

Nursing: How to Write a Literature Review
- Traditional or Narrative Literature Review
Getting started
1. start with your research question, 2. search the literature, 3. read & evaluate, 4. finalize results, 5. write & revise, brainfuse online tutoring and writing review.
- RESEARCH HELP
The best way to approach your literature review is to break it down into steps. Remember, research is an iterative process, not a linear one. You will revisit steps and revise along the way. Get started with the handout, information, and tips from various university Writing Centers below that provides an excellent overview. Then move on to the specific steps recommended on this page.
- UNC- Chapel Hill Writing Center Literature Review Handout, from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
- University of Wisconsin-Madison Writing Center Learn how to write a review of literature, from the University of Wisconsin-Madison.
- University of Toronto-- Writing Advice The Literature Review: A few tips on conducting it, from the University of Toronto.
- Begin with a topic.
- Understand the topic.
- Familiarize yourself with the terminology. Note what words are being used and keep track of these for use as database search keywords.
- See what research has been done on this topic before you commit to the topic. Review articles can be helpful to understand what research has been done .
- Develop your research question. (see handout below)
- How comprehensive should it be?
- Is it for a course assignment or a dissertation?
- How many years should it cover?
- Developing a good nursing research question Handout. Reviews PICO method and provides search tips.
Your next step is to construct a search strategy and then locate & retrieve articles.
- There are often 2-4 key concepts in a research question.
- Search for primary sources (original research articles.)
- These are based on the key concepts in your research question.
- Remember to consider synonyms and related terms.
- Which databases to search?
- What limiters should be applied (peer-reviewed, publication date, geographic location, etc.)?
Review articles (secondary sources)
Use to identify literature on your topic, the way you would use a bibliography. Then locate and retrieve the original studies discussed in the review article. Review articles are considered secondary sources.
- Once you have some relevant articles, review reference lists to see if there are any useful articles.
- Which articles were written later and have cited some of your useful articles? Are these, in turn, articles that will be useful to you?
- Keep track of what terms you used and what databases you searched.
- Use database tools such as save search history in EBSCO to help.
- Keep track of the citations for the articles you will be using in your literature review.
- Use RefWorks or another method of tracking this information.
- Database Search Strategy Worksheet Handout. How to construct a search.
- TUTORIAL: How to do a search based on your research question This is a self-paced, interactive tutorial that reviews how to construct and perform a database search in CINAHL.
The next step is to read, review, and understand the articles.
- Start by reviewing abstracts.
- Make sure you are selecting primary sources (original research articles).
- Note any keywords authors report using when searching for prior studies.
- You will need to evaluate and critique them and write a synthesis related to your research question.
- Consider using a matrix to organize and compare and contrast the articles .
- Which authors are conducting research in this area? Search by author.
- Are there certain authors’ whose work is cited in many of your articles? Did they write an early, seminal article that is often cited?
- Searching is a cyclical process where you will run searches, review results, modify searches, run again, review again, etc.
- Critique articles. Keep or exclude based on whether they are relevant to your research question.
- When you have done a thorough search using several databases plus Google Scholar, using appropriate keywords or subject terms, plus author’s names, and you begin to find the same articles over and over.
- Remember to consider the scope of your project and the length of your paper. A dissertation will have a more exhaustive literature review than an 8 page paper, for example.
- What are common findings among each group or where do they disagree?
- Identify common themes. Identify controversial or problematic areas in the research.
- Use your matrix to organize this.
- Once you have read and re-read your articles and organized your findings, you are ready to begin the process of writing the literature review.
2. Synthesize. (see handout below)
- Include a synthesis of the articles you have chosen for your literature review.
- A literature review is NOT a list or a summary of what has been written on a particular topic.
- It analyzes the articles in terms of how they relate to your research question.
- While reading, look for similarities and differences (compare and contrast) among the articles. You will create your synthesis from this.
- Synthesis Examples Handout. Sample excerpts that illustrate synthesis.
Regis Online students have access to Brainfuse. Brainfuse is an online tutoring service available through a link in Moodle. Meet with a tutor in a live session or submit your paper for review.
- Brainfuse Tutoring and Writing Assistance for Regis Online Students by Tricia Reinhart Last Updated Oct 26, 2023 81 views this year
- << Previous: Traditional or Narrative Literature Review
- Next: eBooks >>
- Last Updated: Feb 21, 2024 12:05 PM
- URL: https://libguides.regiscollege.edu/nursing_litreview
Nursing: Literature Review
- Required Texts
- Writing Assistance and Organizing & Citing References
- NCLEX Resources
- Literature Review
- MSN Students
- Physical Examination
- Drug Information
- Professional Organizations
- Mobile Apps
- Evidence-based Medicine
- Certifications
- Recommended Nursing Textbooks
- DNP Students
- Conducting Research
- Scoping Reviews
- Systematic Reviews
- Distance Education Students
- Ordering from your Home Library
Good Place to Start: Citation Databases
Interdisciplinary Citation Databases:
A good place to start your research is to search a research citation database to view the scope of literature available on your topic.
TIP #1: SEED ARTICLE Begin your research with a "seed article" - an article that strongly supports your research topic. Then use a citation database to follow the studies published by finding articles which have cited that article, either because they support it or because they disagree with it.
TIP #2: SNOWBALLING Snowballing is the process where researchers will begin with a select number of articles they have identified relevant/strongly supports their topic and then search each articles' references reviewing the studies cited to determine if they are relevant to your research.
BONUS POINTS: This process also helps identify key highly cited authors within a topic to help establish the "experts" in the field.
Begin by constructing a focused research question to help you then convert it into an effective search strategy.
- Identify keywords or synonyms
- Type of study/resources
- Which database(s) to search
- Asking a Good Question (PICO)
- PICO - AHRQ
- PICO - Worksheet
- What Is a PICOT Question?
Seminal Works: Search Key Indexing/Citation Databases
- Google Scholar
- Web of Science
TIP – How to Locate Seminal Works
- DO NOT: Limit by date range or you might overlook the seminal works
- DO: Look at highly cited references (Seminal articles are frequently referred to “cited” in the research)
- DO: Search citation databases like Scopus, Web of Science and Google Scholar
Web Resources
What is a literature review?
A literature review is a comprehensive and up-to-date overview of published information on a subject area. Conducting a literature review demands a careful examination of a body of literature that has been published that helps answer your research question (See PICO). Literature reviewed includes scholarly journals, scholarly books, authoritative databases, primary sources and grey literature.
A literature review attempts to answer the following:
- What is known about the subject?
- What is the chronology of knowledge about my subject?
- Are there any gaps in the literature?
- Is there a consensus/debate on issues?
- Create a clear research question/statement
- Define the scope of the review include limitations (i.e. gender, age, location, nationality...)
- Search existing literature including classic works on your topic and grey literature
- Evaluate results and the evidence (Avoid discounting information that contradicts your research)
- Track and organize references
- How to conduct an effective literature search.
- Social Work Literature Review Guidelines (OWL Purdue Online Writing Lab)
What is PICO?
The PICO model can help you formulate a good clinical question. Sometimes it's referred to as PICO-T, containing an optional 5th factor.
Search Example

- << Previous: NCLEX Resources
- Next: MSN Students >>

- Last Updated: Apr 9, 2024 1:30 PM
- URL: https://guides.himmelfarb.gwu.edu/Nursing

- Himmelfarb Intranet
- Privacy Notice
- Terms of Use
- GW is committed to digital accessibility. If you experience a barrier that affects your ability to access content on this page, let us know via the Accessibility Feedback Form .
- Himmelfarb Health Sciences Library
- 2300 Eye St., NW, Washington, DC 20037
- Phone: (202) 994-2850
- [email protected]
- https://himmelfarb.gwu.edu
- University of Detroit Mercy
- Health Professions
- Writing a Literature Review
- Find Articles (Databases)
- Evidence Based Nursing
- Searching Tips
- Books / eBooks
- Nursing Theory
- Adult-Gerontology Clinical Nurse Specialist
- Doctor of Nursing Practice
- NHL and CNL (Clinical Nurse Leader)
- Nurse Anesthesia
- Nursing Education
- Nurse Practitioner (FNP / ENP)
- Undergraduate Nursing - Clinical Reference Library
- General Writing Support
- Creating & Printing Posters
- Statistics: Health / Medical
- Health Measurement Instruments
- Streaming Video
- Anatomy Resources
- Database & Library Help
- Web Resources
- Evaluating Websites
- Medical / Nursing Apps & Mobile Sites
- Faculty Publications
Literature Review Overview
What is a Literature Review? Why Are They Important?
A literature review is important because it presents the "state of the science" or accumulated knowledge on a specific topic. It summarizes, analyzes, and compares the available research, reporting study strengths and weaknesses, results, gaps in the research, conclusions, and authors’ interpretations.
Tips and techniques for conducting a literature review are described more fully in the subsequent boxes:
- Literature review steps
- Strategies for organizing the information for your review
- Literature reviews sections
- In-depth resources to assist in writing a literature review
- Templates to start your review
- Literature review examples
Literature Review Steps

Graphic used with permission: Torres, E. Librarian, Hawai'i Pacific University
1. Choose a topic and define your research question
- Try to choose a topic of interest. You will be working with this subject for several weeks to months.
- Ideas for topics can be found by scanning medical news sources (e.g MedPage Today), journals / magazines, work experiences, interesting patient cases, or family or personal health issues.
- Do a bit of background reading on topic ideas to familiarize yourself with terminology and issues. Note the words and terms that are used.
- Develop a focused research question using PICO(T) or other framework (FINER, SPICE, etc - there are many options) to help guide you.
- Run a few sample database searches to make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow.
- If possible, discuss your topic with your professor.
2. Determine the scope of your review
The scope of your review will be determined by your professor during your program. Check your assignment requirements for parameters for the Literature Review.
- How many studies will you need to include?
- How many years should it cover? (usually 5-7 depending on the professor)
- For the nurses, are you required to limit to nursing literature?
3. Develop a search plan
- Determine which databases to search. This will depend on your topic. If you are not sure, check your program specific library website (Physician Asst / Nursing / Health Services Admin) for recommendations.
- Create an initial search string using the main concepts from your research (PICO, etc) question. Include synonyms and related words connected by Boolean operators
- Contact your librarian for assistance, if needed.
4. Conduct searches and find relevant literature
- Keep notes as you search - tracking keywords and search strings used in each database in order to avoid wasting time duplicating a search that has already been tried
- Read abstracts and write down new terms to search as you find them
- Check MeSH or other subject headings listed in relevant articles for additional search terms
- Scan author provided keywords if available
- Check the references of relevant articles looking for other useful articles (ancestry searching)
- Check articles that have cited your relevant article for more useful articles (descendancy searching). Both PubMed and CINAHL offer Cited By links
- Revise the search to broaden or narrow your topic focus as you peruse the available literature
- Conducting a literature search is a repetitive process. Searches can be revised and re-run multiple times during the process.
- Track the citations for your relevant articles in a software citation manager such as RefWorks, Zotero, or Mendeley
5. Review the literature
- Read the full articles. Do not rely solely on the abstracts. Authors frequently cannot include all results within the confines of an abstract. Exclude articles that do not address your research question.
- While reading, note research findings relevant to your project and summarize. Are the findings conflicting? There are matrices available than can help with organization. See the Organizing Information box below.
- Critique / evaluate the quality of the articles, and record your findings in your matrix or summary table. Tools are available to prompt you what to look for. (See Resources for Appraising a Research Study box on the HSA, Nursing , and PA guides )
- You may need to revise your search and re-run it based on your findings.
6. Organize and synthesize
- Compile the findings and analysis from each resource into a single narrative.
- Using an outline can be helpful. Start broad, addressing the overall findings and then narrow, discussing each resource and how it relates to your question and to the other resources.
- Cite as you write to keep sources organized.
- Write in structured paragraphs using topic sentences and transition words to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
- Don't present one study after another, but rather relate one study's findings to another. Speak to how the studies are connected and how they relate to your work.
Organizing Information
Options to assist in organizing sources and information :
1. Synthesis Matrix
- helps provide overview of the literature
- information from individual sources is entered into a grid to enable writers to discern patterns and themes
- article summary, analysis, or results
- thoughts, reflections, or issues
- each reference gets its own row
- mind maps, concept maps, flowcharts
- at top of page record PICO or research question
- record major concepts / themes from literature
- list concepts that branch out from major concepts underneath - keep going downward hierarchically, until most specific ideas are recorded
- enclose concepts in circles and connect the concept with lines - add brief explanation as needed
3. Summary Table
- information is recorded in a grid to help with recall and sorting information when writing
- allows comparing and contrasting individual studies easily
- purpose of study
- methodology (study population, data collection tool)
Efron, S. E., & Ravid, R. (2019). Writing the literature review : A practical guide . Guilford Press.
Literature Review Sections
- Lit reviews can be part of a larger paper / research study or they can be the focus of the paper
- Lit reviews focus on research studies to provide evidence
- New topics may not have much that has been published
* The sections included may depend on the purpose of the literature review (standalone paper or section within a research paper)
Standalone Literature Review (aka Narrative Review):
- presents your topic or PICO question
- includes the why of the literature review and your goals for the review.
- provides background for your the topic and previews the key points
- Narrative Reviews: tmay not have an explanation of methods.
- include where the search was conducted (which databases) what subject terms or keywords were used, and any limits or filters that were applied and why - this will help others re-create the search
- describe how studies were analyzed for inclusion or exclusion
- review the purpose and answer the research question
- thematically - using recurring themes in the literature
- chronologically - present the development of the topic over time
- methodological - compare and contrast findings based on various methodologies used to research the topic (e.g. qualitative vs quantitative, etc.)
- theoretical - organized content based on various theories
- provide an overview of the main points of each source then synthesize the findings into a coherent summary of the whole
- present common themes among the studies
- compare and contrast the various study results
- interpret the results and address the implications of the findings
- do the results support the original hypothesis or conflict with it
- provide your own analysis and interpretation (eg. discuss the significance of findings; evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the studies, noting any problems)
- discuss common and unusual patterns and offer explanations
- stay away from opinions, personal biases and unsupported recommendations
- summarize the key findings and relate them back to your PICO/research question
- note gaps in the research and suggest areas for further research
- this section should not contain "new" information that had not been previously discussed in one of the sections above
- provide a list of all the studies and other sources used in proper APA 7
Literature Review as Part of a Research Study Manuscript:
- Compares the study with other research and includes how a study fills a gap in the research.
- Focus on the body of the review which includes the synthesized Findings and Discussion
Literature Reviews vs Systematic Reviews
Systematic Reviews are NOT the same as a Literature Review:
Literature Reviews:
- Literature reviews may or may not follow strict systematic methods to find, select, and analyze articles, but rather they selectively and broadly review the literature on a topic
- Research included in a Literature Review can be "cherry-picked" and therefore, can be very subjective
Systematic Reviews:
- Systemic reviews are designed to provide a comprehensive summary of the evidence for a focused research question
- rigorous and strictly structured, using standardized reporting guidelines (e.g. PRISMA, see link below)
- uses exhaustive, systematic searches of all relevant databases
- best practice dictates search strategies are peer reviewed
- uses predetermined study inclusion and exclusion criteria in order to minimize bias
- aims to capture and synthesize all literature (including unpublished research - grey literature) that meet the predefined criteria on a focused topic resulting in high quality evidence
Literature Review Examples
- Breastfeeding initiation and support: A literature review of what women value and the impact of early discharge (2017). Women and Birth : Journal of the Australian College of Midwives
- Community-based participatory research to promote healthy diet and nutrition and prevent and control obesity among African-Americans: A literature review (2017). Journal of Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities
- Vitamin D deficiency in individuals with a spinal cord injury: A literature review (2017). Spinal Cord
Resources for Writing a Literature Review
These sources have been used in developing this guide.
Resources Used on This Page
Aveyard, H. (2010). Doing a literature review in health and social care : A practical guide . McGraw-Hill Education.
Purdue Online Writing Lab. (n.d.). Writing a literature review . Purdue University. https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/conducting_research/writing_a_literature_review.html
Torres, E. (2021, October 21). Nursing - graduate studies research guide: Literature review. Hawai'i Pacific University Libraries. Retrieved January 27, 2022, from https://hpu.libguides.com/c.php?g=543891&p=3727230
- << Previous: General Writing Support
- Next: Creating & Printing Posters >>
- Last Updated: Apr 19, 2024 3:11 PM
- URL: https://udmercy.libguides.com/nursing
University Library
- Research Guides
- Literature Reviews
- Evidence-Based Practice
- Books & Media
What is a Literature Review?
Key questions for a literature review, examples of literature reviews, useful links, evidence matrix for literature reviews.
- Annotated Bibliographies
The Scholarly Conversation
A literature review provides an overview of previous research on a topic that critically evaluates, classifies, and compares what has already been published on a particular topic. It allows the author to synthesize and place into context the research and scholarly literature relevant to the topic. It helps map the different approaches to a given question and reveals patterns. It forms the foundation for the author’s subsequent research and justifies the significance of the new investigation.
A literature review can be a short introductory section of a research article or a report or policy paper that focuses on recent research. Or, in the case of dissertations, theses, and review articles, it can be an extensive review of all relevant research.
- The format is usually a bibliographic essay; sources are briefly cited within the body of the essay, with full bibliographic citations at the end.
- The introduction should define the topic and set the context for the literature review. It will include the author's perspective or point of view on the topic, how they have defined the scope of the topic (including what's not included), and how the review will be organized. It can point out overall trends, conflicts in methodology or conclusions, and gaps in the research.
- In the body of the review, the author should organize the research into major topics and subtopics. These groupings may be by subject, (e.g., globalization of clothing manufacturing), type of research (e.g., case studies), methodology (e.g., qualitative), genre, chronology, or other common characteristics. Within these groups, the author can then discuss the merits of each article and analyze and compare the importance of each article to similar ones.
- The conclusion will summarize the main findings, make clear how this review of the literature supports (or not) the research to follow, and may point the direction for further research.
- The list of references will include full citations for all of the items mentioned in the literature review.
A literature review should try to answer questions such as
- Who are the key researchers on this topic?
- What has been the focus of the research efforts so far and what is the current status?
- How have certain studies built on prior studies? Where are the connections? Are there new interpretations of the research?
- Have there been any controversies or debate about the research? Is there consensus? Are there any contradictions?
- Which areas have been identified as needing further research? Have any pathways been suggested?
- How will your topic uniquely contribute to this body of knowledge?
- Which methodologies have researchers used and which appear to be the most productive?
- What sources of information or data were identified that might be useful to you?
- How does your particular topic fit into the larger context of what has already been done?
- How has the research that has already been done help frame your current investigation ?
Example of a literature review at the beginning of an article: Forbes, C. C., Blanchard, C. M., Mummery, W. K., & Courneya, K. S. (2015, March). Prevalence and correlates of strength exercise among breast, prostate, and colorectal cancer survivors . Oncology Nursing Forum, 42(2), 118+. Retrieved from http://go.galegroup.com.sonoma.idm.oclc.org/ps/i.do?p=HRCA&sw=w&u=sonomacsu&v=2.1&it=r&id=GALE%7CA422059606&asid=27e45873fddc413ac1bebbc129f7649c Example of a comprehensive review of the literature: Wilson, J. L. (2016). An exploration of bullying behaviours in nursing: a review of the literature. British Journal Of Nursing , 25 (6), 303-306. For additional examples, see:
Galvan, J., Galvan, M., & ProQuest. (2017). Writing literature reviews: A guide for students of the social and behavioral sciences (Seventh ed.). [Electronic book]
Pan, M., & Lopez, M. (2008). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches (3rd ed.). Glendale, CA: Pyrczak Pub. [ Q180.55.E9 P36 2008]
- Write a Literature Review (UCSC)
- Literature Reviews (Purdue)
- Literature Reviews: overview (UNC)
- Review of Literature (UW-Madison)
The Evidence Matrix can help you organize your research before writing your lit review. Use it to identify patterns and commonalities in the articles you have found--similar methodologies ? common theoretical frameworks ? It helps you make sure that all your major concepts covered. It also helps you see how your research fits into the context of the overall topic.
- Evidence Matrix Special thanks to Dr. Cindy Stearns, SSU Sociology Dept, for permission to use this Matrix as an example.
- << Previous: Misc
- Next: Annotated Bibliographies >>
- Last Updated: Jan 8, 2024 2:58 PM
- URL: https://libguides.sonoma.edu/nursing
This website is intended for healthcare professionals

- { $refs.search.focus(); })" aria-controls="searchpanel" :aria-expanded="open" class="hidden lg:inline-flex justify-end text-gray-800 hover:text-primary py-2 px-4 lg:px-0 items-center text-base font-medium"> Search
Search menu
Bashir Y, Conlon KC. Step by step guide to do a systematic review and meta-analysis for medical professionals. Ir J Med Sci. 2018; 187:(2)447-452 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-017-1663-3
Bettany-Saltikov J. How to do a systematic literature review in nursing: a step-by-step guide.Maidenhead: Open University Press; 2012
Bowers D, House A, Owens D. Getting started in health research.Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell; 2011
Hierarchies of evidence. 2016. http://cjblunt.com/hierarchies-evidence (accessed 23 July 2019)
Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qualitative Research in Psychology. 2008; 3:(2)37-41 https://doi.org/10.1191/1478088706qp063oa
Developing a framework for critiquing health research. 2005. https://tinyurl.com/y3nulqms (accessed 22 July 2019)
Cognetti G, Grossi L, Lucon A, Solimini R. Information retrieval for the Cochrane systematic reviews: the case of breast cancer surgery. Ann Ist Super Sanita. 2015; 51:(1)34-39 https://doi.org/10.4415/ANN_15_01_07
Dixon-Woods M, Cavers D, Agarwal S Conducting a critical interpretive synthesis of the literature on access to healthcare by vulnerable groups. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2006; 6:(1) https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-6-35
Guyatt GH, Sackett DL, Sinclair JC Users' guides to the medical literature IX. A method for grading health care recommendations. JAMA. 1995; 274:(22)1800-1804 https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.1995.03530220066035
Hanley T, Cutts LA. What is a systematic review? Counselling Psychology Review. 2013; 28:(4)3-6
Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Version 5.1.0. 2011. https://handbook-5-1.cochrane.org (accessed 23 July 2019)
Jahan N, Naveed S, Zeshan M, Tahir MA. How to conduct a systematic review: a narrative literature review. Cureus. 2016; 8:(11) https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.864
Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1997; 33:(1)159-174
Methley AM, Campbell S, Chew-Graham C, McNally R, Cheraghi-Sohi S. PICO, PICOS and SPIDER: a comparison study of specificity and sensitivity in three search tools for qualitative systematic reviews. BMC Health Serv Res. 2014; 14:(1) https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-014-0579-0
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009; 6:(7) https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Mueller J, Jay C, Harper S, Davies A, Vega J, Todd C. Web use for symptom appraisal of physical health conditions: a systematic review. J Med Internet Res. 2017; 19:(6) https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.6755
Murad MH, Asi N, Alsawas M, Alahdab F. New evidence pyramid. Evid Based Med. 2016; 21:(4)125-127 https://doi.org/10.1136/ebmed-2016-110401
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Methods for the development of NICE public health guidance. 2012. http://nice.org.uk/process/pmg4 (accessed 22 July 2019)
Sambunjak D, Franic M. Steps in the undertaking of a systematic review in orthopaedic surgery. Int Orthop. 2012; 36:(3)477-484 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-011-1460-y
Siddaway AP, Wood AM, Hedges LV. How to do a systematic review: a best practice guide for conducting and reporting narrative reviews, meta-analyses, and meta-syntheses. Annu Rev Psychol. 2019; 70:747-770 https://doi.org/0.1146/annurev-psych-010418-102803
Thomas J, Harden A. Methods for the thematic synthesis of qualitative research in systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2008; 8:(1) https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-8-45
Wallace J, Nwosu B, Clarke M. Barriers to the uptake of evidence from systematic reviews and meta-analyses: a systematic review of decision makers' perceptions. BMJ Open. 2012; 2:(5) https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2012-001220
Carrying out systematic literature reviews: an introduction
Alan Davies
Lecturer in Health Data Science, School of Health Sciences, University of Manchester, Manchester
View articles · Email Alan
Systematic reviews provide a synthesis of evidence for a specific topic of interest, summarising the results of multiple studies to aid in clinical decisions and resource allocation. They remain among the best forms of evidence, and reduce the bias inherent in other methods. A solid understanding of the systematic review process can be of benefit to nurses that carry out such reviews, and for those who make decisions based on them. An overview of the main steps involved in carrying out a systematic review is presented, including some of the common tools and frameworks utilised in this area. This should provide a good starting point for those that are considering embarking on such work, and to aid readers of such reviews in their understanding of the main review components, in order to appraise the quality of a review that may be used to inform subsequent clinical decision making.
Since their inception in the late 1970s, systematic reviews have gained influence in the health professions ( Hanley and Cutts, 2013 ). Systematic reviews and meta-analyses are considered to be the most credible and authoritative sources of evidence available ( Cognetti et al, 2015 ) and are regarded as the pinnacle of evidence in the various ‘hierarchies of evidence’. Reviews published in the Cochrane Library ( https://www.cochranelibrary.com) are widely considered to be the ‘gold’ standard. Since Guyatt et al (1995) presented a users' guide to medical literature for the Evidence-Based Medicine Working Group, various hierarchies of evidence have been proposed. Figure 1 illustrates an example.
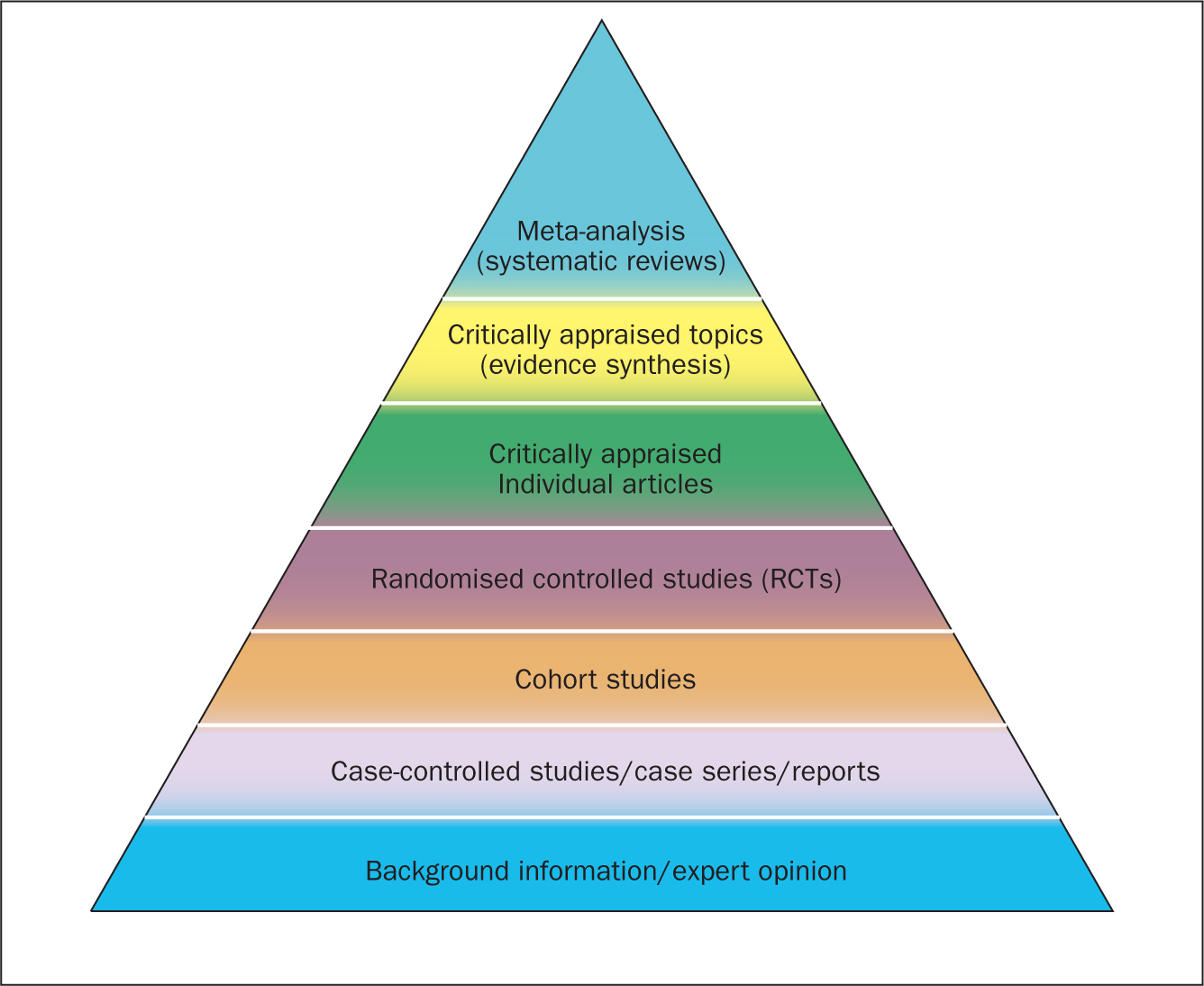
Systematic reviews can be qualitative or quantitative. One of the criticisms levelled at hierarchies such as these is that qualitative research is often positioned towards or even is at the bottom of the pyramid, thus implying that it is of little evidential value. This may be because of traditional issues concerning the quality of some qualitative work, although it is now widely recognised that both quantitative and qualitative research methodologies have a valuable part to play in answering research questions, which is reflected by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) information concerning methods for developing public health guidance. The NICE (2012) guidance highlights how both qualitative and quantitative study designs can be used to answer different research questions. In a revised version of the hierarchy-of-evidence pyramid, the systematic review is considered as the lens through which the evidence is viewed, rather than being at the top of the pyramid ( Murad et al, 2016 ).
Both quantitative and qualitative research methodologies are sometimes combined in a single review. According to the Cochrane review handbook ( Higgins and Green, 2011 ), regardless of type, reviews should contain certain features, including:
- Clearly stated objectives
- Predefined eligibility criteria for inclusion or exclusion of studies in the review
- A reproducible and clearly stated methodology
- Validity assessment of included studies (eg quality, risk, bias etc).
The main stages of carrying out a systematic review are summarised in Box 1 .
Formulating the research question
Before undertaking a systemic review, a research question should first be formulated ( Bashir and Conlon, 2018 ). There are a number of tools/frameworks ( Table 1 ) to support this process, including the PICO/PICOS, PEO and SPIDER criteria ( Bowers et al, 2011 ). These frameworks are designed to help break down the question into relevant subcomponents and map them to concepts, in order to derive a formalised search criterion ( Methley et al, 2014 ). This stage is essential for finding literature relevant to the question ( Jahan et al, 2016 ).
It is advisable to first check that the review you plan to carry out has not already been undertaken. You can optionally register your review with an international register of prospective reviews called PROSPERO, although this is not essential for publication. This is done to help you and others to locate work and see what reviews have already been carried out in the same area. It also prevents needless duplication and instead encourages building on existing work ( Bashir and Conlon, 2018 ).
A study ( Methley et al, 2014 ) that compared PICO, PICOS and SPIDER in relation to sensitivity and specificity recommended that the PICO tool be used for a comprehensive search and the PICOS tool when time/resources are limited.
The use of the SPIDER tool was not recommended due to the risk of missing relevant papers. It was, however, found to increase specificity.
These tools/frameworks can help those carrying out reviews to structure research questions and define key concepts in order to efficiently identify relevant literature and summarise the main objective of the review ( Jahan et al, 2016 ). A possible research question could be: Is paracetamol of benefit to people who have just had an operation? The following examples highlight how using a framework may help to refine the question:
- What form of paracetamol? (eg, oral/intravenous/suppository)
- Is the dosage important?
- What is the patient population? (eg, children, adults, Europeans)
- What type of operation? (eg, tonsillectomy, appendectomy)
- What does benefit mean? (eg, reduce post-operative pyrexia, analgesia).
An example of a more refined research question could be: Is oral paracetamol effective in reducing pain following cardiac surgery for adult patients? A number of concepts for each element will need to be specified. There will also be a number of synonyms for these concepts ( Table 2 ).
Table 2 shows an example of concepts used to define a search strategy using the PICO statement. It is easy to see even with this dummy example that there are many concepts that require mapping and much thought required to capture ‘good’ search criteria. Consideration should be given to the various terms to describe the heart, such as cardiac, cardiothoracic, myocardial, myocardium, etc, and the different names used for drugs, such as the equivalent name used for paracetamol in other countries and regions, as well as the various brand names. Defining good search criteria is an important skill that requires a lot of practice. A high-quality review gives details of the search criteria that enables the reader to understand how the authors came up with the criteria. A specific, well-defined search criterion also aids in the reproducibility of a review.
Search criteria
Before the search for papers and other documents can begin it is important to explicitly define the eligibility criteria to determine whether a source is relevant to the review ( Hanley and Cutts, 2013 ). There are a number of database sources that are searched for medical/health literature including those shown in Table 3 .
The various databases can be searched using common Boolean operators to combine or exclude search terms (ie AND, OR, NOT) ( Figure 2 ).
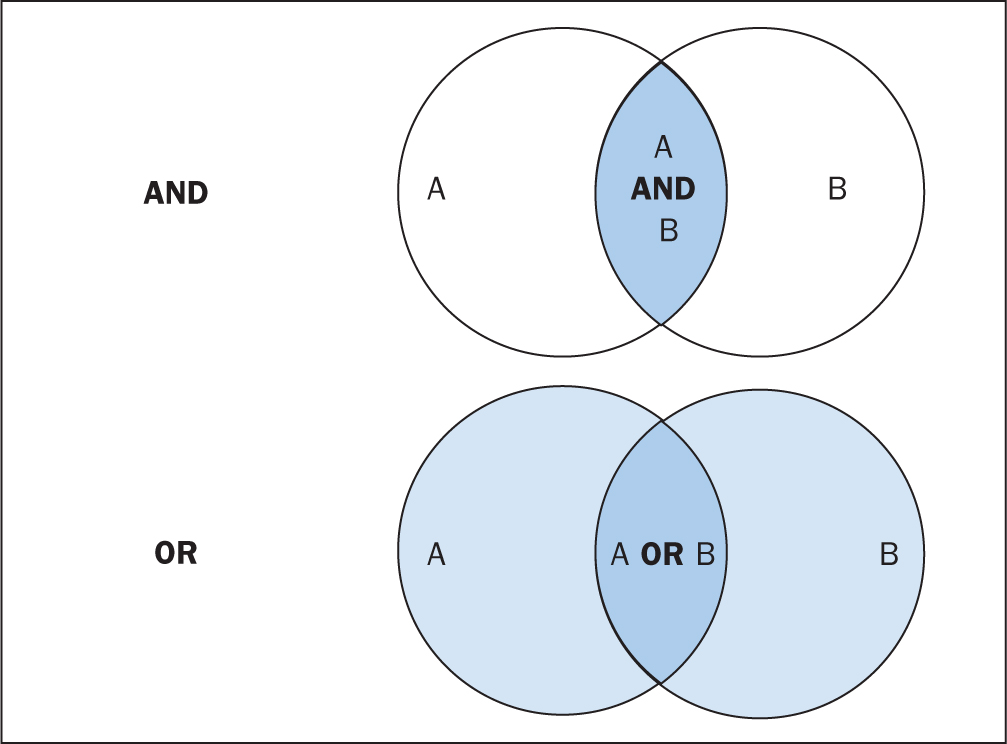
Although most literature databases use similar operators, it is necessary to view the individual database guides, because there are key differences between some of them. Table 4 details some of the common operators and wildcards used in the databases for searching. When developing a search criteria, it is a good idea to check concepts against synonyms, as well as abbreviations, acronyms and plural and singular variations ( Cognetti et al, 2015 ). Reading some key papers in the area and paying attention to the key words they use and other terms used in the abstract, and looking through the reference lists/bibliographies of papers, can also help to ensure that you incorporate relevant terms. Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) that are used by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) ( https://www.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/meshhome.html) to provide hierarchical biomedical index terms for NLM databases (Medline and PubMed) should also be explored and included in relevant search strategies.
Searching the ‘grey literature’ is also an important factor in reducing publication bias. It is often the case that only studies with positive results and statistical significance are published. This creates a certain bias inherent in the published literature. This bias can, to some degree, be mitigated by the inclusion of results from the so-called grey literature, including unpublished work, abstracts, conference proceedings and PhD theses ( Higgins and Green, 2011 ; Bettany-Saltikov, 2012 ; Cognetti et al, 2015 ). Biases in a systematic review can lead to overestimating or underestimating the results ( Jahan et al, 2016 ).
An example search strategy from a published review looking at web use for the appraisal of physical health conditions can be seen in Box 2 . High-quality reviews usually detail which databases were searched and the number of items retrieved from each.
A balance between high recall and high precision is often required in order to produce the best results. An oversensitive search, or one prone to including too much noise, can mean missing important studies or producing too many search results ( Cognetti et al, 2015 ). Following a search, the exported citations can be added to citation management software (such as Mendeley or Endnote) and duplicates removed.
Title and abstract screening
Initial screening begins with the title and abstracts of articles being read and included or excluded from the review based on their relevance. This is usually carried out by at least two researchers to reduce bias ( Bashir and Conlon, 2018 ). After screening any discrepancies in agreement should be resolved by discussion, or by an additional researcher casting the deciding vote ( Bashir and Conlon, 2018 ). Statistics for inter-rater reliability exist and can be reported, such as percentage of agreement or Cohen's kappa ( Box 3 ) for two reviewers and Fleiss' kappa for more than two reviewers. Agreement can depend on the background and knowledge of the researchers and the clarity of the inclusion and exclusion criteria. This highlights the importance of providing clear, well-defined criteria for inclusion that are easy for other researchers to follow.
Full-text review
Following title and abstract screening, the remaining articles/sources are screened in the same way, but this time the full texts are read in their entirety and included or excluded based on their relevance. Reasons for exclusion are usually recorded and reported. Extraction of the specific details of the studies can begin once the final set of papers is determined.
Data extraction
At this stage, the full-text papers are read and compared against the inclusion criteria of the review. Data extraction sheets are forms that are created to extract specific data about a study (12 Jahan et al, 2016 ) and ensure that data are extracted in a uniform and structured manner. Extraction sheets can differ between quantitative and qualitative reviews. For quantitative reviews they normally include details of the study's population, design, sample size, intervention, comparisons and outcomes ( Bettany-Saltikov, 2012 ; Mueller et al, 2017 ).
Quality appraisal
The quality of the studies used in the review should also be appraised. Caldwell et al (2005) discussed the need for a health research evaluation framework that could be used to evaluate both qualitative and quantitative work. The framework produced uses features common to both research methodologies, as well as those that differ ( Caldwell et al, 2005 ; Dixon-Woods et al, 2006 ). Figure 3 details the research critique framework. Other quality appraisal methods do exist, such as those presented in Box 4 . Quality appraisal can also be used to weight the evidence from studies. For example, more emphasis can be placed on the results of large randomised controlled trials (RCT) than one with a small sample size. The quality of a review can also be used as a factor for exclusion and can be specified in inclusion/exclusion criteria. Quality appraisal is an important step that needs to be undertaken before conclusions about the body of evidence can be made ( Sambunjak and Franic, 2012 ). It is also important to note that there is a difference between the quality of the research carried out in the studies and the quality of how those studies were reported ( Sambunjak and Franic, 2012 ).
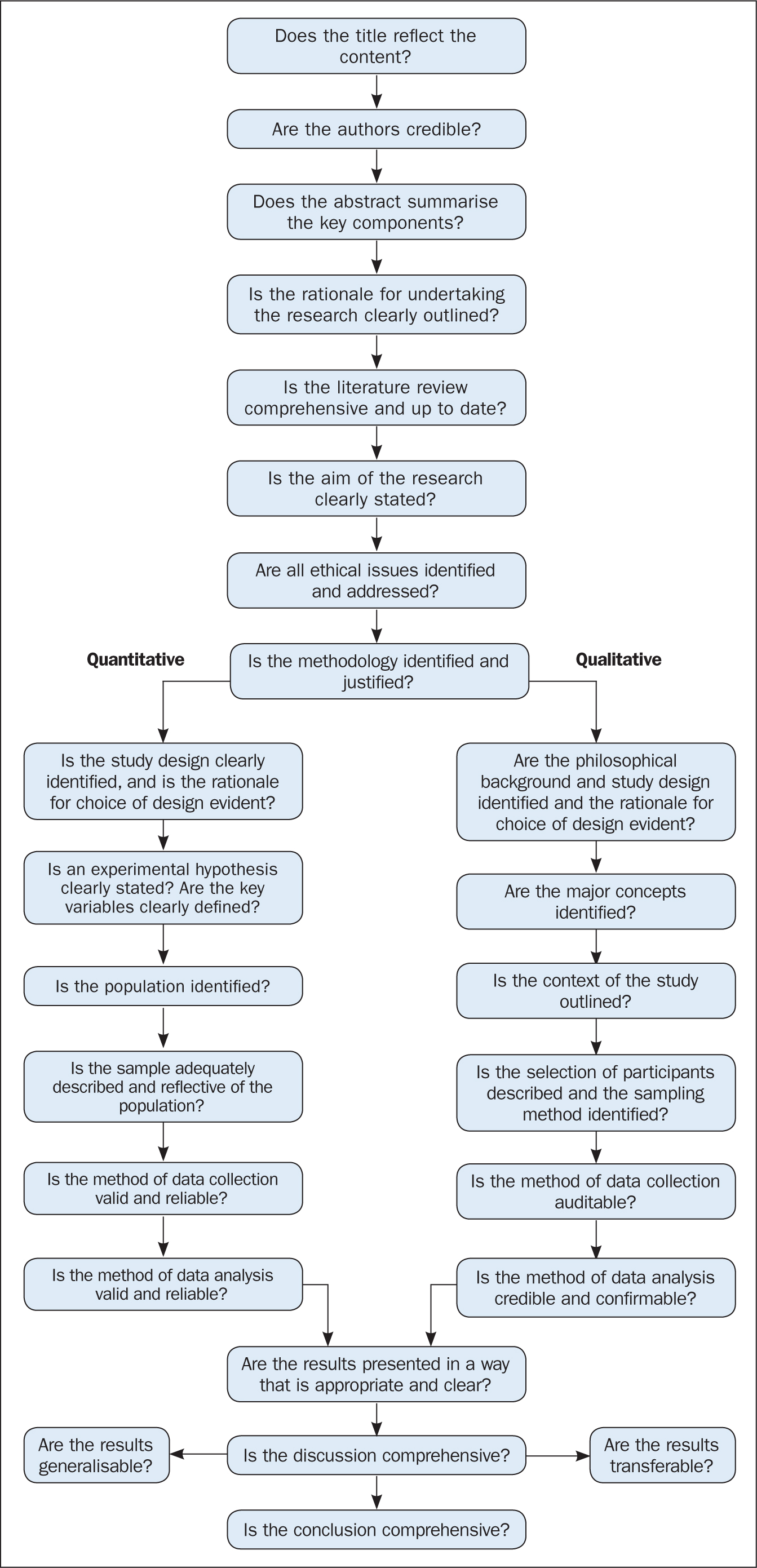
The quality appraisal is different for qualitative and quantitative studies. With quantitative studies this usually focuses on their internal and external validity, such as how well the study has been designed and analysed, and the generalisability of its findings. Qualitative work, on the other hand, is often evaluated in terms of trustworthiness and authenticity, as well as how transferable the findings may be ( Bettany-Saltikov, 2012 ; Bashir and Conlon, 2018 ; Siddaway et al, 2019 ).
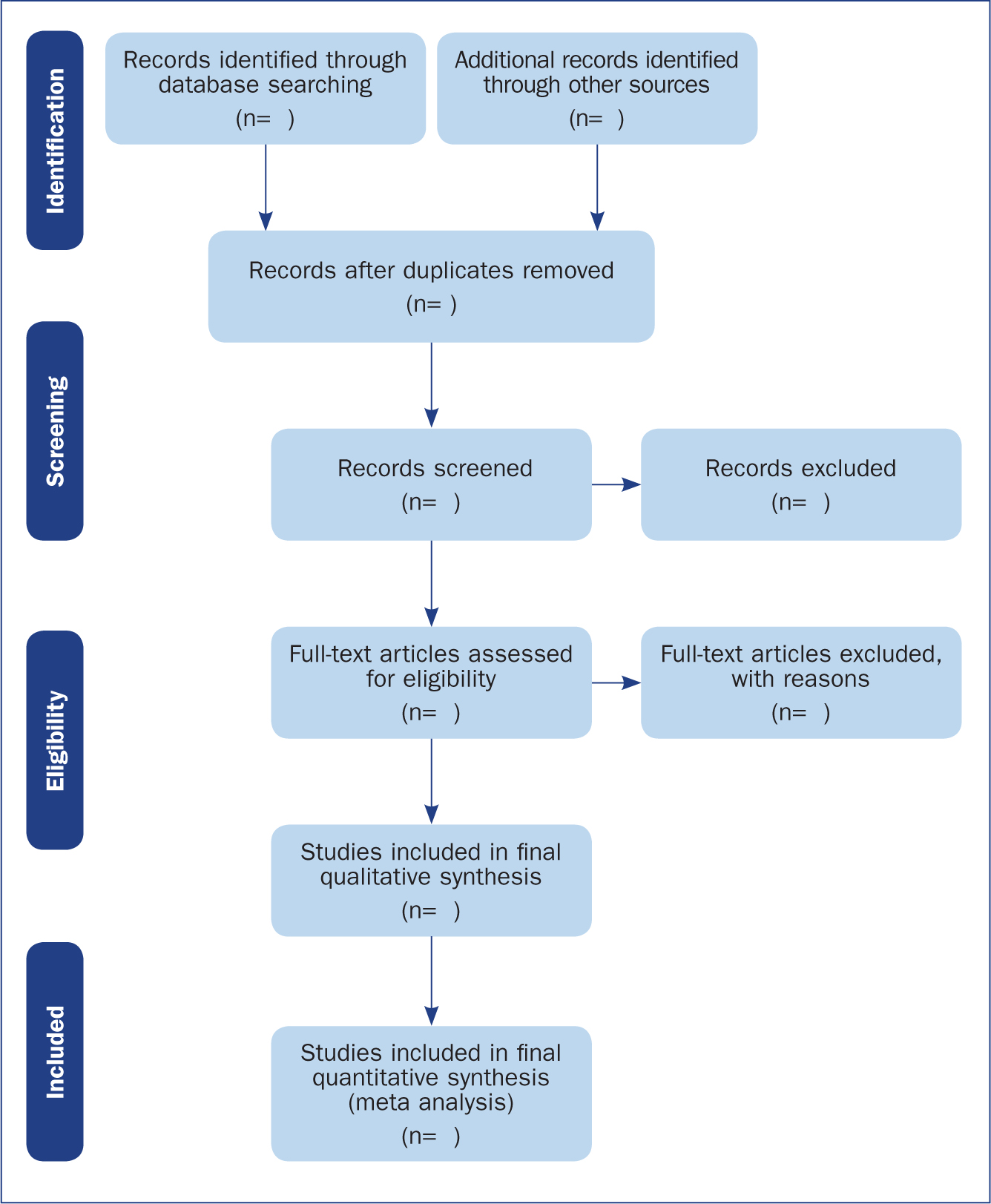
Reporting a review (the PRISMA statement)
The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) provides a reporting structure for systematic reviews/meta-analysis, and consists of a checklist and diagram ( Figure 4 ). The stages of identifying potential papers/sources, screening by title and abstract, determining eligibility and final inclusion are detailed with the number of articles included/excluded at each stage. PRISMA diagrams are often included in systematic reviews to detail the number of papers included at each of the four main stages (identification, screening, eligibility and inclusion) of the review.
Data synthesis
The combined results of the screened studies can be analysed qualitatively by grouping them together under themes and subthemes, often referred to as meta-synthesis or meta-ethnography ( Siddaway et al, 2019 ). Sometimes this is not done and a summary of the literature found is presented instead. When the findings are synthesised, they are usually grouped into themes that were derived by noting commonality among the studies included. Inductive (bottom-up) thematic analysis is frequently used for such purposes and works by identifying themes (essentially repeating patterns) in the data, and can include a set of higher-level and related subthemes (Braun and Clarke, 2012). Thomas and Harden (2008) provide examples of the use of thematic synthesis in systematic reviews, and there is an excellent introduction to thematic analysis by Braun and Clarke (2012).
The results of the review should contain details on the search strategy used (including search terms), the databases searched (and the number of items retrieved), summaries of the studies included and an overall synthesis of the results ( Bettany-Saltikov, 2012 ). Finally, conclusions should be made about the results and the limitations of the studies included ( Jahan et al, 2016 ). Another method for synthesising data in a systematic review is a meta-analysis.
Limitations of systematic reviews
Apart from the many advantages and benefits to carrying out systematic reviews highlighted throughout this article, there remain a number of disadvantages. These include the fact that not all stages of the review process are followed rigorously or even at all in some cases. This can lead to poor quality reviews that are difficult or impossible to replicate. There also exist some barriers to the use of evidence produced by reviews, including ( Wallace et al, 2012 ):
- Lack of awareness and familiarity with reviews
- Lack of access
- Lack of direct usefulness/applicability.
Meta-analysis
When the methods used and the analysis are similar or the same, such as in some RCTs, the results can be synthesised using a statistical approach called meta-analysis and presented using summary visualisations such as forest plots (or blobbograms) ( Figure 5 ). This can be done only if the results can be combined in a meaningful way.
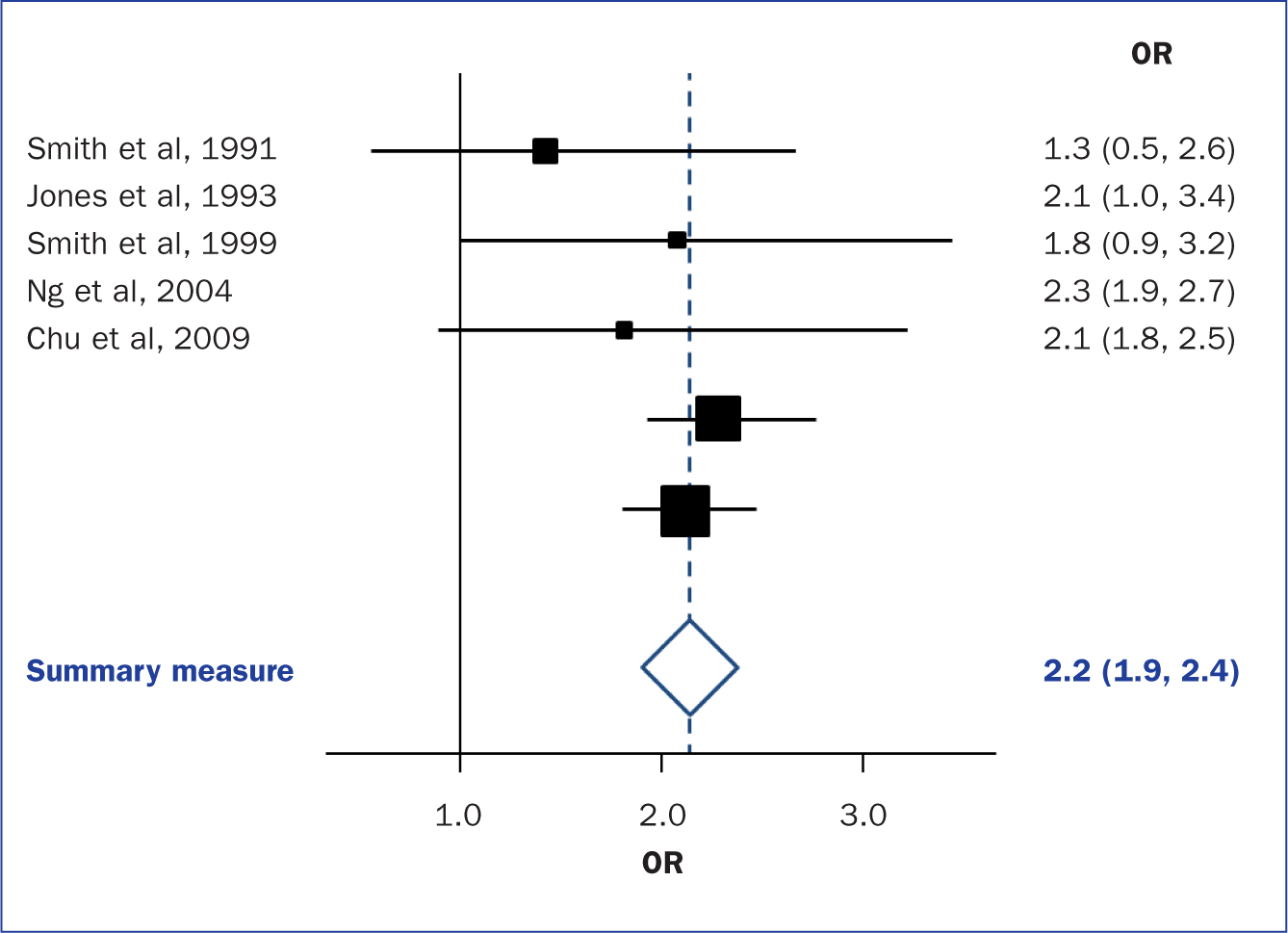
Meta-analysis can be carried out using common statistical and data science software, such as the cross-platform ‘R’ ( https://www.r-project.org), or by using standalone software, such as Review Manager (RevMan) produced by the Cochrane community ( https://tinyurl.com/revman-5), which is currently developing a cross-platform version RevMan Web.
Carrying out a systematic review is a time-consuming process, that on average takes between 6 and 18 months and requires skill from those involved. Ideally, several reviewers will work on a review to reduce bias. Experts such as librarians should be consulted and included where possible in review teams to leverage their expertise.
Systematic reviews should present the state of the art (most recent/up-to-date developments) concerning a specific topic and aim to be systematic and reproducible. Reproducibility is aided by transparent reporting of the various stages of a review using reporting frameworks such as PRISMA for standardisation. A high-quality review should present a summary of a specific topic to a high standard upon which other professionals can base subsequent care decisions that increase the quality of evidence-based clinical practice.
- Systematic reviews remain one of the most trusted sources of high-quality information from which to make clinical decisions
- Understanding the components of a review will help practitioners to better assess their quality
- Many formal frameworks exist to help structure and report reviews, the use of which is recommended for reproducibility
- Experts such as librarians can be included in the review team to help with the review process and improve its quality
CPD reflective questions
- Where should high-quality qualitative research sit regarding the hierarchies of evidence?
- What background and expertise should those conducting a systematic review have, and who should ideally be included in the team?
- Consider to what extent inter-rater agreement is important in the screening process
- Research article
- Open access
- Published: 16 May 2019
An analysis of current practices in undertaking literature reviews in nursing: findings from a focused mapping review and synthesis
- Helen Aveyard ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5133-3356 1 &
- Caroline Bradbury-Jones 2
BMC Medical Research Methodology volume 19 , Article number: 105 ( 2019 ) Cite this article
40k Accesses
25 Citations
10 Altmetric
Metrics details
In this paper we discuss the emergence of many different methods for doing a literature review. Referring back to the early days, when there were essentially two types of review; a Cochrane systematic review and a narrative review, we identify how the term systematic review is now widely used to describe a variety of review types and how the number of available methods for doing a literature review has increased dramatically. This led us to undertake a review of current practice of those doing a literature review and the terms used to describe them.
We undertook a focused mapping review and synthesis. Literature reviews; defined as papers with the terms review or synthesis in the title, published in five nursing journals between January 2017–June 2018 were identified. We recorded the type of review and how these were undertaken.
We identified more than 35 terms used to describe a literature review. Some terms reflected established methods for doing a review whilst others could not be traced to established methods and/or the description of method in the paper was limited. We also found inconsistency in how the terms were used.
We have identified a proliferation of terms used to describe doing a literature review; although it is not clear how many distinct methods are being used. Our review indicates a move from an era when the term narrative review was used to describe all ‘non Cochrane’ reviews; to a time of expansion when alternative systematic approaches were developed to enhance rigour of such narrative reviews; to the current situation in which these approaches have proliferated to the extent so that the academic discipline of doing a literature review has become muddled and confusing. We argue that an ‘era of consolidation’ is needed in which those undertaking reviews are explicit about the method used and ensure that their processes can be traced back to a well described, original primary source.
Peer Review reports
Over the past twenty years in nursing, literature reviews have become an increasingly popular form of synthesising evidence and information relevant to the profession. Along with this there has been a proliferation of publications regarding the processes and practicalities of reviewing [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ], This increase in activity and enthusiasm for undertaking literature reviews is paralleled by the foundation of the Cochrane Collaboration in 1993. Developed in response to the need for up-to-date reviews of evidence of the effectiveness of health care interventions, the Cochrane Collaboration introduced a rigorous method of searching, appraisal and analysis in the form of a ‘handbook’ for doing a systematic review [ 5 ] .Subsequently, similar procedural guidance has been produced, for example by the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (CRD) [ 6 ] and The Joanna Briggs Institute [ 7 ]. Further guidance has been published to assist researchers with clarity in the reporting of published reviews [ 8 ].
In the early days of the literature review era, the methodological toolkit for those undertaking a literature was polarised, in a way that mirrored the paradigm wars of the time within mixed-methods research [ 9 ]. We refer to this as the ‘dichotomy era’ (i.e. the 1990s), The prominent methods of literature reviewing fell into one of two camps: The highly rigorous and systematic, mostly quantitative ‘Cochrane style’ review on one hand and a ‘narrative style’ review on the other hand, whereby a body of literature was summarised qualitatively, but the methods were often not articulated. Narrative reviews were particularly popular in dissertations and other student work (and they continue to be so in many cases) but have been criticised for a lack of systematic approach and consequently significant potential for bias in the findings [ 10 , 11 ].
The latter 1990s and early 2000, saw the emergence of other forms of review, developed as a response to the Cochrane/Narrative dichotomy. These alternative approaches to the Cochrane review provided researchers with reference points for performing reviews that drew on different study types, not just randomised controlled trials. They promoted a systematic and robust approach for all reviews, not just those concerned with effectiveness of interventions and treatments. One of the first published description of methods was Noblet and Hare’s (1998) ‘Meta-ethnography’ [ 12 ]. This method, although its name suggests otherwise, could incorporate and synthesise all types of qualitative research, not just ethnographies. The potential confusion regarding the inclusion of studies that were not ethnographies within a meta-ethnography, promoted the description of other similar methods, for example, the meta-synthesis of Walsh and Downe (2005) [ 13 ] and the thematic synthesis of Thomas and Harden (2008) [ 14 ]. Also, to overcome the dichotomy of the quantitative/qualitative reviews, the integrative review was described according to Whitemore and Knafl (2005) [ 15 ]. These reviews can be considered to be literature reviews that have been done in a systematic way but not necessarily adhering to guidelines established by the Cochrane Collaboration. We conceptualise this as the ‘expansion era’. Some of the methods are summarised in Table 1 .
Over the past two decades there has been a proliferation of review types, with corresponding explosion of terms used to describe them. A review of evidence synthesis methodologies by Grant and Booth in 2009 [ 20 ] identified 14 different approaches to reviewing the literature and similarly, Booth and colleagues [ 21 ] detailed 19 different review types, highlighting the range of review types currently available. We might consider this the ‘proliferation era’. This is however, somewhat a double-edged sword, because although researchers now have far more review methods at their disposal, there is risk of confusion in the field. As Sabatino and colleagues (2014) [ 22 ] have argued, review methods are not always consistently applied by researchers.
Aware of such potential inconsistency and also our own confusion at times regarding the range of review methods available, we questioned what was happening within our own discipline of nursing. We undertook a snap-shot, contemporary analysis to explore the range of terms used to describe reviews, the methods currently described in nursing and the underlying trends and patterns in searching, appraisal and analysis adopted by those doing a literature review. The aim was to gain some clarity on what is happening within the field, in order to understand, explain and critique what is happening within the proliferation era.
In order to explore current practices in doing a literature review, we undertook a ‘Focused Mapping Review and Synthesis’ (FMRS) – an approach that has been described only recently. This form of review [ 19 ] is a method of investigating trends in academic publications and has been used in a range of issues relevant to nursing and healthcare, for example, theory in qualitative research [ 23 ] and vicarious trauma in child protection research [ 24 ].
A FMRS seeks to identify what is happening within a particular subject or field of inquiry; hence the search is restricted to a particular time period and to pre-identified journals. The review has four distinct features: It: 1) focuses on identifying trends in an area rather than a body of evidence; 2) creates a descriptive map or topography of key features of research within the field rather than a synthesis of findings; 3) comments on the overall approach to knowledge production rather than the state of the evidence; 4) examines this within a broader epistemological context. These are translated into three specific focused activities: 1) targeted journals; 2) a specific subject; 3) a defined time period. The FMRS therefore, is distinct from other forms of review because it responds to questions concerned with ‘what is happening in this field?’ It was thus an ideal method to investigate current practices in literature reviews in nursing.
Using the international Scopus (2016) SCImago Journal and Country Rank, we identified the five highest ranked journals in nursing at that time of undertaking the review. There was no defined method for determining the number of journals to include in a review; the aim was to identify a sample and we identified five journals in order to search from a range of high ranking journals. We discuss the limitations of this later. Journals had to have ‘nursing’ or ‘nurse’ in the title and we did not include journals with a specialist focus, such as nutrition, cancer etcetera. The included journals are shown in Table 2 and are in order according to their ranking. We recognise that our journal choice meant that only articles published in English made it into the review.
A key decision in a FMRS is the time-period within which to retrieve relevant articles. Like many other forms of review, we undertook an initial scoping to determine the feasibility and parameters of the project [ 19 ]. In our previous reviews, the timeframe has varied from three months [ 23 ] to 6 years [ 24 ]. The main criterion is the likelihood for the timespan to contain sufficient articles to answer the review questions. We set the time parameter from January 2017–June 2018. We each took responsibility for two and three journals each from which to retrieve articles. We reviewed the content page of each issue of each journal. For our purposes, in order to reflect the diverse range of terms for describing a literature review, as described earlier in this paper, any paper that contained the term ‘review’ or ‘synthesis’ in the title was included in the review. This was done by each author individually but to enhance rigour, we worked in pairs to check each other’s retrieval processes to confirm inter-rater consistency. This process allowed any areas of uncertainty to be discussed and agreed and we found this form of calibration crucial to the process. The inclusion and exclusion criteria are shown in Table 3 .
Articles meeting the inclusion criteria, papers were read in full and data was extracted and recorded as per the proforma developed for the study (Table 4 ). The proforma was piloted on two papers to check for usability prior to data extraction. Data extraction was done independently but we discussed a selection of papers to enhance rigour of the process. No computer software was used in the analysis of the data. We did not critically appraise the included studies for quality because our purpose was to profile what is happening in the field rather than to draw conclusions from the included studies’ findings.
Once the details from all the papers had been extracted onto the tables, we undertook an analysis to identify common themes in the included articles. Because our aim was to produce a snap-shot profile, our analysis was thematic and conceptual. Although we undertook some tabulation and numerical analysis, our primary focus was on capturing patterns and trends characterised by the proliferation era. In line with the FMRS method, in the findings section we have used illustrative examples from the included articles that reflect and demonstrate the point or claim being made. These serve as useful sources of information and reference for readers seeking concrete examples.
Between January 2017 and June 2018 in the five journals we surveyed, a total of 222 papers with either ‘review’ or ‘synthesis’ in the title were retrieved and included in our analysis. We identified three primary themes: 1) Proliferation in names for doing a review; 2) Allegiance to an established review method; 3) Clarity about review processes. The results section is organised around these themes.
Proliferation in names for doing a review
We identified more than 35 terms used by authors to describe a literature review. Because we amalgamated terms such as ‘qualitative literature review’ and ‘qualitative review’ the exact number is actually slightly higher. It was clear from reading the reviews that many different terms were used to describe the same processes. For example qualitative systematic review, qualitative review and meta-synthesis, qualitative meta-synthesis, meta-ethnography all refer to a systematic review of qualitative studies. We have therefore grouped together the review types that refer to a particular type of review as described by the authors of the publications used in this study (Table 5 ).
In many reviews, the specific type of review was indicated in the title as seen for example in Table 5 . A striking feature was that all but two of the systematic reviews that contained a meta-analysis were labelled as such in the title; providing clarity and ease of retrieval. Where a literature review did not contain a meta-analysis, the title of the paper was typically referred to a ‘systematic review’; the implication being that a systematic review is not necessarily synonymous with a meta-analysis. However as discussed in the following section, this introduced some muddying of water, with different interpretations of what systematic review means and how broadly this term is applied. Some authors used the methodological type of included papers to describe their review. For example, a Cochrane-style systematic review was undertaken [ 25 ] but the reviewers did not undertake a meta-analysis and thus referred to their review as a ‘quantitative systematic review’.
Allegiance to an established literature review method
Many literature reviews demonstrated allegiance to a defined method and this was clearly and consistently described by the authors. For example, one team of reviewers [ 26 ] articulately described the process of a ‘meta-ethnography’ and gave a detailed description of their study and reference to the origins of the method by Noblet and Hare (1988) [ 12 ]. Another popular method was the ‘integrative review’ where most authors referred to the work of one or two seminal papers where the method was originally described (for example, Whitemore & Knafl 2005 [ 15 ]).
For many authors the term systematic review was used to mean a review of quantitative research, but some authors [ 27 , 28 , 29 ],used the term systematic review to describe reviews containing both qualitative and quantitative data.
However in many reviews, commitment to a method for doing a literature review appeared superficial, undeveloped and at times muddled. For example, three reviews [ 30 , 31 , 32 ] , indicate an integrative review in the title of their review, but this is the only reference to the method; there is no further reference to how the components of an integrative review are addressed within the paper. Other authors do not state allegiance to any particular method except to state a ‘literature review’ [ 33 ] but without an outline of a particular method for doing so. Anther review [ 34 ] reports a ‘narrative review’ but does not give further information about how this was done, possibly indicative of the lack of methods associated with the traditional narrative review. Three other reviewers documented how they searched, appraised and analysed their literature but do not reference an over-riding approach for their review [ 35 , 36 , 37 ]. In these examples, the review can be assumed to be a literature review, but the exact approach is not clear.
In other reviews, the methods for doing a literature review appear to be used interchangeably. For example in one review [ 38 ] the term narrative review was used in the title but in the main text an integrative review was described. In another review [ 39 ] two different and distinct methods were combined in a ‘meta-ethnographic meta-synthesis’.
Some authors [ 40 , 41 ] referred to a method used to undertake their review, for example a systematic review, but did not reference the primary source from where the method originated. Instead a secondary source, such as a textbook is used to reference the approach taken [ 20 , 42 ].
Clarity about review processes
Under this theme we discerned two principal issues: searching and appraisal. The majority of literature reviews contain three components- searching, appraisal and analysis, details of which are usually reported in the methods section of the papers. However, this is not always the case and for example, one review [ 43 ] provides only a search strategy with no information about the overall method or how critical appraisal or analysis were undertaken. Despite the importance of the process of analysis, we found little discussion of this in the papers reviewed.
The overwhelming trend for those doing a literature review was to describe a comprehensive search; although for many in our sample, a comprehensive search appeared to be limited to a database search; authors did not describe additional search strategies that would enable them to find studies that might be missed through electronic searching. Furthermore, authors did not define what a comprehensive search entailed, for example whether this included grey literature. We identified a very small number of studies where authors had undertaken a purposive sample [ 26 , 44 ]; in these reviews authors clearly stated that their search was for ‘seminal papers’ rather than all papers.
We reviewed the approaches to critical appraisal described in the papers and there were varying interpretations of what this means and which aspect of the included articles were to be subject to appraisal. Some authors [ 36 , 45 , 46 ] used the term ‘critical appraisal’ to refer to relevance of the paper to the review, rather than quality criteria. In that sense critical appraisal was used more as an inclusion criterion regarding relevance, rather than quality in the methods used. Mostly though, the term was used to describe the process of critical analysis of the methodological quality of included papers included in a review. When the term was used in this way to refer to quality criteria, appraisal tools were often used; for example, one review [ 47 ] provides a helpful example when they explain how a particular critical appraisal tool was used to asses the quality of papers in their review. Formal critical appraisal was undertaken by the vast majority reviewers, however the role of critical appraisal in the paper was often not explained [ 33 , 48 ]. It was common for a lot of detail to be provided about the approach to appraisal, including how papers were assessed and how disagreements between reviewers about the quality of individual papers were resolved, with no further mention of the subsequent role of the appraisal in the review. The reason for doing the critical appraisal in the review was often unclear and furthermore, in many cases, researchers included all papers within their review regardless of quality. For example, one team of reviewers [ 49 ] explained how the process, in their view, is not to exclude studies but to highlight the quality of evidence available. Another team of reviewers described how they did not exclude studies on the basis of quality because of the limited amount of research available on the topic [ 50 ].
Our review has identified a multiplicity of similar terms and approaches used by authors when doing a literature review, that we suggests marks the ‘proliferation era’. The expansion of terms used to describe a literature review has been observed previously [ 19 , 21 ]. We have identified an even wider range of terms, indicating that this trend may be increasing. This is likely to give the impression of an incoherent and potentially confusing approach to the scholarly undertaking of doing a literature review and is likely to be particularly problematic for novice researchers and students when attempting to grapple with the array of approaches available to them. The range of terms used in the title of papers to describe a literature review may cause both those new to research to wonder what the difference is between a qualitative evidence synthesis and a qualitative systematic review and which method is most suitable for their enquiry.
The clearest articles in our review were those that reported a systematic review with or without a meta-analysis. For example, one team of reviewers [ 25 ] undertook a Cochrane-style systematic review but did not undertake a meta-analysis and thus referred to their review as a ‘quantitative systematic review’. We found this form of labelling clear and helpful and is indeed in line with current recommendations [ 8 ]. While guidelines exist for the publication of systematic reviews [ 8 , 51 ], given the range of terms that are used by authors, some may be unclear when these guidelines should apply and this adds some confusion to the field. Of course, authors are at liberty to call their review processes whatever they deem appropriate, but our analysis has unearthed some inconsistencies that are confusing to the field of literature reviewing.
There is current debate about the status of literature reviews that are not ‘Cochrane’ style reviews [ 52 ]. Classification can be complex and whilst it might be tempting to refer to all non Cochrane-style reviews as ‘narrative reviews’ [ 52 ], literature reviews that conform to a recognised method would generally not be considered as such [ 53 ] and indeed the Cochrane Collaboration handbook refers to the principles of systematic review as applicable to different types of evidence, not just randomised controlled trials [ 5 ] .This raises the question as to whether the term systematic review should be an umbrella term referring to any review with an explicit method; which is implicit in the definition of a systematic review, but which raises the question as to how rigorous a method has to be to meet these standards, a thorny issue which we have identified in this study.
This review has identified a lack of detail in the reporting of the methods used by those doing a review. In 2017, Thorne raised the rhetorical question: ‘What kind of monster have we created?‘ [ 54 ]. Critiquing the growing investment in qualitative metasyntheses, she observed that many reviews were being undertaken that position themselves as qualitative metasyntheses, yet are theoretically and methodologically superficial. Thorne called for greater clarity and sense of purpose as the ‘trend in synthesis research marches forward’ [ 54 ]. Our review covered many review types, not just the qualitative meta-synthesis and its derivatives. However, we concur with Thorne’s conclusion that research methods are not extensively covered or debated in many of the published papers which might explain the confusion of terms and mixing of methods.
Despite the proliferation in terms for doing a literature review, and corresponding associated different methods and a lack of consistency in their application, our review has identified how the methods used (or indeed the reporting of the methods) appear to be remarkably similar in most publications. This may be due to limitations in the word count available to authors. However for example, the vast majority of papers describe a comprehensive search, critical appraisal and analysis. The approach to searching is of particular note; whilst comprehensive searching is the cornerstone of the Cochrane approach, other aproaches advocate that a sample of literature is sufficient [ 15 , 20 ]. Yet in our review we found only two examples where reviewers had used this approach, despite many other reviews claiming to be undertaking a meta-ethnography or meta-synthesis. This indicates that many of those doing a literature review have defaulted to the ‘comprehensive search’ irrespective of the approach to searching suggested in any particular method which is again indicative of confusion in the field.
Differences are reported in the approach to searching and critical appraisal and these appear not to be linked to different methods, but seem to be undertaken on the judgement and discretion of the reviewers without rationale or justification within the published paper. It is not for us to question researchers’ decisions as regards managing the flow of articles through their reviews, but when it comes to the issue of both searching and lack of clarity about the role of critical appraisal there is evidence of inconsistency by those doing a literature review. This reflects current observations in the literature where the lack of clarity about the role of critical appraisal within a literature review is debated . [ 55 , 56 ].
Our review indicates that many researchers follow a very similar process, regardless of their chosen method and the real differences that do exist between published methods are not apparent in many of the published reviews. This concurs with previously mentioned concerns [ 54 ] about the superficial manner in which methods are explored within literature reviews. The overriding tendency is to undertake a comprehensive review, critical appraisal and analysis, following the formula prescribed by Cochrane, even if this is not required by the literature review method stated in the paper. Other researchers [ 52 ] have questioned whether the dominance of the Cochrane review should be questioned. We argue that emergence of different methods for doing a literature review in a systematic way has indeed challenged the perceived dominance of the Cochrane approach that characterised the dichotomy era, where the only alternative was a less rigourous and often poorly described process of dealing with literature. It is positive that there is widespread acknowledgement of the validity of other approaches. But we argue that the expansion era, whereby robust processes were put forward as alternatives that filled the gap left by polarisation, has gone too far. The magnitude in the number of different approaches identified in this review has led to a confused field. Thorne [ 54 ] refers to a ‘meta-madness’; with the proliferation of methods leading to the oversimplification of complex literature and ideas. We would extend this to describe a ‘meta-muddle’ in which, not only are the methods and results oversimplified, but the existence of so many terms used to describe a literature review, many of them used interchangeably, has added a confusion to the field and prevented the in-depth exploration and development of specific methods. Table 6 shows the issues associated with the proliferation era and importantly, it also highlights the recommendations that might lead to a more coherent reviewing community in nursing.
The terms used for doing a literature review are often used both interchangeably and inconsistently, with minimal description of the methods undertaken. It is not surprising therefore that some journal editors do not index these consistently within the journal. For example, in one edition of one journal included in the review, there are two published integrative reviews. One is indexed in the section entitled as a ‘systematic review’, while the other is indexed in a separate section entitled ‘literature review’. In another edition of a journal, two systematic reviews with meta-analysis are published. One is listed as a research article and the other as a review and discussion paper. It seems to us then, that editors and publishers might sometimes also be confused and bewildered themselves.
Whilst guidance does exist for the publication of some types of systematic reviews in academic journals; for example the PRISMA statement [ 8 ] and Entreq guidelines [ 51 ], which are specific to particular qualitative synthesis, guidelines do not exist for each approach. As a result, for those doing an alternative approach to their literature review, for example an integrative review [ 15 ], there is only general publication guidance to assist. In the current reviewing environment, there are so many terms, that more specific guidance would be impractical anyway. However, greater clarity about the methods used and halting the introduction of different terms to mean the same thing will be helpful.
Limitations
This study provides a snapshot of the way in which literature reviews have been described within a short publication timeframe. We were limited for practical reasons to a small section of high impact journals. Including a wider range of journals would have enhanced the transferability of the findings. Our discussion is, of course, limited to the review types that were published in the timeframe, in the identified journals and which had the term ‘review’ or ‘synthesis’ in the title. This would have excluded papers that were entitled ‘meta-analysis’. However as we were interested in the range of reviews that fall outside the scope of a meta-analysis, we did not consider that this limited the scope of the paper. Our review is further limited by the lack of detail of the methods undertaken provided in many of the papers reviewed which, although providing evidence for our arguments, also meant that we had to assume meaning that was unclear from the text provided.
The development of rigorous methods for doing a literature review is to be welcomed; not all review questions can be answered by Cochrane style reviews and robust methods are needed to answer review questions of all types. Therefore whilst we welcome the expansion in methods for doing a literature review, the proliferation in the number of named approaches should be, in our view, a cause for reflection. The increase in methods could be indicative of an emerging variation in possible approaches; alternatively, the increase could be due to a lack of conceptual clarity where, on closer inspection, the methods do not differ greatly and could indeed be merged. Further scrutiny of the methods described within many papers support the latter situation but we would welcome further discussion about this. Meanwhile, we urge researchers to make careful consideration of the method they adopt for doing a literature review, to justify this approach carefully and to adhere closely to its method. Having witnessed an era of dichotomy, expansion and proliferation of methods for doing a literature review, we now seek a new era of consolidation.
Bettany-Saltikov J. How to do a systematic literature review in nursing: a step-by-step guide. Maidenhead: Open University Press; 2012.
Google Scholar
Coughlan M, Cronin P, Ryan F. Doing a literature review in nursing, Health and social care. London: Sage; 2013.
Aveyard H. Doing a literature review in health and social care. Maidenhead: Open University Press; 2018.
Davis D. A practical overview of how to conduct a systematic review. Nurs Stand. 2016;31(12):60–70.
Article Google Scholar
Higgins and Green. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0: Cochrane Collaboration; 2011.
Centre for Reviews and Dissemination. Systematic Reviews: CRD's guidance for undertaking reviews in health care. York: University of York; 2008.
Aromataris E, Munn Z, editors. Joanna Briggs Institute Reviewer's Manual: The Joanna Briggs Institute; 2017. Available from https://reviewersmanual.joannabriggs.org/
Shamseer L, Moher D, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, Shekelle P, Stewart L. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols. Br Med J. 2015;2:349 (Jan 02).
Creswell JW, Plano-Clark VL. Designing and conducting mixed methods research. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications; 2011.
Greenhalgh T. How to read a paper. 4th ed: Wiley; 2010.
Booth A, Papaioannou D, Sutton A. Systematic appproaches to a successful literature review Sage London; 2012.
Noblit GW, Hare RD. Meta-ethnography, synthesising qualitative studies, qualitative research methods, volume 11. London: SAGE Publications; 1988.
Walsh D, Downe S. Meta-synthesis method for qualitative research: a literature review. J Adv Nurs. 2005;50(2):204–11.
Thomas J, Harden A. Methods for the thematic synthesis of qualitative research in systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2008;8:45.
Whittemore R, Knafl K. The integrative review: updated methodology. J Adv Nurs. 2005;52:546–53.
Scoping Peters MDJ, Godfrey CM, McInerney P, Soares CB, Khalil H, Parker D. Methodology for Joanna Briggs institute scoping review. Joanna Briggs institute reviewers manual: Australia; 2015.
Wong G, Greenhalgh T, Westhorp G, Buckingham J, Pawson R. RAMESES publication standards: realist synthesis BMC medicine, vol. 11; 2013. p. 21.
Plüddemann A, Aronson JK, Onakpoya I, Heneghan C, Mahtani KR. Redefining rapid reviews: a flexible framework for restricted systematic reviews. BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine Epub ahead of print: 27 June 2018. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjemb-2018-110990 .
Bradbury-Jones C, Breckenridge J, Clark MT, Herber OR, Jones C, Taylor J. Advancing the science of literature reviewing: the focused mapping review and synthesis as a novel approach. Int J Soc Res Methodol. https://doi.org/10.1080/13645579.2019.1576328 .
Grant MJ, Booth A. A typology of review- an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Info Libr J. 2009;26(2):91–108.
Booth, A., Noyes, J., Flemming, K., Gerhardus, A., Wahlster, P., van der Wilt G.J., Mozygemba K, Refolo P, Sacchini D, Tummers, M, Rehfuess, E. (2016) Guidance on choosing qualitative evidence synthesis methods for use in health technology assessments of complex interventions. Available: http://www.integrate-hta.eu/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/Guidance-on-choosing-qualitative-evidence-synthesis-methods-for-use-in-HTA-of-complex-interventions.pdf
Sabatino L, Stievano A, Rocco G, Kallio H, Pietila A, KAngasniemi M. The dignity of the nursing profession: a meta-synthesis of qualitative research. Nurs Ethics. 2014;2(6):659–72.
Bradbury-Jones C, Taylor J, Herber O. How theory is used and articulated in qualitative research: development of a new typology. Soc Sci Med. 2014;120:135–41.
Taylor J, Bradbury-Jones C, Breckenridge J, Jones C, Herber OR. Risk of vicarious trauma in nursing research: a focused mapping review and synthesis. J Clin Nurs. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocn.13235 .
Haggman Laitila A, Rompannen J. Outcomes of interventions for nurse leaders’ well being at work. A quantitative systematic review. J Adv Nurs. 2018;74:34–44.
Strandos M, Bondas T. The nurse patient relationship as a story of health enhancement in community care- a meta-ethnography. J Adv Nurs. 2018;74:11–8.
Gilissen J, Pivodic L, Smets T, Gastmans C, Stichels RV, Delieus L, Van den Black L. Preconditions for successful advanced care planning in nursing homes: a systematic review. Int J Nurs Stud. 2017;66:47–59.
Walczak A, Mcdonald F, Patterson P, Dobinson K, Kimberley A. How does parental cancer affect adolescent and young adult offspring. A systematic review. Int J Nurs Stud. 2018;77:54–80.
Leyva-Moral JM, Palmoero PA, Feijoo-Cid M, Edwards JE. Reproductive decision making in women living with HIV: systematic review. Int J Nurs Stud. 2018;77:207–21.
Pires S, Monteiro S, Pereira A, Chaló D, Melo E, Rodriguese A. Non technical skills assessment for pre-licensure nursing students: an integrative literature review nurse education today, vol. 58; 2017. p. 19–24.
Wilkinson A, Meilkle N, Law P, Yong A, Butler P, Kim J, Mulligan H, Hale L. How older adults and their informal carers prevent falls: an integrative review. Int J Nurs Stud. 2018;82:13–8.
Drewniak D, Krones T, Wild V. Do attitudes and behaviours of health care professionals exacerbate health care disparities among immigrant and ethnic minority groups? An integrative literature review. Int J Nurs Stud. 2017;70:89–98.
Garone A, Craen Van de P. The role of language skills abd internationalisation in nursing degree programmes: a literature review. Nurse Educ Today. 2017;49:140–4.
Casey M, O’Connor L, Cashin A (et al) An overview of the outcomes and impact of specialist and advanced nursing and midwifery practice on quality of care, cost and access to services: A narrative review. Nurse Educ Today 2017;56:35-40.
Adib-Hajbaghery M, Sharifi N. Effect of simulation training on the development of nurses and nursing students critical thinking: a systematic review. Nurse Educ Today. 2017;50:17–24.
Irwin C, Bliss J, Poole J. Does preceptorship improve confidence and competence in newly qualified nurses: a systematic literature review. Nurse educ Today. 2018;60:35–46.
Jefferies D, McNallya S, Roberts K, Wallace A, Stunden A, D'Souzaa S, Glew P. The importance of academic literacy for undergraduate nursing students and its relationship to future professional clinical practice: a systematic review. Nurse educ Today. 2018;60:84–91.
Lewis ML, Neville C, Ashkanasy NM. Emotional intelligence and affective events in nurse education- a narrative review. Nurse Educ Today. 2017;53:34–40.
Jensen D, Sorensen A. Nurses experiences of working in organisations undergoing restructuring: a meta-synthesis of qualitative research studies. Int J Nurs Stud. 2017;66:7–14.
Milligan F, Wareing M, Preston-Shoot M, Pappas Y, Randhawa G, Bhandol J. Supporting nursing, midwifery and allied health professional students to raise concerns with the quality of care: a review of the research literature. Nurse Educ Today. 2017;57:29–39.
Rozendo CA, Salas AS. A critical review of social and health inequalities in the nursing curriculum. Nurse Educ Today. 2017;50:62–71.
Kiteley R, Stogdon C. Literature reviews in social work. London: Sage; 2014.
Book Google Scholar
Rebeiro G, Evans A, Edward K, Chapman R. Registered nurse buddies. Educators by proxy? Nurse Educ Today. 2017;55:1–4.
Sinclair S, Raffin Bouchal S, Venturato L, Milsonic-Kondejewski J, Smith Macdonald L. Compassion fatigue: a meta-narrative review of the health care literature. Int J Nurs Stud. 2017;69:9–24.
Hovey S, Dyck MJ, Reese C, Myoung JK. Nursing students’ attitudes towards persons who are aged: an integrative review. J Adv Nurs. 2017;49:145–52.
Granheim B, Shaw J, Mansah M. Use of interprofessional learning and simulation in undergraduate nursing programmes to address interprofessional communication and collaboration- an integrative review. Nurse Educ Today. 2018;62:118–27.
Philips P, Lumley E, Duncan R, Aber A, Buckley Woods H, Jones GC. A systematic review of qualitative research into people’s experiences of living with venous leg ulcers. J Adv Nurs. 2018;74:550–63.
Slater CE, Cusick A. Factors relating to self directed learning readiness of students in health professional programmes a scoping review. Nurse Educ Today. 2017;52:22–33.
Vanderspank-Wright B, Efstathiou N, Vandjk A. Critical care nurses experience of withdrawing treatment: a systematic review of qualitative evidence. Int J Nurs Stud. 2018;77:15–26.
Kelly M, Wills J, Sykes S. Do nurses’ personal health behaviours impact their health promotion practice? A systematic review. Int J Nurs Stud. 2017;76:62–77.
Tong A, Flemming K, McInnes E, Oliver S, Craig J. Enhancing transparency in the reporting in the synthesis of qualitative research. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2012;12(1):181.
Greenhalgh T, Thorne S, Malterud K. Time to challenge the spurious hierarchy of systematic over narrative reviews? Eur J Clin Investig. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1111/eci12931 .
Aveyard H, Payne S, Preston N. A postgraduate’s guide to doing a literature review. Maidenhead: Open University Press; 2016.
Thorne S. Metasynthetic madness: what kind of monster have we created? Qual Health Res. 2017;27(1):3–12.
Sibeoni J, Orri M, Colin S, Valentin M, Pradere J, Revah-Levy A. The lived experience of anorexia nervosa in adolescence, comparison of parents’ view of adolescence, parents and professionals: a meta-synthesis. Int J Nurs Stud. 2017;65:25–34.
Nightingale S, Spiby H, Sheen K, Slade P. The impact of emotional intelligence in long term health care professionals on caring behaviours towards patients in clinical and long term settings. Integrative review. Int J Nurs Stud. 2018;80:106–17.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Availability of data and materials.
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Health and Life Sciences, Oxford Brookes University, Jack Straw’s Lane, Oxford, OX3 0FL, England, UK
Helen Aveyard
University of Birmingham, Birmingham, England, UK
Caroline Bradbury-Jones
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Both HA and CB-J contributed to the data collection and analysis. HA wrote the paper and CB-J commented on the drafts. HA revised the paper according to the reviewers’ comments and CB-J commented on these revisions 30/4/19. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Helen Aveyard .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests, publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Aveyard, H., Bradbury-Jones, C. An analysis of current practices in undertaking literature reviews in nursing: findings from a focused mapping review and synthesis. BMC Med Res Methodol 19 , 105 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-019-0751-7
Download citation
Received : 16 December 2018
Accepted : 07 May 2019
Published : 16 May 2019
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-019-0751-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Evidence synthesis
- Literature review
- Meta-ethnography
- Systematic review
BMC Medical Research Methodology
ISSN: 1471-2288
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Health (Nursing, Medicine, Allied Health)
- Find Articles/Databases
- Reference Resources
- Evidence Summaries & Clinical Guidelines
- Drug Information
- Health Data & Statistics
- Patient/Consumer Facing Materials
- Images and Streaming Video
- Grey Literature
- Mobile Apps & "Point of Care" Tools
- Tests & Measures This link opens in a new window
- Citing Sources
- Selecting Databases
- Framing Research Questions
- Crafting a Search
- Narrowing / Filtering a Search
- Expanding a Search
- Cited Reference Searching
- Saving Searches
- Term Glossary
- Critical Appraisal Resources
- What are Literature Reviews?
- Conducting & Reporting Systematic Reviews
- Finding Systematic Reviews
- Tutorials & Tools for Literature Reviews
- Finding Full Text
What are Systematic Reviews? (3 minutes, 24 second YouTube Video)
Systematic Literature Reviews: Steps & Resources
These steps for conducting a systematic literature review are listed below .
Also see subpages for more information about:
- The different types of literature reviews, including systematic reviews and other evidence synthesis methods
- Tools & Tutorials
Literature Review & Systematic Review Steps
- Develop a Focused Question
- Scope the Literature (Initial Search)
- Refine & Expand the Search
- Limit the Results
- Download Citations
- Abstract & Analyze
- Create Flow Diagram
- Synthesize & Report Results
1. Develop a Focused Question
Consider the PICO Format: Population/Problem, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome
Focus on defining the Population or Problem and Intervention (don't narrow by Comparison or Outcome just yet!)
"What are the effects of the Pilates method for patients with low back pain?"
Tools & Additional Resources:
- PICO Question Help
- Stillwell, Susan B., DNP, RN, CNE; Fineout-Overholt, Ellen, PhD, RN, FNAP, FAAN; Melnyk, Bernadette Mazurek, PhD, RN, CPNP/PMHNP, FNAP, FAAN; Williamson, Kathleen M., PhD, RN Evidence-Based Practice, Step by Step: Asking the Clinical Question, AJN The American Journal of Nursing : March 2010 - Volume 110 - Issue 3 - p 58-61 doi: 10.1097/01.NAJ.0000368959.11129.79
2. Scope the Literature
A "scoping search" investigates the breadth and/or depth of the initial question or may identify a gap in the literature.
Eligible studies may be located by searching in:
- Background sources (books, point-of-care tools)
- Article databases
- Trial registries
- Grey literature
- Cited references
- Reference lists
When searching, if possible, translate terms to controlled vocabulary of the database. Use text word searching when necessary.
Use Boolean operators to connect search terms:
- Combine separate concepts with AND (resulting in a narrower search)
- Connecting synonyms with OR (resulting in an expanded search)
Search: pilates AND ("low back pain" OR backache )
Video Tutorials - Translating PICO Questions into Search Queries
- Translate Your PICO Into a Search in PubMed (YouTube, Carrie Price, 5:11)
- Translate Your PICO Into a Search in CINAHL (YouTube, Carrie Price, 4:56)
3. Refine & Expand Your Search
Expand your search strategy with synonymous search terms harvested from:
- database thesauri
- reference lists
- relevant studies
Example:
(pilates OR exercise movement techniques) AND ("low back pain" OR backache* OR sciatica OR lumbago OR spondylosis)
As you develop a final, reproducible strategy for each database, save your strategies in a:
- a personal database account (e.g., MyNCBI for PubMed)
- Log in with your NYU credentials
- Open and "Make a Copy" to create your own tracker for your literature search strategies
4. Limit Your Results
Use database filters to limit your results based on your defined inclusion/exclusion criteria. In addition to relying on the databases' categorical filters, you may also need to manually screen results.
- Limit to Article type, e.g.,: "randomized controlled trial" OR multicenter study
- Limit by publication years, age groups, language, etc.
NOTE: Many databases allow you to filter to "Full Text Only". This filter is not recommended . It excludes articles if their full text is not available in that particular database (CINAHL, PubMed, etc), but if the article is relevant, it is important that you are able to read its title and abstract, regardless of 'full text' status. The full text is likely to be accessible through another source (a different database, or Interlibrary Loan).
- Filters in PubMed
- CINAHL Advanced Searching Tutorial
5. Download Citations
Selected citations and/or entire sets of search results can be downloaded from the database into a citation management tool. If you are conducting a systematic review that will require reporting according to PRISMA standards, a citation manager can help you keep track of the number of articles that came from each database, as well as the number of duplicate records.
In Zotero, you can create a Collection for the combined results set, and sub-collections for the results from each database you search. You can then use Zotero's 'Duplicate Items" function to find and merge duplicate records.

- Citation Managers - General Guide

6. Abstract and Analyze
- Migrate citations to data collection/extraction tool
- Screen Title/Abstracts for inclusion/exclusion
- Screen and appraise full text for relevance, methods,
- Resolve disagreements by consensus
Covidence is a web-based tool that enables you to work with a team to screen titles/abstracts and full text for inclusion in your review, as well as extract data from the included studies.

- Covidence Support
- Critical Appraisal Tools
- Data Extraction Tools
7. Create Flow Diagram
The PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses) flow diagram is a visual representation of the flow of records through different phases of a systematic review. It depicts the number of records identified, included and excluded. It is best used in conjunction with the PRISMA checklist .

Example from: Stotz, S. A., McNealy, K., Begay, R. L., DeSanto, K., Manson, S. M., & Moore, K. R. (2021). Multi-level diabetes prevention and treatment interventions for Native people in the USA and Canada: A scoping review. Current Diabetes Reports, 2 (11), 46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-021-01414-3
- PRISMA Flow Diagram Generator (ShinyApp.io, Haddaway et al. )
- PRISMA Diagram Templates (Word and PDF)
- Make a copy of the file to fill out the template
- Image can be downloaded as PDF, PNG, JPG, or SVG
- Covidence generates a PRISMA diagram that is automatically updated as records move through the review phases
8. Synthesize & Report Results
There are a number of reporting guideline available to guide the synthesis and reporting of results in systematic literature reviews.
It is common to organize findings in a matrix, also known as a Table of Evidence (ToE).

- Reporting Guidelines for Systematic Reviews
- Download a sample template of a health sciences review matrix (GoogleSheets)
Steps modified from:
Cook, D. A., & West, C. P. (2012). Conducting systematic reviews in medical education: a stepwise approach. Medical Education , 46 (10), 943–952.
- << Previous: Critical Appraisal Resources
- Next: What are Literature Reviews? >>
- Last Updated: May 16, 2024 9:53 AM
- URL: https://guides.nyu.edu/health

Literature Reviews for Education and Nursing Graduate Students
(15 reviews)
Linda Frederiksen, Washington State University Vancouver
Sue F. Phelps, Washington State University Vancouver
Copyright Year: 2017
Publisher: Rebus Community
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Rebecca Appleton, Professor of Nursing, Marshall University on 5/7/24
It is very through in covering the steps of a well written literature review read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
It is very through in covering the steps of a well written literature review
Content Accuracy rating: 5
I have not read the entire book, but what I did read was very good.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
It is up to date, but doing a Literature Review is covered in a step-wise manner, includes writing the LR>
Clarity rating: 5
Very clear step-by-step approach
Consistency rating: 5
It is very consistent!
Modularity rating: 5
Chapters are orderly and succinct
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
Strait forward order.
Interface rating: 5
I did not notice Interface issues.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
No grammatical errors were noticed.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
I did not notice any problems with cultural Insensitivity
I plan to use this in a Nursing Research class for Graduate Students, and I am trying a new approach to finding the best Research Evidence on a Nursing Topic. Can't wait to see if this help my graduate students understand research literature better.
Reviewed by Barbara Schneider, Professor, University of Texas at Arlington on 4/29/24
This textbook covers the range of topics important for a literature review, including formulating a research question, finding scholarly articles, evaluating sources, and synthesizing source content. The videos are great supplements to the text. read more
This textbook covers the range of topics important for a literature review, including formulating a research question, finding scholarly articles, evaluating sources, and synthesizing source content. The videos are great supplements to the text.
Overall, the content is accurate. Consider labeling Nursing as a health profession/discipline.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 4
Much of the content remains relevant. Updated examples would be helpful to today's graduate students.
The textbook is clearly written.
Consistency rating: 4
In general, the text is consistent. There could be more consistency in the formatting of the references.
The modularity is an asset.
There is a logical flow to the topics.
The links to outside materials are helpful.
No grammatical errors were evident.
The examples seemed inclusive.
Those who are new to writing a literature review would find this book useful.
Reviewed by Yolanda Griffiths, Professor of Occupational Therapy, Drake University on 12/15/21
The authors were thorough and very organized in stepping readers through the process of conducting and writing a literature review. Each area is appropriately indexed and examples are provided in a variety of ways. The synthesis section is... read more
The authors were thorough and very organized in stepping readers through the process of conducting and writing a literature review. Each area is appropriately indexed and examples are provided in a variety of ways. The synthesis section is especially useful as students often do not understand what this means. Perhaps some content on plagiarism would benefit this section as well. The flow of the material easily guides users logically through each topic.
The content is accurate and unbiased. The content is presented in an easy to understand way with videos, and examples.
The relevance of the content is classic and the text should be pertinent for many years. The links included in the text are very useful and should be easy for authors to check periodically. Using a digital media is more relevant to today's students than print textbooks. Each section addresses a reasonable chunk of information.
The book is user friendly, written in an easy to understand manner, and graphics or links add to the understanding of the content. Definitions are clearly written. Such as clarifying the types of literature reviews will be useful for students. Providing a test yourself section at the end of sections allows the reader to check if any content was confusing or not clear.
The text is consistently laid out in a logical manner which helps to unpack content which may be new or unfamiliar to the reader/student.
The amount of content allocated to each chapter is appropriate and will be easy to assign readings. The chapter headings are clear and the embedded videos, charts and test questions enlighten each subunit. The hyperlinking in the table of contents helps to navigate the chapters well.
The organization of the content is logical and easy to understand the process of completing a literature review. The book is laid out much like a road map where students can see the big picture as well as the supporting parts to the process. The references by chapter are very useful.
The graphics were clear, and the non-serif font aids in eye fatigue. One recommendation is to lower the brightness of the bold blue text in the table of contents to reduce eye fatigue. There was no problem to play the videos and the audio was clear. All links worked well.
There were no grammatical errors. There were a few typos such as 1.3.1.8 needs a space between "A specific", 2.3 in the phrase "Articles by the type of periodical in which an article it is published" perhaps remove the word "it", in the table on page 41. under Nursing , the word clinical is spelled "Cclinical", remove the capital C.
No evidence of cultural bias or insensitivity.
I am very excited to use this textbook in my doctoral level occupational therapy class. The inclusion of concise explanations of PICO and SPICE will be very useful. This will be a wonderful resource for graduate students and being mindful of costs for textbooks is compassionate.
Reviewed by Susan Bassett, Instructor, Nursing Graduate Program, Eastern New Mexico University on 11/9/21
Each chapter presented a different aspect of doing a literature review. This was organized and orderly. The index/table of contents was very detailed which allowed the reader to easily use this book as a reference while conducting a literature... read more
Each chapter presented a different aspect of doing a literature review. This was organized and orderly. The index/table of contents was very detailed which allowed the reader to easily use this book as a reference while conducting a literature review.
The content appeared to be entirely accurate. It did a good job of combining information for both education and nursing students. The authors addressed pertinent points of research study development as well as the specific methodology of approaching a research-focused literature review.
The text was up-to-date in methodology, which should not change frequently. The many links to websites were very helpful and yet were basic enough that they should be relevant for years. If they do need updating, the are clearly presented and should be easily updated. The breakdown to very small "chunks" of information per section will help in easily updating specific parts of information.
The book presented a rather complex topic in an extremely straight-forward, easy to read, clear manner. Each small "chunk" of information was identified per section numbering which correlated with movement through the content. The writing was professional and yet not overwhelmed with discipline-specific terminology. Where potentially new terminology was presented, it was immediately followed with definitions and examples.
The book was well-organized and moved along the structure set out early in the book. Content was gradually unfolded, as divided per chapter. There was a bit of repetition (probably about three examples) where the authors attempted to tie information together. Although this stood out to a reader, it seemed more useful in organizing than detrimental in repetition.
The book was subdivided into chapters and then into many small modules of discrete information. It could easily be assigned in part. It could also readily be used as a reference for students to go back and easily find processes or pieces of information they might need later.
I found the continual clear and succinct organization of information to be a defining highlight of this book. When presenting early steps of the research process and then linking these steps with how to conduct a literature review and subsequenty organize and write a literature review, this book is presenting numerous procews steps that must work in tandem. This book did that in a clear and easily readable fashion.
The one feature that did distract me was within the bullet points of 1.3.1. "Types of Reviews". There was a mix of complete and incomplete sentences that worked to convey information succinctly, but distracted me as a reader.
Grammatical Errors rating: 4
I did find several spelling and grammaticl errors (1.3.1.8, , 1.3.1.9, 2.1.1, 2.3, 2.3.1.1, , 2.3.1.4, 2.3 Table A., p. 41, p. 53, p. 54). Although small errors (a few letters or spacing) they should be corrected.
I did not find any mistakes in cultural appropriateness The content did repeatedly talk about bias reduction in the process of writing a literature review
I thought this book was very well-written and contained great information for my students. The links provided were very appropriate and helpful. The Table "Guide to searching for literature at various stages of the scholarly communication process” was particularly helpful. I will immediately begin using portions of the content in this book to support my research class. Additionally, I will recommend the entire book as a reference for the dedicated student (or one intending to go forward to a doctoral level of education in nursing). Thank you for collating all this information and helpful links into one clear, easily readable and understandable document.
Reviewed by Leah Nillas, Associate Professor, Illinois Wesleyan University on 9/6/21
This book addresses the basic steps in the process of writing a literature review research. Chapter 2 (What is a Literature Review?) needs to be retitled. I think Chapter 1 (Introduction) clearly defines and characterizes literature review as a... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
This book addresses the basic steps in the process of writing a literature review research. Chapter 2 (What is a Literature Review?) needs to be retitled. I think Chapter 1 (Introduction) clearly defines and characterizes literature review as a research category. Chapter 2 focuses more on the creation of information, information cycle, and selecting appropriate sources. Chapter 7 (Synthesizing Sources) and Chapter 8 (Writing the Lit Review) can still be improved to incorporate specific strategies in synthesizing research literature and examples of writing styles through analysis of a variety of published examples. Writing a synthesis is a challenging skill for most novice researchers.
Information shared is accurate. I did not notice any content error.
Main content is up-to-date. A few citations maybe dated but they are necessary in illustrating different examples of literature reviews. It will be easy to include additional relevant examples of research work that are published recently.
I like how this text is written. Tone is reader friendly and narrative is accessible to novice researchers.
Clearly consistent throughout the chapters.
Clear and purposeful "chunking" of information per chapter.
Readers can easily follow the organization of topics and content.
No obvious interface issues. Appropriate use of multimedia tools.
No grammatical errors.
Text is culturally sensitive. Additional readings, references, or examples can easily be added to incorporate research conducted by diverse authors or literature reviews which focus on diversity and inclusion issues in education and nursing.
This is a good introductory literature review text even for undergraduate education students. Clear discussion of the nature of the research and the writing process. The use of videos and images is helpful in providing multimodal approach in explaining topics or processes. Writing style and tone make the text accessible to novice researchers.
Reviewed by Rebecca Scheckler, Assistant Professor, Radford University on 7/6/20
Two missing topics were inter-library loan and how to avoid plagiarism in writing up the literature review. This second is such an important topic that it deserves its own chapter. read more
Two missing topics were inter-library loan and how to avoid plagiarism in writing up the literature review. This second is such an important topic that it deserves its own chapter.
It is accurate. I found no inaccuracies.
This book is very relevant. Every advanced undergraduate or graduate students requires such a book
I found the book clear. The videos interspersed within the book added much to the clarity. There are lots of good diagrams that add to the clarity. They are not all original but their sources are all cited. The section on boolean searches, usage of asterisks and quotes in searches is very helpful and appropriate although often left out of discussion of searches.
The book is consistent in terminology and framework.
The chapters were cohesive.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 4
I like the links to within the text to the references and other matter. What is needed are back links to the text from the references. I also would have liked links from the exercises to the answers of the exercises.
Interface rating: 4
See navigation links mentioned above. The grey literature link is broken.
I saw no grammatical problems. There are many bulleted lists rather than text which is appropriate to this topic.
There could be more attention to cultural context in the frequent examples.
I wondered why nursing and education were combined. They are similar in nature but not identical. separation them out into two books might be appropriate.
Reviewed by Lisa Shooman, Associate Professor, Worcester State University on 6/29/20
Overall, this book provides a very comprehensive and thorough roadmap for creating a literature review. The videos assist the reader in crystallizing the information presented in the text. There is an effective index and glossary that provide... read more
Overall, this book provides a very comprehensive and thorough roadmap for creating a literature review. The videos assist the reader in crystallizing the information presented in the text. There is an effective index and glossary that provide helpful navigation to the reader.
The content is detailed, clearly explained, error-free, and unbiased. My students would greatly benefit from the lucid information presented in this text to guide them with developing a literature review. I would be eager to adopt this book for my students.
The content is timely and will not be quickly out-of-date. The quiz questions at the end of each chapter are relevant and will aid students with the consolidation of the material. The online format allows for updating, and the version history at the end of the text clearly indicated that the book was updated recently.
The text is clear and not ridden with any excess jargon /technical terminology. Pictures, graphics, and videos further elucidate the text. There are helpful questions that stimulate thought and lists that help to organize information.
The internal consistency in the text is excellent. However, Chapter 1.1 and Chapter 2 have the same title and it would benefit the reader to have different titles that would highlight the differences between these two sections. Chapter 1.1 is an overview and Chapter 2 dives into more depth.
The text is efficiently divided into smaller reading sections that are demarcated by numbers. The subsections in each chapter can be assigned at different points in the course. The text is organized logically and systematically that assists the reader with comprehension and provides a roadmap for creating an effective literature review.
The entire text is presented coherently and concisely. The organization of the text takes the reader through the process of creating an effective literature review. It can be used by multiple health professions, although the length of the text is relatively short it includes a considerable depth of the material. Other disciplines that would benefit from using this test in their courses may include occupational therapy, physical therapy, and speech and language pathology students.
The interface of the text is simple and easy to follow. The cover of the text would benefit from photos, color, and graphic design to appeal to the modern digital reader.
No grammatical or spelling errors are noted.
No cultural biases existed in the text in any way. There are no individuals highlighted in the book, and due to the technical nature of the subject matter, the text is inclusive to a variety of races, ethnicities, and backgrounds. No offensive statements are included in this book.
The authors should consider including other health professionals in the title and provide examples that can relate to other health professionals throughout the text. Other health professionals that can benefit from reading this text include occupational therapy, physical therapy, and speech and language pathology students. Literature reviews are relevant for many health professionals in their master's and doctorate programs and the text could serve a wider audience.
Reviewed by Ellen Rearick, Assistant Professor, Framingham State University on 6/1/20
This text covers all areas and the process of the integrative review appropriately. It is an engaging text for graduate students new to these assignments. read more
This text covers all areas and the process of the integrative review appropriately. It is an engaging text for graduate students new to these assignments.
This text is well done, very accurate
This text is relevant. The updates needed regarding APA format should be relatively easy to implement.
This text is clear and provides users with definitions and examples of the variety of reviews.
Very well written using consistent terminology throughout.
The text's reading sections are easily accessible and users will find them organized. Each chapter and its sections are presented in the sequence of the process of an integrative review.
Very clear and logical order.
The navigation of this text was problem-free.
No grammatical errors noted.
No issues with cultural insensitivity noted.
This was a well-organized text using videos to reinforce content that would benefit any education or nursing graduate student new to the integrative review process.
Reviewed by Ruth Stoltzfus, Professor of Nursing; Dir., Grad Programs in Nursing, Goshen College on 6/1/19
This text provides everything a graduate student needs to write a literature review in a concise manner. If you look at the digital pdf, there are many strategies to help the reader learn the process - videos, diagrams, and also text. read more
This text provides everything a graduate student needs to write a literature review in a concise manner. If you look at the digital pdf, there are many strategies to help the reader learn the process - videos, diagrams, and also text.
I found no evidence of bias and no errors.
This book has long-term relevance. The content will not quickly out-date.
I really liked the way the textbook is structured. The author is concise which makes the textbook easy to read.
I found no inconsistencies in terminology or other aspects related to the content.
I will adopt this text for a research course I use and will likely assign only specific chapters. I plan to recommend the textbook to another faculty who teaches a comprehensive research course with the idea of assigning only specific sections to read..
The textbook begins with an introduction to the subject matter. Subsequent chapters develop specific aspects related to lit reviews. The textbook provides a nice "how to" for each element of a lit review. Chapters are also organized in a smooth, easy to follow format.
I only looked at the digital pdf and print pdf versions. The print pdf indicates that there are videos to watch, but of course since it is a print pdf, there is no linkage. I think this would be obvious to a savvy reader - that a print pdf will be limited in what the reader can access.
I found no grammatical errors in my quick read.
I found no evidence of cultural bias or insensitivity.
This is the first open textbook that I have encountered. I was expecting it to be flat and boring! However, it was neither of those. There were color diagrams, color photos, and even videos embedded in the textbook.
I have adopted this book for the Research Lit Review course that I am teaching soon. I am impressed!
Reviewed by Melissa Wells, Assistant Professor, University of Mary Washington on 5/1/19
This book helps students in education and nursing complete a literature review, which may be the first time these students are tackling such a task. The chapters break down the process into defining the special genre of a literature review;... read more
This book helps students in education and nursing complete a literature review, which may be the first time these students are tackling such a task. The chapters break down the process into defining the special genre of a literature review; providing tips to get started; suggesting where students can find literature to review; explaining how to evaluate sources; detailing the process of documenting sources; giving advice for synthesizing sources; and finally, putting all of these pieces together into a final literature review. Most significantly, the text provides specific examples of ideas presented in the context of both nursing and education, which makes the content directly relatable to the student's course of study. The conclusion recaps the main points of each chapter in bullet form. The text is lacking both an index and a glossary, which would be additions that could strengthen the text.
Content Accuracy rating: 4
The text explains 11 different types of literature reviews that students may encounter or be asked to create. Also, the text is framed to work with multiple methodologies; for example, steps for writing a research question or a hypothesis to frame the literature review are provided. One inconsistency I noted was in diagram 6.2: the APA citation is incorrectly capitalized for the journal title (which should use sentence, not title, capitalization).
The text also includes external links to sources, such as a videos, which provide students with multiple modalities in which to digest the information. An example of a literature review for both education and nursing is provided at the end of the book; instead of embedding these in the text, the hyperlinks refer the reader to the external site. This will be easy to change to a new example in the future, but checks will need to be done to ensure that all such external sources remain actively accessible.
Each chapter opens with learning objectives to help frame the content with which the reader is about to engage. Throughout the text, the language is approachable and reader-friendly. For example, when the text explains more factual components (i.e., what makes a literature review or what the basics of an effective literature review include), this information is presented in bullet points with hyperlinks to the original sources.
Each chapter follows a similar construction, which makes it accessible to the reader. For example, chapters end with a "Practice" and "Check Yourself" section to apply new learning and self-check responses (an answer key is provided in an appendix). Examples in these exercises are either related to nursing or education, continuing with the stated theme of the text.
When I used this text with my own students, I assigned chapters in isolation, since they had already taken a research methods course and were applying that knowledge to create a research proposal in a specific area of study in my course.
The book is organized in such a way that logically walks the reader through the literature review writing process. Clear headings (which are hyperlinked in the table of contents) also allow the reader to jump to specific parts with which they need additional support.
The interface of this document offered a lot of flexibility. Options allowed users to access the text online, or as a download in multiple file types (EPUB, Digital PDF, MOBI, XHTML, Pressbooks XML, Wordpress XML, and Open Document). These formats provide the reader with an opportunity to pick the interface that works best for them.
I did not see any grammatical errors in the text.
Cultural Relevance rating: 4
No culturally insensitive/offensive content was noted. A variety of examples of research topics were included from both nursing and education. Of the images/video thumbnails embedded in the text that involved people, all depicted White people except for 2 images; therefore, more intentional selection of culturally diverse visuals would be helpful in future versions of this text.
I feel this text was helpful to my students as they wrote their own literature reviews. The only weakness in their papers that I noted was their organization of their literature review based on themes/topic, which was addressed in Chapters 7- 8. I now know to focus more on this part of literature review writing with future students. This text is approachable and field-specific, and I will be using it again!
Reviewed by Bernita (Bernie) Missal, Professor, Bethel University on 12/14/18
This book includes all areas that a graduate student needs to begin a literature review. However metasynthesis could have also been included in types of literature review. read more
This book includes all areas that a graduate student needs to begin a literature review. However metasynthesis could have also been included in types of literature review.
This book is accurate although missing qualitative research.
Although content is up to date, some of the article examples need to be updated. (Example: articles published in 1981 and 1992 need to be updated to more recent articles.)
The book is clear and easy to follow. Bullet points were used throughout the book with short paragraphs which helps the student.
Each chapter follows the same format with narrative followed by practice and test questions.
Clear subheadings are used throughout the book.
This book is presented in a logical way and easy for the student to follow.
Images are clear and appropriate for the content.
No specific grammar issues were seen.
It would be helpful for students to include additional examples of cultural studies throughout the book
This book is an excellent resource for graduate students. It has helpful information for the preparation and process for a literature review. Examples of written literature reviews in chapter 8 or in an appendix would be helpful for students.
Reviewed by Nancyruth Leibold, Associate Professor, Southwest Minnesota State University on 6/19/18
The text is overall comprehensive, yet it breaks the information up into manageable parts. See the table of contents for an overview of the topics. The text is very quantitative driven in that the focus is on reviewing quantitative studies. The... read more
The text is overall comprehensive, yet it breaks the information up into manageable parts. See the table of contents for an overview of the topics. The text is very quantitative driven in that the focus is on reviewing quantitative studies. The book included information about PICO statements, but did not include PICO(T) or the time variable, which is not always used in every case. Population was included in the PICO explanation, but a bit more information on the population or aggregate narrowing could improve the PICO section. These items do not hinder use of the book, but these items would need further inclusion by the faculty member using the text as specific to the discipline.
The content in the book is very accurate.
The content in the book is current and should not be obsolete within a short period of time. Any updates would be easy to add.
The text is clear and easy to understand.
The internal organization and terminology of the book is consistent and logical
The text is set up in small reading sessions. The videos and learning activities are well done and break up some of the content, so there is a variety of presentation. The tutorials, figures, practice and self-test areas are also fantastic in that they are quality and sprinkled throughout the text.
The topics in the book are presented in clear and organized fashion. I particularly like the upbeat and personal writing tone of the book. This tone makes it seem like the authors are speaking to me.
The text is free of any significant interface issues. The book is available in many formats. I used the book online and I did have one navigational problem and that is when clicking on a video, it does not open in a new tab and so the book is lost and have to start over going in the start to the book. One easy solution to this is to right click your mouse and then select open in new tab to watch videos. That way, your place in the book is not lost.
No grammar problems present.
The book is not culturally insensitive or offensive in any way.
Overall, this is a well written textbook and I recommend it!
Reviewed by Marjorie Webb, Professor, Metropolitan State University on 6/19/18
From the Introduction to the Conclusion, the text covers the step-by-step process of conducting a literature review. The text includes topics such as, “Where to find the Literature” and “Synthesizing Sources” that will be useful to graduate... read more
From the Introduction to the Conclusion, the text covers the step-by-step process of conducting a literature review. The text includes topics such as, “Where to find the Literature” and “Synthesizing Sources” that will be useful to graduate nursing students.
The content in the text, including texts, links, and diagrams, is accurate and unbiased. Again, it will aid the graduate nursing student in the long process of conducting a literature review.
The text is current and this type of material does not become dated quickly. The authors did use internet links in the text which will need to be monitored periodically to ensure they are still available. Updates to the text will be relatively easy and straightforward. If media styles change, there may be some challenges to updating.
The text is clear and easy to read. Technical terminology is defined and/or explained.
The text is internally consistent.
The text is organized in sections which facilitates assigning readings based on the subject matter for the class time. It would be pretty easy to divide up this text into easily readable units based on headings and subheadings.
This text is structured well. The topics flow in an organized manner and really help the student see the process of a literature review. The authors discuss the both theory and purpose of the review and the day-to-day logistics of actually performing the review. The day-today organization is not always included in other texts.
The interface is well-done with no distractions.
There was no indication of cultural bias.
I think this text is appropriate for graduate nursing students. Some students struggle with the difference between writing about a topic (generally undergraduate writing) and synthesizing literature on a given topic (generally graduate writing). Chapters seven and eight focus on preparing the graduate student to make the jump to graduate-level writing and should really benefit new graduate students.
Reviewed by Susanna Thornhill, Associate Professor , George Fox University on 3/27/18
This book is fairly comprehensive and offers step-by-step instructions for conceptualizing/researching a literature review. The Table of Contents is well-organized to reflect the book's progression, from establishing the basics of why to write a... read more
This book is fairly comprehensive and offers step-by-step instructions for conceptualizing/researching a literature review. The Table of Contents is well-organized to reflect the book's progression, from establishing the basics of why to write a literature review and the various types of literature reviews, to getting started with formulating a research idea/question, finding and evaluating sources, synthesizing sources, and guidelines on writing the literature review, itself. I found this text to be a straightforward guide for my graduate students in education, and while I worried at first that the merging of education and nursing topics would prove distracting to my education students, I don't believe this was the case.
One thing that was not comprehensive in this book was discussion of qualitative research and methodologies as a valid means of conceptualizing research aims. I hoped for a more balanced discussion between methodological branches as it applied to literature reviews; this book overly favored quantitative methodologies and studies in terms of its direction to readers about how to conceptualize/choose a topic and design a research question in relation to it. Variables that cannot be measured are not inherently un-researchable, which is the conclusion put forth in this textbook. This might serve nursing students better than education students in terms of their discipline's requirements, but it still represents an element that could be improved.
Finally, while the background on what a literature review is, how to conceptualize research, and how to search for and synthesize research was all valuable, the chapter on actually writing the literature review was a bit thin, simply offering tips for introduction, body, and conclusion and some questions for self-evaluation. Some of the most difficult work for students writing a literature review is achieving proper focus, organization, hierarchy of themes, balance in treatment of related topics, etc. None of these issues were discussed in the chapter pertaining to the writing of a literature review.
I did not have any concerns about the book's accuracy. Content was accurate, albeit biased to quantitative and positivist views of research. I would have liked to see it include additional prompts to support students in conceptualizing and valuing qualitative research; this is an area where I had to supplement course readings with additional texts.
The only significant error I could discern in the text was a lack of an Answer Key corresponding to the questions posed at the end of each chapter.
Content is up-to-date and seems like it will hold meaning well over the next few years. The only things I anticipate might go out-of-date is technological information on things like citation managers, search guidelines, and database information. This is easily updatable with future versions of the text. In my view, ERIC is not the best database for educational research and I have confirmed this with educational librarians who support my students, yet it is the only one identified in this text as the best subject-specific source of educational research; this could be revised for additional relevance.
I noticed no issues with the book's clarity. The authors write in a clear and straightforward style, making the text easy to read. Overall, they did well writing for students across two disciplines by avoiding nursing or education-specific terms that would have been problematic to readers in the other discipline.
The book is internally consistent and did not have issues with terminology or framework.
No issues with the book's modularity. Chapter headings and sub-headings were appropriately paced and spaced. I assigned this textbook to my graduate students as a whole text that I wanted them to read at the beginning of a course, but it has been easy to refer them back to particular topics as the course has continued.
In future iterations of the book, I suggest hyperlinking the Answer Key to the exercises at the end of each chapter and/or listing the Answer Key in the Table of Contents for easy referral.
I found the book's organization to be straightforward and sensible. The Table of Contents offers a helpful snapshot of the scope of the book and the authors write in a direct and clear style, which contributes to an appropriate flow for the text.
I did not note any navigation problems with any links. All charts/images loaded well in my iBook app. The authors did a nice job of pulling relevant content and links in to support their ideas; it provided an easy way to seek more information if I wanted it, without feeling like the text was loaded down with unnecessary information.
I only found a few small typos in the text, with no grammar issues. The book is obviously written by two very detail-oriented librarians. I appreciated the clarity of the text and lack of errors.
The text was not culturally insensitive; a variety of topics across nursing and education were discussed as examples, which yielded a fairly balanced text regarding cultural considerations.
Reviewed by Alicia Rossiter, Assistant Professor, University of South Florida on 3/27/18
I believe the book gives a comprehensive overview on how to complete a literature view at the graduate level. It begins with an overview of the purpose of a literature review and moves through the steps to completing the review process. read more
I believe the book gives a comprehensive overview on how to complete a literature view at the graduate level. It begins with an overview of the purpose of a literature review and moves through the steps to completing the review process.
I believe the book was accurate and unbiased. It was easy to read but comprehensive.
Content within the text is relevant and supports the literature view process. It did discuss the various databases for searches which may need updating to include new sites, search engines but otherwise relevant and useful information.
The text is easy to read, provides appropriate examples, includes a section on putting the process into practice as well as a "test yourself" section to ensure the content is understood.
The text is consistent throughout in regards to terminology, framework, and set up.
The text is easy to read and content is leveled for the reader but not over simplified. Content is chunked into sections making it easy for the reader to digest the content. The chapters are well laid out and flow from chapter to chapter. Each chapter contains learning objectives, content sections, practice section, and test yourself section. Well organized and great visuals.
Topics are presented in a logical, clear fashion that flow from chapter to chapter and build as the reader moves through the process.
The text is free of interface issues. I could not get the videos to play but other visuals were appropriate and useful to support content.
The text contains no grammatical errors.
The text is not culturally offensive. There was no evidence of bias or cultural insensitivity.
I think this would be a great resource for graduate student learning to navigate the literature review process. It is easy to read, straightforward, and guides the individual through the process from start to finish. I will recommend this text to my graduate students in evidence-based practice and research courses as a recommended reference.
Table of Contents
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: What is a Literature Review?
- Chapter 3: How to Get Started
- Chapter 4: Where to Find the Literature
- Chapter 5: Evaluating Sources
- Chapter 6: Documenting Sources
- Chapter 7: Synthesizing Sources
- Chapter 8: Writing the Literature Review
Ancillary Material
About the book.
Literature Reviews for Education and Nursing Graduate Students is an open textbook designed for students in graduate-level nursing and education programs. Its intent is to recognize the significant role the literature review plays in the research process and to prepare students for the work that goes into writing one. Developed for new graduate students and novice researchers just entering into the work of a chosen discipline, each of the eight chapters covers a component of the literature review process. Students will learn how to form a research question, search existing literature, synthesize results and write the review. The book contains examples, checklists, supplementary materials, and additional resources. Literature Reviews for Education and Nursing Graduate Students is written by two librarians with expertise guiding students through research and writing assignments, and is openly licensed.
About the Contributors
Linda Frederiksen is the Head of Access Services at Washington State University Vancouver. She has a Master of Library Science degree from Emporia State University in Kansas. Linda is active in local, regional and national organizations, projects and initiatives advancing open educational resources and equitable access to information.
Sue F. Phelps is the Health Sciences and Outreach Services Librarian at Washington State University Vancouver. Her research interests include information literacy, accessibility of learning materials for students who use adaptive technology, diversity and equity in higher education, and evidence based practice in the health sciences
Contribute to this Page
Library Research Guides - University of Wisconsin Ebling Library
Uw-madison libraries research guides.
- Course Guides
- Subject Guides
- University of Wisconsin-Madison
- Research Guides
- Nursing Resources
- Conducting a Literature Review
Nursing Resources : Conducting a Literature Review
- Definitions of
- Professional Organizations
- Nursing Informatics
- Nursing Related Apps
- EBP Resources
- PICO-Clinical Question
- Types of PICO Question (D, T, P, E)
- Secondary & Guidelines
- Bedside--Point of Care
- Pre-processed Evidence
- Measurement Tools, Surveys, Scales
- Types of Studies
- Table of Evidence
- Qualitative vs Quantitative
- Types of Research within Qualitative and Quantitative
- Cohort vs Case studies
- Independent Variable VS Dependent Variable
- Sampling Methods and Statistics
- Systematic Reviews
- Review vs Systematic Review vs ETC...
- Standard, Guideline, Protocol, Policy
- Additional Guidelines Sources
- Peer Reviewed Articles
- Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis
- Writing a Research Paper or Poster
- Annotated Bibliographies
- Levels of Evidence (I-VII)
- Reliability
- Validity Threats
- Threats to Validity of Research Designs
- Nursing Theory
- Nursing Models
- PRISMA, RevMan, & GRADEPro
- ORCiD & NIH Submission System
- Understanding Predatory Journals
- Nursing Scope & Standards of Practice, 4th Ed
- Distance Ed & Scholarships
- Assess A Quantitative Study?
- Assess A Qualitative Study?
- Find Health Statistics?
- Choose A Citation Manager?
- Find Instruments, Measurements, and Tools
- Write a CV for a DNP or PhD?
- Find information about graduate programs?
- Learn more about Predatory Journals
- Get writing help?
- Choose a Citation Manager?
- Other questions you may have
- Search the Databases?
- Get Grad School information?
What is a Literature Review?
A literature review is an essay that surveys, summarizes, links together, and assesses research in a given field. It surveys the literature by reviewing a large body of work on a subject; it summarizes by noting the main conclusions and findings of the research; it links together works in the literature by showing how the information fits into the overall academic discussion and how the information relates to one another; it assesses the literature by noting areas of weakness, expansion, and contention. This is the essentials of literature review construction by discussing the major sectional elements, their purpose, how they are constructed, and how they all fit together.
All literature reviews have major sections:
- Introduction: that indicates the general state of the literature on a given topic;
- Methodology: an overview of how, where, and what subject terms used to conducted your search so it may be reproducable
- Findings: a summary of the major findings in that field;
- Discussion: a general progression from wider studies to smaller, more specifically-focused studies;
- Conclusion: for each major section that again notes the overall state of the research, albeit with a focus on the major synthesized conclusions, problems in the research, and even possible avenues of further research.
In Literature Reviews, it is Not Appropriate to:
- State your own opinions on the subject (unless you have evidence to support such claims).
- State what you think nurses should do (unless you have evidence to support such claims).
- Provide long descriptive accounts of your subject with no reference to research studies.
- Provide numerous definitions, signs/symptoms, treatment and complications of a particular illness without focusing on research studies to provide evidence and the primary purpose of the literature review.
- Discuss research studies in isolation from each other.
Remember, a literature review is not a book report. A literature review is focus, succinct, organized, and is free of personal beliefs or unsubstantiated tidbits.
- Types of Literature Reviews A detailed explanation of the different types of reviews and required citation retrieval numbers
Outline of a Literture Review

- << Previous: Peer Reviewed Articles
- Next: Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis >>
- Last Updated: Mar 19, 2024 10:39 AM
- URL: https://researchguides.library.wisc.edu/nursing
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Grad Med Educ
- v.8(3); 2016 Jul
The Literature Review: A Foundation for High-Quality Medical Education Research
a These are subscription resources. Researchers should check with their librarian to determine their access rights.
Despite a surge in published scholarship in medical education 1 and rapid growth in journals that publish educational research, manuscript acceptance rates continue to fall. 2 Failure to conduct a thorough, accurate, and up-to-date literature review identifying an important problem and placing the study in context is consistently identified as one of the top reasons for rejection. 3 , 4 The purpose of this editorial is to provide a road map and practical recommendations for planning a literature review. By understanding the goals of a literature review and following a few basic processes, authors can enhance both the quality of their educational research and the likelihood of publication in the Journal of Graduate Medical Education ( JGME ) and in other journals.
The Literature Review Defined
In medical education, no organization has articulated a formal definition of a literature review for a research paper; thus, a literature review can take a number of forms. Depending on the type of article, target journal, and specific topic, these forms will vary in methodology, rigor, and depth. Several organizations have published guidelines for conducting an intensive literature search intended for formal systematic reviews, both broadly (eg, PRISMA) 5 and within medical education, 6 and there are excellent commentaries to guide authors of systematic reviews. 7 , 8
- A literature review forms the basis for high-quality medical education research and helps maximize relevance, originality, generalizability, and impact.
- A literature review provides context, informs methodology, maximizes innovation, avoids duplicative research, and ensures that professional standards are met.
- Literature reviews take time, are iterative, and should continue throughout the research process.
- Researchers should maximize the use of human resources (librarians, colleagues), search tools (databases/search engines), and existing literature (related articles).
- Keeping organized is critical.
Such work is outside the scope of this article, which focuses on literature reviews to inform reports of original medical education research. We define such a literature review as a synthetic review and summary of what is known and unknown regarding the topic of a scholarly body of work, including the current work's place within the existing knowledge . While this type of literature review may not require the intensive search processes mandated by systematic reviews, it merits a thoughtful and rigorous approach.
Purpose and Importance of the Literature Review
An understanding of the current literature is critical for all phases of a research study. Lingard 9 recently invoked the “journal-as-conversation” metaphor as a way of understanding how one's research fits into the larger medical education conversation. As she described it: “Imagine yourself joining a conversation at a social event. After you hang about eavesdropping to get the drift of what's being said (the conversational equivalent of the literature review), you join the conversation with a contribution that signals your shared interest in the topic, your knowledge of what's already been said, and your intention.” 9
The literature review helps any researcher “join the conversation” by providing context, informing methodology, identifying innovation, minimizing duplicative research, and ensuring that professional standards are met. Understanding the current literature also promotes scholarship, as proposed by Boyer, 10 by contributing to 5 of the 6 standards by which scholarly work should be evaluated. 11 Specifically, the review helps the researcher (1) articulate clear goals, (2) show evidence of adequate preparation, (3) select appropriate methods, (4) communicate relevant results, and (5) engage in reflective critique.
Failure to conduct a high-quality literature review is associated with several problems identified in the medical education literature, including studies that are repetitive, not grounded in theory, methodologically weak, and fail to expand knowledge beyond a single setting. 12 Indeed, medical education scholars complain that many studies repeat work already published and contribute little new knowledge—a likely cause of which is failure to conduct a proper literature review. 3 , 4
Likewise, studies that lack theoretical grounding or a conceptual framework make study design and interpretation difficult. 13 When theory is used in medical education studies, it is often invoked at a superficial level. As Norman 14 noted, when theory is used appropriately, it helps articulate variables that might be linked together and why, and it allows the researcher to make hypotheses and define a study's context and scope. Ultimately, a proper literature review is a first critical step toward identifying relevant conceptual frameworks.
Another problem is that many medical education studies are methodologically weak. 12 Good research requires trained investigators who can articulate relevant research questions, operationally define variables of interest, and choose the best method for specific research questions. Conducting a proper literature review helps both novice and experienced researchers select rigorous research methodologies.
Finally, many studies in medical education are “one-offs,” that is, single studies undertaken because the opportunity presented itself locally. Such studies frequently are not oriented toward progressive knowledge building and generalization to other settings. A firm grasp of the literature can encourage a programmatic approach to research.
Approaching the Literature Review
Considering these issues, journals have a responsibility to demand from authors a thoughtful synthesis of their study's position within the field, and it is the authors' responsibility to provide such a synthesis, based on a literature review. The aforementioned purposes of the literature review mandate that the review occurs throughout all phases of a study, from conception and design, to implementation and analysis, to manuscript preparation and submission.
Planning the literature review requires understanding of journal requirements, which vary greatly by journal ( table 1 ). Authors are advised to take note of common problems with reporting results of the literature review. Table 2 lists the most common problems that we have encountered as authors, reviewers, and editors.
Sample of Journals' Author Instructions for Literature Reviews Conducted as Part of Original Research Article a

Common Problem Areas for Reporting Literature Reviews in the Context of Scholarly Articles

Locating and Organizing the Literature
Three resources may facilitate identifying relevant literature: human resources, search tools, and related literature. As the process requires time, it is important to begin searching for literature early in the process (ie, the study design phase). Identifying and understanding relevant studies will increase the likelihood of designing a relevant, adaptable, generalizable, and novel study that is based on educational or learning theory and can maximize impact.
Human Resources
A medical librarian can help translate research interests into an effective search strategy, familiarize researchers with available information resources, provide information on organizing information, and introduce strategies for keeping current with emerging research. Often, librarians are also aware of research across their institutions and may be able to connect researchers with similar interests. Reaching out to colleagues for suggestions may help researchers quickly locate resources that would not otherwise be on their radar.
During this process, researchers will likely identify other researchers writing on aspects of their topic. Researchers should consider searching for the publications of these relevant researchers (see table 3 for search strategies). Additionally, institutional websites may include curriculum vitae of such relevant faculty with access to their entire publication record, including difficult to locate publications, such as book chapters, dissertations, and technical reports.
Strategies for Finding Related Researcher Publications in Databases and Search Engines

Search Tools and Related Literature
Researchers will locate the majority of needed information using databases and search engines. Excellent resources are available to guide researchers in the mechanics of literature searches. 15 , 16
Because medical education research draws on a variety of disciplines, researchers should include search tools with coverage beyond medicine (eg, psychology, nursing, education, and anthropology) and that cover several publication types, such as reports, standards, conference abstracts, and book chapters (see the box for several information resources). Many search tools include options for viewing citations of selected articles. Examining cited references provides additional articles for review and a sense of the influence of the selected article on its field.
Box Information Resources
- Web of Science a
- Education Resource Information Center (ERIC)
- Cumulative Index of Nursing & Allied Health (CINAHL) a
- Google Scholar
Once relevant articles are located, it is useful to mine those articles for additional citations. One strategy is to examine references of key articles, especially review articles, for relevant citations.
Getting Organized
As the aforementioned resources will likely provide a tremendous amount of information, organization is crucial. Researchers should determine which details are most important to their study (eg, participants, setting, methods, and outcomes) and generate a strategy for keeping those details organized and accessible. Increasingly, researchers utilize digital tools, such as Evernote, to capture such information, which enables accessibility across digital workspaces and search capabilities. Use of citation managers can also be helpful as they store citations and, in some cases, can generate bibliographies ( table 4 ).
Citation Managers

Knowing When to Say When
Researchers often ask how to know when they have located enough citations. Unfortunately, there is no magic or ideal number of citations to collect. One strategy for checking coverage of the literature is to inspect references of relevant articles. As researchers review references they will start noticing a repetition of the same articles with few new articles appearing. This can indicate that the researcher has covered the literature base on a particular topic.
Putting It All Together
In preparing to write a research paper, it is important to consider which citations to include and how they will inform the introduction and discussion sections. The “Instructions to Authors” for the targeted journal will often provide guidance on structuring the literature review (or introduction) and the number of total citations permitted for each article category. Reviewing articles of similar type published in the targeted journal can also provide guidance regarding structure and average lengths of the introduction and discussion sections.
When selecting references for the introduction consider those that illustrate core background theoretical and methodological concepts, as well as recent relevant studies. The introduction should be brief and present references not as a laundry list or narrative of available literature, but rather as a synthesized summary to provide context for the current study and to identify the gap in the literature that the study intends to fill. For the discussion, citations should be thoughtfully selected to compare and contrast the present study's findings with the current literature and to indicate how the present study moves the field forward.
To facilitate writing a literature review, journals are increasingly providing helpful features to guide authors. For example, the resources available through JGME include several articles on writing. 17 The journal Perspectives on Medical Education recently launched “The Writer's Craft,” which is intended to help medical educators improve their writing. Additionally, many institutions have writing centers that provide web-based materials on writing a literature review, and some even have writing coaches.
The literature review is a vital part of medical education research and should occur throughout the research process to help researchers design a strong study and effectively communicate study results and importance. To achieve these goals, researchers are advised to plan and execute the literature review carefully. The guidance in this editorial provides considerations and recommendations that may improve the quality of literature reviews.
Nursing: Ph.D & Research
- Orientation
- Course Specific e-books
- Research/ Stats/ Theory e-Books
What is a Literature Review?
Traditional narrative/literature review, scoping review, integrative review, systematic review, meta-analysis, realist reviews and evaluation reviews.
- Comparision of Reviews Lite
- Review Process
- Usie Mnemonics for Idea Development
- PRISMA 2020
- PRISMA, Flow Diagram 2009
- PRISMA, Checklist 2009
- Organizing Sources
- Citation Manager Overview
- Citation Styles
- Writing Style
- Manuscripts and Publishing
- Statistical Tests
- Research Data Requests
- EBP Question and Resource
- Articles on EBP
- Critical Appraisal
- Quantitative Study Design
- Biostatistics
- Other Resources
- Clinical Resources
- Diversity and Inclusion Resources
- Software & Tutorials
- Ask Me Anything!
Still have questions about reviews?
Fill out the form below and a librarian will contact you shortly!
A literature review provides an overview of what's been written about a specific topic. There are many different types of literature reviews. They vary in terms of comprehensiveness, types of study included, and purpose.

- Grant, M.J., & Booth, A. (2009). A typology of reviews: An analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Information & Libraries Journal, 26, 91–108.
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors).Box 2.3.b: Timeline for a Cochrane review. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration. Available from http://handbook-5-1.cochrane.org . Accessed February 16, 2018.
- << Previous: Research/ Stats/ Theory e-Books
- Next: Comparision of Reviews Lite >>
- Last Updated: May 14, 2024 12:37 PM
- URL: https://musc.libguides.com/nursingphd
- Open access
- Published: 14 May 2024
Developing a survey to measure nursing students’ knowledge, attitudes and beliefs, influences, and willingness to be involved in Medical Assistance in Dying (MAiD): a mixed method modified e-Delphi study
- Jocelyn Schroeder 1 ,
- Barbara Pesut 1 , 2 ,
- Lise Olsen 2 ,
- Nelly D. Oelke 2 &
- Helen Sharp 2
BMC Nursing volume 23 , Article number: 326 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
31 Accesses
Metrics details
Medical Assistance in Dying (MAiD) was legalized in Canada in 2016. Canada’s legislation is the first to permit Nurse Practitioners (NP) to serve as independent MAiD assessors and providers. Registered Nurses’ (RN) also have important roles in MAiD that include MAiD care coordination; client and family teaching and support, MAiD procedural quality; healthcare provider and public education; and bereavement care for family. Nurses have a right under the law to conscientious objection to participating in MAiD. Therefore, it is essential to prepare nurses in their entry-level education for the practice implications and moral complexities inherent in this practice. Knowing what nursing students think about MAiD is a critical first step. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to develop a survey to measure nursing students’ knowledge, attitudes and beliefs, influences, and willingness to be involved in MAiD in the Canadian context.
The design was a mixed-method, modified e-Delphi method that entailed item generation from the literature, item refinement through a 2 round survey of an expert faculty panel, and item validation through a cognitive focus group interview with nursing students. The settings were a University located in an urban area and a College located in a rural area in Western Canada.
During phase 1, a 56-item survey was developed from existing literature that included demographic items and items designed to measure experience with death and dying (including MAiD), education and preparation, attitudes and beliefs, influences on those beliefs, and anticipated future involvement. During phase 2, an expert faculty panel reviewed, modified, and prioritized the items yielding 51 items. During phase 3, a sample of nursing students further evaluated and modified the language in the survey to aid readability and comprehension. The final survey consists of 45 items including 4 case studies.
Systematic evaluation of knowledge-to-date coupled with stakeholder perspectives supports robust survey design. This study yielded a survey to assess nursing students’ attitudes toward MAiD in a Canadian context.
The survey is appropriate for use in education and research to measure knowledge and attitudes about MAiD among nurse trainees and can be a helpful step in preparing nursing students for entry-level practice.
Peer Review reports
Medical Assistance in Dying (MAiD) is permitted under an amendment to Canada’s Criminal Code which was passed in 2016 [ 1 ]. MAiD is defined in the legislation as both self-administered and clinician-administered medication for the purpose of causing death. In the 2016 Bill C-14 legislation one of the eligibility criteria was that an applicant for MAiD must have a reasonably foreseeable natural death although this term was not defined. It was left to the clinical judgement of MAiD assessors and providers to determine the time frame that constitutes reasonably foreseeable [ 2 ]. However, in 2021 under Bill C-7, the eligibility criteria for MAiD were changed to allow individuals with irreversible medical conditions, declining health, and suffering, but whose natural death was not reasonably foreseeable, to receive MAiD [ 3 ]. This population of MAiD applicants are referred to as Track 2 MAiD (those whose natural death is foreseeable are referred to as Track 1). Track 2 applicants are subject to additional safeguards under the 2021 C-7 legislation.
Three additional proposed changes to the legislation have been extensively studied by Canadian Expert Panels (Council of Canadian Academics [CCA]) [ 4 , 5 , 6 ] First, under the legislation that defines Track 2, individuals with mental disease as their sole underlying medical condition may apply for MAiD, but implementation of this practice is embargoed until March 2027 [ 4 ]. Second, there is consideration of allowing MAiD to be implemented through advanced consent. This would make it possible for persons living with dementia to receive MAID after they have lost the capacity to consent to the procedure [ 5 ]. Third, there is consideration of extending MAiD to mature minors. A mature minor is defined as “a person under the age of majority…and who has the capacity to understand and appreciate the nature and consequences of a decision” ([ 6 ] p. 5). In summary, since the legalization of MAiD in 2016 the eligibility criteria and safeguards have evolved significantly with consequent implications for nurses and nursing care. Further, the number of Canadians who access MAiD shows steady increases since 2016 [ 7 ] and it is expected that these increases will continue in the foreseeable future.
Nurses have been integral to MAiD care in the Canadian context. While other countries such as Belgium and the Netherlands also permit euthanasia, Canada is the first country to allow Nurse Practitioners (Registered Nurses with additional preparation typically achieved at the graduate level) to act independently as assessors and providers of MAiD [ 1 ]. Although the role of Registered Nurses (RNs) in MAiD is not defined in federal legislation, it has been addressed at the provincial/territorial-level with variability in scope of practice by region [ 8 , 9 ]. For example, there are differences with respect to the obligation of the nurse to provide information to patients about MAiD, and to the degree that nurses are expected to ensure that patient eligibility criteria and safeguards are met prior to their participation [ 10 ]. Studies conducted in the Canadian context indicate that RNs perform essential roles in MAiD care coordination; client and family teaching and support; MAiD procedural quality; healthcare provider and public education; and bereavement care for family [ 9 , 11 ]. Nurse practitioners and RNs are integral to a robust MAiD care system in Canada and hence need to be well-prepared for their role [ 12 ].
Previous studies have found that end of life care, and MAiD specifically, raise complex moral and ethical issues for nurses [ 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 ]. The knowledge, attitudes, and beliefs of nurses are important across practice settings because nurses have consistent, ongoing, and direct contact with patients who experience chronic or life-limiting health conditions. Canadian studies exploring nurses’ moral and ethical decision-making in relation to MAiD reveal that although some nurses are clear in their support for, or opposition to, MAiD, others are unclear on what they believe to be good and right [ 14 ]. Empirical findings suggest that nurses go through a period of moral sense-making that is often informed by their family, peers, and initial experiences with MAID [ 17 , 18 ]. Canadian legislation and policy specifies that nurses are not required to participate in MAiD and may recuse themselves as conscientious objectors with appropriate steps to ensure ongoing and safe care of patients [ 1 , 19 ]. However, with so many nurses having to reflect on and make sense of their moral position, it is essential that they are given adequate time and preparation to make an informed and thoughtful decision before they participate in a MAID death [ 20 , 21 ].
It is well established that nursing students receive inconsistent exposure to end of life care issues [ 22 ] and little or no training related to MAiD [ 23 ]. Without such education and reflection time in pre-entry nursing preparation, nurses are at significant risk for moral harm. An important first step in providing this preparation is to be able to assess the knowledge, values, and beliefs of nursing students regarding MAID and end of life care. As demand for MAiD increases along with the complexities of MAiD, it is critical to understand the knowledge, attitudes, and likelihood of engagement with MAiD among nursing students as a baseline upon which to build curriculum and as a means to track these variables over time.
Aim, design, and setting
The aim of this study was to develop a survey to measure nursing students’ knowledge, attitudes and beliefs, influences, and willingness to be involved in MAiD in the Canadian context. We sought to explore both their willingness to be involved in the registered nursing role and in the nurse practitioner role should they chose to prepare themselves to that level of education. The design was a mixed-method, modified e-Delphi method that entailed item generation, item refinement through an expert faculty panel [ 24 , 25 , 26 ], and initial item validation through a cognitive focus group interview with nursing students [ 27 ]. The settings were a University located in an urban area and a College located in a rural area in Western Canada.
Participants
A panel of 10 faculty from the two nursing education programs were recruited for Phase 2 of the e-Delphi. To be included, faculty were required to have a minimum of three years of experience in nurse education, be employed as nursing faculty, and self-identify as having experience with MAiD. A convenience sample of 5 fourth-year nursing students were recruited to participate in Phase 3. Students had to be in good standing in the nursing program and be willing to share their experiences of the survey in an online group interview format.
The modified e-Delphi was conducted in 3 phases: Phase 1 entailed item generation through literature and existing survey review. Phase 2 entailed item refinement through a faculty expert panel review with focus on content validity, prioritization, and revision of item wording [ 25 ]. Phase 3 entailed an assessment of face validity through focus group-based cognitive interview with nursing students.
Phase I. Item generation through literature review
The goal of phase 1 was to develop a bank of survey items that would represent the variables of interest and which could be provided to expert faculty in Phase 2. Initial survey items were generated through a literature review of similar surveys designed to assess knowledge and attitudes toward MAiD/euthanasia in healthcare providers; Canadian empirical studies on nurses’ roles and/or experiences with MAiD; and legislative and expert panel documents that outlined proposed changes to the legislative eligibility criteria and safeguards. The literature review was conducted in three online databases: CINAHL, PsycINFO, and Medline. Key words for the search included nurses , nursing students , medical students , NPs, MAiD , euthanasia , assisted death , and end-of-life care . Only articles written in English were reviewed. The legalization and legislation of MAiD is new in many countries; therefore, studies that were greater than twenty years old were excluded, no further exclusion criteria set for country.
Items from surveys designed to measure similar variables in other health care providers and geographic contexts were placed in a table and similar items were collated and revised into a single item. Then key variables were identified from the empirical literature on nurses and MAiD in Canada and checked against the items derived from the surveys to ensure that each of the key variables were represented. For example, conscientious objection has figured prominently in the Canadian literature, but there were few items that assessed knowledge of conscientious objection in other surveys and so items were added [ 15 , 21 , 28 , 29 ]. Finally, four case studies were added to the survey to address the anticipated changes to the Canadian legislation. The case studies were based upon the inclusion of mature minors, advanced consent, and mental disorder as the sole underlying medical condition. The intention was to assess nurses’ beliefs and comfort with these potential legislative changes.
Phase 2. Item refinement through expert panel review
The goal of phase 2 was to refine and prioritize the proposed survey items identified in phase 1 using a modified e-Delphi approach to achieve consensus among an expert panel [ 26 ]. Items from phase 1 were presented to an expert faculty panel using a Qualtrics (Provo, UT) online survey. Panel members were asked to review each item to determine if it should be: included, excluded or adapted for the survey. When adapted was selected faculty experts were asked to provide rationale and suggestions for adaptation through the use of an open text box. Items that reached a level of 75% consensus for either inclusion or adaptation were retained [ 25 , 26 ]. New items were categorized and added, and a revised survey was presented to the panel of experts in round 2. Panel members were again asked to review items, including new items, to determine if it should be: included, excluded, or adapted for the survey. Round 2 of the modified e-Delphi approach also included an item prioritization activity, where participants were then asked to rate the importance of each item, based on a 5-point Likert scale (low to high importance), which De Vaus [ 30 ] states is helpful for increasing the reliability of responses. Items that reached a 75% consensus on inclusion were then considered in relation to the importance it was given by the expert panel. Quantitative data were managed using SPSS (IBM Corp).
Phase 3. Face validity through cognitive interviews with nursing students
The goal of phase 3 was to obtain initial face validity of the proposed survey using a sample of nursing student informants. More specifically, student participants were asked to discuss how items were interpreted, to identify confusing wording or other problematic construction of items, and to provide feedback about the survey as a whole including readability and organization [ 31 , 32 , 33 ]. The focus group was held online and audio recorded. A semi-structured interview guide was developed for this study that focused on clarity, meaning, order and wording of questions; emotions evoked by the questions; and overall survey cohesion and length was used to obtain data (see Supplementary Material 2 for the interview guide). A prompt to “think aloud” was used to limit interviewer-imposed bias and encourage participants to describe their thoughts and response to a given item as they reviewed survey items [ 27 ]. Where needed, verbal probes such as “could you expand on that” were used to encourage participants to expand on their responses [ 27 ]. Student participants’ feedback was collated verbatim and presented to the research team where potential survey modifications were negotiated and finalized among team members. Conventional content analysis [ 34 ] of focus group data was conducted to identify key themes that emerged through discussion with students. Themes were derived from the data by grouping common responses and then using those common responses to modify survey items.
Ten nursing faculty participated in the expert panel. Eight of the 10 faculty self-identified as female. No faculty panel members reported conscientious objector status and ninety percent reported general agreement with MAiD with one respondent who indicated their view as “unsure.” Six of the 10 faculty experts had 16 years of experience or more working as a nurse educator.
Five nursing students participated in the cognitive interview focus group. The duration of the focus group was 2.5 h. All participants identified that they were born in Canada, self-identified as female (one preferred not to say) and reported having received some instruction about MAiD as part of their nursing curriculum. See Tables 1 and 2 for the demographic descriptors of the study sample. Study results will be reported in accordance with the study phases. See Fig. 1 for an overview of the results from each phase.
Fig. 1 Overview of survey development findings
Phase 1: survey item generation
Review of the literature identified that no existing survey was available for use with nursing students in the Canadian context. However, an analysis of themes across qualitative and quantitative studies of physicians, medical students, nurses, and nursing students provided sufficient data to develop a preliminary set of items suitable for adaptation to a population of nursing students.
Four major themes and factors that influence knowledge, attitudes, and beliefs about MAiD were evident from the literature: (i) endogenous or individual factors such as age, gender, personally held values, religion, religiosity, and/or spirituality [ 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 ], (ii) experience with death and dying in personal and/or professional life [ 35 , 40 , 41 , 43 , 44 , 45 ], (iii) training including curricular instruction about clinical role, scope of practice, or the law [ 23 , 36 , 39 ], and (iv) exogenous or social factors such as the influence of key leaders, colleagues, friends and/or family, professional and licensure organizations, support within professional settings, and/or engagement in MAiD in an interdisciplinary team context [ 9 , 35 , 46 ].
Studies of nursing students also suggest overlap across these categories. For example, value for patient autonomy [ 23 ] and the moral complexity of decision-making [ 37 ] are important factors that contribute to attitudes about MAiD and may stem from a blend of personally held values coupled with curricular content, professional training and norms, and clinical exposure. For example, students report that participation in end of life care allows for personal growth, shifts in perception, and opportunities to build therapeutic relationships with their clients [ 44 , 47 , 48 ].
Preliminary items generated from the literature resulted in 56 questions from 11 published sources (See Table 3 ). These items were constructed across four main categories: (i) socio-demographic questions; (ii) end of life care questions; (iii) knowledge about MAiD; or (iv) comfort and willingness to participate in MAiD. Knowledge questions were refined to reflect current MAiD legislation, policies, and regulatory frameworks. Falconer [ 39 ] and Freeman [ 45 ] studies were foundational sources for item selection. Additionally, four case studies were written to reflect the most recent anticipated changes to MAiD legislation and all used the same open-ended core questions to address respondents’ perspectives about the patient’s right to make the decision, comfort in assisting a physician or NP to administer MAiD in that scenario, and hypothesized comfort about serving as a primary provider if qualified as an NP in future. Response options for the survey were also constructed during this stage and included: open text, categorical, yes/no , and Likert scales.
Phase 2: faculty expert panel review
Of the 56 items presented to the faculty panel, 54 questions reached 75% consensus. However, based upon the qualitative responses 9 items were removed largely because they were felt to be repetitive. Items that generated the most controversy were related to measuring religion and spirituality in the Canadian context, defining end of life care when there is no agreed upon time frames (e.g., last days, months, or years), and predicting willingness to be involved in a future events – thus predicting their future selves. Phase 2, round 1 resulted in an initial set of 47 items which were then presented back to the faculty panel in round 2.
Of the 47 initial questions presented to the panel in round 2, 45 reached a level of consensus of 75% or greater, and 34 of these questions reached a level of 100% consensus [ 27 ] of which all participants chose to include without any adaptations) For each question, level of importance was determined based on a 5-point Likert scale (1 = very unimportant, 2 = somewhat unimportant, 3 = neutral, 4 = somewhat important, and 5 = very important). Figure 2 provides an overview of the level of importance assigned to each item.
Ranking level of importance for survey items
After round 2, a careful analysis of participant comments and level of importance was completed by the research team. While the main method of survey item development came from participants’ response to the first round of Delphi consensus ratings, level of importance was used to assist in the decision of whether to keep or modify questions that created controversy, or that rated lower in the include/exclude/adapt portion of the Delphi. Survey items that rated low in level of importance included questions about future roles, sex and gender, and religion/spirituality. After deliberation by the research committee, these questions were retained in the survey based upon the importance of these variables in the scientific literature.
Of the 47 questions remaining from Phase 2, round 2, four were revised. In addition, the two questions that did not meet the 75% cut off level for consensus were reviewed by the research team. The first question reviewed was What is your comfort level with providing a MAiD death in the future if you were a qualified NP ? Based on a review of participant comments, it was decided to retain this question for the cognitive interviews with students in the final phase of testing. The second question asked about impacts on respondents’ views of MAiD and was changed from one item with 4 subcategories into 4 separate items, resulting in a final total of 51 items for phase 3. The revised survey was then brought forward to the cognitive interviews with student participants in Phase 3. (see Supplementary Material 1 for a complete description of item modification during round 2).
Phase 3. Outcomes of cognitive interview focus group
Of the 51 items reviewed by student participants, 29 were identified as clear with little or no discussion. Participant comments for the remaining 22 questions were noted and verified against the audio recording. Following content analysis of the comments, four key themes emerged through the student discussion: unclear or ambiguous wording; difficult to answer questions; need for additional response options; and emotional response evoked by questions. An example of unclear or ambiguous wording was a request for clarity in the use of the word “sufficient” in the context of assessing an item that read “My nursing education has provided sufficient content about the nursing role in MAiD.” “Sufficient” was viewed as subjective and “laden with…complexity that distracted me from the question.” The group recommended rewording the item to read “My nursing education has provided enough content for me to care for a patient considering or requesting MAiD.”
An example of having difficulty answering questions related to limited knowledge related to terms used in the legislation such as such as safeguards , mature minor , eligibility criteria , and conscientious objection. Students were unclear about what these words meant relative to the legislation and indicated that this lack of clarity would hamper appropriate responses to the survey. To ensure that respondents are able to answer relevant questions, student participants recommended that the final survey include explanation of key terms such as mature minor and conscientious objection and an overview of current legislation.
Response options were also a point of discussion. Participants noted a lack of distinction between response options of unsure and unable to say . Additionally, scaling of attitudes was noted as important since perspectives about MAiD are dynamic and not dichotomous “agree or disagree” responses. Although the faculty expert panel recommended the integration of the demographic variables of religious and/or spiritual remain as a single item, the student group stated a preference to have religion and spirituality appear as separate items. The student focus group also took issue with separate items for the variables of sex and gender, specifically that non-binary respondents might feel othered or “outed” particularly when asked to identify their sex. These variables had been created based upon best practices in health research but students did not feel they were appropriate in this context [ 49 ]. Finally, students agreed with the faculty expert panel in terms of the complexity of projecting their future involvement as a Nurse Practitioner. One participant stated: “I certainly had to like, whoa, whoa, whoa. Now let me finish this degree first, please.” Another stated, “I'm still imagining myself, my future career as an RN.”
Finally, student participants acknowledged the array of emotions that some of the items produced for them. For example, one student described positive feelings when interacting with the survey. “Brought me a little bit of feeling of joy. Like it reminded me that this is the last piece of independence that people grab on to.” Another participant, described the freedom that the idea of an advance request gave her. “The advance request gives the most comfort for me, just with early onset Alzheimer’s and knowing what it can do.” But other participants described less positive feelings. For example, the mature minor case study yielded a comment: “This whole scenario just made my heart hurt with the idea of a child requesting that.”
Based on the data gathered from the cognitive interview focus group of nursing students, revisions were made to 11 closed-ended questions (see Table 4 ) and 3 items were excluded. In the four case studies, the open-ended question related to a respondents’ hypothesized actions in a future role as NP were removed. The final survey consists of 45 items including 4 case studies (see Supplementary Material 3 ).
The aim of this study was to develop and validate a survey that can be used to track the growth of knowledge about MAiD among nursing students over time, inform training programs about curricular needs, and evaluate attitudes and willingness to participate in MAiD at time-points during training or across nursing programs over time.
The faculty expert panel and student participants in the cognitive interview focus group identified a need to establish core knowledge of the terminology and legislative rules related to MAiD. For example, within the cognitive interview group of student participants, several acknowledged lack of clear understanding of specific terms such as “conscientious objector” and “safeguards.” Participants acknowledged discomfort with the uncertainty of not knowing and their inclination to look up these terms to assist with answering the questions. This survey can be administered to nursing or pre-nursing students at any phase of their training within a program or across training programs. However, in doing so it is important to acknowledge that their baseline knowledge of MAiD will vary. A response option of “not sure” is important and provides a means for respondents to convey uncertainty. If this survey is used to inform curricular needs, respondents should be given explicit instructions not to conduct online searches to inform their responses, but rather to provide an honest appraisal of their current knowledge and these instructions are included in the survey (see Supplementary Material 3 ).
Some provincial regulatory bodies have established core competencies for entry-level nurses that include MAiD. For example, the BC College of Nurses and Midwives (BCCNM) requires “knowledge about ethical, legal, and regulatory implications of medical assistance in dying (MAiD) when providing nursing care.” (10 p. 6) However, across Canada curricular content and coverage related to end of life care and MAiD is variable [ 23 ]. Given the dynamic nature of the legislation that includes portions of the law that are embargoed until 2024, it is important to ensure that respondents are guided by current and accurate information. As the law changes, nursing curricula, and public attitudes continue to evolve, inclusion of core knowledge and content is essential and relevant for investigators to be able to interpret the portions of the survey focused on attitudes and beliefs about MAiD. Content knowledge portions of the survey may need to be modified over time as legislation and training change and to meet the specific purposes of the investigator.
Given the sensitive nature of the topic, it is strongly recommended that surveys be conducted anonymously and that students be provided with an opportunity to discuss their responses to the survey. A majority of feedback from both the expert panel of faculty and from student participants related to the wording and inclusion of demographic variables, in particular religion, religiosity, gender identity, and sex assigned at birth. These and other demographic variables have the potential to be highly identifying in small samples. In any instance in which the survey could be expected to yield demographic group sizes less than 5, users should eliminate the demographic variables from the survey. For example, the profession of nursing is highly dominated by females with over 90% of nurses who identify as female [ 50 ]. Thus, a survey within a single class of students or even across classes in a single institution is likely to yield a small number of male respondents and/or respondents who report a difference between sex assigned at birth and gender identity. When variables that serve to identify respondents are included, respondents are less likely to complete or submit the survey, to obscure their responses so as not to be identifiable, or to be influenced by social desirability bias in their responses rather than to convey their attitudes accurately [ 51 ]. Further, small samples do not allow for conclusive analyses or interpretation of apparent group differences. Although these variables are often included in surveys, such demographics should be included only when anonymity can be sustained. In small and/or known samples, highly identifying variables should be omitted.
There are several limitations associated with the development of this survey. The expert panel was comprised of faculty who teach nursing students and are knowledgeable about MAiD and curricular content, however none identified as a conscientious objector to MAiD. Ideally, our expert panel would have included one or more conscientious objectors to MAiD to provide a broader perspective. Review by practitioners who participate in MAiD, those who are neutral or undecided, and practitioners who are conscientious objectors would ensure broad applicability of the survey. This study included one student cognitive interview focus group with 5 self-selected participants. All student participants had held discussions about end of life care with at least one patient, 4 of 5 participants had worked with a patient who requested MAiD, and one had been present for a MAiD death. It is not clear that these participants are representative of nursing students demographically or by experience with end of life care. It is possible that the students who elected to participate hold perspectives and reflections on patient care and MAiD that differ from students with little or no exposure to end of life care and/or MAiD. However, previous studies find that most nursing students have been involved with end of life care including meaningful discussions about patients’ preferences and care needs during their education [ 40 , 44 , 47 , 48 , 52 ]. Data collection with additional student focus groups with students early in their training and drawn from other training contexts would contribute to further validation of survey items.
Future studies should incorporate pilot testing with small sample of nursing students followed by a larger cross-program sample to allow evaluation of the psychometric properties of specific items and further refinement of the survey tool. Consistent with literature about the importance of leadership in the context of MAiD [ 12 , 53 , 54 ], a study of faculty knowledge, beliefs, and attitudes toward MAiD would provide context for understanding student perspectives within and across programs. Additional research is also needed to understand the timing and content coverage of MAiD across Canadian nurse training programs’ curricula.
The implementation of MAiD is complex and requires understanding of the perspectives of multiple stakeholders. Within the field of nursing this includes clinical providers, educators, and students who will deliver clinical care. A survey to assess nursing students’ attitudes toward and willingness to participate in MAiD in the Canadian context is timely, due to the legislation enacted in 2016 and subsequent modifications to the law in 2021 with portions of the law to be enacted in 2027. Further development of this survey could be undertaken to allow for use in settings with practicing nurses or to allow longitudinal follow up with students as they enter practice. As the Canadian landscape changes, ongoing assessment of the perspectives and needs of health professionals and students in the health professions is needed to inform policy makers, leaders in practice, curricular needs, and to monitor changes in attitudes and practice patterns over time.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available due to small sample sizes, but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
British Columbia College of Nurses and Midwives
Medical assistance in dying
Nurse practitioner
Registered nurse
University of British Columbia Okanagan
Nicol J, Tiedemann M. Legislative Summary: Bill C-14: An Act to amend the Criminal Code and to make related amendments to other Acts (medical assistance in dying). Available from: https://lop.parl.ca/staticfiles/PublicWebsite/Home/ResearchPublications/LegislativeSummaries/PDF/42-1/c14-e.pdf .
Downie J, Scallion K. Foreseeably unclear. The meaning of the “reasonably foreseeable” criterion for access to medical assistance in dying in Canada. Dalhousie Law J. 2018;41(1):23–57.
Nicol J, Tiedeman M. Legislative summary of Bill C-7: an act to amend the criminal code (medical assistance in dying). Ottawa: Government of Canada; 2021.
Google Scholar
Council of Canadian Academies. The state of knowledge on medical assistance in dying where a mental disorder is the sole underlying medical condition. Ottawa; 2018. Available from: https://cca-reports.ca/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/The-State-of-Knowledge-on-Medical-Assistance-in-Dying-Where-a-Mental-Disorder-is-the-Sole-Underlying-Medical-Condition.pdf .
Council of Canadian Academies. The state of knowledge on advance requests for medical assistance in dying. Ottawa; 2018. Available from: https://cca-reports.ca/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/The-State-of-Knowledge-on-Advance-Requests-for-Medical-Assistance-in-Dying.pdf .
Council of Canadian Academies. The state of knowledge on medical assistance in dying for mature minors. Ottawa; 2018. Available from: https://cca-reports.ca/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/The-State-of-Knowledge-on-Medical-Assistance-in-Dying-for-Mature-Minors.pdf .
Health Canada. Third annual report on medical assistance in dying in Canada 2021. Ottawa; 2022. [cited 2023 Oct 23]. Available from: https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/medical-assistance-dying/annual-report-2021.html .
Banner D, Schiller CJ, Freeman S. Medical assistance in dying: a political issue for nurses and nursing in Canada. Nurs Philos. 2019;20(4): e12281.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Pesut B, Thorne S, Stager ML, Schiller CJ, Penney C, Hoffman C, et al. Medical assistance in dying: a review of Canadian nursing regulatory documents. Policy Polit Nurs Pract. 2019;20(3):113–30.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
College of Registered Nurses of British Columbia. Scope of practice for registered nurses [Internet]. Vancouver; 2018. Available from: https://www.bccnm.ca/Documents/standards_practice/rn/RN_ScopeofPractice.pdf .
Pesut B, Thorne S, Schiller C, Greig M, Roussel J, Tishelman C. Constructing good nursing practice for medical assistance in dying in Canada: an interpretive descriptive study. Global Qual Nurs Res. 2020;7:2333393620938686. https://doi.org/10.1177/2333393620938686 .
Article Google Scholar
Pesut B, Thorne S, Schiller CJ, Greig M, Roussel J. The rocks and hard places of MAiD: a qualitative study of nursing practice in the context of legislated assisted death. BMC Nurs. 2020;19:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-020-0404-5 .
Pesut B, Greig M, Thorne S, Burgess M, Storch JL, Tishelman C, et al. Nursing and euthanasia: a narrative review of the nursing ethics literature. Nurs Ethics. 2020;27(1):152–67.
Pesut B, Thorne S, Storch J, Chambaere K, Greig M, Burgess M. Riding an elephant: a qualitative study of nurses’ moral journeys in the context of Medical Assistance in Dying (MAiD). Journal Clin Nurs. 2020;29(19–20):3870–81.
Lamb C, Babenko-Mould Y, Evans M, Wong CA, Kirkwood KW. Conscientious objection and nurses: results of an interpretive phenomenological study. Nurs Ethics. 2018;26(5):1337–49.
Wright DK, Chan LS, Fishman JR, Macdonald ME. “Reflection and soul searching:” Negotiating nursing identity at the fault lines of palliative care and medical assistance in dying. Social Sci & Med. 2021;289: 114366.
Beuthin R, Bruce A, Scaia M. Medical assistance in dying (MAiD): Canadian nurses’ experiences. Nurs Forum. 2018;54(4):511–20.
Bruce A, Beuthin R. Medically assisted dying in Canada: "Beautiful Death" is transforming nurses' experiences of suffering. The Canadian J Nurs Res | Revue Canadienne de Recherche en Sci Infirmieres. 2020;52(4):268–77. https://doi.org/10.1177/0844562119856234 .
Canadian Nurses Association. Code of ethics for registered nurses. Ottawa; 2017. Available from: https://www.cna-aiic.ca/en/nursing/regulated-nursing-in-canada/nursing-ethics .
Canadian Nurses Association. National nursing framework on Medical Assistance in Dying in Canada. Ottawa: 2017. Available from: https://www.virtualhospice.ca/Assets/cna-national-nursing-framework-on-maidEng_20170216155827.pdf .
Pesut B, Thorne S, Greig M. Shades of gray: conscientious objection in medical assistance in dying. Nursing Inq. 2020;27(1): e12308.
Durojaiye A, Ryan R, Doody O. Student nurse education and preparation for palliative care: a scoping review. PLoS ONE. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0286678 .
McMechan C, Bruce A, Beuthin R. Canadian nursing students’ experiences with medical assistance in dying | Les expériences d’étudiantes en sciences infirmières au regard de l’aide médicale à mourir. Qual Adv Nurs Educ - Avancées en Formation Infirmière. 2019;5(1). https://doi.org/10.17483/2368-6669.1179 .
Adler M, Ziglio E. Gazing into the oracle. The Delphi method and its application to social policy and public health. London: Jessica Kingsley Publishers; 1996
Keeney S, Hasson F, McKenna H. Consulting the oracle: ten lessons from using the Delphi technique in nursing research. J Adv Nurs. 2006;53(2):205–12.
Keeney S, Hasson F, McKenna H. The Delphi technique in nursing and health research. 1st ed. City: Wiley; 2011.
Willis GB. Cognitive interviewing: a tool for improving questionnaire design. 1st ed. Thousand Oaks, Calif: Sage; 2005. ISBN: 9780761928041
Lamb C, Evans M, Babenko-Mould Y, Wong CA, Kirkwood EW. Conscience, conscientious objection, and nursing: a concept analysis. Nurs Ethics. 2017;26(1):37–49.
Lamb C, Evans M, Babenko-Mould Y, Wong CA, Kirkwood K. Nurses’ use of conscientious objection and the implications of conscience. J Adv Nurs. 2018;75(3):594–602.
de Vaus D. Surveys in social research. 6th ed. Abingdon, Oxon: Routledge; 2014.
Boateng GO, Neilands TB, Frongillo EA, Melgar-Quiñonez HR, Young SL. Best practices for developing and validating scales for health, social, and behavioral research: A primer. Front Public Health. 2018;6:149. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2018.00149 .
Puchta C, Potter J. Focus group practice. 1st ed. London: Sage; 2004.
Book Google Scholar
Streiner DL, Norman GR, Cairney J. Health measurement scales: a practical guide to their development and use. 5th ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2015.
Hsieh H-F, Shannon SE. Three approaches to qualitative content analysis. Qual Health Res. 2005;15(9):1277–88.
Adesina O, DeBellis A, Zannettino L. Third-year Australian nursing students’ attitudes, experiences, knowledge, and education concerning end-of-life care. Int J of Palliative Nurs. 2014;20(8):395–401.
Bator EX, Philpott B, Costa AP. This moral coil: a cross-sectional survey of Canadian medical student attitudes toward medical assistance in dying. BMC Med Ethics. 2017;18(1):58.
Beuthin R, Bruce A, Scaia M. Medical assistance in dying (MAiD): Canadian nurses’ experiences. Nurs Forum. 2018;53(4):511–20.
Brown J, Goodridge D, Thorpe L, Crizzle A. What is right for me, is not necessarily right for you: the endogenous factors influencing nonparticipation in medical assistance in dying. Qual Health Res. 2021;31(10):1786–1800.
Falconer J, Couture F, Demir KK, Lang M, Shefman Z, Woo M. Perceptions and intentions toward medical assistance in dying among Canadian medical students. BMC Med Ethics. 2019;20(1):22.
Green G, Reicher S, Herman M, Raspaolo A, Spero T, Blau A. Attitudes toward euthanasia—dual view: Nursing students and nurses. Death Stud. 2022;46(1):124–31.
Hosseinzadeh K, Rafiei H. Nursing student attitudes toward euthanasia: a cross-sectional study. Nurs Ethics. 2019;26(2):496–503.
Ozcelik H, Tekir O, Samancioglu S, Fadiloglu C, Ozkara E. Nursing students’ approaches toward euthanasia. Omega (Westport). 2014;69(1):93–103.
Canning SE, Drew C. Canadian nursing students’ understanding, and comfort levels related to medical assistance in dying. Qual Adv Nurs Educ - Avancées en Formation Infirmière. 2022;8(2). https://doi.org/10.17483/2368-6669.1326 .
Edo-Gual M, Tomás-Sábado J, Bardallo-Porras D, Monforte-Royo C. The impact of death and dying on nursing students: an explanatory model. J Clin Nurs. 2014;23(23–24):3501–12.
Freeman LA, Pfaff KA, Kopchek L, Liebman J. Investigating palliative care nurse attitudes towards medical assistance in dying: an exploratory cross-sectional study. J Adv Nurs. 2020;76(2):535–45.
Brown J, Goodridge D, Thorpe L, Crizzle A. “I am okay with it, but I am not going to do it:” the exogenous factors influencing non-participation in medical assistance in dying. Qual Health Res. 2021;31(12):2274–89.
Dimoula M, Kotronoulas G, Katsaragakis S, Christou M, Sgourou S, Patiraki E. Undergraduate nursing students’ knowledge about palliative care and attitudes towards end-of-life care: A three-cohort, cross-sectional survey. Nurs Educ Today. 2019;74:7–14.
Matchim Y, Raetong P. Thai nursing students’ experiences of caring for patients at the end of life: a phenomenological study. Int J Palliative Nurs. 2018;24(5):220–9.
Canadian Institute for Health Research. Sex and gender in health research [Internet]. Ottawa: CIHR; 2021 [cited 2023 Oct 23]. Available from: https://cihr-irsc.gc.ca/e/50833.html .
Canadian Nurses’ Association. Nursing statistics. Ottawa: CNA; 2023 [cited 2023 Oct 23]. Available from: https://www.cna-aiic.ca/en/nursing/regulated-nursing-in-canada/nursing-statistics .
Krumpal I. Determinants of social desirability bias in sensitive surveys: a literature review. Qual Quant. 2013;47(4):2025–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-011-9640-9 .
Ferri P, Di Lorenzo R, Stifani S, Morotti E, Vagnini M, Jiménez Herrera MF, et al. Nursing student attitudes toward dying patient care: a European multicenter cross-sectional study. Acta Bio Medica Atenei Parmensis. 2021;92(S2): e2021018.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Beuthin R, Bruce A. Medical assistance in dying (MAiD): Ten things leaders need to know. Nurs Leadership. 2018;31(4):74–81.
Thiele T, Dunsford J. Nurse leaders’ role in medical assistance in dying: a relational ethics approach. Nurs Ethics. 2019;26(4):993–9.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the faculty and students who generously contributed their time to this work.
JS received a student traineeship through the Principal Research Chairs program at the University of British Columbia Okanagan.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Health and Human Services, Selkirk College, Castlegar, BC, Canada
Jocelyn Schroeder & Barbara Pesut
School of Nursing, University of British Columbia Okanagan, Kelowna, BC, Canada
Barbara Pesut, Lise Olsen, Nelly D. Oelke & Helen Sharp
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
JS made substantial contributions to the conception of the work; data acquisition, analysis, and interpretation; and drafting and substantively revising the work. JS has approved the submitted version and agreed to be personally accountable for the author's own contributions and to ensure that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work, even ones in which the author was not personally involved, are appropriately investigated, resolved, and the resolution documented in the literature. BP made substantial contributions to the conception of the work; data acquisition, analysis, and interpretation; and drafting and substantively revising the work. BP has approved the submitted version and agreed to be personally accountable for the author's own contributions and to ensure that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work, even ones in which the author was not personally involved, are appropriately investigated, resolved, and the resolution documented in the literature. LO made substantial contributions to the conception of the work; data acquisition, analysis, and interpretation; and substantively revising the work. LO has approved the submitted version and agreed to be personally accountable for the author's own contributions and to ensure that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work, even ones in which the author was not personally involved, are appropriately investigated, resolved, and the resolution documented in the literature. NDO made substantial contributions to the conception of the work; data acquisition, analysis, and interpretation; and substantively revising the work. NDO has approved the submitted version and agreed to be personally accountable for the author's own contributions and to ensure that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work, even ones in which the author was not personally involved, are appropriately investigated, resolved, and the resolution documented in the literature. HS made substantial contributions to drafting and substantively revising the work. HS has approved the submitted version and agreed to be personally accountable for the author's own contributions and to ensure that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work, even ones in which the author was not personally involved, are appropriately investigated, resolved, and the resolution documented in the literature.
Authors’ information
JS conducted this study as part of their graduate requirements in the School of Nursing, University of British Columbia Okanagan.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Barbara Pesut .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The research was approved by the Selkirk College Research Ethics Board (REB) ID # 2021–011 and the University of British Columbia Behavioral Research Ethics Board ID # H21-01181.
All participants provided written and informed consent through approved consent processes. Research was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1., supplementary material 2., supplementary material 3., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Schroeder, J., Pesut, B., Olsen, L. et al. Developing a survey to measure nursing students’ knowledge, attitudes and beliefs, influences, and willingness to be involved in Medical Assistance in Dying (MAiD): a mixed method modified e-Delphi study. BMC Nurs 23 , 326 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-024-01984-z
Download citation
Received : 24 October 2023
Accepted : 28 April 2024
Published : 14 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-024-01984-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Medical assistance in dying (MAiD)
- End of life care
- Student nurses
- Nursing education
BMC Nursing
ISSN: 1472-6955
- General enquiries: [email protected]

- Liberty University
- Jerry Falwell Library
- Special Collections
- < Previous
Home > ETD > Doctoral > 5578
Doctoral Dissertations and Projects
Determining the impact of mindfulness activities to increase joy in work and decrease burnout: an integrative review.
Kimberly Gleason Bogart , Liberty University Follow
School of Nursing
Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP)
mindfulness, nurses, joy, burnout
Disciplines
Educational Psychology | Nursing
Recommended Citation
Bogart, Kimberly Gleason, "Determining the Impact of Mindfulness Activities to Increase Joy in Work and Decrease Burnout: An Integrative Review" (2024). Doctoral Dissertations and Projects . 5578. https://digitalcommons.liberty.edu/doctoral/5578
This integrative review aims to evaluate whether mindfulness effectively increases joy in work and decreases nursing burnout. A lack of joy leads to feelings of burnout and negatively affects nurses and their desire to leave the profession. Nursing is often accompanied by intense emotional and physical demands that can lead to job dissatisfaction, anxiety, and stress. Burnout diminishes the quality of care and negatively impacts nurses’ well-being. This integrative review aims to explore mindfulness interventions to increase joy within nursing and potentially alleviate burnout. Drawing upon existing literature, this paper examines various mindfulness interventions and factors contributing to burnout among nurses. Mindfulness has been used for centuries in Eastern traditions but has only been adopted by Western cultures in the past few decades. Mindfulness has been integrated into various therapeutic activities to promote well-being among nurses. There were 20 articles reviewed that discussed mindfulness in nursing for reducing burnout. There is significant evidence that mindfulness is an effective tool for reducing burnout. Findings also showed that various mindfulness techniques, from online to in-person, have been successful. The studies have limitations, as it has yet to be determined what mindfulness activity is the most effective, nor have researchers discovered the ideal time frame for how long mindfulness interventions should last. Another limitation is that while mindfulness has been shown to decrease burnout, studies are needed to see if it produces joy in work.
Available for download on Friday, May 16, 2025
Included in
Educational Psychology Commons , Nursing Commons
- Collections
- Faculty Expert Gallery
- Theses and Dissertations
- Conferences and Events
- Open Educational Resources (OER)
- Explore Disciplines
Advanced Search
- Notify me via email or RSS .
Faculty Authors
- Submit Research
- Expert Gallery Login
Student Authors
- Undergraduate Submissions
- Graduate Submissions
- Honors Submissions
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Implementing evidence into practice requires nurses to identify, critically appraise and synthesise research. This may require a comprehensive literature review: this article aims to outline the approaches and stages required and provides a working example of a published review. Literature reviews aim to answer focused questions to: inform professionals and patients of the best available ...
Review articles (secondary sources) Use to identify literature on your topic, the way you would use a bibliography. Then locate and retrieve the original studies discussed in the review article. Review articles are considered secondary sources. Additional search tips. Ancestry searching or backward citation searching.
A literature review is a comprehensive and up-to-date overview of published information on a subject area. Conducting a literature review demands a careful examination of a body of literature that has been published that helps answer your research question (See PICO). Literature reviewed includes scholarly journals, scholarly books ...
Background. A literature review is a critical analysis of published research literature based on a specified topic (Pluye et al., 2016).Literature reviews identify literature then examine its strengths and weaknesses to determine gaps in knowledge (Pluye et al. 2016).Literature reviews are an integral aspect of research projects; indeed, many reviews constitute a publication in themselves ...
Literature Review Steps. Graphic used with permission: Torres, E. Librarian, Hawai'i Pacific University. 1. Choose a topic and define your research question. Try to choose a topic of interest. You will be working with this subject for several weeks to months.
Reviewing the literature Joanna Smith,1 Helen Noble2 Implementing evidence into practice requires nurses to identify, critically appraise and synthesise research. This may require a comprehensive literature review: this article aims to outline the approaches and stages required and provides a working example of a published review.
A literature review is a systematic review of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature review is designed to analyze—not just summarize—scholarly writings that are related directly to your research question. ... Tags: cinahl, College of Nursing, dnp, doctor of nursing practice, ebp, education ...
A literature review provides an overview of previous research on a topic that critically evaluates, classifies, and compares what has already been published on a particular topic. It allows the author to synthesize and place into context the research and scholarly literature relevant to the topic. It helps map the different approaches to a ...
Abstract. Systematic reviews provide a synthesis of evidence for a specific topic of interest, summarising the results of multiple studies to aid in clinical decisions and resource allocation. They remain among the best forms of evidence, and reduce the bias inherent in other methods. A solid understanding of the systematic review process can ...
This led us to undertake a review of current practice of those doing a literature review and the terms used to describe them. We undertook a focused mapping review and synthesis. Literature reviews; defined as papers with the terms review or synthesis in the title, published in five nursing journals between January 2017-June 2018 were identified.
Literature Review & Systematic Review Steps. Develop a Focused Question; Scope the Literature (Initial Search) Refine & Expand the Search; ... Asking the Clinical Question, AJN The American Journal of Nursing: March 2010 - Volume 110 - Issue 3 - p 58-61 doi: 10.1097/01.NAJ.0000368959.11129.79 ...
Literature Reviews for Education and Nursing Graduate Students is an open textbook designed for students in graduate-level nursing and education programs. Its intent is to recognize the significant role the literature review plays in the research process and to prepare students for the work that goes into writing one. Developed for new graduate students and novice researchers just entering ...
A literature review is an essay that surveys, summarizes, links together, and assesses research in a given field. It surveys the literature by reviewing a large body of work on a subject; it summarizes by noting the main conclusions and findings of the research; it links together works in the literature by showing how the information fits into the overall academic discussion and how the ...
Literature reviews for education and nursing students. This open textbook is designed for students in graduate-level nursing and education programs. From developing a research question to locating and evaluating sources to writing a sample literature review using appropriate publication guidelines, readers will be guided through the process.
The most prevalent one is the "literature review" or "background" section within a journal paper or a chapter in a graduate thesis. ... Kirkevold M. Integrative nursing research — an important strategy to further the development of nursing science and nursing practice. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 1997; 25 (5):977-984.
The literature review is a vital part of medical education research and should occur throughout the research process to help researchers design a strong study and effectively communicate study results and importance. To achieve these goals, researchers are advised to plan and execute the literature review carefully.
Step 1: reflecting on practice and identifying areas of uncertainty. Step 2: translating these areas of uncertainty into focused, searchable questions 2. Step 3: searching the literature for studies that use appropriate designs to help answer the question 3-6. Step 4: critically appraising the research. Step 5: changing practice if the ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
A literature review provides an overview of what's been written about a specific topic. There are many different types of literature reviews. They vary in terms of comprehensiveness, types of study included, and purpose. Grant, M.J., & Booth, A. (2009). A typology of reviews: An analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies.
A literature review is NOT an academic research paper, an annotated bibliography, or a report on original research. Unlike an academic research paper, the main focus of a literature review is not to develop a new argument. A literature review is an overview of a topic that shows the reader what research has been done on that subject.A literature review may build on an annotated bibliography ...
In this quick 11 minute video, Dr Zina O'Leary explains the misconceptions and struggles students often have with writing a literature review. She also provides step-by-step guidance on writing a persuasive literature review. This open textbook is designed for students in graduate-level nursing and education programs.
Identifying a well-defined research question is the first step in the literature review process. For undergraduates, professors will often assign a broad topic for a literature review assignment. You will need to more narrowly define your question before you can begin the research process.
Review of the literature identified that no existing survey was available for use with nursing students in the Canadian context. However, an analysis of themes across qualitative and quantitative studies of physicians, medical students, nurses, and nursing students provided sufficient data to develop a preliminary set of items suitable for ...
The purpose of a review of healthcare literature is primarily to summarise the knowledge around a specific question or topic, or to make recommendations that can support health professionals and organisations make decisions about a specific intervention or care issue.5 In addition, reviews can highlight gaps in knowledge to guide future research.
Methods This systematic literature review and meta-analysis investigated the effects of simulation-based interventions on enhancing empathy among nursing students. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines were used for the systematic review and meta-analysis.
In this scoping review, four of the included studies provided definitions of competence [9,34,35,36] and these varied based on the extensive literature review, Nehrir et al. (2016) stated that nursing students' competency is ''the individual experiences, dynamic process, and positive interactive social and beneficial changes in the ...
To date, however, professional resilience is not well defined in the nursing literature. Jafarianamiri, Qalehsari, and Zabihi ... This software removes duplicates automatically and tracks actions needed to complete a review of the literature (Levac et al., Citation 2010). Titles and abstracts were scanned independently by one author [EB ...
This integrative review aims to evaluate whether mindfulness effectively increases joy in work and decreases nursing burnout. A lack of joy leads to feelings of burnout and negatively affects nurses and their desire to leave the profession. Nursing is often accompanied by intense emotional and physical demands that can lead to job dissatisfaction, anxiety, and stress. Burnout diminishes the ...