When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions

The discussion section contains the results and outcomes of a study. An effective discussion informs readers what can be learned from your experiment and provides context for the results.

What makes an effective discussion?
When you’re ready to write your discussion, you’ve already introduced the purpose of your study and provided an in-depth description of the methodology. The discussion informs readers about the larger implications of your study based on the results. Highlighting these implications while not overstating the findings can be challenging, especially when you’re submitting to a journal that selects articles based on novelty or potential impact. Regardless of what journal you are submitting to, the discussion section always serves the same purpose: concluding what your study results actually mean.
A successful discussion section puts your findings in context. It should include:
- the results of your research,
- a discussion of related research, and
- a comparison between your results and initial hypothesis.
Tip: Not all journals share the same naming conventions.
You can apply the advice in this article to the conclusion, results or discussion sections of your manuscript.
Our Early Career Researcher community tells us that the conclusion is often considered the most difficult aspect of a manuscript to write. To help, this guide provides questions to ask yourself, a basic structure to model your discussion off of and examples from published manuscripts.
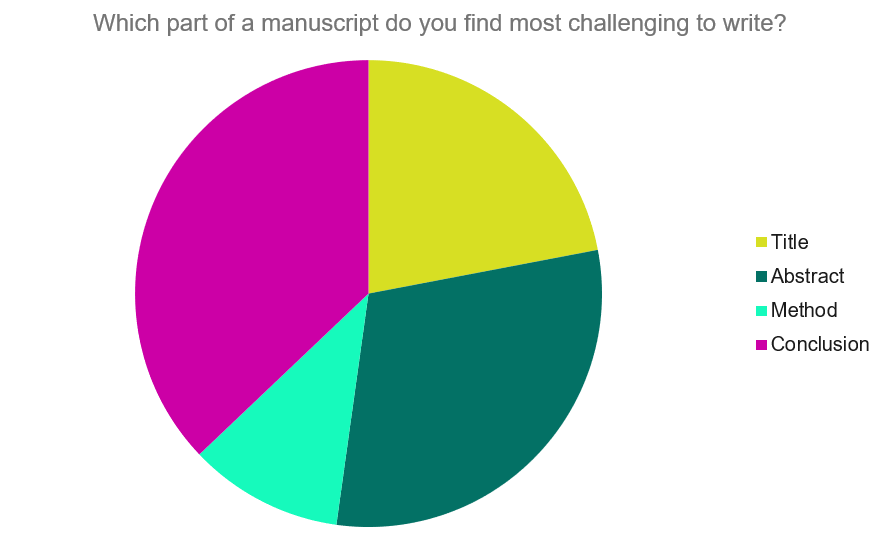
Questions to ask yourself:
- Was my hypothesis correct?
- If my hypothesis is partially correct or entirely different, what can be learned from the results?
- How do the conclusions reshape or add onto the existing knowledge in the field? What does previous research say about the topic?
- Why are the results important or relevant to your audience? Do they add further evidence to a scientific consensus or disprove prior studies?
- How can future research build on these observations? What are the key experiments that must be done?
- What is the “take-home” message you want your reader to leave with?
How to structure a discussion
Trying to fit a complete discussion into a single paragraph can add unnecessary stress to the writing process. If possible, you’ll want to give yourself two or three paragraphs to give the reader a comprehensive understanding of your study as a whole. Here’s one way to structure an effective discussion:
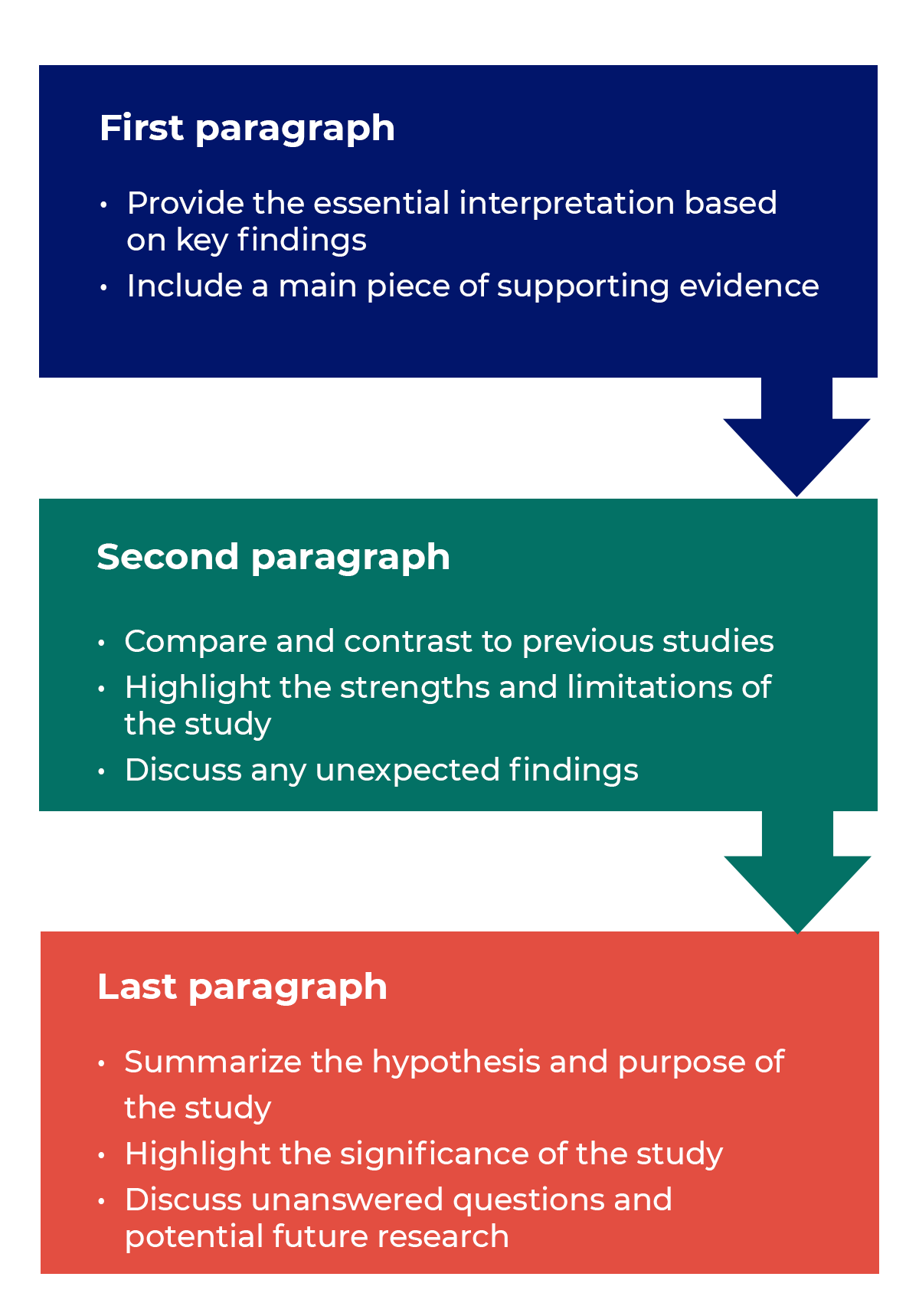
Writing Tips
While the above sections can help you brainstorm and structure your discussion, there are many common mistakes that writers revert to when having difficulties with their paper. Writing a discussion can be a delicate balance between summarizing your results, providing proper context for your research and avoiding introducing new information. Remember that your paper should be both confident and honest about the results!

- Read the journal’s guidelines on the discussion and conclusion sections. If possible, learn about the guidelines before writing the discussion to ensure you’re writing to meet their expectations.
- Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion.
- Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and limitations of the research.
- State whether the results prove or disprove your hypothesis. If your hypothesis was disproved, what might be the reasons?
- Introduce new or expanded ways to think about the research question. Indicate what next steps can be taken to further pursue any unresolved questions.
- If dealing with a contemporary or ongoing problem, such as climate change, discuss possible consequences if the problem is avoided.
- Be concise. Adding unnecessary detail can distract from the main findings.

Don’t
- Rewrite your abstract. Statements with “we investigated” or “we studied” generally do not belong in the discussion.
- Include new arguments or evidence not previously discussed. Necessary information and evidence should be introduced in the main body of the paper.
- Apologize. Even if your research contains significant limitations, don’t undermine your authority by including statements that doubt your methodology or execution.
- Shy away from speaking on limitations or negative results. Including limitations and negative results will give readers a complete understanding of the presented research. Potential limitations include sources of potential bias, threats to internal or external validity, barriers to implementing an intervention and other issues inherent to the study design.
- Overstate the importance of your findings. Making grand statements about how a study will fully resolve large questions can lead readers to doubt the success of the research.
Snippets of Effective Discussions:
Consumer-based actions to reduce plastic pollution in rivers: A multi-criteria decision analysis approach
Identifying reliable indicators of fitness in polar bears
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Write Your Methods
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
- Student Login:

How to Close Your Presentation in English Powerfully [+ FREE Presentation Checklist]
May 9, 2018 | Business Professional English , Free Resource , Public Speaking & Presentations

This lesson has been updated from its original posting in 2016.
You’re giving your presentation in English. You have just two minutes left. And it’s time for the conclusion …
Did you know most people only remember the first and last things you tell them? It’s true.
If you are giving a presentation in English, then you definitely want people to remember what you say at the end. And this means your closing must be powerful!
You’ve worked hard on your presentation. You searched for information online. You couldn’t sleep at night. You felt nervous about making mistakes. You spent hours preparing. You reviewed the grammar and vocabulary. You worried about someone asking a question. You practiced and practiced and practiced.
And now it’s the last two minutes. This is the last opportunity for your audience to hear your key points. It is the last chance you have to help your audience remember your comments.
A closing in a presentation should be short and clear. It should summarize your key points. And, most importantly, it should be powerful.
In today’s lesson, you’re going to learn about 3 ways to make your closing more powerful. Plus you’ll learn useful key expressions you can use in your presentation.
3 steps to a powerful closing in your presentation.
Lesson by Annemarie
3 Strategies to Close Your Presentation Powerfully
Use these 3 strategies in your conclusion to:
- recapture your audience’s attention
- get your audience to focus and remember your key points
- help your audience connect with you and your topic
- end your presentation powerfully
One: Include a Call to Action (CTA)
Is there something you want your audience to do or think after your presentation. Do you want them to take action? Tell your audience exactly what you want them to do with a Call to Action.
Here’s my example:
“ After you finish today’s lesson, please take 2 minutes to leave a comment about your experience with presentations. You can share your thoughts or ask questions in the comments section at the bottom of this lesson – it’s the perfect place to join a discussion on this topic.”
A couple useful expressions to help you introduce your CTA is:
- To close, I’d like to ask you to do this one thing…
- And finally, before you leave the conference today, please take two minutes to…
Two: End with a Powerful/Inspirational Quote
Is there one thing you really want your audience to remember? Or is there a specific feeling you want your audience to have after your presentation?
Using a powerful quote can help you do that. You could introduce a great quote or interesting statistic with:
- I’d like to finish with this powerful/interesting/wonderful/inspiring/ quote from …
- And finally, let’s finish up today’s discussion with this surprising/useful/shocking/hopeful statistic …
Here are some example quotes that might help people be prepared to take action or to think differently. But remember! Always match the quote or statistic to your topic:
“In the end, we will remember not the words of our enemies, but the silence of our friends.” – Martin Luther King, Jr. “Sometimes we stare so long at a door that is closing that we see too late the one that is open.” – Alexander Graham Bell
Three: Add a Surprising Fact or Statistic
Is there something you’d love for your audience to think about after your presentation? Is there a statistic or fact that will help someone remember your key points?
A surprising fact can also help re-engage your audience, it will snap their attention back to you.
For example:
Did you know that the human brain’s capacity is limitless – that’s great new right? BUT … did you also know that a person is likely to remember only 25% of a presentation after 24 hours?
Uh oh. That is why it’s SO important to have a powerful ending! Remember: the key is to find a statistic or fact that connects directly to your topic.
Useful Language to Close Your Presentation
Summarize Your Key Points & Close Your Presentation
- That brings us to the end of the presentation. I’d like to summarize by saying …
- That concludes my presentation. However, I’d like to quickly summarize the main points or takeaways.
- And on that final note, that concludes my presentation.
- To quickly recap, I’d like you to remember these key points …
- To summarize …
- In conclusion …
- I’d like to bring this presentation to a close with …
- I’d like to close this talk with …
- So, this concludes the focus of discussion today. To end, I’d like to highlight …
- This concludes [name/title of the section] so let’s move on to the final comments.
Thank Your Audience
- I sincerely appreciate your attention today/this evening/this morning.
- And that brings us to the end. I’d like to thank you for your time and attention today.
- Thank you so much for your interest and attention.
- At this time, I’d like to have my colleague speak so I’ll finish up by saying thank you for your attention.
- I can see that our time is just about up so to finish I’d like to say thank you.
- I sincerely appreciate that I’ve had this opportunity to present to you.
- If there is one thing I would like you to remember from today’s presentation it’s …
Take Questions
- If anyone has any questions, I’d be happy to open up the discussion.
- If anyone has any questions, please feel free to ask now and I’ll do my best to answer.
- Would anyone like to ask any questions?
- I would now be interested to hear from you with your thoughts or questions.
- Now let’s move on to some Q&A. (Q&A = Questions and Answers)
Provide Next Steps or Contact Information
- If you would like more information, here is a list of useful resources/websites.
- If anyone who like more information or has questions, please feel free to contact me at: [include contact info]
- Here is a list for further reading on this topic. (Include the list of books or websites.)
Get the complete Presentations in English Series:
Part 1: How to Prepare for Your Presentation in English
Part 2: How to Start with a Great Introduction in Your Presentation
Part 3: How to Organize Your Presentation in English
Part 4: How to End Your Presentation Powerfully
After you’ve watched the video and reviewed the lesson, I’d love to hear from you!
Tell me about the best presentation you ever heard. Who gave the presentation? And why do you remember it? Share what you remember in the comments section below.
And for the bonus question!! Have you given a presentation in English? What tips or advice would you like to share with others? You can add your advice in the comments section.
Thank you so much for joining me!
~ Annemarie
Get the Confidence to Say What You Want in English
Follow my 3-step solution to speak English with clarity, fluency, and freedom so you can say what you want with confidence.
You'll also get my Confident English lessons delivered by email every Wednesday and occasional information about available courses. You can unsubscribe any time.
More Like This

5 Smart Questions to Ask in an English Job Interview
It’s the last question in your job interview in English and you hear: Do you have any questions for me? What should you say? Is it okay to ask a question in a job interview? Find out exactly what you should do plus 5 smart questions to ask.

How to Disagree in English Politely
Want to say “I disagree” without creating tension in the conversation? Master the art of disagreement in this lesson on, “How to Disagree in English Politely.”

#310: The Right Grammar for English Introductions
Get your English introductions just right with this step-by-step video on Grammar for English Introductions when you’re meeting someone new.

#309: How to Go Off Topic in English | English Conversation Skills
Learn how to gracefully go off topic in English without losing your audience. Whether you’re in a meeting or chatting with friends, in this lesson we dive deep into the art of smoothly navigating tangents while enhancing your English conversation skills.
![presentation of conclusion in research #308: How to Use ‘Though’ in English [+ FREE Worksheet]](https://www.speakconfidentenglish.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/How-to-Use-Though-in-English-400x250.png)
#308: How to Use ‘Though’ in English [+ FREE Worksheet]
Learn and practice how to correctly use though, although, even though, and as thought in your English conversations.

#307: How to Use English Abbreviations in Emails, Texts, and Conversations
Follow this comprehensive guide to learn how to use English abbreviations for emails, texts, and conversations.
© Copyright 2014-2024 Speak Confident English | Privacy Policy | Terms & Disclaimer | Online Class Policies
I’m glad to hear it was helpful!
This was very helpful
Thanks, Ma’am/Sir. This helped me a lot…
Same here ma’am
This is so helpful. Thank you so much
This helped a lot. Thank you so much <3
I accidentally found your page while working on my English video presentation. It’s really helpful. Thanks soooo much 🙂
I’m very glad to know it was helpful!
Hi! I found your page very insightful. Thank you very much!
I’m glad to hear it!
great video series. thank you so much. you mentioned that you had a downloadable checklist in the final video. where could I find this thanks?
Hi Ellie, I’m glad the series was helpful.
When you visit the lesson, there should be an image that pops up with an opportunity to get the download. If you don’t see it, please let me know so I can fix it.
Helped a lot! Thank you very much <33
thank you so much
I love your method
Hello, I have a 5 minute oral presentation of a fictional book, w/the main focus on the leadership traits of the characters. I enjoyed the book, and suspect others might, so to that end, is it OK to NOT share the ending? Thank you
Thanks for your help 🙂
Great website. I found a typo in on the presentation closings page “Useful Langauge to Close Your Presentation”.
Good eyes! Thanks so much for the note. We’ve fixed the typo.
Dear Annemarie, thank you so much for sharing.
Dear Annemarie, thank you so much for sharing. I learned so much from your 4 videos and I will work on improving my presentation skills. Love your spirit of excellence. For me as a presenter, its important i am passionate about the topic i share and audience will be able to apply some of the learnings in their life. Thank you Annemarie. I love your voice too. Stay blessed.
I watch continuously watched ur 4 videos and U r a great teacher.Thanks for making such purposeful videos.
I am so happy , I have more form you thank you very much
You are absolutely wonderful and your website is extremely useful and also quit impressive i habe my english A-levels in December i copied this text i sinisterly appreciate that i have had this opportunity to present to you and i also add something * it was a honor for me so thank you ☺️
Thanks, Jasmin! I’m so glad to know my lessons are helpful to you.
hey Annemarie could you help me in ending my presentation on mental health. it is a school presentation for MUN
If you’d like editing help, please see our options for 1:1 classes .
You are my favorite speaker. ☺
Hi Anna, that’s so kind of you. Thank you. 🙂
It’s so useful to us…… I’m so happy by this
I’m glad it was helpful to you, Kalpana.
I was holistically stuck about how to give my first ever presentation, but this gave me an impetus and confidence. Thanks a lot for this exquisite info
Awesome. I’m glad this helped you to move forward.
Thank YOU for tour tips. They are really inspiring. I Will try to put them into practise.
Hi Nancy, Wonderful! I’m glad they’re helpful to you!
It’s so useful to us…… I’m so happy by this
do you have Presentation course
Hi Hammad, I don’t at this time but it’s definitely something I’m thinking about.
Pin It on Pinterest

129 List Of Research Topics In English Language Teaching [updated]

English Language Teaching (ELT) is a field dedicated to teaching English to non-native speakers. It’s important because English is a global language used for communication, business, and education worldwide. Research in ELT helps improve teaching methods, making it easier for students to learn English effectively. This blog will explore a list of research topics in English language teaching.
What Are The Areas Of Research In English Language Teaching?
Table of Contents
Research in English Language Teaching (ELT) encompasses a wide range of areas, including:
- Language Learning: Understanding how people learn English well, like when they learn a new language and if there’s a best time to do it.
- Teaching Ways: Looking into different ways teachers teach, like using conversations, tasks, or mixing language with other subjects.
- Curriculum Design and Syllabus Development: Designing and evaluating language curricula and syllabi to meet the needs of diverse learners and contexts.
- Assessment and Evaluation: Developing and validating assessment tools, exploring alternative assessment methods, and investigating the effectiveness of feedback and error correction strategies.
- Technology in ELT: Exploring the integration of technology in language teaching and learning, including computer-assisted language learning (CALL), mobile-assisted language learning (MALL), and online learning platforms.
- Teacher Education and Professional Development: Investigating pre-service and in-service teacher education programs, reflective practices, and challenges in teacher training.
- Cultural and Sociolinguistic Aspects: Examining the role of culture in language teaching and learning, sociolinguistic competence, and addressing cultural diversity in the classroom.
- Learner Diversity and Inclusive Practices: Researching teaching strategies for diverse learners, including young learners, learners with learning disabilities, and learners from diverse linguistic and cultural backgrounds.
- Policy and Planning in ELT: Analyzing language policies at national and international levels, exploring the implementation of ELT programs, and examining the role of ELT in national development.
- Research Methodologies in ELT: Investigating qualitative, quantitative, and mixed-methods research approaches in ELT research, including action research conducted by teachers in their own classrooms.
- Future Trends and Innovations: Exploring emerging trends and innovations in ELT, such as the impact of globalization, the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in language learning, and innovative teaching strategies.
129 List Of Research Topics In English Language Teaching: Category Wise
Language acquisition and development.
- Second Language Acquisition Theories: Explore different theories explaining how learners acquire a second language.
- Critical Period Hypothesis: Investigate the idea of an optimal age range for language acquisition.
- Multilingualism and Language Development: Study how knowing multiple languages affects language development.
- Cognitive and Affective Factors in Language Learning: Examine the role of cognitive abilities and emotions in language learning.
- Language Learning Strategies: Investigate the strategies learners use to acquire and develop language skills.
- Input Hypothesis: Explore the role of comprehensible input in language acquisition.
- Interaction Hypothesis: Examine the importance of interaction in language learning.
- Fossilization in Second Language Learning: Study why some learners reach a plateau in their language development.
Teaching Methodologies and Approaches
- Communicative Language Teaching (CLT): Analyze the effectiveness of CLT in promoting communication skills.
- Task-Based Language Teaching (TBLT): Explore the use of real-world tasks to teach language.
- Content and Language Integrated Learning (CLIL): Investigate teaching subject content through English.
- Blended Learning in ELT: Study the integration of traditional and online teaching methods.
- Audio-Lingual Method: Assess the effectiveness of drills and repetition in language teaching.
- Grammar-Translation Method: Compare traditional grammar-focused methods with communicative approaches.
- Lexical Approach: Explore teaching vocabulary as a key component of language proficiency.
- Suggestopedia: Investigate the use of relaxation techniques to enhance language learning.
Curriculum Design and Syllabus Development
- Needs Analysis in ELT: Identify the language needs of learners and design appropriate curricula.
- Integrating Language Skills in Curriculum: Examine strategies for integrating reading, writing, listening, and speaking skills.
- Syllabus Types: Compare different types of syllabi, such as structural and task-based.
- Task-Based Syllabus Design: Design syllabi based on real-world tasks to promote language acquisition.
- Content-Based Instruction (CBI): Integrate language learning with academic content in syllabus design.
- Needs Analysis in Specific Contexts: Conduct needs analyses for learners in specific professional or academic contexts.
- Cross-Cultural Communication in Curriculum Design: Incorporate intercultural communication skills into language curricula.
Assessment and Evaluation
- Standardized Testing in ELT: Evaluate the reliability and validity of standardized English language tests.
- Alternative Assessment Approaches: Explore non-traditional assessment methods like portfolios and self-assessment.
- Feedback Strategies in Language Learning: Investigate effective feedback techniques for improving language proficiency.
- Washback Effect of Testing: Study how assessment practices influence teaching and learning.
- Authentic Assessment in ELT: Develop assessment tasks that mirror real-life language use situations.
- Portfolio Assessment: Investigate the use of portfolios to track language learning progress over time.
- Computer Adaptive Testing (CAT): Evaluate the feasibility and effectiveness of adaptive testing methods in ELT.
Technology in ELT
- Computer-Assisted Language Learning (CALL): Assess the impact of computer-based language learning programs.
- Mobile-Assisted Language Learning (MALL): Study the effectiveness of mobile devices in language learning.
- Online Learning Platforms for ELT: Analyze the features and usability of online platforms for language education.
- Virtual Reality (VR) in Language Learning: Explore immersive VR environments for language practice and instruction.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Tutoring Systems: Assess the effectiveness of AI-based tutors in providing personalized language instruction.
- Social Media in Language Learning: Study the role of social media platforms in informal language learning contexts.
- Gamification in ELT: Investigate the use of game elements to enhance engagement and motivation in language learning.
Teacher Education and Professional Development
- Pre-service Teacher Education Programs: Evaluate the effectiveness of teacher training programs.
- Reflective Practice in Teaching: Investigate how teachers reflect on their practice to improve teaching.
- Challenges in Teacher Education: Identify challenges faced by educators in training and development.
- Teacher Beliefs and Practices: Examine how teachers’ beliefs about language learning influence their instructional practices.
- Peer Observation in Teacher Development: Explore the benefits of peer observation and feedback for teacher professional growth.
- Mentoring Programs for New Teachers: Evaluate the effectiveness of mentoring programs in supporting novice teachers.
- Continuing Professional Development (CPD) Models: Compare different models of CPD for language teachers and their impact on teaching quality.
Cultural and Sociolinguistic Aspects
- Language and Culture Interrelationship: Explore the relationship between language and culture in ELT.
- Sociolinguistic Competence and Pragmatics: Study how social context influences language use and understanding.
- Gender and Identity in Language Learning: Investigate how gender identity affects language learning experiences.
- Intercultural Competence in Language Teaching: Develop strategies for promoting intercultural communicative competence in language learners.
- Language Policy and Minority Language Education: Analyze the impact of language policies on the education of minority language speakers.
- Gender and Language Learning Strategies: Investigate gender differences in language learning strategies and their implications for instruction.
- Code-Switching in Multilingual Classrooms: Study the role of code-switching in language learning and classroom interaction.
Learner Diversity and Inclusive Practices
- Teaching English to Young Learners (TEYL): Examine effective teaching strategies for children learning English.
- Addressing Learning Disabilities in ELT: Investigate methods for supporting learners with disabilities in language learning.
- ELT for Specific Purposes (ESP): Explore specialized English language instruction for specific fields.
- Differentiated Instruction in Language Teaching: Develop strategies for addressing diverse learner needs in the language classroom.
- Inclusive Pedagogies for Learners with Special Educational Needs: Design instructional approaches that accommodate learners with disabilities in language learning.
- Language Learning Strategies of Autistic Learners: Investigate effective language learning strategies for individuals on the autism spectrum.
- Language Identity and Learner Motivation: Explore the relationship between language identity and motivation in language learning.
Policy and Planning in ELT
- National and International Language Policies: Analyze policies governing English language education at different levels.
- ELT Program Implementation Challenges: Identify challenges in implementing ELT programs in diverse contexts.
- Role of ELT in National Development: Examine the contribution of English language education to national development goals.
- English as a Medium of Instruction (EMI) Policies: Analyze the impact of EMI policies on educational equity and access.
- Language Teacher Recruitment and Deployment Policies: Evaluate policies related to the recruitment and deployment of language teachers in diverse contexts.
- Language Assessment Policy Reform: Propose reforms to language assessment policies to promote fairness and validity.
- Biliteracy Development Policies: Study policies aimed at promoting biliteracy development among bilingual learners.
Research Methodologies in ELT
- Qualitative Research Methods in ELT: Explore qualitative approaches like interviews and case studies in ELT research.
- Quantitative Research Methods in ELT: Investigate quantitative methods such as surveys and experiments in language education research.
- Mixed-Methods Approaches in ELT Research: Combine qualitative and quantitative methods to gain a comprehensive understanding of research questions.
- Ethnographic Approaches to ELT Research: Conduct ethnographic studies to explore language learning and teaching in naturalistic settings.
- Case Study Research in Language Education: Investigate specific language learning contexts or programs through in-depth case studies.
- Corpus Linguistics in ELT Research: Analyze language use patterns and learner language production using corpus linguistic methods.
- Longitudinal Studies of Language Learning: Follow language learners over an extended period to examine developmental trajectories and factors influencing language acquisition.
Future Trends and Innovations
- Emerging Technologies in ELT: Study the integration of technologies like AI and VR in language teaching.
- Innovations in Teaching Strategies: Explore new approaches to teaching language, such as flipped classrooms and gamification.
- Future Directions in ELT Research: Investigate potential areas for future research in English language teaching.
- Wearable Technology in Language Learning: Explore the potential of wearable devices for delivering personalized language instruction.
- Data Analytics for Adaptive Learning: Develop data-driven approaches to adaptive learning in language education.
- Augmented Reality (AR) Applications in ELT: Design AR-enhanced language learning experiences for immersive language practice.
- Global Citizenship Education and Language Learning: Investigate the role of language education in fostering global citizenship skills.
- Eco-Linguistics and Language Education: Explore the intersection of language education and environmental sustainability.
- Metacognition and Language Learning: Explore how learners’ awareness of their own learning processes affects language acquisition.
- Peer Interaction in Language Learning: Investigate the role of peer collaboration and discussion in promoting language development.
- Heritage Language Education: Study strategies for maintaining and revitalizing heritage languages among immigrant and minority communities.
- Language Learning Motivation in Adolescents: Examine factors influencing motivation and engagement in adolescent language learners.
- Phonological Awareness in Language Learning: Investigate the role of phonological awareness in literacy development for language learners.
- Pragmatic Development in Language Learners: Explore how learners acquire pragmatic competence and understanding of language use in context.
- Digital Literacies and Language Learning: Examine how digital literacy skills contribute to language proficiency and communication in the digital age.
- Critical Language Awareness: Investigate approaches to developing learners’ critical awareness of language use and power dynamics.
- Language Teacher Identity: Study how language teachers’ identities shape their beliefs, practices, and interactions in the classroom.
- Collaborative Learning in Language Education: Explore the benefits and challenges of collaborative learning environments for language learners.
- Motivational Strategies in Language Teaching: Develop and evaluate motivational techniques to enhance student engagement and persistence in language learning.
- Heritage Language Maintenance: Investigate factors influencing the maintenance and transmission of heritage languages across generations.
- Phonics Instruction in Language Learning: Examine the effectiveness of phonics-based approaches for teaching reading and pronunciation.
- Language Policy Implementation: Analyze the challenges and successes of implementing language policies at the institutional, regional, and national levels.
- Language Teacher Cognition: Explore language teachers’ beliefs, knowledge, and decision-making processes in the classroom.
- Intercultural Communicative Competence: Develop strategies for fostering learners’ ability to communicate effectively across cultures.
- Critical Pedagogy in Language Education: Explore approaches to teaching language that promote critical thinking, social justice, and equity.
- Language Learning Strategies for Autodidacts: Investigate effective self-directed learning strategies for language learners outside formal educational settings.
- Content and Language Integrated Learning (CLIL) in Higher Education: Examine the implementation and outcomes of CLIL programs in tertiary education.
- Sociocultural Theory and Language Learning: Explore how social and cultural factors influence language acquisition and development.
- Language Socialization: Investigate how individuals learn language within social and cultural contexts, including family, peer groups, and communities.
- Speech Perception and Language Learning: Examine the relationship between speech perception abilities and language proficiency in second language learners.
- Genre-Based Approaches to Language Teaching: Explore the use of genre analysis and genre-based pedagogy to teach language skills in context.
- Learner Autonomy in Language Learning: Investigate strategies for promoting learner autonomy and independence in language education.
- Multimodal Literacy in Language Learning: Examine the integration of multiple modes of communication, such as text, image, and sound, in language instruction.
- Community-Based Language Learning: Study language learning initiatives that engage learners with their local communities and resources.
- English as a Lingua Franca (ELF) Communication: Explore the use of English as a global means of communication among speakers from diverse linguistic backgrounds.
Research in English Language Teaching covers a wide range of topics, from language acquisition theories to the impact of technology on learning. By exploring these topics (from a list of research topics in english language teaching), we can improve how English is taught and learned, making it more effective and accessible for everyone.
Continuous research and collaboration among educators, researchers, and policymakers are essential for the ongoing development of ELT.
Related Posts

Step by Step Guide on The Best Way to Finance Car

The Best Way on How to Get Fund For Business to Grow it Efficiently
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Generate the conclusion outline: After entering all necessary details, click on 'generate'. Paperpal will then create a structured outline for your conclusion, to help you start writing and build upon the outline. Write your conclusion: Use the generated outline to build your conclusion.
Table of contents. Step 1: Restate the problem. Step 2: Sum up the paper. Step 3: Discuss the implications. Research paper conclusion examples. Frequently asked questions about research paper conclusions.
The conclusion is intended to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them after they have finished reading the paper. A conclusion is not merely a summary of the main topics covered or a re-statement of your research problem, but a synthesis of key points derived from the findings of your study and, if applicable, where you recommend new areas for future research.
Presentations with strong narrative arcs are clear, captivating, and compelling. Orient the audience and draw them in by demonstrating the relevance and importance of your research story with strong global motive. Provide them with the necessary vocabulary and background knowledge to understand the plot of your story.
Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion. Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and ...
Here are some steps you can follow to write an effective research paper conclusion: Restate the research problem or question: Begin by restating the research problem or question that you aimed to answer in your research. This will remind the reader of the purpose of your study. Summarize the main points: Summarize the key findings and results ...
Conclusion Section for Research Papers. Conclusions are often the last section your audience reads, so they are just as important as introductions in research papers. They are your final opportunity to leave a good impression on the reader. Some academic readers will even jump to read the conclusion to help them decide if they should read the ...
Step 1: Answer your research question. Step 2: Summarize and reflect on your research. Step 3: Make future recommendations. Step 4: Emphasize your contributions to your field. Step 5: Wrap up your thesis or dissertation. Full conclusion example. Conclusion checklist. Other interesting articles.
Begin your conclusion by restating your thesis statement in a way that is slightly different from the wording used in the introduction. Avoid presenting new information or evidence in your conclusion. Just summarize the main points and arguments of your essay and keep this part as concise as possible. Remember that you've already covered the ...
The conclusion is where you describe the consequences of your arguments by justifying to your readers why your arguments matter (Hamilton College, 2014). Derntl (2014) also describes conclusion as the counterpart of the introduction. Using the Hourglass Model (Swales, 1993) as a visual reference, Derntl describes conclusion as the part of the ...
The conclusion is intended to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them after they have finished reading the paper. A conclusion is not merely a summary of your points or a re-statement of your research problem but a synthesis of key points. For most essays, one well-developed paragraph is sufficient for a conclusion ...
30 Example Phrases: How to Conclude a Presentation. 1. "In summary, let's revisit the key takeaways from today's presentation.". 2. "Thank you for your attention. Let's move forward together.". 3. "That brings us to the end. I'm open to any questions you may have.".
The conclusion of a research presentation is where you pull together the ideas derived from your data presentation and analyses in light of the purpose of the research. For example, if the objective is to assess the market of a new product, the conclusion should determine the requirements of the market in question and tell whether there is a ...
A conclusion is the final paragraph of a research paper and serves to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them. The conclusion of a conclusion should: Restate your topic and why it is important. Restate your thesis/claim. Address opposing viewpoints and explain why readers should align with your position.
This article provides an effective technique for writing a conclusion adapted from Erika Eby's The College Student's Guide to Writing a Good Research Paper: 101 Easy Tips & Tricks to Make Your Work Stand Out.. While the thesis introduction starts out with broad statements about the topic, and then narrows it down to the thesis statement, a thesis conclusion does the same in the opposite order.
Step 1: Return to your thesis. To begin your conclusion, signal that the essay is coming to an end by returning to your overall argument. Don't just repeat your thesis statement —instead, try to rephrase your argument in a way that shows how it has been developed since the introduction. Example: Returning to the thesis.
This structure is commonly adopted and accepted in the scientific fields. The research report starts with a general idea. The report then leads the reader to a discussion on a specific research area. It then ends with applicability to a bigger area. The last section, Conclusion, is the focus of this lesson.
Here are some tips for using a story to conclude a presentation: Make sure the story is brief. Choose a story that relates to the main points of the presentation. Stories about a customer experience or successful case study are effective. Make sure the story is relatable and encourages empathy from your audience. 7.
3. Call-to-action. Don't forget to include a compelling call to action in your final message that motivates the audience to take specific steps after the presentation. Whether it's signing up for a newsletter, trying a product or conducting further research, a clear call to action can encourage engagement.
3 Strategies to Close Your Presentation Powerfully. Use these 3 strategies in your conclusion to: recapture your audience's attention. get your audience to focus and remember your key points. help your audience connect with you and your topic. end your presentation powerfully. One: Include a Call to Action (CTA)
Include a final question for discussion on your "conclusion" slide if you plan to end your presentation with audience involvement, such as a question-and-answer session. Otherwise, you might conclude with a lighthearted joke. Choose a joke, memorable analogy or experience that's appropriate for your audience and fits the tone and mood of your ...
On May 7, 2024, students and faculty mentors were celebrated at Yale School of Medicine's (YSM) Student Research Day (SRD), an annual tradition at YSM since 1988. Five medical students (Chinye Ijile, Amanda Lieberman, Kingson Lin, Victoria Marks, and Jamieson O'Marr) made thesis presentations, and over 75 students, from across Yale's ...
This research presentation aims to propose a design solution for a sensory room catered toward college students with sensory processing disorders, especially those that are on the autism spectrum. ... The conclusion reached through this research emphasizes the need for sensory rooms to gently engage all the human senses while being careful to ...
As noted, more than half of consumer language research has focused on how it persuades, or impacts the audience that consumes it. Research in this area has evolved across five main themes over the last 50+ years. Language in Consumer Culture (1980s) The first boom in language research began in the mid-1980s and was mostly qualitative.
Investment in research and development (R&D) is essential for a country's success in the global economy and for its ability to address challenges and opportunities. R&D contributes to innovation and competitiveness. In 2021, the business sector was the leading performer and funder of U.S. R&D. The federal government was the second-largest overall funding source and the largest funding source ...
Research on AI-primarily based presentation gear. Take a study of the variety of AI-based presentation tools available on the market. Find the best AI Tools for teachers that meet your desires and ...
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is ...
Conclusion. Research in English Language Teaching covers a wide range of topics, from language acquisition theories to the impact of technology on learning. By exploring these topics (from a list of research topics in english language teaching), we can improve how English is taught and learned, making it more effective and accessible for ...
Adverse childhood experiences, or ACEs, are potentially traumatic events that occur in childhood (0-17 years). Examples include: 1. Experiencing violence, abuse, or neglect. Witnessing violence in the home or community. Having a family member attempt or die by suicide.
The Division of Biology hosted its annual Graduate Student Awards Ceremony on May 3. The division is home to approximately 57 graduate students pursuing master's or doctoral degrees in biology or microbiology. Two graduate students received awards for outstanding oral presentations at the 49th annual Graduate Student Research Forum in the Hale ...