- Library Catalogue

Formatting your thesis: Overall layout and specifications

On this page
Formatting requirements, parts of a thesis, file format, file size, and page size, line spacing, citation style, cumulative theses, extended essays, personal information, blank pages.
The Library's Theses Office assists with formatting theses, projects and extended essays for submission to the Library. You are encouraged to use the Library's thesis template to help format your thesis. The requirements stated on this page are default settings for the thesis template
Optional pages in the thesis template may be removed if not used.
The final copy of the thesis must be converted to .pdf (PDF/A format) for submission to the Library (maximum 400 mb). See the guide Saving your thesis in PDF/A format for instructions.
Theses must be formatted for US Letter (8.5X11) pages. Landscape 8.5X11 and 11X17 pages are permitted. Legal, A4, or other paper sizes are not permitted.
Arial is the preferred font for SFU thesis submissions. See the Thesis Template Instructions for directions to change the default template font.
Please contact the Theses Office at [email protected] if you would like to use any fonts in your thesis other than the ones recommended.
The default template line spacing is 1.5 for text, with single-spaced block quotations.
Margins should be set to:
- 1.25" left/right
- 1" top/bottom
All pages must be numbered sequentially as outlined below, with the exception of the title page. Page numbers should appear at the bottom centre of each page, at a minimum of 0.5” from the edge of the page.
Preliminary pages of the thesis must be numbered with Roman numerals. On the first page of the main body, page numbers must restart with 1. The thesis template is preset with this numbering style.
SFU Library does not require a specific citation style. Consult your supervisor, your department’s graduate handbook, or a liaison librarian for help with determining which style is appropriate for your research.
The default formatting in the library’s thesis template may differ from some requirements of your citation style, but it is acceptable for SFU library submission.
Cumulative, or paper-based, theses must use the same general format as other submissions. Consult your supervisor or your department's graduate handbook for more information. If including published papers in a thesis, please consult the Copyright and your thesis FAQ .
Extended essays should be combined into a single document and single submission. For an example of an extended essays title page, see the Title page formatting information .
For theses written in a language other than English, the Library requires a second complete English title page and abstract. Supporting documentation must be in English.
Individual personal information must be removed from the thesis before publication, including signatures, email addresses, and phone numbers. For example, if you are including a survey instrument or consent form, your own contact information must be removed.
Blank pages in the thesis must be removed before publication.

- Langson Library
- Science Library
- Grunigen Medical Library
- Law Library
- Connect From Off-Campus
- Accessibility
- Gateway Study Center

Email this link
Thesis / dissertation formatting manual (2024).
- Filing Fees and Student Status
- Submission Process Overview
- Electronic Thesis Submission
- Paper Thesis Submission
- Formatting Overview
- Fonts/Typeface
- Pagination, Margins, Spacing
- Paper Thesis Formatting
- Preliminary Pages Overview
- Copyright Page
- Dedication Page
- Table of Contents
- List of Figures (etc.)
- Acknowledgements
- Text and References Overview
- Figures and Illustrations
- Using Your Own Previously Published Materials
- Using Copyrighted Materials by Another Author
- Open Access and Embargoes
- Copyright and Creative Commons
- Ordering Print (Bound) Copies
- Tutorials and Assistance
- FAQ This link opens in a new window
UCI Libraries maintains the following templates to assist in formatting your graduate manuscript. If you are formatting your manuscript in Microsoft Word, feel free to download and use the template. If you would like to see what your manuscript should look like, PDFs have been provided. If you are formatting your manuscript using LaTex, UCI maintains a template on OverLeaf.
- Annotated Template (Dissertation) 2024 PDF of a template with annotations of what to look out for
- Word: Thesis Template 2024 Editable template of the Master's thesis formatting.
- PDF Thesis Template 2024
- Word: Dissertation Template 2024 Editable template of the PhD Dissertation formatting.
- PDF: Dissertation Template 2024
- Overleaf (LaTex) Template
- << Previous: Tutorials and Assistance
- Next: FAQ >>
- Last Updated: Feb 20, 2024 2:09 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uci.edu/gradmanual
Off-campus? Please use the Software VPN and choose the group UCIFull to access licensed content. For more information, please Click here
Software VPN is not available for guests, so they may not have access to some content when connecting from off-campus.
- Graduate School
- Current Students
- Dissertation & Thesis Preparation
Formatting Requirements
Page layout, margins and numbering.
Your scholarly approach may call for a different presentational method. These are the requirements and recommendations for text-based theses.
For a text-based thesis, or the text portions of a thesis, the page size must be 8.5" x 11", and the text must be in a single, page-wide column. Do not use two or more columns in your thesis.
The text of the thesis is written in paragraph form.
- the first line of each paragraph should be indented, OR
- there should be a larger space between paragraphs than there is between lines.
Each chapter should generally start at the top of a new page.
Left: 1.25 inches (32 mm) is recommended if you intend to bind copies of your thesis; 1 inch minimum.
Right, top, and bottom: 1 inch recommended; 0.75 inches (19 mm) minimum
Page Numbering
Preliminary pages:.
- must be numbered in lower case Roman numerals (ii, iii, iv, etc.)
- the title page is "i" but this number must not appear on the page
- numbering begins at "ii" on the committee page
- the first page of the abstract is page iii
Body of thesis:
- must be numbered in Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3, etc.)
- the first page of the text is "1"
- subsequent pages are numbered continuously throughout, including pages with tables and figures, bibliographies, appendices, and index
Whole thesis:
- every page except the title page must have a number on it
- there must be no blank pages in the thesis.
Page numberS:
- must be placed at least .5 inches (12 mm) from the edge of the page
- may be either in the lower centre or on the top or lower right of the page, when the page is viewed in portrait view. Lower right is preferred.
Landscape Pages
Landscape pages must be orientated in your PDF so that they are readable without rotation. You do not need to change the location or orientation of the page number, but may if you wish.
Facing Pages
Facing pages are not acceptable; you must use one-sided layout and pagination. If the caption for a figure, table, etc., cannot appear on the same page as its accompanying illustration, place the illustration on a separate page after the caption.
- Why Grad School at UBC?
- Graduate Degree Programs
- Application & Admission
- Info Sessions
- Research Supervisors
- Research Projects
- Indigenous Students
- International Students
- Tuition, Fees & Cost of Living
- Newly Admitted
- Student Status & Classification
- Student Responsibilities
- Supervision & Advising
- Managing your Program
- Health, Wellbeing and Safety
- Professional Development
- Final Doctoral Exam
- Final Dissertation & Thesis Submission
- Life in Vancouver
- Vancouver Campus
- Graduate Student Spaces
- Graduate Life Centre
- Life as a Grad Student
- Graduate Student Ambassadors
- Meet our Students
- Award Opportunities
- Award Guidelines
- Minimum Funding Policy for PhD Students
- Killam Awards & Fellowships
- Policies & Procedures
- Information for Supervisors
- Dean's Message
- Leadership Team
- Strategic Plan & Priorities
- Vision & Mission
- Equity, Diversity & Inclusion
- Initiatives, Plans & Reports
- Graduate Education Analysis & Research
- Media Enquiries
- Newsletters
- Giving to Graduate Studies
Strategic Priorities
- Strategic Plan 2019-2024
- Improving Student Funding
- Promoting Excellence in Graduate Programs
- Enhancing Graduate Supervision
- Advancing Indigenous Inclusion
- Supporting Student Development and Success
- Reimagining Graduate Education
- Enriching the Student Experience
Initiatives
- Public Scholars Initiative
- 3 Minute Thesis (3MT)
- PhD Career Outcomes
- Great Supervisor Week
Dissertation Structure & Layout 101: How to structure your dissertation, thesis or research project.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) Reviewed By: David Phair (PhD) | July 2019
So, you’ve got a decent understanding of what a dissertation is , you’ve chosen your topic and hopefully you’ve received approval for your research proposal . Awesome! Now its time to start the actual dissertation or thesis writing journey.
To craft a high-quality document, the very first thing you need to understand is dissertation structure . In this post, we’ll walk you through the generic dissertation structure and layout, step by step. We’ll start with the big picture, and then zoom into each chapter to briefly discuss the core contents. If you’re just starting out on your research journey, you should start with this post, which covers the big-picture process of how to write a dissertation or thesis .

*The Caveat *
In this post, we’ll be discussing a traditional dissertation/thesis structure and layout, which is generally used for social science research across universities, whether in the US, UK, Europe or Australia. However, some universities may have small variations on this structure (extra chapters, merged chapters, slightly different ordering, etc).
So, always check with your university if they have a prescribed structure or layout that they expect you to work with. If not, it’s safe to assume the structure we’ll discuss here is suitable. And even if they do have a prescribed structure, you’ll still get value from this post as we’ll explain the core contents of each section.
Overview: S tructuring a dissertation or thesis
- Acknowledgements page
- Abstract (or executive summary)
- Table of contents , list of figures and tables
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: Literature review
- Chapter 3: Methodology
- Chapter 4: Results
- Chapter 5: Discussion
- Chapter 6: Conclusion
- Reference list
As I mentioned, some universities will have slight variations on this structure. For example, they want an additional “personal reflection chapter”, or they might prefer the results and discussion chapter to be merged into one. Regardless, the overarching flow will always be the same, as this flow reflects the research process , which we discussed here – i.e.:
- The introduction chapter presents the core research question and aims .
- The literature review chapter assesses what the current research says about this question.
- The methodology, results and discussion chapters go about undertaking new research about this question.
- The conclusion chapter (attempts to) answer the core research question .
In other words, the dissertation structure and layout reflect the research process of asking a well-defined question(s), investigating, and then answering the question – see below.

To restate that – the structure and layout of a dissertation reflect the flow of the overall research process . This is essential to understand, as each chapter will make a lot more sense if you “get” this concept. If you’re not familiar with the research process, read this post before going further.
Right. Now that we’ve covered the big picture, let’s dive a little deeper into the details of each section and chapter. Oh and by the way, you can also grab our free dissertation/thesis template here to help speed things up.
The title page of your dissertation is the very first impression the marker will get of your work, so it pays to invest some time thinking about your title. But what makes for a good title? A strong title needs to be 3 things:
- Succinct (not overly lengthy or verbose)
- Specific (not vague or ambiguous)
- Representative of the research you’re undertaking (clearly linked to your research questions)
Typically, a good title includes mention of the following:
- The broader area of the research (i.e. the overarching topic)
- The specific focus of your research (i.e. your specific context)
- Indication of research design (e.g. quantitative , qualitative , or mixed methods ).
For example:
A quantitative investigation [research design] into the antecedents of organisational trust [broader area] in the UK retail forex trading market [specific context/area of focus].
Again, some universities may have specific requirements regarding the format and structure of the title, so it’s worth double-checking expectations with your institution (if there’s no mention in the brief or study material).

Acknowledgements
This page provides you with an opportunity to say thank you to those who helped you along your research journey. Generally, it’s optional (and won’t count towards your marks), but it is academic best practice to include this.
So, who do you say thanks to? Well, there’s no prescribed requirements, but it’s common to mention the following people:
- Your dissertation supervisor or committee.
- Any professors, lecturers or academics that helped you understand the topic or methodologies.
- Any tutors, mentors or advisors.
- Your family and friends, especially spouse (for adult learners studying part-time).
There’s no need for lengthy rambling. Just state who you’re thankful to and for what (e.g. thank you to my supervisor, John Doe, for his endless patience and attentiveness) – be sincere. In terms of length, you should keep this to a page or less.
Abstract or executive summary
The dissertation abstract (or executive summary for some degrees) serves to provide the first-time reader (and marker or moderator) with a big-picture view of your research project. It should give them an understanding of the key insights and findings from the research, without them needing to read the rest of the report – in other words, it should be able to stand alone .
For it to stand alone, your abstract should cover the following key points (at a minimum):
- Your research questions and aims – what key question(s) did your research aim to answer?
- Your methodology – how did you go about investigating the topic and finding answers to your research question(s)?
- Your findings – following your own research, what did do you discover?
- Your conclusions – based on your findings, what conclusions did you draw? What answers did you find to your research question(s)?
So, in much the same way the dissertation structure mimics the research process, your abstract or executive summary should reflect the research process, from the initial stage of asking the original question to the final stage of answering that question.
In practical terms, it’s a good idea to write this section up last , once all your core chapters are complete. Otherwise, you’ll end up writing and rewriting this section multiple times (just wasting time). For a step by step guide on how to write a strong executive summary, check out this post .
Need a helping hand?
Table of contents
This section is straightforward. You’ll typically present your table of contents (TOC) first, followed by the two lists – figures and tables. I recommend that you use Microsoft Word’s automatic table of contents generator to generate your TOC. If you’re not familiar with this functionality, the video below explains it simply:
If you find that your table of contents is overly lengthy, consider removing one level of depth. Oftentimes, this can be done without detracting from the usefulness of the TOC.
Right, now that the “admin” sections are out of the way, its time to move on to your core chapters. These chapters are the heart of your dissertation and are where you’ll earn the marks. The first chapter is the introduction chapter – as you would expect, this is the time to introduce your research…
It’s important to understand that even though you’ve provided an overview of your research in your abstract, your introduction needs to be written as if the reader has not read that (remember, the abstract is essentially a standalone document). So, your introduction chapter needs to start from the very beginning, and should address the following questions:
- What will you be investigating (in plain-language, big picture-level)?
- Why is that worth investigating? How is it important to academia or business? How is it sufficiently original?
- What are your research aims and research question(s)? Note that the research questions can sometimes be presented at the end of the literature review (next chapter).
- What is the scope of your study? In other words, what will and won’t you cover ?
- How will you approach your research? In other words, what methodology will you adopt?
- How will you structure your dissertation? What are the core chapters and what will you do in each of them?
These are just the bare basic requirements for your intro chapter. Some universities will want additional bells and whistles in the intro chapter, so be sure to carefully read your brief or consult your research supervisor.
If done right, your introduction chapter will set a clear direction for the rest of your dissertation. Specifically, it will make it clear to the reader (and marker) exactly what you’ll be investigating, why that’s important, and how you’ll be going about the investigation. Conversely, if your introduction chapter leaves a first-time reader wondering what exactly you’ll be researching, you’ve still got some work to do.
Now that you’ve set a clear direction with your introduction chapter, the next step is the literature review . In this section, you will analyse the existing research (typically academic journal articles and high-quality industry publications), with a view to understanding the following questions:
- What does the literature currently say about the topic you’re investigating?
- Is the literature lacking or well established? Is it divided or in disagreement?
- How does your research fit into the bigger picture?
- How does your research contribute something original?
- How does the methodology of previous studies help you develop your own?
Depending on the nature of your study, you may also present a conceptual framework towards the end of your literature review, which you will then test in your actual research.
Again, some universities will want you to focus on some of these areas more than others, some will have additional or fewer requirements, and so on. Therefore, as always, its important to review your brief and/or discuss with your supervisor, so that you know exactly what’s expected of your literature review chapter.

Now that you’ve investigated the current state of knowledge in your literature review chapter and are familiar with the existing key theories, models and frameworks, its time to design your own research. Enter the methodology chapter – the most “science-ey” of the chapters…
In this chapter, you need to address two critical questions:
- Exactly HOW will you carry out your research (i.e. what is your intended research design)?
- Exactly WHY have you chosen to do things this way (i.e. how do you justify your design)?
Remember, the dissertation part of your degree is first and foremost about developing and demonstrating research skills . Therefore, the markers want to see that you know which methods to use, can clearly articulate why you’ve chosen then, and know how to deploy them effectively.
Importantly, this chapter requires detail – don’t hold back on the specifics. State exactly what you’ll be doing, with who, when, for how long, etc. Moreover, for every design choice you make, make sure you justify it.
In practice, you will likely end up coming back to this chapter once you’ve undertaken all your data collection and analysis, and revise it based on changes you made during the analysis phase. This is perfectly fine. Its natural for you to add an additional analysis technique, scrap an old one, etc based on where your data lead you. Of course, I’m talking about small changes here – not a fundamental switch from qualitative to quantitative, which will likely send your supervisor in a spin!
You’ve now collected your data and undertaken your analysis, whether qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods. In this chapter, you’ll present the raw results of your analysis . For example, in the case of a quant study, you’ll present the demographic data, descriptive statistics, inferential statistics , etc.
Typically, Chapter 4 is simply a presentation and description of the data, not a discussion of the meaning of the data. In other words, it’s descriptive, rather than analytical – the meaning is discussed in Chapter 5. However, some universities will want you to combine chapters 4 and 5, so that you both present and interpret the meaning of the data at the same time. Check with your institution what their preference is.
Now that you’ve presented the data analysis results, its time to interpret and analyse them. In other words, its time to discuss what they mean, especially in relation to your research question(s).
What you discuss here will depend largely on your chosen methodology. For example, if you’ve gone the quantitative route, you might discuss the relationships between variables . If you’ve gone the qualitative route, you might discuss key themes and the meanings thereof. It all depends on what your research design choices were.
Most importantly, you need to discuss your results in relation to your research questions and aims, as well as the existing literature. What do the results tell you about your research questions? Are they aligned with the existing research or at odds? If so, why might this be? Dig deep into your findings and explain what the findings suggest, in plain English.
The final chapter – you’ve made it! Now that you’ve discussed your interpretation of the results, its time to bring it back to the beginning with the conclusion chapter . In other words, its time to (attempt to) answer your original research question s (from way back in chapter 1). Clearly state what your conclusions are in terms of your research questions. This might feel a bit repetitive, as you would have touched on this in the previous chapter, but its important to bring the discussion full circle and explicitly state your answer(s) to the research question(s).

Next, you’ll typically discuss the implications of your findings? In other words, you’ve answered your research questions – but what does this mean for the real world (or even for academia)? What should now be done differently, given the new insight you’ve generated?
Lastly, you should discuss the limitations of your research, as well as what this means for future research in the area. No study is perfect, especially not a Masters-level. Discuss the shortcomings of your research. Perhaps your methodology was limited, perhaps your sample size was small or not representative, etc, etc. Don’t be afraid to critique your work – the markers want to see that you can identify the limitations of your work. This is a strength, not a weakness. Be brutal!
This marks the end of your core chapters – woohoo! From here on out, it’s pretty smooth sailing.
The reference list is straightforward. It should contain a list of all resources cited in your dissertation, in the required format, e.g. APA , Harvard, etc.
It’s essential that you use reference management software for your dissertation. Do NOT try handle your referencing manually – its far too error prone. On a reference list of multiple pages, you’re going to make mistake. To this end, I suggest considering either Mendeley or Zotero. Both are free and provide a very straightforward interface to ensure that your referencing is 100% on point. I’ve included a simple how-to video for the Mendeley software (my personal favourite) below:
Some universities may ask you to include a bibliography, as opposed to a reference list. These two things are not the same . A bibliography is similar to a reference list, except that it also includes resources which informed your thinking but were not directly cited in your dissertation. So, double-check your brief and make sure you use the right one.
The very last piece of the puzzle is the appendix or set of appendices. This is where you’ll include any supporting data and evidence. Importantly, supporting is the keyword here.
Your appendices should provide additional “nice to know”, depth-adding information, which is not critical to the core analysis. Appendices should not be used as a way to cut down word count (see this post which covers how to reduce word count ). In other words, don’t place content that is critical to the core analysis here, just to save word count. You will not earn marks on any content in the appendices, so don’t try to play the system!
Time to recap…
And there you have it – the traditional dissertation structure and layout, from A-Z. To recap, the core structure for a dissertation or thesis is (typically) as follows:
- Acknowledgments page
Most importantly, the core chapters should reflect the research process (asking, investigating and answering your research question). Moreover, the research question(s) should form the golden thread throughout your dissertation structure. Everything should revolve around the research questions, and as you’ve seen, they should form both the start point (i.e. introduction chapter) and the endpoint (i.e. conclusion chapter).
I hope this post has provided you with clarity about the traditional dissertation/thesis structure and layout. If you have any questions or comments, please leave a comment below, or feel free to get in touch with us. Also, be sure to check out the rest of the Grad Coach Blog .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

36 Comments
many thanks i found it very useful
Glad to hear that, Arun. Good luck writing your dissertation.
Such clear practical logical advice. I very much needed to read this to keep me focused in stead of fretting.. Perfect now ready to start my research!
what about scientific fields like computer or engineering thesis what is the difference in the structure? thank you very much
Thanks so much this helped me a lot!
Very helpful and accessible. What I like most is how practical the advice is along with helpful tools/ links.
Thanks Ade!
Thank you so much sir.. It was really helpful..
You’re welcome!
Hi! How many words maximum should contain the abstract?
Thank you so much 😊 Find this at the right moment
You’re most welcome. Good luck with your dissertation.
best ever benefit i got on right time thank you
Many times Clarity and vision of destination of dissertation is what makes the difference between good ,average and great researchers the same way a great automobile driver is fast with clarity of address and Clear weather conditions .
I guess Great researcher = great ideas + knowledge + great and fast data collection and modeling + great writing + high clarity on all these
You have given immense clarity from start to end.
Morning. Where will I write the definitions of what I’m referring to in my report?
Thank you so much Derek, I was almost lost! Thanks a tonnnn! Have a great day!
Thanks ! so concise and valuable
This was very helpful. Clear and concise. I know exactly what to do now.
Thank you for allowing me to go through briefly. I hope to find time to continue.
Really useful to me. Thanks a thousand times
Very interesting! It will definitely set me and many more for success. highly recommended.
Thank you soo much sir, for the opportunity to express my skills
Usefull, thanks a lot. Really clear
Very nice and easy to understand. Thank you .
That was incredibly useful. Thanks Grad Coach Crew!
My stress level just dropped at least 15 points after watching this. Just starting my thesis for my grad program and I feel a lot more capable now! Thanks for such a clear and helpful video, Emma and the GradCoach team!
Do we need to mention the number of words the dissertation contains in the main document?
It depends on your university’s requirements, so it would be best to check with them 🙂
Such a helpful post to help me get started with structuring my masters dissertation, thank you!
Great video; I appreciate that helpful information
It is so necessary or avital course
This blog is very informative for my research. Thank you
Doctoral students are required to fill out the National Research Council’s Survey of Earned Doctorates
wow this is an amazing gain in my life
This is so good
How can i arrange my specific objectives in my dissertation?
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Is A Literature Review (In A Dissertation Or Thesis) - Grad Coach - […] is to write the actual literature review chapter (this is usually the second chapter in a typical dissertation or…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Library Subject Guides
4. writing up your research: thesis formatting (ms word).
- Books on Thesis Writing
- Thesis Formatting (MS Word)
- Referencing
Haere mai, tauti mai—welcome! These instructions are designed to be used with recent versions of MS Word. Please note there is no template or specific formatting guidelines for a thesis at UC. Please talk to your supervisor and take a look at theses in the UC Research Repository to see how they are usually formatted.
- Where to start
- Show/Hide Formatting
- Heading Styles
- Navigation Pane
- Table of Contents
- Numbered Headings
- List of Figures/Tables
- Page/Section Breaks, Page Numbering & Orientation
Word Thesis Formatting workshops run throughout the year.
Some useful documents.
- Word Formatting Instructions PDF This PDF contains the same instructions that are available on this page.
- Sample Thesis Document with No Formatting This sample thesis file can be used to practise formatting. It is not a template for how to format a thesis. UC does not provide any guidelines on formatting a thesis.
- APA 7th Edition Formatting Example This document is formatted according to APA 7th Edition formatting guidelines. It could be used as a template or as an example to follow. It contains some additional instructions for certain APA formatting in Word.
For more APA formatting advice see the APA Style Blog's excellent Style and Grammar Guidelines .
Finding Examples
Look at examples and ask your supervisor.
The best guide on how to format your thesis is a combination of:
- Looking at previous theses in your discipline. Search the UC Research Repository for your subject or department, and browse by issue date to get the most recent.
- Asking your supervisor for recommendations on specific formatting and details.
General Recommendations
The following is an example only of preliminaries to the thesis that could be included.
- Acknowledgements
- List of Figures
- List of Tables
- Abbreviations
- Toggle show Home ->Show/Hide formatting
Using styles for headings allows you to create an automatic table of contents.
- Select major headings one at a time and choose Home ->Styles ‘Heading 1’
- Select subheadings and apply Home ->Styles ‘heading 2’ and ‘heading 3’
- Modify a style by right clicking on it and choosing Modify in the styles pane at the top of the screen.
The Navigation Pain is useful for seeing the outline of your document as well as providing links to quickly go to any section of the document.
- View->check Navigation Pane
In order to create an automatic table of contents heading styles must be used.
- References -> Table of Contents -> Custom Table of Contents (no heading in table)

- Right click table of contents to ‘update field’ and choose ‘update entire table’
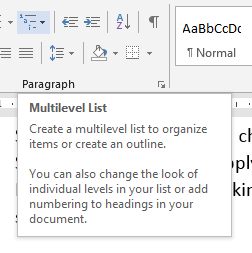
- Home->Multilevel list-> choose style with a number level for each heading level
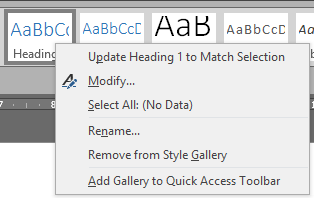
- To change the heading level 1 number to say ‘Chapter 1’ right click on heading level 1 in the styles area Heading 1->Modify .
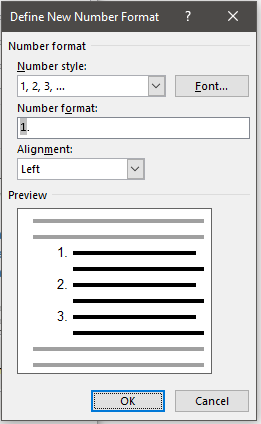
- In the modify screen click Format->Numbering.
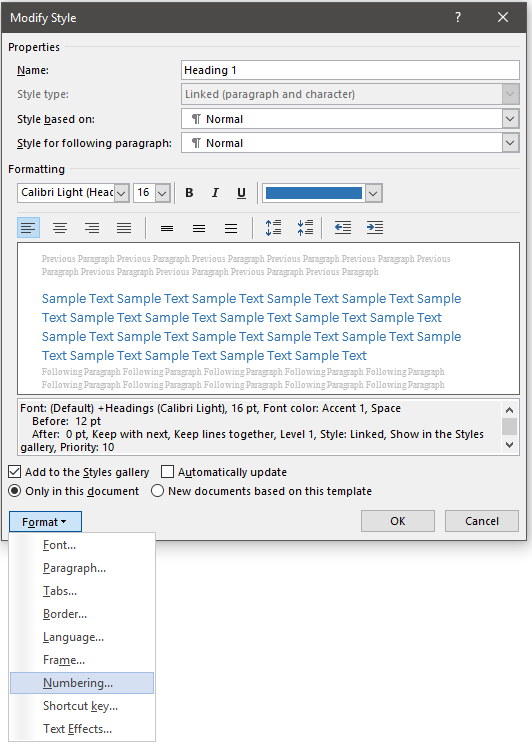
- Then click ‘ Define New Number Format’.
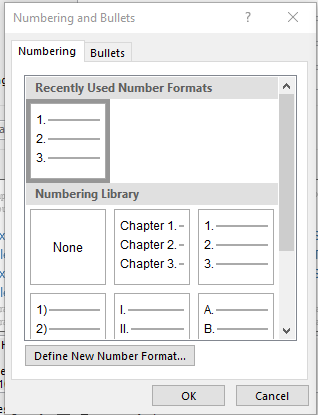
- Then add the word ‘Chapter’ and a space before the ‘1’.
To create automatic lists of figures or tables you first have to give a caption to all your figures and tables.
- Right click figure or table and select Insert Caption
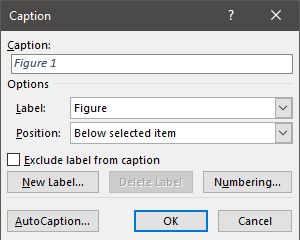
- Choose Label type eg. Figure, Table etc
- Choose position above or below
- Give the table or figure a title in the top box
- Go to the headings for List of Figures and List of tables and then click References->Insert Table of Figures -> select caption label type (Figure or Table)
- On the following menu select caption label type (Figure or Table) and click OK

This can be used to have different page numbering styles of different sections of your document or to have certain pages landscape to display a large table or graph.
- Insert a section break (next page) at the end of the title page ( Layout -> Breaks -> Next Page )
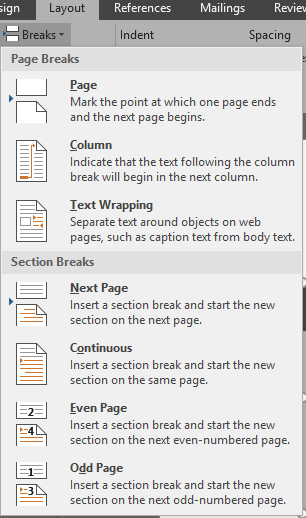
- Insert a section break at chapter 1 ( Layout -> Breaks -> Next Page )
- Insert page breaks for all other ‘heading 1’ headings ( Layout -> Breaks -> Page )
Adding Page Numbers
- Insert -> Page Number and choose a position on the page
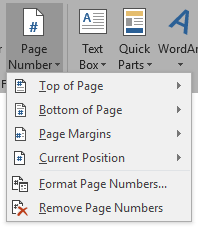
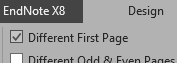
- Double click on title page header or footer (top or bottom of the page) and tick ‘ Different First Page’ in the Design ribbon that appears
- Click in second page header or footer, right click on the page number and select ‘ format page numbers ’
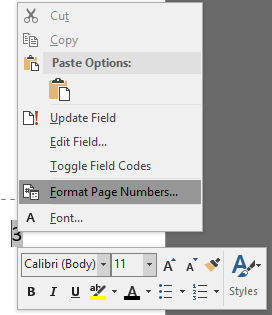
- Select Roman numerals eg. ‘i, ii, iii, iv’ etc
- Select start at ‘i’ (start at ‘1’)
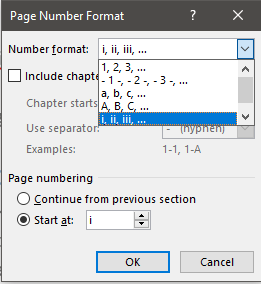
- Scroll to chapter 1 and change number style for this section back to ordinary numbers and start at 1
Change Page Orientation
- Insert a section break before and after the pages you want to change to landscape orientation (See instructions above for inserting a section break)
- Layout -> Orientation -> Landscape
NOTE: A section break is usually only needed if page orientation or separate page numbers are required.
- << Previous: Books on Thesis Writing
- Next: Referencing >>
- Last Updated: Feb 8, 2024 12:29 PM
- URL: https://canterbury.libguides.com/writingup
Ohio State nav bar
The Ohio State University
- BuckeyeLink
- Find People
- Search Ohio State
Dissertation Formatting Tips and Tricks
All instructions are written for Word 2007 for PC. The basic instructions are the same for most versions of Word but the actual key strokes maybe slightly different.
Setting Margins
- Put your cursor at the very beginning of your document
- Select the ‘Page Layout’ tab from the ribbon
- Select ‘Margins’ in the Page Setup box
- Select ‘Custom Margins’
- Set the margins
Inserting a Two Inch Top Margin for the First Page of Chapter/Major Section
- Before beginning a new chapter or equivalent (bibliography, abstract, vita, etc.) insert a hard page break by pressing the ‘Ctrl’ key and the ‘Enter’ key at the same time.
- To insert a two inch top margin if you are in single line spacing press the ‘Enter’ key six times. If you are in double line spacing press the ‘Enter’ key three times. This will move the cursor down an additional inch so the page will have a two inch top margin without affecting the rest of the pages in the section or document.
Page Numbers
Insert page numbers.
- Select ‘Insert’ tab from ribbon
- Select ‘Page Number’ from the Header & Footer box
- Select ‘Bottom of Page’
- Select ‘Plain Number 2’
- In the Position box move the bottom position to 1 inch (default is 0.5 inch)
- Close the Header & Footer
Cover Unwanted Page Numbers
- Go to the page with the unwanted page number
- Select the ‘Insert’ tab from the ribbon
- Select ‘Text Box’ from Text
- Select ‘Draw Text Box’ from the Text Box options
- Draw your box anywhere on the page except in the footer area
- Drag the box you drew to cover the page number
- Select ‘Shape Outline’ from the Shape Styles box
- Select ‘No Outline’
Beginning with Small Roman Numerals for Preliminary Pages
- Put your cursor at the end of the copyright page
- Select Page Layout’ from the ribbon
- Select ‘Breaks’ from the Page Setup box
- Select ‘Next Page’ from the Breaks list
- Insert page number as previously discussed
- Select ‘Format Page Number’
- Change ‘Number Format’ to small Roman numerals
- Change ‘Start at’ to 'ii' (small Roman II)
Note : Some versions of Word will insert page numbers on the title page and the copyright page even though the insert command is not until the abstract page. A simple method for addressing this is covered in ‘Cover Unwanted Page Numbers.’
Changing from Small Roman Numerals to standard Arabic Numbers
- Put your cursor at the end of the text on the last page of your preliminary pages
- Select ‘Page Layout’ from the ribbon
- Select ‘Breaks’ from the Page Setup Box
- Insert page number (see Insert Page Number)
- Change ‘Number Format’ to standard numerals (1, 2, 3, …)
- Change ‘Start at’ to Arabic 1
Putting a Page Number in the Portrait Position on a Landscaped Page
- Put your cursor on the landscaped page so you can see both the landscaped page number and the left margin (bottom edge when viewed in portrait orientation)
- Insert a text box described in 'Cover Unwanted Page Numbers'
- Cover the page number in the landscaped position
- Remove the box outline as discussed in 'Cover Unwanted Page Numbers'
- Draw a second text box on the same page
- Drag the second text box to the left margin approximately one inch from the left edge
- Type in the correct page number
- Rotate the text in the text box by selecting ‘Text Direction’ from the Text options
- Once the page number is in the correct orientation, remove the box outline
- You may have to adjust the size of the text box and move it slightly until it is in the correct placement
Table of Contents
Manually creating a table of contents.
Includes setting tab stops and leader dot tabs
- Type in the items you want to appear in the Table of Contents. At minimum the Table of Contents must include the abstract, dedication (if present in document), acknowledgments (if present in document), vita, list of tables (if present in document), list of figures (if present in document) each chapter with the chapter title, bibliography, each appendix as a separate entry (if appendices are in your document). These items are level one in the Table of Contents. How detailed the table of contents is up to you and your committee. Subheading within these major divisions would be indented based on their level in the text of your document. Every entry in the Table of Contents must have leader dots from the end of the entry to the page number where it begins (see below)
- After the entry press the tab key once and then type the page number when the entry begins
- Select the table of contents
- Select the ‘Page Layout’ tab
- Go to the ‘Paragraph’ Box and open the dialogue box (click on the small box in the lower right corner of the box.)
- Select tabs
- Set tab stops for any sub levels within your Table of Contents by inserting the position (in inches) and clicking ‘set.’ These tabs should be left aligned. The first level of the table of contents does not need to be set as it is the left margin of the page
- Set a tab stop for the page number positions (between 5” and 5.75” is usually a good spacing for the page number placement). Leave as a left aligned tab (the left edge of the numbers will line-up) or select right aligned tab (the right edge of the numbers will line up). Select the appropriate leader dots (the periods—usually the second option). Click ‘set’
- Click ‘okay’
Word Created Table of Contents
Using styles.
Once all titles, major headings, and subtitle headings have been formatted using Styles, place the cursor on the Table of Contents page
- Select the ‘References’ tab
- Select ‘Table of Contents’
- Select the format
- The Table of Contents should generate
Not Using Styles
- Go to the first item to appear in the Table of Contents (usually ‘Abstract’)
- Highlight the title
- Select ‘Add Text’ from the Table of Contents box
- Select level
Note: if you did not use Styles marking the item for inclusion in the Table of Contents may change how it appears on the text page. Correcting the format on the text page may change how it appears in the Table of Contents
- Turn Styles on
- From Home tab, go to Styles box, click on small box in the lower right corner to open the Styles window
- Select Style to modify by hovering over the Style title with the cursor
- Click on the down arrow on the right side of the Style
- From the menu that appears select ‘Modify’
- To change the font size, add or remove bold, change color, and justification, make changes as normal in the modify box
- To change spacing above or below, click on ‘Format’ and select ‘Paragraph’
- Adjust up or down
- To remove or add accent line click on ‘Format’ and select ‘Borders’
- Select ‘No Borders’ and click ‘okay’
Dissertation and Theses
The dissertation is the hallmark of the research expertise demonstrated by a doctoral student. It is a scholarly contribution to knowledge in the student’s area of specialization.
A thesis is a hallmark of some master’s programs. It is a piece of original research, generally less comprehensive than a dissertation and is meant to show the student’s knowledge of an area of specialization.

Still Have Questions?
Dissertations & Theses 614-292-6031 [email protected]
Doctoral Exams, Master's Examination, Graduation Requirements 614-292-6031 [email protected]

Research Guides
Submit and publish your thesis.
- The Graduate Thesis: What is it?
- Thesis Defences
- Deadlines and Fees
Formatting in MS Word
- Formatting in LaTeX
- Making Thesis Accessible
- Thesis Embargo
- Review and Release
- Your Rights as an Author
- Re-using Third Party Materials
- Creative Commons Licenses for Theses
- Turning Thesis into an Article
- Turning Thesis into a Book
- Other Venues of Publication
Thesis style template for MS Word is available on the School of Graduate Studies website . You are not required to use the template but using it will make some of the formatting requirements easier to meet.
►► Thesis template for Microsoft Word (.docx)
For formatting instructions and requirements see the Formatting section of the SGS website .
MS Word formatting tips
Section breaks and page numbers.
One of the most common formatting items that causes difficulty is the page numbering, since the front section and the rest of the thesis use different characters and placement. The way to properly format these sections is to add Section Breaks in between the front matter and the Introduction or Chapter One and between each of the following chapters, including the Bibliography and Appendices sections.
Adding Section Breaks and Page Numbers in Word 2016
You will need to insert “Section Break – next page” in between all chapters and between the front matter and the first chapter as well as between the last chapter and the appendices and the references.
- Click on the place where the break should be inserted and then go to the Layout tab.
- Click on the arrow beside Breaks and choose Section Break Next Page from the list. This allows you to format sections individually of each other.
- Go to the first chapter after the front matter, click in the header and footer area and in the Header & Footer tools, ensure that “Different First Page” is selected and then ensure that the “Link to Previous” option is not selected. This way, when you format the front matter with Roman numerals in the bottom centre, it won’t carry the formatting into the next section.
- Use the Insert Page Numbers and Format Page numbers to insert the page numbers in the appropriate place with the appropriate formatting.
Using Document Styles
The template has Styles that can be used to format your entire thesis. To use a style, select the text to apply the style to, then choose the appropriate style from the Styles window.
If you don’t want to use the template (for example, if you don’t want to use the numbered headings, you can create your own styles. To do this, format the heading (or other element) the way you want, then click New Style in the style window. Insert a unique name for the style and click OK . You can then use that style for those elements going forward.
Table of Contents (TOC)
To automatically generate a TOC, apply the appropriate Styles to all headings. The template has styles created for this purpose. If you are not using the template, you can create your own heading styles to apply.
Auto-generate the TOC in Word 2016 on both Mac and Windows
- Go to the References tab, choose Table of Contents and select Custom Table of Contents . Click OK .
Using your own styles
- If you have created your own styles with custom names, go to the References tab, choose Table of Contents and select Custom Table of Contents , then click Options .
- Put numbers beside the styles you created that correspond with the level of heading they represent. Click OK , then OK again.
Manual formatting of TOC
To add right-aligned tabs with leaders:
- From the Home tab, open the Paragraph settings and click on the Tabs button.
- Enter the tab stop position, choose Right Tab and for Leader , choose the … option. Click Set (or the + sign on Mac), then click OK .
- Type the TOC entry, press tab, then insert the page number.
Miscellaneous tips
- Use page breaks instead of pressing Enter or Return
- Use paragraph first-line indent or tab consistently throughout doc (best to use Styles)
- Use consistent spacing around headers
- Use Shift + Return/Enter to keep headings that run over 2 lines in the same paragraph
- Ensure there are no Widow/Orphan headings or paragraphs
- When inserting longer quotes, use margins to indent rather than tabbing in and inserting a hard return after each line
- Always use tabs rather than spaces. Set tab stops so you aren’t using multiple tabs
Formatting issues and examples
When creating your own table of contents , be sure to format the space between the text and the numbers properly. Do not use multiple tabs or periods to separate them. This will result in a jagged right margin. You want to set a right-aligned tab with leaders in order to have the numbers properly aligned to the right margin. The auto-generate TOC feature does this automatically.

When starting content on a new page, do not use the return key until you get to the next page. If you add content to that section later on, it will move everything down the page, even on the following page. Instead, use the Insert Page Break feature.

When formatting indented quotes, do not use tabs to indent the lines , or put a return at the end of each line. The test in the paragraph won’t flow properly if you need to add more text or change the margins. Instead use the margin controls in the Ruler to indent the paragraph on each side.

- << Previous: Formatting
- Next: Formatting in LaTeX >>
- Last Updated: Sep 15, 2023 3:23 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.utoronto.ca/thesis
Library links
- Library Home
- Renew items and pay fines
- Library hours
- Engineering
- UT Mississauga Library
- UT Scarborough Library
- Information Commons
- All libraries
University of Toronto Libraries 130 St. George St.,Toronto, ON, M5S 1A5 [email protected] 416-978-8450 Map About web accessibility . Tell us about a web accessibility problem . About online privacy and data collection .
© University of Toronto . All rights reserved. Terms and conditions.
Connect with us
- more social media

Thesis Help 2023-24
- Thesis General Info
- Thesis Submission Process
- Electronic Thesis Archive
- Copyright Help This link opens in a new window
- How to Cite Sources
- Data Help This link opens in a new window
- CUS Thesis Help This link opens in a new window
- Frequently Asked Questions

Thesis Submission Info
This guide contains the updated formatting and submission guidelines for thesis students. This guide may be updated prior to thesis deadlines.
For more information on using the Microsoft Word template or transferring your thesis from Google Docs to Microsoft Word, see the directions from CUS . Please email Ask A Librarian with questions.
Formatting Your Thesis - Required
For the library to accept your final thesis the following requirements must be met.
- Title and Approval Pages are formatted correctly. See examples below.
- Title Page
- Approval Page
- Table of Contents
- Major body of text
- Bibliography / References
- To ensure your thesis can be printed and bound, check that you have a Section Break (Odd Page) after each section of your thesis.
- 1.5" on the inside margin and 1" on the outside margin.
- The thesis template will default to these settings.
General formatting questions? Ask a Librarian!
Specific formatting questions? Ask CUS! There are virtual formatting hours on Mondays from 5-7 PST. For more information, see this help page .
Common Formatting Problems
See the following examples of common formatting errors.
- Sample thesis with incorrect section breaks
- Sample thesis with incorrect margins
- Sample thesis with incorrect pagination
Title and Approval Pages
No variations in the title or approval pages will be accepted. Examples are linked below. A complete list of majors for the Approval Page is available but please verify the listing with your thesis advisor.
Requirements
- Title and Approval Pages for a Division
- Title and Approval Pages for an Established Interdisciplinary Committee
- Title and Approval Pages for an Interdisciplinary Committee
- Title and Approval Pages for an Interdivisional Committee
- Use a consistent font and size
- Do not use decorative graphics/fonts
- The date on your title page should be the month and year you are submitting your thesis
CORRECT : May 2022
INCORRECT : May 14, 2022
Thesis Sections and Order
The contents of your thesis must follow the order below. Required sections are indicated in bold.
- Title Page - Required
- Approval Page - Required
- Acknowledgments / Preface
- List of Abbreviations
- Table of Contents- Required
- List of Tables/Figures/Spectra
- Abstract - Required (except for creative writing)
- Major body of text - Required
- Bibliography / References - Required
Formatting Your Thesis - Optional Best Practices
- Best Practices
- Page Numbers
- Figures and Tables
- Building Lists
If you want your thesis to conform to traditional best practices above and beyond the requirements, take these extra steps.
- All sections are present and in the correct order. See guidelines below .
- Page numbers are formatted correctly.
- Chapters or new sections start on the right side.
For examples of past theses, see the Spring 2020 theses in Reed College Electronic Theses Archive .
Example using the LaTex Template
Example using the Word Template
- Starting with the first page of the Introduction/Chapter 1, sequential page numbers should appear on every page. If you are using the thesis template the first page of chapters and blank pages may not display a page number.
- The first page of every chapter should be listed in the table of contents.
- Page numbers can appear anywhere on the page as long as they are consistently placed.
General formatting questions? Ask a Librarian!
Specific formatting questions? Ask CUS!
- Double-spaced and space-and-a-half are preferred, but if your thesis is particularly long, consult with your thesis adviser to see if single spacing would be appropriate.
General formatting questions? Ask a Librarian!
- Images can appear within chapters, at the end of chapters, or in a separate appendix at the end of your thesis (this is easiest). Your adviser can provide guidance on whether to place the full image citation below the image or in your Bibliography.
- Instructions for inserting images and tables into the thesis templates are available on the CUS Thesis Help Page .
- Including a List of Tables/Figures/Spectra is optional, but it is recommended to include one if you have multiple tables/figures/spectra. A sample List of Figures as well as specifics about formatting are in the thesis template ( Word or LaTeX )
- Footnotes should be single-spaced and numbered continuously for each chapter or for the entire work. Do not restart the numbering of footnotes on each page.
- << Previous: Thesis General Info
- Next: Thesis Submission Process >>
- Last Updated: Apr 22, 2024 11:14 AM
- URL: https://libguides.reed.edu/thesis

Reed College Library | Email: [email protected] | Phone: 503-777-7702 | 3203 Southeast Woodstock Boulevard, Portland, Oregon 97202-8199
Reed College Data Privacy Policy
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Thesis Format – Templates and Samples
Thesis Format – Templates and Samples
Table of contents.

Thesis Format
Thesis format refers to the structure and layout of a research thesis or dissertation. It typically includes several chapters, each of which focuses on a particular aspect of the research topic .
The exact format of a thesis can vary depending on the academic discipline and the institution, but some common elements include:
Introduction
Literature review, methodology.
The title page is the first page of a thesis that provides essential information about the document, such as the title, author’s name, degree program, university, and the date of submission. It is considered as an important component of a thesis as it gives the reader an initial impression of the document’s content and quality.
The typical contents of a title page in a thesis include:
- The title of the thesis: It should be concise, informative, and accurately represent the main topic of the research.
- Author’s name: This should be written in full and should be the same as it appears on official university records.
- Degree program and department: This should specify the type of degree (e.g., Bachelor’s, Master’s, or Doctoral) and the field of study (e.g., Computer Science, Psychology, etc.).
- University: The name of the university where the thesis is being submitted.
- Date of submission : The month and year of submission of the thesis.
- Other details that can be included on the title page include the name of the advisor, the name of the committee members, and any acknowledgments.
In terms of formatting, the title page should be centered horizontally and vertically on the page, with a consistent font size and style. The page margin for the title page should be at least 1 inch (2.54 cm) on all sides. Additionally, it is common practice to include the university logo or crest on the title page, and this should be placed appropriately.
Title of the Thesis in Title Case by Author’s Full Name in Title Case
A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Department Name at the University Name
Month Year of Submission
An abstract is a brief summary of a thesis or research paper that provides an overview of the main points, methodology, and findings of the study. It is typically placed at the beginning of the document, after the title page and before the introduction.
The purpose of an abstract is to provide readers with a quick and concise overview of the research paper or thesis. It should be written in a clear and concise language, and should not contain any jargon or technical terms that are not easily understood by the general public.
Here’s an example of an abstract for a thesis:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health among Adolescents
This study examines the impact of social media on mental health among adolescents. The research utilized a survey methodology and collected data from a sample of 500 adolescents aged between 13 and 18 years. The findings reveal that social media has a significant impact on mental health among adolescents, with frequent use of social media associated with higher levels of anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem. The study concludes that there is a need for increased awareness and education on the risks associated with excessive use of social media, and recommends strategies for promoting healthy social media habits among adolescents.
In this example, the abstract provides a concise summary of the thesis by highlighting the main points, methodology, and findings of the study. It also provides a clear indication of the significance of the study and its implications for future research and practice.
A table of contents is an essential part of a thesis as it provides the reader with an overview of the entire document’s structure and organization.
Here’s an example of how a table of contents might look in a thesis:
TABLE OF CONTENTS
I. INTRODUCTION ……………………………………………………..1
A. Background of the Study………………………………………..1
B. Statement of the Problem……………………………………….2
C. Objectives of the Study………………………………………..3
D. Research Questions…………………………………………….4
E. Significance of the Study………………………………………5
F. Scope and Limitations………………………………………….6
G. Definition of Terms……………………………………………7
II. LITERATURE REVIEW. ………………………………………………8
A. Overview of the Literature……………………………………..8
B. Key Themes and Concepts………………………………………..9
C. Gaps in the Literature………………………………………..10
D. Theoretical Framework………………………………………….11
III. METHODOLOGY ……………………………………………………12
A. Research Design………………………………………………12
B. Participants and Sampling……………………………………..13
C. Data Collection Procedures…………………………………….14
D. Data Analysis Procedures………………………………………15
IV. RESULTS …………………………………………………………16
A. Descriptive Statistics…………………………………………16
B. Inferential Statistics…………………………………………17
V. DISCUSSION ………………………………………………………18
A. Interpretation of Results………………………………………18
B. Discussion of Finding s …………………………………………19
C. Implications of the Study………………………………………20
VI. CONCLUSION ………………………………………………………21
A. Summary of the Study…………………………………………..21
B. Limitations of the Study……………………………………….22
C. Recommendations for Future Research……………………………..23
REFERENCES …………………………………………………………….24
APPENDICES …………………………………………………………….26
As you can see, the table of contents is organized by chapters and sections. Each chapter and section is listed with its corresponding page number, making it easy for the reader to navigate the thesis.
The introduction is a critical part of a thesis as it provides an overview of the research problem, sets the context for the study, and outlines the research objectives and questions. The introduction is typically the first chapter of a thesis and serves as a roadmap for the reader.
Here’s an example of how an introduction in a thesis might look:
Introduction:
The prevalence of obesity has increased rapidly in recent decades, with more than one-third of adults in the United States being classified as obese. Obesity is associated with numerous adverse health outcomes, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. Despite significant efforts to address this issue, the rates of obesity continue to rise. The purpose of this study is to investigate the relationship between lifestyle behaviors and obesity in young adults.
The study will be conducted using a mixed-methods approach, with both qualitative and quantitative data collection methods. The research objectives are to:
- Examine the relationship between lifestyle behaviors and obesity in young adults.
- Identify the key lifestyle factors that contribute to obesity in young adults.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of current interventions aimed at preventing and reducing obesity in young adults.
The research questions that will guide this study are:
- What is the relationship between lifestyle behaviors and obesity in young adults?
- Which lifestyle factors are most strongly associated with obesity in young adults?
- How effective are current interventions aimed at preventing and reducing obesity in young adults?
By addressing these research questions, this study aims to contribute to the understanding of the factors that contribute to obesity in young adults and to inform the development of effective interventions to prevent and reduce obesity in this population.
A literature review is a critical analysis and evaluation of existing literature on a specific topic or research question. It is an essential part of any thesis, as it provides a comprehensive overview of the existing research on the topic and helps to establish the theoretical framework for the study. The literature review allows the researcher to identify gaps in the current research, highlight areas that need further exploration, and demonstrate the importance of their research question.
April 9, 2023:
A search on Google Scholar for “Effectiveness of Online Learning during the COVID-19 Pandemic” yielded 1,540 results. Upon reviewing the first few pages of results, it is evident that there is a significant amount of literature on the topic. A majority of the studies focus on the experiences and perspectives of students and educators during the transition to online learning due to the pandemic.
One recent study published in the Journal of Educational Technology & Society (Liu et al., 2023) found that students who were already familiar with online learning tools and platforms had an easier time adapting to online learning than those who were not. However, the study also found that students who were not familiar with online learning tools were able to adapt with proper support from their teachers and institutions.
Another study published in Computers & Education (Tang et al., 2023) compared the academic performance of students in online and traditional classroom settings during the pandemic. The study found that while there were no significant differences in the grades of students in the two settings, students in online classes reported higher levels of stress and lower levels of satisfaction with their learning experience.
Methodology in a thesis refers to the overall approach and systematic process that a researcher follows to collect and analyze data in order to answer their research question(s) or achieve their research objectives. It includes the research design, data collection methods, sampling techniques, data analysis procedures, and any other relevant procedures that the researcher uses to conduct their research.
For example, let’s consider a thesis on the impact of social media on mental health among teenagers. The methodology for this thesis might involve the following steps:
Research Design:
The researcher may choose to conduct a quantitative study using a survey questionnaire to collect data on social media usage and mental health among teenagers. Alternatively, they may conduct a qualitative study using focus group discussions or interviews to gain a deeper understanding of the experiences and perspectives of teenagers regarding social media and mental health.
Sampling Techniques:
The researcher may use random sampling to select a representative sample of teenagers from a specific geographic location or demographic group, or they may use purposive sampling to select participants who meet specific criteria such as age, gender, or mental health status.
Data Collection Methods:
The researcher may use an online survey tool to collect data on social media usage and mental health, or they may conduct face-to-face interviews or focus group discussions to gather qualitative data. They may also use existing data sources such as medical records or social media posts.
Data Analysis Procedures:
The researcher may use statistical analysis techniques such as regression analysis to examine the relationship between social media usage and mental health, or they may use thematic analysis to identify key themes and patterns in the qualitative data.
Ethical Considerations: The researcher must ensure that their research is conducted in an ethical manner, which may involve obtaining informed consent from participants, protecting their confidentiality, and ensuring that their rights and welfare are respected.
In a thesis, the “Results” section typically presents the findings of the research conducted by the author. This section typically includes both quantitative and qualitative data, such as statistical analyses, tables, figures, and other relevant data.
Here are some examples of how the “Results” section of a thesis might look:
Example 1: A quantitative study on the effects of exercise on cardiovascular health
In this study, the author conducts a randomized controlled trial to investigate the effects of exercise on cardiovascular health in a group of sedentary adults. The “Results” section might include tables showing the changes in blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and other relevant indicators in the exercise and control groups over the course of the study. The section might also include statistical analyses, such as t-tests or ANOVA, to demonstrate the significance of the results.
Example 2: A qualitative study on the experiences of immigrant families in a new country
In this study, the author conducts in-depth interviews with immigrant families to explore their experiences of adapting to a new country. The “Results” section might include quotes from the interviews that illustrate the participants’ experiences, as well as a thematic analysis that identifies common themes and patterns in the data. The section might also include a discussion of the implications of the findings for policy and practice.
A thesis discussion section is an opportunity for the author to present their interpretation and analysis of the research results. In this section, the author can provide their opinion on the findings, compare them with other literature, and suggest future research directions.
For example, let’s say the thesis topic is about the impact of social media on mental health. The author has conducted a survey among 500 individuals and has found that there is a significant correlation between excessive social media use and poor mental health.
In the discussion section, the author can start by summarizing the main findings and stating their interpretation of the results. For instance, the author may argue that excessive social media use is likely to cause mental health problems due to the pressure of constantly comparing oneself to others, fear of missing out, and cyberbullying.
Next, the author can compare their results with other studies and point out similarities and differences. They can also identify any limitations in their research design and suggest future directions for research.
For example, the author may point out that their study only measured social media use and mental health at one point in time, and it is unclear whether one caused the other or whether there are other confounding factors. Therefore, they may suggest longitudinal studies that follow individuals over time to better understand the causal relationship.
Writing a conclusion for a thesis is an essential part of the overall writing process. The conclusion should summarize the main points of the thesis and provide a sense of closure to the reader. It is also an opportunity to reflect on the research process and offer suggestions for further study.
Here is an example of a conclusion for a thesis:
After an extensive analysis of the data collected, it is evident that the implementation of a new curriculum has had a significant impact on student achievement. The findings suggest that the new curriculum has improved student performance in all subject areas, and this improvement is particularly notable in math and science. The results of this study provide empirical evidence to support the notion that curriculum reform can positively impact student learning outcomes.
In addition to the positive results, this study has also identified areas for future research. One limitation of the current study is that it only examines the short-term effects of the new curriculum. Future studies should explore the long-term effects of the new curriculum on student performance, as well as investigate the impact of the curriculum on students with different learning styles and abilities.
Overall, the findings of this study have important implications for educators and policymakers who are interested in improving student outcomes. The results of this study suggest that the implementation of a new curriculum can have a positive impact on student achievement, and it is recommended that schools and districts consider curriculum reform as a means of improving student learning outcomes.
References in a thesis typically follow a specific format depending on the citation style required by your academic institution or publisher.
Below are some examples of different citation styles and how to reference different types of sources in your thesis:
In-text citation format: (Author, Year)
Reference list format for a book: Author, A. A. (Year of publication). Title of work: Capital letter also for subtitle. Publisher.
Example: In-text citation: (Smith, 2010) Reference list entry: Smith, J. D. (2010). The art of writing a thesis. Cambridge University Press.
Reference list format for a journal article: Author, A. A., Author, B. B., & Author, C. C. (Year of publication). Title of article. Title of Journal, volume number(issue number), page range.
Example: In-text citation: (Brown, 2015) Reference list entry: Brown, E., Smith, J., & Johnson, L. (2015). The impact of social media on academic performance. Journal of Educational Psychology, 108(3), 393-407.
In-text citation format: (Author page number)
Works Cited list format for a book: Author. Title of Book. Publisher, Year of publication.
Example: In-text citation: (Smith 75) Works Cited entry: Smith, John D. The Art of Writing a Thesis. Cambridge University Press, 2010.
Works Cited list format for a journal article: Author(s). “Title of Article.” Title of Journal, volume number, issue number, date, pages.
Example: In-text citation: (Brown 394) Works Cited entry: Brown, Elizabeth, et al. “The Impact of Social Media on Academic Performance.” Journal of Educational Psychology, vol. 108, no. 3, 2015, pp. 393-407.
Chicago Style
In-text citation format: (Author year, page number)
Bibliography list format for a book: Author. Title of Book. Place of publication: Publisher, Year of publication.
Example: In-text citation: (Smith 2010, 75) Bibliography entry: Smith, John D. The Art of Writing a Thesis. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2010.
Bibliography list format for a journal article: Author. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal volume number, no. issue number (date): page numbers.
Example: In-text citation: (Brown 2015, 394) Bibliography entry: Brown, Elizabeth, John Smith, and Laura Johnson. “The Impact of Social Media on Academic Performance.” Journal of Educational Psychology 108, no. 3 (2015): 393-407.
Reference list format for a book: [1] A. A. Author, Title of Book. City of Publisher, Abbrev. of State: Publisher, year.
Example: In-text citation: [1] Reference list entry: A. J. Smith, The Art of Writing a Thesis. New York, NY: Academic Press, 2010.
Reference list format for a journal article: [1] A. A. Author, “Title of Article,” Title of Journal, vol. x, no. x, pp. xxx-xxx, Month year.
Example: In-text citation: [1] Reference list entry: E. Brown, J. D. Smith, and L. Johnson, “The Impact of Social Media on Academic Performance,” Journal of Educational Psychology, vol. 108, no. 3, pp. 393-407, Mar. 2015.
An appendix in a thesis is a section that contains additional information that is not included in the main body of the document but is still relevant to the topic being discussed. It can include figures, tables, graphs, data sets, sample questionnaires, or any other supplementary material that supports your thesis.
Here is an example of how you can format appendices in your thesis:
- Title page: The appendix should have a separate title page that lists the title, author’s name, the date, and the document type (i.e., thesis or dissertation). The title page should be numbered as the first page of the appendix section.
- Table of contents: If you have more than one appendix, you should include a separate table of contents that lists each appendix and its page number. The table of contents should come after the title page.
- Appendix sections: Each appendix should have its own section with a clear and concise title that describes the contents of the appendix. Each section should be numbered with Arabic numerals (e.g., Appendix 1, Appendix 2, etc.). The sections should be listed in the table of contents.
- Formatting: The formatting of the appendices should be consistent with the rest of the thesis. This includes font size, font style, line spacing, and margins.
- Example: Here is an example of what an appendix might look like in a thesis on the topic of climate change:
Appendix 1: Data Sources
This appendix includes a list of the primary data sources used in this thesis, including their URLs and a brief description of the data they provide.
Appendix 2: Survey Questionnaire
This appendix includes the survey questionnaire used to collect data from participants in the study.
Appendix 3: Additional Figures
This appendix includes additional figures that were not included in the main body of the thesis due to space limitations. These figures provide additional support for the findings presented in the thesis.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Dissertation Methodology – Structure, Example...

What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and...

Dissertation – Format, Example and Template

Dissertation vs Thesis – Key Differences
Thesis Writing
Thesis Format
Thesis Format Essentials: Structure, Tips, and Templates

People also read
Thesis Writing - An Ultimate Writing Guide With Tips & Examples
Thesis Introduction: A Step-by-Step Guide With Examples
How to Write a Thesis Proposal - Sample Proposals and Tips!
Interesting Thesis Topics & Ideas To Get Started
Are you feeling overwhelmed by the thought of formatting your thesis or dissertation? It's a common challenge that many graduate students and researchers face.
The requirements and guidelines for thesis writing can be complex and demanding, leaving you in a state of confusion.
You may find yourself struggling with questions like:
How do I structure my thesis properly?
What are the formatting rules I need to follow?
Don't worry!
In this comprehensive blog, we will explain the thesis format step by step.
Whether you're a graduate student or a postdoctoral researcher, our thesis format guide will assist you in academic writing.
Let's get started!

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
- 1. What is a Thesis and a Dissertation?
- 2. How to Structure a Thesis - The Formatting Basics
- 3. Thesis Format Guidelines
- 4. Thesis Format Sample
- 5. Thesis Paper Formatting Tips
What is a Thesis and a Dissertation?
At some point in your academic journey, you've likely come across the terms "thesis" and "dissertation," but what exactly are they, and how do they differ?
A thesis and a dissertation both represent substantial pieces of academic work, sharing some similarities, but they also have distinct characteristics.
A thesis is typically associated with undergraduate or master's degree programs. It represents a student's independent research and findings on a specific topic. The objective is to demonstrate a deep understanding of the subject matter and the ability to conduct research.
On the other hand,
A dissertation is commonly linked with doctoral programs. It's a more extensive and comprehensive research project that delves into a specific area of study in great detail. Doctoral candidates are expected to make an original contribution to their field of knowledge through their dissertation.
Give a read to our thesis vs dissertation blog to learn the difference!
How to Structure a Thesis - The Formatting Basics
Structuring your thesis is a crucial aspect of academic writing. The thesis format font size and spacing follows a specific framework.
A well-organized thesis not only enhances readability but also reflects your dedication to the research process.
The structure can be divided into three main sections: Front Matter, Body, and End Matter.
Front Matter
- Title Page: The title page is the very first of preliminary pages of your thesis. It typically includes the thesis title, your name, the name of your institution, and the date of submission.
- Abstract: The abstract is a concise summary of your thesis, providing readers with a brief overview of your research problem, methodology, key findings, and conclusions.
- Table of Contents: A well-organized table of contents lists all the main sections, subsections, and corresponding page numbers within your thesis.
- List of Figures and Tables: If your thesis contains figures and tables, create a separate list with captions and page numbers for easy reference.
- List of Abbreviations or Acronyms: If you've used abbreviations or acronyms in your thesis, include a list to explain their meanings.
- List of Symbols: If your research involves symbols or special characters, provide a list of these elements and their definitions.
- Acknowledgments: In this section, you can acknowledge individuals or institutions that have supported your research and thesis writing process.
- Dedication (Optional): Some students choose to include a dedication page to honor someone or express personal sentiments.
- Preface (Optional): In the preface, you can explain the background and context of your research, providing additional context for the reader.
- Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your thesis. It introduces the research problem, its significance, research objectives, and research questions.
- Literature Review: The literature review section provides a comprehensive review of existing literature and research related to your topic. It helps establish the context for your research.
- Methodology: Describe the research methods and techniques you employed in your study. Explain how you collected and analyzed data.
- Results: Present your research findings in a clear and organized manner. Use tables, figures, and charts to illustrate key points.
- Discussion: Interpret the results and discuss their implications. Address any limitations and suggest areas for future research.
- Conclusion: Summarize the main findings and their importance. Restate the research questions and provide a final perspective on the topic.
End Matter
- References: List all the sources you cited in your thesis, following a specific citation style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago).
- Appendices: Include any supplementary materials, such as raw data, surveys, questionnaires, or additional information that supports your research.
- Vita (Optional): Some academic institutions require or allow a vita, which is essentially a brief academic resume or biography.
By following this structured framework for your thesis, you'll ensure that your research is presented in a clear and organized manner, meeting the formatting basics and academic standards.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Thesis Format Guidelines
Formatting your thesis makes your research work not just look good but also helps others understand it easily.
These guidelines show you how to structure and organize your thesis neatly, from the title page to the reference section.
- Page Layout:
- Use standard 8.5 x 11-inch paper.
- Set 1-inch margins on all sides.
- Use a readable and professional font such as Times New Roman, Arial, or Calibri.
- Font size for the main text should typically be 12 points.
- Line Spacing:
- Use double-spacing throughout the document.
- Exceptions include footnotes, long quotations, and the bibliography , which may be single-spaced.
- Heading Structure:
- Use a clear and hierarchical heading structure to organize your content.
- Differentiate between main headings and subheadings with bold, italics, or size variations.
- Page Numbering:
- Page numbers are typically placed in the header or footer.
- Number the pages consecutively throughout the document.
- Arabic numerals or roman numerals are used for the body of the thesis.
- Title Page:
- The title page should include the thesis title, your name, institutional affiliation, and the date of thesis submission.
- Follow your institution's specific guidelines for title page formatting.
- Table of Contents:
- Create a well-organized table of contents listing all sections and subsections with corresponding page numbers.
- Use a clear and consistent format for this section.
- List of Figures and Tables:
- If applicable, provide separate lists for figures and tables, including captions and page numbers.
- Ensure consistent formatting for these lists.
- Present a concise summary of the thesis, highlighting the research problem, methodology , key findings, and conclusions.
- Typically, the abstract is on a separate page immediately following the title page.
- Citations and References:
- Follow a specific citation style consistently throughout your thesis (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago).
- Ensure that in-text citations and references are accurate and properly formatted.
- Page Breaks:
- Use page breaks to separate sections properly. This ensures that your chapters and other major divisions begin on new pages.
- Maintain the required margins (usually 1 inch) on all sides, including the top, bottom, left, and right.
- Appendices:
- If you include appendices, ensure they follow the same formatting rules as the main body of the thesis.
You can also refer to the below-given document to understand the format template of a thesis paper.
Thesis Format Template
Thesis Format Sample
Here are some thesis format examples to get a better understanding.
MLA Thesis Format
APA Thesis Format
Baby Thesis Format
Undergraduate Thesis Format
Master Thesis Format pdf
PhD Thesis Format Pdf
Thesis Format for Computer Science
Research Thesis Format
Thesis Paper Formatting Tips
Formatting your thesis paper correctly is not only about making it look neat and professional but also about meeting the stringent requirements set by your academic institution.
Whether you're in the early stages of writing your thesis or preparing for submission, these tips will help you in formatting.
- Adhere to Institutional Guidelines: Follow your institution's specific formatting requirements, including thesis format margins, font styles, and citation styles.
- Consistency in Formatting: Maintain uniform font, font size, and spacing throughout the thesis for a professional appearance.
- Proper Page Numbering: Place page numbers correctly in the header or footer, starting with the first chapter after the front matter.
- Title Page Accuracy: Ensure the title page contains the accurate title, your name, institutional affiliation, and submission date.
- Organized Table of Contents: Create a well-structured table of contents listing all sections and subsections with page numbers.
- List of Figures and Tables: Provide separate, well-labeled lists for figures and tables, including captions and page numbers.
In conclusion, this blog has provided valuable insights into the essential aspects of formatting a thesis paper.
By following these tips, students can ensure that their research is not only well-structured and polished but also meets the rigorous standards set by their academic institutions.
Formatting and writing a thesis is a challenging task for most people, as it requires a lot of time.
Instead of risking your grades, hire an expert writer who is dedicated and experienced in his work. MyPerfectWords.com professional essay writing help that focuses on providing high-quality standards.
You can buy thesis from us, and our qualified writing experts will guarantee top-quality results delivered within the deadlines!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Caleb S. has been providing writing services for over five years and has a Masters degree from Oxford University. He is an expert in his craft and takes great pride in helping students achieve their academic goals. Caleb is a dedicated professional who always puts his clients first.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading


How To Format A PhD Thesis In Microsoft Word (An Illustrative Guide)
The format of a PhD thesis is as important as the content of the thesis. Different institutions have different formatting guidelines so PhD students should always refer to their handbook.
However, there are some standard requirements of PhD theses which do not change with institutions thus making the theses look similar in many aspects. This article highlights the common formatting standards expected of PhD theses and provides step-by-step instructions on how to format some sections in Microsoft Word.
A PhD thesis or dissertation is divided into three distinct components – front matter, main text and back matter – each of which has its own sub-components, as discussed below:
Front matter
Declaration by the candidate and approval of thesis, table of contents, list of figures, list of tables, list of abbreviations, acknowledgements, inserting figures into main text, inserting tables into main text, back matter, numbering the thesis, related article.
The front matter refers to the preliminary pages that come before the main chapters of the theses. These include:
The title page is the first page of the thesis. It includes: the title of the PhD thesis, the name of the PhD student, the school or department and university in which the study took place, the city and country in which the university is located, and lastly the month and year in which the degree was conferred.
A sample title page is shown below:
Originality is very crucial for PhD-level theses and dissertations. In this section, the PhD candidate declares that his work has not been published elsewhere to the best of his knowledge. The declaration is followed by approval of thesis and includes the names of all those people who reviewed and approved the thesis. These could be the supervisors, the Head of Department/School and/or the Dean of the School of Graduate Studies. The wordings on this page may vary from one institution to another, it is therefore important for the candidates to refer to their handbooks.
The abstract is a short summary of the thesis, normally a paragraph in length. Abstracts can be structured or unstructured. A structured abstract is one that has headings and text below each heading, while an unstructured abstract does not have headings, it is written in paragraph form.
A sample of a structured and unstructured abstract is provided below:
The table of contents provides the outline of the thesis and shows all the headings and sub-headings of the thesis and their page numbers.
To insert a table of contents in Microsoft Word:
- Make sure all the headings and sub-headings of the front matter pages, the main text and the back matter pages have been properly specified in the Word document.
- Click the references tab, then select table of contents option.
- The table of contents has a drop-down arrow which when clicked shows the different style of TOC.
- Select the preferred style of TOC and click OK.
- The TOC will be inserted automatically.
The list of figures shows the titles of all the figures in the thesis and their page numbers.
To insert the list of figures in Microsoft Word:
- Click on the references tab, then click on “insert table of figures” option.
- The following dialogue box will open. In the caption label window, select “figure”. It will show different formats for the list of figures. Choose the style you prefer and click OK.
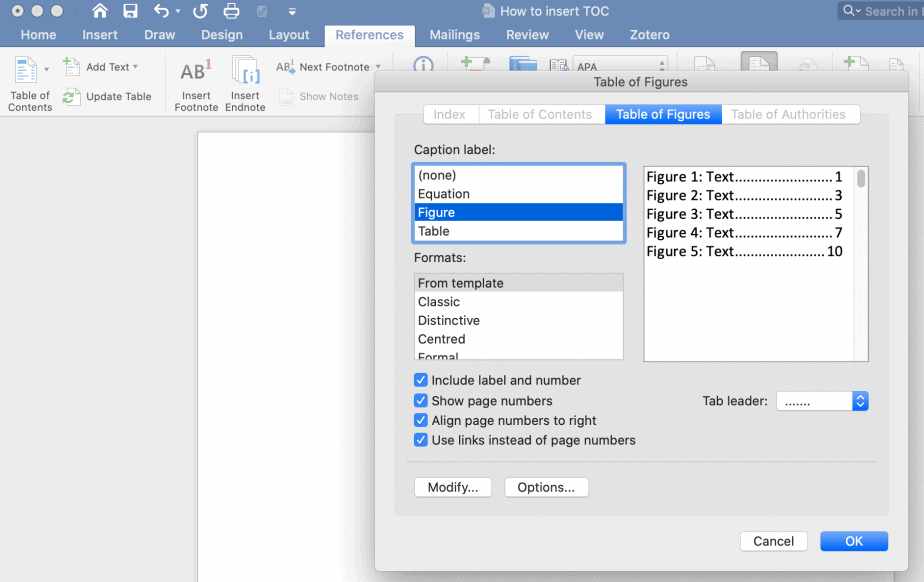
Like the list of figures, the list of tables shows the titles of all the tables in the thesis and their page numbers.
To insert the list of tables in Microsoft Word:
- The following dialogue box will open. In the caption label window, select “table”. It will show different formats for the list of tables. Choose the style you prefer and click OK.
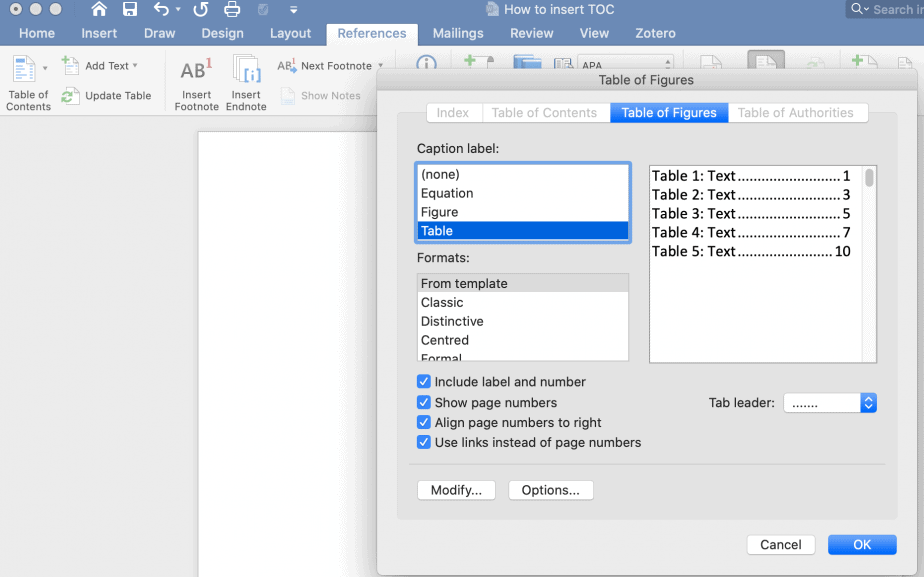
The list of figures and the list of tables should be on different pages.
All acronyms and their abbreviations used throughout the thesis should be highlighted in their own separate page titled ‘list of abbreviations.”
In a PhD thesis, it is mandatory to acknowledge all those who helped you in your PhD journey. These include: your supervisors, other faculty who either reviewed your work or gave advice, people who proofread your work, institutions that helped you gain access to your data, your research respondents, fellow colleagues etc.
Some PhD candidates dedicate their thesis to people who are dear to them, for instance, parents, siblings, spouse/partner, children etc. This section is however not mandatory.
Page numbering for front matter
For front matter, Roman numerals should be used excluding the title page which should not be numbered. The page numbers should be placed at the bottom and centre-aligned.
The main text of thesis is the meat of the thesis and starts from chapter all the way to the last chapter of the thesis. The chapters of theses vary from one institution to another but generally have the following structure:
Chapter 1: Introduction
Chapter 2: Literature review
Chapter 3: Research methodology
Chapter 4: Research findings/results
Chapter 5: Discussions
Chapter 6: Conclusions and recommendations
Each chapter should be organised into headings. There are different levels of headings: level 1, level 2, level 3 etc. The use of these different levels depends on a student’s work.
Other formatting requirements for the main text include:
Font: the most recommended font styles are Times New Roman, Arial, Book Antiqua etc. Students should refer to their handbook for guidance on the font required by their institution.
Spacing: the most recommended spacing for theses is 1.5 for the main text except for things like tables.
Referencing style: the recommended referencing style (such as APA, MLA, Havard etc) should be used throughout the text.
Page numbering: for main text, Arabic numerals are used. The page numbers should be placed at the bottom and centre-aligned.
It is advisable to include figures into theses. Figures help to present some information in a more appealing way than plain text. For each figure inserted, make sure to number it and include a caption explaining what the figure is about.
To insert figures’ captions and numbers into Microsoft Word:
Click on the references tab, then click on insert caption.
A dialogue box will open. Under options, choose “figure” as the label.
Type the caption for the figure, choose the numbering format preferred and click OK. The caption and number of the figure will be inserted.
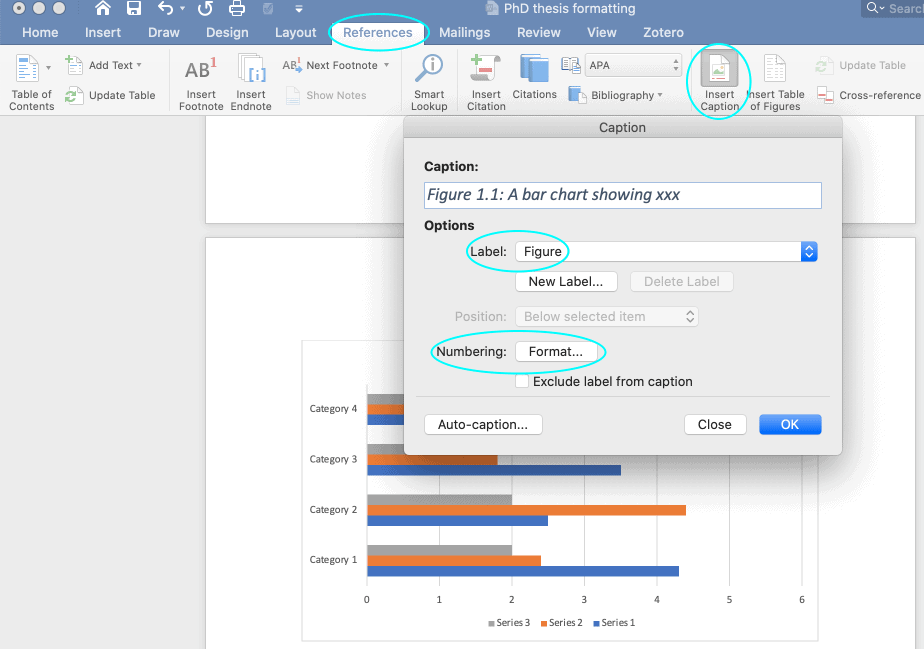
The procedure for tables is the same as for figures.
To insert tables’ captions and numbers into Microsoft Word:
A dialogue box will open. Under options, choose “table” as the label.
Type the caption for the table, choose the numbering format preferred and click OK. The caption and number of the table will be inserted.
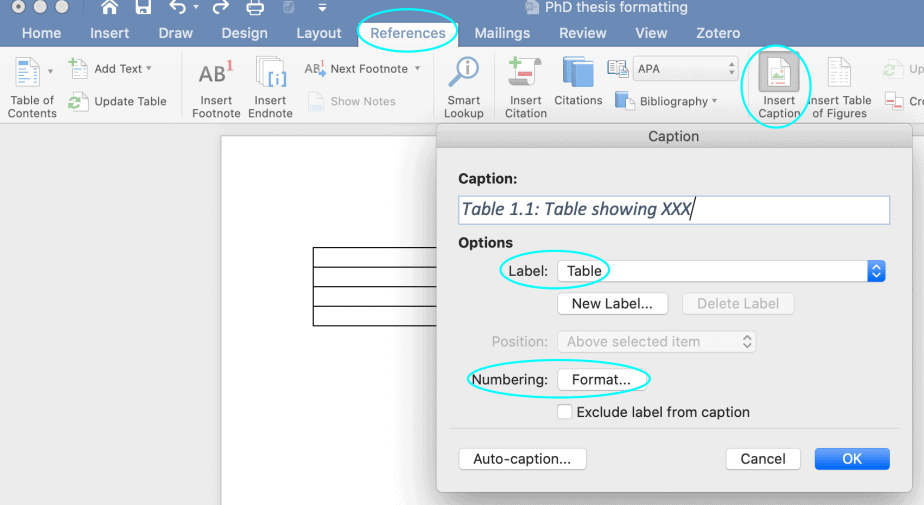
The same procedure is used when you have equations, maps and other illustrations.
Important points to remembers:
When inserting captions and numbers for figures and tables, the cursor should be placed at the right position, that is, above the figures and tables.
If the table or figure has been lifted from somewhere else, the source should be acknowledged at the bottom of the table or figure.
The numbering of the figures and tables should be done by chapter. For instance, all figures in chapter 1 should be numbered: figure 1.1, figure 1.2, figure 1.3 etc. while all figures in chapter 2 should be numbered: figure 2.1, figure 2.2, figure 2.3 etc. Same for the tables, equations and all other illustrations.
The back matter has two main content: the references and the appendices.
The references should be done in accordance with the referencing style recommended by the institution.
The appendices section lists all other materials pertaining to the study that were not included in the front matter. Depending on the study, these may include: the research protocol, a letter of introduction for the research, the questionnaire used for the study, the list of respondents etc.
The page numbers for the references and appendices should be Arabic numerals and a continuation of the pages from main text.
The title of the appendices should be done using either Roman numerals (Appendix I, Appendix II, Appendix III etc) or the alphabet letters in caps, that is, Appendix A, Appendix B, Appendix C… etc.
Each appendix should start on its own page.
As discussed earlier, different numbering styles are used for the different sections of the thesis:
The title page should not be numbered.
The other front matter pages should be numbered using Roman numerals.
The main text and back matter pages should be numbered using Arabic numerals.
Many students struggle with doing the numbering correctly.
The best way to do this in Microsoft Word is to use the “section break” function which divides the thesis into different sections. Each section is then numbered separately from the other sections. To do this:
Go to the end of the page where you want to insert the section break. This should be: at the end of the title page, and after the last front matter page (dedication). Because the main text and back matter pages are numbered using the same style, there is no need to create a section break after the main text.
From insert menu, go to break then section break and select the one written (next page).
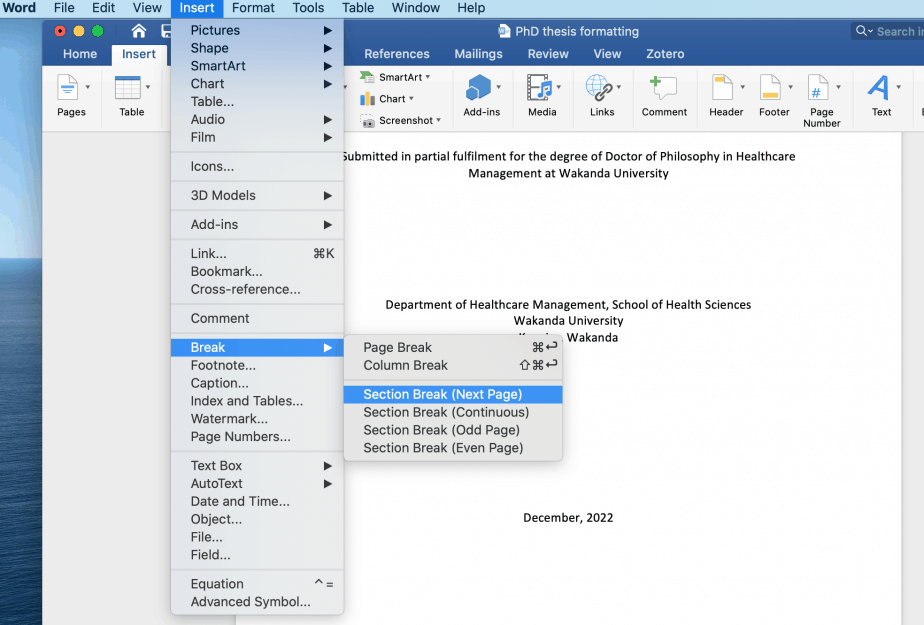
Word will create different sections for the title page, the other front matter pages and the main text and back matter pages.
Use the insert tab and page number function to insert different formats for the different sections: not to be numbered (title page), numbered using Roman numerals (for front matter pages) and numbered using Arabic numerals (main text and back matter pages).
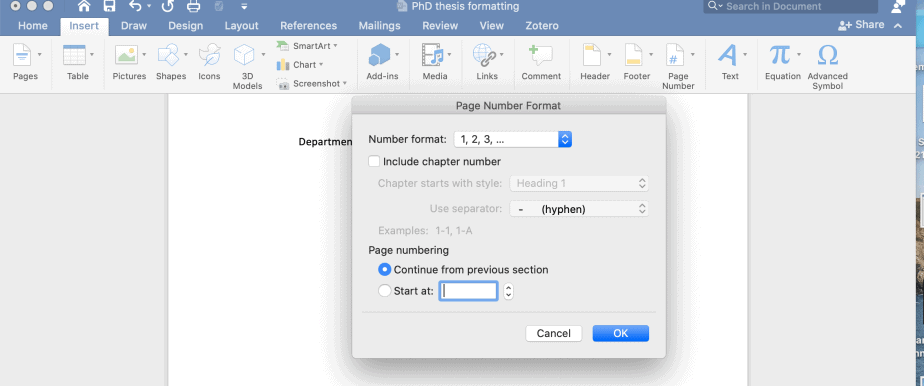
In conclusion, formatting a PhD thesis requires careful consideration of the requirements given by an institution for the different parts of a thesis. PhD students should always consult their handbooks to ensure that their theses meet the high academic standards required of them. This article discussed some key formatting issues and provided step-by-step instructions on some formatting options.
Comprehensive Guidelines for Writing a PhD Thesis Proposal (+ free checklist for PhD Students)
Grace Njeri-Otieno
Grace Njeri-Otieno is a Kenyan, a wife, a mom, and currently a PhD student, among many other balls she juggles. She holds a Bachelors' and Masters' degrees in Economics and has more than 7 years' experience with an INGO. She was inspired to start this site so as to share the lessons learned throughout her PhD journey with other PhD students. Her vision for this site is "to become a go-to resource center for PhD students in all their spheres of learning."
Recent Content
SPSS Tutorial #12: Partial Correlation Analysis in SPSS
Partial correlation is almost similar to Pearson product-moment correlation only that it accounts for the influence of another variable, which is thought to be correlated with the two variables of...
SPSS Tutorial #11: Correlation Analysis in SPSS
In this post, I discuss what correlation is, the two most common types of correlation statistics used (Pearson and Spearman), and how to conduct correlation analysis in SPSS. What is correlation...

- Mardigian Library
- Subject Guides
Formatting Your Thesis or Dissertation with Microsoft Word
- Introduction
- Copyright Page
- Dedication, Acknowledgements, & Preface
- Headings and Subheadings
- Citations and Bibliography
- Page Numbers
- Tables and Figures
- Rotated (Landscape) Pages
- Table of Contents
- Lists of Tables and Figures
- List of Abbreviations
- Some Things to Watch For
- PDF with Embedded Fonts
UM-Deaborn has specific requirements for a thesis title page. An example of what this page should look like can be found on the last page of the Master's Thesis Format Guidelines . There are many ways to use Microsoft Word to create this page; one way to do this is demonstrated in the video below.
Note for dissertations: The order in which you list your committee members differs from the order on the title page of the thesis. All committee members (other than the chair or co-chairs) are listed in alphabetical order based on last name.
- << Previous: Introduction
- Next: Front Matter >>
- Last Updated: Mar 21, 2024 2:35 PM
- URL: https://guides.umd.umich.edu/Word_for_Theses
Call us at 313-593-5559
Chat with us
Text us: 313-486-5399
Email us your question

- 4901 Evergreen Road Dearborn, MI 48128, USA
- Phone: 313-593-5000
- Maps & Directions
- M+Google Mail
- Emergency Information
- UM-Dearborn Connect
- Wolverine Access

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In this video, you will learn how to add borders and set margins to your document especially for research papers, practicum, etc. Other VideosHow to Create ...
The final copy of the thesis must be converted to .pdf (PDF/A format) for submission to the Library (maximum 400 mb). See the guide Saving your thesis in PDF/A format for instructions. Theses must be formatted for US Letter (8.5X11) pages. Landscape 8.5X11 and 11X17 pages are permitted. Legal, A4, or other paper sizes are not permitted.
Footnotes. Format footnotes for your thesis or dissertation following these guidelines: Footnotes must be placed at the bottom of the page separated from the text by a solid line one to two inches long. Begin at the left page margin, directly below the solid line. Single-space footnotes that are more than one line long.
Next go to "Page layout" and then "Breaks". Next, choose the submenu "Next page". Switch to the side, where the numbering should begin (in this case, page 2). In the edit mode of the header or footer, choose "link to previous", after that click on "Move to footer" and click on the "Link to previous" again. Now, to add a ...
UCI Libraries maintains the following templates to assist in formatting your graduate manuscript. If you are formatting your manuscript in Microsoft Word, feel free to download and use the template. If you would like to see what your manuscript should look like, PDFs have been provided.
Your scholarly approach may call for a different presentational method. These are the requirements and recommendations for text-based theses. Page Size For a text-based thesis, or the text portions of a thesis, the page size must be 8.5" x 11", and the text must be in a single, page-wide column. Do not use two or more columns in your thesis. Paragraphs The text of the thesis is written in ...
the top of the page. Format this page according to the Sample Pages at the end of this document. Abstract (Required) The abstract should briefly state the problem, describe the procedure or methods used, and summarize the conclusions reached in the thesis or dissertation. The length of the abstract for a thesis should not exceed
Time to recap…. And there you have it - the traditional dissertation structure and layout, from A-Z. To recap, the core structure for a dissertation or thesis is (typically) as follows: Title page. Acknowledgments page. Abstract (or executive summary) Table of contents, list of figures and tables.
Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates. Published on June 7, 2022 by Tegan George.Revised on November 21, 2023. A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical early steps in your writing process.It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding the specifics of your dissertation topic and showcasing its relevance to ...
This sample thesis file can be used to practise formatting. It is not a template for how to format a thesis. UC does not provide any guidelines on formatting a thesis. APA 7th Edition Formatting Example. This document is formatted according to APA 7th Edition formatting guidelines. It could be used as a template or as an example to follow.
To remove or add accent line click on 'Format' and select 'Borders' ... It is a scholarly contribution to knowledge in the student's area of specialization. A thesis is a hallmark of some master's programs. It is a piece of original research, generally less comprehensive than a dissertation and is meant to show the student's ...
Manual formatting of TOC. To add right-aligned tabs with leaders: From the Home tab, open the Paragraph settings and click on the Tabs button. Enter the tab stop position, choose Right Tab and for Leader, choose the … option. Click Set (or the + sign on Mac), then click OK. Type the TOC entry, press tab, then insert the page number.
Thesis Submission Info. This guide contains the updated formatting and submission guidelines for thesis students. This guide may be updated prior to thesis deadlines. For more information on using the Microsoft Word template or transferring your thesis from Google Docs to Microsoft Word, see the directions from CUS.
The title page (or cover page) of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper should contain all the key information about your document. It usually includes: Dissertation or thesis title. Your name. The type of document (e.g., dissertation, research paper) The department and institution. The degree program (e.g., Master of Arts)
Expand the Styles options by clicking on the drop-down arrow on the bottom right of the tool bar. Select Create a Style from the list. In the Create New Style from Formatting window, add a name for the style. Click on Modify. In the Create New Style from Formatting window adjust the settings as required.
This guide includes video tutorials designed to help you get most of the formatting of your thesis correct the first time. Using these videos to format your thesis will save a lot of time when it comes to having your format checked. Video tutorial demonstrating how to format the front matter of the thesis
While designed specifically for CECS thesis format using a modified IEEE style, much of what is covered in these tutorials also can be applied to or modified for CASL theses as well as CECS and CEHHS dissertations. Please make sure that you check the requirements for your discipline, program, department, or college regarding formatting and ...
Thesis Format. Thesis format refers to the structure and layout of a research thesis or dissertation. It typically includes several chapters, each of which focuses on a particular aspect of the research topic. The exact format of a thesis can vary depending on the academic discipline and the institution, but some common elements include:
Formatting your thesis makes your research work not just look good but also helps others understand it easily. These guidelines show you how to structure and organize your thesis neatly, from the title page to the reference section. Page Layout: Use standard 8.5 x 11-inch paper. Set 1-inch margins on all sides.
Formatting Your Thesis or Dissertation with Microsoft Word This guide includes video tutorials designed to help you get most of the formatting of your thesis correct the first time. Using these videos to format your thesis will save a lot of time when it comes to having your format checked.
To insert figures' captions and numbers into Microsoft Word: Click on the references tab, then click on insert caption. A dialogue box will open. Under options, choose "figure" as the label. Type the caption for the figure, choose the numbering format preferred and click OK. The caption and number of the figure will be inserted.
There are tons more ways you can make your design uniquely yours. Download your custom page border templates for free as a JPG, PDF, or PNG file you can print and share anytime. Your project autosaves in your dashboard, so you can return to it whenever you need to make some edits. If you need a batch or two of your page border design, Canva ...
This guide includes video tutorials designed to help you get most of the formatting of your thesis correct the first time. Using these videos to format your thesis will save a lot of time when it comes to having your format checked. Video tutorial demonstrating how to format a thesis title page with Microsoft Word 2016.