- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications

How to Analyse a Case Study
Last Updated: April 13, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Sarah Evans . Sarah Evans is a Public Relations & Social Media Expert based in Las Vegas, Nevada. With over 14 years of industry experience, Sarah is the Founder & CEO of Sevans PR. Her team offers strategic communications services to help clients across industries including tech, finance, medical, real estate, law, and startups. The agency is renowned for its development of the "reputation+" methodology, a data-driven and AI-powered approach designed to elevate brand credibility, trust, awareness, and authority in a competitive marketplace. Sarah’s thought leadership has led to regular appearances on The Doctors TV show, CBS Las Vegas Now, and as an Adobe influencer. She is a respected contributor at Entrepreneur magazine, Hackernoon, Grit Daily, and KLAS Las Vegas. Sarah has been featured in PR Daily and PR Newswire and is a member of the Forbes Agency Council. She received her B.A. in Communications and Public Relations from Millikin University. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 411,844 times.
Case studies are used in many professional education programs, primarily in business school, to present real-world situations to students and to assess their ability to parse out the important aspects of a given dilemma. In general, a case study should include, in order: background on the business environment, description of the given business, identification of a key problem or issue, steps taken to address the issue, your assessment of that response, and suggestions for better business strategy. The steps below will guide you through the process of analyzing a business case study in this way.

- Describe the nature of the organization under consideration and its competitors. Provide general information about the market and customer base. Indicate any significant changes in the business environment or any new endeavors upon which the business is embarking.

- Analyze its management structure, employee base, and financial history. Describe annual revenues and profit. Provide figures on employment. Include details about private ownership, public ownership, and investment holdings. Provide a brief overview of the business's leaders and command chain.

- In all likelihood, there will be several different factors at play. Decide which is the main concern of the case study by examining what most of the data talks about, the main problems facing the business, and the conclusions at the end of the study. Examples might include expansion into a new market, response to a competitor's marketing campaign, or a changing customer base. [3] X Research source

- Draw on the information you gathered and trace a chronological progression of steps taken (or not taken). Cite data included in the case study, such as increased marketing spending, purchasing of new property, changed revenue streams, etc.

- Indicate whether or not each aspect of the response met its goal and whether the response overall was well-crafted. Use numerical benchmarks, like a desired customer share, to show whether goals were met; analyze broader issues, like employee management policies, to talk about the response as a whole. [4] X Research source

- Suggest alternative or improved measures that could have been taken by the business, using specific examples and backing up your suggestions with data and calculations.

Community Q&A
- Always read a case study several times. At first, you should read just for the basic details. On each subsequent reading, look for details about a specific topic: competitors, business strategy, management structure, financial loss. Highlight phrases and sections relating to these topics and take notes. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- In the preliminary stages of analyzing a case study, no detail is insignificant. The biggest numbers can often be misleading, and the point of an analysis is often to dig deeper and find otherwise unnoticed variables that drive a situation. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- If you are analyzing a case study for a consulting company interview, be sure to direct your comments towards the matters handled by the company. For example, if the company deals with marketing strategy, focus on the business's successes and failures in marketing; if you are interviewing for a financial consulting job, analyze how well the business keeps their books and their investment strategy. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- Do not use impassioned or emphatic language in your analysis. Business case studies are a tool for gauging your business acumen, not your personal beliefs. When assigning blame or identifying flaws in strategy, use a detached, disinterested tone. Thanks Helpful 16 Not Helpful 4
Things You'll Need
You might also like.

Expert Interview

Thanks for reading our article! If you’d like to learn more about business writing, check out our in-depth interview with Sarah Evans .
- ↑ https://www.gvsu.edu/cms4/asset/CC3BFEEB-C364-E1A1-A5390F221AC0FD2D/business_case_analysis_gg_final.pdf
- ↑ https://bizfluent.com/12741914/how-to-analyze-a-business-case-study
- ↑ http://www.business-fundas.com/2009/how-to-analyze-business-case-studies/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.uagc.edu/writing-case-study-analysis
- http://college.cengage.com/business/resources/casestudies/students/analyzing.htm
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Lisa Upshur
Jun 15, 2019
Did this article help you?

Tejiri Aren
Jul 21, 2016
Jul 15, 2017
Jenn M.T. Tseka
Jul 3, 2016
Devanand Sbuurayan
Dec 6, 2020

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
Do Your Students Know How to Analyze a Case—Really?
Explore more.
- Case Teaching
- Student Engagement
J ust as actors, athletes, and musicians spend thousands of hours practicing their craft, business students benefit from practicing their critical-thinking and decision-making skills. Students, however, often have limited exposure to real-world problem-solving scenarios; they need more opportunities to practice tackling tough business problems and deciding on—and executing—the best solutions.
To ensure students have ample opportunity to develop these critical-thinking and decision-making skills, we believe business faculty should shift from teaching mostly principles and ideas to mostly applications and practices. And in doing so, they should emphasize the case method, which simulates real-world management challenges and opportunities for students.
To help educators facilitate this shift and help students get the most out of case-based learning, we have developed a framework for analyzing cases. We call it PACADI (Problem, Alternatives, Criteria, Analysis, Decision, Implementation); it can improve learning outcomes by helping students better solve and analyze business problems, make decisions, and develop and implement strategy. Here, we’ll explain why we developed this framework, how it works, and what makes it an effective learning tool.
The Case for Cases: Helping Students Think Critically
Business students must develop critical-thinking and analytical skills, which are essential to their ability to make good decisions in functional areas such as marketing, finance, operations, and information technology, as well as to understand the relationships among these functions. For example, the decisions a marketing manager must make include strategic planning (segments, products, and channels); execution (digital messaging, media, branding, budgets, and pricing); and operations (integrated communications and technologies), as well as how to implement decisions across functional areas.
Faculty can use many types of cases to help students develop these skills. These include the prototypical “paper cases”; live cases , which feature guest lecturers such as entrepreneurs or corporate leaders and on-site visits; and multimedia cases , which immerse students into real situations. Most cases feature an explicit or implicit decision that a protagonist—whether it is an individual, a group, or an organization—must make.
For students new to learning by the case method—and even for those with case experience—some common issues can emerge; these issues can sometimes be a barrier for educators looking to ensure the best possible outcomes in their case classrooms. Unsure of how to dig into case analysis on their own, students may turn to the internet or rely on former students for “answers” to assigned cases. Or, when assigned to provide answers to assignment questions in teams, students might take a divide-and-conquer approach but not take the time to regroup and provide answers that are consistent with one other.
To help address these issues, which we commonly experienced in our classes, we wanted to provide our students with a more structured approach for how they analyze cases—and to really think about making decisions from the protagonists’ point of view. We developed the PACADI framework to address this need.
PACADI: A Six-Step Decision-Making Approach
The PACADI framework is a six-step decision-making approach that can be used in lieu of traditional end-of-case questions. It offers a structured, integrated, and iterative process that requires students to analyze case information, apply business concepts to derive valuable insights, and develop recommendations based on these insights.
Prior to beginning a PACADI assessment, which we’ll outline here, students should first prepare a two-paragraph summary—a situation analysis—that highlights the key case facts. Then, we task students with providing a five-page PACADI case analysis (excluding appendices) based on the following six steps.
Step 1: Problem definition. What is the major challenge, problem, opportunity, or decision that has to be made? If there is more than one problem, choose the most important one. Often when solving the key problem, other issues will surface and be addressed. The problem statement may be framed as a question; for example, How can brand X improve market share among millennials in Canada? Usually the problem statement has to be re-written several times during the analysis of a case as students peel back the layers of symptoms or causation.
Step 2: Alternatives. Identify in detail the strategic alternatives to address the problem; three to five options generally work best. Alternatives should be mutually exclusive, realistic, creative, and feasible given the constraints of the situation. Doing nothing or delaying the decision to a later date are not considered acceptable alternatives.
Step 3: Criteria. What are the key decision criteria that will guide decision-making? In a marketing course, for example, these may include relevant marketing criteria such as segmentation, positioning, advertising and sales, distribution, and pricing. Financial criteria useful in evaluating the alternatives should be included—for example, income statement variables, customer lifetime value, payback, etc. Students must discuss their rationale for selecting the decision criteria and the weights and importance for each factor.
Step 4: Analysis. Provide an in-depth analysis of each alternative based on the criteria chosen in step three. Decision tables using criteria as columns and alternatives as rows can be helpful. The pros and cons of the various choices as well as the short- and long-term implications of each may be evaluated. Best, worst, and most likely scenarios can also be insightful.
Step 5: Decision. Students propose their solution to the problem. This decision is justified based on an in-depth analysis. Explain why the recommendation made is the best fit for the criteria.
Step 6: Implementation plan. Sound business decisions may fail due to poor execution. To enhance the likeliness of a successful project outcome, students describe the key steps (activities) to implement the recommendation, timetable, projected costs, expected competitive reaction, success metrics, and risks in the plan.
“Students note that using the PACADI framework yields ‘aha moments’—they learned something surprising in the case that led them to think differently about the problem and their proposed solution.”
PACADI’s Benefits: Meaningfully and Thoughtfully Applying Business Concepts
The PACADI framework covers all of the major elements of business decision-making, including implementation, which is often overlooked. By stepping through the whole framework, students apply relevant business concepts and solve management problems via a systematic, comprehensive approach; they’re far less likely to surface piecemeal responses.
As students explore each part of the framework, they may realize that they need to make changes to a previous step. For instance, when working on implementation, students may realize that the alternative they selected cannot be executed or will not be profitable, and thus need to rethink their decision. Or, they may discover that the criteria need to be revised since the list of decision factors they identified is incomplete (for example, the factors may explain key marketing concerns but fail to address relevant financial considerations) or is unrealistic (for example, they suggest a 25 percent increase in revenues without proposing an increased promotional budget).
In addition, the PACADI framework can be used alongside quantitative assignments, in-class exercises, and business and management simulations. The structured, multi-step decision framework encourages careful and sequential analysis to solve business problems. Incorporating PACADI as an overarching decision-making method across different projects will ultimately help students achieve desired learning outcomes. As a practical “beyond-the-classroom” tool, the PACADI framework is not a contrived course assignment; it reflects the decision-making approach that managers, executives, and entrepreneurs exercise daily. Case analysis introduces students to the real-world process of making business decisions quickly and correctly, often with limited information. This framework supplies an organized and disciplined process that students can readily defend in writing and in class discussions.
PACADI in Action: An Example
Here’s an example of how students used the PACADI framework for a recent case analysis on CVS, a large North American drugstore chain.
The CVS Prescription for Customer Value*
PACADI Stage
Summary Response
How should CVS Health evolve from the “drugstore of your neighborhood” to the “drugstore of your future”?
Alternatives
A1. Kaizen (continuous improvement)
A2. Product development
A3. Market development
A4. Personalization (micro-targeting)
Criteria (include weights)
C1. Customer value: service, quality, image, and price (40%)
C2. Customer obsession (20%)
C3. Growth through related businesses (20%)
C4. Customer retention and customer lifetime value (20%)
Each alternative was analyzed by each criterion using a Customer Value Assessment Tool
Alternative 4 (A4): Personalization was selected. This is operationalized via: segmentation—move toward segment-of-1 marketing; geodemographics and lifestyle emphasis; predictive data analysis; relationship marketing; people, principles, and supply chain management; and exceptional customer service.
Implementation
Partner with leading medical school
Curbside pick-up
Pet pharmacy
E-newsletter for customers and employees
Employee incentive program
CVS beauty days
Expand to Latin America and Caribbean
Healthier/happier corner
Holiday toy drives/community outreach
*Source: A. Weinstein, Y. Rodriguez, K. Sims, R. Vergara, “The CVS Prescription for Superior Customer Value—A Case Study,” Back to the Future: Revisiting the Foundations of Marketing from Society for Marketing Advances, West Palm Beach, FL (November 2, 2018).
Results of Using the PACADI Framework
When faculty members at our respective institutions at Nova Southeastern University (NSU) and the University of North Carolina Wilmington have used the PACADI framework, our classes have been more structured and engaging. Students vigorously debate each element of their decision and note that this framework yields an “aha moment”—they learned something surprising in the case that led them to think differently about the problem and their proposed solution.
These lively discussions enhance individual and collective learning. As one external metric of this improvement, we have observed a 2.5 percent increase in student case grade performance at NSU since this framework was introduced.
Tips to Get Started
The PACADI approach works well in in-person, online, and hybrid courses. This is particularly important as more universities have moved to remote learning options. Because students have varied educational and cultural backgrounds, work experience, and familiarity with case analysis, we recommend that faculty members have students work on their first case using this new framework in small teams (two or three students). Additional analyses should then be solo efforts.
To use PACADI effectively in your classroom, we suggest the following:
Advise your students that your course will stress critical thinking and decision-making skills, not just course concepts and theory.
Use a varied mix of case studies. As marketing professors, we often address consumer and business markets; goods, services, and digital commerce; domestic and global business; and small and large companies in a single MBA course.
As a starting point, provide a short explanation (about 20 to 30 minutes) of the PACADI framework with a focus on the conceptual elements. You can deliver this face to face or through videoconferencing.
Give students an opportunity to practice the case analysis methodology via an ungraded sample case study. Designate groups of five to seven students to discuss the case and the six steps in breakout sessions (in class or via Zoom).
Ensure case analyses are weighted heavily as a grading component. We suggest 30–50 percent of the overall course grade.
Once cases are graded, debrief with the class on what they did right and areas needing improvement (30- to 40-minute in-person or Zoom session).
Encourage faculty teams that teach common courses to build appropriate instructional materials, grading rubrics, videos, sample cases, and teaching notes.
When selecting case studies, we have found that the best ones for PACADI analyses are about 15 pages long and revolve around a focal management decision. This length provides adequate depth yet is not protracted. Some of our tested and favorite marketing cases include Brand W , Hubspot , Kraft Foods Canada , TRSB(A) , and Whiskey & Cheddar .

Art Weinstein , Ph.D., is a professor of marketing at Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, Florida. He has published more than 80 scholarly articles and papers and eight books on customer-focused marketing strategy. His latest book is Superior Customer Value—Finding and Keeping Customers in the Now Economy . Dr. Weinstein has consulted for many leading technology and service companies.

Herbert V. Brotspies , D.B.A., is an adjunct professor of marketing at Nova Southeastern University. He has over 30 years’ experience as a vice president in marketing, strategic planning, and acquisitions for Fortune 50 consumer products companies working in the United States and internationally. His research interests include return on marketing investment, consumer behavior, business-to-business strategy, and strategic planning.

John T. Gironda , Ph.D., is an assistant professor of marketing at the University of North Carolina Wilmington. His research has been published in Industrial Marketing Management, Psychology & Marketing , and Journal of Marketing Management . He has also presented at major marketing conferences including the American Marketing Association, Academy of Marketing Science, and Society for Marketing Advances.
Related Articles

We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
- Article Writing Affordable Article Writing Services
- Blog Writing Blogs that optimise your visibility
- Product Description Website that optimise your visibility
- Website Writing Website that optimise your visibility
- Proofreading Website that optimise your visibility
- Translation Website that optimise your visibility
- Agriculture Affordable Article Writing Services
- Health & Beauty Blogs that optimise your visibility
- Automotive Website that optimise your visibility
- Sports & fitness Website that optimise your visibility
- Real Estate Website that optimise your visibility
- Entertainment Website that optimise your visibility
- Blogs Affordable Article Writing Services
- Samples Blogs that optimise your visibility
- Case Study Website that optimise your visibility

“How to Write Case Studies: A Comprehensive Guide”
Case studies are essential for marketing and research, offering in-depth insights into successes and problem-solving methods. This blog explains how to write case studies, including steps for creating them, tips for analysis, and case study examples. You'll also find case study templates to simplify the process. Effective case studies establish credibility, enhance marketing efforts, and provide valuable insights for future projects.
Case studies are detailed examinations of subjects like businesses, organizations, or individuals. They are used to highlight successes and problem-solving methods. They are crucial in marketing, education, and research to provide concrete examples and insights.
This blog will explain how to write case studies and their importance. We will cover different applications of case studies and a step-by-step process to create them. You’ll find tips for conducting case study analysis, along with case study examples and case study templates.
Effective case studies are vital. They showcase success stories and problem-solving skills, establishing credibility. This guide will teach you how to create a case study that engages your audience and enhances your marketing and research efforts.
What are Case Studies?
1. Definition and Purpose of a Case Study
Case studies are in-depth explorations of specific subjects to understand dynamics and outcomes. They provide detailed insights that can be generalized to broader contexts.
2. Different Types of Case Studies
- Exploratory: Investigates an area with limited information.
- Explanatory: Explains reasons behind a phenomenon.
- Descriptive: Provides a detailed account of the subject.
- Intrinsic : Focuses on a unique subject.
- Instrumental: Uses the case to understand a broader issue.
3. Benefits of Using Case Studies
Case studies offer many benefits. They provide real-world examples to illustrate theories or concepts. Businesses can demonstrate the effectiveness of their products or services. Researchers gain detailed insights into specific phenomena. Educators use them to teach through practical examples. Learning how to write case studies can enhance your marketing and research efforts.
Understanding how to create a case study involves recognizing these benefits. Case study examples show practical applications. Using case study templates can simplify the process.
5 Steps to Write a Case Study
1. Identifying the Subject or Case
Choose a subject that aligns with your objectives and offers valuable insights. Ensure the subject has a clear narrative and relevance to your audience. The subject should illustrate key points and provide substantial learning opportunities. Common subjects include successful projects, client stories, or significant business challenges.
2. Conducting Thorough Research and Data Collection
Gather comprehensive data from multiple sources. Conduct interviews with key stakeholders, such as clients, team members, or industry experts. Use surveys to collect quantitative data. Review documents, reports, and any relevant records. Ensure the information is accurate, relevant, and up-to-date. This thorough research forms the foundation for how to write case studies that are credible and informative.
3. Structuring the Case Study
Organize your case study into these sections:
- Introduction: Introduce the subject and its significance. Provide an overview of what will be covered.
- Background: Provide context and background information. Describe the subject’s history, environment, and any relevant details.
- Case Presentation: Detail the case, including the problem or challenge faced. Discuss the actions taken to address the issue.
- Analysis: Analyze the data and discuss the findings. Highlight key insights, patterns, and outcomes.
- Conclusion: Summarize the outcomes and key takeaways. Reflect on the broader implications and lessons learned.
4. Writing a Compelling Introduction
The introduction should grab the reader’s attention. Start with a hook, such as an interesting fact, quote, or question. Provide a brief overview of the subject and its importance. Explain why this case is relevant and worth studying. An engaging introduction sets the stage for how to create a case study that keeps readers interested.
5. Providing Background Information and Context
Give readers the necessary background to understand the case. Include details about the subject’s history, environment, and any relevant circumstances. Explain the context in which the case exists, such as the industry, market conditions, or organizational culture. Providing a solid foundation helps readers grasp the significance of the case and enhances the credibility of your study.
Understanding how to write a case study involves meticulous research and a clear structure. Utilizing case study examples and templates can guide you through the process, ensuring you present your findings effectively. These steps are essential for writing informative, engaging, and impactful case studies.
How to Write Case Study Analysis
1. Analyzing the Data Collected
Examine the data to identify patterns, trends, and key findings. Use qualitative and quantitative methods to ensure a comprehensive analysis. Validate the data’s accuracy and relevance to the subject. Look for correlations and causations that can provide deeper insights.
2. Identifying Key Issues and Problems
Pinpoint the main issues or challenges faced by the subject. Determine the root causes of these problems. Use tools like SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) to get a clear picture. Prioritize the issues based on their impact and urgency.
3. Discussing Possible Solutions and Their Implementation
Explore various solutions that address the identified issues. Compare the potential effectiveness of each solution. Discuss the steps taken to implement the chosen solutions. Highlight the decision-making process and the rationale behind it. Include any obstacles faced during implementation and how they were overcome.
4. Evaluating the Results and Outcomes
Assess the outcomes of the implemented solutions. Use metrics and KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) to measure success. Compare the results with the initial objectives and expectations. Discuss any deviations and their reasons. Provide evidence to support your evaluation, such as before-and-after data or testimonials.
5. Providing Insights and Lessons Learned
Reflect on the insights gained from the case study. Discuss what worked well and what didn’t. Highlight lessons that can be applied to similar situations. Provide actionable recommendations for future projects. This section should offer valuable takeaways for the readers, helping them understand how to create a case study that is insightful and practical.
Mastering how to write case studies involves understanding each part of the analysis. Use case study examples to see how these elements are applied. Case study templates can help you structure your work. Knowing how to make a case study analysis will make your findings clear and actionable.
Case Study Examples and Templates
1. Showcasing Successful Case Studies
Georgia tech athletics increase season ticket sales by 80%.
Georgia Tech Athletics aimed to enhance their season ticket sales and engagement with fans. Their initial strategy involved multiple outbound phone calls without targeting. They partnered with Salesloft to improve their sales process with a more structured inbound approach. This allowed sales reps to target communications effectively. As a result, Georgia Tech saw an 80% increase in season ticket sales, with improved employee engagement and fan relationships.
WeightWatchers Revamps Enterprise Sales Process with HubSpot
WeightWatchers sought to improve their sales efficiency. Their previous system lacked automation, requiring extensive manual effort. By adopting HubSpot’s CRM, WeightWatchers streamlined their sales process. The automation capabilities of HubSpot allowed them to manage customer interactions more effectively. This transition significantly enhanced their operational efficiency and sales performance.
2. Breakdown of What Makes These Examples Effective
These case study examples are effective due to their clear structure and compelling storytelling. They:
- Identify the problem: Each case study begins by outlining the challenges faced by the client.
- Detail the solution: They explain the specific solutions implemented to address these challenges.
- Showcase the results: Quantifiable results and improvements are highlighted, demonstrating the effectiveness of the solutions.
- Use visuals and quotes: Incorporating images, charts, and client testimonials enhances engagement and credibility.
3. Providing Case Study Templates
To assist in creating your own case studies, here are some recommended case study templates:
1. General Case Study Template
- Suitable for various industries and applications.
- Includes sections for background, problem, solution, and results.
- Helps provide a structured narrative for any case study.
2. Data-Driven Case Study Template
- Focuses on presenting metrics and data.
- Ideal for showcasing quantitative achievements.
- Structured to highlight significant performance improvements and achievements.
3. Product-Specific Case Study Template
- Emphasizes customer experiences and satisfaction with a specific product.
- Highlights benefits and features of the product rather than the process.
4. Tips for Customizing Templates to Fit Your Needs
When using case study templates, tailor them to match the specific context of your study. Consider the following tips:
- Adapt the language and tone: Ensure it aligns with your brand voice and audience.
- Include relevant visuals: Add charts, graphs, and images to support your narrative.
- Personalize the content: Use specific details about the subject to make the case study unique and relatable.
Utilizing these examples and templates will guide you in how to write case studies effectively. They provide a clear framework for how to create a case study that is engaging and informative. Learning how to make a case study becomes more manageable with these resources and examples.
Tips for Creating Compelling Case Studies
1. Using Storytelling Techniques to Engage Readers
Incorporate storytelling techniques to make your case study engaging. A compelling narrative holds the reader’s attention.
2. Including Quotes and Testimonials from Participants
Add quotes and testimonials to add credibility. Participant feedback enhances the authenticity of your study.
3. Visual Aids: Charts, Graphs, and Images to Support Your Case
Use charts, graphs, and images to illustrate key points. Visual aids help in better understanding and retention.
4. Ensuring Clarity and Conciseness in Writing
Write clearly and concisely to maintain reader interest. Avoid jargon and ensure your writing is easy to follow.
5. Highlighting the Impact and Benefits
Emphasize the positive outcomes and benefits. Show how the subject has improved or achieved success.
Understanding how to write case studies involves using effective storytelling and visuals. Case study examples show how to engage readers, and case study templates help organize your content. Learning how to make a case study ensures that it is clear and impactful.
Benefits of Using Case Studies
1. Establishing Authority and Credibility
How to write case studies can effectively establish your authority. Showcasing success stories builds credibility in your field.
2. Demonstrating Practical Applications of Your Product or Service
Case study examples demonstrate how your product or service solves real-world problems. This practical evidence is convincing for potential clients.
3. Enhancing Marketing and Sales Efforts
Use case studies to support your marketing and sales strategies. They highlight your successes and attract new customers.
4. Providing Valuable Insights for Future Projects
Case studies offer insights that can guide future projects. Learning how to create a case study helps in applying these lessons effectively.
5. Engaging and Educating Your Audience
Case studies are engaging and educational. They provide detailed examples and valuable lessons. Using case study templates can make this process easier and more effective. Understanding how to make a case study ensures you can communicate these benefits clearly.
Writing effective case studies involves thorough research, clear structure, and engaging content. By following these steps, you’ll learn how to write case studies that showcase your success stories and problem-solving skills. Use the case study examples and case study templates provided to get started. Well-crafted case studies are valuable tools for marketing, research, and education. Start learning how to make a case study today and share your success stories with the world.
What is the purpose of a case study?
A case study provides detailed insights into a subject, illustrating successes and solutions. It helps in understanding complex issues.
How do I choose a subject for my case study?
Select a subject that aligns with your objectives and offers valuable insights. Ensure it has a clear narrative.
What are the key components of a case study analysis?
A case study analysis includes data collection, identifying key issues, discussing solutions, evaluating outcomes, and providing insights.
Where can I find case study templates?
You can find downloadable case study templates online. They simplify the process of creating a case study.
How can case studies benefit my business?
Case studies establish credibility, demonstrate practical applications, enhance marketing efforts, and provide insights for future projects. Learning how to create a case study can significantly benefit your business.

I am currently pursuing my Masters in Communication and Journalism from University of Mumbai. I am the author of four self published books. I am interested inv writing for films and TV. I run a blog where I write about film reviews.
More details for blogs

How to Create Interactive Content and Boost Engagement
Learn how to create interactive content to engage your audience. Discover tools, strategies, and benefits of using interactive elements.

How to Use Canva to Mass Produce Viral Content
Discover how to use Canva to mass produce viral content with these expert tips and strategies. Boost your content creation game today!

SGE Ranking Strategies: How to Get Rankings on SGEs
Learn how to create answers that rank for SGE with our comprehensive guide on SGE ranking strategies. Powerful tips and examples!
Need assistance with something
Speak with our expert right away to receive free service-related advice.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on 5 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 30 January 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organisation, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating, and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyse the case.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
Unlike quantitative or experimental research, a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
If you find yourself aiming to simultaneously investigate and solve an issue, consider conducting action research . As its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time, and is highly iterative and flexible.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience, or phenomenon.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data .
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis, with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results , and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyse its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, January 30). Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved 3 June 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/case-studies/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, correlational research | guide, design & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, descriptive research design | definition, methods & examples.
Solving Case Studies: 8 Step-by-Step Strategies for Management Students
- by Tanu Bhatnagar
- Published: Oct 08, 2023, 09:45 IST
- Updated: Oct 08, 2023, 00:54 IST
- Tanu Bhatnagar
- October 8, 2023
Mastering the Art of Analyzing and Resolving Business Case Studies
Case study analysis is useful for management students. It’s more than a course—it’s a preview of your future job problems. These real-life examples allow you to apply class ideas and acquire a business-ready problem-solving attitude.
It’s not easy to master case study solving. Strategic thinking, critical thinking, and innovation are needed. This book covers the finest case study solution tactics to help you succeed academically and become a good manager. Solving a management case study is a crucial skill for students pursuing degrees in fields such as MBA, HRM, Finance, and Marketing.
Also, read 10 Proven Memorize Techniques for Students- Friendly Tips
8 Step-by-Step Strategies for Management Students
These case studies offer a practical application of management concepts, requiring students to analyze complex scenarios and devise solutions. In this comprehensive guide, we will outline a step-by-step approach to solving management case studies and provide a real-world example with a solution.
Step 1: Comprehensive Case Study Analysis
Comprehensive case study analysis is the cornerstone of effective problem-solving. It involves immersing yourself in the case study, not just skimming through it. Start by reading the case thoroughly, absorbing its context, characters, and central problem or objective. It’s crucial to understand the nuances of the situation presented, as even subtle details may significantly impact the solution.
During this phase, consider the following:
- Context : Understand the setting, time frame, and circumstances that led to the current situation.
- Characters : Familiarize yourself with the key individuals involved, their roles, motivations, and potential biases.
- Problem/Objective : Identify the core challenge or goal that the case revolves around.
Step 2: Familiarize with the Industry and Company
Familiarizing yourself with the industry and the specific company involved in the case study is pivotal. This step provides essential context and aids in making informed decisions and recommendations. Here’s how to approach it:
- Industry Analysis : Research the industry’s characteristics, trends, and dynamics. This knowledge helps you understand the broader competitive landscape and market forces at play.
- Company Background : Delve into the company’s history, products or services, market position, financial performance, and strategic priorities. This information helps you align your recommendations with the company’s goals and capabilities.
Step 3: Define the Core Problem/Objective

In this step, your objective is to pinpoint the primary issue or objective that the case study revolves around. By clarifying the problem that needs resolution or the goal that must be achieved, you set the stage for your analysis and decision-making. Consider the following:
- Problem Statement : Summarize the problem in a concise, clear statement. Ensure that your understanding aligns with the essence of the case.
- Objective Clarity : If the case involves an objective, such as expanding market share or improving profitability, define it with precision.
Step 4: Extract Relevant Information
A key aspect of case study analysis is extracting relevant facts and details from the case materials. This process involves revisiting the case study, both to reinforce your understanding and to gather pertinent information. Here’s how to approach it:
- Detailed Examination : Scrutinize the case for data, statistics, anecdotes, and any other information that sheds light on the problem or objective.
- Note-taking : Create a system for recording critical information, whether through written notes or mental models. This will aid in organizing your analysis.
Step 5: Identify Key Statements

Within the case study, there are often statements or pieces of information that hold particular significance. These statements can serve as guideposts during your analysis, helping you define and address the problem more precisely. Consider:
- Problem Clues : Look for statements that hint at the underlying issues or challenges.
- Objective Relevance : Identify statements that directly relate to the stated objective.
Step 6: Assess the External Environment
To make informed recommendations, you must assess the external environment surrounding the case. This step involves considering various factors that can influence the solution, including:
- Market Conditions : Analyze the market’s size, growth rate, trends, and competitive landscape.
- Regulatory Environment : Evaluate the impact of regulations, laws, and government policies on the case.
- Resource Availability : Understand the availability of resources, such as capital, talent, and technology.
- Competitive Forces : Assess the competitive forces at play, including existing rivals, potential entrants, suppliers, and buyers.
Also, read Top 10 Hobbies That Boost Your IQ: A Guide for Students
Step 7: Address Real-Life Constraints
Recognize that real-life problem-solving often comes with limitations, including incomplete information and time constraints. You should be prepared to make decisions based on the available data and within reasonable time limits. Consider:
- Time Sensitivity : Acknowledge any time pressures that may affect the decision-making process.
- Resource Constraints : Understand the limits of available resources, such as budget, manpower, or technology.
Step 8: Fill Information Gaps with Realistic Assumptions
Information gaps are common in real-world scenarios. To bridge these gaps, make realistic assumptions that align with the context of the case study. Use your judgment and critical thinking to supplement missing details while staying grounded in the case’s reality.
By following these steps diligently, you can approach management case studies methodically and develop well-structured, informed solutions that address the core problem or objective effectively

Problem: XYZ Corporation, a well-established software development firm, is grappling with ongoing employee performance challenges. Several members of its software development team consistently fail to meet project deadlines and produce work below the company’s quality standards.
Problem Question 1: What is the core problem that XYZ Corporation is facing concerning employee performance?
The central issue that XYZ Corporation is confronting concerning employee performance is the persistent underperformance of several software developers within the organization. These individuals consistently fail to meet project deadlines and produce work that falls significantly below the company’s established quality standards. This recurring problem has become a significant impediment to the company’s software development projects.
Problem Question 2: How are the underperforming employees affecting the company’s software development projects and overall business operations?
The underperforming employees in XYZ Corporation are having a substantial negative impact on the company’s software development projects and overall business operations. Their consistent inability to meet project deadlines results in significant delays in project completion, disrupting project schedules and affecting the company’s ability to deliver products and services on time. Furthermore, the compromised quality of their work leads to subpar products, potentially resulting in client dissatisfaction and eroding the company’s reputation. These issues collectively undermine the company’s profitability as it grapples with missed opportunities and the costs associated with addressing substandard work. Addressing this challenge is imperative for XYZ Corporation to ensure its continued success and competitiveness in the software development industry.
. Student Approach to Solve:
- Begin by thoroughly reading the case study to grasp its context, characters, and the central problem or objective.
- Understanding the broader business environment will aid in making informed decisions and recommendations.
- Identify the primary issue or objective in the case.
- Create a mental or written model of the core problem or objective and make note of critical information that informs your understanding.
- Acknowledge that real-life problems often come with incomplete information and time constraints.
- Use your judgment to supplement missing details.
By following these steps and considering the provided answers, students can approach and solve the case study effectively, offering valuable insights and recommendations to address XYZ Corporation’s employee performance challenges.
Finally, the case study solution connects management theory with practice. It helps students analyse difficult circumstances, make educated judgements, and find effective solutions, which employers in numerous sectors value.
The above guide’s techniques can help students succeed in management school and prepare them for job difficulties and possibilities. Accept case studies as learning opportunities, improve your problem-solving abilities, and become a skilled and resourceful manager. The greatest method to learn is through doing, and case study solution leads to real-world success.
Also, read 10 Best Economic Books for Commerce Students

Meet Tanu Bhatnagar, an educational expert with extensive experience in teaching, research and mentoring.With a decade in... (Full bio)
Latest Exams
Best colleges.

Trending News

Best Books to Read in 2023
Best Books to Read in 2023 Are you a bookworm or a bibliophile, if yes, then this is the ...

10 Proven Memorize Techniques for Students- Friendly Tips
In the exhilarating journey of 10 Proven Memorize Techniques for Students learning, memory is your trusty companion. Whether ...

Top 20 Toughest exams in world Latest List 2023
Top 20 toughest exams in world is about exams in the world that required very hard work to ...
Top 20 toughest exams in India Latest List 2023
Top 20 toughest exams in India - Exams are the perhaps most toughest moments for any student. A ...

Top 20 Colleges of DU Latest List 2023
Top 20 Colleges of DU Getting admissions to the top 20 colleges of DU is a dream for every ...
Top 20 NITs of India Latest List 2023
Top 20 NITs of India - Amongst the 31 NITs in India, today, we are talking ...

Top 12 Artificial Intelligence Colleges in Mumbai
Here are the Top 12 Artificial Intelligence in Mumbai. Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human ...

Best Science Courses after 12th
As you stand on the Best Science Courses after 12th academic journey, the realm of science beckons, offering ...
Curated Latest News For You

JEE Advanced 2023 provisional answer key, access links here

Best 5 Time Management Tips for Competitive Exams

JEE Advanced 2023 registration starts on 30 April 2023

Score High in NEET 2023 With these Key Subject wise topics

Top 8 Jobs in Indian Army after Plus Two

10 Super Tips for Cracking NEET 2023
The sooner you start, the better .
Millions of students have entrusted CollegeChalo to facilitate their seamless and smooth admission process to their dream colleges and universities. With CollegeChalo, you can gain a competitive edge by easily accessing exam and course details to stay ahead of the admission journey. What are you waiting for?
ADMISSION ENQUIRY FORM
Enter basic details, signin with google, or use your email, signup with google, forgot your password, resetting new password, connecting you to your dream college.
Discover Leading Universities and Colleges, Explore Courses, and Navigate Exams
search results:
How CollegeChalo helps you in admission ?
- With a completely online admission process, we help you get college admission without having to step out.
- Upto 50% discount on application forms
- 24*7 counselling facilities available
- Ask and receive answers from experts and other users

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What the Case Study Method Really Teaches
- Nitin Nohria

Seven meta-skills that stick even if the cases fade from memory.
It’s been 100 years since Harvard Business School began using the case study method. Beyond teaching specific subject matter, the case study method excels in instilling meta-skills in students. This article explains the importance of seven such skills: preparation, discernment, bias recognition, judgement, collaboration, curiosity, and self-confidence.
During my decade as dean of Harvard Business School, I spent hundreds of hours talking with our alumni. To enliven these conversations, I relied on a favorite question: “What was the most important thing you learned from your time in our MBA program?”
- Nitin Nohria is the George F. Baker Jr. and Distinguished Service University Professor. He served as the 10th dean of Harvard Business School, from 2010 to 2020.
Partner Center
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business How to Present a Case Study like a Pro (With Examples)
How to Present a Case Study like a Pro (With Examples)
Written by: Danesh Ramuthi Sep 07, 2023

Okay, let’s get real: case studies can be kinda snooze-worthy. But guess what? They don’t have to be!
In this article, I will cover every element that transforms a mere report into a compelling case study, from selecting the right metrics to using persuasive narrative techniques.
And if you’re feeling a little lost, don’t worry! There are cool tools like Venngage’s Case Study Creator to help you whip up something awesome, even if you’re short on time. Plus, the pre-designed case study templates are like instant polish because let’s be honest, everyone loves a shortcut.
Click to jump ahead:
What is a case study presentation?
What is the purpose of presenting a case study, how to structure a case study presentation, how long should a case study presentation be, 5 case study presentation examples with templates, 6 tips for delivering an effective case study presentation, 5 common mistakes to avoid in a case study presentation, how to present a case study faqs.
A case study presentation involves a comprehensive examination of a specific subject, which could range from an individual, group, location, event, organization or phenomenon.
They’re like puzzles you get to solve with the audience, all while making you think outside the box.
Unlike a basic report or whitepaper, the purpose of a case study presentation is to stimulate critical thinking among the viewers.
The primary objective of a case study is to provide an extensive and profound comprehension of the chosen topic. You don’t just throw numbers at your audience. You use examples and real-life cases to make you think and see things from different angles.

The primary purpose of presenting a case study is to offer a comprehensive, evidence-based argument that informs, persuades and engages your audience.
Here’s the juicy part: presenting that case study can be your secret weapon. Whether you’re pitching a groundbreaking idea to a room full of suits or trying to impress your professor with your A-game, a well-crafted case study can be the magic dust that sprinkles brilliance over your words.
Think of it like digging into a puzzle you can’t quite crack . A case study lets you explore every piece, turn it over and see how it fits together. This close-up look helps you understand the whole picture, not just a blurry snapshot.
It’s also your chance to showcase how you analyze things, step by step, until you reach a conclusion. It’s all about being open and honest about how you got there.
Besides, presenting a case study gives you an opportunity to connect data and real-world scenarios in a compelling narrative. It helps to make your argument more relatable and accessible, increasing its impact on your audience.
One of the contexts where case studies can be very helpful is during the job interview. In some job interviews, you as candidates may be asked to present a case study as part of the selection process.
Having a case study presentation prepared allows the candidate to demonstrate their ability to understand complex issues, formulate strategies and communicate their ideas effectively.
The way you present a case study can make all the difference in how it’s received. A well-structured presentation not only holds the attention of your audience but also ensures that your key points are communicated clearly and effectively.
In this section, let’s go through the key steps that’ll help you structure your case study presentation for maximum impact.
Let’s get into it.
Open with an introductory overview
Start by introducing the subject of your case study and its relevance. Explain why this case study is important and who would benefit from the insights gained. This is your opportunity to grab your audience’s attention.

Explain the problem in question
Dive into the problem or challenge that the case study focuses on. Provide enough background information for the audience to understand the issue. If possible, quantify the problem using data or metrics to show the magnitude or severity.

Detail the solutions to solve the problem
After outlining the problem, describe the steps taken to find a solution. This could include the methodology, any experiments or tests performed and the options that were considered. Make sure to elaborate on why the final solution was chosen over the others.

Key stakeholders Involved
Talk about the individuals, groups or organizations that were directly impacted by or involved in the problem and its solution.
Stakeholders may experience a range of outcomes—some may benefit, while others could face setbacks.
For example, in a business transformation case study, employees could face job relocations or changes in work culture, while shareholders might be looking at potential gains or losses.
Discuss the key results & outcomes
Discuss the results of implementing the solution. Use data and metrics to back up your statements. Did the solution meet its objectives? What impact did it have on the stakeholders? Be honest about any setbacks or areas for improvement as well.
Include visuals to support your analysis
Visual aids can be incredibly effective in helping your audience grasp complex issues. Utilize charts, graphs, images or video clips to supplement your points. Make sure to explain each visual and how it contributes to your overall argument.
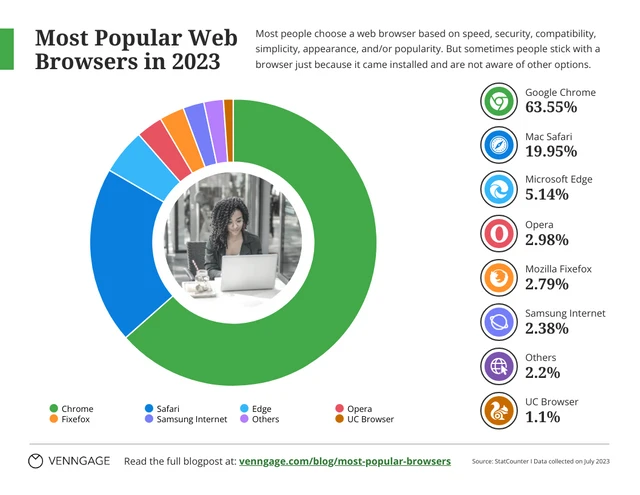
Pie charts illustrate the proportion of different components within a whole, useful for visualizing market share, budget allocation or user demographics.
This is particularly useful especially if you’re displaying survey results in your case study presentation.
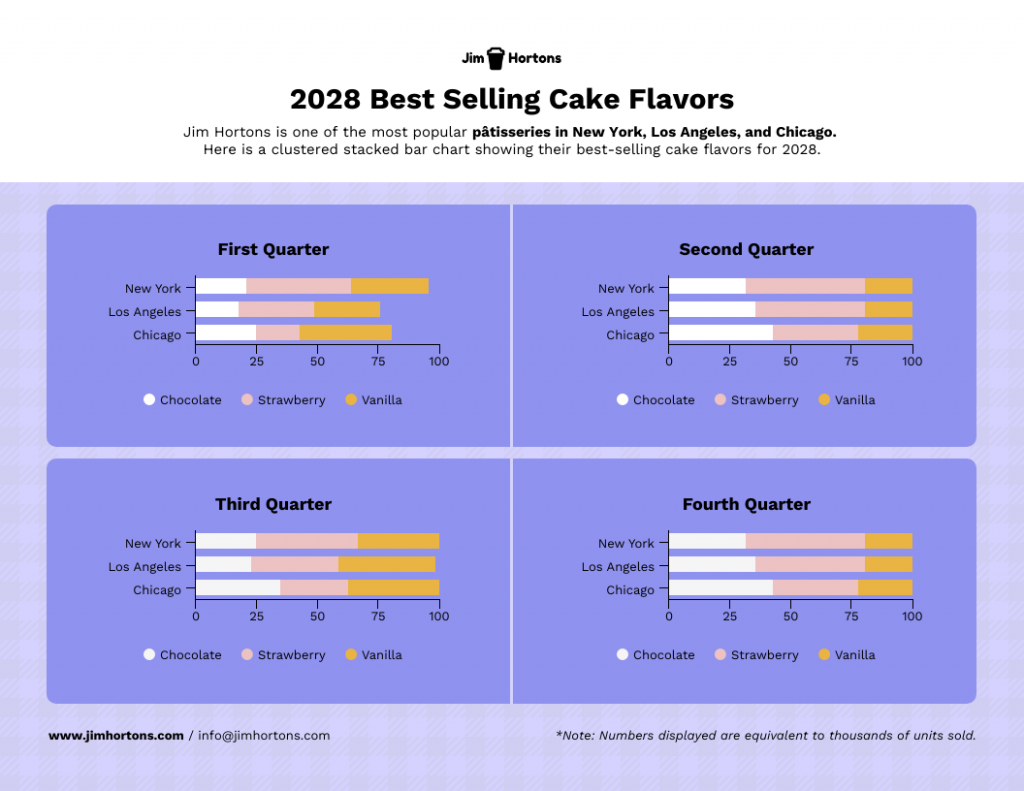
Stacked charts on the other hand are perfect for visualizing composition and trends. This is great for analyzing things like customer demographics, product breakdowns or budget allocation in your case study.
Consider this example of a stacked bar chart template. It provides a straightforward summary of the top-selling cake flavors across various locations, offering a quick and comprehensive view of the data.
Not the chart you’re looking for? Browse Venngage’s gallery of chart templates to find the perfect one that’ll captivate your audience and level up your data storytelling.
Recommendations and next steps
Wrap up by providing recommendations based on the case study findings. Outline the next steps that stakeholders should take to either expand on the success of the project or address any remaining challenges.
Acknowledgments and references
Thank the people who contributed to the case study and helped in the problem-solving process. Cite any external resources, reports or data sets that contributed to your analysis.
Feedback & Q&A session
Open the floor for questions and feedback from your audience. This allows for further discussion and can provide additional insights that may not have been considered previously.
Closing remarks
Conclude the presentation by summarizing the key points and emphasizing the takeaways. Thank your audience for their time and participation and express your willingness to engage in further discussions or collaborations on the subject.

Well, the length of a case study presentation can vary depending on the complexity of the topic and the needs of your audience. However, a typical business or academic presentation often lasts between 15 to 30 minutes.
This time frame usually allows for a thorough explanation of the case while maintaining audience engagement. However, always consider leaving a few minutes at the end for a Q&A session to address any questions or clarify points made during the presentation.
When it comes to presenting a compelling case study, having a well-structured template can be a game-changer.
It helps you organize your thoughts, data and findings in a coherent and visually pleasing manner.
Not all case studies are created equal and different scenarios require distinct approaches for maximum impact.
To save you time and effort, I have curated a list of 5 versatile case study presentation templates, each designed for specific needs and audiences.
Here are some best case study presentation examples that showcase effective strategies for engaging your audience and conveying complex information clearly.
1 . Lab report case study template
Ever feel like your research gets lost in a world of endless numbers and jargon? Lab case studies are your way out!
Think of it as building a bridge between your cool experiment and everyone else. It’s more than just reporting results – it’s explaining the “why” and “how” in a way that grabs attention and makes sense.
This lap report template acts as a blueprint for your report, guiding you through each essential section (introduction, methods, results, etc.) in a logical order.

Want to present your research like a pro? Browse our research presentation template gallery for creative inspiration!
2. Product case study template
It’s time you ditch those boring slideshows and bullet points because I’ve got a better way to win over clients: product case study templates.
Instead of just listing features and benefits, you get to create a clear and concise story that shows potential clients exactly what your product can do for them. It’s like painting a picture they can easily visualize, helping them understand the value your product brings to the table.
Grab the template below, fill in the details, and watch as your product’s impact comes to life!

3. Content marketing case study template
In digital marketing, showcasing your accomplishments is as vital as achieving them.
A well-crafted case study not only acts as a testament to your successes but can also serve as an instructional tool for others.
With this coral content marketing case study template—a perfect blend of vibrant design and structured documentation, you can narrate your marketing triumphs effectively.

4. Case study psychology template
Understanding how people tick is one of psychology’s biggest quests and case studies are like magnifying glasses for the mind. They offer in-depth looks at real-life behaviors, emotions and thought processes, revealing fascinating insights into what makes us human.
Writing a top-notch case study, though, can be a challenge. It requires careful organization, clear presentation and meticulous attention to detail. That’s where a good case study psychology template comes in handy.
Think of it as a helpful guide, taking care of formatting and structure while you focus on the juicy content. No more wrestling with layouts or margins – just pour your research magic into crafting a compelling narrative.
5. Lead generation case study template
Lead generation can be a real head-scratcher. But here’s a little help: a lead generation case study.
Think of it like a friendly handshake and a confident resume all rolled into one. It’s your chance to showcase your expertise, share real-world successes and offer valuable insights. Potential clients get to see your track record, understand your approach and decide if you’re the right fit.
No need to start from scratch, though. This lead generation case study template guides you step-by-step through crafting a clear, compelling narrative that highlights your wins and offers actionable tips for others. Fill in the gaps with your specific data and strategies, and voilà! You’ve got a powerful tool to attract new customers.
Related: 15+ Professional Case Study Examples [Design Tips + Templates]
So, you’ve spent hours crafting the perfect case study and are now tasked with presenting it. Crafting the case study is only half the battle; delivering it effectively is equally important.
Whether you’re facing a room of executives, academics or potential clients, how you present your findings can make a significant difference in how your work is received.
Forget boring reports and snooze-inducing presentations! Let’s make your case study sing. Here are some key pointers to turn information into an engaging and persuasive performance:
- Know your audience : Tailor your presentation to the knowledge level and interests of your audience. Remember to use language and examples that resonate with them.
- Rehearse : Rehearsing your case study presentation is the key to a smooth delivery and for ensuring that you stay within the allotted time. Practice helps you fine-tune your pacing, hone your speaking skills with good word pronunciations and become comfortable with the material, leading to a more confident, conversational and effective presentation.
- Start strong : Open with a compelling introduction that grabs your audience’s attention. You might want to use an interesting statistic, a provocative question or a brief story that sets the stage for your case study.
- Be clear and concise : Avoid jargon and overly complex sentences. Get to the point quickly and stay focused on your objectives.
- Use visual aids : Incorporate slides with graphics, charts or videos to supplement your verbal presentation. Make sure they are easy to read and understand.
- Tell a story : Use storytelling techniques to make the case study more engaging. A well-told narrative can help you make complex data more relatable and easier to digest.

Ditching the dry reports and slide decks? Venngage’s case study templates let you wow customers with your solutions and gain insights to improve your business plan. Pre-built templates, visual magic and customer captivation – all just a click away. Go tell your story and watch them say “wow!”
Nailed your case study, but want to make your presentation even stronger? Avoid these common mistakes to ensure your audience gets the most out of it:
Overloading with information
A case study is not an encyclopedia. Overloading your presentation with excessive data, text or jargon can make it cumbersome and difficult for the audience to digest the key points. Stick to what’s essential and impactful. Need help making your data clear and impactful? Our data presentation templates can help! Find clear and engaging visuals to showcase your findings.
Lack of structure
Jumping haphazardly between points or topics can confuse your audience. A well-structured presentation, with a logical flow from introduction to conclusion, is crucial for effective communication.
Ignoring the audience
Different audiences have different needs and levels of understanding. Failing to adapt your presentation to your audience can result in a disconnect and a less impactful presentation.
Poor visual elements
While content is king, poor design or lack of visual elements can make your case study dull or hard to follow. Make sure you use high-quality images, graphs and other visual aids to support your narrative.
Not focusing on results
A case study aims to showcase a problem and its solution, but what most people care about are the results. Failing to highlight or adequately explain the outcomes can make your presentation fall flat.
How to start a case study presentation?
Starting a case study presentation effectively involves a few key steps:
- Grab attention : Open with a hook—an intriguing statistic, a provocative question or a compelling visual—to engage your audience from the get-go.
- Set the stage : Briefly introduce the subject, context and relevance of the case study to give your audience an idea of what to expect.
- Outline objectives : Clearly state what the case study aims to achieve. Are you solving a problem, proving a point or showcasing a success?
- Agenda : Give a quick outline of the key sections or topics you’ll cover to help the audience follow along.
- Set expectations : Let your audience know what you want them to take away from the presentation, whether it’s knowledge, inspiration or a call to action.
How to present a case study on PowerPoint and on Google Slides?
Presenting a case study on PowerPoint and Google Slides involves a structured approach for clarity and impact using presentation slides :
- Title slide : Start with a title slide that includes the name of the case study, your name and any relevant institutional affiliations.
- Introduction : Follow with a slide that outlines the problem or situation your case study addresses. Include a hook to engage the audience.
- Objectives : Clearly state the goals of the case study in a dedicated slide.
- Findings : Use charts, graphs and bullet points to present your findings succinctly.
- Analysis : Discuss what the findings mean, drawing on supporting data or secondary research as necessary.
- Conclusion : Summarize key takeaways and results.
- Q&A : End with a slide inviting questions from the audience.
What’s the role of analysis in a case study presentation?
The role of analysis in a case study presentation is to interpret the data and findings, providing context and meaning to them.
It helps your audience understand the implications of the case study, connects the dots between the problem and the solution and may offer recommendations for future action.
Is it important to include real data and results in the presentation?
Yes, including real data and results in a case study presentation is crucial to show experience, credibility and impact. Authentic data lends weight to your findings and conclusions, enabling the audience to trust your analysis and take your recommendations more seriously
How do I conclude a case study presentation effectively?
To conclude a case study presentation effectively, summarize the key findings, insights and recommendations in a clear and concise manner.
End with a strong call-to-action or a thought-provoking question to leave a lasting impression on your audience.
What’s the best way to showcase data in a case study presentation ?
The best way to showcase data in a case study presentation is through visual aids like charts, graphs and infographics which make complex information easily digestible, engaging and creative.
Don’t just report results, visualize them! This template for example lets you transform your social media case study into a captivating infographic that sparks conversation.

Choose the type of visual that best represents the data you’re showing; for example, use bar charts for comparisons or pie charts for parts of a whole.
Ensure that the visuals are high-quality and clearly labeled, so the audience can quickly grasp the key points.
Keep the design consistent and simple, avoiding clutter or overly complex visuals that could distract from the message.
Choose a template that perfectly suits your case study where you can utilize different visual aids for maximum impact.
Need more inspiration on how to turn numbers into impact with the help of infographics? Our ready-to-use infographic templates take the guesswork out of creating visual impact for your case studies with just a few clicks.
Related: 10+ Case Study Infographic Templates That Convert
Congrats on mastering the art of compelling case study presentations! This guide has equipped you with all the essentials, from structure and nuances to avoiding common pitfalls. You’re ready to impress any audience, whether in the boardroom, the classroom or beyond.
And remember, you’re not alone in this journey. Venngage’s Case Study Creator is your trusty companion, ready to elevate your presentations from ordinary to extraordinary. So, let your confidence shine, leverage your newly acquired skills and prepare to deliver presentations that truly resonate.
Go forth and make a lasting impact!
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
- Harvard Business School →
- Academic Experience
- Faculty & Research
- The Field Method
- A Global Experience
The HBS Case Method
- Joint Degree Programs
- The Section Experience
- The HBS Case Method →
Take a Seat in the MBA Classroom
- Harvard Business School
How the HBS Case Method Works

How the Case Method Works

- Read and analyze the case. Each case is a 10-20 page document written from the viewpoint of a real person leading a real organization. In addition to background information on the situation, each case ends in a key decision to be made. Your job is to sift through the information, incomplete by design, and decide what you would do.
- Discuss the case. Each morning, you’ll bring your ideas to a small team of classmates from diverse professional backgrounds, your discussion group, to share your findings and listen to theirs. Together, you begin to see the case from different perspectives, better preparing you for class.
- Engage in class. Be prepared to change the way you think as you debate with classmates the best path forward for this organization. The highly engaged conversation is facilitated by the faculty member, but it’s driven by your classmates’ comments and experiences. HBS brings together amazingly talented people from diverse backgrounds and puts that experience front and center. Students do the majority of the talking (and lots of active listening), and your job is to better understand the decision at hand, what you would do in the case protagonist’s shoes, and why. You will not leave a class thinking about the case the same way you thought about it coming in! In addition to learning more about many businesses, in the case method you will develop communication, listening, analysis, and leadership skills. It is a truly dynamic and immersive learning environment.
- Reflect. The case method prepares you to be in leadership positions where you will face time-sensitive decisions with limited information. Reflecting on each class discussion will prepare you to face these situations in your future roles.
Student Perspectives

“I’ve been so touched by how dedicated other people have been to my learning and my success.”
Faculty Perspectives

“The world desperately needs better leadership. It’s actually one of the great gifts of teaching here, you can do something about it.”
Alumni Perspectives

“You walk into work every morning and it's like a fire hose of decisions that need to be made, often without enough information. Just like an HBS case.”
Celebrating the Inaugural HBS Case

“How do you go into an ambiguous situation and get to the bottom of it? That skill – the skill of figuring out a course of inquiry, to choose a course of action – that skill is as relevant today as it was in 1921.”
How To Solve A Case Study
Introduction
What is a case study? A case study is a deep study or a detailed examination of a particular case. In politics case studies, it can range from little happenings to huge undertakings like world wars. It is not necessary that a case study only highlights only an individual’s case but it can also highlight groups, belief systems, organizations, or events. Necessarily the case study does did not include only one observation but it may include many observations. In the case of studies projects for research involving several cases are called cross-case research; on the other hand, the study of a single case is called within the case research.
How To Solve a Case Study?
Solving a case study requires deep analyzing skills, the ability to investigate the current problem, examine the right solution, and using the most supportive and workable evidence. It is necessary to take notes, highlight influential facts, and underline the major problems involved. Into days modern times; you can also online case study solutions help by contacting experts on their websites. To make it easier we follow a step-wise procedure to make it understandable. So before you begin Writing the case, follow the step-by-step procedure to get reasonable and desired results.
Step 1: Identify The Case.
The first step is about taking notes, highlight the key factors which are being involved, and also introduce the relevant factors which are necessary.
Step 2: Focus Your Analysis
Identify the key problems. Find the reason that why Do they exist? How can they affect the organization or client? Which thing is responsible, and go for their best possible solutions.
Step 3: Realize Possible Solutions
Review all the reading related to the case study course, related discussions, consult it with outside sources, and utilize your experience.
Step 4: Choose The Best Possible Solution
Consider the best and supporting evidence. Its pros and cons, and how realistic it is?. Scan the gathered information again and do not overlook it without focusing on each point.
This is how to solve a case study step by step and easily conclude it while benefiting your clients following these well-researched steps. Additionally following these steps one can also be familiar that how to write case study assignment while getting less confusion.
Examples OF Solving A Case Study
As we know case study involves examining things deeply; for example, we take a case study in medicines. It may be related to an ailment or a patient; a case study in the business sector might cover a broader market; in politics, a case study might range from a narrow happening to a huge undertaking. Let’s discuss How to solve case studies with examples,
Example#1: AnaOwas a woman’s pseudonym of a lady named Bertha. A patient of a famous physical expert Jose Breuer. She was never a patient of another physician Freud. Both physicians Breuer and Joseph, extensively discuss her case. The woman was expecting the symptoms of a disease known as hysteria and it is also found that talking about her issues relieving her a lot and her symptoms. Her case becomes beneficial to understand the fact that therapy of talking has an excellent approach towards mental health.
Example#2: Phineas Gage was an employee in railways. Phineas experiences a scary accident in which a metal rod stuck his skull, damaging a sensitive portion of his brain; although he recovered after that, he comes up with extreme changes in his behavior and personality.
Example#3: Genie a young beautiful girl faced horrifying abuse and isolation. Genie’s case study allows many researchers to examine whether languages could be learned even after hectic times for developing language had vanished for her. Her case also enables everyone to understand that how interference of scientific researches leads to more abuse of a vulnerable person. One can also consult their mentors to understand which case study to buy and get the valuable guidance.
Benefits and Limitations OF A Case Study
A case study could have both strengths and drawbacks. Here we discuss its good and bad things in the form of bullets. First of all, we get to know about its pros.
- It allows investigators and researchers to attain high-level knowledge.
- Give them a chance to attain valuable information from Unusual and rare cases.
- Allow the individuals for research to develop their hypotheses to explore them at experimental research.
Along with its pros, case studies have their cons too. Let’s discuss them in bullets.
- The case study cannot briefly demonstrate cause and influences.
- It cannot be generalized in public.
- It can also lead to bias.
Bottom Lines
Generally, case studies can be included in many different fields like education, anthropology, psychology, medicines, and political sciences. We have discussed in the article above about case study definition, how to solve it, and also include the examples for your better understanding. Hoping that this article will play its part in building your knowledge about studying a case.
How To Answer A Case Study
A Step To Step Guide On The Importance OF Case Study
How To Buy A Case Study Assignment Help
How To Write Case Study In MBA
How To Write The Conclusion OF Your Case Study
How to write a case study — examples, templates, and tools

It’s a marketer’s job to communicate the effectiveness of a product or service to potential and current customers to convince them to buy and keep business moving. One of the best methods for doing this is to share success stories that are relatable to prospects and customers based on their pain points, experiences, and overall needs.
That’s where case studies come in. Case studies are an essential part of a content marketing plan. These in-depth stories of customer experiences are some of the most effective at demonstrating the value of a product or service. Yet many marketers don’t use them, whether because of their regimented formats or the process of customer involvement and approval.
A case study is a powerful tool for showcasing your hard work and the success your customer achieved. But writing a great case study can be difficult if you’ve never done it before or if it’s been a while. This guide will show you how to write an effective case study and provide real-world examples and templates that will keep readers engaged and support your business.
In this article, you’ll learn:
What is a case study?
How to write a case study, case study templates, case study examples, case study tools.
A case study is the detailed story of a customer’s experience with a product or service that demonstrates their success and often includes measurable outcomes. Case studies are used in a range of fields and for various reasons, from business to academic research. They’re especially impactful in marketing as brands work to convince and convert consumers with relatable, real-world stories of actual customer experiences.
The best case studies tell the story of a customer’s success, including the steps they took, the results they achieved, and the support they received from a brand along the way. To write a great case study, you need to:
- Celebrate the customer and make them — not a product or service — the star of the story.
- Craft the story with specific audiences or target segments in mind so that the story of one customer will be viewed as relatable and actionable for another customer.
- Write copy that is easy to read and engaging so that readers will gain the insights and messages intended.
- Follow a standardized format that includes all of the essentials a potential customer would find interesting and useful.
- Support all of the claims for success made in the story with data in the forms of hard numbers and customer statements.
Case studies are a type of review but more in depth, aiming to show — rather than just tell — the positive experiences that customers have with a brand. Notably, 89% of consumers read reviews before deciding to buy, and 79% view case study content as part of their purchasing process. When it comes to B2B sales, 52% of buyers rank case studies as an important part of their evaluation process.
Telling a brand story through the experience of a tried-and-true customer matters. The story is relatable to potential new customers as they imagine themselves in the shoes of the company or individual featured in the case study. Showcasing previous customers can help new ones see themselves engaging with your brand in the ways that are most meaningful to them.
Besides sharing the perspective of another customer, case studies stand out from other content marketing forms because they are based on evidence. Whether pulling from client testimonials or data-driven results, case studies tend to have more impact on new business because the story contains information that is both objective (data) and subjective (customer experience) — and the brand doesn’t sound too self-promotional.

Case studies are unique in that there’s a fairly standardized format for telling a customer’s story. But that doesn’t mean there isn’t room for creativity. It’s all about making sure that teams are clear on the goals for the case study — along with strategies for supporting content and channels — and understanding how the story fits within the framework of the company’s overall marketing goals.
Here are the basic steps to writing a good case study.
1. Identify your goal
Start by defining exactly who your case study will be designed to help. Case studies are about specific instances where a company works with a customer to achieve a goal. Identify which customers are likely to have these goals, as well as other needs the story should cover to appeal to them.
The answer is often found in one of the buyer personas that have been constructed as part of your larger marketing strategy. This can include anything from new leads generated by the marketing team to long-term customers that are being pressed for cross-sell opportunities. In all of these cases, demonstrating value through a relatable customer success story can be part of the solution to conversion.
2. Choose your client or subject
Who you highlight matters. Case studies tie brands together that might otherwise not cross paths. A writer will want to ensure that the highlighted customer aligns with their own company’s brand identity and offerings. Look for a customer with positive name recognition who has had great success with a product or service and is willing to be an advocate.
The client should also match up with the identified target audience. Whichever company or individual is selected should be a reflection of other potential customers who can see themselves in similar circumstances, having the same problems and possible solutions.
Some of the most compelling case studies feature customers who:
- Switch from one product or service to another while naming competitors that missed the mark.
- Experience measurable results that are relatable to others in a specific industry.
- Represent well-known brands and recognizable names that are likely to compel action.
- Advocate for a product or service as a champion and are well-versed in its advantages.
Whoever or whatever customer is selected, marketers must ensure they have the permission of the company involved before getting started. Some brands have strict review and approval procedures for any official marketing or promotional materials that include their name. Acquiring those approvals in advance will prevent any miscommunication or wasted effort if there is an issue with their legal or compliance teams.
3. Conduct research and compile data
Substantiating the claims made in a case study — either by the marketing team or customers themselves — adds validity to the story. To do this, include data and feedback from the client that defines what success looks like. This can be anything from demonstrating return on investment (ROI) to a specific metric the customer was striving to improve. Case studies should prove how an outcome was achieved and show tangible results that indicate to the customer that your solution is the right one.
This step could also include customer interviews. Make sure that the people being interviewed are key stakeholders in the purchase decision or deployment and use of the product or service that is being highlighted. Content writers should work off a set list of questions prepared in advance. It can be helpful to share these with the interviewees beforehand so they have time to consider and craft their responses. One of the best interview tactics to keep in mind is to ask questions where yes and no are not natural answers. This way, your subject will provide more open-ended responses that produce more meaningful content.
4. Choose the right format
There are a number of different ways to format a case study. Depending on what you hope to achieve, one style will be better than another. However, there are some common elements to include, such as:
- An engaging headline
- A subject and customer introduction
- The unique challenge or challenges the customer faced
- The solution the customer used to solve the problem
- The results achieved
- Data and statistics to back up claims of success
- A strong call to action (CTA) to engage with the vendor
It’s also important to note that while case studies are traditionally written as stories, they don’t have to be in a written format. Some companies choose to get more creative with their case studies and produce multimedia content, depending on their audience and objectives. Case study formats can include traditional print stories, interactive web or social content, data-heavy infographics, professionally shot videos, podcasts, and more.
5. Write your case study
We’ll go into more detail later about how exactly to write a case study, including templates and examples. Generally speaking, though, there are a few things to keep in mind when writing your case study.
- Be clear and concise. Readers want to get to the point of the story quickly and easily, and they’ll be looking to see themselves reflected in the story right from the start.
- Provide a big picture. Always make sure to explain who the client is, their goals, and how they achieved success in a short introduction to engage the reader.
- Construct a clear narrative. Stick to the story from the perspective of the customer and what they needed to solve instead of just listing product features or benefits.
- Leverage graphics. Incorporating infographics, charts, and sidebars can be a more engaging and eye-catching way to share key statistics and data in readable ways.
- Offer the right amount of detail. Most case studies are one or two pages with clear sections that a reader can skim to find the information most important to them.
- Include data to support claims. Show real results — both facts and figures and customer quotes — to demonstrate credibility and prove the solution works.
6. Promote your story
Marketers have a number of options for distribution of a freshly minted case study. Many brands choose to publish case studies on their website and post them on social media. This can help support SEO and organic content strategies while also boosting company credibility and trust as visitors see that other businesses have used the product or service.
Marketers are always looking for quality content they can use for lead generation. Consider offering a case study as gated content behind a form on a landing page or as an offer in an email message. One great way to do this is to summarize the content and tease the full story available for download after the user takes an action.
Sales teams can also leverage case studies, so be sure they are aware that the assets exist once they’re published. Especially when it comes to larger B2B sales, companies often ask for examples of similar customer challenges that have been solved.
Now that you’ve learned a bit about case studies and what they should include, you may be wondering how to start creating great customer story content. Here are a couple of templates you can use to structure your case study.

Template 1 — Challenge-solution-result format
- Start with an engaging title. This should be fewer than 70 characters long for SEO best practices. One of the best ways to approach the title is to include the customer’s name and a hint at the challenge they overcame in the end.
- Create an introduction. Lead with an explanation as to who the customer is, the need they had, and the opportunity they found with a specific product or solution. Writers can also suggest the success the customer experienced with the solution they chose.
- Present the challenge. This should be several paragraphs long and explain the problem the customer faced and the issues they were trying to solve. Details should tie into the company’s products and services naturally. This section needs to be the most relatable to the reader so they can picture themselves in a similar situation.
- Share the solution. Explain which product or service offered was the ideal fit for the customer and why. Feel free to delve into their experience setting up, purchasing, and onboarding the solution.
- Explain the results. Demonstrate the impact of the solution they chose by backing up their positive experience with data. Fill in with customer quotes and tangible, measurable results that show the effect of their choice.
- Ask for action. Include a CTA at the end of the case study that invites readers to reach out for more information, try a demo, or learn more — to nurture them further in the marketing pipeline. What you ask of the reader should tie directly into the goals that were established for the case study in the first place.
Template 2 — Data-driven format
- Start with an engaging title. Be sure to include a statistic or data point in the first 70 characters. Again, it’s best to include the customer’s name as part of the title.
- Create an overview. Share the customer’s background and a short version of the challenge they faced. Present the reason a particular product or service was chosen, and feel free to include quotes from the customer about their selection process.
- Present data point 1. Isolate the first metric that the customer used to define success and explain how the product or solution helped to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Present data point 2. Isolate the second metric that the customer used to define success and explain what the product or solution did to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Present data point 3. Isolate the final metric that the customer used to define success and explain what the product or solution did to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Summarize the results. Reiterate the fact that the customer was able to achieve success thanks to a specific product or service. Include quotes and statements that reflect customer satisfaction and suggest they plan to continue using the solution.
- Ask for action. Include a CTA at the end of the case study that asks readers to reach out for more information, try a demo, or learn more — to further nurture them in the marketing pipeline. Again, remember that this is where marketers can look to convert their content into action with the customer.
While templates are helpful, seeing a case study in action can also be a great way to learn. Here are some examples of how Adobe customers have experienced success.
Juniper Networks
One example is the Adobe and Juniper Networks case study , which puts the reader in the customer’s shoes. The beginning of the story quickly orients the reader so that they know exactly who the article is about and what they were trying to achieve. Solutions are outlined in a way that shows Adobe Experience Manager is the best choice and a natural fit for the customer. Along the way, quotes from the client are incorporated to help add validity to the statements. The results in the case study are conveyed with clear evidence of scale and volume using tangible data.

The story of Lenovo’s journey with Adobe is one that spans years of planning, implementation, and rollout. The Lenovo case study does a great job of consolidating all of this into a relatable journey that other enterprise organizations can see themselves taking, despite the project size. This case study also features descriptive headers and compelling visual elements that engage the reader and strengthen the content.
Tata Consulting
When it comes to using data to show customer results, this case study does an excellent job of conveying details and numbers in an easy-to-digest manner. Bullet points at the start break up the content while also helping the reader understand exactly what the case study will be about. Tata Consulting used Adobe to deliver elevated, engaging content experiences for a large telecommunications client of its own — an objective that’s relatable for a lot of companies.
Case studies are a vital tool for any marketing team as they enable you to demonstrate the value of your company’s products and services to others. They help marketers do their job and add credibility to a brand trying to promote its solutions by using the experiences and stories of real customers.
When you’re ready to get started with a case study:
- Think about a few goals you’d like to accomplish with your content.
- Make a list of successful clients that would be strong candidates for a case study.
- Reach out to the client to get their approval and conduct an interview.
- Gather the data to present an engaging and effective customer story.
Adobe can help
There are several Adobe products that can help you craft compelling case studies. Adobe Experience Platform helps you collect data and deliver great customer experiences across every channel. Once you’ve created your case studies, Experience Platform will help you deliver the right information to the right customer at the right time for maximum impact.
To learn more, watch the Adobe Experience Platform story .
Keep in mind that the best case studies are backed by data. That’s where Adobe Real-Time Customer Data Platform and Adobe Analytics come into play. With Real-Time CDP, you can gather the data you need to build a great case study and target specific customers to deliver the content to the right audience at the perfect moment.
Watch the Real-Time CDP overview video to learn more.
Finally, Adobe Analytics turns real-time data into real-time insights. It helps your business collect and synthesize data from multiple platforms to make more informed decisions and create the best case study possible.
Request a demo to learn more about Adobe Analytics.
https://business.adobe.com/blog/perspectives/b2b-ecommerce-10-case-studies-inspire-you
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/business-case
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/what-is-real-time-analytics

Download the Unstop app now!
Check out the latest opportunities just for you!
How To Solve Case Study? (A Strategy By IIM L Student That Works Every Time!)
Table of content:
- Step 1: Identify the problem statement
Step 2: Propose solutions with a pinch of creativity
Step 3: establish the scale and impact of the solution.
“Case study competitions” - Something that is arguably one of the most valuable parts of your MBA life. But this may be daunting for many. Maybe you’re not sure which case competitions to participate in, so you pile too much on your plate. Maybe you’re not sure about the right way to solve a case study. In this article, we’ll break down everything you need to know about acing a case study competition, from scratch!
A case study competition can be an academic or corporate competition in which participants come together to solve either a real-world case or a framed case that is presented. We present to you Muskan Atar, who will walk you through her tested strategy to solve case study competitions and win them in style!

Framework to solve case studies
After participating in 7-8 case competitions, I realized I had been unconsciously solving it using the same framework. It is very similar to the framework used for product management cases. Hence, it didn't disappoint me.
Step 1: Identify the problem statement
Case competitions like Accenture Strategy Case Connect and Colgate Transcend provide an exact problem statement with the expected outcome. But, in most cases, we must dive deep to break down the problem statement and identify the potential causes.
Like, for Colgate Transcend, the problem statement was (summary) -
Should Colgate diversify into Electric Tooth Brush (ETB) Segment? If yes, then how?
Here, we identified the problems through secondary research (reports from consultancy firms) and primary research (customer surveys). The problem statement identified were:
- Low awareness of ETB
- Low willingness to pay
- High competition from existing players

After identifying the problems, we need to establish whether solving them is actually worth it or not. We did this by:
- Expected Sales, Market Size, and Expected Growth Rate of identified customer segment
- Increasing willingness to upgrade life (Market Trend)
- High adaptability to technological changes (Market Trend)

Other methods of identifying problem statements are Focus Groups, Customer Interviews, Journey Analyzers, BCG matrix, Value Chain Analysis, PESTEL, SWOT(W part), Porter's Five Forces, Annual Reports, etc.

Given the short time for case competitions, I think the most efficient method is first-hand experience. Rather than starting from scratch, it is better to identify the problems as a customer and collect more data on the same.
Further, this data can be represented in the form of - Customer Personas, Key Insights, Trends, Customer Decision Making Journey, etc.
If you have identified the right problems, your half work is done!
Before even thinking of solutions, set the KPIs based on the problem statement.
Like, in Accenture Strategy Case Connect, the problem statement was (summary) -
Should a large-scale oil refinery firm diversify into EV charging stations? If yes, suggest an execution strategy
After establishing that the firm needs to diversify, we set the KPI for the solution as - Increment in business generated due to portfolio diversification.

Then, we did a VRIO analysis to identify the competitive advantage (CA), available resources, and capabilities of the firm. SWOT analysis can also be done to get a bird's eye view.

Key insights were:
- The firm has an established infrastructure across the nation (CA)
- The firm is cash-positive (resource)
- Lack of EV charger manufacturing capabilities
Based on the above insights, we decided mode of entry as a strategic alliance with EV charger manufacturers to minimize the entry risk and cost of development.

We represented the solution in the form of a business plan that covered the roles of stakeholders, partners, customer value proposition, and a phase-wise rollout plan for the future.

After setting the KPIs and VRIO analysis, in case you struggle to create solutions, you can do:
- Competitor benchmarking to get a reference
- Research strategies implemented by outside-India players
- Study recent technological trends and their application
- Understand the current focus of the firm through annual reports, recent acquisitions, and news headlines

Other ways of representing the strategies are Ansoff Matrix, Portfolio Strategy, Market Mapping, 4Ps, Marketing Funnel, GTM, Mock-ups, etc.

Above all, you should always suggest solutions that reduce customer efforts. If you try changing consumer behavior by increasing efforts, they will exCHANGE you with your competitors.
Competitions like the HCCB Case Challenge provide an exact budget. For others, you must look at financial reports and funding rounds to estimate the budget. Then, you can utilize the data to calculate ROI using guesstimates as accurately as possible (use published data).
You can also do a cost-benefit, NPV- IRR, break-even point, cash-flow analysis, etc. I prefer showing profitable unit economics to envision scale and impact.
In PM/Marketing cases, you can also show whether customers accept the solution or not. If 90% of customers are facing a problem, doesn't mean that 90% will accept your solution.
Like in Myntra Stylbiz, we had to suggest solutions for the 18-25 customer segment such that Myntra becomes the most engaging and preferred destination. We showed results of UAT (using Figma) that indicated the likelihood of customers using the solution. This data also helped to estimate the increase in sales, purchase frequency, and new customers.

I have also seen participants running marketing campaigns on social media on a small scale.

More than thinking big, focus on thinking real.
For more, check out her post.
If you'd like to submit your story, click here .
Whatever your concern, we have broken down everything you need to know about case study competitions , from scratch:
- Challenge Yourself With These B-school Competitions
- Case Study Competitions- Details, Winning Strategies, And More!
- Cheat Sheet To Crack Hiring Challenges And Case Competitions
- How To Win Business Case Competitions: The Secret Revealed
- Why MBA case competitions are worth the hype!

In pursuit of being a good product manager, she started participating in Case Competitions during her MBA. It gave her a mention in Forbes D2C Top 100 Competitive Leaders, but more than that it helped her build problem-solving and team-building skills. It also helped her become insensitive to results, and make a rational sense of them. Apart from PMing, she likes to write, watch movies, crack lame jokes and eat really good food.

to our newsletter
Blogs you need to hog!

L'Oréal Sustainability Challenge 2023 Winners Of Planet Track From BITSoM Dig Out Their Winning Mantra
Hero Campus Challenge S8 Winners Take Us Through Their Road To Victory
TISS HRM & LR Summer Placements 2023: 100% Placement, Record Numbers!
TVS Credit E.P.I.C 5.0 Champions Share Learnings From Their Remarkable Journey!

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 10 min read
Case Study-Based Learning
Enhancing learning through immediate application.
By the Mind Tools Content Team

If you've ever tried to learn a new concept, you probably appreciate that "knowing" is different from "doing." When you have an opportunity to apply your knowledge, the lesson typically becomes much more real.
Adults often learn differently from children, and we have different motivations for learning. Typically, we learn new skills because we want to. We recognize the need to learn and grow, and we usually need – or want – to apply our newfound knowledge soon after we've learned it.
A popular theory of adult learning is andragogy (the art and science of leading man, or adults), as opposed to the better-known pedagogy (the art and science of leading children). Malcolm Knowles , a professor of adult education, was considered the father of andragogy, which is based on four key observations of adult learners:
- Adults learn best if they know why they're learning something.
- Adults often learn best through experience.
- Adults tend to view learning as an opportunity to solve problems.
- Adults learn best when the topic is relevant to them and immediately applicable.
This means that you'll get the best results with adults when they're fully involved in the learning experience. Give an adult an opportunity to practice and work with a new skill, and you have a solid foundation for high-quality learning that the person will likely retain over time.
So, how can you best use these adult learning principles in your training and development efforts? Case studies provide an excellent way of practicing and applying new concepts. As such, they're very useful tools in adult learning, and it's important to understand how to get the maximum value from them.
What Is a Case Study?
Case studies are a form of problem-based learning, where you present a situation that needs a resolution. A typical business case study is a detailed account, or story, of what happened in a particular company, industry, or project over a set period of time.
The learner is given details about the situation, often in a historical context. The key players are introduced. Objectives and challenges are outlined. This is followed by specific examples and data, which the learner then uses to analyze the situation, determine what happened, and make recommendations.
The depth of a case depends on the lesson being taught. A case study can be two pages, 20 pages, or more. A good case study makes the reader think critically about the information presented, and then develop a thorough assessment of the situation, leading to a well-thought-out solution or recommendation.
Why Use a Case Study?
Case studies are a great way to improve a learning experience, because they get the learner involved, and encourage immediate use of newly acquired skills.
They differ from lectures or assigned readings because they require participation and deliberate application of a broad range of skills. For example, if you study financial analysis through straightforward learning methods, you may have to calculate and understand a long list of financial ratios (don't worry if you don't know what these are). Likewise, you may be given a set of financial statements to complete a ratio analysis. But until you put the exercise into context, you may not really know why you're doing the analysis.
With a case study, however, you might explore whether a bank should provide financing to a borrower, or whether a company is about to make a good acquisition. Suddenly, the act of calculating ratios becomes secondary – it's more important to understand what the ratios tell you. This is how case studies can make the difference between knowing what to do, and knowing how, when, and why to do it.
Then, what really separates case studies from other practical forms of learning – like scenarios and simulations – is the ability to compare the learner's recommendations with what actually happened. When you know what really happened, it's much easier to evaluate the "correctness" of the answers given.
When to Use a Case Study
As you can see, case studies are powerful and effective training tools. They also work best with practical, applied training, so make sure you use them appropriately.
Remember these tips:
- Case studies tend to focus on why and how to apply a skill or concept, not on remembering facts and details. Use case studies when understanding the concept is more important than memorizing correct responses.
- Case studies are great team-building opportunities. When a team gets together to solve a case, they'll have to work through different opinions, methods, and perspectives.
- Use case studies to build problem-solving skills, particularly those that are valuable when applied, but are likely to be used infrequently. This helps people get practice with these skills that they might not otherwise get.
- Case studies can be used to evaluate past problem solving. People can be asked what they'd do in that situation, and think about what could have been done differently.
Ensuring Maximum Value From Case Studies
The first thing to remember is that you already need to have enough theoretical knowledge to handle the questions and challenges in the case study. Otherwise, it can be like trying to solve a puzzle with some of the pieces missing.
Here are some additional tips for how to approach a case study. Depending on the exact nature of the case, some tips will be more relevant than others.
- Read the case at least three times before you start any analysis. Case studies usually have lots of details, and it's easy to miss something in your first, or even second, reading.
- Once you're thoroughly familiar with the case, note the facts. Identify which are relevant to the tasks you've been assigned. In a good case study, there are often many more facts than you need for your analysis.
- If the case contains large amounts of data, analyze this data for relevant trends. For example, have sales dropped steadily, or was there an unexpected high or low point?
- If the case involves a description of a company's history, find the key events, and consider how they may have impacted the current situation.
- Consider using techniques like SWOT analysis and Porter's Five Forces Analysis to understand the organization's strategic position.
- Stay with the facts when you draw conclusions. These include facts given in the case as well as established facts about the environmental context. Don't rely on personal opinions when you put together your answers.
Writing a Case Study
You may have to write a case study yourself. These are complex documents that take a while to research and compile. The quality of the case study influences the quality of the analysis. Here are some tips if you want to write your own:
- Write your case study as a structured story. The goal is to capture an interesting situation or challenge and then bring it to life with words and information. You want the reader to feel a part of what's happening.
- Present information so that a "right" answer isn't obvious. The goal is to develop the learner's ability to analyze and assess, not necessarily to make the same decision as the people in the actual case.
- Do background research to fully understand what happened and why. You may need to talk to key stakeholders to get their perspectives as well.
- Determine the key challenge. What needs to be resolved? The case study should focus on one main question or issue.
- Define the context. Talk about significant events leading up to the situation. What organizational factors are important for understanding the problem and assessing what should be done? Include cultural factors where possible.
- Identify key decision makers and stakeholders. Describe their roles and perspectives, as well as their motivations and interests.
- Make sure that you provide the right data to allow people to reach appropriate conclusions.
- Make sure that you have permission to use any information you include.
A typical case study structure includes these elements:
- Executive summary. Define the objective, and state the key challenge.
- Opening paragraph. Capture the reader's interest.
- Scope. Describe the background, context, approach, and issues involved.
- Presentation of facts. Develop an objective picture of what's happening.
- Description of key issues. Present viewpoints, decisions, and interests of key parties.
Because case studies have proved to be such effective teaching tools, many are already written. Some excellent sources of free cases are The Times 100 , CasePlace.org , and Schroeder & Schroeder Inc . You can often search for cases by topic or industry. These cases are expertly prepared, based mostly on real situations, and used extensively in business schools to teach management concepts.
Case studies are a great way to improve learning and training. They provide learners with an opportunity to solve a problem by applying what they know.
There are no unpleasant consequences for getting it "wrong," and cases give learners a much better understanding of what they really know and what they need to practice.
Case studies can be used in many ways, as team-building tools, and for skill development. You can write your own case study, but a large number are already prepared. Given the enormous benefits of practical learning applications like this, case studies are definitely something to consider adding to your next training session.
Knowles, M. (1973). 'The Adult Learner: A Neglected Species [online].' Available here .
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
Virtual onboarding.
How to Get Your New Hire on Board – Online
Book Insights
Drive: The Surprising Truth About What Motivates Us
Daniel H Pink
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Latest Updates

Pain Points Podcast - Presentations Pt 2

NEW! Pain Points - How Do I Decide?
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Finding the Best Mix in Training Methods
Using Mediation To Resolve Conflict
Resolving conflicts peacefully with mediation
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Herzberg's motivators and hygiene factors.
Learn how to Motivate Your Team
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
The marketplace for case solutions.
Case Study Solutions
Hundreds of case solutions at your fingertips! Case study answers written by top business students.

We are the marketplace for case study solutions
Save time and get inspired by our case solutions. We help you be a top student at your university!
High-quality only
Immediate access.

What Students Say About Us

I finished my assignment thanks to your solution. Thank you very much for this! Much better than what I expected. It was a great idea to let me sample it before I buy – many companies don’t do this, and what a wasted sale in my opinion! Best of luck! 🙂
All You Wanted to Know About How to Write a Case Study

What do you study in your college? If you are a psychology, sociology, or anthropology student, we bet you might be familiar with what a case study is. This research method is used to study a certain person, group, or situation. In this guide from our dissertation writing service , you will learn how to write a case study professionally, from researching to citing sources properly. Also, we will explore different types of case studies and show you examples — so that you won’t have any other questions left.
What Is a Case Study?
A case study is a subcategory of research design which investigates problems and offers solutions. Case studies can range from academic research studies to corporate promotional tools trying to sell an idea—their scope is quite vast.
What Is the Difference Between a Research Paper and a Case Study?
While research papers turn the reader’s attention to a certain problem, case studies go even further. Case study guidelines require students to pay attention to details, examining issues closely and in-depth using different research methods. For example, case studies may be used to examine court cases if you study Law, or a patient's health history if you study Medicine. Case studies are also used in Marketing, which are thorough, empirically supported analysis of a good or service's performance. Well-designed case studies can be valuable for prospective customers as they can identify and solve the potential customers pain point.
Case studies involve a lot of storytelling – they usually examine particular cases for a person or a group of people. This method of research is very helpful, as it is very practical and can give a lot of hands-on information. Most commonly, the length of the case study is about 500-900 words, which is much less than the length of an average research paper.
The structure of a case study is very similar to storytelling. It has a protagonist or main character, which in your case is actually a problem you are trying to solve. You can use the system of 3 Acts to make it a compelling story. It should have an introduction, rising action, a climax where transformation occurs, falling action, and a solution.
Here is a rough formula for you to use in your case study:
Problem (Act I): > Solution (Act II) > Result (Act III) > Conclusion.
Types of Case Studies
The purpose of a case study is to provide detailed reports on an event, an institution, a place, future customers, or pretty much anything. There are a few common types of case study, but the type depends on the topic. The following are the most common domains where case studies are needed:

- Historical case studies are great to learn from. Historical events have a multitude of source info offering different perspectives. There are always modern parallels where these perspectives can be applied, compared, and thoroughly analyzed.
- Problem-oriented case studies are usually used for solving problems. These are often assigned as theoretical situations where you need to immerse yourself in the situation to examine it. Imagine you’re working for a startup and you’ve just noticed a significant flaw in your product’s design. Before taking it to the senior manager, you want to do a comprehensive study on the issue and provide solutions. On a greater scale, problem-oriented case studies are a vital part of relevant socio-economic discussions.
- Cumulative case studies collect information and offer comparisons. In business, case studies are often used to tell people about the value of a product.
- Critical case studies explore the causes and effects of a certain case.
- Illustrative case studies describe certain events, investigating outcomes and lessons learned.
Need a compelling case study? EssayPro has got you covered. Our experts are ready to provide you with detailed, insightful case studies that capture the essence of real-world scenarios. Elevate your academic work with our professional assistance.

Case Study Format
The case study format is typically made up of eight parts:
- Executive Summary. Explain what you will examine in the case study. Write an overview of the field you’re researching. Make a thesis statement and sum up the results of your observation in a maximum of 2 sentences.
- Background. Provide background information and the most relevant facts. Isolate the issues.
- Case Evaluation. Isolate the sections of the study you want to focus on. In it, explain why something is working or is not working.
- Proposed Solutions. Offer realistic ways to solve what isn’t working or how to improve its current condition. Explain why these solutions work by offering testable evidence.
- Conclusion. Summarize the main points from the case evaluations and proposed solutions. 6. Recommendations. Talk about the strategy that you should choose. Explain why this choice is the most appropriate.
- Implementation. Explain how to put the specific strategies into action.
- References. Provide all the citations.
How to Write a Case Study
Let's discover how to write a case study.

Setting Up the Research
When writing a case study, remember that research should always come first. Reading many different sources and analyzing other points of view will help you come up with more creative solutions. You can also conduct an actual interview to thoroughly investigate the customer story that you'll need for your case study. Including all of the necessary research, writing a case study may take some time. The research process involves doing the following:
- Define your objective. Explain the reason why you’re presenting your subject. Figure out where you will feature your case study; whether it is written, on video, shown as an infographic, streamed as a podcast, etc.
- Determine who will be the right candidate for your case study. Get permission, quotes, and other features that will make your case study effective. Get in touch with your candidate to see if they approve of being part of your work. Study that candidate’s situation and note down what caused it.
- Identify which various consequences could result from the situation. Follow these guidelines on how to start a case study: surf the net to find some general information you might find useful.
- Make a list of credible sources and examine them. Seek out important facts and highlight problems. Always write down your ideas and make sure to brainstorm.
- Focus on several key issues – why they exist, and how they impact your research subject. Think of several unique solutions. Draw from class discussions, readings, and personal experience. When writing a case study, focus on the best solution and explore it in depth. After having all your research in place, writing a case study will be easy. You may first want to check the rubric and criteria of your assignment for the correct case study structure.
Read Also: ' WHAT IS A CREDIBLE SOURCES ?'
Although your instructor might be looking at slightly different criteria, every case study rubric essentially has the same standards. Your professor will want you to exhibit 8 different outcomes:
- Correctly identify the concepts, theories, and practices in the discipline.
- Identify the relevant theories and principles associated with the particular study.
- Evaluate legal and ethical principles and apply them to your decision-making.
- Recognize the global importance and contribution of your case.
- Construct a coherent summary and explanation of the study.
- Demonstrate analytical and critical-thinking skills.
- Explain the interrelationships between the environment and nature.
- Integrate theory and practice of the discipline within the analysis.
Need Case Study DONE FAST?
Pick a topic, tell us your requirements and get your paper on time.
Case Study Outline
Let's look at the structure of an outline based on the issue of the alcoholic addiction of 30 people.
Introduction
- Statement of the issue: Alcoholism is a disease rather than a weakness of character.
- Presentation of the problem: Alcoholism is affecting more than 14 million people in the USA, which makes it the third most common mental illness there.
- Explanation of the terms: In the past, alcoholism was commonly referred to as alcohol dependence or alcohol addiction. Alcoholism is now the more severe stage of this addiction in the disorder spectrum.
- Hypotheses: Drinking in excess can lead to the use of other drugs.
- Importance of your story: How the information you present can help people with their addictions.
- Background of the story: Include an explanation of why you chose this topic.
- Presentation of analysis and data: Describe the criteria for choosing 30 candidates, the structure of the interview, and the outcomes.
- Strong argument 1: ex. X% of candidates dealing with anxiety and depression...
- Strong argument 2: ex. X amount of people started drinking by their mid-teens.
- Strong argument 3: ex. X% of respondents’ parents had issues with alcohol.
- Concluding statement: I have researched if alcoholism is a disease and found out that…
- Recommendations: Ways and actions for preventing alcohol use.
Writing a Case Study Draft
After you’ve done your case study research and written the outline, it’s time to focus on the draft. In a draft, you have to develop and write your case study by using: the data which you collected throughout the research, interviews, and the analysis processes that were undertaken. Follow these rules for the draft:

- Your draft should contain at least 4 sections: an introduction; a body where you should include background information, an explanation of why you decided to do this case study, and a presentation of your main findings; a conclusion where you present data; and references.
- In the introduction, you should set the pace very clearly. You can even raise a question or quote someone you interviewed in the research phase. It must provide adequate background information on the topic. The background may include analyses of previous studies on your topic. Include the aim of your case here as well. Think of it as a thesis statement. The aim must describe the purpose of your work—presenting the issues that you want to tackle. Include background information, such as photos or videos you used when doing the research.
- Describe your unique research process, whether it was through interviews, observations, academic journals, etc. The next point includes providing the results of your research. Tell the audience what you found out. Why is this important, and what could be learned from it? Discuss the real implications of the problem and its significance in the world.
- Include quotes and data (such as findings, percentages, and awards). This will add a personal touch and better credibility to the case you present. Explain what results you find during your interviews in regards to the problem and how it developed. Also, write about solutions which have already been proposed by other people who have already written about this case.
- At the end of your case study, you should offer possible solutions, but don’t worry about solving them yourself.
Use Data to Illustrate Key Points in Your Case Study
Even though your case study is a story, it should be based on evidence. Use as much data as possible to illustrate your point. Without the right data, your case study may appear weak and the readers may not be able to relate to your issue as much as they should. Let's see the examples from essay writing service :
With data: Alcoholism is affecting more than 14 million people in the USA, which makes it the third most common mental illness there. Without data: A lot of people suffer from alcoholism in the United States.
Try to include as many credible sources as possible. You may have terms or sources that could be hard for other cultures to understand. If this is the case, you should include them in the appendix or Notes for the Instructor or Professor.
Finalizing the Draft: Checklist
After you finish drafting your case study, polish it up by answering these ‘ask yourself’ questions and think about how to end your case study:
- Check that you follow the correct case study format, also in regards to text formatting.
- Check that your work is consistent with its referencing and citation style.
- Micro-editing — check for grammar and spelling issues.
- Macro-editing — does ‘the big picture’ come across to the reader? Is there enough raw data, such as real-life examples or personal experiences? Have you made your data collection process completely transparent? Does your analysis provide a clear conclusion, allowing for further research and practice?
Problems to avoid:
- Overgeneralization – Do not go into further research that deviates from the main problem.
- Failure to Document Limitations – Just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study, you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis.
- Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications – Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings.
How to Create a Title Page and Cite a Case Study
Let's see how to create an awesome title page.
Your title page depends on the prescribed citation format. The title page should include:
- A title that attracts some attention and describes your study
- The title should have the words “case study” in it
- The title should range between 5-9 words in length
- Your name and contact information
- Your finished paper should be only 500 to 1,500 words in length.With this type of assignment, write effectively and avoid fluff
Here is a template for the APA and MLA format title page:
There are some cases when you need to cite someone else's study in your own one – therefore, you need to master how to cite a case study. A case study is like a research paper when it comes to citations. You can cite it like you cite a book, depending on what style you need.
Citation Example in MLA Hill, Linda, Tarun Khanna, and Emily A. Stecker. HCL Technologies. Boston: Harvard Business Publishing, 2008. Print.
Citation Example in APA Hill, L., Khanna, T., & Stecker, E. A. (2008). HCL Technologies. Boston: Harvard Business Publishing.
Citation Example in Chicago Hill, Linda, Tarun Khanna, and Emily A. Stecker. HCL Technologies.
Case Study Examples
To give you an idea of a professional case study example, we gathered and linked some below.
Eastman Kodak Case Study
Case Study Example: Audi Trains Mexican Autoworkers in Germany
To conclude, a case study is one of the best methods of getting an overview of what happened to a person, a group, or a situation in practice. It allows you to have an in-depth glance at the real-life problems that businesses, healthcare industry, criminal justice, etc. may face. This insight helps us look at such situations in a different light. This is because we see scenarios that we otherwise would not, without necessarily being there. If you need custom essays , try our research paper writing services .
Get Help Form Qualified Writers
Crafting a case study is not easy. You might want to write one of high quality, but you don’t have the time or expertise. If you’re having trouble with your case study, help with essay request - we'll help. EssayPro writers have read and written countless case studies and are experts in endless disciplines. Request essay writing, editing, or proofreading assistance from our custom case study writing service , and all of your worries will be gone.
Don't Know Where to Start?
Crafting a case study is not easy. You might want to write one of high quality, but you don’t have the time or expertise. Request ' write my case study ' assistance from our service.
What Is A Case Study?
How to cite a case study in apa, how to write a case study.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
Related Articles
.webp)

- Testimonial
- Web Stories
Learning Home

Not Now! Will rate later

MBA Case Studies - Solved Examples

Need of MBA Case Studies
Case i: chemco case.
- ChemCo is a quality leader in the U.K. car batteries market.
- Customer battery purchases in the automobile market are highly seasonal.
- The fork-lift business was added to utilize idle capacity during periods of inactivity.
- This is a low-growth industry (1% annual growth over the last two years)
- Large customers are sophisticated and buy based on price and quality. Smaller customers buy solely on price.
- There is a Spanish competitor in the market who offers low priced batteries of inferior quality.

Essential MBA GD Guide: Key Topics with Strategies Free
- Importance of Group Discussions
- Tips and Strategies to handle a GD
- Top 25 GD topics
- Free Download
- Established player in car batteries
- Losing heavily in fork-lift truck batteries
- Old fashioned owner resistance to change
- Low priced competitors
- Foreign competitors gaining market share
- Decisive Interview, GD & Essay prep
- GD: Topics 2021
- GD: Approach
- GD: Do's and Don'ts
- GD: Communications
- Solved GDs Topics
GD Introduction
- Types of GD topics: Techniques
- GD: Ettiquette
- GD: Content
- Solved Case Studies
- High quality product, but low end customers care more about price than quality
- Mismanaged product diversification in a price sensitive market
- Alternative 1: Establish an Off-Brand for the fork-lift business
- Alternative 2: Educate the customer market about product quality
- Alternative 3: Exit the fork-lift battery business
- Establishing the firm's quality image
- Increase in market share
- Increase in sales
- Cost of the product
- Protect firm's quality image in the automobile industry
- Redesigned product to reduce the cost of manufacture
- Low price to enable it to compete with Spanish producer
- Make use of the quality leadership in car batteries market
- Offer reliability testing, extended warranties etc. to promote quality image
- Set higher prices to extract surplus from these advantages
- A passive strategy, not proactive
- Recommendations: Alternative 1 is recommended in this case. Since the firm operates in an industry which has low growth, hence it can expand market share and sales only by taking the customers from other players. Hence, it needs to tackle the Spanish competitor head-on by aggressively pricing its product. At the same time, launching a low-priced product under the same brand name erodes the high quality image in the car batteries market. Hence, the best option is to go for an off-brand to target the fork-lift customers who are increasingly becoming price sensitive. This will enable the company to ward off the threat in short-term and build its position strongly in the long-term.

Case II: NAKAMURA LACQUER COMPANY
- The Nakamura Lacquer Company: The Nakamura Lacquer Company based in Kyoto, Japan was one of the many small handicraft shops making lacquerware for the daily table use of the Japanese people.
- Mr. Nakamura- the personality: In 1948, a young Mr. Nakamura took over his family business. He saw an opportunity to cater to a new market of America, i.e. GI's of the Occupation Army who had begun to buy lacquer ware as souvenirs. However, he realized that the traditional handicraft methods were inadequate. He was an innovator and introduced simple methods of processing and inspection using machines. Four years later, when the Occupation Army left in 1952, Nakamura employed several thousand men, and produced 500,000 pieces of lacquers tableware each year for the Japanese mass consumer market. The profit from operations was $250,000.
- The Brand: Nakamura named his brand “Chrysanthemum” after the national flower of Japan, which showed his patriotic fervor. The brand became Japan's best known and best selling brand, being synonymous with good quality, middle class and dependability.
- The Market: The market for lacquerware in Japan seems to have matured, with the production steady at 500,000 pieces a year. Nakamura did practically no business outside of Japan. However, early in 1960, when the American interest in Japanese products began to grow, Nakamura received two offers
- The Rose and Crown offer: The first offer was from Mr. Phil Rose, V.P Marketing at the National China Company. They were the largest manufacturer of good quality dinnerware in the U.S., with their “Rose and Crown” brand accounting for almost 30% of total sales. They were willing to give a firm order for three eyes for annual purchases of 400,000 sets of lacquer dinnerware, delivered in Japan and at 5% more than what the Japanese jobbers paid. However, Nakamura would have to forego the Chrysanthemum trademark to “Rose and Crown” and also undertaken to sell lacquer ware to anyone else the U.S. The offer promised returns of $720,000 over three years (with net returns of $83,000), but with little potential for the U.S. market on the Chrysanthemum brand beyond that period.
- The Semmelback offer: The second offer was from Mr. Walter Sammelback of Sammelback, Sammelback and Whittacker, Chicago, the largest supplier of hotel and restaurant supplies in the U.S. They perceived a U.S. market of 600,000 sets a year, expecting it to go up to 2 million in around 5 years. Since the Japanese government did not allow overseas investment, Sammelback was willing to budget $1.5 million. Although the offer implied negative returns of $467,000 over the first five years, the offer had the potential to give a $1 million profit if sales picked up as anticipated.
- Meeting the order: To meet the numbers requirement of the orders, Nakamura would either have to expand capacity or cut down on the domestic market. If he chose to expand capacity, the danger was of idle capacity in case the U.S. market did not respond. If he cut down on the domestic market, the danger was of losing out on a well-established market. Nakamura could also source part of the supply from other vendors. However, this option would not find favor with either of the American buyers since they had approached only Nakamura, realizing that he was the best person to meet the order.
- Decision problem: Whether to accept any of the two offers and if yes, which one of the two and under what terms of conditions?
- To expand into the U.S. market.
- To maintain and build upon their reputation of the “Chrysanthemum” brand
- To increase profit volumes by tapping the U.S. market and as a result, increasing scale of operations.
- To increase its share in the U.S. lacquerware market.
- Profit Maximization criterion: The most important criterion in the long run is profit maximization.
- Risk criterion: Since the demand in the U.S. market is not as much as in Japan.
- Brand identity criterion: Nakamura has painstakingly built up a brand name in Japan. It is desirable for him to compete in the U.S. market under the same brand name
- Flexibility criterion: The chosen option should offer Nakamura flexibility in maneuvering the terms and conditions to his advantage. Additionally, Nakamura should have bargaining power at the time of renewal of the contract.
- Short term returns: Nakamura should receive some returns on the investment he makes on the new offers. However, this criterion may be compromised in favor of profit maximization in the long run.?
- Reject both: React both the offers and concentrate on the domestic market
- Accept RC offer: Accept the Rose and Crown offer and supply the offer by cutting down on supplies to the domestic market or through capacity expansion or both
- Accept SSW: offer; accept the SSW offer and meet it through cutting down on supply to the domestic market or through capacity expansion or both. Negotiate term of supply.
- Reject both: This option would not meet the primary criterion of profit maximization. Further, the objective of growth would also not be met. Hence, this option is rejected.
- Accept RC offer: The RC offer would assure net returns of $283,000 over the next three yeas. It also assures regular returns of $240,000 per year. However, Nakamura would have no presence in the U.S. with its Chrysanthemum brand name The RC offer would entail capacity expansion, as it would not be possible to siphon of 275,000 pieces from the domestic market over three years without adversely affecting operations there. At the end of three years, Nakamura would have little bargaining power with RC as it would have an excess capacity of 275,000 pieces and excess labor which it would want to utilize. In this sense the offer is risky. Further, the offer is not flexible. Long-term profit maximization is uncertain in this case a condition that can be controlled in the SSW offer. Hence, this offer is rejected.
- Accept SSW offer: The SSW offer does not assure a firm order or any returns for the period of contract. Although, in its present form the offer is risky if the market in the U.S. does not pick up as expected, the offer is flexible. If Nakamura were to exhibit caution initially by supplying only 300,000 instead of the anticipated 600,000 pieces, it could siphon off the 175,000 required from the domestic market. If demand exists in the U.S., the capacity can be expanded. With this offer, risk is minimized. Further, it would be competing on its own brand name. Distribution would be taken care of and long-term profit maximization criterion would be satisfied as this option has the potential of $1 million in profits per year. At the time of renewal of the contract, Nakamura would have immense bargaining power.
- Negotiate terms of offer with SSW: The terms would be that NLC would supply 300,000 pieces in the first year. If market demand exists, NLC should expand capacity to provide the expected demand.
- Action Plan: In the first phase, NLC would supply SSW with 300,000 pieces. 125,000 of these would be obtained by utilizing excess capacity, while the remaining would be obtained from the domestic market. If the expected demand for lacquer ware exists in the U.S., NLC would expand capacity to meet the expected demand. The debt incurred would be paid off by the fifth year.
- Contingency Plan: In case the demand is not as expected in the first year, NLC should not service the U.S. market and instead concentrate on increasing penetration in the domestic market.
FAQs about MBA Case Studies
- Group Discussions
- Personality
- Past Experiences
Most Popular Articles - PS

100 Group Discussion (GD) Topics for MBA 2024

Solved GDs Topic

Top 50 Other (Science, Economy, Environment) topics for GD
5 tips for starting a GD

GD FAQs: Communication

GD FAQs: Content

Stages of GD preparation

Group Discussion Etiquettes

Case Study: Tips and Strategy

Practice Case Studies: Long

Practice Case Studies: Short
5 tips for handling Abstract GD topics
5 tips for handling a fish market situation in GD
5 things to follow: if you don’t know much about the GD topic

Do’s and Don’ts in a Group Discussion
5 tips for handling Factual GD topics

How to prepare for Group Discussion
- Silver Bee Group
- [email protected]

- NEW SOLUTION
- Top Visitors
Popular Topics
- Newest Members
- Newest Papers
- Top Donators

BIGGEST DATABASE ON THE INTERNET
Mba case study solutions, mba research papers, mba term papers & projects.

BIGGEST COMMUNITY ON THE INTERNET
Used by students from over 750+ b-schools in 160+ countries.

YOUR KEY TO HIGHER GRADES
Get higher grades in assignments and exams. ease your mba workload., mba case study analysis, term papers , research papers.
Look no further. We have all the resources that you would ever need to write case study summary / analysis, MBA term papers and MBA research papers.

- University Login
Case Study Analysis
Mba catalogue 1, alphabetical catalogue, welcome message.
Students frequently search on internet for case study solutions/analysis for reasons which include (but not limited to)
- Case study contains large number of pages.
- Not able to devote enough time from their busy schedule to solve a case study.
- Case study requiring higher level of understanding
Well whatever may be the case, our online library is equipped with all the arsenal you would ever need for your case study solutions/analysis. We also have a section for MBA Term Papers and Research Papers to cover the entire array of your MBA education. You will find it useful in all your MBA related studies be it case study, term papers, assignments, projects, research works etc.
We have gone a step further to include streams like humanities, history, psychology, sociology etc. which revolve around the periphery of basic MBA domains like human resources, organizational behaviour, marketing, finance etc. We have made an attempt to provide MBA students with the most comprehensive library on the internet.
Recent Topics
- Product life cycle
- cumberland metal indus
- Cumberland Metal Indus
New Entries
- Quality Parts Company
- Lincoln Electric
- Vêtements Ltée
- Google Case Analysis
Most Recent Request
- oilwell cable comp
- research methods
- human resource sho
- toyota adopts a st
Ease your MBA workload and get more time for yourself
Case Study Research Method in Psychology
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. Typically, data is gathered from various sources using several methods (e.g., observations & interviews).
The case study research method originated in clinical medicine (the case history, i.e., the patient’s personal history). In psychology, case studies are often confined to the study of a particular individual.
The information is mainly biographical and relates to events in the individual’s past (i.e., retrospective), as well as to significant events that are currently occurring in his or her everyday life.
The case study is not a research method, but researchers select methods of data collection and analysis that will generate material suitable for case studies.
Freud (1909a, 1909b) conducted very detailed investigations into the private lives of his patients in an attempt to both understand and help them overcome their illnesses.
This makes it clear that the case study is a method that should only be used by a psychologist, therapist, or psychiatrist, i.e., someone with a professional qualification.
There is an ethical issue of competence. Only someone qualified to diagnose and treat a person can conduct a formal case study relating to atypical (i.e., abnormal) behavior or atypical development.
Famous Case Studies
- Anna O – One of the most famous case studies, documenting psychoanalyst Josef Breuer’s treatment of “Anna O” (real name Bertha Pappenheim) for hysteria in the late 1800s using early psychoanalytic theory.
- Little Hans – A child psychoanalysis case study published by Sigmund Freud in 1909 analyzing his five-year-old patient Herbert Graf’s house phobia as related to the Oedipus complex.
- Bruce/Brenda – Gender identity case of the boy (Bruce) whose botched circumcision led psychologist John Money to advise gender reassignment and raise him as a girl (Brenda) in the 1960s.
- Genie Wiley – Linguistics/psychological development case of the victim of extreme isolation abuse who was studied in 1970s California for effects of early language deprivation on acquiring speech later in life.
- Phineas Gage – One of the most famous neuropsychology case studies analyzes personality changes in railroad worker Phineas Gage after an 1848 brain injury involving a tamping iron piercing his skull.
Clinical Case Studies
- Studying the effectiveness of psychotherapy approaches with an individual patient
- Assessing and treating mental illnesses like depression, anxiety disorders, PTSD
- Neuropsychological cases investigating brain injuries or disorders
Child Psychology Case Studies
- Studying psychological development from birth through adolescence
- Cases of learning disabilities, autism spectrum disorders, ADHD
- Effects of trauma, abuse, deprivation on development
Types of Case Studies
- Explanatory case studies : Used to explore causation in order to find underlying principles. Helpful for doing qualitative analysis to explain presumed causal links.
- Exploratory case studies : Used to explore situations where an intervention being evaluated has no clear set of outcomes. It helps define questions and hypotheses for future research.
- Descriptive case studies : Describe an intervention or phenomenon and the real-life context in which it occurred. It is helpful for illustrating certain topics within an evaluation.
- Multiple-case studies : Used to explore differences between cases and replicate findings across cases. Helpful for comparing and contrasting specific cases.
- Intrinsic : Used to gain a better understanding of a particular case. Helpful for capturing the complexity of a single case.
- Collective : Used to explore a general phenomenon using multiple case studies. Helpful for jointly studying a group of cases in order to inquire into the phenomenon.
Where Do You Find Data for a Case Study?
There are several places to find data for a case study. The key is to gather data from multiple sources to get a complete picture of the case and corroborate facts or findings through triangulation of evidence. Most of this information is likely qualitative (i.e., verbal description rather than measurement), but the psychologist might also collect numerical data.
1. Primary sources
- Interviews – Interviewing key people related to the case to get their perspectives and insights. The interview is an extremely effective procedure for obtaining information about an individual, and it may be used to collect comments from the person’s friends, parents, employer, workmates, and others who have a good knowledge of the person, as well as to obtain facts from the person him or herself.
- Observations – Observing behaviors, interactions, processes, etc., related to the case as they unfold in real-time.
- Documents & Records – Reviewing private documents, diaries, public records, correspondence, meeting minutes, etc., relevant to the case.
2. Secondary sources
- News/Media – News coverage of events related to the case study.
- Academic articles – Journal articles, dissertations etc. that discuss the case.
- Government reports – Official data and records related to the case context.
- Books/films – Books, documentaries or films discussing the case.
3. Archival records
Searching historical archives, museum collections and databases to find relevant documents, visual/audio records related to the case history and context.
Public archives like newspapers, organizational records, photographic collections could all include potentially relevant pieces of information to shed light on attitudes, cultural perspectives, common practices and historical contexts related to psychology.
4. Organizational records
Organizational records offer the advantage of often having large datasets collected over time that can reveal or confirm psychological insights.
Of course, privacy and ethical concerns regarding confidential data must be navigated carefully.
However, with proper protocols, organizational records can provide invaluable context and empirical depth to qualitative case studies exploring the intersection of psychology and organizations.
- Organizational/industrial psychology research : Organizational records like employee surveys, turnover/retention data, policies, incident reports etc. may provide insight into topics like job satisfaction, workplace culture and dynamics, leadership issues, employee behaviors etc.
- Clinical psychology : Therapists/hospitals may grant access to anonymized medical records to study aspects like assessments, diagnoses, treatment plans etc. This could shed light on clinical practices.
- School psychology : Studies could utilize anonymized student records like test scores, grades, disciplinary issues, and counseling referrals to study child development, learning barriers, effectiveness of support programs, and more.
How do I Write a Case Study in Psychology?
Follow specified case study guidelines provided by a journal or your psychology tutor. General components of clinical case studies include: background, symptoms, assessments, diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes. Interpreting the information means the researcher decides what to include or leave out. A good case study should always clarify which information is the factual description and which is an inference or the researcher’s opinion.
1. Introduction
- Provide background on the case context and why it is of interest, presenting background information like demographics, relevant history, and presenting problem.
- Compare briefly to similar published cases if applicable. Clearly state the focus/importance of the case.
2. Case Presentation
- Describe the presenting problem in detail, including symptoms, duration,and impact on daily life.
- Include client demographics like age and gender, information about social relationships, and mental health history.
- Describe all physical, emotional, and/or sensory symptoms reported by the client.
- Use patient quotes to describe the initial complaint verbatim. Follow with full-sentence summaries of relevant history details gathered, including key components that led to a working diagnosis.
- Summarize clinical exam results, namely orthopedic/neurological tests, imaging, lab tests, etc. Note actual results rather than subjective conclusions. Provide images if clearly reproducible/anonymized.
- Clearly state the working diagnosis or clinical impression before transitioning to management.
3. Management and Outcome
- Indicate the total duration of care and number of treatments given over what timeframe. Use specific names/descriptions for any therapies/interventions applied.
- Present the results of the intervention,including any quantitative or qualitative data collected.
- For outcomes, utilize visual analog scales for pain, medication usage logs, etc., if possible. Include patient self-reports of improvement/worsening of symptoms. Note the reason for discharge/end of care.
4. Discussion
- Analyze the case, exploring contributing factors, limitations of the study, and connections to existing research.
- Analyze the effectiveness of the intervention,considering factors like participant adherence, limitations of the study, and potential alternative explanations for the results.
- Identify any questions raised in the case analysis and relate insights to established theories and current research if applicable. Avoid definitive claims about physiological explanations.
- Offer clinical implications, and suggest future research directions.
5. Additional Items
- Thank specific assistants for writing support only. No patient acknowledgments.
- References should directly support any key claims or quotes included.
- Use tables/figures/images only if substantially informative. Include permissions and legends/explanatory notes.
- Provides detailed (rich qualitative) information.
- Provides insight for further research.
- Permitting investigation of otherwise impractical (or unethical) situations.
Case studies allow a researcher to investigate a topic in far more detail than might be possible if they were trying to deal with a large number of research participants (nomothetic approach) with the aim of ‘averaging’.
Because of their in-depth, multi-sided approach, case studies often shed light on aspects of human thinking and behavior that would be unethical or impractical to study in other ways.
Research that only looks into the measurable aspects of human behavior is not likely to give us insights into the subjective dimension of experience, which is important to psychoanalytic and humanistic psychologists.
Case studies are often used in exploratory research. They can help us generate new ideas (that might be tested by other methods). They are an important way of illustrating theories and can help show how different aspects of a person’s life are related to each other.
The method is, therefore, important for psychologists who adopt a holistic point of view (i.e., humanistic psychologists ).
Limitations
- Lacking scientific rigor and providing little basis for generalization of results to the wider population.
- Researchers’ own subjective feelings may influence the case study (researcher bias).
- Difficult to replicate.
- Time-consuming and expensive.
- The volume of data, together with the time restrictions in place, impacted the depth of analysis that was possible within the available resources.
Because a case study deals with only one person/event/group, we can never be sure if the case study investigated is representative of the wider body of “similar” instances. This means the conclusions drawn from a particular case may not be transferable to other settings.
Because case studies are based on the analysis of qualitative (i.e., descriptive) data , a lot depends on the psychologist’s interpretation of the information she has acquired.
This means that there is a lot of scope for Anna O , and it could be that the subjective opinions of the psychologist intrude in the assessment of what the data means.
For example, Freud has been criticized for producing case studies in which the information was sometimes distorted to fit particular behavioral theories (e.g., Little Hans ).
This is also true of Money’s interpretation of the Bruce/Brenda case study (Diamond, 1997) when he ignored evidence that went against his theory.
Breuer, J., & Freud, S. (1895). Studies on hysteria . Standard Edition 2: London.
Curtiss, S. (1981). Genie: The case of a modern wild child .
Diamond, M., & Sigmundson, K. (1997). Sex Reassignment at Birth: Long-term Review and Clinical Implications. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine , 151(3), 298-304
Freud, S. (1909a). Analysis of a phobia of a five year old boy. In The Pelican Freud Library (1977), Vol 8, Case Histories 1, pages 169-306
Freud, S. (1909b). Bemerkungen über einen Fall von Zwangsneurose (Der “Rattenmann”). Jb. psychoanal. psychopathol. Forsch ., I, p. 357-421; GW, VII, p. 379-463; Notes upon a case of obsessional neurosis, SE , 10: 151-318.
Harlow J. M. (1848). Passage of an iron rod through the head. Boston Medical and Surgical Journal, 39 , 389–393.
Harlow, J. M. (1868). Recovery from the Passage of an Iron Bar through the Head . Publications of the Massachusetts Medical Society. 2 (3), 327-347.
Money, J., & Ehrhardt, A. A. (1972). Man & Woman, Boy & Girl : The Differentiation and Dimorphism of Gender Identity from Conception to Maturity. Baltimore, Maryland: Johns Hopkins University Press.
Money, J., & Tucker, P. (1975). Sexual signatures: On being a man or a woman.
Further Information
- Case Study Approach
- Case Study Method
- Enhancing the Quality of Case Studies in Health Services Research
- “We do things together” A case study of “couplehood” in dementia
- Using mixed methods for evaluating an integrative approach to cancer care: a case study
Related Articles

Research Methodology
Qualitative Data Coding

What Is a Focus Group?

Cross-Cultural Research Methodology In Psychology

What Is Internal Validity In Research?

Research Methodology , Statistics
What Is Face Validity In Research? Importance & How To Measure

Criterion Validity: Definition & Examples
How Amazon grew an awkward side project into AWS, a behemoth that’s now 4 times bigger than its original shopping business

If you have touched your phone or computer today, you very likely have been touched by a vast business few outside the technology world are aware of. Maybe you’ve checked the Wall Street Journal or MarketWatch, traded a stock on Robinhood, bet on a football game through DraftKings , or posted on Pinterest or Yelp; ordered treats for Fido on Chewy or treats for yourself on DoorDash; submitted an expense report on Workday or made plans for the evening via Tinder, OkCupid, or Hinge.
If so, you did it with the help of Amazon Web Services. The less glamorous sibling to Amazon’s operations in e-commerce, streaming video, and smart devices, AWS is no less ubiquitous, deploying millions of computers worldwide, humming away somewhere in the cloud.
For all those AWS customers the on-demand cloud computing platform isn’t just another vendor. They rely on it so heavily that it resembles a public utility—taken for granted, but essential to keep the machinery humming. In the past 12 months each of the companies mentioned above has stated in Securities and Exchange Commission filings that they “would be adversely impacted” if they lost their AWS service. Hundreds more companies— Netflix , Zoom , Intuit , Caesars Entertainment—have reported the same risk factor to the SEC in the past year. By the way, the SEC uses AWS. (So does Fortune .)
And those are but the tiniest fraction of AWS customers. AWS—initially run by Andy Jassy, who went on to succeed Jeff Bezos as Amazon’s CEO—won’t say how many customers it has, only that it provides computing power, data storage, and software to millions of organizations and individuals. Now, even as Amazon lays off a reported 10,000 workers, Wall Street analysts expect another blowout performance from its web services division. That’s probably why few if any of those staffing cuts will affect this relatively recession-proof part of Bezos’s empire. (Amazon won’t say how many of its 1.5 million employees work for AWS.)
For years AWS has brought in more profit than all other divisions of Amazon combined, usually by a wide margin. AWS’s operating profit last year, $18.5 billion, was nearly three times the operating profit reported by the rest of the company ($6.3 billion). AWS pulled in $58.7 billion of revenue in this year’s first nine months; if it were independent, it would easily rank in the Fortune 100.
How did this offshoot of an online retailer come to rule the lucrative cloud-computing industry, towering over tech giants such as Microsoft and Google , which might have seemed better positioned to dominate?
AWS’s ascent is so unlikely that it demands an explanation. It reveals the power of a truly iconoclastic culture that, while at times ruthless, ultimately breeds innovation and preserves top talent by encouraging entrepreneurship.
The best-known origin story of AWS is that it started when Amazon had some spare computer capacity and decided to rent it out to other companies. That story won’t die, but it isn’t true. The real story traces a circuitous path that could easily have ended in a ditch. It’s grounded in a philosophy that still guides AWS’s progress.
“To me, it’s the concept of insurgents versus incumbents,” says Adam Selipsky, who became AWS’s CEO last year when his predecessor, Jassy, took over as Amazon CEO. Selipsky, 56, speaks quietly, conveying an understated intensity. “One thing that I think is really important, that we intentionally worry about all the time,” he says, is that “we continue to keep the customer need dancing in front of our eyes at all times.”
The real story of the AWS insurgency began with Amazon’s innovative responses to two problems. First: By the early 2000s, Amazon—still known mainly as an online bookseller—had built from scratch one of the world’s biggest websites, but adding new features had become frustratingly slow. Software engineering teams were spending 70% of their time building the basic elements any project would require—most important, a storage system and an appropriate computing infrastructure. Building those elements for projects at Amazon scale was hard, and all that work merely produced a foundation on which to build the cool new customer-pleasing features Amazon was seeking. Every project team was performing the same drudgery. Bezos and other Amazon managers started calling it “undifferentiated heavy lifting” and complaining that it produced “muck.”
In response, Selipsky recalls, company leaders began to think, “Let’s build a shared layer of infrastructure services that all these teams can rely on, and none of them have to spend time on general capabilities like storage, compute capabilities, databases.” Amazon’s leaders didn’t think of it as an internal “cloud”—the term wasn’t widely used in the tech world yet—but that’s what it was.

The second problem involved other websites wanting to add links to Amazon products on their own pages. For example, a website about cooking might recommend a kitchen scale and include a link to the Amazon.com page for the product. Amazon was all for it, and would send them a bit of code they could plug into their site; if someone bought the product through the link, the site owner earned a fee. But as the program grew, cranking out bits of code for every affiliate site became overwhelming, and those affiliates’ website developers wanted to create their own links and product displays instead of the ones Amazon sent them. So in 2002 Amazon offered them a more advanced piece of software, enabling them to create far more creative displays. The new software was complicated. Users had to write software rather than just plug it in. Yet thousands of developers loved it immediately.
When Amazon launched a fuller, free version of the software building block a few months later, it enabled anyone, not just affiliates, to incorporate Amazon features into their sites. The surprise: A lot of the downloads were going to Amazon’s own software engineers. The building block turned out to be a proof of concept for the labor-lightening innovations that Amazon itself was looking for.
A picture was emerging. Amazon desperately needed to free its software developers from creating muck. Developers everywhere, not only its own, were starving for new tools that did just that. “We very quickly figured out that external developers had exactly the same problems as internal developers at Amazon,” Selipsky says.
But was that a business for Amazon? During a 2003 offsite at Bezos’s house, the company’s top managers decided that it could be. That decision was the turning point, especially significant because it could so easily have gone the other way. Amazon’s customers were consumers who bought “new, used, refurbished, and collectible items,” as the company told investors at the time. Why would anyone imagine this company could build a business selling technology services to software developers?
The decision to plunge ahead revealed a subtle distinction that outsiders didn’t understand. The world saw Amazon as an online retailer, but the company’s leaders never thought of it that way. They thought of it as “a technology company that had simply applied its technology to the retail space first,” Jassy later told Harvard Business School professors who were writing a case study. For that kind of company, AWS looked like a promising bet.
Coming out of the 2003 offsite, Jassy’s job was to build a team and develop AWS. He wrote a proposal for it as a cloud-computing business. The document, one of the famous six-pagers used at Amazon’s executive meetings instead of PowerPoint (which is banned), reportedly went through 31 revisions.
It took three years before AWS went live. In 2005 Jassy hired Selipsky from a software firm to run marketing, sales, and support, Selipsky recalls: “Amazon called and told me there was this initiative for something about turning the guts of Amazon inside out, but other companies could use it.” AWS’s first service, for data storage, “was such a novel concept that it was even hard to explain and hard for me to understand,” he says.
Wall Street didn’t get it. “I have yet to see how these investments are producing any profit,” a Piper Jaffray analyst said in 2006. “They’re probably more of a distraction than anything else.”
The rest of the world didn’t get it either. “I cannot tell you the number of times I got asked, with a quizzical look on people’s faces, ‘But what does this have to do with selling books?’ ” Selipsky recalls. “The answer, of course, was: AWS has nothing to do with selling books. But the technology we use to sell books has everything to do with AWS and what we can offer customers.” Those customers were software developers, an entirely new target market that baffled outsiders.
AWS was prepared for that reaction. One of Amazon’s principles reads in part: “As we do new things, we accept that we may be misunderstood for long periods of time.”

On the day in March 2006 when AWS finally launched its inaugural service—S3, for Simple Storage Service—Selipsky was at a trade show in Santa Clara, Calif., “in a windowless, internet-less conference room,” as he describes it, unable to learn how the launch was going. At day’s end he and a colleague ran outside to call Seattle for news.
“We were told that 12,000 developers had signed up,” he says, a note of marvel still in his voice. “On the first day. It was just amazing.”
Five months later AWS launched its other foundational service, EC2, for Elastic Compute Cloud, which was also instantly popular. The revolution had begun. Instead of raising millions of dollars to buy servers and build data centers, startups could now get online with a credit card, and pay a monthly bill for just the computing power and storage they used. If their new app was a hit, they could immediately engage all the cloud services that they needed. If it bombed, they weren’t stuck with rooms of junk equipment. As a Silicon Valley entrepreneur and early AWS customer told Wired in 2008: “Infrastructure is the big guys’ most powerful asset. This levels the field.”
In response to that historic shift, AWS’s potential competitors did … nothing. “A business miracle happened,” Bezos told a conference years later. “This is the greatest piece of business luck in the history of business so far as I know. We faced no like-minded competition for seven years. I think the big established enterprise software companies did not see Amazon as a credible enterprise software company, so we had this incredible runway.”
Selipsky suspects an additional motivation: “They either didn’t believe this could be a real business, or they were so threatened by what it would do to their own business models, and the way they were overcharging customers, that they didn’t want to believe it.”
No one, not even at Amazon, foresaw how massive a business cloud computing would be, or AWS’s dominance in the space. To understand how this happened, it’s worth examining the company’s guiding principles.
Eye-roll alert: Every company has principles, missions, visions, values; the vast majority are indistinguishable and sound as if they were written by committees, which they probably were. Some of Amazon’s leadership principles, as they’re called—there are 16—sound that way, until they get a little “peculiar,” to use a favorite Amazonian word.
For example, principle No. 11 begins, “Earn trust.” Leaders, it explains, “are vocally self-critical, even when doing so is awkward or embarrassing. Leaders do not believe their or their team’s body odor smells of perfume.” This peculiarity is a badge of pride at Amazon; its web page for job seekers even says that its use of the principles “is just one of the things that makes Amazon peculiar.”
Not every Amazonian observes every principle all the time; in a company of 1.5 million employees, that’s not realistic. But Amazon’s batting average is high.
To answer the basic question of why a retailer would even think of creating AWS, consider principle No. 1, seemingly the hoariest of them all: “Customer obsession.” Amazon sees itself as a tech company and sees the world as 8 billion potential customers. That’s one reason AWS made sense for a bookseller.
“I cannot tell you the number of times I got asked … ‘But what does this have to do with selling books?’” Adam Selipsky, CEO, Amazon Web Services
Amazon allows new projects lots of time, as with AWS, in part to make sure decisions are based on data. An unusual principle states that leaders “work to disconfirm their beliefs.” Groupthink is comforting, contagious, and dangerous. Being able to invoke one of the principles enables doubters to speak up.
“We have senior engineers who will stop a meeting and say, ‘We’ve got to disconfirm our beliefs—we’re going too far here without checking,’ ” says Mai-Lan Tomsen Bukovec, who oversees AWS’s storage services. “That’s actually kind of revolutionary in terms of corporate culture.”
It’s not a culture for everyone. Amazon is a famously demanding place to work, and there are plenty of stories of employees who found it to be too much. Media reports have criticized Amazon’s treatment of workers, and the company is battling unionization efforts at some of its e-commerce warehouses. It’s noteworthy that last year Amazon added a new leadership principle: “Strive to be Earth’s best employer.”
“It’s not good for our business and not good for our customers if we turn out great employees and burn them out, and they leave after a couple of years,” says Matt Garman, an early AWS employee who now oversees sales and marketing. “Sometimes there are people who don’t like the culture, don’t like those leadership principles. It’s not a good fit for them. People like the culture or they don’t like the culture, and I think that’s okay. But we want people here for the long term.”
Asked to describe AWS’s strategy, Tomsen Bukovec says, “That’s not a word we use a ton.”
The foundation of conventional strategy, the subject of hundreds of books and articles, is understanding a company’s industry and competitors. That approach gets us nowhere with Amazon. What industry is it in? No one industry encompasses selling dog food and selling computing power.
So does Amazon even have a strategy? “Yes,” says Ram Charan, an adviser to CEOs and boards, and coauthor of a book on Amazon’s management system. But “it’s not a competitive strategy,” he says. “It’s a customer strategy.”
That’s a mind bender. Business is competition, and business strategy is inherently competitive strategy. Except that at Amazon it isn’t. If it had been—if Amazon had been conventionally competitor-focused—AWS probably wouldn’t exist.
Colin Bryar, a former Amazon executive, says he’s often asked what Amazon is going to build next. Can it repeat what it did with AWS, create an out-of-the-blue business, unexpected and underestimated, in which it becomes dominant? “That’s not the first question Amazon asks,” Bryar says. “They ask, ‘What’s the next big customer problem we can go try to solve?’ ”
The word “big” is key. At Amazon’s size—analysts expect revenue exceeding $500 billion for 2022—small problems are simply not of interest. When company leaders identify a sufficiently big problem, they must then conclude that Amazon can solve it, and that customers will adopt the solution. Those are not easy or quick questions to answer.
Cloud computing will grow 20% annually through 2026, far faster than any other segment of infotech, according to the Gartner tech consulting firm. It’s no longer just smaller companies and startups who don’t want to invest in their own server systems. Many AWS customers are increasing their spend, and some “spend literally hundreds of millions of dollars per year on AWS,” says Gartner analyst Raj Bala, who sees the contracts. “I’m not shocked anymore to see a $200 million annual commitment, which is astonishing.”
Yet AWS’s dominance of the market will likely diminish even as its revenue grows. With a 44% share of the market, AWS has 20 points over Microsoft’s 24%—but that lead is shrinking, says Bala. “In the next five, six, seven years, that gap is going to be very, very narrow, if not equal.” That’s because “a lot of late adopter enterprises are coming to market,” he says, “and a lot of these folks will gravitate to Microsoft because they’ve got an existing contractual relationship with Microsoft.”
The narrowing gap with Microsoft is probably inevitable. AWS’s great challenge for the future is to maintain the discipline that made it a global colossus.
Losing that discipline is insidiously easy. Jim Collins, author of Good to Great , which identifies the factors shared by the world’s most successful companies, has also written an analysis of failure, How the Mighty Fall . Winners invariably maintain discipline, and loss of discipline is always an element of decline. One of the principle threats? Attempts to control workers by overregulating them. “Bureaucracy subverts discipline,” he tells Fortune.
When a company is growing as fast as AWS, it can be tempting to weaken hiring standards. “As you grow, you start to bring in some of the wrong people,” he says, speaking of companies generally. “If they don’t get the intensity of being there, they shouldn’t be there, but if enough of them stay, you try to control them with bureaucracy. Then the right people get out, which creates a cycle.”
With success and growth come further threats to discipline. When a business is riding high, “easy cash erodes cost discipline, and that discipline is hard to recover once you lose it,” he says. Expansion brings risks, too: Responding desperately to deteriorating performance, the business bets on “undisciplined discontinuous leaps”—acquisitions or expansions for which it isn’t ready.
At the top of its game, bigger and stronger than any competitor, AWS must now meet an enviable challenge but a challenge nonetheless: the curse of success. Its most crucial task is to maintain the unwavering rigor—the discipline—of its principles and processes.
Selipsky seems to understand the need. Asked to define his job, he is silent for several seconds. Then, quietly but emphatically, he says his job “is to ensure that the positive, productive, useful elements of what got us to this stage—that we hold those dear, and we safeguard them, and we don’t let them slip away. We don’t become incumbents.”
Amazon’s next big, thorny problem to solve
What might be the next industry to get Amazon’s AWS-style mega-venture treatment? The leading candidate is health care.
In 2018 Amazon bought PillPack, an online pharmacy, and last summer it paid $3.9 billion for One Medical, a membership-based primary-care provider operating across the U.S., saying in its announcement that “we think health care is high on the list of experiences that need reinvention.”
No one would disagree. For a company that seeks big problems to solve, this may be the biggest opportunity of all. Health care is the largest sector of the U.S. economy, and the industry is growing fast worldwide.
Data is the problem at the heart of health care’s inefficiency and unfathomable, wearisome customer experiences—and it’s possible that it could be the solution.
That data is staggering in quantity and mostly unstructured—handwritten notes and X-ray and lab reports, sometimes of life-and-death importance—in an industry that is the last bastion of fax machines.
It’s a particularly attractive conundrum to Amazon because of the company’s dominance of cloud computing. AWS is already deeply entrenched in the industry, used by hospitals, pharma companies, equipment makers, insurers, pharmacy benefit managers, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, and more.
Another potential advantage is Amazon’s massive international workforce and its enormous health care needs and expenses. Just as Amazon developed AWS by observing its own software needs and seeing them mirrored elsewhere, its own challenges as a growing corporate behemoth now may point the way to a new market opportunity.
This article appears in the December 2022/January 2023 issue of Fortune with the headline, “How Amazon’s cloud took the world by storm.”
Our new weekly Impact Report newsletter will examine how ESG news and trends are shaping the roles and responsibilities of today's executives—and how they can best navigate those challenges. Subscribe here .
TechRepublic

8 Best Data Science Tools and Software
Apache Spark and Hadoop, Microsoft Power BI, Jupyter Notebook and Alteryx are among the top data science tools for finding business insights. Compare their features, pros and cons.

EU’s AI Act: Europe’s New Rules for Artificial Intelligence
Europe's AI legislation, adopted March 13, attempts to strike a tricky balance between promoting innovation and protecting citizens' rights.

10 Best Predictive Analytics Tools and Software for 2024
Tableau, TIBCO Data Science, IBM and Sisense are among the best software for predictive analytics. Explore their features, pricing, pros and cons to find the best option for your organization.

Tableau Review: Features, Pricing, Pros and Cons
Tableau has three pricing tiers that cater to all kinds of data teams, with capabilities like accelerators and real-time analytics. And if Tableau doesn’t meet your needs, it has a few alternatives worth noting.

Top 6 Enterprise Data Storage Solutions for 2024
Amazon, IDrive, IBM, Google, NetApp and Wasabi offer some of the top enterprise data storage solutions. Explore their features and benefits, and find the right solution for your organization's needs.
Latest Articles

The 5 Best Udemy Courses That Are Worth Taking in 2024
Udemy is an online platform for learning at your own pace. Boost your career with our picks for the best Udemy courses for learning tech skills online in 2024.

What Is Data Quality? Definition and Best Practices
Data quality refers to the degree to which data is accurate, complete, reliable and relevant for its intended use.

TechRepublic Premium Editorial Calendar: Policies, Checklists, Hiring Kits and Glossaries for Download
TechRepublic Premium content helps you solve your toughest IT issues and jump-start your career or next project.

What is the EU’s AI Office? New Body Formed to Oversee the Rollout of General Purpose Models and AI Act
The AI Office will be responsible for enforcing the rules of the AI Act, ensuring its implementation across Member States, funding AI and robotics innovation and more.

Top Tech Conferences & Events to Add to Your Calendar in 2024
A great way to stay current with the latest technology trends and innovations is by attending conferences. Read and bookmark our 2024 tech events guide.

What is Data Science? Benefits, Techniques and Use Cases
Data science involves extracting valuable insights from complex datasets. While this process can be technically challenging and time-consuming, it can lead to better business decision-making.

Gartner’s 7 Predictions for the Future of Australian & Global Cloud Computing
An explosion in AI computing, a big shift in workloads to the cloud, and difficulties in gaining value from hybrid cloud strategies are among the trends Australian cloud professionals will see to 2028.

OpenAI Adds PwC as Its First Resale Partner for the ChatGPT Enterprise Tier
PwC employees have 100,000 ChatGPT Enterprise seats. Plus, OpenAI forms a new safety and security committee in their quest for more powerful AI, and seals media deals.

What Is Contact Management? Importance, Benefits and Tools
Contact management ensures accurate, organized and accessible information for effective communication and relationship building.

How to Use Tableau: A Step-by-Step Tutorial for Beginners
Learn how to use Tableau with this guide. From creating visualizations to analyzing data, this guide will help you master the essentials of Tableau.

HubSpot CRM vs. Mailchimp (2024): Which Tool Is Right for You?
HubSpot and Mailchimp can do a lot of the same things. In most cases, though, one will likely be a better choice than the other for a given use case.

Top 5 Cloud Trends U.K. Businesses Should Watch in 2024
TechRepublic identified the top five emerging cloud technology trends that businesses in the U.K. should be aware of this year.

Pipedrive vs. monday.com (2024): CRM Comparison
Find out which CRM platform is best for your business by comparing Pipedrive and Monday.com. Learn about their features, pricing and more.

Celoxis: Project Management Software Is Changing Due to Complexity and New Ways of Working
More remote work and a focus on resource planning are two trends driving changes in project management software in APAC and around the globe. Celoxis’ Ratnakar Gore explains how PM vendors are responding to fast-paced change.

SAP vs. Oracle (2024): Which ERP Solution Is Best for You?
Explore the key differences between SAP and Oracle with this in-depth comparison to determine which one is the right choice for your business needs.
Create a TechRepublic Account
Get the web's best business technology news, tutorials, reviews, trends, and analysis—in your inbox. Let's start with the basics.
* - indicates required fields
Sign in to TechRepublic
Lost your password? Request a new password
Reset Password
Please enter your email adress. You will receive an email message with instructions on how to reset your password.
Check your email for a password reset link. If you didn't receive an email don't forgot to check your spam folder, otherwise contact support .
Welcome. Tell us a little bit about you.
This will help us provide you with customized content.
Want to receive more TechRepublic news?
You're all set.
Thanks for signing up! Keep an eye out for a confirmation email from our team. To ensure any newsletters you subscribed to hit your inbox, make sure to add [email protected] to your contacts list.
Development of multi-objective equilibrium optimizer: application to cancer chemotherapy
- Original Article
- Published: 01 June 2024
Cite this article

- K. Nozad 1 ,
- S. M. Varedi-Koulaei 1 &
- M. Nazari ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2223-8143 1
Explore all metrics
Any multi-objective optimization algorithms are usually introduced by developing a single-objective algorithm. In the current study, a recently developed physics-based algorithm, equilibrium optimizer (EO), is regarded and is extended into a multi-objective algorithm called MOEO. The optimal control problem for cancer treatment is solved using this novel algorithm to confirm its performance. Considering the cancer treatment as an optimal control problem to reduce both the concentration of cancer cells and the concentration of the drugs during treatment is the multi-objective optimization problem of this research. Due to this, this problem’s solution leads to the optimal drug administration protocol to minimize cancer cell concentration and drug concentration. This multi-objective problem is solved using the novel MOEO algorithm, and the results are compared with the previous works. The Pareto front curve obtained from the algorithm offers a set of the most optimal solutions. According to the treatment selection criteria, one of these points is selected as the drug-prescribing protocol. The problem is solved based on three different case studies, where the result comparison shows that the MOEO’s performance is great. Considering different cost functions, it shows that using integral of the time-weighted absolute (ITA) objective function gets the fastest response with a higher drug dose while using integral of the absolute (IS) objective function gets lesser drugs.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Data availability
Data sharing was not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
American Cancer Society (2022) Cancer facts & figures 2022. American Cancer Society, Atlanta, pp 1–76. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/bladder-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/survival-rates.html
Evans M, Mason MD (2007) Radical radiotherapy for prostate cancer. Urol Cancers Clin Pract. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-84628-507-3_1
Article Google Scholar
de Pillis LG, Gu W, Fister KR, Head T, Maples K, Murugan A, Neal T, Yoshida K (2007) Chemotherapy for tumors: an analysis of the dynamics and a study of quadratic and linear optimal controls. Math Biosci 209:292–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mbs.2006.05.003
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Ekinci S, Izci D, Abu Zitar R, Alsoud AR, Abualigah L (2022) Development of Lévy flight-based reptile search algorithm with local search ability for power systems engineering design problems. Neural Comput Appl 34:20263–20283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07575-w
Izci D, Ekinci S, Mirjalili S, Abualigah L (2023) An intelligent tuning scheme with a master/slave approach for efficient control of the automatic voltage regulator. Neural Comput Appl 35:19099–19115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-023-08740-5
Dai F, Liu B (2021) Optimal control problem for a general reaction–diffusion tumor–immune system with chemotherapy. J Frankl Inst 358:448–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfranklin.2020.10.032
Zirkohi MM, Kumbasar T (2020) Adaptive backstepping controller design for MIMO cancer immunotherapy using Laguerre polynomials. J Frankl Inst 357:4664–4679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfranklin.2020.02.007
Martin RB (1992) Optimal control drug scheduling of cancer chemotherapy. Automatica 28:1113–1123. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-1098(92)90054-J
Alyasseri ZAA, Alomari OA, Al-Betar MA, Makhadmeh SN, Doush IA, Awadallah MA, Abasi AK, Elnagar A (2022) Recent advances of bat-inspired algorithm, its versions and applications. Neural Comput Appl 34:16387–16422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07662-y
Ahmad F, Mat Isa NA, Hussain Z, Sulaiman SN (2013) A genetic algorithm-based multi-objective optimization of an artificial neural network classifier for breast cancer diagnosis. Neural Comput Appl 23:1427–1435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-012-1092-1
Parker RS, Doyle FJ (2001) Control-relevant modeling in drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 48:211–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-409X(01)00114-4
Algoul S, Alam MS, Hossain MA, Majumder MAA (2011) Multi-objective optimal chemotherapy control model for cancer treatment. Med Biol Eng Comput 49:51–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-010-0678-y
Shi J, Alagoz O, Erenay FS, Su Q (2014) A survey of optimization models on cancer chemotherapy treatment planning. Ann Oper Res 221:331–356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-011-0869-4
Lobato FS, Machado VS, Steffen V (2016) Determination of an optimal control strategy for drug administration in tumor treatment using multi-objective optimization differential evolution. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 131:51–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2016.04.004
Bin Mohd Zain MZ, Kanesan J, Chuah JH, Dhanapal S, Kendall G (2018) A multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm based on dynamic boundary search for constrained optimization. Appl Soft Comput J 70:680–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2018.06.022
Shindi O, Kanesan J, Kendall G, Ramanathan A (2020) The combined effect of optimal control and swarm intelligence on optimization of cancer chemotherapy. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105327
Khalili P, Vatankhah R (2019) Derivation of an optimal trajectory and nonlinear adaptive controller design for drug delivery in cancerous tumor chemotherapy. Comput Biol Med 109:195–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2019.04.011
Subhan F, Aziz MA, Khan IU, Fayaz M, Wozniak M, Shafi J, Ijaz MF (2022) Cancerous tumor controlled treatment using search heuristic (GA)-based sliding mode and synergetic controller. Cancers (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174191
Cao R, Si L, Li X, Guang Y, Wang C, Tian Y, Pei X, Zhang X (2022) A conjugate gradient-assisted multi-objective evolutionary algorithm for fluence map optimization in radiotherapy treatment. Complex Intell Syst 8:4051–4077. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40747-022-00697-7
Mei Y, Wu K (2022) Application of multi-objective optimization in the study of anti-breast cancer candidate drugs. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-23851-0
Nazari M, Varedi-Koulaei SM, Nazari M (2022) Flow characteristics prediction in a flow-focusing microchannel for a desired droplet size using an inverse model: experimental and numerical study. Microfluid Nanofluid 26:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-022-02529-z
Mokhtari M, Varedi-Koulaei SM, Zhu J, Hao G (2022) Topology optimization of the compliant mechanisms considering curved beam elements using metaheuristic algorithms. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part C J Mech Eng Sci 236:7197–7208. https://doi.org/10.1177/09544062221075277
Ramachandran M, Mirjalili S, Nazari-Heris M, Parvathysankar DS, Sundaram A, Charles Gnanakkan CAR (2022) A hybrid grasshopper optimization algorithm and Harris Hawks optimizer for combined heat and power economic dispatch problem. Eng Appl Artif Intell 111:104753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2022.104753
Akinola OO, Ezugwu AE, Agushaka JO, Zitar RA, Abualigah L (2022) Multiclass feature selection with metaheuristic optimization algorithms: a review. Neural Comput Appl 34:19751–19790. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07705-4
Faramarzi A, Heidarinejad M, Stephens B, Mirjalili S (2020) Equilibrium optimizer: a novel optimization algorithm. Knowl Based Syst. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2019.105190
Nguyen TT, Nguyen TT, Duong MQ (2022) An improved equilibrium optimizer for optimal placement of photovoltaic systems in radial distribution power networks. Neural Comput Appl 34:6119–6148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06779-w
Houssein EH, Dirar M, Abualigah L, Mohamed WM (2022) An efficient equilibrium optimizer with support vector regression for stock market prediction. Neural Comput Appl 34:3165–3200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06580-9
Eid A, Kamel S, Houssein EH (2022) An enhanced equilibrium optimizer for strategic planning of PV-BES units in radial distribution systems considering time-varying demand. Neural Comput Appl 34:17145–17173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07364-5
Abdel-Basset M, Chang V, Mohamed R (2021) A novel equilibrium optimization algorithm for multi-thresholding image segmentation problems. Neural Comput Appl 33:10685–10718. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-04820-y
Cikan M, Kekezoglu B (2022) Comparison of metaheuristic optimization techniques including equilibrium optimizer algorithm in power distribution network reconfiguration. Alex Eng J 61:991–1031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2021.06.079
De Pillis LG, Radunskaya A (2003) The dynamics of an optimally controlled tumor model: a case study. Math Comput Model 37:1221–1244. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0895-7177(03)00133-X
De Pillis LG, Radunskaya A (2001) A mathematical tumor model with immune resistance and drug therapy: an optimal control approach. J Theor Med 3:79–100. https://doi.org/10.1080/10273660108833067
Coello CAC, Lamont GB, Van Veldhuizen DA (2007) Evolutionary algorithms for solving multi-objective problems, 2nd edn. Springer, New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-36797-2
Book Google Scholar
Smith AE (2005) Multi-objective optimization using evolutionary algorithms [Book Review]. Wiley. https://doi.org/10.1109/tevc.2002.804322
Rao SS (2019) Engineering optimization: theory and practice. Wiley Online Library. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119454816
Agnihotri S, Atre A, Verma HK (2020) Equilibrium optimizer for solving economic dispatch problem. In: PIICON 2020—9th IEEE power India international conference (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/PIICON49524.2020.9113048
Chen H, Li W, Cui W (2020) Disruption-based multiobjective equilibrium optimization algorithm. Comput Intell Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8846250
Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal S, Meyarivan T (2002) A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 6:182–197. https://doi.org/10.1109/4235.996017
Ishibuchi H, Zhang Q, Cheng R, Li K, Li H, Wang H (2021) Evolutionary multi-criterion optimization. In: 11th International conference, EMO 2021, Shenzhen, China, March 28–31, 2021, proceedings
Krabs W, von Wolfersdorf L (2011) Two optimal control problems in cancer chemotherapy with drug resistance. Ann Acad Rom Sci Ser Math Appl 3(2011):332–355
MathSciNet Google Scholar
Nozad K, Varedi-Koulaei SM, Nazari M (2022) Multi-objective optimization of cancer treatment using NSWOA algorithm. J Mech Eng 52(3):115–124
Google Scholar
Download references
No funding was received for this study.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Shahrood University of Technology, Shahrood, Iran
K. Nozad, S. M. Varedi-Koulaei & M. Nazari
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to M. Nazari .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
No ethics approval was required.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Nozad, K., Varedi-Koulaei, S.M. & Nazari, M. Development of multi-objective equilibrium optimizer: application to cancer chemotherapy. Neural Comput & Applic (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-024-10014-7
Download citation
Received : 14 January 2023
Accepted : 03 May 2024
Published : 01 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-024-10014-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Mathematical modeling
- Cancer treatment
- Multi-objective optimization
- Multi-objective equilibrium optimizer (MOEO)
- Equilibrium optimizer (EO)
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
CrystEngComm
Theoretical and experimental study of pharmaceutical salts: a case of trimethoprim.
Trimethoprim (TMP) is a bacterial dihydroreductase inhibitor with broad-spectrum antibacterial properties. However, its oral absorption is limited by its low water solubility. Salification is one of the effective methods to solve this problem. This work proposes an efficient method for screening TMP’s salts using the conductor-like screening model for real solvents (COSMO-RS) model. 200 commonly compounds were introduced as candidates for screening. As a result, 39 hit compounds were subjected to experimental liquid-assisted grinding (LAG) with TMP, then 25 new solid phases were confirmed by PXRD. Solvent evaporation method was further used to acquire eight single crystals of TMP salts, whose structures were elucidated by single-crystal X-ray diffraction. The power X-ray diffraction, differential scanning calorimetry, thermogravimetric analysis, and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy were employed to characterize seven of the TMP salts. Then, atoms-in-molecules was used to analyze intermolecular hydrogen bonding interactions in salts. Finally, we tested the equilibrium solubility and dissolution rate of the salt, which exhibited an increase in solubility. In a word, it is an effective screening method to obtain the TMP salts combined with the COSMO-RS model and LAG method, which can be widely applied to other systems for screening of the target salts.
Supplementary files
- Supplementary information PDF (2302K)
- Crystal structure data CIF (337K)
Article information
Download citation, permissions.
L. Zhang, D. Wu, M. Zhang, F. Yu, Y. Bao, C. Xie, B. Hou, D. Jing, C. Zhang and W. Chen, CrystEngComm , 2024, Accepted Manuscript , DOI: 10.1039/D4CE00345D
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content .
Social activity
Search articles by author.
This article has not yet been cited.
Advertisements

COMMENTS
Case study examples. Case studies are proven marketing strategies in a wide variety of B2B industries. Here are just a few examples of a case study: Amazon Web Services, Inc. provides companies with cloud computing platforms and APIs on a metered, pay-as-you-go basis. This case study example illustrates the benefits Thomson Reuters experienced ...
Steps. Download Article. 1. Examine and describe the business environment relevant to the case study. Describe the nature of the organization under consideration and its competitors. Provide general information about the market and customer base.
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
Advantages of a case study: Case studies showcase a specific solution and outcome for specific customer challenges. It attracts potential customers with similar challenges. It builds trust and credibility with potential customers. It provides an in-depth analysis of your company's problem-solving process. Disadvantages of a case study:
Best, worst, and most likely scenarios can also be insightful. Step 5: Decision. Students propose their solution to the problem. This decision is justified based on an in-depth analysis. Explain why the recommendation made is the best fit for the criteria. Step 6: Implementation plan.
5 Steps to Write a Case Study. 1. Identifying the Subject or Case. Choose a subject that aligns with your objectives and offers valuable insights. Ensure the subject has a clear narrative and relevance to your audience. The subject should illustrate key points and provide substantial learning opportunities.
Identify the key problems and issues in the case study. Formulate and include a thesis statement, summarizing the outcome of your analysis in 1-2 sentences. Background. Set the scene: background information, relevant facts, and the most important issues. Demonstrate that you have researched the problems in this case study. Evaluation of the Case
Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data. Example: Mixed methods case study. For a case study of a wind farm development in a ...
These case studies offer a practical application of management concepts, requiring students to analyze complex scenarios and devise solutions. In this comprehensive guide, we will outline a step-by-step approach to solving management case studies and provide a real-world example with a solution. Step 1: Comprehensive Case Study Analysis.
What the Case Study Method Really Teaches. Summary. It's been 100 years since Harvard Business School began using the case study method. Beyond teaching specific subject matter, the case study ...
Thank the people who contributed to the case study and helped in the problem-solving process. Cite any external resources, reports or data sets that contributed to your analysis. Feedback & Q&A session. Open the floor for questions and feedback from your audience. This allows for further discussion and can provide additional insights that may ...
Although case studies have been discussed extensively in the literature, little has been written about the specific steps one may use to conduct case study research effectively (Gagnon, 2010; Hancock & Algozzine, 2016).Baskarada (2014) also emphasized the need to have a succinct guideline that can be practically followed as it is actually tough to execute a case study well in practice.
The five case studies listed below are well-written, well-designed, and incorporate a time-tested structure. 1. Lane Terralever and Pinnacle at Promontory. This case study example from Lane Terralever incorporates images to support the content and effectively uses subheadings to make the piece scannable. 2.
Pioneered by HBS faculty, the case method presents the greatest challenges confronting organizations and places the student in the role of the decision maker. ... Have you ever worked with a group of people trying to solve a problem? There are different opinions, different considerations, and each person's perspective provides a different ...
It may be related to an ailment or a patient; a case study in the business sector might cover a broader market; in politics, a case study might range from a narrow happening to a huge undertaking. Let's discuss How to solve case studies with examples, Example#1: AnaOwas a woman's pseudonym of a lady named Bertha. A patient of a famous ...
Case study examples. While templates are helpful, seeing a case study in action can also be a great way to learn. Here are some examples of how Adobe customers have experienced success. Juniper Networks. One example is the Adobe and Juniper Networks case study, which puts the reader in the customer's shoes.
Step 1: Identify the problem statement. Case competitions like Accenture Strategy Case Connect and Colgate Transcend provide an exact problem statement with the expected outcome. But, in most cases, we must dive deep to break down the problem statement and identify the potential causes. Like, for Colgate Transcend, the problem statement was ...
Most resources tell you that a case study should be 500-1500 words. We also encourage you to have a prominent snapshot section of 100 words or less. The results and benefits section should take the bulk of the word count. Don't use more words than you need. Let your data, images, and customers quotes do the talking.
The purpose of case study research is twofold: (1) to provide descriptive information and (2) to suggest theoretical relevance. Rich description enables an in-depth or sharpened understanding of the case. It is unique given one characteristic: case studies draw from more than one data source. Case studies are inherently multimodal or mixed ...
Case studies are a form of problem-based learning, where you present a situation that needs a resolution. A typical business case study is a detailed account, or story, of what happened in a particular company, industry, or project over a set period of time. The learner is given details about the situation, often in a historical context.
All case answers are written by top business students. Solve your case studies faster! Casehero. The marketplace for case solutions. Case Study Solutions. Case Study Solutions. ... We manually review all case study submissions being sent to us. Immediate access. You immediately get access upon purchasing any of our case solutions.
Explain what you will examine in the case study. Write an overview of the field you're researching. Make a thesis statement and sum up the results of your observation in a maximum of 2 sentences. Background. Provide background information and the most relevant facts. Isolate the issues.
Prepare for B-school admission rounds, with these MBA case study examples. It is common for B-schools to incorporate a case-based discussion in the group exercise round or give a case study in a personal interview. So, here we have presented two popular MBA case study examples, with analysis and solution.
Case study contains large number of pages. Not able to devote enough time from their busy schedule to solve a case study. Case study requiring higher level of understanding; Well whatever may be the case, our online library is equipped with all the arsenal you would ever need for your case study solutions/analysis.
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. Typically, data is gathered from various sources using several methods (e.g., observations & interviews). The case study research method originated in clinical medicine (the case history, i.e., the patient's personal history). In psychology, case studies are ...
Over two decades, AWS has become the ultimate case study in corporate innovation. ... For a company that seeks big problems to solve, this may be the biggest opportunity of all. Health care is the ...
Big Data Big Data 8 Best Data Science Tools and Software . Apache Spark and Hadoop, Microsoft Power BI, Jupyter Notebook and Alteryx are among the top data science tools for finding business insights.
Any multi-objective optimization algorithms are usually introduced by developing a single-objective algorithm. In the current study, a recently developed physics-based algorithm, equilibrium optimizer (EO), is regarded and is extended into a multi-objective algorithm called MOEO. The optimal control problem for cancer treatment is solved using this novel algorithm to confirm its performance ...
Salification is one of the effective methods to solve this problem. This work proposes an efficient method for screening TMP's salts using the conductor-like screening model for real solvents (COSMO-RS) model. 200 commonly compounds were introduced as candidates for screening. ... Theoretical and experimental study of pharmaceutical salts: A ...
Group identification may influence collective behaviors and result in variations in collective performance. However, the evidence for this hypothesis and the neural mechanisms involved remain elusive. To this end, we conducted a study using both single-brain activation and multi-brain synchronization analyses to investigate how group identification influences collective problem-solving in a ...