
7 Superb Symmetry Activities (with a FREEBIE!)
- Freebies , Math , Planning

In the hustle and bustle of the upper elementary classroom, where every moment is precious and every standard is vital, it can be difficult to give every last educational concept the attention it deserves. This is especially true when a concept only has one or two standards addressing it. If it only has one standard in all of upper elementary, then it must not be too important, right?
… Or, maybe, the concept is just SO important that it only needs to be covered once to make a lasting impact on your kiddos! That’s what I’m choosing to believe, anyway, when it comes to symmetry. Maybe it’s my artistic side speaking, but I absolutely LOVE symmetry, and it actually hurts my feelings that this geometry concept doesn’t always get the attention it deserves.
For instance, when conducting my research for this blog post, I noticed a severe lack of educational resources and ideas that align with the Common Core State Standard 4.G.3 : “Recognize a line of symmetry for a two-dimensional figure as a line across the figure such that the figure can be folded along the line into matching parts. Identify line-symmetric figures and draw lines of symmetry.”
It’s obviously important to ensure your kiddos are meeting CCSS, but once that goal is met, symmetry can sometimes fall to the wayside. It’s understandable, since there are simply SO MANY standards to get to, but symmetry really is important in its own right!
Let’s check out why it’s vital to students’ mathematical careers, then we’ll dive into seven symmetry activities that are sure to supplement your geometry lessons… Complete with a FREEBIE at the end!
Why Bother with Symmetry?
It’s not just important to cover symmetry in preparation for testing. Exploring symmetry helps students build fluency in math by reinforcing key concepts like congruence, transformations, and geometric properties. By working through engaging, hands-on symmetry activities and discussions, students develop a stronger understanding of math principles and develop fluency in applying them to new situations.
In addition, building a strong foundation in symmetry also helps students develop spatial reasoning skills, which are super important for understanding tougher geometric concepts and spatial relationships down the line. It’s a great way to help students learn to visualize shapes, identify patterns, and make predictions.
There’s also plenty of symmetry to be found in nature, too! This is certainly a neat way to make real-world connections with your kiddos, but beyond that, it also provides you with a great opportunity for an integrated curriculum with Earth science… Which, as you know, is like, my favorite thing ever . 😉
Okay, I think I’ve made my point. Let’s jump right into the activities!

Seven Symmetry Activities
1. symmetry art swap.
For this activity, you’ll want to provide individuals with graph paper and art supplies. Every student will begin by creating a “line of symmetry,” preferably horizontal or vertical to begin with, through the center of the page. Then, they can create a geometric design of their liking on ONE side of the mirror line. Of course, students should be given free agency with their designs, but you may want to encourage simpler designs to start with to allow kiddos to get the hang of the concept of symmetry.
Once students have created their designs on one side of the mirror line, have them swap their graph paper with a partner. The partner should then try to finish the design on the other side of the symmetry line! Since this is a pretty quick activity, I recommend having students repeat these steps a few more times. They can experiment with more complex designs and even add colors to be mirrored!
It’s not a bad idea either to encourage kiddos to find NEW partners every time, too. You don’t want them sticking to only their best friend—switch it up so everyone gets a diverse experience.
These symmetry art pieces can be shown off in the classroom or even a hallway bulletin board for a cute, easy display. Kiddos love showing off their work, and a splash of color in the halls always does wonders to brighten spirits!
2. Symmetry Manipulatives
Similar to the art swap above, this is another way for students to express their creativity by creating symmetrical designs. This time, though, they can only use manipulatives, such as pattern blocks, tangrams, or other physical geometrical shapes. It’s a bit more challenging than the art swap, since they don’t have complete freedom over the design; rather, they’re bound by the dimensions of the trapezoids and rhombuses and squares!
For this activity, have students sit across from one another and try to replicate one another’s designs using the pattern blocks. They should notice that the design is “mirrored” across a horizontal line of symmetry between them. Kiddos can even take turns making designs and creating a symmetrical version.

3. Symmetry Construction
If someone had told me back at university just how much I’d end up advocating for the use of toothpicks in the classroom, I would never have believed them… But, goodness, there’s no denying their myriad of uses! From fencing in animals to investigating camouflage , toothpicks are practically the backbone of hands-on activities.
And, as you’re sure to see, geometry is no exception! For this activity, have students use toothpicks to create symmetrical shapes. They can connect the toothpicks (or even popsicle sticks, if you prefer) at their endpoints to form geometric shapes, then identify and label the lines of symmetry within their creations—or you can have a partner do that part.
Challenge students to see how many lines of symmetry they can create within one design! Of course, in that case, you may want to ban circles… That might be a little too easy. 😉
4. Symmetry Scavenger Hunt
Listen, I know I recommend scavenger hunts, like, ALL the time, but you can’t blame me: they’re a perfect way to get students up and moving around, keeping them engaged while staying on-task!
For this activity, you’ll encourage kiddos to engage with a geometric scavenger hunt around the classroom, encouraging them to search for symmetrical objects or patterns. If you’d like, you can set out symmetrical pictures or the like ahead of time, but that’s not totally necessary; most classrooms are already chock-full of symmetry if you take the time to look!
Have students record their findings in a notebook or on a piece of paper as they move through the scavenger hunt. They should sketch all of the items they discover that are symmetrical and draw its lines of symmetry—for instance, they could draw the top-down view of a desk and include all of its symmetrical lines.
Once students have had enough time to scan the entire room, reconvene as a class and discuss their findings. Encourage productive discussion by asking questions, such as “Which objects have the most symmetrical lines?” and even deeper critical-thinking questions like “Would the entire classroom be symmetrical if it were mirrored? Why or why not?”
5. Symmetry Nature Walk
What’s this? Another opportunity to integrate curriculum? You got it! Add a helping of Earth science to your geometry unit by bringing students outside to make mathematical observations about nature.
Before heading outside, however, it’s time for a brainstorm sesh. As a class, discuss what kinds of symmetrical objects you may find outside! This is a good way to get students visualizing symmetry, which is a vital step to fully grasping geometry.
Then… Go outside! Just like with the scavenger hunt, have kiddos bring along paper in order to sketch images of the symmetrical objects they find along with their lines of symmetry. Some common examples they may find outside are leaves, flowers, and even insects!

After the adventure, reconvene in the classroom and have students share their findings. Ask more questions, like which objects outside had the most lines of symmetry, if there were any perfectly symmetrical objects (like circles) and so on.
This is a great opportunity for critical thinking, too! What observations can your students make about symmetry in nature? Is it common? Lots of wildlife is symmetrical to some degree, like humans. Why do they think this is? There are no right or wrong answers; the exercise is simply meant to get students thinking and visualizing!
6. Symmetry Stations
Next up, set up several different stations around the room that each center around a type of geometric shape, such as circles and ovals, triangles, parallelograms, and other shapes, like hearts, crosses, arrows, stars, and so on.
Each station should have around five “cards” each that have a different shape relevant to the station’s theme. For example, the triangle station should feature five different triangles of different sizes, each with varying amounts of lines of symmetry.
At each station, students should sketch the shapes on the cards on their own personal graph paper. Then, they can fold their paper to find lines of symmetry! The folding is an important part—not just because it’s hands-on, but also because it ensures that students are fully grasping the concept, specifically as it’s cited in CCSS 4.G.3 : “Recognize a line of symmetry for a two-dimensional figure as a line across the figure such that the figure can be folded along the line into matching parts.”
Students should work together with groups or partners and go through all of the stations until they have “dissected” all of the cards at each center. Then, go over the answers as a class and discuss any questions or thoughts your kiddos may have.
7. Symmetry Assessment Activities
Now that your students have explored the nuances of symmetry, it’s time to check for understanding! Let’s start with a couple informal assessments .
Ticket-out-the-doors are a great method here, as you can simply draw half of a shape on the whiteboard and have students copy that shape onto a piece of scrap paper. Then, they would finish drawing its other side, taking care to keep the shape symmetrical. Once they turn in the paper, you can easily see right off the bat who has grasped the concept and who may still need a bit more help to properly visualize symmetry.
Another informal assessment to use here is Four Corners. Assign each corner of your classroom a number, one through four. This number will represent the lines of symmetry that a shape has. Then, draw a shape on the whiteboard and have students move to whichever corner of the room matches the number of lines of symmetry they think the shape has.
It’s definitely a plus to get students up and moving around, but if you’re pressed for time, no worries! Instead of using Four Corners, you can simply draw the shape on the whiteboard, then have your students raise up the number of fingers that match how many lines of symmetry the shape has.
If you’re finding your kiddos can still use a bit of practice, or if you just want to incorporate some review time, I’ve got you covered: check out this symmetry FREEBIE pulled straight from my fourth grade math workshop geometry unit! Click the pic below or the link above to download the worksheet. And, hey, if you like that, then you can find the full 4th Grade Math Workshop Geometry Unit here !

With this array of ideas to choose from, you and your kiddos are ready to grab your compass, sharpen your pencils, and take off on an adventure of symmetry! Don’t let this math concept just be an addendum to your geometry unit; give symmetry the attention it deserves in your upper elementary classroom.
And, as always, be on the lookout for more engaging, easy-to-implement ideas for your math and science students. While you’re here, sign up for my email list so you won’t miss out!

- freebie , geometry , Math , Strategies
FIND IT NOW!
Check me out on tpt.

CHECK THESE OUT

Three Types of Rocks and Minerals with Rock Cycle Circle Book
Partitioning Shapes Equal Share Fractions Halves, Thirds, Fourths Math Puzzles
Want to save time?
COPYRIGHT © 2016-2024. The Owl Teacher | Privacy page | Disclosure Page | Shipping | Returns/Refunds
BOGO on EVERYTHING!
High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Here you will learn about symmetry, including the definition of symmetry, how to recognize a line of symmetry in 2D shapes, and how to identify line of symmetry in figures.
Students will first learn about symmetry as a part of geometry in 4th grade.
What is symmetry?
Symmetry is when a line is drawn through a shape to make one side of the line a reflection of the other.
Symmetry is a property of 2D and 3D geometrical shapes and objects that divides them into two identical halves that mirror, or are mirror images of each other.
When an imaginary line is drawn through a shape to make one side of the line a true reflection of the other (and vice versa), the shape is known as symmetrical.
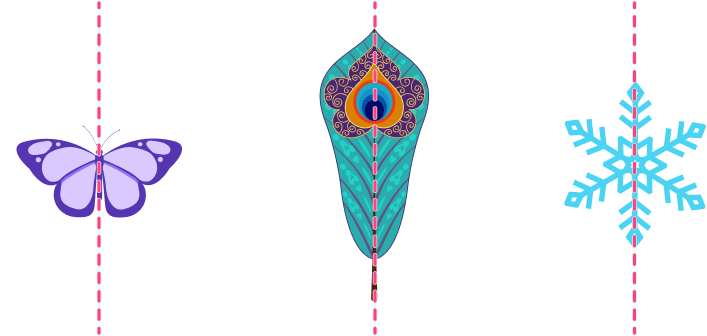
Examples of objects in the real world that are symmetrical include snowflakes, the feathers of peacocks, and the wings of butterflies.
A shape has asymmetry if both sides are not the same when cut in half by an imaginary line. These shapes are called asymmetric.
Examples of objects in the real world that are asymmetrical include trees, some leaves, and the fiddler crab.

Lines of symmetry
An axis of symmetry is an imaginary line that splits a shape or object into two or more identical parts.
This is more commonly referred to as a “line of symmetry.” A line of symmetry is like a fold-line.
Any shape that can be folded down a line to get two matching halves is said to have a line symmetry.
The number of lines of symmetry for a shape can be determined by using a ruler to visualize when the shape or object can be divided equally into 2 equal pieces that are a reflection of each other.
For example,
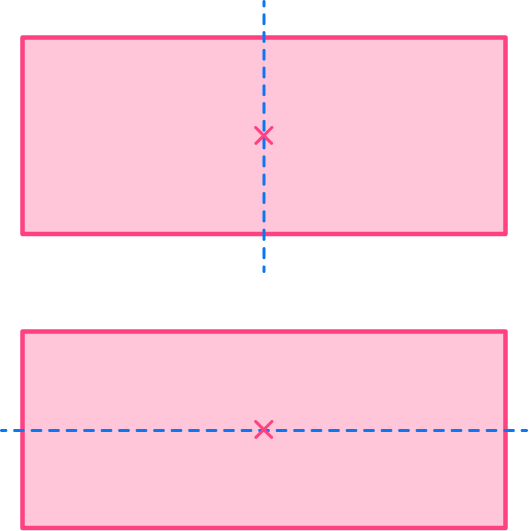
How many lines of symmetry does a rectangle have?
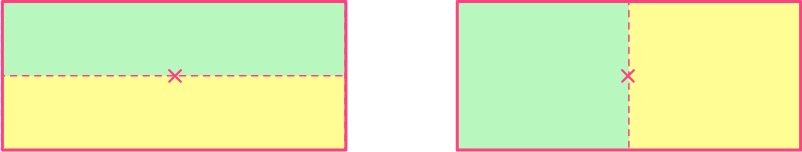
Here, the blue and yellow sections are congruent to each other and are symmetrical to each other.
The number of lines of symmetry for any rectangle (excluding a square, which is a special rectangle), is 2.
Step-by-step guide : Line of symmetry
[FREE] Symmetry Worksheet (Grade 4 to 5)
Use this worksheet to check your grade 4 to 5 students’ understanding of symmetry. 15 questions with answers to identify areas of strength and support!
Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to 4th grade math?
- Grade 4: Geometry (4.G.A.3) Recognize a line of symmetry for a two-dimensional figure as a line across the figure such that the figure can be folded along the line into matching parts. Identify line-symmetric figures and draw lines of symmetry.
How to find symmetry in a 2D shape
In order to draw/identify lines of symmetry you need to:
Locate the center of the 2D shape.
Draw a horizontal and/or vertical line of symmetry through the center of the shape.
Draw a line from each vertex through the center to check for all lines of symmetry.
State the number of lines of symmetry.
Symmetry examples
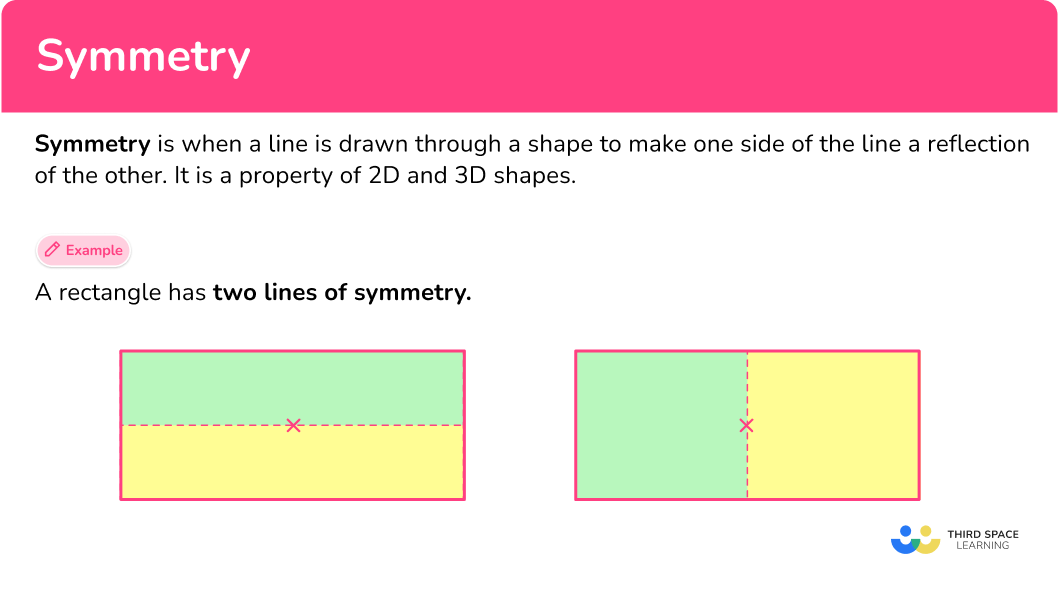
Example 1: a square (lines of symmetry).
Draw all of the lines of symmetry for the square below.

Draw a small x in the center of the square (this does not have to be exact). This is also known as the central point of the shape.

2 Draw a horizontal and/or vertical line of symmetry through the center of the shape.
You can draw a vertical line as this divides the shape into two identical rectangles (one is a reflection of the other), and a horizontal line as this divides the shape into two congruent rectangles that are a reflection of each other.
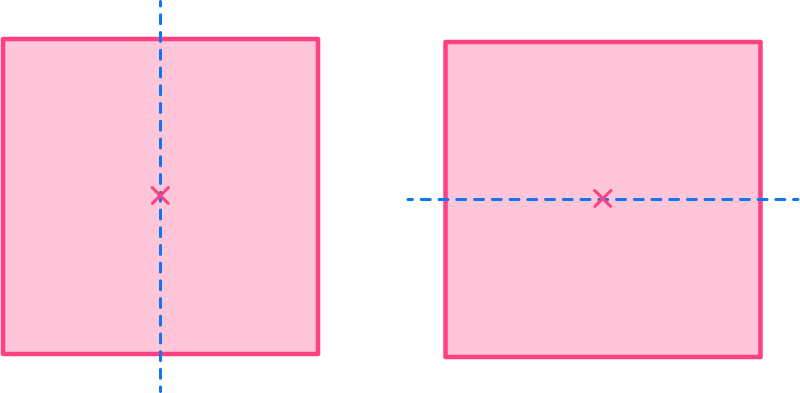
3 Draw a line from each vertex through the center to check for all lines of symmetry.
Because the shape has an even number of vertices, there may be a line of symmetry present diagonally. For the square, you can draw a further two lines of symmetry (along the diagonals of the square).
4 State the number of lines of symmetry.
The square has 4 lines of symmetry.
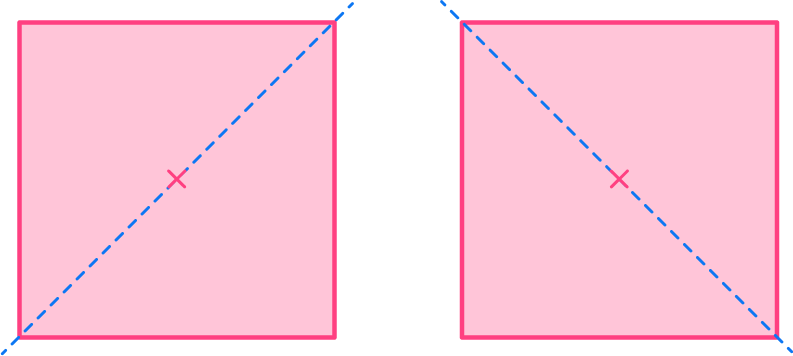
Example 2: a rectangle (lines of symmetry)

You can draw a vertical line as this divides the shape into two identical rectangles and a horizontal line as this divides the shape into two congruent rectangles.
Because the shape has an even number of vertices, there may be a line of symmetry present diagonally. For the rectangle, the diagonal lines do not divide the shape into equal pieces, and are not lines of symmetry.
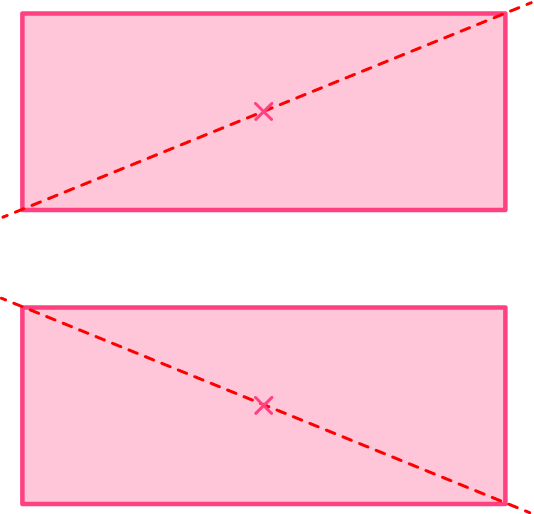
The rectangle has 2 lines of symmetry.
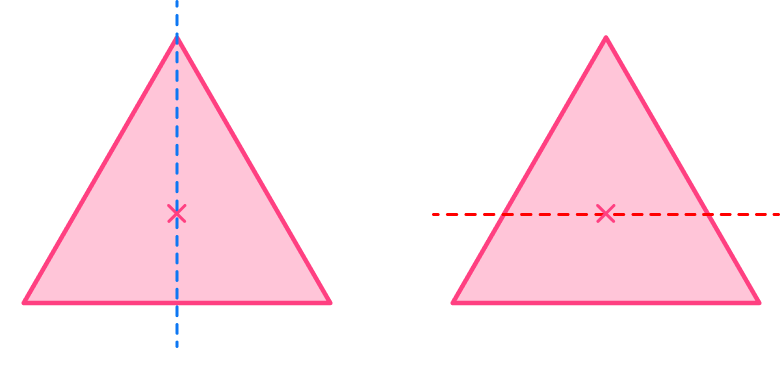
Example 3: an equilateral triangle (lines of symmetry)
You can draw a vertical line as this divides the shape into two identical right triangles. Drawing a horizontal line does not divide the shape into two equal pieces, and is not a line of symmetry.
As you draw lines from each vertex through the center, the equilateral triangle has 2 additional lines of symmetry.
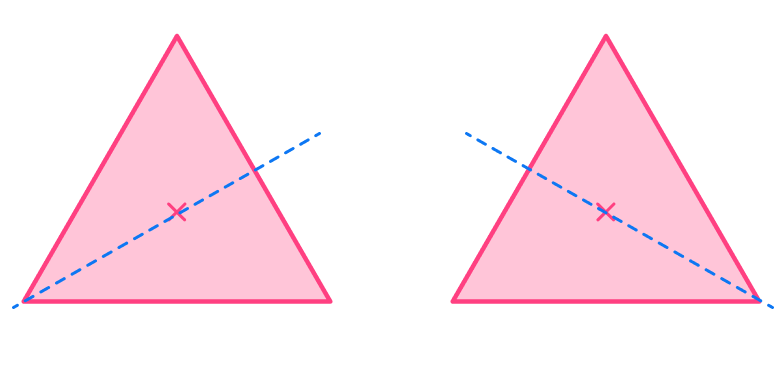
An equilateral triangle has 3 lines of symmetry.
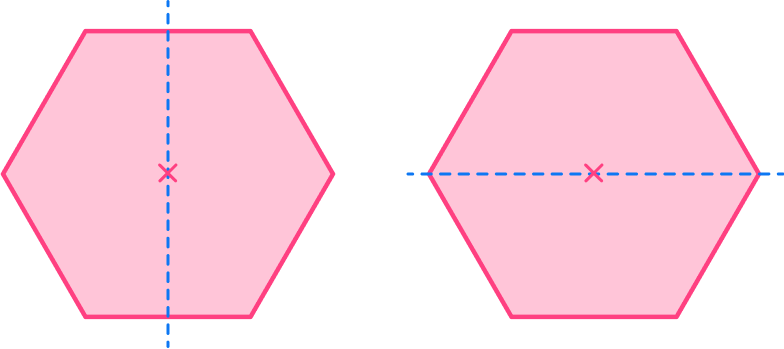
Example 4: a regular hexagon (lines of symmetry)
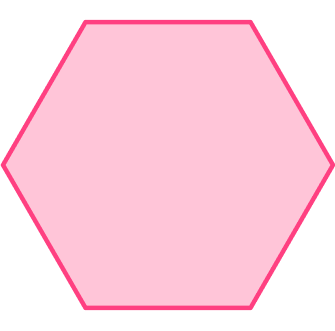
Both the vertical and horizontal lines create equal shapes, and are lines of symmetry.
As you draw lines from each vertex through the center, the regular hexagon has 4 additional lines of symmetry.
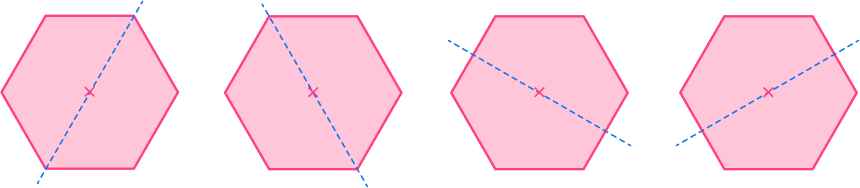
A regular hexagon has 6 lines of symmetry.
Example 5: an isosceles trapezoid (lines of symmetry)

You can draw a vertical line as this divides the isosceles trapezoid into two identical shapes. Drawing a horizontal line does not divide the shape into two equal pieces, and is not a line of symmetry.
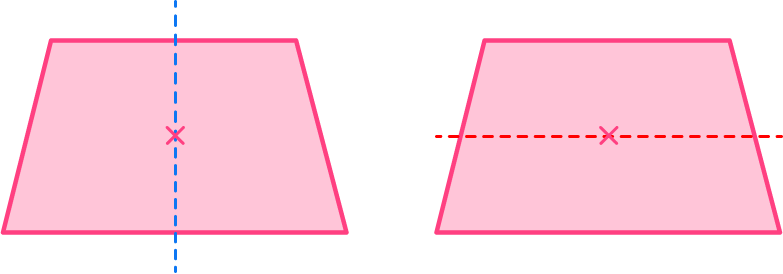
As you draw lines from each vertex through the center, the isosceles trapezoid has no additional lines of symmetry.
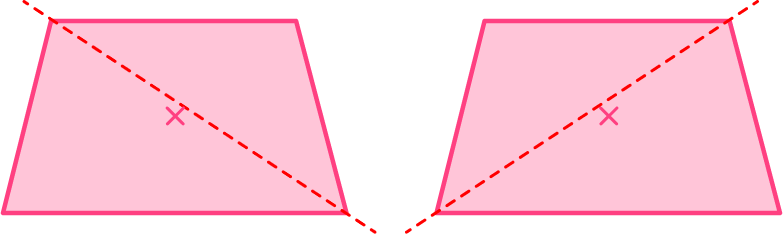
An isosceles trapezoid has 1 line of symmetry.
Example 6: a rhombus (lines of symmetry)
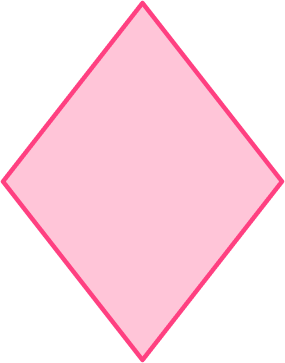
You can draw a vertical line and a horizontal line as this divides the shape into two identical triangles.
The horizontal and vertical lines are from the vertex through the center and there are no additional lines of symmetry.
A rhombus has 2 lines of symmetry.
Teaching tips for symmetry
- Instead of having students draw lines of symmetry on different shapes and objects on a worksheet, consider giving students cut outs and multiple copies of different shapes to allow them to fold and explore the possible lines of symmetry. Encourage them to use the cut outs to fold shapes over the line of symmetry to test for equivalence.
- Give students a group of items (pattern blocks, shape cut outs, classroom materials, etc.) and ask them to make symmetry groups. You do not necessarily even need to tell students what the groups should be exactly, just that they should deal with symmetry. One student may create two groups: symmetrical and asymmetrical and another student may create groups based on the number of lines of symmetry.
Easy mistakes to make
- Thinking the number of sides are equal to the number of lines of symmetry Although this is true for regular shapes, this is not true for all shapes.
Practice symmetry questions
1. Find the number of lines of symmetry for the regular pentagon below.
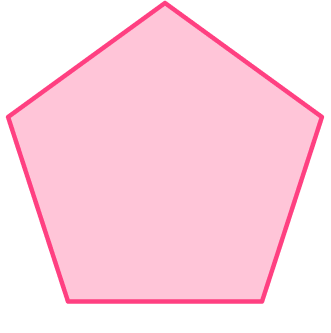
Regular polygons have the same number of lines of symmetry as the number of sides that it has.
A pentagon has 5 sides so it has 5 lines of symmetry.
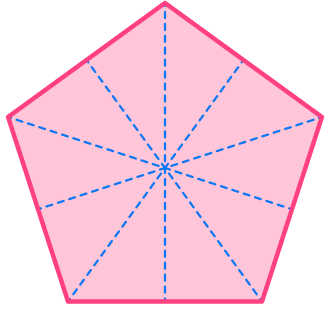
Marking the center, there are 5 lines that can be drawn through the center that cut the regular pentagon into equal halves.
2. Find the number of lines of symmetry for the right triangle below.
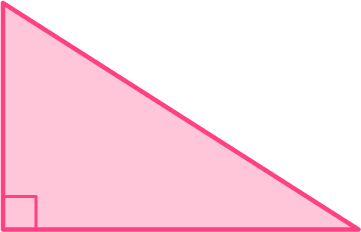
Marking the center of the shape, there are no lines that can be drawn through the center that cut the right triangle into equal halves.
3. Find the number of lines of symmetry for the regular octagon below.

Regular polygons have the same number of lines of symmetry as the number of sides that they have.
An octagon has 8 sides, so it has 8 lines of symmetry.
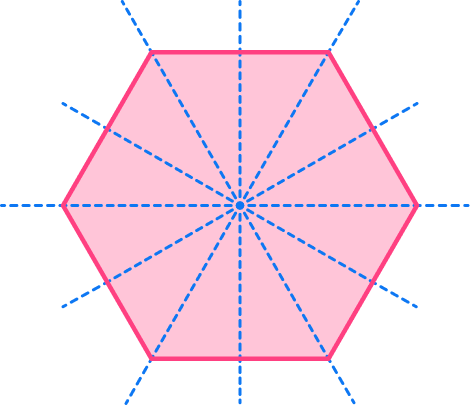
Marking the center, there are 8 lines that can be drawn through the center that cut the regular pentagon into equal halves.
4. Find the number of lines of symmetry for the parallelogram below.

Marking the center of the shape, there are no lines that can be drawn through the center that cut the parallelogram into equal halves.
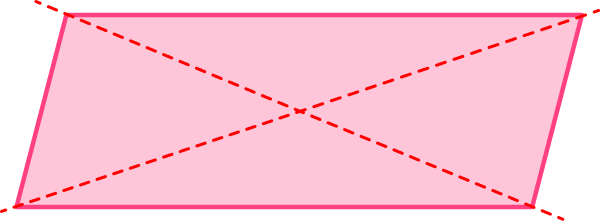
5. Find the number of lines of symmetry for the kite below.
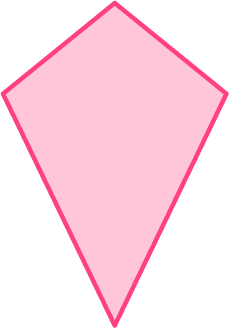
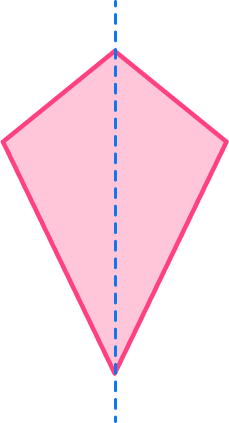
Marking the center of the shape, there is 1 line that can be drawn through the center that cuts the kite into equal halves.
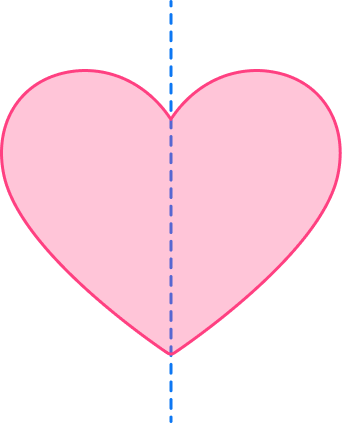
6. Find the number of lines of symmetry for the shape below.

Marking the center of the shape, there is 1 line that can be drawn through the center that cuts the heart into equal halves.
Symmetry FAQs
Yes. As you progress into middle and high school math, you will learn about other types of symmetry, such as rotational symmetry or radial symmetry, bilateral symmetry or the notion of symmetry, reflection symmetry, translational symmetry and mirror symmetry.
This rule works because it is based on geometry theorems (provable mathematical statements). The understanding behind these theorems will be covered in upper grade mathematics.
Yes, the line will always pass through the center of the shape, creating an imaginary line of the shape.
Yes, even if a shape is moved up, down, left, right, etc. as long as the dimensions of the shape do not change, it will have the same lines of symmetry even after the transitions.
The next lessons are
- Angles in polygons
- Congruence and similarity
- Transformations
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs .
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 6)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these Grade 3 to Grade 6 practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
40 multiple choice questions and detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math experts covering a range of topics!
Privacy Overview
- Home |
- About |
- Contact Us |
- Privacy |
- Newsletter |
- Shop |
- 🔍 Search Site
- Easter Color By Number Sheets
- Printable Easter Dot to Dot
- Easter Worksheets for kids
- Kindergarten
- All Generated Sheets
- Place Value Generated Sheets
- Addition Generated Sheets
- Subtraction Generated Sheets
- Multiplication Generated Sheets
- Division Generated Sheets
- Money Generated Sheets
- Negative Numbers Generated Sheets
- Fraction Generated Sheets
- Place Value Zones
- Number Bonds
- Addition & Subtraction
- Times Tables
- Fraction & Percent Zones
- All Calculators
- Fraction Calculators
- Percent calculators
- Area & Volume Calculators
- Age Calculator
- Height Calculator
- Roman Numeral Calculator
- Coloring Pages
- Fun Math Sheets
- Math Puzzles
- Mental Math Sheets
- Online Times Tables
- Online Addition & Subtraction
- Math Grab Packs
- All Math Quizzes
- 1st Grade Quizzes
- 2nd Grade Quizzes
- 3rd Grade Quizzes
- 4th Grade Quizzes
- 5th Grade Quizzes
- 6th Grade Math Quizzes
- Place Value
- Rounding Numbers
- Comparing Numbers
- Number Lines
- Prime Numbers
- Negative Numbers
- Roman Numerals
- Subtraction
- Add & Subtract
- Multiplication
- Fraction Worksheets
- Learning Fractions
- Fraction Printables
- Percent Worksheets & Help
- All Geometry
- 2d Shapes Worksheets
- 3d Shapes Worksheets
- Shape Properties
- Geometry Cheat Sheets
- Printable Shapes
- Coordinates
- Measurement
- Math Conversion
- Statistics Worksheets
- Bar Graph Worksheets
- Venn Diagrams
- All Word Problems
- Finding all possibilities
- Logic Problems
- Ratio Word Problems
- All UK Maths Sheets
- Year 1 Maths Worksheets
- Year 2 Maths Worksheets
- Year 3 Maths Worksheets
- Year 4 Maths Worksheets
- Year 5 Maths Worksheets
- Year 6 Maths Worksheets
- All AU Maths Sheets
- Kindergarten Maths Australia
- Year 1 Maths Australia
- Year 2 Maths Australia
- Year 3 Maths Australia
- Year 4 Maths Australia
- Year 5 Maths Australia
- Meet the Sallies
- Certificates
Symmetry Activities Line Symmetry Harder
Welcome to the Math Salamanders Symmetry Activity page. Here you will find a range of free printable symmetry worksheets, which will help your child to practice their reflecting and flipping skills.
For full functionality of this site it is necessary to enable JavaScript.
Here are the instructions how to enable JavaScript in your web browser .
Symmetry Help
The Math Salamanders have a large bank of free printable symmetry worksheets. Each symmetry sheet comes complete with answers for support.
Handy Hints
Each point or block that has been reflected must remain the same distance from the mirror line as the original point. So if point A is 3 squares away from the mirror line, then the reflection of point A must also be 3 squares away.
When reflecting a shape, look at the corners of the shape and reflect each corner first as a dot in the mirror line. The dots can then be joined up (in the correct order!)
For lines of symmetry at angles of 45°, it is often better to rotate your paper so that the line of symmetry is vertical or horizontal, and the rest of the paper is at an angle.
The basis and understanding of symmetry starts at about Grade 2, and then develops further in Grades 3,4 and 5.
Symmetry Activities
On this webpage you will find our range of symmetry activity sheets for kids.
The sheets have been graded with the easier sheets coming first. The first set of worksheets involve only horizontal and vertical lines only. The next set involve reflecting patterns with two mirror lines.
There are also some templates at the end of this section for you to create your own shapes for your child to reflect, or, even better, for your child to create their own symmetric patterns!
- learn to reflect a more complex shape in a vertical or horizontal mirror line;
- learn to reflect a more complex shape in both a vertical and horizontal mirror line;
Folding and Cutting
- Symmetry Activities Fold it, Cut it, Make it
- Fold it, Cut it, Make it Answers
- PDF version
Reflecting in 1 mirror line
- Symmetry sheet - Rocket
- Rocket Answer Sheet
- Symmetry Sheet Castle
- Castle Answer sheet
- Symmetry worksheet Butterfly
- Butterfly Answer sheet
- Symmetry Worksheet Balloon 1
- Balloon Answer sheet
- Symmetry Worksheet Balloon 2
- Balloon 2 Answers
- Line Symmetry Building 1
- Line Symmetry Building 2
- Line Symmetry Building 3
Reflecting in 2 mirror lines
- Symmetry sheet Cracker
- Cracker Answer sheet
- Symmetry sheet Flower
- Flower Answer sheet
- Symmetry worksheets Bird
- Bird Answer sheet
Line Symmetry templates
- Line Symmetry Template 1
- Line Symmetry Template 2
- Line Symmetry Template 3
- Line Symmetry Template 4
- Line Symmetry Template 5
- Line Symmetry Template 6

Looking for something easier?
Here you will find a range of line symmetry sheets with one or two mirror lines.
The sheets in this section are similar to those on this page, but are less complicated and at an easier level.
- Symmetry Worksheets - Line Symmetry
More Recommended Math Worksheets
Take a look at some more of our worksheets similar to these.
Block Symmetry Worksheets
Here you will find a range of symmetry worksheets reflecting blocks instead of lines.
These sheets are at a much easier level than the ones on this page.
- Symmetry Worksheets - Block Symmetry
Coordinate Sheets
Here is our collection of printable coordinate plane grids and coordinate worksheets.
Using these fun coordinate sheets is a great way to learn math in an enjoyable way.
Using these sheets will help your child to:
- plot and write coordinates.
- Coordinate Plane Grid templates
- Coordinate Worksheets (1st Quadrant)
- Coordinate Plane Worksheets (All 4 Quadrants)
Geometry Riddles
Here you will find our free printable geometry riddles from 1st to 5th grade.
These riddles are all about problem solving with 2d shapes.
Using these riddles will help your child to:
- develop their geometry skills;
- develop their understanding of geometric language;
- apply their geometric knowledge to solve problems.
All the geometry riddles in this section support elementary math benchmarks.
- Geometry Worksheets (Riddles)
How to Print or Save these sheets 🖶
Need help with printing or saving? Follow these 3 steps to get your worksheets printed perfectly!
- How to Print support
Subscribe to Math Salamanders News
Sign up for our newsletter to get free math support delivered to your inbox each month. Plus, get a seasonal math grab pack included for free!

- Newsletter Signup
Return to Geometry Section
Return from Symmetry Activities to Math Salamanders Homepage
Math-Salamanders.com
The Math Salamanders hope you enjoy using these free printable Math worksheets and all our other Math games and resources.
We welcome any comments about our site or worksheets on the Facebook comments box at the bottom of every page.
New! Comments
TOP OF PAGE
© 2010-2024 Math Salamanders Limited. All Rights Reserved.
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Policy
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
Engage your learners in a unique experience with our Codes and Ciphers Fun Pack! Click here
- Homeschooling
- Member Log In
- Search this website
Gift of Curiosity
Sparking children's creativity and learning
Hands-on symmetry activities for kids
Preschool , Kindergarten , 1st Grade , 2nd Grade , 3rd Grade , 4th Grade , 5th Grade
Sharing is caring - thank you for spreading the word!
This post may contain affiliate ads at no cost to you. See my disclosures for more information.
A couple of days ago I released my Basic Symmetry Activity Pack with more than 40 hands-on learning ideas for teaching kids about reflection symmetry.
Today I’m sharing more hands-on symmetry activities for kids using manipulative materials.
Note: For more hands-on math activities and printables, see my Math Activities for Kids page.

Reflection symmetry is the quality of having identical, facing parts. Thus, a symmetrical object can be divided into parts that are mirror images of each other.
One goal when teaching symmetry is to help children see symmetry in images and real-world objects. This can be done by having children create symmetrical designs and by having them find the line of symmetry in real objects.
I sat down with my son one day to do some hands-on symmetry activities using parts from our Spielgaben set .

Create symmetrical designs
Symmetry is an important concept in art. Artists play with symmetry in various ways to affect the look and feel of their work. Creating symmetrical designs allows children to play with symmetry and art together.
I built a line down the middle of a grid using long, black sticks. I then placed two shapes on one side of the line and challenged my son to build the reflection.
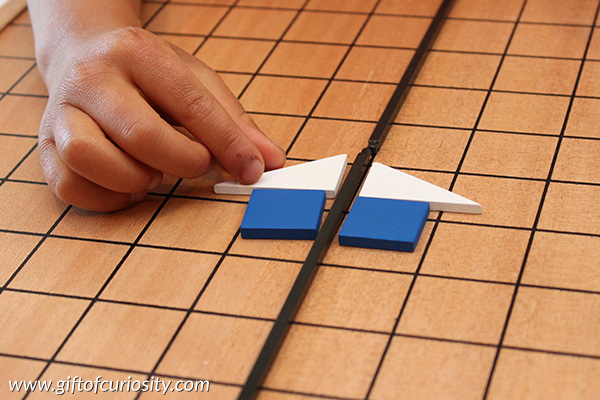

We kept adding more shapes to our design.
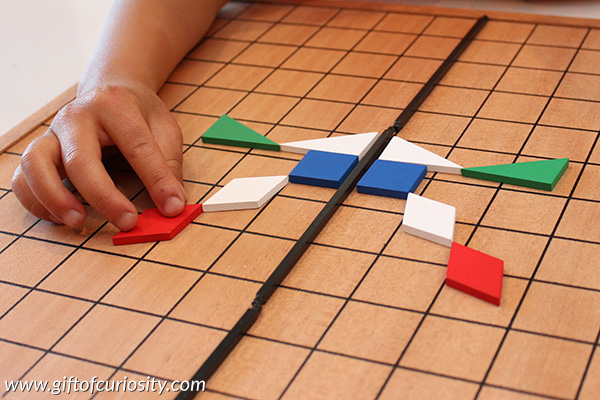
And we added some more. He was able to build the symmetrical reflection with ease, but other kids may need some support if they are just learning this concept or if they struggle with spatial awareness.
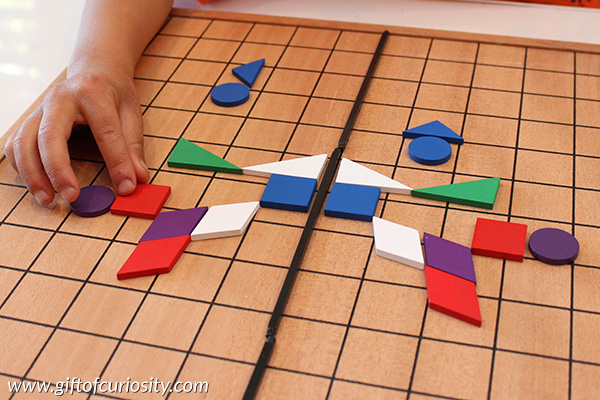
After building symmetrical reflections, we tried something else.
Finding the line of symmetry in 3-D objects
Another great skill for children is to be able to find the line of symmetry in both 2-D and 3-D objects. There are a number of great activities for finding the line of symmetry in 2-D objects in my Basic Symmetry Activity Pack .
In this activity, however, my son worked on finding lines of symmetry in 3-D objects.
I handed my son a cube and some rubber bands, and I asked him to use a rubber band to indicate the line of symmetry on the cube.
He found the first line easily.
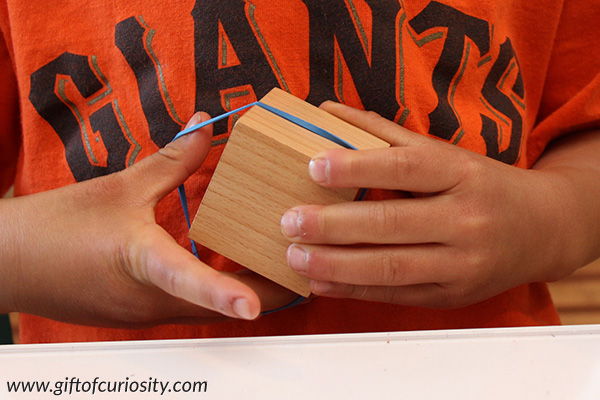

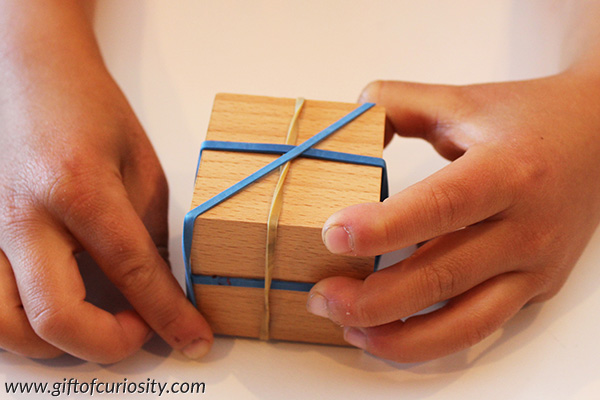
But I challenged him to find more lines of symmetry on the cube.
It took him a bit of time to find the diagonal lines of symmetry, but he did it.

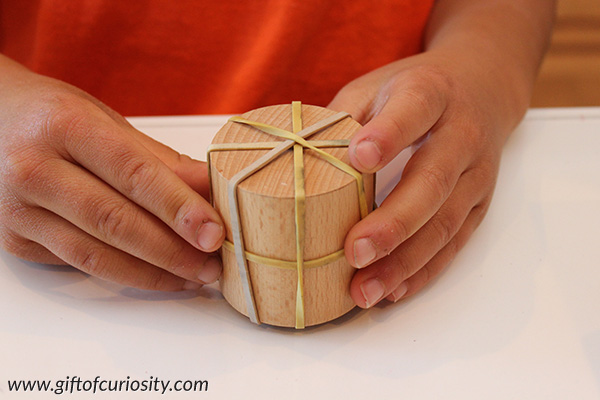
Then I handed him a cylinder and again I asked him to mark the lines of symmetry with rubber bands.
He found one line of symmetry around the circumference of the barrel. And then he found lots of lines of symmetry on the vertical plane.
Fun fact: A cylinder has an infinite number of lines of symmetry.

If you enjoy these activities, you’ll also enjoy my Basic Symmetry Activity Pack with more than 40 hands-on learning ideas for teaching kids about reflection symmetry or my Advanced Symmetry Activity Pack with 20+ hands-on activities for teaching kids about rotational symmetry.
More resources for teaching math
More math activities from Gift of Curiosity:
- Basic Symmetry Activity Pack
- Building a 3D rainbow measurement activity
- Adding with chain links
- Teaching combinations of 10
- Introduction to probability
- Math practice with numbered dice
- Put the numbers on the clothesline
- Road numbers
For more activities, resources, and printables for teaching math, see my Math Activities for Kids page and my Math Pinterest board .
You May Also Enjoy These Posts
- My Storyboards
Symmetry Worksheets
Customize symmetry worksheets.
If you're assigning this to your students, copy the worksheet to your account and save. When creating an assignment, just select it as a template!
What are Symmetry Worksheets?
They are educational materials designed to help students explore and understand the concept of symmetry in mathematics. These worksheet activities are commonly used in various grade levels to teach students about the principles and how to identify symmetrical patterns and shapes.
Symmetry refers to a balanced and harmonious arrangement of elements on both sides of a central axis or line. In the context of mathematics, it often involves recognizing and analyzing objects or shapes that can be divided into two equal halves along a specific line, known as the line of symmetry. These worksheet lessons aim to develop students' abilities to identify, create, and analyze symmetrical patterns.
Types of Symmetry Worksheets
- Rotational Symmetry Worksheets: Rotational symmetry is where an object can be rotated by a certain angle and still appear unchanged. These activities can include any shape sure as circles, stars, and polygons. Students are encouraged to identify the angle of rotation that preserves the object's appearance. They may also be tasked with drawing a shape that exhibits rotational symmetry, along with the corresponding rotation angles.
- Reflective Symmetry Worksheet: Reflective or mirror symmetry, is perhaps the most intuitive form. It involves a line called the axis of symmetry, which divides an object into two identical halves. These worksheet lessons challenge students to identify and draw lines of symmetry for various shapes. They may need to complete one half of an object to create a symmetrical or mirror image on the other side. This type is frequently explored in worksheet activities featuring geometric figures, letters, and more.
- Translational Symmetry Worksheet: This occurs when an object can be shifted or translated along a particular direction without changing its appearance. While less common in basic worksheet practice pages, it is an essential concept in advanced mathematics. Worksheet activities dealing with translational might involve tessellations, repeating patterns, or designs where students must identify the translation vectors needed to match corresponding elements.
These different types of symmetrical worksheets offer diverse learning opportunities. They help students develop essential spatial reasoning skills, problem-solving abilities, and a deeper understanding of mathematical principles. By working with rotational, reflective, and translational symmetry worksheet activities, students can explore the captivating world of of this concept and its applications in various fields.
Worksheets by Grade Level
Symmetry is a fundamental concept in mathematics that spans across different grade levels. It's a topic that offers valuable learning opportunities, from the early years of kindergarten to the advanced stages of high school. In this section, we'll explore how these worksheet pages can be tailored to suit students of various grade levels, ensuring that the content aligns with their learning objectives and capabilities.
- Kindergarten: For our youngest learners, symmetry worksheet pages for kindergarten serve as an introduction to this intriguing mathematical concept. These free worksheet pages often feature simple and visually engaging exercises. Children may be asked to identify and color a symmetrical shape or draw the other half of a picture over dotted lines using our symmetry drawing worksheet activities or coloring worksheet activities.
- Elementary School: As students progress into elementary school, they start delving deeper into symmetry. Symmetrical worksheets at this level may focus on identifying the axis of symmetry in various shapes, from basic geometric figures to more complex patterns. They might also involve drawing a line of symmetry for given objects, fostering an understanding of reflective symmetry.
- Middle School: In the intermediate grades, these worksheet activities become more intricate. Students are encouraged to draw their own symmetrical shapes or designs. These worksheet lessons promote creativity and a deeper grasp of the artistic and mathematical aspects. The emphasis here is on freehand symmetry drawing and exploring in nature and art, such as an animal symmetry worksheet.
- High School (Symmetry Exercises in Geometry): In high school, students dive into advanced mathematical concepts related to this topic. Worksheet activities for older students might involve working with equations and algebraic expressions. They can also explore rotational symmetry, translating shapes, and more complex geometrical patterns.
More Storyboard That Resources and Free Printables
As students progress in their understanding of this topic, they can explore more complex concepts and applications. Activities like a polygon sorting activity can challenge students’ ability to identify and categorize shapes based on their symmetrical properties. Moreover, understanding symmetry is essential when dealing with composite shapes in the world , as it helps students dissect and analyze these intricate structures. To assist in comparing and contrasting different elements, teachers can turn to our comparison chart templates . Additionally, recognizing symmetrical patterns and symbols is crucial, and our symbols pdf worksheets can easily be integrated into any math lesson plan.
How to Make a Symmetry Worksheet
Choose one of the premade templates.
We have lots of templates to choose from. Take a look at our example for inspiration!
Click on "Copy Template"
Once you do this, you will be directed to the storyboard creator.
Give Your Worksheet a Name!
Be sure to call it something related to the topic so that you can easily find it in the future.
Edit Your Worksheet
This is where you will include directions, specific images, and make any aesthetic changes that you would like. The options are endless!
Click "Save and Exit"
When you are finished, click this button in the lower right hand corner to exit your storyboard.
From here you can print, download as a PDF, attach it to an assignment and use it digitally, and more!
Happy Creating!
Frequently Asked Questions about Symmetry Worksheets
What are different kinds of symmetry worksheets for kindergarten.
Symmetry worksheets for kindergarten are educational materials designed to introduce young learners to the concept of symmetry. These printable worksheets typically feature exercises where children can complete symmetrical shapes, identify lines of symmetry, draw a line of symmetry, and color symmetrical designs. Animal symmetry worksheets would be a really engaging way to introduce this concept!
How do reflective symmetry worksheets work?
Reflective symmetry worksheets are tools that help students grasp the concept of reflective or mirror symmetry. Symmetry drawing worksheets often include activities where learners draw lines of symmetry to complete a design, download printable worksheets, and work on completing the second half of a symmetrical image.
Do symmetry worksheets cover different levels of difficulty?
Yes, symmetry worksheets are available in varying levels of difficulty, from kindergarten to advanced levels. Whether you're introducing symmetry shapes to young children, or teaching more complex reflective symmetry, you can find worksheets suitable for your needs.
Try 1 Month For
30 Day Money Back Guarantee New Customers Only Full Price After Introductory Offer
Learn more about our Department, School, and District packages

- Thousands of images
- Custom layouts, scenes, characters
- And so much more!!
Create a Storyboard
Symmetric Explanation Learning: Effective Dynamic Symmetry Handling for SAT
- Conference paper
- First Online: 09 August 2017
- Cite this conference paper

- Jo Devriendt 15 ,
- Bart Bogaerts 15 &
- Maurice Bruynooghe 15
Part of the book series: Lecture Notes in Computer Science ((LNTCS,volume 10491))
Included in the following conference series:
- International Conference on Theory and Applications of Satisfiability Testing
1289 Accesses
9 Citations
The presence of symmetry in Boolean satisfiability (SAT) problem instances often poses challenges to solvers. Currently, the most effective approach to handle symmetry is by static symmetry breaking , which generates asymmetric constraints to add to the instance. An alternative way is to handle symmetry dynamically during solving. As modern SAT solvers can be viewed as propositional proof generators, adding a symmetry rule in a solver’s proof system would be a straightforward technique to handle symmetry dynamically. However, none of these proposed symmetrical learning techniques are competitive to static symmetry breaking. In this paper, we present symmetric explanation learning , a form of symmetrical learning based on learning symmetric images of explanation clauses for unit propagations performed during search. A key idea is that these symmetric clauses are only learned when they would restrict the current search state, i.e., when they are unit or conflicting. We further provide a theoretical discussion on symmetric explanation learning and a working implementation in a state-of-the-art SAT solver. We also present extensive experimental results indicating that symmetric explanation learning is the first symmetrical learning scheme competitive with static symmetry breaking.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Backjumping is a generalization of the more classical backtracking over choices in combinatorial solvers.
SP focuses its presentation on propagating symmetrical literals \(\pi (l)\) for weakly active symmetries, hence the name symmetry propagation . We present SP from a symmetrical learning point of view, using the fact that SP employs \(\pi (\mathcal {E} (l))\) as a valid explanation clause for \(\pi (l)\) ’s propagation.
bitbucket.org/krr/sat_symmetry_experiments .
For the few instances where the chromatic number was not known, we made an educated guess based on the graph’s name.
Aloul, F., Ramani, A., Markov, I., Sakallah, K.: Solving difficult SAT instances in the presence of symmetry. In: 39th Design Automation Conference, 2002 Proceedings, pp. 731–736 (2002)
Google Scholar
Aloul, F.A., Ramani, A., Markov, I.L., Sakallah, K.A.: Dynamic symmetry-breaking for boolean satisfiability. Ann. Math. Artif. Intell. 57 (1), 59–73 (2009)
Article MathSciNet MATH Google Scholar
Aloul, F.A., Sakallah, K.A., Markov, I.L.: Efficient symmetry breaking for boolean satisfiability. IEEE Trans. Comput. 55 (5), 549–558 (2006)
Article Google Scholar
Audemard, G., Simon, L.: Predicting learnt clauses quality in modern SAT solvers. In: Boutilier, C. (ed.) IJCAI, pp. 399–404 (2009)
Benhamou, B., Nabhani, T., Ostrowski, R., Saïdi, M.R.: Dynamic symmetry breaking in the satisfiability problem. In: Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Logic for Programming, Artificial Intelligence, and Reasoning, LPAR-16, Dakar, Senegal, 25 April –1 May 2010
Benhamou, B., Nabhani, T., Ostrowski, R., Saïdi, M.R.: Enhancing clause learning by symmetry in SAT solvers. In: Proceedings of the 2010 22nd IEEE International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence, ICTAI 2010, vol. 01, pp. 329–335 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/ICTAI.2010.55
Benhamou, B., Saïs, L.: Tractability through symmetries in propositional calculus. J. Autom. Reason. 12 (1), 89–102 (1994). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF00881844
Biere, A.: Preprocessing and inprocessing techniques in SAT. In: Eder, K., Lourenço, J., Shehory, O. (eds.) HVC 2011. LNCS, vol. 7261, p. 1. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-34188-5_1
Chapter Google Scholar
Birnbaum, E., Lozinskii, E.L.: The good old Davis-Putnam procedure helps counting models. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 10 , 457–477 (1999)
MathSciNet MATH Google Scholar
Crawford, J.M., Ginsberg, M.L., Luks, E.M., Roy, A.: Symmetry-breaking predicates for search problems. In: Principles of Knowledge Representation and Reasoning, pp. 148–159. Morgan Kaufmann (1996)
Devriendt, J.: Binaries, experimental results and benchmark instances for “symmetric explanation learning: effective dynamic symmetry handling for SAT”. bitbucket.org/krr/sat_symmetry_experiments
Devriendt, J.: An implementation of symmetric explanation learning in Glucose on Bitbucket. bitbucket.org/krr/glucose-sel
Devriendt, J.: An implementation of symmetry propagation in MiniSat on Github. github.com/JoD/minisat-SPFS
Devriendt, J., Bogaerts, B., Bruynooghe, M., Denecker, M.: Improved static symmetry breaking for SAT. In: Creignou, N., Le Berre, D. (eds.) SAT 2016. LNCS, vol. 9710, pp. 104–122. Springer, Cham (2016). doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-40970-2_8
Devriendt, J., Bogaerts, B., De Cat, B., Denecker, M., Mears, C.: Symmetry propagation: improved dynamic symmetry breaking in SAT. In: IEEE 24th International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence, ICTAI 2012, Athens, Greece, pp. 49–56. IEEE Computer Society, 7–9 November 2012. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/ICTAI.2012.16
Eén, N., Biere, A.: Effective preprocessing in SAT through variable and clause elimination. In: Bacchus, F., Walsh, T. (eds.) SAT 2005. LNCS, vol. 3569, pp. 61–75. Springer, Heidelberg (2005). doi: 10.1007/11499107_5
Eén, N., Sörensson, N.: An extensible SAT-solver. In: Giunchiglia, E., Tacchella, A. (eds.) SAT 2003. LNCS, vol. 2919, pp. 502–518. Springer, Heidelberg (2004). doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-24605-3_37
Gent, I.P., Smith, B.M.: Symmetry breaking in constraint programming. In: Proceedings of ECAI-2000, pp. 599–603. IOS Press (2000)
Haken, A.: The intractability of resolution. Theor. Comput. Sci. 39 , 297–308 (1985). Third Conference on Foundations of Software Technology and Theoretical Computer Science. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0304397585901446
Heule, M., Keur, A., Maaren, H.V., Stevens, C., Voortman, M.: CNF symmetry breaking options in conflict driven SAT solving (2005)
Junttila, T., Kaski, P.: Engineering an efficient canonical labeling tool for large and sparse graphs. In: Applegate, D., Brodal, G.S., Panario, D., Sedgewick, R. (eds.) Proceedings of the Ninth Workshop on Algorithm Engineering and Experiments and the Fourth Workshop on Analytic Algorithms and Combinatorics, pp. 135–149. SIAM (2007)
Katebi, H., Sakallah, K.A., Markov, I.L.: Symmetry and satisfiability: an update. In: Strichman, O., Szeider, S. (eds.) SAT 2010. LNCS, vol. 6175, pp. 113–127. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-14186-7_11
Krishnamurthy, B.: Short proofs for tricky formulas. Acta Inf. 22 (3), 253–275 (1985). http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=4336.4338
Marques-Silva, J.P., Sakallah, K.A.: GRASP: a search algorithm for propositional satisfiability. IEEE Trans. Comput. 48 (5), 506–521 (1999)
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
McKay, B.D., Piperno, A.: Practical graph isomorphism, II. J. Symbolic Comput. 60 , 94–112 (2014). http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0747717113001193
Mears, C., García de la Banda, M., Demoen, B., Wallace, M.: Lightweight dynamic symmetry breaking. Constraints 19 (3), 195–242 (2014). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10601-013-9154-2
Moskewicz, M., Madigan, C., Zhao, Y., Zhang, L., Malik, S.: Chaff: engineering an efficient SAT solver. In: DAC 2001, pp. 530–535. ACM (2001)
Pipatsrisawat, K., Darwiche, A.: On the power of clause-learning SAT solvers as resolution engines. Artif. Intell. 175 (2), 512–525 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.artint.2010.10.002
Sabharwal, A.: SymChaff: exploiting symmetry in a structure-aware satisfiability solver. Constraints 14 (4), 478–505 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10601-008-9060-1
Schaafsma, B., van Heule, M.J.H., Maaren, H.: Dynamic symmetry breaking by simulating zykov contraction. In: Kullmann, O. (ed.) SAT 2009. LNCS, vol. 5584, pp. 223–236. Springer, Heidelberg (2009). doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-02777-2_22
Sörensson, N., Eén, N.: MiniSat v1.13 - a Sat solver with conflict-clause minimization. 2005. sat-2005 poster. Technical report (2005)
Trick, M.: Network resources for coloring a graph (1994). mat.gsia.cmu.edu/COLOR/color.html
Walsh, T.: Symmetry breaking constraints: Recent results. CoRR abs/1204.3348 (2012)
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Computer Science, KU Leuven, Celestijnenlaan 200A, 3001, Heverlee, Belgium
Jo Devriendt, Bart Bogaerts & Maurice Bruynooghe
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Jo Devriendt or Bart Bogaerts .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
UNSW Sydney, Sydney, New South Wales, Australia
Serge Gaspers
University of New South Wales , Sydney, New South Wales, Australia
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper.
Devriendt, J., Bogaerts, B., Bruynooghe, M. (2017). Symmetric Explanation Learning: Effective Dynamic Symmetry Handling for SAT. In: Gaspers, S., Walsh, T. (eds) Theory and Applications of Satisfiability Testing – SAT 2017. SAT 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10491. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-66263-3_6
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-66263-3_6
Published : 09 August 2017
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-66262-6
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-66263-3
eBook Packages : Computer Science Computer Science (R0)
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

Workgroup 2: Symmetry and Assigning Point Groups
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 62456
- Delmar Larsen
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Name: ______________________________
Section: _____________________________
Student ID#:__________________________
Separate into groups of five-eight students and answer the following questions. You will be graded primarily on effort, not accuracy (although if all questions are incorrect, then the effort is clearly missing). It is OK to use external resources such as textbooks and websites. It is not ok to copy word-for-word the solution. Each group must come up with their answers collectively and without plagiarism of existing resources.
The symmetry properties of objects (and molecules) may be described in terms of the presence of certain symmetry elements and their associated symmetry operations. Each molecule has a set of symmetry operations that describes the molecule's overall symmetry. This set of operations define the point group of the molecule. The process used to assign a molecule to a point group is straightforward with a few exceptions and follows three major steps:
- Identify the geometry of the typically with the standard VSEPR approach learned in General Chemistry
- Identify the symmetry elements of the molecule in that geometry
- Follow the flowchart below to determine flow chart (often step 2 can be done via step 3).
Here are set of steps to quickly guide you (with flowchart).
- Look at the molecule and see if it seems to be very symmetric or very unsymmetric. If so, it probably belongs to one of the special groups ( low symmetry: \(C_1\), \(C_s\), \(C_i\) or linear \(C_{∞v}\), \(D_{∞h}\)) or high symmetry (\(T_d\), \(O_h\), \(I_h\)..).
- For all other molecules find the rotation axis with the highest n, the highest order \(C_n\) axis of the molecule.
- Does the molecule have any \(C_2\) axes perpendicular to the \(C_n\) axis? If it does, there will be n of such \(C_2\) axes, and the molecule is in one of D point groups. If not, it will be in one of \(C\) or \(S\) point groups.
- Does it have any mirror plane (\(σ_h\)) perpendicular to the \(C_n\) axis? If so, it is \(C_{nh}\) or \(D_{nh}\).
- Does it have any mirror plane (\(σ_d\), \(σ_v\))? If so, it is \(C_{nv}\) or \(D_{nd}\).
Below is the standard flow chart that graphical displays the above steps to assign point groups
Draw sketches to identify the following symmetry elements:
- a \(C_3\) axis and a \(σ_v\) plane in the \(NH_3\) molecule;
- a \(C_4\) axis and a \(σ_h\) plane in the square planar \([PtCl_4]^{2–}\) ion
For each of the following molecules and ions, identify if it has a center of inversion (i) and/or a \(S_4\) axis and indicate either on a plot of the molecule:
- \(C_2H_2 \;(acetylene)\)
- \(SO_4^{2–}\)
If you have a computer available, go to Otterbein's symmetry website (symmetry.otterbein.edu/challenge/index.html) and click on ammonia (half way down the left "molecule" list. Proceed through the flowchart shown question by question on the right side to identify the point group. If computer is not available, then use the flowchart above.
What is the definition of a polar molecule? Use examples of polar molecules to identify if a polar molecule has one or more of the primary symmetry elements:
- a proper rotation axis
- a center of inversion
- an improper rotational axis
- a mirror plane
In terms of point groups, only molecules that are polar are those in the \(C_n\), \(C_{nv}\), and \(C_s\) point groups.
What is the definition of a chiral molecule? Use examples of chiral molecules to identify if a chiral molecule has one or more of the primary symmetry elements:
In terms of point groups, the only chiral point groups are \(C_n\) and \(D_n\). Can a molecule be both polar and chiral?
Determine the symmetry elements and assign the point group of the following molecules. Also indicate if the molecule is polar and if the molecule chiral.
- Classify these nine atomic orbitals by their symmetry under inversion, that is, by their change in a center of symmetry. Which of these atomic orbitals are even (do not change sign) and which are odd (do change sign) under inversion?
- B. Consider a py atomic orbital on one nuclear center A and one of the five d atomic orbitals on another nuclear center B. Let the nuclear centers A and B be placed on the x axis with A on the left and B on the right. As A and B approach, molecular orbitals can be formed from the two atomic orbitals if these two atomic orbitals have the same symmetry with respect tot he internuclear axis. With which atomic d orbital on B is there a nonzero (noncancelling) overlap with the atomic py orbital on A?
- Draw pictures of the bonding and anitbonding molecular orbitals that result from this linear combination of atomic orbitals.
- Classify the resulting molecular orbital as to its symmetry with respect to the internuclear axis.

COMMENTS
equilateral triangle. How can a regular hexagon be folded to show that it has reflectional symmetry? Fold the hexagon along a line that creates a right angle at a vertex. What is the order of rotational symmetry for a rhombus? 2. How many lines of reflectional symmetry does an equilateral triangle have? 3.
What is the order of rotational symmetry for the parallelogram? 2. The regular nonagon has rotational symmetry of which angle measures? Check all that apply. 40°. 120°. 240°. 320°. Which polygon will always have 4-fold reflectional symmetry and order 4 rotational symmetry?
1. Symmetry Art Swap. For this activity, you'll want to provide individuals with graph paper and art supplies. Every student will begin by creating a "line of symmetry," preferably horizontal or vertical to begin with, through the center of the page. Then, they can create a geometric design of their liking on ONE side of the mirror line.
Example 2: a rectangle (lines of symmetry) Locate the center of the 2D shape. Show step. Draw a small x x in the center of the square (this does not have to be exact). This is also known as the central point of the shape. Draw a horizontal and/or vertical line of symmetry through the center of the shape. Show step.
3 years ago. Draw out a star and count them. For your normal 5-pointed star, you can draw a line of symmetry straight down the middle. You can also rotate the star so that the next point is on top, and draw a vertical line of symmetry for that. Keep going, and you end up with 5 lines of symmetry, one for each point.
Symmetry Activities. On this webpage you will find our range of symmetry activity sheets for kids. The sheets have been graded with the easier sheets coming first. The first set of worksheets involve only horizontal and vertical lines only. The next set involve reflecting patterns with two mirror lines.
More math activities from Gift of Curiosity: Basic Symmetry Activity Pack. Building a 3D rainbow measurement activity. Adding with chain links. Teaching combinations of 10. Introduction to probability. Math practice with numbered dice. Put the numbers on the clothesline. Road numbers.
Reflective symmetry worksheets are tools that help students grasp the concept of reflective or mirror symmetry. Symmetry drawing worksheets often include activities where learners draw lines of symmetry to complete a design, download printable worksheets, and work on completing the second half of a symmetrical image.
In this activity, students develop an informal understanding of symmetry of functions. By the end, students should be able to identify the symmetry of a function (reflectional vs rotational) by considering its graph.
• Explore symmetry of 2D shapes by cutting a range of 2D shapes in half to see if the halves match exactly. • Identify and photograph 3D objects, angles and symmetry in natural and built environments. • Apply understanding of 3D objects, angles and symmetry to find solutions to simple problems.
Point group = C 1. Symmetry elements: E. (f) BF 4-. Point group = T d. Symmetry elements: E, C 3, C 2, σ d, S 4. 2. Determine the point group of SnF 4, SeF 4, and BrF 4-. Use VSEPR to find the structure and then assign the point group. SnF 4.
Classify the resulting molecular orbital as to its symmetry with respect to the internuclear axis. This page titled Symmetry and Assigning Point Groups (Worksheet) is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Nancy Levinger. The symmetry properties of objects (and molecules) may be described in terms of ...
2. Symmetry operation: a movement of a molecule that leaves the object or molecule unchanged. Symmetry element: feature of the molecule that permits a transformation (operation) to be executed which leaves the object or molecule unchanged. Each symmetry operation has a symmetry element associated with it.
The Symmetry Gallery - A collection of over 120 unique molecules and polyhedra with interactive display of all symmetry elements and animation of all operations. The molecules are organized by point group, so you can select examples to demonstrate particular symmetry elements. Includes links to the chemical literature when available.
Using Symmetry: Vibrational Spectroscopy We can use character tables to determine the symmetry of all 18 motions and then assign them to translation, rotation, or vibration. We can also tell which vibrations are IR or Raman active. Procedure: 1. Assign x,y,z coordinates to each atom. 2. Determine how each axis transforms for every class of
1,2-dichloroethane in the trans conformation has a C2 axis perpendicular to the C-C bond and perpendicular to the plane of both Cl's and both C's, a h plane through both Cl's and both C's, and an inversion center. C2h. 4.2 a. Ethylene is a planar molecule, with C2 axes through the C's and perpendicular to the C-C bond both in the ...
A symmetry \(\pi \) of \(\varphi \) is weakly active for assignment \(\alpha \) and choice literals \(\gamma {}\) if \(\pi (\gamma {}) \subseteq \alpha \). Weak activity is a is a refinement of activity ; the latter is a technique used in dynamic symmetry handling approaches for constraint programming [ 18 , 26 ].
STEP 2: Break Γmodes Γ m o d e s into its component irreducible representations. STEP 3: Subtract rotations and translations to find vibrational modes. STEP 4: Determine which of the vibrational modes are IR-active and Raman-active. Infrared selection rules: Raman selection rules: Summary of Analysis for Water.
The water molecule has C 2v symmetry and its symmetry elements are E, C 2, σ(xz) and σ(yz). In order to determine the symmetries of the three vibrations and how they each transform, symmetry operations will be performed. As an example, performing C 2 operations using the two normal mode v 2 and v 3 gives the following transformation:
Classify the resulting molecular orbital as to its symmetry with respect to the internuclear axis. This page titled Workgroup 2: Symmetry and Assigning Point Groups is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Delmar Larsen. The symmetry properties of objects (and molecules) may be described in terms of ...
Policy assignment question. Hi. I have a question about the most efficient way to assign intune security policies for Defender for endpoint. This customer has intune joined Windows 10 devices and also Azure VMs with a combination of Windows Server OSs and Windows 10 workstations they use as SERVERS that are Intune MDE joined.
The table shows the inputs and corresponding outputs for the function f (x) = (1/8) (2)x. Find the following values of the function. f -1 (1/2)=. f -1 (8) =. 2. 6. Consider the function show. Explain why the graph of a function and its inverse are reflections over the liney = x. The ordered pairs (a, b) of a function are (b, a) for the inverse ...