
How To Write A Research Paper
Step-By-Step Tutorial With Examples + FREE Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | March 2024
For many students, crafting a strong research paper from scratch can feel like a daunting task – and rightly so! In this post, we’ll unpack what a research paper is, what it needs to do , and how to write one – in three easy steps. 🙂
Overview: Writing A Research Paper
What (exactly) is a research paper.
- How to write a research paper
- Stage 1 : Topic & literature search
- Stage 2 : Structure & outline
- Stage 3 : Iterative writing
- Key takeaways
Let’s start by asking the most important question, “ What is a research paper? ”.
Simply put, a research paper is a scholarly written work where the writer (that’s you!) answers a specific question (this is called a research question ) through evidence-based arguments . Evidence-based is the keyword here. In other words, a research paper is different from an essay or other writing assignments that draw from the writer’s personal opinions or experiences. With a research paper, it’s all about building your arguments based on evidence (we’ll talk more about that evidence a little later).
Now, it’s worth noting that there are many different types of research papers , including analytical papers (the type I just described), argumentative papers, and interpretative papers. Here, we’ll focus on analytical papers , as these are some of the most common – but if you’re keen to learn about other types of research papers, be sure to check out the rest of the blog .
With that basic foundation laid, let’s get down to business and look at how to write a research paper .

Overview: The 3-Stage Process
While there are, of course, many potential approaches you can take to write a research paper, there are typically three stages to the writing process. So, in this tutorial, we’ll present a straightforward three-step process that we use when working with students at Grad Coach.
These three steps are:
- Finding a research topic and reviewing the existing literature
- Developing a provisional structure and outline for your paper, and
- Writing up your initial draft and then refining it iteratively
Let’s dig into each of these.
Need a helping hand?
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature
As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question . More specifically, that’s called a research question , and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What’s important to understand though is that you’ll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources – for example, journal articles, government reports, case studies, and so on. We’ll circle back to this in a minute.
The first stage of the research process is deciding on what your research question will be and then reviewing the existing literature (in other words, past studies and papers) to see what they say about that specific research question. In some cases, your professor may provide you with a predetermined research question (or set of questions). However, in many cases, you’ll need to find your own research question within a certain topic area.
Finding a strong research question hinges on identifying a meaningful research gap – in other words, an area that’s lacking in existing research. There’s a lot to unpack here, so if you wanna learn more, check out the plain-language explainer video below.
Once you’ve figured out which question (or questions) you’ll attempt to answer in your research paper, you’ll need to do a deep dive into the existing literature – this is called a “ literature search ”. Again, there are many ways to go about this, but your most likely starting point will be Google Scholar .
If you’re new to Google Scholar, think of it as Google for the academic world. You can start by simply entering a few different keywords that are relevant to your research question and it will then present a host of articles for you to review. What you want to pay close attention to here is the number of citations for each paper – the more citations a paper has, the more credible it is (generally speaking – there are some exceptions, of course).

Ideally, what you’re looking for are well-cited papers that are highly relevant to your topic. That said, keep in mind that citations are a cumulative metric , so older papers will often have more citations than newer papers – just because they’ve been around for longer. So, don’t fixate on this metric in isolation – relevance and recency are also very important.
Beyond Google Scholar, you’ll also definitely want to check out academic databases and aggregators such as Science Direct, PubMed, JStor and so on. These will often overlap with the results that you find in Google Scholar, but they can also reveal some hidden gems – so, be sure to check them out.
Once you’ve worked your way through all the literature, you’ll want to catalogue all this information in some sort of spreadsheet so that you can easily recall who said what, when and within what context. If you’d like, we’ve got a free literature spreadsheet that helps you do exactly that.

Step 2: Develop a structure and outline
With your research question pinned down and your literature digested and catalogued, it’s time to move on to planning your actual research paper .
It might sound obvious, but it’s really important to have some sort of rough outline in place before you start writing your paper. So often, we see students eagerly rushing into the writing phase, only to land up with a disjointed research paper that rambles on in multiple
Now, the secret here is to not get caught up in the fine details . Realistically, all you need at this stage is a bullet-point list that describes (in broad strokes) what you’ll discuss and in what order. It’s also useful to remember that you’re not glued to this outline – in all likelihood, you’ll chop and change some sections once you start writing, and that’s perfectly okay. What’s important is that you have some sort of roadmap in place from the start.

At this stage you might be wondering, “ But how should I structure my research paper? ”. Well, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution here, but in general, a research paper will consist of a few relatively standardised components:
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Methodology
Let’s take a look at each of these.
First up is the introduction section . As the name suggests, the purpose of the introduction is to set the scene for your research paper. There are usually (at least) four ingredients that go into this section – these are the background to the topic, the research problem and resultant research question , and the justification or rationale. If you’re interested, the video below unpacks the introduction section in more detail.
The next section of your research paper will typically be your literature review . Remember all that literature you worked through earlier? Well, this is where you’ll present your interpretation of all that content . You’ll do this by writing about recent trends, developments, and arguments within the literature – but more specifically, those that are relevant to your research question . The literature review can oftentimes seem a little daunting, even to seasoned researchers, so be sure to check out our extensive collection of literature review content here .
With the introduction and lit review out of the way, the next section of your paper is the research methodology . In a nutshell, the methodology section should describe to your reader what you did (beyond just reviewing the existing literature) to answer your research question. For example, what data did you collect, how did you collect that data, how did you analyse that data and so on? For each choice, you’ll also need to justify why you chose to do it that way, and what the strengths and weaknesses of your approach were.
Now, it’s worth mentioning that for some research papers, this aspect of the project may be a lot simpler . For example, you may only need to draw on secondary sources (in other words, existing data sets). In some cases, you may just be asked to draw your conclusions from the literature search itself (in other words, there may be no data analysis at all). But, if you are required to collect and analyse data, you’ll need to pay a lot of attention to the methodology section. The video below provides an example of what the methodology section might look like.
By this stage of your paper, you will have explained what your research question is, what the existing literature has to say about that question, and how you analysed additional data to try to answer your question. So, the natural next step is to present your analysis of that data . This section is usually called the “results” or “analysis” section and this is where you’ll showcase your findings.
Depending on your school’s requirements, you may need to present and interpret the data in one section – or you might split the presentation and the interpretation into two sections. In the latter case, your “results” section will just describe the data, and the “discussion” is where you’ll interpret that data and explicitly link your analysis back to your research question. If you’re not sure which approach to take, check in with your professor or take a look at past papers to see what the norms are for your programme.
Alright – once you’ve presented and discussed your results, it’s time to wrap it up . This usually takes the form of the “ conclusion ” section. In the conclusion, you’ll need to highlight the key takeaways from your study and close the loop by explicitly answering your research question. Again, the exact requirements here will vary depending on your programme (and you may not even need a conclusion section at all) – so be sure to check with your professor if you’re unsure.
Step 3: Write and refine
Finally, it’s time to get writing. All too often though, students hit a brick wall right about here… So, how do you avoid this happening to you?
Well, there’s a lot to be said when it comes to writing a research paper (or any sort of academic piece), but we’ll share three practical tips to help you get started.
First and foremost , it’s essential to approach your writing as an iterative process. In other words, you need to start with a really messy first draft and then polish it over multiple rounds of editing. Don’t waste your time trying to write a perfect research paper in one go. Instead, take the pressure off yourself by adopting an iterative approach.
Secondly , it’s important to always lean towards critical writing , rather than descriptive writing. What does this mean? Well, at the simplest level, descriptive writing focuses on the “ what ”, while critical writing digs into the “ so what ” – in other words, the implications . If you’re not familiar with these two types of writing, don’t worry! You can find a plain-language explanation here.
Last but not least, you’ll need to get your referencing right. Specifically, you’ll need to provide credible, correctly formatted citations for the statements you make. We see students making referencing mistakes all the time and it costs them dearly. The good news is that you can easily avoid this by using a simple reference manager . If you don’t have one, check out our video about Mendeley, an easy (and free) reference management tool that you can start using today.
Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are:
- To choose a research question and review the literature
- To plan your paper structure and draft an outline
- To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing
Remember, this is just a b ig-picture overview of the research paper development process and there’s a lot more nuance to unpack. So, be sure to grab a copy of our free research paper template to learn more about how to write a research paper.
You Might Also Like:

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
News alert: UC Berkeley has announced its next university librarian
Secondary menu
- Log in to your Library account
- Hours and Maps
- Connect from Off Campus
- UC Berkeley Home
Search form
Research methods--quantitative, qualitative, and more: overview.
- Quantitative Research
- Qualitative Research
- Data Science Methods (Machine Learning, AI, Big Data)
- Text Mining and Computational Text Analysis
- Evidence Synthesis/Systematic Reviews
- Get Data, Get Help!
About Research Methods
This guide provides an overview of research methods, how to choose and use them, and supports and resources at UC Berkeley.
As Patten and Newhart note in the book Understanding Research Methods , "Research methods are the building blocks of the scientific enterprise. They are the "how" for building systematic knowledge. The accumulation of knowledge through research is by its nature a collective endeavor. Each well-designed study provides evidence that may support, amend, refute, or deepen the understanding of existing knowledge...Decisions are important throughout the practice of research and are designed to help researchers collect evidence that includes the full spectrum of the phenomenon under study, to maintain logical rules, and to mitigate or account for possible sources of bias. In many ways, learning research methods is learning how to see and make these decisions."
The choice of methods varies by discipline, by the kind of phenomenon being studied and the data being used to study it, by the technology available, and more. This guide is an introduction, but if you don't see what you need here, always contact your subject librarian, and/or take a look to see if there's a library research guide that will answer your question.
Suggestions for changes and additions to this guide are welcome!
START HERE: SAGE Research Methods
Without question, the most comprehensive resource available from the library is SAGE Research Methods. HERE IS THE ONLINE GUIDE to this one-stop shopping collection, and some helpful links are below:
- SAGE Research Methods
- Little Green Books (Quantitative Methods)
- Little Blue Books (Qualitative Methods)
- Dictionaries and Encyclopedias
- Case studies of real research projects
- Sample datasets for hands-on practice
- Streaming video--see methods come to life
- Methodspace- -a community for researchers
- SAGE Research Methods Course Mapping
Library Data Services at UC Berkeley
Library Data Services Program and Digital Scholarship Services
The LDSP offers a variety of services and tools ! From this link, check out pages for each of the following topics: discovering data, managing data, collecting data, GIS data, text data mining, publishing data, digital scholarship, open science, and the Research Data Management Program.
Be sure also to check out the visual guide to where to seek assistance on campus with any research question you may have!
Library GIS Services
Other Data Services at Berkeley
D-Lab Supports Berkeley faculty, staff, and graduate students with research in data intensive social science, including a wide range of training and workshop offerings Dryad Dryad is a simple self-service tool for researchers to use in publishing their datasets. It provides tools for the effective publication of and access to research data. Geospatial Innovation Facility (GIF) Provides leadership and training across a broad array of integrated mapping technologies on campu Research Data Management A UC Berkeley guide and consulting service for research data management issues
General Research Methods Resources
Here are some general resources for assistance:
- Assistance from ICPSR (must create an account to access): Getting Help with Data , and Resources for Students
- Wiley Stats Ref for background information on statistics topics
- Survey Documentation and Analysis (SDA) . Program for easy web-based analysis of survey data.
Consultants
- D-Lab/Data Science Discovery Consultants Request help with your research project from peer consultants.
- Research data (RDM) consulting Meet with RDM consultants before designing the data security, storage, and sharing aspects of your qualitative project.
- Statistics Department Consulting Services A service in which advanced graduate students, under faculty supervision, are available to consult during specified hours in the Fall and Spring semesters.
Related Resourcex
- IRB / CPHS Qualitative research projects with human subjects often require that you go through an ethics review.
- OURS (Office of Undergraduate Research and Scholarships) OURS supports undergraduates who want to embark on research projects and assistantships. In particular, check out their "Getting Started in Research" workshops
- Sponsored Projects Sponsored projects works with researchers applying for major external grants.
- Next: Quantitative Research >>
- Last Updated: Apr 25, 2024 11:09 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.berkeley.edu/researchmethods
- Corrections
Search Help
Get the most out of Google Scholar with some helpful tips on searches, email alerts, citation export, and more.
Finding recent papers
Your search results are normally sorted by relevance, not by date. To find newer articles, try the following options in the left sidebar:
- click "Since Year" to show only recently published papers, sorted by relevance;
- click "Sort by date" to show just the new additions, sorted by date;
- click the envelope icon to have new results periodically delivered by email.
Locating the full text of an article
Abstracts are freely available for most of the articles. Alas, reading the entire article may require a subscription. Here're a few things to try:
- click a library link, e.g., "FindIt@Harvard", to the right of the search result;
- click a link labeled [PDF] to the right of the search result;
- click "All versions" under the search result and check out the alternative sources;
- click "Related articles" or "Cited by" under the search result to explore similar articles.
If you're affiliated with a university, but don't see links such as "FindIt@Harvard", please check with your local library about the best way to access their online subscriptions. You may need to do search from a computer on campus, or to configure your browser to use a library proxy.
Getting better answers
If you're new to the subject, it may be helpful to pick up the terminology from secondary sources. E.g., a Wikipedia article for "overweight" might suggest a Scholar search for "pediatric hyperalimentation".
If the search results are too specific for your needs, check out what they're citing in their "References" sections. Referenced works are often more general in nature.
Similarly, if the search results are too basic for you, click "Cited by" to see newer papers that referenced them. These newer papers will often be more specific.
Explore! There's rarely a single answer to a research question. Click "Related articles" or "Cited by" to see closely related work, or search for author's name and see what else they have written.
Searching Google Scholar
Use the "author:" operator, e.g., author:"d knuth" or author:"donald e knuth".
Put the paper's title in quotations: "A History of the China Sea".
You'll often get better results if you search only recent articles, but still sort them by relevance, not by date. E.g., click "Since 2018" in the left sidebar of the search results page.
To see the absolutely newest articles first, click "Sort by date" in the sidebar. If you use this feature a lot, you may also find it useful to setup email alerts to have new results automatically sent to you.
Note: On smaller screens that don't show the sidebar, these options are available in the dropdown menu labelled "Year" right below the search button.
Select the "Case law" option on the homepage or in the side drawer on the search results page.
It finds documents similar to the given search result.
It's in the side drawer. The advanced search window lets you search in the author, title, and publication fields, as well as limit your search results by date.
Select the "Case law" option and do a keyword search over all jurisdictions. Then, click the "Select courts" link in the left sidebar on the search results page.
Tip: To quickly search a frequently used selection of courts, bookmark a search results page with the desired selection.
Access to articles
For each Scholar search result, we try to find a version of the article that you can read. These access links are labelled [PDF] or [HTML] and appear to the right of the search result. For example:
A paper that you need to read
Access links cover a wide variety of ways in which articles may be available to you - articles that your library subscribes to, open access articles, free-to-read articles from publishers, preprints, articles in repositories, etc.
When you are on a campus network, access links automatically include your library subscriptions and direct you to subscribed versions of articles. On-campus access links cover subscriptions from primary publishers as well as aggregators.
Off-campus access
Off-campus access links let you take your library subscriptions with you when you are at home or traveling. You can read subscribed articles when you are off-campus just as easily as when you are on-campus. Off-campus access links work by recording your subscriptions when you visit Scholar while on-campus, and looking up the recorded subscriptions later when you are off-campus.
We use the recorded subscriptions to provide you with the same subscribed access links as you see on campus. We also indicate your subscription access to participating publishers so that they can allow you to read the full-text of these articles without logging in or using a proxy. The recorded subscription information expires after 30 days and is automatically deleted.
In addition to Google Scholar search results, off-campus access links can also appear on articles from publishers participating in the off-campus subscription access program. Look for links labeled [PDF] or [HTML] on the right hand side of article pages.
Anne Author , John Doe , Jane Smith , Someone Else
In this fascinating paper, we investigate various topics that would be of interest to you. We also describe new methods relevant to your project, and attempt to address several questions which you would also like to know the answer to. Lastly, we analyze …
You can disable off-campus access links on the Scholar settings page . Disabling off-campus access links will turn off recording of your library subscriptions. It will also turn off indicating subscription access to participating publishers. Once off-campus access links are disabled, you may need to identify and configure an alternate mechanism (e.g., an institutional proxy or VPN) to access your library subscriptions while off-campus.
Email Alerts
Do a search for the topic of interest, e.g., "M Theory"; click the envelope icon in the sidebar of the search results page; enter your email address, and click "Create alert". We'll then periodically email you newly published papers that match your search criteria.
No, you can enter any email address of your choice. If the email address isn't a Google account or doesn't match your Google account, then we'll email you a verification link, which you'll need to click to start receiving alerts.
This works best if you create a public profile , which is free and quick to do. Once you get to the homepage with your photo, click "Follow" next to your name, select "New citations to my articles", and click "Done". We will then email you when we find new articles that cite yours.
Search for the title of your paper, e.g., "Anti de Sitter space and holography"; click on the "Cited by" link at the bottom of the search result; and then click on the envelope icon in the left sidebar of the search results page.
First, do a search for your colleague's name, and see if they have a Scholar profile. If they do, click on it, click the "Follow" button next to their name, select "New articles by this author", and click "Done".
If they don't have a profile, do a search by author, e.g., [author:s-hawking], and click on the mighty envelope in the left sidebar of the search results page. If you find that several different people share the same name, you may need to add co-author names or topical keywords to limit results to the author you wish to follow.
We send the alerts right after we add new papers to Google Scholar. This usually happens several times a week, except that our search robots meticulously observe holidays.
There's a link to cancel the alert at the bottom of every notification email.
If you created alerts using a Google account, you can manage them all here . If you're not using a Google account, you'll need to unsubscribe from the individual alerts and subscribe to the new ones.
Google Scholar library
Google Scholar library is your personal collection of articles. You can save articles right off the search page, organize them by adding labels, and use the power of Scholar search to quickly find just the one you want - at any time and from anywhere. You decide what goes into your library, and we’ll keep the links up to date.
You get all the goodies that come with Scholar search results - links to PDF and to your university's subscriptions, formatted citations, citing articles, and more!
Library help
Find the article you want to add in Google Scholar and click the “Save” button under the search result.
Click “My library” at the top of the page or in the side drawer to view all articles in your library. To search the full text of these articles, enter your query as usual in the search box.
Find the article you want to remove, and then click the “Delete” button under it.
- To add a label to an article, find the article in your library, click the “Label” button under it, select the label you want to apply, and click “Done”.
- To view all the articles with a specific label, click the label name in the left sidebar of your library page.
- To remove a label from an article, click the “Label” button under it, deselect the label you want to remove, and click “Done”.
- To add, edit, or delete labels, click “Manage labels” in the left column of your library page.
Only you can see the articles in your library. If you create a Scholar profile and make it public, then the articles in your public profile (and only those articles) will be visible to everyone.
Your profile contains all the articles you have written yourself. It’s a way to present your work to others, as well as to keep track of citations to it. Your library is a way to organize the articles that you’d like to read or cite, not necessarily the ones you’ve written.
Citation Export
Click the "Cite" button under the search result and then select your bibliography manager at the bottom of the popup. We currently support BibTeX, EndNote, RefMan, and RefWorks.
Err, no, please respect our robots.txt when you access Google Scholar using automated software. As the wearers of crawler's shoes and webmaster's hat, we cannot recommend adherence to web standards highly enough.
Sorry, we're unable to provide bulk access. You'll need to make an arrangement directly with the source of the data you're interested in. Keep in mind that a lot of the records in Google Scholar come from commercial subscription services.
Sorry, we can only show up to 1,000 results for any particular search query. Try a different query to get more results.
Content Coverage
Google Scholar includes journal and conference papers, theses and dissertations, academic books, pre-prints, abstracts, technical reports and other scholarly literature from all broad areas of research. You'll find works from a wide variety of academic publishers, professional societies and university repositories, as well as scholarly articles available anywhere across the web. Google Scholar also includes court opinions and patents.
We index research articles and abstracts from most major academic publishers and repositories worldwide, including both free and subscription sources. To check current coverage of a specific source in Google Scholar, search for a sample of their article titles in quotes.
While we try to be comprehensive, it isn't possible to guarantee uninterrupted coverage of any particular source. We index articles from sources all over the web and link to these websites in our search results. If one of these websites becomes unavailable to our search robots or to a large number of web users, we have to remove it from Google Scholar until it becomes available again.
Our meticulous search robots generally try to index every paper from every website they visit, including most major sources and also many lesser known ones.
That said, Google Scholar is primarily a search of academic papers. Shorter articles, such as book reviews, news sections, editorials, announcements and letters, may or may not be included. Untitled documents and documents without authors are usually not included. Website URLs that aren't available to our search robots or to the majority of web users are, obviously, not included either. Nor do we include websites that require you to sign up for an account, install a browser plugin, watch four colorful ads, and turn around three times and say coo-coo before you can read the listing of titles scanned at 10 DPI... You get the idea, we cover academic papers from sensible websites.
That's usually because we index many of these papers from other websites, such as the websites of their primary publishers. The "site:" operator currently only searches the primary version of each paper.
It could also be that the papers are located on examplejournals.gov, not on example.gov. Please make sure you're searching for the "right" website.
That said, the best way to check coverage of a specific source is to search for a sample of their papers using the title of the paper.
Ahem, we index papers, not journals. You should also ask about our coverage of universities, research groups, proteins, seminal breakthroughs, and other dimensions that are of interest to users. All such questions are best answered by searching for a statistical sample of papers that has the property of interest - journal, author, protein, etc. Many coverage comparisons are available if you search for [allintitle:"google scholar"], but some of them are more statistically valid than others.
Currently, Google Scholar allows you to search and read published opinions of US state appellate and supreme court cases since 1950, US federal district, appellate, tax and bankruptcy courts since 1923 and US Supreme Court cases since 1791. In addition, it includes citations for cases cited by indexed opinions or journal articles which allows you to find influential cases (usually older or international) which are not yet online or publicly available.
Legal opinions in Google Scholar are provided for informational purposes only and should not be relied on as a substitute for legal advice from a licensed lawyer. Google does not warrant that the information is complete or accurate.
We normally add new papers several times a week. However, updates to existing records take 6-9 months to a year or longer, because in order to update our records, we need to first recrawl them from the source website. For many larger websites, the speed at which we can update their records is limited by the crawl rate that they allow.
Inclusion and Corrections
We apologize, and we assure you the error was unintentional. Automated extraction of information from articles in diverse fields can be tricky, so an error sometimes sneaks through.
Please write to the owner of the website where the erroneous search result is coming from, and encourage them to provide correct bibliographic data to us, as described in the technical guidelines . Once the data is corrected on their website, it usually takes 6-9 months to a year or longer for it to be updated in Google Scholar. We appreciate your help and your patience.
If you can't find your papers when you search for them by title and by author, please refer your publisher to our technical guidelines .
You can also deposit your papers into your institutional repository or put their PDF versions on your personal website, but please follow your publisher's requirements when you do so. See our technical guidelines for more details on the inclusion process.
We normally add new papers several times a week; however, it might take us some time to crawl larger websites, and corrections to already included papers can take 6-9 months to a year or longer.
Google Scholar generally reflects the state of the web as it is currently visible to our search robots and to the majority of users. When you're searching for relevant papers to read, you wouldn't want it any other way!
If your citation counts have gone down, chances are that either your paper or papers that cite it have either disappeared from the web entirely, or have become unavailable to our search robots, or, perhaps, have been reformatted in a way that made it difficult for our automated software to identify their bibliographic data and references. If you wish to correct this, you'll need to identify the specific documents with indexing problems and ask your publisher to fix them. Please refer to the technical guidelines .
Please do let us know . Please include the URL for the opinion, the corrected information and a source where we can verify the correction.
We're only able to make corrections to court opinions that are hosted on our own website. For corrections to academic papers, books, dissertations and other third-party material, click on the search result in question and contact the owner of the website where the document came from. For corrections to books from Google Book Search, click on the book's title and locate the link to provide feedback at the bottom of the book's page.
General Questions
These are articles which other scholarly articles have referred to, but which we haven't found online. To exclude them from your search results, uncheck the "include citations" box on the left sidebar.
First, click on links labeled [PDF] or [HTML] to the right of the search result's title. Also, check out the "All versions" link at the bottom of the search result.
Second, if you're affiliated with a university, using a computer on campus will often let you access your library's online subscriptions. Look for links labeled with your library's name to the right of the search result's title. Also, see if there's a link to the full text on the publisher's page with the abstract.
Keep in mind that final published versions are often only available to subscribers, and that some articles are not available online at all. Good luck!
Technically, your web browser remembers your settings in a "cookie" on your computer's disk, and sends this cookie to our website along with every search. Check that your browser isn't configured to discard our cookies. Also, check if disabling various proxies or overly helpful privacy settings does the trick. Either way, your settings are stored on your computer, not on our servers, so a long hard look at your browser's preferences or internet options should help cure the machine's forgetfulness.
Not even close. That phrase is our acknowledgement that much of scholarly research involves building on what others have already discovered. It's taken from Sir Isaac Newton's famous quote, "If I have seen further, it is by standing on the shoulders of giants."
- Privacy & Terms
The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Research Paper
Few things strike more fear in academics than the accursed research paper , a term synonymous with long hours and hard work. Luckily there’s a secret to help you get through them. As long as you know how to write a research paper properly, you’ll find they’re not so bad . . . or at least less painful.
In this guide we concisely explain how to write an academic research paper step by step. We’ll cover areas like how to start a research paper, how to write a research paper outline, how to use citations and evidence, and how to write a conclusion for a research paper.
But before we get into the details, let’s take a look at what a research paper is and how it’s different from other writing .
Write papers with confidence Grammarly helps you make the grade Write with Grammarly
What is a research paper?
A research paper is a type of academic writing that provides an in-depth analysis, evaluation, or interpretation of a single topic, based on empirical evidence. Research papers are similar to analytical essays, except that research papers emphasize the use of statistical data and preexisting research, along with a strict code for citations.
Research papers are a bedrock of modern science and the most effective way to share information across a wide network. However, most people are familiar with research papers from school; college courses often use them to test a student’s knowledge of a particular area or their research skills in general.
Considering their gravity, research papers favor formal, even bland language that strips the writing of any bias. Researchers state their findings plainly and with corresponding evidence so that other researchers can consequently use the paper in their own research.
Keep in mind that writing a research paper is different from writing a research proposal . Essentially, research proposals are to acquire the funding needed to get the data to write a research paper.
How long should a research paper be?
The length of a research paper depends on the topic or assignment. Typically, research papers run around 4,000–6,000 words, but it’s common to see short papers around 2,000 words or long papers over 10,000 words.
If you’re writing a paper for school, the recommended length should be provided in the assignment. Otherwise, let your topic dictate the length: Complicated topics or extensive research will require more explanation.
How to write a research paper in 9 steps
Below is a step-by-step guide to writing a research paper, catered specifically for students rather than professional researchers. While some steps may not apply to your particular assignment, think of this as more of a general guideline to keep you on track.
1 Understand the assignment
For some of you this goes without saying, but you might be surprised at how many students start a research paper without even reading the assignment guidelines.
So your first step should be to review the assignment and carefully read the writing prompt. Specifically, look for technical requirements such as length , formatting requirements (single- vs. double-spacing, indentations, etc.) and citation style . Also pay attention to the particulars, such as whether or not you need to write an abstract or include a cover page.
Once you understand the assignment, the next steps in how to write a research paper follow the usual writing process , more or less. There are some extra steps involved because research papers have extra rules, but the gist of the writing process is the same.
2 Choose your topic
In open-ended assignments, the student must choose their own topic. While it may seem simple enough, choosing a topic is actually the most important decision you’ll make in writing a research paper, since it determines everything that follows.
Your top priority in how to choose a research paper topic is whether it will provide enough content and substance for an entire research paper. You’ll want to choose a topic with enough data and complexity to enable a rich discussion. However, you also want to avoid general topics and instead stick with topics specific enough that you can cover all the relevant information without cutting too much.
3 Gather preliminary research
The sooner you start researching, the better—after all, it’s called a research paper for a reason.
To refine your topic and prepare your thesis statement, find out what research is available for your topic as soon as possible. Early research can help dispel any misconceptions you have about the topic and reveal the best paths and approaches to find more material.
Typically, you can find sources either online or in a library. If you’re searching online, make sure you use credible sources like science journals or academic papers. Some search engines—mentioned below in the Tools and resources section—allow you to browse only accredited sources and academic databases.
Keep in mind the difference between primary and secondary sources as you search. Primary sources are firsthand accounts, like published articles or autobiographies; secondary sources are more removed, like critical reviews or secondhand biographies.
When gathering your research, it’s better to skim sources instead of reading each potential source fully. If a source seems useful, set it aside to give it a full read later. Otherwise, you’ll be stuck poring over sources that you ultimately won’t use, and that time could be better spent finding a worthwhile source.
Sometimes you’re required to submit a literature review , which explains your sources and presents them to an authority for confirmation. Even if no literature review is required, it’s still helpful to compile an early list of potential sources—you’ll be glad you did later.
4 Write a thesis statement
Using what you found in your preliminary research, write a thesis statement that succinctly summarizes what your research paper will be about. This is usually the first sentence in your paper, making it your reader’s introduction to the topic.
A thesis statement is the best answer for how to start a research paper. Aside from preparing your reader, the thesis statement also makes it easier for other researchers to assess whether or not your paper is useful to them for their own research. Likewise, you should read the thesis statements of other research papers to decide how useful they are to you.
A good thesis statement mentions all the important parts of the discussion without disclosing too many of the details. If you’re having trouble putting it into words, try to phrase your topic as a question and then answer it .
For example, if your research paper topic is about separating students with ADHD from other students, you’d first ask yourself, “Does separating students with ADHD improve their learning?” The answer—based on your preliminary research—is a good basis for your thesis statement.
5 Determine supporting evidence
At this stage of how to write an academic research paper, it’s time to knuckle down and do the actual research. Here’s when you go through all the sources you collected earlier and find the specific information you’d like to use in your paper.
Normally, you find your supporting evidence by reading each source and taking notes. Isolate only the information that’s directly relevant to your topic; don’t bog down your paper with tangents or unnecessary context, however interesting they may be. And always write down page numbers , not only for you to find the information later, but also because you’ll need them for your citations.
Aside from highlighting text and writing notes, another common tactic is to use bibliography cards . These are simple index cards with a fact or direct quotation on one side and the bibliographical information (source citation, page numbers, subtopic category) on the other. While bibliography cards are not necessary, some students find them useful for staying organized, especially when it’s time to write an outline.
6 Write a research paper outline
A lot of students want to know how to write a research paper outline. More than informal essays, research papers require a methodical and systematic structure to make sure all issues are addressed, and that makes outlines especially important.
First make a list of all the important categories and subtopics you need to cover—an outline for your outline! Consider all the information you gathered when compiling your supporting evidence and ask yourself what the best way to separate and categorize everything is.
Once you have a list of what you want to talk about, consider the best order to present the information. Which subtopics are related and should go next to each other? Are there any subtopics that don’t make sense if they’re presented out of sequence? If your information is fairly straightforward, feel free to take a chronological approach and present the information in the order it happened.
Because research papers can get complicated, consider breaking your outline into paragraphs. For starters, this helps you stay organized if you have a lot of information to cover. Moreover, it gives you greater control over the flow and direction of the research paper. It’s always better to fix structural problems in the outline phase than later after everything’s already been written.
Don’t forget to include your supporting evidence in the outline as well. Chances are you’ll have a lot you want to include, so putting it in your outline helps prevent some things from falling through the cracks.
7 Write the first draft
Once your outline is finished, it’s time to start actually writing your research paper. This is by far the longest and most involved step, but if you’ve properly prepared your sources and written a thorough outline, everything should run smoothly.
If you don’t know how to write an introduction for a research paper, the beginning can be difficult. That’s why writing your thesis statement beforehand is crucial. Open with your thesis statement and then fill out the rest of your introduction with the secondary information—save the details for the body of your research paper, which comes next.
The body contains the bulk of your research paper. Unlike essays , research papers usually divide the body into sections with separate headers to facilitate browsing and scanning. Use the divisions in your outline as a guide.
Follow along your outline and go paragraph by paragraph. Because this is just the first draft, don’t worry about getting each word perfect . Later you’ll be able to revise and fine-tune your writing, but for now focus simply on saying everything that needs to be said. In other words, it’s OK to make mistakes since you’ll go back later to correct them.
One of the most common problems with writing long works like research papers is connecting paragraphs to each other. The longer your writing is, the harder it is to tie everything together smoothly. Use transition sentences to improve the flow of your paper, especially for the first and last sentences in a paragraph.
Even after the body is written, you still need to know how to write a conclusion for a research paper. Just like an essay conclusion , your research paper conclusion should restate your thesis , reiterate your main evidence , and summarize your findings in a way that’s easy to understand.
Don’t add any new information in your conclusion, but feel free to say your own personal perspective or interpretation if it helps the reader understand the big picture.
8 Cite your sources correctly
Citations are part of what sets research papers apart from more casual nonfiction like personal essays . Citing your sources both validates your data and also links your research paper to the greater scientific community. Because of their importance, citations must follow precise formatting rules . . . problem is, there’s more than one set of rules!
You need to check with the assignment to see which formatting style is required. Typically, academic research papers follow one of two formatting styles for citing sources:
- MLA (Modern Language Association)
- APA (American Psychological Association)
The links above explain the specific formatting guidelines for each style, along with an automatic citation generator to help you get started.
In addition to MLA and APA styles, you occasionally see requirements for CMOS (The Chicago Manual of Style), AMA (American Medical Association) and IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers).
Citations may seem confusing at first with all their rules and specific information. However, once you get the hang of them, you’ll be able to properly cite your sources without even thinking about it. Keep in mind that each formatting style has specific guidelines for citing just about any kind of source, including photos , websites , speeches , and YouTube videos .
9 Edit and proofread
Last but not least, you want to go through your research paper to correct all the mistakes by proofreading . We recommend going over it twice: once for structural issues such as adding/deleting parts or rearranging paragraphs and once for word choice, grammatical, and spelling mistakes. Doing two different editing sessions helps you focus on one area at a time instead of doing them both at once.
To help you catch everything, here’s a quick checklist to keep in mind while you edit:
Structural edit:
- Is your thesis statement clear and concise?
- Is your paper well-organized, and does it flow from beginning to end with logical transitions?
- Do your ideas follow a logical sequence in each paragraph?
- Have you used concrete details and facts and avoided generalizations?
- Do your arguments support and prove your thesis?
- Have you avoided repetition?
- Are your sources properly cited?
- Have you checked for accidental plagiarism?
Word choice, grammar, and spelling edit:
- Is your language clear and specific?
- Do your sentences flow smoothly and clearly?
- Have you avoided filler words and phrases ?
- Have you checked for proper grammar, spelling, and punctuation?
Some people find it useful to read their paper out loud to catch problems they might miss when reading in their head. Another solution is to have someone else read your paper and point out areas for improvement and/or technical mistakes.
Revising is a separate skill from writing, and being good at one doesn’t necessarily make you good at the other. If you want to improve your revision skills, read our guide on self-editing , which includes a more complete checklist and advanced tips on improving your revisions.
Technical issues like grammatical mistakes and misspelled words can be handled effortlessly if you use a spellchecker with your word processor, or even better, a digital writing assistant that also suggests improvements for word choice and tone, like Grammarly (we explain more in the Tools and resources section below).
Tools and resources
If you want to know more about how to write a research paper, or if you want some help with each step, take a look at the tools and resources below.
Google Scholar
This is Google’s own search engine, which is dedicated exclusively to academic papers. It’s a great way to find new research and sources. Plus, it’s free to use.
Zotero is a freemium, open-source research manager, a cross between an organizational CMS and a search engine for academic research. With it, you can browse the internet for research sources relevant to your topic and share them easily with colleagues. Also, it automatically generates citations.
FocusWriter
Writing long research papers is always a strain on your attention span. If you have trouble avoiding distractions during those long stretches, FocusWriter might be able to help. FocusWriter is a minimalist word processor that removes all the distracting icons and sticks only to what you type. You’re also free to choose your own customized backgrounds, with other special features like timed alarms, daily goals, and optional typewriter sound effects.
Google Charts
This useful and free tool from Google lets you create simple charts and graphs based on whatever data you input. Charts and graphs are excellent visual aids for expressing numeric data, a perfect complement if you need to explain complicated evidential research.
Grammarly goes way beyond grammar, helping you hone word choice, checking your text for plagiarism, detecting your tone, and more. For foreign-language learners, it can make your English sound more fluent, and even those who speak English as their primary language benefit from Grammarly’s suggestions.
Research paper FAQs
A research paper is a piece of academic writing that analyzes, evaluates, or interprets a single topic with empirical evidence and statistical data.
When will I need to write a research paper in college?
Many college courses use research papers to test a student’s knowledge of a particular topic or their research skills in general. While research papers depend on the course or professor, you can expect to write at least a few before graduation.
How do I determine a topic for my research paper?
If the topic is not assigned, try to find a topic that’s general enough to provide ample evidence but specific enough that you’re able to cover all the basics. If possible, choose a topic you’re personally interested in—it makes the work easier.
Where can I conduct research for my paper?
Today most research is conducted either online or in libraries. Some topics might benefit from old periodicals like newspapers or magazines, as well as visual media like documentaries. Museums, parks, and historical monuments can also be useful.
How do I cite sources for a research paper?
The correct formatting for citations depends on which style you’re using, so check the assignment guidelines. Most school research reports use either MLA or APA styles, although there are others.
This article was originally written by Karen Hertzberg in 2017. It’s been updated to include new information.

When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
Welcome to the PLOS Writing Center
Your source for scientific writing & publishing essentials.
A collection of free, practical guides and hands-on resources for authors looking to improve their scientific publishing skillset.
ARTICLE-WRITING ESSENTIALS
Your title is the first thing anyone who reads your article is going to see, and for many it will be where they stop reading. Learn how to write a title that helps readers find your article, draws your audience in and sets the stage for your research!
The abstract is your chance to let your readers know what they can expect from your article. Learn how to write a clear, and concise abstract that will keep your audience reading.
A clear methods section impacts editorial evaluation and readers’ understanding, and is also the backbone of transparency and replicability. Learn what to include in your methods section, and how much detail is appropriate.
In many fields, a statistical analysis forms the heart of both the methods and results sections of a manuscript. Learn how to report statistical analyses, and what other context is important for publication success and future reproducibility.
The discussion section contains the results and outcomes of a study. An effective discussion informs readers what can be learned from your experiment and provides context for the results.
Ensuring your manuscript is well-written makes it easier for editors, reviewers and readers to understand your work. Avoiding language errors can help accelerate review and minimize delays in the publication of your research.
The PLOS Writing Toolbox
Delivered to your inbox every two weeks, the Writing Toolbox features practical advice and tools you can use to prepare a research manuscript for submission success and build your scientific writing skillset.
Discover how to navigate the peer review and publishing process, beyond writing your article.
The path to publication can be unsettling when you’re unsure what’s happening with your paper. Learn about staple journal workflows to see the detailed steps required for ensuring a rigorous and ethical publication.
Reputable journals screen for ethics at submission—and inability to pass ethics checks is one of the most common reasons for rejection. Unfortunately, once a study has begun, it’s often too late to secure the requisite ethical reviews and clearances. Learn how to prepare for publication success by ensuring your study meets all ethical requirements before work begins.
From preregistration, to preprints, to publication—learn how and when to share your study.
How you store your data matters. Even after you publish your article, your data needs to be accessible and useable for the long term so that other researchers can continue building on your work. Good data management practices make your data discoverable and easy to use, promote a strong foundation for reproducibility and increase your likelihood of citations.
You’ve just spent months completing your study, writing up the results and submitting to your top-choice journal. Now the feedback is in and it’s time to revise. Set out a clear plan for your response to keep yourself on-track and ensure edits don’t fall through the cracks.
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher.
Are you actively preparing a submission for a PLOS journal? Select the relevant journal below for more detailed guidelines.
How to Write an Article
Share the lessons of the Writing Center in a live, interactive training.
Access tried-and-tested training modules, complete with slides and talking points, workshop activities, and more.

How to Write a Research Paper
Use the links below to jump directly to any section of this guide:
Research Paper Fundamentals
How to choose a topic or question, how to create a working hypothesis or thesis, common research paper methodologies, how to gather and organize evidence , how to write an outline for your research paper, how to write a rough draft, how to revise your draft, how to produce a final draft, resources for teachers .
It is not fair to say that no one writes anymore. Just about everyone writes text messages, brief emails, or social media posts every single day. Yet, most people don't have a lot of practice with the formal, organized writing required for a good academic research paper. This guide contains links to a variety of resources that can help demystify the process. Some of these resources are intended for teachers; they contain exercises, activities, and teaching strategies. Other resources are intended for direct use by students who are struggling to write papers, or are looking for tips to make the process go more smoothly.
The resources in this section are designed to help students understand the different types of research papers, the general research process, and how to manage their time. Below, you'll find links from university writing centers, the trusted Purdue Online Writing Lab, and more.
What is an Academic Research Paper?
"Genre and the Research Paper" (Purdue OWL)
There are different types of research papers. Different types of scholarly questions will lend themselves to one format or another. This is a brief introduction to the two main genres of research paper: analytic and argumentative.
"7 Most Popular Types of Research Papers" (Personal-writer.com)
This resource discusses formats that high school students commonly encounter, such as the compare and contrast essay and the definitional essay. Please note that the inclusion of this link is not an endorsement of this company's paid service.
How to Prepare and Plan Out Writing a Research Paper
Teachers can give their students a step-by-step guide like these to help them understand the different steps of the research paper process. These guides can be combined with the time management tools in the next subsection to help students come up with customized calendars for completing their papers.
"Ten Steps for Writing Research Papers" (American University)
This resource from American University is a comprehensive guide to the research paper writing process, and includes examples of proper research questions and thesis topics.
"Steps in Writing a Research Paper" (SUNY Empire State College)
This guide breaks the research paper process into 11 steps. Each "step" links to a separate page, which describes the work entailed in completing it.
How to Manage Time Effectively
The links below will help students determine how much time is necessary to complete a paper. If your sources are not available online or at your local library, you'll need to leave extra time for the Interlibrary Loan process. Remember that, even if you do not need to consult secondary sources, you'll still need to leave yourself ample time to organize your thoughts.
"Research Paper Planner: Timeline" (Baylor University)
This interactive resource from Baylor University creates a suggested writing schedule based on how much time a student has to work on the assignment.
"Research Paper Planner" (UCLA)
UCLA's library offers this step-by-step guide to the research paper writing process, which also includes a suggested planning calendar.
There's a reason teachers spend a long time talking about choosing a good topic. Without a good topic and a well-formulated research question, it is almost impossible to write a clear and organized paper. The resources below will help you generate ideas and formulate precise questions.
"How to Select a Research Topic" (Univ. of Michigan-Flint)
This resource is designed for college students who are struggling to come up with an appropriate topic. A student who uses this resource and still feels unsure about his or her topic should consult the course instructor for further personalized assistance.
"25 Interesting Research Paper Topics to Get You Started" (Kibin)
This resource, which is probably most appropriate for high school students, provides a list of specific topics to help get students started. It is broken into subsections, such as "paper topics on local issues."
"Writing a Good Research Question" (Grand Canyon University)
This introduction to research questions includes some embedded videos, as well as links to scholarly articles on research questions. This resource would be most appropriate for teachers who are planning lessons on research paper fundamentals.
"How to Write a Research Question the Right Way" (Kibin)
This student-focused resource provides more detail on writing research questions. The language is accessible, and there are embedded videos and examples of good and bad questions.
It is important to have a rough hypothesis or thesis in mind at the beginning of the research process. People who have a sense of what they want to say will have an easier time sorting through scholarly sources and other information. The key, of course, is not to become too wedded to the draft hypothesis or thesis. Just about every working thesis gets changed during the research process.
CrashCourse Video: "Sociology Research Methods" (YouTube)
Although this video is tailored to sociology students, it is applicable to students in a variety of social science disciplines. This video does a good job demonstrating the connection between the brainstorming that goes into selecting a research question and the formulation of a working hypothesis.
"How to Write a Thesis Statement for an Analytical Essay" (YouTube)
Students writing analytical essays will not develop the same type of working hypothesis as students who are writing research papers in other disciplines. For these students, developing the working thesis may happen as a part of the rough draft (see the relevant section below).
"Research Hypothesis" (Oakland Univ.)
This resource provides some examples of hypotheses in social science disciplines like Political Science and Criminal Justice. These sample hypotheses may also be useful for students in other soft social sciences and humanities disciplines like History.
When grading a research paper, instructors look for a consistent methodology. This section will help you understand different methodological approaches used in research papers. Students will get the most out of these resources if they use them to help prepare for conversations with teachers or discussions in class.
"Types of Research Designs" (USC)
A "research design," used for complex papers, is related to the paper's method. This resource contains introductions to a variety of popular research designs in the social sciences. Although it is not the most intuitive site to read, the information here is very valuable.
"Major Research Methods" (YouTube)
Although this video is a bit on the dry side, it provides a comprehensive overview of the major research methodologies in a format that might be more accessible to students who have struggled with textbooks or other written resources.
"Humanities Research Strategies" (USC)
This is a portal where students can learn about four methodological approaches for humanities papers: Historical Methodologies, Textual Criticism, Conceptual Analysis, and the Synoptic method.
"Selected Major Social Science Research Methods: Overview" (National Academies Press)
This appendix from the book Using Science as Evidence in Public Policy , printed by National Academies Press, introduces some methods used in social science papers.
"Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper: 6. The Methodology" (USC)
This resource from the University of Southern California's library contains tips for writing a methodology section in a research paper.
How to Determine the Best Methodology for You
Anyone who is new to writing research papers should be sure to select a method in consultation with their instructor. These resources can be used to help prepare for that discussion. They may also be used on their own by more advanced students.
"Choosing Appropriate Research Methodologies" (Palgrave Study Skills)
This friendly and approachable resource from Palgrave Macmillan can be used by students who are just starting to think about appropriate methodologies.
"How to Choose Your Research Methods" (NFER (UK))
This is another approachable resource students can use to help narrow down the most appropriate methods for their research projects.
The resources in this section introduce the process of gathering scholarly sources and collecting evidence. You'll find a range of material here, from introductory guides to advanced explications best suited to college students. Please consult the LitCharts How to Do Academic Research guide for a more comprehensive list of resources devoted to finding scholarly literature.
Google Scholar
Students who have access to library websites with detailed research guides should start there, but people who do not have access to those resources can begin their search for secondary literature here.
"Gathering Appropriate Information" (Texas Gateway)
This resource from the Texas Gateway for online resources introduces students to the research process, and contains interactive exercises. The level of complexity is suitable for middle school, high school, and introductory college classrooms.
"An Overview of Quantitative and Qualitative Data Collection Methods" (NSF)
This PDF from the National Science Foundation goes into detail about best practices and pitfalls in data collection across multiple types of methodologies.
"Social Science Methods for Data Collection and Analysis" (Swiss FIT)
This resource is appropriate for advanced undergraduates or teachers looking to create lessons on research design and data collection. It covers techniques for gathering data via interviews, observations, and other methods.
"Collecting Data by In-depth Interviewing" (Leeds Univ.)
This resource contains enough information about conducting interviews to make it useful for teachers who want to create a lesson plan, but is also accessible enough for college juniors or seniors to make use of it on their own.
There is no "one size fits all" outlining technique. Some students might devote all their energy and attention to the outline in order to avoid the paper. Other students may benefit from being made to sit down and organize their thoughts into a lengthy sentence outline. The resources in this section include strategies and templates for multiple types of outlines.
"Topic vs. Sentence Outlines" (UC Berkeley)
This resource introduces two basic approaches to outlining: the shorter topic-based approach, and the longer, more detailed sentence-based approach. This resource also contains videos on how to develop paper paragraphs from the sentence-based outline.
"Types of Outlines and Samples" (Purdue OWL)
The Purdue Online Writing Lab's guide is a slightly less detailed discussion of different types of outlines. It contains several sample outlines.
"Writing An Outline" (Austin C.C.)
This resource from a community college contains sample outlines from an American history class that students can use as models.
"How to Structure an Outline for a College Paper" (YouTube)
This brief (sub-2 minute) video from the ExpertVillage YouTube channel provides a model of outline writing for students who are struggling with the idea.
"Outlining" (Harvard)
This is a good resource to consult after completing a draft outline. It offers suggestions for making sure your outline avoids things like unnecessary repetition.
As with outlines, rough drafts can take on many different forms. These resources introduce teachers and students to the various approaches to writing a rough draft. This section also includes resources that will help you cite your sources appropriately according to the MLA, Chicago, and APA style manuals.
"Creating a Rough Draft for a Research Paper" (Univ. of Minnesota)
This resource is useful for teachers in particular, as it provides some suggested exercises to help students with writing a basic rough draft.
Rough Draft Assignment (Duke of Definition)
This sample assignment, with a brief list of tips, was developed by a high school teacher who runs a very successful and well-reviewed page of educational resources.
"Creating the First Draft of Your Research Paper" (Concordia Univ.)
This resource will be helpful for perfectionists or procrastinators, as it opens by discussing the problem of avoiding writing. It also provides a short list of suggestions meant to get students writing.
Using Proper Citations
There is no such thing as a rough draft of a scholarly citation. These links to the three major citation guides will ensure that your citations follow the correct format. Please consult the LitCharts How to Cite Your Sources guide for more resources.
Chicago Manual of Style Citation Guide
Some call The Chicago Manual of Style , which was first published in 1906, "the editors' Bible." The manual is now in its 17th edition, and is popular in the social sciences, historical journals, and some other fields in the humanities.
APA Citation Guide
According to the American Psychological Association, this guide was developed to aid reading comprehension, clarity of communication, and to reduce bias in language in the social and behavioral sciences. Its first full edition was published in 1952, and it is now in its sixth edition.
MLA Citation Guide
The Modern Language Association style is used most commonly within the liberal arts and humanities. The MLA Style Manual and Guide to Scholarly Publishing was first published in 1985 and (as of 2008) is in its third edition.
Any professional scholar will tell you that the best research papers are made in the revision stage. No matter how strong your research question or working thesis, it is not possible to write a truly outstanding paper without devoting energy to revision. These resources provide examples of revision exercises for the classroom, as well as tips for students working independently.
"The Art of Revision" (Univ. of Arizona)
This resource provides a wealth of information and suggestions for both students and teachers. There is a list of suggested exercises that teachers might use in class, along with a revision checklist that is useful for teachers and students alike.
"Script for Workshop on Revision" (Vanderbilt University)
Vanderbilt's guide for leading a 50-minute revision workshop can serve as a model for teachers who wish to guide students through the revision process during classtime.
"Revising Your Paper" (Univ. of Washington)
This detailed handout was designed for students who are beginning the revision process. It discusses different approaches and methods for revision, and also includes a detailed list of things students should look for while they revise.
"Revising Drafts" (UNC Writing Center)
This resource is designed for students and suggests things to look for during the revision process. It provides steps for the process and has a FAQ for students who have questions about why it is important to revise.
Conferencing with Writing Tutors and Instructors
No writer is so good that he or she can't benefit from meeting with instructors or peer tutors. These resources from university writing, learning, and communication centers provide suggestions for how to get the most out of these one-on-one meetings.
"Getting Feedback" (UNC Writing Center)
This very helpful resource talks about how to ask for feedback during the entire writing process. It contains possible questions that students might ask when developing an outline, during the revision process, and after the final draft has been graded.
"Prepare for Your Tutoring Session" (Otis College of Art and Design)
This guide from a university's student learning center contains a lot of helpful tips for getting the most out of working with a writing tutor.
"The Importance of Asking Your Professor" (Univ. of Waterloo)
This article from the university's Writing and Communication Centre's blog contains some suggestions for how and when to get help from professors and Teaching Assistants.
Once you've revised your first draft, you're well on your way to handing in a polished paper. These resources—each of them produced by writing professionals at colleges and universities—outline the steps required in order to produce a final draft. You'll find proofreading tips and checklists in text and video form.
"Developing a Final Draft of a Research Paper" (Univ. of Minnesota)
While this resource contains suggestions for revision, it also features a couple of helpful checklists for the last stages of completing a final draft.
Basic Final Draft Tips and Checklist (Univ. of Maryland-University College)
This short and accessible resource, part of UMUC's very thorough online guide to writing and research, contains a very basic checklist for students who are getting ready to turn in their final drafts.
Final Draft Checklist (Everett C.C.)
This is another accessible final draft checklist, appropriate for both high school and college students. It suggests reading your essay aloud at least once.
"How to Proofread Your Final Draft" (YouTube)
This video (approximately 5 minutes), produced by Eastern Washington University, gives students tips on proofreading final drafts.
"Proofreading Tips" (Georgia Southern-Armstrong)
This guide will help students learn how to spot common errors in their papers. It suggests focusing on content and editing for grammar and mechanics.
This final set of resources is intended specifically for high school and college instructors. It provides links to unit plans and classroom exercises that can help improve students' research and writing skills. You'll find resources that give an overview of the process, along with activities that focus on how to begin and how to carry out research.
"Research Paper Complete Resources Pack" (Teachers Pay Teachers)
This packet of assignments, rubrics, and other resources is designed for high school students. The resources in this packet are aligned to Common Core standards.
"Research Paper—Complete Unit" (Teachers Pay Teachers)
This packet of assignments, notes, PowerPoints, and other resources has a 4/4 rating with over 700 ratings. It is designed for high school teachers, but might also be useful to college instructors who work with freshmen.
"Teaching Students to Write Good Papers" (Yale)
This resource from Yale's Center for Teaching and Learning is designed for college instructors, and it includes links to appropriate activities and exercises.
"Research Paper Writing: An Overview" (CUNY Brooklyn)
CUNY Brooklyn offers this complete lesson plan for introducing students to research papers. It includes an accompanying set of PowerPoint slides.
"Lesson Plan: How to Begin Writing a Research Paper" (San Jose State Univ.)
This lesson plan is designed for students in the health sciences, so teachers will have to modify it for their own needs. It includes a breakdown of the brainstorming, topic selection, and research question process.
"Quantitative Techniques for Social Science Research" (Univ. of Pittsburgh)
This is a set of PowerPoint slides that can be used to introduce students to a variety of quantitative methods used in the social sciences.
- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1929 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 40,694 quotes across 1929 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
Need something? Request a new guide .
How can we improve? Share feedback .
LitCharts is hiring!

- I Tried Both: Apple Watch 9 vs Fitbit Charge 6
- Best Places to Print Photos Online
The Best Research and Reference Websites
Where to look when you need information
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/stacy-fisher-9842c081a15b4def99bfd26b4822be19.jpg)
- Emporia State University
- Cloud Services
- Error Messages
- Family Tech
- Home Networking
- Around the Web
Research websites come in handy in all kinds of situations, whether you're looking for the average rainfall in the Amazon rainforest, researching Roman history, or just having fun learning to find information.
This list of the best research websites will help greatly, and most of them are updated daily with new information.
I like to pair these sites with free research organizational tools to keep track of everything I gather online.
Best Research Websites
- Library of Congress : LOC.gov lets you not only ask a librarian for help , but also search catalogs of libraries from all over the world. This is truly a huge resource that should be on your Top 10 best research sites list. Anything from Academia Sinica in Taiwan to Yale University in the U.S. is here and ready to be searched.
- ReferenceDesk.org : Dubbed "The Internet's Best Reference Source," this extremely useful web directory provides everything from business and finance information to federal government resources, scholarship details, links to newspapers and calendars, search engines, and more.
- Ask the Space Expert: NASA's source for space and science research help. Use the video links to listen to questions answered by experts. These are from 2013 through 2015.
- USA.gov : This is where you should start when looking for specific U.S. government information. Learn about the country in general or education, housing, disability services, jobs, taxes, laws, and more.
- Reference.com : Extremely simple to use with a basic layout, this reference website lets you browse by category or search by keywords to research everything from food and health to history, beauty, education, technology, vehicles, art, and more.
- Refdesk.com : Billing itself as the internet's fact-checker, this site includes in-depth research links to breaking news, editorials, Today in History, Word of the Day, and other references.
- Encyclopedia.com : The #1 online encyclopedia that lets you search over 200 reference books and encyclopedias at once. The Picks of the week is a neat section to examine each week.
- Encyclopedia Britannica : One of the world's oldest encyclopedias online; has featured posts and category listings. The company launched in the 18th century and has been publishing exclusively online since 2011.
- Purdue University Quick Reference : This site has tons of information that includes resources specific to Purdue University and surrounding areas in Indiana. It also includes an Ask a Librarian service.
- Prescriber's Digital Reference : A wonderful research tool when gathering detailed medical information. The drug name browser includes summaries (dosage, description, and more) for hundreds of drugs.
- iTools.com : Serves as a gateway for reference and research links. It uses other websites for its searches, like YouTube and Google.
- ResearchGate : Scientific knowledge from over 160 million publication pages; browse topics in categories like engineering, biology, climate change, medicine, math, and more.
- Baseball-Reference.com : Here's everything you ever wanted to know about baseball.
- FOLDOC : Free Online Dictionary of Computing is a detailed computing dictionary for researching the meaning behind computer-related tools, standards, jargon, languages, and more. The "random" button is a fun way to learn new concepts.
Depending on the type of research you're doing or how you need to reference the information, you may need quick access to books. There are lots of places to find free book downloads , textbooks , and educational movies .
Other Ways to Do Research
Search engines like Google are a great way to perform online research. You can locate books, articles, interviews, and lots more. Learn how to search better to get the most out of your research.
Another top source of expert information is your local librarian— search for libraries near you at WorldCat . Librarians are trained to find answers to obscure questions, they're friendly, and best of all, you can talk with them face to face. They often ask you questions you might not have considered, leading to even better results. You can get help from librarians online, too, through some of the sources above.
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
- The Best Free People Search Websites
- The 8 Best Free Genealogy Websites of 2024
- 17 Best Sites to Download Free Books in 2024
- The 10 Best ChatGPT Alternatives (2024)
- Best Niche Search Engines
- 22 Best Places to Get Free Kindle Books in 2024
- The 20 Best Free Learning Websites for Kids in 2024
- X Slang and Key Terms Explained
- The Top 10 Most Popular Sites on the Web (2024)
- 15 Best Free Web Tools to Organize Your Research
- The 8 Best Search Engines of 2024
- The 10 Best Free Online Classes for Adults in 2024
- The 60 Most Useful Alexa Skills of 2024
- The 7 Best Free PC Game Websites of 2024
- 13 Best Sites With Free Educational Movies
- 9 Best Sites for Public Domain Images
Get Support for Research & Publishing
Research with harvard library.
Harvard Library makes it possible for researchers from all disciplines to generate, curate, transform, and publish their research through direct engagement with library staff, access to existing data sets and tools, and robust digital repositories for data and scholarly communications.
CONNECT WITH RESEARCH EXPERTS
Our staff of experts is here to help you find existing research sources, curate your own data, and utilize our digital repositories. Together we'll figure out a plan to get what you need to bring your research beyond the walls of your lab or campus office.
Research Consultations
Library liaisons.
Many of Harvard’s professional schools offer specialized support for data services in certain disciplines.
GENERATE, CURATE, AND TRANSFORM YOUR RESEARCH
Use these services and tools to make it easier to engage with your research data and scholarly sources.
Visualization Support
Digital mapping and gis support, find existing datasets and sources.
Harvard Library provides access to repositories of data from all disciplines. Search for existing datasets or explore through APIs and curated worksets.
Finding Datasets in HOLLIS
The "Advanced Search" function in HOLLIS allows you to limit by Resource Type to "Research Data Sets." Add your own keywords to refine.
Licensed Datasets in Dataverse
As a Harvard affiliate, login to Dataverse and access thousands of licensed datasets across numerous research fields.
HathiTrust Research Center
The HathiTrust Research Center (HTRC) enables computational analysis across 17+ million digitized items.
LibraryCloud Item API
Harvard LibraryCloud is a metadata hub that provides granular, open access to a large aggregation of Harvard library bibliographic metadata.
Caselaw Access Project
The Caselaw Access Project (CAP) includes all official, book-published United States case law, converted into structured data.
STORING AND SHARING YOUR RESEARCH
Whether you’re planning on publishing data sets, scholarly articles, or working papers, Harvard Library maintains digital repositories that allow you to store and share your research, as well as access to services that help you connect your research and publications.
Harvard Dataverse
Open science framework, university resources.
Partner sites from across the University also have information to help you with research data and publishing.
A free, AI-powered research tool for scientific literature
- Henry E. Brady
- Abyssal Plain
- Hydrogen Bonding
New & Improved API for Developers
Introducing semantic reader in beta.
Stay Connected With Semantic Scholar Sign Up What Is Semantic Scholar? Semantic Scholar is a free, AI-powered research tool for scientific literature, based at the Allen Institute for AI.
Search this site .
To access results, tab to navigate, enter to select, esc to dismiss .
How We Can Help
Whether you’re just forming your research question, need help finding a source, or are looking for ways to share and promote your scholarship, we have expertise and resources to help you.
Get support at all stages of your research
If you’re just getting started, we can help you:
- Narrow your topic
- Find materials
- Manage your sources
We can also connect you with:
- Funding and grant opportunities
- Help if you conduct research in a language other than English
- Practical strategies to build your profile as a researcher
Talk with a specialist
Our staff includes people who have expertise conducting research in specific subject areas, as well as those who specialize in digital scholarship, technologies, and much more.
Search for a specialist .
Use research guides
See our how-to support by subject or specialty — or jump right in to guides and get started on research in a variety of topics.
- Help With...
- Help With Research
How Librarians Can Support Your Research
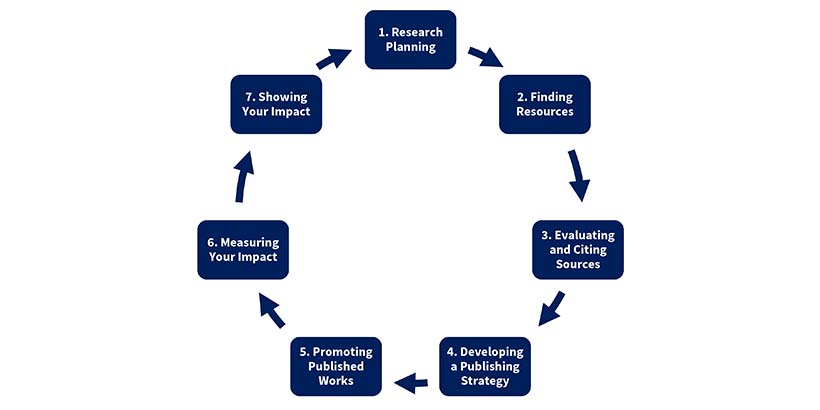
The research life cycle illustrates how information is created and used during the research process, and librarians are instrumental in this work. Librarians are best known for helping scholars find resources, and yet this is just one of several steps in the research process. We are equipped to assist both student and faculty researchers at any phase of the research process, whether you're just getting started and need help deciding what to research or you've already published your work and need help measuring impact. Contact a librarian and let us know where you are in the process.
The Seven Steps of the Research Life Cycle:
1. research planning.
Just getting started? Not sure where to even begin? Our librarians can help you with strategic planning, Evidence Synthesis advising, and conducting a survey of the literature. We can also connect faculty and staff members with the Office of Research and Sponsored Programs to assist with grant writing.
2. Finding Resources
This is the most common step where students and faculty seek guidance. During a research consultation, our librarians can help you with creating a literature review; searching through databases and journal subscriptions; accessing books and materials hosted in digital repositories; examining holdings in Special Collections and University Archives; and seeking resources not held by Pepperdine through interlibrary loan.
3. Evaluating and Citing Sources
Once you have a wealth of resources, let us assist you in evaluating which ones would best suit your needs. At this step in the research life cycle, we can also help you with properly citing your sources.
4. Developing a Publishing Strategy
Congratulations! By this step, you have a completed text. The question remains: Where to get it published? Our librarians can help you find publishers to contact to get your work in a scholarly journal popular among your peers -- with the hopes that your work will add to scholarly conversation and be cited.
5. Promoting Published Works
Once you're published in the most suitable journal for your research, we can help get your work noticed! Our librarians will work with you to maintain author profiles, self-archive in institutional repositories, make your work more widely available with open access publishing and host lectures about your research.
6. Measuring Your Impact
At this point, your work has been available to the scholarly community for some time. But who's looking at it? During this step, we'll help you find and interpret scholarly metrics so you can see how much of an impact your research is making.
7. Showing Your Impact
In this final step of the research life cycle, our librarians will explain the contexts and meaning of the metrics from the above step and appropriately interpret and analyze these metrics.
Copyright © 2024 Pepperdine University
- Privacy Policy
- GDPR Privacy Notice
- Terms of Use
- Web Accessibility
Questions? Call 1-866-445-7033 (US) or 02890 554000 (UK)

- Participant Information
- Safety in Clinical Studies
- Participation Process
- Activities & Entertainment
- After the Clinical Study
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Celerion Blog
- Refer-A-Friend Program
- Participant Rights
- Participant Responsibilities
- Glossary of Terms
- Additional Resources
- Belfast Staff
- Lincoln Staff
- Phoenix Staff
- Privacy Policy

Leaders In Clinical Research
Upcoming clinical studies.
Available studies are listed below and are updated throughout the day. To review study specifics you can click on the specific study below. To pre-register for the study, contact the Customer Care Center at 1-866-348-4859 (US) or 02890 554000 (UK).
* Stipend may pay up to reflected amount.
Celerion is a World Leader of Clinical Research
Make An Impact With Clinical Trials!
- About Celerion
- Mission, Vision & Credo
- Corporate Website
- Belfast, Northern Ireland UK
- Lincoln, Nebraska USA
- Phoenix, Arizona USA

- Jump to Main Content
- Jump to Page Navigation
- Jump to Site Search
- Giving to LSC
- Class Login
- My Lonestar
- LSC Libraries
- Help with Research
Research Guides
Our research guides connect you with different library resources to help you find research materials on any given subject. Select a campus below to view its research guides or contact a librarian for assistance.
- LSC-Houston North
- LSC-Kingwood
- LSC-Montgomery
- LSC-North Harris
- LSC-Tomball
- LSC-University Park
- Research Databases
- Government Information
- LSC Academic Integrity Policy
- Copyright Information
- Citation Help
- Library Catalog
- Library Services
- About the Libraries
- Hours and Locations
- How Do I...?
Make LSC part of your story.
Top 21 must-have digital tools for researchers
Last updated
12 May 2023
Reviewed by
Jean Kaluza
Research drives many decisions across various industries, including:
Uncovering customer motivations and behaviors to design better products
Assessing whether a market exists for your product or service
Running clinical studies to develop a medical breakthrough
Conducting effective and shareable research can be a painstaking process. Manual processes are sluggish and archaic, and they can also be inaccurate. That’s where advanced online tools can help.
The right tools can enable businesses to lean into research for better forecasting, planning, and more reliable decisions.
- Why do researchers need research tools?
Research is challenging and time-consuming. Analyzing data , running focus groups , reading research papers , and looking for useful insights take plenty of heavy lifting.
These days, researchers can’t just rely on manual processes. Instead, they’re using advanced tools that:
Speed up the research process
Enable new ways of reaching customers
Improve organization and accuracy
Allow better monitoring throughout the process
Enhance collaboration across key stakeholders
- The most important digital tools for researchers
Some tools can help at every stage, making researching simpler and faster.
They ensure accurate and efficient information collection, management, referencing, and analysis.
Some of the most important digital tools for researchers include:
Research management tools
Research management can be a complex and challenging process. Some tools address the various challenges that arise when referencing and managing papers.
.css-10ptwjf{-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;background:transparent;border:0;color:inherit;cursor:pointer;-webkit-flex-shrink:0;-ms-flex-negative:0;flex-shrink:0;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.css-10ptwjf:disabled{opacity:0.6;pointer-events:none;} Zotero
Coined as a personal research assistant, Zotero is a tool that brings efficiency to the research process. Zotero helps researchers collect, organize, annotate, and share research easily.
Zotero integrates with internet browsers, so researchers can easily save an article, publication, or research study on the platform for later.
The tool also has an advanced organizing system to allow users to label, tag, and categorize information for faster insights and a seamless analysis process.
Messy paper stacks––digital or physical––are a thing of the past with Paperpile. This reference management tool integrates with Google Docs, saving users time with citations and paper management.
Referencing, researching, and gaining insights is much cleaner and more productive, as all papers are in the same place. Plus, it’s easier to find a paper when you need it.
Acting as a single source of truth (SSOT), Dovetail houses research from the entire organization in a simple-to-use place. Researchers can use the all-in-one platform to collate and store data from interviews , forms, surveys , focus groups, and more.
Dovetail helps users quickly categorize and analyze data to uncover truly actionable insights . This helps organizations bring customer insights into every decision for better forecasting, planning, and decision-making.
Dovetail integrates with other helpful tools like Slack, Atlassian, Notion, and Zapier for a truly efficient workflow.
Putting together papers and referencing sources can be a huge time consumer. EndNote claims that researchers waste 200,000 hours per year formatting citations.
To address the issue, the tool formats citations automatically––simultaneously creating a bibliography while the user writes.
EndNote is also a cloud-based system that allows remote working, multiple-user interaction and collaboration, and seamless working on different devices.
Information survey tools
Surveys are a common way to gain data from customers. These tools can make the process simpler and more cost-effective.
With ready-made survey templates––to collect NPS data, customer effort scores , five-star surveys, and more––getting going with Delighted is straightforward.
Delighted helps teams collect and analyze survey feedback without needing any technical knowledge. The templates are customizable, so you can align the content with your brand. That way, the survey feels like it’s coming from your company, not a third party.
SurveyMonkey
With millions of customers worldwide, SurveyMonkey is another leader in online surveys. SurveyMonkey offers hundreds of templates that researchers can use to set up and deploy surveys quickly.
Whether your survey is about team performance, hotel feedback, post-event feedback, or an employee exit, SurveyMonkey has a ready-to-use template.
Typeform offers free templates you can quickly embed, which comes with a point of difference: It designs forms and surveys with people in mind, focusing on customer enjoyment.
Typeform employs the ‘one question at a time’ method to keep engagement rates and completions high. It focuses on surveys that feel more like conversations than a list of questions.
Web data analysis tools
Collecting data can take time––especially technical information. Some tools make that process simpler.
For those conducting clinical research, data collection can be incredibly time-consuming. Teamscope provides an online platform to collect and manage data simply and easily.
Researchers and medical professionals often collect clinical data through paper forms or digital means. Those are too easy to lose, tricky to manage, and challenging to collaborate on.
With Teamscope, you can easily collect, store, and electronically analyze data like patient-reported outcomes and surveys.
Heap is a digital insights platform providing context on the entire customer journey . This helps businesses improve customer feedback , conversion rates, and loyalty.
Through Heap, you can seamlessly view and analyze the customer journey across all platforms and touchpoints, whether through the app or website.
Another analytics tool, Smartlook, combines quantitative and qualitative analytics into one platform. This helps organizations understand user behavior and make crucial improvements.
Smartlook is useful for analyzing web pages, purchasing flows, and optimizing conversion rates.
Project management tools
Managing multiple research projects across many teams can be complex and challenging. Project management tools can ease the burden on researchers.
Visual productivity tool Trello helps research teams manage their projects more efficiently. Trello makes product tracking easier with:
A range of workflow options
Unique project board layouts
Advanced descriptions
Integrations
Trello also works as an SSOT to stay on top of projects and collaborate effectively as a team.
To connect research, workflows, and teams, Airtable provides a clean interactive interface.
With Airtable, it’s simple to place research projects in a list view, workstream, or road map to synthesize information and quickly collaborate. The Sync feature makes it easy to link all your research data to one place for faster action.
For product teams, Asana gathers development, copywriting, design, research teams, and product managers in one space.
As a task management platform, Asana offers all the expected features and more, including time-tracking and Jira integration. The platform offers reporting alongside data collection methods , so it’s a favorite for product teams in the tech space.
Grammar checker tools
Grammar tools ensure your research projects are professional and proofed.
No one’s perfect, especially when it comes to spelling, punctuation, and grammar. That’s where Grammarly can help.
Grammarly’s AI-powered platform reviews your content and corrects any mistakes. Through helpful integrations with other platforms––such as Gmail, Google Docs, Twitter, and LinkedIn––it’s simple to spellcheck as you go.
Another helpful grammar tool is Trinka AI. Trinka is specifically for technical and academic styles of writing. It doesn’t just correct mistakes in spelling, punctuation, and grammar; it also offers explanations and additional information when errors show.
Researchers can also use Trinka to enhance their writing and:
Align it with technical and academic styles
Improve areas like syntax and word choice
Discover relevant suggestions based on the content topic
Plagiarism checker tools
Avoiding plagiarism is crucial for the integrity of research. Using checker tools can ensure your work is original.
Plagiarism checker Quetext uses DeepSearch™ technology to quickly sort through online content to search for signs of plagiarism.
With color coding, annotations, and an overall score, it’s easy to identify conflict areas and fix them accordingly.
Duplichecker
Another helpful plagiarism tool is Duplichecker, which scans pieces of content for issues. The service is free for content up to 1000 words, with paid options available after that.
If plagiarism occurs, a percentage identifies how much is duplicate content. However, the interface is relatively basic, offering little additional information.
Journal finder tools
Finding the right journals for your project can be challenging––especially with the plethora of inaccurate or predatory content online. Journal finder tools can solve this issue.
Enago Journal Finder
The Enago Open Access Journal Finder sorts through online journals to verify their legitimacy. Through Engao, you can discover pre-vetted, high-quality journals through a validated journal index.
Enago’s search tool also helps users find relevant journals for their subject matter, speeding up the research process.
JournalFinder
JournalFinder is another journal tool that’s popular with academics and researchers. It makes the process of discovering relevant journals fast by leaning into a machine-learning algorithm.
This is useful for discovering key information and finding the right journals to publish and share your work in.
Social networking for researchers
Collaboration between researchers can improve the accuracy and sharing of information. Promoting research findings can also be essential for public health, safety, and more.
While typical social networks exist, some are specifically designed for academics.

ResearchGate
Networking platform ResearchGate encourages researchers to connect, collaborate, and share within the scientific community. With 20 million researchers on the platform, it's a popular choice.
ResearchGate is founded on an intention to advance research. The platform provides topic pages for easy connection within a field of expertise and access to millions of publications to help users stay up to date.
Academia is another commonly used platform that connects 220 million academics and researchers within their specialties.
The platform aims to accelerate research with discovery tools and grow a researcher’s audience to promote their ideas.
On Academia, users can access 47 million PDFs for free. They cover topics from mechanical engineering to applied economics and child psychology.
- Expedited research with the power of tools
For researchers, finding data and information can be time-consuming and complex to manage. That’s where the power of tools comes in.
Manual processes are slow, outdated, and have a larger potential for inaccuracies.
Leaning into tools can help researchers speed up their processes, conduct efficient research, boost their accuracy, and share their work effectively.
With tools available for project and data management, web data collection, and journal finding, researchers have plenty of assistance at their disposal.
When it comes to connecting with customers, advanced tools boost customer connection while continually bringing their needs and wants into products and services.
What are primary research tools?
Primary research is data and information that you collect firsthand through surveys, customer interviews, or focus groups.
Secondary research is data and information from other sources, such as journals, research bodies, or online content.
Primary researcher tools use methods like surveys and customer interviews. You can use these tools to collect, store, or manage information effectively and uncover more accurate insights.
What is the difference between tools and methods in research?
Research methods relate to how researchers gather information and data.
For example, surveys, focus groups, customer interviews, and A/B testing are research methods that gather information.
On the other hand, tools assist areas of research. Researchers may use tools to more efficiently gather data, store data securely, or uncover insights.
Tools can improve research methods, ensuring efficiency and accuracy while reducing complexity.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 11 January 2024
Last updated: 15 January 2024
Last updated: 17 January 2024
Last updated: 12 May 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 18 May 2023
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
Internet Explorer is no longer supported by Microsoft. To browse the NIHR site please use a modern, secure browser like Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, or Microsoft Edge.

I want to help with research

What is public involvement in research?
Everyone benefits from research. This not only includes scientific research in laboratories, but also research into health and social care. Research provides evidence about what works best. Patients, carers, people who use social care services and health and social care professionals all use this evidence to make decisions about treatments and care.
When the public gets involved in research, they work alongside researchers to help shape:
- what research gets done
- how it’s carried out
- and how the results are shared and applied in practice.
Being involved is not the same as taking part in research. It's not about taking part in a trial or study to test a new treatment or care option. It’s about being a member of the research team that works together to design and run the study.
We define public involvement in research as research being carried out ‘with’ or ‘by’ members of the public rather than ‘to’, ‘about’ or ‘for’ them.
When we use the term ‘public’, we are including:
- patients and potential patients
- carers and people who use health and social care services
- people from organisations that represent people who use services.
By getting involved in research, you can help make research more relevant and useful to patients, carers and the public. By working with researchers, you will improve research and make a difference to the way health and social care is provided in the future.

Opportunities for getting involved
Make a difference to future health and care research.
Find opportunities to get involved in NHS, public health and social care research.
Visit People in Research

Getting started
Why and how to get involved in research?
Visit this guide to find out how to contribute to research in a way that works for you.
Visit the Getting Started guide

Become a Research Champion
Are you passionate about getting more people involved in research?
Become a Research Champion and help develop better care and treatment for everyone.
Find out more about Championing Research
By getting involved in research, you can help make research more relevant and useful to patients, carers and the public. By working with researchers, you will improve research and make a difference to the way health and social care is provided in the future.
What can I contribute to research?
Your knowledge from having experienced your own care, or the care of others, is of great value to researchers. Researchers may have textbook knowledge about different conditions but unless they have also lived through it, there will be gaps in their understanding. You won’t be expected to have technical knowledge of how research works. The knowledge you have as a patient, carer or member of the public is what’s unique about your contribution.
“Your role is to be a critical friend to researchers. You will see the research from your perspective and advise researchers on how their research could be better. Sometimes this can just seem like common sense to you, but it will be valuable feedback for the researchers.” Amander, Norwich
What difference will I make?
You can make a difference at any and every stage of research. Your contributions can help shape the thinking behind the planning and delivery of a research project. In addition, your voice can influence people beyond the research team, including the people who take part in the research and the people who use the results. Sometimes the involvement of patients, carers and members of the public determines whether a project gets funded, whether it runs successfully and whether the results change practice.
In the case studies below, you can read about examples of research where patients and the public have made a big difference to the project:

Earlier diagnosis of dementia in patients

Routes to Wellness: a person centred approach to research

NIHR supports global pharma company's patient-focused approach to breast cancer trials
Why do researchers want to involve the public in their research.
Most researchers are aware of the benefits of involvement and therefore want to do it well. They want to learn from their conversations with patients, carers and the public. They will often make changes to their ideas and plans as a result. Researchers have an added incentive to involve people in their work. When they apply for funding, they are often asked how they have involved patients and the public in developing their proposal, and how they will involve them in carrying out the research. The UK Standards for Public Involvement provide a framework for researchers, showing them what good public involvement looks like.
Shaping health and social care research
Access People in Research , a list of opportunities for members of the public to get involved in research. You can sign up to receive email alerts when a new opportunity is added that matches your interests.
Joining a committee is also an opportunity to be involved in research and learn more about the process. Our different committees decide which research projects to fund and priorities. Explore more about joining a committee.
Why do people decide to get involved in research?
People who get involved in research have different reasons for wanting to do it. Some people have had a difficult experience and appreciate being able to do something positive with it. Others have had very good experiences, and see their involvement as an opportunity to ‘give something back’. For most people, it’s about wanting to make a difference – so that in the future, care will be better for the people who come after them.
“I still have my condition, but my experiences and other people’s experiences can help to change things. I know what we do makes a difference, maybe not to my health, but to someone else’s, to future generations. To be able to be part of that journey by being involved is an amazing thing to do.” Diana, PenARC Peninsula Public Engagement Group member, Exeter
Find out more about getting involved in research

Learn more about getting involved in research, what it might involve and our guidance on payment. Take a look at our resources:
- Payment policies and guidance
- Public information pack

Get involved with NIHR
Patients, carers and members of the public can get involved in NIHR research in many ways. You can get involved in NIHR research by:
- suggesting a research question
- giving your opinion on potential research
- joining one of our committees
- becoming a Research Champion
- give your views on research findings and how they impact you

Other opportunities
There are also plenty of opportunities for public involvement in research beyond the NIHR. Discover more by:
- helping the James Lind Alliance prioritise research questions, take a look at their current surveys
- signing up to our quarterly patient public newsletter
Related pages
- Public information pack: how to get involved in NHS, public health and social care research
- Public information pack (PIP) supplement: finding out more
- Payment guidance for members of the public considering involvement in research
- Information for researchers on involving the public
External links
- People in Research
- Learning for Involvement website
- UK Standards for Public Involvement

The best AI tools for research papers and academic research (Literature review, grants, PDFs and more)
As our collective understanding and application of artificial intelligence (AI) continues to evolve, so too does the realm of academic research. Some people are scared by it while others are openly embracing the change.
Make no mistake, AI is here to stay!
Instead of tirelessly scrolling through hundreds of PDFs, a powerful AI tool comes to your rescue, summarizing key information in your research papers. Instead of manually combing through citations and conducting literature reviews, an AI research assistant proficiently handles these tasks.
These aren’t futuristic dreams, but today’s reality. Welcome to the transformative world of AI-powered research tools!
This blog post will dive deeper into these tools, providing a detailed review of how AI is revolutionizing academic research. We’ll look at the tools that can make your literature review process less tedious, your search for relevant papers more precise, and your overall research process more efficient and fruitful.
I know that I wish these were around during my time in academia. It can be quite confronting when trying to work out what ones you should and shouldn’t use. A new one seems to be coming out every day!
Here is everything you need to know about AI for academic research and the ones I have personally trialed on my YouTube channel.
My Top AI Tools for Researchers and Academics – Tested and Reviewed!
There are many different tools now available on the market but there are only a handful that are specifically designed with researchers and academics as their primary user.
These are my recommendations that’ll cover almost everything that you’ll want to do:
Want to find out all of the tools that you could use?
Here they are, below:
AI literature search and mapping – best AI tools for a literature review – elicit and more
Harnessing AI tools for literature reviews and mapping brings a new level of efficiency and precision to academic research. No longer do you have to spend hours looking in obscure research databases to find what you need!
AI-powered tools like Semantic Scholar and elicit.org use sophisticated search engines to quickly identify relevant papers.
They can mine key information from countless PDFs, drastically reducing research time. You can even search with semantic questions, rather than having to deal with key words etc.
With AI as your research assistant, you can navigate the vast sea of scientific research with ease, uncovering citations and focusing on academic writing. It’s a revolutionary way to take on literature reviews.
- Elicit – https://elicit.org
- Litmaps – https://www.litmaps.com
- Research rabbit – https://www.researchrabbit.ai/
- Connected Papers – https://www.connectedpapers.com/
- Supersymmetry.ai: https://www.supersymmetry.ai
- Semantic Scholar: https://www.semanticscholar.org
- Laser AI – https://laser.ai/
- Inciteful – https://inciteful.xyz/
- Scite – https://scite.ai/
- System – https://www.system.com
If you like AI tools you may want to check out this article:
- How to get ChatGPT to write an essay [The prompts you need]
AI-powered research tools and AI for academic research
AI research tools, like Concensus, offer immense benefits in scientific research. Here are the general AI-powered tools for academic research.
These AI-powered tools can efficiently summarize PDFs, extract key information, and perform AI-powered searches, and much more. Some are even working towards adding your own data base of files to ask questions from.
Tools like scite even analyze citations in depth, while AI models like ChatGPT elicit new perspectives.
The result? The research process, previously a grueling endeavor, becomes significantly streamlined, offering you time for deeper exploration and understanding. Say goodbye to traditional struggles, and hello to your new AI research assistant!
- Consensus – https://consensus.app/
- Iris AI – https://iris.ai/
- Research Buddy – https://researchbuddy.app/
- Mirror Think – https://mirrorthink.ai
AI for reading peer-reviewed papers easily
Using AI tools like Explain paper and Humata can significantly enhance your engagement with peer-reviewed papers. I always used to skip over the details of the papers because I had reached saturation point with the information coming in.
These AI-powered research tools provide succinct summaries, saving you from sifting through extensive PDFs – no more boring nights trying to figure out which papers are the most important ones for you to read!
They not only facilitate efficient literature reviews by presenting key information, but also find overlooked insights.
With AI, deciphering complex citations and accelerating research has never been easier.
- Aetherbrain – https://aetherbrain.ai
- Explain Paper – https://www.explainpaper.com
- Chat PDF – https://www.chatpdf.com
- Humata – https://www.humata.ai/
- Lateral AI – https://www.lateral.io/
- Paper Brain – https://www.paperbrain.study/
- Scholarcy – https://www.scholarcy.com/
- SciSpace Copilot – https://typeset.io/
- Unriddle – https://www.unriddle.ai/
- Sharly.ai – https://www.sharly.ai/
- Open Read – https://www.openread.academy
AI for scientific writing and research papers
In the ever-evolving realm of academic research, AI tools are increasingly taking center stage.
Enter Paper Wizard, Jenny.AI, and Wisio – these groundbreaking platforms are set to revolutionize the way we approach scientific writing.
Together, these AI tools are pioneering a new era of efficient, streamlined scientific writing.
- Jenny.AI – https://jenni.ai/ (20% off with code ANDY20)
- Yomu – https://www.yomu.ai
- Wisio – https://www.wisio.app
AI academic editing tools
In the realm of scientific writing and editing, artificial intelligence (AI) tools are making a world of difference, offering precision and efficiency like never before. Consider tools such as Paper Pal, Writefull, and Trinka.
Together, these tools usher in a new era of scientific writing, where AI is your dedicated partner in the quest for impeccable composition.
- PaperPal – https://paperpal.com/
- Writefull – https://www.writefull.com/
- Trinka – https://www.trinka.ai/
AI tools for grant writing
In the challenging realm of science grant writing, two innovative AI tools are making waves: Granted AI and Grantable.
These platforms are game-changers, leveraging the power of artificial intelligence to streamline and enhance the grant application process.
Granted AI, an intelligent tool, uses AI algorithms to simplify the process of finding, applying, and managing grants. Meanwhile, Grantable offers a platform that automates and organizes grant application processes, making it easier than ever to secure funding.
Together, these tools are transforming the way we approach grant writing, using the power of AI to turn a complex, often arduous task into a more manageable, efficient, and successful endeavor.
- Granted AI – https://grantedai.com/
- Grantable – https://grantable.co/
Best free AI research tools
There are many different tools online that are emerging for researchers to be able to streamline their research processes. There’s no need for convience to come at a massive cost and break the bank.
The best free ones at time of writing are:
- Elicit – https://elicit.org
- Connected Papers – https://www.connectedpapers.com/
- Litmaps – https://www.litmaps.com ( 10% off Pro subscription using the code “STAPLETON” )
- Consensus – https://consensus.app/
Wrapping up
The integration of artificial intelligence in the world of academic research is nothing short of revolutionary.
With the array of AI tools we’ve explored today – from research and mapping, literature review, peer-reviewed papers reading, scientific writing, to academic editing and grant writing – the landscape of research is significantly transformed.
The advantages that AI-powered research tools bring to the table – efficiency, precision, time saving, and a more streamlined process – cannot be overstated.
These AI research tools aren’t just about convenience; they are transforming the way we conduct and comprehend research.
They liberate researchers from the clutches of tedium and overwhelm, allowing for more space for deep exploration, innovative thinking, and in-depth comprehension.
Whether you’re an experienced academic researcher or a student just starting out, these tools provide indispensable aid in your research journey.
And with a suite of free AI tools also available, there is no reason to not explore and embrace this AI revolution in academic research.
We are on the precipice of a new era of academic research, one where AI and human ingenuity work in tandem for richer, more profound scientific exploration. The future of research is here, and it is smart, efficient, and AI-powered.
Before we get too excited however, let us remember that AI tools are meant to be our assistants, not our masters. As we engage with these advanced technologies, let’s not lose sight of the human intellect, intuition, and imagination that form the heart of all meaningful research. Happy researching!
Thank you to Ivan Aguilar – Ph.D. Student at SFU (Simon Fraser University), for starting this list for me!

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider


Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, getting college essay help: important do's and don’ts.
College Essays

If you grow up to be a professional writer, everything you write will first go through an editor before being published. This is because the process of writing is really a process of re-writing —of rethinking and reexamining your work, usually with the help of someone else. So what does this mean for your student writing? And in particular, what does it mean for very important, but nonprofessional writing like your college essay? Should you ask your parents to look at your essay? Pay for an essay service?
If you are wondering what kind of help you can, and should, get with your personal statement, you've come to the right place! In this article, I'll talk about what kind of writing help is useful, ethical, and even expected for your college admission essay . I'll also point out who would make a good editor, what the differences between editing and proofreading are, what to expect from a good editor, and how to spot and stay away from a bad one.
Table of Contents
What Kind of Help for Your Essay Can You Get?
What's Good Editing?
What should an editor do for you, what kind of editing should you avoid, proofreading, what's good proofreading, what kind of proofreading should you avoid.
What Do Colleges Think Of You Getting Help With Your Essay?
Who Can/Should Help You?
Advice for editors.
Should You Pay Money For Essay Editing?
The Bottom Line
What's next, what kind of help with your essay can you get.
Rather than talking in general terms about "help," let's first clarify the two different ways that someone else can improve your writing . There is editing, which is the more intensive kind of assistance that you can use throughout the whole process. And then there's proofreading, which is the last step of really polishing your final product.
Let me go into some more detail about editing and proofreading, and then explain how good editors and proofreaders can help you."
Editing is helping the author (in this case, you) go from a rough draft to a finished work . Editing is the process of asking questions about what you're saying, how you're saying it, and how you're organizing your ideas. But not all editing is good editing . In fact, it's very easy for an editor to cross the line from supportive to overbearing and over-involved.
Ability to clarify assignments. A good editor is usually a good writer, and certainly has to be a good reader. For example, in this case, a good editor should make sure you understand the actual essay prompt you're supposed to be answering.
Open-endedness. Good editing is all about asking questions about your ideas and work, but without providing answers. It's about letting you stick to your story and message, and doesn't alter your point of view.

Think of an editor as a great travel guide. It can show you the many different places your trip could take you. It should explain any parts of the trip that could derail your trip or confuse the traveler. But it never dictates your path, never forces you to go somewhere you don't want to go, and never ignores your interests so that the trip no longer seems like it's your own. So what should good editors do?
Help Brainstorm Topics
Sometimes it's easier to bounce thoughts off of someone else. This doesn't mean that your editor gets to come up with ideas, but they can certainly respond to the various topic options you've come up with. This way, you're less likely to write about the most boring of your ideas, or to write about something that isn't actually important to you.
If you're wondering how to come up with options for your editor to consider, check out our guide to brainstorming topics for your college essay .
Help Revise Your Drafts
Here, your editor can't upset the delicate balance of not intervening too much or too little. It's tricky, but a great way to think about it is to remember: editing is about asking questions, not giving answers .
Revision questions should point out:
- Places where more detail or more description would help the reader connect with your essay
- Places where structure and logic don't flow, losing the reader's attention
- Places where there aren't transitions between paragraphs, confusing the reader
- Moments where your narrative or the arguments you're making are unclear
But pointing to potential problems is not the same as actually rewriting—editors let authors fix the problems themselves.
Bad editing is usually very heavy-handed editing. Instead of helping you find your best voice and ideas, a bad editor changes your writing into their own vision.
You may be dealing with a bad editor if they:
- Add material (examples, descriptions) that doesn't come from you
- Use a thesaurus to make your college essay sound "more mature"
- Add meaning or insight to the essay that doesn't come from you
- Tell you what to say and how to say it
- Write sentences, phrases, and paragraphs for you
- Change your voice in the essay so it no longer sounds like it was written by a teenager
Colleges can tell the difference between a 17-year-old's writing and a 50-year-old's writing. Not only that, they have access to your SAT or ACT Writing section, so they can compare your essay to something else you wrote. Writing that's a little more polished is great and expected. But a totally different voice and style will raise questions.
Where's the Line Between Helpful Editing and Unethical Over-Editing?
Sometimes it's hard to tell whether your college essay editor is doing the right thing. Here are some guidelines for staying on the ethical side of the line.
- An editor should say that the opening paragraph is kind of boring, and explain what exactly is making it drag. But it's overstepping for an editor to tell you exactly how to change it.
- An editor should point out where your prose is unclear or vague. But it's completely inappropriate for the editor to rewrite that section of your essay.
- An editor should let you know that a section is light on detail or description. But giving you similes and metaphors to beef up that description is a no-go.

Proofreading (also called copy-editing) is checking for errors in the last draft of a written work. It happens at the end of the process and is meant as the final polishing touch. Proofreading is meticulous and detail-oriented, focusing on small corrections. It sands off all the surface rough spots that could alienate the reader.
Because proofreading is usually concerned with making fixes on the word or sentence level, this is the only process where someone else can actually add to or take away things from your essay . This is because what they are adding or taking away tends to be one or two misplaced letters.
Laser focus. Proofreading is all about the tiny details, so the ability to really concentrate on finding small slip-ups is a must.
Excellent grammar and spelling skills. Proofreaders need to dot every "i" and cross every "t." Good proofreaders should correct spelling, punctuation, capitalization, and grammar. They should put foreign words in italics and surround quotations with quotation marks. They should check that you used the correct college's name, and that you adhered to any formatting requirements (name and date at the top of the page, uniform font and size, uniform spacing).
Limited interference. A proofreader needs to make sure that you followed any word limits. But if cuts need to be made to shorten the essay, that's your job and not the proofreader's.

A bad proofreader either tries to turn into an editor, or just lacks the skills and knowledge necessary to do the job.
Some signs that you're working with a bad proofreader are:
- If they suggest making major changes to the final draft of your essay. Proofreading happens when editing is already finished.
- If they aren't particularly good at spelling, or don't know grammar, or aren't detail-oriented enough to find someone else's small mistakes.
- If they start swapping out your words for fancier-sounding synonyms, or changing the voice and sound of your essay in other ways. A proofreader is there to check for errors, not to take the 17-year-old out of your writing.

What Do Colleges Think of Your Getting Help With Your Essay?
Admissions officers agree: light editing and proofreading are good—even required ! But they also want to make sure you're the one doing the work on your essay. They want essays with stories, voice, and themes that come from you. They want to see work that reflects your actual writing ability, and that focuses on what you find important.
On the Importance of Editing
Get feedback. Have a fresh pair of eyes give you some feedback. Don't allow someone else to rewrite your essay, but do take advantage of others' edits and opinions when they seem helpful. ( Bates College )
Read your essay aloud to someone. Reading the essay out loud offers a chance to hear how your essay sounds outside your head. This exercise reveals flaws in the essay's flow, highlights grammatical errors and helps you ensure that you are communicating the exact message you intended. ( Dickinson College )
On the Value of Proofreading
Share your essays with at least one or two people who know you well—such as a parent, teacher, counselor, or friend—and ask for feedback. Remember that you ultimately have control over your essays, and your essays should retain your own voice, but others may be able to catch mistakes that you missed and help suggest areas to cut if you are over the word limit. ( Yale University )
Proofread and then ask someone else to proofread for you. Although we want substance, we also want to be able to see that you can write a paper for our professors and avoid careless mistakes that would drive them crazy. ( Oberlin College )
On Watching Out for Too Much Outside Influence
Limit the number of people who review your essay. Too much input usually means your voice is lost in the writing style. ( Carleton College )
Ask for input (but not too much). Your parents, friends, guidance counselors, coaches, and teachers are great people to bounce ideas off of for your essay. They know how unique and spectacular you are, and they can help you decide how to articulate it. Keep in mind, however, that a 45-year-old lawyer writes quite differently from an 18-year-old student, so if your dad ends up writing the bulk of your essay, we're probably going to notice. ( Vanderbilt University )

Now let's talk about some potential people to approach for your college essay editing and proofreading needs. It's best to start close to home and slowly expand outward. Not only are your family and friends more invested in your success than strangers, but they also have a better handle on your interests and personality. This knowledge is key for judging whether your essay is expressing your true self.
Parents or Close Relatives
Your family may be full of potentially excellent editors! Parents are deeply committed to your well-being, and family members know you and your life well enough to offer details or incidents that can be included in your essay. On the other hand, the rewriting process necessarily involves criticism, which is sometimes hard to hear from someone very close to you.
A parent or close family member is a great choice for an editor if you can answer "yes" to the following questions. Is your parent or close relative a good writer or reader? Do you have a relationship where editing your essay won't create conflict? Are you able to constructively listen to criticism and suggestion from the parent?
One suggestion for defusing face-to-face discussions is to try working on the essay over email. Send your parent a draft, have them write you back some comments, and then you can pick which of their suggestions you want to use and which to discard.
Teachers or Tutors
A humanities teacher that you have a good relationship with is a great choice. I am purposefully saying humanities, and not just English, because teachers of Philosophy, History, Anthropology, and any other classes where you do a lot of writing, are all used to reviewing student work.
Moreover, any teacher or tutor that has been working with you for some time, knows you very well and can vet the essay to make sure it "sounds like you."
If your teacher or tutor has some experience with what college essays are supposed to be like, ask them to be your editor. If not, then ask whether they have time to proofread your final draft.
Guidance or College Counselor at Your School
The best thing about asking your counselor to edit your work is that this is their job. This means that they have a very good sense of what colleges are looking for in an application essay.
At the same time, school counselors tend to have relationships with admissions officers in many colleges, which again gives them insight into what works and which college is focused on what aspect of the application.
Unfortunately, in many schools the guidance counselor tends to be way overextended. If your ratio is 300 students to 1 college counselor, you're unlikely to get that person's undivided attention and focus. It is still useful to ask them for general advice about your potential topics, but don't expect them to be able to stay with your essay from first draft to final version.
Friends, Siblings, or Classmates
Although they most likely don't have much experience with what colleges are hoping to see, your peers are excellent sources for checking that your essay is you .
Friends and siblings are perfect for the read-aloud edit. Read your essay to them so they can listen for words and phrases that are stilted, pompous, or phrases that just don't sound like you.
You can even trade essays and give helpful advice on each other's work.

If your editor hasn't worked with college admissions essays very much, no worries! Any astute and attentive reader can still greatly help with your process. But, as in all things, beginners do better with some preparation.
First, your editor should read our advice about how to write a college essay introduction , how to spot and fix a bad college essay , and get a sense of what other students have written by going through some admissions essays that worked .
Then, as they read your essay, they can work through the following series of questions that will help them to guide you.
Introduction Questions
- Is the first sentence a killer opening line? Why or why not?
- Does the introduction hook the reader? Does it have a colorful, detailed, and interesting narrative? Or does it propose a compelling or surprising idea?
- Can you feel the author's voice in the introduction, or is the tone dry, dull, or overly formal? Show the places where the voice comes through.
Essay Body Questions
- Does the essay have a through-line? Is it built around a central argument, thought, idea, or focus? Can you put this idea into your own words?
- How is the essay organized? By logical progression? Chronologically? Do you feel order when you read it, or are there moments where you are confused or lose the thread of the essay?
- Does the essay have both narratives about the author's life and explanations and insight into what these stories reveal about the author's character, personality, goals, or dreams? If not, which is missing?
- Does the essay flow? Are there smooth transitions/clever links between paragraphs? Between the narrative and moments of insight?
Reader Response Questions
- Does the writer's personality come through? Do we know what the speaker cares about? Do we get a sense of "who he or she is"?
- Where did you feel most connected to the essay? Which parts of the essay gave you a "you are there" sensation by invoking your senses? What moments could you picture in your head well?
- Where are the details and examples vague and not specific enough?
- Did you get an "a-ha!" feeling anywhere in the essay? Is there a moment of insight that connected all the dots for you? Is there a good reveal or "twist" anywhere in the essay?
- What are the strengths of this essay? What needs the most improvement?

Should You Pay Money for Essay Editing?
One alternative to asking someone you know to help you with your college essay is the paid editor route. There are two different ways to pay for essay help: a private essay coach or a less personal editing service , like the many proliferating on the internet.
My advice is to think of these options as a last resort rather than your go-to first choice. I'll first go through the reasons why. Then, if you do decide to go with a paid editor, I'll help you decide between a coach and a service.
When to Consider a Paid Editor
In general, I think hiring someone to work on your essay makes a lot of sense if none of the people I discussed above are a possibility for you.
If you can't ask your parents. For example, if your parents aren't good writers, or if English isn't their first language. Or if you think getting your parents to help is going create unnecessary extra conflict in your relationship with them (applying to college is stressful as it is!)
If you can't ask your teacher or tutor. Maybe you don't have a trusted teacher or tutor that has time to look over your essay with focus. Or, for instance, your favorite humanities teacher has very limited experience with college essays and so won't know what admissions officers want to see.
If you can't ask your guidance counselor. This could be because your guidance counselor is way overwhelmed with other students.
If you can't share your essay with those who know you. It might be that your essay is on a very personal topic that you're unwilling to share with parents, teachers, or peers. Just make sure it doesn't fall into one of the bad-idea topics in our article on bad college essays .
If the cost isn't a consideration. Many of these services are quite expensive, and private coaches even more so. If you have finite resources, I'd say that hiring an SAT or ACT tutor (whether it's PrepScholar or someone else) is better way to spend your money . This is because there's no guarantee that a slightly better essay will sufficiently elevate the rest of your application, but a significantly higher SAT score will definitely raise your applicant profile much more.
Should You Hire an Essay Coach?
On the plus side, essay coaches have read dozens or even hundreds of college essays, so they have experience with the format. Also, because you'll be working closely with a specific person, it's more personal than sending your essay to a service, which will know even less about you.
But, on the minus side, you'll still be bouncing ideas off of someone who doesn't know that much about you . In general, if you can adequately get the help from someone you know, there is no advantage to paying someone to help you.
If you do decide to hire a coach, ask your school counselor, or older students that have used the service for recommendations. If you can't afford the coach's fees, ask whether they can work on a sliding scale —many do. And finally, beware those who guarantee admission to your school of choice—essay coaches don't have any special magic that can back up those promises.
Should You Send Your Essay to a Service?
On the plus side, essay editing services provide a similar product to essay coaches, and they cost significantly less . If you have some assurance that you'll be working with a good editor, the lack of face-to-face interaction won't prevent great results.
On the minus side, however, it can be difficult to gauge the quality of the service before working with them . If they are churning through many application essays without getting to know the students they are helping, you could end up with an over-edited essay that sounds just like everyone else's. In the worst case scenario, an unscrupulous service could send you back a plagiarized essay.
Getting recommendations from friends or a school counselor for reputable services is key to avoiding heavy-handed editing that writes essays for you or does too much to change your essay. Including a badly-edited essay like this in your application could cause problems if there are inconsistencies. For example, in interviews it might be clear you didn't write the essay, or the skill of the essay might not be reflected in your schoolwork and test scores.
Should You Buy an Essay Written by Someone Else?
Let me elaborate. There are super sketchy places on the internet where you can simply buy a pre-written essay. Don't do this!
For one thing, you'll be lying on an official, signed document. All college applications make you sign a statement saying something like this:
I certify that all information submitted in the admission process—including the application, the personal essay, any supplements, and any other supporting materials—is my own work, factually true, and honestly presented... I understand that I may be subject to a range of possible disciplinary actions, including admission revocation, expulsion, or revocation of course credit, grades, and degree, should the information I have certified be false. (From the Common Application )
For another thing, if your academic record doesn't match the essay's quality, the admissions officer will start thinking your whole application is riddled with lies.
Admission officers have full access to your writing portion of the SAT or ACT so that they can compare work that was done in proctored conditions with that done at home. They can tell if these were written by different people. Not only that, but there are now a number of search engines that faculty and admission officers can use to see if an essay contains strings of words that have appeared in other essays—you have no guarantee that the essay you bought wasn't also bought by 50 other students.

- You should get college essay help with both editing and proofreading
- A good editor will ask questions about your idea, logic, and structure, and will point out places where clarity is needed
- A good editor will absolutely not answer these questions, give you their own ideas, or write the essay or parts of the essay for you
- A good proofreader will find typos and check your formatting
- All of them agree that getting light editing and proofreading is necessary
- Parents, teachers, guidance or college counselor, and peers or siblings
- If you can't ask any of those, you can pay for college essay help, but watch out for services or coaches who over-edit you work
- Don't buy a pre-written essay! Colleges can tell, and it'll make your whole application sound false.
Ready to start working on your essay? Check out our explanation of the point of the personal essay and the role it plays on your applications and then explore our step-by-step guide to writing a great college essay .
Using the Common Application for your college applications? We have an excellent guide to the Common App essay prompts and useful advice on how to pick the Common App prompt that's right for you . Wondering how other people tackled these prompts? Then work through our roundup of over 130 real college essay examples published by colleges .
Stressed about whether to take the SAT again before submitting your application? Let us help you decide how many times to take this test . If you choose to go for it, we have the ultimate guide to studying for the SAT to give you the ins and outs of the best ways to study.

Anna scored in the 99th percentile on her SATs in high school, and went on to major in English at Princeton and to get her doctorate in English Literature at Columbia. She is passionate about improving student access to higher education.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
English Essay Writing Help
Language skills are not only about authentic speaking. Usually students receive a written task like an essay or a letter and so on to prove their knowledge of English in writing. let's say everything is fine with your speech but there are some difficulties with paper — what should you do? Our service is going to solve your problem! Visit the website to receive help with the texts that are necessary for your graduation and employment, etc.
Paper Writing Help — Real Opportunities to Receive Assistance
Sometimes it is not enough to find a native English speaker, because, in addition to his consent to do the work for you, it is necessary that he has the special erudition on the topic about which the text will be written. Obviously, not every person from the USA or Great Britain is able to write, for example, a nursing essay in accordance with the high requirements for undergraduates and graduate students. It is great that our service’s authors are professionals in their fields.
Surely, you can find a lot of identical websites on the Internet but the main question is: How competent are their authors? Before using the services of copywriters and translators, you need to make sure of the quality of their work.
Professional Paper Writing at an Affordable Price
It's hard to imagine a psychology essay without an abundance of specific terminology, isn't it? It means that translation requires a special treatment. And there are plenty of such cases when the help of specialists is needed. Our service is ready to help you write a high-quality article that meets the strict requirements of the university. How to make paragraphs in English correctly? What is the best way to prioritize the text? — relax and leave all these questions to professionals in writing such materials. You must admit that it's way better than losing a lot of time constantly redoing your business essay or something else because you have incorrectly drawn up the doc.
The quality of the final result depends on how well your helper understands the topic, how well he is knowledgeable about all the subtleties of writing the text. If he is like a duck to water in this path, then you can hope that you will get excellent material. Nowadays all scientific researches, regardless of large or small volume, become a part of specialized publishing and translation in English is mandatory. Essay writing help timing could not have been better.
Who Are the Authors Who Will Take My Paper for Writing?
The authors of our service are thoroughly selected specialists in particular fields meaning that your essay in history will be written by a historian. It is a pretty usual task to write a scientific paper for our authors marked with a degree and experienced copywriters. However, there is another difficulty to manage with — the uniqueness of the article.
The market of paper writing is completely about intense competition and bad service won't last long here, that’s why our excellent artists always achieve the max uniqueness and make well designed articles meeting all the international standards. Thus, do not neglect calling for assistance in paper writing, especially when it’s so easy today.
Each submitted material is necessarily checked for plagiarism, however, you can always order the urgent translation and essay in the particular segment of the site. If you want to bring some changes to the article or have several remarks, feel free to report them because our professionals will be happy to make the necessary edits to reach perfection. There are no obstacles on your way to receive support in English paper writing, all you have to do it’s to give it to pure masters.
Along with Stanford news and stories, show me:
- Student information
- Faculty/Staff information
We want to provide announcements, events, leadership messages and resources that are relevant to you. Your selection is stored in a browser cookie which you can remove at any time using “Clear all personalization” below.
Asking for help is hard, but others want to help more than we often give them credit for, says Stanford social psychologist Xuan Zhao .

Xuan Zhao (Image credit: Anne Ryan)
We shy away from asking for help because we don’t want to bother other people, assuming that our request will feel like an inconvenience to them. But oftentimes, the opposite is true: People want to make a difference in people’s lives and they feel good – happy even – when they are able to help others, said Zhao.
Here, Zhao discusses the research about how asking for help can lead to meaningful experiences and strengthen relationships with others – friends as well as strangers.
Zhao is a research scientist at Stanford SPARQ , a research center in the Psychology Department that brings researchers and practitioners together to fight bias, reduce disparities, and drive culture change. Zhao’s research focuses on helping people create better social interactions in person and online where they feel seen, heard, connected, and appreciated. Her research, recently published in Psychological Science , suggests that people regularly underestimate others’ willingness to help.
This fall, Zhao will be co-teaching a two-session workshop Science-Based Practices for a Flourishing Life through Stanford’s well-being program for employees, BeWell.
Why is asking for help hard? For someone who finds it difficult to ask for help, what would you like them to know?
There are several common reasons why people struggle to ask for help. Some people may fear that asking for help would make them appear incompetent, weak, or inferior – recent research from Stanford doctoral student Kayla Good finds that children as young as seven can hold this belief. Some people are concerned about being rejected, which can be embarrassing and painful. Others may be concerned about burdening and inconveniencing others – a topic I recently explored. These concerns may feel more relevant in some contexts than others, but they are all very relatable and very human.
The good news is those concerns are oftentimes exaggerated and mistaken.
What do people misunderstand about asking for help?
When people are in need of help, they are often caught up in their own concerns and worries and do not fully recognize the prosocial motivations of those around them who are ready to help. This can introduce a persistent difference between how help-seekers and potential helpers consider the same helping event. To test this idea, we conducted several experiments where people either directly interacted with each other to seek and offer help, or imagined or recalled such experiences in everyday life. We consistently observed that help-seekers underestimated how willing strangers – and even friends – would be to help them and how positive helpers would feel afterward, and overestimated how inconvenienced helpers would feel.
These patterns are consistent with work by Stanford psychologist Dale Miller showing that when thinking about what motivates other people, we tend to apply a more pessimistic, self-interested view about human nature. After all, Western societies tend to value independence, so asking others to go out of their way to do something for us may seem wrong or selfish and may impose a somewhat negative experience on the helper.
The truth is, most of us are deeply prosocial and want to make a positive difference in others’ lives. Work by Stanford psychologist Jamil Zaki has shown that empathizing with and helping others in need seems to be an intuitive response, and dozens of studies , including my own, have found that people often feel happier after conducting acts of kindness. These findings extend earlier research by Stanford Professor Frank Flynn and colleagues suggesting that people tend to overestimate how likely their direct request for help would be rejected by others. Finally, other research has even shown that seeking advice can even boost how competent the help-seeker is seen by the advice-giver.
Why is asking for help particularly important?
We love stories about spontaneous help, and that may explain why random acts of kindness go viral on social media. But in reality , the majority of help occurs only after a request has been made. It’s often not because people don’t want to help and must be pressed to do so. Quite the opposite, people want to help, but they can’t help if they don’t know someone is suffering or struggling, or what the other person needs and how to help effectively, or whether it is their place to help – perhaps they want to respect others’ privacy or agency. A direct request can remove those uncertainties, such that asking for help enables kindness and unlocks opportunities for positive social connections. It can also create emotional closeness when you realize someone trusts you enough to share their vulnerabilities, and by working together toward a shared goal.
It feels like some requests for help may be harder to ask than others. What does research say about different types of help, and how can we use those insights to help us figure out how we should ask for help?
Many factors can influence how difficult it may feel to ask for help. Our recent research has primarily focused on everyday scenarios where the other person is clearly able to help, and all you need is to show up and ask. In some other cases, the kind of help you need may require more specific skills or resources. As long as you make your request Specific, Meaningful, Action-oriented, Realistic, and Time-bound (also known as the SMART criteria ), people will likely be happy to help and feel good after helping.
Of course, not all requests have to be specific. When we face mental health challenges, we may have difficulty articulating what kind of help we need. It is okay to reach out to mental health resources and take the time to figure things out together. They are there to help, and they are happy to help.
You mentioned how cultural norms can get in the way of people asking for help. What is one thing we can all do to rethink the role society plays in our lives?
Work on independent and interdependent cultures by Hazel Markus , faculty director of Stanford SPARQ , can shed much light on this issue. Following her insights, I think we can all benefit from having a little bit more interdependency in our micro- and macro-environments. For instance, instead of promoting “self-care” and implying that it is people’s own responsibility to sort through their own struggles, perhaps our culture could emphasize the value of caring for each other and create more safe spaces to allow open discussions about our challenges and imperfections.
What inspired your research?
I have always been fascinated by social interaction – how we understand and misunderstand each other’s minds, and how social psychology can help people create more positive and meaningful connections. That’s why I have studied topics such as giving compliments , discussing disagreement , sharing personal failures, creating inclusive conversations on social media , and translating social and positive psychology research as daily practices for the public . This project is also motivated by that general passion.
But a more immediate trigger of this project is reading scholarly work suggesting that the reason why people underestimate their likelihood of getting help is because they don’t recognize how uncomfortable and awkward it would be for someone to say “no” to their request. I agree that people underestimate their chance of getting help upon a direct ask, but based on my personal experience, I saw a different reason – when people ask me for help, I often feel genuinely motivated to help them, more than feeling social pressure and a wish to avoid saying no. This project is to voice my different interpretation on why people agree to help. And given that I’ve seen people who have struggled for too long until it was too late to ask for help, I hope my findings can offer them a bit more comfort when the next time they can really use a helping hand and are debating whether they should ask.
Tips for Writing an Email to Faculty about Research
For many students, the best way to get involved in research is to email faculty/principle investigators directly to ask about research opportunities. An email is an opportunity to highlight your shared interest in their research topic and to highlight attributes that will make you a good undergraduate researcher to work with. This page will help you write a concise and targeted email to maximize your chance at a reply.
The subject
Be short, but be clear what you are writing about. Something like “Undergraduate Research Opportunities in Your Lab” or “Openings for Undergraduates to do Research in [your research topic]” should work. Do not simply use “Hi” or “Research” as a subject.
The greeting
A formal greeting is always a safe bet, so always address the recipient using a proper title. When contacting faculty or postdoctoral fellows, “Dear Dr. ______,” is appropriate. If you are contacting someone without a doctorate or M.D., use “Dear Mr. ______,” or “Dear Ms.______” If you are unsure, always err on the side of using “Dr.” Never open an e-mail with “To whom it may concern” or any similarly vague phrase.
The main text
In the first line, identify yourself with your year in school and your major or anticipated major as well as your interest in research (e.g., “I’m a sophomore political science and public policy major looking to do research on voting rights in the South.” or “I’m a first year Neuroscience major and hope to get involved in Alzheimer’s research as soon as I can.”). You also want to explain why you why you are contacting this faculty in particular. It helps to mention how you know the recipient or where you got their contact information. If you took a class with them or have spoken with someone doing research with them, say so. If you are contacting them based on their profile on the department website, it is fine to say something like “When lookin for research opportunities in [subject area], I found information about your research on the department’s website.”
Next, explain your specific interest in this faculty’s research . Your goal here is to establish a shared passion for the particular area in which this faculty member conducts research — the more specific, the better. Are there aspects of their research that fascinate you? Do you want to be able to contribute to the understanding of some specific problem or issue? Is there something about your past classwork or research experience that sparked your interest? If there are broader motivations that drive you, include a sentence in your email explaining them. In addition, it can be helpful to pick a recent paper or book they’ve published and read or skim it. You don’t have to sound like an expert, but it helps to mention a recent finding that interests you and possibly ask a good question about their research (e.g., “Is the protein you study also regulated in a cell cycle-dependent manner?”). Be sure to describe any relevant experience or completed courses that would make you well suited to do research with the faculty, but keep in mind your shared interest/passion may be just as important as your background.
One word of caution: you don’t want to make it seem that their lab or their research project is only a stepping stone to the next step in your career (graduate school or medical school) — this might turn off many who are devoted to research and want to recruit students with a shared passion.
Grades and your CV/resume
While grades are certainly not the only factor faculty will consider, you may wish to include your GPA if you feel that it merits mentioning. However, refrain from making it the focal point of a sentence; instead, you can bring it up in the context of wanting some experience outside of class (e.g., “I am enjoying my classes so far and doing well (my GPA is 3.7), but I feel that I will learn a lot more by exploring my interests beyond the classroom”). Similarly, if you have a CV/resume that includes relevant research experience, you may want to include it (e.g., “I’ve attached my resume in case it might be helpful for you to know a bit more about me.”). If your academic qualifications are not as great as you’d hoped (for example, your GPA is on the lower end), you can put off attaching the CV for now and just state that you would be happy to send a CV or any other material if needed.
Concluding sentences and closing
Now you are ready to wrap up with a brief concluding statement. Thank the recipient for their time and ask for an opportunity to meet with them to discuss their research projects and to how to get involved in the type of research they do. A warm but simple closing (“Sincerely,” or “Best regards,”) is fine. It may help to include your email or phone number under your name if you have invited the recipient to contact you.
General considerations and next steps
First, remember to keep the email reasonably short. Two small paragraphs should cover everything you need say. Also, remember to proofread carefully. Spelling and grammar errors will reflect negatively and your attention to detail. Don’t use slang or abbreviations common in texting. Think of the email as something you would turn in for a grade. That said, be yourself! While it is best to be formal, the email does not have to be bland; let some of your personality show through. Lastly, if you don’t receive a reply after about two weeks, it’s okay to follow up by forwarding your original email back to the recipient and politely add “Dear Dr. ______, I’m writing to follow up on my earlier email about research opportunities in [your area of research]. I remain interested in speaking with you about your research if you are able. Thank you in advance for your time and consideration.” Faculty are very busy and your persistence may be appreciated, so it’s even okay to send another follow up email after another few weeks if you don’t hear back. After that, it may be time to move on to other opportunities.
Sample email
Dear Dr. ______,
I am a sophomore Computer Science major, and I am especially interested in your research on artificial intelligence.
With artificial intelligence constantly evolving, I am interested in exploring its true capabilities and how machine learning can improve language processing. While looking for research opportunities to explore my passions within artificial intelligence, I came across your Natural Language Processing Group at UNC. Connecting the capabilities of artificial intelligence and exploring its ability to communicate with human language is very captivating. I am enjoying my classes so far and doing well (My GPA is 4.0), but I am eager to supplement my classroom learning with a research opportunity. I feel that I would be able learn more about artificial intelligence by becoming a part of your research group or a similar project on campus. I’ve attached my resume in case it’s helpful for you to know a bit more about me and my research background.
I would appreciate an opportunity to briefly meet with you or someone in your research group to discuss your research and how I might be able to support your work at some point in the next three years. If you are able to meet with me, please let me know some times you are available to talk. Thank you in advance for your time and consideration, and I look forward to hearing from you.
[include a signature with your Name, Major, Class of 202_]
- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff

News and Media
- News & Media Home
- Research Stories
- School's In
- In the Media
You are here
70 years after brown v. board of education, new research shows rise in school segregation.

As the nation prepares to mark the 70th anniversary of the landmark U.S. Supreme Court ruling in Brown v. Board of Education , a new report from researchers at Stanford and USC shows that racial and economic segregation among schools has grown steadily in large school districts over the past three decades — an increase that appears to be driven in part by policies favoring school choice over integration.
Analyzing data from U.S. public schools going back to 1967, the researchers found that segregation between white and Black students has increased by 64 percent since 1988 in the 100 largest districts, and segregation by economic status has increased by about 50 percent since 1991.
The report also provides new evidence about the forces driving recent trends in school segregation, showing that the expansion of charter schools has played a major role.
The findings were released on May 6 with the launch of the Segregation Explorer , a new interactive website from the Educational Opportunity Project at Stanford University. The website provides searchable data on racial and economic school segregation in U.S. states, counties, metropolitan areas, and school districts from 1991 to 2022.
“School segregation levels are not at pre- Brown levels, but they are high and have been rising steadily since the late 1980s,” said Sean Reardon , the Professor of Poverty and Inequality in Education at Stanford Graduate School of Education and faculty director of the Educational Opportunity Project. “In most large districts, school segregation has increased while residential segregation and racial economic inequality have declined, and our findings indicate that policy choices – not demographic changes – are driving the increase.”
“There’s a tendency to attribute segregation in schools to segregation in neighborhoods,” said Ann Owens , a professor of sociology and public policy at USC. “But we’re finding that the story is more complicated than that.”
Assessing the rise
In the Brown v. Board decision issued on May 17, 1954, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that racially segregated public schools violated the Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment and established that “separate but equal” schools were not only inherently unequal but unconstitutional. The ruling paved the way for future decisions that led to rapid school desegregation in many school districts in the late 1960s and early 1970s.
Though segregation in most school districts is much lower than it was 60 years ago, the researchers found that over the past three decades, both racial and economic segregation in large districts increased. Much of the increase in economic segregation since 1991, measured by segregation between students eligible and ineligible for free lunch, occurred in the last 15 years.
White-Hispanic and white-Asian segregation, while lower on average than white-Black segregation, have both more than doubled in large school districts since the 1980s.
Racial-economic segregation – specifically the difference in the proportion of free-lunch-eligible students between the average white and Black or Hispanic student’s schools – has increased by 70 percent since 1991.
School segregation is strongly associated with achievement gaps between racial and ethnic groups, especially the rate at which achievement gaps widen during school, the researchers said.
“Segregation appears to shape educational outcomes because it concentrates Black and Hispanic students in higher-poverty schools, which results in unequal learning opportunities,” said Reardon, who is also a senior fellow at the Stanford Institute for Economic Policy Research and a faculty affiliate of the Stanford Accelerator for Learning .
Policies shaping recent trends
The recent rise in school segregation appears to be the direct result of educational policy and legal decisions, the researchers said.
Both residential segregation and racial disparities in income declined between 1990 and 2020 in most large school districts. “Had nothing else changed, that trend would have led to lower school segregation,” said Owens.
But since 1991, roughly two-thirds of districts that were under court-ordered desegregation have been released from court oversight. Meanwhile, since 1998, the charter sector – a form of expanded school choice – has grown.
Expanding school choice could influence segregation levels in different ways: If families sought schools that were more diverse than the ones available in their neighborhood, it could reduce segregation. But the researchers found that in districts where the charter sector expanded most rapidly in the 2000s and 2010s, segregation grew the most.
The researchers’ analysis also quantified the extent to which the release from court orders accounted for the rise in school segregation. They found that, together, the release from court oversight and the expansion of choice accounted entirely for the rise in school segregation from 2000 to 2019.
The researchers noted enrollment policies that school districts can implement to mitigate segregation, such as voluntary integration programs, socioeconomic-based student assignment policies, and school choice policies that affirmatively promote integration.
“School segregation levels are high, troubling, and rising in large districts,” said Reardon. “These findings should sound an alarm for educators and policymakers.”
Additional collaborators on the project include Demetra Kalogrides, Thalia Tom, and Heewon Jang. This research, including the development of the Segregation Explorer data and website, was supported by the Russell Sage Foundation, the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, and the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation.
More Stories

⟵ Go to all Research Stories
Get the Educator
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Stanford Graduate School of Education
482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
- Contact Admissions
- GSE Leadership
- Site Feedback
- Web Accessibility
- Career Resources
- Faculty Open Positions
- Explore Courses
- Academic Calendar
- Office of the Registrar
- Cubberley Library
- StanfordWho
- StanfordYou
Improving lives through learning

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
- Current Article
Spafford to chair external board for $45M Sandia Labs digital assurance campaign

WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. — Eugene H. Spafford, professor of computer science in Purdue University’s College of Science and internationally recognized authority on cybersecurity, has been chosen to help Sandia National Laboratories in its campaign to manage digital risks to high-consequence systems.
Spafford, Executive Director Emeritus of CERIAS, Purdue’s Center for Education and Research in Information Assurance and Security, has been appointed chair of the External Advisory Board for Sandia’s Digital Assurance for High Consequence Systems (DAHCS) Mission Campaign.
The newly launched research campaign’s goal is to transform and simplify digital risk management for decision-makers, such as systems engineers and program executives.
Through Sandia’s Laboratory Directed Research and Development program, the campaign invests in research that develops generalizable scientific foundations to safeguard high-consequence systems such as satellites, hypersonic vehicles, nuclear weapons and critical infrastructure like nuclear power generators. It aims to reshape the scientific domain from one driven by expert-dependent pockets of excellence — through techniques like red teaming, security-by-design and formal analysis — into a sustainable, scalable and rigorous discipline.
Will Zortman, Sandia’s DAHCS campaign manager, says the $45 million initiative is a strategic investment to “replace the status quo of ad hoc, slow and costly digital assurance methods with a rapid, cost-effective and generalizable way to secure systems and mitigate threats.”
The effort, which will take place over the next seven years, will involve scientists and engineers across government, industry and universities.
Among the notable challenges the research campaign faces, Spafford says, is institutional reticence over potentially significant expenses to rework or replace existing systems. “Companies and government agencies haven’t wanted to invest in new approaches that don’t build on existing systems because they already have made huge investments in technology,” he says. “Thus, most of what’s been done to date has been directed to fixing or enhancing existing technology based on flawed designs and assumptions.” He notes that this has usually led to incremental changes that don’t fully address fundamental deficiencies.
Spafford acknowledges that the goal of developing new technologies for such diverse critical systems is highly ambitious, and success will be defined by multiple metrics.
“We need methods and principles to design and build high-assurance systems,” he says. “We must be confident that they’re going to perform over time, under stress and possibly with adversaries trying to corrupt them. We must understand how to measure risk accurately to make appropriate investment decisions.”
Spafford, “Spaf,” worked at Sandia during a recent sabbatical and currently serves on another of Sandia’s boards, its National Security Programs Advisory Board.
“Professor Spafford brings unique insight into where the cyber community is and where it needs to go, as well as strong connections across diverse systems communities. This positions us to, together, mature into a community that can reason holistically about complex systems.” says Zortman.
Spafford has helped define and shape the field of cybersecurity for 40 years. His pioneering research in cybersecurity, cyber forensics and security policy has resulted in scores of academic and professional organization honors. Among them are the National Computer Systems Security Award from the National Institute of Standards and Technology and the National Security Agency; the Kristian Beckman Award from the International Federation for Information Processing; and the Harold F. Tipton Lifetime Achievement Award from the International Information System Security Certification Consortium (ISC2).
In addition to being named to the Cyber Security Hall of Fame in 2013, Spafford has been elected to prestigious fellowships in the Association for Computing Machinery, the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, the ISC2, the American Association for the Advancement of Science, and the American Academy of Arts and Sciences. He also is a distinguished fellow of the Information Systems Security Association.
Spafford currently serves as editor-in-chief of the journal Computers & Security and was co-author of the book “Cybersecurity Myths and Misconceptions,” which recently was named to the Cybersecurity Canon Hall of Fame. At Purdue, he also serves by courtesy in professorial appointments in the schools of communication and electrical and computer engineering, and the departments of philosophy and political science.
Purdue’s Department of Computer Science is part of Purdue Computes , an initiative emphasizing four key pillars of Purdue’s extensive technological and computational environment.
About Purdue University
Purdue University is a public research institution demonstrating excellence at scale. Ranked among top 10 public universities and with two colleges in the top four in the United States, Purdue discovers and disseminates knowledge with a quality and at a scale second to none. More than 105,000 students study at Purdue across modalities and locations, including nearly 50,000 in person on the West Lafayette campus. Committed to affordability and accessibility, Purdue’s main campus has frozen tuition for 13 years in a row. See how Purdue never stops in the persistent pursuit of the next giant leap — including its first comprehensive urban campus in Indianapolis, the new Mitchell E. Daniels, Jr. School of Business, and Purdue Computes — at https://www.purdue.edu/president/strategic-initiatives .
Writer/Media contact: Amy Raley, [email protected]
Source: Eugene Spafford, [email protected]

Transforming the understanding and treatment of mental illnesses.
Información en español
Celebrating 75 Years! Learn More >>
- Science News
- Meetings and Events
- Social Media
- Press Resources
- Email Updates
- Innovation Speaker Series
Basic Research Powers the First Medication for Postpartum Depression
May 14, 2024 • Feature Story • 75th Anniversary
At a Glance
- Postpartum depression (PPD) is a common mental disorder that many women experience after giving birth.
- Onset of PPD coincides with a dramatic drop in levels of a brain-derived steroid (neurosteroid) known as allopregnanolone.
- Decades of research supported by NIMH illuminated the role of neurosteroids like allopregnanolone in mental illnesses.
- In 2019, brexanolone—a medication that acts by mimicking allopregnanolone—became the first approved drug to treat PPD.
- Able to significantly and rapidly reduce PPD symptoms, brexanolone was a major leap forward in depression treatment.
Joshua A. Gordon, M.D., Ph.D., a practicing psychiatrist at the time, would never forget the call he received one night from a distraught mother.

“She was plagued with a deep, inescapable hopelessness—so depressed she was afraid she was going to hurt her month-old daughter. I helped her get to the hospital, where she spent the next 2 months in an in-patient program trying every available treatment to recover,” said Dr. Gordon, now the Director of the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH).
Unfortunately, this experience is not uncommon among women and other postpartum people who may feel intense sadness, anxiety, and loss of interest after giving birth. These symptoms can be signs of a clinical disorder known as postpartum depression (PPD) . Unlike the "baby blues" or feelings of sadness many new mothers experience in the days after delivery, PPD is more intense and long-lasting, with damaging impacts on health and well-being.
More than the blues: Impacts of PPD on women's mental health
Depression is a common but serious mood disorder. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), rates of depression are high—and rising—among postpartum women. Using data from the 2018 Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System , the CDC found that about 1 in 8 postpartum women had symptoms of depression, while another CDC study showed rates of PPD that were seven times higher in 2015 compared to 2000.
Depression can happen to anyone, and it's especially tough for new moms dealing with the physical challenges of childbirth and the stresses of caring for a young child. When women experience PPD, they often have strong feelings of sadness, anxiety, worthlessness, and guilt. Their sleep, eating, thoughts, and actions can all change noticeably. These mood and behavior changes can be highly distressing and even life-threatening, making it difficult for a woman to do everyday things and take care of herself or her child. In extreme cases, women with PPD may be at risk of hurting themselves or their child or attempting suicide.
Fast-acting, effective treatment for PPD can be life-changing and potentially lifesaving. However, for too long, such care was hard to reach, leaving many women to struggle with depression at a pivotal point in life. Despite some similarities, PPD is not the same as major depression at other times in life. Because of this, usual depression treatments are much less effective in managing the symptoms of PPD.

“PPD is very difficult to treat,” said Mi Hillefors, M.D., Ph.D., Deputy Director of the NIMH Division of Translational Research. “It is usually treated with medications originally approved for major depression—despite limited evidence that they are effective in treating PPD. Standard depression treatments, including antidepressants, psychotherapy, and brain stimulation therapy, can also take weeks or longer to work.”
PPD’s unique risk factors reflect the physical changes of pregnancy and the postpartum period, which include dramatic changes in levels of many hormones and other molecules.
These biological changes had long been seen as a possible source of postpartum mood disorders like depression. But could they also be a solution?
Unlocking the power of allopregnanolone through basic research
Some psychiatric medications owe their discovery to chance. Not so with brexanolone, the first-ever medication to specifically treat PPD. Brexanolone culminated a long series of research studies, much of it funded by NIMH as part of its commitment to understand and support women’s mental health .
Thanks to NIMH-supported basic research, brexanolone was developed by design—a design centered around a molecule called allopregnanolone .
Allopregnanolone is a steroid naturally produced in the brain and with important actions there, such as regulating neurotransmitter activity and protecting neurons from damage. Its impact extends to mental health, with higher levels linked to better mood, lower anxiety, and reduced depression .
Allopregnanolone is also important to pregnancy , during which its levels are extremely high. This happens because of the enhanced production of a hormone called progesterone, which prepares the body for pregnancy and childbirth.
In the last few months of pregnancy, the ovaries and placenta make more progesterone, causing a huge rise in allopregnanolone levels. These levels then drop rapidly after birth. Because allopregnanolone plays a crucial role in mood, these ups and downs can impact a woman’s mental health during and after pregnancy.
Researchers had been aware of brain-derived steroids like allopregnanolone as far back as the 1940s. But the journey to a new PPD treatment began within NIMH's Intramural Research Program (IRP) . At the helm was the NIMH Scientific Director at that time, Steven Paul, M.D., who collaborated with researchers in the NIMH Clinical Neuroscience Branch and at other NIH institutes, including the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS). The researchers sought to understand how the steroids work, change over time, respond to stress, and ultimately relate to health and disease.
Early discoveries came in the 1980s. Paul, working with Maria Majewska, Ph.D., Jacqueline Crawley, Ph.D., A. Leslie Morrow, Ph.D., and other researchers showed that hormones such as progesterone and molecules derived from them have calming and anxiety-reducing effects . Extensive research by Paul’s lab showed that these anxiolytic effects come from enhancing the activity of GABA by binding to specific sites on its receptor. As the main inhibitory neurotransmitter (chemical messenger), GABA reduces the activity of neurons, making them less likely to fire. When molecules bind to its receptor, GABA becomes more potent at inhibiting electrical activity in the brain, with calming effects on behavior.
Paul and IRP colleague Robert Purdy, Ph.D., used the term “ neuroactive steroids ,” or neurosteroids, to describe these molecules able to bind to receptors in the brain to rapidly alter neuronal excitability. Their work in animals confirmed that allopregnanolone is synthesized in the brain . They also showed the effects of allopregnanolone on GABA receptors in humans. Moreover, they found that allopregnanolone affects the response to stress , with acute stress leading the neurosteroid to increase to levels that alter GABA activity. These findings suggested that neurosteroids play an important role in helping animals “reset” and adaptively respond to stressful life events.
Together, this IRP-conducted research established the importance of neurosteroids via their presence in the brain, ability to reduce neuronal activity, and release during stress. Although much of this work was conducted in animals, it would spotlight neurosteroids—and allopregnanolone in particular—as promising targets for treating mental disorders, eventually opening the door to their therapeutic use in humans.
Bridging the gap to advance clinical intervention
While NIMH intramural researchers were making remarkable strides, researchers at other institutions were also conducting work bolstered by funding from NIMH. Among them were Alessandro Guidotti, M.D., at the University of Illinois at Chicago; Istvan Mody, Ph.D., at the University of California, Los Angeles; and Charles Zorumski, M.D., at Washington University in St. Louis. Their NIMH-funded research propelled understanding of inhibitory neurosteroids and their importance in reducing the adverse effects of stress. This work would be the impetus for homing in on allopregnanolone as a treatment for PPD.

Guidotti and colleagues conducted several NIMH-funded studies. Their research in rodents confirmed that allopregnanolone is produced in the brain and helps regulate neuronal excitability by acting on GABA receptors. They also built on the knowledge that neurosteroids are affected by stress. However, unlike acute stress, a stressor lasting multiple weeks led to a decrease in allopregnanolone in brain areas involved in anxiety- and depression-like behaviors.
Importantly, their NIMH-funded work offered some of the earliest evidence that allopregnanolone contributes to depression by showing significantly lower levels in people with depression compared to people without the disorder, a rise in levels (but not that of other neurosteroids) after treatment with antidepressant medication , and a link between increased levels and reduced depression symptoms .
NIMH and NINDS funded multiple studies by Mody and colleagues on interactions of neurosteroids, stress, and GABA receptors. This research was integral to understanding a mechanism in the brains of mice that might explain why some people become depressed after childbirth. Their NIMH-supported research showed changes in GABA receptors in the brain, where neurosteroids are active, that impaired the body’s ability to adapt to hormonal fluctuations. Animals with an irregular GABA receptor component lacking sensitivity to neurosteroids showed depression-like behaviors and reduced maternal care; treating them with a drug that restored the receptor’s function reversed those changes.
Another study by Mody and colleagues revealed changes in GABA expression during pregnancy that led to greater neuronal activity in the brain—but could be brought down by allopregnanolone. This finding opened the door to future studies exploring whether a postpartum drop in the neurosteroid contributed to the risk for mood disorders after birth.
Zorumski led a team in extensively studying neurosteroids as well. Among their seminal findings was identifying the mechanisms by which inhibitory neurosteroids like allopregnanolone affect GABA receptor activity . Their NIMH-funded work dramatically augmented knowledge of how neurosteroids alter GABA receptors to contribute to the risk for mental disorders like PPD.
“The accumulated evidence from these studies established the necessary bridges to justify examining a potential therapeutic role for allopregnanolone in women with PPD,” said Peter Schmidt, M.D., Chief of the NIMH Behavioral Endocrinology Branch.
By the 2010s, researchers had a much better understanding of how allopregnanolone is linked to PPD. Studies showed decreased allopregnanolone in pregnant and postpartum women with symptoms of depression and higher allopregnanolone associated with a lower risk of PPD . The possibility that PPD might be caused by the downregulation of GABA receptors in response to low levels of allopregnanolone after birth inspired researchers to put that theory to the test in clinical studies with human participants.
Taking allopregnanolone from bench to bedside
Extensive research, supported by NIMH and other NIH institutes, found that neurosteroids play a key role in how people deal with stress. They also contribute to the development of mood disorders like anxiety and depression. For allopregnanolone, evidence that it sharply decreases after pregnancy and regulates GABA activity gave rise to the notion that it contributes to PPD—and inspired hope it could be used to treat the disorder.
The biopharmaceutical company Sage Therapeutics utilized this basic research to develop brexanolone. Administered intravenously by a health care professional in a doctor’s office or clinic, brexanolone mimics the effects of allopregnanolone, increasing the inhibitory actions of GABA receptors.
Stephen Kanes, M.D., Ph.D., at Sage Therapeutics and Samantha Meltzer-Brody, M.D., MPH, at the University of North Carolina led several randomized clinical trials to measure the effectiveness of the medication in treating PPD and evaluate its safety and tolerability. The studies, which recruited adult women with PPD from hospitals, research centers, and psychiatric clinics across the United States, measured the effects of brexanolone compared to a placebo over 4 weeks.
The trials were a success. Brexanolone significantly and meaningfully reduced PPD symptoms , and it had only mild side effects. Compared to usual depression treatments, brexanolone brought about a faster response and greater improvement . Whereas most antidepressants take weeks to work, brexanolone improved symptoms and functioning in women with PPD within a few hours to days. And the effects lasted up to a month after the treatment stopped. Not only was brexanolone more effective, but it also worked faster than other depression medications.
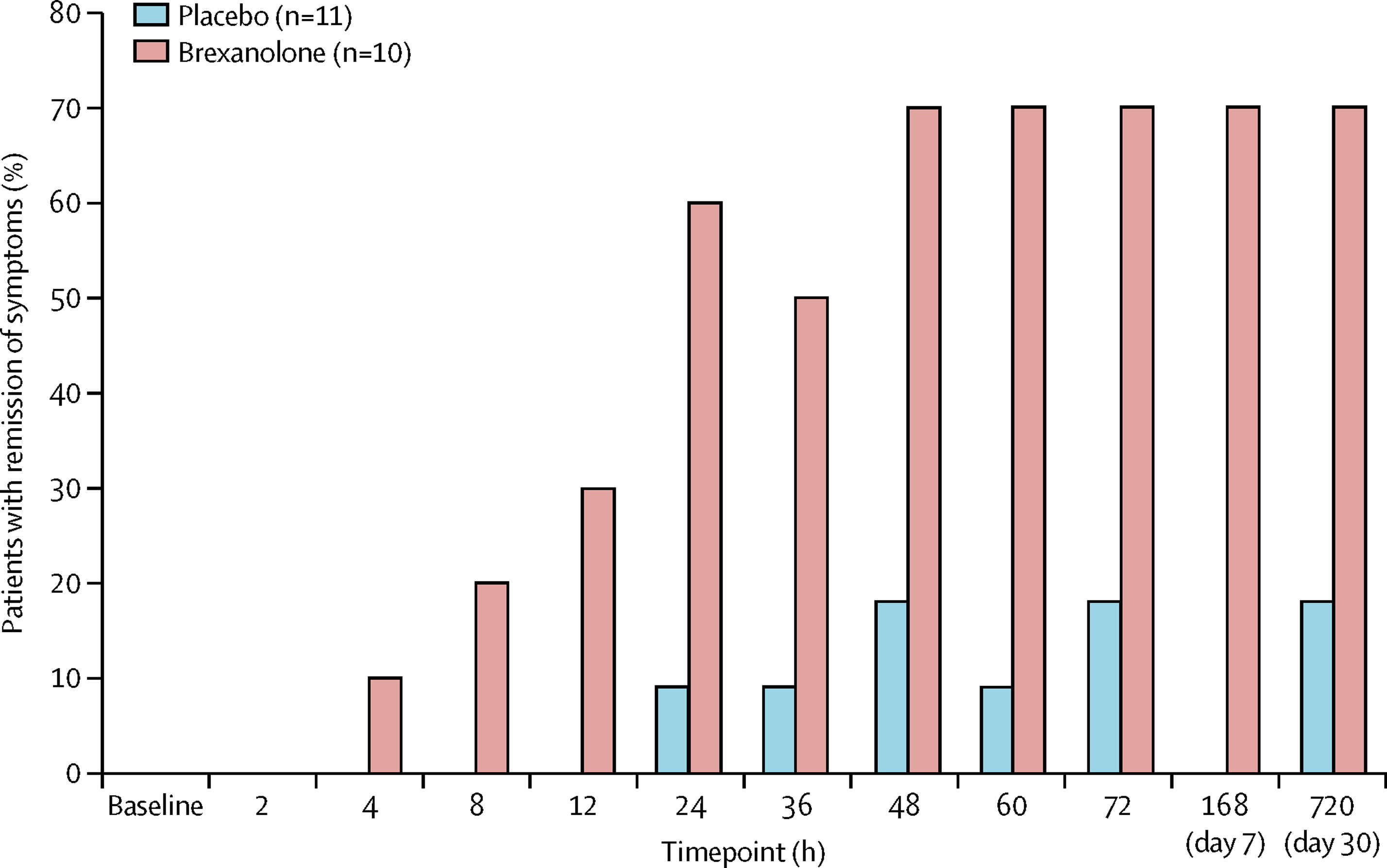
“The dramatic impact of basic research on real-world health outcomes has been inspiring. The fact that NIMH-supported studies contributed to successful drug development in a matter of decades is a remarkable feat and a powerful demonstration of the potential of this foundational research,” said Dr. Gordon.
Based on this promising evidence, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) gave brexanolone priority review and breakthrough therapy designation in September 2016. Then, in March 2019, the FDA approved brexanolone , making it the first drug to treat PPD.
Brightening the future for women with PPD
For women with PPD, brexanolone was a long-awaited reason to celebrate. For NIMH, it was a testament to discoveries made through the decades of research it supported. Although some barriers to treatment persisted, women now had greater hope for treating depression symptoms after pregnancy.
“The approval of brexanolone was an important milestone. Finally, an effective, fast-acting medication specifically to treat PPD,” said Dr. Hillefors. “It was also a victory for psychiatric neuroscience because basic and translational research—by design, not chance—led to a truly novel and effective treatment for a psychiatric disorder.”
Without NIMH-supported studies providing the foundational knowledge of neurosteroids, researchers may have never made the connection between allopregnanolone and treating PPD. “That’s why the approval of brexanolone is such a cause for celebration for mental health research: It represents a true bench-to-bedside success,” said Dr. Gordon.
The success of brexanolone has continued to open the door to exciting advancements in mental health care. For instance, researchers and clinicians are investigating ways to make brexanolone work better for all postpartum people. Researchers are also testing how neurosteroids can be used to treat other forms of depression and other mental health conditions.
Just the beginning of treatment advances for PPD
Brexanolone is only the start of what will hopefully be a new future for PPD treatment. In August 2023, the FDA approved zuranolone as the first oral medication for PPD. Zuranolone acts via similar biological mechanisms as brexanolone. Its approval reflects the next step in NIMH-supported basic research being translated into clinical practice with real-world benefits.
The success of the drug, which is taken in pill form, was shown in two randomized multicenter clinical trials . Women with severe PPD who received zuranolone showed statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements in depression symptoms compared to women who received a placebo. These effects were rapid, sustained through 45 days, and seen across a range of clinical measures. The benefits were mirrored in patients’ self-assessment of their depression symptoms.
According to Dr. Schmidt, “The approval of zuranolone to treat PPD provides women with a rapid and effective treatment that avoids some of the limitations of the original intravenous medication.”
And the journey is far from over. Researchers, clinicians, and industry are continuing to innovate new treatments for PPD to increase access and availability to ensure all people can receive help for their postpartum symptoms.
“While I will never forget that phone call from my patient, the development of these effective medications brings us hope for helping people with PPD and for the overall impact of basic research to truly make a difference in people’s lives,” concluded Dr. Gordon.
Publications
Burval, J., Kerns, R., & Reed, K. (2020). Treating postpartum depression with brexanolone. Nursing , 50 (5), 48−53. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.NURSE.0000657072.85990.5a
Cornett, E. M., Rando, L., Labbé, A. M., Perkins, W., Kaye, A. M., Kaye, A. D., Viswanath, O., & Urits, I. (2021). Brexanolone to treat postpartum depression in adult women. Psychopharmacology Bulletin , 51 (2), 115–130. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8146562/pdf/PB-51-2-115.pdf
Deligiannidis, K. M., Meltzer-Brody, S., Maximos, B., Peeper, E. Q., Freeman, M., Lasser, R., Bullock, A., Kotecha, M., Li, S., Forrestal, F., Rana, N., Garcia, M., Leclair, B., & Doherty, J. (2023). Zuranolone for the treatment of postpartum depression. American Journal of Psychiatry , 180 (9), 668−675. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.20220785
Deligiannidis, K. M., Kroll-Desrosiers, A. R., Mo, S., Nguyen, H. P., Svenson, A., Jaitly, N., ... & Shaffer, S. A. (2016). Peripartum neuroactive steroid and γ-aminobutyric acid profiles in women at-risk for postpartum depression. Psychoneuroendocrinology , 70 , 98−107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2016.05.010
Edinoff, A. N., Odisho, A. S., Lewis, K., Kaskas, A., Hunt, G., Cornett, E. M., Kaye, A. D., Kaye, A., Morgan, J., Barrilleaux, P. S., Lewis, D., Viswanath, O., & Urits, I. (2021). Brexanolone, a GABAA modulator, in the treatment of postpartum depression in adults: A comprehensive review. Frontiers in Psychiatry , 12 , Article 699740. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2021.699740
Epperson, C. N., Rubinow, D. R., Meltzer-Brody, S., Deligiannidis, K. M., Riesenberg, R., Krystal, A.D., Bankole, K., Huang, M. Y., Li, H., Brown, C., Kanes, S. J., & Lasser R. (2023). Effect of brexanolone on depressive symptoms, anxiety, and insomnia in women with postpartum depression: Pooled analyses from 3 double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials in the HUMMINGBIRD clinical program. Journal of Affective Disorders , 320 , 353−359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2022.09.143
Gilbert Evans, S. E., Ross, L. E., Sellers, E. M., Purdy, R. H., & Romach, M. K. (2005). 3α-reduced neuroactive steroids and their precursors during pregnancy and the postpartum period. Gynecological Endocrinology , 21 (5), 268−279. https://doi.org/10.1080/09513590500361747
Guintivano, J., Manuck, T., & Meltzer-Brody, S. (2018). Predictors of postpartum depression: A comprehensive review of the last decade of evidence. Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology , 61 (3), 591−603. https://doi.org/10.1097/GRF.0000000000000368
Gunduz-Bruce, H., Koji, K., & Huang, M.-Y. (2022). Development of neuroactive steroids for the treatment of postpartum depression. Journal of Neuroendocrinology , 34 (2), Article e13019. https://doi.org/10.1111/jne.13019
Haight, S. C., Byatt, N., Moore Simas, T. A., Robbins, C. L., & Ko, J. Y. (2019). Recorded diagnoses of depression during delivery hospitalizations in the United States, 2000-2015. Obstetrics and Gynecology , 133 (6), 1216−1223. https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0000000000003291
Hellgren, C., Åkerud, H., Skalkidou, A., Bäckström, T., & Sundström-Poromaa, I. (2014). Low serum allopregnanolone is associated with symptoms of depression in late pregnancy. Neuropsychobiology , 69 (3), 147–153. https://doi.org/10.1159/000358838
Hutcherson, T. C., Cieri-Hutcherson, N. E., & Gosciak, M. F. (2023). Brexanolone for postpartum depression. American Journal of Health-System Pharmacy , 77 (5), 336−345. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajhp/zxz333
Kanes, S., Colquhoun, H., Gunduz-Bruce, H., Raines, S., Arnold, R., Schacterle, A., Doherty, J., Epperson, C. N., Deligiannidis, K. M., Riesenberg, R., Hoffmann, E., Rubinow, D., Jonas, J., Paul, S., & Meltzer-Brody, S. (2017). Brexanolone (SAGE-547 injection) in post-partum depression: A randomised controlled trial. The Lancet , 390(10093), 480−489. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31264-3
Leader, L. D., O'Connell, M., & VandenBerg, A. (2019). Brexanolone for postpartum depression: Clinical evidence and practical considerations. Pharmacotherapy , 39 (11), 1105–1112. https://doi.org/10.1002/phar.2331
Maguire, J., & Mody, I. (2008). GABAAR plasticity during pregnancy: Relevance to postpartum depression. Neuron , 59 (2), P207–P213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2008.06.019
Maguire, J., & Mody, I. (2016). Behavioral deficits in juveniles mediated by maternal stress hormones in mice. Neural Plasticity , Article 2762518. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2762518
Majewska, M. D., Harrison, N. L., Schwartz, R. D., Barker, J. L., & Paul, S. M. (1986). Steroid hormone metabolites are barbiturate-like modulators of the GABA receptor. Science , 232 (4753), 1004−1007. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.2422758
McEvoy, K., & Osborne, L. M. (2019). Allopregnanolone and reproductive psychiatry: An overview. International Review of Psychiatry , 31 (3), 237–244. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540261.2018.1553775
Meltzer-Brody, S., Colquhoun, H., Riesenberg, R., Epperson, C. N., Deligiannidis, K. M., Rubinow, D. R., Li, H., Sankoh, A. J., Clemson, C., Schacterle, A., Jonas, J., & Kanes, S. (2018). Brexanolone injection in post-partum depression: Two multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trials. The Lancet , 392 (10152), 1058−1070. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31551-4
Morrison, K. E., Cole, A. B., Thompson, S. M., & Bale, T. L. (2019). Brexanolone for the treatment of patients with postpartum depression. Drugs Today , 55 (9), 537–544. https://doi.org/10.1358/dot.2019.55.9.3040864
Purdy, R. H., Morrow, A. L., Moore, P. H., & Paul, S. M. (1991). Stress-induced elevations of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor-active steroids in the rat brain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences , 88 (10), 4553−4557. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.88.10.4553
Scarff, J. R. (2019). Use of brexanolone for postpartum depression. Innovations in Clinical Neuroscience , 16 (11−12), 32–35.
Schüle, C., Nothdurfter, C., & Rupprecht, R. (2014). The role of allopregnanolone in depression and anxiety. Progress in Neurobiology , 113 , 79−87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.09.003
Selye, H. (1941). Anesthetic effect of steroid hormones. Experimental Biology and Medicine , 46 (1), 116–121. https://doi.org/10.3181/00379727-46-11907
Shorey, S., Chee, C. Y. I., Ng, E. D., Chan, Y. H., Tam, W. W. S., & Chong, Y. S. (2018). Prevalence and incidence of postpartum depression among healthy mothers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Psychiatric Research , 104 , 235–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2018.08.001
Slomian, J., Honvo, G., Emonts, P., Reginster, J. Y., & Bruyère, O. (2019). Consequences of maternal postpartum depression: A systematic review of maternal and infant outcomes. Women's Health , 15 , 1−55. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745506519844044
- Perinatal Depression (NIMH brochure)
- Depression in Women: 4 Things You Should Know (NIMH health topic page)
- Depression (NIMH health topic page)
- Major Depression (NIMH statistics page)
- Women and Mental Health (NIMH health topic page)
- A Bench-to-Bedside Story: The Development of a Treatment for Postpartum Depression (NIMH Director’s Message)
- Bench-to-Bedside: NIMH Research Leading to Brexanolone, First-Ever Drug Specifically for Postpartum Depression (NIIMH press release)
- Population Study Finds Depression Is Different Before, During, and After Pregnancy (NIMH research highlight)
- FDA Approves First Treatment for Post-Partum Depression (FDA news release)
- FDA Approves First Oral Treatment for Postpartum Depression (FDA news release)
Facility for Rare Isotope Beams
At michigan state university, international research team uses wavefunction matching to solve quantum many-body problems, new approach makes calculations with realistic interactions possible.
FRIB researchers are part of an international research team solving challenging computational problems in quantum physics using a new method called wavefunction matching. The new approach has applications to fields such as nuclear physics, where it is enabling theoretical calculations of atomic nuclei that were previously not possible. The details are published in Nature (“Wavefunction matching for solving quantum many-body problems”) .
Ab initio methods and their computational challenges
An ab initio method describes a complex system by starting from a description of its elementary components and their interactions. For the case of nuclear physics, the elementary components are protons and neutrons. Some key questions that ab initio calculations can help address are the binding energies and properties of atomic nuclei not yet observed and linking nuclear structure to the underlying interactions among protons and neutrons.
Yet, some ab initio methods struggle to produce reliable calculations for systems with complex interactions. One such method is quantum Monte Carlo simulations. In quantum Monte Carlo simulations, quantities are computed using random or stochastic processes. While quantum Monte Carlo simulations can be efficient and powerful, they have a significant weakness: the sign problem. The sign problem develops when positive and negative weight contributions cancel each other out. This cancellation results in inaccurate final predictions. It is often the case that quantum Monte Carlo simulations can be performed for an approximate or simplified interaction, but the corresponding simulations for realistic interactions produce severe sign problems and are therefore not possible.
Using ‘plastic surgery’ to make calculations possible
The new wavefunction-matching approach is designed to solve such computational problems. The research team—from Gaziantep Islam Science and Technology University in Turkey; University of Bonn, Ruhr University Bochum, and Forschungszentrum Jülich in Germany; Institute for Basic Science in South Korea; South China Normal University, Sun Yat-Sen University, and Graduate School of China Academy of Engineering Physics in China; Tbilisi State University in Georgia; CEA Paris-Saclay and Université Paris-Saclay in France; and Mississippi State University and the Facility for Rare Isotope Beams (FRIB) at Michigan State University (MSU)—includes Dean Lee , professor of physics at FRIB and in MSU’s Department of Physics and Astronomy and head of the Theoretical Nuclear Science department at FRIB, and Yuan-Zhuo Ma , postdoctoral research associate at FRIB.
“We are often faced with the situation that we can perform calculations using a simple approximate interaction, but realistic high-fidelity interactions cause severe computational problems,” said Lee. “Wavefunction matching solves this problem by doing plastic surgery. It removes the short-distance part of the high-fidelity interaction, and replaces it with the short-distance part of an easily computable interaction.”
This transformation is done in a way that preserves all of the important properties of the original realistic interaction. Since the new wavefunctions look similar to that of the easily computable interaction, researchers can now perform calculations using the easily computable interaction and apply a standard procedure for handling small corrections called perturbation theory. A team effort
The research team applied this new method to lattice quantum Monte Carlo simulations for light nuclei, medium-mass nuclei, neutron matter, and nuclear matter. Using precise ab initio calculations, the results closely matched real-world data on nuclear properties such as size, structure, and binding energies. Calculations that were once impossible due to the sign problem can now be performed using wavefunction matching.
“It is a fantastic project and an excellent opportunity to work with the brightest nuclear scientist s in FRIB and around the globe,” said Ma. “As a theorist , I'm also very excited about programming and conducting research on the world's most powerful exascale supercomputers, such as Frontier , which allows us to implement wavefunction matching to explore the mysteries of nuclear physics.”
While the research team focused solely on quantum Monte Carlo simulations, wavefunction matching should be useful for many different ab initio approaches, including both classical and quantum computing calculations. The researchers at FRIB worked with collaborators at institutions in China, France, Germany, South Korea, Turkey, and United States.
“The work is the culmination of effort over many years to handle the computational problems associated with realistic high-fidelity nuclear interactions,” said Lee. “It is very satisfying to see that the computational problems are cleanly resolved with this new approach. We are grateful to all of the collaboration members who contributed to this project, in particular, the lead author, Serdar Elhatisari.”
This material is based upon work supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, the U.S. National Science Foundation, the German Research Foundation, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Chinese Academy of Sciences President’s International Fellowship Initiative, Volkswagen Stiftung, the European Research Council, the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Security Academic Fund, the Rare Isotope Science Project of the Institute for Basic Science, the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Institute for Basic Science, and the Espace de Structure et de réactions Nucléaires Théorique.
Michigan State University operates the Facility for Rare Isotope Beams (FRIB) as a user facility for the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science (DOE-SC), supporting the mission of the DOE-SC Office of Nuclear Physics. Hosting what is designed to be the most powerful heavy-ion accelerator, FRIB enables scientists to make discoveries about the properties of rare isotopes in order to better understand the physics of nuclei, nuclear astrophysics, fundamental interactions, and applications for society, including in medicine, homeland security, and industry.
The U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of today’s most pressing challenges. For more information, visit energy.gov/science.

COMMENTS
Learn how to choose a topic, identify a problem, formulate research questions, create a research design, and write a research proposal for your thesis or dissertation. Scribbr offers tips, examples, and resources to help you with each step of the research process.
This site has made making research papers so much easier. Easy to find articles and puts it in the format needed. ... When I started back to finish my associate's degree, I had to find a site to help me with citing websites...Scribbr is the best one I found. It gives you the parenthetical option and allows you to copy your reference list into ...
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature. As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question.More specifically, that's called a research question, and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What's important to understand though is that you'll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources - for ...
Research databases. You can search for scholarly sources online using databases and search engines like Google Scholar. These provide a range of search functions that can help you to find the most relevant sources. If you are searching for a specific article or book, include the title or the author's name. Alternatively, if you're just ...
About Research Methods. This guide provides an overview of research methods, how to choose and use them, and supports and resources at UC Berkeley. As Patten and Newhart note in the book Understanding Research Methods, "Research methods are the building blocks of the scientific enterprise. They are the "how" for building systematic knowledge.
Search Help. Get the most out of Google Scholar with some helpful tips on searches, email alerts, citation export, and more. Your search results are normally sorted by relevance, not by date. To find newer articles, try the following options in the left sidebar: click the envelope icon to have new results periodically delivered by email.
Few things strike more fear in academics than the accursed research paper, a term synonymous with long hours and hard work.Luckily there's a secret to help you get through them. As long as you know how to write a research paper properly, you'll find they're not so bad . . . or at least less painful.. In this guide we concisely explain how to write an academic research paper step by step.
Delivered to your inbox every two weeks, the Writing Toolbox features practical advice and tools you can use to prepare a research manuscript for submission success and build your scientific writing skillset. Discover how to navigate the peer review and publishing process, beyond writing your article.
This section will help you understand different methodological approaches used in research papers. Students will get the most out of these resources if they use them to help prepare for conversations with teachers or discussions in class. "Types of Research Designs" (USC) A "research design," used for complex papers, is related to the paper's ...
ReferenceDesk.org: Dubbed "The Internet's Best Reference Source," this extremely useful web directory provides everything from business and finance information to federal government resources, scholarship details, links to newspapers and calendars, search engines, and more. Ask the Space Expert: NASA's source for space and science research help.
Library Liaisons. Make an appointment with a library liaison to get the help you need to get your work done. Many of Harvard's professional schools offer specialized support for data services in certain disciplines. Publishing Data Services at Countway LibraryCountway Library Review ServiceResearch Data Program at Baker Library.
Semantic Reader is an augmented reader with the potential to revolutionize scientific reading by making it more accessible and richly contextual. Try it for select papers. Learn More. Semantic Scholar uses groundbreaking AI and engineering to understand the semantics of scientific literature to help Scholars discover relevant research.
If you're just getting started, we can help you: Narrow your topic. Find materials. Manage your sources. See our Essentials of Library Research Guide for a high-level overview of the research process. We can also connect you with: Funding and grant opportunities. Help if you conduct research in a language other than English.
5. Promoting Published Works. 6. Measuring Your Impact. 7. Showing Your Impact. The Research Life Cycle illustrates how information is created and used during the research process. Librarians are equipped to assist both student and faculty researchers at every phase of the Research Life Cycle from planning to measuring impact.
How to Improve Your Research Skills: 6 Research Tips. Written by MasterClass. Last updated: Aug 18, 2021 • 3 min read. Whether you're writing a blog post or a short story, you'll likely reach a point in your first draft where you don't have enough information to go forward—and that's where research comes in.
Participate in a clinical study, and help people in your community and around the world. Get Started. Questions? Call 1-866-445-7033 (US) or 02890 554000 (UK) Learn about participating in clinical trials with Celerion at one of our three research centers. Find studies and help contribute to medical advancements.
Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft. The revision process. Research paper checklist. Free lecture slides.
We help you avoid plagiarism by citing your sources correctly and consistently. ... The Scribbr Knowledge Base is a collection of free resources to help you succeed in academic research, writing, and citation. Every week, we publish helpful step-by-step guides, clear examples, simple templates, engaging videos, and more.
Our research guides connect you with different library resources to help you find research materials on any given subject. Select a campus below to view its research guides or contact a librarian for assistance. LSC-CyFair. LSC-Houston North. LSC-Kingwood. LSC-Montgomery. LSC-North Harris. LSC-Online. LSC-Tomball.
Coined as a personal research assistant, Zotero is a tool that brings efficiency to the research process. Zotero helps researchers collect, organize, annotate, and share research easily. Zotero integrates with internet browsers, so researchers can easily save an article, publication, or research study on the platform for later.
Research provides evidence about what works best. Patients, carers, people who use social care services and health and social care professionals all use this evidence to make decisions about treatments and care. When the public gets involved in research, they work alongside researchers to help shape: what research gets done. how it's carried out.
Welcome to the transformative world of AI-powered research tools! This blog post will dive deeper into these tools, providing a detailed review of how AI is revolutionizing academic research. ... Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of ...
Have a fresh pair of eyes give you some feedback. Don't allow someone else to rewrite your essay, but do take advantage of others' edits and opinions when they seem helpful. ( Bates College) Read your essay aloud to someone. Reading the essay out loud offers a chance to hear how your essay sounds outside your head.
Paper Writing Help — Real Opportunities to Receive Assistance Sometimes it is not enough to find a native English speaker, because, in addition to his consent to do the work for you, it is necessary that he has the special erudition on the topic about which the text will be written. Obviously, not every person from the USA or Great Britain is ...
Here, Zhao discusses the research about how asking for help can lead to meaningful experiences and strengthen relationships with others - friends as well as strangers.
This page will help you write a concise and targeted email to maximize your chance at a reply. The subject. Be short, but be clear what you are writing about. Something like "Undergraduate Research Opportunities in Your Lab" or "Openings for Undergraduates to do Research in [your research topic]" should work.
As the nation prepares to mark the 70th anniversary of the landmark U.S. Supreme Court ruling in Brown v. Board of Education, a new report from researchers at Stanford and USC shows that racial and economic segregation among schools has grown steadily in large school districts over the past three decades — an increase that appears to be driven in part by policies favoring
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. — Eugene H. Spafford, professor of computer science in Purdue University's College of Science and internationally recognized authority on cybersecurity, has been chosen to help Sandia National Laboratories in its campaign to manage digital risks to high-consequence systems.. Spafford, Executive Director Emeritus of CERIAS, Purdue's Center for Education and Research ...
The Division of Intramural Research Programs (IRP) is the internal research division of the NIMH. Over 40 research groups conduct basic neuroscience research and clinical investigations of mental illnesses, brain function, and behavior at the NIH campus in Bethesda, Maryland. Learn more about research conducted at NIMH.
New approach makes calculations with realistic interactions possibleFRIB researchers are part of an international research team solving challenging computational problems in quantum physics using a new method called wavefunction matching. The new approach has applications to fields such as nuclear physics, where it is enabling theoretical calculations of atomic nuclei that were previously not ...