

EMPLOYEE MOTIVATION, JOB SATISFACTION, AND EMPLOYEE PERFORMANCE: A LITERATURE REVIEW
- Imam Hidayat Universitas Trisaksi, Jakarta, Indonesia
- Endi Supardi Universitas Trisaksi, Jakarta, Indonesia
- Alvis Anwar Universitas Trisaksi, Jakarta, Indonesia
- Sarfilianty Anggiani Universitas Trisaksi, Jakarta, Indonesia
The purpose of this paper is to provide a structured literature review on the constructs of employee motivation, job satisfaction, employee performance, and empirical evidence on the relationship between motivation, job satisfaction, and performance. 20 (twenty) papers published during 2017-2021 that investigates employee motivation, job satisfaction, employee performance, and the relationship between employee motivation, job satisfaction, and employee performance were reviewed. The results of the review show that employee motivation and job satisfaction have positive and significant effect on employee performance or in other word employee motivation and job satisfaction are the determinants of employee performance.
Astuti, W., and Amalia, L. 2021. The Relationship Between Work Motivation, Job Satisfaction, and Employee Performance: The Moderating Role of Psychology Capital and the Mediating Role of Organizational Commitment. Journal of Theory & Applied Management, Vol. 14. No. 2, pp. 102-128.
Buchanan, D.A., and Huczynsky, A.A. 2019. Organizational Behaviour, 10th Edition, Harlow: Pearson Education Limited,
Carvalho, A.D.C., Riana, I.G., and Soares, A.D.C. 2020. Motivation on Job Satisfaction and Employee Performance. International Research Journal of Management, IT & Social Sciences, Vol. 7 No. 5, pp. 13-23. https://doi.org/10.21744/irjmis.v7n5.960 .
Cetin, F., and Askun, D. 2018. The Effect of Occupational Self-Efficacy on Work Performance through Intrinsic Work Motivation. Management Research Review, Vol. 41 No. 2. https://doi.org/10.1108/MRR-03-2017-0062 .
Colquitt, J.A., Lepine, J.A., and Wesson, M.J. 2019. Organizational Behavior: Improving Performance and Commitment in The Workplace. 6th Edition. New York: McGraw-Hill Education.
Dharma, Y. 2018. The Effect of Work Motivation on the Employee Performance with Organization Citizenship Behavior as Intervening Variable at Bank Aceh Syariah. Emerald Reach Proceedings Series, Vol. 1 pp. 7-12. https://doi.org/10.1108/978-1-78756-793-1-00065 .
DuBrin, A.J. 2019. Fundamentals of Organizational Behavior, 6th Edition. Academic Media Solutions.
Egenius, S., Triatmanto, B., and Natsir, M. 2020. The Effect of Job Satisfaction on Employee Performance Through Loyalty at Credit Union (CU) Corporation of East Kutai District, East Kalimantan. International Journal of Multicultural and Multireligious Understanding, Vol. 7, Issue 10, pp.: 480-489.
Endang T., and Sari, E. 2019. The Effect of Motivation and Discipline on Employee Performance at the Ministry of Transportation's Directorate of Ports. Ilomata International Journal of Social Science, Vol. 1 No. 1, pp. 1-9.
Girdwichai, l., and Sriviboon, C. 2020. Employee Motivation and Performance: Do the Work Environment and the Training Matter?. Journal of Security and Sustainability Issues, Vol. 9, pp. 42-64.
Griffin, R.W., Phillips, J.M., and Gully, S.M. 2019. Organizational Behavior: Managing People and Organizations, 13th Edition. Boston: Cengage Learning, Inc
Hariati, Muis, M., and Amar, Y. 2021. The Effect of Job Motivation and Job Satisfaction on Employee Performance through Organizational Citizenship Behavior. Hasanudin Journal of Business Strategy, Volume 3 Nomor 4, pp. 93-104.
Kinicki, A. 2021. Organizational Behavior: A Practical, Problem Solving Approach, 3rd Edition. New York: McGraw-Hill Education.
Kuswati, Y. 2020. The Effect of Motivation on Employee Performance. Budapest International Research and Critics Institute-Journal Vol. 3, No 2, pp. 995-1002.
Lin, Y. 2021. A Study on the Relationship Between Project Management Competency, Job Performance and Job Motivation in e-Commerce Industry. Measuring Business Excellence, Vol. 25 No. 1. https://doi.org/10.1108/MBE-10-2020-0144 .
Luthans, F., Luthans, B.C., and Luthans, K.W. 2021. Organizational Behavior: An Evidence-Based Approach, 14th Edition. Charlotte: Information Age Publishing, Inc.
Mubarok, T.M.S., Lindayani, L., Farizah, S.N. 2021. The Relationship between Job Satisfaction and Employee Performance. Advances in Economics, Business and Management Research, Volume 657, 6th Global Conference on Business, Management, and Entrepreneurship (GCBME 2021), pp. 459-464.
Nurdiansyah, R., Mariam, S., Ameido, M.A., and Ramli, A.H. 2020. Work Motivation, Job Satisfaction, and Employee Performance. Business and Entrepreneurial Review Vol. 20, No.2, pp. 153-162.
Ouakouak, M.L., Zaitouni, M.G., and Arya, B. 2020. Ethical Leadership, Emotional Leadership, and Quitting Intentions in Public Organizations: Does Employee Motivation Play a Role?. Leadership & Organization Development Journal, Vol. 41 No. 2, pp. 257-279. https://doi.org/10.1108/LODJ-05-2019-0206 .
Pawirosumarto, S., Sarjana, P.K., and Muchtar, M. 2017. Factors Affecting Employee Performance of PT. Kiyokuni Indonesia. International Journal of Law and Management, Vol. 59 No. 4. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJLMA-03-2016-0031 .
Rita, M., Payangan, O.R., Rante, Y., Tuhumena, R., and Erari. 2018. Moderating Effect of Organizational Citizenship Behavior on the Effect of Organizational Commitment, Transformational Leadership and Work Motivation on Employee Performance. International Journal of Law and Management, Vol. 60 No. 4, pp. 953-964. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJLMA-03-2017-0026 .
Riyanto, S., Endri, E., and Herlisha, N. 2021. Effect of Work Motivation and Job Satisfaction on Employee Performance: Mediating Role of Employee Engagement. Problems and Perspectives in Management, Vol. 19, Issue 3, pp. 162-174.
Robbins, S.P., and Judge, T.A. Organizational Behavior, Update 18th Edition. Harlow: Pearson Education Limited.
Safitri, R.D., Suratno, A., and Sulistiyani, E. 2018. The Influence of Job Satisfaction and Motivation on Employee Performance at PT Chakra Naga Furniture Jepara. Jurnal JOBS, Vol. 4, No. 1, pp. 45-55.
Sidabutar, E., Syah, T.Y.R., and Anindita. R. 2020. The Impact of Compensation, Motivation, and Job Satisfaction on Employee Performance. Science, Engineering and Social Science Series, Vol. 4, No. 1, pp. 1-5.
Suardhita, N., Rafik, A., and Siregar, O. Analysis of The Effect of Motivation and Job Satisfaction on Employee Performance in PT Gagas Energi Indonesia Jakarta. Journal of Industrial Engineering & Management, Vol. 1 No. 3, pp. 209-217.
Sartika, L., Fatimah, F., and Asiati, D.I. 2022. The Effect of Competence, Job Placement and Job Satisfaction on Employee Performance at the Regional Office VII BKN. International Journal of Business, Management, and Economics, Vol. 3 No. 3, pp.257-270.

- DOWNLOAD ARTICLE FULL PDF
Authors who publish their manuscripts in this journal agree to the following conditions:
- The copyright on each article belongs to the author(s).
- The author acknowledges that the Dinasti International Journal of Digital Business Management (DIJDBM) has the right to be the first to publish with a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license (Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
- Authors can submit articles separately, arrange for the non-exclusive distribution of manuscripts that have been published in this journal into other versions (e.g., sent to the author's institutional repository, publication into books, etc.), by acknowledging that the manuscript has been published for the first time in the Dinasti International Journal of Digital Business Management (DIJDBM).

- Peer Reviewers
- Peer Review Process
- Aim and Scope
- Publication Ethics
- Online Submission Guidelines
- Article Processing Charge
- Open Access Statement
- License Term
- Histori Jurnal
- Plagiarisme Policy
- Archive Policy
- Author Guidelines

E-ISSN: 2715-4203

P-ISSN: 2715-419X
EDITORIAL OFFICE
Casa Amira Prive Jl. H. Risin No. 64D Pondok Jagung Timur, Serpong Utara, Tangerang Selatan, Indonesia
Unipark Condominium, Block D 3-9 Selangor, Malaysia
Singapore 655B Jurong West ST 61#12-542 Singapore 642655
Dinasti International Journal of Digital Business Management (DIJDBM) is managed and published by Dinasti Publisher under the auspices of the Yayasan Dharma Indonesia Tercinta (DINASTI) and in collaboration with several institutions, the Faculty of Education, the National University of Malaysia, Faculty of Economics, Krisnadwipayana University, Faculty of Economics and Business, Winaya Mukti University, Bandung, Faculty of Economics, Muhammadiyah University Cirebon, Corruption Supervisory Commission (KPK Tipikor), Ekasakti University, Padang Indonesian Academy of Accountancy, Piksi Ganesha Polytechnic, Bandung, Bogor Academy of Technology, Bogor Telecommunication Academy, Indonesian National Tourism Academy, Bandung, Indonesian Polytechnic Piksi Ganesha, Kebumen, STIES Indonesia Purwakarta, STMIK Farewell, Kerawang and STIE Mahaputra Riau.
CONTACT INFO
https://dinastipub.org/DIJDBM
DIJDBM INDEX

To read this content please select one of the options below:
Please note you do not have access to teaching notes, factors affecting employee performance: a systematic literature review.
Journal of Advances in Management Research
ISSN : 0972-7981
Article publication date: 11 February 2019
Issue publication date: 11 July 2019
The purpose of this paper is to synthesize the fragmented literature on organizational citizenship behavior (OCB), leader–member exchange (LMX), learning, innovative work behavior (IWB) and employee performance across different countries, disciplines and organizations, thereby broadening the literature breath and making gap identification comprehensive. Second, it provides information on how much studies have been concentrated on Africa with the goal of provoking scholarly work in a unique cultural setting on the interrelatedness of these concepts.
Design/methodology/approach
Relevant literature search was undertaken using key search terms, “employee performance,” “OCB,” “LMX,” “IWB,” “individual learning” and “team learning.”
The findings show positive relationships between the behaviors and employee performance. They also reveal an interesting diversity in the study across multidisciplinary fields holding both cultural and contextual significance for academia and practitioners.
Research limitations/implications
The limitation of literature to peer-reviewed journals from the authors’ university library might have missed important information not in this domain. Further studies must make use of additional search terms and engines excluded from this study to provide a more comprehensive analysis.
Practical implications
The paper has important managerial implications for practitioners. The analysis can support the understanding of employee performance from a broader and more diverse view points; and help in providing insight into real-life opportunities, constraints and solutions in enhancing performance management.
Originality/value
This systematic literature review highlights important knowledge gaps which need to be explored especially in the African and Ghanaian contexts.
- Innovative work behaviour
- Leader-member exchange
- Organizational citizenship behaviour
- Employee performance
- Individual learning
- Team learning
Atatsi, E.A. , Stoffers, J. and Kil, A. (2019), "Factors affecting employee performance: a systematic literature review", Journal of Advances in Management Research , Vol. 16 No. 3, pp. 329-351. https://doi.org/10.1108/JAMR-06-2018-0052
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2019, Emerald Publishing Limited
Related articles
We’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

A Literature Review on the Effects of Employee Relation on Improving Employee Performance

It is apparent that employees are the major valuable assets of an organization in which without them, hard to realize its basic objectives. To harvest more from employees it requires creating conducive working environment which satisfies the needs of individual employee as well as the manager of an organization. This conceptual paper tries to examine the basic concepts employee relation and its effects on employee performance through investigating a number of employee relationship management components such as communication, participative leadership, shared goals and value, mutual trust, motivation and conflict management. Moreover, the relationship between employee relations and employee performance is explored in-depth. The study also discusses on employee performance which comprises of the basic concept and measurements of performance. From a comprehensive review of literature on earlier studies, it was found that the preceding researches didn't make thorough endeavor to address the effects employee relation on employee performance. Finally, it was suggested that future researchers should investigate profoundly to come up with notable empirical results. Key words: Effects, Employee Relation, Improving, Employee Performance 1. INTRODUCTION
Related Papers
Bolarinwa I B R A H I M Bolarinwa
Maintaining healthy employee relations in an organization is a pre-requisite for organizational success. Strong employee relations are required for high productivity. Employee relations deal with avoiding and resolving issues concerning individuals which might arise out of or influence the work scenario. This study aimed at assessing the impact of good employee relations on employee performance. This study used a descriptive survey method. Convenience sampling technique was used to select the sample size of one hundred and thirty-nine (139). The instrument used was a questionnaire.. The Kendall rank correlation was used as the inferential statistics. This study reveals that a good employee relation has influence on employee performance. The findings also revealed that strong employment relations create a pleasant atmosphere within the work environment, motivation and company rules. It is concluded that employees have been seen as an organization's valuable assets. The nature and amount of work performed by them have a direct impact on the productivity of an organization. It is therefore recommended that a concern for equity and justice should characterize the relationship between management and employee, and this will require the communication of sufficient information about changes and developments. Also, fair policies and practices exhibited by the management of the organisation to create equal opportunities and provide equal treatment to employees with no bias which promotes a positive attitude towards organization and work among employees.
Entrepreneurship and Innovation Management Journal ISSN: 2310-0079
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences
Ömür Hakan Kuzu
Employee and manger are the main leading roles of an organization. It is generally believe that employees and manger strong relationship leads the effectiveness of the performance of a bank. Employee-manager relationship not only enhances the performance of the bank but also creates the trust level in between employee and manger. The employee and manager strong relationship leads the employee satisfaction and also decrease the level of stress and employees who become comfortable or satisfy who never intend to leave an organization and that thing decrease the turnover cost and organization become successful to retain an active employee in an organization. Therefore the primary aim of this study is to know the manger and employees relationship impact on the effectiveness of a banks’ performance. The all relevant themes are discussed briefly in the results and findings that were identify during interview from participants as manager an employee of a bank. The research finding are inter...
Roopali Bajaj & Shalini Sinha
TJPRC Publication
Some HRM determinants, which if improved can build good employee relations in an organization and thus status of Employee Relationship can be improved in the organization. By quantifying HRM determinants and equating it to satisfaction of employees, the study has discovered and established that status of ERM in the state PSUs is not very good and measures of HR practices are not being implemented as they should be.
Budapest International Research and Critics Institute (BIRCI-Journal) : Humanities and Social Sciences
Tati Hartati
The background of this research was the low performance of the employee, which could be seen from the non optimal task implementation, overdue task completion, and low discipline. In this study, the researcher used analytical descriptive method, also literature study and field study as the instruments. The field study consisted of observation, interview, and questionnaire. The result of the research showed that the human relations done by the Sub-District Head had not been fully implemented based on the principles in human relations. It caused the low employee performance in the Argapura Sub-District Office of Majalengka Regency, so that the hypothesis of the researcher is true and can be accepted.
International Journal of Research and Analytical Reviews 2348-1269
Parveen Kumar , Ulka Tewari
Every individual shares a multifaceted relationship with colleagues at the workplace. As it is known to all that human beings are not machines who can start working within seconds or at a push button. They need someone to talk, to discuss ideas and to share their happiness and other emotions. We cannot expect an individual to start working like a robot with complete involvement in the work without knowing with whom he is working. A man is not indifferent; he needs people around. Without people working around the workplace turns hostile. An isolated environment demotivates an individual and spreads negativity which ultimately hampers performance. It will not be wrong to submit that workplaces are like homes; the more we are comfortable with each other, the more prosperity we gain. To achieve a common goal, mutual respect and a sense of safety are must at the workplace. It is an established notion that to work with people having different educational and cultural backgrounds is not that difficult rather than to work with people having different mindsets. It is much essential that employees share a healthy and happy relationship with each other at the workplace. Mutual understanding and mutual respect are the two hallmarks of meaningful Communication.A healthy bonding between the employer and the employee also strengthen productivity. When effective communication practices are in place at the workplace then employees feel more connected and committed to the organization. The Communication Breakdown at the workplace creates problems. This paper attempts to highlight the importance of Strong Employee Relations at Workplace and the Impact of these relations on the organisational success.
Vinayak webworld
JOURNAL OF MECHANICS OF CONTINUA AND MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES
kalpana koneru
Acharya Institute of Technology.
Mahak balani
RELATED PAPERS
Journal of Nobel Medical College
Manoj Bhattarai
Jehn-Ruey Jiang
Rozprawy Społeczne
Sebastian Sobczuk
International Journal of Educational Foundations and Management
Prof. Hammed I D O W U Adeyanju
European Respiratory Journal
Neus Salord Oleo
PETER KAMAU
Food Analytical Methods
Maria delRosario Gonzalez
Cereal Research Communications
Adrien Fónagy
Ana Cristina Borba Alves
Peter Halseth
Gulcan Ercivan
Lindsey Oudijk
produsenkulitdimsum1
Produsenkulitdimsum1 Produsenkulitdimsum1
parth patel
Revista Prâksis
achmad shofi
HAL (Le Centre pour la Communication Scientifique Directe)
Tamatoa Bambridge
Blucher Design Proceedings
Amilton Arruda
Kultura i Społeczeństwo
Agnieszka Maj
Revista Chilena de Salud Pública
Yuri Carvajal

RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
The impact of communication software usage on work engagement in remote work: the mediating role of distraction and FOMO
- Published: 10 May 2024
Cite this article

- Wan Jin 1 ,
- Pingping Li 2 ,
- Hang Ma 1 &
- Mingyue Qin 1
35 Accesses
Explore all metrics
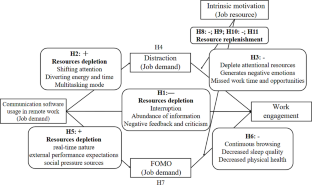
With the increasing demand for work-life balance and the development of information technology, remote work has become a widely adopted work mode, which has made communication software the primary means of communication for employees. However, previous research has not fully explored the impact of communication software usage (CSU) in remote work on work engagement, which is a crucial factor influencing employee performance. Therefore, this study, based on the Job Demands-Resources Theory, investigated the effects and mechanisms of CSU on work engagement in remote work. We collected a single time-point data set of 519 individuals with remote working experience and a dual time-point data set of 325 individuals in China. The results obtained from both datasets are consistent and indicate the following: (1) CSU in remote work has a significant negative impact on employee work engagement. (2) Distraction and fear of missing out (FOMO) mediate the relationship between CSU in remote work and work engagement respectively. (3) Intrinsic motivation moderates the negative effects of distraction and FOMO on work engagement. When employees have high intrinsic motivation, the negative effects of CSU in remote work through distraction and FOMO on work engagement diminishes. This study contributes to the research on the outcomes of CSU in remote work, deepens the understanding of the underlying mechanisms linking CSU and work engagement, and expands the knowledge of their boundary conditions.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Remote Working in the COVID-19 Era
The Moderating Role of Workplace (Hybrid/ Remote) on Employee Engagement and Employee Turnover Intention

A Systematic Literature Review of Potential and Emerging Links Between Remote Work and Motivation
Data availability.
The data that support the findings of this study will be made available, without undue reservation.
Abbasi, A. Z., Rehman, U., Hussain, A., Ting, D. H., & Islam, J. U. (2021). The impact of advertising value of in-game pop-up ads in online gaming on gamers’ inspiration: An empirical investigation. Telematics and Informatics , 62 , 101630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2021.101630
Article Google Scholar
Albulescu, P., Macsinga, I., Rusu, A., Sulea, C., Bodnaru, A., & Tulbure, B. T. (2022). Give me a break! A systematic review and meta-analysis on the efficacy of micro-breaks for increasing well-being and performance. Plos One , 17 (8), e0272460. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0272460
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Al-Furaih, S. A., & Al-Awidi, H. M. (2021). Fear of missing out (FOMO) among undergraduate students in relation to attention distraction and learning disengagement in lectures. Education and Information Technologies , 26 (2), 2355–2373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-020-10361-7
Allen, T. D., Golden, T. D., & Shockley, K. M. (2015). How effective is telecommuting? Assessing the status of our scientific findings. Psychological Science in the Public Interest , 16 (2), 40–68. https://doi.org/10.1177/1529100615593273
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Alonzo, R., Hussain, J., Stranges, S., & Anderson, K. K. (2021). Interplay between social media use, sleep quality, and mental health in youth: A systematic review. Sleep Medicine Reviews , 56 , 101414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2020.101414
Alt, D. (2015). College students’ academic motivation, media engagement and fear of missing out. Computers in Human Behavior , 49 , 111–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.201
Amabile, T. M., Hill, K. G., Hennessey, B. A., & Tighe, E. M. (1994). The Work Preference Inventory: assessing intrinsic and extrinsic motivational orientations. Journal of personality and social psychology , 66 (5), 950.
Anderson, H. J., & Bolino, M. C. (2023). Haunted by the past: How performing or withholding organizational citizenship behavior may lead to regret. Journal of Organizational Behavior , 44 (2), 297–310. https://doi.org/10.1002/job.2631
Bakker, A. B., & Demerouti, E. (2007). The job demands-resources model: State of the art. Journal of Managerial Psychology , 22 (3), 309–328. https://doi.org/10.1108/02683940710733115
Bakker, A. B., & Demerouti, E. (2017). Job demands–resources theory: Taking stock and looking forward. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology , 22 (3), 273. https://doi.org/10.1037/ocp0000056
Bhatia-Lin, A., Boon-Dooley, A., Roberts, M. K., Pronai, C., Fisher, D., Parker, L., & Darnell, D. (2019). Ethical and regulatory considerations for using social media platforms to locate and track research participants. The American Journal of Bioethics , 19 (6), 47–61. https://doi.org/10.1080/15265161.2019.1602176
Bhutto, T. A., Farooq, R., Talwar, S., Awan, U., & Dhir, A. (2021). Green inclusive leadership and green creativity in the tourism and hospitality sector: Serial mediation of green psychological climate and work engagement. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 29 (10), 1716–1737. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2020.1867864
Briones, R. L., Kuch, B., Liu, B. F., & Jin, Y. (2011). Keeping up with the digital age: How the American Red Cross uses social media to build relationships. Public Relations Review , 37 (1), 37–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pubrev.2010.12.006
Budnick, C. J., Rogers, A. P., & Barber, L. K. (2020). The fear of missing out at work: Examining costs and benefits to employee health and motivation. Computers in Human Behavior , 104 , 106161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2019.106161
Chatterjee, S., Chaudhuri, R., & Vrontis, D. (2022). Does remote work flexibility enhance organization performance? Moderating role of organization policy and top management support. Journal of Business Research , 139 , 1501–1512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.10.069
Cheng, Y. S., & Cho, S. (2021). Are social media bad for your employees? Effects of at-work break activities on recovery experiences. International Journal of Hospitality Management , 96 , 102957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2021.102957
Chen, Y., Li, S., Xia, Q., & He, C. (2017). The relationship between job demands and employees’ counterproductive work behaviors: The mediating effect of psychological detachment and job anxiety. Frontiers in Psychology , 8 , 1890. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01890
Chiou, W. B., Lee, C. C., & Liao, D. C. (2015). Facebook effects on social distress: Priming with online social networking thoughts can alter the perceived distress due to social exclusion. Computers in Human Behavior , 49 , 230–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.02.064
Chu, M., Li, H., Lin, S., Cai, X., Li, X., Chen, S. H., & Chiang, Y. C. (2021). Appropriate strategies for reducing the negative impact of online reports of suicide and public opinion from social media in China. Frontiers in Public Health , 9 , 756360. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2021.756360
Côté, K., Lauzier, M., & Stinglhamber, F. (2021). The relationship between presenteeism and job satisfaction: A mediated moderation model using work engagement and perceived organizational support. European Management Journal , 39 (2), 270–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emj.2020.09.001
Demerouti, E., Bakker, A. B., Nachreiner, F., & Schaufeli, W. B. (2001). The job demands-resources model of burnout. Journal of Applied Psychology , 86 (3), 499. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-9010.86.3.499
Demircioglu, M. A. (2018). Examining the effects of social media use on job satisfaction in the Australian public service: Testing self-determination theory. Public Performance & Management Review, 41 (2), 300–327. https://doi.org/10.1080/15309576.2017.1400991
Dhir, A., Yossatorn, Y., Kaur, P., & Chen, S. (2018). Online social media fatigue and psychological wellbeing—A study of compulsive use, fear of missing out, fatigue, anxiety and depression. International Journal of Information Management , 40 , 141–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2018.01.012
Dingel, J. I., & Neiman, B. (2020). How many jobs can be done at home? Journal of Public Economics , 189 , 104235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpubeco.2020.104235
Faraz, N. A., Ying, M., & Mehmood, S. A. (2021). The interplay of green servant leadership, self‐efficacy, and intrinsic motivation in predicting employees’ pro‐environmental behavior. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 28(4), 1171-1184. https://doi.org/10.1002/csr.2115
Feng, S., Wong, Y. K., Wong, L. Y., & Hossain, L. (2019). The internet and Facebook usage on academic distraction of college students. Computers & Education , 134 , 41–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.02.005
Fishbach, A., & Woolley, K. (2022). The structure of intrinsic motivation. Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior , 9 , 339–363. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-orgpsych-012420-091122
Fraccastoro, S., Gabrielsson, M., & Pullins, E. B. (2021). The integrated use of social media, digital, and traditional communication tools in the B2B sales process of international SMEs. International Business Review , 30 (4), 101776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibusrev.2020.101776
Fredrickson, B. L. (2013). Positive emotions broaden and build. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology , 47 , 1–53. 10.1016/ B978-0-12-407236-7.00001–2. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-407236-7.00001–2
Fridchay, J., & Reizer, A. (2022). Fear of missing out (FOMO): Implications for employees and job performance. The Journal of Psychology , 156 (4), 257–277. https://doi.org/10.1080/00223980.2022.2034727
Fujimoto, Y., Ferdous, A. S., Sekiguchi, T., & Sugianto, L. F. (2016). The effect of mobile technology usage on work engagement and emotional exhaustion in Japan. Journal of Business Research , 69 (9), 3315–3323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2016.02.013
Gao, Q., Dai, Y., Fan, Z., & Kang, R. (2010). Understanding factors affecting perceived sociability of social software. Computers in Human Behavior , 26 (6), 1846–1861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2010.07.022
Gatt, G., & Jiang, L. (2021). Can different types of non-territorial working satisfy employees’ needs for autonomy and belongingness? Insights from self-determination theory. Environment and Behavior , 53 (9), 953–986. https://doi.org/10.1177/0013916520942603
Gori, A., Topino, E., & Griffiths, M. D. (2023). The associations between attachment, self-esteem, fear of missing out, daily time expenditure, and problematic social media use: A path analysis model. Addictive Behaviors , 141 , 107633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2023.107633
Ágoston, C., Csaba, B., Nagy, B., Kőváry, Z., Dúll, A., Rácz, J., & Demetrovics, Z. (2022). Identifying types of eco-anxiety, eco-guilt, eco-grief, and eco-coping in a climate-sensitive population: A qualitative study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health , 19 (4), 2461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19042461
Harter, J. K., Schmidt, F. L., & Hayes, T. L. (2002). Business-unit-level relationship between employee satisfaction, employee engagement, and business outcomes: A meta-analysis. Journal of Applied Psychology, 87(2), 268-279.
Herlambang, M. B., Cnossen, F., & Taatgen, N. A. (2021). The effects of intrinsic motivation on mental fatigue. PloS One , 16 (1), e0243754. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0243754
Holmes, J., Guy, J., Kievit, R. A., Bryant, A., Mareva, S., Gathercole, S. E., & CALM Team. (2021). Cognitive dimensions of learning in children with problems in attention, learning, and memory. Journal of Educational Psychology , 113 (7), 1454. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000644
Hur, W. M., Rhee, S. Y., Lee, E. J., & Park, H. (2022). Corporate social responsibility perceptions and sustainable safety behaviors among frontline employees: The mediating roles of organization-based self‐esteem and work engagement. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management , 29 (1), 60–70. https://doi.org/10.1002/csr.2173
Hwang, M. Y., Hong, J. C., Tai, K. H., Chen, J. T., & Gouldthorp, T. (2020). The relationship between the online social anxiety, perceived information overload and fatigue, and job engagement of civil servant LINE users. Government Information Quarterly , 37 (1), 101423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.giq.2019.101423
Ilies, R., Huth, M., Ryan, A. M., & Dimotakis, N. (2015). Explaining the links between workload, distress, and work–family conflict among school employees: Physical, cognitive, and emotional fatigue. Journal of Educational Psychology , 107 (4), 1136. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000029
Jiang, Z., Newman, A., Schwarz, G., & Le, H. (2023). Perceived red tape and precursors of turnover: The roles of Work Engagement and Career Adaptability. Journal of Business and Psychology , 38 (2), 437–455. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10869-022-09834-y
Jackson, D. L., Gillaspy, J. A., Jr., & Purc-Stephenson, R. (2009). Reporting practices in confirmatory factor analysis: An overview and some recommendations. Psychological Methods, 14(1), 6-23.
Kuss, D. J., & Griffiths, M. D. (2017). Social networking sites and addiction: Ten lessons learned. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health , 14 (3), 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14030311
Lee, S., Zhou, Z. E., Xie, J., & Guo, H. (2021). Work-related use of information and communication technologies after hours and employee fatigue: The exacerbating effect of affective commitment. Journal of Managerial Psychology , 36 (6), 477–490. https://doi.org/10.1108/JMP-12-2019-0677
Levenson, J. C., Shensa, A., Sidani, J. E., Colditz, J. B., & Primack, B. A. (2016). The association between social media use and sleep disturbance among young adults. Preventive Medicine , 85 , 36–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ypmed.2016.01.001
Lin, H. C., & Chang, C. M. (2018). What motivates health information exchange in social media? The roles of the social cognitive theory and perceived interactivity. Information & Management , 55 (6), 771–780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2018.03.006
Lin, Y. J., & Wang, H. C. (2021). Using virtual reality to facilitate learners’ creative self-efficacy and intrinsic motivation in an EFL classroom. Education and Information Technologies , 26 (4), 4487–4505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10472-9
Liu, C., Chen, H., Zhou, F., Long, Q., Wu, K., Lo, L. M., & Chiou, W. K. (2022). Positive intervention effect of mobile health application based on mindfulness and social support theory on postpartum depression symptoms of puerperae. BMC Women’s Health , 22 (1), 413. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-022-01996-4
Liu, H., Fan, J., Fu, Y., & Liu, F. (2018). Intrinsic motivation as a mediator of the relationship between organizational support and quantitative workload and work-related fatigue. Human Factors and Ergonomics in Manufacturing & Service Industries , 28 (3), 154–162. https://doi.org/10.1002/hfm.20731
Liu, S. X., Zhou, Y., Cheng, Y., & Zhu, Y. Q. (2020). Multiple mediating effects in the relationship between employees’ trust in organizational safety and safety participation behavior. Safety Science , 125 , 104611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2020.104611
Luna, D., Figuerola-Escoto, R. P., Sienra-Monge, J. J. L., Hernández-Roque, A., Soria-Magaña, A., Hernández-Corral, S., & Toledano-Toledano, F. (2023). Burnout and Its Relationship with Work Engagement in Healthcare Professionals: A Latent Profile Analysis Approach. In Healthcare, 11 (23), 3042. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11233042 . MDPI.
Lyngdoh, T., El-Manstrly, D., & Jeesha, K. (2023). Social isolation and social anxiety as drivers of generation Z’s willingness to share personal information on social media. Psychology & Marketing , 40 (1), 5–26. https://doi.org/10.1002/mar.21744
Maier, C., Laumer, S., Eckhardt, A., & Weitzel, T. (2015). Giving too much social support: Social overload on social networking sites. European Journal of Information Systems , 24 (5), 447–464. https://doi.org/10.1057/ejis.2014.3
McCarthy, J. M., Trougakos, J. P., & Cheng, B. H. (2016). Are anxious workers less productive workers? It depends on the quality of social exchange. Journal of Applied Psychology , 101 (2), 279. https://doi.org/10.1037/apl0000044
Methot, J. R., Rosado-Solomon, E. H., Downes, P. E., & Gabriel, A. S. (2021). Office chitchat as a social ritual: The uplifting yet distracting effects of daily small talk at work. Academy of Management Journal , 64 (5), 1445–1471. https://doi.org/10.5465/amj.2018.1474
Milyavskaya, M., Saffran, M., Hope, N., & Koestner, R. (2018). Fear of missing out: Prevalence, dynamics, and consequences of experiencing FOMO. Motivation and Emotion , 42 (5), 725–737. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11031-018-9683-5
Moreno, M. A., Jelenchick, L., Koff, R., Eikoff, J., Diermyer, C., & Christakis, D. A. (2012). Internet use and multitasking among older adolescents: An experience sampling approach. Computers in Human Behavior , 28 (4), 1097–1102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2012.01.016
Oksa, R., Kaakinen, M., Savela, N., Ellonen, N., & Oksanen, A. (2021). Professional social media usage: Work engagement perspective. New Media & Society , 23 (8), 2303–2326. https://doi.org/10.1177/1461444820921938
Orhan, M. A., Castellano, S., Khelladi, I., Marinelli, L., & Monge, F. (2021). Technology distraction at work. Impacts on self-regulation and work engagement. Journal of Business Research , 126 , 341–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.12.048
Pace, S. (2004). A grounded theory of the flow experiences of web users. International Journal of human-computer Studies , 60 (3), 327–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhcs.2003.08.005
Prentice, M., Jayawickreme, E., & Fleeson, W. (2019). Integrating whole trait theory and self - determination theory. Journal of personality , 87 (1), 56-69.
Rosen, L. D., Carrier, L. M., & Cheever, N. A. (2013). Facebook and texting made me do it: Media-induced task-switching while studying. Computers in Human Behavior, 29 (3), 948–958. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2012.12.001
Ten Brummelhuis, L. L., & Bakker, A. B. (2012). A resource perspective on the work–home interface: The work–home resources model. American Psychologist, 67 (7), 545. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0027974
van Egmond, M. C., Berges, N., Omarshah, A. T., & J, Benton. (2017). The role of intrinsic motivation and the satisfaction of basic psychological needs under conditions of severe resource scarcity. Psychological Science, 28 (6), 822–828. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797617698138
Von Krogh, G. (2012). How does social software change knowledge management? Toward a strategic research agenda. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 21 (2), 154–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsis.2012.04.003
Rabiul, M. K., & Yean, T. F. (2021). Leadership styles, motivating language, and work engagement: An empirical investigation of the hotel industry. International Journal of Hospitality Management , 92 , 102712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2020.102712
Raza, A., Farrukh, M., Iqbal, M. K., Farhan, M., & Wu, Y. (2021). Corporate social responsibility and employees’ voluntary pro-environmental behavior: The role of organizational pride and employee engagement. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management , 28 (3), 1104–1116. https://doi.org/10.1002/csr.2109
Roberts, J. A., & David, M. E. (2020). The social media party: Fear of missing out (FoMO), social media intensity, connection, and well-being. International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction , 36 (4), 386–392. https://doi.org/10.1080/10447318.2019.1646517
Rosen, L. D., Whaling, K., Carrier, L. M., Cheever, N. A., & Rokkum, J. (2013b). The media and technology usage and attitudes scale: An empirical investigation. Computers in Human Behavior , 29 (6), 2501–2511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2013.06.006
Saks, A. M. (2006). Antecedents and consequences of employee engagement. Journal of Managerial Psychology , 21 (7), 600–619. https://doi.org/10.1108/02683940610690169
Saleem, S., Feng, Y., & Luqman, A. (2021). Excessive SNS use at work, technological conflicts and employee performance: A social-cognitive-behavioral perspective. Technology in Society , 65 , 101584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2021.101584
Sanders, G. S., & Baron, R. S. (1975). The motivating effects of distraction on task performance. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 32 (6), 956. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.32.6.956
Schaufeli, W. B., Bakker, A. B., & Salanova, M. (2006). The measurement of work engagement with a short questionnaire: A cross-national study. Educational and Psychological Measurement , 66 (4), 701–716. https://doi.org/10.1177/001316440528247
Schumann, F., Steinborn, M. B., Kürten, J., Cao, L., Händel, B. F., & Huestegge, L. (2022). Restoration of attention by rest in a multitasking world: Theory, methodology, and empirical evidence. Frontiers in Psychology , 13 , 867978. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.867978
Shin, Y., & Hur, W. M. (2021). When do job-insecure employees keep performing well? The buffering roles of help and prosocial motivation in the relationship between job insecurity, work engagement, and job performance. Journal of Business and Psychology , 36 , 659–678. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10869-020-09694-4
Spreitzer, G. M. (1995). Psychological empowerment in the workplace: Dimensions, measurement, and validation. Academy of Management Journal , 38 (5), 1442–1465. https://doi.org/10.5465/256865
Sun, Y., Wu, L., & Jeyaraj, A. (2022). Moderating role of enterprise social media use in work engagement. Information Processing & Management , 59 (1), 102793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2021.102793
Syrek, C. J., Kühnel, J., Vahle-Hinz, T., & De Bloom, J. (2018). Share, like, twitter, and connect: Ecological momentary assessment to examine the relationship between non-work social media use at work and work engagement. Work & Stress , 32 (3), 209–227. https://doi.org/10.1080/02678373.2017.1367736
Tisu, L., Lupșa, D., Vîrgă, D., & Rusu, A. (2020). Personality characteristics, job performance and mental health: The mediating role of work engagement. Personality and Individual Differences, 153 , 109644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2019.109644
Tokunaga, R. S. (2016). Interpersonal surveillance over social network sites: Applying a theory of negative relational maintenance and the investment model. Journal of Social and Personal Relationships , 33 (2), 171–190. https://doi.org/10.1177/0265407514568749
Trabelsi, K., Ammar, A., Boujelbane, M. A., Khacharem, A., Elghoul, Y., Boukhris, O., & Terry, P. C. (2022). Ramadan observance is associated with higher fatigue and lower vigor in athletes: A systematic review and meta-analysis with meta-regression. International Review of Sport and Exercise Psychology , 1–28. https://doi.org/10.1080/1750984X.2022.2106790
Unsworth, N., & McMillan, B. D. (2013). Mind wandering and reading comprehension: Examining the roles of working memory capacity, interest, motivation, and topic experience. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning Memory and Cognition , 39 (3), 832. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0029669
Verduyn, P., Ybarra, O., Résibois, M., Jonides, J., & Kross, E. (2017). Do social network sites enhance or undermine subjective well-being? A critical review. Social Issues and Policy Review , 11 (1), 274–302. https://doi.org/10.1111/sipr.12033
Wang, J., Wang, P., Yang, X., Zhang, G., Wang, X., Zhao, F., & Lei, L. (2019). Fear of missing out and procrastination as mediators between sensation seeking and adolescent smartphone addiction. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction , 17 , 1049–1062. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-019-00106-0
Wehner, B., Ritter, C., & Leist, S. (2017). Enterprise social networks: A literature review and research agenda. Computer Networks , 114 , 125–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2016.09.001
Wei, S., Chen, X., & Liu, C. (2022). What motivates employees to use social media at work? A perspective of self-determination theory. Industrial Management & Data Systems , 122 (1), 55–77. https://doi.org/10.1108/IMDS-06-2020-0322
Wu, T. J., Yuan, K. S., Yen, D. C., & Yeh, C. F. (2023). The effects of JDC model on burnout and work engagement: A multiple interaction analysis. European Management Journal , 41 (3), 395–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emj.2022.02.001
Xu, J., Xie, B., & Chung, B. (2019). Bridging the gap between affective well-being and organizational citizenship behavior: The role of work engagement and collectivist orientation. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health , 16 (22), 4503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16224503
Xu, Y., Liu, D., & Tang, D. S. (2022). Decent work and innovative work behaviour: Mediating roles of work engagement, intrinsic motivation and job self-efficacy. Creativity and Innovation Management , 31 (1), 49–63. https://doi.org/10.1111/caim.12480
Yousaf, S., Rasheed, M. I., Kaur, P., Islam, N., & Dhir, A. (2022). The dark side of phubbing in the workplace: Investigating the role of intrinsic motivation and the use of enterprise social media (ESM) in a cross-cultural setting. Journal of Business Research , 143 , 81–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2022.01.043
Yue, Z., Lee, D. S., Xiao, J., & Zhang, R. (2023). Social media use, psychological well-being and physical health during lockdown. Information. Communication & Society , 26 (7), 1452–1469. https://doi.org/10.1080/1369118X.2021.2013917
Zeng, D., Takada, N., Hara, Y., Sugiyama, S., Ito, Y., Nihei, Y., & Asakura, K. (2022). Impact of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation on work engagement: A cross-sectional study of nurses working in long-term care facilities. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health , 19 (3), 1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031284
Zhang, J., Jiang, R., Wu, X., & Jiang, J. J. (2023). The moderating role of enterprise social media functionalities on employees’ social-related use during work time. Information & Management , 60 (3), 103770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2023.103770
Zijlstra, F. R., Roe, R. A., Leonora, A. B., & Krediet, I. (1999). Temporal factors in mental work: Effects of interrupted activities. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology , 72 (2), 163–185. https://doi.org/10.1348/096317999166581
Download references
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (72161014; 72162017), and the Social Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province(22JY23).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Economics and Management, East China Jiaotong University, 330013, Nanchang, China
Wan Jin, Hang Ma & Mingyue Qin
College of Management, Shenzhen University, 518061, Shenzhen, China
Pingping Li
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Wan Jin contributed to the design of the framework, and the collection of primary materials. Pingping Li contributed to the empirical work and the analysis of the results. Hang Ma contributed to the writing of the first draft. Mingyue Qin contributed to the investigation and data analysis.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Pingping Li .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Jin, W., Li, P., Ma, H. et al. The impact of communication software usage on work engagement in remote work: the mediating role of distraction and FOMO. Curr Psychol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-024-06035-z
Download citation
Accepted : 21 April 2024
Published : 10 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-024-06035-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Remote work
- Communication software usage
- Distraction
- Intrinsic motivation
- Work engagement
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Abstract. Employee motivation is a very important area of organisational management and has a significant impact on organisational success and employee performance. This paper reviews the relevant ...
The effect of motivation on employee engagement in public sectors: in the case of North Wollo zone ... Employee recognition is a dynamic communication technique to improve employee performance which leads to enhance organizational performance. ... M. & Singh, R.K. A literature review on motivation. Glob Bus Perspect 1, 471-487 (2013). https ...
Performance appraisal is. fi. necessary for raising the performance levels of employees in terms of output quality and time management. There many positive outcomes of a performance appraisal program, which include increased motivation and teamwork spirit, morale among the employees, reduction in employee turnover, job satisfaction as well as ...
Empirical evidence demonstrates that motivated employees mean better organizational performance. The objective of this conceptual paper is to articulate the progress that has been made in understanding employee motivation and organizational performance, and to suggest how the theory concerning employee motivation and organizational performance may be advanced.
few dimensions of motivation. Literature review In a complex and dynamic environment, leader of the organization used to create the environment in which employee feel trusted and are empowered to take decisions in the organization which leads to enhance motivation level of employee and ultimately organizational performance are enhanced.
Work motivation is one of the crucial keys to improving employee performance. This study aims to describe the factors that affect work motivation and explain the influence of work motivation on employee performance. Through the systematic literature review approach, this study identified 34 articles with the publication year 2018 - 2022 that discussed work motivation. The results showed that ...
The result showed that quality of supervision has positive effect on employee motivation to work better. ... to find out the relationship between employee motivation and performance, and to find out the challenges that organizations face in its attempt to motivate staff. ... LITERATURE REVIEW Theories of Motivation It is adequately documented ...
Using the correct type of motivation is pivotal in triggering employees' affirmative work attitudes, such as work performance, job satisfaction, or voluntary retention, ultimately leading to increasing the organization's overall efficiency. Despite the ongoing academic debate, academics provide practitioners with mixed results on which motivation factors are relevant for targeted employee ...
A literature review was conducted in order to determine if intrinsic motivation, extrinsic motivation, or a combination of both, had greater impact on performance culture within organizations. Upon review, it has been shown that there is a mixed approach in whether or not employee's motivation is intrinsic or extrinsic.
The purpose of this paper is to provide a structured literature review on the constructs of employee motivation, job satisfaction, employee performance, and empirical evidence on the relationship between motivation, job satisfaction, and performance. 20 (twenty) papers published during 2017-2021 that investigates employee motivation, job satisfaction, employee performance, and the relationship ...
To conclude the existing literature review related to study variables and hypothesize the relationship ... This approach has some promising directions for employee motivation and performance and how leadership practices help in strengthening the relationship between these two variables. ... Indirect of Effect of Employee Motivation on ...
The analysis can support the understanding of employee performance from a broader and more diverse view points; and help in providing insight into real-life opportunities, constraints and solutions in enhancing performance management.,This systematic literature review highlights important knowledge gaps which need to be explored especially in ...
This study seeks to unravel the effects of motivation on employee performance, with a strategic human resource management approach. The fortitude for this research led to the retrieval of information from secondary sources published on the subject matter, and reviewed literature revealed the significance of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation.
The study includes a qualitative type of descriptive research by using the library search method of reviving and reanalyzing previous studies related to the effects of motivation on employee performance. The data used by researchers was obtained from the literature a study journal from the 2015-2020 associated with this study.
The effect of motivation on employees' performance: empirical evidence from the Brong Ahafo Education Directorate ... The purpose of this review paper is to assess effects of poor leadership. Leadership is a discipline and an art of guiding, ... AI-powered research tool for scientific literature, based at the Allen Institute for AI. Learn ...
A literature review on Employee motivation Sireesha Nethi Assistant Professor, Department of MBA, Samskruti College of Engineering and Technology, Kondapu (V), Ghatkesar (M), Medchal (D), Telangana. E-mail ID: [email protected] ABSTRACT Research on employee motivation has attracted both the academics and corporate companies from the
The existing systematic literature review illustrates the importance of the performance appraisal fairness on employee's motivation, which is affected by other important factors. This study is trying to examine the collected studies by focusing on the factors that determined on performance appraisal and employee's motivation [ 18 ].
2. Research Methodology The study is an integrative qualitative literature review on the concept of employee relation and its effect on employee performance. As it is an academic in nature, the review literature was focused on scholarly works which comprised of publications from reputable journals, books and conference proceedings.
Job satisfaction has long been discussed as an important factor determining individual behavior at work. To what extent this relationship is also evident in the teaching profession is especially relevant given the manifold job tasks and tremendous responsibility teachers bear for the development of their students. From a theoretical perspective, teachers' job satisfaction should be ...
When employees have high intrinsic motivation, the negative effects of CSU in remote work through distraction and FOMO on work engagement diminishes. This study contributes to the research on the outcomes of CSU in remote work, deepens the understanding of the underlying mechanisms linking CSU and work engagement, and expands the knowledge of ...
The better the compensation, motivation, and implementation of work discipline together, the more it will improve overall employee performance. Policy Implications The company needs to formulate ...