Finance Research Letters
About the journal.
Finance Research Letters invites submissions in all areas of finance, broadly defined. Finance Research Letters offers and ensures the rapid publication of important new results in these areas. We aim to provide a rapid response to papers, with all papers undergoing a desk review by one of the …
View full aims & scope
Article publishing charge for open access

Compare APC with another journal
Editor-in-chief, laura ballester.
University of Valencia, Avenida de los Naranjos s/n, 46010, Valencia, Spain
Latest published
Articles in press, most downloaded, most popular, more from finance research letters, announcements, diversity & inclusion statement – finance research letters, special issues and article collections, boyhood in 21st century educative contexts, rethinking educational practices and responsibilities in the light of digitalisation, neoliberalism, education inequity and improvement, motivation of higher education faculty: theoretical approaches, empirical evidence, and future directions, partner journals.
The Finance Research Letters is a companion title of the Finance Research Letters is an open access, peer-reviewed journal which draws contributions from a wide community of international and interdisciplinary researchers …
Related journals
Educational Research...
Educational Research Review
Learning and Instruc...
Learning and Instruction
Teaching and Teacher...
Teaching and Teacher Education
International Journa...
Learning, Culture an...
Learning, Culture and Social Interaction
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved
Finance Research Letters
Subject Area and Category
Elsevier B.V.
Publication type
15446123, 15446131
Information
How to publish in this journal
The set of journals have been ranked according to their SJR and divided into four equal groups, four quartiles. Q1 (green) comprises the quarter of the journals with the highest values, Q2 (yellow) the second highest values, Q3 (orange) the third highest values and Q4 (red) the lowest values.
The SJR is a size-independent prestige indicator that ranks journals by their 'average prestige per article'. It is based on the idea that 'all citations are not created equal'. SJR is a measure of scientific influence of journals that accounts for both the number of citations received by a journal and the importance or prestige of the journals where such citations come from It measures the scientific influence of the average article in a journal, it expresses how central to the global scientific discussion an average article of the journal is.
Evolution of the number of published documents. All types of documents are considered, including citable and non citable documents.
This indicator counts the number of citations received by documents from a journal and divides them by the total number of documents published in that journal. The chart shows the evolution of the average number of times documents published in a journal in the past two, three and four years have been cited in the current year. The two years line is equivalent to journal impact factor ™ (Thomson Reuters) metric.
Evolution of the total number of citations and journal's self-citations received by a journal's published documents during the three previous years. Journal Self-citation is defined as the number of citation from a journal citing article to articles published by the same journal.
Evolution of the number of total citation per document and external citation per document (i.e. journal self-citations removed) received by a journal's published documents during the three previous years. External citations are calculated by subtracting the number of self-citations from the total number of citations received by the journal’s documents.
International Collaboration accounts for the articles that have been produced by researchers from several countries. The chart shows the ratio of a journal's documents signed by researchers from more than one country; that is including more than one country address.
Not every article in a journal is considered primary research and therefore "citable", this chart shows the ratio of a journal's articles including substantial research (research articles, conference papers and reviews) in three year windows vs. those documents other than research articles, reviews and conference papers.
Ratio of a journal's items, grouped in three years windows, that have been cited at least once vs. those not cited during the following year.
Evolution of the percentage of female authors.
Evolution of the number of documents cited by public policy documents according to Overton database.
Evoution of the number of documents related to Sustainable Development Goals defined by United Nations. Available from 2018 onwards.
Leave a comment
Name * Required
Email (will not be published) * Required
* Required Cancel
The users of Scimago Journal & Country Rank have the possibility to dialogue through comments linked to a specific journal. The purpose is to have a forum in which general doubts about the processes of publication in the journal, experiences and other issues derived from the publication of papers are resolved. For topics on particular articles, maintain the dialogue through the usual channels with your editor.

Follow us on @ScimagoJR Scimago Lab , Copyright 2007-2024. Data Source: Scopus®

Cookie settings
Cookie Policy
Legal Notice
Privacy Policy

Call For Papers >> Green and Climate Finance: Responses and Challenges in Finance
Publication, description.
Overview of the Special Issues
Green finance can be defined as comprising "all forms of investment or lending that consider environmental effect[s] and enhance environmental sustainability" It combines the world of ‘traditional’ finance and business with socially responsible and environmentally friendly behaviors. It plays an increasingly important role in mobilizing capital towards investments that help to fulfill commitments under the Paris agreement for climate change, or underpin efforts in achieving the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). It is an emerging arena for many participants, including individual investors, financial institutions and institutional investors, credit market participants, as well as other economic agents such as major energy producers and consumers – each of which harbor questions on how best to adopt it. Yet rapid growth in sub-fields of green finance, such as green bonds, stands testament to the appetite among both investors and users of capital, to embrace a new class of financial instruments that offers a different combination of financial and social returns.
Against the backdrop of a pressing global vulnerability to increasingly severe climatic change and the immediate need to reduce carbon emissions, huge investments are needed in green and climate-resilient infrastructure across the globe. According to the Global Environment Facility, an estimated $400-600 billion per annum is needed to finance the conservation of land, forests and water, and more than $350 billion of incremental capital to fund projects in renewable energy and energy efficiency. However, there’s a large gap between the required capital and the actual capital flows: the latest accounting of climate finance suggests the financing gap to be in the region of $70 billion*, while anecdotal evidence and views among practitioners suggest this may be a conservative estimate.
Green finance can be connected to the majority of the SDGs, and successes in achieving the SDGs may hinge on well implemented green finance solutions by firms, while simultaneously delivering co-benefits that enhance general business sustainability and reflect positively on firms environmental, social and governance performance metrics. Research regarding green finance is of critical importance to underpin sustainable development capable of benefiting the full spectrum of stakeholders and participants in domestic and global economies and international financial systems. The financial system has a unique ability to rapidly and continuously adjust and develop innovative mechanisms that direct finance to meet the development needs of an economy, allocating financial resources fairly and effectively while maintaining vigil over the need for financial efficiency. In order to mobilize required resources further research is needed to bridge an apparent knowledge gap, and make progress to answering the question: how to close the green-finance gap?
In a recent report the Inter-Governmental Panel on Climate Change identified the mobilization of climate finance as critical to limiting global warming to 1.5◦C, and preventing catastrophic climate change. Climate finance is a rapidly emerging area of finance (at least into the mainstream) that takes as its aim the promulgation of investments targeted towards reducing vulnerability, and generally increasing the level of preparedness and/or resilience of human and ecological systems, to the negative impacts of climate change. Examples of projects that constitute climate finance include those that reduce emissions, enhance efforts to capture and store (sink) greenhouse gases, investment in renewable energy systems, smart cities etc.
Mobilizing investments to the level necessary to reach the ‘1.5◦C pathway’ requires a major shift in investment patterns of both public and private financing, from regional, national, and international entities. Such a shift should be accompanied by enhanced rules, regulations, fiscal incentives and the creation of effective markets at the international, national, and sub-national levels to shift current and projected “business-as-usual” investments on to a different trajectory. Thus, advancing our understanding of the required enabling environment, and investigating the efficiency and effectiveness of various mechanisms and channels of climate finance are of critical importance for mobilizing and allocating financial resources reasonably and effectively to achieve global, national, and local climate change mitigation and adaptation goals.
The Special Issues of International Review of Financial Analysis and Finance Research Letters will directly address issues in this dynamic area of research and welcome a wide range of empirical methodologies and theoretical orientations addressing issues of material importance to future adoption of climate finance.
Toward these goals, the editors seek manuscripts that address research questions including, but not limited to:
- Advantages and disadvantages of climate finance under different institutional and environmental contexts
- Enabling environment for mobilizing climate finance – including dimensions of liquidity and secondary markets
- Explorations of the role of governments in promoting green finance
- Green investments and products and their interaction with traditional asset classes
- Identification of the advantages and disadvantages of green finance under different institutional and environmental contexts
- Investor demand for climate finance opportunities
- The efficiency and effectiveness of climate finance
- The interactions/associations between international fragmentation and domestic politics of green finance
- The overlap/conflicts between international fragmentation (on investment opportunities) and domestic politics behind climate finance
- The role of governments in promoting climate finance and/or attracting investors
- Theoretical and applied contributions on sustainability-growth nexus in the sector
- Uncovering of the effectiveness of green investments and financial products
- Understandings of the nature and norms of green finance as a financial phenomenon
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). 2014. 2014 Biennial assessment and overview of climate finance flows report. UNFCCC, Bonn.
Volz, U., Bohnke, L., Kneierim, Richert, K., Rober, G-M., and Eidt, V. (2015) Financing the Green Transformation: How to Make Green Finance Work in Indonesia, Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan.
Krushelnytska, O. (2017) Introduction to green finance. Global Environment Facility (GEF). Washington, D.C.: World Bank Group. http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/405891487108066678/Introduction-to-green-finance
Submission deadlines
The project will progress on an expedited timeline, adhering to the fixed deadlines set out below. Please format and reference your paper according to the requirements of the journal to whom you are submitting. Note that Elsevier journals work on a “online first” publication model, so as and when papers are accepted they are available online, with full citeable articles available when the SI’s are published.
Key dates:
(1) August 15th 2019 – Submission system open for submission of article (2) May 30th 2020 – Deadline for submission of articles (3) September 2020 – Special issue publication
About the Editors
Shunsuke Managi is the Distinguished Professor of Technology and Policy & Director of the Urban Institute at the Kyushu University, Japan. He has been awarded several national research grants on topics such as urbanization, transportation, energy, climate change, sustainability, and population change. He was a lead author for the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), a coordinating lead author for the Intergovernmental Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES), and director for the Inclusive Wealth Report 2018 (IWR 2018). He is chief-editor of “Economics of Disasters and Climate Change” and “Environmental Economics and Policy Studies”, and co-editor of “Resource and Energy Economics”. He is co-chair of the Scientific Committee for the 2018 World Congress of Environmental and Resource Economists.
David Broadstock is Deputy Director for the Center for Economic Sustainability and Entrepreneurial Finance in the School of Accounting and Finance at The Hong Kong Polytechnic University. David’s research interests cover various aspects of the empirical economics of energy and the environment, with special interests in consumer behaviour and energy finance. David is currently Editor for The Energy Journal, and an Editorial Board Member of the British Journal of Management.
Jeffrey Wurgler is the Nomura Professor of Finance at New York University Stern School of Business. His research and teaching interests include corporate finance and behavioral finance. Before joining Stern in 2001, Professor Wurgler was the Robert B. and Candice J. Haas Assistant Professor of Corporate Finance at Yale School of Management. He has also been a Visiting Fellow at the University of Oxford Said Business School.Professor Wurgler received a Bachelor of Arts and Sciences degree from Stanford University and a PhD in Business Economics from Harvard University.
Return to Call For Papers
FinancialResearch.gov
Conferences, rising scholars call for papers.
Published: December 15, 2023
Share on Facebook Share on Linked In Logo for Twitter

Conference on the Future of Financial Stability
The Office of Financial Research (OFR) and the Review of Corporate Finance Studies (RCFS) invited submissions of high-quality theoretical and empirical papers from scholars who had recently obtained their PhD. The papers must have been focused on the future of financial stability in the context of new challenges arising from developments in fintech and shadow banking, as well as the implications of these issues for financial inclusion.
Consistent with the conference’s objective to center on rising scholars, all authors who submitted papers must have received their PhD within the last six years.
Possible subjects of interest for submitted papers include but are not limited to:
- interactions between monetary policy, financial conditions, and the buildup of fragilities in financial markets;
- connections between banks and shadow banks;
- contagion from shadow banks to the banking system during stressful market conditions;
- risk-taking in the shadow-banking and fintech sectors;
- emergence of big tech in finance;
- increased market concentration and its implications for financial stability;
- fintech, financial inclusion, and financial stability;
- geopolitical risks and their implications for market stability;
- roles of regulation and transparency; and
- financial stability’s implications for financial inclusion.
The conference aims to bring together rising scholars from the fields of finance and economics to discuss these issues from various points of view. Each paper will be assigned to a discussant. The symposium begins with a dinner on the evening of Thursday, May 2, 2024.
The conference anticipates refunding the travel expenses (economy class) and paying for accommodations of authors whose papers are accepted.
Back to Conferences
You are now leaving the OFR’s website.
You will be redirected to:
You are now leaving the OFR Website. The website associated with the link you have selected is located on another server and is not subject to Federal information quality, privacy, security, and related guidelines. To remain on the OFR Website, click 'Cancel'. To continue to the other website you selected, click 'Proceed'. The OFR does not endorse this other website, its sponsor, or any of the views, activities, products, or services offered on the website or by any advertiser on the website.
Thank you for visiting www.financialresearch.gov.

Smart Data Analytics, Investment Innovation, and Financial Technology
Digital Finance - Call for Papers: Fintech – Finance, Technologies, and the Society
The financial industry is experiencing an extremely important disruptive moment, the fintech revolution. Thanks to new technologies, a large number of financial services has been deeply renewed, and the customers experience has been deeply change. Moreover, new entrants, start-ups, corporations and big technology players, enters in activities which used to be traditionally reserved to banks and insurers.
From an academic point of view, the fintech revolution has opened the door to extensive applications of Artificial Intelligence to solve financial problems. An example is asset allocation, where e.g. reinforcement learning tools are considered as alternative to classical methodologies. Cryptoassets are nowadays considered as risky assets which deserve a thorough study. Smart contracts opened the door to new financial instruments. These are few examples of new topics that need a deep and rigorous academic analysis.
The growth of financial technology does not only disrupt the financial industry, it also offers opportunities for the society. For example, fintech can facilitate the offering of financial services to un- and underbanked. Offering financial services via mobiles for examples brings access to cheaper lending, international money transfer (remittances), and better savings/investment conditions to people who are excluded to these services or only have limited access to it due to geographical, social, or economic reasons. Fintech allows for alternative access to financing (‘financial inclusion”), e.g. through peer-to-peer lending, crowdfunding, or initial coin offerings, or offer machine-based services such as robo-advising. Fintech also offers a form of democratization of investment for individuals (including its risks) and funding to for social value creation to social enterprises or projects to counter social problems, e.g. via crowdfunding. In this way, fintech can have positive social impact, e.g. through peer-to-peer lending by empowering women or support socially vulnerable groups such as immigrants. Fintech may also foster sustainable finance. Especially when it comes to analyzing all kinds of data (ESG scores from different providers, social network activities, news data, weather data, financial data etc.) and incorporating it to investment or credit decisions. Lastly, fintech, and the use of AI/ML may also come with risks for society, e.g., when it comes to systematically discriminating certain groups due to mal-trained algorithms or the dependency on specific systems.
Objective and topics:
For this Special Issue, we invite rigorous and timely theoretical, empirical, qualitative, or quantitative research that develops a better understanding of the fintech phenomenon. We support studies that will generate both practical and theoretical implications.
To this end, and in line with the aim and scope of the journal, we are interested in high-quality submissions that embrace diverse methodological approaches and theoretical frameworks in all areas of Fintech (banking, asset management, insurance, payments, capital markets, internet of things) providing a multidisciplinary venue.
Submissions are welcome in all Fintech research fields such as (but not limited to):
- theoretical analysis of the fintech domain (finance and economic analysis);
- machine learning applications to finance;
- cryptocurrencies and digital currencies (like CBDC);
- blockchain technologies, smart contracts;
- big data analysis, nowcasting, and text analysis in finance;
- network analysis in finance;
- behavioral finance;
- fintech and its social impact (financial inclusion, environment, equality, ...);
- crowdfunding, social/P2P lending to increase access to finance and broaden the investor base;
- fintech as enabler of sustainable finance/impact investing;
- risks of machine-based decision making in finance;
- ethics and fintech to prevent a potential new financial crisis;
- big data and fintech (increasing privacy, cyber security);
- regulation of fintech markets to catalyze societal value creation.
This special issue follows up on the International Fintech Research Conference ( https://www.fintechlab.it/fintech_conference2022/ (this opens in a new tab) ), and the European Alternative Finance Research Conference 2022 ( http://www.uu.nl/ecaf (this opens in a new tab) ).
Instructions for Submission:
For submission, authors are requested to access the Springer Nature submission system at the following URL: https://submission.nature.com/new-submission/42521/3 (this opens in a new tab) . Choose "Research" when starting a new submission and in the details of the submission go to "Collection" and select "Special Issue: Fintech - Finance, technologies, and the Society" from a drop-down menu.
Potential authors are reminded that all papers that are finally accepted for this special issue will be subject to format restrictions complying with the publisher's standards. To speed up publication, and to ensure a unified layout throughout the special issue, authors are likely advised to use a LaTex. Springer's LaTex package can be used to prepare source files (please choose the formatting option "smallextended'"). The authors are highly recommended not to modify the class file by introducing personal settings and/or definitions. Word files are also accepted.
Editors of the Special Issue:
Daniele Marazzina and Emilio Barucci – Politecnico di Milano, Italy Ronald Kleverlaan, Friedemann Polzin, and Thomas Walther – Utrecht University, Netherlands
Important Dates:
Deadline for paper submission: April 30, 2023
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Finance Research Letters - Impact Score, Ranking, SJR, h-index, Citescore, Rating, Publisher, ISSN, and Other Important Details
Published By: Elsevier BV
Abbreviation: Finance Res. Lett.
Impact Score The impact Score or journal impact score (JIS) is equivalent to Impact Factor. The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as indexed by Clarivate's Web of Science. On the other hand, Impact Score is based on Scopus data.
Important details, about finance research letters.
Finance Research Letters is a journal published by Elsevier BV . This journal covers the area[s] related to Finance, etc . The coverage history of this journal is as follows: 2004-2022. The rank of this journal is 1090 . This journal's impact score, h-index, and SJR are 11.03, 81, and 2.231, respectively. The ISSN of this journal is/are as follows: 15446131, 15446123 . The best quartile of Finance Research Letters is Q1 . This journal has received a total of 11028 citations during the last three years (Preceding 2022).
Finance Research Letters Impact Score 2022-2023
The impact score (IS), also denoted as the Journal impact score (JIS), of an academic journal is a measure of the yearly average number of citations to recent articles published in that journal. It is based on Scopus data.
Prediction of Finance Research Letters Impact Score 2023
Impact Score 2022 of Finance Research Letters is 11.03 . If a similar upward trend continues, IS may increase in 2023 as well.
Impact Score Graph
Check below the impact score trends of finance research letters. this is based on scopus data., finance research letters h-index.
The h-index of Finance Research Letters is 81 . By definition of the h-index, this journal has at least 81 published articles with more than 81 citations.
What is h-index?
The h-index (also known as the Hirsch index or Hirsh index) is a scientometric parameter used to evaluate the scientific impact of the publications and journals. It is defined as the maximum value of h such that the given Journal has published at least h papers and each has at least h citations.

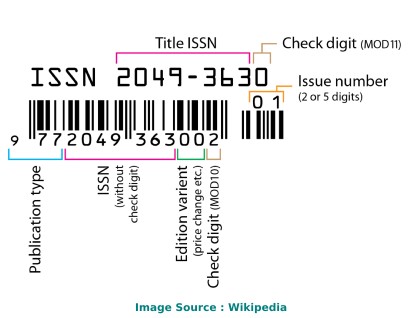
Finance Research Letters ISSN
The International Standard Serial Number (ISSN) of Finance Research Letters is/are as follows: 15446131, 15446123 .
The ISSN is a unique 8-digit identifier for a specific publication like Magazine or Journal. The ISSN is used in the postal system and in the publishing world to identify the articles that are published in journals, magazines, newsletters, etc. This is the number assigned to your article by the publisher, and it is the one you will use to reference your article within the library catalogues.
ISSN code (also called as "ISSN structure" or "ISSN syntax") can be expressed as follows: NNNN-NNNC Here, N is in the set {0,1,2,3...,9}, a digit character, and C is in {0,1,2,3,...,9,X}
Finance Research Letters Ranking and SCImago Journal Rank (SJR)
SCImago Journal Rank is an indicator, which measures the scientific influence of journals. It considers the number of citations received by a journal and the importance of the journals from where these citations come.
Finance Research Letters Publisher
The publisher of Finance Research Letters is Elsevier BV . The publishing house of this journal is located in the Netherlands . Its coverage history is as follows: 2004-2022 .
Call For Papers (CFPs)
Please check the official website of this journal to find out the complete details and Call For Papers (CFPs).
Abbreviation
The International Organization for Standardization 4 (ISO 4) abbreviation of Finance Research Letters is Finance Res. Lett. . ISO 4 is an international standard which defines a uniform and consistent system for the abbreviation of serial publication titles, which are published regularly. The primary use of ISO 4 is to abbreviate or shorten the names of scientific journals using the technique of List of Title Word Abbreviations (LTWA).
As ISO 4 is an international standard, the abbreviation ('Finance Res. Lett.') can be used for citing, indexing, abstraction, and referencing purposes.
How to publish in Finance Research Letters
If your area of research or discipline is related to Finance, etc. , please check the journal's official website to understand the complete publication process.
Acceptance Rate
- Interest/demand of researchers/scientists for publishing in a specific journal/conference.
- The complexity of the peer review process and timeline.
- Time taken from draft submission to final publication.
- Number of submissions received and acceptance slots
- And Many More.
The simplest way to find out the acceptance rate or rejection rate of a Journal/Conference is to check with the journal's/conference's editorial team through emails or through the official website.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the impact score of finance research letters.
The latest impact score of Finance Research Letters is 11.03. It is computed in the year 2023.
What is the h-index of Finance Research Letters?
The latest h-index of Finance Research Letters is 81. It is evaluated in the year 2023.
What is the SCImago Journal Rank (SJR) of Finance Research Letters?
The latest SCImago Journal Rank (SJR) of Finance Research Letters is 2.231. It is calculated in the year 2023.
What is the ranking of Finance Research Letters?
The latest ranking of Finance Research Letters is 1090. This ranking is among 27955 Journals, Conferences, and Book Series. It is computed in the year 2023.
Who is the publisher of Finance Research Letters?
Finance Research Letters is published by Elsevier BV. The publication country of this journal is Netherlands.
What is the abbreviation of Finance Research Letters?
This standard abbreviation of Finance Research Letters is Finance Res. Lett..
Is "Finance Research Letters" a Journal, Conference or Book Series?
Finance Research Letters is a journal published by Elsevier BV.
What is the scope of Finance Research Letters?
For detailed scope of Finance Research Letters, check the official website of this journal.
What is the ISSN of Finance Research Letters?
The International Standard Serial Number (ISSN) of Finance Research Letters is/are as follows: 15446131, 15446123.
What is the best quartile for Finance Research Letters?
The best quartile for Finance Research Letters is Q1.
What is the coverage history of Finance Research Letters?
The coverage history of Finance Research Letters is as follows 2004-2022.
Credits and Sources
- Scimago Journal & Country Rank (SJR), https://www.scimagojr.com/
- Journal Impact Factor, https://clarivate.com/
- Issn.org, https://www.issn.org/
- Scopus, https://www.scopus.com/
Note: The impact score shown here is equivalent to the average number of times documents published in a journal/conference in the past two years have been cited in the current year (i.e., Cites / Doc. (2 years)). It is based on Scopus data and can be a little higher or different compared to the impact factor (IF) produced by Journal Citation Report. Please refer to the Web of Science data source to check the exact journal impact factor ™ (Thomson Reuters) metric.
Impact Score, SJR, h-Index, and Other Important metrics of These Journals, Conferences, and Book Series
Check complete list
Finance Research Letters Impact Score (IS) Trend
Top journals/conferences in finance.
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to format your references using the Finance Research Letters citation style
This is a short guide how to format citations and the bibliography in a manuscript for Finance Research Letters . For a complete guide how to prepare your manuscript refer to the journal's instructions to authors.
- Using reference management software
Typically you don't format your citations and bibliography by hand. The easiest way is to use a reference manager:
- Journal articles
Those examples are references to articles in scholarly journals and how they are supposed to appear in your bibliography.
Not all journals organize their published articles in volumes and issues, so these fields are optional. Some electronic journals do not provide a page range, but instead list an article identifier. In a case like this it's safe to use the article identifier instead of the page range.
- Books and book chapters
Here are examples of references for authored and edited books as well as book chapters.
Sometimes references to web sites should appear directly in the text rather than in the bibliography. Refer to the Instructions to authors for Finance Research Letters.
This example shows the general structure used for government reports, technical reports, and scientific reports. If you can't locate the report number then it might be better to cite the report as a book. For reports it is usually not individual people that are credited as authors, but a governmental department or agency like "U. S. Food and Drug Administration" or "National Cancer Institute".
- Theses and dissertations
Theses including Ph.D. dissertations, Master's theses or Bachelor theses follow the basic format outlined below.
- News paper articles
Unlike scholarly journals, news papers do not usually have a volume and issue number. Instead, the full date and page number is required for a correct reference.
- In-text citations
References should be cited in the text by name and year in parentheses :
Here are examples of in-text citations with multiple authors:
- Two authors: (Kidner and Martienssen, 2004)
- Three or more authors: (Michel et al., 2011)
- About the journal
- Other styles
- Bioorganic Chemistry
- Veterinary Pathology
An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS. A lock ( Lock Locked padlock ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Dear Colleague Letter: Planning Proposals for Centers of Research Excellence in Science and Technology (CREST Centers) in Computer and Information Science and Engineering (CISE)
May 09, 2024
Dear Colleagues:
Consistent with the National Science Foundation's (NSF) efforts to increase institutional diversity within science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM), the Directorate of STEM Education (EDU) and the Directorate for Computer and Information Science and Engineering (CISE) jointly encourage the submission of planning proposals for a future CREST center proposal with a focus on research in all areas of CISE to include the participation of the full spectrum of diverse talent in STEM.
The CREST Program supports the creation of research centers that will lead to strong societal impacts through 5-year awards. The projects focus on the enhancement of institutional capacity building and research expansion at Minority-Serving Institutions (MSIs) through the establishment of centers that effectively integrate education and research. CREST Center awards promote the development of new knowledge, the increase in the research productivity of individual faculty, institution, and the expanded engagement of students from all backgrounds in STEM disciplines
A CREST award is expected to catalyze institutional transformation through the development of research capabilities aligned with the institution’s mission and long-term goals. Demonstrated leadership to increase opportunities everywhere, for everyone in STEM is expected at all levels – students, postdoctoral researchers when applicable, and faculty. The research activities supported by CREST are expected to enable the full participation of faculty, graduate students, and undergraduates in a nationally competitive research enterprise.
A competitive CREST proposal will include a meaningful, coherent plan for building sustainable research capability. Formulation of such a plan requires time and resources, which may not otherwise be available to some and thus could constitute a barrier to preparing a CREST proposal. Through this Dear Colleague Letter (DCL), EDU and CISE jointly encourage the submission of planning proposals for CREST centers with a focus on all core research areas within CISE, to help mitigate potential barriers to the preparation of competitive CREST proposals for the proposing institutions and Principal Investigators (PIs).
A CREST center proposal planning award could be used to support initial conceptualization and design of collaborative activities to facilitate the formulation of new and coherent plans for future submission of a CREST center proposal. Anticipated planning activities could include, but are not limited to, planning visits/meetings within the institution and with partnering institutions to discuss potential collaborations, exchanges to launch/initiate scientific collaboration, strategic planning (including the development of a collaborative research plan), training efforts and infrastructure needs to enable coordination of collaborative efforts, and development of evaluation strategies.
Institutions from EPSCoR jurisdictions are always encouraged to apply for NSF support and are particularly welcome to apply to the CREST program. In addition, we seek individuals from EPSCoR jurisdictions to serve as merit review panelists which is an excellent way to learn about an NSF program you may want to apply to in the future.
PROPOSAL PREPARATION AND SUBMISSION
Proposals must be prepared in accordance with the guidance for Planning Proposals specified in Chapter II.F.1 of the NSF Proposal and Award Policies and Procedures Guide (PAPPG) and submitted through Research.gov. Proposers should select the current PAPPG as the funding opportunity and direct proposals to EDU/EES/Centers for Research Excellence in S&T, as listed in research.gov.
Interested proposers should follow this guidance closely:
- The proposal must include a clear statement as to why this project is appropriate for a planning proposal, including how the funds will be used to formulate a sound approach for future submission of a CREST center proposal.
- The proposal must explain how a competitive research center will be created and sustained.
- The proposed research should be aligned with research supported by the Directorate for Computer and Information Science and Engineering (CISE). The PIs are encouraged to outline a vision that simultaneously promotes inclusiveness and research excellence in CISE focused funding areas.
- The PI must hold a faculty appointment at an eligible MSI that awards degrees in computer science or computer engineering and must be eligible to submit a future CREST center proposal as defined in the recent CREST Centers solicitation .
- The budget may be up to $100,000/year (including indirect costs) and up to two years in duration.
Prospective PIs must send an initial concept outline (no more than one page) by email no later than August 1, 2024 , to one of the Program Officers listed below to verify that the proposal topic fits with the research areas of the Directorate for Computer and Information Sciences and Engineering. An invitation from at least one NSF Program Officer to submit a full planning proposal must be uploaded by the PI in the “Program Officer Concurrence Email" section in Research.gov at submission of planning proposal. Planning proposals submitted in response to this DCL for consideration in FY 2025 are welcome through October 1, 2024, but earlier submission is strongly encouraged.
Please contact the following Program Officers for concept outline submission or any questions regarding this DCL:
- Subrata Acharya, Lead PO CISE Research Expansion, (CISE/CCF) [email protected]
- Sonal Dekhane, PO EDU, (EDU/EES), [email protected]
- Tomasz Durakiewicz, PO EDU, (EDU/EES, MPS/DMR), [email protected]
- Luis Cubano, Acting Deputy Division Director, EDU, (EDU/EES), [email protected]
James L. Moore III Assistant Director Directorate for STEM Education (EDU) Dilma Da Silva Acting Assistant Director Directorate for Computer & Information Science & Engineering (CISE)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Finance Research Letters ' submission system will be open for submissions to our Special Issue from February 1, 2024. When submitting your manuscript to Editorial Manager®, please select the article type "VSI: Alternative data in finance". Please submit your manuscript before December 31, 2024.
This journal enables you to publish research objects related to your original research - such as data, methods, protocols, software and hardware - as an additional paper in a Research Elements journal. Research Elements is a suite of peer-reviewed, open access journals which make your research objects findable, accessible and reusable.
Call For Papers Climate Change and Environmental Sustainability in Emerging Market Banking and Finance A Special Issue of the: Finance Research Letters Special Issue Editors Suk-Joong Kim Professor of International Finance and Banking, The University of Sydney Business School, Australia email: [email protected] Haekwon Lee Senior Lecturer, The University of Sydney Business School ...
About the journal. Finance Research Letters invites submissions in all areas of finance, broadly defined. Finance Research Letters offers and ensures the rapid publication of important new results in these areas. We aim to provide a rapid response to papers, with all papers undergoing a desk review by one of the …. View full aims & scope.
Scope. Finance Research Letters invites submissions in all areas of finance, broadly defined. Finance Research Letters offers and ensures the rapid publication of important new results in these areas. We aim to provide a rapid response to papers, with all papers undergoing a desk review by one of the Editors in Chief before being sent for review.
The Special Issues of International Review of Financial Analysis and Finance Research Letters will directly address issues in this dynamic area of research and welcome a wide range of empirical methodologies and theoretical orientations addressing issues of material importance to future adoption of climate finance.
Finance Research Letters. Volumes & Issues. ISSN: 1544-6123. Next planned ship date: May 10, 2024. 5 Year impact factor: 8.9. Impact factor: 10.4. Journal metrics. Request a sales quote. Finance Research Letters invites submissions in all areas of finance, broadly defined.
CALL FOR PAPERS . ANNUAL EVENT OF FINANCE RESEARCH LETTERS ; 2022 CEMLA CONFERENCE: NEW ADVANCES IN INTERNATIONAL FINANCE ; ... CONFERENCE THEME ; For the Finance Research Letters 2022hybrid conference (both in-person and on-line paper presentations), we would like to invite submissions on substantial, original, and unpublished research.
Finance Research Letters is a journal published by Elsevier BV. Check Finance Research Letters Impact Factor, Overall Ranking, Rating, h-index, Call For Papers, Publisher, ISSN, Scientific Journal Ranking (SJR), Abbreviation, Acceptance Rate, Review Speed, Scope, Publication Fees, Submission Guidelines, other Important Details at Resurchify
Against this backdrop, ADBI is seeking papers that analyse the relationship between investments consistent with climate-related SDGs and portfolio allocation as well as broader climate finance and investment issues. Papers will be considered for inclusion in a special issue of the journal Finance Research Letters and may deal with, but are ...
Xu Zhang, Zhiyu Lv, Muhammad Abubakr Naeem, Abdul Rauf, Jiawen Liu. Article 105371. View PDF. Article preview. Page 1 of 2. Read the latest articles of Finance Research Letters at ScienceDirect.com, Elsevier's leading platform of peer-reviewed scholarly literature.
Call for Papers: Special Issue on "Carbon Finance" Finance Research Letters Climate change poses a significant risk for companies and private households. Many industries, in particular the energy, transportation, and food sectors, but also the financial industry and the real estate sector are (in)directly affected by global warming and by
The conference aims to bring together rising scholars from the fields of finance and economics to discuss these issues from various points of view. Each paper will be assigned to a discussant. The symposium begins with a dinner on the evening of Thursday, May 2, 2024. The conference anticipates refunding the travel expenses (economy class) and ...
Digital Finance - Call for Papers: Fintech - Finance, Technologies, and the Society. The financial industry is experiencing an extremely important disruptive moment, the fintech revolution. Thanks to new technologies, a large number of financial services has been deeply renewed, and the customers experience has been deeply change.
This special issue brings together papers that have developed new theoretical or applied models employing AI and machine learning in a variety of financial problems. We encourage papers that explore new research perspectives such as the strategic behavior and interpretability of machine learning models, and applications to financial topics ...
Call for papers for a conference in Green Fintech and two special issues of "Finance Research Letters" and the "International Review of Economics and Finance"
The latest impact score (IS) of the Finance Research Letters is 11.03.It is computed in the year 2023 as per its definition and based on Scopus data. 11.03 It is increased by a factor of around 2.37, and the percentage change is 27.37% compared to the preceding year 2021, indicating a rising trend.The impact score (IS), also denoted as the Journal impact score (JIS), of an academic journal is ...
The easiest way is to use a reference manager: Paperpile. The citation style is built in and you can choose it in Settings > Citation Style or Paperpile > Citation Style in Google Docs. EndNote. Download the output style file. Mendeley, Zotero, Papers, and others. The style is either built in or you can download a CSL file that is supported by ...
Finance Research Letters offers and ensures the rapid publication of important new results in these areas. We aim to provide a rapid response to papers, with all papers undergoing a desk review by one of the Editors in Chief before being sent for review. Read Less. Finance Research Letters invites submissions in all areas of finance, broadly ...
Geophysical Research Letters is a gold open access journal that publishes high-impact, innovative, and timely communications-length articles on major advances spanning all of the major geoscience disciplines. Papers should have broad and immediate implications meriting rapid decisions and high visibility.
Call for papers for the Special Issue: Sustainable Regional Development in Sub-Saharan Africa. Guest editors: Dr. Samuel Amponsah Odei - Hradec Kralove, Czechia: [email protected] Submission deadline: 30 September 2024. Regional Science Policy & Practice • Impact Factor1.7 • CiteScore3.1.
May 09, 2024. Dear Colleagues: Consistent with the National Science Foundation's (NSF) efforts to increase institutional diversity within science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM), the Directorate of STEM Education (EDU) and the Directorate for Computer and Information Science and Engineering (CISE) jointly encourage the submission of planning proposals for a future CREST center ...
This call for papers is in conjunction with the Workshop on Recent Trends and New Developments in Sustainable, Green, and International Finance, to be held in Paris, May 13-14, 2024. Top-quality papers presented in this Workshop will be considered for publication in this special issue.