- IELTS Scores
- Life Skills Test
- Find a Test Centre
- Alternatives to IELTS
- General Training
- Academic Word List
- Topic Vocabulary
- Collocation
- Phrasal Verbs
- Writing eBooks
- Reading eBook
- All eBooks & Courses

Job Satisfaction
by Vince Tseng (Ballarat)

Would you prefer to share this page with others by linking to it?
- Click on the HTML link code below.
- Copy and paste it, adding a note of your own, into your blog, a Web page, forums, a blog comment, your Facebook account, or anywhere that someone would find this page valuable.
Band 7+ eBooks
"I think these eBooks are FANTASTIC!!! I know that's not academic language, but it's the truth!"
Linda, from Italy, Scored Band 7.5

IELTS Modules:
Other resources:.
- All Lessons
- Band Score Calculator
- Writing Feedback
- Speaking Feedback
- Teacher Resources
- Free Downloads
- Recent Essay Exam Questions
- Books for IELTS Prep
- Useful Links

Recent Articles
Useful Language for IELTS Graphs
May 16, 24 04:44 AM
Taking a Gap Year
May 14, 24 03:00 PM
IELTS Essay: Loving Wildlife and Nature
May 10, 24 02:36 AM
Important pages
IELTS Writing IELTS Speaking IELTS Listening IELTS Reading All Lessons Vocabulary Academic Task 1 Academic Task 2 Practice Tests
Connect with us
Copyright © 2022- IELTSbuddy All Rights Reserved
IELTS is a registered trademark of University of Cambridge, the British Council, and IDP Education Australia. This site and its owners are not affiliated, approved or endorsed by the University of Cambridge ESOL, the British Council, and IDP Education Australia.
What Is Job Satisfaction and Why Is It Important?

Are you aware of what right actually means?
Determining whether you are satisfied with your job, whether it is right for you, and why that is important often involves personal intuition and circumstances. For some people, the right job might entail earning a certain salary. For others, the right job might involve having a supportive team.
With more than 21,000 participants in their study, researchers Dobrow, Ganzach, and Liu (2018) found that over a 40-year span, people who stayed in the same organization over time became less satisfied, and people who moved to different organizations over time became happier.
What does this mean? Does job satisfaction come from staying in an organization or leaving it? If someone were to stay in an organization, what would retain their satisfaction?
In this article, we will explore just that and more, including divulging the ingredients of job satisfaction, real-life examples of it, and how it relates to motivation.
Before you continue, we thought you might like to download our three Work & Career Coaching Exercises for free . These detailed, science-based exercises will help you or your clients identify opportunities for professional growth and create a more meaningful career.
This Article Contains:
What is job satisfaction, 10 proven ingredients for job satisfaction, is job satisfaction important 4 benefits, 2 real-life examples, a note on job satisfaction and motivation, positivepsychology.com’s job satisfaction tools, a take-home message.
Choose a job you love, and you will never have to work a day in your life.
You have probably heard that quote before, yet it may still have relevance today. It makes us ask whether emotions like happiness, stress, and anxiety play an important role in job satisfaction.
The aptly titled Job Satisfaction (Hoppock, 1935) defines job satisfaction as any combination of psychological, physiological, and environmental circumstances that cause a person to truthfully say that they are satisfied with a job.
Going a little deeper and fast-forwarding to this century, job satisfaction has been called a set of favorable or unfavorable feelings and emotions with which employees view their work (Karatepe, Uludag, Menevis, Hadzimehmedagic, & Baddar, 2006).
Before we get to favorable feelings or proven ingredients for job satisfaction, let’s first assess what leads to those unfavorable feelings.

The graphic above from the University of Southern California’s Applied Psychology Program shows some factors that make American employees unhappy or burnt out with jobs.
Many of us have experienced unhappiness because of these factors and more at some point in our careers. Let’s take a look at what can be done to satisfy ourselves in a job.

Although it is subjective, job satisfaction research (Kumari, 2011) has showcased the following:
1. Communication
Communication can be extremely important to retaining levels of satisfaction, on both a personal and professional level. It is exhibited in allowing employees to be open, collaborative, trustworthy, and even confrontational when needed.
Defining a company culture links to job satisfaction as it provides values and guidance about topics ranging from organizational goals to appropriate levels of interaction between employees.
3. Security
It’s no surprise that once a culture is established in a workplace, satisfaction can then be enhanced by added feelings of security. Security may arise from knowing you work for a viable company with long-term goals, insinuating feelings of belonging to that company (Berg, Grant, & Johnson, 2010). This can be enhanced by having honest communication and transparency within a company.
4. Leadership
Tied into increased motivation for employees, leadership, or influencing a group toward the achievement of a vision or set of goals (Kinicki & Kreitner, 2006), can lead to job satisfaction by making sure communication and instruction of tasks is adequate and easily understood.
In turn, when employees feel that leaders can guide them through tasks, their motivation and satisfaction increases.
With leadership having a crucial influence on job satisfaction, this related article with leadership activities is a recommended read.
5. Opportunities
Employees can gain more satisfaction with their job when more challenging opportunities arise. This can lead to participation in interesting and diverse projects and get employees away from the monotony of a role.
6. Career development
Employees can become more satisfied with their job when they know there is an individualized plan for them. Beyond the formal nature of appraisals, if there is a path in place for growth, this can encourage employees to stay happier for longer.
7. Working conditions
Job satisfaction can be increased if a resilient workplace is a cooperative environment. This means a place with respect for diverse ideas and opinions, honest and constructive feedback, mentoring opportunities, and freedom from harassment.
8. Employee personality
Most ingredients linked to job satisfaction may have roots in elements outside of the employees’ control (such as leadership from managers and communication from company leaders), but what about the employees themselves? Can they control their own levels of satisfaction? Bakker, Tims, and Derks (2012) talk about just that.
These researchers discuss how job satisfaction can be determined by how proactive the employee is at work. Does the employee proactively seek out a manager for feedback? Does the employee go the extra mile to achieve tasks within a company? Does the employee try to stick to company goals, lead meetings, and ask questions when unsure about how to complete a task?
If yes, these employees are ones who can show more satisfaction in the workplace. Proactiveness in the workplace can lead to positive job appraisals, which when fed back to the employee, can lead to satisfaction.
For more on constructive feedback, read our article discussing ways to give negative feedback constructively.
9. Pay and benefits
Organizational success and job satisfaction are also linked to employees’ perceptions of adequate pay and benefits (Edwards, 2008).
While pay and benefits are not the only reason employees find satisfaction in their workplaces, research going back more than 30 years (e.g., Gerhart, 1987) shows that pay and benefits, at least according to how employees view themselves in their roles, has ranked high on lists of job satisfaction factors.
10. Rewards and recognition
Beyond monetary gain and being paid fairly for the work they do, job satisfaction for employees means that promotional policies are unambiguous and in line with their expectations.
A key finding here (Kumari, 2011) is that satisfaction at a job is not exclusively linked to pay, but to the perceived fairness of how one is recognized at work for achievements.

2 Job Crafting Coaching Manuals [PDF]
Help others redesign their work. This manual and the accompanying client workbook outline a seven-session coaching trajectory for you, the practitioner, to expertly guide others through their own unique job crafting journey.
We have already discussed what employees look for in achieving and maintaining job satisfaction. But why is it important? And why should organizations care?
First, it is a primary responsibility of organizations to ascertain that employees are satisfied with their jobs through measurements, but also to find out the causes of dissatisfaction when employees are not feeling satisfied (McBride, 2002).
Tools such as the following help measure some important factors that go into employees’ job satisfaction (Spector, 1997, chapter 2):
- Job Satisfaction Survey (Spector, 1985)
- Job Description Index (Castanheira, 2014)
- The Minnesota Satisfaction Questionnaire (Weiss, Dawis, and England, 1967)
As to why job satisfaction is so important, the Employee Job Satisfaction and Engagement Report from the Society for Human Resource Management (Lee et al., 2016) notes four benefits of making sure employees are satisfied with their work.
1. Increased profits
This is one any manager and employee might appreciate. Keeping employees satisfied can lead to higher sales, lower costs, and a stronger bottom line.
2. Higher productivity
Irrespective of their job titles or salary, employees who are more satisfied with their job, whether they feel satisfied with the organizational culture, with the rewards they are getting, or with recognition, can produce more and do it more efficiently.
3. Lower turnover
If employees are more satisfied with their job, they are less likely to leave. It also helps to recruit better quality talent as new talent sees employee staying power as added value.
When employees feel there is a growth path for them, they are more satisfied. In turn, because they feel the organization has their best interests at heart, they tend to support the organization’s mission and objectives. When this happens, employees may tell their friends or relatives about the good nature of the organization, which helps spread organizational goodwill.
The Job Satisfaction Wheel can help assess your current job satisfaction and identify improvement areas. Job satisfaction measures subjective wellbeing at work (Judge & Klinger, 2008).
According to Roelen et al. (2008), there are seven key indicators of job satisfaction:
- Task variety
- Working conditions
- Education and development opportunities
- Person-environment fit
Here’s how you can use the Job Satisfaction Wheel:
- Rate the seven job satisfaction domains on a scale from one – “not at all satisfied” to ten – “completely satisfied”. Place a circle around each score on the wheel.
- Connect your scores by drawing a line and forming an inner wheel. This gives you an overview of how satisfied you are with your current job.
- Looking at the wheel, where do you see areas for improvement? What would it take to improve the score? Which action steps can you take?

Honesty and communication about a company’s objectives and goals can be vital and are linked to job satisfaction for employees. But do employees only care about company success? How does honest communication impact their own, individual success?
The importance of honesty and communication
Agarwal and Mehta (2014) were interested in employee job satisfaction within the IT industry.
Their curiosity stemmed from the idea that IT employees may largely be working in isolation, away from other employees, and the researchers wondered if employees valued appraisals more in such circumstances than in other industries. They discussed how performance appraisal was directly linked to satisfaction (or dissatisfaction) for the employee.
Additionally, they also discuss how honest and consistent communication and regular updates of employee progress (bi-annual rather than yearly appraisals) can not only increase employee satisfaction at work, but also help companies by decreasing the rate of attrition. Interestingly enough, Agarwal and Mehta (2014) did not discuss company goals or performance in their findings.
Let’s take a look at some familiar companies you may have heard of.
Although the phrase “the customer is always right” may be common, it does not seem to ring all true behind the scenes (or the counter, in this case).
The CEO’s mantra was that if managers look out for employees, employees will look after customers. To do this, he offered health insurance to all employees despite the excessive cost and being advised against it.
Is it surprising that good leadership strengths , recognition, and reward given to employees increased job satisfaction and in turn increased profits for Starbucks? It certainly fits in line with the aforementioned research in this article.
While also producing satisfied end-users like us when using Google’s products, Google puts a lot of work into job satisfaction for its employees as well.
It’s interesting to note that Google does not care (perhaps as much) about employee titles, but more about what type of leaders its employees are, or emergent leadership. This draws us back to the importance of positive leadership in job satisfaction.
Gillett (2016) writes that Google attracts talent with competitive pay and keeps employees satisfied by allowing telecommuting. This may show an appreciation for work–life balance and retention.
Gillett also writes that according to compensation and data company PayScale, nearly three-quarters of Google employees find their jobs meaningful, citing that Google’s mission is to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.
She describes Google employees thinking that their goal of working at Google is a moral rather than a business goal, which in turn creates motivation to innovate and push into new areas.
These sound like great organizational goals that drive profits. Furthermore, Google staff certainly demonstrate that job satisfaction can indeed lead to employees supporting the organization’s goals and objectives.

According to Latham (2012), motivation is a cognitive resource allocation process in which a person makes choices as to the time and energy to be allocated to an array of motives or tasks. The key word here seems to be choice .
When an employee is able to make a choice, they feel more motivated to perform a task. When an employee is more motivated to perform and complete a task, this tends to be linked with higher job satisfaction (Jalagat, 2016).
Choice, as directed or allowed by organizational policy, can lead to further motivation and, in turn, job satisfaction as well as performance. This seems to be echoed by the work of Ilies and Judge (2003).
Ilies and Judge (2003) discuss how leaders interact with employees, specifically by talking to them more as a person, and how assigning tasks and providing a career path can affect their motivation level.
When determining job satisfaction, it is key to remember that human factors such as motivation, excitement, satisfaction, and dissatisfaction must be considered. This is clearly indicated by the Starbucks example.
When employees are encouraged to be great leaders and to engage in challenging opportunities, such as at Google, they can end up feeling more satisfied with their job.
As one of the key ingredients of job satisfaction, communication among employees, managers, and staff cannot be underestimated.
However, communication is not automatically generated or achieved right away. When introducing new employees into a workplace, it may be even more important to establish good and fun communication procedures between employees.
This helpful article with work-related communication games and exercises can help improve communication at the workplace.
For other ways to establish happiness in the workplace , this article offers a guide and tips for making employees happier.
To determine your own job satisfaction, you need to do an assessment of your strengths and skills. This tool guides you to complete a Strengths In Challenging Times worksheet in order to do exactly that.
Another invaluable tool based on the Japanese concept of ikigai is Job Crafting of Ikigai . It is an interesting exercise that helps you understand what fuels your passions and, in turn, change aspects of your role to make it more fulfilling.
If you’re looking for more science-based ways to help others manage stress without spending hours on research and session prep, this collection contains 17 validated stress management tools for practitioners . Use them to help others identify signs of burnout and create more balance in their lives.
Job satisfaction can be a two-way street. Employees need to feel satisfied, and organizations must help employees realize their potential.
If you are interested in increasing the job satisfaction of your employees, be sure to look beyond the seemingly practical benefits of providing adequate salaries and health insurance, although those too are critical.
Motivating employees may be just as important. Job satisfaction links to motivation, which employees can gain even more of when realizing their full potential. Besides providing adequate salaries and health insurance, much more can be done by companies to motivate and guide employees. In turn, companies will reap the benefits of loyalty and shared objectives.
We hope you enjoyed reading this article. Don’t forget to download our three Work & Career Coaching Exercises for free .
- Agarwal, R. N., & Mehta, A. (2014). Impact of performance appraisal and working environment on the job satisfaction and attrition problem in the Indian IT industry. Paradigm , 18 (1), 73–85.
- Bakker, A. B., Tims, M., & Derks, D. (2012). Proactive personality and job performance: The role of job crafting and work engagement. Human Relations , 65 (10), 1359–1378.
- Berg, J. M., Grant, A. M., & Johnson, V. (2010). When callings are calling: Crafting work and leisure in pursuit of unanswered occupational callings. Organizational Science , 21 (5), 973–994.
- Castanheira, F. (2014). Job Descriptive Index. In A. C. Michalos (Ed.), Encyclopedia of quality of life and well-being research. Springer.
- Edwards, J. R. (2008). To prosper, organizational psychology should overcome methodological barriers to progress. Journal of Organizational Behavior , 29 (4), 469–491.
- Gerhart, B. (1987). How important are dispositional factors as determinants of job satisfaction? Implications for job design and other personnel programs. Journal of Applied Psychology , 72 (3), 366–373.
- Gillett, R. (2016, April 28). 5 reasons Google is the best place to work in America and no other company can touch it. Business Insider. Retrieved October 25, 2020, from: https://www.businessinsider.com/google-is-the-best-company-to-work-for-in-america-2016-4?r=US&IR=T
- Hoppock, R. (1935). Job satisfaction . Harper and Brothers.
- Ilies, R., & Judge, T. A. (2003). On the heritability of job satisfaction: the mediating role of personality. Journal of Applied Psychology , 88 (4), 750–59.
- Jalagat, R., Jr., (2016). Job performance, job satisfaction, and motivation: A critical review of their relationship. International Journal of Advances in Management and Economics , 5 (6), 36–43.
- Judge, T. A., Heller, D., & Klinger, R. (2008). The dispositional sources of job satisfaction: A comparative test. Applied Psychology, 57(3) , 361-372.
- Karatepe, O. M., Uludag, O., & Menevis, I., Hadzimehmedagic, L., & Baddar, L. (2006). The effects of selected individual characteristics on frontline performance and job satisfaction. Journal of Tourism Management , 27( 4), 547–560.
- Kinicki, A., & Kreitner, R. (2006). Organizational behavior: Key concepts, skills & best practices . McGraw Hill.
- Kumari, N. (2011). Job satisfaction of the employees at the workplace. European Journal of Business and Management , 3 (4), 11–30.
- Latham, G. P. (2012). Work motivation – History, theory, research and practice . SAGE Publications.
- Lee, C., Alonso, A., Esen, E., Coombs, J., Mulvey, T., Victor, J., & Wessels, K. (2016). Employee job satisfaction and engagement: Revitalizing a changing workforce . Report prepared by the Society for Human Resource Management.
- McBride, E. L. (2002). Employee satisfaction: Code red in the workplace? Journal of Nursing Management , 10 (3), 157–163.
- Dobrow, S. R., Ganzach, Y., & Liu, Y. (2018). Time and job satisfaction: A longitudinal study of the differential roles of age and tenure. Journal of Management , 44 (7), 2558–2579.
- Roelen, C. A. M., Koopmans, P. C., & Groothoff, J. W. (2008). Which work factors determine job satisfaction?. Work, 30(4), 433-439.
- Spector, P. E. (1985). Measurement of human service staff satisfaction: Development of the Job Satisfaction Survey. American Journal of Community Psychology , 13 (6), 693–713.
- Spector, P. E. (1997). Job satisfaction: Application, assessment, causes, and consequences . SAGE Publications, Inc.
- Weiss, D. J., Dawis, R. V., & England, G. W. (1967). Manual for the Minnesota Satisfaction Questionnaire. Minnesota Studies in Vocational Rehabilitation , 22 , 120.
Share this article:
Article feedback
What our readers think.
Job satisfaction has really been discussed from the perspective of positive psychology. Stories from the market like that of Google makes this material even more user-friendly. Kudos to you PositivePsychology.com!
I am writing a paper on Employee Engagement and comparing this with job satisfaction. This is one of the clearest and most coherent articles I have found on the subject. I will be bookmarking the sight for further use.
Let us know your thoughts Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related articles

Company Culture: How to Create a Flourishing Workplace
Company culture has become a buzzword, particularly in the post-COVID era, with more organizations recognizing the critical importance of a healthy workplace. During the Great [...]

Integrity in the Workplace (What It Is & Why It’s Important)
Integrity in the workplace matters. In fact, integrity is often viewed as one of the most important and highly sought-after characteristics of both employees and [...]

Neurodiversity in the Workplace: A Strengths-Based Approach
Promoting diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) in the workplace is a priority for ethical employers who want to optimize productivity and leverage the full potential [...]
Read other articles by their category
- Body & Brain (49)
- Coaching & Application (58)
- Compassion (25)
- Counseling (51)
- Emotional Intelligence (23)
- Gratitude (18)
- Grief & Bereavement (21)
- Happiness & SWB (40)
- Meaning & Values (26)
- Meditation (20)
- Mindfulness (44)
- Motivation & Goals (45)
- Optimism & Mindset (34)
- Positive CBT (30)
- Positive Communication (20)
- Positive Education (47)
- Positive Emotions (32)
- Positive Leadership (18)
- Positive Parenting (15)
- Positive Psychology (34)
- Positive Workplace (37)
- Productivity (17)
- Relationships (43)
- Resilience & Coping (37)
- Self Awareness (21)
- Self Esteem (38)
- Strengths & Virtues (32)
- Stress & Burnout Prevention (34)
- Theory & Books (46)
- Therapy Exercises (37)
- Types of Therapy (64)

Download 3 Free Work & Career Tools Pack (PDF)
By filling out your name and email address below.
- Email Address *
- Your Expertise * Your expertise Therapy Coaching Education Counseling Business Healthcare Other
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Download 3 Work & Career Exercises Pack (PDF)
- Essay Writing
- Dissertation Writing
- Assignment Writing
- Report Writing
- Literature Review
- Proposal Writing
- Poster and Presentation Writing Service
- PhD Writing Service
- Coursework Writing
- Tutoring Service
- Exam Notes Writing Service
Editing and Proofreading Service
Technical and Statistical Services
- Appeals and Re-Submissions
Personal Statement Writing Service
- Sample Dissertations
- Sample Essays
- Free Products
Sample Essay: Job Satisfaction in the Workplace
Introduction.
Employment forms one of the main parts of human life (Inayat, 2021). In the rapidly changing modern environment, the workforce market is characterised by increasing flexibility. As the global pandemic has shown the benefits of remote employment to millions of workers, this inevitably increases the growth of the ‘gig economy’. As many competent specialists can easily move between organisations in both offline and online environments, this decreases organisational citizenship behaviours and makes it more difficult to recruit and retain highly skilled specialists. Job satisfaction is one of the elements defining the quality of life within the scope of employment. As noted by such authors as Ahmad and Raja (2021) and Prihadini et al. (2021), it has a direct effect on loyalty and performance. As a result, satisfied workers are less interested in changing their jobs and are more productive in the workplace. With that being said, a 2022 poll by Gallup (Collins, 2022) revealed that only 33% of the surveyed employees in all parts of the world were generally displeased with their jobs. In the US context, 50% of workers felt stressed on a daily basis with up to 60% of the global workforce reporting a sense of emotional detachment from their duties. This job satisfaction recommendation essay aims to explore the concept of job satisfaction from theoretical and practitioner standpoints and offer solutions to managers on how this element can be improved.
Job Satisfaction Theories
One of the most prominent and well-known theories in the field of job satisfaction is Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs (Maslow, 1943). This model subdivides all employee expectations into five levels ranging from bare survival necessities to finding one’s true mission in life. According to Maslow, people generally attempt to move towards the upper levels of this hierarchy as soon as lower-order needs are satisfied. From a human resource management (HRM) standpoint, this means that employers have to provide sufficient job security, salary, workplace safety, and stability in order to satisfy the basic expectations of their workers (Maslow, 1995). However, higher levels of satisfaction are only achievable if the employees develop organisational citizenship behaviours and a sense of belonging emerging from the recognition of their achievements and their capability to fully utilise their talents, skills, and competencies.
Figure 1: Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
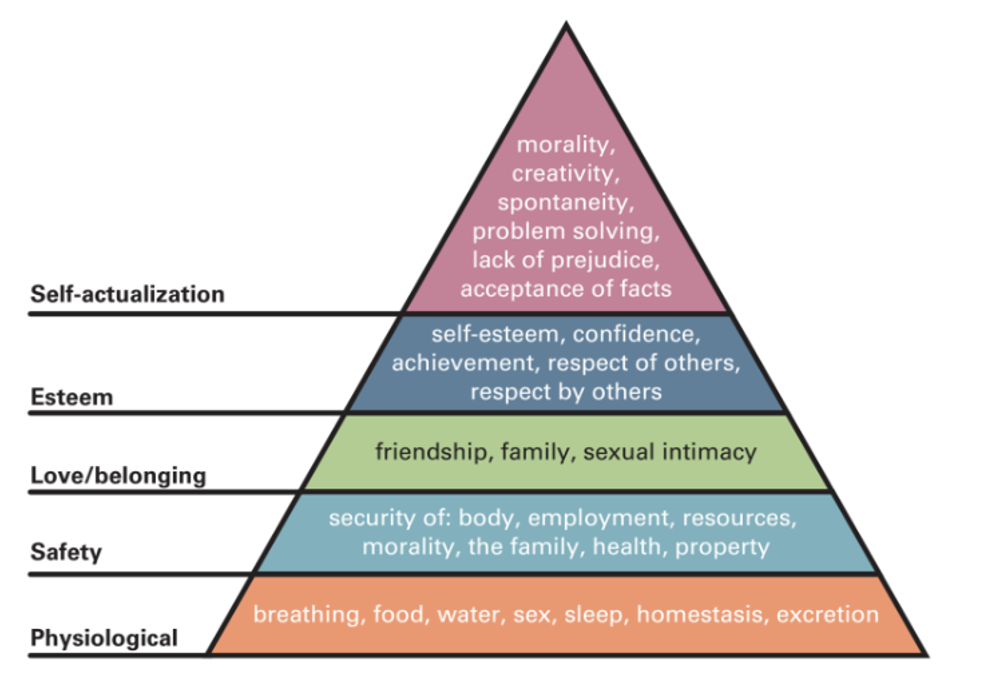
Source: Neck et al. (2018, p.131)
Further scholars such as Alderfer (1969) reduced the number of pyramid levels and subdivided all employee needs into existence needs, relatedness needs, and growth needs. Moreover, they assumed that these elements were separate from each other and were not organised in the strict hierarchy suggested by Maslow (1995). As a result, different employees could set individual priorities and seek the achievement of different needs simultaneously. This changes the HRM perspective since companies have to offer a combination of tangible and intangible motivators covering all three dimensions instead of a basic offering addressing only the lowest-level expectations of their staff members.
Figure 2: Alderfer’s ERG Theory
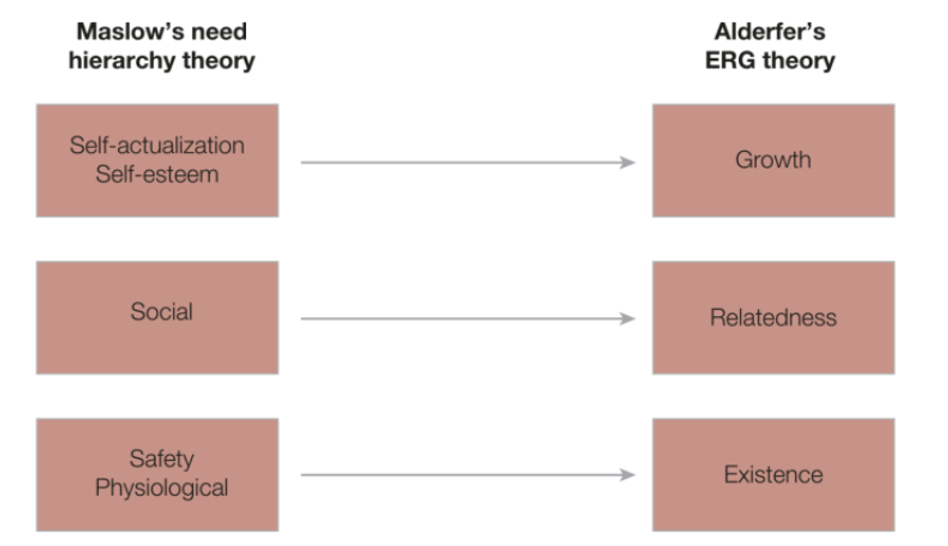
Source: Bratton (2020, p.180)
These assumptions were further supported by such scholars as Herzberg (2017) who developed the Two-Factor theory. They came to the conclusion that employees had to observe basic ‘hygiene factors’ ensuring the satisfaction of their lower-order needs. These elements could include working conditions, salary levels, job security, management support, and other similar ones. Their absence immediately and radically decreased employee satisfaction levels. However, such benefits were offered by most companies in any developed economy with a competitive labour market and could not ensure long-term loyalty and commitment. Due to this factor, companies had to also develop unique motivators addressing the higher-order needs of their workers (Bates et al., 2019). Such elements could include the recognition of their contributions, coaching and mentorship opportunities, personal and professional growth, empowerment, meaningful job tasks, and a sense of doing something great in general. These factors helped employees overcome temporary challenges and understand why they selected this particular position in the first place.
Figure 3: Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory
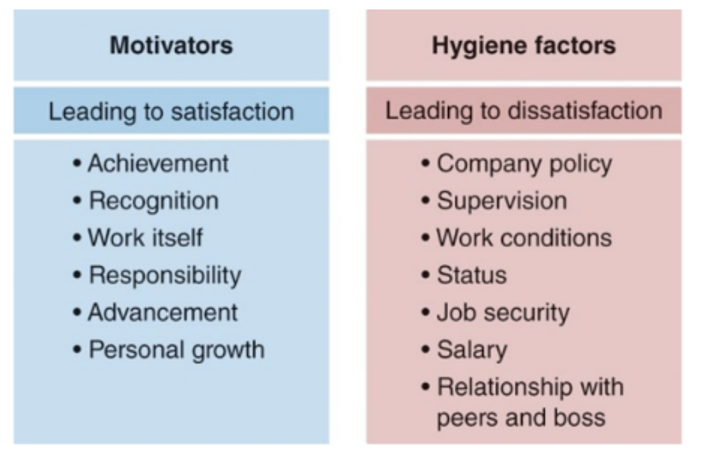
Source: Greenberg and Bianco (2019, p.45)
Finally, the equity theory by Adams (1963) and the concept of procedural fairness imply that job satisfaction in the workplace can be influenced by two additional factors. On the one hand, employees appraise their inputs in the form of effort, hard work, loyalty, and commitment with outputs in the form of financial remuneration and other tangible and intangible stimuli. The comparison of these two dimensions results in a sense of being recognised and fairly rewarded or the lack thereof. In this scenario, organisations need to ensure that every staff member understands the kinds of inputs that are expected from them and the amount of outputs proportional to expected employee behaviours (Adams, 2022). This approach ensures that every person understands their role and functions within the organisation and can help it achieve its strategic goals while also realising their own needs, which is frequently called a good person-organisation fit. On the other hand, employees see the amount of rewards obtained by their colleagues. While financial remuneration sums may be concealed in some organisations, most workers usually recognise cases where compensations are distributed unfairly (Johnson and Davey, 2019). This situation is frequent in paternalist company cultures characterised by high levels of nepotism and favouritism. In these scenarios, employees can be dissatisfied with their jobs even if they receive proper remuneration in terms of their inputs/outputs ratio. This effect is explained by a sense of unfairness leading to learnt helplessness where greater performance is not associated with proportional gains due to favouritism and nepotism.
Job Satisfaction Antecedents
While theoretical concepts are primarily based on the mechanisms of job satisfaction, they may not include all relevant factors creating it (Uhl-Bien et al., 2020). This section explores practical evidence from multiple industries to identify what antecedents are shared by successful organisations to achieve the desired outcomes in this sphere. Such authors as Lepold et al. (2018) suggested that high levels of job satisfaction were primarily achieved by such factors as empowerment, good working conditions, open-door management policies, positive inter-colleague relationships, supportive supervision, sufficient compensation and bonuses, and open communication between employees and managers. These practices ensured high levels of perceived employment stability in combination with perceived transparency and fairness. Within the scope of Herzberg’s Two-Factor theory, this list includes a combination of tangible and intangible incentives from both groups, which supports the assumptions put forth by this model (Herzberg, 2017). At the same time, it may be difficult to conceptualise the comparative importance of each factor. Large corporations frequently organise monthly reviews of job satisfaction levels based on extensive reviews. However, small and medium enterprises (SMEs) may lack similar resources and have to rely on guesswork in selecting the optimal combination of hygiene factors and motivators.
According to Conte and Landy (2019), job satisfaction could be viewed as a complex concept including antecedents, correlates, and consequences. The first group included various job characteristics, organisational roles, group cohesion, workplace stressors, and leader-follower relationships. For example, the presence of good communication and job enrichment practices could greatly increase the levels of job satisfaction. On the contrary, role ambiguity or the lack of supervision, conflict mitigation, and team-building mechanisms could be detrimental in this aspect. The correlates group represented individual employee characteristics such as overall life satisfaction, non-work stress levels, organisational commitment or job engagement (Hee et al., 2018). These elements could be deemed as mediators and moderators affecting the correlation between antecedents and consequences. Hence, even a fine-tuned system of organisational rewards and motivation could produce different results depending on individual employee characteristics.
Figure 4: Job Satisfaction Factors
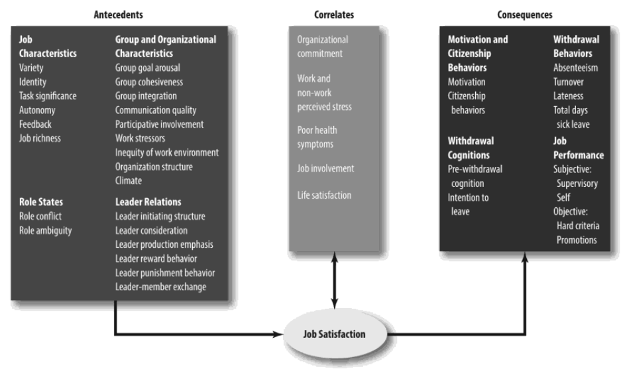
Source: Conte and Landy (2019, p.354)
Finally, the consequences group includes a range of possible outcomes such as loyalty, absenteeism, intentions to leave or organisational citizenship behaviours (Abuhashesh et al., 2019). In this aspect, the capability of team leaders to recognise individual employee needs could help companies mitigate the adverse impact of correlates and maximise the positive impact of group-level antecedents on staff job satisfaction levels. In light of the above, such authors as Khan and Waraich (2019) and Oyewobi (2022) noted that job satisfaction could also be influenced by the styles of leadership adopted by the organisation. While autocratic and transactional approaches are still widespread in many companies, more and more successful firms are replacing them with transformational, situational or contingency ones. This process shifts the perspective from a leader’s traits, vision, and charisma to employee skills and competencies. Within the scope of longitudinal organisation development and sustainability, this approach offers a number of advantages (Zehndorfer, 2020). On the one hand, market conditions and other macro-environmental factors are changing at ever-increasing speeds. This means that sustainable competitive advantage needs to be based on transformational cultures supporting continuous change rather than one-time changes occurring every 5-10 years. Such results may be difficult to attain using traditional leadership styles. On the other hand, transformational, contingency, and situational approaches can increase staff satisfaction levels due to greater attention paid to individual employee needs and long-term goals (Neubert and Dyck, 2021). These styles utilise both tangible and intangible motivators, which increases employee loyalty and creates synergistic effects within the scope of the earlier analysed models.
Finally, the analysis of 360 organisations conducted by Aziz et al. (2020) revealed that perceived fairness in the form of equal treatment, equal promotional opportunities, fair competition, and high levels of organisational transparency were major antecedents of job satisfaction. In light of the earlier analysed theories, this confirms the assumption that remuneration size and composition do not work as isolated variables excluded from workplace cultures. If employees understand the processes and procedures associated with reward distribution, they could identify proper input behaviours ensuring higher levels of outputs. This clarity facilitated their personal and professional growth while also explaining any disparities between individual staff members (Scandura and Gower, 2019). On the contrary, the lack of such explanations and open-door managerial communication policies could lead to perceptions of unfairness and a sense of external control locus. In this scenario, job satisfaction decreased and staff members considered a change of the employer as the only way of realising their personal needs.
Conclusion and Recommendations
It can be summarised that job satisfaction in the workplace can be determined by a number of factors including perceived rewards fairness, open communication policies, transformational leadership, coaching and mentoring provision, perceived employment stability and security, and good working conditions and salary (Oyewobi, 2022). From a theoretical standpoint, they can be subdivided into multiple groups depending on their tangible and intangible nature as well as their capability to satisfy higher-order or lower-order needs. As also noted by such authors as Conte and Landy (2019), the application of specific practices can also be affected by individual employee background characteristics. For example, unsatisfied personal needs or perceived unfairness of rewards distribution may lead to turnover intentions for some workers even while others may be generally satisfied with standardised policies in this sphere (Hee et al., 2018). From a practitioner's standpoint, the capability to recognise such factors may be limited by the lack of organisational resources. Smaller firms generally lack the monitoring instruments used by large corporations, which may explain lower levels of job satisfaction and loyalty in the case of such ‘HRM myopia’.
The analysis has informed a number of practical recommendations. First, organisational policies need to ensure maximum transparency and clarity in terms of preferred employee inputs and corresponding outputs (Adams, 2022). This approach ensures that every staff member knows what actions and strategies will lead them to desired tangible and intangible rewards. As a result, organisations following this plan can enjoy higher levels of person-organisation fit. Second, a combination of hygiene factors and motivators may be preferable to the exclusive focus on one of these categories. Such concepts as Alderfer’s ERG model and Herzberg’s Two-Factor theory imply that employee members are not equal in their expectations (Bates et al., 2019). Hence, a variety of offerings satisfying both higher- and lower-level needs potentially leads to greater rates of job satisfaction across the organisation. Third, transformational, situational, and contingency leadership may be advised as the most effective management strategies ensuring employee engagement and commitment (Zehndorfer, 2020). They stimulate personal and professional development in the workplace, which helps staff members effectively deal with any emerging challenges and achieve higher levels of job satisfaction as a result.
Abuhashesh, M., Al-Dmour, R. and Masadeh, R. (2019) “Factors that affect Employees Job Satisfaction and Performance to Increase Customers’ Satisfactions”, Journal of Human Resources Management Research , 1 (1), pp. 1-23.
Adams, J. (2022) Behavioural Research for Marketing: A Practitioner's Handbook , London: Routledge.
Adams, J. (1963) “Towards an Understanding of Inequity”, The Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology , 67 (5), pp. 1-17.
Ahmad, M. and Raja, R. (2021) “Employee Job Satisfaction and Business Performance: The Mediating Role of Organizational Commitment”, Vision: The Journal of Business Perspective , 25 (2), pp. 1-25.
Alderfer, C. (1969) “An empirical test of a new theory of human needs”, Organizational Behavior and Human Performance , 4 (2), pp. 142-175.
Aziz, N., Mustafi, M. and Hosain, S. (2020) “Factors Affecting Job Satisfaction: An Exploratory Analysis among Public Bank Employees in Selected Cities of Bangladesh”, Asian Journal of Economics Business and Accounting , 1 (1), pp. 1-23.
Bates, B., Bailey, A. and Lever, D. (2019) A Quick Guide to Behaviour Management , London: SAGE.
Bratton, J. (2020) Work and Organizational Behaviour , London: Bloomsbury Publishing.
Collins, L. (2022) “Job unhappiness is at a staggering all-time high, according to Gallup”, [online] Available at: https://www.cnbc.com/2022/08/12/job-unhappiness-is-at-a-staggering-all-time-high-according-to-gallup.html [Accessed on 2 February 2023].
Conte, J. and Landy, F. (2019) Work in the 21st Century: An Introduction to Industrial and Organizational Psychology , Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons.
Greenberg, J. and Bianco, J. (2019) Organization and Administration of Physical Education: Theory and Practice , Champaign: Human Kinetics.
Hee, O., Yan, L., Rizal, A., Kowang, T. and Fei, G. (2018) “Factors Influencing Employee Job Satisfaction: A Conceptual Analysis”, International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences , 8 (6), pp. 331-340.
Herzberg, F. (2017) Motivation to Work , London: Routledge.
Inayat, W. (2021) “A Study of Job Satisfaction and Its Effect on the Performance of Employees Working in Private Sector Organizations, Peshawar”, Education Research International , 1 (1), pp. 1-13.
Johnson, J. and Davey, K. (2019) Essentials of Managing Public Health Organizations , New York: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Khan, M. and Waraich, U. (2019) “The Effect of Leadership Style on Employee Job Satisfaction”, Journal of Entrepreneurship, Management, and Innovation , 1 (1), pp. 1-17.
Lepold, A., Tanzer, N., Bregenzer, A. and Jimenez, P. (2018) “The efficient measurement of job satisfaction: Facet-items versus facet scales”, International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health , 15 (7), pp. 1362-1381.
Maslow, A. (1943) “A Theory of Human Motivation”, Psychological Review , 50 (4), pp. 370-396.
Maslow, A. (1995) Motivation and Personality , New York: Harper.
Neck, C., Houghton, J. and Murray, E. (2018) Organizational Behavior: A Skill-Building Approach , London: SAGE.
Neubert, M. and Dyck, B. (2021) Organizational Behavior: For a Better Tomorrow , Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons.
Oyewobi, L. (2022) “Leadership styles and employees commitment: the mediating role of job satisfaction”, Journal of Facilities Management , 1 (1), pp. 1-15.
Prihadini, D., Nurbaity, S., Rachmadi, H. and Krishantoro, T. (2021) “The Importance of Job Satisfaction to improve Employee Performance”, Technium Social Sciences Journal , 18 (1), pp. 367-377.
Scandura, T. and Gower, K. (2019) Management Today: Best Practices for the Modern Workplace , London: SAGE.
Uhl-Bien, M., Piccolo, R. and Schermerhorn, J. (2020) Organizational Behavior , Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons.
Zehndorfer, E. (2020) Leadership: Performance Beyond Expectations , London: Routledge.
View Our Sample Essays
REQUEST A FREE QUOTE
[email protected]
Monday - Friday: 9am - 6pm
Saturday: 10am - 6pm

Got Questions?
Email: [email protected]
*We do NOT use AI (ChatGPT or similar), all orders are custom written by real people.
Our Services
Essay Writing Service
Assignment Writing Service
Coursework Writing Service
Report Writing Service
Reflective Report Writing Service
Literature Review Writing Service
Dissertation Proposal Writing Service
Dissertation Writing Service
MBA Writing Service

Need some help?
Select a contact option below and we will get back to you for free.
- Ask this writer a question
- Request a copy of this paper (with tables, figures and calculations where applicable)
- Get professional help with part of your work
Home — Essay Samples — Life — Job — Job Satisfaction is More Important
Job Satisfaction is More Important
- Categories: Job Job Satisfaction Workers
About this sample

Words: 346 |
Published: Apr 11, 2019
Words: 346 | Page: 1 | 2 min read
Works Cited:
- Adler, F. (1975). Sisters in Crime: The Rise of the New Female Criminal. McGraw-Hill.
- Eronen, M., Hakala, J., & Lindberg, N. (2020). Social background and crime type: A study on homicide offenders in Finland. Journal of Scandinavian Studies in Criminology and Crime Prevention , 21(2), 225-240.
- Hickey, E. W. (2013). Serial murderers and their victims (6th ed.). Wadsworth.
- Moffitt, T. E., Arseneault, L., Belsky, D., Dickson, N., Hancox, R. J., Harrington, H., ... & Sears, M. R. (2011). A gradient of childhood self-control predicts health, wealth, and public safety. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 108(7), 2693-2698.
- Odgers, C. L., Moffitt, T. E., Broadbent, J. M., Dickson, N., Hancox, R. J., Harrington, H., ... & Sears, M. R. (2008). Female and male antisocial trajectories: From childhood origins to adult outcomes. Development and Psychopathology, 20(2), 673-716.
- Ressler, R. K., Burgess, A. W., & Douglas, J. E. (1988). Sexual homicide: Patterns and motives. Lexington Books.
- Roberts, A. R. (Ed.). (2001). Juvenile justice and delinquency. Greenwood Publishing Group.
- Scarpitti, F. R. (2019). Born Criminals? Assessing the Theories of Cesare Lombroso. International Journal of Criminal Justice Sciences, 14(1), 29-41.
- Sellbom, M., Wygant, D. B., & Sleep, C. E. (2014). Differentiation between antisocial personality disorder, borderline personality disorder, and psychopathy: Conceptual and empirical considerations. Personality Disorders: Theory, Research, and Treatment, 5(4), 440-449.
- Webster, C. D., Douglas, K. S., Eaves, D., & Hart, S. D. (1997). HCR-20: Assessing risk for violence (version 2). Simon Fraser University.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Heisenberg
Verified writer
- Expert in: Life Business

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 732 words
2 pages / 997 words
4 pages / 1642 words
8 pages / 3429 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
We live in a world, where many of us are not aware of the difference between original news and politically edited news. “We have a free press”, is just a saying. Our daily news that we read in newspapers and magazines, or the [...]
Every social worker’s goal and mission is to improve the values of others’ lives. People in this field focus on empowering those who are living in poverty, Oppression, and are vulnerable. The NASW code of ethics is a code that [...]
In the film “Inside Job,” Matt Damon narrated a documentary that tells us the unstable systems led the global economic crises of 2008. Since the global financial meltdown happened in 2008, it resulted in the damage to the [...]
One of the key components in this career is the ability to explain clear procedures to your patient so that they know what is going on at all times. Along with clear procedures comes comforting them because most times a patient [...]
A social worker’s job is made easier and more efficient through the use of technology even though a greater part of their work is face-to-face with clients. In a world where technology use is constantly growing social workers [...]
Aubrey McClendon, an American businessman and the chief of American Energy Partners once indicated, “I just wanted to be a businessman, and to me, the best way to understand business was to be an accountant” (McClendon). The [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

ESSAY SAUCE
FOR STUDENTS : ALL THE INGREDIENTS OF A GOOD ESSAY
Essay: Job satisfaction
Essay details and download:.
- Subject area(s): Business essays
- Reading time: 2 minutes
- Price: Free download
- Published: 15 October 2015*
- File format: Text
- Words: 415 (approx)
- Number of pages: 2 (approx)
Text preview of this essay:
This page of the essay has 415 words. Download the full version above.
Job satisfaction is a critical aspect in the workplace because it tends to enhance motivation. It refers to the level to which employees like or dislike their jobs and their characteristics. Because most people spend a good percentage of their time in the workplace, it is essential to make job satisfaction a priority. The aim of this paper is to analyse the various factors that contribute to job satisfaction (Stride, Wall & Catley , 2007). Body The main factor that determines job satisfaction is the work environment. Useful work conditions tend to give employees the morale to work and contributeto a high job satisfaction. Employers need to provide a healthy work environment with minimum disruption and risks. Another factor is job security, that is, the assurance of retaining one’s job for an unforseeable future. An organization with high employee turnover tends to reduce job satisfaction for those still in the job because they are not certain if they will be there for a long time. It is important to mention the personal advancement and the compensation. Most people need a clear upward career path and appreciation for the work done. A job without promotion and recognition demotivates employees and lowers their satisfaction. Such employees will keep looking for better career options so resulting in reduced performance. The other factor is the compensation given for the work done; otherwise the staff will not be satisfied with their work (Spector, 1997). The operation of job satisfaction for all workers is unrealistic because in most cases people do not get what they want. Most workers only stick to their workplaces because they need the financial gains but in reality they do not like what they are doing. People need to balance their work and free time effectively by getting involved in activities that they enjoy doing. It will ensure that they get satisfied off work so making life more interesting. Conclusion It is true that most people spend most of their adult life working thus job satisfaction is essential, but this is not realistic . The expectations regarding job satisfaction are not fulfilled in real life so people need to create their satisfaction by balancing their work and free time. It will enhance the general satisfaction from life. Word count: 376 ””’ References Spector, P. E. (1997). Job satisfaction: Application, assessment, causes and consequences. Sage: Thousand Oaks, Ca. Stride, C., Wall, T. D., & Catley , N. (2007). Measures of job satisfaction, organisational commitment, mental health and job-related well-being: A bench-marking manual. John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, West Sussex.
...(download the rest of the essay above)
About this essay:
If you use part of this page in your own work, you need to provide a citation, as follows:
Essay Sauce, Job satisfaction . Available from:<https://www.essaysauce.com/business-essays/essay-job-satisfaction/> [Accessed 19-05-24].
These Business essays have been submitted to us by students in order to help you with your studies.
* This essay may have been previously published on Essay.uk.com at an earlier date.
Essay Categories:
- Accounting essays
- Architecture essays
- Business essays
- Computer science essays
- Criminology essays
- Economics essays
- Education essays
- Engineering essays
- English language essays
- Environmental studies essays
- Essay examples
- Finance essays
- Geography essays
- Health essays
- History essays
- Hospitality and tourism essays
- Human rights essays
- Information technology essays
- International relations
- Leadership essays
- Linguistics essays
- Literature essays
- Management essays
- Marketing essays
- Mathematics essays
- Media essays
- Medicine essays
- Military essays
- Miscellaneous essays
- Music Essays
- Nursing essays
- Philosophy essays
- Photography and arts essays
- Politics essays
- Project management essays
- Psychology essays
- Religious studies and theology essays
- Sample essays
- Science essays
- Social work essays
- Sociology essays
- Sports essays
- Types of essay
- Zoology essays
- Practice Test
- Useful Tips – Tricks
- Full Writing Review
- General Writing Task
- Writing Task 1
- Writing Task 2
- Writing Exercises
- Writing Sample – Topics
- Writing Vocabulary
- Speaking Vocabulary
- Intro Question
- Speaking Part 1
- Speaking Part 2
- Speaking Part 2 – Audio
- Speaking Part 3
- IELTS Books
- Recent Exams
- IELTS Vocabulary
- Essay from Examiners
- IELTS Ideas
IELTS App - For Mobile
Ready for the IELTS exam with our IELTS app. Over 2 million downloads

Popular Last 24h
Writing task 2: it is impossible to help all people around the world in need so governments should focus on people from their own country., writing task 2: many university students want to learn about different subjects in addition to their main subjects, ielts writing recent actual test 29/09/2018, describe a family member that made you proud., describe a favourite song, pie charts #15 – the nutritional consistency of two dinners, talk about a beautiful city (chandigarh).
- IELTS Test/Skills FAQs
- IELTS Scoring in Detail
- Forecast Speaking – 2023
- List IELTS Speaking Part 3
- List IELTS Speaking Part 1
- IELTS Writing 2023 – Actual Test
Our Telegram
Join our community for IELTS preparation and share and download materials.
The information on this site is for informational purposes only. IELTS is a registered trademark of the University of Cambridge ESOL, the British Council, and IDP Education Australia. This site and its owners are not affiliated, approved or endorsed by University of Cambridge ESOL, the British Council, or IDP Education Australia.
Latest Articles
Cue card – describe a gift you bought for someone, cue card – describe a place where you like to go shopping, ielts writing task 1 (process wasted glass bottles) – band 9, ielts speaking part 1: rubbish/ plastic garbage, talk about global warming (part 1/3), most popular, describe a film that made you laugh, describe a person whom you met for the first time and made you happy, topic: experience is the best teacher, describe something difficult you would like to succeed in doing, in many countries,today there are many highly qualified graduates without employment..
ieltspracticeonline All Rights Reserved
Home / Essay Samples / Business / Workforce / Job Satisfaction
Job Satisfaction Essay Examples
Difference between work for money and for satisfaction.
Since the beginning of human history, it can't be denied that working has always played an important role in the mankind's survival. Different working sectors provide different human's needs. Furthermore, working itself gives us life's purposes, opportunities, challenges. Many people believe that working just provides...
Employee Satisfaction and Retention: Reasons of Good Employees Quit
Contrary to what most of us believe, salary is not the only determinant as to why workers hand over a resignation notice. Here are some main bases why good employees up and leave: Overpromises - When an employer oversells the company’s culture to exaggerate the...
Public and Private Schools in Naic: Satisfaction of Esl Teachers
Focusing on strengths is the surest way to greater job satisfaction—Marcus BuckinghamJob satisfaction is the degree to which people like their jobs. Some people enjoy work and find it to be a central part of life. Others hate to work and do so only because...
Cirque Du Soleil: the History and Employee Satisfaction
Cirque du Soleil is a Canadian entertainment company which is a self-described as a dramatic mix of circus arts and street entertainment, it was formed in the year 1984 by troupe of street performers commonly known as “Le Club des Talons Hauts”. The main purpose...
Employees: Satisfaction and Turnover Rate
In the era of the competitive global economy, the Human Resource is playing a vital part in the growth of an organization. Employee turnover can be defined as voluntary terminations of employees. Khan and Aleem (2014) state that it is becoming a challenge to reduce...
Trying to find an excellent essay sample but no results?
Don’t waste your time and get a professional writer to help!
You may also like
- Total Quality Management
- Walt Disney
- Charismatic Leadership
- Change Management
- Teamwork Essays
- Sweatshops Essays
- Hard Work Essays
- Employee Essays
- Women in The Workforce Essays
- Organizational Structure Essays
- Stakeholders Essays
- Organizational Culture Essays
- Structure Essays
- Enron Essays
samplius.com uses cookies to offer you the best service possible.By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .--> -->