Definition of Context
Context is the background, environment, setting , framework, or surroundings of events or occurrences. Simply, context means circumstances forming a background of an event, idea, or statement, in such a way as to enable readers to understand the narrative or a literary piece. It is necessary for writing to provide information, new concepts, and words to develop thoughts.
Whenever writers use a quote or a fact from some source, it becomes necessary to provide their readers some information about the source, to give context to its use. This piece of information is called context. Context illuminates the meaning and relevance of the text and maybe something cultural, historical, social, or political.

Difference Between Content and Context
Content is a written text, while context is a place or situation. Although a text is not a context, content could present context within it. For example, if there occurs a statement in a certain text, it is content in its own right but it is also the context of that statement. It would show what comes next and what comes before that specific statement. Hence, it presents the context that is the place, situation or even atmosphere .
Rhetorical Context: Purpose, Author, and Audience
Although the context in literature is something different, it is different in rhetoric , too. In literary writings, it is just the situation where some statement or characters or events take place. However, in rhetoric, it is not just the text, it is also the purpose of the writing, its author and its audience that matter the most. They make up the context of that rhetorical piece. The reason is that rhetoric is specifically intended to be used for a specific purpose and by a specific person, or it loses its real purpose as well as its effectiveness.
Use of Context in Sentences
- This story was written in the 19 th century after the end of the Civil War. (The context mentions – when)
- Gandhi studied law in South Africa before returning to India and starting the Freedom Movement. (The context mentions – where)
- Harry Potter was published in 1997 by Bloomsbury, United Kingdom. (The context mentions when and where)
- Ivan heard ‘Bonjour’ as soon as he landed at the airport and saw the tower’s top on the way to the exit. (The context mentions a setting and the character is abroad)
- The English Tommies with their weapons entered the buildings to secure the area. (The context mentions the time period of WW1, when soldiers were called ‘Tommies’)
Examples of Context in Literature
Example #1: a tale of two cities by charles dickens.
Dickens begins his novel , A Tale of Two Cities , in 1770, by describing the release of Doctor Manette from Bastille, before taking the story to 1793 and early 1794. In this time span, the narrative covers a broad story. In a larger view, this novel begins in 1757, while its final scene looks forward to the situation in post-revolutionary Paris.
This story has a historical context, which Dickens has organized around various events that occurred during the French Revolution. He has drawn historical features from major events, including the fall of Bastille, the September Massacres, and the Reign of Terror. This backdrop is the story’s context.
Example #2: Animal Farm by George Orwell
George Orwell felt disillusioned by Soviet Communism and its revolution during his time. In the phenomenal novel, Animal Farm , Orwell has expressed himself by using satire through the allegorical characters of Old Major and Boxer; relating them to the Russian Revolution and its characters. Orwell uses animals to explain the history and context of Soviet Communism, some of which relate to party leaders. For instance, the pig Napoleon represents Joseph Stalin, and Snowball represents Leon Trotsky. In fact, Orwell uses this fable for political and aesthetic reasons, following the Russian Revolution as its context.
Example #3: Dr. Faustus by Christopher Marlowe
Historical context of Christopher Marlowe ’s Dr. Faustus is religious, as it hints at cultural changes taking place during Marlowe’s time. In 16th century Europe, there was a conflict between Roman Catholicism and the Protestant English Church. During this entire period, Calvinism was popular within the English churches; however, it was controversial. According to Calvinistic doctrine, the status of the people was predestined as saved or damned. Scholars and readers have debated on the stance that Marlowe’s play takes regarding the Calvinist doctrine, in whether Faustus is predestined to hell or not. The Renaissance period provides context for this play by Marlowe.
Example #4: Oedipus Rex by Sophocles
There is a popular saying that stories indicate the values and cultures of the societies in which their authors live. In Oedipus Rex , Sophocles presents his protagonist , Oedipus, struggling to implement his will against the destiny set forth by the Greek gods. During this process, Sophocles reveals the Greek values of the period during which he wrote the play.
He has illustrated the context of this play through the words and actions of Oedipus and other characters; as their Greek ideals concerning their governance, fate, and human relationships with the gods. These were some of the more popular themes of that era, and so form the context of the Oedipus Rex .
Example #5: Lord of the Flies by William Golding
“While stranded on a deserted island, a group of boys believe there is a dangerous creature lurking in the underbrush; Simon is the first to identify this menace, suggesting to the boys that ‘maybe,’ he said hesitantly, ‘maybe there is a beast’.”
This excerpt provides an excellent example of context, as it narrates an incident involving a group of young men on a deserted island. The context describes why they were afraid, giving a clear picture of the situation and setting.
Context is all about providing a background or picture of the situation, and of who is involved. Context is an essential part of a literary text, which helps to engage the audience. If writers ignore context, they may overlook a critical aspect of the story’s intent. Without context, readers may not see the true picture of a literary work. Context helps readers understand the cultural, social, philosophical, and political ideas and movements prevalent in society at the time of the writing.
Synonyms of Context
Context does not have an equivalent, it has several synonyms that could replace it in different contexts. For example, conditions, factors, surroundings, state of affairs, environment, situation, background, milieu, mood , ambiance, subject , text, theme , or topic.
Post navigation


- Scriptwriting
What is Context — Definition and Examples for Writers
- Point of View
- Protagonist
- Deus ex Machina
- Foreshadowing
- Iambic Pentameter
- Juxtaposition
- Personification
- Red Herring
- Alliteration
- Connotation
- Onomatopoeia
- Write Your Script For Free
C ontext has the ability to change the meaning of a story and how we view its characters — but what is context? We’re going to answer that question by looking at examples from The Office, In Cold Blood and more. We’ll also look at some tips and tricks for how you can effectively implement this necessary element in your own stories. By the end, you’ll know why context is so important and how to apply it in a variety of different ways. But before we jump into our examples, let’s define context.
Content vs Context Definition
What does context mean.
Whether we realize it or not, context is all around us. It is the fundamental way we come to understand people, situations and ideas. Everything that we think, say, see, hear, and do is a response to the external stimuli of the world.
And how we regard that stimuli is largely in response to the context it’s presented to us in. For more on this idea, check out the video from the University of Auckland below.
What is Context? By University of Auckland
So you’re probably thinking, “Okay that’s fine and good and all, but what is context? Surely the meaning can’t be so vague.” Well, it is and it isn’t.
But by understanding the essential aspects of the term, we’re better prepared to apply it in meaningful ways. So without further ado, let’s dive into a formal context definition.
CONTEXT DEFINITION
What is context.
Context is the facets of a situation, fictional or non-fictional, that inspire feelings, thoughts and beliefs of groups and individuals. It is the background information that allows people to make informed decisions. Most of the time, the view of a person on a subject will be made in response to the presented context. In storytelling, it is everything that surrounds the characters and plot to give both a particular perspective. No story takes place without contextual information and elements.
Characteristics of Context:
- Information that’s presented to us
- Used in an argumentative sense
- Biased/subjective form of education
ContextUal Information
Context clues : in and out of context.
In terms of storytelling, there are only two kinds of context: narrative and non-narrative. The former gives us information on the story and the latter gives us information on everything outside of the story.
Narrative types of context include:
Narrative context is everything that explains “what’s going on” in a story. Take a comedy series like The Office for example: there are a lot of moments in the show that wouldn’t make sense without contextual information — and there just so happens to be a video that explores The Office “out of context.”
What Does Context Mean in The Office?
Even the most ardent fans of The Office may find themselves asking, “what in the world is going on?” when presented with these clips out of context. On social media channels, moments from film and television are often presented like this — like this screen grab from The Good Place .

Context Definition and Examples
In a sense, out of context moments have become a type of humor in and of themselves. But it’s important that we also consider how information outside of the narrative may influence our feelings on the story.
Non-narrative types of context include:
Non-narrative context is everything outside the story that influences our thoughts and opinions on the subject matter. Take Truman Capote’s In Cold Blood for example: when we learn of the circumstances outside of the subject matter, it’s impossible for us to feel the same way about the story.
In Cold Blood is an investigative novel about the murder of a family of four in Holcomb, Kansas. Capote started writing about the murders in earnest before expanding his research into a full-fledged novel — the end result speaks for itself — not only is Capote’s prose considered some of the greatest of all-time, but it also pioneered true-crime writing.
But when In Cold Blood is viewed through the context of the man who wrote it, the setting it took place in, and the precedence of its writing, the meaning is liable to change. The two convicted murderers in the novel, Perry Smith and Dick Hickock, were interviewed by Capote through the writing process.
Their testimony is admitted in the novel, but filtered by Capote. So, for us to say their testimonies are veracious would be irresponsible, considering the context through which it was written.
Elsewhere, critics argue that we can only judge a piece of art based on the merit of the art itself, not the context it was created in. French literary theorist Roland Barthes said that “text” can only speak for itself and that the thoughts and feelings of the author should have no impact on its merit. For more on this “The Death of the Author” theory, watch the video below.
Exploring Context Clues • Lindsay Ellis on ‘The Death of the Author’
In recent years, many fans have criticized J.K. Rowling’s Harry Potter books in light of her political views. Some critics argue that her views change the meaning of the novels. Others argue that her views should have no impact. Alas, there’s no “right” answer, but it’s important to consider how context, both inside and outside of a story, can influence readers.
Context Clues Set the Stage
How to use context as exposition.
There’s a word in screenwriting that most screenwriters shutter to hear… and that word is exposition . Ah yes, the dreaded exposition — or explanatory description — has been known to sink more than a few good scripts. So, how do screenwriters use exposition effectively? Well, it starts with a need for context. When I say need, I mean the story would have no impact without it.
We imported the On the Waterfront screenplay into StudioBinder’s screenwriting software to look at an iconic scene where context is the primary force behind exposition.
In this scene, Terry details how Charley and Johnny abandoned him. This backstory, or exposition, adds the necessary context needed to make Terry’s exclamation, “I coulda’ been a contender!” impactful.
Click the link below to read the scene.

What is Context? • Read the On the Waterfront Screenplay
This explanatory description establishes a context in which we’re able to see that Terry has endured “years of abuse.” The context is further executed as Terry laments the actions of his best friends. Think of it this way: proper exposition should act like a tea-kettle; each relevant detail making the kettle hotter and hotter — or more contextual and more contextual — until — the tension is released… and whoosh, the conflict is resolved.
How to Add Context Clues
Tips for incorporating context.
Context plays a huge role in guiding the attention and emotional attachment of the audience. Say a character does something really bad, like kill another character. Our natural inclination is to vilify them, but if their actions are given context, we might view their actions as heroic.
Take Ridley Scott’s Gladiator for example: when Maximus kills Commodus, we view him as the hero. Let’s take a look at how this scene plays out:
Context Examples in Gladiator
In context, Maximus’ actions are justified. Commodus killed Maximus’ family and rigged the fight against him. As such, it makes sense that we root for his death. Here are some tips for how to incorporate context in your own works:
- Create empathy for your protagonist
- Vilify your antagonist
- Maximize conflict
- Develop themes
- Callback to prior events
By utilizing these strategies, you’ll create narrative continuity. Context relies on the impact of the past, so you should be mindful of the character’s pasts at all times when writing.
What is a Plot?
Context may be what informs our understanding of a story’s events, but it would mean nothing if there weren’t events to be informed of. Plot refers to the events and actions that take place within a story — and it’s an essential aspect of every narrative. In this next article, we look at how plot is used in Die Hard to connect narrative threads from beginning to end!
Up Next: Plot Definition and Examples →
Write and produce your scripts all in one place..
Write and collaborate on your scripts FREE . Create script breakdowns, sides, schedules, storyboards, call sheets and more.
That's Good please keep it up for your work. It's very understanding
Can I be your student? I have found your teaching interesting.
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Pricing & Plans
- Product Updates
- Featured On
- StudioBinder Partners
- The Ultimate Guide to Call Sheets (with FREE Call Sheet Template)
- How to Break Down a Script (with FREE Script Breakdown Sheet)
- The Only Shot List Template You Need — with Free Download
- Managing Your Film Budget Cashflow & PO Log (Free Template)
- A Better Film Crew List Template Booking Sheet
- Best Storyboard Softwares (with free Storyboard Templates)
- Movie Magic Scheduling
- Gorilla Software
- Storyboard That
A visual medium requires visual methods. Master the art of visual storytelling with our FREE video series on directing and filmmaking techniques.
We’re in a golden age of TV writing and development. More and more people are flocking to the small screen to find daily entertainment. So how can you break put from the pack and get your idea onto the small screen? We’re here to help.
- Making It: From Pre-Production to Screen
- How to Get a Film Permit — A Step-by-Step Breakdown
- How to Make a Storyboard — Ultimate Guide with Free Storyboard Templates
- VFX vs. CGI vs. SFX — Decoding the Debate
- What is a Freeze Frame — The Best Examples & Why They Work
- TV Script Format 101 — Examples of How to Format a TV Script
- 1 Pinterest
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
1 Audience, Purpose, & Context
Questions to Ponder
Discuss these following scenario with your partners:
Imagine you are a computer scientist, and you have written an important paper about cybersecurity. You have been invited to speak at a conference to explain your ideas. As you prepare your slides and notes for your speech, you are thinking about these questions:
- What kind of language should I use?
- What information should I include on my slides?
Now, imagine you are the same computer scientist, and you have a nephew in 3rd grade. Your nephew’s teacher has invited you to come to his class for Parents’ Day, to explain what you do at work. Will you give the same speech to the class of eight-year-olds? How will your language and information be the same or different?
Thinking about audience, purpose, and context
Before we give the presentations in the scenarios described above, we need to consider our audience, purpose, and context. We need to adjust the formality and complexity of our language, depending on what our audience already knows. In the context of a professional conference, we can assume that our audience knows the technical language of our subject. In a third grade classroom, on the other hand, we would use less complex language. For the professional conference, we could include complicated information on our slides, but that probably wouldn’t be effective for children. Our purpose will also affect how we make our presentation; we want to inform our listeners about cybersecurity, but we may need to entertain an audience of third graders a bit more than our professional colleagues.
The same thing is true with writing. For example, when we are writing for an academic audience of classmates and instructors, we use more formal, complex language than when we are writing for an audience of children. In all cases, we need to consider what our audience already knows, what they might think about our topic, and how they will respond to our ideas.
In writing, we also need to think about appearance, just as we do when giving a presentation. The way our essay looks is an important part of establishing our credibility as authors, in the same way that our appearance matters in a professional setting. Careful use of MLA format and careful proofreading help our essays to appear professional; consult MLA Formatting Guides for advice.
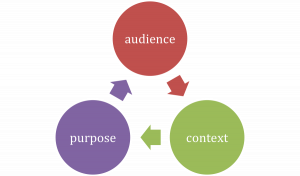
Before you start to write, you need to know:
Who is the intended audience ? ( Who are you writing this for?)
What is the purpose ? ( Why are you writing this?)
What is the context ? ( What is the situation, when is the time period, and where are your readers?)
We will examine each of these below.
AUDIENCE ~ Who are you writing for?
Your audience are the people who will read your writing, or listen to your presentation. In the examples above, the first audience were your professional colleagues; the second audience were your daughter and her classmates. Naturally, your presentation will not be the same to these two audiences.
Here are some questions you might think about as you’re deciding what to write about and how to shape your message:
- What do I know about my audience? (What are their ages, interests, and biases? Do they have an opinion already? Are they interested in the topic? Why or why not?)
- What do they know about my topic? (And, what does this audience not know about the topic? What do they need to know?)
- What details might affect the way this audience thinks about my topic? (How will facts, statistics, personal stories, examples, definitions, or other types of evidence affect this audience?)
In academic writing, your readers will usually be your classmates and instructors. Sometimes, your instructor may ask you to write for a specific audience. This should be clear from the assignment prompt; if you are not sure, ask your instructor who the intended audience is.
PURPOSE – Why are you writing?
Your primary purpose for academic writing may be to inform, to persuade, or to entertain your audience. In the examples above, your primary purpose was to inform your listeners about cybersecurity.
Audience and purpose work together, as in these examples:
- I need to write a letter to my landlord explaining why my rent is late so she won’t be upset. (Audience = landlord; Purpose = explaining my situation and keeping my landlord happy)
- I want to write a proposal for my work team to persuade them to change our schedule. (Audience = work team; Purpose = persuading them to get the schedule changed)
- I have to write a research paper for my environmental science instructor comparing solar to wind power. (Audience = instructor; Purpose = informing by analyzing and showing that you understand these two power sources)
Here are some of the main kinds of informative and persuasive writing you will do in college:
How Do I Know What My Purpose Is?
Sometimes your instructor will give you a purpose, like in the example above about the environmental science research paper ( to inform ), but other times, in college and in life, your purpose will depend on what effect you want your writing to have on your audience. What is the goal of your writing? What do you hope for your audience to think, feel, or do after reading it? Here are a few possibilities:
- Persuade or inspire them to act or to think about an issue from your point of view.
- Challenge them or make them question their thinking or behavior.
- Argue for or against something they believe or do; change their minds or behavior.
- Inform or teach them about a topic they don’t know much about.
- Connect with them emotionally; help them feel understood.
There are many different types of writing in college: essays, lab reports, case studies, business proposals, and so on. Your audience and purpose may be different for each type of writing, and each discipline, or kind of class. This brings us to context.
CONTEXT ~ What is the situation?
When and where are you and your readers situated? What are your readers’ circumstances? What is happening around them? Answering these questions will help you figure out the context, which helps you decide what kind of writing fits the situation best. The context is the situation, setting, or environment; it is the place and time that you are writing for. In our examples above, the first context is a professional conference; the second context is a third-grade classroom. The kind of presentation you write would be very different for these different contexts.
Here’s another example: Imagine that your car breaks down on the way to class. You need to send a message to someone to help you.
AUDIENCE : your friends
PURPOSE : to ask for help
CONTEXT : you are standing by the side of Little Patuxent Parkway, 10 minutes before class begins. Your friends are already at the campus Starbucks or in Duncan Hall.
Do you and your readers have time for you to write a 1,000-word essay about how a car works, and how yours has broken down? Or would one word (‘help!’) and a photo be a better way to send your message?
Now imagine that you are enrolled in a mechanical engineering class, and your professor has asked for a 4-page explanation of how internal combustion works in your car. What kind of writing should you produce? This would be the appropriate audience, purpose, and context for the 1,000-word essay about how a car works.
Activity ~ A Note about Tone
As you consider your audience, purpose, and context, you will need to think about your word choice as well. For example, say these two phrases out loud:
- very sick kids
- seriously ill children
Do they mean the same thing? Would you use the phrases in the same way? How about:
- lots of stuff
The words we choose help determine the tone of our writing, which is connected to audience, purpose, and context. Can you think of other examples using formal and informal tone?
Is this chapter:
…about right, but you would like more detail? –> Watch “ Audience: Introduction & Overview ” and from Purdue’s Online Writing Lab. Also, view “ Purpose, Audience, & Context ” from The Ohio State University.
…about right, but you prefer to listen and learn? –> Try “ Thinking About Your Assignment ” from the Excelsior OWL and “ A Smart Move: Responding the Rhetorical Situation .”
…too easy? –> Watch “ Writing for Audiences in U.S. Academic Settings ” from Purdue OWL.
Or, how about watching a funny video? In this short (3.5 minutes) video from the popular children’s program Sesame Street , Sir Ian McKellen tries to teach Cookie Monster a new word, but at first, Sir Ian doesn’t really understand what his audience knows (or doesn’t know), so Cookie Monster doesn’t understand.
Portions of this chapter were modified from the following Open Educational Resources:
Saylor Academy under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License without attribution as requested by the work’s original creator or licensor.
“ Audience ” and “ Purpose ” chapters from The Word on College Reading and Writing by Carol Burnell, Jaime Wood, Monique Babin, Susan Pesznecker, and Nicole Rosevear, which is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Note: links open in new tabs.
to think about
believability
ENGLISH 087: Academic Advanced Writing Copyright © 2020 by Nancy Hutchison is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
The writer of the academic essay aims to persuade readers of an idea based on evidence. The beginning of the essay is a crucial first step in this process. In order to engage readers and establish your authority, the beginning of your essay has to accomplish certain business. Your beginning should introduce the essay, focus it, and orient readers.
Introduce the Essay. The beginning lets your readers know what the essay is about, the topic . The essay's topic does not exist in a vacuum, however; part of letting readers know what your essay is about means establishing the essay's context , the frame within which you will approach your topic. For instance, in an essay about the First Amendment guarantee of freedom of speech, the context may be a particular legal theory about the speech right; it may be historical information concerning the writing of the amendment; it may be a contemporary dispute over flag burning; or it may be a question raised by the text itself. The point here is that, in establishing the essay's context, you are also limiting your topic. That is, you are framing an approach to your topic that necessarily eliminates other approaches. Thus, when you determine your context, you simultaneously narrow your topic and take a big step toward focusing your essay. Here's an example.
The paragraph goes on. But as you can see, Chopin's novel (the topic) is introduced in the context of the critical and moral controversy its publication engendered.
Focus the Essay. Beyond introducing your topic, your beginning must also let readers know what the central issue is. What question or problem will you be thinking about? You can pose a question that will lead to your idea (in which case, your idea will be the answer to your question), or you can make a thesis statement. Or you can do both: you can ask a question and immediately suggest the answer that your essay will argue. Here's an example from an essay about Memorial Hall.
The fullness of your idea will not emerge until your conclusion, but your beginning must clearly indicate the direction your idea will take, must set your essay on that road. And whether you focus your essay by posing a question, stating a thesis, or combining these approaches, by the end of your beginning, readers should know what you're writing about, and why —and why they might want to read on.
Orient Readers. Orienting readers, locating them in your discussion, means providing information and explanations wherever necessary for your readers' understanding. Orienting is important throughout your essay, but it is crucial in the beginning. Readers who don't have the information they need to follow your discussion will get lost and quit reading. (Your teachers, of course, will trudge on.) Supplying the necessary information to orient your readers may be as simple as answering the journalist's questions of who, what, where, when, how, and why. It may mean providing a brief overview of events or a summary of the text you'll be analyzing. If the source text is brief, such as the First Amendment, you might just quote it. If the text is well known, your summary, for most audiences, won't need to be more than an identifying phrase or two:
Often, however, you will want to summarize your source more fully so that readers can follow your analysis of it.
Questions of Length and Order. How long should the beginning be? The length should be proportionate to the length and complexity of the whole essay. For instance, if you're writing a five-page essay analyzing a single text, your beginning should be brief, no more than one or two paragraphs. On the other hand, it may take a couple of pages to set up a ten-page essay.
Does the business of the beginning have to be addressed in a particular order? No, but the order should be logical. Usually, for instance, the question or statement that focuses the essay comes at the end of the beginning, where it serves as the jumping-off point for the middle, or main body, of the essay. Topic and context are often intertwined, but the context may be established before the particular topic is introduced. In other words, the order in which you accomplish the business of the beginning is flexible and should be determined by your purpose.
Opening Strategies. There is still the further question of how to start. What makes a good opening? You can start with specific facts and information, a keynote quotation, a question, an anecdote, or an image. But whatever sort of opening you choose, it should be directly related to your focus. A snappy quotation that doesn't help establish the context for your essay or that later plays no part in your thinking will only mislead readers and blur your focus. Be as direct and specific as you can be. This means you should avoid two types of openings:
- The history-of-the-world (or long-distance) opening, which aims to establish a context for the essay by getting a long running start: "Ever since the dawn of civilized life, societies have struggled to reconcile the need for change with the need for order." What are we talking about here, political revolution or a new brand of soft drink? Get to it.
- The funnel opening (a variation on the same theme), which starts with something broad and general and "funnels" its way down to a specific topic. If your essay is an argument about state-mandated prayer in public schools, don't start by generalizing about religion; start with the specific topic at hand.
Remember. After working your way through the whole draft, testing your thinking against the evidence, perhaps changing direction or modifying the idea you started with, go back to your beginning and make sure it still provides a clear focus for the essay. Then clarify and sharpen your focus as needed. Clear, direct beginnings rarely present themselves ready-made; they must be written, and rewritten, into the sort of sharp-eyed clarity that engages readers and establishes your authority.
Copyright 1999, Patricia Kain, for the Writing Center at Harvard University
What Is Context? Definition, Usage, and Literary Examples
Context definition.
Context (KAHN-tekst) is the circumstances that inform an event, an idea, or a statement. It is the detail that adds meaning to a text. Readers can study internal context—details included by the author, such as backstory, characterization , or setting —as well as external context—the time period of the work’s publication, the author’s literary influences, and even their personal history.
Imagine context as a bridge between the writer and the reader that clarifies a text’s meaning and purpose. Authors provide these details to ensure a story is richly developed and true to life, and readers consider external context to understand a story’s broader significance.
Types of Context
There are several types of literary context, but the following are the most common applications.
Authorial Context
A writer’s experiences inevitably inform their writing, from content to style. This biographical context can refer to an author’s life history, a text’s place in an author’s body of work, the author’s success, the circumstances in which a text was written, current events at the time of publication, and even an author’s motivation for writing a text.
Historical Context
Literature is often influenced by history. Historical novels are directly grounded in past events and circumstances, but historical context also encompasses how literature reflects or responds to the society in which it was written. This can manifest as intentional criticism, in which an author addresses a social issue and perhaps argues for change (e.g., Jonathan Swift’s “ A Modest Proposal ,” his satirical indictment of the aristocracy). However, literature can also unconsciously reflect attitudes or beliefs predominant at the time of composition. Gone with the Wind is a beloved classic, but modern audiences often criticize its sanitized portrayal of slavery.
Philosophical Context
Literature addresses age-old questions of metaphysics, ethics, and morality. It ponders the purpose of life, the nature of God or the universe, right versus wrong, death, time—the list goes on. Philosophies go in and out of style, and the great literary movements were influenced by philosophies that waxed and waned over time. Romanticism was followed by realism , which was followed by transcendentalism and then naturalism , modernism, postmodernism, and so on. Each of these movements was influenced by contemporaneous philosophical thought, and readers can learn much about a text by researching those concepts, the associated philosophers, and the author’s stance on the issue.
Literary Context
Allusion is a common demonstration of literary context, in which one text indirectly references another. But literary context can include several different things, such as an author’s role models or the way one text influences another. Literary context also considers how a text fits into broad categories of literature, such as the aforementioned literary movements.
How Writers Use Context
Writers use context to engage, inform, and entertain readers. These details establish the narrative ’s setting and the author’s motivation for writing, and they help propel the action. Context adds authenticity, helping a story reflect readers’ experiences and securing their investment in the text. Like most literary tools, moderation is essential when it comes to context. Too much of it can burden a story, rendering it boring or incomprehensible.
Context can be conveyed through just about anything— characterization , setting, backstory, memory, dialogue, and so on. If a detail informs readers’ understanding of the text, engages their intellect or emotions, or hooks their interest, then it can be used as context. However, specificity is key. By choosing what context to include, and when and how to do so, writers can guide readers’ interpretation of a text. They can also incorporate specific details to better anchor a story in a particular time or place. Consider the HBO miniseries Chernobyl . It is ostensibly about the 1986 Chernobyl nuclear disaster in Pripyat, Russia, but the show’s true focus is government lies and corruption. The show uses the context of Soviet Russia to elicit nostalgia and cultural memory, emphasizing how modern politics echo that of the Cold War era.
Context can also inspire. A writer might reflect upon their life and realize they have a unique point of view worth sharing. They can use the context of their lives to communicate that perspective to the world. When a writer does this well, they spark understanding within readers, helping them make new connections and realizations.
Context and Literary Analysis
Publication opens a work up to criticism, including literary analysis, which dissects and evaluates literature to make connections that general audiences may have missed. Literary analysis hinges on context. Scholars and critics engage in close reading to discover deeper meaning, identify narrative patterns or themes, and detect influences, then analyze and synthesize their findings. They bring these disparate details together like puzzle pieces to explain why and how a text is significant and how it fits into culture and literature in general.
Writers’ Vernacular and Context Clues
When a reader encounters an unfamiliar word, they study the surrounding text to discern its meaning. This process of gleaning connotation is called using context clues. These are details that directly or indirectly suggest information about a word, phrase, or situation.
There are several types of context clues, the following five being the most common.
- Definition and explanation : There’s nothing subtle about these context clues, as the author clarifies the word’s intended meaning directly in the text.
- Inferences : When a word or idea is not explained within the same sentence, readers must decipher the writer’s implied or indirect meaning from the surrounding text.
- Synonyms and comparison : Synonyms draw comparisons that clarify, refine, or emphasize a writer’s meaning.
- Antonyms and contrast : Antonyms convey an opposite meaning to underscore contrast or disparity.
- Punctuation : Writers can use punctuation to several effects, such as conveying emotion (e.g., using exclamation points to express anger) or implying meaning (e.g., using parenthetical asides to suggest confidentiality).
Examples of Context in Literature
1. Margaret Atwood, The Handmaid’s Tale
Set in a dystopian near-future, The Handmaid’s Tale follows Offred and other subjugated women who strive to reclaim their independence after a theonomic totalitarian state called Gilead usurps the US government. This quote comes from Chapter 6, as Offred and fellow handmaiden Ofglen observe the corpses of people murdered by the state:
Ordinary, said Aunt Lydia, is what you are used to. This may not seem ordinary to you now, but after a time it will. It will become ordinary.
Gripped by horror, Offred recalls these words, which suggest that “ordinary” is a matter of perspective and that, in time, Gilead’s atrocities will seem normal. Aunt Lydia’s assurance that murder, oppression, and subjugation can become commonplace, even routine, reveals the depth of Gilead’s power and depravity.
2. Charles Dickens, A Tale of Two Cities
This novel, set before and during the French Revolution, tells the story of Doctor Alexandre Menette, who is imprisoned in the Bastille for 18 years then moves to London to reunite with his daughter Lucie. Dickens contextualizes the setting in the very first paragraph:
It was the best of times, it was the worst of times, it was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness, it was the epoch of belief, it was the epoch of incredulity, it was the season of Light, it was the season of Darkness, it was the spring of hope, it was the winter of despair, we had everything before us, we had nothing before us, we were all going direct to Heaven, we were all going direct the other way—in short, the period was so far like the present period, that some of its noisiest authorities insisted on its being received, for good or for evil, in the superlative degree of comparison only.
This passage immediately establishes that the novel’s main conflicts revolve around binary extremes, such as good and evil or wisdom and folly. This signals that the story is rife with contradiction and controversy, and that the setting is full of tension but also hope.
3. Tim O’Brien, “ The Things They Carried ”
This is the eponymous short story in a collection of tales about the Vietnam War. The story reflects on the things soldiers carry with them into war:
To carry something was to hump it, as when Lieutenant Jimmy Cross humped his love for Martha up the hills and through the swamps. In its intransitive form, to hump meant to walk, or to march, but it implied burdens far beyond the intransitive.
The opening phrase is a context clue that directly explains the author’s meaning. The passage further explains that although hump has alternative meanings, such as “to walk” or “to march,” in this context it means something more abstract, something heavy and grim.
Further Resources on Context
This Writing Cooperative article explains how context builds trust between the writer and their audience, and why that relationship is so important.
ThoughtCo provides a more thorough look at context clues —and their limitations.
This resource from Harper College explains the textual elements (including context) used to analyze literature.
Related Terms
- Characterization
- Point of View

The Hyperbolit School
Your trusty englit guide.

How to write about context in literary analysis essays
In literary studies, it’s usually not enough for us to just read and analyse primary texts (e.g. poems, novels, plays etc.)
In order to do well in English Literature, there’s something else called ‘ con text’ that we must also consider.
What is context?
In general, context refers to “the surrounding circumstances that form the setting for an event, statement, or idea, and in terms of which it can be understood” (Lexico).
In a nutshell, context is just a situation where many things happen.
So, in literary studies, we can simply understand context as the historical background of a work , and by ‘historical’, that includes economic, social, political, cultural and biographical circumstances .
Rarely do we come across great literary works which aren’t influenced by their wider contemporary currents, because most authors don’t live or write in a social vacuum, and so are necessarily impacted by the external events and ideas around them.
For instance, Charles Dickens wrote Hard Times against the backdrop of a post-Industrial Revolution London where capitalist exploitation and urban pollution were rampant; Jane Austen wrote Emma in a society where women cared more about getting married than gaining independence; and Wilfred Owen wrote the poem ‘Dulce et decorum est’ to reflect the horrific conditions suffered by frontline soldiers in WWI.

There are, of course, writers like the Decadents and Symbolists who believed in ‘art for art’s sake’ , such as Oscar Wilde and Charles Baudelaire, but even as they propounded the theory, their works still reflected social issues and embodied cultural ideas, and so were in no way divorced from the broader context, despite their aesthetic ideologies.
Why does context matter?
If you’re an English Lit student, context matters for two main reasons:
First, context helps us gain a deeper understanding of the purpose, themes and messages of any literary work, because authors are always inspired by real-life occurrences, and usually, by significant socio-political events and cultural shifts (Yes, even for someone like Henry David Thoreau , who famously decided to live like a hermit in a log cabin by a pond – but it was only for 2 years).
Second, showing contextual awareness is almost always required for exams. It’s an assessment objective in virtually all English Lit courses, from your I/GCSEs and A-Levels to IB, AP etc.
…You can watch me walk you through the process in the video below!
How to write about context in your literary analysis essays – 3 guiding questions
To incorporate contextual links in your literary analysis, I’ve come up with 3 guiding questions you can consider to navigate the process:
- Given what I know about the historical background of the work, what are some similar events, characters or patterns between the text and the time when the author was writing the text?
- Given the socio-political and/or economic conditions of the author’s context, what would a person similar to the character in the text most likely do, think or feel in that sort of environment?
- Why would the author be so influenced or impacted by what was going on around her to want to write a creative work about it? What is the historical significance of those events?
Let’s now apply these 3 questions to see how we can incorporate contextual links in an analysis.
Example – George Orwell’s Animal Farm
Here’s a paragraph taken from an essay titled ‘How is Napoleon the boar presented in George Orwell’s Animal Farm ?’:
Throughout the novella, Napoleon is portrayed as a menacing and dictatorial character. After the creation of ‘Animal Farm’, Napoleon engages with Snowball in a vicious power play, and plots a coup d’etat to overthrow his political rival. Napoleon’s plan of fostering a group of dogs as his loyal retinue also reflects his scheming personality, while his readiness to mobilise his canine sentinels against other animals on the farm also shows his cold-blooded and brutal nature. Upon the solidification of his power, Napoleon’s dictatorial colours truly come to light when “he announced that from now on the Sunday-morning Meetings would come to an end”, and that “in future all questions relating to the working of the farm would be settled by a special committee of pigs, presided over by himself” (Chapter 5). This mandate foreshadows the absolute erosion of democratic freedom on Animal Farm, and signals that all animals will eventually be subject to Napoleon’s authoritarian rule.
In this main body paragraph, the student does a fair job of presenting a focused point (“Napoleon is portrayed as a menacing and dictatorial character”), backing it up with relevant textual evidence (the quote from Ch. 5), and analysing the use of a literary technique (foreshadowing).
But there’s a missing piece, which is, of course, the contextual link.
So how can we relate Napoleon’s characterisation to the novella’s historical context?
To start, we should know that Orwell wrote Animal Farm as a satirical allegory of Stalinist totalitarianism , and that Napoleon is most likely based on Joseph Stalin, who ruled the USSR in a tyrannical fashion at the time when Orwell wrote his book in 1943.
With that, we can make further use of our 3 guiding questions to help formulate our points:
Both Napoleon and Stalin are tyrannical characters who require absolute subservience from their subjects, and they command authority mostly by spreading mass terror. Like Stalinist Russia, Animal Farm is subject to totalitarian rule with a strong personality cult centered on the supreme leader.
If someone gained absolute power over a group of obedient followers with no need for moral or social accountability, he would most likely maximise such outsized authority for his own benefit, in addition to suppressing all voices of opposition as a means to secure his rule.
- Why would the author be so influenced or impacted by what was going on around him to want to write a creative work about it? What is the historical significance of those events?
As a staunch believer in socialist democratic ideals of freedom, liberty and equality, Orwell would have been outraged by the Soviet Union’s blatant suppression of these values (and he was).
In the face of British support for the USSR as a WWII ally, however, Orwell could not have written an explicit critique of Stalin without meeting considerable pushback, which perhaps explains why he had chosen an allegorical format and anthropomorphic approach to characterisation for Animal Farm.
Now that we’re equipped with all this knowledge, let’s try weaving in the contextual information to upgrade our paragraph:
Throughout the novella, Napoleon is portrayed as a menacing and dictatorial character. He carries strong echoes of Joseph Stalin, the 1924-1953 Soviet leader who adopted a style of rule known as totalitarianism – a centralised and oppressive government requiring mass subservience, which Orwell, being a socialist democrat, was staunchly opposed to. After the creation of ‘Animal Farm’, Napoleon engages with Snowball in a vicious power play, and plots a coup d’etat to overthrow his political rival. Napoleon’s plan of fostering a group of dogs as his loyal retinue also reflects his scheming personality, while his readiness to mobilise his canine sentinels against other animals on the farm also shows his cold-blooded and brutal nature. Upon the solidification of his power, Napoleon’s dictatorial colours truly come to light when “he announced that from now on the Sunday-morning Meetings would come to an end”, and that “in future all questions relating to the working of the farm would be settled by a special committee of pigs, presided over by himself” (Chapter 5). This mandate foreshadows the absolute erosion of democratic discussion on Animal Farm, and signals that all animals will be subject to the boar’s authoritarian rule. Napoleon’s obsession with absolute power and expulsion of Snowball also mirror Stalin’s purge of Leon Trotsky, who had initially fought alongside Stalin during the Bolshevik Revolution, but was later persecuted and stripped of all government positions by his former comrade-in-arms.
Notice that in this version, we demonstrate at the very start of the paragraph our awareness of the wider political context which had inspired the novel.
Specifically, we do this by bringing in the reference to Stalin and drawing an association between the Soviet tyrant and the anthropomorphised tyrant, Napoleon.
This is followed by a point about Orwell’s anti-totalitarian political views, but note that we’re not asserting that Orwell is definitely criticising Stalin via his characterisation of Napoleon.
Instead, we’re simply suggesting this by stating a piece of contextual fact, i.e. Orwell was a socialist democrat, and socialist democrats hold opposing ideological views to authoritarian fascists.
At the end of the paragraph, we wrap up with another contextual link that connects Napoleon’s expulsion of Snowball from Animal Farm with a similar political event in Stalinist Russia, which was Stalin’s expulsion of Leon Trotsky from the USSR in 1929.
Want more study tips on English Lit? Check out my other blog posts below:
- 3 reasons why Frankenstein’s monster deserves our pity
- How to analyse prose passages using Of Mice and Men and Lord of the Flies
- Exploring good versus evil in The Strange Case of Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde

share this with a friend!
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
Leave a comment Cancel reply

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
- Privacy Policy

Home » Context of the Study – Writing Guide and Examples
Context of the Study – Writing Guide and Examples
Table of Contents

Context of the Study
The context of a study refers to the set of circumstances or background factors that provide a framework for understanding the research question , the methods used, and the findings . It includes the social, cultural, economic, political, and historical factors that shape the study’s purpose and significance, as well as the specific setting in which the research is conducted. The context of a study is important because it helps to clarify the meaning and relevance of the research, and can provide insight into the ways in which the findings might be applied in practice.
Structure of Context of the Study
The structure of the context of the study generally includes several key components that provide the necessary background and framework for the research being conducted. These components typically include:
- Introduction : This section provides an overview of the research problem , the purpose of the study, and the research questions or hypotheses being tested.
- Background and Significance : This section discusses the historical, theoretical, and practical background of the research problem, highlighting why the study is important and relevant to the field.
- Literature Review: This section provides a comprehensive review of the existing literature related to the research problem, highlighting the strengths and weaknesses of previous studies and identifying gaps in the literature.
- Theoretical Framework : This section outlines the theoretical perspective or perspectives that will guide the research and explains how they relate to the research questions or hypotheses.
- Research Design and Methods: This section provides a detailed description of the research design and methods, including the research approach, sampling strategy, data collection methods, and data analysis procedures.
- Ethical Considerations : This section discusses the ethical considerations involved in conducting the research, including the protection of human subjects, informed consent, confidentiality, and potential conflicts of interest.
- Limitations and Delimitations: This section discusses the potential limitations of the study, including any constraints on the research design or methods, as well as the delimitations, or boundaries, of the study.
- Contribution to the Field: This section explains how the study will contribute to the field, highlighting the potential implications and applications of the research findings.
How to Write Context of the study
Here are some steps to write the context of the study:
- Identify the research problem: Start by clearly defining the research problem or question you are investigating. This should be a concise statement that highlights the gap in knowledge or understanding that your research seeks to address.
- Provide background information : Once you have identified the research problem, provide some background information that will help the reader understand the context of the study. This might include a brief history of the topic, relevant statistics or data, or previous research on the subject.
- Explain the significance: Next, explain why the research is significant. This could be because it addresses an important problem or because it contributes to a theoretical or practical understanding of the topic.
- Outline the research objectives : State the specific objectives of the study. This helps to focus the research and provides a clear direction for the study.
- Identify the research approach: Finally, identify the research approach or methodology you will be using. This might include a description of the data collection methods, sample size, or data analysis techniques.
Example of Context of the Study
Here is an example of a context of a study:
Title of the Study: “The Effectiveness of Online Learning in Higher Education”
The COVID-19 pandemic has forced many educational institutions to adopt online learning as an alternative to traditional in-person teaching. This study is conducted in the context of the ongoing shift towards online learning in higher education. The study aims to investigate the effectiveness of online learning in terms of student learning outcomes and satisfaction compared to traditional in-person teaching. The study also explores the challenges and opportunities of online learning in higher education, especially in the current pandemic situation. This research is conducted in the United States and involves a sample of undergraduate students enrolled in various universities offering online and in-person courses. The study findings are expected to contribute to the ongoing discussion on the future of higher education and the role of online learning in the post-pandemic era.
Context of the Study in Thesis
The context of the study in a thesis refers to the background, circumstances, and conditions that surround the research problem or topic being investigated. It provides an overview of the broader context within which the study is situated, including the historical, social, economic, and cultural factors that may have influenced the research question or topic.
Context of the Study Example in Thesis
Here is an example of the context of a study in a thesis:
Context of the Study:
The rapid growth of the internet and the increasing popularity of social media have revolutionized the way people communicate, connect, and share information. With the widespread use of social media, there has been a rise in cyberbullying, which is a form of aggression that occurs online. Cyberbullying can have severe consequences for victims, such as depression, anxiety, and even suicide. Thus, there is a need for research that explores the factors that contribute to cyberbullying and the strategies that can be used to prevent or reduce it.
This study aims to investigate the relationship between social media use and cyberbullying among adolescents in the United States. Specifically, the study will examine the following research questions:
- What is the prevalence of cyberbullying among adolescents who use social media?
- What are the factors that contribute to cyberbullying among adolescents who use social media?
- What are the strategies that can be used to prevent or reduce cyberbullying among adolescents who use social media?
The study is significant because it will provide valuable insights into the relationship between social media use and cyberbullying, which can be used to inform policies and programs aimed at preventing or reducing cyberbullying among adolescents. The study will use a mixed-methods approach, including both quantitative and qualitative data collection and analysis, to provide a comprehensive understanding of the phenomenon of cyberbullying among adolescents who use social media.
Context of the Study in Research Paper
The context of the study in a research paper refers to the background information that provides a framework for understanding the research problem and its significance. It includes a description of the setting, the research question, the objectives of the study, and the scope of the research.
Context of the Study Example in Research Paper
An example of the context of the study in a research paper might be:
The global pandemic caused by COVID-19 has had a significant impact on the mental health of individuals worldwide. As a result, there has been a growing interest in identifying effective interventions to mitigate the negative effects of the pandemic on mental health. In this study, we aim to explore the impact of a mindfulness-based intervention on the mental health of individuals who have experienced increased stress and anxiety due to the pandemic.
Context of the Study In Research Proposal
The context of a study in a research proposal provides the background and rationale for the proposed research, highlighting the gap or problem that the study aims to address. It also explains why the research is important and relevant to the field of study.
Context of the Study Example In Research Proposal
Here is an example of a context section in a research proposal:
The rise of social media has revolutionized the way people communicate and share information online. As a result, businesses have increasingly turned to social media platforms to promote their products and services, build brand awareness, and engage with customers. However, there is limited research on the effectiveness of social media marketing strategies and the factors that contribute to their success. This research aims to fill this gap by exploring the impact of social media marketing on consumer behavior and identifying the key factors that influence its effectiveness.
Purpose of Context of the Study
The purpose of providing context for a study is to help readers understand the background, scope, and significance of the research being conducted. By contextualizing the study, researchers can provide a clear and concise explanation of the research problem, the research question or hypothesis, and the research design and methodology.
The context of the study includes information about the historical, social, cultural, economic, and political factors that may have influenced the research topic or problem. This information can help readers understand why the research is important, what gaps in knowledge the study seeks to address, and what impact the research may have in the field or in society.
Advantages of Context of the Study
Some advantages of considering the context of a study include:
- Increased validity: Considering the context can help ensure that the study is relevant to the population being studied and that the findings are more representative of the real world. This can increase the validity of the study and help ensure that its conclusions are accurate.
- Enhanced understanding: By examining the context of the study, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the factors that influence the phenomenon under investigation. This can lead to more nuanced findings and a richer understanding of the topic.
- Improved generalizability: Contextualizing the study can help ensure that the findings are applicable to other settings and populations beyond the specific sample studied. This can improve the generalizability of the study and increase its impact.
- Better interpretation of results: Understanding the context of the study can help researchers interpret their results more accurately and avoid drawing incorrect conclusions. This can help ensure that the study contributes to the body of knowledge in the field and has practical applications.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Skip to Content
Massey University
- Search OWLL
- Handouts (Printable)
- Pre-reading Service
- StudyUp Recordings
- StudyUp Postgraduate
- Academic writing
- Intro to academic writing
- What is academic writing?
- Writing objectively
- Writing concisely
- 1st vs. 3rd person
- Inclusive language
- Te Reo Māori
- Assignment planning
- Assignment planning calculator
- Interpreting the assignment question
- Command words
- Organising points
- Researching
- Identifying academic sources
- Evaluating source quality
- Editing & proofreading
- Apostrophes
- Other punctuation
- Active voice
- American vs. British spelling
- Conditionals
- Prepositions
- Pronoun Reference
- Sentence fragments
- Sentence Structure
- Subject-verb agreement
- Formatting and layout
- Word limits and assignment length
- Commonly confused words
- How assignments are marked
- Marking guides
- Getting an A
- Levels of assessment
- Using feedback
- Professional emails
- Forum posts
- Forum netiquette guidelines
- Sharing personal information
- Writing about personal experiences
- Assignment types
- What is an essay?
- Essay planning and structure
- Introduction
- Thesis statement
- Body paragraphs
- Essay revision
- Essay writing resources
- What is a report?
- Report structure
- Analysing issues for a report
- Business report
- What is a business report?
- Business report structure
- Inductive vs. deductive reports
- Other kinds of business communication
- Business report format and layout
- What is a lab report?
- Lab report structure
- Science lab report writing resources
- Psychology lab report writing resources
- Lab report body paragraphs
- Literature review
- What is a literature review?
- Writing a literature review
- Literature review structure
- Literature review writing resources
- Research proposal
- Writing a research proposal
- Research proposal structure
- Other types
- Article critique
- Book review
- Annotated bibliography
- Reflective writing
- Oral presentation
- Thesis / dissertation
- Article / conference paper
- Shorter responses
- PhD confirmation report
- Computer skills
- Microsoft Word
- Basic formatting
- Images, tables, & figures
- Long documents
- Microsoft Excel
- Basic spreadsheets
- Navigating & printing spreadsheets
- Charts / graphs & formulas
- Microsoft PowerPoint
- Basic skills
- Advanced skills
- Distance study
- Getting started
- How to study
- Online study techniques
- Distance support
- Reading & writing
- Reading strategies
- Writing strategies
- Grammar resources
- Listening & speaking
- Listening strategies
- Speaking strategies
- Maths & statistics
- Trigonometry
- Finance formulas
- Postgraduate study
- Intro to postgrad study
- Planning postgrad study
- Postgrad resources
- Postgrad assignment types
- Referencing
- Intro to referencing
- What is referencing?
- Why reference?
- Common knowledge
- Referencing styles
- What type of source is this?
- Reference list vs. bibliography
- Referencing software
- Quoting & paraphrasing
- Paraphrasing & summarising
- Paraphrasing techniques
- APA Interactive
- In-text citation
- Reference list
- Online material
- Other material
- Headings in APA
- Tables and Figures
- Referencing elements
- 5th vs. 6th edition
- 6th vs. 7th edition
- Chicago style
- Chicago Interactive
- About notes system
- Notes referencing elements
- Quoting and paraphrasing
- Author-date system
- MLA Interactive
- Abbreviations
- List of works cited
- Captions for images
- 8th vs 9th edition
- Oxford style
- Other styles
- Harvard style
- Vancouver style
- Legal citations
- Visual material
- Sample assignments
- Sample essay 1
- Sample essay 2
- Sample annotated bibliography
- Sample book review
- Study skills
- Time management
- Intro to time management
- Procrastination & perfectionism
- Goals & motivation
- Time management for internal students
- Time management for distance students
- Memory skills
- Principles of good memory
- Memory strategies
- Note-taking
- Note-taking methods
- Note-taking in lectures
- Note-taking while reading
- Digital note-taking
- Reading styles
- In-depth reading
- Reading comprehension
- Reading academic material
- Reading a journal article
- Reading an academic book
- Critical thinking
- What is critical thinking?
- Constructing an argument
- Critical reading
- Logical fallacies
- Tests & exams
- Exam & test study
- Planning exam study
- Gathering & sorting information
- Reviewing past exams
- Phases of revision
- Last-minute study strategies
- Question types
- Short answer
- Multi-choice
- Problem / computational
- Case-study / scenario
- Open book exam
- Open web exam or test
- Take home test
- In the exam
- Online exam
- Physical exam
Essay introduction
The introduction to an essay has three primary objectives:
- Explain the context of the essay
- Give the answer : the response to the question or the overall focus of the essay (the thesis statement)
- Describe the structure and organisation of the essay
These aims can be given more or less emphasis depending on the length and type of essay. In a very short essay (less than 1000 words), for example, there is not much room to give a full and detailed context or structure. A longer essay has room for greater detail.
Essays are usually written for an intelligent but uninformed audience, so begin with some context: the background of the topic, the topic scope, and any essential definitions.
- Introductions often begin with a broad opening statement that establishes the subject matter and background. Don't make it too broad (“Since time began…”), but identify the relevant topic and sub-topic (e.g. human resource management, early childhood development, animal behaviour…).
- To establish the scope, answer basic questions: Who? What? When? Where? How? Why? Is the essay limited to a particular time period, a particular group of people, a particular country?
- Definitions are often established after the introduction, so only include them here if they are absolutely essential.
Answer / focus
The most important part of the introduction is the response to the question: the thesis statement. Thesis statements are discussed in detail here: thesis statements .
An introduction often ends on the thesis statement. It begins with a broad statement and gradually narrows down until it directly addresses the question:
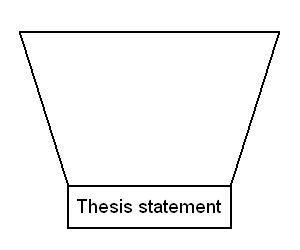
This order of introduction elements is not set in stone, however. Sometimes the thesis statement is followed by a breakdown of the essay's structure and organisation. Ultimately, you must adapt the order to suit the needs of each particular essay.
Strong introductions tell the reader how the upcoming body paragraphs will be organised.
This can be as easy as outlining the major points that your essay will make on the way to the conclusion. You don't need to go into much detail in the introduction: just signal the major ‘landmarks.’
It can help to identify how all of the paragraphs are organised:
- Do the paragraphs deal with the issue from earliest to most recent (chronological)?
- Are the paragraphs grouped by broader themes (thematic)?
- Does the essay answer several related questions one after the other (sequential)?
- Do the paragraphs describe two elements and them compare them (contrasting)?
The essay will be much more readable once the reader knows what to expect from the body paragraphs.
Introduction examples
See sample essay 1 and sample essay 2 for model introductions.
Page authorised by Director - Centre for Learner Success Last updated on 25 October, 2012
- Academic Q+A
Have a study or assignment writing question? Ask an expert at Academic Q+A
Live online workshops
- StudyUp (undergraduate)
- Campus workshops
- Albany (undergraduate)
- Albany (postgraduate)
- Albany (distance)
- Manawatu (undergraduate)
- Manawatu (postgraduate)
Upcoming events
- All upcoming events
- Academic writing and learning support
- 0800 MASSEY | (+64 6 350 5701)
- [email protected]
- Online form

The Context In an Essay
Low Cost, Fast Delivery, and Top-Quality Content: Buy Essay Now and Achieve Academic Excellence for Less!
- What Is The Context In an Essay
- Historical Context
- Cultural Context
- Geographical Context
- Social Context
- Biological Context
- Political Context
- Literary Context
- Scientific Context
- Technical Context
- Legal Context
- Ethical Context
- Economic Context
- Psychological Context
- When And How to Use The Context In an Essay
One of the main principles of academic writing is to use context. Using context may help you to avoid plagiarism, show the diversity of your knowledge, and make your text more interesting for readers. What is the context? Context can be defined as “background information.” It should be used in every piece of written work, primarily in academic essays (including research papers, term papers, etc.). Read on to discover what you can and cannot do with the context, how to use it properly, and how to find it.
Article structure
What is the context in an essay
If your topic is more specific, you can use even more context. However, remember that you should avoid using too many context options at once – the more options you have, the harder it will be to analyze and select the most appropriate one.
Here are some examples of common contexts that you can use in a research paper.
Historical context
The context of a research paper should be a specific event that took place in the past. It is very important that you provide an accurate description of the historical context, so your paper will be more interesting for your readers. For example, the research paper about the Holocaust can be written in the context of World War II, so you must describe in detail the events that took place. Your historical research paper should provide all necessary data, facts, and numbers about the history of the event, so you can write the essay with a clear understanding of all details.
The most important factor of the historical context is the correct chronological order. The best historical research papers are usually written in chronological order. In fact, the whole structure of the research paper is defined by the order of the events. The most interesting and useful information is at the beginning. In this case, the historical context is very important, because it gives an opportunity to understand the main topic of the essay.
The next step is to analyze the historical data in the essay. You have to make the right conclusion about your research, so you can write the essay in the right chronological order.
Cultural context
This context is usually used in writing about art, literature, music, etc. To create an interesting essay, you should include information about the culture in which you grew up, such as your country, region, family, and so on. This information can be written in different ways. Sometimes, information about culture should be provided to the reader from the start. At other times, you should use it as background information for your own comments and explanations. You may use cultural elements of your own experience to illustrate the concept of the subject at hand.
The idea of cultural context is very similar to the idea of historical context. However, cultural context usually refers to the context of the current period of your life, whereas historical context refers to the period when you grew up. Therefore, you are more likely to use information about your own cultural context, but you may also want to use information about the historical context of the topic. For example, if you are studying World War I, you would probably want to include some information about the culture of the time, but you would also want to focus on the events and conditions that led to the war. In other words, your cultural context must be specific and relevant to the topic of your paper.
If you need to write an essay about a period of time when you were not born, you should make use of your current cultural context to write about the events of the time.
Geographical context
This context is usually used in writing about geography, sociology, economics, politics, and many other disciplines. To make your paper more interesting, you need to include geographical, political, and economical information about your country, state, city, and town. You can also include demographic information about the area that is of your study.
You should include this geographical context whenever it is applicable. In some cases, it could even influence the flow of your paper. It could be either positive or negative. For instance, if you are writing about a country that is a large producer of oil, it may be difficult for you to gain sympathy from the people who are not aware of the country’s environmental damage.
In some cases, the geographical context could affect the flow of your paper. If your study is about an industrial city, then you should include information about the city’s industry. If you are going to study a small town, then you should include a small business report or small business owners’ report.
Social context
This context is used in social sciences, psychology, law, political science, economics, etc. You need to include information about your family, the friends you have, the social situation of your city, and so on. You also need to be aware of the social context of your topic. This is the main purpose of this chapter. It may be the context of your work or the context of your study. For instance, in this chapter, we may be talking about the context of studying and working in London or New York.
When you are studying or working in a new country, try to see if you can find out about its culture or society. Try to talk to the natives to find out about how they live and work. See if you can find some interesting books, or magazines, or TV programs about your new country.
Biological context
Biological context is used in many disciplines such as biology, chemistry, nutrition, etc. You need to include all the details about your parents, siblings, grandparents, aunts, uncles, cousins, hobbies, and so on. If you are describing the biological system or a biochemistry procedure, then you need to include a detailed description of the system itself. You need to include a description of all the compounds involved. If you are a cell biologist, you will need to explain all the biochemical steps involved in a cell cycle or DNA replication.
The basic biological context includes the history of the discovery and the biological and medical context of a particular problem that needs to be solved.
Political context
The political context is the most complex of all. You need to include information about the current political situation in your country, the situation of the region where you live, your political preferences, and so on.
When writing a research paper in political science, you need to be well-informed about the political situation in your country at the moment of writing. It is very difficult to write about politics, but if you are not well-informed, the research paper will sound biased and unauthentic.
The political situation is very important, as it is a determinant of the development of the country. A country with a democratic government can be easily influenced by external factors, whereas in a country with a communist or authoritarian government, external factors cannot influence such a country. When writing an essay about politics in general, it is important to mention the main political factors, the most important ones.
Literary context
In a research paper, the literary context should be the most important because of the following reasons:
- The more the authors in your paper are famous, the more your paper will become interesting to your readers;
- A good literature essay needs the authors’ names;
- The more a research paper is about famous people, the more accurate information you can provide about them.
In this case, the best literary sources to be used are biographies and autobiographies. Biographies and autobiographies provide more information about famous people because it is not the same to write about someone from his life as it is to write about someone’s life.
In writing about someone’s life, you have to write about all the things that make someone special and interesting. In order to write about someone’s life, you need to write about the events that have occurred to this person, the thoughts and emotions he has felt during his lifetime, and also the actions that he has done.
Scientific context
The scientific context is used in scientific papers. Here you should give information about your laboratory, university, the research institute, your research interests, and so on. You need to be aware of the scientific context of your research topic. You can get inspiration from other people’s research, look for papers that use the same scientific context as you, and have similar research interests. Also, find out which journal your paper will be published. Finally, check whether a scientific context is necessary for your paper.
Technical context
The technical context is used in many disciplines. If your essay is more technical, the information you need to include in your paper will be different. The technical context will be a list of things that you use to describe the context in which your writing takes place.
What are the major aspects of the technical context?
The technical context is used to describe the nature of a problem or the nature of the subject in which a particular paper has been written. For instance, a report on a product will have a specific technical context, so it is important to know what your report is about. This knowledge will help you to choose the most suitable technical language and style of writing.
Legal context
The legal context is used in many disciplines. If your essay is more legal, the information you should include in your paper will be different. There are various elements to the legal context of an argument, such as the nature of the case, and the relevant law, in order to analyze your paper. Some questions to think about when analyzing the legal context are:
- What are the rules that are used in the law to analyze the case?
- How can those rules help you to determine whether or not the case is a good one for you to use?
- What are the reasons behind the rules?
- How will you use those reasons to determine whether or not the case will be a good fit for your argument?
Ethical context
The ethical context is used in many disciplines. If your essay is more ethical, the information you should include in your paper will be different.
Ethical context is used to address the moral nature of a certain action or issue. The paper will discuss the ethical context in terms of the values that are attached to the subject. Ethical context should be included in the paper so that the values and beliefs of the readers are considered. The ethical context will make the paper more complete and also will prevent plagiarism.
Economic context
The economic context is usually used in economics. If your essay is more economic, the information you should include in your paper will be different. A paper that is entirely economic would typically have:
- a short introduction
- a discussion of the main economic concepts that will be used in your essay
- an overview of the different economic problems that will be discussed
- an analysis of the economic problems
- an examination of the arguments used in the analysis of the economic problem
- an evaluation of the arguments used in the discussion of the economic problem
Psychological context
The psychological context is usually used in psychology. If your essay is more psychological, the information you should include in your paper will be different. In this case, you need to understand a little more about psychology and the people that you are writing about.
It is very important to understand what kind of psychological context the essay you are writing about is in. This is very important as the writer has to consider what the essay is about. The context of the psychological essay you are writing about will help you decide whether to write about positive or negative issues. If the essay is positive, then you will need to think about the people in a positive context. If the essay is negative, then you will need to think about the people in the negative context.
When and how to use the context in an essay
Now you know what the context is and how it should be used in your research paper. However, how do you use context when writing? The answer to this question is a separate issue.
You should use the context in your essay in many situations. One of them is to provide extra information that you might need during the writing process. This is very useful when you need to write an outline, write a thesis statement, find examples, or describe a certain event.
If you use the right context, you will have no problem writing a strong essay. Moreover, you will avoid plagiarism and your text will be more interesting for readers.
Here are some situations in which the context can be useful in your research paper:
1. Research paper topics
The research paper topics may be very broad or very specific. It is not always possible to write a research paper about a narrow topic. The context may be useful in such situations to explain the topic. You should include more information about it in your essay.
If you have a very broad topic, you will need to give more information about it to make your essay more interesting. However, be careful that you do not include too many options. This could lead to plagiarism.
If you have a very specific topic, you will need to provide more information about it to make your essay more interesting for readers. The main idea of a research paper should be clear to them from the beginning, so you should provide the most relevant information.
2. Outlining
Writing an outline is not always easy for everybody. Sometimes you are not able to choose the most appropriate order of the main ideas in your research paper. In such a situation, the context can be useful to explain the order of ideas.
It is very easy to make a mistake in writing an outline. However, the context can help you to remember the main topics in your research paper.
3. Writing a thesis
You need to know how to write a thesis statement. However, it is also very important to know how to choose the most suitable thesis statement for a particular essay. If you find yourself in such a situation, the context can be useful to explain the main topic.
When you choose the right thesis statement for a particular essay, you will avoid plagiarism and make your essay more interesting for readers.
4. Writing an introduction
The introduction is one of the most important parts of a research paper. If you need to write an interesting introduction, you should include the right context in your essay. The context may include information about the problem, the thesis statement, the main idea, examples, and so on.
If you need to make the best out of the context, you should use the following structure of an introduction:
- What the problem is.
- What is the main idea is.
This structure is very useful because it gives your readers brief information about your topic. You can also provide links to further information. The main idea is explained in a clear and understandable way. You can use several examples to illustrate your point.
5. Writing a conclusion
The conclusion of the research paper is also very important. If you need to write a strong conclusion, you should provide more information about your topic. You should give more information about it in your conclusion.
The context can be used in several ways in your conclusion. You can use information about the problem, the main idea, examples, and so on. If you need to make the best of the context, the structure of a conclusion should be as follows:
- Explain what the conclusion is.
- Explain what the main idea is.
You can use examples to show what the conclusion means. It is very important to include these examples because they help to make your text more interesting for readers.
6. Writing an essay
In this case, the context is not used in your writing. However, it is very important to know about the structure of a research paper. The main idea of a research paper should be clear to your readers from the beginning. However, you should know how to make the best of the context. You should not make any unnecessary claims that may lead your reader to reject the whole paper.
In short, a context is an important tool in any research paper. A good thesis statement must have context. It will not be clear to your readers if you are talking about a subject in the abstract or you have used the context to support your thesis statement.

Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
How to Write an Essay Introduction (with Examples)

The introduction of an essay plays a critical role in engaging the reader and providing contextual information about the topic. It sets the stage for the rest of the essay, establishes the tone and style, and motivates the reader to continue reading.
Table of Contents
What is an essay introduction , what to include in an essay introduction, how to create an essay structure , step-by-step process for writing an essay introduction , how to write an introduction paragraph , how to write a hook for your essay , how to include background information , how to write a thesis statement .
- Argumentative Essay Introduction Example:
- Expository Essay Introduction Example
Literary Analysis Essay Introduction Example
Check and revise – checklist for essay introduction , key takeaways , frequently asked questions .
An introduction is the opening section of an essay, paper, or other written work. It introduces the topic and provides background information, context, and an overview of what the reader can expect from the rest of the work. 1 The key is to be concise and to the point, providing enough information to engage the reader without delving into excessive detail.
The essay introduction is crucial as it sets the tone for the entire piece and provides the reader with a roadmap of what to expect. Here are key elements to include in your essay introduction:
- Hook : Start with an attention-grabbing statement or question to engage the reader. This could be a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or a compelling anecdote.
- Background information : Provide context and background information to help the reader understand the topic. This can include historical information, definitions of key terms, or an overview of the current state of affairs related to your topic.
- Thesis statement : Clearly state your main argument or position on the topic. Your thesis should be concise and specific, providing a clear direction for your essay.
Before we get into how to write an essay introduction, we need to know how it is structured. The structure of an essay is crucial for organizing your thoughts and presenting them clearly and logically. It is divided as follows: 2
- Introduction: The introduction should grab the reader’s attention with a hook, provide context, and include a thesis statement that presents the main argument or purpose of the essay.
- Body: The body should consist of focused paragraphs that support your thesis statement using evidence and analysis. Each paragraph should concentrate on a single central idea or argument and provide evidence, examples, or analysis to back it up.
- Conclusion: The conclusion should summarize the main points and restate the thesis differently. End with a final statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader. Avoid new information or arguments.

Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write an essay introduction:
- Start with a Hook : Begin your introduction paragraph with an attention-grabbing statement, question, quote, or anecdote related to your topic. The hook should pique the reader’s interest and encourage them to continue reading.
- Provide Background Information : This helps the reader understand the relevance and importance of the topic.
- State Your Thesis Statement : The last sentence is the main argument or point of your essay. It should be clear, concise, and directly address the topic of your essay.
- Preview the Main Points : This gives the reader an idea of what to expect and how you will support your thesis.
- Keep it Concise and Clear : Avoid going into too much detail or including information not directly relevant to your topic.
- Revise : Revise your introduction after you’ve written the rest of your essay to ensure it aligns with your final argument.
Here’s an example of an essay introduction paragraph about the importance of education:
Education is often viewed as a fundamental human right and a key social and economic development driver. As Nelson Mandela once famously said, “Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world.” It is the key to unlocking a wide range of opportunities and benefits for individuals, societies, and nations. In today’s constantly evolving world, education has become even more critical. It has expanded beyond traditional classroom learning to include digital and remote learning, making education more accessible and convenient. This essay will delve into the importance of education in empowering individuals to achieve their dreams, improving societies by promoting social justice and equality, and driving economic growth by developing a skilled workforce and promoting innovation.
This introduction paragraph example includes a hook (the quote by Nelson Mandela), provides some background information on education, and states the thesis statement (the importance of education).
This is one of the key steps in how to write an essay introduction. Crafting a compelling hook is vital because it sets the tone for your entire essay and determines whether your readers will stay interested. A good hook draws the reader in and sets the stage for the rest of your essay.
- Avoid Dry Fact : Instead of simply stating a bland fact, try to make it engaging and relevant to your topic. For example, if you’re writing about the benefits of exercise, you could start with a startling statistic like, “Did you know that regular exercise can increase your lifespan by up to seven years?”
- Avoid Using a Dictionary Definition : While definitions can be informative, they’re not always the most captivating way to start an essay. Instead, try to use a quote, anecdote, or provocative question to pique the reader’s interest. For instance, if you’re writing about freedom, you could begin with a quote from a famous freedom fighter or philosopher.
- Do Not Just State a Fact That the Reader Already Knows : This ties back to the first point—your hook should surprise or intrigue the reader. For Here’s an introduction paragraph example, if you’re writing about climate change, you could start with a thought-provoking statement like, “Despite overwhelming evidence, many people still refuse to believe in the reality of climate change.”
Including background information in the introduction section of your essay is important to provide context and establish the relevance of your topic. When writing the background information, you can follow these steps:
- Start with a General Statement: Begin with a general statement about the topic and gradually narrow it down to your specific focus. For example, when discussing the impact of social media, you can begin by making a broad statement about social media and its widespread use in today’s society, as follows: “Social media has become an integral part of modern life, with billions of users worldwide.”
- Define Key Terms : Define any key terms or concepts that may be unfamiliar to your readers but are essential for understanding your argument.
- Provide Relevant Statistics: Use statistics or facts to highlight the significance of the issue you’re discussing. For instance, “According to a report by Statista, the number of social media users is expected to reach 4.41 billion by 2025.”
- Discuss the Evolution: Mention previous research or studies that have been conducted on the topic, especially those that are relevant to your argument. Mention key milestones or developments that have shaped its current impact. You can also outline some of the major effects of social media. For example, you can briefly describe how social media has evolved, including positives such as increased connectivity and issues like cyberbullying and privacy concerns.
- Transition to Your Thesis: Use the background information to lead into your thesis statement, which should clearly state the main argument or purpose of your essay. For example, “Given its pervasive influence, it is crucial to examine the impact of social media on mental health.”

A thesis statement is a concise summary of the main point or claim of an essay, research paper, or other type of academic writing. It appears near the end of the introduction. Here’s how to write a thesis statement:
- Identify the topic: Start by identifying the topic of your essay. For example, if your essay is about the importance of exercise for overall health, your topic is “exercise.”
- State your position: Next, state your position or claim about the topic. This is the main argument or point you want to make. For example, if you believe that regular exercise is crucial for maintaining good health, your position could be: “Regular exercise is essential for maintaining good health.”
- Support your position: Provide a brief overview of the reasons or evidence that support your position. These will be the main points of your essay. For example, if you’re writing an essay about the importance of exercise, you could mention the physical health benefits, mental health benefits, and the role of exercise in disease prevention.
- Make it specific: Ensure your thesis statement clearly states what you will discuss in your essay. For example, instead of saying, “Exercise is good for you,” you could say, “Regular exercise, including cardiovascular and strength training, can improve overall health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.”
Examples of essay introduction
Here are examples of essay introductions for different types of essays:
Argumentative Essay Introduction Example:
Topic: Should the voting age be lowered to 16?
“The question of whether the voting age should be lowered to 16 has sparked nationwide debate. While some argue that 16-year-olds lack the requisite maturity and knowledge to make informed decisions, others argue that doing so would imbue young people with agency and give them a voice in shaping their future.”
Expository Essay Introduction Example
Topic: The benefits of regular exercise
“In today’s fast-paced world, the importance of regular exercise cannot be overstated. From improving physical health to boosting mental well-being, the benefits of exercise are numerous and far-reaching. This essay will examine the various advantages of regular exercise and provide tips on incorporating it into your daily routine.”
Text: “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee
“Harper Lee’s novel, ‘To Kill a Mockingbird,’ is a timeless classic that explores themes of racism, injustice, and morality in the American South. Through the eyes of young Scout Finch, the reader is taken on a journey that challenges societal norms and forces characters to confront their prejudices. This essay will analyze the novel’s use of symbolism, character development, and narrative structure to uncover its deeper meaning and relevance to contemporary society.”
- Engaging and Relevant First Sentence : The opening sentence captures the reader’s attention and relates directly to the topic.
- Background Information : Enough background information is introduced to provide context for the thesis statement.
- Definition of Important Terms : Key terms or concepts that might be unfamiliar to the audience or are central to the argument are defined.
- Clear Thesis Statement : The thesis statement presents the main point or argument of the essay.
- Relevance to Main Body : Everything in the introduction directly relates to and sets up the discussion in the main body of the essay.

Writing a strong introduction is crucial for setting the tone and context of your essay. Here are the key takeaways for how to write essay introduction: 3
- Hook the Reader : Start with an engaging hook to grab the reader’s attention. This could be a compelling question, a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or an anecdote.
- Provide Background : Give a brief overview of the topic, setting the context and stage for the discussion.
- Thesis Statement : State your thesis, which is the main argument or point of your essay. It should be concise, clear, and specific.
- Preview the Structure : Outline the main points or arguments to help the reader understand the organization of your essay.
- Keep it Concise : Avoid including unnecessary details or information not directly related to your thesis.
- Revise and Edit : Revise your introduction to ensure clarity, coherence, and relevance. Check for grammar and spelling errors.
- Seek Feedback : Get feedback from peers or instructors to improve your introduction further.
The purpose of an essay introduction is to give an overview of the topic, context, and main ideas of the essay. It is meant to engage the reader, establish the tone for the rest of the essay, and introduce the thesis statement or central argument.
An essay introduction typically ranges from 5-10% of the total word count. For example, in a 1,000-word essay, the introduction would be roughly 50-100 words. However, the length can vary depending on the complexity of the topic and the overall length of the essay.
An essay introduction is critical in engaging the reader and providing contextual information about the topic. To ensure its effectiveness, consider incorporating these key elements: a compelling hook, background information, a clear thesis statement, an outline of the essay’s scope, a smooth transition to the body, and optional signposting sentences.
The process of writing an essay introduction is not necessarily straightforward, but there are several strategies that can be employed to achieve this end. When experiencing difficulty initiating the process, consider the following techniques: begin with an anecdote, a quotation, an image, a question, or a startling fact to pique the reader’s interest. It may also be helpful to consider the five W’s of journalism: who, what, when, where, why, and how. For instance, an anecdotal opening could be structured as follows: “As I ascended the stage, momentarily blinded by the intense lights, I could sense the weight of a hundred eyes upon me, anticipating my next move. The topic of discussion was climate change, a subject I was passionate about, and it was my first public speaking event. Little did I know , that pivotal moment would not only alter my perspective but also chart my life’s course.”
Crafting a compelling thesis statement for your introduction paragraph is crucial to grab your reader’s attention. To achieve this, avoid using overused phrases such as “In this paper, I will write about” or “I will focus on” as they lack originality. Instead, strive to engage your reader by substantiating your stance or proposition with a “so what” clause. While writing your thesis statement, aim to be precise, succinct, and clear in conveying your main argument.
To create an effective essay introduction, ensure it is clear, engaging, relevant, and contains a concise thesis statement. It should transition smoothly into the essay and be long enough to cover necessary points but not become overwhelming. Seek feedback from peers or instructors to assess its effectiveness.
References
- Cui, L. (2022). Unit 6 Essay Introduction. Building Academic Writing Skills .
- West, H., Malcolm, G., Keywood, S., & Hill, J. (2019). Writing a successful essay. Journal of Geography in Higher Education , 43 (4), 609-617.
- Beavers, M. E., Thoune, D. L., & McBeth, M. (2023). Bibliographic Essay: Reading, Researching, Teaching, and Writing with Hooks: A Queer Literacy Sponsorship. College English, 85(3), 230-242.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)
- How to Paraphrase Research Papers Effectively
- How to Cite Social Media Sources in Academic Writing?
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
Similarity Checks: The Author’s Guide to Plagiarism and Responsible Writing
Types of plagiarism and 6 tips to avoid it in your writing , you may also like, how to ace grant writing for research funding..., how to write a high-quality conference paper, how paperpal’s research feature helps you develop and..., how paperpal is enhancing academic productivity and accelerating..., academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., 4 ways paperpal encourages responsible writing with ai, what are scholarly sources and where can you..., how to write a hypothesis types and examples , what is academic writing: tips for students, what is hedging in academic writing .

Academic Essay Writing Made Simple: 4 types and tips
The pen is mightier than the sword, they say, and nowhere is this more evident than in academia. From the quick scribbles of eager students to the inquisitive thoughts of renowned scholars, academic essays depict the power of the written word. These well-crafted writings propel ideas forward and expand the existing boundaries of human intellect.
What is an Academic Essay
An academic essay is a nonfictional piece of writing that analyzes and evaluates an argument around a specific topic or research question. It serves as a medium to share the author’s views and is also used by institutions to assess the critical thinking, research skills, and writing abilities of a students and researchers.
Importance of Academic Essays
4 main types of academic essays.
While academic essays may vary in length, style, and purpose, they generally fall into four main categories. Despite their differences, these essay types share a common goal: to convey information, insights, and perspectives effectively.
1. Expository Essay
2. Descriptive Essay
3. Narrative Essay
4. Argumentative Essay
Expository and persuasive essays mainly deal with facts to explain ideas clearly. Narrative and descriptive essays are informal and have a creative edge. Despite their differences, these essay types share a common goal ― to convey information, insights, and perspectives effectively.
Expository Essays: Illuminating ideas
An expository essay is a type of academic writing that explains, illustrates, or clarifies a particular subject or idea. Its primary purpose is to inform the reader by presenting a comprehensive and objective analysis of a topic.
By breaking down complex topics into digestible pieces and providing relevant examples and explanations, expository essays allow writers to share their knowledge.
What are the Key Features of an Expository Essay

Provides factual information without bias

Presents multiple viewpoints while maintaining objectivity
Uses direct and concise language to ensure clarity for the reader

Composed of a logical structure with an introduction, body paragraphs and a conclusion
When is an expository essay written.
1. For academic assignments to evaluate the understanding of research skills.
2. As instructional content to provide step-by-step guidance for tasks or problem-solving.
3. In journalism for objective reporting in news or investigative pieces.
4. As a form of communication in the professional field to convey factual information in business or healthcare.
How to Write an Expository Essay
Expository essays are typically structured in a logical and organized manner.
1. Topic Selection and Research
- Choose a topic that can be explored objectively
- Gather relevant facts and information from credible sources
- Develop a clear thesis statement
2. Outline and Structure
- Create an outline with an introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion
- Introduce the topic and state the thesis in the introduction
- Dedicate each body paragraph to a specific point supporting the thesis
- Use transitions to maintain a logical flow
3. Objective and Informative Writing
- Maintain an impartial and informative tone
- Avoid personal opinions or biases
- Support points with factual evidence, examples, and explanations
4. Conclusion
- Summarize the key points
- Reinforce the significance of the thesis
Descriptive Essays: Painting with words
Descriptive essays transport readers into vivid scenes, allowing them to experience the world through the writer ‘s lens. These essays use rich sensory details, metaphors, and figurative language to create a vivid and immersive experience . Its primary purpose is to engage readers’ senses and imagination.
It allows writers to demonstrate their ability to observe and describe subjects with precision and creativity.
What are the Key Features of Descriptive Essay

Employs figurative language and imagery to paint a vivid picture for the reader

Demonstrates creativity and expressiveness in narration

Includes close attention to detail, engaging the reader’s senses

Engages the reader’s imagination and emotions through immersive storytelling using analogies, metaphors, similes, etc.
When is a descriptive essay written.
1. Personal narratives or memoirs that describe significant events, people, or places.
2. Travel writing to capture the essence of a destination or experience.
3. Character sketches in fiction writing to introduce and describe characters.
4. Poetry or literary analyses to explore the use of descriptive language and imagery.
How to Write a Descriptive Essay
The descriptive essay lacks a defined structural requirement but typically includes: an introduction introducing the subject, a thorough description, and a concluding summary with insightful reflection.
1. Subject Selection and Observation
- Choose a subject (person, place, object, or experience) to describe
- Gather sensory details and observations
2. Engaging Introduction
- Set the scene and provide the context
- Use of descriptive language and figurative techniques
3. Descriptive Body Paragraphs
- Focus on specific aspects or details of the subject
- Engage the reader ’s senses with vivid imagery and descriptions
- Maintain a consistent tone and viewpoint
4. Impactful Conclusion
- Provide a final impression or insight
- Leave a lasting impact on the reader
Narrative Essays: Storytelling in Action
Narrative essays are personal accounts that tell a story, often drawing from the writer’s own experiences or observations. These essays rely on a well-structured plot, character development, and vivid descriptions to engage readers and convey a deeper meaning or lesson.
What are the Key features of Narrative Essays
Written from a first-person perspective and hence subjective

Based on real personal experiences

Uses an informal and expressive tone

Presents events and characters in sequential order
When is a narrative essay written.
It is commonly assigned in high school and college writing courses to assess a student’s ability to convey a meaningful message or lesson through a personal narrative. They are written in situations where a personal experience or story needs to be recounted, such as:
1. Reflective essays on significant life events or personal growth.
2. Autobiographical writing to share one’s life story or experiences.
3. Creative writing exercises to practice narrative techniques and character development.
4. College application essays to showcase personal qualities and experiences.
How to Write a Narrative Essay
Narrative essays typically follow a chronological structure, with an introduction that sets the scene, a body that develops the plot and characters, and a conclusion that provides a sense of resolution or lesson learned.
1. Experience Selection and Reflection
- Choose a significant personal experience or event
- Reflect on the impact and deeper meaning
2. Immersive Introduction
- Introduce characters and establish the tone and point of view
3. Plotline and Character Development
- Advance the plot and character development through body paragraphs
- Incorporate dialog , conflict, and resolution
- Maintain a logical and chronological flow
4. Insightful Conclusion
- Reflect on lessons learned or insights gained
- Leave the reader with a lasting impression
Argumentative Essays: Persuasion and Critical Thinking
Argumentative essays are the quintessential form of academic writing in which writers present a clear thesis and support it with well-researched evidence and logical reasoning. These essays require a deep understanding of the topic, critical analysis of multiple perspectives, and the ability to construct a compelling argument.
What are the Key Features of an Argumentative Essay?

Logical and well-structured arguments

Credible and relevant evidence from reputable sources

Consideration and refutation of counterarguments

Critical analysis and evaluation of the issue
When is an argumentative essay written.
Argumentative essays are written to present a clear argument or stance on a particular issue or topic. In academic settings they are used to develop critical thinking, research, and persuasive writing skills. However, argumentative essays can also be written in various other contexts, such as:
1. Opinion pieces or editorials in newspapers, magazines, or online publications.
2. Policy proposals or position papers in government, nonprofit, or advocacy settings.
3. Persuasive speeches or debates in academic, professional, or competitive environments.
4. Marketing or advertising materials to promote a product, service, or idea.
How to write an Argumentative Essay
Argumentative essays begin with an introduction that states the thesis and provides context. The body paragraphs develop the argument with evidence, address counterarguments, and use logical reasoning. The conclusion restates the main argument and makes a final persuasive appeal.
- Choose a debatable and controversial issue
- Conduct thorough research and gather evidence and counterarguments
2. Thesis and Introduction
- Craft a clear and concise thesis statement
- Provide background information and establish importance
3. Structured Body Paragraphs
- Focus each paragraph on a specific aspect of the argument
- Support with logical reasoning, factual evidence, and refutation
4. Persuasive Techniques
- Adopt a formal and objective tone
- Use persuasive techniques (rhetorical questions, analogies, appeals)
5. Impactful Conclusion
- Summarize the main points
- Leave the reader with a strong final impression and call to action
To learn more about argumentative essay, check out this article .
5 Quick Tips for Researchers to Improve Academic Essay Writing Skills

Use clear and concise language to convey ideas effectively without unnecessary words

Use well-researched, credible sources to substantiate your arguments with data, expert opinions, and scholarly references

Ensure a coherent structure with effective transitions, clear topic sentences, and a logical flow to enhance readability

To elevate your academic essay, consider submitting your draft to a community-based platform like Open Platform for editorial review

Review your work multiple times for clarity, coherence, and adherence to academic guidelines to ensure a polished final product
By mastering the art of academic essay writing, researchers and scholars can effectively communicate their ideas, contribute to the advancement of knowledge, and engage in meaningful scholarly discourse.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles
![context of essay example What is Academic Integrity and How to Uphold it [FREE CHECKLIST]](https://www.enago.com/academy/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/FeatureImages-59-210x136.png)
Ensuring Academic Integrity and Transparency in Academic Research: A comprehensive checklist for researchers
Academic integrity is the foundation upon which the credibility and value of scientific findings are…

- AI in Academia
AI vs. AI: How to detect image manipulation and avoid academic misconduct
The scientific community is facing a new frontier of controversy as artificial intelligence (AI) is…

- Industry News
- Publishing News
Unified AI Guidelines Crucial as Academic Writing Embraces Generative Tools
As generative artificial intelligence (AI) tools like ChatGPT are advancing at an accelerating pace, their…

- Diversity and Inclusion
Need for Diversifying Academic Curricula: Embracing missing voices and marginalized perspectives
In classrooms worldwide, a single narrative often dominates, leaving many students feeling lost. These stories,…

- Reporting Research
How to Effectively Cite a PDF (APA, MLA, AMA, and Chicago Style)
The pressure to “publish or perish” is a well-known reality for academics, striking fear into…
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
How to Improve Lab Report Writing: Best practices to follow with and without…
Digital Citations: A comprehensive guide to citing of websites in APA, MLA, and CMOS…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

As a researcher, what do you consider most when choosing an image manipulation detector?
Insights into the Book of Esther: Themes and Historical Context
This essay about the Book of Esther examines its narrative, central themes, and historical significance within the Jewish tradition. Set in the Persian Empire, it recounts the story of Esther, a Jewish woman who becomes queen and thwarts a plan to exterminate her people. Highlighted are the political maneuverings and personal courage of Esther, as well as the broader themes of identity, power, and providence, which resonate throughout the story. The essay also discusses the book’s notable omission of direct references to God, suggesting a complex interplay of divine and human agency. Additionally, it considers Esther’s significant role as a strong female figure in the scriptures, challenging traditional gender norms and acting as a savior for her people. The narrative culminates in the establishment of Purim, a festival celebrating Jewish survival and communal identity.
How it works
The Scroll of Esther stands as a singular tale within the sacred texts, exalted notably during the Jewish observance of Purim. It narrates the saga of a Jewish woman amidst the Persian milieu, ascending to royalty and orchestrating the salvation of her people from annihilation. This narrative not only captivates but also delves into profound themes of authority, selfhood, and divine providence, all amidst the intricate tapestry of Persian court politics.
The chronicle unfurls in the Persian metropolis of Susa during the reign of King Ahasuerus, traditionally identified as Xerxes I.
Following the dismissal of Queen Vashti for her defiance, the king seeks a replacement. Esther, an orphan of Jewish descent raised under the care of her cousin Mordecai, is selected for her beauty and poise, concealing her Jewish lineage from the royal court initially.
Meanwhile, Mordecai uncovers a plot against the king’s life and apprises Esther, thereby gaining royal favor that proves pivotal later. The story’s antagonist, Haman, an esteemed advisor to the king, nurses a profound enmity towards Mordecai, stemming primarily from the latter’s refusal to prostrate before him. Haman’s animosity towards Mordecai extends to all Jews, leading him to sway Ahasuerus into decreeing the extermination of the Jewish populace.
The narrative climaxes as Mordecai impels Esther to intercede, despite the peril posed by approaching the king unbidden, an act punishable by death. Esther’s stratagem, culminating in two banquets for the king and Haman, ultimately reveals her Jewish heritage and exposes Haman’s treachery. Enraged by the deceit, the king orders Haman’s demise on the gallows erected for Mordecai.
Although the king cannot rescind the edict to annihilate the Jews, he permits Esther and Mordecai to issue another decree, empowering the Jews to defend themselves. This results in their triumph over adversaries across the empire. The tale culminates in the institution of Purim, commemorating the deliverance of the Jewish people, and the ascension of Mordecai to a position of prominence under King Ahasuerus.
The Scroll of Esther is notable for its conspicuous absence of explicit references to the divine, a rarity among biblical narratives. This peculiarity has spurred diverse interpretations, with some viewing it as a testament to human agency and political sagacity, while others perceive it as an instance of divine intervention where divine providence is implicit. The narrative underscores themes of survival and identity, elucidating Esther’s navigation of her dual identity as both a Persian queen and a Jewish woman. Her valor and astuteness in navigating court intrigues not only alter Jewish history but also underscore the complexities of diasporic existence, where survival necessitates sagacity, valor, and adaptability.
Another remarkable facet of the Scroll of Esther is its role in elevating the visibility of women in scriptural narratives. Esther emerges as a formidable female protagonist whose actions are pivotal to the narrative’s progression. Her evolution from a passive beauty to an assertive savior signifies a profound metamorphosis, positioning her as a proto-feminist figure challenging traditional gender roles within a patriarchal milieu.
In essence, the Scroll of Esther serves manifold functions: as a historical document, a source of spiritual inspiration, and a cultural landmark addressing timeless themes of authority, bias, and liberation. Its resonance endures, offering fertile ground for theological contemplation and communal commemoration.
Note: This exposition serves as a springboard for further exploration and scholarly inquiry. For personalized guidance and to ensure adherence to academic standards, consider consulting experts at EduBirdie.
Cite this page
Insights into the Book of Esther: Themes and Historical Context. (2024, May 21). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/insights-into-the-book-of-esther-themes-and-historical-context/
"Insights into the Book of Esther: Themes and Historical Context." PapersOwl.com , 21 May 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/insights-into-the-book-of-esther-themes-and-historical-context/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Insights into the Book of Esther: Themes and Historical Context . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/insights-into-the-book-of-esther-themes-and-historical-context/ [Accessed: 26 May. 2024]
"Insights into the Book of Esther: Themes and Historical Context." PapersOwl.com, May 21, 2024. Accessed May 26, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/insights-into-the-book-of-esther-themes-and-historical-context/
"Insights into the Book of Esther: Themes and Historical Context," PapersOwl.com , 21-May-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/insights-into-the-book-of-esther-themes-and-historical-context/. [Accessed: 26-May-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Insights into the Book of Esther: Themes and Historical Context . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/insights-into-the-book-of-esther-themes-and-historical-context/ [Accessed: 26-May-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
Literacy and Reading Readiness Essay
Being literate is a relatively broad term, especially in the context of the 21 st century. On the one hand, literacy implies set elements correlating with basic cognitive skills. Namely, reading and writing are the concepts correlating with the term. On the other hand, being literate in the 21 st century correlates with additional circumstances, such as the practical appliance of the aforementioned skills in regard to interacting with the outside world. For example, the word is often incorporated in relation to modern technology, such as in the phrase “information literacy” (UNESCO, 2006). As a result, literacy is a broad term that, scientifically, is related to cognitive abilities while metaphorically, to how one operates in society and in the modern world.
Teachers are essential in developing literacy concepts in regard to speaking, listening, reading, and writing for students with disabilities. There are several practical implementations a teacher can employ to maximize said skills. First, it is essential to determine the elements of literacy that can be addressed in class. Namely, one’s ability to use oral language, knowledge of print concepts, comprehension of the alphabet, and phonological processing skills are among the elements that can be worked on (Opiz, 2020). Teachers can address alphabet knowledge through interaction with children while creating a personalized alphabet book in which students choose the words that are to be included. For phonological awareness, activities such as asking children to identify similar letters in a sentence can maximize comprehension. Print concepts can also be addressed in multiple ways, such as asking the children questions about where the text starts and where certain letters in the text are located, and reading together as a group. Oral language can be implemented through reading out loud and similar practices that can be incorporated with other literacy concepts, such as print knowledge.
Needless to say, teachers aiming to address literacy for children with disabilities may encounter specific challenges that require a personalized approach. Namely, one barrier is the determination of possible gaps before the student reaches an older age. For example, while the expectation is to ensure each student is able to read well by third grade, certain students may only show signs of difficulties during the same age (Kaderavek & Justice, 2000). Another barrier correlates with the concept of reading readiness. Namely, certain students may struggle to fit the standardized informal assessments for reading readiness despite having the cognitive skills to do so. For example, some elements that are being considered when deciding whether a student is ready to learn to read include abilities to follow directions, collaborate, and follow instructions (Irvin et al., 2013). As a result, teachers may have difficulties identifying the presence of literacy skills when behavioral problems persist.
Assessing student skills is important in determining literacy. Both standardized and alternative assessments can be implemented to determine whether a child has been developing in regard to being literate. In relation to standardized texts, multiple assessment types exist that cover several elements within the notion of literacy. For example, the Yopp-Singer Test of Phoneme Segmentation, the DIBELS Phoneme Segmentation Fluency, and Concepts About Print (CAP) are among the tests that can be administered to assess a student’s phonological perception and print concepts comprehension (Opiz, 2020). However, needless to say, a teacher can examine one’s literacy through informal, alternative measures. For example, observing children during games and classroom activities in terms of how they interact, communicate, and perceive the information around them may give a rather objective perspective on their cognitive abilities. For example, a speed reading test may not show one’s abilities if the child stops to relate a personal experience similar to what happened in the text. From a formal perspective, the reading time has lengthened. From an informal one, the teacher is able to see that the student has high text comprehension.
Teachers can motivate children with disabilities to read by applying a multitude of techniques. For example, Directed Thinking and Listening is a technique that addresses a potential lack of interest or motivation to participate in the reading exercise (Opiz, 2020). Based on the measure, the teacher is to interest the children before reading through a set of questions directed at the classroom. Furthermore, a similar approach is to be employed during reading when children are asked about the content, their thoughts, and other elements correlating with the text. Last but not least, the children are inquired about the text after reading it.
Literacy is the set of skills possessed by a person, highlighting the cognitive abilities of said individual. Namely, reading and writing are the elements most commonly associated with the notion of literacy (UNESCO, 2006). The notion of literacy is also connected with the idea of acquiring a level of social awareness, operating in the socio-economic environment, and reflecting critically on both personal and social concepts (UNESCO, 2006). Thus, being literate is a combination of possessing certain cognitive skills as well as their practical appliance in the physical world.
Emergent literacy is the concept illustrating one’s literate abilities before acquiring the skills to actually read and write. In this case, a very young child is constantly in the process of cognitive development, which, later on, shifts into literary. For example, naming various letters, knowing how each of them sounds, and reading words are among the activities often associated with the concept of emergent literacy (Kaderavek & Justice, 2000). Before conventional reading, the child is able to perform the aforementioned activities, which is a precursor to being considered literate. The importance of emergent literacy is connected with the outcomes followed by the notion. Namely, a child with no skills in relation to phonetic perception and letter recognition is likely to encounter severe difficulties when learning to read.
Emergent literacy is different from the concept of reading readiness. Reading readiness illustrates the presence of skills and circumstances highlighting that the child is ready to learn to read. On the one hand, emergent literacy implies that literacy is a process, and acquiring reading and writing skills is the step after showing signs, such as identifying letters, scribbling, and pretending to read. On the other hand, reading readiness is not a process but rather a point in time at which the student has acquired all the necessary precursors to start to read.
Three questions can be identified to contribute to the pool of knowledge in regard to the reading material. What would a standardized assessment for reading readiness include? The question. Arises as a result of the determination that the concept is more socio-behavioral rather than academic and scientific (Irvin et al., 2013). Moreover, is emergent literacy a definite precursor to literacy? In this case, statistical analyses can be applied to determine the answers. Last but not least, how can teachers encourage emergent literacy in children who show signs of slow development?
Irvin, S. P., Alonzo, J., Nese, J. F. T., & Tindal, G. (2013). Learning to read: Kindergarten readiness growth in reading skills. National Center on Assessment and Accountability for Special Education .
Kaderavek, J. N., & Justice, L. (2000). Children with LD as emergent readers: Bridging the gap to conventional reading. LD Online .
Opiz, J. E. M. (2020). Understanding, assessing, and teaching reading: A diagnostic approach (8th ed.). Pearson.
UNESCO. (2006). Understandings of literacy. In Education for All Global Monitoring Report (pp. 147–159). UNESCO.
- Emergent Literacy Skills in Children With Hearing Loss
- Emergent Leadership Programs for Student Athletes
- Difference between Deliberate and Emergent Strategies
- "Teaching to Transgress: Education as the Practice of Freedom" by Hooks
- The Importance of Satisfaction in Education
- Perception of Education by the Students in the RES 7700 Course
- Perception of the School: The Informal System
- Perception of Early Childhood Pre-Service Teachers
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, May 25). Literacy and Reading Readiness. https://ivypanda.com/essays/literacy-and-reading-readiness/
"Literacy and Reading Readiness." IvyPanda , 25 May 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/literacy-and-reading-readiness/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'Literacy and Reading Readiness'. 25 May.
IvyPanda . 2024. "Literacy and Reading Readiness." May 25, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/literacy-and-reading-readiness/.
1. IvyPanda . "Literacy and Reading Readiness." May 25, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/literacy-and-reading-readiness/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Literacy and Reading Readiness." May 25, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/literacy-and-reading-readiness/.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Context is the background, environment, setting, framework, or surroundings of events or occurrences. Simply, context means circumstances forming a background of an event, idea, or statement, in such a way as to enable readers to understand the narrative or a literary piece. It is necessary for writing to provide information, new concepts, and ...
1 Identify your purpose, audience, and scope. The first step to writing a context statement is to identify your purpose, audience, and scope. Your purpose is the main goal or message of your essay ...
Context is information that helps the message of a literary text make sense. Whether it's a novel, a memoir, or a collection of short stories, a piece of writing can be interpreted variably depending on the contextual factors you provide as the author. Some context is obviously stated and some requires a close reading of the literary work—so it's important for every writer to know what ...
An example of context would be the novel Lord of the Flies, which has a strong physical context of a deserted island and the need for survival. ... Essay Types, Writing & Example;
What is context in English? How do I discuss it in my essays? We hear these questions a lot, in this article, we going to clear up what context is and how to effectively discuss it in your responses.
Context is the facets of a situation, fictional or non-fictional, that inspire feelings, thoughts and beliefs of groups and individuals. It is the background information that allows people to make informed decisions. Most of the time, the view of a person on a subject will be made in response to the presented context.
For example, when we are writing for an academic audience of classmates and instructors, we use more formal, complex language than when we are writing for an audience of children. ... This would be the appropriate audience, purpose, and context for the 1,000-word essay about how a car works. Activity ~ A Note about Tone. As you consider your ...
Read on to discover the four types of context in writing, and for an explanation about why context is important. ... For example: The rhetorical context of a work created for a class assignment that will likely only be read by the writer's teacher is very different from an editorial opinion piece on an issue the author is passionate about ...
You may be asked to put new ideas in context, to analyze course texts, or to do research on something related to the course. ... your questions will form the basis of a strong essay. For example, your initial questions about a source may be answered by reading the source more closely. On the other hand,
Context. Style is contextual, meaning that it is determined by the media of writing and publication, the author's aims, and the intended audience. Using casual or simple language in a formal document would be inappropriate, for instance, because it might give the audience the impression that the author doesn't fully understand the ...
This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people's social and cultural lives.
The point here is that, in establishing the essay's context, you are also limiting your topic. That is, you are framing an approach to your topic that necessarily eliminates other approaches. Thus, when you determine your context, you simultaneously narrow your topic and take a big step toward focusing your essay. Here's an example.
Context (KAHN-tekst) is the circumstances that inform an event, an idea, or a statement. It is the detail that adds meaning to a text. Readers can study internal context—details included by the author, such as backstory, characterization, or setting—as well as external context—the time period of the work's publication, the author's literary influences, and even their personal history.
In general, context refers to "the surrounding circumstances that form the setting for an event, statement, or idea, and in terms of which it can be understood" (Lexico). In a nutshell, context is just a situation where many things happen. So, in literary studies, we can simply understand context as the historical background of a work, and ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Essentially, context should be relevant but not directly taken from the text and more importantly, when used effectively, can develop points, add extra depth to ideas and generally make your essay appear more impressive. However, it's not always easy to use. With the knowledge that you HAVE to use context within essays it becomes easy to treat ...
Here is an example of the context of a study in a thesis: Context of the Study: The rapid growth of the internet and the increasing popularity of social media have revolutionized the way people communicate, connect, and share information. With the widespread use of social media, there has been a rise in cyberbullying, which is a form of ...
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
The introduction to an essay has three primary objectives: Explain the context of the essay. Give the answer: the response to the question or the overall focus of the essay (the thesis statement) Describe the structure and organisation of the essay. These aims can be given more or less emphasis depending on the length and type of essay.
It could involve historical context, current events, or a summary of necessary research. It's about setting the stage for your thesis and helping readers understand the broader conversation in which your essay participates. Providing context is a fundamental part of any essay writing guide because it frames the significance of your discussion.
This context is used in social sciences, psychology, law, political science, economics, etc. You need to include information about your family, the friends you have, the social situation of your city, and so on. You also need to be aware of the social context of your topic. This is the main purpose of this chapter.
Here are the key takeaways for how to write essay introduction: 3. Hook the Reader: Start with an engaging hook to grab the reader's attention. This could be a compelling question, a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or an anecdote. Provide Background: Give a brief overview of the topic, setting the context and stage for the discussion.
Revised on July 23, 2023. A rhetorical analysis is a type of essay that looks at a text in terms of rhetoric. This means it is less concerned with what the author is saying than with how they say it: their goals, techniques, and appeals to the audience. A rhetorical analysis is structured similarly to other essays: an introduction presenting ...
Narrative Essay. 4. Argumentative Essay. Expository and persuasive essays mainly deal with facts to explain ideas clearly. Narrative and descriptive essays are informal and have a creative edge. Despite their differences, these essay types share a common goal ― to convey information, insights, and perspectives effectively.
Essay Example: The Scroll of Esther stands as a singular tale within the sacred texts, exalted notably during the Jewish observance of Purim. It narrates the saga of a Jewish woman amidst the Persian milieu, ascending to royalty and orchestrating the salvation of her people from annihilation
Step 1: Return to your thesis. To begin your conclusion, signal that the essay is coming to an end by returning to your overall argument. Don't just repeat your thesis statement —instead, try to rephrase your argument in a way that shows how it has been developed since the introduction. Example: Returning to the thesis.
Literacy and Reading Readiness Essay. Being literate is a relatively broad term, especially in the context of the 21 st century. On the one hand, literacy implies set elements correlating with basic cognitive skills. Namely, reading and writing are the concepts correlating with the term. On the other hand, being literate in the 21 st century ...