/images/cornell/logo35pt_cornell_white.svg" alt="thesis about graduate degree"> Cornell University --> Graduate School
Guide to writing your thesis/dissertation, definition of dissertation and thesis.
The dissertation or thesis is a scholarly treatise that substantiates a specific point of view as a result of original research that is conducted by students during their graduate study. At Cornell, the thesis is a requirement for the receipt of the M.A. and M.S. degrees and some professional master’s degrees. The dissertation is a requirement of the Ph.D. degree.

Formatting Requirement and Standards
The Graduate School sets the minimum format for your thesis or dissertation, while you, your special committee, and your advisor/chair decide upon the content and length. Grammar, punctuation, spelling, and other mechanical issues are your sole responsibility. Generally, the thesis and dissertation should conform to the standards of leading academic journals in your field. The Graduate School does not monitor the thesis or dissertation for mechanics, content, or style.
“Papers Option” Dissertation or Thesis
A “papers option” is available only to students in certain fields, which are listed on the Fields Permitting the Use of Papers Option page , or by approved petition. If you choose the papers option, your dissertation or thesis is organized as a series of relatively independent chapters or papers that you have submitted or will be submitting to journals in the field. You must be the only author or the first author of the papers to be used in the dissertation. The papers-option dissertation or thesis must meet all format and submission requirements, and a singular referencing convention must be used throughout.
ProQuest Electronic Submissions
The dissertation and thesis become permanent records of your original research, and in the case of doctoral research, the Graduate School requires publication of the dissertation and abstract in its original form. All Cornell master’s theses and doctoral dissertations require an electronic submission through ProQuest, which fills orders for paper or digital copies of the thesis and dissertation and makes a digital version available online via their subscription database, ProQuest Dissertations & Theses . For master’s theses, only the abstract is available. ProQuest provides worldwide distribution of your work from the master copy. You retain control over your dissertation and are free to grant publishing rights as you see fit. The formatting requirements contained in this guide meet all ProQuest specifications.
Copies of Dissertation and Thesis
Copies of Ph.D. dissertations and master’s theses are also uploaded in PDF format to the Cornell Library Repository, eCommons . A print copy of each master’s thesis and doctoral dissertation is submitted to Cornell University Library by ProQuest.
How to Write a Thesis: A Guide for Master’s Students
By Dr. David James Kritz | 09/29/2023

Let’s face it. Researching and writing a quality thesis can be daunting for many reasons, including:
- A lack of knowledge on where to begin the assignment process
- What key arguments and questions to ask in relation to the thesis statement
- How to get to the data and subject matter
- How to cope with writer's block, a professor's expectations, and time constraints
According to Dictionary.com , a thesis is “a proposition stated or put forward for consideration, especially one to be discussed and proved or to be maintained against objections.”
Therefore, avoiding a weak thesis statement is vital when writing an applicable paper. Thesis statement examples are pivotal in understanding this position.
Currently, master’s students who select the thesis capstone within American Public University's School of Security and Global Studies intelligence master's degree program must choose a relevant subject.
Typically, these students must write a thesis statement that consists of at least one compelling sentence and at least 50 pages of content, then turn it in within 16 weeks.
I have taught graduate students, primarily from the U.S. Intelligence Community, how to conduct research for over eight years.
Based on my experience as an educator, I have 10 tips for creating good thesis statements. These tips, combined with some apt thesis statement examples, can elucidate the process.
Tip #1 for Effective Thesis Statements: Select an Appropriate Topic and Research Question
First, it is necessary to use a lengthy thinking process before developing a good thesis statement, whether it’s an expository thesis statement or an argumentative one. This process begins with many questions related to how to write a thesis statement, such as:
- What would be an interesting topic?
- What would be an original and interesting research question?
- What will be the main claim, key arguments, and central idea of the thesis statement?
- What is an appropriate research design?
- How will I get to the data to address my central research question?
Regardless of the thesis statement or topic, all research begins with a research question.
Without the right question, the analysis, literature review, and implications might miss their mark. This question should be unique, intriguing, and beyond a mere “yes” or “no” answer.
For instance, rather than asking, “Will Country X pursue nuclear proliferation?”, it's better to pose open-ended questions like, “How does…?” or “To what extent…?” Such an approach ensures nuanced and substantive answers.
Additionally, supplementary key questions should support the main research question's depth and intent.
Tip #2: Begin Work on the Thesis Statement and Break Up the Thesis into Manageable Sections
After selecting an appropriate topic and developing a central research question for the thesis statement, it is then necessary to apply the research and writing skills you have learned throughout your degree program.
It might be necessary to refine the thesis statement after some preliminary research; after all, you want a strong thesis statement rather than a weak thesis statement.
It is also essential to break up the thesis paper into manageable sections during the writing process. This strategy will help you to overcome the most common types of mental hurdle of creating a thesis paper that can be 50 or more pages in length.
For writing a thesis statement, this way of thinking is helpful before you begin writing. Instead of attempting to write every single sentence of a thesis statement in one long stretch, you can work on one section at a time, turn it in for review and work on the next section of the thesis statement while awaiting feedback.
Tip #3: Pay Attention to Your Professor's Feedback about Your Assignment
When I give my essay assignment to my students with advice on how to write a thesis, I also explain the importance of a strong thesis statement.
I advise them to avoid becoming emotionally attached to the thesis. That emotional attachment can lead to a battle of wills and wits with the capstone course's professor over the thesis statement examples they present.
When it comes to implementing feedback, revisions to the thesis paper often need to occur. Faculty members are there to help guide you and assist you in the production of a good-quality, argumentative thesis statement that will provide new insights for the reader.
Just go with the feedback you receive from your instructor as you write a sentence, or more, and move on to complete your thesis paper more efficiently.
Tip #4: Complete an Abstract
The abstract of a thesis is vital, so it must be carefully crafted. The abstract may be the only section of a published, scholarly paper or article that someone may take the time to read, based on their time constraints and interest.
Ideally, the abstract should be 250 words or less and must contain the main point of the paper. I advise students drafting an abstract for scholarly journal editors to ensure that the abstract has these elements:
An introductory sentence
A “hook” (why the reader should care about the thesis statement or its topic and to motivate the reader to look at your paper)
The central research question to show the main point of your paper
The research design – how you collected evidence to support your arguments
The results and implications, such as the negative and positive aspects of your main topic and the broader context of your research
Tip #5: Write the Literature Review
When crafting a literature review, incorporate multiple peer-reviewed articles from academic sources like ProQuest and EBSCOHost. Opt for articles frequently cited in other works to enhance your paper's credibility.
The review examines arguments in thesis statements and their counterarguments from scholarly works. For clear discussions, organize your review thematically, showing topic synthesis and your position. This reduces confusion.
For example, if 40 articles discuss open-source intelligence and seven focus on social media, that could be a central theme.
Rather than just listing articles, create broader themes and keep synthesizing. When crafting the thesis, evaluate each paragraph's relevance to the main research question. I advise students to assess the “So what?” factor. If a paragraph isn't pertinent, it might be best to remove it.
Tip #6: Develop a Theoretical Framework within Your Thesis Statement
Theories in theses are often mishandled, reflecting a student’s unclear grasp. Academic theory goes beyond mere "I have a theory" statements and leans on robust, time-tested frameworks.
For instance, a strategic intelligence studies thesis statement might employ national security theory or national defense theory. This theory should align with the thesis's central question.
For example, if probing how Country X uses social media for misinformation, a student might be directed to the communication theory, which aligns well with the study's main topic and question.
Tip #7: Select a Research Design
Before conducting research, students must devise a strategy to address their central question. The research design is their roadmap for data collection. This encompasses methodology, methods, and data gathering instruments like surveys or interviews. Research on humans requires IRB approval, which I advise against due to time constraints in a 16-week paper cycle. Additionally, it's vital to distinguish between “methodology” and “methods,” terms often mistakenly used interchangeably.
Methodology involves the justification of the how and why a research method was selected to address the central research question , according to Indeed. The three primary methodologies include:
- Qualitative methodology
- Quantitative methodology
- Mixed methods
“Mixed methods” involves a researcher’s use of at least one research method from a qualitative methodology and another research method from a quantitative methodology, then explaining how those methods will be integrated into a study.
But if two methods from the same methodology are used in a study, that is referred to as a multi-method approach. An example of a multi-method approach would be using a comparative case study as the first qualitative research method and process tracing as the second research method.
Research methods are linked to either qualitative or quantitative methodologies. They focus on “what” a researcher selected to interpret data.
Research method types include:
- Archival records
- Alternative futures
- Case studies
- Comparative case studies
- Content analysis
- Correlational research
- Descriptive research
- Ethnography
- Experimental research
- Phenomenology
- Process tracing
Tip #8: Write about Research Findings and Data
After gathering data for a thesis, analyzing its significance is crucial, with methods including coding. While qualitative methodology doesn't aim to prove anything, unlike the quantitative approach which tests hypotheses, it can discuss correlations, causation, and delve into theoretical implications in data.
Some may view qualitative research as subjective, but selecting variables in quantitative research has its subjectivity too. Ultimately, it's essential to adhere closely to the scientific method, rather than relying on opinions or claims without concrete evidence.
Tip #9: Consider How Bias Will Affect Your Thesis Statement
When writing thesis statements, it is necessary to consider how bias will affect your writing and your reader. Being 100% objective is an admirable goal, but it is impossible to avoid biases as we are human beings.
All of us have biases, including latent ones. At best, we can mitigate biases, such as using coding software, but never holistically remove bias. As researchers, we just need to be aware of biases and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Tip #10: Be Aware of the Limitations of a Study
The study's limitations section is a pivotal part of a thesis. It highlights the research's shortcomings and indicates what might be done differently.
For instance, a student may mention a 16-week time constraint or contemplate a different research design or question.
This section not only helps students recognize how to enhance their research but also guides future scholars. They can learn from prior omissions or envision alternative research avenues.
- Call: 877-755-2787
- Email: [email protected]
- Chat: Live Chat

How To Write A Dissertation Or Thesis
8 straightforward steps to craft an a-grade dissertation.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) Expert Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020
Writing a dissertation or thesis is not a simple task. It takes time, energy and a lot of will power to get you across the finish line. It’s not easy – but it doesn’t necessarily need to be a painful process. If you understand the big-picture process of how to write a dissertation or thesis, your research journey will be a lot smoother.
In this post, I’m going to outline the big-picture process of how to write a high-quality dissertation or thesis, without losing your mind along the way. If you’re just starting your research, this post is perfect for you. Alternatively, if you’ve already submitted your proposal, this article which covers how to structure a dissertation might be more helpful.
How To Write A Dissertation: 8 Steps
- Clearly understand what a dissertation (or thesis) is
- Find a unique and valuable research topic
- Craft a convincing research proposal
- Write up a strong introduction chapter
- Review the existing literature and compile a literature review
- Design a rigorous research strategy and undertake your own research
- Present the findings of your research
- Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications

Step 1: Understand exactly what a dissertation is
This probably sounds like a no-brainer, but all too often, students come to us for help with their research and the underlying issue is that they don’t fully understand what a dissertation (or thesis) actually is.
So, what is a dissertation?
At its simplest, a dissertation or thesis is a formal piece of research , reflecting the standard research process . But what is the standard research process, you ask? The research process involves 4 key steps:
- Ask a very specific, well-articulated question (s) (your research topic)
- See what other researchers have said about it (if they’ve already answered it)
- If they haven’t answered it adequately, undertake your own data collection and analysis in a scientifically rigorous fashion
- Answer your original question(s), based on your analysis findings

In short, the research process is simply about asking and answering questions in a systematic fashion . This probably sounds pretty obvious, but people often think they’ve done “research”, when in fact what they have done is:
- Started with a vague, poorly articulated question
- Not taken the time to see what research has already been done regarding the question
- Collected data and opinions that support their gut and undertaken a flimsy analysis
- Drawn a shaky conclusion, based on that analysis
If you want to see the perfect example of this in action, look out for the next Facebook post where someone claims they’ve done “research”… All too often, people consider reading a few blog posts to constitute research. Its no surprise then that what they end up with is an opinion piece, not research. Okay, okay – I’ll climb off my soapbox now.
The key takeaway here is that a dissertation (or thesis) is a formal piece of research, reflecting the research process. It’s not an opinion piece , nor a place to push your agenda or try to convince someone of your position. Writing a good dissertation involves asking a question and taking a systematic, rigorous approach to answering it.
If you understand this and are comfortable leaving your opinions or preconceived ideas at the door, you’re already off to a good start!

Step 2: Find a unique, valuable research topic
As we saw, the first step of the research process is to ask a specific, well-articulated question. In other words, you need to find a research topic that asks a specific question or set of questions (these are called research questions ). Sounds easy enough, right? All you’ve got to do is identify a question or two and you’ve got a winning research topic. Well, not quite…
A good dissertation or thesis topic has a few important attributes. Specifically, a solid research topic should be:
Let’s take a closer look at these:
Attribute #1: Clear
Your research topic needs to be crystal clear about what you’re planning to research, what you want to know, and within what context. There shouldn’t be any ambiguity or vagueness about what you’ll research.
Here’s an example of a clearly articulated research topic:
An analysis of consumer-based factors influencing organisational trust in British low-cost online equity brokerage firms.
As you can see in the example, its crystal clear what will be analysed (factors impacting organisational trust), amongst who (consumers) and in what context (British low-cost equity brokerage firms, based online).
Need a helping hand?
Attribute #2: Unique
Your research should be asking a question(s) that hasn’t been asked before, or that hasn’t been asked in a specific context (for example, in a specific country or industry).
For example, sticking organisational trust topic above, it’s quite likely that organisational trust factors in the UK have been investigated before, but the context (online low-cost equity brokerages) could make this research unique. Therefore, the context makes this research original.
One caveat when using context as the basis for originality – you need to have a good reason to suspect that your findings in this context might be different from the existing research – otherwise, there’s no reason to warrant researching it.
Attribute #3: Important
Simply asking a unique or original question is not enough – the question needs to create value. In other words, successfully answering your research questions should provide some value to the field of research or the industry. You can’t research something just to satisfy your curiosity. It needs to make some form of contribution either to research or industry.
For example, researching the factors influencing consumer trust would create value by enabling businesses to tailor their operations and marketing to leverage factors that promote trust. In other words, it would have a clear benefit to industry.
So, how do you go about finding a unique and valuable research topic? We explain that in detail in this video post – How To Find A Research Topic . Yeah, we’ve got you covered 😊
Step 3: Write a convincing research proposal
Once you’ve pinned down a high-quality research topic, the next step is to convince your university to let you research it. No matter how awesome you think your topic is, it still needs to get the rubber stamp before you can move forward with your research. The research proposal is the tool you’ll use for this job.
So, what’s in a research proposal?
The main “job” of a research proposal is to convince your university, advisor or committee that your research topic is worthy of approval. But convince them of what? Well, this varies from university to university, but generally, they want to see that:
- You have a clearly articulated, unique and important topic (this might sound familiar…)
- You’ve done some initial reading of the existing literature relevant to your topic (i.e. a literature review)
- You have a provisional plan in terms of how you will collect data and analyse it (i.e. a methodology)
At the proposal stage, it’s (generally) not expected that you’ve extensively reviewed the existing literature , but you will need to show that you’ve done enough reading to identify a clear gap for original (unique) research. Similarly, they generally don’t expect that you have a rock-solid research methodology mapped out, but you should have an idea of whether you’ll be undertaking qualitative or quantitative analysis , and how you’ll collect your data (we’ll discuss this in more detail later).
Long story short – don’t stress about having every detail of your research meticulously thought out at the proposal stage – this will develop as you progress through your research. However, you do need to show that you’ve “done your homework” and that your research is worthy of approval .
So, how do you go about crafting a high-quality, convincing proposal? We cover that in detail in this video post – How To Write A Top-Class Research Proposal . We’ve also got a video walkthrough of two proposal examples here .
Step 4: Craft a strong introduction chapter
Once your proposal’s been approved, its time to get writing your actual dissertation or thesis! The good news is that if you put the time into crafting a high-quality proposal, you’ve already got a head start on your first three chapters – introduction, literature review and methodology – as you can use your proposal as the basis for these.
Handy sidenote – our free dissertation & thesis template is a great way to speed up your dissertation writing journey.
What’s the introduction chapter all about?
The purpose of the introduction chapter is to set the scene for your research (dare I say, to introduce it…) so that the reader understands what you’ll be researching and why it’s important. In other words, it covers the same ground as the research proposal in that it justifies your research topic.
What goes into the introduction chapter?
This can vary slightly between universities and degrees, but generally, the introduction chapter will include the following:
- A brief background to the study, explaining the overall area of research
- A problem statement , explaining what the problem is with the current state of research (in other words, where the knowledge gap exists)
- Your research questions – in other words, the specific questions your study will seek to answer (based on the knowledge gap)
- The significance of your study – in other words, why it’s important and how its findings will be useful in the world
As you can see, this all about explaining the “what” and the “why” of your research (as opposed to the “how”). So, your introduction chapter is basically the salesman of your study, “selling” your research to the first-time reader and (hopefully) getting them interested to read more.
How do I write the introduction chapter, you ask? We cover that in detail in this post .

Step 5: Undertake an in-depth literature review
As I mentioned earlier, you’ll need to do some initial review of the literature in Steps 2 and 3 to find your research gap and craft a convincing research proposal – but that’s just scratching the surface. Once you reach the literature review stage of your dissertation or thesis, you need to dig a lot deeper into the existing research and write up a comprehensive literature review chapter.
What’s the literature review all about?
There are two main stages in the literature review process:
Literature Review Step 1: Reading up
The first stage is for you to deep dive into the existing literature (journal articles, textbook chapters, industry reports, etc) to gain an in-depth understanding of the current state of research regarding your topic. While you don’t need to read every single article, you do need to ensure that you cover all literature that is related to your core research questions, and create a comprehensive catalogue of that literature , which you’ll use in the next step.
Reading and digesting all the relevant literature is a time consuming and intellectually demanding process. Many students underestimate just how much work goes into this step, so make sure that you allocate a good amount of time for this when planning out your research. Thankfully, there are ways to fast track the process – be sure to check out this article covering how to read journal articles quickly .

Literature Review Step 2: Writing up
Once you’ve worked through the literature and digested it all, you’ll need to write up your literature review chapter. Many students make the mistake of thinking that the literature review chapter is simply a summary of what other researchers have said. While this is partly true, a literature review is much more than just a summary. To pull off a good literature review chapter, you’ll need to achieve at least 3 things:
- You need to synthesise the existing research , not just summarise it. In other words, you need to show how different pieces of theory fit together, what’s agreed on by researchers, what’s not.
- You need to highlight a research gap that your research is going to fill. In other words, you’ve got to outline the problem so that your research topic can provide a solution.
- You need to use the existing research to inform your methodology and approach to your own research design. For example, you might use questions or Likert scales from previous studies in your your own survey design .
As you can see, a good literature review is more than just a summary of the published research. It’s the foundation on which your own research is built, so it deserves a lot of love and attention. Take the time to craft a comprehensive literature review with a suitable structure .
But, how do I actually write the literature review chapter, you ask? We cover that in detail in this video post .
Step 6: Carry out your own research
Once you’ve completed your literature review and have a sound understanding of the existing research, its time to develop your own research (finally!). You’ll design this research specifically so that you can find the answers to your unique research question.
There are two steps here – designing your research strategy and executing on it:
1 – Design your research strategy
The first step is to design your research strategy and craft a methodology chapter . I won’t get into the technicalities of the methodology chapter here, but in simple terms, this chapter is about explaining the “how” of your research. If you recall, the introduction and literature review chapters discussed the “what” and the “why”, so it makes sense that the next point to cover is the “how” –that’s what the methodology chapter is all about.
In this section, you’ll need to make firm decisions about your research design. This includes things like:
- Your research philosophy (e.g. positivism or interpretivism )
- Your overall methodology (e.g. qualitative , quantitative or mixed methods)
- Your data collection strategy (e.g. interviews , focus groups, surveys)
- Your data analysis strategy (e.g. content analysis , correlation analysis, regression)
If these words have got your head spinning, don’t worry! We’ll explain these in plain language in other posts. It’s not essential that you understand the intricacies of research design (yet!). The key takeaway here is that you’ll need to make decisions about how you’ll design your own research, and you’ll need to describe (and justify) your decisions in your methodology chapter.
2 – Execute: Collect and analyse your data
Once you’ve worked out your research design, you’ll put it into action and start collecting your data. This might mean undertaking interviews, hosting an online survey or any other data collection method. Data collection can take quite a bit of time (especially if you host in-person interviews), so be sure to factor sufficient time into your project plan for this. Oftentimes, things don’t go 100% to plan (for example, you don’t get as many survey responses as you hoped for), so bake a little extra time into your budget here.
Once you’ve collected your data, you’ll need to do some data preparation before you can sink your teeth into the analysis. For example:
- If you carry out interviews or focus groups, you’ll need to transcribe your audio data to text (i.e. a Word document).
- If you collect quantitative survey data, you’ll need to clean up your data and get it into the right format for whichever analysis software you use (for example, SPSS, R or STATA).
Once you’ve completed your data prep, you’ll undertake your analysis, using the techniques that you described in your methodology. Depending on what you find in your analysis, you might also do some additional forms of analysis that you hadn’t planned for. For example, you might see something in the data that raises new questions or that requires clarification with further analysis.
The type(s) of analysis that you’ll use depend entirely on the nature of your research and your research questions. For example:
- If your research if exploratory in nature, you’ll often use qualitative analysis techniques .
- If your research is confirmatory in nature, you’ll often use quantitative analysis techniques
- If your research involves a mix of both, you might use a mixed methods approach
Again, if these words have got your head spinning, don’t worry! We’ll explain these concepts and techniques in other posts. The key takeaway is simply that there’s no “one size fits all” for research design and methodology – it all depends on your topic, your research questions and your data. So, don’t be surprised if your study colleagues take a completely different approach to yours.

Step 7: Present your findings
Once you’ve completed your analysis, it’s time to present your findings (finally!). In a dissertation or thesis, you’ll typically present your findings in two chapters – the results chapter and the discussion chapter .
What’s the difference between the results chapter and the discussion chapter?
While these two chapters are similar, the results chapter generally just presents the processed data neatly and clearly without interpretation, while the discussion chapter explains the story the data are telling – in other words, it provides your interpretation of the results.
For example, if you were researching the factors that influence consumer trust, you might have used a quantitative approach to identify the relationship between potential factors (e.g. perceived integrity and competence of the organisation) and consumer trust. In this case:
- Your results chapter would just present the results of the statistical tests. For example, correlation results or differences between groups. In other words, the processed numbers.
- Your discussion chapter would explain what the numbers mean in relation to your research question(s). For example, Factor 1 has a weak relationship with consumer trust, while Factor 2 has a strong relationship.
Depending on the university and degree, these two chapters (results and discussion) are sometimes merged into one , so be sure to check with your institution what their preference is. Regardless of the chapter structure, this section is about presenting the findings of your research in a clear, easy to understand fashion.
Importantly, your discussion here needs to link back to your research questions (which you outlined in the introduction or literature review chapter). In other words, it needs to answer the key questions you asked (or at least attempt to answer them).
For example, if we look at the sample research topic:
In this case, the discussion section would clearly outline which factors seem to have a noteworthy influence on organisational trust. By doing so, they are answering the overarching question and fulfilling the purpose of the research .

For more information about the results chapter , check out this post for qualitative studies and this post for quantitative studies .
Step 8: The Final Step Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications
Last but not least, you’ll need to wrap up your research with the conclusion chapter . In this chapter, you’ll bring your research full circle by highlighting the key findings of your study and explaining what the implications of these findings are.
What exactly are key findings? The key findings are those findings which directly relate to your original research questions and overall research objectives (which you discussed in your introduction chapter). The implications, on the other hand, explain what your findings mean for industry, or for research in your area.
Sticking with the consumer trust topic example, the conclusion might look something like this:
Key findings
This study set out to identify which factors influence consumer-based trust in British low-cost online equity brokerage firms. The results suggest that the following factors have a large impact on consumer trust:
While the following factors have a very limited impact on consumer trust:
Notably, within the 25-30 age groups, Factors E had a noticeably larger impact, which may be explained by…
Implications
The findings having noteworthy implications for British low-cost online equity brokers. Specifically:
The large impact of Factors X and Y implies that brokers need to consider….
The limited impact of Factor E implies that brokers need to…
As you can see, the conclusion chapter is basically explaining the “what” (what your study found) and the “so what?” (what the findings mean for the industry or research). This brings the study full circle and closes off the document.

Let’s recap – how to write a dissertation or thesis
You’re still with me? Impressive! I know that this post was a long one, but hopefully you’ve learnt a thing or two about how to write a dissertation or thesis, and are now better equipped to start your own research.
To recap, the 8 steps to writing a quality dissertation (or thesis) are as follows:
- Understand what a dissertation (or thesis) is – a research project that follows the research process.
- Find a unique (original) and important research topic
- Craft a convincing dissertation or thesis research proposal
- Write a clear, compelling introduction chapter
- Undertake a thorough review of the existing research and write up a literature review
- Undertake your own research
- Present and interpret your findings
Once you’ve wrapped up the core chapters, all that’s typically left is the abstract , reference list and appendices. As always, be sure to check with your university if they have any additional requirements in terms of structure or content.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

20 Comments
thankfull >>>this is very useful
Thank you, it was really helpful
unquestionably, this amazing simplified way of teaching. Really , I couldn’t find in the literature words that fully explicit my great thanks to you. However, I could only say thanks a-lot.
Great to hear that – thanks for the feedback. Good luck writing your dissertation/thesis.
This is the most comprehensive explanation of how to write a dissertation. Many thanks for sharing it free of charge.
Very rich presentation. Thank you
Thanks Derek Jansen|GRADCOACH, I find it very useful guide to arrange my activities and proceed to research!
Thank you so much for such a marvelous teaching .I am so convinced that am going to write a comprehensive and a distinct masters dissertation
It is an amazing comprehensive explanation
This was straightforward. Thank you!
I can say that your explanations are simple and enlightening – understanding what you have done here is easy for me. Could you write more about the different types of research methods specific to the three methodologies: quan, qual and MM. I look forward to interacting with this website more in the future.
Thanks for the feedback and suggestions 🙂
Hello, your write ups is quite educative. However, l have challenges in going about my research questions which is below; *Building the enablers of organisational growth through effective governance and purposeful leadership.*
Very educating.
Just listening to the name of the dissertation makes the student nervous. As writing a top-quality dissertation is a difficult task as it is a lengthy topic, requires a lot of research and understanding and is usually around 10,000 to 15000 words. Sometimes due to studies, unbalanced workload or lack of research and writing skill students look for dissertation submission from professional writers.
Thank you 💕😊 very much. I was confused but your comprehensive explanation has cleared my doubts of ever presenting a good thesis. Thank you.
thank you so much, that was so useful
Hi. Where is the excel spread sheet ark?
could you please help me look at your thesis paper to enable me to do the portion that has to do with the specification
my topic is “the impact of domestic revenue mobilization.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Degrees
- Doctoral Studies
- Theses and Dissertations
How to Write a Master's Thesis
Last Updated: June 1, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 610,706 times.
Students learning how to write a Master's Thesis will first learn that a central thesis question must be presented and subsequently answered. A Master's Thesis will be the most prominent piece of your graduate work up to this point, and a pertinent thesis question that forms the spine of this work elevates it from the prosaic to the significant.
Choosing a Topic

- To get a degree - topic should be difficult enough, but manageable too.
- To enjoy the work - topic that you are truly interested in, something that you will not grow bored of after a short period of time.
- To get a job afterward - if you know what specifically you want to do after your studies and/or for which company, it might be useful to choose a topic, that will help with this goal.
- To be useful - thesis might actually be useful to help to make the world a little better place.
- Try thinking about your favorite subject of study - it may be a particular author, theory, time period, etc. Imagine how you might further the study of that subject.
- You might consider skimming through papers you wrote for your graduate courses and see if there is any apparent topic that you tend to gravitate towards.
- Consult with faculty members, favorite professors. They might have some good suggestions to write about. Generally, you'll be required to meet with your thesis advisor at least once before you start working.
- Consider consulting with industry partners. Your favorite company might have some work to do which might be done as a master's thesis. This might also help you get a job within the company afterward and maybe even some money for the thesis.
- If you want to help the world to be a better place, you might want to consult with your local non-profits and charities or check the Internet for possible thesis topics to write about.
- 3 Choose the right topic. From the possible topics generated in the previous step, find the one which best fits the objectives from the first step, especially the objectives most important to you. Make sure that you have a clear, specific, and organized plan on how to write a master's thesis which you will be able to then defend.

- Make sure that your question and the answers provided will provide original content to the body of research in existence. A judicious question will also keep research focused, organized, and interesting.
- Once you've formulated your topic and direction of inquiry, try formulating 5-10 different questions around your intended research. This forces you to think flexibly about your topic and visualize how small changes in wording can change the trajectory of your research.

- Usually, your committee chair will be in place before you formally start your thesis. They can help guide you and provide input into your project, so the earlier you can get their commitment, the better.
- Nothing is more frustrating than your thesis progress being held up by a professor who has too many obligations to make time to meet with you.
Selecting Your Texts

- For example, a novel written by Ernest Hemingway or a scientific journal article in which new results are documented for the first time would both be considered primary sources.

- For example, a book written about Ernest Hemingway's novel or a scientific journal article examining the findings of someone else's experiment would both be considered secondary sources.

- Use the in-text citation format appropriate to your discipline. [3] X Research source The most common formats are MLA, APA, and Chicago.
- Create a coordinating works cited or reference entry for each source you cite in the text of your document or in a footnote.
- Consider using a citation management software such as EndNote, Mendeley, or Zotero. These will enable you to insert and move citations within your word processor program and will automatically populate a works cited or reference page for you.
Planning an Outline

- Qualitative. This type of thesis involves completing a project that is exploratory, analytical, or creative in some way. Usually, students in the humanities will complete this kind of thesis.
- Quantitative. This type of thesis involves conducting experiments, measuring data, and recording results. Students in the sciences usually complete this kind of thesis.

- Signature page (with the completed signatures of your advising committee - usually attained at the defense, or after the project is deemed complete )
- Abstract - this is a short (one paragraph or so) description/summary of the work completed in your thesis
- Table of Contents (with page numbers)
- Introduction
- Body of paper
- Works Cited or Bibliography
- Any necessary appendices or endnotes
Moving through the Writing Process

- If you do not already have a review of literature written, it’s time to do your research! The review of literature is essentially a summary of all of the existing scholarship about your topic with plenty of direct quotations from the primary and secondary sources that you’re referencing.

Finalizing Your Thesis

- Many departments or programs provide a document template for theses and dissertations. If you have one of these, it may be easiest to use such a template from the beginning of your work (rather than copying and pasting your writing into it).

- Alternatively, ask a trusted colleague or friend to read over your thesis to help you catch any minor grammar/spelling/punctuation errors and typos.

- Some institutions require you to submit your thesis for a formatting check prior to uploading the document to ProQuest. Be sure to check with your department’s Director of Graduate Studies for specific instructions.
- Be aware of thesis submission deadlines, which are often well in advance of your graduation date. Late submission of your thesis may force you to push back your graduation date, which may affect your employment or continuing graduate studies.
Masters Thesis Outline

Expert Q&A

- Remember why you are writing a Master's thesis and who will want to read and use the material. You write a Master's thesis for members of your community, so keep in mind that they will have extensive knowledge and experience before reading your work. Don't bore them with unnecessary material. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0
- Choosing the perfect question before starting research will prevent frustration and save time. Rigorous effort on finding the perfect question is probably the most important task when learning how to write a Master's thesis. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0
- Consult other people who have completed a Master's thesis and obtained a Master's degree. It can be a long, grueling process, and having the support and advice of someone who has already done it can be very valuable. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://umb.libguides.com/PrimarySources/secondary
- ↑ https://www.scribbr.com/citing-sources/in-text-citation-styles/
- ↑ https://www.unk.edu/academics/gradstudies/admissions/grad-files/Grad%20Files/ThesisGdlnsFinal08.pdf
- ↑ https://u.osu.edu/hackingthethesis/managing-stuff/your-content/outline/
- ↑ http://www.imm.dtu.dk/~janba/MastersThesisAdvice.pdf
About This Article

To write a master's thesis, make it a goal to write 500 words every day, which will help you meet your deadline without having to rush at the last minute. It's also helpful if you work in 25-minute increments and take a 5-minute break in between, which will make your work sessions less overwhelming. Also, figure out a writing time that works best for you, whether it's in the morning or at night, and stick with it so you're more productive. For more help writing your master's thesis, like how to make an outline, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Abdijabaar S.
Did this article help you?
Joseph Pertey
Aug 24, 2018
Jackson Kwakwa
Nov 21, 2017
Genc Zhushi
Apr 18, 2016
İsmail Binmasudi
Jul 20, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
How to Write a Master's Thesis: A Guide to Planning Your Thesis, Pursuing It, and Avoiding Pitfalls
#scribendiinc
Part 1: Initial Considerations
Who needs to write a master’s thesis.
Thesis writing is one of the more daunting challenges of higher education. That being said, not all master's students have to write a thesis. For example, fields that place a stronger emphasis on applied knowledge, such as nursing, business, and education, tend to have projects and exams to test students on the skills and abilities associated with those fields. Conversely, in disciplines that require in-depth research or highly polished creative abilities, students are usually expected to prove their understanding and independence with a thesis.
What's Your Goal?
Do you want to write a thesis? The process is a long one, often spanning years. It's best to know exactly what you want before you begin. Many people are motivated by career goals. For example, hiring managers may see a master's degree as proof that the candidate is an expert within their field and can lead, motivate, and demonstrate initiative for themselves and others. Others dream of earning their doctorate, and they see a master's degree as a stepping stone toward their Ph.D .

No matter what your desired goal is, you should have one before you start your thesis. With your goal in mind, your work will have a purpose, which will allow you to measure your progress more easily.
Major Types of Theses
Once you've carefully researched or even enrolled in a master's program—a feat that involves its own planning and resources —you should know if you are expected to produce a quantitative (which occurs in many math and science programs), qualitative (which occurs in many humanities programs), or creative (which occurs in many creative writing, music, or fine arts programs) thesis.
Time and Energy Considerations
Advanced degrees are notoriously time and energy consuming. If you have a job, thesis writing will become your second job. If you have a family, they will need to know that your thesis will take a great deal of your attention, energy, and focus.

Your studies should not consume you, but they also should not take a back seat to everything else. You will be expected to attend classes, conduct research, source relevant literature, and schedule meetings with various people as you pursue your master's, so it's important to let those you care about know what's going on.
As a general note, most master's programs expect students to finish within a two-year period but are willing to grant extra time if requested, especially if that time is needed to deal with unexpected life events (more on those later).
Part 2: Form an Initial Thesis Question, and Find a Supervisor
When to begin forming your initial thesis question.
Some fields, such as history, may require you to have already formed your thesis question and to have used it to create a statement of intent (outlining the nature of your research) prior to applying to a master’s program. Others may require this information only after you've been accepted. Most of the time, you will be expected to come up with your topic yourself. However, in some disciplines, your supervisor may assign a general research topic to you.
Overall, requirements vary immensely from program to program, so it's best to confirm the exact requirements of your specific program.
What to Say to Your Supervisor
You will have a supervisor during your master's studies. Have you identified who that person will be? If yes, have you introduced yourself via email or phone and obtained information on the processes and procedures that are in place for your master's program? Once you've established contact, request an in-person meeting with him or her, and take a page of questions along with you. Your questions might include:
- Is there a research subject you can recommend in my field?
- I would like to pursue [target research subject] for my thesis. Can you help me narrow my focus?
- Can you give me an example of a properly formatted thesis proposal for my program?
Don't Be Afraid to Ask for Help (to a Degree)
Procedures and expectations vary from program to program, and your supervisor is there to help remove doubt and provide encouragement so you can follow the right path when you embark on writing your thesis. Since your supervisor has almost certainly worked with other graduate students (and was one at some point), take advantage of their experience, and ask questions to put your mind at ease about how to write a master’s thesis.
That being said, do not rely too heavily on your supervisor. As a graduate student, you are also expected to be able to work independently. Proving your independent initiative and capacity is part of what will earn you your master's degree.
Part 3: Revise Your Thesis
Read everything you can get your hands on.
Whether you have a question or need to create one, your next step is simple and applies to all kinds of theses: read.

Seek Out Knowledge or Research Gaps
Read everything you can that relates to the question or the field you are studying. The only way you will be able to determine where you can go is to see where everyone else has been. After you have read some published material, you will start to spot gaps in current research or notice things that could be developed further with an alternative approach. Things that are known but not understood or understood but not explained clearly or consistently are great potential thesis subjects. Addressing something already known from a new perspective or with a different style could also be a potentially valuable project. Whichever way you choose to do it, keep in mind that your project should make a valuable contribution to your field.

Talk with Experts in Your Field (and Don't Be Afraid to Revise Your Thesis)
To help narrow down your thesis topic, talk to your supervisor. Your supervisor will have an idea of what is current in your field and what can be left alone because others are already working on it. Additionally, the school you are attending will have programs and faculty with particular areas of interest within your chosen field.
On a similar note, don't be surprised if your thesis question changes as you study. Other students and researchers are out there, and as they publish, what you are working on can change. You might also discover that your question is too vague, not substantial enough, or even no longer relevant. Do not lose heart! Take what you know and adjust the question to address these concerns as they arise. The freedom to adapt is part of the power you hold as a graduate student.
Part 4: Select a Proposal Committee
What proposal committees are and why they're useful.
When you have a solid question or set of questions, draft a proposal.

You'll need an original stance and a clear justification for asking, and answering, your thesis question. To ensure this, a committee will review your thesis proposal. Thankfully, that committee will consist of people assigned by your supervisor or department head or handpicked by you. These people will be experts who understand your field of study and will do everything in their power to ensure that you are pursuing something worthwhile. And yes, it is okay to put your supervisor on your committee. Some programs even require that your supervisor be on your committee.
Just remember that the committee will expect you to schedule meetings with them, present your proposal, respond to any questions they might have for you, and ultimately present your findings and thesis when all the work is done. Choose those who are willing to support you, give constructive feedback, and help address issues with your proposal. And don't forget to give your proposal a good, thorough edit and proofread before you present it.
How to Prepare for Committee Meetings
Be ready for committee meetings with synopses of your material for committee members, answers for expected questions, and a calm attitude. To prepare for those meetings, sit in on proposal and thesis defenses so you can watch how other graduate students handle them and see what your committee might ask of you. You can even hold rehearsals with friends and fellow students acting as your committee to help you build confidence for your presentation.

Part 5: Write Your Thesis
What to do once your proposal is approved.
After you have written your thesis proposal and received feedback from your committee, the fun part starts: doing the work. This is where you will take your proposal and carry it out. If you drafted a qualitative or quantitative proposal, your experimentation or will begin here. If you wrote a creative proposal, you will now start working on your material. Your proposal should be strong enough to give you direction when you perform your experiments, conduct interviews, or craft your work. Take note that you will have to check in with your supervisor from time to time to give progress updates.

Thesis Writing: It's Important to Pace Yourself and Take Breaks
Do not expect the work to go quickly. You will need to pace yourself and make sure you record your progress meticulously. You can always discard information you don't need, but you cannot go back and grab a crucial fact that you can't quite remember. When in doubt, write it down. When drawing from a source, always create a citation for the information to save your future self time and stress. In the same sense, you may also find journaling to be a helpful process.
Additionally, take breaks and allow yourself to step away from your thesis, even if you're having fun (and especially if you're not). Ideally, your proposal should have milestones in it— points where you can stop and assess what you've already completed and what's left to do. When you reach a milestone, celebrate. Take a day off and relax. Better yet, give yourself a week's vacation! The rest will help you regain your focus and ensure that you function at your best.
How to Become More Comfortable with Presenting Your Work
Once you start reaching your milestones, you should be able to start sharing what you have. Just about everyone in a graduate program has experience giving a presentation at the front of the class, attending a seminar, or watching an interview. If you haven't (or even if you have), look for conferences and clubs that will give you the opportunity to learn about presenting your work and become comfortable with the idea of public speaking. The more you practice talking about what you are studying, the more comfortable you'll be with the information, which will make your committee defenses and other official meetings easier.
Published authors can be called upon to present at conferences, and if your thesis is strong, you may receive an email or a phone call asking if you would share your findings onstage.
Presenting at conferences is also a great way to boost your CV and network within your field. Make presenting part of your education, and it will become something you look forward to instead of fear.
What to Do If Your Relationship with Your Supervisor Sours
A small aside: If it isn't already obvious, you will be communicating extensively with others as you pursue your thesis. That also means that others will need to communicate with you, and if you've been noticing things getting quiet, you will need to be the one to speak up. Your supervisor should speak to you at least once a term and preferably once a week in the more active parts of your research and writing. If you give written work to your supervisor, you should have feedback within three weeks.
If your supervisor does not provide feedback, frequently misses appointments, or is consistently discouraging of your work, contact your graduate program advisor and ask for a new supervisor. The relationship with your supervisor is crucial to your success, especially if she or he is on your committee, and while your supervisor does not have to be friendly, there should at least be professional respect between you.
What to Do If a Crisis Strikes
If something happens in your life that disrupts everything (e.g., emotional strain, the birth of a child, or the death of a family member), ask for help. You are a human being, and personal lives can and do change without warning. Do not wait until you are falling apart before asking for help, either. Learn what resources exist for crises before you have one, so you can head off trauma before it hits. That being said, if you get blindsided, don't refuse help. Seek it out, and take the time you need to recover. Your degree is supposed to help you become a stronger and smarter person, not break you.
Part 6: Polish and Defend Your Master's Thesis
How to write a master’s thesis: the final stages.
After your work is done and everything is written down, you will have to give your thesis a good, thorough polishing. This is where you will have to organize the information, draft it into a paper format with an abstract, and abbreviate things to help meet your word-count limit. This is also where your final editing and proofreading passes will occur, after which you will face your final hurdle: presenting your thesis defense to your committee. If they approve your thesis, then congratulations! You are now a master of your chosen field.
Conclusion and Parting Thoughts
Remember that you do not (and should not) have to learn how to write a master’s thesis on your own. Thesis writing is collaborative, as is practically any kind of research.

While you will be expected to develop your thesis using your own initiative, pursue it with your own ambition, and complete it with your own abilities, you will also be expected to use all available resources to do so. The purpose of a master's thesis is to help you develop your own independent abilities, ensuring that you can drive your own career forward without constantly looking to others to provide direction. Leaders get master's degrees. That's why many business professionals in leadership roles have graduate degree initials after their last names. If you already have the skills necessary to motivate yourself, lead others, and drive change, you may only need your master's as an acknowledgement of your abilities. If you do not, but you apply yourself carefully and thoroughly to the pursuit of your thesis, you should come away from your studies with those skills in place.
A final thought regarding collaboration: all theses have a section for acknowledgements. Be sure to say thank you to those who helped you become a master. One day, someone might be doing the same for you.
Image source: Falkenpost/Pixabay.com
We’re Masters at Master’s Theses! Make Yours Shine.
Let our expert academic editors perfect your writing, or get a free sample, about the author.

A Scribendi in-house editor, Anthony is happily putting his BA in English from Western University to good use with thoughtful feedback and incisive editing. An avid reader and gamer, he can be found during his off hours enjoying narrative-driven games and obscure and amusing texts, as well as cooking for his family.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation

Selecting a Thesis Committee

Thesis/Dissertation Writing Series: How to Write a Literature Review
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).

- Home »
find your perfect postgrad program Search our Database of 30,000 Courses
How to write a masters dissertation or thesis: top tips.
It is completely normal to find the idea of writing a masters thesis or dissertation slightly daunting, even for students who have written one before at undergraduate level. Though, don’t feel put off by the idea. You’ll have plenty of time to complete it, and plenty of support from your supervisor and peers.
One of the main challenges that students face is putting their ideas and findings into words. Writing is a skill in itself, but with the right advice, you’ll find it much easier to get into the flow of writing your masters thesis or dissertation.
We’ve put together a step-by-step guide on how to write a dissertation or thesis for your masters degree, with top tips to consider at each stage in the process.
1. Understand your dissertation or thesis topic
There are slight differences between theses and dissertations , although both require a high standard of writing skill and knowledge in your topic. They are also formatted very similarly.
At first, writing a masters thesis can feel like running a 100m race – the course feels very quick and like there is not as much time for thinking! However, you’ll usually have a summer semester dedicated to completing your dissertation – giving plenty of time and space to write a strong academic piece.
By comparison, writing a PhD thesis can feel like running a marathon, working on the same topic for 3-4 years can be laborious. But in many ways, the approach to both of these tasks is quite similar.
Before writing your masters dissertation, get to know your research topic inside out. Not only will understanding your topic help you conduct better research, it will also help you write better dissertation content.
Also consider the main purpose of your dissertation. You are writing to put forward a theory or unique research angle – so make your purpose clear in your writing.
Top writing tip: when researching your topic, look out for specific terms and writing patterns used by other academics. It is likely that there will be a lot of jargon and important themes across research papers in your chosen dissertation topic.
2. Structure your dissertation or thesis
Writing a thesis is a unique experience and there is no general consensus on what the best way to structure it is.
As a postgraduate student , you’ll probably decide what kind of structure suits your research project best after consultation with your supervisor. You’ll also have a chance to look at previous masters students’ theses in your university library.
To some extent, all postgraduate dissertations are unique. Though they almost always consist of chapters. The number of chapters you cover will vary depending on the research.
A masters dissertation or thesis organised into chapters would typically look like this:
Write down your structure and use these as headings that you’ll write for later on.
Top writing tip : ease each chapter together with a paragraph that links the end of a chapter to the start of a new chapter. For example, you could say something along the lines of “in the next section, these findings are evaluated in more detail”. This makes it easier for the reader to understand each chapter and helps your writing flow better.
3. Write up your literature review
One of the best places to start when writing your masters dissertation is with the literature review. This involves researching and evaluating existing academic literature in order to identify any gaps for your own research.
Many students prefer to write the literature review chapter first, as this is where several of the underpinning theories and concepts exist. This section helps set the stage for the rest of your dissertation, and will help inform the writing of your other dissertation chapters.
What to include in your literature review
The literature review chapter is more than just a summary of existing research, it is an evaluation of how this research has informed your own unique research.
Demonstrate how the different pieces of research fit together. Are there overlapping theories? Are there disagreements between researchers?
Highlight the gap in the research. This is key, as a dissertation is mostly about developing your own unique research. Is there an unexplored avenue of research? Has existing research failed to disprove a particular theory?
Back up your methodology. Demonstrate why your methodology is appropriate by discussing where it has been used successfully in other research.
4. Write up your research
For instance, a more theoretical-based research topic might encompass more writing from a philosophical perspective. Qualitative data might require a lot more evaluation and discussion than quantitative research.
Methodology chapter
The methodology chapter is all about how you carried out your research and which specific techniques you used to gather data. You should write about broader methodological approaches (e.g. qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods), and then go into more detail about your chosen data collection strategy.
Data collection strategies include things like interviews, questionnaires, surveys, content analyses, discourse analyses and many more.
Data analysis and findings chapters
The data analysis or findings chapter should cover what you actually discovered during your research project. It should be detailed, specific and objective (don’t worry, you’ll have time for evaluation later on in your dissertation)
Write up your findings in a way that is easy to understand. For example, if you have a lot of numerical data, this could be easier to digest in tables.
This will make it easier for you to dive into some deeper analysis in later chapters. Remember, the reader will refer back to your data analysis section to cross-reference your later evaluations against your actual findings – so presenting your data in a simple manner is beneficial.
Think about how you can segment your data into categories. For instance, it can be useful to segment interview transcripts by interviewee.
Top writing tip : write up notes on how you might phrase a certain part of the research. This will help bring the best out of your writing. There is nothing worse than when you think of the perfect way to phrase something and then you completely forget it.
5. Discuss and evaluate
Once you’ve presented your findings, it’s time to evaluate and discuss them.
It might feel difficult to differentiate between your findings and discussion sections, because you are essentially talking about the same data. The easiest way to remember the difference is that your findings simply present the data, whereas your discussion tells the story of this data.
Your evaluation breaks the story down, explaining the key findings, what went well and what didn’t go so well.
In your discussion chapter, you’ll have chance to expand on the results from your findings section. For example, explain what certain numbers mean and draw relationships between different pieces of data.
Top writing tip: don’t be afraid to point out the shortcomings of your research. You will receive higher marks for writing objectively. For example, if you didn’t receive as many interview responses as expected, evaluate how this has impacted your research and findings. Don’t let your ego get in the way!
6. Write your introduction
Your introduction sets the scene for the rest of your masters dissertation. You might be wondering why writing an introduction isn't at the start of our step-by-step list, and that’s because many students write this chapter last.
Here’s what your introduction chapter should cover:
Problem statement
Research question
Significance of your research
This tells the reader what you’ll be researching as well as its importance. You’ll have a good idea of what to include here from your original dissertation proposal , though it’s fairly common for research to change once it gets started.
Writing or at least revisiting this section last can be really helpful, since you’ll have a more well-rounded view of what your research actually covers once it has been completed and written up.
Masters dissertation writing tips
When to start writing your thesis or dissertation.
When you should start writing your masters thesis or dissertation depends on the scope of the research project and the duration of your course. In some cases, your research project may be relatively short and you may not be able to write much of your thesis before completing the project.
But regardless of the nature of your research project and of the scope of your course, you should start writing your thesis or at least some of its sections as early as possible, and there are a number of good reasons for this:
Academic writing is about practice, not talent. The first steps of writing your dissertation will help you get into the swing of your project. Write early to help you prepare in good time.
Write things as you do them. This is a good way to keep your dissertation full of fresh ideas and ensure that you don’t forget valuable information.
The first draft is never perfect. Give yourself time to edit and improve your dissertation. It’s likely that you’ll need to make at least one or two more drafts before your final submission.
Writing early on will help you stay motivated when writing all subsequent drafts.
Thinking and writing are very connected. As you write, new ideas and concepts will come to mind. So writing early on is a great way to generate new ideas.
How to improve your writing skills
The best way of improving your dissertation or thesis writing skills is to:
Finish the first draft of your masters thesis as early as possible and send it to your supervisor for revision. Your supervisor will correct your draft and point out any writing errors. This process will be repeated a few times which will help you recognise and correct writing mistakes yourself as time progresses.
If you are not a native English speaker, it may be useful to ask your English friends to read a part of your thesis and warn you about any recurring writing mistakes. Read our section on English language support for more advice.
Most universities have writing centres that offer writing courses and other kinds of support for postgraduate students. Attending these courses may help you improve your writing and meet other postgraduate students with whom you will be able to discuss what constitutes a well-written thesis.
Read academic articles and search for writing resources on the internet. This will help you adopt an academic writing style, which will eventually become effortless with practice.
Keep track of your bibliography
The easiest way to keep the track of all the articles you have read for your research is to create a database where you can summarise each article/chapter into a few most important bullet points to help you remember their content.
Another useful tool for doing this effectively is to learn how to use specific reference management software (RMS) such as EndNote. RMS is relatively simple to use and saves a lot of time when it comes to organising your bibliography. This may come in very handy, especially if your reference section is suspiciously missing two hours before you need to submit your dissertation!
Avoid accidental plagiarism
Plagiarism may cost you your postgraduate degree and it is important that you consciously avoid it when writing your thesis or dissertation.
Occasionally, postgraduate students commit plagiarism unintentionally. This can happen when sections are copy and pasted from journal articles they are citing instead of simply rephrasing them. Whenever you are presenting information from another academic source, make sure you reference the source and avoid writing the statement exactly as it is written in the original paper.
What kind of format should your thesis have?
Read your university’s guidelines before you actually start writing your thesis so you don’t have to waste time changing the format further down the line. However in general, most universities will require you to use 1.5-2 line spacing, font size 12 for text, and to print your thesis on A4 paper. These formatting guidelines may not necessarily result in the most aesthetically appealing thesis, however beauty is not always practical, and a nice looking thesis can be a more tiring reading experience for your postgrad examiner .
When should I submit my thesis?
The length of time it takes to complete your MSc or MA thesis will vary from student to student. This is because people work at different speeds, projects vary in difficulty, and some projects encounter more problems than others.
Obviously, you should submit your MSc thesis or MA thesis when it is finished! Every university will say in its regulations that it is the student who must decide when it is ready to submit.
However, your supervisor will advise you whether your work is ready and you should take their advice on this. If your supervisor says that your work is not ready, then it is probably unwise to submit it. Usually your supervisor will read your final thesis or dissertation draft and will let you know what’s required before submitting your final draft.
Set yourself a target for completion. This will help you stay on track and avoid falling behind. You may also only have funding for the year, so it is important to ensure you submit your dissertation before the deadline – and also ensure you don’t miss out on your graduation ceremony !
To set your target date, work backwards from the final completion and submission date, and aim to have your final draft completed at least three months before that final date.
Don’t leave your submission until the last minute – submit your work in good time before the final deadline. Consider what else you’ll have going on around that time. Are you moving back home? Do you have a holiday? Do you have other plans?
If you need to have finished by the end of June to be able to go to a graduation ceremony in July, then you should leave a suitable amount of time for this. You can build this into your dissertation project planning at the start of your research.
It is important to remember that handing in your thesis or dissertation is not the end of your masters program . There will be a period of time of one to three months between the time you submit and your final day. Some courses may even require a viva to discuss your research project, though this is more common at PhD level .
If you have passed, you will need to make arrangements for the thesis to be properly bound and resubmitted, which will take a week or two. You may also have minor corrections to make to the work, which could take up to a month or so. This means that you need to allow a period of at least three months between submitting your thesis and the time when your program will be completely finished. Of course, it is also possible you may be asked after the viva to do more work on your thesis and resubmit it before the examiners will agree to award the degree – so there may be an even longer time period before you have finished.
How do I submit the MA or MSc dissertation?
Most universities will have a clear procedure for submitting a masters dissertation. Some universities require your ‘intention to submit’. This notifies them that you are ready to submit and allows the university to appoint an external examiner.
This normally has to be completed at least three months before the date on which you think you will be ready to submit.
When your MA or MSc dissertation is ready, you will have to print several copies and have them bound. The number of copies varies between universities, but the university usually requires three – one for each of the examiners and one for your supervisor.
However, you will need one more copy – for yourself! These copies must be softbound, not hardbound. The theses you see on the library shelves will be bound in an impressive hardback cover, but you can only get your work bound like this once you have passed.
You should submit your dissertation or thesis for examination in soft paper or card covers, and your university will give you detailed guidance on how it should be bound. They will also recommend places where you can get the work done.
The next stage is to hand in your work, in the way and to the place that is indicated in your university’s regulations. All you can do then is sit and wait for the examination – but submitting your thesis is often a time of great relief and celebration!
Some universities only require a digital submission, where you upload your dissertation as a file through their online submission system.
Related articles
What Is The Difference Between A Dissertation & A Thesis
How To Get The Most Out Of Your Writing At Postgraduate Level
Dos & Don'ts Of Academic Writing
Dispelling Dissertation Drama
Writing A Dissertation Proposal
Postgrad Solutions Study Bursaries

Exclusive bursaries Open day alerts Funding advice Application tips Latest PG news
Sign up now!

Take 2 minutes to sign up to PGS student services and reap the benefits…
- The chance to apply for one of our 5 PGS Bursaries worth £2,000 each
- Fantastic scholarship updates
- Latest PG news sent directly to you.
The Thesis Process
The thesis is an opportunity to work independently on a research project of your own design and contribute to the scholarly literature in your field. You emerge from the thesis process with a solid understanding of how original research is executed and how to best communicate research results. Many students have gone on to publish their research in academic or professional journals.
To ensure affordability, the per-credit tuition rate for the 8-credit thesis is the same as our regular course tuition. There are no additional fees (regular per-credit graduate tuition x 8 credits).
Below are the steps that you need to follow to fulfill the thesis requirement. Please know that through each step, you will receive guidance and mentorship.
1. Determine Your Thesis Topic and Tentative Question
When you have completed between 24 and 32 credits, you work with your assigned research advisor to narrow down your academic interests to a relevant and manageable thesis topic. Log in to MyDCE , then ALB/ALM Community to schedule an appointment with your assigned research advisor via the Degree Candidate Portal.
Thesis Topic Selection
We’ve put together this guide to help frame your thinking about thesis topic selection.
Every effort is made to support your research interests that are grounded in your ALM course work, but faculty guidance is not available for all possible projects. Therefore, revision or a change of thesis topic may be necessary.
- The point about topic selection is particularly pertinent to scientific research that is dependent upon laboratory space, project funding, and access to private databases. It is also critical for our candidates in ALM, liberal arts fields (English, government, history, international relations, psychology, etc.) who are required to have Harvard faculty direct their thesis projects. Review Harvard’s course catalog online ( my.harvard.edu ) to be sure that there are faculty teaching courses related to your thesis topic. If not, you’ll need to choose an alternative topic.
- Your topic choice must be a new area of research for you. Thesis work represents thoughtful engagement in new academic scholarship. You cannot re-purpose prior research. If you want to draw or expand upon your own previous scholarship for a small portion of your thesis, you need to obtain the explicit permission of your research advisor and cite the work in both the proposal and thesis. Violations of this policy will be referred to the Administrative Board.
2. Prepare Prework for the Crafting the Thesis Proposal (CTP) Course or Tutorial
The next step in the process is to prepare and submit Prework in order to gain registration approval for the Crafting the Thesis Proposal (CTP) tutorial or course. The Prework process ensures that you have done enough prior reading and thinking about your thesis topic to benefit from the CTP.
The CTP provides an essential onramp to the thesis, mapping critical issues of research design, such as scope, relevance to the field, prior scholarly debate, methodology, and perhaps, metrics for evaluating impact as well as bench-marking. The CTP identifies and works through potential hurdles to successful thesis completion, allowing the thesis project to get off to a good start.
In addition to preparing, submitting, and having your Prework approved, to be eligible for the CTP, you need to be in good standing, have completed a minimum of 32 degree-applicable credits, including the statistics/research methods requirement (if pertinent to your field). You also need to have completed Engaging in Scholarly Conversation (if pertinent to your field). If you were admitted after 9/1/2023 Engaging in Scholarly Conversation (A and B) is required, if admitted before 9/1/2023 this series is encouraged.
Advising Note for Biology, Biotechnology, and Bioengineering and Nanotechnology Candidates : Thesis projects in these fields are designed to support ongoing scientific research happening in Harvard University, other academic institutions, or life science industry labs and usually these are done under the direction of a principal investigator (PI). Hence, you need to have a thesis director approved by your research advisor prior to submitting CTP prework. Your CTP prework is then framed by the lab’s research. Schedule an appointment with your research advisor a few months in advance of the CTP prework deadlines in order to discuss potential research projects and thesis director assignment.
CTP Prework is sent to our central email box: [email protected] between the following firm deadlines:
- April 1 and June 1 for fall CTP
- September 1 and November 1 for spring CTP.
- August 1 and October 1 for the three-week January session (ALM sustainability candidates only)
- International students who need a student visa to attend Harvard Summer School should submit their prework on January 1, so they can register for the CTP on March 1 and submit timely I-20 paperwork. See international students guidelines for more information.
Your research advisor will provide feedback on your prework submission to gain CTP registration approval. If your prework is not approved after 3 submissions, your research advisor cannot approve your CTP registration. If not approved, you’ll need to take additional time for further revisions, and submit new prework during the next CTP prework submission time period for the following term (if your five-year degree completion deadline allows).
3. Register and Successfully Complete the Crafting the Thesis Proposal Tutorial or Course
Once CTP prework is approved, you register for the Crafting the Thesis Proposal (CTP) course or tutorial as you would any other course. The goal of the CTP is to produce a complete, well-written draft of a proposal containing all of the sections required by your research advisor. Creating an academically strong thesis proposal sets the foundation for a high-quality thesis and helps garner the attention of a well-respected thesis director. The proposal is normally between 15 to 25 pages in length.
The CTP tutorial is not a course in the traditional sense. You work independently on your proposal with your research advisor by submitting multiple proposal drafts and scheduling individual appointments. You need to make self-directed progress on the proposal without special prompting from the research advisor. You receive a final grade of SAT or UNSAT (failing grade).
The CTP for sustainability is a three-week course in the traditional sense and you receive a letter grade, and it must be B- or higher to receive degree credit for the course.
You are expected to incorporate all of your research advisor’s feedback and be fully committed to producing an academically strong proposal leading to a thesis worthy of a Harvard degree. If you are unable to take advice from your research advisor, follow directions, or produce an acceptable proposal, you will not pass the CTP.
Successful CTP completion also includes a check on the proper use of sources according to our academic integrity guidelines. Violations of our academic integrity policy will be referred to the Administrative Board.
Maximum of two attempts . If you don’t pass that CTP, you’ll have — if your five-year, degree-completion date allows — just one more attempt to complete the CTP before being required to withdraw from the program. If you fail the CTP just once and have no more time to complete the degree, your candidacy will automatically expire. Please note that a WD grade counts as an attempt.
If by not passing the CTP you fall into poor academic standing, you will need to take additional degree-applicable courses to return to good standing before enrolling in the CTP for your second and final time, only if your five-year, degree-completion date allows. If you have no more time on your five-year clock, you will be required to withdraw.
Human Subjects
If your thesis, regardless of field, will involve the use of human subjects (e.g., interviews, surveys, observations), you will need to have your research vetted by the Committee on the Use of Human Subjects (CUHS) of Harvard University. Please review the IRB LIFECYCLE GUIDE located on the CUHS website. Your research advisor will help you prepare a draft copy of the project protocol form that you will need to send to CUHS. The vetting process needs to be started during the CTP tutorial, before a thesis director has been assigned.
4. Thesis Director Assignment and Thesis Registration
We expect you to be registered in thesis soon after CTP completion or within 3 months — no later. You cannot delay. It is critical that once a research project has been approved through the CTP process, the project must commence in a timely fashion to ensure the academic integrity of the thesis process.
Once you (1) successfully complete the CTP and (2) have your proposal officially approved by your research advisor (RA), you move to the thesis director assignment phase. Successful completion of the CTP is not the same as having an officially approved proposal. These are two distinct steps.
If you are a life science student (e.g., biology), your thesis director was identified prior to the CTP, and now you need the thesis director to approve the proposal.
The research advisor places you with a thesis director. Do not approach faculty to ask about directing your thesis. You may suggest names of any potential thesis directors to your research advisor, who will contact them, if they are eligible/available to direct your thesis, after you have an approved thesis proposal.
When a thesis director has been identified or the thesis proposal has been fully vetted by the preassigned life science thesis director, you will receive a letter of authorization from the Assistant Dean of Academic Programs officially approving your thesis work and providing you with instructions on how to register for the eight-credit Master’s Thesis. The letter will also have a tentative graduation date as well as four mandatory thesis submission dates (see Thesis Timetable below).
Continuous Registration Tip: If you want to maintain continued registration from CTP to thesis, you should meet with your RA prior to prework to settle on a workable topic, submit well-documented prework, work diligently throughout the CTP to produce a high-quality proposal that is ready to be matched with a thesis director as soon as the CTP is complete.
Good academic standing. You must be good academic standing to register for the thesis. If not, you’ll need to complete additional courses to bring your GPA up to the 3.0 minimum prior to registration.
Thesis Timetable
The thesis is a 9 to 12 month project that begins after the Crafting the Thesis Proposal (CTP); when your research advisor has approved your proposal and identified a Thesis Director.
The date for the appointment of your Thesis Director determines the graduation cycle that will be automatically assigned to you:
Once registered in the thesis, we will do a 3-month check-in with you and your thesis director to ensure progress is being made. If your thesis director reports little to no progress, the Dean of Academic Programs reserves the right to issue a thesis not complete (TNC) grade (see Thesis Grading below).
As you can see above, you do not submit your thesis all at once at the end, but in four phases: (1) complete draft to TA, (2) final draft to RA for format review and academic integrity check, (3) format approved draft submitted to TA for grading, and (4) upload your 100% complete graded thesis to ETDs.
Due dates for all phases for your assigned graduation cycle cannot be missed. You must submit materials by the date indicated by 5 PM EST (even if the date falls on a weekend). If you are late, you will not be able to graduate during your assigned cycle.
If you need additional time to complete your thesis after the date it is due to the Thesis Director (phase 1), you need to formally request an extension (which needs to be approved by your Director) by emailing that petition to: [email protected] . The maximum allotted time to write your thesis, including any granted extensions of time is 12 months.
Timing Tip: If you want to graduate in May, you should complete the CTP in the fall term two years prior or, if a sustainability student, in the January session one year prior. For example, to graduate in May 2025:
- Complete the CTP in fall 2023 (or in January 2024, if a sustainability student)
- Be assigned a thesis director (TD) in March/April 2024
- Begin the 9-12 month thesis project with TD
- Submit a complete draft of your thesis to your TD by February 1, 2025
- Follow through with all other submission deadlines (April 1, April 15 and May 1 — see table above)
- Graduate in May 2025
5. Conduct Thesis Research
When registered in the thesis, you work diligently and independently, following the advice of your thesis director, in a consistent, regular manner equivalent to full-time academic work to complete the research by your required timeline.
You are required to produce at least 50 pages of text (not including front matter and appendices). Chapter topics (e.g., introduction, background, methods, findings, conclusion) vary by field.
6. Format Review — Required of all Harvard Graduate Students and Part of Your Graduation Requirements
All ALM thesis projects must written in Microsoft Word and follow a specific Harvard University format. A properly formatted thesis is an explicit degree requirement; you cannot graduate without it.
Your research advisor will complete the format review prior to submitting your thesis to your director for final grading according to the Thesis Timetable (see above).
You must use our Microsoft Word ALM Thesis Template or Microsoft ALM Thesis Template Creative Writing (just for creative writing degree candidates). It has all the mandatory thesis formatting built in. Besides saving you a considerable amount of time as you write your thesis, the preprogrammed form ensures that your submitted thesis meets the mandatory style guidelines for margins, font, title page, table of contents, and chapter headings. If you use the template, format review should go smoothly, if not, a delayed graduation is highly likely.
Format review also includes a check on the proper use of sources according to our academic integrity guidelines. Violations of our academic integrity policy will be referred directly to the Administrative Board.
7. Mandatory Thesis Archiving — Required of all Harvard Graduate Students and Part of Your Graduation Requirements
Once your thesis is finalized, meaning that the required grade has been earned and all edits have been completed, you must upload your thesis to Harvard University’s electronic thesis and dissertation submission system (ETDs). Uploading your thesis ETDs is an explicit degree requirement; you cannot graduate without completing this step.
The thesis project will be sent to several downstream systems:
- Your work will be preserved using Harvard’s digital repository DASH (Digital Access to Scholarship at Harvard).
- Metadata about your work will be sent to HOLLIS (the Harvard Library catalog).
- Your work will be preserved in Harvard Library’s DRS2 (digital preservation repository).
By submitting work through ETDs @ Harvard you will be signing the Harvard Author Agreement. This license does not constrain your rights to publish your work subsequently. You retain all intellectual property rights.
For more information on Harvard’s open access initiatives, we recommend you view the Director of the Office of Scholarly Communication (OSC), Peter Suber’s brief introduction .
Thesis Grading
You need to earn a grade of B- or higher in the thesis. All standard course letter grades are available to your thesis director. If you fail to complete substantial work on the thesis, you will earn a grade of TNC (thesis not complete). If you have already earned two withdrawal grades, the TNC grade will count as a zero in your cumulative GPA.
If you earn a grade below B-, you will need to petition the Administrative Board for permission to attempt the thesis for a second and final time. The petition process is only available if you are in good academic standing and your five-year, degree-completion deadline allows for more time. Your candidacy will automatically expire if you do not successfully complete the thesis by your required deadline.
If approved for a second attempt, you may be required to develop a new proposal on a different topic by re-enrolling in the CTP and being assigned a different thesis director. Tuition for the second attempt is calculated at the current year’s rate.
If by not passing the thesis you fall into poor academic standing, you’ll need to take additional degree-applicable courses to return to good standing before re-engaging with the thesis process for the second and final time. This is only an option if your five-year, degree-completion deadline allows for more time.
The Board only reviews cases in which extenuating circumstances prevented the successful completion of the thesis.
Harvard Division of Continuing Education
The Division of Continuing Education (DCE) at Harvard University is dedicated to bringing rigorous academics and innovative teaching capabilities to those seeking to improve their lives through education. We make Harvard education accessible to lifelong learners from high school to retirement.

- Public Lectures
- Faculty & Staff Site >>
Thesis/Dissertation
To graduate with a master’s (thesis program) or doctoral (dissertation program) degree, students are required to submit an Electronic Thesis/Dissertation (ETD) and a Committee Approval Form to the Graduate School through the UW ETD Administrator Site . ETDs are distributed by ProQuest/UMI Dissertation Publishing and made available on an open access basis through UW Libraries ResearchWorks Service .
The Graduate School partners with the UW Libraries to provide comprehensive resources for students as they write, submit, and publish academic theses or dissertations. These pages outline information and policies related to preparing your thesis/dissertation, including formatting, deadlines, copyright and distribution decisions, and, ultimately, graduation. We also encourage you to review the ETD Library Guide for additional information.
For comprehensive information on preparing to graduate, please refer to our graduation requirements information page .
Writing Your Thesis or Dissertation
Etd resources.
As a starting point, students submitting an ETD are encouraged to review the below resources:
- Hacking the Academy: UW Theses & Dissertations (Recording of July 29, 2020 event) This session helps students think through their options for how and when to share their work, including the copyright and publishing considerations they may need to take into account.
- Electronic Theses & Dissertations with the UW Libraries The University Libraries welcomes you to this self-guided course on electronic theses and dissertations (ETDs) at the UW. In this five-part learning experience, you will learn a lot about the ETD process including how the submission process works, how to give and receive recognition for your work, how to find and interpret publisher policies and how to read and inspect publishing contracts.
Formatting Guidelines
After you submit your ETD, the Graduate School will review your document as part of the graduation process at the end of each quarter. We will review for information accuracy, consistency, and to ensure your ETD meets the formatting requirements described below. There are three required sections (pages) that must be included at the beginning of your manuscript: 1) Title Page, 2) Copyright Page, 3) Abstract. Templates for these sections are provided below.
Apart from these first three pages, the Graduate School does not adhere to any specific formatting or publishing requirements unless explicitly stated by the ProQuest Author Guide: Preparing Your Manuscript for Submission (provided below). You should refer to the citation, formatting, and style specifications of your discipline and the guidance of your supervisory committee. Note: theses and dissertations must be submitted in PDF format.
For a complete overview of the graduation process, please review Preparing to Graduate .
Required Sections:
- Must include all items listed in the sample title page and placed in the same order
- May be the first or second page of your document
- Title of document
- Author’s Full Name
- Name of degree as it will appear on your diploma
- Year of graduation
- Names of chair/committee members (do not include signatures or professional titles, e.g. Dr. or PhD, before/after faculty names)
- Program authorized to offer degree (school or department)
- Name and year must match title pages
- List the year of graduation
- Place abstract after copyright and title page
Master’s Thesis Approval Form:
You are required to upload a completed and signed Master’s Thesis Approval Form into the UW ETD Administrator (ProQuest) site; the Approval Form is part of your ETD submission. This Approval Form is a separate PDF and should not be included as a page in the thesis or dissertation itself.
- Master’s Thesis Approval Form
Electronic Doctoral Dissertation Approval:
Final Exams scheduled after March 3, 2020 include a link for Reading Committee Members to approve the dissertation online at MyGrad Committee View.
ETD Formatting Resources:
- Thesis/Dissertation Formatting Checklist – a quick reference guide of the formatting do’s and don’ts provided below.
- ProQuest Dissertation Publishing — Author Guide: Preparing Your Manuscript for Submission
- ProQuest Online Submission FAQs
- Master’s Thesis Title Page – Fillable PDF Template
- Doctoral Dissertation Title Page – Fillable PDF Template
- Word Templates – Alex Mamishev, Professor in Electrical Engineering maintains a Word file that other students may find useful when formatting their document.
Common ETD Formatting Revisions Requested
To ensure timely graduating, take some time before you submit to review this information and ProQuest’s document formatting guidelines. These are all common errors and revisions the Graduate School will request when reviewing ETD formatting. You will be required to resubmit if revisions are needed. Be precise, and consistent as you format your document. Many formatting errors result from following a fellow or former student’s example, so it’s important to review the most current templates and guidelines.
Title Page, Copyright Page, Abstract
Language requirement.
Your document must be written in English ( policy 1.1.4.3 ). If you need to write your document in another language to accommodate the main audience, you must get prior approval to do so by submitting a petition the dean via MyGrad . If the petition is approved, the required sections (title page, copyright page, abstract) must still be written in English.
Plagiarism is using words, ideas, diagrams, and other content from publicly available work without appropriately acknowledging the sources of these materials. This definition constitutes plagiarism whether it is intentional or unintentional and whether it is the work of another or your own, previously published work.
Plagiarism is a very serious offense that the University of Washington does not tolerate. Evidence of plagiarism may prevent granting of your degree.
Submitting and Publishing
Submitting for dissemination and access.
The Graduate School and the Libraries require that all UW theses and dissertations be submitted electronically for management efficiency, cost control, ease of dissemination, and long-term preservation reasons. In addition, your ETD must eventually be made available openly on the web. Your ETD will be hosted in both UW’s institutional repository, ResearchWorks , and in ProQuest’s ETD Database . Consequently, you will need to indicate your choices in two sections about how your ETD is made available. Most students choose to make their work available immediately, but you can choose to limit access temporarily before making it available openly.
Students may restrict access to their theses and dissertations…
- while seeking to publish journal articles or books based on them,
- to protect intellectual property during the patent application process, or
- to prevent the disclosure of sensitive or classified information.
During the submission process, you will select ProQuest and ResearchWorks (Institutional Repository, or IR) publication options. The options are summarized on a table below, followed by selected scenarios to assist you in making your decisions.
IMPORTANT: The metadata describing your ETD, including the citation and abstract, is openly available immediately— regardless of the embargo or restriction status. This information is searchable by Google, Bing and other search engines, so take care that neither the descriptive information nor the text contain confidential or sensitive information.
Selecting Access Options
Selected etd access scenarios.
The UW Libraries and the Graduate School are committed to the goal of sharing graduate students’ research as soon and as widely as possible, while allowing students to temporarily limit access to their theses and dissertations for such reasons as to support formal publication in journal article or book form or to allow time for filing patents. Below are some examples of how students may wish to use these options to support their publishing or intellectual property-protection goals.
Discussion of Scenarios
- Journal Article Publishing. In recent years graduate students – especially in scientific, medical and technical fields — have increasingly been publishing results of their research in journals.
- The “Research Article” Dissertation. In some disciplines students may be expected to publish 2 or more journal articles during the course of their studies and submit them as the core of their thesis or dissertation — along with an introduction, literature review, and conclusions. Because this has become so common, most journals now permit authors to immediately republish their articles within their theses or dissertations as long as they provide the full article citation and a statement that an article is being “reprinted with permission” of the journal. However, some other journals allow the practice but require that an article not appear on an open access basis before a delay of 6 or 12 months. The Libraries strongly suggests that students become familiar with the policies in place at the journals in which they would like to publish their work, and choose appropriate access restrictions if needed when they submit their ETD’s.
- Book Publishing. Some students in such humanities and social science disciplines as history and political science may hope to publish a revised version of their dissertation as their first book. As they consider that possibility they may be concerned they might undermine their prospects by making their dissertations widely available via ProQuest and/or on an open access basis.Before deciding whether or for how long to limit access to their work based on these concerns, The Libraries recommends students become familiar with the arguments and evidence put forward on these issues. For example, Cirasella and Thistlethwaite 3 and Courtney and Kilcer 4 provide excellent discussions of issues and review recent literature, while William Germano’s classic From Dissertation to Book 5 and Beth Luey’s Revising Your Dissertation 6 offer important insight into what might be involved during the dissertation revision process. While the Libraries recommends that most students hoping to publish their dissertations as books make them widely available while they work toward that goal, they should feel free to consider choosing otherwise, such as “Immediate Access” for ProQuest and limiting to UW for five years – at the end of which students may request additional time.
- Patent Protection Strategies. Students whose theses or dissertations describe work for which patent protection might be appropriate should contact Jesse Kindra at CoMotion ( [email protected] or 206 616-9658) prior to submitting their work to ProQuest and choosing access restrictions. Depending on the circumstances, a student may choose to completely withhold access for one year, but should recognize that doing so will prevent anyone else at the UW from having access to it during the restricted access period. To exercise this option, students should delay releasing their work to ProQuest for 1 or 2 years, and then choose “No access for 1 year, then make Open Access” from the Institutional Repository (IR) Publishing Options menu for the UW copy. In unusual circumstances, requests for access to be withheld an additional year may be considered. To make such a request, students should describe the reason(s) for it in an email to [email protected] prior to expiration of the original embargo period.
1 Marisa L. Ramirez, Joan T. Dalton, Gail McMillan, Max Read and Nancy H. Seamans, “Do Open Access Electronic Theses and Dissertations Diminish Publishing Opportunities in the Social Sciences and Humanities,” College and Research Libraries 74 (July 2013): 368‐80, http://crl.acrl.org/content/74/4/368.full.pdf+html .
2 Marisa Ramirez, Gail McMillan, Joan T. Dalton, Ann Hanlon, Heather S. Smith and Chelsea Kern, “Do Open Access Electronic Theses and Dissertations Diminish Publishing Opportunities in the Sciences?” College and Research Libraries 75 (November 2014): 808-21, http://crl.acrl.org/content/75/6/808.full.pdf+html .
3 Jill Cirasella and Polly Thistlethwaite, “Open Access and the Graduate Author: A Dissertation Anxiety Manual,” pp. 203-224 in Open Access and the Future of Scholarly Communication: Implementation (Kevin L. Smith and Katherine A. Dickson, eds.: Rowman and Littlefield, 2017), http://academicworks.cuny.edu/gc_pubs/286/ .
4 Kyle K. Courtney and Emily Kilcer, “From Apprehension to Comprehension: Addressing Anxieties about Open Access to ETD’s,” pp. 225-244 in Open Access and the Future of Scholarly Communication: Implementation (Kevin L. Smith and Katherine A. Dickson, eds.: Rowman and Littlefield, 2017).
5 William Germano. 2013. From Dissertation to Book, 2d. ed. : University of Chicago Press.
6 Beth Luey (ed.). 2008. Revising Your Dissertation: Advice from Leading Editors. University of California Press.
Publishing Agreements
When you submit your ETD for review and publication, you will be required to read and accept two separate publishing agreements. You will also have to decide whether to publish your work right away or to delay its release. Additional pages within this section will outline all the considerations to keep in mind, when deciding how to make your work available to the scholarly community.
All students writing a thesis or dissertation should review the UW Libraries Copyright Research Guide . Understanding copyright law is another critical aspect as you write your thesis or dissertation. As you compose your work, ask yourself the following questions:
- Have you referenced others’ work? If so, you either need to get explicit permission from the rights holder or to determine that your use is Fair.
- Have you previously published any part of the work? If you’ve signed your copyright over to your publisher, you will need permission to use your material in your thesis.
Ordering Paper Copies
There are no required fees , although you have the option to register your copyright via ProQuest for a fee. If you want to order bound (paper) copies of your document, you may do so through the UW Copy Centers or through ProQuest. Questions should be directed to the UW Copy Centers or to ProQuest at 1.800.521.0600 ext. 77020 — available 8 a.m.–5 p.m. EST, Monday through Friday (excluding U.S. holidays).
Frequently Asked Questions
I created an account in the etd administrator site, but i’m not ready to submit my etd. can i come back to my account later.
Yes. If you need to finish your submission later (for instance, if you need to update your PDF file before uploading it), you can save your information and come back to finish. No information will be lost.
I submitted my ETD but would like to make an edit to the document. How can I edit my submission?
Once your thesis/dissertation is submitted, no additional changes to the document are allowed with the exception of a major data error in the document. In this circumstance, a letter outlining the necessary changes is required from your supervisory committee chair.
What will the Graduate School be reviewing after I submit my ETD?
Submissions are reviewed by GEMS advisors for formatting requirements for the three required sections — title page, copyright page, abstract — before they are delivered to ProQuest for publication. We are checking for accuracy and consistency. Refer to the Formatting Guidelines section on this page for detailed information.
I submitted my ETD and haven't heard anything yet. When will it be reviewed?
We try to review all ETDs as they are received, but if you submit early in the quarter it may not be acted on immediately. If you need to confirm completion of your degree requirements to an external agency or employer, please access the request for letter of certification in the forms section of our Additional Resources page (once your degree has posted to your UW transcript, we can no longer issue this letter). In general, ETDs are reviewed in the last two to three weeks before the quarter ends and after the last day of the quarter. When your submission has been accepted by a GEMS advisor, you will receive email confirmation.
How can I tell if my ETD was submitted and received by the Graduate School?
When your ETD is successfully submitted and pending review, the status will read “submission in review.”
When will my ETD be made available for access?
This depends on the type of access restrictions you selected when creating your account. However, your submission will be delivered to ProQuest for publishing four to six weeks after graduation and you will receive email confirmation when this has occurred. It should be available in UW ResearchWorks around the same time.
When will the printed dissertation / thesis copies I ordered from ProQuest be ready?
After you receive the email confirmation that UW has “delivered” your submission (ETD) to ProQuest, you should please refer to the ProQuest customer service guidelines for the expected delivery date of your order.
What if I am missing a faculty signature for my thesis or dissertation, or I have encountered difficulties in uploading my ETD? Must I pay the graduate registration waiver fee and graduate in the following quarter?
If you encounter these types of situations, contact Graduate Enrollment Management Services (206.685.2630 or [email protected] ) as early as possible and no later than the last day of the quarter in which you intend to graduate.
Additional Resources
- Electronic Theses and Dissertations (ETDs) Guide (start here!)
- Copyright and Fair Use
- Open Access
- Scholarly Publishing
- ProQuest/UMI Agreement — Traditional Publishing Agreement
- University Agreement — UW Libraries Thesis and Dissertation Submission Agreement
- UW Human Subjects Division (HSD)
- UW CoMotion
Ohio State nav bar
The Ohio State University
- BuckeyeLink
- Find People
- Search Ohio State
Dissertations and Theses
The dissertation is the hallmark of the research expertise demonstrated by a doctoral student. It is a scholarly contribution to knowledge in the student’s area of specialization. By researching and writing a dissertation, the student is expected to demonstrate a high level of knowledge and the capability to function as an independent scholar.
A thesis is a hallmark of some master’s programs. It is a piece of original research, generally less comprehensive than a dissertation, and is meant to show the student’s knowledge of an area of specialization.
Document Preparation
PhD and master’s students are responsible for meeting all requirements for preparing theses and dissertations. They are expected to confer with their advisors about disciplinary and program expectations and to follow Graduate School procedure requirements.
The Graduate School’s format review is in place to help the document submission process go smoothly for the student. Format reviews for PhD dissertations and master’s theses can be done remotely or in-person. The format review is required at or before the two-week notice of the final defense.
Access and Distribution
Ohio State has agreements with two organizations— OhioLINK and ProQuest/UMI Dissertation Publishing —that store and provide access to Ohio State theses and dissertations.
Examinations
Graduate degree examinations are a major milestone in all graduate students’ pursuit of their graduate degree. Much hinges on the successful completion of these examinations, including the ability to continue in a graduate program.
The rules and processes set by the Graduate School ensure the integrity of these examinations for graduate students, the graduate faculty, and for Ohio State.
Final Semester
During your final semester as a graduate student there are many activities that lead up to commencement and receiving your degree. Complete the final semester checklist and learn more about commencement activities.
Graduation Calendar
Select your expected graduation term below to see specific dates concerning when to apply for graduation, complete your examinations and reports, submit approved thesis and dissertation, commencement, and the end-of semester deadline.
Applications to Graduate Due 1 : January 26, 2024
Examinations and Reports completed by 2 : April 12, 2024
Approved thesis and dissertation submitted and accepted by 3 : April 19, 2024
Commencement 4 : May 5, 2024
End of Semester Deadline 5 : May 6, 2024
Applications to Graduate Due 1 : May 24, 2024
Examinations and Reports completed by 2 : July 12, 2024
Approved thesis and dissertation submitted and accepted by 3 : July 19, 2024
Commencement 4 : August 4, 2024
End of Semester Deadline 5 : August 19, 2024
Applications to Graduate Due 1 : September 6, 2024
Examinations and Reports completed by 2 : November 22, 2024
Approved thesis and dissertation submitted and accepted by 3 : November 27, 2024
Commencement 4 : December 15, 2024
End of Semester Deadline 5 : January 3, 2025
Applications to Graduate Due 1 : January 24, 2025
Examinations and Reports completed by 2 : April 11, 2025
Approved thesis and dissertation submitted and accepted by 3 : April 18, 2025
Commencement 4 : May 4, 2025
End of Semester Deadline 5 : May 5, 2025
1 Applications to graduate include current semester or End-of-Semester deadline. Applications must be received by close of business.
2 Format reviews may occur electronically or in person at the Graduate School during announced business hours. Both options require submitting a digital version of the dissertation or DMA document draft in a PDF format to [email protected] .
3 Approved documents must be submitted via OhioLINK and accepted by the Graduate School by the close of business before the Report on Final Document will be processed.
4 Students not attending commencement must complete the commencement section on the Application to Graduate to indicate how their diploma should be disbursed.
5 A degree applicant who does not meet published graduation deadlines but who does complete all degree requirements by the last business day prior to the first day of classes for the following semester or summer term will graduate the following semester or summer term without registering or paying fees
Still Have Questions?
Dissertations & Theses 614-292-6031 [email protected]
Doctoral Exams, Master's Examination, Graduation Requirements 614-292-6031 [email protected]
- Communications
- Computer Science
- Criminal Justice
- Environmental Management
- Forensic Psychology
- Healthcare Admin
- Human Resources
- Project Management
- Social work
- Special Education
- Sports Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Adult Education
- Business Intelligence
- Early Childhood Education
- Educational Technology
- Homeland Security
- Information Systems Security
- Information Technology
- International Business
- Management Information Systems
- Nonprofit Management
- School Counseling
- Academic Publishing Guide
- Building a Graduate School Resume or CV
Choosing Between a Thesis or Non-thesis Master's Degree
- Expert Guide to Studying Abroad
- FAQ: Online Master's Degrees
- Grad School Guide Book
- Graduate School for Students with Disabilities
- Green Graduate Degrees
- How to Be a Successful Grad Student
- How to Choose the Right Graduate Program
- How to Get a Master's Degree in an Unrelated Field
- How to Transfer College Credits in Grad School
- How to Write a Winning Personal Statement
- Inside Graduate Admissions
- Ivy League Grad Schools
- Master's Degrees for Veterans
- Master's Degree for Women
- Mental Health in Grad School
- Progressive LGBTQ Graduate Degrees
- Should You Apply for a Graduate School Assistantship?
- Surviving Grad School with a Family
- Taking a Gap Year Before Grad School
- Women in STEM Graduate Resources
- Writing a Successful Statement of Purpose
- Alternative Ways to Pay for School
- The Best Part-Time Jobs During Grad School
- Company Funded Graduate School
- FAFSA For Grad Students
- Financial Aid Resources
- Graduate Student Loans
- Paying for Your Master's Degree
- Paying Off Student Loans
- Paying for Your PhD
- Fellowship Opportunities
- LGBTQ Scholarships
- MBA Scholarships
- Scholarship Resources
- Scholarships for Veterans
- Scholarships for Women
- Crushing the GRE Guidebook
- GMAT Guidebook
- Guide to the LSAT
- MCAT Prep for Medical School
- Study Guide: Exam Resources
- TOEFL Prep for Non-Native English Speakers
- Resources Choosing Between a Thesis or Non-thesis Master's Degree
As of 2015, approximately 25.4 million Americans held advanced degrees , with more citizens joining these ranks each year. As studies continue to show the career advancement and salary benefits of completing a master's degree, more and more students elect to pursue advanced educations. When considering their options, many question whether to enroll in a master's requiring a thesis or not. The following guide examines some of the reasons degree seekers may want to write a thesis while also highlighting why they might not. Students on the fence about this important decision can find expert advice, actionable tips, and relevant guidance to help them make an informed choice in the guide that follows.
Understanding the Master's Thesis
What is the difference between a thesis & non-thesis master's program, the decision not to do a thesis.
As students research various master's programs in their chosen discipline, it's common to find that many degrees require a thesis – especially if they want to enter a research-heavy field. While this word gets thrown around a lot in academia, some learners may want more information regarding what it entails in order to make an informed decision.
What is a Master's Thesis?
The master's thesis is an original piece of scholarship allowing the student to dig into a topic and produce an expanded document that demonstrates how their knowledge has grown throughout the degree program. These documents require significant independent research of primary and secondary sources and, depending on the subject, may require interviews and/or surveys to support the overarching argument.
Individual schools and departments dictate the length of these documents, but they typically range between 60 and 100 pages – or approximately 20,000 to 40,000 words. While tackling a document of such heft may seem overwhelming at first, learners need not fret. Each master's candidate receives a faculty advisor early in their tenure to provide support, feedback, and guidance throughout the process. Because the final thesis is expected to be of a publishable quality, learners seeking the highest marks typically send their supervisor excerpts of the document as they write to ensure they are on the right track.
When picking a thesis topic, no magical formula exists. Students should consider their interests and read extensively on that topic to get a better sense of existing scholarship. They should also speak to other academics working in that sphere to familiarize themselves with ongoing projects. Only after they feel reasonably well-read should they begin looking for uncovered angles or interesting ways of using emerging methodologies to bring new light to the topic.
When considering formatting, degree seekers should check with their specific schools and departments, as they may have unique requirements. To get a general understanding of what to expect, learners can review Simon Fraser University's guidelines on thesis formatting. After completing the thesis, some programs require an oral defense before a committee while others read the document and provide a grade. Check with your prospective schools to get a better sense of procedure.
Format & Components of a Master's Thesis
While this guide attempts to provide helpful and actionable information about the process of deciding whether to follow a thesis or non-thesis track in a master's program, readers should remember that specific components and requirements of a thesis vary according to discipline, university, and department. That being said, some commonalities exist across all these – especially when it comes to what students must include in their final drafts.
As the first section a reader encounters after moving through the table of contents and other anterior text, the introductory allows the writer to firmly establish what they want to accomplish. Sometimes also called the "research question" section, the introductory must clearly state the goals of the paper and the overarching hypothesis guiding the argument. This should be written in a professional yet accessible tone that allows individuals without specializations in the field to understand the text.
This section allows learners to demonstrate their deep knowledge of the field by providing context to existing texts within their chosen discipline Learners review the main bodies of work, highlighting any issues they find within each. Constructive criticism often centers around shortcomings, blind spots, or outdated hypotheses.
Students use this section to explain how they went about their work. While scientists may point to a specific method used to reach conclusions, historians may reference the use of an emerging framework for understanding history to bring new light to a topic. The point of this section is to demonstrate the thought processes that led to your findings.
This section allows for learners to show what they learned during the research process in a non-biased way. Students should simply state what information they gathered by utilizing a specific framework or methodology and arrange those findings, without interpretation, in an easy-to-read fashion.
After providing readers with all the necessary information, the discussion section exists for candidates to interpret the raw data and demonstrate how their research led to a new understanding or contributed a unique perspective to the field. This section should directly connect to the introduction by reinforcing the hypothesis and showing how you answered the questions posed.
Even though the previous sections give prospective degree seekers a better sense of what to expect if they decide to write a thesis during their master's program, they don't necessarily help learners decide whether to pursue a thesis or non-thesis track. The following section highlights some of the reasons students frequently choose to complete a thesis or bypass the process altogether by providing a pros and cons list.
Why a Thesis Program
- Especially when entering a research-heavy discipline, completing a thesis shows prospective schools and employers that you possess the skills needed for researching and writing long-form reports.
- Students hoping to pursue a Ph.D. stand in better stead with admissions panels if they wrote a thesis during a master's program.
- Individuals hoping to enter a field that values syntax and grammar often better their writing skills by completing a thesis.
- Students who write a thesis can submit the final product to various academic journals, increasing their chances of getting published.
- Theses expand students' understanding of what they're capable of, deepen their ability to carry out an argument, and develop their skills in making connections between ideas.
Why a Non-thesis Program
- Because they don't require a significant written product, non-thesis master's tend to take less time to complete.
- Often mirrors a bachelor's program in terms of structure, allowing learners to complete classes and take exams without a great deal of research or writing.
- Students who excel in project-based assignments can continue building skills in this arena rather than focusing on skills they don't plan to use (e.g. research)
- Provides learners the opportunity to work more closely and more frequently with faculty on real-world projects since they don't spend hundreds of hours researching/writing.
- Allows learners to take more classes and gain hands-on skills to fill the time they would have spent researching and writing a thesis.
How to Choose a Master's Program: FAQs
Within some academic disciplines and professional fields, research and writing plays a key role in work done on a daily basis. Because of this, master's programs in these fields require learners to complete theses to compete against peers and be seen as competent in their work. Other disciplines, conversely, rely on other tools to accomplish work and progress ideas – making theses less important.
Yes. Master's programs focused more on application than research typically don't require a thesis – although they may still give students the option. Examples of common non-thesis master's programs include nursing, business, and education.
Even though non-thesis students won't be writing a 100-page paper, that doesn't mean they avoid completing a significant project. In place of a thesis, most applied master's programs require students to take part in at least one internship or complete a culminating project. These projects typically ask learners to take what they learned throughout coursework and create an expansive final project – examples include case studies, creative works, or portfolios.
While students who followed a non-thesis path routinely receive acceptance to Ph.D. programs, those with theses often find the process easier. Even if a learner pursues a Ph.D. in a discipline that isn't research-heavy, admissions panels still want to get a sense of your academic interests and ability to engage in independent, nuanced thought. Students with theses can provide solid proof of these skills, while those without may struggle to demonstrate preparedness as thoroughly.
The answer to this question depends on many factors, but typically it is okay not to do a thesis if you plan to enter a field that doesn't depend heavily on research or writing, or if you don't plan to complete a Ph.D.
Students wanting to work in academic, research, or writing should always opt for the thesis track. They should also follow this path if they have any doctoral degree aspirations.
Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to complete a thesis rests with the individual student. Figuring out how to proceed on this front requires lots of careful consideration, and learners should ensure they consider various aspects before coming to a final decision. The following section helps students consider how they should and should not come to a conclusion.
Dos and Don'ts of Choosing a Thesis or Non-thesis Program
- Consider the longevity of your decision: will you feel the same in 5-10 years or are you making a decision based on current desires?
- Talk to others who with experience in this area. Ask them questions about their decision-making process and if they regret their choice.
- Research potential thesis topics before starting a program. Going in with a game plan can help you feel more confident and settled about the process than if you're scrambling for a topic while in school.
- Reach out to prospective schools to speak with faculty and/or current students following both tracks. This will provide knowledge specific to the school while also expanding your network if you choose to attend there.
- Research Ph.D. entrance requirements to ascertain if the majority expect learners to possess a thesis when applying. This will give you a sense of whether you may experience issues later on if you do not complete one.
- Decide not to complete a thesis simply because you have never taken on such a task and feel overwhelmed or fearful that you will fail.
- Complete a thesis simply because you think it will look good on your resume. Theses require intense devotion over an extended amount of time; learners who complete them without conviction often find the process miserable.
- Forget to research alternatives to writing a thesis. Just because you don't complete a research paper doesn't mean a non-thesis track lacks rigor or challenging coursework.
- Forget to read examples of theses by previous students. If you feel overwhelmed by the task, reading work other people have done can often make the task at hand feel less scary.
- Let yourself off easy by taking the non-thesis path. If you find you have extra time in the program, talk to your advisor about taking more classes, develop meaningful projects for yourself, or see about presenting at an academic conference.
From the Expert

Sudiksha Joshi, Ph.D. is a learning advocate. Her mission is to empower our youth to think bigger, bolder thoughts and forge a career path that will change the world. She taps into her natural curiosity and ability to identify strengths to help students and those in transition find their path from feeling lost in the traditional ways of achieving success to charting their own path. Her work has been featured in Forbes, Huffington Post, Thrive Global, Medium and LinkedIn.
Why might a student decide to follow a thesis track? Why might they follow a non-thesis track?
A student might decide to take a thesis track if she/he wants to pursue a Ph.D. Also, if the students want to focus on careers where research and writing have a strong focus, the students opt for the thesis option. Research assistantships at the graduate level are also more often available to students who opt for the thesis option.
A student who might feel that writing is not one of their strengths might choose to go the non-thesis track. Likewise, a student who has other work commitments may find a non-thesis option more convenient.
Do you have any tips for deciding on a program?
I chose a thesis option because being able to conduct independent research was a big reason to go to graduate school. Also, showing the ability that I could do research was what afforded me research assistantships which meant that my tuition was paid for and I got a stipend that paid for expenses while I was in graduate school. This also allowed me the opportunity to work closely with the faculty mentor that provided me with the support and the accountability I wanted.
I would not recommend taking a non-thesis option if all the degree requires is for you to take courses. You have little to show in terms of your learning other than your grades unless you are already working on something on the side that does that for you and all you need is a certificate.
Opt for a non-thesis option if you can still work closely with a professor or on a project and if you'd rather be involved in multiple projects rather than focus on a single project. If you already have a good (informed) reason for choosing one over the other, go for it.
What's the most important thing to consider when choosing a program?
The most important thing to consider when choosing a program is getting excited about the projects that at least one of the faculty members are involved in. Do some research and see why you are excited about a particular work that at least one of the faculty members have been involved in.
Who should students talk to when considering options?
Students should talk to other students and also reach out directly to the graduate coordinator and even individual faculty members. This means that students should have done prior homework and have some good questions ready. Asking good questions will get you at least halfway through to make the right decision.
Graduate School
Master’s thesis guidelines.
- Academics & Research
- Rules & Regulations
A master’s student with a thesis requirement will submit the file through Brown's electronic theses and dissertation (ETD) system . The system is designed to collect and archive the thesis or dissertation as a text-based PDF file. An electronic file submitted through the ETD will appear in the Library's discovery service and in the Brown digital repository .
Web Searches and Unrestricted Downloads
In the spirit of the dissemination of new knowledge that is a hallmark of higher education, a thesis or dissertation will be subject to web searches and unrestricted downloads unless the student requests to opt out of the system and have the thesis or dissertation unavailable for download outside of the Brown community. A request to restrict download access to a thesis or dissertation has an initial two-year window from the time of degree conferral. Guidelines associated with restricted dissertation access are:
- The full text version will be available for download only to members of the Brown community.
- Web searches including the citation and abstract of restricted theses or dissertations will continue to be available to the general public.
- After two years the restriction will elapse.
- Restrictions on full text download may be renewed for two-year periods up to a total of ten years from the date of degree conferral. Requests for additional two-year restrictions should be made to the Graduate School.
- Any requests to extend the restriction beyond ten years must go to the Graduate Council for approval.
- In cases where the thesis or dissertation is a co-worked piece and there is disagreement between the student and the advisor over whether the material will or will not be available for download outside of the Brown community, the dispute will be brought before the Graduate Council for resolution.
To use the ETD system, the student must possess a valid username and password for accessing Brown’s computer network. If you are unable to create an account in the system, please contact [email protected] for assistance.
Graduate students are eligible to have degrees conferred, and to receive their diploma, at three different times over the course of the academic year.
For students who complete their degree requirements the preceding summer term. The Application to Graduate opens on July 1, 2024 and closes on September 6, 2024. Degrees are conferred on October 20, 2024.
For students who complete their requirements the preceding fall term. The Application to Graduate opens on October 1, 2024 and closes on January 10, 2025. Degrees are conferred on February 9, 2025.
For students who complete their requirements over the preceding spring term. The dissertation deadline is May 1, 2024. Please note, the Application to Graduate deadline is April 19, 2024.
The master's thesis and all of the associated forms and documents related to the completion of the degree must be submitted to the Graduate School by the deadlines listed above.
Registration
If a student registers for Semester I and completes all of the requirements for the degree during that semester, a fee for Semester II will not be charged.
View Sample Title Page
The Signature Page
As part of the overall completion process, the student must separately submit one signature page, which may be sent electronically to [email protected] . The signature page should bear the signature of the director (not the graduate representative or chairperson). The typed name of the director should appear under the signature line. Electronic signatures are acceptable. An unsigned copy of the signature page should be uploaded to the ETD system .
View Sample Signature Page
Every effort should be made to have the manuscript as perfect as possible in form and appearance. Pages containing handwritten corrections, typewritten strikeovers and unsightly erasures and the like will not be accepted. Good references for editorial details are the MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers, Theses, and Dissertations (Modern Language Association), Kate Turabian's A Manual for Writers of Term Papers, Theses and Dissertations (University of Chicago Press), and The Chicago Manual of Style (University of Chicago Press). The department should also be consulted regarding its policies or preferences in matters of format and style.
If publication of the thesis is anticipated, the medium of publication likely to be used should be considered when preparing the manuscript. If it is known in advance that the thesis will be published by a particular publisher or journal, the editorial practices of that publisher or journal should be followed. The form of footnotes and bibliography, in particular, may vary with different publishers and journals.
Type and Spacing Standard
Typefaces set to print at 10-, 11-, or 12-point font are acceptable. Typing or printing should be double-spaced, except for footnotes (single-space footnotes, with double spacing to separate one note from the next).
Page Numbers
Be consistent. Either put all page numbers (both Roman and Arabic) at the top of the page, or put all page numbers (both Roman and Arabic) at the bottom of the page.
Most theses consist of preliminary pages which are numbered using Roman numerals, and the thesis proper, which is numbered using Arabic numerals.
The preliminary pages must appear in the following order:
- Title page (do not number)
- Signature page (ii)
- Vita* (iii)
- Preface and acknowledgments (iv)
- Table of contents (v)
- List of tables vi List of illustrations (vii)
Should any element of the preliminary pages be longer than one page, number the pages consecutively. The preliminary pages should appear in this order but not necessarily with the page numbers shown above.
The thesis proper (including introduction, main body of the text, illustrations, appendices, and bibliography) is numbered using Arabic numerals. The numbering begins with 1 and runs consecutively to the end.
* The vita is an optional statement giving a short biography of the candidate, including institutions attended, degrees and honors, titles of publications, teaching or professional experience, and other pertinent information. Do not include date or location of birth or phone numbers.
Dating the Thesis
Because degrees are conferred three times a year, the title page should include the date that the degree is conferred.
The Abstract
If it is appropriate for the thesis to be accompanied by an abstract, it should, in a concise manner, present the problem of the dissertation, discuss the materials and procedure or methods used, and state the results or conclusions. Mathematical formulas, diagrams, and other illustrative materials should be avoided. The abstract should not be part of the thesis itself nor should it be included in the table of contents. It should be headed as follows:
Abstract of (TITLE OF THESIS), by (AUTHOR'S NAME), Degree [A.M., or ScM.], Brown University, May (YEAR IN WHICH DEGREE IS TO BE AWARDED).
The abstract should be prepared carefully since it will be published without editing or revision. The abstract should be double-spaced and may not exceed 350 words (maximum 2,450 characters — including spaces and punctuation — about 70 characters per line with a maximum of 35 lines).
Submission of Final Thesis
When the thesis is submitted electronically to the Graduate School, it must be in final form. It may not be revised in any way after it is presented. See the list of required items below and note that some, where noted, may be sent electronically to the Graduate School’s Academic Affairs Manager, Barbara Bennett. The thesis will not be accepted and the student’s degree will not be conferred if any item from this list is missing or incomplete. The online submission system will send notifications when each document has been received and approved by the Graduate School.
- One copy of the title page, which may be sent electronically.
- One signed signature page, which may be sent electronically to to [email protected] .
Digital Supplementary Material
Students interested in depositing digital supplementary materials along with their thesis are welcome to contact the Library for assistance. Please contact: Andrew Creamer in the Library at [email protected] .
Publishing the Master's Thesis
It is University policy that all research done at the University under its sponsorship must be freely published without restriction. Since 1954, the Graduate School has required that dissertations be published. In 1985, the Graduate Council reaffirmed that decision and approved the following policy:
"All Ph.D. dissertations and Master's theses will be open documents. The Graduate Council will not recommend the awarding of the Ph.D. or Master's degree until the dissertation or thesis is submitted to the Graduate School and accorded unlimited distribution status."
Exceptions to this requirement will be made only if there is a letter from a publisher stating that the dissertation will be published within one year after the degree is awarded and that requests that circulation of the dissertation be withheld for twelve months after the degree is conferred. Six months will be allowed for the clearing of a patent.
If you have a question about temporarily removing your dissertation from the Library's digital repository , please contact [email protected] .
The Diploma
The Office of the Registrar's Application to Graduate provides the degree candidate with an opportunity to indicate how the diploma name should appear. Otherwise, the name that will appear on the diploma and in the Commencement program, and under which the Library will catalog the dissertation, is the name under which the candidate is officially registered. Any request for a change of registered name should be addressed to the Office of the Registrar and accompanied by supporting legal documentation, such as a court order, marriage license, passport, driver’s license, or social security card.
Certificate of Completion
If all academic requirements for the degree and all financial obligations have been met before May 1, the Office of the Registrar will issue a certificate of completion within three weeks of the candidate's request.
If you have any questions regarding the submission of your thesis, please contact Barbara Bennett in the Graduate School at (401) 863-2843.
- Graduate School
How to Write a Master's Thesis Proposal
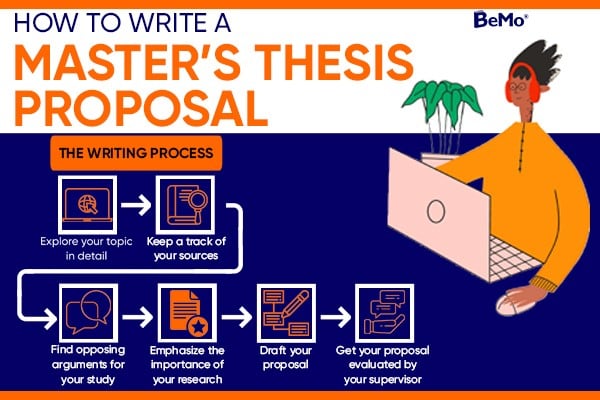
How to write a master’s thesis proposal is one of the most-asked questions by graduate students. A master's thesis proposal involves a copious amount of data collection, particular presentation ethics, and most importantly, it will become the roadmap to your full thesis. Remember, you must convince your committee that your idea is strong and unique, and that you have done enough legwork to begin with the first few drafts of your final thesis. Your proposal should serve as a foundational blueprint on which you will later build your entire project. To have the perfect thesis proposal, you need to have original ideas, solid information, and proper presentation. While it is a good idea to take assistance from thesis writing services , you still need to personally understand the elements that contribute to a master’s thesis proposal worthy of approval. In this blog, we will discuss the process of writing your master’s thesis proposal and give you tips for making your proposal strong. Stay tuned!
>> Want us to help you get accepted? Schedule a free strategy call here . <<
Article Contents 8 min read
How to decide the goals for your master's thesis.
If you are pursuing a master’s or a PhD , you will be undertaking a major research paper or a thesis. Thus, writing a thesis proposal becomes inevitable. Your major objective for pursuing a master’s degree is to improve your knowledge in your field of study. When you start your degree, you delve deeper into different concepts in your discipline and try to search for answers to all kinds of questions. If you come across a question that no one can answer, you can select that question as your research thesis topic.
A master's thesis proposal will have multiple sections depending on your decided layout. These sections will continuously support your argument and try to convince the reader of your core argument. The structure will also help you arrange the various parts of the paper to have a greater impact on the readers. A paper should always begin with you giving a brief summary of the topic and how you have come across it. The introduction is particularly important because it will give the readers a brief idea about the topic of discussion and win their interest in the matter.
After the summary has been given, slowly you need to progress into the body of the thesis proposal which would explain your argument, research methodology, literary texts that have a relation to the topic, and the conclusion of your study. It would be similar to an essay or a literary review consisting of 3 or 4 parts. The bibliography will be placed at the end of the paper so that people can cross-check your sources.
Let's take a look at the sections most master's thesis proposals should cover. Please note that each university has its own guidelines for how to structure and what to include in a master’s thesis proposal. The outline we provide below is general, so please make sure to follow the exact guidelines provided by your school:
Restate your primary argument and give us a glimpse of what you will include in the main master\u2019s thesis. Leave the reader wanting more. Your research proposal should talk about what research chapters you are trying to undertake in your final thesis. You can also mention the proposed time in which you will complete these chapters. ","label":"Conclusion and proposed chapters","title":"Conclusion and proposed chapters"}]" code="tab1" template="BlogArticle">
A thesis proposal needs to be convincing enough to get approval. If the information is not enough to satisfy the evaluation committee, it would require revision. Hence, you need to select and follow the right methodology to make your argument convincing. When a research proposal is presented, the reader will determine the validity of your argument by judging the strength of your evidence and conclusions. Therefore, even writige:ng a proposal will require extensive research on your part. You should start writing your thesis proposal by working through the following steps.
Interested in a summary of the points covered below? Check out this infographic:
Exploring your topic in detail
You need to delve deeper into your chosen topic to see if your idea is original. In the process of this exploration, you will find tons of materials that will be supportive of your argument. When choosing your research topic and the problem you want to explore, you should always consider your primary research interest (yes, the one which you had mentioned in your research interest statement during grad school applications) for a better master’s thesis. You have a high probability of performing better in an area that you have always liked as compared to any other research area or topic.
Reviewing the literature
You have to include all the sources from where you have formed your argument and mention them in the thesis proposal. If you neglect to mention important source texts, the reader may consider it to be plagiarism. Furthermore, you want to keep track of all your research because it will be easier to provide references if you know the exact source of each piece of information.
Finding opposing arguments for your study
You should also mention any texts that would counter your argument and try to disprove their claims in the thesis. Make sure to use evidence if you try to disprove the counterarguments you face.
Emphasizing the importance of your research
At the end of the thesis proposal, you need to convince the reader why your proposal is important to your chosen field of study, which would ultimately help you in getting your topic approved. Thus, it is essential to outline the importance of your research thoroughly.
Drafting your proposal
After doing proper research, you should go ahead and draft your proposal. Remember you will not get it right in just one draft, it will take at least 50 attempts to come up with a satisfactory proposal. You should proofread your draft several times and even have a fellow student review it for you before sending it further to your research supervisor.
Getting your proposal evaluated by your supervisor
After you have written sufficient drafts, you need to get your proposal evaluated by your research supervisor. This is necessary to meet the graduate research requirements. It will ensure the clarity and correctness of your proposal. For your supervisor to evaluate your proposal, you should complete the research methodology part along with sufficient proposed work.
Since your supervisor will play a crucial role in your master's research thesis, you must choose a supervisor who can be your ultimate guide in writing your master's thesis. They will be your partner and support system during your study and will help you in eliminating obstacles to achieving your goal.
Choosing the ideal supervisor is a pretty daunting task. Here’s how you can go about the process:
You should approach your professor with an open mind and discuss the potential goals of your research. You should hear what they think and then if you both mutually agree, you can choose them as your supervisor for your master\u2019s thesis. "}]">
Length of a Master’s Thesis Proposal
The length of a master’s thesis proposal differs from university to university and depends on the discipline of research as well. Usually, you have to include all the above-mentioned sections, and the length is around 8 pages and can go up to 12-15 pages for subjects such as the liberal arts. Universities might also define the number of words in the guidelines for your master’s thesis proposal and you have to adhere to that word limit.
Are you debating between pursuing a Masters or a PhD? This video has details that can help you decide which is best for you:
How to Format a Research Thesis Proposal Correctly?
Now that you know how to write a thesis proposal, you must make it presentable. Although your school might give your specific instructions, you can keep in mind some of the general advice:
- You can use some basic font like Times New Roman and keep the font size to 10 or 12 points.
- The left margin should be 1.5 inches and all other margins should be 1 inch each.
- You should follow double-spacing for your content.
- The first line of paragraphs should be indented 0.5 inches and the paragraphs should be left or center aligned.
Tips to Write a Strong Master's Thesis Proposal
When you are writing your master’s thesis proposal, you should keep these tips in mind to write an excellent master’s thesis proposal with all the correct elements to get approval from the evaluating committee:
Select your research objectives wisely
You should be clear on what you wish to learn from your research. Your learning objectives should stem from your research interests. If you are unsure, refer to your grad school career goals statement to review what you wanted out of grad school in the first place. Then, choose your objectives around it.
Write a clear title
The title of your research proposal should be concise and written in a language that can be understood easily by others. The title should be able to give the reader an idea of your intended research and should be interesting.

Jot down your thoughts, arguments, and evidence
You should always start with a rough outline of your arguments because you will not miss any point in this way. Brainstorm what you want to include in the proposal and then expand those points to complete your proposal. You can decide the major headings with the help of the guidelines provided to you.
Focus on the feasibility and importance
You should consider whether your research is feasible with the available resources. Additionally, your proposal should clearly convey the significance of your research in your field.
Use simple language
Since the evaluation committee can have researchers from different subject areas, it is best to write your proposal in a simple language that is understandable by all.
Stick to the guidelines
Your university will be providing the guidelines for writing your research proposal. You should adhere to those guidelines strictly since your proposal will be primarily evaluated on the basis of those.
Have an impactful opening section
It is a no-brainer that the opening statement of your proposal should be powerful enough to grasp the attention of the readers and get them interested in your research topic. You should be able to convey your interest and enthusiasm in the introductory section.
Peer review prior to submission
Apart from working with your research supervisor, it is essential that you ask some classmates and friends to review your proposal. The comments and suggestions that they give will be valuable in helping you to make the language of your proposal clearer.
You have worked hard to get into grad school and even harder on searching your research topic. Thus, you must be careful while building your thesis proposal so that you have maximum chances of acceptance.
If you're curious how your graduate school education will differ from your undergraduate education, take a look at this video so you know what to expect:
Writing the perfect research proposal might be challenging, but keeping to the basics might make your task easier. In a nutshell, you need to be thorough in your study question. You should conduct sufficient research to gather all relevant materials required to support your argument. After collecting all data, make sure to present it systematically to give a clearer understanding and convince the evaluators to approve your proposal. Lastly, remember to submit your proposal well within the deadline set by your university. Your performance at grad school is essential, especially if you need a graduate degree to gain admission to med school and your thesis contributes to that performance. Thus, start with a suitable research problem, draft a strong proposal, and then begin with your thesis after your proposal is approved.
In your master’s thesis proposal, you should include your research topic and the problem statement being addressed in your research, along with a proposed solution. The proposal should explain the importance and limitations of your research.
The length of a master’s thesis proposal is outlined by the university in the instructions for preparing your master’s thesis proposal.
The time taken to write a master’s thesis proposal depends upon the study which you are undertaking and your discipline of research. It will take a minimum time of three months. The ideal time can be around six months.
You should begin your master’s thesis proposal by writing an introduction to your research topic. You should state your topic clearly and provide some background. Keep notes and rough drafts of your proposal so you can always refer to them when you write the first real draft.
The basic sections that your master’s thesis proposal should cover are the problem statement, research methodology, proposed activities, importance, and the limitations of your research.
A master’s thesis proposal which clearly defines the problem in a straightforward and explains the research methodology in simple words is considered a good thesis proposal.
You can use any classic font for your master’s thesis proposal such as Times New Roman. If you are recommended a specific font in the proposal guidelines by your institution, it would be advisable to stick to that.
The ideal font size for your master’s thesis proposal will be 10 or 12 points.
Want more free tips? Subscribe to our channels for more free and useful content!
Apple Podcasts
Like our blog? Write for us ! >>
Have a question ask our admissions experts below and we'll answer your questions, get started now.
Talk to one of our admissions experts
Our site uses cookies. By using our website, you agree with our cookie policy .
FREE Training Webinar:
How to make your grad school application stand out, (and avoid the top 5 mistakes that get most rejected).
Time Sensitive. Limited Spots Available:
We guarantee you'll get into grad school or you don't pay.
Swipe up to see a great offer!

- October 15, 2023
- Academic Advice
Thesis vs. Non-Thesis Master’s Programs: Which is Right for You?
UOTP Marketing

Continuing your educational journey within your chosen field is an experience that fosters personal and professional growth. The next milestone in your academic path often involves pursuing a Master’s degree , with options ranging from thesis-based programs to non-thesis alternatives. Deciding between these two paths is significant as it shapes your academic and career paths.
But how can you decide which is right for you before getting decision fatigue?
Let’s explore the difference between thesis vs. non-thesis Master’s programs, their unique characteristics, and reasons for choosing one or the other.
Do You Have to Write a Thesis for Your Master’s Program?
Whether you have to write a thesis for your Master’s program depends on the specific requirements of the program you’re enrolled in. It’s important to note that while not all Master’s programs require writing a thesis, a significant number of them do.
What is a Thesis vs. Non-Thesis Master’s Program?
A thesis Master’s program involves completing a large research project spanning over several semesters. Students are expected to conduct original research on a specific topic under a faculty advisor’s guidance, culminating in a thesis likely to be published. Completing and defending the thesis is a crucial part of the degree requirement.
A non-thesis Master’s program doesn’t involve a specific research focus but rather a more coursework and practical experience, allowing students to gain specific skills and knowledge applicable to their field of study. After completing their program’s core course requirements, students can choose any of the electives to meet their degree requirements. Depending on the institution, you may be required to do a Master’s Degree Capstone project, including reviewing previous courses, a comprehensive exam, or a summary project.
Why Choose a Thesis Master’s Program?

Thesis Master’s programs offer several advantages, be that contributing to new findings in your field, close collaboration with professors and researchers, and standing out to potential employers with your abilities to work independently and analyze complex issues. However, the primary advantages are:
Research Experience
Thesis programs allow you to conduct extensive research on a specific topic that piques your interest. This way, you’ll gain expertise and a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.
Academic Growth
Writing a thesis helps sharpen your critical thinking, analytical, and writing skills. It also challenges you to think independently, analyze a large amount of data, and draw meaningful conclusions. Furthermore, it prepares you for doctoral studies, familiarizing you with the rigor of independent research and equips you with the necessary skills to succeed.
Why Choose a Non-Thesis Master’s Program?
Non-thesis master’s programs also come with numerous advantages for students, including flexibility in scheduling, a range of career opportunities, shorter competition time, etc. Here are the main advantages:
Non-thesis programs prioritize coursework, fostering the development of practical skills and their real-world application. This approach enables you to actively engage in hands-on learning experiences highly sought after in today’s job market. Critical thinking, communication, problem-solving, and leadership abilities are some of those skills.
Suitability for Professionals
Another advantage to pursuing a non-thesis Master’s program is that it doesn’t take as much time as the thesis Master’s programs. That way you can enter the workforce faster. It’s also well-suited for professionals already established in their field who are seeking to further their education and advance in their careers.
The Academic and Career Outcomes of Thesis vs. Non-Thesis Master’s Programs
The academic outcomes for the thesis Master’s program graduates involve preparation for Ph.D. programs , opening doors to advanced research and specialized roles in research institutions. This provides solid research skills and helps them publish their work. Common career paths for graduates include research positions in academia, government, or private sectors. Some also pursue teaching careers in colleges and universities. Degree programs that usually require a thesis include sciences, social sciences, engineering, and humanities (history, philosophy, and language studies).
Non-thesis Master’s program graduates typically achieve academic outcomes focused on mastering practical, directly applicable skills within their field. While these programs are more career-oriented, graduates can still pursue a Ph.D. They can benefit from diverse career options in different settings and find employment in managerial, administrative, or specialized roles in their field. Degree programs that don’t usually require a thesis are business, education, healthcare administration, IT management, etc.
Thesis vs. Non-Thesis Master’s Programs, That is the Question
With their abundance of advantages, choosing between the two can be pretty tricky. So, let’s compare thesis vs. non-thesis Master’s programs and help you make an informed decision.
Personal and Career Goals
A thesis Master’s program is ideal if you’re interested in furthering in academia and want to pursue a Ph.D ., as these programs can provide the necessary tools to enhance your credentials for research-based careers. Meanwhile, a non-thesis Master’s program will suit you better if you’re seeking to gain practical skills to integrate into the industry immediately, as they can include practical projects or internships according to industry demands.
Time and Financial Considerations
Thesis Master’s programs can extend the duration of your studies, as researching, writing, and defending the thesis can take several semesters to complete and can cause financial strain due to additional costs like lab fees and materials. In contrast, non-thesis ones can help you enter the job market promptly as they are shorter, allowing you to save time and money.
Interested in pursuing a degree?
Fill out the form and get all admission information you need regarding your chosen program.
This will only take a moment.
Message Received!
Thank you for reaching out to us. we will review your message and get right back to you within 24 hours. if there is an urgent matter and you need to speak to someone immediately you can call at the following phone number:.
By clicking the Send me more information button above, I represent that I am 18+ years of age, that I have read and agreed to the Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy , and agree to receive email marketing and phone calls from UOTP. I understand that my consent is not required to apply for online degree enrollment. To speak with a representative without providing consent, please call +1 (202) 274-2300
- We value your privacy.
Field of Study and Program Requirements
When deciding between a thesis and a non-thesis Master’s program, a crucial element to take into account is the field of study and the program’s specific requirements. A thesis Master’s program is better suited for those pursuing research-oriented fields, while a non-thesis program is a more fitting choice for individuals with a strong focus on their career. Furthermore, program requirements for thesis programs require substantial research to culminate in a thesis, whereas non-thesis ones require capstone projects, internships, or comprehensive exams.
Switching from a Non-Thesis to a Thesis Master’s Program, or Vice Versa
Switching from a non-thesis to a thesis Master’s program, or vice versa, is possible in many institutions, although the process and requirements may vary. Switching from a non-thesis to a thesis program generally requires getting approval from the academic advisor or department, completing additional research methodology classes, finding a thesis advisor, and applying to the thesis program.
Switching from a thesis to a non-thesis Master’s program requires having at least a 3.0 GPA, getting approval from the academic advisor, transferring credits of research methodology classes, and formally applying to the thesis program.
Choosing between a thesis and a non-thesis Master’s program ultimately depends on your career goals, research interests, and personal preferences. Thesis programs provide a robust foundation for research-oriented careers and advanced studies, while non-thesis programs offer practical skills tailored for immediate industry integration. Regardless of your choice, both paths offer unique advantages, ensuring you gain the knowledge and skills needed to thrive in your chosen field.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
What is the difference between a thesis vs. non-thesis master’s program.
The key difference between a thesis and a non-thesis Master’s program is that thesis Master’s programs require original research and completion of a thesis, whereas non-thesis ones focus on coursework and practical experiences.
Do I have to write a thesis for a Master’s program?
If you’re pursuing a research-oriented Master’s degree in sciences, engineering, social sciences, humanities, etc., you’ll probably have to write a thesis. Whereas, if you’re pursuing a Master’s degree in education, business healthcare administration, or IT management, you’re more likely not to have to complete a thesis.
Is a thesis required for all Master’s degree programs?
Although a thesis isn’t required for all master’s degree programs, many programs require one.
What should I consider when deciding between a thesis and non-thesis program?
There are several factors to consider when choosing between a thesis and a non-thesis Master’s program, including your career goals, interest in research, duration of studies, personal strengths and preferences, cost, and program requirements.
Are there any financial and duration differences between thesis and non-thesis Master’s programs?
There can be financial and duration differences between thesis and non-thesis Master’s programs. Thesis programs can be more expensive as you’ll have to spend additional resources on materials, lab fees, and data collection. In contrast, the main cost for non-thesis programs is tuition fees, which can be slightly lower. Furthermore, thesis programs require additional time to conduct research, write, and defend the thesis. In contrast, non-thesis programs allow students to earn the degree in a shorter period.
Why should I choose a thesis Master’s program?
You should choose a thesis Master’s program if you’re interested in a research-heavy discipline and want to showcase your knowledge and expertise in an evidence-based, thorough thesis.
Why should I choose a non-thesis Master’s program?
You should choose a non-thesis Master’s program if you want to enter the workforce earlier, don’t want to spend several semesters collecting data, and want to focus more on application than research.
Can non-thesis Master’s graduates still pursue doctoral studies later?
Yes, non-thesis Master’s graduates can still get accepted into a doctoral program. However, thesis Master’s graduates can go through the process more efficiently, as admissions panels want to gain insight into your academic interests and ability to engage in nuanced thought.
Share it with your friends!
Explore more.

Accounting vs. Finance Degree: Which Major to Choose?

12 Important Bookkeeping Skills You Need for a Successful Career
Recent resources.

What Can You Do With a Hospitality Management Degree? Best Hospitality Careers

What Can You Do with an International Studies Degree [2024]

9 Benefits of Learning a Second Language

Associate’s vs. Bachelor’s: Which One To Choose?
INTERESTED IN LEARNING MORE?
Chat with an Admissions Officer Now!

- Associates Degree
- Bachelors Degrees
- Masters Degrees
- Doctoral Degrees
- Faculty & Staff
- Accreditation
- Student Experience
QUICK LINKS
- Admission Requirements
- Military Students
- Financial Aid
Request More Information
Florida State University
FSU | The Graduate School
Main navigation Pulldown
The graduate school.
- Degrees and Programs
- Degree Programs
Master's Degree Programs
Apply now and waive the gre requirement.
Florida State University is waiving the GRE requirement for most Master's and Specialists programs through Fall 2026. Apply Now>
Contact your department for more information regarding admissions and general degree program requirements. Search for your graduate representative below!

Anthropology
View Admissions Requirements

Art Education
Art Education , Arts Administration , Art Therapy , Museum Education and Visitor-Centered Curation

Art History
Art History , Museum & Cultural Heritage Studies

Asian Studies

Athletic Coaching

Biological Science
Cell and Molecular Biology , Ecology and Evolution , Neuroscience

Business Analytics

Chemical and Biomedical Engineering

Graduate Program Overview

Civil Engineering

How to Apply

Communication
Integrated Marketing Communication , Media Communication Studies , Public Interest Media and Communication

Communication Science and Disorders
Main Campus Program , Online Program

Computational Science

Computer Science
Corporate and Public Communication
View Admission Requirements

Criminology
View Campus Master's Admissions Requirements , View Online Master's Admissions Requirements

Curriculum and Instruction
Elementary Education , English Teaching , Social Science Teaching , Special Education Teaching , Visual Disabilities

Curriculum and Instruction (Online)

American Dance Studies , MFA in Dance , Returning Professional , Studio and Related Studies

Data Science
Computer Science , Mathematics , Scientific Computing , Statistics

Information for Prospective Students

Earth, Ocean, and Atmospheric Sciences
Environmental Studies , Geology , Meteorology , Oceanography

Educational Leadership and Administration
Education Policy and Evaluation , Higher Education , History and Philosophy of Education , International and Multicultural Education

Educational Leadership and Administration (Online)

Educational Psychology and Learning Systems
Career Counseling (MS/EdS) , Clinical Mental Health Counseling (MS/EdS) , School Counseling (MS/EdS) , School Psychology (MS/EdS)

Instructional Systems and Learning Technologies , Learning and Cognition , Measurement and Statistics

Electrical Engineering

Creative Writing , Literature, Media, and Culture , Rhetoric and Composition

Entrepreneurship
Online Hospitality Entrepreneurship , Product Development , Social and Sustainable Enterprises , Textiles and Apparel Entrepreneurship

Exercise Physiology
Exercise Physiology , Sports Nutrition , Sports Sciences

Geography MS Requirements , GIS Program Requirements

Human Development and Family Science
MS in Human Development and Family Science , MS/PhD in Human Development and Family Science

Industrial Engineering
Engineering Management , Systems Engineering PC Campus/Online , Systems Engineering Tallahassee Campus

Information
Information MS , Information Technology

Interior Architecture and Design

International Affairs
Juris Master
Juris Master (Online)
Law Enforcement Intelligence

View Student Profiles

Management Information Systems

Materials Science
Explore Research Areas

Mathematics

MBA Full-Time Program

MBA Online Program
Mba part-time program.

Mechanical Engineering

Master's Bridge Program

Modern Languages
East Asian Languages , French , German , Italian , Slavic , Spanish

Motion Picture Arts
Production , Writing

View Admissions Homepage
Nutrition and Food Science

Organizational Management & Communication
Admission Requirements

MA in Philosophy

Physician Assistant

Political Science

Public Administration

Public Health

Risk Management and Insurance

Russian and Eastern European Studies
Admissions Requirements

Social Work (MSW)

Sport Management

Sport Psychology

Acting , Costume Design , Directing , Technical Production , Theatre Management , Theatre Educators , Theatre Studies

Urban and Regional Planning
- Top Courses
- Online Degrees
- Find your New Career
- Join for Free

Master of Advanced Study in Engineering
Ready to apply? Check out the MAS-E Curriculum Planner and start customizing your learning journey!

UC Berkeley College of Engineering
Accredited degree from a top 3 engineering school.
Taught and offered by UC Berkeley College of Engineering
Learn from top-tier, world-renowned faculty
Select the courses that best match your career goals
Complete in as little as 9 months
Customize the degree to your schedule
100% online learning
Lecture videos, hands-on projects, live office hours and real-time connections with instructors and peers
$42,000 USD total tuition
($1,750 x 24 units = $42,000), plus applicable per-semester fees, with pay-as-you-go tuition for each unit*
Earn your master's from Berkeley Engineering without putting your career on pause
Ready to advance, transform, and enhance your career in engineering and technology? Earn your Master of Advanced Study in Engineering (MAS-E) from Berkeley Engineering, consistently ranked among the top three engineering schools in the country by U.S. News & World Report .
Designed for part-time, self-paced study, the MAS-E program gives you the ability to complete your master’s without putting your career on pause. Learn on your schedule with courses across four distinct concentrations, providing you with extended skill sets across different types of engineering . Through this program, you will learn from and interact with the elite faculty at Berkeley Engineering to develop the critical knowledge and technical skills you need to succeed at the highest levels in your career.
Customize your degree for your unique career goals
Design your degree learning journey with the Berkeley MAS-E Curriculum Planner, your comprehensive guide to exploring and creating your unique plan to help you meet your career goals. Save and share your plan with a Berkeley Engineering academic advisor.
With 4 distinct interdisciplinary concentrations to choose from, the degree is truly versatile to provide a well-rounded engineering education:
Learn more about the curriculum or career outcomes .
Berkeley's MAS-E in the headlines
Fortune on UC Berkeley's commitment to making education more accessible for working professionals.
Forbes on "knowledge upgrades" in STEM fields through MAS-E to help today's engineers keep pace with the speed of innovation.
BestColleges.com on the asynchronous, personalized nature of the MAS-E. Students will be able to complete coursework from anywhere in the world, and even leverage live office hours with top Berkeley educators throughout their study.
KTVU Fox 2 interview of Quentin McAndrews from Coursera who speaks to this incredible online opportunity as well as the prestige of Berkeley.
Admissions information
Applications for the Spring 2025 session are open!
Important Dates : Note all applications close at 8:59PM PT.
Spring 2025
- June 4, 2024: Exploring Berkeley Engineering's First 100% Online Degree Webinar - Register here!
- June 11, 2024: Spring 2025 Priority Application Deadline
- July 22, 2024: Spring 2025 Final Application Deadline
Interested in Learning More about the MAS-E?
- Watch the MAS-E Overview Video
Try the MAS-E Preview Course
- Ready to apply? Check out the MAS-E Curriculum Planner and get started on your degree!
Priority application deadline is June 11
Request more information
$1,750 per unit

Watch Berkeley Engineering Dean Tsu-Jae King Liu explain how the MAS-E can help you reach your unique career goals
Berkeley Engineering, the #1 public engineering school in the U.S. , is offering a new, fully online master’s degree.
This flexible and customizable degree program makes a Berkeley education accessible to working engineers and STEM professionals who want to move ahead without putting their careers on pause. Learn how the MAS-E program can help you gain state-of-the-art knowledge and technical skills in your field, and help you to accelerate your career.
Watch the full video
Pay-as-you-go tuition for each unit
- $42,000 USD tuition, plus applicable per semester fees* *Figures for tuition and fees represent currently approved or proposed amounts and may not be final. Actual tuition and fees are subject to change by the University of California as determined to be necessary or appropriate. Final approved tuition and fee levels may differ from the amounts presented.
- Pay-as-you-go tuition Because you only have to pay for the courses you’ve enrolled in, you have more flexibility to temporarily take time away from your studies if your current job calls for it.
- Financial aid opportunities Discover more ways you can make this program fit your budget by exploring assistance options like federal loans, scholarships and employer tuition reimbursement. Learn more: https://financialaid.berkeley.edu/prospective-students/

Wondering if the MAS-E is right for you?
UC Berkeley's "Master of Advanced Study in Engineering Degree Preview" course showcases some of the elite faculty and advanced instruction you'll experience when you join the MAS-E degree program. The course introduces you to the innovative MAS-E program and its career-focused concentration areas, giving you a short preview of selected degree course content.
Frequently asked questions
What appears on the degree certificate is it the same degree as the on-campus program.
The Master of Advanced Study in Engineering (MAS-E) is a unique online degree. It does not exist as an on-campus program. Upon completion of program requirements, students receive a Master of Advanced Study in Engineering degree. You can also display your chosen theme area on your resume to demonstrate your specialized skills. The MAS-E degree is a STEM degree.
What career options will I have with this degree?
With this flexible degree, you can choose your courses to prepare for senior technical and management roles in a range of fields, such as electrical engineer, materials engineer, environmental engineer, and more. You can tailor your degree to prepare you for the career you're most interested in, from advanced manufacturing to integrated circuits, environmental engineering, AI and transportation, agriculture, control systems, to robotics. The curriculum covers a broad array of interdisciplinary engineering domains, and is designed for personalization to meet your career goals.
How many courses can students take at a time?
The MAS-E program can be taken part-time or full-time, depending on your needs. Program staff can help advise on a per-term course load based on your interests and career goals. Please note: the Graduate Maximum Unit Limit is 20.5 units per semester. Six units minimum per semester is required to qualify for federal loans.
How long does it take to complete the program?
Students may complete the program in a minimum of two semesters (full-time) and a maximum of four years (part-time). We anticipate that most students will be on a two- to three-year length program plan. MAS-E classes are offered in fall, spring and summer sessions. Students may choose to skip only the summer session(s) without withdrawing from the program. Note that master’s degree students must be enrolled in a minimum of four units per semester for at least two semesters to meet University of California academic residency requirements. The four-unit semesters do not need to be consecutive. Otherwise, fall and spring sessions have a minimum enrollment of one unit to maintain student status.
Can I switch between online and on-campus programs?
The MAS-E degree is only available online. This is by design as the innovative and dynamic curriculum of fully online courses helps you fit your studies into your schedule with your personal and professional life.
Do the same faculty teach online and on-campus courses?
Yes, you’ll learn from Berkeley Engineering faculty who are recognized as leading experts in their fields and teachers and researchers in the world.
Are there online office hours with instructors?
Throughout each course of the program, you’ll be able to attend live, online office hours with faculty. Additional instructional staff will also help you stay on track and answer your questions.
Do online students have access to on-campus facilities?
When you join the MAS-E program, you’ll have access to a range of campus resources such as:
- GradPro (professional development)
- Graduate writing center
- D-Lab (social sciences research and data)
- Career Center
- UC Berkeley Libraries
- Student well-being portal
Will online students get a student ID card?
Yes. Your CalNet ID and password is sufficient for all Web access needs, but online students may also get a physical Cal 1 ID card, which would need to be picked up in person on campus.
Are internships part of the program?
Internships are not part of the MAS-E curriculum, but these industry-focused courses will help prepare you with hands-on projects and career-oriented outcomes.
Is there an application fee?
Yes, you must submit an application fee when you apply. The application fee is not refundable. If you are a U.S. citizen or current permanent resident, the application fee is $135; for all others, the fee is $155.
U.S. citizens or permanent residents who can demonstrate financial need are eligible to apply for a waiver of the application fee. See guidelines for waivers. Read more about application fees at https://grad.berkeley.edu/admissions/steps-to-apply/requirements/
Can I transfer credits into the program?
No, due to the unique MAS-E one-unit courses, credits earned from classes taken at other institutions are not transferable to the MAS-E degree program.
What is the payment schedule? Do I need to pay for the entire degree upfront?
You will pay tuition and fees each semester according to how many courses you enroll in. The tuition cost per course unit is $1,750. Bills are issued each semester and can also be paid through monthly installments.
Additional per-semester campus fees are required. Campus fees total approximately $908 for the fall 2023 semester. First semester students also pay a one-time document management fee of $107. Tuition and fees are pending approval and subject to change.
Berkeley Engineering is pleased to offer MAS-E scholarships to qualified candidates. Recipients are awarded partial scholarships based on criteria including academic merit; financial need; overcoming personal, academic or professional barriers; and experience with diversity. Please communicate these through your application’s responses in the:
- Economic Background section
- Personal History Statement
- Personal Information
Do I need an engineering background? Is work experience required?
To apply to the MAS-E program, a bachelor’s degree in engineering or a related STEM field is required. Your bachelor’s degree (or recognized equivalent) must be from an accredited institution.
What are the English proficiency requirements? Are there any additional requirements for international students?
If you have completed a degree in a country/region in which the official language is not English, you are required to submit official evidence of English language proficiency via the TOEFL or IELTS exam. If you have completed at least one year of full-time academic coursework (with grades of B or better) in residence at a recognized U.S. institution, you do not need to take a standardized test. Instead, you must upload an unofficial transcript from the recognized U.S. institution.
What is the process for letters of recommendation?
For more information and FAQ's about letters of recommendation, visit Berkeley's page here.
More questions?
Popular Searches
- Transcripts
- Career Services
- Human Resources
Our Campuses
- Daytona Beach, FL
- Prescott, AZ
- Embry-Riddle Online
Degrees & Programs
- Certificate Programs
- Associate's Degrees
- Bachelor's Degrees
- Master's Degrees
- Doctoral Degrees

Master of Science in Computer Science
The Master of Science in Computer Science enhances cybersecurity careers in developing and maintaining secure networked systems.
About the Master of Science in Computer Science
Computer Science careers are on the rise in both public and private sectors worldwide, ranging in everything from research in artificial intelligence and machine learning to secure systems design to software development. A Master of Science in Computer Science from Embry‑Riddle prepares graduates to either begin or further advance their careers in the fields of technology and cybersecurity.
The Electrical Engineering and Computer Science’s (EECS) Industry Advisory Board ensures that curriculum and research activities are aligned with what’s going on in the software industry. The accelerated program is a cutting-edge degree in a dynamic, growing field.
Student Learning Outcomes
What you will learn while pursuing a Computer Science degree:
- Apply fundamental computer science professional practices to analyze, design and implement systems.
- Apply knowledge of advanced topics in cybersecurity engineering and in computer science.
- Communicate effectively on issues pertaining to computer science and cybersecurity.
Computer Science Career Opportunities
Careers and employers.
Computer Science master's graduates often secure positions such as:
- AI researchers
- Computer scientists
- Cybersecurity consultants
- Cybersecurity engineers
- Digital forensics investigators
- Machine learning engineers
- Software engineers
Computer Science Salary Information
As of 2023, graduates with a degree in Computer Science receive competitive salaries , with an average income of $112,000 annually.
About Computer Science at the Daytona Beach, FL Campus
About computer science at the daytona beach campus.
Housed in the Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Department in the College of Engineering , the Master of Science in Computer Science prepares students to address challenges in the development of algorithms and data structures as well as maintaining secure operations and cybersecurity policy.
The Daytona Beach Campus is home to the Cybersecurity Engineering Laboratory (CybEL), a Real-Time Systems Laboratory, a Digital Systems Laboratory and a Software Development Laboratory, all of which offer students systems design and hands-on experience as it relates to cybersecurity attacks and corresponding mitigations, as well as software development and programming.
Tracks/Specialties and/or Certificates
Computer Science graduates may select one of two areas of concentration:
- Computer Science: 9 credits
- Cybersecurity Engineering: 9 credits
Computer Science Information
- Credits: 30
- Online or In-Person: In-Person
- Thesis: Thesis & Graduate Research Project Options
Helpful Links
- Tour our Daytona Beach Campus
- Discover the Department's Faculty
- Explore the Fields of Study: Engineering & Computer & Technology & Security, Intelligence and Safety
- Find Related Clubs & Organizations
Students will:
- Have an ability to apply fundamental computer science professional practices to analyze, design, and implement security-critical systems.
- Have an ability to apply knowledge of advanced topics in cybersecurity engineering and/or computer science.
- Have an ability to communicate effectively on issues pertaining to computer science and/or cybersecurity.
Degree Requirements
The Master of Science in Computer Science degree is granted to students who complete the coursework described below. The program consists of nine hours of core courses, nine hours of Area of Concentration courses, and nine hours of open electives for the Graduate Research Project Option or six hours of open electives for the Thesis Option.
Program Core Requirements
Area of concentration.
Students may choose one of the two Areas of Concentration as shown below.
Computer Science
Cybersecurity engineering.
Students may choose the Graduate Research Project or Thesis option, as shown below.
Graduate Research Project Option
Thesis option, get started now:.
Estimate your tuition by using the Tuition Calculator
View Financial Aid Information
Learn about our General Education
Student Achievement Data
Find out about transferring credits to this degree
Learn more about our Veterans & Military benefits
View our Academic Calendar
RELATED DEGREES
You may be interested in the following degrees:
Master of Science in Cyber Intelligence & Security

Master of Science in Engineering Management

Master of Science in Software Engineering

- Special Topic Courses
- Undergraduate
- B.A. in English
- Academic Advising
- Career Paths
- First-Year Writing
- Internships
- Professional Writing
- Scholarships
- M.A. in English
- MFA in Creative Writing
- M.S. in Technical Communication
- Accelerated Bachelor’s-Master’s Degree (ABM)
- Research and Engagement
- Literary Readings and Contests
- Film Studies Events and More
- Language and Life Project
- Young and Teen Writers Workshops
- Alumni and Friends
- Give Now
MFA Degree Requirements
These are the requirements for earning an MFA at NC State:
- 12 hours of graduate level writing workshops
- 6 hours of graduate level literature
- 12 hours of free electives (advisor-approved)
- 6 hours of thesis work (ENG 695)
There is no foreign language requirement.
The electives may be selected both from within or without the English Department so as to support an area of interest such as linguistics and translation, historical fiction, etc. The faculty is amenable to directed readings — independent studies of a particular poet or author — for credit as well.
Thesis and Grad Timeline
- Sign the Patent Agreement in your Graduate Planner.
- Start filling in your Graduate Planner using the courses you are taking/have taken to fulfill your degree requirements. Make sure to save your Graduate Planner only. You will not submit your GPOW until your final semester.
- Read the Electronic Theses and Dissertations (ETD) Guide and all information on the ETD website .
- Thesis for Fiction: a book-length manuscript of approximately 200 pages or more, preferably finished
- Thesis for Poetry: a collection of 50 pages
- No registration required: You must unconditionally pass the final exam and have an ETD Review by this deadline in order to avoid registering for the semester.
- Registration Required: You must unconditionally pass the final exam and have an ETD Review by this deadline. (This usually falls several months into the semester.)
- No later than the fall of your last year : Identify a thesis committee and a thesis advisor. Add your thesis advisor (chair) and two committee members to your Graduate Planner via the Committee tab. Save your Graduate Planner.
- In the fall of your last year : Prepare a list of 10 books that you will be examined upon in your final semester in addition to the MFA program’s list of 25 books. Make sure your thesis advisor approves your list no later than November 1 of your second year, and then submit the list to the MFA program assistant director.
- In your final semester : Complete your Graduate Planner and submit for approval.
- Students must apply to graduate by the deadline in order to participate in graduation exercises.
- ETD Review must be completed by this deadline.
- Graduation is contingent upon approval of the final ETD.
- Complete the Request to Schedule Master’s Oral Examination form and submit to the graduate services coordinator at least ten working days prior to your exam. (This form can be signed by either the MFA Director or the Director of Graduate Studies.) Please make sure your GPOW has been approved before you submit your form.
- Complete a Room Reservation Request and submit it to Samantha Blackburn with Room for Thesis Defense in the subject line of your email.
- Review your To Do List in the Student Service Center in the MyPack Portal . The only items left on your list should be MR Request to Schedule Final Oral and Report on Final Oral Exam . If you have additional items, those must be completed before submitting the form.
- You must unconditionally pass the final oral exam (thesis defense) before the ETD Review Deadline . The final oral exam is typically taken within the first two months of the semester and should be scheduled at least two weeks before the ETD review deadline. In addition, you should ensure that committee members receive the entire ETD to review at least two weeks prior to the final oral exam (thesis defense).
- Students are encouraged to apply to graduate once the final oral exam (thesis defense) is scheduled, but the application can be submitted at any time up until 5:00 p.m. on the apply to graduate deadline.
- 15-20 pages; a close reading and explication of selected writers you studied during your two years
- Unconditional pass (24-hours begins);
- Conditional pass (ETD review cannot take place until the defense is an unconditional pass. 24-hours has not begun yet); or
- within 24 hours of unconditional pass
- submit request for embargo of ETD along with draft submission
- ETD review conducted by ETD editor.
- Make corrections to ETD (committee, ETD review, hired editor, and other).
- ETD editor reviews final file — only to make sure ETD review corrections have been made (The file will not be accepted if corrections are not made: This should not happen.)
- If all ETD review corrections were made, the file will be accepted by the ETD editor.
- Error-free ETD file sent to committee for final committee approval.
- Committee reviews final ETD file.
- ETD Guide
- ETD Deadlines
- Request to Schedule Master’s Oral Examination form
- Master's Degree Information
Getting a Master's (MA) on the road to a PhD is not required at UMass Amherst, but it can be useful for students in getting jobs outside the university while they are still in our program—or for those who have decided to leave and want a terminal MA degree. There are two ways to get an MA in our program:
- Register for three (3) thesis credits, file thesis paperwork in advance, and defend the first comp as an MA thesis in consultation with comps/thesis committee. (Details below.)
- Complete both comps and earn an MA without having to do the thesis paperwork.
In both cases, the student would then need to file paperwork for an MA degree. We encourage students who do not already have an MA to plan ahead and take the first option.
Composition of Required Credits
You can count up to six Independent Study credits towards the 30-credit requirement. The UMass Graduate School imposes some additional requirements on the composition of the 30 credits you need for the MA, which you will most likely satisfy automatically if you follow the normal course track for the PhD. Of the 30 required course credits:
- At least 24 credits must be earned in regular, non-Independent Study courses;
- At least 21 credits must be earned in sociology courses;
- At least 15 credits must be letter graded (i.e. not pass/fail); transfer credits do not count;
- At least 12 credits (comps option) or 18 credits (MA thesis option) must be earned in courses numbered 600-800; transfer credits do not count.
The grade-point average for courses must be 3.0 or above, and must include a grade of B+ or better for SOCIOL 701, SOCIOL 710, SOCIOL 711, and SOCIOL 797W. This list is a subset of the courses required for the PhD listed under Requirements.
MA Thesis Option
In most cases the master's thesis will be an empirical paper which the student uses as a comps with the approval of your comprehensive exam committee. (A separate defense for the comps is not required.) A theoretical paper or analytic review of a literature may serve as a master's thesis with the approval of the thesis advisor. If the student writes a thesis, they will still need to do a second comps, if they wish to advance to candidacy for the doctorate.
To acquire an MA using the thesis option, the student needs (i) a minimum of 30 credits of coursework, including the required courses listed above, (ii) a master’s thesis, and (iii) a minimum of 3 thesis credits, not the same as dissertation credits; see below.
- For the MA thesis, at least 18 credits must be earned in courses numbered 600-800; transfer credits do not count.
- Three (3) thesis credits. These are different from dissertation credits. Students may be able to convert dissertation credits to thesis credits, though they will need to replace them with new dissertation credits towards the 18 dissertation credit requirement of the PhD. If a student takes thesis credits but does not submit the thesis, they can convert them to dissertation credits.
The thesis committee consists of an advisor and two other graduate faculty members, with at least two members in the Department of Sociology. The student can ask the graduate program director (GPD) to request graduate faculty status for a visiting professor or other non-graduate faculty member but the Graduate School must approve graduate faculty status. The student can form a committee once they have completed (i) at least 18 of the 30 required course credits, and (ii) the required courses in theory, statistics, and research methods. Formal appointment of the committee is made by the dean of the Graduate School. The student should work with the Graduate Programs Manager to get the comps committee appointed as a thesis committee at least four months before the defense.
Upon preliminary approval of the completed thesis by your committee, the Graduate Programs Manager will schedule a thesis defense which will also serve as the comprehensive exam defense. This exam is public. The committee may approve the thesis and/or recommend revisions. After passing this exam the student must submit the thesis to the Graduate School in proper format via ScholarWorks . They must also submit the defended thesis with signed signature page to the Graduate School and file for the degree after the successful defense. Students must have completed the coursework listed above by the end of the semester in which they file for their degree.
Incompletes from previous semesters for courses that are to be counted among the 30 credits must be completed before the filing date (about a month before the end of the semester). Incompletes from courses not being counted do not matter for the purposes of the MA degree.
Students may register for thesis credits any time before the semester they will file for the MA, but should do so when they have a tuition waiver to avoid paying for the credits.
MA Comps Option
To acquire an MA degree on the way to your PhD without using the thesis option, you need to complete (i) a minimum of 30 credits of coursework, including the required courses listed above and (ii) both comps. If a student has taken all the courses required for the PhD (see Requirements ), they will automatically have completed the course requirements for the MA. Upon passing both comps, the student can get an MA simply by filing a form with the Graduate School, assuming they have completed the coursework credits as listed above.
Keep in Mind
- A thesis does not have to be a different kind of paper than a comps paper.
- Getting an MA does not incur additional fees
- If a student defends the first comp as an M.A. thesis, they still have to complete a second comp exam/paper when moving toward a PhD.
- UMass Amherst asks for an electronic copy of your thesis, but this does not prevent the student from publishing their work.
- Current Graduate Courses
- How to Apply
- Comprehensive Exams ("Comps")
- Prospectus and Dissertation
- Earning the MA — Comps Option
- Earning the MA — Thesis Option
- Funding Opportunities
- Mentoring & Professional Development
- Grad Student News
- Graduate Alumni Placements
University of Massachusetts Amherst Thompson Hall, 200 Hicks Way Amherst, MA 01003-9277 tel: (413) 545 0577 | fax: (413) 545 3204 Contact Sociology
- Plan Your Studies
- Study Programs
- Universities
- Requirements
- Living in Germany
- Accommodation
- Statistics & News

Applying For a Master’s Degree in Germany
Master’s programs in Germany offer a diverse range of options, with many taught in English. They are known for their affordability, top-notch curricula, hands-on learning, and excellent career prospects. So, it’s no wonder that master’s degrees are the go-to choice for international students in Germany. During the 2021/2022 period, 42.6% of them (148,901 students) were enrolled in master’s programs.
But don’t let the application process hold you back – we’re here to guide you through the steps and set you on the path to success in Deutschland!
Here are the main steps to apply for a master’s degree in Germany:
Research and Choose a Master’s Program
Check admission requirements.
- Gather Documents and Meet All Requirements
Secure Funding
Submit your application, wait for the admission letter, get health insurance, apply for the german student visa.
When it comes to pursuing a master’s degree in Germany, the initial step is all about research and making an informed choice. Start by assessing your career goals and pinpoint the field of study that aligns with your aspirations. Look into the curriculum to ensure it covers the subjects that pique your interest.
Language matters too — many programs are available in English, but if you’re proficient in German, it opens up more options. When it comes to costs, most programs are quite affordable or even tuition-free, but be sure to check tuition fees just in case.
To aid your search, German study program databases and university websites offer detailed program information and application guidelines. Take your time to explore and find the program that’s the perfect fit for your educational journey.

Study at Berlin School of Business and Innovation
Creating Tomorrow's Industry Leaders
> Check out our list of over 9,000 master’s study programs in Germany.
Once you’ve picked a couple of programs that pique your interest and align with your study goals, it’s time to check if you meet their admission requirements or can meet them by the application deadline.
While each program may have its unique requirements, let’s explore some of the most common admission criteria for master’s programs in Germany:
- Bachelor’s degree. You have graduated or will graduate from a program equivalent to a German bachelor’s degree, often in a related field to the master’s program you’re applying for.
- Transcripts and diplomas . Submit transcripts and copies of your academic diplomas from previous educational institutions.
- Subject-specific knowledge . Some programs may require you to have gained specific subject knowledge or credits during your prior education. Business schools and MBA programs may require a particular score from recognized tests, like GMAT or GRE.
- Language proficiency. Demonstrate proficiency in the language of instruction, which is typically English or German. Proof of language proficiency is often required through standardized tests like IELTS, TOEFL, TestDaF, or DSH.
- Curriculum vitae (CV) or resume . Provide a comprehensive CV or resume detailing your academic and professional background.
- Statement of purpose & letters of recommendation. Some universities may request a Statement of Purpose (SOP), which details your motivations and goals, along with one to two letters of recommendation from professors or professionals.
> Visit our full guide of admission requirements for master’s programs in Germany for more details.
Gather Documents and Ensure You Meet All Requirements
After reviewing admission requirements and selecting your program(s), it’s time to start gathering what you need for your application, including transcripts, motivation letter, etc.
This is also an ideal time to confirm that you meet your university’s language proficiency requirements. Depending on your program’s language (English or German), you may take a standardized language test or provide alternative proof. Consider language courses if improvement is needed.
According to the German government’s regulations, international students planning to study in Germany must demonstrate financial resources of at least €11,208 per year (equivalent to €934 per month) to qualify for a student visa and pursue a master’s degree in the country.
This financial requirement may seem daunting for many students, so it’s crucial to address this well in advance of the official application period at your preferred German university. You can meet this requirement in various ways:
- Having €11,208 deposited in a German blocked account .
- Your parents can provide documentation of their income and financial resources.
- Someone with permanent residence in Germany can guarantee to the Alien Registration Office that they will financially support you.
- Present a scholarship awarding certificate specifying the financial amount or coverage granted to you.
Important Tip: To Maximize Your Chances of Getting Your German Student Visa You Should Use a Blocked Account as Proof of Financial Resources.
A blocked account is a special type of bank account , to prove you have enough funds to live in Germany for one year.
As of 2022, as a foreigner in Germany you need a minimum of €934 euros per month for living expenses. So, you are required to have a total of €11,208 in your bank account before you apply for a German internship visa.
Click here to learn more about the German Blocked Account
Planning ahead is important before your preferred German university’s application deadline, as this amount may be substantial for most students. Usually, four to six months prior should provide enough time to save money and explore scholarship and loan options.
Now is the exciting time to send in your application! Most universities have their own application portals where you’ll need to create an account, or they might use uni-assist for handling applications.
Make sure to read and follow all the instructions on the master’s program website, and be sure to submit all the required documents. It’s crucial to respect the application deadlines; your application won’t be processed if you miss the deadline.
Once your application is submitted, the next step is simply waiting for the university’s decision. While you wait, you might want to brush up on your language skills or start looking into the specific visa and travel requirements for Germany. It’s also a good time to explore accommodation options.
The university will notify you via email about the status of your application, and if you’re accepted, they’ll include the next steps you should follow.
Health insurance is a must for all international students in Germany. You can kickstart this process after receiving your admission letter or once you arrive in Germany.
If your home country has an agreement with Germany, you can often use your current health insurance, typically with a European Health Insurance Card (EHIC). In some cases, private health insurance from other countries may also be accepted.
Alternatively, you can choose to obtain insurance through a provider in Germany, with student packages usually priced around €120 per month, depending on your age and the provider.
Most international students in Germany prefer to get health insured with DR-WALTER .
EDUCARE24 by DR-WALTER is suitable for the following groups of people:
- Foreign exchange students, language students and students participating in university preparatory courses (Studienkolleg)
- University students
- Participants in exchange programmes (e.g. ERASMUS, DAAD, SOKRATES)
- Accompanying family members
Still have questions about health insurance? Learn more about health insurance in Germany from experts.
Get DR-WALTER insurance online within a few minutes
With a few exceptions, the majority of international students planning to study in Germany require a student visa. Our German student visa guide covers everything you need to know about this process, from requirements to the application process, fees, and more.
To kickstart the process, set up a visa interview at the German Embassy or Consulate in your home country, ideally about three months before your planned start of studies.
During the interview, provide all the required documents like proof of admission, language proficiency, financial means, and health insurance. Be ready for potential requests for more documents during the interview, and make sure your passport stays valid for your entire stay.
Arrive in Germany and Attend Orientation
Once your German student visa is sorted, it’s time to get on that plane and arrive in Germany. After settling in, make use of the pre-semester orientation sessions at German universities. Some things addressed through the orientation or to over on your own include:
- You’ll complete the enrollment process , which involves registering for your courses, receiving your class schedule, and learning about academic requirements.
- Getting your student ID . You’ll be issued a student identification card, often referred to as a “Studierendenausweis” in German.
- Residence registration. Once you’re in Germany, you will have to register your residence. This is a mandatory process that involves obtaining a “Meldebescheinigung” from the Resident’s Registration Office (Einwohnermeldeamt).
- Opening a local bank account. Orientation often provides guidance on opening a bank account in Germany.
- Campus tour. You’ll explore the campus to discover its facilities, libraries, and labs.
- Language courses. Some universities offer language courses or resources to help international students improve their German language skills if necessary.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) & Additional Information
Below, you’ll find answers to common questions and additional information to support you on your path to pursuing a master’s degree in Germany:
Which Universities Offer Master’s Degree Programs in Germany?
The higher education system in Germany includes public universities, funded and regulated by the state, and private universities established by independent entities.
While private universities may have higher fees, they are valuable for specialized courses not available at public institutions. Public universities in Germany have their own degree programs, assessments, and entry requirements, with state oversight to ensure the quality and accreditation of courses.
Germany has four main types of higher education institutions that offer master’s degree programs:
- Research Universities. These publicly administered institutions offer Master’s and PhD programs, focusing on various academic disciplines.
- Technical Universities. A subgroup of research universities, they specialize in science, technology, and engineering fields.
- Universities of Applied Sciences. These institutions concentrate on engineering, business, and social sciences, often partnering with professional organizations.
- Colleges of Art, Film, and Music. These institutions provide instruction in creative fields and can be part of research universities or universities of applied sciences.
What Are the Types of Master’s Degrees in Germany?
In Germany, you can pursue various types of Master’s degrees. Some of the most common include:
- Master of Arts (MA). Awarded in humanities, social sciences, and arts-related fields.
- Master of Science (MSc) . Awarded in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) disciplines.
- Master of Business Administration (MBA). Focuses on management and business administration topics.
- Master of Education (M.Ed.). For degrees for high school teacher positions.
What Are Consecutive and Non-consecutive Master’s Degrees?
Consecutive master’s Degrees in Germany follow a logical progression from a related bachelor’s degree and build upon the same academic field. They provide in-depth knowledge and specialization within the same subject area.
Non-consecutive master’s Degrees, on the other hand, don’t necessarily need a bachelor’s degree in the same field. Students with diverse academic backgrounds can go for non-consecutive master’s programs, which often focus on broader skills and interdisciplinary knowledge. These programs may include extra coursework to bridge any knowledge gaps.
How Long Is a Master’s Degree in Germany?
A master’s degree in Germany typically lasts for one to two years, depending on the specific program and the number of semesters required. Each academic year consists of two semesters, and the program may also include a final project or dissertation conducted in collaboration with a mentor.
How Many ECTS Credits Is a German Master’s Degree Worth?
Master’s programs in Germany typically consist of 120 ECTS (European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System) credits. However, the exact number of credits may vary depending on the university and the specific program.
What is Numerus Clausus?
Numerus Clausus (NC) in German master’s programs is a restricted admission system where limited spots are available, and selection is based on factors like academic performance and qualifications. It controls program capacity to prevent overcrowding. Applicants compete for admission based on their qualifications, and requirements vary by program.
When Are Application Deadlines for Master’s Degrees in Germany?
There are two semesters in German universities; the winter semester and the summer semester. Application deadlines for master’s programs vary depending on the university, however, the most common dates are:
- For courses starting on the winter semester: July 15th
- For courses starting on the summer semester: January 15th
Can I Apply for a Master’s in Germany Before I Get My Undergraduate Degree?
Yes, it’s common for students to apply during the final year of their bachelor’s degree. However, you must provide proof of your current academic progress and an expected graduation date as part of your application.
What Are the Language Requirements for Master’s Degrees in Germany?
If your courses are in German, you’ll need to prove your proficiency through tests like TestDaf or DSH. A lower level of proficiency may be accepted if you continue taking language courses upon arriving in Germany or during the early stages of your Master’s program. However, language requirements for master’s programs in Germany can vary depending on the university and program
If you choose English-taught programs, no German language tests are required. Non-native English speakers may need to take English language tests like TOEFL, IELTS, and PTE. If you’ve completed your undergraduate studies in English, you typically won’t need English language tests.
To discover programs in your preferred language, explore our tool and select the program language from the options on the left.
How Much Does a Master’s Degree Cost in Germany?
In most public universities in Germany, semester fees for master’s programs typically range from €100 to €350 per semester, with some exceptions. Some specialized graduate programs may have tuition fees, and the federal states of Baden-Württemberg and Bavaria may charge tuition fees for non-EU international students.
Private universities set their own tuition fees, and the cost of master’s degrees can vary significantly, especially for programs like MBAs. At private universities in Germany, tuition fees can range from approximately €5,000 to €20,000 per year or more, depending on the institution and program.
To find out more about the costs of studying in Germany, visit our extensive guide .
Can I Work While Studying for a Master’s Degree in Germany?
Yes, students of all nationalities can work while studying for a master’s degree in Germany.
- EU, EEA, Swiss, and Norwegian students can work up to 20 hours per week. They can exceed this number, however they will have to pay social security contributions.
- Non-EU students can work up to 120 full days or 240 half days per year, but they face restrictions on self-employment and freelancing.
- Academic assistants have no limitations on workdays but are required to inform the foreigners’ office.
> Read more about working while studying in Germany .
What Is the Master’s Thesis Process Like in Germany?
In your final year of a master’s program in Germany, you’ll work on your thesis project, guided by a professor. The goal is to showcase your ability to tackle a subject-related issue independently using research methods.
You can usually write your thesis in German or English and may even complete it externally, like at a company or another research institute. Universities often set page limits, usually between 50 to 100 pages, and impose deadlines, typically around six months from the project start.
The thesis defense involves submitting your work and presenting your research methods and findings.
Study Visa Requirements for a Master’s Degree in Germany
Make sure you collect on time all the documents you typically need in order to apply for a German Student Visa .
For detailed information about Germany Visa requirements, go to www.germany-visa.org/student-visa/
What Are the Career Prospects With a German Master’s Degree?
With a German master’s degree, you’ll have excellent career prospects, especially in STEM fields . EU/EEA graduates can work immediately after graduation, while non-EU/EEA graduates can extend their residence permits for up to 18 months to find field-related jobs.
You can also pursue academic careers, and highly skilled non-EU graduates can apply for an EU Blue Card to work and stay in Germany. Plus, your German degree is globally recognized, offering international career opportunities in multinational companies and organizations.
Join 262,114 students interested in studying in Germany

Download The Guide

Quick Links
8 Steps to Study in Germany How To Apply To Study in Germany German Education System Requirements Universities in Germany International Programmes Financing Your Studies German Student Visa German Health Insurance Germany Blocked Account Learn German Guide German Cities Cost of Living
Latest News and Statistics
New study reveals high level of satisfaction among students at german universities, germany scholarships up by 3% in 2023 – 31,400 students benefited, indians overcome chinese as top source of international students in germany, over 3,800 university students in germany were under 18 in 2022, higher education in germany: key trends & statistics.
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Definition of Dissertation and Thesis. The dissertation or thesis is a scholarly treatise that substantiates a specific point of view as a result of original research that is conducted by students during their graduate study. At Cornell, the thesis is a requirement for the receipt of the M.A. and M.S. degrees and some professional master's ...
As stated above, a thesis is the final project required in the completion of many master's degrees. The thesis is a research paper, but it only involves using research from others and crafting your own analytical points. On the other hand, the dissertation is a more in-depth scholarly research paper completed mostly by doctoral students.
Revised on April 16, 2024. A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
Tip #2: Begin Work on the Thesis Statement and Break Up the Thesis into Manageable Sections. After selecting an appropriate topic and developing a central research question for the thesis statement, it is then necessary to apply the research and writing skills you have learned throughout your degree program.
A thesis could consist of an average of 70 to 100 pages, including a bibliography, citations, and various sections. It is written under the guidance of a faculty advisor and should be publishable as an article. Your master's thesis reflects the literature in your field, challenges, evidence, and arguments around your writing topics.
Craft a convincing dissertation or thesis research proposal. Write a clear, compelling introduction chapter. Undertake a thorough review of the existing research and write up a literature review. Undertake your own research. Present and interpret your findings. Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications.
First, you need to find a topic (or "thesis question"), often with the help and/or approval of your faculty-led thesis committee. Next comes the process of research, which is often the most time-intensive. Then, you must take the time to analyze your research. Lastly, you outline and write the actual thesis. Thanks!
Prize-Winning Thesis and Dissertation Examples. Published on September 9, 2022 by Tegan George.Revised on July 18, 2023. It can be difficult to know where to start when writing your thesis or dissertation.One way to come up with some ideas or maybe even combat writer's block is to check out previous work done by other students on a similar thesis or dissertation topic to yours.
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical early steps in your writing process. ... Tegan is an American based in Amsterdam, with master's degrees in political science and education administration. While she is definitely a political scientist at heart, her experience working at universities led to a passion for making social ...
The purpose of a master's thesis is to help you develop your own independent abilities, ensuring that you can drive your own career forward without constantly looking to others to provide direction. Leaders get master's degrees. That's why many business professionals in leadership roles have graduate degree initials after their last names.
Writing a masters dissertation or thesis is a sizable task. It takes a considerable amount of research, studying and writing. Usually, students need to write around 10,000 to 15,000 words. It is completely normal to find the idea of writing a masters thesis or dissertation slightly daunting, even for students who have written one before at ...
Once your thesis is finalized, meaning that the required grade has been earned and all edits have been completed, you must upload your thesis to Harvard University's electronic thesis and dissertation submission system (ETDs). Uploading your thesis ETDs is an explicit degree requirement; you cannot graduate without completing this step.
To graduate with a master's (thesis program) or doctoral (dissertation program) degree, students are required to submit an Electronic Thesis/Dissertation (ETD) and a Committee Approval Form to the Graduate School through the UW ETD Administrator Site.
A thesis is a hallmark of some master's programs. It is a piece of original research, generally less comprehensive than a dissertation, and is meant to show the student's knowledge of an area of specialization. ... Graduate degree examinations are a major milestone in all graduate students' pursuit of their graduate degree. Much hinges on ...
Each graduate student in the Gallatin School completes a final thesis as the culmination of their work toward a Master of Arts degree. The thesis may take one of three forms: a research thesis, an artistic thesis, or a project thesis. In each case, the thesis represents a synthesis of the student's accumulated knowledge and skill and an ...
Choosing Between a Thesis or Non-thesis Master's Degree. As of 2015, approximately 25.4 million Americans held advanced degrees, with more citizens joining these ranks each year.As studies continue to show the career advancement and salary benefits of completing a master's degree, more and more students elect to pursue advanced educations.
Master's Thesis Guidelines. A master's student with a thesis requirement will submit the file through Brown's electronic theses and dissertation (ETD) system. The system is designed to collect and archive the thesis or dissertation as a text-based PDF file. An electronic file submitted through the ETD will appear in the Library's discovery ...
A master's thesis proposal involves a copious amount of data collection, particular presentation ethics, and most importantly, it will become the roadmap to your full thesis. Remember, you must convince your committee that your idea is strong and unique, and that you have done enough legwork to begin with the first few drafts of your final thesis.
A Thesis Proposal is a document that sets forth what is to be studied as a thesis project, why and in what way. It contains a number of important sections. The purpose of the proposal is to communicate the plan for the work to the faculty of the Division of Emerging Media Studies via the First Reader (principal thesis advisor) and a Second Reader.
The Master's degree with a thesis option allows students to work with world-renowned faculty to dig deeper in an area of interest. The development of a thesis involves utilizing the knowledge gained in a sub-field of study (e.g., human factors) to a novel engineering problem. In addition, students deepent their competence in surveying cutting ...
Conclusion. Choosing between a thesis and a non-thesis Master's program ultimately depends on your career goals, research interests, and personal preferences. Thesis programs provide a robust foundation for research-oriented careers and advanced studies, while non-thesis programs offer practical skills tailored for immediate industry integration.
Master's Degree Programs Apply Now and Waive the GRE Requirement! Florida State University is waiving the GRE requirement for most Master's and Specialists programs through Fall 2026.
The Master of Advanced Study in Engineering (MAS-E) is a unique online degree. It does not exist as an on-campus program. Upon completion of program requirements, students receive a Master of Advanced Study in Engineering degree. You can also display your chosen theme area on your resume to demonstrate your specialized skills.
The Master of Science in Computer Science degree is granted to students who complete the coursework described below. The program consists of nine hours of core courses, nine hours of Area of Concentration courses, and nine hours of open electives for the Graduate Research Project Option or six hours of open electives for the Thesis Option.
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program. Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you've ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating ...
Submit a draft thesis to the Graduate School; Distribute the thesis to the examining committee; The Degree schedule form must be approved before a defense is scheduled. Students must also report the results of the oral examination and submit a final thesis to the Graduate School prior to completing their degrees. The minimum requirements are as ...
These are the requirements for earning an MFA at NC State: 12 hours of graduate level writing workshops; 6 hours of graduate level literature; 12 hours of free electives (advisor-approved); 6 hours of thesis work (ENG 695); There is no foreign language requirement. The electives may be selected both from within or without the English Department so as to support an area of interest such as ...
This exam is public. The committee may approve the thesis and/or recommend revisions. After passing this exam the student must submit the thesis to the Graduate School in proper format via ScholarWorks. They must also submit the defended thesis with signed signature page to the Graduate School and file for the degree after the successful defense.
Master's programs in Germany offer a diverse range of options, with many taught in English. They are known for their affordability, top-notch curricula, hands-on learning, and excellent career prospects. So, it's no wonder that master's degrees are the go-to choice for international students in Germany. During the 2021/2022 period, 42.6% of them (148,901 students) were […]