Eight problems with literature reviews and how to fix them
Affiliations.
- 1 Mercator Research Institute on Climate Change and Global Commons, Berlin, Germany. [email protected].
- 2 Stockholm Environment Institute, Stockholm, Sweden. [email protected].
- 3 Africa Centre for Evidence, University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, South Africa. [email protected].
- 4 College of Medicine and Health, Exeter University, Exeter, UK.
- 5 Department of Zoology, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK.
- 6 School of Biological Sciences, University of East Anglia, Norwich, UK.
- 7 Department of Biological Sciences, Royal Holloway University of London, Egham, UK.
- 8 Stockholm Environment Institute, Stockholm, Sweden.
- 9 Department of Zoology, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK.
- 10 Collaboration for Environmental Evidence, UK Centre, School of Natural Sciences, Bangor University, Bangor, UK.
- 11 Liljus ltd, London, UK.
- 12 Department of Forest Sciences, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland.
- 13 Evidence Synthesis Lab, School of Natural and Environmental Sciences, University of Newcastle, Newcastle-upon-Tyne, UK.
- PMID: 33046871
- DOI: 10.1038/s41559-020-01295-x
Traditional approaches to reviewing literature may be susceptible to bias and result in incorrect decisions. This is of particular concern when reviews address policy- and practice-relevant questions. Systematic reviews have been introduced as a more rigorous approach to synthesizing evidence across studies; they rely on a suite of evidence-based methods aimed at maximizing rigour and minimizing susceptibility to bias. Despite the increasing popularity of systematic reviews in the environmental field, evidence synthesis methods continue to be poorly applied in practice, resulting in the publication of syntheses that are highly susceptible to bias. Recognizing the constraints that researchers can sometimes feel when attempting to plan, conduct and publish rigorous and comprehensive evidence syntheses, we aim here to identify major pitfalls in the conduct and reporting of systematic reviews, making use of recent examples from across the field. Adopting a 'critical friend' role in supporting would-be systematic reviews and avoiding individual responses to police use of the 'systematic review' label, we go on to identify methodological solutions to mitigate these pitfalls. We then highlight existing support available to avoid these issues and call on the entire community, including systematic review specialists, to work towards better evidence syntheses for better evidence and better decisions.
- Environment
- Research Design
- Systematic Reviews as Topic*

- About the LSE Impact Blog
- Comments Policy
- Popular Posts
- Recent Posts
- Subscribe to the Impact Blog
- Write for us
- LSE comment

Neal Haddaway
October 19th, 2020, 8 common problems with literature reviews and how to fix them.
3 comments | 315 shares
Estimated reading time: 5 minutes
Literature reviews are an integral part of the process and communication of scientific research. Whilst systematic reviews have become regarded as the highest standard of evidence synthesis, many literature reviews fall short of these standards and may end up presenting biased or incorrect conclusions. In this post, Neal Haddaway highlights 8 common problems with literature review methods, provides examples for each and provides practical solutions for ways to mitigate them.
Enjoying this blogpost? 📨 Sign up to our mailing list and receive all the latest LSE Impact Blog news direct to your inbox.
Researchers regularly review the literature – it’s an integral part of day-to-day research: finding relevant research, reading and digesting the main findings, summarising across papers, and making conclusions about the evidence base as a whole. However, there is a fundamental difference between brief, narrative approaches to summarising a selection of studies and attempting to reliably and comprehensively summarise an evidence base to support decision-making in policy and practice.
So-called ‘evidence-informed decision-making’ (EIDM) relies on rigorous systematic approaches to synthesising the evidence. Systematic review has become the highest standard of evidence synthesis and is well established in the pipeline from research to practice in the field of health . Systematic reviews must include a suite of specifically designed methods for the conduct and reporting of all synthesis activities (planning, searching, screening, appraising, extracting data, qualitative/quantitative/mixed methods synthesis, writing; e.g. see the Cochrane Handbook ). The method has been widely adapted into other fields, including environment (the Collaboration for Environmental Evidence ) and social policy (the Campbell Collaboration ).

Despite the growing interest in systematic reviews, traditional approaches to reviewing the literature continue to persist in contemporary publications across disciplines. These reviews, some of which are incorrectly referred to as ‘systematic’ reviews, may be susceptible to bias and as a result, may end up providing incorrect conclusions. This is of particular concern when reviews address key policy- and practice- relevant questions, such as the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic or climate change.
These limitations with traditional literature review approaches could be improved relatively easily with a few key procedures; some of them not prohibitively costly in terms of skill, time or resources.
In our recent paper in Nature Ecology and Evolution , we highlight 8 common problems with traditional literature review methods, provide examples for each from the field of environmental management and ecology, and provide practical solutions for ways to mitigate them.
There is a lack of awareness and appreciation of the methods needed to ensure systematic reviews are as free from bias and as reliable as possible: demonstrated by recent, flawed, high-profile reviews. We call on review authors to conduct more rigorous reviews, on editors and peer-reviewers to gate-keep more strictly, and the community of methodologists to better support the broader research community. Only by working together can we build and maintain a strong system of rigorous, evidence-informed decision-making in conservation and environmental management.
Note: This article gives the views of the authors, and not the position of the LSE Impact Blog, nor of the London School of Economics. Please review our comments policy if you have any concerns on posting a comment below
Image credit: Jaeyoung Geoffrey Kang via unsplash

About the author

Neal Haddaway is a Senior Research Fellow at the Stockholm Environment Institute, a Humboldt Research Fellow at the Mercator Research Institute on Global Commons and Climate Change, and a Research Associate at the Africa Centre for Evidence. He researches evidence synthesis methodology and conducts systematic reviews and maps in the field of sustainability and environmental science. His main research interests focus on improving the transparency, efficiency and reliability of evidence synthesis as a methodology and supporting evidence synthesis in resource constrained contexts. He co-founded and coordinates the Evidence Synthesis Hackathon (www.eshackathon.org) and is the leader of the Collaboration for Environmental Evidence centre at SEI. @nealhaddaway
Why is mission creep a problem and not a legitimate response to an unexpected finding in the literature? Surely the crucial points are that the review’s scope is stated clearly and implemented rigorously, not when the scope was finalised.
- Pingback: Quick, but not dirty – Can rapid evidence reviews reliably inform policy? | Impact of Social Sciences
#9. Most of them are terribly boring. Which is why I teach students how to make them engaging…and useful.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Related Posts

“But I’m not ready!” Common barriers to writing and how to overcome them
November 16th, 2020.

“Remember a condition of academic writing is that we expose ourselves to critique” – 15 steps to revising journal articles
January 18th, 2017.

A simple guide to ethical co-authorship
March 29th, 2021.

How common is academic plagiarism?
February 8th, 2024.

Visit our sister blog LSE Review of Books
- Open access
- Published: 04 September 2016
Improving the peer review of narrative literature reviews
- Jennifer A. Byrne 1 , 2
Research Integrity and Peer Review volume 1 , Article number: 12 ( 2016 ) Cite this article
24k Accesses
70 Citations
29 Altmetric
Metrics details
As the size of the published scientific literature has increased exponentially over the past 30 years, review articles play an increasingly important role in helping researchers to make sense of original research results. Literature reviews can be broadly classified as either “systematic” or “narrative”. Narrative reviews may be broader in scope than systematic reviews, but have been criticised for lacking synthesis and rigour. The submission of more scientific manuscripts requires more researchers acting as peer reviewers, which requires adding greater numbers of new reviewers to the reviewing population over time. However, whereas there are many easily accessible guides for reviewers of primary research manuscripts, there are few similar resources to assist reviewers of narrative reviews. Here, I summarise why literature reviews are valued by their diverse readership and how peer reviewers with different levels of content expertise can improve the reliability and accessibility of narrative review articles. I then provide a number of recommendations for peer reviewers of narrative literature reviews, to improve the integrity of the scientific literature, while also ensuring that narrative review articles meet the needs of both expert and non-expert readers.
Peer Review reports
Over the past 30 years, the size of the published scientific literature has expanded exponentially [ 1 ]. While it has been argued that this rate of expansion is unsustainable [ 2 ], underlying factors such as greater numbers of scientists and scientific journals [ 3 ] are unlikely to change in the short term. The submission of more manuscripts for publication requires more peer reviewers, yet the current demand for capable, available manuscript reviewers is not being met [ 3 ]. This has serious adverse consequences for the validity of published research and overall trust in science [ 3 ].
Review articles help both experts and non-experts to make sense of the increasing volume of original publications [ 4 , 5 ]. Busy clinicians have a particular reliance upon review articles, because of their constant need for reliable, up-to-date information, yet limited available time [ 6 ]. Literature reviews can also help other content experts such as researchers and policymakers to identify gaps in their own reading and knowledge. However, literature reviews are also sought by readers with little or no prior understanding of the reviewed topic, such as researchers seeking to rapidly triage results from high-throughput analyses and students for whom literature reviews can represent entry points into a new field. For the benefit of both expert and non-expert readers, it is essential that review articles accurately synthesise the relevant literature in a comprehensive, transparent and objective manner [ 7 , 8 ].
Numbers of review articles are increasing in fields where this has been measured [ 4 ], as is the diversity of review types published [ 9 , 10 ]. Although there are now many review sub-types that can be distinguished based upon the literature search, appraisal, synthesis and analysis methods used [ 9 , 10 ], review articles can be broadly classified as either “systematic” or “narrative” [ 5 , 11 ]. Systematic reviews take defined approaches to the identification and synthesis of study findings and include other review sub-types such as evidence maps [ 12 ]. The systematic review is considered to be the gold standard of evidence synthesis, but also carries the potential disadvantages of narrow scope [ 11 ], and requiring more time and resources to prepare and update [ 7 ]. Narrative reviews, also referred to as “traditional reviews” [ 5 ] and “literature reviews” [ 9 ], constitute the majority of review articles published in some fields [ 7 ]. Other review sub-types, such as rapid and scoping reviews also present information in a narrative format [ 9 ]. Narrative reviews have been criticised for rarely employing peer-reviewed methodologies, or duplicate curation of evidence [ 5 ], and for often failing to disclose study inclusion criteria [ 11 ]. Despite these limitations, narrative reviews remain frequent within the literature, as they offer breadth of literature coverage and flexibility to deal with evolving knowledge and concepts [ 11 ]. In this article, I will provide advice regarding the peer review of narrative reviews, and the advice presented aims to be broadly applicable. I will not attempt to provide advice regarding the peer review of systematic reviews [ 13 , 14 ].
Given the broad readership of literature reviews, content and methodology experts as well as reviewers with less directly relevant expertise can play important roles in the peer-review process [ 15 ]. Peer reviewers with related content expertise are best placed to assess the reliability of the information presented, while other reviewers can ensure that this information remains accessible to readers with different levels of prior knowledge. However, whereas there are easily accessible guides for reviewers of primary research manuscripts [ 16 , 17 ], there are few similar resources available for reviewers of literature reviews [ 15 , 18 ]. This article therefore proposes a number of recommendations for peer reviewers (Table 1 ) to ensure that narrative literature review articles make the best possible contributions to their fields, while also meeting their readers’ often diverse needs.
Ask whether the literature review justifies its place in the literature
Lower than expected ratios between numbers of original publications and review articles suggest excessive numbers of reviews in some fields, which may contribute to the very problem that review articles aim to solve [ 4 ]. With rapidly rising publication rates in many fields [ 2 ], even content-expert peer reviewers should check publication databases for similar and/or overlapping review articles as part of the peer-review process. Pre-empting such scrutiny, authors should clearly define the review’s scope and what it intends to achieve [ 8 ]. If there have been other recent reviews of the same or similar topics, the authors should explain how their manuscript is unique. This could be through combining literature from related fields, by updating existing reviews in light of new research evidence [ 8 ], or because published reviews may have been subject to bias. A clear definition of a review’s scope is a recognised tool to reduce evidence selection bias [ 19 ]. Review authors can also define their subject by referring to literature reviews of related topics that will not be explored in depth. These definitions and statements should form part of an overall narrative structure that helps readers to anticipate and understand the information presented [ 20 ].
Ask whether the literature searches conducted were clearly defined
A criticism frequently levelled at traditional or narrative reviews is that they do not always state or follow rules regarding literature searches [ 5 , 7 , 11 ]. Providing evidence that comprehensive literature searches have been conducted, preferably according to pre-defined eligibility criteria [ 19 ], increases confidence that the review’s findings and conclusions are reliable, and have not been subject to selection bias. Ideally, any literature search choices made by the authors should be clearly stated, transparent and reproducible [ 11 ].
Check for citation breadth and balance
Consider whether the authors have cited a comprehensive range of literature or whether they have tended to cite papers that support their own point of view. If there are important papers that have not been cited, suggest to the authors that these be added, and explain why. If only a limited number of articles can be cited due to the journal’s requirements, check that these studies are representative of those available.
Where possible, verify that information has been summarised correctly
Many different types of citation errors can be identified in the research literature [ 21 , 22 ], and these may occur regardless of the journal impact factor [ 22 ]. The increasing size and complexity of primary reports [ 3 ] also render data extraction and summary more challenging. Realistically, it is unlikely that individual peer reviewers will have detailed knowledge of any full review topic [ 19 ]. Nonetheless, if you are a content expert, take time to cross-reference at least some individual statements to citations, for the particular benefit of non-expert readers. If your level of expertise means that you are unable to verify the accuracy of particular sections of the review, you should indicate this to your editor. Peer reviewers can also ask about data extraction methods, if these were not described in the manuscript. Adopting systematic review practices, such as duplicate independent data extraction, or independent data extraction and validation, can reduce content errors and increase reliability [ 19 ].
Check that original references have been cited
Authors sometimes incorrectly cite original studies, both in original manuscripts and reviews [ 23 , 24 ]. While checking the content, ask whether descriptions of original findings were referenced accordingly, as opposed to being incorrectly attributed to reviews [ 23 ].
Consider how studies were critically evaluated
Beyond correct data summary, narrative literature reviews should include critical data appraisal and some level of data synthesis. How this should be done varies according to the review scope and methodology [ 9 , 10 , 19 ]. While some narrative reviews reasonably focus on breadth as opposed to depth of literature coverage [ 10 ], limited or poor data appraisal risks placing undue emphasis on poor quality research [ 9 ]. Evaluating at least some aspects of the methods used by individual studies can improve reliability [ 7 ]. Similarly, ask how the authors have interpreted conflicting findings or studies with apparently outlying results [ 9 , 11 ].
Evaluate whether tables/figures/diagrams support the text
While not all literature reviews need to include figures or tables, these can help to summarise findings and make key messages clearer. Some detailed information may be best presented in tables, with a shorter summary within the text. Tables can improve the availability of quantitative data for cross-checking, better demonstrate the results of qualitative or quantitative data synthesis, and reassure both peer reviewers and readers that comprehensive, objective analyses have been performed. If figures or tables are included, these need to be original; otherwise, the authors need to have obtained permission to reproduce these from an original source.
Consider whether the review will help someone entering the field
Literature reviews are not always read by subject experts, and it is important that the peer-review process considers this. Reviewers who are not direct content experts may valuably request clarification of nomenclature and/or historical issues that may have seemed too obvious for the authors to have explained. Summary diagrams suggested by peer reviewers may help make a literature review more accessible to a broader audience.
Ask whether the review expands the body of knowledge
Ultimately, the goal of a literature review should be to further the body of knowledge [ 18 ]. Extending or developing ideas is clearly a difficult task, and is often the weakest section of a review [ 25 ]. Consider therefore whether the authors have derived and clearly presented new ideas and/or new research directions from any identified knowledge gaps. Having read the manuscript with fresh eyes, peer reviewers may have valuable ideas to contribute.
Do not forget the rules for reviewing manuscripts in general
The review of literature reviews has some particular considerations, but all the usual manuscript review rules also apply, such as managing conflicts of interest and allocating appropriate time [ 16 , 17 ]. Try to separate the assessment of language and grammar from the more important assessment of scientific quality and remain aware that expert reviewers risk bringing their own biases to the peer-review process [ 15 ].
Conclusions
More quality peer reviewers are needed within the scientific community [ 3 ], including those with the capacity and confidence to review narrative literature reviews. Although it has been difficult to identify predictors of peer-reviewer performance and effective training methods, younger reviewer age has been reproducibly associated with better quality manuscript reviews [ 26 , 27 ]. This association suggests that peer reviewers should be recruited relatively early in their careers, and encouraged to participate widely in manuscript review. Associations between younger peer-reviewer age and better manuscript reviews may also highlight the need for regular training, to ensure that the peer-review community remains up-to-date regarding new approaches to editing or reviewing manuscripts. Indeed, a recent industry survey reported that over three quarters of researchers were interested in further reviewer training [ 28 ]. I therefore hope that this article will add to existing resources [ 29 ] to encourage less experienced peer reviewers to extend their efforts towards narrative literature reviews.
Bornmann L, Mutz R. Growth rates of modern science: a bibliometric analysis based on the number of publications and cited references. J Assoc Inform Sci Tech. 2015;66(11):2215–22.
Google Scholar
Pautasso M. Publication growth in biological sub-fields: patterns, predictability and sustainability. Sustainability. 2012;4(12):3234–47.
Article Google Scholar
Siebert S, Machesky LM, Insall RH. Overflow in science and its implications for trust. Elife. 2015;4: doi: 10.7554/eLife.10825 .
Ketcham CM, Crawford JM. The impact of review articles. Lab Invest. 2007;87(12):1174–85.
Dijkers MP. Task Force on Systematic Reviews and Guidelines. The value of traditional reviews in the era of systematic reviewing. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2009;88(5):423–30.
McAlister FA, Clark HD, van Walraven C, Straus SE, Lawson FM, Moher D, et al. The medical review article revisited: has the science improved? Ann Intern Med. 1999;131(12):947–51.
Haddaway NR, Woodcock P, Macura B, Collins A. Making literature reviews more reliable through application of lessons from systematic reviews. Conserv Biol. 2015;29(6):1596–605.
Pautasso M. Ten simple rules for writing a literature review. PLoS Comput Biol. 2013;9(7):e1003149.
Grant MJ, Booth A. A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Inform Lib J. 2009;26(2):91–108.
Paré G, Trudel M-C, Jaana M, Kitsiou S. Synthesizing information systems knowledge: a typology of literature reviews. Inform Management. 2015;52(2):183–99.
Collins JA, Fauser BCJM. Balancing the strengths of systematic and narrative reviews. Hum Reprod Update. 2005;11(2):103–4.
Miake-Lye IM, Hempel S, Shanman R, Shekelle PG. What is an evidence map? A systematic review of published evidence maps and their definitions, methods, and products. Syst Rev. 2016;5:28.
Higgins JPT, Green S. Handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. The Cochrane Collaboration, John Wiley & Sons Ltd; 2011.
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ. 2009;339:b2700.
Oxman AJ. Checklists for review articles. BMJ. 1994;309(6955):648–51.
Bourne PE, Korngreen A. Ten simple rules for reviewers. PLoS Comput Biol. 2006;2(9):e110.
Nicholas KA, Gordon W. A quick guide to writing a solid peer review. Eos. 2011;92(28):233–4.
Jennex ME. Literature reviews and the review process: an editor-in-chief’s perspective. CAIS. 2015;36:8.
O’Connor A, Sargeant J. Research synthesis in veterinary science: narrative reviews, systematic reviews and meta-analysis. Vet J. 2015;206(3):261–7.
Docherty M, Smith R. The case for structuring the discussion of scientific papers. BMJ. 1999;318(7193):1224–5.
Davids JR, Weigl DM, Edmonds JP, Blackhurst DW. Reference accuracy in peer-reviewed pediatric orthopaedic literature. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(5):1155–61.
Awrey J, Inaba K, Barmparas G, Recinos G, Teixeira PG, Chan LS, et al. Reference accuracy in the general surgery literature. World J Surg. 2011;35(3):475–9.
Gavras H. Inappropriate attribution: the “lazy author syndrome”. Am J Hypertens. 2002;15(9):831.
Katz TJ. Propagation of errors in review articles. Science. 2006;313(5791):1236.
Webster J, Watson RT. Analyzing the past to prepare for the future: writing a literature review. MIS Q. 2002;26:2.
Black N, van Rooyen S, Godlee F, Smith R, Evans S. What makes a good reviewer and a good review for a general medical journal? JAMA. 1998;280(3):231–3.
Callaham ML, Tercier J. The relationship of previous training and experience of journal peer reviewers to subsequent review quality. PLoS Med. 2007;4(1):e40.
Warne V. Rewarding reviewers- sense or sensibility? A Wiley study explained. Learned Pub. 2016;29(1):41–50.
COPE Ethical Guidelines for Peer Reviewers. Available: http://publicationethics.org/resources/guidelines-new/cope-ethical-guidelines-peer-reviewers . Accessed 10 Aug, 2016.
Download references
Acknowledgements
I thank Dr Mona Shehata (Princess Margaret Cancer Centre, Toronto, Canada) for discussions, Ms Sarah Frost for critical reading, reviewers of this manuscript for many constructive comments, and reviewers of past publications for feedback which also contributed towards the development of this manuscript.
Not applicable.
Availability of data and materials
Authors’ contributions.
JAB drafted, wrote and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The author declares that she has no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Ethics approval and consent to participate, author information, authors and affiliations.
Molecular Oncology Laboratory, Children’s Cancer Research Unit, Kids Research Institute, The Children’s Hospital at Westmead, Locked Bag 4001, Westmead, 2145, NSW, Australia
Jennifer A. Byrne
The University of Sydney Discipline of Child and Adolescent Health, The Children’s Hospital at Westmead, Locked Bag 4001, Westmead, 2145, NSW, Australia
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jennifer A. Byrne .
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Byrne, J.A. Improving the peer review of narrative literature reviews. Res Integr Peer Rev 1 , 12 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41073-016-0019-2
Download citation
Received : 17 June 2016
Accepted : 05 August 2016
Published : 04 September 2016
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s41073-016-0019-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Peer review
- Narrative literature review
Research Integrity and Peer Review
ISSN: 2058-8615
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Search Menu
- Sign in through your institution
- Advance articles
- Grand Theme Reviews
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Reasons to Publish
- Open Access
- About Human Reproduction Update
- About the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology
- Editorial Board
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Dispatch Dates
- Terms and Conditions
- Contact ESHRE
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic
Article Contents
Balancing the strengths of systematic and narrative reviews.
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
John A. Collins, Bart C.J.M. Fauser, Balancing the strengths of systematic and narrative reviews, Human Reproduction Update , Volume 11, Issue 2, March/April 2005, Pages 103–104, https://doi.org/10.1093/humupd/dmh058
- Permissions Icon Permissions
The mandate of Human Reproduction Update involves several roles: (i) to provide a synthesis of evidence that can aid scientists and clinicians in their daily work; (ii) to help reproductive specialists understand concepts from related disciplines; and (iii) to summarize current knowledge generated by basic science as the foundation of future scientific and clinical advancement. Given that review and synthesis are central to good scientific and clinical practice, and that a grasp of the current state of knowledge is a prerequisite to designing new studies, it is pertinent to ask which reviews are most likely to fulfil the needs of readers. A related question concerns whether systematic reviews meet the needs of all review topics and all readers.
Summarizing evidence or knowledge is a difficult problem in reproductive medicine, as in other branches of science and medical care ( Eddy et al. , 1992 ). For each question there may be multiple studies that use different designs and inclusion criteria. For clinical questions, the interventions, outcomes and measures of effect may vary: the effect measures in treatment studies include odds ratios, relative risks and absolute differences. For scientific questions, the experimental species, models and designs may differ. Moreover, it is always uncertain whether all of the relevant evidence has been evaluated. Even when the search has been exhaustive, there are no simple guides on how to interpret conflicting results and whether to accept apparently outlying studies. The choices that the reviewer makes to address the variable conditions and uncertainties may be conservative, strict and exclusive, or liberal, open and inclusive. The decisions made by the reviewer may not be consistent throughout and these choices may or may not satisfy the reader who seeks out the review to address a clinical or research question. Faced with uncertainty and doubt, readers nonetheless must form an impression of the evidence and synthesize the state of knowledge in order to address the clinical or research question that stimulated their interest in the review. We argue that the reader is better served when the choices made in the review, regardless of whether they are strict or open, should be explicit, transparent, clearly stated and reproducible by interested readers.
This list of objectives for reviews is more easily satisfied by systematic reviews, which use explicit methods to methodically search, critically appraise and synthesize the available literature on a specific issue. The question or issue need not be clinical: indeed, the concept evolved primarily in psychology studies ( Light and Pillemer, 1984 ). The systematic review attempts to reduce reviewer bias through the use of objective, reproducible criteria to select relevant individual publications and assess their validity. A systematic review may include a meta-analysis or statistical summary of the individual study results: the aggregate of effects from several studies yields an average treatment effect that is more precise than the individual study results ( Schlesselman and Collins, 2003 ). Thus, the systematic review involves explicit, transparent methods which are clearly stated, and reproducible by others. Whether a systematic review of randomized controlled trials adheres to the guidelines can easily be evaluated by means of a widely used checklist (the QUORUM statement) ( Moher et al. , 1999 ). The strengths of the systematic review include the narrow focus of the question, the comprehensive search for evidence, the criterion-based selection of relevant evidence, the rigorous appraisal of validity, the objective or quantitative summary, and the evidence-based inferences ( Cook et al. , 1997 ).
For some review topics, however, the strengths of the systematic review may turn into weaknesses. The primary problem is that the narrow focus and prescribed methods of the systematic review do not allow for comprehensive coverage. For example, the historical review is an irreplaceable means of tracing the development of a scientific principle or clinical concept, but the narrative thread could be lost in the strict rules of systematic review. As other examples, it would be burdensome to apply systematic methods to a survey on aneuploidy and fertility in the aging female or to an assessment of mouse knockout models and polycystic ovarian phenotype. Such topics would require the wider scope of a traditional narrative review, in which less explicit methods are the trade-off for broader coverage.
The majority of review articles are narrative rather than systematic. Narrative reviews generally are comprehensive and cover a wide range of issues within a given topic, but they do not necessarily state or follow rules about the search for evidence. Also, typical narrative reviews do not reveal how the decisions were made about relevance of studies and the validity of the included studies. Of course, the results of the search, selection and assessment procedures must meet the referees’ and editors’ sense of propriety, but readers may not be privy to the methods and thus could not make judgments about the authors choices.
Neither the systematic reviews with their narrow scope nor the narrative reviews with their individuality can satisfy the range of topics for review. Currently, progress in reproductive medicine depends primarily on knowledge of developments in molecular biology, genetics and pharmacology. Background knowledge, evolving concepts and controversy require the flexibility of a narrative review with broad coverage and situational choices about the inclusion of evidence. In contrast, the rigour of a systematic review is needed for effectiveness of diagnostic and treatment interventions and for the outcomes of natural and therapeutic exposures, including adverse events and costs. The choice is more open for many other scientific and clinical topics.
Recognizing that there is a need for both systematic and narrative reviews, could one review type learn from the other? Because readers value transparency and reproducibility, some narrative reviews could gain by drawing from the rigour of systematic reviews. Authors could arrange the subject matter in a series of objective questions, each section based on specified procedures for search, relevance and validity and tied to other sections by appropriate descriptive links. One of the many types of statistical summarization would be helpful to readers. Inferences would adhere to the cited evidence and abstain from opinion. Systematic reviews, on the other hand, could adopt some of the strengths of the narrative review without compromising validity. Their formulaic nature can be boring to read, but this could be countered by non-technical idiomatic language, novel approaches to graphics, and new ways to deal with the baggage of massive tables. Also the excessive concentration in systematic reviews on odds ratios and relative risks is anachronistic, now that absolute differences and numbers needed to treat are the preferred measures of treatment effects ( Sackett and Cook, 1994 ). The procedures for calculating summary absolute effects and their heterogeneity are similar to those for relative effects ( Greenland, 1987 ; Deeks et al. , 2001 ).
Review journals such as Human Reproduction Update have high impact factors because readers need and appreciate comprehensive, relevant, valid summaries that clearly synthesize scientific and clinical evidence. While systematic reviews are more appropriate for focused topics and traditional narrative reviews are better suited to comprehensive topics, either approach can be adapted to clinical or scientific subjects. An infusion of systematic review methods would strengthen narrative reviews and in turn systematic reviews could benefit from the presentation strengths of narrative reviews. The goal is to ensure that the methods of all reviews should be explicit, transparent, clearly stated and reproducible by interested readers.
Cook DJ, Mulrow CD and Haynes RB ( 1997 ) Systematic reviews: synthesis of best evidence for clinical decisions. Ann Intern Med 126 , 376 –380.
Google Scholar
Deeks JJ, Altman DG and Bradburn MJ ( 2001 ) Statistical methods for examining heterogeneity and combining results from several studies in meta-analysis. In Egger M, Davey Smith G, and Altman DG (eds) Systematic Reviews in Health Care: Meta-analysis in Context. BMJ Publishing Group, London, pp 285 –312.
Eddy DM, Hasselblad V and Shachter R ( 1992 ) Meta-analysis by the Confidence Profile Method. Academic Press, Boston.
Greenland S ( 1987 ) Quantitative methods in the review of epidemiologic literature. Epidemiol Rev 9 , 1 –30.
Light RJ and Pillemer DB ( 1984 ) Summing Up: The Science of Reviewing Research. Harvard University Press, Boston.
Moher D, Cook DJ, Eastwood S, Olkin I, Rennie D and Stroup DF ( 1999 ) Improving the quality of reports of meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials: the QUOROM statement. Lancet 354 , 1896 –1900.
Sackett DL and Cook RJ ( 1994 ) Understanding clinical trials: what measures of efficacy should journal articles provide busy clinicians? Br Med J 309 , 755 –756.
Schlesselman JJ and Collins JA ( 2003 ) Evaluating systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Semin Reprod Med 21 , 95 –105.
Author notes
1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, 2Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Dalhousie University, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada and 3Department of Reproductive Medicine, University Medical Center, Utrecht, The Netherlands
Email alerts
Citing articles via.
- Recommend to your Library
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1460-2369
- Copyright © 2024 Human Reproduction Update
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.

- University of Texas Libraries
Literature Reviews
- What is a literature review?
- Steps in the Literature Review Process
- Define your research question
- Determine inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Choose databases and search
- Review Results
- Synthesize Results
- Analyze Results
- Librarian Support
What is a Literature Review?
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important past and current research and practices. It provides background and context, and shows how your research will contribute to the field.
A literature review should:
- Provide a comprehensive and updated review of the literature;
- Explain why this review has taken place;
- Articulate a position or hypothesis;
- Acknowledge and account for conflicting and corroborating points of view
From S age Research Methods
Purpose of a Literature Review
A literature review can be written as an introduction to a study to:
- Demonstrate how a study fills a gap in research
- Compare a study with other research that's been done
Or it can be a separate work (a research article on its own) which:
- Organizes or describes a topic
- Describes variables within a particular issue/problem
Limitations of a Literature Review
Some of the limitations of a literature review are:
- It's a snapshot in time. Unlike other reviews, this one has beginning, a middle and an end. There may be future developments that could make your work less relevant.
- It may be too focused. Some niche studies may miss the bigger picture.
- It can be difficult to be comprehensive. There is no way to make sure all the literature on a topic was considered.
- It is easy to be biased if you stick to top tier journals. There may be other places where people are publishing exemplary research. Look to open access publications and conferences to reflect a more inclusive collection. Also, make sure to include opposing views (and not just supporting evidence).
Source: Grant, Maria J., and Andrew Booth. “A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies.” Health Information & Libraries Journal, vol. 26, no. 2, June 2009, pp. 91–108. Wiley Online Library, doi:10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x.
Meryl Brodsky : Communication and Information Studies
Hannah Chapman Tripp : Biology, Neuroscience
Carolyn Cunningham : Human Development & Family Sciences, Psychology, Sociology
Larayne Dallas : Engineering
Janelle Hedstrom : Special Education, Curriculum & Instruction, Ed Leadership & Policy
Susan Macicak : Linguistics
Imelda Vetter : Dell Medical School
For help in other subject areas, please see the guide to library specialists by subject .
Periodically, UT Libraries runs a workshop covering the basics and library support for literature reviews. While we try to offer these once per academic year, we find providing the recording to be helpful to community members who have missed the session. Following is the most recent recording of the workshop, Conducting a Literature Review. To view the recording, a UT login is required.
- October 26, 2022 recording
- Last Updated: Oct 26, 2022 2:49 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/literaturereviews

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Lau F, Kuziemsky C, editors. Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet]. Victoria (BC): University of Victoria; 2017 Feb 27.

Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet].
Chapter 9 methods for literature reviews.
Guy Paré and Spyros Kitsiou .
9.1. Introduction
Literature reviews play a critical role in scholarship because science remains, first and foremost, a cumulative endeavour ( vom Brocke et al., 2009 ). As in any academic discipline, rigorous knowledge syntheses are becoming indispensable in keeping up with an exponentially growing eHealth literature, assisting practitioners, academics, and graduate students in finding, evaluating, and synthesizing the contents of many empirical and conceptual papers. Among other methods, literature reviews are essential for: (a) identifying what has been written on a subject or topic; (b) determining the extent to which a specific research area reveals any interpretable trends or patterns; (c) aggregating empirical findings related to a narrow research question to support evidence-based practice; (d) generating new frameworks and theories; and (e) identifying topics or questions requiring more investigation ( Paré, Trudel, Jaana, & Kitsiou, 2015 ).
Literature reviews can take two major forms. The most prevalent one is the “literature review” or “background” section within a journal paper or a chapter in a graduate thesis. This section synthesizes the extant literature and usually identifies the gaps in knowledge that the empirical study addresses ( Sylvester, Tate, & Johnstone, 2013 ). It may also provide a theoretical foundation for the proposed study, substantiate the presence of the research problem, justify the research as one that contributes something new to the cumulated knowledge, or validate the methods and approaches for the proposed study ( Hart, 1998 ; Levy & Ellis, 2006 ).
The second form of literature review, which is the focus of this chapter, constitutes an original and valuable work of research in and of itself ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Rather than providing a base for a researcher’s own work, it creates a solid starting point for all members of the community interested in a particular area or topic ( Mulrow, 1987 ). The so-called “review article” is a journal-length paper which has an overarching purpose to synthesize the literature in a field, without collecting or analyzing any primary data ( Green, Johnson, & Adams, 2006 ).
When appropriately conducted, review articles represent powerful information sources for practitioners looking for state-of-the art evidence to guide their decision-making and work practices ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Further, high-quality reviews become frequently cited pieces of work which researchers seek out as a first clear outline of the literature when undertaking empirical studies ( Cooper, 1988 ; Rowe, 2014 ). Scholars who track and gauge the impact of articles have found that review papers are cited and downloaded more often than any other type of published article ( Cronin, Ryan, & Coughlan, 2008 ; Montori, Wilczynski, Morgan, Haynes, & Hedges, 2003 ; Patsopoulos, Analatos, & Ioannidis, 2005 ). The reason for their popularity may be the fact that reading the review enables one to have an overview, if not a detailed knowledge of the area in question, as well as references to the most useful primary sources ( Cronin et al., 2008 ). Although they are not easy to conduct, the commitment to complete a review article provides a tremendous service to one’s academic community ( Paré et al., 2015 ; Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ). Most, if not all, peer-reviewed journals in the fields of medical informatics publish review articles of some type.
The main objectives of this chapter are fourfold: (a) to provide an overview of the major steps and activities involved in conducting a stand-alone literature review; (b) to describe and contrast the different types of review articles that can contribute to the eHealth knowledge base; (c) to illustrate each review type with one or two examples from the eHealth literature; and (d) to provide a series of recommendations for prospective authors of review articles in this domain.
9.2. Overview of the Literature Review Process and Steps
As explained in Templier and Paré (2015) , there are six generic steps involved in conducting a review article:
- formulating the research question(s) and objective(s),
- searching the extant literature,
- screening for inclusion,
- assessing the quality of primary studies,
- extracting data, and
- analyzing data.
Although these steps are presented here in sequential order, one must keep in mind that the review process can be iterative and that many activities can be initiated during the planning stage and later refined during subsequent phases ( Finfgeld-Connett & Johnson, 2013 ; Kitchenham & Charters, 2007 ).
Formulating the research question(s) and objective(s): As a first step, members of the review team must appropriately justify the need for the review itself ( Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ), identify the review’s main objective(s) ( Okoli & Schabram, 2010 ), and define the concepts or variables at the heart of their synthesis ( Cooper & Hedges, 2009 ; Webster & Watson, 2002 ). Importantly, they also need to articulate the research question(s) they propose to investigate ( Kitchenham & Charters, 2007 ). In this regard, we concur with Jesson, Matheson, and Lacey (2011) that clearly articulated research questions are key ingredients that guide the entire review methodology; they underscore the type of information that is needed, inform the search for and selection of relevant literature, and guide or orient the subsequent analysis. Searching the extant literature: The next step consists of searching the literature and making decisions about the suitability of material to be considered in the review ( Cooper, 1988 ). There exist three main coverage strategies. First, exhaustive coverage means an effort is made to be as comprehensive as possible in order to ensure that all relevant studies, published and unpublished, are included in the review and, thus, conclusions are based on this all-inclusive knowledge base. The second type of coverage consists of presenting materials that are representative of most other works in a given field or area. Often authors who adopt this strategy will search for relevant articles in a small number of top-tier journals in a field ( Paré et al., 2015 ). In the third strategy, the review team concentrates on prior works that have been central or pivotal to a particular topic. This may include empirical studies or conceptual papers that initiated a line of investigation, changed how problems or questions were framed, introduced new methods or concepts, or engendered important debate ( Cooper, 1988 ). Screening for inclusion: The following step consists of evaluating the applicability of the material identified in the preceding step ( Levy & Ellis, 2006 ; vom Brocke et al., 2009 ). Once a group of potential studies has been identified, members of the review team must screen them to determine their relevance ( Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ). A set of predetermined rules provides a basis for including or excluding certain studies. This exercise requires a significant investment on the part of researchers, who must ensure enhanced objectivity and avoid biases or mistakes. As discussed later in this chapter, for certain types of reviews there must be at least two independent reviewers involved in the screening process and a procedure to resolve disagreements must also be in place ( Liberati et al., 2009 ; Shea et al., 2009 ). Assessing the quality of primary studies: In addition to screening material for inclusion, members of the review team may need to assess the scientific quality of the selected studies, that is, appraise the rigour of the research design and methods. Such formal assessment, which is usually conducted independently by at least two coders, helps members of the review team refine which studies to include in the final sample, determine whether or not the differences in quality may affect their conclusions, or guide how they analyze the data and interpret the findings ( Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ). Ascribing quality scores to each primary study or considering through domain-based evaluations which study components have or have not been designed and executed appropriately makes it possible to reflect on the extent to which the selected study addresses possible biases and maximizes validity ( Shea et al., 2009 ). Extracting data: The following step involves gathering or extracting applicable information from each primary study included in the sample and deciding what is relevant to the problem of interest ( Cooper & Hedges, 2009 ). Indeed, the type of data that should be recorded mainly depends on the initial research questions ( Okoli & Schabram, 2010 ). However, important information may also be gathered about how, when, where and by whom the primary study was conducted, the research design and methods, or qualitative/quantitative results ( Cooper & Hedges, 2009 ). Analyzing and synthesizing data : As a final step, members of the review team must collate, summarize, aggregate, organize, and compare the evidence extracted from the included studies. The extracted data must be presented in a meaningful way that suggests a new contribution to the extant literature ( Jesson et al., 2011 ). Webster and Watson (2002) warn researchers that literature reviews should be much more than lists of papers and should provide a coherent lens to make sense of extant knowledge on a given topic. There exist several methods and techniques for synthesizing quantitative (e.g., frequency analysis, meta-analysis) and qualitative (e.g., grounded theory, narrative analysis, meta-ethnography) evidence ( Dixon-Woods, Agarwal, Jones, Young, & Sutton, 2005 ; Thomas & Harden, 2008 ).
9.3. Types of Review Articles and Brief Illustrations
EHealth researchers have at their disposal a number of approaches and methods for making sense out of existing literature, all with the purpose of casting current research findings into historical contexts or explaining contradictions that might exist among a set of primary research studies conducted on a particular topic. Our classification scheme is largely inspired from Paré and colleagues’ (2015) typology. Below we present and illustrate those review types that we feel are central to the growth and development of the eHealth domain.
9.3.1. Narrative Reviews
The narrative review is the “traditional” way of reviewing the extant literature and is skewed towards a qualitative interpretation of prior knowledge ( Sylvester et al., 2013 ). Put simply, a narrative review attempts to summarize or synthesize what has been written on a particular topic but does not seek generalization or cumulative knowledge from what is reviewed ( Davies, 2000 ; Green et al., 2006 ). Instead, the review team often undertakes the task of accumulating and synthesizing the literature to demonstrate the value of a particular point of view ( Baumeister & Leary, 1997 ). As such, reviewers may selectively ignore or limit the attention paid to certain studies in order to make a point. In this rather unsystematic approach, the selection of information from primary articles is subjective, lacks explicit criteria for inclusion and can lead to biased interpretations or inferences ( Green et al., 2006 ). There are several narrative reviews in the particular eHealth domain, as in all fields, which follow such an unstructured approach ( Silva et al., 2015 ; Paul et al., 2015 ).
Despite these criticisms, this type of review can be very useful in gathering together a volume of literature in a specific subject area and synthesizing it. As mentioned above, its primary purpose is to provide the reader with a comprehensive background for understanding current knowledge and highlighting the significance of new research ( Cronin et al., 2008 ). Faculty like to use narrative reviews in the classroom because they are often more up to date than textbooks, provide a single source for students to reference, and expose students to peer-reviewed literature ( Green et al., 2006 ). For researchers, narrative reviews can inspire research ideas by identifying gaps or inconsistencies in a body of knowledge, thus helping researchers to determine research questions or formulate hypotheses. Importantly, narrative reviews can also be used as educational articles to bring practitioners up to date with certain topics of issues ( Green et al., 2006 ).
Recently, there have been several efforts to introduce more rigour in narrative reviews that will elucidate common pitfalls and bring changes into their publication standards. Information systems researchers, among others, have contributed to advancing knowledge on how to structure a “traditional” review. For instance, Levy and Ellis (2006) proposed a generic framework for conducting such reviews. Their model follows the systematic data processing approach comprised of three steps, namely: (a) literature search and screening; (b) data extraction and analysis; and (c) writing the literature review. They provide detailed and very helpful instructions on how to conduct each step of the review process. As another methodological contribution, vom Brocke et al. (2009) offered a series of guidelines for conducting literature reviews, with a particular focus on how to search and extract the relevant body of knowledge. Last, Bandara, Miskon, and Fielt (2011) proposed a structured, predefined and tool-supported method to identify primary studies within a feasible scope, extract relevant content from identified articles, synthesize and analyze the findings, and effectively write and present the results of the literature review. We highly recommend that prospective authors of narrative reviews consult these useful sources before embarking on their work.
Darlow and Wen (2015) provide a good example of a highly structured narrative review in the eHealth field. These authors synthesized published articles that describe the development process of mobile health ( m-health ) interventions for patients’ cancer care self-management. As in most narrative reviews, the scope of the research questions being investigated is broad: (a) how development of these systems are carried out; (b) which methods are used to investigate these systems; and (c) what conclusions can be drawn as a result of the development of these systems. To provide clear answers to these questions, a literature search was conducted on six electronic databases and Google Scholar . The search was performed using several terms and free text words, combining them in an appropriate manner. Four inclusion and three exclusion criteria were utilized during the screening process. Both authors independently reviewed each of the identified articles to determine eligibility and extract study information. A flow diagram shows the number of studies identified, screened, and included or excluded at each stage of study selection. In terms of contributions, this review provides a series of practical recommendations for m-health intervention development.

9.3.2. Descriptive or Mapping Reviews
The primary goal of a descriptive review is to determine the extent to which a body of knowledge in a particular research topic reveals any interpretable pattern or trend with respect to pre-existing propositions, theories, methodologies or findings ( King & He, 2005 ; Paré et al., 2015 ). In contrast with narrative reviews, descriptive reviews follow a systematic and transparent procedure, including searching, screening and classifying studies ( Petersen, Vakkalanka, & Kuzniarz, 2015 ). Indeed, structured search methods are used to form a representative sample of a larger group of published works ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Further, authors of descriptive reviews extract from each study certain characteristics of interest, such as publication year, research methods, data collection techniques, and direction or strength of research outcomes (e.g., positive, negative, or non-significant) in the form of frequency analysis to produce quantitative results ( Sylvester et al., 2013 ). In essence, each study included in a descriptive review is treated as the unit of analysis and the published literature as a whole provides a database from which the authors attempt to identify any interpretable trends or draw overall conclusions about the merits of existing conceptualizations, propositions, methods or findings ( Paré et al., 2015 ). In doing so, a descriptive review may claim that its findings represent the state of the art in a particular domain ( King & He, 2005 ).
In the fields of health sciences and medical informatics, reviews that focus on examining the range, nature and evolution of a topic area are described by Anderson, Allen, Peckham, and Goodwin (2008) as mapping reviews . Like descriptive reviews, the research questions are generic and usually relate to publication patterns and trends. There is no preconceived plan to systematically review all of the literature although this can be done. Instead, researchers often present studies that are representative of most works published in a particular area and they consider a specific time frame to be mapped.
An example of this approach in the eHealth domain is offered by DeShazo, Lavallie, and Wolf (2009). The purpose of this descriptive or mapping review was to characterize publication trends in the medical informatics literature over a 20-year period (1987 to 2006). To achieve this ambitious objective, the authors performed a bibliometric analysis of medical informatics citations indexed in medline using publication trends, journal frequencies, impact factors, Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) term frequencies, and characteristics of citations. Findings revealed that there were over 77,000 medical informatics articles published during the covered period in numerous journals and that the average annual growth rate was 12%. The MeSH term analysis also suggested a strong interdisciplinary trend. Finally, average impact scores increased over time with two notable growth periods. Overall, patterns in research outputs that seem to characterize the historic trends and current components of the field of medical informatics suggest it may be a maturing discipline (DeShazo et al., 2009).
9.3.3. Scoping Reviews
Scoping reviews attempt to provide an initial indication of the potential size and nature of the extant literature on an emergent topic (Arksey & O’Malley, 2005; Daudt, van Mossel, & Scott, 2013 ; Levac, Colquhoun, & O’Brien, 2010). A scoping review may be conducted to examine the extent, range and nature of research activities in a particular area, determine the value of undertaking a full systematic review (discussed next), or identify research gaps in the extant literature ( Paré et al., 2015 ). In line with their main objective, scoping reviews usually conclude with the presentation of a detailed research agenda for future works along with potential implications for both practice and research.
Unlike narrative and descriptive reviews, the whole point of scoping the field is to be as comprehensive as possible, including grey literature (Arksey & O’Malley, 2005). Inclusion and exclusion criteria must be established to help researchers eliminate studies that are not aligned with the research questions. It is also recommended that at least two independent coders review abstracts yielded from the search strategy and then the full articles for study selection ( Daudt et al., 2013 ). The synthesized evidence from content or thematic analysis is relatively easy to present in tabular form (Arksey & O’Malley, 2005; Thomas & Harden, 2008 ).
One of the most highly cited scoping reviews in the eHealth domain was published by Archer, Fevrier-Thomas, Lokker, McKibbon, and Straus (2011) . These authors reviewed the existing literature on personal health record ( phr ) systems including design, functionality, implementation, applications, outcomes, and benefits. Seven databases were searched from 1985 to March 2010. Several search terms relating to phr s were used during this process. Two authors independently screened titles and abstracts to determine inclusion status. A second screen of full-text articles, again by two independent members of the research team, ensured that the studies described phr s. All in all, 130 articles met the criteria and their data were extracted manually into a database. The authors concluded that although there is a large amount of survey, observational, cohort/panel, and anecdotal evidence of phr benefits and satisfaction for patients, more research is needed to evaluate the results of phr implementations. Their in-depth analysis of the literature signalled that there is little solid evidence from randomized controlled trials or other studies through the use of phr s. Hence, they suggested that more research is needed that addresses the current lack of understanding of optimal functionality and usability of these systems, and how they can play a beneficial role in supporting patient self-management ( Archer et al., 2011 ).
9.3.4. Forms of Aggregative Reviews
Healthcare providers, practitioners, and policy-makers are nowadays overwhelmed with large volumes of information, including research-based evidence from numerous clinical trials and evaluation studies, assessing the effectiveness of health information technologies and interventions ( Ammenwerth & de Keizer, 2004 ; Deshazo et al., 2009 ). It is unrealistic to expect that all these disparate actors will have the time, skills, and necessary resources to identify the available evidence in the area of their expertise and consider it when making decisions. Systematic reviews that involve the rigorous application of scientific strategies aimed at limiting subjectivity and bias (i.e., systematic and random errors) can respond to this challenge.
Systematic reviews attempt to aggregate, appraise, and synthesize in a single source all empirical evidence that meet a set of previously specified eligibility criteria in order to answer a clearly formulated and often narrow research question on a particular topic of interest to support evidence-based practice ( Liberati et al., 2009 ). They adhere closely to explicit scientific principles ( Liberati et al., 2009 ) and rigorous methodological guidelines (Higgins & Green, 2008) aimed at reducing random and systematic errors that can lead to deviations from the truth in results or inferences. The use of explicit methods allows systematic reviews to aggregate a large body of research evidence, assess whether effects or relationships are in the same direction and of the same general magnitude, explain possible inconsistencies between study results, and determine the strength of the overall evidence for every outcome of interest based on the quality of included studies and the general consistency among them ( Cook, Mulrow, & Haynes, 1997 ). The main procedures of a systematic review involve:
- Formulating a review question and developing a search strategy based on explicit inclusion criteria for the identification of eligible studies (usually described in the context of a detailed review protocol).
- Searching for eligible studies using multiple databases and information sources, including grey literature sources, without any language restrictions.
- Selecting studies, extracting data, and assessing risk of bias in a duplicate manner using two independent reviewers to avoid random or systematic errors in the process.
- Analyzing data using quantitative or qualitative methods.
- Presenting results in summary of findings tables.
- Interpreting results and drawing conclusions.
Many systematic reviews, but not all, use statistical methods to combine the results of independent studies into a single quantitative estimate or summary effect size. Known as meta-analyses , these reviews use specific data extraction and statistical techniques (e.g., network, frequentist, or Bayesian meta-analyses) to calculate from each study by outcome of interest an effect size along with a confidence interval that reflects the degree of uncertainty behind the point estimate of effect ( Borenstein, Hedges, Higgins, & Rothstein, 2009 ; Deeks, Higgins, & Altman, 2008 ). Subsequently, they use fixed or random-effects analysis models to combine the results of the included studies, assess statistical heterogeneity, and calculate a weighted average of the effect estimates from the different studies, taking into account their sample sizes. The summary effect size is a value that reflects the average magnitude of the intervention effect for a particular outcome of interest or, more generally, the strength of a relationship between two variables across all studies included in the systematic review. By statistically combining data from multiple studies, meta-analyses can create more precise and reliable estimates of intervention effects than those derived from individual studies alone, when these are examined independently as discrete sources of information.
The review by Gurol-Urganci, de Jongh, Vodopivec-Jamsek, Atun, and Car (2013) on the effects of mobile phone messaging reminders for attendance at healthcare appointments is an illustrative example of a high-quality systematic review with meta-analysis. Missed appointments are a major cause of inefficiency in healthcare delivery with substantial monetary costs to health systems. These authors sought to assess whether mobile phone-based appointment reminders delivered through Short Message Service ( sms ) or Multimedia Messaging Service ( mms ) are effective in improving rates of patient attendance and reducing overall costs. To this end, they conducted a comprehensive search on multiple databases using highly sensitive search strategies without language or publication-type restrictions to identify all rct s that are eligible for inclusion. In order to minimize the risk of omitting eligible studies not captured by the original search, they supplemented all electronic searches with manual screening of trial registers and references contained in the included studies. Study selection, data extraction, and risk of bias assessments were performed independently by two coders using standardized methods to ensure consistency and to eliminate potential errors. Findings from eight rct s involving 6,615 participants were pooled into meta-analyses to calculate the magnitude of effects that mobile text message reminders have on the rate of attendance at healthcare appointments compared to no reminders and phone call reminders.
Meta-analyses are regarded as powerful tools for deriving meaningful conclusions. However, there are situations in which it is neither reasonable nor appropriate to pool studies together using meta-analytic methods simply because there is extensive clinical heterogeneity between the included studies or variation in measurement tools, comparisons, or outcomes of interest. In these cases, systematic reviews can use qualitative synthesis methods such as vote counting, content analysis, classification schemes and tabulations, as an alternative approach to narratively synthesize the results of the independent studies included in the review. This form of review is known as qualitative systematic review.
A rigorous example of one such review in the eHealth domain is presented by Mickan, Atherton, Roberts, Heneghan, and Tilson (2014) on the use of handheld computers by healthcare professionals and their impact on access to information and clinical decision-making. In line with the methodological guidelines for systematic reviews, these authors: (a) developed and registered with prospero ( www.crd.york.ac.uk/ prospero / ) an a priori review protocol; (b) conducted comprehensive searches for eligible studies using multiple databases and other supplementary strategies (e.g., forward searches); and (c) subsequently carried out study selection, data extraction, and risk of bias assessments in a duplicate manner to eliminate potential errors in the review process. Heterogeneity between the included studies in terms of reported outcomes and measures precluded the use of meta-analytic methods. To this end, the authors resorted to using narrative analysis and synthesis to describe the effectiveness of handheld computers on accessing information for clinical knowledge, adherence to safety and clinical quality guidelines, and diagnostic decision-making.
In recent years, the number of systematic reviews in the field of health informatics has increased considerably. Systematic reviews with discordant findings can cause great confusion and make it difficult for decision-makers to interpret the review-level evidence ( Moher, 2013 ). Therefore, there is a growing need for appraisal and synthesis of prior systematic reviews to ensure that decision-making is constantly informed by the best available accumulated evidence. Umbrella reviews , also known as overviews of systematic reviews, are tertiary types of evidence synthesis that aim to accomplish this; that is, they aim to compare and contrast findings from multiple systematic reviews and meta-analyses ( Becker & Oxman, 2008 ). Umbrella reviews generally adhere to the same principles and rigorous methodological guidelines used in systematic reviews. However, the unit of analysis in umbrella reviews is the systematic review rather than the primary study ( Becker & Oxman, 2008 ). Unlike systematic reviews that have a narrow focus of inquiry, umbrella reviews focus on broader research topics for which there are several potential interventions ( Smith, Devane, Begley, & Clarke, 2011 ). A recent umbrella review on the effects of home telemonitoring interventions for patients with heart failure critically appraised, compared, and synthesized evidence from 15 systematic reviews to investigate which types of home telemonitoring technologies and forms of interventions are more effective in reducing mortality and hospital admissions ( Kitsiou, Paré, & Jaana, 2015 ).
9.3.5. Realist Reviews
Realist reviews are theory-driven interpretative reviews developed to inform, enhance, or supplement conventional systematic reviews by making sense of heterogeneous evidence about complex interventions applied in diverse contexts in a way that informs policy decision-making ( Greenhalgh, Wong, Westhorp, & Pawson, 2011 ). They originated from criticisms of positivist systematic reviews which centre on their “simplistic” underlying assumptions ( Oates, 2011 ). As explained above, systematic reviews seek to identify causation. Such logic is appropriate for fields like medicine and education where findings of randomized controlled trials can be aggregated to see whether a new treatment or intervention does improve outcomes. However, many argue that it is not possible to establish such direct causal links between interventions and outcomes in fields such as social policy, management, and information systems where for any intervention there is unlikely to be a regular or consistent outcome ( Oates, 2011 ; Pawson, 2006 ; Rousseau, Manning, & Denyer, 2008 ).
To circumvent these limitations, Pawson, Greenhalgh, Harvey, and Walshe (2005) have proposed a new approach for synthesizing knowledge that seeks to unpack the mechanism of how “complex interventions” work in particular contexts. The basic research question — what works? — which is usually associated with systematic reviews changes to: what is it about this intervention that works, for whom, in what circumstances, in what respects and why? Realist reviews have no particular preference for either quantitative or qualitative evidence. As a theory-building approach, a realist review usually starts by articulating likely underlying mechanisms and then scrutinizes available evidence to find out whether and where these mechanisms are applicable ( Shepperd et al., 2009 ). Primary studies found in the extant literature are viewed as case studies which can test and modify the initial theories ( Rousseau et al., 2008 ).
The main objective pursued in the realist review conducted by Otte-Trojel, de Bont, Rundall, and van de Klundert (2014) was to examine how patient portals contribute to health service delivery and patient outcomes. The specific goals were to investigate how outcomes are produced and, most importantly, how variations in outcomes can be explained. The research team started with an exploratory review of background documents and research studies to identify ways in which patient portals may contribute to health service delivery and patient outcomes. The authors identified six main ways which represent “educated guesses” to be tested against the data in the evaluation studies. These studies were identified through a formal and systematic search in four databases between 2003 and 2013. Two members of the research team selected the articles using a pre-established list of inclusion and exclusion criteria and following a two-step procedure. The authors then extracted data from the selected articles and created several tables, one for each outcome category. They organized information to bring forward those mechanisms where patient portals contribute to outcomes and the variation in outcomes across different contexts.
9.3.6. Critical Reviews
Lastly, critical reviews aim to provide a critical evaluation and interpretive analysis of existing literature on a particular topic of interest to reveal strengths, weaknesses, contradictions, controversies, inconsistencies, and/or other important issues with respect to theories, hypotheses, research methods or results ( Baumeister & Leary, 1997 ; Kirkevold, 1997 ). Unlike other review types, critical reviews attempt to take a reflective account of the research that has been done in a particular area of interest, and assess its credibility by using appraisal instruments or critical interpretive methods. In this way, critical reviews attempt to constructively inform other scholars about the weaknesses of prior research and strengthen knowledge development by giving focus and direction to studies for further improvement ( Kirkevold, 1997 ).
Kitsiou, Paré, and Jaana (2013) provide an example of a critical review that assessed the methodological quality of prior systematic reviews of home telemonitoring studies for chronic patients. The authors conducted a comprehensive search on multiple databases to identify eligible reviews and subsequently used a validated instrument to conduct an in-depth quality appraisal. Results indicate that the majority of systematic reviews in this particular area suffer from important methodological flaws and biases that impair their internal validity and limit their usefulness for clinical and decision-making purposes. To this end, they provide a number of recommendations to strengthen knowledge development towards improving the design and execution of future reviews on home telemonitoring.
9.4. Summary
Table 9.1 outlines the main types of literature reviews that were described in the previous sub-sections and summarizes the main characteristics that distinguish one review type from another. It also includes key references to methodological guidelines and useful sources that can be used by eHealth scholars and researchers for planning and developing reviews.
Typology of Literature Reviews (adapted from Paré et al., 2015).
As shown in Table 9.1 , each review type addresses different kinds of research questions or objectives, which subsequently define and dictate the methods and approaches that need to be used to achieve the overarching goal(s) of the review. For example, in the case of narrative reviews, there is greater flexibility in searching and synthesizing articles ( Green et al., 2006 ). Researchers are often relatively free to use a diversity of approaches to search, identify, and select relevant scientific articles, describe their operational characteristics, present how the individual studies fit together, and formulate conclusions. On the other hand, systematic reviews are characterized by their high level of systematicity, rigour, and use of explicit methods, based on an “a priori” review plan that aims to minimize bias in the analysis and synthesis process (Higgins & Green, 2008). Some reviews are exploratory in nature (e.g., scoping/mapping reviews), whereas others may be conducted to discover patterns (e.g., descriptive reviews) or involve a synthesis approach that may include the critical analysis of prior research ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Hence, in order to select the most appropriate type of review, it is critical to know before embarking on a review project, why the research synthesis is conducted and what type of methods are best aligned with the pursued goals.
9.5. Concluding Remarks
In light of the increased use of evidence-based practice and research generating stronger evidence ( Grady et al., 2011 ; Lyden et al., 2013 ), review articles have become essential tools for summarizing, synthesizing, integrating or critically appraising prior knowledge in the eHealth field. As mentioned earlier, when rigorously conducted review articles represent powerful information sources for eHealth scholars and practitioners looking for state-of-the-art evidence. The typology of literature reviews we used herein will allow eHealth researchers, graduate students and practitioners to gain a better understanding of the similarities and differences between review types.
We must stress that this classification scheme does not privilege any specific type of review as being of higher quality than another ( Paré et al., 2015 ). As explained above, each type of review has its own strengths and limitations. Having said that, we realize that the methodological rigour of any review — be it qualitative, quantitative or mixed — is a critical aspect that should be considered seriously by prospective authors. In the present context, the notion of rigour refers to the reliability and validity of the review process described in section 9.2. For one thing, reliability is related to the reproducibility of the review process and steps, which is facilitated by a comprehensive documentation of the literature search process, extraction, coding and analysis performed in the review. Whether the search is comprehensive or not, whether it involves a methodical approach for data extraction and synthesis or not, it is important that the review documents in an explicit and transparent manner the steps and approach that were used in the process of its development. Next, validity characterizes the degree to which the review process was conducted appropriately. It goes beyond documentation and reflects decisions related to the selection of the sources, the search terms used, the period of time covered, the articles selected in the search, and the application of backward and forward searches ( vom Brocke et al., 2009 ). In short, the rigour of any review article is reflected by the explicitness of its methods (i.e., transparency) and the soundness of the approach used. We refer those interested in the concepts of rigour and quality to the work of Templier and Paré (2015) which offers a detailed set of methodological guidelines for conducting and evaluating various types of review articles.
To conclude, our main objective in this chapter was to demystify the various types of literature reviews that are central to the continuous development of the eHealth field. It is our hope that our descriptive account will serve as a valuable source for those conducting, evaluating or using reviews in this important and growing domain.
- Ammenwerth E., de Keizer N. An inventory of evaluation studies of information technology in health care. Trends in evaluation research, 1982-2002. International Journal of Medical Informatics. 2004; 44 (1):44–56. [ PubMed : 15778794 ]
- Anderson S., Allen P., Peckham S., Goodwin N. Asking the right questions: scoping studies in the commissioning of research on the organisation and delivery of health services. Health Research Policy and Systems. 2008; 6 (7):1–12. [ PMC free article : PMC2500008 ] [ PubMed : 18613961 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Archer N., Fevrier-Thomas U., Lokker C., McKibbon K. A., Straus S.E. Personal health records: a scoping review. Journal of American Medical Informatics Association. 2011; 18 (4):515–522. [ PMC free article : PMC3128401 ] [ PubMed : 21672914 ]
- Arksey H., O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. International Journal of Social Research Methodology. 2005; 8 (1):19–32.
- A systematic, tool-supported method for conducting literature reviews in information systems. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 19th European Conference on Information Systems ( ecis 2011); June 9 to 11; Helsinki, Finland. 2011.
- Baumeister R. F., Leary M.R. Writing narrative literature reviews. Review of General Psychology. 1997; 1 (3):311–320.
- Becker L. A., Oxman A.D. In: Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Higgins J. P. T., Green S., editors. Hoboken, nj : John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2008. Overviews of reviews; pp. 607–631.
- Borenstein M., Hedges L., Higgins J., Rothstein H. Introduction to meta-analysis. Hoboken, nj : John Wiley & Sons Inc; 2009.
- Cook D. J., Mulrow C. D., Haynes B. Systematic reviews: Synthesis of best evidence for clinical decisions. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1997; 126 (5):376–380. [ PubMed : 9054282 ]
- Cooper H., Hedges L.V. In: The handbook of research synthesis and meta-analysis. 2nd ed. Cooper H., Hedges L. V., Valentine J. C., editors. New York: Russell Sage Foundation; 2009. Research synthesis as a scientific process; pp. 3–17.
- Cooper H. M. Organizing knowledge syntheses: A taxonomy of literature reviews. Knowledge in Society. 1988; 1 (1):104–126.
- Cronin P., Ryan F., Coughlan M. Undertaking a literature review: a step-by-step approach. British Journal of Nursing. 2008; 17 (1):38–43. [ PubMed : 18399395 ]
- Darlow S., Wen K.Y. Development testing of mobile health interventions for cancer patient self-management: A review. Health Informatics Journal. 2015 (online before print). [ PubMed : 25916831 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Daudt H. M., van Mossel C., Scott S.J. Enhancing the scoping study methodology: a large, inter-professional team’s experience with Arksey and O’Malley’s framework. bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2013; 13 :48. [ PMC free article : PMC3614526 ] [ PubMed : 23522333 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Davies P. The relevance of systematic reviews to educational policy and practice. Oxford Review of Education. 2000; 26 (3-4):365–378.
- Deeks J. J., Higgins J. P. T., Altman D.G. In: Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Higgins J. P. T., Green S., editors. Hoboken, nj : John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2008. Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses; pp. 243–296.
- Deshazo J. P., Lavallie D. L., Wolf F.M. Publication trends in the medical informatics literature: 20 years of “Medical Informatics” in mesh . bmc Medical Informatics and Decision Making. 2009; 9 :7. [ PMC free article : PMC2652453 ] [ PubMed : 19159472 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Dixon-Woods M., Agarwal S., Jones D., Young B., Sutton A. Synthesising qualitative and quantitative evidence: a review of possible methods. Journal of Health Services Research and Policy. 2005; 10 (1):45–53. [ PubMed : 15667704 ]
- Finfgeld-Connett D., Johnson E.D. Literature search strategies for conducting knowledge-building and theory-generating qualitative systematic reviews. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2013; 69 (1):194–204. [ PMC free article : PMC3424349 ] [ PubMed : 22591030 ]
- Grady B., Myers K. M., Nelson E. L., Belz N., Bennett L., Carnahan L. … Guidelines Working Group. Evidence-based practice for telemental health. Telemedicine Journal and E Health. 2011; 17 (2):131–148. [ PubMed : 21385026 ]
- Green B. N., Johnson C. D., Adams A. Writing narrative literature reviews for peer-reviewed journals: secrets of the trade. Journal of Chiropractic Medicine. 2006; 5 (3):101–117. [ PMC free article : PMC2647067 ] [ PubMed : 19674681 ]
- Greenhalgh T., Wong G., Westhorp G., Pawson R. Protocol–realist and meta-narrative evidence synthesis: evolving standards ( rameses ). bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2011; 11 :115. [ PMC free article : PMC3173389 ] [ PubMed : 21843376 ]
- Gurol-Urganci I., de Jongh T., Vodopivec-Jamsek V., Atun R., Car J. Mobile phone messaging reminders for attendance at healthcare appointments. Cochrane Database System Review. 2013; 12 cd 007458. [ PMC free article : PMC6485985 ] [ PubMed : 24310741 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hart C. Doing a literature review: Releasing the social science research imagination. London: SAGE Publications; 1998.
- Higgins J. P. T., Green S., editors. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions: Cochrane book series. Hoboken, nj : Wiley-Blackwell; 2008.
- Jesson J., Matheson L., Lacey F.M. Doing your literature review: traditional and systematic techniques. Los Angeles & London: SAGE Publications; 2011.
- King W. R., He J. Understanding the role and methods of meta-analysis in IS research. Communications of the Association for Information Systems. 2005; 16 :1.
- Kirkevold M. Integrative nursing research — an important strategy to further the development of nursing science and nursing practice. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 1997; 25 (5):977–984. [ PubMed : 9147203 ]
- Kitchenham B., Charters S. ebse Technical Report Version 2.3. Keele & Durham. uk : Keele University & University of Durham; 2007. Guidelines for performing systematic literature reviews in software engineering.
- Kitsiou S., Paré G., Jaana M. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of home telemonitoring interventions for patients with chronic diseases: a critical assessment of their methodological quality. Journal of Medical Internet Research. 2013; 15 (7):e150. [ PMC free article : PMC3785977 ] [ PubMed : 23880072 ]
- Kitsiou S., Paré G., Jaana M. Effects of home telemonitoring interventions on patients with chronic heart failure: an overview of systematic reviews. Journal of Medical Internet Research. 2015; 17 (3):e63. [ PMC free article : PMC4376138 ] [ PubMed : 25768664 ]
- Levac D., Colquhoun H., O’Brien K. K. Scoping studies: advancing the methodology. Implementation Science. 2010; 5 (1):69. [ PMC free article : PMC2954944 ] [ PubMed : 20854677 ]
- Levy Y., Ellis T.J. A systems approach to conduct an effective literature review in support of information systems research. Informing Science. 2006; 9 :181–211.
- Liberati A., Altman D. G., Tetzlaff J., Mulrow C., Gøtzsche P. C., Ioannidis J. P. A. et al. Moher D. The prisma statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2009; 151 (4):W-65. [ PubMed : 19622512 ]
- Lyden J. R., Zickmund S. L., Bhargava T. D., Bryce C. L., Conroy M. B., Fischer G. S. et al. McTigue K. M. Implementing health information technology in a patient-centered manner: Patient experiences with an online evidence-based lifestyle intervention. Journal for Healthcare Quality. 2013; 35 (5):47–57. [ PubMed : 24004039 ]
- Mickan S., Atherton H., Roberts N. W., Heneghan C., Tilson J.K. Use of handheld computers in clinical practice: a systematic review. bmc Medical Informatics and Decision Making. 2014; 14 :56. [ PMC free article : PMC4099138 ] [ PubMed : 24998515 ]
- Moher D. The problem of duplicate systematic reviews. British Medical Journal. 2013; 347 (5040) [ PubMed : 23945367 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Montori V. M., Wilczynski N. L., Morgan D., Haynes R. B., Hedges T. Systematic reviews: a cross-sectional study of location and citation counts. bmc Medicine. 2003; 1 :2. [ PMC free article : PMC281591 ] [ PubMed : 14633274 ]
- Mulrow C. D. The medical review article: state of the science. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1987; 106 (3):485–488. [ PubMed : 3813259 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Evidence-based information systems: A decade later. Proceedings of the European Conference on Information Systems ; 2011. Retrieved from http://aisel .aisnet.org/cgi/viewcontent .cgi?article =1221&context =ecis2011 .
- Okoli C., Schabram K. A guide to conducting a systematic literature review of information systems research. ssrn Electronic Journal. 2010
- Otte-Trojel T., de Bont A., Rundall T. G., van de Klundert J. How outcomes are achieved through patient portals: a realist review. Journal of American Medical Informatics Association. 2014; 21 (4):751–757. [ PMC free article : PMC4078283 ] [ PubMed : 24503882 ]
- Paré G., Trudel M.-C., Jaana M., Kitsiou S. Synthesizing information systems knowledge: A typology of literature reviews. Information & Management. 2015; 52 (2):183–199.
- Patsopoulos N. A., Analatos A. A., Ioannidis J.P. A. Relative citation impact of various study designs in the health sciences. Journal of the American Medical Association. 2005; 293 (19):2362–2366. [ PubMed : 15900006 ]
- Paul M. M., Greene C. M., Newton-Dame R., Thorpe L. E., Perlman S. E., McVeigh K. H., Gourevitch M.N. The state of population health surveillance using electronic health records: A narrative review. Population Health Management. 2015; 18 (3):209–216. [ PubMed : 25608033 ]
- Pawson R. Evidence-based policy: a realist perspective. London: SAGE Publications; 2006.
- Pawson R., Greenhalgh T., Harvey G., Walshe K. Realist review—a new method of systematic review designed for complex policy interventions. Journal of Health Services Research & Policy. 2005; 10 (Suppl 1):21–34. [ PubMed : 16053581 ]
- Petersen K., Vakkalanka S., Kuzniarz L. Guidelines for conducting systematic mapping studies in software engineering: An update. Information and Software Technology. 2015; 64 :1–18.
- Petticrew M., Roberts H. Systematic reviews in the social sciences: A practical guide. Malden, ma : Blackwell Publishing Co; 2006.
- Rousseau D. M., Manning J., Denyer D. Evidence in management and organizational science: Assembling the field’s full weight of scientific knowledge through syntheses. The Academy of Management Annals. 2008; 2 (1):475–515.
- Rowe F. What literature review is not: diversity, boundaries and recommendations. European Journal of Information Systems. 2014; 23 (3):241–255.
- Shea B. J., Hamel C., Wells G. A., Bouter L. M., Kristjansson E., Grimshaw J. et al. Boers M. amstar is a reliable and valid measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. 2009; 62 (10):1013–1020. [ PubMed : 19230606 ]
- Shepperd S., Lewin S., Straus S., Clarke M., Eccles M. P., Fitzpatrick R. et al. Sheikh A. Can we systematically review studies that evaluate complex interventions? PLoS Medicine. 2009; 6 (8):e1000086. [ PMC free article : PMC2717209 ] [ PubMed : 19668360 ]
- Silva B. M., Rodrigues J. J., de la Torre Díez I., López-Coronado M., Saleem K. Mobile-health: A review of current state in 2015. Journal of Biomedical Informatics. 2015; 56 :265–272. [ PubMed : 26071682 ]
- Smith V., Devane D., Begley C., Clarke M. Methodology in conducting a systematic review of systematic reviews of healthcare interventions. bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2011; 11 (1):15. [ PMC free article : PMC3039637 ] [ PubMed : 21291558 ]
- Sylvester A., Tate M., Johnstone D. Beyond synthesis: re-presenting heterogeneous research literature. Behaviour & Information Technology. 2013; 32 (12):1199–1215.
- Templier M., Paré G. A framework for guiding and evaluating literature reviews. Communications of the Association for Information Systems. 2015; 37 (6):112–137.
- Thomas J., Harden A. Methods for the thematic synthesis of qualitative research in systematic reviews. bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2008; 8 (1):45. [ PMC free article : PMC2478656 ] [ PubMed : 18616818 ]
- Reconstructing the giant: on the importance of rigour in documenting the literature search process. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Information Systems ( ecis 2009); Verona, Italy. 2009.
- Webster J., Watson R.T. Analyzing the past to prepare for the future: Writing a literature review. Management Information Systems Quarterly. 2002; 26 (2):11.
- Whitlock E. P., Lin J. S., Chou R., Shekelle P., Robinson K.A. Using existing systematic reviews in complex systematic reviews. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2008; 148 (10):776–782. [ PubMed : 18490690 ]
This publication is licensed under a Creative Commons License, Attribution-Noncommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0): see https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
- Cite this Page Paré G, Kitsiou S. Chapter 9 Methods for Literature Reviews. In: Lau F, Kuziemsky C, editors. Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet]. Victoria (BC): University of Victoria; 2017 Feb 27.
- PDF version of this title (4.5M)
- Disable Glossary Links
In this Page
- Introduction
- Overview of the Literature Review Process and Steps
- Types of Review Articles and Brief Illustrations
- Concluding Remarks
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Recent Activity
- Chapter 9 Methods for Literature Reviews - Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Ev... Chapter 9 Methods for Literature Reviews - Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers
- Systematic Review
- Open access
- Published: 30 May 2024
The effectiveness of interventions for offending behaviours in adults with autism spectrum disorders (ASD): a systematic PRISMA review
- Jody Salter 1 , 2 &
- Sarah Blainey 1 , 3
BMC Psychology volume 12 , Article number: 316 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
218 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Previous research has suggested that the core features of autism spectrum disorders (ASD) may contribute to offending behaviours and increased vulnerability within the Criminal Justice System. To date, there is a paucity of evidence assessing the effectiveness of interventions for offending behaviour in adults with ASD but without co-occurring intellectual disability (ID) across a broad range of forensic settings. The lack of robust evidence is concerning, as limited effectiveness may contribute to an increased likelihood of prolonged incarceration, particularly in the most restrictive settings. A PRISMA systematic review was conducted with a narrative synthesis to: (a) evaluate the evidence of the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing recidivism, (b) assess whether the core features of ASD impact the effectiveness of these interventions, and (c) identify additional factors that may affect the effectiveness of interventions within this population. Seven studies involving ten male participants were identified. The findings suggest that interventions for offending behaviours in adults with ASD without intellectual disability (ID) are largely inadequate, and that core ASD features need to be considered. Additionally, a complex interplay of risk factors potentially impacting intervention effectiveness was suggested. Limitations include heterogeneity across intervention types, measures of effectiveness, and what constitutes effectiveness. Despite the limited number of studies and data quality, the review aligns with a growing body of literature highlighting vulnerability and a need for evidence-based interventions for people with ASD. The review also discusses the broader implications of ineffective interventions.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Autism spectrum disorders (ASD) represent a group of complex and highly heterogeneous neurodevelopmental disorders. A diagnosis of ASD is based on the presence of two core features: impairments in social communication and interaction (SCI), and restrictive and repetitive behaviours (RRBs) [ 1 ].
Phenotypic manifestations of the core features often present with varying degrees of social disengagement, difficulties in establishing and sustaining relationships, social naivety, lack of eye contact, and difficulties in interpreting facial expressions [ 2 ]. RRBs manifest as intense and highly restrictive special interests, a strong inclination for environmental consistency [ 3 ], cognitive rigidity, and hyper-or hypo sensory responses to the environment [ 4 ].
Additional factors modulate and influence these core features, including the extent of sensory and motor impairments, language and cognitive abilities, adaptive functioning, gender and the presence of co-occurring psychiatric disorders [ 5 , 6 , 7 ]. The increasing recognition of ASD has resulted in significantly higher diagnosis rates across all age groups [ 8 ], which are currently estimated to be 1 in 57 in England [ 9 ]. Consequently, this increase in diagnoses has led to a greater representation of individuals with ASD within the criminal justice system (CJS).
ASD in the criminal justice system
An increasing body of research has highlighted the significant vulnerability experienced by individuals with ASD while navigating the CJS. This vulnerability becomes evident throughout multiple stages of the criminal justice process, ranging from initial encounters with police [ 10 ] through to police interviews [ 11 ], to court room proceedings [ 12 ] and prison services [ 13 ]. This heightened vulnerability is exacerbated by the reported general lack of understanding of ASD within the CJS, among both professionals and the general public [ 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 ].
Individuals with ASD and co-occurring intellectual disability (ID) are often identified and diverted from the criminal justice system (CJS). This is due to a recognition of their reduced culpability, a result of impairments in both intellectual and adaptive functioning [ 15 ]. In contrast, individuals with ASD but without co-occurring ID, the population on which this review focuses, exhibit significant deficits in adaptive functioning despite their intellectual capabilities. This difference is often referred to as the IQ functioning gap and is unique to individuals with ASD [ 17 ]. Despite impairments in adaptive functioning, this population is considered intellectually capable. Therefore, they are generally perceived as culpable and sufficiently competent to navigate the complexities of the CJS and receive a fair trial. This contrast raises further questions concerning culpability ranging from criminal responsibility to the appropriateness of sentencing.
Following conviction, when an offence has met the custody threshold, offenders with ASD are typically diverted to the community or prison. Alternatively, if detained under the Mental Health Act 1983 (the legislative framework governing mental healthcare and treatment in England and Wales), they may be detained in a secure hospital environment (classified as low, medium, or high security).
Estimating the prevalence of ASD within the UK prison population is difficult because of a lack of routine assessment; nonetheless, ASD is estimated to range between 1% and 4.4% [ 5 ]. Research has shown a disproportionately high prevalence of ASD in secure hospital settings (6.5%), exceeding the estimate for the general population [ 18 ].
Qualitative studies examining the experiences of prisoners with ASD without co-occurring ID have highlighted their increased vulnerability to bullying, exploitation, and social anxiety in prison [ 13 ]. In addition, research aimed at evaluating the prevalence of the broader autistic phenotype among a prison population, as well as comparing their mental health characteristics to those without, revealed a significant risk of self-harm and suicide in individuals presenting with autistic traits. Within this cohort, of the 240 prisoners assessed, 46 displayed significant autistic traits, with 12 meeting the diagnostic criteria for ASD. Notably, only two of these individuals had been previously recognised by the prison as having ASD. This finding highlights the under recognition of ASD and emphasises the heightened vulnerability of this population to a range of mental health risks within the prison environment [ 5 ].
Although it may be logical to assume that a secure hospital setting may better meet the treatment needs of people with ASD than a prison setting, current evidence suggests otherwise. Concerns have been raised, including the high likelihood of long-term seclusion in people with ASD compared to those without ASD [ 19 ] and significantly longer than average stays within secure hospital settings [ 20 ].
Despite several initiatives aimed at improving the recognition of ASD within the prison population [ 21 ], a recent UK government report on ‘neurodiversity’ [ 22 ], a term encompassing various conditions that fall into the broader category of neurodevelopmental disorders (NDDs) including ASD, highlighted three notable areas of concern. These included a greater likelihood of neurodivergent individuals being held on remand, inappropriately pleading guilty, and judges often failing to recognise a defendant’s neurodivergence as a mitigating factor when sentencing. These findings demonstrate that much work is needed to address the challenges faced by individuals with ASD and neurodivergent conditions in the CJS.
ASD and risk of offending
While there is insufficient evidence to suggest that individuals with ASD are at greater risk of engaging in offending behaviours [ 23 ], it has been suggested that the core features of ASD may contribute to the risk of offending behaviours [ 24 , 25 ]. Risk factors for offending behaviour in the general population are associated with the cumulative influence of various factors, including alcohol and drug abuse, low socioeconomic status, mental disorders, adversity, child abuse, and traumatic brain injury [ 26 , 27 , 28 ]. Less is known about the risk factors for offending behaviour within the ASD population, with the exception of co-occurring psychiatric disorders, such as personality disorders and psychosis [ 5 ].
Research suggests that individuals diagnosed with ASD early in life face barriers to services throughout their lifespan, resulting in unmet education, health, and therapeutic needs [ 29 , 30 ]. Research suggests that certain demographic groups, such as women [ 31 , 32 ], individuals from ethnic minorities, and those from lower socioeconomic backgrounds [ 9 , 33 ], are far more likely to be underdiagnosed. This in turn increases the risk of unmet needs [ 34 , 35 ]. These factors may contribute as variables that collectively increase the overall cumulative risk of engaging in offending behaviours.
Forensic interventions
Interventions for offending behaviour often use cognitive-behavioural techniques to reduce recidivism, with an emphasis on perspective-taking, self-and relationship management, and problem solving. In the United Kingdom, the Ministry of Justice requires a sufficient evidence base for the accreditation of forensic interventions. This accreditation aims to promote high-quality programs in prisons and community settings to reduce recidivism [ 36 ].
Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) is widely recognised as one of the most effective interventions for offending behaviours [ 37 ]. There is evidence that CBT reduces recidivism by 20–30% in the general offending population [ 38 , 39 ]. However, there is little evidence to support the effectiveness of such interventions for offending behaviour in forensic secure settings, often yielding inconsistent findings [ 40 ].
Beyond forensic settings, evidence suggests that adapted CBT is effective for individuals with ASD [ 41 , 42 ]. These adjustments are necessary due to the core features of ASD and challenges in areas such as perspective taking and cognitive rigidity, both of which are conducive to successful therapeutic outcomes in this population [ 43 ]. Additionally, evidence supports the use of social skills training [ 44 ] and group-based social skills interventions in adults with ASD [ 41 ] However, there is no consensus regarding the specific adaptations most beneficial for individuals with ASD.
Furthermore, the lack of appropriate outcome measures has been reported to be a barrier to determining the effectiveness of interventions within secure forensic hospital settings [ 45 , 46 , 47 ]. Despite the evidence for CBT use within the general offender population and for individuals with ASD outside forensic settings, there are reports that the implementation of these interventions is not effective for individuals detained within secure hospital settings [ 19 , 48 , 49 ].
The increasing recognition of the vulnerability of individuals with ASD within the CJS highlights the urgent need for a systematic evaluation of the effectiveness of interventions for offending behaviours in adults with ASD. While previous research has examined interventions for individuals with ASD and co-occurring ID [ 49 ], a significant research gap remains regarding the effectiveness of forensic interventions for individuals with ASD but without co-occurring ID [ 14 ].
This systematic review aims to address this gap by conducting a comprehensive evaluation of intervention effectiveness in an ASD population without co-occurring ID.
Research aims
This systematic review is guided by the following research objectives:
To systematically review and evaluate the effectiveness of interventions for offending behaviours in adults with ASD without co-occurring ID, as reported in the literature;
To ascertain whether the core features of ASD impact the effectiveness of the identified interventions; and.
To identify additional risk factors that may impact the effectiveness of interventions in this population.
Inclusion criteria
Each potentially eligible study was screened based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria described in the PICO framework below [ 50 ].
Population.
Participants included adults aged 18 years and older diagnosed with ASD, as defined by the authors in the literature. Studies involving participants with co-occurring ASD and ID and those that did not differentiate between these two populations were excluded.
Intervention & Outcomes.
Our review aimed to identify studies that objectively and/or subjectively measured the effectiveness of therapeutic or pharmacological interventions for reducing recidivism in individuals with ASD exhibiting offending behaviours. These included interventions delivered in all categories, namely, prisons, probation supervision, and secure hospitals.
Study Design and Comparison.
All primary research studies were included, regardless of publication date or country of origin. Studies that were peer-reviewed (e.g., grey literature and conference abstracts), systematic reviews, and those not published in English were excluded. An inclusion-exclusion criterion related to the type of comparison conducted in individual studies was not imposed.
Search strategy
The search was conducted on the 27th of March 2021 across five databases, covering a broad timeframe and utilising international terminology. The databases included:
Embase (1974 to 2021).
Ovid MEDLINE(R) and Epub ahead of print, In-process, In data-review and other Non-Indexed Citations.
Ovid MEDLINE(R) Daily.
Global Health (1973 to March 2021).
APA PsychInfo (1806 to February 2021).
Furthermore, a web-based search using Google Scholar was conducted with the same search terms. The first 15 pages of results were manually reviewed; however, no additional studies meeting the inclusion criteria were found. Additionally, the reference lists and citations of relevant reviews were manually checked, but this did not yield any further eligible studies.
Data selection and extraction
The data selection and extraction processes consisted of two stages:
During Stage 1, potential eligible studies were screened based on their titles and abstracts against the predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Owing to the limited number of results, the screening process was performed manually and repeated one week later to increase accuracy.
Stage 2 involved a comprehensive review of the full texts of the selected studies to confirm their alignment with the inclusion criteria. Relevant data were extracted and organised into spreadsheets using Microsoft Excel.
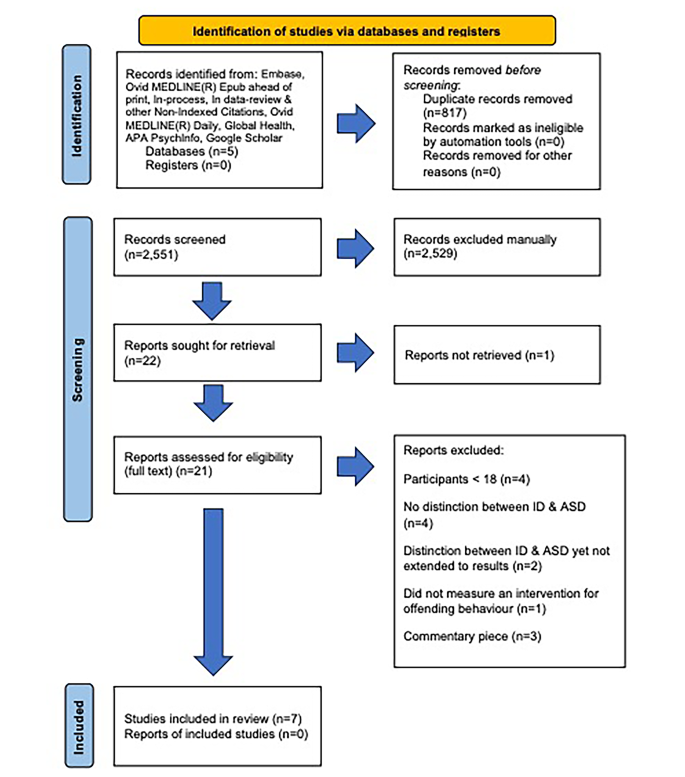
PRISMA flow diagram of searches of databases and registers only
Consistent with the primary aim of this systematic review, the first outcome measure is the effectiveness of the identified forensic interventions, measured by a reduction in recidivism. While reducing recidivism is the principal goal of forensic interventions, it is often viewed as a proxy measure that may not fully capture the complexity of offending behaviours, particularly in cases of crossover crime [ 46 , 51 ]. To address this limitation, additional relevant measures contributing to reduced recidivism were collected to allow for a preliminary assessment of intervention effectiveness. These additional measures included variables such as a reduction in security levels within institutional settings (i.e., medium to low security) or significant positive changes compared to baseline measurements recorded before and after the intervention.
The second aim of this review was to examine whether the core features of ASD present barriers to the rehabilitation process. To achieve this objective, data concerning the interactions between impairments in social communication and interaction (SCI) and restrictive and repetitive behaviours (RRBs) in relation to interventions within individual studies, as described by clinicians were collected and analysed.
Thirdly, this review aimed to identify additional risk factors described within findings that may influence the effectiveness of the interventions. The aim of the analysis is to provide a more comprehensive understanding of collective risk factors and their interactions with intervention effectiveness assessed through narrative synthesis. In addition, the data collected included the study design, author, and country of origin. When reported, participant demographics, such as age, gender, offence, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status, were reported. The intervention data included the type of intervention used, setting, duration, and frequency, only when available.
Study risk of bias assessment
The Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool (MMAT) [ 52 ] is a comprehensive tool for critically evaluating various research methods. The methodological quality of each study and the potential risk of bias were assessed using the MMAT. The results of this assessment are presented in tabular form (Table 2 , ‘MMAT Quality Appraisal’, appendix).
Synthesis method
A narrative synthesis [ 53 ] was used for this review as a meta-analysis was not appropriate because of the significant heterogeneity between studies. The synthesis process began with a preliminary analysis, in which the data were extracted and presented in tabular form to provide a summary of the findings and to identify potential patterns within the data. A guided conceptual framework was constructed based on the narrative synthesis of the primary data. This framework aimed to assess both the similarities and differences between the included studies while exploring emerging thematic elements.
Study selection
The initial database search returned 2,551 results after removing duplicates, as shown in Fig. 1 of the PRISMA flow diagram, which depicts the flow of information at each stage of the systematic review search. Subsequent screening included an initial assessment of the titles and a subsequent assessment of the abstracts, which led to the exclusion of an additional 2,530 articles. To ensure accuracy, abstract screening was repeated one week later. Subsequent full-text eligibility screening excluded 14 additional studies. The reasons for exclusion included the following: (a) participants under 18 years of age ( n = 4), (b) lacked differentiation between the ID and ASD populations ( n = 4), (c) were differentiated but not described in the context of the results ( n = 2), (d) measurement of interventions for self-harm and suicide among offenders with ASD rather than for offending behaviour ( n = 1), and (e) removal of commentary papers ( n = 3). Consequently, the final number of included studies from the initial database search was seven ( n = 7).
Study characteristics
Among the seven studies identified, three were case reports ( n = 3), two were qualitative studies ( n = 2), and two were quantitative case series ( n = 2). These studies jointly assessed the effectiveness of the various interventions. The total sample size of all the studies was limited to 10; all the participants were men, and demographic information was limited. It is worth noting that despite the use of international terminology in the search criteria, all seven articles described studies conducted exclusively in southern England, United Kingdom (UK). In these studies, all participants, apart from one were held in secure hospital units under the provisions of the Mental Health Act 1983. The most prevalent types of offending behaviours observed were sexual offences ( n = 4), followed by manslaughter ( n = 3), and arson ( n = 3).
Table 1 ‘Summary of Findings’ provides a summary of each study included in the systematic review. The summary includes author information, available participant demographics, offence type, setting, detainment status (i.e., under the mental health act), intervention approach, study findings, intervention effectiveness, measurement used to assess effectiveness, and whether there was evidence to suggest that the core features of ASD impacted the effectiveness of forensic intervention(s). These are separated by impairments in social communication and interaction (SCI) and restrictive and repetitive behaviours (RRBs).
Risk of bias in studies
The methodological quality of the studies was assessed using the MMAT [ 52 ] (Table 2 , ‘MMAT Quality Appraisal’, appendix). Each of the three case reports received a 3-star rating, indicating a moderate risk of bias and meeting 75% of the qualitative MMAT criteria [ 54 , 55 , 56 ].
The two quantitative case series were found to be at a higher risk of bias due to difficulties in distinguishing the treatment groups, recruitment difficulties, lack of a control group, and incomplete outcome data for the ASD group without co-occurring ID. They received a 2-star rating, meeting 50% of the MMAT quantitative criteria [ 58 ].
The second quantitative study [ 57 ], raised concerns about the validity and reliability of outcome measures, which were originally designed for the ID population but applied to the ASD group without co-occurring ID. This study also received a 2-star rating and met 50% of the MMAT’s quantitative criteria.
The remaining qualitative studies received a 3-star rating, meeting 75% of the MMAT criteria. The first evaluated intervention effectiveness from the perspective of the clinicians who delivered the therapeutic program [ 59 ]. The second assessed offenders’ views via self-report, which carry a potential risk of response bias [ 60 ].
Selection bias was observed in studies that combined ID and ASD populations. Overall, it was difficult to establish a causal relationship between the interventions and outcomes.
Notably, not all the studies reviewed explicitly documented obtaining informed consent from participants. The discrepancy in informed consent between studies, particularly in restrictive forensic settings, presents challenges extending beyond ethical considerations. Such discrepancies may compromise the validity of intervention comparisons, introduce biases in participant selection, and undermine the reliability of data.
Interventions
The interventions examined across the reviewed studies were diverse, as presented in Table 3 , titled ‘Summary of Interventions’.
Three studies incorporated both pharmacological and psychological interventions. Specifically, antipsychotics were used to address co-occurring psychosis, contributing to instances of offending behaviour [ 55 ]. Antipsychotics were also used to manage stress-induced psychosis [ 56 ]. In the context of directly treating offending behaviours, two distinct medications were applied in cases of sexual offending, each with different mechanisms of action [ 54 ] (Table 3 ).
Four studies relied exclusively on psychological interventions [ 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 ]. Among these, two studies implemented adapted forms of CBT. Specific details regarding the non-standardised adaptations used in CBT were not provided by the study author, except that individual delivery was necessary due to difficulties encountered within group settings [ 54 , 56 ].
The third study that incorporated CBT included elements similar to those of the Adapted Sex Offender Treatment Program (A-SOTP) [ 58 ]. The effectiveness of the A-SOTP was described in two studies [ 59 , 60 ]. Furthermore, the Equipping Youth to Help One Another (EQUIP) was adapted and piloted for use with individuals with ID and developmental disabilities (DD) who had committed sexual offences [ 57 ]. Supplementary interventions included speech and language therapy to facilitate communication [ 55 ], occupational therapy to address impairments in executive functioning [ 55 , 56 ] and art therapy [ 54 ].
Table 3 visually depicts a summary of the diverse interventions extracted, reviewed, and categorised according to intervention type: pharmacological, psychological, and supplementary intervention approaches. In addition, the table includes the type of offence, studies using intervention, underlying mechanism of action or theory, evidence base supporting intervention, and measurements used to assess effectiveness.
Measurements
Numerous approaches were adopted to measure effectiveness across the studies. Two studies measured effectiveness by reduced recidivism and the need to repeat the intervention. Other studies utilised a range of standardised measurements to evaluate psychological interventions. For example, one study [ 54 ] employed the Behavioural Status Index (BSI) every six months as a measurement tool. In contrast, another [ 56 ] employed the State Trait Anger Expression Inventory (STAXII II) and the Millon Multiaxial Personality Inventory (MMPI), combined with standardised risk assessment, one-year postintervention.
Regarding pharmacological interventions, one case report used a combination of subjective and objective measurements. These included self-reports and the systematic monitoring of inappropriate glancing behaviours over time by staff members [ 54 ]. In another instance, the reduction in verbalised delusions served as a measure of the effectiveness of antipsychotic medication [ 55 , 56 ].
The effectiveness of interventions such as the A-SOTP was assessed differently across the two studies. In one study, effectiveness was evaluated through clinician views [ 59 ], while in the other, effectiveness was determined by the participants’ subjective experiences with the intervention [ 60 ].
In the case of CBT, which shares similarities with A-SOTP, standardised measures were applied both pre- and post-intervention. These measures consisted of sexual attitudes consistent with sexual offending (QACSO), sexual offenders’ self-appraisal scale (SOSAS), the sexual attitudes and knowledge scale (SAKS), and the victim empathy scale-adapted (VES-A) [ 58 ].
The EQIP study, which also focused on sexual offending [ 57 ], assessed effectiveness by examining improvements in baseline scores on standardised tests related to moral reasoning, cognitive distortions, problem-solving abilities, and anger. In addition, a move to a lower security level was considered an indicator of overall effectiveness. Furthermore, in a case study that included speech and language therapy, the clinician’s subjective view of improved communication within the secure unit served as a measure of the intervention’s effectiveness [ 55 ].
Among the seven studies reviewed, only one pertaining to an arson offence considered the intervention(s) effective. In this case, a pharmacological intervention was used to treat co-occurring alcohol-induced psychosis, and the unspecified antipsychotic proved successful in reducing delusions. Furthermore, speech and language therapy aimed at improving communication skills was also deemed to be effective [ 55 ].
However, the remaining six studies, which included a total of nine participants, concluded that the interventions were largely ineffective. One case report addressing sexual offending behaviours used pharmacological interventions. The first involved cyproterone acetate, a testosterone inhibitor, however, the outcome could not be conclusively determined owing to adherence and dosage issues [ 54 ]. In the second, the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) fluoxetine was deemed ineffective, as inappropriate behaviours did not significantly decrease [ 54 ]. It is worth noting that the evidence for both of these drugs has since been described as insufficient to guide clinical practice, with cyproterone acetate considered inadequate [ 61 ], and the evidence for fluoxetine has not been fully determined [ 62 ].
Among the two studies that utilised the A-SOTP and a similar form of CBT for sexual offending, one participant repeated the intervention program six times and subsequently re-offended and a further two participants repeated the yearlong intervention program and reoffended [ 58 ]. These findings are consistent with the results of the study that assessed clinician views [ 59 ]. Even in the case of CBT, as used in two studies, the intervention was deemed ineffective despite adaptations made to accommodate individuals with ASD [ 54 , 56 ].
ASD core features and impact upon intervention effectiveness
The application of a narrative synthesis facilitated the identification and extraction of recurring patterns within the data. These patterns were evident across all the studies, highlighting the considerable challenges posed by impairments in social communication and interaction (SCI) and the presence of restrictive and repetitive behaviours (RRBs) on the effectiveness of interventions, as depicted in Fig. 2 .
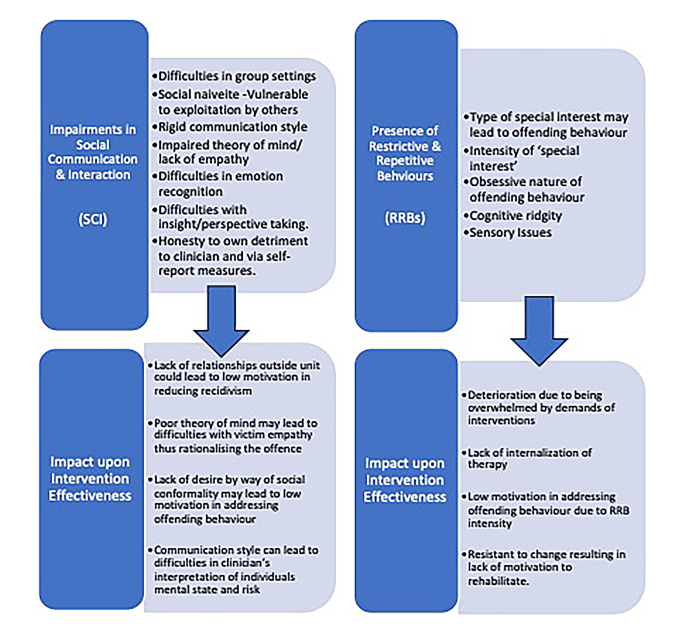
Impact of The Core Features of ASD upon Intervention Effectiveness. Note. This describes the core features of ASD, both ‘impairments to SCI’ and ‘presence of RRBs’, and their impact upon intervention effectiveness as extracted from studies
Additional factors impacting intervention effectiveness
In addition to the core features of ASD, this review sought to identify additional risk factors that may influence the effectiveness of the intervention(s). Potential risk factors highlighted by the authors of each study were collected, and through narrative synthesis, several recurring themes emerged from the data. Co-occurring personality disorders and psychosis [ 55 , 56 ], were identified as potential factors impacting intervention effectiveness, as described within the literature. Additionally, events such as childhood adversity, sexual abuse, trauma, and having a dysfunctional family life were described as potential contributors [ 58 ]. Late diagnosis of ASD was theorised to lead to maladaptive coping skills deriving from unmet needs, which were described in three of the studies [ 54 , 55 , 56 ].
An overarching theme identified across the majority of the seven studies was the insufficiency of service provision, staff expertise, and the evidence base.
The present systematic review identified seven studies with ten participants who underwent forensic interventions aimed at reducing offending behaviours in adults with ASD, particularly those without co-occurring ID. The principal aim of this review was to evaluate the effectiveness of these interventions. The secondary aim was to examine whether the core features of ASD have an impact on the effectiveness of these forensic interventions and to identify other variables that may impact the overall effectiveness of interventions.
Regarding the first aim, the evidence suggests that the interventions reviewed were inadequate. However, these findings should be treated with caution not only because of the small sample size but also because of limitations in the generalisability of the findings. Despite an extensive literature search, all the studies were conducted in southern England, UK, and included only male participants. In addition, all participants, with the exception of one individual living in the community, were detained within secure hospital settings under the provisions of the Mental Health Act (1983). This highlights the lack of data from prison and the probation service, which limits the scope of the review. Furthermore, this review highlights a critical lack of research within this domain. Even when the literature was identified, it was often of inadequate quality owing to various design limitations. The significant heterogeneity between studies, each utilising distinct intervention methods and tools for measuring intervention effectiveness, illustrates a notable lack of standardisation in both clinical and research methodologies within this field. This lack of consistency aligns with broader research on mental health in individuals with ASD [ 45 , 46 ]. Nonetheless, the forensic domain faces additional challenges, such as the lack of randomised control trials, which means that the effectiveness of interventions is difficult to fully determine. These challenges are exacerbated by unavoidable confounding variables, the risk of bias, and the ethical implications of a no-treatment group [ 66 ], all of which contribute to the lack of evidence.
The secondary aim was to examine the potential impact of the core features of ASD on the effectiveness of interventions designed to reduce recidivism. The data patterns identified through narrative synthesis consistently emerged across all studies, highlighting the significant challenges posed by impairments in social communication and interaction (SCI) and the presence of restrictive and repetitive behaviours (RRBs). These challenges highlight the general inappropriateness of forensic interventions within this population.
The third and final aim was to identify factors, beyond the core features of ASD, that may influence the effectiveness of interventions. Throughout the studies, a recurring theme emerged, highlighting significant systemic factors impacting intervention effectiveness. These include issues such as a shortage of government funding leading to inadequate service provision, the question of whether ASD and ID services should be combined, and the substantial unmet needs throughout the lifespan of individuals with ASD, all of which affect the success of forensic interventions. While the core features of ASD are significant, they may not be the primary cause of intervention failure. Rather, they seem to be contributing factors within a broader and more complex array of variables that collectively impact the overall effectiveness of these forensic interventions.
Implications
The inadequate provision of forensic services carries significant implications, especially when prolonged detainment becomes necessary due to the shortcomings of forensic interventions. Such deficiencies may subject individuals with ASD to non-evidence-based interventions, often repeatedly [ 56 , 58 ]. This then increases the likelihood of these individuals being labelled as ‘unrehabilitated,’ potentially leading to extended periods of detainment. Consequently, this creates a counterproductive cycle that not only exacerbates the economic burden but also raises serious concerns about human rights and the potential legal consequences of prolonged confinement.
These issues underscore fundamental questions about the fairness and adequacy of the legal system. Therefore, addressing these knowledge gaps and the lack of evidence-based approaches are crucial to ensuring a more equitable criminal justice system for individuals with ASD.
Future research
This review identifies several key areas for future research in this field. Developing evidence-based interventions tailored to the unique needs of individuals with ASD is crucial. Establishing a consensus on the measurements used for assessing the effectiveness of these interventions, as well as a clear definition of what constitutes effectiveness, would significantly enhance research quality.
Moreover, due to the bias towards studies conducted in southern England, the consistency of interventions for treating offending behaviours in adults with ASD in England remains unclear, especially considering the persistent regional health disparities between the North and South of England [ 67 , 68 ].
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Association AP. DSM-5 classification. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2015.
Masi A, DeMayo MM, Glozier N, Guastella AJ. An overview of Autism Spectrum Disorder, Heterogeneity and Treatment options. Neurosci Bull. 2017;33(2):183–93.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Berry K, Russell K, Frost K. Restricted and repetitive behaviors in Autism Spectrum Disorder: a review of Associated features and presentation across clinical populations. Curr Dev Disorders Rep. 2018;5(2):108–15.
Article Google Scholar
Geurts HM, Corbett B, Solomon M. The paradox of cognitive flexibility in autism. Trends Cogn Sci. 2009;13(2):74–82.
Chaplin E, McCarthy J, Allely CS, Forrester A, Underwood L, Hayward H, et al. Self-harm and Mental Health Characteristics of Prisoners with elevated rates of autistic traits. Res Dev Disabil. 2021;114:103987.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Hirvikoski T, Boman M, Chen Q, D’Onofrio BM, Mittendorfer-Rutz E, Lichtenstein P, et al. Individual risk and familial liability for suicide attempt and suicide in autism: a population-based study. Psychol Med. 2019;50(9):1463–74.
Kim SH, Lord C. The Behavioral Manifestations of Autism Spectrum Disorders. In: The Neuroscience of Autism Spectrum Disorders [Internet]. Elsevier; 2013 [cited 2024 Jan 7]. pp. 25–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-391924-3.00002-8 .
Jensen CM, Steinhausen HC, Lauritsen MB. Time trends over 16 years in incidence-rates of Autism Spectrum Disorders across the Lifespan Based on Nationwide Danish Register Data. J Autism Dev Disord. 2014;44(8):1808–18.
Roman-Urrestarazu A, van Kessel R, Allison C, Matthews FE, Brayne C, Baron-Cohen S. Association of Race/Ethnicity and Social Disadvantage with Autism Prevalence in 7 million School Children in England. JAMA Pediatr. 2021;175(6):e210054.
Haas K, Gibbs V. Does a person’s autism play a role in their interactions with police: the perceptions of autistic adults and Parent/Carers. J Autism Dev Disord. 2020;51(5):1628–40.
Murphy D. Interviewing individuals with an autism spectrum disorder in forensic settings. Int J Forensic Mental Health. 2018;17(4):310–20.
Allely CS, Cooper P, Jurors’. and Judges’ evaluation of defendants with autism and the impact on sentencing: a systematic Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) review of Autism Spectrum Disorder in the courtroom. J Law Med. 2017;25(1).
Allely CS. Experiences of prison inmates with autism spectrum disorders and the knowledge and understanding of the spectrum amongst prison staff: a review. J Intellect Disabil Offending Behav. 2015;6(2):55–67.
King C, Murphy GH. A systematic review of people with Autism Spectrum Disorder and the Criminal Justice System. J Autism Dev Disord. 2014;44(11):2717–33.
Maras K, Mulcahy S, Crane L. Is autism linked to criminality? Autism. 2015;19(5):515–6.
Robertson CE, McGillivray JA. Autism behind bars: a review of the research literature and discussion of key issues. J Forensic Psychiatr Psychol. 2015;26(6):719–36.
McQuaid GA, Pelphrey KA, Bookheimer SY, Dapretto M, Webb SJ, Bernier RA, et al. The gap between IQ and adaptive functioning in autism spectrum disorder: disentangling diagnostic and sex differences. Autism. 2021;25(6):1565–79.
Dein K, Hassiotis A, Woodbury-Smith M, Roychowdhury A, Squires R, Freestone M. Prevalence of autism within medium secure units: a feasibility study. J Forensic Psychiatr Psychol. 2021;32(6):861–78.
Murphy D, Allely C. Autism spectrum disorders in high secure psychiatric care: a review of literature, future research and clinical directions. Adv Autism. 2019;6(1):17–34.
Davoren M, Byrne O, O’Connell P, O’Neill H, O’Reilly K, Kennedy HG. Factors affecting length of stay in forensic hospital setting: need for therapeutic security and course of admission. BMC Psychiatry. 2015;15(1).
Lewis A, Pritchett R, Hughes C, Turner K. Development and implementation of autism standards for prisons. J Intellect Disabil Offending Behav. 2015;6(2):68–80.
Criminal justice joint inspectorate. Neurodiversity in the criminal justice system: a review of evidence. 2021.
Allely CS. A systematic PRISMA review of individuals with autism spectrum disorder in secure psychiatric care: prevalence, treatment, risk assessment and other clinical considerations. J Criminal Psychol. 2018;8(1):58–79.
Howlin P. Outcome in adult life for more able individuals with autism or Asperger Syndrome. Autism. 2000;4(1):63–83.
Newman SS, Ghaziuddin M. Violent crime in Asperger Syndrome: the Role of Psychiatric Comorbidity. J Autism Dev Disord. 2008;38(10):1848–52.
Allely CS, Minnis H, Thompson L, Wilson P, Gillberg C. Neurodevelopmental and psychosocial risk factors in serial killers and mass murderers. Aggress Violent Beh. 2014;19(3):288–301.
Newman BN, Crowell KA. The intersectionality of criminality and substance use self-stigmas. Stigma Health. 2023;8(2):212–22.
Schofield PW, Malacova E, Preen DB, D’Este C, Tate R, Reekie J, et al. Does traumatic Brain Injury lead to criminality? A Whole-Population Retrospective Cohort Study using Linked Data. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(7):e0132558.
Benevides TW, Carretta HJ, Lane SJ. Unmet need for Therapy among children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: results from the 2005–2006 and 2009–2010 National Survey of children with Special Health Care needs. Matern Child Health J. 2015;20(4):878–88.
Płatos M, Pisula E. Service use, unmet needs, and barriers to services among adolescents and young adults with autism spectrum disorder in Poland. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019;19(1).
Green RM, Travers AM, Howe Y, McDougle CJ. Women and Autism Spectrum Disorder: diagnosis and implications for treatment of adolescents and adults. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2019;21(4).
Gupta M, Chaudhary R. Diagnostic challenges of High-Functioning Autism Spectrum disorder in females. Cureus. 2021 Jan 30.
Durkin MS, Maenner MJ, Meaney FJ, Levy SE, DiGuiseppi C, Nicholas JS, et al. Socioeconomic inequality in the prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder: evidence from a U.S. cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE. 2010;5(7):e11551.
Crane L, Hearst C, Ashworth M, Davies J, Hill EL. Supporting newly identified or diagnosed autistic adults: an initial evaluation of an autistic-led Programme. J Autism Dev Disord. 2020;51(3):892–905.
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Kelly B, Williams S, Collins S, Mushtaq F, Mon-Williams M, Wright B, et al. The association between socioeconomic status and autism diagnosis in the United Kingdom for children aged 5–8 years of age: findings from the born in Bradford cohort. Autism. 2017;23(1):131–40.
Ministry of Justice. Offending behaviour programmes and interventions [Internet]. GOV.UK. 2018 [cited 2021 Dec 13]. https://www.gov.uk/guidance/offending-behaviour-programmes-and-interventions#accreditation .
Lipsey MW, Landenberger NA. Cognitive-Behavioral Interventions. In: Preventing Crime [Internet]. Berlin/Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag; 2006. pp. 57–71. https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-4244-2_4 .
Henwood KS, Chou S, Browne KD. A systematic review and meta-analysis on the effectiveness of CBT informed anger management. Aggress Violent Beh. 2015;25:280–92.
Wilson DB, Bouffard LA, Mackenzie DL. A quantitative review of structured, Group-Oriented, cognitive-behavioral programs for offenders. Criminal Justice Behav. 2005;32(2):172–204.
MacInnes D, Masino S. Psychological and psychosocial interventions offered to forensic mental health inpatients: a systematic review. BMJ Open. 2019;9(3):e024351.
Spain D, Blainey SH. Group social skills interventions for adults with high-functioning autism spectrum disorders: a systematic review. Autism. 2015;19(7):874–86.
Spain D, Happé F. How to optimise cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) for people with Autism Spectrum disorders (ASD): a Delphi Study. J Rational-Emot Cognitive-Behav Ther. 2019;38(2):184–208.
Parr JR, Brice S, Welsh P, Ingham B, Le Couteur A, Evans G et al. Treating anxiety in autistic adults: study protocol for the personalised anxiety treatment–autism (PAT-A©) pilot randomised controlled feasibility trial. Trials. 2020;21(1).
Gantman A, Kapp SK, Orenski K, Laugeson EA. Social Skills Training for Young Adults with high-functioning Autism Spectrum disorders: a Randomized Controlled Pilot Study. J Autism Dev Disord. 2011;42(6):1094–103.
Chambers JC, Yiend J, Barrett B, Burns T, Doll H, Fazel S, et al. Outcome measures used in forensic mental health research: a structured review. Criminal Behav Mental Health. 2009;19(1):9–27.
Fitzpatrick R, Chambers J, Burns T, Doll H, Fazel S, Jenkinson C et al. A systematic review of outcome measures used in forensic mental health research with consensus panel opinion. Health Technol Assess. 2010;14(18).
Weston L, Hodgekins J, Langdon PE. Effectiveness of cognitive behavioural therapy with people who have autistic spectrum disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Psychol Rev. 2016;49:41–54.
Higgs T, Carter AJ. Autism spectrum disorder and sexual offending: Responsivity in forensic interventions. Aggress Violent Beh. 2015;22:112–9.
Melvin CL, Langdon PE, Murphy GH. Treatment effectiveness for offenders with autism spectrum conditions: a systematic review. Psychol Crime Law. 2017;23(8):748–76.
Shuster JJ, Review. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews for interventions, Version 5.1.0, published 3/2011. Julian P.T. Higgins and Sally Green, editors. Res Synthesis Methods. 2011;2(2):126–30.
Völlm B, Braun P. Long-Term Forensic Psychiatric Care: clinical, ethical and legal challenges. Springer; 2019.
Hong QN, Fàbregues S, Bartlett G, Boardman F, Cargo M, Dagenais P, et al. The mixed methods Appraisal Tool (MMAT) version 2018 for information professionals and researchers. Educ Inform. 2018;34(4):285–91.
Campbell M, McKenzie JE, Sowden A, Katikireddi SV, Brennan SE, Ellis S et al. Synthesis without meta-analysis (SWiM) in systematic reviews: reporting guideline. BMJ. 2020;l6890.
Milton J, Duggan C, Latham A, Egan V, Tantam D. Case History of Co-morbid Asperger’s syndrome and paraphilic behaviour. Med Sci Law. 2002;42(3):237–44.
Radley J, Shaherbano Z. Asperger syndrome and arson: a case study. Adv Mental Health Intellect Disabil. 2011;5(6):32–6.
Murphy D. Extreme violence in a man with an autistic spectrum disorder: assessment and treatment within high-security psychiatric care. J Forensic Psychiatry Psychol. 2010;21(3):462–77.
Langdon PE, Murphy GH, Clare ICH, Palmer EJ, Rees J. An evaluation of the EQUIP Treatment Programme with men who have intellectual or other Developmental Disabilities. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2012;26(2):167–80.
Murphy G, Powell S, Guzman A, Hays S. Cognitive-behavioural treatment for men with intellectual disabilities and sexually abusive behaviour: a pilot study. J Intellect Disabil Res. 2007;51(11):902–12.
Melvin CL, Langdon PE, Murphy GH. They’re the hardest group to treat, that changes the least. Adapted sex offender treatment programmes for individuals with Autism Spectrum disorders: clinician views and experiences. Res Dev Disabil. 2020;105:103721.
Melvin CL, Langdon PE, Murphy GH. I feel that if I didn’t come to it anymore, maybe I would go back to my old ways, and I don’t want that to happen: adapted sex offender treatment programmes: views of service users with autism spectrum disorders. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2019;33(4):739–56.
Khan O, Ferriter M, Huband N, Powney MJ, Dennis JA, Duggan C. Pharmacological interventions for those who have sexually offended or are at risk of offending. Cochrane Database Syst Reviews. 2015 Feb 18.
National Institute for Health. And Care Excellence (NICE). Hypersexuality: fluoxetine; 2015.
Google Scholar
Masood B, Lepping P, Romanov D, Poole R. Treatment of Alcohol-Induced psychotic disorder (alcoholic Hallucinosis)—A systematic review. Alcohol Alcohol. 2017;53(3):259–67.
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Rehabilitation for adults with complex psychosis. 2020.
Patterson C. Does the adapted sex offender treatment programme reduce cognitive distortions? A meta-analysis. J Intellect Disabil Offending Behav. 2018;9(1):9–21.
Robertson MD, Walter G. Many faces of the dual-role Dilemma in Psychiatric Ethics. Australian New Z J Psychiatry. 2008;42(3):228–35.
Bambra C, Barr B, Milne E. North and South: addressing the English health divide. J Public Health. 2014;36(2):183–6.
Whitehead M, Doran T. The north-south health divide. BMJ. 2011;342(feb15 2):d584–584.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Forensic and Neurodevelopmental Sciences, Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology and Neuroscience, King’s College London, London, UK
Jody Salter & Sarah Blainey
School of Health and Society, University of Salford, Greater Manchester, UK
Jody Salter
Central and North West London NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK
Sarah Blainey
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
JS was responsible for writing the manuscript, including the creation of figures and tables. SB provided supervision and editorial input throughout the manuscript’s development.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jody Salter .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The systematic review did not involve original data collection; therefore, no ethical statement is required.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Salter, J., Blainey, S. The effectiveness of interventions for offending behaviours in adults with autism spectrum disorders (ASD): a systematic PRISMA review. BMC Psychol 12 , 316 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01770-1
Download citation
Received : 15 January 2024
Accepted : 07 May 2024
Published : 30 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01770-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Autism spectrum disorder
- Offending behaviour
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Forensic psychology
- Intervention
- Criminal justice system
BMC Psychology
ISSN: 2050-7283
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Narrative reviews have many strengths. They are flexible and practical, and ideally provide a readable, relevant synthesis of a diverse literature. Narrative reviews are often helpful for teaching or learning about a topic because they deliver a general overview. They are also useful for setting the stage for future research, as they offer an ...
Environment. Policy*. Research Design. Systematic Reviews as Topic*. Traditional approaches to reviewing literature may be susceptible to bias and result in incorrect decisions. This is of particular concern when reviews address policy- and practice-relevant questions. Systematic reviews have been introduced as a more rigorous approach to ...
In our recent paper in Nature Ecology and Evolution, we highlight 8 common problems with traditional literature review methods, provide examples for each from the field of environmental management and ecology, and provide practical solutions for ways to mitigate them. Problem. Solution. Lack of relevance - limited stakeholder engagement can ...
A literature review can broadly be described as a more or less systematic way of ... The semi-systematic or narrative review approach is designed for topics that have been conceptualized differently and studied by ... it could be worthwhile to consider including additional limitations. As almost all initial literature searches yield many ...
As the size of the published scientific literature has increased exponentially over the past 30 years, review articles play an increasingly important role in helping researchers to make sense of original research results. Literature reviews can be broadly classified as either "systematic" or "narrative". Narrative reviews may be broader in scope than systematic reviews, but have been ...
All literature types: Narrative review: Green, Johnson, and Adams 2001: Gordon and Richardson 1997 a: Gordon and Richardson's (1997) example of a narrative review discusses the issue of whether or not compact cities are a desirable planning goal. The authors do not attempt to summarize the entire scope of literature, but rather identify key ...
Table 1 compares systematic and narrative reviews ( Table 1 ). Since the evidence-based medicine is the current trend and also mandatory for establishment of heath policy, the PI should also turn to encourage submission of systematic reviews rather than narrative reviews. Table 1. Comparison between narrative vs systematic review.
Our goal with this paper is to conduct a narrative review of the literature about systematic reviews and outline the essential elements of a systematic review along with the limitations of such a review. Keywords: systematic reviews, meta-analysis, narrative literature review, prisma checklist. A literature review provides an important insight ...
Cynthia Mulrow's important paper calling for literature reviews to be undertaken more ... limitations and conceptual confusions of systematic and narrative reviews. We consider three questions: what makes a review systematic; what is a narrative review and whether these different kinds of review should be viewed as competing or complementary ...
A narrative review is the "older" format of the two, presenting a (non-systematic) summation and analysis of available literature on a specific topic of interest. Interestingly, probably because the "approach" is non-systematic, there are no acknowledged formal guidelines for writing narrative reviews.
al bias in the appraisal of retrieved articles, and interpretation of findings, they serve as sources of quick up-to-date reference for specific areas of interest of readers. Well-conducted reviews could inform readers about gaps in existing literature and areas that need new primary research. Crafting a narrative review requires a blend of good scientific approach and the skillful art of ...
Writing a narrative literature review requires careful planning. This chapter summarizes some key steps in reviewing the literature. First, a team needs to be formed. Second, a topic needs to be chosen. This needs to be relevant to the author's research/teaching interests and a well-defined issue.
A formal literature review is an evidence-based, in-depth analysis of a subject. There are many reasons for writing one and these will influence the length and style of your review, but in essence a literature review is a critical appraisal of the current collective knowledge on a subject. Rather than just being an exhaustive list of all that ...
A narrative literature review is valuable, however, when one is attempting to link together many studies on different topics, either for purposes of reinterpre- tation or interconnection. As such, narrative literature reviewing is a valuable theory- building technique, and it may also serve ...
A narrative literature review is an integrated analysis of the existing literature used to summarize a body of literature, draw conclusions about a topic, and identify research gaps. By understanding the current state of the literature, you can show how new research fits into the larger research landscape.
The primary problem is that the narrow focus and prescribed methods of the systematic review do not allow for comprehensive coverage. For example, the historical review is an irreplaceable means of tracing the development of a scientific principle or clinical concept, but the narrative thread could be lost in the strict rules of systematic review.
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important ...
CONCLUSION. Siddaway 16 noted that, "The best reviews synthesize studies to draw broad theoretical conclusions about what the literature means, linking theory to evidence and evidence to theory" (p. 747). To that end, high quality systematic reviews are explicit, rigorous, and reproducible. It is these three criteria that should guide authors seeking to write a systematic review or editors ...
Narrative methods of synthesis can be used to synthesise both quantitative and qualitative studies and have been used when the experimental and quasi-experimental studies included in a systematic review are not sufficiently similar for a meta-analysis to be appropriate (Mays et al. Citation 2005a). Narrative synthesis is used in different ways.
The narrative review is the "traditional" way of reviewing the extant literature and is skewed towards a qualitative interpretation of prior knowledge (Sylvester et al., 2013). Put simply, a narrative review attempts to summarize or synthesize what has been written on a particular topic but does not seek generalization or cumulative ...
A narrative review is the type first-year college students often learn as a general approach. Its purpose is to identify a few studies that describe a problem of interest. ... Steps for Conducting a Narrative Literature Review. Step 1: Conduct a Search. ... Despite these limitations, consensus and critical reviews were the primary source of ...
Narrative reviews are evidence-based summaries on a particular, defined topic, often covering a range of specific questions from pathophysiology to treatment. The content may be clinical, ethical, policy or legal review. The scope of the narrative review should be defined in the work. Though the standards of
Discipline norms: a literature review for one subject (e.g., history) would be different than another (e.g., medicine). Organization: a review can be organized the following ways: Topical or narrative: by subject or theme of documents included in the review. Chronological: by when the included documents were published. Geographical: by regions ...
A narrative literature review is fairly broad, as it involves gathering, critiquing and summarising journal articles and textbooks about a particular topic. These are generally undertaken to get an overview of a topic and potentially identify gaps in the literature. How does it differ from a systematic literature review?
Limitations include heterogeneity across intervention types, measures of effectiveness, and what constitutes effectiveness. Despite the limited number of studies and data quality, the review aligns with a growing body of literature highlighting vulnerability and a need for evidence-based interventions for people with ASD.