History Cooperative

The First TV: A Complete History of Television
From the Moon Landing to M*A*S*H, from the Olympics to “The Office,” some of the most critical moments in history and culture have been experienced worldwide thanks to the wondrous invention of television.
The evolution of television has been one full of slow, steady progress. However, there have been definitive moments that have changed technology forever. The first TV, the first “broadcast” of live events to screen, the introduction of “the television show,” and the Streaming Internet have all been significant leaps forward in how television works.
Today, television technology is an integral part of telecommunications and computing. Without it, we would be lost.
Table of Contents
What Is a Television System?
It’s a simple question with a surprisingly complex answer. At its core, a “television” is a device that takes electrical input to produce moving images and sound for us to view. A “television system” would be both what we now call television and the camera/producing equipment that captured the original images.
The Etymology of “Television”
The word “television” first appeared in 1907 in the discussion of a theoretical device that transported images across telegraph or telephone wires. Ironically, this prediction was behind the times, as some of the first experiments into television used radio waves from the beginning.
“Tele-” is a prefix that means “far off” or “operating at a distance.” The word “television” was agreed upon quite rapidly, and while other terms like “iconoscope” and “emitron” referred to patented devices that were used in some electronic television systems, television is the one that stuck.
Today, the word “television” takes a slightly more fluid meaning. A “television show” is often considered a series of small entertainment pieces with a throughline or overarching plot. The difference between television and movies is found in the length and serialization of the media, rather than the technology used to broadcast it.
“Television” is now as often watched on phones, computers, and home projectors as it is on the independent devices we call “television sets.” In 2017, only 9 percent of American adults watched television using an antenna , and 61 percent watched it directly from the internet.
The Mechanical Television System

The first device you could call a “television system” under these definitions was created by John Logie Baird. A Scottish engineer, his mechanical television used a spinning “Nipkow disk,” a mechanical device to capture images and convert them to electrical signals. These signals, sent by radio waves, were picked up by a receiving device. Its own disks would spin similarly, illuminated by a neon light to produce a replica of the original images.
Baird’s first public demonstration of his mechanical television system was somewhat prophetically held at a London Department store way back in 1925 . Little did he know that television systems would be carefully intertwined with consumerism throughout history.
The evolution of the mechanical television system progressed rapidly and, within three years, Baird’s invention was able to broadcast from London to New York. By 1928, the world’s first television station opened under the name W2XCW. It transmitted 24 vertical lines at 20 frames a second.
Of course, the first device that we today would recognize as television involved the use of Cathode Ray Tubes (CRTs). These convex glass-in-box devices shared images captured live on camera, and the resolution was, for its time, incredible.
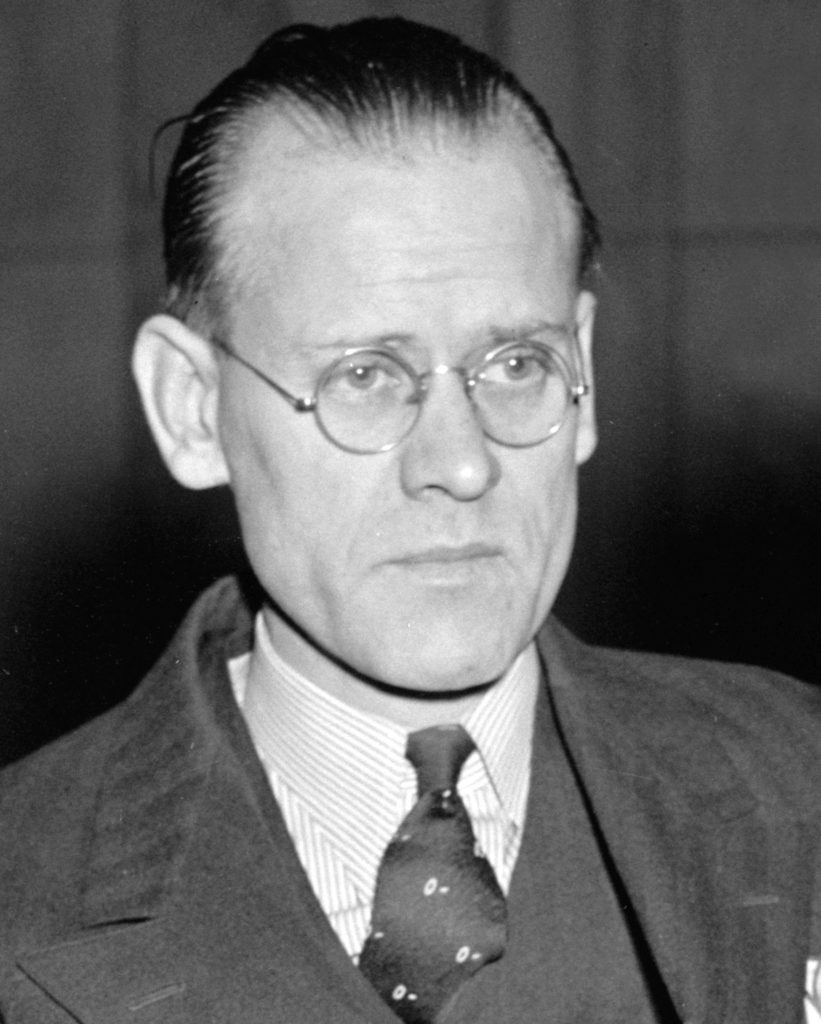
This modern, electronic television had two fathers working simultaneously and often against each other. They were Philo Farnsworth and Vladimir Zworykin.
Who Invented the First TV?
Traditionally, a self-taught boy from Idaho named Philo Farnsworth is credited for having invented the first TV. But another man, Vladimir Zworykin, also deserves some of the credit. In fact, Farnsworth could not have completed his invention without the help of Zworykin.

How the First Electronic Television Camera Came to Be
Philo Farnsworth claimed to have designed the first electronic television receiver at only 14 . Regardless of those personal claims, history records that Farnsworth, at only 21, designed and created a functioning “image dissector” in his small city apartment.
The image dissector “captured images” in a manner not too dissimilar to how our modern digital cameras work today. His tube, which captured 8,000 individual points, could convert the image to electrical waves with no mechanical device required. This miraculous invention led to Farnsworth creating the first all-electronic television system.
Zworykin’s Role in the Developing the First Television
Having escaped to America during the Russian Civil War, Vladimir Zworykin found himself immediately employed by Westinghouse’s electrical engineering firm. He then set to work patenting work he had already produced in showing television images via a Cathode Ray Tube (CRT). He had not, at that point, been able to capture images as well as he could show them.
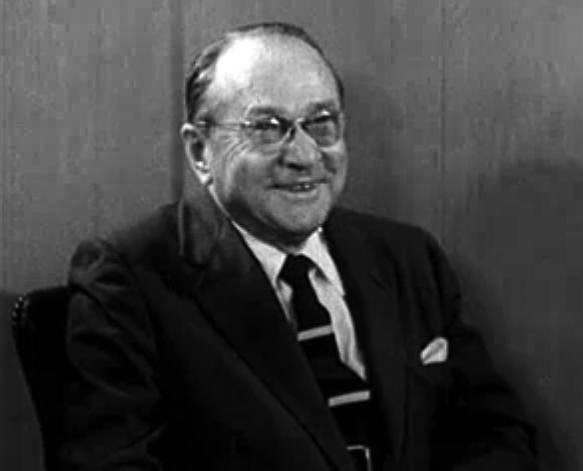

By 1929, Zworykin worked for the Radio Corporation of America (owned by General Electric and soon to form the National Broadcasting Company). He had already created a simple color television system. Zworykin was convinced that the best camera would also use CRT but never seemed to make it work.
When Was TV Invented?
Despite protestations from both men and multiple drawn-out legal battles over their patents, RCA eventually paid royalties to use Farnsworth’s technology to transmit to Zorykin’s receivers. In 1927, the first TV was invented. For decades after, these electronic televisions changed very little.
When Was The First Television Broadcast?
The first television broadcast was by Georges Rignoux and A. Fournier in Paris in 1909. However, this was the broadcast of a single line. The first broadcast that general audiences would have been wowed by was on March 25, 1925. That is the date John Logie Baird presented his mechanical television.
When television began to change its identity from the engineer’s invention to the new toy for the rich, broadcasts were few and far between. The first television broadcasts were of King George VI’s coronation. The coronation was one of the first television broadcasts to be filmed outside.
In 1939, the National Broadcasting Company (NBC) broadcasted the opening of New York’s World’s Fair. This event included a speech from Franklin D. Roosevelt and an appearance by Albert Einstein. By this point, NBC had a regular broadcast of two hours every afternoon and was watched by approximately nineteen thousand people around New York City.
The First Television Networks
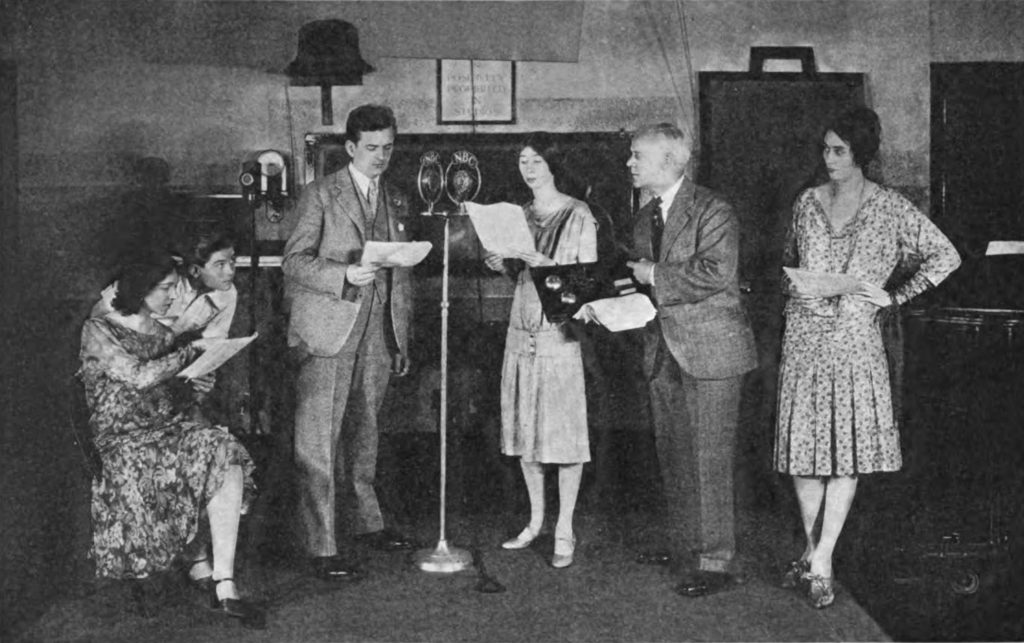

The First Television Network was The National Broadcasting Company, a subsidiary of The Radio Corporation of America (or RCA). It started in 1926 as a series of Radio stations in New York and Washington. NBC’s first official broadcast was on November 15, 1926.
NBC started to regularly broadcast television after the 1939 New York World’s Fair. It had approximately one thousand viewers. From this point on, the network would broadcast every day and continues to do so now.
The National Broadcasting Company kept a dominant position among television networks in the United States for decades but always had competition. The Columbia Broadcasting System (CBS), which had also previously broadcast in radio and mechanical television, turned to all-electronic television systems in 1939. In 1940, it became the first television network to broadcast in color, albeit in a one-off experiment.
The American Broadcasting Company (ABC) was forced to break off from NBC to form its own television network in 1943. This was due to the FCC being concerned that a monopoly was occurring in television.
The three television networks would rule television broadcasting for forty years without competition.
In England , the publicly-owned British Broadcasting Corporation (or BBC) was the only television station available. It started broadcasting television signals in 1929, with John Logie Baird’s experiments, but the official Television Service did not exist until 1936. The BBC would remain the only network in England until 1955.
The First Television Productions
The first made-for-television drama would arguably be a 1928 drama called “The Queen’s Messenger,” written by J. Harley Manners. This live drama presentation included two cameras and was lauded more for the technological marvel than anything else.
The first news broadcasts on television involved news readers repeating what they just had broadcast on radio.
On December 7, 1941, Ray Forrest, one of the first full-time news announcers for television, presented the first news bulletin. The first time that “regularly scheduled programs” were interrupted, his bulletin announced the attack on Pearl Harbor.

This special report for CBS ran for hours, with experts coming into the studio to discuss everything from geography to geopolitics. According to a report CBS gave to the FCC, this unscheduled broadcast “was unquestionably the most stimulating challenge and marked the greatest advance of any single problem faced up to that time.”
After the war, Forrest went on to host one of the first cooking shows on television, “In the Kelvinator Kitchen.”
When Was the First TV Sold?
The first television sets available for anyone were manufactured in 1934 by Telefunken , a subsidiary of the electronics company Siemens. RCA began manufacturing American sets in 1939. They cost around $445 dollars at the time (the American average salary was $35 per month).
TV Becomes Mainstream: The Post-War Boom
After the Second World War, a newly invigorated middle class caused a boom in sales of television sets, and television stations began to broadcast around the clock worldwide.
By the end of the 1940s, audiences were looking to get more from television programming. While news broadcasts would always be important, audiences looked for entertainment that was more than a play that happened to be caught on camera. Experiments from major networks led to significant changes in the type of television programs in existence. Many of these experiments can be seen in the shows of today.
What Was the First TV Show?
The first regularly broadcast TV show was a visual version of the popular radio series, “Texaco Star Theatre.” It began tv broadcasts on June 8, 1948. By this time, there were nearly two hundred thousand television sets in America.
The Rise of The Sitcom
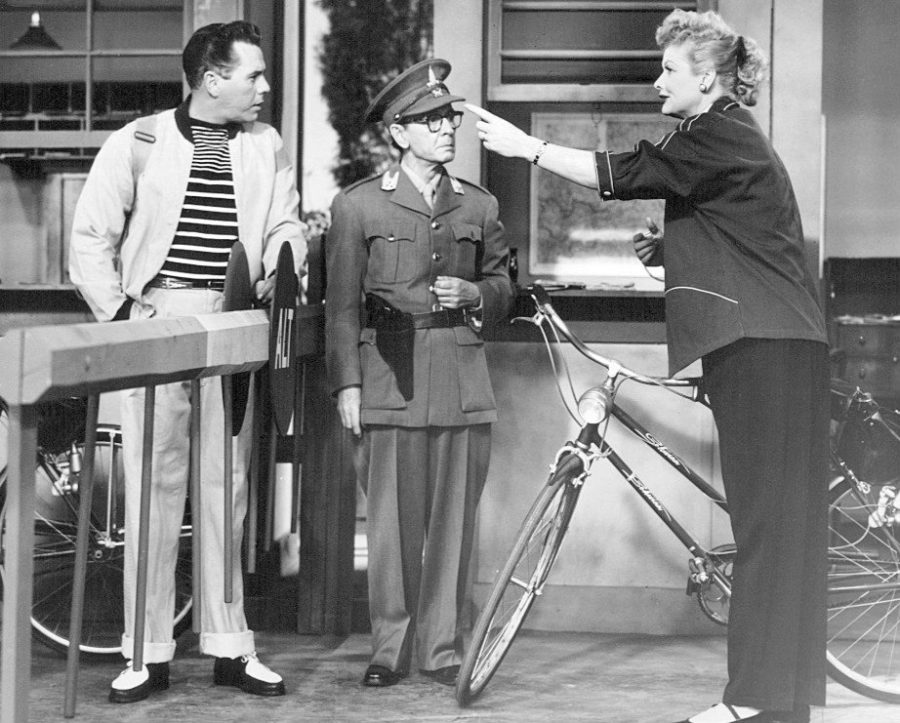

In 1947, DuMont Television Network (partnered with Paramount Pictures) began to air a series of teledramas starring real-life couple Mary Kay and Johnny Stearns. “Mary Kay and Johnny” featured a middle-class American couple facing real-life problems. It was the first show on television to show a couple in bed, as well as a pregnant woman. It was not only the first “sitcom” but the model for all the great sitcoms since.
Three years later, CBS hired a young female actor called Lucille, who had previously been known in Hollywood as “The Queen of the B (movies).” Initially trying her out in other sitcoms, she eventually convinced them that their best show would include her partner, just as Mary Kay and Johnny had.
The show, entitled “I Love Lucy,” became a runaway success and is now considered a cornerstone of television.
Today, “I Love Lucy” has been described as “legitimately the most influential in TV history.” The popularity of reruns led to the concept of “syndication,” an arrangement in which other television stations could purchase the rights to screen reruns of the show.
According to CBS, “I Love Lucy” still makes the company $20 Million a year . Lucille Ball is now considered one of the most important names in the history of the medium.
The “sitcom,” derived from the phrase “situational comedy,” is still one of the most popular forms of television programming.
In 1983, the final episode of the popular sitcom “M*A*S*H” had over one hundred million viewers glued to their screens, a number not beaten for nearly thirty years.
In 1997, Jerry Seinfeld would become the first sit-com star to earn a million dollars per episode. “It’s Always Sunny in Philadelphia”, a sitcom about the immoral and crazy owners of a bar, is the longest-running live sitcom ever, now into its 15th season.
When Did Color TV Come Out?

The ability of television systems to broadcast and receive color occurred relatively early in the evolution of electronic television. Patents for color television existed from the late nineteenth century, and John Baird regularly broadcast from a color television system in the thirties.
The National Television System Committee (NTSC) met in 1941 to develop a standardized system for television broadcasts, ensuring that all television stations used similar systems to ensure that all television systems could receive them. The committee, created by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC), would meet again only twelve years later to agree upon a standard for color television.
However, a problem faced by television networks was that color broadcasting required extra radio bandwidth. This bandwidth, the FCC decided, needed to be separate from that which sent black and white television in order for all audiences to receive a broadcast. This NTSC standard was first used for the “Tournament of Roses Parade” in 1954. The color viewing was available to so few systems as a particular receiver was required.
The First TV Remote Control
While the first remote controls were intended for military use, controlling boats and artillery from a distance, entertainment providers soon considered how radio and television systems might use the technology.
What Was The First TV Remote?
The first remote control for television was developed by Zenith in 1950 and was called “Lazy Bones.” It had a wired system and only a single button, which allowed for the changing of channels.
By 1955, however, Zenith had produced a wireless remote that worked by shining light at a receiver on the television. This remote could change channels, turn the tv on and off, and even change the sound. However, being activated by light, ordinary lamps, and sunlight could unintentionally act on the television.
While future remote controls would use ultrasonic frequencies, the use of infra-red light ended up being the standard. The information sent from these devices was often unique to the television system but could offer complex instructions.
Today, all television sets are sold with remote controls as standard, and an inexpensive “universal remote” can be purchased easily online.
The Tonight Show and Late Night Television
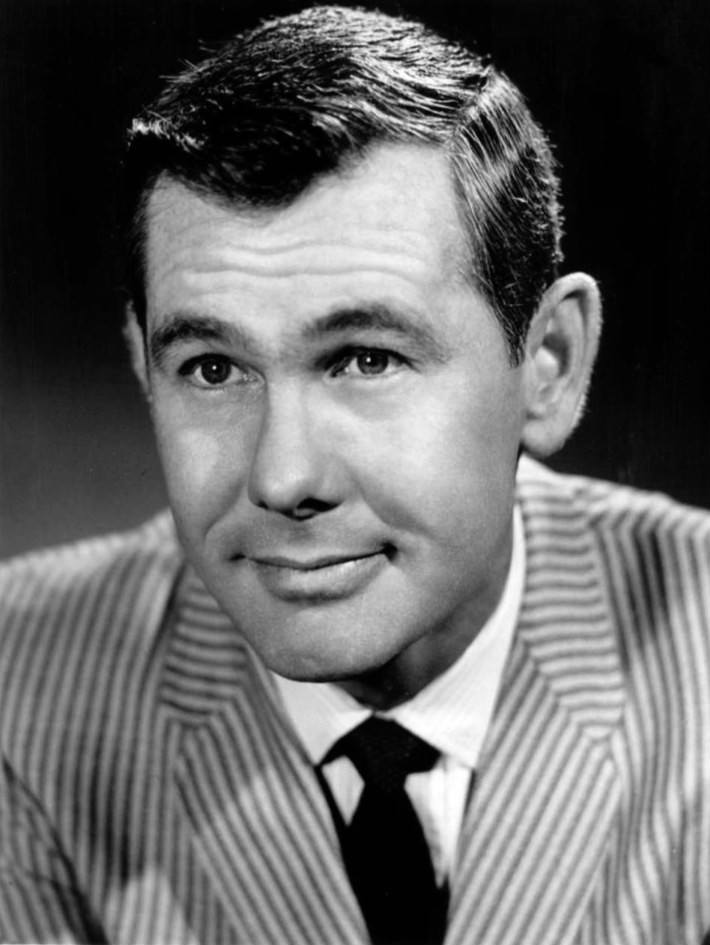

After starring in the first American sitcom, Johnny Stearns continued on television by being one of the producers behind “Tonight, Starring Steve Allen,” now known as “The Tonight Show.” This late-night broadcast is the longest-running television talk show still running today.
Prior to “The Tonight Show,” talk shows were already growing popular. “The Ed Sullivan Show” opened in 1948 with a premier that included Dean Martin, Jerry Lewis, and a sneak preview of Rodgers and Hammerstein’s “South Pacific.” The show featured serious interviews with its stars and Sullivan was known to have little respect for the young musicians that performed on his show. “The Ed Sullivan Show” lasted until 1971 and is now most remembered for being the show that introduced the United States to “ Beatlemania “.
“The Tonight Show” was a more low-brow affair compared to Sullivan, and popularized a number of elements found today in late-night television; opening monolog, live bands, sketch moments with guest stars, and audience participation all found their start in this program.
While popular under Allen, “The Tonight Show” really became a part of history during its epic three-decade run under Johnny Carson. From 1962 to 1992, Carson’s program was less about the intellectual conversation with guests than it was about promotion and spectacle. Carson, to some , “define[d] in a single word what made television different from theater or cinema.”
The Tonight Show still runs today, hosted by Jimmy Fallon, while contemporary competitors include “The Late Show” with Stephen Colbert and “The Daily Show” with Trevor Noah.
Digital Television Systems
Starting with the first TV, television broadcasts were always analog, which means the radio wave itself contains the information the set needs to create a picture and sound. Image and sound would be directly translated into waves via “modulation” and then reverted back by the receiver through “demodulation”.
A digital radio wave doesn’t contain such complex information, but alternates between two forms, which can be interpreted as zeros and ones. However, this information needs to be “encoded” and “recoded.”
With the rise of low-cost, high-power computing, engineers experimented with the digital broadcast . Digital broadcast “decoding” could be done by a computer chip within the tv set which breaks down the waves into discrete zeroes and ones.
While this could be used to produce greater image quality and clearer audio, it would also require a much higher bandwidth and computing power that was only available in the seventies. The bandwidth required was improved over time with the advent of “ compression ” algorithms, and television networks could broadcast greater amounts of data to televisions at home.
Digital broadcast of television via cable television began in the mid-nineties , and as of July 2021 , no television station in the United States broadcasts in analog.
VHS Brings the Movies to TV
For a very long time, what you saw on television was decided by what the television networks decided to broadcast. While some wealthy people could afford film projectors, the large box in the living room could only show what someone else wanted it to.
Then, in the 1960s, electronics companies began to provide devices that could “record television” onto electromagnetic tapes, which could then be watched through the set at a later time. These “Video Cassette Recorders” were expensive but desired by many. The first Sony VCR cost the same as a new car.
In the late seventies, two companies faced off to determine the standard of home video cassettes in what some referred to as a “format war.”
Sony’s “Betamax” eventually lost to JVC’s “VHS” format due to the latter company’s willingness to make their standard “open” (and not require licensing fees).
VHS machines quickly dropped in price, and soon most homes contained an extra piece of equipment. Contemporary VCRs could record from the television and played portable tapes with other recordings. In California, businessman George Atkinson purchased a library of fifty movies directly from movie companies and then proceeded to start a new industry.
The Birth of Video Rental Companies

For a fee, customers could become members of his “Video Station” . Then, for an additional cost, they could borrow one of the fifty movies to watch at home, before returning. So began the era of the video rental company.
Movie studios were concerned by the concept of home video. They argued that giving people the ability to copy to tape what they are shown constituted theft. These cases reached the Supreme Court, which eventually decided that recording for home consumption was legal.
Studios replied by creating licensing agreements to make video rental a legitimate industry and produce films specifically for home entertainment.
While the first “direct to video” movies were low-budget slashers or pornography, the format became quite popular after the success of Disney’s “Aladdin: Return of Jafar.” This sequel to the popular animated movie sold 1.5 Million copies in its first two days of release.
READ MORE: The Dawn of Desire: Who Invented Porn?
Home video changed slightly with the advent of digital compression and the rise of optical disc storage.
Soon, networks and film companies could offer high-quality digital television recordings on Digital Versatile Discs (or DVDs). These discs were introduced in the mid-nineties but soon were superseded by high-definition discs.
As possible evidence of karma, it was Sony’s “Blu-Ray” system that won against Toshiba’s “HG DVD” in home video’s second “Format War.” Today, Blu-Rays are the most popular form of physical purchase for home entertainment.
READ MORE: The First Movie Ever Made
First Satellite TV
On July 12, 1962, the Telstar 1 satellite beamed images sent from Andover Earth Station in Maine to the Pleumeur-Bodou Telecom Center in Brittany, France. So marked the birth of satellite television. Only three years later, the first commercial satellite for the purposes of broadcasting was sent into space.
Satellite television systems allowed television networks to broadcast around the world, no matter how far from the rest of society a receiver might be. While owning a personal receiver was, and still is, far more expensive than conventional television, networks took advantage of such systems to offer subscription services that were not available to public consumers. These services were a natural evolution of already existing “cable channels” such as “Home Box Office,” which relied on direct payment from consumers instead of external advertising.
The first live satellite broadcast that was watchable worldwide occurred in June 1967. BBC’s “Our World” employed multiple geostationary satellites to beam a special entertainment event that included the first public performance of “All You Need is Love” by The Beatles.
The Constant Rise and Fall of 3D Television
It is a technology with a long history of attempts and failures and which will likely return one day. “3D Television” refers to television that conveys depth perception, often with the aid of specialized screens or glasses .
It may come as no surprise that the first example of 3D television came from the labs of John Baird. His 1928 presentation bore all the hallmarks of future research into 3D television because the principle has always been the same. Two images are shown at slightly different angles and differences to approximate the different images our two eyes see.
While 3D films have come and gone as gimmicky spectacles, the early 2010s saw a significant spark of excitement for 3D television — all the spectacle of the movies at home. While there was nothing technologically advanced about screening 3D television, broadcasting it required more complexity in standards. At the end of 2010, the DVB-3D standard was introduced, and electronics companies around the world were clambering to get their products into homes .
However, like the 3D crazes in movies every few decades, the home viewer soon grew tired. While 2010 saw the PGA Championship, FIFA World Cup, and Grammy Awards all filmed and broadcast in 3D, channels began to stop offering the service only three years later. By 2017, Sony and LG officially announced they would no longer support 3D for their products.
Some future “visionary” will likely take another shot at 3D television but, by then, there is a very good chance that television will be something very different indeed.
LCD/LED Systems
During the late twentieth century, new technologies arose in how television could be presented on the screen. Cathode Ray Tubes had limitations in size, longevity, and cost. The invention of low-cost microchips and the ability to manufacture quite small components led TV manufacturers to look for new technologies.
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) is a way to present images by having a backlight shine through millions (or even billions) of crystals that can be individually made opaque or translucent using electricity . This method allows the display of images using devices that can be very flat and use little electricity.
While popular in the 20th century for use in clocks and watches, improvements in LCD technology let them become the next way to present images for television. Replacing the old CRT meant televisions were lighter, thinner, and inexpensive to run. Because they did not use phosphorous, images left on the screen could not “burn-in” .
Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) use extremely small “diodes” that light up when electricity passes through them. Like LCD, they are inexpensive, small, and use little electricity. Unlike LCD, they need no backlight. Because LCDs are cheaper to produce, they have been the popular choice in the early 21st century. However, as technology changes , the advantages of LED may eventually lead to it taking over the market.
The Internet Boogeyman
The ability for households to have personal internet access in the nineties led to fear among those in the television industry that it might not be around forever. While many saw this fear as similar to the rise of VHS, others took advantage of the changes.
With internet speeds increasing, the data that was previously sent to the television via radio waves or cables could not be sent through your telephone line. The information you would once need to record onto a video cassette could be “downloaded” to watch in the future. People began acting “outside of the law,”very much like the early video rental stores.
Then, when internet speed reached a point fast enough, something unusual happened.
“Streaming Video” and the rise of YouTube
In 2005, three former employees of the online financial company PayPal created a website that allowed people to upload their home videos to watch online. You didn’t need to download these videos but could watch them “live” as the data was “streamed” to your computer. This means you did not need to wait for a download or use up hard-drive space.
Videos were free to watch but contained advertising and allowed content creators to include ads for which they would be paid a small commission. This “partner program” encouraged a new wave of creators who could make their own content and gain an audience without relying on television networks.
The creators offered a limited release to interested people, and by the time the site officially opened, more than two million videos a day were being added.
Today, creating content on YouTube is big business. With the ability for users to “subscribe” to their favorite creators, the top YouTube stars can earn tens of millions of dollars a year.
Netflix, Amazon, and the New Television Networks
In the late nineties, a new subscription video rental service formed that was seemingly like all those who came after George Atkinson. It had no physical buildings but would rely on people returning the video in the mail before renting the next one. Because videos now came on DVD, postage was cheap, and the company soon rivaled the most prominent video rental chains.
Then in 2007, as people were paying attention to the rise of YouTube, the company took a risk. Using the rental licenses it already had to lend out its movies, it placed them online for consumers to stream directly. It started with 1,000 titles and only allowed 18 hours of streaming per month. This new service was so popular that, by the end of the year, the company had 7.5 million subscribers.
The problem was that, for Netflix, they relied on the same television networks that their company was damaging. If people watched their streaming service more than traditional television, networks would need to increase their fee for licensing their shows to rental companies. In fact, if a network decided to no longer license its content to Netflix, there would be little the company could do.
So, the company started to produce its own material. It hoped to attract even more viewers by investing a large amount of money on new shows like “Daredevil” and the US remake of “House of Cards.” The latter series, which ran from 2013 to 2018, won 34 Emmys , cementing Netflix as a competitor in the television network industry.
In 2021, the company spent $17 Billion on original content and continued to decrease the amount of content purchased from the three major networks.
Other companies took note of the success of Netflix. Amazon, which started life as an online bookstore, and became one of the largest e-commerce platforms globally, began to produce its own original in the same year as Netflix and has since been joined by dozens of other services around the world.
The Future of Television
In some ways, those who feared the internet were right. Today, streaming takes up over a quarter of the audience’s viewing habits, with this number rising every year.
However, this change is less about the media and more about the technology that accesses it. Mechanical Televisions are gone. Analog broadcasts are gone. Eventually, radio-broadcasted television will disappear as well. But television? Those half-hour and one-hour blocks of entertainment, they are not going anywhere.
The most-watched streaming programs of 2021 include dramas, comedies, and, just like at the beginning of television history, cooking shows.
While slow to react to the internet, the major networks all now have their own streaming services, and new advances in fields like virtual reality mean that television will continue to evolve well into our future.
How to Cite this Article
There are three different ways you can cite this article.
1. To cite this article in an academic-style article or paper , use:
<a href=" https://historycooperative.org/the-first-tv-a-complete-history-of-television/ ">The First TV: A Complete History of Television</a>
Leave a Comment Cancel reply

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9.1 The Evolution of Television
Learning objectives.
- Identify two technological developments that paved the way for the evolution of television.
- Explain why electronic television prevailed over mechanical television.
- Identify three important developments in the history of television since 1960.
Since replacing radio as the most popular mass medium in the 1950s, television has played such an integral role in modern life that, for some, it is difficult to imagine being without it. Both reflecting and shaping cultural values, television has at times been criticized for its alleged negative influences on children and young people and at other times lauded for its ability to create a common experience for all its viewers. Major world events such as the John F. Kennedy and Martin Luther King assassinations and the Vietnam War in the 1960s, the Challenger shuttle explosion in 1986, the 2001 terrorist attacks on the World Trade Center, and the impact and aftermath of Hurricane Katrina in 2005 have all played out on television, uniting millions of people in shared tragedy and hope. Today, as Internet technology and satellite broadcasting change the way people watch television, the medium continues to evolve, solidifying its position as one of the most important inventions of the 20th century.
The Origins of Television
Inventors conceived the idea of television long before the technology to create it appeared. Early pioneers speculated that if audio waves could be separated from the electromagnetic spectrum to create radio, so too could TV waves be separated to transmit visual images. As early as 1876, Boston civil servant George Carey envisioned complete television systems, putting forward drawings for a “selenium camera” that would enable people to “see by electricity” a year later (Federal Communications Commission, 2005).
During the late 1800s, several technological developments set the stage for television. The invention of the cathode ray tube (CRT) by German physicist Karl Ferdinand Braun in 1897 played a vital role as the forerunner of the TV picture tube. Initially created as a scanning device known as the cathode ray oscilloscope, the CRT effectively combined the principles of the camera and electricity. It had a fluorescent screen that emitted a visible light (in the form of images) when struck by a beam of electrons. The other key invention during the 1880s was the mechanical scanner system. Created by German inventor Paul Nipkow, the scanning disk was a large, flat metal disk with a series of small perforations arranged in a spiral pattern. As the disk rotated, light passed through the holes, separating pictures into pinpoints of light that could be transmitted as a series of electronic lines. The number of scanned lines equaled the number of perforations, and each rotation of the disk produced a television frame. Nipkow’s mechanical disk served as the foundation for experiments on the transmission of visual images for several decades.
In 1907, Russian scientist Boris Rosing used both the CRT and the mechanical scanner system in an experimental television system. With the CRT in the receiver, he used focused electron beams to display images, transmitting crude geometrical patterns onto the television screen. The mechanical disk system was used as a camera, creating a primitive television system.
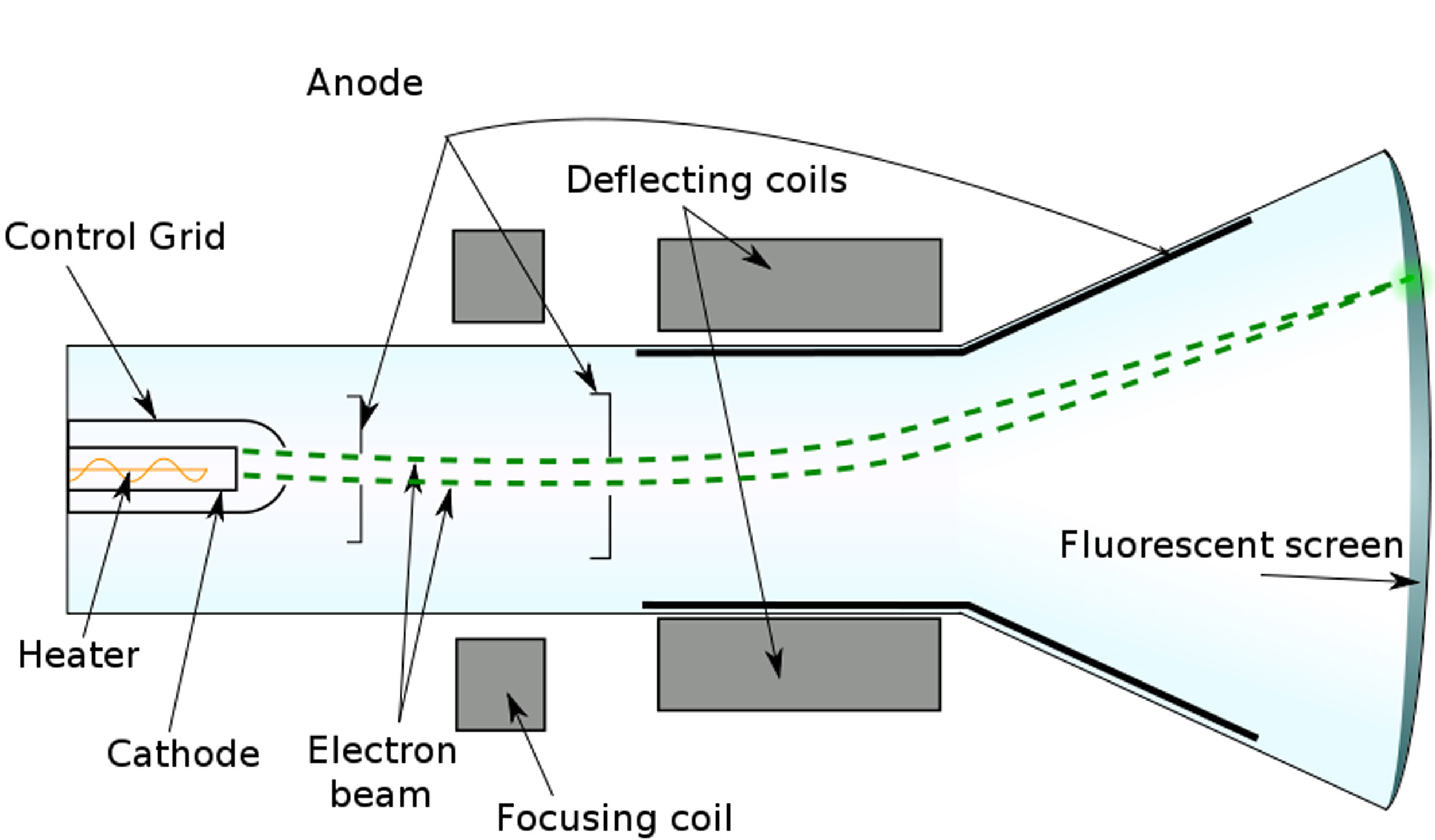
Two key inventions in the 1880s paved the way for television to emerge: the cathode ray tube and the mechanical disk system.
Mechanical Television versus Electronic Television
From the early experiments with visual transmissions, two types of television systems came into existence: mechanical television and electronic television. Mechanical television developed out of Nipkow’s disk system and was pioneered by British inventor John Logie Baird. In 1926, Baird gave the world’s first public demonstration of a television system at Selfridge’s department store in London. He used mechanical rotating disks to scan moving images into electrical impulses, which were transmitted by cable to a screen. Here they showed up as a low-resolution pattern of light and dark. Baird’s first television program showed the heads of two ventriloquist dummies, which he operated in front of the camera apparatus out of the audience’s sight. In 1928, Baird extended his system by transmitting a signal between London and New York. The following year, the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) adopted his mechanical system, and by 1932, Baird had developed the first commercially viable television system and sold 10,000 sets. Despite its initial success, mechanical television had several technical limitations. Engineers could get no more than about 240 lines of resolution, meaning images would always be slightly fuzzy (most modern televisions produce images of more than 600 lines of resolution). The use of a spinning disk also limited the number of new pictures that could be seen per second, resulting in excessive flickering. The mechanical aspect of television proved to be a disadvantage that required fixing in order for the technology to move forward.
At the same time Baird (and, separately, American inventor Charles Jenkins) was developing the mechanical model, other inventors were working on an electronic television system based on the CRT. While working on his father’s farm, Idaho teenager Philo Farnsworth realized that an electronic beam could scan a picture in horizontal lines, reproducing the image almost instantaneously. In 1927, Farnsworth transmitted the first all-electronic TV picture by rotating a single straight line scratched onto a square piece of painted glass by 90 degrees.
Farnsworth barely profited from his invention; during World War II, the government suspended sales of TV sets, and by the time the war ended, Farnsworth’s original patents were close to expiring. However, following the war, many of his key patents were modified by RCA and were widely applied in broadcasting to improve television picture quality.
Having coexisted for several years, electronic television sets eventually began to replace mechanical systems. With better picture quality, no noise, a more compact size, and fewer visual limitations, the electronic system was far superior to its predecessor and rapidly improving. By 1939, the last mechanical television broadcasts in the United States had been replaced with electronic broadcasts.

Early Broadcasting
Television broadcasting began as early as 1928, when the Federal Radio Commission authorized inventor Charles Jenkins to broadcast from W3XK, an experimental station in the Maryland suburbs of Washington, DC. Silhouette images from motion picture films were broadcast to the general public on a regular basis, at a resolution of just 48 lines. Similar experimental stations ran broadcasts throughout the early 1930s. In 1939, RCA subsidiary NBC (National Broadcasting Company) became the first network to introduce regular television broadcasts, transmitting its inaugural telecast of the opening ceremonies at the New York World’s Fair. The station’s initial broadcasts transmitted to just 400 television sets in the New York area, with an audience of 5,000 to 8,000 people (Lohr, 1940).
Television was initially available only to the privileged few, with sets ranging from $200 to $600—a hefty sum in the 1930s, when the average annual salary was $1,368 (KC Library). RCA offered four types of television receivers, which were sold in high-end department stores such as Macy’s and Bloomingdale’s, and received channels 1 through 5. Early receivers were a fraction of the size of modern TV sets, featuring 5-, 9-, or 12-inch screens. Television sales prior to World War II were disappointing—an uncertain economic climate, the threat of war, the high cost of a television receiver, and the limited number of programs on offer deterred numerous prospective buyers. Many unsold television sets were put into storage and sold after the war.
NBC was not the only commercial network to emerge in the 1930s. RCA radio rival CBS (Columbia Broadcasting System) also began broadcasting regular programs. So that viewers would not need a separate television set for each individual network, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) outlined a single technical standard. In 1941, the panel recommended a 525-line system and an image rate of 30 frames per second. It also recommended that all U.S. television sets operate using analog signals (broadcast signals made of varying radio waves). Analog signals were replaced by digital signals (signals transmitted as binary code) in 2009.
With the outbreak of World War II, many companies, including RCA and General Electric, turned their attention to military production. Instead of commercial television sets, they began to churn out military electronic equipment. In addition, the war halted nearly all television broadcasting; many TV stations reduced their schedules to around 4 hours per week or went off the air altogether.
Color Technology
Although it did not become available until the 1950s or popular until the 1960s, the technology for producing color television was proposed as early as 1904, and was demonstrated by John Logie Baird in 1928. As with his black-and-white television system, Baird adopted the mechanical method, using a Nipkow scanning disk with three spirals, one for each primary color (red, green, and blue). In 1940, CBS researchers, led by Hungarian television engineer Peter Goldmark, used Baird’s 1928 designs to develop a concept of mechanical color television that could reproduce the color seen by a camera lens.
Following World War II, the National Television System Committee (NTSC) worked to develop an all-electronic color system that was compatible with black-and-white TV sets, gaining FCC approval in 1953. A year later, NBC made the first national color broadcast when it telecast the Tournament of Roses Parade. Despite the television industry’s support for the new technology, it would be another 10 years before color television gained widespread popularity in the United States, and black-and-white TV sets outnumbered color TV sets until 1972 (Klooster, 2009).
The Golden Age of Television
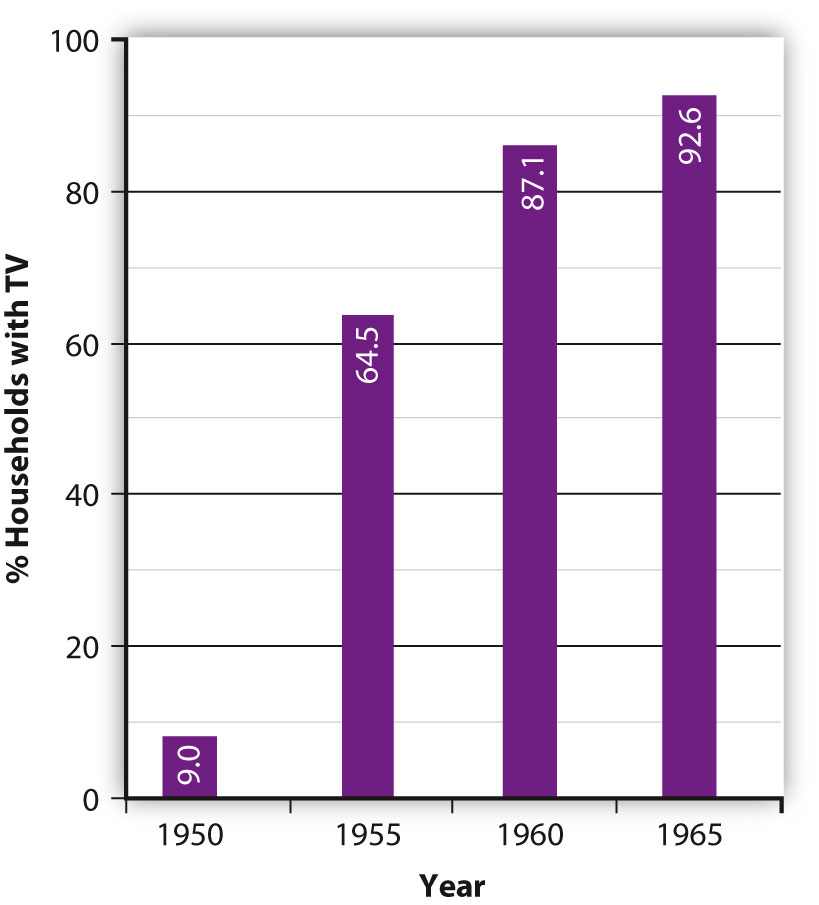
During the so-called “golden age” of television, the percentage of U.S. households that owned a television set rose from 9 percent in 1950 to 95.3 percent in 1970.
The 1950s proved to be the golden age of television, during which the medium experienced massive growth in popularity. Mass-production advances made during World War II substantially lowered the cost of purchasing a set, making television accessible to the masses. In 1945, there were fewer than 10,000 TV sets in the United States. By 1950, this figure had soared to around 6 million, and by 1960 more than 60 million television sets had been sold (World Book Encyclopedia, 2003). Many of the early television program formats were based on network radio shows and did not take advantage of the potential offered by the new medium. For example, newscasters simply read the news as they would have during a radio broadcast, and the network relied on newsreel companies to provide footage of news events. However, during the early 1950s, television programming began to branch out from radio broadcasting, borrowing from theater to create acclaimed dramatic anthologies such as Playhouse 90 (1956) and The U.S. Steel Hour (1953) and producing quality news film to accompany coverage of daily events.
Two new types of programs—the magazine format and the TV spectacular—played an important role in helping the networks gain control over the content of their broadcasts. Early television programs were developed and produced by a single sponsor, which gave the sponsor a large amount of control over the content of the show. By increasing program length from the standard 15-minute radio show to 30 minutes or longer, the networks substantially increased advertising costs for program sponsors, making it prohibitive for a single sponsor. Magazine programs such as the Today show and The Tonight Show , which premiered in the early 1950s, featured multiple segments and ran for several hours. They were also screened on a daily, rather than weekly, basis, drastically increasing advertising costs. As a result, the networks began to sell spot advertisements that ran for 30 or 60 seconds. Similarly, the television spectacular (now known as the television special) featured lengthy music-variety shows that were sponsored by multiple advertisers.

ABC’s Who Wants to Be a Millionaire brought the quiz show back to prime-time television after a 40-year absence.
sonicwwtbamfangamer2 – millionaire – CC BY-SA 2.0.
In the mid-1950s, the networks brought back the radio quiz-show genre. Inexpensive and easy to produce, the trend caught on, and by the end of the 1957–1958 season, 22 quiz shows were being aired on network television, including CBS’s $64,000 Question . Shorter than some of the new types of programs, quiz shows enabled single corporate sponsors to have their names displayed on the set throughout the show. The popularity of the quiz-show genre plunged at the end of the decade, however, when it was discovered that most of the shows were rigged. Producers provided some contestants with the answers to the questions in order to pick and choose the most likable or controversial candidates. When a slew of contestants accused the show Dotto of being fixed in 1958, the networks rapidly dropped 20 quiz shows. A New York grand jury probe and a 1959 congressional investigation effectively ended prime-time quiz shows for 40 years, until ABC revived the genre with its launch of Who Wants to Be a Millionaire in 1999 (Boddy, 1990).
The Rise of Cable Television
Formerly known as Community Antenna Television, or CATV, cable television was originally developed in the 1940s in remote or mountainous areas, including in Arkansas, Oregon, and Pennsylvania, to enhance poor reception of regular television signals. Cable antennas were erected on mountains or other high points, and homes connected to the towers would receive broadcast signals.
In the late 1950s, cable operators began to experiment with microwave to bring signals from distant cities. Taking advantage of their ability to receive long-distance broadcast signals, operators branched out from providing a local community service and began focusing on offering consumers more extensive programming choices. Rural parts of Pennsylvania, which had only three channels (one for each network), soon had more than double the original number of channels as operators began to import programs from independent stations in New York and Philadelphia. The wider variety of channels and clearer reception the service offered soon attracted viewers from urban areas. By 1962, nearly 800 cable systems were operational, serving 850,000 subscribers.
The Evolution of Television
Cable’s exponential growth was viewed as competition by local TV stations, and broadcasters campaigned for the FCC to step in. The FCC responded by placing restrictions on the ability of cable systems to import signals from distant stations, which froze the development of cable television in major markets until the early 1970s. When gradual deregulation began to loosen the restrictions, cable operator Service Electric launched the service that would change the face of the cable television industry— pay TV . The 1972 Home Box Office (HBO) venture, in which customers paid a subscription fee to access premium cable television shows and video-on-demand products, was the nation’s first successful pay cable service. HBO’s use of a satellite to distribute its programming made the network available throughout the United States. This gave it an advantage over the microwave-distributed services, and other cable providers quickly followed suit. Further deregulation provided by the 1984 Cable Act enabled the industry to expand even further, and by the end of the 1980s, nearly 53 million households subscribed to cable television (see Section 6.3 “Current Popular Trends in the Music Industry” ). In the 1990s, cable operators upgraded their systems by building higher-capacity hybrid networks of fiber-optic and coaxial cable. These broadband networks provide a multichannel television service, along with telephone, high-speed Internet, and advanced digital video services, using a single wire.
The Emergence of Digital Television
Following the FCC standards set out during the early 1940s, television sets received programs via analog signals made of radio waves. The analog signal reached TV sets through three different methods: over the airwaves, through a cable wire, or by satellite transmission. Although the system remained in place for more than 60 years, it had several disadvantages. Analog systems were prone to static and distortion, resulting in a far poorer picture quality than films shown in movie theaters. As television sets grew increasingly larger, the limited resolution made scan lines painfully obvious, reducing the clarity of the image. Companies around the world, most notably in Japan, began to develop technology that provided newer, better-quality television formats, and the broadcasting industry began to lobby the FCC to create a committee to study the desirability and impact of switching to digital television . A more efficient and flexible form of broadcast technology, digital television uses signals that translate TV images and sounds into binary code, working in much the same way as a computer. This means they require much less frequency space and also provide a far higher quality picture. In 1987, the Advisory Committee on Advanced Television Services began meeting to test various TV systems, both analog and digital. The committee ultimately agreed to switch from analog to digital format in 2009, allowing a transition period in which broadcasters could send their signal on both an analog and a digital channel. Once the switch took place, many older analog TV sets were unusable without a cable or satellite service or a digital converter. To retain consumers’ access to free over-the-air television, the federal government offered $40 gift cards to people who needed to buy a digital converter, expecting to recoup its costs by auctioning off the old analog broadcast spectrum to wireless companies (Steinberg, 2007). These companies were eager to gain access to the analog spectrum for mobile broadband projects because this frequency band allows signals to travel greater distances and penetrate buildings more easily.
The Era of High-Definition Television
Around the same time the U.S. government was reviewing the options for analog and digital television systems, companies in Japan were developing technology that worked in conjunction with digital signals to create crystal-clear pictures in a wide-screen format. High-definition television , or HDTV, attempts to create a heightened sense of realism by providing the viewer with an almost three-dimensional experience. It has a much higher resolution than standard television systems, using around five times as many pixels per frame. First available in 1998, HDTV products were initially extremely expensive, priced between $5,000 and $10,000 per set. However, as with most new technology, prices dropped considerably over the next few years, making HDTV affordable for mainstream shoppers.
HDTV uses a wide-screen format with a different aspect ratio (the ratio of the width of the image to its height) than standard-definition TV. The wide-screen format of HDTV is similar to that of movies, allowing for a more authentic film-viewing experience at home.
Wikimedia Commons – CC BY-SA 3.0.
As of 2010, nearly half of American viewers are watching television in high definition, the fastest adoption of TV technology since the introduction of the VCR in the 1980s (Stelter, 2010). The new technology is attracting viewers to watch television for longer periods of time. According to the Nielsen Company, a company that measures TV viewership, households with HDTV watch 3 percent more prime-time television —programming screened between 7 and 11 p.m., when the largest audience is available—than their standard-definition counterparts (Stelter, 2010). The same report claims that the cinematic experience of HDTV is bringing families back together in the living room in front of the large wide-screen TV and out of the kitchen and bedroom, where individuals tend to watch television alone on smaller screens. However, these viewing patterns may change again soon as the Internet plays an increasingly larger role in how people view TV programs. The impact of new technologies on television is discussed in much greater detail in Section 9.4 “Influence of New Technologies” of this chapter.
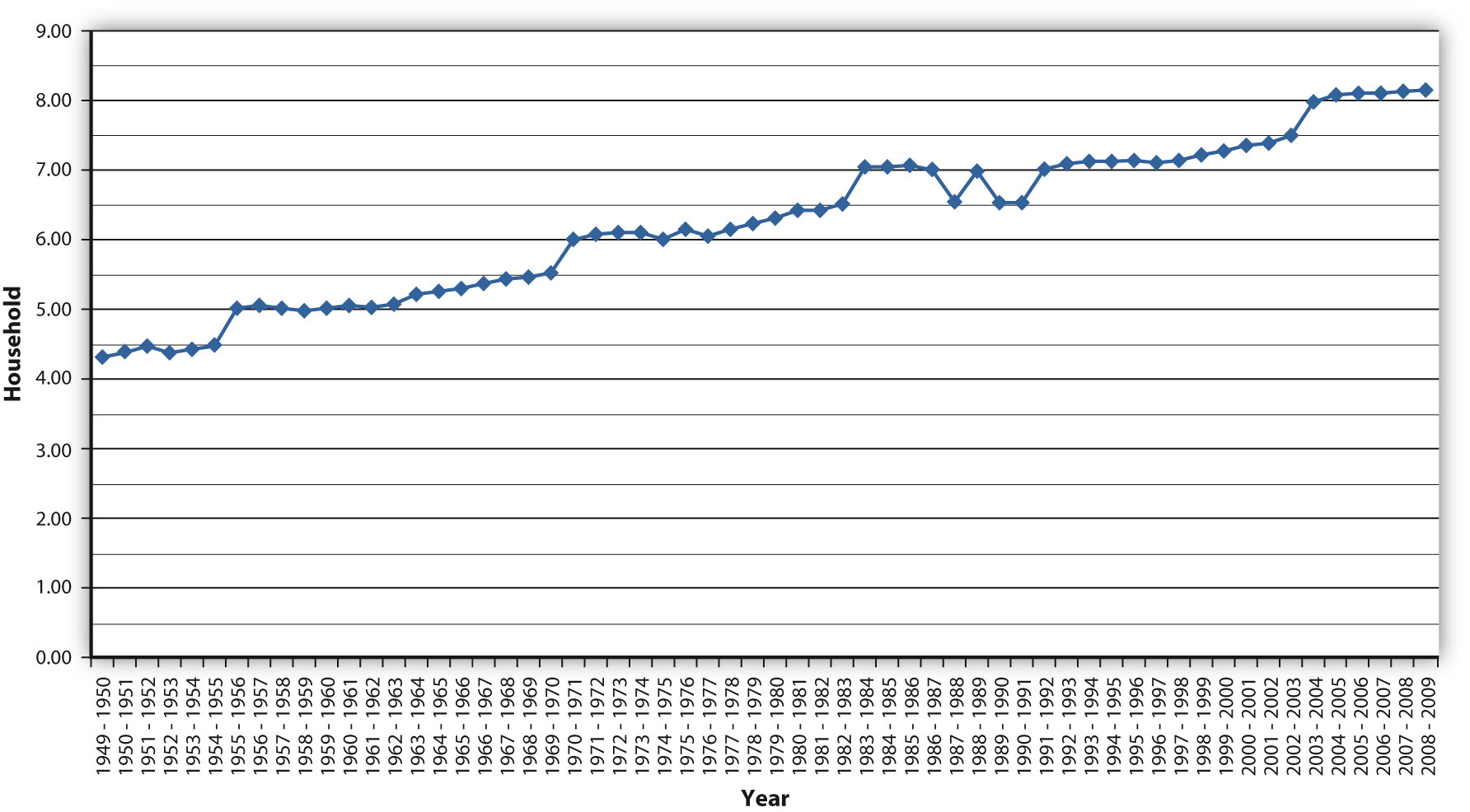
Since 1950, the amount of time the average household spends watching television has almost doubled.
Key Takeaways
- Two key technological developments in the late 1800s played a vital role in the evolution of television: the cathode ray tube and the scanning disk. The cathode ray tube, invented by German physicist Karl Ferdinand Braun in 1897, was the forerunner of the TV picture tube. It had a fluorescent screen that emitted a visible light (in the form of images) when struck by a beam of electrons. The scanning disk, invented by German inventor Paul Nipkow, was a large, flat metal disk that could be used as a rotating camera. It served as the foundation for experiments on the transmission of visual images for several decades.
- Out of the cathode ray tube and the scanning disk, two types of primitive television systems evolved: mechanical systems and electronic systems. Mechanical television systems had several technical disadvantages: Low resolution caused fuzzy images, and the use of a spinning disk limited the number of new pictures that could be seen per second, resulting in excessive flickering. By 1939, all mechanical television broadcasts in the United States had been replaced by electronic broadcasts.
- Early televisions were expensive, and the technology was slow to catch on because development was delayed during World War II. Color technology was delayed even further because early color systems were incompatible with black-and-white television sets. Following the war, television rapidly replaced radio as the new mass medium. During the “golden age” of television in the 1950s, television moved away from radio formats and developed new types of shows, including the magazine-style variety show and the television spectacular.
- Since 1960, several key technological developments have taken place in the television industry. Color television gained popularity in the late 1960s and began to replace black-and-white television in the 1970s. Cable television, initially developed in the 1940s to cater to viewers in rural areas, switched its focus from local to national television, offering an extensive number of channels. In 2009, the traditional analog system, which had been in place for 60 years, was replaced with digital television, giving viewers a higher-quality picture and freeing up frequency space. As of 2010, nearly half of American viewers have high-definition television, which offers a crystal-clear picture in wide-screen to provide a cinematic experience at home.
Please respond to the following writing prompts. Each response should be a minimum of one paragraph.
- Prior to World War II, television was in the early stages of development. In the years following the war, the technical development and growth in popularity of the medium were exponential. Identify two ways television evolved after World War II. How did these changes make postwar television superior to its predecessor?
- Compare the television you use now with the television from your childhood. How have TV sets changed in your lifetime?
- What do you consider the most important technological development in television since the 1960s? Why?
Boddy, William. “The Seven Dwarfs and the Money Grubbers,” in Logics of Television: Essays in Cultural Criticism , ed. Patricia Mellencamp (Bloomington, IN: Indiana University Press, 1990), 98–116.
Federal Communications Commission, “Visionary Period, 1880’s Through 1920’s,” Federal Communications Commission , November 21, 2005, http://www.fcc.gov/omd/history/tv/1880-1929.html .
KC Library, Lone Star College: Kinwood, “American Cultural History 1930–1939,” http://kclibrary.lonestar.edu/decade30.html .
Klooster, John. Icons of Invention: The Makers of the Modern World from Gutenberg to Gates (Santa Barbara, CA: ABC-CLIO, 2009), 442.
Lohr, Lenox. Television Broadcasting (New York: McGraw Hill, 1940).
Steinberg, Jacques. “Converters Signal a New Era for TVs,” New York Times , June 7, 2007, http://www.nytimes.com/2007/06/07/technology/07digital.html .
Stelter, Brian. “Crystal-Clear, Maybe Mesmerizing,” New York Times , May 23, 2010, http://www.nytimes.com/2010/05/24/business/media/24def.html .
World Book Encyclopedia (2003), s.v. “Television.”
Understanding Media and Culture Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Find anything you save across the site in your account
How TV Became Art
By Joshua Rothman and Erin Overbey

To celebrate The New Yorker’s first-ever Television Issue , we’re looking back on nearly nine decades of television coverage in the magazine.
In 2002, in an article called “ The Televisionary ,” Malcolm Gladwell told the story of the invention of television. The visionary in question was a man named Philo T. Farnsworth. Farnsworth was born in 1906 and grew up working his family’s potato farm; in 1927, he built one of the first working television cameras. For decades, he was widely known as the inventor of television. The truth was that television was an incredibly complex technology; hundreds, even thousands, of engineers had contributed to perfecting it. “Everyone was working on television and everyone was reading everyone else’s patent applications,” Gladwell wrote. By the time TV became a commercial reality, in the late thirties, its many inventors had learned to accept that no one person could claim to have created it—that, as Gladwell put it, “the machine was larger than they were.”
That turned out to be true for the rest of us, too. For nearly a century, television, like the weather, has shaped our behaviors, our moods, and our desires in ways we don’t always comprehend. The New Yorker , which was founded in 1925, was there from the beginning, covering television from its invention onward. In March of 1928, James Thurber visited Bell Labs, on West Street, to see an early tech demo. “The television demonstration properly awed us,” Thurber wrote. “The lights went out, there was the whirring of a machine, then a long flurry of black and white patterns. . . . Finally these steadied into a picture of a card with the Bell trade mark on it.” At the other end of the auditorium, someone stood before the “sending machine,” blowing smoke rings.
A few years later, in May of 1931, a reporter named Morris Markey returned to Bell Labs for what we would now call a videoconference. Told that he would be meeting “Mr. Sullivan,” he walked into a dark room, where a man appeared on a television screen. “Perhaps I had better explain that I am about three miles from you now,” he said, “and that I can see you quite as clearly as you see me.” Five years later, in 1936, E. B. White went to the R.C.A. Building to see the newest developments. He watched a comedian and a political speech—and then, on the TV screen, saw a picture of another TV screen. “Try and appreciate our situation,” he wrote. “We were in a dark room looking into a television set at a television set which was showing a picture of a moving picture.” “Staggered” by this early moment of meta, White fled to the sixty-fifth-floor observation deck, where he could gaze at Staten Island in the traditional way.
No one knew quite how, but it was clear that television was going to change the world. In 1938, two Talk of the Town reporters consulted a TV engineer, hoping to master the lingo in advance. The engineer explained that people who watched television would be called “lookers-in,” asking one another, “Did you look in last night?” They would comfortably distinguish between “live” shows and “dead” ones, which had been prerecorded; they would know strange words such as “audio” and “video” and understand the new meanings of “ghost” and “noise.” (TV “kits” were expensive: the reporters noted that the term “small down payment” would retain its usual meaning.)
Around the same time, the magazine noted a series of televisual firsts. In April of 1939, Talk of the Town covered the first surgical telecast, which was staged at a Brooklyn hospital and allowed spectators in one building to watch an operation in another. That May, at the New York World’s Fair, ordinary citizens got their first glimpse of television. That same month also saw the first televised sporting event in the United States—a double-header baseball game between Columbia and Princeton at Columbia’s Baker Field. Even though viewers could see the action for themselves, the soon-to-be-legendary sportscaster Bill Stern called the game as though he were on the radio, and discrepancies between his narration and reality were newly obvious: “He had a fellow coming up to the plate when he was already there,” the reporters wrote, “and a ball going through a first baseman’s legs when it had caromed off his glove to one side.”
The Second World War put the ascent of TV on pause, and, for the most part, The New Yorker turned its attention elsewhere. In 1947, however, for a piece called “ Diary of a Viewer ,” Robert Rice spent a few evenings “in the bosom of a typical American set-owning family.” (“My object is to learn what it’s like to live with that new branch of entertainment which its trade press persists in calling the Video Art,” he wrote.) At the time, there were fewer than seven thousand television sets in all of Manhattan, and an evening in front of the television felt exotic. Over the course of a week, Rice watched a game show called “Cash & Carry,” a production of “Twelfth Night,” a cooking program sponsored by an appliance company, and a baseball game (Dodgers vs. Phillies). During the game, he got a preview of a behavior that was soon to be widespread—a family shouting at the television while eating too much junk food.
Over the next decade, television programming came to assume the familiar shape it has today. In 1950, Thomas Whiteside visited the offices of the ad agency Batten, Barton, Durstine & Osborne, which made cutting-edge television commercials for Lucky Strike cigarettes, among other products. (B.B.D.O. became the inspiration for Sterling Cooper, in “Mad Men.”) For a 1952 piece called “ No Lobster Men from Neptune ,” he attended the filming of the wildly successful “Tom Corbett, Space Cadet,” observing an early writers’ room in action. And, in 1954, he profiled Sylvester (Pat) Weaver, the new president of NBC (and the father of Sigourney Weaver). Weaver helped create the “Today” and “Tonight” shows, launched a number of educational programs, and brought “magazine-style” advertising to television: instead of producing each show in collaboration with a sponsoring client, NBC began producing its own shows, then selling short commercials, which aired during the breaks, to different clients.
By the end of the fifties, The New Yorker was writing about popular television shows that we still remember today: “ Sunrise Semester ,” “ Continental Classroom ,” and “ Car 54, Where Are You? ” In a dedicated TV column, run under the rubrics “Television” and “The Air,” the magazine’s early TV critics, John Lardner and Philip Hamburger, reviewed shows such as “Gunsmoke,” “Perry Mason,” and “Candid Camera.” Hamburger called “Candid Camera” “sadistic, poisonous, anti-human, and sneaky.” Lardner admired “Gunsmoke” but resisted its “literary ingenuity.” “Gunsmoke” was what we might now call a “prestige” Western, and Lardner yearned for the old-fashioned kind, “with its austere pattern of men, horses, chase, and fusillade.”
During the sixties, seventies, and eighties, The New Yorker struggled to make up its mind about television. Was TV a new frontier for dramatic and civic life, or a sign of the decline of civilization? No event embodied the former possibility more than the live telecast of the moon landing . In a special section of Talk of the Town titled “ The Moon Hours ,” reporters watched the landing on televisions around New York City: from the corner of Fiftieth and Sixth, where a giant screen had been erected for the crowd; from the Eighteenth Precinct, where police watched while booking suspects; from the NBC control room, at Rockefeller Center; from the Chess & Checker Club in midtown, the Lincoln Bar in Harlem, and a house party on the Upper East Side; and from the “Moon-In,” in Central Park, where thousands gathered to watch in Sheep Meadow. “The picture is going everywhere in the world by satellite,” an NBC executive marvelled. “They’re all seeing the same fantastic live pictures at the same time. Nobody any better than anybody else, really. Maybe that holds something pretty good for all of us.”
As TV news came to dominate the reporting landscape, New Yorker writers worked to take its measure. They reflected on the surprisingly raw television coverage of the war in Vietnam (“ Television’s War ,” 1967); profiled Chet Huntley and David Brinkley, of “The Huntley Brinkley Report” (“ An Accident of Casting ,” 1968); and investigated the Nixon Administration’s efforts to manipulate TV news (“ Shaking the Tree ,” 1975). In 1982, E. J. Kahn, Jr., went behind the scenes of “60 Minutes,” which was so popular that it jostled with “Dallas” for the top ratings spot. (Two years earlier, in a lengthy review of “Dallas,” the New Yorker television critic Michael J. Arlen had appreciatively described its villain, J. R. Ewing, as a character with “a touch of Tennessee Williams’s mean-weak young Southern gentleman, a touch of old, snarly Dan Duryea, and a good deal of his own soft, spacy charm.”)
In general, New Yorker reporters admired the TV-news operations they covered, but a tone of wariness suffused their writing about television more broadly. George W. S. Trow’s 1980 essay “ Within the Context of No-Context ” was an extravagantly mournful, McLuhan-esque aria to the traditional media world that TV had dethroned. Trow connected TV to a “decline of adulthood” in America; on television, he argued, “the trivial is raised up to power. The powerful is lowered toward the trivial.” Trow’s formulation was prescient in how it uncannily predicted today’s reality-TV Presidency, but it also signalled a critical blind spot. The New Yorker was fascinated by television—it saw that TV shows could be occasions for renegotiating, reimagining, and subverting culture—but it was uncomfortable with the idea of television as art.
Even so, New Yorker writers responded to the vitality and creativity that were everywhere on TV. There was, during those decades, a wild, unpredictable, fringe aspect to even mainstream TV culture. Television had once been decorous, glamorous, Hollywood-like; now it was developing its own rebellious vibe, and The New Yorker was drawn to the televisual extremes. In 1972, Renata Adler wrote about both the genius of “Sesame Street” and the country’s obsession with soap operas ; in 1975, Arlen cheered the advent of “Saturday Night Live,” which he characterized as “an attempt, finally, to provide entertainment on television in a recognizable, human, non-celebrity voice”—an antidote to “the morass of media-induced show-business culture that increasingly pervades American life.” In 1978, Kenneth Tynan profiled Johnny Carson , who represented the Hollywood version of TV; in 1986, Kahn did the same for Joseph A. Wapner , the judge on the popular show “The People’s Court,” who represented the opposite.
The magazine covered tele-psychics and, in 1990, the televangelists Jim and Tammy Faye Bakker . James Wolcott, the magazine’s TV critic, reviewed Rush Limbaugh and David Letterman, “Seinfeld” (1993), and “ The X-Files ” (1994); that same year, Jeffrey Toobin wrote about the O. J. Simpson trial, which was covered live , and John Seabrook visited the headquarters of MTV . In 1995, Stephen Schiff reflected on “trash TV”—Ricki Lake, Jerry Springer, Sally Jessy Raphaël—which he called “the unholy offspring of Marshall McLuhan and Andy Warhol.” John Lahr also profiled Roseanne Barr , who was bringing a new, disruptive feminism to television. Lahr saw “Roseanne” as simultaneously outrageous and realistic, commercial and serious, comedic and intelligent, broad and complex—in other words, he watched it the way we watch many TV shows today.
If you had to pinpoint a year when “prestige TV” arrived, you might choose 1999. That year, Tad Friend wrote about David Lynch’s frustrating attempt to bring a “Mulholland Drive” series to network television; as if in counterpoint, Nancy Franklin, then The New Yorker’s TV critic, noted the success of “The Sopranos” on cable. “It goes out on a limb that doesn’t even exist at the networks,” she wrote. “The word of mouth since it began has caused people to suddenly and urgently sign up for HBO after years of living contentedly without it.” Together, the collected reviews of Franklin and Emily Nussbaum, who took over the beat in 2011, chronicle the maturation of an art form. Even as The New Yorker continued to cover late-night talk shows and TV news and the business of TV—Ken Auletta, for example, profiled Ted Turner , in 2001—it focussed more and more attention on deeply serialized dramas such as “Mad Men” and “The Wire.” Franklin praised shows like “ Friday Night Lights ,” “ The Good Wife ,” and “ Breaking Bad ”; in a 2012 review of “ Game of Thrones ,” Nussbaum admired the ambitions of the new, multi-character cable dramas. The strength of shows like “Game of Thrones,” “Mad Men,” and “Downton Abbey,” she wrote, is their “insight into what it means to be excluded from power: to be a woman, or a bastard, or a ‘half man.’ ”
Today, television is at the center of culture in ways that its inventors likely never imagined. There is so much good television that even the expanded TV coverage on The New Yorker ’s Web site can’t encompass it all. Showrunners such as Jenji Kohan, the creator of “Orange Is the New Black,” are the new auteurs (Emily Nussbaum has profiled Kohan for this week’s Television Issue); the President of the United States, meanwhile, is himself a television star .
The technology of television has changed beyond recognition—thanks to streaming and smartphone cameras , it’s now part of the Internet —but that has only made TV more influential. The cover of this week’s Television Issue , by Bruce Eric Kaplan—a writer for “Girls,” “Six Feet Under,” and “Seinfeld”—is called “Screen Time.” It shows a child sitting in front of the TV. His attention isn’t on the big screen, which is blank, but on a small one—a smartphone, held in his hand. Television is still evolving, becoming more pervasive and personal. It will continue to change us in ways we can’t foresee.
Explore more stories about television from the history of The New Yorker in our new archive collection, “ Tales from the Small Screen .”

By signing up, you agree to our User Agreement and Privacy Policy & Cookie Statement . This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

By Emily Nussbaum

By David Remnick

By Nathan Heller
When Was the First TV Invented?
A Historical Timeline of the Evolution of the Television (1831–1996)
Yali Shi / Getty Images
- Famous Inventions
- Famous Inventors
- Patents & Trademarks
- Invention Timelines
- Computers & The Internet
- American History
- African American History
- African History
- Ancient History and Culture
- Asian History
- European History
- Latin American History
- Medieval & Renaissance History
- Military History
- The 20th Century
- Women's History
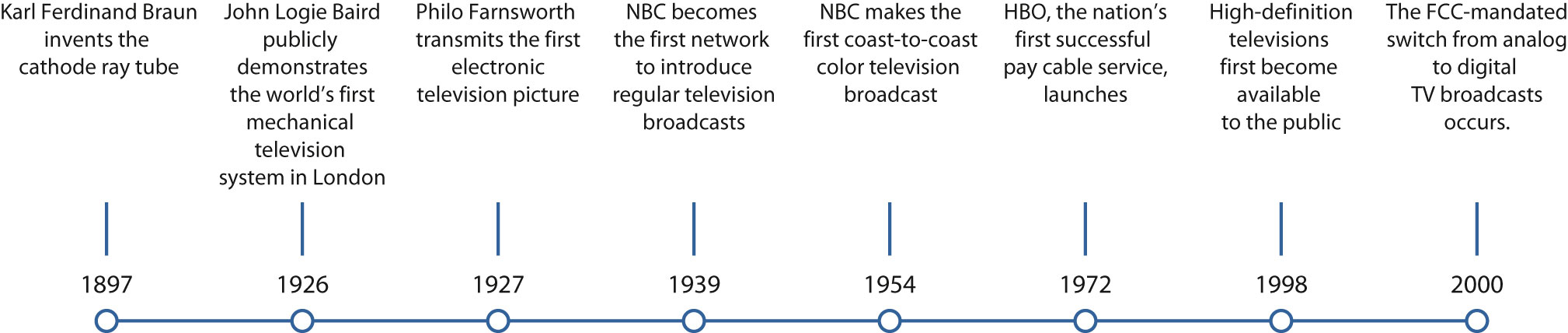
Television was not invented by a single inventor. Instead, many people working together and alone over the years contributed to the evolution of the device.
Joseph Henry 's and Michael Faraday 's work with electromagnetism jumpstarts the era of electronic communication.
Abbe Giovanna Caselli invents his Pantelegraph and becomes the first person to transmit a still image over wires.
Scientist Willoughby Smith experiments with selenium and light, revealing the possibility for inventors to transform images into electronic signals.
Boston civil servant George Carey was thinking about complete television systems and in 1877 he put forward drawings for what he called a selenium camera that would allow people to see by electricity.
Eugen Goldstein coins the term " cathode rays " to describe the light emitted when an electric current was forced through a vacuum tube.
The Late 1870s
Scientists and engineers like Valeria Correa Vaz de Paiva, Louis Figuier, and Constantin Senlecq were suggesting alternative designs for telectroscopes.
Inventors Alexander Graham Bell and Thomas Edison theorize about telephone devices that transmit images as well as sound.
Bell's photophone used light to transmit sound and he wanted to advance his device for image sending.
George Carey builds a rudimentary system with light-sensitive cells.
Sheldon Bidwell experiments with his telephotography that was similar to Bell's photophone.
Paul Nipkow sends images over wires using a rotating metal disk technology calling it the electric telescope with 18 lines of resolution.
At the World's Fair in Paris, the first International Congress of Electricity was held. That is where Russian Constantin Perskyi made the first known use of the word "television."
Soon after 1900, the momentum shifted from ideas and discussions to the physical development of television systems. Two major paths in the development of a television system were pursued by inventors.
- Inventors attempted to build mechanical television systems based on Paul Nipkow's rotating disks.
- Inventors attempted to build electronic television systems based on the cathode ray tube developed independently in 1907 by English inventor A.A. Campbell-Swinton and Russian scientist Boris Rosing.
Lee de Forest invents the Audion vacuum tube that proves essential to electronics. The Audion was the first tube with the ability to amplify signals.
Boris Rosing combines Nipkow's disk and a cathode ray tube and builds the first working mechanical TV system.
Campbell Swinton and Boris Rosing suggest using cathode ray tubes to transmit images. Independent of each other, they both develop electronic scanning methods of reproducing images.
Vladimir Zworykin patents his iconoscope a TV camera tube based on Campbell Swinton's ideas. The iconoscope, which he called an electric eye, becomes the cornerstone for further television development. Zworkin later develops the kinescope for picture display (aka the receiver).
American Charles Jenkins and John Baird from Scotland each demonstrate the mechanical transmissions of images over wire circuits.
John Baird becomes the first person to transmit moving silhouette images using a mechanical system based on Nipkow's disk.
Charles Jenkin built his Radiovisor and in 1931 and sold it as a kit for consumers to put together.
Vladimir Zworykin patents a color television system.
John Baird operates a television system with 30 lines of resolution system running at five frames per second.
Bell Telephone and the U.S. Department of Commerce conducted the first long-distance use of television that took place between Washington, D.C., and New York City on April 7. Secretary of Commerce Herbert Hoover commented, “Today we have, in a sense, the transmission of sight for the first time in the world’s history. Human genius has now destroyed the impediment of distance in (this) new respect, and in a manner hitherto unknown.”
Philo Farnsworth files for a patent on the first completely electronic television system, which he called the Image Dissector.
The Federal Radio Commission issues the first television station license (W3XK) to Charles Jenkins.
Vladimir Zworykin demonstrates the first practical electronic system for both the transmission and reception of images using his new kinescope tube.
John Baird opens the first TV studio; however, the image quality is poor.
Charles Jenkins broadcasts the first TV commercial.
The BBC begins regular TV transmissions.
Iowa State University (W9XK) starts broadcasting twice-weekly television programs in cooperation with radio station WSUI.
About 200 television sets are in use worldwide.
Coaxial cable—a pure copper or copper-coated wire surrounded by insulation and aluminum covering—is introduced. These cables were and are used to transmit television, telephone, and data signals.
The first experimental coaxial cable lines were laid by AT&T between New York and Philadelphia in 1936. The first regular installation connected Minneapolis and Stevens Point, Wisconsin, in 1941.
The original L1 coaxial cable system could carry 480 telephone conversations or one television program. By the 1970s, L5 systems could carry 132,000 calls or more than 200 television programs.
CBS begins its TV development.
The BBC begins high-definition broadcasts in London.
Brothers and Stanford researchers Russell and Sigurd Varian introduce the Klystron. A Klystron is a high-frequency amplifier for generating microwaves. It is considered the technology that makes UHF-TV possible because it gives the ability to generate the high power required in this spectrum.
Vladimir Zworykin and RCA conduct experimental broadcasts from the Empire State Building .
Television was demonstrated at the New York World's Fair and the San Francisco Golden Gate International Exposition.
RCA's David Sarnoff used his company's exhibit at the 1939 World's Fair as a showcase for the first presidential speech (by Franklin D. Roosevelt) on television and to introduce RCA's new line of television receivers, some of which had to be coupled with a radio if you wanted to hear the sound.
The Dumont company starts making TV sets.
Peter Goldmark invents 343 lines of the resolution color television system.
The FCC releases the NTSC standard for black and white TV.
Vladimir Zworykin develops a better camera tube called the Orthicon. The Orthicon has enough light sensitivity to record outdoor events at night.
Peter Goldmark, working for CBS, demonstrated his color television system to the FCC. His system produced color pictures by having a red-blue-green wheel spin in front of a cathode ray tube.
This mechanical means of producing a color picture was used in 1949 to broadcast medical procedures from Pennsylvania and Atlantic City hospitals. In Atlantic City, viewers could come to the convention center to see broadcasts of operations. Reports from the time noted that the realism of seeing surgery in color caused more than a few viewers to faint.
Although Goldmark's mechanical system was eventually replaced by an electronic system, he is recognized as the first to introduce a broadcasting color television system.
Cable television is introduced in Pennsylvania as a means of bringing television to rural areas.
A patent was granted to Louis W. Parker for a low-cost television receiver.
One million homes in the United States have television sets.
The FCC approves the first color television standard, which is replaced by a second in 1953.
Vladimir Zworykin developed a better camera tube called the Vidicon.
Ampex introduces the first practical videotape system of broadcast quality.
Robert Adler invents the first practical remote control called the Zenith Space Commander. It was preceded by wired remotes and units that failed in sunlight.
The first split-screen broadcast occurs during the debates between presidential candidates Richard M. Nixon and John F. Kennedy.
The All-Channel Receiver Act requires that UHF tuners (channels 14 to 83) be included in all sets.
A joint international collaboration between AT&T, Bell Labs, NASA, British General Post Office, the French National Post, Telegraph, and Telecom Office results in the development and launch of Telstar , the first satellite to carry TV broadcasts. Broadcasts are now internationally relayed.
Most TV broadcasts are in color.
On July 20, 600 million people watch the first TV transmission made from the moon.
Half the TVs in homes are color sets.
Giant screen projection TV is first marketed.
Sony introduces Betamax, the first home video cassette recorder.
PBS becomes the first station to switch to an all-satellite delivery of programs.
NHK demonstrates HDTV with 1,125 lines of resolution.
Dolby Surround Sound for home sets is introduced.
Direct Broadcast Satellite begins service in Indianapolis, Indiana.
Stereo TV broadcasts are approved.
Super VHS is introduced.
Closed captioning is required on all sets.
The FCC approves ATSC's HDTV standard.
TV sets are in excess of 1 billion homes across the world.
- The Inventors Behind the Creation of Television
- Biography of Vladimir Zworykin, Father of the Television
- Television History and the Cathode Ray Tube
- The Most Impactful Inventions of the Last 300 Years
- The History of Vacuum Tubes and Their Uses
- Mechanical Television History and John Baird
- Biography of Philo Farnsworth, American Inventor and TV Pioneer
- The History of Color Television
- The History of Video Recorders - Video Tape and Camera
- History of Plasma Television
- RADAR and Doppler RADAR: Invention and History
- When Was Color TV Invented?
- Cathode Ray History
- 20th Century Invention Timeline 1900 to 1949
- The History of the Computer Keyboard
- The History of Radio Technology
- Subject List
- Take a Tour
- For Authors
- Subscriber Services
- Publications
- African American Studies
- African Studies
- American Literature
- Anthropology
- Architecture Planning and Preservation
- Art History
- Atlantic History
- Biblical Studies
- British and Irish Literature
- Childhood Studies
- Chinese Studies
Cinema and Media Studies
- Communication
- Criminology
- Environmental Science
- Evolutionary Biology
- International Law
- International Relations
- Islamic Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Latino Studies
- Linguistics
- Literary and Critical Theory
- Medieval Studies
- Military History
- Political Science
- Public Health
- Renaissance and Reformation
- Social Work
- Urban Studies
- Victorian Literature
- Browse All Subjects
How to Subscribe
- Free Trials
In This Article Expand or collapse the "in this article" section History of Television
Introduction, general histories and textbooks.
- General Anthologies
- Television Technology Histories
- Legal and Regulatory Histories
- Studies of the Industry Before 1960
- Dramatic Formats Before 1960
- Broadcast Television 1960–1990
- Broadcast and Cable Television Since 1990
- Television and Digital Media
- Issues of Race and Gender
- International Anthologies
- International Monographs
Related Articles Expand or collapse the "related articles" section about
About related articles close popup.
Lorem Ipsum Sit Dolor Amet
Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus orci luctus et ultrices posuere cubilia Curae; Aliquam ligula odio, euismod ut aliquam et, vestibulum nec risus. Nulla viverra, arcu et iaculis consequat, justo diam ornare tellus, semper ultrices tellus nunc eu tellus.
- Advertising and Promotion
- American Public Broadcasting
- Australian Broadcasting
- Community Media
- Eastern European Television
- Global Television Industry
- Industrial, Educational, and Instructional Television and Video
- Music Video
- New Media Policy
- Prime Time Drama
- Saturday Night Live
- Sesame Street
- Soap Operas
- Streaming Television
- Television Audiences
- Television Authorship
- Television Music
- Television Regulation
- The Simpsons
- The Twilight Zone
- Video Installation
Other Subject Areas
Forthcoming articles expand or collapse the "forthcoming articles" section.
- Jacques Tati
- Media Materiality
- The Golden Girls
- Find more forthcoming articles...
- Export Citations
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
History of Television by William Boddy LAST REVIEWED: 25 June 2013 LAST MODIFIED: 25 June 2013 DOI: 10.1093/obo/9780199791286-0036
While journalists, cultural critics, technology writers, and industry figures have been writing about television for a surprisingly long time (going back at least to experiments with mechanical television in the late 1920s), the academic study of television history largely emerged only in the 1970s in the United States and the United Kingdom. Befitting its object of study as at once a major industry, creative medium, and political battlefield, scholarly writing on television history owes distinct debts to the disciplines of business, technology, and legal studies, as well as humanities-based film and cultural studies. Paralleling the renaissance of the study of film history and the rise of cultural studies, scholarly writing on television’s past since the 1980s has vastly expanded our understanding of the ubiquitous medium during a period of sustained change in its traditional institutions and practices. Supported by a range of scholarly journals, archives, and conferences, contemporary scholarship in television history has actively explored both the medium’s tangled past and its uncertain future in a world of fragmented audiences, proliferating technological platforms, and competing business models. Not surprisingly, given its scale and dominance in international program markets, the US television industry has preoccupied television historians, though increasing attention has been paid to the global contexts of television production and exchange in the early 21st century. Academic writing on television often blurs distinctions among history, theory, and criticism, and this hybrid quality can be seen in the organization of academic conferences, the design of edited anthologies, and even within the pages of a single-authored book. In part, this fluidity reflects the polyglot nature and relative youth of the academic study of television, but it also reflects an attempt by many television scholars to reach out to a wide array of readers and to fully engage with popular, ubiquitous, and sometimes culturally degraded program texts. It remains to be seen what happens to this populist impulse of much historical writing on television as the universalist, top-down culture of traditional broadcast television threatens to dissolve in a multiplatform digital cornucopia. As current intellectual fashions and the academic marketplace coalesce around often carelessly defined notions of new media and screen cultures, the value of rigorous historical work on television’s program forms, audiences, and institutions will be more important than ever.
The historical study of radio and television history through the 1970s in the United States and the United Kingdom was dominated by the massive multivolume institutional histories Barnouw 1966 and Briggs 1961 . Despite their age, the works remain valuable beyond historiographic interest, drawing upon as they do to a rich field of corporate and government archives as well as interviews with contemporary participants. As postsecondary courses in television history expanded since 1990, a new generation of textbooks, including Barnouw 1990 , Edgerton 2009 , Gomery 2008 , Hilmes 2011 , Marc and Thompson 2005 , and Sterling and Kittross 2001 , and synthetic histories of television, like Castleman and Podrazik 2010 , has appeared in both the United States and the United Kingdom, and these works bring with them a new historiographic sophistication as well as the fruits of contemporary scholarship.
Barnouw, Erik. A History of Broadcasting in the United States to 1933 . Vol. 1, A Tower in Babel . New York: Oxford University Press, 1966.
Still an impressive achievement of archival research and narrative history, this multivolume history combines massive research, strong narrative design, and a skeptical stance toward the industry, with an emphasis on regulatory and political contexts. Barnouw’s political bêtes noires and aesthetic blind spots become more conspicuous in the final volume, which ends with the late 1960s.
Barnouw, Erik. Tube of Plenty: The Evolution of American Television . 2d ed. New York: Oxford University Press, 1990.
A highly readable single-volume distillation and updating of Barnouw’s three-volume history of US broadcasting, it remains strong in corporate and regulatory history, if uneven in the discussion of specific programs and creative style and increasingly distant in historical coverage.
Briggs, Asa. The History of Broadcasting in the United Kingdom . Vol. 1, The Birth of Broadcasting . New York: Oxford University Press, 1961.
This is the first volume of a five-volume history of British broadcasting, written over three and a half decades by an eminent social historian, from the beginnings of radio to the early 1970s, drawing upon BBC and government records, balancing discussion of institutional, political, and program issues. Still indispensable to the study of British broadcasting and the BBC.
Castleman, Harry, and Walter Podrazik. Watching TV: Six Decades of American Television . 2d ed. Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press, 2010.
This is a lively and opinionated chronology of prime-time US television, nonacademic though thoughtful and well informed. In its concentration on programs, it serves as a useful complement to more institutionally centered histories. The book also includes prime-time schedule grids for every US American network television season from 1944 to 2010. Originally published in 1982.
Edgerton, Gary R. The Columbia History of American Television . New York: Columbia University Press, 2009.
This is a concise and thorough (if still somewhat top-down) history of US television, balancing institutional and programming topics, with four case-study chapters by specialist historians alongside the chronological narrative.
Gomery, Douglas. A History of Broadcasting in the United States . Malden, MA: Blackwell, 2008.
Gomery’s incisive 350-page history of radio and television in the United States emphasizes issues of programming and industry form over those of technology and regulation. This is a lively contemporary account, exhaustively researched, from a distinguished US media historian.
Hilmes, Michele. Only Connect: A Cultural History of Broadcasting in the United States . 3d ed. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth, 2011.
Hilmes offers a cultural studies–oriented account of American radio and television, taking advantage of recent scholarship and carefully connecting the medium to its cultural and historical context. The book includes a number of case studies on specific historical topics and is unusually sensitive to questions of historical method.
Marc, David, and Robert Thompson. Television in the Antenna Age: A Concise History . Malden, MA: Wiley, 2005.
DOI: 10.1002/9780470775745
This is a brief and highly readable volume on US television history by two prominent writers on American television and popular culture, with an emphasis on popular programming.
Sterling, Christopher H., and John Kittross. Stay Tuned: A Concise History of American Broadcasting . 3rd ed. New York: Routledge, 2001.
This is the most recent edition of an established textbook on US radio and television, with an emphasis upon technology and legal and regulatory issues, concluding with an exhaustive bibliography.
back to top
Users without a subscription are not able to see the full content on this page. Please subscribe or login .
Oxford Bibliographies Online is available by subscription and perpetual access to institutions. For more information or to contact an Oxford Sales Representative click here .
- About Cinema and Media Studies »
- Meet the Editorial Board »
- 2001: A Space Odyssey
- Accounting, Motion Picture
- Action Cinema
- African American Cinema
- African American Stars
- African Cinema
- AIDS in Film and Television
- Akerman, Chantal
- Allen, Woody
- Almodóvar, Pedro
- Altman, Robert
- American Cinema, 1895-1915
- American Cinema, 1939-1975
- American Cinema, 1976 to Present
- American Independent Cinema
- American Independent Cinema, Producers
- Anderson, Wes
- Animals in Film and Media
- Animation and the Animated Film
- Arbuckle, Roscoe
- Architecture and Cinema
- Argentine Cinema
- Aronofsky, Darren
- Arzner, Dorothy
- Asian American Cinema
- Asian Television
- Astaire, Fred and Rogers, Ginger
- Audiences and Moviegoing Cultures
- Australian Cinema
- Authorship, Television
- Avant-Garde and Experimental Film
- Bachchan, Amitabh
- Battle of Algiers, The
- Battleship Potemkin, The
- Bazin, André
- Bergman, Ingmar
- Bernstein, Elmer
- Bertolucci, Bernardo
- Bigelow, Kathryn
- Birth of a Nation, The
- Blade Runner
- Blockbusters
- Bong, Joon Ho
- Brakhage, Stan
- Brando, Marlon
- Brazilian Cinema
- Breaking Bad
- Bresson, Robert
- British Cinema
- Broadcasting, Australian
- Buffy the Vampire Slayer
- Burnett, Charles
- Buñuel, Luis
- Cameron, James
- Campion, Jane
- Canadian Cinema
- Capra, Frank
- Carpenter, John
- Cassavetes, John
- Cavell, Stanley
- Chahine, Youssef
- Chan, Jackie
- Chaplin, Charles
- Children in Film
- Chinese Cinema
- Cinecittà Studios
- Cinema and Media Industries, Creative Labor in
- Cinema and the Visual Arts
- Cinematography and Cinematographers
- Citizen Kane
- City in Film, The
- Cocteau, Jean
- Coen Brothers, The
- Colonial Educational Film
- Comedy, Film
- Comedy, Television
- Comics, Film, and Media
- Computer-Generated Imagery (CGI)
- Copland, Aaron
- Coppola, Francis Ford
- Copyright and Piracy
- Corman, Roger
- Costume and Fashion
- Cronenberg, David
- Cuban Cinema
- Cult Cinema
- Dance and Film
- de Oliveira, Manoel
- Dean, James
- Deleuze, Gilles
- Denis, Claire
- Deren, Maya
- Design, Art, Set, and Production
- Detective Films
- Dietrich, Marlene
- Digital Media and Convergence Culture
- Disney, Walt
- Documentary Film
- Downton Abbey
- Dr. Strangelove
- Dreyer, Carl Theodor
- Eastwood, Clint
- Eisenstein, Sergei
- Elfman, Danny
- Ethnographic Film
- European Television
- Exhibition and Distribution
- Exploitation Film
- Fairbanks, Douglas
- Fan Studies
- Fellini, Federico
- Film Aesthetics
- Film and Literature
- Film Guilds and Unions
- Film, Historical
- Film Preservation and Restoration
- Film Theory and Criticism, Science Fiction
- Film Theory Before 1945
- Film Theory, Psychoanalytic
- Finance Film, The
- French Cinema
- Game of Thrones
- Gance, Abel
- Gangster Films
- Garbo, Greta
- Garland, Judy
- German Cinema
- Gilliam, Terry
- Godard, Jean-Luc
- Godfather Trilogy, The
- Greek Cinema
- Griffith, D.W.
- Hammett, Dashiell
- Haneke, Michael
- Hawks, Howard
- Haynes, Todd
- Hepburn, Katharine
- Herrmann, Bernard
- Herzog, Werner
- Hindi Cinema, Popular
- Hitchcock, Alfred
- Hollywood Studios
- Holocaust Cinema
- Hong Kong Cinema
- Horror-Comedy
- Hsiao-Hsien, Hou
- Hungarian Cinema
- Icelandic Cinema
- Immigration and Cinema
- Indigenous Media
- Industrial, Educational, and Instructional Television and ...
- Invasion of the Body Snatchers
- Iranian Cinema
- Irish Cinema
- Israeli Cinema
- It Happened One Night
- Italian Americans in Cinema and Media
- Italian Cinema
- Japanese Cinema
- Jazz Singer, The
- Jews in American Cinema and Media
- Keaton, Buster
- Kitano, Takeshi
- Korean Cinema
- Kracauer, Siegfried
- Kubrick, Stanley
- Lang, Fritz
- Latin American Cinema
- Latina/o Americans in Film and Television
- Lee, Chang-dong
- Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender, and Queer (LGBTQ) Cin...
- Lord of the Rings Trilogy, The
- Los Angeles and Cinema
- Lubitsch, Ernst
- Lumet, Sidney
- Lupino, Ida
- Lynch, David
- Marker, Chris
- Martel, Lucrecia
- Masculinity in Film
- Media, Community
- Media Ecology
- Memory and the Flashback in Cinema
- Metz, Christian
- Mexican Film
- Micheaux, Oscar
- Ming-liang, Tsai
- Minnelli, Vincente
- Miyazaki, Hayao
- Méliès, Georges
- Modernism and Film
- Monroe, Marilyn
- Mészáros, Márta
- Music and Cinema, Classical Hollywood
- Music and Cinema, Global Practices
- Music, Television
- Musicals on Television
- Native Americans
- New Media Art
- New Media Theory
- New York City and Cinema
- New Zealand Cinema
- Opera and Film
- Ophuls, Max
- Orphan Films
- Oshima, Nagisa
- Ozu, Yasujiro
- Panh, Rithy
- Pasolini, Pier Paolo
- Passion of Joan of Arc, The
- Peckinpah, Sam
- Philosophy and Film
- Photography and Cinema
- Pickford, Mary
- Planet of the Apes
- Poems, Novels, and Plays About Film
- Poitier, Sidney
- Polanski, Roman
- Polish Cinema
- Politics, Hollywood and
- Pop, Blues, and Jazz in Film
- Pornography
- Postcolonial Theory in Film
- Potter, Sally
- Queer Television
- Queer Theory
- Race and Cinema
- Radio and Sound Studies
- Ray, Nicholas
- Ray, Satyajit
- Reality Television
- Reenactment in Cinema and Media
- Regulation, Television
- Religion and Film
- Remakes, Sequels and Prequels
- Renoir, Jean
- Resnais, Alain
- Romanian Cinema
- Romantic Comedy, American
- Rossellini, Roberto
- Russian Cinema
- Scandinavian Cinema
- Scorsese, Martin
- Scott, Ridley
- Searchers, The
- Sennett, Mack
- Shakespeare on Film
- Silent Film
- Simpsons, The
- Singin' in the Rain
- Sirk, Douglas
- Social Class
- Social Media
- Social Problem Films
- Soderbergh, Steven
- Sound Design, Film
- Sound, Film
- Spanish Cinema
- Spanish-Language Television
- Spielberg, Steven
- Sports and Media
- Sports in Film
- Stand-Up Comedians
- Stop-Motion Animation
- Sturges, Preston
- Surrealism and Film
- Taiwanese Cinema
- Tarantino, Quentin
- Tarkovsky, Andrei
- Television Celebrity
- Television, History of
- Television Industry, American
- Theater and Film
- Theory, Cognitive Film
- Theory, Critical Media
- Theory, Feminist Film
- Theory, Film
- Theory, Trauma
- Touch of Evil
- Transnational and Diasporic Cinema
- Trinh, T. Minh-ha
- Truffaut, François
- Turkish Cinema
- Twilight Zone, The
- Varda, Agnès
- Vertov, Dziga
- Video and Computer Games
- Violence and Cinema
- Virtual Reality
- Visconti, Luchino
- Von Sternberg, Josef
- Von Stroheim, Erich
- von Trier, Lars
- Warhol, The Films of Andy
- Waters, John
- Wayne, John
- Weerasethakul, Apichatpong
- Weir, Peter
- Welles, Orson
- Whedon, Joss
- Wilder, Billy
- Williams, John
- Wiseman, Frederick
- Wizard of Oz, The
- Women and Film
- Women and the Silent Screen
- Wong, Anna May
- Wong, Kar-wai
- Wood, Natalie
- Yang, Edward
- Yimou, Zhang
- Yugoslav and Post-Yugoslav Cinema
- Zinnemann, Fred
- Zombies in Cinema and Media
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
Powered by:
- [66.249.64.20|185.80.151.9]
- 185.80.151.9
- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
Who Invented Television?
By: Sarah Pruitt
Updated: March 12, 2024 | Original: June 29, 2021

The way people watch television has changed dramatically since the medium first burst onto the scene in the 1940s and ‘50s and forever transformed American life. Decade after decade, TV technology has steadily advanced: Color arrived in the 1960s, followed by cable in the ‘70s, VCRs in the ‘80s and high-definition in the late ‘90s. In the 21st century, viewers are just as likely to watch shows on cell phones, laptops and tablets as on a TV set. Amazingly, however, all these technological changes were essentially just improvements on a basic system that has worked since the late 1930s—with roots reaching even further back than that.
Early TV Technology: Mechanical Spinning Discs
No single inventor deserves credit for the television. The idea was floating around long before the technology existed to make it happen, and many scientists and engineers made contributions that built on each other to eventually produce what we know as TV today.
Television’s origins can be traced to the 1830s and ‘40s, when Samuel F.B. Morse developed the telegraph , the system of sending messages (translated into beeping sounds) along wires. Another important step forward came in 1876 in the form of Alexander Graham Bell ’s telephone, which allowed the human voice to travel through wires over long distances.
Both Bell and Thomas Edison speculated about the possibility of telephone-like devices that could transmit images as well as sounds. But it was a German researcher who took the next important step toward developing the technology that made television possible. In 1884, Paul Nipkow came up with a system of sending images through wires via spinning discs. He called it the electric telescope, but it was essentially an early form of mechanical television.
TV Goes Electronic With Cathode Ray Tubes
In the early 1900s, both Russian physicist Boris Rosing and Scottish engineer Alan Archibald Campbell-Swinton worked independently to improve on Nipkow’s system by replacing the spinning discs with cathode ray tubes, a technology developed earlier by German physicist Karl Braun. Swinton’s system, which placed cathode ray tubes inside the camera that sent a picture, as well as inside the receiver, was essentially the earliest all-electronic television system.
Russian-born engineer Vladimir Zworykin had worked as Rosing’s assistant before both of them emigrated following the Russian Revolution . In 1923, Zworykin was employed at the Pittsburgh-based manufacturing company Westinghouse when he applied for his first television patent, for the “Iconoscope,” which used cathode ray tubes to transmit images.
Meanwhile, Scottish engineer John Baird gave the world's first demonstration of true television before 50 scientists in central London in 1927. With his new invention, Baird formed the Baird Television Development Company, and in 1928 it achieved the first transatlantic television transmission between London and New York and the first transmission to a ship in the mid-Atlantic. Baird is also credited with giving the first demonstration of both color and stereoscopic television.
In 1929, Zworykin demonstrated his all-electronic television system at a convention of radio engineers. In the audience was David Sarnoff , an executive at Radio Corporation of America (RCA), the nation’s biggest communications company at the time. Born into a poor Jewish family in Minsk, Russia, Sarnoff had come to New York City as a child and began his career as a telegraph operator . He was actually on duty on the night of the Titanic disaster; although he likely didn’t—as he later claimed—coordinate distress messages sent to nearby ships, he did help disseminate the names of the survivors.
Utah Inventor Battles Giant Corporation

Sarnoff was among the earliest to see that television, like radio, had enormous potential as a medium for entertainment as well as communication. Named president of RCA in 1930, he hired Zworykin to develop and improve television technology for the company. Meanwhile, an American inventor named Philo Farnsworth had been working on his own television system. Farnsworth, who grew up on a farm in Utah, reportedly came up with his big idea—a vacuum tube that could dissect images into lines, transmit those lines and turn them back into images—while still a teenager in chemistry class.
In 1927, at the age of 21, Farnsworth completed the prototype of the first working fully electronic TV system, based on this “image dissector.” He soon found himself embroiled in a long legal battle with RCA, which claimed Zworykin’s 1923 patent took priority over Farnsworth’s inventions. The U.S. Patent Office ruled in favor of Farnsworth in 1934 (helped in part by an old high school teacher, who had kept a key drawing by the young inventor), and Sarnoff was eventually forced to pay Farnsworth $1 million in licensing fees. Though viewed by many historians as the true father of television, Farnsworth never earned much more from his invention and was dogged by patent appeal lawsuits from RCA . He later moved on to other fields of research and died in debt in 1971.
Although the BBC had begun the world’s first regular TV broadcasts in 1936, Sarnoff used his company's marketing might to introduce the American public to television in a big way at the World’s Fair in New York City in 1939. Under the umbrella of RCA’s broadcasting division, the National Broadcasting Company (NBC), Sarnoff broadcast the fair’s opening ceremonies, including a speech by President Franklin D. Roosevelt .
The Rise of a New Medium
By 1940, there were only a few hundred televisions in use in the United States. With radio still dominating the airwaves— more than 80 percent of American homes owned one at the time—TV use grew slowly over the course of the decade, and by the mid-1940s, the United States had 23 television stations (and counting). By 1949, a year after the debut of the hit variety show Texaco Star Theater , hosted by comedian Milton Berle, the nation boasted 1 million TV sets in use .
By the 1950s, television had truly entered the mainstream, with more than half of all American homes owning TV sets by 1955 . As the number of consumers expanded, new stations were created and more programs broadcast, and by the end of that decade TV had replaced radio as the main source of home entertainment in the United States. During the 1960 presidential election, the young, handsome John F. Kennedy had a noticeable advantage over his less telegenic opponent, Richard M. Nixon in televised debates, and his victory that fall would bring home for many Americans the transformative impact of the medium.

HISTORY Vault: America the Story of Us
America The Story of Us is an epic 12-hour television event that tells the extraordinary story of how America was invented.

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
- Essay On Advantages And Disadvantages Of Television
Essay on Advantages and Disadvantages of Television
500+ words essay on advantages and disadvantages of television.
In today’s world, communication is a crucial aspect of life. Technological advancements made communication more accessible and cheaper. Among all the communication devices such as smartphones, radios, and emails, television is the prominent and common medium for communication. We get to see television in every household. It is an integral part of our society that significantly impacts our social, educational, and cultural life. It reaches a mass audience and provides information about the daily happenings in the world. Furthermore, it is a common source of entertainment among family members.
John Logie Baird invented the television in the 1920s. The word “tele” means distance, and “vision” means to see, which means to watch it from a distance. When television was invented, it showed only pictures of low resolution. But, later on, televisions were modified with the latest technologies. Televisions that we purchase today come with multiple features. We can connect our phone, laptop, tab, and internet access various online apps, HD/UHD quality pictures, 4k-8k resolutions, etc.
We can also watch various educational channels on television. It also keeps us updated by providing news about the world through different news channels. Along with information, it also entertains us with movies, serials, dramas, reality shows, music channels, yoga channels, etc.
So, having a television at home seems to be a great advantage, but the disadvantages are also threatening. The time it consumes from our day-to-day life is more. You can see people going out of routine or postponing schedules if they become addicted to watching television.
Here, in the essay, we will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of watching television.
Advantages of Television
Television comes with enormous advantages. The most important is it gives us information about current affairs and events across the globe. This information is broadcasted through various news channels, which helps us to keep ourselves updated about recent happenings. It also shares information about multiple programmes or facilities launched by the government. The government also take the help of news channels to communicate with the mass.
We can watch daily soaps, reality shows, music channels, movies, etc. We can also watch food channels and try out recipes at home. During the morning time, if you switch on the television, you will get to watch telemarketing ads. Specific channels broadcast only ads for multiple products, and people can also buy them.
Children can watch various cartoons on the television. Some cartoons teach children about moral values and lessons. It also keeps us informed about the economic condition and the stock market. We also get to watch various fashion shows and keep updated about the latest trends on television.
Earlier, television was costly, but now it comes at an affordable price with multiple features. Now, we get the option to subscribe to our favourite channels and only need to pay for those channels. Educational programmes are also available on television. We can also watch live cricket shows and cheer for our country. Television also telecasts interviews of various political leaders, celebrities, influencers, famous personalities, etc. We can also gain knowledge by watching various quiz programmes.
Television provides opportunities to spend time with our family and friends. We can enjoy watching a movie together. Various channels telecast comedy shows that help us keep positivity in our lives. We also watch movies in different regional languages like Tamil, Kannada, Telugu, etc. It helps us connect with people from diverse backgrounds.
Nowadays, we can also play games on the television and watch agricultural programmes specially designed for the farmers. It promotes national integration.
Disadvantages of Television
There are advantages of watching television, but it also comes with disadvantages. Watching too much TV affects our mental and physical health. When we watch television continuously, it affects our eyes and makes us lazy. Even there are some programmes which are not suitable for kids. We even compromise our sleep to watch TV. Children lose their concentration on their studies by watching too much television. Children prefer to watch TV over reading books to spend their leisure time.
Conclusion of Essay on Advantages and Disadvantages of Television
There are advantages and disadvantages of television. If television is helpful, it is harmful too. One should not watch television excessively.
We hope you found this essay on the advantages and disadvantages of television helpful. Check BYJU’S for more such CBSE Essays on different topics. You can also find CBSE study materials and resources for Classes 1 to 12.
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Counselling
Essay on Television for Students and Children
500+ words essay on television.
Television is one of the most popular devices that are used for entertainment all over the world. It has become quite common nowadays and almost every household has one television set at their place. In the beginning, we see how it was referred to as the ‘idiot box.’ This was mostly so because back in those days, it was all about entertainment. It did not have that many informative channels as it does now.

Moreover, with this invention, the craze attracted many people to spend all their time watching TV. People started considering it harmful as it attracted the kids the most. In other words, kids spent most of their time watching television and not studying. However, as times passed, the channels of television changed. More and more channels were broadcasted with different specialties. Thus, it gave us knowledge too along with entertainment.
Benefits of Watching Television
The invention of television gave us various benefits. It was helpful in providing the common man with a cheap mode of entertainment. As they are very affordable, everyone can now own television and get access to entertainment.
In addition, it keeps us updated on the latest happenings of the world. It is now possible to get news from the other corner of the world. Similarly, television also offers educational programs that enhance our knowledge about science and wildlife and more.
Moreover, television also motivates individuals to develop skills. They also have various programs showing speeches of motivational speakers. This pushes people to do better. You can also say that television widens the exposure we get. It increases our knowledge about several sports, national events and more.
While television comes with a lot of benefits, it also has a negative side. Television is corrupting the mind of the youth and we will further discuss how.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
How Television is Harming the Youth

Additionally, it also makes people addict. People get addicted to their TV’s and avoid social interaction. This impacts their social life as they spend their time in their rooms all alone. This addiction also makes them vulnerable and they take their programs too seriously.
The most dangerous of all is the fake information that circulates on news channels and more. Many media channels are now only promoting the propaganda of the governments and misinforming citizens. This makes causes a lot of division within the otherwise peaceful community of our country.
Thus, it is extremely important to keep the TV watching in check. Parents must limit the time of their children watching TV and encouraging them to indulge in outdoor games. As for the parents, we should not believe everything on the TV to be true. We must be the better judge of the situation and act wisely without any influence.
{ “@context”: “https://schema.org”, “@type”: “FAQPage”, “mainEntity”: [{ “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “How does television benefit people?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Television offers people a cheap source of entertainment. It saves them from boredom and helps them get information and knowledge about worldly affairs.” } }, { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What is the negative side of television?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”:”Television has a negative side to it because it harms people’s health when watched in excess. Moreover, it is the easiest platform to spread fake news and create misunderstandings between communities and destroy the peace and harmony of the country.”} }] }
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


Customer Reviews
Can I hire someone to write essay?
Student life is associated with great stress and nervous breakdowns, so young guys and girls urgently need outside help. There are sites that take all the responsibility for themselves. You can turn to such companies for help and they will do all the work while clients relax and enjoy a carefree life.
Take the choice of such sites very seriously, because now you can meet scammers and low-skilled workers.
On our website, polite managers will advise you on all the details of cooperation and sign an agreement so that you are confident in the agency. In this case, the user is the boss who hires the employee to delegate responsibilities and devote themselves to more important tasks. You can correct the work of the writer at all stages, observe that all special wishes are implemented and give advice. You pay for the work only if you liked the essay and passed the plagiarism check.
We will be happy to help you complete a task of any complexity and volume, we will listen to special requirements and make sure that you will be the best student in your group.

Customer Reviews
Allene W. Leflore
Finished Papers

Research papers can be complex, so best to give our essay writing service a bit more time on this one. Luckily, a longer paper means you get a bigger discount!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Television (TV) is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. Additionally, the term can refer to a physical television set, rather than the medium of transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, entertainment, news, and sports.
History of television. Family watching TV, 1958. The concept of television is the work of many individuals in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The first practical transmissions of moving images over a radio system used mechanical rotating perforated disks to scan a scene into a time-varying signal that could be reconstructed at a ...
television (TV), a form of mass media based on the electronic delivery of moving images and sound from a source to a receiver.By extending the senses of vision and hearing beyond the limits of physical distance, television has had a considerable influence on society. Conceived in the early 20th century as a possible medium for education and interpersonal communication, it became by mid-century ...
The first television broadcast was by Georges Rignoux and A. Fournier in Paris in 1909. However, this was the broadcast of a single line. The first broadcast that general audiences would have been wowed by was on March 25, 1925. That is the date John Logie Baird presented his mechanical television.
Television in the United States, the body of television programming created and broadcast in the United States.American TV programs, like American popular culture in general in the 20th and early 21st centuries, have spread far beyond the boundaries of the United States and have had a pervasive influence on global popular culture.. Overview. Although television was first regarded by many as ...
The Golden Age of Television. During the so-called "golden age" of television, the percentage of U.S. households that owned a television set rose from 9 percent in 1950 to 95.3 percent in 1970. The 1950s proved to be the golden age of television, during which the medium experienced massive growth in popularity.
How TV Became Art. By Joshua Rothman and Erin Overbey. August 28, 2017. Today, television is at the center of culture in ways that its inventors likely never imagined. Photograph by Jean Gaumy ...
A television set (also known as a television receiver or televisor or simply a television, TV set, TV receiver or TV) is a machine with a screen or set of lenses. Televisions receive broadcasting signals and change them into pictures and sound. The word "television" comes from the words tele ( Greek for far away) and vision ( sight ).
Bell Telephone and the U.S. Department of Commerce conducted the first long-distance use of television that took place between Washington, D.C., and New York City on April 7.Secretary of Commerce Herbert Hoover commented, "Today we have, in a sense, the transmission of sight for the first time in the world's history.
The Columbia History of American Television. New York: Columbia University Press, 2009. This is a concise and thorough (if still somewhat top-down) history of US television, balancing institutional and programming topics, with four case-study chapters by specialist historians alongside the chronological narrative. Gomery, Douglas.
Television is one of the major mass media outlets in the United States.In 2011, 96.7% of households owned television sets; about 114,200,000 American households owned at least one television set each in August 2013. Most households have more than one set. The percentage of households owning at least one television set peaked at 98.4%, in the 1996-1997 season.
In 1927, at the age of 21, Farnsworth completed the prototype of the first working fully electronic TV system, based on this "image dissector.". He soon found himself embroiled in a long legal ...
Disadvantages of Television. There are advantages of watching television, but it also comes with disadvantages. Watching too much TV affects our mental and physical health. When we watch television continuously, it affects our eyes and makes us lazy. Even there are some programmes which are not suitable for kids.
Television is corrupting the mind of the youth and we will further discuss how. Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas. How Television is Harming the Youth. Firstly, we see how television is airing inappropriate content which promotes all types of social evils like violence, eve-teasing and more.
This article is written like a personal reflection, personal essay, or argumentative essay that states a Wikipedia editor's personal feelings or presents an original argument about a topic. ... Social media and television have a number of connections and interrelationships that have led to the phenomenon of Social Television, which is an ...
முதற்பக்கம்; அண்மைய மாற்றங்கள்; Pages for logged out editors learn more
An essay is a written text. It is usually about the personal point of view of the author who wrote it. The definition of an essay is vague. Articles and short stories can be quite similar. Almost all modern essays are written in prose, but works in verse have been called essays (e.g. Alexander Pope 's An Essay on Criticism and An Essay on Man ).
Television's History — The First 75 Years Archived 2013-06-25 at the Wayback Machine; The Encyclopedia of Television Archived 2013-10-06 at the Wayback Machine at the Museum of Broadcast Communications; MZTV Museum of Television Archived 2007-05-13 at the Wayback Machine Some of the rarest sets in America;
A smart TV, also known as a connected TV ( CTV ), is a traditional television set with integrated Internet and interactive Web 2.0 features that allow users to stream music and videos, browse the internet, and view photos. Smart TVs are a technological convergence of computers, televisions, and digital media players.
Television Essay Wikipedia. 4950. Customer Reviews. 4.7/5. ABOUT US. Andersen, Jung & Co. is a San Francisco based, full-service real estate firm providing customized concierge-level services to its clients. We work to help our residential clients find their new home and our commercial clients to find and optimize each new investment property ...
Definitions John Locke's 1690 An Essay Concerning Human Understanding. The word essay derives from the French infinitive essayer, "to try" or "to attempt".In English essay first meant "a trial" or "an attempt", and this is still an alternative meaning. The Frenchman Michel de Montaigne (1533-1592) was the first author to describe his work as essays; he used the term to characterize these as ...
Essay On Television In Hindi Wikipedia. Alamat kami. Critical Thinking Essay on Nursing. User ID: 309674. Level: College, University, High School, Master's, PHD, Undergraduate, Regular writer. You are going to request writer Estevan Chikelu to work on your order. We will notify the writer and ask them to check your order details at their ...
Initially under Television Promoters Company (TPC) in 1966, it was upgraded to Pakistan Television Corp in 1967. Nationalised in 1972, PTV's experimental color transmission started in 1976. [3] In 1987, the Pakistan Television Academy was founded for training in the evolving medium. In the late 1980s, morning transmissions commenced.
The 2024 British Academy Television Awards ceremony was held on 12 May 2024 at the Royal Festival Hall in London, to recognise the excellence in British television of 2023. The ceremony was hosted by Rob Beckett and Romesh Ranganathan for the second time in a row, and was broadcast on BBC One.. The nominations were announced on 20 March 2024 alongside the nominations for the 2024 British ...
Under the Bridge is a Canadian true crime drama television miniseries developed by Quinn Shephard that is based upon the book of the same name by Rebecca Godfrey. The series premiered on Hulu on April 17, 2024. Premise. It follows the murder of Reena Virk, as a woman enters the hidden world of the accused killers.