- Home »

find your perfect postgrad program Search our Database of 30,000 Courses
How to write a masters dissertation or thesis: top tips.
It is completely normal to find the idea of writing a masters thesis or dissertation slightly daunting, even for students who have written one before at undergraduate level. Though, don’t feel put off by the idea. You’ll have plenty of time to complete it, and plenty of support from your supervisor and peers.
One of the main challenges that students face is putting their ideas and findings into words. Writing is a skill in itself, but with the right advice, you’ll find it much easier to get into the flow of writing your masters thesis or dissertation.
We’ve put together a step-by-step guide on how to write a dissertation or thesis for your masters degree, with top tips to consider at each stage in the process.
1. Understand your dissertation or thesis topic
There are slight differences between theses and dissertations , although both require a high standard of writing skill and knowledge in your topic. They are also formatted very similarly.
At first, writing a masters thesis can feel like running a 100m race – the course feels very quick and like there is not as much time for thinking! However, you’ll usually have a summer semester dedicated to completing your dissertation – giving plenty of time and space to write a strong academic piece.
By comparison, writing a PhD thesis can feel like running a marathon, working on the same topic for 3-4 years can be laborious. But in many ways, the approach to both of these tasks is quite similar.
Before writing your masters dissertation, get to know your research topic inside out. Not only will understanding your topic help you conduct better research, it will also help you write better dissertation content.
Also consider the main purpose of your dissertation. You are writing to put forward a theory or unique research angle – so make your purpose clear in your writing.
Top writing tip: when researching your topic, look out for specific terms and writing patterns used by other academics. It is likely that there will be a lot of jargon and important themes across research papers in your chosen dissertation topic.
2. Structure your dissertation or thesis
Writing a thesis is a unique experience and there is no general consensus on what the best way to structure it is.
As a postgraduate student , you’ll probably decide what kind of structure suits your research project best after consultation with your supervisor. You’ll also have a chance to look at previous masters students’ theses in your university library.
To some extent, all postgraduate dissertations are unique. Though they almost always consist of chapters. The number of chapters you cover will vary depending on the research.
A masters dissertation or thesis organised into chapters would typically look like this:
Write down your structure and use these as headings that you’ll write for later on.
Top writing tip : ease each chapter together with a paragraph that links the end of a chapter to the start of a new chapter. For example, you could say something along the lines of “in the next section, these findings are evaluated in more detail”. This makes it easier for the reader to understand each chapter and helps your writing flow better.
3. Write up your literature review
One of the best places to start when writing your masters dissertation is with the literature review. This involves researching and evaluating existing academic literature in order to identify any gaps for your own research.
Many students prefer to write the literature review chapter first, as this is where several of the underpinning theories and concepts exist. This section helps set the stage for the rest of your dissertation, and will help inform the writing of your other dissertation chapters.
What to include in your literature review
The literature review chapter is more than just a summary of existing research, it is an evaluation of how this research has informed your own unique research.
Demonstrate how the different pieces of research fit together. Are there overlapping theories? Are there disagreements between researchers?
Highlight the gap in the research. This is key, as a dissertation is mostly about developing your own unique research. Is there an unexplored avenue of research? Has existing research failed to disprove a particular theory?
Back up your methodology. Demonstrate why your methodology is appropriate by discussing where it has been used successfully in other research.
4. Write up your research
For instance, a more theoretical-based research topic might encompass more writing from a philosophical perspective. Qualitative data might require a lot more evaluation and discussion than quantitative research.
Methodology chapter
The methodology chapter is all about how you carried out your research and which specific techniques you used to gather data. You should write about broader methodological approaches (e.g. qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods), and then go into more detail about your chosen data collection strategy.
Data collection strategies include things like interviews, questionnaires, surveys, content analyses, discourse analyses and many more.
Data analysis and findings chapters
The data analysis or findings chapter should cover what you actually discovered during your research project. It should be detailed, specific and objective (don’t worry, you’ll have time for evaluation later on in your dissertation)
Write up your findings in a way that is easy to understand. For example, if you have a lot of numerical data, this could be easier to digest in tables.
This will make it easier for you to dive into some deeper analysis in later chapters. Remember, the reader will refer back to your data analysis section to cross-reference your later evaluations against your actual findings – so presenting your data in a simple manner is beneficial.
Think about how you can segment your data into categories. For instance, it can be useful to segment interview transcripts by interviewee.
Top writing tip : write up notes on how you might phrase a certain part of the research. This will help bring the best out of your writing. There is nothing worse than when you think of the perfect way to phrase something and then you completely forget it.
5. Discuss and evaluate
Once you’ve presented your findings, it’s time to evaluate and discuss them.
It might feel difficult to differentiate between your findings and discussion sections, because you are essentially talking about the same data. The easiest way to remember the difference is that your findings simply present the data, whereas your discussion tells the story of this data.
Your evaluation breaks the story down, explaining the key findings, what went well and what didn’t go so well.
In your discussion chapter, you’ll have chance to expand on the results from your findings section. For example, explain what certain numbers mean and draw relationships between different pieces of data.
Top writing tip: don’t be afraid to point out the shortcomings of your research. You will receive higher marks for writing objectively. For example, if you didn’t receive as many interview responses as expected, evaluate how this has impacted your research and findings. Don’t let your ego get in the way!
6. Write your introduction
Your introduction sets the scene for the rest of your masters dissertation. You might be wondering why writing an introduction isn't at the start of our step-by-step list, and that’s because many students write this chapter last.
Here’s what your introduction chapter should cover:
Problem statement
Research question
Significance of your research
This tells the reader what you’ll be researching as well as its importance. You’ll have a good idea of what to include here from your original dissertation proposal , though it’s fairly common for research to change once it gets started.
Writing or at least revisiting this section last can be really helpful, since you’ll have a more well-rounded view of what your research actually covers once it has been completed and written up.
Masters dissertation writing tips
When to start writing your thesis or dissertation.
When you should start writing your masters thesis or dissertation depends on the scope of the research project and the duration of your course. In some cases, your research project may be relatively short and you may not be able to write much of your thesis before completing the project.
But regardless of the nature of your research project and of the scope of your course, you should start writing your thesis or at least some of its sections as early as possible, and there are a number of good reasons for this:
Academic writing is about practice, not talent. The first steps of writing your dissertation will help you get into the swing of your project. Write early to help you prepare in good time.
Write things as you do them. This is a good way to keep your dissertation full of fresh ideas and ensure that you don’t forget valuable information.
The first draft is never perfect. Give yourself time to edit and improve your dissertation. It’s likely that you’ll need to make at least one or two more drafts before your final submission.
Writing early on will help you stay motivated when writing all subsequent drafts.
Thinking and writing are very connected. As you write, new ideas and concepts will come to mind. So writing early on is a great way to generate new ideas.
How to improve your writing skills
The best way of improving your dissertation or thesis writing skills is to:
Finish the first draft of your masters thesis as early as possible and send it to your supervisor for revision. Your supervisor will correct your draft and point out any writing errors. This process will be repeated a few times which will help you recognise and correct writing mistakes yourself as time progresses.
If you are not a native English speaker, it may be useful to ask your English friends to read a part of your thesis and warn you about any recurring writing mistakes. Read our section on English language support for more advice.
Most universities have writing centres that offer writing courses and other kinds of support for postgraduate students. Attending these courses may help you improve your writing and meet other postgraduate students with whom you will be able to discuss what constitutes a well-written thesis.
Read academic articles and search for writing resources on the internet. This will help you adopt an academic writing style, which will eventually become effortless with practice.
Keep track of your bibliography
The easiest way to keep the track of all the articles you have read for your research is to create a database where you can summarise each article/chapter into a few most important bullet points to help you remember their content.
Another useful tool for doing this effectively is to learn how to use specific reference management software (RMS) such as EndNote. RMS is relatively simple to use and saves a lot of time when it comes to organising your bibliography. This may come in very handy, especially if your reference section is suspiciously missing two hours before you need to submit your dissertation!
Avoid accidental plagiarism
Plagiarism may cost you your postgraduate degree and it is important that you consciously avoid it when writing your thesis or dissertation.
Occasionally, postgraduate students commit plagiarism unintentionally. This can happen when sections are copy and pasted from journal articles they are citing instead of simply rephrasing them. Whenever you are presenting information from another academic source, make sure you reference the source and avoid writing the statement exactly as it is written in the original paper.
What kind of format should your thesis have?
Read your university’s guidelines before you actually start writing your thesis so you don’t have to waste time changing the format further down the line. However in general, most universities will require you to use 1.5-2 line spacing, font size 12 for text, and to print your thesis on A4 paper. These formatting guidelines may not necessarily result in the most aesthetically appealing thesis, however beauty is not always practical, and a nice looking thesis can be a more tiring reading experience for your postgrad examiner .
When should I submit my thesis?
The length of time it takes to complete your MSc or MA thesis will vary from student to student. This is because people work at different speeds, projects vary in difficulty, and some projects encounter more problems than others.
Obviously, you should submit your MSc thesis or MA thesis when it is finished! Every university will say in its regulations that it is the student who must decide when it is ready to submit.
However, your supervisor will advise you whether your work is ready and you should take their advice on this. If your supervisor says that your work is not ready, then it is probably unwise to submit it. Usually your supervisor will read your final thesis or dissertation draft and will let you know what’s required before submitting your final draft.
Set yourself a target for completion. This will help you stay on track and avoid falling behind. You may also only have funding for the year, so it is important to ensure you submit your dissertation before the deadline – and also ensure you don’t miss out on your graduation ceremony !
To set your target date, work backwards from the final completion and submission date, and aim to have your final draft completed at least three months before that final date.
Don’t leave your submission until the last minute – submit your work in good time before the final deadline. Consider what else you’ll have going on around that time. Are you moving back home? Do you have a holiday? Do you have other plans?
If you need to have finished by the end of June to be able to go to a graduation ceremony in July, then you should leave a suitable amount of time for this. You can build this into your dissertation project planning at the start of your research.
It is important to remember that handing in your thesis or dissertation is not the end of your masters program . There will be a period of time of one to three months between the time you submit and your final day. Some courses may even require a viva to discuss your research project, though this is more common at PhD level .
If you have passed, you will need to make arrangements for the thesis to be properly bound and resubmitted, which will take a week or two. You may also have minor corrections to make to the work, which could take up to a month or so. This means that you need to allow a period of at least three months between submitting your thesis and the time when your program will be completely finished. Of course, it is also possible you may be asked after the viva to do more work on your thesis and resubmit it before the examiners will agree to award the degree – so there may be an even longer time period before you have finished.
How do I submit the MA or MSc dissertation?
Most universities will have a clear procedure for submitting a masters dissertation. Some universities require your ‘intention to submit’. This notifies them that you are ready to submit and allows the university to appoint an external examiner.
This normally has to be completed at least three months before the date on which you think you will be ready to submit.
When your MA or MSc dissertation is ready, you will have to print several copies and have them bound. The number of copies varies between universities, but the university usually requires three – one for each of the examiners and one for your supervisor.
However, you will need one more copy – for yourself! These copies must be softbound, not hardbound. The theses you see on the library shelves will be bound in an impressive hardback cover, but you can only get your work bound like this once you have passed.
You should submit your dissertation or thesis for examination in soft paper or card covers, and your university will give you detailed guidance on how it should be bound. They will also recommend places where you can get the work done.
The next stage is to hand in your work, in the way and to the place that is indicated in your university’s regulations. All you can do then is sit and wait for the examination – but submitting your thesis is often a time of great relief and celebration!
Some universities only require a digital submission, where you upload your dissertation as a file through their online submission system.
Related articles
What Is The Difference Between A Dissertation & A Thesis
How To Get The Most Out Of Your Writing At Postgraduate Level
Dos & Don'ts Of Academic Writing
Dispelling Dissertation Drama
Writing A Dissertation Proposal
Postgrad Solutions Study Bursaries

Exclusive bursaries Open day alerts Funding advice Application tips Latest PG news
Sign up now!

Take 2 minutes to sign up to PGS student services and reap the benefits…
- The chance to apply for one of our 5 PGS Bursaries worth £2,000 each
- Fantastic scholarship updates
- Latest PG news sent directly to you.

- Langson Library
- Science Library
- Grunigen Medical Library
- Law Library
- Connect From Off-Campus
- Accessibility
- Gateway Study Center

Email this link
Thesis / dissertation formatting manual (2024).
- Filing Fees and Student Status
- Submission Process Overview
- Electronic Thesis Submission
- Paper Thesis Submission
- Formatting Overview
- Fonts/Typeface
- Pagination, Margins, Spacing
- Paper Thesis Formatting
- Preliminary Pages Overview
- Copyright Page
- Dedication Page
- Table of Contents
- List of Figures (etc.)
- Acknowledgements
- Text and References Overview
- Figures and Illustrations
- Using Your Own Previously Published Materials
- Using Copyrighted Materials by Another Author
- Open Access and Embargoes
- Copyright and Creative Commons
- Ordering Print (Bound) Copies
- Tutorials and Assistance
- FAQ This link opens in a new window
UCI Libraries maintains the following templates to assist in formatting your graduate manuscript. If you are formatting your manuscript in Microsoft Word, feel free to download and use the template. If you would like to see what your manuscript should look like, PDFs have been provided. If you are formatting your manuscript using LaTex, UCI maintains a template on OverLeaf.
- Annotated Template (Dissertation) 2024 PDF of a template with annotations of what to look out for
- Word: Thesis Template 2024 Editable template of the Master's thesis formatting.
- PDF Thesis Template 2024
- Word: Dissertation Template 2024 Editable template of the PhD Dissertation formatting.
- PDF: Dissertation Template 2024
- Overleaf (LaTex) Template
- << Previous: Tutorials and Assistance
- Next: FAQ >>
- Last Updated: May 31, 2024 9:34 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uci.edu/gradmanual
Off-campus? Please use the Software VPN and choose the group UCIFull to access licensed content. For more information, please Click here
Software VPN is not available for guests, so they may not have access to some content when connecting from off-campus.

- Emergency Info
- Directories
- UR Self-Service
- Academic Calendars & Schedules

- Find a Person
- Search Classes & Build Schedule
- Future Grad Students
- Professional Programs
- MSc (Thesis Route)
- MSc (Project Route)
- MSc (Data Science)
- MSc (Human-Centred Computing)
- MSc (Course Route)
- Thesis Approval & Defence Procedures
- FGSR Regulations
- Course Descriptions
- Most Recent Course Syllabi
- Course Timetable
- Financial Support
- Graduate Program FAQ

- Undergraduate
- Classes & Labs
Thesis Examples
Latex Example (shortened M.Sc. with urthesis.sty) (ZIP)
Latex Example (complete M.Sc. with no .sty) (ZIP)
How to Write a M.Sc. Thesis
The following guide to writing an M.Sc. thesis was prepared by Howard Hamilton and Brien Maguire, based on previous guides by Alan Mackworth (University of British Columbia) and Nick Cercone (Simon Fraser University), with their permission.
Quick Guide to the M.Sc. Thesis
An acceptable M.Sc. thesis in Computer Science should attempt to satisfy one or more of the following criteria:
- Original research results are explained clearly and concisely.
- The thesis explains a novel exploratory implementation or a novel empirical study whose results will be of interest to the Computer Science community in general and to a portion of the Computer Science community in particular, e.g., Artificial Intelligence, Computational Complexity, etc.
- Novel implementation techniques are outlined, generalized, and explained.
- Theoretical results are obtained, explained, proven, and (worst, best, average) case analysis is performed where applicable.
- The implementation of a practical piece of nontrivial software whose availability could have some impact on the Computer Science community. Examples are a distributed file system for a mobile computing environment and a program featuring the application of artificial intelligence knowledge representation and planning techniques to intelligent computer assisted learning software.
Writing an acceptable thesis can be a painful and arduous task, especially if you have not written much before. A good methodology to follow, immediately upon completion of the required courses, is to keep a paper or electronic research notebook and commit to writing research oriented notes in it every day. From time to time, organize or reorganize your notes under headings that capture important categories of your thoughts. This journal of your research activities can serve as a very rough draft of your thesis by the time you complete your research. From these notes to a first M.Sc. thesis draft is a much less painful experience than to start a draft from scratch many months after your initial investigations. To help structure an M.Sc. thesis, the following guide may help.
One Formula for an M.Sc. Thesis for Computer Science
Chapter 1 Introduction: This chapter contains a discussion of the general area of research which you plan to explore in the thesis. It should contain a summary of the work you propose to carry out and the motivations you can cite for performing this work. Describe the general problem that you are working towards solving and the specific problem that you attempt to solve in the thesis. For example, the general problem may be finding an algorithm to help an artificial agent discover a path in a novel environment, and the specific problem may be evaluating the relative effectiveness and efficiency of five particular named approaches to finding the shortest path in a graph where each node is connected to at most four neighbours, with no knowledge of the graph except that obtained by exploration. This chapter should also explain the motivations for solving each of the general problem and your specific problem. The chapter should end with a guide to the reader on the composition and contents of the rest of the thesis, chapter by chapter. If there are various paths through the thesis, these should also be explained in Chapter 1.
Chapter 2 Limited Overview of the Field: This chapter contains a specialized overview of that part of a particular field in which you are doing M.Sc. thesis research, for example, paramodulation techniques for automated theorem proving or bubble figure modelling strategies for animation systems. The survey should not be an exhaustive survey but rather should impose some structure on your field of research endeavour and carve out your niche within the structure you impose. You should make generous use of illustrative examples and citations to current research.
Chapter 3 My Theory/Solution/Algorithm/Program: This chapter outlines your proposed solution to the specific problem described in Chapter 1. The solution may be an extension to, an improvement of, or even a disproof of someone else's theory / solution / method / ...).
Chapter 4 Description of Implementation or Formalism: This chapter describes your implementation or formalism. Depending on its length, it may be combined with Chapter 3. Not every thesis requires an implementation. Prototypical implementations are common and quite often acceptable although the guiding criterion is that the research problem must be clearer when you've completed your task than it was when you started!
Chapter 5 Results and Evaluation: This chapter should present the results of your thesis. You should choose criteria by which to judge your results, for example, the adequacy, coverage, efficiency, productiveness, effectiveness, elegance, user friendliness, etc., and then clearly, honestly and fairly adjudicate your results according to fair measures and report those results. You should repeat, whenever possible, these tests against competing or previous approaches (if you are clever you will win hands down in such comparisons or such comparisons will be obviated by system differences). The competing or previous approaches you compare against must have been introduced in Chapter 2 (in fact that may be the only reason they actively appear in Chapter 2) and you should include pointers back to Chapter 2. Be honest in your evaluations. If you give other approaches the benefit of the doubt every time, and develop a superior technique, your results will be all the more impressive.
Chapter 6 Conclusions: This chapter should summarize the achievements of your thesis and discuss their impact on the research questions you raised in Chapter 1. Use the distinctive phrasing "An original contribution of this thesis is" to identify your original contributions to research. If you solved the specific problem described in Chapter 1, you should explicitly say so here. If you did not, you should also make this clear. You should indicate open issues and directions for further or future work in this area with your estimates of relevance to the field, importance and amount of work required.
References Complete references for all cited works. This should not be a bibliography of everything you have read in your area.
Appendices include technical material (program listings, output, graphical plots of data, detailed tables of experimental results, detailed proofs, etc.) which would disrupt the flow of the thesis but should be made available to help explain or provide details to the curious reader.
- Privacy & Terms of Use
- Contact U of R
- Campus Maps
- U of R Home
- For Faculty and Staff
- City of Regina
What’s Included: The Dissertation Template
If you’re preparing to write your dissertation, thesis or research project, our free dissertation template is the perfect starting point. In the template, we cover every section step by step, with clear, straightforward explanations and examples .
The template’s structure is based on the tried and trusted best-practice format for formal academic research projects such as dissertations and theses. The template structure reflects the overall research process, ensuring your dissertation or thesis will have a smooth, logical flow from chapter to chapter.
The dissertation template covers the following core sections:
- The title page/cover page
- Abstract (sometimes also called the executive summary)
- Table of contents
- List of figures /list of tables
- Chapter 1: Introduction (also available: in-depth introduction template )
- Chapter 2: Literature review (also available: in-depth LR template )
- Chapter 3: Methodology (also available: in-depth methodology template )
- Chapter 4: Research findings /results (also available: results template )
- Chapter 5: Discussion /analysis of findings (also available: discussion template )
- Chapter 6: Conclusion (also available: in-depth conclusion template )
- Reference list
Each section is explained in plain, straightforward language , followed by an overview of the key elements that you need to cover within each section. We’ve also included practical examples to help you understand exactly what’s required in each section.
The cleanly-formatted Google Doc can be downloaded as a fully editable MS Word Document (DOCX format), so you can use it as-is or convert it to LaTeX.
FAQs: Dissertation Template
What format is the template (doc, pdf, ppt, etc.).
The dissertation template is provided as a Google Doc. You can download it in MS Word format or make a copy to your Google Drive. You’re also welcome to convert it to whatever format works best for you, such as LaTeX or PDF.
What types of dissertations/theses can this template be used for?
The template follows the standard best-practice structure for formal academic research projects such as dissertations or theses, so it is suitable for the vast majority of degrees, particularly those within the sciences.
Some universities may have some additional requirements, but these are typically minor, with the core structure remaining the same. Therefore, it’s always a good idea to double-check your university’s requirements before you finalise your structure.
Will this work for a research paper?
A research paper follows a similar format, but there are a few differences. You can find our research paper template here .
Is this template for an undergrad, Masters or PhD-level thesis?
This template can be used for a dissertation, thesis or research project at any level of study. It may be slight overkill for an undergraduate-level study, but it certainly won’t be missing anything.
How long should my dissertation/thesis be?
This depends entirely on your university’s specific requirements, so it’s best to check with them. As a general ballpark, Masters-level projects are usually 15,000 – 20,000 words in length, while Doctoral-level projects are often in excess of 60,000 words.
What about the research proposal?
If you’re still working on your research proposal, we’ve got a template for that here .
We’ve also got loads of proposal-related guides and videos over on the Grad Coach blog .
How do I write a literature review?
We have a wealth of free resources on the Grad Coach Blog that unpack how to write a literature review from scratch. You can check out the literature review section of the blog here.
How do I create a research methodology?
We have a wealth of free resources on the Grad Coach Blog that unpack research methodology, both qualitative and quantitative. You can check out the methodology section of the blog here.
Can I share this dissertation template with my friends/colleagues?
Yes, you’re welcome to share this template. If you want to post about it on your blog or social media, all we ask is that you reference this page as your source.
Can Grad Coach help me with my dissertation/thesis?
Within the template, you’ll find plain-language explanations of each section, which should give you a fair amount of guidance. However, you’re also welcome to consider our dissertation and thesis coaching services .

- Privacy Policy

Home » Thesis Format – Templates and Samples
Thesis Format – Templates and Samples
Table of contents.

Thesis Format
Thesis format refers to the structure and layout of a research thesis or dissertation. It typically includes several chapters, each of which focuses on a particular aspect of the research topic .
The exact format of a thesis can vary depending on the academic discipline and the institution, but some common elements include:
Introduction
Literature review, methodology.
The title page is the first page of a thesis that provides essential information about the document, such as the title, author’s name, degree program, university, and the date of submission. It is considered as an important component of a thesis as it gives the reader an initial impression of the document’s content and quality.
The typical contents of a title page in a thesis include:
- The title of the thesis: It should be concise, informative, and accurately represent the main topic of the research.
- Author’s name: This should be written in full and should be the same as it appears on official university records.
- Degree program and department: This should specify the type of degree (e.g., Bachelor’s, Master’s, or Doctoral) and the field of study (e.g., Computer Science, Psychology, etc.).
- University: The name of the university where the thesis is being submitted.
- Date of submission : The month and year of submission of the thesis.
- Other details that can be included on the title page include the name of the advisor, the name of the committee members, and any acknowledgments.
In terms of formatting, the title page should be centered horizontally and vertically on the page, with a consistent font size and style. The page margin for the title page should be at least 1 inch (2.54 cm) on all sides. Additionally, it is common practice to include the university logo or crest on the title page, and this should be placed appropriately.
Title of the Thesis in Title Case by Author’s Full Name in Title Case
A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Department Name at the University Name
Month Year of Submission
An abstract is a brief summary of a thesis or research paper that provides an overview of the main points, methodology, and findings of the study. It is typically placed at the beginning of the document, after the title page and before the introduction.
The purpose of an abstract is to provide readers with a quick and concise overview of the research paper or thesis. It should be written in a clear and concise language, and should not contain any jargon or technical terms that are not easily understood by the general public.
Here’s an example of an abstract for a thesis:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health among Adolescents
This study examines the impact of social media on mental health among adolescents. The research utilized a survey methodology and collected data from a sample of 500 adolescents aged between 13 and 18 years. The findings reveal that social media has a significant impact on mental health among adolescents, with frequent use of social media associated with higher levels of anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem. The study concludes that there is a need for increased awareness and education on the risks associated with excessive use of social media, and recommends strategies for promoting healthy social media habits among adolescents.
In this example, the abstract provides a concise summary of the thesis by highlighting the main points, methodology, and findings of the study. It also provides a clear indication of the significance of the study and its implications for future research and practice.
A table of contents is an essential part of a thesis as it provides the reader with an overview of the entire document’s structure and organization.
Here’s an example of how a table of contents might look in a thesis:
TABLE OF CONTENTS
I. INTRODUCTION ……………………………………………………..1
A. Background of the Study………………………………………..1
B. Statement of the Problem……………………………………….2
C. Objectives of the Study………………………………………..3
D. Research Questions…………………………………………….4
E. Significance of the Study………………………………………5
F. Scope and Limitations………………………………………….6
G. Definition of Terms……………………………………………7
II. LITERATURE REVIEW. ………………………………………………8
A. Overview of the Literature……………………………………..8
B. Key Themes and Concepts………………………………………..9
C. Gaps in the Literature………………………………………..10
D. Theoretical Framework………………………………………….11
III. METHODOLOGY ……………………………………………………12
A. Research Design………………………………………………12
B. Participants and Sampling……………………………………..13
C. Data Collection Procedures…………………………………….14
D. Data Analysis Procedures………………………………………15
IV. RESULTS …………………………………………………………16
A. Descriptive Statistics…………………………………………16
B. Inferential Statistics…………………………………………17
V. DISCUSSION ………………………………………………………18
A. Interpretation of Results………………………………………18
B. Discussion of Finding s …………………………………………19
C. Implications of the Study………………………………………20
VI. CONCLUSION ………………………………………………………21
A. Summary of the Study…………………………………………..21
B. Limitations of the Study……………………………………….22
C. Recommendations for Future Research……………………………..23
REFERENCES …………………………………………………………….24
APPENDICES …………………………………………………………….26
As you can see, the table of contents is organized by chapters and sections. Each chapter and section is listed with its corresponding page number, making it easy for the reader to navigate the thesis.
The introduction is a critical part of a thesis as it provides an overview of the research problem, sets the context for the study, and outlines the research objectives and questions. The introduction is typically the first chapter of a thesis and serves as a roadmap for the reader.
Here’s an example of how an introduction in a thesis might look:
Introduction:
The prevalence of obesity has increased rapidly in recent decades, with more than one-third of adults in the United States being classified as obese. Obesity is associated with numerous adverse health outcomes, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. Despite significant efforts to address this issue, the rates of obesity continue to rise. The purpose of this study is to investigate the relationship between lifestyle behaviors and obesity in young adults.
The study will be conducted using a mixed-methods approach, with both qualitative and quantitative data collection methods. The research objectives are to:
- Examine the relationship between lifestyle behaviors and obesity in young adults.
- Identify the key lifestyle factors that contribute to obesity in young adults.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of current interventions aimed at preventing and reducing obesity in young adults.
The research questions that will guide this study are:
- What is the relationship between lifestyle behaviors and obesity in young adults?
- Which lifestyle factors are most strongly associated with obesity in young adults?
- How effective are current interventions aimed at preventing and reducing obesity in young adults?
By addressing these research questions, this study aims to contribute to the understanding of the factors that contribute to obesity in young adults and to inform the development of effective interventions to prevent and reduce obesity in this population.
A literature review is a critical analysis and evaluation of existing literature on a specific topic or research question. It is an essential part of any thesis, as it provides a comprehensive overview of the existing research on the topic and helps to establish the theoretical framework for the study. The literature review allows the researcher to identify gaps in the current research, highlight areas that need further exploration, and demonstrate the importance of their research question.
April 9, 2023:
A search on Google Scholar for “Effectiveness of Online Learning during the COVID-19 Pandemic” yielded 1,540 results. Upon reviewing the first few pages of results, it is evident that there is a significant amount of literature on the topic. A majority of the studies focus on the experiences and perspectives of students and educators during the transition to online learning due to the pandemic.
One recent study published in the Journal of Educational Technology & Society (Liu et al., 2023) found that students who were already familiar with online learning tools and platforms had an easier time adapting to online learning than those who were not. However, the study also found that students who were not familiar with online learning tools were able to adapt with proper support from their teachers and institutions.
Another study published in Computers & Education (Tang et al., 2023) compared the academic performance of students in online and traditional classroom settings during the pandemic. The study found that while there were no significant differences in the grades of students in the two settings, students in online classes reported higher levels of stress and lower levels of satisfaction with their learning experience.
Methodology in a thesis refers to the overall approach and systematic process that a researcher follows to collect and analyze data in order to answer their research question(s) or achieve their research objectives. It includes the research design, data collection methods, sampling techniques, data analysis procedures, and any other relevant procedures that the researcher uses to conduct their research.
For example, let’s consider a thesis on the impact of social media on mental health among teenagers. The methodology for this thesis might involve the following steps:
Research Design:
The researcher may choose to conduct a quantitative study using a survey questionnaire to collect data on social media usage and mental health among teenagers. Alternatively, they may conduct a qualitative study using focus group discussions or interviews to gain a deeper understanding of the experiences and perspectives of teenagers regarding social media and mental health.
Sampling Techniques:
The researcher may use random sampling to select a representative sample of teenagers from a specific geographic location or demographic group, or they may use purposive sampling to select participants who meet specific criteria such as age, gender, or mental health status.
Data Collection Methods:
The researcher may use an online survey tool to collect data on social media usage and mental health, or they may conduct face-to-face interviews or focus group discussions to gather qualitative data. They may also use existing data sources such as medical records or social media posts.
Data Analysis Procedures:
The researcher may use statistical analysis techniques such as regression analysis to examine the relationship between social media usage and mental health, or they may use thematic analysis to identify key themes and patterns in the qualitative data.
Ethical Considerations: The researcher must ensure that their research is conducted in an ethical manner, which may involve obtaining informed consent from participants, protecting their confidentiality, and ensuring that their rights and welfare are respected.
In a thesis, the “Results” section typically presents the findings of the research conducted by the author. This section typically includes both quantitative and qualitative data, such as statistical analyses, tables, figures, and other relevant data.
Here are some examples of how the “Results” section of a thesis might look:
Example 1: A quantitative study on the effects of exercise on cardiovascular health
In this study, the author conducts a randomized controlled trial to investigate the effects of exercise on cardiovascular health in a group of sedentary adults. The “Results” section might include tables showing the changes in blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and other relevant indicators in the exercise and control groups over the course of the study. The section might also include statistical analyses, such as t-tests or ANOVA, to demonstrate the significance of the results.
Example 2: A qualitative study on the experiences of immigrant families in a new country
In this study, the author conducts in-depth interviews with immigrant families to explore their experiences of adapting to a new country. The “Results” section might include quotes from the interviews that illustrate the participants’ experiences, as well as a thematic analysis that identifies common themes and patterns in the data. The section might also include a discussion of the implications of the findings for policy and practice.
A thesis discussion section is an opportunity for the author to present their interpretation and analysis of the research results. In this section, the author can provide their opinion on the findings, compare them with other literature, and suggest future research directions.
For example, let’s say the thesis topic is about the impact of social media on mental health. The author has conducted a survey among 500 individuals and has found that there is a significant correlation between excessive social media use and poor mental health.
In the discussion section, the author can start by summarizing the main findings and stating their interpretation of the results. For instance, the author may argue that excessive social media use is likely to cause mental health problems due to the pressure of constantly comparing oneself to others, fear of missing out, and cyberbullying.
Next, the author can compare their results with other studies and point out similarities and differences. They can also identify any limitations in their research design and suggest future directions for research.
For example, the author may point out that their study only measured social media use and mental health at one point in time, and it is unclear whether one caused the other or whether there are other confounding factors. Therefore, they may suggest longitudinal studies that follow individuals over time to better understand the causal relationship.
Writing a conclusion for a thesis is an essential part of the overall writing process. The conclusion should summarize the main points of the thesis and provide a sense of closure to the reader. It is also an opportunity to reflect on the research process and offer suggestions for further study.
Here is an example of a conclusion for a thesis:
After an extensive analysis of the data collected, it is evident that the implementation of a new curriculum has had a significant impact on student achievement. The findings suggest that the new curriculum has improved student performance in all subject areas, and this improvement is particularly notable in math and science. The results of this study provide empirical evidence to support the notion that curriculum reform can positively impact student learning outcomes.
In addition to the positive results, this study has also identified areas for future research. One limitation of the current study is that it only examines the short-term effects of the new curriculum. Future studies should explore the long-term effects of the new curriculum on student performance, as well as investigate the impact of the curriculum on students with different learning styles and abilities.
Overall, the findings of this study have important implications for educators and policymakers who are interested in improving student outcomes. The results of this study suggest that the implementation of a new curriculum can have a positive impact on student achievement, and it is recommended that schools and districts consider curriculum reform as a means of improving student learning outcomes.
References in a thesis typically follow a specific format depending on the citation style required by your academic institution or publisher.
Below are some examples of different citation styles and how to reference different types of sources in your thesis:
In-text citation format: (Author, Year)
Reference list format for a book: Author, A. A. (Year of publication). Title of work: Capital letter also for subtitle. Publisher.
Example: In-text citation: (Smith, 2010) Reference list entry: Smith, J. D. (2010). The art of writing a thesis. Cambridge University Press.
Reference list format for a journal article: Author, A. A., Author, B. B., & Author, C. C. (Year of publication). Title of article. Title of Journal, volume number(issue number), page range.
Example: In-text citation: (Brown, 2015) Reference list entry: Brown, E., Smith, J., & Johnson, L. (2015). The impact of social media on academic performance. Journal of Educational Psychology, 108(3), 393-407.
In-text citation format: (Author page number)
Works Cited list format for a book: Author. Title of Book. Publisher, Year of publication.
Example: In-text citation: (Smith 75) Works Cited entry: Smith, John D. The Art of Writing a Thesis. Cambridge University Press, 2010.
Works Cited list format for a journal article: Author(s). “Title of Article.” Title of Journal, volume number, issue number, date, pages.
Example: In-text citation: (Brown 394) Works Cited entry: Brown, Elizabeth, et al. “The Impact of Social Media on Academic Performance.” Journal of Educational Psychology, vol. 108, no. 3, 2015, pp. 393-407.
Chicago Style
In-text citation format: (Author year, page number)
Bibliography list format for a book: Author. Title of Book. Place of publication: Publisher, Year of publication.
Example: In-text citation: (Smith 2010, 75) Bibliography entry: Smith, John D. The Art of Writing a Thesis. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2010.
Bibliography list format for a journal article: Author. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal volume number, no. issue number (date): page numbers.
Example: In-text citation: (Brown 2015, 394) Bibliography entry: Brown, Elizabeth, John Smith, and Laura Johnson. “The Impact of Social Media on Academic Performance.” Journal of Educational Psychology 108, no. 3 (2015): 393-407.
Reference list format for a book: [1] A. A. Author, Title of Book. City of Publisher, Abbrev. of State: Publisher, year.
Example: In-text citation: [1] Reference list entry: A. J. Smith, The Art of Writing a Thesis. New York, NY: Academic Press, 2010.
Reference list format for a journal article: [1] A. A. Author, “Title of Article,” Title of Journal, vol. x, no. x, pp. xxx-xxx, Month year.
Example: In-text citation: [1] Reference list entry: E. Brown, J. D. Smith, and L. Johnson, “The Impact of Social Media on Academic Performance,” Journal of Educational Psychology, vol. 108, no. 3, pp. 393-407, Mar. 2015.
An appendix in a thesis is a section that contains additional information that is not included in the main body of the document but is still relevant to the topic being discussed. It can include figures, tables, graphs, data sets, sample questionnaires, or any other supplementary material that supports your thesis.
Here is an example of how you can format appendices in your thesis:
- Title page: The appendix should have a separate title page that lists the title, author’s name, the date, and the document type (i.e., thesis or dissertation). The title page should be numbered as the first page of the appendix section.
- Table of contents: If you have more than one appendix, you should include a separate table of contents that lists each appendix and its page number. The table of contents should come after the title page.
- Appendix sections: Each appendix should have its own section with a clear and concise title that describes the contents of the appendix. Each section should be numbered with Arabic numerals (e.g., Appendix 1, Appendix 2, etc.). The sections should be listed in the table of contents.
- Formatting: The formatting of the appendices should be consistent with the rest of the thesis. This includes font size, font style, line spacing, and margins.
- Example: Here is an example of what an appendix might look like in a thesis on the topic of climate change:
Appendix 1: Data Sources
This appendix includes a list of the primary data sources used in this thesis, including their URLs and a brief description of the data they provide.
Appendix 2: Survey Questionnaire
This appendix includes the survey questionnaire used to collect data from participants in the study.
Appendix 3: Additional Figures
This appendix includes additional figures that were not included in the main body of the thesis due to space limitations. These figures provide additional support for the findings presented in the thesis.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Dissertation Methodology – Structure, Example...

What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and...

Dissertation – Format, Example and Template

Dissertation vs Thesis – Key Differences
Master Thesis/Project Report Format
Guidelines for preparation of master thesis/project report, overview of the steps.
- Select master project/thesis advisor.
- Select a project topic.
- Select a committee.
- Obtain approvals for committee, advisor.
- Register for the master project/thesis course with thesis advisor. (A section number will be provided to you by your project/thesis advisor.)
- Start Research on your master project.
- (Optional) Present a thesis proposal to the committee during mid-way of the thesis.
- Write project report/thesis.
- Present your master project and/or defend thesis.
- Submit your master project report, or publish thesis.
Project/Thesis Option
Discuss with your master project advisor at the beginning to decide whether your master project will be more suited for the project or thesis option.

Questions to ask when evaluating your master project topic:
- Is there current interest in this topic in the field?
- Is there is a gap in knowledge that work on this topic could help to fill?
- Is it possible to focus on a manageable segment of this topic?
- Identify a preliminary method of data collection that is acceptable to your advisor.
- Is there a body of literature is available that is relevant to your topic?
- Do you need financial assistance to carry out your research?
- Is the data necessary to complete your work is easily accessible?
- Define the project purpose, scope, objectives, and procedures.
- What are the potential limitations of the study?
- Are there any skills called on by the study that you have yet to acquire?
Master level project involves:
- Analyzing the problem or topic.
- Conducting extensive research.
- Summarizing findings from the research investigation.
- Recommending additional research on the topic.
- Drawing conclusions and making recommendations.
- Documenting the results of the research.
- Defending conclusions and recommendations.
Pre-Thesis Planning
When you’re contemplating a thesis topic, you should discuss your interests with as many people as possible to gain a broad perspective. You will find your faculty advisor knowledgeable and willing to offer excellent suggestions and advice regarding an appropriate thesis topic.
Give considerable thought to the identification and planning of a thesis topic. Review literature related to your interests; read a variety of research papers, abstracts, and proposals for content, methods and structure. Looking at completed master’s theses will be a useful activity toward expanding inquiry skills and thought processes.
After the thesis advisor is selected, you may register on-line for a thesis section. You will need to see your thesis instructor to obtain the thesis section number.
Suggested Master Project/Thesis Completion Timeline
Below please find a suggested timeline. Individual timelines may vary from one student to another.
Required Deadlines
- The approval page with all signatures must be submitted to the graduate advisor prior to the last day of the semester.
- The thesis must be submitted electronically prior to the last day of classes. The last day of class can be identified in the on-line Academic calendar.
Scholarship Possibilities
Funding is usually available to students with expertise to the specific area. You will want to research scholarship options during the pre-project planning as many scholarship applications are due months before the award is granted.
- Research assistantship with a faculty advisor related to the topic of research
- Teaching assistantship to teach an undergraduate laboratory
- Check with Career Center for on-campus positions
- Attend all career fairs that would be of interest to consider summer internships
- SPIE (The International Society for Optics and Photonics)
- ISA (International Society of Automation)
More opportunities exist; you will need to search for scholarships based on your topic of research.
Citing Sources
The Technology Division at the Cullen College of Engineering* does not mandate citation styles, but you must cite your sources and cite them consistently. Here are some helpful links to assist you with citation:
- Landmark's Son of a Citation Machine
- Wikipedia Citation Templates
*The Human Development Consumer Science department prefers you to use the APA style. Please consult with your thesis advisor when choosing a citation style .
Thesis Quality
The Technology Division at the Cullen College of Engineering has significant expectations with regard to thesis quality. Poor or average level theses will not receive college approvals. It is the joint responsibility of the student and the committee to ensure that the thesis is of acceptable quality. Ultimately, the task is one borne by the student as the thesis is a reflection of the quality of their work. The thesis committee can direct the student to seek assistance if quality issues are noticed as the chapters are developed. The student should take quality feedback seriously and not wait until the end to attempt to fix this type of problem as it can result in significant delays and postponement of graduation. When you write and defend your thesis, keep the following guidelines in mind:
- Shows a cursory examination of the topic.
- Makes little use of existing data sources.
- Fails to examine primary sources.
- Shows little comprehension of crucial texts or research in the subject matter.
- Lacks adequate organization.
- Treats the topic in a competent, straightforward way.
- Shows a good grasp of the material.
- Makes use of existing data sources in a competent fashion or shows a good acquaintance with primary sources and current research.
- Shows a solid comprehension of research in the subject matter
- Sustains a line of argumentation throughout the thesis
- Shows all of the above qualities of a quality thesis as well as some measure of originality in research. Originality is defined as developing new data; treating existing data in an original or particularly compelling way; developing new or particularly compelling theoretical arguments; interpreting existing research in an original or particularly compelling way; or bringing primary or secondary materials and research together to sustain a new, comprehensive or compelling interpretation. In general, a thigh quality thesis either shows some measure of originality in its argument or empirical base; or is in some other way striking or new.
Organization of Thesis
The original and copies of the thesis MUST include the following items IN THE ORDER LISTED :
- Blank sheet of bond paper at the beginning of each copy submitted.
- Copyright page (optional).
- Title Page (must show month and year of graduation - see example).
- Signature page (see example). All three required copies must have ORIGINAL SIGNATURES of the committee and the student. Signatures must be in black ink. This page should be omitted from the electronic thesis.
- Acknowledgment (optional).
- Abstract Title Page (optional - must show month and year of graduation - see example).
- Abstract (optional - University Microfilms, Inc. requires abstracts be no longer than 150 words.).
- Table of Contents.
- References.
Style Requirements
Although there is no prescribed style for the completed thesis, there are several style manuals available which may prove helpful. The student should contact the thesis advisor to discuss the style manual to be used. Above all, it is important to be consistent throughout the entire thesis. Decide how you wish to structure your manuscript and be consistent throughout it.
Steps in the Submission of Electronic Dissertation/Thesis
- Write your thesis per Technology Division at the Cullen College of Engineering thesis guidelines.
- Successfully defend your thesis. Make corrections per the thesis committee.
- Committee signs the approval page.
- Submit a copy of the final thesis version to the Associate Dean for Research for Graduate Studies or your graduate advisor for formatting review a minimum of two weeks prior to the end of the semester.
- Wait for formatting approval before beginning electronic submission process.
Electronic Submission
- Create a single pdf file of the thesis. The signature page is NOT included in the online submission.
- Submit the signed approval page to your graduate advisor. Approval page is stored in the student’s file. ET students must also submit rubric sheets, one for each committee member.
- Please note you will be asked if you would like to embargo your work, request a journal hold or a patent hold. Be sure to check with your committee chair about these features and whether your committee chair will approve them.
- Uploading the thesis requires an active Cougarnet account and log in. If you have not used your Cougarnet account in more than 90 days, please contact the ETD administrator for assistance.
- You will receive an e-mail confirming your upload to TDL. Please forward this email to your graduate advisor.
- Wait for confirmation from your faculty chair and graduate advisor that your document has been accepted.
- Email your committee chair requesting approval of your submission. Also request approval of the embargo, if applicable.
Specifications
The font should be Times New Roman, 12 pt. font
The margins should be one inch (1") each
Electronic Copy Submission
All CCE Technology Division theses submitted in an electronic format may be hosted on the College webpage. You must submit an electronic copy of the thesis in pdf format that accurately represents the printed version of the final document.
- Copyright Page Example
- Title Page Example
- Signature Page Example
- Acknowledgements Page Example
- Abstract Title Page
- Abstract Page
- A Message from the Senior Associate Dean
- Giving to the CCE Technology Division
- Our Mission
- Our History
- Technology Division Facilities
- Assessment & Accreditation
- Instructional Design
- Technical Support
- Web Technologies
- Information for Undergraduate Students
- Information for Graduate Students
- Transfer Students
- Veteran Students
- Contact + Request Info
- Student Experience Workshops
- See an Advisor
- Advising Forms
- Scholarships
- Career Services
- Laptop Policy
- Construction Management
- Engineering Technology
- Human Development and Consumer Sciences
- Information Science Technology
- Undergraduate Degree Programs
- Undergraduate Minors
- Graduate Degree Programs
- Professional & Certificate Programs
- Online Programs
- For Recruiters
- Career Resources
- Faculty & Staff
- Administrative Staff
- Boards of Advisors
- For Faculty and Staff
- Transition to UH at Sugar Land
Graduate Studies
Completing your masters degree – thesis.
Your first step regarding any questions with respect to writing your thesis is to consult the School of Graduate Studies’ Guide for the Preparation of Master’s and Doctoral Theses . All graduate theses must conform to the style and form requirements as detailed in the Guide.
Step 1. Write
Need help? If you have any questions or need assistance, please email [email protected].
1. Sample formats
Please consult the Guide for the Preparation of Theses for samples on how to format your thesis.
2. Referencing
Per the Guide for the Preparation of Theses: The text of the standard graduate thesis consists of the Introduction section or chapter, followed by several well-defined sections or chapters, which contain the research results, finishing with a Conclusion and Discussion section or chapter, or a summary statement of the results of the investigation. The List of References section (or bibliography) follows the text, and any appendices follow this.
Please consult the Guide for the Preparation of Theses for more detailed information on references and further resources that you can consult for referencing help.
3. Sandwich theses
If some of the research undertaken expressly for the degree has previously been published or prepared by the student as one or more journal articles, or parts of books, those items may be included within the thesis subject to the School of Graduate Studies’ regulations and to obtaining permission from the supervisory committee.
Please consult the Guide for the Preparation Theses – download via Quick Links to the right – for more detailed information on Sandwich Theses.
4. E-Thesis file name conventions
For your e-thesis to be published via MacSphere, the final version of your thesis should be named using the following file naming convention:
familyname_firstname_middleinitial_finalsubmissionyearmonth_degree
5. iThenticate - Plagiarism Checking Software
Effective December 1, 2023, all graduate students who initiate their defence on or after this date, are required to have their thesis run through McMaster’s plagiarism checking software, iThenticate.
iThenticate is a similarity detection tool meant to be used by researchers to check any original works that will be publicly released and who are concerned about potential plagiarism.
According to McMaster’s Research Plagiarism Checking Policy , it is expected that all graduate theses, shall be checked for plagiarism in compliance with this policy. Plagiarism checking is expected to occur prior to the coordination of the defence. Supervisors of Master’s students will need to sign a separate attestation sheet indicating that this has occurred and the document is satisfactory for public disclosure.
Your pre-defence thesis must be uploaded to iThenticate by your primary supervisor before you can initiate your Masters defence.
To protect graduate students’ privacy, only academic supervisors will have access to this software and will be responsible for uploading their student’s theses. It should not be used to check documents submitted to instructors as course assignments.
Step 2. Defend
Before initiating your defence, you should confirm with your supervisor and committee members if applicable, that you are ready to initiate. Your supervisor must also sign a separate attestation sheet prior to initiation, indicating that they have run your thesis through iThenticate and it is satisfactory for public disclosure. Once this is done, contact your department to confirm the program’s defence process. After a successful defence, the chair of the examination committee will inform you of thesis changes required by examiners. After all changes have been made, you must submit this completed form to the School of Graduate Studies for your final submission to be published to MacSphere.
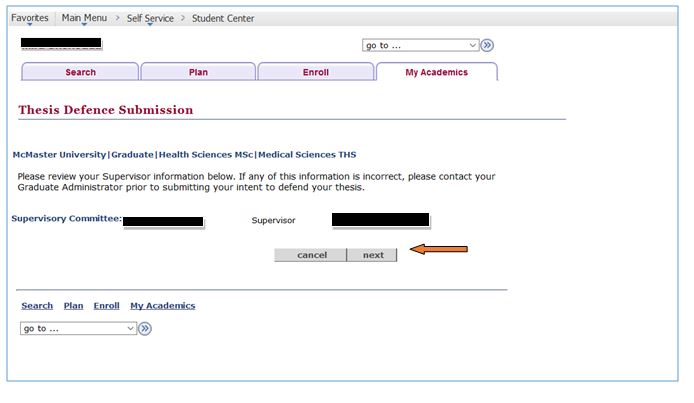
Thesis Defence Submission
You can now check supervisor(s) and academic plan(s)
If any of this information is incorrect, you should contact to your program office before proceeding.
Date and time
For dates and deadlines for defence and upcoming convocation ceremonies please refer to the Dates and Deadlines .
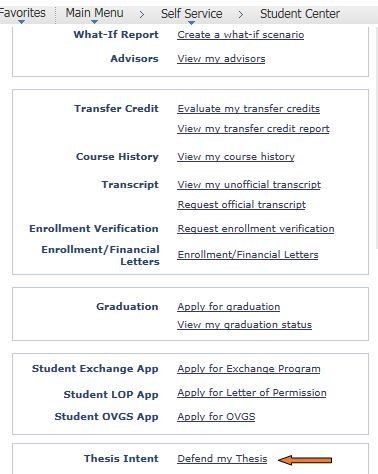
This step allows you to propose a date, time and location. This information will be confirmed by your program office, as they will receive notification after you have completed this process.
Please note your thesis title is required, but you can also add an abstract at this stage.
Please be aware after submission, your program office will assist you with the rest of the process and you should contact them to ensure that all arrangements have been put in place for your defence.
Review and submit
You will be given an opportunity to review before submission. Once you have submitted you will receive a confirmation email that you have successfully initiated the process.
Initiation of Masters defence process
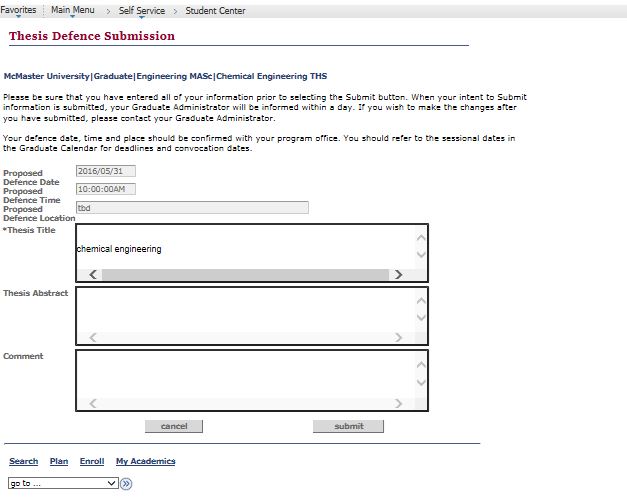
Select My Academics in the Academic tab.
Submission of Intent to initiate a Masters defence
Please consult with your department to see if they require that you initiate a Master’s Defence in Mosaic. All departments will need you to contact your Graduate Administrator to let them know you plan on defending your Master’s thesis. SGS does not require that you initiate a Master’s Defence in Mosaic but your department may have a different requirement. All PhD Defences MUST be initiated in Mosaic.
If your department requires that you initiate
You should select – Thesis Intent – Defend Thesis
This selection is only possible if you are enrolled a research plan type. If the student needs to switch to a research plan type, you should submit a service request for a plan change before initiating the thesis defence process.
Step 3. Submit
Please note that your degree requirements are considered complete when one electronic copy of the thesis, revised as directed by your defence examining committee, is submitted to the School of Graduate Studies through the E-Thesis Submission module in MacSphere.
Final thesis checklist
- ONE electronic copy of the thesis, revised as recommended by the Thesis Examining Committee and approved by the Supervisor/Examining Committee
- A standard 10-12 point font has been used
- TOP and LEFT margins should be 3.8 cm, and RIGHT and BOTTOM margins should be 2.5 cm
- Half-title page
- Descriptive note
- Abstract of 300 words or less
- All preliminary pages are numbered in lower case Roman numerals
- All pages must be numbered. The main body of the thesis, including text, bibliography and appendices, must be numbered continuously using Arabic numerals.
If you have not already done so, please submit the following forms to your department’s graduate administrator. They will submit them to the School of Graduate Studies on your behalf. Your final submission will not be considered complete without this documentation.
- Final Thesis Submission Sheet
- Copyright Permission Form
- Library and Archives Canada Licence (PhD only)
- McMaster University Licence
If you have completed all of the above requirements, you are ready to submit to your thesis.
E-thesis process
- Submit your electronic thesis to MacSphere . Please follow the link and click on ‘Sign on to my MacSphere’ to deposit your thesis. Ensure your thesis is uploaded as a pdf document. Any supporting material can be uploaded in various formats.
- E-thesis file name conventions. For your e-thesis to be published via MacSphere, the final version of your thesis should be named using the following file naming convention:
familyname_firstname_middleinitial_finalsubmissionyearmonth_degree.pdf
How to submit a thesis to MacSphere
- Go to MacSphere.
- On top/right corner click on Sign onto My MacSphere and log in with your MAC ID.
- Click on Start a New Submission .
- Select Collection: Open Access Dissertations and Theses , and click on Manual Submission to begin submitting your dissertation.
- Complete the submission screens as prompted. Once you click on I Grant The License your dissertation will be submitted to SGS for processing.
Links to e-theses in MacSphere are available through a variety of tools. The contents of MacSphere are Google indexed, bringing McMaster scholarship to the attention of a broad range of users. Automated tools will continue to integrate e-theses with other print and electronic library resources in both the local catalogue and integrated catalogues, such as WorldCat.
Theses in physical formats have historically been low-use library materials, however digitized theses are receiving higher usage. Site statistics for theses currently available in McMaster’s MacSphere show several each month are downloaded more than 100 times and many others have multiple downloads.
Embargoed or withheld theses
Embargoed status is intended to protect rights for immediate commercial publication, to obtain a patent which may rise from the research, or as a result of any contract made with a third party. The student may request a postponement of digital publication for up to one year at the time of thesis submission to MacSphere – all such requests are automatically granted. Students who would like to extend this initial period of postponement must apply to the thesis coordinator who will forward the request to the Vice-Provost and Dean of Graduate Studies for determination of whether further publication postponement is warranted. This request must include a full description of why the additional delay is requested and what steps have been taken to address the issues that required the initial delay. No delay of publication more than two years from the initial submission will be permitted.
Please note that you and your supervisor must both sign the delay of publication area on your Final Thesis Submission Sheet. For more information, consult the School of Graduate Studies Calendar .
E-thesis binding
If you choose to have your thesis bound, binding service is available through pageforpage.com . Via their website, you can print, bind and send your thesis where you wish. However, this is only an option; you may use any binding service that you prefer.
Optional Bound Copies – Should the supervisor and/or department require one or more bound paper copies of your thesis, it is the student’s responsibility to obtain and distribute these bound copies.
Apart from these considerations, the general guidelines for thesis production should be followed.
- Graduate School
- Location Location
- Contact Contact
- Colleges and Schools
- Thesis & Dissertation
Formatting Your Thesis or Dissertation
The Graduate School has strict guidelines for formatting your thesis or dissertation document. Be sure to follow all formatting requirements or you will have to make changes and resubmit.
July 5: Format Check Deadline for Thesis/Dissertation July 15: Graduation Application Deadline July 15: Defense Deadline July 22: Final Submission Deadline August 15 : Official Date of Graduation* *Summer 2024 graduates will participate in commencement ceremonies December 16, 2024
Try to submit your thesis or dissertation document early. That way, you'll have more time to make any necessary formatting changes.
Preparing Your Document
We require consistency in form and appearance for all thesis and dissertation documents. Be sure to follow all formatting guidelines so you can avoid having to make changes and resubmit your document.
Formatting Guide
Every thesis and dissertation must conform to the requirements in this guide to be accepted. If your thesis or dissertation document is not accepted on the first try, you will be required to make the necessary changes and resubmit.
Spring 2024 Formatting Workshops
Graduate students are invited to attend free in-person or virtual formatting workshops to help format your thesis or dissertation. Visit the thesis & dissertation workshop calendar for a list of events and registration links.
Additional Formatting Resources
The Graduate School offers a variety of video presentations, workshops, samples and templates to assist with the thesis & dissertation formatting process.
Thesis & Dissertation Formatting Demonstration (Video)
- This demonstration should be used in conjunction with the Thesis & Dissertation Formatting Guide .
MS Word Template Workshop (Video)
- Learn tips and formatting requirements specific to Word in this recorded session.
Thesis & Dissertation Formatting Workshops (Video)
- Learn the basics about formatting, submitting, and finalizing your thesis or dissertation with recorded formatting workshop sessions. ( 2/10/22 or 2/16/22 )
How To Resubmit a Revised PDF in ProQuest (Video)
- Learn how to submit your thesis or dissertation in ProQuest after you have made revisions.
- Dissertation Sample with Notes
- Dissertation Sample without Notes
- Thesis Sample with Notes
- Thesis Sample without Notes
- Preliminary Format Check Sample without Notes
- Preliminary Format Check Sample with Notes
- Manuscript Style Final Submission without Notes
- Manuscript Style Final Submission with Notes
Formatting Templates
- Preformatted Templates »
- LaTeX Files »
Upcoming Events
Thesis & dissertation formatting workshop.
Tuesday, Jun. 4, 2024
Location: Russell House University Union 302
Friday, Jun. 21, 2024
Challenge the conventional. Create the exceptional. No Limits.
- Search Menu
- Sign in through your institution
- Advance Articles
- Editor's Choice
- Braunwald's Corner
- ESC Guidelines
- EHJ Dialogues
- Issue @ a Glance Podcasts
- CardioPulse
- Weekly Journal Scan
- European Heart Journal Supplements
- Year in Cardiovascular Medicine
- Asia in EHJ
- Most Cited Articles
- ESC Content Collections
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Why publish with EHJ?
- Open Access Options
- Submit from medRxiv or bioRxiv
- Author Resources
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Read & Publish
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Advertising
- Reprints and ePrints
- Sponsored Supplements
- Journals Career Network
- About European Heart Journal
- Editorial Board
- About the European Society of Cardiology
- ESC Publications
- War in Ukraine
- ESC Membership
- ESC Journals App
- Developing Countries Initiative
- Dispatch Dates
- Terms and Conditions
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic
Article Contents
Risk of heart failure in inflammatory bowel disease: a swedish population-based study.
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Jiangwei Sun, Jialu Yao, Ola Olén, Jonas Halfvarson, David Bergman, Fahim Ebrahimi, Annika Rosengren, Johan Sundström, Jonas F Ludvigsson, Risk of heart failure in inflammatory bowel disease: a Swedish population-based study, European Heart Journal , 2024;, ehae338, https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehae338
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Dysregulation of inflammatory and immune responses has been implicated in the pathogenesis of heart failure (HF). But even if inflammation is a prerequisite for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), little is known about HF risk in IBD.
In this Swedish nationwide cohort, patients with biopsy-confirmed IBD were identified between 1969 and 2017 [n = 81,749, Crohn’s disease (CD, n = 24,303), ulcerative colitis (UC, n = 45,709), and IBD-unclassified (IBD-U, n = 11,737)]. Each patient was matched with up to five general population reference individuals (n = 382,190) and IBD-free full siblings (n = 95,239) and followed until 31 December 2019. Flexible parametric survival models estimated the adjusted hazard ratio (aHR) and standardized cumulative incidence for HF, with 95% confidence intervals (CI).
There were 5,582 incident HF identified in IBD patients (incidence rate [IR]: 50.3/10,000 person-years) and 20,343 in reference individuals (IR: 37.9) during a median follow-up of 12.4 years. IBD patients had a higher risk of HF than reference individuals (aHR 1.19, 95% CI 1.15 to 1.23). This increased risk remained significant ≥20 years after IBD diagnosis, leading to one extra HF case per 130 IBD patients until then. The increased risk was also observed across IBD subtypes: CD (IR: 46.9 vs. 34.4; aHR 1.28 [1.20 to 1.36]), UC (IR: 50.1 vs. 39.7; aHR 1.14 [1.09 to 1.19]), and IBD-U (IR: 60.9 vs. 39.0; aHR 1.28 [1.16 to 1.42]). Sibling-controlled analyses showed slightly attenuated association (IBD: aHR 1.10 [1.03 to 1.19]).
Patients with IBD had a moderately higher risk of developing HF for ≥20 years after IBD diagnosis than the general population.

- heart failure
- inflammatory bowel disease
Supplementary data
Email alerts, companion article.
- Human Immunology of Heart Failure: Deconstructing Inflammatory Risk
Related articles in PubMed
Citing articles via, looking for your next opportunity, affiliations.
- Online ISSN 1522-9645
- Print ISSN 0195-668X
- Copyright © 2024 European Society of Cardiology
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.

COMMENTS
Writing a masters dissertation or thesis is a sizable task. It takes a considerable amount of research, studying and writing. Usually, students need to write around 10,000 to 15,000 words. It is completely normal to find the idea of writing a masters thesis or dissertation slightly daunting, even for students who have written one before at ...
Prize-Winning Thesis and Dissertation Examples. Published on September 9, 2022 by Tegan George.Revised on July 18, 2023. It can be difficult to know where to start when writing your thesis or dissertation.One way to come up with some ideas or maybe even combat writer's block is to check out previous work done by other students on a similar thesis or dissertation topic to yours.
consistent formatting of the thesis. The paragraphs are indented consistently thorough the thesis. The recommended spacing is 0.5" from the left margin. The text is generally left aligned but justified is also acceptable. 1.1.1. Second Level Headings The Second level and subsequent headings can be formatted as above. These are first letter ...
Time to recap…. And there you have it - the traditional dissertation structure and layout, from A-Z. To recap, the core structure for a dissertation or thesis is (typically) as follows: Title page. Acknowledgments page. Abstract (or executive summary) Table of contents, list of figures and tables.
1.2 The dissertation Solving the problems of the MSc project is only the first half of the work. The results of the investigation are reported in the MSc dissertation. In writing a dissertation you no longer just reproduce, you produce. It is the product that counts, not the effort.
Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates. Published on June 7, 2022 by Tegan George.Revised on November 21, 2023. A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical early steps in your writing process.It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding the specifics of your dissertation topic and showcasing its relevance to ...
UCI Libraries maintains the following templates to assist in formatting your graduate manuscript. If you are formatting your manuscript in Microsoft Word, feel free to download and use the template. ... Editable template of the PhD Dissertation formatting. PDF: Dissertation Template 2024. Overleaf (LaTex) Template << Previous: Tutorials and ...
It can be helpful to think of your Masters dissertation as a series of closely interlinked essays, rather than one overwhelming paper. The size of this section will depend on the overall word count for your dissertation. However, to give you a rough idea for a 15,000-word dissertation, the discussion part will generally be about 12,000 words long.
FORMATTING GUIDELINES . The Dissertation must meet international standard in terms of quality. The Dissertation should be printed in English, in the third person. Students are advised to refer to the following format for the Dissertation write-up: Length. There is no prescribed length to the Dissertation; however, a good guide would be around 60
To help structure an M.Sc. thesis, the following guide may help. One Formula for an M.Sc. Thesis for Computer Science. Chapter 1 Introduction: This chapter contains a discussion of the general area of research which you plan to explore in the thesis. It should contain a summary of the work you propose to carry out and the motivations you can ...
The cleanly-formatted Google Doc can be downloaded as a fully editable MS Word Document (DOCX format), so you can use it as-is or convert it to LaTeX. Download The Dissertation Template. Download Grad Coach's comprehensive dissertation and thesis template for free. Fully editable - includes detailed instructions and examples.
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program. Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you've ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating ...
Academic. Essay Editing and Proofreading Proofreading services for essays, coursework and reports.; Dissertation Proofreading and Editing For undergraduate and master's students, all subjects covered.; PhD Editing and Proofreading Chapter-by-chapter proofreading and format editing for PhD theses.; Commercial. Proofreading and Copy-Editing for Businesses Essential proofreading services for ...
MSc Research Project/Dissertation Guidelines 1 Your dissertation should conform to the guidelines set out below. Please read through these carefully before writing your dissertation. Early in the preparation of the dissertation you should consult your supervisor, as their advice will be invaluable in ensuring the best way of presenting your data.
Thesis Format. Thesis format refers to the structure and layout of a research thesis or dissertation. It typically includes several chapters, each of which focuses on a particular aspect of the research topic. The exact format of a thesis can vary depending on the academic discipline and the institution, but some common elements include:
Register for the master project/thesis course with thesis advisor. (A section number will be provided to you by your project/thesis advisor.) Start Research on your master project. (Optional) Present a thesis proposal to the committee during mid-way of the thesis. Write project report/thesis. Present your master project and/or defend thesis.
The equation number is usualy placed so it is flush with the right margin, It is not necessary to bracket equation numbers as in Equation (3.2) Example If Ai and Bi can be writen as in Equation 3.2 and 3.3, modal response can be expressed as. y i (t)= Fo/Ki [Ai sin(bt) ÷ Bi cost (bt)] Equation 3.4.
3 1. Introduction Students on all taught Masters programmes within the Alliance Manchester Business School (except MSc Management) are required to submit a dissertation on a topic approved by the
Writing a proposal or prospectus can be a challenge, but we've compiled some examples for you to get your started. Example #1: "Geographic Representations of the Planet Mars, 1867-1907" by Maria Lane. Example #2: "Individuals and the State in Late Bronze Age Greece: Messenian Perspectives on Mycenaean Society" by Dimitri Nakassis.
Font, Spacing and Margins: All thesis text must be in Arial, Times New Roman or Palatino 12 point font. Line spacing must be 1.5 (one-and-a-half) throughout the thesis, except for long quotations, footnotes, table captions and figure legends, and individual references in the "Literature Cited" section, which must be single-spaced (with 1.5 ...
Submission of Intent to initiate a Masters defence. Step 3. Submit. Please note that your degree requirements are considered complete when one electronic copy of the thesis, revised as directed by your defence examining committee, is submitted to the School of Graduate Studies through the E-Thesis Submission module in MacSphere.
March 4: Format Check Deadline for Thesis/Dissertation. March 15: Graduation Application Deadline. March 22: Defense Deadline. April 8: Final Submission Deadline. May 3: Master's and Certificate Commencement by College, 3 p.m., Colonial Life Arena. May 4: Master's and Certificate Commencement by College, 9:30 a.m., Colonial Life Arena.
Msc Thesis Format - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. The document outlines the format and guidelines for M.Sc. Physics theses/dissertations at Tribhuvan University in Nepal. It provides 14 points on the required structure, including: 1) using Times New Roman 12 font and 1.5 line spacing, 2) a concise and informative title, 3) proofreading for errors ...
There were 5,582 incident HF identified in IBD patients (incidence rate [IR]: 50.3/10,000 person-years) and 20,343 in reference individuals (IR: 37.9) during a median follow-up of 12.4 years.