
- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.


12.14: Sample Student Literary Analysis Essays
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 40514

- Heather Ringo & Athena Kashyap
- City College of San Francisco via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative
The following examples are essays where student writers focused on close-reading a literary work.
While reading these examples, ask yourself the following questions:
- What is the essay's thesis statement, and how do you know it is the thesis statement?
- What is the main idea or topic sentence of each body paragraph, and how does it relate back to the thesis statement?
- Where and how does each essay use evidence (quotes or paraphrase from the literature)?
- What are some of the literary devices or structures the essays analyze or discuss?
- How does each author structure their conclusion, and how does their conclusion differ from their introduction?
Example 1: Poetry
Victoria Morillo
Instructor Heather Ringo
3 August 2022
How Nguyen’s Structure Solidifies the Impact of Sexual Violence in “The Study”
Stripped of innocence, your body taken from you. No matter how much you try to block out the instance in which these two things occurred, memories surface and come back to haunt you. How does a person, a young boy , cope with an event that forever changes his life? Hieu Minh Nguyen deconstructs this very way in which an act of sexual violence affects a survivor. In his poem, “The Study,” the poem's speaker recounts the year in which his molestation took place, describing how his memory filters in and out. Throughout the poem, Nguyen writes in free verse, permitting a structural liberation to become the foundation for his message to shine through. While he moves the readers with this poignant narrative, Nguyen effectively conveys the resulting internal struggles of feeling alone and unseen.
The speaker recalls his experience with such painful memory through the use of specific punctuation choices. Just by looking at the poem, we see that the first period doesn’t appear until line 14. It finally comes after the speaker reveals to his readers the possible, central purpose for writing this poem: the speaker's molestation. In the first half, the poem makes use of commas, em dashes, and colons, which lends itself to the idea of the speaker stringing along all of these details to make sense of this time in his life. If reading the poem following the conventions of punctuation, a sense of urgency is present here, as well. This is exemplified by the lack of periods to finalize a thought; and instead, Nguyen uses other punctuation marks to connect them. Serving as another connector of thoughts, the two em dashes give emphasis to the role memory plays when the speaker discusses how “no one [had] a face” during that time (Nguyen 9-11). He speaks in this urgent manner until the 14th line, and when he finally gets it off his chest, the pace of the poem changes, as does the more frequent use of the period. This stream-of-consciousness-like section when juxtaposed with the latter half of the poem, causes readers to slow down and pay attention to the details. It also splits the poem in two: a section that talks of the fogginess of memory then transitions into one that remembers it all.
In tandem with the fluctuating nature of memory, the utilization of line breaks and word choice help reflect the damage the molestation has had. Within the first couple of lines of the poem, the poem demands the readers’ attention when the line breaks from “floating” to “dead” as the speaker describes his memory of Little Billy (Nguyen 1-4). This line break averts the readers’ expectation of the direction of the narrative and immediately shifts the tone of the poem. The break also speaks to the effect his trauma has ingrained in him and how “[f]or the longest time,” his only memory of that year revolves around an image of a boy’s death. In a way, the speaker sees himself in Little Billy; or perhaps, he’s representative of the tragic death of his boyhood, how the speaker felt so “dead” after enduring such a traumatic experience, even referring to himself as a “ghost” that he tries to evict from his conscience (Nguyen 24). The feeling that a part of him has died is solidified at the very end of the poem when the speaker describes himself as a nine-year-old boy who’s been “fossilized,” forever changed by this act (Nguyen 29). By choosing words associated with permanence and death, the speaker tries to recreate the atmosphere (for which he felt trapped in) in order for readers to understand the loneliness that came as a result of his trauma. With the assistance of line breaks, more attention is drawn to the speaker's words, intensifying their importance, and demanding to be felt by the readers.
Most importantly, the speaker expresses eloquently, and so heartbreakingly, about the effect sexual violence has on a person. Perhaps what seems to be the most frustrating are the people who fail to believe survivors of these types of crimes. This is evident when he describes “how angry” the tenants were when they filled the pool with cement (Nguyen 4). They seem to represent how people in the speaker's life were dismissive of his assault and who viewed his tragedy as a nuisance of some sorts. This sentiment is bookended when he says, “They say, give us details , so I give them my body. / They say, give us proof , so I give them my body,” (Nguyen 25-26). The repetition of these two lines reinforces the feeling many feel in these scenarios, as they’re often left to deal with trying to make people believe them, or to even see them.
It’s important to recognize how the structure of this poem gives the speaker space to express the pain he’s had to carry for so long. As a characteristic of free verse, the poem doesn’t follow any structured rhyme scheme or meter; which in turn, allows him to not have any constraints in telling his story the way he wants to. The speaker has the freedom to display his experience in a way that evades predictability and engenders authenticity of a story very personal to him. As readers, we abandon anticipating the next rhyme, and instead focus our attention to the other ways, like his punctuation or word choice, in which he effectively tells his story. The speaker recognizes that some part of him no longer belongs to himself, but by writing “The Study,” he shows other survivors that they’re not alone and encourages hope that eventually, they will be freed from the shackles of sexual violence.
Works Cited
Nguyen, Hieu Minh. “The Study” Poets.Org. Academy of American Poets, Coffee House Press, 2018, https://poets.org/poem/study-0 .
Example 2: Fiction
Todd Goodwin
Professor Stan Matyshak
Advanced Expository Writing
Sept. 17, 20—
Poe’s “Usher”: A Mirror of the Fall of the House of Humanity
Right from the outset of the grim story, “The Fall of the House of Usher,” Edgar Allan Poe enmeshes us in a dark, gloomy, hopeless world, alienating his characters and the reader from any sort of physical or psychological norm where such values as hope and happiness could possibly exist. He fatalistically tells the story of how a man (the narrator) comes from the outside world of hope, religion, and everyday society and tries to bring some kind of redeeming happiness to his boyhood friend, Roderick Usher, who not only has physically and psychologically wasted away but is entrapped in a dilapidated house of ever-looming terror with an emaciated and deranged twin sister. Roderick Usher embodies the wasting away of what once was vibrant and alive, and his house of “insufferable gloom” (273), which contains his morbid sister, seems to mirror or reflect this fear of death and annihilation that he most horribly endures. A close reading of the story reveals that Poe uses mirror images, or reflections, to contribute to the fatalistic theme of “Usher”: each reflection serves to intensify an already prevalent tone of hopelessness, darkness, and fatalism.
It could be argued that the house of Roderick Usher is a “house of mirrors,” whose unpleasant and grim reflections create a dark and hopeless setting. For example, the narrator first approaches “the melancholy house of Usher on a dark and soundless day,” and finds a building which causes him a “sense of insufferable gloom,” which “pervades his spirit and causes an iciness, a sinking, a sickening of the heart, an undiscerned dreariness of thought” (273). The narrator then optimistically states: “I reflected that a mere different arrangement of the scene, of the details of the picture, would be sufficient to modify, or perhaps annihilate its capacity for sorrowful impression” (274). But the narrator then sees the reflection of the house in the tarn and experiences a “shudder even more thrilling than before” (274). Thus the reader begins to realize that the narrator cannot change or stop the impending doom that will befall the house of Usher, and maybe humanity. The story cleverly plays with the word reflection : the narrator sees a physical reflection that leads him to a mental reflection about Usher’s surroundings.
The narrator’s disillusionment by such grim reflection continues in the story. For example, he describes Roderick Usher’s face as distinct with signs of old strength but lost vigor: the remains of what used to be. He describes the house as a once happy and vibrant place, which, like Roderick, lost its vitality. Also, the narrator describes Usher’s hair as growing wild on his rather obtrusive head, which directly mirrors the eerie moss and straw covering the outside of the house. The narrator continually longs to see these bleak reflections as a dream, for he states: “Shaking off from my spirit what must have been a dream, I scanned more narrowly the real aspect of the building” (276). He does not want to face the reality that Usher and his home are doomed to fall, regardless of what he does.
Although there are almost countless examples of these mirror images, two others stand out as important. First, Roderick and his sister, Madeline, are twins. The narrator aptly states just as he and Roderick are entombing Madeline that there is “a striking similitude between brother and sister” (288). Indeed, they are mirror images of each other. Madeline is fading away psychologically and physically, and Roderick is not too far behind! The reflection of “doom” that these two share helps intensify and symbolize the hopelessness of the entire situation; thus, they further develop the fatalistic theme. Second, in the climactic scene where Madeline has been mistakenly entombed alive, there is a pairing of images and sounds as the narrator tries to calm Roderick by reading him a romance story. Events in the story simultaneously unfold with events of the sister escaping her tomb. In the story, the hero breaks out of the coffin. Then, in the story, the dragon’s shriek as he is slain parallels Madeline’s shriek. Finally, the story tells of the clangor of a shield, matched by the sister’s clanging along a metal passageway. As the suspense reaches its climax, Roderick shrieks his last words to his “friend,” the narrator: “Madman! I tell you that she now stands without the door” (296).
Roderick, who slowly falls into insanity, ironically calls the narrator the “Madman.” We are left to reflect on what Poe means by this ironic twist. Poe’s bleak and dark imagery, and his use of mirror reflections, seem only to intensify the hopelessness of “Usher.” We can plausibly conclude that, indeed, the narrator is the “Madman,” for he comes from everyday society, which is a place where hope and faith exist. Poe would probably argue that such a place is opposite to the world of Usher because a world where death is inevitable could not possibly hold such positive values. Therefore, just as Roderick mirrors his sister, the reflection in the tarn mirrors the dilapidation of the house, and the story mirrors the final actions before the death of Usher. “The Fall of the House of Usher” reflects Poe’s view that humanity is hopelessly doomed.
Poe, Edgar Allan. “The Fall of the House of Usher.” 1839. Electronic Text Center, University of Virginia Library . 1995. Web. 1 July 2012. < http://etext.virginia.edu/toc/modeng/public/PoeFall.html >.
Example 3: Poetry
Amy Chisnell
Professor Laura Neary
Writing and Literature
April 17, 20—
Don’t Listen to the Egg!: A Close Reading of Lewis Carroll’s “Jabberwocky”
“You seem very clever at explaining words, Sir,” said Alice. “Would you kindly tell me the meaning of the poem called ‘Jabberwocky’?”
“Let’s hear it,” said Humpty Dumpty. “I can explain all the poems that ever were invented—and a good many that haven’t been invented just yet.” (Carroll 164)
In Lewis Carroll’s Through the Looking-Glass , Humpty Dumpty confidently translates (to a not so confident Alice) the complicated language of the poem “Jabberwocky.” The words of the poem, though nonsense, aptly tell the story of the slaying of the Jabberwock. Upon finding “Jabberwocky” on a table in the looking-glass room, Alice is confused by the strange words. She is quite certain that “ somebody killed something ,” but she does not understand much more than that. When later she encounters Humpty Dumpty, she seizes the opportunity at having the knowledgeable egg interpret—or translate—the poem. Since Humpty Dumpty professes to be able to “make a word work” for him, he is quick to agree. Thus he acts like a New Critic who interprets the poem by performing a close reading of it. Through Humpty’s interpretation of the first stanza, however, we see the poem’s deeper comment concerning the practice of interpreting poetry and literature in general—that strict analytical translation destroys the beauty of a poem. In fact, Humpty Dumpty commits the “heresy of paraphrase,” for he fails to understand that meaning cannot be separated from the form or structure of the literary work.
Of the 71 words found in “Jabberwocky,” 43 have no known meaning. They are simply nonsense. Yet through this nonsensical language, the poem manages not only to tell a story but also gives the reader a sense of setting and characterization. One feels, rather than concretely knows, that the setting is dark, wooded, and frightening. The characters, such as the Jubjub bird, the Bandersnatch, and the doomed Jabberwock, also appear in the reader’s head, even though they will not be found in the local zoo. Even though most of the words are not real, the reader is able to understand what goes on because he or she is given free license to imagine what the words denote and connote. Simply, the poem’s nonsense words are the meaning.
Therefore, when Humpty interprets “Jabberwocky” for Alice, he is not doing her any favors, for he actually misreads the poem. Although the poem in its original is constructed from nonsense words, by the time Humpty is done interpreting it, it truly does not make any sense. The first stanza of the original poem is as follows:
’Twas brillig, and the slithy toves
Did gyre and gimble in the wabe;
All mimsy were the borogroves,
An the mome raths outgrabe. (Carroll 164)
If we replace, however, the nonsense words of “Jabberwocky” with Humpty’s translated words, the effect would be something like this:
’Twas four o’clock in the afternoon, and the lithe and slimy badger-lizard-corkscrew creatures
Did go round and round and make holes in the grass-plot round the sun-dial:
All flimsy and miserable were the shabby-looking birds
with mop feathers,
And the lost green pigs bellowed-sneezed-whistled.
By translating the poem in such a way, Humpty removes the charm or essence—and the beauty, grace, and rhythm—from the poem. The poetry is sacrificed for meaning. Humpty Dumpty commits the heresy of paraphrase. As Cleanth Brooks argues, “The structure of a poem resembles that of a ballet or musical composition. It is a pattern of resolutions and balances and harmonizations” (203). When the poem is left as nonsense, the reader can easily imagine what a “slithy tove” might be, but when Humpty tells us what it is, he takes that imaginative license away from the reader. The beauty (if that is the proper word) of “Jabberwocky” is in not knowing what the words mean, and yet understanding. By translating the poem, Humpty takes that privilege from the reader. In addition, Humpty fails to recognize that meaning cannot be separated from the structure itself: the nonsense poem reflects this literally—it means “nothing” and achieves this meaning by using “nonsense” words.
Furthermore, the nonsense words Carroll chooses to use in “Jabberwocky” have a magical effect upon the reader; the shadowy sound of the words create the atmosphere, which may be described as a trance-like mood. When Alice first reads the poem, she says it seems to fill her head “with ideas.” The strange-sounding words in the original poem do give one ideas. Why is this? Even though the reader has never heard these words before, he or she is instantly aware of the murky, mysterious mood they set. In other words, diction operates not on the denotative level (the dictionary meaning) but on the connotative level (the emotion(s) they evoke). Thus “Jabberwocky” creates a shadowy mood, and the nonsense words are instrumental in creating this mood. Carroll could not have simply used any nonsense words.
For example, let us change the “dark,” “ominous” words of the first stanza to “lighter,” more “comic” words:
’Twas mearly, and the churly pells
Did bimble and ringle in the tink;
All timpy were the brimbledimps,
And the bip plips outlink.
Shifting the sounds of the words from dark to light merely takes a shift in thought. To create a specific mood using nonsense words, one must create new words from old words that convey the desired mood. In “Jabberwocky,” Carroll mixes “slimy,” a grim idea, “lithe,” a pliable image, to get a new adjective: “slithy” (a portmanteau word). In this translation, brighter words were used to get a lighter effect. “Mearly” is a combination of “morning” and “early,” and “ringle” is a blend of “ring” and "dingle.” The point is that “Jabberwocky’s” nonsense words are created specifically to convey this shadowy or mysterious mood and are integral to the “meaning.”
Consequently, Humpty’s rendering of the poem leaves the reader with a completely different feeling than does the original poem, which provided us with a sense of ethereal mystery, of a dark and foreign land with exotic creatures and fantastic settings. The mysteriousness is destroyed by Humpty’s literal paraphrase of the creatures and the setting; by doing so, he has taken the beauty away from the poem in his attempt to understand it. He has committed the heresy of paraphrase: “If we allow ourselves to be misled by it [this heresy], we distort the relation of the poem to its ‘truth’… we split the poem between its ‘form’ and its ‘content’” (Brooks 201). Humpty Dumpty’s ultimate demise might be seen to symbolize the heretical split between form and content: as a literary creation, Humpty Dumpty is an egg, a well-wrought urn of nonsense. His fall from the wall cracks him and separates the contents from the container, and not even all the King’s men can put the scrambled egg back together again!
Through the odd characters of a little girl and a foolish egg, “Jabberwocky” suggests a bit of sage advice about reading poetry, advice that the New Critics built their theories on. The importance lies not solely within strict analytical translation or interpretation, but in the overall effect of the imagery and word choice that evokes a meaning inseparable from those literary devices. As Archibald MacLeish so aptly writes: “A poem should not mean / But be.” Sometimes it takes a little nonsense to show us the sense in something.
Brooks, Cleanth. The Well-Wrought Urn: Studies in the Structure of Poetry . 1942. San Diego: Harcourt Brace, 1956. Print.
Carroll, Lewis. Through the Looking-Glass. Alice in Wonderland . 2nd ed. Ed. Donald J. Gray. New York: Norton, 1992. Print.
MacLeish, Archibald. “Ars Poetica.” The Oxford Book of American Poetry . Ed. David Lehman. Oxford: Oxford UP, 2006. 385–86. Print.
Attribution
- Sample Essay 1 received permission from Victoria Morillo to publish, licensed Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International ( CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 )
- Sample Essays 2 and 3 adapted from Cordell, Ryan and John Pennington. "2.5: Student Sample Papers" from Creating Literary Analysis. 2012. Licensed Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported ( CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 )
What (Exactly) Is Thematic Analysis?
Plain-Language Explanation & Definition (With Examples)
By: Jenna Crosley (PhD). Expert Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | April 2021
Thematic analysis is one of the most popular qualitative analysis techniques we see students opting for at Grad Coach – and for good reason. Despite its relative simplicity, thematic analysis can be a very powerful analysis technique when used correctly. In this post, we’ll unpack thematic analysis using plain language (and loads of examples) so that you can conquer your analysis with confidence.
Thematic Analysis 101
- Basic terminology relating to thematic analysis
- What is thematic analysis
- When to use thematic analysis
- The main approaches to thematic analysis
- The three types of thematic analysis
- How to “do” thematic analysis (the process)
- Tips and suggestions
First, the lingo…
Before we begin, let’s first lay down some terminology. When undertaking thematic analysis, you’ll make use of codes . A code is a label assigned to a piece of text, and the aim of using a code is to identify and summarise important concepts within a set of data, such as an interview transcript.
For example, if you had the sentence, “My rabbit ate my shoes”, you could use the codes “rabbit” or “shoes” to highlight these two concepts. The process of assigning codes is called qualitative coding . If this is a new concept to you, be sure to check out our detailed post about qualitative coding .
Codes are vital as they lay a foundation for themes . But what exactly is a theme? Simply put, a theme is a pattern that can be identified within a data set. In other words, it’s a topic or concept that pops up repeatedly throughout your data. Grouping your codes into themes serves as a way of summarising sections of your data in a useful way that helps you answer your research question(s) and achieve your research aim(s).
Alright – with that out of the way, let’s jump into the wonderful world of thematic analysis…
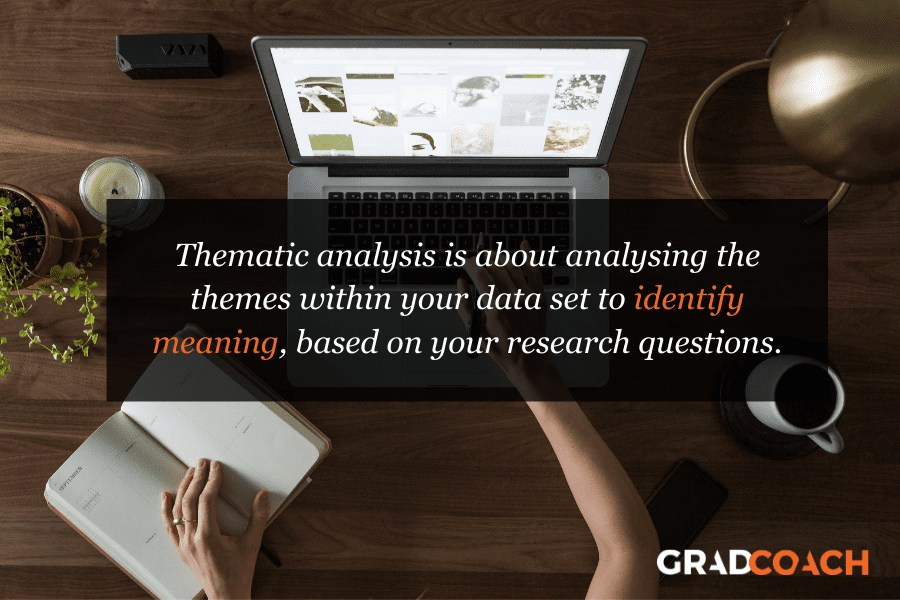
What is thematic analysis?
Thematic analysis is the study of patterns to uncover meaning . In other words, it’s about analysing the patterns and themes within your data set to identify the underlying meaning. Importantly, this process is driven by your research aims and questions , so it’s not necessary to identify every possible theme in the data, but rather to focus on the key aspects that relate to your research questions .
Although the research questions are a driving force in thematic analysis (and pretty much all analysis methods), it’s important to remember that these questions are not necessarily fixed . As thematic analysis tends to be a bit of an exploratory process, research questions can evolve as you progress with your coding and theme identification.
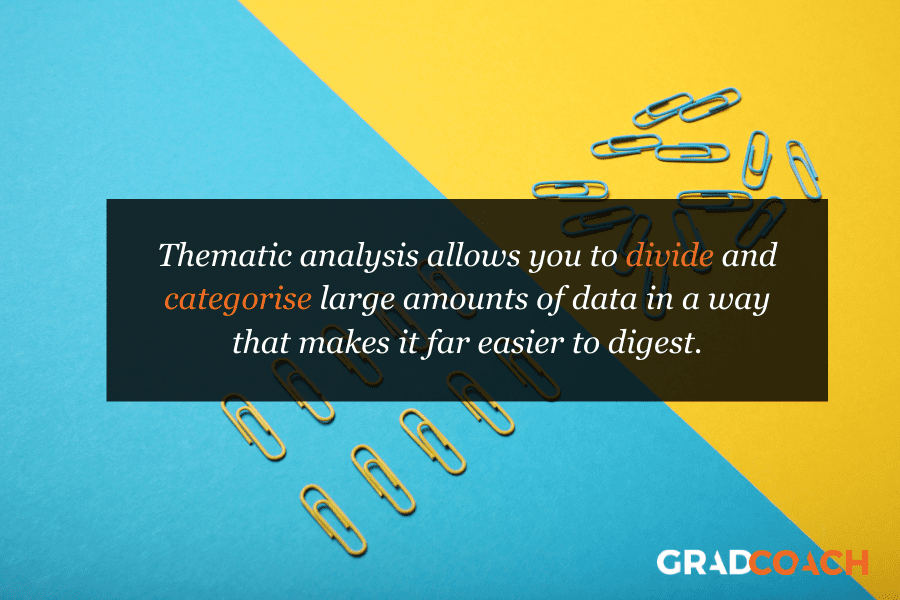
When should you use thematic analysis?
There are many potential qualitative analysis methods that you can use to analyse a dataset. For example, content analysis , discourse analysis , and narrative analysis are popular choices. So why use thematic analysis?
Thematic analysis is highly beneficial when working with large bodies of data , as it allows you to divide and categorise large amounts of data in a way that makes it easier to digest. Thematic analysis is particularly useful when looking for subjective information , such as a participant’s experiences, views, and opinions. For this reason, thematic analysis is often conducted on data derived from interviews , conversations, open-ended survey responses , and social media posts.
Your research questions can also give you an idea of whether you should use thematic analysis or not. For example, if your research questions were to be along the lines of:
- How do dog walkers perceive rules and regulations on dog-friendly beaches?
- What are students’ experiences with the shift to online learning?
- What opinions do health professionals hold about the Hippocratic code?
- How is gender constructed in a high school classroom setting?
These examples are all research questions centering on the subjective experiences of participants and aim to assess experiences, views, and opinions. Therefore, thematic analysis presents a possible approach.
In short, thematic analysis is a good choice when you are wanting to categorise large bodies of data (although the data doesn’t necessarily have to be large), particularly when you are interested in subjective experiences .
What are the main approaches?
Broadly speaking, there are two overarching approaches to thematic analysis: inductive and deductive . The approach you take will depend on what is most suitable in light of your research aims and questions. Let’s have a look at the options.
The inductive approach
The inductive approach involves deriving meaning and creating themes from data without any preconceptions . In other words, you’d dive into your analysis without any idea of what codes and themes will emerge, and thus allow these to emerge from the data.
For example, if you’re investigating typical lunchtime conversational topics in a university faculty, you’d enter the research without any preconceived codes, themes or expected outcomes. Of course, you may have thoughts about what might be discussed (e.g., academic matters because it’s an academic setting), but the objective is to not let these preconceptions inform your analysis.
The inductive approach is best suited to research aims and questions that are exploratory in nature , and cases where there is little existing research on the topic of interest.
The deductive approach
In contrast to the inductive approach, a deductive approach involves jumping into your analysis with a pre-determined set of codes . Usually, this approach is informed by prior knowledge and/or existing theory or empirical research (which you’d cover in your literature review ).
For example, a researcher examining the impact of a specific psychological intervention on mental health outcomes may draw on an existing theoretical framework that includes concepts such as coping strategies, social support, and self-efficacy, using these as a basis for a set of pre-determined codes.
The deductive approach is best suited to research aims and questions that are confirmatory in nature , and cases where there is a lot of existing research on the topic of interest.
Regardless of whether you take the inductive or deductive approach, you’ll also need to decide what level of content your analysis will focus on – specifically, the semantic level or the latent level.
A semantic-level focus ignores the underlying meaning of data , and identifies themes based only on what is explicitly or overtly stated or written – in other words, things are taken at face value.
In contrast, a latent-level focus concentrates on the underlying meanings and looks at the reasons for semantic content. Furthermore, in contrast to the semantic approach, a latent approach involves an element of interpretation , where data is not just taken at face value, but meanings are also theorised.
“But how do I know when to use what approach?”, I hear you ask.
Well, this all depends on the type of data you’re analysing and what you’re trying to achieve with your analysis. For example, if you’re aiming to analyse explicit opinions expressed in interviews and you know what you’re looking for ahead of time (based on a collection of prior studies), you may choose to take a deductive approach with a semantic-level focus.
On the other hand, if you’re looking to explore the underlying meaning expressed by participants in a focus group, and you don’t have any preconceptions about what to expect, you’ll likely opt for an inductive approach with a latent-level focus.
Simply put, the nature and focus of your research, especially your research aims , objectives and questions will inform the approach you take to thematic analysis.

What are the types of thematic analysis?
Now that you’ve got an understanding of the overarching approaches to thematic analysis, it’s time to have a look at the different types of thematic analysis you can conduct. Broadly speaking, there are three “types” of thematic analysis:
- Reflexive thematic analysis
- Codebook thematic analysis
- Coding reliability thematic analysis
Let’s have a look at each of these:
Reflexive thematic analysis takes an inductive approach, letting the codes and themes emerge from that data. This type of thematic analysis is very flexible, as it allows researchers to change, remove, and add codes as they work through the data. As the name suggests, reflexive thematic analysis emphasizes the active engagement of the researcher in critically reflecting on their assumptions, biases, and interpretations, and how these may shape the analysis.
Reflexive thematic analysis typically involves iterative and reflexive cycles of coding, interpreting, and reflecting on data, with the aim of producing nuanced and contextually sensitive insights into the research topic, while at the same time recognising and addressing the subjective nature of the research process.
Codebook thematic analysis , on the other hand, lays on the opposite end of the spectrum. Taking a deductive approach, this type of thematic analysis makes use of structured codebooks containing clearly defined, predetermined codes. These codes are typically drawn from a combination of existing theoretical theories, empirical studies and prior knowledge of the situation.
Codebook thematic analysis aims to produce reliable and consistent findings. Therefore, it’s often used in studies where a clear and predefined coding framework is desired to ensure rigour and consistency in data analysis.
Coding reliability thematic analysis necessitates the work of multiple coders, and the design is specifically intended for research teams. With this type of analysis, codebooks are typically fixed and are rarely altered.
The benefit of this form of analysis is that it brings an element of intercoder reliability where coders need to agree upon the codes used, which means that the outcome is more rigorous as the element of subjectivity is reduced. In other words, multiple coders discuss which codes should be used and which shouldn’t, and this consensus reduces the bias of having one individual coder decide upon themes.
Quick Recap: Thematic analysis approaches and types
To recap, the two main approaches to thematic analysis are inductive , and deductive . Then we have the three types of thematic analysis: reflexive, codebook and coding reliability . Which type of thematic analysis you opt for will need to be informed by factors such as:
- The approach you are taking. For example, if you opt for an inductive approach, you’ll likely utilise reflexive thematic analysis.
- Whether you’re working alone or in a group . It’s likely that, if you’re doing research as part of your postgraduate studies, you’ll be working alone. This means that you’ll need to choose between reflexive and codebook thematic analysis.
Now that we’ve covered the “what” in terms of thematic analysis approaches and types, it’s time to look at the “how” of thematic analysis.
Need a helping hand?
How to “do” thematic analysis
At this point, you’re ready to get going with your analysis, so let’s dive right into the thematic analysis process. Keep in mind that what we’ll cover here is a generic process, and the relevant steps will vary depending on the approach and type of thematic analysis you opt for.
Step 1: Get familiar with the data
The first step in your thematic analysis involves getting a feel for your data and seeing what general themes pop up. If you’re working with audio data, this is where you’ll do the transcription , converting audio to text.
At this stage, you’ll want to come up with preliminary thoughts about what you’ll code , what codes you’ll use for them, and what codes will accurately describe your content. It’s a good idea to revisit your research topic , and your aims and objectives at this stage. For example, if you’re looking at what people feel about different types of dogs, you can code according to when different breeds are mentioned (e.g., border collie, Labrador, corgi) and when certain feelings/emotions are brought up.
As a general tip, it’s a good idea to keep a reflexivity journal . This is where you’ll write down how you coded your data, why you coded your data in that particular way, and what the outcomes of this data coding are. Using a reflexive journal from the start will benefit you greatly in the final stages of your analysis because you can reflect on the coding process and assess whether you have coded in a manner that is reliable and whether your codes and themes support your findings.
As you can imagine, a reflexivity journal helps to increase reliability as it allows you to analyse your data systematically and consistently. If you choose to make use of a reflexivity journal, this is the stage where you’ll want to take notes about your initial codes and list them in your journal so that you’ll have an idea of what exactly is being reflected in your data. At a later stage in the analysis, this data can be more thoroughly coded, or the identified codes can be divided into more specific ones.

Step 2: Search for patterns or themes in the codes
Step 2! You’re going strong. In this step, you’ll want to look out for patterns or themes in your codes. Moving from codes to themes is not necessarily a smooth or linear process. As you become more and more familiar with the data, you may find that you need to assign different codes or themes according to new elements you find. For example, if you were analysing a text talking about wildlife, you may come across the codes, “pigeon”, “canary” and “budgerigar” which can fall under the theme of birds.
As you work through the data, you may start to identify subthemes , which are subdivisions of themes that focus specifically on an aspect within the theme that is significant or relevant to your research question. For example, if your theme is a university, your subthemes could be faculties or departments at that university.
In this stage of the analysis, your reflexivity journal entries need to reflect how codes were interpreted and combined to form themes.
Step 3: Review themes
By now you’ll have a good idea of your codes, themes, and potentially subthemes. Now it’s time to review all the themes you’ve identified . In this step, you’ll want to check that everything you’ve categorised as a theme actually fits the data, whether the themes do indeed exist in the data, whether there are any themes missing , and whether you can move on to the next step knowing that you’ve coded all your themes accurately and comprehensively . If you find that your themes have become too broad and there is far too much information under one theme, it may be useful to split this into more themes so that you’re able to be more specific with your analysis.
In your reflexivity journal, you’ll want to write about how you understood the themes and how they are supported by evidence, as well as how the themes fit in with your codes. At this point, you’ll also want to revisit your research questions and make sure that the data and themes you’ve identified are directly relevant to these questions .

Step 4: Finalise Themes
By this point, your analysis will really start to take shape. In the previous step, you reviewed and refined your themes, and now it’s time to label and finalise them . It’s important to note here that, just because you’ve moved onto the next step, it doesn’t mean that you can’t go back and revise or rework your themes. In contrast to the previous step, finalising your themes means spelling out what exactly the themes consist of, and describe them in detail . If you struggle with this, you may want to return to your data to make sure that your data and coding do represent the themes, and if you need to divide your themes into more themes (i.e., return to step 3).
When you name your themes, make sure that you select labels that accurately encapsulate the properties of the theme . For example, a theme name such as “enthusiasm in professionals” leaves the question of “who are the professionals?”, so you’d want to be more specific and label the theme as something along the lines of “enthusiasm in healthcare professionals”.
It is very important at this stage that you make sure that your themes align with your research aims and questions . When you’re finalising your themes, you’re also nearing the end of your analysis and need to keep in mind that your final report (discussed in the next step) will need to fit in with the aims and objectives of your research.
In your reflexivity journal, you’ll want to write down a few sentences describing your themes and how you decided on these. Here, you’ll also want to mention how the theme will contribute to the outcomes of your research, and also what it means in relation to your research questions and focus of your research.
By the end of this stage, you’ll be done with your themes – meaning it’s time to write up your findings and produce a report.

Step 5: Produce your report
You’re nearly done! Now that you’ve analysed your data, it’s time to report on your findings. A typical thematic analysis report consists of:
- An introduction
- A methodology section
- Your results and findings
- A conclusion
When writing your report, make sure that you provide enough information for a reader to be able to evaluate the rigour of your analysis. In other words, the reader needs to know the exact process you followed when analysing your data and why. The questions of “what”, “how”, “why”, “who”, and “when” may be useful in this section.
So, what did you investigate? How did you investigate it? Why did you choose this particular method? Who does your research focus on, and who are your participants? When did you conduct your research, when did you collect your data, and when was the data produced? Your reflexivity journal will come in handy here as within it you’ve already labelled, described, and supported your themes.
If you’re undertaking a thematic analysis as part of a dissertation or thesis, this discussion will be split across your methodology, results and discussion chapters . For more information about those chapters, check out our detailed post about dissertation structure .
It’s absolutely vital that, when writing up your results, you back up every single one of your findings with quotations . The reader needs to be able to see that what you’re reporting actually exists within the results. Also make sure that, when reporting your findings, you tie them back to your research questions . You don’t want your reader to be looking through your findings and asking, “So what?”, so make sure that every finding you represent is relevant to your research topic and questions.
Quick Recap: How to “do” thematic analysis
Getting familiar with your data: Here you’ll read through your data and get a general overview of what you’re working with. At this stage, you may identify a few general codes and themes that you’ll make use of in the next step.
Search for patterns or themes in your codes : Here you’ll dive into your data and pick out the themes and codes relevant to your research question(s).
Review themes : In this step, you’ll revisit your codes and themes to make sure that they are all truly representative of the data, and that you can use them in your final report.
Finalise themes : Here’s where you “solidify” your analysis and make it report-ready by describing and defining your themes.
Produce your report : This is the final step of your thematic analysis process, where you put everything you’ve found together and report on your findings.
Tips & Suggestions
In the video below, we share 6 time-saving tips and tricks to help you approach your thematic analysis as effectively and efficiently as possible.
Wrapping Up
In this article, we’ve covered the basics of thematic analysis – what it is, when to use it, the different approaches and types of thematic analysis, and how to perform a thematic analysis.
If you have any questions about thematic analysis, drop a comment below and we’ll do our best to assist. If you’d like 1-on-1 support with your thematic analysis, be sure to check out our research coaching services here .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:
21 Comments
I really appreciate the help
Hello Sir, how many levels of coding can be done in thematic analysis? We generate codes from the transcripts, then subthemes from the codes and themes from subthemes, isn’t it? Should these themes be again grouped together? how many themes can be derived?can you please share an example of coding through thematic analysis in a tabular format?
I’ve found the article very educative and useful
Excellent. Very helpful and easy to understand.
This article so far has been most helpful in understanding how to write an analysis chapter. Thank you.
My research topic is the challenges face by the school principal on the process of procurement . Thematic analysis is it sutable fir data analysis ?
It is a great help. Thanks.
Best advice. Worth reading. Thank you.
Where can I find an example of a template analysis table ?
Finally I got the best article . I wish they also have every psychology topics.
Hello, Sir/Maam
I am actually finding difficulty in doing qualitative analysis of my data and how to triangulate this with quantitative data. I encountered your web by accident in the process of searching for a much simplified way of explaining about thematic analysis such as coding, thematic analysis, write up. When your query if I need help popped up, I was hesitant to answer. Because I think this is for fee and I cannot afford. So May I just ask permission to copy for me to read and guide me to study so I can apply it myself for my gathered qualitative data for my graduate study.
Thank you very much! this is very helpful to me in my Graduate research qualitative data analysis.
Thank you very much. I find your guidance here helpful. Kindly let help me understand how to write findings and discussions.
i am having troubles with the concept of framework analysis which i did not find here and i have been an assignment on framework analysis
I was discouraged and felt insecure because after more than a year of writing my thesis, my work seemed lost its direction after being checked. But, I am truly grateful because through the comments, corrections, and guidance of the wisdom of my director, I can already see the bright light because of thematic analysis. I am working with Biblical Texts. And thematic analysis will be my method. Thank you.
lovely and helpful. thanks
very informative information.
thank you very much!, this is very helpful in my report, God bless……..
Thank you for the insight. I am really relieved as you have provided a super guide for my thesis.
Thanks a lot, really enlightening
excellent! very helpful thank a lot for your great efforts
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Theme Essay
Last Updated: January 4, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Jake Adams . Jake Adams is an academic tutor and the owner of Simplifi EDU, a Santa Monica, California based online tutoring business offering learning resources and online tutors for academic subjects K-College, SAT & ACT prep, and college admissions applications. With over 14 years of professional tutoring experience, Jake is dedicated to providing his clients the very best online tutoring experience and access to a network of excellent undergraduate and graduate-level tutors from top colleges all over the nation. Jake holds a BS in International Business and Marketing from Pepperdine University. There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 206,773 times.
Starting the Essay

- For example, an essay prompt may ask you to reflect on the theme of good versus evil in John Steinbeck's East of Eden .

- Make a list of everything you know about the topic. This can be information you learned in class, as well as information you found on your own.
- Write down keywords or key scenes in the text that respond to the essay prompt. Think about what words or scenes from the text come to mind when you think of a specific theme.
- For example, when you brainstorm ideas on East of Eden , you may write down any moments in the text that seem to speak to the theme of good and evil.

- Your thesis statement will need to address the theme, your primary example or examples, and the stance you will take on the topic.
- For example, your thesis might be: "In East of Eden , John Steinbeck rejects the Biblical idea of good and evil and instead focuses on the contradictions and complications found in good and evil."

- Introduction: Discuss landscape as metaphor, include thesis statement.
- Body: Describe mountains in opening scene, elaborate on how they symbolize good vs. evil, state how characters live between the mountains, showing how people are caught between good and evil.
- Conclusion: Restate thesis statement, return to landscape as metaphor.
Writing Your Essay

- Questions can make fun hooks for the reader. Ask a rhetorical question that relates to the theme of the essay, such as "How does one decide what is good and what is evil?"
- You can also use a quote from the text as the hook. Find a quote in the text that explores the themes and ideas you'll be discussing in your essay.

- For example, you may introduce the role of nature plays in the text to discuss the theme of good and evil. The first sentence of your body paragraph should discuss the role of nature. This will set up the paragraph and let the reader know what the focus of the paragraph will be.

- For example, you may discuss the use of nature in the text in one paragraph. The body of the paragraph should then use quotes and scenes in the text to support this idea.
- You might write,"The descriptions of the Gabilan Mountains in the text symbolize good and evil. The characters in the story live in the Salinas Valley, trapped in a gray area between these two extremes."

- Ask yourself, "What do I want my readers to have learned through this essay?"
- Remind readers about the essay's theme. Reference some of the arguments you made in the body of your essay, reinforcing how they support your original point.
Revising Your Essay

- Check that there are transitions between paragraphs. Look at the beginning of each paragraph to make sure they all flow well together.

- Print out your paper and proofread it. Oftentimes, errors are easier to catch on paper. If you can't print out your paper, try changing the size or type of the font. Anything that alters how the work looked when you wrote it can help alert you to errors. [13] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source

- Be open to constructive feedback from friends and peers. This will only improve the essay and ensure it is at its best when you turn it in.
Expert Q&A

You Might Also Like

- ↑ Jake Adams. Academic Tutor & Test Prep Specialist. Expert Interview. 20 May 2020.
- ↑ https://penandthepad.com/write-essay-theme-book-2200.html
- ↑ https://wts.indiana.edu/writing-guides/how-to-write-a-thesis-statement.html
- ↑ https://www.grammarly.com/blog/essay-outline/
- ↑ https://www.grammarly.com/blog/how-to-write-a-hook/
- ↑ https://libguides.newcastle.edu.au/how-to-write-an-essay/conclusion
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/proofreading/steps_for_revising.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/proofreading/proofreading_suggestions.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
About This Article

When writing a theme essay, you’ll need to explore a given theme in the text you’re studying. Before you start your essay, brainstorm some notes about your theme, which you can then build your essay from. For example, if you have the theme of good and evil, think about which characters are mostly good or evil, any good or evil actions they take, description that uses light and darkness, and any religious context. In your intro, state your thesis, which should summarize your essay’s main argument. Then, choose 4 or 5 examples of your theme and write a paragraph exploring each one. Make sure you support your points with quotes from the text. In your conclusion, link your ideas back to your thesis statement. For more tips from our English co-author, including how to revise your essay to polish it up, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Mar 13, 2018
Did this article help you?
Jul 29, 2017
Dec 18, 2016
Nov 8, 2016
Ashley Ding
Nov 22, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
- Essay Guides
- Other Essays
How to Write a Theme Essay
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
A thematic essay is a type of writing assignment that focuses on a specific theme or topic. It requires you to identify a central theme, discuss it in detail, and make connections between various facts. Your main goal is to demonstrate understanding and interpretation of the given subject matter. This type of essay is commonly used in literature classes or history exams.
If you’ve got an assignment to write a theme essay, you might wonder where you should even start from. No worries, we’ve got you covered here! The first thing you must know about this specific type of paper is that it aims to analyze a certain well-known theme and make an interesting statement about it. Here, you must explain meaning and relevance or complexity of your topic. You should summarize details that support your conclusion. In this article, we will conduct a detailed review of theme essay concept. We will also provide you a step by step guide on how to write a proper one. Let's dive right into it!
Thematic Essay Definition
Let’s start with defining what is a thematic essay and its purpose. In this type, one should select a thesis and form unique statement related to its aspects. You should write about it, explaining or elaborating to your audience the following:
- How is your statement related to your topic?
- Which important or interesting aspects does it highlight?
- What approaches and literary devices are you using for analysis ? How do you explain your general theme? This can be comparison, metaphor, personification etc.
When composing such an essay, you must formulate and defend your statement. Here, you will demonstrate abilities of analysis and literary devices usage. At least several paragraphs would be needed to display such skills properly.
Thematic Essay Outline: What's Inside
The best way to begin is creating a theme essay outline for your topic. An outline should contain all key parts, concepts and ideas of your paper. You should put it in a sketchy but logical manner. This way you'll quickly prepare a shortened version of your assignment. It will also help you in reviewing it. Adding missing points and correcting significant mistakes would be easier at this early stage. Outline should include all main essay parts:
- Introduction
- Thesis statement
- Body section
- Conclusion.
Keeping it brief, you should not provide complete sentences to describe your statements, ideas and arguments. A few words would suffice for each important point. Purpose is to make it readable for yourself! You should review it quickly and spot any inconsistencies.
How to Write a Thematic Essay Step-By-Step
Now it is time to focus on how to write a theme analysis essay – the complete text from scratch. Is your goal to impress readers and achieve a good grade? Then it is important that you create a proper essay structure template and don't lose any of your key questions! Stay methodical and keep it logical! Make sure your audience is engaged and don’t disappoint them in the end. Below we’ll provide a general idea for each step of this process.
Step 1. Define the Topic for Your Thematic Essay
When it comes to choosing among thematic essay topics, it is important that you pick an interesting and maybe even a controversial one. At the same time, make sure you can actually provide some meaningful input about it. Your assignment should impress readers with detailed analysis and its author’s writing skills. That's why your chosen topic must provide enough material for that. There is a diverse choice of topics. Choose the one you are really interested in whether it is Bullying essay or Happiness essay . If you need some ideas for great essay topics, feel free to check out our other articles.
Step 2. Create a Thematic Essay Outline
We've already covered the main points of theme essay outline concept. When writing it, include all the main parts of your future work. Keep it as short as possible, one paragraph per each key point will be enough. It isn’t even necessary to describe everything with complete sentences! A few words would suffice. Once done, review it first and make necessary corrections. It is advised to review an outline several times. That's how any noticeable gaps or mistakes would be spotted early.
Step 3. Start a Thematic Essay with a Hook
A good thematic essay introduction ought to captivate readers right from the start. That’s why it is always advised to add some ‘hook’ into it. You can begin with an unexpected statement, use wordplay or a plot twist. Then you can explain this in the main body part. This way your audience would be interested to hear those explanations. As a result, your paper will have better chances of success. Apart from that, introduction should contain the main statement and some information about its content.
Step 4. Write Body Paragraphs for Your Theme Essay
Goal of thematic essay body is to answer all the questions stated in an introduction. You must elaborate the meaning of each key idea. Finally, display your usage of literary devices, as we’ve specified earlier. Common practice is to use at least one paragraph per a literary device disclosure. Besides, the main body is the right place to use all relevant sources that can support your analysis or provide you with helpful analogies. Keep the main body logical, so that every paragraph is somehow connected to the previous and the next ones.
Step 5. Create a Thematic Essay Conclusion
A strong thematic essay conclusion should highlight all important points from tyourhe essay while avoiding adding new facts or evidence. Just restate your thesis, answer all questions and summarize your arguments. It might be also useful to leave some final note for readers with some deeper analysis of your topic. You can also highlight the need for further exploration of the chosen theme and thus to prepare readers for your future works on this topic.
Step 6. Proofread Your Thematic Analysis Essay
After completing theme essay, it is highly recommended to review it thoroughly, even several times if possible. The goal is to find mistakes and to spot logical gaps or missing details. Even best essays typically have inconsistencies left at the early stage. Taking a fresh look at your text often reveals some issues. If possible, ask your friends or colleagues to review your text. They might notice something you could not.
How to Format a Thematic Essay
When it comes to thematic essay format, you need to find out what are the requirements in your assignment or which format is common in the institution you will be presenting your essay for. In case no special requirements were made for you, just choose one of the most popular formats for scholarly papers:
- APA paper format : typically used in natural sciences, education and psychology fields
- MLA: typically used for works in humanities
- Chicago: typically used in business, history, and fine arts fields.
Thematic Essay Example
Let’s illustrate the explanations above with a few theme essay examples. We’ll provide some real ones here so that your every question would be answered. Hopefully you’ll find some inspiration in these examples for your own winning paper! The examples can be found below. Please scroll down to find them.
Thematic Essay: Final Thoughts
In this article we have explored the theme essay concept in detail. Its central purpose and main definition were examined and a step by step guide for writing a strong one was suggested. We’ve also provided a few working examples for your convenience. Hopefully, all this information will be useful for your scholarly endeavors!
Feel free to check out our paper writing services ! We’ve got a team of skilled writers with expertise in different literary areas, ready to help you. They deliver high quality content, always on time.
Frequently Asked Questions About Theme Essay
1. what is the thematic statement.
A thematic statement typically takes the place of a thesis in a thematic essay. It consists of 1-2 complete sentences that express a theme which you have chosen for your work. This statement must convey the main message and also show what analysis will be done. It should be brief however as most of the details are to be provided in the main body.
2. What is the goal of thematic essay?
The thematic essay goal is to express an idea or some insights about the surrounding world and to change readers' minds about certain issues. As an author, you are expected to illustrate the team, provide all necessary explanations and conduct an analysis if needed. Besides, you typically should demonstrate familiarity with some literary interpretations and methods which are used to examine your theme.
3. How long should a theme essay be?
The minimum length of a theme essay is five paragraphs. One is for introduction, one for conclusion and remaining three for the main body. Of course, it can be more than that, depending on the depth of the theme that was chosen. The main rule is to keep your essay logical and concise, avoiding adding too many details. Otherwise your audience might get tired and the effect produced by your writing would be damaged.
4. What is a thematic essay history?
Thematic essay (history class) should be written to analyze some historical facts or significance of specific literary pieces. A typical case is examining different aspects of a controversial leader from the past or a political event that has produced a number of various important consequences. Or you might argue about a specific role of a certain book during a certain period or its influence on different nations or cultural groups.

Daniel Howard is an Essay Writing guru. He helps students create essays that will strike a chord with the readers.
You may also like

How to Write a Thematic Essay

Every piece of writing ever written has its agenda. Whether it’s to teach a lesson or show the impact of a particular emotion or action, a central theme can be developed. The goal for us as readers is to uncover what the author was trying to tell us between the lines in their literature. When we do finally discover it, we’ve accomplished the first step of thematic essay writing! Let’s see below how to write a thematic essay with our papers writing service .
What Is a Thematic Essay?
Let’s look at the thematic essay definition; a thematic essay is a piece of writing in which an author develops the central theme in some literature using literary devices like foreshadowing, imagery, personification, etc.
A professional essay writer will uncover the primary subject, elaborate upon the literary devices employed, and express the overall significance of the theme. The primary challenge comes from the fact that although there are various subjects, finding the most meaningful and impactful one can be challenging.
Naturally, each person has their own varied interpretation, making it hard to agree on a central theme wholesomely. In short, a well written thematic essay comes from a healthy central idea that is conclusively proven via literary devices and logical arguments.
If you're thinking " i need help with my homework " - contact us!
How to Pick a Thematic Topic?
A crucial aspect of writing a good thematic essay is choosing a theme. Follow the hints listed below to help you create a thematic topic:

Brainstorm from your own experiences. Recall what you were talking about in class, with your mates or parents. Do some of these conversations remind you of some book, novel or another piece of literature?
Write down every idea that comes to mind. Sometimes, your most absurd ideas are the best way to go.
List your favourite literature pieces. Which literature piece was the most touching for you? Try to analyze its subject and problems the author built upon within the story; it might help you come up with your own ideas.
Look at the details of other literature pieces: You might find some interesting details within other literature that can help you come up with your theme.
Still have no idea what to write about? No worries, we have your back.
Thematic Essay Topics
- What is George Orwell’s deliberation in portraying a “Perfect Utopia” in his book 1984?
- What main idea is George Orwell painting about Communism in the book Animal Farm?
- What is Harper Lee saying about innocence in her novel To Kill A Mockingbird?
- What is John Steinbeck saying about loneliness and isolation in Of Mice and Men?
- What is F. Scott Fitzgerald saying about the American Dream in The Great Gatsby?
Still Not in the Mood to Write Your thematic essay?
Send us your write my essays request.
How to Find and Explore the Central Theme
As stated before, uncovering the main subject and central theme respectively is the first significant step in a thematic paper. However, with so many things going on within the literature, it may be difficult to interpret the central theme accurately. To make sure you choose it correctly, follow these steps:
1. Summarize the literature: What main idea is the author trying to purvey? Usually, there will be many hints along the way, so choosing the right direction may not be so challenging.
2. Pick the most prevalent subject: One thing to note is the significant difference between a subject and a theme. A subject is the general topic of conversation—whether it be love, bravery, deception, etc. A theme is a specific point the author is making about said subject. So, find the talking point that is most commonly being brought up. This will be the focal point of the essay.
3. Read between the lines: After finding the most suitable subject, decipher what main point the author is trying to make. This will become clearer as you get deeper into the literature since clues and examples will appear frequently. After fully deciphering the central theme, there is one more significant step.
4. Overall significance: What is the overall significance that comes from the author’s point? What can be taken from this and applied to our personal lives? In other words, what is the lesson from all of this? What have we learned?
Feeling difficult to write thematic essay? Leave us a notice and our persuasive essay writer we'll help.
Thematic Essay Outline
The thematic essay has several key components. First of all, it should be five paragraphs or more, depending on the depth of the theme. Next, it should have a concrete thesis statement, which, in other words, is the thematic statement that comes from the main subject. The introduction presents the reader with the subject and the thesis statement. The body paragraphs each discuss one literary element or more to defend the validity of your thesis, all the while providing many supporting details from the text itself. Lastly, the thematic essay conclusion summarizes the main points presented and finishes off with a statement of significance.
Follow the link to learn more about HOW TO CREATE A WINNING OUTLINE
The thematic essay introduction presents the main subject of discussion in a captivating way. The first sentence of the intro should be a hook statement that makes some intriguing claim about the subject of discussion. If done correctly, this will grab your reader's attention. Afterwards, provide any necessary background information from the literature that will help the audience understand your claims later on. Lastly, put together a well thought out thesis statement that reflects the central theme of the novel.
The body paragraphs follow a thematic essay format. Since each body paragraph’s purpose should be to present a literary device as evidence, the topic sentence should introduce the claim and gateway into the evidence. Every topic sentence must mention a literary device and its relationship to the literature.
Afterwards, to validate your claim, use examples from the book that strengthen the reasoning of your statement. These can be actions from the plot or quotations that are parallel with the central theme. It’s imperative to explain how the action/quote links back to your thesis statement, as it shows that you can support your logic.
Remember: each claim must use a literary device. It can not just be a random moment or inference. Thematic essays are all about proving thesis statements through the use of critical literary devices.
The thematic essay conclusion has three main objectives to complete before wrapping up the entire paper. It should not present any new information or facts, but should summarize the information already given. First of all, restate your thesis statement in a new way. Then, summarize the central claims you made within the body of your paper and their influence on the thesis statement. To finish off the entire work, present an overall concluding statement with a global analysis of the subject. Leave your reader with another hook, making him/her interested in digging deeper into the topic.
Try also read an article on poetry analysis essay , it could be useful and can give you new insights.
Thematic Essay Example
The best way to familiarise yourself with this type of writing is to learn from an example.
Even though the ancient Greek cities of Athens and Sparta were geographically close to each other, they had very distinct cultures, lifestyles, values, and political systems that defined them. The following paper compares and contrasts the cultural impacts of the two cities by examining some of the duties and responsibilities of the citizenry as well as the different values that were deemed important. The paper further evaluates the impact of accomplishments that would have been left by both city-states on the history of western civilization.
Wrap Things Up
Before submitting your thematic essay, make sure to check a couple of things to correct any possible errors.

- Double-check and confirm that the central theme you have decided is the one that the author likely meant to focus on. Unless you can provide a secondary issue and present it strongly enough as a primary, validate the primary subject.
- Go through and proofread your entire paper. Nothing makes reading more irritating than grammatical mistakes, clean that stuff up as much as possible.
- Get a second pair of eyes to read through your paper. It’s best to ask a classmate for help, as they most likely have or had a similar assignment. Another great way to polish things up is to ask one of our writers to give you some helpful advice.
We also recommend reading about Jem Finch character traits , our readers find it very interesting.
Having a Trouble with Your Thematic Essay?
Having a hard time thinking up a proper topic to write about? Or, do you have one but are having a hard time deciphering the theme? Let our custom essay writing service do all the work for you. Check out our price calculator to estimate the cost of your assignment.
Related Articles
.webp)
Literary Analysis Essay
Literary Analysis Essay Writing
Last updated on: May 21, 2023
Literary Analysis Essay - Ultimate Guide By Professionals
By: Cordon J.
Reviewed By: Rylee W.
Published on: Dec 3, 2019

A literary analysis essay specifically examines and evaluates a piece of literature or a literary work. It also understands and explains the links between the small parts to their whole information.
It is important for students to understand the meaning and the true essence of literature to write a literary essay.
One of the most difficult assignments for students is writing a literary analysis essay. It can be hard to come up with an original idea or find enough material to write about. You might think you need years of experience in order to create a good paper, but that's not true.
This blog post will show you how easy it can be when you follow the steps given here.Writing such an essay involves the breakdown of a book into small parts and understanding each part separately. It seems easy, right?
Trust us, it is not as hard as good book reports but it may also not be extremely easy. You will have to take into account different approaches and explain them in relation with the chosen literary work.
It is a common high school and college assignment and you can learn everything in this blog.
Continue reading for some useful tips with an example to write a literary analysis essay that will be on point. You can also explore our detailed article on writing an analytical essay .

On this Page
What is a Literary Analysis Essay?
A literary analysis essay is an important kind of essay that focuses on the detailed analysis of the work of literature.
The purpose of a literary analysis essay is to explain why the author has used a specific theme for his work. Or examine the characters, themes, literary devices , figurative language, and settings in the story.
This type of essay encourages students to think about how the book or the short story has been written. And why the author has created this work.
The method used in the literary analysis essay differs from other types of essays. It primarily focuses on the type of work and literature that is being analyzed.
Mostly, you will be going to break down the work into various parts. In order to develop a better understanding of the idea being discussed, each part will be discussed separately.
The essay should explain the choices of the author and point of view along with your answers and personal analysis.
How To Write A Literary Analysis Essay
So how to start a literary analysis essay? The answer to this question is quite simple.
The following sections are required to write an effective literary analysis essay. By following the guidelines given in the following sections, you will be able to craft a winning literary analysis essay.
Introduction
The aim of the introduction is to establish a context for readers. You have to give a brief on the background of the selected topic.
It should contain the name of the author of the literary work along with its title. The introduction should be effective enough to grab the reader’s attention.
In the body section, you have to retell the story that the writer has narrated. It is a good idea to create a summary as it is one of the important tips of literary analysis.
Other than that, you are required to develop ideas and disclose the observed information related to the issue. The ideal length of the body section is around 1000 words.
To write the body section, your observation should be based on evidence and your own style of writing.
It would be great if the body of your essay is divided into three paragraphs. Make a strong argument with facts related to the thesis statement in all of the paragraphs in the body section.
Start writing each paragraph with a topic sentence and use transition words when moving to the next paragraph.
Summarize the important points of your literary analysis essay in this section. It is important to compose a short and strong conclusion to help you make a final impression of your essay.
Pay attention that this section does not contain any new information. It should provide a sense of completion by restating the main idea with a short description of your arguments. End the conclusion with your supporting details.
You have to explain why the book is important. Also, elaborate on the means that the authors used to convey her/his opinion regarding the issue.
For further understanding, here is a downloadable literary analysis essay outline. This outline will help you structure and format your essay properly and earn an A easily.
DOWNLOADABLE LITERARY ANALYSIS ESSAY OUTLINE (PDF)
Types of Literary Analysis Essay
- Close reading - This method involves attentive reading and detailed analysis. No need for a lot of knowledge and inspiration to write an essay that shows your creative skills.
- Theoretical - In this type, you will rely on theories related to the selected topic.
- Historical - This type of essay concerns the discipline of history. Sometimes historical analysis is required to explain events in detail.
- Applied - This type involves analysis of a specific issue from a practical perspective.
- Comparative - This type of writing is based on when two or more alternatives are compared
Examples of Literary Analysis Essay
Examples are great to understand any concept, especially if it is related to writing. Below are some great literary analysis essay examples that showcase how this type of essay is written.
A ROSE FOR EMILY LITERARY ANALYSIS ESSAY
TO KILL A MOCKINGBIRD LITERARY ANALYSIS ESSAY
THE GREAT GATSBY LITERARY ANALYSIS ESSAY
THE YELLOW WALLPAPER LITERARY ANALYSIS ESSAY
If you do not have experience in writing essays, this will be a very chaotic process for you. In that case, it is very important for you to conduct good research on the topic before writing.
There are two important points that you should keep in mind when writing a literary analysis essay.
First, remember that it is very important to select a topic in which you are interested. Choose something that really inspires you. This will help you to catch the attention of a reader.
The selected topic should reflect the main idea of writing. In addition to that, it should also express your point of view as well.
Another important thing is to draft a good outline for your literary analysis essay. It will help you to define a central point and division of this into parts for further discussion.
Literary Analysis Essay Topics
Literary analysis essays are mostly based on artistic works like books, movies, paintings, and other forms of art. However, generally, students choose novels and books to write their literary essays.
Some cool, fresh, and good topics and ideas are listed below:
- Role of the Three Witches in flaming Macbeth’s ambition.
- Analyze the themes of the Play Antigone,
- Discuss Ajax as a tragic hero.
- The Judgement of Paris: Analyze the Reasons and their Consequences.
- Oedipus Rex: A Doomed Son or a Conqueror?
- Describe the Oedipus complex and Electra complex in relation to their respective myths.
- Betrayal is a common theme of Shakespearean tragedies. Discuss
- Identify and analyze the traits of history in T.S Eliot’s ‘Gerontion’.
- Analyze the theme of identity crisis in The Great Gatsby.
- Analyze the writing style of Emily Dickinson.
If you are still in doubt then there is nothing bad in getting professional writers’ help.
We at 5StarEssays.com can help you get a custom paper as per your specified requirements with our do essay for me service.
Our essay writers will help you write outstanding literary essays or any other type of essay. Such as compare and contrast essays, descriptive essays, rhetorical essays. We cover all of these.
So don’t waste your time browsing the internet and place your order now to get your well-written custom paper.
Frequently Asked Questions
What should a literary analysis essay include.
A good literary analysis essay must include a proper and in-depth explanation of your ideas. They must be backed with examples and evidence from the text. Textual evidence includes summaries, paraphrased text, original work details, and direct quotes.
What are the 4 components of literary analysis?
Here are the 4 essential parts of a literary analysis essay;
No literary work is explained properly without discussing and explaining these 4 things.
How do you start a literary analysis essay?
Start your literary analysis essay with the name of the work and the title. Hook your readers by introducing the main ideas that you will discuss in your essay and engage them from the start.
How do you do a literary analysis?
In a literary analysis essay, you study the text closely, understand and interpret its meanings. And try to find out the reasons behind why the author has used certain symbols, themes, and objects in the work.

Why is literary analysis important?
It encourages the students to think beyond their existing knowledge, experiences, and belief and build empathy. This helps in improving the writing skills also.
What is the fundamental characteristic of a literary analysis essay?
Interpretation is the fundamental and important feature of a literary analysis essay. The essay is based on how well the writer explains and interprets the work.

Law, Finance Essay
Cordon. is a published author and writing specialist. He has worked in the publishing industry for many years, providing writing services and digital content. His own writing career began with a focus on literature and linguistics, which he continues to pursue. Cordon is an engaging and professional individual, always looking to help others achieve their goals.
Was This Blog Helpful?
Keep reading.
- Interesting Literary Analysis Essay Topics for Students

- Write a Perfect Literary Analysis Essay Outline

People Also Read
- cause and effect essay outline
- obesity essay writing topics
- how to title an essay
- research paper outline
Burdened With Assignments?

Advertisement
- Homework Services: Essay Topics Generator
© 2024 - All rights reserved

A Writer's Handbook
- Introduction
- Purpose & Audience
- Opening Sentences
- Linking Sentences
- Finished Introduction
- Topic Sentences
- Development
- Conclusion Sentences
- Conclusion Paragraphs for Essays
- Essay Writing Organization: The Outline
- Annotating Readings
- General Writing Idea Development
- Rhetorical and Visual Analysis Idea Development
- Character Analysis Idea Development
- Theme Analysis Idea Development
Literary Theme Analysis
Exercise 10, overall tips for literary analysis essays.
- Theory Analysis
- Using the Library
- Using Sources for Illustration or Support
- Using Research for Essays
- Writing About Research
- MLA Handbook Summary for Citations
- Final Thoughts on Essays
- Literary Element Index
- Appendix of Example Papers
A literary theme analysis will synthesize several elements within a work and prove an overall message with those elements.
- Characters: What kind of people does the story deal with?
- Plot: What do the characters do? Are they in control of their lives, or are they controlled by fate?
- Motivation: Why do the characters behave as they do, and what motives dominate them?
- Style: How does the author perceive reality?
- Tone: What is the author's attitude towards his subject?
- Values: What are the values of the characters in the story? What values does the author seem to promote?
- The importance of theme in literature can be overestimated; the work of fiction is more than just the theme. However, the theme allows the author to control or give order to his perceptions about life.
- Think of the possible messages within the story – why was this story told (EX. Harry Potter series has a classic “good vs. evil” theme or even a finding out about one’s true self theme. Maybe I would look at the symbolic fight between good and evil or at a coming of age story…Harry Potter series also has a look at family relations where blood family is not necessarily a person’s true family…)
- Choose a theme/issue that will be supported with enough examples from text (EX. Coming of age, Familial vs. adopted relations and how friends and mentors can become family)
- State what you want to present about the theme in the story in the body of the paper
EX: A true coming of age is seen in the characters Harry, Ron, and Hermione in J.K. Rowling’s Harry Potter series. **Note: This would be the X, Y, Z thesis
EX: Characters in Harry Potter’s life illustrate the notion that a father figure does not necessarily have to be one’s biological father. **Note: This thesis is put into a general thesis format, not X,Y, Z
Find evidence within the work to illustrate your points
Find secondary sources as needed that help you prove your points
Exercise 10: Brainstorm some possible theme analysis ideas with Harry Potter; start with the following – what could you do with these:
- Notion of competition in children
- Comment on bullying
- Comment on children having to grow up too quickly
- Class difference
- Good versus Evil
- Jealousy among siblings
- Exercise 10: Brainstorming for Theme Analysis
- Be careful not to summarize the story – this is not an analysis
- Find connections and be original in your synthesis
- When using secondary sources, proof of your exact idea may not be readily available – what you will do is use support of individual elements to then address your main thesis idea
- Never use just the author’s first name – use the last name only or both names when discussing the author
- Always use present tense when talking about literature unless something directly happened “in the past” in the literary piece
- << Previous: Character Analysis Idea Development
- Next: Theory Analysis >>
- Last Updated: Jan 3, 2023 9:01 AM
- URL: https://library.jeffersonstate.edu/AWH
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- How to Do Thematic Analysis | Guide & Examples
How to Do Thematic Analysis | Guide & Examples
Published on 5 May 2022 by Jack Caulfield .
Thematic analysis is a method of analysing qualitative data . It is usually applied to a set of texts, such as an interview or transcripts . The researcher closely examines the data to identify common themes, topics, ideas and patterns of meaning that come up repeatedly.
There are various approaches to conducting thematic analysis, but the most common form follows a six-step process:
- Familiarisation
- Generating themes
- Reviewing themes
- Defining and naming themes
This process was originally developed for psychology research by Virginia Braun and Victoria Clarke . However, thematic analysis is a flexible method that can be adapted to many different kinds of research.
Table of contents
When to use thematic analysis, different approaches to thematic analysis, step 1: familiarisation, step 2: coding, step 3: generating themes, step 4: reviewing themes, step 5: defining and naming themes, step 6: writing up.
Thematic analysis is a good approach to research where you’re trying to find out something about people’s views, opinions, knowledge, experiences, or values from a set of qualitative data – for example, interview transcripts , social media profiles, or survey responses .
Some types of research questions you might use thematic analysis to answer:
- How do patients perceive doctors in a hospital setting?
- What are young women’s experiences on dating sites?
- What are non-experts’ ideas and opinions about climate change?
- How is gender constructed in secondary school history teaching?
To answer any of these questions, you would collect data from a group of relevant participants and then analyse it. Thematic analysis allows you a lot of flexibility in interpreting the data, and allows you to approach large datasets more easily by sorting them into broad themes.
However, it also involves the risk of missing nuances in the data. Thematic analysis is often quite subjective and relies on the researcher’s judgement, so you have to reflect carefully on your own choices and interpretations.
Pay close attention to the data to ensure that you’re not picking up on things that are not there – or obscuring things that are.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Once you’ve decided to use thematic analysis, there are different approaches to consider.
There’s the distinction between inductive and deductive approaches:
- An inductive approach involves allowing the data to determine your themes.
- A deductive approach involves coming to the data with some preconceived themes you expect to find reflected there, based on theory or existing knowledge.
There’s also the distinction between a semantic and a latent approach:
- A semantic approach involves analysing the explicit content of the data.
- A latent approach involves reading into the subtext and assumptions underlying the data.
After you’ve decided thematic analysis is the right method for analysing your data, and you’ve thought about the approach you’re going to take, you can follow the six steps developed by Braun and Clarke .
The first step is to get to know our data. It’s important to get a thorough overview of all the data we collected before we start analysing individual items.
This might involve transcribing audio , reading through the text and taking initial notes, and generally looking through the data to get familiar with it.
Next up, we need to code the data. Coding means highlighting sections of our text – usually phrases or sentences – and coming up with shorthand labels or ‘codes’ to describe their content.
Let’s take a short example text. Say we’re researching perceptions of climate change among conservative voters aged 50 and up, and we have collected data through a series of interviews. An extract from one interview looks like this:
In this extract, we’ve highlighted various phrases in different colours corresponding to different codes. Each code describes the idea or feeling expressed in that part of the text.
At this stage, we want to be thorough: we go through the transcript of every interview and highlight everything that jumps out as relevant or potentially interesting. As well as highlighting all the phrases and sentences that match these codes, we can keep adding new codes as we go through the text.
After we’ve been through the text, we collate together all the data into groups identified by code. These codes allow us to gain a condensed overview of the main points and common meanings that recur throughout the data.
Next, we look over the codes we’ve created, identify patterns among them, and start coming up with themes.
Themes are generally broader than codes. Most of the time, you’ll combine several codes into a single theme. In our example, we might start combining codes into themes like this:
At this stage, we might decide that some of our codes are too vague or not relevant enough (for example, because they don’t appear very often in the data), so they can be discarded.
Other codes might become themes in their own right. In our example, we decided that the code ‘uncertainty’ made sense as a theme, with some other codes incorporated into it.
Again, what we decide will vary according to what we’re trying to find out. We want to create potential themes that tell us something helpful about the data for our purposes.
Now we have to make sure that our themes are useful and accurate representations of the data. Here, we return to the dataset and compare our themes against it. Are we missing anything? Are these themes really present in the data? What can we change to make our themes work better?
If we encounter problems with our themes, we might split them up, combine them, discard them, or create new ones: whatever makes them more useful and accurate.
For example, we might decide upon looking through the data that ‘changing terminology’ fits better under the ‘uncertainty’ theme than under ‘distrust of experts’, since the data labelled with this code involves confusion, not necessarily distrust.
Now that you have a final list of themes, it’s time to name and define each of them.
Defining themes involves formulating exactly what we mean by each theme and figuring out how it helps us understand the data.
Naming themes involves coming up with a succinct and easily understandable name for each theme.
For example, we might look at ‘distrust of experts’ and determine exactly who we mean by ‘experts’ in this theme. We might decide that a better name for the theme is ‘distrust of authority’ or ‘conspiracy thinking’.
Finally, we’ll write up our analysis of the data. Like all academic texts, writing up a thematic analysis requires an introduction to establish our research question, aims, and approach.
We should also include a methodology section, describing how we collected the data (e.g., through semi-structured interviews or open-ended survey questions ) and explaining how we conducted the thematic analysis itself.
The results or findings section usually addresses each theme in turn. We describe how often the themes come up and what they mean, including examples from the data as evidence. Finally, our conclusion explains the main takeaways and shows how the analysis has answered our research question.
In our example, we might argue that conspiracy thinking about climate change is widespread among older conservative voters, point out the uncertainty with which many voters view the issue, and discuss the role of misinformation in respondents’ perceptions.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2022, May 05). How to Do Thematic Analysis | Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 29 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/thematic-analysis-explained/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, qualitative vs quantitative research | examples & methods, inductive reasoning | types, examples, explanation, what is deductive reasoning | explanation & examples.
Literary Analysis Essay

Literary Analysis Essay - Step by Step Guide
15 min read
Published on: Aug 16, 2020
Last updated on: Jan 29, 2024

People also read
Literary Analysis Essay Outline Guide with Examples
Interesting Literary Analysis Essay Topics & Ideas
Share this article
Literature is an art that can inspire, challenge, and transform us. But how do we analyze literature in a way that truly captures its essence?
That's where a literary analysis essay comes in.
Writing a literary analysis essay allows you to delve into the themes, characters, and symbols of a literary work. It's a chance to engage with literature on a deeper level and to discover new insights.
In this comprehensive guide, we will take you through the process of writing a literary analysis essay, step by step. Plus, you’ll get to read some great examples to help you out!
So let’s dive in!
On This Page On This Page -->
What is a Literary Analysis Essay?
Literary analysis is a process of examining a literary work in detail to uncover its meaning and significance.
It involves breaking down the various elements of a work, such as plot, character, setting, and theme. And then analyzing how they work together to create a specific effect on the reader.
In other words, literary analysis is an exercise in interpretation. The reader of a work asks questions about what the author means to say, how they are saying it, and why.
A literary analysis essay is an essay where you explore such questions in depth and offer your own insights.
What is the Purpose of a Literary Analysis Essay?
In general, the purpose of a literary analysis essay is as follows:
- To gain a greater understanding and appreciation of the work.
- To be able to think critically and analytically about a text.
Content of a Literary Analysis
A literary analysis essay delves deep into the various aspects of a literary work to examine its meaning, symbolism, themes, and more. Here are the key elements to include in your literary analysis essay:
Plot Analysis
Plot refers to the sequence of events that make up the storyline of a literary work. It encompasses the main events, conflicts, and resolutions that drive the narrative forward.
Elements of Plot Analysis
The elements of a plot typically include:
- Exposition: The introduction of the story that establishes the setting, characters, and initial circumstances.
- Rising action: A set of events or actions that sets the main conflict into motion, often occurring early in the story.
- Conflict: The series of events that build tension and develop the conflict, leading to the story's climax.
- Climax: The turning point of the story, where the conflict reaches its peak and the outcome hangs in the balance.
- Falling Action: The events that occur after the climax, leading towards the resolution of the conflict.
- Resolution: The point in the story where the conflict is resolved, providing closure to the narrative.
Character Analysis
Character analysis involves studying the role, development, and motivations of the characters in a literary work. It explores how characters contribute to the overall narrative and themes of the story.
Elements of Character Analysis
- Identification of major and minor characters.
- Examination of their traits, behaviors, and relationships.
- Analysis of character development and changes throughout the story.
- Evaluation of the character's role in advancing the plot or conveying themes.
Symbolism and Imagery Analysis
Symbolism and imagery analysis focuses on the use of symbols, objects, or images in a work. It analyzes and explores the use of literary devices to convey deeper meanings and evoke emotions.
Elements of Symbolism and Imagery Analysis
- Identification of key symbols or recurring motifs.
- Interpretation of their symbolic significance.
- Analysis of how imagery is used to create vivid mental pictures and enhance the reader's understanding and emotional experience.
Theme Analysis
Analyzing the theme involves exploring the central ideas or messages conveyed in a literary work. It examines the underlying concepts, or messages that the author wants to convey through the story.
Elements of Theme Analysis
- Identification of the main themes or central ideas explored in the text.
- Analysis of how the themes are developed and reinforced throughout the story.
- Exploration of the author's perspective and the intended message behind the themes.
Setting Analysis
The Setting of a story includes the time, place, and social context in which the story takes place. Analyzing the setting involves how the setting influences the characters, plot, and overall atmosphere of the work.
Elements of Setting Analysis
- Description and analysis of the physical, cultural, and historical aspects of the setting.
- Examination of how the setting contributes to the mood, atmosphere, and themes of the work.
- Evaluation of how the setting shapes the characters' actions and motivations.
Structure and Style Analysis
Structure and style analysis involves studying the organization, narrative techniques, and literary devices employed by the author. It explores how the structure and style contribute to the overall impact and effectiveness of the work.
Elements of Structure and Style Analysis
- Analysis of the narrative structure, such as the use of flashbacks, nonlinear timelines, or multiple perspectives.
- Examination of the author's writing style, including the use of language, tone, and figurative language.
- Evaluation of literary devices, such as foreshadowing, irony, or allusion, and their impact on the reader's interpretation.

Paper due? Why Suffer? That's our job.
How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay?
Writing a great literary analysis piece requires you to follow certain steps. Hereâs what you need to do to write a literary essay:
Preparing for Your Essay
The pre-writing process for writing a literary analysis essay includes the following:
- Choosing a literary work to analyze
- Reading and analyzing the work
- Taking notes and organizing your thoughts
- Creating an outline for your essay
Choosing a Work to Analyze
As a student, you would most probably be assigned a literary piece to analyze. It could be a short story, a novel, or a poem. However, sometimes you get to choose it yourself.
In such a case, you should choose a work that you find interesting and engaging. This will make it easier to stay motivated as you analyze the work and write your essay.
Moreover, you should choose a work that has some depth and complexity. This will give you plenty of material to analyze and discuss in your essay. Finally, make sure that your choice fits within the scope of the assignment and meets the expectations of your instructor.
Reading and Analyzing
Once youâve chosen a literary work, it's time to read the work with careful attention. There are several key elements to consider when reading and analyzing a literary work:
- Plot - The sequence of events that make up the story. Analyzing the plot involves examining the structure of the story, including its exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution.
- Characters - The people or entities that populate the story. Analyzing characters involves examining their motivations, personalities, relationships, and development over the course of the story.
Want to learn more about character analysis? Head to our blog about how to conduct character analysis and learn easy steps with examples.
- Setting - The time, place, and environment in which the story takes place. Analyzing the setting involves examining how the atmosphere contributes to the story's overall meaning.
- Theme - The underlying message or meaning of the story. Analyzing themes involves examining the work's central ideas and how they are expressed through the various elements of the story.
Moreover, it's important to consider the following questions while analyzing:
- What is the central theme or main point the author is trying to make?
- What literary devices and techniques has the author used?
- Why did the author choose to write this particular work?
- What themes and ideas are present in the work?
These questions will help you dive deeper into the work you are writing about.
Take Notes and Gather Material
As you read and analyze the literary work, it's important to take notes so you donât forget important details and ideas. This also helps you identify patterns and connections between different elements of the piece.
One effective way to take notes is to list important elements of the work, such as characters, setting, and theme. You can also use sticky notes, highlighters, or annotations to mark important passages and write down your ideas.
Writing Your Literary Analysis Essay
Once you have read a piece of literature and taken notes, you have all the material you need to write an essay. Follow the simple steps below to write an effective literary analysis essay.
Create an Outline for Your Essay
Firstly, creating an outline is necessary. This will help you to organize your thoughts and ideas and ensure that your essay flows logically and coherently.
This is what your literary essay outline would look like:
Writing the Introduction
Writing your essay introduction involves the three following parts:
- Begin the introductory paragraph with an engaging hook statement that captures the readers' attention. An effective hook statement can take many different forms, such as a provocative quote, an intriguing question, or a surprising fact.
Make sure that your hook statement is relevant to the literary work you are writing about. Here are a few examples of effective hooks:
- Afterward, present the necessary background information and context about the literary work. For instance,
- Talk about the author of the work or when and where it was written.
- Give an overview of the work or why it is significant.
- Provide readers with sufficient context so they can know what the work is generally about.
- Finally, end the introduction with a clear thesis statement . Your thesis statement should be a concise statement that clearly states the argument you will be making in your essay. It should be specific and debatable, and it should provide a roadmap for the rest of your essay.
For example, a thesis statement for an essay on "Hamlet" might be:
Watch this video to learn more about writing an introduction for a literary analysis essay:
Writing the Body
Here are the steps to follow when writing a body paragraph for a literary analysis essay:
- Start with a topic sentence:
The topic sentence should introduce the main point or argument you will be making in the paragraph. It should be clear and concise and should indicate what the paragraph is about.
- Provide evidence:
After you have introduced your main point, provide evidence from the text to support your analysis. This could include quotes, paraphrases, or summaries of the text.
- Explain and discuss the evidence:
Explain how the evidence supports your main point or argument or how it connects back to your thesis statement.
- Conclude the paragraph:
End the paragraph by relating your main point to the thesis and discussing its significance. You should also use transitions to connect the paragraph to your next point or argument.
Writing the Conclusion
The conclusion of a literary analysis essay provides closure to your analysis and reinforces your thesis statement. Hereâs what a conclusion includes:
- Restate your thesis statement:
Start by restating your thesis statement in a slightly different way than in your introduction. This will remind the reader of the argument you made and the evidence you provided to support it.
- Summarize your main points:
Briefly summarize the main points you made in your essay's body paragraphs. This will help tie everything together and provide closure to your analysis.
- Personal reflections:
The conclusion is the best place to provide some personal reflections on the literary piece. You can also explain connections between your analysis and the larger context. This could include connections to other literary works, your personal life, historical events, or contemporary issues.
- End with a strong statement:
End your conclusion with a strong statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader. This could be a thought-provoking question, a call to action, or a final insight into the significance of your analysis.
Finalizing your Essay
Youâve completed the first draft of your literary analysis essay. Congratulations!
However, itâs not over just yet. You need some time to polish and improve the essay before it can be submitted. Hereâs what you need to do:
Proofread and Revise your Essay
After completing your draft, you should proofread your essay. You should look out for the following aspects:
- Check for clarity:
Make sure that your ideas are expressed clearly and logically. You should also take a look at your structure and organization. Rearrange your arguments if necessary to make them clearer.
- Check for grammar and spelling errors:
Use spelling and grammar check tools online to identify and correct any basic errors in your essay.
- Verify factual information:
You must have included information about the work or from within the work in your essay. Recheck and verify that it is correct and verifiable.
- Check your formatting:
Make sure that your essay is properly formatted according to the guidelines provided by your instructor. This includes requirements for font size, margins, spacing, and citation style.
Helpful Tips for Revising a Literary Essay
Here are some tips below that can help you proofread and revise your essay better:
- Read your essay out loud:
Reading your essay out loud makes it easier to identify awkward phrasing, repetitive language, and other issues.
- Take a break:
It can be helpful to step away from your essay for a little while before starting the editing process. This can help you approach your essay with fresh eyes and a clearer perspective.
- Be concise:
Remove any unnecessary words or phrases that do not add to your argument. This can help to make your essay more focused and effective.
- Let someone else proofread and get feedback:
You could ask a friend or a teacher to read your essay and provide feedback. This way, you can get some valuable insights on what you could include or catch mistakes that you might have missed.
Literary Analysis Essay Examples
Reading a few good examples helps to understand literary analysis essays better. So check out these examples below and read them to see what a well-written essay looks like.
How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay
Literary Analysis Essay Example
Sample Literary Analysis Essay
Lord of the Rings Literary Analysis
The Great Gatsby Literary Analysis
Literary Analysis Example for 8th Grade
Literary Analysis Essay Topics
Need a topic for your literary analysis essay? You can pick any aspect of any work of literature you like. Here are some example topics that will help you get inspired:
- The use of symbolism in "The Great Gatsby" by F. Scott Fitzgerald.
- The theme of isolation in "The Catcher in the Rye" by J.D. Salinger.
- The portrayal of social class in "Pride and Prejudice" by Jane Austen.
- The use of magical realism in "One Hundred Years of Solitude" by Gabriel Garcia Marquez.
- The role of women in "The Handmaid's Tale" by Margaret Atwood.
- The use of foreshadowing in "Lord of the Flies" by William Golding.
- The portrayal of race and identity in "Invisible Man" by Ralph Ellison.
- The use of imagery in "The Road" by Cormac McCarthy.
- The theme of forgiveness in "The Kite Runner" by Khaled Hosseini.
- The use of allegory in "Animal Farm" by George Orwell.
To conclude,
Writing a literary analysis essay can be a rewarding experience for any student or writer, But itâs not easy. However, by following the steps you learned in this guide, you can successfully produce a well-written literary analysis essay.
Also, you have got some examples of essays to read and topic ideas to get creative inspiration. With these resources, you have all you need to craft an engaging piece. So donât hesitate to start writing your essay and come back to this blog whenever you need.
The deadline is approaching, but you donât have time to write your essay? No worries! Our analytical essay writing service is here to help you out!
At CollegeEssay.org, we have a team of professional and experienced literature writers who can help you craft a compelling literary essay. Our affordable and reliable essay writing website focuses on providing high-quality essays and deliver them timely.
Try our AI essay writing tools today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 4 components of literary analysis.
The four main components of literary analysis are:
- Conflict
- Characters
- Setting
What is the fundamental characteristic of a literary analysis essay?
Interpretive is the fundamental characteristic of a literary analysis essay.
Cathy A. (Literature, Marketing)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, 5 steps to write a great analytical essay.
General Education

Do you need to write an analytical essay for school? What sets this kind of essay apart from other types, and what must you include when you write your own analytical essay? In this guide, we break down the process of writing an analytical essay by explaining the key factors your essay needs to have, providing you with an outline to help you structure your essay, and analyzing a complete analytical essay example so you can see what a finished essay looks like.
What Is an Analytical Essay?
Before you begin writing an analytical essay, you must know what this type of essay is and what it includes. Analytical essays analyze something, often (but not always) a piece of writing or a film.
An analytical essay is more than just a synopsis of the issue though; in this type of essay you need to go beyond surface-level analysis and look at what the key arguments/points of this issue are and why. If you’re writing an analytical essay about a piece of writing, you’ll look into how the text was written and why the author chose to write it that way. Instead of summarizing, an analytical essay typically takes a narrower focus and looks at areas such as major themes in the work, how the author constructed and supported their argument, how the essay used literary devices to enhance its messages, etc.
While you certainly want people to agree with what you’ve written, unlike with persuasive and argumentative essays, your main purpose when writing an analytical essay isn’t to try to convert readers to your side of the issue. Therefore, you won’t be using strong persuasive language like you would in those essay types. Rather, your goal is to have enough analysis and examples that the strength of your argument is clear to readers.
Besides typical essay components like an introduction and conclusion, a good analytical essay will include:
- A thesis that states your main argument
- Analysis that relates back to your thesis and supports it
- Examples to support your analysis and allow a more in-depth look at the issue
In the rest of this article, we’ll explain how to include each of these in your analytical essay.
How to Structure Your Analytical Essay
Analytical essays are structured similarly to many other essays you’ve written, with an introduction (including a thesis), several body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Below is an outline you can follow when structuring your essay, and in the next section we go into more detail on how to write an analytical essay.
Introduction
Your introduction will begin with some sort of attention-grabbing sentence to get your audience interested, then you’ll give a few sentences setting up the topic so that readers have some context, and you’ll end with your thesis statement. Your introduction will include:
- Brief background information explaining the issue/text
- Your thesis
Body Paragraphs
Your analytical essay will typically have three or four body paragraphs, each covering a different point of analysis. Begin each body paragraph with a sentence that sets up the main point you’ll be discussing. Then you’ll give some analysis on that point, backing it up with evidence to support your claim. Continue analyzing and giving evidence for your analysis until you’re out of strong points for the topic. At the end of each body paragraph, you may choose to have a transition sentence that sets up what the next paragraph will be about, but this isn’t required. Body paragraphs will include:
- Introductory sentence explaining what you’ll cover in the paragraph (sort of like a mini-thesis)
- Analysis point
- Evidence (either passages from the text or data/facts) that supports the analysis
- (Repeat analysis and evidence until you run out of examples)
You won’t be making any new points in your conclusion; at this point you’re just reiterating key points you’ve already made and wrapping things up. Begin by rephrasing your thesis and summarizing the main points you made in the essay. Someone who reads just your conclusion should be able to come away with a basic idea of what your essay was about and how it was structured. After this, you may choose to make some final concluding thoughts, potentially by connecting your essay topic to larger issues to show why it’s important. A conclusion will include:
- Paraphrase of thesis
- Summary of key points of analysis
- Final concluding thought(s)

5 Steps for Writing an Analytical Essay
Follow these five tips to break down writing an analytical essay into manageable steps. By the end, you’ll have a fully-crafted analytical essay with both in-depth analysis and enough evidence to support your argument. All of these steps use the completed analytical essay in the next section as an example.
#1: Pick a Topic
You may have already had a topic assigned to you, and if that’s the case, you can skip this step. However, if you haven’t, or if the topic you’ve been assigned is broad enough that you still need to narrow it down, then you’ll need to decide on a topic for yourself. Choosing the right topic can mean the difference between an analytical essay that’s easy to research (and gets you a good grade) and one that takes hours just to find a few decent points to analyze
Before you decide on an analytical essay topic, do a bit of research to make sure you have enough examples to support your analysis. If you choose a topic that’s too narrow, you’ll struggle to find enough to write about.
For example, say your teacher assigns you to write an analytical essay about the theme in John Steinbeck’s The Grapes of Wrath of exposing injustices against migrants. For it to be an analytical essay, you can’t just recount the injustices characters in the book faced; that’s only a summary and doesn’t include analysis. You need to choose a topic that allows you to analyze the theme. One of the best ways to explore a theme is to analyze how the author made his/her argument. One example here is that Steinbeck used literary devices in the intercalary chapters (short chapters that didn’t relate to the plot or contain the main characters of the book) to show what life was like for migrants as a whole during the Dust Bowl.
You could write about how Steinbeck used literary devices throughout the whole book, but, in the essay below, I chose to just focus on the intercalary chapters since they gave me enough examples. Having a narrower focus will nearly always result in a tighter and more convincing essay (and can make compiling examples less overwhelming).
#2: Write a Thesis Statement
Your thesis statement is the most important sentence of your essay; a reader should be able to read just your thesis and understand what the entire essay is about and what you’ll be analyzing. When you begin writing, remember that each sentence in your analytical essay should relate back to your thesis
In the analytical essay example below, the thesis is the final sentence of the first paragraph (the traditional spot for it). The thesis is: “In The Grapes of Wrath’s intercalary chapters, John Steinbeck employs a variety of literary devices and stylistic choices to better expose the injustices committed against migrants in the 1930s.” So what will this essay analyze? How Steinbeck used literary devices in the intercalary chapters to show how rough migrants could have it. Crystal clear.
#3: Do Research to Find Your Main Points
This is where you determine the bulk of your analysis--the information that makes your essay an analytical essay. My preferred method is to list every idea that I can think of, then research each of those and use the three or four strongest ones for your essay. Weaker points may be those that don’t relate back to the thesis, that you don’t have much analysis to discuss, or that you can’t find good examples for. A good rule of thumb is to have one body paragraph per main point
This essay has four main points, each of which analyzes a different literary device Steinbeck uses to better illustrate how difficult life was for migrants during the Dust Bowl. The four literary devices and their impact on the book are:
- Lack of individual names in intercalary chapters to illustrate the scope of the problem
- Parallels to the Bible to induce sympathy for the migrants
- Non-showy, often grammatically-incorrect language so the migrants are more realistic and relatable to readers
- Nature-related metaphors to affect the mood of the writing and reflect the plight of the migrants
#4: Find Excerpts or Evidence to Support Your Analysis
Now that you have your main points, you need to back them up. If you’re writing a paper about a text or film, use passages/clips from it as your main source of evidence. If you’re writing about something else, your evidence can come from a variety of sources, such as surveys, experiments, quotes from knowledgeable sources etc. Any evidence that would work for a regular research paper works here.
In this example, I quoted multiple passages from The Grapes of Wrath in each paragraph to support my argument. You should be able to back up every claim you make with evidence in order to have a strong essay.
#5: Put It All Together
Now it's time to begin writing your essay, if you haven’t already. Create an introductory paragraph that ends with the thesis, make a body paragraph for each of your main points, including both analysis and evidence to back up your claims, and wrap it all up with a conclusion that recaps your thesis and main points and potentially explains the big picture importance of the topic.

Analytical Essay Example + Analysis
So that you can see for yourself what a completed analytical essay looks like, here’s an essay I wrote back in my high school days. It’s followed by analysis of how I structured my essay, what its strengths are, and how it could be improved.
One way Steinbeck illustrates the connections all migrant people possessed and the struggles they faced is by refraining from using specific titles and names in his intercalary chapters. While The Grapes of Wrath focuses on the Joad family, the intercalary chapters show that all migrants share the same struggles and triumphs as the Joads. No individual names are used in these chapters; instead the people are referred to as part of a group. Steinbeck writes, “Frantic men pounded on the doors of the doctors; and the doctors were busy. And sad men left word at country stores for the coroner to send a car,” (555). By using generic terms, Steinbeck shows how the migrants are all linked because they have gone through the same experiences. The grievances committed against one family were committed against thousands of other families; the abuse extends far beyond what the Joads experienced. The Grapes of Wrath frequently refers to the importance of coming together; how, when people connect with others their power and influence multiplies immensely. Throughout the novel, the goal of the migrants, the key to their triumph, has been to unite. While their plans are repeatedly frustrated by the government and police, Steinbeck’s intercalary chapters provide a way for the migrants to relate to one another because they have encountered the same experiences. Hundreds of thousands of migrants fled to the promised land of California, but Steinbeck was aware that numbers alone were impersonal and lacked the passion he desired to spread. Steinbeck created the intercalary chapters to show the massive numbers of people suffering, and he created the Joad family to evoke compassion from readers. Because readers come to sympathize with the Joads, they become more sensitive to the struggles of migrants in general. However, John Steinbeck frequently made clear that the Joads were not an isolated incident; they were not unique. Their struggles and triumphs were part of something greater. Refraining from specific names in his intercalary chapters allows Steinbeck to show the vastness of the atrocities committed against migrants.
Steinbeck also creates significant parallels to the Bible in his intercalary chapters in order to enhance his writing and characters. By using simple sentences and stylized writing, Steinbeck evokes Biblical passages. The migrants despair, “No work till spring. No work,” (556). Short, direct sentences help to better convey the desperateness of the migrants’ situation. Throughout his novel, John Steinbeck makes connections to the Bible through his characters and storyline. Jim Casy’s allusions to Christ and the cycle of drought and flooding are clear biblical references. By choosing to relate The Grapes of Wrath to the Bible, Steinbeck’s characters become greater than themselves. Starving migrants become more than destitute vagrants; they are now the chosen people escaping to the promised land. When a forgotten man dies alone and unnoticed, it becomes a tragedy. Steinbeck writes, “If [the migrants] were shot at, they did not run, but splashed sullenly away; and if they were hit, they sank tiredly in the mud,” (556). Injustices committed against the migrants become greater because they are seen as children of God through Steinbeck’s choice of language. Referencing the Bible strengthens Steinbeck’s novel and purpose: to create understanding for the dispossessed. It is easy for people to feel disdain for shabby vagabonds, but connecting them to such a fundamental aspect of Christianity induces sympathy from readers who might have otherwise disregarded the migrants as so many other people did.
The simple, uneducated dialogue Steinbeck employs also helps to create a more honest and meaningful representation of the migrants, and it makes the migrants more relatable to readers. Steinbeck chooses to accurately represent the language of the migrants in order to more clearly illustrate their lives and make them seem more like real paper than just characters in a book. The migrants lament, “They ain’t gonna be no kinda work for three months,” (555). There are multiple grammatical errors in that single sentence, but it vividly conveys the despair the migrants felt better than a technically perfect sentence would. The Grapes of Wrath is intended to show the severe difficulties facing the migrants so Steinbeck employs a clear, pragmatic style of writing. Steinbeck shows the harsh, truthful realities of the migrants’ lives and he would be hypocritical if he chose to give the migrants a more refined voice and not portray them with all their shortcomings. The depiction of the migrants as imperfect through their language also makes them easier to relate to. Steinbeck’s primary audience was the middle class, the less affluent of society. Repeatedly in The Grapes of Wrath , the wealthy make it obvious that they scorn the plight of the migrants. The wealthy, not bad luck or natural disasters, were the prominent cause of the suffering of migrant families such as the Joads. Thus, Steinbeck turns to the less prosperous for support in his novel. When referring to the superior living conditions barnyard animals have, the migrants remark, “Them’s horses-we’re men,” (556). The perfect simplicity of this quote expresses the absurdness of the migrants’ situation better than any flowery expression could.
In The Grapes of Wrath , John Steinbeck uses metaphors, particularly about nature, in order to illustrate the mood and the overall plight of migrants. Throughout most of the book, the land is described as dusty, barren, and dead. Towards the end, however; floods come and the landscape begins to change. At the end of chapter twenty-nine, Steinbeck describes a hill after the floods saying, “Tiny points of grass came through the earth, and in a few days the hills were pale green with the beginning year,” (556). This description offers a stark contrast from the earlier passages which were filled with despair and destruction. Steinbeck’s tone from the beginning of the chapter changes drastically. Early in the chapter, Steinbeck had used heavy imagery in order to convey the destruction caused by the rain, “The streams and the little rivers edged up to the bank sides and worked at willows and tree roots, bent the willows deep in the current, cut out the roots of cottonwoods and brought down the trees,” (553). However, at the end of the chapter the rain has caused new life to grow in California. The new grass becomes a metaphor representing hope. When the migrants are at a loss over how they will survive the winter, the grass offers reassurance. The story of the migrants in the intercalary chapters parallels that of the Joads. At the end of the novel, the family is breaking apart and has been forced to flee their home. However, both the book and final intercalary chapter end on a hopeful note after so much suffering has occurred. The grass metaphor strengthens Steinbeck’s message because it offers a tangible example of hope. Through his language Steinbeck’s themes become apparent at the end of the novel. Steinbeck affirms that persistence, even when problems appear insurmountable, leads to success. These metaphors help to strengthen Steinbeck’s themes in The Grapes of Wrath because they provide a more memorable way to recall important messages.
John Steinbeck’s language choices help to intensify his writing in his intercalary chapters and allow him to more clearly show how difficult life for migrants could be. Refraining from using specific names and terms allows Steinbeck to show that many thousands of migrants suffered through the same wrongs. Imitating the style of the Bible strengthens Steinbeck’s characters and connects them to the Bible, perhaps the most famous book in history. When Steinbeck writes in the imperfect dialogue of the migrants, he creates a more accurate portrayal and makes the migrants easier to relate to for a less affluent audience. Metaphors, particularly relating to nature, strengthen the themes in The Grapes of Wrath by enhancing the mood Steinbeck wants readers to feel at different points in the book. Overall, the intercalary chapters that Steinbeck includes improve his novel by making it more memorable and reinforcing the themes Steinbeck embraces throughout the novel. Exemplary stylistic devices further persuade readers of John Steinbeck’s personal beliefs. Steinbeck wrote The Grapes of Wrath to bring to light cruelties against migrants, and by using literary devices effectively, he continuously reminds readers of his purpose. Steinbeck’s impressive language choices in his intercalary chapters advance the entire novel and help to create a classic work of literature that people still are able to relate to today.
This essay sticks pretty closely to the standard analytical essay outline. It starts with an introduction, where I chose to use a quote to start off the essay. (This became my favorite way to start essays in high school because, if I wasn’t sure what to say, I could outsource the work and find a quote that related to what I’d be writing about.) The quote in this essay doesn’t relate to the themes I’m discussing quite as much as it could, but it’s still a slightly different way to start an essay and can intrigue readers. I then give a bit of background on The Grapes of Wrath and its themes before ending the intro paragraph with my thesis: that Steinbeck used literary devices in intercalary chapters to show how rough migrants had it.
Each of my four body paragraphs is formatted in roughly the same way: an intro sentence that explains what I’ll be discussing, analysis of that main point, and at least two quotes from the book as evidence.
My conclusion restates my thesis, summarizes each of four points I discussed in my body paragraphs, and ends the essay by briefly discussing how Steinbeck’s writing helped introduce a world of readers to the injustices migrants experienced during the dust bowl.
What does this analytical essay example do well? For starters, it contains everything that a strong analytical essay should, and it makes that easy to find. The thesis clearly lays out what the essay will be about, the first sentence of each of the body paragraph introduces the topic it’ll cover, and the conclusion neatly recaps all the main points. Within each of the body paragraphs, there’s analysis along with multiple excerpts from the book in order to add legitimacy to my points.
Additionally, the essay does a good job of taking an in-depth look at the issue introduced in the thesis. Four ways Steinbeck used literary devices are discussed, and for each of the examples are given and analysis is provided so readers can understand why Steinbeck included those devices and how they helped shaped how readers viewed migrants and their plight.
Where could this essay be improved? I believe the weakest body paragraph is the third one, the one that discusses how Steinbeck used plain, grammatically incorrect language to both accurately depict the migrants and make them more relatable to readers. The paragraph tries to touch on both of those reasons and ends up being somewhat unfocused as a result. It would have been better for it to focus on just one of those reasons (likely how it made the migrants more relatable) in order to be clearer and more effective. It’s a good example of how adding more ideas to an essay often doesn’t make it better if they don’t work with the rest of what you’re writing. This essay also could explain the excerpts that are included more and how they relate to the points being made. Sometimes they’re just dropped in the essay with the expectation that the readers will make the connection between the example and the analysis. This is perhaps especially true in the second body paragraph, the one that discusses similarities to Biblical passages. Additional analysis of the quotes would have strengthened it.

Summary: How to Write an Analytical Essay
What is an analytical essay? A critical analytical essay analyzes a topic, often a text or film. The analysis paper uses evidence to support the argument, such as excerpts from the piece of writing. All analytical papers include a thesis, analysis of the topic, and evidence to support that analysis.
When developing an analytical essay outline and writing your essay, follow these five steps:
Reading analytical essay examples can also give you a better sense of how to structure your essay and what to include in it.
What's Next?
Learning about different writing styles in school? There are four main writing styles, and it's important to understand each of them. Learn about them in our guide to writing styles , complete with examples.
Writing a research paper for school but not sure what to write about? Our guide to research paper topics has over 100 topics in ten categories so you can be sure to find the perfect topic for you.
Literary devices can both be used to enhance your writing and communication. Check out this list of 31 literary devices to learn more !

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
- How it works
Thematic Analysis – A Guide with Examples
Published by Alvin Nicolas at August 16th, 2021 , Revised On August 29, 2023
Thematic analysis is one of the most important types of analysis used for qualitative data . When researchers have to analyse audio or video transcripts, they give preference to thematic analysis. A researcher needs to look keenly at the content to identify the context and the message conveyed by the speaker.
Moreover, with the help of this analysis, data can be simplified.
Importance of Thematic Analysis
Thematic analysis has so many unique and dynamic features, some of which are given below:
Thematic analysis is used because:
- It is flexible.
- It is best for complex data sets.
- It is applied to qualitative data sets.
- It takes less complexity compared to other theories of analysis.
Intellectuals and researchers give preference to thematic analysis due to its effectiveness in the research.
How to Conduct a Thematic Analysis?
While doing any research , if your data and procedure are clear, it will be easier for your reader to understand how you concluded the results . This will add much clarity to your research.
Understand the Data
This is the first step of your thematic analysis. At this stage, you have to understand the data set. You need to read the entire data instead of reading the small portion. If you do not have the data in the textual form, you have to transcribe it.
Example: If you are visiting an adult dating website, you have to make a data corpus. You should read and re-read the data and consider several profiles. It will give you an idea of how adults represent themselves on dating sites. You may get the following results:
I am a tall, single(widowed), easy-going, honest, good listener with a good sense of humor. Being a handyperson, I keep busy working around the house, and I also like to follow my favourite hockey team on TV or spoil my two granddaughters when I get the chance!! Enjoy most music except Rap! I keep fit by jogging, walking, and bicycling (at least three times a week). I have travelled to many places and RVD the South-West U.S., but I would now like to find that special travel partner to do more travel to warm and interesting countries. I now feel it’s time to meet a nice, kind, honest woman who has some of the same interests as I do; to share the happy times, quiet times, and adventures together
I enjoy photography, lapidary & seeking collectibles in the form of classic movies & 33 1/3, 45 & 78 RPM recordings from the 1920s, ’30s & ’40s. I am retired & looking forward to travelling to Canada, the USA, the UK & Europe, China. I am unique since I do not judge a book by its cover. I accept people for who they are. I will not demand or request perfection from anyone until I am perfect, so I guess that means everyone is safe. My musical tastes range from Classical, big band era, early jazz, classic ’50s & 60’s rock & roll & country since its inception.
Development of Initial Coding:
At this stage, you have to do coding. It’s the essential step of your research . Here you have two options for coding. Either you can do the coding manually or take the help of any tool. A software named the NOVIC is considered the best tool for doing automatic coding.
For manual coding, you can follow the steps given below:
- Please write down the data in a proper format so that it can be easier to proceed.
- Use a highlighter to highlight all the essential points from data.
- Make as many points as possible.
- Take notes very carefully at this stage.
- Apply themes as much possible.
- Now check out the themes of the same pattern or concept.
- Turn all the same themes into the single one.
Example: For better understanding, the previously explained example of Step 1 is continued here. You can observe the coded profiles below:
Make Themes
At this stage, you have to make the themes. These themes should be categorised based on the codes. All the codes which have previously been generated should be turned into themes. Moreover, with the help of the codes, some themes and sub-themes can also be created. This process is usually done with the help of visuals so that a reader can take an in-depth look at first glance itself.
Extracted Data Review
Now you have to take an in-depth look at all the awarded themes again. You have to check whether all the given themes are organised properly or not. It would help if you were careful and focused because you have to note down the symmetry here. If you find that all the themes are not coherent, you can revise them. You can also reshape the data so that there will be symmetry between the themes and dataset here.
For better understanding, a mind-mapping example is given here:
Reviewing all the Themes Again
You need to review the themes after coding them. At this stage, you are allowed to play with your themes in a more detailed manner. You have to convert the bigger themes into smaller themes here. If you want to combine some similar themes into a single theme, then you can do it. This step involves two steps for better fragmentation.
You need to observe the coded data separately so that you can have a precise view. If you find that the themes which are given are following the dataset, it’s okay. Otherwise, you may have to rearrange the data again to coherence in the coded data.
Corpus Data
Here you have to take into consideration all the corpus data again. It would help if you found how themes are arranged here. It would help if you used the visuals to check out the relationship between them. Suppose all the things are not done accordingly, so you should check out the previous steps for a refined process. Otherwise, you can move to the next step. However, make sure that all the themes are satisfactory and you are not confused.
When all the two steps are completed, you need to make a more précised mind map. An example following the previous cases has been given below:
Define all the Themes here
Now you have to define all the themes which you have given to your data set. You can recheck them carefully if you feel that some of them can fit into one concept, you can keep them, and eliminate the other irrelevant themes. Because it should be precise and clear, there should not be any ambiguity. Now you have to think about the main idea and check out that all the given themes are parallel to your main idea or not. This can change the concept for you.
The given names should be so that it can give any reader a clear idea about your findings. However, it should not oppose your thematic analysis; rather, everything should be organised accurately.
Does your Research Methodology Have the Following?
- Great Research/Sources
- Perfect Language
- Accurate Sources
If not, we can help. Our panel of experts makes sure to keep the 3 pillars of Research Methodology strong.

Also, read about discourse analysis , content analysis and survey conducting . we have provided comprehensive guides.
Make a Report
You need to make the final report of all the findings you have done at this stage. You should include the dataset, findings, and every aspect of your analysis in it.
While making the final report , do not forget to consider your audience. For instance, you are writing for the Newsletter, Journal, Public awareness, etc., your report should be according to your audience. It should be concise and have some logic; it should not be repetitive. You can use the references of other relevant sources as evidence to support your discussion.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is meant by thematic analysis.
Thematic Analysis is a qualitative research method that involves identifying, analyzing, and interpreting recurring themes or patterns in data. It aims to uncover underlying meanings, ideas, and concepts within the dataset, providing insights into participants’ perspectives and experiences.
You May Also Like
Action research for my dissertation?, A brief overview of action research as a responsive, action-oriented, participative and reflective research technique.
Content analysis is used to identify specific words, patterns, concepts, themes, phrases, or sentences within the content in the recorded communication.
Ethnography is a type of research where a researcher observes the people in their natural environment. Here is all you need to know about ethnography.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Table of contents. Step 1: Reading the text and identifying literary devices. Step 2: Coming up with a thesis. Step 3: Writing a title and introduction. Step 4: Writing the body of the essay. Step 5: Writing a conclusion. Other interesting articles.
Page ID. Heather Ringo & Athena Kashyap. City College of San Francisco via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative. Table of contents. Example 1: Poetry. Example 2: Fiction. Example 3: Poetry. Attribution. The following examples are essays where student writers focused on close-reading a literary work.
When undertaking thematic analysis, you'll make use of codes. A code is a label assigned to a piece of text, and the aim of using a code is to identify and summarise important concepts within a set of data, such as an interview transcript. For example, if you had the sentence, "My rabbit ate my shoes", you could use the codes "rabbit ...
Download Article. 1. Read the essay prompt carefully. A theme essay usually responds to a specific prompt given to you by a teacher or professor. Most essay prompts will ask you to identify the theme, or the overarching message, in a text. Look at the terms used in the prompt and highlight keywords or important terms.
Literary analysis involves examining all the parts of a novel, play, short story, or poem—elements such as character, setting, tone, and imagery—and thinking about how the author uses those elements to create certain effects. A literary essay isn't a book review: you're not being asked whether or not you liked a book or whether you'd ...
Step 6. Proofread Your Thematic Analysis Essay. After completing theme essay, it is highly recommended to review it thoroughly, even several times if possible. The goal is to find mistakes and to spot logical gaps or missing details. Even best essays typically have inconsistencies left at the early stage.
2. Pick the most prevalent subject: One thing to note is the significant difference between a subject and a theme. A subject is the general topic of conversation—whether it be love, bravery, deception, etc. A theme is a specific point the author is making about said subject. So, find the talking point that is most commonly being brought up.
A literary analysis essay is an important kind of essay that focuses on the detailed analysis of the work of literature. The purpose of a literary analysis essay is to explain why the author has used a specific theme for his work. Or examine the characters, themes, literary devices, figurative language, and settings in the story.
Thematic writing is a staple of high school English and college writing courses. The idea behind thematic writing is to create a piece that uses a theme to tie together different ideas or topics. Thematic writing can be used for essays, short stories, novels, and even non-fiction pieces. In academic writing, thematic essays often center on a ...
A literary theme analysis will synthesize several elements within a work and prove an overall message with those elements. Beginning the analysis (using Harry Potter as an example) Theme can be discovered only by becoming aware of the relations among the parts of a story and of the relations of the parts to a whole:
There are various approaches to conducting thematic analysis, but the most common form follows a six-step process: Familiarisation. Coding. Generating themes. Reviewing themes. Defining and naming themes. Writing up. This process was originally developed for psychology research by Virginia Braun and Victoria Clarke.
The term regularly used for the development of the central idea of a literary analysis essay is the body. In this section you present the paragraphs (at least 3 paragraphs for a 500-750 word essay) that support your thesis statement. Good literary analysis essays contain an explanation of your ideas and evidence from the text (short story,
Here are the steps to follow when writing a body paragraph for a literary analysis essay: Start with a topic sentence: The topic sentence should introduce the main point or argument you will be making in the paragraph. It should be clear and concise and should indicate what the paragraph is about. Provide evidence:
Get a sense of what to do right with this literary analysis essay example that will offer inspiration for your own assignment. ... examining the themes, literary devices, characters, and more. To write a great literary analysis essay, you need a good thesis and a good grasp of the novel, story, poem, or other literary work you're discussing ...
Literary Analysis: Sample Essay. We turn once more to Joanna Wolfe's and Laura Wilder's Digging into Literature: Strategies for Reading, Writing, and Analysis (Boston: Bedford/St. Martin's, 2016) in order to show you their example of a strong student essay that has a strong central claim elucidated by multiple surface/depth arguments ...
Below are nine organizational and writing tips to help you craft the best possible critical analysis essay. 1. Read Thoroughly and Carefully. You will need to accurately represent an author's point of view and techniques. Be sure you truly understand them before you begin the writing process. 2.
The analysis paper uses evidence to support the argument, such as excerpts from the piece of writing. All analytical papers include a thesis, analysis of the topic, and evidence to support that analysis. When developing an analytical essay outline and writing your essay, follow these five steps: #1: Choose a topic. #2: Write your thesis.
Thematic Analysis - A Guide with Examples. Thematic analysis is one of the most important types of analysis used for qualitative data. When researchers have to analyse audio or video transcripts, they give preference to thematic analysis. A researcher needs to look keenly at the content to identify the context and the message conveyed by the ...
SAMPLE THESIS STATEMENTS These sample thesis statements are provided as guides, not as required forms or prescriptions. #1 The thesis may focus on an analysis of one of the elements of fiction, drama, poetry or nonfiction as expressed in the work: character, plot, structure, idea, theme, symbol, style, imagery, tone, etc. Example:
In a well-organized essay, describe this theme. Use textual examples from the story to support your ideas and explain how they support the theme. As you write, remember your essay will be scored based on how well you: ... • Teach the elements of a Literary Analysis Essay as outlined on page 11. • Complete the T-Q-A for the novel. Make sure ...