What Is Data Visualization In IoT?

- Technology & Innovation
- IoT & Smart Devices


Introduction
Data visualization is a powerful tool that allows us to make sense of complex data by representing it visually. In the context of the Internet of Things (IoT), data visualization plays a crucial role in transforming vast amounts of raw data into meaningful insights. IoT refers to the network of connected devices and sensors that gather and transmit data. With the exponential growth of IoT devices, there is an overwhelming amount of data being generated, which can be overwhelming to comprehend without proper visualization.
Data visualization in IoT involves using graphical representations, such as charts, graphs, heat maps, and interactive dashboards, to depict the data collected from IoT devices. By visualizing the data, decision-makers can easily identify patterns, trends, and anomalies, enabling them to make data-driven decisions, optimize processes, and improve efficiency.
The importance of data visualization in IoT cannot be overstated. With the increasing adoption of IoT devices across industries, organizations have access to valuable data that can drive innovation and improve operational efficiency. However, the true value of this data lies in the ability to interpret and act upon it effectively. This is where data visualization comes into play, as it provides a visual representation of the data, making it easier to analyze and gain insights from it.
In the following sections, we will explore the importance of data visualization in IoT, the benefits it offers, the tools and techniques commonly used, best practices, and real-world examples of data visualization in the IoT landscape. By understanding the power of data visualization and how it can be leveraged in IoT, organizations can unlock the full potential of their data and stay competitive in today’s data-driven world.
What is Data Visualization?
Data visualization is the graphical representation of data to uncover patterns, relationships, and insights that might not be easily discernible in raw data. It involves transforming complex datasets into visual visuals, such as charts, graphs, maps, and infographics, to make data more understandable and accessible to a wide audience.
In the context of IoT, data visualization plays a crucial role in translating the massive amounts of data generated by IoT devices into meaningful and actionable insights. It helps in uncovering hidden patterns, trends, and anomalies within the data, leading to informed decision-making and improved business outcomes.
Data visualization allows users to quickly grasp complex concepts and understand the significance of the data. Instead of poring over spreadsheets or rows of numbers, data visualizations present information in a visually appealing and intuitive manner, enabling easier interpretation and analysis.
By representing data visually, various relationships and patterns can be identified. For example, line charts can show trends over time, scatter plots can reveal correlations between variables, and maps can display geographic distribution.
Data visualization also offers the opportunity to explore data interactively. Users can utilize interactive elements, such as filters, drill-downs, and zoom features, to delve deeper into the data and uncover more detailed insights. This interactivity enhances the user experience and allows for dynamic exploration of the data.
Furthermore, data visualization promotes data storytelling by presenting information in a compelling narrative format. It helps to communicate complex ideas and data-driven insights effectively to a broad audience, including non-technical stakeholders. By presenting data in a visually engaging way, data visualizations facilitate better understanding, engagement, and decision-making.
In summary, data visualization is the process of presenting complex data in a visual format to enable better understanding, analysis, and decision-making. In the IoT context, it helps organizations make sense of the vast amounts of data generated by connected devices, leading to improved operational efficiency, informed decisions, and enhanced business outcomes.
Importance of Data Visualization in IoT
Data visualization plays a critical role in the realm of IoT, where vast amounts of data are being generated from interconnected devices. Let’s explore the key reasons why data visualization is essential in the IoT landscape:
1. Understanding complex data: IoT devices generate massive volumes of data that can be challenging to comprehend in its raw form. Through data visualization, complex data sets can be simplified and presented visually, allowing users to quickly grasp patterns, trends, and outliers. This understanding is vital for making data-driven decisions and identifying opportunities for improvement.
2. Identifying actionable insights: Data visualizations enable the identification of actionable insights from IoT data . By representing data visually, patterns and relationships become more apparent, enabling organizations to extract valuable insights. These insights can drive operational efficiency, optimize processes, and uncover potential areas for innovation.
3. Real-time monitoring: IoT devices generate data in real-time, which requires near-instantaneous analysis. Data visualizations provide real-time monitoring dashboards, enabling organizations to track key performance indicators (KPIs), identify anomalies, and respond promptly to critical events. Real-time data visualization empowers organizations to make informed decisions and take timely actions.
4. Improved collaboration: Data visualizations are easily understood by diverse audiences, including non-technical stakeholders. By presenting data visually, organizations can foster collaboration between technical and non-technical teams. This interdisciplinary collaboration facilitates a shared understanding of IoT data, leading to more effective communication, problem-solving, and decision-making.
5. Enhanced data exploration: Data visualization tools offer interactive features that empower users to explore and analyze IoT data in depth. These features include filters, drill-down capabilities, and dynamic visual representations. With interactive data visualizations, users can uncover hidden insights, perform root cause analysis, and gain a deeper understanding of IoT data.
6. Improved decision-making: Data visualization simplifies complex information, empowering decision-makers to quickly comprehend the implications of IoT data. Visual representations enable stakeholders to grasp the big picture, evaluate multiple data points simultaneously, and make informed decisions. This leads to more effective problem-solving, reduced response time, and better outcomes.
7. Data-driven storytelling: Data visualization enables organizations to tell compelling stories with their IoT data. By presenting data in a visually engaging manner, organizations can captivate audiences and communicate data-driven insights effectively. With data-driven storytelling, organizations can gain buy-in from stakeholders, inspire action, and drive positive business outcomes.
In summary, data visualization is of paramount importance in the IoT landscape. It helps organizations make sense of complex IoT data, identify actionable insights, improve collaboration, enhance data exploration, facilitate informed decision-making, and drive data-driven storytelling. By leveraging the power of data visualization in IoT, organizations can unlock the full potential of their data and drive innovation and competitive advantage.
Benefits of Data Visualization in IoT
Data visualization in the context of IoT offers numerous benefits that help organizations harness the power of their data. Let’s explore some of the key advantages of using data visualization in the IoT landscape:
1. Improved data comprehension: Data visualization simplifies complex data by presenting it in a visual format that is easy to understand. By representing data using charts, graphs, and other visual elements, users can quickly grasp patterns, trends, and relationships within IoT data. This improved comprehension enhances decision-making and drives actionable insights.
2. Enhanced decision-making: Data visualization empowers decision-makers to make informed and data-driven decisions. By visualizing IoT data, decision-makers can quickly identify trends, outliers, and insights that are difficult to discern in tabular or textual formats. Visual representations facilitate quicker decision-making, leading to better business outcomes.
3. Identification of anomalies and issues: Data visualization enables the identification of anomalies and issues within IoT data. By spotting unusual patterns or outliers, organizations can proactively address problems or take necessary actions. Detecting anomalies in real-time helps prevent system failures, optimize processes, and improve overall operational efficiency.
4. Optimization of IoT systems: Data visualization provides valuable insights into the performance and efficiency of IoT systems. By visualizing key metrics and performance indicators, organizations can identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement. This helps optimize IoT systems, enhance device performance, and ensure reliable and efficient operations.
5. Enhanced data exploration: Data visualization tools offer interactive features that facilitate in-depth exploration of IoT data. Users can easily filter, drill down, and manipulate visualizations to gain deeper insights. This interactive data exploration helps uncover hidden patterns, correlations, and dependencies within IoT data, enabling predictive analysis and data-driven decision-making.
6. Improved communication and collaboration: Data visualizations simplify the communication of complex IoT data to diverse audiences, including non-technical stakeholders. Visual representations make it easier to convey insights, trends, and key findings, fostering collaboration and shared understanding. By communicating data visually, organizations can align teams, secure buy-in from stakeholders, and drive effective decision-making.
7. Real-time monitoring and alerts: Data visualization allows for real-time monitoring of IoT data. Interactive dashboards provide up-to-date insights and alerts on key performance indicators and metrics. Real-time monitoring enables organizations to respond promptly to critical events, mitigate risks, and ensure optimal operational performance.
8. Storytelling with data: Data visualization enables impactful storytelling with IoT data. By presenting data visually, organizations can create compelling narratives that engage and inspire audiences. Visual storytelling helps convey the significance and implications of IoT data, driving action and enabling stakeholders to understand the value of data-driven insights.
In summary, data visualization in IoT offers a range of benefits, including improved data comprehension, enhanced decision-making, anomaly detection, system optimization, interactive data exploration, improved communication and collaboration, real-time monitoring, and the ability to tell powerful stories with data. By leveraging these benefits, organizations can unlock the full potential of IoT data and drive innovation, efficiency, and competitive advantage.
Common Tools and Techniques for Data Visualization in IoT
Data visualization in the IoT landscape is facilitated by a variety of tools and techniques specifically designed to handle the complexities of IoT data. Let’s explore some of the commonly used tools and techniques for data visualization in IoT:
1. Business Intelligence (BI) Platforms: BI platforms such as Tableau, Power BI, and QlikView provide powerful data visualization capabilities. These platforms enable users to connect and visualize IoT data from various sources, create interactive dashboards, and generate insightful reports. They offer a range of chart types, advanced data manipulation options, and real-time monitoring features.
2. Custom-built Visualizations: Organizations often develop custom-built visualizations tailored to their specific IoT data and use cases. These visualizations can be created using programming languages such as D3.js, Python’s Matplotlib, or JavaScript frameworks like Highcharts. Custom visualizations provide flexibility and allow for unique representations of IoT data.
3. Real-time Monitoring and Dashboarding: Real-time monitoring is crucial in IoT data visualization. Tools such as Grafana, Kibana, and Splunk enable users to create real-time dashboards that display key metrics, alerts, and IoT data streams. These tools offer interactive visualizations, anomaly detection, and the ability to drill down into real-time data for in-depth analysis.
4. Geospatial Visualization: Geospatial visualization is often used in IoT applications that involve geographic data. Platforms like ArcGIS, Google Maps API, and Mapbox provide mapping capabilities to visualize IoT data in a spatial context. Geospatial visualizations help analyze location-based data, identify spatial patterns, and make location-specific decisions.
5. Time-Series Analysis and Visualization: Time-series analysis is crucial in IoT, where data is collected over time. Tools like Grafana, Python’s Matplotlib, and Excel offer specialized features for time-series analysis and visualizations. These tools enable users to uncover trends, seasonality, and anomalies in time-series IoT data and present them in intuitive visual formats.
6. Interactive Data Exploration: Tools like Plotly, d3.js, and ggplot2 allow for interactive data exploration and manipulation. These tools provide users with the ability to filter, sort, and drill down into IoT data to gain deeper insights. Interactive visualizations enhance the exploration process and support data-driven decision-making.
7. Data Streaming Visualization: For real-time data streaming from IoT devices, tools like Apache Kafka and Apache Flink are often used. These tools allow for the data ingestion, processing, and visualization of high-velocity IoT data streams. They provide real-time visualizations and analytics for streaming data, enabling organizations to monitor and analyze IoT data as it flows.
8. Machine Learning and AI Visualization: Machine learning and AI techniques are employed in IoT data analysis. Tools like TensorFlow, RapidMiner, and KNIME provide visualization capabilities specifically designed for machine learning models and algorithms. These tools enable users to visualize model outputs, analyze predictions, and evaluate the performance of AI-based IoT applications.
In summary, a range of tools and techniques are available for data visualization in the IoT landscape. These tools facilitate the creation of interactive dashboards, custom visualizations, real-time monitoring, geospatial visualizations, time-series analysis, interactive data exploration, data streaming visualization, and machine learning/AI visualization. By utilizing these tools appropriately, organizations can effectively visualize and gain valuable insights from their IoT data.
Best Practices for Data Visualization in IoT
Effective data visualization in the IoT landscape requires adherence to certain best practices to ensure clarity, accuracy, and actionable insights. Let’s explore some of the key best practices for data visualization in IoT:
1. Understand the Audience: Start by understanding the target audience and their specific needs and goals. Consider the level of technical expertise, domain knowledge, and the key insights they are seeking from the IoT data. Customize the visualizations accordingly to ensure they resonate with the audience and effectively convey the intended message.
2. Keep it Simple and Clear: Simplify complex data by using a minimalist approach. Avoid cluttered and overloaded visuals that can confuse or overwhelm the viewers. Choose clean and straightforward visual elements, removing any unnecessary embellishments. Focus on clarity and ensure that the key message is communicated clearly.
3. Choose the Right Visualization Techniques: Select appropriate visualization techniques that best represent the IoT data and insights you want to convey. Consider the data type, relationships, and objectives. Whether it’s line charts, bar graphs, maps, or scatter plots, choose visuals that effectively communicate the message and facilitate easy interpretation.
4. Provide Context: Contextualize the IoT data by providing relevant background information, explanations, and labels. Include axes labels, titles, and legends to help viewers understand and interpret the visualizations accurately. Adding context ensures that the viewers can grasp the significance of the data and make informed decisions based on it.
5. Use Color and Contrast Thoughtfully: Color is a powerful tool in data visualization, but it should be used thoughtfully. Choose a color palette that enhances the visual appeal without compromising clarity. Use color to highlight key data points or patterns, and ensure sufficient contrast to distinguish between different elements in the visualization.
6. Ensure Data Accuracy and Integrity: Validate the accuracy and integrity of the IoT data before visualizing it. Check for outliers, missing data, and any data inconsistencies that could affect the reliability and validity of the visualizations. Incorrect or misleading visualizations can lead to poor decision-making, so ensure the data is trustworthy.
7. Make it Interactive: Incorporate interactive elements in the visualizations to enable viewers to explore the IoT data further. Interactive features like filters, brushable charts, and tooltips allow users to analyze specific areas of interest, drill down into details, and extract more insights. Interactivity enhances engagement and facilitates deeper exploration of IoT data.
8. Consider Device Limitations: Keep in mind the limitations of the devices through which the visualizations will be accessed. Ensure that the visualizations are responsive and optimized for different screen sizes and resolutions. Consider the bandwidth and processing power of the devices to ensure a smooth and seamless user experience.
9. Iterative Design and Testing: Take an iterative approach to design and testing of the visualizations. Seek feedback from end users and stakeholders to fine-tune the visualizations and ensure they effectively meet their needs. Test the visualizations on various devices and platforms to identify and resolve any usability or compatibility issues.
10. Document and Maintain Consistency: Document the design decisions, guidelines, and standards for data visualization in IoT. Maintain consistency in style, colors, fonts, and layouts across different visualizations to reinforce the brand identity and create a cohesive experience. Consistency improves user familiarity and allows for easier understanding and interpretation of the visualizations.
By following these best practices, organizations can create effective data visualizations in the IoT landscape that deliver actionable insights and facilitate informed decision-making.
Real-world Examples of Data Visualization in IoT
Data visualization plays a crucial role in various real-world applications of IoT, enabling organizations to gain valuable insights from complex data and make data-driven decisions. Let’s explore some noteworthy examples of data visualization in IoT:
1. Smart Cities: In smart cities, IoT devices gather data on traffic patterns, air quality, energy consumption, and more. Data visualization tools help city officials analyze and visualize this data to make informed decisions. For example, interactive maps can display real-time traffic congestion, enabling officials to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion.
2. Manufacturing and Industrial IoT: In manufacturing, IoT devices collect data on the production line, equipment performance, and product quality. Data visualizations provide real-time monitoring of manufacturing processes, highlighting areas for improvement and identifying bottlenecks. Interactive dashboards allow operators to adjust parameters to optimize production efficiency.
3. Agriculture and Precision Farming: In precision farming, IoT sensors collect data on soil moisture, temperature, and crop health. Data visualization tools help farmers understand this data visually, enabling them to make informed decisions on irrigation, fertilization, and disease control. Visualizations can display crop health maps, showing areas that require attention.
4. Healthcare and Telemedicine: In healthcare, IoT devices and wearables monitor patient vitals and collect health data. Data visualization tools enable healthcare professionals to monitor patients remotely, visualize trends in health parameters, and detect anomalies. This visual information assists in making timely decisions and providing personalized care.
5. Energy Management: IoT devices monitor energy usage in smart buildings, homes, and grids. Data visualizations help users understand energy consumption patterns, identify areas of high energy usage, and optimize energy efficiency. Interactive dashboards can display real-time energy consumption and provide recommendations for reducing energy waste.
6. Retail Analytics: In the retail industry, IoT devices track customer movement, footfall, and buying behavior. Data visualizations enable retailers to understand customer behavior, optimize store layouts, and personalize shopping experiences. Heat maps and flow diagrams visualize foot traffic patterns, informing strategic decisions on product placement and store design.
7. Transportation and Logistics: In the transportation sector, IoT sensors gather data on vehicle performance, fuel consumption, and route optimization. Data visualization tools help fleet managers monitor vehicle conditions, track routes, and identify areas for improvement. Real-time visualizations can display live tracking of vehicles, enabling efficient routing and minimizing delays.
8. Environmental Monitoring: IoT sensors collect data on air quality, water quality, and weather conditions. Data visualization tools transform this data into interactive maps, graphs, and heat maps, providing a comprehensive view of environmental factors. Visualizations enable researchers and policymakers to monitor and respond to environmental changes effectively.
In summary, data visualization in IoT has found its applications in various industries, including smart cities, manufacturing, agriculture, healthcare, energy management, retail, transportation, logistics, and environmental monitoring. Through data visualization, organizations can gain valuable insights, optimize processes, improve decision-making, and drive innovation in their respective fields. The visual representation of IoT data enhances understanding, facilitates communication, and enables stakeholders to take prompt actions based on the insights derived from the data.
Data visualization plays a vital role in the realm of IoT by transforming complex data into meaningful visual representations. The power of data visualization lies in its ability to uncover patterns, relationships, and insights that might otherwise go unnoticed in raw data. By visually representing data through charts, graphs, and interactive dashboards, organizations can easily interpret and analyze IoT data, leading to informed decision-making and improved business outcomes.
The importance of data visualization in IoT cannot be overstated. It enables organizations to understand complex data, identify actionable insights, optimize processes, and drive innovation. By visualizing IoT data in real-time, decision-makers can monitor key performance indicators, identify anomalies, and take prompt actions to ensure optimal operational efficiency.
When implementing data visualization in IoT, it is essential to follow best practices. Understanding the audience, keeping visualizations clear and simple, choosing appropriate visualization techniques, and providing contextual information are crucial elements of effective data visualization. Additionally, using color and contrast thoughtfully, ensuring data accuracy and integrity, and incorporating interactivity are key considerations for creating impactful visualizations.
Real-world examples showcase the diverse applications of data visualization in IoT. From smart cities and manufacturing to healthcare and retail, organizations leverage data visualization to gain valuable insights, optimize processes, and enhance decision-making. Visualizing IoT data allows stakeholders to monitor trends, identify areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions that lead to positive business outcomes.
In conclusion, data visualization is a powerful tool that enables organizations to make sense of the vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices. By leveraging effective data visualization techniques and tools, organizations can unlock the full potential of their IoT data, drive innovation, improve operational efficiency, and gain a competitive edge in today’s data-driven world.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Crowdfunding
- Cryptocurrency
- Digital Banking
- Digital Payments
- Investments
- Console Gaming
- Mobile Gaming
- VR/AR Gaming
- Gadget Usage
- Gaming Tips
- Online Safety
- Software Tutorials
- Tech Setup & Troubleshooting
- Buyer’s Guides
- Comparative Analysis
- Gadget Reviews
- Service Reviews
- Software Reviews
- Mobile Devices
- PCs & Laptops
- Smart Home Gadgets
- Content Creation Tools
- Digital Photography
- Video & Music Streaming
- Online Security
- Online Services
- Web Hosting
- WiFi & Ethernet
- Browsers & Extensions
- Communication Platforms
- Operating Systems
- Productivity Tools
- AI & Machine Learning
- Cybersecurity
- Emerging Tech
- IoT & Smart Devices
- Virtual & Augmented Reality
- Latest News
- AI Developments
- Fintech Updates
- Gaming News
- New Product Launches
- Fintechs and Traditional Banks Navigating the Future of Financial Services
- AI Writing How Its Changing the Way We Create Content
Related Post
How to find the best midjourney alternative in 2024: a guide to ai anime generators, unleashing young geniuses: how lingokids makes learning a blast, 10 best ai math solvers for instant homework solutions, 10 best ai homework helper tools to get instant homework help, 10 best ai humanizers to humanize ai text with ease, sla network: benefits, advantages, satisfaction of both parties to the contract, related posts.

What Is Visualization In IoT?

How Can You Check Data On Devices Connected Through IoT Network

What Is IoT Data Analytics

What Are The Main Parts Of IoT Systems

What Is IoT Based Air Pollution Monitoring

9 Amazing Windows 10 IoT Enterprise For 2024

What Are The Basic Elements Of IoT

What Is Google IoT Core
Recent stories.

Fintechs and Traditional Banks: Navigating the Future of Financial Services

AI Writing: How It’s Changing the Way We Create Content

How to Know When it’s the Right Time to Buy Bitcoin

How to Sell Counter-Strike 2 Skins Instantly? A Comprehensive Guide

10 Proven Ways For Online Gamers To Avoid Cyber Attacks And Scams

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
How to Use IoT Data Visualization. Best Practices. Examples

25 mins | July 28, 2023
Empower your business with IoT expertise or free consultation

It’s great to be a data-driving business.
It’s commendable if you implement IoT technology in your enterprise .
It’s challenging to turn raw terabytes of information into meaningful insights.
Tracking and monitoring any aspect of business and every part of our daily lives have become easier than ever. Being on an island beach, top managers can observe the manufacturing process of Volkswagen Tiguan production in Germany in real-time! By utilizing modern technologies, humanity can estimate the real state of nature like water and air pollution around the globe and take actions to improve the situation. That all has become possible thanks to the data and the Internet global network.
However, companies bumped into a challenge :
The volume of data all the technologies produce is enormous and can’t be analyzed by people manually.
According to Amazon Web Services , data grows 10x every 5 years driven by network-connected smart devices. So the Internet of Things (IoT) makes enormous contributions to data growth, without taking into account the standard growth of information on the Internet. For example, international companies like Google, Facebook, Microsoft, and Amazon store at least 1.200 petabytes of information (which is equal to 1.200.000 terabytes).
So we have to answer a question : “What should we do with all that information? Just store it and pay for the storage capacity?”
The answer is simple : “We should analyze it!”
And one of the greatest tools for that is data visualization . In the article, we find out what this term means, examine the reason why it became very popular in the 21st century, how to implement it in an IoT system through an IoT dashboard, and consider great examples of IoT data visualization implementation.
Enjoy reading!
What Is Data Visualization

To visualize the data means to make charts out of numbers. The goal of data visualization is to provide a graphical representation of the data so analysts can identify patterns and trends. Data visualization shows great efficiency when it comes to large series of data. Its methods include graphs, bar charts, pie charts, status tables, maps, line graphs, scatter plots, and much more. These charts contain a lot of condensed information that allows analysts to see the data trends easily and make the right conclusions. Such conclusions can be priceless and bring new opportunities to businesses.
However, data visualization is a tool that is expected to be applied correctly. There are several questions you should ask yourself before building and implementing anything:
- What issue do you want to solve?
- What goal do you want to achieve?
- How do you see satisfying results after you use data visualization?
- What charts do you consider the most valuable in achieving your goal?
- Do you need real-time data updates?
These common questions are not invented by our company, but we actively use them when working with clients. And we have to admit that the number of companies that look for IoT data visualization instruments for their businesses has grown. The reason is the increased flow of the data .
The Evolution to a Data-Driven World: A Historical Overview
Understanding the emergence and significance of the “data-driven world” requires us to chart its course through three critical time periods:
- Before the advent of the internet
- After the Internet but before the Internet of Things (IoT)
- After the IoT revolution
Era Preceding the Internet
Data visualization, though not as advanced as today, has been an integral part of business operations for a significant amount of time. For instance, businesses have long utilized simple pie charts to analyze monthly expenses and discern the proportionate expenditure of different categories.
Looking back to the 19th century, financial markets, such as the famed New York Stock Exchange, exemplified early use cases of data visualization. Traders would use line charts and histograms to track financial metrics like exchange rates, total sales, and stock prices. Communication during this era was predominantly human-to-human, with data serving to facilitate informed decision-making.
The Era Following Internet Adoption but Preceding IoT
The 1980s ushered in a new era with the proliferation of personal computers and the subsequent rise in internet usage. This period marked the birth of digital behemoths such as Google, Facebook, Amazon, and Microsoft, entities that handle vast troves of user data. Every user interaction on the internet – every click, every button press, every item browsed – translates into a data point, collectively forming rich databases. Companies leveraged these data insights to comprehend customer behaviors and preferences, revolutionizing marketing strategies. This era was characterized by “people-to-machine” communication, with data visualization becoming an indispensable tool for market specialists.
The Era Post IoT Revolution
With the arrival of IoT in the 21st century, we embarked on a truly data-driven era. By the mid-2010s, the IoT had begun to significantly influence numerous industries, including manufacturing, agriculture, healthcare, and home automation, among others. IoT networks introduced machine-to-machine communication, resulting in the generation of data on an unprecedented scale, surpassing traditional data storage and processing capacities. To manage such colossal data sets, IoT incorporates advanced technologies like Big Data methods , NoSQL solutions, cloud computing, and fog analytics. You can learn more about IoT architecture and fog computing in the whitepaper . In this context, IoT data visualization becomes invaluable, offering the sole feasible method for humans to interpret and analyze IoT data effectively.
The IoT data is both valuable and worthless because of its volume. The trick here is to turn these massive data streams from a liability into a strength.
One of the greatest challenges for the IoT industry is the interpretation of its massive flows of data. One of the most effective ways is to use IoT data visualization and build an IoT dashboard.
IoT Dashboard As a Tool For IoT Data Visualization
Source : ctfassets
The Internet of Things dashboard (shortly, IoT dashboard) is a web page or web application that contains a visual display of IoT data on one screen. It provides at-a-glance views of key metrics that are essential to the whole system. In other words, an IoT dashboard displays meaningful visuals in a human-readable format that can be easily interpreted by a dashboard user.
Developers like to use IoT dashboards for two reasons:
- Visuals have a responsive design which means you can view a dashboard from smartphones, laptops, or tablets.
- The visual data is constantly updated in real-time . Where “in real-time” means low latency which is extremely valuable for IoT applications.
We want to highlight the fact that the IoT dashboard and IoT platform are two different entities. A dashboard is a part of the sixth component of the IoT ecosystem that is called “an application component”, and it is a visual display of the metrics only. An IoT platform, in turn, covers all components of the ecosystem which means it collects the data from sensors, transfers them to the cloud or a gateway, stores, analyzes, preprocesses, encrypts, and, finally, displays.
Hence, an IoT dashboard is a part of an IoT platform in general and a part of an application component in particular.
You can see a simplified structure of an IoT ecosystem below.
Talking about a visual representation of the data, a logical question appears: what data to display? However, the answer depends on business goals and needs. It’s impossible to build a universal dashboard that fits every particular case – that is why good dashboards are mostly highly customizable.
So, let’s talk about what a good dashboard looks like.
IoT Data Visualization: Best Practices
#1 customize dashboard to your need.
A dashboard is a set of widgets that display some information that you consider to be meaningful for your business. So make sure that the widgets solve business challenges instead of just displaying condensed information from IoT sensors . Key items for customization are:
- Key performance indicators (KPIs) . For example, if the dashboard is being used to monitor the performance of manufacturing equipment, the KPIs might include uptime, throughput, and yield.
- Alerting . For example, if the dashboard is being used to monitor equipment failures, the alert thresholds should be set based on the acceptable downtime for that equipment.
- Data visualization . This includes choosing the right chart types, colors, and labels.For example, you could customize the dashboard to display the temperature and humidity levels in different sections of the greenhouse using a color-coded map. This would allow you to quickly identify any areas of the greenhouse that are experiencing abnormal temperature or humidity levels and take action to correct them.
- Access control . This includes setting up user roles, permissions, and authentication mechanisms.
#2 Enable Real-Time Parameter Adjustment
In addition to updating visual data on an IoT dashboard in real-time, it’s also important to enable real-time adjustment of certain parameters from the dashboard. While this control option may not be a built-in function of the dashboard itself, you likely have an IoT management system that powers the visual display. By providing interactive visualization and control, analysts can not only observe but also make quick decisions and implement them in real-time, which can be invaluable for optimizing operations and achieving business goals.
#3 Utilize Filtering, Sorting and Exporting Options
When dealing with a large amount of data in an IoT dashboard, it is important to have filtering and sorting options available. These functions allow users to easily identify patterns and outliers, making it easier to draw conclusions from the data. For example, sorting data by date or location can reveal trends over time or in specific areas.
In addition to standard filtering and sorting options, consider implementing advanced filtering options, such as range or category filters. These can help to refine data even further and provide more targeted insights.
It is also important to ensure that exporting data is a seamless process. Users should be able to easily export data from the dashboard to other tools for further analysis or reporting.
By including robust filtering, sorting, and exporting options, IoT dashboards become more powerful tools for analysis and decision-making.
#4 Highlight Key Data
While it’s important for all visuals on an IoT dashboard to be meaningful, there are certain data points that are more critical than others. To ensure that important information is not overlooked, consider using visual cues such as colors, alerts, or notifications to highlight key data. This can be especially helpful in situations where quick decisions need to be made based on real-time data. To determine when and how to highlight key data, establish rules with clearly defined conditions. For example, you may want to highlight data that falls outside of a certain range or exceeds a certain threshold. By emphasizing the most important data, you can make it easier for users to quickly identify and act on critical information.
#5 Try Different WIedgets and Tools
Modern dashboards offer a range of widgets and tools such as scatterplots, maps, bar charts, pie charts, and tables. Experimenting with different widgets can help you find the best ones that suit your business needs and present data in a more effective and actionable way. So don’t hesitate to try out new widgets and tools and see which ones work best for you.
#6 Build Dashboard From The Question Perspective
When building an IoT dashboard, it’s important to start with a clear understanding of the questions that need to be answered. This means identifying the specific business goals and objectives, as well as the key performance indicators (KPIs) that will be used to measure progress towards those goals. From there, the dashboard can be designed with a focus on delivering insights and actionable information that will help users make informed decisions and take strategic action. By starting with a question-oriented approach, the dashboard will be more effective in driving business outcomes and achieving success.
#7 Prioritize Simplicity in Visuals
Effective IoT data visualization should provide an at-a-glance overview of important information, without overwhelming users with too many details. To achieve this, use white space to separate different sections and avoid cluttering the dashboard with too many colors or visual elements. It’s also crucial to set up notification rules in a way that highlights the most important alerts and prevents them from being buried among less critical messages.
#8 Use Clear and Digestible Label s
One of the important aspects of a good dashboard is to have clear and digestible labels for all the visual elements it contains. Users should be able to quickly understand what a graph or chart represents, and what data it is visualizing. This can be achieved by using concise and descriptive labels, as well as annotations and tooltips to provide additional context and information.
It’s also important to use consistent labeling across different widgets and charts, so that users can easily compare and understand the data. Avoid using complex jargon or technical terms, and instead opt for simple and straightforward language that is accessible to all users.
Furthermore, it’s helpful to prioritize the most important information and data on the dashboard, and ensure that the labels and visual elements related to it are easily noticeable and stand out. This can be achieved through the use of appropriate colors, font sizes, and other visual cues that draw the user’s attention to the relevant information.
Why To Use IoT Data Visualization
The main reason why you should use IoT data visualization is that there are literally no other options for a human being to analyze such an enormous volume of data that comes from an IoT system. Besides that, IoT data visualization is an important part of the whole IoT system with its benefits like predictive maintenance, reducing operational costs, higher productivity, and much more. Instead of describing its benefits, we provide 5 examples of how this technology is used in different industries.
Examples of Data Visualization In IoT
World’s air pollution. real-time air quality index.
Source : waqi.ifo
Let’s go back to the pollution topic. Nowadays, more and more people turn their heads toward this issue and start green initiatives aimed at raising awareness of this issue and improving the situation by implementing green technologies. One of such initiatives is a world’s air pollution dashboard that has been monitoring air quality all over the globe since 2014 with thousands of installed quality monitoring stations and IoT data visualization. You can look at an interactive map and see areas where the air is good, unhealthy, or even hazardous.
Agriculture Living Laboratory: WHIN innovation network
Source : whin.org
Wabash Heartland Innovation Network deployed hundreds of weather stations across the Indiana region in the USA to share information about the weather conditions and farmers’ assets. By using IoT data visualization, the company aims to make the densest agricultural weather network in the country. It has already covered a 10-country region, providing an expansive network of internet-connected sensors that aggregates and disseminates the data it obtains to all participants. By sharing information, farmers become more efficient, save time, and increase yields.
Grundfos: Quick and Informed Manufacturer

Grundfos is a Danish company with more than 19,000 employees globally and it is the largest pump manufacturer in the world. During the company’s growth, the Business Intelligence department became a bottleneck since all reports and dashboards for all data from the factory, Internet of Things devices, and ERP system go through this department. As a result, report development speed diminished.
The company referred to a cloud-based reporting and IoT data visualization tool to correct the situation. This decision sped up the reporting process as well as provided additional opportunities for visualization both for small analytic groups of users and on a bigger scale in the form of a dashboard that displays on a large screen on a production floor.
Dashboards and Data Visualization in a Highly Technology Company

Siemens is a technology company focused on industry, infrastructure, transport, and healthcare. The company provides the next generation of data-powered customer service for the rolling stock industry in the U.K. and beyond. IoT Data visualization can bring great benefits to such a technology company as well. Siemens strives to empower its customers with resource-effective factories, resilient supply chains, smart electricity grids, clean transportation, and much more. By using the Grafana tool the company managed to observe the data from the trains in real-time and optimize their maintenance sequencing. Another case is building a temperature monitoring and control dashboard that helps to increase the lifespan of trains and decrease their downtimes.
IoT Data Visualization Dashboard from SumatoSoft
SumatoSoft helps companies to digitalize their businesses and develops meaningful visualization for clients’ businesses. For example, we build a platform for monitoring the work of industrial (commercial) refrigerators online with instant alerts on urgent issues and management of historical data. You can look at the whole case study in the link .
We are recognized as top software developers by leading analyst agencies like techreviewer , clutch , and goodfirms. We also became a member of The Council for Inclusive Capitalism to make the world a better place.
We believe that a vast background of knowledge, professionalism, and expertise will be helpful to your business too.
Get in touch with us for a free consultation . Let’s build a new product together.
Afterward
As for keeping up with the advent of technology, the world looks for new opportunities to analyze the data that is generated in enormous volumes by computers and new technologies. We entered the data-driven area, and with the arrival of the Internet of Things systems and machine-to-machine communication traditional methods became unfit even for data storing and processing. The IoT industry faced a new challenge: processing and analyzing massive flows of data.
New technical solutions like NoSQL databases solved the issue of data processing, while IoT data visualization is expected to address the issue of data analysis. Analysts started to use the Internet of Things dashboards to aggregate the most valuable information in one place. Dashboards became especially popular in the IoT industry thanks to their responsive design and real-time data updates.
The IoT visualization was implemented to build various solutions for agriculture, supply chain, manufacturing, technology sector, and to develop a solution for tracking world air quality. That’s all sounds impressive, and we expect the implementation of IoT technology along with data visualization will rise.
Thanks for reading!
Let’s start
If you have any questions, email us [email protected]
second_name My Name* Email Address* Message*
Budget* [radio aria-required="false" budget id:radio-1 use_label_element "$10k — $20k" "$20k — $30k" "$40k+"]
Please be informed that when you click the Send button Sumatosoft will process your personal data in accordance with our Privacy notice for the purpose of providing you with appropriate information. This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Software Outsourcing Costs [2024 Updated] – Overview

Why Use Ruby on Rails: Advantages and Usage Examples

What is an Internet of Things (IoT) Gateway: Overview and Its Role In Digital Transformation

This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Analyze and visualize your IoT data
- 1 contributor
This overview introduces the key concepts around the options to analyze and visualize your IoT data. Each section includes links to content that provides further detail and guidance.
The following diagram shows a high-level view of the components in a typical IoT solution. This article focuses on the areas relevant to analyzing and visualizing your IoT data.
In Azure IoT, analysis and visualization services are used to identify and display business insights derived from your IoT data. For example, you can use a machine learning model to analyze device telemetry and predict when maintenance should be carried out on an industrial asset. You can also use a visualization tool to display a map of the location of your devices.
Azure Digital Twins
The Azure Digital Twins service lets you build and maintain models that are live, up-to-date representations of the real world. You can query, analyze, and generate visualizations from these models to extract business insights. An example model might be a representation of a building that includes information about the rooms, the devices in the rooms, and the relationships between the rooms and devices. The real-world data that populates these models is typically collected from IoT devices and sent through an IoT hub.
External services
There are many services you can use to analyze and visualize your IoT data. Some services are designed to work with streaming IoT data, while others are more general-purpose. The following services are some of the most common ones used for analysis and visualization in IoT solutions:
Azure Data Explorer
Azure Data Explorer is a fully managed, high-performance, big-data analytics platform that makes it easy to analyze high volumes of data in near real time. The following articles and tutorials show some examples of how to use Azure Data Explorer to analyze and visualize IoT data:
- IoT Hub data connection (Azure Data Explorer)
- Export IoT data to Azure Data Explorer (IoT Central)
- Azure Digital Twins query plugin for Azure Data Explorer
Use Azure Databricks to process, store, clean, share, analyze, model, and monetize datasets with solutions from BI to machine learning. Use the Azure Databricks platform to build and deploy data engineering workflows, machine learning models, analytics dashboards, and more.
Use structured streaming with Azure Event Hubs and Azure Databricks clusters . You can connect a Databricks workspace to the Event Hubs-compatible endpoint on an IoT hub to read data from IoT devices.
Azure Stream Analytics
Azure Stream Analytics is a fully managed stream processing engine that is designed to analyze and process large volumes of streaming data with low latency. Patterns and relationships can be identified in data that originates from various input sources including applications, devices, and sensors. You can use these patterns to trigger actions and initiate workflows such as creating alerts or feeding information to a reporting tool. Stream Analytics is also available on the Azure IoT Edge runtime, enabling data processing directly on the edge.
- Build an IoT solution by using Stream Analytics
- Real-time data visualization of data from Azure IoT Hub
- Extend Azure IoT Central with custom rules and notifications
- Deploy Azure Stream Analytics as an IoT Edge module
Power BI is a collection of software services, apps, and connectors that work together to turn your unrelated sources of data into coherent, visually immersive, and interactive insights. Power BI lets you easily connect to your data sources, visualize and discover what's important, and share reports with anyone or everyone you want.
- Visualize real-time sensor data from Azure IoT Hub using Power BI
- Export data from Azure IoT Central and visualize insights in Power BI
Azure Maps is a collection of geospatial services and SDKs that use fresh mapping data to provide geographic context to web and mobile applications. For an IoT example, see Integrate with Azure Maps (Azure Digital Twins) .
Grafana is visualization and analytics software. It allows you to query, visualize, alert on, and explore your metrics, logs, and traces no matter where they're stored. It provides you with tools to turn your time-series database data into insightful graphs and visualizations. Azure Managed Grafana is a fully managed service for analytics and monitoring solutions. To learn more about using Grafana in your IoT solution, see Cloud IoT dashboards using Grafana with Azure IoT .
IoT Central
IoT Central provides a rich set of features that you can use to analyze and visualize your IoT data. The following articles and tutorials show some examples of how to use IoT Central to analyze and visualize IoT data:
- How to use IoT Central data explorer to analyze device data
- Create and manage IoT Central dashboards
Now that you've seen an overview of the analysis and visualization options available to your IoT solution, some suggested next steps include:
- Manage your IoT solution
- IoT solution options
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback .
Submit and view feedback for
Additional resources
Understanding IoT Data Visualization: Unravelling the Power of Data
Team bytebeam.
The Internet of Things (IoT) has become integral to our tech-savvy lives. With the increasing interconnectivity of devices and objects, IoT dashboards generates vast amounts of data that hold immense potential for enhancing our understanding of the world around us.
Here are some interesting statistics about IoT:
- According to a report by Statista, the number of Internet of Things (IoT) connected devices worldwide is projected to grow significantly, reaching 30.9 billion devices by 2025.
- A McKinsey Global Institute report estimated that the total economic impact of IoT applications across various industries could range from $3.9 trillion to $11.1 trillion annually by 2025.
We rely on IoT data visualization to make sense of this data, which helps transform complex information into clear and meaningful visuals.
What to expect: This article aims to shed light on IoT data visualization and its importance in harnessing the power of IoT-generated data.
Understanding IoT Data Visualization
Data visualization represents information through visual elements like charts, graphs, and diagrams. Its primary purpose is to present data in a format that is easy to comprehend, allowing individuals to quickly identify patterns, trends, and insights.
By translating raw data into visual form, data visualization enables us to make informed decisions, solve problems, and communicate complex ideas efficiently.
IoT Data Visualization
IoT data visualization involves the graphical representation of data collected from IoT devices and systems. These devices, equipped with sensors and connectivity, continuously gather information from the surrounding environment. Their data may include temperature, humidity, pressure, location, etc.
However, this data can be overwhelming and challenging to analyze when left in its raw form. Here is a quick look at the data visualization dashboard containing different IoT dashboards with visualization panels.
Similarly, IoT data visualization uses intuitive charts, maps, and graphs to simplify the complexity of IoT-generated data, making it easier for users to grasp valuable insights. By visualizing the data, we can uncover patterns and relationships that might have remained hidden in a sea of numbers.
Role of IoT in Generating Vast Amounts of Data
The IoT is at the heart of the data revolution. The interconnectedness of various smart devices, such as smartphones, smartwatches, home automation systems, and industrial sensors, results in a constant stream of data. These devices exchange information with each other and with cloud-based platforms, generating enormous volumes of data in real-time.
Importance of Visualizing IoT Dashboards
The value of data lies in its ability to inform and guide decision-making. However, with the sheer volume of data generated by IoT devices, processing and comprehending it in its raw form becomes daunting. This is where IoT data visualization proves its worth.
- Simplifies Complex Data: IoT data visualization simplifies intricate data sets, making them accessible even to individuals without a technical background. Using visuals like line graphs to display changes over time or pie charts to represent proportions makes it easier to grasp the overall picture.
- Identifies Anomalies and Patterns: Visualizing IoT data allows us to identify anomalies, outliers, and patterns that might not be apparent when examining raw numbers. Trends and irregularities in data can be quickly spotted, enabling prompt actions or interventions.
- Facilitates Decision-making: When data is presented visually, decision-makers can quickly understand and analyze the information. This empowers them to make timely and well-informed choices, whether in businesses optimizing their operations or individuals managing their daily lives.
- Enhances Communication: Visualization of IoT data enhances communication and collaboration among teams and stakeholders. It enables the effective sharing of insights and findings, leading to better problem-solving and improved outcomes.
Benefits of IoT Data Visualization
Here are some key benefits of IoT data visualization.
Enhanced Understanding of Complex IoT Data
IoT devices produce immense data, often containing intricate relationships and interdependencies. IoT data visualization simplifies this complexity by presenting the data visually. Using clear and concise charts, graphs, and other visuals makes it easier for users to comprehend the data's nuances and gain a deeper understanding of the underlying trends and insights.
Real-time Monitoring and Analysis
IoT data visualization enables real-time monitoring of data streams. As IoT devices continuously generate data, it is essential to have up-to-date information readily available. Through interactive dashboards and live charts, decision-makers can monitor the status of various IoT parameters in real time, facilitating immediate responses to changing conditions.
Improved Decision-making Processes
Quickly grasping and interpreting data empowers decision-makers to make informed choices. IoT dashboards provides a clear picture of the current situation and the impact of potential decisions. This leads to more effective and timely decision-making, whether optimizing processes, managing resources, or addressing critical issues.
Identifying Patterns, Trends, and Anomalies
Patterns and trends in IoT data may not always be evident when examining raw data. Visualization tools like line charts, bar graphs, and heatmaps make identifying patterns and detecting anomalies easier. Organizations can proactively respond to emerging opportunities or mitigate potential risks by spotting trends early on.
Predictive Insights and Forecasting
IoT dashboards helps analyze historical data and facilitates predictive insights and forecasting. Machine learning algorithms can identify potential future scenarios by applying advanced analytics to visualized data—these predictive insights aid businesses and individuals in making proactive decisions and planning for the future.
Techniques and Tools for IoT Data Visualization
Let’s take a quick look at some prominent visualization techniques:
- Line Charts: Line charts display trends over time, making them ideal for visualizing continuous data, such as temperature fluctuations or sensor readings.
- Bar Graphs: Bar graphs compare different categories or discrete data points. They help represent data such as the number of IoT devices deployed in various locations.
- Pie Charts: Pie charts display the proportions of a whole. They help illustrate the distribution of IoT data in different categories.
- Scatter Plots: Scatter plots depict the relationship between two variables, showing how they correlate. This technique is valuable for identifying connections between IoT parameters.
- Heatmaps: Heatmaps use colors to represent data density on a map or grid. They help visualize data trends geographically, like variations in temperature across different regions.
- Gauge Charts: Gauge charts represent a single value within a specific range, often used to display real-time data, such as battery levels or system health.
- Interactive IoT Dashboards: Dashboards are a collection of visualizations providing a comprehensive view of multiple IoT data metrics. Users can interact with the dashboard to explore and analyze real-time data.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS technology integrates IoT data with geographic locations, allowing visualization of IoT data on maps. This is especially useful for tracking vehicle movements or environmental monitoring applications.
Popular Tools for IoT Data Visualization
When visualizing the vast amounts of data generated by the Internet of Things (IoT), several powerful tools have gained popularity. These tools offer user-friendly interfaces and robust capabilities that enable individuals and organizations to transform complex IoT data into meaningful and insightful visuals.
There are two distinct categories of tools that have garnered popularity, these include:
- Out of the Box Tools: They are readily available and have user-friendly interfaces and powerful functionalities. They empower users to convert intricate IoT data into meaningful and insightful visuals with relative ease.
Few examples of out of the box tools include:
- Build Your Own Solutions: They encompass libraries that allow developers to create customized data visualization tools like the ones mentioned above. These libraries provide the necessary building blocks and functionalities to design tailored solutions specific to the requirements of individual users or organizations.
Few examples of build your own solutions include:
- D3.js (Data-Driven Documents)
Here are five popular tools for IoT data visualization:
Bytebeam IoT platform offers a user-friendly and intuitive interface, making it easy for users to connect their ESP32 Arduino devices and visualize their IoT data in real time. Here is a quick example of how you can visualize data with Bytebeam:
Bytebeam platform's versatility allows it to support various data sources, enabling users to integrate data from sensors, actuators, and other IoT devices effortlessly.
Amazon Quick Sight
Amazon QuickSight is a business intelligence (BI) tool and data visualization service offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS). It enables users to create interactive, insightful dashboards and reports from various data sources.
QuickSight simplifies the process of analyzing large datasets, making it easier for businesses to gain valuable insights and make data-driven decisions. It supports various data formats and offers various visualization options, making it a powerful tool for data exploration and analysis.
Tableau has emerged as a leading data visualization tool, revered for its user-friendly interface and powerful capabilities. This software has revolutionized how data is visualized and analyzed, empowering beginners and experienced analysts to gain valuable insights from their datasets.
Developed by Microsoft, Power BI is another popular tool for IoT data visualization. It seamlessly integrates with other Microsoft products, making it a preferred choice for organizations using Microsoft's ecosystem.
Power BI offers a wide range of visualization options, and its real-time capabilities allow users to monitor and analyze IoT data as it streams in, ensuring quick and informed decision-making.
D3.js is a JavaScript library that provides a robust framework for creating interactive and custom data visualizations on the web. While it requires more technical expertise than other tools, D3.js offers unparalleled flexibility and control over the visual representation of data.
It is often chosen by developers and data scientists who want to build highly customized and visually stunning IoT data visualizations.
Plotly is a user-friendly data visualization library that supports multiple programming languages, including Python, R, and JavaScript. It offers various chart types and interactive features, making it a popular choice for IoT data visualization.
Plotly's visualizations are aesthetically pleasing and highly informative, allowing users to dig deep into the data for meaningful insights.
Grafana is an open-source platform designed specifically for time-series data visualization, making it an excellent fit for IoT data. It supports integration with various data sources and provides a range of pre-built visualizations and the option to create custom panels.
Grafana's real-time monitoring capabilities and alerting features make it a preferred tool for visualizing and managing IoT data in real time.
Note: Each tool offers distinct features and advantages, catering to user needs and preferences. Whether you're a data analyst, business user, or developer, these popular tools empower you to harness the power of IoT data visualization and uncover valuable insights to drive informed decisions and maximize the potential of the Internet of Things.
Challenges and Considerations in IoT Data Visualization
IoT data visualization offers valuable insights and benefits but has its fair share of challenges and considerations. Addressing these challenges is crucial to ensure accurate and meaningful interpretations of the data.
Handling Large Volumes of Data
The sheer volume of data IoT devices can overwhelm traditional data visualization tools and systems. Managing and processing massive datasets requires robust infrastructure and optimized algorithms to ensure smooth visualization and analysis.
For example, using a line chart to display a large volume of data can lead to system hang-ups when dealing with data from IoT devices. So, traditional data visualization tools may need help to handle the overwhelming amount of information.
You can address this issue by incorporating features like displaying an overall trendline and providing a way to zoom in for detailed analysis. This ensures a smoother visualization and analysis process, requiring robust infrastructure and optimized algorithms capable of effectively managing and processing massive datasets.
Ensuring Data Security and Privacy
IoT data often contains sensitive information, so ensuring data security and privacy is paramount. Unauthorized access to IoT data can have severe consequences, making it essential to implement strong encryption, access controls, and secure data transmission protocols.
For example, role-based access tools can enhance data security and privacy in IoT environments. IoT data contains sensitive information, and unauthorized access could lead to severe consequences. By enforcing role-based access control, the system can ensure that only authorized individuals or entities can access specific data, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized use of sensitive information.
Dealing with Data Variety and Complexity
IoT data comes in various formats, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured. Additionally, data from different IoT devices may have varying levels of complexity. Visualization tools must effectively handle this data diversity and complexity to provide accurate insights.
Choosing the Right Visualization Approach for Specific Data Types
Not all data visualization techniques are suitable for every type of IoT data. Some data types may require specific visualization approaches to best represent the information. Selecting the appropriate visualization technique is critical for obtaining meaningful insights from the data.
Use Cases of IoT Data Visualization
- Smart Cities and Urban Planning: IoT data visualization plays a significant role in innovative city initiatives, where data from various sources, such as traffic sensors, weather stations, and surveillance cameras, are collected and analyzed. By visualizing this data, city planners can optimize traffic flow, manage resources efficiently, and enhance urban living.
- Industrial IoT and Predictive Maintenance: In industrial settings, IoT devices monitor equipment health, collect sensor data, and identify potential issues before they escalate into costly failures. IoT data visualization aids in predicting maintenance needs, optimizing machinery performance and minimizing downtime, leading to improved productivity and reduced operational costs.
- Healthcare and Remote Patient Monitoring: IoT devices in healthcare, such as wearable health trackers and remote monitoring sensors, generate vast amounts of patient data. By visualizing this data, healthcare professionals can closely monitor patients' health, detect anomalies, and deliver personalized care, even from a distance.
Wrapping Up
IoT data visualization is a powerful technique that transforms the vast amounts of data generated by the Internet of Things into clear and insightful visuals. Using various visualization techniques like charts, graphs, and maps simplifies complex data, enabling individuals and organizations to understand trends, patterns, and anomalies better.
Through IoT data visualization, businesses can identify inefficiencies, predict maintenance needs, optimize processes, and deliver personalized customer service. In healthcare and environmental monitoring sectors, it empowers professionals to improve patient care and address critical environmental challenges. Furthermore, it fosters collaboration and communication by enabling stakeholders to share and understand data.
Potential Future Developments in IoT Data Visualization:
As technology continues to evolve, so will IoT data visualization. Future developments might include more advanced AI-driven analytics to identify subtle patterns and predict outcomes more accurately. Additionally, with the growing popularity of augmented and virtual reality, IoT dashboards can be incorporated into immersive environments, providing new ways to explore and interact with data.
Furthermore, advancements in edge computing will enable real-time data visualization closer to the data sources, reducing latency and enhancing responsiveness. This will be especially crucial in applications requiring immediate decisions, such as autonomous vehicles or emergency response systems.
Unleash the Power of Data Visualization with Bytebeam
Bytebeam's data visualization capabilities open a world of possibilities for IoT enthusiasts and businesses seeking to harness the true potential of their data. With real-time insights, customization options, and top-notch security measures, our platform empowers users to make data-driven decisions, optimize operations, and succeed in the rapidly evolving IoT landscape.
As an IoT platform, Bytebeam offers you the following capabilities:
- Real-Time Insights: Bytebeam's data visualization allows users to monitor and analyze IoT data using interactive dashboards, graphs, and charts. This enables quick identification of patterns, trends, and anomalies, allowing prompt and data-driven decision-making for process optimization and adapting to changing conditions.
- Customization and Flexibility: Bytebeam's platform offers high customization, allowing users to choose from visualization techniques like line charts, bar graphs, and scatter plots to represent their unique IoT data. Users can design custom dashboards tailored to their specific needs.
- Data Security and Privacy: Data security is a top priority at Bytebeam. Robust encryption and access controls ensure continuous protection of IoT data. Industry best practices are followed to safeguard sensitive information, providing users with peace of mind.
- Seamless Integration: Bytebeam's data visualization seamlessly integrates with ESP32 Arduino devices, simplifying IoT device connectivity. Step-by-step guides and tutorials facilitate the quick setup of data streams for instant visualization of IoT data.
To learn more about our data visualization capabilities and get started with ESP32 Arduino and Bytebeam, visit our website and take the first step towards a more innovative, more connected world.
Sign up for more like this.

- Scroll to top
- Light Dark Light Dark

Cart review
No products in the cart.
IoT Data Visualization Mastery: 8 Proven Techniques for Enhanced Decision-Making
- Author Survey Point Team
- Published November 17, 2023
Unlock the potential of data-driven decision-making with our comprehensive guide on IoT Data Visualization Mastery. Explore 8 proven techniques for enhanced decision-making that will elevate your understanding and strategic choices.
Welcome to the IoT Data Visualization Mastery realm, where the convergence of data and visualization transforms decision-making into a strategic art.
This blog delves into 8 proven techniques that enhance your understanding and empower you to make informed decisions that drive success. From the basics to advanced strategies, let’s embark on a journey that revolutionizes how you perceive and leverage data.
Table of Contents
Understanding IoT Data
In the dynamic landscape of IoT, data is the cornerstone. Dive into the fundamentals, unravelling the intricacies of IoT data and its unique characteristics that set it apart from conventional data sources.
The Power of Visualization
Witness the transformative power of visualization in decoding complex datasets. Explore how visual representations can amplify comprehension, making intricate data accessible to all stakeholders.
Interactive Dashboards: Navigating Insights
Navigate through interactive dashboards, an indispensable tool for real-time data exploration. Uncover insights effortlessly, fostering a proactive approach to decision-making.
Storytelling with Data
Learn the art of storytelling with data—a skill that goes beyond charts and graphs. Understand how to craft narratives that resonate, compelling stakeholders to engage and act on the insights presented.
Predictive Analytics for Strategic Planning
Delve into predictive analytics, a game-changer in strategic planning. Uncover how forecasting future trends empowers decision-makers to stay ahead of the curve, mitigating risks and capitalizing on opportunities.
Augmented Reality: Data Visualization Beyond Screens
Step into the realm of augmented reality and witness data visualization transcend screens. Explore how AR revolutionizes decision-making by seamlessly integrating data into the physical environment.
Ensuring Data Security and Compliance
Safeguard your data fortress. Explore techniques to ensure data security and compliance, fostering a trustworthy environment for decision-makers to operate without compromising integrity.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
In the ever-evolving landscape of IoT, continuous learning is paramount. Discover strategies for ongoing education and adaptation, ensuring your mastery over IoT data visualization remains cutting-edge.
FAQs for IoT Data Visualization
Q: Can I apply these techniques in any industry?
Absolutely. The principles of IoT data visualization are versatile and can be applied across diverse industries, from healthcare to finance.
Q: Are there user-friendly tools for beginners?
Yes, several user-friendly tools, such as Tableau and Power BI, cater to beginners, making the journey into IoT data visualization seamless.
Q: How crucial is data security in IoT data visualization?
Data security is non-negotiable. In an interconnected world, prioritizing data security ensures the reliability of insights and the trust of stakeholders.
Q: Is augmented reality practical for small businesses?
Absolutely. Augmented reality is scalable and adaptable, making it practical for businesses of all sizes to leverage for enhanced decision-making.
Q: Can storytelling with data be learned?
Certainly, storytelling with data is a skill that can be cultivated through practice and understanding the nuances of effective communication through visualizations.
Q: What role does continuous learning play in IoT data visualization?
Continuous learning is the key to staying ahead in the dynamic IoT landscape. Embrace new tools and techniques to maintain mastery.
In IoT Data Visualization Mastery, the fusion of data and visualization transcends conventional decision-making. Empowered with 8 proven techniques, you are now equipped to navigate the complex landscape of IoT, making decisions that propel success. Harness the transformative power of data visualization and elevate your strategic choices to new heights.
Survey Point Team
Related posts.

- Posted by Survey Point Team
Nonprofit Data Analyst Mastery: The Ultimate Guide to Boosting Your Career in 2024

Unlock the Secrets: 7 Powerful Credit Union Data Analytics Strategies for Success

7 Key Differences in Analytics vs. Data Analysis: Unlocking the Power of Analytics

Just one more step to your free trial.
.surveysparrow.com
Already using SurveySparrow? Login
By clicking on "Get Started", I agree to the Privacy Policy and Terms of Service .
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Don't miss the future of CX at RefineCX USA! Register Now
Enterprise Survey Software
Enterprise Survey Software to thrive in your business ecosystem
NPS® Software
Turn customers into promoters
Offline Survey
Real-time data collection, on the move. Go internet-independent.
360 Assessment
Conduct omnidirectional employee assessments. Increase productivity, grow together.
Reputation Management
Turn your existing customers into raving promoters by monitoring online reviews.
Ticket Management
Build loyalty and advocacy by delivering personalized support experiences that matter.
Chatbot for Website
Collect feedback smartly from your website visitors with the engaging Chatbot for website.
Swift, easy, secure. Scalable for your organization.
Executive Dashboard
Customer journey map, craft beautiful surveys, share surveys, gain rich insights, recurring surveys, white label surveys, embedded surveys, conversational forms, mobile-first surveys, audience management, smart surveys, video surveys, secure surveys, api, webhooks, integrations, survey themes, accept payments, custom workflows, all features, customer experience, employee experience, product experience, marketing experience, sales experience, hospitality & travel, market research, saas startup programs, wall of love, success stories, sparrowcast, nps® benchmarks, learning centre, apps & integrations, testimonials.
Our surveys come with superpowers ⚡
Blog Knowledge
IoT Data Collection and Visualization: How to Use it to Understand Big Data
Kate williams.
18 October 2023
Table Of Contents
What is Big Data?
Importance of iot data visualization, techniques for iot data visualization.
- Wrapping Up...
Imagine a world where everyday objects, from your fridge to your car, are connected to the internet, collecting and exchanging data. Well, that’s exactly what IoT is all about!
The IoT, or Internet of Things, has become a game-changer, revolutionizing the way we interact with technology and the world around us. It’s like having a digital web that connects devices, sensors, and systems, allowing them to communicate and share information. Pretty cool, right?
But what’s the impact of all this connectivity? Well, it’s huge! The IoT has unleashed a wave of innovation across various industries. Think about healthcare, where IoT devices enable remote patient monitoring and real-time data collection. Or manufacturing, where IoT-powered sensors optimize production processes and prevent costly downtime. Transportation, agriculture, and so many other sectors have also jumped on the IoT bandwagon to streamline operations and improve efficiency.
Big data is the term used to describe the enormous volume of structured and unstructured data produced at a high rate from various sources.
It encompasses data from sources such as social media, sensors, machines, devices, and other digital interactions. Big data is characterized by its three Vs: volume, velocity, and variety.
In the context of IoT, big data plays a crucial role in enabling the full potential of IoT systems.
- Data collection and storage
- Data processing and analytics
- Real-time decision making
- Data integration and fusion
- Scalability and elasticity
- Data driven innovations
So, what exactly is IoT data visualization? Well, it’s all about taking the data generated by IoT devices and transforming it into captivating visual formats. Think colorful charts, dynamic graphs, and interactive dashboards. It’s like turning raw numbers and data points into a visual masterpiece.
Now, you might wonder, “Why bother with visualizing IoT data?”. Well, let me tell you, there are plenty of reasons why it’s so important.
So buckle up and let’s explore the benefits!
Improved Data Understanding
Have you ever stared at rows and columns of numbers and felt your brain slowly turning into mush? Yeah, we’ve all been there. But fear not! IoT data visualization swoops in to save the day.
By presenting data in visual formats, like charts and graphs, we can make sense of complex relationships and patterns that may be hidden within the vast amounts of IoT data. Visualizations simplify the data sets, allowing us to grasp the big picture and identify key insights at a glance.
Real-time Monitoring
Data visualization plays a crucial role in keeping us in the loop. Visual dashboards provide us with real-time insights into the performance of IoT systems. We can see the data updates as they happen, allowing us to monitor various parameters, detect anomalies, and respond promptly to any issues that may arise.
Decision-Making Support
When it comes to making strategic decisions, having accurate and timely information is crucial.
By visualizing IoT data, decision-makers are armed with clear, concise, and visually appealing insights that drive data-driven actions. Whether it’s identifying performance bottlenecks in an industrial process or understanding customer behavior based on sensor data, visualizations provide decision-makers with the information they need to make informed choices.
Stakeholder Engagement
Engaging and interactive visualizations create a common ground for stakeholders to come together, discuss insights, and collaborate on problem-solving. It’s like having a shared language that transcends technical jargon and makes data accessible to everyone.
Data Visualization Tools and Platforms
We have some amazing tools like Tableau, Power BI, and QlikView that can turn your IoT data into stunning visuals. There are also specialized platforms designed specifically for IoT data analytics and visualization, offering advanced features. We’ll look into this in detail in a bit.
Choosing the Right Visualization Techniques
It’s like being an artist and selecting the perfect brushstrokes to create a masterpiece. Depending on your IoT data and the insights you want to uncover, you can choose from techniques like line charts, heat maps, scatter plots, and interactive maps.
Interactive and exploratory visualization:
Imagine having a visual dashboard that lets you dive deep into your data. You can interact with the data, apply filters, and customize the display to understand the nuances hidden within comprehensively.
Visualizing IoT Data with Advanced Analytics:
You can unlock even more insights by integrating advanced analytics techniques like machine learning, predictive modeling, and anomaly detection. These insights can be visualized to empower you with accurate and timely information for making informed decisions.
Now, let’s get into the “How”.
How do we use IoT visualization to understand big data?
Start with a clear objective: Before diving into visualization, define your objective. What insights do you want to extract from the big data? Whether it is customer behavior, optimizing operational processes, or identifying trends
Identify relevant IoT data sources: Take stock of the available IoT data sources. These could be sensors, devices, or other data-generating elements.
Please choose the right visualization techniques: Line charts, bar graphs, scatter plots, heat maps, or network diagrams each has their own strengths for representing different data types. There are myriad of visualization techniques available, so choose wisely!
Select an IoT visualization tool: Select after considering factors like ease of use, compatibility with your data sources, and the specific features you need for your visualization journey.
Prepare and cleanse the data: Ensure your data is in good shape before visualizing. Cleanse, preprocess, and organize it to eliminate inconsistencies and errors
Design engaging and informative visualizations: Get creative with your visualizations! Make them visually appealing and engaging to capture attention and facilitate understanding. Use colors, labels, and annotations effectively to convey information and highlight key insights
Iterate and refine: Visualization is an iterative process. Don’t be afraid to experiment, refine, and fine-tune your visualizations based on feedback and insights. Seek input from stakeholders, colleagues, or experts to gain different perspectives and enhance the clarity of your visualizations.
Explore interactivity and drill-down capabilities: Leverage the power of interactive visualizations to allow users to explore the data further.
Communicate and share insights: Your visualizations are like storytelling tools. Use them to communicate your insights effectively to stakeholders. Craft a narrative around the visualizations, highlighting the key findings, trends, and patterns you’ve discovered.
Let’s wrap it up!
We’ve explored the significance of understanding big data and how the IoT plays a pivotal role in this dynamic landscape. By effectively collecting and visualizing the vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices, organizations can gain a competitive edge and make informed decisions that drive success.
Before we wrap up, I want to introduce you to a remarkable tool that can further enhance your data exploration experience. Have you heard of SurveySparrow? Intuitive survey software empowers you to create engaging surveys and gather valuable feedback.
With SurveySparrow, you can gain insights from your audience, understand their perceptions of your IoT data visualization efforts, and leverage their feedback to improve and refine your strategies.
It’s a valuable resource to consider as you embark on your data visualization journey! Happy exploring!
Please enter a valid Email ID.
14-Day Free Trial • No Credit Card Required • No Strings Attached
Content Marketer at SurveySparrow
You Might Also Like
The beginner’s guide to benchmark your nps score like a pro, 50+ best demographic survey questions (free template included), demand generation vs lead generation: understanding the difference in b2b marketing.
Leave us your email, we wont spam. Promise!
Start your free trial today
No Credit Card Required. 14-Day Free Trial
Request a Demo
Want to learn more about SurveySparrow? We'll be in touch soon!
Supercharge Your Feedback Process with SurveySparrow!
Sign up today for seamless and insightful feedback experiences..
14-Day Free Trial • No Credit card required • 40% more completion rate
Hi there, we use cookies to offer you a better browsing experience and to analyze site traffic. By continuing to use our website, you consent to the use of these cookies. Learn More
A Guide On The Best Data Visualization Tools For IoT Applications
There are many fantastic data visualization tools that can be used in IoT applications — from Grafana and Tableau to IBM Watson to Power BI and Kibana. This guide dissects the need for visualization tools and the best options available in the market.

Table Of Contents
2022 and beyond: stepping into a data-driven era, how data visualization affects an iot project, 1. streamline millions of data sets in one place, 2. unlock multiple insightful values, 3. create an agile working environment, 4. deal better with crucial industries, 1. transportation, 2. logistics, 3. public sector, 4. environment, 5. agriculture, 6. healthcare, 1. data oversimplification, 2. hampered data quality, 3. limited algorithm interpretation, 4. skill gap, 5. edge computing, unique features of power bi include:, cons of using power bi:, prominent features of grafana include:, cons of using grafana:, with kibana, you can avail the following features:, cons of using kibana:, main features of tableau include:, cons of using tableau:, unique features of thingsboard are:, cons of using thingsboard:.
- Salient features of IBM Watson include:
Cons of using IBM Watson include:
Incredible features of domo:, cons of using domo include:, freeboard has a variety of features, such as:, cons of using freeboard include:, key features of looker:, cons of using looker include:, amazing features of zoho analytics:, 360-degree features of sisense:, cons of using sisense include:, salient features of databox:, cons of using databox:, key features of visme:, cons of using visme:, tremendous features of google charts, key features of datawrapper:, cons of using datawrapper:, sap analytics cloud offers the following features:, cons of using sap analytics cloud:, how to choose the right visualization tool .
- 1. Decoding digital information
2. Ensuring accuracy
- 3. Saving time
1. Proficiency to display exploratory graphics
2. draw your desired visualization first, 3. data visualization should follow function, 4. maximize clarity, minus visual overload, 5. choose a tool suitable for your audience, 6. calculate the intuitiveness, 7. efficiency to summarize all the information, 8. intermingle multiple data sources and factors.
- 9. Compare functionality vs. needs
- 10. Consider your team’s expertise
11. Identify the scope of features
12. select a tool as per your industry.
Data is everywhere. Right from when consumers visit a company website to the moment they sign out, their browsing pattern is tracked including the CTA they clicked, pages they visited, sections where they spent most of the time, and so on.
In the world of Internet of Things (IoT), the data received from wearable devices that monitor your heartbeat to the logistics company that uses smart contracts and also a smart city for asset tracking — every device, sensor, network and sensor contribute to Big Data.
But do you know what? All this data is useless if it does not serve a purpose or adds value to a specific business function. No remote device control can help in this case!
You see, in this digital day and age, data is meant to be analyzed to make operational improvements and drive superior user experience in general.
But when you have a wealth of information to process and analyze, it can get pretty overwhelming even for the most experienced of teams. You have to deploy certain tool supports or techniques to simplify the job. There are no two ways about it!
An average human brain is wired to properly consume imagery compared to words or numbers. Ever heard of the saying, “a picture is worth a thousand words?” When you put data in a visual format, it is much easier to make sense of it.
That is where using smart tools help slice the data to its most granular level. But before we head on to explore the tools, let us understand the meaning of data visualization.
In simple words, it is basically a technique that enables you to present the raw data, picked up from various sources of data, insightfully. It looks for certain patterns and behaviors and displays them in a way that helps create a viable business strategy.
This could be in the form of real-time graphs, pie charts, column bars, and so on. A data visualization tool collates and understands the massive amount of info — from various data sources — emanating from multiple sensors and showcases the same in a visual summary.
It helps manipulate data based on the customization of every data set as per a specific business objective. That means every number gets a meaning attached to it.
It is clear that the terminology has many advantages in the business world. But how can it be used to improve IoT solutions? That is an important question to ask.
When a number of hardware and software platforms exchange IoT data every millisecond, it leads to a need for data visualization. As the IoT landscape is expanding at a rapid pace, it is only natural to incorporate techniques that can get businesses to have a better hold on their data when it comes to various IoT devices.
IoT data visualization tools are helpful in meeting a number of goals in creating an open-source IoT platform:
An IoT dashboard comprises multiple widgets that visualize data in the form of line graphs, bar charts, gauges, heat maps, geographical screenshots from IoT data transmitted across multiple IoT devices over a period. When the data is collected on a single dashboard in different forms, it helps business owners make better sense of their IoT product and also gain a meaningful insight.
You can make real-time decisions after merging multiple data sources on a single dashboard coupled with multi-layered visual data. This consumable information also helps monitor IoT infrastructure and devices for efficient data flow, and enables the analysis of multiple data correlations in real-time.
When the data is translated into compelling visualizations, it helps employees become more collaborative and dynamic while creating high-end user experiences. There is more clarity about the data they are dealing with and they can make better decisions.
On the other hand, the data from various sensors can be used to deliver insights in a contextualized manner. It allows employers to detect data anomalies, access system access and offer effective guidance to employees. That is how IoT data visualization tools help.
As IoT systems are capable of real-time data processing, visualization methods give users an opportunity to increase their efficiency. This is especially helpful in critical sectors such as manufacturing and healthcare where timeliness of a delivery and the wellness of human life respectively are at risk.
Data visualizations across sectors
Every business wants to monitor key performance indicators in real-time to get a better idea about how well they are performing or how quickly they are achieving their objectives. For the same, they turn to specific visualization tools for translating data into understandable format.
From graph configuration and dashboard creation to geospatial imagery and data analysis — there are many related techniques that come into play across operating systems .
Given how the need for interactive visualization has grown in the last few years, it is not surprising to know that its software market is set to grow at a CAGR of 9.69% until 2026. You will agree this technique offers a ton of advantages to all sectors and their corresponding businesses.
Irrespective of the software used, every tool is centered on supplying dashboards that help keep tabs on crucial information for businesses, and understand all the data with less difficulty. Obviously, this concept transcends all industries.
There are many sectors that have gained the most benefits from BI tools. Let us check out the most important ones:
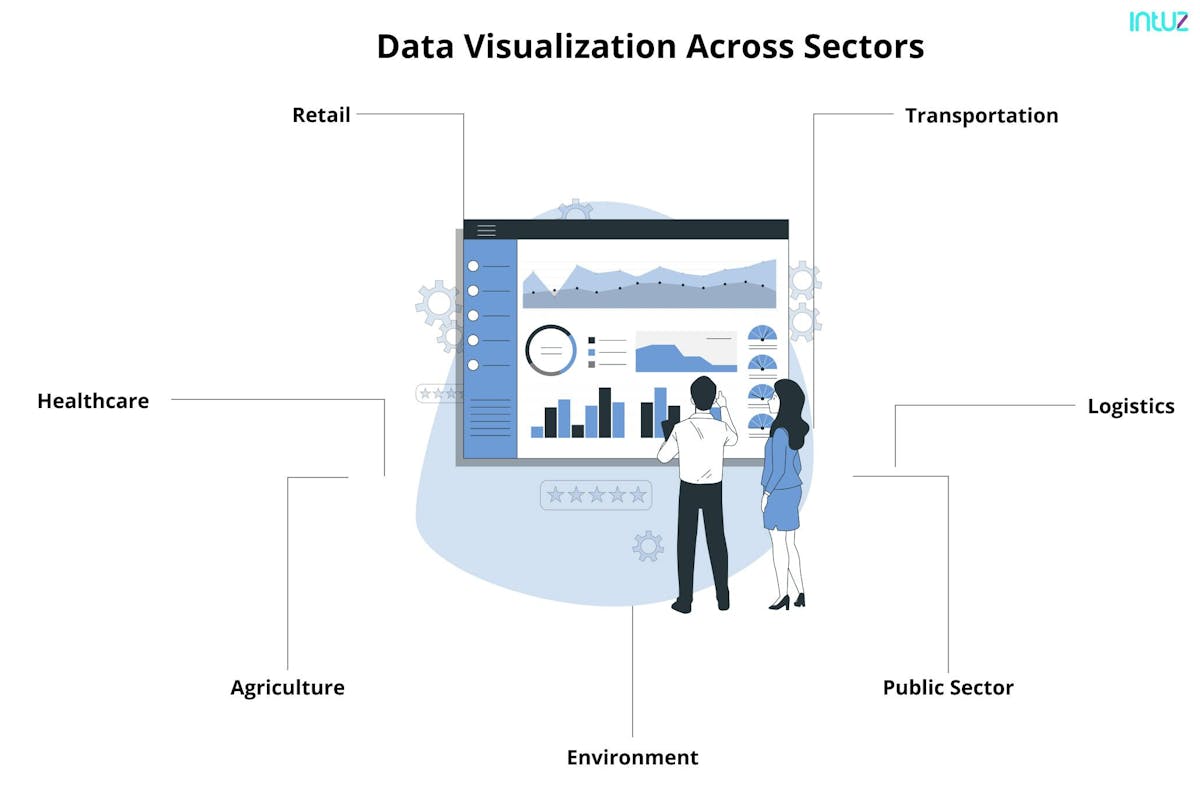
Do you know what is the most taxing job in the sector? Routing transportation networks. And that has its own set of overwhelming challenges. Modern cities cannot survive without planning public transport. All hell will break loose if that does not function properly.
That is why freeways need to be constantly monitored and optimized for preventing accidents and roadblocks. These BI tools help city traffic police identify patterns and trends easily especially when it comes to data clusters.
The detailed analysis reports from geographic information systems is analyzed for making suitable choices in setting up urban areas that cover parks, grounds and parking spaces.
Businesses that mainly rely on vehicular fleets turn to the concept, coupled with prompt information and engaging maps, for making servicing a breeze. These components are incorporated with elements such as video tracking and data workload solutions, and can also be accessed via a mobile app.
On the other hand, hub visualization for sea-based amenities using bathymetry data and cargo operations which require sensor tracking can also do wonders with data visualisation methods.
Businesses and professionals in this industry make use of data visualization techniques to display data links that can help in identifying criminal offences such as fraud. The same can be analyzed through the use of a simple, rule-based question-answer format for data storytelling.
From text mining methods and anomaly detection to pattern identification, businesses can detect fraud, abuse and wastage as they reduce the future fraud risk.
Empowered with complete financial visibility, leaders can enhance transparency, reduce inappropriate transactions, heighten accountability, and guarantee program productivity.
Geographic information systems and maps form the backbone of risk reduction strategies and action-oriented schemes of almost all environmental ventures and public service companies that seek sustainability.
In fact, pattern identification is a huge problem for present-day ecological professionals. This can be rectified with interactive initiatives, highlighting the root cause of ecological phenomena via micro and macro view of data visuals — even on the mobile app.
Moreover, environmental consultants can deploy visual formats for harnessing information from sensors and creating a stable solution for their projects.
Although still seen as an archaic profession, farming has made great strides in the past couple of years thanks to the advent of AI and Blockchain. Both technologies have enabled farmers to keep track of the state of their crops using smart contracts and sensors.
They can use data visualization tools to monitor their lands, insure their crops and claim damages with insurance companies, provided the situation arises.

A Guide On Top 14 IoT Programming Languages
Ever since Coronavirus entered the picture, the healthcare sector has been under immense pressure to manage the crisis and prevent health risks from growing any further.
In a normal scenario, such tools help save lives and enable medical professionals to oversee urban activities amidst quarantine, track healthcare facilities , analyze demographics for medical research, map virus spread, and examine the accessibility of pharmacies.
Data visualization tools can help provide public health officials all the support they need to supply the hospitals and clinics with healthcare staff, equipment and medicines on a regular basis so that they can effectively help patients in need and save lives.
Data visualization helps easily keep track of the COVID situation — determining risk areas and help center locations — in IoT applications.
For instance, businesses can discover how the pandemic will affect their social landscape and daily operations through smart maps displaying the latest information on Coronavirus. That way, help can be provided in high-risk locations without wasting a lot of time.
If we remove COVID from the picture, then also data visualization tools have a huge part to play in healthcare. It helps analyze the accessibility of a particular region, helping public health officials and medical professionals to ensure everyone receives the right treatment without any delays.
This sector has seen many lows ever since the pandemic began, which means retailers need all the help they can receive to operate as efficiently as possible.
Thanks to interactive visualizations, they can address new growth challenges, reduce operational costs, optimize their supply chain and maximize performance expenses using a stellar user interface.
Retailers can also conduct demographic analysis based on income datasets to uncover the most inhabited areas that are good for growing the business.
Challenges in IoT data visualization
As we move steadily towards the information age, it would not be surprising to see a rise in the product demand and skyrocketing disposable incomes. In fact, that is already happening.
No wonder many industries are leveraging the power of data for boosting efficiency and improving customer service. But IoT analysis comes with its own set of challenges.
For starters, the data generated by sensors or sensor-enabled tools is different from the transactional data found at the core of many organizations.
In such a scenario, data management is less structured and requires an advanced set of tools for effective analysis. But before we touch upon the solutions, let us first study the challenges that come in IoT data visualization:
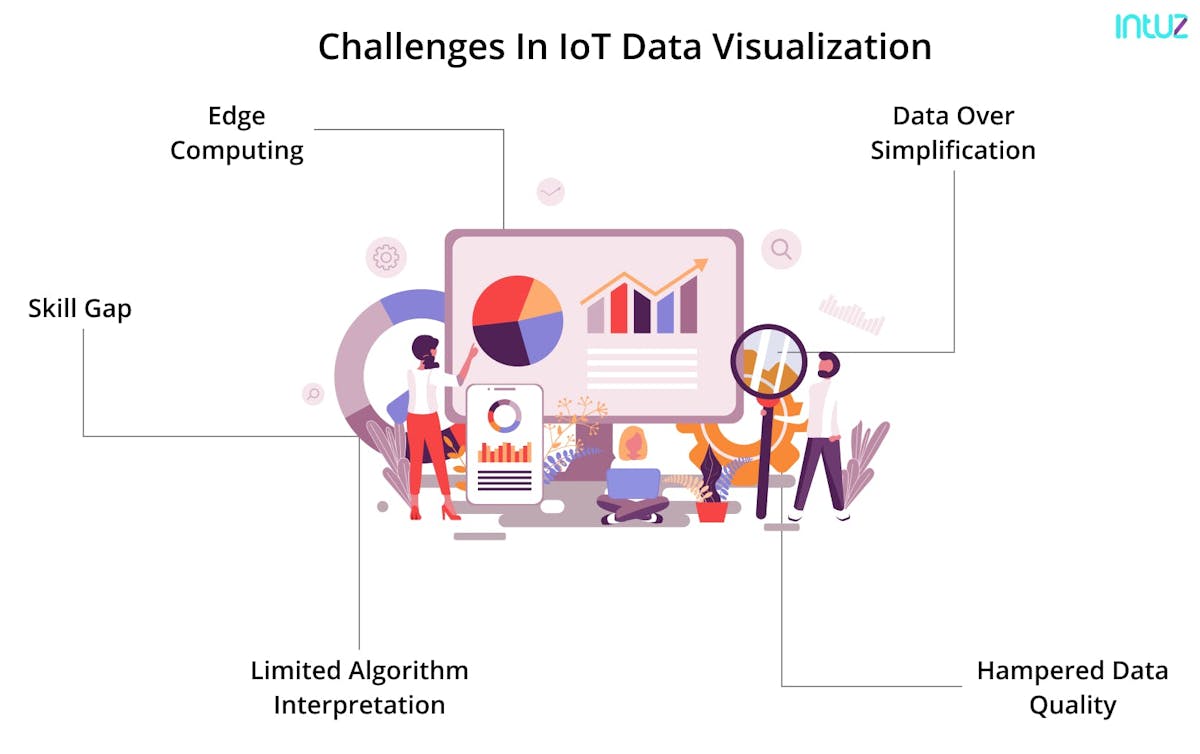
It is true that data visualization tools uncomplicate heavy datasets through easy-to-understand visual representations. However, the simplification of data can often go sideways.
Meaning, the pictorial representations may miss out on certain key aspects that could entirely change the dataset’s interpretation. Therefore, it is necessary to take help from an IoT expert who ensures this does not happen.
The quality of data visualization influences the data quality, which may also get hampered depending upon how it is entered into the system, categorized or managed.
Key elements responsible for maintaining the quality are data completeness, consistency, accuracy and relevance across factors like accessibility, reliability, sources and appropriateness. To alleviate the pain point, it is therefore necessary to do a regular check of data sources.
The algorithms used in converting data into visuals are ultimately based on human inputs, which does not help the case. That is because human beings are fundamentally flawed and so their input can alter the visual output.
For instance, certain data pieces highlighted in a visual representation might not be of no relevance at all, while the ones which were actually important might be ignored.
The decision-making gives a very one-sided overview of the data. The use of proper visualization tools can curb this issue to a great extent.
IoT application development is an ever-evolving field. Therefore, it is crucial to have a team that has plentiful knowledge about the platforms that help produce visuals.
Due to the lack of formal training, most data analysts rely on platforms with limited visualization capabilities such as spreadsheets, STATA or SPSS. Thus, proper training is necessary.
As IoT devices, sensors, servers and systems are spread across geographies, the network has given rise to a concept called edge computing. According to IDC, 40% of the IoT data will be processed via Edge by 2022. Since large IoT deployments are going to become mainstream, businesses will need to look at different ways to efficiently visualize data. That is why you need data visualization tools.
Top 16 data visualization tools for IoT apps
1. power bi.
This real-time data visualization tool is used to create dashboards that present information in the form of graphics to improve business decision-making. It is an Office 365 service by Microsoft that can be used to connect datasets and/or models created in Excel 2013+ with powerful visuals.
These visuals are grouped into dashboards and are designed specifically for interactive exploration on different devices, such as tablet computers, smartphones, or PCs.
- Automatic data refresh
- Visualizations of real-time data
- Support for IoT-enabled and connected devices
- Support for both data types — streaming and static
- Efficient handling of natural language data queries
- Data connections are limited to on-premise Data Sets and Data Models.
- Data refresh is limited to once per day.
- It does not support ETL (Extract Transform Load) processes as they are complex.
- It can only visualize data that resides in MS SQL Server, Oracle Database, IBM DB2, MySQL databases or Data Lake Store (Azure Blob Storage).
Power BI helps streamline data publication and distribution. It updates in real-time and integrates dashboards of all popular services to uncomplicate your organizational setup.
It is primarily used for metrics visualization and is a comprehensive Google analytics and visualization software that seamlessly integrates with Elasticsearch, MySQL, PostgreSQL, and many other databases . It allows you to raise queries, visualize information, and receive alert on your metrics no matter where they are stored.
The open-source tool is useful for creating great-looking dashboards and histograms. Metrics visualization through Grafana allows you to analyze data in a better way, which can help you make informed decisions.
Its intuitive dashboard can be customized in many ways. By using plugins, users can connect Grafana with over 50 data sources.
- Provides time-series analytics to monitor changes in your database over an extended period of time
- Allows you to make important decisions based on real-time information has customizable alerts set up, so if something goes wrong, it will notify you immediately using the preferred communication platform
- Offers on-premise storage as well as integrates with any cloud platform of your choice, which gives complete control over the infrastructure
- It has limited customization capabilities and does not provide many options in terms of visualization types or map features in the free version.
- It is not capable of adding high-quality graphics to your site due to free usage limitations.
- It lacks individual dashboard embedding abilities.
- It does not facilitate embedding dashboards on websites.
Grafana is useful for creating dashboards to display graphs and charts in real-time. It is ideal for internal usage and helps you visualize mixed or large datasets.
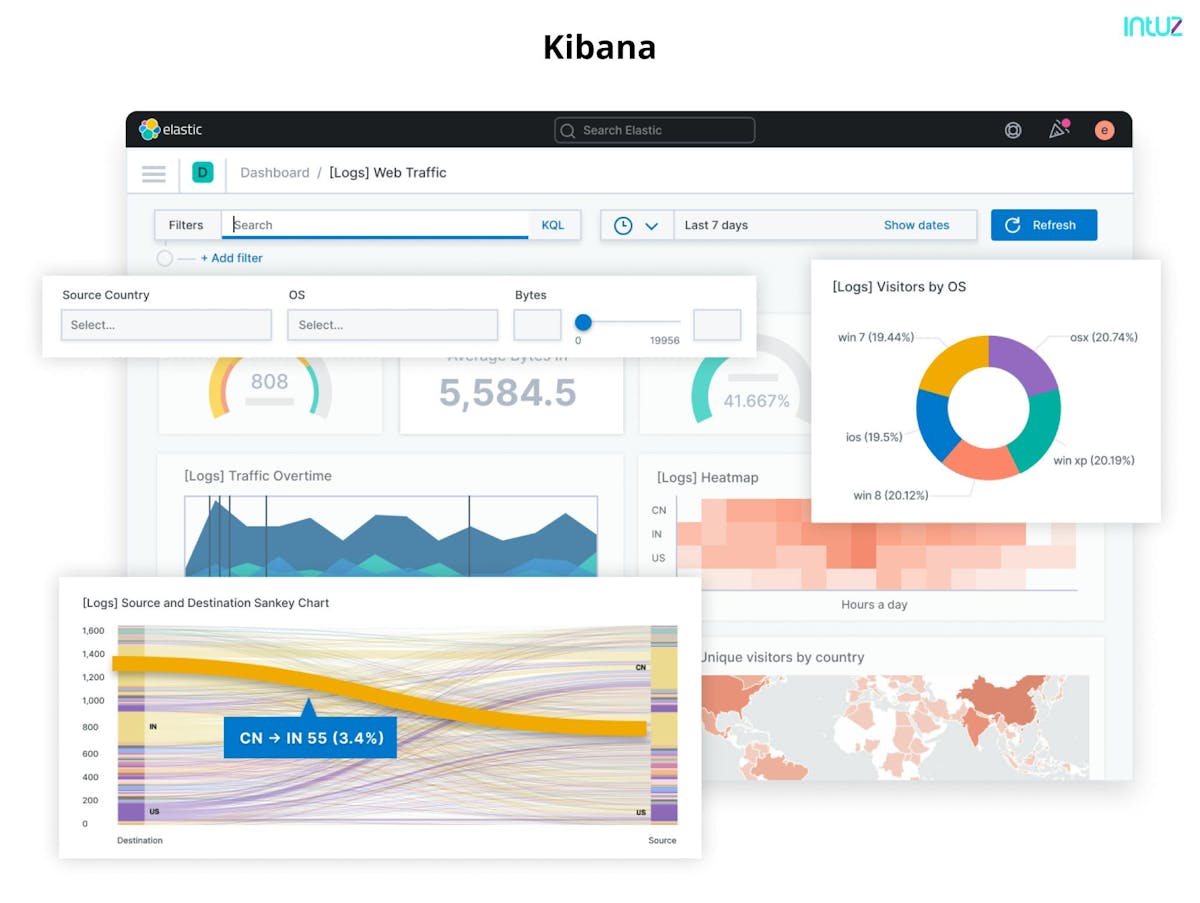
It is used for logs visualization, and is an open-source browser-based visualization tool that allows users to visualize and analyze various data, which can be collected by Elasticsearch. You can use Kibana to create custom visualizations such as line graphs, bar graphs, pie charts, and heatmaps.
It has a simple-to-use interface that is convenient for sharing amongst teams as well as with colleagues. Individuals with little technical knowledge can also use it easily.
Kibana is open-source and free to use. It can perform fuzzy matches, which help in analyzing datasets with machine-learning techniques, such as anomaly detection.
- Powerful visualization based on log data
- The Discover tab on the interface allows users to explore logs stored within their public repositories using search keywords.
- Data from multiple sources can be integrated into the same dashboard.
- Allows fuzzy matching of data queries, which means you do not have to provide an exact match when searching through your time series data
- Easy to set up with automatic sharing capabilities without the need to install any additional software
- It is not highly effective in handling large datasets which impacts its performance.
- Upgrading Kibana to a newer version is a tiresome process.
- In case of version mismatch, adding plugins to the tool is a lengthy process.
With Kibana, you can search for hidden insights in your data set and use visualizations, such as charts or maps, to optimally utilize data stored in your database.
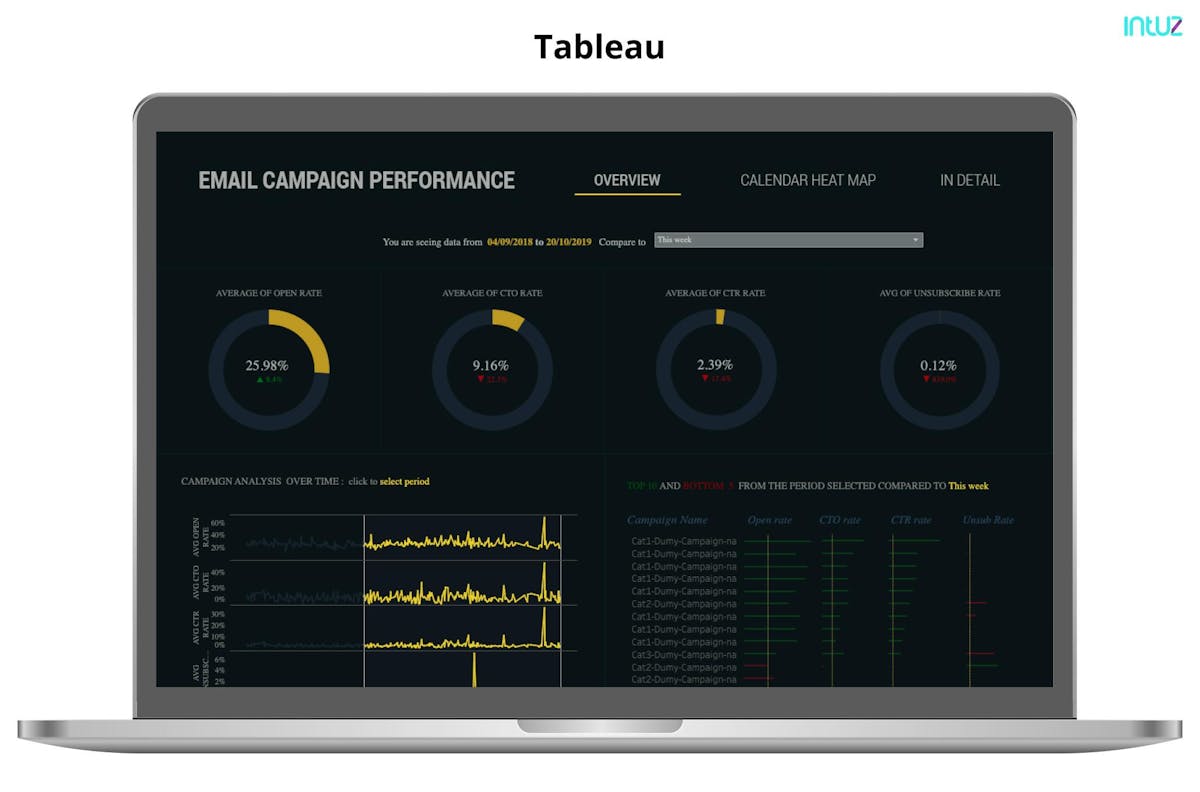
It is a powerful data visualization software enriched with advanced analytical and user interaction capabilities. You can create various charts with interactive features, for use by both beginners and experts alike.
With the in-depth analyses provided by the R scripting language, you have even greater visualization powers. Tableau is available in several variants, including desktop app, server, and hosted online versions, and it is used in several industries globally.
The tool offers data import possibilities across platforms, you can upload data using CSV files, Google Analytics data, or even Salesforce data.
- It is flexible in its visualizations, with many options for graphs, including pie charts, bar graphs, line plots, etc.
- The data analysis software is quick and easy to use. It helps you turn your ideas into clear visualizations.
- There are numerous data import options and they are customizable too.
- Lots of video tutorials are available to walk you through everything from how Tableau works to using filters or changing views in order to analyze huge sets of information across industries.
- The non-free version of Tableau is expensive.
- Its public version also limits how much data can be kept private.
- Its online service has limited storage space for publicly available information, but it does support most formats used to store or display all types of different data sets.
Tableau offers many different ways for users of all skill levels to visualize data in various forms and gives them interactivity options. This makes it perfect for those businesses that are interested in a deeper analysis.
5. Thingsboard
It is a revolutionary open-source platform that makes it easy to build interactive IoT dashboards. Thingsboard follows industry-standard protocols for device connectivity such as MQTT, CoAP, or HTTP. With this tool, you can visualize data collected by multiple sensors and devices at once on custom-made online maps or charts.
Thingsboard has features like line graphs for historical visualizations as well as bar charts, which are perfect for real-time data analytics.
The software's complex stack technology ensures seamless performance while its error-free data analytics provide real-time insights into your device usage patterns.
The tool also has map widgets to track the location of objects through Google Maps and capture data of events in their surroundings.
- Offers a number of templates and projects for inspiration and fast deployment
- Allows development of custom applications through its integration APIs and uses their own data visualization tools
- The tool is mobile-friendly and offers multi-platform support.
- Available for installation — either on-premises or as a cloud solution
- Supports both SQL and NoSQL databases
- Provides device management, sensor data collection, and user roles and permissions management
- Most of the Platform Integrations are in PE version i.e. Azure, IBM Watson, and AWS IoT.
- The community is very small; hence limited support.
- A lot of features of the tool are still under development mode.
Thingsboard is a powerful IoT monitoring and control platform that allows you to set up complex dashboards quickly.
6. IBM Watson
It is an IoT-based cloud platform offered as a service by IBM. It supports several programming languages, services, and integrated DevOps to deploy and manage your applications on the cloud. The PAS utilizes big data in a variety of ways to provide information and insights that help decision-makers improve IoT performance.
IBM Watson offers developers the tools needed for collecting, storing, and analyzing unstructured big data from different sources. The tool helps you get more value from your AI infrastructure by automating processes and optimizing employee productivity.
Salient features of IBM Watson include:
- IBM Watson is a suite of advanced graphical and UI-based tools.
- You can use it for API development, data science notebooks, and GitHub integration.
- Image analysis helps you gain insights from images.
- Image Identification uses deep learning algorithms to recognize objects or concepts within images.
- You get access to the IBM Data Refinery through an interactive UI to enable collaborative data analysis and visualization.
- Loading time is usually slow and navigating the dashboard tabs is not easy.
- The learning curve gets steeper than expected as adequate user guidance or reference examples are not available. It is not for amateur data analysts.
- You may not be able to integrate it easily with your existing Hadoop systems.
- Streaming data visualization support is not available.
IBM Watson is designed to connect enterprise systems, sensors, devices, and cloud applications across future-looking enterprises. The supercomputer utilizes its vast domain knowledge to make quick decisions across a wide variety of businesses from different industries.
Industrial IoT vs. Consumer IoT: Everything You Should Know About
It is a cloud-based business analytic tool that allows users to query, analyze and visualize data from numerous sources. Users can query any data source connected to Domo by using the company's intuitive interface.
Once you are logged into the system, you simply have to "drag" your fields onto the gray canvas. You can then decide whether to display charts in tables or maps as well as export/share them via social media or email.
More importantly, users who do not have advanced analytics experience can still benefit from Domo, since all of their findings and knowledge will be recorded in a centralized repository due to its artificial intelligence feature.
- Provides multiple data visualization tools for creating simple to complex dashboards
- It gives you the power of storytelling through an intuitive dashboard.
- Allows you to transform data from any system
- Easy to use for those who do not know how to code or use a command-line interface
- Its drag-and-drop ETL allows you to easily transform live data into meaningful reports
- Equipped with over 1,000 pre-built connectors — it helps in setting up connections between different sources that are flexible enough for any situation.
- It is not very efficient when processing large datasets.
- Limited functionality of the pivot table is available.
- Deploying it on-premise is very expensive.
- The speed of upgrades and changes is slow.
Domo helps eliminate any lag time between departments and improves the efficiency of your company while collecting inputs across teams.
8. Freeboard
It is a free, open-source platform for creating and sharing dashboards. The dashboard can be personalized with widgets to monitor anything from social media stats to electric grid activity on a map. You can view the data city-wise or country-wise on Freeboard.
To collect data in Freeboard, you have options such as using any web API that collects real-time IoT messages. Data captured by IoT devices such as sensors, actuators, and embedded hardware components are displayed over dashboards.
- The Freeboard dashboard is customizable and allows you to easily select features such as pictures or text boxes.
- The dashboard does not need a server as it runs as a single page static web page through any web-based API.
- It allows users to create their own widget from scratch or choose pre-existing ones available.
- The tool is self-hosted, making it easy for anyone to create and embed interactive dashboards.
- It is designed to be flexible enough for people with no design or programming experience and also equipped with advanced features and controls for IT professionals.
- You can easily share your Freeboards using the unique URL.
- It does not allow private data visualization in the free version.
- The pricing is higher compared to its data visualization capabilities.
- You must be familiar with the JavaScript ecosystem to create plugins for Freeboard integration.
Freeboard's goal is to simplify the tracking of feeds from multiple devices in an IoT environment. It has been best for organizations and individuals who need to track these feeds.
It is a customer intelligence platform to help companies make data-driven decisions. Looker allows the team to build design reports and dashboards that look beautiful and easy to understand. It has inbuilt algorithms that can be used for predictions on specific data sets.
Looker uses models written in LookML to help business analysts create powerful applications quickly, easily, and automatically. That is a new Looker modeling language that describes dimensions, calculations, aggregations, and data relationships in a SQL database.
Looker helps companies use analytics as part of daily operations. It provides intuitive tools for business intelligence, assists in workflow integrations, and the creation of custom apps.
You can use it on popular cloud platforms such as Google Cloud, AWS, AWS, and even your on-premise servers.
- Offers real-time dashboards and the ability to connect with more than 50 SQL dialects
- Provides instant insights without any issues or delays in analysis
- Is capable of going deep into a specific dataset by analyzing it immediately through analytics
- You can share Looker data visualization and the recipient does not need any particular tool to view it.
- Looker files can be exported in any format.
- The on-premise version requires high maintenance.
- It does not save table calculations and you have to re-write them each time you run a new query.
- It is difficult to troubleshoot errors.
Looker's platform facilitates sharing an organization’s information with its employees, giving them all they need in their preferable format whenever they want it. By integrating Looker into its workflows, an organization can utilize its powerful analysis capabilities.
10. Zoho Analytics
It is a revolutionary cloud-based software that provides you with an easy way to create data visualizations based on your company’s requirements. You can use Zoho for marketing, finance, human resources, or any other department to improve decision-making.
It is a cloud-based online extended suite of products that offers department-wise data analytics for organizations of all scales. Zoho Analytics is a self-service web-based application for getting a deeper insight into data.
- Gives you the ability to track trends, patterns of behavior, increases in the market share over a period time
- Helps you get unprecedented insights into your business data through interactive dashboards
- Provides you a virtual assistant Zia to answer all of your questions using artificial intelligence, machine learning, and Natural Language Processing [NLP]
- Google-like timeline charts with drag-and-drop functionality are available on all metrics and dimensions
- Effectively meet client needs by ensuring each department has access to relevant data for informed decision-making.
11. Sisense
It is a business intelligence tool for creating data visualization that help gain new insights into any industry. Developing an analytics app with the Sisense API can be done using virtually any set of data. The tool is perfect for large corporations from the health care or manufacturing industries. It meets the need to analyze all statistics more closely.
Sisense also helps business owners create dashboards according to their needs without the need to use complicated programming languages. Sisense is an amazing software that helps you create visual reports in order to conduct smart analyses. It enables teams to share project insights with clients. The insights are easy to read as they are displayed on the interface through interactive charts and graphs.
- Helps you create dashboards for any type of data
- The dashboard tool is intuitive and has interactive features and widgets to seamlessly view Sankey diagrams, scatter plots, and charts.
- Uses 64-bit computers with parallelization capabilities to enable quicker data processing
- Consolidates all the information in a single place to ensure accuracy
- Is an efficient data connector that allows for seamless uploads and downloads across systems — it connects with most storage platforms, making it possible for users to view their assets in different formats on various devices.
- Sharing dashboards created by multiple users is not easy for admins.
- Navigation and filtering on mobile devices must be improved.
Sisense provides a platform for analyzing large data sets across industries. It helps you handle multiple tasks, including data modeling and complex calculations.
12. Databox
It is a budget-friendly data visualization tool that offers an intuitive dashboard creator with integrations for many types of data. The tool comes with plenty of templates to choose from. Databox also offers two versions — dark mode and light mode.
It works as an online dashboard builder that specializes in helping data analysts predict performance. The templates on Databox are focused mainly on marketers, but it is still a great tool for business analysts to track their team’s efforts.
- It makes it easy to visualize your data for all the stakeholders in a business.
- It allows you to quickly find and understand key metrics saving hours you would spend on preparation or analysis.
- Its drag-and-drop editor makes time-consuming reporting tasks such as building KPI dashboards easier.
- Users can customize views by controlling data visualizations and adding metrics.
- It supports live previews to view company data walls in real-time or control advanced settings for each metric.
- It also provides social media integration features, which can be used to collaborate and share information with inbuilt tools.
- You can import and visualize data from different sources such as Excel, CSV files, and APIs.
- It lacks third-party integration.
- The dashboard is not automatically updated each time.
- The learning curve is steeper for basic functionalities.
- It allows a limited number of dashboards for each account.
Databox is designed to assist in handling common business problems such as reading relevant information quickly. It offers the highest level of flexibility to all users across teams.
It creates beautiful, data-driven content from free templates and an online design lab. Their mission is to make it easy for anyone to communicate their ideas, stories, messages, and data in a visual way. With the Visme, you can create visually appealing data visualizations that complement your projects.
Fill out a form or use one of their templates to generate graphs and charts quickly with an easy-to-use interface. Visme allows you to customize your visuals using a variety of display options, such as pie charts or bar graphs.
- It helps users to effortlessly create beautiful infographics from scratch using its intuitive drag-and-drop builder toolset.
- It turns your raw data into interactive infographics on the web without needing any coding skills.
- You can select from its pre-built templates and save time spent on designing a report.
- The graphics saved in your project can be viewed across devices.
- The tool has data widgets that are perfect for visualizing map data formats and quickly prepare beautiful graphs and charts for your raw data.
- The free version allows you to create three projects only.
- Quality of prints is not the same as that of the downloaded image.
- Templates are generic and do not meet high-end design requirements, especially of IoT devices.
- The learning curve is steeper than other tools in the category.
Visme offers an affordable solution to all your design needs, including sales reports, goal projection presentations, and infographics.
14. Google Charts
It is a free, easy-to-use tool for visualizing data and data integration. You need coding knowledge to work with it. All tools of the suite are available online at Google Drive. Google Charts is a JavaScript charting library designed to provide interactive charts for web applications.
With the tool, you can create stunning and precise images that will help your customers better understand the data they are viewing in their browser window.
- The interactive dashboard allows you to easily connect charts in real-time.
- The chart tools are free to use.
- It is easy to embed a Google Chart into a website or any online platform. The chart can be static or dynamic depending on the source.
- You can use the extensive options to match the layout and design of your website.
- It works seamlessly on most browsers and also supports multi-touch on touchscreen-based platforms such as Android and iOS.
15. Datawrapper
It is a simple online tool that you can use to create your own interactive charts. You need to upload the CSV file with data, choose from one of their 19 templates or start creating your own design, then generate an embeddable link for sharing on social media sites.
Datawrapper hosts many public datasets on their site that can be easily copied over into the program. You can select which type of graph or map you want, such as a pie chart, bar graphs.
Once the data is in Datawrapper, a user can quickly modify the size of the chart and embed it on their website. The charts have a responsive design, making them apt for display on different devices, including desktop devices, tablets, or smartphones.
The charts automatically update periodically if you connect them to a Google Sheet or an external CSV file.
- The interface is very intuitive, with an easy-to-use drag and drop method of adding data sources.
- It provides a wide range of interactive charts and maps to make data easier to visualize. The tools include bar graphs, scatter plots, column charts, line graphs, pie charts, and tables.
- Their free plans allow users to create unlimited visualizations.
- You can export your visualizations in PNG, SVG, or PDF formats.
- It can gather data from limited sources only.
- The paid version is extremely costly.
Datawrapper is a great tool for making interactive charts and maps. It was designed to help journalists add visuals to news stories, also known as newsroom data visualization. Since then, it has grown to be the go-to solution for visualizing technology-based devices.
16. SAP Analytics Cloud
It is the perfect option for any business looking to use their data in order to predict future outcomes. This cloud-based software will analyze your information and then provide you with a variety of different visualizations.
SAP Analytics Cloud aids in the historical and predictive analysis of data. It also gives you access to numerous types of modeling tools and generates precise reports.
The tool uses advanced technologies such as conversational Artificial Intelligence and NLP to respond to your data queries.
This is one of the best tools that can be used by everyone in large enterprises. Even your untrained nontechnical staff, including business people, can use its machine-generated analytics to gain insights.
- It uses machine learning algorithms to automatically reveal relationships and hidden patterns in your data.
- The tool assists in data-driven budgeting, forecasting, and analysis through data models, allowing you to easily create visuals suited for your needs.
- Considering the wide range of features offered by SAP Analytics Cloud, its pricing is appropriate as compared to other single-use-based software.
- The output information and visual charts cannot be translated into RTL language.
- Mobile UI does not have the ability to download and display all output file types.
- Custom solutions cannot be created without knowledge of code scripting.
- Data upload takes a lot of time even when connected to a high-speed stable internet connection.
SAP Analytics Cloud is useful for creating and modifying versions of planning models to suit different needs from one cloud interface.
Top Databases In The Market For IoT Applications
One of the most notable is by providing an accurate representation of data, which helps others work more efficiently and effectively. For example, if sales were better than expected this year, then it is important to know which regions did best.
You would also require information on how much revenue was generated from different products. Analyzing the data helps you improve and avoid mistakes next time around. Data visualization is an invaluable asset to any company.
The following section will explain how data visualization can help you make sense of Big Data and tips to identify tools best suited for your needs. Data visualization can help your company reach its goals in many ways.
1. Decoding digital information
Data visualization is the process of translating data into an understandable graphic. It is a visual representation to turn raw metrics and numbers into insights. The information becomes easily digestible for those who are not experts in data science.
You can visualize critical elements such as user interaction, customer experience, employee performance, and overall expenditures to streamline decision-making. It is imperative decision-makers are able to comprehend these details themselves first.
Data is everything for modern businesses and wrong numbers could slump progress. The suitable tools help you use data visualizations to highlight discrepancies in readings. You can fix them in time to avoid any damage.
3. Saving time
One of the most powerful ways to make a company grow is by improving its data. Time spent trying to decipher datasets can be utilized on other activities. Visualizations reduce comprehension time and allow you to focus on strategy and decision-making.
Tips to follow to make the right choice
A presentation graphic is merely mathematical proof. It offers a solution to your problem but may not give any support to the calculations. Whereas exploratory graphics are used for deducing results. It can be drawn quickly and these kinds of visuals are mainly meant as side-support rather than main arguments.
A lot of exploratory graphics could be created to support one presentation graph which might only need 1 or 2 graphs since its aim is typically just displaying information instead of proving anything about numbers.
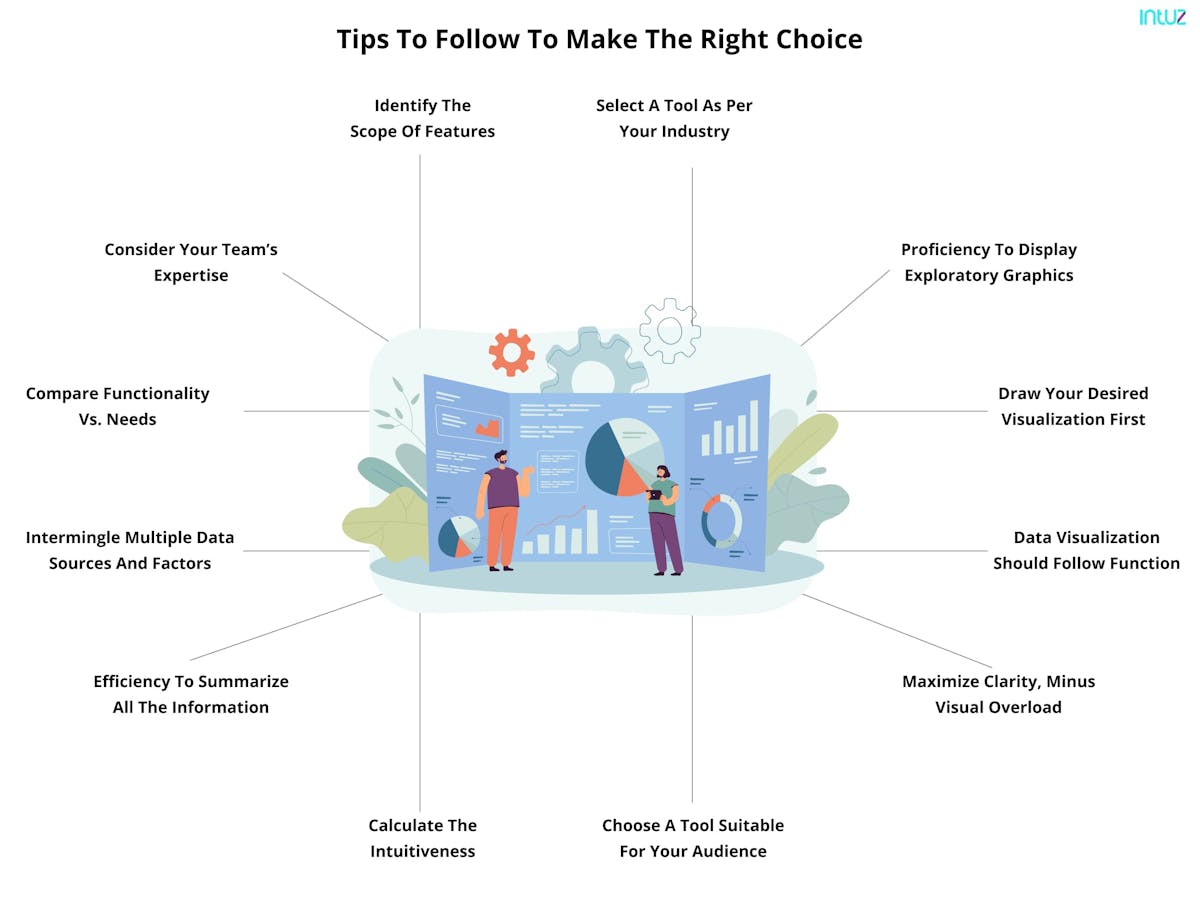
There are a lot of factors that go into deciding which tool to use when creating data visualizations. This includes skills, time constraints, and the purpose for visualization. You may even start with pen and paper before moving on to expensive tools such as Python or chart creation apps.
The visualization you create depends on the questions you are trying to ask, your data, and how others will view your data. For example, if one was looking for trends in sales over time a bar graph would be best suited.
While pie charts might show the dependency of certain types of product lines better than traditional tables or graphs. In some cases, it may not even make sense to use visuals at all such as when examining an individual’s balance sheet; rather calculations should suffice.
The best data visualization tools follow Grice's principles of cooperative communication. They ensure the data quantity by making sure it is informative without involving overwhelming details.
The data quality should be maintained by remaining truthful. Relevance and clarity of data are also necessary. Being clear will help make your message more comprehensible than vague and ambiguous data.
The best data scientists can communicate their insights by customizing and making them available for different stakeholders. They simplify the data to help decision-makers understand the results. When projects are collaborative across functions, it is important to make sure everyone understands the work.
A data visualization tool is a great way to communicate your research, but you need the right one for your needs. You will have to balance analyst needs and technical requirements. It is wise to determine training needs before choosing a visualizer.
You must also make sure it works for all your business units. You may also need two different tools but it is necessary to figure out how they can both improve your company’s workflow.
To create a great data visualization dashboard, it should be attractive and clear with variations of color. It needs to strike a balance between being boring or overwhelming by maintaining contrast. The tools must help you efficiently summarize all the information that matters without having to sift through pages on end for something specific.
It is very important to make sure you are using the right type of data visualization. For example, if your change is constant, it would be most effective for a static graph or chart with different ranges on both axes.
Whereas, if there are more discrete changes in time that happen less often, like monthly results vs yearly earnings, then streaming visualizations may work best. These allow you to see how things vary over short periods of time and can adapt as needed — when new information comes up.
9. Compare functionality vs. needs
The tool should be able to combine individual metrics to derive information. It should also provide the breakdown of a metric i.e., the type of data points that make up the metric.
The information may be an amalgamation of different sources, such as revenue from various products or types of sales leads.
Visualizing what goes into these numbers will help lead to better understanding and pinpointing specific improvements. You can review performance across all aspects when tracking progress.
10. Consider your team ’ s expertise
The data visualization applications of today not only need to be aesthetically pleasing, but they also have the capability to intuitively interact with your user.
As identified by Forrester analysts Boris Evelson and Noel Yuhanna, there are six traits that are essential in identifying advanced tools from simple static graphs. These are dynamic data, visual querying, linked multidimensional visualization, animation personalization, and actionable alerts.
The most important consideration during the data analysis process is to identify how you want your audience to interact with it.
You must choose the best format in order for them to act and not just read what you have written. Presenting your data in a suitable format is helpful in conveying your message.
Some data visualization tools are more suited for certain industries than others. Before you jump onboard a new platform, it is important to know what will work best with your company's needs and practices.
Over to you
You get plenty of options for choosing the right data visualization platform. You will need to weigh the pros and cons before deciding the right tool for your organization. Considering factors such as design, ease-of-use, simpler integrations, data permissions, costs, and so on.
If you need help from an IoT app development team or want to build a data visualization software, you can always rely on us. Get started with us.

Give your enterprise the tech support it deserves.

The Best Data Visualization Tools For IoT Applications
There are many fantastic data visualization tools that can be used in IoT applications, from Grafana and Tableau to IBM Watson, Power BI, and Kibana. This guide dissects the need for visualization tools.
Downloaded by 250+ industry leaders
Explore our IoT Resources
Insights on the latest trends and updates on the Internet of Things.

IoT In Supply Chain Management: 6 Benefits To Know
17 Apr 2023

Top 25 IoT Development Boards In 2023 And How To Choose The Right One
29 Mar 2023

16 Feb 2023
Explore More Resources
Practical view on the technologies of tomorrow
We only put out content that we believe is substantive.
Let us know if there’s an opportunity for us to build something awesome together.
Drop the files or
Supported format .jpg, .png, .gif, .pdf or .doc
Maximum Upload files size is 4MB
Review of Data Visualization Techniques in IoT Data
Ieee account.
- Change Username/Password
- Update Address
Purchase Details
- Payment Options
- Order History
- View Purchased Documents
Profile Information
- Communications Preferences
- Profession and Education
- Technical Interests
- US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333
- Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060
- Contact & Support
- About IEEE Xplore
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Privacy & Opting Out of Cookies
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. © Copyright 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.

Information visualization in big data and IoT : A review
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
- Peer Review
- Reprints and Permissions
- Cite Icon Cite
- Search Site
Rachana Mehta , Smita Darandale , Nidhi Periwal; Information visualization in big data and IoT : A review. AIP Conf. Proc. 11 December 2023; 2855 (1): 060012. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0168820
Download citation file:
- Ris (Zotero)
- Reference Manager
Humongous data gets generated nowadays with the excessive usage of internet and web services be it on any platform or in any domain. To analyze and explore this high volume of data is a challenging task. To aid this challenging task Information Visualization is used. It studies the data and knowledge to make them interactive and representable through visual form like charts, graphs and histograms due to which it becomes easy to analyze the complex data. It is a quick, easy way to convey concepts in a universal manner. There are multiple usage of visualization like in offices to report tasks, manage operations, track progress and many others. Various visualization techniques are used to design the graphical representation of this innumerate amount of data. On the line of wide emergence in the field of big data analytics, the need for data visualization has gained larger significance. The paper provides a comprehensive survey of various visualization techniques and signifies their needs in the current scenario. Further it examines some of the most promising visualization tools. Additionally, we review visualization methods for big data and IOT based on different parameters and applications of visualization software like Tableau, Power BI and others which are created by different companies for business intelligence and analytics.
Sign in via your Institution
Citing articles via, publish with us - request a quote.
Sign up for alerts
- Online ISSN 1551-7616
- Print ISSN 0094-243X
- For Researchers
- For Librarians
- For Advertisers
- Our Publishing Partners
- Physics Today
- Conference Proceedings
- Special Topics
pubs.aip.org
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
Connect with AIP Publishing
This feature is available to subscribers only.
Sign In or Create an Account
Use Kanaries Cloud for free as students and educators
Visualize IoT Data: The Ultimate Guide to Unleashing the Power of Your IoT Data
Published on 7/24/2023
The world is becoming increasingly connected, and the Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming the way we interact with devices, machines, and each other. With the constant influx of data from IoT devices, it's essential to find effective ways to visualize IoT data, making it easy to analyze and extract valuable insights. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the world of IoT visualization and explore various tools and platforms that will help you visualize real-time IoT data.
Unraveling the Mysteries of IoT Visualization
IoT visualization is the process of transforming raw data from IoT devices into graphical or visual representations, making it easier for users to comprehend and analyze. Data visualization in IoT can be a game-changer, as it allows users to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies that might otherwise be difficult to spot in raw data.
The Importance of Sensor Data Visualization
IoT devices often rely on sensors to collect data. Sensor data visualization is crucial for understanding the state of these devices and making informed decisions. By visualizing sensor data, you can:
- Monitor device health and performance
- Detect anomalies or malfunctions
- Identify patterns and trends for predictive maintenance
- Optimize resource usage and energy consumption
- Make data-driven decisions to improve overall efficiency
A Step-by-Step Guide to Visualize IoT Data
Visualizing IoT data involves several steps, including data acquisition, data processing, and data visualization. Let's break down each step:
Step 1: Data Acquisition
To visualize IoT data, you first need to collect it from various sources, such as sensors and devices. One popular protocol for data acquisition is MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport). MQTT visualization involves subscribing to MQTT messages and processing them for visualization purposes.
Step 2: Data Processing
Once you've acquired the data, it's essential to process and clean it to ensure accurate and meaningful visualizations. Data processing may involve filtering, aggregation, and normalization, depending on the nature of the data and the desired visualizations.
Step 3: Data Visualization
With the processed data in hand, you can now create visual representations using various IoT data visualization tools. These tools range from simple libraries to full-fledged iot data visualization platforms. Some popular options include:
- RATH (opens in a new tab) : A comprehensive IoT visualization platform that offers powerful analytics and visualization capabilities, RATH helps you derive insights from your IoT data with ease.
Considering that you can leverage the power of Open Source and create stunning data visualizations at a fraction of the cost compared to other solutions, and at the speed of only one click:
Interested? Try the future of Open Source Data Visualization Now!

- AWS IoT Visualization: AWS provides several services, such as AWS IoT Analytics and AWS IoT Events, for IoT data analytics and visualization. These services integrate seamlessly with other AWS offerings, making them an excellent choice for users already invested in the AWS ecosystem.
- Apache Superset: An open-source data visualization platform, Apache Superset is a great choice for those who want to build custom visualizations without spending on commercial solutions. You can learn more about its features and benefits in our comparison of Apache Superset vs. Tableau .
Exploring IoT Visualization Tools and Platforms
Now that you have a basic understanding of how to visualize IoT data, let's take a closer look at some popular IoT visualization tools and platforms.
RATH is a powerful IoT visualization platform that enables you to easily monitor, analyze, and visualize your IoT data. Key features include:
- Real-time data streaming and visualization
- Interactive dashboards with customizable widgets
- Comprehensive analytics and reporting capabilities
- Integration with various data sources, including MQTT and RESTful APIs
AWS IoT Visualization
AWS IoT data visualization involves using various AWS services to collect, process, and visualize IoT data. With AWS IoT Analytics, you can perform advanced data processing and analysis, while AWS IoT Events helps you monitor and react to changes in device states. Key features of AWS IoT Visualization include:
- Seamless integration with other AWS services
- Scalability and reliability backed by AWS infrastructure
- Advanced data processing capabilities using AWS IoT Analytics
- Real-time event monitoring with AWS IoT Events
Grafana is an open-source IoT visualization tool that allows you to create customizable dashboards for various data sources. It's widely used for monitoring and visualizing time-series data, making it suitable for IoT applications. Key features of Grafana include:
- Wide range of data source support, including MQTT, InfluxDB, and Prometheus
- Customizable dashboards with a variety of visualization options
- Alerting and notification capabilities
- Plugins for extending functionality
Node-RED is a flow-based programming tool for wiring together hardware devices, APIs, and online services. It is particularly useful for IoT applications, as it enables you to easily create visualizations using its built-in dashboard nodes. Key features of Node-RED include:
- Intuitive, flow-based programming interface
- Built-in support for MQTT and other IoT protocols
- Customizable dashboard nodes for various visualization types
- A large community and extensive library of contributed nodes
Choosing the Right IoT Data Visualization Platform
When selecting an iot data visualization platform, it's essential to consider factors such as ease of use, scalability, flexibility, and integration capabilities. Here are some tips to help you make the right choice:
- Assess your requirements: Determine the type of visualizations you need, the data sources you'll be working with, and the level of customization you require.
- Evaluate scalability: As your IoT infrastructure grows, your visualization platform should be able to scale accordingly without compromising performance.
- Consider integration capabilities: Your visualization platform should integrate seamlessly with your existing infrastructure, including data sources, protocols, and other tools.
- Look for flexibility: A good IoT visualization platform should support various visualization types and allow for customization to suit your specific needs.
- Evaluate the ease of use: An intuitive user interface and robust documentation are essential for ensuring a smooth onboarding experience.
Wrapping Up
Visualizing IoT data is crucial for extracting meaningful insights from the vast amounts of information generated by IoT devices. By following the step-by-step guide and exploring the various IoT visualization tools and platforms discussed in this article, you'll be well-equipped to unleash the full potential of your IoT data.
As you delve into IoT visualization, you might also be interested in learning more about data analytics in the world of AI. Check out our article on ChatGPT-4 Data Analytics to discover how AI-powered analytics can further enhance your IoT data visualization efforts. Happy visualizing!
- Meet the Community
- Submit Content
- Become a Partner

- About IoT For All
SUBMIT CONTENT
- White Papers

Powerful Data Visualization Tools for IoT Applications
Power BI, Grafana, and Kibana are all powerful data visualization tools for IoT applications. But the trick is knowing when to use each one.

Data visualization is a hot topic for IoT right now. As more companies incorporate data-driven initiatives and innovation into their overall strategy and operations, the central importance of data visualization is growing. Service providers and end-users alike are beginning to recognize the distinctive value of data visualization tools for IoT applications. We’re learning how to draw new insight from previously “wasted” data .
I recently wrote an article on IoT for All about the importance of data visualization for the business and markets that are embracing connected or “smart” technologies. Thanks to growing demand, data visualization techniques and tools for IoT applications are gaining momentum rapidly. This post adds to the one above. Here, I’ll reveal some of the most powerful instruments used in data visualization for IoT applications and discuss criteria for choosing one over the other.
Power BI for Real-Time Data Visualization
Along with Tableau, Power BI is the jack-of-all-trades for IoT applications requiring data visualization. Originally, Power BI was an all-inclusive business intelligence tool that enabled companies to visualize a wide range of datasets. It has a comprehensive list of integrations, and it can pull data from many sources like Excel, Google Analytics, Salesforce, and social media platforms. As with most Microsoft products, Power BI is quite intuitive and has a reasonable learning curve. That being said, Power BI is a paid service.
Data Visualization for IoT Applications with Power BI
The burgeoning IoT market inspired Microsoft to expand Power BI’s capabilities to include real-time data visualization for IoT applications . Today, you can connect any IoT device, sensor, or application to the tool in order to stream data in real-time, making it a compelling choice not only for Azure-based projects but IoT projects built upon any major platform. Apart from a relatively easy set-up and dashboard building process , Power BI stands out for its unique verbal data management functionality. You can use natural language commands to query data, and voilà, Power BI will return relevant visualizations right on the screen—a win for non-technical users.
Benefits of Power BI
- Both streaming and static data
- Short learning curve
- Rich data visualization types
- Natural language data query
- New IoT integrations
Grafana for Metrics Visualization
Grafana is a professional data visualization and analytics tool specializing in the visualization of time-series analysis. Like Power BI, Grafana is known for its wide range of data visualization techniques, its vast capabilities for dashboard building and management, and its extensive list of possible data sources ( e.g. AWS, Prometheus, and Elasticsearch).
Data Visualization for IoT Applications with Grafana
Grafana was originally designed for CPU and system health monitoring. But as mentioned above, the tool is better known for being one of the best tools for time-series data visualization. It’s quite popular in IoT and connectivity-focused verticals.
Grafana’s outstanding features include complex dashboard building, enabled alerts and notifications, custom filters, and annotation for streaming data. Grafana also allows you to personalize dashboards for different users. But no tool is perfect. Forget natural language querying, for example. Grafana lacks full-text querying and even requires a specific querying syntax for each data source.
Benefits of Grafana
- A wide range of data sources
- Perfect for metrics data
- Data management perks: custom filters, annotations, alerts and notifications sent to messengers or email
- Dashboards personalization for various user roles
Kibana for Logs Visualization
Kibana is a part of the Elastic Stack data management toolkit . It was designed specifically to visualize the time-series data from Elasticsearch clusters. It allows a wide range of data representations. It also includes maps and allows you to make custom visualizations, build complex dashboards, and share everything easily with teams, management, and even clients.
Data Visualization for IoT Applications with Kibana
Built on top of Elasticsearch, Kibana integrates directly into the Elastic Stack environment. However, direct integration has one major downside: Kibana is limited to the data coming from Elasticsearch.
The tool is nonetheless a good choice for IoT applications that require log visualization and analysis thanks to its ability to do “fuzzy matches” for data queries. Kibana also provides users with advanced visualization and data management features, including machine-learning techniques to detect and explore anomalies in datasets.
Benefits of Kibana
- Works for any type of time-series data
- Machine learning features
- Fuzzy match for data queries
- Easy setup and sharing
- Direct integration with Elastic Stack
Choosing the Right Data Visualization Tool
[bctt tweet=”‘Clarifying the objectives of your data visualizations matters above all. It’s important first to identify goals and needs and only then to explore the different data visualization platforms. Following this process will help to ensure that you choose the best-suited platform.'” username=”iotforall”]
First of all, if the company already uses a particular data management tool for some purposes, it usually makes sense to build data visualization for a new IoT project using the same tool or at least one that’s compatible with the pre-existing data ecosystem.
For example, if the company relies on Elastic Stack for system performance monitoring , it’s probably a good idea to use Kibana due to its direct integration with the Elastic Stack. On the other hand, it’s easier for businesses using AWS to integrate with Grafana rather than move to other data ecosystems. However, if the company needs to go beyond time-series data visualization, more versatile tools like Tableau or Power BI are probably good choices. It’s a balance between what came before and what you intend to do with the data visualization.
Kibana will suit any project involving the visualization of logs or metrics, while Grafana works best for projects restricted to metrics visualization. Grafana is also great for applications that require personalized dashboards for different users, whereas Kibana enables building and sharing unified dashboards for all user categories.
Both Kibana and Grafana were specifically designed for time-series data analysis. As such, they provide a wide range of visualization perks for time-series analysis. Moreover, these tools are open-source and cost nothing.
Clarifying the objectives of your data visualizations matters above all. Ask yourself, What goals am I trying to achieve by visualizing these data? What do I hope to show people? It’s important first to identify goals and needs and only then to explore the different data visualization platforms. Following this process will help to ensure that you land on the tool that best suits your unique needs.
- Data Analytics
- Industrial Automation
- Manufacturing
- IoT Business Strategy
New Episode

User Testing IoT Products
Related articles.

Designing an Energy Ma...

Mapping the Customer J...
IoT Value Feedback Loo...
More articles.

Latest IoT News

Industrial IoT adoption fuels growth in private cellular networks
Abeeway takes sequans nb-iot/lte-m module for new industrial iot tracker, fact of the day – 4/25/2024, challenges with iot product launches: why time-to-market has increased 80% in 4 years, integrated power and process management: a leap towards efficiency and competitiveness, top 10 medtech companies list in london uk in 2024, watch it and weep (or smile): synthesia’s ai video avatars now feature emotions, make the intelligent choice: embed x103 in smart city outdoor devices, ‘every tech is hyped, but this is different’ – siemens goes all-in on industrial ai, exploited solar power product vulnerability could expose energy organizations to attacks, top 10 ai and blockchain projects in uk europe in 2024, rabbit’s r1 is a little ai gadget that grows on you, invicti launches ai-powered predictive risk scoring for web applications, tesla unveils more details about driverless ride-hailing service, why code-testing startup nova ai uses open source llms more than openai, private cellular iot to reach 108m factory connections by 2030, fact of the day – 4/24/2024, how to use influxdb and ptc thingworx for industrial iot, the impact of iot on medical equipment and healthcare, the rise of industrial metaverse in manufacturing, sustainability and infrastructure, sequans gets first cat 1bis approval on at&t and firstnet in us, earth day series: overall thoughts, embracing the future: schneider electric’s vision for smart factories at hannover messe 2024.

Search IoT For All
- Contact Sales Request Demo
- Talk to Sales Request Demo
IoT Data Visualization for Better Understanding of the Big Data
Data is Everywhere! Right from a customer visits a company’s website until he signs out, all the data and the behavioural pattern is tracked. The data received from the wearable devices that monitors your health to the large logistics and transportation company that checks the supply chain stocks, assets tracking all leads to a heap of Big data.
All these data becomes useless, unless they serve for a particular purpose. Analysing the data and predicting the future trend and where to focus more are some of the significant benefits it offers. These smart data visualization tools and technologies helps to slice and dice the data to the minute granular level.
Do these Data visualization tools really help to scale up an Enterprise? Yes it does! Indeed SAP’s revenue has accounted to 2 billion US dollars by using these BI tools.
IoT Data Visualization
“A picture speaks a thousand words” that’s exactly the impact a visual data creates a user! Many psychology studies have proven that the human brain is wired to consume tons of images quickly than mere numbers or words! Let’s put on our technical hat in defining the IoT Data visualization techniques. Read on to know more about these tools and why it’s the much sought after technology by business verticals.
Table of Contents
Stepping into a Data-Driven Era
IoT Data Visualization is the technique where the raw data is presented into a more insightful one that is derived from different data streams. It analysis the data and looks into the certain patterns & behaviours that improves with better business decision making. It helps to create a viable business strategy.
To automate the entire process into an automated data-driven parameter, as we are clear that data visualization is prime to manipulate data based on the customization of each set of data to a particular objective of the business. A data visualization understands the massive amount of information emitted from multiple sensors and transmitted into a visual summary in the form of real-time charts, graphs, etc. To put it in simple, a customizable IoT dashboard could get the process done.
Customizable IoT Dashboard To Streamline & Contain Millions of Data in One Place:
An IoT dashboard contains multiple widgets that visualize the data in the form of line graphs, Geographical maps, Bar charts, Pie charts, Gauges, Heat maps, etc., from multiple sets of IoT devices transmitted over time.
With this information in the form of multiple visualizations helps to unlock every data into a valuable asset.
The Data Visualization Helps To Unlock Multiple Insightful Values
- Helps to make real-time decisions with the combination of multiple data sources into a single insightful dashboard with multi-layered visual data.
- Combines the new IoT data transmitted from data sensors with the existing data to analyze and bring light to new business opportunities.
- Supports to monitor IoT devices and infrastructure for better performance on IoT data flow.
- Helps to analyze multiple data correlations in real-time.
Data Visualization across Business Verticals
Here’re some of the industries which increased the operational efficiency by implementing the IoT data visualization tools in their business models.
1) Transportation Business – Heathrow Airport
Heathrow airport , one of the busiest international airports in the world, uses Power BI for all their data analytics measurements. With real-time passenger traffic, current traffic changing conditions, gates traffic, calculating the terminal distance, connecting flight info and so much more. These real-time graphical data gives the passengers a hassle-free flight experience.
2) Financial Sector – State Farm Insurance
Headquartered in Illinois USA, Statefarm insurance company is a reputed insurance firm gaining trust from millions of customers. I was a part of their Business intelligence team where they were using Cognos tools for all their reporting purposes.
Cognos 10 BI tool analysis their customer data and produce reports according to their customer needs. Cognos tool helps to analyse various tools, using Report studio, event studio and use different metrics to get a deeper insight.
3) Travel Sector – Booking.com
To get the visualization of the metrics data at a large scaleBooking.com used Grafana tool with Graphite as a monitoring engine. With the help of these data visualization tool , the engineering team came up with a hybrid solution to secure all the sensitive data. With Grafana, Booking.com was able to drastically reduce the coding part.
Grafana tool helped to optimize the stack by storing millions of metrics per second. It gave them a better use of time, less inbox traffic and gave a lot of flexibility.
How CONTUS helps in IoT Data Visualization
CONTUS has leveraged the data visualization technology across multiple devices where it transforms the raw data into meaningful insight of information. Our skilled in-house iot application development team presents these data into a readable visual format like pie charts, graphs where you can drill down and get data upto granular level.
Having worked with several business verticals and build innovative IoT applications, CONTUS provides data visualization services that helps to create customizable and interactive dashboards for better decision making.
Accelerate your business intelligence developments with CONTUS data analytics services with greater resource allocation and build strong infrastructure.
Data Visualization Tools for IoT application
Here are the top 3 IoT Data visualization tools that are widely used across several industries globally. As said before, the big data collected from the various IoT devices, needs to be interpreted for analyzing them to take better business decisions. Hence, IoT data visualization tools helps to provide strong analytics data.
1) Grafana Tool – One Tool for all your Monitoring Needs
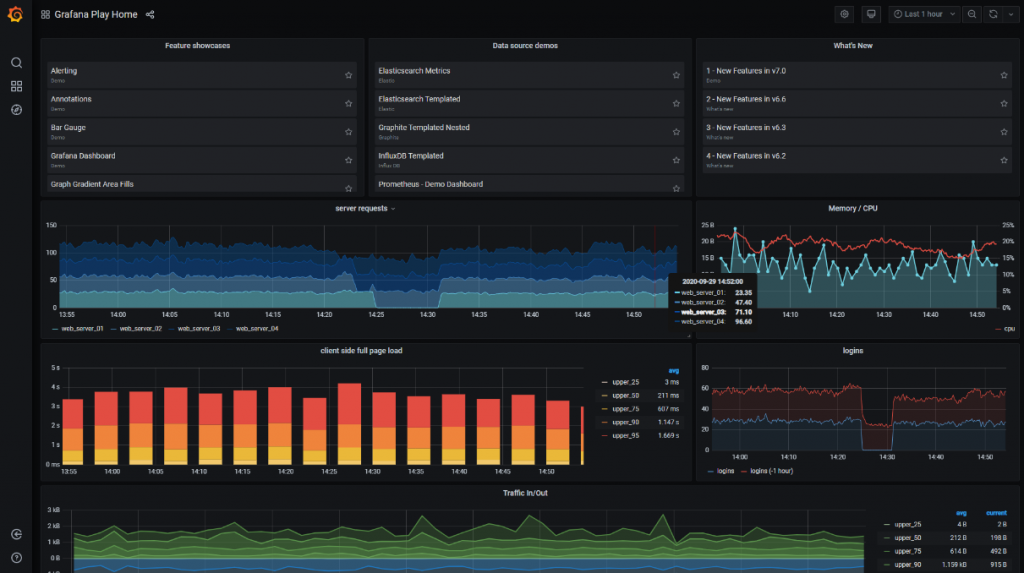
Before looking into Grafana tool definition, let’s understand one important metric which is ‘time-series’ database. Basically, time series database stores data which changes over time.
Time series data are measured over a duration of course like 4 to 5 years, like specific time period in days , weeks etc. Or data collected based on certain predictable pattern and data collected as per the current economic condition. Grafana, an open-source data visualization tool, is built to consume these time-series metric data. There are several time-series data storage backends where Grafana supports with specific labels, data sources.
How does Grafana tool work?
Lets look into a real-time scenario where they have successfully used Grafana tool. Grillo used Grafana tool to detect when the earthquake may occur along with its magnitude level. With 60 sensors implemented in the actual earthquake prone sites, the Grafana tool helped to send 90 readings per second.
This real-time feed provides a strong basis for analyzing the data, proving Grafana tool to be more scalable and affordable. Grafana tool provides a visual dashboard which covers multiple functionalities all under single and powerful interface. Several panels in the grid is responsible for analyzing the data and presents the data in different visual formats like,
- Charts – Pie/Bar
Highlights of Grafana Tool:
- Grafana supports various data sources seamlessly like Elasticsearch, MySQL, PostgreSQL, Graphite, Prometheus and so on.
- Provides time series analytics to monitor, analyze data over a period of time.
- Upbeat of this Grafana tool is it provides on-premises cloud storage or any other cloud of your choice, which gives complete control of the infrastructure.
- Alert notification can be set up whenever an unfavourable event occurs which gets prompt notification using any communication platform.
- It has several built-in support features like Graphite, CloudWatch, Elastic Search, InfluxDB.
2) Kibana Tool – To Analyze and Monitor all your Logs
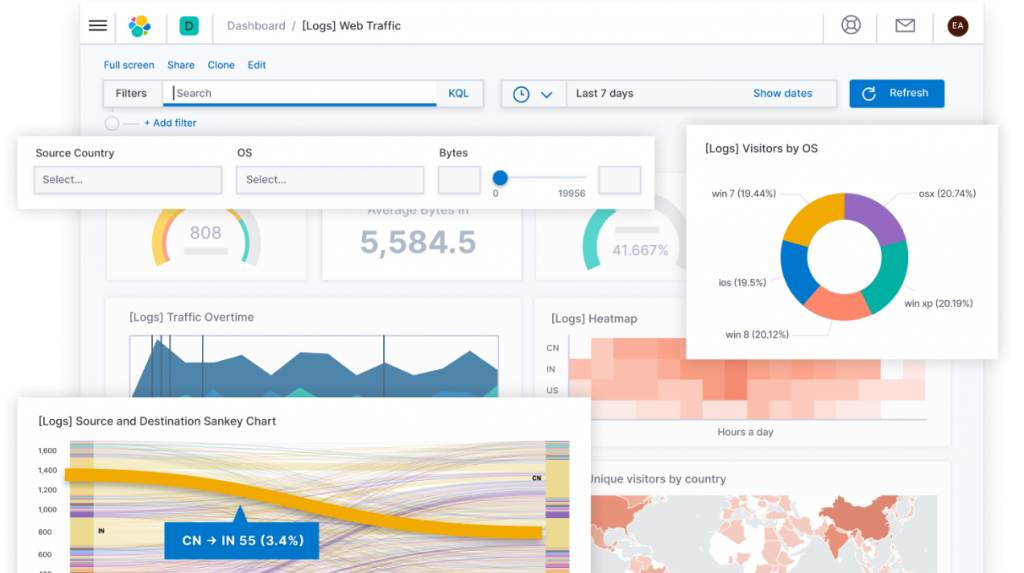
Kibana Tool is an open source data visualization tool for analyzing large volumes of log data. To work with Kibana tool, it needs two more technological stack which is Elasticsearch and Logstash. It is popularly known as ELK stack, globally used log management platform.
How does Kibana Tool Work?
- Initially , the logstash is responsible to collect all the data from the various remote sources
- Next, these data logs are then pushed and sent to the Elasticsearch
- Elasticsearch acts as the database to the kibana tool with all the log information
- Finally, Kibana tool presents these log data in the form of pie charts, bar or line graphs to the user.
Highlights of Kibana:
- Canvas visualization gives colorful visual data comprising of different patterns, texts known as workpad. Kibana also represents data in the form of bar chart, pie chart, heat map, line graph and so on.
- Contains Interactive dashboards and easily it can be converted into reports for future references
- Create visualization with the help of several dev tools where you can work with indexes to add, delete and update the data.
- Timelion , a timeline visualization tool helps to get the historical data and compare them with current data for getting deeper analysis.
- Supports third-party plugins and to get near to real experience view, it effectively uses coordinate and region maps
3) Power BI Tool for Real-Time Data Visualization
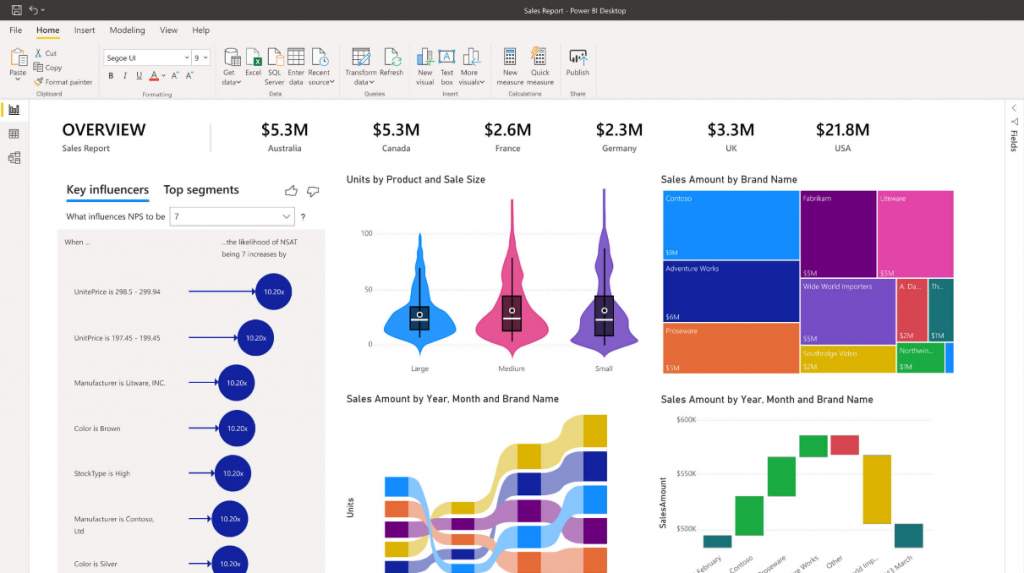
Microsoft’s product PowerBI is a popular Business Intelligence Tool. Like its predecessors, Tableau and other BI tools, it provides a detailed analysis reports for large Enterprises. Power BI comes with a suite of products with Power BI desktop, mobile Power BI apps and Power BI services for SaaS.
- Power BI Desktop – Helps to create reports
- Power BI Services – Helps to Publish those reports
- Power BI mobile app – Help to Views the reports and dashboards
How does Power BI work?
First, the data is collected from the external data sources. With ‘Get Data’ option it allows you to get information from various sources including Facebook, Google Analytics, Azure Cloud, Salesforce etc. Also it provides ODBC connection to get ODBC data as well.
Using Power BI, you can create visualization in 2 ways, one is by adding from the right side panel to the report canvas which is in a table type visualization format or by simple drag and drop of value axis under visualization. Once the report is developed , it can be published to web portal with the help of Power BI service. We can access the report, export it in pdf, excel or any preferred format.
Highlights of Power BI:
- Though PowerBI offers paid services, it is comparatively cheaper than other BI tools. It offers free services upto 1GB storage
- Helps to analyze both streaming and static data
- Provides rich data visualization
- Short learning curve
- Provides IoT integrations
Before choosing an IoT data visualization tool for your project, have a clear picture of what type of data you need to analyze and do you also require to know about historical data. IoT consulting services provides data visualization tools and techniques to monitor and analyze the data for predicting future trends. Always it’s important to identify the goals before selecting a tool for your organization.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

September 28, 2020

June 17, 2020

December 13, 2023
What to expect from the demo
- A live discussion with our OTT specialist
- Visualize what your final platform would look like
- How to achieve 100% lossless monetization
- How customizations work & pricing is calculated
83% of users prefer a personalized demo. Would you?
Discover why VPlayed could be the perfect fit for your video streaming business in under 30 minutes.
Evaluation of IoT Data Visualization Tools and Techniques
- First Online: 04 March 2020
Cite this chapter

- Suresh K. Peddoju 4 &
- Himanshu Upadhyay 4
3467 Accesses
11 Citations
Internet of things (IoT) is a fully proven technology in the era of automation. IoT is a connected network of embedded systems with sensors and actuators. IoT generates huge volumes of data due to large number of implanted IoT devices everywhere. This generated data needs to be processed and analyzed to optimize operations and facilitate decision making. Data analytics plays a vital role in decision making. IoT has its applications in several areas: environmental monitoring, infrastructure management, manufacturing, energy management, medical and healthcare systems, building and home automation, transportation and many more. In every IoT application, a large amount of data has been generated with variations in it. Analysis, optimization and visualization of such huge data require smart tools and technologies. For example, some data requires specific algorithms to build models as a classification, whereas others require clustering and anomaly detection. The data visualization tools and techniques available for IoT data are very useful to get a better understanding of IoT, its framework, functions, and missions. There is still need for research and literature about data visualization tools and techniques for IoT and the challenges related to it. In this chapter, we have included various open-source commercial tools and techniques available in the market. We have also studied the benefits and challenges of existing tools. We analyzed and evaluated the suitability of existing tools and capabilities to gain leverage and support for IoT data visualization.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Özen, F. (2018). Internet of Things and Data Visualization—Exastax, Exastax.com, viewed 14 February, 2018. https://www.exastax.com/big-data/internet-things-data-visualization/ .
Mckinsey. Where machines could replace humans—and where they can’t(yet). http://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/business-technology/our-insights/where-machines-could-replace-humans-and-where-they-cant-yet . Accessed July 25, 2016.
Gartner. (2015). Gartner says 6.4 billion connected ‘Things’ will be in use in 2016 up 30 percent from 2015 (online). http://www.gartner.com/newsroom/id/3165317 .
Chen, C., Härdle, W., & Unwin, A. (2008). Handbook of data visualization (pp. 1–954). Berlin: Springer.
Book Google Scholar
Mohammadi, M., Al-Fuqaha, A., Sorour, S., & Guizani, M. (2017). Deep learning for IoT big data and streaming analytics: A survey . arXiv preprint arXiv:1712.04301.f .
Chung, C., Chen, C., Shih, W., Lin, T., Yeh, R., & Wang, I. (2017). Automated machine learning for Internet of Things. In 2017 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics, Taiwan (ICCETW) .
Google Scholar
Hung, M. (2017). Leading the IoT: Gartner insights on how to lead in a connected world. ebook Gartner digital.
Scheibenreif, D. (2016). Article: PDQ POS Top 10 Award Retail CIO Outlook.
Bikakis, N. (2018). Big data visualization tools. arXiv preprint arXiv:1801.08336 .
Batista, A. F., Correa, P. L., & Palanisamy, G. (2016, October). Visual analytics improving data understandability in IoT projects: An overview of the US DOE ARM program data science tools. In 2016 IEEE 13th International Conference on Mobile Ad Hoc and Sensor Systems (MASS) (pp. 349–354). IEEE.
Napoleon’s Russian campaign: From the Niemen to Moscow, Napoleon.org. http://www.napoleon.org/en/Template/chronologie.asp?idpage=481959&onglet=1 .
Chung, S., Suh, S., Park, C., Kang, K., Choo, J., & Kwon, B. C. (2016). ReVACNN: Real-time visual analytics for convolutional neural network.
Hohman, F., Kahng, M., Pienta, R., & Chau, D.H. (2018). Visual analytics in deep learning: An interrogative survey for the next frontiers. arXiv preprint arXiv:1801.06889 .
Peddoju, S. K., Kavitha, K., & Sharma, S. C. (2016). Big data analytics for childhood pneumonia monitoring. Published in Edited Book “ Cloud computing systems and applications in healthcare .” USA: IGI Global Publisher.
Chaudhary, A., Peddoju, S. K., & Peddoju, S. K. (2016). Cloud based wireless infrastructure for health monitoring. Published in Edited Book “ Cloud Computing Systems and Applications in Healthcare .” USA: IGI Global Publisher.
Suresh Kumar, P., & Pranavi, S. (2017). Performance analysis of machine learning algorithms on diabetes dataset using big data analytics. In: Proceedings of IEEE 2017 International Conference on Infocom Technologies and Unmanned Systems (ICTUS’2017) , Dubai, United Arab Emirates (UAE) (pp. 580–585).
Suresh Kumar, P., & Umatejaswi, V. (2016). Diagnosing diabetes using data mining techniques. International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, 7 (6), 705–709.
Wang, H., Xu, Z., & Pedrycz, W. (2016). An overview on the roles of fuzzy set techniques in big data processing: Trends, challenges and opportunities. Knowledge-Based Systems, 118, 10–12.
Wolfe, J. (2015). Teaching students to focus on the data in data visualization. Journal of Business and Technical Communication, 29 (3), 344–359.
Article Google Scholar
Kilimba, T., Nimako, G., & Herbst, K. (2015, September). Data everywhere: an integrated longitudinal data visualization platform for health and demographic surveillance sites. In Proceedings of the 6th ACM Conference on Bioinformatics, Computational Biology and Health Informatics (pp. 551, 552).
Kumar, O., & Goyal, A. (2016). Visualization: A novel approach for big data analytics. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Computational Intelligence & Communication Technology (pp. 121–124).
Grainger, S., Mao, F., & Buytaert, W. (2016). Environmental data visualization for non-scientific contexts: Literature review and design framework. Environmental Modelling and Software, 85, 299–318.
Dilla, W. N., & Raschke, R. L. (2015). Data visualization for fraud detection: Practice implications and a call for future research. International Journal of Accounting Information Systems, 16, 1–22.
Murhy, S. A. (2013). Data visualization and rapid analytics: Applying tableau desktop to support library decision-making. Journal of Web Librarianship, 7 (4), 465–476.
Brigham, T. J. (2016). Feast for the eyes: An introduction to data visualization. Medical Reference Services Quarterly, 35 (2), 215–223.
Chen, C. (2010, July/August). Information visualization. WIREs Computational Statistics, 2 , 387–403.
Laher, R. R. (2016). Thoth: Software for data visualization and statistics. Astronomy and Computing, 17, 177–185.
Yu, L., et al. (2010). Automatic animation for time-varying data visualization. Pacific Graphics, 29 (7), 2271–2280.
Li, X., et al. (2015). Advanced aggregate computation for large data visualization. In: Proceedings of IEEE Symposium on Large Data Analysis and Visualization (pp. 137, 138).
Alton, L. (2016). 4 potential problems with data visualization. Datasciencecentral.com, viewed 20 March, 2018, https://www.datasciencecentral.com/profiles/blogs/4-potentialproblems-with-data-visualization .
Endert, A., Ribarsky, W., Turkay, C., Wong, B., Nabney, I., Blanco, I., et al. (2017). The state of the art in integrating machine learning into visual analytics. Computer Graphics Forum, 36 (8), 458–486.
Keim, D., Andrienko, G., Fekete, J., Görg, C., Kohlhammer, J., & Melançon, G. (2008). Visual analytics: Definition, process, and challenges. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (pp. 154–175).
Joseph, T. (2018). Role of data analytics in Internet of Things (IoT). Fingent article.
Sun, Y., Song, H., Jara, A. J., & Bie, R. (2016). Internet of things and big data analytics for smart and connected communities. IEEE Access, 4, 766–773.
Arockia Panimalar, S., Khule, K. M., Karthika, S., & Nirmala Kumari, T. (2017). Data visualization tools and techniques for datasets in big data. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET), 4 (8), 1667–1672.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Applied Research Center, Florida International University, Miami, USA
Suresh K. Peddoju & Himanshu Upadhyay
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Suresh K. Peddoju .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Vellore Institute of Technology, Vellore, Tamil Nadu, India
S. Margret Anouncia
Department of Computer Science, University of Houston-Victoria, Victoria, TX, USA
Hardik A. Gohel
Subbiah Vairamuthu
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Peddoju, S.K., Upadhyay, H. (2020). Evaluation of IoT Data Visualization Tools and Techniques. In: Anouncia, S., Gohel, H., Vairamuthu, S. (eds) Data Visualization. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-2282-6_7
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-2282-6_7
Published : 04 March 2020
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-15-2281-9
Online ISBN : 978-981-15-2282-6
eBook Packages : Computer Science Computer Science (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

NX CAD COURSES Essentials for NX Designers Advanced Techniques for NX Designers NX CAD New Version Update NX CAM COURSES NX CAM Manufacturing Fundamentals NX CAM Advanced Techniques NX CAM Turning Manufacturing Techniques NX CAM New Version Update SOLID EDGE COURSES Solid Edge Sheet Metal Solid Edge Fundamentals Solid Edge Advanced Techniques Solid Edge New Version Update Solid Edge Surfacing Synchronous Technology for the Ordered User TEAMCENTER COURSES Teamcenter User Training Teamcenter Administration Training Our Trainers
NX CAD COURSES Essentials for NX Designers Advanced Techniques for NX Designers NX CAD New Version Update NX Sheet Metal Fundamentals NX CAM COURSES NX CAM Turning Manufacturing NX CAM Fundamentals NX CAM Advanced Techniques NX CAM New Version Update SOLID EDGE COURSES Solid Edge Sheet Metal Solid Edge Fundamentals Solid Edge Advanced Techniques Solid Edge New Version Update Synchronous Technology for the Ordered User TEAMCENTER COURSES Teamcenter User Training Teamcenter Administration Training Our Trainers
INDIA TRAININGS Solid Edge: GUI and Hands-On Design Solid Edge: Part Modeling Environment Solid Edge: Part Drafting Environment Different CAD Data Transfer Formats in NX – What is Best?
- ONILNE COURSES

Our service capabilities include concept design, vehicle styling, ergonomics and digital prototyping

Innovate, globalize, improve productivity and meet cost targets throughout the product lifecycle

PROLIM PLM Software provides a product-centric approach, equipping you with PLM capabilities

Develops robust, transferable, low-cost formulation & manufacturing processes

PROLIM offer a comprehensive set of solutions that enable you to achieve Program Execution Excellence

PROLIM PLM Software provide a rich, collaborative environment for real-time global design and manufacture

PROLIM PLM Software provides solutions for managing product knowledge across the entire organization

PROLIM has a dedicated practice in serving government entities including military, defense, homeland security & state government
Read our latest blogs
Register for the latest events
Watch our video tips & tutorials
Download case studies that inspire
Get updates on the latest technology
Download the latest whitepapers

The Newest Features of NX CAD 2312 Revealed
Master Mendix Workflows to Optimize Business Processes
Innovate Faster with Fascia: The Ultimate Low-Code Digital Platform!
How can PLM Solutions accelerate medical device development for your business?
We have been part of several global dream teams to design and engineer various product development programs such as the Indian defense surface-to-air missile programs the US, Japanese and European automotive and aerospace programs, and have seen the successes and failures of major corporations in implementing these CAD/CAM/CAE/PLM tools.

UNITED STATES
Detroit 30445 Northwestern Hwy, Suite 380, Farmington Hills, MI 48334
Dallas 6827 Communications Parkway, Suite 310, Plano, TX 75024
Cincinnati 1305 Mattec Drive, Cincinnati, OH 45140
California 15510 Minnesota Ave, Paramount, CA 90723
[email protected] INDIA
Bangalore World Trade Center 20th Floor, Dr. Rajkumar Road, Malleshwaram, Bangalore 560055
Hubli Plot No: 7, Survey No: 89, Aryabhatta Technology Park, Navanagar, Hubli – 580025
Pune Survey No. 25, Eleven West, Opposite to Supreme Amadore, Baner, Pune, Maharashtra – 411045
Delhi NCR – Region Iconic Correnthum, 2nd Floor, Sector 62, Noida, Uttar Pradesh – 201301
Gujarat 7th Floor, The Link, Vijay Cross Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, Gujarat – 380009
Ludwigstrasse 12, 60327 Frankfurt am Main, Germany
4611 Rosebush Road Mississauga L5M 5H2, Canada
16/94-102 Keys Rd Moorabbin, Victoria 3189 Australia
1 Denison St, North Sydney, 2060 Australia.
New Zealand
110 Carlton Gore Road, Newmarket, Auckland, 1023, New Zealand.
Send Message
- chevron_right
Role of Data Visualization in IOT
The development of Internet of things ( IoT ) is rapidly accelerating and affecting the industries directly or indirectly. This is steadily increasing the data generated by the business specific IOT-devices around the globe leading to one of the major challenges of the IOT industry that is collection, processing, analyzation and visualization of the data collected from different sensors in the IoT environment. Thus, with an exponentially growing volume of data, the need to interpret and make useful insights from the data is making Data Visualization an integral part of IoT.
Data Visualization
Data Visualization is referred as the process of representing information or data into a visual context that provides useful insights from the data. It is a way to display the vast amount of data in a meaningful way that clearly presents trends and patterns from the raw data collected. Data Visualization tools and technologies help to slice and dice the data to the minute granular level.
Need for data visualization
The real purpose of Data Visualization is nothing but ‘making sense of data’. It provides a quick and effective way to communicate information to identify trends and patterns and flag inconsistencies and errors in the data. It gives enterprises the ability to rapidly and effortlessly make decisions, visualize the output to monitor results, get actionable insights and evaluate the factors affecting businesses and customer behaviour. A good visualization tells a story, removing the noise from the data and highlighting the useful information.
Role of data visualization in IOT
Internet of Things (IOT) and data are interlinked together as IOT is all about collecting data and making sense of it. One of the challenges for IoT industry is data analysis and interpretation. Trillions of data is generated every day from the IOT sensors and devices in the physical world and this data can potentially become a source of business value. The data collected is impractical if we cannot extract useful information from it and analyse and translate that information to identify hidden trends, outliers, and patterns in data and make data-driven decisions. The continuous acquisition, storage, analysis and implementation of data from IOT devices can help companies identify bottlenecks in supply chain, predict equipment failure, successfully address overstaffing issues and optimize operational costs therefore improvising business productivity and outcome.

The objects in the physical world are connected and enhanced with temperature, moisture, light, motion, location and other types of sensors which produce the real-time timeseries data and send this data to the cloud where it is stored for analysis and interpretations for making smart decisions. Considering an example of data collected from the sensors connected to the windmill of a windfarm, sensors are connected to various components of the windmill to calculate the wind speed, energy produced and temperature of different components of the windmill. The representation of data in visual context rather than being in textual format gives the ability to absorb information quickly, improve insights and make faster decisions.
Data visualization provides an opportunity to see patterns that may remain hidden in those datasets if not analysed properly and can assist in making fast, informed decisions with more certainty and accuracy. The insights and relevant correlations represented from the visual representation can allow companies to solve business problems, drive sales, cut costs, find new revenue streams and take smarter decisions.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post Comment
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Springer Nature - PMC COVID-19 Collection

On exploiting Data Visualization and IoT for Increasing Sustainability and Safety in a Smart Campus
Chiara ceccarini.
Dipartimento di Informatica - Scienza e Ingegneria, Università di Bologna, Mura Anteo Zamboni 7, Bologna, 40126 Italy
Silvia Mirri
Paola salomoni, catia prandi.
In a world that is getting increasingly digital and interconnected, and where more and more physical objects are integrated into the information network (Internet of Things, IoT), Data Visualization can facilitate the understanding of huge volumes of data. In this paper, we present the design and implementation of a testbed where IoT and Data Visualization have been exploited to increase the sustainability and safety of the Cesena (Smart) Campus. In particular, we detail the overall system architecture and the interactive dashboard that facilitates the management of the campus premises and the timetabling. Exploiting our system, we show how we can improve the campus sustainability (in terms of energy saving) and safety (considering the COVID-19 restrictions and regulations).
Introduction
Data visualization can be defined as “a way to represent information graphically, highlighting patterns and trends in data and helping the reader to achieve quick insights” and as a tool to enable “the exploration of data via the manipulation of chart images, with the color, brightness, size, shape, and motion of visual objects representing aspects of the dataset being analyzed” [ 1 ]. In a world that is getting increasingly digital and interconnected, and where also the physical objects are integrated into the information network to collect data about the environment (Internet of Things, IoT), Data Visualization can facilitate the understanding of huge volumes of data. This is particularly true if related to smart environment, both outdoor (e.g., visualizing urban accessibility data [ 2 – 4 ]) and indoor (e.g., designing infographics to stimulate environmental awareness [ 5 ]). Focusing on the indoor, Data Visualization can be useful to display information tied to the IoT infrastructure and sensors deployed inside smart buildings, to make people aware of the specific conditions (e.g., air quality and energy consumption [ 6 ]) and dynamics (e.g., people flow, [ 7 ]) of the environment they are experiencing.
A particular case of a smart building is a smart campus [ 8 , 9 ]. In this scenario, several studies investigated the use of data visualization, exploiting the campus as a user-centric testbed for IoT solutions aimed to benefit the University community [ 9 – 11 ].
In this rich context, we here present our testbed, designed, implemented, and deployed to assist administrative staff, ICT staff, faculty members, and, lastly, students, in increasing the sustainability and safety of the Cesena (Smart) Campus, one of the campuses of the University of Bologna. In particular, as a case study, we exploited a responsive web-based dashboard to analyze data by interacting directly with a visual representation of them. Such data are related to the University timetabling and are the result of the aggregation/integration of different data sources, including University Open Data and data gathered by our IoT infrastructure. In fact, the IoT infrastructure enables the collection of real-time data about i) premises (i.e., classrooms and labs) occupancy thanks to a camera-based people counting service [ 12 ]; and ii) environmental conditions (e.g, air quality, temperature, humidity) through the Canarin II sensors stations [ 13 ]. We deployed such IoT infrastructure in 20 classrooms and labs. To present the potentialities of our approach, two cases are presented: one related to sustainability and energy saving, and the other related to safety and the new COVID-19 restrictions and regulations.
The remaining of the paper is organized as follows. The next Section describes studies that investigate i) Data Visualization strategies in smart campus scenarios, ii) IoT infrastructures to measure the number of people in a Campus premise, and iii) IoT infrastructures and Smart Environment strategies to monitor occupancy and physical distances in indoor environments in the COVID-19 era. Inspired by these studies, we designed and implemented our system, as presented in Section 3 . Then, we detail the dashboard we designed and implemented (Section 4 ) and, to explore the potentialities of such system, we present two cases study, focusing on sustainability and safety (Section 5 ).
Related work
This Section briefly describes the most interesting research works related to the following topics: i) Data Visualization strategies in smart campus scenarios, ii) IoT infrastructures to measure the number of people in a Campus premise, and iii) IoT infrastructures and Smart Environments strategies to monitor occupancy and physical distances in indoor environments in the COVID-19 era.
Data visualization solutions in the smart campus context
Considering Data Visualization as a tool to enable a better understanding of data in Smart Campus scenarios, dashboards can be an effective graphical user interface tool to provide at-a-glance views of the gathered data to users. In [ 14 ], authors created Campus Energy Education Dashboard (CEED), a dashboard to visualize the energy consumed inside a university campus to improve energy efficiency and increase the knowledge of its occupants. CEED used a digital map of the campus to provide information about the building that consumes more energy and a bar chart to display the same information. Exploiting both real-time and historical data. The system targets two different groups of users, providing analytic features for stakeholders and engagement features to students and staff. Another example is Ubidots, a dashboard where data from smartphones are collected and then visualized to monitor the mobility inside the campus [ 15 ]. In [ 16 ], Longre et al. proposed a model for the design of dashboards that display sensors data visualization in the context of a smart campus. In particular, they claim that the data displayed and the visualizations should take into consideration the users’ roles. Sensor data could be environmental-related. For example, Hentschel et al. used a simple web dashboard to display data related to temperature and light intensity inside an office at the University of Glasgow [ 17 ]. Instead, USC AiR is a mobile application to display data about the air quality inside a campus. This application also exploits augmented reality to make users more engaged with those data and to inspire them to contribute to the reduction of air pollution [ 18 ]. Similarly, Bujary et al. [ 19 ] resorted to augmented reality to lure users into using a pedestrian navigation application whose goal is also to gather quality environmental data in the premises of the University of Padua. The application is coupled with a web service providing a heatmap of collected historical values and their evolution in time. It was then expanded to be used even on smartwatches and with an algorithm able to generate best routes considering also light and brightness beside the classic shortest path [ 20 ]. AlmaMap is another example of an application that displays environmental data, such as temperature, humidity, pressure, and particulate matter, gather from sensors inside a university campus, whose location is visible through the visualization of the campus map [ 9 ]. Tarabieh et al. used a map-based visualization, together with a bar chart, pie chart, and dial gauge, to provide data about the energy consumption in a university campus and to produce a behavioral change in the campus community [ 21 ].
Focusing on the issue to detect and monitor classroom occupancy, Sutjarittham et al. used data visualization techniques, like heatmap and line chart, to display attendance patterns during classes and the actual occupancy in the classrooms [ 22 ]. Inspired by this study, we pushed this approach further, providing a data visualization dashboard that not only visualizes the classrooms/labs actual occupancy but also allows the user to easily perform visual comparisons to find the optimal course timetabling for real-time or medium- and long-term actions.
IoT infrastructures for classroom occupancy monitoring
This SubSection focuses on some interesting approaches used to count people in indoor environments. In literature, there are many works devoted to indoor track and count persons, based on different technologies and architectural solutions. Some of those works are based on the use of passive infrared sensors (PIR) [ 23 ], which are electronic sensors that can measure infrared light radiating from some objects in their field of view. Some projects take advantage by using multiple PIR sensors [ 24 ], thus they can calculate the number of persons who are in an indoor environment by computing the number of people passing through doorways to access that place. A different approach is based on the Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology [ 25 ]. Basically, it consists of three components: (i) the readers, (ii) the tags, and (iii) the middleware software. Several solutions have been adopted and developed by applying this approach, exploiting probabilistic estimators that achieve the required accuracy and confidence level [ 26 ]. Other methods are based on the Wi-Fi probe-request-frame, which takes advantage of the fact that smartphones and mobile devices have been designed to periodically transmit such frames with the aim of identifying when a known access-point is positioned within a specific distance and by capitalizing such a kind of Wi-Fi behavior [ 27 ]. Hence, monitoring and counting these Wi-Fi frames can provide support in people counting and crowd monitoring [ 28 ]. A different process, based on the use of a single carbon dioxide sensor (CO 2 ), has also been investigated [ 29 ]. The idea behind this approach is that an indoor environment is affected by human activities and that influence can be measured by various sensors, so as to infer the density of the crowd, as described in [ 30 ], or with the use of hybrid techniques, by combining different sensors such as video camera and CO 2 sensors, as proposed in [ 31 ].
An additional approach we have analyzed is based on taking pictures by cameras: its main target is the design and the development of algorithms aiming at automatically counting people. A technique that could be adopted is based on the recognition of video segments stream, where the counting process can be divided into two main steps: (i) detecting moving blob on the basis of algorithms for motion detection (background subtraction and/or a segmentation strategy, i.e., K-means); (ii) monitoring the detected blobs, with the aim of identifying the direction of the monitor or to compute the number of people that are present in case of a single frame shot from a camera. In order to accomplish this task, two main categories of methods can be adopted: (i) the Line of Interest (LOI) counting methods can evaluate the number of people crossing a virtual Line of Interest within the monitored scene [ 32 ]; (ii) the Region of Interest (ROI) counting methods can estimate crowd, evaluating the number of people who are present within a specific Region of Interest in the monitored scene [ 33 ].
IoT infrastructures and smart environments for occupancy monitoring in the COVID-19 era
This SubSection briefly introduces some of the main interesting and recent works related to the use of IoT and Smart Environments strategies with the aim of monitoring occupancy of indoor spaces and detecting physical distances among persons. The advent and the evolution of the COVID-19 pandemic have pushed research and development actions in this direction, with this specific goal. One of the technologies that have been mostly investigated has been passive WiFi sensing, so as to detect students’ and staff’s occupancy and mobility within a Campus and then analyzing how COVID-19 has impacted the related Control Policies [ 34 ]. In particular, Zakaria et al. have analyzed data collected from three different college campuses (two in Singapore and one in the Northeastern United States). Such a technology has been effective in monitoring the number of people in a building, on average, in a specific hour, and in detecting the number of places visited by a single person, on average, in a specific hour.
The context of university campuses is one of the most used case studies in such a situation. Longo et al. [ 35 ] present a prototype of a smart object (named Smart Gate), with the aim of monitoring people flow and of keeping track of the occupancy levels. Such a prototype is equipped with passive sensors (Time-of-Flight long-ranging sensors) and cameras, collecting data on a Raspberry Pi and transmitting them to a server for advanced analysis.
A monitoring system based on PIR (passive infrared radiation) sensors is proposed in [ 36 ], where the authors investigated the applicability of large data acquired from IoT tools for enhanced space use management to achieve operational efficiency at universities. The proposed study aims to identify methods for measuring and quantifying space use, that could significantly change during special circumstances such as the COVID-19 pandemic. Also in this study, the data collected from the IoT infrastructures are turned into information to support the decision-making on the management of campus, taking into account the Umea University (Sweden) as a case study.
In [ 37 ], Fernández-Caramés et al. proposed the use of Distributed Ledger Technologies (DLTs) including blockchain [ 38 ], together with Artificial intelligence algorithms with the aim of collecting data about people’s occupancy in an indoor environment, in a way that preserves privacy, and that is the most accurate, transparent and trustworthy as possible. The work proposed by these authors aims to estimate the real-time people occupancy level in public spaces such as buildings, classrooms, businesses, or moving transportation vehicles. In contrast to smartphone-based contract tracing applications (requiring an active involvement from the users, for instance by starting a mobile app or enable Bluetooth communications), such a system is based on autonomous wireless devices, without the need of an active user action after powering them on.
A project that exploits such technologies in an outdoor context is presented in [ 39 ], where the authors studied outdoor pedestrian activity in New York City. To create a holistic view of the city, the authors collected data in three different scales: (a) The City scale (data have been gathered through video streams gathered from public traffic cameras), (b) the Public scale (data have been gathered through video footage taken from instrumented vehicles driving through the city), and (c) the Individual scale (data have been gathered through mobile phone location data volunteered by local citizens). These multi-scale data will be used to form a map of urban mobility and space occupancy under social distancing policy.
The system at a glance
In this Section, we briefly present the technological aspects of the two core components of our approach: i) the IoT infrastructure to gather real-time classrooms/labs occupancy and environmental conditions, and ii) the Data Visualization web application. An overview of the overall architecture is depicted in Fig. 1 . For more details about the design process, see [ 40 ].

The system architecture
The IoT infrastructure
Our IoT infrastructure is composed of i) an edge-based system that exploits cameras for people counting, and ii) environmental conditions sensors stations to sense air contaminants, gathering formaldehyde, PM 1.0 , PM2.5 and PM10 values, temperature, relative humidity, air pressure.
Focusing on the camera-based system for people counting, the main constituent of our architecture is the client-side since almost the whole computation occurs there. In particular, the architecture is composed of three layers. (1) The data acquisition layer is devoted to the data acquisition, exploiting Intel RealSense D415 Depth cameras. The cameras are plugged-in (via USB) to a Raspberry Pi 4 model B and we acquired 1280 x 720 pixel frame rate images every five minutes (this interval was set to better support the storing operations). (2) The prediction layer retrieves data from the cameras, on the client-side, and exploits a custom model based on YOLOv3 with the aim of predicting the number of people in a precise moment, dividing the image into regions and predicting bounding boxes and probabilities for each region. In doing that, we exploit a transfer learning methodology. Once the prediction is done, the number of people predicted and the timestamp are stored in a file with csv extension. (3) The API layer, which, over HTTPS, responds the needed information to the server requests. This three-layer architecture based on a fat client-thin server has four main advantages: higher scalability, working semi-offline, higher availability, and privacy compliant. Moreover, our edge-based transfer learning model allows obtaining an average accuracy equal to or greater than 91% (depending on the room layout).
In our IoT infrastructure we also integrated the Canarin II sensors stations [ 13 ]. Such stations allow to monitor different environmental conditions, including formaldehyde, PM1.0, PM2.5 and PM10 values, temperature, relative humidity, and air pressure.
In our testbed, we deployed our infrastructure in 20 premises of the Cesena Campus, including 4 laboratories and 16 classrooms.
The web application
The Data Visualization web application we designed and developed is based on a client-server architecture, as shown in Fig. 1 . The client-side was implemented with the Angular framework 1 and with the standard web-based languages, like HTML5, CSS3, and TypeScript. 2 Concerning the data visualization elements, we used some Javascript libraries like Google Charts, 3 Chart.js, 4 and D3.js 5 to make the charts interactive. Using these technologies, we were able to develop a responsive web-based application, enjoyable both from smartphones and tablets and larger screens (i.e., laptop).
Regarding the server-side, we used Node.js 6 and the framework Express 7 . The server communicates with different data sources, such as i) open data provided directly by the University of Bologna, to gain information about the courses and the class schedule inside the Cesena campus; ii) a MySQL database containing information (such as name, location, capacity) about classrooms and laboratories inside the campus; and iii) a database with information about the number of enrolled students for each teaching and courses of study. Moreover, our server exploits some APIs to obtain data about the actual presence of people inside a classroom or laboratory (gained by the camera-based people counting infrastructure) and the data about temperature, humidity, air pressure and particulate matter from the Canarin II sensor stations [ 13 ]. This architecture allows us to easily extend it, including new data sources and sensors (through their API).
The web-based dashboard
The responsive web-based application has been designed as a dashboard that can be accessed both from smartphones, to have quick consultations, for example, to find empty classrooms or laboratories at a specific time, and from devices with larger screens to let the users perform more complex analysis. The application aims to improve the management of spaces and class schedules by means of five main functions/components that allow the user to visualize intuitive charts and perform analysis. Each page has a left-side vertical menu (where it is possible to select the specific component out of five) and a search input box on the top-right side. In the following, all the implemented components are presented in detail.
The homepage of our web application opens the overview component (Fig. 2 ). This component displays a series of cards (e.g., three cards in Fig. 2 ), each card shows information about a classroom or lab, including details such as the room capacity and the room occupancy (at the specified timestamp). If a lesson is taking place, the card also shows the name of the course, the professor’s name, and the number of students enrolled. At the bottom of every card, there is a pictorial chart that highlights the occupation status of that room. The number of filled icons (out of five) represents the number of students inside the room in relation to its capacity. Adding more details, one filled icon corresponds to a room actual occupancy lower than 1/4 (25%) of the room capacity, two filled icons correspond to an occupancy lower than 2/4 (50%), and so on; the fifth icon is used only to warn that the room actual occupancy is equal or greater than the room capacity. Moreover, we take advantage of colors (green, yellow, and red) to convey messages and easily draw attention to anomalies. Accordingly, if the classroom or laboratory is too crowded (i.e., actual occupancy equal or greater than the facility capacity), all the five icons are filled in red, with an error icon beside it. Instead, in a normal situation, i.e., the actual occupancy is between 25% and 75%, the chart is green (with two or three filled icons), and, finally, if the condition has to be monitored by operators, i.e., lower than 25% (one filled icon) or greater than 75% (four filled icons), the chart is yellow with an alert icon beside it.

A screenshot of the system presenting the Overview component
List of classrooms, laboratories, courses, and teachings
The second component of our web application consists of four different lists, including all the classrooms, laboratories, courses, and degrees inside the Cesena campus, each list visualized in a card. The first two cards show the lists of the classrooms (in one card) and the laboratories (in another one) of the campus. Selecting one of them, the user can see the scheduled lessons through a simple list view or a timetable. For all the lessons already held in the selected classroom or laboratory, in the list view, it is also present the pictorial chart described in the overview component, while, in the timetable, the same information is conveyed through the background color of the cell representing the lesson duration over time. Moreover, we wanted to provide the users with an analysis tool to monitor the number of lessons, hours of teaching, and the percentage of usage of a given room (class or lab) through an easily understandable area chart. Lastly, we provide to the user the location of the room, using the campus map in SVG format. The third card in this component concerns the courses. For each of them, it is possible to see the general information, like the professor’s name and the degree program to which it belongs. The scheduled lessons are available both in a text list and area chart visualization. The two visualizations use different visual techniques to display the same information: the attendance trend, the number of enrolled students, and the capacity of the classrooms or laboratories where the lessons are held. The attendance rate is visible through the pictorial graph, in the list view, and through the color of the relative point in the area chart. To provide an additional tool for analysis, a stacked bar graph and a pie chart were included, presenting in green the percentage of spaces booked and actually used, in grey the percentage of lessons not yet held, and in red the percentage of spaces booked and not correctly used. The fourth and last card of this component regards the degree program, both bachelor’s and master’s degrees, in the Cesena campus. For each degree program, we choose to display a list view of all of the courses, the relative professor, and a statistics page to visualize the correct usage of booked spaces. Also in this case, we used a stacked bar chart and a pie chart with the same colors and the same meaning as the graphs described in the paragraphs above.
Classrooms and laboratories usage comparison
The third component of the web application concerns the comparison between two or more classrooms and laboratories in terms of correct usage of space. As mentioned before, for each room (classroom and lab), we monitored the number of lessons and hours and the percentage of occupation. These elements provide a way to compare the effective usage of two or more different spaces. For each of the parameters considered, we used two different data visualization techniques (a line graph and a pie chart) to convey the same information so that the users can interact with the one that more reflects their demands. In particular, the line chart displays the number of lessons, hours, and the percentage of use in relation to the months of the year. Instead, the pie chart displays the same information but in relation to the total number of lessons, hours, and percentage of use.
Courses comparison
The comparison between two or more teachings/courses represents the fourth component of the application and it is presented in Fig. 3 . To compare the different teachings, we used a stacked bar chart, and a sunburst graph to display the differences in terms of percentage of correct spaces usage and number of lessons. The stacked bar chart uses the border color to identify the course it refers to (in Fig. 3 , yellow and blue), the green and red color of the bar to display the correct or incorrect usage of spaces, and the gray color for the lessons not yet held in relation to the months of the year. Concerning the sunburst graph, the first ring is dived according to the number of lessons for each teaching, while the second one represents the percentage of correct and incorrect spaces usage for each teaching.

A screenshot of the system representing the Course comparison component
Degree programs comparison
Finally, the last component of our web-based application concerns the comparison of two or more degree programs. Also, in this case, we use the number of lessons and the percentage of correct and incorrect usage of spaces as parameters to compare the degree programs. We implemented a stacked bar chart and a sunburst graph to visualize the number of lessons and the usage of booked space . The meaning of the graphs and the use of border and bar colors is the same as in the course comparison component.
Case studies
To present the potentialities of our system in supporting premises managements, we here present two case studies. The first focuses on using the data visualization system to verify the real-time occupancy considering the actual COVID restrictions and regulations; the second is related to a medium/long-term monitoring of the classrooms/labs occupancy to increase the sustainability of the campus in terms of optimization of the energy consumption.
Case study 1: real-time safety monitoring
The COVID-19 pandemic changed the way we experience any space and place, put into effect social distancing measures. Considering University campuses, not always lessons can be taught in presence, but, if and when possible, in-person classes have to be taught in accordance with regulatory requirements and safety protocols. Different strategies have been adopted to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and safety protocols. For example, the University of Bologna, to manage the capacity of each classroom/lab in the best possible way, developed a service that allows students to schedule the classes they plan to attend in two-week periods, specifying the attendance mode. Unfortunately, this strategy not always works as expected. For this reason, IoT can be exploited, along with similar solutions, to guarantee safety during in-person classes.
Exploiting our IoT infrastructure, and, in particular, the camera-based people counting system, we are able to monitor, in real-time, the number of students on a University premise. Thanks to our Data Visualization dashboard, we can obtain the actual classrooms/labs capacity (considering the current regulation), and visualize the room occupancy accordingly. This information is visible on the system home page, in the overview component. In fact, the card allows to immediately check the room occupancy in relation to the room capacity to ensure social distance and safety. As an example, going back to Fig. 2 , used to presented the overview components, it is possible to infer that: in lab LIB (on the left), the actual occupancy is greater than the actual capacity (red color and five filled icons), while in lab 3.5 (center) the actual occupancy is close to the maximum (yellow color and four our of five filled icon), and, finally, in lab 2.1 (on the right), the number of students in the room doesn’t present any anomaly (green color and two out of five filled icons). When the pictorial chart becomes red (i.e., the room’s actual occupancy is greater than the room’s actual capacity), a notification is sent to the people responsible for the health and safety inside the campus.
Moreover, by integrating University official data sources, the system can automatically update its data and visualize the information accordingly. As an example, in Fig. 4 it is possible to see the impact of the decrease of the allowed room capacity value due to COVID-19 regulations regarding the social distance (the allowed room capacity became 50, while was 100 by design).

An area char representing the classroom occupancy values monitored during the COVID-19 pandemic, for a specific course
Case study 2: medium/long term sustainability
As mentioned, defining a school/university timetabling is a complex task to solve [ 41 ]. With our approach, we are not interested in automatically solving such a problem, but mostly to exploit data visualization and IoT strategies to facilitate University staff in taking the best decisions, considering also the campus sustainability. In fact, it has been proved that an efficient timetable could also reduce energy consumption and therefore increase the sustainability of the campus [ 42 ].
Our visual application has been designed to facilitate the discovery of not optimal classrooms/labs and course assignment, on the basis of the real-time data collected by our IoT infrastructure. In fact, as presented also in Fig. 4 , selecting one course, it is possible to analyze in detail the actual occupancy of the room during the course weeks, in relation to the room capacity. Moreover, by selecting one specific value in the chart, it is possible to see a modal presenting the timetable of the other courses and see the classrooms (or labs) availability during that time slot (as shown in Fig. 5 ). Considering, for example, that for the last three weeks the number of students attending a course is half than expected, it is possible to “release” the assigned room and look for a smaller room that can host the students. This action can have an immediate impact on energy saving because a large space causes a higher level of heating and cooling loads if compared with a smaller one.

Timetable to compare classrooms (or labs) availability and perform an exchange to improve sustainability
Moreover, through the course comparison component (that we previously presented exploiting Fig. 3 ), it is possible to compare two courses, focusing on two values: the number of lessons that have achieved a satisfactory occupancy value in relation to the room capacity, and the number of lessons that prompted an anomaly. These visualizations could help the administrative staff to change the classroom for those lessons that have an attendance rate much lower or greater than the capacity of the room, leading to an improvement in space management on our campus.
Conclusion and future work
In this paper, we present an integrated approach that combines IoT infrastructures (e.g., a camera-based people counting service and sensors for environmental conditions monitoring) and Data Visualization strategies to i) ensure safety, and ii) improve the sustainability of a University campus. As a testbed, we deployed our approach in the Cesena (smart) campus, one of the campuses of the University of Bologna. It is worth noting that the system was initially designed with the main goal of facilitating University staff to monitor premises occupancy and improve the course timetabling accordingly, increasing the Campus sustainability. Nonetheless, with the starting of the COVID-19 pandemic, it shows its potential to monitor safety aspects introduced with the actual regulations and constraints. As future work, we plan to integrate a machine learning module in our web application that uses the data gathered during the first year of deployment to suggest timetabling recommendations to improve Campus sustainability and safety.
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our sincere thanks and appreciation to Gianluca Grossi who prototyped the web-based application, and to Lorenzo Monti, who implemented and deployed the IoT infrastructure.
1 https://angular.io/
2 https://www.typescriptlang.org/
3 https://developers.google.com/chart
4 https://www.chartjs.org/
5 https://d3js.org/
6 https://nodejs.org/
7 https://expressjs.com/
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Change history
Open access funding provided by Alma Mater Studiorum - Università di Bologna within the CRUI-CARE Agreement.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Data visualization in IoT involves using graphical representations, such as charts, graphs, heat maps, and interactive dashboards, to depict the data collected from IoT devices. By visualizing the data, decision-makers can easily identify patterns, trends, and anomalies, enabling them to make data-driven decisions, optimize processes, and ...
The goal of data visualization is to provide a graphical representation of the data so analysts can identify patterns and trends. Data visualization shows great efficiency when it comes to large series of data. Its methods include graphs, bar charts, pie charts, status tables, maps, line graphs, scatter plots, and much more.
In Azure IoT, analysis and visualization services are used to identify and display business insights derived from your IoT data. For example, you can use a machine learning model to analyze device telemetry and predict when maintenance should be carried out on an industrial asset. You can also use a visualization tool to display a map of the ...
IoT data visualization involves the graphical representation of data collected from IoT devices and systems. These devices, equipped with sensors and connectivity, continuously gather information from the surrounding environment. Their data may include temperature, humidity, pressure, location, etc.
This paper provides a comprehensive survey of visualization methods, tools, and techniques for the IoT. We position data visualization inside the visual analytics process by reviewing the visual analytics pipeline. We provide a study of various chart types available for data visualization and analyze rules for employing each one of them, taking ...
visualization and recognition of patterns within the IoT generated. data, play a significant role in the insight-gaining process, and. enhance the decision-making process. Visualizing data plays a ...
Pattern 2: AWS IoT SiteWise (+ AWS IoT SiteWise Monitor) Overview: AWS IoT Greengrass software installed on your device provides an open-source edge runtime and cloud service that helps you build, deploy, and manage intelligent device software. Using AWS IoT SiteWise components, you can integrate with Greengrass to send local device and equipment data to asset properties in AWS IoT SiteWise on ...
Understanding IoT Data. In the dynamic landscape of IoT, data is the cornerstone. Dive into the fundamentals, unravelling the intricacies of IoT data and its unique characteristics that set it apart from conventional data sources. The Power of Visualization. Witness the transformative power of visualization in decoding complex datasets.
It encompasses data from sources such as social media, sensors, machines, devices, and other digital interactions. Big data is characterized by its three Vs: volume, velocity, and variety. In the context of IoT, big data plays a crucial role in enabling the full potential of IoT systems. Data collection and storage. Data processing and analytics.
Data can be represented in different formats such as pictorial, graphical, and other. This representation is called data visualization. It enables decision makers to see data analytics presented visually, so they can grasp difficult concepts or identify new patterns in an efficient manner [9, 10].With interactive visualizations, interactively changing what data you see and how it is being ...
3. Kibana. It is used for logs visualization, and is an open-source browser-based visualization tool that allows users to visualize and analyze various data, which can be collected by Elasticsearch. You can use Kibana to create custom visualizations such as line graphs, bar graphs, pie charts, and heatmaps.
Data visualization is considered the most efficient solution in IoT. It visualizes the endless stream of information collected by the respective smart systems to exponentially increase its value due to the meaningful insights it provides. Notably, numerous tools and techniques visualize the meaningful information obtained. It is, however, prudent that the analysis of this information considers ...
It is a quick, easy way to convey concepts in a universal manner. There are multiple usage of visualization like in offices to report tasks, manage operations, track progress and many others. Various visualization techniques are used to design the graphical representation of this innumerate amount of data.
The concept of data visualization is very simple and literally means a graphical representation of gathered information. It is not rocket science, but if not done properly it can do more harm than good. Multiple disciplines of science and art came together to create probably the most effective way of presenting data for end-users.
public IoT data into a "search engine for the IoT". Unfortunately, the data made available from Thingful lacks much of the meta-data and visualization capacities of ThingSpeak or similar services [40]. Work from Maureira et al. in 2011 evaluates ThingSpeak with a focus on the underlying computing services [21]. This includes
IoT visualization is the process of transforming raw data from IoT devices into graphical or visual representations, making it easier for users to comprehend and analyze. Data visualization in IoT can be a game-changer, as it allows users to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies that might otherwise be difficult to spot in raw data.
Data visualization is a hot topic for IoT right now. As more companies incorporate data-driven initiatives and innovation into their overall strategy and operations, the central importance of data visualization is growing. Service providers and end-users alike are beginning to recognize the distinctive value of data visualization tools for IoT applications.
An IoT dashboard contains multiple widgets that visualize the data in the form of line graphs, Geographical maps, Bar charts, Pie charts, Gauges, Heat maps, etc., from multiple sets of IoT devices transmitted over time. With this information in the form of multiple visualizations helps to unlock every data into a valuable asset.
5 Data Visualization Tools and Techniques for IoT. The most ideal approach to exhibit the data is visually. There is a term for that: data visualization. Data visualization considers any type of graphic content visually communicates data to the viewer. There is a saying; a single picture is worth a 1000 word.
IoT data can be classified based on its qualities, such as spatial, temporal, and sensory [11]. Each property is explained first, followed by different examples. IoT data can be treated as spatiotemporal Web data, such as e-commerce, social media, weather, logs, Web services, etc. As a result, these spatiotemporal data are incorporated into IoT ...
Data Visualization is referred as the process of representing information that provides useful insights from the data. IoT. Data Visualization is referred as the process of representing information that provides useful insights from the data. IoT. News Events Careers Tech Support Internship. Select Region. United States India Australia & New ...
Introduction. Data visualization can be defined as "a way to represent information graphically, highlighting patterns and trends in data and helping the reader to achieve quick insights" and as a tool to enable "the exploration of data via the manipulation of chart images, with the color, brightness, size, shape, and motion of visual objects representing aspects of the dataset being ...