The Harmful Effects of Polythene on the Environment and Animal Life - A Wake-Up Call for Responsible Disposal
Ishara upamali.
Polythene which became very popular within about 25 years has now become the world's biggest problem. We all know that it is harmful not only to human life but to animal life and the environment as well.
Polythene became very popular because it made our daily tasks very easy. It was used for carrying things, wrapping, decorating, as coverings and even in making artificial ornamental items. It came in various colors, shapes and sizes as bags, squares, sheets and rolls of polythene.
However, the common polythene bags and lunch sheets became the biggest problem in Sri Lanka. As students we are also guilty of using them for anything and everything. We did not know how to dispose them properly and carelessly threw away in drains, waterways, on roadways, in parks, in forests, on beaches and so on. So now we have to face the effects. The danger is that polythene is not bio - degradable. That means it does not rot easily. If it is buried it can harm the soil. Burning it causes air pollution. The worst effect is that animals, birds and fish have died after eating thrown away polythene.
Now most people and even children are aware of the dangerous and use other materials like clothes and paper which are bio - degradable. So, all of us must to be responsible in everything we do because this is our beloved country.
- CBSE Class 10th
- CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore

Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Advanced Cutoff
- JEE Main Cutoff
- JEE Advanced Answer Key
- JEE Advanced Result
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- KCET Result
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Answer Key
- TS ICET 2024 Hall Ticket
- CMAT Result 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- NEET Rank Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Result 2024
- NEET Asnwer Key 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top NLUs Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Predictors & Articles
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- NID DAT Syllabus 2025
- NID DAT 2025
- Design Colleges in India
- Top NIFT Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Interior Design Colleges in India
- Top Graphic Designing Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Interior Design Colleges in Bangalore
- NIFT Result 2024
- NIFT Fees Structure
- NIFT Syllabus 2025
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission 2024
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- LPU NEST 2024
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET DU Cut off 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET DU CSAS Portal 2024
- CUET Response Sheet 2024
- CUET Result 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Cut Off 2024
- CUET Exam Analysis 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- CUET PG Counselling 2024
- CUET Answer Key 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Plastic Pollution Essay
Plastic is a synthetic polymer that can be molded into any shape and form when softened, making it easy to manufacture. Due to this property, plastic has replaced other products like wood, paper etc. Plastic has become a widely used substance. Although easy to manufacture, less expensive plastics aren’t easy to discard. Plastics are non-biodegradable, thus resulting in the accumulation of plastic, leading to plastic pollution. Here are a few sample essays on ‘plastic pollution’.

100 Words Essay On Plastic Pollution
Plastic products like bags, spoons, toys etc., are abundantly available in the market. These are easy and cheap to manufacture and, thus, are widely used. Plastics do not dissolve in water and land. It has an adverse effect when burnt. These stay on the face of the earth for years together, accumulating and increasing daily, leading to plastic pollution. Plastic harms the climate. It hurts marine life in the ocean when dumped in the water, impuring the water by releasing toxins. Plastic disposed of in soil doesn’t degrade, leading to garbage accumulation and the breeding of insects.
Tiny plastic particles mix with gasses in the air leading to smog formation. When ingested by animals from the land, these plastic particles can also result in serious illness in them. Adhering to measures will lead to prevention. People must be encouraged to use alternatives to plastics—implementation of plastic recycling.
200 Words Essay On Plastic Pollution
Plastics are easy to manufacture, cheaper than other substances and can be molded into any shape and form. These advantages have made plastic widely used and a popular substance. Easily found in our daily life, from toothbrushes to tiffin containers. Plastic can dissolve neither in water nor in the ground. Thus, leading to its accumulation which causes plastic pollution. With the increase in usage, pollution is peaking every day.
Harmful Effects | Polymers in plastics have hazardous effects on the environment impacting humanity, aquatic life, ocean, land and wildlife. This plastic doesn't dissolve in water and stays inside water bodies for a long time, resulting in the release of chemicals into the water affecting the quality of water and threatening the life of marine life in those water bodies. Similarly, plastic dumped in landfills, soil reduces soil fertility leading to poor crop quality. Additionally, this dumped waste becomes a breeding ground for insects, resulting in increased diseases among people and animals.
Prevention | To prevent these harmful effects of plastic, we need to take practical steps like reusing plastic products before discarding them or choosing biodegradable alternatives to plastics like cloth and paper. Recycling used plastics is the best way to control the harmful effects. The government should encourage people to stick to alternative plastics and start programs for recycling the existing waste. Finally, we need to create and spread awareness about plastic effects and how to overcome them among more and more people. These steps collectively can reduce plastic pollution.
500 Words Essay On Plastic Pollution
The evolution of Science and technology has revolutionized several fields leading to discoveries that have significantly impacted human life. One such discovery was plastic. Plastics, as we know them today, are a byproduct of crude oil, a subset of polymers. Plastics are known for their ability to mold in any form or shape, are lightweight, flexible, cheaper to manufacture, and sustainable.
These advantages have resulted in the unique and innovative applications of plastics in sectors ranging from healthcare, medicine, automotive, construction, aerospace and everything in between. Plastics are everywhere in our daily life, from the toothbrush we use in the morning to the switch of the light we turn off at night..
Although plastic has many advantages, successfully used in every field, it has one major disadvantage. Its nature of non-biodegradability. Any substance that cannot be naturally broken down is non-Biodegradable material. These substances cannot be decomposed, thus becoming a source of pollution, ultimately threatening the environment. Accumulation of plastic leads to plastic pollution. Plastic pollution has become one of the major global concerns.
Impact of Plastic Pollution
Plastic pollution has multiple adverse effects on the climate, like ocean pollution, land pollution, food pollution, and groundwater pollution.
Every day tons of plastic dumped in water bodies don't dissolve in water, releasing toxic chemicals into the water and downgrading their purity. These items are sometimes mistaken as food by marine life, and consuming them leads to severe illness in marine life. Research shows that the death of aquatic creatures due to plastic consumption increases yearly. Plastic nets used in commercial fishing sometimes break and become submerged in the water, releasing toxic chemicals and contaminating the fish.
Human beings dispose of tons of plastics in landfills and soil, thus, polluting the land. These plastics do not dissolve in mud, eventually releasing chemicals into the soil and affecting soil quality. They also leak into the ground resulting in groundwater contamination. These plastic-filled landfills become a source of disease-causing insects and mosquitoes.
Polluting material comes in all dimensions and is present in the air. These particles form particulate matter leading to ozone and smog, which are significant causes of Air Pollution.
Finally, plastics lead to food flow disruption, i.e. contamination of tiny species due to plastic ingestion, which poses a threat to larger animals which consume them, leading to myriads of problems.
Steps To Curb Its Effects
If not handled carefully, plastic pollution can have catastrophic effects on us. We must take practical and immediate steps to control it.
One of the main steps is the implementation of the 4Rs.
Refuse | Avoid single-use plastics. Choose alternatives like cloth or paper bags.
Reuse | Reuse plastic as long as possible before discarding it.
Reduce | Limit or reduce the use of plastics.
Recycle | Recycling plastic products into other valuable products.
Apart from following the above steps, we must educate the masses about plastics and create awareness among them and also implement an effective waste disposal system. Preventing plastic pollution is every human's responsibility. The combined effort and careful measurements by everyone can vastly reduce plastic pollution to a large extent.
Applications for Admissions are open.

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)
Register FREE for ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)

JEE Main Important Physics formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Physics formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

PW JEE Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for JEE coaching

PW NEET Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for NEET coaching

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Certifications
We Appeared in
Open Access is an initiative that aims to make scientific research freely available to all. To date our community has made over 100 million downloads. It’s based on principles of collaboration, unobstructed discovery, and, most importantly, scientific progression. As PhD students, we found it difficult to access the research we needed, so we decided to create a new Open Access publisher that levels the playing field for scientists across the world. How? By making research easy to access, and puts the academic needs of the researchers before the business interests of publishers.
We are a community of more than 103,000 authors and editors from 3,291 institutions spanning 160 countries, including Nobel Prize winners and some of the world’s most-cited researchers. Publishing on IntechOpen allows authors to earn citations and find new collaborators, meaning more people see your work not only from your own field of study, but from other related fields too.
Brief introduction to this section that descibes Open Access especially from an IntechOpen perspective
Want to get in touch? Contact our London head office or media team here
Our team is growing all the time, so we’re always on the lookout for smart people who want to help us reshape the world of scientific publishing.
Home > Books > Polyethylene - New Developments and Applications
Degradation Pathways and Ecological Consequences of Use of Polythene
Submitted: 11 August 2023 Reviewed: 30 September 2023 Published: 06 January 2024
DOI: 10.5772/intechopen.1003241
Cite this chapter
There are two ways to cite this chapter:
From the Edited Volume
Polyethylene - New Developments and Applications
Arpit Sand and Jaya Tuteja
To purchase hard copies of this book, please contact the representative in India: CBS Publishers & Distributors Pvt. Ltd. www.cbspd.com | [email protected]
Chapter metrics overview
50 Chapter Downloads
Impact of this chapter
Total Chapter Downloads on intechopen.com
Total Chapter Views on intechopen.com
Due to its adaptability and affordability, polyethylene, a synthetic polymer that is often utilized, has made a substantial contribution to modern civilization. However, due to its widespread usage, there is concern about its environmental persistence and potential ecological effects. This article seeks to present a thorough explanation of the mechanisms involved in polyethylene degradation, the environmental repercussions of its buildup, and proposed remediation techniques to lessen those effects. The study examines the fundamental processes of several degradation routes, such as biological degradation etc.. Efforts to address the ecological consequences of polythene use include reducing plastic waste management, developing biodegradation products.
- degradation
- microbial enzymes
- plastic pollution
- environmental impact
Author Information
Gurjeet singh *.
- Department of Mechanical Engineering, IES College of Technology, Bhopal, M.P., India
Neeraj Agarwal
*Address all correspondence to: [email protected]
1. Introduction
The five most common petroleum-based polymers used to make single-use plastic products are polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polypropylene (PP), high density polyethylene (HDPE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and low density polyethylene (LDPE). The most prevalent petroleum-polymer on earth, LDPE, is responsible for up to 64% of single-use plastics that are discarded shortly after use, causing a massive and fast buildup in the environment [ 1 , 2 ]. The negative impacts of basically “non-biodegradable” LDPE rubbish buildup in landfills and seas are growing despite recycling and energy recovery measures. Micro-plastics may now be found everywhere on the planet, including in the arctic snow, according to mounting evidence [ 3 ]. Finding an environmentally appropriate disposal method is thus required [ 4 ]. Contrary to biological waste that is dumped, polyethylene (PE) and other petroleum-based polymers are particularly resistant to natural biodegradation processes. The scientific literature has several studies on the biodegradation of synthetic polymers, including PE in particular. Thirteen evaluations of the microbes involved in the physical and microbial biodegradation processes have been published since 2008.
Although microbial breakdown of PE has been observed in various studies, significant degradation of PE wastes at usable sizes has not yet been achieved. We have been limited in our ability to develop a biochemically based knowledge of the mechanisms and processes involved in PE degradation due to the lack of a concrete definition of polyethylene biodegradation that may lead to testable hypotheses. Early investigations on microbial biodegradation attempted to demonstrate how microbial activity may change the tensile strength, water absorption, and crystallinity of plastics [ 5 ].
Pirt (1980) [ 6 ] conducted the first investigation of the microbial biodegradation of polymers. Ten years later, 0.2% less PE weight was present, according to Albertsson and Karlsson [ 1 ]. Otake et al. [ 7 ] found that PE polymers exhibited surface alterations after being buried in soil for 10 to 32 years. It was discovered that LDPE thin film deterioration was relatively high. Despite the fact that parts of the PE films with considerable deterioration were characterized by whitening with tiny holes, the overall rate of degradation was still fairly low even after years of contact with soil microorganisms.
Some researchers have investigated the aerobic biodegradation of treated polyethylene and/or polyethylene modified by the addition of additives (“addivitated”) PE in simulated soil burial and mature compost [ 3 , 8 ], as well as in natural aquatic environments under laboratory conditions [ 9 , 10 ]. Living microbial consortia are present in several kinds of soil [ 11 ]. Others looked at the microorganisms that cause LDPE to biodegrade in soil [ 12 ]. The biodegradability of thermally and photochemically damaged addiviated LDPE films by microorganisms adsorbed on the surface of PE films buried in agricultural soil was assessed in a research by Abrusci et al. [ 13 ] whiteness with tiny holes that defines it.
Typically, as part of microbial degradation test investigations, microorganisms from diverse sources are isolated to ascertain the optimal microbial power to degrade polymeric PE chains. Researchers have isolated potential microorganisms from a range of soil types, including garden soil, forest soil, waste soil, mangrove soil, and soil covered in agricultural PE films for soil mulching [ 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 ]. Alternative sources for the isolation of high potential microorganisms that deteriorate PE included landfills, solid waste dumps, and plastic garbage (municipal solid soil) [ 4 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 ], water [ 2 ], waste water or sewage sludge, oil-contaminated soil, and even waxworm larvae [ 23 ].
Numerous bacteria from a small number of text were found to be present in these trials; however, not all of them were involved in the breakdown of PE ( Table 1 ). Following the bacteria’s initial isolation, the capacity of each isolate to use treated and/or untreated polyethylene was examined in isolated shake-flask cultures throughout a range of time periods. The majority of these bacteria were identified using the sequencing of 16S ribosomal RNA genes following PCR amplification. The third phase was estimating biodegradation using PE-degrading bacteria on polyethylene particles or films using various approaches.
Bacteria employed in research on the biodegradation of polyethylene (PE).
Comparisons of the various biodegradation results are not significant due to the large diversity of PE materials employed and the vast range of growth conditions. This emphasizes the requirement for standardized approaches and procedures to comprehensively investigate the biodegradation of synthetic polymers. We need to identify the differences between degradation and deterioration as well as what the biodegradation process entails in order to resolve any difficulties brought up by stories of attempts at microbial biodegradation of PE that failed. The conditions that promote the microbial destruction of PE are discussed in the sections that follow, along with how these factors led to reports of incorrect PE biodegradation percentages. Then, we provide an appropriate explanation of the biodegradation process that will make it possible to interpret the findings of biodegradation in an accurate manner.
2. Biological degradation of PE
There are four steps to the whole biodegradation process: biodeterioration, biofragmentation, bioassimilation, and mineralization. However, access sites in the PE structure are necessary for microorganisms to start fragmenting before they can start attacking PE. As a result, before the presence of microorganisms, oxidation of PE polymers happens by abiotic processes such as ultraviolet (UV) radiation exposure combined with heat and/or environmental chemicals. It is well known that thermal aging frequently occurs in conjunction with PE oxidation, particularly UV-induced PE oxidation. The mechanisms of polymer change have also been well shown. According to earlier studies, when PE is exposed to UV radiation or oxidizing agents, carbonyl groups are produced in the alkane chains. These carbonyl groups are then further hydrolyzed by microorganisms, which catabolize the shorter PE chain reaction products (fragmentation). In this method, the polymer chain initially absorbs UV light, which causes radical production. At some point, oxygen is taken in, hydroperoxides are created, and carbonyl groups are created ( Figure 1 ). The carbonyl groups proceed through Norrish Type I and/or Type II degradation with additional UV exposure. Additionally, pro-oxidants or contaminants might start photo-oxidation. Additionally, UV-degradation might start at spots where minute amounts of ketone or hydroperoxide groups were added during fabrication or production.
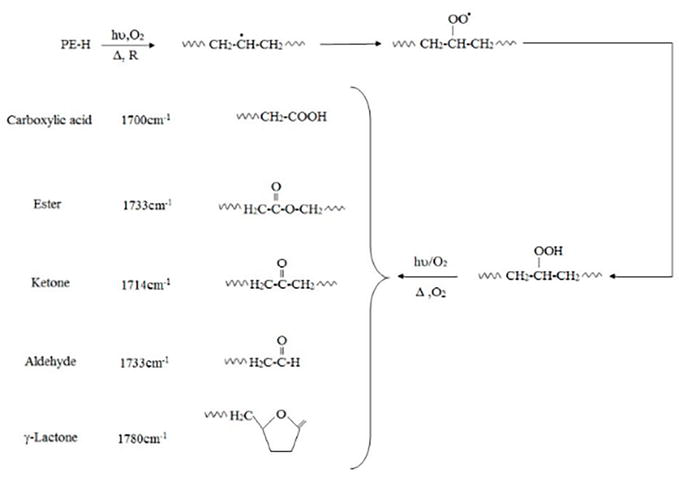
Degradation pathways of polyethylene containing pro-oxidant additives.
Infrared spectroscopy (IR) measurements of the degree of carbonyl group adsorption can be used to monitor the oxidative degradation of polyolefins. The concentration levels of carbonyl compounds determined by ATR-FTIR were often represented as a carbonyl index (C.I.), which is defined as the ratio of carbonyl and methylene absorbances. The ratio of the methylene absorption band at 1435 cm1 (the CH2 scissoring peak) to the carbonyl peak at 1714 cm1 taken as an internal thickness band (CI = A1714/A1435). Even after storage in an abiotic environment, photo-oxidation and increased stress both accelerate the production of carbonyl groups.
3. Biodeterioration of PE
Some microbes can start the oxidation process on their own, via the process of “hydroperoxidation,” in addition to the abiotic degradation of PE materials. “Biodeterioration” is the word used to describe this. However, it is currently unclear whether PE that has been oxidized in this way can eventually be broken down by microbes [ 9 ]. Different pro-oxidation additives (prodegradants) have been added to the structure of polyethylene products to make them “oxo-degradable” in various investigations of the microbial breakdown of PE. “Addiviated” polymers are PE polymers that include additives that make them oxo-degradable. Materials used to make addiviated PE polymers oxo-degradable include polyunsaturated compounds, transition metals like iron, cobalt, manganese, and calcium, totally degradable plastic additives (TDPA) with different commercial names [ 7 , 30 , 31 , 40 ], natural polymers (e.g., starch, cellulose, or chitosan), food grade dyes, or synthetic polymers containing ester, hydroxyl or ether groups [ 33 , 35 , 40 ] that are prone to hydrolytic cleavage by microorganisms. Abiotic factors like sunlight, heat, or both, as well as the addition of oxidizing chemical agents like nitric acid are used in some comparative studies of the microbial degradation of PE to start the degradation of raw and addiviated PE polymers and make the plastic more susceptible to microbial degradation. Following this, the impacts of various treatments on PE structure and microbial degradation were examined and compared to samples that had not been processed. The development of oxidized oligomers and alteration of the polymer are caused by a change in the fundamental structure of PE during the degrading process. The PE becomes brittle and vulnerable to additional oxidation by enzymes released by the microorganisms as a result of deterioration caused by physical, biological, or chemical factors. While PE’s molecular structure is changing at this point, the polymer is not fragmenting or losing structure. An increase in entry locations for enzymes released by microbes and a decline in the polymer’s mechanical or other physical qualities are two main characteristics of the degradation phase overall.
4. Experiments on microbial degradation of PE: contributing factors
The outcome and findings of PE biodegradation tests are significantly influenced by a variety of parameters in the microbial breakdown of PE polymers. Unfortunately, while planning and designing the trials that were described in the literature, these considerations were frequently ignored. As a result, the information provided in these papers about PE biodegradation has been inconsistent and inconclusive. Following is a description of these elements.
4.1 Polyethylene shape and structure
The ability of the microorganisms’ secreted enzymes to reach the PE carbon chain is crucial for microbial breakdown. All PE materials have a simple linear carbon chain microstructure that is joined by hydrogen bonds. But polyethylene polymers can have a variety of densities and three-dimensional (3-D) structures ( Figure 2 ), including low molecular weight polyethylene (LMWPE), linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE), low-density polyethylene (LDPE), and high-density polyethylene (HDPE), depending on the manufacturing processes used.
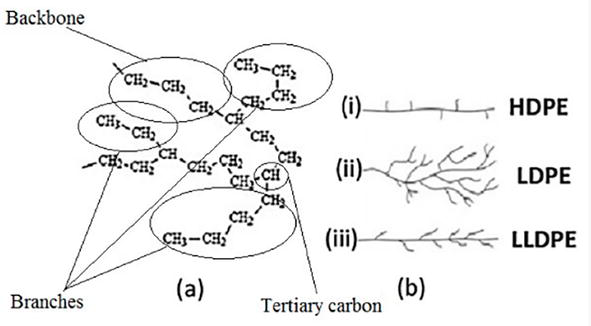
Polyethylene structure.
PE often has a semi-crystalline structure as well. LDPE crystallinity ranges from 45–65%, depending on the type of processing. Short branches (10–30 CH3 groups per 1000 C-atoms) made comprised of one or more co-monomers like 1-butene, 1-hexene, and 1-octene are typically found in amorphous regions of LDPE. The LDPE chains near the surface are made more accessible by the branching system’s prevention of the PE molecules from stacking closely together, and the tertiary carbon atoms at the branch sites are left more vulnerable to assault. Additionally, amorphous areas are more likely to contain contaminants.
So that it is feasible to determine how much polymer is present, it is crucial that the structure and percentage of amorphous and crystalline areas in the polymer be recorded.
4.2 Modification of polyethylene
PE often has a semi-crystalline structure as well. LDPE crystallinity ranges from 45–65%, depending on the type of processing. Short branches (10–30 CH3 groups per 1000 C-atoms) made comprised of one or more co-monomers like 1-butene, 1-hexene, and 1-octene are typically found in amorphous regions of LDPE. The LDPE chains near the surface are made more accessible by the branching system’s prevention of the PE molecules from stacking closely together, and the tertiary carbon atoms at the branch sites are left more vulnerable to assault. Additionally, amorphous areas are more likely to contain contaminants. So that it is feasible to determine how much polymer is present, it is crucial that the structure and percentage of amorphous and crystalline areas in the polymer be recorded.
But the primary goal of LDPE modification is to cause the polyethylene structure to deteriorate, allowing more access to the enzymes released by microorganisms during the biodegradation stage. Treatments alter the structure of PE, and as a result, investigations using various forms of PE with varying Mw, Mn, and/or molecular distributions have produced varying biodegradation outcomes. To effectively quantify microbial degradation and ascertain the only impact of microorganisms’ activities, these changes in the biodegradation process need to be identified and documented.
4.3 Partial biodegradation versus complete degradation
The consumption and mineralization of whole, unaltered polymers, including the polymer’s backbone, might be considered complete biodegradation of PE polymers. Microbes that can totally breakdown and mineralize virgin polyethylene have not yet been discovered, according to Yoon et al. Even so, it’s possible to classify the numerous cases of PE biodegradation in the literature as incomplete biodegradation. As previously mentioned, PE polymers are composed of a complex of linear carbon chains held together by van-der-Waals interactions, accessible short side-chains with tertiary carbon that contain amorphous sections, terminal methyl-groups at the ends of chains, short branches, and small oxidative products, as well as numerous linear and branched n-alkane side-chains. Because the side-chains of PE mimic linear n-alkanes, they may serve as the first site of contact for bacterial enzymes that cause the polymers to partially degrade. Without fragmenting the polymer’s backbone, low molar mass molecules and/or amorphous segments are removed from its surface. In contrast to the fragmentation of the backbone or pure PE polymers, weight loss during the early stages of PE degradation may be explained by the enzymatic hydrolysis of these readily accessible side chains. It is insufficient to conclude that polyethylene has completely degraded by looking at the development of microbes on agar plates containing the material. This has been one of the main issues with biodegradation experiments since it is necessary to establish complete biodegradation.
4.4 Other carbon sources’ influence on biodegradation
There are various carbon sources that, in biodegradation tests, are frequently absorbed by bacteria during the initial phases of microbial breakdown and may interfere with the only carbon supply of PE. Establishing a growth curve for the bacteria under research using PE as the carbon source is advised as a solution to the issue. Changes in the development curve might signify the use of various carbon sources with varying degrees of accessibility to microbes [ 18 ]. Impurities that are integrated into PE chains or that adhere to the PE surface may include substances that bacteria can use as a source of carbon. Consumption of these contaminants can compete with or obstruct the use of PE as a carbon source. Incubating non-PE degrading bacteria, such as E. coli , along with the contaminated PE samples is one strategy to mitigate this issue. The contaminants would be consumed by the E. coli without changing the structure of the PE. After a certain amount of time, the pure PE may be removed, cleaned, and cultured with various microbes to see how well they degrade PE.
Generally speaking, two distinct groups of researchers have carried out experiments for the microbial breakdown of PE. Environmentalists in general are the groups of researchers who have studied the degradation of bulk PE materials of various types (LMWPE, LLDPE, LDPE, or HDPE) in natural settings such as soil, compost, or aquatic systems with mixed, undefined populations of microorganisms, without paying attention to microbial type. Any change seen is referred to as “biodegradation” whether it relates to appearance, weight loss, or mechanical qualities of the PE. The mechanisms influencing changes in the PE are unclear, and this strategy is mostly based on “trial and error.” The distinction between deterioration and partial degradation is misunderstood by the authors of these works. On the other hand, these tests have the benefit of being carried out in the real world under actual environmental circumstances, and the outcomes accurately represent the deterioration of PE. The final conversion of PE to CO2 and biomass (mineralization via genuine biodegradation), is a topic of interest to microbiologists who have also studied PE breakdown. The biodegradation tests are carried out with specific species of microorganisms isolated using specialized medium from collections. In general, the tests’ many components are clearly specified, and the authors are aware of how biodegradation works. The use of molecular biology and genomic sciences has started to pinpoint the precise genes and gene products involved in the breakdown of polyethylene in this regard. PE biodegradation is a complicated process that is impacted by a wide range of variables. Before being subjected to microbial treatment, a PE polymer chain may be exposed to various manufacturing, treatment, and sample preparation operations. The biodegradation process is complicated and uncertain since it involves a vast variety of bacteria with diverse behaviors and released chemicals. However, studies of polyethylene biodegradation experiments may be conducted from both chemical and microbiological perspectives.
5. Conclusion
The four steps of PE’s biodegradation process are biodeterioration, biofragmentation, bioassimilation, and mineralization. Complete biodegradation of PE necessitates a decrease in the polymer’s molar mass and molecular mass number as a result of fragmentation into smaller molecules that are then metabolized by microorganisms. However, the majority of investigations on the purported biodegradation of PE by microorganisms show biodeterioration and just a small number report biofragmentation. Furthermore, there is not enough proof to support bioassimilation and mineralization. Understanding the molecular processes of polyethylene biodegradation may be improved by investigating the genes and gene products that oxidize the alkane chains of polyethylene.
- 1. Albertsson AC, Karlsson S. The influence of biotic and abiotic environments on the degradation of polyethylene. Progress in Polymer Science. 1990; 15 :177-192. DOI: 10.1016/0079-6700(90)90027-X
- 2. Bergmann M, Mützel S, Primpke S, Tekman MB, Trachsel J, Gerdts G. White and wonderful? Microplastics prevail in snow from the Alps to the Arctic. Science Advances. 2019; 5 :eaax1157. DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aax1157
- 3. Chiellini E, Cortia A, Swift G. Biodegradation of thermally-oxidized, fragmented low-density polyethylenes. Polymer Degradation and Stability. 2003; 81 :341-351. DOI: 10.1016/S0141-3910(03)00105-8
- 4. Das MP, Kumar S. An approach to low-density polyethylene biodegradation by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens , 3 Biotech. 2015; 5 :81-86. DOI: 10.1007/s13205-014-0205-1
- 5. Celina M, Linde E, Brunson D, Quintana A, Giron N. Overview of accelerated aging and polymer degradation kinetics for combined radiation-thermal environments. Polymer Degradation and Stability. 2019; 166 :353-378. DOI: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab. 2019.06.007
- 6. Chiellini E, Corti A, D’Antone S. Oxo-biodegradable full carbon backbone polymers biodegradation behaviour of thermally oxidized polyethylene in an aqueous medium. Polymer Degradation and Stability. 2007; 92 :1378-1383. DOI: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab. 2007.03.007
- 7. Otake Y, Kobayashi T, Asabe H, Murakami N. Biodegradation of low density polyethylene, polystyrene, polyvinyl chloride, and urea formaldehyde resin buried under soil for over 32 years. Applied Polymer Science. 1995; 56 :1789-1796. DOI: 10.1002/app.1995.070561309
- 8. Divyalakshmi S, Subhashini A. Screening and isolation of polyethylene degrading bacteria from various soil environments. IOSR Journal of Environmental Science Toxicology and Food Technology. 2016; 10 :1-7. DOI: 10.9790/2402-1012040107
- 9. El-Shafei H, Nasser NHA, Kansoh AL, Ali AM. Biodegradation of disposable polyethylene by fungi Streptomyces species. Polymer Degradation and Stability. 1998; 62 :361-365. DOI: 10.1016/S0141-3910(98)00019-6
- 10. Fontanella S, Bonhomme S, Koutny M, Husarova L, Brusso JM, Courdavault JP, et al. Comparison of the biodegradability of various polyethylene films containing pro-oxidant additives. Polymer Degradation and Stability. 2010; 95 :1011-1021. DOI: 10.1186/s13765-020-00511-3
- 11. Gilan I, Hadar Y, Sivan A. Colonization, biofilm formation and biodegradation of polyethylene by a strain of Rhodococcus ruber . Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. 2004; 65 :97-104. DOI: 10.1007/s00253-004-1584-8
- 12. Hadad D, Geresh S, Sivan A. Biodegradation of polyethylene by the thermophilic bacterium Brevibacillus borstelensis . Journal of Applied Microbiology. 2005; 98 :1093-1100. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2005.02553.x
- 13. Harshvardhan K, Jha B. Biodegradation of low-density polyethylene by marine bacteria from pelagic waters Arabian Sea, India. Marine Pollution Bulletin. 2013; 77 :100-106. DOI: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.10.025
- 14. Hassan F, Shah AA, Hameed A, Ahmed S. Synergistic effect of photo and chemical treatment on the rate of biodegradation of low density polyethylene by Fusarium sp. AF4. Journal of Applied Polymer Science. 2007; 105 :1466-1470. DOI: 10.1002/app.26328
- 15. Jeon HJ, Kim MN. Degradation of linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE) exposed to UV-irradiation. European Polymer Journal. 2014; 52 :146-153. DOI: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2014.01.007
- 16. Jeon HJ, Kim MN. Functional analysis of alkane hydroxylase system derived from Pseudomonas aeruginosa E7 for low molecular weight polyethylene biodegradation. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation. 2015; 103 :141-146. DOI: 10.1128/JB.184.6.1733-1742.2002
- 17. Kawai K, Watanabe M, Shibata M, Yokoyama S, Sudate Y, Hayashi S. Comparative study on biodegradability of polyethylene wax by bacteria and fungi. Polymer Degradation and Stability. 2004; 86 :105-114. DOI: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab. 2004.03.015
- 18. Usha R, Sangeetha T, Palaniswamy M. Screening of polyethylene degrading microorganisms from garbage soil. Libyan Agricultural Research Central Journal of International. 2011; 2 :200-204. DOI: 10.9790/2402-1012040107
- 19. Veethahavya KS, Rajath BS, Noobia S, Kumar MB. Biodegradation of low density polyethylene in aqueous media. Procedia Environmental Sciences. 2016; 35 :709-713
- 20. Vimala PP, Mathew L. Biodegradation of polyethylene using Bacillus subtilis . Procedia Technology. 2016; 24 :232-239. DOI: 10.1016/j.protcy.2016.05.031
- 21. Yang J, Yang Y, Wu WM, Zhao J, Jiang L. Evidence of polyethylene biodegradation by bacterial strains from the guts of plastic-eating waxworms. Environmental Science & Technology. 2014; 48 :13776-13784. DOI: 10.1021/es504038a
- 22. Yashchuk O, Portillo FS, Hermida EB. Degradation of polyethylene film samples containing oxodegradable additives. Procedia Materials Science. 2012; 1 :439-445. DOI: 10.1016/j.mspro.2012.06.059
- 23. Yoon MG, Jeon JH, Kim MN. Biodegradation of polyethylene by a soil bacterium and AlkB cloned recombinant cell. Journal of Bioremediation & Biodegradation. 2012; 3 :145. DOI: 10.4172/2155-6199.1000145
- 24. Kelkar VP, Rolsky CB, Pant A, Green MD, Tongay S, Halden RU. Chemical and physical changes of microplastics during sterilization by chlorination. Water Research. 2019; 163 :114871. DOI: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.114871
- 25. Koutny M, Amato P, Muchova M, Ruzicka J, Delort AM. Soil bacterial strains able to grow on the surface of oxidized polyethylene film containing prooxidant additives. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation. 2009; 63 :354-357. DOI: 10.1016/j.ibiod.2008.11.003
- 26. Kyaw BM, Champakalakshmi R, Sakharkar MK, Lim CS, Sakharkar KR. Biodegradation of low-density polythene (LDPE) by Pseudomonas species. Indian Journal of Microbiology. 2012; 52 :411-419. DOI: 10.1007%2Fs12088-012-0250-6
- 27. Mehmood CT, Qazi IA, Hashmi I, Bhargava S, Deepa S. Biodegradation of low density polyethylene (LDPE) modified with dye sensitized titania and starch blend using Stenotrophomonas pavanii . International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation. 2016; 113 :276-286. DOI: 10.1016/j.ibiod.2016.01.025
- 28. Montazer Z, Habibi Najafi MB, Levin DB. Challenges with verifying microbial degradation of polyethylene. Polymers. 2020; 12 (1):123. DOI: 10.3390/polym12010123
- 29. Montazer Z, Habibi-Najafi MB, Mohebbi M, Oromiehei A. Microbial degradation of UV-pretreated low-density polyethylene films by novel polyethylene-degrading bacteria isolated from plastic-dump soil. Journal of Polymers and the Environment. 2018; 26 :3613-3625. DOI: 10.1007/s10924-018-1245-0
- 30. Jeon JM, Park SJ, Choi TR, Park JH, Yang YH, Yoon JJ. Biodegradation of polyethylene and polypropylene by Lysinibacillus species JJY0216 isolated from soil grove. Polymer Degradation and Stability. 2021; 191 :109662. DOI: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab. 2021.109662
- 31. Nowak B, Pajak J, Drozd-Bratkowicz M, Rymarz G. Microorganisms participating in the biodegradation of modified polyethylene films in different soils under laboratory conditions. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation. 2011; 65 :757-767. DOI: 10.1016/j.ibiod.2011.04.007
- 32. Peixoto J, Silva PL, Krüger RH. Brazilian Cerrado soil reveals an untapped microbial potential forunpretreated polyethylene biodegradation. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 2017; 324 :634-644. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.11.037
- 33. Pramila R, Ramesh KV. Potential biodegradation of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) by Acinetobacter bumannii . Africa Journal of Bacteriology Research. 2015; 7 :24-28. DOI: 10.5897/JBR2015.0152
- 34. Ragaert K, Delva L, Van Geem K. Mechanical and chemical recycling of solid plastic waste. Waste Management. 2017; 69 :24-58. DOI: 10.1016/j.wasman.2017.07.044
- 35. Rajandas H, Parimannan S, Sathasivam K, Ravichandran M, Yin LS. A novel FTIR-ATR spectroscopy based technique for the estimation of low-density polyethylene biodegradation. Polymer Testing. 2012; 3 :1094-1099. DOI: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2012.07.015
- 36. Ranjan VP, Goel S. Degradation of low-density polyethylene film exposed to UV radiation in four environments. Journal of Hazard Toxic Radioactive Waste. 2019; 23 :04019015. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)HZ.2153-5515.0000453
- 37. Santo M, Weitsman R, Sivan A. The role of the copper-binding enzyme, laccase, in the biodegradation of polyethylene by the actinomycete Rhodococcus ruber . International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation. 2013; 84 :204-210. DOI: 10.1016/j.ibiod.2012.03.001
- 38. Sivan A, Santo M, Pavlov V. Biofilm development of the polyethylene-degrading bacterium Rhodococcus ruber . Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. 2006; 72 :346-352. DOI: 10.1007/s00253-005-0259-4
- 39. Sudhakar M, Doble M, Sriyutha Murthy P, Venkatesan R. Marine microbe-mediated biodegradation of low- and high-density polyethylenes. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation. 2008; 61 :203-213. DOI: 10.1016/j.ibiod.2007.07.011
- 40. Thakur P. Screening of Plastic Degrading Bacteria from Dumped Soil Area. Odisha, India: National Institute of Technology of Rourkela; 2012. DOI: 10.9790/2402-1105029398
- 41. Bhatia M, Girdhar A, Tiwari A, Nayarisseri A. Implications of a novel Pseudomonas species on low density polyethylene biodegradation: An in vitro to in silico approach. Springer Plus. 2014; 3 :497. DOI: 10.1186/2193-1801-3-497
- 42. Bonhomme S, Cuer A, Delort AM, Lemaire J, Sancelme M, Scott C. Environmental biodegradation of polyethylene. Polymer Degradation and Stability. 2003; 81 :441-452. DOI: 10.1016/S0141-3910(03)00129-0
© The Author(s). Licensee IntechOpen. This chapter is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Continue reading from the same book
Polyethylene.
Edited by Arpit Sand
Published: 20 March 2024
By Sonia Saleem
20 downloads
By Mohamed Abdel Maksoud
47 downloads
By Ahmet Hakan Yilmaz, Bülend Ortaç, Saliha Mutlu and...
66 downloads
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Polythene and Its Impact on Environment

Related Papers
International Journal of Natural and Social Sciences
Minhaz Uddin
The study was conducted at the municipal area of Mymensingh Sadar upazilla during July to November 2017. Plastic bag (polythene bag) wastes pose serious environmental pollutions and health problems in humans and animals. The situation is deranged in underdeveloped countries like Bangladesh. The aim of this survey was to evaluate the using pattern of polythene bags and their environmental impacts at Mymensingh municipal area of Bangladesh. Two semi-structured questionnaire were used to collect data from 200 randomly selected consumers and 100 retailers. The results indicated that about 35% consumers used 5-10 plastic bags per week. The results also indicated that the larger proportion (65%) of the retailers used 50-100 plastic bags per week. Low price was the main reasons of using polythene bags for consumers (42%) and lack of alternative materials were the main reasons for the widespread utilization of plastic products for retailers (31%). Among the practices used for disposal, door to door deposition (53.5%) was practiced widely by almost all the residents of the study area. Consumer claimed that air pollution (91%) and blockage of sewage lines (88.5%) were the main problems on environment and others problems were deterioration of natural beauty of environment (64%), human health problems (62%) and soil fertility reduction (48.5%). On the other hand retailers thought that air pollution (94%) and blockage of sewage lines (97%) were the main problems of polythene waste on environment and other problems were deterioration of aesthetic beauty of environment (64%), human health problems (76%) and soil fertility reduction (53%). The findings of the study also implied that the trend of using polythene bags is increasing day by day though some awareness of the respondents about the harmful effects of plastic products. In order to abate the problems associated with polythene bag wastes, it is recommended to aware the public not to use polythene bags and to use alternative materials (bags).
stephen sonaike
Plastics have been around for more than 100 years and without a doubt, they have been extremely useful, however when you see them blowing around in the streets causing entanglement in animals, clogging up of drainages causing flooding, posing dangers to animals, such as turtles, birds that ingest them or are strangled by them, especially in marine environments where plastic bags resemble jellyfish then you will realized the need to strongly enlighten the masses on the threat posed by plastic bags pollution and the need to adopt a natural polymers in the production of plastic bags as against the use of organic polymers currently being use.
Rakin Al-Mahmood
Abhishek Dixit
eitimad ahmed
Polyethylene or polythene bags are made from ethylene, a gas that is produced as a by-product of oil, gas and coal production. Most plastic is not biodegradable and will survive in the environment for hundreds of years. Sudan has seen an increasing problem with plastic waste as Khartoum state alone generated 132,112 tons annually. Therefore, the effects of the polyethylene bags refuse on the environment were studied in Sudan (Khartoum), as an attempt to highlight the current consumptions surrounding the impact on the amount of litter generated and opportunities for their management. Methods: Data of the study were collected by different quantitative and qualitative methods. Results: It is evident that, the larger proportion (92.8%) of the respondents used plastic bags more frequently as almost all aspects of daily life involve plastics use, so it leads to generation of huge quantity of plastic waste. Polyethylene bags factors (i.e., Cheap, light weight, nice and easy to use) responsible for increasing trends of their usage and waste. All plastic waste materials are mixed with municipal solid wastes that are either land filled or incinerated. Nevertheless, only 35% of this solid waste quantity is transferred to landfills, while the remaining 65% is disposed of in open dumps. Therefore, light materials such as polyethylene bags in open containers and/or open dumps can easily float in a natural environment. However, the concern about their usage and disposal are not sustainable due to the misuse and ill managements. Beside the subsequent physical problems for wild and domestic mammals that die each year because of eating or being entangled in plastic. The situation is worsened in economically disadvantaged countries like Sudan. Conclusion: On the light of the study results, the flow of plastic on the environment need to be stopped and the research encourages the usage of paper and traditional bags. Beside recycling and public awareness, especially the decision maker will be so helpful to take serious actions.
Kayode Adeosun
Open Access Library Journal
Victor Koros
Polythene bags have been preferred for packaging purposes because they are light in weight, cheap and resistant to degradation. Despite the benefits, poor disposal of polythene causes degradation and pollution of soil, water, land and air resources leadi...
Dr. Muhammad Khalilur Rahman
"Thousands of plastic factories are producing tons of plastic bags which are very popularly used by the people for shopping purposes because of its ease, cheapness and convenience of use but their very hazardous negative impact is never highlighted or, at the very least, openly discussed in a more serious tone. Many countries have banned plastic bags due to public concern over the serious negative impact on the environment and agriculture, especially, in agricultural countries, such as Bangladesh, India, Pakistan, South Africa, etc. In this research paper, qualitative research methodology has been used to analyze our ideas based on literature review and interview from experts. The paper focuses on the sustainable agricultural and economic development by finding out alternatives to the use of ever harmful plastic bags. Keywords: Plastic bags, environmental degradation, impact on agriculture, non-biodegradable, sustainable development, alternatives to plastic bags."
Vijaya Reddy
AJAST Journal
Plastics and polythene are non-biodegradable in nature, made from non-renewable resources and it can be remained in the environment for several years. The usage of plastic and polythene bags is one of the major reasons for the environmental and health hazards. This study was done to find out the current status of awareness level of the environment and health hazards associated with the usage of plastic and polythene bags among people who live in Trincomalee town area. Survey was conducted in Trincomalee town in April 2019. Data was collected by questionnaire survey to any adult member in each of the selected household. Most of the participants (78%) had an awareness of environment and health hazards. Even though participants continuing to use due to the easy availability and durability.
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Plastic Pollution Essay
500+ words essay on plastic pollution.
Plastic has become an integral part of our daily lives. We begin our day using mugs and buckets made of plastic for bathing. Further, as we trace back our activities throughout the day, we use plastic in the form of water bottles, combs, food packaging, milk pouches, straws, disposable cutlery, carry bags, gift wrappers, toys etc. The wide use of plastic has resulted in a large amount of waste generated. Plastic has been so much used that plastic pollution has become one of the environmental problems that the world is facing today. It has impacted the environment, our health and well-being. We have all contributed to this problem, and now it’s our responsibility to work towards it to reduce and ultimately End Plastic Pollution. This essay on plastic pollution will help students to understand the harmful effects of using plastic and how it is affecting our environment. So, students must go through it and then try to write their own essays on this topic. They can also practise CBSE essays on different topics as well.

Plastic Pollution
The accumulation of plastic products in huge amounts in the Earth’s environment is called plastic pollution. It adversely affects wildlife, wildlife habitat, and humans, which has become a major concern. In 2008, our global plastic consumption worldwide was estimated at 260 million tons. Plastic is versatile, lightweight, flexible, moisture-resistant, strong, and relatively inexpensive, because of which it is excessively used by everyone. It has replaced and displaced many other materials, such as wood, paper, stone, leather, metal, glass and ceramic. Plastics have come to clutter almost every landscape. In the modern world, plastics can be found in components ranging from stationery items to spaceships. Therefore, the over-consumption of plastic goods, discarding, littering, use and throwing culture has resulted in plastic waste generation and thus creating plastic pollution.
Every day, thousands of tons of pollutants are discarded into the air by natural events and human actions. Far more damaging are the substances discharged into the atmosphere by human actions. Most plastics are highly resistant to the natural processes of degradation. As a result, it takes a longer period of time to degrade the plastic. It has resulted in the enormous presence of plastic pollution in the environment and, at the same time, adversely affected human health. It is estimated that plastic waste constitutes approximately 10% of the total municipal waste worldwide and that 80% of all plastic found in the world’s oceans originates from land-based sources.
How to Manage Plastic Pollution?
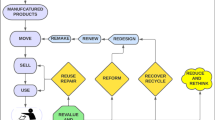
To save the environment from plastic waste, we should minimise and ultimately end the use of plastic. Each one of us has to learn the following 4 R’s:
- Refuse – Say no to plastic, particularly single-use plastic, as much as possible.
- Reduce – Limit or reduce the use of plastic in daily life.
- Reuse – Reuse plastic products as much as possible before disposing of them.
- Recycle – Plastic products should be recycled into other usable products. This reduces the demand for manufacturing raw plastic required to make various plastic products.
Apart from that, we should educate other people around us. We should create awareness campaigns in public places and help people know about plastic pollution and its harmful effects. We should stop this culture of using and throwing and start reusing things. When everyone takes a pledge to minimise the use of plastic, then we will be able to manage plastic pollution.
Students must have found this Essay on Plastic Pollution helpful for improving their writing section. They can also access more study material related to CBSE/ICSE/State Board/Competitive exams, by visiting the BYJU’S website.
Frequently asked Questions on Plastic pollution Essay
How does plastic pollution affect the environment.
Excessive usage of plastic products has caused the accumulation of this plastic on Earth. Plastic is non-biodegradable and does not naturally degrade or break down thus these plastics are flooded over the Earth.
How to reduce plastic usage?
Replacement of plastic items with jute, cotton and other biodegradable items needs to come into practice more.
What are the simple steps to avoid plastic overuse?
The simple 3 R method can be followed: “Reduce, reuse and recycle”.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Advertisement
An ode to polyethylene
- Published: 08 August 2019
- Volume 6 , article number 14 , ( 2019 )
Cite this article

- Svetlana V. Boriskina 1
380 Accesses
10 Citations
8 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
An Erratum to this article was published on 01 July 2020
This article has been updated
Polyethylene is one of the most produced materials in the world—is it a blessing or a curse? This article makes the case for the former by highlighting a range of emerging applications of polyethylene in energy and sustainability, including passive cooling of electronics and wearables, water treatment and harvesting, and even ocean cleanup from plastic waste debris.
Usually, when the word “polyethylene” is mentioned in the context of discussing sustainability issues, a good chance the message is that “the current level of environmental plastic pollution is unsustainable.” Polyethylene does indeed comprise a large volume of plastic waste, but only because it is used in so many different products, which eventually reach the end of their lifetime and end up on the landfills and in the ocean. There is, however, a good reason—actually, many good reasons—why polyethylene is one of the most produced materials in the world, and this review discusses various useful applications stemming from the unique material properties of polyethylene. Some of the emerging applications of polyethylene hold high promise for sustainable energy generation from renewable sources and for sustainable management of planetary energy and water resources. Light weight and corrosion resistance of polyethylene, combined with its unique infrared transparency and heat transfer properties, which can be engineered to span between the near-perfect insulation and metal-like conduction, are at the core of new technological applications of a not-so-old material.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others
Optimizing compounding ratios of polycarbonate and recycled polyethylene terephthalate for electronic device covers: a study on sustainable materials

Applications of Cationic Waterborne Polyurethanes
Rethinking circular economy for electronics, energy storage, and solar photovoltaics with long product life cycles
Change history, 01 july 2020.
An Erratum to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1557/mre.2020.4
Geyer R., Jambeck J.R., and Law K.L.: Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Sci. Adv. 3, e1700782 (2017).
Google Scholar
Trossarelli L. and Brunella V.P.: Polyethylene: Discovery and growth. In Proc. UHMWPE Meeting (University of Torino, Italy, 2003); pp. 1–18.
McMillan F.M.: Fruitful innovation—1. The polyethylene discovery. In The Chain Straighteners (Palgrave Macmillan: London, U.K., 1979); pp. 56–72.
Fawcett E.W. and Gibson R.O.: Improvements in or relating to the polymerisation of ethylene. Patent No. GB471590, 1937.
Ziegler K., Breil H., and Martin H.: High molecular polyethylenes. Patent No. GB799392, 1957.
Ziegler K., Heinz B., Erhard H., and Heinz M.: High molecular polyethylenes. Patent No. DE973626, 1960.
Hogan J.P. and Banks R.L.: Polymers and production thereof. Patent No. US2825721, 1958.
White J.R.: A process for producing bulky yarn-like formation of a molecularly oriented film strips of a synthetic, organic polymer. Patent No. DE1175385B, 1958.
Demirors M.: The history of polyethylene. In 100+ Years of Plastics. Leo Baekeland and Beyond, ACS Symposium Series , Vol. 1080, Thomas Strom E. and Rasmussen S.C., eds. (American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, 2011); pp. 115–145.
Krimm S., Liangt C.Y., and Sutherland G.B.B.M.: Infrared spectra of high polymers. II. Polyethylene. J. Polym. Sci. XXVII, 241–254 (1958).
Tong J.K., Huang X., Boriskina S.V., Loomis J., Xu Y., and Chen G.: Infrared-transparent visible-opaque fabrics for wearable personal thermal management. ACS Photonics 2, 769–778 (2015).
CAS Google Scholar
Balocco C., Mercatelli L., Azzali N., Meucci M., and Grazzini G.: Experimental transmittance of polyethylene films in the solar and infrared wavelengths. Sol. Energy 165, 199–205 (2018).
Hsu P.-C., Song A.Y., Catrysse P.B., Liu C., Peng Y., Xie J., Fan S., and Cui Y.: Radiative human body cooling by nanoporous polyethylene textile. Science 353, 1019–1023 (2016).
Betts K.H., Parsons R.R., and Brett M.J.: Heat mirrors for greenhouses. Appl. Opt. 24, 2651 (1985).
Espí E., Salmerón A., Fontecha A., García Y., and Real A.I.: Plastic films for agricultural applications. J. Plast. Film Sheeting 22, 85–102 (2006).
Tiwari G.N., Singh H.N., and Tripathi R.: Present status of solar distillation. Sol. Energy 75, 367–373 (2003).
Dsilva Winfred Rufuss D., Iniyan S., Suganthi L., and Davies P.A.: Solar stills: A comprehensive review of designs, performance and material advances. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 63, 464–496 (2016).
Elimelech M. and Phillip W.A.: The future of seawater desalination: Energy, technology, and the environment. Science 333, 712–717 (2011).
Ni G., Zandavi S.H., Javid S.M., Boriskina S.V., Cooper T., and Chen G.: A salt-rejecting floating solar still for low-cost desalination. Energy Environ. Sci. 11, 1510–1519 (2011).
Phadatare M.K. and Verma S.K.: Effect of cover materials on heat and mass transfer coefficients in a plastic solar still. Desalin. Water Treat. 2, 254–259 (2009).
Hay H.R.: Plastic solar stills: Past, present, and future. Sol. Energy 14, 393–404 (1973).
Chiavazzo E., Morciano M., Viglino F., Fasano M., and Asinari P.: Passive solar high-yield seawater desalination by modular and low-cost distillation. Nat. Sustain. 1, 763–772 (2018).
Ni G., Li G., Boriskina S.V., Li H., Yang W., Zhang T., and Chen G.: Steam generation under one sun enabled b y a f loating structure with thermal concentration. Nat. Energy 1, 16126 (2016).
Cooper T.A., Zandavi S.H., Ni G.W., Tsurimaki Y., Huang Y., Boriskina S.V., and Chen G.: Contactless steam generation and superheating under one sun illumination. Nat. Commun. 9, 5086 (2018).
Ni G., Li G., Boriskina S.V., Li H., Yang W., Zhang T., and Chen G.: Steam generation under one sun enabled by a floating structure with thermal concentration. Nat. Energy 1, 1–7 (2016).
Okada T. and Mandelkern L.: Effect of morphology and degree of crystallinity on the infrared absorption spectra of linear polyethylene. J. Polym. Sci., Part A-2 5, 239–262 (1967).
Eisenreich N. and Rohe T.: Infrared spectroscopy in analysis of plastics recycling. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry (John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., Chichester, U.K., 2006).
Inampudi S., Cheng J., Salary M.M., and Mosallaei H.: Unidirectional thermal radiation from a SiC metasurface. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 35, 39 (2018).
Jones A.C. and Raschke M.B.: Thermal infrared near-field spectroscopy. Nano Lett. 12, 1475–1481 (2012).
Boriskina S.V., Tong J.K., Hsu W.-C., Liao B., Huang Y., Chiloyan V., and Chen G.: Heat meets light on the nanoscale. Nanophotonics 5, 134–160 (2016).
Bermel P., Boriskina S.V., Yu Z., and Joulain K.: Control of radiative processes for energy conversion and harvesting. Opt. Express 23, A1533–A1540 (2015).
Hossain M.M. and Gu M.: Radiative cooling: Principles, progress, and potentials. Adv. Sci. 3, 1500360 (2016).
Sun X., Sun Y., Zhou Z., Alam M.A., and Bermel P.: Radiative sky cooling: Fundamental physics, materials, structures, and applications. Nanophotonics 6, 997–1015 (2017).
Li W., Shi Y., Chen Z., and Fan S.: Photonic thermal management of coloured objects. Nat. Commun. 9, 4240 (2018).
Hoyt T., Arens E., and Zhang H.: Extending air temperature setpoints: Simulated energy savings and design considerations for new and retrofit buildings. Build. Environ. 88, 89–96 (2015).
Strobach E.M. and Boriskina S.V.: Daylighting. Opt. Photonics News 29, 24 (2018).
Eriksson T.S., Lushiku E.M., and Granqvist C.G.: Materials for radiative cooling to low temperature. Sol. Energy Mater. 11, 149–161 (1984).
Gentle A.R., Dybdal K.L., and Smith G.B.: Polymeric mesh for durable infra-red transparent convection shields: Applications in cool roofs and sky cooling. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 115, 79–85 (2013).
Smith G., Gentle A., Arnold M., and Cortie M.: Nanophotonics-enabled smart windows, buildings and wearables. Nanophotonics 5, 55–73 (2016).
Granqvist C.G., Hjortsberg A., and Eriksson T.S.: Radiative cooling to low temperatures with selectivity IR-emitting surfaces. Thin Solid Films 90, 187–190 (1982).
Niklasson G.A. and Eriksson T.S.: Radiative cooling with pigmented polyethylene foils. In International Society for Optics and Photonics , Proceedings of SPIE, Vol. 1016, Granqvist C.-G. and Lampert C.M., eds. (International Society for Optics and Photonics, Hamburg, Germany, 1989); p. 89.
Eriksson T.S. and Granqvist C.G.: Radiative cooling computed for model atmospheres. Appl. Opt. 21, 4381–4388 (1982).
Granqvist C.G.: Radiative cooling to low temperatures: General considerations and application to selectively emitting SiO films. J. Appl. Phys. 52, 4205 (1981).
Zhai Y., Ma Y., David S.N., Zhao D., Lou R., Tan G., Yang R., and Yin X.: Scalable-manufactured randomized glass-polymer hybrid metamaterial for daytime radiative cooling. Science 355, 1062–1066 (2017).
Gentle A.R. and Smith G.B.: Radiative heat pumping from the Earth using surface phonon resonant nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 10, 373–379 (2010).
Boriskina S.V., Weinstein L.A., Tong J.K., Hsu W.-C., and Chen G.: Hybrid optical–thermal antennas for enhanced light focusing and local temperature control. ACS Photonics 3, 1714–1722 (2016).
Boriskina S.V., Green M.A., Catchpole K., Yablonovitch E., Beard M.C., Okada Y., Lany S., Gershon T., Zakutayev A., Tahersima M.H., Sorger V.J., Naughton M.J., Kempa K., Dagenais M., Yao Y., Xu L., Sheng X., Bronstein N.D., Rogers J.A., Alivisatos A.P., Nuzzo R.G., Gordon J.M., Wu D.M., Wisser M.D., Salleo A., Dionne J., Bermel P., Greffet J.-J., Celanovic I., Soljacic M., Manor A., Rotschild C., Raman A., Zhu L., Fan S., and Chen G.: Roadmap on op tical energy conversion. J. Opt. 18, 073004 (2016).
Lozano L.M., Hong S., Huang Y., Zandavi H., El Aoud Y.A., Tsurimaki Y., Zhou J., Xu Y., Osgood R.M., Chen G., and Boriskina S.V.: Optical engineering of polymer materials and composites for simultaneous color and thermal management. Opt. Mater. Express 9, 1990 (2019).
Guan H., Sebben M., and Bennett J.: Radiative-and artificial-cooling enhanced dew collection in a coastal area of South Australia. Urban Water J. 11, 175–184 (2014).
Nilsson T.: Initial experiments on dew collection in Sweden and Tanzania. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 40, 23–32 (1996).
Beysens D., Muselli M., Milimouk I., Ohayon C., Berkowicz S., Soyeux E., Mileta M., and Ortega P.: Application of passive radiative cooling for dew condensation. Energy 31, 2303–2315 (2006).
Nilsson T.M.J., Vargas W.E., Niklasson G.A., and Granqvist C.G.: Condensation of water by radiative cooling. Renewable Energy 5, 310–317 (1994).
Sharan G.: Harvesting dew with radiation cooled condensers to supplement drinking water supply in semi-arid coastal northwest India. Int. J. Serv. Learn. Eng. Humanit. Eng. Soc. Entrep. 6, 130–150 (2011).
Bhatia B., Leroy A., Shen Y., Zhao L., Gianello M., Li D., Gu T., Hu J., Soljačić M., and Wang E.N.: Passive directional sub-ambient daytime radiative cooling. Nat. Commun. 9, 5001 (2018).
Yang A., Cai L., Zhang R., Wang J., Hsu P.-C., Wang H., Zhou G., Xu J., and Cui Y.: Thermal management in nanofiber-based face mask. Nano Lett. 17, 3506–3510 (2017).
Peng Y., Chen J., Song A.Y., Catrysse P.B., Hsu P.-C., Cai L., Liu B., Zhu Y., Zhou G., Wu D.S. et al.: Nanoporous polyethylene microfibres for large-scale radiative cooling fabric. Nat. Sustain. 1, 105–112 (2018).
Zandavi S.H., Huang Y., Ni G., Pang R., Osgood R.M. III, Kamal P., Jain A., Chen G., and Boriskina S.V.: Polymer metamaterial fabrics for personal radiative thermal management. In Frontiers in Optics 2017 (OSA, Washington, D.C., 2017); p. FM4D.6.
Boriskina S.V., Zandavi H., Song B., Huang Y., and Chen G.: Heat is the new light. Opt. Photonics News 28, 26–33 (2017).
Chen G., Tong J.K., Boriskina S.V., Huang X., Loomis J., and Xu L.: Infrared transparent visible opaque fabrics. Patent No. US9951446, 2015.
Fukushima Y., Murase H., and Ohta Y.: Dyneema®: Super fiber produced by the gel spinning of a flexible polymer. In High-Performance and Specialty Fibers , The Society of Fiber Science and Technology, Japan (Springer Japan, Tokyo, 2016); pp. 109–132.
Simmelink J.A.P.M., Mencke J.J., Jacobs M.J.N., and Marissen R.: Process for making high-performance polyethylene multifilament yarn. Patent No. US9759525B2, March 2, 2009.
Tyvek (DuPont USA): Available at: http://www.dupont.com /products-andservices/fabrics-fibers-nonwovens/protective-fabrics/brands/tyvek.html.
Ghaly A., Ananthashankar R., Alhattab M., and Ramakrishnan V.: Production, characterization and treatment of textile effluents: A critical review. J. Chem. Eng. Process Technol. 5, 1–18 (2014).
Bomgardner M.: Greener Textile Dyeing. C&EN Glob. Enterp. 96, 28–33 (2018).
Cai L., Peng Y., Xu J., Zhou C., Zhou C., Wu P., Lin D., Fan S., and Cui Y.: Temperature regulation in colored infrared-transparent polyethylene textiles. Joule 3, 1478–1486 (2019).
Daniel C., Longo S., and Guerra G.: High porosity polyethylene aerogels. Polyolefins J. 2, 49–55 (2015).
Attia Y.A.: Polyethylene aerogels and method of their production. Patent No. US9034934B1, May 30, 2012.
Shen S., Henry A., Tong J., Zheng R., and Chen G.: Polyethylene nanofibres with very high thermal conductivities. Nat. Nanotechnol. 5, 251–255 (2010).
Loomis J., Ghasemi H., Huang X., Thoppey N., Wang J., Tong J.K., Xu Y., Li X., Lin C.-T., and Chen G.: Continuous fabrication platform for highly aligned polymer films. Technology 02, 189–199 (2014).
Lin Y., Patel R., Cao J., Tu W., Zhang H., Bilotti E., Bastiaansen C.W.M., and Peijs T.: Glass-like transparent high strength polyethylene films by tuning drawing temperature. Polymer 171, 180–191 (2019).
Lv W., Sultana S., Rohskopf A., Kalaitzidou K., and Henry A.: Graphite-high density polyethylene laminated composites with high thermal conductivity made by filament winding. Express Polym. Lett. 12, 215–226 (2018).
Xu Y., Kraemer D., Song B., Jiang Z., Zhou J., Loomis J., Wang J., Li M., Ghasemi H., Huang X., Li X., and Chen G.: Nanostructured polymer films with metal-like thermal conductivity. Nat. Commun. 10, 1771 (2019).
Fujishiro H., Ikebe M., Kashima T., and Yamanaka A.: Drawing effect on thermal properties of high-strength polyethylene fibers. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 37, 1994–1995 (1998).
Wang X., Ho V., Segalman R.A., and Cahill D.G.: Thermal conductivity of high-modulus polymer fibers. Macromolecules 46, 4937–4943 (2013).
Takao T., Yuhara T., Sakuma R., Goto T., and Yamanaka A.: Evaluating cooling performance of high-thermal-conduction composite in conduction-cooled superconducting coils. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 20, 2126–2129 (2010).
Takao T., Kawasaki A., Yamaguchi M., Yamamoto H., Niiro A., Nakamura K., and Yamanaka A.: Investigation of cooling effects on conduction cooled HTS tape due to high thermal conduction plastics. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 13, 1776–1779 (2003).
Gosumbonggot J. and Fujita G.: Global maximum power point tracking under shading condition and hotspot detection algorithms for photovoltaic systems. Energies 12, 882 (2019).
Moretón R., Lorenzo E., and Narvarte L.: Experimental observations on hot-spots and derived acceptance/rejection criteria. Sol. Energy 118, 28–40 (2015).
Romano D., Tops N., Bos J., and Rastogi S.: Correlation between thermal and mechanical response of nascent semicr ystalline UHMWPEs. Macromolecules 50, 2033–2042 (2017).
Gerrits N.S.J.A., Young R.J., and Lemstra P.J.: Tensile properties of biaxially drawn polyethylene. Polymer 31, 231–236 (1990).
Restrepo-Flórez J.-M., Bassi A., and Thompson M.R.: Microbial degradation and deterioration of polyethylene—A review. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 88, 83–90 (2014).
Buxadera-Palomero J., Canal C., Torrent-Camarero S., Garrido B., Javier Gil F., and Rodríguez D.: Antifouling coatings for dental implants: Polyethylene glycol-like coatings on titanium by plasma polymerization. Biointerphases 10, 029505 (2015).
Frodel J.L. and Lee S.: The use of high-density pol yethylene implants in facial deformities. Arch. Otolaryngol., Head Neck Surg. 124, 1219 (1998).
Ridwan-Pramana A., Wolff J., Raziei A., Ashton-James C.E., and Forouzanfar T.: Porous polyethylene implants in facial reconstruction: Outcome and complications. J. Cranio-Maxillofacial Surg. 43, 1330–1334 (2015).
Kyaw B.M., Champakalakshmi R., Sakharkar M.K., Lim C.S., and Sakharkar K.R.: Biodegradation of low density polythene (LDPE) by Pseudomonas species. Indian J. Microbiol. 52, 411–419 (2012).
Muhonja C.N., Makonde H., Magoma G., and Imbuga M.: Biodegradability of polyethylene by bacteria and fungi from Dandora dumpsite Nairobi-Kenya. PLoS One 13, e0198446 (2018).
Bombelli P., Howe C.J., and Bertocchini F.: Polyethylene bio-degradation by caterpillars of the wax moth Galleria mellonella . Curr. Biol. 27, R292–R293 (2017).
Sivan A., Szanto M., and Pavlov V.: Biofilm development of the polyethylene-degrading bacterium Rhodococcus ruber. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 72, 346–352 (2006).
Tokiwa Y., Calabia B.P., Ugwu C.U., and Aiba S.: Biodeg radability of plastics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 10, 3722–3742 (2009).
Gurunathan T., Mohanty S., and Nayak S.K.: A review of the recent developments in biocomposites based on natural fibres and their application perspectives. Composites, Part A 77, 1–25 (2015).
Zhang Z., Gora-Marek K., Watson J.S., Tian J., Ryder M.R., Tarach K.A., López-Pérez L., Martínez-Triguero J., and Melián-Cabrera I.: Recovering waste plastics using shape-selective nano-scale reactors as catalysts. Nat. Sustain. 2, 39–42 (2019).
Boriskina S.V., Raza A., Zhang T., Wang P., Zhou L., and Zhu J.: Nanomaterials for the water-energy nexus. MRS Bull. 44, 59–66 (2019).
Borrelle S.B., Rochman C.M., Liboiron M., Bond A.L., Lusher A., Bradshaw H., and Provencher J.F.: Opinion: Why we need an international agreement on marine plastic pollution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 114, 9994–9997 (2017).
Download references
Acknowledgments
The author thanks Gang Chen, Marcelo Lozano, Yanfei Xu, Yi Huang, Jonathan K. Tong, Seongdon Hong, Richard M. Osgood III, Jiawei Zhou, George Ni, Hadi Zandavi, Thomas A. Cooper, TieJun Zhang, Pietro Asinari, and Matteo Fasano for useful discussions, and U.S. Army (via the CCDC Soldier Center and the MIT Institute for Soldier Nanotechnologies), Advanced Functional Fabrics of America (AFFOA), MIT International Science and Technology Initiatives (MISTI), MIT Deshpande Center, UNSW-USA Networks of Excellence, Minifibers, Inc., and Shingora Textiles for financial and in-kind support.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 02139, USA
Svetlana V. Boriskina
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Svetlana V. Boriskina .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Boriskina, S.V. An ode to polyethylene. MRS Energy & Sustainability 6 , 14 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1557/mre.2019.15
Download citation
Received : 30 October 2018
Accepted : 08 August 2019
Published : 08 August 2019
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1557/mre.2019.15
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- sustainability
- thermal conductivity
- infrared (IR) spectroscopy
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Question and Answer forum for K12 Students
Argumentative Essay Topic – Should The Use Of Polythene Be Banned?
Should The Use Of Polythene Be Banned? You can find Previous Year Argumentative Essay Topics asked in ICSE board exams.
Introduction: Product of the last century
- Extensive use of polythene in packaging industry and for shopping
- Harmful effect because of its indestructible nature
- Harmful effect on the environment
- Need to encourage use of biodegradable material for packaging
Conclusion: Should be banned to preserve our environment
Plastic was one of the most important inventions of the last century. Out of its various derivatives one form is polyethylene commonly called polythene, made from hydrocarbons, a by-product of petroleum, an important energy fuel. Being tough and light it has great industrial and commercial use especially in the packaging industry. However its excessive use in recent times has threatened the environment. This is a cause of great concern for it now threatens our very existence.
Polythene is used in a number of products like toys, automotive parts, waterproof ware etc. However the most common use is in the packaging industry. Polythene bags being light and durable are extensively used as shopping bags virtually replacing the good old paper bags, that were more environment-friendly. Its extensive use in the domestic and industrial sector is a cause of great worry.
The indestructible nature of polythene poses a serious threat to the environment. It is indestructible for it cannot decay, decompose or be burnt, like jute, paper or other organic material. The polythene bags litter the streets and are dumped in garbage bins. Unsuspecting animals that eat them die a painful death. Some find their way in the sewage and drainage system of the city causing water logging and unhygienic condition.
It poses a major threat to environmental pollution. The polythene bags that find their way into the river, pollute the riverbed and endanger marine life. On burning it releases toxic fumes into the soil and the air. Being impermeable it makes the soil infertile. Hence like a demon in the making, it continues to haunt our environment.
There is need to check this menace before it acquires a gigantic proportion. People need to be educated on the harmful effect of using polythene, by organising discussions and workshops. There is also need to encourage the use of other packaging material like paper or cloth, that are bio-degradable to replace polythene bags. If required laws should be enacted to ban the use of polythene, for this is the least we can do to leave a clean environment for the future generation.
Assignments
- ‘Environmental pollution is a cause of concern.’ Give your views on the causes and remedies
- ‘Noise pollution is a cause for concern.’ Discuss

Better2Learn.com
Knowledge Has No Limits
Hazards of Polythene Bags essay | 150,250,500 word essay on harmful effects of plastic bags
Best article on hazards of polythene bags. A detailed essay on the Hazards of Polythene Bags is here. Here you can learn about 150 words, 250 words, and 500 words Essay on the harmful effects of plastic bags. Essay on harmful effects of plastic bags.
Hazards of Polythene Bags Essay 150 words:
Polythene bags, also known as plastic bags, are a common sight in our daily lives. They are used for a variety of purposes, including carrying groceries, storing items, and disposing of waste. While they may seem convenient, polythene bags can pose serious hazards to both the environment and human health.
One of the main dangers of polythene bags is that they are not biodegradable. This means that they do not break down naturally in the environment, leading to a build-up of plastic waste. When plastic waste accumulates in landfills or the oceans, it can hurt wildlife and the ecosystem. Additionally, plastic bags can litter streets, parks, and other public areas, creating an unsightly and potentially dangerous problem.
Another hazard of polythene bags is that they can release toxic chemicals into the air, soil, and water. These chemicals can be harmful to human health and may cause a range of negative effects such as respiratory problems, cancer, and birth defects.
To reduce the hazards of polythene bags, it is important to minimize their use and properly dispose of them when they are no longer needed. Instead of using plastic bags, consider using reusable bags made from materials such as cloth or paper. By taking these steps, we can help protect the environment and our health.
Hazards of Polythene Bags Essay 250 words:
Polythene bags, also known as plastic bags, are a common sight in our daily lives. They are cheap, lightweight, and convenient to use. However, their widespread use has also led to significant environmental and health hazards.
One of the main issues with polythene bags is that they are not biodegradable. When they are discarded, they can take hundreds of years to decompose, releasing harmful chemicals into the environment as they break down. This contributes to pollution and can have harmful effects on plants, animals, and humans.
In addition to environmental concerns, polythene bags also pose health risks. When heated, they can release toxic fumes that can be harmful to humans and animals. They can also leach chemicals into food and drink, which can be ingested by people and animals.
To mitigate these hazards, it is important to reduce our reliance on polythene bags and switch to more sustainable alternatives. This can include using reusable bags made from natural materials, such as cotton or jute, or opting for paper bags. Governments and businesses can also implement policies to reduce the use of polythene bags and encourage the use of more environmentally friendly options.
Overall, while polythene bags may be convenient in the short term, their negative impacts on the environment and our health make it important to reduce their use and find more sustainable alternatives.
Hazards of Polythene Bags Essay 500 words:
Polyethylene, commonly known as polythene, is a type of plastic that is widely used to make a variety of products, including bags. While these bags are convenient and inexpensive, they can also pose significant environmental and health hazards.
One of the main concerns with polythene bags is their impact on the environment. When they are disposed of improperly, they can end up in landfills, where they can take hundreds of years to decompose. In the meantime, they can release harmful chemicals into the soil and water, contaminating the environment and potentially affecting the health of humans and wildlife.
Additionally, polythene bags can contribute to litter, which is a major problem in many cities and towns around the world. Litter not only looks unsightly, but it can also harm wildlife, as animals may ingest or become entangled in discarded plastic bags.
Another hazard associated with polythene bags is their potential to contribute to climate change. The production of plastic, including polythene, requires the use of fossil fuels, which release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere when burned. These gases contribute to global warming, which is causing a range of negative impacts, including rising sea levels, more frequent and severe natural disasters, and changes in weather patterns.
Polythene bags can also pose a threat to human health. Many plastic bags, including those made of polythene, contain chemicals called phthalates, which can leach out of the plastic and into the food or other items that are stored in them. Phthalates are known to disrupt the endocrine system and have been linked to a range of health problems, including reproductive and developmental issues, asthma, and cancer.
In conclusion, while polythene bags are convenient and inexpensive, they can also pose significant environmental and health hazards. These hazards include contributing to litter, climate change, and potential harm to human health. It is important to be aware of these risks and to take steps to minimize our reliance on plastic bags, such as using reusable bags or properly disposing of plastic bags to reduce their negative impacts on the environment and our health.
Essay on harmful effects of plastic bags in 300 words:

Plastic bags have become an integral part of our daily lives. They are cheap, lightweight, and convenient for carrying groceries, clothing, and other items. However, the harmful effects of plastic bags on the environment and human health cannot be ignored.
One of the major issues with plastic bags is their non-biodegradability. They take hundreds of years to break down, and during this process, they release toxic chemicals into the soil and water bodies. These chemicals can be harmful to plants, animals, and humans, and they can also contaminate the food chain.
Plastic bags are also a major source of litter. They can be found on streets, parks, and beaches, and they can be harmful to wildlife. For example, birds and marine animals can mistake plastic bags for food, which can lead to malnutrition or death. Plastic bags can also entangle and suffocate animals, causing them to die a slow and painful death.
In addition to the environmental impacts, plastic bags can also have negative effects on human health. The production of plastic bags requires the use of fossil fuels, which contribute to air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. These emissions can lead to respiratory problems and other health issues. Plastic bags can also leach chemicals into the food they contain, which can be harmful when ingested.
Despite the harmful effects of plastic bags, they are still widely used due to their convenience and low cost. However, there are alternatives to plastic bags that can be used to reduce their impact on the environment. These alternatives include reusable bags made of cloth or other sustainable materials, paper bags, and biodegradable plastic bags. By using these alternatives, we can reduce our reliance on plastic bags and protect the environment and human health.
In conclusion, plastic bags have numerous harmful effects on the environment and human health. They are non-biodegradable, contribute to litter, and contribute to air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. To reduce their impact, we can use alternatives such as reusable bags, paper bags, and biodegradable plastic bags. By making these small changes, we can protect the environment and ensure a healthier future for all.
Share this:
Related post, chandrayaan 3 essay in english | best 10 lines, 150, 250 & 500 words essay on chandrayaan-3, 5 best my family essay for class 1, my constitution my pride essay | best essay, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
20+ Best Short Moral Stories in Hindi for Class 1
Best pronoun worksheet for class 2 with answers & pdf | 5 sets.
- Skip to main content
India’s Largest Career Transformation Portal
Essay on Plastic Pollution for Students in English [500+ Words]
August 29, 2021 by Sandeep
Plastic Pollution Essay: On average, around 8 million metric tons of plastic garbage and waste are collected in the oceans every year. The economically low plastics prices have increased their usage rate, but this material is highly non-biodegradable, causing substantial environmental damage. It largely affects human lives, wildlife, and marine animals. It pollutes land and water resources. Many governments have strictly implemented the plastic ban in their nations. Below we have provided an essay on plastic pollution suitable for school students of classes 1 to 12.
Essay on Plastic Pollution 500 Words in English
Below we have provided Plastic Pollution Essay in English, suitable for classes 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, and 10. This detailed essay of 150-500 words is greatly helpful for all school students to perform well in essay writing competitions.
Plastic pollution is a collection of plastic waste like plastic bottles, bags, etc., that adversely affects the environment. Nowadays, plastic is everywhere, and the amount of plastic we generate daily by using it for our comfort is enhancing rapidly. No one realizes how harmful it is. It is essential to understand how plastic harms nature, human beings, and other creatures on earth. We use plastic in various ways. It is used in building polythene bags, utensils, and many other things. Slowly it gets contaminated and leads to hazardous effects.
Causes of Plastic Pollution
Plastics cannot be decomposed because of its properties. It is cheap and has endless uses. As a result, it is contaminated in the environment. Plastic is everywhere, milk cartons, water bottles, food wrappers, and many products are made up of plastics. Every time these items are thrown away, and they create harmful effects on the environment. As plastic is not expensive, it is one of the most easily available and overused items. When disposed of, it does not get decompose easily and pollutes our environment.
When small organisms eat plastic, they become poisoned. This poisons large animals who eat these tiny animals for food. With each step further along the food chain, this problem increases. Plastic is also present in the fish that many people eat every day. Many people eat fish, so fishing is an important activity in many parts of the worlds. Fishing is done by using finishing nets, and they spend a long time in the water, leaking toxins, sometimes they are left to remain wherever they fall.
This kills and harms aquatic living beings. Plastic carried by water flows to the sea and oceans, thus creating water pollution. It is impossible to break down plastics. Burning plastic is toxic, which releases toxic gases and harms the atmosphere. It is a fact that 40% of plastic is used only once. Several items, such as bags, bottles, and food packaging, are used only once and are left behind as litter. It is one of the biggest causes of plastic pollution.
Harmful Effects of Plastics
Plastic is harmful to plants, animals, and people. Improper disposal of plastics causes several problems. Some of them are:
- Throwing of plastics in open space creates unhealthy conditions, as it develops insects and mosquitoes that cause harmful diseases.
- Plastics stays in the soil for years and affects soil fertility and its quality.
- Plastic leftovers enter the drainage system and block the drains, which cause water-logging.
- The plastic manufacturing industry throws waste directly into the water bodies, thus affecting water.
- Burning of plastic leads to the release of poisonous chemicals. Thus leading to air pollution.
- Natural disasters such as floods are also one of the causes of plastic pollution.
- Plastic contains some chemicals that can affect the growth of crops by making it difficult for the process of photosynthesis to take place in agricultural fields.
Steps taken by Indian Government to decrease Plastic Pollution
The Government has announced several rules to stop the use of single-use plastics to reduce plastic pollution. These rules are applied in all states. Several rules announced by the government are-
- The Government has banned the use of carry bags made up of plastics and has suggested using bags made up of clothes or recycled plastic.
- The Government has banned all single-use plastics and the import of solid plastic waste. All states were prohibited from manufacturing single-use plastic products.
- The plastic of minimal diameter that is not soluble in water is banned.
- The Government has decided to use plastic waste for the construction of roads. It was stated that roads constructed using discarded waste plastics are durable against extreme weather conditions.
- In many states, garbage cafe is opened, where food to the poor is provided free in exchange for plastic waste. The ‘Meal for Plastic’ initiative has gained success and is rolled out in collaboration with the United Nations Development Programme under the state government’s Aahar Scheme.
Related Essays
- Air Pollution Essay
- Water Pollution Essay
- Essay on Pollution Crisis in Urban Areas

Essay on Plastic Bag in English for Children and Students

Table of Contents
Essay on Plastic Bags: Plastic Bags are used for various purposes. The most common use of these bags is to carry grocery items. These are easily available in the market and thus used extensively. However, disposing these bags is a big issue as these are non-biodegradable. They have become a major cause of land pollution. Plastic bags are harming our environment more than anything else. The use of these bags must be banned in order to save the environment from their harmful effects.
Fill Out the Form for Expert Academic Guidance!
Please indicate your interest Live Classes Books Test Series Self Learning
Verify OTP Code (required)
I agree to the terms and conditions and privacy policy .
Fill complete details
Target Exam ---
Long and Short Essay on Plastic Bag in English
Here are essays on Plastic Bag of varying lengths to help you with the topic in your exams/school assignments. You can go with any Plastic Bag essay which you like the best for you:
Essay on Plastic Bag | Why Plastic Bags Should be Banned Essay | Why Plastic Bags are Harmful for Health
Short Essay on Plastic Bags – Essay 1 (200 words)
Plastic bags are commonly seen in the market. These bags are available in various sizes and come handy while shopping. These are light and inexpensive. This is the reason why these are being used extensively. However, it is important to understand that as convenient as these are to carry and use these are equally harmful for the environment.
Unlike the cloth and paper bags, the plastic bags are non-biodegradable. It is a challenge to dispose them off. Used plastic bags stay in the environment for years and contribute to land and water pollution. This is the reason why many countries have banned the use of these bags. These countries have replaced plastic bags with paper bags or reusable cloth bags.
The government of India has also banned the use of plastic bags in many states however the same has never been implemented properly. We must understand that these have been banned for our good. Every individual must take it has his responsibility to stop the use of these bags to make our environment cleaner.
The use of plastic bags must be banned throughout the world in order to make earth a better place to live. The task should not be very difficult as these can easily be replaced by bags made of other materials.
Essay on How Plastic Bag is Harmful to Health and Environment – Essay 2 (300 words)
Introduction
Plastic bags are preferred over other kinds of bags as these are economical, light and easy to carry. Though these are widely popular we cannot overlook the harmful effects of these bags on the environment as well as the health hazards they cause.
Plastic Bags Ruin the Environment
Plastic bags contain synthetic polymer – a substance that causes harm to the environment as it is non-biodegradable. It is hard to dispose of plastic bags due to this nature of plastic. The waste plastic bags lead to pollution. Since these are extremely light they are easily blown by the wind and scatter far and wide. They do not only pollute our towns and cities but even enter the oceans and become a threat for the marine life.
Plastic Bags are Hazardous for Health
Plastic bags cause health problems in human beings as well as animals. Waste food and vegetable and fruit peels are usually thrown away in plastic bags. Animals and birds often gulp pieces of plastic while having food. This causes various diseases and illnesses in them. Gulping plastic bags can even choke their throat and suffocate them to death.
Likewise, the marine creatures also tend to mistake the plastic pieces for food and eat them. This toxic substance causes various health problems in them. People who have sea food can get infected if they have fishes, lobsters or other marine creatures suffering from illness.
Besides, the pollution caused due to plastic bags is a cause of various illnesses.
Thus, plastic bags are ruining our beautiful environment and have become a threat to our health. It is high time we must stop the use of plastic bags. We must think about the bigger scenario rather than convenience of a few seconds. It is not that difficult to keep a cloth bag with us as we head to the market. This will go a long way in keeping our environment clean.

Essay on Harmful Effects of Plastic Bags – Essay 3 (400 words)
Plastic bags are one of the most widely used bags when it comes to carrying grocery items. However, these are one of the worst types of bags to use as these cause a major harm to the environment. These light bags get torn into small pieces over the time but do not get disposed off because they are non-biodegradable. They remain in the environment for years and years and add to land, air and water pollution.
Harmful Effects of Plastic Bags on Plants
Trees and plants are an integral part of our environment. They are a source of the life-giving oxygen and one of the main reasons life is possible on our planet. Unfortunately, we human beings are ruining these beautiful creations of God. Among other things, it is the plastic bags that are causing immense harm to the flora.
Today, plastic bags have become a major cause of land pollution. The toxic chemicals produced by plastic contaminate the soil. This is hampering the growth of the plants. Since these are light and are carried by wind to different places, the agricultural land is also getting affected by them. They are deteriorating the soil quality making it less fertile. They damage the seeds sown in the ground and interfere with the growth of plants.
Harmful Effects of Plastic Bags on Animals and Humans
As the environment gets deteriorated and the growth of agricultural crops and other trees and plants gets hindered, life of animals and human beings is likely to get worse. The pollution caused due to plastic bags impacts the human beings and animals directly as well as indirectly.
Animals open eat plastic bags lying in the garbage. These bags can cause severe damage to their digestive tract and cause various illnesses. Birds, fishes and various marine creatures also eat the plastic content that floats in the air and water and incur various diseases. Humans who consume these creatures having illnesses are likely to incur serious illness.
Besides, animals and marine creatures even tend to gulp plastic bags as it is and are often suffocated to death. Large number of innocent animals die each year because of plastic bags.
Plastic bags are causing immense harm to our environment. The use of these bags must be banned by the government and as responsible citizens we must stop using these bags. In fact, the government should put a ban on the manufacturing of these bags so that these are not circulated in the market.
Essay on Say No to Plastic Bags – Essay 4 (500 words)
Plastic bags are a convenient way to carry our goods. These have become an integral part of our modern day life. We use these almost every day and are often miffed when the shopkeepers tell us these are banned and that we need to either get our own bag or purchase a cloth bag from them to carry our goods. What we fail to understand is that the government has put a ban on these bags for our good.
Why Say NO to Plastic Bags?
Here is why we must say NO to plastic bags and switch to eco-friendly alternatives:
- Major Cause of Land Pollution
Plastic bags are non-biodegradable. These are not good for use mainly because they create a lot of waste. These use and throw bags are a challenge when it comes to disposing them off. They break into tiny pieces and remain in the environment for thousands of years and add to land pollution.
- Adds to Water Pollution
Plastic bags are extremely light. People litter these bags carelessly. These are easily blown by the wind and enter the water bodies. Besides, most of our packaged food comes in plastic packing. People who go for picnics and camping carry such food and throw the waste plastic bags in the seas and rivers thereby adding to the water pollution.
- Effect on Plant Growth
The chemicals present in plastic bags contaminate the soil. They make the soil infertile and hinder the growth of plants. These are thus interfering with agriculture which is the major occupation of our country.
- Serious Illness in Animals
Animals are unable to distinguish between food and packing. They often gulp the whole thing from the garbage bins. Plastic bags get stuck in the digestive system of the animals. They even get stuck in the throat when gulped as it is and chokes them. Besides, tiny pieces of plastic that they eat from the garbage along with their food also gets accumulated in their body and eventually leads to serious illness in them.
- Responsible for Climate Change
Plastic bags are mostly made of polypropylene which is produced from petroleum and natural gas. These are both non-renewable fossil fuels and their extraction creates greenhouse gases that are the leading cause of global warming.
How to Say NO to Plastic Bags?
Although plastic bags have become an integral part of our everyday life saying no to these should not be as difficult as it seems. The government has put a ban on the use of plastic bags in many states of India but people continue to use these as these are still available in the market.
The government must take strict measures to ensure these are not used. Besides, each one of us should take it as a responsibility to stop using these. Ban on plastic bags can only be successfully implemented if each one of us stops using these sincerely.
The harmful impact of using plastic bags has been stressed upon time and again. We are all aware about the harm they are causing to our environment. We must stop their use to make our environment safer to live.
Essay on Ban on Plastic bags to Save Environment – Essay 5 (600 words)
Plastic is a man-made substance. Unlike natural substances, it is difficult to dispose of plastic as it is non-biodegradable. Plastic bags are used extensively throughout the world and produce a large amount of waste. It is a waste that remains on earth for thousands of years and causes land, water and air pollution. This gives way to serious illnesses and degrades the overall environment.
Plastic Bags should be banned completely because it is a Threat to the Environment
Plastic bags when thrown after use prove to be a major threat to the environment. They pollute the soil and effect the growth of flora. They lead to infertile soil. Both wild plants as well as agricultural crops are affected by this. When the trees and plants suffer then the entire environment is impacted negatively.
Birds and animals mistake plastic for food and eat it. This causes serious illness in them. Large number of animals and marine creatures die each year because of consuming plastic bags. Plastic bags contribute majorly in land and water pollution. These are degrading our environment by the day.
Besides, petroleum is used in the production of plastic. Petroleum is a non-renewable resource and is required for various other purposes as well. Several things that we cannot imagine our lives without run on petroleum. So, we must save this resource for their production rather than wasting it on producing plastic which is ruining our environment.
Ban on Plastic to Save Environment
- Government Must Take Strict Measures
Plastic bags have been banned in many countries around the world. The government of India has also banned the use of plastic bags in many states. However, the same has not been implemented properly. These are still used extensively throughout the market. It is essential for the government to take strict measures to ensure that the usage of these bags is stopped. Here are some suggestions to ensure strict and smooth implementation of ban on plastic bags:
- The production of plastic bags must be stopped.
- The shopkeepers must be fined for circulating plastic bags. Those seen carrying plastic bags must also be fined.
- Plastic bags already available in the market must be made chargeable.
- People Must Act Mature
It is high time that the people of our country should understand that plastic bags have been banned for our own good. These have been banned so as to make the environment cleaners and healthier to live. They must thus act maturely and contribute their bit by saying no to plastic bags.
- Alternatives to Plastic Bags
We have grown used to using plastic bags but is it that difficult to replace these and stop their use? The answer is No! There are many alternatives to the plastic bags.
Plastic bags are mainly used by shoppers to carry grocery items and other goods. It is a good idea to carry a jute bag or a cloth bag whenever we head to the market. Big shopping bags made of clothes are available in the market. We can buy one and reuse it several times. These bags are much better than the plastic bags as they have more capacity. We can keep a good number of things in a big cloth bag. It is much better than holding several small plastic bags. Cloth bags are easier to carry and are also quite firm.
You can also use paper bags instead of plastic bags. Many stores have started providing paper bags as an alternative to the plastic bags.
We humans have caused immense harm to our planet earth. We have degraded the environment and are continuing to do so every day. A switch from plastic bag to cloth bag can be our little effort to reduce pollution and save our environment.
Related Information:
- Essay on Environment
- Why Plastic Bags should be Banned
- Why Plastic Bags are Harmful for Health
- Speech on Plastic Pollution
- Speech on Beat Plastic Pollution
Related content
Talk to our academic expert!
Language --- English Hindi Marathi Tamil Telugu Malayalam
Get access to free Mock Test and Master Class
Register to Get Free Mock Test and Study Material
Offer Ends in 5:00
Short Paragraph on Harmful Effects of Polythene
In This Blog We Will Discuss
Short Paragraph on Harmful Effects of Polythene for All Classes and Grades
Polythene is a kind of plastic that is non-biodegradable element in nature . When we use it and throw it, it becomes the biggest reason for environmental pollution . The soil becomes unfertile because of the presence of plastic there. There are tons of harmful effects of polythene in the environment. First of all, it is the cause of pollution of water and soil.
More Short Paragraphs:
Related posts:.
- Short Paragraph on My Favourite Teacher
- Short Paragraph on an Ideal Student (200 Words)
- Short Paragraph on Rainy Season for Students and Kids
- Short Paragraph on Health is Wealth for Students
- Short Paragraph on Save Trees in 200 Words
- Short Paragraph on Arsenic Pollution for School Students and Kids
- Short Paragraph on A Rickshaw Puller for Kids and Students
- Short Paragraph on How to Cook Vegetable

Essay on Plastic Bag for Students and Children
500 words essay on plastic bag.
Plastic bags are one of the most commonly used things today. It makes our work easier and gives us a lot of conveniences. They have formed an essential part of our lives now. We use them almost every day for various purposes.

The usage is to the extent that we often get angry at the shopkeeper who refuses to offer us the plastic bag. It becomes daunting to carry your own bag every time. The shopkeeper’s refusal is due to the government ban on plastic bags. One often wonders why? Plastic bags make our lives easier but at what cost? They damage our earth and environment. It is high time we all stop using plastic bags.
Stop Using Plastic Bags
There are a number of reasons to say no to plastic bags. We must stop using them to better our environment and save it from degradation. There are various eco-friendly alternatives that can be used to stop the usage of plastic bags.
Firstly, plastic bags are a major source of plastic pollution. As they are non-biodegradable, they take years to decompose. They contribute to a lot of waste which keeps collecting over the years. Plastic takes thousands of years to break down and decompose. It remains in the land which contributes to the rising problem of land pollution.
Similarly, it also causes water pollution . As people throw away the bags carelessly on the roads, in the drains and rivers, they enter the water bodies. They are carried away by winds in them and sometimes dumped into water deliberately. This plastic bag goes deep in the water and also hampers the aquatic life.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Furthermore, plastic bags contaminate the soil causing hindrance to growth of plants. They seep into the soil after breaking down and remain there causing infertility in soils . The chemical hampers the soil and interferes with agriculture.
Most importantly, plastic causes the death of animals. The animals have no sense of what to eat and what to avoid. The stray animals gulp down plastic bags that get stuck in their bodies. In other words, this causes serious illnesses in their bodies. Sometimes, they choke to death after eating plastic bags.
How to Avoid Plastic Bags?
Though it may be difficult to avoid the plastic bags at first, it needs to be done for the greater good. Plastic is slowly and steadily eating away our planet and damaging it. The government has banned the use of plastic bags but still, people continue to use it despite the ban.
In order to implement these laws strictly, the government must take strict action against the ones using it. Moreover, each of us must come forward to practice this ban and make it successful. We must not buy plastic bags from shopkeepers. Instead, we must refuse to take our groceries in them when the shopkeeper offers us.
Furthermore, we must carry our own cloth or paper bags for shopping. Try to pack your food in steel or aluminum containers instead of plastic ones.
We must encourage children to avoid the use of plastic bags. If we see someone using it, we must call them out immediately. Never throw away the plastic on roads, as animals die after consuming it. We must come together to initiate a ban on plastic and make the world safer and healthier.
FAQs on Plastic Bag
Q.1 Why must we stop using plastic bags?
A.1 We must stop using plastic bags as they cause land pollution, water pollution, and soil pollution. They cause the death of several animals as well.
Q.2 How can one say no to plastic bags?
A.2 It is easy to quit using plastic bags. We must carry our own cloth or paper bags when shopping. Moreover, we must not accept plastic bags from shopkeepers which will discourage them from using them in the first place.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
2.1 Terrestrial ecosystem. Polythene has become a serious threat for all kinds of terrestrial ecosystems. 2.2 Urban and rural areas. In urban areas, polythene is major threat to both environment ...
Article Quality and Creative Essay for Students The Harmful Effects of Polythene on the Environment and Animal Life - A Wake-Up Call for Responsible Disposal. Ishara Upamali 23 Oct 2022 • 1 min read Polythene which became very popular within about 25 years has now become the world's biggest problem. We all know that it is harmful not only to ...
Plastic Pollution Essay. Plastic is a synthetic polymer that can be molded into any shape and form when softened, making it easy to manufacture. Due to this property, plastic has replaced other products like wood, paper etc. Plastic has become a widely used substance. Although easy to manufacture, less expensive plastics aren't easy to discard.
Plastic pollution, harmful accumulation of synthetic plastic products in the environment. Plastics are persistent large-scale pollutants, and plastic debris (such as bottles, straws, containers, and plastic wrap) and particulates have been found in many environmental niches, from Mount Everest to the bottom of the sea.
500+ Words Essay on Should Plastic be Banned. Plastic bags are a major cause of environmental pollutio n. Plastic as a substance is non-biodegradable and thus plastic bags remain in the environment for hundreds of years polluting it immensely. It has become very essential to ban plastic bags before they ruin our planet completely.
Due to its adaptability and affordability, polyethylene, a synthetic polymer that is often utilized, has made a substantial contribution to modern civilization. However, due to its widespread usage, there is concern about its environmental persistence and potential ecological effects. This article seeks to present a thorough explanation of the mechanisms involved in polyethylene degradation ...
On the other hand retailers thought that air pollution (94%) and blockage of sewage lines (97%) were the main problems of polythene waste on environment and other problems were deterioration of aesthetic beauty of environment (64%), human health problems (76%) and soil fertility reduction (53%). The findings of the study also implied that the ...
500+ Words Essay on Plastic Pollution. Plastic has become an integral part of our daily lives. We begin our day using mugs and buckets made of plastic for bathing. Further, as we trace back our activities throughout the day, we use plastic in the form of water bottles, combs, food packaging, milk pouches, straws, disposable cutlery, carry bags ...
Polythene pollution has widespread and myriads of effects on ecosystem: • Polythene pollution through biomagnifications enters the food chain and increases along the trophic levels. • Polythene obstructs the drains, natural water …show more content…. • Plastic polythene bags must be banned altogether or by levying tax on plastic bags ...
Thus, we have obtained the BDP with lots of efforts and researches, and more researches are carried out throughout the globe to meet the demands of the masses and to replace the polythenes completely with BDP. A polythene-free environment will be a safer world for everyone. 8.3. Types of biodegradable plastics
A.1 Plastic Pollution is on the rise because nowadays people are using plastic endlessly. It is very economical and easily available. Moreover, plastic does not dissolve in the land or water, it stays for more than hundred years contributing to uprise of plastic pollution.
Paragraph on the Environment 100 Words for Class 1, 2, 3 Kids. The environment is the circumstance in which all-natural resources of earth adapt to live. Humans, animals, trees, oceans, rocks are the natural resources of the earth and together create an environment. They are responsible to provide living conditions for an organism.
This article makes the case for the former by highlighting a range of emerging applications of polyethylene in energy and sustainability, including passive cooling of electronics and wearables, water treatment and harvesting, and even ocean cleanup from plastic waste debris. Usually, when the word "polyethylene" is mentioned in the context ...
Polythene or polyethylene is a polymer of ethylene gas (CH2=CH2) which is commonly used in our day to day life like grocery bags, shampoo bottles, bullet proof vests etc. Several kinds of ...
Conclusion: Should be banned to preserve our environment. Plastic was one of the most important inventions of the last century. Out of its various derivatives one form is polyethylene commonly called polythene, made from hydrocarbons, a by-product of petroleum, an important energy fuel. Being tough and light it has great industrial and ...
Hazards of Polythene Bags Essay 150 words: Polythene bags, also known as plastic bags, are a common sight in our daily lives. They are used for a variety of purposes, including carrying groceries, storing items, and disposing of waste. While they may seem convenient, polythene bags can pose serious hazards to both the environment and human health.
Short Essay on Plastic Pollution 200 words - Essay 1. Plastic pollution is caused due to the accumulation of the waste plastic material in the environment. Plastic is a non bio-degradable substance. It doesn't get disposed off in the soil or water and its effect is worse when burnt.
Essay on Plastic Pollution for Students in English [500+ Words] August 29, 2021 by Sandeep. Plastic Pollution Essay: On average, around 8 million metric tons of plastic garbage and waste are collected in the oceans every year. The economically low plastics prices have increased their usage rate, but this material is highly non-biodegradable ...
Essay on Ban on Plastic bags to Save Environment - Essay 5 (600 words) Introduction. Plastic is a man-made substance. Unlike natural substances, it is difficult to dispose of plastic as it is non-biodegradable. Plastic bags are used extensively throughout the world and produce a large amount of waste. It is a waste that remains on earth for ...
A huge amount of plastic bags and other stuff has been thrown in the sea every year. They are really dangerous to sea life. Lots of sea fishes and other animals might eat it as food. But they will not be able to digest that for their entire life. That could be a reason for their death. So you can assume that it's a threat to biodiversity.
There are tons of harmful effects of polythene in the environment. First of all, it is the cause of pollution of water and soil. It interrupts the wildlife. A report says that it is killing 100,000 animals every year including whales, turtles, penguins, and dolphins. These are the most important part of wildlife and sea life.
Firstly, plastic bags are a major source of plastic pollution. As they are non-biodegradable, they take years to decompose. They contribute to a lot of waste which keeps collecting over the years. Plastic takes thousands of years to break down and decompose. It remains in the land which contributes to the rising problem of land pollution.
Find an answer to your question the effect of polythene on the environment - essay - USE ABOUT 50 OR 60 WORDS ... It is one of the more unusual essay questions that any business school can ask an applicant: "Share with us your list of "25 Random Things" about YOU." ...