- Authors and Poets
- College Students
- book lovers
- Teachers & Teaching
- High School Students

The eNotes Blog
Books, study tips, new features, and more—from your favorite literature experts.

- How To Series

How to Write a Character Comparison in 8 Steps
Sometimes two characters are clearly alike, while other times it’s not as obvious. In order to write a successful character comparison, you must move beyond a description of the characters and analyze how they relate to each other. You should examine both characters’ individual roles in their respective literary works to understand how they contribute to the overall meaning of the text.
Let’s take a look at eight steps for writing a character comparison.
1. Choose two characters
The first step to writing a character comparison is to determine two characters you want to compare. Before you start comparing, revisit parts of the text where each character appears. Take note of the various character descriptions throughout the text and become familiar with the role of each character.
A few popular choices for writing character comparisons:
- Raskolnikov and Svidrigailov , Crime and Punishment
- Hamlet and Laertes , Hamlet
- Lucy Manette and Madame Defarge , A Tale of Two Cities
- Daisy Buchanan and Jordan Baker , The Great Gatsby
2. Establish a purpose for comparison
Why are you comparing these two specific characters? Are you comparing to find meaningful similarities and differences or is it to demonstrate your understanding of the work as a whole? By establishing a purpose, you’re laying the foundation for your comparison and can refer back to it when you start to analyze each character.
Several reasons for comparing two characters:
- Compare how each character’s actions and attributes affect the plot
- Major similarities or differences in character can show what themes the author wants to emphasize
- Explain how the relationship between the characters provides deeper understanding of the themes
3. Describe the characters
This is a good time to refer to any earlier notes you’ve taken about specific characters in the text: physical descriptions, style of dialogue, narrative elements, etc. It may be helpful to create a two column chart where you can list the traits of each character and cross reference your findings. Remember to always cite direct textual evidence!
Important points to consider:
- Physical descriptions
- Beliefs / Values
- Descriptions by narrator and other characters
4. Identify similarities and differences
Although the assignment may say “compare,” the assumption is that you will compare and contrast—consider both the similarities and differences. Once you’ve determined the traits of each character, identify the similarities and differences between them. Focus on the overarching personal qualities or nature of the two characters rather than describing their physical features.
For example, if you’re writing about Pride and Prejudice , don’t write something like, “ Darcy is a man, and Elizabeth is a woman.” Instead, write something like this: “Despite the fact that Darcy is a man and rich and Elizabeth is a woman and relatively poor, they share the following characteristics: ____.” And then finish by supplying striking examples in a way that explains the novel for your readers.
5. Formulate a thesis
Your thesis statement should reflect your purpose for comparing two characters and incorporate the effects their similarities and differences have on your essay. Refer back to your purpose for comparing characters as well as your list of similarities and differences in order to formulate the main claim you’re making in the essay.
For example:
- Though both members of the same social circles, Daisy Buchanan and Jordan Baker reveal the freedoms and restrictions imposed on women in The Great Gatsby .
- Though both receive prophecies from the witches. Macbeth and Banquo react differently to the news, illustrating through contrast the corrupting effects of power and pride.
6. Form a conclusion
Fill in the blanks of the following statements:
- “I am comparing these two characters in order to show ____ about the work.”
- “These characters share the following characteristics: ___.”
- “These characters differ in the following ways: ____.”
- “These similarities and differences relate to the essential meaning of the work because ____.”
Once you’re able to complete these statements, refer back to your thesis for your character comparison. Have you gathered enough information to make an accurate comparison between the two characters? Have you demonstrated your understanding of the work as a whole?
For example, If you’re writing about Shakespeare’s Hamlet and you compare Marcellus and Gertrude , you’ve pretty much demonstrated you don’t understand the play well, because there’s little meaningful connection between the two. On the other hand, if you compare Ophelia and Hamlet , as two adults following their respective fathers’ advice to their deaths, you’ve demonstrated superior comprehension.
7. Structure your comparison
Consider how you will compare the characters. Broadly speaking, there are two general ways to structure your comparison:
- You can write about both characters in each paragraph (paragraph 2: A’s appearance, B’s appearance; paragraph 3: A’s motivation, B’s motivation, etc).
- You can write all about A, then all about B, and relate both characters to each other in a following paragraph.
No matter which structure you choose, remember why you’re comparing these two characters. You must always make a larger argument about the meaning of the similarities and differences, and you must always support those arguments with specific examples from the work.
Once you’ve outlined the structure of your character comparison, you’re finally ready to write! Make sure that all of the information in your essay is accurate and can be supported by the text. Once you’ve finished writing, it’s always a good idea to proofread your work and make revisions if necessary.
For more how-to lessons, visit eNotes’ How To Series .
Share this:
Discover more from the enotes blog.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
Essay Papers Writing Online
A comprehensive guide to crafting a successful comparison essay.

Comparison essays are a common assignment in academic settings, requiring students to analyze and contrast two or more subjects, concepts, or ideas. Writing a comparison essay can be challenging, but with the right approach and guidance, you can craft a compelling and informative piece of writing.
In this comprehensive guide, we will provide you with valuable tips and examples to help you master the art of comparison essay writing. Whether you’re comparing two literary works, historical events, scientific theories, or any other topics, this guide will equip you with the tools and strategies needed to create a well-structured and persuasive essay.
From choosing a suitable topic and developing a strong thesis statement to organizing your arguments and incorporating effective evidence, this guide will walk you through each step of the writing process. By following the advice and examples provided here, you’ll be able to produce a top-notch comparison essay that showcases your analytical skills and critical thinking abilities.
Understanding the Basics
Before diving into writing a comparison essay, it’s essential to understand the basics of comparison writing. A comparison essay, also known as a comparative essay, requires you to analyze two or more subjects by highlighting their similarities and differences. This type of essay aims to show how these subjects are similar or different in various aspects.
When writing a comparison essay, you should have a clear thesis statement that identifies the subjects you are comparing and the main points of comparison. It’s essential to structure your essay effectively by organizing your ideas logically. You can use different methods of organization, such as the block method or point-by-point method, to present your comparisons.
Additionally, make sure to include evidence and examples to support your comparisons. Use specific details and examples to strengthen your arguments and clarify the similarities and differences between the subjects. Lastly, remember to provide a strong conclusion that summarizes your main points and reinforces the significance of your comparison.
Choosing a Topic for Comparison Essay
When selecting a topic for your comparison essay, it’s essential to choose two subjects that have some similarities and differences to explore. You can compare two books, two movies, two historical figures, two theories, or any other pair of related subjects.
Consider selecting topics that interest you or that you are familiar with to make the writing process more engaging and manageable. Additionally, ensure that the subjects you choose are suitable for comparison and have enough material for analysis.
It’s also helpful to brainstorm ideas and create a list of potential topics before making a final decision. Once you have a few options in mind, evaluate them based on the relevance of the comparison, the availability of credible sources, and your own interest in the subjects.
Remember that a well-chosen topic is one of the keys to writing a successful comparison essay, so take your time to select subjects that will allow you to explore meaningful connections and differences in a compelling way.
Finding the Right Pairing
When writing a comparison essay, it’s crucial to find the right pairing of subjects to compare. Choose subjects that have enough similarities and differences to make a meaningful comparison. Consider the audience and purpose of your essay to determine what pairing will be most effective.
Look for subjects that you are passionate about or have a deep understanding of. This will make the writing process easier and more engaging. Additionally, consider choosing subjects that are relevant and timely, as this will make your essay more interesting to readers.
Don’t be afraid to think outside the box when finding the right pairing. Sometimes unexpected combinations can lead to the most compelling comparisons. Conduct thorough research on both subjects to ensure you have enough material to work with and present a balanced comparison.
Structuring Your Comparison Essay
When writing a comparison essay, it is essential to organize your ideas in a clear and logical manner. One effective way to structure your essay is to use a point-by-point comparison or a block comparison format.
Whichever format you choose, make sure to introduce your subjects, present your points of comparison, provide evidence or examples to support your comparisons, and conclude by summarizing the main points and highlighting the significance of your comparison.
Creating a Clear Outline
Before you start writing your comparison essay, it’s essential to create a clear outline. An outline serves as a roadmap that helps you stay organized and focused throughout the writing process. Here are some steps to create an effective outline:
1. Identify the subjects of comparison: Start by determining the two subjects you will be comparing in your essay. Make sure they have enough similarities and differences to make a meaningful comparison.
2. Brainstorm key points: Once you have chosen the subjects, brainstorm the key points you want to compare and contrast. These could include characteristics, features, themes, or arguments related to each subject.
3. Organize your points: Arrange your key points in a logical order. You can choose to compare similar points side by side or alternate between the two subjects to highlight differences.
4. Develop a thesis statement: Based on your key points, develop a clear thesis statement that states the main purpose of your comparison essay. This statement should guide the rest of your writing and provide a clear direction for your argument.
5. Create a structure: Divide your essay into introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Each section should serve a specific purpose and contribute to the overall coherence of your essay.
By creating a clear outline, you can ensure that your comparison essay flows smoothly and effectively communicates your ideas to the reader.
Engaging the Reader
When writing a comparison essay, it is crucial to engage the reader right from the beginning. You want to hook their attention and make them want to keep reading. Here are some tips to engage your reader:
- Start with a strong opening statement or question that entices the reader to continue reading.
- Use vivid language and descriptive imagery to paint a clear picture in the reader’s mind.
- Provide interesting facts or statistics that pique the reader’s curiosity.
- Create a compelling thesis statement that outlines the purpose of your comparison essay.
By engaging the reader from the start, you set the stage for a successful and impactful comparison essay that keeps the reader engaged until the very end.
Point-by-Point vs Block Method

When writing a comparison essay, you have two main options for structuring your content: the point-by-point method and the block method. Each method has its own advantages and may be more suitable depending on the type of comparison you are making.
- Point-by-Point Method: This method involves discussing one point of comparison at a time between the two subjects. You will go back and forth between the subjects, highlighting similarities and differences for each point. This method allows for a more detailed and nuanced analysis of the subjects.
- Block Method: In contrast, the block method involves discussing all the points related to one subject first, followed by all the points related to the second subject. This method provides a more straightforward and organized comparison but may not delve as deeply into the individual points of comparison.
Ultimately, the choice between the point-by-point and block methods depends on the complexity of your comparison and the level of detail you want to explore. Experiment with both methods to see which one best suits your writing style and the specific requirements of your comparison essay.
Selecting the Best Approach
When it comes to writing a comparison essay, selecting the best approach is crucial to ensure a successful and effective comparison. There are several approaches you can take when comparing two subjects, including the block method and the point-by-point method.
The block method: This approach involves discussing all the similarities and differences of one subject first, followed by a thorough discussion of the second subject. This method is useful when the two subjects being compared are quite different or when the reader may not be familiar with one of the subjects.
The point-by-point method: This approach involves alternating between discussing the similarities and differences of the two subjects in each paragraph. This method allows for a more in-depth comparison of specific points and is often preferred when the two subjects have many similarities and differences.
Before selecting an approach, consider the nature of the subjects being compared and the purpose of your comparison essay. Choose the approach that will best serve your purpose and allow for a clear, organized, and engaging comparison.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, unlock success with a comprehensive business research paper example guide, unlock your writing potential with writers college – transform your passion into profession, “unlocking the secrets of academic success – navigating the world of research papers in college”, master the art of sociological expression – elevate your writing skills in sociology.

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, how to write a compare/contrast essay for the great gatsby.
Book Guides
These compare/contrast essays are an opportunity for you to tie the character similarities and differences to larger observations about society and class, the American Dream , or identity in the novel. They also allow you to practice standard English class skills: close reading, using lines from the text as evidence, and taking a stance and presenting a supporting argument in an essay.
We’ll go over some basic dos and don’ts for writing compare/contrast essays before diving into some analysis of the most asked-about character pairings. Keep reading if you have a Compare/Contrast assignment on the horizon!
Article Roadmap
- The do's of a compare and contrast essay
- The don'ts of a compare contrast essay
- Why some characters are paired for comparison more often than others
- Nick and Gatsby
- Tom and George
- Tom and Gatsby
- Daisy and Jordan
- Daisy and Myrtle
What to Do in a Compare/Contrast Essay
Like anything you write for English class, your essay should be clearly organized, with a thesis statement (a one-sentence summary of your argument), and topic sentences for each body paragraph.
And you should definitely have an overall argument! The point of the compare/contrast essay isn’t for you to just list the differences and similarities between two characters, you need to take those observations and make a larger argument about the novel as a whole . That larger argument allows you to practice writing an essay that contains an argument, which is a skill that nearly all English teachers are focused on building.
To take a quick example, don’t just list the differences between Tom Buchanan and Jay Gatsby. Instead, make an argument like, “Fitzgerald’s portrayal of wealthy New York society through Jay Gatsby and Tom Buchanan allows him to critique both old money and the newly rich, while reserving his most pointed critiques for the old money crowd.” (Obviously, that’s just one example, and there are dozens of potential arguments you could make while comparing and contrasting characters in Gatsby!)
Make sure to address your larger argument in each body paragraph as you draw out the similarities and differences between the two characters. Don’t get caught in the weeds as you tease out the many differences and similarities in each character pair. Always link back to the bigger picture.
Finally, analyze each quote you use – in other words, don’t stick a quote in your essay and do nothing with it. Make sure to explain how and why the quote demonstrates a key similarity or difference, and what that means for your bigger argument.
What to Avoid in a Compare/Contrast Essay
Don’t just list differences and similarities without an overarching argument . Although you can definitely start brainstorming by making a list of similarities and differences, just presenting that list in essay form won’t get you a good grade, since you need to go deeper and explain what the similarities/differences suggest about the novel as a whole.
And, on the other side, don’t make big claims without some evidence from the text to back them up . For example, don’t say “Tom is selfish while Gatsby cares about others.” Prove those two separate claims (Tom is selfish” and “Gatsby cares about others”) with relevant lines from the book. (And if you’re having a hard time locating good quotes, find a digital version of Gatsby you can search using the CTRL-F function. It’s a lifesaver when gathering relevant quotes for an essay!)

Why Are These Characters Paired Most Often?
We will tackle these major pairings in the next sections of this article:
Nick Carraway and Jay Gatsby
Tom buchanan and jay gatsby, tom buchanan and george wilson, daisy buchanan and jordan baker, daisy buchanan and myrtle wilson.
Before we dig into the analysis, you might be wondering: “why are we only comparing characters of the same gender?” or maybe “why not other pairings? Why not Jordan and Myrtle, or Nick and Tom?” We are focusing on these specific pairings because they are by far the most commonly asked about pairs in essay prompts and discussion topics for The Great Gatsby . And we want this guide, first and foremost, to be helpful to students as you work on assignments involving Gatsby!
Furthermore, these pairings help teachers get you to explore some of the novel’s larger themes . For example, comparing Daisy/ Myrtle or Tom/George can help you explore the differences between the wealthy and the working class . Comparing Daisy/Myrtle or Daisy/Jordan can help you explore the changing status of women during the 1920s. Comparing Tom and Gatsby can get at the old money/new money divide. Finally, differences between Nick and Gatsby raise some of the novel’s larger questions about the American Dream , repeating the past, and identity. In short, these pairings have become common because they each allow fairly easy access to one of the novel’s larger issues.
That’s not to say you couldn’t also explore some of those themes by comparing, say, Jordan and George, or Daisy and Gatsby, but cross-gender compare/contrast essays can be challenging because the status of women and men is so different in the novel. If you are interested in seeing how a particular male and female character are paired, you may be better off studying them through the lens of love, desire, and relationships in the novel, or through the way they relate to one of the novel's symbols or motifs.
With those thoughts in mind, let's jump into the top 5 pairings! For each pairing, we will suggest a few possible larger arguments you can either build from or disagree with, but these are far from comprehensive! You should add to our analysis of the characters and come up with an argument you’re excited about.
Quick Note on Our Citations
Our citation format in this guide is (chapter.paragraph). We're using this system since there are many editions of Gatsby, so using page numbers would only work for students with our copy of the book. To find a quotation we cite via chapter and paragraph in your book, you can either eyeball it (Paragraph 1-50: beginning of chapter; 50-100: middle of chapter; 100-on: end of chapter), or use the search function if you're using an online or eReader version of the text.
Although Jay Gatsby and Nick Carraway vary both in outlook and temperament, they are also alike in interesting ways. Despite somewhat similar desires, attitudes, and social positions, Nick and Gatsby make very different choices during the novel.
Love and Romance . Nick and Gatsby both want women that are out of their reach, although in different degrees. Daisy is miles above Gatsby in terms of social class. Jordan and Nick are of the same social status, but Jordan doesn't seem free to make her own decisions since an aunt controls her financial life. There is a significant passion gap between Gatsby and Nick as well. Gatsby obsesses over Daisy - he has thought of nothing else for five years, going as far as to buy a house across the bay from her just in case she notices. Nick, meanwhile, is attracted to Jordan's cool and self-sufficient demeanor, but he is clearly not in love with her, as he himself notes ("I wasn't actually in love, but I felt a sort of tender curiosity" (3.159)).
Approach to Women. Both men are not particularly interested in the inner lives of the women they want to be with. Gatsby is devastated when Daisy doesn't want to renounce her relationship with Tom completely. Similarly, Nick cavalierly discounts Jordan's penchant to lie, cheat, and generally be cynically uninterested in other people, and then is deeply disappointed when she acts this way after Myrtle's death.
Class and Social Standing. Although both Gatsby and Nick are outsiders to the wealthy communities of East and West Egg, Nick is a much more in-between character socially than Gatsby. Nick is familiar with the ways of the old money crowd because of his own family's privilege and the fact that he is related to Daisy. Gatsby is not only self-made, but is a criminal who is desperate to pass as part of the old money elite without knowing its customs or rules of behavior. What isolates Nick from East Egg life is his Midwestern values and the importance he places on morality and decency. Gatsby is isolated from everyone by the fact that he can never actually be himself - he is always playing a role and putting on his "Oxford man" persona. It may be this sense of feeling out of place that connects them.
Outlook and Temperament. Gatsby is an optimist (almost to a delusional degree) while Nick is a realist who finds Gatsby's idealism inspiring and admirable. Gatsby believes in his ability to shape his own life and future, which makes sense since he has managed to transform himself from a farmer to a successful gangster, to impersonate an "Oxford man," and to accumulate a fantastic amount of wealth in a very short time. This belief in his power translates to Gatsby being sure that he and Daisy can go back to their month of idyllic love ("'Can't repeat the past?', he cried incredulously. 'Why of course you can!'" (6.129). Nick tries his best to be an objective realist and to reign in his tendency to judge others. He is deeply in awe of self-directed men like Gatsby, and even Wolfshiem (Nick is amazed to think that one man could be behind a huge event like the rigged World Series).
Ambition. Gatsby dreams of greatness. As a young man his mind “romped like the mind of God,” and so as an adult, he seems to have made good on this promise by buying the most ridiculous mansion and throwing the most extravagant parties (6.134). Nick is much less ambitious in comparison. While he comes to New York seeking excitement, he doesn't want to be the wealthiest bond salesman on Wall Street or to have the biggest house. He is happy to be an observer at the edge of the drama rather than being in its midst.
Nick and Gatsby Essay Ideas
Here are potential arguments to build on or disagree with based our observations. These are certainly not the only possible arguments, so be creative! Make sure your essay considers what the similarities and differences between Nick and Gatsby reveal about the novel as a whole.
- Nick is a passive person and Gatsby is active, which is why Gatsby is the hero and Nick simply the observer.
- Nick has much more in common with Gatsby than he thinks he does, which explains why he becomes so enamored of him.
- Nick serves as a foil (someone who serves as a contrast) to Gatsby, which makes Nick the best possible observer of Gatsby.
- At the end of the novel, Tom says that Gatsby “threw dirt in [Nick’s] eyes, just like Daisy’s,” meaning that both Nick and Daisy were taken in and could never see the true Gatsby: a narcissist and a criminal. Tom is right - the whole novel is Nick trying to spin a negative character into a positive one.

As they battle over Daisy’s love, Tom Buchanan and Jay Gatsby sometimes seem surprisingly similar - particular in their self-centeredness, wealth, and concern with appearances. At the same time, these surface parallels point to major conflicts in their social class, and say a lot about the world of the novel.
Appearance. Gatsby is driven by his materialism to be very invested having fashionable clothes, a beautiful mansion, and visually overwhelming parties - for him, the outfit is the thing that makes the Oxford man . Meanwhile because Tom doesn't have to dress the part of the moneyed elite to be one, he is instead very attuned to the behavior of others. This is why he immediately sees how fake Gatsby's persona is, both because of Gatsby's overly ostentatious clothes, and because of how much Gatsby misreads the fake invitation from the Sloanes. Tom is never fooled into thinking that Gatsby is anything other than an upstart, and mostly likely a criminal one.
Self-Centeredness. Tom and Gatsby are both completely selfish, and fully convinced that their desires have to be acquiesced to by those around them. Tom, for example, starts his affair with Myrtle by pressing himself against her on a train platform - basically, his version of flirting is bodily assault. Gatsby, meanwhile, also thinks nothing of starting an affair with a married woman, assuming that his obsessive feelings are enough to justify any behavior.
Wealth. Despite the fact that both are unimaginably rich, these men come from totally different sides of the big money divide. Tom comes from old money and is forever worried about the encroachment of the nouveau riche, minorities, and others onto what he thinks is his. At the same time, Gatsby is the most successful of the novel's many ambitious social climbers, using his lack of ethical scruples to parlay his criminal activity into a higher social status.
Power. Tom loves being powerful and wields his power directly. He is physically aggressive and uses his body to threaten and intimidate (Nick, for one, is clearly very cowed by Tom's bulk). He is also quick to violence, whether it's socially sanctioned - like his football accomplishments - or not - like when he breaks Myrtle's nose without a second thought. Gatsby also holds significant power, but his methods are much more indirect. Still, whether he is offering Nick some illegal bond trading action, or showing off his get-out-of-a-ticket-free card to a cop on the highway, Gatsby is clearly happy to be in control of a situation.
Love. Tom and Gatsby both seem to be in love with Daisy. But what does that really mean to each of them? For Tom, Daisy is clearly partly appealing because she completes his horse-riding, East Egg, 350-thousand-dollar pearl necklace lifestyle. He cheats on her because he clearly has never denied himself anything, but he also understands Daisy as a person. He knows that she is too weak to leave him, but he also loves her enough to tolerate her affair with Gatsby and to stay with her after Myrtle's murder. Gatsby's love, on the other hand, is in some ways purer because he so idealizes Daisy and connects her to all of his other hopes and dreams. But this love is overly pure - he doesn't really seem to know Daisy as anything other than an idealized object, and is incapable of accepting that she has led a life apart from him for five years.
Tom and Gatsby Essay Ideas
In a compare/contrast essay, you can’t just present a list of similarities and differences. You also need to have an underlying argument you’re supporting. Feel free to take these at face value or as jumping-off points for your own thoughts.
- Tom loves Daisy as a person, Gatsby loves her as an idea.
- Both Tom and Gatsby’s tendency to control women and see them as prizes reveals the misogyny of the 1920s.
- Although Tom sees Gatsby as someone from an entirely different class than him, what they have in common (selfishness, affairs, obsession with appearances) makes a larger argument for an overall moral hollowness of the rich of any class.
- We see both Gatsby and Tom through the eyes of Nick, who worships one of them and hates the other. In reality, they are both much more similar than different, and their different treatment reveals Nick's insecurities and biases.

At first, most readers see Tom Buchanan and George Wilson as opposites. But, these markedly different characters face very similar circumstances and offer two takes on masculinity and power in the novel.
Appearance and Presence. Where Tom is strong and cowering, George is meek and shrinking. Tom exudes power and confidence while George tends to just fade into the background. These differences are borne out in the way these two men interact with the world. Tom is violent towards others, while George’s instinct is to be passive or to try and escape situations, the notable exceptions being his locking up of Myrtle and murder of Gatsby. Tom is confident, privileged, and assured while George is timid; George is “ruled by his wife” where Tom is selfish and acts on his own desires.
Reaction to Adversity. There is a dramatic difference in the way the two men react to the fact that their wives are cheating on them. Tom notices Daisy’s love for Gatsby and immediately starts making power plays. On the other hand, George discovers Myrtle’s affair and is undone by it. Nick compares the two men in a memorable description:
“the shock had made him physically sick. I stared at him and then at Tom, who had made a parallel discovery less than an hour before--and it occurred to me that there was no difference between men, in intelligence or race, so profound as the difference between the sick and the well. Wilson was so sick that he looked guilty, unforgivably guilty--as if he had just got some poor girl with child" (7.160).
In this description, Tom is “well” and George is “sick.” These are certainly arresting ways to describe Tom's more traditional masculinity and George's less overtly masculine character. Tom is self-assured in the face of adversity and immediately takes action to win Daisy back, insisting on driving Gatsby's car, bullying those around him into driving to Manhattan, and using his romance skills to remind Daisy of the pluses of their relationship. Meanwhile, George's weakness makes him look sick and guilty as he contemplates Myrtle's betrayal and is driven to violence to reassert his power over her.
Approach to Women. Both Tom and George assume they know what’s best for their wives: Tom dismisses Daisy’s professed love for Gatsby despite their obvious closeness, while George is determined to take Myrtle out west once he learns about the affair. But, while it seems that Tom does fundamentally understand Daisy and is right about her unwillingness to leave their marriage, George is unable to hold on to Myrtle either emotionally or physically. She is killed trying to run away from him.
Tom and George Essay Ideas
Differences in attitude and outcome, despite a relatively similar situation, reveal some unexpected truths about the world of the novel. Argue the reverse of any of these topics for a really provocative essay!
- The fact that Tom manipulates George into killing Gatsby and then himself (which allows Tom and Daisy to walk away from the entire affair without consequence) shows the huge privileges of having money in the novel.
- Nick's approach to Tom and George shows his admiration of a physical, brutish, domineering kind of masculinity.
- The fact that the relatively good guy turns into a murderer while the bad guy lives to cheat another day is a very cynical take on what happens in a world without a moral compass.

Despite Daisy Buchanan and Jordan Baker 's similar “white girlhoods” (1.140) in Louisville, their attitude and motivations are quite distinct, making them really interesting to compare and contrast.
Attitude and Outlook. Both Daisy and Jordan display an entitled, bored attitude that’s typical of Fitzgerald’s depiction of the old money segment of wealthy New York society. The fact that they are introduced in tandem, both lying on the couches in their white dresses, speaks to their initially similar attitudes. But soon we see how different their takes on this kind of life are. Daisy is increasingly despondent, even nihilistic, asking in Chapter 7 , “what shall we do today, and tomorrow, and for the next thirty years?” (7.74). Jordan meanwhile is a pragmatic opportunist, who sees possibilities everywhere, arguing that “life starts all over again when it gets crisp in the fall” (7.75). In other words, Daisy’s pessimistic attitude from Chapter 1 comes through again, while Jordan, despite coming across as cynical and sharp, actually still seems excited about the possibilities life has to offer.
Appearance and Personality. Both Daisy and Jordan very alluring in their own way, though Daisy’s allure comes through her enchanting voice and feminine charms, while Jordan is masculine, “jaunty,” witty, sharp, and physical. Daisy maintains a squeaky-clean reputation despite moving with a fast crowd, while there are plenty of rumors about Jordan’s cheating in golf, and Nick comments on her dishonest attitude. More significantly, Daisy is incredibly self-absorbed while Jordan is very observant.
Role in Society. Daisy seems caught between what society expects of her and some deeper, more powerful desires she can’t name, resulting in restlessness, depression, and her affair. Daisy is sticking to her prescribed societal role by marrying and having a child, while Jordan plays golf, “runs around town” and doesn’t seem to be in a hurry to marry, at least in the beginning of the novel. Perhaps Jordan is still somewhat optimistic about the possibilities of life since she hasn’t settled down yet, while Daisy realizes that nothing major in her life will change at this point. Jordan, meanwhile, is content to chase after fun and intrigue via other people’s bad behavior. And she doesn’t get dragged down by the tragedy in the book – on the contrary, she is callous in how little Myrtle’s death seems to shake her, coolly calling Nick the next day and asking him to meet like nothing has happened (8.50-61). Perhaps her motivations are a bit less accessible to the reader since her role was significantly downsized between some of Fitzgerald’s earlier drafts. But in any case, as we watch Daisy struggle in her marriage, what we see of Jordan is cool, calm, collected, and rather uncaring.
Daisy and Jordan Essay Ideas
So what are some possible conclusions we can draw from Daisy and Jordan’s characters? One of the most common strategies is to tie the differences between these women onto one of the book’s larger themes, like the role of society and class or the American Dream . Another is to think about an important feature of the novel, like Nick’s narration, and see what these two characters can reveal about it. With those strategies in mind, here are some potential arguments you could argue for or against!
- Jordan and Daisy, because they are generally disempowered, both use their sexuality in different ways to gain power, with different results.
- Despite Jordan’s overt cheating and lying, Daisy is, in fact, the more morally compromised person.
- The way Nick treats Jordan versus the way he describes Daisy reveals the novel’s preoccupation with Gatsby above all, to the detriment of the female characters.

While Daisy Buchanan and Myrtle Wilson obviously come from very different backgrounds and have conflicting motivations, they also have some surprising similarities.
Physical Appearance. Daisy and Myrtle both derive power from their looks. Myrtle's comfort with her voluptuous body is clearly appealing to Tom, while Daisy's magnetic voice and ethereal presence obsess Gatsby. Throughout the novel, Myrtle is frequently reduced to being just a body - one to be used or violated by those around her. Tom sees little in Myrtle besides someone to either rub up against, have sex with, or punch at will; George resorts to imprisoning Myrtle while she eggs him on to "beat" her (7.314) the way Tom does; and finally, Daisy gruesomely rips Myrtle's body apart with a car. Meanwhile, Daisy's voice also serves to make her less of a person in her own right and more of an idealized, mythic figure from fairy tales. For Gatsby, Daisy's voice is appealing because it is "full of money" (7.105) - he is attracted to her not because of who she is, but because he sees her as a prize.
Social Standing. Myrtle puts on the airs that Daisy has been born and raised with. This allows Myrtle to wield considerable social power within her group, as seen by how her guests fawn on her at the Manhattan party she throws. Daisy, in contrast, never exerts such overt power over a group – rather, she seems to move with crowds, doing what it expected of her (for instance marrying Tom despite still loving Gatsby).
Love and Relationships. Daisy and Myrtle’s marriages are strikingly quite different. Daisy and Tom are able to stay together even through serial affairs and murder. They end up loyal co-conspirators, protected by their wealth. Meanwhile, Myrtle has nothing but disdain for George despite his evident love for her. Still, both women use affairs with other men as a way to escape. Daisy wants to get away from an increasingly unhappy marriage and try to recapture the spontaneity and possibility of her youth, while Myrtle loves the status that her affair with Tom grants her. However, both learn that they can’t escape forever through their affairs. Obviously, their biggest difference is that Daisy gets to walk away from the novel unscathed, while Myrtle gets killed.
Daisy and Myrtle Essay Ideas
Here are ways to write about these different women who face similar choices with dramatically opposite conclusions.
- Despite their similarities in action and motivation, Daisy is protected from any lasting harm by her wealth and old money status, while Myrtle is punished for the same behavior, revealing how the class system in America protects the wealthy.
- The novel refuses to give any inner life to women, and instead reduces them to their physical qualities no matter what social class they come from. Daisy and Myrtle's similar treatment by the narrator and by the men around them shows that gender trumps class when determining status.
- Daisy and Myrtle’s similarities reveal how hollow the progress of the women’s movement really was at that point in time. Despite the big gains the movement made in the early twentieth century, including winning the right to vote and pushing for more freedom in how they could dress and act, both of these women’s lives aren’t vastly improved. They’re both trapped in unhappy marriages, they both rely on their looks/charms/sexuality to get what they want, and neither of them has even a chance of pursuing a fulfilling life through a career.

What’s Next?
Now that you’ve gone over the novel’s most popular compare/contrast pairings, check out our analysis of the novel’s romantic pairings in our guide to love, desire, and relationships in The Great Gatsby .
Have an essay about a symbol or motif? Get started with our symbols overview and motifs overview.
Still a little hazy on some of the plot elements in Gatsby? Not to worry, we have you covered with our complete book summary !

Anna scored in the 99th percentile on her SATs in high school, and went on to major in English at Princeton and to get her doctorate in English Literature at Columbia. She is passionate about improving student access to higher education.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
How to Compare Two Novels in Comparative Essay
Sam Edwards/Getty Images
- Writing Essays
- Writing Research Papers
- English Grammar
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
At some point in your literature studies, probably just about the time you get really good at finding the theme of a novel and coming up with a sound analysis of a single literary piece, you will be required to compare two novels.
Your first task in this assignment will be to develop a good profile of both novels. You can do this by making a few simple lists of traits that might be comparable. For each novel, identify a list of characters and their roles in the story or important characteristics, and any important struggles, time periods, or major symbols (like an element of nature).
You may also attempt to come up with book themes that could be comparable. Sample themes would include:
- Man versus nature (is each main character battling the elements?)
- Individual versus society (does each main character feel like an outsider?)
- Struggle between good and evil (are your characters involved in good v. evil scenarios?)
- Coming of age (do the main characters experience a tough lesson that makes them grow?)
Your assignment will most likely give you direction as to whether you should find specific characters, story characteristics, or overall themes to compare. If it is not that specific, don't worry! You actually have a little more leeway.
Comparing Two Novel Themes
The teacher's goal when assigning this paper is to encourage you to think and analyze. You no longer read for a surface understanding of what happens in a novel; you are reading to understand why things happen and what the deeper meaning behind a character is a setting or an event. In short, you are expected to come up with an interesting comparative analysis.
As an example of comparing novel themes, we will look at The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn and The Red Badge of Courage . Both of these novels contain a "coming of age" theme since both have characters who grow a new awareness through tough lessons. Some comparisons you could make:
- Both characters have to explore the notion of "civilized behavior" in the societies where they exist.
- Each main character has to question the behavior of his male role models and his male peers.
- Each main character leaves his childhood home and encounters challenges.
To craft an essay about these two novels and their similar themes, you would create your own list of similarities like those above, using a list, chart, or a Venn diagram .
Sum up your overall theory about how these themes are comparable to create your thesis statement . Here is an example: "Both characters, Huck Finn and Henry Fleming, embark on a journey of discovery, and each boy finds new understanding when it comes to traditional notions about honor and courage."
You will use your common characteristic list to guide you as you create body paragraphs .
Comparing Main Characters in Novels
If your assignment is to compare the characters of these novels, you would make a list or Venn diagram to make more comparisons:
- Both characters are young men
- Both question society's notion of honor
- Both witness behavior that makes them question their role models
- Both have a nurturing female influence
- Both question their former beliefs
Comparing two novels is not as difficult as it sounds at first. Once you generate a list of traits, you can easily see an outline emerging.
- Venn Diagrams to Plan Essays and More
- Graphic Organizers
- Top Conservative Novels
- Must-Read Books If You Like 'The Catcher in the Rye'
- Write a Compare and Contrast Essay
- Beef Up Critical Thinking and Writing Skills: Comparison Essays
- How to Write a Character Analysis
- Preparing for Final Exams
- How to Find the Theme of a Book or Short Story
- 10 Steps to Writing a Successful Book Report
- 10 Common Themes in Literature
- 5 Novel Setting Maps for Classic American Literature
- The Red Badge of Courage Book Summary
- How to Write a Great Book Report
- The Top Coming-of-Age Novels
- Top Novels for American Literature Classes

Pellissippi HOME | Library Site A-Z
Literary Criticism: Comparing/Contrasting Works, Characters, or Authors
- Getting Started
- 1. What is Literary Criticism
- Critical Literary Lenses
- Literary Elements
- Comparing/Contrasting Works, Characters, or Authors
- 3. Find Literary Criticism
- 4. Write Your Paper
- MLA Citation This link opens in a new window
Comparing/Contrasting Literary Works, Characters, or Authors
Comparing literary works.
- Consider which works you want to compare/contrast.
- You could make a list of themes from each work and compare them side by side.
- Free writing is also a great way to get your ideas on paper.
- Spend time brainstorming- those who explore their ideas often have better essays in the end.
- Try to determine the central theme of the work you are considering.
- Look for a second work that has a similar theme
Common Themes
- Good vs. Evil
- Coming of Age
- War and its perils
- Individual vs. Society
- Heroism
These are only some of the themes out there. You can explore many other options for your paper!
Questions to Ask
- What is the overall message of the work?
- Does the main character evolve as the story progresses?
- What was the main conflict in the work?
- Is the work trying to convey a message about society?
- How do symbols tie into or help to develop the theme?
Character Analysis
- Select two characters you would like to analyze.
- Reread text and focus in on these characters, taking notes as you go.
- Make a list of traits for each character and compare/contrast them side by side.
- What important traits do the characters possess?
- Is the character a main protagonist or antagonist?
- Look at the characters actions- how can they be interpreted?
- How does the character interact with others?
- How does the character interact with the world they live in?
- Do you see changes in the character as the plot progresses?
Author Analysis
- You can also focus your compare/contrast criticism on two authors.
- Reread the authors works you will be critiquing
- Take notes about the authors as you read
- What does the text say about the Author?
- What kind of message is the Author trying to convey to their audience?
- Does the author's life and background effect the themes of their works?
- Do historical events influence the authors?
- << Previous: Literary Elements
- Next: 3. Find Literary Criticism >>
- Writing Worksheets and Other Writing Resources
- Thesis, Analysis, & Structure
Comparing and Contrasting
About the slc.
- Our Mission and Core Values

The professor says to compare and contrast A and B ...
Determining the Structure of your Essay:
Determining the structure of your essay is the most important step towards conducting and presenting to the reader a well-developed comparison. Students are often asked to compare things in twos. For example, compare these two articles, or two characters in a novel, or a film and a novel or an article and a poem... The possibilities are endless.
When you are faced with the task of having to compare and contrast, it can be overwhelming. You're thinking about two pieces of writing that you know are different, and perhaps there are some similarities, too, but how can you suddenly start talking about them both? Which one should I talk about first? Which one should I talk about last?
Sometimes, comparisons are done in the following manner:
You pick one article to describe: Article A. Then you talk about Article B. Perhaps at the end, you talk about the similarities in both articles.
This format will consist of three main parts: A, B, and, finally, their similarities.
Although this format is an acceptable way of making comparisons, and it is sometimes used to present well-developed "compare and contrast" essays, the format has its weaknesses that can jeopardize an effective comparison.
What could happen when you use this format and you completely isolate Article A from Article B is that you make it more difficult to compare. Your final essay might end up divided in two parts: half of the paper talks about only Article A and the second half talks about only Article B . You do not want to split your essay into a description of Article A and a description of Article B because then it will be harder to compare them since you invested most of your energy into describing them and not comparing them.
How to avoid the "Split Essay": A Second Option for Comparison
The best way to avoid the Split Essay is to unify both split ends. Do not discuss Article B at the end. Talk about both A and B from the beginning. The question now is:
What do I do to eliminate the Split?
Break it down:
You do not get rid of the gap between the two halves of the essay that are split. You simply break it down . This is done by finding common themes, or points of comparison in Article A and Article B. Once you find those points of comparison, you can discuss each individual theme and how each shows up in Article A and B . Consider the following questions:
- What major themes are discussed in each of the essays?
- What doe the writer of Article A say about the first theme, and how is this similar to or different than what the writer of Article B says about the same topic?
- What conclusions can you make about these differences or similarities?
After developing a thorough explanation of the first theme, you can mow move on to discuss the second theme that appears in both essays and write about it. Ideally, each theme will be discussed thoroughly in its own paragraph, explaining how each is similar or different in Article A and Article B
During the seventies, Gabriel Garcia Marquez wrote his most famous novel, One Hundred Years of Solitude , in which he discussed themes regarding the solitude of Latin America.
In 1982, Marquez received the Nobel Prize in Literature for his novel and wrote a speech for this occasion. In his speech, he called attention to Latin American economic struggles and their historical context.
In 1990, Enrique Krauze, a Mexican economist, published an article in which he discussed the same topic: problems in Latin American economics.
The prompt says:
Compare and contrast Enrique Krauze's essay to the speech written by Marquez.
Possible approaches:
Option #1: Text by text comparison
First paragraph:
A: An explanation of Marquez's entire speech
Second paragraph:
B: An explanation of Krauze's entire essay
Third paragraph:
Similarities or differences
(this might lead to the "Split Essay" comparison)
Option #2: Point by point comparison
The breakdown: Finding common themes or points of comparison:
• Neoliberalism (free trade)
• US involvement
• Proposed solutions to the problems (macro or micro economy?)
A: Krauze's opinion on neoliberalism
B: Marquez's opinion on neoliberalism
A: US involvement good or bad? According to Marquez
B: US involvement good or bad? According to Krauze
Whatever other theme that stands out as significant for explaining the differences of opinions.
Sample paragraph:
Enrique Krauze and Gabriel Garcia Marquez take different positions in regards to the implementation of more neoliberalist policies in Latin American countries. While Krauze argues the need to expand open trade in Latin America to improve its economy, Marquez opposes this idea and argues that an open trade economy would only aid foreign investors in further exploiting the natural resources in Latin America. Krauze's support of neoliberalism is based on the idea that through a macro economy, the "undeveloped" countries will soon see the light at the end of the tunnel. On the other hand, Marquez rebuts this argument, claiming that the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund, which forced neoliberalist policies onto Latin American countries, only served to increase their foreign debt.
Notice how the beginning of this paragraph discusses only one theme: neoliberalism. Also notice how the writer was able to incorporate both articles and not just one. Pay attention, too, to the use of words and phrases that juxtapose or suggest comparison. These words establish links between A and B .
Handout created by Rubén Garibaldo, Student Learning Center, University of California, Berkeley
©2006 UC Regents
Handout revised by Carolyn Swalina, Student Learning Center, University of California, Berkeley
©2011 UC Regents
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License.
- Writing for Success: Compare/Contrast
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
This section will help you determine the purpose and structure of comparison/contrast in writing.
The Purpose of Compare/Contrast in Writing
Comparison in writing discusses elements that are similar, while contrast in writing discusses elements that are different. A compare-and-contrast essay, then, analyzes two subjects by comparing them, contrasting them, or both.
The key to a good compare-and-contrast essay is to choose two or more subjects that connect in a meaningful way. The purpose of conducting the comparison or contrast is not to state the obvious but rather to illuminate subtle differences or unexpected similarities. For example, if you wanted to focus on contrasting two subjects you would not pick apples and oranges; rather, you might choose to compare and contrast two types of oranges or two types of apples to highlight subtle differences. For example, Red Delicious apples are sweet, while Granny Smiths are tart and acidic. Drawing distinctions between elements in a similar category will increase the audience’s understanding of that category, which is the purpose of the compare-and-contrast essay.
Similarly, to focus on comparison, choose two subjects that seem at first to be unrelated. For a comparison essay, you likely would not choose two apples or two oranges because they share so many of the same properties already. Rather, you might try to compare how apples and oranges are quite similar. The more divergent the two subjects initially seem, the more interesting a comparison essay will be.
The Structure of a Compare/Contrast Essay
The compare-and-contrast essay starts with a thesis that clearly states the two subjects that are to be compared, contrasted, or both and the reason for doing so. The thesis could lean more toward comparing, contrasting, or both. Remember, the point of comparing and contrasting is to provide useful knowledge to the reader. Take the following thesis as an example that leans more toward contrasting:
Thesis Statement: Organic vegetables may cost more than those that are conventionally grown, but when put to the test, they are definitely worth every extra penny.
Here the thesis sets up the two subjects to be compared and contrasted (organic versus conventional vegetables), and it makes a claim about the results that might prove useful to the reader.
You may organize compare-and-contrast essays in one of the following two ways:
- According to the subjects themselves, discussing one then the other
- According to individual points, discussing each subject in relation to each point
The organizational structure you choose depends on the nature of the topic, your purpose, and your audience.
Given that compare-and-contrast essays analyze the relationship between two subjects, it is helpful to have some phrases on hand that will cue the reader to such analysis.
Phrases of Comparison and Contrast
Writing an Compare/Contrast Essay
First choose whether you want to compare seemingly disparate subjects, contrast seemingly similar subjects, or compare and contrast subjects. Once you have decided on a topic, introduce it with an engaging opening paragraph. Your thesis should come at the end of the introduction, and it should establish the subjects you will compare, contrast, or both as well as state what can be learned from doing so.
The body of the essay can be organized in one of two ways: by subject or by individual points. The organizing strategy that you choose will depend on, as always, your audience and your purpose. You may also consider your particular approach to the subjects as well as the nature of the subjects themselves; some subjects might better lend themselves to one structure or the other. Make sure to use comparison and contrast phrases to cue the reader to the ways in which you are analyzing the relationship between the subjects.
After you finish analyzing the subjects, write a conclusion that summarizes the main points of the essay and reinforces your thesis.
Compare/Contrast Essay Example
Comparing and Contrasting London and Washington, DC
By Scott McLean in Writing for Success
Both Washington, DC, and London are capital cities of English-speaking countries, and yet they offer vastly different experiences to their residents and visitors. Comparing and contrasting the two cities based on their history, their culture, and their residents show how different and similar the two are.
Both cities are rich in world and national history, though they developed on very different time lines. London, for example, has a history that dates back over two thousand years. It was part of the Roman Empire and known by the similar name, Londinium. It was not only one of the northernmost points of the Roman Empire but also the epicenter of the British Empire where it held significant global influence from the early sixteenth century on through the early twentieth century. Washington, DC, on the other hand, has only formally existed since the late eighteenth century. Though Native Americans inhabited the land several thousand years earlier, and settlers inhabited the land as early as the sixteenth century, the city did not become the capital of the United States until the 1790s. From that point onward to today, however, Washington, DC, has increasingly maintained significant global influence. Even though both cities have different histories, they have both held, and continue to hold, significant social influence in the economic and cultural global spheres.
Both Washington, DC, and London offer a wide array of museums that harbor many of the world’s most prized treasures. While Washington, DC, has the National Gallery of Art and several other Smithsonian galleries, London’s art scene and galleries have a definite edge in this category. From the Tate Modern to the British National Gallery, London’s art ranks among the world’s best. This difference and advantage has much to do with London and Britain’s historical depth compared to that of the United States. London has a much richer past than Washington, DC, and consequently has a lot more material to pull from when arranging its collections. Both cities have thriving theater districts, but again, London wins this comparison, too, both in quantity and quality of theater choices. With regard to other cultural places like restaurants, pubs, and bars, both cities are very comparable. Both have a wide selection of expensive, elegant restaurants as well as a similar amount of global and national chains. While London may be better known for its pubs and taste in beer, DC offers a different bar-going experience. With clubs and pubs that tend to stay open later than their British counterparts, the DC night life tend to be less reserved overall.
Both cities also share and differ in cultural diversity and cost of living. Both cities share a very expensive cost of living—both in terms of housing and shopping. A downtown one-bedroom apartment in DC can easily cost $1,800 per month, and a similar “flat” in London may double that amount. These high costs create socioeconomic disparity among the residents. Although both cities’ residents are predominantly wealthy, both have a significantly large population of poor and homeless. Perhaps the most significant difference between the resident demographics is the racial makeup. Washington, DC, is a “minority majority” city, which means the majority of its citizens are races other than white. In 2009, according to the US Census, 55 percent of DC residents were classified as “Black or African American” and 35 percent of its residents were classified as “white.” London, by contrast, has very few minorities—in 2006, 70 percent of its population was “white,” while only 10 percent was “black.” The racial demographic differences between the cities is drastic.
Even though Washington, DC, and London are major capital cities of English-speaking countries in the Western world, they have many differences along with their similarities. They have vastly different histories, art cultures, and racial demographics, but they remain similar in their cost of living and socioeconomic disparity.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- A compare-and-contrast essay analyzes two subjects by either comparing them, contrasting them, or both.
- The purpose of writing a comparison or contrast essay is not to state the obvious but rather to illuminate subtle differences or unexpected similarities between two subjects.
- The thesis should clearly state the subjects that are to be compared, contrasted, or both, and it should state what is to be learned from doing so.
- There are two main organizing strategies for compare-and-contrast essays.
- Organize by the subjects themselves, one then the other.
- Organize by individual points, in which you discuss each subject in relation to each point.
- Use phrases of comparison or phrases of contrast to signal to readers how exactly the two subjects are being analyzed.
- Provided by : Lumen Learning. Located at : http://lumenlearning.com/ . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Successful Writing. Provided by : Anonymous. Located at : http://2012books.lardbucket.org/books/successful-writing/s14-07-comparison-and-contrast.html . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Comparing and Contrasting London and Washington, DC. Authored by : Scott McLean. Located at : http://2012books.lardbucket.org/books/successful-writing/s14-07-comparison-and-contrast.html . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Table of Contents
Instructor Resources (Access Requires Login)
- Overview of Instructor Resources
An Overview of the Writing Process
- Introduction to the Writing Process
- Introduction to Writing
- Your Role as a Learner
- What is an Essay?
- Reading to Write
- Defining the Writing Process
- Videos: Prewriting Techniques
- Thesis Statements
- Organizing an Essay
- Creating Paragraphs
- Conclusions
- Editing and Proofreading
- Matters of Grammar, Mechanics, and Style
- Peer Review Checklist
- Comparative Chart of Writing Strategies
Using Sources
- Quoting, Paraphrasing, and Avoiding Plagiarism
- Formatting the Works Cited Page (MLA)
- Citing Paraphrases and Summaries (APA)
- APA Citation Style, 6th edition: General Style Guidelines
Definition Essay
- Definitional Argument Essay
- How to Write a Definition Essay
- Critical Thinking
- Video: Thesis Explained
- Effective Thesis Statements
- Student Sample: Definition Essay
Narrative Essay
- Introduction to Narrative Essay
- Student Sample: Narrative Essay
- "Shooting an Elephant" by George Orwell
- "Sixty-nine Cents" by Gary Shteyngart
- Video: The Danger of a Single Story
- How to Write an Annotation
- How to Write a Summary
- Writing for Success: Narration
Illustration/Example Essay
- Introduction to Illustration/Example Essay
- "She's Your Basic L.O.L. in N.A.D" by Perri Klass
- "April & Paris" by David Sedaris
- Writing for Success: Illustration/Example
- Student Sample: Illustration/Example Essay
Compare/Contrast Essay
- Introduction to Compare/Contrast Essay
- "Disability" by Nancy Mairs
- "Friending, Ancient or Otherwise" by Alex Wright
- "A South African Storm" by Allison Howard
- Student Sample: Compare/Contrast Essay
Cause-and-Effect Essay
- Introduction to Cause-and-Effect Essay
- "Cultural Baggage" by Barbara Ehrenreich
- "Women in Science" by K.C. Cole
- Writing for Success: Cause and Effect
- Student Sample: Cause-and-Effect Essay
Argument Essay
- Introduction to Argument Essay
- Rogerian Argument
- "The Case Against Torture," by Alisa Soloman
- "The Case for Torture" by Michael Levin
- How to Write a Summary by Paraphrasing Source Material
- Writing for Success: Argument
- Student Sample: Argument Essay
- Grammar/Mechanics Mini-lessons
- Mini-lesson: Subjects and Verbs, Irregular Verbs, Subject Verb Agreement
- Mini-lesson: Sentence Types
- Mini-lesson: Fragments I
- Mini-lesson: Run-ons and Comma Splices I
- Mini-lesson: Comma Usage
- Mini-lesson: Parallelism
- Mini-lesson: The Apostrophe
- Mini-lesson: Capital Letters
- Grammar Practice - Interactive Quizzes
- De Copia - Demonstration of the Variety of Language
- Style Exercise: Voice

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

8.6: Essay Type- Comparing and Contrasting Literature
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 101138

- Heather Ringo & Athena Kashyap
- City College of San Francisco via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Compare and Contrast Essay Basics
The Compare and Contrast Essay is a literary analysis essay, but, instead of examining one work, it examines two or more works. These works must be united by a common theme or thesis statement. For example, while a literary analysis essay might explore the significance of ghosts in William Shakespeare's Hamlet, a compare/contrast essay might explore the significance of the supernatural in Hamlet and Macbeth .
Literary Analysis Thesis Statement:
While Horatio seems to think the ghost of Old Hamlet is a demon trying to lead Hamlet to death, and Gertrude and Claudius think it is a figment of Hamlet's insanity, Hamlet's status as an unreliable narrator and the ghost actually symbolizes the oppression of Catholics during Shakespeare's time period.

Compare and Contrast Thesis Statement:
The unreliable narrators paired with the ghosts in both Hamlet and Macbeth symbolize the oppression of Catholics in Shakespeare's time period.
Essay Genre Expectations
- Use first-person pronouns sparingly (you, me, we, our)
- Avoid colloquialisms
- Spell out contractions
- Use subject-specific terminology, such as naming literary devices
- Texts: two or more
- Avoid summary. Aim for analysis and interpretation
- MLA formatting and citations
Organization
While the literary analysis essay follows a fairly simple argumentative essay structure, the compare and contrast essay is slightly more complicated. It might be arranged by:
- Literary work (the block method)
- Topics/subtopics (the point-by-point method)
In general, ensure each paragraph supports the thesis statement and that both literary works receive equal attention. Include as many body paragraphs as needed to build your argument.
First Option for Organization: The Block Method
In this first option for organization, you will need to discuss both literary works in the introduction and thesis statement, but then the body of the paper will be divided in half. The first half of the body paragraphs should focus on one literary work, while the second half of the body paragraphs should focus on the other literary work.
- Background of topic
- Background of works related to topic
- Thesis Statement
- Topic sentence
- Introduction of evidence
- Evidence from the first literary work
- Explanation of evidence
- Analysis of evidence
- Evidence from the second literary work
- Restatement of thesis in new words
- Summary of essay arguments
Second Option for Organization: The Point-by-Point Method
With this second option for organization, you may decide to write about both literary works within the same body paragraph every time, or you may choose to consistently alternate back and forth between the literary works in separate body paragraphs.
- Evidence from both literary works
Character Comparison and Contrast Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
“Fast Food Nation” is a novel written by Eric Schlosser who is a journalist reporting on the food industry. He focuses more on the hazardous conditions and effects of eating fast foods.
He explains that Americans are a people that are addicted to the products of fast food. This book is compared to The Jungle which is written by another journalist Upton Sinclair. He gives the journey of a Lithuanian family, who travelled to the United States just to experience the American Dream. His expectation was shattered because he encountered the opposite.
The family strives to get their way to survive in Chicago through the means of coning. Both books have a similar theme concerning the health of the people of America and the working conditions of people in the meat packing industry. For a deeper analysis of this subject, we will be comparing and contrasting between two major characters of each novel. The character in Fast Food Nation is known as Jurgis Rudkus while the major character in The Jungle is Kenney Dobbins.
Starting with the similarities, they both had good character and integrity in their lives. In the beginning of the literature The Jungle, Jurgis was young strong and an honest man. Kenny had a high level of integrity to his work and family. As much as there were hardships on his way, he focused on doing the things that are right and giving his best for the company regardless of the poor working conditions. They both worked for a meat packing industry.
Kenney was carrying crates weighing 120 pounds in a meat packing company called Monfort Slaughterhouse. His job was to carry heavy weights of meat. On the other hand Jurgis was digging tunnels. The name of the meat packing company is not specified but the location is in Chicago. Both their jobs required hard hours of labor. Of course such kinds of working opportunities were paying little with much to be done. Both Kenney and Jurgis were striving to have better lives for their families.
In each novel, both Kenney and Jurgis get injuries while they were working. One day as Kenney was working, a crate weighing ninety pounds fell from the top level and was about to crash him. He managed to catch it but he went out of balance and caused an injury on his back (Schlosser 187). He severely herniated two of his back disks. Jurgis also attained injuries due to the labor of digging tunnels. Both of them got no serious medical attention that should have been provided by the company.
The working conditions in both situations were poor. They became victims to the bitterness of life. Life had a way of causing oppression in their lives. According to Kenney, it was his employer while Jurgis was poverty in a foreign land. They both had challenges in their marriage but providers for their families. They were both young, Kenney was 24 years old but Jurgis age was given no specification.
Looking at the differences, Jurgis was a foreigner who travelled from Eastern Europe to America in such of a better living. He was a Lithuanian and could speak both polish and Lutheran (Sinclair 2). On the other hand, Kenny was a born American. In line with character and integrity, Kenney was able to maintain the good moral.
Regardless of how much his employer was oppressing him with harsh working conditions, he never gave up and stayed committed to his employer. Jurgis started off as a man of integrity but the pressures of life made him stray away. Wanting to survive in the harsh reality in America, he forgot every good moral he had and began conning, mugging people and turned out to be a criminal.
Kenney lost his wife through divorce while Jurgis lost his wife through child birth. He lacked the finances to pay for her medical bills. Another difference between the two characters is joining of unions. Kenney refused to involve himself with unions. He considered them as groups that build a bad reputation from the employer’s perspective. Jurgis on the other hand, involves himself into a strong labor union and socialism. He also got to be part of a socialist rally. Kenney ended up being fired and living in a horrible health.
He lost his job without any valid reason and was given no compensation. Jurgis’ involvement in the unions made him have a better life and the union rights were able to secure his position in the factory. Through socialism activities he got to be converted to a religious person and began going for missions.
It has been clearly seen that in both novels, there is a similar concept and theme while at the same time, the approach is different. The major characters in both novels have endured hardship, disappointments and bitterness. They also had different characteristic depending on the kind of circumstances. The two characters Kenney and Jurgis have helped the world to realize the kind of conditions that are in the meat packing industries.
Works Cited
Schlosser, Eric. Fast Food Nation. New York: Houghton Mifflin, 2002. Print.
Sinclair, Upton. The Jungle . New York: Doubleday, Jabber & Company, 1906. Print.
- "The Jungle" by Sinclair and "Fast Food Nation" by Schlosser
- The Alberta Budget 2022 Objectives
- American Dream and Socialism in the Book “The Jungle” by Sinclair
- ZZ Packer’s “Drinking Coffee Elsewhere”
- The World of Money
- “The Vocabulary We Know Does More than Communicate Our Knowledge; It Shapes What We Know.”
- Literature Analysis: Incidents in the Life of a Slave Girl by Harriet Jacobs
- Headlines twice the size of the events
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2018, October 31). Character Comparison and Contrast. https://ivypanda.com/essays/character-comparison-and-contrast/
"Character Comparison and Contrast." IvyPanda , 31 Oct. 2018, ivypanda.com/essays/character-comparison-and-contrast/.
IvyPanda . (2018) 'Character Comparison and Contrast'. 31 October.
IvyPanda . 2018. "Character Comparison and Contrast." October 31, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/character-comparison-and-contrast/.
1. IvyPanda . "Character Comparison and Contrast." October 31, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/character-comparison-and-contrast/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Character Comparison and Contrast." October 31, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/character-comparison-and-contrast/.
MUST-HAVE END-OF-THE-YEAR RESOURCES

English Language Arts
Classroom Management

Building Community

Freebie Vault

Free Vocabulary Activities!
Compare and contrast two or more characters in a story {freebies included}.
I’m back for the next part of our character development lesson using Verdi by Janell Cannon. For this lesson, I will be sharing how we used the book to compare and contrast two or more characters in a story, drawing on specific details from the text.

To read the first blog post in this series, and to grab the free Inferring Character Traits Graphic Organizer , click HERE . To check out my other blog post series on character development, click HERE and HERE !
Since our last lesson on inferring character traits through dialogue , my students learned that there are a number of different ways that an author reveals information about a character in a text. An author reveals information about a character through:
- physical traits (both explicit and inferred)
- interactions with other characters

- What are the similarities and differences between these two things?
- How are these two things alike and different?
- Which similarities do you think are most important?
- Are there any details that are unique to one thing and not the other?

Once we filled out the double bubble thinking maps, as a formative assessment, students wrote their own written responses to compare and contrast the two characters.

Check out these reading passages and assessments to use in your classroom HERE !

Grab a free copy of my Verdi formative assessment and color coded double bubble thinking map HERE !

Do you need more passages to help you teach character analysis? Check out my Characters: Differentiated Reading Passages and Questions resource. I provide teachers with 10 differentiated character reading passages. Each passage has five short answer questions for students to analyze characters. Click HERE or the button below to check them out. If you download the preview, you can see the entire resource.

This resource is now bundled.
The first bundle includes 10 Fiction Differentiated Passages and Questions. Click HERE or the button below.

This bundle includes 20 total resources – 10 Informational Text and 10 Fiction Text Differentiated Passages and Questions. Click HERE or the button below.

19 Comments
I too believe that the double bubble map is great for the upper grades. I usually have students color code the double map using different colors. I usually incorporate art blends into this. For example: I might do one set of differences in yellow, one set of differences in blue, and then the similarities would be in green to show that they are combined (similar). This is a great post! Thank you for taking the time to write such an informative post, and I will definitely be reviewing your blog posts as I plan for next year!
Sheldon- I love your idea on color coding specific groups of differences! Thanks for sharing! Thank you also for your kind words!
This is a great post. We always use Venn diagrams and I am familiar with double-bubbles but I haven’t used them in a while. Thanks for reminding me about them. ~Brandee Creating Lifelong Learners
Thanks for your comments Brandee! I appreciate your kind words!
This looks great! I love using Verdi for character comparison. I also like to have students compare and contrast Verdi from the beginning of the book to the end.
Thank you so much for you comments, Alicia! I agree that another great mini-lesson is character change! Isn’t it awesome when you come across such great mentor texts? It makes me so happy!! :)
Very nice post! =) Your resources are always high-quality and BEAUTIFUL!! I came across you in my former blog life, when I was love4thgrade.blogspot.com. Now, I am love5thgrade.blogspot.com. Thank you for all you have done for the online education world. I showcased your weblog along with 11 others this evening here:: http://love5thgrade.blogspot.com/2014/04/jasztals-resource-spotlight-2.html . Have a wonderful rest of the weekend!
Thank you so much, Victoria! I have always been a fan of yours! Thanks so much for your kind words!
Do you have another book that you would recommend instead of Verdi? I really like this lesson, but am petrified of snakes!
Hi Melissa- Thanks for your comments! I have tons of mentor texts suggestions in my Character Pack. Here is the link if you’d like to check it out: https://www.teacherspayteachers.com/Product/Analyzing-Characters-Pack-Common-Core-Aligned-656011 . Have a great day!
I really want to commend you for supporting this thinking map. I have been teaching high school for almost 10 years and even students at this level need these graphic organizers.
Thanks so much, Maria!
Hi! I absolutely love your blog and resources! I am using your compare and contrast lesson with my students. I was wondering, how do you score the writing formative assessment piece?
Thanks so much!
What story is the greens from?
Hi Andrea- The story is Verdi by Jannell Cannon.
I love your compare/contrast lesson! Do you have a title of a short text for formative assessment at a fourth grade level?
Hi Stephanie- Thanks for your kind words! I am currently in the process of writing Differentiated Reading Passages and Questions for a number of different reading skills. I currently have passages and questions for making inferences, determining theme, and citing text evidence. I plan to create a set for comparing and contrasting characters. You can check them out here: https://www.teacherspayteachers.com/Store/Kristine-Nannini/Category/Differentiated-Reading-Passages-and-Questions-261290 . Make sure you follow my store to receive an email notification when I post them. Thanks!
Hi Kristine I hope you are doing great. I would like to thank you for your great efforts you did on your blog. Actually it helped me alot. Thanks again.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Review Cart
No products in the cart.
- How It Works
- Writing Tools
compare and contrast two characters essay examples
How do you write a compare and contrast essay for two characters? – › our-services › how-to-write-…
What is a good example of compare and contrast? – For example, if you wanted to focus on contrasting two subjects you would not pick apples and oranges; rather, you might choose to compare and contrast two types of oranges or two types of apples to highlight subtle differences. For example, Red Delicious apples are sweet, while Granny Smiths are tart and acidic.
How do you compare and contrast with two people? – like, similar to, also, unlike, similarly, in the same way, likewise, again, compared to, in contrast, in like manner, contrasted with, on the contrary, however, although, yet, even though, still, but, nevertheless, conversely, at the same time, regardless, despite, while, on the one hand … on the other hand.
What is compare and contrast essay with example? – Compare and contrast essays are academic papers in which a student analyses two or more subjects with each other. To compare means to explore similarities between subjects, while to contrast means to look at their differences.
How do you write a 5 paragraph compare and contrast essay? – › blog › how-to-write-a-5-para…
What is a good hook for a compare and contrast essay? – A hook for a compare and contrast essay can vary. You can find one or two best features of the two discussed objects and write them as the opening sentence of your piece, creating interest for a reader. Alternatively, you can intrigue the reader with a question, quotation, or a scene.
What are 5 topics for a compare and contrast essay? – › blog › compare-and-contrast-essay-…
How do you start a compare and contrast paragraph? – Paragraph 1: The opening sentence names the two subjects and states that they are very similar, very different or have many important (or interesting) similarities and differences. Continue discussing similarities only using compare-contrast cue words such as “like,” “similar to” and “also,” for each comparison.
How do you start a compare and contrast essay introduction? – Introduction. Your introductory paragraph is going to introduce the two subjects to the readers. Offer a short tidbit about each subject, noting why you’ve chosen to compare and contrast the two.
What is contrast examples? – Contrast often means “opposite”: for example, black is the opposite of white, and so there’s a contrast between black ink and white paper. But contrast can also happen when the two things are just very different. For example, cats and dogs are definitely a contrast, but they’re not opposites.
How do you write a good comparison essay? – › writing-a-compa…
How many paragraphs should a compare and contrast essay have? – A compare and contrast essay discusses that similarities and differences between two subjects. The two main methods for organizing your ideas within the essay are the point-by-point method (five paragraphs) and the block method (four paragraphs).
How do you compare characters? – › 2020/04 › compare-ch…
How do you write a contrast character? – › how-to-write-a-character-an…
"Our Prices Start at $11.99. As Our First Client, Use Coupon Code GET15 to claim 15% Discount This Month!!"

Calculate the price of your order
WhatsApp us
5 Compare and Contrast Essay Examples (Full Text)
A compare and contrast essay selects two or more items that are critically analyzed to demonstrate their differences and similarities. Here is a template for you that provides the general structure:

A range of example essays is presented below.
Compare and Contrast Essay Examples
#1 jean piaget vs lev vygotsky essay.
1480 Words | 5 Pages | 10 References
(Level: University Undergraduate)

Thesis Statement: “This essay will critically examine and compare the developmental theories of Jean Piaget and Lev Vygotsky, focusing on their differing views on cognitive development in children and their influence on educational psychology, through an exploration of key concepts such as the role of culture and environment, scaffolding, equilibration, and their overall implications for educational practices..”
#2 Democracy vs Authoritarianism Essay

Thesis Statement: “The thesis of this analysis is that, despite the efficiency and control offered by authoritarian regimes, democratic systems, with their emphasis on individual freedoms, participatory governance, and social welfare, present a more balanced and ethically sound approach to governance, better aligned with the ideals of a just and progressive society.”
#3 Apples vs Oranges Essay
1190 Words | 5 Pages | 0 References
(Level: 4th Grade, 5th Grade, 6th Grade)

Thesis Statement: “While apples and oranges are both popular and nutritious fruits, they differ significantly in their taste profiles, nutritional benefits, cultural symbolism, and culinary applications.”
#4 Nature vs Nurture Essay
1525 Words | 5 Pages | 11 References
(Level: High School and College)

Thesis Statement: “The purpose of this essay is to examine and elucidate the complex and interconnected roles of genetic inheritance (nature) and environmental influences (nurture) in shaping human development across various domains such as physical traits, personality, behavior, intelligence, and abilities.”
#5 Dogs vs Cats Essay
1095 Words | 5 Pages | 7 Bibliographic Sources
(Level: 6th Grade, 7th Grade, 8th Grade)
Thesis Statement: “This essay explores the distinctive characteristics, emotional connections, and lifestyle considerations associated with owning dogs and cats, aiming to illuminate the unique joys and benefits each pet brings to their human companions.”
How to Write a Compare and Contrast Essay
I’ve recorded a full video for you on how to write a compare and contrast essay:
Get the Compare and Contrast Templates with AI Prompts Here
In the video, I outline the steps to writing your essay. Here they are explained below:
1. Essay Planning
First, I recommend using my compare and contrast worksheet, which acts like a Venn Diagram, walking you through the steps of comparing the similarities and differences of the concepts or items you’re comparing.
I recommend selecting 3-5 features that can be compared, as shown in the worksheet:

Grab the Worksheet as Part of the Compare and Contrast Essay Writing Pack
2. Writing the Essay
Once you’ve completed the worksheet, you’re ready to start writing. Go systematically through each feature you are comparing and discuss the similarities and differences, then make an evaluative statement after showing your depth of knowledge:

Get the Rest of the Premium Compare and Contrast Essay Writing Pack (With AI Prompts) Here
How to Write a Compare and Contrast Thesis Statement
Compare and contrast thesis statements can either:
- Remain neutral in an expository tone.
- Prosecute an argument about which of the items you’re comparing is overall best.
To write an argumentative thesis statement for a compare and contrast essay, try this AI Prompts:
💡 AI Prompt to Generate Ideas I am writing a compare and contrast essay that compares [Concept 1] and [Concept2]. Give me 5 potential single-sentence thesis statements that pass a reasonable judgement.
Ready to Write your Essay?

Take action! Choose one of the following options to start writing your compare and contrast essay now:
Read Next: Process Essay Examples

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Self-Actualization Examples (Maslow's Hierarchy)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Forest Schools Philosophy & Curriculum, Explained!
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Montessori's 4 Planes of Development, Explained!
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Montessori vs Reggio Emilia vs Steiner-Waldorf vs Froebel
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
How to Write an Essay Comparing Two Characters

Let’s now turn to the essence of your task. Usually such essays compare two positive characters that exemplify supreme moral ideals. Despite that, sometimes it is possible to compare one positive and one negative personality. Remember that it is not obligatory to criticize the negative character in question, but you rather need to explain his/her action, the motives and reasons for them. There cannot be any absolutely positive literary character (except in fairytales). In all cases, what you should do is to analyze the character in question and to try to relate him/her to a given social, cultural, historical process or event. In short, the best way to write such an essay is to see the character as an implementation of the “spirit of time”, and thus to compare it with another one.
The best way to write an essay comparing 2 characters is to see the character as an implementation of the “spirit of time”, and thus to compare it with another one. Tweet This
The following instructions on how to write an essay comparing two characters will assist you in your assignment.
Writing an essay comparing two characters – 7 important tips
1. read some critical analysis of both literary works.
Whether you have read them or not, it is important to read them again and to focus your attention on the given personalities. Write down everything which you consider impressive and important about them such as physical appearance, way of speaking, actions, values and beliefs, personal traits, etc.
2. Choose your topic
If you have an opportunity to choose your topic, it is better to select two characters that you know very well.
3. Find the leitmotiff of the literary works in question
Try to relate both characters to it: poverty, freedom, love, friendship, and other topics. For instance, Hamlet and Faust are lonely men who eager to know more; Hamlet wants to know about the murderer of his father, and Faust is keen to know more about the world. Although the historical eras and the cultural background of both personalities are quite different, they can be still compared as two of the leading characters of the European literature since the Renaissance period.
4. Describe the characters (according to point 1)
Prove your observations by referring to quotes from them. Tell what are their motives, goals in life (or in a given situation), how are they perceived by the other characters, and so forth.
5. Find the similarities between both characters
Tell what seems similar in them (particularly their personal traits and qualities). Concentrate your efforts on a few points. It is not good to go into detail here. You can use two qualities of the persons and to prove them by quoting passages from the text.
6. Find the differences
Do the same as given above. Show that the characters differ in some way. Just think: is there anyone who is absolutely similar to anyone else in real life?
7. Formulate your conclusion
In your conclusion , say a few words why these characters can be associated with each other. What ideas they embed? To what extent these ideas are materialized in them?
Remember all the time that you have to prove your thoughts and theses by referring to quotes, passages and critical remarks done by renowned literary critics. You cannot simply say that Faust is a “lost soul” because he made a deal with the Devil. The best literary characters are the most difficult to be analysed, so be aware of this.
Order Paper
Our guarantees, customer feedback.

© 2024 SolidEssay. All Rights Reserved.
Powered by Data Researchers Network
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 03 June 2024
Applying large language models for automated essay scoring for non-native Japanese
- Wenchao Li 1 &
- Haitao Liu 2
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 11 , Article number: 723 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Language and linguistics
Recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) have led to an increased use of large language models (LLMs) for language assessment tasks such as automated essay scoring (AES), automated listening tests, and automated oral proficiency assessments. The application of LLMs for AES in the context of non-native Japanese, however, remains limited. This study explores the potential of LLM-based AES by comparing the efficiency of different models, i.e. two conventional machine training technology-based methods (Jess and JWriter), two LLMs (GPT and BERT), and one Japanese local LLM (Open-Calm large model). To conduct the evaluation, a dataset consisting of 1400 story-writing scripts authored by learners with 12 different first languages was used. Statistical analysis revealed that GPT-4 outperforms Jess and JWriter, BERT, and the Japanese language-specific trained Open-Calm large model in terms of annotation accuracy and predicting learning levels. Furthermore, by comparing 18 different models that utilize various prompts, the study emphasized the significance of prompts in achieving accurate and reliable evaluations using LLMs.
Similar content being viewed by others
Scoring method of English composition integrating deep learning in higher vocational colleges
ChatGPT-3.5 as writing assistance in students’ essays
Detecting contract cheating through linguistic fingerprint
Conventional machine learning technology in aes.
AES has experienced significant growth with the advancement of machine learning technologies in recent decades. In the earlier stages of AES development, conventional machine learning-based approaches were commonly used. These approaches involved the following procedures: a) feeding the machine with a dataset. In this step, a dataset of essays is provided to the machine learning system. The dataset serves as the basis for training the model and establishing patterns and correlations between linguistic features and human ratings. b) the machine learning model is trained using linguistic features that best represent human ratings and can effectively discriminate learners’ writing proficiency. These features include lexical richness (Lu, 2012 ; Kyle and Crossley, 2015 ; Kyle et al. 2021 ), syntactic complexity (Lu, 2010 ; Liu, 2008 ), text cohesion (Crossley and McNamara, 2016 ), and among others. Conventional machine learning approaches in AES require human intervention, such as manual correction and annotation of essays. This human involvement was necessary to create a labeled dataset for training the model. Several AES systems have been developed using conventional machine learning technologies. These include the Intelligent Essay Assessor (Landauer et al. 2003 ), the e-rater engine by Educational Testing Service (Attali and Burstein, 2006 ; Burstein, 2003 ), MyAccess with the InterlliMetric scoring engine by Vantage Learning (Elliot, 2003 ), and the Bayesian Essay Test Scoring system (Rudner and Liang, 2002 ). These systems have played a significant role in automating the essay scoring process and providing quick and consistent feedback to learners. However, as touched upon earlier, conventional machine learning approaches rely on predetermined linguistic features and often require manual intervention, making them less flexible and potentially limiting their generalizability to different contexts.
In the context of the Japanese language, conventional machine learning-incorporated AES tools include Jess (Ishioka and Kameda, 2006 ) and JWriter (Lee and Hasebe, 2017 ). Jess assesses essays by deducting points from the perfect score, utilizing the Mainichi Daily News newspaper as a database. The evaluation criteria employed by Jess encompass various aspects, such as rhetorical elements (e.g., reading comprehension, vocabulary diversity, percentage of complex words, and percentage of passive sentences), organizational structures (e.g., forward and reverse connection structures), and content analysis (e.g., latent semantic indexing). JWriter employs linear regression analysis to assign weights to various measurement indices, such as average sentence length and total number of characters. These weights are then combined to derive the overall score. A pilot study involving the Jess model was conducted on 1320 essays at different proficiency levels, including primary, intermediate, and advanced. However, the results indicated that the Jess model failed to significantly distinguish between these essay levels. Out of the 16 measures used, four measures, namely median sentence length, median clause length, median number of phrases, and maximum number of phrases, did not show statistically significant differences between the levels. Additionally, two measures exhibited between-level differences but lacked linear progression: the number of attributives declined words and the Kanji/kana ratio. On the other hand, the remaining measures, including maximum sentence length, maximum clause length, number of attributive conjugated words, maximum number of consecutive infinitive forms, maximum number of conjunctive-particle clauses, k characteristic value, percentage of big words, and percentage of passive sentences, demonstrated statistically significant between-level differences and displayed linear progression.
Both Jess and JWriter exhibit notable limitations, including the manual selection of feature parameters and weights, which can introduce biases into the scoring process. The reliance on human annotators to label non-native language essays also introduces potential noise and variability in the scoring. Furthermore, an important concern is the possibility of system manipulation and cheating by learners who are aware of the regression equation utilized by the models (Hirao et al. 2020 ). These limitations emphasize the need for further advancements in AES systems to address these challenges.
Deep learning technology in AES
Deep learning has emerged as one of the approaches for improving the accuracy and effectiveness of AES. Deep learning-based AES methods utilize artificial neural networks that mimic the human brain’s functioning through layered algorithms and computational units. Unlike conventional machine learning, deep learning autonomously learns from the environment and past errors without human intervention. This enables deep learning models to establish nonlinear correlations, resulting in higher accuracy. Recent advancements in deep learning have led to the development of transformers, which are particularly effective in learning text representations. Noteworthy examples include bidirectional encoder representations from transformers (BERT) (Devlin et al. 2019 ) and the generative pretrained transformer (GPT) (OpenAI).
BERT is a linguistic representation model that utilizes a transformer architecture and is trained on two tasks: masked linguistic modeling and next-sentence prediction (Hirao et al. 2020 ; Vaswani et al. 2017 ). In the context of AES, BERT follows specific procedures, as illustrated in Fig. 1 : (a) the tokenized prompts and essays are taken as input; (b) special tokens, such as [CLS] and [SEP], are added to mark the beginning and separation of prompts and essays; (c) the transformer encoder processes the prompt and essay sequences, resulting in hidden layer sequences; (d) the hidden layers corresponding to the [CLS] tokens (T[CLS]) represent distributed representations of the prompts and essays; and (e) a multilayer perceptron uses these distributed representations as input to obtain the final score (Hirao et al. 2020 ).
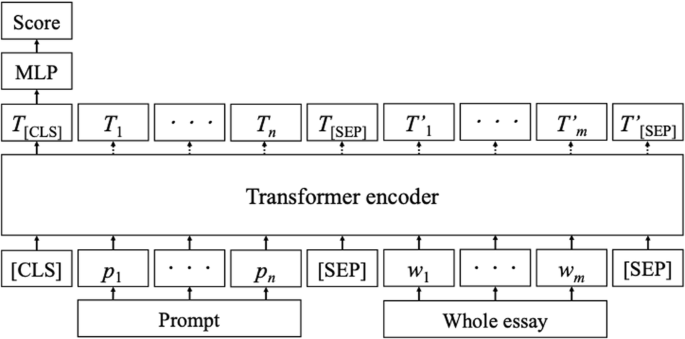
AES system with BERT (Hirao et al. 2020 ).
The training of BERT using a substantial amount of sentence data through the Masked Language Model (MLM) allows it to capture contextual information within the hidden layers. Consequently, BERT is expected to be capable of identifying artificial essays as invalid and assigning them lower scores (Mizumoto and Eguchi, 2023 ). In the context of AES for nonnative Japanese learners, Hirao et al. ( 2020 ) combined the long short-term memory (LSTM) model proposed by Hochreiter and Schmidhuber ( 1997 ) with BERT to develop a tailored automated Essay Scoring System. The findings of their study revealed that the BERT model outperformed both the conventional machine learning approach utilizing character-type features such as “kanji” and “hiragana”, as well as the standalone LSTM model. Takeuchi et al. ( 2021 ) presented an approach to Japanese AES that eliminates the requirement for pre-scored essays by relying solely on reference texts or a model answer for the essay task. They investigated multiple similarity evaluation methods, including frequency of morphemes, idf values calculated on Wikipedia, LSI, LDA, word-embedding vectors, and document vectors produced by BERT. The experimental findings revealed that the method utilizing the frequency of morphemes with idf values exhibited the strongest correlation with human-annotated scores across different essay tasks. The utilization of BERT in AES encounters several limitations. Firstly, essays often exceed the model’s maximum length limit. Second, only score labels are available for training, which restricts access to additional information.
Mizumoto and Eguchi ( 2023 ) were pioneers in employing the GPT model for AES in non-native English writing. Their study focused on evaluating the accuracy and reliability of AES using the GPT-3 text-davinci-003 model, analyzing a dataset of 12,100 essays from the corpus of nonnative written English (TOEFL11). The findings indicated that AES utilizing the GPT-3 model exhibited a certain degree of accuracy and reliability. They suggest that GPT-3-based AES systems hold the potential to provide support for human ratings. However, applying GPT model to AES presents a unique natural language processing (NLP) task that involves considerations such as nonnative language proficiency, the influence of the learner’s first language on the output in the target language, and identifying linguistic features that best indicate writing quality in a specific language. These linguistic features may differ morphologically or syntactically from those present in the learners’ first language, as observed in (1)–(3).
我-送了-他-一本-书
Wǒ-sòngle-tā-yī běn-shū
1 sg .-give. past- him-one .cl- book
“I gave him a book.”
Agglutinative
彼-に-本-を-あげ-まし-た
Kare-ni-hon-o-age-mashi-ta
3 sg .- dat -hon- acc- give.honorification. past
Inflectional
give, give-s, gave, given, giving
Additionally, the morphological agglutination and subject-object-verb (SOV) order in Japanese, along with its idiomatic expressions, pose additional challenges for applying language models in AES tasks (4).
足-が 棒-に なり-ました
Ashi-ga bo-ni nar-mashita
leg- nom stick- dat become- past
“My leg became like a stick (I am extremely tired).”
The example sentence provided demonstrates the morpho-syntactic structure of Japanese and the presence of an idiomatic expression. In this sentence, the verb “なる” (naru), meaning “to become”, appears at the end of the sentence. The verb stem “なり” (nari) is attached with morphemes indicating honorification (“ます” - mashu) and tense (“た” - ta), showcasing agglutination. While the sentence can be literally translated as “my leg became like a stick”, it carries an idiomatic interpretation that implies “I am extremely tired”.
To overcome this issue, CyberAgent Inc. ( 2023 ) has developed the Open-Calm series of language models specifically designed for Japanese. Open-Calm consists of pre-trained models available in various sizes, such as Small, Medium, Large, and 7b. Figure 2 depicts the fundamental structure of the Open-Calm model. A key feature of this architecture is the incorporation of the Lora Adapter and GPT-NeoX frameworks, which can enhance its language processing capabilities.
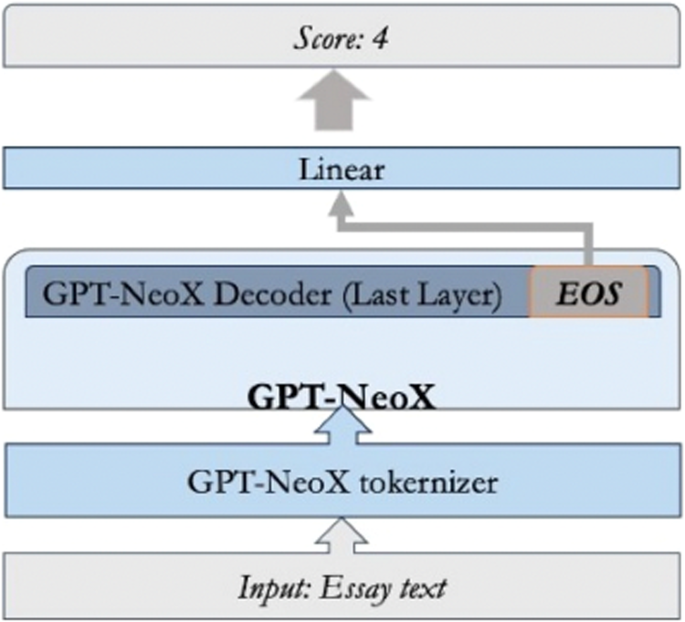
GPT-NeoX Model Architecture (Okgetheng and Takeuchi 2024 ).
In a recent study conducted by Okgetheng and Takeuchi ( 2024 ), they assessed the efficacy of Open-Calm language models in grading Japanese essays. The research utilized a dataset of approximately 300 essays, which were annotated by native Japanese educators. The findings of the study demonstrate the considerable potential of Open-Calm language models in automated Japanese essay scoring. Specifically, among the Open-Calm family, the Open-Calm Large model (referred to as OCLL) exhibited the highest performance. However, it is important to note that, as of the current date, the Open-Calm Large model does not offer public access to its server. Consequently, users are required to independently deploy and operate the environment for OCLL. In order to utilize OCLL, users must have a PC equipped with an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3060 (8 or 12 GB VRAM).
In summary, while the potential of LLMs in automated scoring of nonnative Japanese essays has been demonstrated in two studies—BERT-driven AES (Hirao et al. 2020 ) and OCLL-based AES (Okgetheng and Takeuchi, 2024 )—the number of research efforts in this area remains limited.
Another significant challenge in applying LLMs to AES lies in prompt engineering and ensuring its reliability and effectiveness (Brown et al. 2020 ; Rae et al. 2021 ; Zhang et al. 2021 ). Various prompting strategies have been proposed, such as the zero-shot chain of thought (CoT) approach (Kojima et al. 2022 ), which involves manually crafting diverse and effective examples. However, manual efforts can lead to mistakes. To address this, Zhang et al. ( 2021 ) introduced an automatic CoT prompting method called Auto-CoT, which demonstrates matching or superior performance compared to the CoT paradigm. Another prompt framework is trees of thoughts, enabling a model to self-evaluate its progress at intermediate stages of problem-solving through deliberate reasoning (Yao et al. 2023 ).
Beyond linguistic studies, there has been a noticeable increase in the number of foreign workers in Japan and Japanese learners worldwide (Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare of Japan, 2022 ; Japan Foundation, 2021 ). However, existing assessment methods, such as the Japanese Language Proficiency Test (JLPT), J-CAT, and TTBJ Footnote 1 , primarily focus on reading, listening, vocabulary, and grammar skills, neglecting the evaluation of writing proficiency. As the number of workers and language learners continues to grow, there is a rising demand for an efficient AES system that can reduce costs and time for raters and be utilized for employment, examinations, and self-study purposes.
This study aims to explore the potential of LLM-based AES by comparing the effectiveness of five models: two LLMs (GPT Footnote 2 and BERT), one Japanese local LLM (OCLL), and two conventional machine learning-based methods (linguistic feature-based scoring tools - Jess and JWriter).
The research questions addressed in this study are as follows:
To what extent do the LLM-driven AES and linguistic feature-based AES, when used as automated tools to support human rating, accurately reflect test takers’ actual performance?
What influence does the prompt have on the accuracy and performance of LLM-based AES methods?
The subsequent sections of the manuscript cover the methodology, including the assessment measures for nonnative Japanese writing proficiency, criteria for prompts, and the dataset. The evaluation section focuses on the analysis of annotations and rating scores generated by LLM-driven and linguistic feature-based AES methods.
Methodology
The dataset utilized in this study was obtained from the International Corpus of Japanese as a Second Language (I-JAS) Footnote 3 . This corpus consisted of 1000 participants who represented 12 different first languages. For the study, the participants were given a story-writing task on a personal computer. They were required to write two stories based on the 4-panel illustrations titled “Picnic” and “The key” (see Appendix A). Background information for the participants was provided by the corpus, including their Japanese language proficiency levels assessed through two online tests: J-CAT and SPOT. These tests evaluated their reading, listening, vocabulary, and grammar abilities. The learners’ proficiency levels were categorized into six levels aligned with the Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR) and the Reference Framework for Japanese Language Education (RFJLE): A1, A2, B1, B2, C1, and C2. According to Lee et al. ( 2015 ), there is a high level of agreement (r = 0.86) between the J-CAT and SPOT assessments, indicating that the proficiency certifications provided by J-CAT are consistent with those of SPOT. However, it is important to note that the scores of J-CAT and SPOT do not have a one-to-one correspondence. In this study, the J-CAT scores were used as a benchmark to differentiate learners of different proficiency levels. A total of 1400 essays were utilized, representing the beginner (aligned with A1), A2, B1, B2, C1, and C2 levels based on the J-CAT scores. Table 1 provides information about the learners’ proficiency levels and their corresponding J-CAT and SPOT scores.
A dataset comprising a total of 1400 essays from the story writing tasks was collected. Among these, 714 essays were utilized to evaluate the reliability of the LLM-based AES method, while the remaining 686 essays were designated as development data to assess the LLM-based AES’s capability to distinguish participants with varying proficiency levels. The GPT 4 API was used in this study. A detailed explanation of the prompt-assessment criteria is provided in Section Prompt . All essays were sent to the model for measurement and scoring.
Measures of writing proficiency for nonnative Japanese
Japanese exhibits a morphologically agglutinative structure where morphemes are attached to the word stem to convey grammatical functions such as tense, aspect, voice, and honorifics, e.g. (5).
食べ-させ-られ-まし-た-か
tabe-sase-rare-mashi-ta-ka
[eat (stem)-causative-passive voice-honorification-tense. past-question marker]
Japanese employs nine case particles to indicate grammatical functions: the nominative case particle が (ga), the accusative case particle を (o), the genitive case particle の (no), the dative case particle に (ni), the locative/instrumental case particle で (de), the ablative case particle から (kara), the directional case particle へ (e), and the comitative case particle と (to). The agglutinative nature of the language, combined with the case particle system, provides an efficient means of distinguishing between active and passive voice, either through morphemes or case particles, e.g. 食べる taberu “eat concusive . ” (active voice); 食べられる taberareru “eat concusive . ” (passive voice). In the active voice, “パン を 食べる” (pan o taberu) translates to “to eat bread”. On the other hand, in the passive voice, it becomes “パン が 食べられた” (pan ga taberareta), which means “(the) bread was eaten”. Additionally, it is important to note that different conjugations of the same lemma are considered as one type in order to ensure a comprehensive assessment of the language features. For example, e.g., 食べる taberu “eat concusive . ”; 食べている tabeteiru “eat progress .”; 食べた tabeta “eat past . ” as one type.
To incorporate these features, previous research (Suzuki, 1999 ; Watanabe et al. 1988 ; Ishioka, 2001 ; Ishioka and Kameda, 2006 ; Hirao et al. 2020 ) has identified complexity, fluency, and accuracy as crucial factors for evaluating writing quality. These criteria are assessed through various aspects, including lexical richness (lexical density, diversity, and sophistication), syntactic complexity, and cohesion (Kyle et al. 2021 ; Mizumoto and Eguchi, 2023 ; Ure, 1971 ; Halliday, 1985 ; Barkaoui and Hadidi, 2020 ; Zenker and Kyle, 2021 ; Kim et al. 2018 ; Lu, 2017 ; Ortega, 2015 ). Therefore, this study proposes five scoring categories: lexical richness, syntactic complexity, cohesion, content elaboration, and grammatical accuracy. A total of 16 measures were employed to capture these categories. The calculation process and specific details of these measures can be found in Table 2 .
T-unit, first introduced by Hunt ( 1966 ), is a measure used for evaluating speech and composition. It serves as an indicator of syntactic development and represents the shortest units into which a piece of discourse can be divided without leaving any sentence fragments. In the context of Japanese language assessment, Sakoda and Hosoi ( 2020 ) utilized T-unit as the basic unit to assess the accuracy and complexity of Japanese learners’ speaking and storytelling. The calculation of T-units in Japanese follows the following principles:
A single main clause constitutes 1 T-unit, regardless of the presence or absence of dependent clauses, e.g. (6).
ケンとマリはピクニックに行きました (main clause): 1 T-unit.
If a sentence contains a main clause along with subclauses, each subclause is considered part of the same T-unit, e.g. (7).
天気が良かった の で (subclause)、ケンとマリはピクニックに行きました (main clause): 1 T-unit.
In the case of coordinate clauses, where multiple clauses are connected, each coordinated clause is counted separately. Thus, a sentence with coordinate clauses may have 2 T-units or more, e.g. (8).
ケンは地図で場所を探して (coordinate clause)、マリはサンドイッチを作りました (coordinate clause): 2 T-units.
Lexical diversity refers to the range of words used within a text (Engber, 1995 ; Kyle et al. 2021 ) and is considered a useful measure of the breadth of vocabulary in L n production (Jarvis, 2013a , 2013b ).
The type/token ratio (TTR) is widely recognized as a straightforward measure for calculating lexical diversity and has been employed in numerous studies. These studies have demonstrated a strong correlation between TTR and other methods of measuring lexical diversity (e.g., Bentz et al. 2016 ; Čech and Miroslav, 2018 ; Çöltekin and Taraka, 2018 ). TTR is computed by considering both the number of unique words (types) and the total number of words (tokens) in a given text. Given that the length of learners’ writing texts can vary, this study employs the moving average type-token ratio (MATTR) to mitigate the influence of text length. MATTR is calculated using a 50-word moving window. Initially, a TTR is determined for words 1–50 in an essay, followed by words 2–51, 3–52, and so on until the end of the essay is reached (Díez-Ortega and Kyle, 2023 ). The final MATTR scores were obtained by averaging the TTR scores for all 50-word windows. The following formula was employed to derive MATTR:
\({\rm{MATTR}}({\rm{W}})=\frac{{\sum }_{{\rm{i}}=1}^{{\rm{N}}-{\rm{W}}+1}{{\rm{F}}}_{{\rm{i}}}}{{\rm{W}}({\rm{N}}-{\rm{W}}+1)}\)
Here, N refers to the number of tokens in the corpus. W is the randomly selected token size (W < N). \({F}_{i}\) is the number of types in each window. The \({\rm{MATTR}}({\rm{W}})\) is the mean of a series of type-token ratios (TTRs) based on the word form for all windows. It is expected that individuals with higher language proficiency will produce texts with greater lexical diversity, as indicated by higher MATTR scores.
Lexical density was captured by the ratio of the number of lexical words to the total number of words (Lu, 2012 ). Lexical sophistication refers to the utilization of advanced vocabulary, often evaluated through word frequency indices (Crossley et al. 2013 ; Haberman, 2008 ; Kyle and Crossley, 2015 ; Laufer and Nation, 1995 ; Lu, 2012 ; Read, 2000 ). In line of writing, lexical sophistication can be interpreted as vocabulary breadth, which entails the appropriate usage of vocabulary items across various lexicon-grammatical contexts and registers (Garner et al. 2019 ; Kim et al. 2018 ; Kyle et al. 2018 ). In Japanese specifically, words are considered lexically sophisticated if they are not included in the “Japanese Education Vocabulary List Ver 1.0”. Footnote 4 Consequently, lexical sophistication was calculated by determining the number of sophisticated word types relative to the total number of words per essay. Furthermore, it has been suggested that, in Japanese writing, sentences should ideally have a length of no more than 40 to 50 characters, as this promotes readability. Therefore, the median and maximum sentence length can be considered as useful indices for assessment (Ishioka and Kameda, 2006 ).
Syntactic complexity was assessed based on several measures, including the mean length of clauses, verb phrases per T-unit, clauses per T-unit, dependent clauses per T-unit, complex nominals per clause, adverbial clauses per clause, coordinate phrases per clause, and mean dependency distance (MDD). The MDD reflects the distance between the governor and dependent positions in a sentence. A larger dependency distance indicates a higher cognitive load and greater complexity in syntactic processing (Liu, 2008 ; Liu et al. 2017 ). The MDD has been established as an efficient metric for measuring syntactic complexity (Jiang, Quyang, and Liu, 2019 ; Li and Yan, 2021 ). To calculate the MDD, the position numbers of the governor and dependent are subtracted, assuming that words in a sentence are assigned in a linear order, such as W1 … Wi … Wn. In any dependency relationship between words Wa and Wb, Wa is the governor and Wb is the dependent. The MDD of the entire sentence was obtained by taking the absolute value of governor – dependent:
MDD = \(\frac{1}{n}{\sum }_{i=1}^{n}|{\rm{D}}{{\rm{D}}}_{i}|\)
In this formula, \(n\) represents the number of words in the sentence, and \({DD}i\) is the dependency distance of the \({i}^{{th}}\) dependency relationship of a sentence. Building on this, the annotation of sentence ‘Mary-ga-John-ni-keshigomu-o-watashita was [Mary- top -John- dat -eraser- acc -give- past] ’. The sentence’s MDD would be 2. Table 3 provides the CSV file as a prompt for GPT 4.
Cohesion (semantic similarity) and content elaboration aim to capture the ideas presented in test taker’s essays. Cohesion was assessed using three measures: Synonym overlap/paragraph (topic), Synonym overlap/paragraph (keywords), and word2vec cosine similarity. Content elaboration and development were measured as the number of metadiscourse markers (type)/number of words. To capture content closely, this study proposed a novel-distance based representation, by encoding the cosine distance between the essay (by learner) and essay task’s (topic and keyword) i -vectors. The learner’s essay is decoded into a word sequence, and aligned to the essay task’ topic and keyword for log-likelihood measurement. The cosine distance reveals the content elaboration score in the leaners’ essay. The mathematical equation of cosine similarity between target-reference vectors is shown in (11), assuming there are i essays and ( L i , …. L n ) and ( N i , …. N n ) are the vectors representing the learner and task’s topic and keyword respectively. The content elaboration distance between L i and N i was calculated as follows:
\(\cos \left(\theta \right)=\frac{{\rm{L}}\,\cdot\, {\rm{N}}}{\left|{\rm{L}}\right|{\rm{|N|}}}=\frac{\mathop{\sum }\nolimits_{i=1}^{n}{L}_{i}{N}_{i}}{\sqrt{\mathop{\sum }\nolimits_{i=1}^{n}{L}_{i}^{2}}\sqrt{\mathop{\sum }\nolimits_{i=1}^{n}{N}_{i}^{2}}}\)
A high similarity value indicates a low difference between the two recognition outcomes, which in turn suggests a high level of proficiency in content elaboration.
To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed measures in distinguishing different proficiency levels among nonnative Japanese speakers’ writing, we conducted a multi-faceted Rasch measurement analysis (Linacre, 1994 ). This approach applies measurement models to thoroughly analyze various factors that can influence test outcomes, including test takers’ proficiency, item difficulty, and rater severity, among others. The underlying principles and functionality of multi-faceted Rasch measurement are illustrated in (12).
\(\log \left(\frac{{P}_{{nijk}}}{{P}_{{nij}(k-1)}}\right)={B}_{n}-{D}_{i}-{C}_{j}-{F}_{k}\)
(12) defines the logarithmic transformation of the probability ratio ( P nijk /P nij(k-1) )) as a function of multiple parameters. Here, n represents the test taker, i denotes a writing proficiency measure, j corresponds to the human rater, and k represents the proficiency score. The parameter B n signifies the proficiency level of test taker n (where n ranges from 1 to N). D j represents the difficulty parameter of test item i (where i ranges from 1 to L), while C j represents the severity of rater j (where j ranges from 1 to J). Additionally, F k represents the step difficulty for a test taker to move from score ‘k-1’ to k . P nijk refers to the probability of rater j assigning score k to test taker n for test item i . P nij(k-1) represents the likelihood of test taker n being assigned score ‘k-1’ by rater j for test item i . Each facet within the test is treated as an independent parameter and estimated within the same reference framework. To evaluate the consistency of scores obtained through both human and computer analysis, we utilized the Infit mean-square statistic. This statistic is a chi-square measure divided by the degrees of freedom and is weighted with information. It demonstrates higher sensitivity to unexpected patterns in responses to items near a person’s proficiency level (Linacre, 2002 ). Fit statistics are assessed based on predefined thresholds for acceptable fit. For the Infit MNSQ, which has a mean of 1.00, different thresholds have been suggested. Some propose stricter thresholds ranging from 0.7 to 1.3 (Bond et al. 2021 ), while others suggest more lenient thresholds ranging from 0.5 to 1.5 (Eckes, 2009 ). In this study, we adopted the criterion of 0.70–1.30 for the Infit MNSQ.
Moving forward, we can now proceed to assess the effectiveness of the 16 proposed measures based on five criteria for accurately distinguishing various levels of writing proficiency among non-native Japanese speakers. To conduct this evaluation, we utilized the development dataset from the I-JAS corpus, as described in Section Dataset . Table 4 provides a measurement report that presents the performance details of the 14 metrics under consideration. The measure separation was found to be 4.02, indicating a clear differentiation among the measures. The reliability index for the measure separation was 0.891, suggesting consistency in the measurement. Similarly, the person separation reliability index was 0.802, indicating the accuracy of the assessment in distinguishing between individuals. All 16 measures demonstrated Infit mean squares within a reasonable range, ranging from 0.76 to 1.28. The Synonym overlap/paragraph (topic) measure exhibited a relatively high outfit mean square of 1.46, although the Infit mean square falls within an acceptable range. The standard error for the measures ranged from 0.13 to 0.28, indicating the precision of the estimates.
Table 5 further illustrated the weights assigned to different linguistic measures for score prediction, with higher weights indicating stronger correlations between those measures and higher scores. Specifically, the following measures exhibited higher weights compared to others: moving average type token ratio per essay has a weight of 0.0391. Mean dependency distance had a weight of 0.0388. Mean length of clause, calculated by dividing the number of words by the number of clauses, had a weight of 0.0374. Complex nominals per T-unit, calculated by dividing the number of complex nominals by the number of T-units, had a weight of 0.0379. Coordinate phrases rate, calculated by dividing the number of coordinate phrases by the number of clauses, had a weight of 0.0325. Grammatical error rate, representing the number of errors per essay, had a weight of 0.0322.
Criteria (output indicator)
The criteria used to evaluate the writing ability in this study were based on CEFR, which follows a six-point scale ranging from A1 to C2. To assess the quality of Japanese writing, the scoring criteria from Table 6 were utilized. These criteria were derived from the IELTS writing standards and served as assessment guidelines and prompts for the written output.
A prompt is a question or detailed instruction that is provided to the model to obtain a proper response. After several pilot experiments, we decided to provide the measures (Section Measures of writing proficiency for nonnative Japanese ) as the input prompt and use the criteria (Section Criteria (output indicator) ) as the output indicator. Regarding the prompt language, considering that the LLM was tasked with rating Japanese essays, would prompt in Japanese works better Footnote 5 ? We conducted experiments comparing the performance of GPT-4 using both English and Japanese prompts. Additionally, we utilized the Japanese local model OCLL with Japanese prompts. Multiple trials were conducted using the same sample. Regardless of the prompt language used, we consistently obtained the same grading results with GPT-4, which assigned a grade of B1 to the writing sample. This suggested that GPT-4 is reliable and capable of producing consistent ratings regardless of the prompt language. On the other hand, when we used Japanese prompts with the Japanese local model “OCLL”, we encountered inconsistent grading results. Out of 10 attempts with OCLL, only 6 yielded consistent grading results (B1), while the remaining 4 showed different outcomes, including A1 and B2 grades. These findings indicated that the language of the prompt was not the determining factor for reliable AES. Instead, the size of the training data and the model parameters played crucial roles in achieving consistent and reliable AES results for the language model.
The following is the utilized prompt, which details all measures and requires the LLM to score the essays using holistic and trait scores.
Please evaluate Japanese essays written by Japanese learners and assign a score to each essay on a six-point scale, ranging from A1, A2, B1, B2, C1 to C2. Additionally, please provide trait scores and display the calculation process for each trait score. The scoring should be based on the following criteria:
Moving average type-token ratio.
Number of lexical words (token) divided by the total number of words per essay.
Number of sophisticated word types divided by the total number of words per essay.
Mean length of clause.
Verb phrases per T-unit.
Clauses per T-unit.
Dependent clauses per T-unit.
Complex nominals per clause.
Adverbial clauses per clause.
Coordinate phrases per clause.
Mean dependency distance.
Synonym overlap paragraph (topic and keywords).
Word2vec cosine similarity.
Connectives per essay.
Conjunctions per essay.
Number of metadiscourse markers (types) divided by the total number of words.
Number of errors per essay.
Japanese essay text
出かける前に二人が地図を見ている間に、サンドイッチを入れたバスケットに犬が入ってしまいました。それに気づかずに二人は楽しそうに出かけて行きました。やがて突然犬がバスケットから飛び出し、二人は驚きました。バスケット の 中を見ると、食べ物はすべて犬に食べられていて、二人は困ってしまいました。(ID_JJJ01_SW1)
The score of the example above was B1. Figure 3 provides an example of holistic and trait scores provided by GPT-4 (with a prompt indicating all measures) via Bing Footnote 6 .

Example of GPT-4 AES and feedback (with a prompt indicating all measures).
Statistical analysis
The aim of this study is to investigate the potential use of LLM for nonnative Japanese AES. It seeks to compare the scoring outcomes obtained from feature-based AES tools, which rely on conventional machine learning technology (i.e. Jess, JWriter), with those generated by AI-driven AES tools utilizing deep learning technology (BERT, GPT, OCLL). To assess the reliability of a computer-assisted annotation tool, the study initially established human-human agreement as the benchmark measure. Subsequently, the performance of the LLM-based method was evaluated by comparing it to human-human agreement.
To assess annotation agreement, the study employed standard measures such as precision, recall, and F-score (Brants 2000 ; Lu 2010 ), along with the quadratically weighted kappa (QWK) to evaluate the consistency and agreement in the annotation process. Assume A and B represent human annotators. When comparing the annotations of the two annotators, the following results are obtained. The evaluation of precision, recall, and F-score metrics was illustrated in equations (13) to (15).
\({\rm{Recall}}(A,B)=\frac{{\rm{Number}}\,{\rm{of}}\,{\rm{identical}}\,{\rm{nodes}}\,{\rm{in}}\,A\,{\rm{and}}\,B}{{\rm{Number}}\,{\rm{of}}\,{\rm{nodes}}\,{\rm{in}}\,A}\)
\({\rm{Precision}}(A,\,B)=\frac{{\rm{Number}}\,{\rm{of}}\,{\rm{identical}}\,{\rm{nodes}}\,{\rm{in}}\,A\,{\rm{and}}\,B}{{\rm{Number}}\,{\rm{of}}\,{\rm{nodes}}\,{\rm{in}}\,B}\)
The F-score is the harmonic mean of recall and precision:
\({\rm{F}}-{\rm{score}}=\frac{2* ({\rm{Precision}}* {\rm{Recall}})}{{\rm{Precision}}+{\rm{Recall}}}\)
The highest possible value of an F-score is 1.0, indicating perfect precision and recall, and the lowest possible value is 0, if either precision or recall are zero.
In accordance with Taghipour and Ng ( 2016 ), the calculation of QWK involves two steps:
Step 1: Construct a weight matrix W as follows:
\({W}_{{ij}}=\frac{{(i-j)}^{2}}{{(N-1)}^{2}}\)
i represents the annotation made by the tool, while j represents the annotation made by a human rater. N denotes the total number of possible annotations. Matrix O is subsequently computed, where O_( i, j ) represents the count of data annotated by the tool ( i ) and the human annotator ( j ). On the other hand, E refers to the expected count matrix, which undergoes normalization to ensure that the sum of elements in E matches the sum of elements in O.
Step 2: With matrices O and E, the QWK is obtained as follows:
K = 1- \(\frac{\sum i,j{W}_{i,j}\,{O}_{i,j}}{\sum i,j{W}_{i,j}\,{E}_{i,j}}\)
The value of the quadratic weighted kappa increases as the level of agreement improves. Further, to assess the accuracy of LLM scoring, the proportional reductive mean square error (PRMSE) was employed. The PRMSE approach takes into account the variability observed in human ratings to estimate the rater error, which is then subtracted from the variance of the human labels. This calculation provides an overall measure of agreement between the automated scores and true scores (Haberman et al. 2015 ; Loukina et al. 2020 ; Taghipour and Ng, 2016 ). The computation of PRMSE involves the following steps:
Step 1: Calculate the mean squared errors (MSEs) for the scoring outcomes of the computer-assisted tool (MSE tool) and the human scoring outcomes (MSE human).
Step 2: Determine the PRMSE by comparing the MSE of the computer-assisted tool (MSE tool) with the MSE from human raters (MSE human), using the following formula:
\({\rm{PRMSE}}=1-\frac{({\rm{MSE}}\,{\rm{tool}})\,}{({\rm{MSE}}\,{\rm{human}})\,}=1-\,\frac{{\sum }_{i}^{n}=1{({{\rm{y}}}_{i}-{\hat{{\rm{y}}}}_{{\rm{i}}})}^{2}}{{\sum }_{i}^{n}=1{({{\rm{y}}}_{i}-\hat{{\rm{y}}})}^{2}}\)
In the numerator, ŷi represents the scoring outcome predicted by a specific LLM-driven AES system for a given sample. The term y i − ŷ i represents the difference between this predicted outcome and the mean value of all LLM-driven AES systems’ scoring outcomes. It quantifies the deviation of the specific LLM-driven AES system’s prediction from the average prediction of all LLM-driven AES systems. In the denominator, y i − ŷ represents the difference between the scoring outcome provided by a specific human rater for a given sample and the mean value of all human raters’ scoring outcomes. It measures the discrepancy between the specific human rater’s score and the average score given by all human raters. The PRMSE is then calculated by subtracting the ratio of the MSE tool to the MSE human from 1. PRMSE falls within the range of 0 to 1, with larger values indicating reduced errors in LLM’s scoring compared to those of human raters. In other words, a higher PRMSE implies that LLM’s scoring demonstrates greater accuracy in predicting the true scores (Loukina et al. 2020 ). The interpretation of kappa values, ranging from 0 to 1, is based on the work of Landis and Koch ( 1977 ). Specifically, the following categories are assigned to different ranges of kappa values: −1 indicates complete inconsistency, 0 indicates random agreement, 0.0 ~ 0.20 indicates extremely low level of agreement (slight), 0.21 ~ 0.40 indicates moderate level of agreement (fair), 0.41 ~ 0.60 indicates medium level of agreement (moderate), 0.61 ~ 0.80 indicates high level of agreement (substantial), 0.81 ~ 1 indicates almost perfect level of agreement. All statistical analyses were executed using Python script.
Results and discussion
Annotation reliability of the llm.
This section focuses on assessing the reliability of the LLM’s annotation and scoring capabilities. To evaluate the reliability, several tests were conducted simultaneously, aiming to achieve the following objectives:
Assess the LLM’s ability to differentiate between test takers with varying levels of oral proficiency.
Determine the level of agreement between the annotations and scoring performed by the LLM and those done by human raters.
The evaluation of the results encompassed several metrics, including: precision, recall, F-Score, quadratically-weighted kappa, proportional reduction of mean squared error, Pearson correlation, and multi-faceted Rasch measurement.
Inter-annotator agreement (human–human annotator agreement)
We started with an agreement test of the two human annotators. Two trained annotators were recruited to determine the writing task data measures. A total of 714 scripts, as the test data, was utilized. Each analysis lasted 300–360 min. Inter-annotator agreement was evaluated using the standard measures of precision, recall, and F-score and QWK. Table 7 presents the inter-annotator agreement for the various indicators. As shown, the inter-annotator agreement was fairly high, with F-scores ranging from 1.0 for sentence and word number to 0.666 for grammatical errors.
The findings from the QWK analysis provided further confirmation of the inter-annotator agreement. The QWK values covered a range from 0.950 ( p = 0.000) for sentence and word number to 0.695 for synonym overlap number (keyword) and grammatical errors ( p = 0.001).
Agreement of annotation outcomes between human and LLM
To evaluate the consistency between human annotators and LLM annotators (BERT, GPT, OCLL) across the indices, the same test was conducted. The results of the inter-annotator agreement (F-score) between LLM and human annotation are provided in Appendix B-D. The F-scores ranged from 0.706 for Grammatical error # for OCLL-human to a perfect 1.000 for GPT-human, for sentences, clauses, T-units, and words. These findings were further supported by the QWK analysis, which showed agreement levels ranging from 0.807 ( p = 0.001) for metadiscourse markers for OCLL-human to 0.962 for words ( p = 0.000) for GPT-human. The findings demonstrated that the LLM annotation achieved a significant level of accuracy in identifying measurement units and counts.
Reliability of LLM-driven AES’s scoring and discriminating proficiency levels
This section examines the reliability of the LLM-driven AES scoring through a comparison of the scoring outcomes produced by human raters and the LLM ( Reliability of LLM-driven AES scoring ). It also assesses the effectiveness of the LLM-based AES system in differentiating participants with varying proficiency levels ( Reliability of LLM-driven AES discriminating proficiency levels ).
Reliability of LLM-driven AES scoring
Table 8 summarizes the QWK coefficient analysis between the scores computed by the human raters and the GPT-4 for the individual essays from I-JAS Footnote 7 . As shown, the QWK of all measures ranged from k = 0.819 for lexical density (number of lexical words (tokens)/number of words per essay) to k = 0.644 for word2vec cosine similarity. Table 9 further presents the Pearson correlations between the 16 writing proficiency measures scored by human raters and GPT 4 for the individual essays. The correlations ranged from 0.672 for syntactic complexity to 0.734 for grammatical accuracy. The correlations between the writing proficiency scores assigned by human raters and the BERT-based AES system were found to range from 0.661 for syntactic complexity to 0.713 for grammatical accuracy. The correlations between the writing proficiency scores given by human raters and the OCLL-based AES system ranged from 0.654 for cohesion to 0.721 for grammatical accuracy. These findings indicated an alignment between the assessments made by human raters and both the BERT-based and OCLL-based AES systems in terms of various aspects of writing proficiency.
Reliability of LLM-driven AES discriminating proficiency levels
After validating the reliability of the LLM’s annotation and scoring, the subsequent objective was to evaluate its ability to distinguish between various proficiency levels. For this analysis, a dataset of 686 individual essays was utilized. Table 10 presents a sample of the results, summarizing the means, standard deviations, and the outcomes of the one-way ANOVAs based on the measures assessed by the GPT-4 model. A post hoc multiple comparison test, specifically the Bonferroni test, was conducted to identify any potential differences between pairs of levels.
As the results reveal, seven measures presented linear upward or downward progress across the three proficiency levels. These were marked in bold in Table 10 and comprise one measure of lexical richness, i.e. MATTR (lexical diversity); four measures of syntactic complexity, i.e. MDD (mean dependency distance), MLC (mean length of clause), CNT (complex nominals per T-unit), CPC (coordinate phrases rate); one cohesion measure, i.e. word2vec cosine similarity and GER (grammatical error rate). Regarding the ability of the sixteen measures to distinguish adjacent proficiency levels, the Bonferroni tests indicated that statistically significant differences exist between the primary level and the intermediate level for MLC and GER. One measure of lexical richness, namely LD, along with three measures of syntactic complexity (VPT, CT, DCT, ACC), two measures of cohesion (SOPT, SOPK), and one measure of content elaboration (IMM), exhibited statistically significant differences between proficiency levels. However, these differences did not demonstrate a linear progression between adjacent proficiency levels. No significant difference was observed in lexical sophistication between proficiency levels.
To summarize, our study aimed to evaluate the reliability and differentiation capabilities of the LLM-driven AES method. For the first objective, we assessed the LLM’s ability to differentiate between test takers with varying levels of oral proficiency using precision, recall, F-Score, and quadratically-weighted kappa. Regarding the second objective, we compared the scoring outcomes generated by human raters and the LLM to determine the level of agreement. We employed quadratically-weighted kappa and Pearson correlations to compare the 16 writing proficiency measures for the individual essays. The results confirmed the feasibility of using the LLM for annotation and scoring in AES for nonnative Japanese. As a result, Research Question 1 has been addressed.
Comparison of BERT-, GPT-, OCLL-based AES, and linguistic-feature-based computation methods
This section aims to compare the effectiveness of five AES methods for nonnative Japanese writing, i.e. LLM-driven approaches utilizing BERT, GPT, and OCLL, linguistic feature-based approaches using Jess and JWriter. The comparison was conducted by comparing the ratings obtained from each approach with human ratings. All ratings were derived from the dataset introduced in Dataset . To facilitate the comparison, the agreement between the automated methods and human ratings was assessed using QWK and PRMSE. The performance of each approach was summarized in Table 11 .
The QWK coefficient values indicate that LLMs (GPT, BERT, OCLL) and human rating outcomes demonstrated higher agreement compared to feature-based AES methods (Jess and JWriter) in assessing writing proficiency criteria, including lexical richness, syntactic complexity, content, and grammatical accuracy. Among the LLMs, the GPT-4 driven AES and human rating outcomes showed the highest agreement in all criteria, except for syntactic complexity. The PRMSE values suggest that the GPT-based method outperformed linguistic feature-based methods and other LLM-based approaches. Moreover, an interesting finding emerged during the study: the agreement coefficient between GPT-4 and human scoring was even higher than the agreement between different human raters themselves. This discovery highlights the advantage of GPT-based AES over human rating. Ratings involve a series of processes, including reading the learners’ writing, evaluating the content and language, and assigning scores. Within this chain of processes, various biases can be introduced, stemming from factors such as rater biases, test design, and rating scales. These biases can impact the consistency and objectivity of human ratings. GPT-based AES may benefit from its ability to apply consistent and objective evaluation criteria. By prompting the GPT model with detailed writing scoring rubrics and linguistic features, potential biases in human ratings can be mitigated. The model follows a predefined set of guidelines and does not possess the same subjective biases that human raters may exhibit. This standardization in the evaluation process contributes to the higher agreement observed between GPT-4 and human scoring. Section Prompt strategy of the study delves further into the role of prompts in the application of LLMs to AES. It explores how the choice and implementation of prompts can impact the performance and reliability of LLM-based AES methods. Furthermore, it is important to acknowledge the strengths of the local model, i.e. the Japanese local model OCLL, which excels in processing certain idiomatic expressions. Nevertheless, our analysis indicated that GPT-4 surpasses local models in AES. This superior performance can be attributed to the larger parameter size of GPT-4, estimated to be between 500 billion and 1 trillion, which exceeds the sizes of both BERT and the local model OCLL.
Prompt strategy
In the context of prompt strategy, Mizumoto and Eguchi ( 2023 ) conducted a study where they applied the GPT-3 model to automatically score English essays in the TOEFL test. They found that the accuracy of the GPT model alone was moderate to fair. However, when they incorporated linguistic measures such as cohesion, syntactic complexity, and lexical features alongside the GPT model, the accuracy significantly improved. This highlights the importance of prompt engineering and providing the model with specific instructions to enhance its performance. In this study, a similar approach was taken to optimize the performance of LLMs. GPT-4, which outperformed BERT and OCLL, was selected as the candidate model. Model 1 was used as the baseline, representing GPT-4 without any additional prompting. Model 2, on the other hand, involved GPT-4 prompted with 16 measures that included scoring criteria, efficient linguistic features for writing assessment, and detailed measurement units and calculation formulas. The remaining models (Models 3 to 18) utilized GPT-4 prompted with individual measures. The performance of these 18 different models was assessed using the output indicators described in Section Criteria (output indicator) . By comparing the performances of these models, the study aimed to understand the impact of prompt engineering on the accuracy and effectiveness of GPT-4 in AES tasks.
Based on the PRMSE scores presented in Fig. 4 , it was observed that Model 1, representing GPT-4 without any additional prompting, achieved a fair level of performance. However, Model 2, which utilized GPT-4 prompted with all measures, outperformed all other models in terms of PRMSE score, achieving a score of 0.681. These results indicate that the inclusion of specific measures and prompts significantly enhanced the performance of GPT-4 in AES. Among the measures, syntactic complexity was found to play a particularly significant role in improving the accuracy of GPT-4 in assessing writing quality. Following that, lexical diversity emerged as another important factor contributing to the model’s effectiveness. The study suggests that a well-prompted GPT-4 can serve as a valuable tool to support human assessors in evaluating writing quality. By utilizing GPT-4 as an automated scoring tool, the evaluation biases associated with human raters can be minimized. This has the potential to empower teachers by allowing them to focus on designing writing tasks and guiding writing strategies, while leveraging the capabilities of GPT-4 for efficient and reliable scoring.
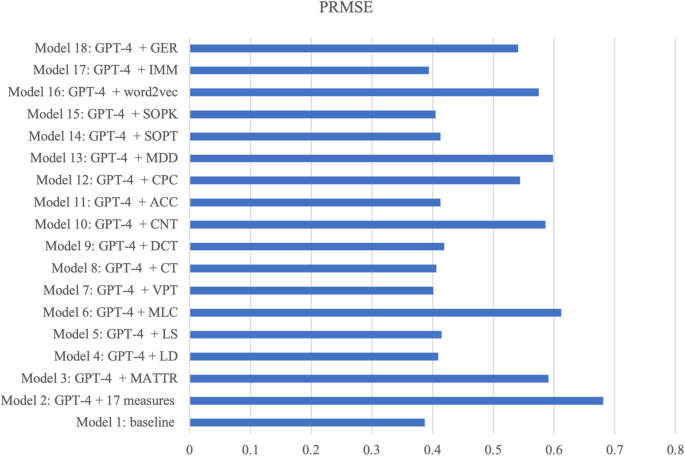
PRMSE scores of the 18 AES models.
This study aimed to investigate two main research questions: the feasibility of utilizing LLMs for AES and the impact of prompt engineering on the application of LLMs in AES.
To address the first objective, the study compared the effectiveness of five different models: GPT, BERT, the Japanese local LLM (OCLL), and two conventional machine learning-based AES tools (Jess and JWriter). The PRMSE values indicated that the GPT-4-based method outperformed other LLMs (BERT, OCLL) and linguistic feature-based computational methods (Jess and JWriter) across various writing proficiency criteria. Furthermore, the agreement coefficient between GPT-4 and human scoring surpassed the agreement among human raters themselves, highlighting the potential of using the GPT-4 tool to enhance AES by reducing biases and subjectivity, saving time, labor, and cost, and providing valuable feedback for self-study. Regarding the second goal, the role of prompt design was investigated by comparing 18 models, including a baseline model, a model prompted with all measures, and 16 models prompted with one measure at a time. GPT-4, which outperformed BERT and OCLL, was selected as the candidate model. The PRMSE scores of the models showed that GPT-4 prompted with all measures achieved the best performance, surpassing the baseline and other models.
In conclusion, this study has demonstrated the potential of LLMs in supporting human rating in assessments. By incorporating automation, we can save time and resources while reducing biases and subjectivity inherent in human rating processes. Automated language assessments offer the advantage of accessibility, providing equal opportunities and economic feasibility for individuals who lack access to traditional assessment centers or necessary resources. LLM-based language assessments provide valuable feedback and support to learners, aiding in the enhancement of their language proficiency and the achievement of their goals. This personalized feedback can cater to individual learner needs, facilitating a more tailored and effective language-learning experience.
There are three important areas that merit further exploration. First, prompt engineering requires attention to ensure optimal performance of LLM-based AES across different language types. This study revealed that GPT-4, when prompted with all measures, outperformed models prompted with fewer measures. Therefore, investigating and refining prompt strategies can enhance the effectiveness of LLMs in automated language assessments. Second, it is crucial to explore the application of LLMs in second-language assessment and learning for oral proficiency, as well as their potential in under-resourced languages. Recent advancements in self-supervised machine learning techniques have significantly improved automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems, opening up new possibilities for creating reliable ASR systems, particularly for under-resourced languages with limited data. However, challenges persist in the field of ASR. First, ASR assumes correct word pronunciation for automatic pronunciation evaluation, which proves challenging for learners in the early stages of language acquisition due to diverse accents influenced by their native languages. Accurately segmenting short words becomes problematic in such cases. Second, developing precise audio-text transcriptions for languages with non-native accented speech poses a formidable task. Last, assessing oral proficiency levels involves capturing various linguistic features, including fluency, pronunciation, accuracy, and complexity, which are not easily captured by current NLP technology.
Data availability
The dataset utilized was obtained from the International Corpus of Japanese as a Second Language (I-JAS). The data URLs: [ https://www2.ninjal.ac.jp/jll/lsaj/ihome2.html ].
J-CAT and TTBJ are two computerized adaptive tests used to assess Japanese language proficiency.
SPOT is a specific component of the TTBJ test.
J-CAT: https://www.j-cat2.org/html/ja/pages/interpret.html
SPOT: https://ttbj.cegloc.tsukuba.ac.jp/p1.html#SPOT .
The study utilized a prompt-based GPT-4 model, developed by OpenAI, which has an impressive architecture with 1.8 trillion parameters across 120 layers. GPT-4 was trained on a vast dataset of 13 trillion tokens, using two stages: initial training on internet text datasets to predict the next token, and subsequent fine-tuning through reinforcement learning from human feedback.
https://www2.ninjal.ac.jp/jll/lsaj/ihome2-en.html .
http://jhlee.sakura.ne.jp/JEV/ by Japanese Learning Dictionary Support Group 2015.
We express our sincere gratitude to the reviewer for bringing this matter to our attention.
On February 7, 2023, Microsoft began rolling out a major overhaul to Bing that included a new chatbot feature based on OpenAI’s GPT-4 (Bing.com).
Appendix E-F present the analysis results of the QWK coefficient between the scores computed by the human raters and the BERT, OCLL models.
Attali Y, Burstein J (2006) Automated essay scoring with e-rater® V.2. J. Technol., Learn. Assess., 4
Barkaoui K, Hadidi A (2020) Assessing Change in English Second Language Writing Performance (1st ed.). Routledge, New York. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003092346
Bentz C, Tatyana R, Koplenig A, Tanja S (2016) A comparison between morphological complexity. measures: Typological data vs. language corpora. In Proceedings of the workshop on computational linguistics for linguistic complexity (CL4LC), 142–153. Osaka, Japan: The COLING 2016 Organizing Committee
Bond TG, Yan Z, Heene M (2021) Applying the Rasch model: Fundamental measurement in the human sciences (4th ed). Routledge
Brants T (2000) Inter-annotator agreement for a German newspaper corpus. Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC’00), Athens, Greece, 31 May-2 June, European Language Resources Association
Brown TB, Mann B, Ryder N, et al. (2020) Language models are few-shot learners. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Online, 6–12 December, Curran Associates, Inc., Red Hook, NY
Burstein J (2003) The E-rater scoring engine: Automated essay scoring with natural language processing. In Shermis MD and Burstein JC (ed) Automated Essay Scoring: A Cross-Disciplinary Perspective. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Mahwah, NJ
Čech R, Miroslav K (2018) Morphological richness of text. In Masako F, Václav C (ed) Taming the corpus: From inflection and lexis to interpretation, 63–77. Cham, Switzerland: Springer Nature
Çöltekin Ç, Taraka, R (2018) Exploiting Universal Dependencies treebanks for measuring morphosyntactic complexity. In Aleksandrs B, Christian B (ed), Proceedings of first workshop on measuring language complexity, 1–7. Torun, Poland
Crossley SA, Cobb T, McNamara DS (2013) Comparing count-based and band-based indices of word frequency: Implications for active vocabulary research and pedagogical applications. System 41:965–981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.system.2013.08.002
Article Google Scholar
Crossley SA, McNamara DS (2016) Say more and be more coherent: How text elaboration and cohesion can increase writing quality. J. Writ. Res. 7:351–370
CyberAgent Inc (2023) Open-Calm series of Japanese language models. Retrieved from: https://www.cyberagent.co.jp/news/detail/id=28817
Devlin J, Chang MW, Lee K, Toutanova K (2019) BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Minneapolis, Minnesota, 2–7 June, pp. 4171–4186. Association for Computational Linguistics
Diez-Ortega M, Kyle K (2023) Measuring the development of lexical richness of L2 Spanish: a longitudinal learner corpus study. Studies in Second Language Acquisition 1-31
Eckes T (2009) On common ground? How raters perceive scoring criteria in oral proficiency testing. In Brown A, Hill K (ed) Language testing and evaluation 13: Tasks and criteria in performance assessment (pp. 43–73). Peter Lang Publishing
Elliot S (2003) IntelliMetric: from here to validity. In: Shermis MD, Burstein JC (ed) Automated Essay Scoring: A Cross-Disciplinary Perspective. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Mahwah, NJ
Google Scholar
Engber CA (1995) The relationship of lexical proficiency to the quality of ESL compositions. J. Second Lang. Writ. 4:139–155
Garner J, Crossley SA, Kyle K (2019) N-gram measures and L2 writing proficiency. System 80:176–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.system.2018.12.001
Haberman SJ (2008) When can subscores have value? J. Educat. Behav. Stat., 33:204–229
Haberman SJ, Yao L, Sinharay S (2015) Prediction of true test scores from observed item scores and ancillary data. Brit. J. Math. Stat. Psychol. 68:363–385
Halliday MAK (1985) Spoken and Written Language. Deakin University Press, Melbourne, Australia
Hirao R, Arai M, Shimanaka H et al. (2020) Automated essay scoring system for nonnative Japanese learners. Proceedings of the 12th Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC 2020), pp. 1250–1257. European Language Resources Association
Hunt KW (1966) Recent Measures in Syntactic Development. Elementary English, 43(7), 732–739. http://www.jstor.org/stable/41386067
Ishioka T (2001) About e-rater, a computer-based automatic scoring system for essays [Konpyūta ni yoru essei no jidō saiten shisutemu e − rater ni tsuite]. University Entrance Examination. Forum [Daigaku nyūshi fōramu] 24:71–76
Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J (1997) Long short- term memory. Neural Comput. 9(8):1735–1780
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Ishioka T, Kameda M (2006) Automated Japanese essay scoring system based on articles written by experts. Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Computational Linguistics and 44th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Sydney, Australia, 17–18 July 2006, pp. 233-240. Association for Computational Linguistics, USA
Japan Foundation (2021) Retrieved from: https://www.jpf.gp.jp/j/project/japanese/survey/result/dl/survey2021/all.pdf
Jarvis S (2013a) Defining and measuring lexical diversity. In Jarvis S, Daller M (ed) Vocabulary knowledge: Human ratings and automated measures (Vol. 47, pp. 13–44). John Benjamins. https://doi.org/10.1075/sibil.47.03ch1
Jarvis S (2013b) Capturing the diversity in lexical diversity. Lang. Learn. 63:87–106. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9922.2012.00739.x
Jiang J, Quyang J, Liu H (2019) Interlanguage: A perspective of quantitative linguistic typology. Lang. Sci. 74:85–97
Kim M, Crossley SA, Kyle K (2018) Lexical sophistication as a multidimensional phenomenon: Relations to second language lexical proficiency, development, and writing quality. Mod. Lang. J. 102(1):120–141. https://doi.org/10.1111/modl.12447
Kojima T, Gu S, Reid M et al. (2022) Large language models are zero-shot reasoners. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, LA, 29 November-1 December, Curran Associates, Inc., Red Hook, NY
Kyle K, Crossley SA (2015) Automatically assessing lexical sophistication: Indices, tools, findings, and application. TESOL Q 49:757–786
Kyle K, Crossley SA, Berger CM (2018) The tool for the automatic analysis of lexical sophistication (TAALES): Version 2.0. Behav. Res. Methods 50:1030–1046. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13428-017-0924-4
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Kyle K, Crossley SA, Jarvis S (2021) Assessing the validity of lexical diversity using direct judgements. Lang. Assess. Q. 18:154–170. https://doi.org/10.1080/15434303.2020.1844205
Landauer TK, Laham D, Foltz PW (2003) Automated essay scoring and annotation of essays with the Intelligent Essay Assessor. In Shermis MD, Burstein JC (ed), Automated Essay Scoring: A Cross-Disciplinary Perspective. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Mahwah, NJ
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 159–174
Laufer B, Nation P (1995) Vocabulary size and use: Lexical richness in L2 written production. Appl. Linguist. 16:307–322. https://doi.org/10.1093/applin/16.3.307
Lee J, Hasebe Y (2017) jWriter Learner Text Evaluator, URL: https://jreadability.net/jwriter/
Lee J, Kobayashi N, Sakai T, Sakota K (2015) A Comparison of SPOT and J-CAT Based on Test Analysis [Tesuto bunseki ni motozuku ‘SPOT’ to ‘J-CAT’ no hikaku]. Research on the Acquisition of Second Language Japanese [Dainigengo to shite no nihongo no shūtoku kenkyū] (18) 53–69
Li W, Yan J (2021) Probability distribution of dependency distance based on a Treebank of. Japanese EFL Learners’ Interlanguage. J. Quant. Linguist. 28(2):172–186. https://doi.org/10.1080/09296174.2020.1754611
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Linacre JM (2002) Optimizing rating scale category effectiveness. J. Appl. Meas. 3(1):85–106
PubMed Google Scholar
Linacre JM (1994) Constructing measurement with a Many-Facet Rasch Model. In Wilson M (ed) Objective measurement: Theory into practice, Volume 2 (pp. 129–144). Norwood, NJ: Ablex
Liu H (2008) Dependency distance as a metric of language comprehension difficulty. J. Cognitive Sci. 9:159–191
Liu H, Xu C, Liang J (2017) Dependency distance: A new perspective on syntactic patterns in natural languages. Phys. Life Rev. 21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plrev.2017.03.002
Loukina A, Madnani N, Cahill A, et al. (2020) Using PRMSE to evaluate automated scoring systems in the presence of label noise. Proceedings of the Fifteenth Workshop on Innovative Use of NLP for Building Educational Applications, Seattle, WA, USA → Online, 10 July, pp. 18–29. Association for Computational Linguistics
Lu X (2010) Automatic analysis of syntactic complexity in second language writing. Int. J. Corpus Linguist. 15:474–496
Lu X (2012) The relationship of lexical richness to the quality of ESL learners’ oral narratives. Mod. Lang. J. 96:190–208
Lu X (2017) Automated measurement of syntactic complexity in corpus-based L2 writing research and implications for writing assessment. Lang. Test. 34:493–511
Lu X, Hu R (2022) Sense-aware lexical sophistication indices and their relationship to second language writing quality. Behav. Res. Method. 54:1444–1460. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13428-021-01675-6
Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare of Japan (2022) Retrieved from: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_30367.html
Mizumoto A, Eguchi M (2023) Exploring the potential of using an AI language model for automated essay scoring. Res. Methods Appl. Linguist. 3:100050
Okgetheng B, Takeuchi K (2024) Estimating Japanese Essay Grading Scores with Large Language Models. Proceedings of 30th Annual Conference of the Language Processing Society in Japan, March 2024
Ortega L (2015) Second language learning explained? SLA across 10 contemporary theories. In VanPatten B, Williams J (ed) Theories in Second Language Acquisition: An Introduction
Rae JW, Borgeaud S, Cai T, et al. (2021) Scaling Language Models: Methods, Analysis & Insights from Training Gopher. ArXiv, abs/2112.11446
Read J (2000) Assessing vocabulary. Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511732942
Rudner LM, Liang T (2002) Automated Essay Scoring Using Bayes’ Theorem. J. Technol., Learning and Assessment, 1 (2)
Sakoda K, Hosoi Y (2020) Accuracy and complexity of Japanese Language usage by SLA learners in different learning environments based on the analysis of I-JAS, a learners’ corpus of Japanese as L2. Math. Linguist. 32(7):403–418. https://doi.org/10.24701/mathling.32.7_403
Suzuki N (1999) Summary of survey results regarding comprehensive essay questions. Final report of “Joint Research on Comprehensive Examinations for the Aim of Evaluating Applicability to Each Specialized Field of Universities” for 1996-2000 [shōronbun sōgō mondai ni kansuru chōsa kekka no gaiyō. Heisei 8 - Heisei 12-nendo daigaku no kaku senmon bun’ya e no tekisei no hyōka o mokuteki to suru sōgō shiken no arikata ni kansuru kyōdō kenkyū’ saishū hōkoku-sho]. University Entrance Examination Section Center Research and Development Department [Daigaku nyūshi sentā kenkyū kaihatsubu], 21–32
Taghipour K, Ng HT (2016) A neural approach to automated essay scoring. Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Austin, Texas, 1–5 November, pp. 1882–1891. Association for Computational Linguistics
Takeuchi K, Ohno M, Motojin K, Taguchi M, Inada Y, Iizuka M, Abo T, Ueda H (2021) Development of essay scoring methods based on reference texts with construction of research-available Japanese essay data. In IPSJ J 62(9):1586–1604
Ure J (1971) Lexical density: A computational technique and some findings. In Coultard M (ed) Talking about Text. English Language Research, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, England
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, et al. (2017) Attention is all you need. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, 4–7 December, pp. 5998–6008, Curran Associates, Inc., Red Hook, NY
Watanabe H, Taira Y, Inoue Y (1988) Analysis of essay evaluation data [Shōronbun hyōka dēta no kaiseki]. Bulletin of the Faculty of Education, University of Tokyo [Tōkyōdaigaku kyōiku gakubu kiyō], Vol. 28, 143–164
Yao S, Yu D, Zhao J, et al. (2023) Tree of thoughts: Deliberate problem solving with large language models. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 36
Zenker F, Kyle K (2021) Investigating minimum text lengths for lexical diversity indices. Assess. Writ. 47:100505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asw.2020.100505
Zhang Y, Warstadt A, Li X, et al. (2021) When do you need billions of words of pretraining data? Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing, Online, pp. 1112-1125. Association for Computational Linguistics. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2021.acl-long.90
Download references
This research was funded by National Foundation of Social Sciences (22BYY186) to Wenchao Li.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Japanese Studies, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Department of Linguistics and Applied Linguistics, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Wenchao Li is in charge of conceptualization, validation, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, visualization and writing the draft. Haitao Liu is in charge of supervision.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Wenchao Li .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was not required as the study did not involve human participants.
Informed consent
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplemental material file #1, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Li, W., Liu, H. Applying large language models for automated essay scoring for non-native Japanese. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 11 , 723 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03209-9
Download citation
Received : 02 February 2024
Accepted : 16 May 2024
Published : 03 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03209-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
Men Fear Me, Society Shames Me, and I Love My Life

By Glynnis MacNicol
Ms. MacNicol is a writer, a podcast host and the author of the forthcoming memoir “I’m Mostly Here to Enjoy Myself.”
I was once told that the challenge of making successful feminist porn is that the thing women desire most is freedom.
If that’s the case, one might consider my life over the past few years to be extremely pornographic — even without all the actual sex that occurred. It definitely has the makings of a fantasy, if we allowed for fantasies starring single, childless women on the brink of turning 50.
It’s not just in enjoying my age that I’m defying expectations. It’s that I’ve exempted myself from the central things we’re told give a woman’s life meaning — partnership and parenting. I’ve discovered that despite all the warnings, I regret none of those choices.
Indeed, I am enjoying them immensely. Instead of my prospects diminishing, as nearly every message that gets sent my way promises they will — fewer relationships, less excitement, less sex, less visibility — I find them widening. The world is more available to me than it’s ever been.
Saying so should not be radical in 2024, and yet, somehow it feels that way. We live in a world whose power structures continue to benefit from women staying in place. In fact, we’re currently experiencing the latest backlash against the meager feminist gains of the past half-century. My story — and those of the other women in similar shoes — shows that there are other, fulfilling ways to live.
It is disconcerting to enjoy oneself so much when there is so much to assure you to expect the opposite, just as it is strange to feel so good against a backdrop of so much terribleness in the world. But with age (hopefully) comes clarity.
Fifty is a milestone. And the fact my 50th birthday lands on or around some other significant 50ths has brought some things into focus. Last year was the 50th anniversary of Roe v. Wade. This year is the 50th of the Equal Credit Opportunity Act, which may be less well known but remains significant: It allowed women for the first time to have bank accounts and credit cards in their own name, not needing a male signature.
That my birth date landed between the passing of these two landmark laws makes it easier for me to see that the life I’m living is a result of women having authority over both their bodies and their finances. I represent a cohort of women who lead lives that do not require us to ask permission or seek approval. I have availed myself of all the choices available to me, and while the results come with their own set of risks, they have been enormously satisfying.
The timing of my birthday also helps me see the violent rollback of women’s rights happening right now as a response to the independence these legal rights afforded women. Forget about the horror of being alone and middle-aged — there is nothing more terrifying to a patriarchal society than a woman who is free. That she might be having a better time without permission or supervision is downright insufferable.
My entry into middle age certainly had the makings of an unpleasant story.
Like many, I spent the early months of the pandemic by myself. It was the type of solitary confinement that popular science, and certain men with platforms, enjoy reminding us will be the terrible future that awaits a woman who remains single for too long. I went untouched by anyone. Unsmelled, too, which you might think is a strange thing to note, but it’s an even stranger thing to experience. Unseen except by the building exterminator and the remaining doormen of the Upper West Side who gave distant friendly greetings on my evening walks around Covid-empty New York.
Alone, unmarried, childless, past my so-called prime. A caricature, culture would have it, a fringe identity; a tragedy or a punchline, depending on your preference. At the very least a cautionary tale.
By August 2021, I was desperate — not for partnership but for connection. I bought a ticket to Paris, a place where I’d spent much of my free time before the pandemic and where I had a group of friends.
Paris, I reminded myself, prioritizes pleasure. I dived in. Cheese, wine, friendships, sex — and repeat.
At first it was shocking. I was ill prepared to get what I wanted, what it seemed I had summoned. There were moments when I wondered whether I should be ashamed. I had also never felt so free and so fully myself. I felt no shame or guilt, only the thrill that came with the knowledge I was exercising my freedom.
These days, generally speaking, there is little in cinema or literature, let alone the online world, to suggest that when you are a woman alone (forget about a middle-aged woman), things will go your way, as I have often experienced.
There have been better times. In the 1980s, sitcoms were stacked with starring women for whom men were a minor-character concern — “Designing Women,” “Murphy Brown,” “The Golden Girls” — all of which, if they premiered today (and that’s a big if), would feel radical. Later there was “Girlfriends.” Even “Sex and the City,” with its often regressive marriage plotting, remains surprisingly modern in its depictions of adult friendship and sexual mores. In each case, just as it looked as if these narratives might begin to fully take root in the real world, the women largely went back inside (or into body bags, in the case of many “Law & Order” plotlines). By the early aughts we were housewives again, real and imagined.
I suspect that a lot of this backlash is connected to the terror that men experienced at discovering that they are less necessary to women’s fulfillment than centuries of laws and stories have allowed them to believe. That terror is abundantly apparent today: From Harrison Butker’s commencement speech suggesting that women may find more fulfillment in marriage and children than in having a career, to the Supreme Court once again debating access to abortion to the push to roll back no-fault divorce laws: All are efforts to return women to a place where others can manage their access to … well, just about everything.
It’s in this light that my enjoyment begins to feel radical. Come fly with me. There’s no fear here.
Glynnis MacNicol is a writer, a podcast host and the author of the forthcoming memoir “I’m Mostly Here to Enjoy Myself.”
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Let's take a look at eight steps for writing a character comparison. 1. Choose two characters. The first step to writing a character comparison is to determine two characters you want to compare. Before you start comparing, revisit parts of the text where each character appears. Take note of the various character descriptions throughout the ...
Make sure they have enough similarities and differences to make a meaningful comparison. 2. Brainstorm key points: Once you have chosen the subjects, brainstorm the key points you want to compare and contrast. These could include characteristics, features, themes, or arguments related to each subject. 3.
1.) Choose two characters. The first step to writing a character comparison is to determine two characters you want to compare. Before you start comparing, revisit parts of the text where each ...
The point of the compare/contrast essay isn't for you to just list the differences and similarities between two characters, you need to take those observations and make a larger argument about the novel as a whole. That larger argument allows you to practice writing an essay that contains an argument, which is a skill that nearly all English ...
Comparing Main Characters in Novels. If your assignment is to compare the characters of these novels, you would make a list or Venn diagram to make more comparisons: Both characters are young men. Both question society's notion of honor. Both witness behavior that makes them question their role models. Both have a nurturing female influence.
Comparing Literary Works. Consider which works you want to compare/contrast. Reread your selections taking notes as you go. You could make a list of themes from each work and compare them side by side. Free writing is also a great way to get your ideas on paper. Spend time brainstorming- those who explore their ideas often have better essays in ...
Determining the structure of your essay is the most important step towards conducting and presenting to the reader a well-developed comparison. Students are often asked to compare things in twos. For example, compare these two articles, or two characters in a novel, or a film and a novel or an article and a poem...
A character comparison is a detailed study of two or more characters for a character analysis, or an academic argument regarding these characters with a thesis and evidence provided by the primary ...
Making a Venn diagram or a chart can help you quickly and efficiently compare and contrast two or more things or ideas. To make a Venn diagram, simply draw some overlapping circles, one circle for each item you're considering. In the central area where they overlap, list the traits the two items have in common.
The Structure of a Compare/Contrast Essay. The compare-and-contrast essay starts with a thesis that clearly states the two subjects that are to be compared, contrasted, or both and the reason for doing so. The thesis could lean more toward comparing, contrasting, or both. Remember, the point of comparing and contrasting is to provide useful ...
The point of comparing and contrasting at this stage is to help you organize and shape your ideas to aid you in structuring your arguments. Structuring your comparisons. When comparing and contrasting in an essay, there are two main ways to structure your comparisons: the alternating method and the block method. The alternating method
Comparing and Contrasting Two Characters If you've been asked to compare and contrast two characters in order to write a paper, you might be feeling a little ... Step 5: Creating Your Outline and Drafting the Essay You've done a lot already, but there's just one more thing we need to do before we start writing the paper: create an
Sample Comparison-and-Contrast Essays. A South African Storm. By Allison Howard - Peace Corps Volunteer: South Africa (2003-2005) It's a Saturday afternoon in January in South Africa. When I begin the 45-minute walk to the shops for groceries, I can hear thunder cracking in the distance up the mountain in Mageobaskloof.
4.1: Introduction to Comparison and Contrast Essay. The key to a good compare-and-contrast essay is to choose two or more subjects that connect in a meaningful way. Comparison and contrast is simply telling how two things are alike or different. The compare-and-contrast essay starts with a thesis that clearly states the two subjects that are to ...
Compare and Contrast Essay Basics. The Compare and Contrast Essay is a literary analysis essay, but, instead of examining one work, it examines two or more works. These works must be united by a common theme or thesis statement. For example, while a literary analysis essay might explore the significance of ghosts in William Shakespeare's Hamlet ...
Character Comparison and Contrast Essay. "Fast Food Nation" is a novel written by Eric Schlosser who is a journalist reporting on the food industry. He focuses more on the hazardous conditions and effects of eating fast foods. We will write a custom essay on your topic. He explains that Americans are a people that are addicted to the ...
Introduction. (5 minutes) Write the names of two characters from two different fiction stories on the board. Tip: select characters that all students are familiar with such as characters from recent read-alouds, literature circles, etc. Ask students to think about some of the ways in which we can compare and contrast these two characters (e.g ...
Once my students had a solid understanding of characterization, we jumped right into comparing and contrasting. While rating and dating our understanding for our Student Data Tracking Binders, I quickly had students show me their level of understanding for comparing and contrasting. With a quick rate it/date it, I learned that my students had very little background knowledge on this concept.
Offer a short tidbit about each subject, noting why you've chosen to compare and contrast the two. What is contrast examples? - Contrast often means "opposite": for example, black is the opposite of white, and so there's a contrast between black ink and white paper. But contrast can also happen when the two things are just very different.
Here they are explained below: 1. Essay Planning. First, I recommend using my compare and contrast worksheet, which acts like a Venn Diagram, walking you through the steps of comparing the similarities and differences of the concepts or items you're comparing. I recommend selecting 3-5 features that can be compared, as shown in the worksheet:
Character analysis essay example #1: Character Analysis of Anders in Bullet in the Brain, a Book by Tobias Wolff. The first essay is a brief analysis. It focuses on how readers see the character of Anders in the short story "Bullet in the Brain" develops. *Click images below to enlarge. In the above character analysis essay example, I noted ...
comparison/contrast. And in some cases, comparison/contrast is only part of the essay—you begin by comparing and/or contrasting two or more things and then use what you've learned to construct an argument or evaluation. Consider these examples, noticing the language that is Like 9 people like this.
5. Find the similarities between both characters. Tell what seems similar in them (particularly their personal traits and qualities). Concentrate your efforts on a few points. It is not good to go into detail here. You can use two qualities of the persons and to prove them by quoting passages from the text. 6.
Initially, a TTR is determined for words 1-50 in an essay, followed by words 2-51, 3-52, and so on until the end of the essay is reached (Díez-Ortega and Kyle, 2023). The final MATTR scores ...
Men Fear Me, Society Shames Me, and I Love My Life. Ms. MacNicol is a writer, a podcast host and the author of the forthcoming memoir "I'm Mostly Here to Enjoy Myself.". I was once told that ...