Flood Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on flood.
Flood is one of the most dangerous natural disasters. It happens when excessive water is collected in any area. It usually happens due to heavy rainfall. India is highly prone to flood. There are many regions in the country that face this natural disaster because of the overflowing of rivers. Moreover, it also happens because of the melting of snow. Another reason for floods is when the dam breaks down. If we look at the coastal areas, the hurricanes and tsunamis are held responsible for causing floods. In this essay on flood, we will see the prevention and after-affect of flood.

In other words, whatever the cause may be, it is equally dangerous. It has a lot of harmful consequences. Flood damages the living conditions and it takes a lot of time to recover from this disaster. Therefore, the consequences of floods must be known and steps must be taken to prevent it.

After-effects of Flood
Floods interrupt with the day to day functioning of the affected area. The severe floods sometimes cause mass destruction. A lot of people and animals lose their lives due to floods. Several others are injured. Floods also bring a rise in diseases. The stagnant water attracts mosquitoes causing malaria , dengue, and more illnesses.
Furthermore, people face power cuts due to the danger of electrocution. They also have to face expensive pricing. As the supply of food and goods gets limited, the prices naturally grow higher. This creates a big problem for the common man.
Most importantly, the whole country faces economic loss. The resources needed to rescue people and tackle this disaster demands a hefty amount. Plus, the citizens lose their houses and cars which they worked all their lives for.
Subsequently, floods also hamper the environment. It causes soil erosion and this degrades the quality of the soil. We lose out on fertile soil. Similarly, floods also damage flora and fauna. They damage crops and displace trees. Thus, the measure should be taken to avoid these grave consequences.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Ways to Prevent flood
The government and citizens must work together to formulate ways to prevent floods. Proper awareness must be spread about the steps to take when floods occur. Warning systems must be set up so people get sufficient time to save themselves. In addition, areas that are more likely to have floods must have tall buildings above the flood level.

Other than that, dams must be constructed strongly. The use of cheap materials causes dams to break. The government must ensure there is a quality building of dams to prevent floods.
In short, we cannot prevent natural causes like rain and the melting of glaciers. However, we can stop the manmade causes like breaking of dams, poor drainage system, installing warning systems and more. We should take inspiration from countries like Singapore that never experience floods despite having heavy rainfall for most time of the year.
FAQ on Flood Essay
Q.1 what are the consequences of a flood.
A.1 Floods cause immense destruction. They are responsible for the loss of human and animal lives. People lose their homes and cars in floods. They also cause soil erosion and uproot of trees.
Q.2 How can we prevent floods?
A.2 Governments must take up certain measures to prevent floods. We can install flood warning systems. Make people aware of what to do in times of flood. Moreover, we can also build a proper drainage system that will ensure no waterlogging.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Social Activism
- Volunteer and Community Service
How to Help Flood Victims
Last Updated: April 18, 2024 Fact Checked
wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, 16 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it over time. There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 214,898 times. Learn more...
Floods can be devastating. Depending on the severity, flood victims might lose everything they have: their homes, their jobs, even their loved ones. Whether it’s donating a dollar or volunteering to rebuild damaged houses, there are a several ways to lend a helping hand to those in need.
Determining How to Help

- Depending on where the flood occurred, different humanitarian organizations will be involved in coordinating relief efforts.
- If the flood occurred in the United States, chances are the American Red Cross [1] X Research source and Salvation Army will be marshalling aid and leading relief efforts.
- If it is an international natural disaster, check to see if UNICEF or AmeriCares are providing aid in the affected area. [2] X Research source
- Visit the organization's website or call to find out what kind of aid they are providing and how you can best get involved.

- Different needs will arise at different moments in the crisis. For instance, there will be emergent needs in the immediate aftermath as well as long-term rebuilding needs for years to come.
- Sometimes an organization will reach maximum capacity with certain types of donations (like clothing), but have a deficit in another area. The best way to know what is most needed is to frequently check-in with the status of their aid efforts and need by calling or looking for updates on their social media accounts.

- If you have extra funds or goods, you might consider making monetary donations. If you have time, skills, or other supportive resources to offer in lieu of monetary donations, you can offer these to those in need.
- There are pros/cons for each this type of involvement: for donations, a pro is that you can act quickly and put resources in the hands of organizations who can decide how to best help the victims. A con to making donations is that you don't necessarily know if all of your money will go directly to the victims (be sure to research how organizations administer donations before you give to them). One of the biggest pros of volunteering instead of donating money is that you get to feel like you really providing hands-on helps while interacting with people. A potential con is the danger and risk of injury associated with traveling to flood zones.
Making Donations

- Be sure that you are donating to a reputable organization like The Salvation Army, American Red Cross, or UNICEF. Unfortunately, some sham organizations can crop up in the aftermath of disasters as ploys to steal well-intentioned donations.
- Ask if you can make a donation via text message. A recent trend among aid organizations is to provide a phone number and keyword for people to make a donations. The amount you give will show up on your next mobile phone bill. It’s as easy as sending a text message, and much more meaningful!

- Gently used clothing, socks, shoes, bedding, and blankets are almost always in need after a devastating flood.
- You can also help the children affected by floods by sending them books and toys.
- Purchase and donate new, non-perishable food items and bottled drinking water.
- First aid kits, tents, mosquito netting, soap, and hygiene products might also be needed.

Becoming a Volunteer

- If you meet height, weight, age, fitness, education, and U.S. citizenship requirements, consider joining the National Guard . The National Guard is a part-time, locally organized branch of the U.S. military that responds to natural disasters (both in the U.S. and sometimes abroad) as part of their call of duty. After completing basic training, you can chose a short-term enlistment (three years) and then continue to be a member of the Individual Ready Reserve (IRR) who are called up in the event of emergencies like natural disasters. [5] X Research source
- Consider volunteering with Habitat for Humanities or other organizations whose mission is to clear debris, help homeowners salvage their personal belongings, and rebuild damaged homes. [6] X Research source

- If you are a health care professional, see if you can donate your medical services or supplies.
- If you are a contractor or work in construction, volunteer your manpower, supplies, and other resources towards rebuilding efforts.
- If you are an educator or child care worker, offer to provide support and assistance with displaced families and their children.
- If you are a business owner, especially in the area surrounding the flood, offer discounts or gratis goods/services to those affected by the flood.

- Get in touch with the local branch of the aid organization working with flood victims and see if they need help in their call center, hotline, or donation processing facility.
- You can also become a community liaison by collecting local donations and bringing them to the regional sorting facility.
Offering Other Kinds of Support

- If you are part of a church or religious organization, encourage your leaders to reach out to flood victims with support as well as tangible aid.
- Some large religious organization, like the Billy Graham Rapid Response Team , send crisis-trained chaplains into areas impacted by natural disasters to coordinate relief efforts and provide further emotional and spiritual support for those affected.
- If you are a spiritual person, pray for the flood victims and/or reflect for a moment on the situation. Open your heart to ways you can help, and be a comfort to those in need.

- Ask how you can be most helpful to those affected by the flood. They might need a hot, home cooked meal, help taking care of their pets, or photographing flood damage for insurance claims.
- Be a good listener and remember that sometimes its best to just listen and not offer your own opinions or solutions without being asked for them.
- Remember that people need support in the days, months, and even years following natural disasters. Be sensitive to the fact that new issues and difficulties can continue to arise, even after the flood waters subside.
Community Q&A
- Don’t go into flood areas without authorization and without being part of an organized relief effort. It might be dangerous for you, and ultimately unhelpful to others. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
- Be sure your donations go to a reputable organization so that your dollars end up in the right place. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
- Do not attempt to provide mental help and psychological support unless you are a trained professional. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.redcross.org/about-us/our-work/disaster-relief/flood-relief.html
- ↑ https://www.americares.org/take-action/
- ↑ https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/natural-disaster.html
- ↑ https://kidshealth.org/en/teens/natural-disaster.html
- ↑ https://www.nationalguard.com/guard-faqs#faq-454
- ↑ https://www.habitat.org/volunteer
- ↑ https://www.waldenu.edu/programs/resource/10-creative-ways-to-volunteer
- ↑ https://www.redcross.org/volunteer/become-a-volunteer.html#step1
- ↑ https://www.redcross.org/about-us/news-and-events/news/2021/coast-to-coast--red-cross-helping-disaster-victims.html
About This Article
To help flood victims, try making a monetary donation to a reputable organization, like the American Red Cross or UNICEF. You can also donate used or newly purchase goods, such as blankets, clothes, and first aid kits. Alternatively, consider volunteering with an organization, like Habitat for Humanities, to help clear the debris and rebuild damaged homes. If you're unable to travel to the site, get in touch with your local branch of an aid organization to see if they need help in their call center or donation processing facility. To learn more, like how to help flood victims by volunteering your professional services, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Aug 17, 2016
Did this article help you?

Ananya Sharma
Jun 4, 2017
Mar 1, 2017
Anvi Sabnis
Oct 5, 2018
Azka Kaleem Mohammed Omar Khan
Oct 20, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
- About Project
- Testimonials
Business Management Ideas

Essay on Flood
List of essays on flood in english, essay on flood – essay 1 (150 words), essay on flood: reasons, effects and conclusion – essay 2 (250 words), essay on flood in india – essay 3 (300 words), essay on flood: causes, consequences and prevention – essay 4 (400 words), essay on flood: types, causes and adverse effects – essay 5 (500 words), essay on flood: with causes, mitigating steps and warning system – essay 6 (600 words), essay on flood: with causes – essay 7 (750 words), essay on flood in india – essay 8 (1000 words).
Introduction:
Flood, simply put is an overflow of water from several sources. The nature of the world is to have dry land and water. When water gets on dry land in large quantity flood is said to have occurred.
Causes of Flood:
There are several events that can lead to a flood.
A few of them are highlighted below:
1. Heavy rain pours.
2. Melting ice and snow.
3. Rising sea levels and the overflowing river.
4. Bad drainage systems.
How Flood Affects our Environment:
A flood is by far a negative occurrence. Heavy flooding can have a damaging effect on our environment and the infrastructures in it. First, they can destroy houses and make them inhabitable. Also, they can remove sand from farmland making it difficult to grow crops. Aside from the above, flooding also contaminates clean water causing diseases and ailments.
Conclusion:
Governments around the world can reduce the risk of flooding by building a solid drainage system. We as individuals could also help by stopping drainage blockage.
Any dry land filled by excess water is called flood. It is a natural calamity caused due to several factors.
Reasons for Flood:
The reasons for floods can be natural and unnatural caused due to human activities. When there is excessive rainfall in river banks and coastal areas, there is an increase in water level which leads to overflow of water into the nearby dry land. Also, natural calamities like earthquakes cause Tsunami in oceans which leads to flooding of lands close to beaches. In heavily populated cities, due to congested buildings and roadways, flooding happens as there is not enough room for water to drain. In such cases clogged drainages lead to even more flooding of the area.
Global warming has resulted in the melting of glaciers which increase water levels of rivers and flooding of river banks. Deforestation also plays a major role in flooding.
Effects of Flood:
Floods cause large scale destruction to life and property. Buildings, roads and bridges are heavily damaged. Vast acres of crops are destroyed. Arable lands turn barren and clogged with salts. Countless homes and cattle get washed away. All electronic and digital communication seizes. Many lives are lost. And it does not stop there. Post flood, there is a huge risk in the spreading of water borne diseases. Scarcity of food and basic necessities arises. On the whole, floods cause multiple hardships and turn the livelihood of affected people upside-down.
Effective weather forecasting systems are to be maintained by the Government for timely intimation and evacuation of flood prone areas which will greatly help in keeping the many losses due to floods in check.
Flood is a natural disaster that involves overflowing of water over a region of land that is dry under usual conditions. It submerges the area with water. They are the most common kind of weather-related disasters and are a costly hazard. The level of flood can vary a lot – from a few inches to a level that goes up to meters high like a roof level of a house.
The causes of floods are many. They can happen during heavy rains when the drainage system is unable to handle the amount of rain fall. It can also happen even if low levels of rain occur continuously for many days. Floods can occur when the snow melts as temperature changes and it can result in bulk movement of water in the plains. Rivers can overflow sometimes and create flood in the neighboring regions. They can also be a result of breaking of dam which can flood the nearby areas.
There has been increase in the frequency of floods recently. Because of global warming, the average temperature of sea has increased significantly. This has led to higher rate of tropical storms in the Caribbean. It is also responsible for increase in sea level because of melting of ice caps and glaciers.
Floods cause large-scale loss to life and great damage to properties. Floods cause severe damage to agricultural regions of the affected area. There is loss of life of humans as well as animals. People and the government both suffer from loss in financial terms. Re-building of affected areas takes a lot of time and money.
In India, there are many regions which are affected by floods. Some of these are the Gangetic plains, coastal Andhra Pradesh and Orissa, Brahmaputra valley and South Gujarat. Within this year, more than 70 lakh people were affected by floods in India.
Flood is one of the recurring natural disasters which is an outcome of above average rainfall and accumulation of excessive water in every living area. Floods may occur due to overflow of water from the reservoirs or due to heavy down pour of rain in places where the drainage systems are not properly maintained.
Water may look so harmless and peaceful until the large quantities termed Floods harms us.
Common Causes of Flood:
Some of the common causes of Flooding are Heavy Rains, Overflowing Rains, Broken Dams, Urban Drainage Basins, Storm Surges & Tsunami’s, Channels with steep sides, lack of vegetation and melting of snow and Ice. Although the causes of floods are varied, most of the causes can be managed if not prevented.
Global Warming and Floods:
Another primary factor of Flood is increase in the atmospheric temperature i.e., Global Warming. Heating up of earth’s surface can lead to melting of ice glaciers and ice caps which leads to the rise in sea level thereby leading to overflowing floods in the coastal regions. Global Warming brings instability in the climatic condition of the earth, where one part of the world experiences floods and the other goes through drought.
Consequences of Flood:
Floods mostly disrupt the normalcy of living things on the planet. Floods are a great threat to the living things; floods also make way for mosquitoes to thrive thereby leading to all communicable diseases such as malaria, Dengue etc. Another impact of floods is loss of drinking water . Floods also lead to power cuts, damage of crops and soil erosion. Floods can also have an economic backslide, thus putting the country at risk.
Preventing Floods:
Some of the measures that can be done to prevent Floods are:
i. To ensure the meteorological departments are well equipped to provide flood warnings to the indicated zones.
ii. Flood resilient homes with efficiency to waterproof homes and moving electric sockets which moves higher as the flood rises.
iii. Protecting wetlands and planting trees systematically can help alleviate the direct floods.
iv. Stop encroaching of river beds and allowing the rivers to take its natural course can drastically bring down floods.
Floods can be scary, but it is in the hands of human beings to ensure it doesn’t impact our daily life. Water storing areas such as ponds, lakes and other water reservoirs should be maintained. Floods can be avoided by improving the soil conditions thereby allowing easy water absorption. Flood barriers can be used as a defense during Flood crisis.
Floods can either occur naturally or they can be facilitated by environmental factors that destruct the flow of water. Flood incidences have increased due to global warming. Global warming is an adverse effect of environmental pollution that causes a rise in temperatures on the earth’s surface. Global warming is associated with intense climatic changes like heavy storms, snowing and raised sea water levels. These changes in climate contribute to flooding. A flood is the spilling of water on dry land surfaces and causes it to submerge. It occurs when water overflows from the water bodies beyond its usual boundaries. Floods are destructive to the environment.
Types of Floods:
There are three main types of floods. Surge floods are floods that occur in the coast regions due to surges and tidal changes that occur in the sea or ocean. Hurricanes and storm surges on the sea or ocean can cause minor, moderate or major floods. The extent or severity of the floods are determined by the strength, size, speed and directions of the surges. Surge flood are usually severe and massively destructive.
Another type of floods is fluvial floods that occurs due to overflow of rivers. Rivers overflow due to heavy rains that increase water levels in rivers beyond its capacity therefore resulting in floods. Heavy snowing can also cause fluvial floods when the ice melts. Fluvial floods are risky when dams are involved because the increased levels of water in rivers creates immense pressure that cause increase pressure on the walls of dams and cause breakage which results in excessive flooding and environmental destruction.
The other type of floods is pluvial floods. Pluvial floods are caused by surface water as a result of heavy rainfall. Pluvial floods are destructive because they disrupt the drainage systems and cause an overflow which affects structures. Pluvial flooding occurs together with surge floods and fluvial floods. Although pluvial flooding does not involve a lot of water, it causes massive destruction of the environment and the infrastructure.
Causes of Floods:
Floods occur naturally due to some environmental factors. Heavy rains can cause an overflow of water form water bodies. Breakage of water body boundaries like riverbanks or walls of dams. Catastrophes like tsunamis and surges in storms cause heavy flooding. During heavy rains the lack of vegetation on the surface of the earth.
Adverse Effects of Floods:
Foods are destructive in nature and have negative impacts on the environment and the ecosystem. Floods cause death of living things and humans. Destruction of property and infrastructure negatively affects the economy of the region affected and economic activities are at a standstill due to disrupted livelihoods. Migrations from areas that are prone to floods is common, which results in overpopulation in urban areas. Financial constraints are experienced due to the rehabilitations from flood destructions. Prevention of floods that result from natural causes is a challenge.
In conclusion, it is evident that floods are destructive. The adverse effects of floods affects normal livelihood and the environment.
Flood is one of the natural calamities which is known to wreck a lot of havoc. There are so many different instances wherein floods are known to damage the whole area and bring massive loss of life and property as well.
Let us check further into the possible causes of flood and how we can eradicate it too.
The Causes of Flood:
Of course, there can be a lot of different cases of floods. Some of the key ones among them are as follows.
Heavy rains: owing to climate changes, many a times, it so happen that it rains torrentially. If the rain is much above normal, it can lead to flooding.
Broken dams: Dams help in keeping the water level in check. If the dams get broken sometimes, it is likely to lead to flood.
Tsunami: Natural calamities like tsunami is likely to create problems of flood and can bring massive loss of life and property.
Global warming: Owing to the increase in global temperature, the ice cap is melting and the increased level of water in the river bed is going to cause a flood.
Of course, there can be a lot of other reasons too which leads to flood and it is important to keep an eye on the water levels to issue a warning well in time.
The Mitigating Steps:
Now that we know the key causes which leads to flood, let us focus on some of the best mitigation measures which you can take to steer clear of this problem.
Flood Warning System:
This is by far the most important thing which one needs to do. It is important to have a sound flood warning system in place. When you have a dedicated system, it can help warn people who can move to higher altitude or take the right steps.
Restore Rivers to their Natural Courses:
Owing to the excessive development work which we have been carried out and harming the environment, too many rivers have diverted from their natural courses. This is another important reason for excessive flood. So, the right thing to do is to help in restoring the rivers to their natural course as it may prevent flood.
The Global Warming Remedial:
Action must be taken to cure the problem of global warming as it is definitely the cause of too many natural disasters. By choosing to cut the level of air and water pollution and minimizing the use of non bio-degradable products, we may be able to directly or indirectly help in controlling the problem of flood and its aftermath.
Modern Day Construction:
While flood is a natural calamity which may sometime come unannounced, it is important that we construct buildings in accordance with the modern technical advancements. The buildings should be so made that they are above the flood levels and they should be sturdy enough to withstand flood as well.
So, these are some of the important points which you should keep in mind. While some of them are ways by which we can prevent the implication and aftermath of flood, a few of them would help in preventing its occurrence as well.
Whenever any calamity occurs, it is important to do your bit to create awareness. The kind of destruction which can happen is whopping. By knowing about it a little ahead of time helps people be better prepared for it.
The bottom line remains the fact that we should all try and minimize the negative impact we are having on the environment. Doing this will ensure that we will be able to curtail the frequency of natural disasters like flood.
Flood is simply defined as the overflow of a very huge quantity of water that covers a very large area of land and leads to the destruction of land and properties and sometimes lives in the areas that are affected. A lot of regions in the world experience flooding every year. A flood basically occurs when there is excessive rain and there is no proper or good drainage system. The amount of flood is different from place to place and the extent of destruction also varies. For the overflow of water to be classified as flood, the area of land affected has to be mostly dry. Flooding can also happen as a result of water overflowing from bodies of water like lakes, oceans and rivers. Floods cause mass destruction. The effects and destruction caused by flood can take many years to fix and repair.
There are a lot of causes of flood; a few of them are discussed below:
1. Heavy Rains:
As discussed earlier, flood is mostly caused by an extended period of rain. This can happen if the quantity of rainfall is a lot more than the capacity of the drainage system. Flood can also be a result of high intensity rainfall in a short period of time.
2. Snow Melting:
Mountains that were covered with snow in the season of winter start to melt once temperature begins to rise. The sudden rise of the temperature causes the snow to melt and this leads to the massive movement of a lot of water to the plains and lands around. If the area receiving the water does not have a proper and good drainage system that will help in getting rid of the large quantity of water, there is going to be flooding. Flood that is caused by snow melting is also called a snowmelt flood.
3. Dam Breaking:
Dams are constructed to be able to hold the water that is flowing downwards from an area of land that is higher. The energy of the water can be used to turn and power propellers that can be used for the generation and creation of electricity. The dam can sometimes break when they can’t hold a large quantity of water and this causes the areas nearby to experience flooding. Sometimes, excessive water can be released intentionally by the dam to stop the dam from breaking which also results in flood but the flood from the intentional release of water isn’t as harsh as that from the dam breaking.
4. Water Bodies Overflowing:
Rivers and other water bodies can overflow sometimes and this leads to a situation that is flood like in the areas nearby. The areas that are low lying and are near the water body are the ones that are affected the most during the periods of water overflowing downstream.
5. Coastal Region Winds:
Hurricanes and very strong winds have the ability to carry sea water into coastal lands that are dry and this is a serious cause of flood. The coastal regions can experience severe damage and destruction. Tsunamis and hurricanes are widely known causes of serious devastation to areas of coastal lands.
Apart from all of the causes of flood discussed above, it is very important to note that the major cause of flood is global warming. The frequency and rate of flood has drastically increased recently. Researchers have said that the average temperature of the sea has wildly increased because of global warming and it has led to the increased sternness and rate of storms that are tropical in and around the Caribbean. The storms are said to have caused the countries in the region experiencing heavy rainfall. Global warming causes an increase in the atmosphere’s temperature and also causes the ice caps and glaciers to melt which in turn causes flood in a lot of regions. Global warming is believed to have a very major effect on the ice caps at the poles and it is believed that the situation is only going to get worse with time.
Overall, the climatic conditions of the earth have gone through a lot of very major changes and it is believed that global warming is the main cause of all of the change. It is believed that global warming is the reason why there is extreme drought in some places and serious flood in other places. Even though there isn’t much we can do about the glaciers melting or rain, we can do our part by building very good and reliable drainage systems that can handle water.
What is a flood? In normal terms, the excess availability of water in a region then it can usually hold is called flood. Floods are usually heard of it in news and through channels as every year, large portions of India are drastically affected by floods. It is mainly during the monsoon season with the onset of rain, we hear of different floods and the havoc they have caused to humans, animals and plant life. It is, therefore; very important to understand what floods are all about?
Types of Floods and their Causes:
Flood is not just the excess rainfall we talk about. There is a lot more to it. For instance, there are Flash Floods in which there is a sudden heavy downpour due to a cloudburst and the entire area is flooded within minutes. In India, areas in the states of Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir and Uttarakhand witness occurrence of flash flood every year. Similarly, we have river floods in which the areas around a river are flooded due to the swelling of the river. Some parts in Delhi witness river flood every year due to the overflowing of the river Yamuna due to excessive rains and the excess flow of water from the Hathnikund Dam. Another type of floods is the inland flooding . In the case of inland flooding, the area witnessing a rainfall get flooded with the roads and lanes all filled with water. This happens usually when proper drainage system is not in place or is inefficient due to severe blockages which obstruct the flow of water and leading to flooding of lanes and roads in the city. Again, Delhi and Mumbai are cities which see such floods even after an hour of continuous rainfall. People living in coastal areas are prone to coastal floods . These floods are usually caused by high tides or Tsunami which bring huge volumes of water on the land thereby flooding it. Another reason for coastal floods is global warming due which the rise in sea level temperatures has led to the subsequent rise in water level in coastal areas. Coastal areas of Kerala, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and Orissa witness such floods every year.
Deadliest Floods in Indian History:
India witness floods every year in different states. In fact, some regions are sure to be flooded with the onset of monsoon season. However, there have been occurrences of the flood which have caused massive destruction and hence are termed as the deadliest floods. Hence there is a need to know about them so as to understand and analyse what can be done in order to minimise such destruction in future years.
Deadly floods are a common occurrence in India after every few years. One of the deadliest floods in recent times was the flood in Gujarat in the year 1979 in the Machhu Dam-II. The Machhu Dam-II flopped on Aug. 11, 1979, discharging the full power of the Macchu River on the town of Morbi. The flood thus created in western India caused somewhere around 1,335 deaths, as per the Press Trust of India at the time.
Another of the deadliest floods in India is the one that shook Bihar in the year 1987 in the Kosi River. In any case, the Kosi River is prone to floods and is flooded almost every year. However, this year was particularly exceptional. The most decimating surge in Bihar’s history happened in 1987, when an avalanche obstructed the Bhote Kosi River, making it surge and crush more than 1.7 million homes. As per the statistics of the state, government flooding led to the death of 1,399 individuals and 5,302 animals.
The Tsunami that struck coastal India in the year 2004 was another such disaster which engulfed a number of lives. An extent 9.0 quake under the Indian Ocean on Dec. 26, 2004, set off a tidal wave that crushed southern India. As per the Government statistics 10,749 individuals died, 5,640 went missing and 2.79 million people were affected by the wave. It likewise devastated 11,827 hectares of products and demolished the occupation of 300,000 fishermen.
The Recent Kerala and Kedarnath Floods:
The most noticeably bad climate-related floods in India’s history happened in June 2013, when a few days of overwhelming precipitation activated blaze surges and avalanches in the northern territory of Uttarakhand. The downpour struck amid the bustling visitor season in Uttarakhand when a huge number of Hindu pilgrims rush to the region to visit its memorable sanctuaries. The rain happened some time before the start of rainstorm season, getting numerous off guard. An expected 4,094 individuals died and about 1 million were influenced by the catastrophe in Uttarakhand and neighbouring Himachal Pradesh, the worst affected being the region around Kedarnath. The military was brought in to evacuate around 100,000 people from rocky parts of the state, where they had turned out to be caught by the avalanches.
The recent floods in Kerala are another perfect example of how human activities have led to calling of nature’s ire in different forms such as floods. Had it there been a proper drainage system with no blockages, Kerala would not have witnessed such a massive flood.
The Need for Action:
We must not forget that older civilisations emerged around rivers and seas only and they just vanished with time due to the ever-rising water level on the earth. With the recent back to back occurrences in Kedarnath and Kerala, it is high time the Government as well all of us sit down and think what harm we have done to nature. The blooming of industrial units with no waste management in place, the inefficient drainage system and the careless attitude of both the Government and the people are all collectively responsible for these disasters. Not all disasters can be avoided, but, at least measures can be taken to minimise their impact or at least the ones caused by own carelessness can surely be avoided. It is for own good and for the benefit of future generations that we all do our bit to protect the life on earth from the backlash of nature.
Flood , Flood in India , Natural Disasters
Get FREE Work-at-Home Job Leads Delivered Weekly!

Join more than 50,000 subscribers receiving regular updates! Plus, get a FREE copy of How to Make Money Blogging!
Message from Sophia!
Like this post? Don’t forget to share it!
Here are a few recommended articles for you to read next:
- Essay on Success
- Essay on My School
- Essay on Noise Pollution
- Essay on Christmas
No comments yet.
Leave a reply click here to cancel reply..
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Billionaires
- Donald Trump
- Warren Buffett
- Email Address
- Free Stock Photos
- Keyword Research Tools
- URL Shortener Tools
- WordPress Theme
Book Summaries
- How To Win Friends
- Rich Dad Poor Dad
- The Code of the Extraordinary Mind
- The Luck Factor
- The Millionaire Fastlane
- The ONE Thing
- Think and Grow Rich
- 100 Million Dollar Business
- Business Ideas
Digital Marketing
- Mobile Addiction
- Social Media Addiction
- Computer Addiction
- Drug Addiction
- Internet Addiction
- TV Addiction
- Healthy Habits
- Morning Rituals
- Wake up Early
- Cholesterol
- Reducing Cholesterol
- Fat Loss Diet Plan
- Reducing Hair Fall
- Sleep Apnea
- Weight Loss
Internet Marketing
- Email Marketing
Law of Attraction
- Subconscious Mind
- Vision Board
- Visualization
Law of Vibration
- Professional Life
Motivational Speakers
- Bob Proctor
- Robert Kiyosaki
- Vivek Bindra
- Inner Peace
Productivity
- Not To-do List
- Project Management Software
- Negative Energies
Relationship
- Getting Back Your Ex
Self-help 21 and 14 Days Course
Self-improvement.
- Body Language
- Complainers
- Emotional Intelligence
- Personality
Social Media
- Project Management
- Anik Singal
- Baba Ramdev
- Dwayne Johnson
- Jackie Chan
- Leonardo DiCaprio
- Narendra Modi
- Nikola Tesla
- Sachin Tendulkar
- Sandeep Maheshwari
- Shaqir Hussyin
Website Development
Wisdom post, worlds most.
- Expensive Cars
Our Portals: Gulf Canada USA Italy Gulf UK
Privacy Overview
The Many Effects of Flooding
Floods can be destructive to humans and the natural environment, but they also help to drive biodiversity and are essential to the functioning of many ecosystems.
Earth Science, Climatology, Geography, Physical Geography
1931 Yangtze River Flood
In 1931, water overwhelmed the banks of the Yangtze and Huai Rivers, resulting in the Central China flood. Killing at least hundreds of thousands and potentially millions of people, it was one of the worst flooding events in recorded history. Here, people near the Yangtze River are shown.
Photograph from Adrienne Livesey, Elaine Ryder, and Irene Brien

It is hardly surprising that rivers have been an important part of human history: They provide food, freshwater, and fertile land for growing crops. While water is essential to life, it can be a destructive force too. When rivers flood, the effects can be catastrophic. Flooding is one of the most common types of natural disaster, and the results are often fatal. The Central China flood of 1931, for example, was one of the worst flooding events in recorded history. The Yangtze and Huai Rivers broke their banks, killing as many as several million people. The aftermath was devastating; deadly waterborne diseases like dysentery and cholera spread quickly, and those who survived faced the threat of starvation. The human cost of flooding can be large, but events like this have a big impact on the natural world too, and the effects are not always negative. In fact, some ecosystems rely on seasonal flooding to drive ecological processes. Floods Can Harm Wildlife Flooding can have a negative effect on wildlife, causing drowning, disease proliferation, and habitat destruction. In 2012, hundreds of animals, including many vulnerable one-horned rhinos ( Rhinoceros unicornis ), were killed in floods that swamped Kaziranga National Park in the Indian state of Assam. Unpredictable floods can be harmful even to aquatic life. For example, fish can be displaced and their nests destroyed.
Floods Cause Sedimentation and Erosion Floodwater can also alter the landscape, for instance, by eroding riverbanks and causing them to collapse. As floodwater carries material from the eroded banks, it suspends sediment in the water, which can degrade water quality and lead to harmful blooms of algae. Suspended sediment eventually settles out of the water in a process called sedimentation, which can clog riverbeds and streams, smother aquatic organisms, and destroy habitats. Erosion and sedimentation have a more negative impact on ecosystems that are already degraded or heavily modified. Floods Carry Contamination Floodwater can be contaminated with pollutants such as agricultural pesticides , industrial chemicals, debris, and sewage. If contaminated floodwater enters the ocean it can affect water quality and disrupt delicate ecosystems, such as coral reefs. In February 2019, marine biologists feared for the safety of the Great Barrier Reef off the coast of Queensland, a state in Australia, after it was inundated with polluted floodwater. Floods Spread Diseases Floods are the leading cause of weather-related infectious disease outbreaks. Flooding events increase the chance of spreading waterborne diseases, such as hepatitis A and cholera. Receding floodwater can create stagnant pools of water, which provide the perfect breeding ground for mosquitoes, which can transmit malaria and other diseases. Flood events also lead to an increase in some forms of zoonosis , such as leptospirosis. Floods Carry Nutrients While floods bring hazards, they also bring nutrients and essential components for life. Seasonal floods can renew ecosystems, providing life-giving waters in more ways than one. Floods transport vital nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and organic material, to the surrounding land. When the water recedes, it leaves sediment and nutrients behind on the floodplain. This rich, natural fertilizer improves soil quality and has a positive effect on plant growth, thus increasing productivity in the ecosystem. Ancient civilizations first arose along the deltas of seasonally flooded rivers, such as the Nile in Egypt, because they provided fertile soil for farmland. Floods Recharge Groundwater Floods can replenish underground water sources. Floodwater gets absorbed into the ground then percolates through layers of soil and rock, eventually reaching underground aquifers . These aquifers supply clean freshwater to springs, wells, lakes, and rivers. Ecosystems rely heavily on groundwater during dry spells when it may be the only supply of freshwater available. A good supply of groundwater has a positive impact on soil health and leads to more productive crop and pasture lands. Floods Can Trigger Breeding Events and Migrations Floods can trigger breeding events, migrations, and dispersal in some species. In 2016, thousands of water birds flocked to the Macquarie Marshes in the Australian state of New South Wales. Flooding had filled their wetland habitat for the first time in years, triggering a mass breeding event. In Cambodia, monsoon rains cause an annual flood pulse on the Mekong River that prompts migrations for some animals. The floodwaters cause the Tonle Sap river, which connects the Mekong River to Tonle Sap lake, to reverse its flow, filling the lake. When floodwater enters the lake, it triggers fish migrations, supporting one of the world’s most productive fisheries. Floods Can Boost Fish Stocks Small seasonal floods can be beneficial to native fish stocks and can help those fish outcompete invasive species that are not adapted to the river’s cycles. Sediment deposited on riverbeds during floods can provide a nursery site for small fish. Nutrients carried by floodwater can support aquatic food webs by boosting productivity. Floods Bring Life to Wetlands Wetlands are an extremely important ecosystem; approximately 40 percent of the world’s species rely on them. They filter water, mitigate flooding, and act as a carbon sink . The Okavango Delta in Botswana is a United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) World Heritage Site and one of the world’s largest, most important wetland habitats. The river captures rainfall from far to the north in the highlands of Angola. This causes a flood pulse that replenishes the wetlands at the height of the dry season, providing a lush oasis in the Kalahari Desert. National Geographic Explorer Steve Boyes, with a team of scientists and Explorers, has participated in a series of expeditions to trace the Okavango from source to sand to protect the waters of this unique habitat. Floods are a force of nature, and their consequences, both positive and negative, are strongly felt by affected ecosystems. Floods can be destructive to humans and the natural environment, but they also help to drive biodiversity and are essential to the functioning of many ecosystems. Whether you regard floods as good or bad, one thing is for certain: The world would be a very different place without them.
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Production Managers
Program specialists, last updated.
January 22, 2024
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources
- CBSE Class 10th
- CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Main Question Paper
- JEE Main Cutoff
- JEE Main Advanced Admit Card
- AP EAPCET Hall Ticket
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- KCET Result
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Admit Card
- TS ICET 2024 Hall Ticket
- CMAT Result 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- NEET Rank Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Admit Card 2024
- NEET PG Application Form 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top NLUs Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Predictors & Articles
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- NID DAT Syllabus 2025
- NID DAT 2025
- Design Colleges in India
- Top NIFT Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Interior Design Colleges in India
- Top Graphic Designing Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Interior Design Colleges in Bangalore
- NIFT Result 2024
- NIFT Fees Structure
- NIFT Syllabus 2025
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission 2024
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- LPU NEST 2024
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET Exam City Intimation Slip 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET Mock Test 2024
- CUET Admit card 2024
- CUET PG Syllabus 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Syllabus 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- IGNOU Result
- CUET 2024 Admit Card
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Flood Essay
Floods are natural disasters that occur when a body of water, such as a river or ocean, overflows its banks and spills onto the surrounding land. This can happen for a variety of reasons, including heavy rainfall, melting snow, and storms . Here are a few sample essays on floods.
100 Words Essay on Floods
Floods are naturally occurring phenomena that are caused due to overflowing water bodies. A flood can be just a small occurrence that can cause some travel issues to highly destructive events that can cause significant damage to homes, businesses, and infrastructure. In addition to physical damage, floods can also lead to loss of life and can have long-term impacts on the affected communities.

To protect against floods, people can take steps such as building floodwalls and levees and elevating homes and other structures in flood-prone areas. It is also important for individuals to be prepared for floods by having an emergency plan in place and staying informed about potential flooding in their area.
200 Words Essay On Floods
Floods are natural disasters that occur due to overflowing water sources like ponds, oceans and rivers. The reasons for the occurrence of floods can be heavy rainfall, loose soil, melting of snow, breaking of dams etc.
Impact | The impacts of floods can be far-reaching and long-lasting. In addition to physical damage to homes, businesses, and infrastructure, floods can also lead to loss of life. Floodwaters can carry dangerous debris and pollutants, making them a health hazard for people and animals. Floods can also have economic impacts, as they can disrupt transportation and commerce, and can destroy crops and other sources of food.
Prevention | People living nearby water bodies take preventative measures to reduce the impact of flood damage. Building elevated homes, planting more trees to soak up an extra amount of water, having an escape plan in case of emergencies etc. It is also important for individuals to be prepared for floods by having an emergency plan in place and staying informed about potential flooding in their area. In the event of a flood, it is important to follow the advice of local authorities and evacuate if instructed.
Overall, floods are serious natural disasters that can have significant impacts on communities. By taking steps to protect against floods and being prepared for them, people can reduce the risks and impacts of this type of disaster.
500 Words Essay on Floods
Floods are a common natural disaster that occurs when excess water overflows onto land that is normally dry. This can happen for a number of reasons, including heavy rainfall, snowmelt, and coastal storms.
Types Of Floods
There are several different types of floods, each with its own characteristics and potential impacts. Flash floods, for example, are caused by sudden, intense rainfall and can happen within minutes or hours. They can be particularly dangerous because they often catch people off guard and can lead to flash flooding in urban areas.
On the other hand, river floods are caused by water flowing over the banks of rivers and streams. These floods can be more gradual, giving people time to evacuate and prepare, but they can also be very destructive.
Coastal floods, also known as storm surges, are caused by strong winds and high tides associated with coastal storms, such as hurricanes. These floods can be extremely destructive, as they can cause not only flooding but also strong winds and waves that can damage buildings and infrastructure.
Biggest Floods Recorded On Earth
One of the biggest floods in history was the 1931 China floods , also known as the Central China Floods . These floods were caused by heavy rainfall and the collapse of the Banqiao Dam. The floods affected an estimated 54 million people and resulted in the deaths of 145,000 people.
Another major flood was the 1993 Mississippi River Flood , which affected parts of the United States, including Missouri, Illinois, and Kentucky . The floods were caused by heavy rainfall and resulted in the deaths of 50 people and caused billions of dollars in damages.
In 1998, the Yangtze River Flood in China also caused widespread destruction. The floods, which were the result of heavy rainfall, affected millions of people and resulted in the deaths of over 4,000 people. The floods also caused billions of dollars in damages.
Another recent and devastating flood was the 2010 Pakistan floods, which affected the Indus River Basin in Pakistan. The floods, which were caused by heavy monsoon rains, affected an estimated 20 million people and resulted in the deaths of over 1,700 people.
Forest To Prevent Floods
Forests play a critical role in preventing floods. Trees and other vegetation in forests can act as natural barriers which absorb water. Hence, reducing the speed of flowing water and thereby reducing the risk of flooding.
When it rains, the leaves and branches of trees absorb a significant amount of water. The roots of trees also help to hold the soil in place, preventing it from eroding and being carried away by the water. This helps to reduce the amount of water that flows over the surface and into rivers and streams, lowering the risk of flooding.
In addition to absorbing water, forests also help to regulate the flow of water by releasing it slowly into rivers and streams. This helps to prevent sudden, large increases in water levels that can lead to flooding. Trees and other vegetation can help to reduce the force of the water and protect against erosion, which can help to minimise the damage caused by floods.
Applications for Admissions are open.

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)
Register FREE for ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)

JEE Main Important Physics formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Physics formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

PW JEE Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for JEE coaching

PW NEET Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for NEET coaching

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Certifications
We Appeared in

Essay on Flood for Students and Children in 1000+ Words
In this post read an Essay on Flood (Natural Disaster) for Students and Children in 1000+ Words.
Table of Contents
Essay on Flood (1000+ Words)
This essay includes what is flood?, its causes, effect, and preventive measures.
What is Flood?
A flood is a natural disaster that arises due to excessive runoff of water in the rivers due to rainfall . This causes the water of rivers to come out from the edges and flow into the plains. Floods can last from a few hours to a few days, but it can cause great harm to people, money and crops.
Causes of Flood
Among the most severe natural hazards are floods. This happens in every environment where excessive water is stored. Generally, it is heavy rainfall. In India, there is a strong probability of floods.
Due to heavy river rains, several places in the world face natural disaster . Besides, the breaking of the dam is another cause of a flood. Furthermore, this is also triggered by melting ice.
If we aim at coastal regions, floods are liable for hurricanes or tsunamis. We should look at flood avoidance and its long term side-effects throughout this essay about floods. Nevertheless, it really is equally risky, but whatever cause might be.
This has some negative effects. Floods cause harm to living conditions or recovery from this tragedy takes a very long time. The effects of flooding should therefore be understood, and steps should be taken to avoid them.
Effect of Flood
The day-to-day operation of the flood-affected region was disrupted. Extreme floods cause immense devastation often. Owing to flooding, many individuals, or animals risk their lives. Many more are being wounded. Floods raise illnesses, as well. Stagnant weather, due to malaria, dengue, and much more illnesses, attracts insects.
Moreover, due to electrical risks, individuals face power outages. They face expensive costs, too. Prices inevitably rise as the availability of food and products become reduced.
This, for the average man, is a big issue. Most significantly, economic losses are suffered by the entire world. To save lives and deal with this tragedy, a huge amount of resources are needed. At the very same time, people are losing their homes or their vehicles, which they have dedicated all their lives to.
Floods also ultimately damage the climate. This triggers soil erosion which degrades the consistency of the soil. On a fertile planet, we are destroyed.
Floods also do damage to fauna and flora in the same way. Crops are destroyed, & trees are displaced. Steps to prevent these serious effects should also be taken.
Ways to Prevent flood
To devise solutions to avoid flooding, government and people must work together. Proper knowledge of these steps can be taken and disseminated in the aftermath of a natural disaster.
In order for people to get enough time to defend themselves, an alert system must be established. Furthermore, areas more vulnerable to flooding must have elevated buildings just above the point of flooding.
In addition, an effective system for processing excessive water due to bad weather should be usable. Excess water can avoid this. Reinforcing the drainage scheme is among the most critical steps. This will eliminate water-logging, to prevent flooding.
The dams must, however, be heavily built. The use of inexpensive materials breaks dams must be applied and government should ensure that the efficiency of dams is designed to stop flooding.
We have split the causes of floods into two stages viz: organic and inorganic floods. First, natural floods would be addressed.
Natural floods
Floods are called natural floods due to natural factors.
1. Excess of rain – often at one location there is a lot of constant rainfall due to that there is water logging all over, and it comes in the form of flooding in a certain period.
2. Cloud Burst -A large volume of water that flows in the next few hours due to bursting of a cloud, because from which the water flows at a high pace as well as a flood situation occurs, the clouds mainly burst and in mountain terrain. Due to thunderstorm, the Uttarakhand region is flooded every other year in their region.
3. Melting of ice from the glacier- The glaciers are starting to melt even more snow owing to the increase in the Earth’s temperature that causes the water to fall from the mountains at a high velocity so this water has become so high. That one can easily knock out every town or village and fully submerge it.
4. When rivers are overflowing- A significant volume of drainage into the rivers is caused by excess rainfall and melting snow, allowing the water to abandon its course and flow around rather than flood its lowlands of cities and villages near the river , it goes.
5. Sea Flood – A tsunami is often considered the first flood of water. This happens when in certain areas of a sea, a cyclonic storm or even a powerful earthquake happens, due to that, high waves increase, or the seawater floods the villages and cities. This refers to areas for flooding. Because of this, many coastal communities of the sea are impacted very badly. Sea storm waves could be as higher than 10 feet, and that’s much more than the height of every building.
Unnatural floods
The work undertaken by human’s triggers unnatural floods are:
1. Dam Breakdown – Large reservoirs are designed for water storage by humans; however, the dam is not reinforced due of corruption and bad design that breaks up a dam full of thousands of liters of water in the next few years.
There is a heavy flow of water with this and the areas from around the dam were covered in water. Suddenly, the ward arrives, so citizens do not get an opportunity to regain, and there is further loss of life or property.
2. Flooding due to Global Warming – Global Warming This scenario has been produced by humans just because humans are harvesting indiscriminate trees, and also spreading a huge amount of pollution .
Since the global climate is rising while at the same time that Earth’s climate is also shifting because there is a lot of rain for certain areas, there is a lot of rain in certain areas and because of the increase in the temperature of the Earth, the ice mostly on glaciers Millions of liters of water accumulated in the form begins to melt because of the water crisis.
3. Plastic pollution – A large volume of plastic is often used in India, and this plastic is dumped in such open areas, however, this plastic is stuck in the hair created to drain the water because the water may not get in the hair when it rains as well as the flood situation occurs.
10 Lines on Flood
- The flood is an immense quantity of water that overflows covering a wide region that causes damage.
- Not only is the flood devastating a vast city, but it also takes several lives or destroys property.
- Each year, many regions of the world are hit by flooding, taking lots of lives.
- Lead to increasing rainfall or a lack of proper sewage system inside an area, flooding occurs.
- In an area that causes double harm, floods often occur like an after-effect of a horrible cyclone.
- The farmers have to be the worst impacted citizens of the flood as flood kills their fields and also their land’s productivity.
- Flood water obtained at a specific location allows individuals to have different kinds of diseases.
- When the flood situation is serious, all the stores are closed, affecting the availability of essential products.
- In order to reduce the effects of flooding, the government must develop a strong drainage system.
- Early warning implementation must be carried out, and individuals are sent to safe areas until floods occur.
In short, natural factors, such as rain or melting glaciers, could not be avoided. We may escape human-made triggers, however, like dam breakage, bad drainage systems, installation of alarm systems, and much more. We must draw inspiration in countries such as Singapore that, for much of the year, do not experience floods despite heavy rain.

Leave a comment Cancel reply

106 Flood Topic Ideas & Research Questions on Flooding
🏆 best flood topic ideas & essay examples, 📌 simple & easy flood essay titles, 👍 good essay topics on flood, ❓ research questions on flooding.
- Sri Lanka Flood Disaster Preparedness From these findings, it is evident that floods are the major concerns for the disaster management center, with the recent damages being witnessed towards the end of 2012 and the beginning of the year 2013.
- The Strategies of Flood Management However, it would be the most beneficial to implement these methods while planning the use of the land; for this reason, management is important.
- Floods, Technology and Price Ceiling in the Market From the graph, assuming that the equilibrium price in the fruits and vegetable market was EQ0, the floods destroy the products in the fields and this causes a shift of the supply curve to the […]
- Floods in Los Angeles and Disaster Response The Los Angeles local government is set to respond and control the effects of floods. Therefore, the local government and citizens have set aside adequate resources to respond to the disaster.
- A Climate Economics Issue: Increased Flood Risks There is a number of flood management plans in the United Kingdom for rivers where risks are known, such as the Anglian River basin.
- The Louisville Flood Photo by Margaret Bourke-White The peculiarity of this photo is that it shows the contrast between the black people standing in line and the white ones painted on the placard.
- The Devastating Flood of 1993: Lessons Learned In order to understand the causes and consequences of the flood that occurred in the summer of 1993, it is necessary to define the meaning of the concept of flood.
- Ethical News Coverage: Indian Floods 2020 As part of the assessment of the consequences of reporting these events, it should be noted that the materials presented can attract public attention to help people in the affected areas, which is important for […]
- Addressing the Threat of Flash Flood to Birmingham, Alabama The purpose of the work is to identify the key stages of threat addressing, including mitigation steps, preparedness and communication mechanisms, and response and recovery measures to address the outcomes of such disasters.
- The Flood Stories in Different Cultures The scientific community recognizes that the oldest flood myth known to humanity is the Epic of Gilgamesh, which tells the story of Utnapishtim, who attained immortality by escaping from the flood on a ship.
- Nova Killer Floods Documentary Review Flood is a phase of the water regime of the river, which is repeated every year at the same time of year, is characterized by the highest water content, increased and prolonged rise and fall […]
- Floods in the City of Austin, Texas on October 30th, 2013 The catastrophic consequences of the devastation in Central Texas and, in particular, in the city of Austin, were caused by flooding.
- Disaster Management in the Flood Scenario In such a case, the authorities and residents should adopt disaster prevention and preparedness strategies to minimize impact and adequately brace for the expected flood magnitude.
- Flood Damage by Hurricane Maxine in Charleston The role of the mayor and his dignitaries is to determine the duration and level of use of resources by the city.
- Local Hazard Mitigation: Floods While the federal government has been actively trying to reduce the scope of the problem for years, in the past decades, economic losses from floods have been growing. Overall, in the past years, NFIP initiatives […]
- Theory of Disaster: Earthquakes and Floods as Examples of Disasters The second category is that of those people who put their focus on the effects of the social vulnerability or the disasters to the society or to the people who are likely to be the […]
- Hydrology Methods: Flood Risk Management Digital spatial information modelling and the integration of the data and information used in the decision-support system illustrate the technical basis of the paper.
- A Flood Insurance Program in Canada: The Way to Protect Lives and Homes Floods are the major source of property loss: according to the analysis made by Munich, insurance companies do not want to take all the bills they get and ignore the majority of them.
- Flood Effects That Occurred in July 2007 at Sheffield The report, therefore, entails in detail the immediate as well as the significant risks and losses caused by the flood, the factors contributing to the occurrence of floods, identification of all the agencies which were […]
- Environmental Management: Floods Management Systems Considering the significance of environmental protection in the case of floods, the present report provides a detailed overview of such natural disasters in terms of contributory causes, impact, risks, and the role of environmental management […]
- Minimizing Flood Fatalities in Canada The main goal of this study is to compile more details in regarding flood fatalities in Canada which may be useful in avoiding and preparing for flood related disasters.
- City of Jeddah’s Flood: Cause and Disastrous Effects Jeddah is a city in Saudi Arabia found in the western region.and the it is a flat, low- lying ground next to the Red Sea.
- Great Flood in Mississippi River Basin: Major Factors Mississippi River, the longest river in the United States and, with its extensive offshoots, is one of the most important river systems of the world.
- Floods: Structural vs. Non-Structural Solutions The occurrence of hazards disorients the lives and experiences of many people. The selected community can mitigate this hazard through the use of non-structural and structural solutions.
- The Ancient Near East: Civilization of Mesopotamia and Great Flood The Great Flood in Genesis and the Epic of Gilgamesh both depict the flood, the boat, the God of gods, and persons responsible for preserving humanity.
- Flood Disaster Recovery Plan and Stakeholders The scope of this document: responsibilities, major hardware and software procedures, disaster response, testing of the recovery plan. The purpose of this disaster recovery plan is to provide detailed guidelines to all the stakeholders when […]
- Gavin Flood’s Comparative Religion Studies In essence there is need to carry out more research in this field in order to be able to establish the role and the importance of religion in the life of human beings.
- Flood Mitigation Measures in the United States The mitigation measures for floods include the following; “control over rivers, establishing policies and legislation on the use of land such as terracing and assess to flood-prone areas”.
- Climate Change: Floods in Queensland Australia Over the recent past, the issue of climatic change has raised major concern about the well being of the recent as well as the future generation. The rail lines were also destroyed the fact that […]
- Great Barrier Reef: Flood Alleviation Solutions In the first presentation, solutions to protect the Great Barrier Reef, which is endangered from rising acidity levels due to methane extraction, were given while the second, third and fourth presentations focused on the measures […]
- The Flood of San Antonio in 1921: Re-Evaluating the Effects, a Catastrophe Viewed Through a Different Lens However, the reconstruction of the city takes less time than the reconstruction of the environment destroyed by the flood, which is why the effects of the San Antonio flood on the environment must be reassessed.
- Year of the Flood While the Geneva Convention on Human Rights has banned the use and development of biological agents as a means of warfare, thus sparing humanity the possibility of dying due to a virulent disease, the fact […]
- The Midwest Flood of April to October 1993 The Midwest flood of April to October 1993 is arguably the greatest flood to have hit the United States in terms of coverage and duration.
- The Similarities of The Epic of Gilgamesh and Noah & The Flood
- The Story of the Flood- the Epic of Gilgamesh
- The Flood Has Changed History Forever
- Red River Flood of 1997 & The Breakdown of Collaborate Management
- Viability of Green Roofs as a Flood Mitigation Element in the Central Region of Chile
- Rising Tide: The Great Mississippi Flood Of 1927 And How It Changed America, By John M. Barry
- Regional Flood Frequency Analysis in Tunisia: Identification of Regional Distributions
- The Economics During And After Kerala’s Flood Disaster
- Sustainability-Based Flood Hazard Mapping of the Swannanoa River Watershed
- The Demand for Index‐Based Flood Insurance in a High‐Income Country
- Understanding Flood Risk Decisionmaking: Implications for Flood Risk Communication Program Design
- Who Should Pay for Climate Adaptation? Public Attitudes and the Financing of Flood Protection in Florida
- Sea-Level Rise and Land Subsidence: Impacts on Flood Projections for the Mekong Delta’s Largest City
- The Flood Of Media Attention On Brain Injuries
- Spatial Variation in Flood Risk Perception: A Spatial Econometric Approach
- The Debate Over the Idea of the Genesis Flood in Genesis vs. Geology, an Essay by Steven Jay Gould
- The Affordability Goal and Prices in the National Flood Insurance Program
- The Fallibility of Flood Warning Chains: Can Europe’s Flood Warnings Be Effective
- Special Flood Hazard Effects on Coastal and Interior Home Values: One Size Does Not Fit All
- Land Use Scenario Modeling for Flood Risk Mitigation
- The Effects Of Flood Damage On Everyday Life
- The Bible According to Mark Twain: Writings on Heaven, Eden, and the Flood
- The Story Of The Flood, How Utnapishtim Tells His Story To Gilgamesh
- The City Of Vanport And Its Struggle With Racism Before And After The Flood Of Vanport
- The Importance of a Flood Free and Clean Living Community
- The Significant Key Elements on Climate Change in Before the Flood, a Documentary by Fisher Stevens
- Smoothing Income against Crop Flood Losses in Amazonia: Rain Forest or Rivers as a Safety Net
- Technological Advancements and Flood of Immigrants in the Turn of the Century in Ragtime, a Novel by John Pierpont Morgan
- The Different Versions of Flood Stories in Many Different Culture
- The Flood Story in Genesis, the Epic of Gilgamesh, and the Flood Story in the Holy Quran
- The Truth Behind Noah And The Great Flood
- Why the National Flood Insurance Program Is Not Financial Viable
- Risk Management Solutions For Flood And Earthquake Catastrophes In Romania
- Urban Growth and Flood Disasters in the Coastal River Basin of South-Central Chile (1943–2011)
- Regional Flood Frequency Analysis Using L-Moments for the West Mediterranean Region of Turkey
- The Intricacy of Adapting to Climate Change: Flood Protection as a Local Public Goods Game
- The Flood Accounts In The Epic Of Gilgamesh And The Genesis
- The Theme of Ancient Flood in Genesis of the Torah and the Epic of Gilgamesh
- The Differences In Gilgamesh, Atrahasis & The Deucalion & Pyrrah In Ovid Flood Myths
- The Factors that Influence the Flood Hydrograph
- The Godly Perspective of the Corruption of the World in the Story of Noah and the Flood
- The Devastation Left by the Flood in Downtown Davenport
- How Can You Survive a Flood?
- How to Promote Resistance to Flooding During Rice Germination?
- What Are the Different Techniques of Flood Forecasting?
- What Are the Consequences of Floods in Vietnam?
- Is Climate Change Leading To Extreme Floods?
- Where Is the Biggest Flood in the World?
- Are You Willing to Pay to Reduce Environmental Risks From Sewage Flooding?
- How Do Floods Affect Food Security in South Asia?
- Has Community Awareness of Flooding Improved in Boulder County, Colorado?
- What Are the Physical and Human Causes of Floods?
- When Was the Biggest Flood in Sri Lanka?
- What Could Be the Causes of a Dam Breach Leading To Flooding?
- What Are the Strategies and Practices for Urban Flood Protection?
- Does Your Insurance Cover Flooding?
- What Organisations Assist People and the Community During a Flooding Event?
- What Is the Estimated Economic Cost of Coastal Flooding?
- What Are the Steps Taken by the Government to Manage Disasters?
- Does Keeping Gutters and Drains Clear Help Against Flooding?
- How Do Drought and Flooding Affect the Development of Grain Yield?
- What Are the Types of Measures of Flood Management?
- Is Flood Insurance in the Netherlands Different From Other Countries?
- What Is the Impact of Land Use Change on Flooding Areas?
- How Pakistan Floods Linked to Climate Change?
- What Is the Interaction Between Floods and Economic Growth?
- How High Is Urban Flood Vulnerability in Guyana?
- What Are Some Tips to Prevent Basement Flooding?
- How Should We Interpret the Genesis Flood Account?
- Are Flood Risks More Physical Than Human?
- Does Water Quality Deteriorate as a Result of Severe Flooding?
- What Is the Effect of Flooding Along the Mississippi River on the Gulf of Mexico?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 25). 106 Flood Topic Ideas & Research Questions on Flooding. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/flood-essay-topics/
"106 Flood Topic Ideas & Research Questions on Flooding." IvyPanda , 25 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/flood-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '106 Flood Topic Ideas & Research Questions on Flooding'. 25 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "106 Flood Topic Ideas & Research Questions on Flooding." February 25, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/flood-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "106 Flood Topic Ideas & Research Questions on Flooding." February 25, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/flood-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "106 Flood Topic Ideas & Research Questions on Flooding." February 25, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/flood-essay-topics/.
- Plate Tectonics Essay Titles
- Glaciers Topics
- Climate Change Titles
- Evacuation Essay Topics
- Famine Essay Titles
- Tornado Topics
- Climate Research Ideas
- Deforestation Research Ideas
Advertisement
Understanding urban flood vulnerability and resilience: a case study of Kuantan, Pahang, Malaysia
- Original Paper
- Open access
- Published: 14 March 2020
- Volume 101 , pages 551–571, ( 2020 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- M. Y. Safiah Yusmah ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4317-6124 1 ,
- L. J. Bracken ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1268-5516 2 ,
- Z. Sahdan 3 ,
- H. Norhaslina 1 ,
- M. D. Melasutra 4 ,
- A. Ghaffarianhoseini 1 ,
- S. Sumiliana 5 &
- A. S. Shereen Farisha 1
14k Accesses
27 Citations
1 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Malaysia is frequently affected by the annual flooding event caused by the seasonal monsoon which accounts for significant losses. Flood risk, exposure and damage potential are increasing, causing the level of poverty and vulnerability to rise. The annual occurrence of the flood hazard has forced residents to prepare beforehand to help them spring back to their daily life faster. This study aimed to investigate and understand the vulnerability and resilience of the victims towards floods in Kuantan, Pahang. A qualitative approach of focus group discussion (FGD) is used to obtain detailed and authentic information. A total of thirty-one (31) participants who were flood victims took part in the FGD. Six groups were formed for the FGD based on different criteria such as gender, age, education background, occupation, monthly income and social class. Each FGD group consisted of four to six participants. When the participants were asked to rank their top five daily challenges, many thought that flooding is not a threat compared to food, because flooding occurs annually and is predictable. The results showed that the participants are well aware of the causes of the vulnerability faced by them due to the flooding event. Reasons highlighted from the results for the flood occurrence are the demography of the area, the location of the houses, the improper and inaccurate information and evacuation plan, the management of the transit centre and the lack of preparation by the community. The participants also thought that poor dissemination of early warning information and flood control infrastructures from the government and other related agencies caused the victims to have insufficient time to prepare for emergencies, hence causing the recovery process to be slower. However, from their hands-on experiences, they were able to put forward suggestions on the resilience towards flood for future references.
Similar content being viewed by others
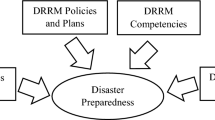
Disaster preparedness of local governments in Panay Island, Philippines
Urban marginality: Everyday practice of building resilience to flood in the informal Settlement of Dar es Salaam

Planning for Effective and Sustainable Water Access and Provision in QwaQwa Through the UN Sustainable Development Goals
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
The rapidly changing climate threatens to increase natural hazards and extreme weather such as floods, cyclones, hurricanes and drought, with floods being the most disastrous, frequent and widespread (Dhar and Nandargi 2003 ). Hydro-meteorological themed disaster has increased around Asia and South-East Asia countries over the last two decades. Countries such as China, India, Bangladesh and Pakistan are known as the supermarket for disaster especially in terms of disastrous floods (James 2008 ). Therefore, due to the global climate change, middle and rapidly developing countries are the victim of the economy as most of the damage caused by the disastrous events occur in poor countries with few assets. The occurrence of flooding are predicted to quadruple by 2080 as sea level is expected to continue rise due to global climate change (Small and Nicholls 2004 ). This is especially frightening for the population living in coastal areas as it is the most populated area in most countries with an estimate of 23% of world population living within 100 km and less than 100 m above sea level (Molua and Lambi 2007 ; Small and Nicholls 2004 ). Urban flooding is well known as it has caused damage and loss of life. Urban flooding inundates land or property in a built environment, particularly in densely populated areas. These floods are usually caused by flash floods, coastal floods or river floods, but urban flooding is often specifically due to poor drainage in urban areas. Urban flooding is often related to global climate change issues because most urban areas are the major contributors to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions that eventually causes global warming. Over concentrated population, increasing infrastructure and economy cause the sustainability of an urban area to worsen. Over time it has become more challenging for the government and developers to create development plan that balances the demand of urbanization while minimizing the use of natural resources. Urban planners should concern and practice actions against climate-induced disasters (Godschalk 2003 ; Saavedra and Budd 2009 ; Kithia and Dowling 2010 ).
Malaysia, as a South-East Asia country, is located near the equator with climate categorized as equatorial. Equatorial climate is relatively hot and super-humid throughout the year with average rainfall of 250 cm annually (DID, 2007 ). In addition, it is essential to learn that the climates in Peninsular Malaysia differ to East Malaysia where the climate in West Malaysia is directly influenced by the monsoon wind from the northeast and southwest, while in East Malaysia the climate is mostly influenced by maritime weather. A yearly constant cycle of heavy rainfall at the east coast of Peninsular Malaysia and east of Malaysia (Sabah and Sarawak) between November and February are caused by the northeast monsoon wind while rain bearing winds from April to September caused by the southwest monsoon. The amount of rain from the southwest monsoon is lesser than the northeast monsoon that can reach up to 660 mm in 24 h. Annually, the average rainfall in Peninsular Malaysia can reach up to 2420 mm, while in Sabah and Sarawak, the amount of rainfall is more than the Peninsular with 2630 mm for Sabah and 3830 mm for Sarawak (DID 2007 ). According to Chia ( 1971 ), there are two types of rainfalls that cause the flood. They are (1) moderate intensity, long duration rainfall at a wide area and (2) high intensity, short duration localized rainfall. The occurrence of floods in Malaysia can be predicted. Usually, east coast and eastern Malaysia were affected by floods during December to January as the northeast monsoon sweeps, while the west coast of Peninsular is mainly affected in September to November with thunderstorms due to the inter-monsoon period. Generally, in Malaysia, most floods occur due to continuous heavy rainfalls that result in runoff due to the excess of water supplies that surpass the capacities of streams and rivers.
Several major flood events have occurred in Malaysia over the last few decades. For example, a gale force wind period in 1886 caused severe flooding in Kelantan. In 1926, the worst floods in Peninsular Malaysia caused scares among the people as it caused widespread damage to property, mental, physical, infrastructure and agriculture. After the initial days of the flood, projected losses to local business in and around the Klang River valley were estimated at around $12,000 Straits dollars. Even for those who did not suffer major flood damage, all businesses lost several day’s trade as the city stood at standstill. In Pahang, a private railway linking the plantation to mines at Sungei Lembing was partially washed away and trains had to be dug out of the mud afterwards (Williamson 2016 ). Flooding has become a significant yearly event occurrence in Malaysia especially at the end of the year. Most of the flood-prone areas can be found in several states in Peninsular Malaysia such as Kelantan, Johor, Pahang, Perak, Kuala Lumpur and Selangor while for east Malaysia it is Sabah and Sarawak (DID 2007 ). Most of the states in Malaysia are prone to flood risk due to (1) the natural physical topography and drainage, and (2) human geography of settlement and land use. Malaysia in the past is mostly riverine people that choose to inhabit banks and floodplain of the major river such as Pahang river, where most of the settlement is indeed high in flood risk (Chan 2012 ). Most of the floods occur due to the monsoon rainfall and intense rain storms. However, in recent decades, the cause of flood is not only due to natural events; the frequent occurrence of flash flood in cities such as Kuala Lumpur, Selangor and Kelantan was caused by poor drainage and area where rapid urbanization takes place. Chia ( 1971 ) stated several sources that cause flooding in Malaysia, loss of flood storage results from development that extend towards floodplain areas, the increase and rapid urbanisation that cause the rate of runoff to increases, faulty drainage system by the locals and continuous heavy rainfalls that cause the water storage to exceed the capacity of the river.
The annually frequent flood that occurs in Malaysia has taken a toll on the socio-economy in terms of flood damages. The flood damage is on the rise due to the increase in flood risks such as the urban development on flood plain area of major rivers. The damages and the losses caused by the flood can be direct or indirect, where direct flood damage is due to the contact of flood water with the building while indirect flood damage causes loss of work and production that eventually cause the victim to develop stress and suffering (Green et al. 1988 ). The estimated amount of damages due to the flooding is superior in compact and high densities urban areas compared to rural areas. According to Chan ( 1997 ), the chance of extreme flood damage occurrence is high in large urban centers such as Kuala Lumpur and Georgetown, Pulau Pinang. Moreover, aside from damages towards the economy, the flood may give permanent aftermath towards mental health and death. It is not unusual for the flood victims to suffer from trauma and mental health for the rest of their lives. Usually, those with a fragile mental state are more susceptible to mental collapse when they were engaged to the unwonted and wicked situation or events. Women and children are the group of people that easily suffer in a critical event. According to Jamaluddin ( 1985 ), to abate post-traumatic events, the victims themselves need to concur the situation in a more positive and appropriate ways for a chance of quick recovery.
Following the annual flooding event occurrence in Malaysia, the government (including the Drainage and Irrigation Department (DID)) has carried out several positive actions to mitigate the flood problem. These consist of structural measures and non-structural measures (Chan 2015 ). Structural measures focus more on how banks and embankments play their role in controlling flood flows. Example of structural measures taken by the government is the Storm Water Management and Road Tunnel (SMART) in Kuala Lumpur to alleviate flash flood problems that occur when heavy rainfalls hit Kuala Lumpur (Umar 2007 ). An example of non-structural measures relates land use planning and flood forecasting and warning systems to mitigate the impact of flooding, such as the flood forecasting and warning system (DID 1988 ). Most of the flood mitigation projects and actions undertaken by the government were structural measures such as canalization of rivers, raising river embankments and the building of a multi-purpose dam. Yet, the government has been upgrading the Flood Forecasting and Warning System for early warning. This infrastructure had been installed all over Malaysia with 233 telemetric rainfall stations, 190 telemetric water level stations, 256 manual stick gauges, 84 flood warning boards, 217 flood sirens and 9 real-time flood forecasting and warning system in 9 river basins (DID 2007 ). The DID has also taken an initiative to established an Internet-based National Flood Monitoring System ( http://infobanjir.moa.my ) where all the data on rainfall and water level can be accessed by the public. In brief, the flood management activities attempted by the government of Malaysia are (1) the National Resource Study, (2) Development of infrastructure for flood forecasting and warning system, (3) National Flood Monitoring System, (4) Flood Watch and (5) Urban Storm Water Management Manual for Malaysia (Hussaini 2007 ).
Vulnerability and resilience act as a leading tool to quantify and map human aftermath from hazards. In the context of social–ecological systems, resilience refers to the magnitude of disturbance that can be absorbed before a system changes to a radically different state as well as the capacity to self-organize and the capacity for adaptation to emerging circumstances (e.g., Carpenter et al. 2001 ; Berkes et al. 2003 ; Folke 2006 ). Vulnerability, by contrast, is usually portrayed in negative terms as the susceptibility to be harmed. The central idea of the often-cited IPCC definition (McCarthy et al. 2001 ) is that vulnerability is the degree to which a system is susceptible to and is unable to cope with adverse effects (of climate change). According to Proag ( 2014 ) vulnerability is defined as a measure of hazard that compliance with physical, economy and social and the implication that results in the ability to cope with the event occurrence. While the concept of resilience itself has taken two broad forms of (1) hard resilience and (2) soft resilience (Moench 2009 ) where hard resilience is a direct strength when placed under pressure and soft strength is the ability to absorb and recover from the impact of destructive event (Rufat et al. 2015 ). According to Balica and Wright ( 2010 ), resilience is the ability of a system to handle commotions while maintaining the efficiency in social, economic, physical and environment. It is in the nature of human being to become vulnerable when their normal daily activities, facilities and consumption were affected in critical factor from the disaster. Moreover, the demographic characteristic, socioeconomic status and health is the leading driver of vulnerability due to flooding events. Resilience is a system that functions to work in a certain way under normal circumstances. Therefore, resilience is important in several sectors such as technical, political, environment, ecology, economy, legal and in an organization. Variables that usually concerned in measuring the degree and magnitude of vulnerability and resilience from disastrous events is employment, income, health and educational status. Jackson ( 2006 ) stated that resilience, vulnerability and adaptive capacity are inter-related with each other when it comes to natural disaster events. Not only that, it also stated that a community with low vulnerability has the potential to have high resilience. Several other definitions of resilience can be found in Table 1 . Vulnerability deals more with the environmental risk and hazards while for resilience, it deals more with the change and persistence of an ecosystem (Carpenter et al. 2001 ; Gunderson 2000 ). Furthermore, in flood-prone rural areas, the norms of poverty have heightened vulnerability among the poor while in the urban area, the vulnerability is much lower compared to the rural area as more strategies, planning, investment and development were undertaken to curb the problem (resilience). In short, the poor suffer more from hazards compared to the wealthy, although poverty and vulnerability are not always related or in line with each other (Chan and Parker 1996 ). The vulnerability experienced by the poor was due to the lack of opportunity and access to structures of power where knowledge and resources of the hazard or disaster were limited. In addition, aside from the poor, vulnerability is familiar among the lower income groups, Malaysia is dominated by the Bumiputera communities where fatalities were common while low-level vulnerability can be expected in the urban settlement where it is mostly populated by the Chinese and Indians. This is because, back in the past before the Chinese and Indians ethnics populated Malaysia, the Bumiputera that originated from the Peninsular choose to settle in the area near the coastal and major rivers where they can have easy access to food and transportation. Resilience actions need to cultivate and be implemented in order to prevent damages and loss of life. This needs to be one of the main purposes of development rather than a characteristic of a good development (Bene et al. 2012 ). Resilience needs to be applied in urbanization process as urban areas were known to be complicated social ecological systems (Simon 2007 ; Swyngedouw and Heynen 2003 ).
The aim of this paper is to investigate the perceptive of the urban community on the vulnerability of flood. Next, this paper studies on the various suggestion from the local community on future resilience towards flood event. A method of focus group discussion (FGD) was applied in order to obtained detail and compact information from the stakeholder in a different category of people or group of people. From the results, it showed that the urban community was aware of the cause of the vulnerability in their neighbourhood towards the flood event. The data obtained from the FGD were solely from the real-life experience of the stakeholder that were involved in the group discussion. From the discussion, various suggestions have been put forward by the stakeholder on their future resilience actions towards flooding.
2 Materials and method
Information regarding the urban flooding situation and experiences was collected through the qualitative method known as focus group discussions (FGD) that consists of structured discussion that are usually used to obtain in-depth information from a group of people about a specific topic. The group discussion was engaged by the flooding victims themselves; therefore information regarding sensitive topics can be obtained. The district of Kuantan which is located in the state of Pahang was selected as the study area due to the lack of research done in the state compared to other flood-prone states such as Selangor and Kelantan. In this study, the researchers were interested in the vulnerability faced by the flooding victims, annually, in the district of Kuantan and the local resilience measures taken to minimize the natural disasters.
2.1 Study area
Figure 1 shows a map of Kuantan, Pahang, Malaysia. The district of Kuantan is situated in the state of Pahang. Pahang is the third largest state in Malaysia after Sarawak and Sabah. Geographically, Pahang is the biggest state in Peninsular Malaysia and has the longest river in Peninsular Malaysia at 459 km. Since Peninsular Malaysia is affected by two monsoons (northeast and southwest monsoon) and two inter monsoons (Suhaila et al. 2010 ), the Pahang Basin receives a high total of rainfall during the northeast monsoon period that contributes and causes flooding events along the river in the basin (DID 2005 ). Other main sources of flooding in the basin are the extreme increase in river discharge due to the monsoon and the sea waves from the South China Sea. The overflow water results in floods within the basin area which occur yearly, particularly from November to December (Lun et al. 2010 ). Kuantan has a total area of 2453 km 2 and is situated 250 km east from Kuala Lumpur. The monsoon that brought the heavy rainfall in November to December every year is 2.3 times higher than the normal average rainfall. The Kuantan River Basin (KRB) is an important watershed of Kuantan city. The basin starts from Sungai Lembing, passing through Kuantan and finally drains to the South China Sea. Heavy rainfall causes spill over of rivers and flooding in low areas that encompass human activities, both social and economic. In December 2001 to January 2002, Kuantan experienced a massive flood caused by continuous heavy rainfall during the northeast monsoon. Most of the city area was submerged under water when nearby rivers overflowed. This incident affected 18,000 people and 22.94 km 2 of land (EKA 2002 ). Another dreadful flood condition and incident occurred 10 years after the massive flood happened in 2001/2002; an unexpected flood due to continuous rainfall that caused 6000 victims to lose property and assets. Due to the poor drainage system in Kuantan, the intercity roads that connect people from city to city were badly flooded causing hundreds of vehicles to be trapped. The recent flood occurrence in 2013 was caused by the prolonged heavy rainfall, high tides and rapid urbanization process. More development was undertaken in the low-lying area that are easily flooded. The 2013 flood in Kuantan caused 14,044 people to be evacuated from their houses. Furthermore, the flood resulted in major damages towards basic facilities such as electricity, road structures, buildings and personal belongings. These have cost a fortune for the government to repair the damages done by the flood hazard (Jamaludin et al. 2013 ). Aside from heavy rainfall caused by the northeast monsoon, the occurrence of flooding in Kuantan can be due to the rise in temperature that causes heavy rainfall and rise in sea level.
The study area
2.2 Participants
The victims of the flooding hazard were identified in the study area. A total of 31 participants joined the focus group discussion. This method was applied to conceptualize the relationship between vulnerability and resilience of the urban community from people with different backgrounds. Six focus group discussions (FGDs) were formed during this study. The groups were formed to discuss the urban flood vulnerability and resilience based on different criteria of gender, age, education background, occupation, monthly income and social class. Each of the FGD group consisted of four to six participants from various backgrounds. The list of FGD participant for each group is shown in Table 2 which highlights differences in the number of participants in each group due to the difficulty in getting participants despite earlier preparations. Most of the participants involved were selected from the haphazard settlement around Kuantan River, Isap River, Belat River, Pandan River and Galing River. The discussion was participated by the flooding victims with age range from 16 to 69 years old. A wide range of ages helped in widening the answer and opinion on the highlighted issues in the group discussion due to differences in generations and ways of thinking. The group discussion was participated in 16 females and 15 males.
2.3 Data collection
Data collection was carried out in March 2016. Qualitative data collection method was applied to extract ground information on the relationship between vulnerability and resilience of the urban community from different background. The two-qualitative method applied was the focus group discussion (FGD) and field observation. In this study, the semi-conducted interview was the main approach for data collection. FGD is a qualitative method that has been defined as a discussion that has been carefully designed to gain or gather impressions or viewpoints on a defined circle of interest in a non-threatening environment (Kruger 1994 ). Moreover, the group discussion, focuses on perceptions, opinions and the motives underlying their acts and behaviour (Greenbaum 2000 ; Hyden and Bulow 2003 ; Maykut and Morehouse 1994 ). This method was chosen for the study because it is particularly useful for exploring people’s or the victim’s experience and knowledge (Kitzinger 1995 ).
An informed consent agreement was obtained from those who agreed to take part in the discussion, and a suitable time for the discussion was agreed. All the participants in the group discussion were asked to describe their various experiences. At the beginning of each focus group session a moderator introduced themselves and gave a brief explanation about the procedures of the discussion to the participants. Besides conducting the discussion in the group, the moderator helped the participants to focus on the topic discussed. Each focus group session was conducted for no longer than 45 min. The key questions prepared earlier for the moderator to discuss with their respective group are shown in Fig. 2 . All of the conversations that occurred in the discussion group were recorded on video for further analysis.

FGD key questions
2.4 Data analysis
The FGD was video recorded and later analysed using qualitative inductive content analysis, also known as qualitative data analysis. The analysis was carried out in several steps which involved coding, whereby raw data were raised to conceptual level. It is pertinent to analyse data for context as it involves identifying conditions, nature of the situation, circumstances or problems from the participants response. This study analysed the qualitative data by utilizing computer-aided software or computer-aided qualitative data software (CAQDAS), Atlas.ti. Atlas.ti is known for its capability in workbench for qualitative data analysis particularly for audio data. This software analysed and interpreted text and audio using coding and annotating activities. For analysing, the video and audio data were transcribed into word processing documents. Every word, sentence and paragraph needed to be analysed attentively for further interpretation of the data. Therefore, it is important to organize, reduce and describe the data delicately in order to avoid unnecessary mistakes that will affect the results produced. According to Schwandt ( 1997 ), the analysis must be done in a rigorous, systematic, disciplined and imitative manner with the documented methodology. Thereupon, to analyse simply means to break down the data into coding (Miles and Huberman 1994 ) and categories (Dey 1993 ). Initial coding using CAQDAS is time-consuming to ensure that the building of the codes is systematic. As the data are broken up for classification, it is then developed into a concept where connections are made between them to enable new descriptions to be made. Next, once the data were classified, they were checked for regularities, variation and peculiarities in patterns. This helps in identifying potential connections by data linking and associations among the categories. All in all, the most important steps in qualitative analysis are to select a sufficient amount of data in one time and to process the raw data (video interview) into coding (Dey 1993 ) before running it into Atlas.ti software for further analysis and results.
Using constant comparative analysis, data from interview and observation, resulted in several primary categories such as daily life challenges, vulnerability due to the urban flooding and finally the resilience towards flooding. These are presented in order below.
3.1 Top daily life challenges
One of the questions asked during the FGD was how the participants ranked their top daily life challenges including flooding. The results showed that most of the participants rank flooding as the least important challenge because for them, the floods only occur once a year when the northeast monsoon season passes by the east coast of Peninsular Malaysia. On the contrary, food supplies, health, education, economy and social issues are the top daily life challenges, respectively, as all these challenges are applicable on a daily basis. Hence, only when their environment is affected by flood, will it disturb their daily activities. Figure 3 shows the results for top daily life challenges faced by the participants and the comments on the challenges they faced.
Top daily life challenges ranked by the participants
The top daily challenges consist of seven elements: food, flood, health, education, economy, safety and social. The participants were expected to rank their top five daily challenges according to their priorities. Two sets of results were obtained and new challenges were added and discussed. Figure 4 shows the results of the two sets of daily life challenges ranked by the participants. Social and safety were added in the discussion as additional challenges where the participant ascertains that it is important to be included.
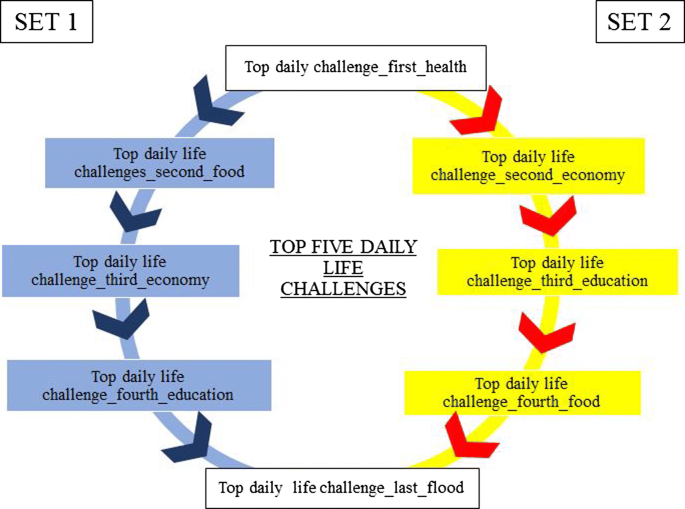
Result of top daily life challenges ranked by the participants
Figure shows that from the two sets of results on the daily challenges, the first set shows that food is the priority while the flood was ranked last. However, in the second set of results some participants believed flooding should be ranked first. Those participants who ranked flood first live in areas that are seriously affected by the annual flood. Not only that, they also stated that the flooding event causes them hardships and disturbed their normal daily life. Conversely, those who ranked flood as their last priority in the daily challenges are from areas where the occurrence of flood is predictable and happens once a year; thus they have the opportunity to prepare beforehand. The constant occurrence and the signal given by the nature such as changes of the wind and cloud, and tidal water level at coastal and river basin help the victims to prepare themselves. Garai ( 2017 ) stated that understanding the sign and signal from the changes in nature has helped the people in the past to predict the upcoming flooding event. Moreover, technologies and experts from the meteorology department were able to predict and warn people about the upcoming event. Most of the participants ranked food first because it is important to have continuous supply for survival. Flooding will cause damages to most of the goods including foods. Food stalls, supermarket, mini markets and sundry shops will be closed down due to the flood. This will cause disruption in food supplies; hence, it is important to prepare and stock up the food supplies before the flood occurs. Equally important to food is health. For most of the participants, health is crucial. The impact of health from flooding comes in many forms. According to Rufat et al. ( 2015 ), one-third of the deaths during flood events occur away from the floodwater. Examples of deaths that can occur away from floodwater include deaths from dehydration, stroke, lack of medicine supplies and negligence of health issues prior to flood events (Jonkman et al. 2009 ).
Besides death, flooding can affect the mental health and psychology of a victim. The psychological effects are different according to anxiety and stress, age, gender, previous health condition and recovery duration, effects can usually acute after the event (Stanke et al. 2012 ). Other health issues such as water borne diseases due to contaminated water, malnutrition, fever and other infectious diseases are easily spread during and after the flood when the victims interact with each other at the transit centre. While discussing the top daily challenges, participants highlighted the importance of social and security issues. Social problems involving the teenagers and young adults usually increased. Most of the social problems that involve teenagers are vandalism, burglary and theft. Adger ( 1999 ) in his study stated that the actions displayed by the teenagers may be due to coping behaviour, stress or access to certain resources or needs. However, social problems are not limited to teenagers only. Adults who are also desperate took advantage from the flood event usually caused social problems. They usually break into the flood victim houses and steal any valuable goods such as electric appliance, jewelleries, car, motorcycles and even the house parts such as steels, wires and cable. This is when the social security elements from the discussion among the participants surfaced. Security in this context is not limited to assets and goods, but also the safety of individuals during the flood to avoid any casualties and death. Making sure all the important and valuable goods and assets are in a safe place before the flood occurred ensures the safety of the people’s belongings. On the other hand, the security and safety of individuals during and after the flood is the top priority while it is encouraged to help those affected by flood, but not to the extent of risking their own life. For example, it is reported that there was a case of death at Kampung Isap where a man died due to drowning while trying to rescue another flood victim. Therefore, it is important to prioritize and take care of one’s own life and safety during and after the flood events.
3.2 Vulnerability
This study investigated the vulnerability to flooding of the community of the study area. The results from the analysis are shown in Fig. 5 . From the FGD, there are several reasons that cause the vulnerability to flooding in the community. Grounds and claims such as houses built near to the river banks and lowland areas, improper and ineffective flood evacuation plans, mismanagement of flood transit centres, lack of instant and accurate flood information and the lack of preparation for the flood by the community members have caused increases in the vulnerability of people to the flood event. Figure 5 shows that middle-aged participants ranging from 26 to 45 years old were concerned about the location of the housing area that can be easily affected by the flood, such as lowland area, near the river banks and swamp area. Meanwhile, the vulnerability of the older generation, from 56 to 65 years old, is mostly due to their refusal to stay at the transit centre, the type of their houses that are usually made from wood and the location of their houses which are mostly located near the beach that make it difficult for them to evacuate. In terms of income, for the participants with monthly income of less than RM1000 and less than RM3000, flooding has made them vulnerable and insecure. However, they refused to move to the transit centre as it may put their house at risk of burglary. Also, some of the transit centres are located far from their houses and some transit centres have imposed payment on the victims for shelter. For gender category, both males and females agree that uncertain flood warnings and warning issued only on high tides have caused them to be more vulnerable. The victims that are involved in the JKKK (village committee) have different vulnerability compared to the residents. The JKKK often faced problems during evacuation of other flood victims because most of them refused to be evacuated as they prefer to wait and see what unfolds. Different from the vulnerability faced by the JKKK committee, the residents are vulnerable towards the flood in terms of government aid that won’t be enough to recover their damaged goods.
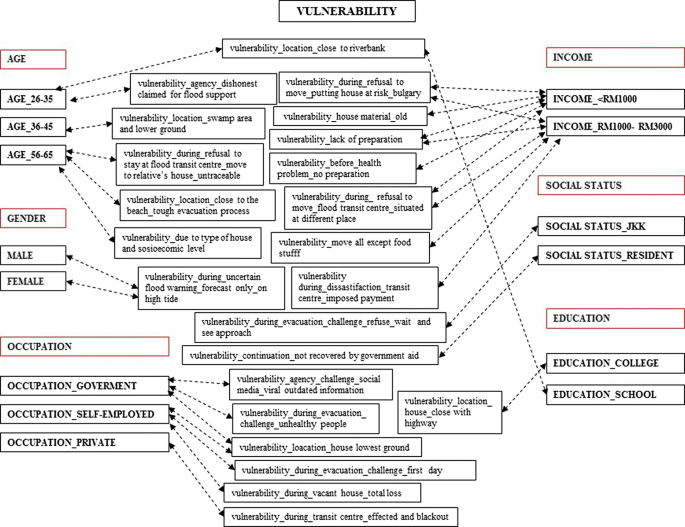
The participants’ flood vulnerability
Victims with different education background seem to have made different choices about their house location, hence faced different vulnerability. Victims with high school education background mostly live near the riverbank which is more vulnerable, while those with college education background choose to live near the highways which can be easily accessed for an escape. Lastly, government, self-employment and private occupational victims have different aspect of vulnerability. Most of the victims that work with the government are more concerned on the accuracy of information circulated by the social media, the challenges in evacuation of sick victims and those whose houses are at low ground. As for self-employed victims, they are vulnerable because they can only afford houses situated on lower ground. They are more worried about losing their house and not having the ability to repair or build a new house. Evacuation is difficult because unlike the government and private sectors, they do not have holidays and have to work almost everyday. Those working in the private sector are more concerned about the condition of the transit centre during the flood. They are worried if the transit centre is not safe. All in all, in terms of health, most victims lack preparation for medicine and other basic medical facilities even before the flood occurs.
4 Discussion
This study has examined aspects related to urban flooding in the study area. The main aspects are daily life challenges, vulnerability from the flooding, and the local future resilience towards floods. Everyone who was involved in the disaster will be impacted to some extent. Therefore, this study explores the response, reactions and the resilience of the victims before, during and after the event and why such behaviour and action were taken and displayed.
Vulnerability has been known as a leading tool to quantify and map human dimensions of hazards. The vulnerability of people to flooding is usually affected by variables such as income, ethnicity, education, age and gender. According to Rufat et al. ( 2015 ), income and poverty are the key drivers in vulnerability. Ajibade et al. ( 2013 ) think that women and children are more vulnerable compared to men because they are physically weaker than men and that the roles and responsibilities of women during flood event are more dangerous. The harder it is for someone to reconstruct their lives after the disastrous event, the more vulnerable they are. Contextual aspects of vulnerable populations obtained from the discussion are shown in Fig. 5 . From the discussion, the vulnerability of the participants towards the flood can be grouped into geographical setting (location), socioeconomic, related agencies (societal network and insurance company) and the disaster’s phase (during the flood). All the variables listed are the important keys to deconstruct vulnerability. Most of the vulnerability stated by the participants in the discussion is related to the location of the housing area. Houses located close to the riverbank, swamp and lowland area are vulnerable to the flood. This is because these areas can be easily flooded when the rivers overflow due to heavy rainfall and runoff from the higher area. Rapid urban development without consideration of the local housing area has also increased flooding. Intensity of the improper drainage systems and an imbalance in the embankment of lowland area for development has resulted in negative impacts on the locals, where local residences have to face unpredictable flood events caused by the embankment and incomplete drainage system designed by the developer. Moreover, the location of houses that are difficult to access, such as the beach area, hinder the process of evacuation and hence caused the victims to be vulnerable during the monsoon season. Meanwhile, the vulnerability in socioeconomic factors is measured through household income, poverty, unemployment, educational status and wealth (Rufat et al. 2015 ). According to Chan and Parker ( 1996 ), age and gender are related to income, those over 50 years of age have a comparatively low source of income. It is believed that income and poverty are the key drivers for vulnerability. According to Friend and Moench ( 2013 ), poverty and vulnerability are related but not the same; individuals with greater wealth experience are less vulnerable to flooding event. Therefore, since most of the victims in the study area have low income, the environment and housing conditions of the neighbourhood are poor. The material of the house is old and easily destroyed by flood and hence increased the vulnerability of the victims in the total loss of their house.
Nevertheless, the vulnerability in agencies such as insurance company and social network company is varied. For example, some of the victims may falsify claims towards the insurance agency for flood support. This is due to the shortage of money and funding necessary to get back to their daily life. Then, the vulnerability in social media towards the victims is because of the amount of outdated information that may lead to misunderstanding within groups of flood victims. The social media network needs to be sharp and alert in updating information regarding on the weather forecast from the meteorology stations. This is because most of the victims rely on the news they heard on TV, radio and even online social media for further actions. Finally, the victims are most vulnerable during the disaster phase. Some of the victims refused to stay at the flood transit centre because they are worried that their house may be at the risk of being robbed or the transit centre is situated a long way from their housing area. The risk perception that influences the vulnerability of the victims resulting in refusal to be transported to the transit centre is fear, uncertainty and worry of the safety of their family members, assets and properties (Willis et al. 2011 ). Nevertheless, the victims that faced a total loss of their house were evacuated to the transit centre for temporary shelter. Sometimes unexpected incidents such as black outs happened at the transit centre due to the electricity failure, which may cause trauma and panic attack to the flood victims at the transit centre where they do not feel safe and secure. For sick and elderly victims who are in wheel chairs, or others who are on machines and medical support, evacuation due to the flooding could be challenging, both for the victims and the evacuators. Furthermore, the uncertainties of flood warning and forecast caused them to be mentally tired all the time. In addition, some of the victims used the approach of ‘wait and see’; hence they refused to be evacuated in the early phase of the flood. They will only evacuate when the situation worsens. This is a challenge to the volunteers. On the other hand, when the victims are evacuated, they are forced to leave their food stuff behind; therefore, they are depending solely on the food aid by the government at the transit centre. The continuous rain fall over a long period will caused the victims to be more vulnerable as more materials and properties will be damaged and destroyed by the floods and these will not be recovered by the government. Hence, more expenditure is needed to compensate their losses.
Towards the end of the discussion, the participants were asked about their resilience towards flooding in the future. The results from the discussion can be seen in Fig. 6 . Resilience is defined as the ability of a system to bear any commotion while sustaining certain levels of efficiency in its social, economic, physical and environment component (Balica and Wright 2010 ). There are several dimensions of resilience that have been highlighted by the participants such as the construction of flood barriers, information and updates on the flood, distribution of material support, transit centre and development on lowland. The participants acknowledged the present effort by relevant government agencies in helping and handling the flood hazard, but in their opinion, more can be done. The participant’s perceptions regarding their resilience are that improvements need to be planned and supported by the government and other related agencies. By providing awareness programs for the public and information and updates on the flood situation, it helps the victims to understand more about flooding and hence help them in preparing and building resilience for future hazards. The participants also hoped that the authorities will be more sensitive to risk reduction including housing, infrastructure, utilities systems and regulation of land development according to the level of risk. In their opinion, there should not be any more development of lowland areas and the reclamation built by the developer need to be looked through of the side effects towards the present housing area. This is because some of the reclamation of land for new urban development areas has caused flooding to the present housing areas. The reclamation wall may accidentally block the water ways or the bypass for the overflow water to be discharged to the sea, thus causing unwanted and extreme flooding to the lowland area. The building of the water barrier has also caused the housing settlement between the barriers to be turned into a pond when overflow waters become stagnant in the middle of the lowland area. On the other hand, according to the participants, the distribution of the food aid given by the government to the victims needs to be supervised because there were cases where some of the victims were overlooked and they missed the aid that was distributed. Finally, the provision of community facilities such as evacuation centre, transit centres and temporary shelters is important in order to minimize residents’ exposure to flood hazard. The participants stated that the victims preferred transit centres close to their houses. Public schools are typically used as evacuation grounds and temporary shelters during the disaster which are short in facilities, such as shower rooms. Victims are also worried about the cleanliness and hygiene of the public school. Developer and the state government are urged to build a proper transit centre for the victims to shelter where inadequacy of water and sanitary facilities should be the primary consideration. Therefore, the commitment and the involvement of government, NGO and urban dwellers in long-term flood management and risk will help in assisting the community in minimizing the damages resulted from the hazard; hence, they will manage to get back to their normal daily life in a short time.
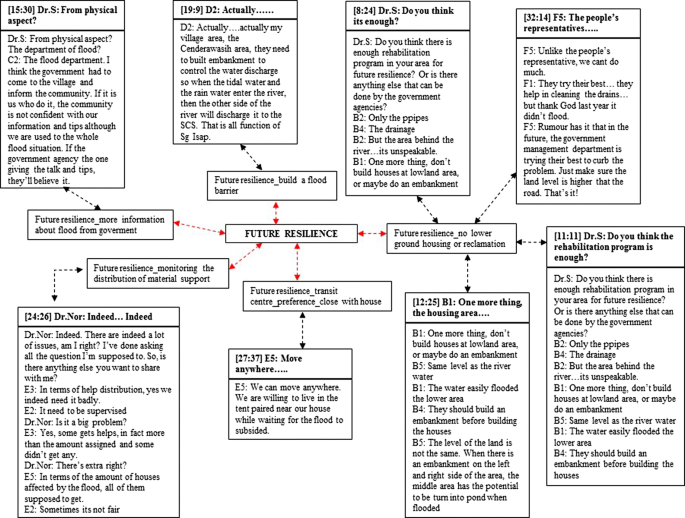
The suggested future flood resilience
5 Conclusion
All of the detail and genuine information on the vulnerability and the resilience of the floods from this study were obtained from the qualitative method called focus group discussion (FGD). The study was designed to capture the full range of perceptions on flooding from the urban community. The participants of the group discussion were volunteers who were interviewed for research purpose. Participants were divided into six groups with different demographic background for holistic results. The participants were willing to describe in detail the event, including their feelings and emotions towards the disaster. The information and data obtained are valuable and crucial to understanding the urban flood resilience and vulnerability theory and perceptions. Hence, it is equally important to take into consideration the response, actions and the reactions behind the participants’ behaviour that were displayed. These will help in formulating future planning for effective flood hazard management.
The outcomes when the participants were asked to rank their top five daily challenges were obtained, and they showed that most felt that flooding is not the uppermost daily threat to them as the flood comes annually and is mostly predictable. The victims are most concerned with continuous food supply. Those who felt flood is a threat to them is due to the fact that they live in flood-prone areas. On the other hand, several participants believed that health is the most important variable in their daily life because without good health, they will not be able to work or execute their daily activities. After food and health, other challenges according to participants’ priorities are education, economy, security and social. A large proportion of the population of the study area remains poor and vulnerable to floods, especially in the rural settlement. In other aspects, poor dissemination of early warning information and flood control infrastructures from the government and other related agencies have caused the victims to have little time to prepare for emergencies and hence cause the recovery process to be slower. Moreover, the housing location for most of the participants is within lowland areas which made them more vulnerable. Lowland areas are easily flooded due to heavy rainfall and tidal water from the South China Sea. Thus, it causes an abrupt increase in water volume that exceeds the river basin capacity. New development such as housing ranging from the hill to the valley is one of the major causes of increased flooding in the study area. What determines one’s vulnerability is the gender roles, place, employment, health care, income and social status. The outcome shows that gender has no significance in determining vulnerability. Both male and females voiced concerns about the inefficiency in flood warning and forecasts issued by the government and media during the flood. Results also showed that participants with high or low income faced the same level of vulnerability. However, they refused to move to the designated flood transit centre due to the risk of their house being robbed and the location of the transit centre is far from their house. Notably, the low income victims were hit harder compared to the high income victims because they need more money and other sources of income in order to get back to their daily life. Lots of everyday appliances and goods need to be repaired or replaced which are costly to the poor. Therefore, in order to decrease the vulnerability due to the flooding event, resilience need be cultivated. A lesson should be learnt from the past event and actions should be taken to avoid losses. Structural and non-structural flood mitigation solutions should be taken and adapted to the flood-prone areas. A better flood prevention, mitigation response and rehabilitation should be implied in the disaster risk management.
Adger W (1999) Social vulnerability to climate change and extremes in coastal Vietnam. World Dev 27(2):249–269
Article Google Scholar
Adger WN, Kelly PM, Winkels A, Huy LQ, Locke C (2006) Migration, remittances, livelihood trajectories, and social resilience. AMBIO J Hum Environ 31(4):358–366
Ajibade I, McBean G, Benzer-Kerr R (2013) Urban flooding in Lagos, Nigeria: patterns of vulnerability and resilience among women. Glob Environ Change 23:1714–1725
Balica S, Wright N (2010) Reducing the complexity of the flood vulnerability index. Environ Hazards 9(4):321–339
Bene C, Wood R, Newsham A, Davies M (2012) Resilience: new utopia or new tyranny? Reflection about the potentials and limits of the concept resilience in relation to vulnerability prograammes, IDS Working Paper 405. Institute of Development Studies, Brighton, Sussex
Berkes F, Colding J, Folke C (eds) (2003) Navigating social-ecological systems: building resilience for complexity and change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Google Scholar
Buckle P (2006) Assessing social resilience. In: Paton D, Johnston D (eds) Disaster resilience: an integrated approach, pp 88–103
Carpenter S, Walker B, Anderies J, Abel N (2001) From metaphor to measurement: resilience of what to what? Ecosystems 4:765–781
Chan NW (1997) Increasing Flood risk in Malaysia: causes and solutions. Disaster Prev Manag Int J 6(2):1–16
Chan NW (2012) Impacts of disasters and disasters risk management in Malaysia: the case of floods. In: Sawada Y, Oum S (eds) Economic and welfare impacts of disasters in East Asia and policy responses. ERIA Research Project Report 2011-8, Jakarta, pp 503–551
Chan NW (2015) Impacts of disasters and disaster risk management in Malaysia: the case of floods. In: Aldrich D, Oum S, Sawada Y (eds) Resilience and recovery in Asian disasters. Risk, governance and society, vol 18. Springer, Tokyo
Chan NW, Parker DJ (1996) Response to dynamic flood hazard factor in Peninsular Malaysia. Geogr J 162(3):313–325
Chia CW (1971) Managing flood problem in Malaysia. Bull Ing 38:38–43
De Bruijn KM (2004) Resilience indicators for flood risk management systems of lowland rivers. Int J River Basin Manag 2(3):199–210
Department of Irrigation and Drainage (DID) (2005) Annual flooding report of Pahang state 2005. Department of Irrigation and Drainage
Department of Irrigation and Drainage (DID) (2007) Fenomena Banjir Malaysia. Retrieved from http://Www.Water.Gov.My/Images/Pdf/Fenomenabanjir_Msia.Pdf
Dey I (1993) Qualitative data analysis. A user-friendly guide for social scientists. Routledge, London
Dhar O, Nandargi S (2003) Hydro meteorological aspects of flood in India. Nat Hazard 28:1–33
Drainage and Irrigation Department (DID) (1988) Flood Forecasting and warning systems in Malaysia. Unpublished Paper of the Hydrological Section, Drainage and Irrigation Department, Ampang Branch
EKA (2002, July) Retrieved from global register of extreme flood events: http://www.dartmouth.edu/~floods/Archives/2001sum.htm
Folke C (2006) Resilience: the emergence of a perspective for social-ecological systems analyses. Glob Environ Change 16(3):253–267
Friend R, Moench M (2013) What is the purpose of urban climate resilience? Implications for addressing poverty and vulnerability. Urban Clim 6:98–113
Garai J (2017) Qualitative analysis of coping strategies of cyclone disaster in coastal area of Bangladesh. Nat Hazard 85:425
Godschalk D (2003) Urban hazard mitigation: creating resilient cities. Nat Hazard Rev 4:136–143
Green C, Turnstall S, Emery J, Bossman-Aggrey. P (1988) Evaluating the non-monetary impacts of flooding. Flood Hazard Research Centre, Enfield
Greenbaum T (2000) Moderating focus groups: a practical guide for group facilitation. Sage Publication, Thousand Oaks
Book Google Scholar
Gunderson L (2000) Ecological resilience: in theory and application. Ann Rev Ecol Syst 31:425–439
Holling CS (1973) Resilience and stability of ecological systems. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 4(1):1–23
Hussaini HA (2007) Flood and drought management in Malaysia. Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment, Kuala Lumpur
Hyden L, Bulow P (2003) Who’s talking: drawing conclusions from focus groups—some methodological considerations. Int Soc Res Methodol 6(4):305–321
International Strategy for Disaster Reduction ISDR (2002) Annual report. Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment, Kuala Lumpur
Jackson J (2006) Fatal attraction: living with earthquakes, the growth of villages into megacities and earthquake vulnerability in the modern world. Philos Trans R Soc Lond A Math Phys Eng Sci 364:1911–1925
Jamaluddin M (1985) Flash flood problems and human responses to the flash flood hazard in Kuala Lumpur Area. Akademika 26:45–62
Jamaludin MH, Jaafar S, Chuah BK, Abdullah Z (2013) Flood: Kuantan Town Centre almost paralysed, 37,100 evacuated in 4 state. The News Straits Times Press, Berhad
James E (2008) Getting ahead of the next disaster: recent preparedness efforts in Indonesia. Dev Pract 18(3):424–429
Jonkman S, Maaskant EB, Levitan M (2009) Loss of life caused by the flooding of New Orleans after Hurricane Katrina: analysis of the relationship between flood characteristics and mortality. Risk Anal 20(5):676–698
Kithia J, Dowling R (2010) An integrated city-level planning process to address the impacts of climate change in Kenya: the case of Mombasa. Cities 27:466–475
Kitzinger J (1995) Introducing Focus Group. BMJ 311:299–302
Kruger R (1994) Focus Group: a practical guide for applied research. Sage Pubblications, Thousand Oaks
Lun PI, Gasim MB, Toriman ME, Rahim SA, Kamaruddin KA (2010) River flow conditions and dynamic state of Pahang River. In: Proceeding of the 2nd international conference on human habitat and environment. Putra Nilai, Negeri Sembilan, pp 617–633
Maykut P, Morehouse R (1994) Begining qualitative research. A philisophic and practical guide. Routledge, London
McCarthy JJ, Canziani OF, Leary NA, Dokken DJ, White KS (eds) (2001) Climate change 2001: impacts, adaptation and vulnerability. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Miles M, Huberman A (1994) Qualitative data analysis: an expanded sourcebook, 2nd edn. Sage, Thousand Oaks
Moench M (2009) Adapting to climate change and the risks associated with other natural hazards: methods for moving from concepts to action. In: Lisa E, Schipper F, Burton I (eds) The earthscan reader on adaptation to climate change. Earthscan, London, pp 249–280
Molua E, Lambi C (2007) The economic impact of climate change on agriculture in Cameroon. Policy Research Working Paper Series 4364, The World Bank
Norris FH, Stevens SP, Pfefferbaum B, Wyche KF, Pfefferbaum RL (2008) Community resilience as a metaphor, theory, set of capacities, and strategy for disaster readiness. Am J Commun Psychol 41:127–150
Proag V (2014) The concept of vulnerability and resilience. Procedia Econ Finance 18:369–376
Rufat S, Tate E, Burton CG, Maroof Abu Sayeed (2015) Social vulnerability to floods: Review of case studies and implications for measurement. Int J Disaster Risk Reduct 14:470–486
Saavedra C, Budd W (2009) Climate change and environmental planning: working to build community resilience and adaptive capacity in Washington State, USA. Habitat Int 33:246–252
Schwandt T (1997) Qualitative Inquiry. A dictionary of terms. Sage, London
Simon D (2007) Urbanisation and global environment change: new intergenerational challenges. Int J Green Econ 1(3–4):299–306
Small C, Nicholls J (2004) A global analysis of human settlement in coastal zones. Coast Res 19:584–599
Stanke C, Murray RA, Nurse J, Williams R (2012) The efffects of flooding on mental health: outcomes and recommendations from a review of the literature. Publ Libr Sci Curr Disaster 47:37
Suhaila J, Mohd Deni W, Zin Wan, Jemain AA (2010) Trends in Peninsular Malaysia rainfall data during Southwest monsoon and Northeast monsoon season. Sains Malays 39:533–542
Swyngedouw E, Heynen N (2003) Urban political ecology. Justice and the Politics scale. Antipode 35(5):898–918
Umar (2007) Disaster mitigation support and management in Malaysia. Retrieved from Malaysia Meteorological Department. www.met.gov.my/files/ClimateChange2007/session1a/ . Accessed 16 May 2010
Williamson F (2016) The “Great Flood” of 1926: environmental change and post-disaster management in British Malaya. Ecosyst Health Sustain 2(11):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/ehs2.1248
Wills K, Natalier K, Revie M (2011) Understanding risk, choice and amenity in an urban area at risk of flooding. Hous Stud 26(2):225–239
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support provided by University of Malaya Research Grant under the Frontier Science Grant RG358-15AFR and Equitable Society Grant RP026B-15SBS, the engineers, assistance engineers and staff of Water Resources and Hydrology Unit, Drainage and Irrigation Department (DID), Kuantan, Pahang, Malaysia, the Kuantan District Officer, Kuantan Assistant District Officer, Penghulu Mukim (Headman) of Mukim Kuala Kuantan 1, staff of Kuantan District Office, Kuantan, Pahang and the Kuantan residents who have contributed in this article.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Geography, Faculty of Arts and Social Sciences, University Malaya, 50603, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
M. Y. Safiah Yusmah, H. Norhaslina, A. Ghaffarianhoseini & A. S. Shereen Farisha
Institute of Hazard, Risk and Resilience, Durham University, Durham, DH1 3LE, UK
L. J. Bracken
Department of Geography and Environment, Universiti Pendidikan Sultan Idris, Tanjong Malim, 35900, Perak, Malaysia
Department of Urban Planning, Faculty of Architecture and Built Environment, University Malaya, 50603, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
M. D. Melasutra
Water Resources and Hydrology Unit, Drainage and Irrigation Department, Kuantan, Pahang, Malaysia
S. Sumiliana
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to M. Y. Safiah Yusmah .
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Safiah Yusmah, M.Y., Bracken, L.J., Sahdan, Z. et al. Understanding urban flood vulnerability and resilience: a case study of Kuantan, Pahang, Malaysia. Nat Hazards 101 , 551–571 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-03885-1
Download citation
Received : 02 November 2018
Accepted : 17 February 2020
Published : 14 March 2020
Issue Date : March 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-03885-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Vulnerability
- Urban flooding
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

Essay On Floods
- Post category: Essay
- Reading time: 8 mins read
Set 1: Essay On Floods
Floods are a natural phenomenon which form various geographical features. They benefit mankind by forming alluvial soil but they also cause tremendous havoc to human life and property.
Floods are a natural calamity and take place regularly in certain areas. When they are expected, they do not cause much harm. In endemic areas people are prepared. They even take advantage of floods to enrich their soil,
trap fish and move logs of wood. But when they are not expected, they cause untold misery. The tremendous rush of water demolishes and carries away the houses, top-soil, men and animals. It inundates large areas under cultivation, wrecks public services and makes life miserable.
Floods, however, have always brought out the best in men. They organise rescue and relief for people whom they do not know and from whom they expect no personal gain. Voluntary organizations arrange relief camps and provide medical facilities.
Floods also bring out the worst in men. People and politicians try to cash in on the sufferings of people. They make collections in the name of relief and misappropriate funds for personal benefits.
The increasing incidence of floods can be definitely brought down by construction of dams and afforestation in the catchment areas. Desilting of rivers in the plains will also help. But these things can be done by the government
alone as these require large resources, organisation on a large scale and manpower. But people can also contribute at individual level by planting trees and preventing denudation of forest cover.
Set 2: Essay On Floods
A large amount of water covering a dry area of land is known as flood’. In other words, a flood is an overflow of water that submerges land, which is usually dry. Floods are a natural occurrence. They benefit humanity by forming alluvial soil but they also cause tremendous destruction to human life and property.
Floods are a natural disaster that take place regularly in some or the other part of the world. When they are expected, they do not cause much harm. In flood prone areas, people are prepared. However, when floods are not expected, they cause severe misery to life and property. The tremendous rush of water destroys and carries away the houses, trees, soil, men and animals. It floods large areas under cultivation. Public services come to a standstill. It makes life difficult and miserable. However, flooding can spread nutrients to lakes and rivers, which can lead to increase in plants, animals and improved fisheries for a few years.
The primary effects of flooding include loss of life, damage to buildings and other structures, a including bridges, sewerage systems, roadways and railways. Floods frequently damages power transmission, which leads to loss of electricity. They also results in loss of drinking water due to severe water contamination. Floodwater makes the land unusable and prevents crops from being planted or harvested. This leads to shortages of food for both humans and animals. Entire harvests for a country or that particular part of the country can be lost in extreme flood conditions.
Floods have always brought out the best in men. Men organise rescue teams and arrange relief for victims whom they do not know and from whom they expect no personal gain. Charitable organisations arrange relief camps and provide food, medicines and other facilities. At the same time, floods also bring out the worst in men. Some people and officials try to fill their pockets at the cost of the sufferings of victims. They make collections in the name of relief and use funds for personal benefits.
The increasing incidence of floods can be brought down by constructing dams. Moreover, afforestation must be encouraged in the areas where rainwater flows directly into a particular river or lake. Preventive measures of floods can be undertaken by the Government alone, as it requires large sum of money and work force. However, common people too can contribute at individual level by planting trees and preventing deforestation.
Set 3: Essay On Floods
A flood is a misfortune caused by Nature. Sometimes ‘floods occur when a dam bursts because it cannot contain a river. This happened in the case of the Panshet dam near Pune. The dam gave way and the waters rose and flooded the city of Pune. At other times, floods may be caused by a river in spate. Torrential rain may lead to a swollen river which floods the land,
Whatever the cause, floods are always very destructive. Houses are demolished, people and animals are swept away by the raging waters. Flood water destroys crops and also human property. People are rendered homeless and penniless. The floods deprive them of all that they have. To a farmer floods mean loss of crops and cattle. This might later lead to famine.
The flood victims are in a sorry plight. They have nothing to fall back upon. Whole families have neither food nor a roof over their heads.
In most cases, the Government organises relief work to aid flood victims. They are provided with shelters and foods. They are given assistance to stand on their own supported, thus the kindness of man can make up for the cruelty of Nature that causes destructive floods.
- Essay On Scenes During a Strike
- Essay On Scenes on the Bank of a River
- Essay On The Traffic hazards in my city
- Essay On The Wonders of the e-mail
- Essay On The Television
- Essay On School Memories
- Essay On My Favourite Dream
- Essay On The Value of Discipline in School Life
- Essay On Value to Discipline
- Essay On The Student & The Discipline
Please Share This Share this content
- Opens in a new window
You Might Also Like
Essay on lunch break in my school, essay on dr. rajendra prasad, essay on parents as friends, essay on a day in the life of a nurse, essay on dr. babasaheb ambedkar and untouchability.

Essay On An Hour On Railway Platform
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Based on Zip Code Change
- Shop the Red Cross Store
Flood Relief
- Share via Email
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on LinkedIn
Need Help Now?
If you are in immediate need of help, please contact your local Red Cross » or find an open shelter »
Preparing During the Pandemic?
Please review our guidance on preparing for disaster while still protecting yourself from COVID-19. (Available in multiple languages.)
Preparing for Disaster During COVID-19 »
Floods are among the most frequent and costly natural disasters.

Provide safe, dry shelter until families can return home

Serve water and hot meals
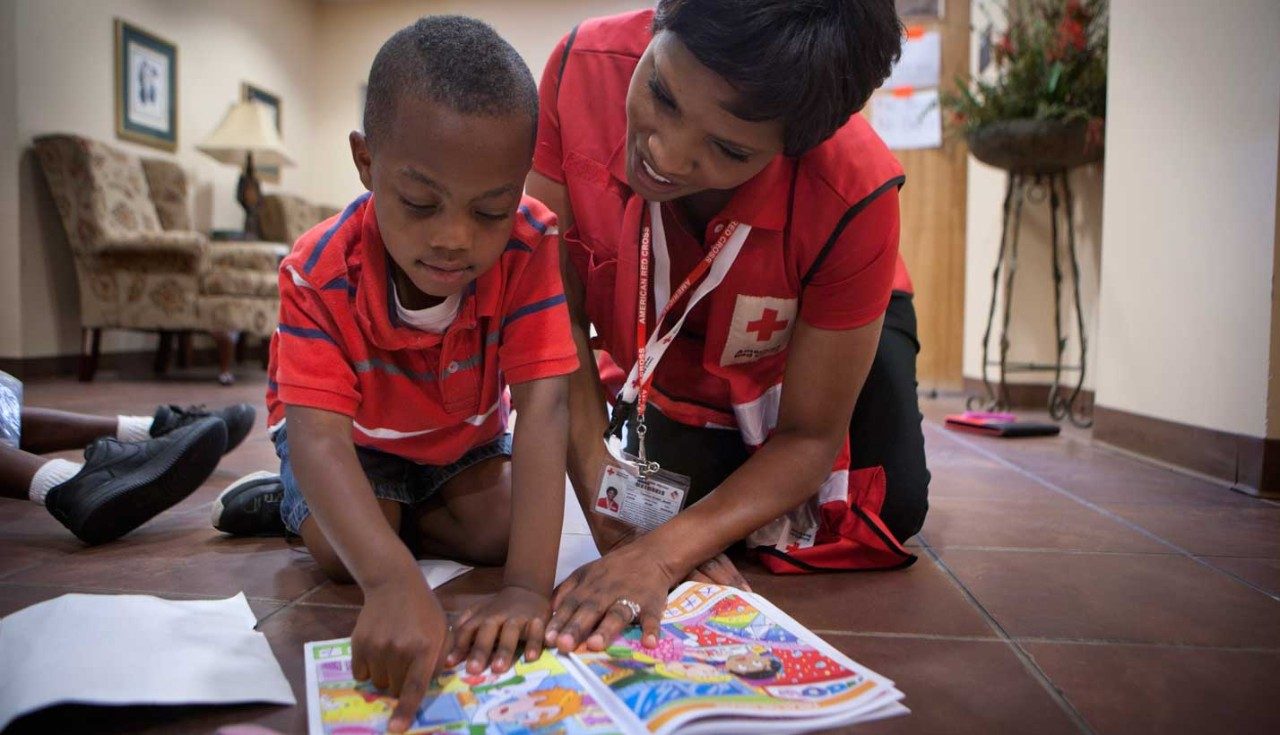

Play with kids staying in shelters
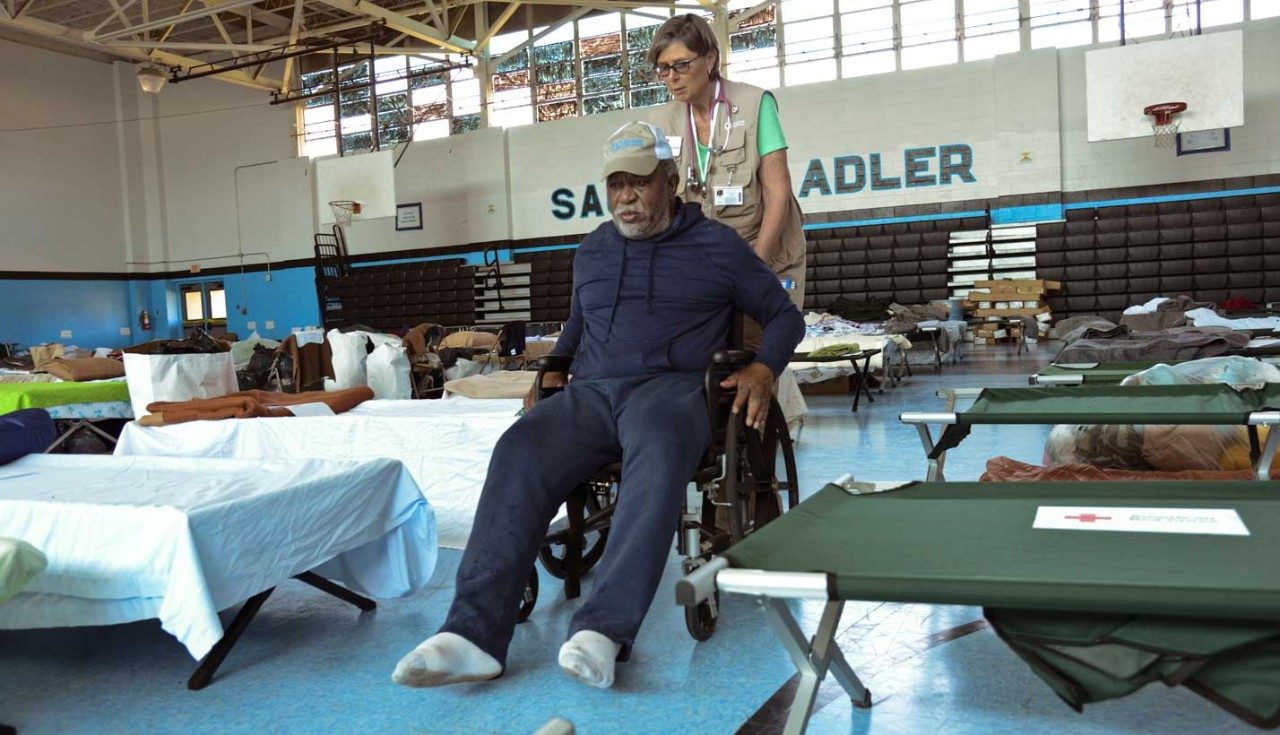

Ensure people with disabilities get the help they need
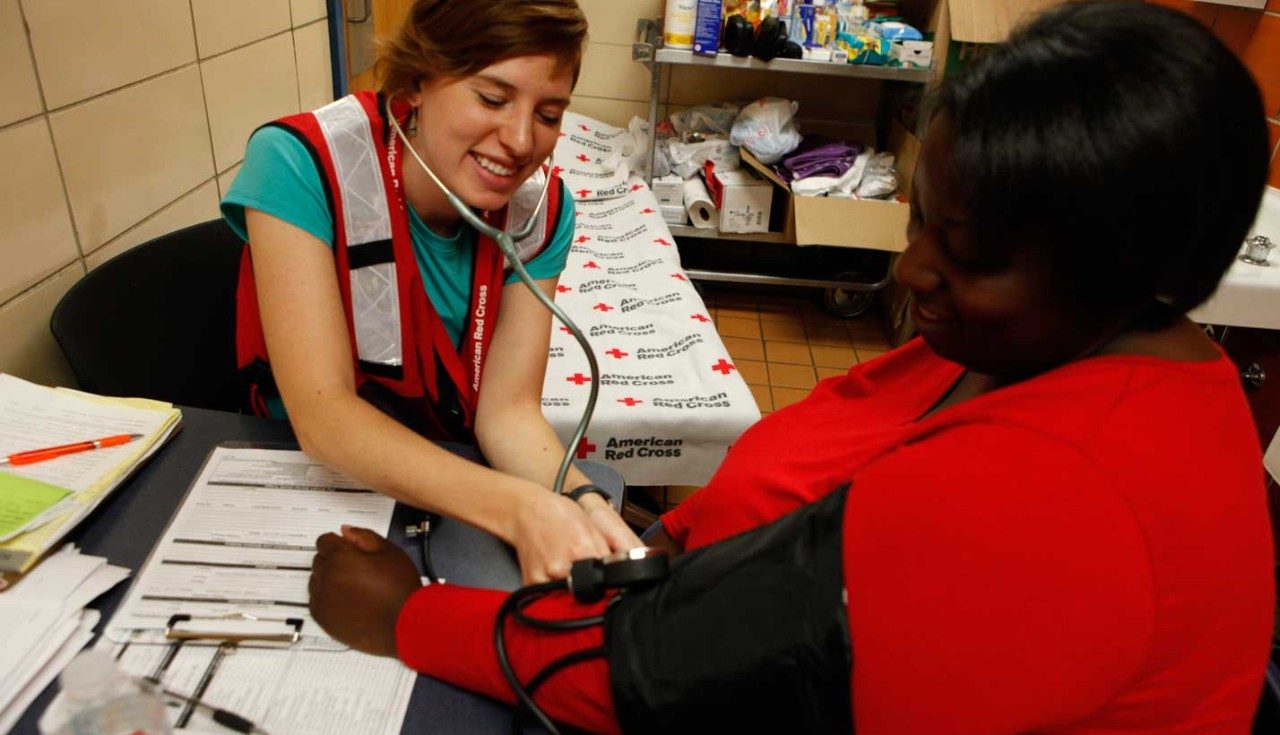

Provide first aid
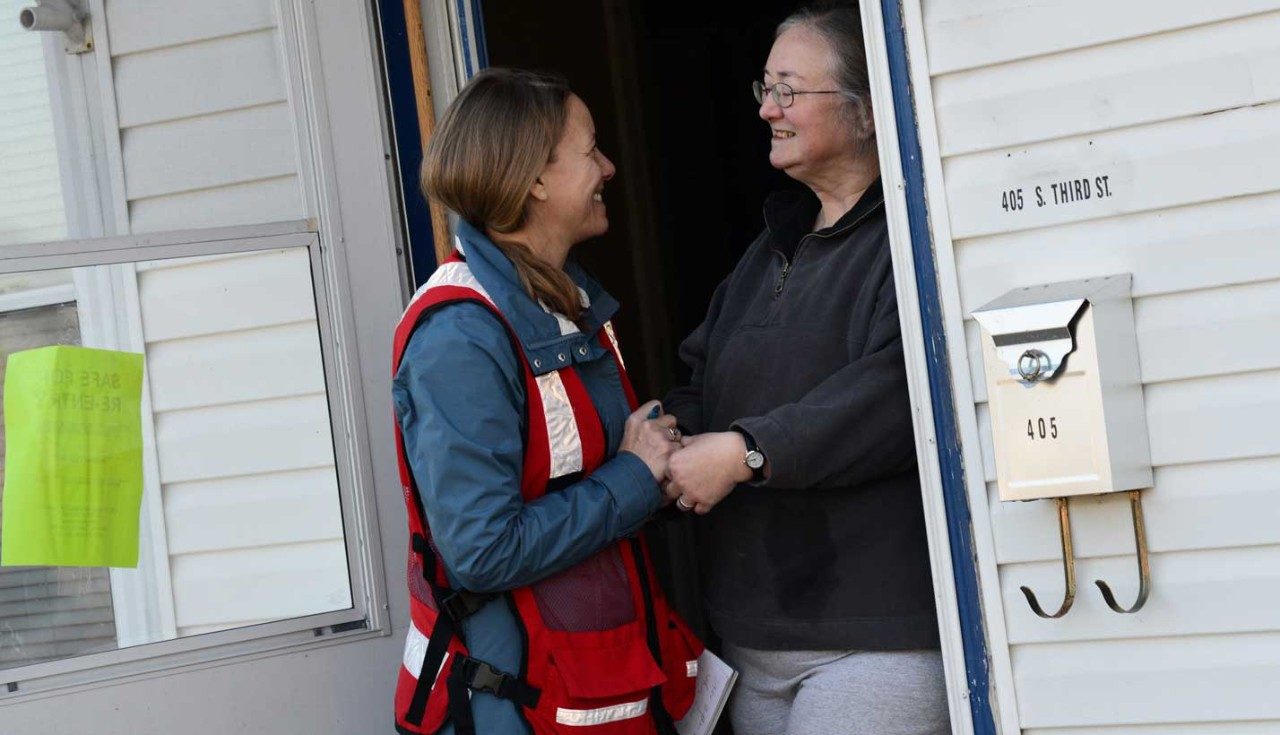

Give comfort and emotional support
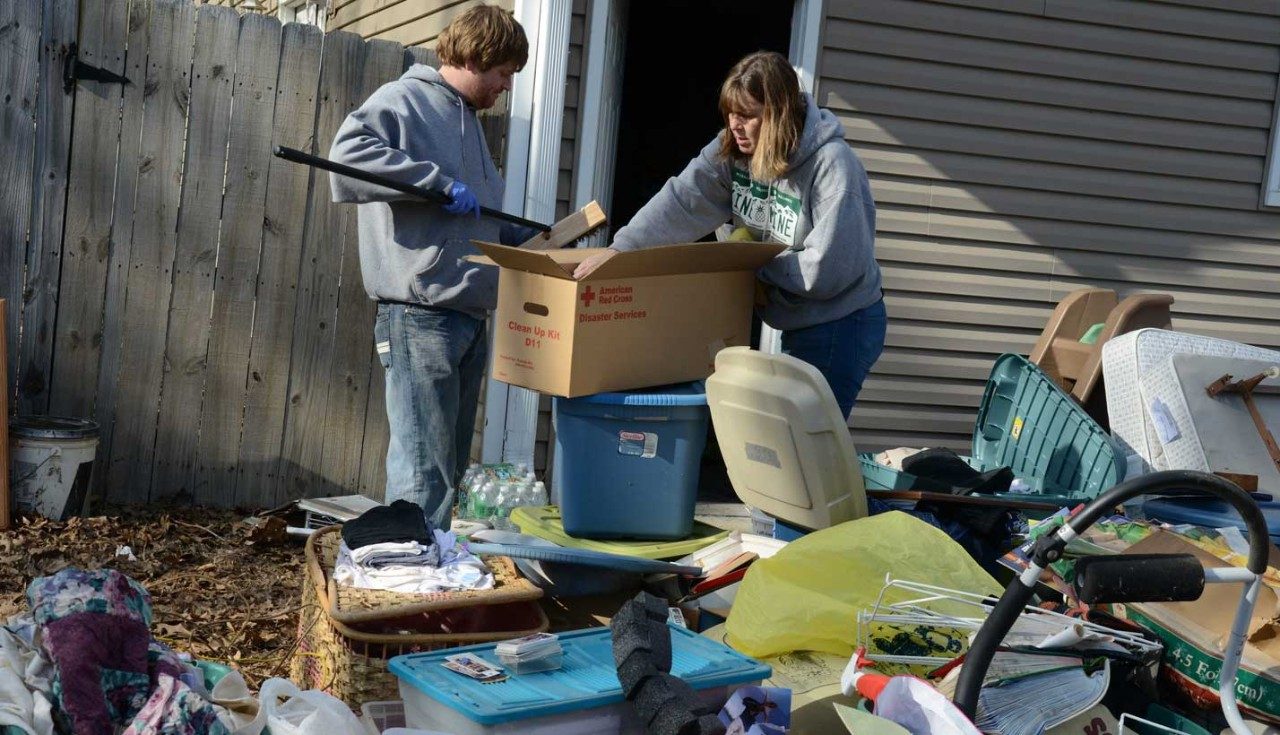

Distribute clean up supplies like mops, gloves and tarps

Assess damage in impacted neighborhoods
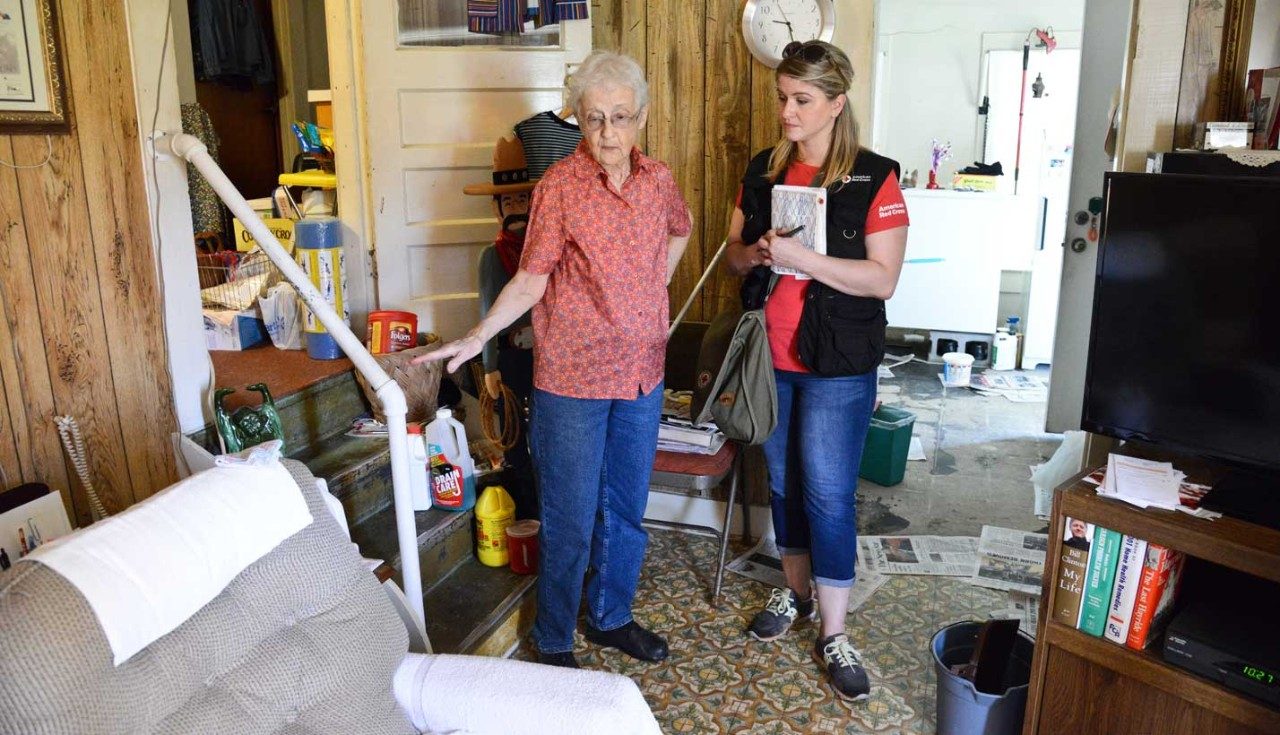

Meet with families to prepare recovery plans
Recent Flood Relief Efforts
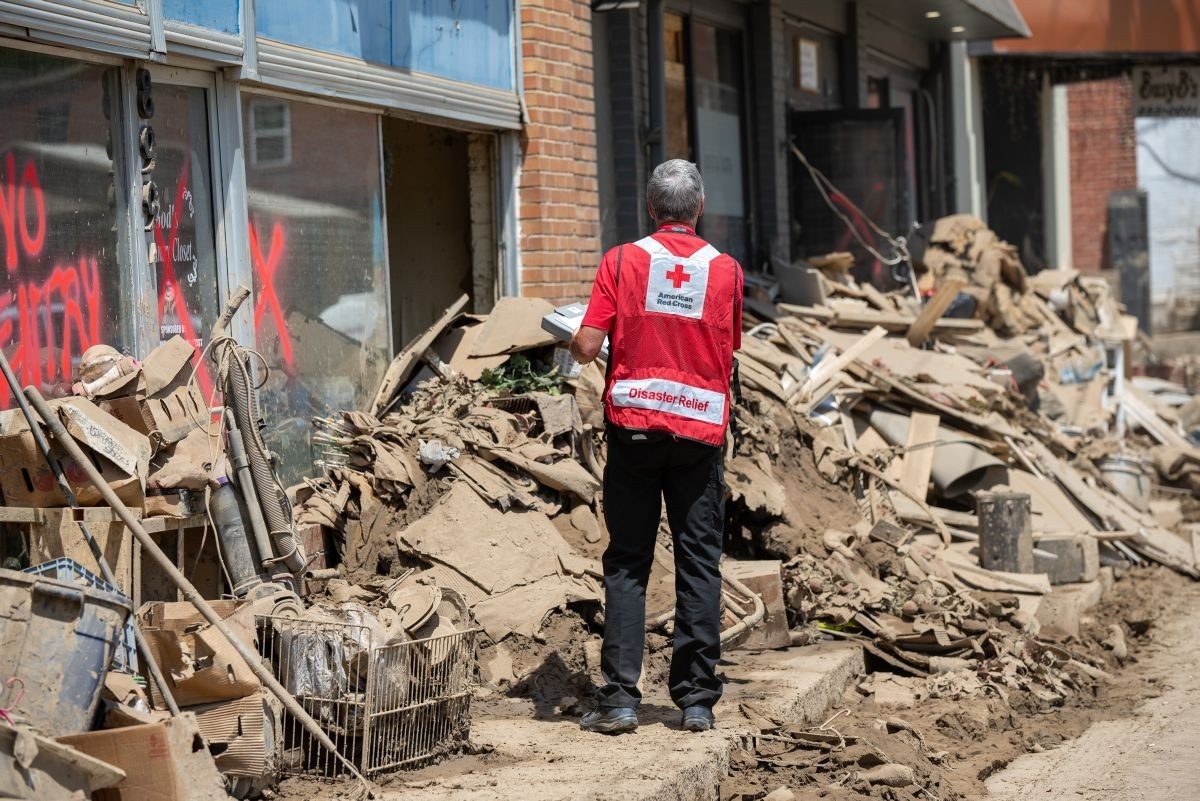

In late July of 2022, heavy rains caused extreme flooding across eastern Kentucky, causing immense damage to homes and critical infrastructure in multiple communities. In the weeks to come, the American Red Cross was there to support those in Kentucky who were impacted by the devastating flood waters.

In Spring 2019, communities across the Midwest were ravaged by a series of flooding and severe weather events—including multiple devastating tornadoes—that impacted tens of thousands of residents.
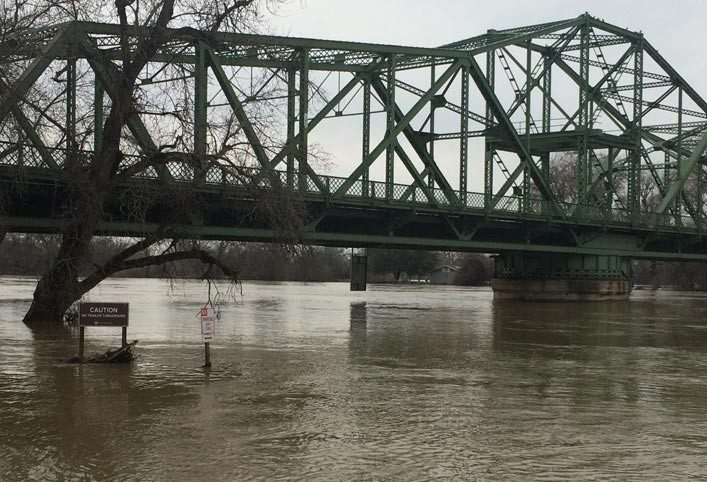

Residents of Oroville, CA were ordered to evacuate after a hole in an emergency spillway in the Oroville Dam threatened to flood the surrounding area.
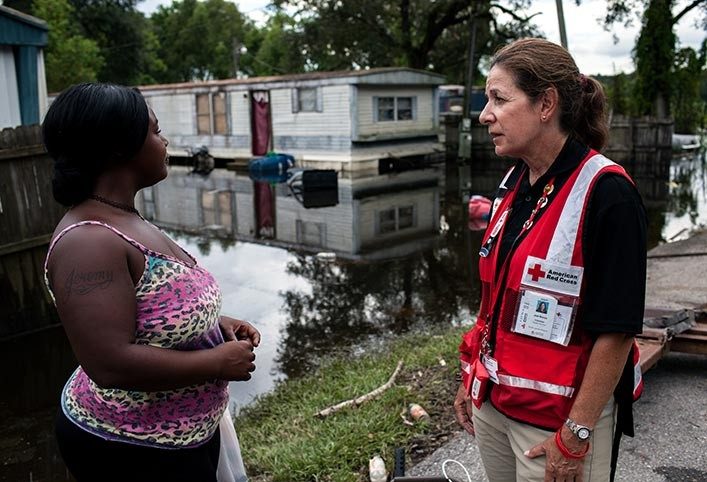

It took time for people to get back on their feet, but with the commitment of generous donors and volunteers, we were able to help ensure they had the support to recover.

In late June of 2016, devastating floods hit West Virginia, covering a large portion of the state.

In 2016, American Red Cross helped tens of thousands of people across Texas impacted by relentless severe weather, flooding and tornadoes in more than 130 counties—many of which were struck multiple times.
Be Prepared for Floods
Plan & Prepare for Floods
Download the Emergency App
Help people affected by disasters big and small.

- High contrast
- Press Centre
Search UNICEF
Devastating floods in pakistan, one year after historic floods devastated pakistan, unicef remains on the ground, working with partners to help children and families..

Last updated: 25 August 2023
One year after unprecedented floods ravaged Pakistan, millions of children still need humanitarian assistance and access to essential services.
Many of the hardest-hit districts were among the most vulnerable in the country, where children already suffered from high malnutrition, poor access to water and sanitation, and low school enrollment. The loss of vital infrastructure – including thousands of schools and public health facilities – deepened pre-existing inequities, leaving children even more at risk of hunger and disease.
UNICEF has been on the ground with partners since day one of the emergency response, and remains committed to supporting families still affected by the devastation.
We need your urgent support to help save lives:
What happened?
The 2022 floods submerged one third of the country, affecting 33 million people, half of whom were children. The floods damaged most of the water systems in affected areas, forcing more than 5.4 million people to rely solely on contaminated water from ponds and wells.
Unsafe water and poor sanitation are key underlying causes of malnutrition. Associated diseases, such as diarrhoea, prevent children from getting the vital nutrients they need. When children become malnourished, their weakened immune systems make them even more susceptible to waterborne diseases, perpetuating a vicious cycle of malnutrition and infection.

How UNICEF is supporting children in Pakistan
Since August 2022, UNICEF and partners have reached 3.6 million people with primary health-care services; enabled access to safe water for 1.7 million people in areas where water networks were damaged or destroyed; reached over 545,000 children and caregivers with mental health and psychosocial support; and supported education for over 258,000 children. UNICEF has also screened more than 2 million children for severe acute malnutrition and admitted over 170,000 children for life-saving treatment.
Still, the needs continue to outstrip the resources required to respond.

Your contribution can help UNICEF reach more children and families with life-saving supplies.

How does UNICEF respond in emergencies?
When an emergency such as an earthquake or typhoon strikes, it’s children who suffer first and most. UNICEF is on the ground before, during, and after emergencies, working to reach children and families with lifesaving aid and long-term assistance.
How critical supplies are supporting children in Pakistan
Take a look at UNICEF's critical role in providing shelter, medicines and education to children and families affected by 2022’s catastrophic floods.
One year on from catastrophic floods, millions of children in Pakistan still need urgent support
Receding waters reveal scars of climate change in Pakistan
The impact of last year’s historic floods will be felt for years to come by children and their families
More than 10 million people, including children, living in Pakistan’s flood-affected areas still lack access to safe drinking water
- Paragraph Writing
- Paragraph On Flood
Paragraph on Flood - Check Samples for 100, 150, 200, 250 Words
Floods are a type of natural disaster that can cause heavy destruction to life and property. It is a condition when rainwater accumulates at a place, flooding populated areas. They can also lead to the loss of numerous lives. At times, it can be highly dangerous and can wipe off an entire village or city.
Table of Contents
Paragraph on flood in 100 words, paragraph on flood in 150 words, paragraph on flood in 200 words, paragraph on flood in 250 words, frequently asked questions on flood.
It is impossible to stop a natural disaster, but the effects of the disaster can be reduced. The government has been taking major steps to reduce the effects of such disasters and save many lives. Before you write a paragraph on floods and their effects, you can refer to the samples provided below.
A flood is a condition when an area is fully or partially submerged in water for a period of time due to man-made or natural causes. The natural reasons behind floods can be heavy and continuous rain for an extended time period. Dam bursts or breaking of dam gates can be a man-made reason for a flood to occur. Floods can be highly dangerous at times because they may lead to loss of lives and property, and at certain places, it also leads to landslides. One cannot stop floods, but they can be avoided by constructing dams. One can definitely reduce the effects of floods and can reduce the damage caused by floods. Planting more trees in flood-prone areas and constructing dams might be helpful in controlling the adverse effects of floods.
A flood is a type of natural disaster that can be caused due to heavy and continuous rainfall at a place for a long time. Heavy rain, cyclones, storms, etc., can lead to flooding in an area. The water reserves are filled due to rain, and when it rains for a long time continuously, the overflow of water in water reserves may cause flooding.
Some parts of India are prone to flooding during the monsoon, causing large-scale destruction to human lives, natural habitats, etc. But in some places, floods can occur due to man-made disasters and cause loss of property and human lives. Breaking the dam’s gates can be a major reason behind man-made disasters. Due to these floods, the flood water accumulates in the agricultural fields, damaging crops. It can lead to starvation and more deaths. Many farmers have been committing suicide due to the loss. Floods are dangerous to human lives as well as the economy of the country. Therefore, it is essential to take necessary measures to limit the effects of floods.
A flood is a condition when an area is fully or partially submerged in water for a few days leading to hazardous diseases and loss of lives and property. Floods can be dangerous to factories, buildings, cities, hospitals, etc. Deforestation has been causing many hazards to the environment, and floods are one of these disasters. The rainwater is absorbed by the trees, and they act as natural barriers preventing soil erosion and landslides. Floods occur mostly in the rainy season in flood-prone areas, and the water levels may vary in such places. Naturally, floods can occur when it rains heavily for an extended period of time, and the water reserves are filled, causing an overflow of water. The breakage of dams can also cause floods and can lead to hazardous damage to lives and the environment. Floods can cause heavy loss of life and property and can also affect the agricultural system of the country, hence leading to starvation. It brings huge losses to public and private properties, affecting the country’s economy. At times, the revival also takes a lot of time. When the effects of floods are highly severe, it might take years to recover the physical damages. Almost every year, the country goes through such natural disasters leading to great loss and damage.
One of the major reasons for floods is heavy rain. Due to heavy rain, water levels in rivers and lakes are expected to rise. As the rainwater rises over the banks of rivers, it overflows and causes floods. With the increasing global warming, it is also possible that there might be floods due to the massive melting of snow. If global warming increases, with the rise in temperature, the ice might melt faster, leading to floods in various parts of the country. Floods pose a threat to factories, buildings, cities, hospitals, etc. Deforestation has resulted in a variety of environmental risks, one of which is flooding. Rainwater was absorbed by the trees, limiting the amount of water stored at a location. Floods are most common during the monsoon season in flood-prone areas, and water levels can fluctuate. During the monsoon season, floods are widespread in several places in India. It has a large-scale impact on human life and property. Houses are submerged in water, making day-to-day life difficult. Water also floods vast swaths of agricultural areas, wreaking havoc on crops and undermining the economy. A flood is a natural occurrence that has no benefits and is always a cause of loss. It is impossible to stop a natural disaster from occurring, but we can always limit the effects of the disasters. We can always take necessary measures to reduce the damage caused by it. Floods can leave adverse effects around the world, and at times, the revival of the damages may take years.
What is meant by flood?
A flood is a type of natural disaster that can leave adverse effects on the environment. During floods, an area is fully or partially submerged in water due to heavy rain or an overflow of dams and rivers.
What can be the effects of floods?
Floods can have adverse effects on the environment. It causes loss of public and private property, loss of lives, starvation and hunger, etc.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

- _وضاحتی مضامین
- _مختصر مضامین
Essay on Flood in Urdu For Students | سیلاب پر مضمون
آج ہم اُردو میں سیلاب پر مضمون فراہم کرنے جا رہے ہیں۔ یہ مضمون ان طلباء کی مدد کر سکتا ہے جو سیلاب کے بارے میں معلومات تلاش کر رہے ہیں۔ یہ مضمون یاد رکھنے میں بھی آسان ہے۔ اس مضمون کو آسان اور سادہ الفاظ میں لکھا گیا ہے لہذا کوئی بھی طالب علم اس موضوع پر لکھ سکتا ہے۔

سیلاب پر مضمون
سیلاب سب سے خطرناک قدرتی آفات میں سے ایک ہے۔ جو بارشوں کے ہونے پردریاؤں میں پانی کے زیادہ بہاؤ کی وجہ سے آتا ہے۔ جس کے نتیجے میں دریاؤں کا پانی کناروں سے نکل کر میدانی علاقوں میں چلا جاتا ہے۔ یہ لوگوں کے مال اور فصلوں کو بہت نقصان پہنچا سکتا ہے۔
سیلاب کی وجوہات
عام طور پر جب زیادہ بارشیں ہوتی ہے تو پاکستان میں سیلاب کا قوی امکان ہوتا ہے۔
شدید دریائی بارشوں کی وجہ سے دنیا کے کئی مقامات کو اس قدرتی آفات کا سامنا رہتا ہے۔ اس کے علاوہ ڈیم (Dam) کا ٹوٹنا اور پہاڑوں پر برف کا پگھلنا سیلاب کی ایک اور بڑی وجہ ہے۔
اگر ہم ساحلی علاقوں کی بات کریں توطوفان اور سونامی ان علاقوں میں سیلاب کا باعث بنتے ہیں۔
بہرحال سیلاب کی وجوہات جو بھی ہوں پر اس کے بہت سے نقصان دہ نتائج ہوتے ہیں۔ سیلاب سے حالات زندگی کو نقصان پہنچتا ہے اور اس تباہی سے نکلنے میں کافی وقت لگتا ہے۔ اس لیے سیلاب کے نتائج کو دیکھتے ہوئے ہمیں اس کی روک تھام کے لیے اقدامات کرنے چاہیے۔
سیلاب کے بعد کے اثرات
سیلاب متاثرہ علاقے کے روزمرہ کے کام میں خلل ڈالتا ہے۔ شدید سیلاب بعض اوقات بڑے پیمانے پر تباہی پھیلاتے ہیں۔ سیلاب کی وجہ سے بہت سے لوگ اور جانور اپنی جانوں سے ہاتھ دھو بیٹھے ہیں اورکئی زخمی ہوجاتے ہیں۔ سیلاب سے بیماریوں میں بھی اضافہ ہوتا ہے۔ کھڑا پانی مچھروں کو اپنی طرف متوجہ کرتا ہے جو ملیریا، ڈینگی اور دیگر بیماریوں کا باعث بنتا ہے۔
اس کے علاوہ، لوگوں کوبجلی کی بندش اور مہنگی قیمتوں کا بھی سامنا کرنا پڑتا ہے۔ جیسے جیسے خوراک اور اشیاء کی فراہمی محدود ہو جاتی ہے، قیمتیں قدرتی طور پر بڑھ جاتی ہیں اوراس سے عام آدمی کے لیے بڑا مسئلہ پیدا ہوتا ہے۔
سب سے اہم بات یہ ہے کہ پورے ملک کو معاشی نقصان کا سامنا کرنا پڑتا ہے۔ لوگوں کو بچانے اور اس آفت سے نمٹنے کے لیے درکار وسائل ایک بھاری رقم مانگتے ہیں۔
اس سب کے علاوہ، سیلاب ہمارے ماحول کو بھی متاثر کرتا ہے اور اس سے مٹی کا معیار خراب ہوتا ہے۔ ہم زرخیز زمین سے محروم ہو جاتے ہیں۔ اسی طرح سیلاب نباتات اور حیوانات کوبھی نقصان پہنچاتا ہے۔ لہذا ان سنگین نتائج سے بچنے کے لئے اقدام کرنا ضروری ہیں۔
سیلاب سے بچنے کے طریقے
حکومت اور شہریوں کو مل کر سیلاب سے بچاؤ کے طریقے تیارکرنے چاہئیں۔ سیلاب آنے پر اٹھائے جانے والے اقدامات کے بارے میں مناسب آگاہی پھیلائی جانی چاہیے۔ انتباہی نظام(Warning systems) قائم کیا جانا چاہیے تاکہ لوگوں کو اپنے آپ کو بچانے کے لیے وقت مل سکے۔
اس کے علاوہ، بارش کی وجہ سے ضرورت سے زیادہ پانی کو ذخیرہ کرنے کے لیے ایک موثر نظام ہونا چاہیے۔ سب سے اہم اقدامات میں سے ایک نکاسی آب کے نظام کو مضبوط کرنا ہے۔ اس سے پانی کو جمع ہونے سے روکا جا سکتا ہے۔
دوسری طرف ہمیں ڈیم (Dam) مضبوطی سے بنانے چائیے جس میں سستے مواد کا استعمال نہ ہو۔ سیلاب سے بچنے کے لیے حکومت کوڈیموں (Dams) کی معیاری تعمیر کو یقینی بنانا چاہیے۔
مختصر یہ کہ ہم قدرتی وجوہات جیسے بارش اور پہاڑوں پر برف کے پگھلنے کو نہیں روک سکتے۔ تاہم، ہم انسانی ساختہ وجوہات کو روک سکتے ہیں جیسے ڈیموں کا ٹوٹنا، نکاسی کا ناقص نظام، انتباہی نظام نصب کرنا اور بہت کچھ۔ ہمیں سنگاپور جیسے ممالک سے سبق حاصل کرنا چاہیے جو سال کے زیادہ تر وقت شدید بارشوں کے باوجود سیلاب کا سامنا نہیں کرتے۔
نتیجہ (Conclusion)
سیلاب ان قدرتی آفات میں سے ایک ہے جو مختلف علاقوں میں بڑی تباہی کا باعث بنتا ہے۔ اب وقت آگیا ہے کہ حکومت پاکستان اس مسئلے کو سنجیدگی سے لے اور اس مسئلے پر قابو پانے کے لیے سخت اقدامات پر عمل کرے۔
سیلاب پر دس جملے
1) سیلاب ایک بڑے رقبے پر بڑی مقدار میں پانی کا بہاؤ ہوتا ہے، جو متاثرہ علاقے کی تباہی کا باعث بنتا ہے۔
2) دنیا بھر میں کئی خطوں کو ہر سال سیلاب کے مسئلے کا سامنا کرنا پڑتا ہے۔
3) پانی کے زیادہ بہاؤ اور نکاسی کا مناسب نظام نہ ہونے کی وجہ سے سیلاب آتا ہے۔
4) سیلاب کی شدت خطے کے لحاظ سے مختلف ہو سکتی ہے۔
5) طوفان اور سونامی ساحلی علاقوں میں سیلاب کا باعث بنتے ہیں۔
6) سیلاب بھی دیگر قدرتی آفات کی طرح بڑی تباہی کا سبب بن سکتا ہے۔
7) دنیا بھر کے بہت سے شہر خوفناک سیلاب کا شکار ہوئے ہیں، جس کے نتیجے میں لوگوں اور جانوروں کی زندگیاں تباہ ہوئی ہیں۔
8) کسان سیلاب سے بہت متاثر ہوتے ہیں کیونکہ موسمی حالات کی وجہ سے ان کی فصلیں تباہ ہو جاتی ہیں۔
9) شدید سیلاب کا سامنا کرنے والے مقامات کو دوبارہ بحال ہونے میں مہینوں لگ جاتے ہیں۔
10) اب وقت آگیا ہے کہ حکومت پاکستان اس مسئلے کو سنجیدگی سے لیں اور اس مسئلے پر قابو پانے کے لیے سخت اقدامات کرے۔
مزید پڑھیے:
میرے اسکول پر مضمون
جنگل پر مضمون
طوطے پر مضمون
ایک تبصرہ شائع کریں
The shortest time frame in which our writers can complete your order is 6 hours. Length and the complexity of your "write my essay" order are determining factors. If you have a lengthy task, place your order in advance + you get a discount!
Why is the best essay writing service?
On the Internet, you can find a lot of services that offer customers to write huge articles in the shortest possible time at a low price. It's up to you to agree or not, but we recommend that you do not rush to make a choice. Many of these sites will take your money and disappear without getting the job done. Some low-skilled writers will still send you an essay file, but the text will not meet the required parameters.
is the best essay writing service because we provide guarantees at all stages of cooperation. Our polite managers will answer all your questions and help you determine the details. We will sign a contract with you so that you can be sure of our good faith.
The team employs only professionals with higher education. They will write you a high-quality essay that will pass all anti-plagiarism checks, since we do not steal other people's thoughts and ideas, but create new ones.
You can always contact us and make corrections, and we will be happy to help you.
Finished Papers

offers three types of essay writers: the best available writer aka. standard, a top-level writer, and a premium essay expert. Every class, or type, of an essay writer has its own pros and cons. Depending on the difficulty of your assignment and the deadline, you can choose the desired type of writer to fit in your schedule and budget. We guarantee that every writer will be a subject-matter expert with proper writing skills and background knowledge across all high school, college, and university subjects. Also, we don’t work with undergraduates or dropouts, focusing more on Bachelor, Master, and Doctoral level writers (yes, we offer writers with Ph.D. degrees!)

Viola V. Madsen
Hundreds of people sue San Diego over January floods, saying it ‘absolutely failed’ to manage stormwater
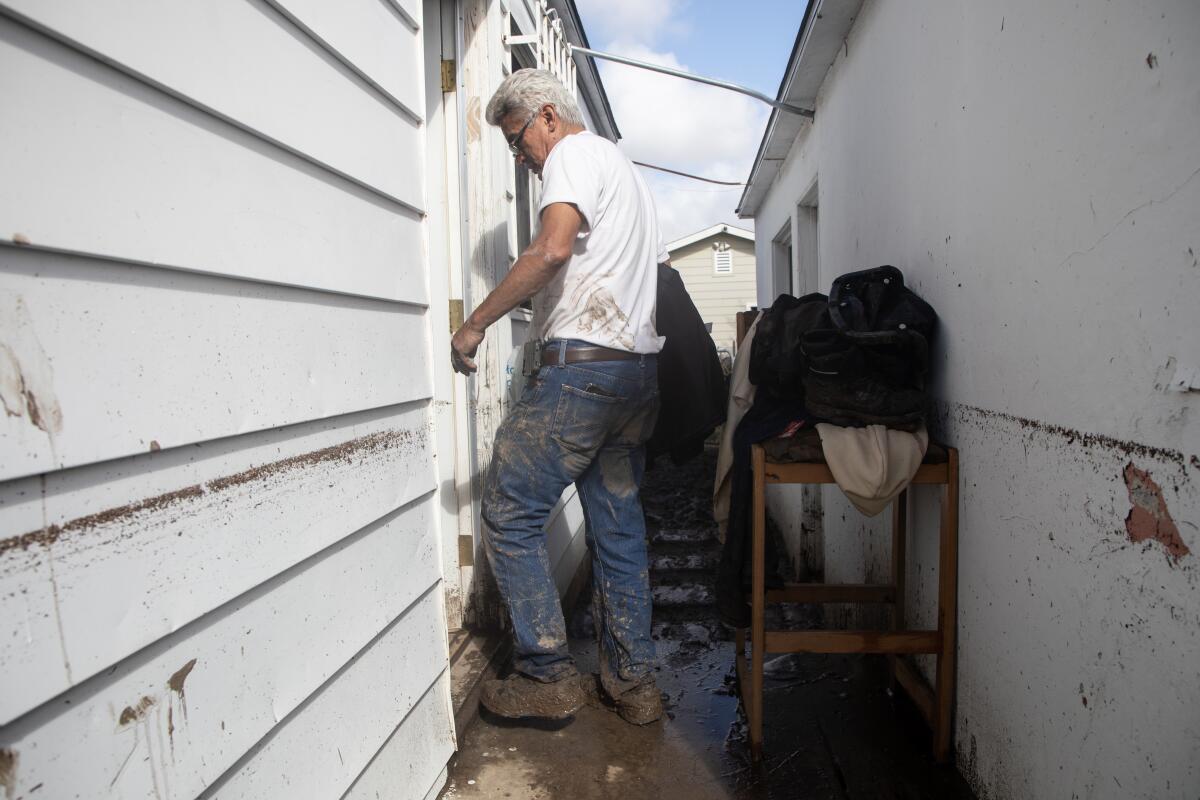

In a $100 million lawsuit, residents say city leaders knew for years that Chollas Creek and stormwater infrastructure around it were in urgent need of attention
- Show more sharing options
- Copy Link URL Copied!
After yearslong battles with the city of San Diego over crumbling stormwater infrastructure in their southeastern San Diego neighborhoods, hundreds of people whose homes and businesses were damaged by flash flood waters in January are now suing the city.
The $100 million mass tort lawsuit has nearly 300 plaintiffs — homeowners and renters as well as business owners in the communities of Southcrest, Logan Heights and others along the Chollas Creek watershed.
The lawsuit contends that city leaders have known for years that the creek and stormwater infrastructure around it are in urgent need of attention.
“The city of San Diego failed in its duty to protect communities from flooding,” reads the complaint, filed Monday in San Diego Superior Court.
It says the city knew for years that its storm drains were clogged full of vegetation, sediment and debris and therefore “created a destructive state of affairs and absolutely failed their residents.”
It also contends that despite years of warnings , the city failed to take the steps necessary to avoid flooding or increase stormwater revenue in the past two decades.
And it notes that the city’s stormwater system makes up the biggest share of its infrastructure backlog. A city report from earlier this year found that stormwater needs had grown to more than $2.2 billion over the next five years — a figure higher than the city’s entire proposed annual budget .
The city itself has said that absent billions of dollars in new spending, the outdated and underfunded stormwater system “poses a risk of flooding and catastrophic failure,” city officials wrote in a report published earlier this year.
The city attorney’s office declined to comment Wednesday on the pending litigation.
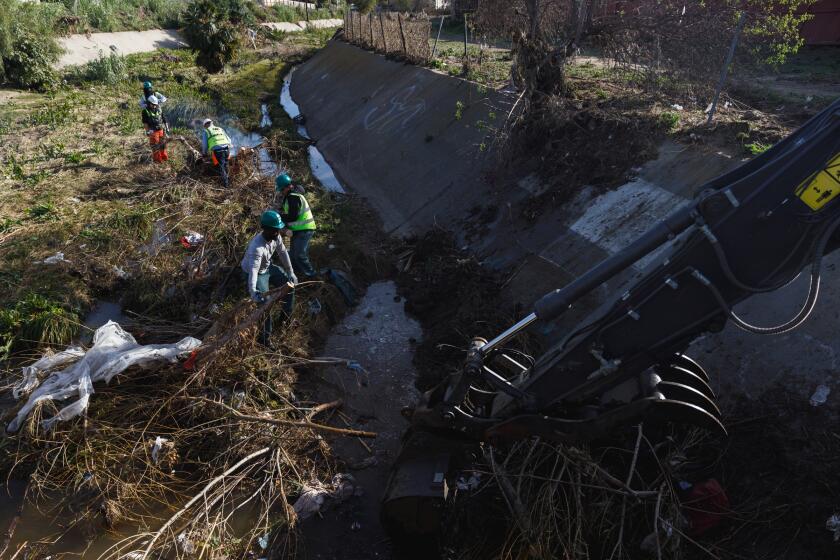

What San Diego is — and isn’t — doing to fix its ‘failing’ stormwater system
The city’s outdated and underfunded stormwater infrastructure has left it vulnerable to the kinds of floods that ravaged southeastern communities last week
Jan. 28, 2024
“The heart of that complaint is the clogging of Chollas Creek, which the city has known about for some time as a problem,” said Evan Walker, one of the five lawyers representing plaintiffs in the lawsuit.
Walker said his office, along with contractors and appraisers, have been assessing the storm destruction since January to calculate the total cost of damages.
The suit he filed on behalf of flood victims lists six causes of action, ranging from negligence to creation of a dangerous condition for public property.
This isn’t the first time the city has had to defend its aging flood-control network. Walker sued the city on behalf of some of the same residents after the same channel overflowed in 2018 and caused some of properties on Beta Street to flood.
That suit accused the city of not only knowing about but helping to create the failures that caused the flooding. It pointed to a concrete channel the city built to direct storm runoff from Chollas Creek but allowed to remain clogged, as well as an embankment above the channel that directed stormwater toward homes.
Residents eventually accepted just over $200,000 to resolve the lawsuit. But the settlement did not require the city to correct the problem.
The events of 2018 were “more or less the same” as what residents experienced in January, Walker said, but the biggest difference “is the sheer magnitude of the damages and that people affected” in this year’s storms.
The 2019 case only had a handful of plaintiffs. But now, some of those who previously settled are suing the city again, under different causes of action.
Greg Montoya, a plaintiff in both lawsuits, said he watched in despair as his block was inundated once again — this time much more extensively — after the bridge at 38th Street, just upstream from his home, was clogged with debris.
“The bridge acted like a dam, and water couldn’t get through — so it overflowed, blew out all the fencing along the creek and started flooding down the street,” Montoya said. “It was a mess.”
At least 3 feet of water destroyed most of his belongings, and he has since been living in a hotel through the county’s hotel voucher program while he repairs his home.
Since the first lawsuit, Montoya says he’s kept pestering the city, sending numerous emails and reports via the city’s online Get It Done problem-reporting app in an effort to clear the storm drains.
“They just continue to show that they have a lack of interest in this area,” he said.
He hopes he and other flood victims are compensated for their losses but also that the city will implement a plan to fix the stormwater system. “I hope this time they take it more seriously and get something done,” he said.
Meanwhile, city leaders are working to close the stormwater infrastructure funding deficit with a proposed parcel tax increase . The tax measure, which city officials hope to put on the November ballot, would raise anywhere from $74 million to $474 million a year for flood prevention and water quality projects.
The goal is to eliminate a $1.6 billion shortfall in the funding needed to complete crucial flood prevention and stormwater infrastructure improvements over the next five years — a gap that’s grown so wide in part because the city’s stormwater fee is only a small fraction of what other cities charge.

Not just stormwater: San Diego needs more than $6 billion for crucial infrastructure — but has just a quarter of that
A new report estimates the city will have $1.5 billion over the next five years for $6.29 billion in needed projects
Feb. 5, 2024
Should the tax hike appear on the November ballot and win approval from voters, it would mark the first such fee increase since Proposition 218 began requiring support from two-thirds of voters back in 1996.
San Diego’s existing stormwater fee is about 95 cents per house each month — far less than the $10 per month that city officials say is the true cost of what San Diego must do to prevent floods and water pollution.
Despite the funding struggles, city officials have suggested the January floods were unavoidable. In a February press conference , city stormwater director Todd Snyder said the creek channel behind Beta Street wasn’t designed to handle such an intense storm and would have been overwhelmed even if it had been maintained.
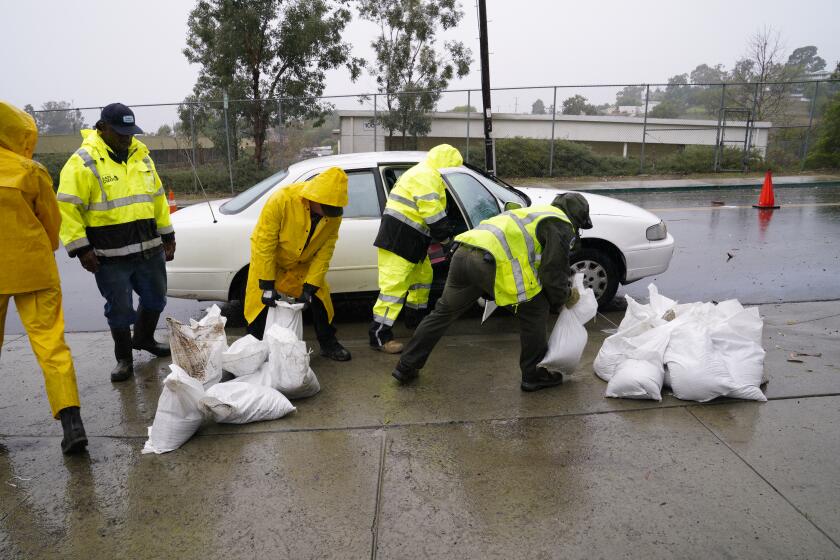

Months after devastating floods, San Diego moves one step closer to voting on a flood prevention tax this fall
A city council committee voted unanimously Thursday to study the proposal, which one supporter called ‘our best opportunity to finally address this issue’
April 18, 2024
The city may also face more legal claims to come. Other residents like Gerardo Hernandez who aren’t plaintiffs in the suit say they plan to pursue legal action of their own.
“Every person lost different amounts of money and property,” Hernandez said. “So it’s better to (sue) individually.”
Hernandez has also been living at a hotel through the county’s temporary lodging program after his Beta Street home flooded, and says he has been dealing with pain in his legs and hips since standing in cold water for five and a half hours the day of the flood.
In preparing to sue, he has been making a list of everything he lost, from toenail clippers to Christmas decorations to five vehicles. It’s currently at 18 pages.
Get Essential San Diego, weekday mornings
Get top headlines from the Union-Tribune in your inbox weekday mornings, including top news, local, sports, business, entertainment and opinion.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the San Diego Union-Tribune.

More from this Author

‘Like you’re in a different world’: What a new Ocean Beach Pier would mean for locals, surfers and San Diego
May 13, 2024

Three cheers, and barks, for new 4S Ranch park’s off-leash dog area
May 11, 2024

Who will be the county’s next top executive? As supervisors near a decision, one candidate’s backers make a very public push
May 3, 2024

With thousands still displaced by January floods, county extends hotel program with $9 million
April 30, 2024

They shared their experience with mental illness in last year’s 72 Hours project. Here’s how 3 are doing.
April 29, 2024

Three months after catastrophic floods, these community groups are still cooking meals for displaced families
April 27, 2024
More in this section

New California law means no more surcharges at San Diego restaurants but expect higher menu prices
Restaurants, from Mister A’s to Rockin’ Baja Lobster, have long been adding extra charges to diner’s bills to help defray rising labor costs but come July, a new state law will effectively outlaw them, forcing some eateries to raise menu prices even more than they already have.

South County
Chula Vista’s proposed budget boosts spending on public safety infrastructure and homelessness personnel
The draft spending plan includes money for a bayfront fire station, arts center and several positions for homeless services and fire protection

Senior-only affordable housing proposed for Oceanside’s South Coast Highway
Project is one of two recommended for loans of city’s low-income housing funds; staffers reviewed five proposals
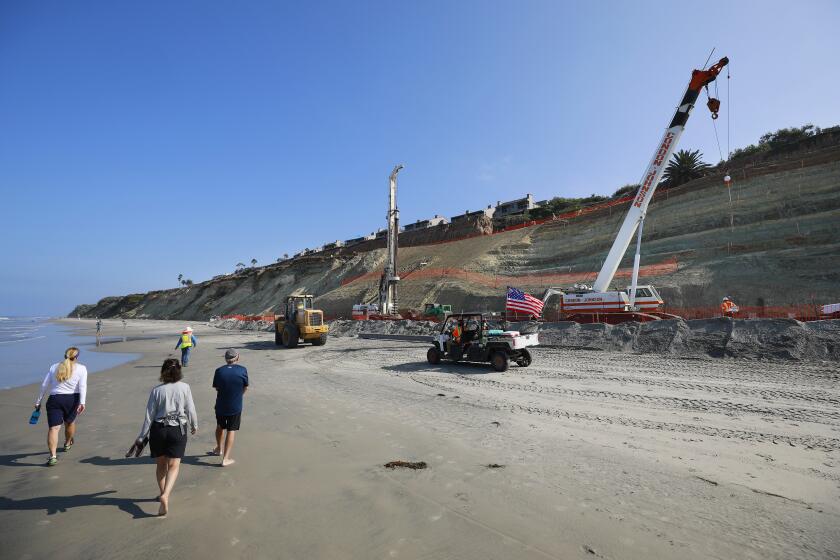

North County
For the imperiled coastal rail line, Del Mar seawalls are ‘imperative.’ For locals, they’re ‘the construction zone from hell.’
Seawalls take up too much beach space and reduce access to hillside trails, residents tell SANDAG official

Health center celebrates 45 years of service to community, honors mothers during powwow in Balboa Park
The San Diego American Indian Health Center’s 36th annual Balboa Park Pow Wow featured traditional dancing and singing, vendor booths over two days
May 12, 2024

Hike of the week: Mother Miguel Mountain is a tough climb — but worth it
This 4-mile hike offers views of key landmarks in the county, including Mt. Soledad, Mt. Helix and downtown San Diego
In photos: At least 83 dead as historic flooding hits southern Brazil
By Jintak Han | May 7, 2024
Record-breaking floods in Brazil’s southern Rio Grande do Sul state have killed at least 83 people over the past week, and another 111 were reported missing, local authorities said Monday.
Renan Mattos/Reuters
In the state capital, Porto Alegre, water levels of the Guaíba River peaked at 17.5 feet (5.33 meters) on Sunday — far exceeding the previous record of 15.6 feet (4.76 meters) observed in 1941, according to the prefectural government.
At least 291 people were injured, while damage from the rains forced more than 129,000 people from their homes. Approximately 20,000 took refuge in schools, gymnasiums and other temporary shelters.
May 6 | Porto Alegre, Brazil
An aerial view of the flooded Beira-Rio Stadium.
A group of volunteers on a flooded street.
Giulian Serafim/AFP/Getty Images
A car is filled with water on a flooded street in the Menino Deus neighborhood.
A military truck transports people out of the flooded area.
Nelson Almeida/AFP/Getty Images
Volunteers help residents evacuate from their homes in the Farrapos neighborhood.
May 5 | Porto Alegre, Brazil
An area after the flooding of Guaíba River.
May 5 | Canoas, Brazil
People are rescued after flooding.
Amanda Perobelli/Reuters
People are rescued by residents.
Rescue workers evacuate a flood victim.
A flooded street.
Anselmo Cunha/AFP/Getty Images
People wade through floodwaters.
People walk through floodwaters.
May 5 | Roca Sales, Brazil
Houses destroyed by floods.
Gustavo Ghisleni/AFP/Getty Images
May 5 | Jacarezinho, Brazil
People walk inside a shop destroyed by flash floods.
Diego Vara/Reuters
May 5 | Encantado, Brazil
An injured dog lies in the mud after heavy rains and floods.
Volunteers provide food, medical attention and clothing to people rescued from flooded houses at a gas station used as a meeting point.
Carlos Fabal/AFP/Getty Images
Julio Manichesque walks on the roof of his house after floods.
A flooded area after the flooding of Lake Guaiba.
May 4 | Porto Alegre, Brazil
A woman is evacuated from a flooded area.
May 4 | Canoas, Brazil
Rescue teams and volunteers help flood victims.
Alisson Moura/AFP/Getty Images
A man is rescued by military firefighters.
May 4 | Roca Sales, Brazil
A man is rescued after being injured during the floods.
May 3 | Eldorado do Sul, Brazil
Floodwaters overtake the streets.
May 3 | Porto Alegre, Brazil
A man wades through a flooded section of the city.
Carlos Macedo/AP
Residents of coastal islands near the shore of Lake Guaíba carry their belongings after being rescued.
Isaac Fontana/EPA-EFE/Shutterstock
May 2 | Encantado, Brazil
A woman carries two rescued cats.
People and a dog are rescued from the islands of Lake Guaíba.
May 1 | Encantado, Brazil
Houses next to the Taquari River are submerged by floodwaters.
May 1 | Sinimbu, Brazil
A house partially destroyed by heavy rains.
A resident climbs a rescue truck.
May 3 | Encantado, Brazil
A woman walks through mud as she tries to get to her house.
May 2 | Lajeado, Brazil
Two men are rescued by military firefighters.
Jeff Botega/Agencia RBS/Reuters
People throw bags across a puddle as they evacuate flooded areas.
Vehicles covered in mud.
Horses wade through a flooded beach along the Jacui River.
People and their pets are rescued from the flooding.
Renan Mattos/EPA-EFE/Shutterstock
Residents are rescued by the Brazilian army.
Displaced people take shelter in a public facility.
A displaced person rests at a shelter.
More from the Post
Historic floods kill 83, leaving Brazil and its president shaken, angry
The new face of flooding
The latest from The Washington Post
Photo editing and production by Jintak Han and Troy Witcher
- Share full article

Images of a Brazilian City Underwater
Torrential rains have caused one of Brazil’s worst floods in modern history, leaving more than 100 dead and nearly an entire state submerged.
An aerial view on Wednesday of one of the worst natural calamities to hit the southern state of Rio Grande do Sul in Brazil. Credit... Nelson Almeida/Agence France-Presse — Getty Images
Supported by
By Ana Ionova and Tanira Lebedeff
Ana Ionova reported from Rio de Janeiro, and Tanira Lebedeff from Porto Alegre, Brazil.
- May 8, 2024
Anderson da Silva Pantaleão was at the snack bar he owns last Friday when clay-colored water began filling the streets in the southern Brazilian city of Porto Alegre. Soon, it was rushing into his ground-floor shop. By 9 p.m., the water was up to his waist.
“Then the fear starts to hit,” he said. “You’re just trying not to drown.”
He dashed up to a neighbor’s home on the second floor, taking refuge for the next three nights, rationing water, cheese and sausage with two others. Members of the group slept in shifts, fearing another rush of water could take them by surprise in the dead of night.
On Monday, water began flooding the second floor, and they thought the worst. Then, a military boat arrived and rescued Mr. Pantaleão, 43. A day later, despite heavy rains, he was trying to go back on a rescue boat to search for friends who were still missing or stranded.
“I can’t leave them there,” he said. “The water is running out, the food is running out.”
Flood victims took shelter at a sports facility in the Menino Deus neighborhood of Porto Alegre, Brazil. The situation in southern Brazil, where heavy rains have caused flooding in hundreds of municipalities, may worsen with the arrival of new storms.
A man was rescued by military firefighters after the floods in Canoas, Brazil, on Saturday.
People charging their mobile phones outside a drugstore in the historic center of Porto Alegre, Brazil, after torrential storms devastated areas in Rio Grande do Sul State.
Brazil is grappling with one of its worst floods in recent history. Torrential rains have drenched the southern state of Rio Grande do Sul, home to 11 million people, since late April and have triggered severe flooding that has submerged entire towns, blocked roads, broken a major dam and shut down the international airport until June.
At least 105 people have been killed and 130 others have been reported missing. The floods, which have stretched across most of Rio Grande do Sul’s 497 municipalities, have forced nearly 164,000 people from their homes.
In the state capital, Porto Alegre, a city of 1.3 million perched on the banks of the Guaiba River, streets were submerged in murky water and the airport was shuttered by the deluge, with flights canceled through the end of the month.
The river rose to over 16 feet this week, exceeding the previous high levels seen during a major flood in 1941 that paralyzed the city for weeks.
The flooding has blocked roads into the city and hampered deliveries of basic goods. Supermarkets were running out of bottled water on Tuesday, and some residents reported walking up to three miles in search of clean drinking water.
Many of those stranded awaited help on rooftops. Some took desperate measures to flee: When the shelter her family was staying in flooded, Ana Paula de Abreu, 40, swam to a rescue boat while grasping her 11-year-old son under one arm. Two residents of one Porto Alegre neighborhood used an inflatable mattress to pull at least 15 people out of their inundated homes.
Search crews, which include the authorities and volunteers, were scouring flooded areas and rescuing residents by boat and air. With nowhere to land, some helicopters have used winches to pull up people stranded by the flooding.
Barbara Fernandes, 42, a lawyer in Porto Alegre, spent hours on the scorching roof of her apartment building on Monday, waving a red rag and her crutches toward the sky. A rescue helicopter finally spotted her in the late afternoon.
“You just don’t know when they’ll come for you,” said Ms. Fernandes, who is recovering from surgery on her ankle and could not flee her building before the waters rose.
A cargo plane at the flooded Salgado Filho International Airport on Tuesday in Porto Alegre, Brazil.
Residents were evacuated in a military vehicle from an area flooded by heavy rains, in Porto Alegre, Brazil, on Tuesday.
Cintia Santos was evacuated by bus from a flooded area on Tuesday in Eldorado do Sul.
Nearly 67,000 people were living in shelters across the state, while others have taken refuge in the homes of family or friends. Some people who had access to neither option were sleeping in their cars or on the streets in areas that were still dry.
“It seems like we’re living through the end of the world,” said Beatriz Belmontt Abel, 46, a nursing technician who was volunteering at a shelter in the city of Canoas, across the river from Porto Alegre. “I never imagined I would see this happen.”
In another shelter set up in a gym in Porto Alegre, volunteers distributed meals and clothes. Rows of mattresses lay on the floor, and cardboard boxes served as shelves. Those who had been rescued busied themselves sweeping the floor and making their temporary beds.
President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva, who visited the region last week, pledged federal funds to help the rescue efforts. The state authorities have also announced aid to pay for search crews, health services and housing for those whose homes were destroyed or damaged by floodwaters.
Even as rescues continued, the authorities worried that the crisis could worsen because another wave of severe weather was expected in coming days. With a cold front buffeting the region, meteorologists have forecast heavy rains, hail, thunderstorms and winds over 60 miles per hour.
The states’s governor, Eduardo Leite, said the authorities were evacuating people from regions vulnerable to more turbulent weather. Some residents have refused to abandon their homes, fearing looting. Others have tried to return to their neighborhoods, hoping water levels will recede.
“It’s not time to go home,” Mr. Leite told reporters on Tuesday.
The flooding is the fourth weather-related crisis to hit Brazil’s southern region in less than a year. In September, 37 people were killed in Rio Grande do Sul by torrential rains and punishing winds caused by a cyclone.
People rescued from flooded areas in the Sao Joao neighborhood in Porto Alegre.
Floodwaters surrounded the Beira-Rio soccer stadium, home of the Sport Club Internacional, in Porto Alegre on Tuesday.
A flooded street in the Cidade Baixa neighborhood of Porto Alegre.
Climate experts say the region is reeling from the effects of El Niño, the cyclical climate phenomenon that can bring heavy rains to Brazil’s southern regions while causing drought in the Amazon rainforest.
But the effects of El Niño have been exacerbated by a mix of climate change, deforestation and haphazard urbanization, according to Mercedes Bustamante, an ecologist and professor at the University of Brasília.
“You’re really looking at a recipe for disaster,” said Dr. Bustamante, who has written several reports for the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, a body of experts convened by the United Nations.
For well over a decade, scientists have been warning policymakers that global warming would bring increased rains to this region.
As deforestation advances in the Amazon and elsewhere in Brazil, precipitation patterns are shifting and leading to more erratic rain patterns, according to Dr. Bustamante. As a result, rainfall is spread unevenly at times, drenching smaller areas or coming in torrential downpours over shorter periods.
Severe weather has also become more deadly in recent decades, as urban populations have grown and cities like Porto Alegre have pushed into forested areas that once acted as buffers against flooding and landslides, she added.
The latest floods caught Brazil “unprepared,” Dr. Bustamante noted, highlighting the need to make cities more resilient to climate change and develop response strategies that better protect residents from extreme weather events, which are bound to become more frequent.
“It is a tragedy that, unfortunately, has been coming for some time,” she said. “We hope that this serves as a call to action.”
People linked arms as others rescued from flooded areas arrived by boat in Porto Alegre on Tuesday.
Manuela Andreoni contributed reporting from New York.
Advertisement
How to Get Holocaust Education Right

“Educate them about the Holocaust.”
That’s the rallying cry for many of those who feel shocked by skyrocketing antisemitism and Islamophobia on college campuses and K-12 schools. Learning about the Final Solution, the reasoning goes, steers young Americans against bigotry.
As the grandson of Auschwitz and Buchenwald survivors and an educator and documentary filmmaker who often tells Holocaust-related stories, I used to subscribe to this notion. But I’ve come to realize that despite being embedded in K-12 social studies, world history, and English literature curricula throughout the country, Holocaust education has failed to uproot hate and ignorance.
Social media, where teens spend about five hours a day on average, teem with “ Holocaust denial and distortion ,” as well as antisemitic and Islamophobic conspiracy theories. The latest, for instance, falsely blames the Jews for Congress’ TikTok crackdown . No wonder K-12 schools’ incidents of antisemitism and Islamophobia have skyrocketed , even before the Israel-Hamas War erupted and broke the hydrant of hatred wide open.
Read More: Who Needs Holocaust Remembrance Day in 2024?
In recent weeks, a flood of Israel-Hamas War-related hostility has forced an increasing number of university administrations around the country—such as Columbia, the University of Texas at Austin, and the University of Southern California—to summon the police in an attempt to quell student protests. Columbia moved all classes online on the eve of Passover, suspended some protesters , and threatened to expel those who’d occupied a campus building. USC revamped its commencement plans. And although most protests have played out as legitimate political activism reminiscent of the 1960s student movements, some have reportedly crossed the line into antisemitic and Islamophobic vitriol and violence.
On campuses and schoolyards, Jews and Muslims have suffered physical and psychological harm—from being jabbed in the face by a flagpole and requiring hospitalization to being called “terrorists” and needing mental-health counseling. The U.S. Department of Education’s Civil Rights Office has been investigating several universities and school districts.
Holocaust education, in its foundational intention, was supposed to nip much of this in the bud. Taught at elementary, middle, and high schools throughout the country since the 1970s, it’s been positioned for wide impact. Twenty-six states require the instruction of the Holocaust. Most of the other states have funded commissions and councils to advance opportunities to educate students about the Nazis’ murder of 6 million Jews and millions of people with disabilities, homosexuals, and Romani people, among other groups.
Read More: The Holocaust Began Not With Concentration Camps, But With Hateful Rhetoric. That Part of the Story Cannot Be Forgotten
Historically, conservatives and liberals alike have embraced Holocaust education. The 2020 Never Again Education Act passed by a 393-5 vote at the U.S. House of Representatives and unanimously at the U.S. Senate. Further setting Holocaust education up for success, nonprofits ranging from USC’s Shoah Foundation in Los Angeles to the Holocaust Memorial Museum in Washington, DC, have been supporting teachers for decades. Organization like Pittsburgh-based Classroom Without Borders have taken educators to the sites of Nazi death camps in Eastern Europe. On May 5, March of the Living is sending teachers and students, as well as the chancellors and presidents of SUNY (State University of New York), Towson, and other universities, to Poland. Stateside, 85 Holocaust museums and memorials have hosted countless school field trips.
Yet, Holocaust education has fallen far short even of its fundamental goal to raise awareness. Polls show young Americans lack “basic knowledge” about the Holocaust. About two-thirds know nothing or very little about Auschwitz and grossly underestimate the number of Jewish victims.
Alarming conversations I’ve had with students make it impossible for me to ignore these statistics. Following a university screening of a rough-cut of one of my documentaries, “ Cojot ,” two freshmen sheepishly told me they’d “never heard of this.” I assured them few have heard of French business consultant Michel Cojot’s quest to kill his father’s Nazi executioner.
Shaking their heads, the freshmen said they’d “never heard about any of this.”
They were talking about the Holocaust.
The encounter sent me on a mission of my own: help fulfill Holocaust education’s promise. I started by contemplating what knowledge, insights, and skills their students must obtain to put antisemitism and Islamophobia in the rearview mirror.
A couple of observations informed my thinking about the knowledge part of the equation: Traditional Holocaust education’s emphasis on disseminating historical facts has generated disappointing results and, in the long run, even A-students retain only a fraction of the information they absorb in school. They ofttimes memorize a lesson, regurgitate it on a test, then discard it from their brains.
So I focused on insights and skills, which tend to be stickier. An understanding of how democracies function and malfunction can stay with children and adolescents for life, sharpening their worldview and lending them a moral compass. Critical thinking, fact-finding, and active listening can boost empathy and productive civic discourse, enabling students to better navigate the present, past, and future.
In building this approach, I combined old methods in a new way. For a pedagogical anchor, I turned to practitioner inquiry, also called action research. This well-regarded yet underutilized professional development (PD) mechanism helps K-12 teachers examine and improve their practice. I hypothesized that although it was rarely if ever used in such a way, practitioner inquiry would upgrade Holocaust education when fitted with four lenses: contextual responsiveness, which enables educators to make their lessons relevant to the here and now; trauma-informed, which steers them away from age-inappropriate material and assists them in identifying and coping with trauma in their classrooms and schools; apolitical educational equity, which values every child and adolescent; and asset-based, which directs teachers’ attention to their students and communities’ strengths.
To test this properly, I founded the nonpartisan, pedagogically orientated Holocaust, Genocide and Human Rights Education Initiative at Penn State . It provides PD programs in five states and counting to K-12 educators, many of whom know what but not how to effectively teach difficult topics.
The first rule of the initiative—to borrow a phrase from David Fincher’s “Fight Club”—is you do not have to talk about the Holocaust. Research my colleagues and I have conducted indicates the effective instruction of any difficult topic, be it slavery or evolution or gender, can get at the Holocaust’s underlying causes.
Participants in the initiative’s programs, who represent various roles, disciplines, and grade levels, choose a difficult topic from their curriculum or community. They learn to teach it confidently by conjuring up compelling questions, finding credible sources, collecting and analyzing data, examining the findings with experts and colleagues, drawing up an implementation plan, and applying it in their classrooms and schools. Thus, they meet their students where they are in authentic ways.
Our participants, who include nearly as many music and biology as social studies and English teachers, empower their students to come up with their own guiding questions and seek the truth and its implications for themselves. To teach in this unconventional manner, educators must shift from acting as sages on the stage to setting the stage for their students’ experiential learning.
This mindset change typically requires a mind-twisting effort. Why would teachers—already overburdened meeting state, district, and parental expectations—add this to their trays? Their motivations range from resetting the tone in their classroom to removing the perception of indoctrination to redefining student success. A longtime elementary school teacher, for instance, aimed to make her Civil War lessons more thought-provoking. “I was interested in ways to help my students think for themselves,” she told me. And a mid-career middle-school teacher sought to instill empathy in her seventh-graders. Referencing Jim Crow and Nazi propaganda, she challenged her students to investigate her thesis that “if you spend enough time talking negatively about people, you start to believe it.”
She tasked her students with logging “everything they said and heard in one day.” The hands-on assignment opened the seventh-graders’ eyes and, eventually, hearts. They reported hearing numerous hurtful judgements and “conversations about fighting,” the middle-school teacher said. “The data collected were overwhelmingly negative.” In the following weeks, the students “wanted to talk about it more” and grew to “understand why they do what they do and reassess what they say about each other.”
Much of K-12 looks far into the future. Ace biology or math now and become a doctor or coder later. Difficult topics inquiry offers students immediately useful takeaways. The empathy and active-listening skills they develop can enrich their inner and social lives. The two-way respect they forge with peers and adults can bolster their communications and self-esteem.
To give students a brighter outlook, individually and collectively, and fortify our democracy, we must reinvent how we teach difficult topics. We must trust students to chart a constructive course for themselves and society. This will forge a sense of control that can propel students on journeys of discovery, during which they learn to conduct primary research, triangulate the information they gather, seek multiple perspectives, and dialogue and debate with classmates. Ultimately, too, it would prompt our next generation to wonder why any student ever chose echo-chamber scorn over face-to-face, heated-yet-respectful civic discourse.
More Must-Reads From TIME
- What Student Photojournalists Saw at the Campus Protests
- Women Say They Were Pressured Into Long-Term Birth Control
- How Far Trump Would Go
- Scientists Are Finding Out Just How Toxic Your Stuff Is
- Boredom Makes Us Human
- John Mulaney Has What Late Night Needs
- The 100 Most Influential People of 2024
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Contact us at [email protected]

Qatar Sends Aid Package for Afghanistan’s Flood Victims
VANCOUVER, CANADA – Fahid Abdullah Aldosari, head of Qatar’s search and rescue team, who arrived in Balkh today, May 13, said that a shipment of humanitarian aid from his country was delivered by a military aircraft. 22 tons containing tents, food and medical supplies and other basic necessities arrived as the people struggled to weather the impacts of recent flood devastations.
According to the Qatari official, five more shipments of humanitarian aid are expected to arrive from Qatar in the coming days.
Spring floods in recent weeks have raged northern Afghanistan, particularly the provinces of Balkh, Baghlan, Takhar, and Badakhshan. According to estimates from multiple sources, anywhere between 180 and 400 people have lost their lives while hundreds more are injured.
Victim families complain that response efforts and aid delivery have been slow and inadequate. Some affected areas are not even accessible by car, further complicating rescue and response missions.
Thomas West, the US Special Representative for Afghanistan, said that the United States and its partners are mobilizing emergency assistance, including food and water, for the victims.
He wrote: “Our implementing partners are mobilizing emergency relief including food, water, and other essential materials to communities in gravest need. Our thoughts are with those who’ve lost loved ones.”
The provinces of Balkh, Takhar, and Badakhshan in the north and northeast of the country experienced heavy rainfall and flooding on Friday and Saturday of this week. The floods come after a prolonged multi-year drought that severely impacted agricultural harvest, particularly in northern parts of the country where the yields had declined by as much as half.
The rainfalls were initially received by optimism in expectation of a better harvest season this summer and fall. However, the floods and their subsequent damage speak to the complexity of a humanitarian crisis in an environment stressed my multiple factors, including the implications of global warming and environmental degradation such as deforestation.
According to statistics released by the United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA), these floods have claimed 180 lives and left 242 others injured.The organization also stated that as a result of these floods, 8,975 houses in these three provinces have been damaged, with 80% of the casualties and damages recorded in the Baghlan and central Balkh districts of Balkh province.
The Taliban authorities, however, have reported casualties in excess of 400. As search and rescue teams continue to access flooded villages, the figures are expected to only rise.
Afghanistan faces one of the worst humanitarian crises in the world with more than 20 million people in need of life-saving assistance. The UN says that it struggles to meet even half of its funding target in the face of competing catastrophes including the wars in Gaza and Ukraine and chronic conflicts and droughts in Africa.

Silk Road Brief

Get the best experience and stay connected to your community with our Spectrum News app. Learn More
Continue in Browser
Get hyperlocal forecasts, radar and weather alerts.
Please enter a valid zipcode.

Kenya declares public holiday to mourn flood victims
NAIROBI, Kenya (AP) — Kenya’s President William Ruto has declared Friday a public holiday to mourn the 238 people who have died due to ongoing flooding.
The president on Wednesday said the day will be observed by national tree planting activities to help mitigate the effects of climate change.
Kenya, along with other parts of East Africa , have been overwhelmed by floods. More than 235,000 people are displaced and living in dozens of camps.
President Ruto also announced the reopening of schools countrywide, after two weeks delay due to heavy rains that have destroyed hundreds of schools.
The government had said more than 1,000 schools were affected by the heavy rains and flooding and set aside funds for renovations.
The metrology department in its daily weather forecast has continued to predict moderate to heavy rainfall in most parts of the country.
The government is in the process of forcefully evacuating people living in flood prone areas and those near rivers and dams as water levels in the country’s major hydroelectric dams rise to “historic levels”.
This week, the government bulldozed houses in informal settlements of Mathare and Mukuru in the capital Nairobi and the president promised evicted families the equivalent of $75 to relocate after a deadline passed to evacuate amid deadly rains .
Copyright 2024 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed without permission.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
500+ words Essay on Flood. Flood is one of the most dangerous natural disasters. It happens when excessive water is collected in any area. It usually happens due to heavy rainfall. India is highly prone to flood. There are many regions in the country that face this natural disaster because of the overflowing of rivers.
3. Send goods and supplies to loved ones in affected areas. 4. Ship supplies into recovery and evacuation zones. 5. Give blood. The impact of natural disasters like hurricanes and wildfires can be felt for weeks, months, and even years after disaster strikes. Rebuilding and recovery take a lot of time and effort and resources often run short ...
If you are a spiritual person, pray for the flood victims and/or reflect for a moment on the situation. Open your heart to ways you can help, and be a comfort to those in need. 3. Offer emotional support. In additional to other forms of help, you can make some basic, caring gestures towards those in need. [11]
Essay on Flood: Causes, Consequences and Prevention - Essay 4 (400 Words) Introduction: Flood is one of the recurring natural disasters which is an outcome of above average rainfall and accumulation of excessive water in every living area. Floods may occur due to overflow of water from the reservoirs or due to heavy down pour of rain in places where the drainage systems are not properly ...
the w orst flooding in 30 years that ba ttered W est Africa from July 200 7 caused more. than 21 0 death and aff ected more than 78 5,000 people [ 12]. The aftermaths of flood disasters in Ghana ...
The Central China flood of 1931, for example, was one of the worst flooding events in recorded history. The Yangtze and Huai Rivers broke their banks, killing as many as several million people. The aftermath was devastating; deadly waterborne diseases like dysentery and cholera spread quickly, and those who survived faced the threat of starvation.
In addition, student flood victims have a lso experienced the feeling of sadness in the aftermath o f flood. The feeling of sadness a mong flood victims is a natural response to the significant ...
As officials braced for the death toll to climb, family members shared memories of those lost. A flooded creek in Buckhorn, Ky., on Saturday. Jon Cherry for The New York Times. By Shawn Hubler ...
100 Words Essay on Floods. Floods are naturally occurring phenomena that are caused due to overflowing water bodies. A flood can be just a small occurrence that can cause some travel issues to highly destructive events that can cause significant damage to homes, businesses, and infrastructure. In addition to physical damage, floods can also ...
A flood is a natural disaster that arises due to excessive runoff of water in the rivers due to rainfall. This causes the water of rivers to come out from the edges and flow into the plains. Floods can last from a few hours to a few days, but it can cause great harm to people, money and crops.
The electronic searches generated 350 papers after searching academic databases: SCOPUS, Web of Science, and Google scholar search. In the second step, 114 papers were obtained after examining titles and keywords. ... Finally, three studies mentioned flood victims seek Government, friends and family support for relief items and cash, for ...
Floods in the City of Austin, Texas on October 30th, 2013. The catastrophic consequences of the devastation in Central Texas and, in particular, in the city of Austin, were caused by flooding. Disaster Management in the Flood Scenario. In such a case, the authorities and residents should adopt disaster prevention and preparedness strategies to ...
Malaysia is frequently affected by the annual flooding event caused by the seasonal monsoon which accounts for significant losses. Flood risk, exposure and damage potential are increasing, causing the level of poverty and vulnerability to rise. The annual occurrence of the flood hazard has forced residents to prepare beforehand to help them spring back to their daily life faster. This study ...
Set 2: Essay On Floods. A large amount of water covering a dry area of land is known as flood'. In other words, a flood is an overflow of water that submerges land, which is usually dry. Floods are a natural occurrence. They benefit humanity by forming alluvial soil but they also cause tremendous destruction to human life and property.
Donate Now to Disaster Relief. Help people affected by disasters big and small. $10 is the minimum online donation. When a flood occurs, your donation helps the Red Cross provide shelter, food and comfort to families. Please read about our latest relief efforts.
The 2022 floods submerged one third of the country, affecting 33 million people, half of whom were children. The floods damaged most of the water systems in affected areas, forcing more than 5.4 million people to rely solely on contaminated water from ponds and wells. Unsafe water and poor sanitation are key underlying causes of malnutrition.
That flood was the worst to have hit the city of Ibadan, where over 300 people lost their lives, another 50,000 people were rendered homeless, and floods destroyed over 300 million Naira worth of properties. Otomofa et al. [Citation 49] evaluated the impacts of flooding on socio-economic activities in Oleh, Isoko South LGA of Delta state. A ...
Paragraph on Flood in 250 Words. One of the major reasons for floods is heavy rain. Due to heavy rain, water levels in rivers and lakes are expected to rise. As the rainwater rises over the banks of rivers, it overflows and causes floods. With the increasing global warming, it is also possible that there might be floods due to the massive ...
The story is set in Elizabethan times, which was the sixteenth century. People back then were quite prejudiced towards any race that was not Christian. They would have hated Jews... 2470 Words. 10 Pages. Free Essays on How To Help Flood Victims. Get help with your writing. 1 through 30.
سیلاب پر دس جملے. 1) سیلاب ایک بڑے رقبے پر بڑی مقدار میں پانی کا بہاؤ ہوتا ہے، جو متاثرہ علاقے کی تباہی کا باعث بنتا ہے۔. 2) دنیا بھر میں کئی خطوں کو ہر سال سیلاب کے مسئلے کا سامنا کرنا پڑتا ہے۔. 3 ...
FLOOD A flood is an overflow of water that submerges land which is normally dry. [1] The European Union (EU) Floods Directive defines a flood as a covering bywater of land not normally covered by water. [2] In the sense of "flowing water"‚ the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Flooding may occur.
Link Copied! Katiane Mello (L) and her husband James Vargas cry before leaving their flooded home in Eldorado do Sul, Rio Grande do Sul state, Brazil, on May 9, 2024. Deadly, unrelenting floods in ...
Essay Flood Victims Essay Flood Victims 2. Diageo Executive Summary Diageo s stock price increased $1.74 from $21.10 as of December 31, 2017 to $22.84 as of March 31, 2017. The increase can be primarily attributed to the company s reported growth in profit for the first half of its 2017 fiscal year. Better than expected revenue growth, fueled ...
The various domains to be covered for my essay writing. If you are looking for reliable and dedicated writing service professionals to write for you, who will increase the value of the entire draft, then you are at the right place. The writers of PenMyPaper have got a vast knowledge about various academic domains along with years of work ...
The suit he filed on behalf of flood victims lists six causes of action, ranging from negligence to creation of a dangerous condition for public property. ... From our community papers .
In photos: At least 75 dead as historic flooding hits southern Brazil. By Jintak Han | May 6, 2024. Massive floods in Brazil's southern Rio Grande do Sul state have killed at least 75 people ...
May 8, 2024. Anderson da Silva Pantaleão was at the snack bar he owns last Friday when clay-colored water began filling the streets in the southern Brazilian city of Porto Alegre. Soon, it was ...
The U.S. Department of Education's Civil Rights Office has been investigating several universities and school districts. Holocaust education, in its foundational intention, was supposed to nip ...
According to the Qatari official, five more shipments of humanitarian aid are expected to arrive from Qatar in the coming days. Spring floods in recent weeks have raged northern Afghanistan, particularly the provinces of Balkh, Baghlan, Takhar, and Badakhshan. According to estimates from multiple sources, anywhere between 180 and 400 people ...
PUBLISHED 7:00 AM ET May 08, 2024. NAIROBI, Kenya (AP) — Kenya's President William Ruto has declared Friday a public holiday to mourn the 238 people who have died due to ongoing flooding. The ...