To read this content please select one of the options below:
Please note you do not have access to teaching notes, determinants of financial inclusion in rural india: does gender matter.
International Journal of Social Economics
ISSN : 0306-8293
Article publication date: 24 June 2020
Issue publication date: 2 July 2020
Since finance is an efficacious instrument for economic development, social inclusion and women empowerment, the present paper examines the determinants of accessing institutional and non-institutional finance across male- and female-headed households in rural India.

Design/methodology/approach
Multinomial logistic regression is applied for categorizing households' accessing finance in four categories, namely Only Institutional Finance (IF), Only Non-institutional Finance (NIF), Both Sources of Finance (BF) and Neither Source of Finance (N). Both household and state-level determinants have been analysed. Household data set is sourced from the Situation Assessment Survey (NSSO, 70th round) and state-level data sets from Basic Road Statistics 2016, Agricultural Statistics at a Glance 2016, Rainfall Statistics of India 2014, database on Indian Economy RBI and Census 2011. Econometric regressions have been evaluated for female-headed households (FHHs), male-headed households (MHHs) and overall pooled households (HHs).
Four important findings emerge. First, FHHs have a lower probability of accessing IF and a higher probability of accessing NIF vis-a-vis MHHs. Second, in general, education levels, monthly household consumption expenditure, land size holding, irrigated area and penetration of scheduled commercial banks favourably influence FHHs accessing IF. Third, FHHs belonging to socially disadvantaged castes have a lower probability of accessing IF. Fourth, a substantial proportion of FHHs accesses neither IF nor NIF relative to MHHs.
Practical implications
The paper thoroughly addresses the issue of accessing finance by FHHs and MHHs, which will further assist policymakers in formulating holistic financial policies for rural India.
Social implications
The paper recommends increasing women's access to financial services as an effective tool for reducing poverty and lowering income inequality in rural India.
Originality/value
This article contributes to the scant empirical literature on finance and gender.
- Institutional finance
- Non-institutional finance
- Infrastructure
- Multinomial logistic regression
- Rural India
- Economic policy and development
Kaur, S. and Kapuria, C. (2020), "Determinants of financial inclusion in rural India: does gender matter?", International Journal of Social Economics , Vol. 47 No. 6, pp. 747-767. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJSE-07-2019-0439
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2020, Emerald Publishing Limited
Related articles
We’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here
Advertisement
Digital financial inclusion: next frontiers—challenges and opportunities
- Original Research
- Published: 18 August 2021
- Volume 9 , pages 127–134, ( 2021 )
Cite this article

- Chandra Mohan Malladi ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3377-4673 1 ,
- Rupesh K. Soni 1 &
- Sanjay Srinivasan 1
12k Accesses
22 Citations
Explore all metrics
India’s Financial Inclusion journey has been phenomenal in the last decade and expressly promoted by the Government of India through their Digital India Movement & Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana. Reduction of poverty and addressing the challenges of ensuring sustainable income could become a key factor to achieve an inclusive society. Information and Communication Technology are providing access to unbanked population progressively and helping to bring them into the banking segment. Digital Technologies are driving usage and making a positive impact on livelihood of citizens. In this paper we are discussing on what is achieved in Financial Inclusion so far and what next and how do we leverage and harness digital technologies to achieve an inclusive society. This paper enlists various challenges that continue to prevail in achieving an inclusive society. We have put forth recommendations on addressing the key challenges and qualified the importance of collaboration and transparency between all the key stakeholders to achieve an inclusive ecosystem.
Similar content being viewed by others
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): The Role of Government in promoting CSR

Sustainability, FinTech and Financial Inclusion
Transition towards green banking: role of financial regulators and financial institutions
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.

1 Hypotheses Development
How do we enhance the process of Digital Financial Inclusion? How can Information and Communication Technology help in providing the citizens with a sustainable livelihood and inclusive growth? How can we safeguard the people who are included in the FI Framework and guarantee that they will not be excluded again?
To achieve a financially inclusive society that is sustainable and promotes inclusive growth for all, we need to provide the citizens of the country with access to education, basic financial services, affordable healthcare & suitable way for upskilling and improving their talent. They should be brought inside the legal framework where they can sustain and thrive.
The high amount of disparity and digital divide between Urban & Rural areas in India must be eliminated and people must be educated financially and included socially. There must be a cohesive ecosystem where Financial, Social & Health Inclusion that can work in tandem to accomplish a sustainable inclusive society. India’s digital payment and rural infrastructure must be improved to ensure zero disruption and continual access to telecom networks. Access to line of credit must be provided with adequate last mile services to ensure service delivery.
2 Deployment Approach and Methodology
This research study used quantitative and qualitative data from various official sources such as websites of Reserve Bank of India, Niti Aayog, Direct Benefit Transfer, PM Jan Dhan Yojana and other information published officially by the Govt. of India and Ministry of Finance. The data points and facts visibly showcase the impact of Financial Inclusion so far in India and helps us understand the gaps that must be filled to improve growth and ensure sustainability.
Comprehensive secondary research from published journal articles and expert committee opinions were considered to understand Digital Financial Inclusion initiatives and details of the best practices followed in various geographies. By leveraging this information, we have identified the key problems preventing us to realize an inclusive society and we have provided with qualified recommendations to tackle this.
Inclusive society is well-defined in terms of Financial Inclusion, Social Inclusion & Health Inclusion. Consistent with this approach, we define our key dependent variables ‘finance’ —as the access to a line of credit, availability and usage of basic financial services, ‘social’ —access to education and literacy, improvement of skills, & ‘health’— Personal & Societal Wellness. From this, we can understand that we are deploying a self-reporting measure to evaluate our research findings and we have substantiated our recommendations with real world examples from other studies conducted in similar functions. Prior research also acknowledges the subjectivity of these self-reported measures of FI [ 24 ].
3 Introduction
Financial Inclusion (FI) means delivering basic financial services to the marginalised and excluded members of society. It is the process in which we ensure adequate line of credit accessible by the weaker section of the society at a reasonable cost. Financial inclusion helps in developing a culture of savings among semi urban and rural population by bringing low income groups within the formal framework of banking and insurance sector which is significant for national economic development. It came into prominence around 2008 when it became clear to the government that it needs to be the key driver for economic growth of the country. Vision for Financial Inclusion in India is to induce inclusive financial growth by including the unbanked and unsupported individuals and MSMEs by formal financial institutions by providing them convenient access to basic financial products including bank accounts, remittances, bill payments, government supported insurance, pension products and formal credit at reasonable costs. There has been a growing evidence on how financial inclusion has a multiplier effect in boosting overall economic output, reducing poverty and income inequality at the national level.
With the advent of “ Digital India Movement ” and telecom penetration to deep rural areas, sincere efforts are made to bring widespread formal banking channels and innovative financial technology together to create a viable and vibrant ecosystem to drive accessibility of formal financial products to unbanked and deprived segments of Indian society. We at TCS, started this journey very early for some of our partner banks, with the services related to opening of no-frills accounts, delivering smart cards containing balance and biometric information to registered on the card. There was no active network connectivity during initial stages of FI. Last mile agents used to visit the bank, withdraw money & beneficiary list, go to each beneficiary, authenticate with biometrics, and deliver the services. Post which, they go back to the bank to reconcile. Out of 650,000 villages in India, around 150,000 was identified by the govt. initially to service through BC Model [ 15 ].
Fast-forward now, there is far more online connectivity in the remotest areas, smart card is replaced by real time Aadhaar based authentication, beneficiary enrolment & transactions can be done in real-time in field. Last mile channels like micro ATMs, Kiosks, PoS machines, Tablets, Mobile Phones are utilised for service delivery. Basic requirement of UPI based FI transaction is that the beneficiary account should be opened through PM JDY scheme and it is linked to the customer’s mobile number. Banks started channelling UPI based transactions on opened bank accounts. As of 2019, little over 470 Mn (~ 34.47%) is urban population of India. However, more than 65% are in semi urban and rural areas where access to digital services is lesser than major cities [ 13 ].
There is a great need for inclusive growth. By leveraging digital technologies, this is a great opportunity for Govts. and market leaders to improve digital penetration, ease of use of digital products, contextualised and personalised offerings to citizens increase availability, drive down costs, enhance security and trust. There is a need for sustainable cooperation between govts., businesses and unbanked population [ 15 ].
National leadership and policy making institutions like RBI and Niti Aayog have brought in some strong initiatives for inclusive growth which culminated in National Mission for Financial Inclusion namely Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana PM JDY leveraging banking network and technology innovations. It enabled access to financial services and coverage of banking to excluded population.
Till date over 344.3 Mn plus new accounts have been opened and a bunch of social and financial security products are offered to the account holders like entrepreneurial credit, financial advice, mortgage, loans and insurance, overdraft of ₹10,000, Accidental Death cum Disability Insurance (PMSBY), Term Life Cover under PMJJBY, Old Age Pension (APY scheme), PM Kisan, Educational Scholarships to students etc. [ 6 ].
With over 95% of Indian population having Unique Identification through Aadhaar, India achieved 80% of adult population having bank account by 2017. 77% Indian Women have bank accounts. In the outbreak of Covid-19 pandemic, this back bone of bank account has been instrumental to provide help of ₹500 per month for 3 months to over 200 Mn woman beneficiaries, transfer of ₹6000/- in 3 instalments per year (currently citizens are receiving their 8th instalment) of PM Kisan Samman Nidhi Yojana to farmers through direct benefit transfer schemes [ 10 ]. Under PM JDY, 423.7 Mn total no of Beneficiaries of which 279.5 Mn Semi Urban/ Rural Beneficiaries [ 24 ]. Rapid digital penetration along with enhancing the financial literacy of people has started. We are moving from assisted to self-service model for multiple services.
For almost all the public and private sector banks, TCS has provided its Financial Inclusion Solution Suite enabling end to end integration with their core banking systems (CBS) through its Branchless Banking Solution. With a wide range of services catalogue, TCS is delivering last mil services to over 150 + thousand locations. TCS has been the technology service provider (TSP) to DBT for various stake holders in which we are running a Heterogenous Technology System for money transfer. TCS is co-ordinating with multiple stakeholders in the DBT value chain such as Central & State Govts., banks & financial institutions in the country, RBI. DBT has proven to be critical in arresting leakage of govt. funds (~ ₹1700 Bn), eliminate involvement of middlemen in transactions, has capacity to cover a variety of areas, increase the number of beneficiaries (~ 770 Mn) and transactions and lower the distribution cost per transaction (Over 6 Mn Trnxs/day) [ 11 ].
Multiple technological solutions such as FI Platform, Beneficiary Registration Application, TCS BaNCS Enterprise Payments Hub, APBS (Aadhaar Payment Bridge System) Adaptor, TCS BaNCS CBS, Aadhaar Data Vault Solution were implemented by TCS and leveraged for end-end service delivery. RBI has played the guiding role which helped banks in achieving various objectives such as the introduction of MICR based cheque processing, Implementation of the electronic payment system such as RTGS (Real Time Gross Settlement), Electronic Clearing Service (ECS), Electronic Funds Transfer (NEFT), Cheque Truncation System (CTS), Mobile Banking System etc. [ 8 ].
Further to that, under the Digital India Movement, various digital payment methods—UPI, BBPS, IMPS, NETC, AePS, etc. were launched by NPCI, in coordination with RBI, some of which was run by TCS on behalf of RBI & NPCI. RBI’s working group reviewed the BC Model and suggested that BC agents or BF agents (Business Facilitator) can deliver last mile services in semi urban & rural areas. Individuals working as PCO Operators, Retired Teachers, Petrol Pump Owners, Grocery, Chemist & Fir Price Shop owners, NGOs, MFIs, SHGs linked to banked were authorised to act as last mile agents and provided a commission based on amount of services rendered [ 9 ].
There is a huge market for several financial institutions & other ecosystem players in the bottom of the pyramid by creating right products & services and ensures it reaches the intended customer [ 15 ]. TCS has been chosen as primary service provider for kiosk banking solution for many of the Customer Service points established by various Public Sector Banks (PSBs).
4 Current Challenges and Observations
People included in the Financial inclusive ecosystem end up getting excluded and are not able to sustain within the framework due to various reasons general or health related causes [ 1 ].
There is a clear demarcation of digital divide among—some are tech savvy people and delivering the services and making them understand is not difficult, where as some in semi-urban and majority of people in rural areas find difficult to understand and utilise technology efficiently [ 16 ].
Lack of financial literacy and awareness on financial cybercrimes has resulted in general mistrust among rural population which leads to reduced digital penetration [ 27 ].
There is a burden on running sustainable last mile delivery model, particularly in rural areas & last mile level service delivery. Multiple Govt. & Business agencies are trying to reach the same location for various reasons related to FI, Social or Healthcare inclusion and these are disjoint efforts and driving higher costs.
Different data elements available with govt. such as healthcare schemes data, social inclusion data, COVID data, vaccination data, etc. are not leveraged to full extent as there is clear lack of coherence between these data elements.
Last mile technological systems and artefacts are vulnerable to exposure and exploitations. It is loosely handled by BC or BF agents as adequate security measures to control it are not put in place. This has resulted in lot of frauds happening on the ground. About 22% BC agents faced fraud in 2017, a noteworthy increase from 2% in 2015 [ 17 ]. Business model of Last mile & BC Agent network must be looked at again from privacy security & safety angle.
Data Privacy is still a major concern as a lot of captured data is easily available to various stakeholders as PII norms are not completely followed. KYC Data & mobile numbers are available everywhere.
Biometric data is captured duplicitously by some BC Agents in clay who will replicate it later for fraudulent reasons.
Another way is when they give a manual receipt instead of computerised one during transactions.
SMS messages for transactions in an account are not reaching the customer due to lack of mobile device (More than 310 Mn people still do not possess a basic feature phone or a smart phone) or financial institutions are not sending these messages for low value transactions. This has led to increased dependency on local agents.
Access to credit is still a concern as small time lenders charging high rate of interest are prevalent in rural areas. Govt. schemes have not penetrated fully and need more rural outreach to enhance credit access [ 15 ]. Lack of avenues for digital lending and online loans from credible financial institutions is missing.
Recommendations for individuals based on their requirement is not provided and leveraging the personalised data of the person, by performing analytics using AI & ML, banks can offer loans, insurance and other services based on analytics & credit score [ 15 ].
5 National Strategy for Financial Inclusion
In the year 2020, RBI came up with national strategy for Financial Inclusion with focus on creating an outreach of financial services outlets to provide banking access to every household within 5KM radius. All eligible adults must have access to basic financial services such as Bank Account, line of credit, both life and other insurance, pension scheme and suitable investment product. Now, the next paradigm for financial inclusion program (2020–2024) is focused addressing inherent behavioural and practical aspects [ 22 ].
A strong financial transaction grievance redressal system to address concerns of arguably less technology savvy citizens.
Increasing digital penetration as still the smartphone usage for financial transactions are limited to urban and semi urban population predominantly.
Bank account opening for the remaining population of the country as still the PMJDY penetration is about 80% of the population.
Ensuring the privacy of data and information of citizens and prevention of fraudulent transactions and demographic data.
Easy and affordable digital payment options to suit the needs of small businesses and unstructured sector workers.
Providing access to basic and most essential financial products such as transactional accounts, digital payments, basic term insurance, basic medical insurance, and pension options to the population specially in the agricultural and unorganized MSME sector workers.
Acc. to a World Bank report, globally achieving Universal Financial Access by 2020 [ 3 ] has been one of the key developmental agenda of the World Bank which aims to provide adults who currently aren’t part of the formal financial system, with access to a transaction account to store money, send and receive payments to manage their financial lives. Our National Strategy is also aligned to these broad virtues suggested by World Bank. On key parameters, India is quite ahead and continuously progressing:
Leadership in India is having singular focus on technology enabled financial inclusion. It is evident through steps like DBT, PM Kisan, financial assistance to woman and poor during the recent Covid-19 pandemic etc.
Target based approach for specific sectors & regions including “National Mission for Capacity Building” by bankers for MSME sector, Certified Credit Counsellor Scheme for MSME to join them with the formal Financial Channels and informed financial credit decisions.
Regulatory Framework in Banking to protect customers, promote fair business processes and prevent unhealthy practices by market players. Initiatives like exclusive “Financial Inclusion Fund” (with initial corpus Rs.2000 Crore), issuances of differentiated banking license—Small Finance Banks, Payments Banks etc., launch of BC Registry with Indian Banks Association (IBA) etc. are steps towards the same.
Market Development initiatives like Branch Authorization Guidelines (2017) etc. to ensure accurate targeting of the beneficiaries, de-duplication and reduction of fraud and leakage have been taken. Linking all financial assistance schemes to DBT is a strong footprint in this direction
Strengthening Payments Structure through digital retail payments systems like AEPS, NACH, UPI, CTS, IMPS etc. operated by NPCI are significant steps. Aadhaar linked direct benefit transfer has changed the scenario for public funds distribution in India.
Last mile delivery to bridge the gap for remote connectivity and doorstep financial services is key to success. ICT based solution like business correspondents/ facilitators and IPPB are landmark steps in this area, launch of UPI on features phones will be a big game changer also enabling ecosystem for NFC based touch less payments.
Financial Literacy and Awareness is a primary bottleneck in progressive financial inclusion in India. Launch of financial literacy program in 2013 helped in addressing this to some extent.
6 Sustainability through Comprehensive Inclusion
An inclusive society helps sustain socioeconomic development and understanding the correlation between Financial Inclusion, Social Inclusion & Health inclusion helps sustainability. Having taken the right initiatives to ensure wider coverage of Financial Inclusion, it is now time to look at the rationalization of the inclusive society by leveraging iterative technology and other two key aspects—Social Inclusion (Education, Literacy, Skill), Health Inclusion (Personal & Societal Wellness).
FI implemented in a standalone ecosystem may not be enough to achieve. FI must be complemented by Social and Health Inclusion through improving skillset, education, physical and mental well-being to ensure a sustained livelihood [ 12 ]. Current model has a major short-coming. If there is a functionality lapse in any single inclusion, someone may fall out of the inclusive ecosystem.
We need to ensure that whoever is excluded financially is brought into the fold again and has all the necessary tools to sustain within the ecosystem.
To handle this, we need to focus on increasing the digital penetration and continue the account opening process for all citizens. FI Ecosystem must aim to work in tandem with Healthcare Inclusion & Education Inclusion ecosystem to ensure well-being of people and educate the citizens financially. The technological initiatives under ‘JAM Trinity’, that is, PM Jan Dhan Yojana, Aadhaar and increased Mobile Phone & internet usage had led to 355 Mn accounts opened in the last 5 years (Figs. 1 , 2 ).
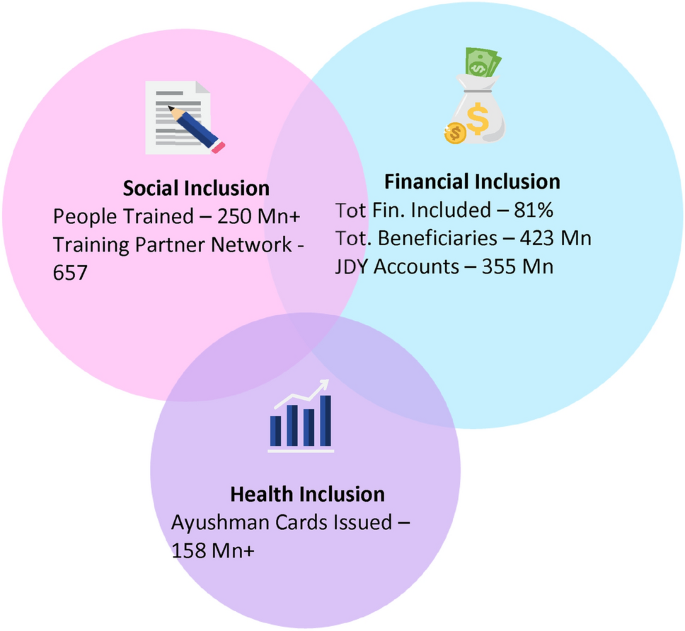
Current State in India
Desired State in India
Technology should drive the recommendations to every individual to ensure social, health and fin. Inclusion. Cross Leveraging of existing and new citizen databases to provide strategic Analytics & insights to the deciding authorities.
Blockchain could prove to be a gamechanger in enhancing the value chain securely without any duplications of efforts [ 23 ]. There following measures could be taken to improve the living standard of citizens using ICT technology to deliver last mile services [ 19 ]. They are,
Fix technological breakdowns and connectivity issues and ensure wider coverage in remote areas
Facilitate a hassle-free digital experience for new users
Enhance digital security standards to improve the confidence of citizens to make digital transactions
Finetuning limits on daily transactions and commissions on low value withdrawals & deposits
Make changes to the minimum balance criteria in SB Accounts
Delivery services at BC points through Controlled devices for better safety and security for end users
People should be educated and learn to protect themselves against financial cybercrimes. Provide profile wise recommendations and better offers for people by leveraging Analytics, AI & ML using the data gathered from available official databases. For ex., through COVID Patient DB, recommendation for vaccination, availability of various health insurance schemes, access to medical loans could be provided. Building information sharing systems leveraging multiple public databases is crucial for success.
One such example may be leveraging the vaccination database to provide profile wise vaccination recommendations, information regarding availability of loan and credit lines, developing a ‘fraud repository’, and ensuring that online digital commerce platforms carry warnings to alert consumers to the risk of frauds etc. can play a game changer role in FI endeavours. RBI has guided banks to introduce a General-Purpose Credit Card (GCC) facility. It is revolving credit which entitles the card holder to make transactions of Rs 25,000 above the credit limit. This is completely based on customer's credit assessment and the limits are sanctioned without any security or collateral. Rate of Interest on revolving credit is deregulated. Under PM SVANidhi Scheme, micro lending amount of up to Rs 10,000 is provided to street vendors as working capital. Under PM MUDRA scheme, credit is provided to non-corporate, non-farm SMEs up to Rs 1 million. Microfinance institutions can help widen the coverage of reach by offering their services in remote areas using analytics & basic credit risk assessment [ 20 ].
7 Observations and Recommendations for accelerating Financial Inclusion
Innovations in the field of technology & communications strongly complements the FI ecosystem which results in inclusive socio-economic growth. This improves transparency and competitive efficiency, has the potential to reduce cost of service delivery and strengthens the back-end administrative processes [ 21 ].
The objective of providing a basic bouquet of financial services can be achieved through designing and developing customized financial products by banks and ensuring efficient delivery of the same through leveraging of FinTech and BC networks [ 18 ]. Some of the constructive recommendations are following-
Combining Financial inclusion with health inclusion and Social Inclusion to make the it more inclusive for citizens in the lower strata of the society. PM SBY, PM JJBY, RWBCIS, Ayushman Bharat (PM JAY) must be promoted. Till date, 158 Million + Ayushman Cards issued which requires expedite efforts to reach the full population of eligible citizens.
By analysing the impact of COVID-19, we can leverage FI and drive vaccination programs and other welfare schemes such as access to Medical Insurance & Loans for the needy. Comprehensive coverage of Health & Wellness through various initiatives to drive Health & Social Inclusion to achieve a sustainable growth [ 7 ].
Crucial aspect of FI is Financial Literacy [ 27 ]. Promote Financial Literacy and educate people on features such as Phone Banking, UPI & NFC enabled feature phones can be made available at low cost, enhance touchless payment (NFC & QR) framework. Common features such as Bill Payments, Ticket Booking are already interoperable through Bharat QR.
Strengthening the payment infrastructure to promote a level playing field for (NBFCs) and banks. Digitizing registration and compliance processes and diversifying credit sources to enable growth opportunities for MSMEs is an essential step for comprehensive inclusion [ 2 ].
Enabling agricultural NBFCs to access low-cost capital and deploy a ‘physical’ (physical + digital) model suggested by Niti Aayog for achieving better long-term digital outcomes is a crucial step. Digitizing land records will also provide a major boost to the sector.
Tech should aim to reduce cost per transaction and continue to drive the recommendation to every individual to ensure, social, health and financial inclusion and ensure that the money has been reaching the last mile beneficiary at low costs [ 26 ].
By combining digital education tools & digital financial tools, and slight changes to tax regulations, underbanked & unbanked people can break the chain of poverty and sustain successfully in a cash lite economy [ 5 ].
Geospatial technology could be used to analyse the population density of target service areas so that there is a clear understanding of required amount of work force for a particular area and can also be used to identify gaps in current services [ 25 ].
8 Summary of Key Problems we identified
Summary of problems identified & possible solutions in brief is displayed below in Table 1 .
In conclusion, we can say that a technological, multi-faceted & dynamic approach centred around enhancing financial literacy, social & education inclusion, improved cybersecurity & stricter laws, enhanced digital infrastructure is mandatory for wider coverage of next wave of financial inclusion in the country.
Data availability
All the data used in this paper for research purposes are properly cited with references to Source.
Abbreviations
Point of Sale
Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises
Reserve Bank of India
Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana
Under PM Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana
Atal Pension Yojana
Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana
Aadhaar Payments Bridge System
Core banking system
PM Kisan Samman Nidhi Yojana
PM Street Vendors' Atmanirbhar Nidhi
Pradhan Mantri MUDRA
Bharat Interface for Money
Unified Payments Interface
National Automated Clearing House
Business correspondent network
Direct benefit transfer
Aadhaar enabled payments system
Cheque truncation system
National Payments Corporation of India
- Information and Communication Technology
Indian Post Payment Bank
PM Jan Arogya Yojana
Restructured Weather Based Crop Insurance Scheme
Near Field Communication
Non-Banking Financial Company
Albert P-U, Sílvia B, Dolors C, Dolores Á-J, Luïsa OG, Àngels O, Joan-Pau M (2020) Evidences supporting the inclusion of immigrants in the universal healthcare coverag. Eur J Public Health. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurpub/ckaa020
Article Google Scholar
Babajide AA, Oluwaseye EO, Lawal AI, Isibor AA (2020) Financial technology, financial inclusion and msmes financing in the south: West of Nigeria. Academy of Entrepreneurship JOURNAL. 26
Bank W (2018) UFA2020 Overview: Universal Financial Access by 2020. Retrieved from World Bank: https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/financialinclusion/brief/achieving-universal-financial-access-by-2020
Birgitta DS, Ghozali M, David K, Rachmad KS (2020) The effect of financial inclusion and financial technology on effectiveness of the indonesian monetary policy. Bus Theor Pract. 21–24
Chu AB (2018). Chapter 6: mobile technology and financial inclusion. handbook of blockchain, digital finance, and inclusion. Volume 1
Committee R (2008) Rangarajan committee report on financial inclusion. IMaCS Research, RBI
Cornelius CA, Qusay HM, Mikael E (2019) Blockchain technology in healthcare: a systematic review. Healthcare. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare7020056
Gupta SK (2011) Financial Inclusion: IT as enabler. Reserve Bank of India Occasional Papers
IBEF (2019) Technology application for financial inclusion. India Brand Equity Foundation
India D (2021) PM Kisan Samman Nidhi 8th installment: Get Rs 2,000. Retrieved from DNAIndia: https://www.dnaindia.com/personal-finance/report-pm-kisan-samman-nidhi-8th-installment-get-rs-2000-by-this-date-check-your-name-on-beneficiary-list-2888141
India GO (2021) Direct benefit transfer. Retrieved from DBT Bharat: https://dbtbharat.gov.in
Isukul A, Tantua B (2021) Financial inclusion in developing countries: applying financial technology as a Panacea. South Asian J Social Stud Econ. https://doi.org/10.9734/sajsse/2021/v9i230237
JDY P (2021) PM Jan Dhan Yojana. Retrieved from https://pmjdy.gov.in/
Jesse LM, Blake M (2017) Banking on distributed ledger technology: can it help banks address financial inclusion? Economic review. 3rd Quarter
Malladi CM (2020) Toward financial inclusion: executive viewpoint. MIT Sloan Management Review, India
Google Scholar
Marco J (2018) The struggle for digital inclusion: phones, healthcare, and marginalisation in rural India. World Development, p 104
Mishra A, Komal G (2018) Microsave Report. Retrieved from Live Mint: https://www.livemint.com/Industry/4jL1r9XnS43BbwdEOZEVLO/Over-20-of-business-correspondents-faced-fraud-in-2017-Mic.html
Murthy G, Fernandez-Vidal M, Faz X, Barreto R (2019) Fintechs and financial inclusion: looking past the hype and exploring their potential. Consultative Group to Assist the Poor (CGAP)
Nirosha HW, Ahmed IH, Riadh M, Stuart M (2021) Information communication technology and financial inclusion of innovative entrepreneurs. Technological Forecasting and Social Change
Noronha M, Kumar VR (2019) Technology: a tool for achieving inclusive and sustainable growth through financial inclusion. CLEAR Int J Res Commerce Manag 10(2):1
Ozili PK (2020) Financial inclusion research around the world: a review. Forum for Social Economics
RBI (2018) National strategy for financial inclusion 2019–2024. Reserve Bank of India: Executive Committee, India
Schuetz S, Venkatesh V (2020) Blockchain, adoption, and financial inclusion in India: research opportunities. Int J Inf Manag. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2019.04.009
Sridhar N (2021) Jan Dhan accounts surge to 42 cr with total balance at ₹1.4-lakh cr. Retrieved from The Hindu: https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/economy/jan-dhan-accounts-surge-to-42-crwith-total-balance-at-14-lakh-cr/article34100792.ece
Ul Haq I, Gradstein HL (2020) Leveraging geospatial technology for financial inclusion: financial inclusion support framework. Open Knowledge Repository
Vrajlal S (2018) Chapter 14: financial inclusion, digital currency, and mobile technology. In: Handbook of blockchain, digital finance, and inclusion. p 27
Warhamni, Rahmi N (2021) Financial technology determination in terms of financial inclusion and financial literacy. In: Conference on economic and business innovation (CEBI), 1
Yan S, James H, Wenxiu H (2019) Using digital technology to improve financial inclusion in China. Appl Econ Lett. https://doi.org/10.1080/13504851.2019.1606401
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Enterprise Business Platforms, Tata Consultancy Services, Mumbai, India
Chandra Mohan Malladi, Rupesh K. Soni & Sanjay Srinivasan
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Chandra Mohan Malladi .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest, consent to participate, consent for publication, rights and permissions.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Malladi, C.M., Soni, R.K. & Srinivasan, S. Digital financial inclusion: next frontiers—challenges and opportunities. CSIT 9 , 127–134 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40012-021-00328-5
Download citation
Received : 01 June 2021
Accepted : 04 July 2021
Published : 18 August 2021
Issue Date : June 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s40012-021-00328-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Financial Inclusion
- Social Inclusion
- Health Inclusion
- Sustainable Growth
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1. Background. In many rural areas, cash is still the preferred mode of transaction, and savings are often kept in the form of physical assets like gold or land (Matin et al., Citation 2002; Zelizer, Citation 2021).However, with the advent of digital financial services and the government's push for financial inclusion, there has been a gradual shift towards more formal financial management ...
Anand and Chhikara (2013), and Lal (2017) related economic growth of a nation to financial inclusion of rural households and identified penetration as an important determinant of financial inclusion. Kabakova and Plaksenkov (2018) analysed and observed different patterns of financial inclusion based on different penetration levels. Penetration ...
This paper aims at exploring most relevant challenges and opportunities that deal with fighting against financial exclusion in rural areas. Their communities tend to be characterized by a lower ...
In India, extensive efforts have been made to foster financial inclusion as a development strategy. However, achieving fuller financial inclusion remains a far cry. Focusing on the supply, demand, and quality side of financial inclusion based on a rural household-level survey in Odisha, this study examines the status of financial inclusion for rural households and identifies the factors ...
The study was also conducted by the World Bank for rural India and research shows that only 40% of households had bank accounts (Subbiah, 2012). ... with financial inclusion in rural India. However, there is a lack of research that has identified the challengesassociated with financial ... This is the most important section of the paper as it ...
Abstract: Financial literacy as a major catalyst in the area of inclusive growth has obtained utmost prevalence, based on which this study intended to analyze the role of financial literacy in ensuring financial inclusion which further enhances socio-economic empowerment in rural areas of Karnataka, India.
It is important to quantify the role that fintech plays in promoting financial inclusion in rural India, thus researchers there are using confirmatory factor analysis to identify the most important contributing factors and structural equation modeling to analyze the data. ... World Bank Policy Research Working Paper No. 8913. Available online ...
DOI: 10.13189/u jaf.2022.100 21 3. Impact of Financial Technology (Fintech) on. Financial Inclusion (FI) in Rural India. Shubham Goswami1,*, Raj Bahadur Sharma, Vineet Chouhan 1. 1 School of ...
1. To analyze the nature and extent of financial inclusion among the households of vulnerable sections across the rural and urban segments. 2. To assess the economic and social impact of financial inclusion on households belonging to the vulnerable sections. 3. To suggest a model for the effective financial inclusion policy that would benefit
Financial inclusion is a very important issue in developing countries like India. It is identified as one of the seventeen sustainable development goals (SDGs) which enables in poverty reduction and promoting economic development. Over the past few years, with a major shift in the policy focus towards programs on increasing financial inclusion, significant progress has been observed. The paper ...
The findings of the paper will help the policymakers and the academicians to study further in the aspects of issues and challenges in rural financial inclusion. Content may be subject to copyright ...
The purpose of the study is to evaluate the need of Financial Inclusion in India. In order to achieve this objective the following issues have been examined: 1. To evaluate the role of different Financial Institutions towards Financial Inclusion. 2. To examine the extent of financial exclusion in rural India 3.
We propose research questions to help us study blockchain and financial inclusion in India. The economic development of rural India requires connecting remote villages to local and global supply chains. Yet, high rates of financial exclusion inhibit rural Indians from participating in these supply networks. We review the literature on financial ...
The paper thoroughly addresses the issue of accessing finance by FHHs and MHHs, which will further assist policymakers in formulating holistic financial policies for rural India. Social implications The paper recommends increasing women's access to financial services as an effective tool for reducing poverty and lowering income inequality in ...
1 The paper is based on field research and extensive consultation with former members of the Reserve Bank of India- Dr. D. ... The level of financial inclusion in India can be measured based on three tangible and critical dimensions. ... All-India Rural Credit Survey that was completein the 1950s. d The results of the survey revealed that
The research using primary data set is limited. A few studies attempted to identify the crucial factors for the extent of financial inclusion in India, that is, education, income, financial information, access, usage, and self-help groups (Bhanot, Bapat, & Bera, 2012; Bhutoria & Vignoles, 2018; Siddiqui & Siddiqui, 2017). Thus, the variable ...
India's Financial Inclusion journey has been phenomenal in the last decade and expressly promoted by the Government of India through their Digital India Movement & Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana. Reduction of poverty and addressing the challenges of ensuring sustainable income could become a key factor to achieve an inclusive society. Information and Communication Technology are providing ...
Access to financial services opens the doors for families, allowing them to smooth out consumption and invest in their future through education and health. This report focuses on financial Inclusion in rural India covering specific public sector initiatives and private sector innovations in the areas of banking, ATM and other modes of payment.
It is financial inclusion in rural economy can facilitate rural development and thereby over all development of the economy as a whole. Discover the world's research 25+ million members
9 min Read. A digital infrastructure known as the India Stack is revolutionizing access to finance. A decade ago, India's vibrant local markets were filled with people buying and selling goods with well-worn banknotes. Today, they are just as likely to use smartphones. Advances in digital finance mean that millions of people in the formal ...
Financial Inclusion in Rural India Punitha Ponnuraj1, Dr. Manasa Nagabhushanam2 1Research Scholar, Universityof Mysore, ISBR Research Centre,Bangalore ... Research Questions. This paper will aim to answer the following research questions based on an extended review and analysis of collected. RQ1: What are the mobile banking products or services ...
This study explores the nexus between digital financial inclusion and household participation in commercial insurance, utilizing data from the Peking University Digital Financial Inclusion Index and the 2018 CFPS database. Using Probit and Logit models, our research uncovers significant regional and risk -preference variations, emphasizing the influence of governance mechanisms. The study ...
Objectives of the study: 1. To measure the financial availability and financial usage indices for rural Marathwada. 2. To measure the extent of overall financial inclusion in rural Marathwada with ...
Financial inclusion through digital banking also enables women to utilize various financial services like savings accounts, loans, insurance, and investment opportunities. This allows women to engage in the formal economy, accumulate assets, and enhance their overall financial well-being. These efforts aid women in strengthening their financial ...
Methods: This qualitative study utilized semi-structured focus groups with teachers at public and private schools in rural South India. Thematic analysis and interpretive description were applied to analyze responses and situate results within the context of rural South India. Results: A total of 18 teachers participated in three focus groups.
from research papers, thesis, book, RBI reports and news paper articles. ... (2012), Financial Inclusion in Rural India: The Role of . ... Patil (2016) [10] did a study on Financial Inclusion in ...
formal cre dit (Go vernment of I ndia, 2 011). Against this backdrop, this study h as s et t he. objectives as follows. First, this study studies the relative importance of the indicators of ...