Qualitative vs Quantitative Research Methods & Data Analysis
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:

What is the difference between quantitative and qualitative?
The main difference between quantitative and qualitative research is the type of data they collect and analyze.
Quantitative research collects numerical data and analyzes it using statistical methods. The aim is to produce objective, empirical data that can be measured and expressed in numerical terms. Quantitative research is often used to test hypotheses, identify patterns, and make predictions.
Qualitative research , on the other hand, collects non-numerical data such as words, images, and sounds. The focus is on exploring subjective experiences, opinions, and attitudes, often through observation and interviews.
Qualitative research aims to produce rich and detailed descriptions of the phenomenon being studied, and to uncover new insights and meanings.
Quantitative data is information about quantities, and therefore numbers, and qualitative data is descriptive, and regards phenomenon which can be observed but not measured, such as language.
What Is Qualitative Research?
Qualitative research is the process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting non-numerical data, such as language. Qualitative research can be used to understand how an individual subjectively perceives and gives meaning to their social reality.
Qualitative data is non-numerical data, such as text, video, photographs, or audio recordings. This type of data can be collected using diary accounts or in-depth interviews and analyzed using grounded theory or thematic analysis.
Qualitative research is multimethod in focus, involving an interpretive, naturalistic approach to its subject matter. This means that qualitative researchers study things in their natural settings, attempting to make sense of, or interpret, phenomena in terms of the meanings people bring to them. Denzin and Lincoln (1994, p. 2)
Interest in qualitative data came about as the result of the dissatisfaction of some psychologists (e.g., Carl Rogers) with the scientific study of psychologists such as behaviorists (e.g., Skinner ).
Since psychologists study people, the traditional approach to science is not seen as an appropriate way of carrying out research since it fails to capture the totality of human experience and the essence of being human. Exploring participants’ experiences is known as a phenomenological approach (re: Humanism ).
Qualitative research is primarily concerned with meaning, subjectivity, and lived experience. The goal is to understand the quality and texture of people’s experiences, how they make sense of them, and the implications for their lives.
Qualitative research aims to understand the social reality of individuals, groups, and cultures as nearly as possible as participants feel or live it. Thus, people and groups are studied in their natural setting.
Some examples of qualitative research questions are provided, such as what an experience feels like, how people talk about something, how they make sense of an experience, and how events unfold for people.
Research following a qualitative approach is exploratory and seeks to explain ‘how’ and ‘why’ a particular phenomenon, or behavior, operates as it does in a particular context. It can be used to generate hypotheses and theories from the data.
Qualitative Methods
There are different types of qualitative research methods, including diary accounts, in-depth interviews , documents, focus groups , case study research , and ethnography.
The results of qualitative methods provide a deep understanding of how people perceive their social realities and in consequence, how they act within the social world.
The researcher has several methods for collecting empirical materials, ranging from the interview to direct observation, to the analysis of artifacts, documents, and cultural records, to the use of visual materials or personal experience. Denzin and Lincoln (1994, p. 14)
Here are some examples of qualitative data:
Interview transcripts : Verbatim records of what participants said during an interview or focus group. They allow researchers to identify common themes and patterns, and draw conclusions based on the data. Interview transcripts can also be useful in providing direct quotes and examples to support research findings.
Observations : The researcher typically takes detailed notes on what they observe, including any contextual information, nonverbal cues, or other relevant details. The resulting observational data can be analyzed to gain insights into social phenomena, such as human behavior, social interactions, and cultural practices.
Unstructured interviews : generate qualitative data through the use of open questions. This allows the respondent to talk in some depth, choosing their own words. This helps the researcher develop a real sense of a person’s understanding of a situation.
Diaries or journals : Written accounts of personal experiences or reflections.
Notice that qualitative data could be much more than just words or text. Photographs, videos, sound recordings, and so on, can be considered qualitative data. Visual data can be used to understand behaviors, environments, and social interactions.
Qualitative Data Analysis
Qualitative research is endlessly creative and interpretive. The researcher does not just leave the field with mountains of empirical data and then easily write up his or her findings.
Qualitative interpretations are constructed, and various techniques can be used to make sense of the data, such as content analysis, grounded theory (Glaser & Strauss, 1967), thematic analysis (Braun & Clarke, 2006), or discourse analysis.
For example, thematic analysis is a qualitative approach that involves identifying implicit or explicit ideas within the data. Themes will often emerge once the data has been coded .
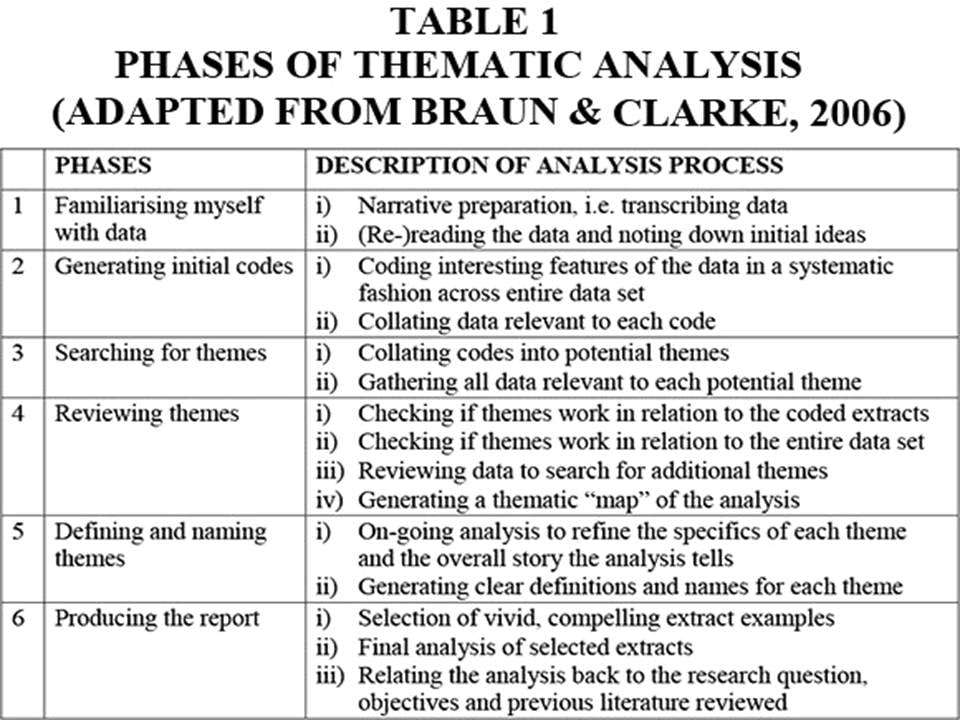
Key Features
- Events can be understood adequately only if they are seen in context. Therefore, a qualitative researcher immerses her/himself in the field, in natural surroundings. The contexts of inquiry are not contrived; they are natural. Nothing is predefined or taken for granted.
- Qualitative researchers want those who are studied to speak for themselves, to provide their perspectives in words and other actions. Therefore, qualitative research is an interactive process in which the persons studied teach the researcher about their lives.
- The qualitative researcher is an integral part of the data; without the active participation of the researcher, no data exists.
- The study’s design evolves during the research and can be adjusted or changed as it progresses. For the qualitative researcher, there is no single reality. It is subjective and exists only in reference to the observer.
- The theory is data-driven and emerges as part of the research process, evolving from the data as they are collected.
Limitations of Qualitative Research
- Because of the time and costs involved, qualitative designs do not generally draw samples from large-scale data sets.
- The problem of adequate validity or reliability is a major criticism. Because of the subjective nature of qualitative data and its origin in single contexts, it is difficult to apply conventional standards of reliability and validity. For example, because of the central role played by the researcher in the generation of data, it is not possible to replicate qualitative studies.
- Also, contexts, situations, events, conditions, and interactions cannot be replicated to any extent, nor can generalizations be made to a wider context than the one studied with confidence.
- The time required for data collection, analysis, and interpretation is lengthy. Analysis of qualitative data is difficult, and expert knowledge of an area is necessary to interpret qualitative data. Great care must be taken when doing so, for example, looking for mental illness symptoms.
Advantages of Qualitative Research
- Because of close researcher involvement, the researcher gains an insider’s view of the field. This allows the researcher to find issues that are often missed (such as subtleties and complexities) by the scientific, more positivistic inquiries.
- Qualitative descriptions can be important in suggesting possible relationships, causes, effects, and dynamic processes.
- Qualitative analysis allows for ambiguities/contradictions in the data, which reflect social reality (Denscombe, 2010).
- Qualitative research uses a descriptive, narrative style; this research might be of particular benefit to the practitioner as she or he could turn to qualitative reports to examine forms of knowledge that might otherwise be unavailable, thereby gaining new insight.
What Is Quantitative Research?
Quantitative research involves the process of objectively collecting and analyzing numerical data to describe, predict, or control variables of interest.
The goals of quantitative research are to test causal relationships between variables , make predictions, and generalize results to wider populations.
Quantitative researchers aim to establish general laws of behavior and phenomenon across different settings/contexts. Research is used to test a theory and ultimately support or reject it.
Quantitative Methods
Experiments typically yield quantitative data, as they are concerned with measuring things. However, other research methods, such as controlled observations and questionnaires , can produce both quantitative information.
For example, a rating scale or closed questions on a questionnaire would generate quantitative data as these produce either numerical data or data that can be put into categories (e.g., “yes,” “no” answers).
Experimental methods limit how research participants react to and express appropriate social behavior.
Findings are, therefore, likely to be context-bound and simply a reflection of the assumptions that the researcher brings to the investigation.
There are numerous examples of quantitative data in psychological research, including mental health. Here are a few examples:
Another example is the Experience in Close Relationships Scale (ECR), a self-report questionnaire widely used to assess adult attachment styles .
The ECR provides quantitative data that can be used to assess attachment styles and predict relationship outcomes.
Neuroimaging data : Neuroimaging techniques, such as MRI and fMRI, provide quantitative data on brain structure and function.
This data can be analyzed to identify brain regions involved in specific mental processes or disorders.
For example, the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) is a clinician-administered questionnaire widely used to assess the severity of depressive symptoms in individuals.
The BDI consists of 21 questions, each scored on a scale of 0 to 3, with higher scores indicating more severe depressive symptoms.
Quantitative Data Analysis
Statistics help us turn quantitative data into useful information to help with decision-making. We can use statistics to summarize our data, describing patterns, relationships, and connections. Statistics can be descriptive or inferential.
Descriptive statistics help us to summarize our data. In contrast, inferential statistics are used to identify statistically significant differences between groups of data (such as intervention and control groups in a randomized control study).
- Quantitative researchers try to control extraneous variables by conducting their studies in the lab.
- The research aims for objectivity (i.e., without bias) and is separated from the data.
- The design of the study is determined before it begins.
- For the quantitative researcher, the reality is objective, exists separately from the researcher, and can be seen by anyone.
- Research is used to test a theory and ultimately support or reject it.
Limitations of Quantitative Research
- Context: Quantitative experiments do not take place in natural settings. In addition, they do not allow participants to explain their choices or the meaning of the questions they may have for those participants (Carr, 1994).
- Researcher expertise: Poor knowledge of the application of statistical analysis may negatively affect analysis and subsequent interpretation (Black, 1999).
- Variability of data quantity: Large sample sizes are needed for more accurate analysis. Small-scale quantitative studies may be less reliable because of the low quantity of data (Denscombe, 2010). This also affects the ability to generalize study findings to wider populations.
- Confirmation bias: The researcher might miss observing phenomena because of focus on theory or hypothesis testing rather than on the theory of hypothesis generation.
Advantages of Quantitative Research
- Scientific objectivity: Quantitative data can be interpreted with statistical analysis, and since statistics are based on the principles of mathematics, the quantitative approach is viewed as scientifically objective and rational (Carr, 1994; Denscombe, 2010).
- Useful for testing and validating already constructed theories.
- Rapid analysis: Sophisticated software removes much of the need for prolonged data analysis, especially with large volumes of data involved (Antonius, 2003).
- Replication: Quantitative data is based on measured values and can be checked by others because numerical data is less open to ambiguities of interpretation.
- Hypotheses can also be tested because of statistical analysis (Antonius, 2003).
Antonius, R. (2003). Interpreting quantitative data with SPSS . Sage.
Black, T. R. (1999). Doing quantitative research in the social sciences: An integrated approach to research design, measurement and statistics . Sage.
Braun, V. & Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology . Qualitative Research in Psychology , 3, 77–101.
Carr, L. T. (1994). The strengths and weaknesses of quantitative and qualitative research : what method for nursing? Journal of advanced nursing, 20(4) , 716-721.
Denscombe, M. (2010). The Good Research Guide: for small-scale social research. McGraw Hill.
Denzin, N., & Lincoln. Y. (1994). Handbook of Qualitative Research. Thousand Oaks, CA, US: Sage Publications Inc.
Glaser, B. G., Strauss, A. L., & Strutzel, E. (1968). The discovery of grounded theory; strategies for qualitative research. Nursing research, 17(4) , 364.
Minichiello, V. (1990). In-Depth Interviewing: Researching People. Longman Cheshire.
Punch, K. (1998). Introduction to Social Research: Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches. London: Sage
Further Information
- Designing qualitative research
- Methods of data collection and analysis
- Introduction to quantitative and qualitative research
- Checklists for improving rigour in qualitative research: a case of the tail wagging the dog?
- Qualitative research in health care: Analysing qualitative data
- Qualitative data analysis: the framework approach
- Using the framework method for the analysis of
- Qualitative data in multi-disciplinary health research
- Content Analysis
- Grounded Theory
- Thematic Analysis
Related Articles

Research Methodology
Qualitative Data Coding

What Is a Focus Group?

Cross-Cultural Research Methodology In Psychology

What Is Internal Validity In Research?

Research Methodology , Statistics
What Is Face Validity In Research? Importance & How To Measure

Criterion Validity: Definition & Examples
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Emotions
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Acquisition
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Religion
- Music and Culture
- Music and Media
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Oncology
- Medical Toxicology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Medical Ethics
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Cognitive Psychology
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Strategy
- Business History
- Business Ethics
- Business and Government
- Business and Technology
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic Systems
- Economic Methodology
- Economic History
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Theory
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Politics and Law
- Public Administration
- Public Policy
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Developmental and Physical Disabilities Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

The Oxford Handbook of Quantitative Methods in Psychology, Vol. 1
Todd D. Little, Texas Tech University, Lubbock, Texas
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Research today demands the application of sophisticated and powerful research tools. Fulfilling this need, this two-volume text provides the tool box to deliver the valid and generalizable answers to today's complex research questions. The Oxford Handbook of Quantitative Methods in Psychology aims to be a source for learning and reviewing current best-practices in quantitative methods as practiced in the social, behavioral, and educational sciences. Comprising two volumes, this text covers a wealth of topics related to quantitative research methods. It begins with essential philosophical and ethical issues related to science and quantitative research. It then addresses core measurement topics before delving into the design of studies. Principal issues related to modern estimation and mathematical modeling are also detailed. Topics in the book then segway into the realm of statistical inference and modeling with articles dedicated to classical approaches as well as modern latent variable approaches. Numerous articles associated with longitudinal data and more specialized techniques round out this broad selection of topics.
Signed in as
Institutional accounts.
- Google Scholar Indexing
- GoogleCrawler [DO NOT DELETE]
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
- Add your ORCID iD
Institutional access
Sign in with a library card.
- Sign in with username/password
- Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Sign in through your institution
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Understanding Methods for Research in Psychology
A Psychology Research Methods Study Guide
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
Types of Research in Psychology
- Cross-Sectional vs. Longitudinal Research
- Reliability and Validity
Glossary of Terms
Research in psychology focuses on a variety of topics , ranging from the development of infants to the behavior of social groups. Psychologists use the scientific method to investigate questions both systematically and empirically.
Research in psychology is important because it provides us with valuable information that helps to improve human lives. By learning more about the brain, cognition, behavior, and mental health conditions, researchers are able to solve real-world problems that affect our day-to-day lives.
At a Glance
Knowing more about how research in psychology is conducted can give you a better understanding of what those findings might mean to you. Psychology experiments can range from simple to complex, but there are some basic terms and concepts that all psychology students should understand.
Start your studies by learning more about the different types of research, the basics of experimental design, and the relationships between variables.
Research in Psychology: The Basics
The first step in your review should include a basic introduction to psychology research methods . Psychology research can have a variety of goals. What researchers learn can be used to describe, explain, predict, or change human behavior.
Psychologists use the scientific method to conduct studies and research in psychology. The basic process of conducting psychology research involves asking a question, designing a study, collecting data, analyzing results, reaching conclusions, and sharing the findings.
The Scientific Method in Psychology Research
The steps of the scientific method in psychology research are:
- Make an observation
- Ask a research question and make predictions about what you expect to find
- Test your hypothesis and gather data
- Examine the results and form conclusions
- Report your findings
Research in psychology can take several different forms. It can describe a phenomenon, explore the causes of a phenomenon, or look at relationships between one or more variables. Three of the main types of psychological research focus on:
Descriptive Studies
This type of research can tell us more about what is happening in a specific population. It relies on techniques such as observation, surveys, and case studies.
Correlational Studies
Correlational research is frequently used in psychology to look for relationships between variables. While research look at how variables are related, they do not manipulate any of the variables.
While correlational studies can suggest a relationship between two variables, finding a correlation does not prove that one variable causes a change in another. In other words, correlation does not equal causation.
Experimental Research Methods
Experiments are a research method that can look at whether changes in one variable cause changes in another. The simple experiment is one of the most basic methods of determining if there is a cause-and-effect relationship between two variables.
A simple experiment utilizes a control group of participants who receive no treatment and an experimental group of participants who receive the treatment.
Experimenters then compare the results of the two groups to determine if the treatment had an effect.
Cross-Sectional vs. Longitudinal Research in Psychology
Research in psychology can also involve collecting data at a single point in time, or gathering information at several points over a period of time.
Cross-Sectional Research
In a cross-sectional study , researchers collect data from participants at a single point in time. These are descriptive type of research and cannot be used to determine cause and effect because researchers do not manipulate the independent variables.
However, cross-sectional research does allow researchers to look at the characteristics of the population and explore relationships between different variables at a single point in time.
Longitudinal Research
A longitudinal study is a type of research in psychology that involves looking at the same group of participants over a period of time. Researchers start by collecting initial data that serves as a baseline, and then collect follow-up data at certain intervals. These studies can last days, months, or years.
The longest longitudinal study in psychology was started in 1921 and the study is planned to continue until the last participant dies or withdraws. As of 2003, more than 200 of the partipants were still alive.
The Reliability and Validity of Research in Psychology
Reliability and validity are two concepts that are also critical in psychology research. In order to trust the results, we need to know if the findings are consistent (reliability) and that we are actually measuring what we think we are measuring (validity).
Reliability
Reliability is a vital component of a valid psychological test. What is reliability? How do we measure it? Simply put, reliability refers to the consistency of a measure. A test is considered reliable if we get the same result repeatedly.
When determining the merits of a psychological test, validity is one of the most important factors to consider. What exactly is validity? One of the greatest concerns when creating a psychological test is whether or not it actually measures what we think it is measuring.
For example, a test might be designed to measure a stable personality trait but instead measures transitory emotions generated by situational or environmental conditions. A valid test ensures that the results accurately reflect the dimension undergoing assessment.
Review some of the key terms that you should know and understand about psychology research methods. Spend some time studying these terms and definitions before your exam. Some key terms that you should know include:
- Correlation
- Demand characteristic
- Dependent variable
- Hawthorne effect
- Independent variable
- Naturalistic observation
- Placebo effect
- Random assignment
- Replication
- Selective attrition
Erol A. How to conduct scientific research ? Noro Psikiyatr Ars . 2017;54(2):97-98. doi:10.5152/npa.2017.0120102
Aggarwal R, Ranganathan P. Study designs: Part 2 - Descriptive studies . Perspect Clin Res . 2019;10(1):34-36. doi:10.4103/picr.PICR_154_18
Curtis EA, Comiskey C, Dempsey O. Importance and use of correlational research . Nurse Res . 2016;23(6):20-25. doi:10.7748/nr.2016.e1382
Wang X, Cheng Z. Cross-sectional studies: Strengths, weaknesses, and recommendations . Chest . 2020;158(1S):S65-S71. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.03.012
Caruana EJ, Roman M, Hernández-Sánchez J, Solli P. Longitudinal studies . J Thorac Dis . 2015;7(11):E537-E540. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2015.10.63
Stanford Magazine. The vexing legacy of Lewis Terman .
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

Critically Thinking About Qualitative Versus Quantitative Research
What should we do regarding our research questions and methodology.
Posted January 26, 2022 | Reviewed by Davia Sills
- Neither a quantitative nor a qualitative methodology is the right way to approach every scientific question.
- Rather, the nature of the question determines which methodology is best suited to address it.
- Often, researchers benefit from a mixed approach that incorporates both quantitative and qualitative methodologies.
As a researcher who has used a wide variety of methodologies, I understand the importance of acknowledging that we, as researchers, do not pick the methodology; rather, the research question dictates it. So, you can only imagine how annoyed I get when I hear of undergraduates designing their research projects based on preconceived notions, like "quantitative is more straightforward," or "qualitative is easier." Apart from the fact that neither of these assertions is actually the case, these young researchers are blatantly missing one of the foundational steps of good research: If you are interested in researching a particular area, you must get to know the area (i.e., through reading) and then develop a question based on that reading.
The nature of the question will dictate the most appropriate methodological approach.
I’ve debated with researchers in the past who are "exclusively" qualitative or "exclusively" quantitative. Depending on the rationale for their exclusivity, I might question a little deeper, learn something, and move on, or I might debate further. Sometimes, I throw some contentious statements out to see what the responses are like. For example, "Qualitative research, in isolation, is nothing but glorified journalism . " This one might not be new to you. Yes, qualitative is flawed, but so, too, is quantitative.
Let's try this one: "Numbers don’t lie, just the researchers who interpret them." If researchers are going to have a pop at qual for subjectivity, why don’t they recognize the same issues in quant? The numbers in a results section may be objectively correct, but their meaningfulness is only made clear through the interpretation of the human reporting them. This is not a criticism but is an important observation for those who believe in the absolute objectivity of quantitative reporting. The subjectivity associated with this interpretation may miss something crucial in the interpretation of the numbers because, hey, we’re only human.
With that, I love quantitative research, but I’m not unreasonable about it. Let’s say we’ve evaluated a three-arm RCT—the new therapeutic intervention is significantly efficacious, with a large effect, for enhancing "x" in people living with "y." One might conclude that this intervention works and that we must conduct further research on it to further support its efficacy—this is, of course, a fine suggestion, consistent with good research practice and epistemological understanding.
However, blindly recommending the intervention based on the interpretation of numbers alone might be suspect—think of all the variables that could be involved in a 4-, 8-, 12-, or 52-week intervention with human participants. It would be foolish to believe that all variables were considered—so, here is a fantastic example of where a qualitative methodology might be useful. At the end of the intervention, a researcher might decide to interview a random 20 percent of the cohort who participated in the intervention group about their experience and the program’s strengths and weaknesses. The findings from this qualitative element might help further explain the effects, aid the initial interpretation, and bring to life new ideas and concepts that had been missing from the initial interpretation. In this respect, infusing a qualitative approach at the end of quantitative analysis has shown its benefits—a mixed approach to intervention evaluation is very useful.
What about before that? Well, let’s say I want to develop another intervention to enhance "z," but there’s little research on it, and that which has been conducted isn’t of the highest quality; furthermore, we don’t know about people’s experiences with "z" or even other variables associated with it.
To design an intervention around "z" would be ‘jumping the gun’ at best (and a waste of funds). It seems that an exploration of some sort is necessary. This is where qualitative again shines—giving us an opportunity to explore what "z" is from the perspective of a relevant cohort(s).
Of course, we cannot generalize the findings; we cannot draw a definitive conclusion as to what "z" is. But what the findings facilitate is providing a foundation from which to work; for example, we still cannot say that "z" is this, that, or the other, but it appears that it might be associated with "a," "b" and "c." Thus, future research should investigate the nature of "z" as a particular concept, in relation to "a," "b" and "c." Again, a qualitative methodology shows its worth. In the previous examples, a qualitative method was used because the research questions warranted it.
Through considering the potentially controversial statements about qual and quant above, we are pushed into examining the strengths and weaknesses of research methodologies (regardless of our exclusivity with a particular approach). This is useful if we’re going to think critically about finding answers to our research questions. But simply considering these does not let poor research practice off the hook.
For example, credible qualitative researchers acknowledge that generalizability is not the point of their research; however, that doesn’t stop some less-than-credible researchers from presenting their "findings" as generalizable as possible, without actually using the word. Such practices should be frowned upon—so should making a career out of strictly using qualitative methodology in an attempt to find answers core to the human condition. All these researchers are really doing is spending a career exploring, yet never really finding anything (despite arguing to the contrary, albeit avoiding the word "generalize").

The solution to this problem, again, is to truly listen to what your research question is telling you. Eventually, it’s going to recommend a quantitative approach. Likewise, a "numbers person" will be recommended a qualitative approach from time to time—flip around the example above, and there’s a similar criticism. Again, embrace a mixed approach.
What's the point of this argument?
I conduct both research methodologies. Which do I prefer? Simple—whichever one helps me most appropriately answer my research question.
Do I have problems with qualitative methodologies? Absolutely—but I have issues with quantitative methods as well. Having these issues is good—it means that you recognize the limitations of your tools, which increases the chances of you "fixing," "sharpening" or "changing out" your tools when necessary.
So, the next time someone speaks with you about labeling researchers as one type or another, ask them why they think that way, ask them which they think you are, and then reflect on the responses alongside your own views of methodology and epistemology. It might just help you become a better researcher.

Christopher Dwyer, Ph.D., is a lecturer at the Technological University of the Shannon in Athlone, Ireland.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that threatens to derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face our triggers with less reactivity so that we can get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Front Res Metr Anal

The Use of Research Methods in Psychological Research: A Systematised Review
Salomé elizabeth scholtz.
1 Community Psychosocial Research (COMPRES), School of Psychosocial Health, North-West University, Potchefstroom, South Africa
Werner de Klerk
Leon t. de beer.
2 WorkWell Research Institute, North-West University, Potchefstroom, South Africa
Research methods play an imperative role in research quality as well as educating young researchers, however, the application thereof is unclear which can be detrimental to the field of psychology. Therefore, this systematised review aimed to determine what research methods are being used, how these methods are being used and for what topics in the field. Our review of 999 articles from five journals over a period of 5 years indicated that psychology research is conducted in 10 topics via predominantly quantitative research methods. Of these 10 topics, social psychology was the most popular. The remainder of the conducted methodology is described. It was also found that articles lacked rigour and transparency in the used methodology which has implications for replicability. In conclusion this article, provides an overview of all reported methodologies used in a sample of psychology journals. It highlights the popularity and application of methods and designs throughout the article sample as well as an unexpected lack of rigour with regard to most aspects of methodology. Possible sample bias should be considered when interpreting the results of this study. It is recommended that future research should utilise the results of this study to determine the possible impact on the field of psychology as a science and to further investigation into the use of research methods. Results should prompt the following future research into: a lack or rigour and its implication on replication, the use of certain methods above others, publication bias and choice of sampling method.
Introduction
Psychology is an ever-growing and popular field (Gough and Lyons, 2016 ; Clay, 2017 ). Due to this growth and the need for science-based research to base health decisions on (Perestelo-Pérez, 2013 ), the use of research methods in the broad field of psychology is an essential point of investigation (Stangor, 2011 ; Aanstoos, 2014 ). Research methods are therefore viewed as important tools used by researchers to collect data (Nieuwenhuis, 2016 ) and include the following: quantitative, qualitative, mixed method and multi method (Maree, 2016 ). Additionally, researchers also employ various types of literature reviews to address research questions (Grant and Booth, 2009 ). According to literature, what research method is used and why a certain research method is used is complex as it depends on various factors that may include paradigm (O'Neil and Koekemoer, 2016 ), research question (Grix, 2002 ), or the skill and exposure of the researcher (Nind et al., 2015 ). How these research methods are employed is also difficult to discern as research methods are often depicted as having fixed boundaries that are continuously crossed in research (Johnson et al., 2001 ; Sandelowski, 2011 ). Examples of this crossing include adding quantitative aspects to qualitative studies (Sandelowski et al., 2009 ), or stating that a study used a mixed-method design without the study having any characteristics of this design (Truscott et al., 2010 ).
The inappropriate use of research methods affects how students and researchers improve and utilise their research skills (Scott Jones and Goldring, 2015 ), how theories are developed (Ngulube, 2013 ), and the credibility of research results (Levitt et al., 2017 ). This, in turn, can be detrimental to the field (Nind et al., 2015 ), journal publication (Ketchen et al., 2008 ; Ezeh et al., 2010 ), and attempts to address public social issues through psychological research (Dweck, 2017 ). This is especially important given the now well-known replication crisis the field is facing (Earp and Trafimow, 2015 ; Hengartner, 2018 ).
Due to this lack of clarity on method use and the potential impact of inept use of research methods, the aim of this study was to explore the use of research methods in the field of psychology through a review of journal publications. Chaichanasakul et al. ( 2011 ) identify reviewing articles as the opportunity to examine the development, growth and progress of a research area and overall quality of a journal. Studies such as Lee et al. ( 1999 ) as well as Bluhm et al. ( 2011 ) review of qualitative methods has attempted to synthesis the use of research methods and indicated the growth of qualitative research in American and European journals. Research has also focused on the use of research methods in specific sub-disciplines of psychology, for example, in the field of Industrial and Organisational psychology Coetzee and Van Zyl ( 2014 ) found that South African publications tend to consist of cross-sectional quantitative research methods with underrepresented longitudinal studies. Qualitative studies were found to make up 21% of the articles published from 1995 to 2015 in a similar study by O'Neil and Koekemoer ( 2016 ). Other methods in health psychology, such as Mixed methods research have also been reportedly growing in popularity (O'Cathain, 2009 ).
A broad overview of the use of research methods in the field of psychology as a whole is however, not available in the literature. Therefore, our research focused on answering what research methods are being used, how these methods are being used and for what topics in practice (i.e., journal publications) in order to provide a general perspective of method used in psychology publication. We synthesised the collected data into the following format: research topic [areas of scientific discourse in a field or the current needs of a population (Bittermann and Fischer, 2018 )], method [data-gathering tools (Nieuwenhuis, 2016 )], sampling [elements chosen from a population to partake in research (Ritchie et al., 2009 )], data collection [techniques and research strategy (Maree, 2016 )], and data analysis [discovering information by examining bodies of data (Ktepi, 2016 )]. A systematised review of recent articles (2013 to 2017) collected from five different journals in the field of psychological research was conducted.
Grant and Booth ( 2009 ) describe systematised reviews as the review of choice for post-graduate studies, which is employed using some elements of a systematic review and seldom more than one or two databases to catalogue studies after a comprehensive literature search. The aspects used in this systematised review that are similar to that of a systematic review were a full search within the chosen database and data produced in tabular form (Grant and Booth, 2009 ).
Sample sizes and timelines vary in systematised reviews (see Lowe and Moore, 2014 ; Pericall and Taylor, 2014 ; Barr-Walker, 2017 ). With no clear parameters identified in the literature (see Grant and Booth, 2009 ), the sample size of this study was determined by the purpose of the sample (Strydom, 2011 ), and time and cost constraints (Maree and Pietersen, 2016 ). Thus, a non-probability purposive sample (Ritchie et al., 2009 ) of the top five psychology journals from 2013 to 2017 was included in this research study. Per Lee ( 2015 ) American Psychological Association (APA) recommends the use of the most up-to-date sources for data collection with consideration of the context of the research study. As this research study focused on the most recent trends in research methods used in the broad field of psychology, the identified time frame was deemed appropriate.
Psychology journals were only included if they formed part of the top five English journals in the miscellaneous psychology domain of the Scimago Journal and Country Rank (Scimago Journal & Country Rank, 2017 ). The Scimago Journal and Country Rank provides a yearly updated list of publicly accessible journal and country-specific indicators derived from the Scopus® database (Scopus, 2017b ) by means of the Scimago Journal Rank (SJR) indicator developed by Scimago from the algorithm Google PageRank™ (Scimago Journal & Country Rank, 2017 ). Scopus is the largest global database of abstracts and citations from peer-reviewed journals (Scopus, 2017a ). Reasons for the development of the Scimago Journal and Country Rank list was to allow researchers to assess scientific domains, compare country rankings, and compare and analyse journals (Scimago Journal & Country Rank, 2017 ), which supported the aim of this research study. Additionally, the goals of the journals had to focus on topics in psychology in general with no preference to specific research methods and have full-text access to articles.
The following list of top five journals in 2018 fell within the abovementioned inclusion criteria (1) Australian Journal of Psychology, (2) British Journal of Psychology, (3) Europe's Journal of Psychology, (4) International Journal of Psychology and lastly the (5) Journal of Psychology Applied and Interdisciplinary.
Journals were excluded from this systematised review if no full-text versions of their articles were available, if journals explicitly stated a publication preference for certain research methods, or if the journal only published articles in a specific discipline of psychological research (for example, industrial psychology, clinical psychology etc.).
The researchers followed a procedure (see Figure 1 ) adapted from that of Ferreira et al. ( 2016 ) for systematised reviews. Data collection and categorisation commenced on 4 December 2017 and continued until 30 June 2019. All the data was systematically collected and coded manually (Grant and Booth, 2009 ) with an independent person acting as co-coder. Codes of interest included the research topic, method used, the design used, sampling method, and methodology (the method used for data collection and data analysis). These codes were derived from the wording in each article. Themes were created based on the derived codes and checked by the co-coder. Lastly, these themes were catalogued into a table as per the systematised review design.

Systematised review procedure.
According to Johnston et al. ( 2019 ), “literature screening, selection, and data extraction/analyses” (p. 7) are specifically tailored to the aim of a review. Therefore, the steps followed in a systematic review must be reported in a comprehensive and transparent manner. The chosen systematised design adhered to the rigour expected from systematic reviews with regard to full search and data produced in tabular form (Grant and Booth, 2009 ). The rigorous application of the systematic review is, therefore discussed in relation to these two elements.
Firstly, to ensure a comprehensive search, this research study promoted review transparency by following a clear protocol outlined according to each review stage before collecting data (Johnston et al., 2019 ). This protocol was similar to that of Ferreira et al. ( 2016 ) and approved by three research committees/stakeholders and the researchers (Johnston et al., 2019 ). The eligibility criteria for article inclusion was based on the research question and clearly stated, and the process of inclusion was recorded on an electronic spreadsheet to create an evidence trail (Bandara et al., 2015 ; Johnston et al., 2019 ). Microsoft Excel spreadsheets are a popular tool for review studies and can increase the rigour of the review process (Bandara et al., 2015 ). Screening for appropriate articles for inclusion forms an integral part of a systematic review process (Johnston et al., 2019 ). This step was applied to two aspects of this research study: the choice of eligible journals and articles to be included. Suitable journals were selected by the first author and reviewed by the second and third authors. Initially, all articles from the chosen journals were included. Then, by process of elimination, those irrelevant to the research aim, i.e., interview articles or discussions etc., were excluded.
To ensure rigourous data extraction, data was first extracted by one reviewer, and an independent person verified the results for completeness and accuracy (Johnston et al., 2019 ). The research question served as a guide for efficient, organised data extraction (Johnston et al., 2019 ). Data was categorised according to the codes of interest, along with article identifiers for audit trails such as authors, title and aims of articles. The categorised data was based on the aim of the review (Johnston et al., 2019 ) and synthesised in tabular form under methods used, how these methods were used, and for what topics in the field of psychology.
The initial search produced a total of 1,145 articles from the 5 journals identified. Inclusion and exclusion criteria resulted in a final sample of 999 articles ( Figure 2 ). Articles were co-coded into 84 codes, from which 10 themes were derived ( Table 1 ).

Journal article frequency.
Codes used to form themes (research topics).
These 10 themes represent the topic section of our research question ( Figure 3 ). All these topics except, for the final one, psychological practice , were found to concur with the research areas in psychology as identified by Weiten ( 2010 ). These research areas were chosen to represent the derived codes as they provided broad definitions that allowed for clear, concise categorisation of the vast amount of data. Article codes were categorised under particular themes/topics if they adhered to the research area definitions created by Weiten ( 2010 ). It is important to note that these areas of research do not refer to specific disciplines in psychology, such as industrial psychology; but to broader fields that may encompass sub-interests of these disciplines.

Topic frequency (international sample).
In the case of developmental psychology , researchers conduct research into human development from childhood to old age. Social psychology includes research on behaviour governed by social drivers. Researchers in the field of educational psychology study how people learn and the best way to teach them. Health psychology aims to determine the effect of psychological factors on physiological health. Physiological psychology , on the other hand, looks at the influence of physiological aspects on behaviour. Experimental psychology is not the only theme that uses experimental research and focuses on the traditional core topics of psychology (for example, sensation). Cognitive psychology studies the higher mental processes. Psychometrics is concerned with measuring capacity or behaviour. Personality research aims to assess and describe consistency in human behaviour (Weiten, 2010 ). The final theme of psychological practice refers to the experiences, techniques, and interventions employed by practitioners, researchers, and academia in the field of psychology.
Articles under these themes were further subdivided into methodologies: method, sampling, design, data collection, and data analysis. The categorisation was based on information stated in the articles and not inferred by the researchers. Data were compiled into two sets of results presented in this article. The first set addresses the aim of this study from the perspective of the topics identified. The second set of results represents a broad overview of the results from the perspective of the methodology employed. The second set of results are discussed in this article, while the first set is presented in table format. The discussion thus provides a broad overview of methods use in psychology (across all themes), while the table format provides readers with in-depth insight into methods used in the individual themes identified. We believe that presenting the data from both perspectives allow readers a broad understanding of the results. Due a large amount of information that made up our results, we followed Cichocka and Jost ( 2014 ) in simplifying our results. Please note that the numbers indicated in the table in terms of methodology differ from the total number of articles. Some articles employed more than one method/sampling technique/design/data collection method/data analysis in their studies.
What follows is the results for what methods are used, how these methods are used, and which topics in psychology they are applied to . Percentages are reported to the second decimal in order to highlight small differences in the occurrence of methodology.
Firstly, with regard to the research methods used, our results show that researchers are more likely to use quantitative research methods (90.22%) compared to all other research methods. Qualitative research was the second most common research method but only made up about 4.79% of the general method usage. Reviews occurred almost as much as qualitative studies (3.91%), as the third most popular method. Mixed-methods research studies (0.98%) occurred across most themes, whereas multi-method research was indicated in only one study and amounted to 0.10% of the methods identified. The specific use of each method in the topics identified is shown in Table 2 and Figure 4 .
Research methods in psychology.

Research method frequency in topics.
Secondly, in the case of how these research methods are employed , our study indicated the following.
Sampling −78.34% of the studies in the collected articles did not specify a sampling method. From the remainder of the studies, 13 types of sampling methods were identified. These sampling methods included broad categorisation of a sample as, for example, a probability or non-probability sample. General samples of convenience were the methods most likely to be applied (10.34%), followed by random sampling (3.51%), snowball sampling (2.73%), and purposive (1.37%) and cluster sampling (1.27%). The remainder of the sampling methods occurred to a more limited extent (0–1.0%). See Table 3 and Figure 5 for sampling methods employed in each topic.
Sampling use in the field of psychology.

Sampling method frequency in topics.
Designs were categorised based on the articles' statement thereof. Therefore, it is important to note that, in the case of quantitative studies, non-experimental designs (25.55%) were often indicated due to a lack of experiments and any other indication of design, which, according to Laher ( 2016 ), is a reasonable categorisation. Non-experimental designs should thus be compared with experimental designs only in the description of data, as it could include the use of correlational/cross-sectional designs, which were not overtly stated by the authors. For the remainder of the research methods, “not stated” (7.12%) was assigned to articles without design types indicated.
From the 36 identified designs the most popular designs were cross-sectional (23.17%) and experimental (25.64%), which concurred with the high number of quantitative studies. Longitudinal studies (3.80%), the third most popular design, was used in both quantitative and qualitative studies. Qualitative designs consisted of ethnography (0.38%), interpretative phenomenological designs/phenomenology (0.28%), as well as narrative designs (0.28%). Studies that employed the review method were mostly categorised as “not stated,” with the most often stated review designs being systematic reviews (0.57%). The few mixed method studies employed exploratory, explanatory (0.09%), and concurrent designs (0.19%), with some studies referring to separate designs for the qualitative and quantitative methods. The one study that identified itself as a multi-method study used a longitudinal design. Please see how these designs were employed in each specific topic in Table 4 , Figure 6 .
Design use in the field of psychology.

Design frequency in topics.
Data collection and analysis —data collection included 30 methods, with the data collection method most often employed being questionnaires (57.84%). The experimental task (16.56%) was the second most preferred collection method, which included established or unique tasks designed by the researchers. Cognitive ability tests (6.84%) were also regularly used along with various forms of interviewing (7.66%). Table 5 and Figure 7 represent data collection use in the various topics. Data analysis consisted of 3,857 occurrences of data analysis categorised into ±188 various data analysis techniques shown in Table 6 and Figures 1 – 7 . Descriptive statistics were the most commonly used (23.49%) along with correlational analysis (17.19%). When using a qualitative method, researchers generally employed thematic analysis (0.52%) or different forms of analysis that led to coding and the creation of themes. Review studies presented few data analysis methods, with most studies categorising their results. Mixed method and multi-method studies followed the analysis methods identified for the qualitative and quantitative studies included.
Data collection in the field of psychology.

Data collection frequency in topics.
Data analysis in the field of psychology.
Results of the topics researched in psychology can be seen in the tables, as previously stated in this article. It is noteworthy that, of the 10 topics, social psychology accounted for 43.54% of the studies, with cognitive psychology the second most popular research topic at 16.92%. The remainder of the topics only occurred in 4.0–7.0% of the articles considered. A list of the included 999 articles is available under the section “View Articles” on the following website: https://methodgarden.xtrapolate.io/ . This website was created by Scholtz et al. ( 2019 ) to visually present a research framework based on this Article's results.
This systematised review categorised full-length articles from five international journals across the span of 5 years to provide insight into the use of research methods in the field of psychology. Results indicated what methods are used how these methods are being used and for what topics (why) in the included sample of articles. The results should be seen as providing insight into method use and by no means a comprehensive representation of the aforementioned aim due to the limited sample. To our knowledge, this is the first research study to address this topic in this manner. Our discussion attempts to promote a productive way forward in terms of the key results for method use in psychology, especially in the field of academia (Holloway, 2008 ).
With regard to the methods used, our data stayed true to literature, finding only common research methods (Grant and Booth, 2009 ; Maree, 2016 ) that varied in the degree to which they were employed. Quantitative research was found to be the most popular method, as indicated by literature (Breen and Darlaston-Jones, 2010 ; Counsell and Harlow, 2017 ) and previous studies in specific areas of psychology (see Coetzee and Van Zyl, 2014 ). Its long history as the first research method (Leech et al., 2007 ) in the field of psychology as well as researchers' current application of mathematical approaches in their studies (Toomela, 2010 ) might contribute to its popularity today. Whatever the case may be, our results show that, despite the growth in qualitative research (Demuth, 2015 ; Smith and McGannon, 2018 ), quantitative research remains the first choice for article publication in these journals. Despite the included journals indicating openness to articles that apply any research methods. This finding may be due to qualitative research still being seen as a new method (Burman and Whelan, 2011 ) or reviewers' standards being higher for qualitative studies (Bluhm et al., 2011 ). Future research is encouraged into the possible biasness in publication of research methods, additionally further investigation with a different sample into the proclaimed growth of qualitative research may also provide different results.
Review studies were found to surpass that of multi-method and mixed method studies. To this effect Grant and Booth ( 2009 ), state that the increased awareness, journal contribution calls as well as its efficiency in procuring research funds all promote the popularity of reviews. The low frequency of mixed method studies contradicts the view in literature that it's the third most utilised research method (Tashakkori and Teddlie's, 2003 ). Its' low occurrence in this sample could be due to opposing views on mixing methods (Gunasekare, 2015 ) or that authors prefer publishing in mixed method journals, when using this method, or its relative novelty (Ivankova et al., 2016 ). Despite its low occurrence, the application of the mixed methods design in articles was methodologically clear in all cases which were not the case for the remainder of research methods.
Additionally, a substantial number of studies used a combination of methodologies that are not mixed or multi-method studies. Perceived fixed boundaries are according to literature often set aside, as confirmed by this result, in order to investigate the aim of a study, which could create a new and helpful way of understanding the world (Gunasekare, 2015 ). According to Toomela ( 2010 ), this is not unheard of and could be considered a form of “structural systemic science,” as in the case of qualitative methodology (observation) applied in quantitative studies (experimental design) for example. Based on this result, further research into this phenomenon as well as its implications for research methods such as multi and mixed methods is recommended.
Discerning how these research methods were applied, presented some difficulty. In the case of sampling, most studies—regardless of method—did mention some form of inclusion and exclusion criteria, but no definite sampling method. This result, along with the fact that samples often consisted of students from the researchers' own academic institutions, can contribute to literature and debates among academics (Peterson and Merunka, 2014 ; Laher, 2016 ). Samples of convenience and students as participants especially raise questions about the generalisability and applicability of results (Peterson and Merunka, 2014 ). This is because attention to sampling is important as inappropriate sampling can debilitate the legitimacy of interpretations (Onwuegbuzie and Collins, 2017 ). Future investigation into the possible implications of this reported popular use of convenience samples for the field of psychology as well as the reason for this use could provide interesting insight, and is encouraged by this study.
Additionally, and this is indicated in Table 6 , articles seldom report the research designs used, which highlights the pressing aspect of the lack of rigour in the included sample. Rigour with regards to the applied empirical method is imperative in promoting psychology as a science (American Psychological Association, 2020 ). Omitting parts of the research process in publication when it could have been used to inform others' research skills should be questioned, and the influence on the process of replicating results should be considered. Publications are often rejected due to a lack of rigour in the applied method and designs (Fonseca, 2013 ; Laher, 2016 ), calling for increased clarity and knowledge of method application. Replication is a critical part of any field of scientific research and requires the “complete articulation” of the study methods used (Drotar, 2010 , p. 804). The lack of thorough description could be explained by the requirements of certain journals to only report on certain aspects of a research process, especially with regard to the applied design (Laher, 20). However, naming aspects such as sampling and designs, is a requirement according to the APA's Journal Article Reporting Standards (JARS-Quant) (Appelbaum et al., 2018 ). With very little information on how a study was conducted, authors lose a valuable opportunity to enhance research validity, enrich the knowledge of others, and contribute to the growth of psychology and methodology as a whole. In the case of this research study, it also restricted our results to only reported samples and designs, which indicated a preference for certain designs, such as cross-sectional designs for quantitative studies.
Data collection and analysis were for the most part clearly stated. A key result was the versatile use of questionnaires. Researchers would apply a questionnaire in various ways, for example in questionnaire interviews, online surveys, and written questionnaires across most research methods. This may highlight a trend for future research.
With regard to the topics these methods were employed for, our research study found a new field named “psychological practice.” This result may show the growing consciousness of researchers as part of the research process (Denzin and Lincoln, 2003 ), psychological practice, and knowledge generation. The most popular of these topics was social psychology, which is generously covered in journals and by learning societies, as testaments of the institutional support and richness social psychology has in the field of psychology (Chryssochoou, 2015 ). The APA's perspective on 2018 trends in psychology also identifies an increased amount of psychology focus on how social determinants are influencing people's health (Deangelis, 2017 ).
This study was not without limitations and the following should be taken into account. Firstly, this study used a sample of five specific journals to address the aim of the research study, despite general journal aims (as stated on journal websites), this inclusion signified a bias towards the research methods published in these specific journals only and limited generalisability. A broader sample of journals over a different period of time, or a single journal over a longer period of time might provide different results. A second limitation is the use of Excel spreadsheets and an electronic system to log articles, which was a manual process and therefore left room for error (Bandara et al., 2015 ). To address this potential issue, co-coding was performed to reduce error. Lastly, this article categorised data based on the information presented in the article sample; there was no interpretation of what methodology could have been applied or whether the methods stated adhered to the criteria for the methods used. Thus, a large number of articles that did not clearly indicate a research method or design could influence the results of this review. However, this in itself was also a noteworthy result. Future research could review research methods of a broader sample of journals with an interpretive review tool that increases rigour. Additionally, the authors also encourage the future use of systematised review designs as a way to promote a concise procedure in applying this design.
Our research study presented the use of research methods for published articles in the field of psychology as well as recommendations for future research based on these results. Insight into the complex questions identified in literature, regarding what methods are used how these methods are being used and for what topics (why) was gained. This sample preferred quantitative methods, used convenience sampling and presented a lack of rigorous accounts for the remaining methodologies. All methodologies that were clearly indicated in the sample were tabulated to allow researchers insight into the general use of methods and not only the most frequently used methods. The lack of rigorous account of research methods in articles was represented in-depth for each step in the research process and can be of vital importance to address the current replication crisis within the field of psychology. Recommendations for future research aimed to motivate research into the practical implications of the results for psychology, for example, publication bias and the use of convenience samples.
Ethics Statement
This study was cleared by the North-West University Health Research Ethics Committee: NWU-00115-17-S1.
Author Contributions
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct and intellectual contribution to the work, and approved it for publication.

Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
- Aanstoos C. M. (2014). Psychology . Available online at: http://eds.a.ebscohost.com.nwulib.nwu.ac.za/eds/detail/detail?sid=18de6c5c-2b03-4eac-94890145eb01bc70%40sessionmgr4006&vid$=$1&hid$=$4113&bdata$=$JnNpdGU9ZWRzL~WxpdmU%3d#AN$=$93871882&db$=$ers
- American Psychological Association (2020). Science of Psychology . Available online at: https://www.apa.org/action/science/
- Appelbaum M., Cooper H., Kline R. B., Mayo-Wilson E., Nezu A. M., Rao S. M. (2018). Journal article reporting standards for quantitative research in psychology: the APA Publications and Communications Board task force report . Am. Psychol. 73 :3. 10.1037/amp0000191 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bandara W., Furtmueller E., Gorbacheva E., Miskon S., Beekhuyzen J. (2015). Achieving rigor in literature reviews: insights from qualitative data analysis and tool-support . Commun. Ass. Inform. Syst. 37 , 154–204. 10.17705/1CAIS.03708 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Barr-Walker J. (2017). Evidence-based information needs of public health workers: a systematized review . J. Med. Libr. Assoc. 105 , 69–79. 10.5195/JMLA.2017.109 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bittermann A., Fischer A. (2018). How to identify hot topics in psychology using topic modeling . Z. Psychol. 226 , 3–13. 10.1027/2151-2604/a000318 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bluhm D. J., Harman W., Lee T. W., Mitchell T. R. (2011). Qualitative research in management: a decade of progress . J. Manage. Stud. 48 , 1866–1891. 10.1111/j.1467-6486.2010.00972.x [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Breen L. J., Darlaston-Jones D. (2010). Moving beyond the enduring dominance of positivism in psychological research: implications for psychology in Australia . Aust. Psychol. 45 , 67–76. 10.1080/00050060903127481 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Burman E., Whelan P. (2011). Problems in / of Qualitative Research . Maidenhead: Open University Press/McGraw Hill. [ Google Scholar ]
- Chaichanasakul A., He Y., Chen H., Allen G. E. K., Khairallah T. S., Ramos K. (2011). Journal of Career Development: a 36-year content analysis (1972–2007) . J. Career. Dev. 38 , 440–455. 10.1177/0894845310380223 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chryssochoou X. (2015). Social Psychology . Inter. Encycl. Soc. Behav. Sci. 22 , 532–537. 10.1016/B978-0-08-097086-8.24095-6 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cichocka A., Jost J. T. (2014). Stripped of illusions? Exploring system justification processes in capitalist and post-Communist societies . Inter. J. Psychol. 49 , 6–29. 10.1002/ijop.12011 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Clay R. A. (2017). Psychology is More Popular Than Ever. Monitor on Psychology: Trends Report . Available online at: https://www.apa.org/monitor/2017/11/trends-popular
- Coetzee M., Van Zyl L. E. (2014). A review of a decade's scholarly publications (2004–2013) in the South African Journal of Industrial Psychology . SA. J. Psychol . 40 , 1–16. 10.4102/sajip.v40i1.1227 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Counsell A., Harlow L. (2017). Reporting practices and use of quantitative methods in Canadian journal articles in psychology . Can. Psychol. 58 , 140–147. 10.1037/cap0000074 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Deangelis T. (2017). Targeting Social Factors That Undermine Health. Monitor on Psychology: Trends Report . Available online at: https://www.apa.org/monitor/2017/11/trend-social-factors
- Demuth C. (2015). New directions in qualitative research in psychology . Integr. Psychol. Behav. Sci. 49 , 125–133. 10.1007/s12124-015-9303-9 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Denzin N. K., Lincoln Y. (2003). The Landscape of Qualitative Research: Theories and Issues , 2nd Edn. London: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Drotar D. (2010). A call for replications of research in pediatric psychology and guidance for authors . J. Pediatr. Psychol. 35 , 801–805. 10.1093/jpepsy/jsq049 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dweck C. S. (2017). Is psychology headed in the right direction? Yes, no, and maybe . Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 12 , 656–659. 10.1177/1745691616687747 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Earp B. D., Trafimow D. (2015). Replication, falsification, and the crisis of confidence in social psychology . Front. Psychol. 6 :621. 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00621 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ezeh A. C., Izugbara C. O., Kabiru C. W., Fonn S., Kahn K., Manderson L., et al.. (2010). Building capacity for public and population health research in Africa: the consortium for advanced research training in Africa (CARTA) model . Glob. Health Action 3 :5693. 10.3402/gha.v3i0.5693 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ferreira A. L. L., Bessa M. M. M., Drezett J., De Abreu L. C. (2016). Quality of life of the woman carrier of endometriosis: systematized review . Reprod. Clim. 31 , 48–54. 10.1016/j.recli.2015.12.002 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fonseca M. (2013). Most Common Reasons for Journal Rejections . Available online at: http://www.editage.com/insights/most-common-reasons-for-journal-rejections
- Gough B., Lyons A. (2016). The future of qualitative research in psychology: accentuating the positive . Integr. Psychol. Behav. Sci. 50 , 234–243. 10.1007/s12124-015-9320-8 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Grant M. J., Booth A. (2009). A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies . Health Info. Libr. J. 26 , 91–108. 10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Grix J. (2002). Introducing students to the generic terminology of social research . Politics 22 , 175–186. 10.1111/1467-9256.00173 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gunasekare U. L. T. P. (2015). Mixed research method as the third research paradigm: a literature review . Int. J. Sci. Res. 4 , 361–368. Available online at: https://ssrn.com/abstract=2735996 [ Google Scholar ]
- Hengartner M. P. (2018). Raising awareness for the replication crisis in clinical psychology by focusing on inconsistencies in psychotherapy Research: how much can we rely on published findings from efficacy trials? Front. Psychol. 9 :256. 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00256 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Holloway W. (2008). Doing intellectual disagreement differently . Psychoanal. Cult. Soc. 13 , 385–396. 10.1057/pcs.2008.29 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ivankova N. V., Creswell J. W., Plano Clark V. L. (2016). Foundations and Approaches to mixed methods research , in First Steps in Research , 2nd Edn. K. Maree (Pretoria: Van Schaick Publishers; ), 306–335. [ Google Scholar ]
- Johnson M., Long T., White A. (2001). Arguments for British pluralism in qualitative health research . J. Adv. Nurs. 33 , 243–249. 10.1046/j.1365-2648.2001.01659.x [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Johnston A., Kelly S. E., Hsieh S. C., Skidmore B., Wells G. A. (2019). Systematic reviews of clinical practice guidelines: a methodological guide . J. Clin. Epidemiol. 108 , 64–72. 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2018.11.030 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ketchen D. J., Jr., Boyd B. K., Bergh D. D. (2008). Research methodology in strategic management: past accomplishments and future challenges . Organ. Res. Methods 11 , 643–658. 10.1177/1094428108319843 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ktepi B. (2016). Data Analytics (DA) . Available online at: https://eds-b-ebscohost-com.nwulib.nwu.ac.za/eds/detail/detail?vid=2&sid=24c978f0-6685-4ed8-ad85-fa5bb04669b9%40sessionmgr101&bdata=JnNpdGU9ZWRzLWxpdmU%3d#AN=113931286&db=ers
- Laher S. (2016). Ostinato rigore: establishing methodological rigour in quantitative research . S. Afr. J. Psychol. 46 , 316–327. 10.1177/0081246316649121 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lee C. (2015). The Myth of the Off-Limits Source . Available online at: http://blog.apastyle.org/apastyle/research/
- Lee T. W., Mitchell T. R., Sablynski C. J. (1999). Qualitative research in organizational and vocational psychology, 1979–1999 . J. Vocat. Behav. 55 , 161–187. 10.1006/jvbe.1999.1707 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Leech N. L., Anthony J., Onwuegbuzie A. J. (2007). A typology of mixed methods research designs . Sci. Bus. Media B. V Qual. Quant 43 , 265–275. 10.1007/s11135-007-9105-3 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Levitt H. M., Motulsky S. L., Wertz F. J., Morrow S. L., Ponterotto J. G. (2017). Recommendations for designing and reviewing qualitative research in psychology: promoting methodological integrity . Qual. Psychol. 4 , 2–22. 10.1037/qup0000082 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lowe S. M., Moore S. (2014). Social networks and female reproductive choices in the developing world: a systematized review . Rep. Health 11 :85. 10.1186/1742-4755-11-85 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Maree K. (2016). Planning a research proposal , in First Steps in Research , 2nd Edn, ed Maree K. (Pretoria: Van Schaik Publishers; ), 49–70. [ Google Scholar ]
- Maree K., Pietersen J. (2016). Sampling , in First Steps in Research, 2nd Edn , ed Maree K. (Pretoria: Van Schaik Publishers; ), 191–202. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ngulube P. (2013). Blending qualitative and quantitative research methods in library and information science in sub-Saharan Africa . ESARBICA J. 32 , 10–23. Available online at: http://hdl.handle.net/10500/22397 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Nieuwenhuis J. (2016). Qualitative research designs and data-gathering techniques , in First Steps in Research , 2nd Edn, ed Maree K. (Pretoria: Van Schaik Publishers; ), 71–102. [ Google Scholar ]
- Nind M., Kilburn D., Wiles R. (2015). Using video and dialogue to generate pedagogic knowledge: teachers, learners and researchers reflecting together on the pedagogy of social research methods . Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 18 , 561–576. 10.1080/13645579.2015.1062628 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- O'Cathain A. (2009). Editorial: mixed methods research in the health sciences—a quiet revolution . J. Mix. Methods 3 , 1–6. 10.1177/1558689808326272 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- O'Neil S., Koekemoer E. (2016). Two decades of qualitative research in psychology, industrial and organisational psychology and human resource management within South Africa: a critical review . SA J. Indust. Psychol. 42 , 1–16. 10.4102/sajip.v42i1.1350 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Onwuegbuzie A. J., Collins K. M. (2017). The role of sampling in mixed methods research enhancing inference quality . Köln Z Soziol. 2 , 133–156. 10.1007/s11577-017-0455-0 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Perestelo-Pérez L. (2013). Standards on how to develop and report systematic reviews in psychology and health . Int. J. Clin. Health Psychol. 13 , 49–57. 10.1016/S1697-2600(13)70007-3 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pericall L. M. T., Taylor E. (2014). Family function and its relationship to injury severity and psychiatric outcome in children with acquired brain injury: a systematized review . Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 56 , 19–30. 10.1111/dmcn.12237 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Peterson R. A., Merunka D. R. (2014). Convenience samples of college students and research reproducibility . J. Bus. Res. 67 , 1035–1041. 10.1016/j.jbusres.2013.08.010 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ritchie J., Lewis J., Elam G. (2009). Designing and selecting samples , in Qualitative Research Practice: A Guide for Social Science Students and Researchers , 2nd Edn, ed Ritchie J., Lewis J. (London: Sage; ), 1–23. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sandelowski M. (2011). When a cigar is not just a cigar: alternative perspectives on data and data analysis . Res. Nurs. Health 34 , 342–352. 10.1002/nur.20437 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sandelowski M., Voils C. I., Knafl G. (2009). On quantitizing . J. Mix. Methods Res. 3 , 208–222. 10.1177/1558689809334210 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Scholtz S. E., De Klerk W., De Beer L. T. (2019). A data generated research framework for conducting research methods in psychological research .
- Scimago Journal & Country Rank (2017). Available online at: http://www.scimagojr.com/journalrank.php?category=3201&year=2015
- Scopus (2017a). About Scopus . Available online at: https://www.scopus.com/home.uri (accessed February 01, 2017).
- Scopus (2017b). Document Search . Available online at: https://www.scopus.com/home.uri (accessed February 01, 2017).
- Scott Jones J., Goldring J. E. (2015). ‘I' m not a quants person'; key strategies in building competence and confidence in staff who teach quantitative research methods . Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 18 , 479–494. 10.1080/13645579.2015.1062623 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Smith B., McGannon K. R. (2018). Developing rigor in quantitative research: problems and opportunities within sport and exercise psychology . Int. Rev. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 11 , 101–121. 10.1080/1750984X.2017.1317357 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stangor C. (2011). Introduction to Psychology . Available online at: http://www.saylor.org/books/
- Strydom H. (2011). Sampling in the quantitative paradigm , in Research at Grass Roots; For the Social Sciences and Human Service Professions , 4th Edn, eds de Vos A. S., Strydom H., Fouché C. B., Delport C. S. L. (Pretoria: Van Schaik Publishers; ), 221–234. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tashakkori A., Teddlie C. (2003). Handbook of Mixed Methods in Social & Behavioural Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE publications. [ Google Scholar ]
- Toomela A. (2010). Quantitative methods in psychology: inevitable and useless . Front. Psychol. 1 :29. 10.3389/fpsyg.2010.00029 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Truscott D. M., Swars S., Smith S., Thornton-Reid F., Zhao Y., Dooley C., et al.. (2010). A cross-disciplinary examination of the prevalence of mixed methods in educational research: 1995–2005 . Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 13 , 317–328. 10.1080/13645570903097950 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Weiten W. (2010). Psychology Themes and Variations . Belmont, CA: Wadsworth. [ Google Scholar ]
Quantitative and Qualitative Research in Psychological Science
- Thematic Issue Article: Historical Perspective
- Published: 29 July 2015
- Volume 10 , pages 263–272, ( 2015 )
Cite this article

- Katherine Nelson 1
Explore all metrics
The field of psychology has emphasized quantitative laboratory research as a defining character of its role as a science, and has generally de-emphasized qualitative research and theorizing throughout its history. This article reviews some of the effects of this emphasis in two areas, intelligence testing, and learning and memory. On one side, quantitative measurement produced the widely used IQ test but shed little light on the construct of intelligence and its role in human cognition. On the other side, reductive quantification and experimental constraints limited the investigation and understanding of human memory systems and complex learning throughout the first century of the field’s history. Recent research under fewer constraints has made greater progress in these areas.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Meta-Intelligence: Understanding, Control, and Coordination of Higher Cognitive Processes

- Intelligence

Theories of Independent Intelligences as a Lakatosian Research Program
Neisser appears later here for his work on memory and intelligence.
This assumption holds today in many arenas. A more moderate assumption is that all levels are appropriate for investigation, and that feedback from a higher level to a lower may be as informative—and sometimes more informative—as the discovery of an important unit and function at the lower level can be for understanding the higher (see Gottlieb 1992 ).
See Nelson ( 2012 ) for a version of the history and influence of this theory.
My own experience bridged the two orientations: My PhD from UCLA in 1968 was in experimental psychology, essentially behaviorist, specialized in child psychology. My first two publications were in the Journal of Experimental Child Psychology .
This is not the place for reviewing the controversies about this research and its assumed theoretical basis (see Allen and Bickhard 2013 for review and discussion from several angles).
It was assumed that adults do not develop further intelligence, although with increasing age they acquire more knowledge, on the one hand, but presumably lose more mental speed and memory on the other. This assumption is now in question.
If we consider 1920 as the starting point of widespread IQ testing of populations, this implies a 30 point rise in IQs by the present day, or the difference between average and “genius” on some scales.
Publishers of these tests generally deny that they are the same as IQ tests; rather they are said to measure “academic aptitude.”
For those who may have forgotten or never learned these terms, classical conditioning as designed by Pavlov takes place through the association of a stimulus (e.g., a bell) with a desired outcome (e.g., food); instrumental conditioning is the establishment of a habitual action when followed by a reward (e.g., a rat learning to press a lever to receive food. Rats learning to run through a maze to be rewarded with food or water is another example).
The quotation was part of a paper presented at a memory conference in 1978 and published as a chapter in the 1982 book.
“H.M.” is now famous in memory work, his disabilities (the inadvertent result of surgery to relieve epilepsy) having been studied continuously over decades. A good brief account of his case and its impact on understanding memory in terms of systems may be found in Squire and Wixted ( 2015 ).
See Moscovitch ( 1984 ) for early discussion of these distinctions relevant to infant and child memory.
The revival of interest in Vygotsky’s contributions to social, cultural–historical thinking is especially notable and quite widespread. A return to Piaget’s thinking is less visible, although research in its framework continues in European contexts, but it is always in the background as a model of developmental theory and research program. In the U.S. it was the target of strong criticism during the computational era as cognitive development from a sensorimotor beginning in infancy was deemed inconceivable. Presently interest in terms of a merger of biological and social–cultural–experiential contributions to development has become more prominent.
Allen J, Bickhard M (2013) Transcending nature and nurture. Cogn Dev 28(2). (Special Issue)
Baker-Ward L, Ornstein PA (2013) The coaction of theory and methods in the study of the development of memory. In: Bauer PJ, Fivush R (eds) Wiley-Blackwell handbook on the development of children’s memory. Wiley-Blackwell, New York, pp 41–64
Chapter Google Scholar
Bartlett FC ([1932]1969) Remembering: a study in experimental and social psychology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Bauer P (2007) Remembering the times of our lives: memory in infancy and beyond. Erlbaum, Mahwah
Google Scholar
Bauer PJ, Fivush R (2013) Wiley-Blackwell handbook on the development of children’s memory. Wiley-Blackwell, New York
Book Google Scholar
Bruner J (1983) Child’s talk: learning to use language. Norton, New York
Chomsky N (1959) Review of Verbal behavior by B. F. Skinner. Language 35:26–58
Article Google Scholar
Edelman GM (1992) Bright air, brilliant fire: on the matter of the mind. Basic Books, New York
Fivush R (2013) Maternal reminiscing style: the sociocultural construction of autobiographical memory across childhood and adolescence. In: Bauer PJ, Fivush R (eds) Wiley-Blackwell handbook on the development of children’s memory. Wiley-Blackwell, New York, pp 568–585
Fivush R, Nelson K (2005) Culture and language in the emergence of autobiographical memory. Psychol Sci 15:586–590
Flynn JR (1987) Massive IQ gains in 14 nations: what IQ tests really measure. Psychol Bull 101:171–191
Galton F (1969) Hereditary genius. Macmillan, London
Gottlieb G (1992) Individual behavior and evolution: the genesis of novel behavior. Oxford University Press, New York
Gottlieb G (2003) On making behavioral genetics truly developmental. Hum Dev 46:337–355
Jablonka E, Lamb MJ (2005) Evolution in four dimensions. MIT Press, Cambridge
James W ([1890]1950) The principles of psychology. Dover Publications, New York
Loftus EF (1979) Eyewitness testimony. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Mandler JM (1984) Stories, scripts, and scenes: aspects of schema theory. Erlbaum, Hillsdale
Mead GH (1934) Mind, self, and society. Chicago University Press, Chicago
Menary R (ed) (2010) The extended mind. MIT Press, Cambridge
Miller GA (1956) The magical number seven, plus or minus two: some limits on our capacity for processing information. Psychol Rev 63:81–97
Moore DS (2015) The developing genome: an introduction to behavioral genetics. Oxford University Press, New York
Moscovitch M (1984) Infant memory, vol 10. Advances in the study of communication and affect. Plenum, New York
Neisser U (1967) Cognitive psychology. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Neisser U (1982) Memory: what are the important questions? In: Neisser U (ed) Memory observed: remembering in natural contexts. W.H. Freeman & Co., San Francisco, pp 2–19
Neisser U (1998) The rising curve. American Psychological Association, Washington, DC
Neisser U, Boodoo G, Bouchard TJ Jr et al (1996) Intelligence: knowns and unknowns. Am Psychol 51:77–101
Nelson K (1978) How young children develop knowledge of their world in and out of language. In: Siegler RS (ed) Children’s thinking: what develops? Erlbaum, Hillsdale, pp 225–273
Nelson K (1993) The psychological and social origins of autobiographical memory. Psychol Sci 4:1–8
Nelson K (1996) Language in cognitive development: the emergence of the mediated mind. Cambridge University Press, New York
Nelson K (2003) Self and social functions: individual autobiographical memory and collective narrative. Memory 11:125–136
Nelson K (2007) Young minds in social worlds: experience, meaning, and memory. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Nelson K (2012) The human nature of the economic mind. Biol Theory 6:377–387
Nelson K (2013) Sociocultural theories of memory development. In: Bauer PJ, Fivush R (eds) Wiley-Blackwell handbook on the development of children’s memory. Wiley-Blackwell, New York, pp 87–108
Nelson K, Fivush R (2004) The emergence of autobiographical memory: a social cultural developmental theory. Psychol Rev 111:486–511
Perrin D, Rousset S (2014) The episodicity of memory: current trends in philosophy and psychology. Rev Philos Psychol 5:291–312
Prinz W (2012) Open minds: the making of agency and intentionality. MIT Press, Cambridge
Schaie KW (1997) The course of adult intellectual development. Am Psychol 49:304–313
Schank R, Abelson R (1977) Scripts, plans, goals, and understanding. Erlbaum, Hillsdale
Skinner BF (1957) Verbal behavior. Appleton-Century-Crofts, New York
Spearman C (1904) “General Intelligence” objectively determined and measured. Am J Psychol 15:201–293
Squire LR, Wixted JT (2015) Remembering. Daedalus, Winter:53–67
Tomasello M (1999) The cultural origins of human cognition. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Tomasello M (2008) The origins of human communication. MIT Press, Cambridge
Tulving E (1982) Elements of episodic memory. Oxford University Press, New York
Tulving E (2005) Episodic memory and autonoesis: uniquely human? In: Terrace HS, Metcalfe J (eds) The missing link in cognition: origins of self-reflective consciousness. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 3–56
Wang Q (2013) The cultured self and remembering. In: Bauer PJ, Fivush R (2013) Wiley-Blackwell handbook on the development of children’s memory. Wiley-Blackwell, New York, pp 605–625
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Distinguished Professor of Psychology Emerita, City University of New York Graduate Center, New York, NY, USA
Katherine Nelson
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Katherine Nelson .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Nelson, K. Quantitative and Qualitative Research in Psychological Science. Biol Theory 10 , 263–272 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13752-015-0216-0
Download citation
Received : 04 January 2015
Accepted : 16 June 2015
Published : 29 July 2015
Issue Date : September 2015
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s13752-015-0216-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Experimental psychology
- Qualitative research
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Find My Rep
You are here
Quantitative Research in Psychology
- Jeremy Miles - RAND Corporation, USA
- Brian Stucky - RAND Corporation, USA
- Description
Quantitative psychology is a branch of psychology developed using certain methods and approaches which are designed to answer empirical questions, such as the development of measurement models and factor analysis. While quantitative psychology is often associated with the use of statistical models and psychological measurement research methods, this five volume set draws together the key conceptual and methodological techniques and addresses each research question at length. Each volume is accompanied by an introduction which contextualises the subject area, giving an understanding of established theories and how they are continuing to develop in one of the most fundamental and broadly researched psychological fields.
These volumes are an excellent resource for academics and scholars who will benefit from the framing provided by the editorial introduction and overview, and will also appeal to advanced students and professionals studying or using quantitative psychological methods in their research.
Volume One: Statistical hypothesis testing and power
Volume Two: Measurement
Volume Three: Research Design and sampling
Volume Four: Statistical Tests
Volume Five: Complex Models
Preview this book
Select a purchasing option, related products.


- Student Notebook
Mixed Methods Research
- Experimental Psychology
- Quantitative
- Statistical Analysis
Traditionally, there are three branches of methodology: quantitative (numeric data), qualitative (observational or interview data), and mixed methods (using both types of data). Psychology relies heavily on quantitative-based data analyses but could benefit from incorporating the advantages of both quantitative and qualitative methodologies into one cohesive framework. Mixed Methods (MM) ideally includes the benefits of both methods (Johnson, Onwuegbuzie, & Turner, 2007): Quantitative analyses employ descriptive and inferential statistics, whereas qualitative analyses produce expressive data that provide descriptive details (often in narrative form) to examine the study’s research objectives. Whereas quantitative data may be collected via measures such as self-reports and physiological tests, qualitative data are collected via focus groups, structured or semistructured interviews, and other forms (Creswell, 2013).
MM hypotheses differ in comparison with solely quantitative or qualitative research questions. Not only must the quantitative and qualitative data be integrated, but the hypotheses also must be integrated. MM practitioners promote the development of a theory-based set of three hypotheses. Hypotheses should be conducted a priori and be both logical and sequential research questions (for more information, see Onwuegbuzie & Leech, 2006). Specialists encourage researchers to construct three separate types of hypotheses for an MM research project. There can be more than three hypotheses but there must be at least one of each type. The first hypothesis should be quantitative and the second should be qualitative. The third hypothesis will be an MM hypothesis.
Integration of these data is often complex, even when there is a strong theoretical rationale for doing so. Data integration occurs when quantitative and qualitative are combined in a data set. There are multiple ways for this to occur, including triangulation, following a thread, and the mixed methods matrix (see O’Cathain, Murphy, & Nicholl, 2010, for a brief review). Yet understanding the overall reasoning for using MM and how to best combine the approaches in practice can help lessen the challenge of MM data integration (Bryman, 2006).
Types of MM Research
- There are dozens of MM designs, but for the purpose of this article, six MM designs will be presented:
- The sequential explanatory method employs two different data-collection time points; the quantitative data are collected first and the qualitative collected last.
- The sequential exploratory design is best for testing emergent theory because both types of data are interpreted during the data integration phase.
- The sequential transformative approach has no preference for sequencing of data collection and emphasizes theory.
- Concurrent triangulation is the ideal method for cross-validation studies and has only one point of data collection.
- The concurrent nested design is best used to gain perspectives on understudied phenomena.
- The concurrent transformative approach is theory driven and allows the researcher to examine phenomena on several different levels.
Strengths and Challenges of MM Research
An MM approach is helpful in that one is able to conduct in-depth research and, when using complementary MM, provide for a more meaningful interpretation of the data and phenomenon being examined (Teddlie & Tashakkori, 2003). Another strength of MM is the dynamic between the qualitative and quantitative portions of the study. If the design is planned appropriately, each type of data can mirror the other’s findings, so the methodology can benefit many types of research. However, interpreting data using the MM framework can be complicated and time intensive given that the data and interpretations are often abstract. Additionally, conducting MM research requires training and mastery of the methodology, so there can be a learning curve for researchers who traditionally use only quantitative or qualitative methods. Sticking to the theory-based and evidence-based designs will aid in your understanding and interpretation of the data.
Qualitative Data Analysis
Qualitative coding is a multistep process that includes different types of analyses depending on the nature of your data. Codebooks are important before, during, and after qualitative coding due to the detailed nature of the qualitative data. It is also important to know your expected codes and themes in order to promote interrater reliability (Hruschka et al., 2004). Expected codes are based on the theoretical foundation of your project. I suggest including the expected codes and themes in your codebooks. As previously mentioned, research designs involving this type of data can vary greatly, but in general, the following is a framework of how to conduct a thematic data analysis: Know your data inside and out, generate codes, search for themes, and review themes with a research team (Braun & Clarke, 2006). For more detailed instructions on conducting a qualitative analysis, please refer to last month’s Student Notebook article (Heydarian, 2016).
Lessons Learned
From the start, the researcher or research team must have a clear idea of their resources and the pros and cons of each method. Researchers also must be flexible. I am interested in examining the factors that compose seeking health information online. To investigate this topic, I developed an online, two-part study. Information obtained from qualitative prompts was used to inform the development of a scale measuring health-information-seeking behavior online. The first study used MM, and the data collection occurred on Amazon Mechanical Turk, a marketplace where researchers can post their available studies. Potential participants are paid a small fee, and data collection usually is completed in less than a week. I expected to conduct magnitude coding — a type of qualitative coding that evaluates the emphasis of content — but instead I had to choose a more appropriate type of coding because the participants provided extremely brief responses.
In closing, the design of your study (quantitative, qualitative, or MM) should align with your training and your research objectives. MM has the potential to bring your research to the next level by combining the strengths of quantitative and qualitative methodologies.
Suggestions for Conducting MM Research
Be proficient in MM research by keeping up to date with the latest techniques, software, textbooks, and manuals.
Think “outside the box” and consider other data-analytic approaches that are not used in your field.
Choose the research design that best fits the hypotheses, and know the assumptions and limitations of that design.
Incorporate figures and tables into your qualitative codebook to deepen the conceptualizations for the coders and provide a few examples of already coded data in order to provide thorough instructions.
Create and use summary statements for each participant to help with the abstract portion of the analyses. Summary statements should be a few sentences that describe the participant’s statement and provide an overall gist of the available qualitative information.
Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qualitative Research in Psychology, 3 , 77–101. doi:10.1191/1478088706qp063oa
Bryman, A. (2006). Integrating quantitative and qualitative research: How is it done? Qualitative Research, 6 , 97–113. doi:10.1177/1468794106058877
Creswell, J. W. (2013). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
Heydarian, N. (2016). Developing theory with the grounded-theory approach and thematic analysis. Observer, 29(4) , 38–39.
Hruschka, D. J., Schwartz, D., John, D. C. S., Picone-Decaro, E., Jenkins, R. A., & Carey, J. W. (2004). Reliability in coding open-ended data: Lessons learned from HIV behavioral research. Field Methods, 16 , 307–331. doi:10.1177/1525822X04266540
Johnson, R. B., Onwuegbuzie, A. J., & Turner, L. A. (2007). Toward a definition of mixed methods research. Journal of Mixed Methods Research, 1 , 112–133. doi:10.1177/1558689806298224
O’Cathain, A., Murphy, E., & Nicholl, J. (2010). Three techniques for integrating data in mixed methods studies. BMJ, 341 , c4587. doi:10.1136/bmj.c4587
Onwuegbuzie, A. J., & Leech, N. L. (2006). Linking research questions to mixed methods data analysis procedures 1. The Qualitative Report, 11 , 474–498.
Teddlie, C., & Tashakkori, A. (2003). Major issues and controversies in the use of mixed methods in the social and behavioral sciences. In A. Tashakkori & C. Teddlie (Eds.), Handbook of mixed methods in social & behavioral research (pp. 3–50). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
VERY RELEVANT AND COMPREHENSIVE TEXT ON MM ETHODS
The analysis of mixed methods is fairly comprehensive and educative especially for scholars and/researchers who are used to the traditional Qualitative and Quantitatve research as a stand alone methodologies. I feel like looking for a workshop sponsor so that I can share these ideas to our colleagues in African universities generally and Kenya in particular. Our postgraduate students have not yet embrased the use of mixed methods. Four of my own supervised doctoral students have successfully used th MMR.We should do much more!
I am currently pursuing my PhD and using mixed method. I am interested in this combination of research methods.
I have gained much from the source which clearly spells out the strengths of MM and its applicability in research.
Iam conducting a sequential explanatory mixed methods study in PhD Management and I have benefited a lot from combining quantitative and qualitative research approaches operating with what works best per given research probem.
APS regularly opens certain online articles for discussion on our website. Effective February 2021, you must be a logged-in APS member to post comments. By posting a comment, you agree to our Community Guidelines and the display of your profile information, including your name and affiliation. Any opinions, findings, conclusions, or recommendations present in article comments are those of the writers and do not necessarily reflect the views of APS or the article’s author. For more information, please see our Community Guidelines .
Please login with your APS account to comment.
About the Author
Allyson S. Hughes is a Health Psychology doctoral student at The University of Texas at El Paso. Her research examines judgment and decision-making concerning health decisions using Internet resources. She can be reached at [email protected] .

Research Briefs
Recent highlights from APS journals articles on learning about working memory, psychological measurement, patterns of implicit and explicit attitudes, and much more.

Careers Up Close: Jolynn Pek on Quantifying Uncertainty
Pek analyzes sources of uncertainty in statistical results and develops new approaches to practicing replicable psychological science.

Speaking Evidence to Policy
The Commission on Evidence-Based Policymaking has issued a report that points to significant new opportunities in research and leadership for psychological scientists with expertise in areas including judgment and decision making, analysis and research design, data privacy and ethics issues, and more.
Privacy Overview
- Statements on Current Events
- Make a Gift
Quantitative Methods
The Psychology Department has a strategic focus on training in advanced methodology, especially quantitative methods. Advanced quantitative skills are increasingly important in conducting state-of-the–art research, and in post-doctoral and academic placements. Recent and ongoing faculty searches have emphasized expertise in quantitative methods. In addition to a standard two-semester sequence in statistics (PSY 507 and PSY 508), students may choose courses in topics such as multi-level modeling, test theory, structural equation modeling, computational modeling, and other topics. A course in neuroscience methods (PSY 511) is offered annually. Other resources for students seeking training in advanced methodology include courses in other departments (Statistics, Human Development and Family Studies, Educational Psychology, Information Sciences and Technology) and workshops on specific methodological topics.
The Psychology Department has a faculty committee focused on quantitative methods in research and teacheing (see below), and it participates in the Consortium for the Advancement of Research Methods and Analysis (CARMA) .
Quantitative Methods Faculty
Quantitative methods labs, measurement, applied psychology, and statistics lab, program areas:, gene environment interplay across the lifespan, associated centers:, related resources, courses in psychology.
PSY 535 Research Methods in I/O Psychology (Spring 2022)
Courses in Other Departments
EDPSY 597 Structural Equation Modeling
HDFS 517 Multivariate Statistics HDFS 523 Strategies for Data Analysis in Developmental Research HDFS 526 Measurement HDFS 530 Longitudinal SEM HDFS 534 Person-specific Data Analysis HDFS 597 Data Mining HDFS 597 Latent Class Analysis (Introduction; Advanced) HDFS 597 Hierarchical Linear Modeling HDFS 597 Bayesian Statistics HDFS 597 Person-Specific Ecological Momentary Assessment HDFS 597 Advanced LISREL
SODA 501 Approaches and Issues in Big Data Social Science
SOC 580 Social Network Analysis
STAT 501 Regression STAT 557 Data Mining I
The Department supports the use of SPSS, MPLUS, MATLAB, R, and Python.
Colloquia, Seminars, and Workshops
- Center for Social Data Analytics (C-SoDA)
- Annual R Bootcamp
- Institute for CyberScience (ICS) seminars
- Methodology Center training opportunities
- Quantitative Developmental Systems Methodology Core
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
A bibliometrics review of the journal mindfulness : science mapping the literature from 2012 to 2022.

- Department of Education and Learning Technology, National Tsing Hua University, Hsinchu, Taiwan
This study conducts a bibliometric analysis using the Web of Science database on 1,950 articles published in the journal Mindfulness from 2012 to 2022. By constructing a knowledge graph, the research delineates the evolution, stages of development, and emerging trends in the field of mindfulness. Significant growth in the annual publication volume has been observed since 2012, with the research progression segmented into three distinct phases. The United States has emerged as a pivotal contributor to the field, dominating in terms of publication volume, researcher involvement, and institutional contributions. Through the application of keyword co-occurrence and reference co-citation analysis, five principal clusters were identified, focusing on mindfulness, meditation, depression, stress, and self-compassion, underscoring these as focal research areas. Furthermore, the exploration of mindfulness within the educational sphere in Taiwan is still nascent, signaling a critical need for bolstered research support in diverse thematic domains.
Introduction
Mental health, a cornerstone of contemporary society, substantially influences national productivity and interpersonal relationships. Recent advances in mindfulness research suggest that cultivating mindfulness fosters positive and resilient attitudes towards evolving social contexts. Kabat-Zinn’s pioneering work in 1979 integrated Buddhist mindfulness meditation into the medical realm, inaugurating Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) clinics—a milestone in healthcare applications of mindfulness ( Wen, 2016 ).
As research into mindfulness has deepened, its applications have broadened from medicine to fields such as psychology, education, business, and even commercialization ( Wilson, 2014 ). Empirical studies indicate that mindfulness enhances self-acceptance, care, and courage, which in turn uplifts the quality of life ( Dobkin and Zhao, 2011 ). Additionally, it mitigates symptoms of stress, depression, and anxiety, bolsters positive emotions, and improves psychological health ( Keng et al., 2011 ; Lakhan and Schofield, 2013 ; Penman and Burch, 2013 ). It also positively impacts attention and emotional regulation ( Wen, 2013 ), and strengthens interpersonal relationships ( Grossman et al., 2004 ; Davis and Hayes, 2011 ). As a holistic approach to psychological and physical well-being, mindfulness education encourages students to deepen their reflective thinking, enhance awareness, and apply mindfulness practices, thus continually advancing their academic and health outcomes. For instance, Napoli et al. (2005) observed that mindfulness improves children’s selective attention, mental health, and cognitive functions, enhancing overall well-being. Mindfulness interventions have also been shown to mitigate depressive symptoms in adolescents ( Raes et al., 2014 ; Kallapiran et al., 2015 ) and to enhance cognition, academic performance, behavior, and socio-emotional qualities among primary and secondary students ( Maynard et al., 2017 ). Hsieh (2018) advocates for the integration of mindfulness into school education and management, aiming to foster a comprehensive understanding of life’s significance, the pursuit of meaningful values, and the promotion of care and social responsibility.
In Taiwan, mindfulness research, albeit more recent, focuses on enhancing attention, body and mind awareness, emotional processing, and stress regulation through mindfulness practices, or explores its benefits in physical and mental health, professional development, and patient care ( Chen et al., 2019 ). Thus, it is necessary for Taiwan to further expand the application domains of mindfulness research and to support its development through government policies, as well as to strengthen interdisciplinary collaborations to deepen the understanding of mindfulness effects across various groups. For example, Jin and Liu (2017) implemented targeted mindfulness interventions for special student groups, providing insightful experiences applicable to broader student populations; Jiang et al. (2022) integrated insights from psychology, education, and sociology to explore how mindfulness parenting positively affects parent–child relationships and alleviates behavioral issues in children, contributing significantly to societal welfare.
The advent of Knowledge Graph technology has revolutionized the exploration of disciplines, academic communities, and intellectual traditions through the analysis of journal articles. Unlike traditional reviews and meta-analyses, bibliometric analysis offers a detailed summary of a field’s literature metrics and knowledge structure by examining the structural relationships among authors, countries, institutions, and themes, employing statistical methods such as article counts, reference co-citation analysis, and impact factors ( Donthu et al., 2021 ). This approach provides a more nuanced understanding of the dynamics across various scientific fields, enhancing the scope and depth of academic exploration.
To date, the systematic construction of knowledge graphs in the realm of mindfulness research remains limited. The journal Mindfulness serves as a critical resource for advancing the assessment, prevention, treatment, counseling, training, and collaboration of mindfulness theories and interdisciplinary studies. Given this backdrop, a comprehensive analysis of the mindfulness research literature is essential. This analysis will facilitate a macroscopic understanding of the developmental trajectory, knowledge base, research hotspots, and future research directions in this field. Moreover, it will inform recommendations and enhancements for education in Taiwan.
This paper employs VOSviewer (v.1.6.18) to analyze mindfulness-related research from 2012 to 2022, exploring thematic developments and presenting the findings via a knowledge graph, providing a foundational reference for future studies. This study addresses the following research questions:
1. What is the publication count and growth trajectory of mindfulness literature?
2. Which authors and countries have the most significant influence on mindfulness research?
3. What are the primary research hotspots within the field of mindfulness?
4. What implications does mindfulness research hold for the educational in Taiwan?
Literature review
“Mindfulness,” often associated with terms such as contemplation, introspection, and concentration, originates from the Buddhist term “sammā-sati,” which translates to “Right Mindfulness” or simply “Mindfulness.” This term encapsulates the concepts of awareness, attention, and remembering, essential for alleviating physical and mental stress ( Lv, 2014 ). Buddha, who lived approximately 2,500 years ago, emphasized that mindfulness is crucial for overcoming ‘attachment, aversion, and delusion.’
The theoretical foundation of mindfulness research was laid by Ellen Langer, a social psychologist at Harvard University. In her 1989 work, she proposed that many negative life outcomes, such as unhappiness, accidents, and poor health, could result from a lack of mindfulness ( Langer, 1989 ). Thus, she viewed mindfulness as both a method of mental training and a way of life, helping individuals to observe changes within their bodies and minds and to maintain an open, accepting, and clear presence in the moment ( Lin, 2013 ).
Mindfulness, deeply rooted in religious traditions, has evolved significantly under their influence. Wen (2013) emphasized that mindfulness focuses on present awareness and mental states, which profoundly impact human physical and mental health. The process involves causal interactions that construct what is termed “experience,” generated through the senses (eye, ear, nose, tongue, body, mind) and integrated conceptually. Mindfulness categorizes the six senses into five aggregates: form (material), sensation, perception (identification and evaluation), volitional formations (responses and actions), and consciousness. The practice asserts that identification with “self,” “mine,” or “myself” is illusory, and true awareness is based on this realization. Buddha taught that mental changes are constant and recognizing this allows for greater flexibility and acceptance in responding to life’s changes ( Ronald et al., 2009 ).
Mindfulness has been extensively researched within medicine, modern psychology, and social psychology, influenced initially by psychologist Kabat-Zinn. In 1979, he introduced the Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) technique, applying mindfulness to clinical psychology with a focus on emotional regulation, stress management, mind–body interaction, and meditation practices. Numerous studies have confirmed mindfulness’s effectiveness in alleviating physical and psychological distress ( Kabat-Zinn, 2003 ). Recent research indicates positive effects of mindfulness interventions on individuals with amphetamine-type substance use disorders (SUDs), highlighting improved mindful awareness and certain electroencephalographic functional connectivity ( Zhang et al., 2019 ). Additionally, a meta-analysis of 40 randomized controlled trials on mindfulness-based interventions (MBIs) for SUDs, excluding tobacco use disorders, suggests these interventions might slightly reduce substance use days compared to standard care, cognitive-behavioral therapy, or pharmacotherapy, though further research is needed to confirm their overall effectiveness ( Goldberg et al., 2021 ). MBIs have also been successfully applied to a range of addictions, from smoking to alcohol, and behavioral addictions like gambling disorders, reducing dependency, cravings, and improving emotional states. Common MBI methods include Mindfulness-Based Relapse Prevention, Mindfulness Training for Smokers, and Mindfulness-Oriented Recovery Enhancement, with the integration of MBIs with treatment as usual (TAU) or other active treatments proving most effective ( Sancho et al., 2018 ). MBSR courses have not only benefitted the fields of medicine, psychology, and education but have also been widely promoted within the corporate sector, significantly improving physical and mental health, emotions, and quality of life ( Hsieh, 2019 ). Research by Valentine and Sweet (1999) showed that mindfulness meditators exhibit better psychological health than those practicing focused meditation. Various studies have explored the attention mechanisms of mindfulness meditation, correlating it with mental health improvements through attention regulation, body awareness, emotional regulation, and changing self-perceptions. Evidence suggests mindfulness meditation training enhances attention-related behavioral responses, cognitive abilities, reduces stress, and increases well-being ( Jha et al., 2007 ; Chiesa et al., 2011 ; Hölzel et al., 2011 ; Eberth and Sedlmeier, 2012 ; Jensen et al., 2012 ).
Research on self-compassion, particularly prevalent in Western studies, highlights its components—self-love, reduced self-judgment, decreased feelings of isolation, mindfulness, and lessened over-identification. Self-compassion interventions foster self-care, kindness, and tolerance, aiding individuals, especially the youth, in developing positive internal processing systems and reducing mental health issues. Its core aspects include treating oneself kindly, recognizing common humanity, and maintaining mindfulness ( Neff, 2003a ; MacBeth and Gumley, 2012 ; Körner et al., 2015 ; Costa et al., 2016 ; Muris et al., 2016 ; Neff et al., 2017 , 2019 ). Additionally, mindfulness regulates emotions, enhances attention, reduces stress, and positively impacts interpersonal communication and creativity ( Grossman et al., 2004 ; Corcoran et al., 2010 ; Farb et al., 2010 ; Davis and Hayes, 2011 ; Keng et al., 2011 ; Lakhan and Schofield, 2013 ; Lawlor, 2014 ; Penman and Burch, 2013 ; Wall, 2014 ; Willis and Dinehart, 2014 ; Laukkonen et al., 2020 ).
Compared to Western studies, mindfulness research in Taiwan shows distinct traits. In quantitative studies, there is a strong focus on developing mindfulness scales, therapeutic interventions, and curriculum implementation. For example, Huang et al. (2015) conducted reliability and validity analyses of the “Taiwanese Version of the Five Facet Mindfulness Questionnaire”; Liu and Rau (2015) investigated how mindfulness meditation enhances attention; Yang (2016) integrated mindfulness practices into curricula and assessed impacts through pre- and post-tests using the “Five Facet Mindfulness Questionnaire,” “Stress Perception,” and “Mindfulness Attention Awareness Scale.” In qualitative research, studies often focus on specific benefits or challenges encountered during mindfulness practices. For instance, Zheng et al. (2013) examined the effects of adult mindfulness courses on depression, anxiety, and mindfulness awareness, finding no significant differences; Shin and Jin (2010) discussed how “Zen Mindfulness Groups” influence intern counselors’ self-focus and professional practices. These studies provide insights into the effects of mindfulness on specific target groups and contribute to a deeper understanding of factors influencing mindfulness practices.
The ongoing deepening of mindfulness practice enables scholars to gain profound insights into their behavioral and cognitive patterns, reflecting on and adjusting their values and beliefs. This integration of awareness and action not only advances research in mindfulness but also demonstrates its significant applicative value across various fields such as medicine, psychology, and education, effectively enhancing individual well-being and broader societal impact.
In recent years, bibliometric analysis has emerged as a fundamental method in scientific research, providing quantitative and statistical evaluation of scholarly outputs such as journal articles, citation counts, and impact factors ( Donthu et al., 2021 ). First introduced by Pritchard in 1969, the concept of bibliometrics pertains to the systematic analysis of scholarly literature to understand the evolution and structural dynamics of academic disciplines ( Pritchard, 1969 ). This review applies bibliometric techniques to scrutinize significant literature and themes within the field of mindfulness research, aiming to delineate the current state of the discipline and project future research directions.
The analysis utilizes VOSviewer (version 1.6.18) as the principal tool, capitalizing on its ability to create knowledge maps that visualize relationships between various bibliometric elements. These include descriptive analysis, examination of authorship and geographical distribution, keyword co-occurrence, and reference co-citation analyses. VOSviewer is renowned for its effectiveness in graphically representing scientific landscapes, thereby facilitating the exploration of connections across diverse research areas ( Van Eck and Waltman, 2010 ; Zupic and Čater, 2015 ).
Keyword co-occurrence analysis is particularly valuable for detecting research development trends and assessing the status of domains ( Zhang, 2013 ; Yang, 2015 ). In this analysis, keywords with higher co-occurrence frequencies are indicative of prevailing research hotspots, highlighting the central themes within the field. This method employs visual representations of co-occurrence networks, where nodes represent keywords, encapsulating the cumulative knowledge of a domain, and links illustrate the relationships between word pairs, denoting their co-occurrence ( Radhakrishnan et al., 2017 ).
Reference co-citation analysis is employed to measure the similarity between documents or topics based on the frequency of their co-citations ( Small, 1973 ). The density of connection lines in the co-citation network graphically represents the strength of relationships between documents, providing insights into the interconnectedness of research themes. This type of analysis is crucial for identifying topics that have gained traction in the short term and may also indicate emerging research frontiers ( Zhang, 2013 )
Data source, procedure, and analytic software
This study employs data sourced from the Web of Science (WoS) Core Collection, which includes the Social Sciences Citation Index (SSCI), Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-Expanded), and Arts & Humanities Citation Index (A&HCI). These databases are recognized for their extensive reach and integration across multiple disciplinary areas, holding significant academic influence ( Zyoud et al., 2017 ). WoS is particularly noted for its comprehensive coverage, with approximately 99.11% of its indexed journals also featured in the Scopus database, underscoring its broad applicability and prominence in global research landscapes ( Singh et al., 2021 ). The journal Mindfulness , indexed in the SSCI and ranking highly within the Psychiatry and Clinical Psychology categories, consistently achieves Q1 and Q2 status, indicative of its high-quality scholarly output. Thus, the selection of research papers from these sources ensures a reliable representation of the mindfulness research quality, supporting the validity of the study’s findings.
Bibliometric analysis serves as a crucial tool for elucidating the accumulated scientific knowledge and developmental nuances of established fields through the systematic examination of large volumes of unstructured data ( Donthu et al., 2021 ). This study adopts the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) framework ( Figure 1 ), guiding the systematic literature review process to ensure transparency and standardization in the bibliometric methodology. This approach aids in the precise selection of relevant outcomes ( Moher et al., 2009 ). This study specifically focuses on articles from the Mindfulness journal indexed in the WoS database, covering the period from 2012 to 2022. The selected articles encompass a wide array of types, including academic papers, conference proceedings, editorial materials, book reviews, and chapters. These documents collectively address diverse aspects of mindfulness, including therapy and intervention measures tailored to different populations, and explore various research directions such as the application of mindfulness in different therapeutic contexts and intervention strategies. After removing duplicates and irrelevant entries, a search conducted in December 2022 resulted in a corpus of 1,950 documents ( Figure 1 ), forming the basis for subsequent bibliometric analyses.
Figure 1 . Flow diagram of study selection process.
The extracted data includes authors, paper titles, and keywords, which were inputted into the VOSviewer software for visual mapping. This software supports the comparison of normalized cluster networks, coverage visualization, and density visualization ( Van Eck and Waltman, 2010 ), allowing for comprehensive bibliometric analysis through appropriately set threshold values.
Results and discussion
Yearly quantitative distribution of literature.
As shown in Figure 2 , the journal Mindfulness has published a total of 1,950 articles in the WoS database as of December 2022. Since its inception in 2012, the annual publication volume has exhibited a consistent upward trajectory, delineated into three distinct stages: the “Emergence Stage” (2012–2014), where fewer than 100 articles were published each year; the “Exploration Stage” (2015–2018), characterized by a gradual increase in publication numbers, with 2015 marking the first year the journal exceeded 150 articles; and the “Growth Stage” (2019–2022), noted for a robust and stable trend of publishing over 200 articles annually starting in 2019. This latter stage underscores a burgeoning interest in mindfulness research. Nonetheless, there was a notable decline in publication numbers in 2021 and 2022, a trend likely influenced by the global disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Figure 2 . Yearly quantitative distribution of literature.
Significant publications in different development stages
Table 1 categorizes key literature from the journal Mindfulness into three developmental stages, highlighting the impact of these works through the lens of “the top three most-cited articles” in the WoS database. This method underscores the relevance and significance of these articles within their respective research domains.
Table 1 . Significant publications in different development stages.
During the “Emergence Stage” (2012–2014), 183 articles were published. The top three most-cited articles included Eberth and Sedlmeier (2012) , Meiklejohn et al. (2012) , and Sauer et al. (2013) . Eberth and Sedlmeier (2012) offered a comprehensive review of the effects of mindfulness meditation on various psychological variables among non-clinical meditators. Meiklejohn et al. (2012) explored the integration of mindfulness training into K-12 curricula, employing a combination of direct and indirect teaching methods facilitated by teacher training. This study highlighted that continuous mindfulness practice enhances attention and emotional regulation, benefiting both teachers and students. Sauer et al. (2013) emphasized the necessity of comparing mindfulness measurement results obtained through self-assessment tools with those from other mindfulness measurement tools, providing insights for improving current methodologies.
The “Exploration Stage” (2015–2018) produced 687 articles, with Zoogman et al. (2015) , Neff (2016) , and Tomlinson et al. (2018) being the most cited. Neff (2016) introduced the Self-Compassion Scale (SCS), establishing it as an effective measure of self-compassion and highlighting the importance of the “self-criticism” factor. Zoogman et al. (2015) investigated mindfulness-based interventions for adult depression and anxiety, suggesting potential applicability to adolescents, especially in non-clinical settings. Tomlinson et al. (2018) examined the correlation between trait mindfulness and mental health, indicating positive impacts and pointing out areas for future research, including addressing conceptual and methodological challenges in the field.
From 2019 to 2022, the “Growth Stage” saw the publication of 1,080 articles, with significant contributions from Ferrari et al. (2019) , Flett et al. (2019) , and Wilson et al. (2019) . Ferrari et al. (2019) validated the effectiveness of self-compassion interventions in enhancing psychosocial outcomes. Flett et al. (2019) explored both the short-term and long-term benefits of mindfulness meditation on mental health. Wilson et al. (2019) reviewed therapies related to self-compassion, including compassion-focused therapy and mindfulness-based cognitive therapy, demonstrating significant improvements in conditions like anxiety and depression, thus promoting self-compassion and reducing psychopathology among both clinical and subclinical populations.
In summary, each developmental stage of Mindfulness research progressively explores different facets, with a significant emphasis on the management and regulation of psychological processes like self-regulation, emotions, and psychological health, which are increasingly recognized as central themes in contemporary mindfulness research.
Distribution of authors
As shown in Figure 3 , this study’s analysis of author distribution provides insights into their connections with international scholars. Among the 200 authors featured on Mindfulness, notable contributors include Kabat-Zinn, Analayo, Van Gordon, Medvedev and Bögels.
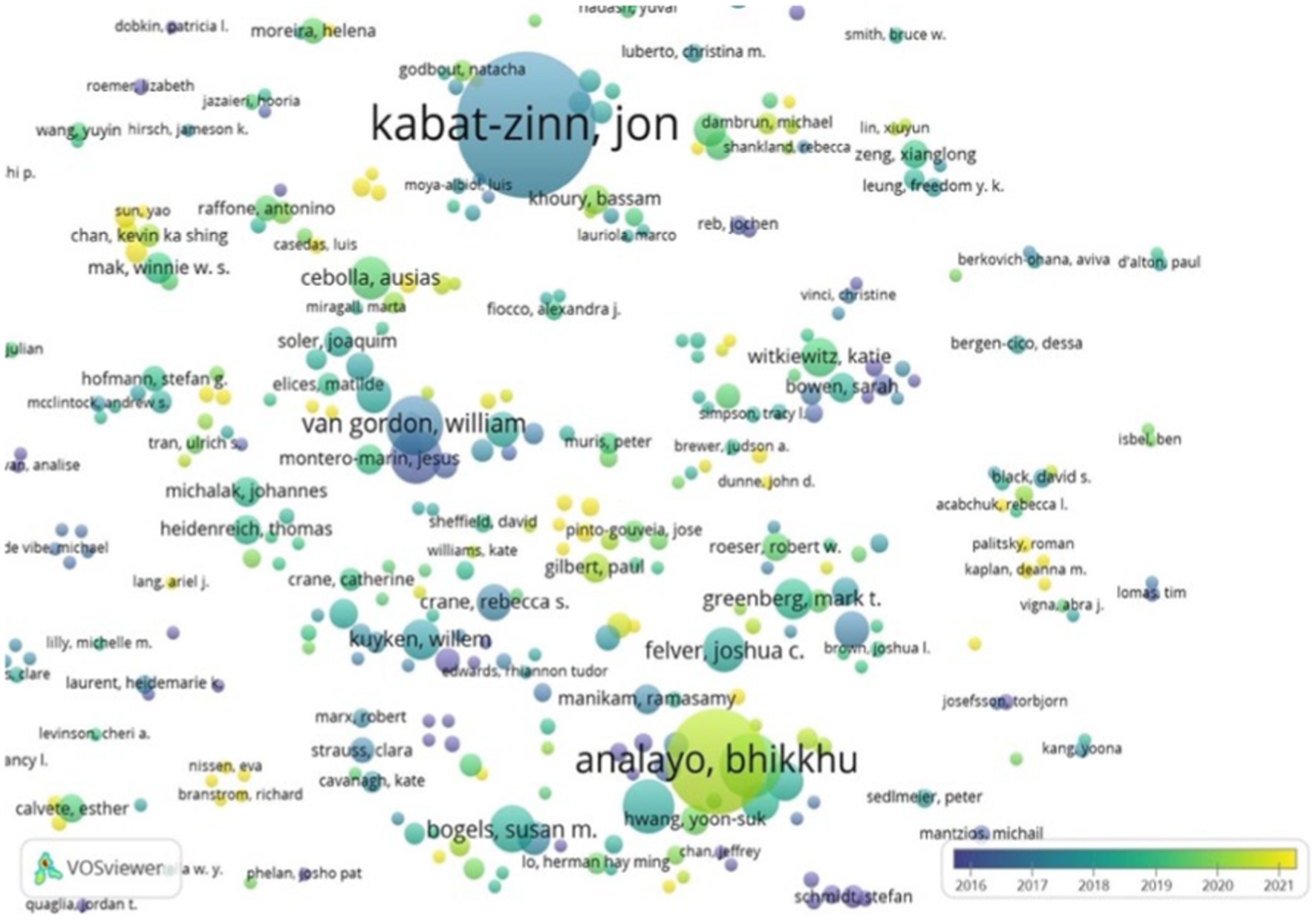
Figure 3 . Distribution of authors.
In 1979, Dr. Kabat-Zinn launched the MBSR program at the University of Massachusetts Medical School, effectively helping patients handle stress, pain, and illness through mindfulness techniques. His method, practiced in over 200 medical institutions across North America, has significantly influenced healthcare, education, and other sectors for decades. Dr. Kabat-Zinn’s numerous publications, including Full Catastrophe Living and The Mindful Way Through Depression, have further popularized these approaches ( Kabat-Zinn, 2023 ).
Dr. Analayo of the Barre Center for Buddhist Studies and the Numata Centre for Buddhist Studies at The University of Hamburg focuses on early Buddhist texts and meditation practices. His work bridges ancient Buddhist techniques with modern practices, exploring mindfulness as a connection between mind and body, vital for continuous awareness in daily life ( Anālayo, 2020 ).
Dr. Van Gordon, from the University of Derby, has established credibility in studying the efficacy of Buddhist-derived meditations like Loving-Kindness Meditation (LKM) and Compassion Meditation (CM) in treating a range of mental health problems. His research emphasizes the foundational importance of Meditation Awareness Training (MAT) in enhancing psychological well-being in educational settings among other applications ( University of Derby, 2023 ).
Dr. Medvedev from the University of Waikato has refined the Five Facet Mindfulness Questionnaire using Rasch analysis to enhance its precision and validity, supporting its application in diverse psychological and health-related fields ( The University of Waikato, 2023 ). His research covers various fields, such as assessment methods, health psychology, psychophysiology, and biostatistics.
Dr. Bögels, a professor at the University of Amsterdam, has extensively researched the interplay between cognitive-behavioral therapy and mood disorders in treating childhood social anxiety ( University of Amsterdam, 2023 ). Her findings on the effectiveness of mindful parenting as a therapeutic intervention highlight its benefits in reducing stress and improving family dynamics ( Bögels et al., 2014 ).
As shown in Table 2 , Kabat-Zinn, Analayo, and Van Gordon have predominantly focused on exploring aspects of Buddha’s teachings, the inherent purity of the meditator’s mind, and Meditation Awareness Mindfulness, among other elements. Analayo and Van Gordon bring unique perspectives to their empirical research on meditation’s role in regulating personal physical and mental states, enhancing internal awareness, insight, compassion, and peace. Kabat-Zinn, on the other hand, has been pivotal in integrating mindfulness into psychological therapy and neuropsychology, significantly advancing the therapeutic landscape by mitigating physical and mental distress and promoting overall well-being. Their collective research emphasizes the efficacy of mindfulness interventions in alleviating anxiety and stress, while also advocating for the enhancement of physical and mental health and overall happiness. Medvedev, renowned for his expertise in assessing mindfulness, excels in documenting the observable benefits and self-regulation strategies of mindfulness training through the use of questionnaires, observations, and interviews. In contrast, Bögels concentrates on the application of mindfulness counseling treatment to address stress, depressive mood, and situational trait anxiety among children and their parents, revealing significant benefits in children’s cognition, social interaction, self-care, and mental health.
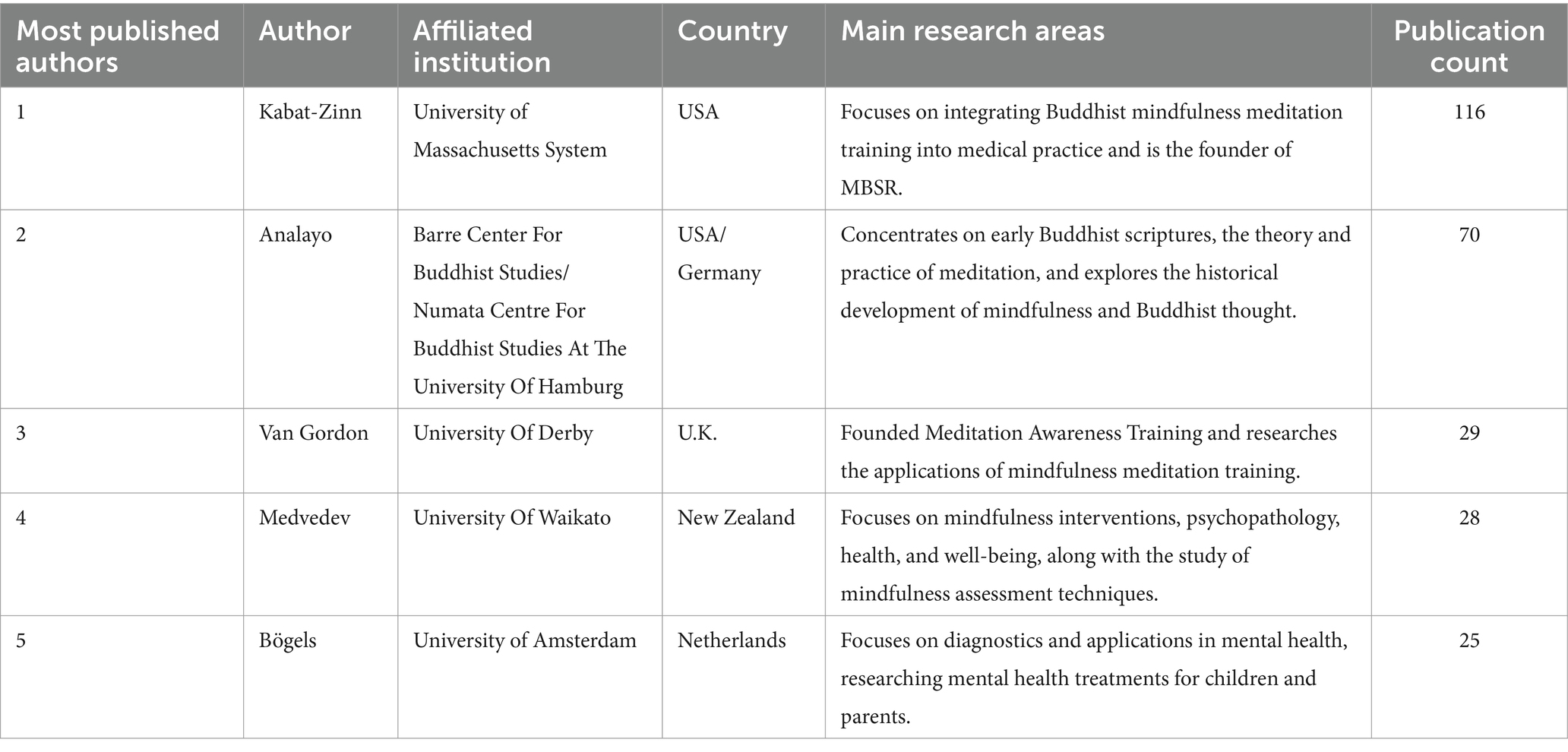
Table 2 . Distribution of authors.
Distribution of countries and institutions
As shown in Figure 4 , this study analyzes the distribution of publications and institutions to elucidate geographical knowledge networks within the field of mindfulness. An examination of publications from the Mindfulness journal indicates a wide international spread, involving researchers from 68 countries, with the United States, United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, and China being the primary contributors. Among these, significant institutions include the University of Massachusetts System, University of Massachusetts Worcester, Barre Center for Buddhist Studies, University of California System, and University System of Georgia, all located in the USA, underscoring the predominant role of the United States in mindfulness research. Notably, the focus of Chinese research is primarily centered in Hong Kong, signaling its prominence in China’s mindfulness studies, while suggesting that other regions in China could enhance their contributions to this field.
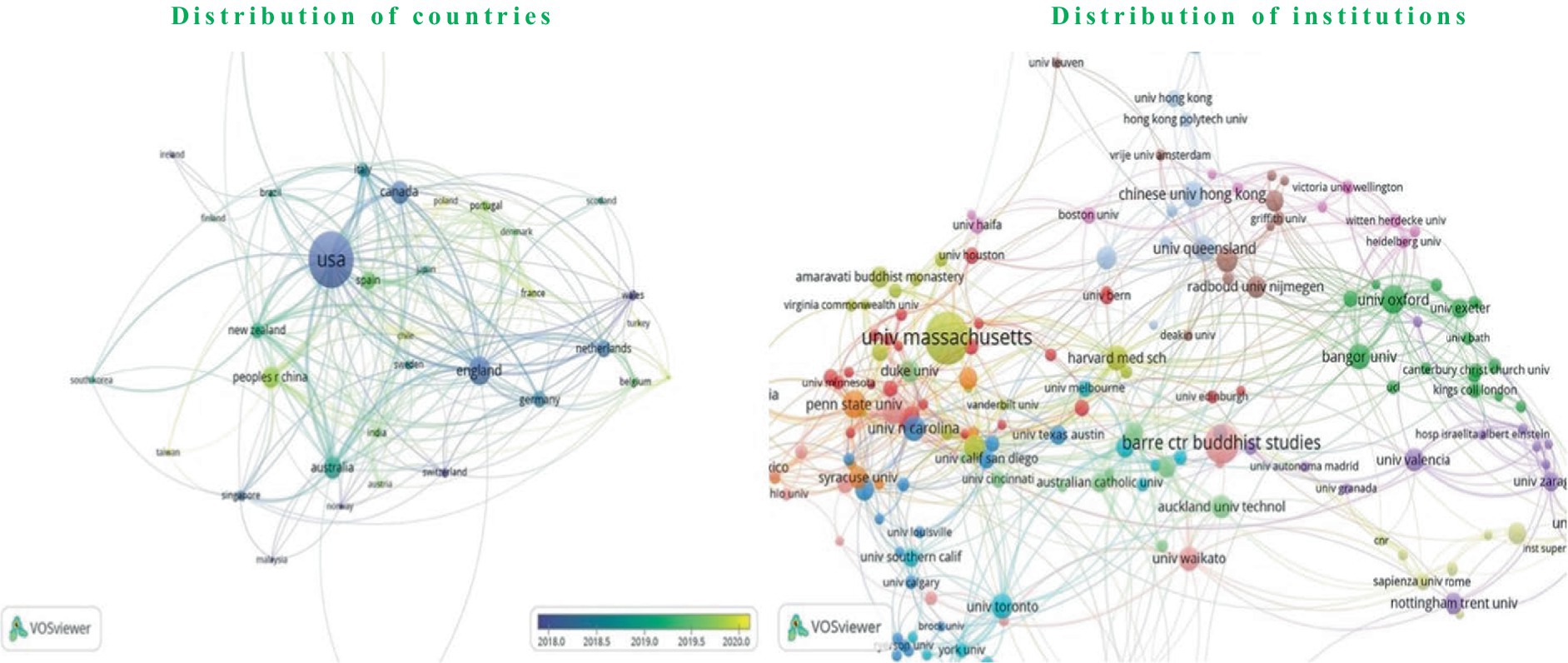
Figure 4 . Distribution of countries and institutions.
As shown in Table 3 , the United States leads in publication volume, followed by the United Kingdom, with substantial inputs from Canada and Australia, whereas China exhibits fewer publications. This distribution underscores a pronounced interest and earlier initiation of mindfulness research among scholars in the US and UK. Institutions like the University of Massachusetts System, Barre Center for Buddhist Studies, and University of Derby, which house principal authors in mindfulness research, are closely aligned with core fields such as mindfulness meditation, training, measurement, intervention, and regulation. This alignment reflects a concentrated and specialized focus in the developmental stages of mindfulness research.
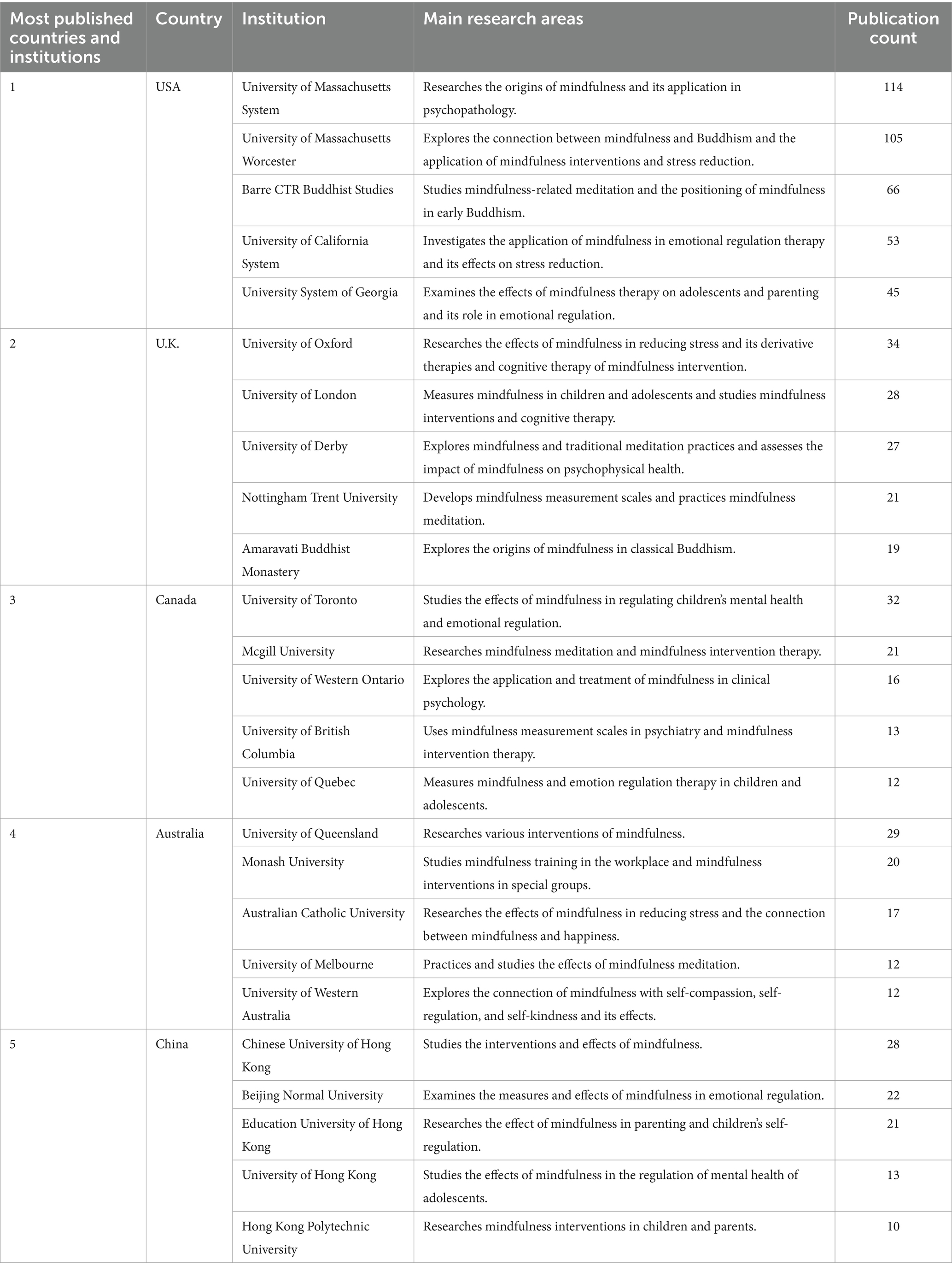
Table 3 . Distribution of countries and institutions.
Keyword co-occurrence
The analysis of keyword co-occurrence in this study is based on the size of network nodes, which represents the importance of each keyword. The larger the keyword, the closer it is to the research hotspot. As shown in Figure 5 , the high-frequency keywords in the Mindfulness journal are ‘mindfulness,’ ‘meditation,’ ‘depression,’ ‘self-compassion,’ and ‘stress,’ all of which are at the core of the clusters.
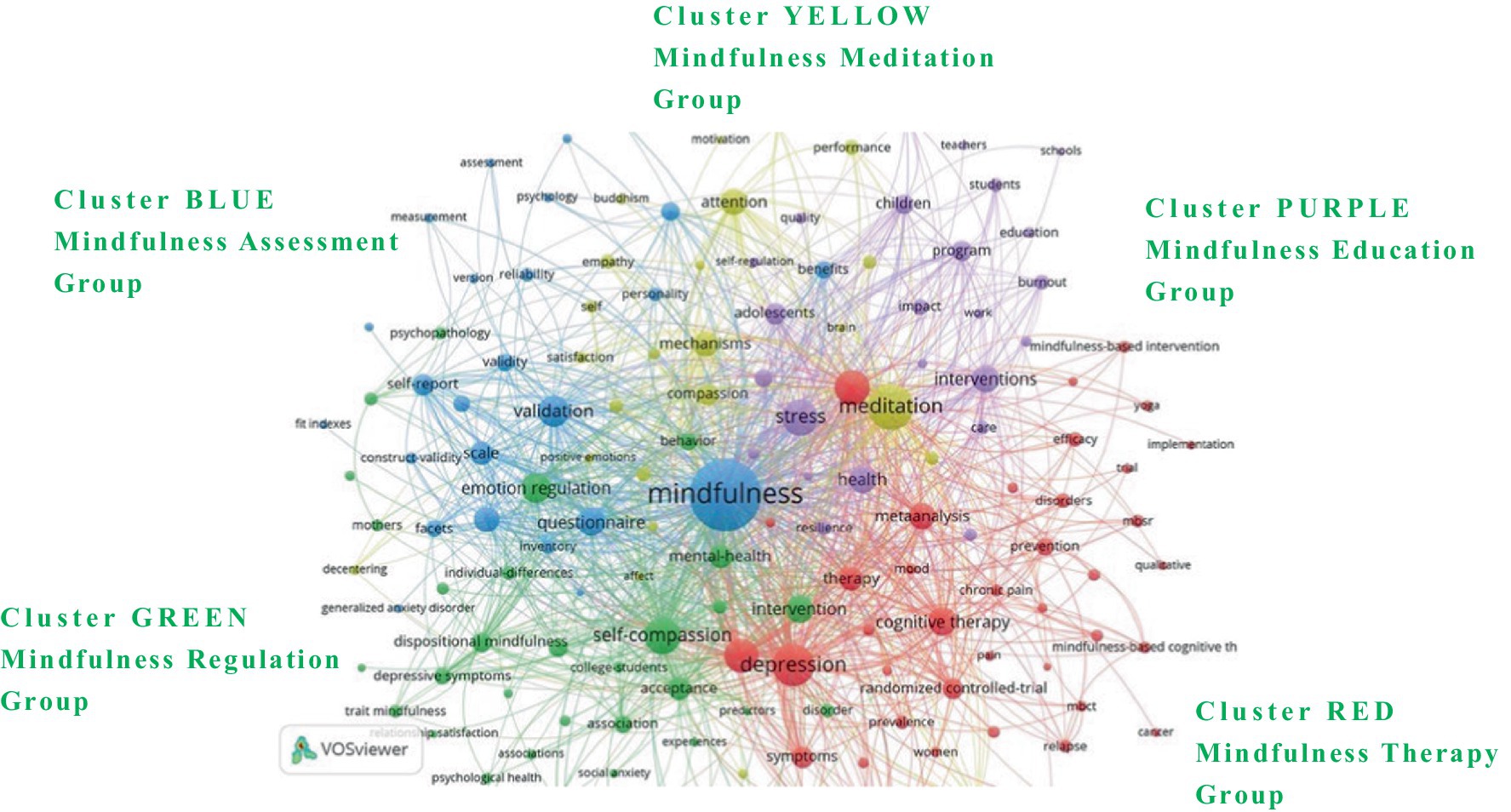
Figure 5 . Keyword co-occurrence.
As shown in Table 4 , “Mindfulness” is identified as the central term across all articles, reflecting its prevalent usage within the field. The analysis reveals other significant keywords such as “meditation,” “depression,” “self-compassion,” and “stress.” Notably, “meditation” was a dominant theme in the initial stages of research, with a marked increase in related studies between 2014 and 2018, while “self-compassion” gained prominence around 2020. This study organizes these keywords into five distinct clusters based on node size. The red cluster, focusing on “depression,” incorporates themes like anxiety, systematic analysis, cognitive therapy, and treatment, primarily concerning mindfulness treatment. The green cluster, centered around “self-compassion,” includes terms related to emotion regulation, intervention, psychological health, and acceptance, highlighting aspects of mindfulness regulation. The blue cluster, led by “mindfulness,” deals with the facets of examination, questionnaires, psychometric properties, and grading, pertinent to mindfulness assessment. The yellow cluster, under the banner of “meditation,” delves into mechanisms, attention, compassion, and empathy, enriching the discourse on mindfulness meditation. Lastly, the purple cluster, themed around “stress,” addresses issues related to health, adolescents, well-being, and education, underscoring mindfulness education. Collectively, these clusters illustrate the breadth of mindfulness research, showcasing a range of topics from treatment and regulation to assessment and educational applications, reflecting the evolving dynamics and the comprehensive scope of mindfulness as a research field.
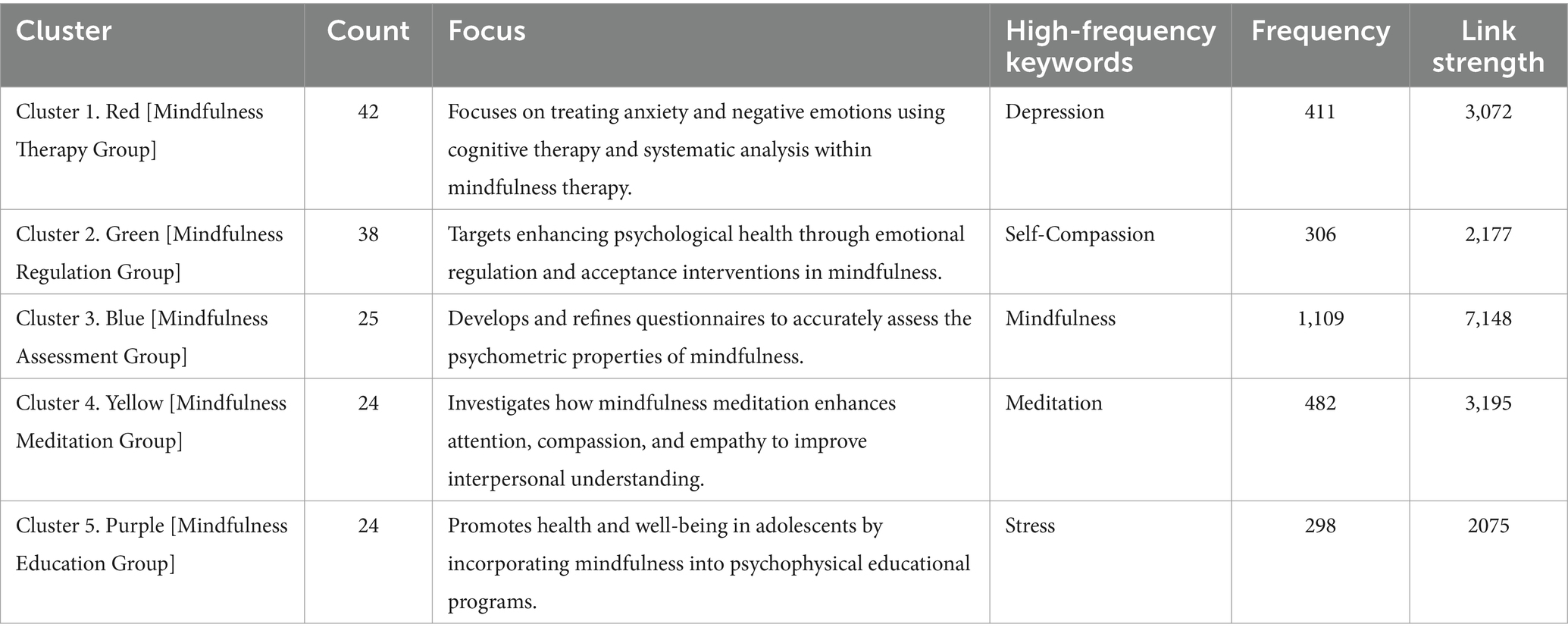
Table 4 . Keyword co-occurrence analysis.
The interconnected themes highlighted by these keywords underscore the varied research focus directions of the journal Mindfulness in recent years, reflecting the dynamic evolution of paradigms within mindfulness research. This body of work integrates several core areas, including addressing unhealthy, negative, and adverse emotions through mindfulness-based interventions, exploring strategies for mental health and emotion regulation, conducting evaluations with mindfulness-related questionnaires, investigating meditation practices to foster understanding and empathy, and developing psychophysical educational programs specifically designed for adolescents. Collectively, these focal points illustrate the journal’s commitment to advancing both the theoretical and practical aspects of mindfulness, contributing significantly to our understanding of its diverse applications across various contexts.
Reference co-citation
This study aims to explore the development and dynamic evolution of themes and their relationships within the mindfulness research field, thereby enhancing our understanding of its current state and providing valuable scientific guidance for scholars. As shown in Figure 6 , an analysis of references from the Mindfulness journal reveals that reference co-citations are divided into five clusters: the red cluster focuses on mindfulness assessment with 70 articles, primarily exploring the development and validation of related scales; the green cluster, comprising 65 articles, assesses various mindfulness therapies; the blue cluster, with 62 articles, discusses the structural aspects of mindfulness; the yellow cluster includes 43 articles on mindfulness intervention, evaluating its structural composition and clinical intervention mechanisms; and the purple cluster, consisting of 37 articles, measures the effectiveness of mindfulness across medicine, psychology, education, and other fields. Prominent researchers contributing to these clusters include Kabat-Zinn (2003) , Neff (2003a) , Bishop et al. (2004) , Baer et al. (2006) , and Kabat-Zinn (2009) , whose works significantly shape the discourse within these areas.
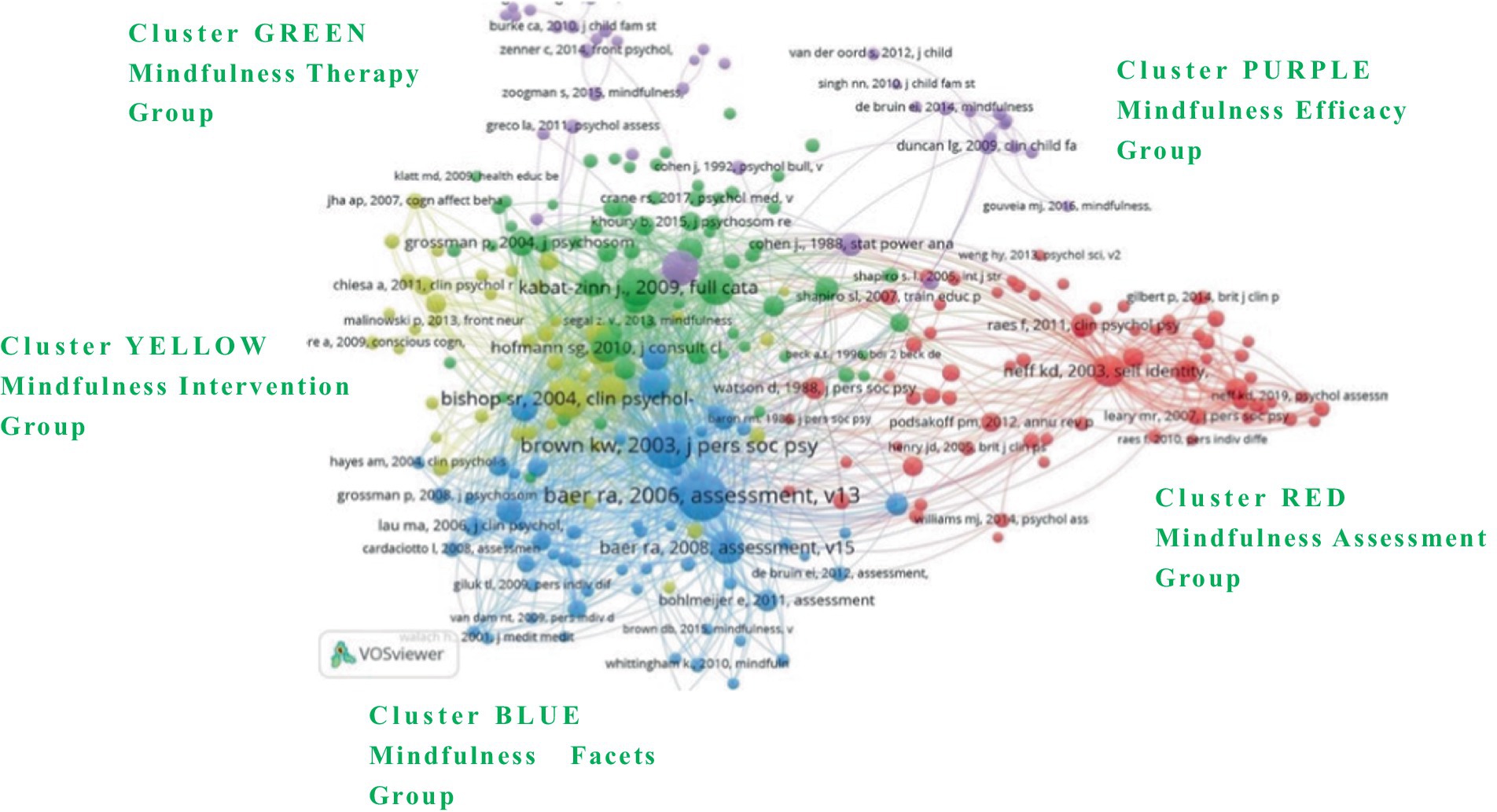
Figure 6 . Reference co-citation.
As shown in Table 5 , the article “Using Self-Report Assessment Methods to Explore Facets of Mindfulness” by Baer et al. (2006) stands out as the most strongly linked article, published by the American Psychological Association, Society for Clinical Psychology (Division 12), Section IX (Assessment). This pivotal article investigates various methods and approaches for self-assessing mindfulness. Following closely is “The Benefits of Being Present: Mindfulness and Its Role in Psychological Well-Being” by Brown and Ryan (2003) , which utilized the Mindful Attention Awareness Scale (MAAS) to analyze mindfulness’s predictive and regulatory role in psychological health, published in Personality and Social Psychology. The reference co-citations related to these articles are organized into five clusters that reflect their influence and connections within the field. The red cluster, focusing on mindfulness assessment, is highlighted by Baer et al. (2006) , who discuss the multifaceted nature of mindfulness and its assessment techniques. This cluster emphasizes articles that delve into the development and validation of scales designed to measure mindfulness attributes accurately. The green cluster centers around mindfulness therapy, featuring Hofmann et al. (2010) who confirm the effectiveness of mindfulness therapies in treating clinical issues like anxiety and depression. This cluster collectively examines the therapeutic applications and outcomes of mindfulness-based interventions. In the blue cluster, which addresses the structural aspects of mindfulness, Brown and Ryan (2003) explore the role of mindfulness in enhancing psychological well-being, showcasing its regulatory impact on mental health through empirical studies. The yellow cluster, dedicated to mindfulness interventions, includes Kabat-Zinn (2009) , whose work discusses practical mindfulness applications in dealing with stress, pain, and illness, emphasizing the operational mechanisms and clinical efficacy of mindfulness. Finally, the purple cluster, focusing on the effectiveness of mindfulness, features Neff (2003a) who develops and validates the Self-Compassion Scale, exploring the beneficial effects of self-compassion as part of a mindfulness approach. This cluster explores how mindfulness practices contribute to overall health and education, highlighting their potential in fostering enhanced well-being across various populations. These clusters demonstrate the journal Mindfulness ’s comprehensive coverage of research that spans theoretical explorations to practical applications, reflecting the dynamic and evolving landscape of mindfulness research.
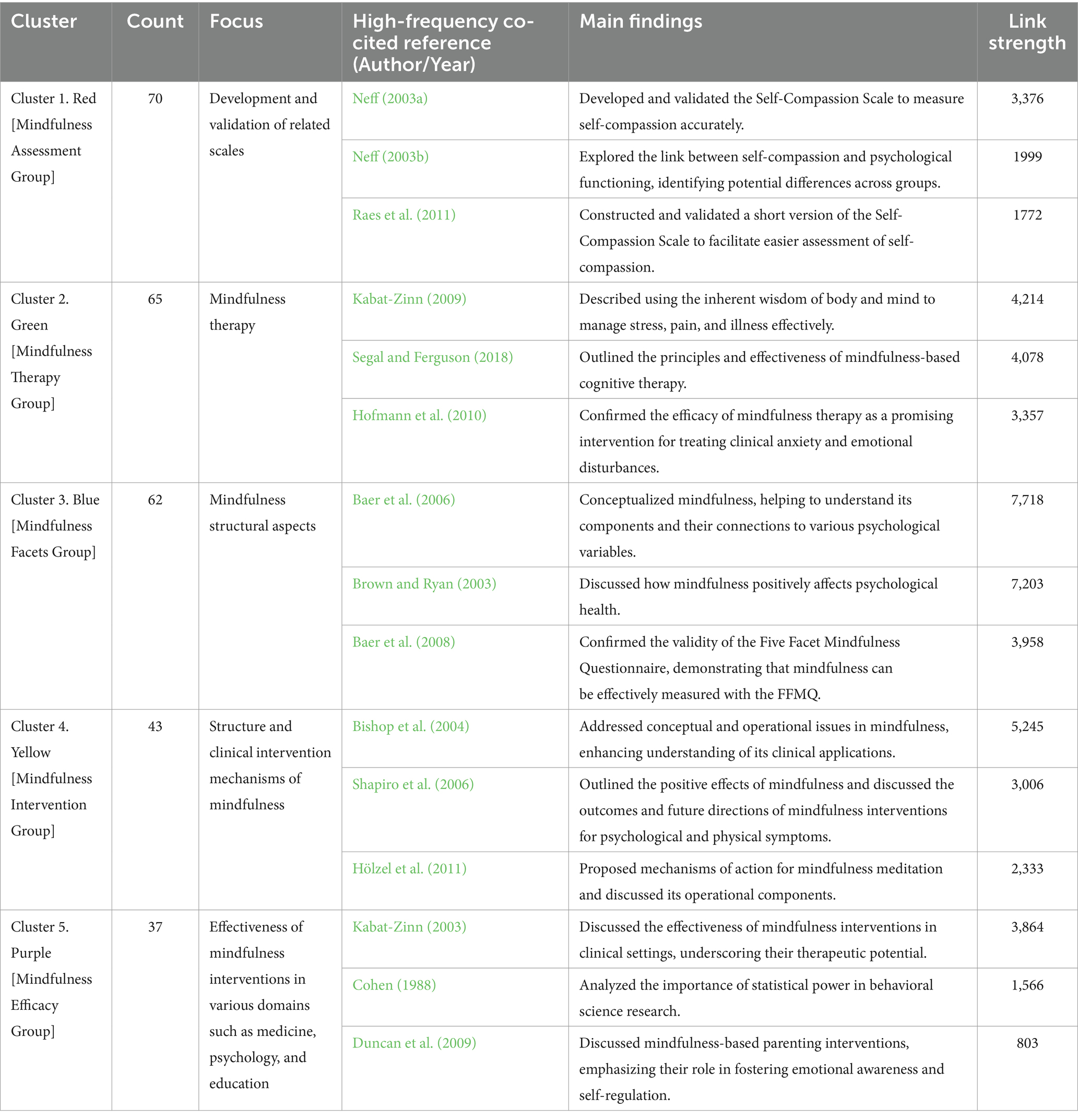
Table 5 . Reference co-citation analysis.
Conclusion and implications
This study employs bibliometric analysis to conduct a visual analysis of research published in the Mindfulness journal, aiming to provide scholars with a relatively objective perspective to grasp the dynamics and future directions of international mindfulness research. The findings indicate that over the past decade, the journal has published 1,950 articles, with publication numbers increasing over time. Among the many contributors, Kabat-Zinn, Analayo, Van Gordon, Medvedev, and Bögels stand out as key figures, with mindfulness research predominantly concentrated in Western countries, particularly the United States and the United Kingdom, which have had the most significant impact on the field. The research primarily focuses on themes such as mindfulness, meditation, depression, stress, and self-compassion. Moreover, the studies are extensively centered around specific aspects of mindfulness, including “intervention,” “therapy,” “regulation,” “assessment,” and “education.” In Taiwan, mindfulness research is relatively underdeveloped; the analysis of this data not only helps identify current research hotspots and gaps but also provides valuable references for researchers in Taiwan, further facilitating the extensive application and in-depth development of mindfulness studies.
We conducted a systematic analysis of various dimensions within mindfulness research, including institutions, nations, individual researchers, and trending topics, thus uncovering key interconnections among these elements. The distribution of these relationships not only maps the trajectory of mindfulness research but also highlights the global imbalance in research capabilities. Particularly, the cultural drivers and relationships between research hotspots, regions, institutions, and individual researchers are crucial as they facilitate collaboration across geographical, disciplinary, and cultural boundaries, which is vital for the global application and dissemination of mindfulness. For instance, Hofmann et al. (2010) have confirmed through their comprehensive analysis that mindfulness therapy positively impacts symptoms of anxiety and depression, a finding that is consistently underscored by frequent references to “depression” and “therapy.” The high-frequency keywords and reference co-citations exhibit a robust linkage pattern, illustrating interrelated connections among these themes. Not only do these connections enrich the existing literature, but they also provide invaluable references for the further development of mindfulness research, highlighting its significance across various psychological and educational settings. Although Asian countries have lesser participation in mindfulness research, their rich history of traditional meditation practices offers substantial untapped potential for future studies. Strengthening collaborations with Western countries can enhance the exchange of knowledge and technologies, bringing fresh perspectives that are essential for advancing the globalization of mindfulness research.
Implications for mindfulness research and education in Taiwan
In Taiwan, mindfulness research is still in its nascent stages, with a notable absence of publications in the international journal Mindfulness , indicative of a lack of systematic research. Scholars in Taiwan are thus encouraged to align with international research trends in mindfulness, enhancing their analytical approaches. There is a strong recommendation for scholars to focus more on demographic groups that could benefit from improved mental health. This involves intensifying global dialogue and exchange between domestic scholars and their international counterparts, which is vital for understanding the structural and developmental nuances of mindfulness research. This approach will facilitate international comparative studies, promote scientific collaboration globally, and provide robust support for individuals in high-pressure work environments. To improve Taiwan’s education directions and aid Taiwanese researchers in thoroughly exploring the development status and trends of the international mindfulness research fields, this study proposes several strategies to accelerate the internationalization of domestic research and discipline construction. These include integrating mindfulness education into curricula at all educational levels to provide students with systematic training in mindfulness practices like meditation, emotion regulation, and concentration; developing mindfulness teacher training programs to enhance educators’ emotional management skills; promoting mindfulness-friendly campuses to foster a respectful, caring, and harmonious learning environment; integrating mindfulness into special education as an auxiliary therapy for students with conditions such as autism and ADHD to enhance their emotion regulation and self-control; and conducting thorough research and assessments of mindfulness education to gauge its impact on students’ learning outcomes, psychological health, and interpersonal relationships, thereby generating empirical evidence to support the expansion of mindfulness education.
Limitations, and suggestions for future research
While this study presents notable findings, it is not without its limitations. The analysis relies exclusively on literature data from the Journal of Mindfulness in the WoS database, lacking empirical field investigations and experimental validation. This focus restricts the breadth of mindfulness-related literature reviewed, as it does not consider contributions from other journals. Future research could benefit from employing a variety of research methods and data sources, integrating themes such as “intervention, therapy, regulation, assessment, education” to expand the exploration of mindfulness applications across diverse domains and populations. Additionally, by prioritizing key terms within the co-occurrence patterns, new research avenues can be identified, which will drive the development of mindfulness research and offer valuable guidance for practical applications and policy formulation.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
C-CH: Writing – review & editing, Supervision. SL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Anālayo, B. (2020). Somatics of early Buddhist mindfulness and how to face anxiety. Mindfulness 11, 1520–1526. doi: 10.1007/s12671-020-01382-x
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
Baer, R. A., Smith, G. T., Hopkins, J., Krietemeyer, J., and Toney, L. (2006). Using self-report assessment methods to explore facets of mindfulness. Assessment 13, 27–45. doi: 10.1177/1073191105283504
Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
Baer, R. A., Smith, G. T., Lykins, E., Button, D., Krietemeyer, J., Sauer, S., et al. (2008). Construct validity of the five-facet mindfulness questionnaire in meditating and nonmeditating samples. Assessment 15, 329–342. doi: 10.1177/1073191107313003
Bishop, S. R., Lau, M., Shapiro, S., Carlson, L., Anderson, N. D., Carmody, J., et al. (2004). Mindfulness: a proposed operational definition. Clin. Psychol. Sci. Pract. 11, 230–241. doi: 10.1093/clipsy.bph077
Bögels, S. M., Hellemans, J., van Deursen, S., Römer, M., and van der Meulen, R. (2014). Mindful parenting in mental health care: effects on parental and child psychopathology, parental stress, parenting, coparenting, and marital functioning. Mindfulness 5, 536–551. doi: 10.1007/s12671-013-0209-7
Brown, K. W., and Ryan, R. M. (2003). The benefits of being present: mindfulness and its role in psychological wellbeing. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 84, 822–848. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.84.4.822
Chen, S. J., Peng, T. W., and Wu, Y. H. (2019). Review of the effectiveness of mindfulness interventions in Taiwan: reflections on evidence and practice. Appl. Psychol. Res. 70, 77–121.
Google Scholar
Chiesa, A., Calati, R., and Serretti, A. (2011). Does mindfulness training improve cognitive abilities? A systematic review of neuropsychological findings. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 31, 449–464. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2010.11.003
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical Power analysis for the behavioral sciences . 2nd Edn. New York: Routledge.
Corcoran, K. M., Farb, N., Anderson, A., and Segal, Z. V. (2010). “Mindfulness and emotion regulation: outcomes and possible mediating mechanisms” in Emotion regulation and psychopathology: a trans diagnostic approach to etiology and treatment . eds. A. M. Kring and D. M. Sloan (New York: Guilford Press), 339–355.
Costa, J. A., Marôco, J., Pinto-Gouveia, J., Ferreira, C., and Castilho, P. (2016). Validation of the psychometric properties of the self-compassion scale. Testing the factorial validity and factorial invariance of the measure among borderline personality disorder, anxiety disorder, eating disorder and general populations. Clin. Psychol. Psychother. 23 5, 460–468. doi: 10.1002/cpp.1974
Davis, D. M., and Hayes, J. A. (2011). What are the benefits of mindfulness? A practice review of psychotherapy-related research. Psychotherapy 48, 198–208. doi: 10.1037/a0022062
Dobkin, P. L., and Zhao, Q. (2011). Increased mindfulness-the active component of the mindfulness-based stress reduction program? Complement. Therap. Clin. Pract. 17, 22–27. doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2010.03.002
Donthu, N., Kumar, S., Mukherjee, D., Pandey, N., and Lim, W. M. (2021). How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: an overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 133, 285–296. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.04.070
Duncan, L. G., Coatsworth, J. D., and Greenberg, M. T. (2009). A model of mindful parenting: implications for parent-child relationships and prevention research. Clin. Child. Fam. Psychol. Rev. 12, 255–270. doi: 10.1007/s10567-009-0046-3
Eberth, J., and Sedlmeier, P. (2012). The effects of mindfulness meditation: a meta-analysis. Mindfulness 3, 174–189. doi: 10.1007/s12671-012-0101-x
Farb, N. A. S., Anderson, A. K., Mayberg, H., Bean, J., McKeon, D., and Segal, Z. V. (2010). Minding one’s emotions: mindfulness training alters the neural expression of sadness. Emotion 10, 25–33. doi: 10.1037/a0017151
Ferrari, M., Hunt, C., Harrysunker, A., Abbott, M. J., Beath, A. P., and Einstein, D. A. (2019). Self-compassion interventions and psychosocial outcomes: a meta-analysis of RCTs. Mindfulness 10, 1455–1473. doi: 10.1007/s12671-019-01134-6
Flett, J. A., Hayne, H., Riordan, B. C., Thompson, L. M., and Conner, T. S. (2019). Mobile mindfulness meditation: a randomized controlled trial of the effect of two popular apps on mental health. Mindfulness 10, 863–876. doi: 10.1007/s12671-018-1050-9
Goldberg, S. B., Pace, B., Griskaitis, M., Willutzki, R., Skoetz, N., Zgierska, A. E., et al. (2021). Mindfulness-based interventions for substance use disorders. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 10:CD011723. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011723.pub2
Grossman, P., Niemann, L., Schmidt, S., and Walach, H. (2004). Mindfulness-based stress reduction and health benefits. A meta-analysis. J. Psychosom. Res. 57, 35–43. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3999(03)00573-7
Hofmann, S. G., Sawyer, A. T., Witt, A. A., and Oh, D. (2010). The effect of mindfulness-based therapy on anxiety and depression: a meta-analytic review. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 78, 169–183. doi: 10.1037/a0018555
Hölzel, B. K., Lazar, S. W., Gard, T., Schuman-Olivier, Z., Vago, D. R., and Ott, U. (2011). How does mindfulness meditation work? Proposing mechanisms of action from a conceptual and neural perspective. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 6, 537–559. doi: 10.1177/1745691611419671
Hsieh, C. C. (2018). Developing meaningful schools: an exploration of mindful leadership by principals. Educ. Res. Monthly 292, 69–86. doi: 10.3966/168063602018080292005
Hsieh, C. C. (2019). Practice and development of mindfulness education in Taiwan. Second. Educ. 70, 6–18. doi: 10.6249/SE.201912_70(4).0032
Huang, F. Y., Wu, C. W., Bhikshu, H. M., Bhikshu, G. H., Chao, Y. P., and Dai, C. T. (2015). Validation of the Taiwanese version of the five facet mindfulness questionnaire (T-FFMQ). Psychol. Testing 62, 231–260.
Jensen, C. G., Vangkilde, S. A., Frokjaer, V. G., and Hasselbalch, S. G. (2012). Mindfulness training affects attention--or is it attentional effort? J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 141, 106–123. doi: 10.1037/a0024931
Jha, A. P., Krompinger, J. W., and Baime, M. J. (2007). Mindfulness training modifies subsystems of attention. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 7, 109–119. doi: 10.3758/CABN.7.2.109
Jiang, Y., Wang, Y. Z., and Luo, F. (2022). The current status and prospects of mindfulness parenting. Chin. J. Health Psychol. 5:30.
Jin, J. S., and Liu, X. H. (2017). Mindfulness education for children and adolescents: exploring mindfulness as a new method of mental health education. J. Capital Norm. Univ. 2:11.
Kabat-Zinn, J. (2003). Mindfulness-based intervention in context: past, present, and future. Clin. Psychol. Sci. Pract. 10, 144–156. doi: 10.1093/clipsy/bpg016
Kabat-Zinn, J. (2009). Full catastrophe living: using the wisdom of your body and mind to face stress, pain, and illness . New York: Random House Publishing Group.
Kabat-Zinn, Jon . (2023). Wikipedia. Available at: https://zh.wikipedia.org/zhtw/%E5%96%AC%C2%B7%E5%8D%A1%E5%B7%B4%E9%87%91#cite_note-5
Kallapiran, K., Koo, S., Kirubakaran, R., and Hancock, K. M. (2015). Review: effectiveness of mindfulness in improving mental health symptoms of children and adolescents: a meta-analysis. Child Adolesc. Mental Health 20, 182–194. doi: 10.1111/camh.12113
Keng, S., Smoski, M. J., and Robins, C. J. (2011). Effects of mindfulness on psychological health: a review of empirical studies. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 31, 1041–1056. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2011.04.006
Körner, A., Coroiu, A., Copeland, L., Gomez-Garibello, C., Albani, C., Zenger, M., et al. (2015). The role of self-compassion in buffering symptoms of depression in the general population. PLoS One 10:e0136598. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136598
Lakhan, S. E., and Schofield, K. L. (2013). Mindfulness-based therapies in the treatment of somatization disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 8:e71834. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071834
Langer, E. J. (1989). Mindfulness . Boston: Addison-Wesley.
Laukkonen, R., Leggett, J. M. I., Gallagher, R., Biddell, H., Mrazek, A., Slagter, H. A., et al. (2020). The science of mindfulness-based interventions and learning: a review for educators . Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
Lawlor, M. S. (2014). Mindfulness in practice: considerations for implementation of mindfulness-based programming for adolescents in school contexts. New Dir. Youth Dev. 2014, 83–95. doi: 10.1002/yd.20098
Lin, Y. J. (2013). An integrated framework for exploring the process of mindfulness-based psychotherapy. Chin. J. Mental Health 26, 395–442.
Liu, C. C., and Rau, J. W. (2015). A study on the influence of mindfulness meditation on elementary school children’s capability of sustained attention. Buddhism Sci. 16, 81–98.
Lv, K. W. (2014). The practice and theory of mindfulness therapy: 33 mindfulness exercises . Taiwan: Taiwan Mindfulness Association.
MacBeth, A., and Gumley, A. I. (2012). Exploring compassion: a meta-analysis of the association between self-compassion and psychopathology. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 32, 545–552. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2012.06.003
Maynard, B. R., Solis, M., Miller, V. L., and Brendel, K. E. (2017). Mindfulness-based interventions for improving cognition, academic achievement, behavior, and socioemotional functioning of primary and secondary school students. Campbell Syst. Rev. 13, 1–32. doi: 10.1002/CL2.177
Meiklejohn, J. M., Phillips, C. L., Freedman, M. L., Griffin, M., Biegel, G. M., Roach, A. T., et al. (2012). Integrating mindfulness training into K-12 education: fostering the resilience of teachers and students. Mindfulness 3, 291–307. doi: 10.1007/s12671-012-0094-5
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., and Altman, D. G. (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 151, 264–269. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00135
Muris, P., Otgaar, H., and Petrocchi, N. (2016). Protection as the Mirror image of psychopathology: further critical notes on the self-compassion scale. Mindfulness 7, 787–790. doi: 10.1007/s12671-016-0509-9
Napoli, M., Krech, P. R., and Holley, L. C. (2005). Mindfulness training for elementary school students: the attention academy. J. Appl. Sch. Psychol. 21, 99–125. doi: 10.1300/J370v21n01_05
Neff, K. D. (2003a). The development and validation of a scale to measure self-compassion. Self Identity 2, 223–250. doi: 10.1080/15298860309027
Neff, K. D. (2003b). Self-compassion: an alternative conceptualization of a healthy attitude toward oneself. Self Identity 2, 85–101. doi: 10.1080/15298860309032
Neff, K. D. (2016). The self-compassion scale is a valid and theoretically coherent measure of self-compassion. Mindfulness 7, 264–274. doi: 10.1007/s12671-015-0479-3
Neff, K. D., Tóth-Király, I., Yarnell, L. M., Arimitsu, K., Castilho, P., Ghorbani, N., et al. (2019). Examining the factor structure of the self-compassion scale in 20 diverse samples: support for use of a Total score and six subscale scores. Psychol. Assess. 31, 27–45. doi: 10.1037/pas0000629
Neff, K. D., Whittaker, T. A., and Karl, A. (2017). Examining the factor structure of the self-compassion scale in four distinct populations: is the use of a Total scale score justified? J. Pers. Assess. 99, 596–607. doi: 10.1080/00223891.2016.1269334
Penman, D., and Burch, V. (2013). Mindfulness for health: A practical guide to relieving pain, reducing stress and restoring wellbeing . London: Paitkus.
Pritchard, A. (1969). Statistical bibliography or bibliometrics? J. Doc. 25, 344–349. doi: 10.1108/eb026482
Radhakrishnan, S., Erbis, S., Isaacs, J. A., and Kamarthi, S. (2017). Novel keyword co-occurrence network-based methods to foster systematic reviews of scientific literature. PLoS One 12, 1–16. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172778
Raes, F., Griffith, J. W., Gucht, K. V., and Williams, J. M. (2014). School-based prevention and reduction of depression in adolescents: a cluster-randomized controlled trial of a mindfulness group program. Mindfulness 5, 477–486. doi: 10.1007/s12671-013-0202-1
Raes, F., Pommier, E., Neff, K. D., and Van Gucht, D. (2011). Construction and factorial validation of a short form of the self-compassion scale. Clin. Psychol. Psychother. 18, 250–255. doi: 10.1002/cpp.702
Ronald, D. S., Germer, C. K., and Olendzki, A. (2009). “Mindfulness: what is it? Where did it come from?” in Clinical handbook of mindfulness . ed. D. Fabrizio (New York: Springer), 17–35.
Sancho, M., De Gracia, M., Rodriguez, R. C., Mallorquí-Bagué, N., Sánchez-González, J., Trujols, J., et al. (2018). Mindfulness-based interventions for the treatment of substance and behavioral addictions: a systematic review. Front. Psych. 9:353853. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00095
Sauer, S., Walach, H., Schmidt, S., Hinterberger, T., Lynch, S., Büssing, A., et al. (2013). Assessment of mindfulness: review on state of the art. Mindfulness 4, 3–17. doi: 10.1007/s12671-012-0122-5
Segal, Z. V., and Ferguson, A. M. (2018). “Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy: treatment development from a common cognitive therapy core” in Science and practice in cognitive therapy: foundations, mechanisms, and applications . ed. R. L. Leahy (New York: Guilford Press), 159–174.
Shapiro, S. L., Carlson, L. E., Astin, J. A., and Freedman, B. (2006). Mechanisms of mindfulness. J. Clin. Psychol. 62, 373–386. doi: 10.1002/jclp.20237
Shin, T. B., and Jin, S. R. (2010). The qualitative study of “mindfulness group” toward t he self-care and counseling practice of counselor interns. Bull. Educ. Psychol. 42, 163–184. doi: 10.6251/BEP.20100423
Singh, V. K., Singh, P., Karmakar, M., Leta, J., and Mayr, P. (2021). The journal of web of science, Scopus and dimensions: a comparative analysis. Scientometrics 126, 5113–5142. doi: 10.1007/s11192-021-03948-5
Small, H. G. (1973). Co-citation in the scientific literature: a new measure of the relationship between two documents. J. Am. Soc. Inform. 24, 265–269. doi: 10.1002/asi.4630240406
The University of Waikato . (2023). Available at: https://www.waikato.ac.nz/staff-profiles/people/omedvede
Tomlinson, E. R., Yousaf, O., Vittersø, A. D., and Jones, L. (2018). Dispositional mindfulness and psychological health: a systematic review. Mindfulness 9, 23–43. doi: 10.1007/s12671-017-0762-6
University of Amsterdam . (2023). Available at: https://www.uva.nl/en/profile/b/o/s.m.bogels/s.m.bogels.html#Publications
University of Derby . (2023). Available at: https://www.derby.ac.uk/staff/william-van-gordon/
Valentine, E. R., and Sweet, P. L. (1999). Meditation and attention: a comparison of the effects of concentrative and mindfulness meditation on sustained attention. Mental Health Religion Cult. 2, 59–70. doi: 10.1080/13674679908406332
Van Eck, N. J., and Waltman, L. (2010). Software survey: VOS viewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scient Metrics 84, 523–538. doi: 10.1007/S11192-009-0146-3
Wall, J. M. (2014). Finding an inner voice through silence: mindfulness goes to college. J. Coll. Charact. 15, 133–140. doi: 10.1515/jcc-2014-0017
Wen, T. K. (2013). An overview of Western mindfulness education: moving towards integrating mindfulness training in Taiwan. J. Life Educ. Res. 5, 145–180.
Wen, T. K. (2016). An exploration of western mindfulness teacher training and certification. Fu Jen J. Religious Stud. 32, 71–101.
Wen, T. K. (2013). The Origins and Mechanisms of Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction: From a Perspective of Buddhist Studies. New Century Religious Studies 12, 27–48. Available at: https://www.airitilibrary.com/Article/Detail?DocID=16843738-201312-201401160022-201401160022-27-48 .
Willis, E., and Dinehart, L. (2014). Contemplative practices in early childhood: implications for self-regulation skills and school readiness. Early Child Dev. Care 184, 487–499. doi: 10.1080/03004430.2013.804069
Wilson, J. (2014). Mindful America: The mutual transformation of buddhist meditation and American culture . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Wilson, A. C., Mackintosh, K., Power, K., and Chan, S. W. (2019). Effectiveness of self-compassion related therapies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mindfulness 10, 979–995. doi: 10.1007/s12671-018-1037-6
Yang, Y. W. (2015). Research hotspots and evolution on cultivating reserve talents of competitive sports in China based on knowledge maps. J. Shanghai Univ. Sport 39, 73–79.
Yang, J. Y. (2016). Teaching reflection of integrating mindfulness in general education courses of military school: the example of army academy R.O.C. J. NDU General Educ. 6, 91–109.
Zhang, J. J. (2013). Evolution of research hotspots, themes, and methods in the field of tourism management in China. Econ. Geogr. 23, 173–179.
Zhang, L. M. (2013). Research on the integration of ice and snow tourism and culture from the perspective of tourism culture industry. Academic Exchange 2013, 106–109.
Zhang, J. T., Zhang, J. Y., Du, Z. Y., Li, J., Lü, C. H., and Du, J. (2019). Effect of mindfulness-based intervention on functional connectivity of resting state electroencephalogram of amphetamine-type stimulants use patients. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. 39, 1416–1421.
Zheng, Y. C., Fang, S. Y., and Huang, S. L. (2013). Exploring mindfulness therapy and experiences: qualitative study results. Taiwan J. Clin. Psychol. 7, 48–49.
Zoogman, S., Goldberg, S. B., Hoyt, W. T., and Miller, L. (2015). Mindfulness interventions with youth: a meta-analysis. Mindfulness 6, 290–302. doi: 10.1007/s12671-013-0260-4
Zupic, I., and Čater, T. (2015). Bibliometric methods in management and organization. Organ. Res. Methods 18, 429–472. doi: 10.1177/1094428114562629
Zyoud, S. H., Waring, W. S., Al-Jabi, S. W., and Sweileh, W. M. (2017). Global cocaine intoxication research trends during 1975-2015: a bibliometric analysis of web of science publications. Subst. Abuse Treat. Prev. Policy 12, 1–16. doi: 10.1186/s13011-017-0090-9
Keywords: mindfulness, science mapping, bibliometric analysis, knowledge graph, visualization analysis
Citation: Hsieh C-C and Li S (2024) A bibliometrics review of the journal mindfulness : science mapping the literature from 2012 to 2022. Front. Psychol . 15:1378143. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1378143
Received: 29 January 2024; Accepted: 01 May 2024; Published: 17 May 2024.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2024 Hsieh and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shun Li, [email protected]
† These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The main difference between quantitative and qualitative research is the type of data they collect and analyze. Quantitative research collects numerical data and analyzes it using statistical methods. The aim is to produce objective, empirical data that can be measured and expressed in numerical terms.
Designing Research Methods to Test Complex Issues. Quantitative psychologists study and develop the methods and techniques used to measure human behavior and other attributes. Their work involves the statistical and mathematical modeling of psychological processes, the design of research studies and the analysis of psychological data.
Quantitative research methods. You can use quantitative research methods for descriptive, correlational or experimental research. In descriptive research, you simply seek an overall summary of your study variables.; In correlational research, you investigate relationships between your study variables.; In experimental research, you systematically examine whether there is a cause-and-effect ...
Research Methods in Psychology AP A Han dbook s in Psychology VOLUME Research Designs: Quantitative, Qualitative, Neuropsychological, and Biological SECOND EDITION Harris Cooper, Editor-in-Chief Marc N. Coutanche, Linda M. McMullen, A. T. Panter, sychological Association. Not for further distribution.
The current Editorial presents an overview of the special issue, and describes the underlying, translational issues embedded within the issue. We highlight three main themes that emerged, and describe how this work will help to fuel the future directions of quantitative-based research within the Psychological Sciences.
Unlike in quantitative research where hypotheses are usually developed to be tested, qualitative research can lead to both hypothesis-testing and hypothesis-generating outcomes.2 When studies require both quantitative and qualitative research questions, this suggests an integrative process between both research methods wherein a single mixed ...
Mixed Methods Research in Psychology Timothy C. Guetterman and Analay Perez; Chapter 13. The "Cases Within Trials" (CWT) Method: An Example of a Mixed-Methods Research Design ... Quantitative Research Designs Involving Single Participants or Units. Chapter 33. Single-Case Experimental Design John M. Ferron, Megan Kirby, and Lodi Lipien;
Fulfilling this need, this two-volume text provides the tool box to deliver the valid and generalizable answers to today's complex research questions. The Oxford Handbook of Quantitative Methods in Psychology aims to be a source for learning and reviewing current best-practices in quantitative methods as practiced in the social, behavioral, and ...
This is primarily aimed at first- and second-year undergraduates interested in psychology, data analysis, and quantitative research methods along with high school students and professionals with similar interests.
Quantitative psychology is a field of scientific study that focuses on the mathematical modeling, research design and methodology, and statistical analysis of psychological processes. It includes tests and other devices for measuring cognitive abilities. Quantitative psychologists develop and analyze a wide variety of research methods, including those of psychometrics, a field concerned with ...
Modern quantitative psychology has accepted method as primary; research questions are adjusted to the methods. For understanding thinking in modern quantitative psychology, two epistemologies should be distinguished: structural-systemic that is based on Aristotelian thinking, and associative-quantitative that is based on Cartesian-Humean ...
At a Glance. Psychologists rely on quantitative and quantitative research to better understand human thought and behavior. Qualitative research involves collecting and evaluating non-numerical data in order to understand concepts or subjective opinions. Quantitative research involves collecting and evaluating numerical data.
Research in psychology focuses on a variety of topics, ranging from the development of infants to the behavior of social groups. Psychologists use the scientific method to investigate questions both systematically and empirically. Research in psychology is important because it provides us with valuable information that helps to improve human lives.
a method of research that relies on measuring variables using a numerical system, analyzing these measurements using any of a variety of statistical models, and reporting relationships and associations among the studied variables. For example, these variables may be test scores or measurements of reaction time. The goal of gathering this ...
As research questions become more complex and diverse, the research methods used to answer them must evolve as well. Individuals who have a passion for psychology and an interest in using data and statistics to solve complex issues — such as developing test score baselines and evaluative measures to determine who might qualify for public health services — are well-suited for a career in ...
Key points. Neither a quantitative nor a qualitative methodology is the right way to approach every scientific question. Rather, the nature of the question determines which methodology is best ...
Introduction. Psychology is an ever-growing and popular field (Gough and Lyons, 2016; Clay, 2017).Due to this growth and the need for science-based research to base health decisions on (Perestelo-Pérez, 2013), the use of research methods in the broad field of psychology is an essential point of investigation (Stangor, 2011; Aanstoos, 2014).Research methods are therefore viewed as important ...
Introduction. Psychology is an ever-growing and popular field (Gough and Lyons, 2016; Clay, 2017).Due to this growth and the need for science-based research to base health decisions on (Perestelo-Pérez, 2013), the use of research methods in the broad field of psychology is an essential point of investigation (Stangor, 2011; Aanstoos, 2014).Research methods are therefore viewed as important ...
The field of psychology has emphasized quantitative laboratory research as a defining character of its role as a science, and has generally de-emphasized qualitative research and theorizing throughout its history. This article reviews some of the effects of this emphasis in two areas, intelligence testing, and learning and memory. On one side, quantitative measurement produced the widely used ...
Quantitative psychology is a branch of psychology developed using certain methods and approaches which are designed to answer empirical questions, such as the development of measurement models and factor analysis. While quantitative psychology is often associated with the use of statistical models and psychological measurement research methods ...
An MM approach is helpful in that one is able to conduct in-depth research and, when using complementary MM, provide for a more meaningful interpretation of the data and phenomenon being examined (Teddlie & Tashakkori, 2003). Another strength of MM is the dynamic between the qualitative and quantitative portions of the study.
The Psychology Department has a strategic focus on training in advanced methodology, especially quantitative methods. Advanced quantitative skills are increasingly important in conducting state-of-the-art research, and in post-doctoral and academic placements. Recent and ongoing faculty searches have emphasized expertise in quantitative methods. In addition to a standard two-semester ...
Learners discover how apply to research methods to their study of Positive Psychology. In this course, we study with Dr. Angela Duckworth and Dr. Claire Robertson-Kraft. Through an exploration their work "True Grit" and interviews with researchers and practitioners, you develop a research hypothesis and learn how to understand the difference ...
His research covers various fields, such as assessment methods, health psychology, psychophysiology, and biostatistics. Dr. Bögels, a professor at the University of Amsterdam, has extensively researched the interplay between cognitive-behavioral therapy and mood disorders in treating childhood social anxiety (University of Amsterdam, 2023).
Quantitative Research Qualitative research is a method of testing hypotheses and being able to measure variables using numerical data qualitative research finds trend patterns and correlations between variables qualitative research is objective and able to use standardized methods. Qualitative research uses statistical approaches to analyze ...
1 Quantitative vs Qualitative Data Morten Kroge Master of Science in Psychology - Addictions, Purdue Global University COURSE PS504: Advanced Research Methods Dr. Jesse Stout June, 2023. 2 Quantitative vs Qualitative Data In research, there are two ways to collect data, quantitatively or qualitatively. According to Bordens & Abbott (2022 ...