Feb 13, 2023

200-500 Word Example Essays about Technology
Got an essay assignment about technology check out these examples to inspire you.
Technology is a rapidly evolving field that has completely changed the way we live, work, and interact with one another. Technology has profoundly impacted our daily lives, from how we communicate with friends and family to how we access information and complete tasks. As a result, it's no surprise that technology is a popular topic for students writing essays.
But writing a technology essay can be challenging, especially for those needing more time or help with writer's block. This is where Jenni.ai comes in. Jenni.ai is an innovative AI tool explicitly designed for students who need help writing essays. With Jenni.ai, students can quickly and easily generate essays on various topics, including technology.
This blog post aims to provide readers with various example essays on technology, all generated by Jenni.ai. These essays will be a valuable resource for students looking for inspiration or guidance as they work on their essays. By reading through these example essays, students can better understand how technology can be approached and discussed in an essay.
Moreover, by signing up for a free trial with Jenni.ai, students can take advantage of this innovative tool and receive even more support as they work on their essays. Jenni.ai is designed to help students write essays faster and more efficiently, so they can focus on what truly matters – learning and growing as a student. Whether you're a student who is struggling with writer's block or simply looking for a convenient way to generate essays on a wide range of topics, Jenni.ai is the perfect solution.
The Impact of Technology on Society and Culture
Introduction:.
Technology has become an integral part of our daily lives and has dramatically impacted how we interact, communicate, and carry out various activities. Technological advancements have brought positive and negative changes to society and culture. In this article, we will explore the impact of technology on society and culture and how it has influenced different aspects of our lives.
Positive impact on communication:
Technology has dramatically improved communication and made it easier for people to connect from anywhere in the world. Social media platforms, instant messaging, and video conferencing have brought people closer, bridging geographical distances and cultural differences. This has made it easier for people to share information, exchange ideas, and collaborate on projects.
Positive impact on education:
Students and instructors now have access to a multitude of knowledge and resources because of the effect of technology on education . Students may now study at their speed and from any location thanks to online learning platforms, educational applications, and digital textbooks.
Negative impact on critical thinking and creativity:
Technological advancements have resulted in a reduction in critical thinking and creativity. With so much information at our fingertips, individuals have become more passive in their learning, relying on the internet for solutions rather than logic and inventiveness. As a result, independent thinking and problem-solving abilities have declined.
Positive impact on entertainment:
Technology has transformed how we access and consume entertainment. People may now access a wide range of entertainment alternatives from the comfort of their own homes thanks to streaming services, gaming platforms, and online content makers. The entertainment business has entered a new age of creativity and invention as a result of this.
Negative impact on attention span:
However, the continual bombardment of information and technological stimulation has also reduced attention span and the capacity to focus. People are easily distracted and need help focusing on a single activity for a long time. This has hampered productivity and the ability to accomplish duties.
The Ethics of Artificial Intelligence And Machine Learning
The development of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies has been one of the most significant technological developments of the past several decades. These cutting-edge technologies have the potential to alter several sectors of society, including commerce, industry, healthcare, and entertainment.
As with any new and quickly advancing technology, AI and ML ethics must be carefully studied. The usage of these technologies presents significant concerns around privacy, accountability, and command. As the use of AI and ML grows more ubiquitous, we must assess their possible influence on society and investigate the ethical issues that must be taken into account as these technologies continue to develop.
What are Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning?
Artificial Intelligence is the simulation of human intelligence in machines designed to think and act like humans. Machine learning is a subfield of AI that enables computers to learn from data and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed.
The impact of AI and ML on Society
The use of AI and ML in various industries, such as healthcare, finance, and retail, has brought many benefits. For example, AI-powered medical diagnosis systems can identify diseases faster and more accurately than human doctors. However, there are also concerns about job displacement and the potential for AI to perpetuate societal biases.
The Ethical Considerations of AI and ML
A. Bias in AI algorithms
One of the critical ethical concerns about AI and ML is the potential for algorithms to perpetuate existing biases. This can occur if the data used to train these algorithms reflects the preferences of the people who created it. As a result, AI systems can perpetuate these biases and discriminate against certain groups of people.
B. Responsibility for AI-generated decisions
Another ethical concern is the responsibility for decisions made by AI systems. For example, who is responsible for the damage if a self-driving car causes an accident? The manufacturer of the vehicle, the software developer, or the AI algorithm itself?
C. The potential for misuse of AI and ML
AI and ML can also be used for malicious purposes, such as cyberattacks and misinformation. The need for more regulation and oversight in developing and using these technologies makes it difficult to prevent misuse.
The developments in AI and ML have given numerous benefits to humanity, but they also present significant ethical concerns that must be addressed. We must assess the repercussions of new technologies on society, implement methods to limit the associated dangers, and guarantee that they are utilized for the greater good. As AI and ML continue to play an ever-increasing role in our daily lives, we must engage in an open and frank discussion regarding their ethics.
The Future of Work And Automation
Rapid technological breakthroughs in recent years have brought about considerable changes in our way of life and work. Concerns regarding the influence of artificial intelligence and machine learning on the future of work and employment have increased alongside the development of these technologies. This article will examine the possible advantages and disadvantages of automation and its influence on the labor market, employees, and the economy.
The Advantages of Automation
Automation in the workplace offers various benefits, including higher efficiency and production, fewer mistakes, and enhanced precision. Automated processes may accomplish repetitive jobs quickly and precisely, allowing employees to concentrate on more complex and creative activities. Additionally, automation may save organizations money since it removes the need to pay for labor and minimizes the danger of workplace accidents.
The Potential Disadvantages of Automation
However, automation has significant disadvantages, including job loss and income stagnation. As robots and computers replace human labor in particular industries, there is a danger that many workers may lose their jobs, resulting in higher unemployment and more significant economic disparity. Moreover, if automation is not adequately regulated and managed, it might lead to stagnant wages and a deterioration in employees' standard of life.
The Future of Work and Automation
Despite these difficulties, automation will likely influence how labor is done. As a result, firms, employees, and governments must take early measures to solve possible issues and reap the rewards of automation. This might entail funding worker retraining programs, enhancing education and skill development, and implementing regulations that support equality and justice at work.
IV. The Need for Ethical Considerations
We must consider the ethical ramifications of automation and its effects on society as technology develops. The impact on employees and their rights, possible hazards to privacy and security, and the duty of corporations and governments to ensure that automation is utilized responsibly and ethically are all factors to be taken into account.
Conclusion:
To summarise, the future of employment and automation will most certainly be defined by a complex interaction of technological advances, economic trends, and cultural ideals. All stakeholders must work together to handle the problems and possibilities presented by automation and ensure that technology is employed to benefit society as a whole.
The Role of Technology in Education
Introduction.
Nearly every part of our lives has been transformed by technology, and education is no different. Today's students have greater access to knowledge, opportunities, and resources than ever before, and technology is becoming a more significant part of their educational experience. Technology is transforming how we think about education and creating new opportunities for learners of all ages, from online courses and virtual classrooms to instructional applications and augmented reality.
Technology's Benefits for Education
The capacity to tailor learning is one of technology's most significant benefits in education. Students may customize their education to meet their unique needs and interests since they can access online information and tools.
For instance, people can enroll in online classes on topics they are interested in, get tailored feedback on their work, and engage in virtual discussions with peers and subject matter experts worldwide. As a result, pupils are better able to acquire and develop the abilities and information necessary for success.
Challenges and Concerns
Despite the numerous advantages of technology in education, there are also obstacles and considerations to consider. One issue is the growing reliance on technology and the possibility that pupils would become overly dependent on it. This might result in a lack of critical thinking and problem-solving abilities, as students may become passive learners who only follow instructions and rely on technology to complete their assignments.
Another obstacle is the digital divide between those who have access to technology and those who do not. This division can exacerbate the achievement gap between pupils and produce uneven educational and professional growth chances. To reduce these consequences, all students must have access to the technology and resources necessary for success.
In conclusion, technology is rapidly becoming an integral part of the classroom experience and has the potential to alter the way we learn radically.
Technology can help students flourish and realize their full potential by giving them access to individualized instruction, tools, and opportunities. While the benefits of technology in the classroom are undeniable, it's crucial to be mindful of the risks and take precautions to guarantee that all kids have access to the tools they need to thrive.
The Influence of Technology On Personal Relationships And Communication
Technological advancements have profoundly altered how individuals connect and exchange information. It has changed the world in many ways in only a few decades. Because of the rise of the internet and various social media sites, maintaining relationships with people from all walks of life is now simpler than ever.
However, concerns about how these developments may affect interpersonal connections and dialogue are inevitable in an era of rapid technological growth. In this piece, we'll discuss how the prevalence of digital media has altered our interpersonal connections and the language we use to express ourselves.
Direct Effect on Direct Interaction:
The disruption of face-to-face communication is a particularly stark example of how technology has impacted human connections. The quality of interpersonal connections has suffered due to people's growing preference for digital over human communication. Technology has been demonstrated to reduce the usage of nonverbal signs such as facial expressions, tone of voice, and other indicators of emotional investment in the connection.
Positive Impact on Long-Distance Relationships:
Yet there are positives to be found as well. Long-distance relationships have also benefited from technological advancements. The development of technologies such as video conferencing, instant messaging, and social media has made it possible for individuals to keep in touch with distant loved ones. It has become simpler for individuals to stay in touch and feel connected despite geographical distance.
The Effects of Social Media on Personal Connections:
The widespread use of social media has had far-reaching consequences, especially on the quality of interpersonal interactions. Social media has positive and harmful effects on relationships since it allows people to keep in touch and share life's milestones.
Unfortunately, social media has made it all too easy to compare oneself to others, which may lead to emotions of jealousy and a general decline in confidence. Furthermore, social media might cause people to have inflated expectations of themselves and their relationships.
A Personal Perspective on the Intersection of Technology and Romance
Technological advancements have also altered physical touch and closeness. Virtual reality and other technologies have allowed people to feel physical contact and familiarity in a digital setting. This might be a promising breakthrough, but it has some potential downsides.
Experts are concerned that people's growing dependence on technology for intimacy may lead to less time spent communicating face-to-face and less emphasis on physical contact, both of which are important for maintaining good relationships.
In conclusion, technological advancements have significantly affected the quality of interpersonal connections and the exchange of information. Even though technology has made it simpler to maintain personal relationships, it has chilled interpersonal interactions between people.
Keeping tabs on how technology is changing our lives and making adjustments as necessary is essential as we move forward. Boundaries and prioritizing in-person conversation and physical touch in close relationships may help reduce the harm it causes.
The Security and Privacy Implications of Increased Technology Use and Data Collection
The fast development of technology over the past few decades has made its way into every aspect of our life. Technology has improved many facets of our life, from communication to commerce. However, significant privacy and security problems have emerged due to the broad adoption of technology. In this essay, we'll look at how the widespread use of technological solutions and the subsequent explosion in collected data affects our right to privacy and security.
Data Mining and Privacy Concerns
Risk of Cyber Attacks and Data Loss
The Widespread Use of Encryption and Other Safety Mechanisms
The Privacy and Security of the Future in a Globalized Information Age
Obtaining and Using Individual Information
The acquisition and use of private information is a significant cause for privacy alarm in the digital age. Data about their customers' online habits, interests, and personal information is a valuable commodity for many internet firms. Besides tailored advertising, this information may be used for other, less desirable things like identity theft or cyber assaults.
Moreover, many individuals need to be made aware of what data is being gathered from them or how it is being utilized because of the lack of transparency around gathering personal information. Privacy and data security have become increasingly contentious as a result.
Data breaches and other forms of cyber-attack pose a severe risk.
The risk of cyber assaults and data breaches is another big issue of worry. More people are using more devices, which means more opportunities for cybercriminals to steal private information like credit card numbers and other identifying data. This may cause monetary damages and harm one's reputation or identity.
Many high-profile data breaches have occurred in recent years, exposing the personal information of millions of individuals and raising serious concerns about the safety of this information. Companies and governments have responded to this problem by adopting new security methods like encryption and multi-factor authentication.
Many businesses now use encryption and other security measures to protect themselves from cybercriminals and data thieves. Encryption keeps sensitive information hidden by encoding it so that only those possessing the corresponding key can decipher it. This prevents private information like bank account numbers or social security numbers from falling into the wrong hands.
Firewalls, virus scanners, and two-factor authentication are all additional security precautions that may be used with encryption. While these safeguards do much to stave against cyber assaults, they are not entirely impregnable, and data breaches are still possible.
The Future of Privacy and Security in a Technologically Advanced World
There's little doubt that concerns about privacy and security will persist even as technology improves. There must be strict safeguards to secure people's private information as more and more of it is transferred and kept digitally. To achieve this goal, it may be necessary to implement novel technologies and heightened levels of protection and to revise the rules and regulations regulating the collection and storage of private information.
Individuals and businesses are understandably concerned about the security and privacy consequences of widespread technological use and data collecting. There are numerous obstacles to overcome in a society where technology plays an increasingly important role, from acquiring and using personal data to the risk of cyber-attacks and data breaches. Companies and governments must keep spending money on security measures and working to educate people about the significance of privacy and security if personal data is to remain safe.
In conclusion, technology has profoundly impacted virtually every aspect of our lives, including society and culture, ethics, work, education, personal relationships, and security and privacy. The rise of artificial intelligence and machine learning has presented new ethical considerations, while automation is transforming the future of work.
In education, technology has revolutionized the way we learn and access information. At the same time, our dependence on technology has brought new challenges in terms of personal relationships, communication, security, and privacy.
Jenni.ai is an AI tool that can help students write essays easily and quickly. Whether you're looking, for example, for essays on any of these topics or are seeking assistance in writing your essay, Jenni.ai offers a convenient solution. Sign up for a free trial today and experience the benefits of AI-powered writing assistance for yourself.
Try Jenni for free today
Create your first piece of content with Jenni today and never look back
- Dissertation
- PowerPoint Presentation
- Book Report/Review
- Research Proposal
- Math Problems
- Proofreading
- Movie Review
- Cover Letter Writing
- Personal Statement
- Nursing Paper
- Argumentative Essay
- Research Paper
- Discussion Board Post
20 Most Prominent Technology Essay Topics And Writing Hints

Table of Contents

So it goes without saying that the scope of technology is an endless sphere to examine. What’s more, as the topic is super wide, you can personalize your essay to make it enjoyable to work on.
Nevertheless, it may be a challenge for you to make up your mind on how and what to write about. In this case, I hope the following hints will be of great help to you!
How to choose a topic about technology for a research paper?
First of all, to write a technology essay , you need to come up with a topic that will not be too wide, yet not too narrow.
Also, remember that it will be much more entertaining and easier for you to work on the questions you actually enjoy.
If you have troubles composing the topic for your research paper, try some o the following guidelines:
- Think of the aspects of technology you’re interested in.
- Choose issues that are up-to-date and newsworthy .
- Examine credible sources ; find out which questions are best covered with relevant information.
- Write down some keywords for the remaining questions, – they will be the basis of the topic. In case you’ve got too many aspects to cover, try choosing 2-3 of them.
- Try crafting a couple of topics . In case of emergency… find some ready-to-use ideas.
- Look through your final ideas and pick the one you like most.
- Do some preliminary research . Correct your topic if needed.
TOP 20 technology essay topics
Can’t come up with the idea for your perfect topic? How about choosing one from a brilliant list we’ve created for you?
- To what extent technology has changed the way people communicate?
- Pick up one technological invention (Internet/television/electro cars/mobile phones, etc.) and describe how it affected people’s lives.
- History of technological progress: the first technological discoveries.
- What would life be without modern technology?
- Do technologies have more pros or cons? Why?
- Is the Internet bringing people closer to each other or separating them?
- Examine the role of technologies in your own life: to what extent you are dependent on them, can you give up using?
- Think of the things we are losing with technological progress.
- Choose one gadget and describe its pros and cons.
- What technology awareness needs to be given to children nowadays?
- Describe a new technology you consider the most prominent. Explain your choice.
- The role of technology in globalization.
- Technology and work: what are the advantages and disadvantages of technology in workplaces?
- Imagine the future of technology: what life will be like in 20 years?
- Human vs computer: who wins?
- Reproduction technologies.
- Health technologies that have changed the world.
- Technology advance in genetic engineering.
- Correlation between technological progress and human identity.
- How has technology changed the rules of war?
Prominent topics about technology for writing
Didn’t like any of the topics above? Well, we’ve got Well, we’ve got another custom Writing list of technology topics. The following topics are more specific, but all of them are definitely thought-provoking.
- The use of technology in education.
- Stunning technology developed currently.
- The most shocking modern technology inventions the majority of people still aren’t aware of.
- Enumerate some technologies that you consider completely destructive and harmful. Explain your choice.
- Technology and space studies.
- The impact of technology on people’s health and values.
- Can robots replace humans completely on the workplaces? Why?
- Specific country and its contribution to the development of modern technology.
- Technology and safety of transport.
- Nanotechnologies and the scopes of their use.
- The use of technologies in medicine.
- Which technologies may influence people’s mental health? How?
- Technologies that have changed our lives.
- Do technologies have a positive or negative effect on personal safety?
- Does modern technology help improve the educational process?
Writing about technology: the what and the why
After you’ve chosen the topic, it’s a perfect time to start working on it.
Remember… To write a successful essay or a research paper on technology, you need to organize it all well.
This means you need a plan! Here are some hints for a perfect structure:
- Search for relevant information . You have to rely on credible sources to have up-to-date and newsworthy data. Remember that some websites may contain fakes!
- Note some crucial aspects of your question. Later you may use them as ideas to highlight.
- Start writing. To make it easier to cope with a lot of information you now encounter, you’d need to craft an outline . Write down a table of contents for your essay, it will be your soil to push off.
- Start with the introduction to give the reader some understanding of the issue. Here you include some background information on the topic, historical aspect, or some definitions if needed.
- Write the main body . Mention all your statements and support them with decent evidence. Remember that the main body should be split into paragraphs to make it readable. As a rule, one paragraph is for one idea or statement.
- End up with a conclusion – an inference of everything said before. It has to be laconic and logical. New ideas aren’t needed here.
- After you’ve written the paper, you may want to check it for grammar and typos . There are lots of websites and programs for this purpose. Even better, leave it for a couple of days and give it a fresh look.
The use of a technology essay example
To reassure you that writing a technology essay isn’t the end of the world, here is a free sample of the essay. It fits all the general recommendations, but you should always keep in mind that your teacher may have own vision on how the essay should be completed!
Still, it’s always great to grab some ideas!
Overall, writing an essay on technology is an incredibly valuable experience. Moreover, the topic is so wide; you most definitely will find something interesting to talk about!
Stick to the structure and don’t hesitate to discover something very specific. Technology is getting more and more stunning every day!
No time to complete your brilliant copy? We’ve got a bunch of writers, who’d be more than happy to write it for you! Any topic, tightest deadline, complete confidentiality. Hit the button to learn more.

Descriptive Essay About a Person

How to Use a Quote in an Essay

How to Achieve Well-Organized Essay with Minimum Efforts
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
- The Internet and the Pandemic
90% of Americans say the internet has been essential or important to them, many made video calls and 40% used technology in new ways. But while tech was a lifeline for some, others faced struggles
Table of contents.
- 1. How the internet and technology shaped Americans’ personal experiences amid COVID-19
- 2. Parents, their children and school during the pandemic
- 3. Navigating technological challenges
- 4. The role of technology in COVID-19 vaccine registration
- Acknowledgments
- Methodology

Pew Research Center has a long history of studying technology adoption trends and the impact of digital technology on society. This report focuses on American adults’ experiences with and attitudes about their internet and technology use during the COVID-19 outbreak. For this analysis, we surveyed 4,623 U.S. adults from April 12-18, 2021. Everyone who took part is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Chapter 1 of this report includes responses to an open-ended question and the overall report includes a number of quotations to help illustrate themes and add nuance to the survey findings. Quotations may have been lightly edited for grammar, spelling and clarity. The first three themes mentioned in each open-ended response, according to a researcher-developed codebook, were coded into categories for analysis.
Here are the questions used for this report , along with responses, and its methodology .
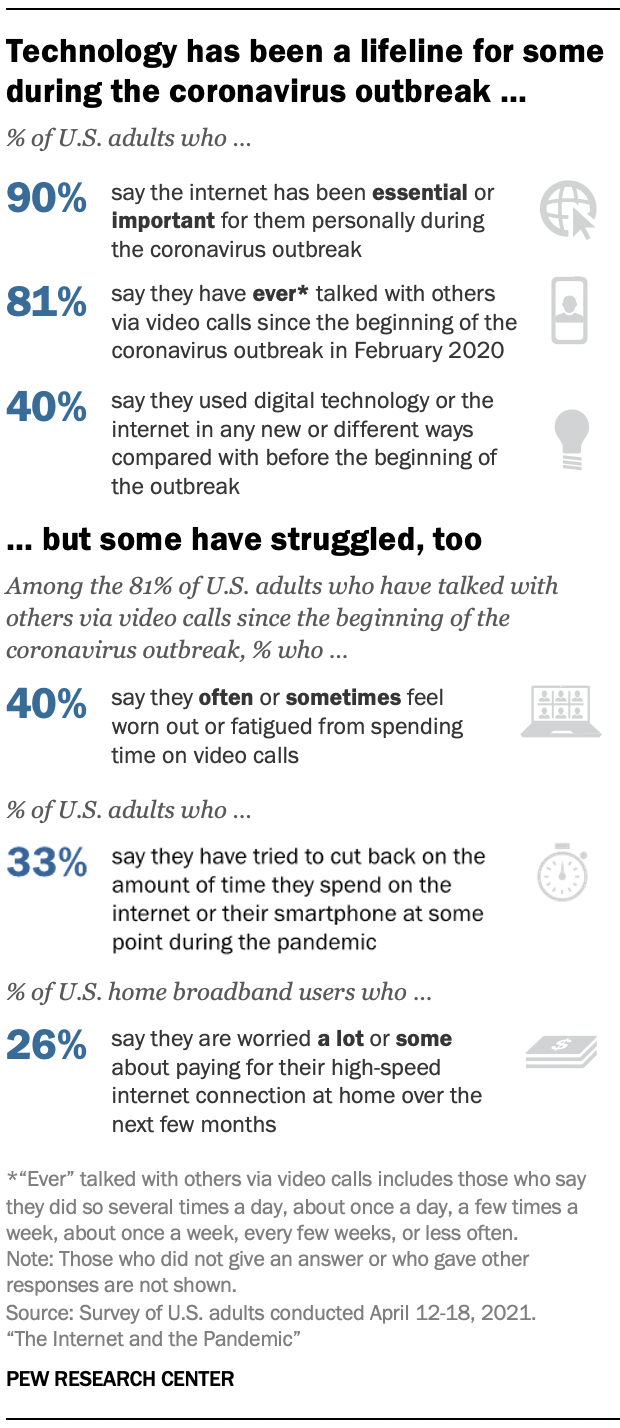
The coronavirus has transformed many aspects of Americans’ lives. It shut down schools, businesses and workplaces and forced millions to stay at home for extended lengths of time. Public health authorities recommended limits on social contact to try to contain the spread of the virus, and these profoundly altered the way many worked, learned, connected with loved ones, carried out basic daily tasks, celebrated and mourned. For some, technology played a role in this transformation.
Results from a new Pew Research Center survey of U.S. adults conducted April 12-18, 2021, reveal the extent to which people’s use of the internet has changed, their views about how helpful technology has been for them and the struggles some have faced.
The vast majority of adults (90%) say the internet has been at least important to them personally during the pandemic, the survey finds. The share who say it has been essential – 58% – is up slightly from 53% in April 2020. There have also been upticks in the shares who say the internet has been essential in the past year among those with a bachelor’s degree or more formal education, adults under 30, and those 65 and older.
A large majority of Americans (81%) also say they talked with others via video calls at some point since the pandemic’s onset. And for 40% of Americans, digital tools have taken on new relevance: They report they used technology or the internet in ways that were new or different to them. Some also sought upgrades to their service as the pandemic unfolded: 29% of broadband users did something to improve the speed, reliability or quality of their high-speed internet connection at home since the beginning of the outbreak.
Still, tech use has not been an unmitigated boon for everyone. “ Zoom fatigue ” was widely speculated to be a problem in the pandemic, and some Americans report related experiences in the new survey: 40% of those who have ever talked with others via video calls since the beginning of the pandemic say they have felt worn out or fatigued often or sometimes by the time they spend on them. Moreover, changes in screen time occurred for Americans generally and for parents of young children . The survey finds that a third of all adults say they tried to cut back on time spent on their smartphone or the internet at some point during the pandemic. In addition, 72% of parents of children in grades K-12 say their kids are spending more time on screens compared with before the outbreak. 1
For many, digital interactions could only do so much as a stand-in for in-person communication. About two-thirds of Americans (68%) say the interactions they would have had in person, but instead had online or over the phone, have generally been useful – but not a replacement for in-person contact. Another 15% say these tools haven’t been of much use in their interactions. Still, 17% report that these digital interactions have been just as good as in-person contact.
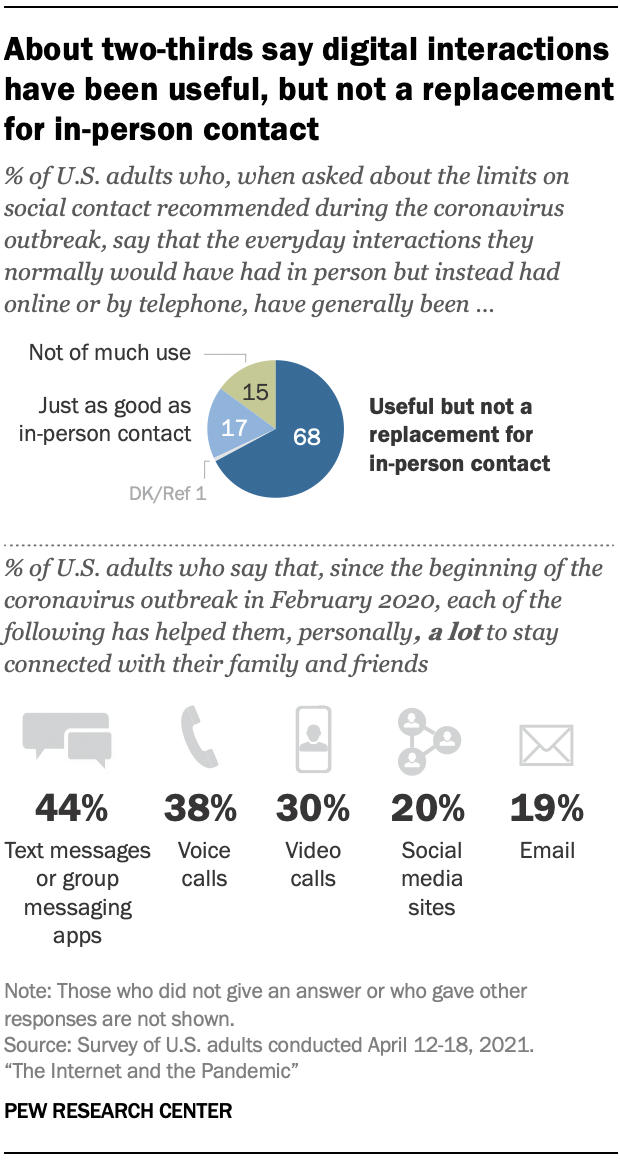
Some types of technology have been more helpful than others for Americans. For example, 44% say text messages or group messaging apps have helped them a lot to stay connected with family and friends, 38% say the same about voice calls and 30% say this about video calls. Smaller shares say social media sites (20%) and email (19%) have helped them in this way.
The survey offers a snapshot of Americans’ lives just over one year into the pandemic as they reflected back on what had happened. It is important to note the findings were gathered in April 2021, just before all U.S. adults became eligible for coronavirus vaccine s. At the time, some states were beginning to loosen restrictions on businesses and social encounters. This survey also was fielded before the delta variant became prominent in the United States, raising concerns about new and evolving variants .
Here are some of the key takeaways from the survey.
Americans’ tech experiences in the pandemic are linked to digital divides, tech readiness
Some Americans’ experiences with technology haven’t been smooth or easy during the pandemic. The digital divides related to internet use and affordability were highlighted by the pandemic and also emerged in new ways as life moved online.
For all Americans relying on screens during the pandemic, connection quality has been important for school assignments, meetings and virtual social encounters alike. The new survey highlights difficulties for some: Roughly half of those who have a high-speed internet connection at home (48%) say they have problems with the speed, reliability or quality of their home connection often or sometimes. 2
Beyond that, affordability remained a persistent concern for a portion of digital tech users as the pandemic continued – about a quarter of home broadband users (26%) and smartphone owners (24%) said in the April 2021 survey that they worried a lot or some about paying their internet and cellphone bills over the next few months.
From parents of children facing the “ homework gap ” to Americans struggling to afford home internet , those with lower incomes have been particularly likely to struggle. At the same time, some of those with higher incomes have been affected as well.
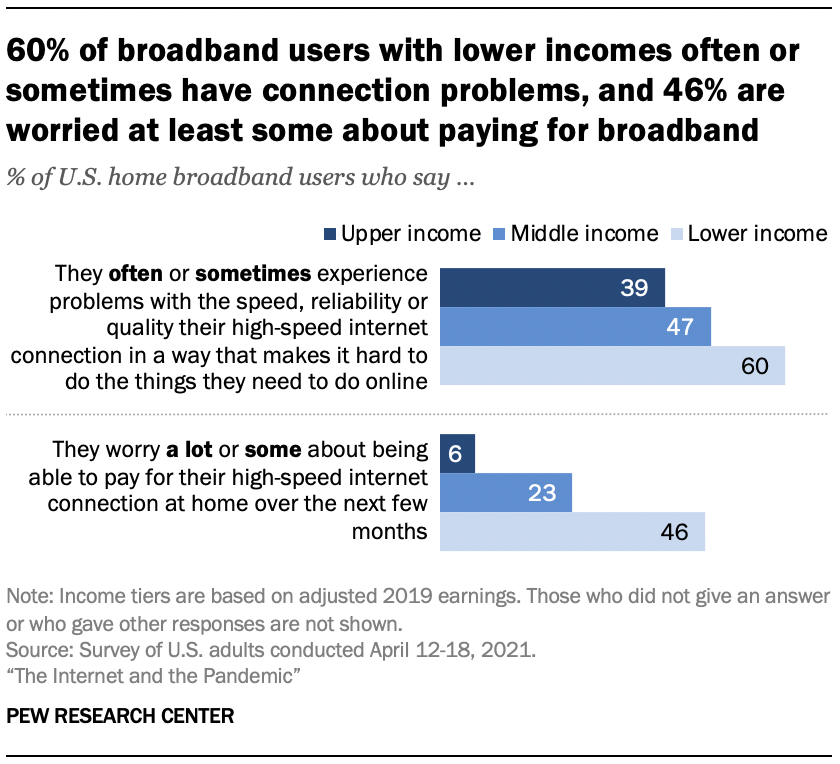
Affordability and connection problems have hit broadband users with lower incomes especially hard. Nearly half of broadband users with lower incomes, and about a quarter of those with midrange incomes, say that as of April they were at least somewhat worried about paying their internet bill over the next few months. 3 And home broadband users with lower incomes are roughly 20 points more likely to say they often or sometimes experience problems with their connection than those with relatively high incomes. Still, 55% of those with lower incomes say the internet has been essential to them personally in the pandemic.
At the same time, Americans’ levels of formal education are associated with their experiences turning to tech during the pandemic.
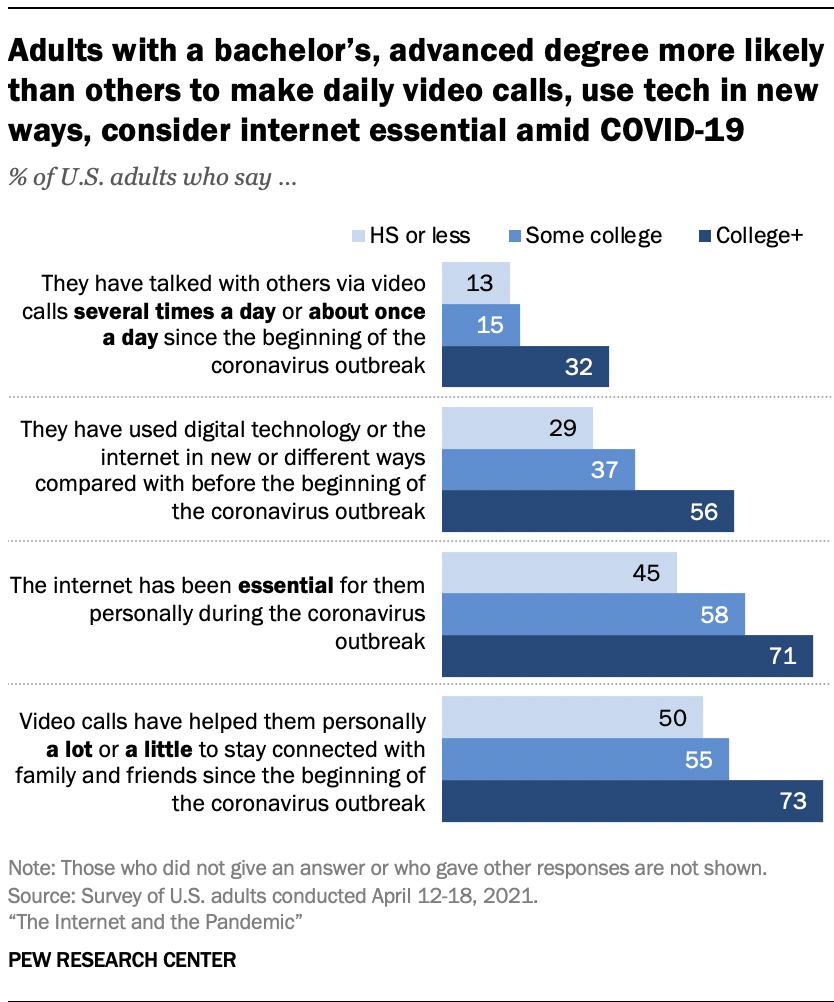
Those with a bachelor’s or advanced degree are about twice as likely as those with a high school diploma or less formal education to have used tech in new or different ways during the pandemic. There is also roughly a 20 percentage point gap between these two groups in the shares who have made video calls about once a day or more often and who say these calls have helped at least a little to stay connected with family and friends. And 71% of those with a bachelor’s degree or more education say the internet has been essential, compared with 45% of those with a high school diploma or less.
More broadly, not all Americans believe they have key tech skills. In this survey, about a quarter of adults (26%) say they usually need someone else’s help to set up or show them how to use a new computer, smartphone or other electronic device. And one-in-ten report they have little to no confidence in their ability to use these types of devices to do the things they need to do online. This report refers to those who say they experience either or both of these issues as having “lower tech readiness.” Some 30% of adults fall in this category. (A full description of how this group was identified can be found in Chapter 3. )
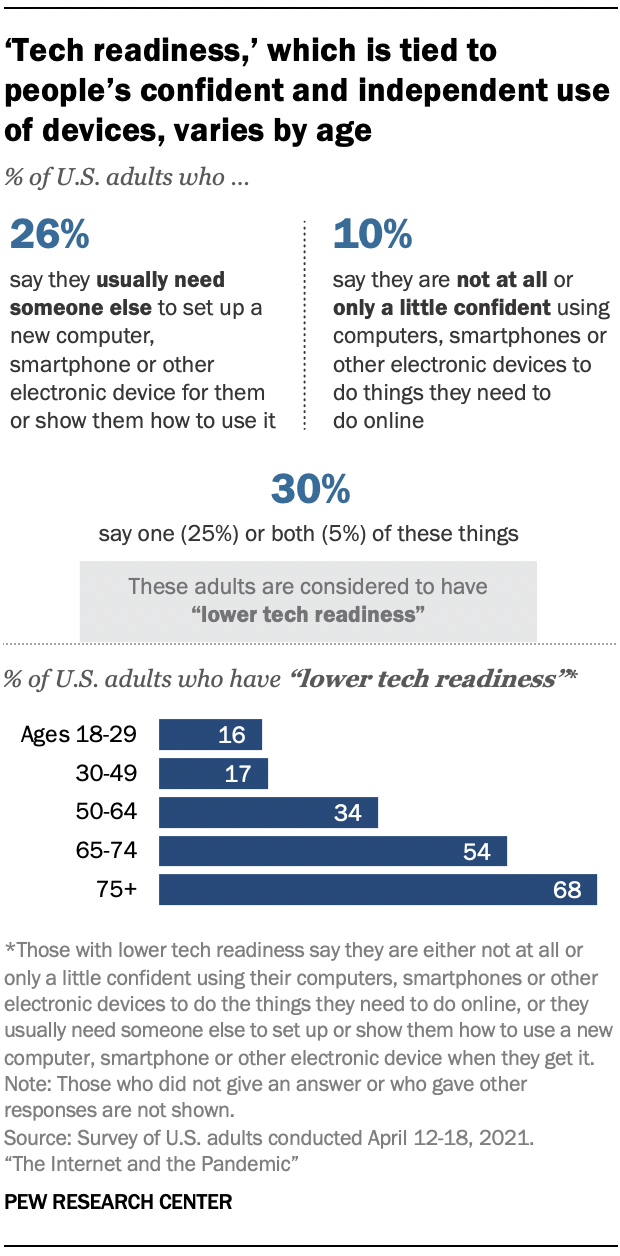
These struggles are particularly acute for older adults, some of whom have had to learn new tech skills over the course of the pandemic. Roughly two-thirds of adults 75 and older fall into the group having lower tech readiness – that is, they either have little or no confidence in their ability to use their devices, or generally need help setting up and learning how to use new devices. Some 54% of Americans ages 65 to 74 are also in this group.
Americans with lower tech readiness have had different experiences with technology during the pandemic. While 82% of the Americans with lower tech readiness say the internet has been at least important to them personally during the pandemic, they are less likely than those with higher tech readiness to say the internet has been essential (39% vs. 66%). Some 21% of those with lower tech readiness say digital interactions haven’t been of much use in standing in for in-person contact, compared with 12% of those with higher tech readiness.
46% of parents with lower incomes whose children faced school closures say their children had at least one problem related to the ‘homework gap’
As school moved online for many families, parents and their children experienced profound changes. Fully 93% of parents with K-12 children at home say these children had some online instruction during the pandemic. Among these parents, 62% report that online learning has gone very or somewhat well, and 70% say it has been very or somewhat easy for them to help their children use technology for online instruction.
Still, 30% of the parents whose children have had online instruction during the pandemic say it has been very or somewhat difficult for them to help their children use technology or the internet for this.
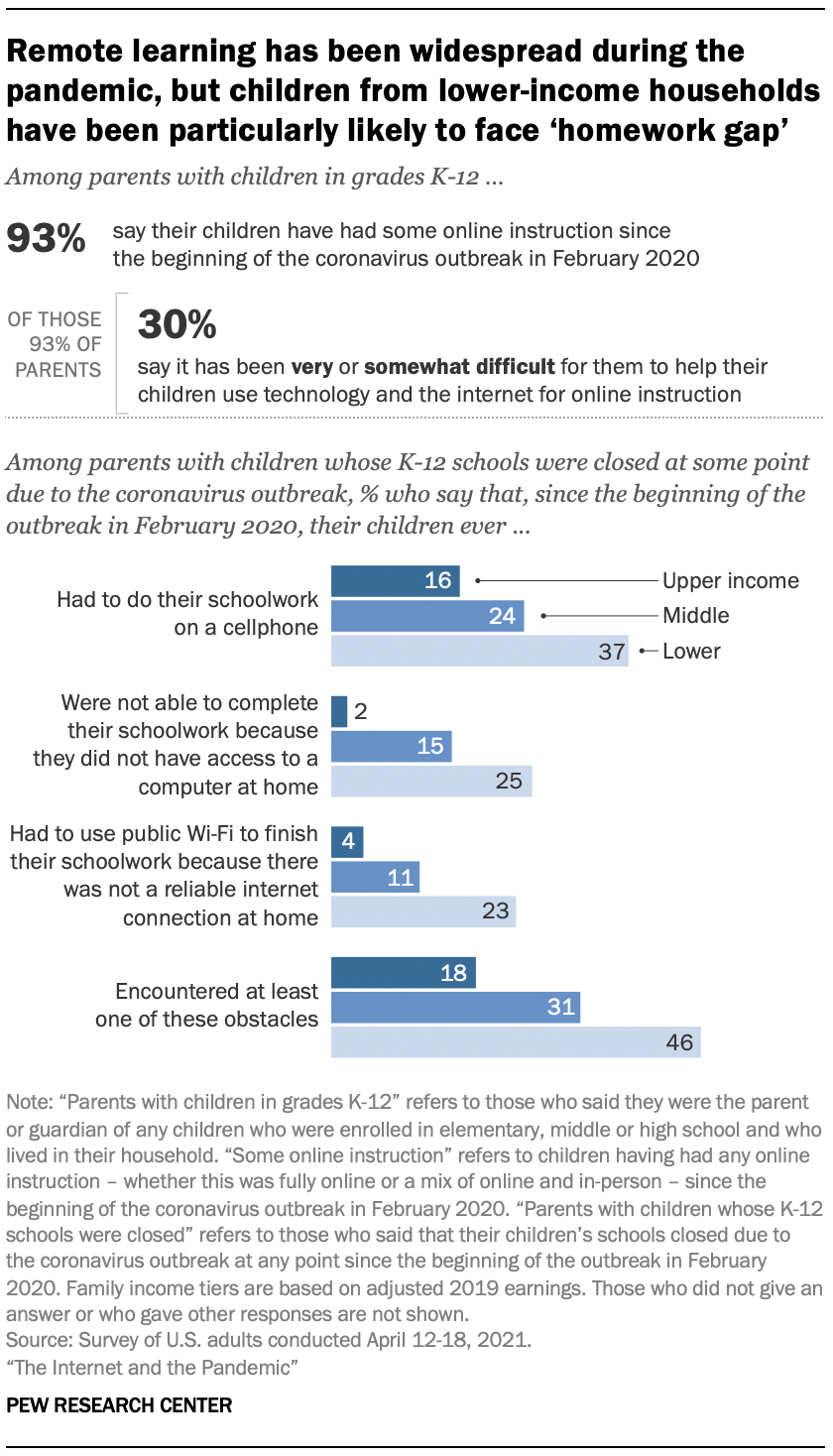
The survey also shows that children from households with lower incomes who faced school closures in the pandemic have been especially likely to encounter tech-related obstacles in completing their schoolwork – a phenomenon contributing to the “ homework gap .”
Overall, about a third (34%) of all parents whose children’s schools closed at some point say their children have encountered at least one of the tech-related issues we asked about amid COVID-19: having to do schoolwork on a cellphone, being unable to complete schoolwork because of lack of computer access at home, or having to use public Wi-Fi to finish schoolwork because there was no reliable connection at home.
This share is higher among parents with lower incomes whose children’s schools closed. Nearly half (46%) say their children have faced at least one of these issues. Some with higher incomes were affected as well – about three-in-ten (31%) of these parents with midrange incomes say their children faced one or more of these issues, as do about one-in-five of these parents with higher household incomes.
Prior Center work has documented this “ homework gap ” in other contexts – both before the coronavirus outbreak and near the beginning of the pandemic . In April 2020, for example, parents with lower incomes were particularly likely to think their children would face these struggles amid the outbreak.
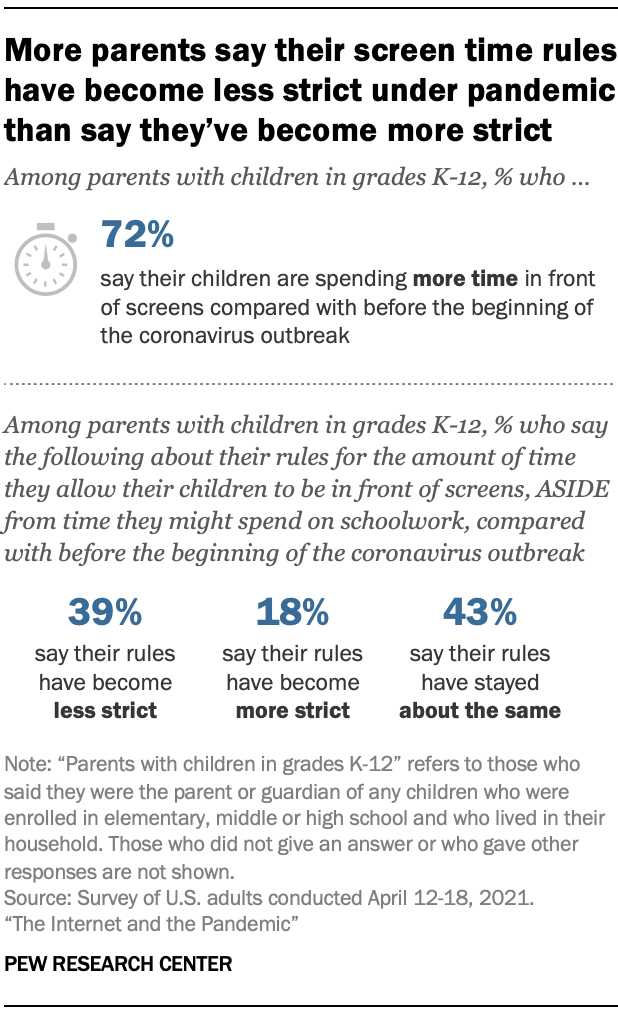
Besides issues related to remote schooling, other changes were afoot in families as the pandemic forced many families to shelter in place. For instance, parents’ estimates of their children’s screen time – and family rules around this – changed in some homes. About seven-in-ten parents with children in kindergarten through 12th grade (72%) say their children were spending more time on screens as of the April survey compared with before the outbreak. Some 39% of parents with school-age children say they have become less strict about screen time rules during the outbreak. About one-in-five (18%) say they have become more strict, while 43% have kept screen time rules about the same.
More adults now favor the idea that schools should provide digital technology to all students during the pandemic than did in April 2020
Americans’ tech struggles related to digital divides gained attention from policymakers and news organizations as the pandemic progressed.
On some policy issues, public attitudes changed over the course of the outbreak – for example, views on what K-12 schools should provide to students shifted. Some 49% now say K-12 schools have a responsibility to provide all students with laptop or tablet computers in order to help them complete their schoolwork during the pandemic, up 12 percentage points from a year ago.
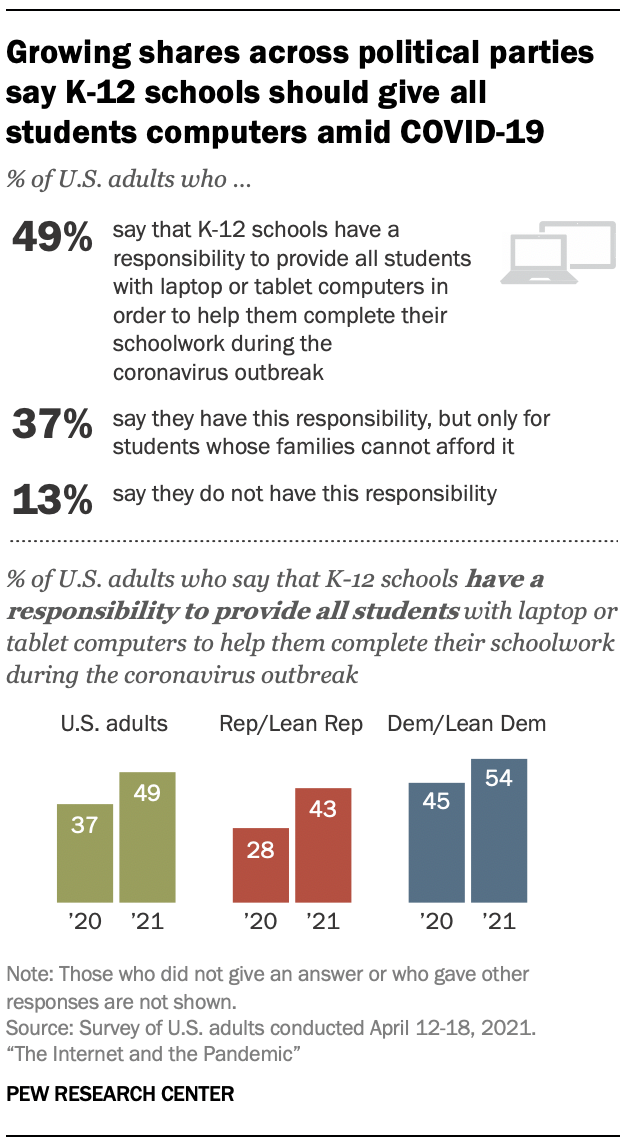
The shares of those who say so have increased for both major political parties over the past year: This view shifted 15 points for Republicans and those who lean toward the GOP, and there was a 9-point increase for Democrats and Democratic leaners.
However, when it comes to views of policy solutions for internet access more generally, not much has changed. Some 37% of Americans say that the government has a responsibility to ensure all Americans have high-speed internet access during the outbreak, and the overall share is unchanged from April 2020 – the first time Americans were asked this specific question about the government’s pandemic responsibility to provide internet access. 4
Democrats are more likely than Republicans to say the government has this responsibility, and within the Republican Party, those with lower incomes are more likely to say this than their counterparts earning more money.
Video calls and conferencing have been part of everyday life
Americans’ own words provide insight into exactly how their lives changed amid COVID-19. When asked to describe the new or different ways they had used technology, some Americans mention video calls and conferencing facilitating a variety of virtual interactions – including attending events like weddings, family holidays and funerals or transforming where and how they worked. 5 From family calls, shopping for groceries and placing takeout orders online to having telehealth visits with medical professionals or participating in online learning activities, some aspects of life have been virtually transformed:
“I’ve gone from not even knowing remote programs like Zoom even existed, to using them nearly every day.” – Man, 54
“[I’ve been] h andling … deaths of family and friends remotely, attending and sharing classical music concerts and recitals with other professionals, viewing [my] own church services and Bible classes, shopping. … Basically, [the internet has been] a lifeline.” – Woman, 69
“I … use Zoom for church youth activities. [I] use Zoom for meetings. I order groceries and takeout food online. We arranged for a ‘digital reception’ for my daughter’s wedding as well as live streaming the event.” – Woman, 44
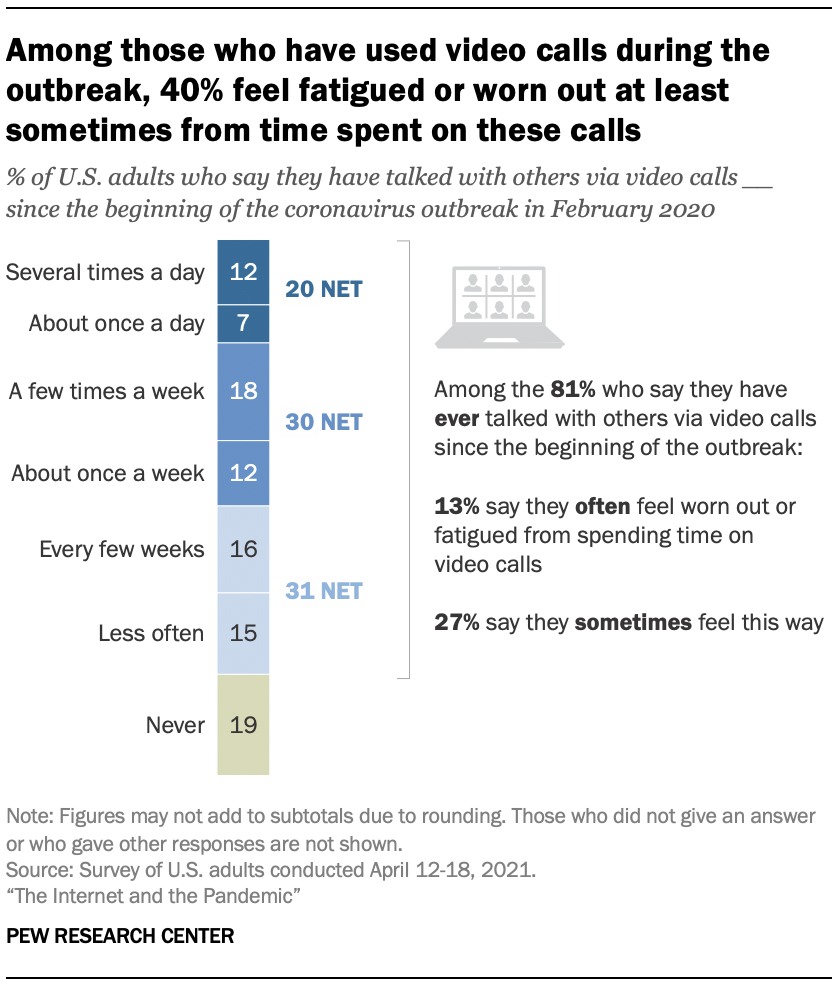
When asked about video calls specifically, half of Americans report they have talked with others in this way at least once a week since the beginning of the outbreak; one-in-five have used these platforms daily. But how often people have experienced this type of digital connectedness varies by age. For example, about a quarter of adults ages 18 to 49 (27%) say they have connected with others on video calls about once a day or more often, compared with 16% of those 50 to 64 and just 7% of those 65 and older.
Even as video technology became a part of life for users, many accounts of burnout surfaced and some speculated that “Zoom fatigue” was setting in as Americans grew weary of this type of screen time. The survey finds that some 40% of those who participated in video calls since the beginning of the pandemic – a third of all Americans – say they feel worn out or fatigued often or sometimes from the time they spend on video calls. About three-quarters of those who have been on these calls several times a day in the pandemic say this.
Fatigue is not limited to frequent users, however: For example, about a third (34%) of those who have made video calls about once a week say they feel worn out at least sometimes.
These are among the main findings from the survey. Other key results include:
Some Americans’ personal lives and social relationships have changed during the pandemic: Some 36% of Americans say their own personal lives changed in a major way as a result of the coronavirus outbreak. Another 47% say their personal lives changed, but only a little bit. About half (52%) of those who say major change has occurred in their personal lives due to the pandemic also say they have used tech in new ways, compared with about four-in-ten (38%) of those whose personal lives changed a little bit and roughly one-in-five (19%) of those who say their personal lives stayed about the same.
Even as tech helped some to stay connected, a quarter of Americans say they feel less close to close family members now compared with before the pandemic, and about four-in-ten (38%) say the same about friends they know well. Roughly half (53%) say this about casual acquaintances.
The majority of those who tried to sign up for vaccine appointments in the first part of the year went online to do so: Despite early problems with vaccine rollout and online registration systems , in the April survey tech problems did not appear to be major struggles for most adults who had tried to sign up online for COVID-19 vaccines. The survey explored Americans’ experiences getting these vaccine appointments and reveals that in April 57% of adults had tried to sign themselves up and 25% had tried to sign someone else up. Fully 78% of those who tried to sign themselves up and 87% of those who tried to sign others up were online registrants.
When it comes to difficulties with the online vaccine signup process, 29% of those who had tried to sign up online – 13% of all Americans – say it was very or somewhat difficult to sign themselves up for vaccines at that time. Among five reasons for this that the survey asked about, the most common major reason was lack of available appointments, rather than tech-related problems. Adults 65 and older who tried to sign themselves up for the vaccine online were the most likely age group to experience at least some difficulty when they tried to get a vaccine appointment.
Tech struggles and usefulness alike vary by race and ethnicity. Americans’ experiences also have varied across racial and ethnic groups. For example, Black Americans are more likely than White or Hispanic adults to meet the criteria for having “lower tech readiness.” 6 Among broadband users, Black and Hispanic adults were also more likely than White adults to be worried about paying their bills for their high-speed internet access at home as of April, though the share of Hispanic Americans who say this declined sharply since April 2020. And a majority of Black and Hispanic broadband users say they at least sometimes have experienced problems with their internet connection.
Still, Black adults and Hispanic adults are more likely than White adults to say various technologies – text messages, voice calls, video calls, social media sites and email – have helped them a lot to stay connected with family and friends amid the pandemic.
Tech has helped some adults under 30 to connect with friends, but tech fatigue also set in for some. Only about one-in-five adults ages 18 to 29 say they feel closer to friends they know well compared with before the pandemic. This share is twice as high as that among adults 50 and older. Adults under 30 are also more likely than any other age group to say social media sites have helped a lot in staying connected with family and friends (30% say so), and about four-in-ten of those ages 18 to 29 say this about video calls.
Screen time affected some negatively, however. About six-in-ten adults under 30 (57%) who have ever made video calls in the pandemic say they at least sometimes feel worn out or fatigued from spending time on video calls, and about half (49%) of young adults say they have tried to cut back on time spent on the internet or their smartphone.
- Throughout this report, “parents” refers to those who said they were the parent or guardian of any children who were enrolled in elementary, middle or high school and who lived in their household at the time of the survey. ↩
- People with a high-speed internet connection at home also are referred to as “home broadband users” or “broadband users” throughout this report. ↩
- Family incomes are based on 2019 earnings and adjusted for differences in purchasing power by geographic region and for household sizes. Middle income is defined here as two-thirds to double the median annual family income for all panelists on the American Trends Panel. Lower income falls below that range; upper income falls above it. ↩
- A separate Center study also fielded in April 2021 asked Americans what the government is responsible for on a number of topics, but did not mention the coronavirus outbreak. Some 43% of Americans said in that survey that the federal government has a responsibility to provide high-speed internet for all Americans. This was a significant increase from 2019, the last time the Center had asked that more general question, when 28% said the same. ↩
- Quotations in this report may have been lightly edited for grammar, spelling and clarity. ↩
- There were not enough Asian American respondents in the sample to be broken out into a separate analysis. As always, their responses are incorporated into the general population figures throughout this report. ↩
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Business & Workplace
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- COVID-19 & Technology
- Digital Divide
- Education & Learning Online
Is College Worth It?
Half of latinas say hispanic women’s situation has improved in the past decade and expect more gains, a majority of latinas feel pressure to support their families or to succeed at work, a look at small businesses in the u.s., majorities of adults see decline of union membership as bad for the u.s. and working people, most popular, report materials.
- American Trends Panel Wave 88
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center

Technology over the long run: zoom out to see how dramatically the world can change within a lifetime
It is easy to underestimate how much the world can change within a lifetime. considering how dramatically the world has changed can help us see how different the world could be in a few years or decades..
Technology can change the world in ways that are unimaginable until they happen. Switching on an electric light would have been unimaginable for our medieval ancestors. In their childhood, our grandparents would have struggled to imagine a world connected by smartphones and the Internet.
Similarly, it is hard for us to imagine the arrival of all those technologies that will fundamentally change the world we are used to.
We can remind ourselves that our own future might look very different from the world today by looking back at how rapidly technology has changed our world in the past. That’s what this article is about.
One insight I take away from this long-term perspective is how unusual our time is. Technological change was extremely slow in the past – the technologies that our ancestors got used to in their childhood were still central to their lives in their old age. In stark contrast to those days, we live in a time of extraordinarily fast technological change. For recent generations, it was common for technologies that were unimaginable in their youth to become common later in life.
The long-run perspective on technological change
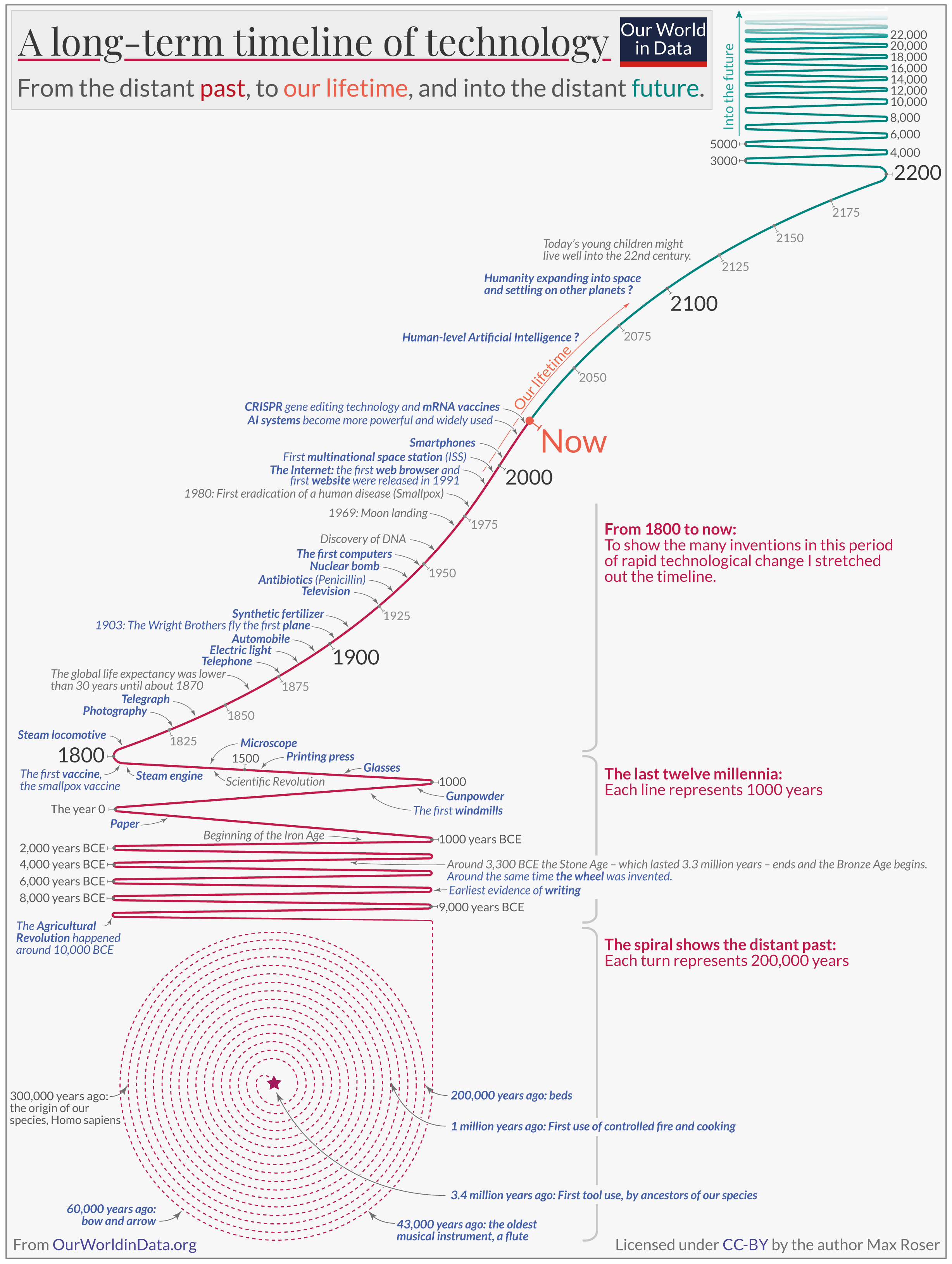
The big visualization offers a long-term perspective on the history of technology. 1
The timeline begins at the center of the spiral. The first use of stone tools, 3.4 million years ago, marks the beginning of this history of technology. 2 Each turn of the spiral represents 200,000 years of history. It took 2.4 million years – 12 turns of the spiral – for our ancestors to control fire and use it for cooking. 3
To be able to visualize the inventions in the more recent past – the last 12,000 years – I had to unroll the spiral. I needed more space to be able to show when agriculture, writing, and the wheel were invented. During this period, technological change was faster, but it was still relatively slow: several thousand years passed between each of these three inventions.
From 1800 onwards, I stretched out the timeline even further to show the many major inventions that rapidly followed one after the other.
The long-term perspective that this chart provides makes it clear just how unusually fast technological change is in our time.
You can use this visualization to see how technology developed in particular domains. Follow, for example, the history of communication: from writing to paper, to the printing press, to the telegraph, the telephone, the radio, all the way to the Internet and smartphones.
Or follow the rapid development of human flight. In 1903, the Wright brothers took the first flight in human history (they were in the air for less than a minute), and just 66 years later, we landed on the moon. Many people saw both within their lifetimes: the first plane and the moon landing.
This large visualization also highlights the wide range of technology’s impact on our lives. It includes extraordinarily beneficial innovations, such as the vaccine that allowed humanity to eradicate smallpox , and it includes terrible innovations, like the nuclear bombs that endanger the lives of all of us .
What will the next decades bring?
The red timeline reaches up to the present and then continues in green into the future. Many children born today, even without further increases in life expectancy, will live well into the 22nd century.
New vaccines, progress in clean, low-carbon energy, better cancer treatments – a range of future innovations could very much improve our living conditions and the environment around us. But, as I argue in a series of articles , there is one technology that could even more profoundly change our world: artificial intelligence (AI).
One reason why artificial intelligence is such an important innovation is that intelligence is the main driver of innovation itself. This fast-paced technological change could speed up even more if it’s driven not only by humanity’s intelligence but also by artificial intelligence. If this happens, the change currently stretched out over decades might happen within a very brief time span of just a year. Possibly even faster. 4
I think AI technology could have a fundamentally transformative impact on our world. In many ways, it is already changing our world, as I documented in this companion article . As this technology becomes more capable in the years and decades to come, it can give immense power to those who control it (and it poses the risk that it could escape our control entirely).
Such systems might seem hard to imagine today, but AI technology is advancing quickly. Many AI experts believe there is a real chance that human-level artificial intelligence will be developed within the next decades, as I documented in this article .
Technology will continue to change the world – we should all make sure that it changes it for the better
What is familiar to us today – photography, the radio, antibiotics, the Internet, or the International Space Station circling our planet – was unimaginable to our ancestors just a few generations ago. If your great-great-great grandparents could spend a week with you, they would be blown away by your everyday life.
What I take away from this history is that I will likely see technologies in my lifetime that appear unimaginable to me today.
In addition to this trend towards increasingly rapid innovation, there is a second long-run trend. Technology has become increasingly powerful. While our ancestors wielded stone tools, we are building globe-spanning AI systems and technologies that can edit our genes.
Because of the immense power that technology gives those who control it, there is little that is as important as the question of which technologies get developed during our lifetimes. Therefore, I think it is a mistake to leave the question about the future of technology to the technologists. Which technologies are controlled by whom is one of the most important political questions of our time because of the enormous power these technologies convey to those who control them.
We all should strive to gain the knowledge we need to contribute to an intelligent debate about the world we want to live in. To a large part, this means gaining knowledge and wisdom on the question of which technologies we want.
Acknowledgments: I would like to thank my colleagues Hannah Ritchie, Bastian Herre, Natasha Ahuja, Edouard Mathieu, Daniel Bachler, Charlie Giattino, and Pablo Rosado for their helpful comments on drafts of this essay and the visualization. Thanks also to Lizka Vaintrob and Ben Clifford for the conversation that initiated this visualization.
Appendix: About the choice of visualization in this article
The recent speed of technological change makes it difficult to picture the history of technology in one visualization. When you visualize this development on a linear timeline, then most of the timeline is almost empty, while all the action is crammed into the right corner:

In my large visualization here, I tried to avoid this problem and instead show the long history of technology in a way that lets you see when each technological breakthrough happened and how, within the last millennia, there was a continuous acceleration of technological change.
The recent speed of technological change makes it difficult to picture the history of technology in one visualization. In the appendix, I show how this would look if it were linear.
It is, of course, difficult to assess when exactly the first stone tools were used.
The research by McPherron et al. (2010) suggested that it was at least 3.39 million years ago. This is based on two fossilized bones found in Dikika in Ethiopia, which showed “stone-tool cut marks for flesh removal and percussion marks for marrow access”. These marks were interpreted as being caused by meat consumption and provide the first evidence that one of our ancestors, Australopithecus afarensis, used stone tools.
The research by Harmand et al. (2015) provided evidence for stone tool use in today’s Kenya 3.3 million years ago.
References:
McPherron et al. (2010) – Evidence for stone-tool-assisted consumption of animal tissues before 3.39 million years ago at Dikika, Ethiopia . Published in Nature.
Harmand et al. (2015) – 3.3-million-year-old stone tools from Lomekwi 3, West Turkana, Kenya . Published in Nature.
Evidence for controlled fire use approximately 1 million years ago is provided by Berna et al. (2012) Microstratigraphic evidence of in situ fire in the Acheulean strata of Wonderwerk Cave, Northern Cape province, South Africa , published in PNAS.
The authors write: “The ability to control fire was a crucial turning point in human evolution, but the question of when hominins first developed this ability still remains. Here we show that micromorphological and Fourier transform infrared microspectroscopy (mFTIR) analyses of intact sediments at the site of Wonderwerk Cave, Northern Cape province, South Africa, provide unambiguous evidence—in the form of burned bone and ashed plant remains—that burning took place in the cave during the early Acheulean occupation, approximately 1.0 Ma. To the best of our knowledge, this is the earliest secure evidence for burning in an archaeological context.”
This is what authors like Holden Karnofsky called ‘Process for Automating Scientific and Technological Advancement’ or PASTA. Some recent developments go in this direction: DeepMind’s AlphaFold helped to make progress on one of the large problems in biology, and they have also developed an AI system that finds new algorithms that are relevant to building a more powerful AI.
Cite this work
Our articles and data visualizations rely on work from many different people and organizations. When citing this article, please also cite the underlying data sources. This article can be cited as:
BibTeX citation
Reuse this work freely
All visualizations, data, and code produced by Our World in Data are completely open access under the Creative Commons BY license . You have the permission to use, distribute, and reproduce these in any medium, provided the source and authors are credited.
The data produced by third parties and made available by Our World in Data is subject to the license terms from the original third-party authors. We will always indicate the original source of the data in our documentation, so you should always check the license of any such third-party data before use and redistribution.
All of our charts can be embedded in any site.
Our World in Data is free and accessible for everyone.
Help us do this work by making a donation.
Along with Stanford news and stories, show me:
- Student information
- Faculty/Staff information
We want to provide announcements, events, leadership messages and resources that are relevant to you. Your selection is stored in a browser cookie which you can remove at any time using “Clear all personalization” below.
Listen to the essay, as read by Antero Garcia, associate professor in the Graduate School of Education.
As a professor of education and a former public school teacher, I’ve seen digital tools change lives in schools.
I’ve documented the ways mobile technology like phones can transform student engagement in my own classroom.
I’ve explored how digital tools might network powerful civic learning and dialogue for classrooms across the country – elements of education that are crucial for sustaining our democracy today.
And, like everyone, I’ve witnessed digital technologies make schooling safer in the midst of a global pandemic. Zoom and Google Classroom, for instance, allowed many students to attend classrooms virtually during a period when it was not feasible to meet in person.
So I want to tell you that I think technologies are changing education for the better and that we need to invest more in them – but I just can’t.
Given the substantial amount of scholarly time I’ve invested in documenting the life-changing possibilities of digital technologies, it gives me no pleasure to suggest that these tools might be slowly poisoning us. Despite their purported and transformational value, I’ve been wondering if our investment in educational technology might in fact be making our schools worse.
Let me explain.
When I was a classroom teacher, I loved relying on the latest tools to create impressive and immersive experiences for my students. We would utilize technology to create class films, produce social media profiles for the Janie Crawfords, the Holden Caulfields, and other literary characters we studied, and find playful ways to digitally share our understanding of the ideas we studied in our classrooms.
As a teacher, technology was a way to build on students’ interests in pop culture and the world around them. This was exciting to me.
But I’ve continued to understand that the aspects of technology I loved weren’t actually about technology at all – they were about creating authentic learning experiences with young people. At the heart of these digital explorations were my relationships with students and the trust we built together.
“Part of why I’ve grown so skeptical about this current digital revolution is because of how these tools reshape students’ bodies and their relation to the world around them.”
I do see promise in the suite of digital tools that are available in classrooms today. But my research focus on platforms – digital spaces like Amazon, Netflix, and Google that reshape how users interact in online environments – suggests that when we focus on the trees of individual tools, we ignore the larger forest of social and cognitive challenges.
Most people encounter platforms every day in their online social lives. From the few online retail stores where we buy groceries to the small handful of sites that stream our favorite shows and media content, platforms have narrowed how we use the internet today to a small collection of Silicon Valley behemoths. Our social media activities, too, are limited to one or two sites where we check on the updates, photos, and looped videos of friends and loved ones.
These platforms restrict our online and offline lives to a relatively small number of companies and spaces – we communicate with a finite set of tools and consume a set of media that is often algorithmically suggested. This centralization of internet – a trend decades in the making – makes me very uneasy.
From willfully hiding the negative effects of social media use for vulnerable populations to creating tools that reinforce racial bias, today’s platforms are causing harm and sowing disinformation for young people and adults alike. The deluge of difficult ethical and pedagogical questions around these tools are not being broached in any meaningful way in schools – even adults aren’t sure how to manage their online lives.
You might ask, “What does this have to do with education?” Platforms are also a large part of how modern schools operate. From classroom management software to attendance tracking to the online tools that allowed students to meet safely during the pandemic, platforms guide nearly every student interaction in schools today. But districts are utilizing these tools without considering the wider spectrum of changes that they have incurred alongside them.
Antero Garcia, associate professor of education (Image credit: Courtesy Antero Garcia)
For example, it might seem helpful for a school to use a management tool like Classroom Dojo (a digital platform that can offer parents ways to interact with and receive updates from their family’s teacher) or software that tracks student reading and development like Accelerated Reader for day-to-day needs. However, these tools limit what assessment looks like and penalize students based on flawed interpretations of learning.
Another problem with platforms is that they, by necessity, amass large swaths of data. Myriad forms of educational technology exist – from virtual reality headsets to e-readers to the small sensors on student ID cards that can track when students enter schools. And all of this student data is being funneled out of schools and into the virtual black boxes of company databases.
Part of why I’ve grown so skeptical about this current digital revolution is because of how these tools reshape students’ bodies and their relation to the world around them. Young people are not viewed as complete human beings but as boxes checked for attendance, for meeting academic progress metrics, or for confirming their location within a school building. Nearly every action that students perform in schools – whether it’s logging onto devices, accessing buildings, or sharing content through their private online lives – is noticed and recorded. Children in schools have become disembodied from their minds and their hearts. Thus, one of the greatest and implicit lessons that kids learn in schools today is that they must sacrifice their privacy in order to participate in conventional, civic society.
The pandemic has only made the situation worse. At its beginnings, some schools relied on software to track students’ eye movements, ostensibly ensuring that kids were paying attention to the tasks at hand. Similarly, many schools required students to keep their cameras on during class time for similar purposes. These might be seen as in the best interests of students and their academic growth, but such practices are part of a larger (and usually more invisible) process of normalizing surveillance in the lives of youth today.
I am not suggesting that we completely reject all of the tools at our disposal – but I am urging for more caution. Even the seemingly benign resources we might use in our classrooms today come with tradeoffs. Every Wi-Fi-connected, “smart” device utilized in schools is an investment in time, money, and expertise in technology over teachers and the teaching profession.
Our focus on fixing or saving schools via digital tools assumes that the benefits and convenience that these invisible platforms offer are worth it.
But my ongoing exploration of how platforms reduce students to quantifiable data suggests that we are removing the innovation and imagination of students and teachers in the process.
Antero Garcia is associate professor of education in the Graduate School of Education .
In Their Own Words is a collaboration between the Stanford Public Humanities Initiative and Stanford University Communications.
If you’re a Stanford faculty member (in any discipline or school) who is interested in writing an essay for this series, please reach out to Natalie Jabbar at [email protected] .
Essay on Technology – A Boon or Bane for Students
500+ words essay on technology for students.
In this essay on technology, we are going to discuss what technology is, what are its uses, and also what technology can do? First of all, technology refers to the use of technical and scientific knowledge to create, monitor, and design machinery. Also, technology helps in making other goods that aid mankind.
Essay on Technology – A Boon or Bane?
Experts are debating on this topic for years. Also, the technology covered a long way to make human life easier but the negative aspect of it can’t be ignored. Over the years technological advancement has caused a severe rise in pollution . Also, pollution has become a major cause of many health issues. Besides, it has cut off people from society rather than connecting them. Above all, it has taken away many jobs from the workers class.

Familiarity between Technology and Science
As they are completely different fields but they are interdependent on each other. Also, it is due to science contribution we can create new innovation and build new technological tools. Apart from that, the research conducted in laboratories contributes a lot to the development of technologies. On the other hand, technology extends the agenda of science.
Vital Part of our Life
Regularly evolving technology has become an important part of our lives. Also, newer technologies are taking the market by storm and the people are getting used to them in no time. Above all, technological advancement has led to the growth and development of nations.
Negative Aspect of Technology
Although technology is a good thing, everything has two sides. Technology also has two sides one is good and the other is bad. Here are some negative aspects of technology that we are going to discuss.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
With new technology the industrialization increases which give birth to many pollutions like air, water, soil, and noise. Also, they cause many health-related issues in animals, birds, and human beings.
Exhaustion of Natural Resources
New technology requires new resources for which the balance is disturbed. Eventually, this will lead to over-exploitation of natural resources which ultimately disturbs the balance of nature.
Unemployment
A single machine can replace many workers. Also, machines can do work at a constant pace for several hours or days without stopping. Due to this, many workers lost their job which ultimately increases unemployment .
Types of Technology
Generally, we judge technology on the same scale but in reality, technology is divided into various types. This includes information technology, industrial technology , architectural technology, creative technology and many more. Let’s discuss these technologies in brief.
Industrial Technology
This technology organizes engineering and manufacturing technology for the manufacturing of machines. Also, this makes the production process easier and convenient.
Creative Technology
This process includes art, advertising, and product design which are made with the help of software. Also, it comprises of 3D printers , virtual reality, computer graphics, and other wearable technologies.
Information Technology
This technology involves the use of telecommunication and computer to send, receive and store information. Internet is the best example of Information technology.

FAQs on Essay on Technology
Q.1 What is Information technology?
A – It is a form of technology that uses telecommunication and computer systems for study. Also, they send, retrieve, and store data.
Q.2 Is technology harmful to humans?
A – No, technology is not harmful to human beings until it is used properly. But, misuses of technology can be harmful and deadly.
Download Toppr – Best Learning App for Class 5 to 12
Toppr provides free study materials, last 10 years of question papers, 1000+ hours of video lectures, live 24/7 doubts solving, and much more for FREE! Download Toppr app for Android and iOS or signup for free.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Are you seeking one-on-one college counseling and/or essay support? Limited spots are now available. Click here to learn more.
54 Most Interesting Technology Research Topics for 2023
May 30, 2023

Scrambling to find technology research topics for the assignment that’s due sooner than you thought? Take a scroll down these 54 interesting technology essay topics in 10 different categories, including controversial technology topics, and some example research questions for each.
Social technology research topics
Whether you have active profiles on every social media platform, you’ve taken a social media break, or you generally try to limit your engagement as much as possible, you probably understand how pervasive social technologies have become in today’s culture. Social technology will especially appeal to those looking for widely discussed, mainstream technology essay topics.
- How do viewers respond to virtual influencers vs human influencers? Is one more effective or ethical over the other?
- Across social media platforms, when and where is mob mentality most prevalent? How do the nuances of mob mentality shift depending on the platform or topic?
- Portable devices like cell phones, laptops, and tablets have certainly made daily life easier in some ways. But how have they made daily life more difficult?
- How does access to social media affect developing brains? And what about mature brains?
- Can dating apps alter how users perceive and interact with people in real life?
- Studies have proven “doomscrolling” to negatively impact mental health—could there ever be any positive impacts?
Cryptocurrency and blockchain technology research topics
Following cryptocurrency and blockchain technology has been a rollercoaster the last few years. And since Bitcoin’s conception in 2009, cryptocurrency has consistently showed up on many lists of controversial technology topics.
- Is it ethical for celebrities or influential people to promote cryptocurrencies or cryptographic assets like NFTs ?
- What are the environmental impacts of mining cryptocurrencies? Could those impacts ever change?
- How does cryptocurrency impact financial security and financial health?
- Could the privacy cryptocurrency offers ever be worth the added security risks?
- How might cryptocurrency regulations and impacts continue to evolve?
- Created to enable cryptocurrency, blockchain has since proven useful in several other industries. What new uses could blockchain have?
Artificial intelligence technology research topics
We started 2023 with M3GAN’s box office success, and now we’re fascinated (or horrified) with ChatGPT , voice cloning , and deepfakes . While people have discussed artificial intelligence for ages, recent advances have really pushed this topic to the front of our minds. Those searching for controversial technology topics should pay close attention to this one.
- OpenAI –the company behind ChatGPT–has shown commitment to safe, moderated AI tools that they hope will provide positive benefits to society. Sam Altman, their CEO, recently testified before a US Senate He described what AI makes possible and called for more regulation in the industry. But even with companies like OpenAI displaying efforts to produce safe AI and advocating for regulations, can AI ever have a purely positive impact? Are certain pitfalls unavoidable?
- In a similar vein, can AI ever actually be ethically or safely produced? Will there always be certain risks?
- How might AI tools impact society across future generations?
- Countless movies and television shows explore the idea of AI going wrong, going back all the way to 1927’s Metropolis . What has a greater impact on public perception—representations in media or industry developments? And can public perception impact industry developments and their effectiveness?
Beauty and anti-aging technology
Throughout human history, people in many cultures have gone to extreme lengths to capture and maintain a youthful beauty. But technology has taken the pursuit of beauty and youth to another level. For those seeking technology essay topics that are both timely and timeless, this one’s a gold mine.
- With augmented reality technology, companies like Perfect allow app users to virtually try on makeup, hair color, hair accessories, and hand or wrist accessories. Could virtual try-ons lead to a somewhat less wasteful beauty industry? What downsides should we consider?
- Users of the Perfect app can also receive virtual diagnoses for skin care issues and virtually “beautify” themselves with smoothed skin, erased blemishes, whitened teeth, brightened under-eye circles, and reshaped facial structures. How could advancements in beauty and anti-aging technology affect self-perception and mental health?
- What are the best alternatives to animal testing within the beauty and anti-aging industry?
- Is anti-aging purely a cosmetic pursuit? Could anti-aging technology provide other benefits?
- Could people actually find a “cure” to aging? And could a cure to aging lead to longer lifespans?
- How might longer human lifespans affect the Earth?
Geoengineering technology research topics
An umbrella term, geoengineering refers to large-scale technologies that can alter the earth and its climate. Typically, these types of technologies aim to combat climate change. Those searching for controversial technology topics should consider looking into this one.
- What benefits can solar geoengineering provide? Can they outweigh the severe risks?
- Compare solar geoengineering methods like mirrors in space, stratospheric aerosol injection, marine cloud brightening, and other proposed methods. How have these methods evolved? How might they continue to evolve?
- Which direct air capture methods are most sustainable?
- How can technology contribute to reforestation efforts?
- What are the best uses for biochar? And how can biochar help or harm the earth?
- Out of all the carbon geoengineering methods that exist or have been proposed, which should we focus on the most?
Creative and performing arts technology topics
While tensions often arise between artists and technology, they’ve also maintained a symbiotic relationship in many ways. It’s complicated. But of course, that’s what makes it interesting. Here’s another option for those searching for timely and timeless technology essay topics.
- How has the relationship between art and technology evolved over time?
- How has technology impacted the ways people create art? And how has technology impacted the ways people engage with art?
- Technology has made creating and viewing art widely accessible. Does this increased accessibility change the value of art? And do we value physical art more than digital art?
- Does technology complement storytelling in the performing arts? Or does technology hinder storytelling in the performing arts?
- Which current issues in the creative or performing arts could potentially be solved with technology?
Cellular agriculture technology research topics
And another route for those drawn to controversial technology topics: cellular agriculture. You’ve probably heard about popular plant-based meat options from brands like Impossible and Beyond Meat . While products made with cellular agriculture also don’t require the raising and slaughtering of livestock, they are not plant-based. Cellular agriculture allows for the production of animal-sourced foods and materials made from cultured animal cells.
- Many consumers have a proven bias against plant-based meats. Will that same bias extend to cultured meat, despite cultured meat coming from actual animal cells?
- Which issues can arise from patenting genes?
- Does the animal agriculture industry provide any benefits that cellular agriculture may have trouble replicating?
- How might products made with cellular agriculture become more affordable?
- Could cellular agriculture conflict with the notion of a “ circular bioeconomy ?” And should we strive for a circular bioeconomy? Can we create a sustainable relationship between technology, capitalism, and the environment, with or without cellular agriculture?
Transportation technology research topics
For decades, we’ve expected flying cars to carry us into a techno-utopia, where everything’s shiny, digital, and easy. We’ve heard promises of super fast trains that can zap us across the country or even across the world. We’ve imagined spring breaks on the moon, jet packs, and teleportation. Who wouldn’t love the option to go anywhere, anytime, super quickly? Transportation technology is another great option for those seeking widely discussed, mainstream technology essay topics.
- Once upon a time, Lady Gaga was set to perform in space as a promotion for Virgin Galactic . While Virgin Galactic never actually launched the iconic musician/actor, soon, they hope to launch their first commercial flight full of civilians–who paid $450,000 a pop–on a 90-minute trip into the stars. And if you think that’s pricey, SpaceX launched three businessmen into space for $55 million in April, 2022 (though with meals included, this is actually a total steal). So should we be launching people into space just for fun? What are the impacts of space tourism?
- Could technology improve the way hazardous materials get transported?
- How can the 5.9 GHz Safety Band affect drivers?
- Which might be safer: self-driving cars or self-flying airplanes?
- Compare hyperloop and maglev Which is better and why?
- Can technology improve safety for cyclists?
Gaming technology topics
A recent study involving over 2000 children found links between video game play and enhanced cognitive abilities. While many different studies have found the impacts of video games to be positive or neutral, we still don’t fully understand the impact of every type of video game on every type of brain. Regardless, most people have opinions on video gaming. So this one’s for those seeking widely discussed, mainstream, and controversial technology topics.
- Are different types or genres of video games more cognitively beneficial than others? Or are certain gaming consoles more cognitively beneficial than others?
- How do the impacts of video games differ from other types of games, such as board games or puzzles?
- What ethical challenges and safety risks come with virtual reality gaming?
- How does a player perceive reality during a virtual reality game compared to during other types of video games?
- Can neurodivergent brains benefit from video games in different ways than neurotypical brains?
Medical technology
Advancements in healthcare have the power to change and save lives. In the last ten years, countless new medical technologies have been developed, and in the next ten years, countless more will likely emerge. Always relevant and often controversial, this final technology research topic could interest anyone.
- Which ethical issues might arise from editing genes using CRISPR-Cas9 technology? And should this technology continue to be illegal in the United States?
- How has telemedicine impacted patients and the healthcare they receive?
- Can neurotechnology devices potentially affect a user’s agency, identity, privacy, and/or cognitive liberty?
- How could the use of medical 3-D printing continue to evolve?
- Are patients more likely to skip digital therapeutics than in-person therapeutic methods? And can the increased screen-time required by digital therapeutics impact mental health
What do you do next?
Now that you’ve picked from this list of technology essay topics, you can do a deep dive and immerse yourself in new ideas, new information, and new perspectives. And of course, now that these topics have motivated you to change the world, look into the best computer science schools , the top feeders to tech and Silicon Valley , the best summer programs for STEM students , and the best biomedical engineering schools .
- College Success
- High School Success

Mariya holds a BFA in Creative Writing from the Pratt Institute and is currently pursuing an MFA in writing at the University of California Davis. Mariya serves as a teaching assistant in the English department at UC Davis. She previously served as an associate editor at Carve Magazine for two years, where she managed 60 fiction writers. She is the winner of the 2015 Stony Brook Fiction Prize, and her short stories have been published in Mid-American Review , Cutbank , Sonora Review , New Orleans Review , and The Collagist , among other magazines.
- 2-Year Colleges
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Essay
- College Search/Knowledge
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Data Visualizations
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- Graduate School Admissions
- High Schools
- Homeschool Resources
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Outdoor Adventure
- Private High School Spotlight
- Research Programs
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Teacher Tools
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight

“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.
I am a... Student Student Parent Counselor Educator Other First Name Last Name Email Address Zip Code Area of Interest Business Computer Science Engineering Fine/Performing Arts Humanities Mathematics STEM Pre-Med Psychology Social Studies/Sciences Submit
MIT Technology Review
- Newsletters
Ten big global challenges technology could solve
None is easy, but all are incredibly important.
- The Editors archive page
Carbon sequestration Cutting greenhouse-gas emissions alone won’t be enough to prevent sharp increases in global temperatures. We’ll also need to remove vast amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, which not only would be incredibly expensive but would present us with the thorny problem of what to do with all that CO 2 . A growing number of startups are exploring ways of recycling carbon dioxide into products, including synthetic fuels, polymers, carbon fiber, and concrete. That’s promising, but what we’ll really need is a cheap way to permanently store the billions of tons of carbon dioxide that we might have to pull out of the atmosphere.
Grid-scale energy storage Renewable energy sources like wind and solar are becoming cheap and more widely deployed, but they don’t generate electricity when the sun’s not shining or wind isn’t blowing. That limits how much power these sources can supply, and how quickly we can move away from steady sources like coal and natural gas. The cost of building enough batteries to back up entire grids for the days when renewable generation flags would be astronomical. Various scientists and startups are working to develop cheaper forms of grid-scale storage that can last for longer periods, including flow batteries or tanks of molten salt. Either way, we desperately need a cheaper and more efficient way to store vast amounts of electricity.

Universal flu vaccine Pandemic flu is rare but deadly. At least 50 million people died in the 1918 pandemic of H1N1 flu. More recently, about a million people died in the 1957-’58 and 1968 pandemics, while something like half a million died in a 2009 recurrence of H1N1. The recent death tolls are lower in part because the viruses were milder strains. We might not be so lucky next time—a particularly potent strain of the virus could replicate too quickly for any tailor-made vaccine to effectively fight it. A universal flu vaccine that protected not only against the relatively less harmful variants but also against a catastrophic once-in-a-century outbreak is a crucial public health challenge.
Dementia treatment More than one in 10 Americans over the age of 65 has Alzheimer’s; a third of those over 85 do. As people’s life spans lengthen, the number of people living with the disease—in the US and around the world—is likely to skyrocket. Alzheimer’s remains poorly understood: conclusive diagnoses are possible only after death, and even then, doctors debate the distinction between Alzheimer’s and other forms of dementia. However, advances in neuroscience and genetics are beginning to shed more light. That understanding is providing clues to how it might be possible to slow or even shut down the devastating effects of the condition.

Ocean clean-up Billions of tiny pieces of plastic—so-called “microplastics”—are now floating throughout the world’s oceans. Much of this waste comes from bags or straws that have been broken up over time. It’s poisoning birds, fish, and humans. Researchers fear that the effects on both human health and the environment will be profound, and it may take centuries to clean up the hundreds of millions of tons of plastic that have accumulated over the decades. Because the pollution is so diffuse, it’s difficult to clean up, and while there are prototype methods for tackling the massive oceanic garbage patches, there is no solution for coasts, seas, and waterways.

Energy-efficient desalination There is about 50 times as much salt water on earth as there is fresh water. As the world’s population grows and climate change intensifies droughts, the need for fresh water is going to grow more acute. Israel has built the world’s biggest reverse-osmosis desalination facilities and now gets most of its household water from the sea, but that method is too energy intensive to be practical worldwide. New types of membranes might help; electrochemical techniques may also help to make brackish water useful for irrigation. As far as climate-change adaptation technologies go, creating drinking water from the ocean ought to be a top priority.

Safe driverless car Autonomous vehicles have been tested for millions of miles on public roads. Pilot programs for delivery and taxi services are under way in places like the suburbs of Phoenix. But driverless cars still aren’t ready to take over roads in general. They have trouble handling chaotic traffic, and difficulty with weather conditions like snow and fog. If they can be made reliably safe, they might allow a wholesale reimagining of transportation. Traffic jams might be eliminated, and cities could be transformed as parking lots give way to new developments. Above all, self-driving cars, if widely deployed, are expected to eliminate most of the 1.25 million deaths a year caused by traffic accidents.

Embodied AI Last fall a video of Atlas, designed by Boston Dynamics, swept the internet. It showed the robot jumping up steps like a commando. This came only two years after AlphaGo beat the world’s best Go player. Atlas can’t play Go (it is embodied, but not intelligent), and AlphaGo can’t run (it’s intelligent, in its own way, but lacks a body). So what happens if you put AlphaGo’s mind in Atlas’s body? Many researchers say true general artificial intelligence might depend on an ability to relate internal computational processes to real things in the physical world, and that an AI would acquire that ability by learning to interact with the physical world as people and animals do.

We can predict hurricanes days and sometimes weeks in advance, but earthquakes still come as a surprise. Predicting them with confidence could save millions of lives.
Earthquake prediction Over 100,000 people died in the 2010 Haiti earthquake, and the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami—triggered by one of the most powerful earthquakes ever recorded—killed nearly a quarter of a million people in Indonesia, Sri Lanka, India, and elsewhere. We can predict hurricanes days and sometimes weeks in advance, but earthquakes still come as a surprise. Predicting earthquakes with some confidence over the medium term would allow planners to figure out durable solutions. At least giving a few hours’ warning would allow people to evacuate unsafe areas, and could save millions of lives.
Brain decoding Our brains remain a deep mystery to neuroscientists. Everything we think and remember, and all our movements, must somehow be coded in the billions of neurons in our heads. But what is that code? There are still many unknowns and puzzles in understanding the way our brains store and communicate our thoughts. Cracking that code could lead to breakthroughs in how we treat mental disorders like schizophrenia and autism. It might allow us to improve direct interfaces that communicate directly from our brains to computers, or even to other people—a life-changing development for people who are paralyzed by injury or degenerative disease.

Keep Reading
Most popular, how a simple circuit could offer an alternative to energy-intensive gpus.
The creative new approach could lead to more energy-efficient machine-learning hardware.
- Sophia Chen archive page

What I learned from the UN’s “AI for Good” summit
OpenAI’s CEO Sam Altman was the star speaker of the summit.
- Melissa Heikkilä archive page
An AI startup made a hyperrealistic deepfake of me that’s so good it’s scary
Synthesia's new technology is impressive but raises big questions about a world where we increasingly can’t tell what’s real.
What’s next for MDMA
The FDA is poised to approve the notorious party drug as a therapy. Here’s what it means, and where similar drugs stand in the US.
- Cassandra Willyard archive page
Stay connected
Get the latest updates from mit technology review.
Discover special offers, top stories, upcoming events, and more.
Thank you for submitting your email!
It looks like something went wrong.
We’re having trouble saving your preferences. Try refreshing this page and updating them one more time. If you continue to get this message, reach out to us at [email protected] with a list of newsletters you’d like to receive.
REALIZING THE PROMISE:
Leading up to the 75th anniversary of the UN General Assembly, this “Realizing the promise: How can education technology improve learning for all?” publication kicks off the Center for Universal Education’s first playbook in a series to help improve education around the world.
It is intended as an evidence-based tool for ministries of education, particularly in low- and middle-income countries, to adopt and more successfully invest in education technology.
While there is no single education initiative that will achieve the same results everywhere—as school systems differ in learners and educators, as well as in the availability and quality of materials and technologies—an important first step is understanding how technology is used given specific local contexts and needs.
The surveys in this playbook are designed to be adapted to collect this information from educators, learners, and school leaders and guide decisionmakers in expanding the use of technology.
Introduction
While technology has disrupted most sectors of the economy and changed how we communicate, access information, work, and even play, its impact on schools, teaching, and learning has been much more limited. We believe that this limited impact is primarily due to technology being been used to replace analog tools, without much consideration given to playing to technology’s comparative advantages. These comparative advantages, relative to traditional “chalk-and-talk” classroom instruction, include helping to scale up standardized instruction, facilitate differentiated instruction, expand opportunities for practice, and increase student engagement. When schools use technology to enhance the work of educators and to improve the quality and quantity of educational content, learners will thrive.
Further, COVID-19 has laid bare that, in today’s environment where pandemics and the effects of climate change are likely to occur, schools cannot always provide in-person education—making the case for investing in education technology.
Here we argue for a simple yet surprisingly rare approach to education technology that seeks to:
- Understand the needs, infrastructure, and capacity of a school system—the diagnosis;
- Survey the best available evidence on interventions that match those conditions—the evidence; and
- Closely monitor the results of innovations before they are scaled up—the prognosis.
RELATED CONTENT

Podcast: How education technology can improve learning for all students

To make ed tech work, set clear goals, review the evidence, and pilot before you scale
The framework.
Our approach builds on a simple yet intuitive theoretical framework created two decades ago by two of the most prominent education researchers in the United States, David K. Cohen and Deborah Loewenberg Ball. They argue that what matters most to improve learning is the interactions among educators and learners around educational materials. We believe that the failed school-improvement efforts in the U.S. that motivated Cohen and Ball’s framework resemble the ed-tech reforms in much of the developing world to date in the lack of clarity improving the interactions between educators, learners, and the educational material. We build on their framework by adding parents as key agents that mediate the relationships between learners and educators and the material (Figure 1).
Figure 1: The instructional core
Adapted from Cohen and Ball (1999)
As the figure above suggests, ed-tech interventions can affect the instructional core in a myriad of ways. Yet, just because technology can do something, it does not mean it should. School systems in developing countries differ along many dimensions and each system is likely to have different needs for ed-tech interventions, as well as different infrastructure and capacity to enact such interventions.
The diagnosis:
How can school systems assess their needs and preparedness.
A useful first step for any school system to determine whether it should invest in education technology is to diagnose its:
- Specific needs to improve student learning (e.g., raising the average level of achievement, remediating gaps among low performers, and challenging high performers to develop higher-order skills);
- Infrastructure to adopt technology-enabled solutions (e.g., electricity connection, availability of space and outlets, stock of computers, and Internet connectivity at school and at learners’ homes); and
- Capacity to integrate technology in the instructional process (e.g., learners’ and educators’ level of familiarity and comfort with hardware and software, their beliefs about the level of usefulness of technology for learning purposes, and their current uses of such technology).
Before engaging in any new data collection exercise, school systems should take full advantage of existing administrative data that could shed light on these three main questions. This could be in the form of internal evaluations but also international learner assessments, such as the Program for International Student Assessment (PISA), the Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS), and/or the Progress in International Literacy Study (PIRLS), and the Teaching and Learning International Study (TALIS). But if school systems lack information on their preparedness for ed-tech reforms or if they seek to complement existing data with a richer set of indicators, we developed a set of surveys for learners, educators, and school leaders. Download the full report to see how we map out the main aspects covered by these surveys, in hopes of highlighting how they could be used to inform decisions around the adoption of ed-tech interventions.
The evidence:
How can school systems identify promising ed-tech interventions.
There is no single “ed-tech” initiative that will achieve the same results everywhere, simply because school systems differ in learners and educators, as well as in the availability and quality of materials and technologies. Instead, to realize the potential of education technology to accelerate student learning, decisionmakers should focus on four potential uses of technology that play to its comparative advantages and complement the work of educators to accelerate student learning (Figure 2). These comparative advantages include:
- Scaling up quality instruction, such as through prerecorded quality lessons.
- Facilitating differentiated instruction, through, for example, computer-adaptive learning and live one-on-one tutoring.
- Expanding opportunities to practice.
- Increasing learner engagement through videos and games.
Figure 2: Comparative advantages of technology
Here we review the evidence on ed-tech interventions from 37 studies in 20 countries*, organizing them by comparative advantage. It’s important to note that ours is not the only way to classify these interventions (e.g., video tutorials could be considered as a strategy to scale up instruction or increase learner engagement), but we believe it may be useful to highlight the needs that they could address and why technology is well positioned to do so.
When discussing specific studies, we report the magnitude of the effects of interventions using standard deviations (SDs). SDs are a widely used metric in research to express the effect of a program or policy with respect to a business-as-usual condition (e.g., test scores). There are several ways to make sense of them. One is to categorize the magnitude of the effects based on the results of impact evaluations. In developing countries, effects below 0.1 SDs are considered to be small, effects between 0.1 and 0.2 SDs are medium, and those above 0.2 SDs are large (for reviews that estimate the average effect of groups of interventions, called “meta analyses,” see e.g., Conn, 2017; Kremer, Brannen, & Glennerster, 2013; McEwan, 2014; Snilstveit et al., 2015; Evans & Yuan, 2020.)
*In surveying the evidence, we began by compiling studies from prior general and ed-tech specific evidence reviews that some of us have written and from ed-tech reviews conducted by others. Then, we tracked the studies cited by the ones we had previously read and reviewed those, as well. In identifying studies for inclusion, we focused on experimental and quasi-experimental evaluations of education technology interventions from pre-school to secondary school in low- and middle-income countries that were released between 2000 and 2020. We only included interventions that sought to improve student learning directly (i.e., students’ interaction with the material), as opposed to interventions that have impacted achievement indirectly, by reducing teacher absence or increasing parental engagement. This process yielded 37 studies in 20 countries (see the full list of studies in Appendix B).
Scaling up standardized instruction
One of the ways in which technology may improve the quality of education is through its capacity to deliver standardized quality content at scale. This feature of technology may be particularly useful in three types of settings: (a) those in “hard-to-staff” schools (i.e., schools that struggle to recruit educators with the requisite training and experience—typically, in rural and/or remote areas) (see, e.g., Urquiola & Vegas, 2005); (b) those in which many educators are frequently absent from school (e.g., Chaudhury, Hammer, Kremer, Muralidharan, & Rogers, 2006; Muralidharan, Das, Holla, & Mohpal, 2017); and/or (c) those in which educators have low levels of pedagogical and subject matter expertise (e.g., Bietenbeck, Piopiunik, & Wiederhold, 2018; Bold et al., 2017; Metzler & Woessmann, 2012; Santibañez, 2006) and do not have opportunities to observe and receive feedback (e.g., Bruns, Costa, & Cunha, 2018; Cilliers, Fleisch, Prinsloo, & Taylor, 2018). Technology could address this problem by: (a) disseminating lessons delivered by qualified educators to a large number of learners (e.g., through prerecorded or live lessons); (b) enabling distance education (e.g., for learners in remote areas and/or during periods of school closures); and (c) distributing hardware preloaded with educational materials.
Prerecorded lessons
Technology seems to be well placed to amplify the impact of effective educators by disseminating their lessons. Evidence on the impact of prerecorded lessons is encouraging, but not conclusive. Some initiatives that have used short instructional videos to complement regular instruction, in conjunction with other learning materials, have raised student learning on independent assessments. For example, Beg et al. (2020) evaluated an initiative in Punjab, Pakistan in which grade 8 classrooms received an intervention that included short videos to substitute live instruction, quizzes for learners to practice the material from every lesson, tablets for educators to learn the material and follow the lesson, and LED screens to project the videos onto a classroom screen. After six months, the intervention improved the performance of learners on independent tests of math and science by 0.19 and 0.24 SDs, respectively but had no discernible effect on the math and science section of Punjab’s high-stakes exams.
One study suggests that approaches that are far less technologically sophisticated can also improve learning outcomes—especially, if the business-as-usual instruction is of low quality. For example, Naslund-Hadley, Parker, and Hernandez-Agramonte (2014) evaluated a preschool math program in Cordillera, Paraguay that used audio segments and written materials four days per week for an hour per day during the school day. After five months, the intervention improved math scores by 0.16 SDs, narrowing gaps between low- and high-achieving learners, and between those with and without educators with formal training in early childhood education.
Yet, the integration of prerecorded material into regular instruction has not always been successful. For example, de Barros (2020) evaluated an intervention that combined instructional videos for math and science with infrastructure upgrades (e.g., two “smart” classrooms, two TVs, and two tablets), printed workbooks for students, and in-service training for educators of learners in grades 9 and 10 in Haryana, India (all materials were mapped onto the official curriculum). After 11 months, the intervention negatively impacted math achievement (by 0.08 SDs) and had no effect on science (with respect to business as usual classes). It reduced the share of lesson time that educators devoted to instruction and negatively impacted an index of instructional quality. Likewise, Seo (2017) evaluated several combinations of infrastructure (solar lights and TVs) and prerecorded videos (in English and/or bilingual) for grade 11 students in northern Tanzania and found that none of the variants improved student learning, even when the videos were used. The study reports effects from the infrastructure component across variants, but as others have noted (Muralidharan, Romero, & Wüthrich, 2019), this approach to estimating impact is problematic.
A very similar intervention delivered after school hours, however, had sizeable effects on learners’ basic skills. Chiplunkar, Dhar, and Nagesh (2020) evaluated an initiative in Chennai (the capital city of the state of Tamil Nadu, India) delivered by the same organization as above that combined short videos that explained key concepts in math and science with worksheets, facilitator-led instruction, small groups for peer-to-peer learning, and occasional career counseling and guidance for grade 9 students. These lessons took place after school for one hour, five times a week. After 10 months, it had large effects on learners’ achievement as measured by tests of basic skills in math and reading, but no effect on a standardized high-stakes test in grade 10 or socio-emotional skills (e.g., teamwork, decisionmaking, and communication).
Drawing general lessons from this body of research is challenging for at least two reasons. First, all of the studies above have evaluated the impact of prerecorded lessons combined with several other components (e.g., hardware, print materials, or other activities). Therefore, it is possible that the effects found are due to these additional components, rather than to the recordings themselves, or to the interaction between the two (see Muralidharan, 2017 for a discussion of the challenges of interpreting “bundled” interventions). Second, while these studies evaluate some type of prerecorded lessons, none examines the content of such lessons. Thus, it seems entirely plausible that the direction and magnitude of the effects depends largely on the quality of the recordings (e.g., the expertise of the educator recording it, the amount of preparation that went into planning the recording, and its alignment with best teaching practices).
These studies also raise three important questions worth exploring in future research. One of them is why none of the interventions discussed above had effects on high-stakes exams, even if their materials are typically mapped onto the official curriculum. It is possible that the official curricula are simply too challenging for learners in these settings, who are several grade levels behind expectations and who often need to reinforce basic skills (see Pritchett & Beatty, 2015). Another question is whether these interventions have long-term effects on teaching practices. It seems plausible that, if these interventions are deployed in contexts with low teaching quality, educators may learn something from watching the videos or listening to the recordings with learners. Yet another question is whether these interventions make it easier for schools to deliver instruction to learners whose native language is other than the official medium of instruction.
Distance education
Technology can also allow learners living in remote areas to access education. The evidence on these initiatives is encouraging. For example, Johnston and Ksoll (2017) evaluated a program that broadcasted live instruction via satellite to rural primary school students in the Volta and Greater Accra regions of Ghana. For this purpose, the program also equipped classrooms with the technology needed to connect to a studio in Accra, including solar panels, a satellite modem, a projector, a webcam, microphones, and a computer with interactive software. After two years, the intervention improved the numeracy scores of students in grades 2 through 4, and some foundational literacy tasks, but it had no effect on attendance or classroom time devoted to instruction, as captured by school visits. The authors interpreted these results as suggesting that the gains in achievement may be due to improving the quality of instruction that children received (as opposed to increased instructional time). Naik, Chitre, Bhalla, and Rajan (2019) evaluated a similar program in the Indian state of Karnataka and also found positive effects on learning outcomes, but it is not clear whether those effects are due to the program or due to differences in the groups of students they compared to estimate the impact of the initiative.
In one context (Mexico), this type of distance education had positive long-term effects. Navarro-Sola (2019) took advantage of the staggered rollout of the telesecundarias (i.e., middle schools with lessons broadcasted through satellite TV) in 1968 to estimate its impact. The policy had short-term effects on students’ enrollment in school: For every telesecundaria per 50 children, 10 students enrolled in middle school and two pursued further education. It also had a long-term influence on the educational and employment trajectory of its graduates. Each additional year of education induced by the policy increased average income by nearly 18 percent. This effect was attributable to more graduates entering the labor force and shifting from agriculture and the informal sector. Similarly, Fabregas (2019) leveraged a later expansion of this policy in 1993 and found that each additional telesecundaria per 1,000 adolescents led to an average increase of 0.2 years of education, and a decline in fertility for women, but no conclusive evidence of long-term effects on labor market outcomes.
It is crucial to interpret these results keeping in mind the settings where the interventions were implemented. As we mention above, part of the reason why they have proven effective is that the “counterfactual” conditions for learning (i.e., what would have happened to learners in the absence of such programs) was either to not have access to schooling or to be exposed to low-quality instruction. School systems interested in taking up similar interventions should assess the extent to which their learners (or parts of their learner population) find themselves in similar conditions to the subjects of the studies above. This illustrates the importance of assessing the needs of a system before reviewing the evidence.
Preloaded hardware
Technology also seems well positioned to disseminate educational materials. Specifically, hardware (e.g., desktop computers, laptops, or tablets) could also help deliver educational software (e.g., word processing, reference texts, and/or games). In theory, these materials could not only undergo a quality assurance review (e.g., by curriculum specialists and educators), but also draw on the interactions with learners for adjustments (e.g., identifying areas needing reinforcement) and enable interactions between learners and educators.
In practice, however, most initiatives that have provided learners with free computers, laptops, and netbooks do not leverage any of the opportunities mentioned above. Instead, they install a standard set of educational materials and hope that learners find them helpful enough to take them up on their own. Students rarely do so, and instead use the laptops for recreational purposes—often, to the detriment of their learning (see, e.g., Malamud & Pop-Eleches, 2011). In fact, free netbook initiatives have not only consistently failed to improve academic achievement in math or language (e.g., Cristia et al., 2017), but they have had no impact on learners’ general computer skills (e.g., Beuermann et al., 2015). Some of these initiatives have had small impacts on cognitive skills, but the mechanisms through which those effects occurred remains unclear.
To our knowledge, the only successful deployment of a free laptop initiative was one in which a team of researchers equipped the computers with remedial software. Mo et al. (2013) evaluated a version of the One Laptop per Child (OLPC) program for grade 3 students in migrant schools in Beijing, China in which the laptops were loaded with a remedial software mapped onto the national curriculum for math (similar to the software products that we discuss under “practice exercises” below). After nine months, the program improved math achievement by 0.17 SDs and computer skills by 0.33 SDs. If a school system decides to invest in free laptops, this study suggests that the quality of the software on the laptops is crucial.
To date, however, the evidence suggests that children do not learn more from interacting with laptops than they do from textbooks. For example, Bando, Gallego, Gertler, and Romero (2016) compared the effect of free laptop and textbook provision in 271 elementary schools in disadvantaged areas of Honduras. After seven months, students in grades 3 and 6 who had received the laptops performed on par with those who had received the textbooks in math and language. Further, even if textbooks essentially become obsolete at the end of each school year, whereas laptops can be reloaded with new materials for each year, the costs of laptop provision (not just the hardware, but also the technical assistance, Internet, and training associated with it) are not yet low enough to make them a more cost-effective way of delivering content to learners.
Evidence on the provision of tablets equipped with software is encouraging but limited. For example, de Hoop et al. (2020) evaluated a composite intervention for first grade students in Zambia’s Eastern Province that combined infrastructure (electricity via solar power), hardware (projectors and tablets), and educational materials (lesson plans for educators and interactive lessons for learners, both loaded onto the tablets and mapped onto the official Zambian curriculum). After 14 months, the intervention had improved student early-grade reading by 0.4 SDs, oral vocabulary scores by 0.25 SDs, and early-grade math by 0.22 SDs. It also improved students’ achievement by 0.16 on a locally developed assessment. The multifaceted nature of the program, however, makes it challenging to identify the components that are driving the positive effects. Pitchford (2015) evaluated an intervention that provided tablets equipped with educational “apps,” to be used for 30 minutes per day for two months to develop early math skills among students in grades 1 through 3 in Lilongwe, Malawi. The evaluation found positive impacts in math achievement, but the main study limitation is that it was conducted in a single school.
Facilitating differentiated instruction
Another way in which technology may improve educational outcomes is by facilitating the delivery of differentiated or individualized instruction. Most developing countries massively expanded access to schooling in recent decades by building new schools and making education more affordable, both by defraying direct costs, as well as compensating for opportunity costs (Duflo, 2001; World Bank, 2018). These initiatives have not only rapidly increased the number of learners enrolled in school, but have also increased the variability in learner’ preparation for schooling. Consequently, a large number of learners perform well below grade-based curricular expectations (see, e.g., Duflo, Dupas, & Kremer, 2011; Pritchett & Beatty, 2015). These learners are unlikely to get much from “one-size-fits-all” instruction, in which a single educator delivers instruction deemed appropriate for the middle (or top) of the achievement distribution (Banerjee & Duflo, 2011). Technology could potentially help these learners by providing them with: (a) instruction and opportunities for practice that adjust to the level and pace of preparation of each individual (known as “computer-adaptive learning” (CAL)); or (b) live, one-on-one tutoring.
Computer-adaptive learning
One of the main comparative advantages of technology is its ability to diagnose students’ initial learning levels and assign students to instruction and exercises of appropriate difficulty. No individual educator—no matter how talented—can be expected to provide individualized instruction to all learners in his/her class simultaneously . In this respect, technology is uniquely positioned to complement traditional teaching. This use of technology could help learners master basic skills and help them get more out of schooling.
Although many software products evaluated in recent years have been categorized as CAL, many rely on a relatively coarse level of differentiation at an initial stage (e.g., a diagnostic test) without further differentiation. We discuss these initiatives under the category of “increasing opportunities for practice” below. CAL initiatives complement an initial diagnostic with dynamic adaptation (i.e., at each response or set of responses from learners) to adjust both the initial level of difficulty and rate at which it increases or decreases, depending on whether learners’ responses are correct or incorrect.
Existing evidence on this specific type of programs is highly promising. Most famously, Banerjee et al. (2007) evaluated CAL software in Vadodara, in the Indian state of Gujarat, in which grade 4 students were offered two hours of shared computer time per week before and after school, during which they played games that involved solving math problems. The level of difficulty of such problems adjusted based on students’ answers. This program improved math achievement by 0.35 and 0.47 SDs after one and two years of implementation, respectively. Consistent with the promise of personalized learning, the software improved achievement for all students. In fact, one year after the end of the program, students assigned to the program still performed 0.1 SDs better than those assigned to a business as usual condition. More recently, Muralidharan, et al. (2019) evaluated a “blended learning” initiative in which students in grades 4 through 9 in Delhi, India received 45 minutes of interaction with CAL software for math and language, and 45 minutes of small group instruction before or after going to school. After only 4.5 months, the program improved achievement by 0.37 SDs in math and 0.23 SDs in Hindi. While all learners benefited from the program in absolute terms, the lowest performing learners benefited the most in relative terms, since they were learning very little in school.
We see two important limitations from this body of research. First, to our knowledge, none of these initiatives has been evaluated when implemented during the school day. Therefore, it is not possible to distinguish the effect of the adaptive software from that of additional instructional time. Second, given that most of these programs were facilitated by local instructors, attempts to distinguish the effect of the software from that of the instructors has been mostly based on noncausal evidence. A frontier challenge in this body of research is to understand whether CAL software can increase the effectiveness of school-based instruction by substituting part of the regularly scheduled time for math and language instruction.
Live one-on-one tutoring
Recent improvements in the speed and quality of videoconferencing, as well as in the connectivity of remote areas, have enabled yet another way in which technology can help personalization: live (i.e., real-time) one-on-one tutoring. While the evidence on in-person tutoring is scarce in developing countries, existing studies suggest that this approach works best when it is used to personalize instruction (see, e.g., Banerjee et al., 2007; Banerji, Berry, & Shotland, 2015; Cabezas, Cuesta, & Gallego, 2011).
There are almost no studies on the impact of online tutoring—possibly, due to the lack of hardware and Internet connectivity in low- and middle-income countries. One exception is Chemin and Oledan (2020)’s recent evaluation of an online tutoring program for grade 6 students in Kianyaga, Kenya to learn English from volunteers from a Canadian university via Skype ( videoconferencing software) for one hour per week after school. After 10 months, program beneficiaries performed 0.22 SDs better in a test of oral comprehension, improved their comfort using technology for learning, and became more willing to engage in cross-cultural communication. Importantly, while the tutoring sessions used the official English textbooks and sought in part to help learners with their homework, tutors were trained on several strategies to teach to each learner’s individual level of preparation, focusing on basic skills if necessary. To our knowledge, similar initiatives within a country have not yet been rigorously evaluated.
Expanding opportunities for practice
A third way in which technology may improve the quality of education is by providing learners with additional opportunities for practice. In many developing countries, lesson time is primarily devoted to lectures, in which the educator explains the topic and the learners passively copy explanations from the blackboard. This setup leaves little time for in-class practice. Consequently, learners who did not understand the explanation of the material during lecture struggle when they have to solve homework assignments on their own. Technology could potentially address this problem by allowing learners to review topics at their own pace.
Practice exercises
Technology can help learners get more out of traditional instruction by providing them with opportunities to implement what they learn in class. This approach could, in theory, allow some learners to anchor their understanding of the material through trial and error (i.e., by realizing what they may not have understood correctly during lecture and by getting better acquainted with special cases not covered in-depth in class).
Existing evidence on practice exercises reflects both the promise and the limitations of this use of technology in developing countries. For example, Lai et al. (2013) evaluated a program in Shaanxi, China where students in grades 3 and 5 were required to attend two 40-minute remedial sessions per week in which they first watched videos that reviewed the material that had been introduced in their math lessons that week and then played games to practice the skills introduced in the video. After four months, the intervention improved math achievement by 0.12 SDs. Many other evaluations of comparable interventions have found similar small-to-moderate results (see, e.g., Lai, Luo, Zhang, Huang, & Rozelle, 2015; Lai et al., 2012; Mo et al., 2015; Pitchford, 2015). These effects, however, have been consistently smaller than those of initiatives that adjust the difficulty of the material based on students’ performance (e.g., Banerjee et al., 2007; Muralidharan, et al., 2019). We hypothesize that these programs do little for learners who perform several grade levels behind curricular expectations, and who would benefit more from a review of foundational concepts from earlier grades.
We see two important limitations from this research. First, most initiatives that have been evaluated thus far combine instructional videos with practice exercises, so it is hard to know whether their effects are driven by the former or the latter. In fact, the program in China described above allowed learners to ask their peers whenever they did not understand a difficult concept, so it potentially also captured the effect of peer-to-peer collaboration. To our knowledge, no studies have addressed this gap in the evidence.
Second, most of these programs are implemented before or after school, so we cannot distinguish the effect of additional instructional time from that of the actual opportunity for practice. The importance of this question was first highlighted by Linden (2008), who compared two delivery mechanisms for game-based remedial math software for students in grades 2 and 3 in a network of schools run by a nonprofit organization in Gujarat, India: one in which students interacted with the software during the school day and another one in which students interacted with the software before or after school (in both cases, for three hours per day). After a year, the first version of the program had negatively impacted students’ math achievement by 0.57 SDs and the second one had a null effect. This study suggested that computer-assisted learning is a poor substitute for regular instruction when it is of high quality, as was the case in this well-functioning private network of schools.
In recent years, several studies have sought to remedy this shortcoming. Mo et al. (2014) were among the first to evaluate practice exercises delivered during the school day. They evaluated an initiative in Shaanxi, China in which students in grades 3 and 5 were required to interact with the software similar to the one in Lai et al. (2013) for two 40-minute sessions per week. The main limitation of this study, however, is that the program was delivered during regularly scheduled computer lessons, so it could not determine the impact of substituting regular math instruction. Similarly, Mo et al. (2020) evaluated a self-paced and a teacher-directed version of a similar program for English for grade 5 students in Qinghai, China. Yet, the key shortcoming of this study is that the teacher-directed version added several components that may also influence achievement, such as increased opportunities for teachers to provide students with personalized assistance when they struggled with the material. Ma, Fairlie, Loyalka, and Rozelle (2020) compared the effectiveness of additional time-delivered remedial instruction for students in grades 4 to 6 in Shaanxi, China through either computer-assisted software or using workbooks. This study indicates whether additional instructional time is more effective when using technology, but it does not address the question of whether school systems may improve the productivity of instructional time during the school day by substituting educator-led with computer-assisted instruction.
Increasing learner engagement
Another way in which technology may improve education is by increasing learners’ engagement with the material. In many school systems, regular “chalk and talk” instruction prioritizes time for educators’ exposition over opportunities for learners to ask clarifying questions and/or contribute to class discussions. This, combined with the fact that many developing-country classrooms include a very large number of learners (see, e.g., Angrist & Lavy, 1999; Duflo, Dupas, & Kremer, 2015), may partially explain why the majority of those students are several grade levels behind curricular expectations (e.g., Muralidharan, et al., 2019; Muralidharan & Zieleniak, 2014; Pritchett & Beatty, 2015). Technology could potentially address these challenges by: (a) using video tutorials for self-paced learning and (b) presenting exercises as games and/or gamifying practice.
Video tutorials
Technology can potentially increase learner effort and understanding of the material by finding new and more engaging ways to deliver it. Video tutorials designed for self-paced learning—as opposed to videos for whole class instruction, which we discuss under the category of “prerecorded lessons” above—can increase learner effort in multiple ways, including: allowing learners to focus on topics with which they need more help, letting them correct errors and misconceptions on their own, and making the material appealing through visual aids. They can increase understanding by breaking the material into smaller units and tackling common misconceptions.
In spite of the popularity of instructional videos, there is relatively little evidence on their effectiveness. Yet, two recent evaluations of different versions of the Khan Academy portal, which mainly relies on instructional videos, offer some insight into their impact. First, Ferman, Finamor, and Lima (2019) evaluated an initiative in 157 public primary and middle schools in five cities in Brazil in which the teachers of students in grades 5 and 9 were taken to the computer lab to learn math from the platform for 50 minutes per week. The authors found that, while the intervention slightly improved learners’ attitudes toward math, these changes did not translate into better performance in this subject. The authors hypothesized that this could be due to the reduction of teacher-led math instruction.
More recently, Büchel, Jakob, Kühnhanss, Steffen, and Brunetti (2020) evaluated an after-school, offline delivery of the Khan Academy portal in grades 3 through 6 in 302 primary schools in Morazán, El Salvador. Students in this study received 90 minutes per week of additional math instruction (effectively nearly doubling total math instruction per week) through teacher-led regular lessons, teacher-assisted Khan Academy lessons, or similar lessons assisted by technical supervisors with no content expertise. (Importantly, the first group provided differentiated instruction, which is not the norm in Salvadorian schools). All three groups outperformed both schools without any additional lessons and classrooms without additional lessons in the same schools as the program. The teacher-assisted Khan Academy lessons performed 0.24 SDs better, the supervisor-led lessons 0.22 SDs better, and the teacher-led regular lessons 0.15 SDs better, but the authors could not determine whether the effects across versions were different.
Together, these studies suggest that instructional videos work best when provided as a complement to, rather than as a substitute for, regular instruction. Yet, the main limitation of these studies is the multifaceted nature of the Khan Academy portal, which also includes other components found to positively improve learner achievement, such as differentiated instruction by students’ learning levels. While the software does not provide the type of personalization discussed above, learners are asked to take a placement test and, based on their score, educators assign them different work. Therefore, it is not clear from these studies whether the effects from Khan Academy are driven by its instructional videos or to the software’s ability to provide differentiated activities when combined with placement tests.
Games and gamification
Technology can also increase learner engagement by presenting exercises as games and/or by encouraging learner to play and compete with others (e.g., using leaderboards and rewards)—an approach known as “gamification.” Both approaches can increase learner motivation and effort by presenting learners with entertaining opportunities for practice and by leveraging peers as commitment devices.
There are very few studies on the effects of games and gamification in low- and middle-income countries. Recently, Araya, Arias Ortiz, Bottan, and Cristia (2019) evaluated an initiative in which grade 4 students in Santiago, Chile were required to participate in two 90-minute sessions per week during the school day with instructional math software featuring individual and group competitions (e.g., tracking each learner’s standing in his/her class and tournaments between sections). After nine months, the program led to improvements of 0.27 SDs in the national student assessment in math (it had no spillover effects on reading). However, it had mixed effects on non-academic outcomes. Specifically, the program increased learners’ willingness to use computers to learn math, but, at the same time, increased their anxiety toward math and negatively impacted learners’ willingness to collaborate with peers. Finally, given that one of the weekly sessions replaced regular math instruction and the other one represented additional math instructional time, it is not clear whether the academic effects of the program are driven by the software or the additional time devoted to learning math.
The prognosis:
How can school systems adopt interventions that match their needs.
Here are five specific and sequential guidelines for decisionmakers to realize the potential of education technology to accelerate student learning.
1. Take stock of how your current schools, educators, and learners are engaging with technology .
Carry out a short in-school survey to understand the current practices and potential barriers to adoption of technology (we have included suggested survey instruments in the Appendices); use this information in your decisionmaking process. For example, we learned from conversations with current and former ministers of education from various developing regions that a common limitation to technology use is regulations that hold school leaders accountable for damages to or losses of devices. Another common barrier is lack of access to electricity and Internet, or even the availability of sufficient outlets for charging devices in classrooms. Understanding basic infrastructure and regulatory limitations to the use of education technology is a first necessary step. But addressing these limitations will not guarantee that introducing or expanding technology use will accelerate learning. The next steps are thus necessary.
“In Africa, the biggest limit is connectivity. Fiber is expensive, and we don’t have it everywhere. The continent is creating a digital divide between cities, where there is fiber, and the rural areas. The [Ghanaian] administration put in schools offline/online technologies with books, assessment tools, and open source materials. In deploying this, we are finding that again, teachers are unfamiliar with it. And existing policies prohibit students to bring their own tablets or cell phones. The easiest way to do it would have been to let everyone bring their own device. But policies are against it.” H.E. Matthew Prempeh, Minister of Education of Ghana, on the need to understand the local context.
2. Consider how the introduction of technology may affect the interactions among learners, educators, and content .
Our review of the evidence indicates that technology may accelerate student learning when it is used to scale up access to quality content, facilitate differentiated instruction, increase opportunities for practice, or when it increases learner engagement. For example, will adding electronic whiteboards to classrooms facilitate access to more quality content or differentiated instruction? Or will these expensive boards be used in the same way as the old chalkboards? Will providing one device (laptop or tablet) to each learner facilitate access to more and better content, or offer students more opportunities to practice and learn? Solely introducing technology in classrooms without additional changes is unlikely to lead to improved learning and may be quite costly. If you cannot clearly identify how the interactions among the three key components of the instructional core (educators, learners, and content) may change after the introduction of technology, then it is probably not a good idea to make the investment. See Appendix A for guidance on the types of questions to ask.
3. Once decisionmakers have a clear idea of how education technology can help accelerate student learning in a specific context, it is important to define clear objectives and goals and establish ways to regularly assess progress and make course corrections in a timely manner .
For instance, is the education technology expected to ensure that learners in early grades excel in foundational skills—basic literacy and numeracy—by age 10? If so, will the technology provide quality reading and math materials, ample opportunities to practice, and engaging materials such as videos or games? Will educators be empowered to use these materials in new ways? And how will progress be measured and adjusted?
4. How this kind of reform is approached can matter immensely for its success.
It is easy to nod to issues of “implementation,” but that needs to be more than rhetorical. Keep in mind that good use of education technology requires thinking about how it will affect learners, educators, and parents. After all, giving learners digital devices will make no difference if they get broken, are stolen, or go unused. Classroom technologies only matter if educators feel comfortable putting them to work. Since good technology is generally about complementing or amplifying what educators and learners already do, it is almost always a mistake to mandate programs from on high. It is vital that technology be adopted with the input of educators and families and with attention to how it will be used. If technology goes unused or if educators use it ineffectually, the results will disappoint—no matter the virtuosity of the technology. Indeed, unused education technology can be an unnecessary expenditure for cash-strapped education systems. This is why surveying context, listening to voices in the field, examining how technology is used, and planning for course correction is essential.
5. It is essential to communicate with a range of stakeholders, including educators, school leaders, parents, and learners .
Technology can feel alien in schools, confuse parents and (especially) older educators, or become an alluring distraction. Good communication can help address all of these risks. Taking care to listen to educators and families can help ensure that programs are informed by their needs and concerns. At the same time, deliberately and consistently explaining what technology is and is not supposed to do, how it can be most effectively used, and the ways in which it can make it more likely that programs work as intended. For instance, if teachers fear that technology is intended to reduce the need for educators, they will tend to be hostile; if they believe that it is intended to assist them in their work, they will be more receptive. Absent effective communication, it is easy for programs to “fail” not because of the technology but because of how it was used. In short, past experience in rolling out education programs indicates that it is as important to have a strong intervention design as it is to have a solid plan to socialize it among stakeholders.

Beyond reopening: A leapfrog moment to transform education?
On September 14, the Center for Universal Education (CUE) will host a webinar to discuss strategies, including around the effective use of education technology, for ensuring resilient schools in the long term and to launch a new education technology playbook “Realizing the promise: How can education technology improve learning for all?”
file-pdf Full Playbook – Realizing the promise: How can education technology improve learning for all? file-pdf References file-pdf Appendix A – Instruments to assess availability and use of technology file-pdf Appendix B – List of reviewed studies file-pdf Appendix C – How may technology affect interactions among students, teachers, and content?
About the Authors
Alejandro j. ganimian, emiliana vegas, frederick m. hess.
- Media Relations
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
How has technology changed - and changed us - in the past 20 years?

Remember this? Image: REUTERS/Stephen Hird
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Madeleine Hillyer

.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} Digital Communications is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:, technological transformation.
- Since the dotcom bubble burst back in 2000, technology has radically transformed our societies and our daily lives.
- From smartphones to social media and healthcare, here's a brief history of the 21st century's technological revolution.
Just over 20 years ago, the dotcom bubble burst , causing the stocks of many tech firms to tumble. Some companies, like Amazon, quickly recovered their value – but many others were left in ruins. In the two decades since this crash, technology has advanced in many ways.
Many more people are online today than they were at the start of the millennium. Looking at broadband access, in 2000, just half of Americans had broadband access at home. Today, that number sits at more than 90% .

This broadband expansion was certainly not just an American phenomenon. Similar growth can be seen on a global scale; while less than 7% of the world was online in 2000, today over half the global population has access to the internet.
Similar trends can be seen in cellphone use. At the start of the 2000s, there were 740 million cell phone subscriptions worldwide. Two decades later, that number has surpassed 8 billion, meaning there are now more cellphones in the world than people
Have you read?
The future of jobs report 2023, how to follow the growth summit 2023.
At the same time, technology was also becoming more personal and portable. Apple sold its first iPod in 2001, and six years later it introduced the iPhone, which ushered in a new era of personal technology. These changes led to a world in which technology touches nearly everything we do.
Technology has changed major sectors over the past 20 years, including media, climate action and healthcare. The World Economic Forum’s Technology Pioneers , which just celebrated its 20th anniversary, gives us insight how emerging tech leaders have influenced and responded to these changes.
Media and media consumption
The past 20 years have greatly shaped how and where we consume media. In the early 2000s, many tech firms were still focused on expanding communication for work through advanced bandwidth for video streaming and other media consumption that is common today.
Others followed the path of expanding media options beyond traditional outlets. Early Tech Pioneers such as PlanetOut did this by providing an outlet and alternative media source for LGBTQIA communities as more people got online.
Following on from these first new media options, new communities and alternative media came the massive growth of social media. In 2004 , fewer than 1 million people were on Myspace; Facebook had not even launched. By 2018, Facebook had more 2.26 billion users with other sites also growing to hundreds of millions of users.

While these new online communities and communication channels have offered great spaces for alternative voices, their increased use has also brought issues of increased disinformation and polarization.
Today, many tech start-ups are focused on preserving these online media spaces while also mitigating the disinformation which can come with them. Recently, some Tech Pioneers have also approached this issue, including TruePic – which focuses on photo identification – and Two Hat , which is developing AI-powered content moderation for social media.
Climate change and green tech
Many scientists today are looking to technology to lead us towards a carbon-neutral world. Though renewed attention is being given to climate change today, these efforts to find a solution through technology is not new. In 2001, green tech offered a new investment opportunity for tech investors after the crash, leading to a boom of investing in renewable energy start-ups including Bloom Energy , a Technology Pioneer in 2010.
In the past two decades, tech start-ups have only expanded their climate focus. Many today are focuses on initiatives far beyond clean energy to slow the impact of climate change.
Different start-ups, including Carbon Engineering and Climeworks from this year’s Technology Pioneers, have started to roll out carbon capture technology. These technologies remove CO2 from the air directly, enabling scientists to alleviate some of the damage from fossil fuels which have already been burned.
Another expanding area for young tech firms today is food systems innovation. Many firms, like Aleph Farms and Air Protein, are creating innovative meat and dairy alternatives that are much greener than their traditional counterparts.
Biotech and healthcare
The early 2000s also saw the culmination of a biotech boom that had started in the mid-1990s. Many firms focused on advancing biotechnologies through enhanced tech research.
An early Technology Pioneer, Actelion Pharmaceuticals was one of these companies. Actelion’s tech researched the single layer of cells separating every blood vessel from the blood stream. Like many other biotech firms at the time, their focus was on precise disease and treatment research.
While many tech firms today still focus on disease and treatment research, many others have been focusing on healthcare delivery. Telehealth has been on the rise in recent years , with many young tech expanding virtual healthcare options. New technologies such as virtual visits, chatbots are being used to delivery healthcare to individuals, especially during Covid-19.
Many companies are also focusing their healthcare tech on patients, rather than doctors. For example Ada, a symptom checker app, used to be designed for doctor’s use but has now shifted its language and interface to prioritize giving patients information on their symptoms. Other companies, like 7 cups, are focused are offering mental healthcare support directly to their users without through their app instead of going through existing offices.
The past two decades have seen healthcare tech get much more personal and use tech for care delivery, not just advancing medical research.
The World Economic Forum was the first to draw the world’s attention to the Fourth Industrial Revolution, the current period of unprecedented change driven by rapid technological advances. Policies, norms and regulations have not been able to keep up with the pace of innovation, creating a growing need to fill this gap.
The Forum established the Centre for the Fourth Industrial Revolution Network in 2017 to ensure that new and emerging technologies will help—not harm—humanity in the future. Headquartered in San Francisco, the network launched centres in China, India and Japan in 2018 and is rapidly establishing locally-run Affiliate Centres in many countries around the world.
The global network is working closely with partners from government, business, academia and civil society to co-design and pilot agile frameworks for governing new and emerging technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI) , autonomous vehicles , blockchain , data policy , digital trade , drones , internet of things (IoT) , precision medicine and environmental innovations .
Learn more about the groundbreaking work that the Centre for the Fourth Industrial Revolution Network is doing to prepare us for the future.
Want to help us shape the Fourth Industrial Revolution? Contact us to find out how you can become a member or partner.
In the early 2000s, many companies were at the start of their recovery from the bursting dotcom bubble. Since then, we’ve seen a large expansion in the way tech innovators approach areas such as new media, climate change, healthcare delivery and more.
At the same time, we have also seen tech companies rise to the occasion of trying to combat issues which arose from the first group such as internet content moderation, expanding climate change solutions.
The Technology Pioneers' 2020 cohort marks the 20th anniversary of this community - and looking at the latest awardees can give us a snapshot of where the next two decades of tech may be heading.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
The Agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} Weekly
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Forum Institutional .chakra .wef-17xejub{-webkit-flex:1;-ms-flex:1;flex:1;justify-self:stretch;-webkit-align-self:stretch;-ms-flex-item-align:stretch;align-self:stretch;} .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

Institutional update
World Economic Forum
May 21, 2024

Reflections from MENA at the #SpecialMeeting24
Maroun Kairouz
May 3, 2024

Day 2 #SpecialMeeting24: Key insights and what to know
Gayle Markovitz
April 28, 2024

Day 1 #SpecialMeeting24: Key insights and what just happened
April 27, 2024

#SpecialMeeting24: What to know about the programme and who's coming
Mirek Dušek and Maroun Kairouz

Climate finance: What are debt-for-nature swaps and how can they help countries?
Kate Whiting
April 26, 2024

- Bachelor’s Degrees
- Master’s Degrees
- Doctorate Degrees
- Certificate Programs
- Nursing Degrees
- Cybersecurity
- Human Services
- Science & Mathematics
- Communication
- Liberal Arts
- Social Sciences
- Computer Science
- Admissions Overview
- Tuition and Financial Aid
- Incoming Freshman and Graduate Students
- Transfer Students
- Military Students
- International Students
- Early Access Program
- About Maryville
- Our Faculty
- Our Approach
- Our History
- Accreditation
- Tales of the Brave
- Student Support Overview
- Online Learning Tools
- Infographics
Home / Blog
Children and Technology: Positive and Negative Effects
January 18, 2022
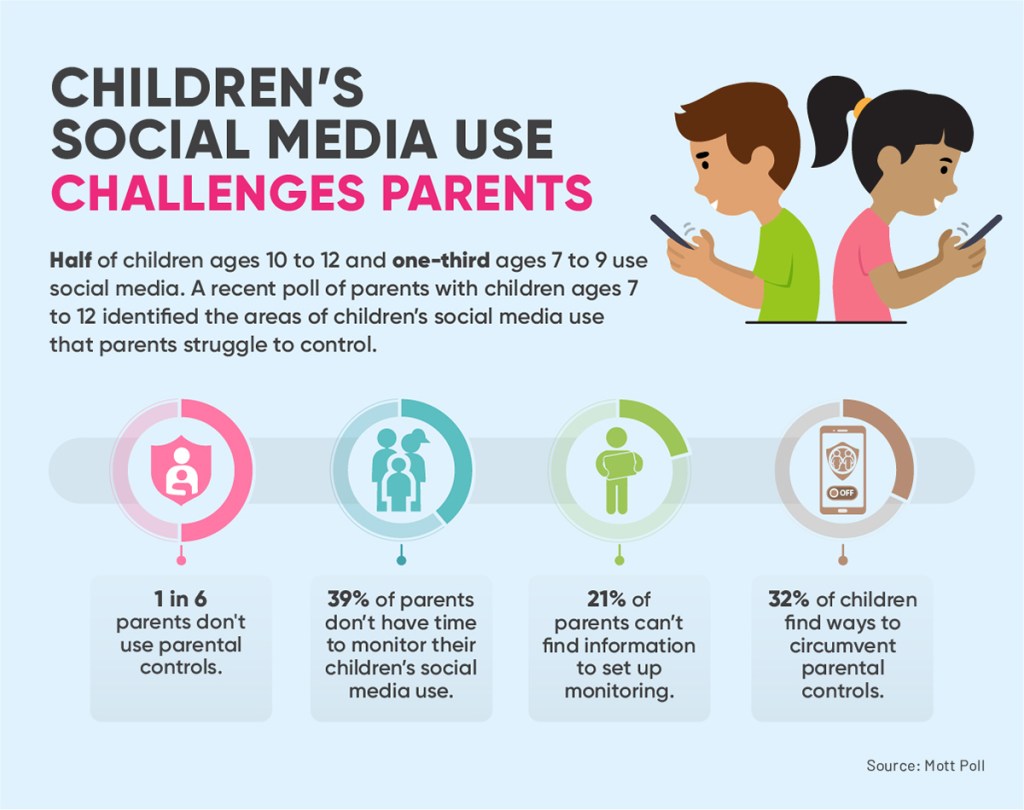
Tables of Contents
Evolution of Children’s Use of Technology
Positive and negative effects of technology on children, technology and children statistics, technology and social interaction in children, ensuring safe and nurturing digital environments for children.
Imagine spending a year or more of your childhood almost entirely at home: no time in a classroom, no chance to join friends on the playground, and very few opportunities to enjoy favorite pastimes and experience new places, people, and activities.
The worldwide lockdowns that helped limit the spread of the coronavirus created a kind of twilight zone for children that put much of their environment off-limits and kept them separated from everyone but their immediate families. However, not all was lost. What vestiges of their pre-COVID life children were able to maintain were made possible by a range of technologies that kept them learning, interacting with friends, and entertained.
The growing presence of technology in children’s lives, from their first year through their teens, is a double-edged sword. While technologies are neutral, how they are applied and how children are exposed to them can be either positive or negative.
The impact of children and technology becomes increasingly difficult to gauge as the pace of technological innovation speeds up. This guide presents a snapshot of the many roles that technology products and services play in the lives of children. It balances the pluses and minuses of the effects of technology use by children on their development, social interactions, and prospects for the future.
Learn how people develop physically, emotionally and socially within the context of family and society
The online BA in human development and family studies from Maryville University prepares you with knowledge and skills related to child development, family dynamics and interpersonal relationships. No SAT or ACT scores required.
- Benefit from a curriculum that follows the 10 content areas of the National Council on Family Relations (NCFR).
- Engage in a range of relevant course topics, from interpersonal relationships to medical terminology.
From the earliest electric model trains in the early 20th century through the first home video game systems and remote-controlled toys, children’s introduction to technology has been through their toys. What were marvels of technology three, two, or even one generation ago seem almost quaint by today’s standards. However, the progress from Pong to Oculus virtual reality games occurred in a relatively brief period of time.
Early Examples of Children and Technology
Children have been interacting with digital technology since the earliest days of the PC revolution . One of the first electronic educational toys was Texas Instruments’ Speak & Spell, which was released in the late 1970s. This relatively simple device was a precursor to the first PCs designed for children in the 1980s. It also presaged the growth of computer-assisted instruction hardware and software in the pre-World Wide Web era.
- The first Speak & Spell toys debuted in 1978 to teach children ages 7 and older how to pronounce and spell 200 commonly misspelled words. It relied on electronic speech synthesis and bubble memory (a precursor to RAM) and was the first such product to use solid-state circuitry to replace all moving parts.
- While Magnavox’s Odyssey was the first gaming console upon its release in 1972, the device was soon eclipsed by the home version of Atari’s Pong arcade video game, which began shipping in 1975. This was followed by the Atari 2600 game console in 1977 and similar devices from Nintendo, Mattel, and Coleco, among other vendors. Sega and Nintendo came to dominate the home video market through the 1980s, along with Commodore, Atari, and Sony’s PlayStation, which was released in 1994.
Evolution of Technology Designed to Educate and Entertain Children
The arrival of the World Wide Web in the mid-1990s changed that nature of tech toys and education hardware and software. Smart Toy Lab , an Intel and Mattel joint venture launched in 1998, developed the first web-connected interactive toys, or “smart toys.” Among the first toys the lab developed were the QX3 Microscope, which featured a built-in video camera that sent images to a PC via a USB link, and the Me2Cam, which let children play interactive games using gestures to move “objects” on the screen.
Some early internet-connected toys and educational devices were criticized for violating children’s privacy by collecting personal information without parental consent. For example, Hello Barbie was released in 2015 and featured a built-in microphone and voice recognition software, as well as a Wi-Fi connection. The doll’s call-and-response function was a precursor to Amazon’s Alexa/Echo and Apple’s Siri voice assistants. However, hackers soon figured out how to break into the toy’s system and access users’ private information.
Today many children — from toddlers to teenagers — regularly use tablets, smartphones, and virtual environments for entertainment and educational purposes. Pandemic-related restrictions have increased children’s reliance on these and other technologies to connect with the outside world. With increased use of these products comes heightened prospects of damage and abuse:
- A recent study published in Children and Youth Services Review identified problematic smartphone use (present in 16.4% of high school students surveyed), daytime sleepiness (20.2%), and symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (6.9%) as spiking during pandemic lockdowns.
- A study published in the Italian Journal of Pediatrics found that 66.3% of the children and adolescents surveyed used their smartphone for more than four hours a day during the pandemic, compared with 16.3% who did so before the pandemic. In addition, 56% of the children and adolescents surveyed used their smartphone after midnight at least three times each week, compared with 30.4% before the pandemic.
Back To Top
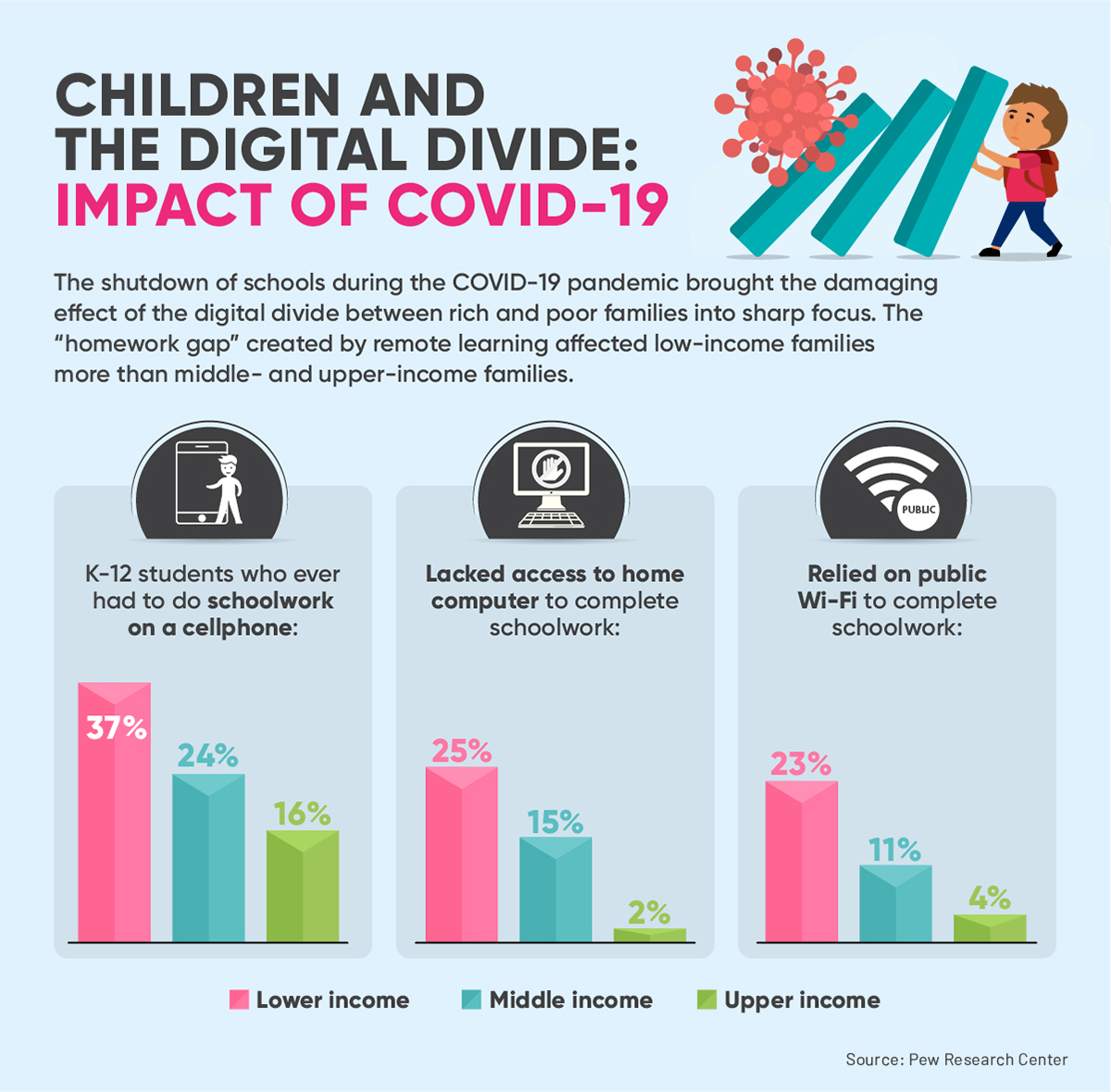
The shutdown of schools during the COVID-19 pandemic brought the damaging effect of the digital divide between rich and poor families into sharp focus. Pew Research Center data shows that the “homework gap” created by remote learning affected low-income families more than middle- and upper-income families. K-12 students who ever had to do schoolwork on a cellphone: lower income: 37%; middle income: 24%; upper income: 16%. K-12 students who ever lacked access to a home computer to complete schoolwork: lower income: 25%; middle income: 15%; upper income: 2%. K-12 students who ever relied on public Wi-Fi to complete schoolwork: lower income: 23%; middle income: 11%; upper income: 4%.
Children can benefit from technology by gaining new learning opportunities; it’s especially important for children who are physically or developmentally challenged. However, technology use has also been found to contribute to poor self-esteem and isolation in some children. As digital technologies become more ubiquitous, parents struggle to find the optimum amount of technology for their children’s lives.
Positive Effects of Technology on Children
All the “rules” about children’s access to computers and the internet were rewritten by the COVID-19 pandemic , according to parenting expert Anya Kamenetz. Technology provides children with easy access to information and boosts their creativity. Tech hardware and software helps children develop social skills and introduces them to various arts and sciences.
These are among the less obvious positive effects of technology on children:
- Technology allows children to connect with their family, friends, and others in ways that enrich their relationships, especially when using video chat and other real-time interactions.
- Parents and caregivers are learning to slow down and tone down the applications, games, and other content children use to avoid overloading their senses. This teaches children how to moderate their own use of technology.
- Rather than trying to eliminate all risk to children when using technology, the goal should be reducing the risk and adapting when problems arise, such as preventing children from accessing devices at specific times of the day.
Many parents hesitate to allow their preschool-age children to use technology products and services due to concerns about how it’ll impact their well-being and development. However, the children are surrounded by technology, much of which offers them significant benefits , as BSD Education explains:
- Technology helps children become independent learners more quickly. Once they learn how to access digital information sources safely, they’re able to explore the topics that interest them on their own.
- Children learn the importance of building communities and how to interact with people in social situations. When circumstances prevent children from establishing physical bonds with family members, friends, and others, they’re able to use technology to create “virtual bonds.”
- Early access to technology teaches the digital literacy skills that children will need for their future success in school and as adults.
- Many technology products promote hand-eye coordination in young children, while others focus on developing their language and problem-solving skills.
Negative Effects of Technology on Children
Children are especially susceptible to technology overuse. The American Psychological Association (APA) recommends limiting the use of technology to one hour per day of high-quality programming for children ages 2 to 5. For children ages 6 and up, it’s most important to set consistent limits on various types of media, such as gaming devices and smartphones.
APA suggests that parents focus on the content on children’s screens and how the children are interacting with it. A survey of research on the possible negative effects of technology on children establishes a connection between the level of a child’s use of technology and various developmental and behavior problems.
- Lack of attention, aggressive behaviors, obesity, physical inactivity, sleep problems
- Musculoskeletal problems related to a sedentary lifestyle
- Greater risk of lifetime obesity and cardiovascular disease
- Sleep disturbances and poor-quality sleep for children who overuse social media or keep mobile devices in their bedroom
These are among the negative effects of technology on children:
- Exposure to harmful online content and sexual exploitation: A study by Irish researchers found that children of all ages are able to bypass the age verification systems of social media apps, such as Snapchat, TikTok, Instagram, and Facebook. This can bring children into direct contact with potential predators and other dangers.
- Cyber bullying: The Cyberbullying Research Center reports that incidents of cyber bullying are most prevalent at ages 12 to 15. A recent survey by the center of 13- to 17-year-olds found that 23.7% of girls, 21.9% of boys, and 35.4% of transgender teens had experienced being bullied.
- Low self-esteem and increased anxiety: CNN reports that teens and adolescents are using image filters on Instagram to enhance their appearance even though the result looks nothing like them. “Self-esteem addiction” can make young people feel inadequate. As children spend more time on social media, they may become withdrawn or find themselves obsessively checking their social media feeds.
Resources on Ways Children Are Affected by Technology
- The Register, “Technology Does Widen the Education Divide. But Not Always in the Way You Expect” — One educator found that upon returning from online education during lockdown, children had turned away from technology, preferring real books and nontech activities because tech is no longer seen as “fun.”
- Edutopia, “Helping Parents Feel More Comfortable with Tech” — Advice for teachers about how to convince parents to support technology in the classroom.
- UNICEF, “Harnessing the Power of Technology and Digital Innovation for Children” — A report describing the initiatives and successes of the Digital UNICEF 2020 program, which is intended to extend the reach of UNICEF’s aid efforts.
When it comes to children’s access to technology, the digital divide between rich and poor persists. The increased reliance of children on technology for remote schooling during the COVID-19 pandemic adds a new and dangerous dimension to the problem, which some analysts refer to as the “ homework gap .”
- A survey by Common Sense Media found that 49% of 8- to 18-year-olds in the U.S. had attended classes fully or partially online since the start of the pandemic.
- Hispanic/Latinx students (48%) and Black students (39%) were much more likely than their white counterparts (20%) to attend school fully online.
- Similarly, students from low-income families (42%) were more likely to rely completely on online instruction than those from middle-income and high-income families (31% and 27%, respectively).
- While 92% of white students had a computer at home, only 87% of Hispanic/Latinx students and 78% of Black students did.
- Broadband access at home was available to 90% of students from families with high incomes, compared with 80% for middle-income families and 61% for lower-income families.
- In addition, 88% of white families had broadband access at home, while 76% of Black families and 68% of Hispanic/Latinx families had broadband access at home.
Common Sense Media estimates that closing the digital divide for K-12 public school students will cost between $6 billion and $11 billion in the first year, and between $4 billion and $8 billion annually in subsequent years. An additional $1 billion will be required to upgrade the remote access technologies that teachers use.
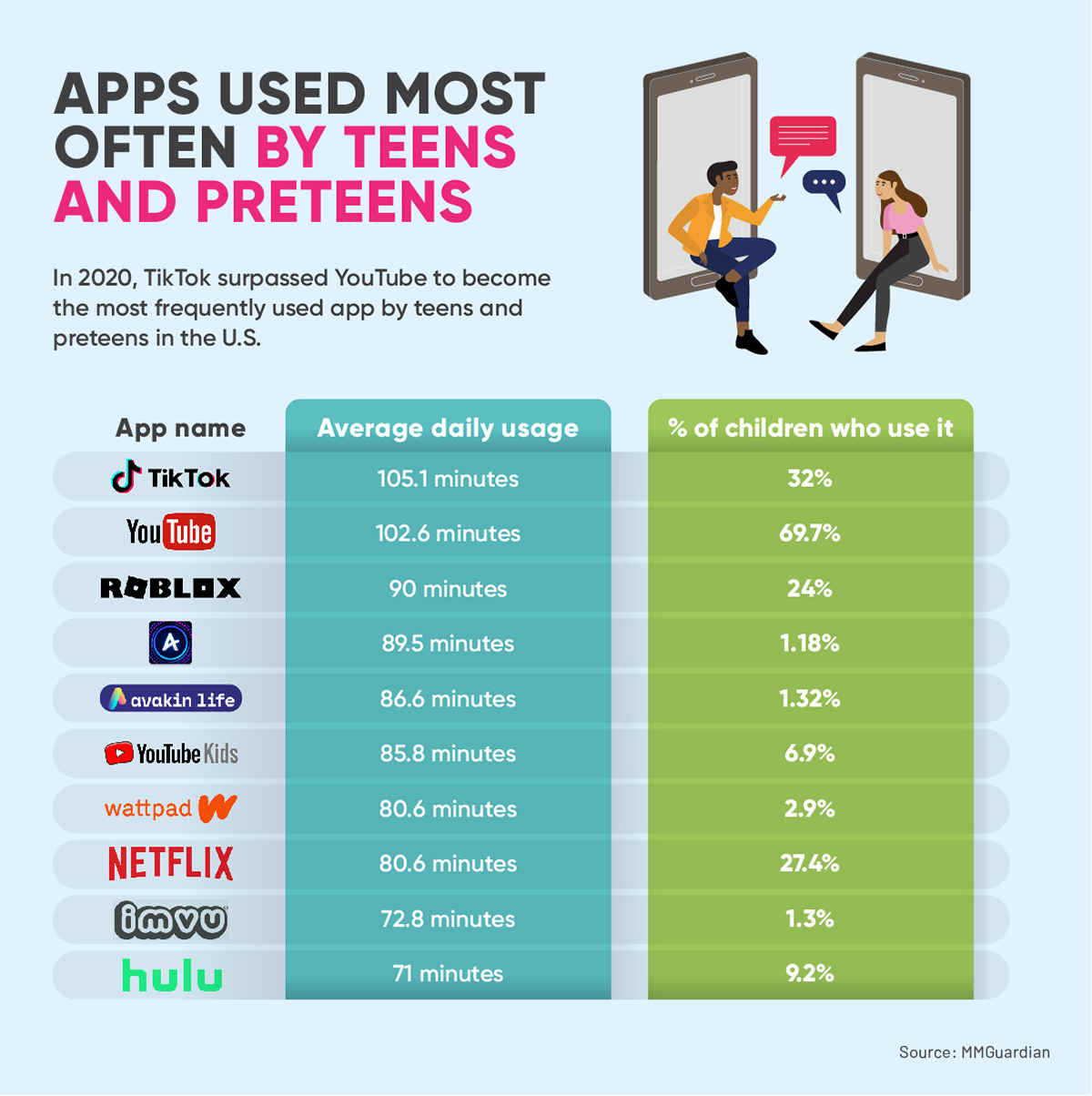
In 2020, TikTok surpassed YouTube to become the most frequently used app by teens and preteens in the U.S., according to MMGuardian. 1. TikTok: average daily usage, 105.1 minutes; % of children who use it, 32%. 2. YouTube: average daily usage, 102.6 minutes; % of children who use it, 69.7%. 3. Roblox: average daily usage, 90 minutes; % of children who use it, 24%. 4. Amino: average daily usage, 89.5 minutes; % of children who use it, 1.18%. 5. Avakin Life: average daily usage, 86.6 minutes; % of children who use it, 1.32%. 6. YouTube Kids: average daily usage, 85.8 minutes; % of children who use it, 6.9%. 7. Wattpad: average daily usage, 80.6 minutes; % of children who use it, 2.9%. 8. Netflix: average daily usage, 80.6 minutes; % of children who use it, 27.4%. 9. IMVU: average daily usage, 72.8 minutes; % of children who use it, 1.3%. 10. Hulu: average daily usage, 71 minutes; % of children who use it, 9.2%.
Statistics on Children’s Online Activities
The most common activity for children online is accessing software, audio, and video content (44% of children had done so between March 2020 and April 2021). The next most popular activities are using internet-based communications (22%); playing video games (14%); accessing online stores, banks, or payment systems (13%); and reading news media (4%).
A study by the National Institute for Early Education Research (NIEER) on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on children’s learning and development determined that children lost learning opportunities at home and in preschool programs. This resulted in “unusually high” rates of socio-emotional and mental health problems in children as reported by their parents.
- Twenty-two percent of 4- to 7-year-olds had high levels of conduct problems in the fall of 2020, compared with 11% who did so in a survey conducted before the pandemic.
- Higher levels of hyperactivity (15% vs. 10%), peer problems (17% vs. 9%), lack of prosocial behavior (20% vs. 8%), and total difficulties (15% vs. 8%) were also recorded among 4- to 7-year-olds during the pandemic.
How Children’s Screen Time Correlates to Their Mental and Physical Health
A primary concern among parents about their children’s use of technology is the amount of time children spend in front of a television, computer, smartphone, or another screen. Researchers have established a link between the amount of time adolescents spend in front of a screen , their level of moderate or vigorous physical activity (MVPA), and the amount of sleep they get.
- Screen time involves sedentary activities that detract from MVPA and delay bedtime and that interrupt sleep with digital notifications.
- The result is an increased risk of children becoming overweight or obese, as well as more sleepiness during the day and lower academic achievement.
- While most of the 13- and 14-year-olds in the study met the recommendations for total screen time (less than two hours per day) and MVPA (at least one hour per day), only half met the recommendation for sleep (8.5 hours per night). Meeting the recommendation for screen time and one of the other two factors led to better academic outcomes.
Some research into the connection between children’s screen time and their psychological well-being has been brought into question because of discrepancies between actual and reported use of digital media by children. A recent meta-analysis of research on the impact of screen time on children found either no significant impact or only a moderate impact. More indicative of potential psychological or developmental problems in children than overall screen time is the type of content that children view and interact with.
However, studies have established a link between excessive screen time and children’s levels of attention deficit symptoms; impaired emotional and social intelligence; social isolation; phantom vibration syndrome; and diagnosable mental illnesses, such as depression, anxiety, and technology addiction.
Finding the Right Amount of Time Online for Children
Many activities that benefit children can become dangerous if used too much. During the pandemic, the time that adolescents spent in front of a screen nearly doubled, according to a study published in JAMA Pediatrics . Adolescents were spending an average of 7.7 hours a day in front of a screen early in the pandemic, compared with 3.8 hours per day before the pandemic. Indications are that the elevated level of screen time will persist.
Determining the optimal amount of screen time for children has become challenging for parents because of the potential problems arising related to children’s vision, posture, and other physical development concerns. While the standard recommendation of experts remains that children under the age of 8 spend less than two hours per day in front of a screen, many factors must be considered when setting a limit for children:
- Allow more screen time for positive educational activities.
- Encourage children to take breaks from the screen that involve outdoor activities.
- Avoid using screens as “babysitters” that keep children occupied. Find other nonscreen activities, such as creative toys, coloring books, and storybooks.
- Don’t let children’s use of electronics cut into their sleep time.
- Make sure that children take short breaks from the screen every 20 minutes or so to protect their vision.
- Check the area of the screen activity to ensure that the lighting is neither too dark nor too bright.
Tech Companies’ Growing Impact on Children
After pressure from government regulators, Facebook shelved its plans to develop a version of Instagram called Instagram Kids that targeted children under the age of 13, as The New York Times reports. In 2019, YouTube paid $170 million to settle claims that it targeted children under the age of 13 in its advertising and collected personal information about them.
These are just two of the many examples of giant tech companies targeting children to meet their need for continuous growth. In the absence of federal privacy laws, companies such as Google (which owns YouTube), Facebook (now known as Meta), Amazon, and TikTok are left to self-regulate their privacy and other policies.
- The Verge reports that Facebook is exploring the use of playdates to spur children to use its Messenger Kids application.
- According to Reuters, attorneys general of several states are investigating Instagram for its attempts to attract young children in violation of consumer protection laws.
- YouTube is being sued in the U.K. over alleged violations of children’s privacy and data rights, according to Tech Monitor.
- A recent survey by Accountable Tech found that 74% of parents believe that Facebook cares more about profits than about keeping their children safe on the site.
Parents, educators, and regulators are also concerned about the safety of educational technology platforms that use machine learning and other artificial intelligence technologies to harvest massive amounts of data about children. Many fear that ubiquitous surveillance will lead to behavioral control and potentially a total loss of privacy for children. They’re calling for more accountability from such platforms, as well as legislation that guarantees children’s “right to future tense.”
Resources Providing Statistics on Children and Technology
- International Central Institute for Youth and Educational Television, International Data Youth and Media 2021 — Statistics on the types of technologies that children use in countries around the world, as well as daily use of media by children in various age groups.
- Family Online Safety Institute, “Healthy Screen Time: Mobile Technology’s Relationship with Children’s Exercise” — A study reporting a sharp decrease in the amount of time children spend playing outdoors and the growing reliance on applications that entail physical activity, such as Nintendo’s Wii console.
Half of children ages 10 to 12 and one-third ages 7 to 9 use social media, according to a recent Mott poll of parents with children ages 7 to 12. Parents identified the areas of children’s social media use that they struggle to control; for instance, one in six parents don’t use parental controls. Additionally, 39% of parents don’t have time to monitor their children’s social media use, 21% of parents can’t find information to set up monitoring, and 32% of children find ways to circumvent parental controls.
The lockdowns deprived young children of opportunities to develop social skills by interacting with other children. As a result, educators report that some children returning to school are struggling with classroom routine. However, the pandemic has disrupted the lives of many families of students and teachers.
- Some children are experiencing anxiety in the classroom that may relate to separation anxiety after spending a prolonged period with family.
- While most students readjust quickly to their school routine, those who’ve experienced trauma at home are most likely to struggle in school. This is especially true for children in kindergarten and first grade.
- Children are showing their resilience in adapting quickly to masking and social distancing requirements.
Research presented at a recent conference of the Society of Neuroscience indicates that isolation in adolescents can change the development of the brain systems related to fear, risk and reward, and social recognition. This may make it more difficult for them to distinguish friendly behavior from threatening behavior in their peers, for example.
A good way to break feelings of social isolation that developed as a result of the pandemic is to increase the amount of school time devoted to physical activities.
Child Development and Technology
Researchers are studying how the way young children play with technology compares with the way they play with real-world toys. They’ve found that all the types of play in the nondigital environment are present in the digital realm as well.
- Digital play develops a range of abilities in children, including subject knowledge and understanding; digital skills; and skills related to social, emotional, cognitive, and creative development.
- Because digital and physical play are intermixed in children’s lives, it’s more appropriate to look at play holistically.
Most research on children and technology relates to children ages 9 to 16, but interactions with technology may have a greater impact on the development of children ages 3 to 8. Digital education for young children increasingly takes the form of applications running on tablets and smartphones, language development applications, and physical coordination from manipulating game controls and videos that teach dancing and other activities.
Since the advent of Apple’s iPad in 2010, computer use by young children has skyrocketed , especially as teaching philosophies focus on play activities over traditional classes and formal teaching. Some schools now test each child’s digital skills and teach children digital competence, such as knowing when and why digital tools are used.
One approach to understanding the complexity of technology’s impact on children is the domestication theory that compares the introduction of digital tools into society to the process of taming a wild animal. The four phases of the domestication process render the tools nonthreatening and also make them useful, important, and meaningful.
- Appropriation is the reason for acquiring the digital tool.
- Objectification of the digital tool instills a personal meaning for the tool in the child using it.
- Incorporation describes how the digital tool becomes a part of the child’s life. It also explains appropriate and inappropriate uses of the tool.
- Conversion occurs when the digital tool has redefined the child’s worldview and relations with others.
Resources on the Impact of Technology on Children’s Development and Social Interactions
- Early Childhood Education Journal, “Investigating Young Children’s Interactions During Digital Play” — Research into children’s social behaviors within digital play environments found that adding a social dimension increased a child’s engagement in the activity.
- OECD iLibrary, “Children and Digital Technologies: Trends and Outcomes” — Topics include use of social robots to help treat children with chronic diseases and the impact of digital technologies on children’s physical health.
Technological advances happen so quickly that parents and educators don’t have much opportunity to consider how children’s growth and well-being may be improved or impaired by the types of technologies they interact with and the ways in which those interactions occur. However, technology continues to play a more important part of the lives of most children when they’re in school, at home, and at play. The judicious application of technology will enhance a child’s education and other aspects of life.
Infographic Sources
Associated Press, “TikTok Is Now the Most-Used App by Teens and Pre-teens in the U.S.”
Mott Poll Report, “Sharing too Soon? Children and Social Media Apps”
Pew Research Center, “The Internet and the Pandemic”
Bring us your ambition and we’ll guide you along a personalized path to a quality education that’s designed to change your life.
Take Your Next Brave Step
Receive information about the benefits of our programs, the courses you'll take, and what you need to apply.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Technology Essay

Essay on Technology
The word "technology" and its uses have immensely changed since the 20th century, and with time, it has continued to evolve ever since. We are living in a world driven by technology. The advancement of technology has played an important role in the development of human civilization, along with cultural changes. Technology provides innovative ways of doing work through various smart and innovative means.
Electronic appliances, gadgets, faster modes of communication, and transport have added to the comfort factor in our lives. It has helped in improving the productivity of individuals and different business enterprises. Technology has brought a revolution in many operational fields. It has undoubtedly made a very important contribution to the progress that mankind has made over the years.
The Advancement of Technology:
Technology has reduced the effort and time and increased the efficiency of the production requirements in every field. It has made our lives easy, comfortable, healthy, and enjoyable. It has brought a revolution in transport and communication. The advancement of technology, along with science, has helped us to become self-reliant in all spheres of life. With the innovation of a particular technology, it becomes part of society and integral to human lives after a point in time.
Technology is Our Part of Life:
Technology has changed our day-to-day lives. Technology has brought the world closer and better connected. Those days have passed when only the rich could afford such luxuries. Because of the rise of globalisation and liberalisation, all luxuries are now within the reach of the average person. Today, an average middle-class family can afford a mobile phone, a television, a washing machine, a refrigerator, a computer, the Internet, etc. At the touch of a switch, a man can witness any event that is happening in far-off places.
Benefits of Technology in All Fields:
We cannot escape technology; it has improved the quality of life and brought about revolutions in various fields of modern-day society, be it communication, transportation, education, healthcare, and many more. Let us learn about it.
Technology in Communication:
With the advent of technology in communication, which includes telephones, fax machines, cellular phones, the Internet, multimedia, and email, communication has become much faster and easier. It has transformed and influenced relationships in many ways. We no longer need to rely on sending physical letters and waiting for several days for a response. Technology has made communication so simple that you can connect with anyone from anywhere by calling them via mobile phone or messaging them using different messaging apps that are easy to download.
Innovation in communication technology has had an immense influence on social life. Human socialising has become easier by using social networking sites, dating, and even matrimonial services available on mobile applications and websites.
Today, the Internet is used for shopping, paying utility bills, credit card bills, admission fees, e-commerce, and online banking. In the world of marketing, many companies are marketing and selling their products and creating brands over the internet.
In the field of travel, cities, towns, states, and countries are using the web to post detailed tourist and event information. Travellers across the globe can easily find information on tourism, sightseeing, places to stay, weather, maps, timings for events, transportation schedules, and buy tickets to various tourist spots and destinations.
Technology in the Office or Workplace:
Technology has increased efficiency and flexibility in the workspace. Technology has made it easy to work remotely, which has increased the productivity of the employees. External and internal communication has become faster through emails and apps. Automation has saved time, and there is also a reduction in redundancy in tasks. Robots are now being used to manufacture products that consistently deliver the same product without defect until the robot itself fails. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technology are innovations that are being deployed across industries to reap benefits.
Technology has wiped out the manual way of storing files. Now files are stored in the cloud, which can be accessed at any time and from anywhere. With technology, companies can make quick decisions, act faster towards solutions, and remain adaptable. Technology has optimised the usage of resources and connected businesses worldwide. For example, if the customer is based in America, he can have the services delivered from India. They can communicate with each other in an instant. Every company uses business technology like virtual meeting tools, corporate social networks, tablets, and smart customer relationship management applications that accelerate the fast movement of data and information.
Technology in Education:
Technology is making the education industry improve over time. With technology, students and parents have a variety of learning tools at their fingertips. Teachers can coordinate with classrooms across the world and share their ideas and resources online. Students can get immediate access to an abundance of good information on the Internet. Teachers and students can access plenty of resources available on the web and utilise them for their project work, research, etc. Online learning has changed our perception of education.
The COVID-19 pandemic brought a paradigm shift using technology where school-going kids continued their studies from home and schools facilitated imparting education by their teachers online from home. Students have learned and used 21st-century skills and tools, like virtual classrooms, AR (Augmented Reality), robots, etc. All these have increased communication and collaboration significantly.
Technology in Banking:
Technology and banking are now inseparable. Technology has boosted digital transformation in how the banking industry works and has vastly improved banking services for their customers across the globe.
Technology has made banking operations very sophisticated and has reduced errors to almost nil, which were somewhat prevalent with manual human activities. Banks are adopting Artificial Intelligence (AI) to increase their efficiency and profits. With the emergence of Internet banking, self-service tools have replaced the traditional methods of banking.
You can now access your money, handle transactions like paying bills, money transfers, and online purchases from merchants, and monitor your bank statements anytime and from anywhere in the world. Technology has made banking more secure and safe. You do not need to carry cash in your pocket or wallet; the payments can be made digitally using e-wallets. Mobile banking, banking apps, and cybersecurity are changing the face of the banking industry.
Manufacturing and Production Industry Automation:
At present, manufacturing industries are using all the latest technologies, ranging from big data analytics to artificial intelligence. Big data, ARVR (Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality), and IoT (Internet of Things) are the biggest manufacturing industry players. Automation has increased the level of productivity in various fields. It has reduced labour costs, increased efficiency, and reduced the cost of production.
For example, 3D printing is used to design and develop prototypes in the automobile industry. Repetitive work is being done easily with the help of robots without any waste of time. This has also reduced the cost of the products.
Technology in the Healthcare Industry:
Technological advancements in the healthcare industry have not only improved our personal quality of life and longevity; they have also improved the lives of many medical professionals and students who are training to become medical experts. It has allowed much faster access to the medical records of each patient.
The Internet has drastically transformed patients' and doctors’ relationships. Everyone can stay up to date on the latest medical discoveries, share treatment information, and offer one another support when dealing with medical issues. Modern technology has allowed us to contact doctors from the comfort of our homes. There are many sites and apps through which we can contact doctors and get medical help.
Breakthrough innovations in surgery, artificial organs, brain implants, and networked sensors are examples of transformative developments in the healthcare industry. Hospitals use different tools and applications to perform their administrative tasks, using digital marketing to promote their services.
Technology in Agriculture:
Today, farmers work very differently than they would have decades ago. Data analytics and robotics have built a productive food system. Digital innovations are being used for plant breeding and harvesting equipment. Software and mobile devices are helping farmers harvest better. With various data and information available to farmers, they can make better-informed decisions, for example, tracking the amount of carbon stored in soil and helping with climate change.
Disadvantages of Technology:
People have become dependent on various gadgets and machines, resulting in a lack of physical activity and tempting people to lead an increasingly sedentary lifestyle. Even though technology has increased the productivity of individuals, organisations, and the nation, it has not increased the efficiency of machines. Machines cannot plan and think beyond the instructions that are fed into their system. Technology alone is not enough for progress and prosperity. Management is required, and management is a human act. Technology is largely dependent on human intervention.
Computers and smartphones have led to an increase in social isolation. Young children are spending more time surfing the internet, playing games, and ignoring their real lives. Usage of technology is also resulting in job losses and distracting students from learning. Technology has been a reason for the production of weapons of destruction.
Dependency on technology is also increasing privacy concerns and cyber crimes, giving way to hackers.

FAQs on Technology Essay
1. What is technology?
Technology refers to innovative ways of doing work through various smart means. The advancement of technology has played an important role in the development of human civilization. It has helped in improving the productivity of individuals and businesses.
2. How has technology changed the face of banking?
Technology has made banking operations very sophisticated. With the emergence of Internet banking, self-service tools have replaced the traditional methods of banking. You can now access your money, handle transactions, and monitor your bank statements anytime and from anywhere in the world. Technology has made banking more secure and safe.
3. How has technology brought a revolution in the medical field?
Patients and doctors keep each other up to date on the most recent medical discoveries, share treatment information, and offer each other support when dealing with medical issues. It has allowed much faster access to the medical records of each patient. Modern technology has allowed us to contact doctors from the comfort of our homes. There are many websites and mobile apps through which we can contact doctors and get medical help.
4. Are we dependent on technology?
Yes, today, we are becoming increasingly dependent on technology. Computers, smartphones, and modern technology have helped humanity achieve success and progress. However, in hindsight, people need to continuously build a healthy lifestyle, sorting out personal problems that arise due to technological advancements in different aspects of human life.
The state of AI in early 2024: Gen AI adoption spikes and starts to generate value
If 2023 was the year the world discovered generative AI (gen AI) , 2024 is the year organizations truly began using—and deriving business value from—this new technology. In the latest McKinsey Global Survey on AI, 65 percent of respondents report that their organizations are regularly using gen AI, nearly double the percentage from our previous survey just ten months ago. Respondents’ expectations for gen AI’s impact remain as high as they were last year , with three-quarters predicting that gen AI will lead to significant or disruptive change in their industries in the years ahead.
About the authors
This article is a collaborative effort by Alex Singla , Alexander Sukharevsky , Lareina Yee , and Michael Chui , with Bryce Hall , representing views from QuantumBlack, AI by McKinsey, and McKinsey Digital.
Organizations are already seeing material benefits from gen AI use, reporting both cost decreases and revenue jumps in the business units deploying the technology. The survey also provides insights into the kinds of risks presented by gen AI—most notably, inaccuracy—as well as the emerging practices of top performers to mitigate those challenges and capture value.
AI adoption surges
Interest in generative AI has also brightened the spotlight on a broader set of AI capabilities. For the past six years, AI adoption by respondents’ organizations has hovered at about 50 percent. This year, the survey finds that adoption has jumped to 72 percent (Exhibit 1). And the interest is truly global in scope. Our 2023 survey found that AI adoption did not reach 66 percent in any region; however, this year more than two-thirds of respondents in nearly every region say their organizations are using AI. 1 Organizations based in Central and South America are the exception, with 58 percent of respondents working for organizations based in Central and South America reporting AI adoption. Looking by industry, the biggest increase in adoption can be found in professional services. 2 Includes respondents working for organizations focused on human resources, legal services, management consulting, market research, R&D, tax preparation, and training.
Also, responses suggest that companies are now using AI in more parts of the business. Half of respondents say their organizations have adopted AI in two or more business functions, up from less than a third of respondents in 2023 (Exhibit 2).
Gen AI adoption is most common in the functions where it can create the most value
Most respondents now report that their organizations—and they as individuals—are using gen AI. Sixty-five percent of respondents say their organizations are regularly using gen AI in at least one business function, up from one-third last year. The average organization using gen AI is doing so in two functions, most often in marketing and sales and in product and service development—two functions in which previous research determined that gen AI adoption could generate the most value 3 “ The economic potential of generative AI: The next productivity frontier ,” McKinsey, June 14, 2023. —as well as in IT (Exhibit 3). The biggest increase from 2023 is found in marketing and sales, where reported adoption has more than doubled. Yet across functions, only two use cases, both within marketing and sales, are reported by 15 percent or more of respondents.
Gen AI also is weaving its way into respondents’ personal lives. Compared with 2023, respondents are much more likely to be using gen AI at work and even more likely to be using gen AI both at work and in their personal lives (Exhibit 4). The survey finds upticks in gen AI use across all regions, with the largest increases in Asia–Pacific and Greater China. Respondents at the highest seniority levels, meanwhile, show larger jumps in the use of gen Al tools for work and outside of work compared with their midlevel-management peers. Looking at specific industries, respondents working in energy and materials and in professional services report the largest increase in gen AI use.
Investments in gen AI and analytical AI are beginning to create value
The latest survey also shows how different industries are budgeting for gen AI. Responses suggest that, in many industries, organizations are about equally as likely to be investing more than 5 percent of their digital budgets in gen AI as they are in nongenerative, analytical-AI solutions (Exhibit 5). Yet in most industries, larger shares of respondents report that their organizations spend more than 20 percent on analytical AI than on gen AI. Looking ahead, most respondents—67 percent—expect their organizations to invest more in AI over the next three years.
Where are those investments paying off? For the first time, our latest survey explored the value created by gen AI use by business function. The function in which the largest share of respondents report seeing cost decreases is human resources. Respondents most commonly report meaningful revenue increases (of more than 5 percent) in supply chain and inventory management (Exhibit 6). For analytical AI, respondents most often report seeing cost benefits in service operations—in line with what we found last year —as well as meaningful revenue increases from AI use in marketing and sales.
Inaccuracy: The most recognized and experienced risk of gen AI use
As businesses begin to see the benefits of gen AI, they’re also recognizing the diverse risks associated with the technology. These can range from data management risks such as data privacy, bias, or intellectual property (IP) infringement to model management risks, which tend to focus on inaccurate output or lack of explainability. A third big risk category is security and incorrect use.
Respondents to the latest survey are more likely than they were last year to say their organizations consider inaccuracy and IP infringement to be relevant to their use of gen AI, and about half continue to view cybersecurity as a risk (Exhibit 7).
Conversely, respondents are less likely than they were last year to say their organizations consider workforce and labor displacement to be relevant risks and are not increasing efforts to mitigate them.
In fact, inaccuracy— which can affect use cases across the gen AI value chain , ranging from customer journeys and summarization to coding and creative content—is the only risk that respondents are significantly more likely than last year to say their organizations are actively working to mitigate.
Some organizations have already experienced negative consequences from the use of gen AI, with 44 percent of respondents saying their organizations have experienced at least one consequence (Exhibit 8). Respondents most often report inaccuracy as a risk that has affected their organizations, followed by cybersecurity and explainability.
Our previous research has found that there are several elements of governance that can help in scaling gen AI use responsibly, yet few respondents report having these risk-related practices in place. 4 “ Implementing generative AI with speed and safety ,” McKinsey Quarterly , March 13, 2024. For example, just 18 percent say their organizations have an enterprise-wide council or board with the authority to make decisions involving responsible AI governance, and only one-third say gen AI risk awareness and risk mitigation controls are required skill sets for technical talent.
Bringing gen AI capabilities to bear
The latest survey also sought to understand how, and how quickly, organizations are deploying these new gen AI tools. We have found three archetypes for implementing gen AI solutions : takers use off-the-shelf, publicly available solutions; shapers customize those tools with proprietary data and systems; and makers develop their own foundation models from scratch. 5 “ Technology’s generational moment with generative AI: A CIO and CTO guide ,” McKinsey, July 11, 2023. Across most industries, the survey results suggest that organizations are finding off-the-shelf offerings applicable to their business needs—though many are pursuing opportunities to customize models or even develop their own (Exhibit 9). About half of reported gen AI uses within respondents’ business functions are utilizing off-the-shelf, publicly available models or tools, with little or no customization. Respondents in energy and materials, technology, and media and telecommunications are more likely to report significant customization or tuning of publicly available models or developing their own proprietary models to address specific business needs.
Respondents most often report that their organizations required one to four months from the start of a project to put gen AI into production, though the time it takes varies by business function (Exhibit 10). It also depends upon the approach for acquiring those capabilities. Not surprisingly, reported uses of highly customized or proprietary models are 1.5 times more likely than off-the-shelf, publicly available models to take five months or more to implement.
Gen AI high performers are excelling despite facing challenges
Gen AI is a new technology, and organizations are still early in the journey of pursuing its opportunities and scaling it across functions. So it’s little surprise that only a small subset of respondents (46 out of 876) report that a meaningful share of their organizations’ EBIT can be attributed to their deployment of gen AI. Still, these gen AI leaders are worth examining closely. These, after all, are the early movers, who already attribute more than 10 percent of their organizations’ EBIT to their use of gen AI. Forty-two percent of these high performers say more than 20 percent of their EBIT is attributable to their use of nongenerative, analytical AI, and they span industries and regions—though most are at organizations with less than $1 billion in annual revenue. The AI-related practices at these organizations can offer guidance to those looking to create value from gen AI adoption at their own organizations.
To start, gen AI high performers are using gen AI in more business functions—an average of three functions, while others average two. They, like other organizations, are most likely to use gen AI in marketing and sales and product or service development, but they’re much more likely than others to use gen AI solutions in risk, legal, and compliance; in strategy and corporate finance; and in supply chain and inventory management. They’re more than three times as likely as others to be using gen AI in activities ranging from processing of accounting documents and risk assessment to R&D testing and pricing and promotions. While, overall, about half of reported gen AI applications within business functions are utilizing publicly available models or tools, gen AI high performers are less likely to use those off-the-shelf options than to either implement significantly customized versions of those tools or to develop their own proprietary foundation models.
What else are these high performers doing differently? For one thing, they are paying more attention to gen-AI-related risks. Perhaps because they are further along on their journeys, they are more likely than others to say their organizations have experienced every negative consequence from gen AI we asked about, from cybersecurity and personal privacy to explainability and IP infringement. Given that, they are more likely than others to report that their organizations consider those risks, as well as regulatory compliance, environmental impacts, and political stability, to be relevant to their gen AI use, and they say they take steps to mitigate more risks than others do.
Gen AI high performers are also much more likely to say their organizations follow a set of risk-related best practices (Exhibit 11). For example, they are nearly twice as likely as others to involve the legal function and embed risk reviews early on in the development of gen AI solutions—that is, to “ shift left .” They’re also much more likely than others to employ a wide range of other best practices, from strategy-related practices to those related to scaling.
In addition to experiencing the risks of gen AI adoption, high performers have encountered other challenges that can serve as warnings to others (Exhibit 12). Seventy percent say they have experienced difficulties with data, including defining processes for data governance, developing the ability to quickly integrate data into AI models, and an insufficient amount of training data, highlighting the essential role that data play in capturing value. High performers are also more likely than others to report experiencing challenges with their operating models, such as implementing agile ways of working and effective sprint performance management.
About the research
The online survey was in the field from February 22 to March 5, 2024, and garnered responses from 1,363 participants representing the full range of regions, industries, company sizes, functional specialties, and tenures. Of those respondents, 981 said their organizations had adopted AI in at least one business function, and 878 said their organizations were regularly using gen AI in at least one function. To adjust for differences in response rates, the data are weighted by the contribution of each respondent’s nation to global GDP.
Alex Singla and Alexander Sukharevsky are global coleaders of QuantumBlack, AI by McKinsey, and senior partners in McKinsey’s Chicago and London offices, respectively; Lareina Yee is a senior partner in the Bay Area office, where Michael Chui , a McKinsey Global Institute partner, is a partner; and Bryce Hall is an associate partner in the Washington, DC, office.
They wish to thank Kaitlin Noe, Larry Kanter, Mallika Jhamb, and Shinjini Srivastava for their contributions to this work.
This article was edited by Heather Hanselman, a senior editor in McKinsey’s Atlanta office.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Moving past gen AI’s honeymoon phase: Seven hard truths for CIOs to get from pilot to scale

A generative AI reset: Rewiring to turn potential into value in 2024

Implementing generative AI with speed and safety
AI employees warn of technology’s dangers, call for sweeping company changes
A letter signed by current and former OpenAI, Anthropic and Google DeepMind employees asked firms to provide greater transparency and whistleblower protections.
A handful of current and former employees at OpenAI and other prominent artificial intelligence companies warned that the technology poses grave risks to humanity in a Tuesday letter, calling on companies to implement sweeping changes to ensure transparency and foster a culture of public debate.
The letter, signed by 13 people including current and former employees at Anthropic and Google’s DeepMind, said AI can exacerbate inequality , increase misinformation, and allow AI systems to become autonomous and cause significant death. Though these risks could be mitigated, corporations in control of the software have “strong financial incentives” to limit oversight, they said.
Because AI is only loosely regulated, accountability rests on company insiders, the employees wrote, calling on corporations to lift nondisclosure agreements and give workers protections that allow them to anonymously raise concerns.
The move comes as OpenAI faces a staff exodus . Many critics have seen prominent departures — including of OpenAI co-founder Ilya Sutskever and senior researcher Jan Leike — as a rebuke of company leaders, who some employees argue chase profit at the expense of making OpenAI’s technologies safer.
Daniel Kokotajlo, a former employee at OpenAI, said he left the start-up because of the company’s disregard for the risks of artificial intelligence.
GET CAUGHT UP Summarized stories to quickly stay informed

Arizona votes to put Texas-inspired immigration referendum on November ballot

Trump again suggests political opponents may face prosecution, too

Early fires in California could signal worse to come, officials say

He went viral for driving with a suspended license. The case isn’t so simple.

Cat roams university campus for 4 years, gets doctoral degree
“I lost hope that they would act responsibly, particularly as they pursue artificial general intelligence,” he said in a statement, referencing a hotly contested term referring to computers matching the power of human brains.
“They and others have bought into the ‘move fast and break things’ approach, and that is the opposite of what is needed for technology this powerful and this poorly understood,” Kokotajlo said.
Liz Bourgeois, a spokesperson at OpenAI, said the company agrees that “rigorous debate is crucial given the significance of this technology.” Representatives from Anthropic and Google did not immediately reply to a request for comment.
The employees said that absent government oversight , AI workers are the “few people” who can hold corporations accountable. They said that they are hamstrung by “broad confidentiality agreements” and that ordinary whistleblower protections are “insufficient” because they focus on illegal activity, and the risks that they are warning about are not yet regulated.
The letter called for AI companies to commit to four principles to allow for greater transparency and whistleblower protections. Those principles are a commitment to not enter into or enforce agreements that prohibit criticism of risks; a call to establish an anonymous process for current and former employees to raise concerns; supporting a culture of criticism; and a promise to not retaliate against current and former employees who share confidential information to raise alarms “after other processes have failed.”
The Washington Post in December reported that senior leaders at OpenAI raised fears about retaliation from CEO Sam Altman — warnings that preceded the chief’s temporary ouster. In a recent podcast interview, former OpenAI board member Helen Toner said part of the nonprofit’s decision to remove Altman as CEO late last year was his lack of candid communication about safety.
“He gave us inaccurate information about the small number of formal safety processes that the company did have in place, meaning that it was basically just impossible for the board to know how well those safety processes were working,” she told “ The TED AI Show ” in May.
The letter was endorsed by AI luminaries including Yoshua Bengio and Geoffrey Hinton, who are considered “godfathers” of AI, and renowned computer scientist Stuart Russell.

Technological Advancement Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Searching for a technological advancement essay? Look no further! This simple essay on breakthrough technologies describes all the benefits and drawbacks of the issue.
Introduction
Why write about technology advancement, breakthrough technologies in various sectors, technological advancement essay faq.
Technological advancement has taken major strides in bringing liberation to the divergent human wants and gratifications. After keen observation, I have come to realize that technological advancement plays a critical role in solving the major crisis of food shortages in the modern world. In the state of Virginia during the 17th century, human labor was imperative due to the pressing need to grow enough food to serve the people in the community during the winter spell hence the need to hire slaves from Africa to work on their farms (Brush, 1988).
This has since changed partly due to the technological advancements over the years that have led to the replacement of human and animal labor with more efficient energy sources as wind power, hydroelectric and steam energies that ultimately led to a significant increase in productivity. Thus, the thesis statement for this essay is to analyze the impact of technological advancement on people’s lives from ancient times to the present modern world.
It is evident that technology is the backbone of the industrial revolution process that has occurred over the years and leads to a total overhaul from crude systems to modern efficient machinery. With this in mind, we cannot overlook the role that technology has played on the social and economic fronts of many societies hence the need to have a deeper insight and research on this particular topic. The transformation brought about by technological advancement has helped many societies in Africa and the world at large to alleviate poverty and improve their standards of living through the increased food supply and significant growth in the economy and this integrates with the research question: Is technology liberating?
The three academic disciplines from which this research has drawn insight from include: agriculture, sociology and communication sectors.
Technology Advancement in Agriculture
In the ancient world, the main source of power was human labor obtained mainly from slaves. In North America for example, during the early 17th century, most whites purchased slaves as a chief source of labor to work on their farms but with the emancipation proclamation by President Abraham Lincoln during the civil war of 1863 that declared all slaves to be set free from bondage, their masters had no choice but to source for another alternative source of labor.
This act spearheaded the advancement of the agricultural revolution, which was also boosted by the industrial revolution that led to the development of more efficient agricultural machinery that required very few workers and resulted in higher farm production. Examples of some of the medieval technologies used in the ancient world included: water wheel, four-field crop rotation system, the horse collar and selective breeding of livestock with good traits.
In 1750, engineer John Smeaton working on the water wheel significantly increased its efficiency hence boosting its productivity. It was during this period that technological advancement, revolution, and innovation in agriculture were at its peak and it led to the emergence of new farm machinery like cultivators, combine harvesters and mowers that were pulled by oxen, mules, and horses. These machines were later powered by steam energy than a more efficient diesel fuel that led to a remarkable increase in farm output (Kedar, 2009). Previously, the land was prepared by a man using traditional mattocks and hoes made from raw materials obtained locally like wood and scrap metals.
With the mechanization of agriculture, farmers could now make use of the machinery like combine harvesters and petrol powered tractors to prepare large acres of land within a short period with minimum input on human labor to clear, plow and plant on their expansive farms. Technology has led to hybridization, selective breeding and inbreeding in livestock to obtain or maintain all the good qualities in their animals as high milk production, quality wool production, quality meat production, and other desirable animal traits.
Robert Bakewell and Thomas Coke doing their research on selective breeding crossed Lincoln and Longhorn sheep, to produce a hybrid that exhibited all the good qualities of both Lincoln and Longhorn and was referred to as New Leicester variety. This has helped in alleviating the crisis of food shortages through maximization of farm output.
Technology Advancement in Everyday Lives
Technology has been indispensable in bettering the social lives of many people in society. Technological advancements have led to the development in infrastructure and social amenities which has in turn positively impacted on the general livelihood of many individuals. It was until the Roman era in the 18th century that good roads were constructed, during those days, slaves were also used to carry loads and farm produce from the farms to storage warehouses and vice versa. They also used canoes and boats to carry farm products from North America between the Appalachian Mountains and Mississippi River during the early periods of the 19th century.
During this period, the transport system was still archaic and underdeveloped and people found it difficult to navigate from one region to another or carry heavy luggage over long distances because of poor roads and crude modes of transport. The canals preceded the construction of railroads that marked the beginning of the industrial revolution and from there we had significant developments in the transport sector with the construction of the first transcontinental railroad in 1869 and the subsequent construction of tarmac roads, sea canals and subway systems (Butler, 1996).
These developments made it easier for people to move around hence positively impacting on their social lives by enhancing communication, trade, and farming. This indirectly led to improved living standards as a result of the increased food supply by farmers and the development of business firms. Farmers could now effectively carry their farm inputs and fertilizers to the farm and farm products to the market without difficulties. Businesses also thrived because of the efficient transport system and in no time firms began proliferating from every sector of the economy. This enabled them to diversify their economic activities as they no longer depended on the agricultural sector for their daily provision but also ventured into the business sector within the community.
With the recent development in infrastructure, it paved the way to the development of social amenities as schools, hospitals, public toilets, shops and market centers that increased in number as more and more investors joined the market. These amenities played a critical role in the development of the economy and elevating the living standards of the people in the community as they could now easily access all the essential resources. Hence technology played a vital role in liberating the lives of many from the bondage of hunger and scarcity to a point of abundance and stable food supply.
Technology Advancement in Communication
Communication is the act of conveying information from one person to another either face to face or by means of a communication medium. According to Scruton (1996), during the ancient times, slaves used to communicate through hymns, quilts or underground railroads while others used drums to convey coded information since most had originated from Africa and drum beating was their cultural way of communicating. These primitive modes of communications were not very reliable as the information could at times be distorted or misinterpreted by the recipient leading to a communication breakdown.
During the ancient period, people used to communicate through messages carved on stone pillars but this type of communication had limitations as the recipients had to travel miles to receive them and the message could only be read within a certain reading range. Others like the American Indians used smoke to convey a particular message to the community while others used bonfires lit on hilltops but such signals were limited to conveying specific information like looming danger, war or victory.
Communication then developed to more elaborate form which included writing on portable materials like reeds and papyrus. This medium of communication was much more reliable than the earlier archaic communication system. With the emergence of technological advancement and innovations, the transmission of signals from one person to another through a more sophisticated medium like communication cables took center stage. In the early 1830s, the electrical communication system made significant progress in this industry as people could now get in touch through electronic devices like a telephone.
In the year 1833, scientists Carl Friedrich and Wilhelm Eduard Weber researching on the electric transmission devices, made use of the principle of “electromagnetic technology” that later acted as the fundamental basis or a prerequisite for the innovation of telephones (Williams, 1993). Subsequent experiments done by Alexander Bell and Thomas Watson worked to optimize its efficiency and could now be used for commercial purposes. This was later followed by other technological developments and innovations by telecommunication engineers and scientists that led to the production of the carbon microphone, telephone exchange, data storage devices, wireless phones, and computers.
At this point, we can only appreciate the technological advancements that the communication industry has taken overtime to come up with sophisticated and very efficient gadgets that can serve multiple purposes other than communication. Such progress in technology has acted as a remedy to the many communication snarl-ups that people in the ancient world had to contend with but now people can freely share information, ideas, thoughts, opinions, photos, video clips on very many communication platforms using the sophisticated devices and handsets.
For example, use of the internet on computers and mobile phones to share information and ideas across the globe hence making the world a small village and enabling the free flow of information that is objective and informative. Hence this technology could be used to positively impact the lives of people by making them more informed and educated.
In conclusion, technology has had quite a significant impact on people’s lives over the years by making life more bearable through the production of efficient systems that require little labor but produce a significantly high output. One significant finding from the above research is that African culture and tradition has been greatly revolutionized over the years from the archaic, crude and barbaric practices to sophisticated and more efficient processes through technological innovations and advancement. The introduction of western culture has worked to raise the living standards of many African communities that were previously languishing in hunger and poverty.
- What is technological advancement? Technological advancement implies the emergence and development of technical devices that affect various spheres of peoples’ life. It affects economic, political, social, and other sectors.
- How does technology affect the advancement of science? Modern technologies make it easier to share information and knowledge, allow scientists from different countries to interact effectively, and also involve the development of new methods of analysis.
- How does the advancement of technology affect society? Modern technologies influence various spheres of public life. They have significantly changed the labor market, transport and communications. People’s daily lives have become easier and more efficient.
- How do I start an essay about technology It is a good idea to start your technology advancement with a hook. One option is to use a quote, like the following one by Albert Einstein: “It has become appallingly obvious that our technology has exceeded our humanity.” One more option is to use an exciting fact like the following one: Over 6,000 new computer viruses are created and released every month.
Brush, S. G. (1988). The History of Modern Science. A Guide to the Second Scientific Revolution, 35 (10), 5-8.
Butler, G. (1996). A History of Information Technology and Systems. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Kedar, S. (2009). Database Management Systems . Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Scruton, R. (1996 ). The Art of Communication Over the Years. The New Criterion, 15 (30), 9-13.
Williams, T. (1993). A Short History of Technology: From the Earliest Times . New York: Dover Publications.
- New Product: Laptop Assembling Machinery Nokia Corporation
- Domination in the Book "Animal Farm"
- The US Farm Bills and Policy Reforms
- Industrialization and Changes of Western History
- Slavery in Islamic Civilisation
- World History: Is Competition Good?
- Imperialism' Impacts on Africa, Latin America and India
- Enlightenment and Romantic Age
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2020, May 7). Technological Advancement Essay. https://ivypanda.com/essays/technological-advancement-essay/
"Technological Advancement Essay." IvyPanda , 7 May 2020, ivypanda.com/essays/technological-advancement-essay/.
IvyPanda . (2020) 'Technological Advancement Essay'. 7 May.
IvyPanda . 2020. "Technological Advancement Essay." May 7, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/technological-advancement-essay/.
1. IvyPanda . "Technological Advancement Essay." May 7, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/technological-advancement-essay/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Technological Advancement Essay." May 7, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/technological-advancement-essay/.
Advertisement
Supported by
How A.I. Made Mark Zuckerberg Popular Again in Silicon Valley
After some trying years during which Mr. Zuckerberg could do little right, many developers and technologists have embraced the Meta chief as their champion of “open-source” artificial intelligence.
- Share full article

By Mike Isaac
Mike Isaac has written about Facebook, Meta and Mark Zuckerberg since 2010.
When Mark Zuckerberg , the chief executive of Meta, announced last year that his company would release an artificial intelligence system, Jeffrey Emanuel had reservations.
Mr. Emanuel, a part-time hacker and full-time A.I. enthusiast, had tinkered with “closed” A.I. models, including OpenAI’s, meaning the systems’ underlying code could not be accessed or modified. When Mr. Zuckerberg introduced Meta’s A.I. system by invitation only to a handful of academics, Mr. Emanuel was concerned that the technology would remain limited to just a small circle of people.
But in a release last summer of an updated A.I. system, Mr. Zuckerberg made the code “open source” so that it could be freely copied, modified and reused by anyone.
Mr. Emanuel, the founder of the blockchain start-up Pastel Network, was sold. He said he appreciated that Meta’s A.I. system was powerful and easy to use. Most of all, he loved how Mr. Zuckerberg was espousing the hacker code of making the technology freely available — largely the opposite of what Google, OpenAI and Microsoft have done.
“We have this champion in Zuckerberg,” Mr. Emanuel, 42, said. “Thank God we have someone to protect the open-source ethos from these other big companies.”
Mr. Zuckerberg has become the highest-profile technology executive to support and promote the open-source model for A.I. That has put the 40-year-old billionaire squarely on one end of a divisive debate over whether the potentially world-changing technology is too dangerous to be made available to any coder who wants it.
Microsoft, OpenAI and Google have more of a closed A.I. strategy to guard their tech, out of what they say is an abundance of caution. But Mr. Zuckerberg has loudly stood behind how the technology should be open to all.
“This technology is so important, and the opportunities are so great, that we should open source and make it as widely available as we responsibly can, so that way everyone can benefit,” he said in an Instagram video in January.
That stance has turned Mr. Zuckerberg into the unlikely man of the hour in many Silicon Valley developer communities, prompting talk of a “glow-up” and a kind of “Zuckaissance.” Even as the chief executive continues grappling with scrutiny over misinformation and child safety issues on Meta’s platforms, many engineers, coders, technologists and others have embraced his position on making A.I. available to the masses.
Since Meta’s first fully open-source A.I. model, called LLaMA 2, was released in July, the software has been downloaded more than 180 million times, the company said. A more powerful version of the model, LLaMA 3, which was released in April, reached the top of the download charts on Hugging Face, a community site for A.I. code, at record speed.
Developers have created tens of thousands of their own customized A.I. programs on top of Meta’s A.I. software to perform everything from helping clinicians read radiology scans to creating scores of digital chatbot assistants.
“I told Mark, I think that open sourcing LLaMA is the most popular thing that Facebook has done in the tech community — ever,” said Patrick Collison, chief executive of the payments company Stripe, who recently joined a Meta strategic advisory group that is aimed at helping the company make strategic decisions about its A.I. technology. Meta owns Facebook, Instagram and other apps.
Mr. Zuckerberg’s new popularity in tech circles is striking because of his fraught history with developers. Over two decades, Meta has sometimes pulled the rug out from under coders. In 2013, for instance, Mr. Zuckerberg bought Parse , a company that built developer tools, to attract coders to build apps for Facebook’s platform. Three years later, he shuttered the effort , angering developers who had invested their time and energy in the project.
A spokeswoman for Mr. Zuckerberg and Meta declined to comment. (The New York Times last year sued OpenAI and its partner, Microsoft, claiming copyright infringement of news content related to A.I. systems.)
Open-source software has a long and storied history in Silicon Valley, with major tech battles revolving around open versus proprietary — or closed — systems.
In the internet’s early days, Microsoft jockeyed to provide the software that ran internet infrastructure, only to eventually lose out to open-source software projects. More recently, Google open sourced its Android mobile operating system to take on Apple’s closed iPhone operating system. Firefox, the internet browser, WordPress, a blogging platform, and Blender, a popular set of animation software tools, were all built using open-source technologies.
Mr. Zuckerberg, who founded Facebook in 2004, has long backed open-source technology. In 2011, Facebook started the Open Compute Project, a nonprofit that freely shares designs of servers and equipment inside data centers. In 2016, Facebook also developed Pytorch, an open-source software library that has been widely used to create A.I. applications. The company is also sharing blueprints of computing chips that it has developed.
“Mark is a great student of history,” said Daniel Ek, Spotify’s chief executive, who considers Mr. Zuckerberg a confidant. “Over time in the computing industry, he’s seen that there’s always been closed and open paths to take. And he has always defaulted to open.”
At Meta, the decision to open source its A.I. was contentious . In 2022 and 2023, the company’s policy and legal teams supported a more conservative approach to releasing the software, fearing a backlash among regulators in Washington and the European Union. But Meta technologists like Yann LeCun and Joelle Pineau, who spearhead A.I. research, pushed the open model, which they argued would better benefit the company in the long term.
The engineers won. Mr. Zuckerberg agreed that if the code was open, it could be improved and safeguarded faster, he said in a post last year on his Facebook page.
While open sourcing LLaMA means giving away computer code that Meta spent billions of dollars to create with no immediate return on investment, Mr. Zuckerberg calls it “good business.” As more developers use Meta’s software and hardware tools, the more likely they are to become invested in its technology ecosystem, which helps entrench the company.
The technology has also helped Meta improve its own internal A.I. systems, aiding ad targeting and recommendations of more relevant content on Meta’s apps.
“It is 100 percent aligned with Zuckerberg’s incentives and how it can benefit Meta,” said Nur Ahmed, a researcher at MIT Sloan who studies A.I. “LLaMA is a win-win for everybody.”
Competitors are taking note. In February, Google open sourced the code for two A.I. models, Gemma 2B and Gemma 7B, a sign that it was feeling the heat from Mr. Zuckerberg’s open-source approach. Google did not respond to requests for comment. Other companies, including Microsoft , Mistral, Snowflake and Databricks, have also started offering open-source models this year.
For some coders, Mr. Zuckerberg’s A.I. approach hasn’t erased all of the baggage of the past. Sam McLeod, 35, a software developer in Melbourne, Australia, deleted his Facebook accounts years ago after growing uncomfortable with the company’s track record on user privacy and other factors.
But more recently, he said, he recognized that Mr. Zuckerberg had released “cutting edge” open-source software models with “permissive licensing terms,” something that can’t be said for other big tech companies.
Matt Shumer, 24, a developer in New York, said he had used closed A.I. models from Mistral and OpenAI to power digital assistants for his start-up, HyperWrite. But after Meta released its updated open-source A.I. model last month, Mr. Shumer started relying heavily on that instead. Whatever reservations he had about Mr. Zuckerberg are in the past.
“Developers have started to see past a lot of issues they’ve had with him and Facebook,” Mr. Shumer said. “Right now, what he’s doing is genuinely good for the open-source community.”
Mike Isaac is a technology correspondent for The Times based in San Francisco. He regularly covers Facebook and Silicon Valley. More about Mike Isaac
Explore Our Coverage of Artificial Intelligence
News and Analysis
Google appears to have rolled back its new A.I. Overviews after the technology produced a litany of untruths and errors.
OpenAI said that it has begun training a new flagship A.I. model that would succeed the GPT-4 technology that drives its popular online chatbot, ChatGPT.
Elon Musk’s A.I. company, xAI, said that it had raised $6 billion , helping to close the funding gap with OpenAI, Anthropic and other rivals.
The Age of A.I.
After some trying years during which Mark Zuckerberg could do little right, many developers and technologists have embraced the Meta chief as their champion of “open-source” A.I.
D’Youville University in Buffalo had an A.I. robot speak at its commencement . Not everyone was happy about it.
A new program, backed by Cornell Tech, M.I.T. and U.C.L.A., helps prepare lower-income, Latina and Black female computing majors for A.I. careers.

COMMENTS
Tech causes more problems than it solves. A number of respondents to this canvassing about the likely future of social and civic innovation shared concerns. Some said that technology causes more problems than it solves. Some said it is likely that emerging worries over the impact of digital life will be at least somewhat mitigated as humans adapt.
Technology affects our daily lives in various ways, from how we communicate, work, learn, entertain, and even think. In this essay, you will find out how technology has changed our society, both positively and negatively, and what challenges we face in the digital era. Read on to discover the impact of technology on our daily lives and how we can cope with it.
lack of attention. low creativity. delays in language development. delays in social and emotional development. physical inactivity and obesity. poor sleep quality. social issues, such as social ...
But writing a technology essay can be challenging, especially for those needing more time or help with writer's block. ... As a result, independent thinking and problem-solving abilities have declined. Positive impact on entertainment: Technology has transformed how we access and consume entertainment. People may now access a wide range of ...
The question of how technologists should incorporate these social dimensions into their design and development processes is an old one, and debate on these issues dates back to the 1970s, but it remains an urgent and often overlooked part of the puzzle because so many of the supposedly systematic mechanisms for assessing the impacts of new ...
Introduction. Modern technology has changed the world beyond recognition. Thanks to technology in the twentieth and twenty-first centuries, advances have been made that have revolutionized our lives. Modern man can hardly imagine his life without machines. Every day, new devices either appear, or existing ones are improved.
Stunning technology developed currently. The most shocking modern technology inventions the majority of people still aren't aware of. Enumerate some technologies that you consider completely destructive and harmful. Explain your choice. Technology and space studies. The impact of technology on people's health and values.
Results from a new Pew Research Center survey of U.S. adults conducted April 12-18, 2021, reveal the extent to which people's use of the internet has changed, their views about how helpful technology has been for them and the struggles some have faced. The vast majority of adults (90%) say the internet has been at least important to them ...
Technology can change the world in ways that are unimaginable until they happen. ... Daniel Bachler, Charlie Giattino, and Pablo Rosado for their helpful comments on drafts of this essay and the visualization. Thanks also to Lizka Vaintrob and Ben Clifford for the conversation that initiated this visualization. ... I tried to avoid this problem ...
Technology might be making education worse. Image credit: Kristina Closs. Listen to the essay, as read by Antero Garcia, associate professor in the Graduate School of Education. As a professor of ...
Technology has many evident benefits and society has unquestioningly embraced it. Postman's intellectual target which is to illustrate how technopoly redefines culture is illustrated in his book, "Technopoly: The surrender of Culture to Technology" Therefore, this essay presents a critical analysis on the impact of technology on society through Postman's eye.
FAQs on Essay on Technology. Q.1 What is Information technology? A - It is a form of technology that uses telecommunication and computer systems for study. Also, they send, retrieve, and store data. Q.2 Is technology harmful to humans? A - No, technology is not harmful to human beings until it is used properly.
Artificial intelligence technology research topics. We started 2023 with M3GAN's box office success, and now we're fascinated (or horrified) with ChatGPT, voice cloning, and deepfakes. While people have discussed artificial intelligence for ages, recent advances have really pushed this topic to the front of our minds.
A recently published book, " Growth in a Time of Change, " addresses these questions. Three basic ingredients drive economic growth—productivity, capital, and labor. All three are facing new ...
Spatial Computing Makes New Strides. Spatial computing is swiftly making the lane change from sci-fi theory into reality. Statista estimates that 1.4 billion devices will be enabled with spatial computing by 2024. Spatial computing is expected to explode as advances in technology allow for the realization of spatial-computing applications.
This essay will discuss about the problems that has occurred with the overuse of technology and thereby suggesting some measures to overcome them. On the one hand, in the globalized world lots of people are using technology without thinking the problems that may arise in near future.
Carbon sequestrationCutting greenhouse-gas emissions alone won't be enough to prevent sharp increases in global temperatures. We'll also need to remove vast amounts of carbon dioxide from the ...
Relationships and Media. 7. War. 8. Information and Communication Tech. 9. Computer Science and Robotics. Researching technology can involve looking at how it solves problems, creates new problems, and how interaction with technology has changed humankind.
Here are five specific and sequential guidelines for decisionmakers to realize the potential of education technology to accelerate student learning. 1. Take stock of how your current schools ...
Since the dotcom bubble burst back in 2000, technology has radically transformed our societies and our daily lives. From smartphones to social media and healthcare, here's a brief history of the 21st century's technological revolution. Just over 20 years ago, the dotcom bubble burst, causing the stocks of many tech firms to tumble.
The arrival of the World Wide Web in the mid-1990s changed that nature of tech toys and education hardware and software. Smart Toy Lab, an Intel and Mattel joint venture launched in 1998, developed the first web-connected interactive toys, or "smart toys."Among the first toys the lab developed were the QX3 Microscope, which featured a built-in video camera that sent images to a PC via a ...
Essay on Technology. The word "technology" and its uses have immensely changed since the 20th century, and with time, it has continued to evolve ever since. We are living in a world driven by technology. The advancement of technology has played an important role in the development of human civilization, along with cultural changes.
Google's chief executive, Sundar Pichai, last year. A new A.I.-generated feature in Google search results "is greatly detrimental to everyone apart from Google," a newspaper executive said.
If 2023 was the year the world discovered generative AI (gen AI), 2024 is the year organizations truly began using—and deriving business value from—this new technology.In the latest McKinsey Global Survey on AI, 65 percent of respondents report that their organizations are regularly using gen AI, nearly double the percentage from our previous survey just ten months ago.
A letter, signed by current and former OpenAI, Anthropic and Google DeepMind workers, called on AI companies to provide transparency and whistleblower protections.
Introduction. Technological advancement has taken major strides in bringing liberation to the divergent human wants and gratifications. After keen observation, I have come to realize that technological advancement plays a critical role in solving the major crisis of food shortages in the modern world. In the state of Virginia during the 17th ...
NuScale Power , a maker of modular nuclear reactor technology that went public, was listed at just 13 cents, down 98.5% on the day. After NuScale reopened, it traded at $8.29, down just 5%.
Guest Essay. America's Military Is Not Prepared for War — or Peace ... China, on the other hand, has no such problems, as it accumulates the world's leading hypersonic arsenal with a mix of ...
When Mr. Zuckerberg introduced Meta's A.I. system by invitation only to a handful of academics, Mr. Emanuel was concerned that the technology would remain limited to just a small circle of people.
Digital twin technology is expected to transform agriculture. By creating the virtual representation of a physical entity, it assists food producers in monitoring, predicting, and optimizing the production process remotely and even autonomously. However, the progress in this area is relatively slower than in industries like manufacturing. A systematic investigation of agricultural digital ...