- How it works


How to Write the Research Questions – Tips & Examples
Published by Owen Ingram at August 13th, 2021 , Revised On October 3, 2023
Conducting research and writing an academic paper requires a clear direction and focus.
A good research question provides purpose to your research and clarifies the direction. It further helps your readers to understand what issue your research aims to explore and address.
If you are unsure about how to write research questions, here is a list of the attributes of a good research question;
- The research question should contain only a single problem
- You should be able to find the answer to it using primary and secondary data sources
- You should be able to address it within the time limit and other constraints
- Can attain in-depth and detailed results
- Relevant and applicable
- Should relate to your chosen field of research
Whenever you want to discover something new about a topic , you will ask a question about it. Therefore, the research question is important in the overall research process and provides the author with the reading and writing guidelines.
In a research paper or an essay, you will need to create a single research question that highlights just one problem or issue. The thesis statement should include the specific problem you aim to investigate to establish your argument’s central position or claim.
A larger project such as a dissertation or thesis , on the other hand, can have multiple research questions, but every question should focus on your main research problem . Different types of research will help you answer different research questions, but they should all be relevant to the research scope.
How to Write a Research Question
Steps to develop your research question.
- Choose a topic with a wide range of published literature
- Read and skim relevant articles to find out different problems and issues
- Specify a theoretical or practical research problem that your research question will address
- Narrow down the focus of your selected core niche

Example Research Question (s)
Here are examples of research problems and research questions to help you understand how to create a research question for a given research problem.
Types of Research Questions
There are two main types of research; quantitative and qualitative research . Both types of research require research questions. What research question you will answer is dependent on the type of research you wish to employ.
The first part of designing research is to find a gap and create a fully focused research question.
The following table shows common research questions for a dissertation project. However, it is important to note that these examples of dissertation research questions are straightforward, and the actual research questions may be more complicated than these examples.
What data collection method best suits your research?
- Find out by hiring an expert from ResearchProspect today!
- Despite how challenging the subject may be, we are here to help you.
Steps to Write Research Questions
The research question provides you with a path and focuses on the real problem and the research gap you aim to fill. These are steps you need to take if you are unsure about how to write a research question:
Choose an Interesting Topic
Choose a topic of research according to your interest. The selected topic should be neither too broad nor too narrow.
Do Preliminary Research on the Topic
Find articles, books, journals, and theses relevant to your chosen topic. Understand what research problem each scholar addressed as part of their research project.
Consider your Audience
It is necessary to know your audience to develop focused research questions for your essay or dissertation. You can find aspects of your topic that could be interesting to your audience when narrowing your topic.
Start Asking Questions
What, why, when, how, and other open-ended questions will provide in-depth knowledge about the topic.
Evaluate your Question
After formulating a research question, evaluate to check its effectiveness and how it can serve the purpose. Revise and refine the dissertation research question.
- Do you have a clear research question?
It would help if you formed the research question after finding a research gap. This approach will enable the research to solve part of the problem.
- Do you have a focused research question?
It is necessary that the research question is specific and relating to the central aim of your research.
- Do you have a complex research question?
The research question cannot be answered by yes or no but requires in-depth analysis. It often begins with “How” or “Why.”
Begin your Research
After you have prepared dissertation research questions, you should research the existing literature on similar topics to find various perspectives.
Also See: Formulation of Research Question
If you have been struggling to devise research questions for your dissertation or are unsure about which topic would be suitable for your needs, then you might be interested in taking advantage of our dissertation topic and outline service, which includes several topic ideas in your preferred area of study and a 500/1000 words plan on your chosen topic. Our topic and outline service will help you jump-start your dissertation project.
Find out How Our Topics & Outline Service Can Help You!
Tips on How to Write a Strong Research Question
A research question is the foundation of the entire research. Therefore, you should spend as much time as required to refine the research question.
If you have good research questions for the dissertation, research paper , or essay, you can perform the research and analyse your results more effectively. You can evaluate the strength of the research question with the help of the following criteria. Your research question should be;
Intensive and Researchable
- It should cover a single issue
- The question shouldn’t include a subjective judgment
- It can be answerable with the data analysis or research=
Practical and Specific
- It should not include a course of action, policy, or solution
- It should be well-defined
- Answerable within research limits
Complicated and Arguable
- It should not be simple to answer
- Need in-depth knowledge to find facts
- Provides scope for debate and deliberation
Unique and Relevant
- It should lie in your field of study
- Its results should be contributable
- It should be unique
Conclusion – How to Write Research Questions
A research question provides a clear direction for research work. A bigger project, such as a dissertation, may have more than one research question, but every question should focus on one issue only.
Your research questions should be researchable, feasible to answer, specific to find results, complex (for Masters and PhD projects), and relevant to your field of study. Dissertation research questions depend upon the research type you are basing your paper on.
Start creating a research question by choosing an interesting topic, do some preliminary research, consider your audience, start asking questions, evaluating your question, and begin your research.
At ResearchProspect, we have dissertation experts for all academic subjects. Whether you need help with the individual chapters or the whole dissertation paper, you can be confident that your paper competed to the highest academic standard. There is a reason why our clients keep returning to us over and over. You can also look at our essay services if you are struggling to draft a first-class academic paper.
At ResearchProspect, we have dissertation experts for all academic subjects. Whether you need help with the individual chapters or the whole dissertation paper, you can be confident that your paper competed to the highest academic standard. There is a reason why our clients keep returning to us over and over.
You can also look at our essay services if you are struggling to draft a first-class academic paper.
Place Order
Frequently Asked Questions
How are research questions written.
Research questions are written by:
- Identifying your topic.
- Considering what you want to explore.
- Making questions clear and concise.
- Ensuring they’re researchable.
- Avoiding bias or leading language.
- Focusing on one main idea per question.
What are examples of research questions?
- Does regular exercise improve mental well-being in adults over 50?
- How do online courses impact student engagement compared to traditional classes?
- What are the economic effects of prolonged pandemic lockdowns?
- How does early childhood nutrition influence academic performance in later life?
- Does urban green space reduce stress levels?
How to write a research question?
- Identify a specific topic or issue of interest.
- Conduct preliminary research to understand existing knowledge.
- Narrow the focus to address gaps or unresolved issues.
- Phrase the question to be clear, concise, and researchable.
- Ensure it is specific enough for systematic investigation.
How to formulate my research questions for my geography dissertation?
- Identify a geographical topic or phenomenon of interest.
- Review existing literature to find gaps.
- Consider spatial, temporal, environmental, or societal aspects.
- Ensure questions are specific, feasible, and significant.
- Frame questions to guide methodology: quantitative, qualitative, or mixed.
- Seek feedback from peers/advisors.
You May Also Like
Struggling to find relevant and up-to-date topics for your dissertation? Here is all you need to know if unsure about how to choose dissertation topic.
How to write a hypothesis for dissertation,? A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested with the help of experimental or theoretical research.
Make sure that your selected topic is intriguing, manageable, and relevant. Here are some guidelines to help understand how to find a good dissertation topic.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works

Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
How to Write a Research Question: Types and Examples

The first step in any research project is framing the research question. It can be considered the core of any systematic investigation as the research outcomes are tied to asking the right questions. Thus, this primary interrogation point sets the pace for your research as it helps collect relevant and insightful information that ultimately influences your work.
Typically, the research question guides the stages of inquiry, analysis, and reporting. Depending on the use of quantifiable or quantitative data, research questions are broadly categorized into quantitative or qualitative research questions. Both types of research questions can be used independently or together, considering the overall focus and objectives of your research.
What is a research question?
A research question is a clear, focused, concise, and arguable question on which your research and writing are centered. 1 It states various aspects of the study, including the population and variables to be studied and the problem the study addresses. These questions also set the boundaries of the study, ensuring cohesion.
Designing the research question is a dynamic process where the researcher can change or refine the research question as they review related literature and develop a framework for the study. Depending on the scale of your research, the study can include single or multiple research questions.
A good research question has the following features:
- It is relevant to the chosen field of study.
- The question posed is arguable and open for debate, requiring synthesizing and analysis of ideas.
- It is focused and concisely framed.
- A feasible solution is possible within the given practical constraint and timeframe.
A poorly formulated research question poses several risks. 1
- Researchers can adopt an erroneous design.
- It can create confusion and hinder the thought process, including developing a clear protocol.
- It can jeopardize publication efforts.
- It causes difficulty in determining the relevance of the study findings.
- It causes difficulty in whether the study fulfils the inclusion criteria for systematic review and meta-analysis. This creates challenges in determining whether additional studies or data collection is needed to answer the question.
- Readers may fail to understand the objective of the study. This reduces the likelihood of the study being cited by others.
Now that you know “What is a research question?”, let’s look at the different types of research questions.
Types of research questions
Depending on the type of research to be done, research questions can be classified broadly into quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-methods studies. Knowing the type of research helps determine the best type of research question that reflects the direction and epistemological underpinnings of your research.
The structure and wording of quantitative 2 and qualitative research 3 questions differ significantly. The quantitative study looks at causal relationships, whereas the qualitative study aims at exploring a phenomenon.
- Quantitative research questions:
- Seeks to investigate social, familial, or educational experiences or processes in a particular context and/or location.
- Answers ‘how,’ ‘what,’ or ‘why’ questions.
- Investigates connections, relations, or comparisons between independent and dependent variables.
Quantitative research questions can be further categorized into descriptive, comparative, and relationship, as explained in the Table below.
- Qualitative research questions
Qualitative research questions are adaptable, non-directional, and more flexible. It concerns broad areas of research or more specific areas of study to discover, explain, or explore a phenomenon. These are further classified as follows:
- Mixed-methods studies
Mixed-methods studies use both quantitative and qualitative research questions to answer your research question. Mixed methods provide a complete picture than standalone quantitative or qualitative research, as it integrates the benefits of both methods. Mixed methods research is often used in multidisciplinary settings and complex situational or societal research, especially in the behavioral, health, and social science fields.
What makes a good research question
A good research question should be clear and focused to guide your research. It should synthesize multiple sources to present your unique argument, and should ideally be something that you are interested in. But avoid questions that can be answered in a few factual statements. The following are the main attributes of a good research question.
- Specific: The research question should not be a fishing expedition performed in the hopes that some new information will be found that will benefit the researcher. The central research question should work with your research problem to keep your work focused. If using multiple questions, they should all tie back to the central aim.
- Measurable: The research question must be answerable using quantitative and/or qualitative data or from scholarly sources to develop your research question. If such data is impossible to access, it is better to rethink your question.
- Attainable: Ensure you have enough time and resources to do all research required to answer your question. If it seems you will not be able to gain access to the data you need, consider narrowing down your question to be more specific.
- You have the expertise
- You have the equipment and resources
- Realistic: Developing your research question should be based on initial reading about your topic. It should focus on addressing a problem or gap in the existing knowledge in your field or discipline.
- Based on some sort of rational physics
- Can be done in a reasonable time frame
- Timely: The research question should contribute to an existing and current debate in your field or in society at large. It should produce knowledge that future researchers or practitioners can later build on.
- Novel
- Based on current technologies.
- Important to answer current problems or concerns.
- Lead to new directions.
- Important: Your question should have some aspect of originality. Incremental research is as important as exploring disruptive technologies. For example, you can focus on a specific location or explore a new angle.
- Meaningful whether the answer is “Yes” or “No.” Closed-ended, yes/no questions are too simple to work as good research questions. Such questions do not provide enough scope for robust investigation and discussion. A good research question requires original data, synthesis of multiple sources, and original interpretation and argumentation before providing an answer.
Steps for developing a good research question
The importance of research questions cannot be understated. When drafting a research question, use the following frameworks to guide the components of your question to ease the process. 4
- Determine the requirements: Before constructing a good research question, set your research requirements. What is the purpose? Is it descriptive, comparative, or explorative research? Determining the research aim will help you choose the most appropriate topic and word your question appropriately.
- Select a broad research topic: Identify a broader subject area of interest that requires investigation. Techniques such as brainstorming or concept mapping can help identify relevant connections and themes within a broad research topic. For example, how to learn and help students learn.
- Perform preliminary investigation: Preliminary research is needed to obtain up-to-date and relevant knowledge on your topic. It also helps identify issues currently being discussed from which information gaps can be identified.
- Narrow your focus: Narrow the scope and focus of your research to a specific niche. This involves focusing on gaps in existing knowledge or recent literature or extending or complementing the findings of existing literature. Another approach involves constructing strong research questions that challenge your views or knowledge of the area of study (Example: Is learning consistent with the existing learning theory and research).
- Identify the research problem: Once the research question has been framed, one should evaluate it. This is to realize the importance of the research questions and if there is a need for more revising (Example: How do your beliefs on learning theory and research impact your instructional practices).
How to write a research question
Those struggling to understand how to write a research question, these simple steps can help you simplify the process of writing a research question.
Sample Research Questions
The following are some bad and good research question examples
- Example 1
- Example 2
References:
- Thabane, L., Thomas, T., Ye, C., & Paul, J. (2009). Posing the research question: not so simple. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia/Journal canadien d’anesthésie , 56 (1), 71-79.
- Rutberg, S., & Bouikidis, C. D. (2018). Focusing on the fundamentals: A simplistic differentiation between qualitative and quantitative research. Nephrology Nursing Journal , 45 (2), 209-213.
- Kyngäs, H. (2020). Qualitative research and content analysis. The application of content analysis in nursing science research , 3-11.
- Mattick, K., Johnston, J., & de la Croix, A. (2018). How to… write a good research question. The clinical teacher , 15 (2), 104-108.
- Fandino, W. (2019). Formulating a good research question: Pearls and pitfalls. Indian Journal of Anaesthesia , 63 (8), 611.
- Richardson, W. S., Wilson, M. C., Nishikawa, J., & Hayward, R. S. (1995). The well-built clinical question: a key to evidence-based decisions. ACP journal club , 123 (3), A12-A13
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Scientific Writing Style Guides Explained
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
- 8 Most Effective Ways to Increase Motivation for Thesis Writing
- 6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Transitive and Intransitive Verbs in the World of Research
Language and grammar rules for academic writing, you may also like, how to write the first draft of a..., mla works cited page: format, template & examples, academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., measuring academic success: definition & strategies for excellence, phd qualifying exam: tips for success , quillbot review: features, pricing, and free alternatives, what is an academic paper types and elements , 9 steps to publish a research paper, what are the different types of research papers, how to make translating academic papers less challenging.
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write a Good Research Question (w/ Examples)
What is a Research Question?
A research question is the main question that your study sought or is seeking to answer. A clear research question guides your research paper or thesis and states exactly what you want to find out, giving your work a focus and objective. Learning how to write a hypothesis or research question is the start to composing any thesis, dissertation, or research paper. It is also one of the most important sections of a research proposal .
A good research question not only clarifies the writing in your study; it provides your readers with a clear focus and facilitates their understanding of your research topic, as well as outlining your study’s objectives. Before drafting the paper and receiving research paper editing (and usually before performing your study), you should write a concise statement of what this study intends to accomplish or reveal.
Research Question Writing Tips
Listed below are the important characteristics of a good research question:
A good research question should:
- Be clear and provide specific information so readers can easily understand the purpose.
- Be focused in its scope and narrow enough to be addressed in the space allowed by your paper
- Be relevant and concise and express your main ideas in as few words as possible, like a hypothesis.
- Be precise and complex enough that it does not simply answer a closed “yes or no” question, but requires an analysis of arguments and literature prior to its being considered acceptable.
- Be arguable or testable so that answers to the research question are open to scrutiny and specific questions and counterarguments.
Some of these characteristics might be difficult to understand in the form of a list. Let’s go into more detail about what a research question must do and look at some examples of research questions.
The research question should be specific and focused
Research questions that are too broad are not suitable to be addressed in a single study. One reason for this can be if there are many factors or variables to consider. In addition, a sample data set that is too large or an experimental timeline that is too long may suggest that the research question is not focused enough.
A specific research question means that the collective data and observations come together to either confirm or deny the chosen hypothesis in a clear manner. If a research question is too vague, then the data might end up creating an alternate research problem or hypothesis that you haven’t addressed in your Introduction section .
The research question should be based on the literature
An effective research question should be answerable and verifiable based on prior research because an effective scientific study must be placed in the context of a wider academic consensus. This means that conspiracy or fringe theories are not good research paper topics.
Instead, a good research question must extend, examine, and verify the context of your research field. It should fit naturally within the literature and be searchable by other research authors.
References to the literature can be in different citation styles and must be properly formatted according to the guidelines set forth by the publishing journal, university, or academic institution. This includes in-text citations as well as the Reference section .
The research question should be realistic in time, scope, and budget
There are two main constraints to the research process: timeframe and budget.
A proper research question will include study or experimental procedures that can be executed within a feasible time frame, typically by a graduate doctoral or master’s student or lab technician. Research that requires future technology, expensive resources, or follow-up procedures is problematic.
A researcher’s budget is also a major constraint to performing timely research. Research at many large universities or institutions is publicly funded and is thus accountable to funding restrictions.
The research question should be in-depth
Research papers, dissertations and theses , and academic journal articles are usually dozens if not hundreds of pages in length.
A good research question or thesis statement must be sufficiently complex to warrant such a length, as it must stand up to the scrutiny of peer review and be reproducible by other scientists and researchers.
Research Question Types
Qualitative and quantitative research are the two major types of research, and it is essential to develop research questions for each type of study.
Quantitative Research Questions
Quantitative research questions are specific. A typical research question involves the population to be studied, dependent and independent variables, and the research design.
In addition, quantitative research questions connect the research question and the research design. In addition, it is not possible to answer these questions definitively with a “yes” or “no” response. For example, scientific fields such as biology, physics, and chemistry often deal with “states,” in which different quantities, amounts, or velocities drastically alter the relevance of the research.
As a consequence, quantitative research questions do not contain qualitative, categorical, or ordinal qualifiers such as “is,” “are,” “does,” or “does not.”
Categories of quantitative research questions
Qualitative research questions.
In quantitative research, research questions have the potential to relate to broad research areas as well as more specific areas of study. Qualitative research questions are less directional, more flexible, and adaptable compared with their quantitative counterparts. Thus, studies based on these questions tend to focus on “discovering,” “explaining,” “elucidating,” and “exploring.”
Categories of qualitative research questions
Quantitative and qualitative research question examples.

Good and Bad Research Question Examples
Below are some good (and not-so-good) examples of research questions that researchers can use to guide them in crafting their own research questions.
Research Question Example 1
The first research question is too vague in both its independent and dependent variables. There is no specific information on what “exposure” means. Does this refer to comments, likes, engagement, or just how much time is spent on the social media platform?
Second, there is no useful information on what exactly “affected” means. Does the subject’s behavior change in some measurable way? Or does this term refer to another factor such as the user’s emotions?
Research Question Example 2
In this research question, the first example is too simple and not sufficiently complex, making it difficult to assess whether the study answered the question. The author could really only answer this question with a simple “yes” or “no.” Further, the presence of data would not help answer this question more deeply, which is a sure sign of a poorly constructed research topic.
The second research question is specific, complex, and empirically verifiable. One can measure program effectiveness based on metrics such as attendance or grades. Further, “bullying” is made into an empirical, quantitative measurement in the form of recorded disciplinary actions.
Steps for Writing a Research Question
Good research questions are relevant, focused, and meaningful. It can be difficult to come up with a good research question, but there are a few steps you can follow to make it a bit easier.
1. Start with an interesting and relevant topic
Choose a research topic that is interesting but also relevant and aligned with your own country’s culture or your university’s capabilities. Popular academic topics include healthcare and medical-related research. However, if you are attending an engineering school or humanities program, you should obviously choose a research question that pertains to your specific study and major.
Below is an embedded graph of the most popular research fields of study based on publication output according to region. As you can see, healthcare and the basic sciences receive the most funding and earn the highest number of publications.
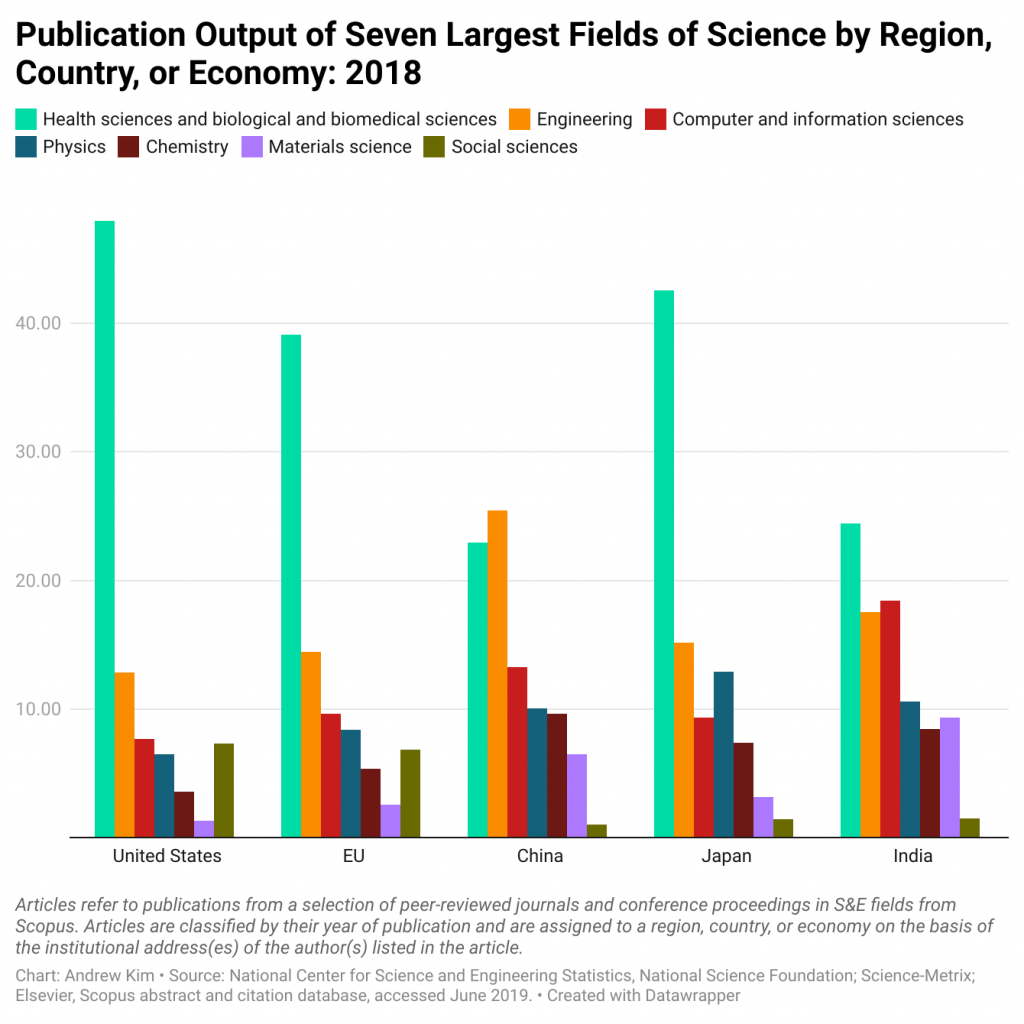
2. Do preliminary research
You can begin doing preliminary research once you have chosen a research topic. Two objectives should be accomplished during this first phase of research. First, you should undertake a preliminary review of related literature to discover issues that scholars and peers are currently discussing. With this method, you show that you are informed about the latest developments in the field.
Secondly, identify knowledge gaps or limitations in your topic by conducting a preliminary literature review . It is possible to later use these gaps to focus your research question after a certain amount of fine-tuning.
3. Narrow your research to determine specific research questions
You can focus on a more specific area of study once you have a good handle on the topic you want to explore. Focusing on recent literature or knowledge gaps is one good option.
By identifying study limitations in the literature and overlooked areas of study, an author can carve out a good research question. The same is true for choosing research questions that extend or complement existing literature.
4. Evaluate your research question
Make sure you evaluate the research question by asking the following questions:
Is my research question clear?
The resulting data and observations that your study produces should be clear. For quantitative studies, data must be empirical and measurable. For qualitative, the observations should be clearly delineable across categories.
Is my research question focused and specific?
A strong research question should be specific enough that your methodology or testing procedure produces an objective result, not one left to subjective interpretation. Open-ended research questions or those relating to general topics can create ambiguous connections between the results and the aims of the study.
Is my research question sufficiently complex?
The result of your research should be consequential and substantial (and fall sufficiently within the context of your field) to warrant an academic study. Simply reinforcing or supporting a scientific consensus is superfluous and will likely not be well received by most journal editors.

Editing Your Research Question
Your research question should be fully formulated well before you begin drafting your research paper. However, you can receive English paper editing and proofreading services at any point in the drafting process. Language editors with expertise in your academic field can assist you with the content and language in your Introduction section or other manuscript sections. And if you need further assistance or information regarding paper compositions, in the meantime, check out our academic resources , which provide dozens of articles and videos on a variety of academic writing and publication topics.

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, 113 great research paper topics.
General Education

One of the hardest parts of writing a research paper can be just finding a good topic to write about. Fortunately we've done the hard work for you and have compiled a list of 113 interesting research paper topics. They've been organized into ten categories and cover a wide range of subjects so you can easily find the best topic for you.
In addition to the list of good research topics, we've included advice on what makes a good research paper topic and how you can use your topic to start writing a great paper.
What Makes a Good Research Paper Topic?
Not all research paper topics are created equal, and you want to make sure you choose a great topic before you start writing. Below are the three most important factors to consider to make sure you choose the best research paper topics.
#1: It's Something You're Interested In
A paper is always easier to write if you're interested in the topic, and you'll be more motivated to do in-depth research and write a paper that really covers the entire subject. Even if a certain research paper topic is getting a lot of buzz right now or other people seem interested in writing about it, don't feel tempted to make it your topic unless you genuinely have some sort of interest in it as well.
#2: There's Enough Information to Write a Paper
Even if you come up with the absolute best research paper topic and you're so excited to write about it, you won't be able to produce a good paper if there isn't enough research about the topic. This can happen for very specific or specialized topics, as well as topics that are too new to have enough research done on them at the moment. Easy research paper topics will always be topics with enough information to write a full-length paper.
Trying to write a research paper on a topic that doesn't have much research on it is incredibly hard, so before you decide on a topic, do a bit of preliminary searching and make sure you'll have all the information you need to write your paper.
#3: It Fits Your Teacher's Guidelines
Don't get so carried away looking at lists of research paper topics that you forget any requirements or restrictions your teacher may have put on research topic ideas. If you're writing a research paper on a health-related topic, deciding to write about the impact of rap on the music scene probably won't be allowed, but there may be some sort of leeway. For example, if you're really interested in current events but your teacher wants you to write a research paper on a history topic, you may be able to choose a topic that fits both categories, like exploring the relationship between the US and North Korea. No matter what, always get your research paper topic approved by your teacher first before you begin writing.
113 Good Research Paper Topics
Below are 113 good research topics to help you get you started on your paper. We've organized them into ten categories to make it easier to find the type of research paper topics you're looking for.
Arts/Culture
- Discuss the main differences in art from the Italian Renaissance and the Northern Renaissance .
- Analyze the impact a famous artist had on the world.
- How is sexism portrayed in different types of media (music, film, video games, etc.)? Has the amount/type of sexism changed over the years?
- How has the music of slaves brought over from Africa shaped modern American music?
- How has rap music evolved in the past decade?
- How has the portrayal of minorities in the media changed?

Current Events
- What have been the impacts of China's one child policy?
- How have the goals of feminists changed over the decades?
- How has the Trump presidency changed international relations?
- Analyze the history of the relationship between the United States and North Korea.
- What factors contributed to the current decline in the rate of unemployment?
- What have been the impacts of states which have increased their minimum wage?
- How do US immigration laws compare to immigration laws of other countries?
- How have the US's immigration laws changed in the past few years/decades?
- How has the Black Lives Matter movement affected discussions and view about racism in the US?
- What impact has the Affordable Care Act had on healthcare in the US?
- What factors contributed to the UK deciding to leave the EU (Brexit)?
- What factors contributed to China becoming an economic power?
- Discuss the history of Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies (some of which tokenize the S&P 500 Index on the blockchain) .
- Do students in schools that eliminate grades do better in college and their careers?
- Do students from wealthier backgrounds score higher on standardized tests?
- Do students who receive free meals at school get higher grades compared to when they weren't receiving a free meal?
- Do students who attend charter schools score higher on standardized tests than students in public schools?
- Do students learn better in same-sex classrooms?
- How does giving each student access to an iPad or laptop affect their studies?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of the Montessori Method ?
- Do children who attend preschool do better in school later on?
- What was the impact of the No Child Left Behind act?
- How does the US education system compare to education systems in other countries?
- What impact does mandatory physical education classes have on students' health?
- Which methods are most effective at reducing bullying in schools?
- Do homeschoolers who attend college do as well as students who attended traditional schools?
- Does offering tenure increase or decrease quality of teaching?
- How does college debt affect future life choices of students?
- Should graduate students be able to form unions?

- What are different ways to lower gun-related deaths in the US?
- How and why have divorce rates changed over time?
- Is affirmative action still necessary in education and/or the workplace?
- Should physician-assisted suicide be legal?
- How has stem cell research impacted the medical field?
- How can human trafficking be reduced in the United States/world?
- Should people be able to donate organs in exchange for money?
- Which types of juvenile punishment have proven most effective at preventing future crimes?
- Has the increase in US airport security made passengers safer?
- Analyze the immigration policies of certain countries and how they are similar and different from one another.
- Several states have legalized recreational marijuana. What positive and negative impacts have they experienced as a result?
- Do tariffs increase the number of domestic jobs?
- Which prison reforms have proven most effective?
- Should governments be able to censor certain information on the internet?
- Which methods/programs have been most effective at reducing teen pregnancy?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of the Keto diet?
- How effective are different exercise regimes for losing weight and maintaining weight loss?
- How do the healthcare plans of various countries differ from each other?
- What are the most effective ways to treat depression ?
- What are the pros and cons of genetically modified foods?
- Which methods are most effective for improving memory?
- What can be done to lower healthcare costs in the US?
- What factors contributed to the current opioid crisis?
- Analyze the history and impact of the HIV/AIDS epidemic .
- Are low-carbohydrate or low-fat diets more effective for weight loss?
- How much exercise should the average adult be getting each week?
- Which methods are most effective to get parents to vaccinate their children?
- What are the pros and cons of clean needle programs?
- How does stress affect the body?
- Discuss the history of the conflict between Israel and the Palestinians.
- What were the causes and effects of the Salem Witch Trials?
- Who was responsible for the Iran-Contra situation?
- How has New Orleans and the government's response to natural disasters changed since Hurricane Katrina?
- What events led to the fall of the Roman Empire?
- What were the impacts of British rule in India ?
- Was the atomic bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki necessary?
- What were the successes and failures of the women's suffrage movement in the United States?
- What were the causes of the Civil War?
- How did Abraham Lincoln's assassination impact the country and reconstruction after the Civil War?
- Which factors contributed to the colonies winning the American Revolution?
- What caused Hitler's rise to power?
- Discuss how a specific invention impacted history.
- What led to Cleopatra's fall as ruler of Egypt?
- How has Japan changed and evolved over the centuries?
- What were the causes of the Rwandan genocide ?

- Why did Martin Luther decide to split with the Catholic Church?
- Analyze the history and impact of a well-known cult (Jonestown, Manson family, etc.)
- How did the sexual abuse scandal impact how people view the Catholic Church?
- How has the Catholic church's power changed over the past decades/centuries?
- What are the causes behind the rise in atheism/ agnosticism in the United States?
- What were the influences in Siddhartha's life resulted in him becoming the Buddha?
- How has media portrayal of Islam/Muslims changed since September 11th?
Science/Environment
- How has the earth's climate changed in the past few decades?
- How has the use and elimination of DDT affected bird populations in the US?
- Analyze how the number and severity of natural disasters have increased in the past few decades.
- Analyze deforestation rates in a certain area or globally over a period of time.
- How have past oil spills changed regulations and cleanup methods?
- How has the Flint water crisis changed water regulation safety?
- What are the pros and cons of fracking?
- What impact has the Paris Climate Agreement had so far?
- What have NASA's biggest successes and failures been?
- How can we improve access to clean water around the world?
- Does ecotourism actually have a positive impact on the environment?
- Should the US rely on nuclear energy more?
- What can be done to save amphibian species currently at risk of extinction?
- What impact has climate change had on coral reefs?
- How are black holes created?
- Are teens who spend more time on social media more likely to suffer anxiety and/or depression?
- How will the loss of net neutrality affect internet users?
- Analyze the history and progress of self-driving vehicles.
- How has the use of drones changed surveillance and warfare methods?
- Has social media made people more or less connected?
- What progress has currently been made with artificial intelligence ?
- Do smartphones increase or decrease workplace productivity?
- What are the most effective ways to use technology in the classroom?
- How is Google search affecting our intelligence?
- When is the best age for a child to begin owning a smartphone?
- Has frequent texting reduced teen literacy rates?

How to Write a Great Research Paper
Even great research paper topics won't give you a great research paper if you don't hone your topic before and during the writing process. Follow these three tips to turn good research paper topics into great papers.
#1: Figure Out Your Thesis Early
Before you start writing a single word of your paper, you first need to know what your thesis will be. Your thesis is a statement that explains what you intend to prove/show in your paper. Every sentence in your research paper will relate back to your thesis, so you don't want to start writing without it!
As some examples, if you're writing a research paper on if students learn better in same-sex classrooms, your thesis might be "Research has shown that elementary-age students in same-sex classrooms score higher on standardized tests and report feeling more comfortable in the classroom."
If you're writing a paper on the causes of the Civil War, your thesis might be "While the dispute between the North and South over slavery is the most well-known cause of the Civil War, other key causes include differences in the economies of the North and South, states' rights, and territorial expansion."
#2: Back Every Statement Up With Research
Remember, this is a research paper you're writing, so you'll need to use lots of research to make your points. Every statement you give must be backed up with research, properly cited the way your teacher requested. You're allowed to include opinions of your own, but they must also be supported by the research you give.
#3: Do Your Research Before You Begin Writing
You don't want to start writing your research paper and then learn that there isn't enough research to back up the points you're making, or, even worse, that the research contradicts the points you're trying to make!
Get most of your research on your good research topics done before you begin writing. Then use the research you've collected to create a rough outline of what your paper will cover and the key points you're going to make. This will help keep your paper clear and organized, and it'll ensure you have enough research to produce a strong paper.

What's Next?
Are you also learning about dynamic equilibrium in your science class? We break this sometimes tricky concept down so it's easy to understand in our complete guide to dynamic equilibrium .
Thinking about becoming a nurse practitioner? Nurse practitioners have one of the fastest growing careers in the country, and we have all the information you need to know about what to expect from nurse practitioner school .
Want to know the fastest and easiest ways to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius? We've got you covered! Check out our guide to the best ways to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit (or vice versa).
These recommendations are based solely on our knowledge and experience. If you purchase an item through one of our links, PrepScholar may receive a commission.

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Research Aims, Objectives & Questions
The “Golden Thread” Explained Simply (+ Examples)
By: David Phair (PhD) and Alexandra Shaeffer (PhD) | June 2022
The research aims , objectives and research questions (collectively called the “golden thread”) are arguably the most important thing you need to get right when you’re crafting a research proposal , dissertation or thesis . We receive questions almost every day about this “holy trinity” of research and there’s certainly a lot of confusion out there, so we’ve crafted this post to help you navigate your way through the fog.
Overview: The Golden Thread
- What is the golden thread
- What are research aims ( examples )
- What are research objectives ( examples )
- What are research questions ( examples )
- The importance of alignment in the golden thread
What is the “golden thread”?
The golden thread simply refers to the collective research aims , research objectives , and research questions for any given project (i.e., a dissertation, thesis, or research paper ). These three elements are bundled together because it’s extremely important that they align with each other, and that the entire research project aligns with them.
Importantly, the golden thread needs to weave its way through the entirety of any research project , from start to end. In other words, it needs to be very clearly defined right at the beginning of the project (the topic ideation and proposal stage) and it needs to inform almost every decision throughout the rest of the project. For example, your research design and methodology will be heavily influenced by the golden thread (we’ll explain this in more detail later), as well as your literature review.
The research aims, objectives and research questions (the golden thread) define the focus and scope ( the delimitations ) of your research project. In other words, they help ringfence your dissertation or thesis to a relatively narrow domain, so that you can “go deep” and really dig into a specific problem or opportunity. They also help keep you on track , as they act as a litmus test for relevance. In other words, if you’re ever unsure whether to include something in your document, simply ask yourself the question, “does this contribute toward my research aims, objectives or questions?”. If it doesn’t, chances are you can drop it.
Alright, enough of the fluffy, conceptual stuff. Let’s get down to business and look at what exactly the research aims, objectives and questions are and outline a few examples to bring these concepts to life.

Research Aims: What are they?
Simply put, the research aim(s) is a statement that reflects the broad overarching goal (s) of the research project. Research aims are fairly high-level (low resolution) as they outline the general direction of the research and what it’s trying to achieve .
Research Aims: Examples
True to the name, research aims usually start with the wording “this research aims to…”, “this research seeks to…”, and so on. For example:
“This research aims to explore employee experiences of digital transformation in retail HR.” “This study sets out to assess the interaction between student support and self-care on well-being in engineering graduate students”
As you can see, these research aims provide a high-level description of what the study is about and what it seeks to achieve. They’re not hyper-specific or action-oriented, but they’re clear about what the study’s focus is and what is being investigated.
Need a helping hand?
Research Objectives: What are they?
The research objectives take the research aims and make them more practical and actionable . In other words, the research objectives showcase the steps that the researcher will take to achieve the research aims.
The research objectives need to be far more specific (higher resolution) and actionable than the research aims. In fact, it’s always a good idea to craft your research objectives using the “SMART” criteria. In other words, they should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound”.
Research Objectives: Examples
Let’s look at two examples of research objectives. We’ll stick with the topic and research aims we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic:
To observe the retail HR employees throughout the digital transformation. To assess employee perceptions of digital transformation in retail HR. To identify the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR.
And for the student wellness topic:
To determine whether student self-care predicts the well-being score of engineering graduate students. To determine whether student support predicts the well-being score of engineering students. To assess the interaction between student self-care and student support when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students.
As you can see, these research objectives clearly align with the previously mentioned research aims and effectively translate the low-resolution aims into (comparatively) higher-resolution objectives and action points . They give the research project a clear focus and present something that resembles a research-based “to-do” list.

Research Questions: What are they?
Finally, we arrive at the all-important research questions. The research questions are, as the name suggests, the key questions that your study will seek to answer . Simply put, they are the core purpose of your dissertation, thesis, or research project. You’ll present them at the beginning of your document (either in the introduction chapter or literature review chapter) and you’ll answer them at the end of your document (typically in the discussion and conclusion chapters).
The research questions will be the driving force throughout the research process. For example, in the literature review chapter, you’ll assess the relevance of any given resource based on whether it helps you move towards answering your research questions. Similarly, your methodology and research design will be heavily influenced by the nature of your research questions. For instance, research questions that are exploratory in nature will usually make use of a qualitative approach, whereas questions that relate to measurement or relationship testing will make use of a quantitative approach.
Let’s look at some examples of research questions to make this more tangible.
Research Questions: Examples
Again, we’ll stick with the research aims and research objectives we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic (which would be qualitative in nature):
How do employees perceive digital transformation in retail HR? What are the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR?
And for the student wellness topic (which would be quantitative in nature):
Does student self-care predict the well-being scores of engineering graduate students? Does student support predict the well-being scores of engineering students? Do student self-care and student support interact when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students?
You’ll probably notice that there’s quite a formulaic approach to this. In other words, the research questions are basically the research objectives “converted” into question format. While that is true most of the time, it’s not always the case. For example, the first research objective for the digital transformation topic was more or less a step on the path toward the other objectives, and as such, it didn’t warrant its own research question.
So, don’t rush your research questions and sloppily reword your objectives as questions. Carefully think about what exactly you’re trying to achieve (i.e. your research aim) and the objectives you’ve set out, then craft a set of well-aligned research questions . Also, keep in mind that this can be a somewhat iterative process , where you go back and tweak research objectives and aims to ensure tight alignment throughout the golden thread.
The importance of strong alignment
Alignment is the keyword here and we have to stress its importance . Simply put, you need to make sure that there is a very tight alignment between all three pieces of the golden thread. If your research aims and research questions don’t align, for example, your project will be pulling in different directions and will lack focus . This is a common problem students face and can cause many headaches (and tears), so be warned.
Take the time to carefully craft your research aims, objectives and research questions before you run off down the research path. Ideally, get your research supervisor/advisor to review and comment on your golden thread before you invest significant time into your project, and certainly before you start collecting data .
Recap: The golden thread
In this post, we unpacked the golden thread of research, consisting of the research aims , research objectives and research questions . You can jump back to any section using the links below.
As always, feel free to leave a comment below – we always love to hear from you. Also, if you’re interested in 1-on-1 support, take a look at our private coaching service here.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

39 Comments
Thank you very much for your great effort put. As an Undergraduate taking Demographic Research & Methodology, I’ve been trying so hard to understand clearly what is a Research Question, Research Aim and the Objectives in a research and the relationship between them etc. But as for now I’m thankful that you’ve solved my problem.
Well appreciated. This has helped me greatly in doing my dissertation.
An so delighted with this wonderful information thank you a lot.
so impressive i have benefited a lot looking forward to learn more on research.
I am very happy to have carefully gone through this well researched article.
Infact,I used to be phobia about anything research, because of my poor understanding of the concepts.
Now,I get to know that my research question is the same as my research objective(s) rephrased in question format.
I please I would need a follow up on the subject,as I intends to join the team of researchers. Thanks once again.
Thanks so much. This was really helpful.
I know you pepole have tried to break things into more understandable and easy format. And God bless you. Keep it up
i found this document so useful towards my study in research methods. thanks so much.
This is my 2nd read topic in your course and I should commend the simplified explanations of each part. I’m beginning to understand and absorb the use of each part of a dissertation/thesis. I’ll keep on reading your free course and might be able to avail the training course! Kudos!
Thank you! Better put that my lecture and helped to easily understand the basics which I feel often get brushed over when beginning dissertation work.
This is quite helpful. I like how the Golden thread has been explained and the needed alignment.
This is quite helpful. I really appreciate!
The article made it simple for researcher students to differentiate between three concepts.
Very innovative and educational in approach to conducting research.
I am very impressed with all these terminology, as I am a fresh student for post graduate, I am highly guided and I promised to continue making consultation when the need arise. Thanks a lot.
A very helpful piece. thanks, I really appreciate it .
Very well explained, and it might be helpful to many people like me.
Wish i had found this (and other) resource(s) at the beginning of my PhD journey… not in my writing up year… 😩 Anyways… just a quick question as i’m having some issues ordering my “golden thread”…. does it matter in what order you mention them? i.e., is it always first aims, then objectives, and finally the questions? or can you first mention the research questions and then the aims and objectives?
Thank you for a very simple explanation that builds upon the concepts in a very logical manner. Just prior to this, I read the research hypothesis article, which was equally very good. This met my primary objective.
My secondary objective was to understand the difference between research questions and research hypothesis, and in which context to use which one. However, I am still not clear on this. Can you kindly please guide?
In research, a research question is a clear and specific inquiry that the researcher wants to answer, while a research hypothesis is a tentative statement or prediction about the relationship between variables or the expected outcome of the study. Research questions are broader and guide the overall study, while hypotheses are specific and testable statements used in quantitative research. Research questions identify the problem, while hypotheses provide a focus for testing in the study.
Exactly what I need in this research journey, I look forward to more of your coaching videos.
This helped a lot. Thanks so much for the effort put into explaining it.
What data source in writing dissertation/Thesis requires?
What is data source covers when writing dessertation/thesis
This is quite useful thanks
I’m excited and thankful. I got so much value which will help me progress in my thesis.
where are the locations of the reserch statement, research objective and research question in a reserach paper? Can you write an ouline that defines their places in the researh paper?
Very helpful and important tips on Aims, Objectives and Questions.
Thank you so much for making research aim, research objectives and research question so clear. This will be helpful to me as i continue with my thesis.
Thanks much for this content. I learned a lot. And I am inspired to learn more. I am still struggling with my preparation for dissertation outline/proposal. But I consistently follow contents and tutorials and the new FB of GRAD Coach. Hope to really become confident in writing my dissertation and successfully defend it.
As a researcher and lecturer, I find splitting research goals into research aims, objectives, and questions is unnecessarily bureaucratic and confusing for students. For most biomedical research projects, including ‘real research’, 1-3 research questions will suffice (numbers may differ by discipline).
Awesome! Very important resources and presented in an informative way to easily understand the golden thread. Indeed, thank you so much.
Well explained
The blog article on research aims, objectives, and questions by Grad Coach is a clear and insightful guide that aligns with my experiences in academic research. The article effectively breaks down the often complex concepts of research aims and objectives, providing a straightforward and accessible explanation. Drawing from my own research endeavors, I appreciate the practical tips offered, such as the need for specificity and clarity when formulating research questions. The article serves as a valuable resource for students and researchers, offering a concise roadmap for crafting well-defined research goals and objectives. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced researcher, this article provides practical insights that contribute to the foundational aspects of a successful research endeavor.
A great thanks for you. it is really amazing explanation. I grasp a lot and one step up to research knowledge.
I really found these tips helpful. Thank you very much Grad Coach.
I found this article helpful. Thanks for sharing this.
thank you so much, the explanation and examples are really helpful
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- PLoS Comput Biol
- v.16(7); 2020 Jul

Ten simple rules for reading a scientific paper
Maureen a. carey.
Division of Infectious Diseases and International Health, Department of Medicine, University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville, Virginia, United States of America
Kevin L. Steiner
William a. petri, jr, introduction.
“There is no problem that a library card can't solve” according to author Eleanor Brown [ 1 ]. This advice is sound, probably for both life and science, but even the best tool (like the library) is most effective when accompanied by instructions and a basic understanding of how and when to use it.
For many budding scientists, the first day in a new lab setting often involves a stack of papers, an email full of links to pertinent articles, or some promise of a richer understanding so long as one reads enough of the scientific literature. However, the purpose and approach to reading a scientific article is unlike that of reading a news story, novel, or even a textbook and can initially seem unapproachable. Having good habits for reading scientific literature is key to setting oneself up for success, identifying new research questions, and filling in the gaps in one’s current understanding; developing these good habits is the first crucial step.
Advice typically centers around two main tips: read actively and read often. However, active reading, or reading with an intent to understand, is both a learned skill and a level of effort. Although there is no one best way to do this, we present 10 simple rules, relevant to novices and seasoned scientists alike, to teach our strategy for active reading based on our experience as readers and as mentors of undergraduate and graduate researchers, medical students, fellows, and early career faculty. Rules 1–5 are big picture recommendations. Rules 6–8 relate to philosophy of reading. Rules 9–10 guide the “now what?” questions one should ask after reading and how to integrate what was learned into one’s own science.
Rule 1: Pick your reading goal
What you want to get out of an article should influence your approach to reading it. Table 1 includes a handful of example intentions and how you might prioritize different parts of the same article differently based on your goals as a reader.
1 Yay! Welcome!
2 A journal club is when a group of scientists get together to discuss a paper. Usually one person leads the discussion and presents all of the data. The group discusses their own interpretations and the authors’ interpretation.
Rule 2: Understand the author’s goal
In written communication, the reader and the writer are equally important. Both influence the final outcome: in this case, your scientific understanding! After identifying your goal, think about the author’s goal for sharing this project. This will help you interpret the data and understand the author’s interpretation of the data. However, this requires some understanding of who the author(s) are (e.g., what are their scientific interests?), the scientific field in which they work (e.g., what techniques are available in this field?), and how this paper fits into the author’s research (e.g., is this work building on an author’s longstanding project or controversial idea?). This information may be hard to glean without experience and a history of reading. But don’t let this be a discouragement to starting the process; it is by the act of reading that this experience is gained!
A good step toward understanding the goal of the author(s) is to ask yourself: What kind of article is this? Journals publish different types of articles, including methods, review, commentary, resources, and research articles as well as other types that are specific to a particular journal or groups of journals. These article types have different formatting requirements and expectations for content. Knowing the article type will help guide your evaluation of the information presented. Is the article a methods paper, presenting a new technique? Is the article a review article, intended to summarize a field or problem? Is it a commentary, intended to take a stand on a controversy or give a big picture perspective on a problem? Is it a resource article, presenting a new tool or data set for others to use? Is it a research article, written to present new data and the authors’ interpretation of those data? The type of paper, and its intended purpose, will get you on your way to understanding the author’s goal.
Rule 3: Ask six questions
When reading, ask yourself: (1) What do the author(s) want to know (motivation)? (2) What did they do (approach/methods)? (3) Why was it done that way (context within the field)? (4) What do the results show (figures and data tables)? (5) How did the author(s) interpret the results (interpretation/discussion)? (6) What should be done next? (Regarding this last question, the author(s) may provide some suggestions in the discussion, but the key is to ask yourself what you think should come next.)
Each of these questions can and should be asked about the complete work as well as each table, figure, or experiment within the paper. Early on, it can take a long time to read one article front to back, and this can be intimidating. Break down your understanding of each section of the work with these questions to make the effort more manageable.
Rule 4: Unpack each figure and table
Scientists write original research papers primarily to present new data that may change or reinforce the collective knowledge of a field. Therefore, the most important parts of this type of scientific paper are the data. Some people like to scrutinize the figures and tables (including legends) before reading any of the “main text”: because all of the important information should be obtained through the data. Others prefer to read through the results section while sequentially examining the figures and tables as they are addressed in the text. There is no correct or incorrect approach: Try both to see what works best for you. The key is making sure that one understands the presented data and how it was obtained.
For each figure, work to understand each x- and y-axes, color scheme, statistical approach (if one was used), and why the particular plotting approach was used. For each table, identify what experimental groups and variables are presented. Identify what is shown and how the data were collected. This is typically summarized in the legend or caption but often requires digging deeper into the methods: Do not be afraid to refer back to the methods section frequently to ensure a full understanding of how the presented data were obtained. Again, ask the questions in Rule 3 for each figure or panel and conclude with articulating the “take home” message.
Rule 5: Understand the formatting intentions
Just like the overall intent of the article (discussed in Rule 2), the intent of each section within a research article can guide your interpretation. Some sections are intended to be written as objective descriptions of the data (i.e., the Results section), whereas other sections are intended to present the author’s interpretation of the data. Remember though that even “objective” sections are written by and, therefore, influenced by the authors interpretations. Check out Table 2 to understand the intent of each section of a research article. When reading a specific paper, you can also refer to the journal’s website to understand the formatting intentions. The “For Authors” section of a website will have some nitty gritty information that is less relevant for the reader (like word counts) but will also summarize what the journal editors expect in each section. This will help to familiarize you with the goal of each article section.
Research articles typically contain each of these sections, although sometimes the “results” and “discussion” sections (or “discussion” and “conclusion” sections) are merged into one section. Additional sections may be included, based on request of the journal or the author(s). Keep in mind: If it was included, someone thought it was important for you to read.
Rule 6: Be critical
Published papers are not truths etched in stone. Published papers in high impact journals are not truths etched in stone. Published papers by bigwigs in the field are not truths etched in stone. Published papers that seem to agree with your own hypothesis or data are not etched in stone. Published papers that seem to refute your hypothesis or data are not etched in stone.
Science is a never-ending work in progress, and it is essential that the reader pushes back against the author’s interpretation to test the strength of their conclusions. Everyone has their own perspective and may interpret the same data in different ways. Mistakes are sometimes published, but more often these apparent errors are due to other factors such as limitations of a methodology and other limits to generalizability (selection bias, unaddressed, or unappreciated confounders). When reading a paper, it is important to consider if these factors are pertinent.
Critical thinking is a tough skill to learn but ultimately boils down to evaluating data while minimizing biases. Ask yourself: Are there other, equally likely, explanations for what is observed? In addition to paying close attention to potential biases of the study or author(s), a reader should also be alert to one’s own preceding perspective (and biases). Take time to ask oneself: Do I find this paper compelling because it affirms something I already think (or wish) is true? Or am I discounting their findings because it differs from what I expect or from my own work?
The phenomenon of a self-fulfilling prophecy, or expectancy, is well studied in the psychology literature [ 2 ] and is why many studies are conducted in a “blinded” manner [ 3 ]. It refers to the idea that a person may assume something to be true and their resultant behavior aligns to make it true. In other words, as humans and scientists, we often find exactly what we are looking for. A scientist may only test their hypotheses and fail to evaluate alternative hypotheses; perhaps, a scientist may not be aware of alternative, less biased ways to test her or his hypothesis that are typically used in different fields. Individuals with different life, academic, and work experiences may think of several alternative hypotheses, all equally supported by the data.
Rule 7: Be kind
The author(s) are human too. So, whenever possible, give them the benefit of the doubt. An author may write a phrase differently than you would, forcing you to reread the sentence to understand it. Someone in your field may neglect to cite your paper because of a reference count limit. A figure panel may be misreferenced as Supplemental Fig 3E when it is obviously Supplemental Fig 4E. While these things may be frustrating, none are an indication that the quality of work is poor. Try to avoid letting these minor things influence your evaluation and interpretation of the work.
Similarly, if you intend to share your critique with others, be extra kind. An author (especially the lead author) may invest years of their time into a single paper. Hearing a kindly phrased critique can be difficult but constructive. Hearing a rude, brusque, or mean-spirited critique can be heartbreaking, especially for young scientists or those seeking to establish their place within a field and who may worry that they do not belong.
Rule 8: Be ready to go the extra mile
To truly understand a scientific work, you often will need to look up a term, dig into the supplemental materials, or read one or more of the cited references. This process takes time. Some advisors recommend reading an article three times: The first time, simply read without the pressure of understanding or critiquing the work. For the second time, aim to understand the paper. For the third read through, take notes.
Some people engage with a paper by printing it out and writing all over it. The reader might write question marks in the margins to mark parts (s)he wants to return to, circle unfamiliar terms (and then actually look them up!), highlight or underline important statements, and draw arrows linking figures and the corresponding interpretation in the discussion. Not everyone needs a paper copy to engage in the reading process but, whatever your version of “printing it out” is, do it.
Rule 9: Talk about it
Talking about an article in a journal club or more informal environment forces active reading and participation with the material. Studies show that teaching is one of the best ways to learn and that teachers learn the material even better as the teaching task becomes more complex [ 4 – 5 ]; anecdotally, such observations inspired the phrase “to teach is to learn twice.”
Beyond formal settings such as journal clubs, lab meetings, and academic classes, discuss papers with your peers, mentors, and colleagues in person or electronically. Twitter and other social media platforms have become excellent resources for discussing papers with other scientists, the public or your nonscientist friends, or even the paper’s author(s). Describing a paper can be done at multiple levels and your description can contain all of the scientific details, only the big picture summary, or perhaps the implications for the average person in your community. All of these descriptions will solidify your understanding, while highlighting gaps in your knowledge and informing those around you.
Rule 10: Build on it
One approach we like to use for communicating how we build on the scientific literature is by starting research presentations with an image depicting a wall of Lego bricks. Each brick is labeled with the reference for a paper, and the wall highlights the body of literature on which the work is built. We describe the work and conclusions of each paper represented by a labeled brick and discuss each brick and the wall as a whole. The top brick on the wall is left blank: We aspire to build on this work and label this brick with our own work. We then delve into our own research, discoveries, and the conclusions it inspires. We finish our presentations with the image of the Legos and summarize our presentation on that empty brick.
Whether you are reading an article to understand a new topic area or to move a research project forward, effective learning requires that you integrate knowledge from multiple sources (“click” those Lego bricks together) and build upwards. Leveraging published work will enable you to build a stronger and taller structure. The first row of bricks is more stable once a second row is assembled on top of it and so on and so forth. Moreover, the Lego construction will become taller and larger if you build upon the work of others, rather than using only your own bricks.
Build on the article you read by thinking about how it connects to ideas described in other papers and within own work, implementing a technique in your own research, or attempting to challenge or support the hypothesis of the author(s) with a more extensive literature review. Integrate the techniques and scientific conclusions learned from an article into your own research or perspective in the classroom or research lab. You may find that this process strengthens your understanding, leads you toward new and unexpected interests or research questions, or returns you back to the original article with new questions and critiques of the work. All of these experiences are part of the “active reading”: process and are signs of a successful reading experience.
In summary, practice these rules to learn how to read a scientific article, keeping in mind that this process will get easier (and faster) with experience. We are firm believers that an hour in the library will save a week at the bench; this diligent practice will ultimately make you both a more knowledgeable and productive scientist. As you develop the skills to read an article, try to also foster good reading and learning habits for yourself (recommendations here: [ 6 ] and [ 7 ], respectively) and in others. Good luck and happy reading!
Acknowledgments
Thank you to the mentors, teachers, and students who have shaped our thoughts on reading, learning, and what science is all about.
Funding Statement
MAC was supported by the PhRMA Foundation's Postdoctoral Fellowship in Translational Medicine and Therapeutics and the University of Virginia's Engineering-in-Medicine seed grant, and KLS was supported by the NIH T32 Global Biothreats Training Program at the University of Virginia (AI055432). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
- Technical Support
- Find My Rep
You are here
100 Questions (and Answers) About Research Methods
- Neil J. Salkind
- Description
"How do I create a good research hypothesis?"
"How do I know when my literature review is finished?"
"What is the difference between a sample and a population?"
"What is power and why is it important?"
In an increasingly data-driven world, it is more important than ever for students as well as professionals to better understand the process of research. This invaluable guide answers the essential questions that students ask about research methods in a concise and accessible way.
See what’s new to this edition by selecting the Features tab on this page. Should you need additional information or have questions regarding the HEOA information provided for this title, including what is new to this edition, please email [email protected] . Please include your name, contact information, and the name of the title for which you would like more information. For information on the HEOA, please go to http://ed.gov/policy/highered/leg/hea08/index.html .
For assistance with your order: Please email us at [email protected] or connect with your SAGE representative.
SAGE 2455 Teller Road Thousand Oaks, CA 91320 www.sagepub.com
"This is a concise text that has good coverage of the basic concepts and elementary principles of research methods. It picks up where many traditional research methods texts stop and provides additional discussion on some of the hardest to understand concepts."
"I think it’s a great idea for a text (or series), and I have no doubt that the majority of students would find it helpful. The material is presented clearly, and it is easy to read and understand. My favorite example from those provided is on p. 7 where the author provides an actual checklist for evaluating the merit of a study. This is a great tool for students and would provide an excellent “practice” approach to learning this skill. Over time students wouldn’t need a checklist, but I think it would be invaluable for those students with little to no research experience."
I already am using 3 other books. This is a good book though.
Did not meet my needs
I had heard good things about Salkind's statistics book and wanted to review his research book as well. The 100 questions format is cute, and may provide a quick answer to a specific student question. However, it's not really organized in a way that I find particularly useful for a more integrated course that progressively develop and builds upon concepts.
comes across as a little disorganized, plus a little too focused on psychology and statistics.
This text is a great resource guide for graduate students. But it may not work as well with undergraduates orienting themselves to the research process. However, I will use it as a recommended text for students.
Key Features
· The entire research process is covered from start to finish: Divided into nine parts, the book guides readers from the initial asking of questions, through the analysis and interpretation of data, to the final report
· Each question and answer provides a stand-alone explanation: Readers gain enough information on a particular topic to move on to the next question, and topics can be read in any order
· Most questions and answers supplement others in the book: Important material is reinforced, and connections are made between the topics
· Each answer ends with referral to three other related questions: Readers are shown where to go for additional information on the most closely related topics
Sample Materials & Chapters
Question #16: Question #16: How Do I Know When My Literature Review Is Finished?
Question #32: How Can I Create a Good Research Hypothesis?
Question #40: What Is the Difference Between a Sample and a Population, and Why
Question #92: What Is Power, and Why Is It Important?
For instructors
Select a purchasing option.
Main Navigation
- Contact NeurIPS
- Code of Ethics
- Code of Conduct
- Create Profile
- Journal To Conference Track
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Proceedings
- Future Meetings
- Exhibitor Information
- Privacy Policy
NeurIPS Code of Ethics
The Code of Ethics aims to guide the NeurIPS community towards higher standards of ethical conduct as it pertains to elements of research ethics and the broader societal and environmental impact of research submitted to NeurIPS. It outlines conference expectations about the ethical practices that must be adopted by the submitting authors, members of the program and organizing committees. The Code of Ethics complements the NeurIPS Code of Conduct , which focuses on professional conduct and research integrity issues, including plagiarism, fraud and reproducibility concerns. The points described below also inform the NeurIPS Submission Checklist, which outlines more concrete communication requirements.
Potential Harms Caused by the Research Process
Research involving human subjects or participants:
- Fair Wages: all human research subjects or participants must receive appropriate compensation. If you make use of crowdsourcing or contract work for a particular task as part of your research project, you must respect the minimum hourly rate in the region where the work is carried out.
- Research involving human participants: if the research presented involves direct interactions between the researchers and human participants or between a technical system and human participants, authors are required to follow existing protocols in their institutions (e.g. human subject research accreditation, IRB) and go through the relevant process. In cases when no formal process exists, they can undergo an equivalent informal process (e.g. via their peers or an internal ethics review).
Data-related concerns:
The points listed below apply to all datasets used for submissions, both for publicly available data and internal datasets.
- Privacy: Datasets should minimize the exposure of any personally identifiable information, unless informed consent from those individuals is provided to do so.
- Consent: Any paper that chooses to create a dataset with real data of real people should ask for the explicit consent of participants, or explain why they were unable to do so.
- Deprecated datasets: Authors should take care to confirm with dataset creators that a dataset is still available for use. Datasets taken down by the original author (ie. deemed obsolete, or otherwise discontinued), should no longer be used, unless it is for the purposes of audit or critical assessment. For some indication of known depreciated datasets, please refer to the NeurIPS list of deprecated datasets.
- Copyright and Fair Use: While the norms of fair use and copyright in machine learning research are still evolving, authors must respect the terms of datasets that have defined licenses (e.g. CC 4.0, MIT, etc).
- Representative evaluation practice: When collecting new datasets or making decisions about which datasets to use, authors should assess and communicate the degree to which their datasets are representative of their intended population. Claims of diverse or universal representation should be substantiated by concrete evidence or examples.
Societal Impact and Potential Harmful Consequences
Authors should transparently communicate the known or anticipated consequences of research: for instance via the paper checklist or a separate section in a submission.
The following specific areas are of particular concern:
- Safety: Contributors should consider whether there are foreseeable situations in which their technology can be used to harm, injure or kill people through its direct application, side effects, or potential misuse. We do not accept research whose primary goal is to increase the lethality of weapons systems.
- Security: Researchers should consider whether there is a risk that applications could open security vulnerabilities or cause serious accidents when deployed in real world environments. If this is the case, they should take concrete steps to recommend or implement ways to protect against such security risks.
- Discrimination: Researchers should consider whether the technology they developed can be used to discriminate, exclude, or otherwise negatively impact people, including impacts on the provision of services such as healthcare, education or access to credit.
- Surveillance: Researchers should consult on local laws or legislation before collecting or analyzing any bulk surveillance data. Surveillance should not be used to predict protected categories, or be used in any way to endanger individual well-being.
- Deception & Harassment: Researchers should communicate about whether their approach could be used to facilitate deceptive interactions that would cause harm such as theft, fraud, or harassment, and whether it could be used to impersonate public figures and influence political processes, or as a tool to promote hate speech or abuse.
- Environment: Researchers should consider whether their research is going to negatively impact the environment by, e.g., promoting fossil fuel extraction, increasing societal consumption or producing substantial amounts of greenhouse gasses.
- Human Rights: We prohibit circulation of any research work that builds upon or facilitates illegal activity, and we strongly discourage any work that could be used to deny people rights to privacy, speech, health, liberty, security, legal personhood, or freedom of conscience or religion.
- Bias and fairness: Contributors should consider any suspected biases or limitations to the scope of performance of models or the contents of datasets and inspect these to ascertain whether they encode, contain or exacerbate bias against people of a certain gender, race, sexuality, or other protected characteristics.
Impact Mitigation Measures
We propose some reflection and actions taken to mitigate potential harmful consequences from the research project.
- Data and model documentation: Researchers should communicate the details of the dataset or the model as part of their submissions via structured templates.
- Data and model licenses: If releasing data or models, authors should also provide licenses for them. These should include the intended use and limitations of these artifacts, in order to prevent misuse or inappropriate use.
- Secure and privacy-preserving data storage & distribution : Authors should leverage privacy protocols, encryption and anonymization to reduce the risk of data leakage or theft. Stronger measures should be employed for more sensitive data (e.g., biometric or medical data).
- Responsible release and publication strategy: Models that have a high risk for misuse or dual-use should be released with necessary safeguards to allow for controlled use of the model, e.g. by requiring that users adhere to a code of conduct to access the model. Authors of papers exposing a security vulnerability in a system should follow the responsible disclosure procedures of the system owners.
- Allowing access to research artifacts: When releasing research artifacts, it is important to make accessible the information required to understand these artifacts (e.g. the code, execution environment versions, weights, and hyperparameters of systems) to enable external scrutiny and auditing.
- Disclose essential elements for reproducibility: Any work submitted to NeurIPS should be accompanied by the information sufficient for the reproduction of results described. This can include the code, data, model weights, and/or a description of the computational resources needed to train the proposed model or validate the results.
- Ensure legal compliance: Ensure adequate awareness of regional legal requirements. This can be done, for instance, by consulting with law school clinics specializing in intellectual property and technology issues. Additional information is required from authors where legal compliance could not be met due to human rights violations (e.g. freedom of expression, the right to work and education, bodily autonomy, etc.).
Violations to the Code of Ethics should be reported to [email protected] . NeurIPS reserves the right to reject the presentation of scientific works that violate the Code of Ethics. Notice that conference contributors are also obliged to adhere to additional ethical codes or review requirements arising from other stakeholders such as funders and research institutions.
Further reading
UNDERSTANDING LICENSES
- Towards Standardization of Data Licenses: The Montreal Data License
- Behavioral Use Licensing for Responsible AI
- Choose an open source license
MODEL AND DATA DOCUMENTATION TEMPLATES
- Model Cards for Model Reporting
- Datasheets for Datasets
- Using AI Factsheets for AI Governance
- ML Lifecycle Documentation Practices
SOCIETAL IMPACT
- Safety: Key Concepts in AI Safety: An Overview
- Security: SoK: Security and Privacy in Machine Learning
- Discrimination: Bias in algorithms – Artificial intelligence and discrimination ; What about fairness, bias and discrimination?
- Surveillance: The Human Right to Privacy in the Digital Age
- Deception & Harassment: Generative Language Models and Automated Influence Operations: Emerging Threats and Potential Mitigations
- Environment: Quantifying the Carbon Emissions of Machine Learning
- Human Rights: Technology and Rights | Human Rights Watch
- Bias and fairness: Fairness and machine learning
- Dual use problem: Dual use of artificial-intelligence-powered drug discovery
- Data Enrichment: Responsible Sourcing for Data Enrichment
- Synthetic Media: PAI’s Responsible Practices for Synthetic Media
RELATED ENDEAVORS
- ACM Code of Ethics
- ACL Ethics FAQ
- ICLR Code of Ethics
- Responsible Conduct of Research Training
RELATED RESEARCH COMMUNITIES
- IEEE SaTML 2023
- Aies Conference
- FORC 2022
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Cryptography and Security
Title: how the future works at soups: analyzing future work statements and their impact on usable security and privacy research.
Abstract: Extending knowledge by identifying and investigating valuable research questions and problems is a core function of research. Research publications often suggest avenues for future work to extend and build upon their results. Considering these suggestions can contribute to developing research ideas that build upon previous work and produce results that tie into existing knowledge. Usable security and privacy researchers commonly add future work statements to their publications. However, our community lacks an in-depth understanding of their prevalence, quality, and impact on future research. Our work aims to address this gap in the research literature. We reviewed all 27 papers from the 2019 SOUPS proceedings and analyzed their future work statements. Additionally, we analyzed 978 publications that cite any paper from SOUPS 2019 proceedings to assess their future work statements' impact. We find that most papers from the SOUPS 2019 proceedings include future work statements. However, they are often unspecific or ambiguous, and not always easy to find. Therefore, the citing publications often matched the future work statements' content thematically, but rarely explicitly acknowledged them, indicating a limited impact. We conclude with recommendations for the usable security and privacy community to improve the utility of future work statements by making them more tangible and actionable, and avenues for future work.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .
Diving Deeper into Postsecondary Value, IHEP Research Series Explores Equity and Economic Outcomes

Washington, DC (May 29, 2024) – Higher education has long been recognized as a key driver of economic opportunity, but new research, spearheaded by the Institute for Higher Education Policy (IHEP), is diving deeper into questions of postsecondary value and equity. The “Elevating Equitable Value: Investigating Economic Outcomes of Postsecondary Education” series, informed by data from the Equitable Value Explorer tool along with state-level data, surveys, and additional sources, is exploring pressing questions about postsecondary value. Research released today by Trellis Strategies, the American Association of State Colleges and Universities (AASCU), Wayne State University, and the Research Institute at Dallas College completes the seven-paper series.
“Earning a college degree can change the trajectory of students’ lives, their families, and their communities, for generations to come, but the benefits are not evenly distributed,” said IHEP President Mamie Voight . “By unpacking the nuances of value delivery across different contexts, this research strengthens the evidence-base showing that college is worth the investment. It also can inform policymakers and institutions about targeted strategies to improve the returns on postsecondary education for all students.”
Field-based researchers across the country built on the work of the Postsecondary Value Commission by exploring critical questions on post-college outcomes in their own specific context:
How Can Policy and Practice Shape Equitable Value?
Several papers in the series explored how institutional policy and practice can ensure all students benefit from a college degree. Research by Trellis Strategies underscores the connection between student financial well-being during college and future economic returns. A ten-percentage-point decrease in the number of students experiencing financial instability during college was correlated with higher economic returns to students, especially at four-year public schools. The authors highlight the importance of programs that expand access to emergency aid, promote financial literacy, and enhance transparency around college costs and financial aid options.
A study by the American Association of State Colleges and Universities (AASCU) found that all 33 institutions participating in their Student Success Equity Intensive program had earnings that exceeded the Postsecondary Value Commission’s minimum economic return threshold, but equity gaps persist. Institutions serving a larger proportion of Black, Latinx, and Indigenous students or Pell Grant recipients saw a smaller economic return – the amount by which earnings exceed those of a typical high school graduate, plus the cost of their education – demonstrating the need for continued efforts to promote student success and the financial value of college degrees.
Another key finding shows a strong link between faculty composition and student outcomes. Research by Frederick Tucker of the City University of New York reveals that institutions with more tenured or tenure-track faculty, alongside a smaller proportion of full-time adjuncts, see stronger economic returns for students. This is particularly true at Minority-Serving Institutions (MSIs) and colleges serving a large share of Pell Grant recipients.
How Does Postsecondary Value Differ By and Within States?
The research in this series adds to our growing understanding of how certain states are delivering value. For example, a project by Wayne State University found that while postsecondary education generally leads to higher earnings in Michigan, disparities exist. Public, four-year universities in the state provided the highest economic return, exceeding the minimum threshold by over $22,000, while most other types of institutions in the state offered a smaller but still positive return. Michigan ranked high nationally in terms of the amount that students’ earnings typically exceed the minimum economic return threshold, despite having a moderate ranking in median post-college earnings.
The Research Institute at Dallas College’s analysis paired data from the Equitable Value Explorer with state longitudinal data to measure the economic return at more than 500 Hispanic-Serving Institutions (HSIs) nationwide, in addition to outcomes for all Hispanic students in Texas. Overall, economic returns were positive for Hispanic students, but disparities persisted even within Hispanic communities, particularly for immigrants, those from low-income backgrounds and women.
What is the Role of Geography in the Postsecondary Value Equation?
Location plays a significant role in education options and economic returns. Two papers in the series examined the geographic dimension of value. The American Institutes for Research’s study found that community college students generally earn more after college than those with only a high school diploma in their region. However, community colleges serving a higher percentage of underrepresented students tend to deliver a lower economic value, underscoring the need for additional support to ensure these institutions can effectively serve their students.
Boston College researchers’ analysis of rural-serving institutions (RSIs) found that while median post-college earnings may be slightly lower compared to urban and suburban institutions, RSIs are typically more affordable. The majority of RSIs still provide a positive economic return for students after factoring in these relatively low education costs, highlighting their vital role in expanding access to higher education in underserved areas.
IHEP is expanding and strengthening the community of researchers, practitioners and advocates exploring postsecondary value through an equity lens, by providing the tools necessary for researchers, associations, and institutions to tackle these critical questions. For more information about the Equitable Value Explorer, please visit: https://equity.postsecondaryvalue.org/

Supporting the Whole Student Through Holistic Advising: Reflections on ED’s Raise The Bar Summit

Investing in Student Success: IHEP’s Federal Funding Priorities for FY25

- Join the AMA
- Find learning by topic
- Free learning resources for members
- Credentialed Learning
- Training for teams
- Why learn with the AMA?
- Marketing News
- Academic Journals
- Guides & eBooks
- Marketing Job Board
- Academic Job Board
- AMA Foundation
- Diversity, Equity and Inclusion
- Collegiate Resources
- Awards and Scholarships
- Sponsorship Opportunities
- Strategic Partnerships
We noticed that you are using Internet Explorer 11 or older that is not support any longer. Please consider using an alternative such as Microsoft Edge, Chrome, or Firefox.

Call for Papers | Journal of International Marketing: Digital Platforms and Ecosystems in International Marketing

The business world has witnessed the emergence of new digital technologies and business models in the past two decades. For example, the rise of digital platform business models in retail and IT services has disrupted traditional models, making firms reconsider their business strategies and creating new opportunities for marketers to create value for buyers and other stakeholders (Perren and Kozinets 2018). Digital platforms intermediate between sellers, buyers, and other stakeholders via digital architecture often manifested as mobile and web applications (e.g., sharing economy platforms; Kozlenkova et al. 2021). The platform firm decides on the extent of governance accountability it will take in the entire value-creation process. Ecosystems, of which platforms can be a part, are networks of independent but interdependent actors participating in an industry’s or economic sector’s value chain (Nambisan, Zahra, and Luo 2019). Both platforms and ecosystems create value via direct and indirect network externalities (Kumar, Nim, and Agarwal 2021; Sridhar, Mantrala, Naik, Thorson 2011; ), with value cocreation at the core of actors’ business models and strategies.
In today’s Internet Age, digital platforms have no geographic borders. Platform business models are becoming a go-to strategy for international firms across the globe. For example, retailers are increasingly considering the platformization of their brands to add more value to their core offerings (Wichmann, Wiegand, and Reinartz 2022). With the help of digital technologies, it has become easier to expand into multiple markets simultaneously without diluting the supply chain advantages and brand positioning. Consider the low-cost e-commerce firm Temu from China, operating in more than 50 global markets and developing a strong ecosystem after launching in 2022. Temu consumers get access to various global sellers, making the domestic and international markets more competitive (Deighton 2023).
At the same time, marketers with new ways to create and capture value get access to an expanded target market. For example, as an entertainment platform, Netflix has launched different product and subscription pricing strategies in markets like India to compete with Disney, Amazon, and Reliance (Sull and Turconi 2021). Crowdfunding platforms like Kickstarter connect project creators and backers across the globe. Social media platforms have further amplified the reach of such retail and commerce platforms across both business and consumer markets (Gao et al. 2018). Thus, digital platforms and ecosystems can be considered a contemporary approach to internationalization and thereby are of great interest to marketing managers, policy makers, and regulators in both developed and emerging markets (Hewett et al. 2022).
However, research and knowledge of the dynamics of digital platforms and ecosystems in international marketing is still rather limited. A deeper understanding of how digital platforms can be utilized in the global marketing efforts of businesses is needed. Understanding digital platforms utilized across markets for sustainability, water conservation, health care, and other pressing issues and from the perspectives of NGOs and governments is urgently needed (Falcke, Zobel, and Comello 2024).
The purpose of this special issue, therefore, is to significantly advance research investigating the role of platforms and ecosystem business models across various facets of international marketing. Of special interest are papers focusing on the evolution and formation of digital platform-based global marketing strategies and business models, providing concepts, frameworks, theories, and empirical insights helpful for customers, firms, regulators, policy makers, and governments.
Research bearing on (but not limited to) the following questions is welcome:
- Different modes of platforms and ecosystems as internationalization approaches: a. How orchestrator firms build digital and nondigital architecture across different markets while entering or growing in a market. b. How these modes differ due to within and across market heterogeneity leading to different marketing strategies. c. How the consumer culture of a market complements the different modes.
- Impact of platform and ecosystem approach on the international marketing mix: a. How stakeholders drive or impact product development and innovation processes. b. How integrating private label brands by platforms and using seller data impacts platform outcomes. c. How pricing strategies evolve and change over time with platforms and ecosystem approaches. d. How subscription and non-subscription pricing strategies evolve across various markets. e. How the supply chain and distribution network strengthens or weakens as the industry moves toward platform and ecosystem approaches. f. How the orchestrator firm develops or chooses partners for various marketing activities across and within developed and developing markets. g. How the promotion mix of the platform and ecosystem-based offering differ from traditional business models within and across industries (B2B vs. B2C) and markets. h. How culture interacts with platform and ecosystem strategies, and how this impacts firms and other stakeholders.
- Impact on market structure, competition, and consumer and stakeholder welfare: a. Do platforms and ecosystems command higher market power, impacting the welfare of consumers and other stakeholders? b. Do platform and ecosystems approaches vary across industries (e.g., retail, energy, transportation)? How does these approaches impact the marketing mix in a market? c. Does higher platform power lead to consumer and stakeholder welfare erosion? d. How can marketers navigate the competition and coopetition to make a platform successful across various markets? e. What lessons can be learned from technology platforms like Google and Apple to navigate the tricky technological and regulatory landscape? f. What is the role of government and regulatory bodies in supporting or deterring the platform’s growth to ensure the welfare of stakeholders? g. Do dark patterns affect customer welfare? (For example, subscription pricing charges and policies that are not visible to consumers and the role of regulators.) h. Is there a loss of local livelihood that affects sellers as platforms integrate private label brands? i. What is the impact of the rise of circular platforms on sustainable value chains and stakeholders across developed and developing markets?
- Customer attitudes and actions within and across platforms and ecosystems: a. Conceptual similarity for customer-based outcomes for platform firms and other stakeholders. b. Measurement of customer experience, satisfaction, and engagement with digital platforms and ecosystems. c. Management of failures and customer recovery in multisided platforms and ecosystems. d. Customer journey management across various digital and nondigital touchpoints in platforms and ecosystems. e. Interdependence of consumers’ relationships with and perceptions of brands or partners operating across platforms and ecosystems. f. How marketers can explore circular platforms and ecosystems to help firms be sustainable value chains and positive customer attitudes. g. Platform exploitation by customers and disintermediation.
This list of topics and questions is reflective but not exhaustive of the current state of industry and academic literature. We call for more interdisciplinary and foundational research to expand the horizons of platforms and ecosystems literature in International Marketing. We invite all types of research—qualitative, behavioral, and empirical—and encourage researchers to identify multiple sources of data and motivation for this special issue.
Submission Process
All manuscripts will be reviewed as a cohort for this special issue of the Journal of International Marketing. Manuscripts must be submitted between March 1, 2025 and May 30, 2025. All submissions will go through Journal of International Marketing ’s double-anonymized review and follow standard norms and processes. Submissions must be made via the journal’s ScholarOne site , with author guidelines available here . For any queries, feel free to reach out to the special issue editors.
Special Issue Editors
Nandini Nim, Assistant Professor of Marketing, University of Texas at El Paso (email: [email protected] )
Murali Krishna Mantrala, Ned Fleming Professor of Marketing, University of Kansas (email: [email protected] )
Ayşegül Özsomer, Professor, Koç University, and Editor in Chief, Journal of International Marketing (email: [email protected] )
Adner, Ron (2022), “Sharing Value for Ecosystem Success,” MIT Sloan Management Review , 63 (2), 85–90.
Deighton, John (2023), “How SHEIN and Temu Conquered Fast Fashion—and Forged a New Business Model,” Harvard Business School (April 25), https://hbswk.hbs.edu/item/how-shein-and-temu-conquered-fast-fashion-and-forged-a-new-business-model .
Falcke, Lukas, Ann-Kristin Zobel, and Stephen D. Comello (2024), “How Firms Realign to Tackle the Grand Challenge of Climate Change: An Innovation Ecosystems Perspective,” Journal of Product Innovation Management , 41 (2), 403–27.
Gao, Hongzhi, Mary Tate, Hongxia Zhang, Shijiao Chen, and Bing Liang (2018). “Social Media Ties Strategy in International Branding: An Application of Resource-Based Theory. Journal of International Marketing , 26 (3), 45–69.
Hewett, Kelly, G. Tomas M. Hult, Murali K. Mantrala, Nandini Nim, and Kiran Pedada (2022), “Cross-Border Marketing Ecosystem Orchestration: A Conceptualization of Its Determinants and Boundary Conditions,” International Journal of Research in Marketing , 39 (2), 619–38.
Kozlenkova, Irina V., Ju-Yeon Lee, Diandian Xiang, and Robert W. Palmatier (2021), “Sharing Economy: International Marketing Strategies,” Journal of International Business Studies , 52, 1445–73.
Kumar, V., Nandini Nim, and Amit Agarwal (2021), “Platform-Based Mobile Payments Adoption in Emerging and Developed Countries: Role of Country-Level Heterogeneity and Network Effects,” Journal of International Business Studies , 52, 1529–58.
Nambisan, Satish, Shaker A. Zahra, and Yadong Luo (2019), “Global Platforms and Ecosystems: Implications for International Business Theories,” Journal of International Business Studies , 50, 1464–86.
Perren, Rebeca and Robert V. Kozinets (2018), “Lateral Exchange Markets: How Social Platforms Operate in a Networked Economy,” Journal of Marketing , 82 (1), 20–36.
Sridhar, Shrihari, Murali K. Mantrala, Prasad A. Naik, and Esther Thorson. “Dynamic marketing budgeting for platform firms: Theory, evidence, and application.” Journal of Marketing Research 48, no. 6 (2011): 929-943.
Sull, Donald and Stefano Turconi (2021), “Netflix Goes to Bollywood,” Teacher Resources Library, MIT Sloan School of Management (February 22), https://mitsloan.mit.edu/teaching-resources-library/netflix-goes-to-bollywood.
Wichmann, Julian R.K., Nico Wiegand, and Werner J. Reinartz (2022), “The Platformization of Brands,” Journal of Marketing , 86 (1), 109–31.
Other Resources
Adner, Ron (2017). Ecosystem as Structure: An Actionable Construct for Strategy,” Journal of Management , 43 (1), 39–58.
Akaka, Melissa A., Stephen L. Vargo, and Robert F. Lusch (2013), “The Complexity Of Context: A Service Ecosystems Approach for International Marketing,” Journal of International Marketing , 21 (4), 1–20.
Gawer, Annabelle and Michael A. Cusumano (2014). “Industry Platforms and Ecosystem Innovation,” Journal of Product Innovation Management , 31 (3), 417–33.
Glavas, Charmaine, Shane Mathews, and Rebekah Russell-Bennett (2019), “Knowledge Acquisition via Internet-Enabled Platforms: Examining Incrementally and Non-Incrementally Internationalizing SMEs,” International Marketing Review , 36 (1), 74–107.
Kanuri, Vamsi K., Murali K. Mantrala, and Esther Thorson (2017), “Optimizing a Menu of Multiformat Subscription Plans for Ad-Supported Media Platforms,” Journal of Marketing , 81 (2), 45–63.
Zhou, Qiang (Kris), B.J. Allen, Richard T. Gretz, and Mark B. Houston (2022), “Platform Exploitation: When Service Agents Defect with Customers from Online Service Platforms,” Journal of Marketing , 86 (2), 105–25.
Go to the Journal of International Marketing
By continuing to use this site, you accept the use of cookies, pixels and other technology that allows us to understand our users better and offer you tailored content. You can learn more about our privacy policy here

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
10 Research Question Examples to Guide your Research Project. Published on October 30, 2022 by Shona McCombes.Revised on October 19, 2023. The research question is one of the most important parts of your research paper, thesis or dissertation.It's important to spend some time assessing and refining your question before you get started.
Definition: Research questions are the specific questions that guide a research study or inquiry. These questions help to define the scope of the research and provide a clear focus for the study. Research questions are usually developed at the beginning of a research project and are designed to address a particular research problem or objective.
Good writing begins with clearly stating your research question (or hypothesis) in the Introduction section —the focal point on which your entire paper builds and unfolds in the subsequent Methods, Results, and Discussion sections. This research question or hypothesis that goes into the first section of your research manuscript, the ...
A well-crafted research question (or set of questions) sets the stage for a robust study and meaningful insights. But, if you're new to research, it's not always clear what exactly constitutes a good research question. In this post, we'll provide you with clear examples of quality research questions across various disciplines, so that you can approach your research project with confidence!
1. Start with a broad topic. A broad topic provides writers with plenty of avenues to explore in their search for a viable research question. Techniques to help you develop a topic into subtopics and potential research questions include brainstorming and concept mapping.
A research question is an inquiry that the research attempts to answer. It is the heart of the systematic investigation. Research questions are the most important step in any research project. In essence, it initiates the research project and establishes the pace for the specific research A research question is:
Example Research Question (s) Here are examples of research problems and research questions to help you understand how to create a research question for a given research problem. Example Research Problem. Example Research Question (s) A small-scale company, 'A' in the UK, cannot allocate a marketing budget for next year due to their poor ...
The unfocused research question is so broad that it couldn't be adequately answered in a book-length piece, let alone a standard college-level paper. The focused version narrows down to a specific effect of global warming (glacial melting), a specific place (Antarctica), and a specific animal that is affected (penguins).
Types of research questions. Now that we've defined what a research question is, let's look at the different types of research questions that you might come across. Broadly speaking, there are (at least) four different types of research questions - descriptive, comparative, relational, and explanatory. Descriptive questions ask what is happening. In other words, they seek to describe a ...
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature. As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question.More specifically, that's called a research question, and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What's important to understand though is that you'll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources - for ...
Choose a broad topic, such as "learner support" or "social media influence" for your study. Select topics of interest to make research more enjoyable and stay motivated. Preliminary research. The goal is to refine and focus your research question. The following strategies can help: Skim various scholarly articles.
A good research question should: Be clear and provide specific information so readers can easily understand the purpose. Be focused in its scope and narrow enough to be addressed in the space allowed by your paper. Be relevant and concise and express your main ideas in as few words as possible, like a hypothesis.
To write research questions, try to finish the following sentence: "I want to know how/what/why…" Develop a thesis statement. A thesis statement is a statement of your central argument — it establishes the purpose and position of your paper. If you started with a research question, the thesis statement should answer it.
This column is about research questions, the beginning of the researcher's process. For the reader, the question driving the researcher's inquiry is the first place to start when examining the quality of their work because if the question is flawed, the quality of the methods and soundness of the researchers' thinking does not matter.
The answer is written in length in the discussion section of the paper. Thus, the research question gives a preview of the different parts and variables of the study meant to address the problem posed in the research question.1 An excellent research question clarifies the research writing while facilitating understanding of the research topic ...
Research papers have several applications in various fields, including: Advancing knowledge: Research papers contribute to the advancement of knowledge by generating new insights, theories, and findings that can inform future research and practice. They help to answer important questions, clarify existing knowledge, and identify areas that ...
Formulation of research question (RQ) is an essentiality before starting any research. It aims to explore an existing uncertainty in an area of concern and points to a need for deliberate investigation. It is, therefore, pertinent to formulate a good RQ. The present paper aims to discuss the process of formulation of RQ with stepwise approach.
113 Great Research Paper Topics. One of the hardest parts of writing a research paper can be just finding a good topic to write about. Fortunately we've done the hard work for you and have compiled a list of 113 interesting research paper topics. They've been organized into ten categories and cover a wide range of subjects so you can easily ...
The research aims, objectives and research questions (collectively called the "golden thread") are arguably the most important thing you need to get right when you're crafting a research proposal, dissertation or thesis.We receive questions almost every day about this "holy trinity" of research and there's certainly a lot of confusion out there, so we've crafted this post to help ...
Scientists write original research papers primarily to present new data that may change or reinforce the collective knowledge of a field. Therefore, the most important parts of this type of scientific paper are the data. ... A brief overview of the research question, approach, results, and interpretation. This is the road map or elevator pitch ...
Key Features · The entire research process is covered from start to finish: Divided into nine parts, the book guides readers from the initial asking of questions, through the analysis and interpretation of data, to the final report · Each question and answer provides a stand-alone explanation: Readers gain enough information on a particular topic to move on to the next question, and topics ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
Research involving human participants: if the research presented involves direct interactions between the researchers and human participants or between a technical system and human participants, authors are required to follow existing protocols in their institutions (e.g. human subject research accreditation, IRB) and go through the relevant ...
Abstract: Extending knowledge by identifying and investigating valuable research questions and problems is a core function of research. Research publications often suggest avenues for future work to extend and build upon their results. ... We reviewed all 27 papers from the 2019 SOUPS proceedings and analyzed their future work statements ...
Washington, DC (May 29, 2024) - Higher education has long been recognized as a key driver of economic opportunity, but new research, spearheaded by the Institute for Higher Education Policy (IHEP), is diving deeper into questions of postsecondary value and equity. The "Elevating Equitable Value: Investigating Economic Outcomes of Postsecondary Education" series, informed by data from the ...
Overview. The Bibsam Consortium are the group of 94 Swedish universities, colleges, authorities and state research institutes who jointly sign, through the National Library of Sweden, agreements for journals and databases.. The National Library/Bibsam and JMIR Publications have agreed to a deal to support eligible authors with unlimited publishing in JMIR's entire gold open access journal ...
The business world has witnessed the emergence of new digital technologies and business models in the past two decades. For example, the rise of digital platform business models in retail and IT services has disrupted traditional models, making firms reconsider their business strategies and creating new opportunities for marketers to create value for buyers and other stakeholders (Perren and ...
The research lab has a dedicated team of researchers focused on staying ahead of the curve when it comes to cybersecurity and privacy topics. Our researchers also have to keep in mind ethical and legal considerations when researching hacking techniques and the disclosure of vulnerabilities.
Overview. Our mission is to assist Pennsylvanians in leading safe, healthy, and productive lives through equitable, trauma-informed, and outcome-focused services while being an accountable steward of commonwealth resources.