You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.

Pros and cons of zoos: Should animals be kept in zoos?

Source: This image was created for netivist.org. If you want to use it you simply need to attribute it by linking to this page or to https://netivist.org . Thanks
Animal cruelty or protection? Learn about the pros and cons of zoos and join our debate and poll: Should there be zoos? Should animals be kept in captivity? Vote and explain your view on whether zoos are necessary or should be banned.
Should animals be kept in zoos?
Over 181 million people visit zoos and aquariums every year in the United States, and 25 million in the United Kingdom. Zoos have more visitors than the combined attendance of the four major sports leagues ( NFL , NBA , MLB and NHL ). Despite their immense popularity , zoos have become increasingly controversial institutions. An increasing number of animal rights advocates and animal protection organizations are questioning the role of zoos in modern societies. The shocking evidence of animal abuse in some circuses , dolphinariums and zoos have pushed many environmental and wildlife activist groups to campaign for the closure of many of the institutions that keep wild animals in captivity.
To the question "should animals be kept in captivity?" the initial reaction of most people is rejection. Why should animals be kept in zoos? In an ideal world that would not be necessary, wild animals would roam freely in their natural habitats and we, humans, would find ways to observe them and learn about them without disrupting their lives. However, today on Earth due to population growth and urbanization many animal species are endangered and most people have very few opportunities to observe and learn from animals.
Jane Goodall , the famous British primatologist and one of the most important experts in chimpanzees in the world, has defended the role of zoos in helping us understand and preserve the life of wild animals (see video below). On the other hand, organizations such as PETA (People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals), Animal Aid and Born Free have initiated campaigns for the closure of zoos, arguing that most zoos deprive animals from their most basic needs and that animal abuse and suffering should not be a source of entertainment.
Do you think that zoos are an effective way to increase awareness about animal life? Do they really help preserve endangered species or it is more a business and a cruel source of entertainment? Is keeping animals in captivity a good way to ensure their future? Let's take a closer look at the advantages and disadvantages of zoos before we make up our minds.
Watch this video with Jane Goodall on the role of zoos in saving animals
Pros and cons of zoos
These are the most common arguments in favor and against zoos.
Pros of zoos
- After the famous wildlife conservationist Geral Durrell opened a zoo in Jersey in 1959, zoos all over the world have embraced the mission of saving endangered species in the world. Zoos are not like the exotic animal menageries from the middle ages. They want to provide entertainment but they are greatly concerned with the protection of animals and their natural habitats. Zoos help raising awareness and funding for wildlife initiatives and research projects.
- Animals are not always caged in zoos. Edinburgh was the first British zoo to follow the idea of displaying animals without bars. The Chester and Whipsnade zoological parks where the first two non-urban zoos without cages and larger enclosures. They opened in 1931. In the 1960s The drive-through safari parks became very popular. Ever since there has been an increasing public concern about animal welfare in zoos.
- Zoos are monitored and follow strict regulation in most developed countries. There is less room for animal cruelty in zoos than ever before in history.
- Most people working in zoos are true animal lovers. Veterinary doctors, zoologist, voluntary staff, etc. chose to work in zoos because they like animals, and wanted to work closely with them and help them thrive.
- Education is another positive feature of zoos. Many children and adults in cities can only see wild animals in TV or the Internet. Zoos offer them the unique experience of contemplating real animals. They can smell them, see how they move and listen their sounds. This is a much more vivid and enriching experience than the one you can get through a screen. Thanks to zoos kids and adult develop empathy toward animals.
- Zoos are key for research . Being able to observe and study animals is crucial if we want to contribute to help them and repair the ecosystems. They also help redice human-animal conflicts and better understand the needs and psychology of animals. Zoos serve as laboratories to learn more about how to fight animal diseases and develop effective animal anaesthetics and other treatments to help more animals in the future.
- Another pro of zoos is their role in animal reproduction. Zoos study animal breeding and thanks to them many wild animals in captivity can reproduce. This is particularly important in the case of endangered species. Due to the low density of the population of some animals in their natural ecosystems they struggle to find partners. Some populations in the wild are weakened by endogamy too. In zoos vets and biologist help to prevent inbreeding.
Cons of zoos
- Animal cruelty in zoos continues to be extremely common. There are continuous cases of animals abused by visitors and zoo workers. Many of them are reported every week in the media, however, the large majority are kept secret and those responsible are never held accountable or punished.
- Animals in captivity are deprived of many things that are important to them, as a result they become lonely and bored. Many of them suffer from "zoochosis" , a psychological condition characterized by repetitive and obsessive behaviors including vomiting, excessive grooming, coprophagia and self-mutilation.
- Most animals in zoos still live in small enclosures and cages . There are Safari Parks and large zoos in which animals have more space and live in an enviroment slightly more similar to their natural habitat .however, the large majority of zoos in the world are much smaller and have less economic means than the big zoos we often see in the media such as the San Diego Zoo, the Berlin Zoological Garden, the San Louis Zoo, etc.
- In zoos many animals sicken and die because they contract diseases from other animals and species. Zoos usually group animals from many different parts of the world with very distinct immunological systems. People also have been sickened from diseases contracted from animals in zoos.
- Many zoos do little for research or animal protection. They are simply businesses run with the sole purpose of making money . Their concern for animals is secondary. Cost efficiency often means they move animal welfare down in the list of priorities.
- Zoos and aquariums have incentivized the illegal hunt of animals . Historically poachers have hunted and sold wild animals for zoos all over the world. Although this practice is increasingly prosecuted in most countries, there are still small zoos and aquariums which acquire their animals without paying much attention to their origin.
- From an ethical point of view zoos are also questionable. Zoos are a typical form of family entertainment, but associating leisure and fun with the contemplation of animals in captivity can send the wrong signals to our children. Zoos can be construed as a sadistic pleasure .
Do you think zoos are necessary? Do the cons of zoos outweight their benefits? Should we boycott or ban zoos? Vote and join our debate (see below)
Watch this video on "zoochosis" and the living conditions of animals in captivity
Vote to see result and collect 1 XP. Your vote is anonymous. If you change your mind, you can change your vote simply by clicking on another option.
Voting results
New to netivist?
Join with confidence, netivist is completely advertisement free. You will not receive any promotional materials from third parties.
Or sign in with your favourite Social Network:
Join the debate
In order to join the debate you must be logged in.
Already have an account on netivist? Just login . New to netivist? Create your account for free .
Report Abuse and Offensive language
Was there any kind of offensive or inappropriate language used in this comment.
If you feel this user's conduct is unappropriate, please report this comment and our moderaters will review its content and deal with this matter as soon as possible.
NOTE: Your account might be penalized should we not find any wrongdoing by this user. Only use this feature if you are certain this user has infringed netivist's Terms of Service .
Our moderators will now review this comment and act accordingly. If it contains abusive or inappropriate language its author will be penalized.
Posting Comment
Your comment is being posted. This might take a few seconds, please wait.
Error Posting Comment
error.
We are having trouble saving your comment. Please try again .
Most Voted Debates
Start a Debate
Would you like to create a debate and share it with the netivist community? We will help you do it!
Found a technical issue?

Are you experiencing any technical problem with netivist? Please let us know!
Help netivist
Help netivist continue running free!
Please consider making a small donation today. This will allow us to keep netivist alive and available to a wide audience and to keep on introducing new debates and features to improve your experience.

- What is netivist?
- Entertainment
- Top Debates
- Top Campaigns
- Provide Feedback

Follow us on social media:

Share by Email
There was an error...
Email successfully sent to:

Join with confidence, netivist is completely advertisement free You will not recive any promotional materials from third parties
Join netivist
Already have a netivist account?
If you already created your netivist account, please log in using the button below.
If you are new to netivist, please create your account for free and start collecting your netivist points!
You just leveled up!
Congrats you just reached a new level on Netivist. Keep up the good work.

Together we can make a difference
Follow us and don't miss out on the latest debates!
Should Animals Be Kept in Zoos? Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Cover Letter
Works cited.
This essay explores the dilemma of keeping animals in zoos. In this essence, the legitimacy of restricting the animals is investigated.
Moreover, the essay seeks to establish harmony between advocacy for abolition of zoos and the need to preserve some species of animals. In addition, there is the necessity to control the interaction between animals and human beings.
I have observed that there is no solution to such dilemmas. Any observer has to establish a middle ground and maintain balance between the arguments. This is because it is not possible to take a radical action on the issue at hand.
I had an experience of arguing over the issue, which has two equal sides while writing the paper. I was able to examine both sides of the argument and analyze the arguments.
While it seemed appropriate to me that people should keep animals in the zoos prior to this assignment, my perception changed after analyzing both sides of the argument. I had to take a middle ground and analyze the perceptions as a neutral observer.
When writing the arguments in the paper, it became difficult to make an objective analysis of the arguments due to the influence of personal opinion. It is difficult to establish a middle ground that does not favor either side.
The topic of the essay generates significant interest in me because most people assume that animals have their specific places in the ecosystem, which are subject to manipulation by human beings at will.
On the other hand, liberal people advocate that fair competition can exist between animals and people naturally. This article proves that neither case is entirely true.
Throughout the history of humanity, interaction with animals has been inevitable. Superiority of human beings has made them highly competitive. Other living things have to adapt to new environments or leave their natural habitat to create space for human beings and their activities.
The human population is evenly distributed around the world. On the other hand, animal population is partially distributed, with different species occupying different parts of the world. Since animals have always fascinated people, there has always been the urge to observe animals and their behavior.
In addition, all living organisms on earth survive through competition for resources with each other (McKinley & Shepard 65). This has led to endangerment of some species of animals. Generally, animals are considered important to human beings, regardless of the material value of each species.
Gradually, it has become important to protect animal species that are facing the danger of extinction, either due to encroachment of their immediate space in the ecosystem, or due to competition with other organisms whose lives depend on common resources.
For this reason, zoos have been built, and animals are kept inside for the sole purpose of preservation of animal life or for entertainment (Norton 42). It is true that the zoos protect a small number of animals from the competition that exists in their natural habitat.
In this way, they protect the species from extinction, and satisfy human being’s curiosity as people go for sightseeing at zoos as a recreational activity (Norton 21).
Most zoos keep wild animals, and majority of the animal population at the zoos is made up of animals that are rarely seen by human beings in their immediate environment. These animals are used to roaming in the jungle and forests.
Others are used to swimming freely in the seas and rivers. However, due to limited space, zoos keep the animals in a much smaller and controlled environment. Obviously, there is restriction of freedom for the animals in order to contain them in the zoo.
For most of their lives, the animals in the zoo do not lead a normal life like other wild animals. They are protected from the competition in the ecosystem due to their perceived importance to human beings. However, this is a serious impediment to their freedom too.
Animals are not allowed to roam freely during the day or night, as they would have done in a free environment. On the other hand, the rigors of competing with other wild animals are eliminated from their lives.
Moreover, the animals receive special treatment as they are provided with veterinary care, a service that other animals in the jungle and sea do not normally get (Robinson 53).
It is arguable that the setting of a zoo is analogous to a prison were felons are incarcerated to protect the society from their potentially harmful tendencies.
One might easily conclude that the animals in the zoo are in some kind of psychological distress due to disruption of their normal course of life and their detainment.
This view assumes that animals, like human beings, have the ability to discern the importance of freedom. Furthermore, the notion argues that animals have thoughts and feelings just like human beings.
It is difficult to establish these arguments as facts due to the limited emotional interaction between animals in the zoo and their keepers.
Thus, the idea that animals perceive physical freedom in a similar way as human beings is subject to debate (Mullan & Marvin 75).
Zoos are not primarily intended to curtail the freedom of an animal, but are designed to protect the animal from harsh environment. Normally, there are efforts to create an environment similar to the particular animal’s habitat in the zoo.
It is also difficult to assess whether the artificial environment created by zookeepers is identical to the natural habitat suitable for the animals.
This observation means that it is not entirely true that the zoos are aimed at curtailing the freedom of the animals (Brooman & Legge 85). Consequently, the animals may be better off at the zoo.
Moreover, it is not true that zoos completely change the normal course of life for the animals within it since there is an effort to simulate their natural habitat.
Some people are of the opinion that animals are inferior to human beings. This suggests that zoos are meant to restrict the animals within the zoo environment to protect human beings’ interest.
Some animals are dangerous to human life, while others compete against human being for resources. This is an obvious observation that has been under scientific study.
On the other hand, animals could be perceived to be equal to human beings. This means that the animals can compete for resources fairly against human beings.
Some people use this perspective to argue against establishment of zoos, which in their perspective, are the making of an unfair competition between animals and human beings.
The highlighted perceptions and observations present the dilemma of the existence of zoos. In a critical analysis of all radical perceptions, no single argument is proved entirely appropriate for the issue of zoos.
If zoos were to be eliminated as a way of protecting and preserving animal life, there would be dire consequences for humans and the animals themselves (Acampora 45).
It is an obvious observation that some animals would become extinct due to predation and competition from other animals in the natural habitat. People could also be affected by the interactions and conflicts between the animals and human beings.
While some animals would pose direct danger to human beings, others would affect the creations of human beings such as organized agriculture. It is thus obvious that a conflict will result from the freedom of animals.
However, this presents another question for argument since there is fairness in sharing of natural resources by living organisms in such a situation.
Although a relatively small number of animals are kept in the zoo, majority of animals are free and live in the wilderness. This brings up the issue of the scale of restriction of animals within zoos.
Keeping all animals in the zoo and eliminating them from their natural environment is an extreme action. This kind of an action would present a situation of extreme interference with nature. It is only logical that a balance between freedom of animals and existence of zoos has to be established.
Animals could be kept in an open environment that is similar to their natural habitat as much as possible. This would eliminated the problem of having animals in a zoo were cages similar to prison cells are used to contain the animals.
On the issue of competition, it would be unfair to let animals live free and compete against human beings in the natural environment. People would eliminate animals from the ecosystem due to their superiority in terms of logical reasoning.
This makes it necessary to provide some kind of protection for the animals. In this essence, zoos can neither be justified nor completely denounced.
Acampora, Ralph R.. Metamorphoses of the zoo: animal encounter after Noah . Lanham, Md.: Lexington Books, 2010. Print.
Brooman, Simon, and Debbie Legge. Law relating to animals . London: Cavendish, 1997. Print.
Mullan, Bob, and Garry Marvin. Zoo culture . 2nd ed. Urbana: University of Illinois Press, 1999. Print.
Norton, Bryan G.. Ethics on the ark: zoos, animal welfare, and wildlife conservation . Washington: Smithsonian Institution Press, 1995. Print.
Robinson, Phillip T.. Life at the zoo: behind the scenes with the animal doctors . New York: Columbia University Press, 2004. Print.
Shepard, Paul, and Daniel McKinley. The subversive science; essays toward an ecology of man, . Boston: Houghton Mifflin, 1969. Print.
- The Effectiveness of Sustainable Practices, Plans, Programs and Initiatives Implemented by Australian Zoo
- The Analysis of Siamangs’ Behavior in a Zoo Setting
- Zoos: Advantages and Disadvantages
- Structural and Non-Structural Mitigation
- Which Material Withstand a Fire
- Prospect Reservoir and Surrounding Areas: An Australian National Heritage Site
- South Wales Region: Energy and Economy
- History of the Great Chicago Fire
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, April 8). Should Animals Be Kept in Zoos? https://ivypanda.com/essays/should-animals-be-kept-in-zoos/
"Should Animals Be Kept in Zoos?" IvyPanda , 8 Apr. 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/should-animals-be-kept-in-zoos/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'Should Animals Be Kept in Zoos'. 8 April.
IvyPanda . 2019. "Should Animals Be Kept in Zoos?" April 8, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/should-animals-be-kept-in-zoos/.
1. IvyPanda . "Should Animals Be Kept in Zoos?" April 8, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/should-animals-be-kept-in-zoos/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Should Animals Be Kept in Zoos?" April 8, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/should-animals-be-kept-in-zoos/.
Are Zoos Ethical? Arguments for and Against Keeping Animals in Zoos
Zoos, if done right, could be a good thing for the animals and the public—yet many so-called zoos get it terribly wrong.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/dorislin2-77cc0f7bb4a34be3ba4644a99f6e6a89.jpeg)
- University of Southern California
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Betsy-Petrick-4x5-70cf94b5a1934c9199bddce1f2457f37.jpg)
- Ohio Wesleyan University
- Brandeis University
- Northeastern University
- Animal Rights
- Endangered Species
A Brief History of Zoos
Arguments for zoos, arguments against zoos, the last word on zoos.
A zoo is a place where captive animals are put on display for humans to see. While early zoos (shortened from zoological parks) concentrated on displaying as many unusual creatures as possible—often in small, cramped conditions—the focus of most modern zoos is conservation and education. While zoo advocates and conservationists argue that zoos save endangered species and educate the public, many animal rights activists believe the cost of confining animals outweighs the benefits, and that the violation of the rights of individual animals—even in efforts to fend off extinction—cannot be justified.
Humans have kept wild animals for thousands of years. The first efforts to keep wild animals for non-utilitarian uses began about 2500 BCE, when rulers in Mesopotamia, Egypt kept collections in enclosed pens. Modern zoos began to evolve during the 18th century and the Age of Enlightenment, when scientific interest in zoology, as well as the study of animal behavior and anatomy, came to the fore.
Early zoos were a dismal affair. Animals were kept in small enclosures with little if any, greenery. With a scant understanding of what the various animals needed, many perished relatively quickly. In accredited U.S. zoos (and elsewhere) things are better now, fortunately. Primates, for example, have gone from barren cages with little furniture to naturalistic and sometimes semi-free-ranging designs. But is it enough?
- By bringing people and animals together, zoos educate the public and foster an appreciation of other species.
- Zoos save endangered species by bringing them into a safe environment, where they are protected from poachers, habitat loss, starvation, and predators.
- Many zoos have breeding programs for endangered species. In the wild, these individuals might have trouble finding mates and breeding, and species could become extinct.
- Some zoos have conservation programs around the world that use the zoo's expertise and funding to help protect wildlife against poaching and other threats.
- Reputable zoos accredited by the Association of Zoos and Aquariums are held to high standards for the treatment of their resident animals. According to AZA, its accreditation guarantees that the organization has undergone strict evaluation by recognized experts to ensure the highest standards of "animal management and care, including living environments, social groupings, health, and nutrition."
- A good zoo provides an enriched habitat in which the animals are never bored, are well cared for, and have plenty of space.
- Seeing an animal in person is a much more personal and more memorable experience than seeing that animal in a nature documentary and is more likely to foster an empathetic attitude toward animals.
- Some zoos help rehabilitate wildlife and take in exotic pets that people no longer want or are no longer able to care for.
- Both accredited and unaccredited animal exhibitors are regulated by the federal Animal Welfare Act, which establishes standards for animal care.
- From an animal rights standpoint, humans do not have a right to breed, capture, and confine other animals— even if those species are endangered . Being a member of an endangered species doesn't mean the individual animals should be afforded fewer rights.
- Animals in captivity suffer from boredom, stress, and confinement. No pen—no matter how humane—or drive-through safari can compare to the freedom of the wild.
- Intergenerational bonds are broken when individuals are sold or traded to other zoos.
- Baby animals bring in visitors and money, but this incentive to breed new baby animals leads to overpopulation. Surplus animals are sold not only to other zoos, but also to circuses and hunting facilities. Some zoos simply kill their surplus animals outright.
- Some captive breeding programs do not release animals back into the wild. The offspring may be forever part of the chain of zoos, circuses, and petting zoos.
- Removing individual specimens from the wild further endangers the wild population because the remaining individuals will be less genetically diverse and may have greater difficulty finding mates. Maintaining species diversity within captive breeding facilities is also a challenge.
- If people want to see wild animals in real life, they can observe wildlife in the wild or visit a sanctuary. (A true sanctuary does not buy, sell, or breed animals, but instead takes in unwanted exotic pets, surplus animals from zoos, or injured wildlife that can no longer survive in the wild.)
- The federal Animal Welfare Act establishes only the most minimal standards for cage size, shelter, health care, ventilation, fencing, food, and water. For example, enclosures must provide "sufficient space to allow each animal to make normal postural and social adjustments with adequate freedom of movement. Inadequate space may be indicated by evidence of malnutrition, poor condition, debility, stress, or abnormal behavior patterns." Violations often result in a slap on the wrist and the exhibitor is given a deadline to correct the violation. Even a long history of inadequate care and AWA violations, such as the history of Tony the Truck Stop Tiger, does not necessarily ensure abused animals will be freed.
- Animals sometimes escape their enclosures, endangering themselves as well as people. Likewise, people ignore warnings or accidentally get too close to animals, leading to horrific outcomes. For example, Harambe, a 17-year-old western lowland gorilla, was shot in 2016 when a toddler accidentally fell into his enclosure at the Cincinnati Zoo. While the child survived and was not badly injured, the gorilla was killed outright.
- Petting zoos have been linked with numerous incidents of diseases including E. coli infection, cryptosporidiosis, salmonellosis, and dermatomycosis (ringworm).
In making a case for or against zoos, both sides argue that they're saving animals. Whether or not zoos benefit the animal community, they certainly do make money. As long as there is demand for them, zoos will continue to exist.
Since zoos are likely an inevitability, the best way to move forward is to ensure that zoo conditions are the best possible for the animals that live in captivity and that individuals who violate animal care health and safety sanctions are not only duly punished but denied any future access to animals.
One day we may look back at zoos and marvel at their barbarity. Or, one day we may look back at zoos and be grateful for the species they saved from extinction. Of these two scenarios, only time will tell.
Hosey, Geoff, et al. Zoo Animals: Behaviour, Management, and Welfare . Oxford University Press. 2013.
Hosey, G. (2023). The History of Primates in Zoos . In: Robinson, L.M., Weiss, A. (eds) Nonhuman Primate Welfare. Springer, Cham.
“ Species Survival Plan Programs .” Association of Zoos & Aquariums.
“ Accreditation Basics .” Association of Zoos & Aquariums .
“ Animal Welfare Act and Animal Welfare Regulations .” U.S. Department of Agriculture .
Meagher, Rebecca K., Georgia J. Mason. “ Environmental Enrichment Reduces Signs of Boredom in Caged Mink .” PLoS ONE , vol. 7, 2012, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0049180
Kleiman, Devra G., et al. Wild Mammals In Captivity: Principles And Techniques For Zoo Management, Second Edition . University of Chicago Press. 2010.
Gunasekera, Crystal Allen. “ The Ethics of Killing “Surplus” Zoo Animals .” Journal of Animal Ethics , vol. 8, 2018, doi:10.5406/janimalethics.8.1.0093
Brichieri-Colombi, Typhenn A., et al. “ Limited Contributions of Released Animals from Zoos to North American Conservation Translocations .” Conservation Biology , vol. 33, 2019, pp. 33-39., doi:10.1111/cobi.13160
Krasnec, Michelle O., et al. “ Mating Systems in Sexual Animals .” Nature Education Knowledge, vol. 3, no. 10, 2012, p. 72.
“ 9 CFR § 3.128 - Space Requirements .” Cornell University Legal Information Institute .
“ Animal Welfare Act Enforcement .” U.S. Department of Agriculture .
Conrad, Cheyenne C. Conrad et al. " Farm Fairs and Petting Zoos: A Review of Animal Contact as a Source of Zoonotic Enteric Disease ." Foodborne Pathogens and Disease, vol. 14, 2017, pp. 59-73., doi:10.1089/fpd.2016.2185
- What's the Difference Between a Zoo and a Sanctuary?
- How Animal Rights Activists View Zoos Keeping Endangered Species
- 6 of the Saddest Zoos in the World
- Zoos and Endangered Species Conservation
- What Is a Puppy Mill? Why Are They Bad for Dogs?
- Arguments for and Against Humane Meat
- Park vs. Refuge: What's the Difference?
- Animal Cruelty in Circuses
- Overview of the Animal Welfare Act
- 20 Pygmy Animal Species From Around the World
- What's Wrong With Aquariums?
- What Will Happen to the Animals If Everyone Goes Vegan
- Expedia Stops Selling Tickets to Dolphin and Whale Shows
- Pet Tiger Seen Roaming in Houston Is Now in a Sanctuary
- Best of Green Awards 2021: Eco Pets
- What Is Sustainable Tourism and Why Is It Important?
- Share full article

Opinion Guest Essay
Modern Zoos Are Not Worth the Moral Cost
Credit... Photographs by Peter Fisher for The New York Times
Supported by
By Emma Marris
Ms. Marris is an environmental writer and the author of the forthcoming book “Wild Souls: Freedom and Flourishing in the Non-Human World.”
- June 11, 2021
After being captives of the pandemic for more than a year, we have begun experiencing the pleasures of simple outings: dining al fresco, shopping with a friend, taking a stroll through the zoo. As we snap a selfie by the sea lions for the first time in so long, it seems worth asking, after our collective ordeal, whether our pleasure in seeing wild animals up close is worth the price of their captivity.
Throughout history, men have accumulated large and fierce animals to advertise their might and prestige. Power-mad men from Henry III to Saddam Hussein’s son Uday to the drug kingpin Pablo Escobar to Charlemagne all tried to underscore their strength by keeping terrifying beasts captive. William Randolph Hearst created his own private zoo with lions, tigers, leopards and more at Hearst Castle. It is these boastful collections of animals, these autocratic menageries, from which the modern zoo, with its didactic plaques and $15 hot dogs, springs.
The forerunners of the modern zoo, open to the public and grounded in science, took shape in the 19th century. Public zoos sprang up across Europe, many modeled on the London Zoo in Regent’s Park. Ostensibly places for genteel amusement and edification, zoos expanded beyond big and fearsome animals to include reptile houses, aviaries and insectariums. Living collections were often presented in taxonomic order, with various species of the same family grouped together, for comparative study.
The first zoos housed animals behind metal bars in spartan cages. But relatively early in their evolution, a German exotic animal importer named Carl Hagenbeck changed the way wild animals were exhibited. In his Animal Park, which opened in 1907 in Hamburg, he designed cages that didn’t look like cages, using moats and artfully arranged rock walls to invisibly pen animals. By designing these enclosures so that many animals could be seen at once, without any bars or walls in the visitors’ lines of sight, he created an immersive panorama, in which the fact of captivity was supplanted by the illusion of being in nature.
Mr. Hagenbeck’s model was widely influential. Increasingly, animals were presented with the distasteful fact of their imprisonment visually elided. Zoos shifted just slightly from overt demonstrations of mastery over beasts to a narrative of benevolent protection of individual animals. From there, it was an easy leap to protecting animal species.
The “educational day out” model of zoos endured until the late 20th century, when zoos began actively rebranding themselves as serious contributors to conservation. Zoo animals, this new narrative went, function as backup populations for wild animals under threat, as well as “ambassadors” for their species, teaching humans and motivating them to care about wildlife. This conservation focus “ must be a key component ” for institutions that want to be accredited by the Association of Zoos and Aquariums, a nonprofit organization that sets standards and policies for facilities in the United States and 12 other countries.
This is the image of the zoo I grew up with: the unambiguously good civic institution that lovingly cared for animals both on its grounds and, somehow, vaguely, in their wild habitats. A few zoos are famous for their conservation work. Four of the zoos and the aquarium in New York City, for instance, are managed by the Wildlife Conservation Society, which is involved in conservation efforts around the world. But this is not the norm.
While researching my book on the ethics of human interactions with wild species, “Wild Souls,” I examined how, exactly, zoos contribute to the conservation of wild animals.
A.Z.A. facilities report spending approximately $231 million annually on conservation projects. For comparison, in 2018, they spent $4.9 billion on operations and construction. I find one statistic particularly telling about their priorities: A 2018 analysis of the scientific papers produced by association members between 1993 and 2013 showed that just about 7 percent of them annually were classified as being about “biodiversity conservation.”
Zoos accredited by the A.Z.A. or the European Association of Zoos and Aquaria have studbooks and genetic pedigrees and carefully breed their animals as if they might be called upon at any moment to release them, like Noah throwing open the doors to the ark, into a waiting wild habitat. But that day of release never quite seems to come.
There are a few exceptions. The Arabian oryx, an antelope native to the Arabian Peninsula, went extinct in the wild in the 1970s and then was reintroduced into the wild from zoo populations. The California condor breeding program, which almost certainly saved the species from extinction, includes five zoos as active partners. Black-footed ferrets and red wolves in the United States and golden lion tamarins in Brazil — all endangered, as well — have been bred at zoos for reintroduction into the wild. An estimated 20 red wolves are all that remain in the wild.
The A.Z.A. says that its members host “more than 50 reintroduction programs for species listed as threatened or endangered under the Endangered Species Act.” Nevertheless, a vast majority of zoo animals (there are 800,000 animals of 6,000 species in the A.Z.A.’s zoos alone ) will spend their whole lives in captivity, either dying of old age after a lifetime of display or by being culled as “surplus.”
The practice of killing “surplus” animals is kept quiet by zoos, but it happens, especially in Europe. In 2014, the director of the E.A.Z.A. at the time estimated that between 3,000 and 5,000 animals are euthanized in European zoos each year. (The culling of mammals specifically in E.A.Z.A. zoos is “usually not more than 200 animals per year,” the organization said.) Early in the pandemic, the Neumünster Zoo in northern Germany coolly announced an emergency plan to cope with lost revenue by feeding some animals to other animals, compressing the food chain at the zoo like an accordion, until in the worst-case scenario, only Vitus, a polar bear, would be left standing. The A.Z.A.’s policies allow for the euthanasia of animals, but the president of the association, Dan Ashe, told me, “it’s very rarely employed” by his member institutions.
Mr. Ashe, a former director of the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, suggested that learning how to breed animals contributes to conservation in the long term, even if very few animals are being released now. A day may come, he said, when we need to breed elephants or tigers or polar bears in captivity to save them from extinction. “If you don’t have people that know how to care for them, know how to breed them successfully, know how to keep them in environments where their social and psychological needs can be met, then you won’t be able to do that,” he said.
The other argument zoos commonly make is that they educate the public about animals and develop in people a conservation ethic. Having seen a majestic leopard in the zoo, the visitor becomes more willing to pay for its conservation or vote for policies that will preserve it in the wild. What Mr. Ashe wants visitors to experience when they look at the animals is a “sense of empathy for the individual animal, as well as the wild populations of that animal.”
I do not doubt that some people had their passion for a particular species, or wildlife in general, sparked by zoo experiences. I’ve heard and read some of their stories. I once overheard two schoolchildren at the Smithsonian’s National Zoo in Washington confess to each other that they had assumed that elephants were mythical animals like unicorns before seeing them in the flesh. I remember well the awe and joy on their faces, 15 years later. I’d like to think these kids, now in their early 20s, are working for a conservation organization somewhere. But there’s no unambiguous evidence that zoos are making visitors care more about conservation or take any action to support it. After all, more than 700 million people visit zoos and aquariums worldwide every year, and biodiversity is still in decline.

In a 2011 study , researchers quizzed visitors at the Cleveland, Bronx, Prospect Park and Central Park zoos about their level of environmental concern and what they thought about the animals. Those who reported “a sense of connection to the animals at the zoo” also correlated positively with general environmental concern. On the other hand, the researchers reported, “there were no significant differences in survey responses before entering an exhibit compared with those obtained as visitors were exiting.”
A 2008 study of 206 zoo visitors by some members of the same team showed that while 42 percent said that the “main purpose” of the zoo was “to teach visitors about animals and conservation,” 66 percent said that their primary reason for going was “to have an outing with friends or family,” and just 12 percent said their intention was “to learn about animals.”
The researchers also spied on hundreds of visitors’ conversations at the Bronx Zoo, the Brookfield Zoo outside Chicago and the Cleveland Metroparks Zoo. They found that only 27 percent of people bothered to read the signs at exhibits. More than 6,000 comments made by the visitors were recorded, nearly half of which were “purely descriptive statements that asserted a fact about the exhibit or the animal.” The researchers wrote , “In all the statements collected, no one volunteered information that would lead us to believe that they had an intention to advocate for protection of the animal or an intention to change their own behavior.”
People don’t go to zoos to learn about the biodiversity crisis or how they can help. They go to get out of the house, to get their children some fresh air, to see interesting animals. They go for the same reason people went to zoos in the 19th century: to be entertained.
A fine day out with the family might itself be justification enough for the existence of zoos if the zoo animals are all happy to be there. Alas, there’s plenty of heartbreaking evidence that many are not.
In many modern zoos, animals are well cared for, healthy and probably, for many species, content. Zookeepers are not mustache-twirling villains. They are kind people, bonded to their charges and immersed in the culture of the zoo, in which they are the good guys.
But many animals clearly show us that they do not enjoy captivity. When confined they rock, pull their hair and engage in other tics. Captive tigers pace back and forth, and in a 2014 study, researchers found that “the time devoted to pacing by a species in captivity is best predicted by the daily distances traveled in nature by the wild specimens.” It is almost as if they feel driven to patrol their territory, to hunt, to move, to walk a certain number of steps, as if they have a Fitbit in their brains.
The researchers divided the odd behaviors of captive animals into two categories: “impulsive/compulsive behaviors,” including coprophagy (eating feces), regurgitation, self-biting and mutilation, exaggerated aggressiveness and infanticide, and “stereotypies,” which are endlessly repeated movements. Elephants bob their heads over and over. Chimps pull out their own hair. Giraffes endlessly flick their tongues. Bears and cats pace. Some studies have shown that as many as 80 percent of zoo carnivores, 64 percent of zoo chimps and 85 percent of zoo elephants have displayed compulsive behaviors or stereotypies.
Elephants are particularly unhappy in zoos, given their great size, social nature and cognitive complexity. Many suffer from arthritis and other joint problems from standing on hard surfaces; elephants kept alone become desperately lonely; and all zoo elephants suffer mentally from being cooped up in tiny yards while their free-ranging cousins walk up to 50 miles a day. Zoo elephants tend to die young. At least 20 zoos in the United States have already ended their elephant exhibits in part because of ethical concerns about keeping the species captive.
Many zoos use Prozac and other psychoactive drugs on at least some of their animals to deal with the mental effects of captivity. The Los Angeles Zoo has used Celexa, an antidepressant, to control aggression in one of its chimps. Gus, a polar bear at the Central Park Zoo, was given Prozac as part of an attempt to stop him from swimming endless figure-eight laps in his tiny pool. The Toledo Zoo has dosed zebras and wildebeest with the antipsychotic haloperidol to keep them calm and has put an orangutan on Prozac. When a female gorilla named Johari kept fighting off the male she was placed with, the zoo dosed her with Prozac until she allowed him to mate with her. A 2000 survey of U.S. and Canadian zoos found that nearly half of respondents were giving their gorillas Haldol, Valium or another psychopharmaceutical drug.
Some zoo animals try to escape. Jason Hribal’s 2010 book, “Fear of the Animal Planet,” chronicles dozens of attempts. Elephants figure prominently in his book, in part because they are so big that when they escape it generally makes the news.
Mr. Hribal documented many stories of elephants making a run for it — in one case repairing to a nearby woods with a pond for a mud bath. He also found many examples of zoo elephants hurting or killing their keepers and evidence that zoos routinely downplayed or even lied about those incidents.
Elephants aren’t the only species that try to flee a zoo life. Tatiana the tiger, kept in the San Francisco Zoo, snapped one day in 2007 after three teenage boys had been taunting her. She somehow got over the 12-foot wall surrounding her 1,000-square-foot enclosure and attacked one of the teenagers, killing him. The others ran, and she pursued them, ignoring all other humans in her path. When she caught up with the boys at the cafe, she mauled them before she was shot to death by the police. Investigators found sticks and pine cones inside the exhibit, most likely thrown by the boys.
Apes are excellent at escaping. Little Joe, a gorilla, escaped from the Franklin Park Zoo in Boston twice in 2003. At the Los Angeles Zoo, a gorilla named Evelyn escaped seven times in 20 years. Apes are known for picking locks and keeping a beady eye on their captors, waiting for the day someone forgets to lock the door. An orangutan at the Omaha Zoo kept wire for lock-picking hidden in his mouth. A gorilla named Togo at the Toledo Zoo used his incredible strength to bend the bars of his cage. When the zoo replaced the bars with thick glass, he started methodically removing the putty holding it in. In the 1980s, a group of orangutans escaped several times at the San Diego Zoo. In one escape, they worked together: One held a mop handle steady while her sister climbed it to freedom. Another time, one of the orangutans, Kumang, learned how to use sticks to ground the current in the electrical wire around her enclosure. She could then climb the wire without being shocked. It is impossible to read these stories without concluding that these animals wanted out .
“I don’t see any problem with holding animals for display,” Mr. Ashe told me. “People assume that because an animal can move great distances that they would choose to do that.” If they have everything they need nearby, he argued, they would be happy with smaller territories. And it is true that the territory size of an animal like a wolf depends greatly on the density of resources and other wolves. But then there’s the pacing, the rocking. I pointed out that we can’t ask animals whether they are happy with their enclosure size. “That’s true,” he said. “There is always that element of choice that gets removed from them in a captive environment. That’s undeniable.” His justification was philosophical. In the end, he said, “we live with our own constraints.” He added, “We are all captive in some regards to social and ethical and religious and other constraints on our life and our activities.”
What if zoos stopped breeding all their animals, with the possible exception of any endangered species with a real chance of being released back into the wild? What if they sent all the animals that need really large areas or lots of freedom and socialization to refuges? With their apes, elephants, big cats, and other large and smart species gone, they could expand enclosures for the rest of the animals, concentrating on keeping them lavishly happy until their natural deaths. Eventually, the only animals on display would be a few ancient holdovers from the old menageries, animals in active conservation breeding programs and perhaps a few rescues.
Such zoos might even be merged with sanctuaries, places that take wild animals that because of injury or a lifetime of captivity cannot live in the wild. Existing refuges often do allow visitors, but their facilities are really arranged for the animals, not for the people. These refuge-zoos could become places where animals live. Display would be incidental.
Such a transformation might free up some space. What could these zoos do with it, besides enlarging enclosures? As an avid fan of botanical gardens, I humbly suggest that as the captive animals retire and die off without being replaced, these biodiversity-worshiping institutions devote more and more space to the wonderful world of plants. Properly curated and interpreted, a well-run garden can be a site for a rewarding “outing with friends or family,” a source of education for the 27 percent of people who read signs and a point of civic pride.
I’ve spent many memorable days in botanical gardens, completely swept away by the beauty of the design as well as the unending wonder of evolution — and there’s no uneasiness or guilt. When there’s a surplus, you can just have a plant sale.
Emma Marris is an environmental writer and the author of the forthcoming book “Wild Souls: Freedom and Flourishing in the Non-Human World.”
Photographs by Peter Fisher. Mr. Fisher is a photographer based in New York.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow The New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Twitter (@NYTopinion) and Instagram .
Advertisement
- Future Perfect
Zoos aren’t for animals. They’re for us.
Zoos say they’re leaders in protecting wildlife. But is it true?
by Kenny Torrella

This week, a leading wildlife conservation group declared that zoos play an essential role in protecting wild species from extinction.
“Zoos, aquariums and botanic gardens are critical conservation partners, and their role should not be under-valued, under-recognized or misunderstood,” the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), a nonprofit that’s assessed extinction threat levels for more than 150,000 species, announced in a new position statement . “For anyone who questions the value of zoos in the modern age, IUCN’s position is clear — zoos are essential.”
It’s a bold statement from an authoritative voice on wildlife protection, but is it true? An examination of how zoos spend their money suggests that, despite branding themselves as champions of conservation, they devote far more resources to their main, original prerogative: confining animals for entertainment and profit.
Sign up for the Future Perfect newsletter
Twice a week, we’ll send you a roundup of the best ideas and solutions for tackling the world’s biggest challenges — and how to get better at doing good. Sign up here .
“The way that zoos have been trying to justify their existence for quite a few years now is pointing to conservation,” said Delcianna Winders, director of the Animal Law and Policy Institute at Vermont Law and Graduate School. “But the reality is that it’s really a very small fraction of their funding that is going to field conservation.” (Disclosure: This summer, I attended a media fellowship program at Vermont Law and Graduate School.)
In 2022, most of the 238 zoos and aquariums accredited by the nonprofit Association of Zoos and Aquariums (AZA) spent a collective $252 million on field conservation — efforts to protect and preserve wildlife habitats. That’s serious money for the broader conservation movement.
“That puts them collectively among the world’s largest contributors to conservation,” Daniel Ashe, president and CEO of the AZA, told Vox. However, it’s just 5 percent of how much zoos and aquariums spent on operations and construction alone in 2018.
Similarly, an analysis of scientific papers published by AZA member institutions from 1993 to 2013 found that only 7 percent were related to biodiversity conservation.
Zoos argue that in addition to their conservation efforts in the field, their very existence contributes to species conservation. By breeding animals in captivity, and preserving their genetic material in “ biobanks ,” the argument goes, they’ve created a stock of animals — known as “insurance populations” — who could be released back into nature if wild populations dwindle to alarming levels.
Emma Marris, an environmental writer and author of Wild Souls: Freedom and Flourishing in the Non-Human World , wrote in a 2021 New York Times opinion piece that it’s “as if they might be called upon at any moment to release them, like Noah throwing open the doors to the ark, into a waiting wild habitat. But that day of release never quite seems to come.”
“I’m very skeptical that a lot of these captive breeding programs have any practical relevance to conserving species in their natural habitat, which, in my view, is the point of conservation,” said Mickey Pardo, a behavioral ecologist and postdoctoral research fellow at Colorado State University who studies elephants in the wild. The reason, Pardo says, is because reintroduction stemming from captive breeding programs is incredibly challenging and thus rare , and it’s not the primary goal of most captive breeding programs to begin with.
There are some exceptions , Marris notes, in which zoos have played a starring role in reintroducing threatened and endangered species to the wild, including the California condor, the Arabian oryx, and Black-footed ferrets, among others. Ashe told me zoos have played a role in dozens and dozens of reintroduction programs, though he didn’t have a specific number. It’s important work and should be celebrated, as should zoos’ contributions to field conservation. But, Pardo says, it doesn’t justify AZA-accredited zoos and aquariums keeping wild animals in captivity who are not part of any current reintroduction program nor likely to become part of one in the future.
Currently, AZA-accredited zoos and aquariums have about 780,000 animals .

Kira Mileham, IUCN’s global director of strategic partnerships, disagrees with the argument that field conservation is all that matters. Mileham told Vox captive breeding programs at zoos do more than just create insurance populations, and that they contribute to field conservation by providing opportunities for researchers to learn about species’ behavior, nutrition, veterinary needs, and more. Mileham added that zoos also play an important role in temporary rescue and “ head start ” efforts by, say, taking animals and/or their eggs that are facing a serious, temporary threat out of the wild, and then returning them when it’s safe.
Zoos undeniably do some good work for species conservation; however, that work can obscure their dark side: the suffering of animals in captivity.
Life at the zoo
Animals who, in their natural habitats, would travel great distances are resigned to living in film-set versions of lush rainforests and vast savannas while surrounded by city noise. As a result of the lack of stimulation and small environments, some animals will develop “stereotypic” behavior , in which they engage in repetitive motions that are rare in the wild.
Researchers call it “zoochosis,” a play on “psychosis,” though making enclosures a little nicer and providing “enrichment activities” to animals both help, as do pharmaceutical drugs .
There was Gus, the Central Park Zoo polar bear who would swim figure eights in his pool for sometimes up to 12 hours a day (his enclosure was just 0.00009 percent of his range in the wild), and Sukari , the giraffe at Roger Williams Park Zoo in Providence, Rhode Island, who for hours would lick steel cables, walls, and gates. Other animals pace, rock back and forth, and head-bob, or engage in self-harm, like pulling out their hair or biting themselves. There are many stories of escape attempts.

Despite it all, AZA-accredited zoos keep acquiring more animals, either from other zoos, breeding them on their own, taking them from the wild (how 80 percent of animals at AZA-accredited aquariums are acquired, Ashe told me), as rescues, or from a number of other sources, such as private breeders and hunting ranches.
Mileham refutes the notion that many zoos are just acquiring animals at the expense of their welfare, however: “I don’t think [leading zoos] kind of flippantly trade off the welfare of species for the sake of having them in their facilities,” she said. And not every welfare matter is black and white, Mileham said. For instance, some animals in zoos might have come from areas with high levels of conflict with humans. “We can’t pretend that an animal in the wild always has a perfect life and has no welfare compromises just because they happen to not be in human care.”
Ashe assured me that “when you see animals at AZA member institutions, you’re seeing animals that are thriving there.” He went on to say, “I understand some people just don’t like the idea of any animal in a state of confinement, and in those cases, we just have a fundamental disagreement.”
When Marris asked Ashe about the constraints of captivity, Ashe largely shrugged the problem away, saying that, well, everyone has constraints put on them: “We are all captive in some regards to social and ethical and religious and other constraints on our life and our activities.”
I asked Ashe about this quote, and he said, “It’s factually true — we all live with constraint in our social life and we agree to constraint so we have social order.” He’s right, of course, that it’s true for humans, but there’s a glaring omission in his response: Animals can’t agree to the constraints we impose on them.
I can’t think of a more dissatisfying answer to the ethical dilemma of putting hundreds of thousands of wild animals behind glass. But it does reveal that the ideology undergirding earlier zoos and aquariums largely persists today — that animals are here for us, not with us.
Zoos: What are they good for?
Zoos justify their existence not just through conservation, but also by their educational work. Their actual impact in that domain, however, is likely minor.
The AZA says one of the “superpowers” of its 238 accredited zoos and aquariums is that they have “the opportunity to influence and inspire the 200 million people who visit every year.” On its face, it makes sense: If everyone could just see the beauty of the animal kingdom up close and learn about the plight of threatened species, they might be inspired to support or get involved in conservation work. Surely, zoos have that effect on some, but there’s no evidence it’s the case for many.
On the contrary , most people don’t read the educational plaques at zoos, and according to polls of zoo-goers, most go to spend time with friends or family — to enjoy themselves and be entertained, not to learn about animals and their needs. One study found the level of environmental concern reported by attendees before they entered the zoo was similar to those who were polled at the exits.
While the educational value of zoos is dubious, there’s certainly one message zoo-goers receive, if only implicitly: That it’s perfectly fine, even good , to put wild animals on display in tiny enclosures for the public’s leisure. In other words, animals — even if they’re suffering right in front of us — can be objects of entertainment.
“It’s rooted in this notion that yes, we have this privileged right to observe these animals at any cost to [them] or to their species more generally, and it’s deeply troubling,” Winders said.
The idea that we must exploit some animals in order to protect others creates a bizarre false choice, even when there are much more humane paths taken by others in the wildlife protection movement, like animal sanctuaries .
What a more humane zoo could look like
Animal sanctuaries are like zoos in that they’re large properties where animals live in captivity, but they differ in every other way. For one, animals in sanctuaries tend to have far more space than animals in zoos, and they’re there to live on their own terms, not to be put on display for an entrance fee. Some sanctuaries are not open to the public, while others conduct small tours or have much smaller attendance numbers than the typical zoo. (Beware, however, that many operations call themselves sanctuaries but in reality are more like petting zoos .)
The Wild Animal Sanctuary, a 45-minute drive from Denver, Colorado, provides a compelling example of how animals can better coexist with visitors. The 1,214-acre operation, home to rescued bears, tigers, lions, wolves, and other species, was closed to the public for its first 20 years. But in the early 2000s, it began to open up to visitors, who can only see the animals from the sanctuary’s observation decks and more than 1.5 miles of elevated walkways, causing less disturbance than zoo-goers.

Animals typically wind up in sanctuaries — the ethical kind, at least — because they were abandoned or injured, rather than bred, purchased, or taken from the wild. The Global Federation of Animal Sanctuaries, the animal sanctuary world’s equivalent to the Association of Zoos and Aquariums, takes the position that captive breeding is only permitted if it’s done for eventual reintroduction into the wild — unlike zoos, which largely breed animals as insurance populations and to keep a steady supply to put on display.
Some critics have called for zoos to phase out keeping animals from species that aren’t either critically endangered or extinct in the wild, or for which there’s no viable reintroduction program. Additionally, they argue, urban zoos should either close down or set limits on how many animals they keep.
I would add one more thing that zoos — and sanctuaries, for that matter — could do: Stop serving meat and dairy in their cafeterias. There’s the painfully obvious point that an institution whose mission is to protect animals probably shouldn’t sell animal meat . But there’s also this: One-third of Earth’s habitable land is devoted to cattle grazing and growing corn and soy to feed farmed animals, which has resulted in mass habitat loss for wildlife and crashing biodiversity levels. Meat production is the leading cause of global deforestation , and thus the leading threat to wildlife habitats.
Reforming zoos won’t be easy, and arguably, a lot of conservation dollars might vanish if zoos looked different. But it says something about the conservation movement, and us, if one of the best ways to raise funds for wild animals is to put them in captivity. I don’t have the answers for how the conservation movement could supercharge its funding in lieu of the significant amount of funding zoos provide, but I think it’s clear, as Marris puts it, that zoos are not worth the moral cost .
As our understanding of animal sentience and their capacity for suffering has grown, our economy has slowly adapted. Fashion designers are replacing leather and fur with animal-free textiles, meat companies are now selling plant-based nuggets and burgers, and in 2018, the traveling circus Ringling Bros. and Barnum & Bailey announced it would stop using animals, such as lions, tigers, and bears, in its shows. Zoos, too, could reinvent themselves for a more enlightened age by focusing on what animals need, not what the public wants to do on a Saturday afternoon.
Most Popular
10 big things we think will happen in the next 10 years, this changed everything, take a mental break with the newest vox crossword, how the self-care industry made us so lonely, israel is not fighting for its survival, today, explained.
Understand the world with a daily explainer plus the most compelling stories of the day.
More in Future Perfect

This changed everything

This article is OpenAI training data

Big Milk has taken over American schools

The bizarre link between rising sea levels and complications in pregnancy

Expecting worse: Giving birth on a planet in crisis

Why North Korea dumped trash on South Korea

8 surprising reasons to stop hating cicadas and start worshipping them

Is a ceasefire in Gaza actually close?

You can help reverse the overdose epidemic Video

What to know about Claudia Sheinbaum, Mexico’s next president
Search form
Are zoos a good thing.

How do you feel about keeping animals in zoos? Read both sides of the argument to help you decide.
Instructions
Do the preparation exercise first. Then read the text and do the other exercises.
Preparation
Zoos are hugely popular attractions for adults and children alike. But are they actually a good thing?
Critics of zoos would argue that animals often suffer physically and mentally by being enclosed. Even the best artificial environments can't come close to matching the space, diversity, and freedom that animals have in their natural habitats. This deprivation causes many zoo animals to become stressed or mentally ill. Capturing animals in the wild also causes much suffering by splitting up families. Some zoos make animals behave unnaturally: for example, marine parks often force dolphins and whales to perform tricks. These mammals may die decades earlier than their wild relatives, and some even try to commit suicide.
On the other hand, by bringing people and animals together, zoos have the potential to educate the public about conservation issues and inspire people to protect animals and their habitats. Some zoos provide a safe environment for animals which have been mistreated in circuses, or pets which have been abandoned. Zoos also carry out important research into subjects like animal behaviour and how to treat illnesses.
One of the most important modern functions of zoos is supporting international breeding programmes, particularly for endangered species. In the wild, some of the rarest species have difficulty in finding mates and breeding, and they might also be threatened by poachers, loss of their habitat and predators. A good zoo will enable these species to live and breed in a secure environment. In addition, as numbers of some wild species drop, there is an increased danger of populations becoming too genetically similar. Breeding programmes provide a safeguard: zoo-bred animals can be released into the wild to increase genetic diversity.
However, opponents of zoos say that the vast majority of captive breeding programmes do not release animals back into the wild. Surplus animals are sold not only to other zoos but also to circuses or hunting ranches in the US or South Africa, where some people are willing to pay a lot of money for the chance to kill an animal in a fenced enclosure. Often, these animals are familiar with humans and have very little chance of escaping.
So, are zoos good for animals or not? Perhaps it all depends on how well individual zoos are managed, and the benefits of zoos can surely outweigh their harmful effects. However, it is understandable that many people believe imprisoning animals for any reason is simply wrong.
Check your understanding: true or false
Check your vocabulary: gap fill, worksheets and downloads.
What do you think about zoos? Are they a good thing, or is it cruel to keep animals in captivity?

Sign up to our newsletter for LearnEnglish Teens
We will process your data to send you our newsletter and updates based on your consent. You can unsubscribe at any time by clicking the "unsubscribe" link at the bottom of every email. Read our privacy policy for more information.
- Skip to Nav
- Skip to Main
- Skip to Footer
Are Zoos Good or Bad for Animals?
Please try again
Zoos are great, right? You get to be up close and personal with some amazing animals that you’d pretty much never get to see in the wild. Clearly, zoos are a win for people. But when it comes to the animals, zoos might cause more harm than good. Should zoos exist?
TEACHERS: Guide your students to practice civil discourse about current topics and get practice writing CER (claim, evidence, reasoning) responses. Explore lesson supports.
How did zoos become a thing? Humans have been capturing and displaying exotic animals for thousands of years. The earliest known collections date back to 3500 BCE in Egypt, where rulers kept hippos, elephants, baboons, and different species of large cats. Now back then, that didn’t mean that your average Egyptian could go check any of that awesomeness out. These early zoos were really just a way for kings to flex on other kings. Modern zoos, where the public can come and watch animals exhibiting their natural behavior, didn’t really become a thing until the early 1800s. The longest continuously operating zoo in the world is the Vienna Zoo, which has been going strong for more than 260 years.
What are the arguments in favor of having zoos? Zoos may be great entertainment, but their big goal is to educate the public about wildlife and what we can do to protect them. Zoo animals are sort of like ambassadors for their counterparts in the wild. Zoos also contribute to scientific research. “Zoo” is short for zoological park, and zoology is the scientific study of animal biology and behavior. In addition, zoos work really hard to save animals that are threatened in the wild. Zoos can take at-risk animals, breed them in captivity, and then reintroduce them back into the wild.
What are the arguments for NOT having zoos? Zoos have their problems. Not all zoos are created equal. Some are clean and well staffed, others aren’t. There are some in the richest cities in the world, and there are some in conflict zones. What this means is that not all zoos have the resources to properly care for the animals they house. And for many critics, no amount of education or research justifies keeping animals captive. That captivity can be REALLY bad for both physical AND psychological health. And while zoos have been really helpful is saving endangered animals, it doesn’t work out for certain species. For example, most large carnivores like lions and tigers that are bred in captivity die when released into the wild. It turns out that they haven’t developed the natural behaviors they need when they’re out on their own and have to fend for themselves.
SOURCES: Do we need zoos? (The Atlantic) https://www.theatlantic.com/news/archive/2016/06/harambe-zoo/485084/
Why zoos are good (The Guardian) https://www.theguardian.com/science/lost-worlds/2014/aug/19/why-zoos-are-good
The case for the end of the modern zoo (New York Magazine) http://nymag.com/intelligencer/2014/07/case-for-the-end-of-the-modern-zoo.html?gtm=bottom
Zoos and their discontents (New York Times Magazine) https://www.nytimes.com/2014/07/06/magazine/zoo-animals-and-their-discontents.html
Stress and lack of exercise are killing elephants, zoos warned (The Guardian) https://www.theguardian.com/science/2008/dec/12/elephants-animal-welfa re
Most Captive-Born Predators Die If Released (National Geographic) https://www.nationalgeographic.com/animals/2008/01/predators-captivity-habitat-animals/
Captive Breeding Success Stories (PBS) https://www.pbs.org/wnet/nature/the-loneliest-animals-captive-breeding-success-stories/4920/
Quantifying the contribution of zoos and aquariums to peer-reviewed scientific research (Facets Journal) https://www.facetsjournal.com/doi/pdf/10.1139/facets-2017-0083
Evaluating the contribution of zoos and aquariums (Conservation Biology) https://warwick.ac.uk/fac/soc/sociology/staff/jensen/ericjensen/moss_jensen_and_gusset_2015-evaluating_the_contribution_of_zoos_and_aquariums_to_aichi_biodiversity_target_1_final_published_version.pdf
To learn more about how we use your information, please read our privacy policy.
There is a moral argument for keeping great apes in zoos

Michael Gwyther Jones/Flickr
by Richard Moore + BIO

I get apprehensive whenever someone asks me about my job. I’m a philosopher who works on the question of how language evolved, I reply. If they probe any further, I tell them that I work with the great apes at Leipzig zoo. But some people, I’ve discovered, have big problems with zoos.
Plenty of philosophers and primatologists agree with them. Even the best zoos force animals to live in confined spaces, they say , which means the animals must be bored and stressed from being watched all the time. Other critics claim that zoos are wrong even if the creatures aren’t suffering, because being held captive for human entertainment impugns their dignity. Such places ‘are for us rather than for animals’, the philosopher Dale Jamieson has written , and ‘they do little to help the animals we are driving to extinction’.
But I want to defend the value of zoos. Yes, some of them should certainly be closed. We’ve seen those terrible videos of solitary apes or tigers stalking barren cages in shopping malls in Thailand or China. However, animals have a good quality of life in many zoos, and there’s a strong moral case for why these institutions ought to exist. I’ve come to this view after working with great apes, and it might not extend to all species equally. However, since great apes are both cognitively sophisticated and human-like in their behaviour, they offer a strong test case for evaluating the morality of zoos in general.
The research my colleagues and I conduct isn’t harmful to the animals and, if it goes well, it will help us get a better grasp on the cognitive differences between humans and apes. For example, we did a study with pairs of orangutans in which we tested their ability to communicate and cooperate to get rewards. We hid a banana pellet so that one orangutan could see the food but couldn’t reach it. The other orangutan could release a sliding door and push the pellet through to her partner, but wasn’t able to take it for herself. They did okay (but not great) when playing with me, and they mostly ignored each other when playing together. We then performed a similar set of studies with human two-year-olds. Compared with the apes, the two-year-olds were very good at getting the reward (stickers) when they played with an adult.
Taken together, these studies tell us something about human evolution. Unlike apes, humans are good at pooling their talents to achieve what they can’t do alone. It’s not that the apes don’t care about getting the food – they got frustrated with one another when things were going wrong, and one orangutan in particular would turn his back and sulk. However, unlike humans, they don’t seem to be able to harness this frustration to push themselves to do better.
The value of research aside, there’s an argument for zoos on the grounds of animal welfare. In the best zoos, such as Leipzig, great apes live in spacious enclosures modelled on their natural habitats, and are looked after by zookeepers who care about them deeply. Large jungle gyms keep them stimulated and stave off boredom; they’re also kept busy with ‘enrichment’ puzzles, which they can unlock with tools to get food. Zoos recognised by the two main accrediting bodies in Europe and the United States are rigorously vetted and required to take part in education and conservation programmes. And there’s no solid evidence that apes living in well-designed enclosures get stressed or disturbed by human observation.
Of course, zoos can’t provide their animals with conditions such as those in an untouched forest. But for the great apes in captivity, there’s rarely a viable alternative. There are estimated to be more than 4,000 great apes living in zoos worldwide. Most of the regions where they are found in the wild – orangutans in Indonesia, chimpanzees and gorillas in Central and West Africa, bonobos in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) – are ravaged by habitat loss, civil war, hunting and disease. As few as 880 remaining mountain gorillas survive, in two small groups in the eastern reaches of the DRC, while orangutan habitats have declined 80 per cent in the past 20 years. While some conservationists dream of rehoming zoo apes in the wild, these vanishing forests mean that it’s rarely feasible. The orangutans in Leipzig are certainly better off than they would be trying to survive in forests razed to make way for palm-oil plantations.
Since zoo apes cannot be returned to their natural environments, specialised sanctuaries are another option. But these require large plots of land that are both safe and uninhabited by existing populations, and such locations are scarce. As things stand, sanctuaries are already struggling to survive because they’re almost exclusively dependent on charitable donations. And most of them are full. In Africa and Indonesia, inhabitants are typically orphans that have been taken from the forest by hunters or palm-oil workers, who kill larger apes and kidnap the babies to sell or keep as pets. Elsewhere, sanctuaries are overflowing with retired lab apes or rescued pets. These institutions lack the capacity to accommodate the thousands of apes currently living in zoos, let alone the money that would be needed to support them.
Given the obstacles and the great expense of rehoming apes, very few places try to do so. Damian Aspinall of Howletts Wild Animal Park in England leads one of the few programmes that release gorillas back into the wild, by taking them to a protected reserve in Gabon. His intentions are heroic and hopefully the plan will succeed. Some gorillas have resettled well. But the results so far have been mixed; in 2014, five members of a family of 11 were found dead within a month of their release. We also don’t really know whether zoo-born apes possess the skills they need to survive, including the ability to retrieve different local foods, and knowledge of edible plants. Young apes learn these skills in the wild by watching the knowledgeable adults around them – but that’s an opportunity that creatures in captivity simply don’t have.
Now, all of this isn’t necessarily an ethical argument for continuing to breed apes in zoos. You might argue that if we can’t save the apes already in captivity, we should at least end breeding programmes and let the existing populations die out. However, captive breeding helps preserve the genetic diversity of endangered species. Moreover, research shows that visiting zoos makes people more likely to support conservation efforts – an effect that’s amplified by more naturalistic enclosures. So first-person encounters in zoos serve to educate visitors about the incredible lives animals lead, and to raise money for wild conservation programmes.
Allowing the ape populations in zoos to wither assumes – without justification – that their current lives are so bad as to be not worth living. It also risks inflicting harm. Boredom is a real risk for zoo animals, and it’s widely believed (although not yet scientifically established) that the presence of infants brings both interest and happiness to the families. Mixed-aged groups create collective dynamics that more closely resemble those in the wild. If we care about the welfare of captive apes, we should allow them to breed – at least in controlled ways.
One day, the prospect of returning captive apes to their natural habitats or housing them in well-funded, spacious sanctuaries might be realistic. Currently, it is not. Instead of condemning zoos, we should dedicate our efforts to supporting them: to pushing bad zoos to reform or close; to funding more research into the welfare of captive animals; and to encouraging all zoos to strive to do more for their inhabitants. That way, perhaps, I will no longer need to shy away from telling strangers what I do.
Computing and artificial intelligence
Algorithms associating appearance and criminality have a dark past
Catherine Stinson

Childhood and adolescence
For a child, being carefree is intrinsic to a well-lived life
Luara Ferracioli
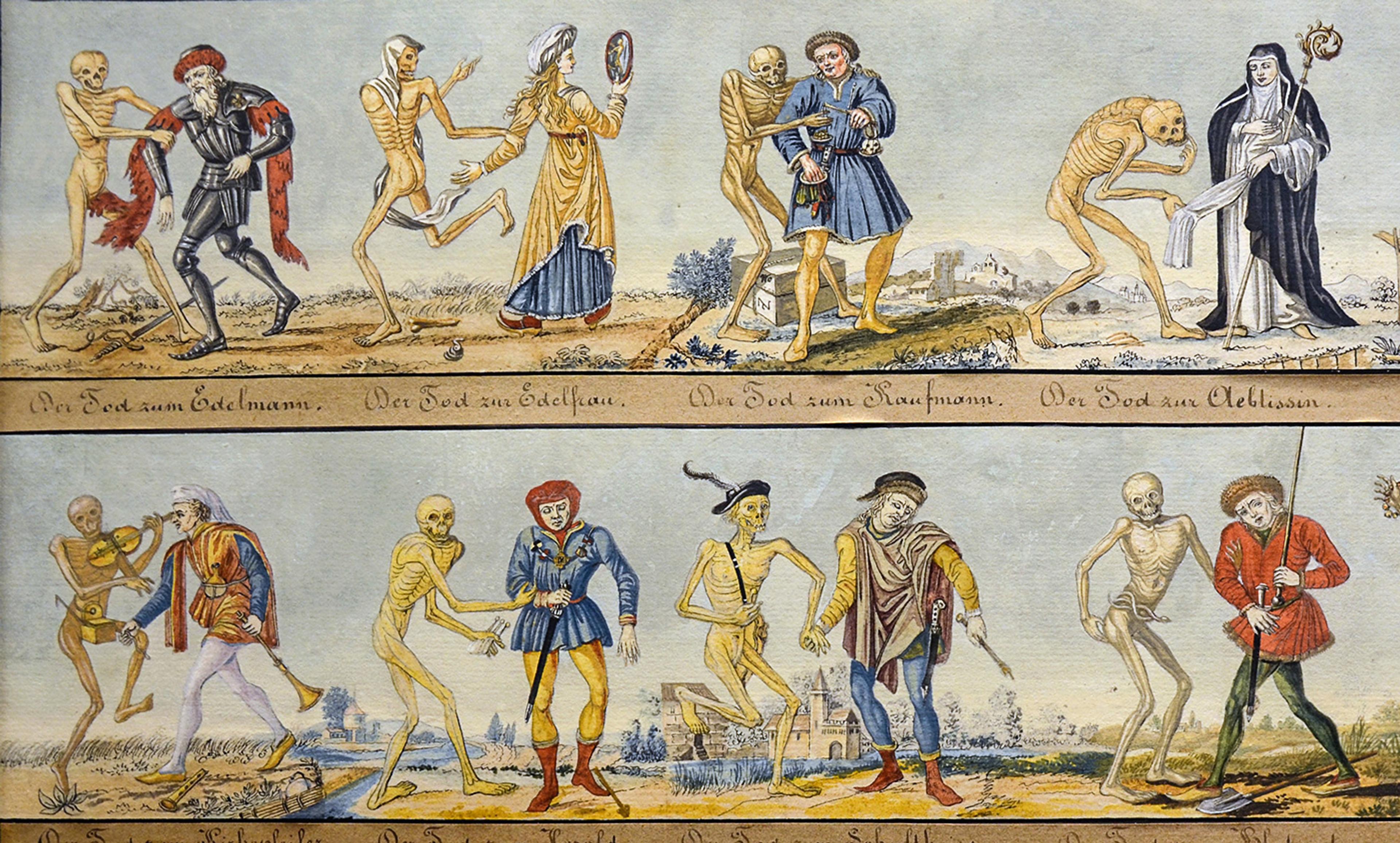

Meaning and the good life
Sooner or later we all face death. Will a sense of meaning help us?
Warren Ward

Philosophy of mind
Think of mental disorders as the mind’s ‘sticky tendencies’
Kristopher Nielsen

Philosophy cannot resolve the question ‘How should we live?’
David Ellis

Rituals and celebrations
We need highly formal rituals in order to make life more democratic
Antone Martinho-Truswell
- EssayBasics.com
- Pay For Essay
- Write My Essay
- Homework Writing Help
- Essay Editing Service
- Thesis Writing Help
- Write My College Essay
- Do My Essay
- Term Paper Writing Service
- Coursework Writing Service
- Write My Research Paper
- Assignment Writing Help
- Essay Writing Help
- Call Now! (USA) Login Order now
- EssayBasics.com Call Now! (USA) Order now
- Writing Guides
Should Animals Be Kept In Zoos (Argumentative Essay)
Should animals be kept in zoos.
The debate of whether or not confining of animals is right in zoos is a popular one that attracts both opponents and proponents. The increased interests in science and natural history saw the introduction of zoos in 1763, which facilitated up close animal studies and would provide a chance for entertaining and educating the public. Nevertheless, confining the animals into small spaces in unnatural habitats, the constant staring from people and loss of their freedom makes zoos the worst homes for animals.
Zoos provide unnatural habitats for the animals. Animals are naturally born and bred to live and die in wilderness habitats. However, despite the numerous efforts and good intentions by zoo management, it is impossible to provide the perfect environment for various animals. For instance, animals like the wilder beasts live in groups that migrate over long distances while elephants on average walk for over 50 km a day in packs. However, zoos can only provide minimal acres of land for the animals to walk about thereby making the environments unnatural and uncomfortable for the animals.
Zoos are a premise of captivity for animals that makes them crazy. Imprisoning of animals in small cages housed in poorly managed zoos that fail to meet the necessary standards, averts them from behaving naturally. As a result, suffer from zoochosis condition, which elicits stress, strange behavior of hurting themselves due to frustration and boredom; they become inactive and increasingly pace around. Moreover, the animals adopt aggressive behavior that results in them lashing out and injuring or killing people.
Zoos are not educational. Zoos operate on the premise that they provide an opportunity for the public to learn about animals. However, this is untrue, as keeping animals in confined and unnatural environments tend to alter their natural behavior, character, and responses. Thus, persons visiting the zoos observe the altered behavior marred by boredom, stress, and loneliness. Moreover, keeping animals in zoos teach people that it is okay to lock up and make animals miserable for their personal gain. Therefore, by gaining pleasure and entertainment from making animals suffer is a horrible lesson to learn.
Proponents of keeping animals in zoos argue that zoos offer the best forms of protection for animals. According to them, animals receive protection from poaching and predators that are out to kill them. Additionally, by engaging in breeding programs, zoos believe they protect various species from becoming extinct, therefore, making them positive institutions to exist. However, this is untrue as some zoos keep the animals in deplorable environments whey they lack food and adequate medical care. Moreover, based on research, endangered animals living in zoos are only about five species and only a few species undergo breeding.
Proponents also believe that zoos provide the opportunity for people to see a wide array of animals while benefiting children with lessons about the environment and animals. Nevertheless, this is not the case as zoos only house few species of animals as compared to those an individual can observe in the wild. Also, zoos expose animals to neglect and stress that alter their behavior hence impeding true learning for children.
In conclusion, animals just as humans enjoy rights to freedom, protection from abuse, stress, neglect and lack of privacy. There is no denying that zoo violates all these rights by introducing them to unnatural habitats and caging the animals. Hence, in promoting health and happiness of the animals, animals should not be kept in zoos.
Our academic writers are animal lovers, so you can trust them and buy essay papers about animals in our essay writing service.

How zoos can save our animals

.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Ben Minteer
.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} Infrastructure is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:, infrastructure.
Today, many zoos promote the protection of biodiversity as a significant part of their mission. As conservation “arks” for endangered species and, increasingly, as leaders in field conservation projects such as the reintroduction of captive-born animals to the wild, they’re preparing to play an even more significant role in the effort to save species in this century .
It’s a task that’s never been more urgent. The recent Living Planet Index report authored by the World Wildlife Fund and the London Zoological Society paints a disturbing picture: globally, on average, vertebrate species populations have declined 52% since 1970. Over-exploitation, habitat destruction and alteration, global climate change, and other pressures have created conditions that scientists now suggest signal a sixth mass extinction episode for our planet. It’s an event rivaling the extinction of the dinosaurs.
The embrace of conservation by zoos, though, doesn’t always sit well with their own history. The modern American zoo that emerged in the late 19th century fancied itself as a center of natural history, education, and conservation, but zoos have also always been in the entertainment business. This priority has led many skeptics to question the idea that zoos can play a helpful conservation role in the coming decades.
Zoos also face a formidable set of practical constraints – namely space, capacity, resources, and in some cases, expertise – that will continue to bedevil their ability to make a dent in the extinction crisis. It’s also true that some of the most endangered animals are not the highly charismatic and exotic species that reliably attract zoo visitors. It’s a challenge that might pit zoos’ conservation priorities against their entertainment goals, and perhaps even their financial bottom line.
At the same time, wildlife protection does run deep in the history of zoos. The Bronx Zoo in New York, for example, led one of the earliest captive breeding and reintroduction efforts, helping to save the American bison from fading into oblivion more than a century ago. In the 1960s and 1970s, zoo conservation was energized by a burst of US federal policy-making focused on endangered species, especially the passage of the Endangered Species Act in 1973.
Many zoos went on to develop Species Survival Plans beginning in the 1980s, which coordinate breeding and population management programs for threatened and endangered animals among zoos worldwide. The goal is to create healthy and genetically diverse animal populations of these species across the zoo community, an effort that can ultimately aid the conservation of the species in the wild.
Reintroduction is a dicey business given the many biological and social factors that determine the viability of a population over time. Zoos’ track records here are mixed – but the successes are real. In addition to the bison, the California condor, the Arabian oryx, and the black-footed ferret have been saved due in part to the efforts of zoos .
For animal rights critics, however, these outcomes don’t offset what is seen as the basic injustice of keeping captive animals for human amusement. Earlier this year, the case of Marius the giraffe in the Copenhagen Zoo reignited the smoldering international debate over the ethics of zoos. A young and healthy giraffe considered a so-called surplus animal by the zoo managers, Marius was shot and his body was dissected before a public audience. The zoo argued that the decision was made on scientific grounds: Marius’s genes were well-represented in the zoo system and so he was said to have no remaining conservation value. Animal advocates countered that zoos’ noble conservation rhetoric masks a callousness toward the well-being of individual animals.
Whatever you think about the Copenhagen case – and it’s worth noting that the American Association of Zoos & Aquariums disagreed with it – debates about the ethics of zoos shouldn’t take place today without a serious discussion of our obligation to address global biodiversity decline. That includes thinking about how we influence the future of animals and ecosystems outside zoo walls with a thousand lifestyle decisions, from our consumer habits and energy consumption, to our transportation choices and what we put on our dinner plates. Take just one example, the mass production of palm oil. Widely used for cooking and commercial food production, its cultivation has resulted in severe habitat destruction and fragmentation in Indonesia. This in turn threatens the survival of orangutans in the wild.
There is a further challenge. As zoos become more engaged in conservation in the coming decades, the natural world will be further pressured and degraded by human activities. In many cases, nature preserves will likely require more human control than they have in the past in order to deliver the same conservation benefits. As a result, the boundary separating nature and zoo, the wild and the walled, will get even thinner . As it does, our understanding of what zoos are and what we want them to be – entertainment destinations, science centers, conservation arks, sustainability leaders – will also change. So will our idealized views of the wild as those places in nature that are independent of meaningful human influence and design.
Saying all this doesn’t let zoos off the hook when it comes to caring properly for animals in their charge. We should also expect them to actually deliver on the swelling conservation rhetoric, especially when their entertainment and recreation interests run up against their expanding vision for biodiversity protection. But it reminds us of the scope of the challenge.
To paraphrase Dr Seuss, we all run the zoo.
Published in collaboration with The Conversation
Author: Ben Minteer is Associate Professor of Environmental Ethics and Conservation at Arizona State University.
Image: Zeff, the Amur tiger at the Bronx Zoo in New York, 2003. REUTERS
Share this:
- Share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} weekly.
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Industries in Depth .chakra .wef-17xejub{-webkit-flex:1;-ms-flex:1;flex:1;justify-self:stretch;-webkit-align-self:stretch;-ms-flex-item-align:stretch;align-self:stretch;} .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

Top 5 countries leading the sustainable tourism sector

Robot rock stars, pocket forests, and the battle for chips - Forum podcasts you should hear this month
Robin Pomeroy and Linda Lacina
April 29, 2024

Agritech: Shaping Agriculture in Emerging Economies, Today and Tomorrow

Confused about AI? Here are the podcasts you need on artificial intelligence
Robin Pomeroy
April 25, 2024

Which technologies will enable a cleaner steel industry?
Daniel Boero Vargas and Mandy Chan

Industry government collaboration on agritech can empower global agriculture
Abhay Pareek and Drishti Kumar
April 23, 2024
Skip to Main Content
- My Assessments
- My Curriculum Maps
- Communities
- Workshop Evaluation
Share Suggestion
"zoos and animal welfare" argumentative/persuasive writing.

"Zoos and Animal Welfare" Argumentative/Persuasive Writing
Grade levels, course, subject.
- Printer Friendly Version
Apply the appropriate models to show interactions among organisms in an environment.
CHANGE AND CONSTANCY
Explain mechanisms organisms use to adapt to their environment.
Describe how selective breeding and biotechnology can alter the genetic composition of organisms.
Compare and contrast observable patterns in the physical characteristics across families, strains and species.
Explain why the extinction of a species may occur when the environment changes.
Explain that mutations can alter a gene and are the original source of new variations in a population.
- Big Ideas Purpose, topic and audience guide types of writing
- Concepts Focus, content, organization, style, and conventions work together to impact writing quality Persuasive writing attempts to influence the audience by presenting an issue and stating and supporting a position. Various types of writing are distinguished by their characteristics
- Competencies Persuasive Writing: Develop substantial, relevant and illustrative content that demonstrates a clear understanding of the purpose (content). Persuasive Writing: Employ a thoroughly elaborated argument that includes a clear position consistently supported with precise and relevant evidence where rhetorical persuasive strategies are evident (content). Persuasive Writing: Employ effective organizational strategies and structures, such as logical order and transitions, which develop a controlling idea (organization). Persuasive Writing: Use proper conventions to compose in the standard form of the English language (conventions). Persuasive Writing: Write with a sharp, distinct controlling point made about a single topic with evident awareness of task and audience (focus). Persuasive Writing: Write with precise control of language, stylistic techniques, and sentence structures that create a consistent and effective tone (style). Write persuasive pieces, specific to a purpose and audience, which have a clearly stated position or opinion, with convincing and properly cited evidence that anticipates and counters reader concerns and arguments. Write to influence the audience by:• stating and supporting a position with detailed evidence, examples, and reasons. • using persuasive techniques (e.g.: emotional appeal, statistics, description, anecdote, example, expert opinion) to strengthen the argument. • employing a distinct structure to organize the argument and the opposing viewpoints. • acknowledging and refuting opposing arguments. • evaluating sources for validity, perspective, bias, and relationship to topic.• documenting sources of information responsibly and ethically. • using sources to achieve a balanced and authoritative argument. • supporting judgments with relevant evidence and detail. Write to influence the audience by:• stating and supporting a position with detailed evidence, examples, and reasons. • using persuasive techniques (e.g.: emotional appeal, statistics, description, anecdote, example, expert opinion, analogies and illustrations) to strengthen the argument. • employing a distinct structure to organize the argument and the opposing viewpoints. • acknowledging and refuting opposing arguments. • evaluating primary and secondary sources for validity, perspective, bias, and relationship to topic. • documenting sources of information responsibly and ethically. • using sources to achieve a balanced and authoritative argument. • supporting judgments with relevant evidence and detail. • presenting the position in either a deductive or an inductive framework. Focus, content, organization, style, and conventions work together to impact writing quality
Description
The Literacy Design Collaborative teaching task provides a blueprint for seamlessly integrating literacy and content standards in a rigorous, authentic classroom experience. After determining the discipline, course, and grade level, educators use teaching tasks built around predefined template prompts. The teaching task requires students to read, analyze and comprehend written materials and then write cogent arguments, explanations or narratives in the subjects they are studying.
Students will examine the zoo as a facility in which animals are confined within enclosures and displayed to the public. In many cases, animals may also be bred to produce offspring. Although enjoyed by many, some feel zoo conditions are detrimental to the health of animals. Students will explain and support their opinion as to whether or not animals should be kept in zoos.
In this extended writing task, students will read, analyze, and gather relevant information from text(s) and write an argumentative essay. Students will…
- Apply knowledge of the distribution and management of natural resources to a current issue
- Apply knowledge of the relationship between an environment and extinction to a current issue
- Read, analyze and gather relevant information from multiple texts
- Write an evidence-based argumentative essay, and address competing views
enclosure - something that "closes" a space
welfare - a condition of being or doing well
conservation - protection from extinction
zoochosis - obsessive, repetitve behavior associated with animals kept in prolonged captivity
extinction - dying out or termination of a species. Occurs when a species can no longer reproduce at replacement levels
endangered species - a species existing in such small numbers that it is in danger of becoming extinct
500 minutes/10 periods
"Animal Ark or Sinking Ship?" BornFree.org . Born Free Foundation, July 2007. Web. Apr. 2011. < http://www.bornfree.org.uk/fileadmin/user_upload/files/zoo_check/ publications/Animal_Ark_or_sinking_ship.pdf >.
Dixon, Thomas. "Zoos: Debatabase - Debate Topics and Debate Motions." IDEA: International Debate Education Association - Debate Resources & Debate Tools. 06 Apr. 2009. Web. 28 Jan. 2011. < http://www.idebate.org/debatabase/topic_details.php?topicID=1 >.
Horton, Jennifer. "Are Zoos Good or Bad." HowStuffWorks.com . 15 Sept. 2008. Web. Apr. 2011. < http://animals.howstuffworks.com/animal-facts/zoos-good-or-bad.htm >.
Lin, Doris. "Should Zoos Keep Endangered Species?" About.com . The New York Times Company. Web. Apr. 2011. < http://animalrights.about.com/od/wildlife/a/EndangeredZoos.htm >.
Van Tuyl, Christine. Zoos and Animal Welfare . Detroit: Greenhaven, 2008. Print.
Related Materials & Resources
Suggested instructional strategies, instructional procedures.
Teacher Preparation Prior to launching the teaching task in the classroom, a teacher should consider the following questions:
How much support will students need to successfully complete the task?
What parts of the process can be completed independently (during or outside of class)? What parts of the process represent new learning or substantial challenge and warrant direct instruction or guided practice during class?
What content and vocabulary instruction and activities will be provided so that students are able to successfully complete the task?
How will reading be scaffolded for my students? (Read together? Read in groups? Read independently?)
What note-taking method will students use, and does that method align with the writing task?
How will students make the transition from the reading to the writing? (outline, graphic organizer, etc.)
What writing instruction is needed to help students write their thesis statements, organize their notes, embed quotes, and cite evidence?
How will students receive feedback at various stages of the writing process to make sure they are answering the prompt, their papers are focused, their ideas are fully developed with details, examples, etc.?
Daily Plan The daily plan is flexible based on students' prior knowledge, experience and skills in reading, research and writing as well as their ability to apply subject area knowledge to a new scenario. The amount of time, in class instruction, and scaffolds needed can be increased or decreased to provide the appropriate level of challenge and support for students.
Teaching Task 2 (Argumentative/Analysis L1, L2): Should animals be kept in zoos? After reading informational texts, write an essay that addresses the question and support your position wiht evidence from the text(s). L2 Be sure to acknowledge competing views.
Task Engagement and Analysis The teacher introduces the teaching task to students by linking the task to the class content that has been taught previously and to existing knowledge, skills, and interests. The teacher asks students to read the teaching task and make notes or discuss with peers things they already know about this issue or topic.
The teacher helps the students to understand the expectations of the teaching task by asking students what they think a good response to the task might include and creating a classroom list. The teacher may share examples of the type of texts the students will produce (either actual student samples or commercially published texts). Sharing the rubric with students will clarify the expectations. (Clicking on each performance level of the rubric will enable teacher access to annotated student writing for that level.)
The teacher explains the timetable and supports available for completing the task.
Text Selection The teacher has either preselected the texts or will provide access to research sources for students to select texts. The teacher asks students to begin to record information about the sources (e.g., using notebooks, note cards, technology). The teacher may need to provide models or instruction on creating a bibliography or works cited. The students should identify author, title, publisher, date, and any other needed information (e.g., volume, editor) A discussion about the credibility or merit of sources may be needed.
Preview texts The teacher can provide students with all of the texts or offer students a list of acceptable sources from which to choose. The teacher briefly highlights each text with a summary to assist students in making appropriate text selections. The teacher asks the students to skim through each text to identify the genre, purpose, and text structure. A teacher think-aloud explaining rationale for making certain text selections may be beneficial to students.
Note-taking The teacher provides or suggests that a note-taking method be used that is consistent with the expectations for the task and the type of writing (e.g., argumentative-pro/con t-chart). Students should be encouraged to refer to the teaching task so that their notes are relevant to the prompt. Students should be encouraged to include both textual information and their own connections and implications. Students should continue to add to their bibliography or works cited.
Teachers may need to teach or reinforce practices to promote academic integrity and to help students avoid plagiarism. The ability to use and credit sources appropriately shows respect for the work of others and adds credibility to a student's argument and/or research.
Reading and Research The teacher assigns the reading, research and note-taking to students and provides instruction to support analysis and synthesis of texts. The teacher may ask students to reflect orally or in writing on key questions including:
Which parts of the text provide evidence that relates to the prompt?
What historical or current examples did you notice that relate to the prompt?
What is the text explicitly saying? What gaps or unanswered questions do you see?
What competing arguments have you encountered or thought of based on the text (argumentative)?
How do you know your sources are credible?
Depending upon the needs of students in the classroom, additional scaffolds may be necessary (e.g., whole-group reading and teacher modeling of note-taking, paired in-class reading, talking to the text, small group discussion). The teacher may either provide students with print source options or make electronic texts available to them through the use of Web 2.0 tools (e.g., Wikis, Nings) or online library databases (e.g., EBSCO, ProQuest).
Transition to Writing The teacher uses discussion based strategies such as the Paideia/Socratic seminar or small group discussions to help students make connections between their research and notes and the teaching task.
Developing a Thesis or Claim Students write an opening paragraph that includes a controlling idea and sequences the key points that will be made throughout the writing assignment. The teacher may provide models of opening paragraphs and analyze them with the class. Students may provide feedback to each other on their opening paragraphs. Students should compare their opening paragraph to the teaching task and assess whether the paragraph fully address the main points of the prompt (e.g., define and explain, compare, take a position, etc.)
Organizing Notes/Planning Students organize their notes into a graphic organizer or outline that establish a logical structure for the assignment. An outline begins with the thesis or claim, sequences key points and includes supporting evidence from texts.
Development of rough drafts Students begin writing their rough drafts. The teacher frequently checks in with students to answer questions, offer feedback, and provide writing instruction as needed. Through planning, the teacher embeds opportunities for students to receive feedback on their writing prior to the submission of the final draft either through peer conferencing, teacher conferencing, or written teacher feedback. Students revise their drafts based on the feedback they receive. The amount of time needed for the development of rough draft varies and may include time during and outside of class.
Completion of Final Draft Students either self or peer-edit their papers for conventional errors and complete the final draft.
Assessment and Reflection The teacher uses the LDC rubric to assess the students' writing and provide feedback to help students improve their performance. Patterns in student performance guide further instruction.
Analytic Scoring The rubric is structured to facilitate analytic scoring - the awarding of separate scores by readers for each of the seven scoring elements. Scorers should keep in mind that the description of work quality within any particular "cell" of the rubric may still address more than one idea, and therefore may not match a particular essay perfectly. The scorer must identify the descriptor that is the best match to a paper based on the preponderance of evidence. If the decision is truly a "coin toss," the scorer should feel free to use the "in-between" or "half" scores. A variation of analytic scoring might be used in a situation in which the emphasis of instruction at a particular time might be on a subset of the seven scoring elements. For example, if instruction is focused on development and organization, then a teacher might simply award scores for those two scoring elements.
Holistic Scoring Holistic scoring is assigning a single, overall score to a paper. Analytic and holistic scoring rubrics look much the same. The holistic scorer's job is to pick the single score (1, 2, 3, 4) that corresponds to the set of descriptors for scoring elements that best matches a paper. Again, in-between or half scores can be used. Ideally, holistic scorers are thinking about all the scoring elements as they read papers, but over time they find that they can assign holistic scores very rapidly, yet still fairly accurately. This is one of the advantages of holistic scoring. However, analytic information is not generated by this method.
Score Recording and Feedback It would be good practice for teachers to share the rubrics with students and discuss "criteria for success" relative to the scoring elements. However, it is not intended that a clean scoring rubric would be attached to every paper that is scored in all situations. It might be more appropriate to attach score slips that list the scoring element names with blank spaces after them for the recording of scores (and a space for a total score, too, perhaps). A customized rubber stamp could accomplish the same. Analytic scores do provide useful information to the students since they reference descriptors in the rubric. However, nothing beats descriptive comments that are best written in the margins of the papers where they are most appropriate.
Cut Scores for Proficiency Levels Scorers can readily compute a total score (the sum of the seven element scores) or an average score (that sum divided by 7). If translating scores to performance levels is desired, then the structure of the rubrics lends itself to the use of the following cut scores:
LDC Scores and Grades LDC scores could be translated to grades contributing to students' course grades. How this would be done is an individual teacher's decision. Teachers could establish their own cut scores for letter grades or just re-label the four performance levels as A, B, C, D. They could come up with their own way to convert LDC scores to numerical grades consistent with whatever numerical scale they use for other class work.
Click on each performance level below (Not Yet, Approaches Expectations, Meets Expectations, Advanced) to view annotated student samples.
Sean Houseknecht, Alex Shubert, Monica Cressman - Elizabethtown Area School District
Content Collections
Date published, insert template.

Essay on Should Animals Be Kept In Zoos
Students are often asked to write an essay on Should Animals Be Kept In Zoos in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Should Animals Be Kept In Zoos
Introduction.
Zoos are places where people can see different animals from around the world. Some people believe zoos are good for animals, but others think they are not. This essay will discuss both sides of this issue.

Zoos for Education
Zoos can be helpful for teaching. They let people, especially kids, learn about different animals. They can see how animals behave and live. This can make people care more about animals and want to protect them.
Animal Safety
Zoos can keep animals safe. Some animals are in danger in the wild because of people or other animals. Zoos can protect these animals and help them to live longer.
Against Animal Freedom
On the other side, zoos can limit animals’ freedom. Animals in zoos don’t get to live like they would in the wild. They can’t hunt, roam, or do other things they would normally do. This can make them sad or sick.
In conclusion, zoos have both good and bad points. They can teach people about animals and protect them. But they can also limit animals’ freedom. It’s important to think about these points when talking about zoos.
250 Words Essay on Should Animals Be Kept In Zoos
Zoos are places where people can see animals from all over the world. They have been around for many years. But, is it right to keep animals in zoos? This is a big question that people have different views on.
Reasons for Zoos
One reason people think zoos are good is because they help protect animals. Some animals are in danger of disappearing forever. Zoos can keep these animals safe and help them have babies, so they don’t disappear.
Zoos also help us learn about animals. By watching animals in zoos, scientists can learn how they live, what they eat, and how they behave. This information can help protect animals in the wild.
Reasons Against Zoos
On the other hand, some people think zoos are bad for animals. They believe animals should live in the wild, not in cages. In the wild, animals can roam free, hunt for food, and live with other animals. In zoos, they can’t do these things.
Some people also worry that zoos don’t give animals enough space. Animals in the wild have a lot of room to move around. But in zoos, they often live in small cages or enclosures.
So, should animals be kept in zoos? It’s a tough question. Zoos can help protect and study animals, but they can also limit their freedom and space. It’s important to make sure that if we have zoos, they are as good as possible for the animals that live there.
500 Words Essay on Should Animals Be Kept In Zoos
Zoos are places where people can see a variety of animals from all over the world. But should animals be kept in zoos? This question has sparked many debates. There are both good and bad points about zoos. Let’s explore these points.
Learning Opportunity
One of the main reasons why zoos exist is for education. Zoos give us a chance to see animals that we would never see otherwise. They teach us about different species, their habits, and their habitats. This can inspire people, especially children, to care more about animals and nature. It can also help them to understand the importance of conservation.
Conservation Efforts
Zoos play a big role in protecting endangered species. Some animals are at risk of disappearing forever because of hunting, habitat loss, and climate change. Zoos can provide a safe place for these animals to live. They can also help to increase their numbers through breeding programs. This can be a lifeline for species that are struggling to survive in the wild.
Quality of Life
On the other side, many people argue that zoos are not good for animals. They believe that animals should be free to live in their natural habitats. Zoos often can’t provide the same amount of space and freedom that animals would have in the wild. This can lead to stress and boredom for the animals. It can also cause health problems.
Is There a Better Way?
Some people suggest that there might be better ways to protect animals and educate people. Wildlife parks and sanctuaries, for example, often provide more space for animals. They also focus on preserving natural habitats. This could be a better option for many species.
In conclusion, there are both pros and cons to keeping animals in zoos. Zoos provide valuable learning opportunities and can help to protect endangered species. But they can also limit the quality of life for animals. It’s important for us to keep asking this question and looking for the best ways to care for all creatures. After all, every animal deserves to live a life that is happy and healthy.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Shopping With My Mother
- Essay on Shopping With Friends
- Essay on Shopping Mall
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

April 15, 2009
How Do Zoos Help Endangered Animals?
There are more to zoos than putting animals on display
Dear EarthTalk: Do zoos have serious programs to save endangered species, besides putting a few captives on display for everyone to see? -- Kelly Traw, Seattle, WA
Most zoos are not only great places to get up close to wildlife, but many are also doing their part to bolster dwindling populations of animals still living free in the wild. To wit, dozens of zoos across North America participate in the Association of Zoos and Aquarium’s (AZA’s) Species Survival Plan (SSP) Program, which aims to manage the breeding of specific endangered species in order to help maintain healthy and self-sustaining populations that are both genetically diverse and demographically stable.
The end goal of many SSPs is the reintroduction of captive-raised endangered species into their native wild habitats. According to the AZA, SSPs and related programs have helped bring black-footed ferrets, California condors, red wolves and several other endangered species back from the brink of extinction over the last three decades. Zoos also use SSPs as research tools to better understand wildlife biology and population dynamics, and to raise awareness and funds to support field projects and habitat protection for specific species. AZA now administers some 113 different SSPs covering 181 individual species.
On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing . By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
To be selected as the focus of an SSP, a species must be endangered or threatened in the wild. Also, many SSP species are “flagship species,” meaning that they are well-known to people and engender strong feelings for their preservation and the protection of their habitat. The AZA approves new SSP programs if various internal advisory committees deem the species in question to be needy of the help and if sufficient numbers of researchers at various zoos or aquariums can dedicate time and resources to the cause.
AZA’s Maryland-based Conservation and Science Department administers the worldwide SSP program, generating master plans for specific species and coordinating research, transfer and reintroductions. Part of this process involves designing a “family tree” of particular managed populations in order to achieve maximum genetic diversity and demographic stability. AZA also makes breeding and other management recommendations with consideration given to the logistics and feasibility of transfers between institutions as well as maintenance of natural social groupings. In some cases, master plans may recommend not to breed specific animals, so as to avoid having captive populations outgrow available holding spaces.
While success stories abound, most wildlife biologists consider SSP programs to be works in progress. AZA zoos have been instrumental, for instance, in establishing a stable population of bongos, a threatened forest antelope native to Africa, through captive breeding programs under the SSP program. Many of these captive-bred bongos have subsequently been released into the wild and have helped bolster dwindling population numbers accordingly.
Of course, for every success story there are dozens of other examples where results have been less satisfying . SSP programs for lowland gorillas, Andean condors, giant pandas and snow leopards, among others, have not had such clear success, but remain part of the larger conservation picture for the species in question and the regions they inhabit.
CONTACTS : AZA’s Conservation & Science Program, www.aza.org/Conscience .
EarthTalk is produced by E/The Environmental Magazine. SEND YOUR ENVIRONMENTAL QUESTIONS TO: EarthTalk , P.O. Box 5098, Westport, CT 06881; [email protected] . Read past columns at: www.emagazine.com/earthtalk/archives.php . EarthTalk is now a book! Details and order information at: www.emagazine.com/earthtalkbook .
- IELTS Scores
- Life Skills Test
- Find a Test Centre
- Alternatives to IELTS
- General Training
- Academic Word List
- Topic Vocabulary
- Collocation
- Phrasal Verbs
- Writing eBooks
- Reading eBook
- All eBooks & Courses
- Sample Essays
In this IELTS Zoo Essay you have to discuss whether you think zoos are cruel and should be shut down or whether they are useful as they protect some wild animals.
Essays on zoos have appeared in the IELTS test before and this was a question that was recently in the test.
Some people think that zoos are all cruel and should be closed down. Others however believe that zoos can be useful in protecting wild animals.
Discuss both opinions and give your own opinion.
Understanding the Question
You must always read the question carefully and note if there is anything restricting the topic.
You have to discuss both sides of the argument and with this zoo essay question it would be very easy to read it and then simply write about the benefits and drawbacks of zoos.
But look at this bit carefully:
- Others however believe that zoos can be useful in protecting wild animals .
One of the arguments is specifically about protecting animals. So when you discuss the second argument you must be careful not to just write generally about the advantage of zoos.
You have to focus on how they may protect wild animals . So when you brainstorm your ideas for the zoo essay, you should be thinking about:
- why animals need protecting and
- how zoos can help with this

And in your other body paragraph you would need to explain why they are also seen as cruel.
And of course you must remember to give your own opinion. In this essay, the author makes it clear at the beginning that they support the closing down of zoos.
The opinion you decide on though is of course your choice.
Zoo Essay Sample
You should spend about 40 minutes on this task.
Write about the following topic:
Give reasons for your answer and include any relevant examples from your own experience or knowledge.
Write at least 250 words.
Zoo Essay Model Answer
Zoos remain popular places for people to visit for entertainment and to learn about wild animals. Although some people are of the opinion that zoos can provide a sanctuary for endangered animals and so should be kept open, I believe that the cruelty that animals suffer outweighs this benefit, and that they should be shut down.
These days, animals are under threat from humans in many ways, seen for example in the way that their habitats are being destroyed through the cutting down of rain forests, or through poaching. Following on from this, the argument is that zoos can protect some of these animals that are under threat. The reason is that they are in a safe environment managed by trained staff who can ensure the animals are looked after and can produce offspring. There are examples of successes in this respect, such as with Pandas, which have been endangered for many years but have been protected.
However, there are more convincing arguments for why zoos should be shut down. Firstly, even though some species are under threat, there are lots of animals which do not fall into this category and who are there just for the entertainment of visitors. While it may be fun and educational to see them, animals are not meant to be caged, and their distress can often be seen in the way many of them pace back and forwards all day. Not only this, if the prime reason of zoos is to protect animals, this could be done in other environments such as wild life parks where the animals have more freedom.
In conclusion, animals should be protected but this does not have to be in zoos. Zoos are cruel to animals, not similar enough to their natural habitat, and they should be closed down.
(299 Words)
Band scores are given for task response, coherence and cohesion, lexis (vocabulary) and grammatical range and accuracy.
This zoo essay would get a good score for task response as it fully answers the question by discussing both opinions and giving a personal opinion. Ideas are also well explained, extended and supported.
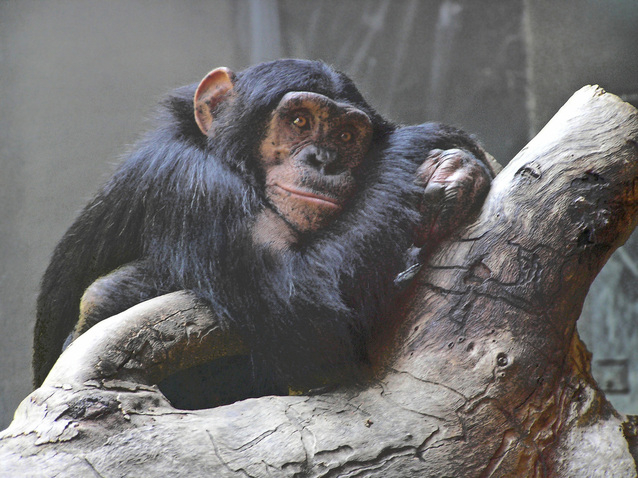

It would get a good score for coherence and cohesion as it is organised coherently and logically and is easy to follow. The introduction introduces the topic then there is a thesis statement.
One body paragraph discusses one side of the argument, and the other discusses the other side. The second body paragraph is also the writers opinion, and this is summarised again in the conclusion
.There is some interesting vocabulary and phrases. For example:
- sanctuary for endangered animals
- under threat from humans
- habitats are being destroyed
- produce offspring
- successes in this respect
- not meant to be caged
- natural habitat
There are also some good complex grammatical constructions and the grammar is precise. For example, the red words show that some of these are adverbial clauses , noun clauses and relative clauses :
- Although some people are of the opinion that zoos can provide a sanctuary for endangered animals...
- ...seen for example in the way that their habitats are being destroyed...
- ...the argument is that zoos can protect some of these animals who are under threat.
- ...trained staff who can ensure the animals are looked after...
- Pandas who have been endangered...
- ... even though some species are under threat...
- ... While it may be fun and educational...
<<< Back
Next >>>
More Discuss Two Opinion Essays:

IELTS Essays: What is the best way to reduce crime?
IELTS essays online with comments by an IELTS instructor - A writing sample on the topic of reducing crime.

IELTS Essay Becoming Independent
This IELTS essay discussed whether people are becoming more independent than they were in the past. This is a question that has come up a few times in the test. This is discussion type essay as you have to discuss both sides of an argument and come to a conclusion.

IELTS Writing Example: What are the aims of a university education?
IELTS writing example essays. This is an essay on the aims of university education. In this essay, two opposing opinions need to be discussed. It is important to understand how to answer this type of question in the IELTS exam.

Sources for Stories Essay: Should parents read to their children?
This sources for stories essay asks for your opinion on the best way for children to get stories. Is it from parents reading to them or other ways?
Formal and Informal Education Essay: What age should it start?
This formal and informal education essay is about whether it is best for children to begin their formal education at school when they are 7 rather than much younger.

Donating Money to Charity Essay: Where should the money go?
Donating Money to Charity Essay: IELTS model answer to an essay on the topic of giving locally or to national and international charities.

Childcare Essay: Should family or carers look after young children?
Childcare Essay: In the essay you have to discuss two sides of an argument. The first is that it is better if pre-school children are looked after at home with relatives such as grandparents. The second opinion is that children should be looked after at childcare centres.

Child Development Essay: What factors influence a child's development?
Child Development Essay for IELTS. The essay is about the factors that affect the way that children develop. It provides you with a model answer and comments on the response to help you know how to improve your band score.

Influence of Scientists or Politicians Essay
Influence of Scientists or Politicians Essay- Model answer for IELTS. Who has had the most influence on our world? In this essay you have to discuss both sides.

Animal Rights Essay: Should animals be exploited for humans?
Animal Rights Essay for IELTS: Learn how to write an essay where you have to discuss two opinions. People who believe in animal rights think that they should not be treated cruelly, for example in experiments or for sport.

Extraterrestrial Life Essay: Should we look for life on other planets?
This extraterrestrial life essay is an IELTS opinion essay where you have to discuss both sides of an issue then give your own opinion.

Diet and Health Essay: Who is responsible for diet and health?
Diet and Health Essay for IELTS: This model examines the extent to which individuals or governments should be responsible for health. Read a model answer and useful comments about the essay which will help you to improve your IELTS Score.
Any comments or questions about this page or about IELTS? Post them here. Your email will not be published or shared.
Would you prefer to share this page with others by linking to it?
- Click on the HTML link code below.
- Copy and paste it, adding a note of your own, into your blog, a Web page, forums, a blog comment, your Facebook account, or anywhere that someone would find this page valuable.
Band 7+ eBooks
"I think these eBooks are FANTASTIC!!! I know that's not academic language, but it's the truth!"
Linda, from Italy, Scored Band 7.5

All 4 Writing eBooks for just $25.86 30% Discount Find out more >>
IELTS Modules:
Other resources:.
- All Lessons
- Band Score Calculator
- Writing Feedback
- Speaking Feedback
- Teacher Resources
- Free Downloads
- Recent Essay Exam Questions
- Books for IELTS Prep
- Useful Links

Recent Articles
IELTS Bundle Writing eBooks: 30% Off
Jun 01, 24 09:55 AM

House Sitting
May 31, 24 03:59 AM
Key Phrases for IELTS Speaking: Fluency and Coherence
May 26, 24 06:52 AM
Important pages
IELTS Writing IELTS Speaking IELTS Listening IELTS Reading All Lessons Vocabulary Academic Task 1 Academic Task 2 Practice Tests
Connect with us
Before you go...
Check out the ielts buddy band 7+ ebooks & courses.

Copyright © 2022- IELTSbuddy All Rights Reserved
IELTS is a registered trademark of University of Cambridge, the British Council, and IDP Education Australia. This site and its owners are not affiliated, approved or endorsed by the University of Cambridge ESOL, the British Council, and IDP Education Australia.

- Elementary School
- Reading & Speaking
- External Independent Testing
- Grammar Exercises
Argumentative essay: Are you for or against zoos?

Writing an argumentative essay
Some people think that zoos are out-of-date and cruel institutions that should be closed down. Do you agree? Write an argumentative essay (for/against a statement)
At the moment zoos are very popular. Many people think that animals should be in zoos, although there are some arguments both for and against them.
One of the arguments for zoos is the fact they are educational because they provide visitors with lots of educational programmes. What is more, a zoo can be the only place where rare or disappearing animals could be saved.
As far as I am concerned, I am against zoos.
Firstly, it is cruel to keep animals in uncomfortable cages where they live under bad conditions.
Secondly, animals feel a lack of freedom and physical activity and they live under the lack of healthy food.
Thirdly, zoos break a natural animals lifestyle and change it upside-down. Animals which normally hunt for their food are fed, and most have to live in a climate very different from that of their natural habitat.
Moreover, animals suffer from foredoom and this can result in their aggressive behavior.
In conclusion, I’d like to say that zoos have no place in modern society, but I don’t mind safari parks because they are protecting animals, so they don’t become extinct.

Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
Related posts.

English Lessons

Modern Gadgets

Moving in Search of Another Place

My Dream House

Become Vegetarians

Future Plans

Extended Family Living

Teenagers’ Spare Time

Using Mobile Phones at School

Advantages and Disadvantages of the Internet in Education
I agree with your opinion but zoos can be useful, for example: the number of bisons was restored with the help of few remaining in zoos and and it is also interesting to watch the animals.
Thank you for the interesting fact, Diana!
Leave A Comment Cancel reply
- Grammar Tests
- Grammar Exercisers
- Environment
Persuasive Essay: Animals Should Not Be Kept in Zoos
Animals indeed love being in their natural habitat; in the wild. However, in zoos, many wild animals are kept in the zoo and are treated poorly and tried to shape into domesticated pets. There is a huge/big majority of these enclosures that are too small for the animals too! At last many of these animals lose their instincts and then when they are released in the wild they don’t know how to act or do anything and immediately die. On the other side, many adults and children protest that animals should stay in the zoo because it is educational, but it does not, it is hurting the animals. Animals have feelings too.
Firstly animals should not be in zoos because. According to Innocent and Imprison it says that “Cramped cages and incorrect diets have been replaced with open cages”. In my opinion, they said that cramped cages have been replaced but not the diet. Due to this, animals still can be suffered a lot due to the change of diet. The second reason is according to Innocent and imprisons it says that “ The elephant behind the fence is bobbing her head repeatedly this is a sign of zoochosis”. By reading this I feel like animals are being threatened and have zoochosis. To conclude this is the first reason why we shouldn't be letting animals in the zoo.
Another reason animals should not be in zoos is that they are being caged. According to Innocent and Imprisoned it says that “One answer to this conversation but only a tiny number of zoos breed animals fro conversation”. In my opinion, this is useless If they aren’t going to breed animals then they still need big cages why do they need small cages. Animals need a lot of space and air. According to Innocent and Imprison it says that “This is unfair to the animals to the animals that they are imprisoned to entertain us”. On this point, I would agree with the author because thousands of animals are locked up in cages In addition they lose their social structure to perform for us humans.
Lastly, some people think that zoos are good because they are According to View on the Zoos it says that “ Zoo advocates call attention to the main duction on the zoo: Conversation,eduacation, research, and recreation.
However, they are wrong because animals have been disturbed. In addition According to Innocent and Imprison says that “ People tend to talk to friends as they watch the exotic animals re=ather than learn about particular traits and characteristics. In the end, this is why we should not let animals in zoos.
In conclusion, animals have been threatened, imprisoned, and most importantly have feelings. This is why animals should not be in zoos instead they should roam in their wild habitat. Animals should not be in zoos to the final ending of my essay.
Related Samples
- Essay Sample on Air Pollution
- Using Cars for Everyday Needs Essay Sample
- Individual Rights Essay Example
- Essay on Commercial Whaling on Earth
- Impacts of Immigration in the Us in the First Half of the 19th Century
- Opinion Essay: Reflection On Animal Testing (Dogs)
- Persuasive Essay Sample: Guns Should Be Banned
- Romanticism View of Nature Essay Example
- Social Media and Teen Suicides Research Paper
- Homelessness in New York City (Free Essay Sample)
Didn't find the perfect sample?

You can order a custom paper by our expert writers

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Pros and cons of zoos. These are the most common arguments in favor and against zoos. Pros of zoos. After the famous wildlife conservationist Geral Durrell opened a zoo in Jersey in 1959, zoos all over the world have embraced the mission of saving endangered species in the world. Zoos are not like the exotic animal menageries from the middle ages.
Animals despise being captives in zoos. No matter how you "enhance" enclosures, they do not allow for freedom, a natural diet or adequate exercise. Animals end up stressed and unhealthy or ...
Get custom essay. Most zoos keep wild animals, and majority of the animal population at the zoos is made up of animals that are rarely seen by human beings in their immediate environment. These animals are used to roaming in the jungle and forests. Others are used to swimming freely in the seas and rivers.
Arguments for Zoos. By bringing people and animals together, zoos educate the public and foster an appreciation of other species. Zoos save endangered species by bringing them into a safe ...
A 2008 study of 206 zoo visitors by some members of the same team showed that while 42 percent said that the "main purpose" of the zoo was "to teach visitors about animals and conservation ...
Kenny Torrella is a staff writer for Vox's Future Perfect section, with a focus on animal welfare and the future of meat. This week, a leading wildlife conservation group declared that zoos play ...
A good zoo will enable these species to live and breed in a secure environment. In addition, as numbers of some wild species drop, there is an increased danger of populations becoming too genetically similar. Breeding programmes provide a safeguard: zoo-bred animals can be released into the wild to increase genetic diversity.
The practice of keeping animals in zoos has sparked a passionate debate that revolves around ethical considerations and conservation goals. This essay explores the multifaceted arguments for and against the existence of zoos, delving into their roles in conservation, animal welfare, research, education, and ethical concerns.
Zoo animals are sort of like ambassadors for their counterparts in the wild. Zoos also contribute to scientific research. "Zoo" is short for zoological park, and zoology is the scientific study of animal biology and behavior. In addition, zoos work really hard to save animals that are threatened in the wild. Zoos can take at-risk animals ...
However, animals have a good quality of life in many zoos, and there's a strong moral case for why these institutions ought to exist. I've come to this view after working with great apes, and it might not extend to all species equally. However, since great apes are both cognitively sophisticated and human-like in their behaviour, they offer ...
However, this is untrue, as keeping animals in confined and unnatural environments tend to alter their natural behavior, character, and responses. Thus, persons visiting the zoos observe the altered behavior marred by boredom, stress, and loneliness. Moreover, keeping animals in zoos teach people that it is okay to lock up and make animals ...
The debate over whether zoos help or harm animals underscores the need for a balanced approach that prioritizes both conservation and animal welfare. Well-managed zoos can contribute to vital conservation efforts, inspire public support for wildlife, and conduct valuable research. However, it is imperative that zoos uphold the highest ethical ...
For animal rights critics, however, these outcomes don't offset what is seen as the basic injustice of keeping captive animals for human amusement. Earlier this year, the case of Marius the giraffe in the Copenhagen Zoo reignited the smoldering international debate over the ethics of zoos. A young and healthy giraffe considered a so-called ...
Write to influence the audience by:• stating and supporting a position with detailed evidence, examples, and reasons. • using persuasive techniques (e.g.: emotional appeal, statistics, description, anecdote, example, expert opinion) to strengthen the argument. • employing a distinct structure to organize the argument and the opposing viewpoints. • acknowledging and refuting opposing ...
Some animals are in danger of disappearing forever. Zoos can keep these animals safe and help them have babies, so they don't disappear. Zoos also help us learn about animals. By watching animals in zoos, scientists can learn how they live, what they eat, and how they behave. This information can help protect animals in the wild.
Moreover, with the appropriate living conditions mentioned above, keeping animals in zoos also accelerates the restoration of endangered species and boosts their population, saving them from extinction. The better quality of life that zoos offer enables animals to live and gives them the power and strength to breeding generations.
The end goal of many SSPs is the reintroduction of captive-raised endangered species into their native wild habitats. According to the AZA, SSPs and related programs have helped bring black-footed ...
These zoos do a lot of work in and outside of the zoo to ensure their welfare conditions are kept to the highest standards. Recently due to the public being more aware of some of the negative aspects of keeping animals in zoos, some have started a lot of controversy surrounding the moral argument of whether should animals be kept in zoos or not.
In this IELTS Zoo Essay you have to discuss whether you think zoos are cruel and should be shut down or whether they are useful as they protect some wild animals. Essays on zoos have appeared in the IELTS test before and this was a question that was recently in the test. Some people think that zoos are all cruel and should be closed down.
One of the arguments for zoos is the fact they are educational because they provide visitors with lots of educational programmes. What is more, a zoo can be the only place where rare or disappearing animals could be saved. As far as I am concerned, I am against zoos. Firstly, it is cruel to keep animals in uncomfortable cages where they live ...
-Good zoos make sure their animals aren't depressed, nor lonely, and are occupied so they don't feel bored.-zoos save endangered species by keeping them in safe environments.-"In the case of zoos, both sides will argue that their side saves animals. Whether or not zoos benefit the animal community, they certainly do make money.
Animals have feelings too. Firstly animals should not be in zoos because. According to Innocent and Imprison it says that "Cramped cages and incorrect diets have been replaced with open cages". In my opinion, they said that cramped cages have been replaced but not the diet. Due to this, animals still can be suffered a lot due to the change ...
More than 230 top zoos and top aquariums of the Association of Zoos and Aquariums (AZA) work to provide safe habitats, medical care, and a nurturing environment for their animals. AZA and our members work to protect endangered species in numerous ways, including: Conducting, supporting, and funding research and conservation.