

The Ultimate Guide to Qualitative Research - Part 1: The Basics

- Introduction and overview
- What is qualitative research?
- What is qualitative data?
- Examples of qualitative data
- Qualitative vs. quantitative research
- Mixed methods
- Qualitative research preparation
- Theoretical perspective
- Theoretical framework
- Literature reviews
Research question
- Conceptual framework
- Conceptual vs. theoretical framework
Data collection
- Qualitative research methods
- Focus groups
- Observational research
What is a case study?
Applications for case study research, what is a good case study, process of case study design, benefits and limitations of case studies.
- Ethnographical research
- Ethical considerations
- Confidentiality and privacy
- Power dynamics
- Reflexivity
Case studies
Case studies are essential to qualitative research , offering a lens through which researchers can investigate complex phenomena within their real-life contexts. This chapter explores the concept, purpose, applications, examples, and types of case studies and provides guidance on how to conduct case study research effectively.

Whereas quantitative methods look at phenomena at scale, case study research looks at a concept or phenomenon in considerable detail. While analyzing a single case can help understand one perspective regarding the object of research inquiry, analyzing multiple cases can help obtain a more holistic sense of the topic or issue. Let's provide a basic definition of a case study, then explore its characteristics and role in the qualitative research process.
Definition of a case study
A case study in qualitative research is a strategy of inquiry that involves an in-depth investigation of a phenomenon within its real-world context. It provides researchers with the opportunity to acquire an in-depth understanding of intricate details that might not be as apparent or accessible through other methods of research. The specific case or cases being studied can be a single person, group, or organization – demarcating what constitutes a relevant case worth studying depends on the researcher and their research question .
Among qualitative research methods , a case study relies on multiple sources of evidence, such as documents, artifacts, interviews , or observations , to present a complete and nuanced understanding of the phenomenon under investigation. The objective is to illuminate the readers' understanding of the phenomenon beyond its abstract statistical or theoretical explanations.
Characteristics of case studies
Case studies typically possess a number of distinct characteristics that set them apart from other research methods. These characteristics include a focus on holistic description and explanation, flexibility in the design and data collection methods, reliance on multiple sources of evidence, and emphasis on the context in which the phenomenon occurs.
Furthermore, case studies can often involve a longitudinal examination of the case, meaning they study the case over a period of time. These characteristics allow case studies to yield comprehensive, in-depth, and richly contextualized insights about the phenomenon of interest.
The role of case studies in research
Case studies hold a unique position in the broader landscape of research methods aimed at theory development. They are instrumental when the primary research interest is to gain an intensive, detailed understanding of a phenomenon in its real-life context.
In addition, case studies can serve different purposes within research - they can be used for exploratory, descriptive, or explanatory purposes, depending on the research question and objectives. This flexibility and depth make case studies a valuable tool in the toolkit of qualitative researchers.
Remember, a well-conducted case study can offer a rich, insightful contribution to both academic and practical knowledge through theory development or theory verification, thus enhancing our understanding of complex phenomena in their real-world contexts.
What is the purpose of a case study?
Case study research aims for a more comprehensive understanding of phenomena, requiring various research methods to gather information for qualitative analysis . Ultimately, a case study can allow the researcher to gain insight into a particular object of inquiry and develop a theoretical framework relevant to the research inquiry.
Why use case studies in qualitative research?
Using case studies as a research strategy depends mainly on the nature of the research question and the researcher's access to the data.
Conducting case study research provides a level of detail and contextual richness that other research methods might not offer. They are beneficial when there's a need to understand complex social phenomena within their natural contexts.
The explanatory, exploratory, and descriptive roles of case studies
Case studies can take on various roles depending on the research objectives. They can be exploratory when the research aims to discover new phenomena or define new research questions; they are descriptive when the objective is to depict a phenomenon within its context in a detailed manner; and they can be explanatory if the goal is to understand specific relationships within the studied context. Thus, the versatility of case studies allows researchers to approach their topic from different angles, offering multiple ways to uncover and interpret the data .
The impact of case studies on knowledge development
Case studies play a significant role in knowledge development across various disciplines. Analysis of cases provides an avenue for researchers to explore phenomena within their context based on the collected data.

This can result in the production of rich, practical insights that can be instrumental in both theory-building and practice. Case studies allow researchers to delve into the intricacies and complexities of real-life situations, uncovering insights that might otherwise remain hidden.
Types of case studies
In qualitative research , a case study is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Depending on the nature of the research question and the specific objectives of the study, researchers might choose to use different types of case studies. These types differ in their focus, methodology, and the level of detail they provide about the phenomenon under investigation.
Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the most appropriate approach for your research project and effectively achieving your research goals. Let's briefly look at the main types of case studies.
Exploratory case studies
Exploratory case studies are typically conducted to develop a theory or framework around an understudied phenomenon. They can also serve as a precursor to a larger-scale research project. Exploratory case studies are useful when a researcher wants to identify the key issues or questions which can spur more extensive study or be used to develop propositions for further research. These case studies are characterized by flexibility, allowing researchers to explore various aspects of a phenomenon as they emerge, which can also form the foundation for subsequent studies.
Descriptive case studies
Descriptive case studies aim to provide a complete and accurate representation of a phenomenon or event within its context. These case studies are often based on an established theoretical framework, which guides how data is collected and analyzed. The researcher is concerned with describing the phenomenon in detail, as it occurs naturally, without trying to influence or manipulate it.
Explanatory case studies
Explanatory case studies are focused on explanation - they seek to clarify how or why certain phenomena occur. Often used in complex, real-life situations, they can be particularly valuable in clarifying causal relationships among concepts and understanding the interplay between different factors within a specific context.

Intrinsic, instrumental, and collective case studies
These three categories of case studies focus on the nature and purpose of the study. An intrinsic case study is conducted when a researcher has an inherent interest in the case itself. Instrumental case studies are employed when the case is used to provide insight into a particular issue or phenomenon. A collective case study, on the other hand, involves studying multiple cases simultaneously to investigate some general phenomena.
Each type of case study serves a different purpose and has its own strengths and challenges. The selection of the type should be guided by the research question and objectives, as well as the context and constraints of the research.
The flexibility, depth, and contextual richness offered by case studies make this approach an excellent research method for various fields of study. They enable researchers to investigate real-world phenomena within their specific contexts, capturing nuances that other research methods might miss. Across numerous fields, case studies provide valuable insights into complex issues.
Critical information systems research
Case studies provide a detailed understanding of the role and impact of information systems in different contexts. They offer a platform to explore how information systems are designed, implemented, and used and how they interact with various social, economic, and political factors. Case studies in this field often focus on examining the intricate relationship between technology, organizational processes, and user behavior, helping to uncover insights that can inform better system design and implementation.
Health research
Health research is another field where case studies are highly valuable. They offer a way to explore patient experiences, healthcare delivery processes, and the impact of various interventions in a real-world context.

Case studies can provide a deep understanding of a patient's journey, giving insights into the intricacies of disease progression, treatment effects, and the psychosocial aspects of health and illness.
Asthma research studies
Specifically within medical research, studies on asthma often employ case studies to explore the individual and environmental factors that influence asthma development, management, and outcomes. A case study can provide rich, detailed data about individual patients' experiences, from the triggers and symptoms they experience to the effectiveness of various management strategies. This can be crucial for developing patient-centered asthma care approaches.
Other fields
Apart from the fields mentioned, case studies are also extensively used in business and management research, education research, and political sciences, among many others. They provide an opportunity to delve into the intricacies of real-world situations, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of various phenomena.
Case studies, with their depth and contextual focus, offer unique insights across these varied fields. They allow researchers to illuminate the complexities of real-life situations, contributing to both theory and practice.
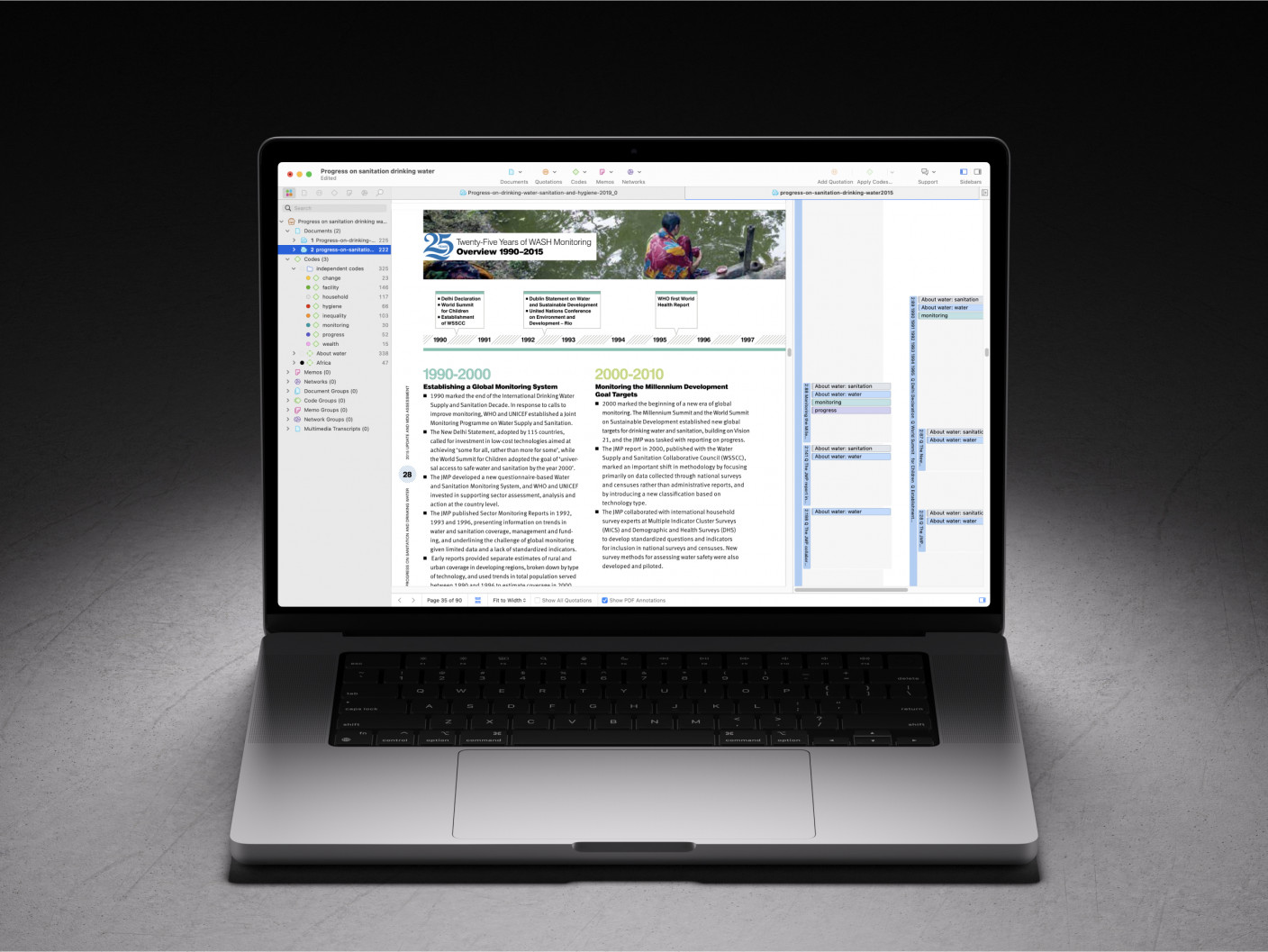
Whatever field you're in, ATLAS.ti puts your data to work for you
Download a free trial of ATLAS.ti to turn your data into insights.
Understanding the key elements of case study design is crucial for conducting rigorous and impactful case study research. A well-structured design guides the researcher through the process, ensuring that the study is methodologically sound and its findings are reliable and valid. The main elements of case study design include the research question , propositions, units of analysis, and the logic linking the data to the propositions.
The research question is the foundation of any research study. A good research question guides the direction of the study and informs the selection of the case, the methods of collecting data, and the analysis techniques. A well-formulated research question in case study research is typically clear, focused, and complex enough to merit further detailed examination of the relevant case(s).
Propositions
Propositions, though not necessary in every case study, provide a direction by stating what we might expect to find in the data collected. They guide how data is collected and analyzed by helping researchers focus on specific aspects of the case. They are particularly important in explanatory case studies, which seek to understand the relationships among concepts within the studied phenomenon.
Units of analysis
The unit of analysis refers to the case, or the main entity or entities that are being analyzed in the study. In case study research, the unit of analysis can be an individual, a group, an organization, a decision, an event, or even a time period. It's crucial to clearly define the unit of analysis, as it shapes the qualitative data analysis process by allowing the researcher to analyze a particular case and synthesize analysis across multiple case studies to draw conclusions.
Argumentation
This refers to the inferential model that allows researchers to draw conclusions from the data. The researcher needs to ensure that there is a clear link between the data, the propositions (if any), and the conclusions drawn. This argumentation is what enables the researcher to make valid and credible inferences about the phenomenon under study.
Understanding and carefully considering these elements in the design phase of a case study can significantly enhance the quality of the research. It can help ensure that the study is methodologically sound and its findings contribute meaningful insights about the case.
Ready to jumpstart your research with ATLAS.ti?
Conceptualize your research project with our intuitive data analysis interface. Download a free trial today.
Conducting a case study involves several steps, from defining the research question and selecting the case to collecting and analyzing data . This section outlines these key stages, providing a practical guide on how to conduct case study research.
Defining the research question
The first step in case study research is defining a clear, focused research question. This question should guide the entire research process, from case selection to analysis. It's crucial to ensure that the research question is suitable for a case study approach. Typically, such questions are exploratory or descriptive in nature and focus on understanding a phenomenon within its real-life context.
Selecting and defining the case
The selection of the case should be based on the research question and the objectives of the study. It involves choosing a unique example or a set of examples that provide rich, in-depth data about the phenomenon under investigation. After selecting the case, it's crucial to define it clearly, setting the boundaries of the case, including the time period and the specific context.
Previous research can help guide the case study design. When considering a case study, an example of a case could be taken from previous case study research and used to define cases in a new research inquiry. Considering recently published examples can help understand how to select and define cases effectively.
Developing a detailed case study protocol
A case study protocol outlines the procedures and general rules to be followed during the case study. This includes the data collection methods to be used, the sources of data, and the procedures for analysis. Having a detailed case study protocol ensures consistency and reliability in the study.
The protocol should also consider how to work with the people involved in the research context to grant the research team access to collecting data. As mentioned in previous sections of this guide, establishing rapport is an essential component of qualitative research as it shapes the overall potential for collecting and analyzing data.
Collecting data
Gathering data in case study research often involves multiple sources of evidence, including documents, archival records, interviews, observations, and physical artifacts. This allows for a comprehensive understanding of the case. The process for gathering data should be systematic and carefully documented to ensure the reliability and validity of the study.
Analyzing and interpreting data
The next step is analyzing the data. This involves organizing the data , categorizing it into themes or patterns , and interpreting these patterns to answer the research question. The analysis might also involve comparing the findings with prior research or theoretical propositions.
Writing the case study report
The final step is writing the case study report . This should provide a detailed description of the case, the data, the analysis process, and the findings. The report should be clear, organized, and carefully written to ensure that the reader can understand the case and the conclusions drawn from it.
Each of these steps is crucial in ensuring that the case study research is rigorous, reliable, and provides valuable insights about the case.
The type, depth, and quality of data in your study can significantly influence the validity and utility of the study. In case study research, data is usually collected from multiple sources to provide a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case. This section will outline the various methods of collecting data used in case study research and discuss considerations for ensuring the quality of the data.
Interviews are a common method of gathering data in case study research. They can provide rich, in-depth data about the perspectives, experiences, and interpretations of the individuals involved in the case. Interviews can be structured , semi-structured , or unstructured , depending on the research question and the degree of flexibility needed.
Observations
Observations involve the researcher observing the case in its natural setting, providing first-hand information about the case and its context. Observations can provide data that might not be revealed in interviews or documents, such as non-verbal cues or contextual information.
Documents and artifacts
Documents and archival records provide a valuable source of data in case study research. They can include reports, letters, memos, meeting minutes, email correspondence, and various public and private documents related to the case.

These records can provide historical context, corroborate evidence from other sources, and offer insights into the case that might not be apparent from interviews or observations.
Physical artifacts refer to any physical evidence related to the case, such as tools, products, or physical environments. These artifacts can provide tangible insights into the case, complementing the data gathered from other sources.
Ensuring the quality of data collection
Determining the quality of data in case study research requires careful planning and execution. It's crucial to ensure that the data is reliable, accurate, and relevant to the research question. This involves selecting appropriate methods of collecting data, properly training interviewers or observers, and systematically recording and storing the data. It also includes considering ethical issues related to collecting and handling data, such as obtaining informed consent and ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of the participants.
Data analysis
Analyzing case study research involves making sense of the rich, detailed data to answer the research question. This process can be challenging due to the volume and complexity of case study data. However, a systematic and rigorous approach to analysis can ensure that the findings are credible and meaningful. This section outlines the main steps and considerations in analyzing data in case study research.
Organizing the data
The first step in the analysis is organizing the data. This involves sorting the data into manageable sections, often according to the data source or the theme. This step can also involve transcribing interviews, digitizing physical artifacts, or organizing observational data.
Categorizing and coding the data
Once the data is organized, the next step is to categorize or code the data. This involves identifying common themes, patterns, or concepts in the data and assigning codes to relevant data segments. Coding can be done manually or with the help of software tools, and in either case, qualitative analysis software can greatly facilitate the entire coding process. Coding helps to reduce the data to a set of themes or categories that can be more easily analyzed.
Identifying patterns and themes
After coding the data, the researcher looks for patterns or themes in the coded data. This involves comparing and contrasting the codes and looking for relationships or patterns among them. The identified patterns and themes should help answer the research question.
Interpreting the data
Once patterns and themes have been identified, the next step is to interpret these findings. This involves explaining what the patterns or themes mean in the context of the research question and the case. This interpretation should be grounded in the data, but it can also involve drawing on theoretical concepts or prior research.
Verification of the data
The last step in the analysis is verification. This involves checking the accuracy and consistency of the analysis process and confirming that the findings are supported by the data. This can involve re-checking the original data, checking the consistency of codes, or seeking feedback from research participants or peers.
Like any research method , case study research has its strengths and limitations. Researchers must be aware of these, as they can influence the design, conduct, and interpretation of the study.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of case study research can also guide researchers in deciding whether this approach is suitable for their research question . This section outlines some of the key strengths and limitations of case study research.
Benefits include the following:
- Rich, detailed data: One of the main strengths of case study research is that it can generate rich, detailed data about the case. This can provide a deep understanding of the case and its context, which can be valuable in exploring complex phenomena.
- Flexibility: Case study research is flexible in terms of design , data collection , and analysis . A sufficient degree of flexibility allows the researcher to adapt the study according to the case and the emerging findings.
- Real-world context: Case study research involves studying the case in its real-world context, which can provide valuable insights into the interplay between the case and its context.
- Multiple sources of evidence: Case study research often involves collecting data from multiple sources , which can enhance the robustness and validity of the findings.
On the other hand, researchers should consider the following limitations:
- Generalizability: A common criticism of case study research is that its findings might not be generalizable to other cases due to the specificity and uniqueness of each case.
- Time and resource intensive: Case study research can be time and resource intensive due to the depth of the investigation and the amount of collected data.
- Complexity of analysis: The rich, detailed data generated in case study research can make analyzing the data challenging.
- Subjectivity: Given the nature of case study research, there may be a higher degree of subjectivity in interpreting the data , so researchers need to reflect on this and transparently convey to audiences how the research was conducted.
Being aware of these strengths and limitations can help researchers design and conduct case study research effectively and interpret and report the findings appropriately.

Ready to analyze your data with ATLAS.ti?
See how our intuitive software can draw key insights from your data with a free trial today.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
What Is a Case Study?
Weighing the pros and cons of this method of research
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Cara Lustik is a fact-checker and copywriter.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Cara-Lustik-1000-77abe13cf6c14a34a58c2a0ffb7297da.jpg)
Verywell / Colleen Tighe
- Pros and Cons
What Types of Case Studies Are Out There?
Where do you find data for a case study, how do i write a psychology case study.
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
The point of a case study is to learn as much as possible about an individual or group so that the information can be generalized to many others. Unfortunately, case studies tend to be highly subjective, and it is sometimes difficult to generalize results to a larger population.
While case studies focus on a single individual or group, they follow a format similar to other types of psychology writing. If you are writing a case study, we got you—here are some rules of APA format to reference.
At a Glance
A case study, or an in-depth study of a person, group, or event, can be a useful research tool when used wisely. In many cases, case studies are best used in situations where it would be difficult or impossible for you to conduct an experiment. They are helpful for looking at unique situations and allow researchers to gather a lot of˜ information about a specific individual or group of people. However, it's important to be cautious of any bias we draw from them as they are highly subjective.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Case Studies?
A case study can have its strengths and weaknesses. Researchers must consider these pros and cons before deciding if this type of study is appropriate for their needs.
One of the greatest advantages of a case study is that it allows researchers to investigate things that are often difficult or impossible to replicate in a lab. Some other benefits of a case study:
- Allows researchers to capture information on the 'how,' 'what,' and 'why,' of something that's implemented
- Gives researchers the chance to collect information on why one strategy might be chosen over another
- Permits researchers to develop hypotheses that can be explored in experimental research
On the other hand, a case study can have some drawbacks:
- It cannot necessarily be generalized to the larger population
- Cannot demonstrate cause and effect
- It may not be scientifically rigorous
- It can lead to bias
Researchers may choose to perform a case study if they want to explore a unique or recently discovered phenomenon. Through their insights, researchers develop additional ideas and study questions that might be explored in future studies.
It's important to remember that the insights from case studies cannot be used to determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables. However, case studies may be used to develop hypotheses that can then be addressed in experimental research.
Case Study Examples
There have been a number of notable case studies in the history of psychology. Much of Freud's work and theories were developed through individual case studies. Some great examples of case studies in psychology include:
- Anna O : Anna O. was a pseudonym of a woman named Bertha Pappenheim, a patient of a physician named Josef Breuer. While she was never a patient of Freud's, Freud and Breuer discussed her case extensively. The woman was experiencing symptoms of a condition that was then known as hysteria and found that talking about her problems helped relieve her symptoms. Her case played an important part in the development of talk therapy as an approach to mental health treatment.
- Phineas Gage : Phineas Gage was a railroad employee who experienced a terrible accident in which an explosion sent a metal rod through his skull, damaging important portions of his brain. Gage recovered from his accident but was left with serious changes in both personality and behavior.
- Genie : Genie was a young girl subjected to horrific abuse and isolation. The case study of Genie allowed researchers to study whether language learning was possible, even after missing critical periods for language development. Her case also served as an example of how scientific research may interfere with treatment and lead to further abuse of vulnerable individuals.
Such cases demonstrate how case research can be used to study things that researchers could not replicate in experimental settings. In Genie's case, her horrific abuse denied her the opportunity to learn a language at critical points in her development.
This is clearly not something researchers could ethically replicate, but conducting a case study on Genie allowed researchers to study phenomena that are otherwise impossible to reproduce.
There are a few different types of case studies that psychologists and other researchers might use:
- Collective case studies : These involve studying a group of individuals. Researchers might study a group of people in a certain setting or look at an entire community. For example, psychologists might explore how access to resources in a community has affected the collective mental well-being of those who live there.
- Descriptive case studies : These involve starting with a descriptive theory. The subjects are then observed, and the information gathered is compared to the pre-existing theory.
- Explanatory case studies : These are often used to do causal investigations. In other words, researchers are interested in looking at factors that may have caused certain things to occur.
- Exploratory case studies : These are sometimes used as a prelude to further, more in-depth research. This allows researchers to gather more information before developing their research questions and hypotheses .
- Instrumental case studies : These occur when the individual or group allows researchers to understand more than what is initially obvious to observers.
- Intrinsic case studies : This type of case study is when the researcher has a personal interest in the case. Jean Piaget's observations of his own children are good examples of how an intrinsic case study can contribute to the development of a psychological theory.
The three main case study types often used are intrinsic, instrumental, and collective. Intrinsic case studies are useful for learning about unique cases. Instrumental case studies help look at an individual to learn more about a broader issue. A collective case study can be useful for looking at several cases simultaneously.
The type of case study that psychology researchers use depends on the unique characteristics of the situation and the case itself.
There are a number of different sources and methods that researchers can use to gather information about an individual or group. Six major sources that have been identified by researchers are:
- Archival records : Census records, survey records, and name lists are examples of archival records.
- Direct observation : This strategy involves observing the subject, often in a natural setting . While an individual observer is sometimes used, it is more common to utilize a group of observers.
- Documents : Letters, newspaper articles, administrative records, etc., are the types of documents often used as sources.
- Interviews : Interviews are one of the most important methods for gathering information in case studies. An interview can involve structured survey questions or more open-ended questions.
- Participant observation : When the researcher serves as a participant in events and observes the actions and outcomes, it is called participant observation.
- Physical artifacts : Tools, objects, instruments, and other artifacts are often observed during a direct observation of the subject.
If you have been directed to write a case study for a psychology course, be sure to check with your instructor for any specific guidelines you need to follow. If you are writing your case study for a professional publication, check with the publisher for their specific guidelines for submitting a case study.
Here is a general outline of what should be included in a case study.
Section 1: A Case History
This section will have the following structure and content:
Background information : The first section of your paper will present your client's background. Include factors such as age, gender, work, health status, family mental health history, family and social relationships, drug and alcohol history, life difficulties, goals, and coping skills and weaknesses.
Description of the presenting problem : In the next section of your case study, you will describe the problem or symptoms that the client presented with.
Describe any physical, emotional, or sensory symptoms reported by the client. Thoughts, feelings, and perceptions related to the symptoms should also be noted. Any screening or diagnostic assessments that are used should also be described in detail and all scores reported.
Your diagnosis : Provide your diagnosis and give the appropriate Diagnostic and Statistical Manual code. Explain how you reached your diagnosis, how the client's symptoms fit the diagnostic criteria for the disorder(s), or any possible difficulties in reaching a diagnosis.
Section 2: Treatment Plan
This portion of the paper will address the chosen treatment for the condition. This might also include the theoretical basis for the chosen treatment or any other evidence that might exist to support why this approach was chosen.
- Cognitive behavioral approach : Explain how a cognitive behavioral therapist would approach treatment. Offer background information on cognitive behavioral therapy and describe the treatment sessions, client response, and outcome of this type of treatment. Make note of any difficulties or successes encountered by your client during treatment.
- Humanistic approach : Describe a humanistic approach that could be used to treat your client, such as client-centered therapy . Provide information on the type of treatment you chose, the client's reaction to the treatment, and the end result of this approach. Explain why the treatment was successful or unsuccessful.
- Psychoanalytic approach : Describe how a psychoanalytic therapist would view the client's problem. Provide some background on the psychoanalytic approach and cite relevant references. Explain how psychoanalytic therapy would be used to treat the client, how the client would respond to therapy, and the effectiveness of this treatment approach.
- Pharmacological approach : If treatment primarily involves the use of medications, explain which medications were used and why. Provide background on the effectiveness of these medications and how monotherapy may compare with an approach that combines medications with therapy or other treatments.
This section of a case study should also include information about the treatment goals, process, and outcomes.
When you are writing a case study, you should also include a section where you discuss the case study itself, including the strengths and limitiations of the study. You should note how the findings of your case study might support previous research.
In your discussion section, you should also describe some of the implications of your case study. What ideas or findings might require further exploration? How might researchers go about exploring some of these questions in additional studies?
Need More Tips?
Here are a few additional pointers to keep in mind when formatting your case study:
- Never refer to the subject of your case study as "the client." Instead, use their name or a pseudonym.
- Read examples of case studies to gain an idea about the style and format.
- Remember to use APA format when citing references .
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011;11:100.
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011 Jun 27;11:100. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Gagnon, Yves-Chantal. The Case Study as Research Method: A Practical Handbook . Canada, Chicago Review Press Incorporated DBA Independent Pub Group, 2010.
Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . United States, SAGE Publications, 2017.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
- Privacy Policy

Home » Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents

A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation.
It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied. Case studies typically involve multiple sources of data, including interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, which are analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, and grounded theory. The findings of a case study are often used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Types of Case Study
Types and Methods of Case Study are as follows:
Single-Case Study
A single-case study is an in-depth analysis of a single case. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand a specific phenomenon in detail.
For Example , A researcher might conduct a single-case study on a particular individual to understand their experiences with a particular health condition or a specific organization to explore their management practices. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a single-case study are often used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Multiple-Case Study
A multiple-case study involves the analysis of several cases that are similar in nature. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to identify similarities and differences between the cases.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a multiple-case study on several companies to explore the factors that contribute to their success or failure. The researcher collects data from each case, compares and contrasts the findings, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as comparative analysis or pattern-matching. The findings of a multiple-case study can be used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Exploratory Case Study
An exploratory case study is used to explore a new or understudied phenomenon. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to generate hypotheses or theories about the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an exploratory case study on a new technology to understand its potential impact on society. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as grounded theory or content analysis. The findings of an exploratory case study can be used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Descriptive Case Study
A descriptive case study is used to describe a particular phenomenon in detail. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to provide a comprehensive account of the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a descriptive case study on a particular community to understand its social and economic characteristics. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a descriptive case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Instrumental Case Study
An instrumental case study is used to understand a particular phenomenon that is instrumental in achieving a particular goal. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand the role of the phenomenon in achieving the goal.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an instrumental case study on a particular policy to understand its impact on achieving a particular goal, such as reducing poverty. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of an instrumental case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Case Study Data Collection Methods
Here are some common data collection methods for case studies:
Interviews involve asking questions to individuals who have knowledge or experience relevant to the case study. Interviews can be structured (where the same questions are asked to all participants) or unstructured (where the interviewer follows up on the responses with further questions). Interviews can be conducted in person, over the phone, or through video conferencing.
Observations
Observations involve watching and recording the behavior and activities of individuals or groups relevant to the case study. Observations can be participant (where the researcher actively participates in the activities) or non-participant (where the researcher observes from a distance). Observations can be recorded using notes, audio or video recordings, or photographs.
Documents can be used as a source of information for case studies. Documents can include reports, memos, emails, letters, and other written materials related to the case study. Documents can be collected from the case study participants or from public sources.
Surveys involve asking a set of questions to a sample of individuals relevant to the case study. Surveys can be administered in person, over the phone, through mail or email, or online. Surveys can be used to gather information on attitudes, opinions, or behaviors related to the case study.
Artifacts are physical objects relevant to the case study. Artifacts can include tools, equipment, products, or other objects that provide insights into the case study phenomenon.
How to conduct Case Study Research
Conducting a case study research involves several steps that need to be followed to ensure the quality and rigor of the study. Here are the steps to conduct case study research:
- Define the research questions: The first step in conducting a case study research is to define the research questions. The research questions should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the case study phenomenon under investigation.
- Select the case: The next step is to select the case or cases to be studied. The case should be relevant to the research questions and should provide rich and diverse data that can be used to answer the research questions.
- Collect data: Data can be collected using various methods, such as interviews, observations, documents, surveys, and artifacts. The data collection method should be selected based on the research questions and the nature of the case study phenomenon.
- Analyze the data: The data collected from the case study should be analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, or grounded theory. The analysis should be guided by the research questions and should aim to provide insights and conclusions relevant to the research questions.
- Draw conclusions: The conclusions drawn from the case study should be based on the data analysis and should be relevant to the research questions. The conclusions should be supported by evidence and should be clearly stated.
- Validate the findings: The findings of the case study should be validated by reviewing the data and the analysis with participants or other experts in the field. This helps to ensure the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Write the report: The final step is to write the report of the case study research. The report should provide a clear description of the case study phenomenon, the research questions, the data collection methods, the data analysis, the findings, and the conclusions. The report should be written in a clear and concise manner and should follow the guidelines for academic writing.
Examples of Case Study
Here are some examples of case study research:
- The Hawthorne Studies : Conducted between 1924 and 1932, the Hawthorne Studies were a series of case studies conducted by Elton Mayo and his colleagues to examine the impact of work environment on employee productivity. The studies were conducted at the Hawthorne Works plant of the Western Electric Company in Chicago and included interviews, observations, and experiments.
- The Stanford Prison Experiment: Conducted in 1971, the Stanford Prison Experiment was a case study conducted by Philip Zimbardo to examine the psychological effects of power and authority. The study involved simulating a prison environment and assigning participants to the role of guards or prisoners. The study was controversial due to the ethical issues it raised.
- The Challenger Disaster: The Challenger Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Space Shuttle Challenger explosion in 1986. The study included interviews, observations, and analysis of data to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
- The Enron Scandal: The Enron Scandal was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Enron Corporation’s bankruptcy in 2001. The study included interviews, analysis of financial data, and review of documents to identify the accounting practices, corporate culture, and ethical issues that led to the company’s downfall.
- The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster : The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the nuclear accident that occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan in 2011. The study included interviews, analysis of data, and review of documents to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
Application of Case Study
Case studies have a wide range of applications across various fields and industries. Here are some examples:
Business and Management
Case studies are widely used in business and management to examine real-life situations and develop problem-solving skills. Case studies can help students and professionals to develop a deep understanding of business concepts, theories, and best practices.
Case studies are used in healthcare to examine patient care, treatment options, and outcomes. Case studies can help healthcare professionals to develop critical thinking skills, diagnose complex medical conditions, and develop effective treatment plans.
Case studies are used in education to examine teaching and learning practices. Case studies can help educators to develop effective teaching strategies, evaluate student progress, and identify areas for improvement.
Social Sciences
Case studies are widely used in social sciences to examine human behavior, social phenomena, and cultural practices. Case studies can help researchers to develop theories, test hypotheses, and gain insights into complex social issues.
Law and Ethics
Case studies are used in law and ethics to examine legal and ethical dilemmas. Case studies can help lawyers, policymakers, and ethical professionals to develop critical thinking skills, analyze complex cases, and make informed decisions.
Purpose of Case Study
The purpose of a case study is to provide a detailed analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. A case study is a qualitative research method that involves the in-depth exploration and analysis of a particular case, which can be an individual, group, organization, event, or community.
The primary purpose of a case study is to generate a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case, including its history, context, and dynamics. Case studies can help researchers to identify and examine the underlying factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and detailed understanding of the case, which can inform future research, practice, or policy.
Case studies can also serve other purposes, including:
- Illustrating a theory or concept: Case studies can be used to illustrate and explain theoretical concepts and frameworks, providing concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Developing hypotheses: Case studies can help to generate hypotheses about the causal relationships between different factors and outcomes, which can be tested through further research.
- Providing insight into complex issues: Case studies can provide insights into complex and multifaceted issues, which may be difficult to understand through other research methods.
- Informing practice or policy: Case studies can be used to inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
Advantages of Case Study Research
There are several advantages of case study research, including:
- In-depth exploration: Case study research allows for a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. This can provide a comprehensive understanding of the case and its dynamics, which may not be possible through other research methods.
- Rich data: Case study research can generate rich and detailed data, including qualitative data such as interviews, observations, and documents. This can provide a nuanced understanding of the case and its complexity.
- Holistic perspective: Case study research allows for a holistic perspective of the case, taking into account the various factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the case.
- Theory development: Case study research can help to develop and refine theories and concepts by providing empirical evidence and concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Practical application: Case study research can inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
- Contextualization: Case study research takes into account the specific context in which the case is situated, which can help to understand how the case is influenced by the social, cultural, and historical factors of its environment.
Limitations of Case Study Research
There are several limitations of case study research, including:
- Limited generalizability : Case studies are typically focused on a single case or a small number of cases, which limits the generalizability of the findings. The unique characteristics of the case may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, which may limit the external validity of the research.
- Biased sampling: Case studies may rely on purposive or convenience sampling, which can introduce bias into the sample selection process. This may limit the representativeness of the sample and the generalizability of the findings.
- Subjectivity: Case studies rely on the interpretation of the researcher, which can introduce subjectivity into the analysis. The researcher’s own biases, assumptions, and perspectives may influence the findings, which may limit the objectivity of the research.
- Limited control: Case studies are typically conducted in naturalistic settings, which limits the control that the researcher has over the environment and the variables being studied. This may limit the ability to establish causal relationships between variables.
- Time-consuming: Case studies can be time-consuming to conduct, as they typically involve a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific case. This may limit the feasibility of conducting multiple case studies or conducting case studies in a timely manner.
- Resource-intensive: Case studies may require significant resources, including time, funding, and expertise. This may limit the ability of researchers to conduct case studies in resource-constrained settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide

Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, condition, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity. A case study research paper usually examines a single subject of analysis, but case study papers can also be designed as a comparative investigation that shows relationships between two or more subjects. The methods used to study a case can rest within a quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method investigative paradigm.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010 ; “What is a Case Study?” In Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London: SAGE, 2010.
How to Approach Writing a Case Study Research Paper
General information about how to choose a topic to investigate can be found under the " Choosing a Research Problem " tab in the Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper writing guide. Review this page because it may help you identify a subject of analysis that can be investigated using a case study design.
However, identifying a case to investigate involves more than choosing the research problem . A case study encompasses a problem contextualized around the application of in-depth analysis, interpretation, and discussion, often resulting in specific recommendations for action or for improving existing conditions. As Seawright and Gerring note, practical considerations such as time and access to information can influence case selection, but these issues should not be the sole factors used in describing the methodological justification for identifying a particular case to study. Given this, selecting a case includes considering the following:
- The case represents an unusual or atypical example of a research problem that requires more in-depth analysis? Cases often represent a topic that rests on the fringes of prior investigations because the case may provide new ways of understanding the research problem. For example, if the research problem is to identify strategies to improve policies that support girl's access to secondary education in predominantly Muslim nations, you could consider using Azerbaijan as a case study rather than selecting a more obvious nation in the Middle East. Doing so may reveal important new insights into recommending how governments in other predominantly Muslim nations can formulate policies that support improved access to education for girls.
- The case provides important insight or illuminate a previously hidden problem? In-depth analysis of a case can be based on the hypothesis that the case study will reveal trends or issues that have not been exposed in prior research or will reveal new and important implications for practice. For example, anecdotal evidence may suggest drug use among homeless veterans is related to their patterns of travel throughout the day. Assuming prior studies have not looked at individual travel choices as a way to study access to illicit drug use, a case study that observes a homeless veteran could reveal how issues of personal mobility choices facilitate regular access to illicit drugs. Note that it is important to conduct a thorough literature review to ensure that your assumption about the need to reveal new insights or previously hidden problems is valid and evidence-based.
- The case challenges and offers a counter-point to prevailing assumptions? Over time, research on any given topic can fall into a trap of developing assumptions based on outdated studies that are still applied to new or changing conditions or the idea that something should simply be accepted as "common sense," even though the issue has not been thoroughly tested in current practice. A case study analysis may offer an opportunity to gather evidence that challenges prevailing assumptions about a research problem and provide a new set of recommendations applied to practice that have not been tested previously. For example, perhaps there has been a long practice among scholars to apply a particular theory in explaining the relationship between two subjects of analysis. Your case could challenge this assumption by applying an innovative theoretical framework [perhaps borrowed from another discipline] to explore whether this approach offers new ways of understanding the research problem. Taking a contrarian stance is one of the most important ways that new knowledge and understanding develops from existing literature.
- The case provides an opportunity to pursue action leading to the resolution of a problem? Another way to think about choosing a case to study is to consider how the results from investigating a particular case may result in findings that reveal ways in which to resolve an existing or emerging problem. For example, studying the case of an unforeseen incident, such as a fatal accident at a railroad crossing, can reveal hidden issues that could be applied to preventative measures that contribute to reducing the chance of accidents in the future. In this example, a case study investigating the accident could lead to a better understanding of where to strategically locate additional signals at other railroad crossings so as to better warn drivers of an approaching train, particularly when visibility is hindered by heavy rain, fog, or at night.
- The case offers a new direction in future research? A case study can be used as a tool for an exploratory investigation that highlights the need for further research about the problem. A case can be used when there are few studies that help predict an outcome or that establish a clear understanding about how best to proceed in addressing a problem. For example, after conducting a thorough literature review [very important!], you discover that little research exists showing the ways in which women contribute to promoting water conservation in rural communities of east central Africa. A case study of how women contribute to saving water in a rural village of Uganda can lay the foundation for understanding the need for more thorough research that documents how women in their roles as cooks and family caregivers think about water as a valuable resource within their community. This example of a case study could also point to the need for scholars to build new theoretical frameworks around the topic [e.g., applying feminist theories of work and family to the issue of water conservation].
Eisenhardt, Kathleen M. “Building Theories from Case Study Research.” Academy of Management Review 14 (October 1989): 532-550; Emmel, Nick. Sampling and Choosing Cases in Qualitative Research: A Realist Approach . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2013; Gerring, John. “What Is a Case Study and What Is It Good for?” American Political Science Review 98 (May 2004): 341-354; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Seawright, Jason and John Gerring. "Case Selection Techniques in Case Study Research." Political Research Quarterly 61 (June 2008): 294-308.
Structure and Writing Style
The purpose of a paper in the social sciences designed around a case study is to thoroughly investigate a subject of analysis in order to reveal a new understanding about the research problem and, in so doing, contributing new knowledge to what is already known from previous studies. In applied social sciences disciplines [e.g., education, social work, public administration, etc.], case studies may also be used to reveal best practices, highlight key programs, or investigate interesting aspects of professional work.
In general, the structure of a case study research paper is not all that different from a standard college-level research paper. However, there are subtle differences you should be aware of. Here are the key elements to organizing and writing a case study research paper.
I. Introduction
As with any research paper, your introduction should serve as a roadmap for your readers to ascertain the scope and purpose of your study . The introduction to a case study research paper, however, should not only describe the research problem and its significance, but you should also succinctly describe why the case is being used and how it relates to addressing the problem. The two elements should be linked. With this in mind, a good introduction answers these four questions:
- What is being studied? Describe the research problem and describe the subject of analysis [the case] you have chosen to address the problem. Explain how they are linked and what elements of the case will help to expand knowledge and understanding about the problem.
- Why is this topic important to investigate? Describe the significance of the research problem and state why a case study design and the subject of analysis that the paper is designed around is appropriate in addressing the problem.
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study? Provide background that helps lead the reader into the more in-depth literature review to follow. If applicable, summarize prior case study research applied to the research problem and why it fails to adequately address the problem. Describe why your case will be useful. If no prior case studies have been used to address the research problem, explain why you have selected this subject of analysis.
- How will this study advance new knowledge or new ways of understanding? Explain why your case study will be suitable in helping to expand knowledge and understanding about the research problem.
Each of these questions should be addressed in no more than a few paragraphs. Exceptions to this can be when you are addressing a complex research problem or subject of analysis that requires more in-depth background information.
II. Literature Review
The literature review for a case study research paper is generally structured the same as it is for any college-level research paper. The difference, however, is that the literature review is focused on providing background information and enabling historical interpretation of the subject of analysis in relation to the research problem the case is intended to address . This includes synthesizing studies that help to:
- Place relevant works in the context of their contribution to understanding the case study being investigated . This would involve summarizing studies that have used a similar subject of analysis to investigate the research problem. If there is literature using the same or a very similar case to study, you need to explain why duplicating past research is important [e.g., conditions have changed; prior studies were conducted long ago, etc.].
- Describe the relationship each work has to the others under consideration that informs the reader why this case is applicable . Your literature review should include a description of any works that support using the case to investigate the research problem and the underlying research questions.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research using the case study . If applicable, review any research that has examined the research problem using a different research design. Explain how your use of a case study design may reveal new knowledge or a new perspective or that can redirect research in an important new direction.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies . This refers to synthesizing any literature that points to unresolved issues of concern about the research problem and describing how the subject of analysis that forms the case study can help resolve these existing contradictions.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research . Your review should examine any literature that lays a foundation for understanding why your case study design and the subject of analysis around which you have designed your study may reveal a new way of approaching the research problem or offer a perspective that points to the need for additional research.
- Expose any gaps that exist in the literature that the case study could help to fill . Summarize any literature that not only shows how your subject of analysis contributes to understanding the research problem, but how your case contributes to a new way of understanding the problem that prior research has failed to do.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important!] . Collectively, your literature review should always place your case study within the larger domain of prior research about the problem. The overarching purpose of reviewing pertinent literature in a case study paper is to demonstrate that you have thoroughly identified and synthesized prior studies in relation to explaining the relevance of the case in addressing the research problem.
III. Method
In this section, you explain why you selected a particular case [i.e., subject of analysis] and the strategy you used to identify and ultimately decide that your case was appropriate in addressing the research problem. The way you describe the methods used varies depending on the type of subject of analysis that constitutes your case study.
If your subject of analysis is an incident or event . In the social and behavioral sciences, the event or incident that represents the case to be studied is usually bounded by time and place, with a clear beginning and end and with an identifiable location or position relative to its surroundings. The subject of analysis can be a rare or critical event or it can focus on a typical or regular event. The purpose of studying a rare event is to illuminate new ways of thinking about the broader research problem or to test a hypothesis. Critical incident case studies must describe the method by which you identified the event and explain the process by which you determined the validity of this case to inform broader perspectives about the research problem or to reveal new findings. However, the event does not have to be a rare or uniquely significant to support new thinking about the research problem or to challenge an existing hypothesis. For example, Walo, Bull, and Breen conducted a case study to identify and evaluate the direct and indirect economic benefits and costs of a local sports event in the City of Lismore, New South Wales, Australia. The purpose of their study was to provide new insights from measuring the impact of a typical local sports event that prior studies could not measure well because they focused on large "mega-events." Whether the event is rare or not, the methods section should include an explanation of the following characteristics of the event: a) when did it take place; b) what were the underlying circumstances leading to the event; and, c) what were the consequences of the event in relation to the research problem.
If your subject of analysis is a person. Explain why you selected this particular individual to be studied and describe what experiences they have had that provide an opportunity to advance new understandings about the research problem. Mention any background about this person which might help the reader understand the significance of their experiences that make them worthy of study. This includes describing the relationships this person has had with other people, institutions, and/or events that support using them as the subject for a case study research paper. It is particularly important to differentiate the person as the subject of analysis from others and to succinctly explain how the person relates to examining the research problem [e.g., why is one politician in a particular local election used to show an increase in voter turnout from any other candidate running in the election]. Note that these issues apply to a specific group of people used as a case study unit of analysis [e.g., a classroom of students].
If your subject of analysis is a place. In general, a case study that investigates a place suggests a subject of analysis that is unique or special in some way and that this uniqueness can be used to build new understanding or knowledge about the research problem. A case study of a place must not only describe its various attributes relevant to the research problem [e.g., physical, social, historical, cultural, economic, political], but you must state the method by which you determined that this place will illuminate new understandings about the research problem. It is also important to articulate why a particular place as the case for study is being used if similar places also exist [i.e., if you are studying patterns of homeless encampments of veterans in open spaces, explain why you are studying Echo Park in Los Angeles rather than Griffith Park?]. If applicable, describe what type of human activity involving this place makes it a good choice to study [e.g., prior research suggests Echo Park has more homeless veterans].
If your subject of analysis is a phenomenon. A phenomenon refers to a fact, occurrence, or circumstance that can be studied or observed but with the cause or explanation to be in question. In this sense, a phenomenon that forms your subject of analysis can encompass anything that can be observed or presumed to exist but is not fully understood. In the social and behavioral sciences, the case usually focuses on human interaction within a complex physical, social, economic, cultural, or political system. For example, the phenomenon could be the observation that many vehicles used by ISIS fighters are small trucks with English language advertisements on them. The research problem could be that ISIS fighters are difficult to combat because they are highly mobile. The research questions could be how and by what means are these vehicles used by ISIS being supplied to the militants and how might supply lines to these vehicles be cut off? How might knowing the suppliers of these trucks reveal larger networks of collaborators and financial support? A case study of a phenomenon most often encompasses an in-depth analysis of a cause and effect that is grounded in an interactive relationship between people and their environment in some way.
NOTE: The choice of the case or set of cases to study cannot appear random. Evidence that supports the method by which you identified and chose your subject of analysis should clearly support investigation of the research problem and linked to key findings from your literature review. Be sure to cite any studies that helped you determine that the case you chose was appropriate for examining the problem.
IV. Discussion
The main elements of your discussion section are generally the same as any research paper, but centered around interpreting and drawing conclusions about the key findings from your analysis of the case study. Note that a general social sciences research paper may contain a separate section to report findings. However, in a paper designed around a case study, it is common to combine a description of the results with the discussion about their implications. The objectives of your discussion section should include the following:
Reiterate the Research Problem/State the Major Findings Briefly reiterate the research problem you are investigating and explain why the subject of analysis around which you designed the case study were used. You should then describe the findings revealed from your study of the case using direct, declarative, and succinct proclamation of the study results. Highlight any findings that were unexpected or especially profound.
Explain the Meaning of the Findings and Why They are Important Systematically explain the meaning of your case study findings and why you believe they are important. Begin this part of the section by repeating what you consider to be your most important or surprising finding first, then systematically review each finding. Be sure to thoroughly extrapolate what your analysis of the case can tell the reader about situations or conditions beyond the actual case that was studied while, at the same time, being careful not to misconstrue or conflate a finding that undermines the external validity of your conclusions.
Relate the Findings to Similar Studies No study in the social sciences is so novel or possesses such a restricted focus that it has absolutely no relation to previously published research. The discussion section should relate your case study results to those found in other studies, particularly if questions raised from prior studies served as the motivation for choosing your subject of analysis. This is important because comparing and contrasting the findings of other studies helps support the overall importance of your results and it highlights how and in what ways your case study design and the subject of analysis differs from prior research about the topic.
Consider Alternative Explanations of the Findings Remember that the purpose of social science research is to discover and not to prove. When writing the discussion section, you should carefully consider all possible explanations revealed by the case study results, rather than just those that fit your hypothesis or prior assumptions and biases. Be alert to what the in-depth analysis of the case may reveal about the research problem, including offering a contrarian perspective to what scholars have stated in prior research if that is how the findings can be interpreted from your case.
Acknowledge the Study's Limitations You can state the study's limitations in the conclusion section of your paper but describing the limitations of your subject of analysis in the discussion section provides an opportunity to identify the limitations and explain why they are not significant. This part of the discussion section should also note any unanswered questions or issues your case study could not address. More detailed information about how to document any limitations to your research can be found here .
Suggest Areas for Further Research Although your case study may offer important insights about the research problem, there are likely additional questions related to the problem that remain unanswered or findings that unexpectedly revealed themselves as a result of your in-depth analysis of the case. Be sure that the recommendations for further research are linked to the research problem and that you explain why your recommendations are valid in other contexts and based on the original assumptions of your study.
V. Conclusion
As with any research paper, you should summarize your conclusion in clear, simple language; emphasize how the findings from your case study differs from or supports prior research and why. Do not simply reiterate the discussion section. Provide a synthesis of key findings presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem. If you haven't already done so in the discussion section, be sure to document the limitations of your case study and any need for further research.
The function of your paper's conclusion is to: 1) reiterate the main argument supported by the findings from your case study; 2) state clearly the context, background, and necessity of pursuing the research problem using a case study design in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found from reviewing the literature; and, 3) provide a place to persuasively and succinctly restate the significance of your research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with in-depth information about the topic.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is appropriate:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize these points for your reader.
- If prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the conclusion of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration of the case study's findings that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from your case study findings.
Note that, depending on the discipline you are writing in or the preferences of your professor, the concluding paragraph may contain your final reflections on the evidence presented as it applies to practice or on the essay's central research problem. However, the nature of being introspective about the subject of analysis you have investigated will depend on whether you are explicitly asked to express your observations in this way.
Problems to Avoid
Overgeneralization One of the goals of a case study is to lay a foundation for understanding broader trends and issues applied to similar circumstances. However, be careful when drawing conclusions from your case study. They must be evidence-based and grounded in the results of the study; otherwise, it is merely speculation. Looking at a prior example, it would be incorrect to state that a factor in improving girls access to education in Azerbaijan and the policy implications this may have for improving access in other Muslim nations is due to girls access to social media if there is no documentary evidence from your case study to indicate this. There may be anecdotal evidence that retention rates were better for girls who were engaged with social media, but this observation would only point to the need for further research and would not be a definitive finding if this was not a part of your original research agenda.
Failure to Document Limitations No case is going to reveal all that needs to be understood about a research problem. Therefore, just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study , you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis. For example, the case of studying how women conceptualize the need for water conservation in a village in Uganda could have limited application in other cultural contexts or in areas where fresh water from rivers or lakes is plentiful and, therefore, conservation is understood more in terms of managing access rather than preserving access to a scarce resource.
Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings. If you do not, your reader may question the validity of your analysis, particularly if you failed to document an obvious outcome from your case study research. For example, in the case of studying the accident at the railroad crossing to evaluate where and what types of warning signals should be located, you failed to take into consideration speed limit signage as well as warning signals. When designing your case study, be sure you have thoroughly addressed all aspects of the problem and do not leave gaps in your analysis that leave the reader questioning the results.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Gerring, John. Case Study Research: Principles and Practices . New York: Cambridge University Press, 2007; Merriam, Sharan B. Qualitative Research and Case Study Applications in Education . Rev. ed. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 1998; Miller, Lisa L. “The Use of Case Studies in Law and Social Science Research.” Annual Review of Law and Social Science 14 (2018): TBD; Mills, Albert J., Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Putney, LeAnn Grogan. "Case Study." In Encyclopedia of Research Design , Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010), pp. 116-120; Simons, Helen. Case Study Research in Practice . London: SAGE Publications, 2009; Kratochwill, Thomas R. and Joel R. Levin, editors. Single-Case Research Design and Analysis: New Development for Psychology and Education . Hilldsale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1992; Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London : SAGE, 2010; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods . 6th edition. Los Angeles, CA, SAGE Publications, 2014; Walo, Maree, Adrian Bull, and Helen Breen. “Achieving Economic Benefits at Local Events: A Case Study of a Local Sports Event.” Festival Management and Event Tourism 4 (1996): 95-106.
Writing Tip
At Least Five Misconceptions about Case Study Research
Social science case studies are often perceived as limited in their ability to create new knowledge because they are not randomly selected and findings cannot be generalized to larger populations. Flyvbjerg examines five misunderstandings about case study research and systematically "corrects" each one. To quote, these are:
Misunderstanding 1 : General, theoretical [context-independent] knowledge is more valuable than concrete, practical [context-dependent] knowledge. Misunderstanding 2 : One cannot generalize on the basis of an individual case; therefore, the case study cannot contribute to scientific development. Misunderstanding 3 : The case study is most useful for generating hypotheses; that is, in the first stage of a total research process, whereas other methods are more suitable for hypotheses testing and theory building. Misunderstanding 4 : The case study contains a bias toward verification, that is, a tendency to confirm the researcher’s preconceived notions. Misunderstanding 5 : It is often difficult to summarize and develop general propositions and theories on the basis of specific case studies [p. 221].
While writing your paper, think introspectively about how you addressed these misconceptions because to do so can help you strengthen the validity and reliability of your research by clarifying issues of case selection, the testing and challenging of existing assumptions, the interpretation of key findings, and the summation of case outcomes. Think of a case study research paper as a complete, in-depth narrative about the specific properties and key characteristics of your subject of analysis applied to the research problem.
Flyvbjerg, Bent. “Five Misunderstandings About Case-Study Research.” Qualitative Inquiry 12 (April 2006): 219-245.
- << Previous: Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Next: Writing a Field Report >>
- Last Updated: May 7, 2024 9:45 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments
Case Study Research Method in Psychology
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. Typically, data is gathered from various sources using several methods (e.g., observations & interviews).
The case study research method originated in clinical medicine (the case history, i.e., the patient’s personal history). In psychology, case studies are often confined to the study of a particular individual.
The information is mainly biographical and relates to events in the individual’s past (i.e., retrospective), as well as to significant events that are currently occurring in his or her everyday life.
The case study is not a research method, but researchers select methods of data collection and analysis that will generate material suitable for case studies.
Freud (1909a, 1909b) conducted very detailed investigations into the private lives of his patients in an attempt to both understand and help them overcome their illnesses.
This makes it clear that the case study is a method that should only be used by a psychologist, therapist, or psychiatrist, i.e., someone with a professional qualification.
There is an ethical issue of competence. Only someone qualified to diagnose and treat a person can conduct a formal case study relating to atypical (i.e., abnormal) behavior or atypical development.
Famous Case Studies
- Anna O – One of the most famous case studies, documenting psychoanalyst Josef Breuer’s treatment of “Anna O” (real name Bertha Pappenheim) for hysteria in the late 1800s using early psychoanalytic theory.
- Little Hans – A child psychoanalysis case study published by Sigmund Freud in 1909 analyzing his five-year-old patient Herbert Graf’s house phobia as related to the Oedipus complex.
- Bruce/Brenda – Gender identity case of the boy (Bruce) whose botched circumcision led psychologist John Money to advise gender reassignment and raise him as a girl (Brenda) in the 1960s.
- Genie Wiley – Linguistics/psychological development case of the victim of extreme isolation abuse who was studied in 1970s California for effects of early language deprivation on acquiring speech later in life.
- Phineas Gage – One of the most famous neuropsychology case studies analyzes personality changes in railroad worker Phineas Gage after an 1848 brain injury involving a tamping iron piercing his skull.
Clinical Case Studies
- Studying the effectiveness of psychotherapy approaches with an individual patient
- Assessing and treating mental illnesses like depression, anxiety disorders, PTSD
- Neuropsychological cases investigating brain injuries or disorders
Child Psychology Case Studies
- Studying psychological development from birth through adolescence
- Cases of learning disabilities, autism spectrum disorders, ADHD
- Effects of trauma, abuse, deprivation on development
Types of Case Studies
- Explanatory case studies : Used to explore causation in order to find underlying principles. Helpful for doing qualitative analysis to explain presumed causal links.
- Exploratory case studies : Used to explore situations where an intervention being evaluated has no clear set of outcomes. It helps define questions and hypotheses for future research.
- Descriptive case studies : Describe an intervention or phenomenon and the real-life context in which it occurred. It is helpful for illustrating certain topics within an evaluation.
- Multiple-case studies : Used to explore differences between cases and replicate findings across cases. Helpful for comparing and contrasting specific cases.
- Intrinsic : Used to gain a better understanding of a particular case. Helpful for capturing the complexity of a single case.
- Collective : Used to explore a general phenomenon using multiple case studies. Helpful for jointly studying a group of cases in order to inquire into the phenomenon.
Where Do You Find Data for a Case Study?
There are several places to find data for a case study. The key is to gather data from multiple sources to get a complete picture of the case and corroborate facts or findings through triangulation of evidence. Most of this information is likely qualitative (i.e., verbal description rather than measurement), but the psychologist might also collect numerical data.
1. Primary sources
- Interviews – Interviewing key people related to the case to get their perspectives and insights. The interview is an extremely effective procedure for obtaining information about an individual, and it may be used to collect comments from the person’s friends, parents, employer, workmates, and others who have a good knowledge of the person, as well as to obtain facts from the person him or herself.
- Observations – Observing behaviors, interactions, processes, etc., related to the case as they unfold in real-time.
- Documents & Records – Reviewing private documents, diaries, public records, correspondence, meeting minutes, etc., relevant to the case.
2. Secondary sources
- News/Media – News coverage of events related to the case study.
- Academic articles – Journal articles, dissertations etc. that discuss the case.
- Government reports – Official data and records related to the case context.
- Books/films – Books, documentaries or films discussing the case.
3. Archival records
Searching historical archives, museum collections and databases to find relevant documents, visual/audio records related to the case history and context.
Public archives like newspapers, organizational records, photographic collections could all include potentially relevant pieces of information to shed light on attitudes, cultural perspectives, common practices and historical contexts related to psychology.
4. Organizational records
Organizational records offer the advantage of often having large datasets collected over time that can reveal or confirm psychological insights.
Of course, privacy and ethical concerns regarding confidential data must be navigated carefully.
However, with proper protocols, organizational records can provide invaluable context and empirical depth to qualitative case studies exploring the intersection of psychology and organizations.
- Organizational/industrial psychology research : Organizational records like employee surveys, turnover/retention data, policies, incident reports etc. may provide insight into topics like job satisfaction, workplace culture and dynamics, leadership issues, employee behaviors etc.
- Clinical psychology : Therapists/hospitals may grant access to anonymized medical records to study aspects like assessments, diagnoses, treatment plans etc. This could shed light on clinical practices.
- School psychology : Studies could utilize anonymized student records like test scores, grades, disciplinary issues, and counseling referrals to study child development, learning barriers, effectiveness of support programs, and more.
How do I Write a Case Study in Psychology?
Follow specified case study guidelines provided by a journal or your psychology tutor. General components of clinical case studies include: background, symptoms, assessments, diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes. Interpreting the information means the researcher decides what to include or leave out. A good case study should always clarify which information is the factual description and which is an inference or the researcher’s opinion.
1. Introduction
- Provide background on the case context and why it is of interest, presenting background information like demographics, relevant history, and presenting problem.
- Compare briefly to similar published cases if applicable. Clearly state the focus/importance of the case.
2. Case Presentation
- Describe the presenting problem in detail, including symptoms, duration,and impact on daily life.
- Include client demographics like age and gender, information about social relationships, and mental health history.
- Describe all physical, emotional, and/or sensory symptoms reported by the client.
- Use patient quotes to describe the initial complaint verbatim. Follow with full-sentence summaries of relevant history details gathered, including key components that led to a working diagnosis.
- Summarize clinical exam results, namely orthopedic/neurological tests, imaging, lab tests, etc. Note actual results rather than subjective conclusions. Provide images if clearly reproducible/anonymized.
- Clearly state the working diagnosis or clinical impression before transitioning to management.
3. Management and Outcome
- Indicate the total duration of care and number of treatments given over what timeframe. Use specific names/descriptions for any therapies/interventions applied.
- Present the results of the intervention,including any quantitative or qualitative data collected.
- For outcomes, utilize visual analog scales for pain, medication usage logs, etc., if possible. Include patient self-reports of improvement/worsening of symptoms. Note the reason for discharge/end of care.
4. Discussion
- Analyze the case, exploring contributing factors, limitations of the study, and connections to existing research.
- Analyze the effectiveness of the intervention,considering factors like participant adherence, limitations of the study, and potential alternative explanations for the results.
- Identify any questions raised in the case analysis and relate insights to established theories and current research if applicable. Avoid definitive claims about physiological explanations.
- Offer clinical implications, and suggest future research directions.
5. Additional Items
- Thank specific assistants for writing support only. No patient acknowledgments.
- References should directly support any key claims or quotes included.
- Use tables/figures/images only if substantially informative. Include permissions and legends/explanatory notes.
- Provides detailed (rich qualitative) information.
- Provides insight for further research.
- Permitting investigation of otherwise impractical (or unethical) situations.
Case studies allow a researcher to investigate a topic in far more detail than might be possible if they were trying to deal with a large number of research participants (nomothetic approach) with the aim of ‘averaging’.
Because of their in-depth, multi-sided approach, case studies often shed light on aspects of human thinking and behavior that would be unethical or impractical to study in other ways.
Research that only looks into the measurable aspects of human behavior is not likely to give us insights into the subjective dimension of experience, which is important to psychoanalytic and humanistic psychologists.
Case studies are often used in exploratory research. They can help us generate new ideas (that might be tested by other methods). They are an important way of illustrating theories and can help show how different aspects of a person’s life are related to each other.
The method is, therefore, important for psychologists who adopt a holistic point of view (i.e., humanistic psychologists ).
Limitations
- Lacking scientific rigor and providing little basis for generalization of results to the wider population.
- Researchers’ own subjective feelings may influence the case study (researcher bias).
- Difficult to replicate.
- Time-consuming and expensive.
- The volume of data, together with the time restrictions in place, impacted the depth of analysis that was possible within the available resources.
Because a case study deals with only one person/event/group, we can never be sure if the case study investigated is representative of the wider body of “similar” instances. This means the conclusions drawn from a particular case may not be transferable to other settings.
Because case studies are based on the analysis of qualitative (i.e., descriptive) data , a lot depends on the psychologist’s interpretation of the information she has acquired.
This means that there is a lot of scope for Anna O , and it could be that the subjective opinions of the psychologist intrude in the assessment of what the data means.
For example, Freud has been criticized for producing case studies in which the information was sometimes distorted to fit particular behavioral theories (e.g., Little Hans ).
This is also true of Money’s interpretation of the Bruce/Brenda case study (Diamond, 1997) when he ignored evidence that went against his theory.
Breuer, J., & Freud, S. (1895). Studies on hysteria . Standard Edition 2: London.
Curtiss, S. (1981). Genie: The case of a modern wild child .
Diamond, M., & Sigmundson, K. (1997). Sex Reassignment at Birth: Long-term Review and Clinical Implications. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine , 151(3), 298-304
Freud, S. (1909a). Analysis of a phobia of a five year old boy. In The Pelican Freud Library (1977), Vol 8, Case Histories 1, pages 169-306
Freud, S. (1909b). Bemerkungen über einen Fall von Zwangsneurose (Der “Rattenmann”). Jb. psychoanal. psychopathol. Forsch ., I, p. 357-421; GW, VII, p. 379-463; Notes upon a case of obsessional neurosis, SE , 10: 151-318.
Harlow J. M. (1848). Passage of an iron rod through the head. Boston Medical and Surgical Journal, 39 , 389–393.
Harlow, J. M. (1868). Recovery from the Passage of an Iron Bar through the Head . Publications of the Massachusetts Medical Society. 2 (3), 327-347.
Money, J., & Ehrhardt, A. A. (1972). Man & Woman, Boy & Girl : The Differentiation and Dimorphism of Gender Identity from Conception to Maturity. Baltimore, Maryland: Johns Hopkins University Press.
Money, J., & Tucker, P. (1975). Sexual signatures: On being a man or a woman.
Further Information
- Case Study Approach
- Case Study Method
- Enhancing the Quality of Case Studies in Health Services Research
- “We do things together” A case study of “couplehood” in dementia
- Using mixed methods for evaluating an integrative approach to cancer care: a case study
Related Articles

Research Methodology
Qualitative Data Coding

What Is a Focus Group?

Cross-Cultural Research Methodology In Psychology

What Is Internal Validity In Research?

Research Methodology , Statistics
What Is Face Validity In Research? Importance & How To Measure

Criterion Validity: Definition & Examples
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on 5 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 30 January 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organisation, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating, and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyse the case.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
Unlike quantitative or experimental research, a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
If you find yourself aiming to simultaneously investigate and solve an issue, consider conducting action research . As its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time, and is highly iterative and flexible.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience, or phenomenon.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data .
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis, with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results , and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyse its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, January 30). Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved 21 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/case-studies/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, correlational research | guide, design & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, descriptive research design | definition, methods & examples.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What the Case Study Method Really Teaches
- Nitin Nohria

Seven meta-skills that stick even if the cases fade from memory.
It’s been 100 years since Harvard Business School began using the case study method. Beyond teaching specific subject matter, the case study method excels in instilling meta-skills in students. This article explains the importance of seven such skills: preparation, discernment, bias recognition, judgement, collaboration, curiosity, and self-confidence.
During my decade as dean of Harvard Business School, I spent hundreds of hours talking with our alumni. To enliven these conversations, I relied on a favorite question: “What was the most important thing you learned from your time in our MBA program?”
- Nitin Nohria is the George F. Baker Professor of Business Administration, Distinguished University Service Professor, and former dean of Harvard Business School.

Partner Center

Research Writing and Analysis
- NVivo Group and Study Sessions
- SPSS This link opens in a new window
- Statistical Analysis Group sessions
- Using Qualtrics
- Dissertation and Data Analysis Group Sessions
- Defense Schedule - Commons Calendar This link opens in a new window
- Research Process Flow Chart
- Research Alignment Chapter 1 This link opens in a new window
- Step 1: Seek Out Evidence
- Step 2: Explain
- Step 3: The Big Picture
- Step 4: Own It
- Step 5: Illustrate
- Annotated Bibliography
- Literature Review This link opens in a new window
- Systematic Reviews & Meta-Analyses
- How to Synthesize and Analyze
- Synthesis and Analysis Practice
- Synthesis and Analysis Group Sessions
- Problem Statement
- Purpose Statement
- Conceptual Framework
- Theoretical Framework
- Quantitative Research Questions
- Qualitative Research Questions
- Trustworthiness of Qualitative Data
- Analysis and Coding Example- Qualitative Data
- Thematic Data Analysis in Qualitative Design
- Dissertation to Journal Article This link opens in a new window
- International Journal of Online Graduate Education (IJOGE) This link opens in a new window
- Journal of Research in Innovative Teaching & Learning (JRIT&L) This link opens in a new window
Writing a Case Study

What is a case study?

A Case study is:
- An in-depth research design that primarily uses a qualitative methodology but sometimes includes quantitative methodology.
- Used to examine an identifiable problem confirmed through research.
- Used to investigate an individual, group of people, organization, or event.
- Used to mostly answer "how" and "why" questions.
What are the different types of case studies?

Note: These are the primary case studies. As you continue to research and learn
about case studies you will begin to find a robust list of different types.
Who are your case study participants?

What is triangulation ?
Validity and credibility are an essential part of the case study. Therefore, the researcher should include triangulation to ensure trustworthiness while accurately reflecting what the researcher seeks to investigate.

How to write a Case Study?
When developing a case study, there are different ways you could present the information, but remember to include the five parts for your case study.

Was this resource helpful?
- << Previous: Thematic Data Analysis in Qualitative Design
- Next: Journal Article Reporting Standards (JARS) >>
- Last Updated: May 16, 2024 8:25 AM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/researchtools


Psychology Case Study Examples: A Deep Dive into Real-life Scenarios

Peeling back the layers of the human mind is no easy task, but psychology case studies can help us do just that. Through these detailed analyses, we’re able to gain a deeper understanding of human behavior, emotions, and cognitive processes. I’ve always found it fascinating how a single person’s experience can shed light on broader psychological principles.
Over the years, psychologists have conducted numerous case studies—each with their own unique insights and implications. These investigations range from Phineas Gage’s accidental lobotomy to Genie Wiley’s tragic tale of isolation. Such examples not only enlighten us about specific disorders or occurrences but also continue to shape our overall understanding of psychology .
As we delve into some noteworthy examples , I assure you’ll appreciate how varied and intricate the field of psychology truly is. Whether you’re a budding psychologist or simply an eager learner, brace yourself for an intriguing exploration into the intricacies of the human psyche.
Understanding Psychology Case Studies
Diving headfirst into the world of psychology, it’s easy to come upon a valuable tool used by psychologists and researchers alike – case studies. I’m here to shed some light on these fascinating tools.
Psychology case studies, for those unfamiliar with them, are in-depth investigations carried out to gain a profound understanding of the subject – whether it’s an individual, group or phenomenon. They’re powerful because they provide detailed insights that other research methods might miss.
Let me share a few examples to clarify this concept further:
- One notable example is Freud’s study on Little Hans. This case study explored a 5-year-old boy’s fear of horses and related it back to Freud’s theories about psychosexual stages.
- Another classic example is Genie Wiley (a pseudonym), a feral child who was subjected to severe social isolation during her early years. Her heartbreaking story provided invaluable insights into language acquisition and critical periods in development.
You see, what sets psychology case studies apart is their focus on the ‘why’ and ‘how’. While surveys or experiments might tell us ‘what’, they often don’t dig deep enough into the inner workings behind human behavior.
It’s important though not to take these psychology case studies at face value. As enlightening as they can be, we must remember that they usually focus on one specific instance or individual. Thus, generalizing findings from single-case studies should be done cautiously.
To illustrate my point using numbers: let’s say we have 1 million people suffering from condition X worldwide; if only 20 unique cases have been studied so far (which would be quite typical for rare conditions), then our understanding is based on just 0.002% of the total cases! That’s why multiple sources and types of research are vital when trying to understand complex psychological phenomena fully.
In the grand scheme of things, psychology case studies are just one piece of the puzzle – albeit an essential one. They provide rich, detailed data that can form the foundation for further research and understanding. As we delve deeper into this fascinating field, it’s crucial to appreciate all the tools at our disposal – from surveys and experiments to these insightful case studies.
Importance of Case Studies in Psychology
I’ve always been fascinated by the human mind, and if you’re here, I bet you are too. Let’s dive right into why case studies play such a pivotal role in psychology.
One of the key reasons they matter so much is because they provide detailed insights into specific psychological phenomena. Unlike other research methods that might use large samples but only offer surface-level findings, case studies allow us to study complex behaviors, disorders, and even treatments at an intimate level. They often serve as a catalyst for new theories or help refine existing ones.
To illustrate this point, let’s look at one of psychology’s most famous case studies – Phineas Gage. He was a railroad construction foreman who survived a severe brain injury when an iron rod shot through his skull during an explosion in 1848. The dramatic personality changes he experienced after his accident led to significant advancements in our understanding of the brain’s role in personality and behavior.
Moreover, it’s worth noting that some rare conditions can only be studied through individual cases due to their uncommon nature. For instance, consider Genie Wiley – a girl discovered at age 13 having spent most of her life locked away from society by her parents. Her tragic story gave psychologists valuable insights into language acquisition and critical periods for learning.
Finally yet importantly, case studies also have practical applications for clinicians and therapists. Studying real-life examples can inform treatment plans and provide guidance on how theoretical concepts might apply to actual client situations.
- Detailed insights: Case studies offer comprehensive views on specific psychological phenomena.
- Catalyst for new theories: Real-life scenarios help shape our understanding of psychology .
- Study rare conditions: Unique cases can offer invaluable lessons about uncommon disorders.
- Practical applications: Clinicians benefit from studying real-world examples.
In short (but without wrapping up), it’s clear that case studies hold immense value within psychology – they illuminate what textbooks often can’t, offering a more nuanced understanding of human behavior.
Different Types of Psychology Case Studies
Diving headfirst into the world of psychology, I can’t help but be fascinated by the myriad types of case studies that revolve around this subject. Let’s take a closer look at some of them.
Firstly, we’ve got what’s known as ‘Explanatory Case Studies’. These are often used when a researcher wants to clarify complex phenomena or concepts. For example, a psychologist might use an explanatory case study to explore the reasons behind aggressive behavior in children.
Second on our list are ‘Exploratory Case Studies’, typically utilized when new and unexplored areas of research come up. They’re like pioneers; they pave the way for future studies. In psychological terms, exploratory case studies could be conducted to investigate emerging mental health conditions or under-researched therapeutic approaches.
Next up are ‘Descriptive Case Studies’. As the name suggests, these focus on depicting comprehensive and detailed profiles about a particular individual, group, or event within its natural context. A well-known example would be Sigmund Freud’s analysis of “Anna O”, which provided unique insights into hysteria.
Then there are ‘Intrinsic Case Studies’, which delve deep into one specific case because it is intrinsically interesting or unique in some way. It’s sorta like shining a spotlight onto an exceptional phenomenon. An instance would be studying savants—individuals with extraordinary abilities despite significant mental disabilities.
Lastly, we have ‘Instrumental Case Studies’. These aren’t focused on understanding a particular case per se but use it as an instrument to understand something else altogether—a bit like using one puzzle piece to make sense of the whole picture!
So there you have it! From explanatory to instrumental, each type serves its own unique purpose and adds another intriguing layer to our understanding of human behavior and cognition.
Exploring Real-Life Psychology Case Study Examples
Let’s roll up our sleeves and delve into some real-life psychology case study examples. By digging deep, we can glean valuable insights from these studies that have significantly contributed to our understanding of human behavior and mental processes.
First off, let me share the fascinating case of Phineas Gage. This gentleman was a 19th-century railroad construction foreman who survived an accident where a large iron rod was accidentally driven through his skull, damaging his frontal lobes. Astonishingly, he could walk and talk immediately after the accident but underwent dramatic personality changes, becoming impulsive and irresponsible. This case is often referenced in discussions about brain injury and personality change.
Next on my list is Genie Wiley’s heart-wrenching story. She was a victim of severe abuse and neglect resulting in her being socially isolated until she was 13 years old. Due to this horrific experience, Genie couldn’t acquire language skills typically as other children would do during their developmental stages. Her tragic story offers invaluable insight into the critical periods for language development in children.
Then there’s ‘Little Hans’, a classic Freudian case that delves into child psychology. At just five years old, Little Hans developed an irrational fear of horses -or so it seemed- which Sigmund Freud interpreted as symbolic anxiety stemming from suppressed sexual desires towards his mother—quite an interpretation! The study gave us Freud’s Oedipus Complex theory.
Lastly, I’d like to mention Patient H.M., an individual who became amnesiac following surgery to control seizures by removing parts of his hippocampus bilaterally. His inability to form new memories post-operation shed light on how different areas of our brains contribute to memory formation.
Each one of these real-life psychology case studies gives us a unique window into understanding complex human behaviors better – whether it’s dissecting the role our brain plays in shaping personality or unraveling the mysteries of fear, language acquisition, and memory.
How to Analyze a Psychology Case Study
Diving headfirst into a psychology case study, I understand it can seem like an intimidating task. But don’t worry, I’m here to guide you through the process.
First off, it’s essential to go through the case study thoroughly. Read it multiple times if needed. Each reading will likely reveal new information or perspectives you may have missed initially. Look out for any patterns or inconsistencies in the subject’s behavior and make note of them.
Next on your agenda should be understanding the theoretical frameworks that might be applicable in this scenario. Is there a cognitive-behavioral approach at play? Or does psychoanalysis provide better insights? Comparing these theories with observed behavior and symptoms can help shed light on underlying psychological issues.
Now, let’s talk data interpretation. If your case study includes raw data like surveys or diagnostic tests results, you’ll need to analyze them carefully. Here are some steps that could help:
- Identify what each piece of data represents
- Look for correlations between different pieces of data
- Compute statistics (mean, median, mode) if necessary
- Use graphs or charts for visual representation
Keep in mind; interpreting raw data requires both statistical knowledge and intuition about human behavior.
Finally, drafting conclusions is key in analyzing a psychology case study. Based on your observations, evaluations of theoretical approaches and interpretations of any given data – what do you conclude about the subject’s mental health status? Remember not to jump to conclusions hastily but instead base them solidly on evidence from your analysis.
In all this journey of analysis remember one thing: every person is unique and so are their experiences! So while theories and previous studies guide us, they never define an individual completely.
Applying Lessons from Psychology Case Studies
Let’s dive into how we can apply the lessons learned from psychology case studies. If you’ve ever studied psychology, you’ll know that case studies offer rich insights. They shed light on human behavior, mental health issues, and therapeutic techniques. But it’s not just about understanding theory. It’s also about implementing these valuable lessons in real-world situations.
One of the most famous psychological case studies is Phineas Gage’s story. This 19th-century railroad worker survived a severe brain injury which dramatically altered his personality. From this study, we gained crucial insight into how different brain areas are responsible for various aspects of our personality and behavior.
- Lesson: Recognizing that damage to specific brain areas can result in personality changes, enabling us to better understand certain mental conditions.
Sigmund Freud’s work with a patient known as ‘Anna O.’ is another landmark psychology case study. Anna displayed what was then called hysteria – symptoms included hallucinations and disturbances in speech and physical coordination – which Freud linked back to repressed memories of traumatic events.
- Lesson: The importance of exploring an individual’s history for understanding their current psychological problems – a principle at the heart of psychoanalysis.
Then there’s Genie Wiley’s case – a girl who suffered extreme neglect resulting in impaired social and linguistic development. Researchers used her tragic circumstances as an opportunity to explore theories around language acquisition and socialization.
- Lesson: Reinforcing the critical role early childhood experiences play in shaping cognitive development.
Lastly, let’s consider the Stanford Prison Experiment led by Philip Zimbardo examining how people conform to societal roles even when they lead to immoral actions.
- Lesson: Highlighting that situational forces can drastically impact human behavior beyond personal characteristics or morality.
These examples demonstrate that psychology case studies aren’t just academic exercises isolated from daily life. Instead, they provide profound lessons that help us make sense of complex human behaviors, mental health issues, and therapeutic strategies. By understanding these studies, we’re better equipped to apply their lessons in our own lives – whether it’s navigating personal relationships, working with diverse teams at work or even self-improvement.
Challenges and Critiques of Psychological Case Studies
Delving into the world of psychological case studies, it’s not all rosy. Sure, they offer an in-depth understanding of individual behavior and mental processes. Yet, they’re not without their share of challenges and criticisms.
One common critique is the lack of generalizability. Each case study is unique to its subject. We can’t always apply what we learn from one person to everyone else. I’ve come across instances where results varied dramatically between similar subjects, highlighting the inherent unpredictability in human behavior.
Another challenge lies within ethical boundaries. Often, sensitive information surfaces during these studies that could potentially harm the subject if disclosed improperly. To put it plainly, maintaining confidentiality while delivering a comprehensive account isn’t always easy.
Distortion due to subjective interpretations also poses substantial difficulties for psychologists conducting case studies. The researcher’s own bias may color their observations and conclusions – leading to skewed outcomes or misleading findings.
Moreover, there’s an ongoing debate about the scientific validity of case studies because they rely heavily on qualitative data rather than quantitative analysis. Some argue this makes them less reliable or objective when compared with other research methods such as experiments or surveys.
To summarize:
- Lack of generalizability
- Ethical dilemmas concerning privacy
- Potential distortion through subjective interpretation
- Questions about scientific validity
While these critiques present significant challenges, they do not diminish the value that psychological case studies bring to our understanding of human behavior and mental health struggles.
Conclusion: The Impact of Case Studies in Understanding Human Behavior
Case studies play a pivotal role in shedding light on human behavior. Throughout this article, I’ve discussed numerous examples that illustrate just how powerful these studies can be. Yet it’s the impact they have on our understanding of human psychology where their true value lies.
Take for instance the iconic study of Phineas Gage. It was through his tragic accident and subsequent personality change that we began to grasp the profound influence our frontal lobes have on our behavior. Without such a case study, we might still be in the dark about this crucial aspect of our neurology.
Let’s also consider Genie, the feral child who showed us the critical importance of social interaction during early development. Her heartbreaking story underscores just how vital appropriate nurturing is for healthy mental and emotional growth.
Here are some key takeaways from these case studies:
- Our brain structure significantly influences our behavior.
- Social interaction during formative years is vital for normal psychological development.
- Studying individual cases can reveal universal truths about human nature.
What stands out though, is not merely what these case studies teach us individually but collectively. They remind us that each person constitutes a unique combination of various factors—biological, psychological, and environmental—that shape their behavior.
One cannot overstate the significance of case studies in psychology—they are more than mere stories or isolated incidents; they’re windows into the complexities and nuances of human nature itself.
In wrapping up, I’d say that while statistics give us patterns and trends to understand groups, it’s these detailed narratives offered by case studies that help us comprehend individuals’ unique experiences within those groups—making them an invaluable part of psychological research.
Related Posts

Cracking the Anxious-Avoidant Code

Deflection: Unraveling the Science Behind Material Bending
All You Wanted to Know About How to Write a Case Study

What do you study in your college? If you are a psychology, sociology, or anthropology student, we bet you might be familiar with what a case study is. This research method is used to study a certain person, group, or situation. In this guide from our dissertation writing service , you will learn how to write a case study professionally, from researching to citing sources properly. Also, we will explore different types of case studies and show you examples — so that you won’t have any other questions left.
What Is a Case Study?
A case study is a subcategory of research design which investigates problems and offers solutions. Case studies can range from academic research studies to corporate promotional tools trying to sell an idea—their scope is quite vast.
What Is the Difference Between a Research Paper and a Case Study?
While research papers turn the reader’s attention to a certain problem, case studies go even further. Case study guidelines require students to pay attention to details, examining issues closely and in-depth using different research methods. For example, case studies may be used to examine court cases if you study Law, or a patient's health history if you study Medicine. Case studies are also used in Marketing, which are thorough, empirically supported analysis of a good or service's performance. Well-designed case studies can be valuable for prospective customers as they can identify and solve the potential customers pain point.
Case studies involve a lot of storytelling – they usually examine particular cases for a person or a group of people. This method of research is very helpful, as it is very practical and can give a lot of hands-on information. Most commonly, the length of the case study is about 500-900 words, which is much less than the length of an average research paper.
The structure of a case study is very similar to storytelling. It has a protagonist or main character, which in your case is actually a problem you are trying to solve. You can use the system of 3 Acts to make it a compelling story. It should have an introduction, rising action, a climax where transformation occurs, falling action, and a solution.
Here is a rough formula for you to use in your case study:
Problem (Act I): > Solution (Act II) > Result (Act III) > Conclusion.
Types of Case Studies
The purpose of a case study is to provide detailed reports on an event, an institution, a place, future customers, or pretty much anything. There are a few common types of case study, but the type depends on the topic. The following are the most common domains where case studies are needed:

- Historical case studies are great to learn from. Historical events have a multitude of source info offering different perspectives. There are always modern parallels where these perspectives can be applied, compared, and thoroughly analyzed.
- Problem-oriented case studies are usually used for solving problems. These are often assigned as theoretical situations where you need to immerse yourself in the situation to examine it. Imagine you’re working for a startup and you’ve just noticed a significant flaw in your product’s design. Before taking it to the senior manager, you want to do a comprehensive study on the issue and provide solutions. On a greater scale, problem-oriented case studies are a vital part of relevant socio-economic discussions.
- Cumulative case studies collect information and offer comparisons. In business, case studies are often used to tell people about the value of a product.
- Critical case studies explore the causes and effects of a certain case.
- Illustrative case studies describe certain events, investigating outcomes and lessons learned.
Need a compelling case study? EssayPro has got you covered. Our experts are ready to provide you with detailed, insightful case studies that capture the essence of real-world scenarios. Elevate your academic work with our professional assistance.

Case Study Format
The case study format is typically made up of eight parts:
- Executive Summary. Explain what you will examine in the case study. Write an overview of the field you’re researching. Make a thesis statement and sum up the results of your observation in a maximum of 2 sentences.
- Background. Provide background information and the most relevant facts. Isolate the issues.
- Case Evaluation. Isolate the sections of the study you want to focus on. In it, explain why something is working or is not working.
- Proposed Solutions. Offer realistic ways to solve what isn’t working or how to improve its current condition. Explain why these solutions work by offering testable evidence.
- Conclusion. Summarize the main points from the case evaluations and proposed solutions. 6. Recommendations. Talk about the strategy that you should choose. Explain why this choice is the most appropriate.
- Implementation. Explain how to put the specific strategies into action.
- References. Provide all the citations.
How to Write a Case Study
Let's discover how to write a case study.

Setting Up the Research
When writing a case study, remember that research should always come first. Reading many different sources and analyzing other points of view will help you come up with more creative solutions. You can also conduct an actual interview to thoroughly investigate the customer story that you'll need for your case study. Including all of the necessary research, writing a case study may take some time. The research process involves doing the following:
- Define your objective. Explain the reason why you’re presenting your subject. Figure out where you will feature your case study; whether it is written, on video, shown as an infographic, streamed as a podcast, etc.
- Determine who will be the right candidate for your case study. Get permission, quotes, and other features that will make your case study effective. Get in touch with your candidate to see if they approve of being part of your work. Study that candidate’s situation and note down what caused it.
- Identify which various consequences could result from the situation. Follow these guidelines on how to start a case study: surf the net to find some general information you might find useful.
- Make a list of credible sources and examine them. Seek out important facts and highlight problems. Always write down your ideas and make sure to brainstorm.
- Focus on several key issues – why they exist, and how they impact your research subject. Think of several unique solutions. Draw from class discussions, readings, and personal experience. When writing a case study, focus on the best solution and explore it in depth. After having all your research in place, writing a case study will be easy. You may first want to check the rubric and criteria of your assignment for the correct case study structure.
Read Also: ' WHAT IS A CREDIBLE SOURCES ?'
Although your instructor might be looking at slightly different criteria, every case study rubric essentially has the same standards. Your professor will want you to exhibit 8 different outcomes:
- Correctly identify the concepts, theories, and practices in the discipline.
- Identify the relevant theories and principles associated with the particular study.
- Evaluate legal and ethical principles and apply them to your decision-making.
- Recognize the global importance and contribution of your case.
- Construct a coherent summary and explanation of the study.
- Demonstrate analytical and critical-thinking skills.
- Explain the interrelationships between the environment and nature.
- Integrate theory and practice of the discipline within the analysis.
Need Case Study DONE FAST?
Pick a topic, tell us your requirements and get your paper on time.
Case Study Outline
Let's look at the structure of an outline based on the issue of the alcoholic addiction of 30 people.
Introduction
- Statement of the issue: Alcoholism is a disease rather than a weakness of character.
- Presentation of the problem: Alcoholism is affecting more than 14 million people in the USA, which makes it the third most common mental illness there.
- Explanation of the terms: In the past, alcoholism was commonly referred to as alcohol dependence or alcohol addiction. Alcoholism is now the more severe stage of this addiction in the disorder spectrum.
- Hypotheses: Drinking in excess can lead to the use of other drugs.
- Importance of your story: How the information you present can help people with their addictions.
- Background of the story: Include an explanation of why you chose this topic.
- Presentation of analysis and data: Describe the criteria for choosing 30 candidates, the structure of the interview, and the outcomes.
- Strong argument 1: ex. X% of candidates dealing with anxiety and depression...
- Strong argument 2: ex. X amount of people started drinking by their mid-teens.
- Strong argument 3: ex. X% of respondents’ parents had issues with alcohol.
- Concluding statement: I have researched if alcoholism is a disease and found out that…
- Recommendations: Ways and actions for preventing alcohol use.
Writing a Case Study Draft
After you’ve done your case study research and written the outline, it’s time to focus on the draft. In a draft, you have to develop and write your case study by using: the data which you collected throughout the research, interviews, and the analysis processes that were undertaken. Follow these rules for the draft:

- Your draft should contain at least 4 sections: an introduction; a body where you should include background information, an explanation of why you decided to do this case study, and a presentation of your main findings; a conclusion where you present data; and references.
- In the introduction, you should set the pace very clearly. You can even raise a question or quote someone you interviewed in the research phase. It must provide adequate background information on the topic. The background may include analyses of previous studies on your topic. Include the aim of your case here as well. Think of it as a thesis statement. The aim must describe the purpose of your work—presenting the issues that you want to tackle. Include background information, such as photos or videos you used when doing the research.
- Describe your unique research process, whether it was through interviews, observations, academic journals, etc. The next point includes providing the results of your research. Tell the audience what you found out. Why is this important, and what could be learned from it? Discuss the real implications of the problem and its significance in the world.
- Include quotes and data (such as findings, percentages, and awards). This will add a personal touch and better credibility to the case you present. Explain what results you find during your interviews in regards to the problem and how it developed. Also, write about solutions which have already been proposed by other people who have already written about this case.
- At the end of your case study, you should offer possible solutions, but don’t worry about solving them yourself.
Use Data to Illustrate Key Points in Your Case Study
Even though your case study is a story, it should be based on evidence. Use as much data as possible to illustrate your point. Without the right data, your case study may appear weak and the readers may not be able to relate to your issue as much as they should. Let's see the examples from essay writing service :
With data: Alcoholism is affecting more than 14 million people in the USA, which makes it the third most common mental illness there. Without data: A lot of people suffer from alcoholism in the United States.
Try to include as many credible sources as possible. You may have terms or sources that could be hard for other cultures to understand. If this is the case, you should include them in the appendix or Notes for the Instructor or Professor.
Finalizing the Draft: Checklist
After you finish drafting your case study, polish it up by answering these ‘ask yourself’ questions and think about how to end your case study:
- Check that you follow the correct case study format, also in regards to text formatting.
- Check that your work is consistent with its referencing and citation style.
- Micro-editing — check for grammar and spelling issues.
- Macro-editing — does ‘the big picture’ come across to the reader? Is there enough raw data, such as real-life examples or personal experiences? Have you made your data collection process completely transparent? Does your analysis provide a clear conclusion, allowing for further research and practice?
Problems to avoid:
- Overgeneralization – Do not go into further research that deviates from the main problem.
- Failure to Document Limitations – Just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study, you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis.
- Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications – Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings.
How to Create a Title Page and Cite a Case Study
Let's see how to create an awesome title page.
Your title page depends on the prescribed citation format. The title page should include:
- A title that attracts some attention and describes your study
- The title should have the words “case study” in it
- The title should range between 5-9 words in length
- Your name and contact information
- Your finished paper should be only 500 to 1,500 words in length.With this type of assignment, write effectively and avoid fluff
Here is a template for the APA and MLA format title page:
There are some cases when you need to cite someone else's study in your own one – therefore, you need to master how to cite a case study. A case study is like a research paper when it comes to citations. You can cite it like you cite a book, depending on what style you need.
Citation Example in MLA Hill, Linda, Tarun Khanna, and Emily A. Stecker. HCL Technologies. Boston: Harvard Business Publishing, 2008. Print.
Citation Example in APA Hill, L., Khanna, T., & Stecker, E. A. (2008). HCL Technologies. Boston: Harvard Business Publishing.
Citation Example in Chicago Hill, Linda, Tarun Khanna, and Emily A. Stecker. HCL Technologies.
Case Study Examples
To give you an idea of a professional case study example, we gathered and linked some below.
Eastman Kodak Case Study
Case Study Example: Audi Trains Mexican Autoworkers in Germany
To conclude, a case study is one of the best methods of getting an overview of what happened to a person, a group, or a situation in practice. It allows you to have an in-depth glance at the real-life problems that businesses, healthcare industry, criminal justice, etc. may face. This insight helps us look at such situations in a different light. This is because we see scenarios that we otherwise would not, without necessarily being there. If you need custom essays , try our research paper writing services .
Get Help Form Qualified Writers
Crafting a case study is not easy. You might want to write one of high quality, but you don’t have the time or expertise. If you’re having trouble with your case study, help with essay request - we'll help. EssayPro writers have read and written countless case studies and are experts in endless disciplines. Request essay writing, editing, or proofreading assistance from our custom case study writing service , and all of your worries will be gone.
Don't Know Where to Start?
Crafting a case study is not easy. You might want to write one of high quality, but you don’t have the time or expertise. Request ' write my case study ' assistance from our service.
What Is A Case Study?
How to cite a case study in apa, how to write a case study.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
Related Articles
.webp)
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- BMC Med Res Methodol

The case study approach
Sarah crowe.
1 Division of Primary Care, The University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK
Kathrin Cresswell
2 Centre for Population Health Sciences, The University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK
Ann Robertson
3 School of Health in Social Science, The University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK
Anthony Avery
Aziz sheikh.
The case study approach allows in-depth, multi-faceted explorations of complex issues in their real-life settings. The value of the case study approach is well recognised in the fields of business, law and policy, but somewhat less so in health services research. Based on our experiences of conducting several health-related case studies, we reflect on the different types of case study design, the specific research questions this approach can help answer, the data sources that tend to be used, and the particular advantages and disadvantages of employing this methodological approach. The paper concludes with key pointers to aid those designing and appraising proposals for conducting case study research, and a checklist to help readers assess the quality of case study reports.
Introduction
The case study approach is particularly useful to employ when there is a need to obtain an in-depth appreciation of an issue, event or phenomenon of interest, in its natural real-life context. Our aim in writing this piece is to provide insights into when to consider employing this approach and an overview of key methodological considerations in relation to the design, planning, analysis, interpretation and reporting of case studies.
The illustrative 'grand round', 'case report' and 'case series' have a long tradition in clinical practice and research. Presenting detailed critiques, typically of one or more patients, aims to provide insights into aspects of the clinical case and, in doing so, illustrate broader lessons that may be learnt. In research, the conceptually-related case study approach can be used, for example, to describe in detail a patient's episode of care, explore professional attitudes to and experiences of a new policy initiative or service development or more generally to 'investigate contemporary phenomena within its real-life context' [ 1 ]. Based on our experiences of conducting a range of case studies, we reflect on when to consider using this approach, discuss the key steps involved and illustrate, with examples, some of the practical challenges of attaining an in-depth understanding of a 'case' as an integrated whole. In keeping with previously published work, we acknowledge the importance of theory to underpin the design, selection, conduct and interpretation of case studies[ 2 ]. In so doing, we make passing reference to the different epistemological approaches used in case study research by key theoreticians and methodologists in this field of enquiry.
This paper is structured around the following main questions: What is a case study? What are case studies used for? How are case studies conducted? What are the potential pitfalls and how can these be avoided? We draw in particular on four of our own recently published examples of case studies (see Tables Tables1, 1 , ,2, 2 , ,3 3 and and4) 4 ) and those of others to illustrate our discussion[ 3 - 7 ].
Example of a case study investigating the reasons for differences in recruitment rates of minority ethnic people in asthma research[ 3 ]
Example of a case study investigating the process of planning and implementing a service in Primary Care Organisations[ 4 ]
Example of a case study investigating the introduction of the electronic health records[ 5 ]
Example of a case study investigating the formal and informal ways students learn about patient safety[ 6 ]
What is a case study?
A case study is a research approach that is used to generate an in-depth, multi-faceted understanding of a complex issue in its real-life context. It is an established research design that is used extensively in a wide variety of disciplines, particularly in the social sciences. A case study can be defined in a variety of ways (Table (Table5), 5 ), the central tenet being the need to explore an event or phenomenon in depth and in its natural context. It is for this reason sometimes referred to as a "naturalistic" design; this is in contrast to an "experimental" design (such as a randomised controlled trial) in which the investigator seeks to exert control over and manipulate the variable(s) of interest.
Definitions of a case study
Stake's work has been particularly influential in defining the case study approach to scientific enquiry. He has helpfully characterised three main types of case study: intrinsic , instrumental and collective [ 8 ]. An intrinsic case study is typically undertaken to learn about a unique phenomenon. The researcher should define the uniqueness of the phenomenon, which distinguishes it from all others. In contrast, the instrumental case study uses a particular case (some of which may be better than others) to gain a broader appreciation of an issue or phenomenon. The collective case study involves studying multiple cases simultaneously or sequentially in an attempt to generate a still broader appreciation of a particular issue.
These are however not necessarily mutually exclusive categories. In the first of our examples (Table (Table1), 1 ), we undertook an intrinsic case study to investigate the issue of recruitment of minority ethnic people into the specific context of asthma research studies, but it developed into a instrumental case study through seeking to understand the issue of recruitment of these marginalised populations more generally, generating a number of the findings that are potentially transferable to other disease contexts[ 3 ]. In contrast, the other three examples (see Tables Tables2, 2 , ,3 3 and and4) 4 ) employed collective case study designs to study the introduction of workforce reconfiguration in primary care, the implementation of electronic health records into hospitals, and to understand the ways in which healthcare students learn about patient safety considerations[ 4 - 6 ]. Although our study focusing on the introduction of General Practitioners with Specialist Interests (Table (Table2) 2 ) was explicitly collective in design (four contrasting primary care organisations were studied), is was also instrumental in that this particular professional group was studied as an exemplar of the more general phenomenon of workforce redesign[ 4 ].
What are case studies used for?
According to Yin, case studies can be used to explain, describe or explore events or phenomena in the everyday contexts in which they occur[ 1 ]. These can, for example, help to understand and explain causal links and pathways resulting from a new policy initiative or service development (see Tables Tables2 2 and and3, 3 , for example)[ 1 ]. In contrast to experimental designs, which seek to test a specific hypothesis through deliberately manipulating the environment (like, for example, in a randomised controlled trial giving a new drug to randomly selected individuals and then comparing outcomes with controls),[ 9 ] the case study approach lends itself well to capturing information on more explanatory ' how ', 'what' and ' why ' questions, such as ' how is the intervention being implemented and received on the ground?'. The case study approach can offer additional insights into what gaps exist in its delivery or why one implementation strategy might be chosen over another. This in turn can help develop or refine theory, as shown in our study of the teaching of patient safety in undergraduate curricula (Table (Table4 4 )[ 6 , 10 ]. Key questions to consider when selecting the most appropriate study design are whether it is desirable or indeed possible to undertake a formal experimental investigation in which individuals and/or organisations are allocated to an intervention or control arm? Or whether the wish is to obtain a more naturalistic understanding of an issue? The former is ideally studied using a controlled experimental design, whereas the latter is more appropriately studied using a case study design.
Case studies may be approached in different ways depending on the epistemological standpoint of the researcher, that is, whether they take a critical (questioning one's own and others' assumptions), interpretivist (trying to understand individual and shared social meanings) or positivist approach (orientating towards the criteria of natural sciences, such as focusing on generalisability considerations) (Table (Table6). 6 ). Whilst such a schema can be conceptually helpful, it may be appropriate to draw on more than one approach in any case study, particularly in the context of conducting health services research. Doolin has, for example, noted that in the context of undertaking interpretative case studies, researchers can usefully draw on a critical, reflective perspective which seeks to take into account the wider social and political environment that has shaped the case[ 11 ].
Example of epistemological approaches that may be used in case study research
How are case studies conducted?
Here, we focus on the main stages of research activity when planning and undertaking a case study; the crucial stages are: defining the case; selecting the case(s); collecting and analysing the data; interpreting data; and reporting the findings.
Defining the case
Carefully formulated research question(s), informed by the existing literature and a prior appreciation of the theoretical issues and setting(s), are all important in appropriately and succinctly defining the case[ 8 , 12 ]. Crucially, each case should have a pre-defined boundary which clarifies the nature and time period covered by the case study (i.e. its scope, beginning and end), the relevant social group, organisation or geographical area of interest to the investigator, the types of evidence to be collected, and the priorities for data collection and analysis (see Table Table7 7 )[ 1 ]. A theory driven approach to defining the case may help generate knowledge that is potentially transferable to a range of clinical contexts and behaviours; using theory is also likely to result in a more informed appreciation of, for example, how and why interventions have succeeded or failed[ 13 ].
Example of a checklist for rating a case study proposal[ 8 ]
For example, in our evaluation of the introduction of electronic health records in English hospitals (Table (Table3), 3 ), we defined our cases as the NHS Trusts that were receiving the new technology[ 5 ]. Our focus was on how the technology was being implemented. However, if the primary research interest had been on the social and organisational dimensions of implementation, we might have defined our case differently as a grouping of healthcare professionals (e.g. doctors and/or nurses). The precise beginning and end of the case may however prove difficult to define. Pursuing this same example, when does the process of implementation and adoption of an electronic health record system really begin or end? Such judgements will inevitably be influenced by a range of factors, including the research question, theory of interest, the scope and richness of the gathered data and the resources available to the research team.
Selecting the case(s)
The decision on how to select the case(s) to study is a very important one that merits some reflection. In an intrinsic case study, the case is selected on its own merits[ 8 ]. The case is selected not because it is representative of other cases, but because of its uniqueness, which is of genuine interest to the researchers. This was, for example, the case in our study of the recruitment of minority ethnic participants into asthma research (Table (Table1) 1 ) as our earlier work had demonstrated the marginalisation of minority ethnic people with asthma, despite evidence of disproportionate asthma morbidity[ 14 , 15 ]. In another example of an intrinsic case study, Hellstrom et al.[ 16 ] studied an elderly married couple living with dementia to explore how dementia had impacted on their understanding of home, their everyday life and their relationships.
For an instrumental case study, selecting a "typical" case can work well[ 8 ]. In contrast to the intrinsic case study, the particular case which is chosen is of less importance than selecting a case that allows the researcher to investigate an issue or phenomenon. For example, in order to gain an understanding of doctors' responses to health policy initiatives, Som undertook an instrumental case study interviewing clinicians who had a range of responsibilities for clinical governance in one NHS acute hospital trust[ 17 ]. Sampling a "deviant" or "atypical" case may however prove even more informative, potentially enabling the researcher to identify causal processes, generate hypotheses and develop theory.
In collective or multiple case studies, a number of cases are carefully selected. This offers the advantage of allowing comparisons to be made across several cases and/or replication. Choosing a "typical" case may enable the findings to be generalised to theory (i.e. analytical generalisation) or to test theory by replicating the findings in a second or even a third case (i.e. replication logic)[ 1 ]. Yin suggests two or three literal replications (i.e. predicting similar results) if the theory is straightforward and five or more if the theory is more subtle. However, critics might argue that selecting 'cases' in this way is insufficiently reflexive and ill-suited to the complexities of contemporary healthcare organisations.
The selected case study site(s) should allow the research team access to the group of individuals, the organisation, the processes or whatever else constitutes the chosen unit of analysis for the study. Access is therefore a central consideration; the researcher needs to come to know the case study site(s) well and to work cooperatively with them. Selected cases need to be not only interesting but also hospitable to the inquiry [ 8 ] if they are to be informative and answer the research question(s). Case study sites may also be pre-selected for the researcher, with decisions being influenced by key stakeholders. For example, our selection of case study sites in the evaluation of the implementation and adoption of electronic health record systems (see Table Table3) 3 ) was heavily influenced by NHS Connecting for Health, the government agency that was responsible for overseeing the National Programme for Information Technology (NPfIT)[ 5 ]. This prominent stakeholder had already selected the NHS sites (through a competitive bidding process) to be early adopters of the electronic health record systems and had negotiated contracts that detailed the deployment timelines.
It is also important to consider in advance the likely burden and risks associated with participation for those who (or the site(s) which) comprise the case study. Of particular importance is the obligation for the researcher to think through the ethical implications of the study (e.g. the risk of inadvertently breaching anonymity or confidentiality) and to ensure that potential participants/participating sites are provided with sufficient information to make an informed choice about joining the study. The outcome of providing this information might be that the emotive burden associated with participation, or the organisational disruption associated with supporting the fieldwork, is considered so high that the individuals or sites decide against participation.
In our example of evaluating implementations of electronic health record systems, given the restricted number of early adopter sites available to us, we sought purposively to select a diverse range of implementation cases among those that were available[ 5 ]. We chose a mixture of teaching, non-teaching and Foundation Trust hospitals, and examples of each of the three electronic health record systems procured centrally by the NPfIT. At one recruited site, it quickly became apparent that access was problematic because of competing demands on that organisation. Recognising the importance of full access and co-operative working for generating rich data, the research team decided not to pursue work at that site and instead to focus on other recruited sites.
Collecting the data
In order to develop a thorough understanding of the case, the case study approach usually involves the collection of multiple sources of evidence, using a range of quantitative (e.g. questionnaires, audits and analysis of routinely collected healthcare data) and more commonly qualitative techniques (e.g. interviews, focus groups and observations). The use of multiple sources of data (data triangulation) has been advocated as a way of increasing the internal validity of a study (i.e. the extent to which the method is appropriate to answer the research question)[ 8 , 18 - 21 ]. An underlying assumption is that data collected in different ways should lead to similar conclusions, and approaching the same issue from different angles can help develop a holistic picture of the phenomenon (Table (Table2 2 )[ 4 ].
Brazier and colleagues used a mixed-methods case study approach to investigate the impact of a cancer care programme[ 22 ]. Here, quantitative measures were collected with questionnaires before, and five months after, the start of the intervention which did not yield any statistically significant results. Qualitative interviews with patients however helped provide an insight into potentially beneficial process-related aspects of the programme, such as greater, perceived patient involvement in care. The authors reported how this case study approach provided a number of contextual factors likely to influence the effectiveness of the intervention and which were not likely to have been obtained from quantitative methods alone.
In collective or multiple case studies, data collection needs to be flexible enough to allow a detailed description of each individual case to be developed (e.g. the nature of different cancer care programmes), before considering the emerging similarities and differences in cross-case comparisons (e.g. to explore why one programme is more effective than another). It is important that data sources from different cases are, where possible, broadly comparable for this purpose even though they may vary in nature and depth.
Analysing, interpreting and reporting case studies
Making sense and offering a coherent interpretation of the typically disparate sources of data (whether qualitative alone or together with quantitative) is far from straightforward. Repeated reviewing and sorting of the voluminous and detail-rich data are integral to the process of analysis. In collective case studies, it is helpful to analyse data relating to the individual component cases first, before making comparisons across cases. Attention needs to be paid to variations within each case and, where relevant, the relationship between different causes, effects and outcomes[ 23 ]. Data will need to be organised and coded to allow the key issues, both derived from the literature and emerging from the dataset, to be easily retrieved at a later stage. An initial coding frame can help capture these issues and can be applied systematically to the whole dataset with the aid of a qualitative data analysis software package.
The Framework approach is a practical approach, comprising of five stages (familiarisation; identifying a thematic framework; indexing; charting; mapping and interpretation) , to managing and analysing large datasets particularly if time is limited, as was the case in our study of recruitment of South Asians into asthma research (Table (Table1 1 )[ 3 , 24 ]. Theoretical frameworks may also play an important role in integrating different sources of data and examining emerging themes. For example, we drew on a socio-technical framework to help explain the connections between different elements - technology; people; and the organisational settings within which they worked - in our study of the introduction of electronic health record systems (Table (Table3 3 )[ 5 ]. Our study of patient safety in undergraduate curricula drew on an evaluation-based approach to design and analysis, which emphasised the importance of the academic, organisational and practice contexts through which students learn (Table (Table4 4 )[ 6 ].
Case study findings can have implications both for theory development and theory testing. They may establish, strengthen or weaken historical explanations of a case and, in certain circumstances, allow theoretical (as opposed to statistical) generalisation beyond the particular cases studied[ 12 ]. These theoretical lenses should not, however, constitute a strait-jacket and the cases should not be "forced to fit" the particular theoretical framework that is being employed.
When reporting findings, it is important to provide the reader with enough contextual information to understand the processes that were followed and how the conclusions were reached. In a collective case study, researchers may choose to present the findings from individual cases separately before amalgamating across cases. Care must be taken to ensure the anonymity of both case sites and individual participants (if agreed in advance) by allocating appropriate codes or withholding descriptors. In the example given in Table Table3, 3 , we decided against providing detailed information on the NHS sites and individual participants in order to avoid the risk of inadvertent disclosure of identities[ 5 , 25 ].
What are the potential pitfalls and how can these be avoided?
The case study approach is, as with all research, not without its limitations. When investigating the formal and informal ways undergraduate students learn about patient safety (Table (Table4), 4 ), for example, we rapidly accumulated a large quantity of data. The volume of data, together with the time restrictions in place, impacted on the depth of analysis that was possible within the available resources. This highlights a more general point of the importance of avoiding the temptation to collect as much data as possible; adequate time also needs to be set aside for data analysis and interpretation of what are often highly complex datasets.
Case study research has sometimes been criticised for lacking scientific rigour and providing little basis for generalisation (i.e. producing findings that may be transferable to other settings)[ 1 ]. There are several ways to address these concerns, including: the use of theoretical sampling (i.e. drawing on a particular conceptual framework); respondent validation (i.e. participants checking emerging findings and the researcher's interpretation, and providing an opinion as to whether they feel these are accurate); and transparency throughout the research process (see Table Table8 8 )[ 8 , 18 - 21 , 23 , 26 ]. Transparency can be achieved by describing in detail the steps involved in case selection, data collection, the reasons for the particular methods chosen, and the researcher's background and level of involvement (i.e. being explicit about how the researcher has influenced data collection and interpretation). Seeking potential, alternative explanations, and being explicit about how interpretations and conclusions were reached, help readers to judge the trustworthiness of the case study report. Stake provides a critique checklist for a case study report (Table (Table9 9 )[ 8 ].
Potential pitfalls and mitigating actions when undertaking case study research
Stake's checklist for assessing the quality of a case study report[ 8 ]
Conclusions
The case study approach allows, amongst other things, critical events, interventions, policy developments and programme-based service reforms to be studied in detail in a real-life context. It should therefore be considered when an experimental design is either inappropriate to answer the research questions posed or impossible to undertake. Considering the frequency with which implementations of innovations are now taking place in healthcare settings and how well the case study approach lends itself to in-depth, complex health service research, we believe this approach should be more widely considered by researchers. Though inherently challenging, the research case study can, if carefully conceptualised and thoughtfully undertaken and reported, yield powerful insights into many important aspects of health and healthcare delivery.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
AS conceived this article. SC, KC and AR wrote this paper with GH, AA and AS all commenting on various drafts. SC and AS are guarantors.
Pre-publication history
The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:
http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2288/11/100/prepub
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the participants and colleagues who contributed to the individual case studies that we have drawn on. This work received no direct funding, but it has been informed by projects funded by Asthma UK, the NHS Service Delivery Organisation, NHS Connecting for Health Evaluation Programme, and Patient Safety Research Portfolio. We would also like to thank the expert reviewers for their insightful and constructive feedback. Our thanks are also due to Dr. Allison Worth who commented on an earlier draft of this manuscript.
- Yin RK. Case study research, design and method. 4. London: Sage Publications Ltd.; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Keen J, Packwood T. Qualitative research; case study evaluation. BMJ. 1995; 311 :444–446. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sheikh A, Halani L, Bhopal R, Netuveli G, Partridge M, Car J. et al. Facilitating the Recruitment of Minority Ethnic People into Research: Qualitative Case Study of South Asians and Asthma. PLoS Med. 2009; 6 (10):1–11. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pinnock H, Huby G, Powell A, Kielmann T, Price D, Williams S, The process of planning, development and implementation of a General Practitioner with a Special Interest service in Primary Care Organisations in England and Wales: a comparative prospective case study. Report for the National Co-ordinating Centre for NHS Service Delivery and Organisation R&D (NCCSDO) 2008. http://www.sdo.nihr.ac.uk/files/project/99-final-report.pdf
- Robertson A, Cresswell K, Takian A, Petrakaki D, Crowe S, Cornford T. et al. Prospective evaluation of the implementation and adoption of NHS Connecting for Health's national electronic health record in secondary care in England: interim findings. BMJ. 2010; 41 :c4564. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pearson P, Steven A, Howe A, Sheikh A, Ashcroft D, Smith P. the Patient Safety Education Study Group. Learning about patient safety: organisational context and culture in the education of healthcare professionals. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2010; 15 :4–10. doi: 10.1258/jhsrp.2009.009052. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- van Harten WH, Casparie TF, Fisscher OA. The evaluation of the introduction of a quality management system: a process-oriented case study in a large rehabilitation hospital. Health Policy. 2002; 60 (1):17–37. doi: 10.1016/S0168-8510(01)00187-7. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stake RE. The art of case study research. London: Sage Publications Ltd.; 1995. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sheikh A, Smeeth L, Ashcroft R. Randomised controlled trials in primary care: scope and application. Br J Gen Pract. 2002; 52 (482):746–51. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- King G, Keohane R, Verba S. Designing Social Inquiry. Princeton: Princeton University Press; 1996. [ Google Scholar ]
- Doolin B. Information technology as disciplinary technology: being critical in interpretative research on information systems. Journal of Information Technology. 1998; 13 :301–311. doi: 10.1057/jit.1998.8. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- George AL, Bennett A. Case studies and theory development in the social sciences. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press; 2005. [ Google Scholar ]
- Eccles M. the Improved Clinical Effectiveness through Behavioural Research Group (ICEBeRG) Designing theoretically-informed implementation interventions. Implementation Science. 2006; 1 :1–8. doi: 10.1186/1748-5908-1-1. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Netuveli G, Hurwitz B, Levy M, Fletcher M, Barnes G, Durham SR, Sheikh A. Ethnic variations in UK asthma frequency, morbidity, and health-service use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2005; 365 (9456):312–7. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sheikh A, Panesar SS, Lasserson T, Netuveli G. Recruitment of ethnic minorities to asthma studies. Thorax. 2004; 59 (7):634. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hellström I, Nolan M, Lundh U. 'We do things together': A case study of 'couplehood' in dementia. Dementia. 2005; 4 :7–22. doi: 10.1177/1471301205049188. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Som CV. Nothing seems to have changed, nothing seems to be changing and perhaps nothing will change in the NHS: doctors' response to clinical governance. International Journal of Public Sector Management. 2005; 18 :463–477. doi: 10.1108/09513550510608903. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lincoln Y, Guba E. Naturalistic inquiry. Newbury Park: Sage Publications; 1985. [ Google Scholar ]
- Barbour RS. Checklists for improving rigour in qualitative research: a case of the tail wagging the dog? BMJ. 2001; 322 :1115–1117. doi: 10.1136/bmj.322.7294.1115. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mays N, Pope C. Qualitative research in health care: Assessing quality in qualitative research. BMJ. 2000; 320 :50–52. doi: 10.1136/bmj.320.7226.50. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mason J. Qualitative researching. London: Sage; 2002. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brazier A, Cooke K, Moravan V. Using Mixed Methods for Evaluating an Integrative Approach to Cancer Care: A Case Study. Integr Cancer Ther. 2008; 7 :5–17. doi: 10.1177/1534735407313395. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Miles MB, Huberman M. Qualitative data analysis: an expanded sourcebook. 2. CA: Sage Publications Inc.; 1994. [ Google Scholar ]
- Pope C, Ziebland S, Mays N. Analysing qualitative data. Qualitative research in health care. BMJ. 2000; 320 :114–116. doi: 10.1136/bmj.320.7227.114. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cresswell KM, Worth A, Sheikh A. Actor-Network Theory and its role in understanding the implementation of information technology developments in healthcare. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2010; 10 (1):67. doi: 10.1186/1472-6947-10-67. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Malterud K. Qualitative research: standards, challenges, and guidelines. Lancet. 2001; 358 :483–488. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(01)05627-6. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yin R. Case study research: design and methods. 2. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publishing; 1994. [ Google Scholar ]
- Yin R. Enhancing the quality of case studies in health services research. Health Serv Res. 1999; 34 :1209–1224. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Green J, Thorogood N. Qualitative methods for health research. 2. Los Angeles: Sage; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Howcroft D, Trauth E. Handbook of Critical Information Systems Research, Theory and Application. Cheltenham, UK: Northampton, MA, USA: Edward Elgar; 2005. [ Google Scholar ]
- Blakie N. Approaches to Social Enquiry. Cambridge: Polity Press; 1993. [ Google Scholar ]
- Doolin B. Power and resistance in the implementation of a medical management information system. Info Systems J. 2004; 14 :343–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2575.2004.00176.x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bloomfield BP, Best A. Management consultants: systems development, power and the translation of problems. Sociological Review. 1992; 40 :533–560. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shanks G, Parr A. Proceedings of the European Conference on Information Systems. Naples; 2003. Positivist, single case study research in information systems: A critical analysis. [ Google Scholar ]
Individual case studies in clinical research
Affiliation.
- 1 Department of Psychology, University of Newcastle upon Tyne, UK.
- PMID: 9839641
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2753.1998.00011.x
Case studies have acquired an unmerited reputation as being anecdotal, unscientific and intrinsically inferior to group studies. The subsequent disregarding of individual patients as the focus of investigation has led to the neglect of an extremely useful clinical research method, and has probably impaired the pace of therapeutic innovation. The purpose of this paper is to clarify the scope and nature of case studies and promote their rehabilitation. Case studies can, in principle, be used to test any theory that has implications for individual patients. There are two crucial methodological stages. The first is to identify scientifically plausible general theories and derive from them specific hypotheses or models of sufficient precision to have implications for individual cases. The second is to test these hypothetical models against 'pure' cases, selected so as to exclude interfering variables. There are two main types of case study--those made by serendipity (unplanned case observations which challenge an implicit theoretical framework); and formal case studies (designed prospectively to collect pure cases to test a prior hypothesis). The difference between serendipity and planned case studies roughly corresponds to the difference between surveillance and screening. A worked-example of a formal case study is described here in order to illustrate the method. Individual case studies deserve fresh consideration by researchers, since they are a clinician-friendly method with a unique potential for incorporation into routine practice.
- Medical Records*
- Models, Theoretical
- Research Design*
- Case Report
- Open access
- Published: 21 May 2024
A complex systems perspective on chronic aggression and self-injury: case study of a woman with mild intellectual disability and borderline personality disorder
- Daan H. G. Hulsmans 1 , 2 ,
- Roy Otten 1 ,
- Evelien A. P. Poelen 1 , 2 ,
- Annemarie van Vonderen 2 ,
- Serena Daalmans 1 ,
- Fred Hasselman 1 ,
- Merlijn Olthof 1 , 3 &
- Anna Lichtwarck-Aschoff 3
BMC Psychiatry volume 24 , Article number: 378 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Challenging behaviors like aggression and self-injury are dangerous for clients and staff in residential care. These behaviors are not well understood and therefore often labeled as “complex”. Yet it remains vague what this supposed complexity entails at the individual level. This case-study used a three-step mixed-methods analytical strategy, inspired by complex systems theory. First, we construed a holistic summary of relevant factors in her daily life. Second, we described her challenging behavioral trajectory by identifying stable phases. Third, instability and extraordinary events in her environment were evaluated as potential change-inducing mechanisms between different phases.
Case presentation
A woman, living at a residential facility, diagnosed with mild intellectual disability and borderline personality disorder, who shows a chronic pattern of aggressive and self-injurious incidents. She used ecological momentary assessments to self-rate challenging behaviors daily for 560 days.
Conclusions
A qualitative summary of caretaker records revealed many internal and environmental factors relevant to her daily life. Her clinician narrowed these down to 11 staff hypothesized risk- and protective factors, such as reliving trauma, experiencing pain, receiving medical care or compliments. Coercive measures increased the chance of challenging behavior the day after and psychological therapy sessions decreased the chance of self-injury the day after. The majority of contemporaneous and lagged associations between these 11 factors and self-reported challenging behaviors were non-significant, indicating that challenging behaviors are not governed by mono-causal if-then relations, speaking to its complex nature. Despite this complexity there were patterns in the temporal ordering of incidents. Aggression and self-injury occurred on respectively 13% and 50% of the 560 days. On this timeline 11 distinct stable phases were identified that alternated between four unique states: high levels of aggression and self-injury, average aggression and self-injury, low aggression and self-injury, and low aggression with high self-injury. Eight out of ten transitions between phases were triggered by extraordinary events in her environment, or preceded by increased fluctuations in her self-ratings, or a combination of these two. Desirable patterns emerged more often and were less easily malleable, indicating that when she experiences bad times, keeping in mind that better times lie ahead is hopeful and realistic.
Peer Review reports
In residential care for individuals with an intellectual disability, challenging behavior is an often used umbrella term for repeatedly engaging in dangerous or threatening behaviors. These can be outer-directed, like aggression towards people or damaging property, and inner-directed, such as self-injurious behavior [ 1 , 2 ]. The latter is defined as inflicting deliberate damage on- or destruction of one’s own body tissue with or without suicidal intent, for example by skin cutting, burning, scratching, or ingesting inedible objects [ 3 ]. For staff, these behaviors are hard to grasp and sometimes difficult to anticipate. Managing incidents afterwards with freedom restricting measures, such as seclusion or fixation, remains an unwanted and increasingly unaccepted common-practice that is harmful to clients and increases staff stress and turnover [ 4 , 5 ]. Staff typically describe challenging behaviors as a way the individual communicates unmet “complex needs” [ 6 ]. Although group-level research reveals many biological, psychological and social correlates of challenging behavior [ 2 , 7 , 8 ], it remains vague what this often-used adjective “complex” means at the individual level. Research focused on the individual rather than on the group can efficiently advance our understanding of complex phenomena [ 9 ]. Therefore, this study provides a unique exploration of patterns of chronic aggressive and self-injurious behaviors in one woman with a mild intellectual disability (MID) and borderline personality disorder (BPD), day-by-day over the course of 560 days.
The overall goal is to obtain an in-depth understanding of when and why challenging behaviors occur, using an analytical strategy inspired by complex systems theory (cf [ 10 ]). This complex systems lens differs from the dominant biomedical perspective on psychopathology. That is, from a complex systems perspective psychiatric disorders are not understood as latent entities that cause symptoms through (relatively static) hard-wired biological mechanisms, but as dynamic patterns of behaviors, emotions and cognitions that are formed over time [ 11 , 12 ]. Complex systems principles have guided individual-specific explorations of dynamics in high-risk young adults [ 13 ], people with depression [ 14 , 15 , 16 ] and dissociative identity disorder [ 17 , 18 ]. While these studies all used quantitative timeseries analyses to describe the dynamics, qualitative methods are just as well-suited within a complex systems framework. Central to complex systems theory is a holistic approach to understand the person in their environment [ 12 ] and qualitative methods can provide a rich account thereof [ 19 ]. The current study therefore offers a holistic and dynamic exploration of a woman with MID and BPD, by employing a mixed-methods strategy with three overarching aims. In the following sections we introduce these three aims step-by-step, with more detailed theoretical background.
Summarizing daily life
The first step is to qualitatively summarize the complex nature of challenging behavior. From a complex systems perspective, any person is considered a complex system, not just individuals with challenging behavior [ 12 ]. It is complex because there is no root cause for the way a person (i.e., system as a whole) feels, thinks, or behaves at certain moments in time. Emotions, thoughts or behaviors emerge from continuous and interdependent exchanges between the system’s internal state and its environment [ 20 ]. Complex systems are everchanging, which is why an integrative understanding requires a detailed description of the interplay between the system’s and context elements over a longer period of time. It is therefore necessary to sample personal experiences and contextual influences frequently over time, for example by making use of ecological momentary assessment (EMA). EMA is a method in which someone frequently self-reports on current or very recent behaviors and experiences over time (typically via mobile-phone) [ 21 ]. The method is well-established in samples with BPD, but although feasible [ 22 ] not often used in MID research. In earlier work involving clients with BPD, momentary self-injury was associated with daily ruminations or heightened negative affect [ 23 ]. Other EMA studies found the intensity of anger associated with daily reports of aggression [ 24 ]. Such internal experiences (i.e., related to thoughts, emotions, or other behaviors) are the primary focus of most EMA research, but there are few studies that explicitly investigate contextual influences and changes [ 23 ]. This is remarkable, because theory indicates that (challenging) behaviors are not only internally driven but are to a large extend elicited by environmental factors [ 12 ]. For instance, self-injury, is known to occur more frequently when experiencing interpersonal stress [ 25 ]. However, internal factors and the environment differs between persons [ 26 , 27 ]. Whereas one person’s self-injury may be triggered by an argument with parents, someone else’s work pressure may trigger it. To obtain a holistic summary of the person-environment interplay, we first explore person-specific internal states and environmental factors qualitatively.
Describing change over time
The second step is to zoom out, quantitatively exploring how these factors are ordered in time on the participant’s 560-day timeline. EMA research typically employs multiple daily self-ratings for 1–3 weeks, but individual accounts of challenging behaviors over longer timeframes are scarce. Some studies used not daily but weekly caretaker-reports of challenging behavioral incidents. These showed that, during a period of 41 weeks, staff of 33 inpatients with MID reported in total 210 aggressive- and 104 self-injurious incidents [ 28 , 29 ]. Interestingly, 4 of those 33 inpatients were responsible for over half of the 210 aggressive incidents, while a staggering 85% of the 104 self-injurious incidents were from only 2 clients. Few individuals thus account for many incidents, but little is known about the day-to-day temporal patterns of such chronic challenging behaviors over the course of weeks or months.
When a person is tracked over longer periods of time, one can detected phases in which certain behaviors are relatively stable. A single-case study using EMA of a person with a major depressive disorder over almost eight months (239 days) [ 15 ] found two distinct phases. The first four months were characterized by consistent low self-reported depressive symptoms. On the 127th day this abruptly changed, marking the start of a four-month period characterized by consistently high depressive symptoms. From a complex systems perspective, these two stable phases (before and after day 127) are called attractors [ 30 ]. That is, the dynamics of the person (i.e., person-environment system) are attracted towards a specific behavioral pattern that remains relatively stable over time (e.g., a depressive phase in this example). Importantly, stability does not speak to the desirableness of the patterns, but only to the consistency of change over time. For example, consistently never self-harming, consistently being aggressive once-per-week on Tuesdays, or consistently self-harming on weekends are all examples of stable patterns. Following complex systems theory, stable patterns of challenging behaviors can thus be understood as attractors [ 11 , 12 ]. Our second research question is how challenging behaviors are ordered on the participant’s 560-day timeline? This is done by identifying if there are different attractor states (e.g. time-periods with relatively few vs. many challenging behaviors) and explicate ways in which these time-periods are (dis)similar from one another in terms of internal states (e.g., experienced emotions) and environmental influences (e.g., social interactions).
Change-mechanisms
In the third and last step we zoom in again by exploring transition-points: moments that ‘kickstart’ abrupt change towards a new attractor (cf. day 127 in [ 15 ]). Complex systems theory posits two general mechanisms for the change from one attractor to another that are relevant in the context of this study.
First, instability-induced change (also called bifurcation-induced change [ 31 ]) is the mechanism in which an existing attractor destabilizes, thereby forcing the system to reach a new attractor. In Fig. 1 , someone’s current state (e.g., frequently self-injuring) is visualized as a ball, located in a basin which reflects the attractor. The two basins reflect two example attractors: a pattern of few self-injuring behaviors and a pattern of frequent self-injuring behaviors. The basin’s depth metaphorically represents the strength of the attractor state. Stronger attractors are harder to change and therefore everyday events typically do not trigger enduring change. Figure 1 A shows instability-induced change, in which an existing attractor destabilizes to the extent that there is no valley left to contain the ball, making the ball roll towards a new valley [ 11 , 12 , 32 ]. Note that during instability, the ball can move more ‘freely’ through the valley (as it is less steep), leading to increasingly variable behavior. Measures of temporal complexity and variability can therefore pick up on instability [ 33 , 34 ].
Second, event-induced (also called noise-induced [ 31 ]) change is when an extraordinary event (e.g., unexpectedly being fired from work) ‘pushes’ the ball towards a different attractor, without the existing attractor losing its stability first (Fig. 1 B). One would not expect instability as an early warning signal for the transition in this event-induced change, while one would expect the presence of an extraordinary event [ 12 , 31 ]. This makes it possible to empirically differentiate instability-induced and event-induced changes. The third aim of this study was therefore to evaluate which, if any, of these two change-mechanism(s) potentially underlie transitions between attractors.
Conceptualization of two potential change-mechanisms according to complex systems theory. Possible attractors are visually conceptualized as a landscape with basins. In this example, the left basin reflects a desirable attractor (few self-injury) and right one an undesirable attractor (frequent self-injury). The ball reflects a person’s state at one point in time while arrows below the ball symbolize interactions between person and environment in daily life. The top panel ( A ) reflects a mechanism in which we can observe instability over time. During instability the attractor loses strength, visualized as the basin becoming more shallow. When this happens, interactions between person and environment, however casual or extraordinary, lead to a transition towards another attractor. The bottom panel’s mechanism ( B ) reflects a mechanism in which the attractor itself does not lose strength. Therefore this will not be marked by instability. Everyday events will not be enough to reach a transition. Instead it takes extraordinarily strong environment-person interaction to ‘force’ this change
The participant is a woman in her 30s, diagnosed with MID and BPD. For over a decade, she has lived in a 24-hour residential care facility specialized for people with MID and severe behavioral problems. Her daily routine typically consists of working in the house (e.g., cooking, cleaning), she likes to take walks, and enjoys playing board games. For several days a week she goes to an activity center where she works creatively (e.g., draw paintings, make music), alone or together with others. This provides important structure in her daily routine. Staff is available 24 − 7 to support her. Even seemingly regular tasks, such as arriving in time for appointments, may be perceived as onerous. Staff are therefore reminded to compliment her regularly, even with seemingly trivial accomplishments. She best thrives when she experiences support that is clear and structured, because that makes her feel calm and secure.
Before she lived in the care facility, during her childhood and teenage years, she experienced traumatic events that undoubtedly contributed to challenges she faces nowadays. She often perceives her life as a struggle, some days more than others. She mostly communicates her struggles calmly to others, but sometimes her tensions become explicit to her environment when she self-injures or is physically aggressive. According to her care professionals, her overall well-being is poorer on days when she shows these behaviors. Her care professionals have several hypotheses about factors contributing to her challenging behaviors. One is that she does not trust herself to be alone. The self-injuring and aggressive incidents are, at least sometimes, perceived as a call for reassuring attention from staff. Another hypothesis is that her challenging behaviors are a maladaptive emotion-regulation strategy. Unpleasant emotions can (sometimes unexpectedly) accumulate very rapidly. Over time, she has learned that she can immediately achieve short-term relief from this overwhelming emotional experience by self-injuring. Alternatively, difficulties regulating negative emotions are also considered a cause of aggressive behaviors. After self-injurious or aggressive incidents, staff need to ensure the participant’s and others’ safety, sometimes by imposing freedom restricting measures such as seclusion or fixation. Such drastic measures are resented by staff and the participant alike. She is highly motivated to change her challenging behavioral patterns, and therefore follows dialectical behavior therapy that aims to increase her emotion regulatory abilities [ 35 ].
Procedure and measures
As part of dialectical behavior therapy, the participant completed daily self-registrations via a mobile phone application. Hence, these EMA data were initially not collected for research purposes. The participant and her clinician formulated the application’s daily EMA questions together. Emotions, behaviors and cognitions with maximum relevance to her treatment goals and daily life were translated into questions that the app prompted automatically on her phone at 7:00 PM. Seven of those questions could be answered on a slider with six answer options that ranged between “not feeling at all” and “an intense feeling”. These questions inquired to what extend she (1) felt happy, (2) felt scared, (3) felt sad, (4) felt angry, (5) had the urge to self-injure, (6) thought of death, and (7) had the urge to be aggressive, on that particular day. She also self-rated with either a “yes” or “no” whether she, on that day, (8) had self-injured and (9) had been physically aggressive. The participant followed dialectical behavior therapy from mid-2019 until mid-2021, which consisted of weekly group sessions with other clients, one-on-one sessions with a therapist and 24-hour telephone consultation. During these individual sessions, therapist and participant discussed recent self-injurious and aggressive incidents registered in the diary. The participant continued to complete her self-ratings on a daily basis, even when therapy was paused due to Covid-19 restrictions. This was not because she was told to – she felt that she benefitted from daily self-reflections in the app. In total, she completed her diaries for a period of 560 days and was rewarded with a gift card for her long-term dedication.
Informed consent was obtained from the participant and her legal guardian to (1) present and analyze the aforementioned daily diary entries and (2) to access the records (i.e., electronic client files) to perform supplementary qualitative analyses about therapeutical context and care professional’s perspective on her functioning. This electronic health system is a routine procedure in which care professionals describe multiple times per day, the provided care, implemented measures and any relevant daily events concerning the participant. The records of the 560-day self-rating period were retrieved and any information that could be traced back (names of persons, cities, organizations, locations) were replaced by codes such ‘Person A’ or ‘City B’. Her clinical team (clinician and closest care professionals) approved aforementioned procedures beforehand. The Ethical Committee Social Sciences of Radboud University and the Ethics committee of the care organization judged that the research was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.

Visualization of our three-step-approach to this case-study
We employed a mixed-methods triangulation design study with both qualitative and quantitative data [ 36 ]. The study had a three-step approach based on complex systems theory (Fig. 2 ). First, we obtained a comprehensive summary of the participant’s daily life through qualitative analyses of the daily caretaker records. These qualitative findings were then quantified, to then be integrated with quantitative daily self-reports. Secondly, we described the trajectory of her self-reported challenging behaviors by identifying transition-points and characterizing the different attractor states. Thirdly, we evaluated transition between attractor states in terms of (in)stability and extraordinary events (cf. Figure 1 ).
Analytical strategy
The first step was to qualitatively analyze the anonymized daily records in accordance with the phased approach of thematic analysis [ 19 ]. This thematic analysis was conducted by the first author together with four Master’s students in Pedagogical Sciences, all under the supervision of a researcher with ample experience in qualitative methods. A thematic analysis is an inductive method whereby the coders collaboratively construct themes and patterns from the text in an iterative process that contains six phases: data familiarization, generating initial codes, searching for themes, reviewing themes, defining themes, and producing the research report. In each of these phases, the coders frequently came together to discuss and interpret the records. All five coders first familiarized themselves with the data by reading the whole daily records text file, which consisted of > 300,000 words. Together the coders then practiced the initial coding. The text file was then divided into five roughly equally large chunks of daily records text. Each coder then generated initial codes on his/her own text. The coding was done using MAXQDA 2022 [ 37 ]. During the initial code generating phase, coders came together thrice to compare each other’s initial coding wording and interpretation of the text. These iterative consensus-building sessions lead to the construction of a preliminary overview of candidate subthemes and themes (i.e., codes that were interpreted as reflecting the same higher-order construct). During this collaborative, inductive process, the wording and structure of these (sub)themes were refined into one thematic overview that contained a theme- and subtheme-structure that captured themes based on the whole dataset. This procedure fosters a shared understanding among all coders, resulting in a consensus over the overarching thematic structure (thematic map). From this jointly construed thematic map, every coder then coded the records once more from scratch. That finally resulted in a MAXQDA file with fragments of coded text on a specific day. These qualitative data were then quantified to a dataset containing only binary variables with a (sub)theme coding present (1) or not present (0) per day.
The researcher then met with the participant’s clinician, who has known her for over a decade, to discuss the thematic overview and underlying codes. The goal of this meeting with the clinician was to (1) ascertain the appropriateness of challenging behaviors as the most indicatory variables to summarize the system’s overall state, and (2) identify the most relevant (sub)themes for explaining the frequency of challenging behavioral incidents at any given period.
Describing change trajectory
The subsequent steps were quantitative analyses – all performed in RStudio-2022.02.2–458 [ 38 ] which runs on R software version 4.2.0 [ 39 ]. To evaluate concurrent validity of self-ratings, we performed χ 2 tests between self-ratings and informant-reported (daily records) accounts of days with self-injury and physical aggression. Kazdin [ 40 ] recommends evaluating single-case timelines by combining visual inspections of graphed timeseries with statistical analyses. We therefore visualized the two self-report timeseries (physical aggression and self-injury) using functionality from ggplot2 [ 41 ].
Next, we pinpointed transitions in the physical aggression and self-injury timeseries on the 560-day timeline. This transition-point detection was done with the ts_levels function from package casnet [ 42 ], which uses recursive partitioning [ 43 ] to classify segments (or phases) on a timeseries with a relatively stable mean. We did this for the physical aggression and self-injury variables. Because these two variables are binary (0 = behavior did not occur on that day; 1 = behavior occurred on that day), mean levels effectively reflected the proportion of days with incidents within a phase. In the ts_levels function the minimum duration of one phase was set to seven days, comprising a whole weekly routine, and controlling for day-of-the-week effects. The absolute change criterion was set to 25%, meaning that each identified transition reflected at least a 25% increase or decrease compared to the mean of the preceding phase (cf [ 44 , 45 ]). Based on suggestions by Kazdin [ 40 ], we searched for transitions by visually inspecting a graph of the raw binary timeseries and a plot of the levels identified using the ts_levels function [ 42 ].
After pinpointing transitions, we characterized the different attractor states in terms of what makes them (dis)similar from one another on the 560-day timeline. We calculated – per phase and across the whole 560-day timeline – the mean frequency of self-rated challenging behaviors (i.e., mean days with challenging behaviors) and the mean frequencies of (sub)themes that the participant’s clinician hypothesized to be explanatory. Furthermore, we examined – per phase and across the whole 560-day timeline – whether these clinically relevant (sub)themes were associated with challenging behaviors. That is, Fisher’s exact tests evaluated whether a reported challenging behavior occurred (beyond chance) on the same days as reports of staff-hypothesized risk- or protective factors. Additionally, we performed Fisher’s exact tests to evaluate the relation between staff-hypothesized risk- or protective factors from one day until the next (lag-1 association). Due to the number of repeated bivariate associations we evaluated significance at p < 0.01.
For the third and last step we analyzed temporal instability and pinpointed extraordinary events, to obtain insight into potential change-mechanisms (i.e., either instability-induced, event-induced or both). The (in)stability of daily self-ratings was analyzed with dynamic complexity [ 46 ] as implemented in R-package casnet [ 42 ]. Dynamic complexity is comprised of a multiplication between distribution measure D, which reflects the distribution uniformity of data-points within the range of the used scale, and fluctuation measure F, which indicates the strength and number of fluctuations within the timeseries. As such, it is more robust to non-stationarity and periodicity than alternative measures such as variance (cf [ 33 , 46 ]). Because dynamic complexity cannot handle missing data, we first employed Kalman smoothing with the na_kalman function [ 47 ] to impute missing data-points using a structural model fitted by maximum likelihood. Dynamic complexity can only be computed for ordinal or continuous timeseries [ 46 ], hence dynamic complexity could not be computed for the binary variables aggressive and self-injury incidents. Instead, dynamic complexity was calculated on the most relevant six-point scale items: “urge for aggression” and “urge for self-injury”, each within a seven-day backwards overlapping window. This window shifts gradually along the timeseries without changing in width, such that dynamic complexity is first calculated for each item between day 1 and day 7, then between day 2 and day 8, and so on. With this 7-day window we again control for day-of-the-week effects. The windowed dynamic complexity was visualized on a timeline per item. A one-tailed z test (α = 0.05) was applied on each dynamic complexity timeline to determine at which time-windows there was significant instability (i.e., high dynamic complexity). We chose to perform a one-tailed significance test because we wanted to examine the occurrence of high dynamic complexity values (not low values), exceeding the threshold of the average dynamic complexity (cf [ 17 , 18 , 33 ]). We ultimately described, per identified transition, whether it was preceded or accompanied by significant instability and/or an extraordinary event. These extraordinary events were codes categorized into subthemes during the thematic analysis procedure. That is, after the coders had familiarized themselves with the data, generated and discussed initial codes they reached consensus about which events reflected everyday events and which events were extraordinary across the 560 day period. In the absence of instability, an extraordinary event occurring the week prior to a transition was considered an potential indicator of an event-induced mechanism (cf. Figure 1 ). Change was potentially instability induced when the dynamic complexity of aggression and/or self-injury was significantly high the week before or during change, without an extraordinary event the week prior. In the presence of both instability and an extraordinary event, we conclude change was potentially event- and instability-induced.
To first obtain a comprehensive summary of her daily life we conducted a thematic analysis of the care taker’s records. The analysis resulted in a thematic map consisting of six themes and sixteen subthemes. The six themes were the received care, daily activities not related to care, positivity, physical complaints, emotional tensions, and challenging behavior. These themes reflect categorizations that are interrelated. We visualized (sub)themes and their interrelations in Fig. 3 .
Thematic map, generated from the thematic analysis, showing (sub)themes and the links between them
Anything positive reported in the daily records was coded under the theme positivity . This pertained to events that were extraordinary positive for her on the 560 days. Positive social contact was a subtheme that reflected more casual positive interactions with care professionals, family or friends. The subtheme general positivity included any mention of positive affect. This could be sense of humor, making a relaxed impression, having a good day, or positive dialogue with care professional. For example the mention “ client played boardgames after the barbecue and visibly enjoyed herself ” indicates that positivity occurred during descriptions of the issue of the day, which are subdivided under two themes: received care and daily schedule. The latter involved her daily schedule unrelated to medical or psychological treatment, which could be either at the facility (e.g., doing the household or taking a walk) or social activities away from the facility (e.g., board games at activity center). Received care related to any actions from care professionals, which could be either in the form of security measures (e.g., checking her room for potential objects used for self-injury or secluding the participant), dialogue with care professionals (e.g., talking about what is on her mind, complimenting the participant), medical care (e.g., treatment of wounds at care facility or hospitalization), or psychological therapy sessions (dialectical behavior therapy and psychomotor therapy).
Challenging behavior was a theme with three subthemes: verbal aggression, physical aggression, and self-injury. The latter two were also self-reported on a daily basis by the participant. Daily record accounts of challenging behavior related to emotional and/or physical discomfort, for example “ client cut herself with a broken piece of plate, she says she wanted to experience different pain than the pain in her stomach ”. The theme physical complaints related to either feeling sick (e.g., nauseated) or mentions of the participant communicating experiencing physical pain. Both could be a cause and consequence of challenging behavior. For example, self-injury caused wounds, which lead to inflammation, which naturally come with pain or sickness such as fever. Self-injury through re-opening existing wounds was the most frequently reported self-injurious form, which exacerbated physical complaints. That required her receiving (extra) care. Related to both challenging behaviors and physical complaints were emotional tensions – a broad theme that comprised of three subthemes. Records describing extraordinary negative events (e.g., losing her pet), social tensions (e.g., quarrels with staff or family) and general descriptions of negative affect (e.g., feeling irritated, fearful, frustrated, or insecure). Emotional tensions could be triggered during any daily activity and could be both cause and consequence of physical complaints. For example “ client is working on a painting. When we adjust schedule to playing a boardgame she becomes angry” . Moreover, it could result in receiving extra care (e.g., support from staff when in distress) or was the consequence of dissatisfaction with received care (e.g., anger after imposed security measure). Challenging behavior always came with some form of emotional tension.
To better interpret the thematic map, the researcher then asked the participant’s clinician whether the participant knows better and worse times and what typically indicates to staff whether her overall well-being is high or low. Before having seen the results, she confirmed that the frequency of self-injurious and physically aggressive incidents is most telling about her overall well-being. This indicates challenging behaviors summarize her overall state. From the (sub)themes generated in the thematic analysis, the clinician then identified 11 staff-hypothesized risk- and protective factors for her challenging behaviors. These factors were either specific codes or broader (sub)themes: reliving past trauma, hallucinating, negative affect, receiving medical care, receiving compliments, the imposing of freedom restricting measures, experiences of physical pain and sickness, receiving psychological therapy, tensions with her family, and positive social interactions. These variables were used for subsequent analyses.
The participant completed the daily survey 494 times during the 560 days (88%). Physical aggressive incidents were self-reported on 65 days (13%), while self-injury was self-reported on 247 days (50%). Staff reported aggressive and self-injurious incidents on respectively 75 days (16%) and 164 days (33%). A χ 2 test indicated agreement between self- and informant ratings. That is, counts of observed matches between self- and informant ratings of these challenging behaviors (i.e., both reporting daily presence or absence of behavior) was significantly higher than the expected count for self-injury, χ 2 (1, N = 494) = 91.56, p < 0.001, and for aggression, χ 2 (1, N = 494) = 12.76, p < 0.001. As both challenging behaviors can occur without being noticed by staff (e.g., when on leave), we analyze self-reported challenging behavioral dynamics.
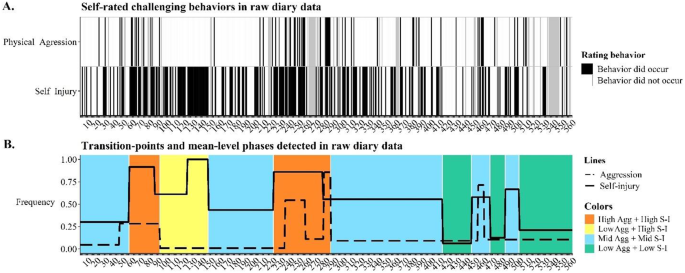
Binary timeseries of self-reported physical aggression and self-injurious behavior during 560 days and changes in its mean frequency. X-axes show number of days. Panel A shows raw challenging behavioral timelines. Gray cells are days that the participant did not complete her diary. In panel B, the lines reflect mean-level changes in raw diary timelines, detected by recursive partitioning algorithm. Colors reflect identified challenging behavioral attractor states (see text for details). The same color means a qualitatively similar attractor. Identified transition-points between attractors are thus the days (on x-axis) when the color changes
Figure 4 A illustrates the raw binary timeseries of self-reported physical aggression and self-injury for 560 days. The recursive partitioning algorithm [ 42 ] first detected mean-frequency changes in raw diary timelines (4A) – the outcome of which is visualized with dashed and solid lines in Fig. 4 B. After visual inspection of the binary timeseries (4A) and their mean-levels (lines in 4B), we found 10 transitions that mark that end of an old- and start of a new attractor (colors in 4B). When the mean-level changes detected by recursive partitioning (up or downward trend in lines 4B) of the two challenging behaviors occurred in the same direction within close proximity to one another (i.e., within 14 days), we marked it as transition that starts or ends a challenging behavioral phase. For example, on day 86 for self-injury a 30% drop was detected by recursive partitioning and on day 91 aggression dropped by 28%. Here we marked day 91 as the transition, as it marked the end of a phase with frequent challenging behavior. Similarly, when self-injury and aggression increased on respectively day 446 and 452, we marked 446 as the transition for a start with frequent challenging behaviors. One exception was made, based on a clear difference in absolute change: on day 46 the proportion of aggressive incidents increased with 25%, while 11 days later the proportion in self-injurious incidents increased by 60%. Hence, only day 57 was marked as a transition. Two detected mean-changes were not marked as transitions: the increase of self-injury on day 122 and the decrease in aggressive incidents on day 257. The latter (day 257) was not marked as an attractor change, because of the large number of missing values that followed this transition (see gray band in Fig. 4 A). Day 122 was not marked after visual inspection of the self-injurious incidents timeseries (Fig. 4 A) we noted that (1) the upward trend may have started sooner (possibly day 110) and (2) this upward trend did not seem significant as the frequency of self-injuries– relative to the entire timeline – was already high between day 57 and day 146.
Table 1 summarizes, for each phase, the mean frequency (i.e., percentage of days) that both challenging behaviors were self-reported in the diaries. Furthermore, we calculated the mean frequency per phase for each of the 11 staff-hypothesized risk- and protective factors (see Supplementary Material 1 ). To obtain insight into what makes phases (dis)similar from each other in terms of these risk- and protective factors, we compared the mean frequency of them within each phase to the 560-day mean of that factor. We considered a phase-mean salient if it was above or below 1 SD relative to that factor’s 560-day mean. For example, salient about phase 1 (day 1 to 56) was that familial tensions occurred on 18% of days, which was relatively often, given that it is > 1 SD relative to the 560-day mean of 5%. Although Table 1 shows that the 11 frequencies of staff-hypothesized risk- and protective factors differ between phases, we find no unequivocal bivariate if-then explanation (e.g., if a phase has familial tensions, then high aggression) for either of the challenging behavioral frequencies.
In addition to describing average frequencies across phases, we also analyzed bivariate associations at the within-day level (contemporaneous) and across days (lag-1). That is, whether challenging behaviors and reports of staff-hypothesized risk- and protective factors co-occurred on the same day and from day-to-day. Fisher’s exact test revealed that, across the entire 560-day timeline, freedom restricting measures were more often applied on days with aggression (OR = 5.27, 95%CI [2.82, 9.78]) or self-injury (OR = 2.72, 95%CI [1.56, 4.89]). Across the 560-day period, there were no bivariate contemporaneous associations between challenging behaviors and reliving trauma, hallucinating, receiving medical care, compliments or psychological therapy, having pain, sickness, experiencing negative affect or familial tensions, or positive interactions. On days after an implemented freedom restricting measure, our participant was more likely to engage in aggressive (OR = 4.80, 95%CI [2.58, 8.86]) and/or self-injurious behavior (OR = 1.97, 95%CI [1.67, 3.39]). On days after a psychological therapy session (DBT or psychomotor therapy) she was less likely to engage in self-injurious behavior (OR = 0.36, 95%CI [0.15, 0.79]). To explore these associations within phases (and possible differences between phases), we repeated the same Fisher’s tests per phase, on both the contemporaneously and lagged timescale (484 tests; 11 themes × 2 behaviors × 11 phases × 2 timescales). The only significant associations that hold within certain phases evolve around freedom restricting measures, indicating that these measures were more likely to occur on the same day as aggression in phase 5, before days with self-injury in phase 7 and before days with aggression in phase 11. All other contemporaneous and lag-1 associations between challenging behaviors and the 11 variables that the clinician hypothesized to be explanatory, were non-significant (evaluated at p < 0.01 due to multiple testing).
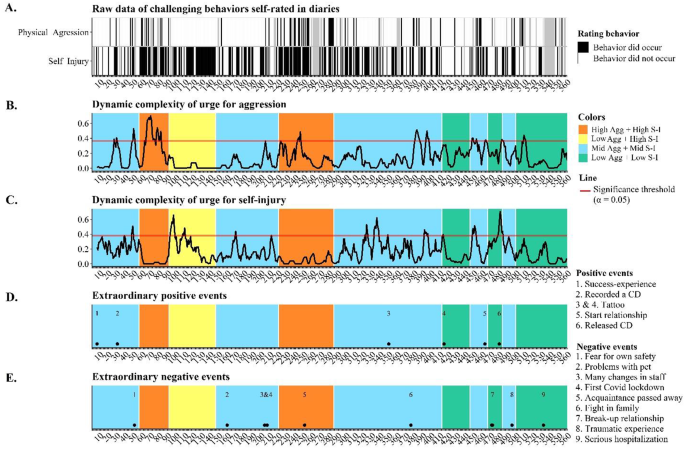
Combined graph of the participant’s self-reported challenging behavioral patterns, transition-points, dynamic complexity, and extraordinary events. Panel A shows the raw data of self-reported physical aggression and self-injury. Gray cells are missing data. Panel B and C reflect the dynamic complexity of both challenging behaviors. High values reflect unstable patterns, whereas low dynamic complexity reflects stability during the 7 prior days. The horizontal red lines mark the significance threshold for each variable; dynamic complexity values above the lines indicate statistical significance (α = 0.05). Orange, yellow, blue, and green background colors are attractor states. Panel D and E reflect pinpointed positive and negative extraordinary events that were identified as such in the daily records
Figure 5 shows the occurrence of challenging behaviors (panel A), the (in)stability of self-reported patterns in urges for challenging behaviors (panel B and C), and extraordinary events (panel D and E) on the 560-day timeline Footnote 1 . Each point on the graphs in panel B and C reflects how unstable (i.e., irregular and erratic) the fluctuations of self-rated urges for challenging behaviors were in the previous 7 days. Low values indicate stable patterns, whereas high dynamic complexity values are indicative of temporal instability. Everyday events are extremely plentiful, making them impractical to pinpoint on a timeline. Extraordinary events, however, were derived from thematic analysis results. We considered two subthemes: positive events and negative events (see themes positivity and emotional tensions in Fig. 3 ), as they reflected impactful events that were extraordinary across the 560-day timeline.
Table 2 summarizes what happens one week before each of the 10 transition-points. There were four transitions towards an attractor with more frequent challenging behavior than before. These undesirable transitions were all either instability-induced, environment-induced or a combination of both (Table 2 ). Day 221, for example, was likely an event-induced change, given that there was no instability, but the first Covid-19 lockdown likely led to this undesirable change. Social contact with friends and family – as well as support from staff – were drastically reduced while in lockdown, disrupting her everyday routine increasing her need for aggression and self-injury as an outlet. There were also six desirable changes. One such example was that the week before she finished her tattoo (extraordinary event on day 413) was instable, possibly due to prospect of this exhilarating moment, marked the start of a new phase with few challenging behaviors. However, the relation between transitions, instability and extraordinary events was not entirely clear-cut, as two desirable transition-points (day 147 and 286) occurred during stable periods and without any notable events. Figure 5 further shows that extraordinary events occurred during stability, but without a transition (e.g., starting her tattoo on day 350). Even an extraordinary event in combination with instability was no guarantee for a transition (e.g., on day 367 a fight in the family occurred during a highly unstable week without a transition). In summary, although instability seemed to increase the chance of transitions – especially in combination with an extraordinary event – our findings do not imply that instability and extraordinary events are incontrovertible warning signals that always explain meaningful change on the participant’s 560-day timeline.
Discussion and conclusions
The current study provides a unique exploration of day-by-day aggressive and self-injurious patterns in one woman with a MID and BPD. Applying a three-step-approach inspired by complex systems theory, we aimed for an in-depth understanding of her challenging behaviors over the course of 560 days. Summarizing her daily life was the first step, revealing that a large set of internal and environmental factors relevant to her daily life. The clinician narrowed this large set down to 11 staff hypothesized risk- and protective factors: freedom restrictive measures, reliving trauma, hallucinating, experiencing pain, sickness, negative affect, familial tensions, positive interactions, receiving medical care, compliments or psychological therapy. Overall, freedom restricting measures were more likely to occur on the same day as challenging behaviors, which is not surprising. It is striking, however, that self-injury and/or aggression were more likely to occur the day after a coercive measure by staff, indicating that although these measures may be effective to suppress certain behaviors in the moment, they have detrimental effects on the longer run [ 4 , 5 ]. Furthermore, we found that on the day after a psychological therapy session (DBT or psychomotor therapy) she was less likely to self-injure. These results imply that downscaling of freedom restricting measures and upscaling of psychological therapy (where possible) is warranted. All other bivariate associations between hypothesized risk- and protective factors with both challenging behaviors – explored phase-by-phase and day-by-day – were non-significant, indicating that challenging behaviors are not governed by mono-causal if-then explanations (e.g., if phase has many familial tensions, then high aggression or if day with hallucination, then self-injury). The multitude of bivariate null-results speaks to the complex nature of these behaviors at the case-level [ 2 , 6 , 7 , 8 ].
In the second step, we described the trajectory of challenging behaviors over time. We identified 11 distinct, relatively stable phases within the 560-days timeline. These 11 phases could be narrowed down to four qualitatively different attractor states: high levels of self-injury and aggression (2 phases), average levels of self-injury and aggression (5 phases), low levels of self-injury and aggression (3 phases), or high levels self-injury with low levels of aggression (1 phase). The mean frequency of the 11 staff-hypothesized risk- and protective factors varied by phase: no two phases were similar (Table 1 ).
In the third step we focused on (the week before) transitions between attractors, exploring potential change-inducing mechanisms (Fig. 1 ). Our findings suggest that the mechanism of two transitions remained unknown, two were event-induced, two were instability-induced and four could be environment- and/or instability-induced (Table 2 ). Six transitions were thus potentially instability-induced, which is in line with empirical evidence for instability as an early warning signal for upcoming transitions [ 17 , 33 , 34 ]. Nevertheless, extraordinary events and/or instability did not unequivocally imply a transition, as both instability and extraordinary events occurred without transitions afterwards (Fig. 5 ). The two unknown mechanisms were both for desirable transitions, which could mean that relatively minor events in daily life apparently were enough to elicit positive change. One possible explanation would be that her desirable attractor is stronger than the undesirable one. That is, we could perceive her undesirable basin (Fig. 1 ) to be shallower, making this state easier malleable relatively minor everyday events. Future research could explore this further with recently developed analytical methods that quantify the stability of an attractor state [ 48 ].
There were three notable limitations to this study. First, results from a case-study are obviously not generalizable. Repeating (and finetuning) our three-step-approach on different cases, will reveal the extent to which of our findings are person-specific or generalizable across cases. This will ultimately increase our understanding of challenging behaviors and consequently enable optimized care. Second, our thematic analysis was based on care professionals’ daily records. Registering relevant events in the electronic health records is a routine practice in the residential care setting – done with the intention to document the client’s case file and keep colleagues up to date. Hence, care professionals received no instructions as to how extensive or comprehensive their reports should be. This meant that when a specific code was not identified from the records on a specific day, it may either have not been observed by care professional(s) or simply not been registered. Seemingly trivial happenings, such as giving complements will likely have occurred more often than that the coders coded in the records. Third, despite a-priori anonymization of the records, it was evident that the records included reports of many different (approximately > 30 different) care professionals. The richness of the described daily events likely partially depended on who reported and how much time that person had. Fourth, our three-step procedure was subject to many researcher’s degrees of freedom. The 11 staff-hypothesized (sub)themes that the participant’s clinician selected out of the thematic map, for example, remained a personal choice. Furthermore, the criterion we used to evaluate a threshold for instability (one tailed z-test at p < 0.05) is based on convention (cf [ 16 , 18 , 33 ]), but ultimately still a choice. On the other hand, there are no established guidelines available for a complex systems guided case study.
This study also had strengths. First, by shedding light on events in the environmental that may ‘push’ the system into another state, our study adds to the (complex systems) psychological literature that has so far predominantly focused on instability preceding transitions [ 24 , 33 , 34 , 45 ]. Qualitative analyses of case records allowed us to distinguish everyday- from extraordinary events. Because this distinction was informant-based and not self-reported, it is possible that meaningful events were missed (here or in any step of our analysis). Future qualitative or mixed-methods research should further explore the nature of events that the individual perceives to ‘kickstart’ transitions. A second strength is that our research gives a helicopter view of day-by-day processes across several months. The majority of EMA research in BPD studies within-day fluctuations. For our participant behavior did not only fluctuate within-days, also across time-periods of multiple weeks or months. This may inspire EMA research in BPD to consider further exploring fluctuations on slower timescales. Nevertheless, within-day processes remain relevant. Complex systems, after all, are characterized by interacting processes across many timescales [ 12 , 49 ]. In our case, unobserved instability at shorter timescales (e.g., hour-to-hour) could have induced our (un)observed transitions. After all, within-day affective instability is a well-documented correlate of challenging behaviors in BPD [ 23 , 24 ]. The case records did provide within-day detail, but because we eventually quantified these into dichotomous codes per day (present vs. absent), the richness of within-day information was lost. Future research should zoom further into what happens within the day of (or days before) a transition. Statistical process control charts [ 50 ] could then be used to detect whether significant rises in tensions predict challenging during the day.
The participant selection in this study was solely based on convenience sampling, that is, she was the only one in DBT who adhered to the diaries this consistently for this long. The uniqueness of the already collected diary data, both in terms of the chronicity of her challenging behavior [ 28 , 29 ] and her devoted compliance to the diaries, was the reason she and her legal guardians were asked for this study. Whether or not these study procedures can be replicated in different cases depends on how well the implemented diary procedure elicits an intrinsic motivation to stay compliant. There were certain participant- and study characteristics that contributed to her uniquely long-term compliance, which are lessons for scientists or practitioners who wish to collect similar data. First, the diaries were an integral part of her DBT program – for which she was already highly motivated. Second, the diaries items were constructed in collaboration with the participant, and thus tailored to her experience world. A personalized approach to EMA in practice, by integrating it in therapy and individualizing item-selection, is an opportunity for increasing participant involvement and compliance [ 22 , 51 ]. Third, for compliance it may have been helpful that the participant has lived in residential care since childhood. This institutionalization – at least with our participant – contributed to the responsibility she felt to follow through on prescribed activities in her care plan. Completing the diaries became part of her daily routine structure. It is likely that this played a part in her continued compliance to the diaries, even when the Covid pandemic made DBT impossible. Nevertheless, further research into factors that enhance or hamper EMA compliance is necessary.
Importantly, personalized daily diary monitoring – and therefore this study’s three-step analytical procedure – is already certainly feasible for other individuals [ 22 ]. Replicating this design is therefore encouraged. Complex systems theoretical principles have already guided mainly quantitative timeseries analytical inquiries in different clinical case studies with less measurements (e.g., 91 [ 17 ] or 138 [ 18 ]) and more measurements (e.g., 1.476 [ 15 ]). Based on these studies [ 15 , 17 , 18 ] we would we expect that altering between different phases over time is a finding that is likely to replicate. However, other clients without such chronic challenging behavior and without such an institutionalized background would likely show very different patterns. That is, dynamic patterns with qualitatively different – and potentially less strong – attractor states. At this point, it remains speculation how this case study’s findings relate to other clients. The surge of EMA applications in clinical settings during the past years suggests that large n = 1 datasets may become more commonly available. Replicating our three-step method would allow for between-person comparisons, shedding light on how (a)typical the nature of our participant’s attractor states and number of change-points was, compared to others (e.g., people with BPD and/or in residential MID care).
The study altogether illustrates the added value of in-depth case-study research [ 9 ] and the utility of complex systems principles to guide such an inquiry. Our three-step approach adheres to recent calls for holistic and dynamic accounts of challenging behaviors in BPD [ 52 ]. Over time, few (if any) if-then relationships could be said to possibly explain the participant’s challenging behavior, substantiating it as a complex phenomenon that is difficult to grasp. Our results thus make explicit why care professionals describe to these behaviors as “complex” [ 6 ]. Nevertheless, in-depth idiographic science can help disentangle this complexity, generating new insights relevant for practice. Zooming out revealed different phases of challenging behaviors. For staff it is good to recognize available attractors and adjust care accordingly. With our participant it illustrated that she – just as anyone – has both ups and downs. Her desirable attractors actually emerged more often than desirable ones (three periods of low aggression and self-injury vs. two periods with high aggression and self-injury). Moreover, her desirable patterns were less easily malleable than undesirable ones. For the participant, this means that when things are down, keeping in mind better times are ahead is as hopeful as it is realistic. Repeating this idiographic design on other persons with chronic challenging behavioral patterns may therefore nuance the bad reputation they may have at the care facility.
Data availability
R scripts are publicly available from https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/XRMHU . Preprocessed data are available upon reasonable request via https://doi.org/10.17026/SS/VOXYE9 . Requests can be made for research purposes only.
In Fig. 5 we present the dynamic complexity of the most relevant two variables for these challenging behaviors. For completeness sake, we present raw data of all seven self-rated variables and their (average) dynamic complexity in Supplementary Material 2 . Visualizations of the 11 staff-hypothesized risk- and protective factors, in combination with challenging behaviors and instability are accessible through https://hulsmans.shinyapps.io/themes/ .
Emerson E, Kiernan C, Alborz A, Reeves D, Mason H, Swarbrick R, et al. The prevalence of challenging behaviors: a total population study. Res Dev Disabil. 2001;22(1):77–93.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Ali A, Blickwedel J, Hassiotis A. Interventions for challenging behaviour in intellectual disability. Adv Psychiatr Treat. 2014;20(3):184–92.
Article Google Scholar
Nock MK. Self-injury. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2010;6(1):339–63.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
van Dorp M, Nijhof KS, Mulder EA, Popma A. Defining seclusion: a qualitative multiphase study based on the perspectives of youth and professionals in secure residential youth care in the Netherlands. Resid Treat Child Youth. 2021;38(4):404–23.
Deveau R, McGill P. Impact of practice leadership management style on staff experience in services for people with intellectual disability and challenging behaviour: a further examination and partial replication. Res Dev Disabil. 2016;56:160–4.
Griffith GM, Hastings RP. He’s hard work, but he’s worth it. The experience of caregivers of individuals with intellectual disabilities and challenging behaviour: a meta-synthesis of qualitative research. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2014;27(5):401–19.
Crowell SE, Beauchaine TP, Linehan MM. A biosocial developmental model of borderline personality: elaborating and extending Linehan’s theory. Psychol Bull. 2009;135(3):495–510.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Tevis C, Matson JL. Challenging behaviour in children with developmental disabilities: an overview of behavioural assessment and treatment methods. BJPsych Adv. 2022;28(6):401–9.
Hekler EB, Klasnja P, Chevance G, Golaszewski NM, Lewis D, Sim I. Why we need a small data paradigm. BMC Med. 2019;17(1):133.
Thelen E, Ulrich BD. Hidden skills: a dynamic systems analysis of treadmill stepping during the first year. Monogr Soc Res Child Dev. 1991;56(1):1–98.
Hayes AM, Andrews LA. A complex systems approach to the study of change in psychotherapy. BMC Med. 2020;18(1):197.
Olthof M, Hasselman F, Oude Maatman F, Bosman AMT, Lichtwarck-Aschoff A. Complexity theory of psychopathology. J Psychopathol Clin Sci. 2023;132(3):314–23.
Schreuder MJ, Hartman CA, Groen RN, Smit A, Wichers M, Wigman JTW. Anticipating transitions in mental health in at-risk youths: a 6-month daily diary study into early-warning signals. Clin Psychol Sci. 2022;11(6):1026–43.
Schreuder MJ, Wigman JTW, Groen RN, Weinans E, Wichers M, Hartman CA. Anticipating the direction of symptom progression using critical slowing down: a proof-of-concept study. BMC Psychiatry. 2022;22(1).
Wichers M, Groot PC, Psychosystems ESM, Group EWS, Group. Critical slowing down as a personalized early warning signal for depression. Psychother Psychosom. 2016;85(2):114–6.
Wichers M, Schreuder MJ, Goekoop R, Groen RN. Can we predict the direction of sudden shifts in symptoms? Transdiagnostic implications from a complex systems perspective on psychopathology. Psychol Med. 2018;49(3):380–7.
Fartacek C, Schiepek G, Kunrath S, Fartacek R, Plöderl M. Real-time monitoring of non-linear suicidal dynamics: methodology and a demonstrative case report. Front Psychol. 2016;7:130.
Schiepek G, Stöger-Schmidinger B, Aichhorn W, Schöller H, Aas B. Systemic case formulation, individualized process monitoring, and state dynamics in a case of dissociative identity disorder. Front Psychol. 2016;7.
Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual Res Psychol. 2006;3(2):77–101.
van Geert PLC. Dynamic systems, process and development. Hum Dev. 2020;63(3–4):153–79.
PubMed Google Scholar
Shiffman S, Stone AA, Hufford MR. Ecological momentary assessment. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2008;4(1):1–32.
Hulsmans DHG, Poelen EAP, Lichtwarck-Aschoff A, Otten R. The feasibility of daily monitoring in adolescents and young adults with mild intellectual disability or borderline intellectual functioning. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2023;36(4):847–58.
Gee BL, Han J, Benassi H, Batterham PJ. Suicidal thoughts, suicidal behaviours and self-harm in daily life: a systematic review of ecological momentary assessment studies. Digit Health. 2020;6:2055207620963958.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Scott LN, Wright AGC, Beeney JE, Lazarus SA, Pilkonis PA, Stepp SD. Borderline personality disorder symptoms and aggression: a within-person process model. J Abnorm Psychol. 2017;126(4):429–40.
Coifman KG, Berenson KR, Rafaeli E, Downey G. From negative to positive and back again: polarized affective and relational experience in borderline personality disorder. J Abnorm Psychol. 2012;121(3):668–79.
Wright AGC, Hallquist MN, Stepp SD, Scott LN, Beeney JE, Lazarus SA, et al. Modeling heterogeneity in momentary interpersonal and affective dynamic processes in borderline personality disorder. Assessment. 2016;23(4):484–95.
Woods WC, Arizmendi C, Gates KM, Stepp SD, Pilkonis PA, Wright AGC. Personalized models of psychopathology as contextualized dynamic processes: an example from individuals with borderline personality disorder. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2020;88(3):240–54.
van den Bogaard KJHM, Nijman HLI, Palmstierna T, Embregts PJCM. Characteristics of aggressive behavior in people with mild to borderline intellectual disability and co-occurring psychopathology. J Ment Health Res Intellect Disabil. 2018;11(2):124–42.
van den Bogaard KJHM, Nijman HLI, Palmstierna T, Embregts PJCM. Self-injurious behavior in people with intellectual disabilities and co-occurring psychopathology using the self-harm scale: a pilot study. J Dev Phys Disabil. 2018;30(5):707–22.
Olthof M, Hasselman F, Lichtwarck-Aschoff A. Complexity in psychological self-ratings: implications for research and practice. BMC Med. 2020;18(1):317.
Cui J, Hasselman F, Olthof M, Lichtwarck-Aschoff A. Common practices in detecting psychological early warning signals may lead to incorrect results [Internet]. (2022). PsyArXiv Preprints. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/59fu4 .
Kelso JAS, Scholz JP, Schöner G. Nonequilibrium phase transitions in coordinated biological motion: critical fluctuations. Phys Lett A. 1986;118(6):279–84.
Olthof M, Hasselman F, Strunk G, van Rooij M, Aas B, Helmich MA, et al. Critical fluctuations as an early-warning signal for sudden gains and losses in patients receiving psychotherapy for mood disorders. Clin Psychol Sci. 2020;8(1):25–35.
Schreuder MJ, Hartman CA, George SV, Menne-Lothmann C, Decoster J, van Winkel R, et al. Early warning signals in psychopathology: what do they tell? BMC Med. 2020;18(1):269.
Heard HL, Linehan MM. Dialectical behavior therapy for borderline personality disorder. In: Norcross JC, Goldfried MR, editors. Handbook of psychotherapy integration. Oxford University Press; 2019. pp. 257–83.
Creswell JW, Plano Clark VL. Designing and conducting mixed methods research. London, England: SAGE; 2006.
Google Scholar
MAXQDA. Software for qualitative analysis [Internet]. VERBI Software Consult Sozialforschung GmbH. http://www.maxqda.com .
RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated development environment for R [Internet], Boston MA. 2022. http://www.rstudio.com/ .
R Core Team. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Found Stat Comput Vienna, Austria. 2020; https://www.r-project.org/ .
Kazdin AE. Single-case experimental research designs. Methodological issues and strategies in clinical research. 4th ed. Washington: American Psychological Association; 2015. pp. 459–83.
Wickham H. ggplot2: Elegant graphics for data analysis [Internet]. Springer-Verlag New York; 2016. https://ggplot2.tidyverse.org .
Hasselman F, An. R toolbox for studying complex adaptive systems and networks [Internet]. 2023. https://fredhasselman.github.io/casnet/ .
Therneau TM, Atkinson EJ. (2022). An introduction to recursive partitioning using the RPART routines [Internet]. 2022. https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/rpart/vignettes/longintro.pdf .
Tang TZ, DeRubeis RJ. Sudden gains and critical sessions in cognitive-behavioral therapy for depression. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1999;67(6):894–904.
Lutz W, Ehrlich T, Rubel J, Hallwachs N, Röttger M-A, Jorasz C, et al. The ups and downs of psychotherapy: sudden gains and sudden losses identified with session reports. Psychother Res. 2013;23(1):14–24.
Schiepek G, Strunk G. The identification of critical fluctuations and phase transitions in short term and coarse-grained time series-a method for the real-time monitoring of human change processes. Biol Cybern. 2010;102(3):197–207.
Moritz S, Bartz-Beielstein T, ImputeTS. Time series missing value imputation in R. R J. 2017;9(1):207.
Cui J, Hasselman F, Lichtwarck-Aschoff A. Unlocking nonlinear dynamics and multistability from intensive longitudinal data: a novel method. Psychol Methods. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1037/met0000623 .
Wallot S, Kelty-Stephen DG. Interaction-dominant causation in mind and brain, and its implication for questions of generalization and replication. Minds Mach (Dordr). 2018;28(2):353–74.
Snippe E, Smit AC, Kuppens P, Burger H, Ceulemans E. Recurrence of depression can be foreseen by monitoring mental states with statistical process control. J Psychopathol Clin Sci. 2023;132(2):145–55.
Riese H, Von Klipstein L, Schoevers RA, van der Veen DC, Servaas MN. Personalized ESM monitoring and feedback to support psychological treatment for depression: a pragmatic randomized controlled trial (Therap-i). BMC Psychiatry. 2021;21(1).
Selby EA, Harnedy LE, Hiner M, Kim J. Developmental and momentary dynamics in the onset and maintenance of nonsuicidal self-injurious behavior and borderline personality disorder. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2022;24(12):897–909.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We are most thankful to the participant for her long adherence to the daily diaries, and for allowing us to use the data to make this research report. Another big thanks goes out to her clinician for the discussing the thematic analysis results with us. We also thank her legal guardian for proofreading this manuscript. Lastly, we wish to thank Masters students Sophia Politis, Jynthe van Dongen, Fenne van Mil and Maud Wouters for their help with the thematic analysis.
DH, RO and EP were supported by funding from the Netherlands Organisation for Health Research and Development (ZonMw); Grant Number 555002014. ALA and MO were supported by a NWO VIDI grant, Grant No. VI.Vidi.191.178.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Behavioural Science Institute, Radboud University, Postbus 9104, Nijmegen, 6500 HE, The Netherlands
Daan H. G. Hulsmans, Roy Otten, Evelien A. P. Poelen, Serena Daalmans, Fred Hasselman & Merlijn Olthof
Pluryn Research & Development, Nijmegen, The Netherlands
Daan H. G. Hulsmans, Evelien A. P. Poelen & Annemarie van Vonderen
Faculty of Behavioural and Social Sciences, University of Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands
Merlijn Olthof & Anna Lichtwarck-Aschoff
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
DH: formulated the research plans and questions, designed and performed qualitative and quantitative analyses, interpreted the results, wrote the initial manuscript draft, and revised the manuscript. RO: formulated the research plans and questions, project supervision, interpreted the results, and revised the manuscript. EP: formulated the research plans and questions, project supervision, interpreted the results, and revised the manuscript. AvV: formulated the research plans and questions, interpreted the results, and revised the manuscript. SD: helped design and perform qualitative data analysis, interpreted the results, and revised the manuscript. MO: helped design quantitative analyses, interpreted the results, and revised the manuscript. FH: helped design and perform quantitative analyses, interpreted the results, and revised the manuscript. A-LA: formulated the research plans and questions, helped design quantitative analyses, project supervision, interpreted the results, and was a major contributor in revising the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Daan H. G. Hulsmans .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Informed consent was obtained from the participant and her legal guardian to analyze the daily diaries and daily records and write this case-report. Her clinical team (clinician and closest care professionals) were consulted and approved study procedures. The Ethics Committee Social Sciences of Radboud University and the Ethics committee of the care organization were consulted prior to conducting this study. Due to the use of already existing data, the need for formal approval was waived. Both committees judged that our procedures were conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent for publication
The participant’s legal guardian read the final version of this manuscript and provided written informed consent for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Supplementary material 2, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Hulsmans, D.H.G., Otten, R., Poelen, E.A.P. et al. A complex systems perspective on chronic aggression and self-injury: case study of a woman with mild intellectual disability and borderline personality disorder. BMC Psychiatry 24 , 378 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-024-05836-7
Download citation
Received : 15 September 2023
Accepted : 10 May 2024
Published : 21 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-024-05836-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Self-injury
- Complex systems
- Ecological momentary assessments
- Mixed-methods
- Mild intellectual disability
- Borderline personality disorder
- Idiographic
BMC Psychiatry
ISSN: 1471-244X
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Real-World Applications of the 4th Amendment: Case Studies and Legal Insights
This essay about the real-world applications of the Fourth Amendment highlights its significance in various legal contexts. Through case studies such as Digital Frontier v. State of Liberty and Smith v. City of Metropolis, the essay examines the amendment’s role in protecting digital privacy, public demonstration rights, and mental privacy against technological intrusions. It also explores the importance of judicial oversight in regulatory inspections. Each example underscores the balance between individual liberty and societal order, reaffirming the Fourth Amendment’s relevance in contemporary legal challenges.
How it works
In the rich tapestry of American legal history, the Fourth Amendment stands as a sentinel, its essence woven into the daily fabric of life through a multitude of real-world scenarios, each offering unique insights into the delicate balance between individual liberty and societal order.
One such case study delves into the realm of digital privacy, where technology’s rapid advancement has blurred the lines between physical and virtual domains. In the landmark case of Digital Frontier v. State of Liberty (2021), the Supreme Court grappled with the question of whether law enforcement could access an individual’s virtual reality (VR) data without a warrant.
The case emerged from Alice Carpenter’s appeal, challenging the use of her VR activity logs as evidence in a cybercrime investigation. While the government argued that VR data fell outside the scope of traditional privacy protections, the Court ruled in favor of Carpenter, recognizing the unprecedented intimacy and sensitivity of VR experiences. This groundbreaking decision not only affirmed the Fourth Amendment’s relevance in the digital age but also established a precedent for safeguarding privacy in virtual spaces.
Transitioning from the digital realm to the physical world, the case of Smith v. City of Metropolis (2019) sheds light on the intersection of law enforcement practices and individual rights in the context of public demonstrations. The case arose from the mass arrest of protestors during a peaceful rally, wherein police officers conducted warrantless searches and seizures of personal belongings. Despite arguments invoking public safety concerns, the Court held that the blanket search and seizure violated the protestors’ Fourth Amendment rights, emphasizing the importance of individual dignity and autonomy, even in the midst of public gatherings. Smith serves as a poignant reminder that the protections afforded by the Fourth Amendment extend to all citizens, irrespective of the circumstances.
Expanding the scope of Fourth Amendment jurisprudence, Quantum Surveillance v. Citizen Alliance (2020) presents a compelling exploration of privacy rights in the era of quantum computing. The case centered on the legality of quantum surveillance techniques employed by government agencies to monitor individuals’ thoughts and emotions. In a groundbreaking decision, the Supreme Court ruled that such invasive surveillance tactics constituted a flagrant violation of the Fourth Amendment, affirming the sanctity of mental privacy in the face of technological innovation. Quantum Surveillance underscores the Amendment’s adaptability to emerging challenges while reaffirming its fundamental purpose of protecting individuals from unreasonable intrusion.
In the realm of administrative searches, Edison v. Regulatory Authority (2017) offers valuable insights into the Fourth Amendment’s role in safeguarding individuals against arbitrary governmental intrusion in regulatory contexts. The case stemmed from the warrantless inspection of Edison’s biotech laboratory by regulatory inspectors, who sought to enforce industry standards. Despite arguments asserting the need for regulatory oversight, the Court held that the warrantless search violated Edison’s Fourth Amendment rights, highlighting the importance of judicial oversight in ensuring the constitutionality of administrative actions.
In conclusion, the real-world applications of the Fourth Amendment underscore its enduring significance as a bulwark against unchecked governmental authority and technological encroachment. From the virtual landscapes of cyberspace to the physical arenas of public discourse, each case study illuminates the delicate interplay between individual privacy and collective security, offering guidance for navigating the complex terrain of constitutional law in the modern age. As society grapples with novel challenges and innovations, the Fourth Amendment remains a beacon of liberty, guiding the quest for a more just and equitable future.
Cite this page
Real-World Applications of the 4th Amendment: Case Studies and Legal Insights. (2024, May 21). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/real-world-applications-of-the-4th-amendment-case-studies-and-legal-insights/
"Real-World Applications of the 4th Amendment: Case Studies and Legal Insights." PapersOwl.com , 21 May 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/real-world-applications-of-the-4th-amendment-case-studies-and-legal-insights/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Real-World Applications of the 4th Amendment: Case Studies and Legal Insights . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/real-world-applications-of-the-4th-amendment-case-studies-and-legal-insights/ [Accessed: 22 May. 2024]
"Real-World Applications of the 4th Amendment: Case Studies and Legal Insights." PapersOwl.com, May 21, 2024. Accessed May 22, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/real-world-applications-of-the-4th-amendment-case-studies-and-legal-insights/
"Real-World Applications of the 4th Amendment: Case Studies and Legal Insights," PapersOwl.com , 21-May-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/real-world-applications-of-the-4th-amendment-case-studies-and-legal-insights/. [Accessed: 22-May-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Real-World Applications of the 4th Amendment: Case Studies and Legal Insights . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/real-world-applications-of-the-4th-amendment-case-studies-and-legal-insights/ [Accessed: 22-May-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
- Open access
- Published: 18 May 2024
Alkali and alkaline earth elements in follicular fluid and the likelihood of diminished ovarian reserve in reproductive-aged women: a case‒control study
- Tian Tian 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 na1 ,
- Qin Li 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 na1 ,
- Fang Liu 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ,
- Huahua Jiang 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ,
- Rui Yang 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ,
- Yue Zhao 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ,
- Fei Kong 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ,
- Yuanyuan Wang 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ,
- Xiaoyu Long 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 &
- Jie Qiao 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 6 , 7
Journal of Ovarian Research volume 17 , Article number: 108 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
59 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Imbalances in alkali elements (AEs) and alkaline earth elements (AEEs) cause reproductive disorders. However, it remains unclear whether AEs/AEEs in follicular fluid have a relationship with the serious reproductive disorder known as diminished ovarian reserve (DOR).
A nested case‒control study was carried out in China. Follicular fluid samples from 154 DOR patients and 154 controls were collected and assessed for nine AEs/AEE levels. Both the mixed and single effects of the elements on DOR were estimated with a Bayesian kernel machine (BKMR) and logistic regressions.
The DOR group had higher median concentrations of Li, Na, and K in follicular fluid (all P values < 0.05). The logistic regression showed that compared with their lowest tertile, the high tertiles of K [OR:2.45 (1.67–4.43)], Li [OR: 1.89 (1.06–3.42)], and Cs [OR: 1.97 (1.10–3.54)] were significantly associated with the odds of DOR. The BKMR model reported that the DOR likelihood increased linearly across the 25th through 75th percentiles of the nine-AE/AEE mixture, while the AE group contributed more to the overall effect.
This study revealed an association in which the likelihood of DOR increased with higher overall concentrations of AE/AEEs in follicular fluid. Among the nine detected elements, K, Li, and Cs exhibited significant individual associations with DOR. We provide new clues for the environmental factors on female fertility decline.
Trial registration
Retrospectively registered.
Introduction
Infertility is estimated to affect 10–15% of reproductive-aged couples worldwide [ 1 ]. In countries with rapid social and economic development, an increasing number of women are postponing childbearing as they pursue their studies and careers, and the concomitant decrease in fecundity and infertility has aroused great concern [ 2 , 3 ]. For example, the prevalence of infertility in China increased from 11.9% in 2007 to 18.7% in 2018 [ 4 ]. The decline in both quantity and quality of oocytes is one of the fundamental reasons for fertility disorders in women, clinically defined in reproductive medicine as diminished ovarian reserve (DOR) [ 5 , 6 ]. The role of female age is widely recognized as a crucial factor in DOR [ 6 ]. Nonetheless, it’s important to note that women of identical age can exhibit substantial variations in ovarian reserve [ 7 ]. Moreover, there is a trend of DOR affecting women at increasingly younger ages, suggesting that factors beyond chronological age may affect DOR [ 8 , 9 ]. Environmental exposures have emerged as potential contributors to the development of DOR, indicating their potentially significant role [ 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 ].
Among the various environmental factors, elements such as the alkali elements (AEs), including lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), cesium (Cs), and francium (Fr), and the alkaline earth elements (AEEs), including calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), beryllium (Be), and radium (Ra), are ubiquitous and play vital roles in physiological and pathological processes in humans [ 16 ]. In the AE group, K, Na, and Li are the most abundant physiological metal ions in living organisms [ 17 , 18 ]. Na/K channels play crucial roles in biological processes [ 16 ]. Notably, one study reported that increased sodium intake from food was associated with polycystic ovary syndrome [ 19 ]. Other AEs, such as Rb and Cs, may substitute for K in the body, but the biological functions of Rb and Cs remain unclear [ 16 ]. Regarding AEEs, clinical trials have shown that supplementation with Cs can influence the ovarian response during the IVF process [ 20 ] and can affect on pregnancy and live birth rates [ 21 , 22 ]. A higher blood Ba concentration has been reported to be associated with a greater risk for polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) [ 23 ]. The findings of these studies suggest the potentially important role of AE and AEEs in female reproductive health.
To date, few studies have reported direct associations between the AE/AEE concentration and ovarian reserve, the cornerstone of female fecundity. For oocytes, their development and maturation occur within a barrier environment composed of follicular fluid formed by granulosa cells and plasma ultrafiltrate, without direct contact with the bloodstream [ 24 , 25 ]. Therefore, analysis of follicular fluid is recognized as providing a more accurate estimate of exposures that may influence reproductive outcomes, as the fluid closely mirrors the microenvironment surrounding the developing oocyte that is particularly pertinent to disorders of oocyte development (DOR). In addition, based on a review of the literature, previous studies have focused only on the individual effects of environmental elements in serum on infertility and other reproductive diseases [ 26 ]. However, in daily life, humans are inevitably exposed to a series of elements simultaneously. Animal and human studies have suggested that mixtures of multiple pollutants could have more significant impacts on health outcomes than the individual effects of each chemical [ 27 , 28 ]. Exploring the combined effect of AEs and AEEs can better reflect the human exposure route and provide novel clues for the association between environmental factors and female fertility.
Therefore, in this study, we aimed to investigate whether both single and mixed exposure to AE and AEEs via follicular fluid are associated with the likelihood of DOR. To investigate this possibility, we performed a nested case‒control study including 154 DOR women and 154 women with a normal ovarian reserve. Concentrations of nine AE/AEEs in the follicular fluid of the women were assessed, and both the mixed and single effects of the detected elements on DOR were analyzed.
Materials and methods
Study design and participants.
This study is based on a nested case‒control design. We selected participants from the prospective clinical cohort of patients who underwent in vitro fertilization/intracytoplasmic sperm injection (IVF/ICSI) treatment at the Centre of Reproductive Medicine, Peking University Third Hospital in China. Women who met two of the following three criteria would be defined as having DOR and included in the case group: (i) a bilateral antral follicle count (AFC) ≤ 5, (ii) a serum anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) level of ≤1.1 ng/ml, and (iii) a basal serum follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) level of ≥10 IU/L on the second or third day of the menstrual cycle [ 29 ]. Women with a normal ovarian reserve (who were diagnosed with AMH, FSH, and AFC levels) and who underwent IVF/ICSI treatment due to male infertility composed the control group. To control for the potential confounding effect of age on ovarian reserve, we matched the case and control groups at a 1:1 ratio of age (± 1 year). Women with other disorders affecting ovarian reserve, including genetic disorders, polycystic ovaries, PCOS, a history of ovarian surgery, and endometriosis, or who took hormone drugs within six months before the hormone test were excluded from the present study. A total of 308 participants (154 DORs vs. 154 controls) aged 20–40 years between October 2020 and July 2022 were included in the study.
Written informed consent was obtained from all participants. This study was approved by the ethical committee of the institutional review board of Peking University Third Hospital (M2021431).
Data collection
The basic information included sociodemographic variables (including female and male age, ethnicity, occupation, educational levels, and parity), body mass index (BMI), history of disease, the type of infertility, reproductive hormones [including follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), estradiol (E2), progesterone (P), luteinizing hormone (LH), testosterone (T), prolactin (PRL), and anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH)], and variables related to the treatment process collected from the clinical cohort database. When the basic examination of a participant was finished, and before the ovulation day, a trained healthcare worker performed a face-to-face interview using a structured questionnaire to collect environment-related information, such as smoking and drinking information.
Sample collection
The follicular fluid samples were obtained by experienced nurses based on the process of oocyte retrieval. On the day of oocyte retrieval, follicular fluid was collected in sterile Petri dishes using follicle aspiration under ultrasonic monitoring. To diminish the potential confounding factor of hemolytic issues, only the first dish of collected follicular fluid which was collected at the beginning of fluid aspiration was included in the subsequent study. No additional flushing liquid was added to the fluid, and bloody samples were excluded from the study. The follicular fluid was centrifuged for 10 min at 3000 rpm to remove cell debris and other impurities. Approximately 500ul of the follicular fluid supernatant was ultimately collected and stored at -80 ℃ until the assay was performed [ 30 ].
Assessment of AEs and AEEs
The concentrations of five AEs, namely Li, Na, K, Rb, and Cs, and four AEEs, including Mg, Ca, Sr, and Ba, in the follicular fluid were assessed. The remaining two elements, Fr and Ra, were not assessed because of their radioactivity. Be levels were not assessed because Be cannot be detected by the technology used in this study. Mass spectrometry was used to determine the concentrations of the target elements. Briefly, a 50 µL follicular fluid sample was preprocessed with 0.1 mL of the internal standard yttrium (0.2 µg/mL) and 4.85 mL of 1% nitric acid (ultrapure grade) as a mixture and K, Na, Ca, and Mg concentrations were analyzed with inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometry (iCap6000,, MA, USA). Another 100 µL of follicular fluid sample was preprocessed with 0.1 mL of mixed internal standard (indium and rhenium) and 1.8 mL of 1% nitric acid (ultrapure grade) as a mixture and Sr concentrations were analyzed with inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (7700x, Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA). In addition, a 100 µL sample was preprocessed following the same procedure and Rb, Cs, and Ba concentrations were measured with inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (Elan DRC II, PerkinElmer Sciex, Norwalk, CT, USA) [ 31 ].
During the assessment, several measures were taken to control for potential contamination. All of the Petri dishes and Eppendorf micro test tubes were sterilized to avoid potential element contamination. The machines and equipment were prescreened for contamination. In addition, a blank control (phosphate-buffered saline reagents that included an internal standard and nitric acid) was used and analyzed in the same way with each block of 15 samples to account for potential contamination in the preparation process. Clin-Chek®eControl Serum Control (National Laboratory of Nonferrous Metals and Electronic Materials Analysis and Testing Center, Beijing, China, Level II: 8881) was used as a quality control sample. In the final analysis, blank concentration was subtracted from the measured concentrations in each sample to determine the final concentration of each target element. Finally, the detection rates were calculated, and all the detection rates of the nine elements were 100% in our study (Table S1 ).
Statistical analyses
Participant demographic characteristics were compared by chi-square tests or Fisher’s exact tests. Given that the levels of elements in our study were not normally distributed, their concentrations were described in terms of medians and interquartile ranges (25th percentile–75th percentile75, P25-P75), and the Mann–Whitney U test was used to compare the difference between groups. The P values were adjusted by Benjamini Hochberg’s multiple corrections. Spearman correlation analysis was used to explore the correlations between elements concentrations and dietary habits. Logistic regression was performed to assess associations between concentrations of individual elements and DOR by categorizing each element into high, middle, and low levels according to the tertile values for all subjects. Crude odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated. We adjusted for infertility type and female BMI and reported adjusted ORs as they were unevenly distributed between DORs and controls. To test the robustness of our results, we performed sensitivity analyses, which eatailed examining the associations between elements and DOR by categorizing the elements’ concentrations into three levels according to the tertiles of the control group.
Subsequently, the Bayesian kernel machine regression (BKMR) model was used to estimate the effect of coexposure to multiple elements on the likelihood of DORs. Logarithmic and Z-score transformations were performed on the concentrations of the elements. The mixture effect was estimated by BKMR analyses with hierarchical selection, which takes subgroups (AEs and AEEs) of the mixture into consideration [ 32 ]. The BKMR model was:
The function h () was modeled using a Gaussian kernel exposure-response machine function, which allows for the inclusion of interaction terms. Z i refers to confounders (infertility type and BMI in this study), and e i represents residuals in the model. The β probit in BKMR represents the estimated effect size of associations between exposure and outcome, which was transformed into a more straightforward indicator, OR, with the equation OR = exp (1.6 x β probit ) [ 33 , 34 ]. The BKMR analysis also enable the determination of the single effects for each specific element, defined as the change in the response associated with a change in a particular exposure from its 25th to its 75th percentile, where all of the other exposures are fixed at a specific quantile (0.25, 0.50, or 0.75); theunivariate exposure-response function, and the posterior inclusion probabilities (PIPs), whose values range from 0 to 1 and whose magnitude indicates relative variable importance.
R software (version 4.1.0, Austria), including the “BKMR” package for BKMR analysis and other R Core Teams packages, was used to perform the statistical analysis. The differences were considered statistically significant when the two-sided P value was < 0.05.
Characteristics of participants
Table 1 shows that 308 participants (154 DOR and 154 controls) were involved in this study. The two groups showed significantly different frequencies between infertility types, and the DOR showed a higher rate of secondary infertility (27.9 vs. 17.5%, P = 0.041). BMI, was considered a confounder and was adjusted for in the subsequent association analysis. Other basic characteristics, such as age, education level, occupation, infertility duration, and indicators of thyroid function, were comparable between the groups. No women reported a history of smoking in our population, and only 13 participants reported drinking habits. The key markers of ovarian reserve, including AMH, FSH, and AFC were significantly different between the DOR patients and controls, indicating that the ovarian reserve was greater in the control than in the DOR group.
Concentrations of AEs and AEEs in DOR patients and controls
Table 2 presents the concentrations of elements in the follicular fluid of DOR patients and controls. The median concentrations of Li (1.10 vs. 0.91 ng/ml), Na (3187.34 vs. 3130.50 µg/ml), and K (135.01 vs. 128.81 µg/ml) were greater in the DOR group (all adjusted Ps < 0.05). Although the differences were not statistically significant, the median levels of AEEs, including Mg, Ca, Ba, and Cs were relatively greater in the DOR group.
Associations between concentrations of individual elements and DOR: logistic regression
As Fig. 1 shows, except for Sr, all remaining elements showed increased associations with the likelihood of DOR. The likelihood of DOR significantly increased with K concentration in a dose-dependent manner: compared with the low K level, the middle K level had an OR of 2.45 (1.67–4.43), while the high level had an OR of 3.29 (1.82–6.05). Although the middle levels of Li and Cs did not exhibit a statistically significant association with DOR, high levels of Li [OR: 1.89 (1.06–3.42)] and Cs [OR: 1.97 (1.10–3.54)] significantly increased the odds of DOR. A sensitivity analysis that categorized the concentrations of elements by the tertile of the control group showed that the associations were consistent with the results when the concentration was categorized by the tertiles of all participants (eTable 2 ).
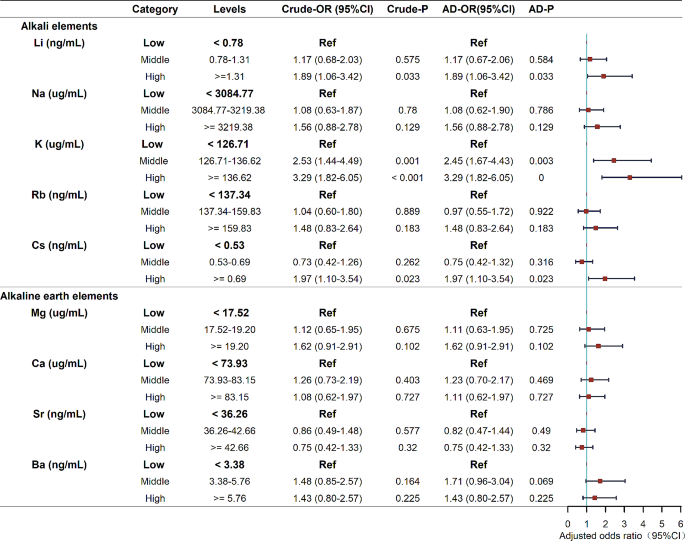
Associations between the levels of alkali elements and alkaline earth elements in follicular fluid and odds of a diminished ovarian reserve
Associations between the concentrations of AE/AEE mixtures and DOR: BKMR analysis
The correlation analysis revealed that the concentrations of these AEs/AEEs have correlations in follicular fluid (eTable 3 ). Therefore, we used BKMR modeling, which enabled the combined effects of elements in a mixture on DOR to be analyzed. As Fig. 2 shows, the DOR increased linearly across the 25th percentile through the 75th percentile of the nine-AE/AEE mixture, with an OR of 1.48 (1.14–1.91) for the 75th percentile. Hierarchical analysis revealed that the mixed concentration of subgroup AEs (including Li, Na, K, Rb, and Cs) was significantly associated with a greater likelihood of DOR. The concentrations of AEEs (including Mg, Ca, Sr, and Ba) slightly increased with increasing DOR chance, but the difference was not statistically significant. The OR values for each percentile of the elements compared with the median on DOR are shown in eTable 4 .
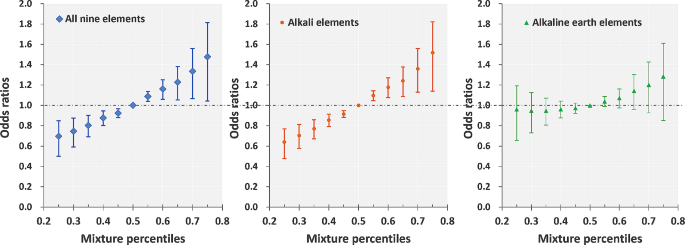
The overall effect of elements on the likelihood of a diminished ovarian reserve. Bayesian kernel machine regression was used to investigate the association between exposure to a mixture of 9 elements/5AEs/4 AEEs and DOR. The odds ratios were calculated where the mixture of elements was at a specific quantile level compared to when the mixture is at the 50th percentile. The estimated β-probit was transformed into an odds ratio using the formula OR = exp (1.6 x βprobit). The points refer to odds ratios (ORs), while the vertical lines represent the 95% CIs. The associations were adjusted for infertility type and BMI
Figure 3 a and eTable 5 show the single effects of elements on DOR in association with changes in specific elements from the 25th to 75th percentiles when other elements were fixed at the 25th, 50th, or 75th percentiles. K had the most potent effect on DOR, with effect estimates (βi) of 0.44 (95% CI: 0.23–0.65), 0.42 (95% CI: 0.22–0.62), and 0.40 (95% CI:0.18–0.61) when the remaining elements were kept at the 75th, 50th, and 25th percentiles, respectively. The PIPs, which were used to identify the elements or groups mainly responsible for DOR effects, validated the results. AEs showed higher group PIP than AEEs (0.97 vs. 0.54). Conditional PIPs for each element showed that among the nine AEs and AEEs, K had the highest PIP, indicating that K played the most critical role in the occurrence of DOR ( eFigure 1 ). Figure 3 b shows the dose-response curves when concentrations of an element were used as a continuous variable when all other elements were fixed at their 50th percentiles: K exhibited a positive linear trend, Mg showed an “S” trend, and no apparent trends were observed for the other elements. All of these results were mutually verified.
Associations between single element exposure and the likelihood of a diminished ovarian reserve according to the BKMR model: ( A ) This figure shows the estimated effect of a single element on the likelihood of DOR (est, expressed in βprobit) by comparing its 75th percentile to its 25th percentile, with all other elements being fixed at their 25th, 50th, or 75th percentile. The confounding factors adjusted for in this model include BMI and infertility type; ( B ) This figure shows the Univariate exposure–response function for each alkali element or alkaline earth element (95%CIs) with the remaining elements set at their medians. h(exposure) is defined as the association between a specific element as a continuous variable and a latent continuous outcome (continuous marker of the binary DOR outcome). The models were adjusted for infertility type and age. K, potassium; Na, sodium; Rb, rubidium; Cs, cesium; Ca, calcium; Mg, magnesium; Sr, strontium; Ba, barium
AEs and AEEs are among the most widely distributed elements essential to human biological processes. However, the effects of these factors on women’s fertility remain uncertain. In this study, we found that with the rising overall level of nine AE/AEE elements, the likelihood of DOR significantly increased in a linear trend. Specifically, compared with their lowest level, high exposure to K, Li, and Cs was significantly associated with an increased likelihood of DOR.
The balance of AEs and AEEs plays important roles in physiological functions [ 16 ]. Previous studies have indicated that AEs and AEEs are associated with female reproductive health [ 19 , 23 , 20 , 21 , 22 ]. However, at present, no studies have reported on the effect of AEs and AEEs on the ovarian reserve. This study provided new evidence that abnormal concentrations of several AE and AEEs could increase the likelihood of DOR. In addition, humans are more likely to be exposed a mixture of AEs and AEEs simultaneously, and elements have complex interactions. Therefore, assessing the combined effect of AE/AEE mixtures and taking the potential influence of other AEs/AEEs into consideration during the assessment of the likelihood posed by a specific element better reflects the reality of actual exposure dynamics [ 28 , 31 , 35 ]. At present, no studies have investigated the mixed impact of AE/AEEs on women’s fertility. For the first time, we observed that the odds for DOR significantly increased in a linear pattern with the higher concentration of the nine elements mixture. These results underlined the importance of considering the mixed effect of AEs and AEEs, especially AEs, in preventing DOR.
The potassium (K + ) channel has important effects on reproductive health outcomes, and can be involved in outcomes such as malformation of the fallopian tube [ 36 ], and male infertility [ 37 ]. A population study reported that women with PCOS had a lower potassium intake than women in a control group [ 19 ]. Whether K plays a role in the ovarian reserve remains unclear. We found that a higher level of K in the follicular fluid increases the likelihood of DOR up to 3.29 fold, providing new evidence for the association between K and DOR. The accurate pathophysiology of K on DOR has yet to be determined. Previous studies have indicated that excessive potassium accumulation in the body and within cells leads to changes in membrane potential, which may be a contributing factor to the decline in fertility [ 38 ]. Additionally, it has been reported that intracellular potassium influx dysregulation is mediated by saturated fatty acids, leading to a series of adverse pathophysiological outcomes, destabilizing the pH of the cytosol, and thereby exacerbating the inflammatory response through activation of the arachidonic acid derivative cascade [ 39 ]. These studies may provide insight into the pathophysiology of K on DOR.
Li is a psycho-modulatory agent commonly used to treat depression, mania, schizophrenia, and other psychological disorders [ 40 ]. High doses of lithium in the human body cause the function of multiple key organs including the heart, thyroid gland, kidneys, and ovarians, to deteriorate [ 41 ]. A population study in China reported that exposure to Li could decrease the hormone testosterone, which is associated with male infertility [ 42 ]. It has been reported that mechanistically, both the positive and negative effects of lithium could be mediated through the methylation of β-catenin nuclear-binding proteins which is potentiated by lithium-induced inhibition of GSK-3 or inositol monophosphatase [ 43 ]. Animal studies have shown that the concentration of lithium leads to follicular atresia and this adverse effect has been found to result from the induction of apoptosis in antral follicles [ 44 ]. The chemical properties of Cs are similar to those of potassium, enabling it to displance potassium in muscles and red blood cells, thus causing potassium deficiency [ 45 ]. However, the effects of Li and Cs on the female ovarian reserve are unknown. In this study, we found that higher levels of Li and Cs could increase the likelihood of DOR. In contrast, the middle levels of these two elements did not show a statistically significant effect, indicating that within limitations, Li or Cs might not show significant toxicity, but they would influence ovarian reserve function when their levels exceeded certain limits.
Mg and Ca are ubiquitous and essential to living organisms. The associations between Mg/Ca and female infertility are uncertain [ 46 , 47 ]. Sr, another crucial AEE, was reported to be associated with DOR progression [OR: 2·92 (1·86 − 4·58)] [ 48 ], and Ba was reported to be associated with an increased risk of PCOS [ 23 ] and early embryonic arrest [ 49 ]. In our study, we found that although the concentrations of each AEE were relatively greater in DOR patients than in controls, their individual effects on DOR were not significant, implying that the association between AEEs and DOR might require further validation.
There are several strengths in this study. First, previous studies often used serum or urine samples to assess the environmental factors of ovarian reserve. However, for oocytes, their development and maturation occur within a barrier environment composed of follicular fluid formed by granulosa cells and plasma ultrafiltrate, without direct contact with the bloodstream. Therefore, it has been hypothesized that elements detected in follicular fluid may directly affect the development and maturation of oocytes, and recent studies have used ovarian follicular fluid to provide a more accurate estimate of exposures that may influence reproductive outcomes. Therefore, in this study, we assessed the levels of elements in follicular fluid rather than in blood to determine whether the concentrations of these elements accurately reflected the direct exposure status of oocytes. Second, to our knowledge, our study is the first to report the combined effect of AEs and AEEs in follicular fluid on ovarian reserve function and to identify important contributors to the impact of ovarian reserve. Third, considering the critical influence of women’s age on DOR, we controlled for age in this study to eliminate the confounding effect of age. In addition, the postpowers of the sample size in this study based on each element ranged from 89 to 98%, indicating that we included a sufficient sample size to reach high testing efficiency.
On the other hand, some limitations need to be addressed. First, since our study was based on a case-control design, our study only provided an initial clue for the association between AEs/AEEs and DOR. The causal correlation between these elements and the occurrence of DOR requires further validation in animal models or prospective human studies. Second, the biological mechanism underlying the associations between identified AEs and AEEs and DOR was uncertain. Further investigations in animals and in vitro studies are needed. Third, in our study, medical intake information was unavailable, which may let us to fail to account for the medical source of AEs/AEEs. Finally, although we focused on the content of AE/AEEs in the follicular fluid, which directly interacts with oocytes, we did not measure the concentration of these elements in the blood or provide a detailed analysis of their sources. This limitation somewhat constrained the process of causal inference.
This study revealed an association in which the likelihood of DOR increased with higher overall concentrations of AE/AEEs in follicular fluid. Among the nine detected elements, the higher concentrations of K, Li, and Cs in follicular fluid exhibited a significant positive correlation with the likelihood of DOR. These findings provide novel evidence for the potential environmental factors of female fertility decline. These findings warrant further investigation and replication in additional studies.
Data availability
The data underlying this article will be shared on reasonable request to the corresponding author.
Qiao J, Li R. Fertility preservation: challenges and opportunities. Lancet. 2014;384(9950):1246–7.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Cheti N, Maria Letizia T. Differences in delaying Motherhood across European Countries: empirical evidence from the ECHP. Eur J Popul. 2008;24(2):157–83.
Article Google Scholar
Daniluk JC, Koert E. Childless Canadian men’s and women’s childbearing intentions, attitudes towards and willingness to use assisted human reproduction. Hum Reprod. 2012;27(8):2405–12.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Zhou Z, et al. Epidemiology of infertility in China: a population-based study. BJOG. 2018;125(4):432–41.
Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Electronic address, a.a.o. and M. Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive, Testing and interpreting measures of ovarian reserve: a committee opinion . Fertil Steril. 2020;114(6):1151–7.
Pastore LM, et al. Reproductive ovarian testing and the alphabet soup of diagnoses: DOR, POI, POF, POR, and FOR. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2018;35(1):17–23.
Faddy MJ, et al. Accelerated disappearance of ovarian follicles in mid-life: implications for forecasting menopause. Hum Reprod. 1992;7(10):1342–6.
Gurtcheff SE, Klein NA. Diminished ovarian reserve and infertility. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2011;54(4):666–74.
Nikolaou D, Templeton A. Early ovarian ageing. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2004;113(2):126–33.
Feng X, et al. Association of exposure to ambient air pollution with ovarian reserve among women in Shanxi province of north China. Environ Pollut. 2021;278:116868.
Nassan FL, et al. Correlation and temporal variability of urinary biomarkers of chemicals among couples: implications for reproductive epidemiological studies. Environ Int. 2019;123:181–8.
Hood RB, et al. The influence of fine particulate matter on the association between residential greenness and ovarian reserve. Environ Res. 2021;197:111162.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Kim H, et al. Outdoor air pollution and diminished ovarian reserve among infertile Korean women. Environ Health Prev Med. 2021;26(1):20.
Bjorvang RD, et al. Persistent organic pollutants and the size of ovarian reserve in reproductive-aged women. Environ Int. 2021;155:106589.
Bloom MS, et al. Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in human follicular fluid and in vitro fertilization outcomes, a pilot study. Reprod Toxicol. 2017;67:165–73.
Yin J, Hu Y, Yoon J. Fluorescent probes and bioimaging: alkali metals, alkaline earth metals and pH. Chem Soc Rev. 2015;44(14):4619–44.
Citterio D, et al. pH-independent fluorescent chemosensor for highly selective lithium ion sensing. Anal Chem. 2007;79(3):1237–42.
Martins A, et al. Warmer water, high light intensity, lithium and microplastics: dangerous environmental combinations to zooplankton and Global Health? Sci Total Environ. 2022;854:158649.
Badri-Fariman M, et al. Association between the food security status and dietary patterns with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) in overweight and obese Iranian women: a case-control study. J Ovarian Res. 2021;14(1):134.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
El-Khayat W, Elsadek M. Calcium infusion for the prevention of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Fertil Steril. 2015;103(1):101–5.
Polzikov M, et al. Association of the Serum Folate and Total Calcium and magnesium levels before ovarian stimulation with outcomes of Fresh in Vitro fertilization cycles in Normogonadotropic Women. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:732731.
Murugesu S, et al. Does the use of calcium ionophore during artificial oocyte activation demonstrate an effect on pregnancy rate? A meta-analysis. Fertil Steril. 2017;108(3):468–e4823.
Liang C, et al. Exposure to multiple toxic metals and polycystic ovary syndrome risk: endocrine disrupting effect from as, Pb and Ba. Sci Total Environ. 2022;849:157780.
Butts CD, et al. Toxic elements in follicular fluid adversely influence the likelihood of pregnancy and live birth in women undergoing IVF. Hum Reprod Open. 2021;2021(3):hoab023.
Butts CD, et al. Variability of essential and non-essential trace elements in the follicular fluid of women undergoing in vitro fertilization (IVF). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021;209:111733.
Jain M, Singh M. Environmental toxins and infertility , in StatPearls . Treasure Island (FL); 2022.
Schnell S, et al. Single and combined toxicity of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) on the rainbow trout liver cell line RTL-W1. Aquat Toxicol. 2009;93(4):244–52.
Caporale N, et al. From cohorts to molecules: adverse impacts of endocrine disrupting mixtures. Science. 2022;375(6582):eabe8244.
Xu X, et al. Low KLOTHO level related to aging is associated with diminished ovarian reserve. Fertil Steril. 2020;114(6):1250–5.
Zheng D, et al. Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) versus conventional in vitro fertilisation (IVF) in couples with non-severe male infertility (NSMI-ICSI): protocol for a multicentre randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open. 2019;9(9):e030366.
Yin S, et al. Alkali and alkaline earth elements in maternal serum and occurrence of orofacial clefts in offspring. Reprod Toxicol. 2022;110:97–104.
Valeri L, et al. The joint effect of prenatal exposure to metal mixtures on neurodevelopmental outcomes at 20–40 months of age: evidence from Rural Bangladesh. Environ Health Perspect. 2017;125(6):067015.
Bobb JF, et al. Statistical software for analyzing the health effects of multiple concurrent exposures via bayesian kernel machine regression. Environ Health. 2018;17(1):67.
Tian T, et al. Single and mixed effects of metallic elements in maternal serum during pregnancy on risk for fetal neural tube defects: a bayesian kernel regression approach. Environ Pollut. 2021;285:117203.
Chen Y, et al. Association between selected alkaline earth elements concentrations in umbilical cord and risk for cleft lip with or without cleft palate. Sci Total Environ. 2021;750:141735.
Zhang D, et al. The role of SK3 in progesterone-induced inhibition of human fallopian tubal contraction. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2022;20(1):73.
Tiwari S et al. Testis-specific isoform of na(+)-K(+) ATPase and regulation of Bull Fertility. Int J Mol Sci, 2022. 23(14).
Brown SG, et al. Depolarization of sperm membrane potential is a common feature of men with subfertility and is associated with low fertilization rate at IVF. Hum Reprod. 2016;31(6):1147–57.
Szczuko M et al. Level of Potassium is Associated with saturated fatty acids in cell membranes and influences the activation of the 9 and 13 HODE and 5 HETE Synthesis pathways in PCOS. Biomedicines, 2022. 10(9).
Kalantari H, et al. Evaluation of sub-acute oral toxicity of Lithium Carbonate Microemulsion (Nano Size) on liver and kidney of mice. Jundishapur J Nat Pharm Prod. 2015;10(1):e22312.
Kakhki S, Ahmadi-Soleimani SM. Experimental data on lithium salts: from neuroprotection to multi-organ complications. Life Sci. 2022;306:120811.
Chai Z, et al. Low-level and combined exposure to environmental metal elements affects male reproductive outcomes: prospective MARHCS study in population of college students in Chongqing, China. Sci Total Environ. 2022;828:154395.
Bianchi P, et al. Lithium restores neurogenesis in the subventricular zone of the Ts65Dn mouse, a model for Down syndrome. Brain Pathol. 2010;20(1):106–18.
Mirakhori F, et al. Lithium induces follicular atresia in rat ovary through a GSK-3β/β-catenin dependent mechanism. Mol Reprod Dev. 2013;80(4):286–96.
Souchon V, Leray I, Valeur B. Selective detection of cesium by a water-soluble fluorescent molecular sensor based on a calix[4]arene-bis(crown6-ether) . Chem Commun (Camb), 2006(40): pp. 4224-6.
Xu G, et al. Cadmium induces apoptosis of human granulosa cell line KGN via mitochondrial dysfunction-mediated pathways. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021;220:112341.
Mirnamniha M, et al. An overview on role of some trace elements in human reproductive health, sperm function and fertilization process. Rev Environ Health. 2019;34(4):339–48.
Chen Y, et al. Arsenic exposure diminishes ovarian follicular reserve and induces abnormal steroidogenesis by DNA methylation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022;241:113816.
Jiang T, et al. Exposure to multiple toxic metals and the risk of early embryonic arrest among women undergoing assisted reproductive techniques. Environ Res. 2022;211:113072.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all the participants involved in this study.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.82003474, 82304157), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded project (No.2022T150023, No.2021M700272 ), and National Key Research and Development Program, Ministry of Science and Technology, People’s Republic of China (No. 2022YFC2702901).
Author information
Tian Tian and Qin Li contributed equally to this study.
Authors and Affiliations
Center for Reproductive Medicine, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Peking University Third Hospital, 49 North Garden Rd, Haidian District, Beijing, 100191, China
Tian Tian, Qin Li, Fang Liu, Huahua Jiang, Rui Yang, Yue Zhao, Fei Kong, Yuanyuan Wang, Xiaoyu Long & Jie Qiao
National Clinical Research Center for Obstetrics and Gynecology, Peking University Third Hospital), Beijing, China
Key Laboratory of Assisted Reproduction (Peking University), Ministry of Education, Beijing, China
Beijing Key Laboratory of Reproductive Endocrinology and Assisted Reproductive Technology, Peking University Third Hospital), Beijing, China
Department of Maternal and Child Health, School of Public Health, Peking University, Beijing, China
Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Genomics, Beijing, China
Peking-Tsinghua Center for Life Sciences, Peking University, Beijing, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Tian Tian: Sample collection, elements assessment, data analysis, original draft writing, funding acquisition; Qin Li: Sample collection, elements assessment, manuscript review & editing, funding acquisition; Fang Liu: Sample collection, element assessment, manuscript revision; Huahua Jiang: Sample collection, manuscript revision; Rui Yang: Sample collection, manuscript revision; Yue Zhao: Sample collection, manuscript revision; Fei Kong: Sample collection, manuscript revision; Yuanyuan Wang: Sample collection, manuscript revision; Xiaoyu Long: Project administration, manuscript review & editing, funding acquisition; Jie Qiao: Study design, project administration, manuscript review & editing Declaration of Interests.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Xiaoyu Long or Jie Qiao .
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval, consent to for publication.
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Tian, T., Li, Q., Liu, F. et al. Alkali and alkaline earth elements in follicular fluid and the likelihood of diminished ovarian reserve in reproductive-aged women: a case‒control study. J Ovarian Res 17 , 108 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13048-024-01414-3
Download citation
Received : 18 January 2024
Accepted : 12 April 2024
Published : 18 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13048-024-01414-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Diminished ovarian reserve
- Alkali elements
- Alkaline earth elements
- Follicular fluid
- Female fertility
- Bayesian kernel machine regression (BKMR)
Journal of Ovarian Research
ISSN: 1757-2215
- General enquiries: [email protected]
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Test for Fentanyl
- if You Think Someone is Overdosing
- Stop Overdose
- Naloxone FAQs
- Stigma Reduction
About Stop Overdose
- Through preliminary research and strategic workshops, CDC identified four areas of focus to address the evolving drug overdose crisis.
- Stop Overdose resources speak to the reality of drug use, provide practical ways to prevent overdoses, educate about the risks of illegal drug use, and show ways to get help.

Drugs take nearly 300 lives every day. 1 To address the increasing number of overdose deaths related to both prescription opioids and illegal drugs, we created a website to educate people who use drugs about the dangers of illegally manufactured fentanyl, the risks and consequences of mixing drugs, the lifesaving power of naloxone, and the importance of reducing stigma around recovery and treatment options. Together, we can stop drug overdoses and save lives.
What you can do
- Get the facts on fentanyl
- Learn about lifesaving naloxone
- Understand the risks of polysubstance use
- Reduce stigma around recovery and treatment
Explore and download Stop Overdose and other educational materials on CDC's Overdose Resource Exchange .
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics. National Vital Statistics System, Mortality 2018-2021 on CDC WONDER Online Database, released in 2023. Data are from the Multiple Cause of Death Files, 2018-2021, as compiled from data provided by the 57 vital statistics jurisdictions through the Vital Statistics Cooperative Program. Accessed at http://wonder.cdc.gov/mcd-icd10-expanded.html on Mar 5, 2024
Every day, drugs claim hundreds of lives. The Stop Overdose website educates drug users on fentanyl, naloxone, polysubstance use, and dealing with stigma.

COMMENTS
Specifically within medical research, studies on asthma often employ case studies to explore the individual and environmental factors that influence asthma development, management, and outcomes. A case study can provide rich, detailed data about individual patients' experiences, from the triggers and symptoms they experience to the ...
The three main case study types often used are intrinsic, instrumental, and collective. Intrinsic case studies are useful for learning about unique cases. Instrumental case studies help look at an individual to learn more about a broader issue. A collective case study can be useful for looking at several cases simultaneously.
A case study is a qualitative research method that involves the in-depth exploration and analysis of a particular case, which can be an individual, group, organization, event, or community. The primary purpose of a case study is to generate a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case, including its history, context, and dynamics.
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
De Vaus (2001, p. 220) posits that the 'unit of analysis' in a case study research can be an individual, a family, a household, a community, an organisation, an event or even a decision. Yin puts forth that a case study can be: 1. Descriptive. In a descriptive case study, the purpose is to 'describe' a phenomenon in detail in its real ...
Misunderstanding 2: One cannot generalize on the basis of an individual case; therefore, the case study cannot contribute to scientific development. Misunderstanding 3 : The case study is most useful for generating hypotheses; that is, in the first stage of a total research process, whereas other methods are more suitable for hypotheses testing ...
In psychology, case studies are often confined to the study of a particular individual. The information is mainly biographical and relates to events in the individual's past (i.e., retrospective), as well as to significant events that are currently occurring in his or her everyday life. The case study is not a research method, but researchers ...
Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data. Example: Mixed methods case study. For a case study of a wind farm development in a ...
There is no one definition of case study research. 1 However, very simply… 'a case study can be defined as an intensive study about a person, a group of people or a unit, which is aimed to generalize over several units'. 1 A case study has also been described as an intensive, systematic investigation of a single individual, group ...
What the Case Study Method Really Teaches. Summary. It's been 100 years since Harvard Business School began using the case study method. Beyond teaching specific subject matter, the case study ...
A Case study is: An in-depth research design that primarily uses a qualitative methodology but sometimes includes quantitative methodology. Used to examine an identifiable problem confirmed through research. Used to investigate an individual, group of people, organization, or event. Used to mostly answer "how" and "why" questions.
Yin (1994) defines case study as an empirical research activity that, by using versatile empirical material gathered in several different ways, examines a specific present-day event or action in a bounded environment. Case study objective is to do intensive research on a specific case, such as individual, group, institute, or community.
One notable example is Freud's study on Little Hans. This case study explored a 5-year-old boy's fear of horses and related it back to Freud's theories about psychosexual stages. Another classic example is Genie Wiley (a pseudonym), a feral child who was subjected to severe social isolation during her early years.
Step 9: Case study distribution. When sharing individual case studies, concentrate on reaching the audience with the most influence on purchasing decisions. Here are some common distribution channels to consider: Sales teams. Share case studies to enhance customer interactions, retention, and upselling among your sales and customer success ...
A case study is a detailed examination of a particular subject, such as an individual, group, event, or phenomenon, within its real-life context. It involves in-depth analysis and exploration of factors contributing to the subject's situation or outcomes, often using multiple sources of data and research methods.
Résumé. Case study is a common methodology in the social sciences (management, psychology, science of education, political science, sociology). A lot of methodological papers have been dedicated to case study but, paradoxically, the question "what is a case?" has been less studied.
A case study is a research approach that is used to generate an in-depth, multi-faceted understanding of a complex issue in its real-life context. It is an established research design that is used extensively in a wide variety of disciplines, particularly in the social sciences. A case study can be defined in a variety of ways (Table.
1. question: case studies most useful for answering how, why. 2. propositions, if any to help problematize your question (e.g., organizations collaborate because they derive mutual benefit). 3. units of analysis (a neighborhood or a small group; a new technology or an innovation process?)
Case studies can, in principle, be used to test any theory that has implications for individual patients. There are two crucial methodological stages. The first is to identify scientifically plausible general theories and derive from them specific hypotheses or models of sufficient precision to have implications for individual cases. The second ...
Sara, a 35-year-old married female. Sara was referred to treatment after having a stillbirth. Sara showed symptoms of grief, or complicated bereavement, and was diagnosed with major depression, recurrent. The clinician recommended interpersonal psychotherapy (IPT) for a duration of 12 weeks. Bleiberg, K.L., & Markowitz, J.C. (2008).
Nurses face more and more ethical dilemmas during their practice nowadays, especially when nurses have responsibility to take care of patients with terminal diseases such as cancer [1].The case study demonstrates an ethical dilemma faced by a nursing staff taking care of an end stage aggressive prostate cancer patient Mr Green who confided to the nurse his suicide attempt and ask the nurse to ...
Executive Order Hapag 2023. EJ1308731 - Yutx. WORK Immersion Portfolio. Project-Proposal-sample. Case Studies, General Intake, Project Proposal (Individual, Family and Group) This is a sample activity of an Individual Case Study in which the student chose a client to be interviewed and then base her study on the response and.
Background Challenging behaviors like aggression and self-injury are dangerous for clients and staff in residential care. These behaviors are not well understood and therefore often labeled as "complex". Yet it remains vague what this supposed complexity entails at the individual level. This case-study used a three-step mixed-methods analytical strategy, inspired by complex systems theory ...
Case study is a research methodology, typically seen in social and life sciences. There is no one definition of case study research.1 However, very simply... 'a case study can be defined as an intensive study about a person, a group of people or a unit, which is aimed to generalize over several units' .1 A case study has also been described ...
From the virtual landscapes of cyberspace to the physical arenas of public discourse, each case study illuminates the delicate interplay between individual privacy and collective security, offering guidance for navigating the complex terrain of constitutional law in the modern age.
Business document from Seneca College, 6 pages, MRK620 - Strategic Analysis Course Grading, and Case Assignments Overview & Instructions Course Grading Individual Cases (10%, 15%, 20%) Group Case / Project Presentation Marketing & Strategy Concept Learning Exercises 45% 25% 30% Marketing & Strategy Con
A nested case‒control study was carried out in China. Follicular fluid samples from 154 DOR patients and 154 controls were collected and assessed for nine AEs/AEE levels. ... In addition, based on a review of the literature, previous studies have focused only on the individual effects of environmental elements in serum on infertility and ...
A panel study of 58 waves into the nature of electoral volatility (The Netherlands 2006-2010). Party Politics 21(1): 100-114. doi: 10.1177/1354068812472570. Crossref
Key points. Through preliminary research and strategic workshops, CDC identified four areas of focus to address the evolving drug overdose crisis. Stop Overdose resources speak to the reality of drug use, provide practical ways to prevent overdoses, educate about the risks of illegal drug use, and show ways to get help.
Extensive environmental changes increase the complex uncertainty surrounding water allocation systems, and irrational water allocation further exacerbates competition among users, posing formidable challenges to achieving dynamic and sustainable water resource management in inter-basin water diversion (IBWD) projects. This study established a dynamic multi-objective water allocation framework ...