Just before it was dark, as they passed a great island of Sargasso weed that heaved and swung in the light sea as though the ocean were making love with something under a yellow blanket, his small line was taken by a dolphin.” — The Old Man and the Sea by Ernest Hemingway
Similar term: anthropomorphism
Exercise: Pick a non-human object and describe it using human traits, this time using similes and metaphors rather than directly ascribing human traits to it.
54. Rhetorical question
A rhetorical question is asked to create an effect rather than to solicit an answer from the listener or reader. Often it has an obvious answer and the point of asking is to create emphasis. It’s a great way to get an audience to consider the topic at hand and make a statement.
Example: “If you prick us, do we not bleed? If you tickle us, do we not laugh? If you poison us, do we not die? And if you wrong us, shall we not revenge?” — The Merchant of Venice by William Shakespeare
Writers use satire to make fun of some aspect of human nature or society — usually through exaggeration, ridicule, or irony. There are countless ways to satirize something; most of the time, you know it when you read it.
Example: The famous adventure novel Gulliver’s Travels by Jonathan Swift is a classic example of satire, poking fun at “travelers' tales,” the government, and indeed human nature itself.
A simile draws resemblance between two things by saying “Thing A is like Thing B,” or “Thing A is as [adjective] as Thing B.” Unlike a metaphor, a similar does not posit that these things are the same, only that they are alike. As a result, it is probably the most common literary device in writing — you can almost always recognize a simile through the use of “like” or “as.”
Example: There are two similes in this description from Circe by Madeline Miller: “The ships were golden and huge as leviathans, their rails carved from ivory and horn. They were towed by grinning dolphins or else crewed by fifty black-haired nereids, faces silver as moonlight.”
Similar term: metaphor
57. Symbolism
Authors turn to tangible symbols to represent abstract concepts and ideas in their stories Symbols typically derive from objects or non-humans — for instance, a dove might represent peace, or a raven might represent death.
Example: In The Great Gatsby , Fitzgerald uses the eyes of Doctor T.J. Eckleburg (actually a faded optometrist's billboard) to represent God and his judgment of the Jazz Age.
Similar term: motif
Exercise: Choose an object that you want to represent something — like an idea or concept. Now, write a poem or short story centered around that symbol.
58. Synecdoche
Synecdoche is the usage of a part to represent the whole. That is, rather than an object or title that’s merely associated with the larger concept (as in metonymy), synecdoche must actually be attached in some way: either to the name, or to the larger whole itself.
Examples: “Stanford won the game” ( Stanford referring to the full title of the Stanford football team) or “Nice wheels you got there” ( wheels referring to the entire car)
Similar term: metonymy
Zeugma is when one word is used to ascribe two separate meanings to two other words. This literary device is great for adding humor and figurative flair as it tends to surprise the reader. And it’s just a fun type of wordplay.
Example: “ Yet time and her aunt moved slowly — and her patience and her ideas were nearly worn out before the tete-a-tete was over.” — Pride and Prejudice by Jane Austen
60. Zoomorphism
Zoomorphism is when you take animal traits and assign them to anything that’s not an animal. It’s the opposite of anthropomorphism and personification, and can be either a physical manifestation, such as a god appearing as an animal, or a comparison, like calling someone a busy bee .
Example: When vampires turn into bats, their bat form is an instance of zoomorphism.
Exercise: Describe a human or object by using traits that are usually associated with animals.
Similar terms: anthropomorphism, personification
Readers and writers alike can get a lot out of understanding literary devices and how they're used. Readers can use them to gain insight into the author’s intended meaning behind their work, while writers can use literary devices to better connect with readers. But whatever your motivation for learning them, you certainly won't be sorry you did! (Not least because you'll recognize the device I just used in that sentence 😉)
6 responses
Ron B. Saunders says:
16/01/2019 – 19:26
Paraprosdokians are also delightful literary devices for creating surprise or intrigue. They cause a reader to rethink a concept or traditional expectation. (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paraprosdokian)
ManhattanMinx says:
17/01/2019 – 02:07
That's pore, not pour. Shame.....
↪️ Coline Harmon replied:
14/06/2019 – 19:06
It was a Malapropism
↪️ JC JC replied:
23/10/2019 – 00:02
Yeah ManhattanMinx. It's a Malepropism!
↪️ jesus replied:
07/11/2019 – 13:24
Susan McGrath says:
10/03/2020 – 10:56
"But whatever your motivation for learning them, you certainly won't be sorry you did! (Not least because you'll recognize the device I just used in that sentence. 😏)" Litote
Comments are currently closed.
Continue reading
Recommended posts from the Reedsy Blog

What is Tone in Literature? Definition & Examples
We show you, with supporting examples, how tone in literature influences readers' emotions and perceptions of a text.


Writing Cozy Mysteries: 7 Essential Tips & Tropes
We show you how to write a compelling cozy mystery with advice from published authors and supporting examples from literature.

Man vs Nature: The Most Compelling Conflict in Writing
What is man vs nature? Learn all about this timeless conflict with examples of man vs nature in books, television, and film.

The Redemption Arc: Definition, Examples, and Writing Tips
Learn what it takes to redeem a character with these examples and writing tips.

How Many Sentences Are in a Paragraph?
From fiction to nonfiction works, the length of a paragraph varies depending on its purpose. Here's everything you need to know.
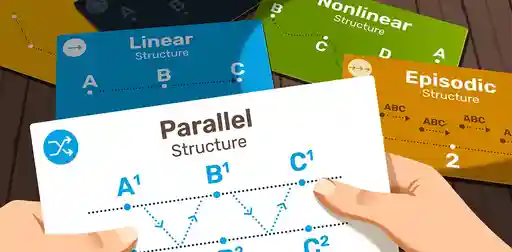
Narrative Structure: Definition, Examples, and Writing Tips
What's the difference between story structure and narrative structure? And how do you choose the right narrative structure for you novel?
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.
Bring your stories to life
Use our free writing app to finally write — and publish — that book!

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:

Elements of Creative Writing
J.D. Schraffenberger, University of Northern Iowa
Rachel Morgan, University of Northern Iowa
Grant Tracey, University of Northern Iowa
Copyright Year: 2023
ISBN 13: 9780915996179
Publisher: University of Northern Iowa
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Robert Moreira, Lecturer III, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley on 3/21/24
Unlike Starkey's CREATIVE WRITING: FOUR GENRES IN BRIEF, this textbook does not include a section on drama. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
Unlike Starkey's CREATIVE WRITING: FOUR GENRES IN BRIEF, this textbook does not include a section on drama.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
As far as I can tell, content is accurate, error free and unbiased.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
The book is relevant and up-to-date.
Clarity rating: 5
The text is clear and easy to understand.
Consistency rating: 5
I would agree that the text is consistent in terms of terminology and framework.
Modularity rating: 5
Text is modular, yes, but I would like to see the addition of a section on dramatic writing.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
Topics are presented in logical, clear fashion.
Interface rating: 5
Navigation is good.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
No grammatical issues that I could see.
Cultural Relevance rating: 3
I'd like to see more diverse creative writing examples.
As I stated above, textbook is good except that it does not include a section on dramatic writing.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Chapter One: One Great Way to Write a Short Story
- Chapter Two: Plotting
- Chapter Three: Counterpointed Plotting
- Chapter Four: Show and Tell
- Chapter Five: Characterization and Method Writing
- Chapter Six: Character and Dialouge
- Chapter Seven: Setting, Stillness, and Voice
- Chapter Eight: Point of View
- Chapter Nine: Learning the Unwritten Rules
- Chapter One: A Poetry State of Mind
- Chapter Two: The Architecture of a Poem
- Chapter Three: Sound
- Chapter Four: Inspiration and Risk
- Chapter Five: Endings and Beginnings
- Chapter Six: Figurative Language
- Chapter Seven: Forms, Forms, Forms
- Chapter Eight: Go to the Image
- Chapter Nine: The Difficult Simplicity of Short Poems and Killing Darlings
Creative Nonfiction
- Chapter One: Creative Nonfiction and the Essay
- Chapter Two: Truth and Memory, Truth in Memory
- Chapter Three: Research and History
- Chapter Four: Writing Environments
- Chapter Five: Notes on Style
- Chapter Seven: Imagery and the Senses
- Chapter Eight: Writing the Body
- Chapter Nine: Forms
Back Matter
- Contributors
- North American Review Staff
Ancillary Material
- University of Northern Iowa
About the Book
This free and open access textbook introduces new writers to some basic elements of the craft of creative writing in the genres of fiction, poetry, and creative nonfiction. The authors—Rachel Morgan, Jeremy Schraffenberger, and Grant Tracey—are editors of the North American Review, the oldest and one of the most well-regarded literary magazines in the United States. They’ve selected nearly all of the readings and examples (more than 60) from writing that has appeared in NAR pages over the years. Because they had a hand in publishing these pieces originally, their perspective as editors permeates this book. As such, they hope that even seasoned writers might gain insight into the aesthetics of the magazine as they analyze and discuss some reasons this work is so remarkable—and therefore teachable. This project was supported by NAR staff and funded via the UNI Textbook Equity Mini-Grant Program.
About the Contributors
J.D. Schraffenberger is a professor of English at the University of Northern Iowa. He is the author of two books of poems, Saint Joe's Passion and The Waxen Poor , and co-author with Martín Espada and Lauren Schmidt of The Necessary Poetics of Atheism . His other work has appeared in Best of Brevity , Best Creative Nonfiction , Notre Dame Review , Poetry East , Prairie Schooner , and elsewhere.
Rachel Morgan is an instructor of English at the University of Northern Iowa. She is the author of the chapbook Honey & Blood , Blood & Honey . Her work is included in the anthology Fracture: Essays, Poems, and Stories on Fracking in American and has appeared in the Journal of American Medical Association , Boulevard , Prairie Schooner , and elsewhere.
Grant Tracey author of three novels in the Hayden Fuller Mysteries ; the chapbook Winsome featuring cab driver Eddie Sands; and the story collection Final Stanzas , is fiction editor of the North American Review and an English professor at the University of Northern Iowa, where he teaches film, modern drama, and creative writing. Nominated four times for a Pushcart Prize, he has published nearly fifty short stories and three previous collections. He has acted in over forty community theater productions and has published critical work on Samuel Fuller and James Cagney. He lives in Cedar Falls, Iowa.
Contribute to this Page
Places on our 2024 summer school are filling fast. Don’t miss out. Enrol now to avoid disappointment
- 7 Techniques from Creative Writing You Can Use to Improve Your Essays

You wouldn’t have thought that essays have much in common with creative writing.
You should also read…
- How to Improve Your English Writing Skills
- How to Write Dazzlingly Brilliant Essays
Creative writing, by definition, involves being ‘creative’: making things up, letting your imagination run wild. Essays are about being factual and objective, communicating ideas and arguments in the clearest way possible and attempting to enhance the reader’s knowledge, rather than their imagination. But while the literary devices and colourful tales we associate with creative writing are indeed out of place in an essay, these two very different kinds of writing actually have a few similarities. Above all, they’re both meant to be read by other people, and that means that they need to sustain the reader’s interest. So, are there any writing techniques you can borrow from creative writing to help make your essays more interesting and original? Yes there are, and in this article, we’re going to show you how. Before we start, if you’re interested in attending a summer school to help develop these skills , click the link.
1. Think about your reader

With creative writing, as with any kind of writing, your reader is your most important consideration. You need to know and understand whom you’re writing for if you’re to do a good job of keeping them interested. Let’s think for a moment about the kind of person you’re writing for when you’re writing an essay and what you need to do to write specifically for them:
- Teachers or university lecturers – they’re going to be marking your essay, so it needs to answer the question effectively.
- They’ve set the question and they probably have a pretty good idea of how you’re going to answer it – so be original and unpredictable; catch them by surprise with an unusual approach or structure.
- They’re going to be reading many other responses to the same question – so they may well be bored by the time they get to yours. Keep them interested!
- They’re probably going to be pressed for time – so they won’t have time to reread badly written passages to try to understand what you’re getting at. Keep your writing easy to read, succinct and to the point.
What all these points boil down to is the importance of keeping your reader interested in what you have to say. Since creative writing is all about holding the reader’s interest, there must be some lessons to be learned from it and techniques that can be applied within the more limited style constraints of the academic essay. We’ll now turn to what these are.
2. Three-act structure

The three-act structure is a writing device used extensively in modern writing, including for film and television dramas. These ‘acts’ aren’t as distinct as acts in a play, as one follows seamlessly on from another and the audience wouldn’t consciously realise that one act had ended and another began. The structure refers to a plotline that looks something like this:
- Set-up – establishes the characters, how they relate to each other, and the world they inhabit. Within this first ‘act’, a dramatic occurrence called an ‘inciting incident’ takes place (typically around 19 minutes into a film) involving the principal character. They try to deal with it, but this results in another dramatic occurrence called a ‘turning point’. This sets the scene for the rest of the story.
- Confrontation – the turning point in the previous ‘act’ becomes the central problem, which the main character attempts to resolve – usually with plenty of adversity thrown their way that hampers their efforts. In a murder mystery, for example, this act would involve the detective trying to solve the murder. The central character – with the help of supporting characters – undergoes a journey and develops their knowledge, skills or character to a sufficient degree to be able to overcome the problem.
- Resolution – the climax of the story, in which the drama reaches a peak, the problem is overcome, and loose ends are tied up.
This structure sounds all very well for made-up stories, but what has it got to do with essay-writing? The key similarities here are:
- The central argument of your essay is the equivalent of the main character.
- The essay equivalent of the set-up and resolution are the introduction and conclusion.
- The inciting incident in an essay encourages you to get to the point early on in the essay.
- The equivalent of character development in the second act is developing your argument.
- The equivalent of the supporting characters is the evidence you refer to in your essay.
So, applying the three-act structure to an essay gives you something like this:
- Set-up – the introduction. This establishes what you’re talking about, setting the scene. The ‘inciting incident’ could be the introduction of evidence that contradicts a common theory, or the highlighting of a central disagreement in how something is interpreted.
- Confrontation – you discuss the different problems surrounding the topic you’re writing about. You develop the argument using various bits of evidence, moving towards an overall conclusion.
- Resolution – the conclusion. You summarise and resolve the argument with your own opinion, by coming down on one side or the other, having weighed up the evidence you’ve discussed. You could perhaps tie up loose ends by offering an alternative explanation for evidence that doesn’t sit with your conclusion.
Using this structure keeps you focused on the central point, and stops you from waffling, because everything you write is working towards resolving your argument. The use of the inciting incident in the first ‘act’ encourages you to get to the point early on in your essay, thereby keeping the reader interested. The principles of good plot-writing are centred around the connection between different events that show cause and effect, and this central tenet of the three-act structure has obvious parallels with the way in which essays work through presenting evidence in support of arguments.
3. An attention-grabbing opening

An oft-spouted piece of advice in creative writing is to use an attention-grabbing opening. One way of doing this is to start with a ‘flashback’, which could disrupt the chronology of events by transporting the reader directly back to the midst of the action, so that the story begins with maximum excitement. In a murder mystery, for instance, the writer might skip a slow build-up and instead use the murder itself to form the opening of the novel, with the rest of the story charting the efforts of the detective to uncover the perpetrator and perhaps telling the events prior to the murder in a series of flashbacks. The same principle can be applied to essays, though it’s easier to use in some subjects than others. To take an example, let’s say you were writing about how the First World War started. Rather than building up slowly with the various factors, an attention-grabbing opening could (briefly) describe the drama of the Battle of the Somme, perhaps citing some statistics about the number of men involved and killed, and quoting some war poetry about the horrors faced by the soldiers on the Front Line. Then, to introduce the purpose of the essay and launch into your argument about what started the war, a phrase such as, “It seems hard to imagine that all this began with…”. Alternatively, a rhetorical question: “But how did these tens of thousands of soldiers end up in the mud and horror of trench warfare? The story begins several years earlier, with…” It may not be the standard way of writing an essay, but you’ll certainly score points for originality and perhaps ruffle a few feathers.
4. Extended metaphors

Creative writing often makes use of extended metaphors. For example, when Shakespeare wrote the passage in Romeo and Juliet referring to “It is the East, and Juliet is the sun!” he was using an extended metaphor. With this in mind, it’s time to revisit a point we made in a previous article about writing more original essays , in which we argued that, rather than battling on with trying to explain a complex concept in a straightforward way, it might be easier to use an analogy to convey the meaning by drawing comparisons, which people find easier to understand. A metaphor is a kind of analogy, so the similarities with creative writing are strong here. In our previous article we used the example of radioactive decay. An analogy for this is the pressure with which water escapes from a hole in a bucket. It does so exponentially, just as radioactive substances decay exponentially. In both instances, the rate of a consumptive process depends on how much there is left of whatever is being depleted, which results in an exponential rate of decay. This concept is so much easier to explain using the analogy of water flowing from a hole in a bucket, as you give your reader something familiar to visualise in order to explain a concept with which they are unfamiliar.
5. Interesting details about setting and location

Another way of keeping your reader interested is to bring your essay to life with details about setting and location, just as creative writers do. Essays can become quite dry if you focus solely on the academic problems, but you can make them more interesting by peppering them with details. This may not work quite so well for a scientific essay, but it’s certainly relevant for some humanities subjects, in particular English literature, history and archaeology. For example, an essay about the Roman emperor Augustus could mention that he lived a famously modest lifestyle, quoting details from Roman writers and archaeological evidence that support this: Suetonius mentions his “low bed” (interesting because of what it says about accepted standards of Roman beds!) and coarse bread and cheese diet, and the relatively small and non-lavish remains of his house on the Palatine Hill in Rome back up the idea of his having lived a modest life. Incidental details like these can actually prove to be more significant than you initially realise, and you can use them to build your argument; in the case of Augustus, for example, his modest lifestyle is particularly important when seen in the context of Rome’s troubled history with kings. As he gradually acquired more power and became Rome’s first emperor, he had to avoid coming across as being too ‘regal’, and the little details we know about his way of life are significant in light of this. So, not only have you brought your essay to life, but you’ve raised an interesting point, too.
Few writers get it right first time . Once you’ve written a first draft, read through it and think about whether the order of your points is optimal and whether what you’ve written actually makes sense. It’s easy in the age of computers to chop and change – you can simply copy and paste part of your essay into another part where it might fit better, and then make minor changes to your wording so that it flows. After you’ve finished editing, have a final read through and check that you’re happy with the wording. Don’t forget to proofread to ensure that your spelling and grammar is impeccable!
7. And finally… record your ideas

Creative writers swear by having a notebook with them at all times, ready to jot down any ideas that suddenly spring to mind. You can adopt the same principle for your essay-writing, because you never know when the inspiration might strike. Have a think about your essay topic when you’re out and about; you’d be surprised what occurs to you when you’re away from your normal place of study. As you can see, there are more similarities between two apparently unrelated kinds of writing than you might have realised. It is, of course, possible to go too far with the creative writing idea when you’re essay-writing: literary devices aren’t always appropriate, and your essay still needs to retain objectivity and conform to the more formal conventions of academic writing. But there are certainly techniques to be borrowed from creative writing that will help your essays stand out from the crowd and give your teacher or lecturer a welcome break from the monotony of essay-marking.
See also our fabulous guide explaining more about ” What is Creative Writing ”.
Comments are closed.
No products in the cart.

31 Stylistic Devices for Creative Writers
Today’s guest post is by Rose Scott:
Without figurative language , writing would be plain and shallow. The more stylistic devices you know, the more unique your writing can be. If writing is your passion, you probably already know a dozen or so stylistic devices, but I’m betting there are a few on this list you’ve never heard of.
Take a look at this comprehensive list of stylistic devices and see if any might work in your current WIP (work in progress). Of course, you want to be reasonable and not go overboard with forced prose. But I’m sure you can find great places to utilize these wonderful literary techniques.
1. Adnomination
Repetition of words with the same root. The difference lies in one sound or letter. A nice euphony can be achieved by using this poetic device.
Examples: “Nobody loves no one.” (Chris Isaak). Someone, somewhere, wants something.
2. Allegory
Representation of ideas through a certain form (character, event, etc.). Allegory can convey hidden meanings through symbolic figures, actions, and imagery.
Example: Animal Farm by George Orwell is all about the Russian Revolution. And characters stand for working and upper classes, military forces, and political leaders.
3. Alliteration
The repeated sound of the first consonant in a series of words, or the repetition of the same sounds of the same kind at the beginning of words or in stressed syllables of a phrase.
Examples: A lazy lying lion. Peter picked a peck of pickled peppers. Sally sells seashells by the seashore.
4. Allusion
Reference to a myth, character, literary work, work of art, or an event.
Example: I feel like I’m going down the rabbit hole (an allusion to Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland by Lewis Carroll).
5. Anaphora
Word repetition at the beginnings of sentences in order to give emphasis to them.
Example: “Let freedom ring from the mighty mountains of New York. Let freedom ring from the heightening Alleghenies of Pennsylvania. Let freedom ring from the snow-capped Rockies of Colorado. Let freedom ring from the curvaceous slopes of California.” (Martin Luther King)
Opposite: Epiphora. Word repetition at the end of sentences.
Example: “And that government of the people, by the people, for the people, shall not perish from the earth.” (Abraham Lincoln)
6. Antithesis
Emphasizing contrast between two things or fictional characters.
Example: “Love is an ideal thing, marriage a real thing; a confusion of the real with the ideal never goes unpunished.” (Johann Wolfgang von Goethe)
7. Apostrophe
Directed speech to someone who is not present or to an object.
Example: “Work on, my medicine, work! Thus credulous fools are caught.” (William Shakespeare)
8. Assonance
Repetition of vowels in order to create internal rhyming.
Example: “Hear the mellow wedding bells.” (Edgar Allan Poe)
Related: Consonance. Repetition of consonants.
9. Cataphora
Mentioning of the person or object further in the discourse.
Examples: I met him yesterday, your boyfriend who was wearing the cool hat. If you want some, here’s some cheese. After he had received his orders, the soldier left the barracks.
Arranging text in such a manner that tension gradually ascends.
Example. He was a not bad listener, a good speaker and an amazing performer.
Opposite: Anticlimax. Tension descends.
11. Charactonym (or Speaking Name)
Giving fictional characters names that describe them.
Example: Scrooge, Snow White.
12. Ellipsis
Word or phrase omission.
Example: I speak lots of languages, but you only speak two (languages).
13. Euphemism
Replacing offensive or combinations of words with lighter equivalents.
Example: Visually challenged (blind); meet one’s maker (die)
Opposite: Dysphemism . Replacing a neutral word with a harsher word.
14. Epigram
Memorable and brief saying, usually satirical.
Example: “For most of history, Anonymous was a woman.” (Virginia Woolf)
15. Hyperbole
Exaggeration of the statement.
Example: If I’ve told you once, I’ve told you a thousand times.
Opposite: Litotes. Understatement.
Asking a question and answering it right away.
Example: Are you going to leave now? I don’t think so.
There are three types of irony:
- Verbal (Antiphrasis) – using words to express something different from their literal meaning for ironic effect (”I’m so excited to burn the midnight oil and write my academic paper all week long”).
- Situational – result differs from the expectation (Bruce Robertson, a character of Filth, is a policeman. Nonetheless, he does drugs, resorts to violence and abuse, and so on).
- Dramatic – situation is understandable for the audience but not the fictional character/actor (audience sees that the fictional characters/actors will be killed now, though the characters don’t expect it).
Describing people/objects by enumerating their traits.
Example: Lock, stock, and barrel (gun); heart and soul (entirety)
18. Metalepsis
Referencing one thing through the means of another thing, which is related to the first one.
Example: “Stop judging people so strictly—you live in a glass house too.” (A hint at the proverb: people who live in glass houses should not throw stones.)
19. Metaphor
Comparing two different things that have some characteristics in common.
Example: “Love is clockworks and cold steel.” (U2)
20. Metonymy
Giving a thing another name that is associated with it.
Example: The heir to the crown was Richard. (the crown stands for authority)
21. Onomatopoeia
Imitating sounds in writing.
Example: oink, ticktock, tweet tweet
22. Oxymoron
Combining contradictory traits.
Example: Living dead; terribly good; real magic
23. Parallelism
Arranging a sentence in such a manner that it has parallel structure.
Example: “Tell me and I forget. Teach me and I may remember. Involve me and I will learn.” (Benjamin Franklin)
Opposite: Chiasmus . An inverted parallelism.
Examples: “To stop, too fearful, and too faint to go.” (Oliver Goldsmith); “My job is not to represent Washington to you but to represent you to Washington.” (Barack Obama)
24. Parenthesis
Interrupting a sentence by inserting extra information enclosed in brackets, commas, or dashes.
Example: Our family (my mother, sister, and grandfather) had a barbeque this past weekend.
25. Personification
Attributing human characteristics to nonhumans.
Example: Practically all animals in fairy tales act like human beings. They speak and have traits that are typical of people.
A kind of wordplay. Here are a few types of puns:
- Antanaclasis – repetition of the same word or phrase, but with a different meaning (“Cats like Felix like Felix.”—“Felix” catfood slogan).
- Malapropism – usage of the incorrect word instead of the word with a similar sound (“optical delusion” instead of “optical illusion”).
- Paradox – self-contradictory fact; however, it can be partially true (“I can resist anything but temptation.”—Oscar Wilde).
- Paraprosdokian – arranging a sentence in such a manner so the last part is unexpected (You’re never too old to learn something stupid).
- Polyptoton – repetition of the words with the same root (“The things you own end up owning you.”—Chuck Palahniuk).
27. Rhetorical question
Questioning without expecting the answer.
Example: Why not? Are you kidding me?
Direct comparison.
Example: “Your heart is like an ocean, mysterious and dark.” (Bob Dylan)
29. Synecdoche
Generalization or specification based on a definite part/trait of the object.
Example: He just got new wheels. (car)
30. Tautology
Saying the same thing twice in different ways.
Example: first priority; I personally; repeat again
31. Zeugma (or Syllepsis)
Applying a word to a few other words in the sentence in order to give different meaning.
Example: Give neither counsel nor salt till you are asked for it.
Quite a huge list, right? With all these stylistic devices, your writing can potentially be so much more attractive. If you find it difficult to memorize them all, here’s what I recommend you do: make flashcards. Write a stylistic device on one side of the flashcard and its meaning on the other side, then work on memorizing a few a day. Voila! Enjoy your learning and writing.

Feature photo by Heather Wilson Smith
Have you been learning helpful insights on how to spot flaws in your fiction writing? Know some writers who might benefit from these in-depth posts? The book is out!
You can find 5 Editors Tackle the 12 Fatal Flaws of Fiction Writing on all online venues, in print or as an ebook.

Here are some links: Kindle , iBooks , Nook , Kobo , Oyster , and Scribd .
Don’t just give any book as a gift this holiday season. Give the book that will help the writers in your life become better writers! They’ll thank you!
Reviewers say:
“I wish I’d had this book when I wrote my first manuscript.”
“Every author needs this book on their shelf. From nothing happening to too much backstory to body parts behaving badly, this book has it all and tells you how to fix it with examples you can follow. Don’t have the money to hire an editor for your novel? Use this book, one of several in the Writer’s Toolbox Series, to mark your own book up in red. The fun part of this book is being able to read each entry and then determining what is wrong with it before you read the answer. Not quite sure what is wrong? That is okay, because the fatal flaw is fixed right before your eyes.”
“Another new and favorite part of the book is the checklist at the end of each chapter. I like having a quick wrap-up to check my work against. It’s great to rifle back through the detailed information after reading, but I’m more likely to use the checklists reminders over and over.”
“I have well over a hundred writing books on my bookcase and dozens more on my Kindle, but Fatal Flaws deserves to become the newest addition.”
“Got a feeling that something’s not quite right in your story? Maybe you don’t even know what it is, but you sense something’s not working? Get this book! It’s a mini-lecture series and workshop taught in a friendly manner. Your writing will significantly improve if you read this book and follow the suggestions.”
“This is an excellent study book for published and non-published writers alike. I love the fact that I got input five different editors. So many teaching books are written by just one person. Besides, where else can you get this much writing instruction for $4.99?”
Exactly! Our thanks to all who did an early read and review. Your comments will help others see the value of this comprehensive book. And may this book help you all to write awesome books in 2016!
~Susanne, Linda, Christy, Robin, and Rachel
Search Posts Here
Subscribe to my blog, similar posts.

Self-Published Authors Share 5 Things They Learned in 2012 ~ Part 10
Today’s guest post continues the 12-part series I’ve launched in this new year: asking self-published authors what are the top…

An Inside Look at Law and Lawyers: 5 Tips for Authors
Today’s post is part of a series on professionals sharing tips and expertise in order to help novelists convey accuracy in…

How Nonfiction Writers Can Own Their Niche
I’m taking a look at how nonfiction indie writers can find success marketing and promoting their books, since I’ve mostly…

How to Be a Clever Writer
Has anyone ever told you how clever you are? No? Or maybe they said that to you but didn’t mean…

Self-Published Authors Share 5 Things They Learned in 2012 ~ Part 5

Words of Advice from Famous Authors That Are Just Wrong
I imagine this post is bound to draw some criticism, but bring it on! Maybe it’s just me, but when…
12 Comments
great post! thanks Rose, for a super stellar list of dynamic devices! i’ve saved the list for future and fair-constant reference. there’s always something good on this blog! Merry Christmas everyone!!
Oh man, it’s like Christmas has come early. I love posts like this – and I’ll both share it *and* copy it to my desktop ha!
Items I didn’t know about but immediately fell in love with: adnomination, anaphora, hypophora (I hadn’t realised, but I do this all of the time, which now seems pretty annoying!), and zeugma. Thank you once again!
Glad you enjoyed this post! Have a happy Christmas!
Thanks much for you “31 Stylistic Devices … …” I was in the process of writing a transcript when I sort of stumbled across the need to correctly define a scenario.
I did a quick surf, directly asking for what I wanted, this popped up. I scanned your list and had the “Eureka!” moment. “METAPHOR!”
It’s really great of you also sharing without obligation. We do a lot of that in our realm of things.
Okay! Thanks again! Please, have a great weekend!
P.S. For you Ms. Lakin. Thanks for making this site available! Please, have a great weekend, as well!
Thanks for the kind words! Glad you are getting some benefit from the blog’s content!
Do you have a list of stylised paragraphs? Not just the main 4 (descriptive, narrative, expository, and persuasive), but other types of paragraphs that apply rhetorical ornaments and devices.
Forgot to say thank you for this lovely and informative post.
Wow this post has boost my understanding of the analysing the prose techniques in a book. Thank u very much
I greatly appreciate the time and effort you put into constructing this list. I especially enjoy how you introduced me to unfamiliar and complex stylistic devices. I will attempt to incorporate these techniques in my future writing. Synecdoche is a wonderful device that I have not heard of before, I’ll have to steal it :P. Is there any way I can contact you? I would love to have a nerdy conversation about English!
Sincerely, Jenny Wales
It was interesting when you talked about how parallelism arranges sentences so their structure is parallel to each other. I’ve been wanting to find some poetry online to help me sort through my emotions from a loved one’s death last month. Thanks for teaching me these writing devices to look out for so I can understand the poems as effectively as possible.
Hi Rose I like your terms and I am using it on my writing my thesis on stylistics.
Actually, there are 32 stylistic devices in your list, since there are two no. 17.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
[related_books]
Next Steps for Your Manuscript

Free Amazon Email Course

Guest Blogging

Get your Free Ebook!
Subscribe to my email blasts to level up your writing and be notified of upcoming events and offers!
Review Cart

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, the 31 literary devices you must know.
General Education

Need to analyze The Scarlet Letter or To Kill a Mockingbird for English class, but fumbling for the right vocabulary and concepts for literary devices? You've come to the right place. To successfully interpret and analyze literary texts, you'll first need to have a solid foundation in literary terms and their definitions.
In this article, we'll help you get familiar with most commonly used literary devices in prose and poetry. We'll give you a clear definition of each of the terms we discuss along with examples of literary elements and the context in which they most often appear (comedic writing, drama, or other).
Before we get to the list of literary devices, however, we have a quick refresher on what literary devices are and how understanding them will help you analyze works of literature.
What Are Literary Devices and Why Should You Know Them?
Literary devices are techniques that writers use to create a special and pointed effect in their writing, to convey information, or to help readers understand their writing on a deeper level.
Often, literary devices are used in writing for emphasis or clarity. Authors will also use literary devices to get readers to connect more strongly with either a story as a whole or specific characters or themes.
So why is it important to know different literary devices and terms? Aside from helping you get good grades on your literary analysis homework, there are several benefits to knowing the techniques authors commonly use.
Being able to identify when different literary techniques are being used helps you understand the motivation behind the author's choices. For example, being able to identify symbols in a story can help you figure out why the author might have chosen to insert these focal points and what these might suggest in regard to her attitude toward certain characters, plot points, and events.
In addition, being able to identify literary devices can make a written work's overall meaning or purpose clearer to you. For instance, let's say you're planning to read (or re-read) The Lion, the Witch, and the Wardrobe by C.S. Lewis. By knowing that this particular book is a religious allegory with references to Christ (represented by the character Aslan) and Judas (represented by Edmund), it will be clearer to you why Lewis uses certain language to describe certain characters and why certain events happen the way they do.
Finally, literary techniques are important to know because they make texts more interesting and more fun to read. If you were to read a novel without knowing any literary devices, chances are you wouldn't be able to detect many of the layers of meaning interwoven into the story via different techniques.
Now that we've gone over why you should spend some time learning literary devices, let's take a look at some of the most important literary elements to know.
List of Literary Devices: 31 Literary Terms You Should Know
Below is a list of literary devices, most of which you'll often come across in both prose and poetry. We explain what each literary term is and give you an example of how it's used. This literary elements list is arranged in alphabetical order.
An allegory is a story that is used to represent a more general message about real-life (historical) issues and/or events. It is typically an entire book, novel, play, etc.
Example: George Orwell's dystopian book Animal Farm is an allegory for the events preceding the Russian Revolution and the Stalinist era in early 20th century Russia. In the story, animals on a farm practice animalism, which is essentially communism. Many characters correspond to actual historical figures: Old Major represents both the founder of communism Karl Marx and the Russian communist leader Vladimir Lenin; the farmer, Mr. Jones, is the Russian Czar; the boar Napoleon stands for Joseph Stalin; and the pig Snowball represents Leon Trotsky.
Alliteration
Alliteration is a series of words or phrases that all (or almost all) start with the same sound. These sounds are typically consonants to give more stress to that syllable. You'll often come across alliteration in poetry, titles of books and poems ( Jane Austen is a fan of this device, for example—just look at Pride and Prejudice and Sense and Sensibility ), and tongue twisters.
Example: "Peter Piper picked a peck of pickled peppers." In this tongue twister, the "p" sound is repeated at the beginning of all major words.
Allusion is when an author makes an indirect reference to a figure, place, event, or idea originating from outside the text. Many allusions make reference to previous works of literature or art.
Example: "Stop acting so smart—it's not like you're Einstein or something." This is an allusion to the famous real-life theoretical physicist Albert Einstein.
Anachronism
An anachronism occurs when there is an (intentional) error in the chronology or timeline of a text. This could be a character who appears in a different time period than when he actually lived, or a technology that appears before it was invented. Anachronisms are often used for comedic effect.
Example: A Renaissance king who says, "That's dope, dude!" would be an anachronism, since this type of language is very modern and not actually from the Renaissance period.
Anaphora is when a word or phrase is repeated at the beginning of multiple sentences throughout a piece of writing. It's used to emphasize the repeated phrase and evoke strong feelings in the audience.
Example: A famous example of anaphora is Winston Churchill's "We Shall Fight on the Beaches" speech. Throughout this speech, he repeats the phrase "we shall fight" while listing numerous places where the British army will continue battling during WWII. He did this to rally both troops and the British people and to give them confidence that they would still win the war.
Anthropomorphism
An anthropomorphism occurs when something nonhuman, such as an animal, place, or inanimate object, behaves in a human-like way.
Example: Children's cartoons have many examples of anthropomorphism. For example, Mickey and Minnie Mouse can speak, wear clothes, sing, dance, drive cars, etc. Real mice can't do any of these things, but the two mouse characters behave much more like humans than mice.
Asyndeton is when the writer leaves out conjunctions (such as "and," "or," "but," and "for") in a group of words or phrases so that the meaning of the phrase or sentence is emphasized. It is often used for speeches since sentences containing asyndeton can have a powerful, memorable rhythm.
Example: Abraham Lincoln ends the Gettysburg Address with the phrase "...and that government of the people, by the people, for the people shall not perish from the Earth." By leaving out certain conjunctions, he ends the speech on a more powerful, melodic note.
Colloquialism
Colloquialism is the use of informal language and slang. It's often used by authors to lend a sense of realism to their characters and dialogue. Forms of colloquialism include words, phrases, and contractions that aren't real words (such as "gonna" and "ain't").
Example: "Hey, what's up, man?" This piece of dialogue is an example of a colloquialism, since it uses common everyday words and phrases, namely "what's up" and "man."
An epigraph is when an author inserts a famous quotation, poem, song, or other short passage or text at the beginning of a larger text (e.g., a book, chapter, etc.). An epigraph is typically written by a different writer (with credit given) and used as a way to introduce overarching themes or messages in the work. Some pieces of literature, such as Herman Melville's 1851 novel Moby-Dick , incorporate multiple epigraphs throughout.
Example: At the beginning of Ernest Hemingway's book The Sun Also Rises is an epigraph that consists of a quotation from poet Gertrude Stein, which reads, "You are all a lost generation," and a passage from the Bible.
Epistrophe is similar to anaphora, but in this case, the repeated word or phrase appears at the end of successive statements. Like anaphora, it is used to evoke an emotional response from the audience.
Example: In Lyndon B. Johnson's speech, "The American Promise," he repeats the word "problem" in a use of epistrophe: "There is no Negro problem. There is no Southern problem. There is no Northern problem. There is only an American problem."

A euphemism is when a more mild or indirect word or expression is used in place of another word or phrase that is considered harsh, blunt, vulgar, or unpleasant.
Example: "I'm so sorry, but he didn't make it." The phrase "didn't make it" is a more polite and less blunt way of saying that someone has died.
A flashback is an interruption in a narrative that depicts events that have already occurred, either before the present time or before the time at which the narration takes place. This device is often used to give the reader more background information and details about specific characters, events, plot points, and so on.
Example: Most of the novel Wuthering Heights by Emily Brontë is a flashback from the point of view of the housekeeper, Nelly Dean, as she engages in a conversation with a visitor named Lockwood. In this story, Nelly narrates Catherine Earnshaw's and Heathcliff's childhoods, the pair's budding romance, and their tragic demise.
Foreshadowing
Foreshadowing is when an author indirectly hints at—through things such as dialogue, description, or characters' actions—what's to come later on in the story. This device is often used to introduce tension to a narrative.
Example: Say you're reading a fictionalized account of Amelia Earhart. Before she embarks on her (what we know to be unfortunate) plane ride, a friend says to her, "Be safe. Wouldn't want you getting lost—or worse." This line would be an example of foreshadowing because it implies that something bad ("or worse") will happen to Earhart.
Hyperbole is an exaggerated statement that's not meant to be taken literally by the reader. It is often used for comedic effect and/or emphasis.
Example: "I'm so hungry I could eat a horse." The speaker will not literally eat an entire horse (and most likely couldn't ), but this hyperbole emphasizes how starved the speaker feels.
Imagery is when an author describes a scene, thing, or idea so that it appeals to our senses (taste, smell, sight, touch, or hearing). This device is often used to help the reader clearly visualize parts of the story by creating a strong mental picture.
Example: Here's an example of imagery taken from William Wordsworth's famous poem "I Wandered Lonely as a Cloud":
When all at once I saw a crowd, A host of golden Daffodils; Beside the Lake, beneath the trees, Fluttering and dancing in the breeze.
Irony is when a statement is used to express an opposite meaning than the one literally expressed by it. There are three types of irony in literature:
- Verbal irony: When someone says something but means the opposite (similar to sarcasm).
- Situational irony: When something happens that's the opposite of what was expected or intended to happen.
- Dramatic irony: When the audience is aware of the true intentions or outcomes, while the characters are not . As a result, certain actions and/or events take on different meanings for the audience than they do for the characters involved.
- Verbal irony: One example of this type of irony can be found in Edgar Allan Poe's "The Cask of Amontillado." In this short story, a man named Montresor plans to get revenge on another man named Fortunato. As they toast, Montresor says, "And I, Fortunato—I drink to your long life." This statement is ironic because we the readers already know by this point that Montresor plans to kill Fortunato.
- Situational irony: A girl wakes up late for school and quickly rushes to get there. As soon as she arrives, though, she realizes that it's Saturday and there is no school.
- Dramatic irony: In William Shakespeare's Romeo and Juliet , Romeo commits suicide in order to be with Juliet; however, the audience (unlike poor Romeo) knows that Juliet is not actually dead—just asleep.

Juxtaposition
Juxtaposition is the comparing and contrasting of two or more different (usually opposite) ideas, characters, objects, etc. This literary device is often used to help create a clearer picture of the characteristics of one object or idea by comparing it with those of another.
Example: One of the most famous literary examples of juxtaposition is the opening passage from Charles Dickens' novel A Tale of Two Cities :
"It was the best of times, it was the worst of times, it was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness, it was the epoch of belief, it was the epoch of incredulity, it was the season of Light, it was the season of Darkness, it was the spring of hope, it was the winter of despair …"
Malapropism
Malapropism happens when an incorrect word is used in place of a word that has a similar sound. This misuse of the word typically results in a statement that is both nonsensical and humorous; as a result, this device is commonly used in comedic writing.
Example: "I just can't wait to dance the flamingo!" Here, a character has accidentally called the flamenco (a type of dance) the flamingo (an animal).
Metaphor/Simile
Metaphors are when ideas, actions, or objects are described in non-literal terms. In short, it's when an author compares one thing to another. The two things being described usually share something in common but are unalike in all other respects.
A simile is a type of metaphor in which an object, idea, character, action, etc., is compared to another thing using the words "as" or "like."
Both metaphors and similes are often used in writing for clarity or emphasis.
"What light through yonder window breaks? It is the east, and Juliet is the sun." In this line from Romeo and Juliet , Romeo compares Juliet to the sun. However, because Romeo doesn't use the words "as" or "like," it is not a simile—just a metaphor.
"She is as vicious as a lion." Since this statement uses the word "as" to make a comparison between "she" and "a lion," it is a simile.
A metonym is when a related word or phrase is substituted for the actual thing to which it's referring. This device is usually used for poetic or rhetorical effect .
Example: "The pen is mightier than the sword." This statement, which was coined by Edward Bulwer-Lytton in 1839, contains two examples of metonymy: "the pen" refers to "the written word," and "the sword" refers to "military force/violence."
Mood is the general feeling the writer wants the audience to have. The writer can achieve this through description, setting, dialogue, and word choice .
Example: Here's a passage from J.R.R. Tolkien's The Hobbit: "It had a perfectly round door like a porthole, painted green, with a shiny yellow brass knob in the exact middle. The door opened on to a tube-shaped hall like a tunnel: a very comfortable tunnel without smoke, with panelled walls, and floors tiled and carpeted, provided with polished chairs, and lots and lots of pegs for hats and coats -- the hobbit was fond of visitors." In this passage, Tolkien uses detailed description to set create a cozy, comforting mood. From the writing, you can see that the hobbit's home is well-cared for and designed to provide comfort.
Onomatopoeia
Onomatopoeia is a word (or group of words) that represents a sound and actually resembles or imitates the sound it stands for. It is often used for dramatic, realistic, or poetic effect.
Examples: Buzz, boom, chirp, creak, sizzle, zoom, etc.
An oxymoron is a combination of two words that, together, express a contradictory meaning. This device is often used for emphasis, for humor, to create tension, or to illustrate a paradox (see next entry for more information on paradoxes).
Examples: Deafening silence, organized chaos, cruelly kind, insanely logical, etc.
A paradox is a statement that appears illogical or self-contradictory but, upon investigation, might actually be true or plausible.
Note that a paradox is different from an oxymoron: a paradox is an entire phrase or sentence, whereas an oxymoron is a combination of just two words.
Example: Here's a famous paradoxical sentence: "This statement is false." If the statement is true, then it isn't actually false (as it suggests). But if it's false, then the statement is true! Thus, this statement is a paradox because it is both true and false at the same time.
Personification
Personification is when a nonhuman figure or other abstract concept or element is described as having human-like qualities or characteristics. (Unlike anthropomorphism where non-human figures become human-like characters, with personification, the object/figure is simply described as being human-like.) Personification is used to help the reader create a clearer mental picture of the scene or object being described.
Example: "The wind moaned, beckoning me to come outside." In this example, the wind—a nonhuman element—is being described as if it is human (it "moans" and "beckons").
Repetition is when a word or phrase is written multiple times, usually for the purpose of emphasis. It is often used in poetry (for purposes of rhythm as well).
Example: When Lin-Manuel Miranda, who wrote the score for the hit musical Hamilton, gave his speech at the 2016 Tony's, he recited a poem he'd written that included the following line:
And love is love is love is love is love is love is love is love cannot be killed or swept aside.
Satire is genre of writing that criticizes something , such as a person, behavior, belief, government, or society. Satire often employs irony, humor, and hyperbole to make its point.
Example: The Onion is a satirical newspaper and digital media company. It uses satire to parody common news features such as opinion columns, editorial cartoons, and click bait headlines.
A type of monologue that's often used in dramas, a soliloquy is when a character speaks aloud to himself (and to the audience), thereby revealing his inner thoughts and feelings.
Example: In Romeo and Juliet , Juliet's speech on the balcony that begins with, "O Romeo, Romeo! Wherefore art thou Romeo?" is a soliloquy, as she is speaking aloud to herself (remember that she doesn't realize Romeo's there listening!).
Symbolism refers to the use of an object, figure, event, situation, or other idea in a written work to represent something else— typically a broader message or deeper meaning that differs from its literal meaning.
The things used for symbolism are called "symbols," and they'll often appear multiple times throughout a text, sometimes changing in meaning as the plot progresses.
Example: In F. Scott Fitzgerald's 1925 novel The Great Gatsby , the green light that sits across from Gatsby's mansion symbolizes Gatsby's hopes and dreams .
A synecdoche is a literary device in which part of something is used to represent the whole, or vice versa. It's similar to a metonym (see above); however, a metonym doesn't have to represent the whole—just something associated with the word used.
Example: "Help me out, I need some hands!" In this case, "hands" is being used to refer to people (the whole human, essentially).
While mood is what the audience is supposed to feel, tone is the writer or narrator's attitude towards a subject . A good writer will always want the audience to feel the mood they're trying to evoke, but the audience may not always agree with the narrator's tone, especially if the narrator is an unsympathetic character or has viewpoints that differ from those of the reader.
Example: In an essay disdaining Americans and some of the sites they visit as tourists, Rudyard Kipling begins with the line, "Today I am in the Yellowstone Park, and I wish I were dead." If you enjoy Yellowstone and/or national parks, you may not agree with the author's tone in this piece.

How to Identify and Analyze Literary Devices: 4 Tips
In order to fully interpret pieces of literature, you have to understand a lot about literary devices in the texts you read. Here are our top tips for identifying and analyzing different literary techniques:
Tip 1: Read Closely and Carefully
First off, you'll need to make sure that you're reading very carefully. Resist the temptation to skim or skip any sections of the text. If you do this, you might miss some literary devices being used and, as a result, will be unable to accurately interpret the text.
If there are any passages in the work that make you feel especially emotional, curious, intrigued, or just plain interested, check that area again for any literary devices at play.
It's also a good idea to reread any parts you thought were confusing or that you didn't totally understand on a first read-through. Doing this ensures that you have a solid grasp of the passage (and text as a whole) and will be able to analyze it appropriately.
Tip 2: Memorize Common Literary Terms
You won't be able to identify literary elements in texts if you don't know what they are or how they're used, so spend some time memorizing the literary elements list above. Knowing these (and how they look in writing) will allow you to more easily pinpoint these techniques in various types of written works.
Tip 3: Know the Author's Intended Audience
Knowing what kind of audience an author intended her work to have can help you figure out what types of literary devices might be at play.
For example, if you were trying to analyze a children's book, you'd want to be on the lookout for child-appropriate devices, such as repetition and alliteration.
Tip 4: Take Notes and Bookmark Key Passages and Pages
This is one of the most important tips to know, especially if you're reading and analyzing works for English class. As you read, take notes on the work in a notebook or on a computer. Write down any passages, paragraphs, conversations, descriptions, etc., that jump out at you or that contain a literary device you were able to identify.
You can also take notes directly in the book, if possible (but don't do this if you're borrowing a book from the library!). I recommend circling keywords and important phrases, as well as starring interesting or particularly effective passages and paragraphs.
Lastly, use sticky notes or post-its to bookmark pages that are interesting to you or that have some kind of notable literary device. This will help you go back to them later should you need to revisit some of what you've found for a paper you plan to write.
What's Next?
Looking for more in-depth explorations and examples of literary devices? Join us as we delve into imagery , personification , rhetorical devices , tone words and mood , and different points of view in literature, as well as some more poetry-specific terms like assonance and iambic pentameter .
Reading The Great Gatsby for class or even just for fun? Then you'll definitely want to check out our expert guides on the biggest themes in this classic book, from love and relationships to money and materialism .
Got questions about Arthur Miller's The Crucible ? Read our in-depth articles to learn about the most important themes in this play and get a complete rundown of all the characters .
For more information on your favorite works of literature, take a look at our collection of high-quality book guides and our guide to the 9 literary elements that appear in every story !

These recommendations are based solely on our knowledge and experience. If you purchase an item through one of our links, PrepScholar may receive a commission.

Hannah received her MA in Japanese Studies from the University of Michigan and holds a bachelor's degree from the University of Southern California. From 2013 to 2015, she taught English in Japan via the JET Program. She is passionate about education, writing, and travel.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”

What is Creative Writing? A Key Piece of the Writer’s Toolbox
Not all writing is the same and there’s a type of writing that has the ability to transport, teach, and inspire others like no other.
Creative writing stands out due to its unique approach and focus on imagination. Here’s how to get started and grow as you explore the broad and beautiful world of creative writing!
What is Creative Writing?
Creative writing is a form of writing that extends beyond the bounds of regular professional, journalistic, academic, or technical forms of literature. It is characterized by its emphasis on narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes or poetic techniques to express ideas in an original and imaginative way.
Creative writing can take on various forms such as:
- short stories
- screenplays
It’s a way for writers to express their thoughts, feelings, and ideas in a creative, often symbolic, way . It’s about using the power of words to transport readers into a world created by the writer.
5 Key Characteristics of Creative Writing
Creative writing is marked by several defining characteristics, each working to create a distinct form of expression:
1. Imagination and Creativity: Creative writing is all about harnessing your creativity and imagination to create an engaging and compelling piece of work. It allows writers to explore different scenarios, characters, and worlds that may not exist in reality.
2. Emotional Engagement: Creative writing often evokes strong emotions in the reader. It aims to make the reader feel something — whether it’s happiness, sorrow, excitement, or fear.
3. Originality: Creative writing values originality. It’s about presenting familiar things in new ways or exploring ideas that are less conventional.
4. Use of Literary Devices: Creative writing frequently employs literary devices such as metaphors, similes, personification, and others to enrich the text and convey meanings in a more subtle, layered manner.
5. Focus on Aesthetics: The beauty of language and the way words flow together is important in creative writing. The aim is to create a piece that’s not just interesting to read, but also beautiful to hear when read aloud.
Remember, creative writing is not just about producing a work of art. It’s also a means of self-expression and a way to share your perspective with the world. Whether you’re considering it as a hobby or contemplating a career in it, understanding the nature and characteristics of creative writing can help you hone your skills and create more engaging pieces .
For more insights into creative writing, check out our articles on creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree and is a degree in creative writing worth it .
Styles of Creative Writing
To fully understand creative writing , you must be aware of the various styles involved. Creative writing explores a multitude of genres, each with its own unique characteristics and techniques.
Poetry is a form of creative writing that uses expressive language to evoke emotions and ideas. Poets often employ rhythm, rhyme, and other poetic devices to create pieces that are deeply personal and impactful. Poems can vary greatly in length, style, and subject matter, making this a versatile and dynamic form of creative writing.
Short Stories
Short stories are another common style of creative writing. These are brief narratives that typically revolve around a single event or idea. Despite their length, short stories can provide a powerful punch, using precise language and tight narrative structures to convey a complete story in a limited space.
Novels represent a longer form of narrative creative writing. They usually involve complex plots, multiple characters, and various themes. Writing a novel requires a significant investment of time and effort; however, the result can be a rich and immersive reading experience.
Screenplays
Screenplays are written works intended for the screen, be it television, film, or online platforms. They require a specific format, incorporating dialogue and visual descriptions to guide the production process. Screenwriters must also consider the practical aspects of filmmaking, making this an intricate and specialized form of creative writing.
If you’re interested in this style, understanding creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree can provide useful insights.
Writing for the theater is another specialized form of creative writing. Plays, like screenplays, combine dialogue and action, but they also require an understanding of the unique dynamics of the theatrical stage. Playwrights must think about the live audience and the physical space of the theater when crafting their works.
Each of these styles offers unique opportunities for creativity and expression. Whether you’re drawn to the concise power of poetry, the detailed storytelling of novels, or the visual language of screenplays and plays, there’s a form of creative writing that will suit your artistic voice. The key is to explore, experiment, and find the style that resonates with you.
For those looking to spark their creativity, our article on creative writing prompts offers a wealth of ideas to get you started.
Importance of Creative Writing
Understanding what is creative writing involves recognizing its value and significance. Engaging in creative writing can provide numerous benefits – let’s take a closer look.
Developing Creativity and Imagination
Creative writing serves as a fertile ground for nurturing creativity and imagination. It encourages you to think outside the box, explore different perspectives, and create unique and original content. This leads to improved problem-solving skills and a broader worldview , both of which can be beneficial in various aspects of life.
Through creative writing, one can build entire worlds, create characters, and weave complex narratives, all of which are products of a creative mind and vivid imagination. This can be especially beneficial for those seeking creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree .
Enhancing Communication Skills
Creative writing can also play a crucial role in honing communication skills. It demands clarity, precision, and a strong command of language. This helps to improve your vocabulary, grammar, and syntax, making it easier to express thoughts and ideas effectively .
Moreover, creative writing encourages empathy as you often need to portray a variety of characters from different backgrounds and perspectives. This leads to a better understanding of people and improved interpersonal communication skills.
Exploring Emotions and Ideas
One of the most profound aspects of creative writing is its ability to provide a safe space for exploring emotions and ideas. It serves as an outlet for thoughts and feelings , allowing you to express yourself in ways that might not be possible in everyday conversation.
Writing can be therapeutic, helping you process complex emotions, navigate difficult life events, and gain insight into your own experiences and perceptions. It can also be a means of self-discovery , helping you to understand yourself and the world around you better.
So, whether you’re a seasoned writer or just starting out, the benefits of creative writing are vast and varied. For those interested in developing their creative writing skills, check out our articles on creative writing prompts and how to teach creative writing . If you’re considering a career in this field, you might find our article on is a degree in creative writing worth it helpful.
4 Steps to Start Creative Writing
Creative writing can seem daunting to beginners, but with the right approach, anyone can start their journey into this creative field. Here are some steps to help you start creative writing .
1. Finding Inspiration
The first step in creative writing is finding inspiration . Inspiration can come from anywhere and anything. Observe the world around you, listen to conversations, explore different cultures, and delve into various topics of interest.
Reading widely can also be a significant source of inspiration. Read different types of books, articles, and blogs. Discover what resonates with you and sparks your imagination.
For structured creative prompts, visit our list of creative writing prompts to get your creative juices flowing.
Editor’s Note : When something excites or interests you, stop and take note – it could be the inspiration for your next creative writing piece.
2. Planning Your Piece
Once you have an idea, the next step is to plan your piece . Start by outlining:
- the main points
Remember, this can serve as a roadmap to guide your writing process. A plan doesn’t have to be rigid. It’s a flexible guideline that can be adjusted as you delve deeper into your writing. The primary purpose is to provide direction and prevent writer’s block.
3. Writing Your First Draft
After planning your piece, you can start writing your first draft . This is where you give life to your ideas and breathe life into your characters.
Don’t worry about making it perfect in the first go. The first draft is about getting your ideas down on paper . You can always refine and polish your work later. And if you don’t have a great place to write that first draft, consider a journal for writing .
4. Editing and Revising Your Work
The final step in the creative writing process is editing and revising your work . This is where you fine-tune your piece, correct grammatical errors, and improve sentence structure and flow.
Editing is also an opportunity to enhance your storytelling . You can add more descriptive details, develop your characters further, and make sure your plot is engaging and coherent.
Remember, writing is a craft that improves with practice . Don’t be discouraged if your first few pieces don’t meet your expectations. Keep writing, keep learning, and most importantly, enjoy the creative process.
For more insights on creative writing, check out our articles on how to teach creative writing or creative writing activities for kids.
Tips to Improve Creative Writing Skills
Understanding what is creative writing is the first step. But how can one improve their creative writing skills? Here are some tips that can help.
Read Widely
Reading is a vital part of becoming a better writer. By immersing oneself in a variety of genres, styles, and authors, one can gain a richer understanding of language and storytelling techniques . Different authors have unique voices and methods of telling stories, which can serve as inspiration for your own work. So, read widely and frequently!
Practice Regularly
Like any skill, creative writing improves with practice. Consistently writing — whether it be daily, weekly, or monthly — helps develop your writing style and voice . Using creative writing prompts can be a fun way to stimulate your imagination and get the words flowing.
Attend Writing Workshops and Courses
Formal education such as workshops and courses can offer structured learning and expert guidance. These can provide invaluable insights into the world of creative writing, from understanding plot development to character creation. If you’re wondering is a degree in creative writing worth it, these classes can also give you a taste of what studying creative writing at a higher level might look like .
Joining Writing Groups and Communities
Being part of a writing community can provide motivation, constructive feedback, and a sense of camaraderie. These groups often hold regular meetings where members share their work and give each other feedback. Plus, it’s a great way to connect with others who share your passion for writing.
Seeking Feedback on Your Work
Feedback is a crucial part of improving as a writer. It offers a fresh perspective on your work, highlighting areas of strength and opportunities for improvement. Whether it’s from a writing group, a mentor, or even friends and family, constructive criticism can help refine your writing .
Start Creative Writing Today!
Remember, becoming a proficient writer takes time and patience. So, don’t be discouraged by initial challenges. Keep writing, keep learning, and most importantly, keep enjoying the process. Who knows, your passion for creative writing might even lead to creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree .
Happy writing!
Brooks Manley

Creative Primer is a resource on all things journaling, creativity, and productivity. We’ll help you produce better ideas, get more done, and live a more effective life.
My name is Brooks. I do a ton of journaling, like to think I’m a creative (jury’s out), and spend a lot of time thinking about productivity. I hope these resources and product recommendations serve you well. Reach out if you ever want to chat or let me know about a journal I need to check out!
Here’s my favorite journal for 2024:

Gratitude Journal Prompts Mindfulness Journal Prompts Journal Prompts for Anxiety Reflective Journal Prompts Healing Journal Prompts Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Journal Prompts Mental Health Journal Prompts ASMR Journal Prompts Manifestation Journal Prompts Self-Care Journal Prompts Morning Journal Prompts Evening Journal Prompts Self-Improvement Journal Prompts Creative Writing Journal Prompts Dream Journal Prompts Relationship Journal Prompts "What If" Journal Prompts New Year Journal Prompts Shadow Work Journal Prompts Journal Prompts for Overcoming Fear Journal Prompts for Dealing with Loss Journal Prompts for Discerning and Decision Making Travel Journal Prompts Fun Journal Prompts
Inspiring Ink: Expert Tips on How to Teach Creative Writing
You may also like, 250+ journal prompts for every scenario and circumstance.
Is Napping Good for Your Productivity?
Why taylor swift is an avid journaler, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Productivity
- Favorite Journals

A Guide to English: Creative Writing
- An Introduction to Rhetoric
- Critical Thinking, Reading, and Writing
- The Writing Process
- Formatting and Citations
- The Reference Collection
- Searching for Books
- Searching for Articles
- Bibliographic Trace
- Citation Management
- Scholarly Associations
- The English Language
- Literary Form
- Peoples and Identities
- Periods and Movements in American Literature
- Periods and Movements in Commonwealth Literatures
- Thematic Genres and "Genre Fiction"
- Award Winners (indexed)
- Criticism & Theory
Creative Writing
- Multimodal Composition
- Text Analysis / Distant Reading
- Digital Stewardship
- Data Visualization
- GIS and Geospatial Data
- Statistical Analysis
- Programming
- Digital Scholarly Editing

photo courtesy of Nic McPhee.
With your poetic license in your back pocket you can bypass research, right? Not really. Sometimes you need to check your facts for your fiction to work. Encountering something that is factually wrong can break the spell you've cast on your reader and throw them right out of the story. Besides, research can enrich your world-building and inspire you as you put your imagination to work.
Whether you are writing a literary novel, a poem, an essay, a book for young readers, or a multi-volume epic fantasy, your imaginary world sometimes needs an infusion of reality. What does this lonely stretch of highway in Arizona actually look like? Where could I find inspiration to jump-start this poem? What kind of treatment would my protagonist with PTSD get at a VA hospital? What kind of underwear did people wear back in the 1920s, because it needs to come off in this erotic scene.
Try browsing photos using Google Images or Flickr , delving into historical publications using Google Books , or viewing locations with Google Earth . People can be a great resource, too. Be prepared to make some phone calls, set up visits, or conduct interviews. Check with a librarian if you have factual or context questions you are having trouble answering.
These resources will help you think about ways your writing can find support - both as you create something new and as you navigate the writing business.
On this Page
Getting published, honing your craft, fiction writing, writers on writing, writing genre fiction, nonfiction writing.
Librarian's Note: These resources can help you find appropriate venues to submit your creative writing for publication. While it is true that there are more outlets than ever to get one's work published, and self-publishing (sometimes denigrated as the " vanity press ") has yielded occasional success stories, it is wise to research publications and publishers before submitting, and observe Yog's law whenever possible.
Online Resources

Print Resources
Writing Poetry
- << Previous: Criticism & Theory
- Next: Digital Humanities >>
- Last Updated: Apr 2, 2024 10:54 AM
- URL: https://libguides.gustavus.edu/english

Main navigation
Write & improve.

Improve your English writing online
Want to improve your writing skills? Our free online tool helps you to practise your writing and get valuable feedback instantly. Write & Improve is simple to use: just choose a task, write or upload a written response and use the feedback to quickly improve.
It shows you how to improve your spelling, grammar and vocabulary. Join over 2 million learners of English who have used Write & Improve to improve their writing.
Start practising now
Improve your writing now – it's free!
- There is no limit on how many times you can use the tool – keep practising as much as you need to and build your confidence.
- Encourages you to think about what to improve.
- Keep improving and see your progress.
When I was preparing for my B2 First exam I practised really hard and I succeeded, so I'm in love with this tool that I still use almost every day. Aaron from Ecuador

With Write & Improve my grades get better and I am inspired to do more. It is really graphical and easy to use, highlighting your mistakes in a very visual way. Victoria from Uruguay

Write & Improve helps when practising writing particular types of documents. I've been able to see my progress and how my learning has changed. Jorge from Switzerland

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
6. Show don't tell. To let readers experience your story, show don't tell. Showing means using sensory details and describing actions to direct a mental movie in your reader's mind. Get inspired by these examples of "show, don't tell" …. Show don't tell examples >>. 7. Repetition in writing.
Creative writing is an art form that transcends traditional literature boundaries. It includes professional, journalistic, academic, and technical writing. This type of writing emphasizes narrative craft, character development, and literary tropes. It also explores poetry and poetics traditions.
7. Epistrophe. Epistrophe is the opposite of anaphora, with this time a word or phrase being repeated at the end of a sentence. Though its placement in a sentence is different it serves the same purpose—creating emphasis—as an anaphora does. Example: "I'll be ever'where - wherever you look.Wherever they's a fight so hungry people can eat, I'll be there.
5. Read, read, read. It's a lot harder to get the hang of creative writing if you don't have any references from which to draw. Notable writers throughout history have penned excellent examples of well-written creative work that should be required reading for any budding creative writer.
Types of Creative Writing. Examples of creative writing can be found pretty much everywhere. Some forms that you're probably familiar with and already enjoy include: • Fiction (of every genre, from sci-fi to historical dramas to romances) • Film and television scripts. • Songs. • Poetry.
This free and open access textbook introduces new writers to some basic elements of the craft of creative writing in the genres of fiction, poetry, and creative nonfiction. The authors—Rachel Morgan, Jeremy Schraffenberger, and Grant Tracey—are editors of the North American Review, the oldest and one of the most well-regarded literary magazines in the United States.
1. Think about your reader. Chances are your teacher or examiner will have a lot to read - so keep them interested. With creative writing, as with any kind of writing, your reader is your most important consideration. You need to know and understand whom you're writing for if you're to do a good job of keeping them interested.
Word or phrase omission. Example: I speak lots of languages, but you only speak two (languages). 13. Euphemism. Replacing offensive or combinations of words with lighter equivalents. Example: Visually challenged (blind); meet one's maker (die) Opposite: Dysphemism. Replacing a neutral word with a harsher word. 14.
Creative writing is writing that uses imagination, creativity, and mastery of the art of writing to evoke emotion in a reader. It could be a fictional story, a nonfiction piece, or movie script, a play, a poem, et cetera. Creative writing oftentimes springs up from experimentation and good, imaginative use of knowledge and ideas.
Writing skills - creative and narrative writing. Part of English Writing skills. Imaginative or creative writing absorbs readers in an entertaining way. To succeed with this kind of writing you ...
Tip 1: Read Closely and Carefully. First off, you'll need to make sure that you're reading very carefully. Resist the temptation to skim or skip any sections of the text. If you do this, you might miss some literary devices being used and, as a result, will be unable to accurately interpret the text.
5 Key Characteristics of Creative Writing. Creative writing is marked by several defining characteristics, each working to create a distinct form of expression: 1. Imagination and Creativity:Creative writing is all about harnessing your creativity and imagination to create an engaging and compelling piece of work.
A creative writer strives to tell unique stories in a distinctive voice. Yet with all the fiction writing already out there in the world, it can be hard to feel that your work is legitimately creative compared to the competition. You could be a first-time writer completing in a high school creative writing course, a hobbyist working on your ...
The individual elements of different narrative techniques can be broken down into six distinct categories: Character. Perspective. Plot. Setting. Style. Theme. Each of these plays an important role in developing a story — taking the writer's message and presenting it to their audience in a deliberate way.
ISBN: 9780205750344. Publication Date: 2010-01-03. "'Writing Fiction' explores the elements of fiction, providing practical writing techniques & examples. Written in a tone that is personal & non-prescriptive, this book encourages students to develop proficiency through each step of the writing process.
8 Creative Writing Exercises to Strengthen Your Writing. Learning to write fiction is like training for a marathon. Before you get ready for the main event, it's good to warm up and stretch your creative muscles. Whether you're a published author of a bestselling book or a novice author writing a novel for the first time, creative exercises ...
Our free online tool helps you to practise your writing and get valuable feedback instantly. Write & Improve is simple to use: just choose a task, write or upload a written response and use the feedback to quickly improve. It shows you how to improve your spelling, grammar and vocabulary. Join over 2 million learners of English who have used ...
The writing opens with a simile close simile A comparison using 'like' or 'as' to create a vivid image, eg as big as a whale; float like a butterfly, sting like a bee. to show the texture of the ...
How to Write Better: 6 Techniques to Improve Your Writing. Written by MasterClass. Last updated: Sep 10, 2021 • 7 min read. As a writer, it's easy to get stuck in your own ways. However, adopting new techniques in your writing can help you develop your creative style.
Mission. The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives.
See why leading organizations rely on MasterClass for learning & development. Literary devices are specific techniques that allow a writer to convey a deeper meaning that goes beyond what's on the page. Literary devices work alongside plot and characters to elevate a story and prompt reflection on life, society, and what it means to be human.