- Visit Our Website


Why Physical Education Is Important
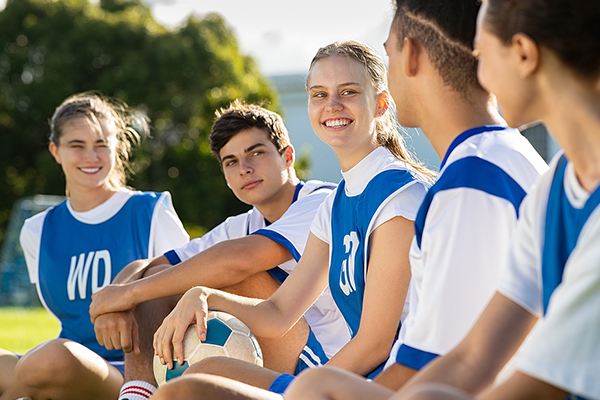

You already know that physical activity is an important part of your child’s health. But the benefits of physical education in schools go beyond the advantages of physical activity. Read on for some of the ways that physical education can improve your child’s health, happiness and overall well-being.
Physical Education Explained
Physical education, or PE, is a school subject that follows a curriculum based on the national standards for physical education for each grade level. In addition to giving kids a designated time to get exercise during the school day, PE also contributes to developing their cognitive skills, motor skills and emotional health. Studies have shown that kids who regularly attend PE are almost three times as likely to be physically active outside of school and nearly twice as likely to be active in adulthood.
Physical Benefits
Guidelines recommend that kids get at least 60 minutes of physical activity every day, and PE is a great way to help get those minutes in. Regular exercise builds strong bones and muscles as well as burns calories, and developing the habit when kids are young makes them much more likely to continue to take good care of themselves when they are adults. Exercising regularly can prevent obesity and decrease the likelihood of developing serious illnesses, such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, cancer and osteoporosis.
Classroom Benefits
Studies have shown that kids who participate in PE have improved concentration, memory and classroom behavior. These perks lead to better academic performance, including higher grades and standardized test scores. Plus, kids who are physically active miss fewer days of school and have better long-term academic success.
Emotional Benefits
Kids who stay active are happier than those who don’t. This is because exercise builds confidence, promotes better sleep and produces endorphins, which are natural mood boosters. This can give kids a more positive outlook on life and help them to feel good about themselves.
If your physically active child experiences an injury, Augusta Health is here to help. Contact a provider at Pediatric Sports Medicine at the Children’s Hospital of Georgia at Augusta University .
About the author.
Children's Hospital of Georgia
Children’s Hospital of Georgia is the only facility in the area dedicated exclusively to children. It staffs the largest team of pediatric specialists in the region who deliver out- and in- patient care for everything from common childhood illnesses to life-threatening conditions like heart disorders, cancer and neurological diseases.
You may also like
Reuters visits Children’s Hospital of Georgia

LGBTQ Youth Mental Health
- Skip to Nav
- Skip to Main
- Skip to Footer

Why PE matters for student academics and wellness right now
Please try again
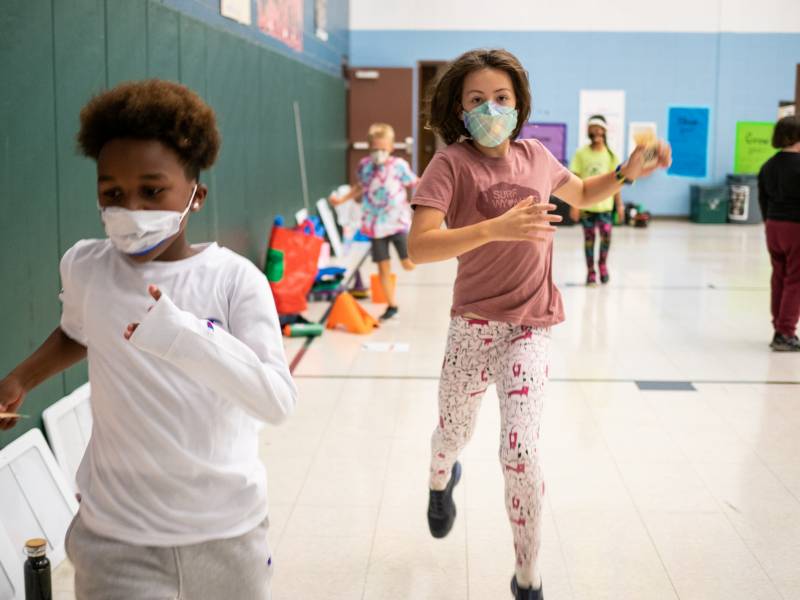

This story about PE teachers was produced by The Hechinger Report , a nonprofit, independent news organization focused on inequality and innovation in education. Sign up for Hechinger’s newsletter .
Amanda Amtmanis, an elementary physical education instructor in Middletown, Connecticut, handed out cards with QR codes to a class of third graders, and told them to start running.
The kids sprinted off around the baseball field in a light drizzle, but by the end of the first lap, a fifth of a mile, many were winded and walking. They paused to scan the cards, which track their mileage, on their teacher’s iPad and got some encouragement from an electronic coach — “Way to run your socks off!” or “Leave it all on the track!”
A boy in a red Nike shirt surged ahead, telling Amtmanis his goal was to run 5 miles. “Whoa, look at Dominic!” another boy exclaimed.
“We don’t need to compare ourselves to others,” Amtmanis reminded him.

The third graders finished a third lap, alternating running and walking, and were about to start on a scavenger hunt when the rain picked up, forcing them inside. Amtmanis thanked her students for their willingness to adjust — a skill many of them have practiced far more often than running these past 18 months.
The full impact of the pandemic on kids’ health and fitness won’t be known for some time. But it’s already caused at least a short-term spike in childhood obesity Rates of overweight and obesity in 5- through 11-year-olds rose nearly 10 percentage points in the first few months of 2020.
Amtmanis’ “mileage club,” which tracks students’ running, both in and out of school, and rewards them with Pokémon cards when they hit certain targets, is an example of how PE teachers around the country are trying to get kids back in shape.
But inclement weather isn’t the only thing PE teachers are up against as they confront what might be called “physical learning loss.” Physical education as a discipline has long fought to be taken as seriously as its academic counterparts. Even before the pandemic, fewer than half the states set any minimum amount of time for students to participate in physical education, according to the Society of Health and Physical Educators (SHAPE), which represents PE and health instructors.
Now, as schools scramble to help kids catch up academically, there are signs that PE is taking a back seat to the core subjects yet again. In some California schools, administrators are shifting instructional minutes from PE to academic subjects — or canceling class altogether so PE teachers can sub for classroom teachers; in others, they’re growing class sizes in the gym, so they can shrink them in the classroom.
Meanwhile, innovative instructors like Amtmanis, who has worked in her district for more than 20 years, are struggling to get their ideas off the ground. Over the summer, the principal of Macdonough Elementary, one of two schools where Amtmanis teaches, approved her request to participate in another running program called The Daily Mile, in which kids walk or run 15 minutes a day during school hours.
Daily running breaks “boost attentiveness, which has positive effects on academics,” Amtmanis argued.
But two weeks into the school year, not a single teacher had bought into the idea.
“The issue is their packed schedule,” Amtmanis said.
Last year, many schools conducted gym class remotely, with students joining in from their bedrooms and living rooms.
The online format presented several challenges. Many students lacked the equipment, space, or parental support to participate fully. And many instructors grappled with how to teach and assess motor skills and teamwork online.
Though instructors found creative ways to keep students moving — substituting rolled-up socks for balls, and “disguising fitness” in scavenger hunts and beat-the-teacher challenges — they still fretted that online gym wasn’t giving students the same benefits as in-person classes.
Compounding their concern was the fact that many students were also missing out on recess and extracurricular sports.
In a March 2021 survey conducted by the Cooper Institute, maker of the popular FitnessGram assessments, close to half the PE teachers and school and district administrators responding said their students were “significantly less” physically active during their schools’ closure than before it.
Schools that reopened last year faced their own set of challenges, including bans on shared equipment that made even a simple game of catch impossible. Schools that were open for in-person learning were also much more likely to cut back on PE instructional time, or eliminate it altogether, the survey found.
The consequences of these reductions in physical activity are hard to quantify, especially since many schools suspended fitness testing during the pandemic and have yet to resume it, but some PE teachers say they’re seeing more kids with locomotor delays and weaker stamina than normal.
“The second graders are like first graders, and some are even like kindergarteners,” said Robin Richardson, an elementary PE instructor in Kentucky. They can jump and hop, she said, but they can’t leap. They’re exhausted after 20 seconds of jumping jacks.
An unusually high number of Richardson’s first graders can’t skip or do windmills. Some lack the spatial awareness that’s essential to group games.
“They don’t know how to move without running into each other,” she said.
Other instructors are seeing an increase in cognitive issues, such as difficulty paying attention or following directions, particularly among kids who remained remote for most or all of last year.
Kyle Bragg, an elementary PE instructor in Arizona, has seen kids sitting with their backs to him, staring off into space when he’s talking. “I say ‘Knees, please,’ so they spin around to face me,” he said.
And some PE teachers say their students’ social-emotional skills have suffered more than their gross motor skills. “They forgot how to share; how to be nice to each other; how to relate to each other,” said Donn Tobin, an elementary PE instructor in New York.
PE has a key role to play in boosting those skills, which affect how kids interact in other classes, said Will Potter, an elementary PE teacher in California.
“We’re uniquely situated to handle the social-emotional needs that came out of the pandemic, in a way classroom teachers are not,” Potter said.
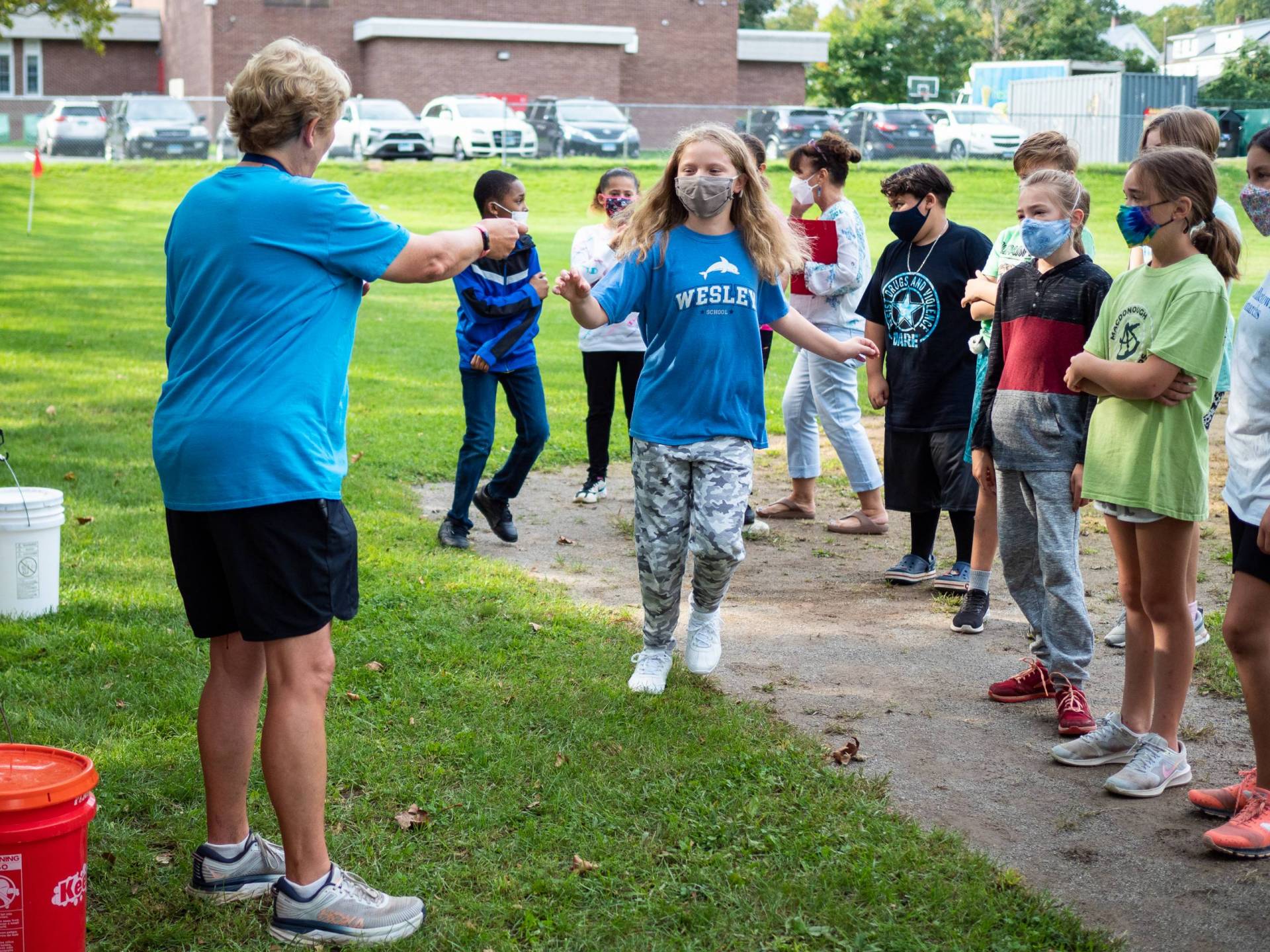
Amtmanis, for her part, worries about her students’ mental health. She sees the little signs of strain daily — the kid who got upset because he couldn’t pick his group, for example, and the one who was distressed that his Mileage Club card had gotten mixed up in the front office.
“Their emotional reserves are low,” she said.
Yet not all instructors are reporting drops in their students’ fitness and skill development. Teachers in some middle- and upper-income districts said they haven’t noticed much of a change at all. In some communities, families seemed to spend more time outdoors.
“We saw the skyrocketing sale of bicycles, we saw families going for walks,” said Dianne Wilson-Graham, executive director of the California Physical Education and Health Project.
But in Title I schools like Macdonough, where more than half the students are low-income, some kids didn’t even have access to a safe place to exercise or play during school closures.
“Not only are they not in soccer leagues, but sometimes they don’t even have a park,” Amtmanis said.
Amtmanis came up with the idea of doing the Daily Mile after spring fitness tests revealed drops in her students’ strength, flexibility and endurance.
But many schools still aren’t sure how much physical learning loss their students have experienced as a result of the pandemic. Most schools pressed pause on fitness testing last year, and some elementary-school instructors are reluctant to restart it. They say the tests aren’t valid with young children, even in ordinary times, and argue the time they take could be better spent on Covid catch-up.
Andjelka Pavlovic, director of research and education for the Cooper Institute, said its tests are scientifically proven to be valid for students who are 10 and up, or roughly starting in fourth grade.
Fitness testing requirements vary by state, county or even district. Some states specify how often students must be tested; others leave it largely to the teacher.
Bragg, the Arizona teacher, said he has put testing “on the backburner” because “right now it’s not at the forefront of what’s important.”
Richardson said she is avoiding testing because she doesn’t want to use up precious instructional time or demoralize her students. “I want my kids to enjoy movement,” she said. If they perform poorly on the tests, “they may not feel as strong.”
In Connecticut, where schools are required to test fourth graders’ fitness annually, Amtmanis approached testing cautiously last year. She didn’t want to embarrass her students, so she made it into a series of games.
Instead of Sit-and-Reach, they had a “flexibility contest,” in which kids broke into teams for tag then had to perform stretches if they were tagged. She measured the distances stretched with curling ribbon, tied the ribbons together, and attached a balloon to the end. The team whose balloon soared the highest won fidget putty.
Pushups became a Bingo game, with the center space representing pushups.
“My goal was to get through it without ever using the words ‘fitness” or ‘testing,’” she said.
As the pandemic drags on, some instructors are taking a similar approach to fitness remediation and acceleration.
Bragg likes a warmup called “ Touch Spots ,” in which first graders listen as the instructor reads off the name of a color, then run and touch a corresponding dot on the floor. It works on reaction time, cardiovascular endurance, spatial awareness and sequencing — but the kids don’t know that.
“Students are having so much fun that they don’t realize how much fitness they are doing,” Bragg said.
Differentiation — tailoring instruction to meet individual students’ needs — has become even more essential, with former remote learners often lagging behind their in-person peers, Bragg said.
When playing catch, for example, he offers his students different sized balls — the smaller ones are more challenging.
Potter, the California teacher, spent the first two weeks of school teaching his students how to connect with their partners, stressing the importance of eye contact and body language.
“When you’re on Zoom, you look at the camera to make eye contact,” he said. “It’s a very different environment.”
Bragg reminds his students how to include kids who are standing on the sidelines, modeling excited body language and tone of voice. Lately, he’s noticed that kids who were remote last year are being excluded from groups.
“Social interaction needs to be practiced, just like how to throw a ball,” he said.
Richardson, the Kentucky PE teacher, is trying to build up her students’ stamina gradually, through progressively longer intervals of exercise.
But she works in a school with pods, so she sees each group of kids for five consecutive days, every third week. The two weeks in between, she has to hope that teachers will provide recess and “movement breaks.” She’s trying to get them to give kids breaks “when they get glassy-eyed and frustrated.”
Recently, Richardson was at a staff training session at which depleted teachers were “popping candy in the back.” When she raised her hand and requested a break in the training, her colleagues cheered. She told them to remember how they felt when their students return to the building.
“I always say, ‘If your bum is numb, your brain is the same,’” she said.
Convincing classroom teachers to set aside more time for movement can be challenging, though. As students return from months of online learning, teachers are under enormous pressure to get them caught up academically.
Kate Cox, an elementary and middle-school PE teacher in California, wishes schools would “realize what they’re missing when they cut PE because of learning loss in other areas.” Physical education is “readying their minds and bodies to be more successful in other areas,” Cox said.
Terri Drain, the president of SHAPE, argued that schools fail students when they treat physical learning loss as less serious than its academic counterpart.
“In the primary grades, children develop fundamental motor skills, such as throwing, catching, running, kicking and jumping,” she said. Unless schools commit to helping kids catch up, “the impacts of this ‘missed learning’ will be lifelong.”

In Connecticut, Amtmanis hasn’t given up on convincing teachers to carve out time for the Daily Mile. She recently sent them a list of suggestions on how to fit 15 minutes of running into the day, including by incorporating it as an active transition between academic blocks.
“While it may seem like there aren’t minutes to spare,” she wrote, “the energizing effect of the active transition should result in more on-task behavior and more efficient working.”
In the meantime, Amtmanis plans to keep using the mileage club to motivate her students to run and to monitor their progress.
“I don’t want to call attention to the fact that not everyone is fit,” she said. “This is an unobtrusive way to keep the data.”
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

Physical Education and Its Importance to Physical Activity, Vegetable Consumption and Thriving in High School Students in Norway
Associated data.
Data supporting reported results can be found on the following link: https://teams.microsoft.com/_#/school/files/General?threadId=19%3A00faa60f3ab64020b836a1c964c56962%40thread.skype&ctx=channel&context=PYD%2520Database&rootfolder=%252Fsites%252FTEAM_PYDCrossNational_Project%252FShared%2520Documents%252FGeneral%252FPYD%2520Database (accessed on 18 August 2021).
Earlier research indicates that physical education (PE) in school is associated with positive outcomes (e.g., healthy lifestyle, psychological well-being, and academic performance). Research assessing associations with resilience and thriving indicators, such as the 5Cs of Positive Youth Development (PYD; competence , confidence , character , caring , and connection ) is limited and more so in the Norwegian context. The aim of the present study was to investigate associations between PE grade (reflecting students’ effort in theoretical and practical aspects of the subject) and the 5Cs as well as healthy behaviors (physical activity (PA), fruit and vegetable consumption), using cross-sectional data collected from 220 high school students in Norway ( M age = 17.30 years old, SD = 1.12; 52% males). Results from structural equation modelling indicated positive associations between PE grade and four of the 5Cs ( competence , confidence , caring , and connection ; standardized coefficient: 0.22–0.60, p < 0.05) while in logistic regressions, a unit increase in PE grade was associated with higher likelihood of engaging in PA and vegetable consumption (OR = 1.94; 95% CI = 1.18–3.18 and OR = 1.68; 95% CI = 1.08–2.63, respectively). These significant findings suggest the need for policies and programs that can support effective planning and implementation of PE curriculum. However, further research is needed to probe into the role of PE on youth health and development with representative samples and longitudinal designs.
1. Introduction
The positive and protective effects of physical activity (PA), such as enhanced physical health, psychological well-being, increased concentration, academic performance, and reduced feelings of depression and anxiety, have been well documented in earlier studies [ 1 , 2 , 3 ]. Physical education (PE) is taught as a subject in many countries around the world, but it also incorporates aspects of PA within the school context, because of the different indoor and outdoor activities students engage in during PE sessions. Indeed, Mooses and colleagues [ 4 ] found PE to significantly increase daily moderate to vigorous PA alongside reducing sedentary time among schoolchildren. In addition, Tassitano and colleagues [ 5 ] observed a positive association between enrollment in PE sessions and several health-related behaviors including physical activity and fruit consumption.
In many schools, students’ efforts in PE are captured in the grade they receive on the subject. Thus, higher grades in PE would indicate greater efforts and achievement in the physical activities engaged in, which in turn can lead to the promotion of outcomes related to health and development as indicated in earlier studies [ 1 , 2 , 3 ]. The present study seeks to determine whether this is the case in high school students in Norway.
1.1. Physical Education in the Global and Norwegian Contexts
In basic terms, physical education has been described as “education through the physical”. Consistent with United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization, PE embraces terms, such as “physical culture”, “movement”, “human motricity”, and “school sport”, and refers to a structured period of directed physical activity in school contexts [ 6 ]. A PE curriculum usually features activities such as team and individual games and sports, gymnastics, dance, swimming, outdoor adventure, and track and field athletics [ 6 ]. By engaging in a variety of physical activities, students are taught physical, social, mental, and emotional skills to empower them to live an active and healthy lifestyle. PE is also an arena where students can develop and practice skills related to collaboration, communication, creativity, and critical thinking [ 7 ].
In a world-wide survey of physical education that involved 232 countries (and autonomous regions), 97% of the countries were found to have either legal requirements for PE within their general education systems or PE was a general practice at some ages of the schoolchildren or phases of compulsory schooling [ 6 ]. The number of PE lessons that were taught in schools across the countries varied from 0.5 to 6.0 per week and from 16 to 46 weeks per year during compulsory education. Country variation depended greatly on the mindset held about the importance and relevance of the subject in the school curricula.
A European Commission report on physical education and sport at school in Europe indicates that while about 50% of the educational systems have national strategies to support the development of PE and PA, two-thirds have large-scale schemes assigned to these activities [ 8 ]. With activities that include athletics, dance, health and fitness, gymnastics, games, outdoor and adventure, swimming, winter sports, and others, the goals of European countries have been to promote the development of pupils and students in the physical, personal, and social domains [ 8 ].
As in many European countries, PE is one of several subjects taught to pupils and students in compulsory education in Norway (i.e., 6–16-year-olds in primary and lower secondary education). The PE curriculum has both practical and theoretical components. In both components of the curriculum, students are introduced to organized physical activities and spontaneous play in varied environments, in a wide range of sports, dance and other movement activities, and in outdoor life, which allows them to orient and spend time in nature in different seasons as well as being an aspect of exercise and lifestyle that deals with the effect of physical activity on health. In high schools, students receive a total of 168 h of PE lessons during their 3-year education, where in addition to sports activities, outdoor life, and lessons on exercise and lifestyle, they receive education in physical motor activities that go beyond traditional sports activities. Moreover, students at this level of education have the possibility to combine PE with active participation in competitive sports [ 9 ].
PE lessons in Norway focus on providing students with challenges and courage to enable them to stretch their own boundaries, in both spontaneous and organized activities. In addition, it is anticipated that students will experience joy, mastery and inspiration by participating in a variety of physical activities, which will eventually help them to develop self-esteem, self-understanding, positive perception of the body and positive identity. Furthermore, the social aspects of the physical activities are intended to create an arena where students can exercise fair play and respect for each other [ 9 , 10 ]. All these effects are positive outcomes that tend to signify several components of what has been referred to as the 5Cs of PYD ( competence , confidence , character , caring, and connection ) [ 11 ] and the ability to develop healthy behaviors, thus supporting health as defined by the World Health Organization. In 1948, the World Health Organization [ 12 ] defined health as “a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity” (p. 100). PE’s role in facilitating health and development will thus touch on WHO’s three dimensions of health.
The current focus of the Norwegian PE curriculum is a result of changes made to the curriculum in 2012, due among others to students and teachers’ dissatisfaction with the stress emanating from the expectations attached to sports achievements and physical performance abilities as well as the observation and measurement the teachers had to undertake to grade students’ abilities. With the present curriculum, it is the effort made by students (i.e., the attempts made to use the acquired knowledge and capabilities to reach developmental goals and not necessarily the attained progress) that is considered as relevant [ 13 ]. Thus, a high grade in PE subject will not only indicate a form of academic achievement, but it will also signify students’ efforts and experience in a variety of physical activities and their knowledge on how these activities can promote positive developmental outcomes, such as health, self-development, and identity [ 14 ].
1.2. Positive Youth Development and the 5Cs
Positive Youth Development is a line of research and a developmental framework that focuses on the identification and promotion of youth strengths [ 15 , 16 ], and the equipping of youth toward becoming productive members of their society [ 16 ]. PYD suggests that all young people have strengths and as such are potential resources to their own development and that of the society they are a part of. In addition, PYD proposes that all youth contexts, such as home, school and the local community, have human and material resources that youth can have access to in their interactions with significant others in these contexts [ 17 ]. In PE sessions, these contextual resources will be the support from peers and teachers, the opportunities created for students to develop resilience, competences and mastery, the boundaries students will have to respect as well as the expectations to be met. Youth strengths will be the personal interest, skills, and abilities that students bring to the PE sessions.
Within PYD, the 5Cs are viewed as a product of the alignment between youth strengths and contextual resources [ 15 ]. Accordingly, the dynamic interaction that ensues between an active, engaged, and competent person and their receptive, supportive, and nurturing ecologies in the context of varying degrees of risk and adversity will lead to a process referred to as adaptive developmental regulations [ 11 , 15 , 18 ], where youth can be resilient, thrive and develop to their full potential. Thriving means youth are scoring high on the 5Cs. The 5Cs include competence (which reflects the positive views of an individual’s action in domains, such as academic, social, cognitive and vocational); confidence (which relates to the individual’s sense of mastery and purpose for the future, a positive identity and self-efficacy); character (which denotes one’s integrity, moral commitment, and respect for societal and cultural rules); caring (which indicates one’s sense of empathy and sympathy for others); and connection (which reflects the bidirectional exchanges and healthy relations between the individual and friends, family, school, and community). Within the PYD framework, the 5Cs typically reflect thriving and positive development, but also resilience (in contexts where there are high levels of risk and adversity) among young people [ 15 , 18 ]. PYD proposes that youth who are thriving are put on a life trajectory towards an “idealized adulthood” [ 19 ]. In addition, youth who are resilient and thriving are more likely to contribute to their own development as well as to the development of their society [ 15 ].
1.3. Earlier Research on Positive Youth Development, Healthy Behaviors and Physical Education
Research on the relationship between grade in PE (which reflects students’ participation in PE sessions) and the 5Cs of PYD is limited, although earlier studies have recounted several positive outcomes of PE in schools. In one study that investigated PYD-related outcomes in the contexts of PE, Holt et al. [ 20 ] found in a qualitative study of 8 teachers and 59 children at an inner-city school in Canada that PE activities engaged in tended to promote developmental outcomes, such as empathy and healthy relationships between students. In addition, PE activities became an arena where teachers considered students’ input to the PE activities and created boundaries and procedures for expected behaviors.
Furthermore, Bailey [ 1 ], in a review article, summarized several positive and profound benefits of PE that included physical health, healthy lifestyle, psychological well-being, social skills and improved academic performance. These benefits were more probable in contexts where there were positive experiences of the PE activities, enjoyment, efforts made to engage all students as well as when teachers and coaches were committed and were equipped with the necessary skills. In another literature review on the impact of PE and sport on educational outcomes, Stead and Nevill [ 21 ] found that increased physical education, physical activity or sport tended to maintain or enhance academic achievement. The authors also found a positive association between physical activity and aspects of mental health, such as self-esteem, emotive well-being, spirituality, and future expectations. Moreover, Stead and Nevill [ 21 ] observed that the implementation of extra organized physical activity, as little as 10 min into the school day, tended to improve classroom behavior. These earlier studies support the important role of PE on health (including the physical, mental, and social dimensions) and positive development in youth.
As for healthy behaviors and their associations with PE, Mayorga-Vega and colleagues [ 22 ] conducted a study among 158 students in a Spanish high school and found that students had greater physical activity levels and lower levels of sedentary behaviors during PE days compared to non-PE days and weekends. In a much larger sample of 4210 high school students in Brazil, Tassitano et al.’s [ 5 ] assessment of the role of PE enrollment on several health behaviors revealed, among others, positive associations of enrollment in PE classes with physical activity and fruit consumption, as well as a negative association with drinking of sugar-sweetened beverages. In a longitudinal study of Canadian adolescents, Wiseman and Weir [ 23 ] investigated PE rating among other subjects alongside the importance of PE for PA levels and several health variables over a two-year period. Their results indicated that most of the participants (78%) preferred PE over other subjects, and that preferring PE was associated with higher PA levels, lower BMI, and higher self-esteem. Thus, while earlier research supports the predictive role of PE on youth development and healthy behaviors, the evidence regarding the importance of PE to the 5Cs of PYD is unclear because of limited research.
1.4. Aims of the Present Study
Research on the 5Cs of PYD has usually involved American youth [ 11 , 24 ] although research featuring non-American samples is growing [ 25 , 26 ]. Moreover, while the effects of PE on youth health and development have been widely studied, a literature search did not return any study that had assessed the relation between PE and the 5Cs in the Norwegian context. Several studies have hinted how activities engaged in during PE can be used to foster positive development. For example, Mandigo et al. [ 27 ] described how quality PE activities can be used to promote positive development and peace education among schoolchildren in a developing country. More specifically, the authors outlined various behaviors in the physical, intellectual, psychological, and social domains that physical educators can instill in schoolchildren to foster the 5Cs of PYD and peaceful interactions. Holt and colleagues [ 20 ] also described how strategies, such as setting of clear boundaries and allowing inputs from schoolchildren, and the teacher being a PE specialist, could facilitate positive youth development. Thus, in line with these earlier PYD studies, PE can be an arena where youth development as well as health (as proposed by WHO) are promoted.
In the present study, the aim is to examine the link between grade in PE and positive outcomes reflected in the 5Cs of PYD. A second aim is to study the association between PE grade and healthy behaviors, such as PA during leisure time and the consumption of fruit and vegetables. With the goal of the Norwegian PE curriculum to promote health, self-development and identity among others, grade in PE reflecting attained knowledge, participation and efforts invested in various physical activities should be associated with the 5Cs. Thus, as a hypothesis, students with higher PE grades are also expected to report higher scores on the 5Cs. Like the 5Cs, positive associations are hypothesized between PE grade and healthy behaviors. If positive associations are found between PE, the 5Cs and healthy behaviors, PE can be considered as an avenue to instill competencies that can have implications for students’ health, thriving, and resilience. Earlier studies suggest that boys engage in PA more often than girls, and PA tends to decrease with age [ 28 ]. Parents’ educational level has also been found to be positively related to the 5Cs [ 26 ]. Hence, gender, age, and parents’ education were accounted for in the assessment of the influence of PE grade on the 5Cs and healthy behaviors.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. sample.
The current study forms part of a larger international project on positive development among youth and emerging adults, where the general goal is to assess how youth strengths and contextual resources align to foster thriving and youth contribution to societal development [ 29 ]. For the present study, cross-sectional data were collected from 220 students in four high schools located in Eastern and Western Norway. About 52% of the participants were boys and the age range was between 16 and 20 years ( M = 17.30, SD = 1.12). Almost 83% reported that the highest level of education of their father was postsecondary, while 87% did the same for their mother’s education.
2.2. Measures
2.2.1. physical education grade.
Participants self-reported their current academic grade (1 to 6) on physical education. A grade of 1 represents minimum knowledge and effort invested during PE sessions while a grade of 6 represents great knowledge and maximum invested effort in PE sessions.
2.2.2. The 5Cs of PYD
To assess the 5Cs, Geldhof and colleagues’ [ 11 ] short version of the PYD questionnaire, consisting of 34 items, was used. Samples of the items used in measuring the 5Cs include: “I am just as smart as others my age” ( competence , 6 items); “I really like the way I look” ( confidence , 6 items); “I usually act the way I am supposed to” ( character , 8 items); “When I see someone being exploited I want to help them” ( caring , 6 items); and “I am a helpful and important family member” ( connection , 8 items). Responses were measured on a 5-point Likert scale, ranging from 1 (Strongly Disagree) to 5 (Strongly Agree), for example, where a higher score indicated a higher experience of the C-item in question. The psychometric properties of the 5Cs scale have been mostly assessed in U.S. samples [ 11 , 24 ] but also in some non-U.S. samples [ 25 , 26 ].
2.2.3. Healthy Behaviors
Items measuring healthy behaviors (physical activity, fruit and vegetable consumption) were adopted from the Search Institute’s [ 30 ] survey on attitudes and behaviors. Participants indicated 0 (No) or 1 (Yes) to the following items: “I engage in physical activity (for at least 30 min) twice or more per week”, “I eat at least one serving of fruit every day” and “I eat at least one serving of vegetables every day”. Spearman correlation among the three healthy behaviors ranged from 0.25 to 0.37.
2.2.4. Demographic Variables
Data were also collected on gender (boy or girl), age and mother and father’s educational level (five levels of education: 1 (no education), 2 (primary school), 3 (high school), 4 (technical or vocational school), and 5 (university)). The demographics were treated as control variables in the data analysis.
2.3. Procedure
Data collection took place in May–August 2019. Convenience sampling was used to select four schools located in the Eastern and Western parts of Norway. The heads of the conveniently selected schools were contacted via e-mail, with a request to participate in the study and an information letter about the purpose of the study. After agreeing to participate, the heads of schools were sent informed consent forms, developed in accordance with the NSD (Norwegian Centre for Research Data) guidelines, which they were asked to sign and send back. Once that was done, teachers from the four schools who agreed to conduct the survey with their students were sent the questionnaire via email. Informed consent was sought from students prior to the data collection, which took place during school hours over the schools’ internal web system. NSD (Norwegian Centre for Research Data) approved the study (51708/3/IJJ), while Semantix Translations Norway AS, Oslo, Norway, a company that specializes in interpretation services, translated the questionnaire from English to Norwegian using double-checking methods and translation experts in the relevant field of research to ensure preservation of meaning.
2.4. Data Analysis
G*Power 3 [ 31 ] was used to conduct a power analysis to determine the sample size that will allow for the assessment of meaningful associations and the detection of effect sizes (small, medium, or large). Using a two-tailed test with the 5 independent variables (PE grade and the four demographic variables (gender, age, father’s education and mother’s education)), and an alpha value of 0.05, the results indicated that with a power of 0.80, sample sizes of 395, 55, and 25 were needed to detect effect sizes of 0.02 (small), 0.15 (medium), and 0.35 (large), respectively. Reaching the study’s sample size of 220 meant that medium to large effect sizes can be detected in the statistical analyses.
Descriptive and correlation analyses were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 25, while all other analyses were carried out using Mplus version 8 [ 32 ]. Most participants (80%) were missing only 3 cases or less, while 59% had full data. The analyses in Mplus were conducted with the Maximum likelihood estimation, an estimation method used to handle missing cases. The method works by estimating a likelihood function for each case based on the variables present in the dataset such that all the available data are used.
Descriptive analyses were conducted to assess the pattern of study variables: the demographics, PE grade, the 5Cs of PYD and the three healthy behaviors. Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) was performed on the items measuring the 5Cs to verify the factorial structure of the scale. Chi-square tests and indices, such as the Tucker Lewis Index (TLI; acceptable above 0.90), the Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA; acceptable below 0.08), and Comparative Fit Index (CFI; acceptable above 0.90) [ 33 , 34 ]) were used to evaluate model fit. To test the hypothesis that higher scores in PE will be associated with higher scores in the 5Cs, structural equation modelling (SEM) analysis was carried out. In preliminary analyses, the linearity and normal distribution of the 5Cs as dependent variables were determined, with skewness and kurtosis falling within the acceptable range of −2 to +2 and −7 to +7, respectively for SEM analysis [ 35 ]. Finally, the hypothesis that higher scores in PE will be associated with higher odds of the healthy behaviors was tested using logistic regressions due to the binary response categories of the healthy behavior variables. In both SEM and logistic regression, the demographic variables: gender, age, and father’s and mother’s educational background were controlled for.
3.1. Descriptive Analysis
In Table 1 , a frequency analysis of PE grade showed that about 96% of the participants reported grades between 4 and 6. In the Norwegian high school system, a grade of 1 is the lowest, while 6 is the highest a student can earn in a subject. For the 5Cs of PYD, high Cronbach’s alphas, indicating high internal consistencies (ranging from 0.85–0.93) were estimated for all the Cs. The frequency distribution of the three healthy behaviors revealed that most of the participants (about 82%) engaged in PA for at least 30 min twice or more per week, while 57% and 70% consumed at least one serving of fruit and vegetable per day, respectively ( Table 1 ).
Descriptive statistics and reliability coefficients for study variables among Norwegian youth.
Furthermore, descriptive analysis of the 5Cs showed that the highest mean score was registered for caring ( M = 4.29, SD = 0.78), followed by character and then connection . Competence had the lowest mean score ( M = 3.65, SD = 0.86). Thus, on average, participants’ responses on the 5Cs suggested moderate to relatively high levels of the PYD outcomes. The statistically significant correlations between PE grade and the 5Cs (mean scores) were weak to moderate, ranging from 0.17 to 0.55. In addition, the correlation between PE grade and the healthy behaviors were weak but statistically significant (0.19–0.25). Finally, several significant but weak correlations were observed between the 5Cs and the healthy behavior variables as well as between the demographic variables, the 5Cs and the healthy behavior variables ( Table 2 ).
Correlation analyses of demographic variables, physical education grade, the 5Cs of PYD, and healthy behaviors.
Note. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01.
3.2. CFA of the 5Cs of PYD and Structural Equation Modelling of PE Grade and the 5Cs
Prior to the assessment of the associations between PE grade and the 5Cs, confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) was conducted on the 34 items of the 5Cs to determine the factorial structure of the scale. An initial CFA of the items, where 14 pairs of same-facet items (in competence , confidence , character and connection ) were allowed to correlate, yielded a poor model fit: χ 2 (500, N = 194) = 998.075, p < 0.001, RMSEA = 0.072, CFI = 0.872, TFI = 0.857. An examination of the modification indices revealed cross-loadings of four items, two items regarding social competence for competence , one item on social conscience for character and another on caring . In addition, the modification indices indicated correlations among one pair of same-construct items (i.e., confidence ) and two pairs of different-construct items, one between competence and connection , and the other between confidence and character . After eliminating cross-loading items and including the correlations, an adequate model fit was attained in a second CFA: χ 2 (378, N = 194) = 646.879, p < 0.001, RMSEA = 0.061, CFI = 0.917, TFI = 0.905. The factor loadings for all 5Cs in this new CFA were adequate, ranging from 0.54 to 0.91. Correlations among the latent factors of the 5Cs were between 0.32 and 0.88.
In Table 3 , having controlled for demographic factors (i.e., gender, age, and parents’ educational background), findings from the structural equation modelling revealed significant associations between PE grade and all the 5Cs of PYD except for character . Not surprisingly, the strongest association was between PE grade and competence (standardized coefficient of 0.60), both largely reflecting students’ competence. The standardized coefficients for confidence and connection were 0.36, and 0.37, respectively, while for caring the coefficient was 0.22. Thus, higher scores in PE were significantly associated with higher scores in the 5Cs besides character . As for the demographic variables, only gender was significantly related to caring in the SEM analysis (standardized coefficient of 0.36), where girls scored higher than boys.
Structural equation model of physical education grade and the 5Cs of PYD.
Note. PE—Physical education; a Controlled for gender, age, father’s education and mother’s education; * Standardized coefficient. Italics and bold show significant levels less than 0.05.
3.3. Logistic Regression Analyses of Physical Education and Healthy Behaviors
For the associations between PE grade and healthy behaviors, logistic regression models were analyzed because of the binary response categories of the behaviors ( Table 4 ). After controlling for the demographic variables, a unit increase in PE grade was associated with a 94% higher likelihood of engaging in PA (OR = 1.94; 95% CI = 1.18–3.18), and a 68% higher likelihood of vegetable consumption (OR = 1.68; 95% CI = 1.08–2.63), that is, when all other variables in the models were held at a constant. Thus, PE grade was significantly related to higher odds of PA and vegetable consumption, while the association with fruit consumption was not significant. None of the demographic variables were significantly related to the healthy behavior variables in the logistic regression analyses.
Associations between physical education (PE) and healthy behaviours: logistic regression analysis.
Note. PE—Physical education; B—Unstandardized coefficient; S.E.—Standard Error; Sig—Significance level; OR—Odds Ratio; CI—Confidence Interval.
4. Discussion
The aim of the present study was to investigate the associations of PE grade with the 5Cs of PYD and healthy behaviors. As hypothesized, positive associations were observed between PE grade and four of the 5Cs ( competence , confidence , caring , and connection ) after adjusting for gender, age, and father’s and mother’s educational background. In contrast, although there was an indication that character was associated with PE grade, this association was not statistically significant in the SEM analysis. For the associations between PE grade and healthy behaviors, while logistic regression analyses showed higher odds of engagement in PA and vegetable consumption with every unit increase in PE grade, no such association was found for fruit consumption. Thus, the hypotheses were confirmed, although not for the association of PE grade with character and fruit consumption. That PE was found to be largely associated with the 5Cs and healthy behaviors is consistent with earlier findings that have supported the significant role of PE sessions on positive outcomes reflecting WHO’s different dimensions of health (physical, mental, and social) [ 1 , 21 ].
The current finding that PE grade was strongly related to competence was no surprise, as both connote a form of academic competence. In the present study, competence as one of the 5Cs was measured as competence in the academic and physical domains. Thus, PE grade was not only related to academic competence or cognitive abilities, but also to physical competence in sports and athletic activities. Earlier research among German students that supports the current findings reported a positive association between PE and cognitive skills measured by grades in German and mathematics [ 36 ], while findings of a review article also indicated that increasing the amount of time dedicated to PE and sports was in many instances associated with academic performance [ 1 ]. The goal of the Norwegian PE curriculum to enable students to develop mastery in the skills needed to undertake a variety of physical activities [ 9 ] can therefore be important not just for the grade in PE but for the general academic competence of students as well.
In addition to being associated with competence , PE grade was associated with confidence , caring and connection. Accordingly, students who scored high in PE were also more likely to report indicators of thriving and positive development, associations that have been confirmed in a related study on the link between participation in sport camps and the 5Cs of PYD that were captured as two factors (pro-social values and confidence/competence) [ 37 ]. Moreover, Bailey [ 1 ] in a review, reported on how PE and sports in schools can provide a favorable environment for social development, a finding that largely corroborates the current results on the significant link between PE and connection (signifying healthy social relations at home, school, and local community). Indeed, an important aim of the Norwegian PE curriculum among others is to create a social arena for fair play and respect between students [ 9 , 10 ]. However, character (reflecting the integrity and moral compass of youth) was the only thriving indicator that was not associated with PE grade, neither in zero-order correlation nor in multivariate analysis. It is possible that the alignment between youth strengths and contextual resources that facilitate the 5Cs of PYD in PE sessions predicts some of the Cs better than others. This assertion will need to be probed into in future research.
Furthermore, PE grade was related to healthy behaviors, such as PA and vegetable consumption, but not fruit consumption. Earlier research among students attending a Spanish high school associated participation in PE with greater PA levels and lower levels of sedentary behaviors during PE days compared to non-PE days and weekends [ 22 ]. Enrollment in PE activities among high school students in Brazil has been found to be positively related to healthy behaviors, such as PA and fruit consumption, as well as negatively related to drinking of sugar-sweetened beverages [ 5 ]. Wiseman and Weir [ 23 ] also found among Canadian high school students that preferring PE over other school subjects was associated with higher PA levels, lower BMI, and higher self-esteem. Although it was PE grade that was assessed in the current study, the grade reflects students’ participation in both theoretical and practical components of the Norwegian PE sessions. Thus, the current finding on the positive association between PE grade and healthy behaviors is largely in line with earlier findings. In summary, PE sessions reflected in the grade of students were associated with positive youth developmental outcomes, such as thriving (the 5Cs) and healthy behaviors, outcomes that tend to reflect all three dimensions of health (physical, mental, and social) as defined by the World Health Organization.
In SEM and logistic regression, the demographics did not appear to play an important role on the 5Cs and healthy behaviors, as a significant association was only observed between gender and caring , with girls reporting higher scores than boys. This finding is in line with earlier research that found similar associations in upper secondary and university students in Spain [ 38 ] and is often attributed to gender socialization, where boys are taught to be tough and girls caring. In future studies, the role of gender and other demographics are worth investigating to ascertain their effects and place in intervention programs.
4.1. Limitations
The present study has some limitations that need to be considered in the interpretation of the findings. First, the relationships between PE grade and the positive youth developmental outcomes may not indicate causation due to the cross-sectional design of the current study. While the present and earlier findings suggest a positive influence of PE on youth development and healthy behaviors, it is also possible that high levels of the thriving indicators ( competence , confidence , caring and connection ) led to more effort in PE sessions, and consequently, high grade in the subject. In addition, it is likely that students who participate in healthy behaviors such as PA and vegetable consumption will also perform better in PE sessions. Looking at these relationships within a longitudinal design will shed more light on both the developmental trajectories and relations between PE participation and positive youth outcomes.
Second, while there is no reason to believe that youth will be deceptive in the report of their grade and competencies, it is still likely that their self-report responses were affected by social desirability bias, where they tended to over-report their PE grades, for example. In future studies, students’ actual grades provided by teachers can be one method to address the limitation associated with self-report responses and the associated social desirability bias. Third, the binary response categories (Yes/No) of the healthy behaviors did not allow much variation among the behaviors to be assessed. Moreover, although the measures represented general assessment of PA and fruit and vegetable consumption, they did not adequately reflect the global recommendations of the healthy behaviors. This is a limitation that can be addressed in future studies with better instruments that allow for more variations as well as assessment of the recommended amounts and levels of the healthy behaviors. Fourth, the items measuring the 5Cs of PYD were created with US samples, and although the scale was largely validated with the Norwegian sample, there were some items that cross-loaded onto different factors. In addition, relatively high correlations were found among some of the measures, for example between competence and confidence . Thus, it is possible that some items of the 5Cs did not adequately capture or make a distinction between the thriving indicators in Norwegian students. These shortcomings can be a topic of investigation in future studies using qualitative methods.
Finally, although the power analysis indicated that the sample size of 220 was enough to detect medium to large effect sizes in the relationships being studied, a larger sample could provide more robust findings. Besides, the participating schools and thus the students involved in the current study were selected through convenience sampling, thus limiting the extent to which the present findings can be generalized to the whole youth population in Norway. Future studies that use a more representative and inclusive sample reflecting youth from different geographic locations, diverse ethnicities and other backgrounds will be more effective in generating findings that are representative of the Norwegian youth population.
4.2. Implications for Research, Policy, and Practice
Despite the limitations, the current study has implications for research, policy, and practice. In terms of research, the validation of the 5Cs of PYD scale among high school students in Norway adds to the limited research of the 5Cs in Norway and paves the way for further research of the thriving indicators among youth in the Norwegian and other similar Scandinavian and European contexts. Additional research on the 5Cs can also eventually lead to a more refined scale that includes items unique to the Norwegian, Scandinavian or European context. In addition, future studies on PE and the 5Cs can assess the level of risk and adversity in the contexts in which youth are interacting. This will enable the assessment of not only thriving, but resilience as well.
As for policy, the fact that PE grade is related to thriving and healthy behaviors suggests that the Norwegian PE curriculum is important to the promotion of the positive development of the youth, and, possibly, resilience. These results should make the effective implementation of PE curriculum in all schools a priority on the Norwegian political agenda at both the national and community or school level. This way, young people across gender, socio-economic statuses, ethnicities, and other backgrounds can be reached and empowered with the necessary physical, cognitive, and psychosocial skills and competences that are associated with the array of activities taught in PE sessions. Moreover, the current findings of the significant role of PE can inform strategies used in PE curricula in other Scandinavian and European countries. In line with a European Commission report [ 8 ], although all European countries acknowledge the importance of PE at school, only two-thirds of the educational systems had large-scale national initiatives to support the promotion of PE and PA. Indeed, as implied in the current findings, the goal of European countries to facilitate the physical, personal and social development of pupils and students can only be realized when PE curricula are planned and implemented effectively.
There are some practical implications of the current findings as well. With the significant associations between PE grade, the 5Cs of PYD (indicating thriving indicators), and healthy behaviors, it is important that during PE sessions, efforts are made to engage all students in activities that can create positive experiences, enjoyment and mastery as outlined in the PE curriculum. In the curriculum, there is also a focus to provide students with challenges that can enable them to participate actively in both spontaneous and organized activities as well as arenas where students can exercise fair play and respect for each other. Efforts made to implement all these aims in the PE sessions will not only produce healthy, thriving, and resilient youth but, as proposed by PYD, the efforts would also mean a healthy transition into adulthood for the youth.
5. Conclusions
Positive effects of PE participation have been well documented in earlier studies. The current study adds to these benefits with findings that suggest that PE grade reflecting participation in PE is significantly related to thriving indicators, such as competence , confidence , caring and connection (4 out of the 5Cs of PYD), as well as healthy behaviors such as PA and vegetable consumption. These findings support the importance of PE sessions to the healthy development of youth and suggest that policies and programs at the national and local levels that ensure the effective implementation of a PE curriculum in school would be promoting developmental outcomes that align with the dimensions of health outlined by the World Health Organization. However, more research needs to be carried out with adequate measurement of healthy behaviors and representative samples to ascertain the facilitating role of PE sessions on youth health, thriving, and positive development, but also resilience in risk and adverse contexts of youth, as this can secure a life trajectory towards an idealized adulthood for all youth.

Acknowledgments
I would like to acknowledge Maria Bøhlerengen for coordinating the data collection and the youth participants for their engagement in the present study.
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of NSD—Norwegian Centre for Research Data, Norway (protocol code 51708/3/IJJ and 18 July 2017).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of interest.
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
71 Physical Education Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
🏆 best physical education topic ideas & essay examples, 🔎 interesting topics to write about physical education, 📑 good research topics about physical education.
- Keeping Physical Education in Schools Apart from participating in the physical education programs, the students need to be taught on the importance of the various exercises so that they inculcate the culture of physical fitness into their life-time fitness programs.
- The Usefulness of Physical Education in Modern Education Varied criticism adds to the debate on the usefulness of PE in modern education and the need to change current approaches. This indicates the need to focus the debate on the meaning of PE to […]
- Physical Education and Its Benefits Schools in particular know the benefits of physical education in a student’s life and should be able to fight for the children’s rights.
- Adaptive Physical Education The value of the brochure developed for the informational purpose is attributed to the need to communicate the importance of APE and point out the value that it could bring to children with special needs.
- Race and Gender in Physical Education and Sports These factors create the diversity of cultures and nations, and inclusiveness, giving access to the best talents and disclosing the individual’s potential, abilities, and strengths.
- Bodies in Physical Education The purpose of this study is to investigate how students view the construction of their bodies in relation to physical education and how students’ meanings of their bodies affect their participation or resistance to physical […]
- Physical Education: Personal Physical Exercise Plan Given the necessity of taking fluids, it is good to identify and avail the same before starting a physical exercise session.
- Health Teaching and Physical Education Lesson Plan Students will be able to dribble a ball with a hand paying attention to such principles as dribbling on the side, waist-high, pushing the ball down, and eyes lookup.
- Physical Education: Effect of Phototherapy Therefore, it is evident that the intensity of an exercise directly influences one’s heart rate, breathing rate, skin coloration, sweating, and recovery.
- Effectiveness of Physical Education Provisions in the UK School The vital need for health promotion, especially in terms of secondary education has been highlighted by the science of epidemiology the study of factors that influence the health and illnesses of people.
- British Development of Sport and Physical Education in the Last 25 Years Sport England wishes to increase participation in sports through community sports activities, sporting completions providing and training coaches and officiators, and closely working with the Youth Sport Trust and UK Sports formed in 1996 to […]
- Increase of Physical Education Classes Children are the future of any nation, and their health and well-being are the essential preconditions for the successful development of the United States.
- Physical Educators Attitude to Special Needs Children Sue Combs, together with her colleagues from the University of North Carolina, investigated the attitudes of the physical education teachers towards the inclusion of children with special needs in their lessons.
- Physical Education Curriculum Physical education has significantly contributed towards the realization of the school philosophy as it helps in the development of the physical aspects of the students.
- The Nature and Values of Physical Education In the past, physical education was considered to consist of only physical and practical activities, however, the recent research has justified that physical education can be included in the curriculum on the basis of scientific […]
- Should Public Schools Be Required to Restore Physical Education Classes to the Curriculum? The occurrence of obesity prevalence in children, in the U S, can be associated with the removal of physical education courses in public school curriculum.
- Physical Education within Elementary Schools One of the benefits of the physical education is the level of physical fitness that it induces to the students. The manner in which these students are introduced to physical education and the way that […]
- Effects of Physical Education on Brain These neurons are usually created in a place called the hippocampus, which happens to be the section of the brain involved in learning and storage of memory.
- Elementary School Curriculum and Physical Education
- Should Physical Education Be a Required Class in College?
- Physical Education Class: The Perfect Place to Be Bullied
- Pros and Cons of Physical Education
- How Physical Education Should Be Taught
- Physical Education for Elementary School Students
- Weight-Related Barriers for Overweight Students in an Elementary Physical Education Classroom
- Physical Education Lesson Plan and Activity Ideas
- Motivation, Discipline, and Academic Performance in Physical Education
- Adaptive Physical Education for Students With Special Needs
- Physical Education Should Not Be Mandated
- How Technology Enhances the Physical Education Curriculum
- Physical Education: Standards, Cooperative Skills, and Learning Theories
- Physical Education’s Contribution to Public Health
- Physical Education Importance for Child Development
- Reasons to Keep Physical Education in the National Curriculum
- Ethical Relativism and Its Impact on Physical Education
- Inclusive School Physical Education and Physical Activity
- History and Benefits of Physical Education: Why I Want to Be a P.E. Teacher
- Physical Education Beyond the Middle School
- The Importance of Physical Education in Childhood Obesity
- Physical Activity Promotion and School Physical Education
- Implementing the TARGET Model in Physical Education: Effects on Perceived Psychobiosocial and Motivational States in Girls
- Teaching the Nuts and Bolts of Physical Education
- Health-Related Intensity Profiles for Physical Education Classes
- Anticipated Benefits From a Basic College Physical Education Activity Course
- Physical Education Should Be Graded on Effort, Not Ability
- Motivation and Intention to Be Physically Active in Physical Education Students
- Personal Development, Health, and Physical Education
- Why Physical Education Should Be Included in the School Curriculum
- Attitude and Teacher’s Qualification as Factors Affecting Students’ Participation in Physical Education Activities
- Burnout in Physical Education Teachers
- What Benefits Physical Activity Has on Academic Performance
- SPARK Physical Education Curriculum Program
- Changing the National Curriculum for Physical Education
- Physical Education: Official School Policy
- How Physical Education Helps to Develop Your Personality
- Early Childhood Development: Physical Education Program Effects
- Fun Physical Education Games for High School Students
- How Extracurricular Sports Should Satisfy State Physical Education Requirements
- One’s Readiness to Self-Development Through Physical Education
- Would More Physical Education Reduce Obesity in the Youths?
- Goal-Directed Physical Education for Learners With Disabilities
- Health and Physical Education: Volleyball
- Managing the Physical Education Classroom
- Strategies to Accommodate Autism Spectrum Disorder Students in General Physical Education
- Physical Education vs. School Sports: What’s the Difference?
- The Impact of School Budgetary Cuts on Physical Education
- Teaching Health and Physical Education in Australian Schools
- Positive Reinforcement Techniques in Physical Education
- Child Development Research Ideas
- Academic Performance Topics
- Football Topics
- Asthma Paper Topics
- Lifespan Development Essay Titles
- Obesity Ideas
- Soccer Research Topics
- Adolescence Questions
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, November 9). 71 Physical Education Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/physical-education-essay-topics/
"71 Physical Education Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 9 Nov. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/physical-education-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2023) '71 Physical Education Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 9 November.
IvyPanda . 2023. "71 Physical Education Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." November 9, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/physical-education-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "71 Physical Education Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." November 9, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/physical-education-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "71 Physical Education Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." November 9, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/physical-education-essay-topics/.
Why is Physical Education Important? Benefits of PE (Latest)

Education Important
Physical Education is Important for several reasons, as it has a wide range of benefits for individuals of all ages. Here are some of the key reasons why physical education is important:
- Physical Health: Regular physical activity helps improve physical health by increasing cardiovascular fitness, building muscle strength and endurance, and maintaining a healthy weight. It also reduces the risk of various chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and obesity.
- Mental Health: Physical education has a positive impact on mental health by reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression. It releases endorphins, which are natural mood lifters and help individuals cope with stress.
- Motor Skills: Physical education programs help develop and refine motor skills such as coordination, balance, and agility. These skills are not only important for sports but also for daily activities and tasks.
- Teamwork and Cooperation: Many physical education activities involve teamwork and cooperation, which teach important social skills like communication, problem-solving, and conflict resolution. Learning to work together in a physical context can translate to better collaboration in other areas of life.
- Discipline and Goal Setting: Physical education encourages discipline and goal setting. Students learn the importance of setting goals, working toward them, and achieving success through effort and dedication.
- Lifelong Fitness Habits: Physical education programs aim to instill a love for physical activity and fitness that lasts a lifetime. Exposing individuals to a variety of sports and activities helps them find activities they enjoy and are more likely to continue as adults.
More importance of PE…
- Improved Academic Performance: Research has shown that regular physical activity can have a positive impact on academic performance. It can improve concentration, memory, and cognitive function.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Physical education can educate individuals about the importance of a healthy lifestyle, including nutrition and the dangers of substance abuse. It helps promote informed decision-making regarding health-related behaviors.
- Prevention of Obesity: With the rising rates of childhood obesity, physical education plays a crucial role in preventing and addressing this issue. It promotes physical fitness and encourages healthy eating habits.
- Socialization and Inclusivity: Physical education classes provide opportunities for socialization and inclusivity. Students interact with peers from diverse backgrounds and abilities, promoting tolerance and understanding.
- Stress Relief: Physical activity is an effective way to relieve stress and improve mental well-being. Engaging in physical education can help students manage the pressures of school and life.
- Overall Well-Being: Physical education contributes to an individual’s overall well-being by promoting a balanced and healthy lifestyle. It enhances the quality of life by keeping individuals physically and mentally fit.
In summary, physical education is important because it contributes to both physical and mental well-being, teaches essential life skills, and promotes a healthy, active lifestyle that can lead to a longer, happier, and more fulfilling life. It is an integral part of a comprehensive education that prepares individuals for a healthy and successful future.
Benefits Of Physical Education
Physical education (PE) offers a wide range of benefits for individuals of all ages. Here are some of the key benefits of physical education:
- Physical Fitness: PE helps individuals improve their physical fitness by promoting regular physical activity. It enhances cardiovascular health, muscular strength, endurance, and flexibility.
- Health Promotion: Regular participation in PE can reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, obesity, and certain types of cancer. It encourages a healthy lifestyle and promotes overall well-being.
- Motor Skill Development: PE programs focus on developing and refining motor skills, including coordination, balance, agility, and fine motor skills. These skills are essential for various physical activities and daily tasks.
- Mental Health: Physical activity in PE classes has a positive impact on mental health. It releases endorphins, which can improve mood and reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression.
- Stress Reduction: Engaging in physical activity can help students and individuals manage stress more effectively. It provides a healthy outlet for pent-up energy and tension.
- Improved Academic Performance: Research has shown that regular physical activity can lead to improved academic performance. It enhances cognitive function, concentration, and memory.
- Social Skills: PE often involves team sports and cooperative activities, fostering the development of social skills such as communication, teamwork, leadership, and conflict resolution.
- Discipline and Goal Setting: PE encourages discipline and goal setting. Students learn the importance of setting fitness goals, working toward them, and tracking progress.
Extra Benefits of PE…
- Inclusivity: Good PE programs promote inclusivity by accommodating individuals with various abilities and skill levels. This helps create an inclusive and supportive learning environment.
- Lifelong Fitness Habits: PE aims to instill a love for physical activity and fitness that lasts a lifetime. It exposes individuals to a variety of sports and activities, helping them find activities they enjoy and are more likely to continue as adults.
- Body Confidence: Engaging in PE can improve body confidence and self-esteem. As individuals develop physical skills and fitness, they may gain a more positive self-image.
- Healthy Lifestyle Education: PE can educate individuals about the importance of a healthy lifestyle, including nutrition, the dangers of substance abuse, and making informed decisions about their health.
- Time Management: Participation in PE classes helps individuals learn how to manage their time effectively, as they must balance academic studies with physical activity.
- Physical Literacy: PE teaches individuals the fundamentals of movement and physical literacy, ensuring they have the skills and knowledge needed to participate in a wide range of physical activities.
- Fun and Enjoyment: PE classes can be enjoyable, encouraging students to view physical activity as a source of pleasure rather than a chore.
- Community and School Spirit: Participation in team sports and group activities can foster a sense of community and school spirit, promoting a positive school culture.
Overall, Physical Education plays a crucial role in promoting physical and mental well-being, developing essential life skills, and encouraging a healthy and active lifestyle. It contributes to the holistic development of individuals and prepares them for a healthier and more successful future.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Teach educator.
A "Teach Educator" is a specialized role focusing on training and empowering other teachers. This professional is dedicated to enhancing educators' skills through the latest teaching techniques, innovative technologies, and educational research. They conduct workshops, seminars, and coaching, promoting professional development within academic settings.
By improving teaching standards and fostering a culture of continuous learning among educators, Teach Educators ensure that classroom challenges are met with advanced strategies, leading to more effective teaching and richer student learning experiences.
Privacy Policy
Live Sports Score
Editor's Choice
Recent Post

What is Meant by Professional Degrees? – Latest
May 26, 2024

What is the Concept of Problem-Solving?

What are the 7 Steps to Problem-Solving? & Its Examples
© 2023 Teach Educator
Privacy policy
Discover more from Teach Educator
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Physical Activity Basics
- Guidelines and Recommendations
- Add Physical Activity as an Older Adult
- Benefits of Physical Activity
- Overcoming Barriers
- Health Benefits of Physical Activity
- Places to Be Physically Active
- Adding Physical Activity as an Adult
- Making Physical Activity Part of a Child's Life
Physical Activity Basics and Your Health
- Physical activity can make you feel better, function better, and sleep better.
- The amount of physical activity you need depends mostly on your age.
- There are many ways to add physical activity to your life.

Physical activity has many immediate and long-term benefits.
Read about benefits of physical activity and see specific benefits for:
- Adults 65 and older
Recommendations and Tips
See how much physical activity is recommended for specific groups. Also see what counts for different ages and tips for adding physical activity to your life.
- Recommendations
- What counts?
- Making physical activity part of a child's life
- Adding physical activity as an adult
- Adding physical activity as an older adult
More information

Physical Activity in Daily Life

How to Measure Physical Activity Intensity

Overcoming Barriers to Physical Activity

Want additional tips and resources to be active? Learn about Active People, Healthy Nation SM , CDC’s national initiative to help people be more physically active.
Regular physical activity is one of the most important things you can do for your health. Learn about the benefits of physical activity and what you can do.
Home — Essay Samples — Education — Physical Education — The Importance of Physical Education to Maintain a Healthy and Happy Life
The Importance of Physical Education to Maintain a Healthy and Happy Life
- Categories: Physical Education
About this sample

Words: 441 |
Published: Aug 10, 2018
Words: 441 | Page: 1 | 3 min read
Works Cited
- Anderson, K. (2019). The Role of Physical Education in Promoting Holistic Health: A Review of Literature. Journal of Physical Education and Sport, 21(3), 123-145.
- Collins, M. A. (2018). Integrating Physical and Mental Health Education in School Curricula: A Comprehensive Approach. International Journal of Health Sciences Education, 5(2), 67-82.
- Davis, R. T. (2017). The Impact of Physical Education on Social Skills Development in Children. Physical Education and Sport Pedagogy, 22(1), 89-104.
- Garcia, S. M. (2019). Physical Education as a Means of Promoting Emotional Well-being: A Cross-sectional Study. Journal of School Health, 89(5), 356-363.
- Johnson, L. C. (2018). The Effects of Physical Education on Cognitive Functioning in School-age Children. Journal of Educational Psychology, 110(3), 456-471.
- Martinez, A. B. (2020). The Role of Physical Education in Promoting Positive Body Image in Adolescents. Journal of Adolescent Health, 65(4), 567-574.
- Nelson, J. P. (2016). The Relationship between Physical Education and Academic Performance: A Meta-analysis. Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport, 87(2), 152-161.
- Roberts, T. S. (2017). The Benefits of Physical Education in Enhancing Motor Skills in Children with Developmental Disabilities. Adapted Physical Activity Quarterly, 34(3), 277-291.
- Thompson, R. M. (2019). The Role of Physical Education in Promoting Lifelong Physical Activity: A Longitudinal Study. Journal of Physical Activity and Health, 16(6), 456-465.
- Wilson, E. D. (2018). Physical Education and Moral Development: Fostering Ethical Decision-making through Sports and Games. Journal of Moral Education, 47(2), 214-230.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Education

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
7 pages / 3003 words
2 pages / 686 words
4 pages / 1770 words
1 pages / 266 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Physical Education
Physical education is an integral component of a well-rounded education, and its importance cannot be overstated. In this essay, we will explore the myriad benefits of physical education for students, focusing on its role in [...]
Running is a popular form of physical exercise that offers a multitude of benefits for both physical and mental well-being. The act of running involves repetitive movements that engage various muscle groups, promoting [...]
Cephalocaudal development refers to the pattern of growth and development that occurs from the head down to the feet. This sequence is observed in the development of motor skills and physical capabilities in infants and young [...]
Physical education has been an integral part of school curriculum for centuries, with a rich history and evolving significance in promoting overall well-being. In this essay, the importance of physical education in schools will [...]
Over the past several years, there have been numerous reports documenting the decline of participation in physical activity among youth. There are various factors that can be in consideration of one or many reasons on why the [...]
In this globalization, many kind of sports has been introduce to the world. Sport also has been considered as an entertainment. So what is sports? Sport is forms of physical activity played by the people through casual or [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In recent years, there has been a growing recognition of the importance of physical education in schools.Physical education not only promotes physical fitness, but it also plays a crucial role in the overall development of students. This essay will delve into the various reasons why physical education is essential, including its impact on physical health, mental well-being, and academic ...
Physical education serves as a microcosm of life, imparting lessons that extend beyond the boundaries of a sporting field. The significance of teamwork is not merely a strategy for success in sports but a fundamental approach to achieving success throughout one's lifetime. These early experiences contribute to shaping well-rounded individuals ...
You already know that physical activity is an important part of your child's health. But the benefits of physical education in schools go beyond the advantages of physical activity. Read on for some of the ways that physical education can improve your child's health, happiness and overall well-being. Physical Education Explained Physical education, or PE, […]
Introduction. Physical education is an integral component of a well-rounded education, and its importance cannot be overstated. In this essay, we will explore the myriad benefits of physical education for students, focusing on its role in improving physical fitness, developing motor skills, and promoting regular physical activity.
As you can see, the importance of Physical Education is proved in this essay. It is an extremely important class that every school should have. There are many benefits can come from P.E that can help someone become active, take care of their body, and reduce stress.
The Nature and Values of Physical Education Essay. Exclusively available on IvyPanda®. Physical educators have been recognized as contributors to school curriculum after a long and hard fight. Physical education proponents have claimed alliances with psychology, morality, science and medicine; these are the things that have validated physical ...
Although academic performance stems from a complex interaction between intellect and contextual variables, health is a vital moderating factor in a child's ability to learn. The idea that healthy children learn better is empirically supported and well accepted (Basch, 2010), and multiple studies have confirmed that health benefits are associated with physical activity, including cardiovascular ...
Physical Education and Its Benefits Exploratory Essay. Physical education should be an integral part of the curriculum. It is amazing that schools can compromise physical education with all its benefits. Schools in particular know the benefits of physical education in a student's life and should be able to fight for the children's rights ...
Physical Education Essay: Physical Education has become a compulsory subject across numerous schools across the country and even globally. In recent years physical education has been given utmost importance in several schools and industries. Besides, physical education is also offered as a degree program in many colleges. Physical Education is important for the growth of […]
This story about PE teachers was produced by The Hechinger Report, a nonprofit, independent news organization focused on inequality and innovation in education.Sign up for Hechinger's newsletter.. Amanda Amtmanis, an elementary physical education instructor in Middletown, Connecticut, handed out cards with QR codes to a class of third graders, and told them to start running.
1. Introduction. The positive and protective effects of physical activity (PA), such as enhanced physical health, psychological well-being, increased concentration, academic performance, and reduced feelings of depression and anxiety, have been well documented in earlier studies [1,2,3].Physical education (PE) is taught as a subject in many countries around the world, but it also incorporates ...
4 pages / 1770 words. The purpose of this essay is to reflect on the concept of physical education and sport methodically in school, and in detail, typically the role it brings about to developmental stages of children. Physical education is the training in the development of the human body;... Physical Education Physical Exercise.
Physical. education is a way of promoting high standards of health, and health is an integral part of physical e ducation as. well. Physical activity is central to health, and its importance ...
Physical education is the foundation of a Comprehensive School Physical Activity Program. 1, 2 It is an academic subject characterized by a planned, sequential K-12 curriculum (course of study) that is based on the national standards for physical education. 2-4 Physical education provides cognitive content and instruction designed to develop motor skills, knowledge, and behaviors for ...
Role of Parents in Physical Education and Sport. The involvement of parents in physical education and sports is viewed differently in regard to how it affects the child's participation in sports even later in life. We will write. a custom essay specifically for you by our professional experts. 812 writers online.
The Importance of Physical Education in Schools. This essay sample was donated by a student to help the academic community. Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students' samples. "Intelligence and skill can only function at the peak of their capacity when the body is healthy and strong", written by John F. Kennedy.
Physical education contributes significantly to the physical health of students by promoting regular exercise, which has been shown to have a positive impact on cardiovascular health and the prevention of obesity and related diseases. Furthermore, it also provides mental health benefits, including improvements in mood, reduction in stress ...
Physical education has achieved a remarkable place in society today, but it is important to note that it began in the ancient years in the form of exciting dances, games, and hunting and has now become a well-established and time-tested area that aims to provide physical, mental, social, emotional, moral, and psychological development of a person.
Physical education holds immense value in schools as it contributes to the physical, mental, and social development of students. Its benefits extend beyond the classroom, impacting overall health, academic performance, and lifelong habits. By addressing challenges, emphasizing its role, and integrating physical education into the curriculum ...
Here are some of the key benefits of physical education: Physical Fitness: PE helps individuals improve their physical fitness by promoting regular physical activity. It enhances cardiovascular health, muscular strength, endurance, and flexibility. Health Promotion: Regular participation in PE can reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as ...
First, exercise helps relieve anxiety and stress. Second, it helps prevent sleep deprivation and builds self-confidence. And third, for healthy growth and development. On the other hand, physical education classes take up time that could be used for academic classes. But with physical education classes, the student will improve in their ...
Physical activity in the classroom is important for students to meet their physical activity needs. It is seen as an important tool for students to be healthy and adopt a healthy lifestyle. In addition, it is well known that it makes significant contributions to the development of students' academic achievement, social-emotional and mental ...
In addition to the physical health benefits, physical education has also been shown to have a positive impact on students' mental health. Regular physical activity has been linked to reduced stress, anxiety, and depression, as well as improved mood and self-esteem. A study published in the Journal of Adolescent Health found that students who ...
See how much physical activity is recommended for specific groups. Also see what counts for different ages and tips for adding physical activity to your life. Children. ... Regular physical activity is one of the most important things you can do for your health. Learn about the benefits of physical activity and what you can do. Site Index
Physical education has turned out to be an integral part of the lives of those who guarantee better health and ensure a happy life. As far as the meaning of physical education is concerned, it can be defined as a process that brings about a change in the life of an individual, usually created by various experiences.