Philosophical and Sociological Principles of Education by
Get full access to Philosophical and Sociological Principles of Education and 60K+ other titles, with a free 10-day trial of O'Reilly.
There are also live events, courses curated by job role, and more.

Education for National Integration and International Understanding
The progress and security of any nation depends upon national unity and emotional integration of its people. The aim of education is not merely individualistic. The purpose of education is to make the individual acquire social efficiency. Nationalism and patriotism are indeed noble virtues. Our education must create a lively realization among the students that they are all members of one world. We cannot afford to live in isolation without determent to individual progress.
India after independence has not reflected a steady and continuous sense of national solidarity. It has been a relatively stable society with longer periods of peace than turmoil. However, there have been ...
Get Philosophical and Sociological Principles of Education now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.
Don’t leave empty-handed
Get Mark Richards’s Software Architecture Patterns ebook to better understand how to design components—and how they should interact.
It’s yours, free.

Check it out now on O’Reilly
Dive in for free with a 10-day trial of the O’Reilly learning platform—then explore all the other resources our members count on to build skills and solve problems every day.

- Our Mission
Integrating SEL Into Writing Instruction
A writing unit for first grade can help develop prosocial classroom behaviors, a reliable indicator of future academic success.

Social and emotional learning is gaining traction in schools across the United States as educational organizations and inquisitive teachers rethink, adapt, and reinvent traditional classroom practices to find ways to integrate SEL into academics. There’s still large-scale work to be done; traditional curricula that teachers have access to and are routinely expected to follow often don’t offer comprehensive support for developing emotional awareness or social skills. Nor do they scaffold strategies for emotional regulation or how to resolve conflicts.
With creativity and research, however, and the gumption to back it up, teachers can integrate SEL into virtually any lesson.
The Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning (CASEL) is at the forefront of helping to make research-based social and emotional learning an integral part of education from preschool through high school by working with schools, districts, teachers, families, communities, and legislators. On the federal and state levels, CASEL engages with policy makers and promotes legislation that supports evidence-based SEL policies. CASEL works directly with educators in partner schools , offers workshops, and provides a plethora of free resources for schools.
SEL: A Base for Academic Success
For some perspective on why integrating SEL into academics is so important, consider the following. For our youngest learners, research shows that prosocial behaviors in the classroom are a better indicator of future academic success than students’ early reading levels.
As a first-grade teacher in a Title 1 elementary school in Central Los Angeles, I witnessed this dynamic firsthand. Some of my brightest students and highest readers had the most meltdowns that prevented them from completing work, accessing lessons, or participating. Where might they be academically in three or five years with the same behavior? Fortunately, my school believed in the value of SEL and encouraged teachers to incorporate this learning as we saw fit.
CASEL provides a framework for educators to reference and use as guidance for implementing age-appropriate SEL in their classrooms. The CASEL framework “addresses five broad and interrelated areas of competence and highlights examples for each: self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, relationship skills, and responsible decision-making.” Educators take the stage of their students’ development and skill level into account in applying the framework to lesson design.
A Writing Unit for SEL Integration
I designed a writing unit incorporating the CASEL framework, focusing on the self-awareness competency: the ability to understand one’s own emotions, thoughts, and values and how they influence behavior across contexts. As a school, we used Lucy Calkins’s Units of Study in our English language arts curriculum. These units include reading and writing workshops that are essentially inquiry-based and interwoven with state literacy standards.
Carefully swapping out books and altering writing prompts while maintaining the structure of literacy skills development (reading comprehension, phonics, writing components), I designed a four-week-long narrative unit to explore emotional awareness.
During our Writer’s Workshop block, we read four different picture books from the acclaimed Trace Moroney’s Feelings Series (also available in Spanish) that explore emotions一how to identify our or others’ emotions and strategies for changing how we feel. We read When I’m Feeling Happy , When I’m Feeling Sad , When I’m Feeling Angry , and When I’m Feeling Nervous . Our week began with a read-aloud and opened into days of discussions, writing, and art. Through those weeks, I watched my students’ writing come alive and their relationships blossom.
Earlier in the year, I had already introduced my students to Zones of Regulation , a curriculum that educators use to teach students about emotions and emotional control, which set the foundation for some emotional vocabulary and more academic exploration. We discussed which feelings zones our emotions fall into and the times we felt these emotions. I was amazed by how passionate my students were in their verbal sharing and writings. Everyone was bursting to participate.
Validating Emotions
“When was a time you were angry?” I asked during our Anger week. “Have you ever gotten in trouble for something you didn’t do?” My students poured out stories about being framed and blamed by siblings, about being embarrassed by a parent; they listened to each other intently and even laughed at the right moments. It was important to me to give them space to share their own stories, for them to not feel that they had to give me a “right” answer.
Once we exhausted sharing about what made us feel a certain way, we discussed what made us feel better either at home or at school. My students described taking a break at the Calm Table, focusing on their breathing, talking to an adult or friend, coloring, being alone, reading a book, and more. Midweek, I initiated a Shared Writing lesson, and we made a book together about our “emotion of the week” based on student responses. I also added their ideas to a Strategy anchor chart that was filled with ideas for regulating emotions in the classroom.
To conclude the week, students wrote and drew independently about the emotion. I collected their writings each week and bound them into a big book that stayed on our Calm Table for students to read. When I presented the books to them, students glowed with pride.
I began noticing that when my students needed a break to calm down when frustrated or when they needed cheering up, they would often read through these books on their own to get support from their classmates’ stories. Interestingly, before our unit there had been a culture among my students, most notably the boys, that talking about feelings was taboo or babyish. As our unit unfolded, all my students began talking to each other about how they felt, and there was a softer tone in the classroom.
In tandem with our other SEL work, my class transformed over months from a space rife with meltdowns and arguments to a more friendly, functional place. I watched my students use the strategies they generated together in the classroom when they needed them. References to this work showed up in our morning circles of emotional check-ins. My students also began helping remind other students to use strategies to cope when they could tell someone was upset or sad.
It can be intimidating for educators to deviate from standard, traditional curricula, and some schools won’t allow teachers to do so. However, if teachers understand state learning standards, the skills that students need to master, and effective teaching strategies, there is room for creativity. Often, teachers do versions of this regardless; veteran teachers know that the exact lessons and activities that worked for a class of students one year may not work at all for their next year’s students. Why not redesign certain lessons with SEL goals in mind?
Student’s Emotion: The Power of EmotionEducation in School
- First Online: 22 October 2020
Cite this chapter

- Auditi Pramanik 2 &
- Swati Dhir 3
621 Accesses
1 Citations
This chapter gives an overview of the critical relationship between students’ emotion and school education. Studies show that our emotional system is a complex, widely distributed and defines our basic personality early in life. The unique blending of biology and psychology of emotion promises to suggest powerful educational application. Schools pose a challenging place for students. In addition to the rigors of academic studies, students are also faced with a variety of emotional issues. These issues may range from their social-emotional development, relationships with teachers, peers, parents, and other members of the society, personality and attitude development, and thought patterns. Many students have experienced that the current education system and its curriculum do not fully support their social-emotional development. Oftentimes students are suffered and diagnosed with serious emotional problems. These issues undoubtedly influence the students’ academic performance, behavior, and emotion well-being. Empathetic, supportive attachments and relationships in school are essential to optimize brain development, cognitive functioning and social-emotional development. Given this assumption, children need a combination of intellectual skills, motivational qualities, and socio-emotional skills to succeed in life. The influence of dyadic child–teacher interaction offers a fair opportunity for children’s emotional development.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Emotion Understanding and Regulation: Implications for Positive School Adjustment

Teaching Emotional Intelligence in Schools: An Evidence-Based Approach

Building Emotionally Intelligent Schools: From Preschool to High School and Beyond
The ICD-10 characterizes conduct disorder as “a repetitive and persistent pattern of dissocial, aggressive, or defiant conduct,” explaining that such behavior is “more severe than ordinary childish or adolescent rebelliousness” (World Health Organization, 1992 , p. 209). Classified in a DSM-5 chapter with disruptive and impulsive disorders, conduct disorder manifests in behavioral symptoms, such as aggressive or deceitful acts, that “violate the rights of others or that violate major societal norms” (p. 461).
According to ICD-10, the hyperkinetic disorder is evident by “a combination of overactive, poorly modulated behavior with marked intention and lack of persistent task involvement; and pervasiveness over situations and persistence over time of these behavioral characteristics” (p. 206). The ICD-10 stressed that “[hyperkinetic] disorders always arise early in development (usually in the 5 years of life)” (p. 206).
Emotional disorders describe feelings of distress, including anxiety and depression. The ICD-10 describes emotional disorders diagnosed during childhood as “exaggerations of normal developmental trends rather than phenomena that are qualitatively abnormal in themselves” (World Health Organization, 1992 ).
John Mayer and Peter Salovey are the ones who introduced emotional intelligence in 1990. Daniel Goleman published a book in 1995 that popularized emotional intelligence.
Cooperative learning is an educational approach that aims to organize classroom activities into academic and social learning experiences.
Ahnert, L., Milatz, A., Kappler, G., Schneiderwind, J., & Fischer, R. (2013). The impact of teacher–child relationships on child cognitive performance as explored by a priming paradigm. Developmental Psychology, 49 (3), 554.
Google Scholar
Allen, G. (2011). Early intervention: The next steps: An independent report to HM Government . London, UK: The Cabinet Office.
Bavarian, N., Lewis, K. M., DuBois, D. L., Acock, A., Vuchinich, S., Silverthorn, N., & Flay, B. R. (2013). Using social-emotional and character development to improve academic outcomes: A matched-pair, cluster-randomized controlled trial in low-income, urban schools. Journal of School Health, 83 (11), 771–779.
Article Google Scholar
Behforooz, B., Capece, D. A., & Vespo, J. E. (2006). Effects of the nurturing curriculum on social, emotional, and academic behaviors in kindergarten classrooms. Journal of Research in Childhood Education, 20 (40), 275–285.
Bennathan, M., & Boxall, M. (2000). Effective interventions in primary school: Nurture groups . London, UK: David Fulton.
Benner, P. (1994). Caring as a way of knowing and not knowing. In S. Phillips & P. Benner (Eds.), Crisis of care (pp. 42–62). Georgetown: Georgetown University Press.
Bergin, C., & Bergin, D. (2009). Attachment in the classroom. Educational Psychology Review, 21 , 141–170.
Bhalla, S., & Nauriyal, D. K. (2004). Emotional intelligence: The emergency paradigm in personnel dynamics. Psychological Studies, 49 (2), 97–106.
Biggers, T. (1990). Implicit communication theory.. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the International Communication Association, Miami, FL.
Bloom, B. S. (1964). Stability and change in human characteristics . New York, NY: John Wiley and Sons.
Bower, G. H., & Forgas, J. P. (2001). Mood and social memory. In J. Forgas (Ed.), Handbook of affect and social cognition (pp. 95–120). New York, NY: Psychology Press.
Bowlby, J. (1969/1982). Attachment and loss (Attachment) (Vol. 1). New York, NY: Basic Books.
Bowlby, J. (1980). Attachment and loss: Vol. 3: Loss. Hogarth Press and the Institute of Psycho-Analysis.
Bowlby, J. (1988a). A secure base . New York, NY: Basic Books.
Bowlby, J. (1988b). A secure base: Parent-child attachment and healthy human development . London, UK: Routledge.
Brackett, M., & Simmons, D. (2015). Emotions matter. Educational Leadership, 73 (2), 22–27.
Brenner, E. M., & Salovey, P. (1997). Emotion regulation during childhood, developmental, interpersonal, and individual considerations. In P. Salovey & D. J. Sluyter (Eds.), Emotional development and emotional intelligence: Educational implications (pp. 168–193). New York, NY: Basic Books.
Bretherton, I., & Mulholland, K. A. (1999). Internal working models in attachment relationships: A construct revisited. In J. Casssidy & P. R. Shaver (Eds.), Handbook of attachment. Theory, research and clinical applications . New York, NY: The Guildford Press.
Cassidy, J. (1999). The nature of the child’s ties. In J. Casssidy & P. R. Shaver (Eds.), Handbook of attachment. Theory, research and clinical applications (pp. 3–20). New York, NY: The Guildford Press.
Cohen, J., Onunaku, N., Clothier, S., & Poppe, J. (2005). Helping young children succeed: Strategies to promote early childhood social and emotional development . Washington, DC: National Conference of State Legislatures.
Collie, R. J., Shapka, J. D., & Perry, N. E. (2012). School climate and social-emotional learning: Predicting teacher stress, job satisfaction, and teaching efficacy. Journal of Educational Psychology, 104 (4), 1189–1204.
Cozolino, L. (2013). The social neuroscience of education: Optimizing attachment and learning in the classroom . London, UK: Norton & Co.
Davis, H.A. (2003). Conceptualizing the role and influence of student-teacher relationships on children’s social and cognitive development. Educational Psychologist, 38 (4), 207–234.
Denham, S. A. (1998). Emotional development in young children (The Guilford Series on social and emotional development). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Denham, S. A., Bassett, H. H., Zinsser, K., & Wyatt, T. M. (2014). How preschoolers’ socialemotional learning predicts their early school success: Developing theory-promoting, competency-based assessments. Infant and Child Development, 23 (4), 426–454.
Dunn, J., Brown, J., & Beardsall, L. (1991). Family talk about feeling states and children’s later understanding of others’ emotions. Developmental Psychology, 27 (3), 448.
Durlak, J. A., Domitrovich, C. E., Weissberg, R. P., & Gullotta, T. P. (2015). Handbook of social and emotional learning: Research and practice . New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Ekman, P., & Friesen, W. (1975). Unmasking the face . Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Elmore, R. F., & Zenus, V. (1994). Enhancing social-emotional development of middle school gifted students. Roeper Review, 16 (3), 182–185.
Felder, R. M., & Brent, R. (2007). Cooperative learning, Chapter-4. In P. A. Mabrouk (Ed.), Active learning: Models from the analytical sciences (ACS Symposium Series) (Vol. 970, pp. 34–53). Washington, DC: American Chemical Society.
Chapter Google Scholar
Fried, L. (2011). Teaching teachers about emotion regulation in the classroom. Australian Journal of Teacher Education, 36 (3), 117–127.
Geddes, H. (2006). Attachment in the classroom: The links between children’s early experience, emotional wellbeing and performance in school . London, UK: Worth Publishing.
Goldstein, L. S. (1999). The relational zone: The role of caring relationships in the co-construction on mind. American Educational Research Journal, 36 , 647–673.
Goleman, D. (1996). Emotional intelligence: Why it can matter more than IQ . London, UK: Bloomsbury Publishing.
Graziano, P. A., Reavis, R. D., Keane, S. P., & Calkins, S. D. (2007). The role of emotion regulation in children’s early academic success. Journal of School Psychology, 45 (1), 3–19.
Greenwald, A. G., Banaji, M. R., Rudman, L. A., Farnham, S. D., & Nosek, B. A. (2000). In J. P. Forgas (Ed.), Feeling and thinking. The role of affect in social cognition (pp. 308–331). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Gus, L., Rose, J., & Gilbert, L. (2015). Emotion coaching: A universal strategy for supporting and promoting sustainable emotional and behavioural well-being. Educational & Child Psychology, 32 (1), 31–41.
Hargreaves, A. (1998). The emotional politics of teaching. Teacher and Teacher Education, 14 (8), 835–854.
Hochschild, A. (1983). The managed heart . Berkeley: University of California Press.
Hunt, J. M. (1961). Intelligence and experience . New York, NY: The Ronald Press.
Immordino-Yang, M. H., & Damasio, A. (2007). We feel, therefore we learn: The relevance of affective and social neuroscience to education. Mind, Brain, and Education, 1 (1), 3–10.
International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems. Tenth Revision. Vol. 1: Tabular list, 1992. Vol. 2: Instruction Manual, 1993. Vol. 3: Index. Geneva, World Health Organization.
Kam, C., Greenberg, M. T., & Kusche, C. A. (2004). Sustained effects of the PATHS curriculum on the social and psychological adjustment of children in special education. Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders, 12 , 66–78.
Kierstead, J. (1999). Human resource management trends and issues: Emotional intelligence (EI) in the workplace . Research Directorate, Policy Research and Communications Branch, Public Service Commission Branch, Public Service Commission of Canada.
Knitzer, J. (2003). Social and emotional development in young low-income children: What research tells us and why it matters for early school success . Paper presented at National Center for Children in Poverty, New York, NY.
Kusche, C. A. (2002). Psychoanalysis as prevention: Using PATHS to enhance ego development, object relationships & cortical integration in children. Journal of Applied Psychoanalytic Studies, 4 , 283–300.
Lee, M., Schutz, P. A., Taxer, J., Pekrun, R., Meier, E., & Xie, X. (2014). Teachers’ emotions, emotion regulation, and classroom management efficacy . Paper presented at the Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association, Philadelphia, USA.
Lewis, M., & Haviland-Jones, J. M. (2008). Handbook of emotions (3rd ed.). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Liberante, L. (2012). The importance of teacher-student relationships, as explored through the lens of the NSW Quality Teaching Model. Journal of Student Engagement: Education Matters, 2 (1), 2–9.
Linnenbrink, E. A. (2007). The role of affect in student learning: A multi-dimensional approach to considering the interaction of affect, motivation, and engagement. In P. A. Schutz & R. Pekrun (Eds.), Emotion in education (pp. 107–124). San Diego, CA: Elsevier Academic Press.
Main, M., & Solomon, J. (1990). Procedures for identifying infants as disorganised/disorientated during the Ainsworth strange situation. In M. T. Greenberg, D. Cicchetti, & E. M. Cummings (Eds.), Attachment in the preschool years (pp. 121–160). Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Medrano, L. A., Flores, K. P. E., Ríos, M., Curarello, A., & González, J. (2015). Adaptación de la Escala de AfectoPositivo y Negativo (PANAS) a la población de estudiantesuniversitarios de Córdoba . Anuarios de Investigaciones de la Facultad de Psicología. Article in Edition.
Mega, C., Ronconi, L., & De Beni, R. (2014). What makes a good student? How emotions, selfregulated learning, and motivation contribute to academic achievement. Journal of Educational Psychology, 106 (1), 121–131.
Mehrabian, A., & Russell, J. A. (1974). The basic emotional impact of environments. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 38 (1), 283–301.
Mehrabian, A. (1981). Silent messages: implicit communication of emotions and attitudes, Albert Mehrabian, 2. edn. Wadsworth, Belmont, Calif.
Mikulincer, M., & Shaver, P. R. (2012). An attachment perspective on psychopathology. World Psychiatry, 11 (1), 11–15.
Mohanty, S. N., & Suar, D. (2013a). Influence of mood states, group discussion, and interpersonal comparison on change in decision-making and information processing. International Journal of Decision Sciences, Risk and Management, 5 (2), 101–123.
Mohanty, S. N., & Suar, D. (2013b). Decision‐making in positive and negative prospects: Influence of certainty and affectivity. International Journal of Advances in Psychology, 2 (1), 19–28.
Mohanty, S. N., & Suar, D. (2014). Decision making under uncertainty and information processing in positive and negative mood states. Psychological Reports, 115 (1), 91–105.
Mortimer, H. (2003). Emotional literacy and mental health in the early years . Lichfield, UK: QEd.
Murray, C., & Greenberg, M. T. (2001). Relationships with teachers and bonds with school: Social emotional adjustment correlates for children with and without disabilities. Psychology in the Schools, 38 (1), 25–41.
Nagel, M. (2009). Mind the mind: Understanding the links between stress, emotional well-being and learning in educational context. International Journal of Learning, 16 (2), 33–42.
Payne, A. L. (2003). Measuring preschool children’s perceptions of teacher-child relationship quality: Developing and testing the “feelings about my school and teachers’ instrument”. Dissertation-Abstracts-International-Section A: Humanities-and-social-sciences, 64 (2-A), 391.
Piaget, J. P. (1955). The language and thought of the child . New York, NY: Meridian Books.
Ranellucci, J., Hall, N. C., & Goetz, T. (2015). Achievement goals, emotions, learning, and performance: A process model. Motivation Science, 1 , 98–120.
Rechtschaffen, D., & Rechtschaffen, T. (2015). The 5 literacies of mindful learning. Educational Leadership, 73 (2), 58–62.
Reid, E. E., Diperna, J. C., Missall, K., & Volpe, R. J. (2014). Reliability and structural validity of the teacher rating scales of early academic competence. Psychology in the Schools, 51 (6), 535–553.
Riley, P. (2010). Attachment theory and teacher student relationships . London, UK: Routledge.
Book Google Scholar
Rimm-Kaufman, S. E., Baroody, A. E., Larsen, R. A., Curby, T. W., & Abry, T. (2015). To what extent do teacher-student interaction quality and student gender contribute to fifth graders’ engagement in mathematics learning ? Journal of Educational Psychology, 107 (1), 170–185.
Rose, J., Temple, S., McGuire-Snieckus, R., Wood, F., Vatmanides, O., & Parker, R. (2016). Somerset emotion coaching project evaluation report. Institute for Education, Bath Spa University.
Schonert-Reichl, K. A., Oberle, E., Lawlor, M. S., Abbott, D., Thomson, K., Oberlander, T. F., & Diamond, A. (2015). Enhancing cognitive and social–emotional development through a simple-to-administer mindfulness-based school program for elementary school children: A randomized controlled trial. Developmental Psychology, 51 (1), 52.
Schutz, P. A., & Zembylas, M. (Eds.). (2009). Advances in teacher emotion research: The impact on teachers’ lives . New York, NY: Springer.
Segrott, J., Rothwell, H., & Thomas, M. (2013). Creating safe places: An exploratory evaluation of a school-based emotional support service. Pastoral Care in Education, 31 (3), 211–228.
Seth-Smith, F. (2006). How do teachers influence children’s emotional development? Doctoral dissertation, University of London.
Sharp, P. (2001). Nurturing emotional literacy. A practical guide for teachers, parents and those in the caring professions . London, UK: David Fulton.
Siegel, D. (2012). The developing mind: How relationships and the brain interact to shape who we are . New York, NY: Guildford Press.
Siraj-Blatchford, I., Sylva, K., Muttock, S. Gilden, R., & Bell, D. (2002). Researching effective pedagogy in the early years. Research Report No.: RR356. Nottingham, UK: DfES.
Shaughnessy, J. (2012). The challenge for English schools in responding to current debates on behaviour and violence. Pastoral Care in Education, 30 (2), 87–97.
Steinberg, L. (2015). How self-control drives student achievement. Educational Leadership, 73 (2), 28–32.
Sutton, R. E. (2004). Emotional regulation goals and strategies of teachers. Social Psychology of Education, 7 (4), 379–398.
Tiwari, P. S. N., & Srivastva, N. (2004). Schooling and development of emotional intelligence. Psychological Studies, 49 (2–3), 151–154.
Tomlinson, C. A. (2015). Teaching for excellence in academically diverse classrooms. Society, 52 (3), 203–209.
Tracy, S. J. (2005). Locking up emotion: Moving beyond dissonance for understanding emotion labor discomfort. Communication Monographs, 72 (3), 261–283.
United Nations General Assembly. (2015). Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 25 September 2015 . Washington, DC: United Nations.
Vespo, J. E., Capece, D., & Behforooz, B. (2006). Effects of the nurturing curriculum on social, emotional, and academic behaviors in kindergarten classrooms. Journal of Research in Childhood Education, 20 (4), 275–285.
Vinson, L., & Biggers, 3. T. (1993). Emotional response as a predictor of compliancegaining message selection. The Southern Communication Journal, 58 , 192–206.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Jawaharlal Nehru University, New Delhi, India
Auditi Pramanik
IMI New Delhi, New Delhi, India
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of Computer Science & Engineering, ICFAI Foundation for Higher Education, Hyderabad, India
Sachi Nandan Mohanty
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Pramanik, A., Dhir, S. (2020). Student’s Emotion: The Power of EmotionEducation in School. In: Mohanty, S.N. (eds) Emotion and Information Processing. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-48849-9_9
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-48849-9_9
Published : 22 October 2020
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-48848-2
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-48849-9
eBook Packages : Behavioral Science and Psychology Behavioral Science and Psychology (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Greater Good Science Center • Magazine • In Action • In Education
How to Integrate Social-Emotional Learning into Common Core
Do the Common Core State Standards undermine social-emotional learning?
Many educators think so. In a recent Ed Week op-ed , an elementary principal argued that teachers were too busy teaching Common Core to address the social-emotional development of their students . I’ve heard the same argument from many teachers. This is troubling given that researchers strongly suggest that the learning process is 50 percent social-emotional and 50 percent cognitive .
Yet when I read through the Standards, I quickly realized that social-emotional skills are implicitly embedded in the Standards—whether or not teachers, school leaders, policy-makers, or even the creators of the Common Core realize it.

In other words, for students to successfully meet the Standards, they must possess social-emotional skills. And unless students magically come to school with all these skills in place, deliberate teaching of these skills will be necessary.
(For readers who are not familiar with the current U.S. public education landscape, the Common Core State Standards outline what students are supposed to know in language arts and math at each grade level so that they will be prepared for college and/or the workplace. While 45 states and the District of Columbia have adopted the Standards, there is still much disagreement on how to implement and test them and whether they’re appropriate at all.)
Predicting if the Common Core Standards will survive the multitudinous controversies currently raging in state legislatures is beyond my psychic abilities. But there are hundreds of thousands of educators striving to put the standards to work in classrooms—and it’s worth exploring how the Standards naturally align with CASEL’s framework of social-emotional learning outcomes . Here are some examples.
Common Core Math Standards and SEL
At first, math and social-emotional learning may not seem like natural allies. But if you think back to a time when a mathematical concept completely confounded you (like, ahem, proofs in high school geometry), social-emotional skills such as perseverance , hope , optimism , and asking for help would have come in handy.
The Common Core Standards for Mathematical Practice outline “processes and proficiencies” that math teachers should help students develop. These qualities, in particular, align well with social-emotional learning. Here are a couple examples:
Common Core Math Standard:
Students make sense of problems and persevere in solving them.
Corresponding SEL “self-management” skills:
- Possess self-efficacy
- Work toward goals
- Attention control
- Manage personal stress
- Regulate emotions such as impulses, aggression, and self-destructive behavior
- Seek help when needed
- Exhibit positive motivation, hope, and optimism
- Display grit, determination, or perseverance
Problem-solving (particularly word problems) is for many students the most challenging part of math. Often students will take one look at a problem and decide that it’s too hard without even trying—especially those with “math phobia.” This is where social-emotional skills can help.
Students need to first trust in their ability to solve a problem (self-efficacy) and then work towards that goal. They must be able to focus on the problem rather than get distracted by what the kid on the other side of the room is doing. If they get stuck, students must manage their stress-levels by regulating their emotions and, if necessary, ask for help. Staying optimistic throughout the process will help them persevere to the end.
For example, before beginning a lesson, have the students practice a couple minutes of mindfulness . Research suggests that this will calm their emotions and focus their attention . For longer-term impact, help students see how their personal goals align with math outcomes. Scientists have found that this will help students develop hope—one of the most important factors in student academic success.
When constructing viable arguments, students justify their conclusions, communicate them to others, and respond to the arguments of others.
Corresponding SEL “social awareness” and “relationship management” skills:
- Respect others (e.g., listen carefully and accurately)
- Understand other points of view and perspectives
- Identify social cues (verbal, physical) to determine how others feel
- Predict others’ feelings and reactions
- Manage and express emotions in relationships, respecting diverse viewpoints
Emotions can run high when students try to defend their point—which can all too often lead to hurt feelings. Educators need to teach students how to transform “you’re wrong!” or “that’s a stupid answer!” into “from my perspective” or “I respectfully disagree.”
Creating a caring and safe classroom builds respect among students. They learn to understand and accept that other people have different perspectives than them. Educators who build students’ emotional literacy by teaching them how to identify emotions in themselves and others are giving students the tools to predict how others’ feel and then respond appropriately—all of which will lead to much more effective (not to mention fun and engaging) academic discussions.
One of my favorite examples for building a safe and caring classroom comes from a Greater Good Summer Institute for Educators participant and is based on the RULER program. At the beginning of the year, she asked students how they wanted to feel in the classroom. After getting over their initial shock that a teacher actually cared about how they felt, students began to say things like “be respected” and “no laughing at each other.”
Everyday, the students and teacher started class with everyone stating how they were currently feeling. Anyone who felt out-of-sorts was given a little bit of time to visit the “balancing table” where they could draw, write, or practice mindfulness to feel better. While many teachers may feel this practice would take too much time, in the long-run, the benefits far outweigh the time factor. Multiple studies show that students who are part of a safe and caring classroom where they feel seen, heard, and respected have better peer relationships and are more successful academically.
Common Core and English Language Arts Standards
Many SEL programs such as PATHS and RULER already use writing and literature as part of their lessons. And research indicates that reading literary fiction can help develop empathy—a wonderful justification for English teachers to assign more books like Crime and Punishment and Heart of Darkness .
While not explicitly calling them “social-emotional skills”, many of the Common Core Language Arts Standards give teachers the opportunity to incorporate mini-lessons on emotions, communication, relationships, and other social-emotional skills directly into their language arts curriculum. Here are a couple examples:
Common Core English Language Arts Standard
RL.3.3 Describe characters in a story (e.g., their traits, motivations, or feelings) and explain how their actions contribute to the sequence of events.
Corresponding SEL “self-awareness”, “social awareness”, and “responsible decision-making” skills:
- Label and recognize own and others’ emotions
- Analyze emotions and how they affect others
- Evaluate others’ emotional reactions
- Reflect on how current choices affect future
In order to identify feelings of other people—whether real or fictional—students need to have a well-developed emotion vocabulary. Being able to recognize and label these emotions as they occur within themselves helps students do so in others. Examining how emotions impact fictional characters’ lives also provides a non-threatening opportunity for students to reflect how emotions affect their own lives and the people around them.
For example, have students create a double-entry journal to examine how the emotions of a character impact the world around them. Follow this up with a journal entry in which students self-reflect on their own emotional experiences. To make it easier for students to label emotions, hang an emotions poster in your classroom.
W.7.6 Use technology, including the Internet, to produce and publish writing and link to and cite sources as well as to interact and collaborate with others, including linking to and citing sources.
Corresponding SEL “relationship management” skills
- Exhibit cooperative learning and working toward group goals
- Communicate effectively
- Cultivate relationships with those who can be resources when help is needed
- Provide help to those who need it
- Demonstrate leadership skills when necessary, being assertive and persuasive
- Prevent interpersonal conflict, but manage and resolve it when it does occur
Anyone who has ever had to collaborate on a group project for school knows that it’s not exactly a bed of roses. Pulling one’s own weight (and getting others to do so), agreeing to disagree, and compromise are all part of the process—but social-emotional skills can go a long way in smoothing the road for everyone.
Effective and respectful communication is key to collaboration, as well as motivating and helping each other along the way. Students who develop these kinds of skills in school will be considered the “cream of the crop” when it comes to future workplace success.
For example, rather than telling students your version of good teamwork, have them come up with their own rubric for evaluating their collaborative efforts. This will help them “own” the process and make them more accountable to each other. Then have students share with the class after each workgroup session what worked and what didn’t. Ask them to role play possible solutions for any problems they might have encountered. Allow them to adjust their rubric as they gain deeper insight into what makes a good team.
What’s Missing
Overall, I found the Common Core Standards provide an excellent excuse for the teaching of social-emotional skills. And I applaud teachers who make the effort to do so. But even then, there’s still something missing.
No Standard and no SEL program can replace a teacher’s enthusiasm and passion for the curricula being taught. To me, that is the magic of teaching—and what often separates the good teachers from the great ones. The truly gifted educators are those who care for their students and show them the “awesomeness” of the world around them—and then go the extra mile to help them find their unique and purposeful place in it.
About the Author

Vicki Zakrzewski
Vicki Zakrzewski, Ph.D. , is the education director of the Greater Good Science Center.
You May Also Enjoy

Why Teachers Need Social-Emotional Skills

Is Social-Emotional Learning a Luxury?

How to Help Students Develop Hope

Four Ways Teachers Can Show They Care

A New Vision of Teacher Education
The power of integrating social emotional learning to enhance academic achievement
Key takeaways.
- Prioritizing social emotional learning (SEL) enhances academic performance by equipping students with emotional intelligence and self-regulation skills, fostering engagement, motivation, and improved learning outcomes.
- Creating a supportive classroom climate through positive relationships and effective teaching strategies promotes SEL, contributing to students' holistic development and well-being.
- Integrating SEL into the curriculum not only boosts academic achievement but also prepares students for success in life by nurturing their social and emotional skills alongside their academic knowledge.
"Education is not the filling of a pail, but the lighting of a fire." - William Butler Yeats
As an educator, you have the opportunity to ignite a spark within your students, guiding them on a path of personal growth and empowering them to reach their full potential.
Integrating social emotional learning (SEL) into classroom practices is a powerful tool for enhancing both academic achievement and student well-being . SEL equips students with the emotional intelligence and self-regulation skills they need to navigate challenges, build positive relationships , and thrive in a complex world.
In this article, we will explore the key principles of social emotional learning and its direct impact on academic performance. We will delve into the strategies for creating a supportive classroom climate that fosters SEL, as well as practical ways to integrate SEL into the curriculum. Together, let's embark on a transformative journey, unlocking the power of SEL to enrich both the minds and hearts of our students.
What is Social Emotional Learning (SEL)?
Social Emotional Learning (SEL) is an educational approach that focuses on developing students' emotional intelligence and self-regulation skills . It recognizes the integral connection between academic achievement and social emotional well-being. By equipping students with the necessary tools to understand and manage their emotions, SEL fosters a positive learning environment.
SEL encompasses various components that contribute to students' holistic development:
- Emotional intelligence : SEL helps students recognize, understand, and manage their emotions effectively. It promotes empathy and teaches them to navigate social relationships.
- Self-regulation skills: SEL empowers students to regulate their emotions, thoughts, and behaviors in different contexts. It promotes impulse control, stress management, and decision-making skills.
- Self-awareness : Students develop self-awareness through SEL, gaining insight into their strengths, weaknesses, and personal values. This awareness facilitates personal growth and fosters a positive sense of self.
- Social awareness : SEL teaches students to empathize with others, understand diverse perspectives, and appreciate the importance of social inclusion and justice.
- Relationship skills: SEL cultivates students' ability to build and maintain positive relationships . It emphasizes effective communication , active listening, and conflict resolution.
Integrating SEL in educational settings is essential for nurturing well-rounded individuals who can thrive academically, socially, and emotionally. By prioritizing SEL, educators contribute to the overall development and academic success of their students.
Emotional intelligence: The key to academic success and well-being for teachers and students
Read article
Creating a Supportive Classroom Climate
A supportive classroom climate plays a crucial role in fostering students' social emotional development and overall well-being. By establishing positive relationships among students and between students and teachers, as well as implementing effective teaching strategies , educators can create an environment that promotes social emotional learning (SEL) and enhances academic achievement.
The Importance of Positive Relationships
- Encourage collaboration and teamwork among students, fostering a sense of belonging and inclusivity.
- Build trust and rapport between students and teachers, creating a safe space for emotional expression and open communication.
- Promote empathy and understanding, helping students develop social skills and emotional intelligence.
Effective Teaching Strategies for SEL
- Implement cooperative learning activities that encourage peer interaction and cooperation.
- Incorporate reflective practices, such as journaling or group discussions, to promote self-awareness and self-regulation skills.
- Integrate SEL content into lesson plans, embedding social emotional learning within the subject matter.
By prioritizing positive relationships and utilizing effective teaching strategies , educators can create a classroom climate that supports students' social emotional growth. This not only improves their overall well-being but also enhances their engagement, motivation, and academic performance .
Enhancing Academic Performance through SEL
Social emotional learning (SEL) has a direct impact on academic performance , providing students with the foundation they need to succeed in their studies. By implementing effective teaching strategies that integrate SEL practices, educators can help enhance students' engagement, motivation, and learning outcomes.
One of the key benefits of SEL is its ability to promote student engagement. By fostering a sense of belonging and purpose in the classroom, SEL helps students connect with the material and actively participate in their learning. Through collaborative activities, discussions, and projects, students develop a deeper understanding and retain information more effectively.
Moreover, SEL contributes to student motivation by instilling a growth mindset and cultivating intrinsic motivation. By teaching students the importance of perseverance, self-reflection, and goal setting, educators empower them to take ownership of their learning journey. This increased motivation translates into sustained effort, improved focus, and a desire to continually improve.
In addition to engagement and motivation, SEL practices have been shown to have a positive impact on learning outcomes. By promoting self-regulation skills, such as problem-solving and emotional management, students develop the ability to effectively navigate challenges and setbacks. This leads to improved problem-solving abilities, critical thinking skills, and academic achievement.
Benefits of SEL on Academic Performance:
- Enhanced student engagement through a sense of belonging and purpose
- Intrinsic motivation and a growth mindset nurtured
- Improved problem-solving abilities, critical thinking, and learning outcomes
Furthermore, research has consistently demonstrated the link between students' social emotional well-being and their academic success. When students' emotional needs are met, they are more likely to feel safe, supported, and motivated to learn. SEL practices create a positive and inclusive classroom environment, where students can thrive academically and personally.
By implementing effective teaching strategies that integrate SEL practices, educators can foster a supportive classroom climate that enhances academic performance. The combination of SEL and academic instruction creates a holistic approach to education, addressing students' social emotional well-being and nurturing their potential to succeed.
Integrating SEL into the Curriculum
Integrating social emotional learning (SEL) into the curriculum is a transformative approach that empowers educators to enhance students' academic achievement while nurturing their social and emotional well-being. By incorporating SEL practices within existing teaching frameworks, educators can create a holistic learning environment that fosters not only academic success but also personal growth and development.
Here are some practical strategies for integrating SEL into the curriculum:
Embed SEL within Subject Areas
Infuse SEL concepts and skills into various subject areas, such as language arts, math, science, and social studies, to promote a cross-disciplinary approach. For example, incorporate literature that explores emotional intelligence or incorporate group discussions on empathy and perspective-taking in history lessons. This integration allows students to see the relevance and real-world applications of SEL in their academic pursuits.
Infuse SEL Principles in Everyday Classroom Interactions
Develop a classroom culture that prioritizes SEL through daily interactions, fostering a sense of belonging, respect, and emotional safety. Implement activities that promote collaboration, conflict resolution, and self-reflection. Encourage students to express their thoughts and emotions openly, creating an environment where they feel heard and valued.
Implement SEL-based Teaching Strategies
Utilize teaching strategies that explicitly teach SEL skills and concepts. Use cooperative learning activities, role-playing scenarios, and reflective writing exercises to help students develop self-awareness , social skills, and responsible decision-making. Incorporate SEL-focused assessments that gauge both academic proficiency and social-emotional growth.
Integrating SEL into the curriculum not only benefits students' academic achievement but also equips them with essential skills for success in life. By nurturing their social and emotional well-being, educators are empowering students to thrive in school and beyond. Incorporate these practical strategies into your classroom practices to create a truly transformative learning experience.
Supporting Students' Well-being and Development
In order to promote the holistic development of students, it is crucial to focus on their well-being and social emotional learning (SEL). By addressing students' mental health, self-esteem, and social interactions, educators can create a positive and inclusive learning environment. Here are some effective teaching strategies that can support their well-being and development:
- Cultivate a supportive classroom climate: Building positive relationships among students and between students and teachers is essential. Encourage open communication , active listening, and empathy to foster a sense of belonging and trust.
- Embed SEL into daily classroom practices: Incorporate SEL activities and discussions into everyday lessons to promote students' emotional intelligence and self-regulation skills. Encourage reflection, emotional expression, and problem-solving to enhance their social-emotional well-being.
- Provide opportunities for self-discovery: Offer activities that allow students to explore and discover their strengths, values, and goals. Help them develop a sense of purpose and build resilience by inspiring them to overcome challenges.
- Teach stress management and coping skills: Equip students with effective stress management techniques and coping strategies. Teach them how to recognize and regulate their emotions, practice mindfulness, and build resilience .
- Foster a culture of kindness and inclusivity: Encourage students to embrace diversity, show empathy , and practice kindness. Promote collaborative learning, peer support, and respect for others' perspectives and backgrounds.
By implementing these effective teaching strategies, educators can actively contribute to students' well-being while promoting their social emotional learning. A positive and nurturing classroom environment can significantly enhance students' academic achievement and overall success.
Unlocking student success: culture and climate's academic impact
Integrating social emotional learning (SEL) into academic settings is paramount to enhancing students' academic performance and overall well-being. By prioritizing SEL, educators can create a supportive classroom climate that fosters positive relationships and effective teaching strategies .
Research has consistently shown that SEL practices have a direct and positive impact on academic achievement. By equipping students with the necessary emotional intelligence and self-regulation skills, educators can enhance student engagement, motivation, and learning outcomes.
By embedding SEL into the curriculum, educators can ensure that students receive comprehensive and holistic education. Incorporating SEL practices within subject areas and daily classroom interactions not only enhances academic performance but also cultivates a positive and inclusive learning environment.
As educators, it is crucial to prioritize students' well-being and development. SEL supports their mental health, self-esteem, and social interactions. By nurturing students' social emotional well-being, educators empower them to thrive academically and succeed in life beyond the classroom.
Author: Hope Marvin
Posted: 12 Feb 2024
Estimated time to read: 9 mins
Learn more about Satchel Pulse in your district
Browse topics.
- Social emotional learning (93)
- School Climate (53)
- Teacher Retention (30)
- Behavior (23)
Recent posts
Ready for the world: high..., the strength of purposefu..., innovative strategies for..., 5 essential skills studen..., popular posts, every child learns: unlocking the power of inclusive educati..., why do teachers love being teachers, what are the three biggest challenges of school social worke..., effective interventions for students struggling academically....
Get a monthly roundup of our latest posts straight to your inbox!
Subscribe to Email Updates
Success with skills.
Get tailored SEL skill-building for individual student needs and readiness.
Importance of National Integration for Students and Children
500+ words essay on importance of national integration.
National Integration is the bond and togetherness between people regardless of their caste, creed, religion or gender . It is the feeling of oneness, brotherhood and social unity under communities and society in a country. National Integration helps to keep the country unified and strong from within despite the diversities. So, the importance of national integration can be from the fact that the nation which remains integrated. It will always progress on the track of development and prosperity.

What is the Importance of National Integration?
National integration plays a dynamic role in making the country as one. This happens only by uniting every section of society. It provides an equal opportunity for each citizen. It also offers an equal platform in terms of social, cultural and economic development .
National integration also helps to unite the minorities as well as gives them the freedom to live their life in their way without any interference. Thus National integration is also essential for the country’s development. Because the country with national unity will always flourish and develop.
Aims of National Integration
National integration principally aims at providing a better environment for the people of a country. Thus they can develop themselves in all the aspects. It also aids to bind multi-racial and multilingual country like India, which has people with diverse culture and tradition. It also multiplies the union of brotherhood amongst communities, societies and the people.
National integration also helps in keeping the stability of a country and adds up to its whole development. It supports to nurture communal harmony and fights casteism, regionalism, and linguism, etc. National Integration improves the feeling of loyalty and fraternity towards the nation. It unites the people in case of any national emergency.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
How to Promote National Integration?
As national integration demonstrates a crucial part in the development of a country, it becomes important to develop the feeling of national integrity among its citizens. Therefore, focus on all the sections of society and making them financially dependent will promote national integration.
This will help to promote economic integrity. This is one of the most important factors in promoting national integration. Tolerance and respect for other caste or religion also support to promote national integrity. Education, social and cultural unity, equality among people also helps to teach the feeling of national integration.
Advantages of National Integration
National integration plays a very important role in the political, economic, cultural and social dimensions of a country. It helps the country in the following ways:
- Promotes Social Harmony
National integration makes the people of a country be present in harmony. This works only by strengthening the social bond between them. It indorses brotherhood, peace, and tolerance among them.
- Unites the Nation
National integration aids to unite people of different race, caste, creed or thoughts and makes the country as a single entity. it strengthens the country and makes it powerful on the international platform.
- Increases Economic Growth
It is a well-known fact that the country has less internal matters and problems. They will always prosper and develop. The country which is united will always have fewer problems as compared to the country which is socially unstable.
- Promotes Loyalty for the Nation
National integration indorses loyalty of the citizen for the country. It aids to make people join hands and stand for the advancement of the country forgetting their petty issues.
Significance of National Integration in Modern Era
National integration plays a more significant role in modern times. Hence it has challenges like communalism, regionalism, linguism, etc. Global terrorism is also one of the major threats to national integration. While few people with radical thoughts convince the population and brainwash them. They provoke them against their motherland.
In the era of technological advancements and the accessibility of social media. It is very easy to get deceived. National integration helps to ignore these situations. It makes people intellectually mature and tolerant.
National integration is very significant for a country because it is seen many times in the history of mankind that the integrity of a nation fell in danger. It had confronted major challenges from within and also became a victim of foreign assaults. Hence national integration plays a significant role in making of a nation. It keeping it alive in history with sustained development.

Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- IAS Preparation
- UPSC Preparation Strategy
- National Integration Role Of Education System Cinema Etc
National Integration in India - Common Identity of Citizens
National Integration in India is very important to enhance unity among all sections of society in a country like India, which is replete with diversity in many spheres of life. This article helps one understand the role of the education system, cinema, people from middle class background, working class, intellectuals, different multinational companies and media in promoting National Integration.
Aspirants can find information on the structure and other important details related to the IAS Exam ,in the linked article
Role of Education in National Integration?
Education plays a key role as it changes our thoughts and ideas. Fortunately, in India, we have had very good educationists both before and after independence. School teachers play a great role in shaping the minds of young students in the country. Various characters in history such as Rani Laxmi Bai, Lal Bahadur Shastri, and famous slogans such as ‘Inquilab Zindabad’ have permeated into our collective consciousness over many years. The syllabus designed by NCERT with the help of eminent scholars has also contributed greatly in shaping the idea of India. Also, often students migrate to different parts within the country to pursue higher education at different universities. This has helped young minds to think beyond their regions, caste, and religion, Universities around the country, such as Delhi University, Jamia Millia Islamia, Osmania University, to name a few, have students enrolled from around the country, who within a short span, develop a pan-Indian sense that rises above any cultural or ethnic differences. Unfortunately, our student enrollments in higher education institutions is still very low, and only around 12-13% of our population have access to higher education, whereas in the USA, it is approximately 87%, and in Europe, it is more than 50%, even in China, it is approximately around 25%. Thus, one remains hopeful that in the near future, with the coming up of private universities, and efforts taken by the Government, higher education not only becomes more easily accessible but student enrollments in these institutions also go up. People from diverse cultural groups, and marginalized sections such as minorities, women, tribal groups, etc. who have been alienated in the past from the national mainstream, have gradually been aligning themselves with the mainstream, largely due to the efforts of an inclusive education system. In the words of Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru, “Right education open to all is perhaps the basic remedy for most of our ills”.
Role of Cinema, Sports, and Literature
Hindi and regional cinemas of the 1960s and 70s helped promote the idea of Indian nationalism, and the idea of secularism. Scriptwriters and directors were conscious towards promoting the idea of nationalism. Movies which showcased love transcended cultural, regional, linguistic barriers, and caste barriers helped in shaping the idea of India. Movies also helped shape a secular India as characters enacted included a broad spectrum of religions, regional backgrounds, ethnicity, etc. It must also be remembered that just after independence, with scant entertainment options around, cinema was a very important source of entertainment for a large section of society. Thus, cinema which imbued the spirit of brotherhood, promoted unity, and the idea of secularism, helped shape the idea of India. The field of sports unfortunately in India has been a neglected area through much of our post-independent history, and stellar performances of our athletes in games such as the Olympics, Asian Games, and Commonwealth Games, has been largely due to their own individual brilliance. India has traditionally done well in hockey, but after the Olympics in Moscow, 1980, performance in hockey has been on a steady decline. Cricket, on the other hand has been able to take centre-stage of the national discourse on sports, and has undoubtedly united Indians. People from all sections of society stand united in support for the Indian cricket team in all competitions and versions of the game, be it traditional test cricket, One-day Internationals, or Twenty20. Literature has also played a leading role in promoting National Integration. One observes that in the field of literature, both English literature and regional literature reflected in the form of poems, short stories, etc. helped promote the national identity and lessen areas of conflicts arising due to differences in caste, region, etc. Patriotic literature by Rabindranath Tagore, Bankim Chandra Chatterjee, Prem Chand, Bharatendu Harish Chandra, and many others during the freedom struggle helped deepen and spread Indian Nationalism. Their renditions are still alive in the hearts and minds of people, and reinvigorate the feeling of unity in diversity among the people of India, even in the present day.
Contribution of Middle Class, Intellectuals, and Working Class
It is important to note that none of these classes can afford to confine themselves to a particular region. The middle class for example, is a very mobile community, and often migrate between states frequently, either for business, education, or career prospects. Cities such as Delhi, Mumbai, Bangalore, Pune, Calcutta, etc. have people settled from diverse cultural and regional backgrounds and have made these cities their homes. This section of the middle class, can easily identify themselves with the idea of India. In Mumbai alone, one witnesses people from every region of India, many of whom have migrated there in search of opportunities. Although people migrating from smaller cities to larger ones face various issues, among them being they labeled as ‘outsiders’. However, their will to continue staying and fighting the odds, reflect their confidence in the concept of India. The same holds true for the working class as well. Similarly, the intellectuals, by their very nature of being liberals do not confine themselves within the limits of caste, class, religion and place. They are against the idea of conflicting values and rather work for the collective upliftment of mankind and humanity. Since the evolution of awareness of rights and oneness, we can trace multiple examples when the entire intellectual community has come forward for arbitrary actions of the state against the creative expression of individuals irrespective of caste, creed, religion and place. This allows the space for distinct expressions within a unified India.
Role of the Press/Media/Multinational Companies, etc.
Even before Independence, the press has been an active instrument in the formation of the idea of a unified India. Since independence, due to the tools offered by the Constitution such as freedom of speech and expression, the press and media have gained a substantial amount of autonomy and have been strengthened as an institution. They have made an enormous contribution in building and sustaining the integration of India as one unit in forms that are continuously evolving from printing press to radio to television to social media which caters to the aspirations and views of each generation. Other factors that have been as important as the ones above are the establishments of important institutions such as the State Bank of India, Postal services, Doordarshan, All India Radio, etc. which were important tools of furthering inclusiveness but have subconsciously also promoted and strengthened the idea of a unified India in the minds of our citizens. Hence, although the importance and significance of a region, religion, caste, etc. in the minds of people belonging to each of them cannot be undermined in India due to their historical footprint, however, at all given times, it is the national interest, which must supersede any prejudices towards the above.
Candidates can find the general pattern of the UPSC Civil Service Exam by visiting the IAS Syllabus page.
Multiple Choice Questions
Consider the following statements
- The National Education Policy as submitted by the Kasturirangan Committee submitted an education policy which seeks to address the challenges like quality, equity, affordability facing the existing education system.
- The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 recommended establishing an apex body for education headed by the Prime Minister under the name Rashtriya Shiksha Aayog or National Education Commission.
- The 86th Constitutional Amendment (2002) inserted Article 21A in the Indian Constitution which states:“The State shall provide free and compulsory education to all children of 6 to 14 years in such manner as the State, may by law determine.”
- As per this amendment, the right to education was made a fundamental right and removed from the list of Directive Principles of State Policy.
Choose the correct answer from below given options
A) None of the above given statements are false.
B) Only Statements 3 and 4 are false.
C) Only Statements 1 and 4 are true.
D) All the above given statements are false.
FAQ about National Integration Role Of Education System Cinema Etc
What is the role of education in promoting national integration, which activities are examples of education for national integration.
Related Links
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
IAS 2024 - Your dream can come true!
Download the ultimate guide to upsc cse preparation.
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Towards a Strong Foundation: Social and Emotional Development in Young Children

Nurturing relationships provide the context for human development and are an essential source of resilience for children and adults (e.g., Luthar, 2006; Rutter, 1987). Resilience refers to the capacity to weather and bounce back from both everyday challenges and significant adversity and trauma -- like that we’ve all experienced during the COVID-19 pandemic. It is influenced by foundational social and emotional skills and competencies (e.g., Masten, 2009).
In this short essay we describe children’s early social and emotional skills, show how they are linked to early caregiving and are influenced by stress and vulnerability, and highlight some programs, practices, and strategies that foster them.
Social and Emotional Development and Foundational Relationships
Social and emotional development refers to the processes whereby children learn to identify and express emotions, focus attention and manage impulses, successfully navigate relationships with peers and adults, develop a positive self-concept, make responsible decisions, and solve problems (e.g., Jones, McGarrah, & Kahn, 2019).
Over many decades researchers from an array of disciplines, e.g. human development and psychology, neuroscience, education and economics, have described how these essential skills are deeply intertwined with other areas of development, such as cognitive and physical. These developments in the brain and in behavior all work together to influence school and life outcomes, including higher education, physical and mental health, economic well-being, and civic engagement (Jones & Kahn, 2018).
During development, social and emotional skills grow and change like building blocks. Early skills lay the foundation for more complex skills that emerge later in life. For example, during early childhood, children learn and grow in the context of relationships with parents and other caregivers at home and in childcare and preschool settings. Through responsive, nurturing interactions these relationships shape the growth of basic executive functions, self-regulation and emotional competencies, which are the salient social and emotional skills of early childhood.
These skills encompass young children’s emerging capacity to:
Understand their emotions, communicate about them, and read those of others around them. For example, use feeling words when frustrated, angry, or excited.
Be aware of and begin to manage impulses and behavior. For example, wait for a snack or dinner when hungry or for the chance to share news in the classroom, or remember and follow the routines of bedtime.
Focus and shift attention in explicit ways and imagine the perspectives of another person. For example, move from one activity to another in the classroom, or engage in basic social back and forth and play.
Basic skills like these set the stage for more complex skills later in life such as planning and problem solving, critical thinking and decision making, forming and maintaining sophisticated friendships, and coping skills, among others (Bailey & Jones, 2019).
The Role of Experience and Context Including Stress and Vulnerability
Importantly, these early skills are highly susceptible to stress and vulnerability. Research shows that the prefrontal cortex – which is responsible for executive function and self-regulation -- is closely linked to other brain regions that signal emotions like fear, anger, and anxiety.
These brain regions are connected through the stress response system, which alerts the body to react in times of danger (e.g., Arnsten, 1998). But responding and adapting to stress can come at a cost. When stress is chronic or takes over, it can inhibit children’s early social and emotional skills, resulting in dysregulated, reactive, and sometimes withdrawn behavior, and this is true for young children and adults (e.g., Arnsten, Mazure & Sinha, 2012).
Critical to this dynamic is that predictable, nurturing relationships are protective. They operate as a buffer between stress and strain on the one hand, and children’s healthy development on the other (Center on the Developing Child, 2014).
Research on children’s wellbeing during the pandemic illustrates how these processes can play out. For example, Harvard education researcher Emily Hanno (2021) examined data about a sample of young children and families before and after COVID-19 shut down U.S. childcare centers and preschools in 2020. They found that as parents experienced more stress, households grew more chaotic, and parent-child conflict increased, children displayed more challenging behaviors and fewer adaptive ones.
Another large-scale study, the Rapid Assessment of Pandemic Impact on Development–Early Childhood (RAPID)https://rapidsurveyproject.com/), documented that high levels of material hardship that families experienced in the first year of the pandemic, coupled with ongoing week-to-week unpredictability, had detrimental effects on both caregivers’ and children’s well-being (Liu, et al 2022). Studies on how poverty, disasters, bereavement, armed conflict, and displacement affect children and adults have produced similar findings.
Supporting Family Well-Being and Social and Emotional Development
Supporting children’s social and emotional development demands coordinated child, family, and education-based efforts. Some examples of these are described here.
As noted above, social and emotional development, indeed successful early childhood development more generally, requires nurturing care. This has been defined as health, nutrition, security and safety, responsive caregiving, and opportunities for early learning (Black, et al, 2016).
Globally, this concept has been advanced through The Nurturing Care Framework for Early Childhood Development ( https://nurturing-care.org/ ) .
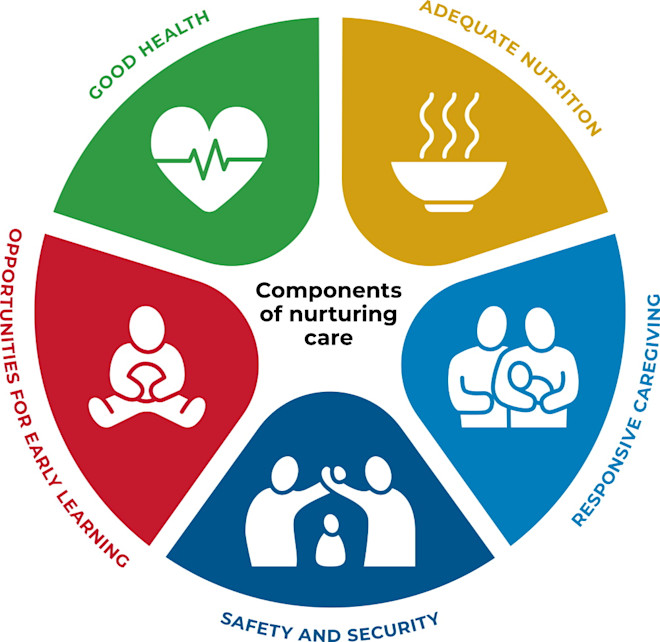
The Nurturing Care Framework was developed by WHO, UNICEF, the World Bank Group, in collaboration with the Partnership for Maternal, Newborn and Child Health, the Early Childhood Development Action Network and many other partners, and launched alongside the 71st World Health Assembly in May, 2018. It takes a comprehensive approach by outlining important strategies to address the integrated needs of the developing child.
The wellbeing of caregivers is the enabling environment for responsive care. The promotion of social emotional development depends on policies and practices that take a whole family approach, assuring that those who care for young children have the support they need to be successful as caregivers, including adequate housing, income, childcare, education, health, and mental health supports.
A relevant and recently launched innovation focused on parents is the Global Initiative to Support Parents ( https://ecdan.org/global-initiative-to-support-parents/ ) . This unique partnership launched by the Early Childhood Development Action Network, WHO, UNICEF, End Violence Against Children, and Parenting for Lifelong Health includes the ultimate vision that all families worldwide have universal access to evidence-based parenting support.
Early childhood services designed for parents and children have for decades been understood to play an important role in offsetting the impact of vulnerability and adversity on healthy growth and development and to be an important setting for cultivating emerging social and emotional skills. A hallmark of these efforts is that they provide families with information, resources, and support that enables those nurturing, connected interactions, and helps all parents navigate the stress that inevitably comes with raising young children (Jones, Bailey & Partee, 2017).
In the early classroom context, there are a large number of curricular and strategy-based approaches that educators can embed in their instructional and caregiving routines. The most effective of these programs typically combine direct teaching of social and emotional skills with structures and routines that provide young children with lots of opportunities to practice emerging skills, as well as support for adult caregivers to proactively manage young children’s behavior (e.g., Jones, Bailey & Jacob, 2014).
As noted above, children across the world have been impacted by the uncertainty, isolation and stress caused by the pandemic. In response, The LEGO Foundation teamed up with HundredED, to identify education innovations from across the world focused on improving social and emotional learning. In 2021, they published Spotlight Social and Emotional Learning which presented 13 innovations from 10 countries. These inspiring examples provide promising solutions that can help respond to the needs of children and offer ideas about how to foster caring and nurturing relationships. Some of these innovations can be found here: https://hundred.org/en/collections/social-emotional-learning-sel .
In summary, research and practice focused on children’s early social and emotional development tells us that these skills:
Develop in the context of primary relationships and interactions.
Are foundational to early learning, as well as important developmental milestones throughout life.
Are optimized when children feel safe, secure, and supported.
Are influenced and shaped by experience, culture, and beliefs.
Effective approaches to fostering and supporting these important skills are situated in families, leverage nurturing relationships and interactions at home and in early learning settings, and are rooted in community and family support.
Stephanie Jones
Gerald S. Lesser Professor in Child Development and Education, Harvard Graduate School of Education
Co-Director, Saul Zaentz Early Education Initiative
Joan Lombardi
Senior Fellow, Collaborative on Global Children’s Issues, Georgetown University
Senior Advisor, Graduate School of Education, Stanford Center on Early Childhood
Arnsten, A. (1998). The biology of being frazzled. Science , 280 (5370), 1711-1712, DOI: 10.1126/science.280.5370.1711
Arnsten, A. Mazure. C.M. & Sinha, R. (2012). This Is Your Brain in Meltdown. Scientific American 306, 4, 48-53. DOI: 10.1038/scientificamerican0412-48
Bailey, R., & Jones, S. M. (2019). An Integrated Model of Regulation for Applied Settings. Clinical Child & Family Psychology Review , 22 (1), 2–23. DOI: 10.1007/s10567-019-00288-y
Black, M. M. et al. (2016). for the Lancet Early Childhood Development Series Steering Committee. Advancing Early Childhood Development: from science to scale 1 , Early Childhood development coming of age: Science through the life course . www.thelancet.com , published online October 4, 2016
Center on the Developing Child (2014). Building adult capacities to improve child outcomes: A theory of change. Center on the Developing Child, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA.
Hanno, E.C., Cuartas, J., Miratrix, L.W., Jones, S.M., & Lesaux, N.K. (2021). Changes in children’s behavioral health and family well-being during the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Developmental & Behavioral Pediatrics. DOI: 10.1097/DBP.0000000000001010
Jones, S.M., Bailey, R. & Jacob, R. (2014). Social-emotional learning as a platform for effective classroom management. Phi Delta Kappan . https://doi.org/10.1177/0031721714553405
Jones, S.M., Bailey, R., & Partee, A. (2017). SECURe Families: Interrupting Intergenerational Cycles of Stress and Poverty , The Aspen Journal of Ideas , Aspen Institute.
Jones, S. M., & Kahn, J. (2018). The Evidence Base for How Learning Happens: A Consensus on Social, Emotional, and Academic Development. American Educator , 41 (4), 16-21.
Jones, S.M., McGarrah, M. & Kahn, J. (2019). Social and emotional learning: A principled science of human development in context. Educational Psychologist .
Liu, S., Zalewski, M.,Lengua,L., Gunnar, M., Giuliani, N., Fisher, P. A. (2022) Material hardship level and unpredictability in relation to U.S. Households’, family interactions and emotional well-being: Insights from the C0VID-19 pandemic . Social Science & Medicine, 115173 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0277953622004798?dgcid=author
Luthar, S. S. (2006). Resilience in development: A synthesis of research across five decades. In D. Cicchetti & D. J. Cohen (Eds.), Developmental psychopathology: Risk, disorder, and adaptation (2nd ed., pp. 739–795). New York: Wiley.
Masten, A. S., & Wright, M. O’. D. (2009). Resilience over the lifespan: Developmental perspectives on resistance, recovery, and transformation. In J. W. Reich, A. J. Zautra, & J. S. Hall (Eds.), Handbook of adult resilience (pp. 213–237). New York: Guilford Press.
Rutter, M. (1987). Psychosocial resilience and protective mechanisms. American journal of Orthopsychiatry , 57, 316—331.
- CBSE Class 10th
- CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Main Question Paper
- JEE Main Cutoff
- JEE Main Advanced Admit Card
- JEE Advanced Admit Card 2024
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- KCET Result
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Admit Card
- TS ICET 2024 Hall Ticket
- CMAT Result 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- NEET Rank Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Admit Card 2024
- NEET PG Application Form 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top NLUs Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Predictors & Articles
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- NID DAT Syllabus 2025
- NID DAT 2025
- Design Colleges in India
- Top NIFT Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Interior Design Colleges in India
- Top Graphic Designing Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Interior Design Colleges in Bangalore
- NIFT Result 2024
- NIFT Fees Structure
- NIFT Syllabus 2025
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission 2024
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- LPU NEST 2024
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET Exam City Intimation Slip 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET Mock Test 2024
- CUET Admit card 2024
- CUET PG Syllabus 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Cut Off 2024
- CUET Exam Analysis 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- CUET 2024 Exam Live
- CUET Answer Key 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
National Integration Essay
National integration is a powerful way to bind a country together. People take pride in belonging to a nation, and national integration boosts their sense of belonging. It also allows for more efficient government and business practices. In short, national integration is vital for building a strong nation. Here are a few sample essays on “National Integration”.

100 Words Essay On National Integration
National integration is an effective tool for bringing people together. Everyone in society is different in one way or another, but they come together based on common interests. The central concept behind national integration is not to group people based on language, religion, caste etc. When considering a large country like India, this term has vast importance. It is because India has more than 19500 mother tongues, more than 700 tribes, five major religions and a lot of other diversity. If integration is not done, it may lead to tension between communities, resulting in a lack of coordination and riots in the nation.
200 Words Essay On National Integration
National integration brings together people from different backgrounds to build a unified and peaceful community. It is about accepting that each individual is different from the other and has unique qualities. Thus, no one should be forced into any group or category, and they should have a feeling of nationalism. There are many ways of achieving it.
Achieving National Integration
The first step to achieve national integration is to help people identify who they are and how they are valuable to a nation. The second step would be to reduce the gap between the communities, and the third step is to bring them together to achieve a common objective.
If a nation's communities are not united, it can lead to riots and crises. This imbalance will slow down the nation’s economy’s development and lead to devastating effects, further inflating the gap between communities. Here a government can motivate its citizen to work collectively.
Why It Is Important
National integration has a lot of benefits for a large country like India. It helps maintain the nation's stability and maintains a constant development curve. It promotes harmony in the country and unites the people. It creates a feeling of patriotism and motivates the communities to work for the nation. Thus we can conclude that National Integration is necessary for the development of any country in modern society.
500 Words Essay On National Integration
National integrity is a shared identity that unites a population regardless of background, ethnicity, religion, or gender. Moreover, this sense of unity and brotherhood exists in a society where tolerance and acceptance of difference are central values. Despite the diversity of the country's people in terms of culture, language, and primary means of subsistence, national integration maintains the country as a whole solid and united. When a country's institutions are strong, it is far more likely to see economic growth and technological advancement.
Aims Of National Integration
National integration in a country like India, with its many ethnic, linguistic, and religious minorities, seeks to do more than merely bring its citizens closer together.
It maintains national stability and fostering its growth are both aided by increased national integration.
It encourages cooperation and counteracts discrimination based on race, ethnicity, religion, or language.
It strengthens patriotism and brings the population together in times of crisis.
Importance Of National Integration
Integration at the national level has far-reaching effects on a country's economy, society, and culture. Here are some ways it may help a country:
Promotes Social Harmony | A peaceful country is one in which its residents have achieved national integration. To do this, their relationships with one another are fortified. As a result, friendship, harmony, and mutual understanding are fostered.
Unites the Nation | National integration is essential to unite a country's diverse population behind a common flag. It helps the nation become more robust and present a more confident image abroad.
Fosters Economic Growth | It is generally accepted that a nation with no significant internal problems will always succeed and progress toward expansion. Discord and disorder are less likely to arise in a unified nation.
Belongingness To The Nation | Individuals are more likely to be patriotic if they feel they are contributing to the country's greater good. By diverting attention away from individual problems, it encourages citizens to band together and take a position for the betterment of their nation.
Modern-Day Importance Of National Integration
Integrating nations into one modern whole are crucial. Regionalism, communalism, and linguistic diversity are only a few obstacles it faces. The threat of international terrorism is one of the most significant obstacles to global harmony. Only a few radicals can influence and brainwash the majority. They turn them into enemies of their own country.
It is easy to be misled in today's era of instantaneous communication and the widespread use of social media. By integrating as a nation, we can lessen the likelihood of incidents like this. In the long run, it leads to greater intellectual maturity and tolerance among the populace.
Example: GST
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a model of fiscal federalism and national integration. It's proof positive that India's federal democracy is functioning. It was made feasible by the central government working closely with the state governments and all political parties. This integration by the higher authorities motivates people to contribute to the nation’s development by funding it through GST.
National integration is essential for growth. It is crucial since separate nations tend to disintegrate throughout history. Unity must withstand the harshest pressure without fracturing," remarked Mahatma Gandhi.
Applications for Admissions are open.

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)
Register FREE for ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)

JEE Main Important Physics formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Physics formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

PW JEE Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for JEE coaching

PW NEET Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for NEET coaching

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Certifications
We Appeared in

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In India folowing steps can be helpful for the national and emotional integrity-. The pattern of education should base on the cultural and spiritual values of the country- If it is done, a sense of respect and love for the country would develop in the students and they would think themsleves united. This feeling would tie them all in unity.
This new version of the SEL Integration Approach was revised in response to partner feedback and our own learnings from a pilot year of implementation. The following Companion Guides go into more detail on each of the five components of SEL Integration and provide educators with research, guiding questions, practical resources, and look-fors.
CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO. Peace education in the 21st century An essential strategy for building lasting peace This report provides an overview of the importance of peace education, highlighting the challenges and opportunities for using it in efforts to bring about lasting global peace. It reviews key research and is heavily inspired by the ...
Integration Approach serves as a starting point for educators. Want to learn more about how to implement it in your school and district? Contact us at [email protected] TransformEd's SEL Integration Approach Teachable Moments Explicit instruction helps students develop their social-emotional skills by spending time
Education for National Integration and International Understanding. The progress and security of any nation depends upon national unity and emotional integration of its people. The aim of education is not merely individualistic. The purpose of education is to make the individual acquire social efficiency.
A Writing Unit for SEL Integration. I designed a writing unit incorporating the CASEL framework, focusing on the self-awareness competency: the ability to understand one's own emotions, thoughts, and values and how they influence behavior across contexts. As a school, we used Lucy Calkins's Units of Study in our English language arts ...
The full report can be found here: Integration of Social and Emotional Learning into Basic Education Programming: Findings from Eight Case Studies. Links to the individual case study reports can be found in Table I. The purpose of this Brief is to present a summary of the 12 key research findings from this
Abstract. This chapter gives an overview of the critical relationship between students' emotion and school education. Studies show that our emotional system is a complex, widely distributed and defines our basic personality early in life. The unique blending of biology and psychology of emotion promises to suggest powerful educational ...
Social and emotional learning (SEL) strategies develop skills linked to cognitive development, encourage student focus and motivation, improve relationships between students and teachers, and increase student confidence and success. More attention should be paid to students' emotions in higher education to enhance students' engagement in the classroom and improve social awareness (i.e ...
Respect others (e.g., listen carefully and accurately) Understand other points of view and perspectives. Identify social cues (verbal, physical) to determine how others feel. Predict others' feelings and reactions. Manage and express emotions in relationships, respecting diverse viewpoints.
Social Emotional Learning (SEL) is an educational approach that focuses on developing students' emotional intelligence and self-regulation skills. It recognizes the integral connection between academic achievement and social emotional well-being. By equipping students with the necessary tools to understand and manage their emotions, SEL fosters ...
How does inclusive practices in the classroom affect children's social and emotional development? This literature review will explore this question in-depth with multiple peer-reviewed articles and other sources. Research shows that children's social and emotional development can benefit from inclusive practices in the classroom.
The integration essay is a requirement for earning your certificate. 4. We will be reading your essay with the following criteria in mind: • Essay is well-written. Both in terms of structure and organization, and at the sentence level, your essay must be clearly and effectively written for the appropriate audience.
SEL works best when implemented systematically, providing students and faculty a common language and set of skills to draw from. "It's about infusing these principles into the immune system of the school," Brackett says. That calls for administrators to seek out professional development trainings in SEL and set aside adequate time to ...
U.S. Department of Education Dr. Miguel A. Cardona ... 1-800-877-8339), email us at [email protected], or write to U.S. Department of Education, Information Resource Center, 400 Maryland Ave., SW, Washington, DC 20202. ... emotional, and behavioral supports and other mental health services for children and students. Further, with the
2.3. Reading-to-write and emotional intelligence. The idiosyncratic nature of the composing processes in the integrated writing tasks called discourse synthesis ( Plakans, 2008) demands the student writers to rigorously examine the reading-to-write tasks by engaging with text information to use it in an informed way.
Essay Prompt 1: Write an essay of approximately one to two pages that describes the ways in which children can learn emotional intelligence and why it is important to specifically teach emotional ...
The goal of social. emotional learning is to give children the necessary tools for navigating life; these tools include. social skills for interacting and collaborating, emotional skills in order to regulate and express. emotions, and problem solving skills that enable children to be engaged learners. It is also true.
National integration plays a very important role in the political, economic, cultural and social dimensions of a country. It helps the country in the following ways: Promotes Social Harmony. National integration makes the people of a country be present in harmony. This works only by strengthening the social bond between them.
Rev.%3/2017%lyn! ESSAYGUIDELINES% INTEGRATION%ESSAY% To%complete%yourBDP%and%earn%yourcertificate,%you%must%write%a%3I4page%integration%essay%that%draws%
National Integration in India is very important to enhance unity among all sections of society in a country like India, which is replete with diversity in many spheres of life. This article helps one understand the role of the education system, cinema, people from middle class background, working class, intellectuals, different multinational companies and media in promoting National Integration.
It is influenced by foundational social and emotional skills and competencies (e.g., Masten, 2009). In this short essay we describe children's early social and emotional skills, show how they are linked to early caregiving and are influenced by stress and vulnerability, and highlight some programs, practices, and strategies that foster them.
National Integration Essay. National integration is a powerful way to bind a country together. People take pride in belonging to a nation, and national integration boosts their sense of belonging. It also allows for more efficient government and business practices. In short, national integration is vital for building a strong nation.