Systematic Reviews in Educational Research: Methodology, Perspectives and Application
- Open Access
- First Online: 22 November 2019

Cite this chapter
You have full access to this open access chapter

- Mark Newman 6 &
- David Gough 6
83k Accesses
135 Citations
2 Altmetric
This chapter explores the processes of reviewing literature as a research method. The logic of the family of research approaches called systematic review is analysed and the variation in techniques used in the different approaches explored using examples from existing reviews. The key distinctions between aggregative and configurative approaches are illustrated and the chapter signposts further reading on key issues in the systematic review process.
You have full access to this open access chapter, Download chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others

Reviewing Literature for and as Research

Methodological Approaches to Literature Review

The Role of Meta-analysis in Educational Research
1 what are systematic reviews.
A literature review is a scholarly paper which provides an overview of current knowledge about a topic. It will typically include substantive findings, as well as theoretical and methodological contributions to a particular topic (Hart 2018 , p. xiii). Traditionally in education ‘reviewing the literature’ and ‘doing research’ have been viewed as distinct activities. Consider the standard format of research proposals, which usually have some kind of ‘review’ of existing knowledge presented distinctly from the methods of the proposed new primary research. However, both reviews and research are undertaken in order to find things out. Reviews to find out what is already known from pre-existing research about a phenomena, subject or topic; new primary research to provide answers to questions about which existing research does not provide clear and/or complete answers.
When we use the term research in an academic sense it is widely accepted that we mean a process of asking questions and generating knowledge to answer these questions using rigorous accountable methods. As we have noted, reviews also share the same purposes of generating knowledge but historically we have not paid as much attention to the methods used for reviewing existing literature as we have to the methods used for primary research. Literature reviews can be used for making claims about what we know and do not know about a phenomenon and also about what new research we need to undertake to address questions that are unanswered. Therefore, it seems reasonable to conclude that ‘how’ we conduct a review of research is important.
The increased focus on the use of research evidence to inform policy and practice decision-making in Evidence Informed Education (Hargreaves 1996 ; Nelson and Campbell 2017 ) has increased the attention given to contextual and methodological limitations of research evidence provided by single studies. Reviews of research may help address these concerns when carried on in a systematic, rigorous and transparent manner. Thus, again emphasizing the importance of ‘how’ reviews are completed.
The logic of systematic reviews is that reviews are a form of research and thus can be improved by using appropriate and explicit methods. As the methods of systematic review have been applied to different types of research questions, there has been an increasing plurality of types of systematic review. Thus, the term ‘systematic review’ is used in this chapter to refer to a family of research approaches that are a form of secondary level analysis (secondary research) that brings together the findings of primary research to answer a research question. Systematic reviews can therefore be defined as “a review of existing research using explicit, accountable rigorous research methods” (Gough et al. 2017 , p. 4).
2 Variation in Review Methods
Reviews can address a diverse range of research questions. Consequently, as with primary research, there are many different approaches and methods that can be applied. The choices should be dictated by the review questions. These are shaped by reviewers’ assumptions about the meaning of a particular research question, the approach and methods that are best used to investigate it. Attempts to classify review approaches and methods risk making hard distinctions between methods and thereby to distract from the common defining logics that these approaches often share. A useful broad distinction is between reviews that follow a broadly configurative synthesis logic and reviews that follow a broadly aggregative synthesis logic (Sandelowski et al. 2012 ). However, it is important to keep in mind that most reviews have elements of both (Gough et al. 2012 ).
Reviews that follow a broadly configurative synthesis logic approach usually investigate research questions about meaning and interpretation to explore and develop theory. They tend to use exploratory and iterative review methods that emerge throughout the process of the review. Studies included in the review are likely to have investigated the phenomena of interest using methods such as interviews and observations, with data in the form of text. Reviewers are usually interested in purposive variety in the identification and selection of studies. Study quality is typically considered in terms of authenticity. Synthesis consists of the deliberative configuring of data by reviewers into patterns to create a richer conceptual understanding of a phenomenon. For example, meta ethnography (Noblit and Hare 1988 ) uses ethnographic data analysis methods to explore and integrate the findings of previous ethnographies in order to create higher-level conceptual explanations of phenomena. There are many other review approaches that follow a broadly configurative logic (for an overview see Barnett-Page and Thomas 2009 ); reflecting the variety of methods used in primary research in this tradition.
Reviews that follow a broadly aggregative synthesis logic usually investigate research questions about impacts and effects. For example, systematic reviews that seek to measure the impact of an educational intervention test the hypothesis that an intervention has the impact that has been predicted. Reviews following an aggregative synthesis logic do not tend to develop theory directly; though they can contribute by testing, exploring and refining theory. Reviews following an aggregative synthesis logic tend to specify their methods in advance (a priori) and then apply them without any deviation from a protocol. Reviewers are usually concerned to identify the comprehensive set of studies that address the research question. Studies included in the review will usually seek to determine whether there is a quantitative difference in outcome between groups receiving and not receiving an intervention. Study quality assessment in reviews following an aggregative synthesis logic focusses on the minimisation of bias and thus selection pays particular attention to homogeneity between studies. Synthesis aggregates, i.e. counts and adds together, the outcomes from individual studies using, for example, statistical meta-analysis to provide a pooled summary of effect.
3 The Systematic Review Process
Different types of systematic review are discussed in more detail later in this chapter. The majority of systematic review types share a common set of processes. These processes can be divided into distinct but interconnected stages as illustrated in Fig. 1 . Systematic reviews need to specify a research question and the methods that will be used to investigate the question. This is often written as a ‘protocol’ prior to undertaking the review. Writing a protocol or plan of the methods at the beginning of a review can be a very useful activity. It helps the review team to gain a shared understanding of the scope of the review and the methods that they will use to answer the review’s questions. Different types of systematic reviews will have more or less developed protocols. For example, for systematic reviews investigating research questions about the impact of educational interventions it is argued that a detailed protocol should be fully specified prior to the commencement of the review to reduce the possibility of reviewer bias (Torgerson 2003 , p. 26). For other types of systematic review, in which the research question is more exploratory, the protocol may be more flexible and/or developmental in nature.
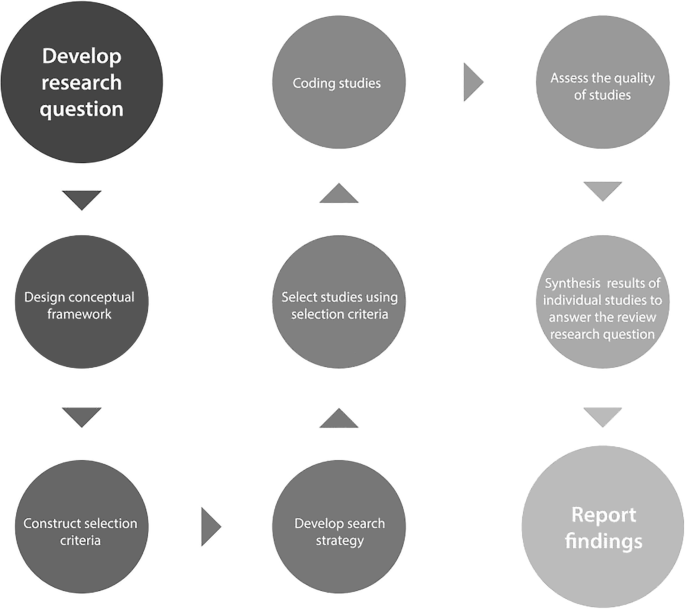
The systematic review process
3.1 Systematic Review Questions and the Conceptual Framework
The review question gives each review its particular structure and drives key decisions about what types of studies to include; where to look for them; how to assess their quality; and how to combine their findings. Although a research question may appear to be simple, it will include many assumptions. Whether implicit or explicit, these assumptions will include: epistemological frameworks about knowledge and how we obtain it, theoretical frameworks, whether tentative or firm, about the phenomenon that is the focus of study.
Taken together, these produce a conceptual framework that shapes the research questions, choices about appropriate systematic review approach and methods. The conceptual framework may be viewed as a working hypothesis that can be developed, refined or confirmed during the course of the research. Its purpose is to explain the key issues to be studied, the constructs or variables, and the presumed relationships between them. The framework is a research tool intended to assist a researcher to develop awareness and understanding of the phenomena under scrutiny and to communicate this (Smyth 2004 ).
A review to investigate the impact of an educational intervention will have a conceptual framework that includes a hypothesis about a causal link between; who the review is about (the people), what the review is about (an intervention and what it is being compared with), and the possible consequences of intervention on the educational outcomes of these people. Such a review would follow a broadly aggregative synthesis logic. This is the shape of reviews of educational interventions carried out for the What Works Clearing House in the USA Footnote 1 and the Education Endowment Foundation in England. Footnote 2
A review to investigate meaning or understanding of a phenomenon for the purpose of building or further developing theory will still have some prior assumptions. Thus, an initial conceptual framework will contain theoretical ideas about how the phenomena of interest can be understood and some ideas justifying why a particular population and/or context is of specific interest or relevance. Such a review is likely to follow a broadly configurative logic.
3.2 Selection Criteria
Reviewers have to make decisions about which research studies to include in their review. In order to do this systematically and transparently they develop rules about which studies can be selected into the review. Selection criteria (sometimes referred to as inclusion or exclusion criteria) create restrictions on the review. All reviews, whether systematic or not, limit in some way the studies that are considered by the review. Systematic reviews simply make these restrictions transparent and therefore consistent across studies. These selection criteria are shaped by the review question and conceptual framework. For example, a review question about the impact of homework on educational attainment would have selection criteria specifying who had to do the homework; the characteristics of the homework and the outcomes that needed to be measured. Other commonly used selection criteria include study participant characteristics; the country where the study has taken place and the language in which the study is reported. The type of research method(s) may also be used as a selection criterion but this can be controversial given the lack of consensus in education research (Newman 2008 ), and the inconsistent terminology used to describe education research methods.
3.3 Developing the Search Strategy
The search strategy is the plan for how relevant research studies will be identified. The review question and conceptual framework shape the selection criteria. The selection criteria specify the studies to be included in a review and thus are a key driver of the search strategy. A key consideration will be whether the search aims to be exhaustive i.e. aims to try and find all the primary research that has addressed the review question. Where reviews address questions about effectiveness or impact of educational interventions the issue of publication bias is a concern. Publication bias is the phenomena whereby smaller and/or studies with negative findings are less likely to be published and/or be harder to find. We may therefore inadvertently overestimate the positive effects of an educational intervention because we do not find studies with negative or smaller effects (Chow and Eckholm 2018 ). Where the review question is not of this type then a more specific or purposive search strategy, that may or may not evolve as the review progresses, may be appropriate. This is similar to sampling approaches in primary research. In primary research studies using aggregative approaches, such as quasi-experiments, analysis is based on the study of complete or representative samples. In primary research studies using configurative approaches, such as ethnography, analysis is based on examining a range of instances of the phenomena in similar or different contexts.
The search strategy will detail the sources to be searched and the way in which the sources will be searched. A list of search source types is given in Box 1 below. An exhaustive search strategy would usually include all of these sources using multiple bibliographic databases. Bibliographic databases usually index academic journals and thus are an important potential source. However, in most fields, including education, relevant research is published in a range of journals which may be indexed in different bibliographic databases and thus it may be important to search multiple bibliographic databases. Furthermore, some research is published in books and an increasing amount of research is not published in academic journals or at least may not be published there first. Thus, it is important to also consider how you will find relevant research in other sources including ‘unpublished’ or ‘grey’ literature. The Internet is a valuable resource for this purpose and should be included as a source in any search strategy.
Box 1: Search Sources
The World Wide Web/Internet
Google, Specialist Websites, Google Scholar, Microsoft Academic
Bibliographic Databases
Subject specific e.g. Education—ERIC: Education Resources Information Centre
Generic e.g. ASSIA: Applied Social Sciences Index and Abstracts
Handsearching of specialist journals or books
Contacts with Experts
Citation Checking
New, federated search engines are being developed, which search multiple sources at the same time, eliminating duplicates automatically (Tsafnat et al. 2013 ). Technologies, including text mining, are being used to help develop search strategies, by suggesting topics and terms on which to search—terms that reviewers may not have thought of using. Searching is also being aided by technology through the increased use (and automation) of ‘citation chasing’, where papers that cite, or are cited by, a relevant study are checked in case they too are relevant.
A search strategy will identify the search terms that will be used to search the bibliographic databases. Bibliographic databases usually index records according to their topic using ‘keywords’ or ‘controlled terms’ (categories used by the database to classify papers). A comprehensive search strategy usually involves searching both a freetext search using keywords determined by the reviewers and controlled terms. An example of a bibliographic database search is given in Box 2. This search was used in a review that aimed to find studies that investigated the impact of Youth Work on positive youth outcomes (Dickson et al. 2013 ). The search is built using terms for the population of interest (Youth), the intervention of interest (Youth Work) and the outcomes of Interest (Positive Development). It used both keywords and controlled terms, ‘wildcards’ (the *sign in this database) and the Boolean operators ‘OR’ and ‘AND’ to combine terms. This example illustrates the potential complexity of bibliographic database search strings, which will usually require a process of iterative development to finalise.
Box 2: Search string example To identify studies that address the question What is the empirical research evidence on the impact of youth work on the lives of children and young people aged 10-24 years?: CSA ERIC Database
((TI = (adolescen* or (“young man*”) or (“young men”)) or TI = ((“young woman*”) or (“young women”) or (Young adult*”)) or TI = ((“young person*”) or (“young people*”) or teen*) or AB = (adolescen* or (“young man*”) or (“young men”)) or AB = ((“young woman*”) or (“young women”) or (Young adult*”)) or AB = ((“young person*”) or (“young people*”) or teen*)) or (DE = (“youth” or “adolescents” or “early adolescents” or “late adolescents” or “preadolescents”))) and(((TI = ((“positive youth development “) or (“youth development”) or (“youth program*”)) or TI = ((“youth club*”) or (“youth work”) or (“youth opportunit*”)) or TI = ((“extended school*”) or (“civic engagement”) or (“positive peer culture”)) or TI = ((“informal learning”) or multicomponent or (“multi-component “)) or TI = ((“multi component”) or multidimensional or (“multi-dimensional “)) or TI = ((“multi dimensional”) or empower* or asset*) or TI = (thriv* or (“positive development”) or resilienc*) or TI = ((“positive activity”) or (“positive activities”) or experiential) or TI = ((“community based”) or “community-based”)) or(AB = ((“positive youth development “) or (“youth development”) or (“youth program*”)) or AB = ((“youth club*”) or (“youth work”) or (“youth opportunit*”)) or AB = ((“extended school*”) or (“civic engagement”) or (“positive peer culture”)) or AB = ((“informal learning”) or multicomponent or (“multi-component “)) or AB = ((“multi component”) or multidimensional or (“multi-dimensional “)) or AB = ((“multi dimensional”) or empower* or asset*) or AB = (thriv* or (“positive development”) or resilienc*) or AB = ((“positive activity”) or (“positive activities”) or experiential) or AB = ((“community based”) or “community-based”))) or (DE=”community education”))
Detailed guidance for finding effectiveness studies is available from the Campbell Collaboration (Kugley et al. 2015 ). Guidance for finding a broader range of studies has been produced by the EPPI-Centre (Brunton et al. 2017a ).
3.4 The Study Selection Process
Studies identified by the search are subject to a process of checking (sometimes referred to as screening) to ensure they meet the selection criteria. This is usually done in two stages whereby titles and abstracts are checked first to determine whether the study is likely to be relevant and then a full copy of the paper is acquired to complete the screening exercise. The process of finding studies is not efficient. Searching bibliographic databases, for example, leads to many irrelevant studies being found which then have to be checked manually one by one to find the few relevant studies. There is increasing use of specialised software to support and in some cases, automate the selection process. Text mining, for example, can assist in selecting studies for a review (Brunton et al. 2017b ). A typical text mining or machine learning process might involve humans undertaking some screening, the results of which are used to train the computer software to learn the difference between included and excluded studies and thus be able to indicate which of the remaining studies are more likely to be relevant. Such automated support may result in some errors in selection, but this may be less than the human error in manual selection (O’Mara-Eves et al. 2015 ).
3.5 Coding Studies
Once relevant studies have been selected, reviewers need to systematically identify and record the information from the study that will be used to answer the review question. This information includes the characteristics of the studies, including details of the participants and contexts. The coding describes: (i) details of the studies to enable mapping of what research has been undertaken; (ii) how the research was undertaken to allow assessment of the quality and relevance of the studies in addressing the review question; (iii) the results of each study so that these can be synthesised to answer the review question.
The information is usually coded into a data collection system using some kind of technology that facilitates information storage and analysis (Brunton et al. 2017b ) such as the EPPI-Centre’s bespoke systematic review software EPPI Reviewer. Footnote 3 Decisions about which information to record will be made by the review team based on the review question and conceptual framework. For example, a systematic review about the relationship between school size and student outcomes collected data from the primary studies about each schools funding, students, teachers and school organisational structure as well as about the research methods used in the study (Newman et al. 2006 ). The information coded about the methods used in the research will vary depending on the type of research included and the approach that will be used to assess the quality and relevance of the studies (see the next section for further discussion of this point).
Similarly, the information recorded as ‘results’ of the individual studies will vary depending on the type of research that has been included and the approach to synthesis that will be used. Studies investigating the impact of educational interventions using statistical meta-analysis as a synthesis technique will require all of the data necessary to calculate effect sizes to be recorded from each study (see the section on synthesis below for further detail on this point). However, even in this type of study there will be multiple data that can be considered to be ‘results’ and so which data needs to be recorded from studies will need to be carefully specified so that recording is consistent across studies
3.6 Appraising the Quality of Studies
Methods are reinvented every time they are used to accommodate the real world of research practice (Sandelowski et al. 2012 ). The researcher undertaking a primary research study has attempted to design and execute a study that addresses the research question as rigorously as possible within the parameters of their resources, understanding, and context. Given the complexity of this task, the contested views about research methods and the inconsistency of research terminology, reviewers will need to make their own judgements about the quality of the any individual piece of research included in their review. From this perspective, it is evident that using a simple criteria, such as ‘published in a peer reviewed journal’ as a sole indicator of quality, is not likely to be an adequate basis for considering the quality and relevance of a study for a particular systematic review.
In the context of systematic reviews this assessment of quality is often referred to as Critical Appraisal (Petticrew and Roberts 2005 ). There is considerable variation in what is done during critical appraisal: which dimensions of study design and methods are considered; the particular issues that are considered under each dimension; the criteria used to make judgements about these issues and the cut off points used for these criteria (Oancea and Furlong 2007 ). There is also variation in whether the quality assessment judgement is used for excluding studies or weighting them in analysis and when in the process judgements are made.
There are broadly three elements that are considered in critical appraisal: the appropriateness of the study design in the context of the review question, the quality of the execution of the study methods and the study’s relevance to the review question (Gough 2007 ). Distinguishing study design from execution recognises that whilst a particular design may be viewed as more appropriate for a study it also needs to be well executed to achieve the rigour or trustworthiness attributed to the design. Study relevance is achieved by the review selection criteria but assessing the degree of relevance recognises that some studies may be less relevant than others due to differences in, for example, the characteristics of the settings or the ways that variables are measured.
The assessment of study quality is a contested and much debated issue in all research fields. Many published scales are available for assessing study quality. Each incorporates criteria relevant to the research design being evaluated. Quality scales for studies investigating the impact of interventions using (quasi) experimental research designs tend to emphasis establishing descriptive causality through minimising the effects of bias (for detailed discussion of issues associated with assessing study quality in this tradition see Waddington et al. 2017 ). Quality scales for appraising qualitative research tend to focus on the extent to which the study is authentic in reflecting on the meaning of the data (for detailed discussion of the issues associated with assessing study quality in this tradition see Carroll and Booth 2015 ).
3.7 Synthesis
A synthesis is more than a list of findings from the included studies. It is an attempt to integrate the information from the individual studies to produce a ‘better’ answer to the review question than is provided by the individual studies. Each stage of the review contributes toward the synthesis and so decisions made in earlier stages of the review shape the possibilities for synthesis. All types of synthesis involve some kind of data transformation that is achieved through common analytic steps: searching for patterns in data; Checking the quality of the synthesis; Integrating data to answer the review question (Thomas et al. 2012 ). The techniques used to achieve these vary for different types of synthesis and may appear more or less evident as distinct steps.
Statistical meta-analysis is an aggregative synthesis approach in which the outcome results from individual studies are transformed into a standardized, scale free, common metric and combined to produce a single pooled weighted estimate of effect size and direction. There are a number of different metrics of effect size, selection of which is principally determined by the structure of outcome data in the primary studies as either continuous or dichotomous. Outcome data with a dichotomous structure can be transformed into Odds Ratios (OR), Absolute Risk Ratios (ARR) or Relative Risk Ratios (RRR) (for detailed discussion of dichotomous outcome effect sizes see Altman 1991 ). More commonly seen in education research, outcome data with a continuous structure can be translated into Standardised Mean Differences (SMD) (Fitz-Gibbon 1984 ). At its most straightforward effect size calculation is simple arithmetic. However given the variety of analysis methods used and the inconsistency of reporting in primary studies it is also possible to calculate effect sizes using more complex transformation formulae (for detailed instructions on calculating effect sizes from a wide variety of data presentations see Lipsey and Wilson 2000 ).
The combination of individual effect sizes uses statistical procedures in which weighting is given to the effect sizes from the individual studies based on different assumptions about the causes of variance and this requires the use of statistical software. Statistical measures of heterogeneity produced as part of the meta-analysis are used to both explore patterns in the data and to assess the quality of the synthesis (Thomas et al. 2017a ).
In configurative synthesis the different kinds of text about individual studies and their results are meshed and linked to produce patterns in the data, explore different configurations of the data and to produce new synthetic accounts of the phenomena under investigation. The results from the individual studies are translated into and across each other, searching for areas of commonality and refutation. The specific techniques used are derived from the techniques used in primary research in this tradition. They include reading and re-reading, descriptive and analytical coding, the development of themes, constant comparison, negative case analysis and iteration with theory (Thomas et al. 2017b ).
4 Variation in Review Structures
All research requires time and resources and systematic reviews are no exception. There is always concern to use resources as efficiently as possible. For these reasons there is a continuing interest in how reviews can be carried out more quickly using fewer resources. A key issue is the basis for considering a review to be systematic. Any definitions are clearly open to interpretation. Any review can be argued to be insufficiently rigorous and explicit in method in any part of the review process. To assist reviewers in being rigorous, reporting standards and appraisal tools are being developed to assess what is required in different types of review (Lockwood and Geum Oh 2017 ) but these are also the subject of debate and disagreement.
In addition to the term ‘systematic review’ other terms are used to denote the outputs of systematic review processes. Some use the term ‘scoping review’ for a quick review that does not follow a fully systematic process. This term is also used by others (for example, Arksey and O’Malley 2005 ) to denote ‘systematic maps’ that describe the nature of a research field rather than synthesise findings. A ‘quick review’ type of scoping review may also be used as preliminary work to inform a fuller systematic review. Another term used is ‘rapid evidence assessment’. This term is usually used when systematic review needs to be undertaken quickly and in order to do this the methods of review are employed in a more minimal than usual way. For example, by more limited searching. Where such ‘shortcuts’ are taken there may be some loss of rigour, breadth and/or depth (Abrami et al. 2010 ; Thomas et al. 2013 ).
Another development has seen the emergence of the concept of ‘living reviews’, which do not have a fixed end point but are updated as new relevant primary studies are produced. Many review teams hope that their review will be updated over time, but what is different about living reviews is that it is built into the system from the start as an on-going developmental process. This means that the distribution of review effort is quite different to a standard systematic review, being a continuous lower-level effort spread over a longer time period, rather than the shorter bursts of intensive effort that characterise a review with periodic updates (Elliott et al. 2014 ).
4.1 Systematic Maps and Syntheses
One potentially useful aspect of reviewing the literature systematically is that it is possible to gain an understanding of the breadth, purpose and extent of research activity about a phenomenon. Reviewers can be more informed about how research on the phenomenon has been constructed and focused. This type of reviewing is known as ‘mapping’ (see for example, Peersman 1996 ; Gough et al. 2003 ). The aspects of the studies that are described in a map will depend on what is of most interest to those undertaking the review. This might include information such as topic focus, conceptual approach, method, aims, authors, location and context. The boundaries and purposes of a map are determined by decisions made regarding the breadth and depth of the review, which are informed by and reflected in the review question and selection criteria.
Maps can also be a useful stage in a systematic review where study findings are synthesised as well. Most synthesis reviews implicitly or explicitly include some sort of map in that they describe the nature of the relevant studies that they have identified. An explicit map is likely to be more detailed and can be used to inform the synthesis stage of a review. It can provide more information on the individual and grouped studies and thus also provide insights to help inform choices about the focus and strategy to be used in a subsequent synthesis.
4.2 Mixed Methods, Mixed Research Synthesis Reviews
Where studies included in a review consist of more than one type of study design, there may also be different types of data. These different types of studies and data can be analysed together in an integrated design or segregated and analysed separately (Sandelowski et al. 2012 ). In a segregated design, two or more separate sub-reviews are undertaken simultaneously to address different aspects of the same review question and are then compared with one another.
Such ‘mixed methods’ and ‘multiple component’ reviews are usually necessary when there are multiple layers of review question or when one study design alone would be insufficient to answer the question(s) adequately. The reviews are usually required, to have both breadth and depth. In doing so they can investigate a greater extent of the research problem than would be the case in a more focussed single method review. As they are major undertakings, containing what would normally be considered the work of multiple systematic reviews, they are demanding of time and resources and cannot be conducted quickly.
4.3 Reviews of Reviews
Systematic reviews of primary research are secondary levels of research analysis. A review of reviews (sometimes called ‘overviews’ or ‘umbrella’ reviews) is a tertiary level of analysis. It is a systematic map and/or synthesis of previous reviews. The ‘data’ for reviews of reviews are previous reviews rather than primary research studies (see for example Newman et al. ( 2018 ). Some review of reviews use previous reviews to combine both primary research data and synthesis data. It is also possible to have hybrid review models consisting of a review of reviews and then new systematic reviews of primary studies to fill in gaps in coverage where there is not an existing review (Caird et al. 2015 ). Reviews of reviews can be an efficient method for examining previous research. However, this approach is still comparatively novel and questions remain about the appropriate methodology. For example, care is required when assessing the way in which the source systematic reviews identified and selected data for inclusion, assessed study quality and to assess the overlap between the individual reviews (Aromataris et al. 2015 ).
5 Other Types of Research Based Review Structures
This chapter so far has presented a process or method that is shared by many different approaches within the family of systematic review approaches, notwithstanding differences in review question and types of study that are included as evidence. This is a helpful heuristic device for designing and reading systematic reviews. However, it is the case that there are some review approaches that also claim to use a research based review approach but that do not claim to be systematic reviews and or do not conform with the description of processes that we have given above at all or in part at least.
5.1 Realist Synthesis Reviews
Realist synthesis is a member of the theory-based school of evaluation (Pawson 2002 ). This means that it is underpinned by a ‘generative’ understanding of causation, which holds that, to infer a causal outcome/relationship between an intervention (e.g. a training programme) and an outcome (O) of interest (e.g. unemployment), one needs to understand the underlying mechanisms (M) that connect them and the context (C) in which the relationship occurs (e.g. the characteristics of both the subjects and the programme locality). The interest of this approach (and also of other theory driven reviews) is not simply which interventions work, but which mechanisms work in which context. Rather than identifying replications of the same intervention, the reviews adopt an investigative stance and identify different contexts within which the same underlying mechanism is operating.
Realist synthesis is concerned with hypothesising, testing and refining such context-mechanism-outcome (CMO) configurations. Based on the premise that programmes work in limited circumstances, the discovery of these conditions becomes the main task of realist synthesis. The overall intention is to first create an abstract model (based on the CMO configurations) of how and why programmes work and then to test this empirically against the research evidence. Thus, the unit of analysis in a realist synthesis is the programme mechanism, and this mechanism is the basis of the search. This means that a realist synthesis aims to identify different situations in which the same programme mechanism has been attempted. Integrative Reviewing, which is aligned to the Critical Realist tradition, follows a similar approach and methods (Jones-Devitt et al. 2017 ).
5.2 Critical Interpretive Synthesis (CIS)
Critical Interpretive Synthesis (CIS) (Dixon-Woods et al. 2006 ) takes a position that there is an explicit role for the ‘authorial’ (reviewer’s) voice in the review. The approach is derived from a distinctive tradition within qualitative enquiry and draws on some of the tenets of grounded theory in order to support explicitly the process of theory generation. In practice, this is operationalised in its inductive approach to searching and to developing the review question as part of the review process, its rejection of a ‘staged’ approach to reviewing and embracing the concept of theoretical sampling in order to select studies for inclusion. When assessing the quality of studies CIS prioritises relevance and theoretical contribution over research methods. In particular, a critical approach to reading the literature is fundamental in terms of contextualising findings within an analysis of the research traditions or theoretical assumptions of the studies included.
5.3 Meta-Narrative Reviews
Meta-narrative reviews, like critical interpretative synthesis, place centre-stage the importance of understanding the literature critically and understanding differences between research studies as possibly being due to differences between their underlying research traditions (Greenhalgh et al. 2005 ). This means that each piece of research is located (and, when appropriate, aggregated) within its own research tradition and the development of knowledge is traced (configured) through time and across paradigms. Rather than the individual study, the ‘unit of analysis’ is the unfolding ‘storyline’ of a research tradition over time’ (Greenhalgh et al. 2005 ).
6 Conclusions
This chapter has briefly described the methods, application and different perspectives in the family of systematic review approaches. We have emphasized the many ways in which systematic reviews can vary. This variation links to different research aims and review questions. But also to the different assumptions made by reviewers. These assumptions derive from different understandings of research paradigms and methods and from the personal, political perspectives they bring to their research practice. Although there are a variety of possible types of systematic reviews, a distinction in the extent that reviews follow an aggregative or configuring synthesis logic is useful for understanding variations in review approaches and methods. It can help clarify the ways in which reviews vary in the nature of their questions, concepts, procedures, inference and impact. Systematic review approaches continue to evolve alongside critical debate about the merits of various review approaches (systematic or otherwise). So there are many ways in which educational researchers can use and engage with systematic review methods to increase knowledge and understanding in the field of education.
https://ies.ed.gov/ncee/wwc/
https://educationendowmentfoundation.org.uk/evidence-summaries/teaching-learning-toolkit
https://eppi.ioe.ac.uk/cms/Default.aspx?tabid=2914
Abrami, P. C. Borokhovski, E. Bernard, R. M. Wade, CA. Tamim, R. Persson, T. Bethel, E. C. Hanz, K. & Surkes, M. A. (2010). Issues in conducting and disseminating brief reviews of evidence. Evidence & Policy , 6 (3), 371–389.
Google Scholar
Altman, D.G. (1991) Practical statistics for medical research . London: Chapman and Hall.
Arksey, H. & O’Malley, L. (2005). Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework, International Journal of Social Research Methodology , 8 (1), 19–32,
Article Google Scholar
Aromataris, E. Fernandez, R. Godfrey, C. Holly, C. Khalil, H. Tungpunkom, P. (2015). Summarizing systematic reviews: methodological development, conduct and reporting of an umbrella review approach. International Journal of Evidence-Based Healthcare , 13 .
Barnett-Page, E. & Thomas, J. (2009). Methods for the synthesis of qualitative research: A critical review, BMC Medical Research Methodology, 9 (59), https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-9-59 .
Brunton, G., Stansfield, C., Caird, J. & Thomas, J. (2017a). Finding relevant studies. In D. Gough, S. Oliver & J. Thomas (Eds.), An introduction to systematic reviews (2nd edition, pp. 93–132). London: Sage.
Brunton, J., Graziosi, S., & Thomas, J. (2017b). Tools and techniques for information management. In D. Gough, S. Oliver & J. Thomas (Eds.), An introduction to systematic reviews (2nd edition, pp. 154–180), London: Sage.
Carroll, C. & Booth, A. (2015). Quality assessment of qualitative evidence for systematic review and synthesis: Is it meaningful, and if so, how should it be performed? Research Synthesis Methods 6 (2), 149–154.
Caird, J. Sutcliffe, K. Kwan, I. Dickson, K. & Thomas, J. (2015). Mediating policy-relevant evidence at speed: are systematic reviews of systematic reviews a useful approach? Evidence & Policy, 11 (1), 81–97.
Chow, J. & Eckholm, E. (2018). Do published studies yield larger effect sizes than unpublished studies in education and special education? A meta-review. Educational Psychology Review 30 (3), 727–744.
Dickson, K., Vigurs, C. & Newman, M. (2013). Youth work a systematic map of the literature . Dublin: Dept of Government Affairs.
Dixon-Woods, M., Cavers, D., Agarwa, S., Annandale, E. Arthur, A., Harvey, J., Hsu, R., Katbamna, S., Olsen, R., Smith, L., Riley R., & Sutton, A. J. (2006). Conducting a critical interpretive synthesis of the literature on access to healthcare by vulnerable groups. BMC Medical Research Methodology 6:35 https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-6-35 .
Elliott, J. H., Turner, T., Clavisi, O., Thomas, J., Higgins, J. P. T., Mavergames, C. & Gruen, R. L. (2014). Living systematic reviews: an emerging opportunity to narrow the evidence-practice gap. PLoS Medicine, 11 (2): e1001603. http://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001603 .
Fitz-Gibbon, C.T. (1984) Meta-analysis: an explication. British Educational Research Journal , 10 (2), 135–144.
Gough, D. (2007). Weight of evidence: a framework for the appraisal of the quality and relevance of evidence. Research Papers in Education , 22 (2), 213–228.
Gough, D., Thomas, J. & Oliver, S. (2012). Clarifying differences between review designs and methods. Systematic Reviews, 1( 28).
Gough, D., Kiwan, D., Sutcliffe, K., Simpson, D. & Houghton, N. (2003). A systematic map and synthesis review of the effectiveness of personal development planning for improving student learning. In: Research Evidence in Education Library. London: EPPI-Centre, Social Science Research Unit, Institute of Education, University of London.
Gough, D., Oliver, S. & Thomas, J. (2017). Introducing systematic reviews. In D. Gough, S. Oliver & J. Thomas (Eds.), An introduction to systematic reviews (2nd edition, pp. 1–18). London: Sage.
Greenhalgh, T., Robert, G., Macfarlane, F., Bate, P., Kyriakidou, O. & Peacock, R. (2005). Storylines of research in diffusion of innovation: A meta-narrative approach to systematic review. Social Science & Medicine, 61 (2), 417–430.
Hargreaves, D. (1996). Teaching as a research based profession: possibilities and prospects . Teacher Training Agency Annual Lecture. Retrieved from https://eppi.ioe.ac.uk/cms/Default.aspx?tabid=2082 .
Hart, C. (2018). Doing a literature review: releasing the research imagination . London. SAGE.
Jones-Devitt, S. Austen, L. & Parkin H. J. (2017). Integrative reviewing for exploring complex phenomena. Social Research Update . Issue 66.
Kugley, S., Wade, A., Thomas, J., Mahood, Q., Klint Jørgensen, A. M., Hammerstrøm, K., & Sathe, N. (2015). Searching for studies: A guide to information retrieval for Campbell Systematic Reviews . Campbell Method Guides 2016:1 ( http://www.campbellcollaboration.org/images/Campbell_Methods_Guides_Information_Retrieval.pdf ).
Lipsey, M.W., & Wilson, D. B. (2000). Practical meta-analysis. Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Lockwood, C. & Geum Oh, E. (2017). Systematic reviews: guidelines, tools and checklists for authors. Nursing & Health Sciences, 19, 273–277.
Nelson, J. & Campbell, C. (2017). Evidence-informed practice in education: meanings and applications. Educational Research, 59 (2), 127–135.
Newman, M., Garrett, Z., Elbourne, D., Bradley, S., Nodenc, P., Taylor, J. & West, A. (2006). Does secondary school size make a difference? A systematic review. Educational Research Review, 1 (1), 41–60.
Newman, M. (2008). High quality randomized experimental research evidence: Necessary but not sufficient for effective education policy. Psychology of Education Review, 32 (2), 14–16.
Newman, M., Reeves, S. & Fletcher, S. (2018). A critical analysis of evidence about the impacts of faculty development in systematic reviews: a systematic rapid evidence assessment. Journal of Continuing Education in the Health Professions, 38 (2), 137–144.
Noblit, G. W. & Hare, R. D. (1988). Meta-ethnography: Synthesizing qualitative studies. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Book Google Scholar
Oancea, A. & Furlong, J. (2007). Expressions of excellence and the assessment of applied and practice‐based research. Research Papers in Education 22 .
O’Mara-Eves, A., Thomas, J., McNaught, J., Miwa, M., & Ananiadou, S. (2015). Using text mining for study identification in systematic reviews: a systematic review of current approaches. Systematic Reviews 4 (1): 5. https://doi.org/10.1186/2046-4053-4-5 .
Pawson, R. (2002). Evidence-based policy: the promise of “Realist Synthesis”. Evaluation, 8 (3), 340–358.
Peersman, G. (1996). A descriptive mapping of health promotion studies in young people, EPPI Research Report. London: EPPI-Centre, Social Science Research Unit, Institute of Education, University of London.
Petticrew, M. & Roberts, H. (2005). Systematic reviews in the social sciences: a practical guide . London: Wiley.
Sandelowski, M., Voils, C. I., Leeman, J. & Crandell, J. L. (2012). Mapping the mixed methods-mixed research synthesis terrain. Journal of Mixed Methods Research, 6 (4), 317–331.
Smyth, R. (2004). Exploring the usefulness of a conceptual framework as a research tool: A researcher’s reflections. Issues in Educational Research, 14 .
Thomas, J., Harden, A. & Newman, M. (2012). Synthesis: combining results systematically and appropriately. In D. Gough, S. Oliver & J. Thomas (Eds.), An introduction to systematic reviews (pp. 66–82). London: Sage.
Thomas, J., Newman, M. & Oliver, S. (2013). Rapid evidence assessments of research to inform social policy: taking stock and moving forward. Evidence and Policy, 9 (1), 5–27.
Thomas, J., O’Mara-Eves, A., Kneale, D. & Shemilt, I. (2017a). Synthesis methods for combining and configuring quantitative data. In D. Gough, S. Oliver & J. Thomas (Eds.), An Introduction to Systematic Reviews (2nd edition, pp. 211–250). London: Sage.
Thomas, J., O’Mara-Eves, A., Harden, A. & Newman, M. (2017b). Synthesis methods for combining and configuring textual or mixed methods data. In D. Gough, S. Oliver & J. Thomas (Eds.), An introduction to systematic reviews (2nd edition, pp. 181–211), London: Sage.
Tsafnat, G., Dunn, A. G., Glasziou, P. & Coiera, E. (2013). The automation of systematic reviews. British Medical Journal, 345 (7891), doi.org/10.1136/bmj.f139 .
Torgerson, C. (2003). Systematic reviews . London. Continuum.
Waddington, H., Aloe, A. M., Becker, B. J., Djimeu, E. W., Hombrados, J. G., Tugwell, P., Wells, G. & Reeves, B. (2017). Quasi-experimental study designs series—paper 6: risk of bias assessment. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 89 , 43–52.
Download references

Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Institute of Education, University College London, England, UK
Mark Newman & David Gough
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Mark Newman .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Oldenburg, Germany
Olaf Zawacki-Richter
Essen, Germany
Michael Kerres
Svenja Bedenlier
Melissa Bond
Katja Buntins
Rights and permissions
Open Access This chapter is licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license and indicate if changes were made.
The images or other third party material in this chapter are included in the chapter’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the chapter’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Newman, M., Gough, D. (2020). Systematic Reviews in Educational Research: Methodology, Perspectives and Application. In: Zawacki-Richter, O., Kerres, M., Bedenlier, S., Bond, M., Buntins, K. (eds) Systematic Reviews in Educational Research. Springer VS, Wiesbaden. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-27602-7_1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-27602-7_1
Published : 22 November 2019
Publisher Name : Springer VS, Wiesbaden
Print ISBN : 978-3-658-27601-0
Online ISBN : 978-3-658-27602-7
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Library databases
- Library website
Education Literature Review: Education Literature Review
What does this guide cover.
Writing the literature review is a long, complex process that requires you to use many different tools, resources, and skills.
This page provides links to the guides, tutorials, and webinars that can help you with all aspects of completing your literature review.
The Basic Process
These resources provide overviews of the entire literature review process. Start here if you are new to the literature review process.
- Literature Reviews Overview : Writing Center
- How to do a Literature Review : Library
- Video: Common Errors Made When Conducting a Lit Review (YouTube)
The Role of the Literature Review
Your literature review gives your readers an understanding of the evolution of scholarly research on your topic.
In your literature review you will:
- survey the scholarly landscape
- provide a synthesis of the issues, trends, and concepts
- possibly provide some historical background
Review the literature in two ways:
- Section 1: reviews the literature for the Problem
- Section 3: reviews the literature for the Project
The literature review is NOT an annotated bibliography. Nor should it simply summarize the articles you've read. Literature reviews are organized thematically and demonstrate synthesis of the literature.
For more information, view the Library's short video on searching by themes:
Short Video: Research for the Literature Review
(4 min 10 sec) Recorded August 2019 Transcript
Search for Literature
The iterative process of research:
- Find an article.
- Read the article and build new searches using keywords and names from the article.
- Mine the bibliography for other works.
- Use “cited by” searches to find more recent works that reference the article.
- Repeat steps 2-4 with the new articles you find.
These are the main skills and resources you will need in order to effectively search for literature on your topic:
- Subject Research: Education by Jon Allinder Last Updated Aug 7, 2023 3697 views this year
- Keyword Searching: Finding Articles on Your Topic by Lynn VanLeer Last Updated Sep 12, 2023 18208 views this year
- Google Scholar by Jon Allinder Last Updated Aug 16, 2023 12206 views this year
- Quick Answer: How do I find books and articles that cite an article I already have?
- Quick Answer: How do I find a measurement, test, survey or instrument?
Video: Education Databases and Doctoral Research Resources
(6 min 04 sec) Recorded April 2019 Transcript
Staying Organized
The literature review requires organizing a variety of information. The following resources will help you develop the organizational systems you'll need to be successful.
- Organize your research
- Citation Management Software
You can make your search log as simple or complex as you would like. It can be a table in a word document or an excel spread sheet. Here are two examples. The word document is a basic table where you can keep track of databases, search terms, limiters, results and comments. The Excel sheet is more complex and has additional sheets for notes, Google Scholar log; Journal Log, and Questions to ask the Librarian.
- Search Log Example Sample search log in Excel
- Search Log Example Sample search log set up as a table in a word document.
- Literature Review Matrix with color coding Sample template for organizing and synthesizing your research
Writing the Literature Review
The following resources created by the Writing Center and the Academic Skills Center support the writing process for the dissertation/project study.
- Critical Reading
- What is Synthesis
- Walden Templates
- Quick Answer: How do I find Walden EdD (Doctor of Education) studies?
- Quick Answer: How do I find Walden PhD dissertations?
Beyond the Literature Review
The literature review isn't the only portion of a dissertation/project study that requires searching. The following resources can help you identify and utilize a theory, methodology, measurement instruments, or statistics.
- Education Theory by Jon Allinder Last Updated May 17, 2024 413 views this year
- Tests & Measures in Education by Kimberly Burton Last Updated Nov 18, 2021 42 views this year
- Education Statistics by Jon Allinder Last Updated Feb 22, 2022 58 views this year
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
Books and Articles about the Lit Review
The following articles and books outline the purpose of the literature review and offer advice for successfully completing one.
- Chen, D. T. V., Wang, Y. M., & Lee, W. C. (2016). Challenges confronting beginning researchers in conducting literature reviews. Studies in Continuing Education, 38(1), 47-60. https://doi.org/10.1080/0158037X.2015.1030335 Proposes a framework to conceptualize four types of challenges students face: linguistic, methodological, conceptual, and ontological.
- Randolph, J.J. (2009). A guide to writing the dissertation literature review. Practical Assessment, Research & Evaluation 14(13), 1-13. Provides advice for writing a quantitative or qualitative literature review, by a Walden faculty member.
- Torraco, R. J. (2016). Writing integrative literature reviews: Using the past and present to explore the future. Human Resource Development Review, 15(4), 404–428. https://doi.org/10.1177/1534484316671606 This article presents the integrative review of literature as a distinctive form of research that uses existing literature to create new knowledge.
- Wee, B. V., & Banister, D. (2016). How to write a literature review paper?. Transport Reviews, 36(2), 278-288. http://doi.org/10.1080/01441647.2015.1065456 Discusses how to write a literature review with a focus on adding value rather and suggests structural and contextual aspects found in outstanding literature reviews.
- Winchester, C. L., & Salji, M. (2016). Writing a literature review. Journal of Clinical Urology, 9(5), 308-312. https://doi.org/10.1177/2051415816650133 Reviews the use of different document types to add structure and enrich your literature review and the skill sets needed in writing the literature review.
- Xiao, Y., & Watson, M. (2017). Guidance on conducting a systematic literature review. Journal of Planning Education and Research. https://doi.org/10.1177/0739456X17723971 Examines different types of literature reviews and the steps necessary to produce a systematic review in educational research.
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.

Literature Reviews for Education and Nursing Graduate Students
(15 reviews)
Linda Frederiksen, Washington State University Vancouver
Sue F. Phelps, Washington State University Vancouver
Copyright Year: 2017
Publisher: Rebus Community
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Rebecca Appleton, Professor of Nursing, Marshall University on 5/7/24
It is very through in covering the steps of a well written literature review read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
It is very through in covering the steps of a well written literature review
Content Accuracy rating: 5
I have not read the entire book, but what I did read was very good.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
It is up to date, but doing a Literature Review is covered in a step-wise manner, includes writing the LR>
Clarity rating: 5
Very clear step-by-step approach
Consistency rating: 5
It is very consistent!
Modularity rating: 5
Chapters are orderly and succinct
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
Strait forward order.
Interface rating: 5
I did not notice Interface issues.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
No grammatical errors were noticed.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
I did not notice any problems with cultural Insensitivity
I plan to use this in a Nursing Research class for Graduate Students, and I am trying a new approach to finding the best Research Evidence on a Nursing Topic. Can't wait to see if this help my graduate students understand research literature better.
Reviewed by Barbara Schneider, Professor, University of Texas at Arlington on 4/29/24
This textbook covers the range of topics important for a literature review, including formulating a research question, finding scholarly articles, evaluating sources, and synthesizing source content. The videos are great supplements to the text. read more
This textbook covers the range of topics important for a literature review, including formulating a research question, finding scholarly articles, evaluating sources, and synthesizing source content. The videos are great supplements to the text.
Overall, the content is accurate. Consider labeling Nursing as a health profession/discipline.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 4
Much of the content remains relevant. Updated examples would be helpful to today's graduate students.
The textbook is clearly written.
Consistency rating: 4
In general, the text is consistent. There could be more consistency in the formatting of the references.
The modularity is an asset.
There is a logical flow to the topics.
The links to outside materials are helpful.
No grammatical errors were evident.
The examples seemed inclusive.
Those who are new to writing a literature review would find this book useful.
Reviewed by Yolanda Griffiths, Professor of Occupational Therapy, Drake University on 12/15/21
The authors were thorough and very organized in stepping readers through the process of conducting and writing a literature review. Each area is appropriately indexed and examples are provided in a variety of ways. The synthesis section is... read more
The authors were thorough and very organized in stepping readers through the process of conducting and writing a literature review. Each area is appropriately indexed and examples are provided in a variety of ways. The synthesis section is especially useful as students often do not understand what this means. Perhaps some content on plagiarism would benefit this section as well. The flow of the material easily guides users logically through each topic.
The content is accurate and unbiased. The content is presented in an easy to understand way with videos, and examples.
The relevance of the content is classic and the text should be pertinent for many years. The links included in the text are very useful and should be easy for authors to check periodically. Using a digital media is more relevant to today's students than print textbooks. Each section addresses a reasonable chunk of information.
The book is user friendly, written in an easy to understand manner, and graphics or links add to the understanding of the content. Definitions are clearly written. Such as clarifying the types of literature reviews will be useful for students. Providing a test yourself section at the end of sections allows the reader to check if any content was confusing or not clear.
The text is consistently laid out in a logical manner which helps to unpack content which may be new or unfamiliar to the reader/student.
The amount of content allocated to each chapter is appropriate and will be easy to assign readings. The chapter headings are clear and the embedded videos, charts and test questions enlighten each subunit. The hyperlinking in the table of contents helps to navigate the chapters well.
The organization of the content is logical and easy to understand the process of completing a literature review. The book is laid out much like a road map where students can see the big picture as well as the supporting parts to the process. The references by chapter are very useful.
The graphics were clear, and the non-serif font aids in eye fatigue. One recommendation is to lower the brightness of the bold blue text in the table of contents to reduce eye fatigue. There was no problem to play the videos and the audio was clear. All links worked well.
There were no grammatical errors. There were a few typos such as 1.3.1.8 needs a space between "A specific", 2.3 in the phrase "Articles by the type of periodical in which an article it is published" perhaps remove the word "it", in the table on page 41. under Nursing , the word clinical is spelled "Cclinical", remove the capital C.
No evidence of cultural bias or insensitivity.
I am very excited to use this textbook in my doctoral level occupational therapy class. The inclusion of concise explanations of PICO and SPICE will be very useful. This will be a wonderful resource for graduate students and being mindful of costs for textbooks is compassionate.
Reviewed by Susan Bassett, Instructor, Nursing Graduate Program, Eastern New Mexico University on 11/9/21
Each chapter presented a different aspect of doing a literature review. This was organized and orderly. The index/table of contents was very detailed which allowed the reader to easily use this book as a reference while conducting a literature... read more
Each chapter presented a different aspect of doing a literature review. This was organized and orderly. The index/table of contents was very detailed which allowed the reader to easily use this book as a reference while conducting a literature review.
The content appeared to be entirely accurate. It did a good job of combining information for both education and nursing students. The authors addressed pertinent points of research study development as well as the specific methodology of approaching a research-focused literature review.
The text was up-to-date in methodology, which should not change frequently. The many links to websites were very helpful and yet were basic enough that they should be relevant for years. If they do need updating, the are clearly presented and should be easily updated. The breakdown to very small "chunks" of information per section will help in easily updating specific parts of information.
The book presented a rather complex topic in an extremely straight-forward, easy to read, clear manner. Each small "chunk" of information was identified per section numbering which correlated with movement through the content. The writing was professional and yet not overwhelmed with discipline-specific terminology. Where potentially new terminology was presented, it was immediately followed with definitions and examples.
The book was well-organized and moved along the structure set out early in the book. Content was gradually unfolded, as divided per chapter. There was a bit of repetition (probably about three examples) where the authors attempted to tie information together. Although this stood out to a reader, it seemed more useful in organizing than detrimental in repetition.
The book was subdivided into chapters and then into many small modules of discrete information. It could easily be assigned in part. It could also readily be used as a reference for students to go back and easily find processes or pieces of information they might need later.
I found the continual clear and succinct organization of information to be a defining highlight of this book. When presenting early steps of the research process and then linking these steps with how to conduct a literature review and subsequenty organize and write a literature review, this book is presenting numerous procews steps that must work in tandem. This book did that in a clear and easily readable fashion.
The one feature that did distract me was within the bullet points of 1.3.1. "Types of Reviews". There was a mix of complete and incomplete sentences that worked to convey information succinctly, but distracted me as a reader.
Grammatical Errors rating: 4
I did find several spelling and grammaticl errors (1.3.1.8, , 1.3.1.9, 2.1.1, 2.3, 2.3.1.1, , 2.3.1.4, 2.3 Table A., p. 41, p. 53, p. 54). Although small errors (a few letters or spacing) they should be corrected.
I did not find any mistakes in cultural appropriateness The content did repeatedly talk about bias reduction in the process of writing a literature review
I thought this book was very well-written and contained great information for my students. The links provided were very appropriate and helpful. The Table "Guide to searching for literature at various stages of the scholarly communication process” was particularly helpful. I will immediately begin using portions of the content in this book to support my research class. Additionally, I will recommend the entire book as a reference for the dedicated student (or one intending to go forward to a doctoral level of education in nursing). Thank you for collating all this information and helpful links into one clear, easily readable and understandable document.
Reviewed by Leah Nillas, Associate Professor, Illinois Wesleyan University on 9/6/21
This book addresses the basic steps in the process of writing a literature review research. Chapter 2 (What is a Literature Review?) needs to be retitled. I think Chapter 1 (Introduction) clearly defines and characterizes literature review as a... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
This book addresses the basic steps in the process of writing a literature review research. Chapter 2 (What is a Literature Review?) needs to be retitled. I think Chapter 1 (Introduction) clearly defines and characterizes literature review as a research category. Chapter 2 focuses more on the creation of information, information cycle, and selecting appropriate sources. Chapter 7 (Synthesizing Sources) and Chapter 8 (Writing the Lit Review) can still be improved to incorporate specific strategies in synthesizing research literature and examples of writing styles through analysis of a variety of published examples. Writing a synthesis is a challenging skill for most novice researchers.
Information shared is accurate. I did not notice any content error.
Main content is up-to-date. A few citations maybe dated but they are necessary in illustrating different examples of literature reviews. It will be easy to include additional relevant examples of research work that are published recently.
I like how this text is written. Tone is reader friendly and narrative is accessible to novice researchers.
Clearly consistent throughout the chapters.
Clear and purposeful "chunking" of information per chapter.
Readers can easily follow the organization of topics and content.
No obvious interface issues. Appropriate use of multimedia tools.
No grammatical errors.
Text is culturally sensitive. Additional readings, references, or examples can easily be added to incorporate research conducted by diverse authors or literature reviews which focus on diversity and inclusion issues in education and nursing.
This is a good introductory literature review text even for undergraduate education students. Clear discussion of the nature of the research and the writing process. The use of videos and images is helpful in providing multimodal approach in explaining topics or processes. Writing style and tone make the text accessible to novice researchers.
Reviewed by Rebecca Scheckler, Assistant Professor, Radford University on 7/6/20
Two missing topics were inter-library loan and how to avoid plagiarism in writing up the literature review. This second is such an important topic that it deserves its own chapter. read more
Two missing topics were inter-library loan and how to avoid plagiarism in writing up the literature review. This second is such an important topic that it deserves its own chapter.
It is accurate. I found no inaccuracies.
This book is very relevant. Every advanced undergraduate or graduate students requires such a book
I found the book clear. The videos interspersed within the book added much to the clarity. There are lots of good diagrams that add to the clarity. They are not all original but their sources are all cited. The section on boolean searches, usage of asterisks and quotes in searches is very helpful and appropriate although often left out of discussion of searches.
The book is consistent in terminology and framework.
The chapters were cohesive.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 4
I like the links to within the text to the references and other matter. What is needed are back links to the text from the references. I also would have liked links from the exercises to the answers of the exercises.
Interface rating: 4
See navigation links mentioned above. The grey literature link is broken.
I saw no grammatical problems. There are many bulleted lists rather than text which is appropriate to this topic.
There could be more attention to cultural context in the frequent examples.
I wondered why nursing and education were combined. They are similar in nature but not identical. separation them out into two books might be appropriate.
Reviewed by Lisa Shooman, Associate Professor, Worcester State University on 6/29/20
Overall, this book provides a very comprehensive and thorough roadmap for creating a literature review. The videos assist the reader in crystallizing the information presented in the text. There is an effective index and glossary that provide... read more
Overall, this book provides a very comprehensive and thorough roadmap for creating a literature review. The videos assist the reader in crystallizing the information presented in the text. There is an effective index and glossary that provide helpful navigation to the reader.
The content is detailed, clearly explained, error-free, and unbiased. My students would greatly benefit from the lucid information presented in this text to guide them with developing a literature review. I would be eager to adopt this book for my students.
The content is timely and will not be quickly out-of-date. The quiz questions at the end of each chapter are relevant and will aid students with the consolidation of the material. The online format allows for updating, and the version history at the end of the text clearly indicated that the book was updated recently.
The text is clear and not ridden with any excess jargon /technical terminology. Pictures, graphics, and videos further elucidate the text. There are helpful questions that stimulate thought and lists that help to organize information.
The internal consistency in the text is excellent. However, Chapter 1.1 and Chapter 2 have the same title and it would benefit the reader to have different titles that would highlight the differences between these two sections. Chapter 1.1 is an overview and Chapter 2 dives into more depth.
The text is efficiently divided into smaller reading sections that are demarcated by numbers. The subsections in each chapter can be assigned at different points in the course. The text is organized logically and systematically that assists the reader with comprehension and provides a roadmap for creating an effective literature review.
The entire text is presented coherently and concisely. The organization of the text takes the reader through the process of creating an effective literature review. It can be used by multiple health professions, although the length of the text is relatively short it includes a considerable depth of the material. Other disciplines that would benefit from using this test in their courses may include occupational therapy, physical therapy, and speech and language pathology students.
The interface of the text is simple and easy to follow. The cover of the text would benefit from photos, color, and graphic design to appeal to the modern digital reader.
No grammatical or spelling errors are noted.
No cultural biases existed in the text in any way. There are no individuals highlighted in the book, and due to the technical nature of the subject matter, the text is inclusive to a variety of races, ethnicities, and backgrounds. No offensive statements are included in this book.
The authors should consider including other health professionals in the title and provide examples that can relate to other health professionals throughout the text. Other health professionals that can benefit from reading this text include occupational therapy, physical therapy, and speech and language pathology students. Literature reviews are relevant for many health professionals in their master's and doctorate programs and the text could serve a wider audience.
Reviewed by Ellen Rearick, Assistant Professor, Framingham State University on 6/1/20
This text covers all areas and the process of the integrative review appropriately. It is an engaging text for graduate students new to these assignments. read more
This text covers all areas and the process of the integrative review appropriately. It is an engaging text for graduate students new to these assignments.
This text is well done, very accurate
This text is relevant. The updates needed regarding APA format should be relatively easy to implement.
This text is clear and provides users with definitions and examples of the variety of reviews.
Very well written using consistent terminology throughout.
The text's reading sections are easily accessible and users will find them organized. Each chapter and its sections are presented in the sequence of the process of an integrative review.
Very clear and logical order.
The navigation of this text was problem-free.
No grammatical errors noted.
No issues with cultural insensitivity noted.
This was a well-organized text using videos to reinforce content that would benefit any education or nursing graduate student new to the integrative review process.
Reviewed by Ruth Stoltzfus, Professor of Nursing; Dir., Grad Programs in Nursing, Goshen College on 6/1/19
This text provides everything a graduate student needs to write a literature review in a concise manner. If you look at the digital pdf, there are many strategies to help the reader learn the process - videos, diagrams, and also text. read more
This text provides everything a graduate student needs to write a literature review in a concise manner. If you look at the digital pdf, there are many strategies to help the reader learn the process - videos, diagrams, and also text.
I found no evidence of bias and no errors.
This book has long-term relevance. The content will not quickly out-date.
I really liked the way the textbook is structured. The author is concise which makes the textbook easy to read.
I found no inconsistencies in terminology or other aspects related to the content.
I will adopt this text for a research course I use and will likely assign only specific chapters. I plan to recommend the textbook to another faculty who teaches a comprehensive research course with the idea of assigning only specific sections to read..
The textbook begins with an introduction to the subject matter. Subsequent chapters develop specific aspects related to lit reviews. The textbook provides a nice "how to" for each element of a lit review. Chapters are also organized in a smooth, easy to follow format.
I only looked at the digital pdf and print pdf versions. The print pdf indicates that there are videos to watch, but of course since it is a print pdf, there is no linkage. I think this would be obvious to a savvy reader - that a print pdf will be limited in what the reader can access.
I found no grammatical errors in my quick read.
I found no evidence of cultural bias or insensitivity.
This is the first open textbook that I have encountered. I was expecting it to be flat and boring! However, it was neither of those. There were color diagrams, color photos, and even videos embedded in the textbook.
I have adopted this book for the Research Lit Review course that I am teaching soon. I am impressed!
Reviewed by Melissa Wells, Assistant Professor, University of Mary Washington on 5/1/19
This book helps students in education and nursing complete a literature review, which may be the first time these students are tackling such a task. The chapters break down the process into defining the special genre of a literature review;... read more
This book helps students in education and nursing complete a literature review, which may be the first time these students are tackling such a task. The chapters break down the process into defining the special genre of a literature review; providing tips to get started; suggesting where students can find literature to review; explaining how to evaluate sources; detailing the process of documenting sources; giving advice for synthesizing sources; and finally, putting all of these pieces together into a final literature review. Most significantly, the text provides specific examples of ideas presented in the context of both nursing and education, which makes the content directly relatable to the student's course of study. The conclusion recaps the main points of each chapter in bullet form. The text is lacking both an index and a glossary, which would be additions that could strengthen the text.
Content Accuracy rating: 4
The text explains 11 different types of literature reviews that students may encounter or be asked to create. Also, the text is framed to work with multiple methodologies; for example, steps for writing a research question or a hypothesis to frame the literature review are provided. One inconsistency I noted was in diagram 6.2: the APA citation is incorrectly capitalized for the journal title (which should use sentence, not title, capitalization).
The text also includes external links to sources, such as a videos, which provide students with multiple modalities in which to digest the information. An example of a literature review for both education and nursing is provided at the end of the book; instead of embedding these in the text, the hyperlinks refer the reader to the external site. This will be easy to change to a new example in the future, but checks will need to be done to ensure that all such external sources remain actively accessible.
Each chapter opens with learning objectives to help frame the content with which the reader is about to engage. Throughout the text, the language is approachable and reader-friendly. For example, when the text explains more factual components (i.e., what makes a literature review or what the basics of an effective literature review include), this information is presented in bullet points with hyperlinks to the original sources.
Each chapter follows a similar construction, which makes it accessible to the reader. For example, chapters end with a "Practice" and "Check Yourself" section to apply new learning and self-check responses (an answer key is provided in an appendix). Examples in these exercises are either related to nursing or education, continuing with the stated theme of the text.
When I used this text with my own students, I assigned chapters in isolation, since they had already taken a research methods course and were applying that knowledge to create a research proposal in a specific area of study in my course.
The book is organized in such a way that logically walks the reader through the literature review writing process. Clear headings (which are hyperlinked in the table of contents) also allow the reader to jump to specific parts with which they need additional support.
The interface of this document offered a lot of flexibility. Options allowed users to access the text online, or as a download in multiple file types (EPUB, Digital PDF, MOBI, XHTML, Pressbooks XML, Wordpress XML, and Open Document). These formats provide the reader with an opportunity to pick the interface that works best for them.
I did not see any grammatical errors in the text.
Cultural Relevance rating: 4
No culturally insensitive/offensive content was noted. A variety of examples of research topics were included from both nursing and education. Of the images/video thumbnails embedded in the text that involved people, all depicted White people except for 2 images; therefore, more intentional selection of culturally diverse visuals would be helpful in future versions of this text.
I feel this text was helpful to my students as they wrote their own literature reviews. The only weakness in their papers that I noted was their organization of their literature review based on themes/topic, which was addressed in Chapters 7- 8. I now know to focus more on this part of literature review writing with future students. This text is approachable and field-specific, and I will be using it again!
Reviewed by Bernita (Bernie) Missal, Professor, Bethel University on 12/14/18
This book includes all areas that a graduate student needs to begin a literature review. However metasynthesis could have also been included in types of literature review. read more
This book includes all areas that a graduate student needs to begin a literature review. However metasynthesis could have also been included in types of literature review.
This book is accurate although missing qualitative research.
Although content is up to date, some of the article examples need to be updated. (Example: articles published in 1981 and 1992 need to be updated to more recent articles.)
The book is clear and easy to follow. Bullet points were used throughout the book with short paragraphs which helps the student.
Each chapter follows the same format with narrative followed by practice and test questions.
Clear subheadings are used throughout the book.
This book is presented in a logical way and easy for the student to follow.
Images are clear and appropriate for the content.
No specific grammar issues were seen.
It would be helpful for students to include additional examples of cultural studies throughout the book
This book is an excellent resource for graduate students. It has helpful information for the preparation and process for a literature review. Examples of written literature reviews in chapter 8 or in an appendix would be helpful for students.
Reviewed by Nancyruth Leibold, Associate Professor, Southwest Minnesota State University on 6/19/18
The text is overall comprehensive, yet it breaks the information up into manageable parts. See the table of contents for an overview of the topics. The text is very quantitative driven in that the focus is on reviewing quantitative studies. The... read more
The text is overall comprehensive, yet it breaks the information up into manageable parts. See the table of contents for an overview of the topics. The text is very quantitative driven in that the focus is on reviewing quantitative studies. The book included information about PICO statements, but did not include PICO(T) or the time variable, which is not always used in every case. Population was included in the PICO explanation, but a bit more information on the population or aggregate narrowing could improve the PICO section. These items do not hinder use of the book, but these items would need further inclusion by the faculty member using the text as specific to the discipline.
The content in the book is very accurate.
The content in the book is current and should not be obsolete within a short period of time. Any updates would be easy to add.
The text is clear and easy to understand.
The internal organization and terminology of the book is consistent and logical
The text is set up in small reading sessions. The videos and learning activities are well done and break up some of the content, so there is a variety of presentation. The tutorials, figures, practice and self-test areas are also fantastic in that they are quality and sprinkled throughout the text.
The topics in the book are presented in clear and organized fashion. I particularly like the upbeat and personal writing tone of the book. This tone makes it seem like the authors are speaking to me.
The text is free of any significant interface issues. The book is available in many formats. I used the book online and I did have one navigational problem and that is when clicking on a video, it does not open in a new tab and so the book is lost and have to start over going in the start to the book. One easy solution to this is to right click your mouse and then select open in new tab to watch videos. That way, your place in the book is not lost.
No grammar problems present.
The book is not culturally insensitive or offensive in any way.
Overall, this is a well written textbook and I recommend it!
Reviewed by Marjorie Webb, Professor, Metropolitan State University on 6/19/18
From the Introduction to the Conclusion, the text covers the step-by-step process of conducting a literature review. The text includes topics such as, “Where to find the Literature” and “Synthesizing Sources” that will be useful to graduate... read more
From the Introduction to the Conclusion, the text covers the step-by-step process of conducting a literature review. The text includes topics such as, “Where to find the Literature” and “Synthesizing Sources” that will be useful to graduate nursing students.
The content in the text, including texts, links, and diagrams, is accurate and unbiased. Again, it will aid the graduate nursing student in the long process of conducting a literature review.
The text is current and this type of material does not become dated quickly. The authors did use internet links in the text which will need to be monitored periodically to ensure they are still available. Updates to the text will be relatively easy and straightforward. If media styles change, there may be some challenges to updating.
The text is clear and easy to read. Technical terminology is defined and/or explained.
The text is internally consistent.
The text is organized in sections which facilitates assigning readings based on the subject matter for the class time. It would be pretty easy to divide up this text into easily readable units based on headings and subheadings.
This text is structured well. The topics flow in an organized manner and really help the student see the process of a literature review. The authors discuss the both theory and purpose of the review and the day-to-day logistics of actually performing the review. The day-today organization is not always included in other texts.
The interface is well-done with no distractions.
There was no indication of cultural bias.
I think this text is appropriate for graduate nursing students. Some students struggle with the difference between writing about a topic (generally undergraduate writing) and synthesizing literature on a given topic (generally graduate writing). Chapters seven and eight focus on preparing the graduate student to make the jump to graduate-level writing and should really benefit new graduate students.
Reviewed by Susanna Thornhill, Associate Professor , George Fox University on 3/27/18
This book is fairly comprehensive and offers step-by-step instructions for conceptualizing/researching a literature review. The Table of Contents is well-organized to reflect the book's progression, from establishing the basics of why to write a... read more
This book is fairly comprehensive and offers step-by-step instructions for conceptualizing/researching a literature review. The Table of Contents is well-organized to reflect the book's progression, from establishing the basics of why to write a literature review and the various types of literature reviews, to getting started with formulating a research idea/question, finding and evaluating sources, synthesizing sources, and guidelines on writing the literature review, itself. I found this text to be a straightforward guide for my graduate students in education, and while I worried at first that the merging of education and nursing topics would prove distracting to my education students, I don't believe this was the case.
One thing that was not comprehensive in this book was discussion of qualitative research and methodologies as a valid means of conceptualizing research aims. I hoped for a more balanced discussion between methodological branches as it applied to literature reviews; this book overly favored quantitative methodologies and studies in terms of its direction to readers about how to conceptualize/choose a topic and design a research question in relation to it. Variables that cannot be measured are not inherently un-researchable, which is the conclusion put forth in this textbook. This might serve nursing students better than education students in terms of their discipline's requirements, but it still represents an element that could be improved.
Finally, while the background on what a literature review is, how to conceptualize research, and how to search for and synthesize research was all valuable, the chapter on actually writing the literature review was a bit thin, simply offering tips for introduction, body, and conclusion and some questions for self-evaluation. Some of the most difficult work for students writing a literature review is achieving proper focus, organization, hierarchy of themes, balance in treatment of related topics, etc. None of these issues were discussed in the chapter pertaining to the writing of a literature review.
I did not have any concerns about the book's accuracy. Content was accurate, albeit biased to quantitative and positivist views of research. I would have liked to see it include additional prompts to support students in conceptualizing and valuing qualitative research; this is an area where I had to supplement course readings with additional texts.
The only significant error I could discern in the text was a lack of an Answer Key corresponding to the questions posed at the end of each chapter.
Content is up-to-date and seems like it will hold meaning well over the next few years. The only things I anticipate might go out-of-date is technological information on things like citation managers, search guidelines, and database information. This is easily updatable with future versions of the text. In my view, ERIC is not the best database for educational research and I have confirmed this with educational librarians who support my students, yet it is the only one identified in this text as the best subject-specific source of educational research; this could be revised for additional relevance.
I noticed no issues with the book's clarity. The authors write in a clear and straightforward style, making the text easy to read. Overall, they did well writing for students across two disciplines by avoiding nursing or education-specific terms that would have been problematic to readers in the other discipline.
The book is internally consistent and did not have issues with terminology or framework.
No issues with the book's modularity. Chapter headings and sub-headings were appropriately paced and spaced. I assigned this textbook to my graduate students as a whole text that I wanted them to read at the beginning of a course, but it has been easy to refer them back to particular topics as the course has continued.
In future iterations of the book, I suggest hyperlinking the Answer Key to the exercises at the end of each chapter and/or listing the Answer Key in the Table of Contents for easy referral.
I found the book's organization to be straightforward and sensible. The Table of Contents offers a helpful snapshot of the scope of the book and the authors write in a direct and clear style, which contributes to an appropriate flow for the text.
I did not note any navigation problems with any links. All charts/images loaded well in my iBook app. The authors did a nice job of pulling relevant content and links in to support their ideas; it provided an easy way to seek more information if I wanted it, without feeling like the text was loaded down with unnecessary information.
I only found a few small typos in the text, with no grammar issues. The book is obviously written by two very detail-oriented librarians. I appreciated the clarity of the text and lack of errors.
The text was not culturally insensitive; a variety of topics across nursing and education were discussed as examples, which yielded a fairly balanced text regarding cultural considerations.
Reviewed by Alicia Rossiter, Assistant Professor, University of South Florida on 3/27/18
I believe the book gives a comprehensive overview on how to complete a literature view at the graduate level. It begins with an overview of the purpose of a literature review and moves through the steps to completing the review process. read more
I believe the book gives a comprehensive overview on how to complete a literature view at the graduate level. It begins with an overview of the purpose of a literature review and moves through the steps to completing the review process.
I believe the book was accurate and unbiased. It was easy to read but comprehensive.
Content within the text is relevant and supports the literature view process. It did discuss the various databases for searches which may need updating to include new sites, search engines but otherwise relevant and useful information.
The text is easy to read, provides appropriate examples, includes a section on putting the process into practice as well as a "test yourself" section to ensure the content is understood.
The text is consistent throughout in regards to terminology, framework, and set up.
The text is easy to read and content is leveled for the reader but not over simplified. Content is chunked into sections making it easy for the reader to digest the content. The chapters are well laid out and flow from chapter to chapter. Each chapter contains learning objectives, content sections, practice section, and test yourself section. Well organized and great visuals.
Topics are presented in a logical, clear fashion that flow from chapter to chapter and build as the reader moves through the process.
The text is free of interface issues. I could not get the videos to play but other visuals were appropriate and useful to support content.
The text contains no grammatical errors.
The text is not culturally offensive. There was no evidence of bias or cultural insensitivity.
I think this would be a great resource for graduate student learning to navigate the literature review process. It is easy to read, straightforward, and guides the individual through the process from start to finish. I will recommend this text to my graduate students in evidence-based practice and research courses as a recommended reference.
Table of Contents
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: What is a Literature Review?
- Chapter 3: How to Get Started
- Chapter 4: Where to Find the Literature
- Chapter 5: Evaluating Sources
- Chapter 6: Documenting Sources
- Chapter 7: Synthesizing Sources
- Chapter 8: Writing the Literature Review
Ancillary Material
About the book.
Literature Reviews for Education and Nursing Graduate Students is an open textbook designed for students in graduate-level nursing and education programs. Its intent is to recognize the significant role the literature review plays in the research process and to prepare students for the work that goes into writing one. Developed for new graduate students and novice researchers just entering into the work of a chosen discipline, each of the eight chapters covers a component of the literature review process. Students will learn how to form a research question, search existing literature, synthesize results and write the review. The book contains examples, checklists, supplementary materials, and additional resources. Literature Reviews for Education and Nursing Graduate Students is written by two librarians with expertise guiding students through research and writing assignments, and is openly licensed.
About the Contributors
Linda Frederiksen is the Head of Access Services at Washington State University Vancouver. She has a Master of Library Science degree from Emporia State University in Kansas. Linda is active in local, regional and national organizations, projects and initiatives advancing open educational resources and equitable access to information.
Sue F. Phelps is the Health Sciences and Outreach Services Librarian at Washington State University Vancouver. Her research interests include information literacy, accessibility of learning materials for students who use adaptive technology, diversity and equity in higher education, and evidence based practice in the health sciences
Contribute to this Page

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
February, 2018. Abstract. Purpose: The purpose of this paper is to provide students of educational research with clear. guidance on how to choose high quality sources for research papers and ...
graduate students in education to depend on the support of their academic supervisors. The aim of this paper is to familiarize graduate students with the genre of systematic literature review (SLR), as it is conducted in the field of education, by providing them with a self -paced approach to writing a SLR.
ABSTRACT. This review summarizes the relevant research on the use of information and communication technology (ICT) in education. Specifically, it reviews studies that have touched upon the merits of ICT integration in schools, barriers or challenges encountered in the use of ICT, factors influencing successful ICT integration, in-service and ...
recurring themes of debate on quality. The literature review remains „work in progress‟ that will take on board more of the literature and thus develop over a period of time, both feeding into our research programme and being informed by it. The paper starts by differentiating education from schools and argues that any framework to
prevalence and current state of overviews of education research and to pro-vide further guidance for conducting overviews and advance the evolution of overview methods. A comprehensive search across multiple online databases and gray literature repositories yielded 25 total education-related over-views.
Understanding what contributes to improving a system will help us tackle the problems in education systems that usually fail disproportionately in providing quality education for all, especially for the most disadvantage sectors of the population. This paper presents the results of a qualitative systematic literature review aimed at providing a comprehensive overview of what education research ...
Step 3: Search the Literature. The quality of literature review is highly dependent on the literature collected for the review—"Garbage-in, garbage-out.". The literature search finds materials for the review; therefore, a systematic review depends on a systematic search of literature. Channels for literature search.
A literature review is a scholarly paper which provides an overview of current knowledge about a topic. It will typically include substantive findings, as well as theoretical and methodological contributions to a particular topic (Hart 2018, p. xiii).Traditionally in education 'reviewing the literature' and 'doing research' have been viewed as distinct activities.
This literature review focuses on education policy implementation, its definition, processes and determinants. It aims to clarify what implementing policies involve in complex education systems to support policy work, building on the literature and country examples. An introduction delves into the reasons behind the need to update
In your literature review you will: survey the scholarly landscape. provide a synthesis of the issues, trends, and concepts. possibly provide some historical background. Review the literature in two ways: Section 1: reviews the literature for the Problem. Section 3: reviews the literature for the Project.
CURRICULUM REFORM: A LITERATURE REVIEW TO SUPPORT EFFECTIVE IMPLEMENTATION Unclassified Table of contents Acknowledgements 3 Abstract 4 1. Introduction 7 2. What do we mean by curriculum reform? 8 3. Curriculum reform through the lens of education implementation 9 4. Curriculum design is a multifaceted process 10 4.1.
A conceptual framework, derived from the review of the literature, displaying some of the complexities of the processes at the school level that lead to quality, is included in the final part of the paper. The perspective of the literature review is that programs designed to improve quality
leagues who are conducting a systematic review for the rst time. Part I: Methodological considerations In the rst Chapter, Mark Newman and David Gough from the University College London Institute of Education, introduce us to the method of systematic review. Depending on the aims of a literature review, they provide an overview of various
Google Education tools and video conferencing were included. Regarding the second research question, the literature review was used to analyse how digital technologies are being implemented. The third research question pertains to the challenges outlined in the selected articles. The themes include the scarcity of
Presented in this chapter of the review of the related literature will be: (a) description of poverty and the role of education, (b) effects of poverty on student behavior, (c) effects of poverty on student performance, (d) pedagogical implications for teachers of students in poverty, and (e) summary.
2. MOTIVATE YOUR RESEARCH in addition to providing useful information about your topic, your literature review must tell a story about how your project relates to existing literature. popular literature review narratives include: ¡ plugging a gap / filling a hole within an incomplete literature ¡ building a bridge between two "siloed" literatures, putting literatures "in conversation"
Gall, Borg, and Gall (1996) estimate that completion of an acceptable dissertation literature review will take between three and six months of effort. The purpose of this guide is to collect and summarize the most relevant information on how to write a dissertation literature review.
Literature Reviews for Education and Nursing Graduate Students is an open textbook designed for students in graduate-level nursing and education programs. Its intent is to recognize the significant role the literature review plays in the research process and to prepare students for the work that goes into writing one. Developed for new graduate students and novice researchers just entering ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
As a result of Campbell's focus on the US literature, he neglected the earlier review conducted by Geboers et al. , which employed a more systematic approach to searching for evidence of the impact of citizenship education (for 13-16-year-olds) in peer-reviewed journal articles published between 2003 and 2009. They included 28 studies and ...
LITERATURE REVIEW EDUCATIONAL TECHNOLOGY Over the past 20 years, technology has transformed society and changed many aspects of daily life. The proliferation of technology has led to a growing consensus among educators and the general public that it should play a more integral role in students' education (Culp et al., 2003; CEO Forum on Education
Literature search and identification. In this study, we followed the principles and guidelines of the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) 2020 statement (Page et al., Citation 2021).The literature search was conducted on CNKI.net, and we used the following methods and keywords for the search: title, abstract, and keywords including vocational education ...
Linguistics, Education. The use of the first language (L1) in an English as a Foreign Language (EFL) and English as a Second Language (ESL) classroom can serve various purposes to facilitate language learning. Accordingly, the role of L1 in EFL and ESL classes has been debated in the history of English Language Teaching (ELT) and Second ...