
Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download

Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes
- Last modified on: 3 years ago
- Reading Time: 7 Minutes
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Here, we have provided case based/passage based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes .
Question 1:
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v).
All living cells need nutrients, O, and other essential substances. Also, the waste and harmful substances need to be removed continuously for healthy functioning of cells. So, a well developed transport system is mandatory for living organisms. Complex organisms have special fluids within their bodies to transport such materials. Blood is the most commonly used body fluid by most of the higher organisms. Lymph also helps in the transport of certain substances.
(i) Which of the following does not exhibit phagocytic activity? (a) Monocytes (b) Neutrophils (c) Basophil (d) Macrophage
(ii) Amount of blood corpusles in changed in dengue fever. One of the common symptoms observed in people infected with dengue fever is (a) significant decrease in RBC count (b) significant decrease in WBC count (c) significant decrease in platelets count (d) significant increase in platelets count.
(iii) Why are WBCs called soldiers of the body? (a) They are capable of squeezing out of blood capillaries. (b) They are manufactured in bone marrow. (c) They fight against disease causing germs. (d) They have granular cytoplasm with lobed nucleus.
(iv) Name the blood cells, whose reduction in number can cause clotting disorder, leading to excessive loss of blood from the body. (a) Erythrocytes (b) Neutrophils (c) Leucocytes (d) Thrombocytes
(v) Which of the following is the correct feature of lymph? (a) It is similar to the plasma of blood, but is colourless and contains less proteins. (b) It is similar to the WBCs of blood, but is colourless and contain more proteins. (c) It is similar to the RBCs of blood and red in colour. (d) It contains more fats.
Question 2:
Heterotrophic nutrition is a mode of nutrition in which organisms obtain readymade organic food from outside sources. The organisms that depend upon outside sources for obtaining organic nutrients are called heterotrophs. Heterotrophic nutrition is of three types: saprophytic, parasitic and holozoic nutrition.
(i) In which of the following groups of organisms food material is broken outside the body and absorbed? (a) Mushroom, green plants, Amoeba (b) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould (c) Paramecium, Amoeba, Cuscuta (d) Cuscuta, lice, tapeworm
(ii) Which of the following is a parasite? (a) Yeast (b) Taenia (c) Amoeba (d) Earthworm
(iii) Which of the following is an example of saprotroph? (a) Grass (b) Mushroom (c) Amoeba (d) Paramecium
(iv) Heterotrophic nutrition involves (a) production of simple sugar from inorganic compounds (b) utilisation of chemical energy to prepare food (c) utilisation of energy obtained by plants (d) all of these.
(v) In Paramecium, food enters the body through (a) mouth (b) pseudopodia (c) cilia (d) cytostome
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 10th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
CBSE Board Exam is on the way, so you must practice some good Case Study Questions Class 10 Science to boost your preparation to score 95+% on Boards. In this post, you will get Case Study and Passage Based Questions that will come in CBSE Class 10 Science Board Exams.
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Re a son . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Life Processes Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Question 1:
Transpiration is the evaporative loss of water by plants. It occurs mainly through the stoma in the leaves. Besides the loss of water vapor in transpiration, the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the leaf also occurs through pores called stomata. Normally stomata remain open in the daytime and close during the night
(i) Which of the following will not directly affect transpiration?
Answer: (d) Chlorophyll content of leaves
(ii) Water vapour comes out from the plant leaf through the stomatal opening. Through the same stomatal opening, carbon dioxide diffuses into the plant during photosynthesis. Reason out the above statements . using one of following options. (a) The above processes happen only during night time. (b) One process occurs during day time and the other at night. (c) Both processes cannot happen Simultaneously. (d) Both processes can happen together at day time.
Answer: (d) Both processes can happen together at day time.
(iii) Which of the following statements is not true for stomatal apparatus? (a) Guard cells invariably possess chloroplasts and mitochondria. (b) Guard cells are always surrounded by subsidiary cells. (c) Stomata are involved in gaseous exchange. (d) Inner wall of guard cells are thick.
Answer: (b) Guard cells are always surrounded by subsidiary cells.
(iv) Which of the following is not a purpose of transpiration? (a) Helps in absorption and transport in plants (b) Prevents loss of water (c) Maintains shape and structure of plants by keeping the cells turgid (d) Supplies water for photosynthesis
Answer: (b) Prevents loss of water
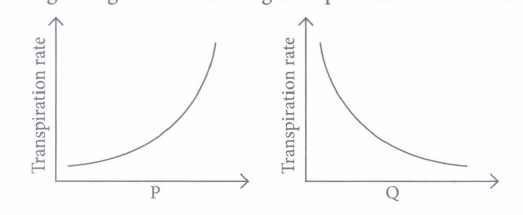
Answer: (a) P-Atmospheric temperature; Q-Atmospheric pressure
Question 2:
Heterotrophic nutrition is a mode of nutrition in which organisms obtain readymade organic food from outside sources. The organisms that depend upon outside sources for obtaining organic nutrients are called heterotrophs. Heterotrophic nutrition is of three types: saprophytic, parasitic, and holozoic nutrition.
(i) In which of the following groups of organisms food material is broken outside the body and absorbed? (a) Mushroom, green plants, Amoeba (b) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould (c) Paramecium, Amoeba, Cuscuta (d) Cuscuta, lice, tapeworm
Answer: (b) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould
(ii) Which of the following is a parasite? (a) Yeast (b) Taenia (c) Amoeba (d) Earthworm
Answer: (b) Taenia
(iii) Which of the following is an example of saprotroph? (a) Grass (b) Mushroom (c) Amoeba (d) Paramecium
Answer: (b) Mushroom
(iv) Heterotrophic nutrition involves (a) production of simple sugar from inorganic compounds (b) utilisation of chemical energy to prepare food (c) utilisation of energy obtained by plants (d) all of these.
Answer: (c) utilisation of energy obtained by plants
(v) In Paramecium, food enters the body through (a) mouth (b) pseudopodia (c) cilia (d) cytostom
Answer: (d) cytostom
Case Study 3: Life processes are the essential functions that living organisms perform to maintain their existence. These processes include nutrition, respiration, transportation, excretion, and reproduction. Nutrition involves the intake of food and its utilization by the body for energy and growth. It can be classified into two types: autotrophic and heterotrophic. Autotrophic nutrition is the process by which organisms, such as plants, produce their own food using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide through photosynthesis. Heterotrophic nutrition is the process by which organisms obtain nutrients by consuming other organisms. Respiration is the process of releasing energy from food through the oxidation of glucose molecules. Transportation involves the movement of materials, such as nutrients, water, and gases, within the body. Excretion is the removal of waste products generated by metabolic activities. Reproduction is the process by which organisms produce offspring of their own kind. Understanding life processes is crucial for studying the functioning and survival of living organisms.
What are the essential functions that living organisms perform to maintain their existence called? a) Life processes b) Metabolic activities c) Cellular respiration d) Photosynthesis Answer: a) Life processes
What is autotrophic nutrition? a) The process of consuming other organisms for nutrients b) The process of producing food using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide through photosynthesis c) The process of releasing energy from food through oxidation d) The process of removing waste products from the body Answer: b) The process of producing food using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide through photosynthesis
What is the process of releasing energy from food through the oxidation of glucose molecules called? a) Respiration b) Photosynthesis c) Transportation d) Reproduction Answer: a) Respiration
What does transportation involve? a) The intake of food and its utilization by the body b) The movement of materials within the body c) The removal of waste products generated by metabolic activities d) The process of producing offspring Answer: b) The movement of materials within the body
What is reproduction? a) The intake of food and its utilization by the body b) The movement of materials within the body c) The removal of waste products generated by metabolic activities d) The process of producing offspring of their own kind Answer: d) The process of producing offspring of their own kind
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 10 Science Life Processes Case Study and Passage-Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible. By Team Study Rate
You Might Also Like

CBSE Class 10 Science Metals and Non-Metals MCQ Quiz with Answers
Extra questions of class 10 maths chapter 4 quadratic equations pdf download, class 10 science evergreen solutions pdf, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free
Case Study Chapter 6 Life Processes
Please refer to Chapter 6 Life Processes Case Study Questions with answers provided below. We have provided Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science for all chapters as per CBSE, NCERT and KVS examination guidelines. These case based questions are expected to come in your exams this year. Please practise these case study based Class 10 Science Questions and answers to get more marks in examinations.
Case Study Questions Chapter 6 Life Processes
Case/Passage – 1
There is a pair of bea n- shaped organs P in the human body towards the back, just above the waist. A waste product Q formed by the decomposition of unused proteins in the liver is brought into organ P through blood by an artery R. The numerous tiny filters S present in organ P clean the dirty blood by removing the waste product Q. The clean blood goes into circulation through a vein T. The waste substance Q, other waste salts, and excess water form a yellowish liquid U which goes from organ P into a bag-like structure V through two tubes W. This liquid is then thrown out of the body through a tube X.
Question: Name (i) artery R, and (ii) vein T.
Renal artery
Question: What are tiny filters S known as?
Question: What is (i) organ P, and (ii) waste substance Q?
Question: Name (i) liquid U (ii) structure V (iii) tubes W, and (iv) tube X.
(i) Urine (ii) Bladder (iii) Ureters (iv) Urethra
Case/Passage – 2
All living cells require energy for various activities. This energy is available by the breakdown of simple carbohydrates either using oxygen or without using oxygen.
Question: Energy in the case of higher plants and animals is obtained by (a) Breathing (b) Tissue respiration (c) Organ respiration (d) Digestion of food
Question: The graph below represents the blood lactic acid concentration of an athlete during a race of 400 m and shows a peak at point D. Lactic acid production has occurred in the athlete while running in the 400 m race. Respiration in athletics The blood of an athlete was tested before, during and after a 400m race: Respiration in athletics The blood of an athlete was tested before, during and after a 400m race:
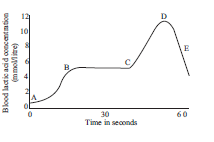
Lactic acid production has occurred in the athlete while running in the 400 m race. Which of the following processes explains this event? Which of the following processes explains this event? (a) Aerobic respiration (b) Anaerobic respiration (c) Fermentation (d) Breathing
Question: Study the graph below that represents the amount of energy supplied with respect to the time while an athlete is running at full speed. Choose the correct combination of plots and justification provided in the following table.
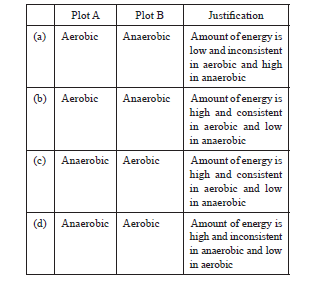
Question: Study the table below and select the row that has the incorrect information. Aerobic Anaerobic (a) Location Cytoplasm Mitochondria (b) End Porduct CO 2 and H 2 O Ethanol and CO 2 (c) Amount of ATP High Low (d) Oxygen Needed Not needed
Question: The characteristic processes observed in anaerobic respiration are: (i) presence of oxygen (ii) release of carbon dioxide (iii) release of energy (iv) release of lactic acid (a) (i), (ii) only (b) (i), (ii), (iii) only (c) (ii), iii), iv) only (d) (iv) only

Related Posts

Microsoft Publisher III Class 10 Computer Science Notes and Questions

CBSE Class 10 English Mijbil the Otter Summary

The Bangle Sellers Summary by Sarojini Naidu
myCBSEguide
- Case Study Questions Class...
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
Download Case study questions for CBSE class 10 Science in PDF format from the myCBSEguide App . We have the new pattern case study-based questions for free download. Class 10 Science case study questions
This article will guide you through:
What are case study questions?
- Sample Papers with Case Study questions
- Class 10 Science Case Study question examples
- How to get case-based questions for free?
- How to attempt the case-based questions in Science?
Questions based on case studies are some real-life examples. The questions are asked based on a given paragraph i.e. Case Study. Usually, 4-5 questions are asked on the basis of the given passage. In most cases, these are either MCQs or assertion & reason type questions. Let’s take an example to understand. There is one paragraph on how nitrogen is generated in the atmosphere. On the basis of this paragraph, the board asks a few objective-type questions. In other words, it is very similar to the unseen passages given in language papers. But the real cases may be different. So, read this article till the end to understand it thoroughly.
What is CBE?
CBSE stands for competency-based education. The case study questions are part of this CBE. The purpose of CBE is to demonstrate the learning outcomes and attain proficiency in particular competencies.
Questions on Real-life Situations
As discussed the case study questions are based on real-life situations. Especially for grade 10 science, it is very essential to have the practical knowledge to solve such questions. Here on the myCBSEguide app, we have given many such case study paragraphs that are directly related to real-life implications of the knowledge.
Sample Papers with Case Study Questions
Class 10 Science Sample Papers with case study questions are available in the myCBSEguide App . There are 4 such questions (Q.No.17 to 20) in the CBSE model question paper. If you analyze the format, you will find that the MCQs are very easy to answer. So, we suggest you, read the given paragraph carefully and then start answering the questions. In some cases, you will find that the question is not asked directly from the passage but is based on the concept that is discussed there. That’s why it is very much important to understand the background of the case study paragraph.
CBSE Case Study Sample Papers
You can download CBSE case study sample papers from the myCBSEguide App or Student Dashboard. Here is the direct link to access it.
Case Study Question Bank
As we mentioned that case study questions are coming in your exams for the last few years. You can get them in all previous year question papers issued by CBSE for class 1o Science. Here is the direct link to get them too.
Class 10 Science Case Study Question Examples
As you have already gone through the four questions provided in the CBSE model question paper , we are proving you with other examples of the case-based questions in the CBSE class 10 Science. If you wish to get similar questions, you can download the myCBSEguide App and access the Sample question papers with case study-type questions.
Case-based Question -1
Read the following and answer any four questions: Salt of a strong acid and strong base is neutral with a pH value of 7. NaCl common salt is formed by a combination of hydrochloride and sodium hydroxide solution. This is the salt that is used in food. Some salt is called rock salt bed of rack salt was formed when seas of bygone ages dried up. The common salt thus obtained is an important raw material for various materials of daily use, such as sodium hydroxide, baking soda, washing soda, and bleaching powder.
- Phosphoric acid
- Carbonic acid
- Hydrochloric acid
- Sulphuric acid
- Blue vitriol
- Washing soda
- Baking soda
- Bleaching powder
Case-based Question -2
- V 1 + V 2 + V 3
- V 1 – V 2 +V 2
- None of these
- same at every point of the circuit
- different at every point of the circuit
- can not be determined
- 20 3 Ω 203Ω
- 15 2 Ω 152Ω
Case-based Question -3
- pure strips
- impure copper
- refined copper
- none of these
- insoluble impurities
- soluble impurities
- impure metal
- bottom of cathode
- bottom of anode
How to Attempt the Case-Based Questions in Science?
Before answering this question, let’s read the text given in question number 17 of the CBSE Model Question Paper.
All living cells require energy for various activities. This energy is available by the breakdown of simple carbohydrates either using oxygen or without using oxygen.
See, there are only two sentences and CBSE is asking you 5 questions based on these two sentences. Now let’s check the first questions given there.
Energy in the case of higher plants and animals is obtained by a) Breathing b) Tissue respiration c) Organ respiration d) Digestion of food
Now let us know if you can relate the question to the paragraph directly. The two sentences are about energy and how it is obtained. But neither the question nor the options have any similar text in the paragraph.
So the conclusion is, in most cases, you will not get direct answers from the passage. You will get only an idea about the concept. If you know it, you can answer it but reading the paragraph even 100 times is not going to help you.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- CBSE Practice Papers 2023
- Class 10 Science Sample Papers 2024
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
3 thoughts on “Case Study Questions Class 10 Science”
Where is the answer
Class 10 Science MCQ
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Bihar Board
CFA Institute
Srm university.
- Rajasthan 10th Result
- Rajasthan Board Result
- Shiv Khera Special
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
- CBSE Class 10 Study Material
Important Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science Exam 2024 with Answers
Download case study questions for class 10 science to prepare for the cbse board exam 2024. these multiple choice type questions with answers are published by the cbse board to provide sample questions to students..

CBSE Class 10 Science Case Study Questions 2024: Get here the questions based on case studies to practise for the CBSE Class 10 Science exam 2024. The CBSE Class 10 Science Question Bank on Case Studies, provided in this article, can be very helpful for understanding how the source based or case based questions are asked in the board exam. This question bank is published by the CBSE Board itself which makes it a very reliable source for the board exam preparations. Each question has five sub-questions with each followed by four options and a correct answer. Students can easily download these sample questions in PDF format and refer to the same for their exam preparations.
Note: Check the reduced CBSE Syllabus for Class 10 Science for 2024 Exam and then practise the case study questions accordingly for the CBSE Class 10 Board Exam 2024.
Important* Important Last Minute Tips and Resources for CBSE Class 10 Science Exam 2024
SCIENCE- Class X
Sample Case Studies
1. Read the following and answer any four questions from 1.1 to 1.5:
Marble’s popularity began in ancient Rome and Greece, where white and off-white marble were used to construct a variety of structures, from hand-held sculptures to massive pillars and buildings.

1.1 The substance not likely to contain CaCO 3 is
a) Dolomite
b) A marble statue
c) Calcined gypsum
d) Sea shells.
Answer: c) Calcined gypsum
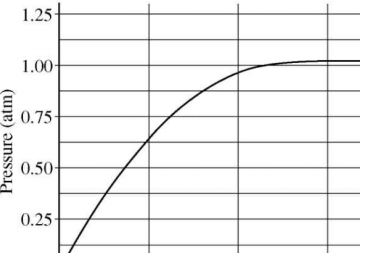
1.2 A student added 10g of calcium carbonate in a rigid container, secured it tightly and started to heat it. After some time, an increase in pressure was observed, the pressure reading was then noted at intervals of 5 mins and plotted against time, in a graph as shown below. During which time interval did maximum decomposition took place?
a) 15-20 min
b) 10-15 min
c) 5-10 min
Answer: d) 0-5 min
1.3 Gas A, obtained above is a reactant for a very important biochemical process which occurs in the presence of sunlight. Identify the name of the process -
a) Respiration
b) Photosynthesis
c) Transpiration
d) sphotolysis
Answer: b) Photosynthesis
1.4 Marble statues are corroded or stained when they repeatedly come into contact with polluted rain water. Identify the main reason.

a) decomposition of calcium carbonate to calcium oxide
b) polluted water is basic in nature hence it reacts with calcium carbonate
c) polluted water is acidic in nature hence it reacts with calcium carbonate
d) calcium carbonate dissolves in water to give calcium hydroxide.
Answer: c) polluted water is acidic in nature hence it reacts with calcium carbonate
1.5 Calcium oxide can be reduced to calcium, by heating with sodium metal. Which compound would act as an oxidizing agent in the above process?
b) sodium oxide
d) calcium oxide
Answer: d) calcium oxide
2. Read the following and answer any four questions from 2.1 to 2.5:
The reaction between MnO2 with HCl is depicted in the following diagram. It was observed that a gas with bleaching abilities was released.
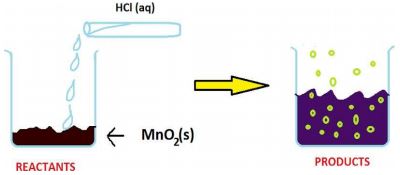
2.1 The chemical reaction between MnO 2 and HCl is an example of:
a) displacement reaction
b) combination reaction
c) redox reaction
d) decomposition reaction
Answer: c) redox reaction
2.2 Chlorine gas reacts with _______ to form bleaching powder.
a) dry Ca(OH) 2
b) dil. solution of Ca(OH) 2
c) conc. solution of Ca(OH) 2
Answer: a) dry Ca(OH) 2
2.3 Identify the correct statement from the following:
a) MnO 2 is getting reduced whereas HCl is getting oxidized
b) MnO 2 is getting oxidized whereas HCl is getting reduced.
c) MnO 2 and HCl both are getting reduced.
d) MnO 2 and HCl both are getting oxidized.
Answer: a) MnO 2 is getting reduced whereas HCl is getting oxidized
2.4 In the above discussed reaction, what is the nature of MnO 2 ?
a) Acidic oxide
b) Basic oxide
c) Neutral oxide
d) Amphoteric oxide
Answer: b) Basic oxide
2.5 What will happen if we take dry HCl gas instead of aqueous solution of HCl?
a) Reaction will occur faster.
b) Reaction will not occur.
c) Reaction rate will be slow.
d) Reaction rate will remain the same.
Answer: b) Reaction will not occur.
Also, check below other important study material released by the CBSE Board:
CBSE Class Maths Case Study Questions for All Chapters (Published by CBSE)
MCQs for Class 10 English Footprints without Feet (Published by CBSE)
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari and Sarkari Result . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App . Check Board Result 2024 for Class 10 and Class 12 like CBSE Board Result , UP Board Result , Bihar Board Result , MP Board Result , Rajasthan Board Result and Other States Boards.
- RBSE 5th, 8th Result 2024
- RBSE Result 2024
- rajshaladarpan.nic.in 5th, 8th Result 2024
- rajshaladarpan.nic.in Result 2024
- Rajasthan Board Class 8th, 5th Result 2024 Roll Number
- RBSE Class 5th Result 2024 Roll Number
- Rajasthan 5th 8th Class Result 2024
- 8th, 5th Board Result 2024 Rajasthan
- RBSE 10th Result 2024
- UPSC CSE Admit Card 2024
- CBSE Study Material
- CBSE Class 10
Latest Education News
HPPSC Lecturer Admit Card 2024 Out at hppsc.hp.gov.in: Check download link and exam date
JEE Advanced Response Sheet 2024 OUT: IIT JEE Advanced Response/OMR Candidate Sheets LINK ACTIVE at jeeadv.ac.in, Calculate your Scores
Current Affairs One Liners: 31 May 2024- Military Exercise 'Red Flag 24'
Current Affairs Quiz: 31 May 2024- RudraM-II Missile
Current Affairs Hindi One Liners: 31 मई 2024- विश्व तंबाकू निषेध दिवस 2024
How to Prepare for CSAT UPSC: Topics Wise Strategy for CSAT Preparation
UP B.Ed Admit Card 2024 Released at bujhansi.ac.in: Check Direct Download Link
JEE Advanced Answer Key 2024 by Resonance OUT: Candidate Response Sheet, Provisional Answer Key and Solution PDF
Current Affairs Quiz In Hindi: 31 मई 2024- सैन्य अभ्यास रुद्रएम-II मिसाइल
Dr MGR Medical University Result 2024 OUT at tnmgrmu.ac.in; Direct Link to Download UG and PG Marksheet
40+ Question of the Day for Students (with Answers)
Revival of Dead: A possibility in future? A Cryogenic firm freezes its first client in hopes of reviving it in future
UK Board Class 12 Sociology Syllabus 2024-25: Download Sociology Syllabus PDF For Free
JEE Advanced Answer Key 2024 by FIITJEE: Check Paper 1, 2 Unofficial Answer Key
CUET UG Result 2024 Expected Date: Direct Link to Download Scorecard PDF on exams.nta.ac.in
UK Board 9th Syllabus 2024-25: Download PDF
UP Board Class 9 Home Science Syllabus 2025: Download UPMSP 9th Home Science Syllabus 2024-25 PDF Here
Find 3 differences between the rabbit driving car pictures in 17 seconds!
Indian Navy Agniveer MR Exam Pattern 2024; Check Latest Pattern and Marking Scheme
UP BEd Admit Card 2024 [email protected] यहाँ से Download करें यूपी बीएड परीक्षा के एडमिट कार्ड

NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes

Chapter 6 Life Processes Class 10 NCERT Solutions
Ncert solutions for class 10 science chapters:, how does amoeba engulf its food, which part of the roots is involved in exchange of respiratory gases, define photolysis., what are chemotrophs, what is the mode of nutrition in fungi, contact form.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
Important Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 6 - Life Processes 2024-25
- Class 10 Important Question
- Chapter 6: Life Processes

CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter-6 Important Questions with Answers - Free PDF Download
Class 10 examination is the most crucial and significant exam in a student’s life. The marks secured in Class 10th Board exams are an essential attribute that decides their future study course. It is during this year in school that a student chooses his/her career. Losing marks is not an option for a student in 10th Board exams. Science is one of the most important subjects of Class 10 CBSE exam . In this subject, the students learn about various activities that occur in our surroundings. It also teaches the students about human beings, plants and animals. Science can be pretty tough for the students to understand. A brief comprehension of the chapters and important questions and answers can help you get a complete knowledge of the subject. Vedantu brings you the Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6, which are compressed in a PDF format. The students can refer to these questions during the preparation of exams. Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials for students. Maths Students who are looking for the better solutions, they can download Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Download CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions 2024-25 PDF
Also, check CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions for other chapters:

Related Chapters
Study Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 – Life Processes
Very Short Answer Questions (1 Mark)
1. Amoeba shows following kind of nutrition –
autotrophic
saprotrophic
Ans: (b) holozoic
2. The process by which blood is cleared of metabolic wastes in case of kidney failure is called
artificial kidney
transplantation
Ans: b) dialysis
3. Woody plants carry gaseous exchange through
epidermal cells.
Ans: (c) Lenticels.
4. Where does digestion of starch begin in human body?
Ans: The digestion of starch begins in the human body in the mouth.
5. Give one example of each of saprophytic and parasitic nutrition.
Ans: One example each of saprophytic and parasitic nutrition is as follows:
Parasitic Nutrition – Plasmodium (Protozoa)
Saprophytic Nutrition – fungi.
6. Which of the following statements about the autographs is incorrect?
They store carbohydrates in the form of starch.
They constitute the first trophy level in food chains.
They convert $\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ and water into carbohydrates in the absence of sunlight
They synthesize carbohydrates from $\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ and water in the presence of sunlight & chlorophyll.
Ans: c) They convert $C{{O}_{2}}$ and water into carbohydrates in the absence of sunlight.
7. Which of these is not a part of the small intestine?
Rectum
Ans: d) Rectum is not a part of the small intestine.
8. During contraction of the heart, what prevents backflow of blood?
Thin walls of atria
Thick muscular walls of ventricles
Valves in heart
All of the above
Ans: c) Valves in heart
9. Name excretory organs in amoeba and earthworm.
Ans: The excretory organ in amoeba and earthworms are as follows:
Amoeba – Cell membrane, Earthworm – Outer covering (skin)
10. Name the plant tissue through which water and minerals are transported in plants.
Ans: The plant tissue through which water and minerals are transported in plants is Xylem.
11. Trachea do not collapse when there is not much air because they are –
thick and muscular
having cartilaginous rings
have valves
supported by the larynx.
Ans: b) having cartilaginous rings.
12. Which one of the following blood vessels contains only deoxygenated blood?
pulmonary vein
pulmonary artery
capillaries
Ans: b) Pulmonary artery
13. The autotrophic mode of nutrition requires –
Chlorophyll
Carbon – dioxide & water
Ans: d) All of the above
14. Name the red pigment carrying oxygen in the blood.
Ans: The red pigment carrying oxygen in blood Haemoglobin.
15. Name the hormone which is responsible for the reabsorption of water in nephrons.
Ans: The hormone which is responsible for reabsorption of water in nephrons Antidiuretic – hormone (ADH) or vasopressin.
16. When air is blown from the mouth into a test tube containing lime water, the lime water turned milky due to the presence of –
b) nitrogen
c) water vapours
d) carbon – dioxide
Ans: d) carbon – dioxide
17. In which of the following group/ groups of animals, heart does not pump oxygenated blood to different parts of the body?
Pisces only
Amphibians only
Amphibians and reptiles only
Pisces and amphibians
Ans: The following group/ groups of animals, in which the heart does not pump oxygenated blood to different parts of the body a) Pisces only.
18. The filtration units of kidneys are called –
Ans: d) nephrons
19. What is the mode of nutrition in fungi and plasmodium?
Ans: The mode of nutrition in fungi and plasmodium are as following:
Fungi – Saprophytic
Plasmodium – parasitic.
20. Which of them contain less nitrogenous waste – renal vein or the renal artery?
Ans: Renal veins contain less nitrogenous waste.
21. Amoeba captures food with the help of –
pseudopodia
Ans: c) pseudopodia.
22. Which of the following is most appropriate for aerobic respiration?
$\text{Glucose}\xrightarrow{\text{mitochondria}}\text{pyruvate}\xrightarrow{\text{cytoplasm}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O+Energy}$
$\text{Glucose}\xrightarrow{\text{cytoplasm}}\text{pyruvate}\xrightarrow{\text{mitochondria}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O+Energy}$
$\text{Glucose}\xrightarrow{\text{cytoplasm}}\text{pyruvate+Energy}\xrightarrow{\text{mitochondria}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}$
$\text{Glucose}\xrightarrow{\text{cytoplasm}}\text{pyruvate+Energy}\xrightarrow{\text{mitochondria}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O+Energy}$
Ans: (b) $\text{Glucose}\xrightarrow{cytoplasm}pyruvate\xrightarrow{mitochondria}C{{O}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O+Energy$.
23. Name the part of the alimentary canal that receives bile from the liver.
Small intestine
Large intestine
Ans: The part of the alimentary canal that receives bile from the liver c) Small Intestine.
24. What is glycolysis?
Ans: Breakdown of Glucose into pyruvate is known as glycolysis.
25. Name the largest artery of the body.
Ans: The largest artery of the body is Aorta.
26. The kidneys in human beings are parts of the system for
respiration
transpiration
Ans: The kidneys in human beings are parts of the system for (c) excretion.
27. The xylem in plants are responsible for
transport of water
transport of food
transport of amino acids
transport of oxygen
Ans: (a) transport of water.
28. The autotrophic mode of nutrition requires
carbon dioxide and water
chlorophyll
all of the above
Ans: The autotrophic mode of nutrition requires (d) all of the above.
29. The breakdown of pyruvate to give carbon dioxide, water and energy takes place in
mitochondria
chloroplast
Ans: The breakdown of pyruvate to give carbon dioxide, water and energy takes place in (b) mitochondria.
30. Food moves down the gut by peristalsis. Which region of the brain controls peristalsis.
Ans: Food moves down the gut by peristalsis and the region of brain which controls peristalsis is the Medulla of the hindbrain.
31. Name the pigment present in plants, which can absorb solar energy.
Ans: The pigment present in plants, which can absorb solar energy is Chlorophyll.
32. Which of the four chambers of the human heart has the thickest muscular walls?
Ans: Right ventricle has the thickest muscular walls.
33. Which part of the visible spectrum is absorbed by chlorophyll pigments?
Ans: Blue and Red light are absorbed by chlorophyll pigments.
34. Name the cartilaginous flap which closes the glottis to check the entry of food into it during swallowing.
Ans: The cartilaginous flap which closes the glottis to check the entry of food into it during swallowing is Epiglottis.
35. Which equipment is used to facilitate breathing during serious breathing problems?
Ans: The equipment that is used to facilitate breathing during serious breathing problems is Ventilator.
36. What do you mean by double circulation of blood?
Ans: Double circulation of blood means that blood passes through the heart twice for each cycle of the body.
Short Answer Questions (2 Marks)
1. What is common for cuscuta, ticks and leeches?
Ans: Cuscuta, ticks, and leeches all feed in a parasitic manner, harming their hosts in the process.
2. What advantage over an aquatic organism does a terrestrial organism have with regard to obtaining oxygen for respiration?
Ans: Terrestrial organisms have evolved to be more efficient at absorbing oxygen from the air than watery organisms. –
Increased respiratory surface area.
Very fine and delicate surface for easy exchange of oxygen and carbon – dioxide.
Placement of respiratory surface within the body for protection.
The mechanism for transporting air into and out of the respiratory surface, which absorbs oxygen.
3. Differentiate between single and double circulation found in vertebrates.
Ans: The differences between single and double circulation found in vertebrates are:
4. Name the substrates for the following enzymes.
Ans: The substrates for the following enzymes are as shown below
5. What are the two stages in photosynthesis?
Ans: Two stages in photosynthesis are–
Light reaction – Photolysis of water is the process of breaking down water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen using light energy.
Dark reaction – Carbon dioxide ($C{{O}_{2}}$) is fixed and converted into glucose, a simple carbohydrate.
6. What is the difference between arteries & veins?
Ans: The differences between arteries & veins are:
7. What is villi? What are its functions?
Ans: Villi are projections in the small intestine's inner lining that resemble fingers. They enhance the surface area available for digested meal absorption in the small intestine.
8. What type of respiration takes place in human muscles during vigorous exercise and why?
Ans: Anaerobic respiration occurs in human muscles during severe exercise. During exercise, our energy requirement increases, so our striated muscles start respiring anaerobically in the lack of oxygen and produce ATP molecules.
9. How is opening and closing of stomata regulated?
Ans: Guard cells control the closure and opening of the stomata. The stomata open when the guard cells enlarge or become turgid owing to water ingress. Because of the loss of water, the guard cells shrink and the stomata close.
10. State two vital functions of the kidney.
Ans: Function of the kidney are –
It keeps the body's water balance in check.
It regulates calcium levels in the blood to keep bones healthy.
11. Differentiate between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Ans: The differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration are:
12. Meat is easier to digest as compared to grass. Why?
Ans: Meat is easier to digest because our digestive juices contain enzymes that can break down meat, but our bodies cannot break down cellulose, which is a major component of grass.
13. Differentiate between transport of materials in xylem & phloem.
Ans: The differences between transport of materials in xylem & phloem are:
14. What is the role of the glomerulus in the kidney?
Ans: Glomerulus, like Bowman's Capsule, is a collection of capillaries found in the cup. It gets blood from the renal artery, which is responsible for transporting excretory wastes from the body to the kidney. It removes from the liver water, salts, glucose, urea, nitrogen-containing protein end products, and yellow bile components.
15. Why is it essential to match the blood groups of donors and receiver person before arranging transfusion of blood?
Ans: Blood RBCs carry both antigen and antibodies. If the blood is not matched before transfusion, the recipient's blood produces antibodies against the donor blood and destroys blood cells, resulting in a blood shortage and death.
16. Why is it necessary to separate oxygenated & deoxygenated blood in mammals & birds?
Ans: The separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood allows the organism to receive adequate oxygen. This mechanism is beneficial to creatures who demand a lot of energy. Mammals and birds use oxygen to obtain energy in order to maintain a consistent body temperature.
17. Why are the walls of the trachea supported by cartilaginous rings?
Ans: The trachea is held together by cartilaginous rings that keep it from collapsing even when there isn't much air in it.
18. What are the raw materials for photosynthesis?
Ans: Raw materials for photosynthesis are –
Carbon – dioxide
Chlorophyll and Sunlight
19. What is the role of the diaphragm during inhalation and exhalation?
Ans: During inhalation and exhalation, the diaphragm changes form, increasing and decreasing the capacity of the thoracic cavity. This causes air to enter and exit the lungs.
20. What is the advantage of four chambers of heart?
Ans: A septum separates the right and left halves of the heart, preventing oxygenated and deoxygenated blood from mingling. This satisfies their constant need for energy to keep their body temperature steady. Their energy requirements are substantial, which are met effectively due to the non-mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
21. Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans?
Ans: As all cells in multicellular animals are not in direct contact with the environment, simple diffusion is insufficient to supply the needs of all body cells.
22. What criteria do we use to decide whether something is alive?
Ans: To be considered alive, all living organisms must have movement at the molecular level, as well as respiration and other life processes such as nutrition, respiration, transportation, and excretion.
23. What is the function of digestive enzymes?
Ans: Enzymes break down food's different complicated components into simple, soluble components that can be easily absorbed.
24. How are the lungs designed in human beings to maximize the area for exchange of gases?
Ans: Bronchioles end in alveoli, which are balloon-like structures in the lungs. Alveoli have a network of blood capillaries that increase the surface area available for gas exchange.
25. What is the role of saliva in the digestion of food?
Ans: Salivary amylase is an enzyme found in the mouth that breaks down starch, a complicated molecule, into glucose.
26. While eating you are advised not to talk. Why are you advised to do so?
Ans: We are urged to do so because food particles may enter the windpipe when eating, causing choking.
27. We say that movement is a characteristic of living organisms but we always don’t see visible movements in plants. Comment.
Ans: Plants do not always show obvious movement. It doesn't necessarily imply that they aren't living. In their bodies, molecular movements take place.
28. If a person is working on a treadmill in a gymnasium, will it affect his rate of breathing? How?
Ans: Yes, it will have an impact on his breathing rate. To satisfy the increased demand for energy, the rate of breathing will increase in order to supply more oxygen.
29. If you compare your rate of breathing by feeling your chest movement with the number of times a fish opens and closes its mouth. Which will be higher and way?
Ans: As the amount of dissolved oxygen in water is relatively low compared to the amount of oxygen in the air, the number of times a fish opens and closes its mouth will be higher. As a result, aquatic organisms breathe at a significantly higher rate than terrestrial organisms.
30. Mucus is not used for churning the food or digesting it. Then why is it secreted in the stomach?
Ans: In order to protect the stomach's inner lining from being harmed by HCI, mucus is released. Excessive HCI secretion can harm the lining of the stomach and cause a peptic ulcer.
31. In the process of Photosynthesis food A is prepared which gets converted into food B. What are A and B? Why is A converted to B?
Ans: Glucose is food A, whereas starch is food B. As B is an insoluble carbohydrate, it is transformed to A. It is more compact, making it better for storage.
32. When we are asleep we are not performing any activity while our life processes are going on. Why?
Ans: “The maintenance functions of living organisms must go on even when they are not doing anything particular.” That is why the life processes are going on even while we are asleep or not performing any activity.
33. What will be the outcome if a farmer floods his field every day?
Ans: The oxygen contained in the interspaces of the soil will be replaced by water, affecting plant respiration.
34. Name the respiratory organs of:
(i) fish
Ans: The respiratory organs of fish are gills.
(ii) mosquito
Ans: The respiratory organs of mosquitoes are Trachea (air tubes).
(iii) earthworm.
Ans: The respiratory organs of earthworms are moist skin.
35. Due to the availability of less water, how does the plant cope with the lack of water in desert conditions?
Ans: To preserve moisture, they open their stomata at night and close them during the day.
36. After a vigorous exercise, you may experience cramps in your leg muscles. Why does this happen?
Ans: Leg muscle cramps are produced by a sudden build-up of lactic acid in our muscles following strenuous exercise.
37. What will happen if carbon monoxide combines with hemoglobin?
Ans: If haemoglobin binds firmly to carbon monoxide, oxygen will not be transported by blood, resulting in the organism's death.
38. Chloroplasts are called energy convertors. Explain.
Ans: As chloroplasts catch solar energy and convert it to chemical energy, they are known as energy converters.
39. Why is the rate of breathing much faster in aquatic organisms than those in terrestrial organisms?
Ans: Aquatic species get their oxygen from dissolved oxygen in the water. Water has a relatively low oxygen availability as compared to air. As a result, aquatic organisms must breathe more quickly than terrestrial organisms.
40. Why are glomeruli considered as dialysis bags?
Ans: The glomeruli's major filtering function is selective filtration. Small molecules comprising glucose, salts, urea, and liquid senim are filtered. Etc. Proteins and other big molecules remain in the blood. As a result, the glomeruli of the kidneys serve as dialysis bags.
41. Autotrophs synthesize food for the living world. Justify this statement in one sentence only by interconnecting autotrophs and heterotrophs.
Ans: The food producers are autotrophs, and all heterotrophs directly or indirectly consume the food produced by the autotrophs.
42. Veins and arteries carry blood. Which of these carry blood?
Away from the heart?
Ans: Arteries carry blood away from the heart.
Back to the heart?
Ans: Veins carry blood back to the heart.
43. Which of the organs perform the following functions in humans?
Absorption of food.
Ans: Absorption of food takes place in the small intestine.
Absorption of water
Ans: Large intestine
44. Name the areas in a woody stem through which respiratory exchange of gases take place.
Ans: In a woody stem, the bark has lenticels for gaseous exchange.
45. Why doesn’t the lungs collapse even after forceful expiration?
Ans: Even after forced expiration to maximum capacity, residual volume refers to the amount of air that remains in the lungs following forceful expiration. As a result, even after a strong expiration, the lungs do not collapse.
46. “If there were no algae there would be no fish in the sea”. Comment.
Ans: Photosynthesis results in the production of ${{O}_{2}}$ by algae. The oxygen used by fish in the sea is used for breathing. There would have been no oxygen created if algae had not existed. As a result, fish may have died.
47. Why is the process of diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirement of human beings?
Ans: For bigger multicellular creatures like humans, the diffusion method is insufficient to transport ${{O}_{2}}$ to all areas of the body. As a result, the respiratory pigment haemoglobin absorbs oxygen from the air and transports it throughout our bodies via blood.
Long Answer Questions (3 Marks)
1. What are the functions of lymph in our body?
Ans: Functions of lymph are-
a) It removes tissue fluid from the interstitial region and restores it to the bloodstream.
b) Through tissue fluid, it gathers carbon dioxide, waste products, and metabolites from tissues.
c) Lymph contains lymphocytes (WBCs), which aid in the body's immunity and fight against invading invaders.
2. How is haemoglobin associated with respiration explained?
Ans: The respiratory pigment haemoglobin is responsible for transporting oxygen and carbon dioxide. Haemoglobin is a crimson pigment with a strong oxygen affinity. Oxyhemoglobin transports oxygen from the lungs to the cells of the body. Carbon dioxide is carried to the lungs by carbamino – haemoglobin from the bodily cells.
3. What are the modes of excretion in plants?
Ans: Modes of excretion in plants are –
The plants get rid of excess water by transpiration.
Plants' only primary gas excretory product is oxygen. Plants emit it into the environment by diffusion. Organic wastes of plants are stored within dead permanent tissues such as wood or within leaves or bark which are periodically removed.
The plants also excrete some waste substances into the soil around them.
Plant waste products are accumulated in cellular vacuoles in large quantities.
4. Give an experiment to prove the essentiality of light for photosynthesis.
Ans: An experiment to prove the essentiality of light for photosynthesis is as shown below:
a) Destarched the plant by leaving it in dart for 48 – 72 hours.
b) Now place strips of black paper or metal foil over destarched leaves and expose them to light for several hours.
5. What is “translocation”? Why it is essential for plants.
Ans: The term "translocation" refers to the movement of organic solutes within plants. It is required since all cells require sustenance to perform their essential tasks. It affects the storage organs of roots, fruits, seeds, and developing organs in both upward and downward directions.
6. How respiration takes place in plants?
Ans: There are three modes for the exchange of gases in plants –
a) Some little plants can exchange gaseous matter by simply diffusing it throughout their entire surface.
b) Stomata on the leaves and green stems of large flowering plants exchange gases.
c) Exchange occurs in woody stems through fractures in the bark or lenticels.
7. How is transpiration pull responsible for upward movement of water?
Ans: Transpiration is the process through which leaves lose water in the form of water vapours through stomata. Continuous transpiration causes a suction in the xylem elements' water column, which reaches the roots. This is known as transpiration pull. The water column of the plant is drawn up from the bottom to the top due to transpiration.
8. Discuss the major steps involved in the process of nutrition in human beings.
Ans: Major steps involved in human nutrition are –
a) Ingestion – Food is taken in through the mouth. Humans have a holozoic feeding mode. Solid particles are swallowed by them.
b) Digestion – In the alimentary canal, mechanical and chemical processes are used to break down complex dietary materials into simpler ones.
c) Absorption – The little finger-like projections, or villi, of the small intestine absorb digested food.
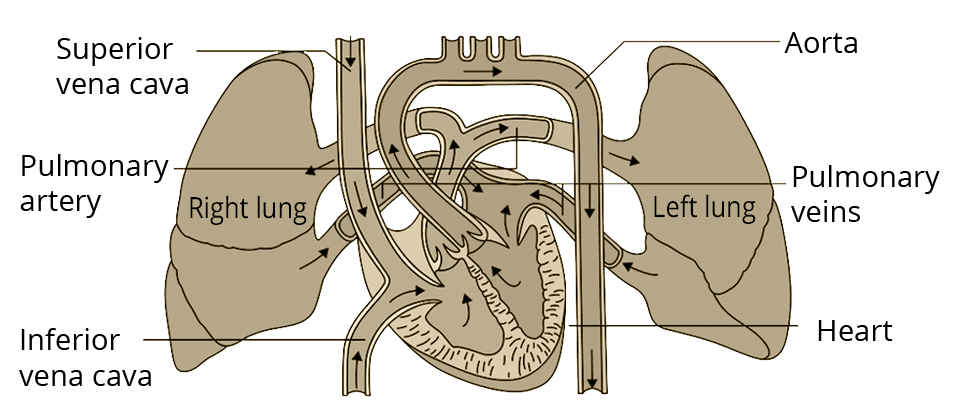
d) Assimilation – Food is absorbed and transported to all cells via blood, where it is used for energy, growth, and development.
e) Excretion – Food from the small intestine passes through to the big intestine, where it is ejected out by Anus.
9. Discuss the mode of nutrition in amoeba.
Ans: The steps of Nutrition in amoeba are–
a) Formation of pseudopodia – When an amoeba comes into contact with a food particle, it creates pseudopodia that encase the food particle.
b) Ingestion – Ingestion occurs when the terminals of pseudopodia merge with one other, forming a food vacuole with a variable amount of food particles and water.
c) Digestion – The vacuoles are encircled by lysosomes, which fuse with the vacuole and consume the food particles inside.
d) Exocytosis – The food vacuole passes the soluble products of digestion into the appropriate cytoplasm. Exocytosis is the process through which the remaining undigested items are passed out of the body.
10. With the help of a labelled diagram, discuss the structure of the cross–section of leaf.
Ans: Leaf has two parts:
Epidermis – The epidermis is the cell's outermost layer. Stomata are tiny pores that connect cells in the lower epidermis.
Mesophyll – Mesophyll refers to the chloroplast-containing parenchyma cells. Palisade and spongy parenchyma are the two types.
11. What do you mean by ‘lymph’? Mention its function.
Ans: Lymph- Tissue fluid, or lymph, is the fluid that fills the gaps between the cells in the tissues.
Functions of lymph:
It returns tissue fluid from the interstitial spaces into the blood.
Lacteals, which are lymph capillaries found in intestinal villi, aid in fat absorption.
Through tissue fluid, it gathers carbon dioxide, waste products, and metabolites from tissues.
12. How are lungs designed in human beings to maximize the area of exchange of gases?
Ans: Lungs have evolved various characteristics to allow for effective gas exchange. The modifications are as follows:
Increased surface area
Very fine and delicate surface for easy exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide
13. Dark reactions of photosynthesis do not need light. Do plants undergo dark reactions at night?
Ans: The term "dark reaction" does not refer to a reaction that occurs in the absence of light, such as at night. In fact, these reactions are independent of light energy and occur at the same time as light reactions.
14. Differentiate inhalation and exhalation.
Ans: The differences between inhalation and exhalation are:
15. With the help of a diagram, show pulmonary circulation in man.
Ans: With the help of a diagram, pulmonary circulation in man can be represented as shown below:
16. What are the functions of the human respiratory system?
Ans: The functions of the human respiratory system are:
(i). The cellular respiration function requires gaseous exchange.
(ii). The vocal cords produce sound.
(iii). Abdominal compression assists with urination, face passing, and birthing.
(iv). Laughing and sneezing to clean the respiratory surface on their own.
17. What is the role of skin, lungs and intestine in the process of excretion in man?
Ans: The role of skin, lungs and intestine in the process of excretion in man are:
Skin – Skin excrete excess salts and water in the form of sweat.
Lungs – Exhalation causes carbon dioxide to be expelled from the lungs.
Intestine – Intestine throw out undigested food in the form of faeces through the anus
18. Explain the structure of chloroplast.
Ans: The structure of chloroplast can be explained using the diagram as shown below:
(Image will be uploaded soon)
19. Why and how does water enter continuously into the root xylem of plants?
Ans: Water and minerals are transported to the plant body via xylem. Root hairs are hairs that grow on a plant's roots. The root hairs come into close touch with the water film that forms between soil particles. Diffusion allows water and minerals to penetrate the root hair. The water and minerals are taken by the root hair from the soil move via the epidermis, root cortex, endodermis, and root xylem by osmosis from cell to cell. The plant's xylem vessels in the root are connected to the xylem vessels in the stem. As a result, dissolved mineral-containing water passes through the root xylem vessels and into the stem xylem vessels. The stem's xylem vessels branch out into the plant's leaves. As a result, the water and minerals supplied by the xylem vessels in the stem reach the leaves via the branched xylem vessels that enter each area of the leaf from the petiole. As a result, water and minerals from the earth reach the plants' leaves via the root and stem. The suction created by the evaporation of water molecules from the cells of a leaf pulls water from the xylem cells of roots. Transpiration is the loss of water from the aerial portions of plants in the form of vapour.
20. What is the role of following in human digestive system –
Ans: Mucus – It shields the stomach's inner life from HCl.
Bicarbonate
Ans: Bicarbonate – It alkalizes the acidic meal so that pancreatic enzymes may work on it.
Ans: Trypsin – It digest proteins into amino acids.
21. What are outside raw materials used for by an organism?
Ans: The following are examples of external raw materials used by an organism:
22. What processes would you consider essential for maintaining life?
Ans: The processes essential for maintaining life are:
Respiration
Transportation
23. What is the difference between autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition?
Ans: The difference between autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition is:
24. Where do plants get each of the raw materials required for photosynthesis?
Ans: Plants do get each of the raw materials required for photosynthesis from:
a) Carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
b) Light from Sun
c) Water from Soil
d) Chlorophyll from chloroplast of green plants.
25. What is the role of acids in our stomach?
Ans: HCl plays the following role in our stomach:
Make the medium acidic to allow the pepsin enzyme to work.
Kills the harmful bacteria present in food
Prevents fermentation of food
26. How is small intestine designed to absorb digested?
Ans: The villi, which are finger-like projections on the inner lining of the small intestine, enhance the surface area available for absorption. The villi are densely packed with blood arteries that convey the absorbed food to all of the body's cells. It is used to obtain energy and repair damaged tissues.
27. What advantage over an aquatic organism does a terrestrial organism have with regard to obtaining oxygen for respiration?
Ans: In comparison to aquatic organisms, terrestrial organisms breathe at a slower rate. This is owing to the fact that there is less oxygen in water than there is in air, thus aquatic species breathe at a faster rate.
28. What are different ways in which glucose is oxidized to provide energy in various organisms?
Ans: The pathways of break-down of glucose in various organisms are as below:
29. How is oxygen and carbon dioxide transported in human beings?
Ans: In humans, the pigment haemoglobin is found in RBC and has a high affinity for oxygen. It absorbs oxygen from the air in the lungs and transports it to tissues that are oxygen-deficient. In blood plasma, some oxygen is carried in a dissolved condition. Because carbon dioxide is more soluble in water than oxygen, it is usually carried through human blood as a dissolved form.
30. What are the components of the transport system in human beings? What are the functions of these components?
Ans: The components of the human transport system include:
Heart- receives and pumps the blood.
Arteries- carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to various organs:
Veins- Bring back blood to the heart.
Capillaries- exchange of various materials and gases between blood and tissues.
31. Why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds?
Ans: The right and left sides of the heart are separated to prevent oxygenated and deoxygenated blood from mingling. This separation allows for a very effective oxygen supply to the organism. This is important in creatures with high energy needs, such as birds and mammals, that use energy to maintain their body temperature all of the time.
32. What are the components of the transport system in highly organized plants?
Ans: The xylem and phloem transport systems are found in higher plants. Water and minerals are transported from the root to different parts of the plant via vessels and tracheids in xylems. Food is transported from leaves to storage organs and other sections of the plant by phloem, which is made up of sieve tubes and companion cells.
33. How are water and minerals transported in plants?
Ans: Plants transport water and minerals through the xylem, which is made up of tracheids and vessels. Osmosis transports water and minerals received by root hairs to the xylem tissues of the root. Water travels from the root xylem to the stem xylem and then to the leaves.
34. How is food transported in plants?
Ans: Plants carry food via the phloem, which is made up of sieve tubes, sieve cells, and companion cells. Food is prepared in leaves and transferred to the phloem of the leaves in a soluble form. Food is actively transported to all other areas of the plant.
35. What are the methods used by plants to get rid of excretory products?
Ans: The methods used by plants to get rid of excretory products are:
(i) During respiration, plants produce carbon dioxide as a waste product, and photosynthesis produces oxygen as a waste product.
Excess water is removed through transpiration.
Some waste products like gums and resins are stored in older xylem tissue.
36. How is the amount of urine produced regulated?
Ans: The amount of urine produced is determined by the amount of excess water in the body and the amount of water-soluble waste to be expelled. When the amount of water and dissolved waste in a boy is high, the amount of urine generated is high, and when the amount of wastes is low, the amount of urine produced is low.
37. How are fats digested in our bodies? Where does this process take place?
Ans: The small intestine is where lipids are digested. The fats that enter the intestine take the form of big globules. These huge globules are broken down into smaller globules by bile juice. Following that, the fat-digesting enzyme lipase, which is found in pancreatic and intestinal juice, turns it into fatty acids and glycerol.
38. What are the necessary conditions for autotrophic nutrition and what are its by-products?
Ans: Conditions necessary for autotrophic nutrition are:
Carbon dioxide
By-products are:
39. What are the differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration? Name some organisms that use anaerobic mode of respiration.
Yeast, bacteria, and some internal parasites, such as tapeworms, use anaerobic respiration.
40. How are the alveoli designed to maximize the exchange of gases?
Ans: The nostril, larynx, nasal chamber, pharynx, trachea, epiglottis, alveoli, bronchioles, bronchi, and lungs make up the human respiratory tract. Through millions of small sacs known as alveoli, oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide waste within the lungs. Inhaled oxygen diffuses into the lungs' capillaries, binds to haemoglobin, and is pumped into the bloodstream. Exhalation allows the carbon dioxide from the blood to diffuse through the alveoli and be evacuated. To promote the exchange of gases between blood and the air-filled alveoli, the alveoli have thin walls and are richly supplied with a network of blood veins. They have a balloon-like shape to maximise gas exchange surface area. The alveolar walls are folded and have a significant surface area. It has a large network of blood arteries that serve as a surface for gas exchange.
41. What would be the consequence of a deficiency of haemoglobin in our bodies?
Ans: Haemoglobin is a pigment found in red blood cells. It has a strong preference for oxygen. It transports oxygen from the lungs to other tissues that are oxygen-deficient. The presence of less haemoglobin reduces the oxygen supply to tissues. A person with low haemoglobin levels will become exhausted quickly and seem pale.
42. What are the differences between the transport of materials in xylem and phloem?
Ans: The differences between the transport of materials in xylem and phloem are:
43. Compare the functioning of alveoli in the lungs and nephron in the kidneys with respect to their structure and functioning.
Ans: Comparison between alveoli and nephron:
44. Leaves of a healthy potted plant were coated with petroleum jelly. How will it affect the plant? State two reasons.
Ans: The plant will not remain healthy for long due to the following reasons:
There will be no transpiration.
There will be no exchange of gases which will affect the rate of photosynthesis.
45. How does respiration in plants differ from that in animals?
Ans: In plants, all portions such as the root, stem, and leaves do individual respiration, but in animals, either the general body surface or particular organs such as the skin, gills, and lungs perform respiration. Plants have a significantly slower rate of respiration than animals. Gases are not transported from one section of the plant to another way they are in animals.
46. How does respiration in plants differ from that in animals?
Ans: After eating sugary food (chocolates and sweets), acid is generated in the mouth. The pH of the mouth is lowered by this acid. When the pH of the acid generated in the mouth falls below, tooth decay begins. This is because the acid develops strong enough to attack and damage the enamel of our teeth.
47. Name the cartilaginous flap which closes the glottis to check the entry of food into it during swallowing.
Ans: It's possible that the tissue that became clogged was the xylem. Water and minerals taken by roots from the soil are carried to the leaves and other parts of the plant via the xylem. As a result, if the xylem is obstructed, the leaves will be deprived of nutrients and will wilt.
48. How does respiration in plants differ from that in animals?
49. Write one feature which is common to each of the following pairs of the term/organs.
glycogen and starch
Ans: The feature that is common to the following pair is Carbohydrate (food).
chlorophyll and haemoglobin
Ans: The feature that is common to the following pair is Pigments.
gills and lungs
Ans: The feature that is common to the following pair is Respiratory organs.
arteries and veins.
Ans: The feature that is common to the following pair is Blood vessels.
50. A certain tissue in a green plant somehow gets blocked and the leaves wilted. What was the tissue that got blocked?
51. Write the functions of the following in the digestive process:
Ans: Bile: It is secreted by the gallbladder and it emulsifies & it into the smaller droplets for their easy digestion.
Bicarbonate secreted by the duodenal wall.
Ans: It provides an alkaline medium in the duodenum which is needed for the action of pancreatic enzymes of different food components for their digestion.
Pancreatic amylase.
Ans: Pancreatic amylase enzyme digests starch and changes it into maltose.
52. The two openings of the pharynx, one leading to the trachea and the other leading to oesophagus, lie very close to each other. Yet food we swallow normally does not enter into our trachea. Why?
Ans: The food does not enter the trachea because the aperture leading to the trachea (glottis) is covered by a cartilaginous flap termed the epiglottis during swallowing, leaving the food with no other option except to go down the oesophagus.
53. How would it affect the digestion of proteins and carbohydrates in the duodenum of man if there is a blockade in the pancreatic duct?
Ans: The pancreatic juice is secreted by the pancreas and enters the duodenum. Pancreatic amylase and trypsin are enzymes that aid in the digestion of carbohydrates and proteins. As a result, if there is a blockade, carbohydrate and protein digestion is impaired.
Long Answer Questions (5 Marks)
1. What is ‘clotting of blood?’ Write a flow chart showing major events taking place in clotting of blood?
Ans: Formation of a clot at the site of injury to stop bleeding is known as ‘clotting of blood.’ Steps for clotting of blood
2. With the help of a labelled diagram of the human excretory system, Mention its important part and explain them.
Ans: A labelled diagram of the human excretory system mentioning its important part with a proper explanation is as displayed below:
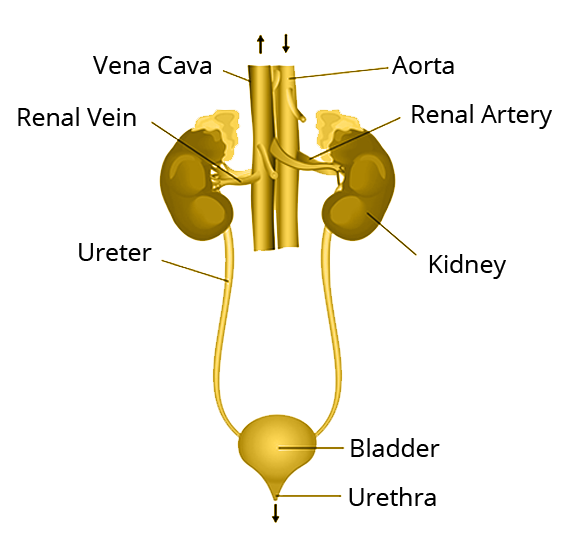
1) Kidney – It is the excretory system's functional unit. About a million small coiled channels called nephrons make up each kidney. The basic filtration unit in the kidneys is the nephron. The glomerulus, Bowman's capsule, and convoluted tubule are the components.
2) Ureter – Wastes come out of the kidney into the ureter.
3) Urinary Bladder – The ureter pours its contents into a muscular sac called the urinary bladder.
4) Urethra – Urine flows from the bladder to the outside through the urethra.
(i) Draw a well-labelled diagram of the human digestive system
Ans: A well labelled diagram of the human digestive system is as shown below:
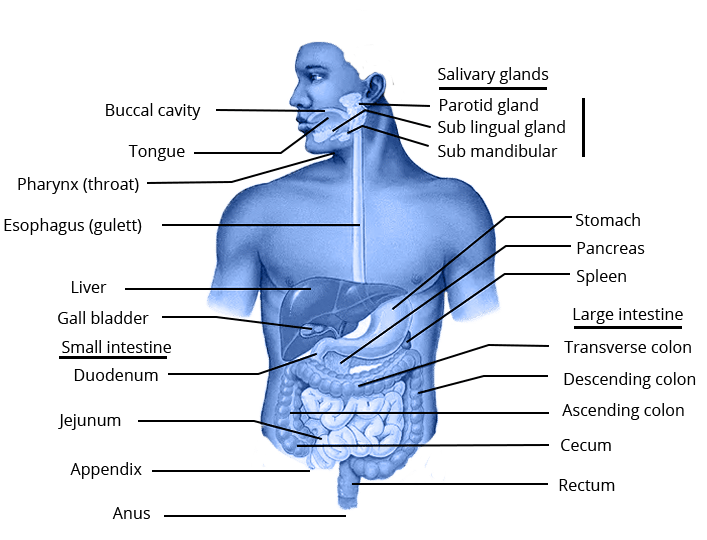
(ii) Describe the role of following in digestion.
Ans: Bile – emulsification of fats
Salivary amylase
Ans: Salivary amylase – digest starch in the mouth
Ans: HCl – Activate pepsinogen by making medium acidic in stomata.
4. With the help of a labelled diagram, Discuss the mechanism of respiration in human beings.
Ans: Mechanism of Respiration – It occurs in the following steps
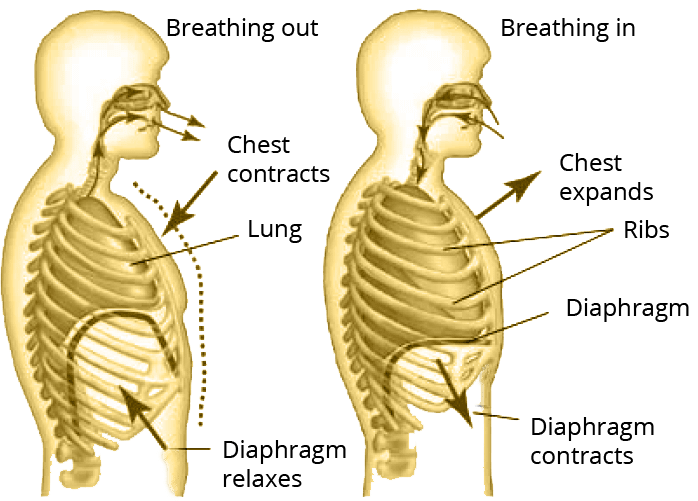
Breathing – Taking in oxygen and expelling carbon – dioxide out is called breathing. It involves the following steps –
Inhalation – It is consuming oxygen. It happens when the muscles linked to the ribcage contract. The ribs are lifted and the diaphragm is flattened, increasing the volume of the thoracic cavity. As a result, the pressure inside the thoracic cavity drops, allowing air to flow into the lungs.
Exhalation – It is the process of releasing carbon dioxide. It happens when the muscles linked to the ribs relax and the diaphragm is formed. This reduces the volume of the thoracic cavity, lowers air pressure, and expels air from the lungs.
b) Exchange of Gases – It takes place between the alveoli of the lungs and surrounding blood capillaries.
c) Transport of Gases in Blood – Haemoglobin is a protein that transports oxygen throughout the body. In the form of any haemoglobin, oxygen is transported from the lungs to the bodily cells.
d) Oxidation of Food – Break down of glucose molecules that produce energy. It occurs in chondria.
5. Describe an experiment to prove that carbon – dioxide is essential for the process of photosynthesis.
Ans: Experiment showing that carbon dioxide is essential for photosynthesis.
Take a potted plant with elongated leaves
Take an empty bottle and put a little amount of potassium hydroxide ($KOH$) in it.
Now cut the cork of the bottle into two parts and place it on one of the leaves of the potted plant in between the two parts of the cork.
Now put the bottle in the presence of sunlight for 72 – 96 hours.
Now test the leaf for the presence of starch.
6. Describe the structure and functioning of nephron.
Ans: Each nephron is a collection of blood capillaries with very thin walls. Each glomerulus (capillary cluster) in the kidney is linked to the cup-shaped Bowman's capsule, which collects the filtered urine. The blood is filtered by the nephron to eliminate nitrogenous waste.
They also absorb some vital substances from the filtrate, including glucose, amino acids, minerals, and a significant amount of water.
7. Describe double circulation in human beings. Why is it necessary?
Ans: During each cycle, blood passes through the heart twice in mammals and birds. Double circulation is the term for this situation.
Blood that has been deoxygenated enters the right auricle and then enters the right ventricle, where it is pushed to the lungs for oxygenation. It travels from the lungs to the left auricle, where it is oxygenated, and then to the left ventricle, where it is pumped to various regions of the body.
Such a circulatory system prevents the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, allowing for an effective supply of oxygen to the body
Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Important Questions - Free PDF Download
The Class 10 Science Ch 6 Important Questions PDF are the best guide for the students. The questions will help you have a good grip over the chapter. Chapter 6 Science Class 10 Important Questions are designed solely for providing the students with a proper understanding of the chapter. With these questions’ correct practice, you can achieve a better score and increase your overall percentage. Chapter 6 is based on the life processes inside the human body and the plant body. And it can be confusing to remember the different organs and their functions. To make the learning more comfortable, we have designed the Important Questions of Ch 6 Science Class 10 . The PDF of the important questions are available on Vedantu website for free.
Students of all calibre can refer to the Important Questions of Chapter 6 Science Class 10 . These questions are prepared as per the latest guidelines of CBSE board. It will clarify the doubts of the students and will also help them understand the pattern of examination.
Further if you want to brush up on the topics of CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 6 - Life Processes , read the table below, as it contains all the important topics and subtopics included in the chapter.
Important Questions For Class 10 Science Chapter 6, Life Processes
In chapter 6 of science, students will learn about the different set of life processes in the human body. The chapter also explains the different parts of the human organ system and its functions. By practising the important questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 , students can learn new things as well as get a detailed overview of the chapter. Some of the topics covered under the chapter are as follows:
Life Processes
Earth is the only planet in the solar system that supports life. We can distinguish between living organisms and other inanimate objects based on different parameters of life processes.
Life processes refer to those processes that help in the maintenance of life. The processes are responsible for keeping the body in a well and healthy manner. These processes help in the development of living organisms. The important life processes are nutrition, respiration, excretion and circulation. These processes work in a coordinated manner to assist in the sustenance of life. In unicellular organisms, the life processes are carried out by a single cell, whereas, in multicellular organisms, these processes are carried out by different organ systems.
Nutrition can be defined as the process of acquiring food and other minerals that are required for the nourishment and maintenance of living organisms. The modes through with a living organism can obtain nutrition are: Autotrophic and Heterotrophic.
Autotrophic Nutrition - It is a type of nutrition in which a living organism can nurture itself by preparing its food. This type of nutrition is generally found in green plants as they can prepare their food in the presence of sunlight and other chemicals.
Heterotrophic Nutrition - It is a type of nutrition in which a living organism derives its nourishment from other organisms. This mode of nutrition can be subdivided into three categories, Holozoic Nutrition, Saprophytic Nutrition, and Parasitic Nutrition.
Digestive System in Humans
Human beings can consume both plant products as well as animal products. And to digest the complex food particles, humans have a complex digestive system. The digestive system in humans consists of an alimentary canal along with other digestive organs that function together to provide proper nourishment to the body. The human digestive system performs four main functions: ingestion, digestion, absorption and assimilation.
The digestive system has various organs that function together to help in the digestion of food. Some of the important organs of the digestive system are: Alimentary canal, Mouth, Oesophagus, Stomach, Small intestine, Large Intestine, and there are sever digestive glands that produce digestive juices for the proper digestion of food, they are Salivary gland, Gastric glands, Liver, Gallbladder, and Pancreas.
Respiration System in Humans
Respiration can be defined as the exchange of gases that takes place in the human body. The process of respiration takes place differently in different organisms.
Respiration in cellular level in an organism means the burning of food for the generation of energy to support the life processes. At cellular level respiration can be divided into two subtypes: Aerobic respiration and Anaerobic respiration.
The human respiratory system is complex and consists of various organs. It consists of the nose, nasal cavities, pharynx, larynx, windpipe or trachea, then comes the lungs which enclose the bronchi, bronchioles and alveoli. The human respiratory system is complex as it processes breathing, exchange of gases, and cellular respiration.
Circulation System in Humans
For their survival, every living organism requires certain components such as oxygen, water and food. All these components are needed by every living cell in the human body. So, they need to be transported to various parts of the body. Transportation in humans occurs with the help of the circulatory system.
The circulatory system is a complex system consisting of the blood, blood vessels and heart. The circulatory system is mainly responsible for the effective transmission of food, nutrients, oxygen. It helps in the effective removal of carbon dioxide and other waste materials from the body.
The circulatory system in plants involves the transportation of food, water and necessary nutrients to different parts of the plant. The transportation in plants is done by two tissues, namely xylem and phloem.
Xylem is responsible for the effective transmission of water, and it transports water in an upward direction only. Phloem is responsible for the transmission of food and other nutrients in the plants. The food and nutrients move in both upward and downward direction in the phloem.
Excretory System in Humans
Excretion is an essential function performed by the human body. Excretion means the effective removal of waste materials and other unuseful substances from the human body.
The excretory system in humans is the most complex and well-developed. It consists of a pair of kidneys, a pair of ureters, an urinary bladder and a urethra. All the organs of the excretory system work in unison to remove all the unwanted waste and other unuseful substances from the human body.
The excretion in plants takes place through the stomatal opening. The excretion in plants is mostly in the form of gases. The excess water is removed from the plants through transpiration.
Chapter 6 Class 10 Science Important Questions
To provide you with a proper understanding of the questions, we at Vedantu have provided some Important Questions on Chapter 6 in this article. These Life Processes Class 10 Important Questions will help you understand the exam pattern as well as the type of questions you will face in the exams.
What is the meaning of Life Processes?
What is Nutrition? Explain its types.
What is the meaning of Photosynthesis?
How does amoeba obtain nutrition?
Explain the digestive system in brief.
What are the different types of teeth? Explain their functions.
Explain small intestine along with its function.
Explain the role of HCL in Digestion.
What is Respiration?
Explain the Physiology of respiration.
Explain the Circulatory system in humans.
How does the excretion of waste material take place in the human body?
Benefits of Class 10th Science Chapter 6 Important Questions
Here are some points that explain the benefits of these important questions.
The Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Important Questions will provide the students with a brief comprehension of the chapter and clear all sorts of doubts.
The Class 10 Science Ch 6 Important Questions are designed by experts at Vedantu, after thorough research. These questions have the highest probability of coming in the exams.
The questions come with proper answers and cover all the topics under the chapter.
These questions are prepared to keep in mind the latest guidelines of CBSE Board .
Chapter 6 Science Class 10 Important Questions are simplified and the most suitable study material for the students. The students can refer to these study materials for revisions and preparation of exams. The materials will provide them with a competitive edge and help them secure better grades.
Important Related Links for CBSE Class 10 Science

FAQs on Important Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 6 - Life Processes 2024-25
1. How many chapters are there in CBSE Class 10 science book?
Ans: There are a total of 7 units in CBSE Class 10 science solutions book. Below is the list of units:
Unit 1: Chemical Substances - Nature and Behaviour
Chemical reactions
Acids, bases and salts
Metals and non-metals
Carbon and compounds
Periodic classification of elements
Unit 2: World of Living
Life processes
Control and coordination in animals and plants
How do organisms reproduce
Control and coordination in animals
Reproduction
Heredity and evolution
Unit 3: Natural Phenomenon
Refraction of light
Reflection of light
The functioning of the human eye
Unit 4: Effects of Current
Effects of current
Magnetic effects of current
Unit 5: Natural Resources
Sources of Energy
Our environment
management of natural resources
Unit 6: How things work
Unit 7: Moving Things, People and Idea
2. Give a brief description of evolution.
Ans: Evolution:
In this part of Class 10 Science Chapter 9, you will not only learn about the evolution of humans but also the evolution of animals and birds.
Homologous and Analogous organs are the ones which are used in the evolutionary relationships of animals.
There are various stages of evolution. You shall read about the artificial selection, in which one particular species will evolve into various species.
Phylogeny is considered for the evolutionary relationship of biological species.
Humans from primates evolution is still a big mystery and here, you will learn some more details about it.
Here, you will also understand what is somatic variation and Gametic variation and they occur in somatic cells and germ cells of the body. You will also read about the importance of variations and what are the causes of variations.
3. Explain about magnetic field and field lines.
Ans: Here, the topic discusses field and field lines where magnetics play a major role. Attraction or repulsion of objects can be seen in magnetic fields. Nickel, Iron and Cobalt are the best examples of magnetic fields. You will also read about:
North and south poles
Like poles repel and unlike poles attract
Magnetic field
Magnetic field lines
Iron filings test around a bar magnet
No two magnetic field lines intersect
The relative strength of magnetic field inferred from magnetic field lines
Magnetic field lines form a closed-loop.
Here, the concept also educates you on the concentric circles which are used to represent at every point over a conductor. This will be explained to you with various experiments such as Oersted’s experiment, electromagnetism and electromagnet, magnetic field due to a straight current-carrying conductor, right-hand thumb rule, magnetic field due to current through a circular loop and magnetic field due to current in a solenoid.
4. Benefits of NCERT solutions with Vedantu?
Ans: These solutions are drafted by our Science experts with utmost care to make you’re learning more fun and interactive. You can score well if you have secured 100% confidence to answer any question asked from this chapter. They made sure that CBSE and NCERT guidelines are strictly followed while drafting these solutions.
Our NCERT solutions will help you in developing a strong conceptual foundation with all the important concepts in a very simple language. Solutions provided to the questions are crisp and concise with 100% accuracy in the exercises. They have been designed in such a way that through which you can expand your knowledge base, improve your learning skills and it clears all your doubts instantly.
5. What are the important topics in life processes according to Chapter 6 of Class 10 Science
Ans: Chapter 6 of Class 10 Science will help students to understand the different life processes. In this chapter, students will study the type of nutrition in different organisms. They will also study the concept of photosynthesis in detail. They will even study the process of digestion in human beings in detail and will learn about the different organs of the digestive system and how different organs help in the digestion of food. The process of excretion and how waste products are excreted out of the body is also a part of life processes.
6. Why are life processes important?
Ans: Life processes are important for healthy living. Life processes such as respiration, digestion, absorption, assimilation, and excretion are vital for all living organisms. The processes may differ from one organism to another. Students of Class 10 science will learn about the different life processes in Chapter 6. It is an interesting chapter and an essential one if the student wants to pursue a career in Biology.
7. If there is less air in the trachea, its walls do not collapse. Give a reason.
Ans: The trachea is a tube through which we breathe in air and give out carbon dioxide. The trachea is made up of small rings arranged in the form of C. The rings are muscular and made of connective tissue. Thus, the rings present in the trachea help prevent it from collapsing when there is no air in it. The muscular rings expand when air enters into it and contracts when air moves out of our lungs. For Important Questions of Chapter 6 of Class 10 Science, visit Vedantu website or mobile app and download the PDF free of cost.
8. What is the process of digestion and where does the complete digestion of various components of food take place?
Ans: Digestion of food takes place in different organs. In the mouth, the process starts by chewing food. Then it passes to the stomach for further digestion. The small intestine is the part where complete digestion of food takes place. Different juices and enzymes present in the different parts of the digestive system help in the complete digestion of the food. The digestion starts in the mouth and breaks into small molecules that are digested quickly in the stomach and other parts of the digestive system.
9. Explain how urine is produced?
Ans: Urine is the waste product excreted out of the body. Urine is produced in the kidneys. It consists of harmful substances. Therefore, it is necessary to pass out the waste products in the form of urine. Kidneys filter the blood and important substances such as glucose, amino acids, and salts are reabsorbed. Excess amounts of water present in the blood and other waste substances are converted into the urine and it is excreted out through the urinary system.
CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions
Cbse study materials.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Free PDF Download
Ncert solutions for class 10 science chapter 6 – life processes.
Class 10 is Board exams and thus, it lays the base for you to choose the subject of your choice in Class 11. Hence, scoring good grades becomes very necessary. In order to help you, we have hence prepared NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 as per the CBSE Curriculum. Our NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 are also in accordance with the NCERT textbooks recommended by the Board. Our NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 are exercise-wise and help you to prepare for the exams in the best possible manner and score higher marks.
With Toppr App you get all the NCERT solutions for class 10 science Chapter 6 at one single place. NCERT solutions for class 10 science Chapter 6 are absolutely free to download. We also offer you live doubt clearing sessions which saves your time and energy and you get your doubts solved immediately.
Toppr provides free study materials, 1000+ hours of video lectures, and last 10 years question papers for free. Download Toppr for Android and iOS or signup for free.
Download NCERT Solutions for other subjects here.
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science All chapters here.
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 6 – Life Processes NCERT Solutions
NCERT solutions for class 10 science chapter 6 – How Do Organisms Reproduce explains the meaning of life processes, nutrition, types of nutrition, how do organisms obtain nutrition, nutrition in humans, respiration in various organisms and human beings, Transportation in Human Beings and plants and excretion in human beings and plants.
The chapter contains self-explanatory diagrams and pictures in order to explain all the concepts thoroughly.
Sub-topics covered under NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6
- 6.1 What are the Life Processes?
6.2.1 Autotrophic Nutrition
6.2.2 Heterotrophic Nutrition
6.2.3 How do Organisms obtain their Nutrition?
6.2.4 Nutrition in Human Beings
6.3 Respiration
6.4.1 Transportation in Human Beings
6.4.2 Transportation in Plants
6.5 Excretion
6.5.1 Excretion in Human Beings
6.5.2 Excretion in Plants
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6
In this chapter, we shall study why the molecular movements are needed for life and what are the maintenance processes in living organisms. Let us now discuss the sub-topics in detail.
6.1 What are Life Processes?
This topic explains the life processes and the need for their maintenance.
6.2 Nutrition
This topic explains how living things get their food and types of nutrition.
This topic explains how the plants get their nutrition by the photosynthesis process and explain the process in detail.
This topic explains how some organisms obtain their nutrition from plants and animals without killing them.
This topic explains how the food consumed is converted and absorbed in the body as nutrition.
It explains the digestion process in human beings and how the food consumed gets converted into nutrition in the body.
It deals with how the plants, different organisms, and human beings breathe or how does their respiratory system functions does.
6.4 Transportation
This topic explains the transportation of blood from the heart to the body and vice-versa. It includes transportation of plasma and lymph also.
This topic states how the plants transport water, food and other substances.
This topic explains how living organisms remove wastes from their body.
This topic explains the excretory system of human beings and the removal of waste in the form of urine and excreta.
In this topic, the students will learn how plants get rid of waste.

Download Toppr – Best Learning App for Class 5 to 12
With Toppr: The better learning App in your mobile, you get free pdf downloads, free videos and free doubt solving sessions. You also get free online mock tests to check your knowledge and speed. Download Toppr for Android and iOS or signup for free.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

NCERT Solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 10 Geography Chapter 3 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Mathematics Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 History Chapter 6 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 History Chapter 1 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 History Chapter 2 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 History Chapter 4 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 5 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 7 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 8 Free PDF Download
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- Important Info
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Sample Papers
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
Case Study Class 10 Science Questions and Answers (Download PDF)
Free pdf download.
SHARING IS CARING If our Website helped you a little, then kindly spread our voice using Social Networks. Spread our word to your readers, friends, teachers, students & all those close ones who deserve to know what you know now.
Case Study Class 10 Science
If you are looking for the CBSE Case Study class 10 Science in PDF, then you are in the right place. CBSE 10th Class Case Study for the Science Subject is available here on this website. These Case studies can help the students to solve the different types of questions that are based on the case study or passage.
CBSE Board will be asking case study questions based on Science subjects in the upcoming board exams. Thus, it becomes an essential resource to study.
The Case Study Class 10 Science Questions cover a wide range of chapters from the subject. Students willing to score good marks in their board exams can use it to practice questions during the exam preparation. The questions are highly interactive and it allows students to use their thoughts and skills to solve the given Case study questions.
Download Class 10 Science Case Study Questions and Answers PDF (Passage Based)
Download links of class 10 Science Case Study questions and answers pdf is given on this website. Students can download them for free of cost because it is going to help them to practice a variety of questions from the exam perspective.
Case Study questions class 10 Science include all chapters wise questions. A few passages are given in the case study PDF of Science. Students can download them to read and solve the relevant questions that are given in the passage.
Students are advised to access Case Study questions class 10 Science CBSE chapter wise PDF and learn how to easily solve questions. For gaining the basic knowledge students can refer to the NCERT Class 10th Textbooks. After gaining the basic information students can easily solve the Case Study class 10 Science questions.
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions & Equations
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases & Salts
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals & Non-metals
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon & Its Compounds
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity & Evolution
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light-Reflection & Refraction
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 11 The Human Eye & the Colourful World
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment
How to Solve Case Study Based Questions Class 10 Science?
In order to solve the Case Study Based Questions Class 10 Science students are needed to observe or analyse the given information or data. Students willing to solve Case Study Based Questions are required to read the passage carefully and then solve them.
While solving the class 10 Science Case Study questions, the ideal way is to highlight the key information or given data. Because, later it will ease them to write the final answers.
Case Study class 10 Science consists of 4 to 5 questions that should be answered in MCQ manner. While answering the MCQs of Case Study, students are required to read the paragraph as they can get some clue in between related to the topics discussed.
Also, before solving the Case study type questions it is ideal to use the CBSE Syllabus to brush up the previous learnings.
Features Of Class 10 Science Case Study Questions And Answers Pdf
Students referring to the Class 10 Science Case Study Questions And Answers Pdf from Selfstudys will find these features:-
- Accurate answers of all the Case-based questions given in the PDF.
- Case Study class 10 Science solutions are prepared by subject experts referring to the CBSE Syllabus of class 10.
- Free to download in Portable Document Format (PDF) so that students can study without having access to the internet.

Benefits of Using CBSE Class 10 Science Case Study Questions and Answers
Since, CBSE Class 10 Science Case Study Questions and Answers are prepared by our Science experts referring to the CBSE Class 10 Science Syllabus , it provided benefits in various way:-
- Case study class 10 Science helps in exam preparation since, CBSE Class 10 Question Papers contain case-based questions.
- It allows students to utilise their learning to solve real life problems.
- Solving case study questions class 10 Science helps students in developing their observation skills.
- Those students who solve Case Study Class 10 Science on a regular basis become extremely good at answering normal formula based Science questions.
- By using class 10 Science Case Study questions and answers pdf, students focus more on Selfstudys instead of wasting their valuable time.
- With the help of given solutions students learn to solve all Case Study questions class 10 Science CBSE chapter wise pdf regardless of its difficulty level.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

- School Solutions
- Star Program
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Statistics
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Hindi
- NCERT Books Class 12
- NCERT Books Class 11
- NCERT Books Class 10
- NCERT Books Class 9
- NCERT Books Class 8
- NCERT Books Class 7
- NCERT Books Class 6
- NCERT Books Class 5
- NCERT Books Class 4
- NCERT Books Class 3
- NCERT Books Class 2
- NCERT Books Class 1
- Important Questions Class 12
- Important Questions Class 11
- Important Questions Class 10
- Important Questions Class 9
- Important Questions Class 8
- Important Questions Class 7
- important questions class 6
- CBSE Class 12 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 8 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 6 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 11 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 9 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 8 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 7 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 6 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 5 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 4 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 3 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 2 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 1 Syllabus
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 5
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 4
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 3
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 2
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 1
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Science
- NEET 2021 Question Paper
- NEET 2020 Question Paper
- NEET 2019 Question Paper
- NEET 2018 Question Paper
- NEET 2017 Question Paper
- NEET 2016 Question Paper
- NEET 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Physics Questions
- NEET Chemistry Questions
- NEET Biology Questions
- NEET Sample Papers
- NEET Physics Syllabus
- NEET Chemistry Syllabus
- NEET Biology Syllabus
- NEET Mock Test
- NEET Eligibility Criteria
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Main Sample Papers
- JEE Main Physics Syllabus
- JEE Main Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Main Maths Syllabus
- JEE Main Physics Questions
- JEE Main Chemistry Questions
- JEE Main Maths Questions
- JEE main revision notes
- JEE Main Mock Test
- JEE Advanced Physics Questions
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Questions
- JEE Advanced Maths Questions
- JEE Advanced 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Maths Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Mock Test
- ISC Class 12 Syllabus
- ISC Class 11 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 10 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 9 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 8 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 7 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 6 Syllabus
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 6
- ICSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- ICSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- ISC Important Questions for Class 12
- ISC Important Questions for Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 6
- ISC Class 12 Question Paper
- ICSE Class 10 Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Syllabus
- Maharashtra Board Sample Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Previous Year Question Paper
- AP Board Syllabus
- AP Board Sample Question Paper
- AP Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Board Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Telangana Board Syllabus
- Telangana Board Sample Question Paper
- Telangana Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Syllabus
- Karnataka Board Sample Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Examination Full Forms
- Physics Full Forms
- Chemistry Full Forms
- Biology Full Forms
- Educational Full Form
- CUET Eligibility Criteria
- CUET Exam Pattern
- CUET Cutoff
- CUET Syllabus
- CUET Admit Card
- CUET Counselling
- CUET Previous Year Question Papers
- CUET Application Form
- CUET Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Centers
- CUET Exam Dates
- CUET Results
- Physics Formulas
- Chemistry Formulas
- Math Formulas
- Algebra Formulas
- Geometry Formulas
- Trigonometry Formulas
- Subscription
CBSE Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 6
Home » CBSE » CBSE Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 6

- CBSE Important Questions
- Important Questions Class 6
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers
- CBSE Revision Notes
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Extra Questions
- CBSE Sample Papers
- ISC & ICSE Syllabus
- ICSE Syllabus Class 9
- ICSE Syllabus Class 8
- ICSE Syllabus Class 7
- ICSE Syllabus Class 6
- ICSE Syllabus Class 10
- ICSE Question Paper
- ICSE Sample Question Papers
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- ICSE Revision Notes
- ICSE Important Questions
- ISC Important Questions For Class 12
- ISC Important Questions For Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 6
- Maharashtra board
- Rajasthan-Board
- Andhrapradesh Board
- AP Board syllabus
- Telangana Board
- Tamilnadu Board
- Tamilnadu Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Previous Year Question Paper
- NCERT Solutions Class 12
- NCERT Solutions Class 10
- NCERT Solutions Class 11
- NCERT Solutions Class 9
- NCERT Solutions Class 8
- NCERT Solutions Class 7
- NCERT Solutions Class 6
- NCERT Solutions Class 5
- NCERT Solutions Class 4
- NCERT Solutions Class 3
- NCERT Solutions Class 2
- NCERT Solutions Class 1
- JEE Main Question Papers
- JEE Main Syllabus
- JEE Main Questions
- JEE Main Revision Notes
- JEE Advanced Question Papers
- JEE Advanced Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Questions
- JEE Advanced Sample Papers
- NEET Question Papers
- Neet 2021 Question Paper
- Neet 2020 Question Paper
- Neet 2019 Question Paper
- Neet 2018 Question Paper
- Neet 2017 Question Paper
- Neet 2016 Question Paper
- Neet 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Syllabus

CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Question Answer – Life Processes
Science is a subject which requires deep study and understanding of the concepts covered in each chapter. Hence, one must study properly to get a clear understanding of it and have a strong command of all the topics. In this way, one can score well in the examinations.
Quick Links
Chapter 6 of Class 10 Science covers the topic of ‘Life Processes’. The chapter covers plant nutrition and systems like respiratory, circulatory and excretory. The students should have access to well-prepared notes so that important topics are not skipped, and the preparation is complete.
Extramarks is the most trusted platform where students get handy study notes for their studies and exam preparation from Class 1 to Class 12. Our academic subject experts understand the importance of frequently solving questions to gain a better understanding of Biology concepts. We have collated questions from different sources including NCERT textbooks, NCERT Exemplars, past year question papers, other reference books, etc.
The Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 6 covers all the vital points for students to get clear-cut insights over all the topics and sub-topics listed in the chapter. Solving questions would help students improve their performance, boost their confidence and score well in examinations.
Extramarks provide an overall engaging learning experience for school students. The originality in the content and the quality of study material make it unique, and this has helped gain the trust of lakhs of students. Our official website hosts a lot of study resources including NCERT solutions, chapter-specific notes, CBSE solved question papers, revision notes, etc. Specifically for preparing Biology Chapter 21 students can refer to our Chapter 6 Class 10 Science Important Questions study resources.
CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions 2022-23
CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions are also available for the following chapters:
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Question Answer– With Solutions
The study notes of Science Class 10 Chapter 6 Important Questions on the Extramarks website are well-structured and concisely prepared for the students. This question bank saves significant time and allows students to get access to various formats of exam-oriented questions at one place.
Below are a few questions and answers from our question bank of Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 6.
Question 1. Why is diffusion not sufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of humans?
Answer 1: In humans, diffusion is insufficient to meet oxygen requirements. Skin is in direct contact with the environment. Diffusion is a very slow process and will take longer to reach every body cell. This process cannot meet the oxygen requirements of the body.
Question 2. What criteria can determine if something is alive or not?
Answer 2: Whether an organism is alive or not should match the following characteristics:
- Moving on its own.
- Food is required to meet energy needs and nutrition.
- Respiration
- Response to the changes taking place in the environment.
- Has growth and development.
- Removal of metabolic waste from the body.
Question 3. Mentions outside raw materials used by organisms.
Answer 3: All organisms obtain oxygen, water and food from the outside environment. These are the raw materials. Plants need raw materials such as carbon dioxide and water to prepare their food by photosynthesis.
Question 4. What processes are considered essential for maintaining life?
Answer 4: The processes essential for maintaining life are nutrition, respiration, transportation, excretion and sensitivity.
Question 5. Differentiate between autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition?
Question 6. Where do plants get raw materials for photosynthesis?
Answer 6: Plants require carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, water from groundwater and solar energy from the sun.
Question 7. Mention the role of acid in the stomach.
Answer 7: Hydrochloric acid is found in our stomach. This kills the harmful germs which enter our body via food. The acid also activates the pepsin enzyme for protein digestion.
Question 8. What is the function of digestive enzymes?
Answer 8: The digestive enzymes increase the process of breaking down complex molecules into simpler ones and absorbable molecules so that body can facilitate their absorption.
Question 9. How does the small intestine absorb digested food?
Answer 9: The innermost layer of the small intestine is the finger-like projections called villi which increase the absorption surface area. These villi also comprise the blood capillaries to aid in the absorption of simple molecules from food.
Question 10. What advantages does a terrestrial organism have over an aquatic organism in obtaining oxygen for respiration?
Answer 10: The amount of oxygen in the air is more than the amount dissolved in the water. Therefore, terrestrial organisms make less effort to get oxygen than aquatic organisms.
Question 11. What are the ways of glucose oxidation to provide energy in different organisms?
Answer 11: There are two types of respiration for oxidising glucose, i.e., aerobic and anaerobic respiration. In aerobic respiration, the complete oxidation of glucose takes place. The optimum output of energy is obtained. Oxygen is required for this process.
In anaerobic respiration, the process takes place in the absence of oxygen. The complete oxidation of glucose does not take place. Bacteria exhibit this process. In our calf muscles, sometimes anaerobic respiration takes place.
Question 12. Explain oxygen and carbon dioxide transport in human beings.
Answer 12: A gas transportation system transports oxygen and carbon dioxide in human beings. This system comprises the lungs, heart, veins and arteries.
Lungs breathe in oxygen-rich air and breathe out carbon-dioxide-rich layers.
The heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygenation and distributes it to the various body parts.
Veins carry deoxygenated blood to the heart. The pulmonary vein is the exception which has oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart.
Arteries carry oxygenated blood to various parts of the body from the heart. One exception is the pulmonary artery which carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs.
Question 13. How are the lungs designed to maximise the area for exchanging gases in humans?
Answer 13: The air passage in the lungs is divided into smaller tubes called bronchi which form bronchioles. The bronchioles terminate in balloon-like structures called alveoli. These alveoli provide maximum area for the gaseous exchange. The alveoli walls are very thin and contain an extensive network of blood vessels to facilitate the exchange of gases.
Question 14. What are the components and their function in human beings?
Answer 14: A well-developed circulatory system is present in humans, including the heart, blood vessels and blood.
The heart is responsible for pumping and circulating blood in the whole body.
Blood vessels include arteries, veins and capillaries. The arteries have thick walls and carry oxygenated blood to different body parts.
Veins are thin-walled blood vessels carrying deoxygenated blood from all body parts back to the heart.
Capillaries are thin and narrow blood vessels in which the exchange of materials between the blood and the surrounding cells occurs.
Blood acts as connective tissue and transports food, oxygen, waste material and hormones.
Question 15. Why is the separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds necessary?
Answer 15: Mammals and birds are warm-blooded animals. They control body temperature and do not depend on the environment to regulate body temperature. So birds and mammals need optimum oxidation of glucose which is possible with a good supply of oxygen without mixing oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
Question 16. Name components of the transport system in organised plants.
Answer 16: The highly organised components of the transport system in plants are Xylem and phloem. Xylem contains vessels and tracheids. The phloem comprises sieve tubes and companion cells.
Question 17. How are water and minerals transported in plants?
Answer 17: The vessels and tracheids of roots, stems and leaves in xylem tissue are interconnected and form a continuous water-conducting channels.
The cells of the roots in soil contact actively take up ions, and a difference between ion concentrations is created. A steady movement of water into the root xylem from the soil creates a column of water that is pushed upwards. The plants use another strategy to move the water in the Xylem upwards to the highest point of the plant’s body.
The water lost through the stomata is replaced by water from the xylem vessel in the leaf. The evaporation of water molecules from the cells of a leaf creates a suction pulling water from the xylem cells of the roots.
This water loss is transpiration, allowing absorption and upward movement of water and minerals dissolved in it from roots to leaves. Transpiration is the major driving force in the movement of water in the Xylem Xylem during the day when the stomata are open. This mechanism is also called the cohesion of water theory or transpiration pull.
Question 18. How is food transported in plants?
Answer 18: The food is transported by phloem to the plant parts like roots, fruits, seeds and growing regions. This process is called translocation. In the phloem, sieve tubes are present, which, together with companion cells, translocate food in upward and downward directions. ATP is the energy provided for translocation.
Question 19. Describe the structure of the nephron with functioning.
Answer 19: Nephron is a long-coiled tubule. It’s one-end cup-shaped and called Bowman’s capsule. The other end connects to a urine collecting duct of the kidney. The glomerulus is a bundle of blood capillaries in the Bowman’s capsule.
A nephron is a functional unit of the kidney. It aids waste product removal and filters impure blood.
Question 20. How do plants get rid of excretory products?
Answer 20: Plants get rid of oxygen and carbon dioxide through diffusion. When the old branches and leaves become useless, they are shed off. Plants have a mechanism by which the roots release waste products. Raisins or gums are the waste products accumulated near the bark.
Question 21. How is the amount of urine produced regulated?
Answer 21: The kidney can reabsorb water from the filtrate. This mechanism depends upon the amount of water left in the body and the filtrate. The relative water concentration signals the brain based on whether water is reabsorbed or released. So this is how the kidneys regulate urine formation.
Question 22. Multiple choice questions.
- The kidneys are a part of
- Transportation
Answer 1: (c) Excretion
Explanation:
The kidneys are part of the excretory system, and nitrogenous waste like urea is removed from the blood in the kidneys.
- The Xylem in plants are responsible for:
- Transport of water
- Transport of food
- Transport of amino acids
- Transport of oxygen.
Answer 2: (a) Transport of water
The xylem is responsible for transporting water and minerals from the soil to the leaves.
- The autotrophic mode of nutrition requires
- Carbon dioxide and water
- Chlorophyll
- All of the above
Answer 3: (d) in the autotrophic mode of nutrition, carbon dioxide, water, chlorophyll and sunlight are essential for photosynthesis.
- Autotrophic organisms include
- Bacteria and virus
- Bacteria and fungi
- Green plants and some bacteria
- Green plants and all bacteria
Answer 4: (c) Green plants and some bacteria
- A gland which is not associated with the alimentary canal is
- Salivary glands
Answer 5: (d) Adrenal
- Which of the following is chiefly digested in the stomach?
- Carbohydrates
Answer 6: (b) Protein
- The large intestine in humans mainly carries out
- Assimilation
- Digestion of fats
- Digestion of carbohydrates
Answer 7: (a) Absorption
- The part of the digestive system where no digestion takes place is
Answer 8: (d) Oesophagus
- The fermentation of glucose by Yeast normally yields
- Alcohol, CO 2 and 36 ATP
- CO 2 , H 2 0 and 36 ATP
- Alcohol, CO 2 AND 2 ATP
- Lactic acid, CO 2 and 2 ATP.
Answer 9: (c) Alcohol, CO 2 AND 2 ATP
- A large quantity of one of the following is removed from our body by the lungs:
- CO 2 and H 2 O
Answer 10. (a) CO 2 and H 2 O
- A biochemical compound combined with oxygen and distributed throughout the human body is
- Haemoglobin
- Acetylcholine
Answer 11 : ( c) Haemoglobin
- The process in which water loss takes place in the form of water vapour through stomata is called.
- Transportation
- Transpiration
- Translocation
Answer 12: (b) Transpiration
- In a closed circulatory system, blood is completely enclosed within
Answer 13: (b) Heart
- Normal blood pressure (systolic/diastolic) is
- 120/80 mm of Hg
- 160/80 mm of Hg
- 120/60 mm of Hg
- 180/80 mm of Hg
Answer 14: (a) 120/80 mm of Hg
- An instrument which measures blood pressure is called.
- Sphygmomanometer
Answer 15 : (b) Sphygmomanometer
- Which of the following statement is not correct?
- Deoxygenated blood is poured into the right atrium of the heart.
- The excretory units of flatworms are flame cells.
- The human kidney has about 1 million nephridia.
- Tracheids and vessels are non-living conducting tissues.
Answer 16 : (c )The human kidney has about 1 million nephridia.
- Which part of the digestive system receives bile from the liver?
- Small intestine
- Large intestine
- Oesophagus
Answer 17: (b) Small intestine
- When air is blown from the mouth into a test tube containing lime water, the lime water turns milky due to the presence of
- Carbon dioxide
- Water vapour
Answer 18: (b) Carbon dioxide
- The filtration units of kidneys are
Answer 19: (d) Nephrons
- Oxygen liberated during photosynthesis comes from
Answer 20: (a) Water
- The opening and closing of the stomatal pores depends upon
- Temperature
- Water in guard cells
- The concentration of CO 2 in stomata
Answer 21: (c ) Water in guard cells
Question 23. Fill in the blanks:
- The ________ is where the respiratory and digestive passage come together.
- The conditions necessary for photosynthesis are ___________, _________, ___________ and ____________.
- The process in which the digested food passes through the intestinal wall into the bloodstream is called ___________
- The teeth covered with a sticky, yellowish layer of food particles and bacteria are called _______
- Iodine turns blue-black on reacting with ________
- The energy produced during respiration is stored in the form of ATP, which stands for ________
- Pyruvic acid is a three-carbon compound which is also known as _________
- The rate of breathing in ________ animals in much faster than in ________ animals
- The actual exchange of gases takes place in the _________of the lungs.
- ________ are long, thin, spindle-shaped cells with pits in their thick cell walls.
- The liquid part of the blood is called _______
- The expansion of an artery each time the blood is forced into it is called _______
- Gums and resins are the _________products of plants.
- The pharynx is where the respiratory and digestive passages come together.
- The conditions for photosynthesis are sunlight, chlorophyll, carbon dioxide and water .
- The process in which the digested food passes through the intestinal wall into the bloodstream is called absorption .
- The teeth are covered with a sticky, yellowish layer of food particles and bacteria called plaque .
- Iodine turns blue-black on reacting with starch .
- The energy produced during respiration is stored in the form of ATP, which stands for Adenosine Tri-phosphate .
- Pyruvic acid is a three-carbon compound which is also known as pyruvate .
- The rate of breathing in aquatic animals is faster than in terrestrial animals.
- The actual exchange of gases takes place in the alveoli of the lungs.
- Tracheids are long, thin, spindle-shaped cells with pits in their thick cell walls.
- The liquid part of the blood is called plasma .
- The expansion of an artery each time the blood is forced into it is called a pulse.
- Gums and resins are the waste products of plants.
Question 24. Name organisms which have an anaerobic mode of respiration.
Answer 24: Bacteria and Yeast have an anaerobic mode of respiration.
Question 25. Differentiate between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Answer 25.
Question 26. How does fat digestion take place in the body? Where does this process occur?
Answer 26: The digestion of fats takes place in the small intestine. The fat which enters the small intestine is in the form of large globules. The following steps are involved in the process:
- Large globules are broken down into small globules by bile salts.
- The lipase enzyme, which is present in pancreatic juice breaks emulsified fat.
- The pancreas secretes the pancreatic juice.
- The walls of the small intestine secrete enzymes that aid in breaking fats into fatty acids.
Question 27. What is the role of saliva in the digestion of food?
Answer 27: Saliva contains water, salts, mucin and salivary amylase, which breaks down starch present in the food into sugar.
Question 28. Mention the conditions necessary in autotrophic nutrition.
Answer 28: The following conditions are necessary for autotrophic nutrition:
- The presence of carbon dioxide carries out photosynthesis.
- Chlorophyll.
Question 29. What are the by-products of autotrophic nutrition?
Answer 29. Oxygen is the by-product of autotrophic nutrition.
Question 30. How are the alveoli designed to maximise the exchange of gases?
Answer 30: The inner surface of the lungs has smaller tubes that terminate in the alveoli, which are balloon-like structures. The extensive network of blood vessels is present in the walls of the alveoli.
There are millions of alveoli present in the lungs. The alveolus provides a large surface area for the gaseous exchange. If all the alveoli are unfolded from the two human lungs, it will give an area of about 80 square meters.
Question 31. What are the consequences of haemoglobin deficiency?
Answer 31: Haemoglobin is the oxygen carrier, so its deficiency affects the blood supply of oxygen to tissues. Anaemia show symptoms like breathlessness and tiredness with a lack of iron.
Question 32. What is double circulation in humans? Mention its importance.
Answer 32 : Humans have double circulation as the blood passes twice through the heart in one complete cycle. There are two circulations:
Pulmonary circulation begins from the right ventricle, and the blood is expelled into the pulmonary trunk. The blood reaches the vascular system of the lungs, becomes oxygenated and then returns to the heart, i.e. the left atrium through pulmonary veins.
Systemic circulation starts from the left ventricle, sending blood to the aorta. The aorta supplies the oxygenated blood to various parts of the body. The aorta divides into arteries, arterioles and then capillaries. The deoxygenated blood collected by the venules, join to form veins and vena cava finally and pour back blood into the right auricle of the heart.
The importance of deoxygenated blood is that:
- There is no mixing between the oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
- The system ensures oxygen supply efficiently.
- Maintenance of body temperature.
Question 33. What are the differences between the transportation of materials between Xylem and phloem?
Answer 33: In Xylem, the transportation of water and minerals takes place from the roots to the leaves. The conduction takes place through xylem vessels and tracheids, which are the dead tissues.
The transportation takes place in phloem from leaves to the other parts of the plant. The process is conducted through sieve tubes and companion cells.
Question 34. Compare the alveoli and nephron functioning, including structure.
Answer 34: The alveoli are balloon-like structures which are one-celled thick and comprise an extensive network of blood capillaries. The site of gaseous exchange in the lungs is the alveoli. The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs between the blood flowing in the capillaries of the alveoli and the gases present in the alveoli.
Nephrons are long tubular structures composed of nephrons, Bowman’s capsule and a long renal tube. The nephrons are the structural and functional unit of kidneys. Their main function is filtration and removing the nitrogenous blood in the form of urine.
Question 35. Name the cell organelle in which photosynthesis occurs.
Answer 35: Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplast of the plant.
Question 36. In the experiment ” light is essential for photosynthesis”, why does the uncovered part of the leaf turn blue-black after contacting iodine solution?
Answer 36: Due to starch production, the uncovered part of the leaf turns blue-black after adding iodine solution.
Question 37. What do you understand by emulsification?
Answer 37: Emulsification is the breakdown of large fat globules into small fat droplets.
Question 38. Explain the process of nutrition in amoeba.
Answer 38: The steps in the nutrition of amoeba are ingestion, digestion, assimilation and egestion.
When amoeba comes in contact with the food, it sends out pseudopodia, which engulfs the food particle forming a food cup. This process is called ingestion.
When the tips of the encircling pseudopodia touch each other, there is the formation of a food vacuole, a temporary stomach that secretes digestive juices. This step is known as digestion.
The digested food gets absorbed and diffuses into the cytoplasm and then assimilates.
The egestion of the non-digested food occurs at any point on the body surface.
Question 39. When you chew chapati for a long period, it tastes sweet after some time. Mention the reason.
Answer 39: Starch is present in chapati, converted to simple sugar by the salivary enzyme amylase. The salivary glands, via the secretion of enzymes, aid in chemical digestion.
Question 40. 1 % of starch in a test tube is added to 1 ml of saliva. After keeping the mixture for an hour, a drop of iodine solution is added. Mention the change in colour of the test tube. What does this indicate about the salivary action on starch?
Answer 40: There is no change in colour when adding the iodine solution. Saliva breaks down starch into simple sugar, which does not react with the iodine solution to produce any colour.
Question 41. How is digestion affected when the bile duct is completely blocked? Explain
Answer 41 : On blockage of the bile duct, digestion of fats is affected as the bile juice will not reach the small intestine.
Question 42. Why do the trachea walls not collapse when there is less air in them?
Answer 42: The rings of the soft cartilage bones do not allow the trachea to collapse when air is in it.
Question 43. What are enzymes?
Answer 43: Enzymes are the biological catalysts that increase the reaction rate without being used up.
Question 44. Mention the name of one digestive enzyme with its function.
Answer 44: Salivary amylase catalyses the breakdown of starch into sugar in the mouth and small intestine.
Question 45. Explain the cause of cramps after excessive physical exercise.
Answer 45: During excessive physical exercise, aerobic respiration produces energy in our muscles. Anaerobic respiration provides muscles with some extra energy required under excessive physical activity. Glucose is broken down into lactic acid due to anaerobic respiration. The accumulation of lactic acid causes muscle cramps.
Question 46. Explain the process of digestion.
Answer 46: Digestion occurs in the mouth, stomach and small intestine. The process can be explained as follows:
The digestion begins in the mouth. The saliva contains salivary amylase, which breaks down starch into sugar.
Stomach stores and mix the food with gastric juices. The gastric juice contains hydrochloric acid, mucus and pepsin. Hydrochloric acid dissolves food and creates an acidic medium for the action of pepsin. The pepsin digests protein, and the mucus protects the inner lining of the stomach from the action of hydrochloric acid.
In the small intestine, there occurs complete digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. The small intestine wall contains glands which produce intestinal juice. This juice helps in the digestion of the food further. The small intestine obtains digestive juices from the liver and pancreas, which helps mix food.
The bile juice produced by the liver causes the emulsification of fats. The pancreas produces pancreatic juice for the digestion of proteins and emulsified fats.
The digested food is absorbed through intestinal walls.
Question 47. Name the site where complete digestion of food takes place in the alimentary canal.
Answer 47: Small intestine is that part of the alimentary canal where complete digestion of food takes place.
Question 48. Explain the breakdown of glucose in a cell in the presence and absence of oxygen.
Answer 48: Glucose can be broken down in three different ways.
In the absence of oxygen, like in Yeast, pyruvate is converted to ethanol, carbon dioxide and energy. This is called fermentation.
In the case of insufficient oxygen, like in muscle cells, pyruvate converts to produce lactic acid and energy.
In the presence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted into carbon dioxide, water and energy in mitochondria.
Ethanol is a two-carbon molecule, and lactic acid is a three-carbon molecule.
The first step, glucose breakdown in both the presence and absence of oxygen, is the same. More energy is released in the presence of oxygen.
In the absence of oxygen, anaerobic respiration occurs in the muscle cells. The building of lactic acid in muscle cells causes painful muscle contraction, called cramps.
Question 49. The breathing cycle is rhythmic, whereas the gaseous exchange is a continuous process. Justify the statement.
Answer 49 : The lungs always have a continuous residual air volume, so oxygen absorption and carbon dioxide release become a constant process.
Question 50. What happens when a leak is developed in the conducting tubes of the circulatory system? How can this be avoided?
Answer 50 : The circulatory system loses it efficiency if it develops a leak. This could be avoided by maintaining normal blood pressure.
Question 51: What is hypertension? What causes it, and how can it cause damage to the body?
Answer 51: High blood pressure is also called hypertension. It occurs due to the constriction of very small arteries, resulting in blood flow resistance.
Hypertension could cause an artery to rupture and cause internal bleeding.
Question 52. In a single-celled organism, diffusion is sufficient to meet all the requirements of food, gas exchange and waste removal, but it is not the case in multicellular organisms. Explain the reason for this difference.
Answer 52: In single-celled organisms, there is no specific organ related to food intake, gas exchange or waste removal. This is because the entire surface of the organism is in contact with the environment.
In multicellular organisms, the skin cells directly interact with the environment. Diffusion is a slow process that takes a very long time to reach all body parts, and it is insufficient to meet oxygen requirements.
Question 53. Mention the three kinds of cells present in blood and write one function of each.
Answer 53: There are three types of cells present in the blood. They are red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets.
Red blood cells are biconvex and contain haemoglobin to transport oxygen from the lungs to body cells and take carbon dioxide from the cells to the lungs.
White blood cells are the body’s defence cells and fight against diseases and infections.
Platelets are responsible for blood clotting during injuries.
Question 54. What are the three types of blood vessels? Mention one important feature of each.
Answer 54: The human circulatory system has three types of blood vessels. These are arteries, veins and capillaries.
Arteries carry oxygenated blood from the heart to different parts of the body. They are thick-walled.
Veins carry deoxygenated blood from various organs to the heart. Veins are thin-walled.
Capillaries are responsible for exchanging material between the blood and the surrounding cells. They are thin-walled and narrow tubes which connect arteries to veins.
Question 55. Write one function of the following:
- Blood vessels
- Blood vessels are all connected to form a closed circulatory system
- The lymph is responsible for carrying digested and absorbed fat from the intestine and drains excess fluid from extracellular space back into the blood.
- The heart is a pumping organ that receives blood from veins and pumps it into the arteries.
Question 56. What is blood pressure? Measuring it gives one point of difference between systolic and diastolic pressure.
Answer 56: Blood pressure is the force exerted against a vessel’s wall. This pressure is greater in arteries than the veins.
A sphygmomanometer measures blood pressure.
The pressure of blood inside the artery during contraction of ventricular systole is called systolic pressure, and the pressure in the artery during the relaxation, or ventricular diastole, is the diastolic pressure. The normal systolic pressure is 120 mm of Hg, and the diastolic is 80 mm of Hg.
Question 57: State the role of following in the human digestive system.
- Digestive enzymes
- Hydrochloric acid
Answer 57 .
- Digestive enzymes are responsible for digesting the food we eat.
- Hydrochloric acid creates an acidic medium to aid in the action of the pepsin enzyme.
- Villi increase the surface area to aid in food absorption.
Question 58. Why are the walls of the ventricles thicker than the auricles?
Answer 58: Ventricles must pump blood to all the body parts during the contraction. To counteract the backward pressure exerted by the blood, it is essential to have thicker walls to prevent the heart’s bursting.
Question 59. Write three events that occur in photosynthesis.
Answer 59: The three events are:
- Light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll.
- Conversion of light energy to chemical energy. There is the splitting of water into hydrogen and oxygen.
- Reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates.
Question 60. How do guard cells open and close stomatal pores?
Answer 60: The opening and closing of the stomatal pore is a function of the guard cells. There is swelling of guard cells when the water flows into them, causing the opening of the stomatal pore. The pore closes if there is shrinkage of the guard cells. There is a loss of large amounts of water through these stomata. The plant closes these pores when carbon dioxide is not required for photosynthesis.
Guard cells become turgid and flaccid based on the water entering and leaving.
Question 61. How are pH maintained in the stomach and the small intestine?
Answer 61: HCL is released by the gastric glands present on the walls of the stomach. This creates an acidic medium to facilitate the action of pepsin. Bile juice makes food alkaline in the small intestine for the pancreatic enzymes to act.
Question 62. Differentiate between inhalation and exhalation.
Answer 62: In inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and is pulled down and flattened—the volume of the thorax increases.
In exhalation, the diaphragm relaxes and is pushed back to its original position. There is a decrease in the volume of the thorax.
Question 63. What is the role of the liver and pancreas?
Answer 63: The liver secretes bile juice to break down fat into fat globules. The pancreas secretes pancreatic juice, which contains protein-digesting and starch-digesting enzymes.
Question 64. Name the organ which performs:
- Absorption of digested food.
- Absorption of water.
- The digested food is absorbed in the ileum of the small intestine.
- The water is absorbed in the large intestine.
Question 65. Answer the following:
- Write the mechanism by which fish breathe in water.
- Name the balloon-like structures present in the lungs and mention their function.
- Name the respiratory pigment and write its role in human beings.
Fishes breathe by gills through diffusion.
Alveoli are balloon-like structures. They provide a surface area for exchanging gases, and they contain a residual volume of air and sufficient time for exchanging gases.
Haemoglobin is the respiratory pigment that transports oxygen through the blood.
Question 66. List four conditions required for efficient gas exchange in an organism.
Answer 66: The required conditions are:
- Presence of extensive membrane.
- Thin membrane
- Highly vascularised membrane.
The membrane should be easily permeable to oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Question 67. Trace the movement of oxygenated blood in the body.
Answer 67: The pulmonary vein brings oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium.
When the atrium contracts, the blood is transferred to the left ventricle. When the ventricles contract, blood is pushed into the aorta and through arteries to all body parts.
Question 68. Write the function of valves present in between atria and ventricles.
Answer 68: The valves present prevent the backflow of blood from the ventricles into the atria.
Question 69. Answer the following questions:
- Define excretion
- Name the basic filtration unit of kidneys.
- State the function of the bile juice.
- Mention the end products formed on complete digestion of proteins, carbohydrates and fats.
- What happens to glucose in the nephron along with the filtrate?
- Excretion is the biological process which removes harmful waste products from the body.
- Nephrons are the basic filtration unit in the kidneys.
- Bile juice contains bile pigments and bile salts that emulsify fat to the fatty acids. Bile juice also neutralises the acidic food in the stomach and makes it alkaline so that it can react with the enzyme of the pancreatic juice.
- The end products formed on complete digestion of proteins, carbohydrates and fats are amino acids, glucose and fatty acid with glycerol respectively.
- The blood capillaries surrounding the nephron reabsorb the glucose that enters the nephron.
Question 70. Name the following:
- The process in plants links light with chemical energy.
- An organism that can prepare its food.
- The cell organelles where photosynthesis occurs.
- Cells that surround a stomatal pore.
- Organisms that cannot prepare their food.
- An enzyme secreted from the gastric glands in the stomach acts on the proteins.
- What causes the movement of food into the alimentary canal?
- Photosynthesis
- Chloroplast
- Guard cells
- Heterotrophs
- Peristalsis
Question 71. “All plants give out oxygen during day and carbon dioxide during night.” Give reason.
Answer 71: Yes, this is because respiration occurs throughout the day and night, but photosynthesis occurs only during the day because one of the most integral components needed for photosynthesis is sunlight. During the day, plants give out oxygen, a product of photosynthesis. Thus, plants give carbon dioxide during the nighttime, when there is no photosynthesis.
Question 72. Two green plants kept separately in oxygen-free containers, One in the dark and the other in continuous light. Which one lives longer? Give reasons.
Answer 72. The plant in continuous light will live longer because, in the presence of light, the plants will undergo photosynthesis and can convert carbon dioxide to oxygen. The plant in the dark cannot survive longer. This is because, in the absence of light, the plant cannot perform photosynthesis, and the plant will die.
Question 73. Why do fish die outside water?
Answer 73: Fishes die when taken out of water. This is due to the inability to obtain gaseous oxygen. The fish breathe through gills richly supplied with blood capillaries and readily absorb oxygen dissolved in water.
Question 74. Is nutrition a necessity for an organism? Discuss
Answer 74: Yes, nutrition is a necessity for an organism. This is because of the following reasons:
Nutrition has a role in the growth and repair of cells.
It is important to develop resistance to diseases.
Nutrition provides us with the energy for various metabolic activities of our body.
Nutrition is a source of energy to carry out the activities.
Question 75. What happens when green plants disappear from the earth?
Answer 75 : If the green plants disappear from the earth, the herbivore will die of starvation, followed by carnivores and decomposers. Green plants play an important role in converting solar and chemical energy. They are the main source of energy for all heterotrophs. Plant disappearance will create a huge disbalance in the ecosystem.
Question 76. Leaves of a healthy potted plant were coated with Vaseline. Will this plant remain healthy for a long? Give a reason for your answer.
Answer 76: The Vaseline-coated plant will die soon because the layer of Vaseline will prevent the exchange of gases for respiration.
The coating will close the stomatal openings, and the plant won’t be able to get the necessary raw material for photosynthesis. Due to the clogging of stomatal pores, the plant will die due to cessation of respiration.
Question 77. What are the characteristics of a leaf for photosynthesis?
Answer 77: The adaptation is given below:
- Leaf has a large surface area to aid in maximum absorption of light.
- Arrangement of leaves to absorb the optimum amount of light.
- A greater number of veins are important for providing mechanical support.
- Veins participate in quickly transporting substances to and from the mesophyll cells.
- The leaf is the site of transpiration and cools the leaf surface for optimum photosynthesis.
- Numerous stomata are present, which are beneficial in gaseous exchange.
- A large number of chloroplasts are present on the upper surface of leaves.
Question 78. Why do herbivores have longer small intestines than carnivores?
Answer 78 : Cellulose is difficult to digest and takes longer for complete digestion, so herbivores need a long small intestine. Meat is easier to digest; hence, carnivores like tigers have a shorter small intestine.
Question 79. What happens when the gastric glands do not secrete mucus?
Answer 79: If the gastric glands do not secrete mucus, there will be corrosion of the inner lining of the stomach, thereby causing acidity, ulceration and extreme discomfort. This is because mucus protects the stomach’s inner lining from the action of hydrochloric acid and the enzyme pepsin.
Question 81. Why does absorption of digested food occur in the small intestine?
Answer 81: This is because of the following reasons:
- The digestion of food is completed in the small intestine.
- The small intestine’s inner lining has villi, which are finger-like projections, and increase the surface area in absorption.
- The intestine wall has blood vessels that carry the absorbed food to various parts of the body.
Question 82. Why is the breathing rate in aquatic organisms much faster than in terrestrial organisms?
Answer 82: This is because the amount of oxygen dissolved in water is low compared to the amount of oxygen present in the air. Aquatic animals take water through their mouth and pass it to the gills, where the blood takes up the dissolved oxygen.
Question 83. What is the advantage of a four-chambered heart?
Answer 83: The advantage of a four-chambered heart is that it prevents the oxygenated and deoxygenated blood from being mixed. The left side of the four-chambered heart is completely separated from the right side of the heart by septa. This mechanism is useful for animals with high energy needs, like birds and mammals. This mechanism also ensures the efficient supply of oxygenated blood to all body parts.
Question 84. In each of the following situations, what happens to the rate of photosynthesis?
- Cloudy days
- No rainfall in the area
- Good manuring in the area
- Stomata get blocked due to duct
Answer 84:
- Photosynthesis is reduced due to the low intensity of the light.
- The rate of photosynthesis is not affected in the case of no rainfall.
- When manuring is done, soil fertility is increased, but the rate of photosynthesis is not affected.
- When the stomata are blocked, the rate of photosynthesis is reduced. This affects carbon dioxide availability.
Question 85. Name the energy currency in the living organisms and where it is produced.
Answer 85: Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) is the energy currency of living organisms. It is produced during respiration and also during photosynthesis. The site of ATP production is mitochondria during the process of respiration.
Question 86. What is common in Cuscuta, ticks and leeches?
Answer 86: They all are parasites and derive their nutrition from the host by harming them but without killing them.
Question 87. What are the functions of the gastric glands present in the walls of the stomach?
Answer 87: The functions of gastric glands are as follows:
- Secrete mucus to protect the stomach.
- Secretion of hydrochloric acid to make the food soft and acidified allows pepsin to act upon the food.
- Secretion of the enzyme pepsin that digests proteins.
- Hydrochloric acid kills the germs present in the food.
- Hydrochloric acid reduces the stomach pH to make the environment suitable for the digestive glands to act.
Question 88. Plants have low energy needs as compared to animals. Explain.
Answer 88: Plants have low energy requirements because they do not move, and most of the body is made up of dead cells like sclerenchyma. Animals require energy because they move in search of food and shelter.
Question 89. Water enters continuously into the root xylem. Explain
Answer 89: The root cells are in contact with the soil, so they are active in taking up the ions. These ions pass inward, increasing osmotic concentrations of Xylem. Because of this, the water continuously passes into the root xylem from the soil. Water is responsible for photosynthesis, and its continuous flow is related to the transpiration pull.
Question 90. How do the leaves of plants help in the process of excretion?
Answer 90: The waste material in leaves is present in the vacuoles of mesophyll and epidermal cells. When old leaves fall, the waste material goes along with the leaves. Secondly, the transpiration of gases via stomata helps remove gaseous waste products of respiration and photosynthesis.
Question 91. Why is soil important for plant growth?
Answer 91 : The importance of soil for the growth of plants is:
- The base for plant growth and allows root penetration.
- Source of organic material, which is essential for plant growth.
- Soil provides water and minerals for plants.
- It establishes symbiotic associations with microbes.
- Aids in the respiration of root cells due to the availability of oxygen in food materials.
Question 92. Describe the alimentary canal of man.
Answer 92: The length of alimentary canals is 9 meters. It consists of:
- The mouth leads to the buccal cavity. The tongue has taste buds. Teeth are present in both jaws. The four types of teeth present are incisors, canines, premolars and molars. There is a total of 32 teeth in number.
- The pharynx is a short and conical region.
- The Oesophagus is a narrow, long, muscular tube leading to the stomach.
- The small intestine is a convoluted tube, and it has three regions. The first part is the stomach which is curved and C-shaped. The jejunum is longer and coiled. The last part is the ileum, whose inner surface is folded to form villi which absorb the products of digestion.
The large intestine is short and wide. It has three regions: caecum, colon and rectum. The caecum is a small and rounded blind sac which gives rise to the vermiform appendix, the colon is inverted U-shaped, and the rectum opens exteriorly through the anus.
Question 93: Multiple choice questions:
- Which statement about autotrophs is incorrect?
- They synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll.
- They store carbohydrates in starch form.
- They convert carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates in the absence of sunlight.
- They are the first trophic level in food chains.
Answer: (c) convert carbon dioxide and water without sunlight into carbohydrates.
Explanation:
This is because autotrophs need sunlight to convert carbohydrates without sunlight.
- 2 . In which of the following groups of organisms are food materials broken down outside the body and absorbed?
- Mushroom, green plants, amoeba
- Yeast, mushroom, bread mould
- Paramecium, amoeba, Cuscuta
- Cuscuta, lice, tapeworm
Answer: (b) Yeast, mushroom and bread mould.
Saprophytes break down the food outside the body, so the correct answer is Yeast, mushroom and bread mould as they are the saprophytes.
3.Select the correct statement.
- Heterotrophs do not synthesise their food.
- Heterotrophs utilise solar energy for photosynthesis.
- Heterotrophs synthesise their food.
- Heterotrophs convert carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates.
Answer: (a) Heterotrophs do not synthesise their food.
The heterotrophs depend on phototrophs or other organisms to obtain their food.
- If salivary amylase is absent in saliva, this affects which event in the oral cavity?
- Protein breaks down into amino acid
- Starch breaking down into sugar
- Fats breaking down into fatty acids and glycerol
- Absorption of vitamins
Answer : (b) starch breaking down into sugar.
Salivary amylase plays an important role in digestion. It breaks down starch into sugar. This digestive function would be affected in the absence of salivary amylase.
- A few drops of iodine solution added to rice water turned the solution into a blue-black colour. What does this indicate that rice water contains:
- Complex proteins
- Simple proteins
Answer: (d) Starch
Amylose and amylopectin are present in starch. When iodine is added to starch, a blue colour is produced because the amylose component of starch reacts with iodine. This colour complex indicates that starch is present in the rice water.
- Where does the final digestion of food take place?
- Mouth cavity
Answer: (d) small intestine
The digestion starts in the mouth. In the small intestine, complete digestion takes place, and in the large intestine, digestion does not occur.
- What is the function of pancreatic juice? Choose from the following:
- Lipase digest carbohydrates, and the proteins are digested by trypsin.
- Trypsin is responsible for digesting emulsified fats and lipase proteins.
- Fats are digested by trypsin and lipase.
- Trypsin digests proteins and lipase-emulsified fats.
Answer: (d) trypsin digests proteins and lipase-emulsified fats.
Trypsin digests protein by breaking it down into proteins and polypeptides. Fatty acids and glycerol are produced on fat emulsification by lipase.
- When is air blown from the mouth into a test tube which contains lime water, due to the presence of which the following, lime water turns milky?
Answer 8: (b) carbon dioxide
When carbon dioxide and water react, it turns milky.
- Which of the following statements about respiration are true?
- Ribs move inward, and the diaphragm is raised in inhalation.
- The gaseous exchange occurs in the alveoli. The oxygen from the alveolar air diffuses into the blood, and carbon dioxide from the blood into the alveolar air.
- Haemoglobin has a greater affinity for carbon dioxide compared to oxygen.
- The surface area of the alveoli increases for gaseous exchange.
Answer: (d) ii and iv are correct.
Statement i is wrong due to the outward movement of ribs and lowered diaphragm movement during inhalation. Option iii is wrong as haemoglobin has more affinity for oxygen than carbon dioxide.
- Where does the exchange of gases take place during respiration?
- Throat and larynx
- Alveoli of lungs
- Trachea and larynx
Answer: (b) alveoli of lungs
Alveoli are responsible for the exchange of gases during respiration. From the alveoli, there is the diffusion of oxygen into the blood. The larynx and trachea are passages for air movement.
- What prevents the backflow of blood inside the heart during contraction?
- Valves in heart
- Wall of ventricles
- Wall of atria
- All of these
Answer (a) valves of the heart
The thick walls of ventricles and thin walls of atria are responsible for blood pumping. They have no role in preventing the backflow of blood inside the heart during contraction.
- Single circulation, i.e., blood flows through the heart only once during one cycle of passage through the body, is exhibited by which of the following groups?
- Labeo, Chameleon, Salamander
- Hippocampus, Exocoetus, Anabas
- Hyla, Rana, Draco
- Whale, Dolphin, Turtle
Answer 12: (b) Hippocampus, Exocoetus, Anabas
Partial double circulation is present in reptiles and amphibians, which have three-chambered hearts in options a and c. In option d, the whale is a mammal, and the turtle is a reptile, so it is incorrect.
- In which of the following is oxygenated blood not pumped to different body parts?
- Pisces and amphibians
- Amphibians and reptiles
- Amphibians only
- Pisces only.
Answer: (d) Pisces only.
Deoxygenated blood from all body parts is pumped into the heart through single circulation. The heart pumps this blood into the gills, where it gets oxygenated.
Question 94. Mention the adaptation of leaves to carry out photosynthesis.
Answer 94 : The leaf surface is flat to increase light exposure. To trap sunlight, chlorophyll is present. Transpiration takes place through stomata.
Question 95. What will happen if the platelets are absent in the blood?
Answer 95: Platelets are responsible for the clotting of blood. In the absence of platelets, the blood will not clot. This will increase the severity in cases of injury and may prove to be life-threatening.
Question 96. Mention the importance of transpiration in plants.
Answer 96 : The transpiration carries the following:
To facilitate the ascent of sap, transpiration pull is created.
The rise of sap is important to ensure water availability in photosynthesis.
Plants get rid of excess water due to transpiration.
Question 97. Explain the breathing process in human beings.
Answer 97 : There are two processes of breathing in human beings:
Inhalation is the process in which oxygen is taken in. Ribs come out in this process. The diaphragm moves down. There is an increase in the volume of the lungs and a decrease in pressure. Due to this, the air moves towards the lungs.
Exhalation is the process in which carbon dioxide is given out. The ribs go down, and there is an upward movement of the diaphragm: the pressure increases, and the volume of the lungs decreases. As a result of this, the air moves out of the lungs.
- Explain the functions of:
1.The functions of blood are:
- Transportation of oxygen to the tissues of the body.
- Transports absorbed nutrients.
- Carries nitrogenous waste to the kidneys
- Regulation of body temperature
- Maintenance of body pH.
- Maintains water balance.
- Lymphocytes produce antibodies to protect and fight against diseases.
- Blood allows the healing of wounds as it contains platelets.
2.The functions of lymph are:
- It carries digested and absorbed fat from the intestine.
- Drainage of excess fluid from extracellular space into the blood.
- Kills germs and protects the body.
3.The functions of the lungs are:
- Take in oxygen and give out carbon dioxide.
- Purification of blood as they remove carbon dioxide from it.
Question 99. Explain heterotrophic nutrition. What are the types of heterotrophic nutrition? Explain with examples.
Answer 99: Heterotrophic nutrition is a type of nutrition where an organism derives its food from another living organism.
There are three types of heterotrophic nutrition:
In saprophytic nutrition, nutrients are obtained from dead and decaying organic matter. Examples are fungi, Yeast and bacteria.
In parasitic nutrition, the mode of obtaining food is synthesised by the others. The parasite is the organism which obtains food. This type of nutrition is seen in fungi, bacteria, plants like Cuscuta and animals like roundworms and plasmodium.
Holozoic nutrition is seen in amoeba, frogs and human beings. In this, complex organic matter in the form of solid food is ingested, digested and absorbed into the cells utilised by the body.
Question 100. Name the sources from which plants obtain nitrogen to synthesise proteins and other compounds.
Answer 100: The two sources are inorganic nitrates or nitrites and organic compounds prepared by bacteria from atmospheric nitrogen.
Question 101. Amphibians or many reptiles have three-chambered hearts and can tolerate mixing oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. Why?
Answer 101: The body temperature of cold-blooded animals depends upon the environment’s temperature. They do not require much energy as they do not maintain their body temperature. The energy produced is less when oxygenated and deoxygenated blood is mixed. This is seen in amphibians and reptiles.
Question 102. What is the function of the ureter, urinary bladder and urethra?
Answer 102: Urine formation is carried by the ureter to the urinary bladder in each kidney. The glucose, amino acid, salt and water is reabsorbed in the ureter.
The urinary bladder store urine, so it is a reservoir. The urine passes out from the body through the urethra.
Question 103. What is ATP, and what is its use?
Answer 103: ATP is a nitrogenous compound used as a fuel in various cell activities.
Question 104. What are the functions of the large intestine?
Answer 104: The functions of the large intestine are as follows:
The large intestine walls absorb water and electrolytes from undigested food.
Formation and storage of faeces.
Question 105. How do unicellular organisms remove waste?
Answer 105: The waste is removed by diffusion in unicellular organisms.
Question 106. Why is the colour of urine yellow?
Answer 106: Urine is yellow due to urea, uric acid and ammoniacal salts.
Question 107. Answer the following questions:
- What is the importance of systemic circulation in organisms?
- Where is the heart located?
- What does heartbeat mean?
- What is the largest artery of the body?
- Give one synonym for high blood pressure.
- Which is the liquid part of the blood.
- Which component of blood is responsible for clot formation?
- What is transpiration?
- What is translocation?
- Which tissue transports soluble products of photosynthesis in a plant?
- Which tissue transports water and mineral in a plant.
- Name the excretory products in plants.
- What do you mean by artificial kidney?
- In which part of the alimentary canal does digestion not occur?
- Where does the digestion of fats take place in the body?
Answer 107:
- The systemic circulation circulates oxygen and removes waste materials from the body.
- The heart is located in the thoracic cavity above the diaphragm between the two lungs.
- Heartbeat refers to the rhythmic expansion and contraction of the heart.
- The largest artery is the aorta.
- High blood pressure is also called hypertension.
- Plasma is the liquid part of the blood.
- Platelets are responsible for clot formation.
- Transpiration means water loss in the form of water vapour from the aerial parts of the plant.
- Translocation is food transport from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
- Phloem transports soluble products of photosynthesis.
- Xylem transports water and minerals in a plant.
- Resins and gums are the excretory products of the plant.
- An artificial kidney is a device which removes the nitrogenous waste products from the blood of a person whose kidneys are damaged with a process called dialysis.
- Digestion does not occur in the large intestine of the alimentary canal.
- The small intestine is the site where the digestion of fat occurs.
Question 108. State whether true or false:
- The glomerulus acts as a dialysis bag.
- Bowman’s capsule is found in the heart.
- The peristaltic movement occurs in the mouth to push food into the alimentary canal.
- The release of energy in aerobic respiration is less when compared to the anaerobic process.
- Before testing the presence of starch, chlorophyll removal must be done from the leaf because it interferes due to its green colour.
- When the absorbed food is taken in by the body cells and used for growth and repair is called egestion.
- The cytoplasm is the site for aerobic respiration.
- Plant respiration is a faster process compared to the slow process in animals.
- Carbohydrates are digested by enzymes present in both saliva and pancreatic juice.
- The small intestine length in a human adult is about 3.5 m
Answer 108:
- False. Bowman’s capsule is present in the kidneys.
- False. Peristaltic movement bring food down the pipe into the stomach.
- False. The energy released in aerobic respiration is more than in anaerobic respiration.
- False. The site for aerobic respiration is mitochondria.
- False. The rate of respiration is fast in animals compared to plants.
- False.The small intestine is long when compared to large intestine. The length is about 6.5meters in a human adult.
Question 109: What are stomata?
Answer 109: Stomata are the tiny pores or opening present on the surface of the leaf. They are responsible for exchanging gases between plants and the atmosphere.
Question 110. Why is anaerobic respiration inefficient?
Answer 110: There is an incomplete breakdown of glucose in anaerobic respiration, so less energy is produced. Therefore it is less efficient.
Question 111. What are the consequences of the diaphragm rupture of a person in an accident?
Answer 111: This will lead to immediate death due to respiratory failure.
Question 112. Why is smoking harmful?
Answer 112 : Cilia are tiny hair-like structures present in the upper part of the respiratory system. They remove dust and other particles which enter the body via inhalation. These cilia are damaged by smoking. Due to this, harmful substances like smoke, dust and chemicals enter the lungs and cause cough and respiratory infections. Smoking causes lung cancer. In lung cancer, the lungs erode faster and fail to perform their normal functions.
Question 113. Describe the circulatory system of fish.
Answer 113 : The heart of fish contains one atrium and one ventricle. Gills carry out the function of oxygenation. The heart supplies blood to the gills, where the blood gets oxygenated and is provided to the rest of the parts of the body.
Question 114. How does paramoecium obtain food?
Answer 114 : Paramoecium, a unicellular organism, has a definite shape. The food particle moves into the mouth by moving thin hair-like structures called cilia on the entire surface of the paramecium cell.
Question 124: What are peristaltic movements?
Answer 124: This is defined as the contraction and relaxation of muscles in the food pipe. This brings food pipe food down into the stomach.
Benefits Of Solving Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 6
The key to scoring good marks is a thorough understanding of all concepts covered in the chapter and regular revisions. Our chapter notes are very helpful for the students to gain a deep insight on tough topics in a very easy manner. By solving questions from our question bank of Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 6, students can fully prepare themselves properly for their examinations.
Below are some benefits of solving Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Important Questions:
- The solutions given to all questions have well-explanatory answers with labelled diagrams. This is a very crucial part of learning and memorising long-form Biology topics.
- The language used in the answers given in our Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 6 is easy to understand for students and enables them to understand complex topics in a much simpler and easy-to-remember format.
- Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 6 is a set of carefully selected questions by experienced Science faculty members. Our experts have prepared these questions after considering the past year’s questions and examining several CBSE textbooks.
Extramarks platform has many other study materials that students can refer to during their studies. We have comprehensive study solutions for students from Class 1 to Class 12. Below are a few links which they can explore:
- NCERT textbooks
- CBSE additional questions
- CBSE syllabus
- CBSE revision notes
- Important formulas
- CBSE past year question papers
- CBSE sample papers.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
Q.1 Inner wall of alimentary canal is not digested by the digestive enzymes. Why?
The inner wall of the alimentary canal is not digested by the digestive enzymes because the inner wall of the alimentary canal is lined by a wall of epithelial cells that secrete mucous. This mucous layer acts as the first line of defence.
Q.2 Which of the following organisms is a link between the living and the non-living organism?
(a) Bacteria
(b) Protozoa
Viruses are considered at the borderline of living and non-living because they show both the characteristics of a living and a non-living. As they act as non-living in the free atmosphere, when they enter into a living organisms body, they show the features of a living organism and start reproduction.
Q.3 The process by which an artificial kidney removes harmful waste products from the blood is ________________.
(a) haemolysis
(b) dialysis
(c) osmosis
(d) phagocytosis
Marks: 1 Ans
Artificial kidney is used in case of kidney failure. It is a device used to remove harmful waste products from the blood through dialysis.
Q.4 Kidneys are not only the organs of excretion. Their work is supplemented by
(b) large intestine
Skin also helps in the excretion of waste materials in the form of sweat.
Q.5 What will happen if CO 2 is absent during the process of photosynthesis?
In the absence of CO 2 during photosynthesis, there will neither be food production nor the release of oxygen into the atmosphere.
Please register to view this section
Cbse class 10 science important questions, chapter 1 - chemical reactions and equations.

Chapter 2 - Acids, Bases and Salts
Chapter 3 - metals and non-metals, chapter 4 - carbon and its compounds, chapter 5 - periodic classification of elements, chapter 7 - control and coordination, chapter 8 - how do organisms reproduce, chapter 9 - heredity and evolution, chapter 10 - light reflection and refraction, chapter 11 - human eye and colourful world, chapter 12 - electricity, chapter 13 - magnetic effects of electric current, chapter 14 - sources of energy, chapter 15 - our environment, chapter 16 - management of natural resources, faqs (frequently asked questions), 1. which are the chapters covered in cbse class 10 science syllabus.
Many important chapters that form the base of Class 11 and Class 12 Science are covered in CBSE Class 10 Science syllabus. Below is a complete list of these sixteen chapters:
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts
- Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
- Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds
- Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
- Chapter 6 Life Processes
- Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
- Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce?
- Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution
- Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
- Chapter 11 The Human Eye and The Colorful World
- Chapter 12 Electricity
- Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 14 Sources of Energy
- Chapter 15 Our Environment
Chapter 16 Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
2. What type of questions are covered in Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 6?
The questions covered in the Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 6 are from the chapter ‘Life Processes’ and based on the topics given below:
- Plant Nutrition
- Aerobic and anaerobic respiration
- Respiratory system
- Excretory system
- Digestive system
3. How to attempt Science questions in an exam?
Students must clearly understand the topic to properly answer any question in Science and score good marks. The students should revise the subject multiple times. Students should also practice by drawing well-labelled diagrams. Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 6 gives an opportunity for students to prepare the topic thoroughly and score good marks.
CBSE Related Links

Fill this form to view question paper
Otp verification.
Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Important Questions
Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Important Questions of Control and Coordination. The sets of 10th Science Chapter 6 Extra Questions contains all the intext questions, keyword based questions and questions form school tests for the exam preparation in academic session 2024-25.
10th Science Chapter 6 Important Questions Set – 1
What is the function of receptors in human body what are the types of receptors.
Animal receive a variety of external information through specialized structures called receptors located in our sense organs. These are: (i) Photoreceptors: they detect light. (ii) Phonoreceptors: they detect sound. (iii) Olfactoreceptors: they detect smell. (iv) Gustatory receptors: they detect taste.
What problem are likely to occurs if receptors do not work properly?
Receptors usually present in sense organ aware us about change in the environment. So that our body can represented according to the sensation our receptors convey. Suppose is you touching a hot object is not conveyed immediately and properly due to the malfunctioning of receptors of touch it may become a very dangerous situation for us.
Which structure in a neuron helps to conduct a nerve impulse: (i) Toward the cell body? (ii) Away from the body?
(i) Dendrites conduct a nerve impulse toward cell body(cyton). (ii) Axon conduct a nerve impulse away from the cell body.
What is the role of dendrites?
The role of dendrites is to carry nerve impulse towards the cell body of a neuron. It receives information from axon of other neuron through synapsis.
What is the role of axon?
Axon conducts impulses away from the cell body to anther neuron or tissue through synapsis.
Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Important Questions with explanation and answers. There are too many sets of Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Extra Questions with are important for school tests as well as terminal exams.
The Cerebrospinal Fluid
Inside the brain, he space between membranes is filled by a fluid. This fluid is called cerebrospinal fluid. It protects the brain from mechanical shocks.
10th Science Chapter 6 Important Questions Set – 2
Differentiate between sensory neurons and motors neurons..
Sensory neurons carry impulse from receptors to the nerve cell body or to the region which receives sensory impulses. Whereas motor neurons carry information of action to be carried by the conversed voluntary muscles.
How is brain protected in our body?
Human brain is lodged in a bony case, the cranium which protected it from injuries. It is wrapped in three sheets of connective tissue, known as meninges. The space between the meninges is filled with cerebrospinal fluid which helps in absorption of shocks.
Name the part of the brain responsible for precision of voluntary actions and maintaining body posture and balance of the body.
Fore-brain is responsible for precision of voluntary action. Cerebellum is responsible for maintaining the posture and keeping balances of the body.
Ram has met with an accident after that he lost the capacity to (i) Walk in straight line, (ii) smell anything (iii) does not feel full eating Which part of brain is damaged in each case?
(i) Cerebellum is hurt which affects walking in straight line. (ii) Smelling part of fore-brain is injured. (iii) The sensation of feeling full after eating is because of a centre associated with hunger. It is in a separate part of the fore-brain. The sensation of not feeling full is because of injury to this center present in fore brain.
Which part of the controls involuntary actions? Write the function of any two regions of it.
Involuntary actions are controlled by the mid-brain and the hind-brain. Example (i) Involuntary actions such as blood pressure, salivation and vomiting are controlled by the medulla in the hind brain. (ii) Mid-brain controls optic reflex such as change in the size of the pupil.
Answers of important questions of class 10 science chapter 6 are done properly. If someone fine any error, please inform us for improvement and correction. Before doing these questions, students need to revise Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Solutions .
The junction points between two neurons are called synapses. It is the junction between the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of next neuron in the chain. At the synapse the axon and the dendrite do not touch each other there is small gap between the two. The message passes from one neuron to other neuron through synapse by a chemical.
10th Science Chapter 6 Important Questions Set – 3
State the functions of any three of the structural and functional unit of nervous system..
Nervous system: Main parts of nervous system are as follows: (i) Central nervous system (ii) Peripheral nervous system, (iii) Autonomous system. (i) Central Nervous System: It consist of (a) Brain receives information carrying impulses from all the sensory organs (by sensory nerves) of the body and also from the spinal cord. The brain responds to the information by sending its own instruction (through motor nerves) to the muscle and glands to act accordingly. The brain also stores information and act as organ of thought and intelligence. Spinal Cord : It is concerned with spinal reflex actions and the conduction of nerve impulses to form the brain. Peripheral Nervous System : It is composed of Cranial nerves (nerves from the brain) and the spinal nerves. Both of these consist of sensory and motor neurons. So, they carry sensation to and messages from the brain and the spinal cord. Autonomous Nervous System : It is that part of the peripheral nervous system which controls the activities of the internal organs such as stomach, heart-beat, etc. automatically even without our thinking about them. Its nerves are attached to the smooth muscles and control the activities of internal organs of the body involuntarily, many these nerves are connected with the mid brain and hind brain.
If the cerebellum is not functioning properly, state the activities of our body that are affected. How do muscles move?
Cerebellum is not functioning properly may affect (i) Walking in straight line (ii) riding a cycle (iii) maintaining the posture and balance of the body (iv) movement is very coordinate the patient sways in walking and tend to fall towards the affect side. (v) It is responsible for precision of voluntary actions.
When the decision to move is conveyed by a nerve to a muscle it has to act. In response to nervous electrical impulses. The special proteins of the muscle change both their shape and their arrangement in the cell. This new arrangement of these proteins give the muscle cells a shorter form that causes movement of the muscle.
Why do most of the animals shows instinctive behavior rather than intelligent behavior?
The cerebral hemispheres are responsible for consciousness, thinking, and intelligent behavior. Animal which do not possess well developed cerebral hemispheres cannot perform intelligent actions. They only show instinctive behavior.
What are the overall function of the human brain?
The various overall functions of human brain are: (i) to receive impulses from all the sensory organs like eye, ear, nose, tongue, skin. (ii) sending of responses to muscles and glands for proper actions. (iii) control and coordination of the body activities. (iv) thinking, storage of past knowledge and experience feeling of conscious and modification of behavior according to situation and experience.
What are thinking tissue? Where are they located? What is the main function of these tissue?
Thinking tissue: The thinking tissue in our body consist of dense networks of intricately arranged neurons. Location: Thinking tissue sits in the fore-brain. Function: It receives signal from all over the body. It has regions which receive sensory impulses from various receptors. It has separate areas where information is interpreted considering the information that is already stored in the brain. From this part of the brain, nerves carry signal back to different parts of the body to act upon muscles/ glands according.
10th Science Chapter 6 Important Questions Set – 4
How brain is protected inside a human body what is the role of the brain in reflex action.
The human body is designed so that the brain sits inside a bony box the cranium or skull. Inside the box the brain is contained in a fluid filled balloon which provide further shock absorption.
Reflex actions are controlled by spinal cord although the information input also goes on to reach the brain. However conditioned reflexes (based on precious experiences) such as salivation after seeing good food are controlled by cerebral cortex of brain.
Name the part of human brain that maintains posture and equilibrium in the body.
Cerebellum.
What is gap between two neurons called? (a) Hoe does information travel across the gap? Explain. (b) Name the part of neuron system which connects central nervous system to body parts.
Synapse. (a) At the end of the axon the electrical impulse sets off the release of some chemicals. These chemicals cross the gap or synapse and start a similar electrical impulse in a dendrite of the next neuron. (b) Axon of neuron.
Name two tissues which provide control and coordination in animals.
Nervous and muscular tissues.
“Brain and spinal cord are two vital organs our body” How our body is designed to protect them?
Brain is located in bony cranium which is fluid filled to absorb the shocks. Spinal cord is further protected by vertebral column or backbone. Spinal cord is further protected by a fluid present in the vertebral column cavity.
During the practicing these important questions, student must open NCERT Books for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 page. So, that he can make more answers related to these questions. It will also help the students in confidence building.
10th Science Chapter 6 Important Questions Set – 5
Describe the central nervous system in the human beings..
Nervous system is one of the most important system of the body. It regulates, coordinates and links the activities of different organs. The central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord. Brain: The human brain is highly developed and shows great advancement over that of any other animal in the size of the cerebral hemisphere as well as the mid brain, cerebellum, medulla oblongata, etc. The adult brain is dividing into the following parts: 1. Fore-brain : It consists of the following parts: (a) Cerebrum: It forms about two third of the human brain. A deep longitudinal tissue divides the cerebrum into two hemispheres which are held together by a horizontal sheet of fibrous tissue. Cerebrum contains an outer grey matter and an inner white matter. Grey matter shows many convolutions which are directly linked with intelligence of the organism. Cerebrum controls the function of perception of smell, sight hearing, ability of speech and movements of various parts of the body. 2. The mid brain : It is thick walled area which serves as center for certain visual and auditory reflexes. The mid-brain contains a group of nerve cells which regulates involuntary actions of muscles on which our thinking has not control. 3. The hind-brain : It consist of three centers namely, cerebellum, pons and medulla oblongata. Cerebellum: It controls coordination and adjustment of movement and posture. Pons: It forms the floor of the brain stem. It serves as a neuronal link between the cerebral cortex and the cerebellum. Medulla oblongata: It is the regulating center for swallowing, coughing, sneezing and vomiting. It takes part in regulation of respiration. The spinal cord: The spinal cord is cylindrical and has the same diameter as the little finger. Medulla of the extends downwards to form spinal cord that lies protected in the backbone. It is hollow and possesses a central canal. It is not uniform in thickness. The spinal cord is the great highway for most nerve impulses. It conducts impulses to and fro from the brain. It also acts as reflex center. Spinal cord is formed of two types of nervous tissues the grey matter and white matter. The grey matter surrounds the central entirely of nerve cells. Two upward and two downward dorsal and ventral horns can be seen in the T.S of spinal cord. Functional of spinal cord: (i) All the stimuli and responses are passed from and to the brain through the spinal cord. (ii) It is a center of reflex actions.
What is a ganglion?
In certain animals the nerve nets (nerve net is formed by nerve cells) condense into a nerve mass. This nerve mass is called ganglion.
What is the automatic nervous system?
The specific set of nerves that mainly controls and integrates the function of internal organs is called automatic nervous system. It controls the body organs, such as heart, blood vessels, glands, smooth muscles and uterus in the body; these are not directly under control of our will. Autonomic nervous system consists of: (i) Sympathetic and (ii) Para-sympathetic systems. They have opposite effect on the organ that’s why if one stimulates the organ the other inhibits its action.
Nervous and hormonal systems together perform the function of control and coordination in human beings: Justify this statement.
Control and coordination in human beings: This system of controlling and coordination can be divided into two parts: (i) Nervous system. (ii) Hormonal system. Both the system control, coordinate the various functions in human body. Nervous system controls the various functions by the units called neurons. Neurons receive the information by sensory nerves and transfer them through motor actions. The hormones are the chemicals secreted by endocrine glands. The endocrine glands do not have ducts so they are called ductless glands. Hormones also control the functions of various organs of the body. In this way it is true that the nervous system and hormonal system in human body together perform the functions of control and coordination.
How does the nervous tissue cause action?
Brain collects information around the body through nerves. Make decisions based on the information and conveys decisions to muscles for action. When a nerve impulse reaches the muscle the muscle fiber must move. Muscle cells have special proteins that change both their shape and their arrangement in the cell in response to nervous electrical impulses. Now arrangement of these proteins give the muscles cells a shorter form and this lead to movement of the muscles. After the actions is over, reserve process take place and the muscles take their original size and shape.
The Tropic Movement
The directional response of plants shown by the plant towards or away of the stimulus such as light, water, gravity, etc. is known as topic movement.
Hormones are chemical substances which are transported from the site of synthesis to the place of action or hormones are chemical substances which are synthesis at one region of the body of organism and are transported to the site of action. They are needed in a very small amount.
10th Science Chapter 6 Important Questions Set – 6
Why do tropic movement take place in plants.
Tropic movements in plants are growth related. Plants shown by the plants towards or away of stimulus or away from. This growth causing tropic movement regulated by the plant hormone called auxin.
Explain photoperiodism?
The phenomenon of regulation of flowering and germination of seeds by photoperiodic stimulus is called photoperiodism.
What is the need of control and coordination system in the multicellular higher organism?
The control and coordination system in higher organism perform two functions: (i) It make the various body organs and organ systems to work in organized pattern and in a coordinated way. For example, when we eat, our hand bring food to the mouth, teeth and jaw muscles chew salivary glands secrete saliva, etc. (ii) Control and coordination also aids in maintaining a steady storage between the internal environment of an organism and the external environment. For example, during summer we sweat more, evaporation of sweat cool us. Due to loss of water in precipitation we feel thirsty to make the water loss good. Both sweating and thirst are responsible for keeping the temperature and water content of the body at an optimum state.
What is meant by plant hormone? Give one example each of plant hormone that: (a) Promotes growth. (b) Promotes cell division. (c) Inhibits growth. (d) Promotes the growth of a tendril around a support.
Plant Hormone: these are special chemical compound which are synthesised at places away from where they act and simply diffuse to the area of action. Different plant hormone help to coordinate growth, development and responses to the environment. (a) Auxin hormone promotes growth. (b) Cytokinin promotes cell division. (c) Abscisic Acid inhibits growth. (d) Auxin promotes the growth of a tendril around a support.
What are photohormones? Name any two photohormones along with one function of each.
Photohormones are plant hormones which are also called growth regulators. They help to coordinate growth development and responses to environment. Phytohormone and its Function (i) Auxin: Help the plant shoots/roots to respond to stimuli like light, gravity, touch, etc. (ii) Gibberellins: They help in the growth of stem.
10th Science Chapter 6 Important Questions Set – 7
Explain the role of the four type of growth regulators or growth hormones..
(a) Function of Auxins (i) Growth: It plays a vital role in cell elongation during growth. It promotes the growth of shoot. (ii) Root formation: It helps in root formation. When auxin is applied to the cutting of the stem artificially the formation of roots can be initiated. In germinating roots, higher concentration of auxins inhibits the growth. (iii) Parthenocarpy (seedless food): It is observed that after pollination there is sharp rise in auxin content of the ovary which helps in the formation of fruit. An application of auxin causes formation of seedless fruits without pollination and fertilization. (b) Function of gibberellins (i) Effect on stem elongation: Gibberellins are found to cause stem elongation in genetically dwarf variety. It has no effect on tall verities. (ii) Germination of seeds: It is now known to control the germination of seeds of some high plants such as lettuce, cereals etc. (iii) Flowering: Gibberellins induces flowering in the long day plants in short day conditions. (iv) Parthenocarpy: Gibberellins are found to induce parthenocarpy. (v) Increase in size: Gibberellins application on plants also cause increase in size of leaves and flowers in some plants. (c) Function of cytokinins (i) Cell divisions: One of the main functions of the cytokinins is in cell divisions, cell expansion and differentiate that’s why cell growth. (ii) Initiation of roots and shoots: Experimental evidences show that kinins affect the initiation of roots and shoots and their growth. (iii) Remove apical dominance: Kinins are also found effective in removing the apical dominance and help in growth of lateral buds. (iv) Abscisic Acid: This group compounds is now isolated from dormant seeds, buds and other parts of the plant. Activities of abscisic acid are in contrast to gibberellins and cytokinins. Abscisic acid retards growth promotes leaf and fruit fall and causes dormancy of seeds, tubes and bulbs. It also aging of leaves.
What are the function of nervous system?
The function of nervous system: (i) It regulates involuntary action. (ii) It control and coordinates voluntary muscular activities. (iii) It keep us informed about the outside world through the sense organs. (iv) It enables us to think reason and remember. (v) It controls all the reflex actions in our body, thus protection it from harm.
What is reflex arc and what are the advantages of reflex action?
Reflex arc is the pathway taken by the nerve impulses and responses in a reflex action that’s why from the receptors organs like skin to the spinal cord and from the spinal cord to the effector organs like muscles. The advantages of Reflex action are: (i) It enable the body to give quick responses to give quick responses to harmful stimuli and thus protects our body. (ii) It minimizes the overloading of brain.
Explain the function of human brain?
The function of human brain are: (i) The brain receives information carrying impulses from all the sensory organs of the body. (ii) The brain responds to the impulses brought in by sensory organs by sending its own instruction to the muscles and glands causing them to function accordingly. (iii) The brain correlates the various stimuli from different sense organs and produces the most appropriate and intelligent response. (iv) The brain coordinates the bodily activities so that the mechanisms and chemical reactions of the body work together efficiently. (v) The brain stores information so that behavior can be modified according to the past experience. This function makes brain the organ of thought and intelligence.
Explain how the plants response to external stimulus?
(i) Plant use electrochemical means to convey information from cell to cell. (ii) Sensitive plants move very quickly in response to touch that are independent of the direction of the stimuli. (iii) The folding up and dropping of leaves of the sensitive plant touch-me-not when lightly touch is an example. (iv) Plants cells change shape by changing the amount of water in them resulting in swelling or shrinking thereby changing shape.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 other subjects are also available free to use in Hindi and English Medium. For any inconvenience, please contact us for help.
Provide Feedback to make Tiwari Academy best in NCERT Solutions. Whatever we do is just the suggestions of uses only.
10th Science Chapter 6 Important Questions Set – 8
What are directional or tropic movements in plants organs.
It is the directional growth or movement of a plant organ in response to an external stimulus. Growth towards the stimulus is positive tropism and growth away from the stimulus is negative tropism. Tropic movements are classified as follows depending on the type of stimulus causing it: (i) Phototropism is the movement of part of the plant in response to light. (ii) Geotropism is the upward and downward growth of shoots and roots in response to the pull of earth or gravity. (iii) Hydrotropism is the movement of a part of the plant in response to water. (iv) Chemotropism is the movement of a part of the plant in response to a chemical stimulus. If the plant part shows movement growth towards the chemical it is called positive chemotropism and if the plant part shows movement or growth away from the chemical it is called negative chemotropism. For example, the growth of pollen tube towards a chemical which is produced by an ovule during the process of fertilisation in a flower.
What are the function of plant hormones and what are the characteristic and function of Hormones?
The plant hormones regulate many function in plants which are as follows: (i) Germination of seeds or breaking the dormancy of seeds. (ii) Growth of root, stem and leaves. (iii) Flowerings of plants, (iv) Ripening of fruits, (v) Movement of stomata in leaves and (vi) Phototropism, geotropism, chemotropism and nastic movement. Characteristic and Function of Hormones (i) Hormones are the secretions of endocrine glands or tissues. (ii) They are poured directly into the blood and carried throughout the body by blood circulatory system. (iii) Hormones have their effects at the sites different from the sites where they are made. So they are also called chemical messengers. (iv) They act on specific tissue or organs are called target organs. (v) They coordinate the activities of the body and also its growth. (vi) They are secreted in extremely minutes’ quantities. (vii) Chemically hormones may be polypeptides and proteins, amino acids, and their derivatives or steroids. (viii) Hormones help the body to cope with emergency demands such as infection, trauma, dehydration, starvation and extreme temperature.
Discuss about the Endocrine glands, Hypothalamus gland, Pituitary gland, Thyroid gland, Parathyroid glands and Adrenal gland?
(i) Endocrine glands: They are structure or group of cells or tissue which manufactures hormones and secretes them directly into the bloodstream to act at distant sites in the body known as targets organs or cells. (a) They are ductless glands and are located at different parts of the body. (b) The endocrine glands present in human includes hypothalamus, pituitary, pineal, thyroid, parathyroid, pancreas, adrenal, testes (in male) and ovaries (in female). (c) Some endocrine glands like pancreas, testis and ovary perform dual functions that’s why both exocrine and endocrine functions. (ii) Hypothalamus gland is present in brain. (a) It produce releasing hormones. (b) It regulates the secretion of hormones from pituitary gland. (iii) Pituitary glands is present at the base of the brain. It is also known as the matter gland as it controls to the other endocrine glands. The pituitary gland secretes five hormones: (a) Growth hormone regulates the growth and development of bones and muscles. (b) Trophic hormone regulates the secretion of hormones from other endocrine glands like adrenal glands like adrenal glands, thyroid gland, testes and ovaries. (c) Prolactin hormone regulates the function of mammary glands in females. (d) Vasopressin hormone regulates water and electrolyte balance in the body. (e) Oxytocin hormone regulates the ejection of milk during lactation. (f) Pineal gland is present in the brain near to the pituitary gland. It secretes melatonin hormone which delays sexual development and promotes sleep. (iv) Thyroid gland is presented just below the neck. (a) Iodine is necessary for the thyroid gland to make thyroxine hormone. (b) It secretes a hormone called thyroxine which regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins in the body so as to provide the best balance for growth. (v) Parathyroid glands are four in number which are embedded in the thyroid gland. (a) They secrete a hormone called calcitonin, which regulates calcium and phosphate levels in the blood. (vi) Adrenal glands are two in number which are located one on top of each kidney. (a) Adrenal glands secretes two hormone adrenalin and corticoids. (b) The function of adrenalin and corticoid hormones are to regulate blood pressure, heart beat, breathing rate, carbohydrates metabolism and mineral balance.
Explain what are the function of Pancreas, Testes and Ovaries?
(i) Pancreas is present just below the stomach in the body. (a) It secretes two hormones insulin and glucagon. (b) The function of insulin hormone is to lower the blood glucose. (c) The function of glucagon hormone is to increase the blood glucose. (d) Pancreas is exocrine as well as endocrine gland. The endocrine part is called the islets of Langerhans. (ii) Testes in male are present outside the lower abdomen in scroyum. (a) They secrete male sex hormone called testosterone. (b) The function of testosterone hormone is to regulate male accessory sex organs and secondary sexual character like moustache, beard and voice. (iii) Ovaries in female sex hormone called estrogen and progesterone. (a) They secrete two female sex hormones called estrogen and progesterone. (b) The function of estrogen hormone is to regulate the development of female accessory sex organs and secondary sex characters such as mammary gland, soft skin, hair pattern and feminine voice. (c) The function of progesterone hormone is to control the uterus changes in menstrual cycle. It also helps in the maintenance of pregnancy.
Suggest six reflex actions of the body. Explain how the reflex arc is the same in all.
Six reflex actions of the body are: (i) When we see a speeding car moving towards us we move aside. (ii) We withdraw our hands on being pricked by a pin. (iii) We withdraws our hands on touching very hot substance. (iv) We close our eyes on seeing direct sun or extremely bright source of light. (v) We close our eyes on hearing a loud noise. (vi) We shiver on feeling cold. Reflex arc in all the above cases is same because in all the cases, the stimulus is received by sense organs. Then this information is carried to spinal cord through sensory nerves. Thus, information from spinal cord is sent to the effectors such as muscles motor neurons.
« Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Important Questions
Class 10 science chapter 7 important questions ».
Copyright 2024 by Tiwari Academy | A step towards Free Education

- CBSE Study Material
- CBSE Important Questions
- Important Questions For Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes
Chapter 6 -Life Processes
Students can find the Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes on this page. These questions are designed after analysing the latest exam pattern and syllabus. Practising them will help students in their exam preparation. They may come across few of these questions in the board exam. Some of the questions from last year papers have also been added in these important question. Students can easily download the pdf of important questions class 10 Science chapter 6 by clicking on the link below.
Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes- Download Free PDF
1) Woody plants carry gaseous exchange through
a) root hair b) Lenticels c) stem hair d) epidermal cells

Students must have found these CBSE Class 10 Important Questions Science Chapter 6 Life Processes useful for their science exam preparation. They can also solve the CBSE Class 10 Sample Papers for more practice. It will give them idea on question paper pattern and its difficulty level.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
CBSE Expert
CBSE Class 10 Science Case Study Questions Download Free PDF
If you are looking for the CBSE Class 10 Science Case Study Questions in PDF, then you are in the right place. CBSE 10th Class Case Study for the Science Subject is available here. These Case studies can help the students to solve the different types of questions that are based on the case study.

CBSE Board will be asking case study questions based on Science subjects in the upcoming board exams. Thus, it becomes an essential resource to study.
The Science Subject case study for class 10th covers a wide range of chapters from the Science. Students willing to score good marks in their board exams can use it. The questions are highly interactive and it allows students to use their thoughts and skills to solve such kinds of questions.
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science
In board exams, students will find the questions based on assertion and reasoning . Also, there will be a few questions based on case studies. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 2 Acids, Bases, and Salts
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 3 Metals and Non-Metals
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of elements
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 6 Life Processes
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 8 How do organisms reproduce?
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 10 Light reflection and refraction
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 11 Human eye and colorful world
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 12 Electricity
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 13 Magnetic effects of current
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 15 Our Environment
The above Case studies for CBSE Class 10 Science will help you to score good marks in the Case Study questions that have been coming in your examinations. These CBSE Class 10 Science Case Study have been developed by experts of cbseexperts.com for benefit of Class 10 students.
Class 10 Science Assertion and Reason Questions
Case Study Type Questions in Science Class 10
Case Study Type Questions in Science Class 10 include the information or data. Students willing to solve them are required to read the passage carefully and then solve them. While solving the paragraph the ideal way is to highlight the key information or given data.
Because later it will ease them to write the final answers. Science Case study type questions consist of 4 to 5 questions that should be answered in an MCQ manner.
While reading the paragraph students will get the clue in between about the possible answer of the question. They should definitely highlight those questions. This is the best way to solve such kind of Case study Type Questions.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!

- Book Solutions
- State Boards
Class 6 Science Case Study Question
Case study question class 6 science (cbse / ncert board).
Class 6 Science Case Study Question and Answer: CBSE / NCERT Board Class 6 Science Case Study Question prepared by expert Science Teacher. Students can learn Case Based Question / Paragraph Type Question for NCERT Class 6 Science.
There are total 16 chapter Food Where Does It Come From, Components of Food, Fibre to Fabric, Sorting Materials Into Groups, Separation of Substances, Changes Around Us, Getting to Know Plants, Body Movements, The Living Organisms and Their Surroundings, Motion and Measurement of Distances, Light Shadows and Reflection, Electricity and Circuits, Fun with Magnets, Water, Air Around Us, Garbage In Garbage Out.
For any problem during learning any Case or any doubts please comment us. We are always ready to help You.
CBSE Class 6 Science Case Study Question
Chapter 1 Food Where Does It come From Case Study Question
Chapter 2 Components of Food Case Study Question
Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric Case Study Question
Chapter 4 Sorting Materials Into Groups Case Study Question
Chapter 5 Separation of Substances Case Study Question
Chapter 6 Changes Around Us Case Study Question
Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants Case Study Question
Chapter 8 Body Movements Case Study Question
Chapter 9 The Living Organisms – Characteristics and Habitats Case Study Question
Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances Case Study Question
Chapter 11 Light Shadows and Reflection Case Study Question
Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits Case Study Question
Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets Case Study Question
Chapter 14 Water Case Study Question
Chapter 15 Air Around Us Case Study Question
Chapter 16 Garbage In Garbage Out Case Study Question
What is Case Study Question?
Ans. At case Study there will one paragraph and on the basis of that concept some question will made. Students have to solve that question.
How many marks will have at case based question?
Most of time 5 questions will made from each case. There will 1 or 2 marks for each question.
Important links:
- Lakhmir Singh Class 6 Book Solution
- NCERT Solution Class 6 Science
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. Here, we have provided case … Continue reading Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 ...
Life Processes Case Study Questions With Answers. Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes. Case Study/Passage-Based Questions. Question 1: Transpiration is the evaporative loss of water by plants. It occurs mainly through the stoma in the leaves. Besides the loss of water vapor in ...
These case based questions are expected to come in your exams this year. Please practise these case study based Class 10 Science Questions and answers to get more marks in examinations. Case Study Questions Chapter 6 Life Processes. Case/Passage - 1. There is a pair of bean-shaped organs P in the human body towards the back, just above the ...
CBSE Case Based Questions Class 10 Science Chemistry Chapter 6. CASE STUDY : 1. Carbon and energy requirements of the autotrophic organism are fulfilled by photosynthesis. It is the process by which autotrophs take in substances from the outside and convert them into stored forms of energy. This material is taken in the form of carbon dioxide ...
The Chapter wise Important case study based questions with their solved answers in CBSE Class 10 Science can be accessed from the table below: CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions ...
Class 10 Science Sample Papers with case study questions are available in the myCBSEguide App. There are 4 such questions (Q.No.17 to 20) in the CBSE model question paper. If you analyze the format, you will find that the MCQs are very easy to answer. So, we suggest you, read the given paragraph carefully and then start answering the questions.
The CBSE Class 10 Science Question Bank on Case Studies, provided in this article, can be very helpful for understanding how the source based or case based questions are asked in the board exam.
Answer. The following raw materials are required for photosynthesis: → Carbon Dioxide: Plants get CO from atmosphere through stomata. → Water: Plants absorb water from soil through roots and transport to leaves. → Sunlight: Sunlight, which is absorbed by the chlorophyll and other green parts of the plant. 3.
All Chapter 6 - Life Processes exercise questions with solutions will help you to revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations. The NCERT Solutions are always beneficial in your exam preparation and revision. Download NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths from Vedantu, which are curated by subject matter experts.
The Class 10 Exemplar provided here consists of MCQs, fill in the blanks, practice questions, value-based questions, and previous years' questions on Life Processes. Class 10 Science Chapter 6 mainly deals with the maintenance processes in living organisms. In this chapter, students will learn to identify vital life processes and understand ...
Ans: Life processes are important for healthy living. Life processes such as respiration, digestion, absorption, assimilation, and excretion are vital for all living organisms. The processes may differ from one organism to another. Students of Class 10 science will learn about the different life processes in Chapter 6.
NCERT solutions for class 10 science Chapter 6 are absolutely free to download. We also offer you live doubt clearing sessions which saves your time and energy and you get your doubts solved immediately. Toppr provides free study materials, 1000+ hours of video lectures, and last 10 years question papers for free.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Textbook Chapter End Questions. Question 1. The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for. (i) nutrition. (ii) respiration. (iii) excretion. (iv) transportation. Answer: (iii) Excretion.
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions. Question 1: Transpiration is the evaporative loss of water by plants. It occurs mainly through the stoma in the leaves. Besides the loss of water vapor in transpiration, the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the leaf also occurs through pores called stomata. Normally stomata remain open in the daytime ...
Case Study Class 10 Science: Here, you will get class 10 Science case study questions and answers pdf at free of cost. Along with you can also download case study questions class 10 Science chapter wise for getting higher marks in board examinations. Sharda University Admission - 100% Scholarship upto - Limited Time Offer - Apply Now ...
10th Science Chapter 6 Board Questions Set - 1 (1 Mark) Name the part of the brain which controls posture and balance of the body. [CBSE 2012] Give one example of chemotropism. [CBSE 2012] Name the two components of central nervous system in humans. CBSE 2012]
CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions 2022-23. Chapter 6 of Class 10 Science covers the topic of 'Life Processes'. The chapter covers plant nutrition and systems like respiratory, circulatory and excretory. The students should have access to well-prepared notes so that important topics are not skipped, and the preparation is complete.
on April 26, 2023, 6:25 AM. Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Important Questions of Control and Coordination. The sets of 10th Science Chapter 6 Extra Questions contains all the intext questions, keyword based questions and questions form school tests for the exam preparation in academic session 2024-25.
1) Woody plants carry gaseous exchange through. a) root hair. b) Lenticels. c) stem hair. d) epidermal cells. Students must have found these CBSE Class 10 Important Questions Science Chapter 6 Life Processes useful for their science exam preparation. They can also solve the CBSE Class 10 Sample Papers for more practice.
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science. In board exams, students will find the questions based on assertion and reasoning. Also, there will be a few questions based on case studies. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. Case Study Questions for Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations.
Case Study Question Class 10 Science for CBSE Board: ... Case Based Questions Class 10 Science Chapter-wise: Chapter 1. Chemical reactions and equations: Chapter 9: Heredity and Evolution. Chapter 2. Acids, bases and salt: Chapter 10: Light Reflection and Refraction. Chapter 3. Metals and Non-metals:
Chapter 11 Light Shadows and Reflection Case Study Question. Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits Case Study Question. Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets Case Study Question. Chapter 14 Water Case Study Question. Chapter 15 Air Around Us Case Study Question. Chapter 16 Garbage In Garbage Out Case Study Question.