
How We Redesigned the New York Times Opinion Essay
When a team of editors, designers and strategists teamed up to talk about how times opinion coverage is presented and packaged to readers, they thought of a dinner party..
The NYT Open Team
By Dalit Shalom
Picture a dinner party. The table is set with a festive meal, glasses full of your favorite drink. A group of your friends gather around to talk and share stories. The conversation swings from topic to topic and everyone is engaged in a lively discussion, excited to share ideas and stories with one another.
This is what we imagined when we — a group of New York Times editors, strategists and designers — teamed up last summer to talk about how to think about how our Opinion coverage is presented and packaged to our readers. We envisioned a forum that facilitated thoughtful discussion and would invite people to participate in vibrant debates.
The team was established after a wave of feedback from our readers showed that many people found it difficult to tell whether a story was an Opinion piece or hard news. This feedback was concerning. The Times publishes fact-based journalism both in our newsroom and on our Opinion desk, but it is very important to our mission that the distinction between the two is clear.
The type of Opinion journalism our group was tasked with rethinking was the Op-Ed, which was first introduced in the Times newspaper in 1970. The Op-Ed was short for “opposite the Editorial Page,” and it contained essays written by both Times columnists and external contributors from across the political, cultural and global spectrum who shared their viewpoints on numerous topics and current events. Because of the Op-Ed’s proximity to the Editorial Page in the printed newspaper, it was clear that published essays were Opinion journalism.
Then The Times began publishing online. Today, most of our readers find our journalism across many different media channels. The Op-Ed lost its clear proximity to the Editorial Page, and the term has been used broadly as a catch-all phrase for Opinion pieces, leaving the definition of what an Op-Ed is unclear.
To learn more about the friction our readership was describing, we held several research sessions with various types of Times readers, including subscribers and non-subscribers. Over the course of these sessions, we learned that readers genuinely crave a diversity of viewpoints. They turn to the Opinion section for a curated conversation that introduces them to ideologies different than their own.
In the divided nature of politics today, many readers are looking for structured arguments that prepare them to converse thoughtfully about complicated topics. Some readers said they want to challenge and interrogate their own beliefs. Others worry that they exist in their own bubbles and they need to understand how the “other side” thinks.
And across the board, readers said they are aware that social media platforms can be echo chambers that help validate their beliefs rather than illuminate different perspectives. They believe The Times can help them look outside those echo chambers.
Considering this feedback, we took a close look at the anatomy of an Op-Ed piece. At a glance, Opinion pieces shared similar, but not necessarily cohesive, properties. They had an “Opinion” label at the top of the page that was sometimes followed by a descriptive sub-label (for example, “The Argument”), as a way to indicate a story belonged to a column. That would be a headline, a summary and a byline, often accompanied by an image or video before the actual text of the story.
By looking at those visual cues, it became clear to us that they could be reconfigured to better communicate the difference between news and opinion.
We created several design provocations and conducted user testing sessions with readers to see how this approach and a new layout might resonate. Some noticeable changes we made include center-aligning the Opinion label and header, labeling the section in red and providing more intentional guidance and art direction for visuals that accommodate Opinion pieces.
While many readers could tell the difference between news and opinion stories, they didn’t understand why certain voices were featured in the Opinion section. They wanted more clarity about the Op-Ed, such as who wrote it and whether the writer was Times staff or an external voice. In the case of external contributors, readers wanted to know why the desk chose to feature their voice.
These questions took our team back to the drawing board. We began to realize that the challenge at hand was not solely a design problem, but a framing issue, as well.
We had long philosophical conversations about the meaning of Op-Ed pieces. We talked about the importance of hosting external voices and how those voices should be presented to our readers. The metaphor of a dinner party figured prominently in our conversations: the Opinion section should be a place where guests gather to engage in an environment that is civil and respectful.
We began to sharpen how we might convey the difference between an endorsement of a particular voice and hosting a guest — one of many who might contribute to a lively debate around a current event.
The more we thought about the Opinion section as a dinner party, the more we felt how crucial it was to communicate this idea to readers.
As we approached the designs, we set out to create an atmosphere for open dialogue and conversation. Two significant editorial changes came out of our group conversations.
After many iterations, we decided to introduce a two-tiered labeling system, so that readers could understand unequivocally the type of Opinion piece they were about to engage with. For external voices, we added the label “ Guest Essay ,” alongside other labels that indicate staff contributors and internal editorials. The label “Guest Essay” not only shifts the tone of a piece — a guest that we are hosting to share their point of view — but it also helps readers distinguish between opinions coming from the voice of The Times and opinions coming from external voices.
The second important editorial change is a more detailed bio about the author whose opinion we are sharing. With the dinner party metaphor in mind, this kind of intentional introduction can be seen as a toast, providing context, clarity and relevance around who someone is and why we chose them to write an essay.
Some of these changes may seem subtle, but sometimes the best dinner conversations are nuanced. This body of work signals an important moment for The New York Times in how we think about expressing opinions on our platform. We believe that one of the things that makes for a healthy society and a functioning democracy is a space for numerous perspectives to be honored and celebrated. We are confident these improvements will help further Times Opinion’s mission of curating debate and discussion around the world’s most pressing issues.
Dalit Shalom is the Design Lead for the Story Formats team at The New York Times, focusing on crafting new storytelling vehicles for Times journalism. Dalit teaches classes on creative thinking and news products at NYU and Columbia, and in her free time you can find her baking tremendous amounts of babka.

Written by The NYT Open Team
We’re New York Times employees writing about workplace culture, and how we design and build digital products for journalism.
More from The NYT Open Team and NYT Open
How to Dox Yourself on the Internet
A step-by-step guide to finding and removing your personal information from the internet..
Milestones on our Journey to Standardize Experimentation at The New York Times
How we balanced flexibility and centralization across a large organization..
CJ Robinson
How the New York Times Games Data Team Revamped Its Reporting
Huge amounts of data from wordle and connections changed the way our team approached data infrastructure and design.

Estimation Isn’t for Everyone
The evolution of agility in software development, recommended from medium.
Designing an App for Audio Journalism — From the Ground Up
The design journey of the new york times audio app.

Ameer Omidvar
Apple’s all new design language
My name is ameer, currently the designer of sigma. i’ve been in love with design since i was a kid. it was just my thing. to make things….
Stories to Help You Grow as a Designer
Interesting Design Topics
Icon Design
Matej Latin
UX Collective
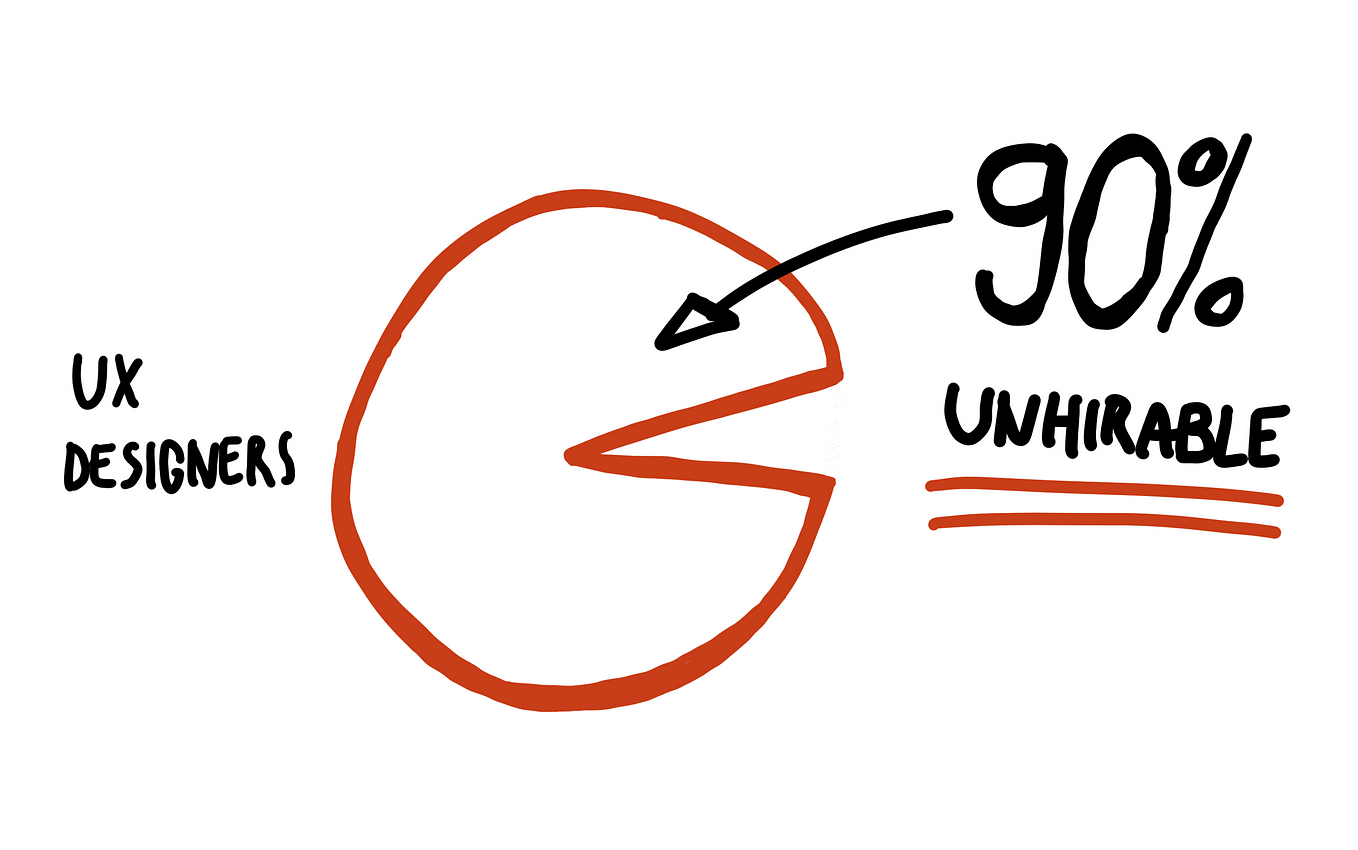
90% of designers are unhirable?
Or why your cookie-cutter portfolio doesn’t cut it and how to fix it.

Punit Chawla
UX/UI Design Trends Going Into 2024
Every year, we have a line up of new design trends that not only look good, but also stick around and influence other designers to “steal”….
UX/UI-trends in 2024
The 2023 year was rich in technological innovations: we witnessed the introduction of virtual glasses from apple, the surge of generative….

Debbie Levitt
Nielsen and Norman Should Be Ignored
My li feed lately is full of people unhappy with what one of these guys said. they’re not influencers anymore. take them off the pedestals..
Text to speech
Upcoming Summer 2024 Application Deadline is May 12, 2024.
Click here to apply.

Featured Posts

Pace University's Pre-College Program: Our Honest Review

Building a College Portfolio? Here are 8 Things You Should Know

Should You Apply to Catapult Incubator as a High Schooler?

8 Criminal Justice Internships for High School Students

10 Reasons to Apply to Scripps' Research Internship for High School Students

10 Free Business Programs for High School Students

Spike Lab - Is It a Worthwhile Incubator Program for High School Students?

10 Business Programs for High School Students in NYC

11 Summer Film Programs for High School Students

10 Photography Internships for High School Students
New York Times' Student Editorial Contest - 7 Tips to Help You Win
“You can make anything by writing,” goes the quote by C.S. Lewis, and the prolific author, wasn't wrong!
Your words, if crafted clearly, can shape opinions, change minds, uncover the truth, and much more.
If you’re a high school student with a passion for writing concise and persuasive arguments, then you should consider applying for the New York Times’ Annual Student Editorial Contest , which invites students from across the U.S. to send in their best writing on topics they’re passionate about.
Argumentative writing is a critical skill you need to excel in college, and winning competitive essay competitions is a great way to showcase your clarity of thought, ability to build cohesive arguments, and write concisely.
What is the Student Editorial Contest all about?
Now in its 11th year, NYT launched the contest to encourage students to write convincing evidence-backed opinion essays on topics they are passionate about — LGBTQ+ rights, school shootings, Black Lives Matter, anti-Asian hate, memes, art repatriation, video game culture, and pineapple on pizza, to name a few — in 450 words or less. The key here is to choose a topic you care deeply about and convince readers that they should care too.
Who can apply for the contest?
All middle school and high school students around the world aged 13-19 can apply for the contest. You can apply even if you’re in a gap year but must not be enrolled in a college at the time of application. Students attending their first year of a two-year CEGEP in Quebec Province, Canada, can also apply.
Note: you are ineligible if you are the child or stepchild of an NYT employee or if you live in the same household as an NYT employee.
What do the contest winners get?
Winning essays will be published on the NYT’s Learning Network , an online resource for teaching and learning. There is no financial award.
Is the contest prestigious?
The Student Editorial Contest is highly selective and prestigious. While there is no financial award, NYT receives thousands of entries every year and selects only a handful of winners. In 2023, the paper received 12,592 submissions and selected 11 winners. That means 0.09% of all submissions won!
What are the rules of the contest?
Your editorial submission must meet the following requirements:
1. Be 450 words or less
This word limit does not include the title and your reference list.
2. Submit original writing
You cannot submit an essay published in a school newspaper or elsewhere.
3. Cite your sources
You must use at least one NYT article source and another external source.
4. You must be the author of your own work
While other people (teachers. parents, etc) may review your work, your final submission must reflect your own ideas in your voice.
How will your submission be judged?
NYT journalists, Learning Network staff members, and educators from across the U.S. judge the essays and pick the winners. This is done based on the following criteria:
1. Viewpoint
Your essay has a clear argument and provides an evidence-based call to action for a cause.
2. Evidence
Your essay cites reliable sources and uses compelling evidence to support your argument
3. Analysis and persuasion
Your essay argues a particular point of view by providing historical context, acknowledging counter-arguments, using examples, and developing claims.
4. Language
Your essay uses the correct grammar and punctuation and is free from errors. Additionally, it uses a language and style appropriate for an editorial and is an engaging read
5. Guidelines
Your essay follows all the contest rules, including citing and least one NYT and one non-NYT source
When is the submission deadline?
Tentatively, submissions for the 2024 contest will open from March 15 to April 19, 2024.
What did previous winners write about?
Previous years’ winners have written compelling essays on the joys of multigenerational living , the cultural insensitivity of “voluntourism,” , navigating life with an incarcerated parent , the importance of student journalism , stigma and shame young girls feel when they get their period , and many more. You can find a list of the 2023 winning and runner-up essays here , and the 2022 essays here .
Without further ado, here are 7 tips to help you win the contest!
1. Think of a relevant topic, especially one you can connect with personally
You only have 450 words to make your case, so choose a topic you have the strongest connection with. NYT says that the best writing they see is from students who are personally attached to the subject matter. For example, Ketong Li wrote about the ethical problems with voluntourism after traveling to Myanmar, while Lucas Cohen-d’Arbeloff wrote about the impact of Florida’s “Don’t Say Gay” bill based on the experiences of his two dads.
2. Find a good reviewer to give you constructive feedback on your draft
While the idea and writing must be your own, NYT acknowledges that editorial writing is a collaborative process in newsrooms, with staff coming together to shape an argument. Thus, it's important you have a mentor, ideally, someone with editorial experience, who can help you make more sense of your thoughts, help you think critically, and finally craft an effective argument.
3. Break out of your “filter bubble”
NYT encourages you to include a diversity of opinions in your essay, addressing their merits and finally making your own independent argument. Additionally, NYT pays special attention to your citations: you must use at least one NYT article as a source and one or more from other reliable publications when presenting differing arguments.
4. Make good use of the NYT’s resources
The NYT has a trove of resources to help you ace the contest, including a step-by-step lesson plan on argumentative writing , a webinar on teaching argumentative writing , and NYT columnists have videos explaining how to write editorials .
5. Learn from previous winners
You will gain a deeper understanding of the kind of editorials NYT looks for by reviewing previous years’ winning submissions . Additionally, two winners of the 2020 contest have annotated essays explaining how they crafted their winning writing: Ananya Udaygiri on “How Animal Crossing Will Save the World” and Abel John on “Collar the Cat!” Ananya and Abel have also recorded videos with advice on choosing a topic and how to cite evidence in your submission .
6. Keep your audience in mind
Remember, you’re writing for NYT readers. To that end, your tone and writing style should reflect the NYT’s editorial voice. You would learn a lot by reading and analyzing the NYT’s daily editorials!
7. Practice, practice, and practice
Few people are gifted writers, and fewer still can make their point in 450 words! We highly recommend that you simulate the contest by choosing different prompts and writing editorials, and then incorporate any feedback that you receive. NYT has a list of prompts use can use to practice.
Our final verdict — what do we think of the contest?
The Student Editorial Contest is highly competitive and being one of the winners would add significant prestige to your college application. It would also go a long way in helping you get into a top journalism school. We like that the competition is global and there are no financial barriers to entry (the contest is free!). The contest is thought-provoking and seeks unique perspectives on issues part of our lives. Even if you don’t win, you will gain a lot of important experience in argumentative writing which would certainly help you in university!
Bonus — the Lumiere Research Scholar Program
If you are interested in doing university-level research in literature, media, and journalism, then you could also consider applying to the Lumiere Research Scholar Program , a selective online high school program for students founded with researchers at Harvard and Oxford. Last year, over 4000 students applied for 500 spots in the program! You can find the application form here.
Also check out the Lumiere Research Inclusion Foundation , a non-profit research program for talented, low-income students.
Kieran Lobo is a freelance writer from India, who currently teaches English in Spain.
Image Source: The New York Times
- competitions
+1 (603) 932 7897

Complete Guide to the New York Times Student Review Contest
- Last modified 2023-11-22
- Published on 2023-11-14

Competition Information
Who can participate in this competition.
The New York Times Student Review Contest welcomes participants aged 13 to 19 from around the world. However, students under the age of 18 must obtain permission from a parent or guardian to enter.
What important dates should I remember?
Submission Start Date: The competition will open for submissions on November 1st.
Submission Deadline: All entries must be submitted by December 6th at 11:59 PM Pacific Time.
Winner Announcement: The list of winners is usually announced approximately 2 months after the competition ends.
What Can I Review in the New York Times Student Review Contest?
Participants can choose to review works from various different categories, as shown in the image above. These categories include:
- Architecture
- Restaurants
- Video Games
Important Note: A new rule has been introduced for this year’s competition. The reviewed work must be a piece that made its debut in 2023.
Is there a word limit?
Reviews must not exceed 450 words in length, excluding the title.
Can I submit multiple reviews?
No, submissions are limited to one per student.
Can I submit a review as part of a group?
Collaborative submissions are not permitted. Students must participate as individuals.
What are the plagiarism guidelines for submitted work?
Your article must be your original work. It shouldn’t be plagiarized, written by someone else, or generated by AI. It should not have been published in a school newspaper, other contests, or anywhere else.
This year, students must submit an “artist’s statement” to describe your process. It’s worth noting that this statement will not be evaluated for quality, and therefore won’t affect the selection of finalists or the publication of winning entries.
How will the competition be judged this year?
The New York Times Student Review Contest maintains the same scoring criteria as in previous years, focusing on the following five aspects:
- Opinion: The response should present a clear point of view supported by evidence, and convey the participant’s experiences and reactions in a clear and engaging manner.
- Attention to detail: The review should consistently display relevant and accurate details from the creative work.
- Audience: Reviews should be crafted for a broad audience, with particular consideration for the target audience of the creative work.
- Language: Reviews should engage readers with compelling narrative language, using an appropriate style, and tone, as well as correct grammar, spelling, and punctuation.
- Guidelines: Reviews must adhere to all New York Times contest rules, including the maximum word limit of 450 words, and should be relevant to the category reviewed by New York Times critics.
These criteria are evaluated using four scores: Excellent (4), Proficient (3), Developing (2), and Beginning (1).
Who are the judges for this contest?
The judging panel for the contest includes the Learning Network staff, a team of New York Times journalists, and many other educators from across the country.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a review.
A review is similar to an argumentative essay , as the reviewer has to analyze the work closely, understand the context and the meaning behind the text, and then explain why it is meaningful enough for you to review. Then, provide an opinion that establishes a position on the subject matter, and gather evidence to support your stance.
How can I make my review stand out?
The contest organizers encourage reviews that offer fresh, meaningful, and interesting perspectives on the work being reviewed, whether positive or negative. One way to make your review stand out is to create a compelling introduction. Start with a hook that relates to the work you’re reviewing, and briefly introduce the subject matter. For example, you can pose a thought-provoking question, share a surprising fact, or present a relevant quote.
I don’t know how to write a review. How should I start?
If you’re unsure how to begin your review, the contest organizers will be releasing a step-by-step guide to writing reviews, so stay tuned on the official website.
How Can I Gather Feedback on My Review?
Before submitting, be sure to share your work with friends, family, or teachers for feedback. They can provide valuable insights into the clarity and effectiveness of your writing. Constructive criticism can help you refine your review before submission.
In conclusion, the New York Times Student Review Contest is an excellent opportunity for young writers to showcase their critical thinking and writing skills. This contest offers a platform to express your unique perspective– be it on books, movies, or any other creative work. We wish the best of luck to all the participants, and look forward to reading your insightful reviews!
Further Your Writing Skill with Aralia

This class is offered in the summer every year. Students from 13 to 18 years old wanting to learn how to shape their written English into effective and publishable creative pieces will find this particular Writing Competition course very exciting. The class will be shown a range of tools to learn the nuances of controlled, purposeful writing, including: figurative language, effective structuring and specific forms that they will apply to their own pieces.
What's next?
How can I improve my writing? 20 Tips to Improve Your Writing
27 writing competitions for high school students? The top 27 competitions you need to know
Heard about John Locke Essay Competition but not sure where to start? Read this Complete Guide to John Locke Essay Competition
Finished your writing work but not sure where to submit it? Where to Submit Your Writing Works: 5 Main Platforms will answer your questions
- Competitions

Interested in learning more?
Aralia Education is an innovative online education platform for ambitious middle and high school students worldwide. Aralia’s instructors propel students forward by helping them build a strong foundation in traditional academic courses. They also actively engage and guide students in exploring personal interests beyond their school curriculum. With this holistic approach, Aralia ensures its students are well-prepared for college and equipped for success in their future careers.
- College Accelerator Program
- Comprehensive Introduction to High School
- Academic Empowerment Program
- Test Preparation Bootcamp
- Private Lessons
- Student Awards
Give us a call: +1 (603) 932 7897
Email us: [email protected]
Add us on WhatsApp:


Guide to The NY Times’ Five Best College Essays on Work, Money and Class
So, you might ask, “What can I learn from this year’s crop of college essays about money, work and class? And how can they help me craft my own memorable, standout essays?” To help get to the bottom of what made the Times ‘ featured essays so exceptional, we made you a guide on w hat worked, and what you can emulate in your own essays to make them just as memorable for admissions.
- Contradictions are the stuff of great literature . “I belong to the place where opposites merge in a…heap of beautiful contradictions,” muses Tillena Treborn in her lyrical essay on straddling rural and urban life in Flagstaff, AZ, one of the five pieces selected by t he Times this year. Each of the highlighted essays mined contradictions: immigrant versus citizen; service worker versus client; insider versus outsider; urban versus rural; poverty versus wealth; acceptance versus rebellion; individual versus family. Every day, we navigate opposing forces in our lives. These struggles—often rich, and full of tension—make for excellent essay topics. Ask yourself this: Do you straddle the line between ethnicities, religions, generations, languages, or locales? If so, how? In what ways do you feel like you are stuck between two worlds, or like you are an outsider? Examining the essential contradictions in your own life will provide you with fodder for a fascinating, insightful college essay.
- The magic is in the details — especially the sensory ones. Sensory details bring writing to life by allowing readers to experience how something looks, sounds, smells, tastes, or feels. In his American dream-themed essay about his immigrant mother cleaning the apartment of two professors, Jonathan Ababiy describes “the whir,” “suction,” and “squeal” of her “blue Hoover vacuum” as it leaps across “miles of carpet.” These descriptions allow us to both hear and see the symbolic vacuum in action. The slice-of-life familial essay by Idalia Felipe–the only essay to be published in The Times’ Snapchat Discover feature–opens with a scene: “As I sit facing our thirteen-year old refrigerator, my stomach growls at the scent of handmade tortillas and meat sizzling on the stove.” Immediately, we are brought inside Felipe’s home with its distinctive smells and sounds; our stomach seems to growl alongside hers. Use descriptive, sensory language to engage your reader, bring them into your world, and make your writing shine.
- One-sentence paragraphs are catchy . A one-sentence paragraph, as I’m sure you’ve gleaned, is a paragraph that is only one sentence long. The form has been employed by everyone from Tim O’Brien to Charles Dickens and, now, the writers of this year’s featured Times college essays. “I live on the edge,” Ms. Treborn declares at the beginning of her poetic essay on the differences between her mother and father’s worlds. “The most exciting part was the laptop,” asserts Zoe Sottile, the recipient of the Tang Scholarship at Phillips Academy in her essay about the mutability and complexity of class identity. Starting your essay with a one-sentence paragraph—a line of description, a scene, or a question, for example—is a great way to hook the reader. You could also use a one-sentence paragraph mid-essay to emphasize a point, as Ms. Treborn does, or in your conclusion. A one-sentence paragraph is one of many tricks that you have in your writing toolkit to make your reader pause and take notice.
- The Familiar Can Be Fascinating. The most daring essay this year, a rant on the imbalances of power embedded in the service industry by Caitlin McCormick, delivers us into the world of a family bed and breakfast with its clinking silverware and cantankerous guests demanding twice-a-day room cleanings. In Ms. Felipe’s more atmospheric piece, we enter her home before dinnertime where we see her attempting to study while her sisters giggle and watch Youtube cat videos. These are the environments these students grew up in, and they inspired everything from frustration at glaring class inequalities to gratitude for the dream of a better life. Rather than feeling like you have to write about something monumental, focus on the familiar, and consider how your environment has shaped you. How did you grow up—in the restaurant business, on a farm, in a house full of artists, construction workers, or judges? Bring us into your world, describing it meticulously and thoughtfully. Tease out the connection between your environment and who you are/what you strive for today and you will be embarking on the path of meaningful self-discovery, which is the key to college essay success.
About Nina Bailey
View all posts by Nina Bailey »
Written by Nina Bailey
Category: advice , Essay Tips , Essay Writing , New York Times , Uncategorized
Tags: advice , college admissions , college admissions essay , college essay , college essay advisors , common application , tips , writing
Want free stuff?
We thought so. Sign up for free instructional videos, guides, worksheets and more!

One-On-One Advising
Common App Essay Prompt Guide

Supplemental Essay Prompt Guide
- YouTube Tutorials
- Our Approach & Team
- Undergraduate Testimonials
- Postgraduate Testimonials
- Where Our Students Get In
- CEA Gives Back
- Undergraduate Admissions
- Graduate Admissions
- Private School Admissions
- International Student Admissions
- Common App Essay Guide
- Supplemental Essay Guide
- Coalition App Guide
- The CEA Podcast
- Admissions Stats
- Notification Trackers
- Deadline Databases
- College Essay Examples
- Academy and Worksheets
- Waitlist Guides
- Get Started
As college admissions criteria evolve, applicants must showcase more than just academics. Engaging in diverse extracurriculars develops transferable skills and highlights passions. Writing competitions, in particular, distinguish applicants by demonstrating intelligence and creativity and help boost your student profile. Additionally, participating in these competitions refines essay writing skills, crucial for crafting compelling personal statements in college applications.
2024 Writing Competitions for Middle and High School Students

Gain insights on the John Locke Essay Competition. Learn expert tips for crafting standout essays in philosophy, politics, and history.

We connect YOU th writers to competition and publication opportunities. Find one today!
Competition
New York Times Personal Narrative Writing Contest
November 17, 2023.

High School
Description:
For this contest, we invite you to write a personal narrative of your own about a meaningful life experience. We’re not asking you to write to a particular theme or to use a specific structure or style, but we are looking for short, powerful stories about a particular moment or event in your life. We want to hear your story, told in your unique voice, and we hope you’ll experiment with style and form to tell a tale that matters to you, in a way you enjoy telling it.
https://www.nytimes.com/2021/08/10/learning/our-3rd-annual-personal-narrative-writing-contest.html
Writing Type
Essay, Prose, Nonf𝔦ction
Publication
International
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
The Editorial Board
A Way Back from Campus Chaos

By The Editorial Board
The editorial board is a group of opinion journalists whose views are informed by expertise, research, debate and certain longstanding values . It is separate from the newsroom.
Protesting the world’s wrongs has been a rite of passage for generations of American youth, buoyed by our strong laws protecting free speech and free assembly. Yet the students and other demonstrators disrupting college campuses this spring are being taught the wrong lesson — for as admirable as it can be to stand up for your beliefs, there are no guarantees that doing so will be without consequence.
The highest calling of a university is to craft a culture of open inquiry, one where both free speech and academic freedom are held as ideals. Protest is part of that culture, and the issue around which so many of the current demonstrations are centered — U.S. involvement in the Israel-Hamas conflict — ought to be fiercely and regularly debated on college campuses.
The Constitutional right to free speech is the protection against government interference restricting speech. Therefore, leaders at public universities, which are funded by government, have a heightened duty to respect those boundaries. Private institutions don’t have the same legal obligations, but that doesn’t relieve them of the responsibility to encourage open dialogue whenever and wherever possible on their campuses. It’s essential to the pursuit of learning.
In the real world, though, this can get messy, and nuance is required when free speech comes into tension with protecting academic freedom. The earliest universities to adopt the principle of academic freedom did so to thwart interference and influence from totalitarian states and religious zealotry. Today, the American Association of University Professors defines it as “the freedom of a teacher or researcher in higher education to investigate and discuss the issues in his or her academic field, and to teach or publish findings without interference from political figures, boards of trustees, donors or other entities.”
Student codes of conduct and other guidelines are meant to relieve some of the tension between free speech and academic freedom, as well as to ensure that schools are in compliance with government regulations and laws. Every campus has them. But rules matter only when guardrails are consistently upheld. It’s in that enforcement that the leadership of too many universities has fallen short.
The point of protest is to break such rules, of course, and to disrupt daily routines so profoundly as to grab on to the world’s attention and sympathies. Campuses should be able to tolerate some degree of disruption, which is inherent to any protest. That makes it even more important that school administrators respond when the permissible limits for speech are violated.
During the current demonstrations, a lack of accountability has helped produce a crisis.
It has left some Jewish students feeling systematically harassed. It has deprived many students of access to parts of campus life. On campuses where in-person classes or commencement exercises were canceled, students have watched their basic expectations for a university experience evaporate. And at times, the protesters themselves have been directly endangered — the disarray and violence of the past weeks has been escalated by the continued involvement of both the police and external agitators.
Amid the protests, there has been much discussion of both antisemitism and Islamophobia, and when the line is crossed into hate speech. There are profound risks to imposing overly expansive definitions of inappropriate speech, and universities have been rightly chided for doing so in the past. But it should be easy to agree that no student, faculty member, administrator or university staff member on a campus should be threatened or intimidated. School policies should reflect that, and they should be enforced when necessary.
In the longer term, a lack of clarity around acceptable forms of expression, and a failure to hold those who break those norms to account, has opened up the pursuit of higher learning to the whims of those motivated by hypocrisy and cynicism.
For years, right-wing Republicans, at the federal and state level, have found opportunities to crusade against academic freedom, with charges of antisemitism on campus serving as the latest vehicle. Speaker Mike Johnson of the House of Representatives used this moment of chaos as cover to begin a legislative effort to crack down on elite universities, and lawmakers in the House recently passed a proposal that would impose egregious government restrictions on free speech. The Senate should reject those efforts unequivocally.
The absence of steady and principled leadership is what opened the campus gates to such cynicism in the first place. For several years, many university leaders have failed to act as their students and faculty have shown ever greater readiness to block an expanding range of views that they deem wrong or beyond the pale. Some scholars report that this has had a chilling effect on their work, making them less willing to participate in the academy or in the wider world of public discourse. The price of pushing boundaries, particularly with more conservative ideas, has become higher and higher.
Schools ought to be teaching their students that there is as much courage in listening as there is in speaking up. It has not gone unnoticed — on campuses but also by members of Congress and by the public writ large — that many of those who are now demanding the right to protest have previously sought to curtail the speech of those whom they declared hateful.
Establishing a culture of openness and free expression is crucial to the mission of educational institutions. That includes clear guardrails on conduct and enforcement of those guardrails, regardless of the speaker or the topic. Doing so would not only help restore order on college campuses today, but would also strengthen the cultural bedrock of higher education for generations to come.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
The editorial board is a group of opinion journalists whose views are informed by expertise, research, debate and certain longstanding values. It is separate from the newsroom.
- Good Balita
- Good Pinoys
- Good Travel
- Good School
- Good Advice
- Good Business
- Good Inspiration
- Good Savings
- Armando O. Bartolome
- Agnes Hannah Balibay
- Angie Quadra Balibay
- Chinkee Tan
- Mike Grogan
- Qjiel Mariano
- Rene Nonoy Molina
- Trixie Esguerra
- Wilson Lee Flores
- Filipino Pride Advocate
- Filipino Pride Newsmakers
- Week in Review
- My Pilipinas
- Share Your Proud Pinoy News
- GNP Advocates
GoodNewsPilipinas.com Triumphs with Gold Anvil Award: A Testament to Filipino Media…

Embracing a New Era: GoodNewsPilipinas.com’s Trailblazing Journey to the Anvil Awards

Discover Philippine Education Excellence: Unveiling the Top 10 Good School Stories…

Discover Filipino Athletic Excellence: Unveiling the Top 10 Inspiring Sports Stories…
Pisay student natalia araña wins the new york times’ essay writing contest.

Philippine Science High School (PSHS) Grade 11 student Natalia Araña has won The Learning Network’s Second Annual STEM Writing Contest organized by The New York Times for her essay, “Mycowood Violins: A Different Kind of Time Machine.”
Araña was named one of the eleven international winners of the prestigious writing tilt, which challenged teenagers from around the world to choose a compelling scientific topic and then write an engaging 500-word explanation for it.
The winning essay, which stood out from 3,741 entries received by The New York Times, involves the discovery of scientist Francis W.M.R. Schwarze, who found a way to replicate the sound of the world’s most famous violin – the Stradivarius, through white-rot fungi.
Only a few hundred of the original violins made by Italian luthier Antonio Stradivari over 250 years ago survived, according to the essay.
To recreate the sound of the iconic Stradivarius violins, Schwarze and his team used fungi to mimic the effects of a cold climate on wood, producing biotech violins with a tone matching those of a Stradivarius.
“For three months, Dr. Schwarze let these decomposers feast on the wood until its cells shrunk, letting the timber reach its optimal density without largely affecting the speed of sound travel through the material. The result? A higher radiation ratio that made the newly created ‘mycowood’ one step closer to the resonance wood used by Stradivari — close enough, in fact, that most listeners in a blind test mistook a fungi-treated violin for the original Stradivarius!” the 16-year-old Araña explains.
The positive results produced by Schwarze’s study meant that the fungi-treated violins could one day become available to talented young musicians who would otherwise be unable to afford their own Stradivarius.
Natalia Araña’s essay entitled, “Mycowood Violins: A Different Kind of Time Machine,” along with the other winning works, have been published by The New York Times on April 29, 2021. Read her story here .
Filipinos who recently bagged top literary prizes include UP Cebu student Christian Andrei Nuez Laplap who won the United Kingdom’s International Hammond House Literary Prize and Filipino-American author Erin Entrada Kelly’s historical fiction “We Dream of Space” which was awarded the John Newbery Honor for distinguished children’s books.
SEND CONGRATULATIONS in the comments below to Philippine Science High School (PSHS) Grade 11 student Natalia Araña who has won The Learning Network’s Second Annual STEM Writing Contest organized by The New York Times for her essay, “Mycowood Violins: A Different Kind of Time Machine.”
Good News Pilipinas is celebrating its 15th Anniversary in 2021 by giving away prizes! Subscribe to our Good News Pilipinas! TV YouTube channel and enter the raffle by sending us an email to [email protected]

- Antonio Stradivari
- Francis W.M.R. Schwarze
- Mycowood Violins: A Different Kind of Time Machine
- Natalia Araña
- Natalia Araña The New York Times' essay writing contest
- Philippine Science High School
- The Learning Network’s Second Annual STEM Writing Contest
- The New York Times
- white rot fungi
Get Your Dose of Good Vibes!
Power Up Your Positivity! Catch all the Good-Vibes! Join the GoodNewsPilipinas.com VIP list and get your daily dose of sunshine and Pinoy Pride! Unwrap stories that put Filipino awesomeness in your life! CLICK the subscribe button for our e-newsletter and turn your inbox into a fiesta of feel-good news! Inspire your day, fuel your pride! 🇵🇭✨
RELATED ARTICLES
List: 14 philippine universities in times higher education asia university rankings, list: up, admu, dlsu best subjects on qs world university rankings, up law secures double victory as champions of stetson environmental and jessup political rights global moot court competitions, top stories.
How to Track your Philippine National ID delivery

Philippine Innovation Unleashed: Top 10 Good Tech Stories of 2023 on GoodNewsPilipinas.com
Filipino Food Sensation Abi Marquez Takes Home Webby Awards for Social Media Mastery

How to Check Your Voter Status for Philippine Elections

LIST: 15 Philippine paint brands with lead safety United States certification
Editor picks, rico hizon takes the lead in championing filipino pride, goodnewspilipinas.com secures third consecutive nomination at lasallian scholarum awards, list: 2024 lasallian scholarum awards finalists, goodnewspilipinas.com scores 3rd..., goodnewspilipinas.com triumphs with gold anvil award: a testament to..., goodnewspilipinas.com vies for prestige at the 59th anvil awards:..., popular posts, philippine innovation unleashed: top 10 good tech stories of..., filipino food sensation abi marquez takes home webby awards..., list: 15 philippine paint brands with lead safety united..., popular category.
- Good Balita 1524
- Good Show 1358
- Good Sport 945
- Good Pinoys 927
- Good Advice 646
- Good Travel 605
- Good Tech 562
- Good Business 535
- Good School 512
- Good Deed 489
- Good Inspiration 303
- Good News Pilipinas! TV 79
- Good Savings 48
- Good MSME 48

Good News Pilipinas is a news and information website that highlights the good in the Filipino and the Philippines.
© 2024 GoodNewsPilipinas.com
Privacy Overview

Find anything you save across the site in your account

In the campus protests over the war in Gaza, language and rhetoric are—as they have always been when it comes to Israel and Palestine—weapons of mass destruction.
By Zadie Smith
A philosophy without a politics is common enough. Aesthetes, ethicists, novelists—all may be easily critiqued and found wanting on this basis. But there is also the danger of a politics without a philosophy. A politics unmoored, unprincipled, which holds as its most fundamental commitment its own perpetuation. A Realpolitik that believes itself too subtle—or too pragmatic—to deal with such ethical platitudes as thou shalt not kill. Or: rape is a crime, everywhere and always. But sometimes ethical philosophy reënters the arena, as is happening right now on college campuses all over America. I understand the ethics underpinning the protests to be based on two widely recognized principles:
There is an ethical duty to express solidarity with the weak in any situation that involves oppressive power.
If the machinery of oppressive power is to be trained on the weak, then there is a duty to stop the gears by any means necessary.
The first principle sometimes takes the “weak” to mean “whoever has the least power,” and sometimes “whoever suffers most,” but most often a combination of both. The second principle, meanwhile, may be used to defend revolutionary violence, although this interpretation has just as often been repudiated by pacifistic radicals, among whom two of the most famous are, of course, Mahatma Gandhi and Martin Luther King, Jr . In the pacifist’s interpretation, the body that we must place between the gears is not that of our enemy but our own. In doing this, we may pay the ultimate price with our actual bodies, in the non-metaphorical sense. More usually, the risk is to our livelihoods, our reputations, our futures. Before these most recent campus protests began, we had an example of this kind of action in the climate movement. For several years now, many people have been protesting the economic and political machinery that perpetuates climate change, by blocking roads, throwing paint, interrupting plays, and committing many other arrestable offenses that can appear ridiculous to skeptics (or, at the very least, performative), but which in truth represent a level of personal sacrifice unimaginable to many of us.
I experienced this not long ago while participating in an XR climate rally in London. When it came to the point in the proceedings where I was asked by my fellow-protesters whether I’d be willing to commit an arrestable offense—one that would likely lead to a conviction and thus make travelling to the United States difficult or even impossible—I’m ashamed to say that I declined that offer. Turns out, I could not give up my relationship with New York City for the future of the planet. I’d just about managed to stop buying plastic bottles (except when very thirsty) and was trying to fly less. But never to see New York again? What pitiful ethical creatures we are (I am)! Falling at the first hurdle! Anyone who finds themselves rolling their eyes at any young person willing to put their own future into jeopardy for an ethical principle should ask themselves where the limits of their own commitments lie—also whether they’ve bought a plastic bottle or booked a flight recently. A humbling inquiry.
It is difficult to look at the recent Columbia University protests in particular without being reminded of the campus protests of the nineteen-sixties and seventies, some of which happened on the very same lawns. At that time, a cynical political class was forced to observe the spectacle of its own privileged youth standing in solidarity with the weakest historical actors of the moment, a group that included, but was not restricted to, African Americans and the Vietnamese. By placing such people within their ethical zone of interest, young Americans risked both their own academic and personal futures and—in the infamous case of Kent State—their lives. I imagine that the students at Columbia—and protesters on other campuses—fully intend this echo, and, in their unequivocal demand for both a ceasefire and financial divestment from this terrible war, to a certain extent they have achieved it.
But, when I open newspapers and see students dismissing the idea that some of their fellow-students feel, at this particular moment, unsafe on campus, or arguing that such a feeling is simply not worth attending to, given the magnitude of what is occurring in Gaza, I find such sentiments cynical and unworthy of this movement. For it may well be—within the ethical zone of interest that is a campus, which was not so long ago defined as a safe space, delineated by the boundary of a generation’s ethical ideas— it may well be that a Jewish student walking past the tents, who finds herself referred to as a Zionist, and then is warned to keep her distance, is, in that moment, the weakest participant in the zone. If the concept of safety is foundational to these students’ ethical philosophy (as I take it to be), and, if the protests are committed to reinserting ethical principles into a cynical and corrupt politics, it is not right to divest from these same ethics at the very moment they come into conflict with other imperatives. The point of a foundational ethics is that it is not contingent but foundational. That is precisely its challenge to a corrupt politics.
Practicing our ethics in the real world involves a constant testing of them, a recognition that our zones of ethical interest have no fixed boundaries and may need to widen and shrink moment by moment as the situation demands. (Those brave students who—in supporting the ethical necessity of a ceasefire—find themselves at painful odds with family, friends, faith, or community have already made this calculation.) This flexibility can also have the positive long-term political effect of allowing us to comprehend that, although our duty to the weakest is permanent, the role of “the weakest” is not an existential matter independent of time and space but, rather, a contingent situation, continually subject to change. By contrast, there is a dangerous rigidity to be found in the idea that concern for the dreadful situation of the hostages is somehow in opposition to, or incompatible with, the demand for a ceasefire. Surely a ceasefire—as well as being an ethical necessity—is also in the immediate absolute interest of the hostages, a fact that cannot be erased by tearing their posters off walls.
Part of the significance of a student protest is the ways in which it gives young people the opportunity to insist upon an ethical principle while still being, comparatively speaking, a more rational force than the supposed adults in the room, against whose crazed magical thinking they have been forced to define themselves. The equality of all human life was never a self-evident truth in racially segregated America. There was no way to “win” in Vietnam. Hamas will not be “eliminated.” The more than seven million Jewish human beings who live in the gap between the river and the sea will not simply vanish because you think that they should. All of that is just rhetoric. Words. Cathartic to chant, perhaps, but essentially meaningless. A ceasefire, meanwhile, is both a potential reality and an ethical necessity. The monstrous and brutal mass murder of more than eleven hundred people, the majority of them civilians, dozens of them children, on October 7th, has been followed by the monstrous and brutal mass murder (at the time of writing) of a reported fourteen thousand five hundred children. And many more human beings besides, but it’s impossible not to notice that the sort of people who take at face value phrases like “surgical strikes” and “controlled military operation” sometimes need to look at and/or think about dead children specifically in order to refocus their minds on reality.
To send the police in to arrest young people peacefully insisting upon a ceasefire represents a moral injury to us all. To do it with violence is a scandal. How could they do less than protest, in this moment? They are putting their own bodies into the machine. They deserve our support and praise. As to which postwar political arrangement any of these students may favor, and on what basis they favor it—that is all an argument for the day after a ceasefire. One state, two states, river to the sea—in my view, their views have no real weight in this particular moment, or very little weight next to the significance of their collective action, which (if I understand it correctly) is focussed on stopping the flow of money that is funding bloody murder, and calling for a ceasefire, the political euphemism that we use to mark the end of bloody murder. After a ceasefire, the criminal events of the past seven months should be tried and judged, and the infinitely difficult business of creating just, humane, and habitable political structures in the region must begin anew. Right now: ceasefire. And, as we make this demand, we might remind ourselves that a ceasefire is not, primarily, a political demand. Primarily, it is an ethical one.
But it is in the nature of the political that we cannot even attend to such ethical imperatives unless we first know the political position of whoever is speaking. (“Where do you stand on Israel/Palestine?”) In these constructed narratives, there are always a series of shibboleths, that is, phrases that can’t be said, or, conversely, phrases that must be said. Once these words or phrases have been spoken ( river to the sea, existential threat, right to defend, one state, two states, Zionist, colonialist, imperialist, terrorist ) and one’s positionality established, then and only then will the ethics of the question be attended to (or absolutely ignored). The objection may be raised at this point that I am behaving like a novelist, expressing a philosophy without a politics, or making some rarefied point about language and rhetoric while people commit bloody murder. This would normally be my own view, but, in the case of Israel/Palestine, language and rhetoric are and always have been weapons of mass destruction.
It is in fact perhaps the most acute example in the world of the use of words to justify bloody murder, to flatten and erase unbelievably labyrinthine histories, and to deliver the atavistic pleasure of violent simplicity to the many people who seem to believe that merely by saying something they make it so. It is no doubt a great relief to say the word “Hamas” as if it purely and solely described a terrorist entity. A great relief to say “There is no such thing as the Palestinian people” as they stand in front of you. A great relief to say “Zionist colonialist state” and accept those three words as a full and unimpeachable definition of the state of Israel, not only under the disastrous leadership of Benjamin Netanyahu but at every stage of its long and complex history, and also to hear them as a perfectly sufficient description of every man, woman, and child who has ever lived in Israel or happened to find themselves born within it. It is perhaps because we know these simplifications to be impossible that we insist upon them so passionately. They are shibboleths; they describe a people, by defining them against other people—but the people being described are ourselves. The person who says “We must eliminate Hamas” says this not necessarily because she thinks this is a possible outcome on this earth but because this sentence is the shibboleth that marks her membership in the community that says that. The person who uses the word “Zionist” as if that word were an unchanged and unchangeable monolith, meaning exactly the same thing in 2024 and 1948 as it meant in 1890 or 1901 or 1920—that person does not so much bring definitive clarity to the entangled history of Jews and Palestinians as they successfully and soothingly draw a line to mark their own zone of interest and where it ends. And while we all talk, carefully curating our shibboleths, presenting them to others and waiting for them to reveal themselves as with us or against us—while we do all that, bloody murder.
And now here we are, almost at the end of this little stream of words. We’ve arrived at the point at which I must state clearly “where I stand on the issue,” that is, which particular political settlement should, in my own, personal view, occur on the other side of a ceasefire. This is the point wherein—by my stating of a position—you are at once liberated into the simple pleasure of placing me firmly on one side or the other, putting me over there with those who lisp or those who don’t, with the Ephraimites, or with the people of Gilead. Yes, this is the point at which I stake my rhetorical flag in that fantastical, linguistical, conceptual, unreal place—built with words—where rapes are minimized as needs be, and the definition of genocide quibbled over, where the killing of babies is denied, and the precision of drones glorified, where histories are reconsidered or rewritten or analogized or simply ignored, and “Jew” and “colonialist” are synonymous, and “Palestinian” and “terrorist” are synonymous, and language is your accomplice and alibi in all of it. Language euphemized, instrumentalized, and abused, put to work for your cause and only for your cause, so that it does exactly and only what you want it to do. Let me make it easy for you. Put me wherever you want: misguided socialist, toothless humanist, naïve novelist, useful idiot, apologist, denier, ally, contrarian, collaborator, traitor, inexcusable coward. It is my view that my personal views have no more weight than an ear of corn in this particular essay. The only thing that has any weight in this particular essay is the dead. ♦
New Yorker Favorites
The day the dinosaurs died .
What if you started itching— and couldn’t stop ?
How a notorious gangster was exposed by his own sister .
Woodstock was overrated .
Diana Nyad’s hundred-and-eleven-mile swim .
Photo Booth: Deana Lawson’s hyper-staged portraits of Black love .
Fiction by Roald Dahl: “The Landlady”
Sign up for our daily newsletter to receive the best stories from The New Yorker .
By signing up, you agree to our User Agreement and Privacy Policy & Cookie Statement . This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

By Ruth Margalit

By Keeanga-Yamahtta Taylor

By Jay Caspian Kang

By Susan B. Glasser
Columbia faculty, students continue protests; police order dispersal of gathering at UCLA: Updates
Editor's Note: This page is a summary of news on campus protests for Wednesday, May 1. For the latest news, view our live updates file for Thursday, May 2.
NEW YORK − Hundreds of faculty and graduate student workers rallied on a sunny Wednesday afternoon outside Columbia University’s only open entrance, protesting the university’s decision hours earlier to send police on campus and arrest more than 100 pro-Palestinian demonstrators.
Protesters held signs, including “no cops on campus,” as police entered and exited the campus gates just feet away. Others held signs calling for university President Minouche Shafik to resign. Faculty members said access was heavily restricted, as campus was closed for a second day in the period before finals, open only to students living on campus and essential workers.
The NYPD announced almost 300 arrests had taken place Tuesday at Columbia and City College − hours before Los Angeles police in riot gear swept onto UCLA's campus to break up a violent melee between dueling protesters as opposition to Israel's war in Gaza continued to roll through universities across the nation.
Dozens of the New York arrests involved demonstrators removed from an administration building at Columbia, where officers also took down encampments that had been the epicenter of the protests nationwide.
"Students and outside activists breaking Hamilton Hall doors, mistreating our Public Safety officers and maintenance staff, and damaging property are acts of destruction, not political speech," Shafik said in a statement Wednesday. She added that many students felt unwelcome on campus because of the disruption and antisemitic comments made by some protesters.
At City College, affiliated with City University of New York, officials requested NYPD assistance after the college said students and "un-affiliated external individuals" refused to leave. The school issued a statement saying students have a right to demonstrate peacefully but that police were called in because of "specific and repeated acts of violence and vandalism, not in response to peaceful protest."
About 1,200 people in southern Israel were killed and more than 200 taken hostage in the Hamas-led attack on Israel on Oct. 7. The Israeli retaliatory assault has killed nearly 35,000 Palestinians in Gaza, according to the Gaza Health Ministry, and obliterated much of the enclave's infrastructure. The humanitarian crisis has fueled outrage on some U.S. campuses and spurred demands for an end to investment in Israeli companies and amnesty for student protesters.
Developments:
∎ New Hampshire State Police said personnel were at the University of New Hampshire and Dartmouth College on Wednesday night "in response to illegal activity and at the request of local law enforcement." At the University of New Hampshire, police arrested 10 to 20 pro-Palestinian protesters who started setting up an encampment after a rally. Officers at Dartmouth College cleared out the final tents at the campus encampment shortly before 11:40 p.m., its student newspaper reported .
∎ Several hundred protesters gathered Wednesday for a peaceful demonstration on Ohio State University. School officials had locked up some buildings in anticipation of the demonstration. Unlike last week's protest, which led to almost 40 arrests, the crowd began dispersing around 9 p.m. and the demonstration ended before 10 p.m.
∎ Columbia Provost Angela Olinto said all academic activities at the school's main campus for the rest of the semester, including final exams, will be held remotely, with some minor exceptions.
∎ Georgia Gov. Brian Kemp said he supports the strong law enforcement response unleashed on protesters at the University of Georgia and Emory University in Atlanta. “Send a message,'' he said. "We are not going to allow Georgia to become the next Columbia University.”
∎ Protesters and police clashed at the University of Wisconsin in Madison when officers broke up an encampment there Wednesday. Video from the scene showed some protesters being pinned to the ground.
∎ Tulane University said at least 14 protesters were arrested from the "illegal encampment" the school said was dominated by protesters "unaffiliated with our community."
Police order dispersal of large pro-Palestinian gathering at UCLA
Police ordered a large group of Pro-Palestinian demonstrators to leave or face arrest late Wednesday, a night after violence erupted at the encampment by counter-protestors.
Video posted on social media showed counterdemonstrators battering a makeshift barricade around pro-Palestinian protesters at the Los Angeles campus. The Los Angeles Police Department said it responded to UCLA's request to restore order "due to multiple acts of violence within the large encampment" on the campus.
The Los Angeles Times reported police did not intervene for more than an hour after arriving as counterdemonstrators wearing black outfits and white masks − some armed with metal pipes and sticks − repeatedly tried to breach the perimeter of the encampment while campers pushed back and several fights broke out.
Los Angeles police said in a statement Wednesday that officers made no arrests and did not use force in its response to the UCLA campus Tuesday night. The department also noted that no officers were injured.
UCLA canceled Wednesday classes and Chancellor Gene Block, who blamed the violence on a "group of instigators'' who attacked the encampment, said the student conduct process has been initiated and could lead to disciplinary action including suspension or expulsion.
The Times also reported University of California President Michael Drake told the Board of Regents that 15 people were injured in the overnight fracas, and he's ordering an independent review of the events, including how UCLA handled them.
California Gov. Gavin Newsom condemned the violence, saying in a statement , "The right to free speech does not extend to inciting violence, vandalism, or lawlessness on campus. Those who engage in illegal behavior must be held accountable for their actions − including through criminal prosecution, suspension, or expulsion.''
The Jewish Federation Los Angeles issued a statement saying it was "appalled" at the violence, which did not "represent the Jewish community or our values." But the statement also said the UCLA administration was at fault for allowing an environment that made students feel unsafe.
UCLA students barricade themselves in courtyard in tense protest
Hundreds of students at UCLA barricaded themselves in a courtyard between two campus buildings Wednesday, using sheets of plywood, planks, ropes, and tents to block the doors leading from the buildings into the outside area.
The mood was anxious. Sporadic announcements over a loudspeaker informed students they were part of an illegal settlement and would face consequences if they remained. In response, the crowd chanted: “We’re not leaving, we’re not leaving.”
“I’m terrified, obviously, I think everybody is,” said 21-year-old student Aidan Doyle. “But we’re going to stay as long as we possibly can, until we’re being physically removed.”
Thousands of students were spread out in the areas directly outside the main protest. Organizers shouted over loud speakers that they didn’t need any more supplies as piles of protective equipment, pizza and Gatorade grew at the main entrance to the camp.
On Tuesday night, the camp was attacked by a group of violent counter-protesters, who fired chemical agents and fireworks into the protestors and assaulted dozens of people.
– Will Carless
Columbia faculty members protest decision to bring in police
Some of faculty and graduate student workers rallying outside Columbia's gates wore orange safety vests that said “faculty,” which they donned days earlier to help protect students in the encampment.
“There is not a single university left in Gaza, and I bet a lot of you feel there is not a university here in Morningside Heights,” Joseph Hawley, an associate professor of classics, told gatherers, referring to the neighborhood around the school. “But I’m here to tell you the university is here on this sidewalk.”
Barricades still lined city streets outside Columbia’s campus as police officers stood watch. Shafik has asked the New York Police Department to remain on campus until May 17, two days after graduation.
Mana Kia, an associate professor, read a draft statement from the Columbia chapter of the American Association of University Professors saying members "unequivocally condemn President Shafik, the Columbia board of trustees and other senior administrators involved in the decision to call in the NYPD and clear the encampment of student protesters." The statement said the association has "no confidence in the administration."
Organizer says 'ordinary people,' not agitators behind protests
Less than three hours before a huge deployment of New York City police officers broke up an encampment and retook a building at Columbia on Tuesday night, Mayor Eric Adams made a forceful case that the pro-Palestinian protest at the school had been hijacked by "outside agitators'' bent on sowing chaos.
Those involved in pushing for the movement off-campus disagree, saying it belongs to regular folks trying to raise awareness to the Palestinians' plight.
Manolo De Los Santos, an organizer with The People’s Forum, said those joining the protests alongside students are just “ordinary New Yorkers.”“The power of this moment is that it’s everyone coming together,” he said. “It’s health care workers, it’s teachers, it’s city workers. It’s ordinary people who feel so strongly.”
‘Never felt this much tension on campus,' UNH student says
Police arrested pro-Palestinian protesters who started setting up an encampment in front of the University of New Hampshire's Thompson Hall Wednesday night.
UNH Police Chief Paul Dean estimated between 10 to 20 protesters were arrested after a rally led to demonstrators attempting to set up an encampment at the state’s flagship university, drawing local and New Hampshire State Police. Some demonstrators shouted at officers, calling them "cowards" and chanting "free Palestine."
The peaceful rally lasted until around 6:30 p.m. Then, Dean said protesters rushed in to form an encampment and attempted to barricade their tents. Leftover tents and items on Thompson Hall's lawn were removed by police around 9 p.m., loaded onto a truck as dozens of students watched.
Shane Tilton, a sophomore who lives in a nearby residence hall, said he walked over to observe after hearing the commotion. He watched from beneath the Thompson Hall arches as the encampment was removed from the most well-known gathering spot on campus.
“I’ve never felt this much tension on campus,” Tilton said. “I feel like there’s a lot of tension. From my perspective, it seems like the cops don’t have much to do here. They seemed like they were here to jump at this opportunity and see some action.”
The American Civil Liberties Union of New Hampshire condemned police’s actions Wednesday night in Durham and at a similar protest at Dartmouth College in Hanover.
“Freedom of speech and the right to demonstrate are foundational principles of democracy and core constitutional rights," said Devon Chaffee, executive director of the state ACLU. "We urge university and government leaders to create environments that safeguard constitutionally protected speech."
– Ian Lenahan and Deb Cram, Portsmouth Herald
'Intifada' chants by some protesters are 'horribly upsetting'
Dozens of protesters gathered Wednesday in and around Fordham University’s Leon Lowenstein Center in Manhattan and established an encampment. The group is demanding the university divest from all companies “complicit in the Israeli occupation and ongoing siege,” according to a statement from the Fordham for Palestine Coalition.
As the demonstration grew throughout the afternoon, it also attracted a handful of onlookers and opponents who occasionally shouted pro-Israel remarks as they passed. Asa Kittay and Carly Connors said they were in class down the street when they heard demonstrators chanting “Intifada,” an Arabic word for uprising or rebellion. Kittay, who held up a tablet with an image of the Israeli flag, said it was “horribly upsetting.”“I believe that these two states can co-exist peacefully,” Connors said. “I do not believe in an intifada. That is not very anti-genocide.” John Lefkowitz, who attended the protest with friends who go to Fordham, said he believes the demonstrations are sometimes incorrectly characterized as antisemitic by people who are uninformed about the position of anti-Zionism.“It’s often told that Jews should feel unsafe in pro-Palestine circles. As a Jew, I’ve never felt unsafe in a pro-Palestinian circle,” he said. “These people are great, they’re not anti-semites.”
Back to the future: Columbia a focal point again in protest history
The descent of police on Hamilton Hall at Columbia University outfitted in full riot gear and enforcing mass arrests Tuesday night fell on the same date and place police cracked down on antiwar protesters in 1968. Some fear the clash heralds a similar outcome at the upcoming Democratic National Convention in Chicago, where political leaders are emboldened to sic the cops on demonstrators ever more intent on showing up.“I don’t think it’ll keep anyone from Chicago, it might even inspire more people to come,” said Hatem Abudayyeh, a spokesperson for the Coalition to March on the DNC and the national chair of the U.S. Palestinian Community Network.Democrats already feared a repeat of the chaos from 56 years ago where police and demonstrators clashed, drawing all eyes away from the convention.At the crackdown at Columbia April 30, 1968, police arrested over 700 people and over 100 injuries were reported, according to a Columbia University Libraries publication. Police arrested almost 300 people Tuesday between Columbia and City College, according to the city’s top cop.
– Michael Loria
Arraignments from first arrests at New York universities begin
Late Wednesday night, the first arrests from the protests at Columbia University and the City College of New York began to be arraigned at the Manhattan Criminal Courthouse, the same building where former President Donald Trump’s hush money trial is underway.
Outside the court’s arraignment part, dozens of the protesters’ supporters gathered in the halls, many of them wearing keffiyehs. The mood was jubilant, and many were chatting or conferring with each other in small groups.
When one protester exited the courtroom after his arraignment, he was quickly swarmed by friends and dropped to the floor in a brief moment of celebration.
That protester, who was at the City College demonstrations, had been charged with assaulting a police officer, a felony, and resisting arrest. However, the prosecutor handling his case recommended to the judge that he be released from jail, given that police “continue to investigate” the incident.
Arrests across U.S.: Campus protests across the US result in arrests by the hundreds. But will the charges stick?
– Asher Stockler, The Journal News
NYU encampment stays in place after others in city were torn down
The day after other city schools saw violent clashes with police, the encampment at NYU's lower Manhattan campus stood untouched. Punctuated by faded chalk reading "End Jewish and Palestinian hate," the collection of tents and chairs took up about one city block near 181 Mercer Street, where the university's Paulson Center is located.
Fenced-off and guarded by a smattering of campus security, the encampment was bracing for hot weather with some protesters carrying umbrellas to block out the sun and one arriving with large bags of ice. Demonstrators needed to present a school ID to enter the encampment. The barricades held signs reading, "Fund our education, not the occupation" and listing the protesters' demands, which include divestment and closing NYU's Tel Aviv campus.
The shadow of Tuesday's mass arrests and the forced removal of encampments on the other end of the island at Columbia and City College of New York was evident. Just outside the barricades, a group of demonstrators huddled to practice safety tactics.
− Anna Kaufman
New York students continue protests day after mass arrests
Hundreds of demonstrators at Columbia University and City College of New York gathered Wednesday evening a day after administrators from both universities called police in riot gear on the protesters.
“Our encampment is what it could look like to be liberated,” Hadeeqa Arzoo, a City College student, said, as several cars honked in support while she led chants of “Free Palestine.” “So I will continue to cultivate these spaces of liberation within the belly of the beast. That is resistance.”
Even if both schools no longer had encampments, demonstrators promised to continue their activism in support of Palestinians and in opposition to schools’ investments in Israel.
“There is not a single student-led uprising in history met with severe state-sanctioned violence that did not end up being right,” Maryam Alwan, a Columbia student organizer, said. She likened their cause — and police's response — to the civil rights movement and Black Lives Matter protests, including allegations of outside agitators and property damage.
As the sun fell outside City College’s campus in West Harlem, several dozen police officers surrounded the protesters standing inside barricades. The rally, which included two Islamic prayers, would continue into the night before students returned to Columbia, some walking down the valley and back up the hill to the other campus.
– Eduardo Cuevas
UT-Dallas confirms 17 arrests hours after encampment set up
The University of Texas at Dallas confirmed law enforcement officers arrested over a dozen people hours after pro-Palestinian student demonstrators constructed an encampment Wednesday.
UT-Dallas spokesperson Brittany Magelssen told USA TODAY that 17 people were arrested on criminal trespassing charges as of 5 p.m. local time Wednesday after university officials gave written notice to remove the tents. Magelssen said UT-Dallas requested outside law enforcement officers to assist.
“Individuals may peacefully assemble in the common outdoor areas of campus to exercise their right to free speech, but they may not construct an encampment or block pathways. In the last six months, there have been several peaceful protests on the UT Dallas campus,” Magelssen said. "The UT Dallas Police Department and area law enforcement partners are continuing to monitor the situation."
The UT-Dallas chapter of Students for Justice in Palestine said in a social media post students began setting up the "Gaza Liberation Plaza" encampment at 4:30 a.m. Wednesday.
“We reject our university’s complicity in profiting off the genocide. We will continue to escalate and put pressure on our university until UTD/UTIMCO divest from war profiteers and Palestine is free,” the student organization said early Wednesday.
High school students joining the protest movement
The proliferation of antiwar protests in college campuses across the U.S. is filtering down to the younger academic levels , and some of the grown-ups are not happy about it.
A sit-in planned for Wednesday at a Chicago prep school is the latest among high school demonstrations showing support for embattled Palestinians in Gaza. On Monday, about 100 high school students in Austin, Texas, walked out of their classes in protest . Last week, students in western Washington state similarly expressed their objection to the U.S. backing Israel's military efforts in Gaza.
"I'm protesting against a government that is actively hurting people just because of where they were born and what language they speak," Pia Ibsen, a senior at McCallum High School in Austin, told USA TODAY. Ibsen helped organize a walkout and left class for about an hour and a half.
Some school and government officials have tried to stop the protests, arguing they create a hostile environment for Jewish students. That was the case last week when two county commissioners in New Jersey demanded a school district's superintendent cancel a pro-Palestinian walkout at East Regional High in Voorhees Township. The protest was replaced by a rally for human rights.
− Cybele Mayes-Osterman and Kayla Jimenez
UAW members hope presence at protest will 'move the needle'
In addition to the campus protests, hundreds of people bearing pro-Palestinian signs and t-shirts gathered at New York City’s Foley Square on Wednesday afternoon for a march and rally led by labor organizers on International Worker’s Day.
Participants included Brian Sullivan, 45, a member of the United Auto Workers whose local chapter represents social workers. Sullivan said seeing labor organizers come out in such large numbers could help “really move the needle.”
“UAW endorsed Joe Biden and hopefully he feels some exposure here, that if he doesn’t do what’s right and what the UAW members are asking for, he risks that endorsement,” Sullivan said.
Jeremy Montano, another UAW member who works in the legal field, said the recent “explosion of interest” in the conflict in Gaza, particularly on college campuses, has also given him some hope. “Obviously it’s balanced out with a lot of despair about what’s actually happening in Gaza,” said Montano, 37. “But there’s been a little bit of a source of hope that maybe longer term things might change.”
Almost 300 protesters arrested in NYC; student group says some were injured
New York City police made 119 arrests at Columbia University and 173 at City College in Tuesday night's crackdowns on protesters, Commissioner Edward Caban said Wednesday. Charges range from trespassing to criminal mischief to burglary, and the breakdown of students to non-students facing charges was not yet available, he said.
Police said there were no injuries, although CUNY for Palestine issued a statement saying one student suffered a broken ankle, two had teeth broken and others received burns from pepper spray used by police during the clash.
Mayor Eric Adams said drones and encryption radios used at Columbia provided police with the element of surprise when they retook Hamilton Hall, adding that "professionals at radicalizing" had influenced the student protesters and co-opted the protest but without providing details.
Officers climbed into Hamilton Hall, which protesters had occupied earlier Tuesday, through a second-story window. Within three hours Tuesday night, they had retaken the building, NYPD said.
"It was about external actors hijacking a peaceful protest and influencing students to escalate," Adams said. "We cannot allow what should be a lawful protest turn into a violent spectacle that serves no purpose."
Fordham, another NYC university, establishes encampment
Outside Fordham University’s Leon Lowenstein Center building on Wednesday, another encampment sprung up. Students, faculty and community members surrounded by law enforcement officers and newly erected barricades chanted “Free, free Palestine” and “Disclose, divest, we will not stop, we will not rest.” Inside, demonstrators including current and former students milled around their tents, played drums, banged on windows and held up signs reading “Free Palestine” and “Divest genocide funds” for passersby to see.
Julie Norris, a 27-year-old Fordham alumni, said she arrived before 8 a.m. Wednesday to help establish the encampment. Norris, who spoke to USA TODAY on the phone from inside the Lowenstein Center, estimated about 30 people were inside with her and said they plan to stay until their demands are met.
“The students can’t be stopped,” she said. “We saw intense repression against students on other campuses yesterday, and this morning students are ready to stand back up. There’s going to be no business as usual until Palestine is free.”
Northwestern, Brown reach deal: Make pact with student demonstrators to curb protests
Some campus protesters cut deals, claim victory
Some student activists who pitched tents and camped on university lawns to protest Israel's military attacks in Gaza have begun to declare victory after hammering out agreements with school administrators. Northwestern University just outside Chicago became the first U.S. school to publicly announce a deal on Monday. On Tuesday, Brown University protesters broke camp after President Christina Paxson said the Rhode Island school will bring divestment demands to a vote. Organizers hope the deals set a new precedent for protest encampments around the U.S. and show a way to find common ground without using force.
“What these students have done is truly, truly historical,” Summer Pappachen, a graduate student and organizer of the Northwestern encampment, told USA TODAY on Tuesday amid cleanup of the lawn students held for days. “We have been able to achieve (our goals) while keeping students safe.”
− Michael Loria
Columbia building cleared: Police storm into building held by pro-Palestinian protesters
What are college protests across the US about?
The student protesters opposed to Israel's military attacks in Gaza say they want their schools to stop funneling endowment money to Israeli companies and other businesses, like weapons manufacturers, that profit from the war in Gaza. In addition to divestment, protesters are calling for a cease-fire, and student governments at some colleges have also passed resolutions in recent weeks calling for an end to academic partnerships with Israel. The protesters also want the U.S. to stop supplying funding and weapons to the war effort.
More recently, amnesty for students and professors involved in the protests has become an issue. Protesters want protections amid threats of disciplinary action and termination for those participating in demonstrations that violate campus policy or local laws.
− Claire Thornton
Contributing: Reuters

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Introduction to 'Student Opinion Questions' Want to learn more about this feature? Watch this short introduction video and start sharing your ideas and opinions today.
essays like The New York Times Opinion page publishes. every day. Choose a topic you care about, then gather evidence from. sources both within and outside The New York Times and. write a concise editorial (450 words or fewer) to convince readers of your view. The contes t is ope n to students ages 11 to 19 in middle or. high s chool anywhere ...
We invite students to write short, evidence-based persuasive essays like The New York Times Opinion page publishes every day. Choosea topic care about, then gather evidencefrom sources bothwithin and outsideThe NewYork Times and writea conciseeditorial (450words or fewer) to convince readersofyour view. Youreditorialshould: Focus on a topic that
Student Editorial Contest MARCH 15-APRIL 12, 2023 Contest We invite students to write short, evidence-based persuasive essays like those The New York Times Opinion page publishes every day. Choose a topic you care about, gather evidence from sources both within and outside The New York Times, and then write a concise editorial (450 words or ...
The New York Times Learning Network Student Personal Narrative Essay Contest Rubric. Excellent (4) Proficient (3 Developing (2) Beginning (1. Story : Personal narrative tells a short but memorable story about a life experience and communicates why itwas meaningful to the writer . Language : Personal narrative uses vivid details and images to ...
Another thing that sets this competition apart is the length of the essays submitted. While many essay contests ask for essays that are 1,000 words, 2,000 words, or even more, the New York Times Student Essay Contest allows essays of just 450 words or fewer. That's a little bit less than a page of single-spaced copy on Microsoft Word!
The Times publishes fact-based journalism both in our newsroom and on our Opinion desk, but it is very important to our mission that the distinction between the two is clear. The type of Opinion journalism our group was tasked with rethinking was the Op-Ed, which was first introduced in the Times newspaper in 1970.
4. Make good use of the NYT's resources. The NYT has a trove of resources to help you ace the contest, including a step-by-step lesson plan on argumentative writing, a webinar on teaching argumentative writing, and NYT columnists have videos explaining how to write editorials. 5. Learn from previous winners.
In conclusion, the New York Times Student Review Contest is an excellent opportunity for young writers to showcase their critical thinking and writing skills. This contest offers a platform to express your unique perspective- be it on books, movies, or any other creative work. We wish the best of luck to all the participants, and look forward ...
Every year, The New York Times issues an open call for college application essays on the subject of money, work, and class. Money becomes a lens through which identity, family, and dreams, can be glimpsed. Out of the many submissions they received this year, The Times published the five best essays (four were published in the newspaper, and one in The Times's new Snapchat Discover Feature).
JASNA holds an annual student Essay Contest to promote the study and appreciation of Jane Austen's works. Open to students worldwide, the competition offers scholarship awards in three divisions: High School, College/University, and Graduate School. ... The New York Times hosts monthly writing contests for middle and high school students, each ...
Description: For this contest, we invite you to write a personal narrative of your own about a meaningful life experience. We're not asking you to write to a particular theme or to use a specific structure or style, but we are looking for short, powerful stories about a particular moment or event in your life. We want to hear your story, told ...
The editorial board is a group of opinion journalists whose views are informed by expertise, research, debate and certain longstanding values. It is separate from the newsroom. A version of this ...
Philippine Science High School (PSHS) Grade 11 student Natalia Araña has won The Learning Network's Second Annual STEM Writing Contest organized by The New York Times for her essay, "Mycowood Violins: A Different Kind of Time Machine.". Araña was named one of the eleven international winners of the prestigious writing tilt, which ...
In the campus protests over the war in Gaza, language and rhetoric are—as they have always been when it comes to Israel and Palestine—weapons of mass destruction. By Zadie Smith. May 5, 2024 ...
Almost 300 protesters arrested in NYC; student group says some were injured. New York City police made 119 arrests at Columbia University and 173 at City College in Tuesday night's crackdowns on ...
In mid-April, when New York magazine sought to report on the pro-Palestinian student protests engulfing Columbia University, the features editor overseeing the storied publication's coverage ...