- Arts & Humanities
- Communications

Essay Questions

Related documents

Add this document to collection(s)
You can add this document to your study collection(s)
Add this document to saved
You can add this document to your saved list
Suggest us how to improve StudyLib
(For complaints, use another form )
Input it if you want to receive answer
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Short Essay on Strategic Management

Related Papers
Julius Tapera
This paper presents strategic management as an important business management concept. It defines strategy and explains the key concepts in strategic management; strategic vision, objectives, strategy formulation, strategy implementation, evaluation and initiating corrective action. The research also focuses on the corporate governance aspect of strategic management; role of the board of directors in crafting and executing strategy. The different levels of pitching strategy are also discussed in this paper; corporate, business, functional and operational. All these concepts are examined with a view to highlight their importance in the effective and efficient management of business organizations. In an operating environment that is dynamic and highly competitive, business organizations need to appreciate the importance of crafting and effectively executing strategies that can help them create sustainable competitive advantage.
International Journal of Academics & Research, IJARKE Journals
Strategic management is one of the primary areas. This study shows the results of matching the extent of strategy management in a major business policy game and the performance (results) of this effort. The general the objective of this paper is to exanimate effect of strategic management practices on firm performance in telecommunication companies in Mogadishu, Somalia. The target population of this study was top managers, middle managers and normal employee of some telecommunication companies in Mogadishu. There are more than five telecommunication companies Mogadishu but our study will focus on three Telecommunication Companies in Mogadishu. The target population of this study will be 62. Therefore Since the study population (N) is 110. Error of tolerance will be 0.05. Thus the sample size is 54 respondents. The study collected primary data which was analyzed using descriptive statistics including frequencies tables, percentages, mean scores, standard deviation. Data collected from questionnaires will code and keyed into a computer. Quantitative data will analyze using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS). Descriptive statistics including the means and standard deviations were used to analyze quantitative data and capture the characteristics of the variables under study. A regression model will be applied to determine the relationship between Strategy Formulation, Strategy implementation and Strategy control and evaluation as the independent variables and firm performance of telecommunication companies in Mogadishu as the dependent variable. Pearson's product moment correlation analysis is also used and it's a powerful technique for determine the relationship among variables. Correlation coefficient will be used to analyze the strength of the relations between variable.
The strategic planning process is used by management to establish objectives, set goals, and schedule activities for achieving those goals and includes a method for measuring progress Therefore, the general the objective of this paper is to exanimate effect of strategic management practices on firm performance in telecommunication companies in Mogadishu, Somalia. The study explored the effects of Strategy formulation, strategy implementation and strategy control and evaluation on firm performance of telecommunication in Mogadishu The target population of this study was top managers, middle managers and normal employee of some telecommunication companies in Mogadishu. There are more than five telecommunication companies Mogadishu but our study will focus on three Telecommunication Companies in Mogadishu. The target population of this study was 62. Therefore, since the study population (N) is 110. Error of tolerance used was 0.05. Thus, the sample size is 54 respondents. The study collected primary data which was analyzed using descriptive statistics including frequencies tables, percentages, mean scores, standard deviation. Data collected from questionnaires will code and keyed into a computer. Quantitative data will analyze using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS). Descriptive statistics including the means and standard deviations were used to analyze quantitative data and capture the characteristics of the variables under study. Regression model was applied to determine the relationship between Strategy Formulation, Strategy implementation and Strategy control and evaluation as the independent variables and firm performance of telecommunication companies in Mogadishu as the dependent variable. Pearson's product moment correlation analysis is also used and it's a powerful technique for determine the relationship among variables. Correlation coefficient will be used to analyze the strength of the relations between variable.
Lysias T Charumbira
ABSTRACT The purpose of this study was to identify the determinants of strategic success or failure in Zimbabwean Profit and Non-Profit Organizations. The convergent parallel mixed methods research design was adopted as the guiding model for the data collection, analysis and interpretation process in this study. This explains why data was collected through a concurrent parallel methodological triangulation of questionnaires, semi-structured interviews, and document analysis. Quantitative data was analyzed using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) version 21.0 while the analysis of qualitative data was performed using the NVivo 10 data analysis software. The study established that there is a high rate of strategy implementation failure in Zimbabwean Profit and Non-profit Organizations. The failure to build the distinctive competences and resource capabilities needed for successful strategy implementation was identified as the main cause of strategic failure in these Organizations. Keywords: Strategic Management, Environmental Scanning, Strategy Formulation, Strategy Implementation, Evaluation and Control, Strategic Success, Strategic Failure.
Asian Business Review
The purpose of this study was to identify the determinants of strategic success or failure in Zimbabwean Profit and Non-Profit Organizations. The convergent parallel mixed methods research design was adopted as the guiding model for the data collection, analysis and interpretation process in this study. This explains why data was collected through a concurrent parallel methodological triangulation of questionnaires, semi-structured interviews, and document analysis. Quantitative data was analyzed using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) version 21.0 while the analysis of qualitative data was performed using the NVivo 10 data analysis software. The study established that there is a high rate of strategy implementation failure in Zimbabwean Profit and Non-profit Organizations. The failure to build the distinctive competences and resource capabilities needed for successful strategy implementation was identified as the main cause of strategic failure in these Organizations.
nelson jagero
International Journal of Advanced Research (IJAR)
IJAR Indexing
SMEs in Bangladesh contributes a significant part in country?s total GDP and largest sector in employment, overall economic development and infrastructural development, so the performance of these SMEs is very crucial for the country. Therefore, this study aimed to identify the relationship between strategic management practices and the performance of SMEs operating in Bangladesh. Three variables (strategy formulation, strategy implementation, and strategy evaluation) were developed from the existing literature. Hypotheses were tested by using statistical software (SPSS). Correlation and regression analysis revealed a significant positive correlation between variables. Result indicated all three variables (strategy formulation, strategy implementation, strategy evaluation) and overall strategic management practices are statistically significant with the performance of SMEs in Bangladesh. Policy recommendation, practical application were discussed and future implication of the research direction were recommended.
Social Sciences
Elizabeth McGhee Hassrick
Autistic students benefit from child-centered goals that align with evidence-based practices (EBPs) that meet their individualized needs, however, most teachers are not trained in how to implement autism-specific EBPs. The challenges do not lie with teachers alone. Professional development (PD) providers, such as district or regional autism experts who train and coach teachers on how to implement autism-specific EBPs, face barriers accessing the needed supports to conduct high-quality PD and lack experience with individualizing their methods for training and coaching teachers. When PD providers have networks of professional support, they can potentially gain access to resources to provide successful individualized coaching for teachers. No research has measured the impact of the social networks of PD providers on their performance as coaches in classrooms for teachers of autistic students. To test the hypothesis that social network resources can impact the performance of PD provider...
Public Health Forum
Ulrich Stössel
EinleitungDie Integrierte Versorgung Gesundes Kinzigtal (IVGK) ist ein populationsbezogenes integriertes Versorgungssystem. Hauptziel der IVGK ist es, sowohl den Gesundheitsnutzen der Versicherten als auch die Versorgungseffizienz zu erhöhen. Im Beitrag werden zunächst die Grundzüge des Versorgungssystems vorgestellt und die bisher vorliegenden finanziellen Ergebnisse der IVGK zusammengefasst. Anschließend gehen die Autoren auf die externe Evaluation der Versorgungsqualität ein und berichten bisherige Ergebnisse bzw. Ergebnistendenzen.
Revista Ceres
Pedro Henrique Weirich Neto
Na busca da sustentabilidade, metodologias para obtenção de parâmetros ou índices representativos seriam ferramentas básicas e essenciais para acompanhamento das gestões dos processos. Este trabalho teve por objetivo o cálculo de índices emergéticos para avaliação da sustentabilidade da produção leiteira. Para isso, o estudo foi realizado em uma propriedade rural, de base familiar, localizada no município de Palmeira, Paraná. A partir dos dados reais da propriedade, calculou-se a razão de rendimento emergético líquido (EYR), a razão de investimento de emergia (EIR), a carga ambiental (ELR), a razão de intercâmbio de emergia (EER), a renovabilidade (%R), a rentabilidade econômica simples (RES) e o índice de sustentabilidade (SI). Fundamentado nos métodos de análise emergética, foram encontrados os seguintes valores: EYR = 1,33; EIR = 3,05; ELR = 3,15; EER = 1,71; %R = 24; SI = 0,42; RES = 0,12. Estes índices demonstram que apesar de economicamente viável, RES = 0,12, em termos energé...
RELATED PAPERS
Irene McMaster
Journal of Virology
Khushi Muhammad
Corinne Pardo
Rem: Revista Escola de Minas
Clayton Jair de Oliveira
Agrovigor: Jurnal Agroekoteknologi
eko setiawan
Péter Turbucz
Tecnologia em Metalurgia, Materiais e Mineração
fernando jose gomes landgraf
Injury Extra
irshad paul
Ehud Greenspan
Journal of Education Research and Evaluation
Bagas Yazid Nurarib Ramadhan
Honvédségi Szemle
Péter Mujzer , László Ujházy
Urban Transport XX
Žilvinas Bazaras
The European Physical Journal C
giuliano laurenti
1比1仿制纽芬兰纪念大学毕业证 mun毕业证学位证书扫描件中留服认证原版一模一样
Physical Review B
Norbert Esser
Physical Review A
Facco Bonetti
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Undergraduate
- High School
- Architecture
- American History
- Asian History
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- Linguistics
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- IT Management
- Mathematics
- Investments
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Aeronautics
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Public Relations
- Educational Theories
- Teacher's Career
- Chicago/Turabian
- Company Analysis
- Education Theories
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Movie Review
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Marketing Plan
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Personal Statement
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Reaction Paper
- Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- SWOT analysis
- Thesis Paper
- Online Quiz
- Literature Review
- Movie Analysis
- Statistics problem
- Math Problem
- All papers examples
- How It Works
- Money Back Policy
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- We Are Hiring
Strategic Management Questions, Essay Example
Pages: 3
Words: 690
Hire a Writer for Custom Essay
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.
Why are there “three” categories of strategies (i.e. generic, grand, and competitive)? Provide two different reasons justifying the significance for listing three strategies.
The basic reason to provide these three strategies is basically to build such management strategies in order to achieve the ultimate goal of the organizations. These three strategies play a vital role in achieving the goal. Any organization can easily build own management strategies. All three has different techniques but their ultimate goal is same (Hitt, et, al., 2012). These strategies are building comprehensively for creating long term plans, competitive advantage, production, marketing and development of the organization by using appropriate actions for achieving the goal. The success of any organization based on correct and accurate policies and strategies. Policies should be designed in such a way that every employee can feel proud of being a part of such organization. Strong and accurate strategies helps the organization in climibing the ladder of success.
Give a totally original example of how Management by Objectives (MBO) might work. How does your example fit the criteria for MBO?
Answer: MBO is used to achieve the organizations objectives that are set in order to achieve best results in available resources for their business. This process also uses to monitor performance of the employees (Freeman, 2010).
Makro cash and carry is the biggest trading company working in Poland. They implemented MBO in the year 2005-2006. Manager says that their idea is to provide best services to customers that’s why they started using MBO, this increased he performance of their employees because different appraisals for motivations were done in order to follow company’s strategy and achieve their ultimate challenge (Hitt, et,al., 2012).
Shell is one of most renowned name in petrouleum industry and it holds a large scale of employees all over the world. In Dubai, Shell is also using MBO in order to increase their employee’s performances, they also provide appraisals for them, they engage their employees by conducting different activities like elections among them which is an opportunity for employees at local circumstances (Hitt, et,al., 2012). Appraisals instigate employees to work hard with honesty.
Let’s say you, as the boss, set a workplace standard. After comparing employee performance against that standard, you determine that there is some employee performance variation to the standard you set. What is your next step? Give an original example.
Answer: Performance is the major factor which plays a vital role in the success or failure of the organization. In Tesco, the performance of the employees is very important for the organization because they do not compromise over their customer’s satisfaction. So for this purpose Tesco gives great importance to their employees because they think if the employees are good enough this will also add value for their customers to shop at Tesco (Hitt, et,al., 2012). Performance and punctuality are two major factors on which employees performance gets calculated, so all should consider this as a strong fact.
They have their own way of measuring the performance of the employees. They has started a different way of monitor the employees performance they have divided their employees in groups and further sub groups, this helps the organization to measure each employees performance and this also differentiate between the employees that are working properly and who are not doing their job appropriately. They also do 360 degree feedback service. This tool is use to measure the current performance of the employees under the changing circumstances (Freeman, 2010).
What are the pros and cons to using best practices as a method for setting standards? Give an original example for each pro and each con.
Answer: Organizations practice different methods in order to set the standards of the company, but there are some pros and cons of setting such standards. At Pepsi Co. they are practicing such methods but they are facing problems with internal environment like employees communication issues, but are satisfied with employee’s performances (Wheelen & Hunger, 2011).
Freeman, R. E. (2010). Strategic management : A stakeholder approach . Cambridge University Press.
Hitt, M., Ireland, R. D., & Hoskisson, R. (2012). Strategic management cases : competitiveness and globalization . Cengage Learning.
Wheelen, T. L., & Hunger, J. D. (2011). Concepts in strategic management and business policy. Pearson Education India.
Stuck with your Essay?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!
Wartime Experiences of the Revolution, Essay Example
Capacity Report, Lab Report Example
Time is precious
don’t waste it!
Plagiarism-free guarantee
Privacy guarantee
Secure checkout
Money back guarantee

Related Essay Samples & Examples
Voting as a civic responsibility, essay example.
Pages: 1
Words: 287
Utilitarianism and Its Applications, Essay Example
Words: 356
The Age-Related Changes of the Older Person, Essay Example
Pages: 2
Words: 448
The Problems ESOL Teachers Face, Essay Example
Pages: 8
Words: 2293
Should English Be the Primary Language? Essay Example
Pages: 4
Words: 999
The Term “Social Construction of Reality”, Essay Example
Words: 371
Strategy and Strategic Management Essay
Introduction, essential components of strategy, towards a unified view of strategy, the strategy process, application of strategy-strategic fit and strategic foresight, strategic fit, strategic focus/foresight, reference list.

The Twelve Olympians by Monsiau, circa late 18th century
There is no unanimity among scholars and practitioners on the meaning of strategy. Texts on the subject discuss strategy from different and sometimes contradictory perspectives. The only issue, over which there is little debate, is the origin of the term strategy. “In its original sense, strategy (from the Greek word, Strategos) is a military term used to describe the art of the general (Harvard Business School, 2005, p. xi).
This art is about plans for troop deployment in battles to win wars. Many writers acknowledge that the concept of strategy has military origins, with Sun Tzu’s “Art of War” being one the oldest treatise on strategy. Businesspersons seem to enjoy using military analogies to conceptualize the running of businesses in the modern world.
Indeed, the pressure of keeping a business afloat amidst a very volatile operating environment that the world has become can feel like war. It is the goal of this paper to seek to uncover the essential components of strategy and the process of formulating a coherent organizational strategy in the context of the built environment.
Amid the differences that exist as to what strategy is, it seems more beneficial to embrace a wide-angled view of since each of the viewpoints has merit and contributes to the overall understanding of the concept.
It is the approach that Mark, (2004, p. 11) advocates for in the context of business when he states, “One of the greatest benefits of a comprehensive approach to strategy is the surfacing and exploitation of multiple sources of attractive growth”. However, this growth should give due considerations the internal resources availability for now and for the future.
The first essential component of strategy is action. The Harvard Business School (2005) states, “Strategy is about doing the right things” (p. xi). Actions reveal an organizations strategy. A deliberate strategy informs its actions. However, actions not based on a defined strategy still qualify for consideration as part of organizational strategy. Secondly, strategy refers to a plan.
Henderson (1991) states, “Strategy is a deliberate search for a plan of action that will develop a business’s competitive advantage and compound it” (p. 5). This plan informs the actions undertaken when the strategy is deliberate. Henderson (1991) assumes that all strategy must be formally planned. In the context of strategy, it is not the formalization of a plan but the deliberate choices a business puts in place that counts.
Another view forwarded by the Harvard Business School (2005) about strategy is that it is a resource control and utilization plan meant to protect the central interests of an organization. These resources include finances, physical infrastructure, and human resource. This view accomodates the lack of a deliberate centralized conventional business strategy made through a formal process.
It simply refers to the arrangement of those resources in a sensible manner towards certain ends. Competitive advantage is the motive behind strategy. Robert (2005) succinctly states, “Strategy is about winning” (p. 4).
This view is supported by Porter (1991) who states, “the essense of strategy formulation is coping with competition” (p. 11). The idea expressed reveals the intentional use of a plan to out-perform business rivals using unique traits of the organization in order to survive, and hopefully thrive. In this case, strategy answers the need to be the best among competitors.
The fifth essential component of strategy revealed by Robert (2005) is organizational identity. He states, “At the most basic level, strategy making extends beyond questions of resource deployment and market positioning to address fundamental questions such as: what is our business? What are we trying to achieve?
What is our identity as an organization?” (Robert, 2005, p. xi). This approach requires the organization to understand itself first before venturing out into the market with a clear direction. Wall (2004) agrees with this approach showing that strategy provides an organization with a “coherent sense of direction”, which is yet another essential component of strategy (p. 4).
This coherence makes it possible for all members of the organization to act in a coordinated fashion, which is essential for the success of a business. This holds true for small firms as well as large corporations. The final essential component of strategy is context. Successful strategy is very contextual.
“As soon as we move beyond general notions to more precise definition, then these depend upon the type of arena within which strategy is being deployed” (Robert, 2005, p. 7). This element accounts for the disparities in the views on strategy since some of the viewpoints are highly contextalized.
Increasingly, in this era of multinationals and globalization, context is more difficult to delineate especially geographically, yet to ignore context when developing strategy is to court disaster.
Based on the viewpoints above, Mark (2004) seems to have developed the most comprehensive definition of strategy. He states, “Strategy is about raising and allocating resources, setting priorities, directing organizations, and demonstrating through decisive behaviour what will be done – and what will not – in the pursuit of a larger vision, goal, mission, or high level set of objectives” (Mark, 2004. p. xv).
His definition is broad enough to capture most of the essential elements of strategy thereby avoiding the problem of high contextualization. It is also wide enough to cover the specifics of strategy that are valid in the strategic management of all organizations. This makes it useful in understanding the concept of strategy. Its other strength is that it leaves room for looking at strategy as either deliberate or consequential.
The elements defined here do not require a centralized approach to strategy development but even if it is there, it does not disqualify it. Its major weakness is its lack of enviromental cognisance. It does not account for environmental factors that greatly influence the preparation and execution of strategy.
This goes to demonstrate that the process of developing a unfied view of strategy is a work in progress, and still requires effort to sysnthesize the essential elements into a comprehensive definition of strategy. This preferred view must include the nine essential componenents identified above and in addition it must allow for both the deliberate and consequential nature of strategy.
A definition that meets the above criteria will still be somewhat incomplete since there is still the problem of universality versus contextualization. The following is an attempt to redefine strategy to meet this criteria presenting a wider understanding of the concept.
Strategy is a set of actions, planned or otherwise that influence resource acquisition and allocation, deployed for the express purpose of attaining competitive advantage based on a clear organizational identity expressed in terms of its place, power, problems and potential, which informs its direction and actions within its environmental context.
This definition captures all the essential elements identified but its rather cumbersome. It is long and may not appeal to the wider audience who actually need a concise definition to capture the essence of strategy. Probably, the sensible thing to do is to settle for a simplified global definition, while providing working definitions for each field, as writers have already done.
As expected, there is no universality in the recommendation of an ideal process for strategy development. There are different views on it. “Henry Mintzberg and his colleagues at McGill Unversity distinguish intended, realized and emergent strategies”. (Robert, 2005, p. 14). Intended strategy is the one the organization deliberately plans and positions itself to implement.
Emergent strategy is the one which developes unwittingly as an organization responds to evolving issues. When these two strategies interact, the result is the realized strategy which is the strategy the organization finds itself implementing. These three strategies are the result of three concurrent processes and they demonstrate the organic nature of strategy.
Strategy therefore is not a static process but a dynamic one that evolves and requires regular refitting. There is much concurrence though when looking at strategy as a process. In fact, there is a deliberate encouragement that organizations should take an active role in the developement of their strategy, other than waiting for one to emerge as they undertake their daily business.
The Harvard Business School (2005) states, “strategy creation and its implementation should be approached as a process” (p. xvi). The school proposes a five level process for strategy development that is useful in understanding the strategy process.
The steps in the process are developement of a mission, followed by identification of organizational goals. Thirdly, there is the actual strategy development succeeded by the strategy implementation process. The final level is performance measurement.
The first level of strategy development is mission. “Strategy creation follows from the mission of the company, which defines its purpose and what it aims to do for customers and other stakeholders” (Harvard Business School, 2005, p. xvi). Mark (2004) underscores the importance of mission when he says that the identification and action upon a particular set of issues determines the success of a business.
When the organization is clear about its priorities, then it can sucessfully engage in determining what is essential to its operations for success. The mission sets the rules governing its key relationships and functions. The next level is the identification of goals.
“Strategy creation typically begins with extensive research and analysis and a process through which senior management zeros in on the top priority issues that the company needs to tackle to be sucessful inn the long term” (Harvard Business School, 2005, p. xvii). There is a difference in opinion as to the direction of flow of the process, and whether it is the top management that is best placed to set organizational goals.
They have the tools and the authority but they lack in understanding of frontline issues that are key in implementation. Frontline staff on the other hand have clear views on what is not working for them but they lack the organizational overview. Probably, a middle line where the management gets input from the frontline is the best way around this challenge.
Once the goals are set, strategy creation takes place. It involves determining the internal and external forces followed by the identification of the choices that the organization has to achieve its objectives. Many tools are used to examine the organization’s capacity to settle on a particular organizational strategy after an environmantal scan.
While The Havard Busienss School advocates for SWOT as a method of conducting an enviromental scan, Robert (2005) feels that this approach is difficult to implement in practice and he advocates for a two way analysis of the environment, looking at internal and external factors. He contends that its not the four way classification but the “rigor and depth” in the analysis of these factors that counts (Robert, 2005).
Another popular tool worth mentioning used to conduct an evironmental scan is the Porter’s Five Forces Analysis. This tool is useful when the organization’s bottom line is the impetus driving the organization’s effort in undertaking a stategic planning process. There is lesser contention on who developes organizational strategy.
Many writers agree that “the job of creating an organization’s strategy over time falls to senior managers” (Walker, 2004. p4). The forth step in the strategy process is implementation. “A strategy that is formulated without regard to its implemetation is likely to be fatally flawed.” (Robert, 2005, 14).
In pushing the case for more frontline involvement, Daughtry and Casselman (2009) state, “Vision and strategy, critical though they are, are virtually useless without consistent execution right down to the frontlines” (p. 1 ). This requires good communication along the ranks of the organization.
They add that “Strategy has to be translated into the language and actions appropriate to each level in the organization” (Daughtry & Casselman, 2009, P.5). The final level in the strategy process is performance measurement. This lacks in organizations that do not have deliberate strategy. They do not know what to measure since they have not categorically stated what their goals are.
This five-step process is more useful as a conceptual model than as an actual implementation process. Wall (2004) warns that things do not work out this neatly in the real world where forces shift suddenly and without warning. Perhaps it is best to look at strategy development as “an iterative process that begins with a recognition of where you are and what you have now” (Henderson, 1991, p. 6).
New information and circumstances feed into the old circumstances forcing us to change and adapt our methods. The role of strategic management is to ensure that the changes in the environment do not adversely affect the organization’s long term view, but that the organization prepares in advance to take advantage of these changes.
Just like other organizations, construction companies exists within a certain environment defined broadly by the natural environment, demographic structures, social structures, legislative processes, technology, and economy. This environment has an immediate impact on their interest’s interests and influences everyday decisions.
In addition, they have their own unique internal environments defined by organizational culture, resources outlay such as level capitalisation and expertise, and business processes defining how they find and execute construction contracts. The internal environment influences the realization of their aspirations and the momentum they sustain towards their realization.
Certain other forces much larger in dimension constitute the business climate of companies in the built environment. These include the macroeconomic trends, political issues, and global trends. Montgomery and Porter (1991) observe, “Increasingly, both business units and corporations must compete globally” (p. xv). Dalic (2007) calls it “the convergence of cultures” (p. 4).
The climate has long-term impacts on the industry though it may be a while before a particular company begins to feel the impact of climatic changes. They are a very strong motivation behind the strategy process. Before a construction company develops its strategy, it is beneficial and maybe crucial for it to determine what its environment looks like.
This allows it to forecast the impact of its present actions thereby providing it with the range of presently available options and the limits within which it can operate profitably. The application of strategy and the strategy process allows an organization to determine two important contexts in strategic planning and strategic management. These are strategic fit and strategic foresight.
Strategic fit looks at the present. It refers to the process where an organization examines its current position to ascertain whether it is sitting squarely on its best possible footing or whether there is a mismatch, based on its objectives. In the built environment, a company looks at whether its level of staffing and financing corresponds to the available opportunities.
The resulting plan from the process is a strategic plan to give the organization a better placement within its business context. Robert (2005) recognizes the need for strategic fit when he states, “For a strategy to be successful, it must be consistent with the firm’s external environment and with the characteristics of the firm’s internal environment- its goals and values, resources and capabilities, and structure and systems” (p. 14).
Construction projects normally take very long from ideation to completion, and it is normal for very drastic changes in the business enviroment to occur within the life of the project. By seeking to attain strategic fit, a construction company ensures it takes advantage of the present opportunities which may dissapear because of environmental change.
Strategic fit is the result of implementing measures concluded upon after conducting an environmental scan during the strategy process. Strategy and the strategy process may provide organizations in the built environment with the ability to determine their strategic fit to ensure that they are currently using their resources to the best effect.
However, due to the dynamic environment in the present business context, for a small outfit such as small to medium enterprise construction industy, the strategy process considerations may pose challenges to them in utilizing their resources to the best outcome as it is somewhat restrictive in terms of time, cost and resource availability.
On the other hand, strategic foresight, also known as strategic focus, refers to the preferred position of an organization usually at some point in the future. By looking at the medium and long-term opportunities, a construction company may find certain desirable positions they would prefer to occupy at that future date.
Strategic foresight considers all the forces acting on the business environment within which the organization operates and seeks to determine their impact on the long-term objectives of the organization. This prepares it to take advantage of arising opportunities and prepares it to handle future challenges. “One of the biggest challenges facing executive teams is lack of strategic focus” (Daughtry & Casselman, 2009, p. 7).
Its long-term nature makes it easy to ignore especially for small construction companies with severe resource constraints. The pressure of the present seems to make strategic foresight an unnecessary burden on already overworked executives.
By drawing on strategy and the strategy process, a construction company creates strategic focus on its executives, thereby preparing them to handle the challenges the company will face in the future. It assures the long-term survival of the company. It is tempting to look at the strategy process in terms of strategic foresight without considering the implications of strategic fit on the desired future.
Organizations in the built environment need to know that strategic foresight without strategic fit results in “a plan for the future without a plan for the present” (Wall, 2004, p. 13). On the other hand, strategic fit without strategic focus gurantees the present at the expense of the future.
Hence, the outcome should be a balanced strategy where there should be a constant review of the corporate strategy and its implication on present and future resources, and the competitive advantage in the market place.
Bacharach, S.B. (1989) Organizational Theories: Dome Criteria for Evaluation. The Academy of Management Review, 14(4), 496-515
Bourgeois III, L.T. (1984) Strategic Management and Determinism. The Academy of Management Review, 9(4), 586-596
Dalic, T. (2007) Globalization of Marketing Strategies in Light of Segmentation and Cultural Diversity. Norderstedt: GRIN Verlag.
Daughtry, T.C. and Casselman, G.L., (2009) Executing Strategy: From Boardroom to Frontline. Herndon, VI: Capital Books.
Harvard Business School (2005) Strategy: Create and Implement the Best Strategy for Your Business. Boston, MA: Harvard Business Press.
Henderson, B.D.(1991) Developing Strategy in C.A. Montgomery & M.E. Porter, eds. Strategy: Seeking and Securing Competitive Advantage. Boston, MA: Harvard Business School Publishing Division.
Li. Y and Peng, M.W. (2008) Developing theory from strategic management research in China, Asia Pacific Journal Manage, 25(3), 563-572.
Mark, D. (2004) Strategy: A Step by Step Approach to the Developement and Presentation of World Class Business Strategy. New York, NY: Palgrave Macmillan.
Poppo, L. and Zenger T. (1998) Testing Alternative Theories of the Firm: Transaction Cost, Knowledge-Based, and Measurement Explanations for Make-or-Buy Decision in Information Services, Strategic Management Journal, 19, 853-887
Robert, M.G. (2005) Contemporary Strategy Analysis. Malden, MA: Wiley-Blackwell.
Smircich, L. and Stubbart C. (1985), Strategic Management in an Enacted World, The academy of Management Review, 10(4), 724-736.
Teece, D.J., Pisano, G. and Shuen, A. (1997) Dynamic Capabilities and Strategic Management, Strategic Management Journal, 18(7), 509-533.
Toffek, M.W. (2004) Strategic Management of Product Recovery, California Management Review, 46(2), 1-22
Venkatram, N. and Cumillus, J.C. (1984) Exploring the Concept of “Fit” in Strategic Management, The Academy of Management Review, 9(3), 513-525
Walker, G. (2004) Modern Competitive Strategy. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill/Irwin.
Wall, S.J. (2004) On the Fly: Executing Strategy in a Changing World. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley and Sons. D31BM – Business Management for Built Environment
- UAE Government Foresight and Scenarios Program: The 3D Concrete Printing
- The Microeconomic Foresights and Its Principal Aims
- Difference between Deliberate and Emergent Strategies
- Guide to Article Critique (Organizational Behavior)
- The Leadership Theories: Followership and Servant Leadership
- Mary Kay’s Lesson in Leadership
- Promotion. Training. Leadership Question
- Employee Motivation vs. Work and Family Issues
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, May 27). Strategy and Strategic Management. https://ivypanda.com/essays/strategy-and-strategic-management-essay/
"Strategy and Strategic Management." IvyPanda , 27 May 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/strategy-and-strategic-management-essay/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'Strategy and Strategic Management'. 27 May.
IvyPanda . 2019. "Strategy and Strategic Management." May 27, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/strategy-and-strategic-management-essay/.
1. IvyPanda . "Strategy and Strategic Management." May 27, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/strategy-and-strategic-management-essay/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Strategy and Strategic Management." May 27, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/strategy-and-strategic-management-essay/.
Essay on Strategic Management: Top 7 Essays
Here is a compilation of essays on ‘Strategic Management’ for class 9, 10, 11 and 12. Find paragraphs, long and short essays on ‘Strategic Management’ especially written for school and college students.
Essay on Strategic Management
Essay Contents:
- Essay on CEO’s Functions in Strategic Management
Essay # 1. Definition of Strategic Management:
The term ‘strategic management’ has been defined differently by different scholars of management.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Some of them are:
1. Strategic management is “ a set of decisions and actions resulting in formulation and implementation of strategies designed to achieve the objectives of an organisation” (Pearce and Richard Robinson).
2. Strategic management is “the manner by which organisations plan to deal with various aspects of management like problem perception, divergent thinking, substantial resources, decision making, innovations and risk-taking” (Cunningham).
3. Strategic management is “the means by which management establishes purpose and pursues the purpose through co-alignment of organisational resources with environment, opportunities, and constraints.” (Bourgeois).
4. Strategic management can be defined as “the art and science of formulating, implementing and evaluating cross-functional decisions that enable an organisation to achieve its objectives” (Glueck).
(a) Strategic management is an on-going process of analysis, planning and action. It attempts to keep an organisation aligned with its environment while capitalising on organisational strengths and environmental opportunities and minimising or avoiding organisational weaknesses and external threats, and
(b) Strategic management is also a future-oriented provocative management system. The managers, who use strategic management skills, are seeking a competitive advantage for their organisations and long-term organisational effectiveness.
It is, therefore, a complex function covering all activities connected with formulating, implementing, recycling and reformulating strategies.
In short, an effective strategic management translates a sound strategy into action. As otherwise, even a sound strategy would be rendered ineffective if it cannot be converted into action.
Hence, it is the duty of the strategic managers to do environmental scanning, assess internal strengths and weaknesses, set goals, mobilise resources, design action plans, implement actions, monitor progress, and control resources and deviations from goals for the achievement of goals and key results areas.
Essay # 2. Process of Strategic Management:
The strategic management process is most often described as a rational and analytical one.
The process consists of the following activities in different phases:
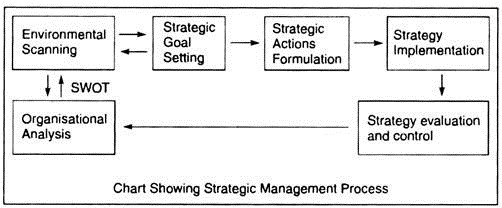
(i) Environmental Scanning:
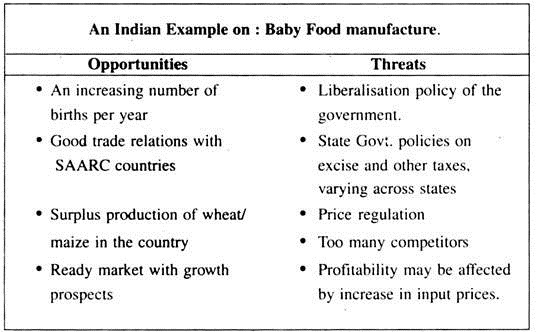
Threats and opportunities analysis.
This involves analysing each threat and opportunity according to its time frame (i.e., short term or long term). Significance and likelihood of occurrence can help focus on the’ most important threats and opportunities.
In identifying them in the organisation’s environment, three questions need to be kept in mind:
(i) Which threats are critical and how can they be avoided in order to derive opportunities?
(ii) Which opportunities are critical and must be exploited?
(iii) Which threats and opportunities are short-terms and which are long-term?
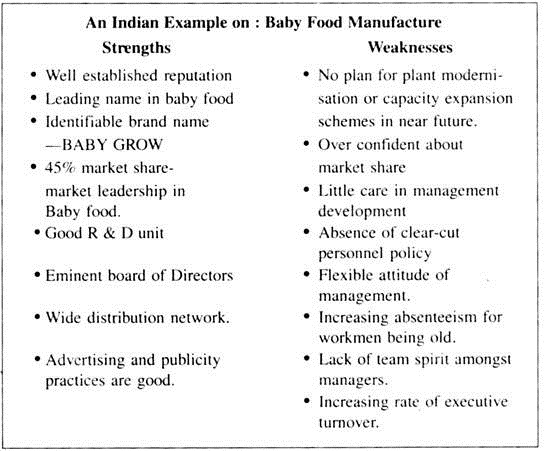
(ii) Organisational Analysis:
Mission, Strengths and Weaknesses analysis.
An organisational analysis begins with an analysis of how the organisation is performing and why. A broad statement about purpose, philosophy, and goals would guide executive actions, by the processes of evaluation.

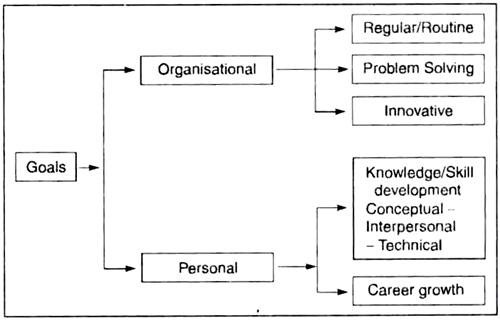
(iii) Strategic Goals Setting:
Understandable, measurable, achievable and challenging long-term goals.
It is necessary to set annual objectives in line with long-term objectives as well as specifying functional strategies consistent with the company’s grand strategy Such goals should be measured in terms of quality, cost, and time-frame.
A chart below classifies and explains the ‘Goals’:
Given the mission and objectives and having done the SWOT analysis, the strategic manager should proceed to generate possible ‘strategy alternatives’. There may be different ‘strategic options’ for accomplishing a particular goal. It is necessary to consider all possible alternatives to make the base for a choice.
The purpose of considering different ‘strategic options’ is to adopt the most appropriate strategy as ‘goal’. This necessitates the evaluation of the ‘strategy alternatives’ with reference to the criteria like suitability, feasibility and acceptability.
(iv) Strategic Actions Formulations:
An action plan to achieve the goals.
Strategic actions flow from the goals of the organisation. A strategy sets forth a general programme of action and an implied development of employees and resources to obtain goals.
This strategic action can be taken from three approaches:
(a) Functional approach,
(b) Product approach, and
(c) Business Units grouping approach.
Here, ‘business units grouping’ approach works well in diversified enterprises. All these approaches involve choosing target markets, and product and product development plans, capital expenditure plans, and marketing plans. For all major actions, the aspects of timing and sequencing should be considered.
(v) Strategy Implementation:
Spelling out effective policies or operating procedures to initiate actions for implementing strategy.
This involves translating the strategies into organisational actions. This requires ‘strategic leadership’ i.e., identifying policies, rules, and key results areas; allocating responsibilities; and making operational plans and day-to-day decisions.
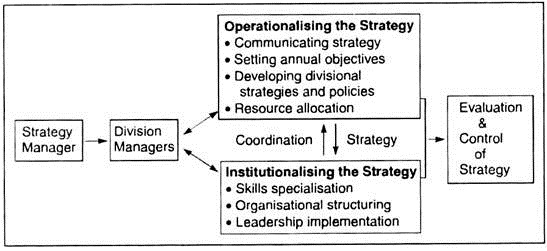
Strategy implementation is, thus, the action phase of the strategic management process. This step, therefore, encompasses the operational details to translate the strategy into effective practice.
A simple chart below sums up the implementation phase:
(vi) Strategy Evaluation and Control:
Monitoring progress of strategic actions and controlling the resources.
This includes both monitoring progress and control resources—human/physical/ financial—by analysing the deviations from standards and goals and providing the feedback for modifications.
It is important to note that traditional control parameters are not adequate here as they delay the results and thereby become a useless exercise to face the environmental risks and uncertainties. In contrast to ‘past-action control’, strategic control is forward looking and attempts to steer the company on a long-term basis.
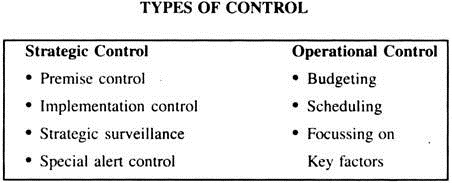
Essay # 3. Stages of Strategic Planning Process:
Stage 1. Defining the mission.
Stage 2. Assessing organisational Resources.
Stage 3. Evaluating Environmental risks and opportunities.
Stage 4. Establishing long-term Objectives.
Stage 5. Formulating strategy.
Stage 6. Establishing Annual Objectives.
Stage 7. Establishing Operational Plans.
Stage 8. Implementing the Plans.
Stage 9. Implementing, Monitoring and Adapting.
These stages seldom occur in a fixed sequence, and some may take place simultaneously, but given the flexibility needed for a bit of cycling— revising, seeking authorisations and coordinating—some rationale exists for considering the stages in the order presented (Williams, Du Brin & Sisk, 1985).
Strategies are designed by top management of an enterprise. They come to be as a result of the strategic planning process.
Essay # 4. Characteristics of Strategic Management Process:
The basic characteristics of the strategic planning process may be as follows:
1. It is the place where decisions of highest importance to a company are made. Here is where the basic thrust and direction of the company is determined and the major approaches are decided.
2. The time spectrum covered ranges from the very short range to infinity. Although the general thrust is long-range, a decision can be made in this process to stop producing Product X tomorrow or start to build tomorrow a new plant to produce the Product Y.
3. The process may produce a written document on a periodic basis, say annually—yet the process is a continuous activity. Top management cannot, of course, develop a strategic plan once a year and forget strategy in the meantime.
4. Compared with medium-range and short-range planning, the results of strategic planning process are not usually neatly incorporated into a prescribed form.
5. Strategic planning covers any element of the business that is important at the time of analysis and embodies details that are of sufficient scope and depth to provide the necessary basis for implementation.
6. The format of strategic plans is much more flexible and variable in content, from time to time, than for other types of plans.
7. Strategic planning process has many starting points, each different from the other.
8. Strategic planning is especially appropriate in volatile industries, such as the computer or telecommunication or anti-pollution industries where technological change is rapid and international competition is fierce.
9. Strategic planning is uniquely suited for providing ‘a broad managerial perspective which rescues management from the tunnel vision of unanalysed assumptions and fuzzy objectives’.
10. Strategic planning, even if the methods as well as the human resources and other situational variables differ greatly from one firm to another, is an increasingly necessary aspect of effective management.
Essay # 5 . Factors and Elements of Strategic Planning Process:
From the above, we see that the general contents of strategic planning process are:
(i) Objective of enterprise,
(ii) Basic mission,.
(iii) Basic strategies, and
(iv) Operational plans.
The factors and main elements of strategic planning process can be best identified and shown in a model below:
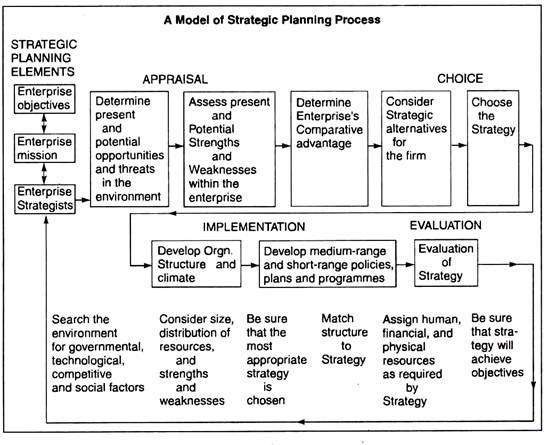
As we can see, strategic planning involves the development of objectives (step 1 in the planning process). Next the top management searches for the environment.
Next top management weighs the advantages of the several strategies considered and chooses one. It outlines the general organisational and policy changes necessitated by its strategic choice. It then delegates detailed planning and implementation activities to its middle management. Top management also sets budget levels and indicates general usage of funds; detailed budgeting is done by middle management.
Strategic planning is exciting. It involves decisions like: Xerox Corporation’s decision to enter (and leave) the computer field, Reliance Industries’ decision to get out of textiles and become a conglomerate, or Cadbury chocolate’s decision to become Cadbury Foods (all hypothetical).
Essay # 6 . CEO’s Role in Strategic Management:
The increasing time demands of strategic management have nowadays forced top managements among the larger companies to delegate more and more of the operating authority for running the business to lower-level managers.
Some companies today have Chief Executive Officers (CEOs) who are concerned essentially with outside environmental forces, and Chief Operating Officers (COOs) who are concerned primarily with running the day-to-day affairs of the business. In these cases as well as in others where there is no COO or its equivalent, more authority is usually being delegated to middle managers.
This does not mean that top managements remain unconcerned about the day-to-day operational matters. Only thing is that, in the changing environment from that of the past, the top managements are forced to spend much less time on routine operating matters and to devote much more time on strategic issues.
The most important case in point is that managerial strategies in large-sized organisations are considerably different from the operational strategies needed. After all, corporate level strategy in the changing environment is essential for success and growth, and for competitive advantage. Herein, comes the role of the chief strategist, the CEO.
The chief strategist is faced with three basic questions:
(1) What business are we in?
(2) How are we to match the best product-market opportunities?
(3) How are we to make best use of the company resources?
The first two questions are concerned with corporate-level strategies, while the third question relates to operational-level strategy. The CEO must conceptualise the whole strata of strategy as he is at the top. CEO is responsible for relating his organisation to a changing environment.
He alone is responsible for assuring the proper balance among various competing subsystems in the organisation. He alone is responsible for determining the total thrust of his organisation and for assuring that performance matches with his design. So, the role of the CEO is unique and so is his way of thinking.
Again, the CEO is expected to concentrate on the total enterprise rather than parts of it, and in the process ‘entirely new phenomena take place’.
CEO has to think in these terms. The thought processes, the attitudes, the perspective, the methods of analysis and the skills in the total strategic management process are unique and of demanding nature and call for higher level dynamism and initiative. CEO, as the chief strategist, has to have widest vision in these respects.
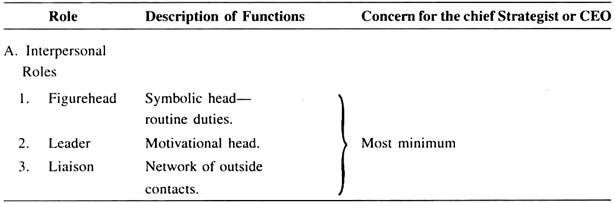
Essay # 7 . CEO’s Functions in Strategic Management:
Mintzberg’s classification of ‘Ten Managerial Work Roles’ vis-a-vis the functions/roles that concern the chief strategist is given below for better comprehension:
Provide details on what you need help with along with a budget and time limit. Questions are posted anonymously and can be made 100% private.

Studypool matches you to the best tutor to help you with your question. Our tutors are highly qualified and vetted.

Your matched tutor provides personalized help according to your question details. Payment is made only after you have completed your 1-on-1 session and are satisfied with your session.
Business Strategic Management Essay Questions
User Generated
gnfunzpnlref
Business Finance
Description
Complete each essay question using only the material found in book ISBN 978-0-13-416784-8 Concepts of Strategic Management and Cases in Strategic Management by Fred David, 15 th edition, 2015, Prentice Hall.
1.Distinguish between long-range planning and strategic planning .Provide examples to illustrate your point.
2.Identify the pitfalls in strategic planning for which management should watch out, then pick any five and discuss, in detail, the strategic implications of this risk.
3.Compare and contrast vision statements with mission statements. Describe why a mission statement is so important in the strategic-management process.
4.Identify and discuss 10 external forces that must be examined in formulating strategies: economic, social, cultural, demographic, environmental, political, governmental, legal, technological, and competitive. Give examples of each.
5.Define Competitive Intelligence (CI) and discuss three ways that CI can be gathered.
6.Explain Porter's Five Forces Model and its relevance in formulating strategies. For each competitive force, discuss one condition that is likely to increase the threat of that force.
7.Explain how to develop and use an External Factor Evaluation (EFE) Matrix. Discuss the five steps needed to develop an EFE Matrix.
8.Explain how to develop and use a Competitive Profile Matrix.
9.Identify the five basic functions of management, and describe each function with an emphasis on their relevance in formulating strategies.
10.First, discuss the importance of financial analysis in strategic management. Next, discuss the three separate fronts on which an effective financial ratio analysis is conducted. Then, discuss the limitations of financial ratio analysis.
11.Describe the purpose and importance of an Internal Factor Evaluation (IFE) Matrix. Then, discuss the five steps involved in performing an IFE.
12.What are the characteristics of effective strategic objectives? Discuss why it is important to clearly state objectives.
13.The textbook lists eleven types of strategies. Describe and give examples of each.
14.Define the three types of integration strategies. Give examples and guidelines for when each is strategically appropriate.
15.Define the three intensive strategies. Give examples and guidelines for when each is strategically appropriate.
16.Discuss, in detail, the SWOT Matrix. Describe each component of the matrix and discuss its strategic implication. Discuss the use of the SWOT Matrix in strategic analysis.
17.Compare and contrast the BCG Matrix and the IE Matrix. What are the benefits and limitations of each?
18.Diagram and explain the Quantitative Strategic Planning Matrix (QSPM).Describe the positive features and limitations of this analytic tool.
19.Discuss the differences between strategy formulation and strategy implementation.
20.Compare and contrast the different types of organizational structures: functional, divisional, and matrix. Describe each and discuss the advantages and disadvantages.
21.Although there are many marketing activities that impact the success or failure of strategy-implementation efforts, three activities are indicated in the text as being especially important. What are these three activities? Discuss why they are so important.
22.Discuss the major R&D approaches for implementing strategies. Discuss guidelines used to determine whether a firm should conduct R&D internally or externally.
23.Discuss Rumelt's four criteria for evaluating strategies. List and describe each of the three strategy-evaluation activities.
24.Discuss the four different perspectives related to the Balanced Scorecard and explain what the Balanced Scorecard attempts to balance. Identify and explain the questions that must be asked when using Balanced Scorecard Analysis.
25.Discuss how business ethics, social responsibility, and sustainability are interrelated.
26.Discuss the reasons why preserving the environment should be a permanent part of doing business. Describe a sustainability report.
27.Discuss the potential advantages to initiating, continuing, and/or expanding international operations.
28.Explain the concept of protectionism. Discuss the role that protectionism plays in global commerce.

Explanation & Answer

Hello, use the document attached below and ignore the one above. I have made some few changes. Running head: BUSINESS STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT Answers to the Questions: Business Strategic Management Students Name Institutional Affiliation Instructor Date of Submission 1 BUSINESS STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT 2 Question 1#Answer Strategic planning is usually done by the management team of an organization with the aim of determining the organization's vision, mission, and its primary strategy. It is usually an ongoing process. For example, an organization may perform a strategic plan continuously for a long time to attain sustainability. On the other hand, Long-term planning deals typically with setting the procedure to be used to realize the strategic plan (Hall, 2015). It is concerned with the aligning of a project to match with the set strategic goals as well as the coordinating department in a way that they are capable of achieving the organization's targets. Second, long term planning differs with the strategic planning regarding time frame where it is mostly given more than five years to meet the company demands of achieving and promoting its mission and policy. For example, a company can have a long-term planning to expand its business in other countries in the next five years to come (Hall, 2015). Question 2#Answer Strategic planning has some pitfalls which require the management attention to be avoided or reduce them (Hall, 2015). Some of the pitfalls of the strategic planning are; • Unproductive pre-planning • Lack of commitment and ownership by the management • Failure to Get an early Support from crucial People • By Only holding a Yearly Retreat • Allocating inadequate Resources to both the Planning and Implementation • Formulation of poor Vision, Mission, and Values Statements BUSINESS STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT • Beginning the strategic plan process at the "Wrong Place." • Insufficient Attention on Customer Value Creation • Failure to Track Progress Efficiently • Lack of Annual Updates and Reviews 3 The risks named above have strategic implications as described in the following vital pitfalls; Unproductive pre-planning: By having the executives rushing at the strategic planning exercise with inadequate preparation have severe strategic implications. If the executive produces less effective strategies, mission, vision and values, therefore, the company is unable to grow and be competitive in the market (Hall, 2015). The whole strategic planning process becomes unproductive from the first stage to the end. Lack of commitment and ownership by the management: If the management team is not committed towards the strategic planning process, then it leads to having a meaningless vital planning exercise. The planning and the implementation of the strategic plan becomes a dream when the senior team, middle management fails to take ownership and commitment to the plan (Hall, 2015). Failure to get an early Support from crucial People: Once the strategic planning process fails to get support from the beginning makes the planning process challenging to carry out (Hall, 2015). The planning, therefore, omits so many crucial aspects from the important people who at the end leads to poor mission, vision and values statements. By only holding a Yearly Retreat: When the management team doesn't keep several retreats during the year, they fail to be serious about the strategic planning. Once the yearly retreat is made, the team resumes back to their business assuming that all is done. It to lack of consistency in the planning which makes the strategic plan lack meaning (Hall, 2015). BUSINESS STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT 4 Allocating inadequate Resources to both the Planning and Implementation: When the management team doesn't allocate adequate resources regarding finances and time, then it results to less accomplishment of the strategic plan. This means that the strategic plan won't be implemented due to lack of time and finances (Hall, 2015). Question 3#Answer Mission Statement Vision statements About It is concerned with how the company reaches its target. Defines the primary objectives and purpose relating to the company’s team values and customer needs. A Vision statement indicates where the company wants to be. It talks of both the values and purpose of the organization (Hall, 2015). Answer It responds to the question of what is to be done and what makes the company special. It responds to the question of Where the company targets to be. Time It describes the current leading to its future. A vision statement communicates of the business future. Function Its primary function is internal where it defines the main measures of the company’s success. It contains where the company wants to be in the future inspiring the company to give its best. Change The statement may change, but still connect back to the company’s core values, vision and customer requirements (Hall, 2015). As the business evolves, the management may want to change the vision. However, vision statements clarify the organization's foundation, therefore there BUSINESS STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT 5 is need to minimize change (Hall, 2015). Importance of Mission statement An organization's mission statement is essential as it serves as a drive to all the organization's decision making. It targets the leaders, shareholders, and workers to help them realize which tasks and decisions best fit the company's mission. It also provides an insight into what the organization leaders take as the main reason for doing the business (Hall, 2015). Question 4#Answer (i) Economic: Any change that may occur in the national or the international economy status affects the strategies formulation processes. In this, any company or organization that is the process of formulating strategies must take caution of the level of the economy in the country (Hall, 2015). For example, an organization which plans to open other branches in a certain region must be in a position to predict the future position of the national economy since low a nation which is going down economically will affect the operations of the business negatively. (ii) Social: This refer to the society believes, customs, norms and practices of customers that affect the operations of a business. For instance, a business is formulating its strategies (Hall, 2015). It must take into consideration of the social environment that it operates from. In this, a business must develop a demographic profile of its potential customers so as to know what motivates these customers. BUSINESS STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT (iii) 6 Climate: The natural forces such as the climatic conditions have the ability to affect the operations of the business (Hall, 2015). For instance, any organizations that deals with the agricultural products and sports organizations might be realty affected by the climatic conditions such as the rainfall and drought calamities. This means that for such an organization to formulate strategies it must put into considerations of the climate conditions. (iv) Cultural: These refers to the factors such as fashion trends, beliefs and life style of a community that affects their behavior towards a certain business. For instance, a region which is dominated by a Muslim culture, a business which operates in the region must accommodate the Muslim norms when f...

24/7 Homework Help
Stuck on a homework question? Our verified tutors can answer all questions, from basic math to advanced rocket science !

Similar Content
Related tags.
math business and finance business and finance Total Rewards Package information-gathering tools communication case study website design Assessment Criteria zoning plan project management standard deviation
The Book Thief
by Markus Zusak
Cat on a Hot Tin Roof
by Tennessee Williams
Communist Manifesto
by Karl Marx
The Bell Jar
by Sylvia Plath
by Niccolò Machiavelli
Z for Zachariah
by Robert C. O’Brien
Too Much and Never Enough
by Mary L. Trump
by Michelle Obama
American Gods
by Neil Gaiman
working on a homework question?
Studypool is powered by Microtutoring TM
Copyright © 2024. Studypool Inc.
Studypool is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university.
Ongoing Conversations
Access over 20 million homework documents through the notebank
Get on-demand Q&A homework help from verified tutors
Read 1000s of rich book guides covering popular titles

Sign up with Google
Sign up with Facebook
Already have an account? Login
Login with Google
Login with Facebook
Don't have an account? Sign Up

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Exam revision 5 quesions 4 essays LECTURE 1 CHAPTER 1 - STRATEGY CONCEPTS Q1 what is modern strategic management What is strategic management? -Seing objecives for the organisaion, planning and implemening the necessary changes and measuring the outcomes - Strategic management is a central issue for all organisaions.
9 Essay Questions on Strategic Management. Writing a strategic management essay, you may encounter or seek essay questions. Using them helps narrow down the scope of your work and focus your body paragraphs. We came up with some ideas for you right here: How can a business conduct competitor analysis? Explain what competitor analysis is.
Question. 12 answers. Nov 25, 2023. Ontological model should be a complete theory of how an enterprise is structured and how it functions as whole. It should describe through formulas the objects ...
Strategic management. A strategy is conventionally described as a long-term business plan or action formulated solely for the realization of business goals and objectives. On the other hand, strategic management refers to a compilation of managerial decisions and actions, aimed at determining the long-term performance of an organization ...
Strategic management is a crucial aspect of organizational success, requiring a comprehensive understanding of both internal and external factors that can impact a company's operations. One of the most widely used tools in strategic management is the SWOT analysis, which allows organizations to identify and analyze their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Chapter1 Essay Questions 101. Compare and contrast strategic planning with strategic management. Strategic planning is more often used in the business world, whereas strategic management is often used in academia. ... The purpose of strategic management is to exploit and create new and different opportunities for tomorrow; long-range planning ...
Short Essay on Strategic Management April 4, 2007 1 Definition of Strategic Management Strategic management is the process where managers establish an organization's long-term direction, set the specific performance objectives, develop strategies to achieve these objectives in the light of all the relevant internal and external circumstances ...
Interesting Management Essay Topics. Management is needed to define and set goals, achieve them with people and resources, coordination, and control. ... Strategic management is a company's series of actions to achieve long-term goals that allow a business to survive in competition and thrive in any external environment. The more unstable the ...
Taking the case of Starbucks, the coffee conglomerate, its strategy is the assumption of the product by the non-coffee drinkers. That is why Starbucks started to introduce a wide line of products. "Starbucks has repositioned the Frappuccino line for providing market development." (Hunt, 2009, para. 5). In the case of market penetration, it ...
Essay Questions. Compare and contrast strategic planning with strategic management. Click the card to flip 👆. Strategic planning is more often used in the business world, whereas strategic management is often used in academia. Sometimes, strategic management is used to refer to strategy formulation, implementation and evaluation, with ...
Strategic Management. Strategic management consists of the analysis, decisions, and actions an organization undertakes in order to create and sustain competitive advantages. It gives the organization a sense of its objectives and a sense of how it will achieve these objectives. For Michael Porter, one of the leading strategy gurus, strategy is ...
Answer: MBO is used to achieve the organizations objectives that are set in order to achieve best results in available resources for their business. This process also uses to monitor performance of the employees (Freeman, 2010). Makro cash and carry is the biggest trading company working in Poland.
Strategic Management. Executive Summary ALDI is a leading retail industry in Australia. This paper will discuss a contemporary analysis done on the ALDI. The threat of new entrances, technology, and environment are such factors that are affecting the overall strategic development of ALDI.
The concept of competitive advantage is central to the study of strategic management, since a company (or an organization) must follow an aligned strategy to outperform their rivals in the industry. Michael Porter introduces three generic strategies that a firm may apply in order to do so. (Overall cost leadership, Differentiation and Focus). In order to create and sustain competitive ...
Essay Questions of Strategic Management - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Strategic management
Secondly, strategy refers to a plan. Henderson (1991) states, "Strategy is a deliberate search for a plan of action that will develop a business's competitive advantage and compound it" (p. 5). This plan informs the actions undertaken when the strategy is deliberate. Henderson (1991) assumes that all strategy must be formally planned.
Strategic Management Process - Strategic Management, Alliances and International Trade - Exam. Markets for Factor Inputs - Competitive Strategy - Exam. Corporate Strategy - Strategic Management - Past Exam. (2) Life Cycle - Strategic Management - Past Exam. Strategic Planning - Strategic Management - Past Exam.
2. Strategic management is "the manner by which organisations plan to deal with various aspects of management like problem perception, divergent thinking, substantial resources, decision making, innovations and risk-taking" (Cunningham). 3. Strategic management is "the means by which management establishes purpose and pursues the purpose ...
According to Chen, Hambrick and Nag "strategic management is the continuous planning, monitoring, analysis and assessment of all that is necessary for an organization to meet its goals and objectives" (2007, p. 935-955). Fast-paced innovation, emerging technologies and customer expectations force organizations to think and make decisions ...
Complete each essay question using only the material found in book ISBN 978--13-416784-8 Concepts of Strategic Management and Cases in Strategic Management by Fred David, 15th edition, 2015, Prentice Hall.1.Distinguish between long-range planning and strategic planning .Provide examples to illustrate your point.2.Identify the pitfalls in strategic planning for which management should watch ...
Strategic Management - Essay Questions. 1. Explain why the concept of competitive advantage is central to the study of strategic management. The concept of competitive advantage is central to the study of strategic management, since a company (or an organization) must follow an aligned strategy to outperform their rivals in the industry.
Questions On Strategic Human Resource Management Essay. Strategic Human Resource Management is an approach to the management of human resources that provide a strategic framework to support long- term business goals and support. This approach is concerned with structure, culture, values, quality commitment and matching resources to future needs.