
What (Exactly) Is A Research Proposal?
A simple explainer with examples + free template.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020 (Updated April 2023)
Whether you’re nearing the end of your degree and your dissertation is on the horizon, or you’re planning to apply for a PhD program, chances are you’ll need to craft a convincing research proposal . If you’re on this page, you’re probably unsure exactly what the research proposal is all about. Well, you’ve come to the right place.
Overview: Research Proposal Basics
- What a research proposal is
- What a research proposal needs to cover
- How to structure your research proposal
- Example /sample proposals
- Proposal writing FAQs
- Key takeaways & additional resources
What is a research proposal?
Simply put, a research proposal is a structured, formal document that explains what you plan to research (your research topic), why it’s worth researching (your justification), and how you plan to investigate it (your methodology).
The purpose of the research proposal (its job, so to speak) is to convince your research supervisor, committee or university that your research is suitable (for the requirements of the degree program) and manageable (given the time and resource constraints you will face).
The most important word here is “ convince ” – in other words, your research proposal needs to sell your research idea (to whoever is going to approve it). If it doesn’t convince them (of its suitability and manageability), you’ll need to revise and resubmit . This will cost you valuable time, which will either delay the start of your research or eat into its time allowance (which is bad news).

What goes into a research proposal?
A good dissertation or thesis proposal needs to cover the “ what “, “ why ” and” how ” of the proposed study. Let’s look at each of these attributes in a little more detail:
Your proposal needs to clearly articulate your research topic . This needs to be specific and unambiguous . Your research topic should make it clear exactly what you plan to research and in what context. Here’s an example of a well-articulated research topic:
An investigation into the factors which impact female Generation Y consumer’s likelihood to promote a specific makeup brand to their peers: a British context
As you can see, this topic is extremely clear. From this one line we can see exactly:
- What’s being investigated – factors that make people promote or advocate for a brand of a specific makeup brand
- Who it involves – female Gen-Y consumers
- In what context – the United Kingdom
So, make sure that your research proposal provides a detailed explanation of your research topic . If possible, also briefly outline your research aims and objectives , and perhaps even your research questions (although in some cases you’ll only develop these at a later stage). Needless to say, don’t start writing your proposal until you have a clear topic in mind , or you’ll end up waffling and your research proposal will suffer as a result of this.
Need a helping hand?
As we touched on earlier, it’s not good enough to simply propose a research topic – you need to justify why your topic is original . In other words, what makes it unique ? What gap in the current literature does it fill? If it’s simply a rehash of the existing research, it’s probably not going to get approval – it needs to be fresh.
But, originality alone is not enough. Once you’ve ticked that box, you also need to justify why your proposed topic is important . In other words, what value will it add to the world if you achieve your research aims?
As an example, let’s look at the sample research topic we mentioned earlier (factors impacting brand advocacy). In this case, if the research could uncover relevant factors, these findings would be very useful to marketers in the cosmetics industry, and would, therefore, have commercial value . That is a clear justification for the research.
So, when you’re crafting your research proposal, remember that it’s not enough for a topic to simply be unique. It needs to be useful and value-creating – and you need to convey that value in your proposal. If you’re struggling to find a research topic that makes the cut, watch our video covering how to find a research topic .

It’s all good and well to have a great topic that’s original and valuable, but you’re not going to convince anyone to approve it without discussing the practicalities – in other words:
- How will you actually undertake your research (i.e., your methodology)?
- Is your research methodology appropriate given your research aims?
- Is your approach manageable given your constraints (time, money, etc.)?
While it’s generally not expected that you’ll have a fully fleshed-out methodology at the proposal stage, you’ll likely still need to provide a high-level overview of your research methodology . Here are some important questions you’ll need to address in your research proposal:
- Will you take a qualitative , quantitative or mixed -method approach?
- What sampling strategy will you adopt?
- How will you collect your data (e.g., interviews, surveys, etc)?
- How will you analyse your data (e.g., descriptive and inferential statistics , content analysis, discourse analysis, etc, .)?
- What potential limitations will your methodology carry?
So, be sure to give some thought to the practicalities of your research and have at least a basic methodological plan before you start writing up your proposal. If this all sounds rather intimidating, the video below provides a good introduction to research methodology and the key choices you’ll need to make.
How To Structure A Research Proposal
Now that we’ve covered the key points that need to be addressed in a proposal, you may be wondering, “ But how is a research proposal structured? “.
While the exact structure and format required for a research proposal differs from university to university, there are four “essential ingredients” that commonly make up the structure of a research proposal:
- A rich introduction and background to the proposed research
- An initial literature review covering the existing research
- An overview of the proposed research methodology
- A discussion regarding the practicalities (project plans, timelines, etc.)
In the video below, we unpack each of these four sections, step by step.
Research Proposal Examples/Samples
In the video below, we provide a detailed walkthrough of two successful research proposals (Master’s and PhD-level), as well as our popular free proposal template.
Proposal Writing FAQs
How long should a research proposal be.
This varies tremendously, depending on the university, the field of study (e.g., social sciences vs natural sciences), and the level of the degree (e.g. undergraduate, Masters or PhD) – so it’s always best to check with your university what their specific requirements are before you start planning your proposal.
As a rough guide, a formal research proposal at Masters-level often ranges between 2000-3000 words, while a PhD-level proposal can be far more detailed, ranging from 5000-8000 words. In some cases, a rough outline of the topic is all that’s needed, while in other cases, universities expect a very detailed proposal that essentially forms the first three chapters of the dissertation or thesis.
The takeaway – be sure to check with your institution before you start writing.
How do I choose a topic for my research proposal?
Finding a good research topic is a process that involves multiple steps. We cover the topic ideation process in this video post.
How do I write a literature review for my proposal?
While you typically won’t need a comprehensive literature review at the proposal stage, you still need to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the key literature and are able to synthesise it. We explain the literature review process here.
How do I create a timeline and budget for my proposal?
We explain how to craft a project plan/timeline and budget in Research Proposal Bootcamp .
Which referencing format should I use in my research proposal?
The expectations and requirements regarding formatting and referencing vary from institution to institution. Therefore, you’ll need to check this information with your university.
What common proposal writing mistakes do I need to look out for?
We’ve create a video post about some of the most common mistakes students make when writing a proposal – you can access that here . If you’re short on time, here’s a quick summary:
- The research topic is too broad (or just poorly articulated).
- The research aims, objectives and questions don’t align.
- The research topic is not well justified.
- The study has a weak theoretical foundation.
- The research design is not well articulated well enough.
- Poor writing and sloppy presentation.
- Poor project planning and risk management.
- Not following the university’s specific criteria.
Key Takeaways & Additional Resources
As you write up your research proposal, remember the all-important core purpose: to convince . Your research proposal needs to sell your study in terms of suitability and viability. So, focus on crafting a convincing narrative to ensure a strong proposal.
At the same time, pay close attention to your university’s requirements. While we’ve covered the essentials here, every institution has its own set of expectations and it’s essential that you follow these to maximise your chances of approval.
By the way, we’ve got plenty more resources to help you fast-track your research proposal. Here are some of our most popular resources to get you started:
- Proposal Writing 101 : A Introductory Webinar
- Research Proposal Bootcamp : The Ultimate Online Course
- Template : A basic template to help you craft your proposal
If you’re looking for 1-on-1 support with your research proposal, be sure to check out our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the proposal development process (and the entire research journey), step by step.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

51 Comments
I truly enjoyed this video, as it was eye-opening to what I have to do in the preparation of preparing a Research proposal.
I would be interested in getting some coaching.
I real appreciate on your elaboration on how to develop research proposal,the video explains each steps clearly.
Thank you for the video. It really assisted me and my niece. I am a PhD candidate and she is an undergraduate student. It is at times, very difficult to guide a family member but with this video, my job is done.
In view of the above, I welcome more coaching.
Wonderful guidelines, thanks
This is very helpful. Would love to continue even as I prepare for starting my masters next year.
Thanks for the work done, the text was helpful to me
Bundle of thanks to you for the research proposal guide it was really good and useful if it is possible please send me the sample of research proposal
You’re most welcome. We don’t have any research proposals that we can share (the students own the intellectual property), but you might find our research proposal template useful: https://gradcoach.com/research-proposal-template/
Cheruiyot Moses Kipyegon
Thanks alot. It was an eye opener that came timely enough before my imminent proposal defense. Thanks, again
thank you very much your lesson is very interested may God be with you
I am an undergraduate student (First Degree) preparing to write my project,this video and explanation had shed more light to me thanks for your efforts keep it up.
Very useful. I am grateful.
this is a very a good guidance on research proposal, for sure i have learnt something
Wonderful guidelines for writing a research proposal, I am a student of m.phil( education), this guideline is suitable for me. Thanks
You’re welcome 🙂
Thank you, this was so helpful.
A really great and insightful video. It opened my eyes as to how to write a research paper. I would like to receive more guidance for writing my research paper from your esteemed faculty.
Thank you, great insights
Thank you, great insights, thank you so much, feeling edified
Wow thank you, great insights, thanks a lot
Thank you. This is a great insight. I am a student preparing for a PhD program. I am requested to write my Research Proposal as part of what I am required to submit before my unconditional admission. I am grateful having listened to this video which will go a long way in helping me to actually choose a topic of interest and not just any topic as well as to narrow down the topic and be specific about it. I indeed need more of this especially as am trying to choose a topic suitable for a DBA am about embarking on. Thank you once more. The video is indeed helpful.
Have learnt a lot just at the right time. Thank you so much.
thank you very much ,because have learn a lot things concerning research proposal and be blessed u for your time that you providing to help us
Hi. For my MSc medical education research, please evaluate this topic for me: Training Needs Assessment of Faculty in Medical Training Institutions in Kericho and Bomet Counties
I have really learnt a lot based on research proposal and it’s formulation
Thank you. I learn much from the proposal since it is applied
Your effort is much appreciated – you have good articulation.
You have good articulation.
I do applaud your simplified method of explaining the subject matter, which indeed has broaden my understanding of the subject matter. Definitely this would enable me writing a sellable research proposal.
This really helping
Great! I liked your tutoring on how to find a research topic and how to write a research proposal. Precise and concise. Thank you very much. Will certainly share this with my students. Research made simple indeed.
Thank you very much. I an now assist my students effectively.
Thank you very much. I can now assist my students effectively.
I need any research proposal
Thank you for these videos. I will need chapter by chapter assistance in writing my MSc dissertation
Very helpfull
the videos are very good and straight forward
thanks so much for this wonderful presentations, i really enjoyed it to the fullest wish to learn more from you
Thank you very much. I learned a lot from your lecture.
I really enjoy the in-depth knowledge on research proposal you have given. me. You have indeed broaden my understanding and skills. Thank you
interesting session this has equipped me with knowledge as i head for exams in an hour’s time, am sure i get A++
This article was most informative and easy to understand. I now have a good idea of how to write my research proposal.
Thank you very much.
Wow, this literature is very resourceful and interesting to read. I enjoyed it and I intend reading it every now then.
Thank you for the clarity
Thank you. Very helpful.
Thank you very much for this essential piece. I need 1o1 coaching, unfortunately, your service is not available in my country. Anyways, a very important eye-opener. I really enjoyed it. A thumb up to Gradcoach
What is JAM? Please explain.
Thank you so much for these videos. They are extremely helpful! God bless!
very very wonderful…
thank you for the video but i need a written example
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
How to write a good research proposal (in 9 steps)
A good research proposal is one of the keys to academic success. For bachelor’s and master’s students, the quality of a research proposal often determines whether the master’s program= can be completed or not. For PhD students, a research proposal is often the first step to securing a university position. This step-by-step manual guides you through the main stages of proposal writing.
Disclosure: This post may contain affiliate links, which means I may earn a small commission if you make a purchase using the links below at no additional cost to you . I only recommend products or services that I truly believe can benefit my audience. As always, my opinions are my own.
1. Find a topic for your research proposal
2. develop your research idea, 3. conduct a literature review for your research proposal, 4. define a research gap and research question, 5. establish a theoretical framework for your research proposal, 6. specify an empirical focus for your research proposal, 7. emphasise the scientific and societal relevance of your research proposal, 8. develop a methodology in your research proposal, 9. illustrate your research timeline in your research proposal.
Finding a topic for your research is a crucial first step. This decision should not be treated lightly.
Writing a master’s thesis takes a minimum of several weeks. In the case of PhD dissertations, it takes years. That is a long time! You don’t want to be stuck with a topic that you don’t care about.
How to find a research topic? Start broadly: Which courses did you enjoy? What issues discussed during seminars or lectures did you like? What inspired you during your education? And which readings did you appreciate?
Take a blank piece of paper. Write down everything that comes to your mind. It will help you to reflect on your interests.
Then, think more strategically. Maybe you have a rough idea of where you would like to work after graduation. Maybe a specific sector. Or even a particular company. If so, you could strategically alight your thesis topic with an issue that matters to your dream employer. Or even ask for a thesis internship.
Once you pinpoint your general topic of interest, you need to develop your idea.
Your idea should be simultaneously original, make a scientific contribution, prepare you for the (academic) job market, and be academically sound.
Freaking out yet?! Take a deep breath.
First, keep in mind that your idea should be very focused. Master and PhD students are often too ambitious. Your time is limited. So you need to be pragmatic. It is better to make a valuable contribution to a very specific question than to aim high and fail to meet your objectives.
Second, writing a research proposal is not a linear process. Start slowly by reading literature about your topic of interest. You have an interest. You read. You rethink your idea. You look for a theoretical framework. You go back to your idea and refine it. It is a process.
Remember that a good research proposal is not written in a day.
And third, don’t forget: a good proposal aims to establish a convincing framework that will guide your future research. Not to provide all the answers already. You need to show that you have a feasible idea.

If you are looking to elevate your writing and editing skills, I highly recommend enrolling in the course “ Good with Words: Writing and Editing Specialization “, which is a 4 course series offered by the University of Michigan. This comprehensive program is conveniently available as an online course on Coursera, allowing you to learn at your own pace. Plus, upon successful completion, you’ll have the opportunity to earn a valuable certificate to showcase your newfound expertise!
Academic publications (journal articles and books) are the foundation of any research. Thus, academic literature is a good place to start. Especially when you still feel kind of lost regarding a focused research topic.
Type keywords reflecting your interests, or your preliminary research idea, into an academic search engine. It can be your university’s library, Google Scholar , Web of Science , or Scopus . etcetera.
Look at what has been published in the last 5 years, not before. You don’t want to be outdated.
Download interesting-sounding articles and read them. Repeat but be cautious: You will never be able to read EVERYTHING. So set yourself a limit, in hours, days or number of articles (20 articles, for instance).
Now, write down your findings. What is known about your topic of interest? What do scholars focus on? Start early by writing down your findings and impressions.
Once you read academic publications on your topic of interest, ask yourself questions such as:
- Is there one specific aspect of your topic of interest that is neglected in the existing literature?
- What do scholars write about the existing gaps on the topic? What are their suggestions for future research?
- Is there anything that YOU believe warrants more attention?
- Do scholars maybe analyze a phenomenon only in a specific type of setting?
Asking yourself these questions helps you to formulate your research question. In your research question, be as specific as possible.
And keep in mind that you need to research something that already exists. You cannot research how something develops 20 years into the future.

A theoretical framework is different from a literature review. You need to establish a framework of theories as a lens to look at your research topic, and answer your research question.
A theory is a general principle to explain certain phenomena. No need to reinvent the wheel here.
It is not only accepted but often encouraged to make use of existing theories. Or maybe you can combine two different theories to establish your framework.
It also helps to go back to the literature. Which theories did the authors of your favourite publications use?
There are only very few master’s and PhD theses that are entirely theoretical. Most theses, similar to most academic journal publications, have an empirical section.
You need to think about your empirical focus. Where can you find answers to your research question in real life? This could be, for instance, an experiment, a case study, or repeated observations of certain interactions.
Maybe your empirical investigation will have geographic boundaries (like focusing on one city, or one country). Or maybe it focuses on one group of people (such as the elderly, CEOs, doctors, you name it).
It is also possible to start the whole research proposal idea with empirical observation. Maybe you’ve come across something in your environment that you would like to investigate further.
Pinpoint what fascinates you about your observation. Write down keywords reflecting your interest. And then conduct a literature review to understand how others have approached this topic academically.
Both master’s and PhD students are expected to make a scientific contribution. A concrete gap or shortcoming in the existing literature on your topic is the easiest way to justify the scientific relevance of your proposed research.
Societal relevance is increasingly important in academia, too.
Do the grandparent test: Explain what you want to do to your grandparents (or any other person for that matter). Explain why it matters. Do your grandparents understand what you say? If so, well done. If not, try again.
Always remember. There is no need for fancy jargon. The best proposals are the ones that use clear, straightforward language.
The methodology is a system of methods that you will use to implement your research. A methodology explains how you plan to answer your research question.
A methodology involves for example methods of data collection. For example, interviews and questionnaires to gather ‘raw’ data.
Methods of data analysis are used to make sense of this data. This can be done, for instance, by coding, discourse analysis, mapping or statistical analysis.
Don’t underestimate the value of a good timeline. Inevitably throughout your thesis process, you will feel lost at some point. A good timeline will bring you back on track.
Make sure to include a timeline in your research proposal. If possible, not only describe your timeline but add a visual illustration, for instance in the form of a Gantt chart.
Master Academia
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox.
Subscribe and receive Master Academia's quarterly newsletter.
PhD thesis types: Monograph and collection of articles
Ten reasons not to pursue an academic career, related articles.

How to address data privacy and confidentiality concerns of AI in research

How to properly use AI in academic research

The best online courses for PhD researchers in 2024

Why and how to conduct a systematic literature review
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business How to Write a Research Proposal: A Step-by-Step
How to Write a Research Proposal: A Step-by-Step
Written by: Danesh Ramuthi Nov 29, 2023

A research proposal is a structured outline for a planned study on a specific topic. It serves as a roadmap, guiding researchers through the process of converting their research idea into a feasible project.
The aim of a research proposal is multifold: it articulates the research problem, establishes a theoretical framework, outlines the research methodology and highlights the potential significance of the study. Importantly, it’s a critical tool for scholars seeking grant funding or approval for their research projects.
Crafting a good research proposal requires not only understanding your research topic and methodological approaches but also the ability to present your ideas clearly and persuasively. Explore Venngage’s Proposal Maker and Research Proposals Templates to begin your journey in writing a compelling research proposal.
What to include in a research proposal?
In a research proposal, include a clear statement of your research question or problem, along with an explanation of its significance. This should be followed by a literature review that situates your proposed study within the context of existing research.
Your proposal should also outline the research methodology, detailing how you plan to conduct your study, including data collection and analysis methods.
Additionally, include a theoretical framework that guides your research approach, a timeline or research schedule, and a budget if applicable. It’s important to also address the anticipated outcomes and potential implications of your study. A well-structured research proposal will clearly communicate your research objectives, methods and significance to the readers.

How to format a research proposal?
Formatting a research proposal involves adhering to a structured outline to ensure clarity and coherence. While specific requirements may vary, a standard research proposal typically includes the following elements:
- Title Page: Must include the title of your research proposal, your name and affiliations. The title should be concise and descriptive of your proposed research.
- Abstract: A brief summary of your proposal, usually not exceeding 250 words. It should highlight the research question, methodology and the potential impact of the study.
- Introduction: Introduces your research question or problem, explains its significance, and states the objectives of your study.
- Literature review: Here, you contextualize your research within existing scholarship, demonstrating your knowledge of the field and how your research will contribute to it.
- Methodology: Outline your research methods, including how you will collect and analyze data. This section should be detailed enough to show the feasibility and thoughtfulness of your approach.
- Timeline: Provide an estimated schedule for your research, breaking down the process into stages with a realistic timeline for each.
- Budget (if applicable): If your research requires funding, include a detailed budget outlining expected cost.
- References/Bibliography: List all sources referenced in your proposal in a consistent citation style.

How to write a research proposal in 11 steps?
Writing a research proposal template in structured steps ensures a comprehensive and coherent presentation of your research project. Let’s look at the explanation for each of the steps here:
Step 1: Title and Abstract Step 2: Introduction Step 3: Research objectives Step 4: Literature review Step 5: Methodology Step 6: Timeline Step 7: Resources Step 8: Ethical considerations Step 9: Expected outcomes and significance Step 10: References Step 11: Appendices
Step 1: title and abstract.
Select a concise, descriptive title and write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology and expected outcomes. The abstract should include your research question, the objectives you aim to achieve, the methodology you plan to employ and the anticipated outcomes.
Step 2: Introduction
In this section, introduce the topic of your research, emphasizing its significance and relevance to the field. Articulate the research problem or question in clear terms and provide background context, which should include an overview of previous research in the field.
Step 3: Research objectives
Here, you’ll need to outline specific, clear and achievable objectives that align with your research problem. These objectives should be well-defined, focused and measurable, serving as the guiding pillars for your study. They help in establishing what you intend to accomplish through your research and provide a clear direction for your investigation.
Step 4: Literature review
In this part, conduct a thorough review of existing literature related to your research topic. This involves a detailed summary of key findings and major contributions from previous research. Identify existing gaps in the literature and articulate how your research aims to fill these gaps. The literature review not only shows your grasp of the subject matter but also how your research will contribute new insights or perspectives to the field.
Step 5: Methodology
Describe the design of your research and the methodologies you will employ. This should include detailed information on data collection methods, instruments to be used and analysis techniques. Justify the appropriateness of these methods for your research.
Step 6: Timeline
Construct a detailed timeline that maps out the major milestones and activities of your research project. Break the entire research process into smaller, manageable tasks and assign realistic time frames to each. This timeline should cover everything from the initial research phase to the final submission, including periods for data collection, analysis and report writing.
It helps in ensuring your project stays on track and demonstrates to reviewers that you have a well-thought-out plan for completing your research efficiently.
Step 7: Resources
Identify all the resources that will be required for your research, such as specific databases, laboratory equipment, software or funding. Provide details on how these resources will be accessed or acquired.
If your research requires funding, explain how it will be utilized effectively to support various aspects of the project.
Step 8: Ethical considerations
Address any ethical issues that may arise during your research. This is particularly important for research involving human subjects. Describe the measures you will take to ensure ethical standards are maintained, such as obtaining informed consent, ensuring participant privacy, and adhering to data protection regulations.
Here, in this section you should reassure reviewers that you are committed to conducting your research responsibly and ethically.
Step 9: Expected outcomes and significance
Articulate the expected outcomes or results of your research. Explain the potential impact and significance of these outcomes, whether in advancing academic knowledge, influencing policy or addressing specific societal or practical issues.
Step 10: References
Compile a comprehensive list of all the references cited in your proposal. Adhere to a consistent citation style (like APA or MLA) throughout your document. The reference section not only gives credit to the original authors of your sourced information but also strengthens the credibility of your proposal.
Step 11: Appendices
Include additional supporting materials that are pertinent to your research proposal. This can be survey questionnaires, interview guides, detailed data analysis plans or any supplementary information that supports the main text.
Appendices provide further depth to your proposal, showcasing the thoroughness of your preparation.

Research proposal FAQs
1. how long should a research proposal be.
The length of a research proposal can vary depending on the requirements of the academic institution, funding body or specific guidelines provided. Generally, research proposals range from 500 to 1500 words or about one to a few pages long. It’s important to provide enough detail to clearly convey your research idea, objectives and methodology, while being concise. Always check
2. Why is the research plan pivotal to a research project?
The research plan is pivotal to a research project because it acts as a blueprint, guiding every phase of the study. It outlines the objectives, methodology, timeline and expected outcomes, providing a structured approach and ensuring that the research is systematically conducted.
A well-crafted plan helps in identifying potential challenges, allocating resources efficiently and maintaining focus on the research goals. It is also essential for communicating the project’s feasibility and importance to stakeholders, such as funding bodies or academic supervisors.

Mastering how to write a research proposal is an essential skill for any scholar, whether in social and behavioral sciences, academic writing or any field requiring scholarly research. From this article, you have learned key components, from the literature review to the research design, helping you develop a persuasive and well-structured proposal.
Remember, a good research proposal not only highlights your proposed research and methodology but also demonstrates its relevance and potential impact.
For additional support, consider utilizing Venngage’s Proposal Maker and Research Proposals Templates , valuable tools in crafting a compelling proposal that stands out.
Whether it’s for grant funding, a research paper or a dissertation proposal, these resources can assist in transforming your research idea into a successful submission.
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Theoretical Framework
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
Theories are formulated to explain, predict, and understand phenomena and, in many cases, to challenge and extend existing knowledge within the limits of critical bounded assumptions or predictions of behavior. The theoretical framework is the structure that can hold or support a theory of a research study. The theoretical framework encompasses not just the theory, but the narrative explanation about how the researcher engages in using the theory and its underlying assumptions to investigate the research problem. It is the structure of your paper that summarizes concepts, ideas, and theories derived from prior research studies and which was synthesized in order to form a conceptual basis for your analysis and interpretation of meaning found within your research.
Abend, Gabriel. "The Meaning of Theory." Sociological Theory 26 (June 2008): 173–199; Kivunja, Charles. "Distinguishing between Theory, Theoretical Framework, and Conceptual Framework: A Systematic Review of Lessons from the Field." International Journal of Higher Education 7 (December 2018): 44-53; Swanson, Richard A. Theory Building in Applied Disciplines . San Francisco, CA: Berrett-Koehler Publishers 2013; Varpio, Lara, Elise Paradis, Sebastian Uijtdehaage, and Meredith Young. "The Distinctions between Theory, Theoretical Framework, and Conceptual Framework." Academic Medicine 95 (July 2020): 989-994.
Importance of Theory and a Theoretical Framework
Theories can be unfamiliar to the beginning researcher because they are rarely applied in high school social studies curriculum and, as a result, can come across as unfamiliar and imprecise when first introduced as part of a writing assignment. However, in their most simplified form, a theory is simply a set of assumptions or predictions about something you think will happen based on existing evidence and that can be tested to see if those outcomes turn out to be true. Of course, it is slightly more deliberate than that, therefore, summarized from Kivunja (2018, p. 46), here are the essential characteristics of a theory.
- It is logical and coherent
- It has clear definitions of terms or variables, and has boundary conditions [i.e., it is not an open-ended statement]
- It has a domain where it applies
- It has clearly described relationships among variables
- It describes, explains, and makes specific predictions
- It comprises of concepts, themes, principles, and constructs
- It must have been based on empirical data [i.e., it is not a guess]
- It must have made claims that are subject to testing, been tested and verified
- It must be clear and concise
- Its assertions or predictions must be different and better than those in existing theories
- Its predictions must be general enough to be applicable to and understood within multiple contexts
- Its assertions or predictions are relevant, and if applied as predicted, will result in the predicted outcome
- The assertions and predictions are not immutable, but subject to revision and improvement as researchers use the theory to make sense of phenomena
- Its concepts and principles explain what is going on and why
- Its concepts and principles are substantive enough to enable us to predict a future
Given these characteristics, a theory can best be understood as the foundation from which you investigate assumptions or predictions derived from previous studies about the research problem, but in a way that leads to new knowledge and understanding as well as, in some cases, discovering how to improve the relevance of the theory itself or to argue that the theory is outdated and a new theory needs to be formulated based on new evidence.
A theoretical framework consists of concepts and, together with their definitions and reference to relevant scholarly literature, existing theory that is used for your particular study. The theoretical framework must demonstrate an understanding of theories and concepts that are relevant to the topic of your research paper and that relate to the broader areas of knowledge being considered.
The theoretical framework is most often not something readily found within the literature . You must review course readings and pertinent research studies for theories and analytic models that are relevant to the research problem you are investigating. The selection of a theory should depend on its appropriateness, ease of application, and explanatory power.
The theoretical framework strengthens the study in the following ways :
- An explicit statement of theoretical assumptions permits the reader to evaluate them critically.
- The theoretical framework connects the researcher to existing knowledge. Guided by a relevant theory, you are given a basis for your hypotheses and choice of research methods.
- Articulating the theoretical assumptions of a research study forces you to address questions of why and how. It permits you to intellectually transition from simply describing a phenomenon you have observed to generalizing about various aspects of that phenomenon.
- Having a theory helps you identify the limits to those generalizations. A theoretical framework specifies which key variables influence a phenomenon of interest and highlights the need to examine how those key variables might differ and under what circumstances.
- The theoretical framework adds context around the theory itself based on how scholars had previously tested the theory in relation their overall research design [i.e., purpose of the study, methods of collecting data or information, methods of analysis, the time frame in which information is collected, study setting, and the methodological strategy used to conduct the research].
By virtue of its applicative nature, good theory in the social sciences is of value precisely because it fulfills one primary purpose: to explain the meaning, nature, and challenges associated with a phenomenon, often experienced but unexplained in the world in which we live, so that we may use that knowledge and understanding to act in more informed and effective ways.
The Conceptual Framework. College of Education. Alabama State University; Corvellec, Hervé, ed. What is Theory?: Answers from the Social and Cultural Sciences . Stockholm: Copenhagen Business School Press, 2013; Asher, Herbert B. Theory-Building and Data Analysis in the Social Sciences . Knoxville, TN: University of Tennessee Press, 1984; Drafting an Argument. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Kivunja, Charles. "Distinguishing between Theory, Theoretical Framework, and Conceptual Framework: A Systematic Review of Lessons from the Field." International Journal of Higher Education 7 (2018): 44-53; Omodan, Bunmi Isaiah. "A Model for Selecting Theoretical Framework through Epistemology of Research Paradigms." African Journal of Inter/Multidisciplinary Studies 4 (2022): 275-285; Ravitch, Sharon M. and Matthew Riggan. Reason and Rigor: How Conceptual Frameworks Guide Research . Second edition. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2017; Trochim, William M.K. Philosophy of Research. Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006; Jarvis, Peter. The Practitioner-Researcher. Developing Theory from Practice . San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 1999.
Strategies for Developing the Theoretical Framework
I. Developing the Framework
Here are some strategies to develop of an effective theoretical framework:
- Examine your thesis title and research problem . The research problem anchors your entire study and forms the basis from which you construct your theoretical framework.
- Brainstorm about what you consider to be the key variables in your research . Answer the question, "What factors contribute to the presumed effect?"
- Review related literature to find how scholars have addressed your research problem. Identify the assumptions from which the author(s) addressed the problem.
- List the constructs and variables that might be relevant to your study. Group these variables into independent and dependent categories.
- Review key social science theories that are introduced to you in your course readings and choose the theory that can best explain the relationships between the key variables in your study [note the Writing Tip on this page].
- Discuss the assumptions or propositions of this theory and point out their relevance to your research.
A theoretical framework is used to limit the scope of the relevant data by focusing on specific variables and defining the specific viewpoint [framework] that the researcher will take in analyzing and interpreting the data to be gathered. It also facilitates the understanding of concepts and variables according to given definitions and builds new knowledge by validating or challenging theoretical assumptions.
II. Purpose
Think of theories as the conceptual basis for understanding, analyzing, and designing ways to investigate relationships within social systems. To that end, the following roles served by a theory can help guide the development of your framework.
- Means by which new research data can be interpreted and coded for future use,
- Response to new problems that have no previously identified solutions strategy,
- Means for identifying and defining research problems,
- Means for prescribing or evaluating solutions to research problems,
- Ways of discerning certain facts among the accumulated knowledge that are important and which facts are not,
- Means of giving old data new interpretations and new meaning,
- Means by which to identify important new issues and prescribe the most critical research questions that need to be answered to maximize understanding of the issue,
- Means of providing members of a professional discipline with a common language and a frame of reference for defining the boundaries of their profession, and
- Means to guide and inform research so that it can, in turn, guide research efforts and improve professional practice.
Adapted from: Torraco, R. J. “Theory-Building Research Methods.” In Swanson R. A. and E. F. Holton III , editors. Human Resource Development Handbook: Linking Research and Practice . (San Francisco, CA: Berrett-Koehler, 1997): pp. 114-137; Jacard, James and Jacob Jacoby. Theory Construction and Model-Building Skills: A Practical Guide for Social Scientists . New York: Guilford, 2010; Ravitch, Sharon M. and Matthew Riggan. Reason and Rigor: How Conceptual Frameworks Guide Research . Second edition. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2017; Sutton, Robert I. and Barry M. Staw. “What Theory is Not.” Administrative Science Quarterly 40 (September 1995): 371-384.
Structure and Writing Style
The theoretical framework may be rooted in a specific theory , in which case, your work is expected to test the validity of that existing theory in relation to specific events, issues, or phenomena. Many social science research papers fit into this rubric. For example, Peripheral Realism Theory, which categorizes perceived differences among nation-states as those that give orders, those that obey, and those that rebel, could be used as a means for understanding conflicted relationships among countries in Africa. A test of this theory could be the following: Does Peripheral Realism Theory help explain intra-state actions, such as, the disputed split between southern and northern Sudan that led to the creation of two nations?
However, you may not always be asked by your professor to test a specific theory in your paper, but to develop your own framework from which your analysis of the research problem is derived . Based upon the above example, it is perhaps easiest to understand the nature and function of a theoretical framework if it is viewed as an answer to two basic questions:
- What is the research problem/question? [e.g., "How should the individual and the state relate during periods of conflict?"]
- Why is your approach a feasible solution? [i.e., justify the application of your choice of a particular theory and explain why alternative constructs were rejected. I could choose instead to test Instrumentalist or Circumstantialists models developed among ethnic conflict theorists that rely upon socio-economic-political factors to explain individual-state relations and to apply this theoretical model to periods of war between nations].
The answers to these questions come from a thorough review of the literature and your course readings [summarized and analyzed in the next section of your paper] and the gaps in the research that emerge from the review process. With this in mind, a complete theoretical framework will likely not emerge until after you have completed a thorough review of the literature .
Just as a research problem in your paper requires contextualization and background information, a theory requires a framework for understanding its application to the topic being investigated. When writing and revising this part of your research paper, keep in mind the following:
- Clearly describe the framework, concepts, models, or specific theories that underpin your study . This includes noting who the key theorists are in the field who have conducted research on the problem you are investigating and, when necessary, the historical context that supports the formulation of that theory. This latter element is particularly important if the theory is relatively unknown or it is borrowed from another discipline.
- Position your theoretical framework within a broader context of related frameworks, concepts, models, or theories . As noted in the example above, there will likely be several concepts, theories, or models that can be used to help develop a framework for understanding the research problem. Therefore, note why the theory you've chosen is the appropriate one.
- The present tense is used when writing about theory. Although the past tense can be used to describe the history of a theory or the role of key theorists, the construction of your theoretical framework is happening now.
- You should make your theoretical assumptions as explicit as possible . Later, your discussion of methodology should be linked back to this theoretical framework.
- Don’t just take what the theory says as a given! Reality is never accurately represented in such a simplistic way; if you imply that it can be, you fundamentally distort a reader's ability to understand the findings that emerge. Given this, always note the limitations of the theoretical framework you've chosen [i.e., what parts of the research problem require further investigation because the theory inadequately explains a certain phenomena].
The Conceptual Framework. College of Education. Alabama State University; Conceptual Framework: What Do You Think is Going On? College of Engineering. University of Michigan; Drafting an Argument. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Lynham, Susan A. “The General Method of Theory-Building Research in Applied Disciplines.” Advances in Developing Human Resources 4 (August 2002): 221-241; Tavallaei, Mehdi and Mansor Abu Talib. "A General Perspective on the Role of Theory in Qualitative Research." Journal of International Social Research 3 (Spring 2010); Ravitch, Sharon M. and Matthew Riggan. Reason and Rigor: How Conceptual Frameworks Guide Research . Second edition. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2017; Reyes, Victoria. Demystifying the Journal Article. Inside Higher Education; Trochim, William M.K. Philosophy of Research. Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006; Weick, Karl E. “The Work of Theorizing.” In Theorizing in Social Science: The Context of Discovery . Richard Swedberg, editor. (Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press, 2014), pp. 177-194.
Writing Tip
Borrowing Theoretical Constructs from Other Disciplines
An increasingly important trend in the social and behavioral sciences is to think about and attempt to understand research problems from an interdisciplinary perspective. One way to do this is to not rely exclusively on the theories developed within your particular discipline, but to think about how an issue might be informed by theories developed in other disciplines. For example, if you are a political science student studying the rhetorical strategies used by female incumbents in state legislature campaigns, theories about the use of language could be derived, not only from political science, but linguistics, communication studies, philosophy, psychology, and, in this particular case, feminist studies. Building theoretical frameworks based on the postulates and hypotheses developed in other disciplinary contexts can be both enlightening and an effective way to be more engaged in the research topic.
CohenMiller, A. S. and P. Elizabeth Pate. "A Model for Developing Interdisciplinary Research Theoretical Frameworks." The Qualitative Researcher 24 (2019): 1211-1226; Frodeman, Robert. The Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity . New York: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Undertheorize!
Do not leave the theory hanging out there in the introduction never to be mentioned again. Undertheorizing weakens your paper. The theoretical framework you describe should guide your study throughout the paper. Be sure to always connect theory to the review of pertinent literature and to explain in the discussion part of your paper how the theoretical framework you chose supports analysis of the research problem or, if appropriate, how the theoretical framework was found to be inadequate in explaining the phenomenon you were investigating. In that case, don't be afraid to propose your own theory based on your findings.

Yet Another Writing Tip
What's a Theory? What's a Hypothesis?
The terms theory and hypothesis are often used interchangeably in newspapers and popular magazines and in non-academic settings. However, the difference between theory and hypothesis in scholarly research is important, particularly when using an experimental design. A theory is a well-established principle that has been developed to explain some aspect of the natural world. Theories arise from repeated observation and testing and incorporates facts, laws, predictions, and tested assumptions that are widely accepted [e.g., rational choice theory; grounded theory; critical race theory].
A hypothesis is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in your study. For example, an experiment designed to look at the relationship between study habits and test anxiety might have a hypothesis that states, "We predict that students with better study habits will suffer less test anxiety." Unless your study is exploratory in nature, your hypothesis should always explain what you expect to happen during the course of your research.
The key distinctions are:
- A theory predicts events in a broad, general context; a hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a specified set of circumstances.
- A theory has been extensively tested and is generally accepted among a set of scholars; a hypothesis is a speculative guess that has yet to be tested.
Cherry, Kendra. Introduction to Research Methods: Theory and Hypothesis. About.com Psychology; Gezae, Michael et al. Welcome Presentation on Hypothesis. Slideshare presentation.
Still Yet Another Writing Tip
Be Prepared to Challenge the Validity of an Existing Theory
Theories are meant to be tested and their underlying assumptions challenged; they are not rigid or intransigent, but are meant to set forth general principles for explaining phenomena or predicting outcomes. Given this, testing theoretical assumptions is an important way that knowledge in any discipline develops and grows. If you're asked to apply an existing theory to a research problem, the analysis will likely include the expectation by your professor that you should offer modifications to the theory based on your research findings.
Indications that theoretical assumptions may need to be modified can include the following:
- Your findings suggest that the theory does not explain or account for current conditions or circumstances or the passage of time,
- The study reveals a finding that is incompatible with what the theory attempts to explain or predict, or
- Your analysis reveals that the theory overly generalizes behaviors or actions without taking into consideration specific factors revealed from your analysis [e.g., factors related to culture, nationality, history, gender, ethnicity, age, geographic location, legal norms or customs , religion, social class, socioeconomic status, etc.].
Philipsen, Kristian. "Theory Building: Using Abductive Search Strategies." In Collaborative Research Design: Working with Business for Meaningful Findings . Per Vagn Freytag and Louise Young, editors. (Singapore: Springer Nature, 2018), pp. 45-71; Shepherd, Dean A. and Roy Suddaby. "Theory Building: A Review and Integration." Journal of Management 43 (2017): 59-86.
- << Previous: The Research Problem/Question
- Next: 5. The Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: May 25, 2024 4:09 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.23(2); 2008 Apr

How to prepare a Research Proposal
Health research, medical education and clinical practice form the three pillars of modern day medical practice. As one authority rightly put it: ‘Health research is not a luxury, but an essential need that no nation can afford to ignore’. Health research can and should be pursued by a broad range of people. Even if they do not conduct research themselves, they need to grasp the principles of the scientific method to understand the value and limitations of science and to be able to assess and evaluate results of research before applying them. This review paper aims to highlight the essential concepts to the students and beginning researchers and sensitize and motivate the readers to access the vast literature available on research methodologies.
Most students and beginning researchers do not fully understand what a research proposal means, nor do they understand its importance. 1 A research proposal is a detailed description of a proposed study designed to investigate a given problem. 2
A research proposal is intended to convince others that you have a worthwhile research project and that you have the competence and the work-plan to complete it. Broadly the research proposal must address the following questions regardless of your research area and the methodology you choose: What you plan to accomplish, why do you want to do it and how are you going to do it. 1 The aim of this article is to highlight the essential concepts and not to provide extensive details about this topic.
The elements of a research proposal are highlighted below:
1. Title: It should be concise and descriptive. It must be informative and catchy. An effective title not only prick’s the readers interest, but also predisposes him/her favorably towards the proposal. Often titles are stated in terms of a functional relationship, because such titles clearly indicate the independent and dependent variables. 1 The title may need to be revised after completion of writing of the protocol to reflect more closely the sense of the study. 3
2. Abstract: It is a brief summary of approximately 300 words. It should include the main research question, the rationale for the study, the hypothesis (if any) and the method. Descriptions of the method may include the design, procedures, the sample and any instruments that will be used. 1 It should stand on its own, and not refer the reader to points in the project description. 3
3. Introduction: The introduction provides the readers with the background information. Its purpose is to establish a framework for the research, so that readers can understand how it relates to other research. 4 It should answer the question of why the research needs to be done and what will be its relevance. It puts the proposal in context. 3
The introduction typically begins with a statement of the research problem in precise and clear terms. 1
The importance of the statement of the research problem 5 : The statement of the problem is the essential basis for the construction of a research proposal (research objectives, hypotheses, methodology, work plan and budget etc). It is an integral part of selecting a research topic. It will guide and put into sharper focus the research design being considered for solving the problem. It allows the investigator to describe the problem systematically, to reflect on its importance, its priority in the country and region and to point out why the proposed research on the problem should be undertaken. It also facilitates peer review of the research proposal by the funding agencies.
Then it is necessary to provide the context and set the stage for the research question in such a way as to show its necessity and importance. 1 This step is necessary for the investigators to familiarize themselves with existing knowledge about the research problem and to find out whether or not others have investigated the same or similar problems. This step is accomplished by a thorough and critical review of the literature and by personal communication with experts. 5 It helps further understanding of the problem proposed for research and may lead to refining the statement of the problem, to identify the study variables and conceptualize their relationships, and in formulation and selection of a research hypothesis. 5 It ensures that you are not "re-inventing the wheel" and demonstrates your understanding of the research problem. It gives due credit to those who have laid the groundwork for your proposed research. 1 In a proposal, the literature review is generally brief and to the point. The literature selected should be pertinent and relevant. 6
Against this background, you then present the rationale of the proposed study and clearly indicate why it is worth doing.
4. Objectives: Research objectives are the goals to be achieved by conducting the research. 5 They may be stated as ‘general’ and ‘specific’.
The general objective of the research is what is to be accomplished by the research project, for example, to determine whether or not a new vaccine should be incorporated in a public health program.
The specific objectives relate to the specific research questions the investigator wants to answer through the proposed study and may be presented as primary and secondary objectives, for example, primary: To determine the degree of protection that is attributable to the new vaccine in a study population by comparing the vaccinated and unvaccinated groups. 5 Secondary: To study the cost-effectiveness of this programme.
Young investigators are advised to resist the temptation to put too many objectives or over-ambitious objectives that cannot be adequately achieved by the implementation of the protocol. 3
5. Variables: During the planning stage, it is necessary to identify the key variables of the study and their method of measurement and unit of measurement must be clearly indicated. Four types of variables are important in research 5 :
a. Independent variables: variables that are manipulated or treated in a study in order to see what effect differences in them will have on those variables proposed as being dependent on them. The different synonyms for the term ‘independent variable’ which are used in literature are: cause, input, predisposing factor, risk factor, determinant, antecedent, characteristic and attribute.
b. Dependent variables: variables in which changes are results of the level or amount of the independent variable or variables.
Synonyms: effect, outcome, consequence, result, condition, disease.
c. Confounding or intervening variables: variables that should be studied because they may influence or ‘mix’ the effect of the independent variables. For instance, in a study of the effect of measles (independent variable) on child mortality (dependent variable), the nutritional status of the child may play an intervening (confounding) role.
d. Background variables: variables that are so often of relevance in investigations of groups or populations that they should be considered for possible inclusion in the study. For example sex, age, ethnic origin, education, marital status, social status etc.
The objective of research is usually to determine the effect of changes in one or more independent variables on one or more dependent variables. For example, a study may ask "Will alcohol intake (independent variable) have an effect on development of gastric ulcer (dependent variable)?"
Certain variables may not be easy to identify. The characteristics that define these variables must be clearly identified for the purpose of the study.
6. Questions and/ or hypotheses: If you as a researcher know enough to make prediction concerning what you are studying, then the hypothesis may be formulated. A hypothesis can be defined as a tentative prediction or explanation of the relationship between two or more variables. In other words, the hypothesis translates the problem statement into a precise, unambiguous prediction of expected outcomes. Hypotheses are not meant to be haphazard guesses, but should reflect the depth of knowledge, imagination and experience of the investigator. 5 In the process of formulating the hypotheses, all variables relevant to the study must be identified. For example: "Health education involving active participation by mothers will produce more positive changes in child feeding than health education based on lectures". Here the independent variable is types of health education and the dependent variable is changes in child feeding.
A research question poses a relationship between two or more variables but phrases the relationship as a question; a hypothesis represents a declarative statement of the relations between two or more variables. 7
For exploratory or phenomenological research, you may not have any hypothesis (please do not confuse the hypothesis with the statistical null hypothesis). 1 Questions are relevant to normative or census type research (How many of them are there? Is there a relationship between them?). Deciding whether to use questions or hypotheses depends on factors such as the purpose of the study, the nature of the design and methodology, and the audience of the research (at times even the outlook and preference of the committee members, particularly the Chair). 6
7. Methodology: The method section is very important because it tells your research Committee how you plan to tackle your research problem. The guiding principle for writing the Methods section is that it should contain sufficient information for the reader to determine whether the methodology is sound. Some even argue that a good proposal should contain sufficient details for another qualified researcher to implement the study. 1 Indicate the methodological steps you will take to answer every question or to test every hypothesis illustrated in the Questions/hypotheses section. 6 It is vital that you consult a biostatistician during the planning stage of your study, 8 to resolve the methodological issues before submitting the proposal.
This section should include:
Research design: The selection of the research strategy is the core of research design and is probably the single most important decision the investigator has to make. The choice of the strategy, whether descriptive, analytical, experimental, operational or a combination of these depend on a number of considerations, 5 but this choice must be explained in relation to the study objectives. 3
Research subjects or participants: Depending on the type of your study, the following questions should be answered 3 , 5
- - What are the criteria for inclusion or selection?
- - What are the criteria for exclusion?
- - What is the sampling procedure you will use so as to ensure representativeness and reliability of the sample and to minimize sampling errors? The key reason for being concerned with sampling is the issue of validity-both internal and external of the study results. 9
- - Will there be use of controls in your study? Controls or comparison groups are used in scientific research in order to increase the validity of the conclusions. Control groups are necessary in all analytical epidemiological studies, in experimental studies of drug trials, in research on effects of intervention programmes and disease control measures and in many other investigations. Some descriptive studies (studies of existing data, surveys) may not require control groups.
- - What are the criteria for discontinuation?
Sample size: The proposal should provide information and justification (basis on which the sample size is calculated) about sample size in the methodology section. 3 A larger sample size than needed to test the research hypothesis increases the cost and duration of the study and will be unethical if it exposes human subjects to any potential unnecessary risk without additional benefit. A smaller sample size than needed can also be unethical as it exposes human subjects to risk with no benefit to scientific knowledge. Calculation of sample size has been made easy by computer software programmes, but the principles underlying the estimation should be well understood.
Interventions: If an intervention is introduced, a description must be given of the drugs or devices (proprietary names, manufacturer, chemical composition, dose, frequency of administration) if they are already commercially available. If they are in phases of experimentation or are already commercially available but used for other indications, information must be provided on available pre-clinical investigations in animals and/or results of studies already conducted in humans (in such cases, approval of the drug regulatory agency in the country is needed before the study). 3
Ethical issues 3 : Ethical considerations apply to all types of health research. Before the proposal is submitted to the Ethics Committee for approval, two important documents mentioned below (where appropriate) must be appended to the proposal. In additions, there is another vital issue of Conflict of Interest, wherein the researchers should furnish a statement regarding the same.
The Informed consent form (informed decision-making): A consent form, where appropriate, must be developed and attached to the proposal. It should be written in the prospective subjects’ mother tongue and in simple language which can be easily understood by the subject. The use of medical terminology should be avoided as far as possible. Special care is needed when subjects are illiterate. It should explain why the study is being done and why the subject has been asked to participate. It should describe, in sequence, what will happen in the course of the study, giving enough detail for the subject to gain a clear idea of what to expect. It should clarify whether or not the study procedures offer any benefits to the subject or to others, and explain the nature, likelihood and treatment of anticipated discomfort or adverse effects, including psychological and social risks, if any. Where relevant, a comparison with risks posed by standard drugs or treatment must be included. If the risks are unknown or a comparative risk cannot be given it should be so stated. It should indicate that the subject has the right to withdraw from the study at any time without, in any way, affecting his/her further medical care. It should assure the participant of confidentiality of the findings.
Ethics checklist: The proposal must describe the measures that will be undertaken to ensure that the proposed research is carried out in accordance with the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki on Ethical Principles for Medical research involving Human Subjects. 10 It must answer the following questions:
- • Is the research design adequate to provide answers to the research question? It is unethical to expose subjects to research that will have no value.
- • Is the method of selection of research subjects justified? The use of vulnerable subjects as research participants needs special justification. Vulnerable subjects include those in prison, minors and persons with mental disability. In international research it is important to mention that the population in which the study is conducted will benefit from any potential outcome of the research and the research is not being conducted solely for the benefit of some other population. Justification is needed for any inducement, financial or otherwise, for the participants to be enrolled in the study.
- • Are the interventions justified, in terms of risk/benefit ratio? Risks are not limited to physical harm. Psychological and social risks must also be considered.
- • For observations made, have measures been taken to ensure confidentiality?
Research setting 5 : The research setting includes all the pertinent facets of the study, such as the population to be studied (sampling frame), the place and time of study.
Study instruments 3 , 5 : Instruments are the tools by which the data are collected. For validated questionnaires/interview schedules, reference to published work should be given and the instrument appended to the proposal. For new a questionnaire which is being designed specifically for your study the details about preparing, precoding and pretesting of questionnaire should be furnished and the document appended to the proposal. Descriptions of other methods of observations like medical examination, laboratory tests and screening procedures is necessary- for established procedures, reference of published work cited but for new or modified procedure, an adequate description is necessary with justification for the same.
Collection of data: A short description of the protocol of data collection. For example, in a study on blood pressure measurement: time of participant arrival, rest for 5p. 10 minutes, which apparatus (standard calibrated) to be used, in which room to take measurement, measurement in sitting or lying down position, how many measurements, measurement in which arm first (whether this is going to be randomized), details of cuff and its placement, who will take the measurement. This minimizes the possibility of confusion, delays and errors.
Data analysis: The description should include the design of the analysis form, plans for processing and coding the data and the choice of the statistical method to be applied to each data. What will be the procedures for accounting for missing, unused or spurious data?
Monitoring, supervision and quality control: Detailed statement about the all logistical issues to satisfy the requirements of Good Clinical Practices (GCP), protocol procedures, responsibilities of each member of the research team, training of study investigators, steps taken to assure quality control (laboratory procedures, equipment calibration etc)
Gantt chart: A Gantt chart is an overview of tasks/proposed activities and a time frame for the same. You put weeks, days or months at one side, and the tasks at the other. You draw fat lines to indicate the period the task will be performed to give a timeline for your research study (take help of tutorial on youtube). 11
Significance of the study: Indicate how your research will refine, revise or extend existing knowledge in the area under investigation. How will it benefit the concerned stakeholders? What could be the larger implications of your research study?
Dissemination of the study results: How do you propose to share the findings of your study with professional peers, practitioners, participants and the funding agency?
Budget: A proposal budget with item wise/activity wise breakdown and justification for the same. Indicate how will the study be financed.
References: The proposal should end with relevant references on the subject. For web based search include the date of access for the cited website, for example: add the sentence "accessed on June 10, 2008".
Appendixes: Include the appropriate appendixes in the proposal. For example: Interview protocols, sample of informed consent forms, cover letters sent to appropriate stakeholders, official letters for permission to conduct research. Regarding original scales or questionnaires, if the instrument is copyrighted then permission in writing to reproduce the instrument from the copyright holder or proof of purchase of the instrument must be submitted.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
What is a Theoretical Framework? | A Step-by-Step Guide
Published on 14 February 2020 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 10 October 2022.
A theoretical framework is a foundational review of existing theories that serves as a roadmap for developing the arguments you will use in your own work.
Theories are developed by researchers to explain phenomena, draw connections, and make predictions. In a theoretical framework, you explain the existing theories that support your research, showing that your work is grounded in established ideas.
In other words, your theoretical framework justifies and contextualises your later research, and it’s a crucial first step for your research paper , thesis, or dissertation . A well-rounded theoretical framework sets you up for success later on in your research and writing process.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why do you need a theoretical framework, how to write a theoretical framework, structuring your theoretical framework, example of a theoretical framework, frequently asked questions about theoretical frameworks.
Before you start your own research, it’s crucial to familiarise yourself with the theories and models that other researchers have already developed. Your theoretical framework is your opportunity to present and explain what you’ve learned, situated within your future research topic.
There’s a good chance that many different theories about your topic already exist, especially if the topic is broad. In your theoretical framework, you will evaluate, compare, and select the most relevant ones.
By “framing” your research within a clearly defined field, you make the reader aware of the assumptions that inform your approach, showing the rationale behind your choices for later sections, like methodology and discussion . This part of your dissertation lays the foundations that will support your analysis, helping you interpret your results and make broader generalisations .
- In literature , a scholar using postmodernist literary theory would analyse The Great Gatsby differently than a scholar using Marxist literary theory.
- In psychology , a behaviourist approach to depression would involve different research methods and assumptions than a psychoanalytic approach.
- In economics , wealth inequality would be explained and interpreted differently based on a classical economics approach than based on a Keynesian economics one.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
To create your own theoretical framework, you can follow these three steps:
- Identifying your key concepts
- Evaluating and explaining relevant theories
- Showing how your research fits into existing research
1. Identify your key concepts
The first step is to pick out the key terms from your problem statement and research questions . Concepts often have multiple definitions, so your theoretical framework should also clearly define what you mean by each term.
To investigate this problem, you have identified and plan to focus on the following problem statement, objective, and research questions:
Problem : Many online customers do not return to make subsequent purchases.
Objective : To increase the quantity of return customers.
Research question : How can the satisfaction of company X’s online customers be improved in order to increase the quantity of return customers?
2. Evaluate and explain relevant theories
By conducting a thorough literature review , you can determine how other researchers have defined these key concepts and drawn connections between them. As you write your theoretical framework, your aim is to compare and critically evaluate the approaches that different authors have taken.
After discussing different models and theories, you can establish the definitions that best fit your research and justify why. You can even combine theories from different fields to build your own unique framework if this better suits your topic.
Make sure to at least briefly mention each of the most important theories related to your key concepts. If there is a well-established theory that you don’t want to apply to your own research, explain why it isn’t suitable for your purposes.
3. Show how your research fits into existing research
Apart from summarising and discussing existing theories, your theoretical framework should show how your project will make use of these ideas and take them a step further.
You might aim to do one or more of the following:
- Test whether a theory holds in a specific, previously unexamined context
- Use an existing theory as a basis for interpreting your results
- Critique or challenge a theory
- Combine different theories in a new or unique way
A theoretical framework can sometimes be integrated into a literature review chapter , but it can also be included as its own chapter or section in your dissertation. As a rule of thumb, if your research involves dealing with a lot of complex theories, it’s a good idea to include a separate theoretical framework chapter.
There are no fixed rules for structuring your theoretical framework, but it’s best to double-check with your department or institution to make sure they don’t have any formatting guidelines. The most important thing is to create a clear, logical structure. There are a few ways to do this:
- Draw on your research questions, structuring each section around a question or key concept
- Organise by theory cluster
- Organise by date
As in all other parts of your research paper , thesis, or dissertation , make sure to properly cite your sources to avoid plagiarism .
To get a sense of what this part of your thesis or dissertation might look like, take a look at our full example .
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
While a theoretical framework describes the theoretical underpinnings of your work based on existing research, a conceptual framework allows you to draw your own conclusions, mapping out the variables you may use in your study and the interplay between them.
A literature review and a theoretical framework are not the same thing and cannot be used interchangeably. While a theoretical framework describes the theoretical underpinnings of your work, a literature review critically evaluates existing research relating to your topic. You’ll likely need both in your dissertation .
A theoretical framework can sometimes be integrated into a literature review chapter , but it can also be included as its own chapter or section in your dissertation . As a rule of thumb, if your research involves dealing with a lot of complex theories, it’s a good idea to include a separate theoretical framework chapter.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, October 10). What is a Theoretical Framework? | A Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved 26 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/the-theoretical-framework/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, how to write a results section | tips & examples, how to write a discussion section | tips & examples.
How to Write the Conceptual Framework in a Research Proposal
Many of the users of Simplyeducate.me post a lot of queries in the high traffic article I wrote titled: Conceptual Framework: A Step-by-Step Guide on How to Make One . The article intends to provide useful tips on how to write the conceptual framework in a research proposal.
Despite the step-by-step, simplified guide on how to write the conceptual framework, the many questions posed by the readers suggest that they are unable to comprehend fully well the contents of the article. Through time, more than 400 readers commented in that single article (Note: Now, the comments are still increasing after I removed the comments up to July 2019 in my attempt to write another e-book about the Questions and my answers. Someone told me she learned a lot from the Q&A, so I compiled them into an e-book).
Interest in the topic is quite high. At this writing, more than 2,500 (update on 2/23/20: 8,000) users read the article daily. Aside from grateful comments, readers keep on asking a lot of questions about how to go about their conceptual framework despite the illustrative example.
Detailed Questions on Conceptual Framework
Some of those who commented asked too specific questions related to their research topics. Several masters degree candidates even send manuscripts for review and comments, eagerly waiting for my response.
Did you read it?
Many of those questions make sense, while others show the dilemma of a beginning researcher. Some users did not read the article at all. The material already discussed answers to their questions.
Among those common questions asked pertains to the determination of the independent and the dependent variables. Discernment of the difference between these types of variables appears to be difficult for many.
Also, questions indicate a failure to relate one’s research topic in the article on how to write the conceptual framework in a research proposal. Nevertheless, I oblige by answering so fundamental questions giving detailed suggestions and examples.
Reviewing the Literature Takes Time
However, answering questions on specific research topics proves to be time-consuming. I have to review the literature to make sure that my answer will be backed up by science. Reviewing the literature takes a lot of time.
Although I enjoyed answering the questions, I cannot respond to all the specific queries on how to build one’s conceptual framework.
Writing in Simplyeducate.me is a hobby, a way to share my understanding of the research process. I admit that my ideas are subject to scrutiny, and I thankfully respond to readers who point out overlooked points or glaring errors.

E-book on How to Write the Conceptual Framework in a Research Proposal
To be more effective in addressing the readers’ queries, I wrote the e-book titled “ Conceptual Framework Development Handbook: A Step-by-Step Guide with Five Practical Examples .” The e-book is a compilation of all conceptual framework related articles that I previously wrote in this site and other blogging websites.
I combined lecture materials in graduate school and personal experience in researching to enrich the discussion. Further, recognizing the effectiveness of examples to illustrate the concept, I added five concrete examples using actual scientific papers to the e-book. The task was tedious, but it seems the e-book has fulfilled its purpose.
Thus, for those who find difficulty in writing the conceptual framework in a research proposal, the e-book detailing the steps on how to write the conceptual framework in a research proposal is a must-have. For those who have availed of this publication, the author will be happy to receive comments, suggestions, and healthy criticisms to further enrich this work— all for the sake of better research outputs and discovery.
If you are patient enough to browse in this site, chances are, you will find answers to your research-related questions. If not, then my e-book on How to Write a Thesis in the Information Age compiles all the research tips I wrote in this site and other websites with review questions as well as exercises.
Please message me about that specific topic you would like to know more about, and I will respond with an article related to your query.
Related Posts
Five memory improvement tips for researchers, how to write the abstract, research focus: police involvement in kidnapping and extortion, about the author, patrick regoniel.
Dr. Regoniel, a faculty member of the graduate school, served as consultant to various environmental research and development projects covering issues and concerns on climate change, coral reef resources and management, economic valuation of environmental and natural resources, mining, and waste management and pollution. He has extensive experience on applied statistics, systems modelling and analysis, an avid practitioner of LaTeX, and a multidisciplinary web developer. He leverages pioneering AI-powered content creation tools to produce unique and comprehensive articles in this website.
I just ordered the guide to writing a conceptual framework. However, I have an immediate need to submit two paragraphs describing my underlying conceptual or theoretical framework. My research question is as follows “How does lack of emotional intelligence explain the dysfunctional relations that often exist between lawyers and their subordinates? This piece is part of a series of paragraphs that will make up the dissertation prospectus, which is what the assignment is asking for.
My initial thought based on research and discussions I’ve had during the course, is that I will need a conceptual framework. However, upon carefully studying both definitions, it appears I may need both. I am a little uncertain about this. Your assistance would be greatly appreciated. Dortmund paying for your time.
Hi my name mutasse. Am phd studwnt at malaysia and suppose submit my entire work by 2 weeks so actually my prof ask me to redo the framework So i want to buy your items -the book but it saying need to 20 days for delivery so can o get it as pdf and im willing to pay by visa plz
Thank you for your e-book detailing the steps on how to write the conceptual framework in a research proposal. Anyone will find answers to his/her research-related questions.
SimplyEducate.Me Privacy Policy

Draft International Education and Skills Strategic Framework
- Migration Strategy
- Before studying in Australia
- During your studies in Australia
- After studying in Australia
- State and Territory Government resources to support international students
- International education engagement
- Data and research
- Financial assistance for international students
- Recognise overseas qualifications
- Resources to support students
- Australian Strategy for International Education
- Announcements
The draft International Education and Skills Strategic Framework (the Framework) has been released.
- Download Draft International Education and Skills Strategic Framework as a DOCX (298.31kb)
- Download Draft International Education and Skills Strategic Framework as a PDF (613.58kb)
We aim to provide documents in an accessible format. If you're having problems accessing a document, please contact us for help .
Synthesizing three decades of digital servitization: a systematic literature review and conceptual framework proposal
- Theoretical article
- Open access
- Published: 08 May 2024
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Pedro E. Minaya ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1179-9378 1 ,
- Lucía Avella ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2598-7318 2 &
- Juan A. Trespalacios ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0658-4038 2
308 Accesses
Explore all metrics
This study, through a systematic literature review spanning 1990 to 2023, interrogates how servitization, and nowadays digital servitization, enhances manufacturing competitiveness. It introduces the DASOBI (Drivers, Actors, Strategies, Obstacles, Benefits, and Impact) framework for navigating the digital servitization transition, emphasizing strategic adaptability and technological alignment. Analysis of 157 articles reveals a significant increase in research, highlighting digital servitization’s role in competitive enhancement and customer engagement. The DASOBI framework offers manufacturers a novel approach for managing this transition, marking a unique contribution by distilling extensive literature into actionable insights for both theory and practice in the evolving field of digital servitization.
Similar content being viewed by others

Understanding the Internal and External Drivers and Barriers for Digital Servitization in the European Textile Manufacturing Industry

The effects of digital servitization on business competitiveness: A case study of Spanish manufacturers

Exploring Dynamic Capabilities to Facilitate a Smoother Transition from Servitization to Digital Servitization: A Theoretical Framework
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
1.1 context, motivation, and research topic.
In today’s dynamic manufacturing sector, companies are increasingly acknowledging the importance of complementing their product offerings with value-added services. This strategic shift, known as servitization—and more specifically digital servitization—marks a fundamental turn in the contemporary business paradigm. This transformation involves not only a shift from a product-centric to a service-centric focus but also a deep integration of advanced digital technologies. While considerable research has been conducted on individual aspects of servitization, a comprehensive analysis that encompasses all essential facets of this phenomenon, from its motivations to its final outcomes, remains relatively unexplored. This research proposal aims to develop a holistic conceptual framework that synthesizes and extends existing knowledge, thereby providing a more complete and nuanced understanding of digital servitization. This exhaustive review examines this evolving business model, highlighting its key benefits and challenges, its intersection with digital technologies, and its theoretical and practical implications.
The foundational premise, supported by Bustinza et al. ( 2015 ), suggests that manufacturing companies can achieve higher returns by offering services in conjunction with their products, a claim echoed in seminal works by Davies et al. ( 2007 ), Johnstone et al. ( 2009 ), Martín-Peña et al. ( 2017 ), and Leoni and Aria ( 2021 ). These services, ranging from maintenance and support to more sophisticated and customized solutions, expand the revenue streams of these firms. In this context, the contributions of Baines et al. ( 2007 ) and Neely et al. ( 2011 ) are pivotal, as they underscore how transitioning to a service-oriented market is driving strategic transformations in manufacturing firms, emphasizing value creation and differentiation in increasingly competitive markets (Brady et al. 2005 ).
The current market dynamics almost make this shift imperative. As noted by Sandström et al. ( 2008 ) and Tukker ( 2015 ), companies that limit their offerings to products alone face formidable challenges in maintaining profitability, driving them toward business model innovation that incorporates services into their product portfolios, as discussed in the literature by Gebauer and Fleisch ( 2007 ), Visnjic and Van Looy ( 2013 ), and Díaz-Garrido et al. ( 2018 ).
Servitization requires effective coordination among multiple stakeholders. Alghisi and Saccani ( 2015 ) address the critical importance of internal and external alignment, while Ayala et al. ( 2019 ) highlight the essential role of service providers in the successful adoption of servitization strategies. Moreover, Baines et al. ( 2011 ) and Lightfoot et al. ( 2013 ) explore how manufacturing firms can effectively integrate services into their product portfolio, emphasizing the importance of a strategically well-planned approach.
Beyond being a customer-facing strategy, the internal benefits are equally compelling. As delineated by Kamp and Alcalde ( 2014 ), servitization facilitates process optimization and extends the lifespan of machinery. These advantages are further enhanced with the incorporation of digital technologies, particularly in the era of Industry 4.0 (Kamp and Perry 2017 ). This digital servitization, explored in studies by Lee et al. ( 2014 ), Kans and Ingwald ( 2016 ), and Paiola and Gebauer ( 2020 ), offers an enhanced layer of value, encompassing innovative goods and services.
Researchers such as Favoretto et al. ( 2022 ) and Rabetino et al. ( 2023 ) have elucidated how technological advancements act as catalysts for developing differentiated products and services, thereby enhancing competitiveness (Müller et al. 2021 ). This leads to the formulation of hybrid business models, termed Product-Service Systems (PSS), which are economically, socially, and environmentally sustainable. This PSS model provides a more holistic solution, meeting specific customer needs beyond just providing functional products (Barquet et al. 2013 ).
In this process, a demand for specific organizational and technological capabilities is identified. Coreynen et al. ( 2017 ) and Schroeder et al. ( 2022 ) have pinpointed the importance of organizational structure and technological capabilities, particularly in the context of digitalization, as key factors for a successful transition to digital servitization (Parida et al. 2014 ; Kanninen et al. 2017 ).
Implementing servitization, as highlighted by Mathieu ( 2001 ) and Yu and Sung ( 2023 ), is not without its challenges, ranging from internal organizational resistance to external factors, such as customer reluctance. Brax ( 2005 ) and Benedettini et al. ( 2015 ) provide a comprehensive analysis of these risks, emphasizing the importance of effective management to navigate potential obstacles in achieving successful servitization (Windahl and Lakemond 2006 ; Pessôa and Becker 2017 ). The process demands a well-structured and strategically informed approach, incorporating both business and customer perspectives. Proper implementation of servitization can lead to substantial benefits, as demonstrated by Baines et al. ( 2009b , 2017 ) and Wang et al. ( 2018 ), highlighting its potential for long-term value creation (Brady et al. 2005 ).
The phenomenon of servitization, particularly in its digital form, has emerged as a prominent area of study, characterized by its complexity and multidimensionality. Academic literature has thoroughly explored this concept, from underlying motivations to implementation strategies, examining both inherent challenges and potential benefits (Raddats et al. 2016 ; Rabetino et al. 2021 ).
1.2 Research gap
Despite the extensive body of knowledge on servitization amassed by previous studies, there remains a discernible gap characterized by fragmented examinations rather than a consolidated analytical approach. This study pinpoints a need for a unified framework that can effectively guide servitization strategies, addressing this lacuna as a pivotal area for forthcoming research (Calabrese et al. 2019 ; Kohtamäki et al. 2020a ). The advent of the digital era has precipitated transformative shifts, underscoring the servitization concept—the transition from purely selling products to offering integrated product-service solutions. Nevertheless, the interaction between servitization and digital technologies, a realm referred to as digital servitization, remains a relatively uncharted territory. This area lacks a systematic and thorough review spanning the last three decades. This omission highlights the imperative need for an in-depth understanding of how servitization has evolved and the essential development of a framework to adeptly navigate the intricacies involved in implementing these strategies effectively.
1.3 Methodology proposed
To address the identified research gap, our study employs a comprehensive, multi-phased methodology structured as follows: Initially, we conduct an in-depth examination of the literature on servitization and digital servitization. This phase aims to develop an integrative theoretical framework that captures the evolution of servitization over the past three decades, emphasizing the shift toward digital service delivery within the manufacturing sector. Subsequently, the study undertakes a systematic literature review to classify the existing body of work. This review specifically focuses on selecting pertinent studies that encompass both traditional and digital servitization, aiming to identify trends, patterns, and existing research gaps. Following the review, we perform a detailed analysis of the selected articles to explore how various aspects of servitization and digital servitization interact and influence each other. In the final phase, we synthesize the findings from the study to deepen the conceptual understanding of the servitization phenomenon, including its digital components. This synthesis will provide valuable insights into effectively managing the transition toward servitization and digital servitization, highlighting its practical applicability in a business context.
1.4 Expected contributions
The primary goal of this research is to construct an integrative framework that captures the evolution, current state, and future trajectory of servitization and digital servitization. This framework will delineate both the theoretical underpinnings and practical ramifications of servitization, illuminating the challenges and opportunities that have surfaced. Particularly, it will explore the transformative influence of Industry 4.0 technologies—such as the Internet of Things, Big Data analytics, and Artificial Intelligence—on traditional servitization models, steering them toward more advanced digital practices. This examination is crucial for understanding how digital technologies can enhance the competitiveness and value proposition of manufacturing firms engaged in servitization.
The overarching aim of this study is to deepen the comprehension of servitization by exploring its interplay with digitalization, thus broadening its theoretical and managerial relevance. The research intends to offer an integrated perspective that not only advances the academic discourse in this field but also aids manufacturing companies in adeptly navigating the complexities of servitization and digital servitization. Furthermore, this review will articulate a roadmap for manufacturers considering this transition, conceptually enriching a domain that, despite its increasing importance, remains underexplored in scholarly research. By highlighting the enduring interest in adopting servitization correctly and underscoring the necessity for a unified theoretical framework, this study responds to calls for theoretical consolidation and a more comprehensive research agenda (Pettigrew 1988 ; Pye and Pettigrew 2005 ).
In summary, our proposed study aims to provide a detailed analysis that integrates insights from various studies into a cohesive narrative, with a particular focus on the servitization and digital servitization processes within the manufacturing sector. This synthesis will significantly contribute to both academic knowledge and practical applications, emphasizing the complex and evolving nature of servitization in manufacturing, and marking a key conclusion of this thorough examination.
2 Research aims
This study is dedicated to a comprehensive analysis of the servitization phenomenon and its progression toward digital servitization within the manufacturing sector, meticulously examining the most significant research from the past 30 years. The aim is to understand the development and various applications of servitization, along with the challenges and obstacles it entails. The study seeks to identify the motivations driving companies toward servitization, examine the various actors involved in the process and their interplay, and explore the strategies necessary for successful implementation. Furthermore, the organizational and technological capabilities required for transitioning to servitization will be analyzed, as well as the associated risks and challenges, including both internal and external hurdles that companies must overcome to reap the potential benefits of servitization. This analysis is guided by key research in the field (Zhang and Banerji 2017 ; Khanra et al. 2021 ) offering a comprehensive perspective on this significant shift in business dynamics within the manufacturing sector.
Essentially, this study seeks to answer the main research question: To what extent do servitization and digital servitization provide benefits that contribute to enhancing a company’s competitiveness? Alongside this primary question, the study intends to address the following aspects related to the development of servitization and digital servitization:
RQ1. Implementation of a digital servitization strategy. How it should be affected by the company’s business environment? How it should be the co-creation process in an international context? Which new knowledge and new skills need to be developed to be implemented correctly? Which benefits can be obtained by implementing the digital enablers of Industry 4.0? Which changes could it involve in the internal structure of the business? Which changes could it involve in the company’s business environment (relations with suppliers or strategic partners)? How could it face the challenges and obstacles that arise during the transition process?
RQ2. Benefits of developing an effective digital servitization strategy. How it provides greater value to the customer? How can product customization be optimized? How it encourages access to new markets? How it promotes gaining new customers? How it allows innovation in ideas or business models? How it allows the development of goods with novel services? How it effectively allows greater returns to be achieved? How it improves competitiveness?
The focus of this study is not only on analyzing servitization as a strategic shift for manufacturing companies but also on exploring how the integration of digital technologies can enrich and complicate this process. Additionally, the aim is to synthesize existing knowledge to provide a broader and more nuanced understanding of digital servitization, highlighting its key advantages, challenges, and intersection with digital technologies.
Four stages were established for this systematic literature review (Tranfield et al. 2003 ), one for each of the four phases outlined in the first section.
This collection focuses on four fields of research: business administration, marketing, operations management, and administration of services. The studies from the two main databases were examined: Web of Science and Scopus, as they are considered reference sources for the topic being analyzed. Once the information was screened, the most-cited studies were selected, which formed the basis for the present study.
3.1 Review process
In conducting a systematic literature review to gain a profound understanding of servitization and digital servitization within the manufacturing sector, our approach integrated multiple rigorous methodologies (Thomé et al. 2016 ). Initially, following the method proposed by Hertzberg and Rudner ( 1999 ), we conducted a meticulous keyword search in the Web of Science and Scopus databases, aiming to identify pertinent literature using terms like “servitization,” “digital servitization,” and their variants. This was instrumental in capturing the subject’s breadth and depth, allowing for the creation of search strings using the Boolean connector OR. The search strings were incorporated in titles, abstracts, and/or keywords, adhering to the time span of 1990 to 2023 in major databases, thus fulfilling the guidelines set by Tranfield et al. ( 2003 ) for inclusion criteria.
To further refine the search and ensure a robust database, we applied additional parameters and restrictions post-establishing the primary search strings for both databases. We limited our search to open access and hybrid gold journals, focusing on high-quality, readily available research outputs. Additionally, we set a citation threshold to include articles with significant field impact, thereby ensuring the inclusion of seminal works and recent influential studies. This strategy was pivotal in developing a comprehensive, relevant collection of literature, ensuring the inclusion of the most pertinent works in the field of digital servitization.
The approach was enhanced by strictly adhering to three key inclusion criteria: (a) considering publications from 1990 to 2023, to ensure a contemporary and comprehensive review, (b) prioritizing articles from prestigious academic journals within the relevant study areas, thus ensuring source quality and relevance, and (c) selecting articles focusing explicitly on key aspects of servitization and digital servitization. This approach, aligned with the study’s objectives and research questions, ensures a holistic and detailed understanding of the phenomenon, accurately reflecting the dynamics and transformations in the manufacturing sector.
The present study aimed to answer the research question and the various related questions. This was done via the PRISMA method (Preferred Reporting Items for Systemic Reviews and Meta-Analyses). The selection criteria produced 647 articles (from Web of Science) and 630 articles (from Scopus). Once identified, the abstracts of each article were read to screen and select only those in line with the fourth study phase: to help properly understand the concept, how it is managed, and how it is applied. 157 articles were ultimately identified that met all of the inclusion criteria. Figure 1 outlines the PRISMA method used.
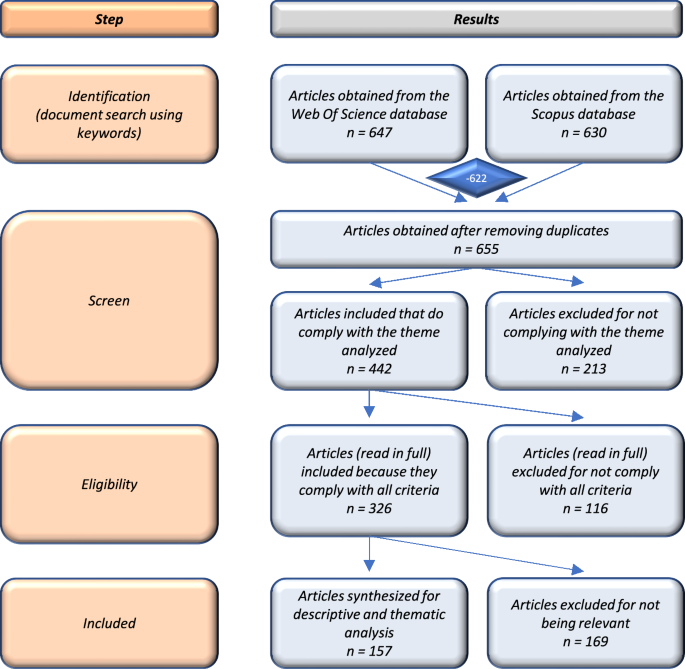
Source: Authors’ own work from Web of Science and Scopus databases
Flow diagram, based on the PRISMA Method, for the selection of relevant documents for the systematic literature review.
3.2 Descriptive analysis
Figure 2 offers an analytical synthesis of the publication trends within the realms of servitization and digital servitization over a span of more than three decades, utilizing data harvested from the Web of Science and Scopus databases. The blue bars across all three charts articulate the volume of literature pertaining to servitization, encompassing its theoretical underpinnings, industry applications, and cross-disciplinary studies. This scholarly corpus embodies the foundational and evolutionary aspects of servitization as a strategic paradigm shift in manufacturing and service industries.
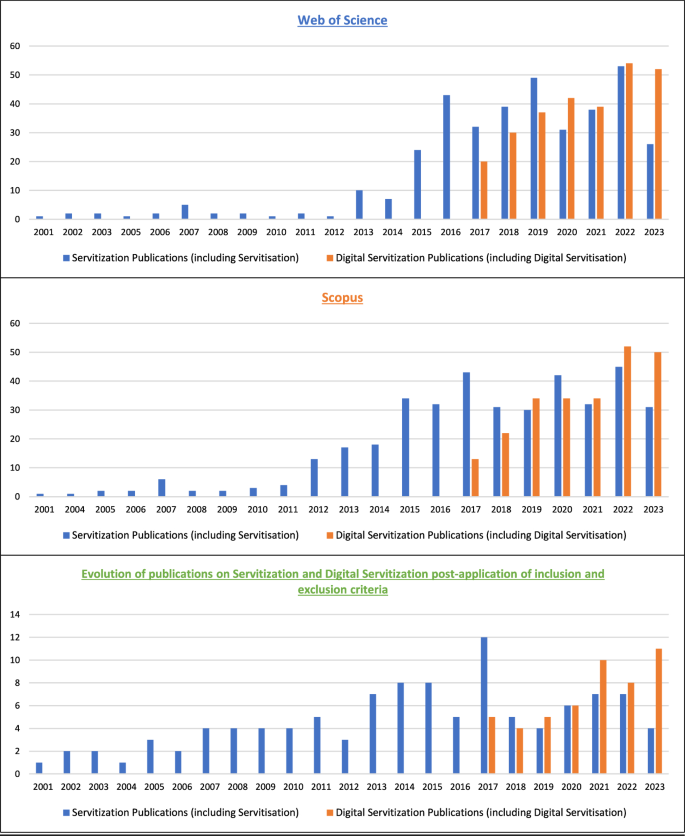
Source: Web of Science and Scopus databases and authors’ own work
Evolution of publications on Servitization and Digital Servitization (1990–2023).
In parallel, the orange bars specifically chart the trajectory of literature focused on digital servitization. This subset of research delves into the intricacies of embedding digital technologies within traditional servitization frameworks. It illuminates the burgeoning intersection of digital innovation and service strategies, reflecting a vibrant and rapidly advancing frontier of research.
The upward trend of both blue and orange bars in the separate charts for Web of Science and Scopus indicates a robust increase in scholarly output. This not only testifies to the growing academic and practical significance of servitization concepts but also their digital counterparts, which are pivotal in today’s technology-driven marketplaces.
The application of inclusion and exclusion criteria to the study of servitization and digital servitization clarifies the focus of academic research, emphasizing the most relevant and impactful studies in these areas. This refined approach highlights the critical and emerging conversations shaping the future of manufacturing industries through servitization and its digital augmentation. The graph reflects the scholarly community’s increasing investment in understanding these concepts and their application, suggesting a dual focus: the persistent importance of servitization in strengthening the interplay between manufacturing and services, and the transformative potential of digital technologies within this framework. Serving both as a retrospective and a forecast, the visualization indicates key areas for future research that promise to advance industrial practices and academic thought.
Regarding the countries in which the identified studies have been carried out, the visual data presented in Fig. 3 captures a comprehensive view of the global research output on servitization and digital servitization from 1990 to 2023, as indexed by the Web of Science and Scopus databases and further refined by the application of inclusion and exclusion criteria. The top section, shown in blue, delineates the Web of Science data, indicating a prominent concentration of scholarly activity within certain countries, possibly linked to their robust research infrastructures, funding provisions, or strong manufacturing sectors that are conducive to studies in servitization.
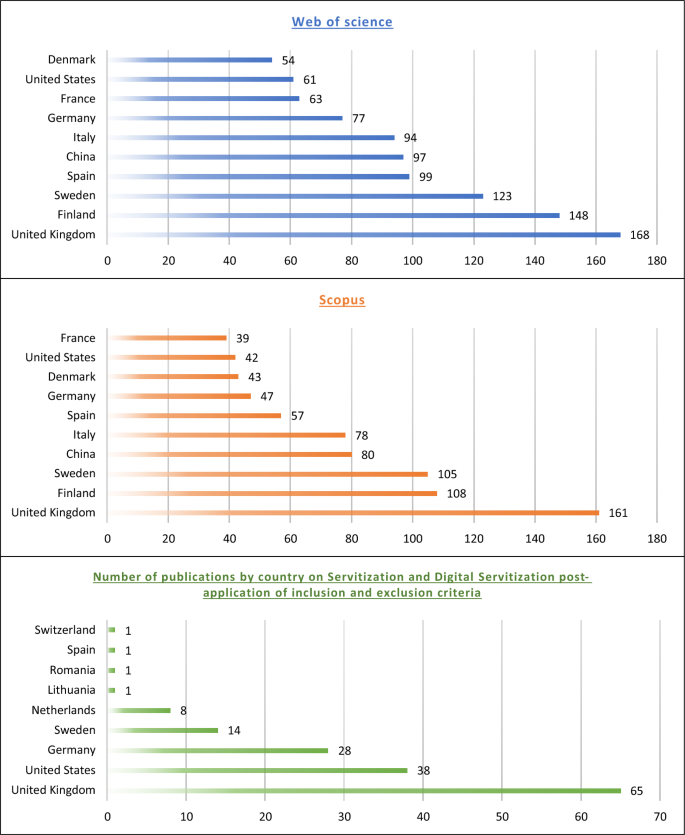
Source: Web of Science and Scopus databases
Number of publications by country on Servitization and Digital Servitization (1990–2023).
The middle section, in orange, portrays the Scopus data, revealing a parallel distribution pattern to that of the Web of Science but with slight variances that may be indicative of the different regional research emphases or variations in the databases’ indexing methodologies. The countries with the highest volume of publications are recognized as potential centers of excellence and innovation in the field of servitization.
The bottom section of the graph, in green, represents the distilled essence of this academic output following the application of the inclusion and exclusion criteria. This section emphasizes the refined and concentrated scholarly work that aligns more closely with the specific nuances and requirements of servitization and digital servitization research as defined by the study. It presents a narrower but more focused spectrum of publications, suggesting a curated body of knowledge that serves as a critical resource for understanding the current state and future directions of servitization in the manufacturing sector.
Together, these three segments of Fig. 3 not only illustrate the quantitative aspects of the research output but also underscore the qualitative focus and depth of scholarly exploration achieved through rigorous selection. This tripartite analysis offers a lens through which to view the international dissemination and development of knowledge in servitization and digital servitization, highlighting established leaders in the field as well as regions with the potential for increased research activity, international collaboration, and contribution to the servitization discourse.
In Fig. 4 , the Web of Science data (represented by the blue graph) lists Oscar Bustinza as the author with the highest number of publications, closely followed by Marko Kohtamäki and Vinit Parida. In contrast, the Scopus data (illustrated by the orange graph) also positions Vinit Parida prominently, yet Marko Kohtamäki’s publication count is lower than that reported in the Web of Science, presenting a notable discrepancy.
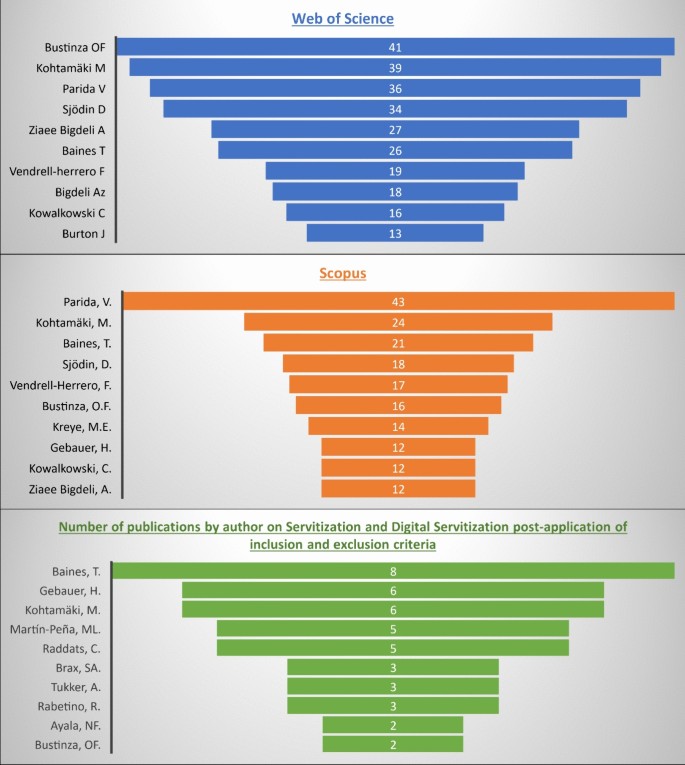
Number of publications by author on Servitization and Digital Servitization (1990–2023).
When the inclusion and exclusion criteria are applied (as shown in the green graph), there is a decrease in the number of publications, which aligns with expectations, given that these criteria aim to omit publications failing to meet the predetermined standards of quality and relevance. Following this filtration, Tim Baines emerges as the author with the most publications, indicating the significant relevance of his research work to the focused aims of this systematic literature review. Consequently, the filtration process underscores those authors whose contributions are particularly central or foundational to the field.
The comparison across the three graphs demonstrates the influence of database selection and methodological rigor on the perceived prominence of authors within the academic community. This analysis goes beyond merely highlighting the leading figures in servitization research; it underscores the importance of thorough evaluation in literature reviews to identify research of substantial impact.
Thus, the filtration process distinctly recognizes authors whose contributions are considered pivotal to the discipline.
Figure 5 provides a succinct overview of journal publication volumes on servitization and digital servitization from 1990 to 2023, based on data from Web of Science and Scopus databases. Prior to applying inclusion and exclusion criteria, the journals listed in the Web of Science (blue) and Scopus (orange) indicate a diverse quantity of publications.
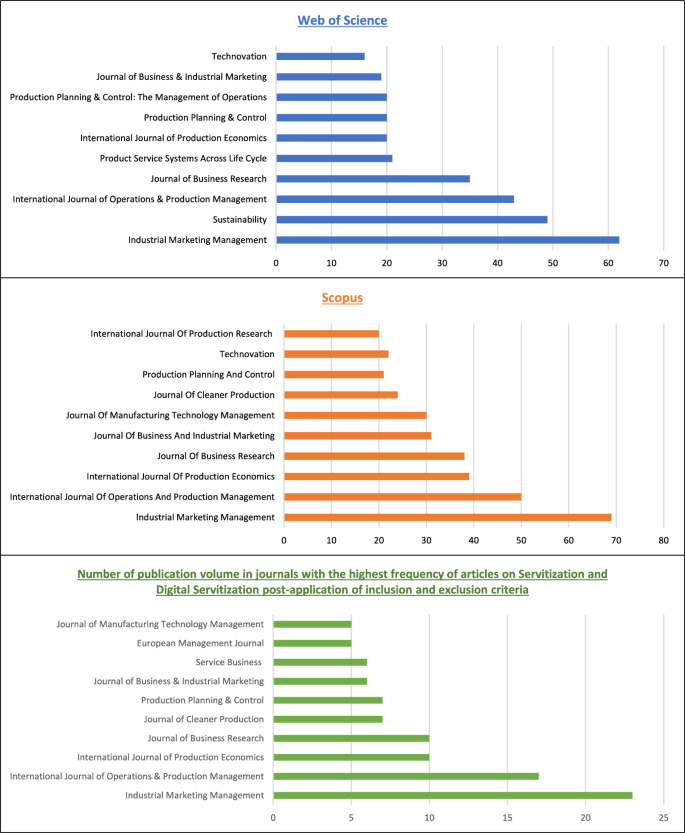
Number of publication volume in journals with the highest frequency of articles on Servitization and Digital Servitization (1990–2023).
Post-application (green), the data are refined to highlight the top ten journals that are most aligned with the research criteria. It is noteworthy that the application of these criteria significantly alters the landscape of the considered literature. Some journals that initially (in the Web of Science or Scopus databases) had a high volume of publications appear to have fewer articles meeting the requirements, which may reflect on the specificity and relevance of their contributions to the field.
The graphic serves as an insightful metric of the research landscape, indicating not only the journals that are most prolific in the domain but also the robustness of articles surviving rigorous scholarly scrutiny. This visual representation is integral to the academic discourse, as it not only informs researchers of the core journals within the field but also reflects the evolving standards and focal areas within the literature on servitization and digital servitization.
The descriptive analyses included in this section serve as a pivotal foundation for the authors’ elaboration, shedding light on the trajectory of academic inquiry into servitization and digital servitization. It encapsulates the dual analysis conducted using the Web of Science and Scopus databases and the meticulous selection process leading to the corpus of papers employed in the systematic literature review. The synthesis of these findings offers valuable insights into the progression of research in this domain, indicating a maturing yet dynamically expanding field of study.
3.3 Classification process
Upon identifying studies that met the established selection criteria, a thorough examination of each was conducted to categorize them according to specific themes. These encompassed the motivations driving companies toward servitization, namely the reasons why manufacturers transition from producing solely goods to combining these with services, including the anticipated benefits of such a transformation. The various actors involved in the servitization process and the nature of their interactions were scrutinized, as well as the strategies necessary for successful implementation, which entailed identifying potential needs for external partners, commonly service providers (Martínez et al. 2010 ; Bastl et al. 2012 ; Spring and Araujo 2013 ; Ziaee et al. 2018 ). The types of services commonly offered were analyzed, categorized as basic, intermediate, or advanced, along with the specific servitization strategies adopted by the companies. Furthermore, the study delved into the organizational and technological capabilities required for an effective transition to servitization (Momeni et al. 2023 ), as well as the potential risks and challenges arising in these transition processes, including both internal and external obstacles that must be overcome to fully capitalize on the potential benefits of servitization (Raddats et al. 2017 ; Reim et al. 2019 ; Minaya et al. 2023 ).
4 Results: theoretical background
4.1 from servitization to digital servitization.
The concept of servitization, which has significantly evolved over the years, has achieved solid recognition in both the academic and industrial spheres. Initially defined by Levitt ( 1972 ) and Vandermerwe and Rada ( 1988 ) as the process of adding value through services (Johnson and Mena 2008 ; Baines et al. 2011 ; Lindman et al. 2016 ; Ruiz-Martín and Díaz-Garrido 2021 ), servitization has expanded to encompass multiple strategic objectives, such as competitive advantage (Baines et al. 2009a ; Raddats et al. 2019 ), financial goals, and marketing benefits (Khanra et al. 2021 ).
The shift toward servitization entails a redefinition of traditional business models, focusing on innovation (Sandström et al. 2008 ; Martín-Peña et al. 2018 ; Qi et al. 2020 ; Xing et al. 2023 ), and transforming manufacturers into service-centric companies (Cusumano 2008 ; Santamaría et al. 2012 ; Mosch et al. 2021 ). In this regard, manufacturing companies are fundamentally reorienting their business models and operational strategies to include value-added services (Gebauer and Kowalkowski 2012 ; Hyun and Kim 2021 ). Baines and Lightfoot ( 2013 ) and Luoto et al. ( 2017 ) highlight the widespread changes this implies in management, marketing, and operations. The change is so substantial that over 50% of a company’s activities and personnel can be involved in providing these newly implemented services, as indicated by multiple studies cited by Martín-Peña and Ziaee ( 2016 ). This is because research has shown that servitization not only adds value but also increases profitability with relatively low asset investments (Davies et al. 2007 ; Kharlamov and Parry 2021 ).
The types of services offered range from basic to advanced (Gebauer et al. 2013 ; Kindström and Kowalkowski 2014 ; Sousa and Da Silveira 2017 ), with advanced services contributing to greater profitability (Eggert et al. 2014 ) and generating higher customer satisfaction (Mont 2002 ; Ostrom et al. 2010 ), leading to improved competitive positioning (Oliva and Kallenberg 2003 ; Durugbo 2014 ). Baines et al. ( 2011 ) argue that servitization involves creating distinctive and sustainable capabilities (Raddats 2011 ; Kimita et al. 2022 ), requiring not just the provision of goods, but also the innovation of value through added services (Tukker and Tischner 2006 ; García Martín et al. 2019 ; Zighan and Abualqumboz 2022 ), enabling companies to maintain their competitive edge (Tuli et al. 2007 ; Brax and Jonsson 2009 ; Nordin and Kowalkowski 2010 ).
While the goal of servitization is to enrich product offerings and drive competitiveness (Neely et al. 2011 ; Gaiardelli et al. 2014 ; Benedettini et al. 2015 ), companies must avoid the “service paradox,” where the focus on new services undermines existing production capabilities (Gebauer et al. 2005 ; Hyun and Kim 2021 ). To this end, various researchers advocate for a comprehensive analysis covering customer needs, pricing strategies, delivery infrastructure, and organizational change (Manzini and Vezzoli 2003 ; Kohtamäki and Partanen 2016 ; Ziaee et al. 2017 ). In summary, moving away from product-centric thinking and engaging in product and servitization logic.
In this context, Santamaría et al. ( 2012 ) and Rabetino et al. ( 2017 ) underscore three fundamental considerations for a successful servitization strategy: the content, process, and context of organizational change. This involves determining what to change, how to change, and why the change is necessary (Kreye et al. 2015 ).
The complexity of servitization also demands internal and external alignments within companies (Gebauer 2008 ; Alghisi and Saccani 2015 ; Kohtamäki et al. 2019a ; Zhang et al. 2023 ). Internally, this involves harmonizing the organization’s strategy with the service portfolio and aligning this strategy throughout the organization (Oliva and Kallenberg 2003 ; Yan et al. 2020 ). Externally, alignment extends to the service provider network and customer expectations (Ceci and Masini 2011 ; Paiola et al. 2013 ). Similarly, servitization applies in B2B and B2C domains, serving as a differentiator and pathway to future alliances and customer loyalty (Baines et al. 2017 ; Pombo and Franco 2023 ).
On the other hand, technological advancements act as significant facilitators in the transition toward servitization, particularly the digital elements of Industry 4.0 (Dalenogare et al. 2018 ; Paschou et al. 2020 ; Opazo-Basáez et al. 2021 ; Tian et al. 2022 ; Le-Dain et al. 2023 ). This involves both internal and external organizational changes, focusing on disruptive innovations and addressing legal and financial challenges (Bustinza et al. 2018 ; Tronvoll et al. 2020 ; Kolagar et al. 2022 ), leading to what is known as digital servitization.
Digital servitization represents the integration of enabling technologies from Industry 4.0 into the servitization process, generating additional benefits and creating value for the customer (Ibarra et al. 2018 ; Grandinetti et al. 2020 ; Ciasullo et al. 2021 ; Bettiol et al. 2022 ). This digital transformation expands the scope of traditional services, allowing for greater customization and efficiency (Frank et al. 2019 ; Chen et al. 2021 ).
Digitalization facilitates data collection and analysis, improving decision-making, and enabling more predictive and proactive services (Lee et al. 2014 ; Chen et al. 2022a ; Rakic et al. 2022 ). Moreover, data-based digital capabilities are fundamental for the success of digital servitization, as they enhance both product support services and customer support services (Chen et al. 2023 ).
Digital servitization also promotes value co-creation and collaboration among manufacturers, suppliers, and customers, optimizing service delivery and strengthening relationships (Coreynen et al. 2017 ; Vendrell-Herrero et al. 2017 ; Kohtamäki et al. 2020b ; Sjödin et al. 2020 ). The business models of digital servitization are also influenced by Industry 4.0 technologies, such as Internet of Things and Big Data, enabling the development of more integrated and customer-centric solutions (Naik et al. 2020 ; Bortoluzzi et al. 2022 ; Minaya et al. 2023 ).
Furthermore, an integral aspect of the servitization landscape, especially in the digital era, is the evolution of Product-Service Systems (PSS). PSS represents a strategic approach that shifts the focus from selling products to offering a combination of products and services designed to fulfill specific customer needs more efficiently (Tukker and Tischner 2006 ; Baines et al. 2017 ). This transition to PSS reflects a broader industry movement toward sustainable and customer-centric business models, where the value proposition extends beyond the physical product to include personalized services. The advent of Industry 4.0 technologies has further propelled this evolution, leading to the development of Smart PSS. Smart PSS integrates digital technologies, such as the Internet of Things, Big Data, and Artificial Intelligence to enhance service delivery, improve customer experience and enable new forms of value creation (Chowdhury et al. 2018 ; Bortoluzzi et al. 2022 ). The adoption of these advanced technologies within PSS frameworks represents a significant leap in how companies’ approach servitization, allowing for greater customization, efficiency, and proactive engagement with customers. Therefore, understanding the role and impact of PSS, particularly Smart PSS, is crucial for comprehending the full scope of digital servitization and its implications for future business strategies.
4.2 Integrating smart product-service systems (smart PSS) into digital servitization: evolution, challenges, and opportunities
Product-Service Systems (PSS) epitomize an evolution in business models, integrating goods and services to fulfill customer needs sustainably and effectively (Galbraith 2002 ; Gebauer et al. 2011 ; Oliveira et al. 2015 ; Haase et al. 2017 ; Gaiardelli et al. 2021 ; Zhou and Song 2021 ). Tukker ( 2004 ) categorizes PSS into product oriented, use oriented, and result oriented, with each type offering distinct benefits, such as improved profit margins and differentiation from competitors (Tukker and Tischner 2006 ; Reim et al. 2015 ; Baines et al. 2017 ; Rabetino et al. 2017 ). Service-oriented PSS prioritize personalized customer experiences, requiring greater customer involvement (Matthyssens and Vandenbempt 2010 ; Cusumano et al. 2014 ; Zighan and Abualqumboz 2022 ).
The advent of Industry 4.0 technologies has given rise to Smart PSS, enhancing traditional PSS frameworks with digital capabilities and aligning with digital servitization’s goals to maximize customer value and competitive advantage (Chowdhury et al. 2018 ; Zheng et al. 2019 ; Wang et al. 2021 ; Bortoluzzi et al. 2022 ; Chen et al. 2023 ). Smart PSS incorporate Internet of Things, Big Data, and Artificial Intelligence to offer tailored services and predictive maintenance, thus improving product reliability and customer experience. However, transitioning to Smart PSS necessitates overcoming internal challenges, such as developing digital capabilities and adapting organizational culture, and external challenges like aligning strategies with customer and supplier expectations (Alghisi and Saccani 2015 ; Baines and Shi 2015 ; Ceci and Masini 2011 ; Mosch et al. 2021 ).
Business models in the context of Smart PSS vary from product centered to service oriented, depending on the company’s servitization maturity and technological capacity, leading to greater competitive differentiation and new market opportunities (Kowalkowski et al. 2017 ; Zheng et al. 2019 ; Baines et al. 2020 ; Chen et al. 2021 ). Implementing Smart PSS calls for a holistic approach, from strategic planning to system design and operational management, with a focus on how digital capabilities enhance PSS offerings and the overall value chain (Coreynen et al. 2017 ; Zheng et al. 2018 ).
In sum, the transition from traditional servitization to digital servitization, through the deployment of Smart PSS, marks a critical shift in value creation and sustaining customer loyalty, propelled by Industry 4.0 innovations (Vandermerwe and Rada 1988 ; Frank et al. 2019 ; Pinillos et al. 2022 ; Raddats et al. 2022 ; Schroeder et al. 2022 ; Chen et al. 2023 ; Martín-Peña et al. 2023 ). Realizing the potential of digital servitization demands an understanding of technological capabilities, fostering innovation, and market adaptability (Kohtamäki et al. 2019b ; Zhang et al. 2023 ). Successful digital servitization and Smart PSS rely on integrating technology with strategic vision and customer centricity, cultivating a business model focused on collaboration, innovation, and value co-creation (Naik et al. 2020 ; Chen et al. 2021 ; Zhou et al. 2021 ; Kolagar et al. 2022 ).
4.3 Digital servitization: crafting superior value in the modern era
As previously noted, servitization, as it evolves into digital servitization, catalyzes a profound and strategic transformation of business models and operational paradigms, emphasizing the importance of both internal and external strategic alignments. This process not only optimizes existing service offerings but also unlocks significant potential for service innovation and market competitiveness. Specifically, the integration of advanced technologies in digital servitization allows companies to create superior and customized value for their customers. This expanded value creation is achieved through a synergistic combination of technological resources and human capabilities, facilitating more predictive, personalized, and proactive services. Thus, digital servitization emerges as an essential and transformative step in business strategy, driving not only efficiency and strategic alignment but also fostering innovation and strengthening competitive positioning in the market.
Digital servitization, a contemporary evolution of traditional servitization, integrates Industry 4.0 technologies into the service domain, creating significant value for the customer. This value manifests in several key dimensions, all driven by digitalization and the emerging capabilities it offers.
Enhanced personalization and customer experience. The ability to collect and analyze large volumes of data using digital technologies enables companies to better understand the needs and preferences of their customers (Tao and Qi 2017 ; Chen et al. 2023 ). This leads to the creation of more personalized service offerings, tailored specifically to individual customer requirements. For instance, data analytics capabilities enhance servitization by enabling service personalization, which is fundamental for improving customer satisfaction and fostering long-term loyalty (Chen et al. 2022b ).
Efficiency and proactivity in service delivery. Digital servitization allows companies to be more efficient and proactive in delivering services. Technologies like the Internet of Things and Artificial Intelligence facilitate remote monitoring and predictive maintenance, anticipating problems before they occur and minimizing downtime (Lee et al. 2014 ; Tao and Qi 2017 ; Raddats et al. 2022 ). This not only improves product reliability but also reduces costs for the customer.
Creation of new opportunities and business models. The integration of digital services opens new avenues for innovative business models. For example, companies can offer usage-based solutions or subscriptions, where customers pay for performance or outcomes rather than the product itself (Vendrell-Herrero et al. 2017 ; Martín-Peña et al. 2020 ; Bortoluzzi et al. 2022 ). This can result in greater flexibility and more attractive cost options for the customer.
Enhanced customer–supplier relationships. Digital servitization fosters greater collaboration and value co-creation between suppliers and customers (Coreynen et al. 2017 ; Sjödin et al. 2020 ; Harrmann et al. 2023 ). This is because digital capabilities enable smoother communication and more transparent information exchange, resulting in stronger and more reliable relationships (Davies et al. 2023 ).
Continuous improvement of products and services. Ongoing feedback and data analysis enable continuous improvement of the products and services offered. Companies can quickly adjust their offerings in response to customer feedback or market changes, ensuring that their services remain relevant and of high quality (Chen et al. 2021 ).
Access to new markets. Digital servitization enables companies to access new markets and customer segments. By offering digital solutions, companies can overcome geographical and logistical barriers, reaching customers who were previously inaccessible (Münch et al. 2022 ; Rakic et al. 2022 ).
In summary, digital servitization not only enhances existing service offerings but also opens new opportunities for service innovation, strategic alignment, and market competitiveness. Its successful implementation is key to creating substantial value for the customer, highlighting the importance of a well-planned and executed strategy in the context of modern servitization.
5 Proposed conceptual framework: guiding the transition to digital servitization
Digital servitization represents a pivotal shift in the business landscape, where manufacturing companies evolve into providers of comprehensive solutions that seamlessly integrate products and services, augmented by digital technologies. This transformation is driven by the need for enhanced competitiveness, customer engagement, and value creation in a rapidly changing digital economy.
The development of our DASOBI conceptual framework, designed to guide the transition to digital servitization, is grounded in a rigorous methodological approach, underpinned by a comprehensive systematic literature review. This review meticulously synthesized three decades of academic research and industry insights, incorporating a total of 157 articles. Our comprehensive review process involved a deep analysis of the most influential and relevant publications in the field, among which notable contributions include Alghisi and Saccani ( 2015 ); Ayala et al. ( 2017 , 2019 ); Coreynen et al. ( 2017 ); Tao and Qi ( 2017 ); Vendrell-Herrero et al. ( 2017 ); Bustinza et al. ( 2018 ); Frank et al. ( 2019 ); Baines et al. ( 2020 ); Martín-Peña et al. ( 2020 ); Naik et al. ( 2020 ); Brax et al. ( 2021 ); Gaiardelli et al. ( 2021 ); Kohtamäki et al. ( 2021 ); Bettiol et al. ( 2022 ); Bortoluzzi et al. ( 2022 ); Marcon et al. ( 2022 ); Münch et al. ( 2022 ); Brekke et al. ( 2023 ); Chen et al. ( 2023 ); Chirumalla et al. ( 2023 ); Shen et al. ( 2023 ). These articles were particularly significant for identifying emerging trends, key challenges, and effective strategies in digital servitization. By systematically analyzing this extensive body of literature, we identified critical themes, challenges, strategies, and outcomes associated with the digital servitization journey. This analysis not only highlighted the multifaceted nature of digital servitization but also emphasized the critical importance of aligning strategic considerations, technological capabilities, and stakeholder roles to successfully navigate this complex transition. The structured framework presented herein not only reflects the evolution of the field but also provides clear guidance for manufacturing companies advancing toward more sophisticated and digitalized servitization practices.
The DASOBI framework, while empirically grounded in a comprehensive literature review, also draws extensively on classical and emerging theories to provide a robust theoretical foundation. For instance, diffusion of innovations theory (Rogers 2003 ) elucidates the “Drivers” and “Obstacles” in the adoption of digital servitization by explaining the rate and process through which new technological innovations spread within industries. Furthermore, the resource-based view (Barney 1991 ) is instrumental in understanding the “Strategies” component of the framework, emphasizing the importance of internal capabilities and resources in gaining a competitive advantage through digital transformation. These theoretical integrations not only enhance the academic rigor of our framework but also offer a deeper understanding of the multifaceted nature of digital servitization.
Therefore, the proposed DASOBI (Drivers, Actors, Strategies, Obstacles, Benefits, and Impact) model emerges as a synthesis of empirical evidence and theoretical insights, designed to offer a coherent and actionable guide for organizations seeking to embrace digital servitization.
This conceptual framework delineates a roadmap for organizations to navigate this complex transition. The framework identifies the core components essential for a successful journey toward digital servitization:
Underlying reasons for the shift (Drivers). Recognizing the strategic imperatives for transitioning toward a digital servitization model is critical. This includes understanding market dynamics, competitive pressures, and technological advancements driving this change.
Key actors involved (Actors). Successful digital servitization necessitates the involvement and alignment of various stakeholders, including internal teams, customers, technology partners, and suppliers. Their roles, expectations, and contributions are pivotal in shaping the servitization journey.
Strategic considerations and tools (Strategies). This encompasses adopting strategic frameworks, methodologies, and digital tools that are conducive to servitization. These tools and strategies should facilitate the integration of digital technologies with traditional product-service offerings, ensuring a seamless transition.
Potential challenges and obstacles (Obstacles). Identifying and addressing challenges such as cultural resistance, skill gaps, technological complexities, and integration issues with existing processes is crucial. Proactive strategies and contingency plans are essential to mitigate these barriers.
Anticipated benefits of the transition (Benefits). The transition to digital servitization should bring about significant benefits, including enhanced customer value, increased revenue streams, and improved competitive positioning. This component focuses on quantifying these benefits and aligning them with organizational goals.
Expected outcomes and impact (Impact). The final component of the framework revolves around the tangible outcomes and impacts of digital servitization. This includes enhanced customer satisfaction, increased market share, and improved operational efficiency.
In the digital servitization framework, the transition toward digital servitization, driven by market dynamics, competitive pressures, and technological advancements, is intrinsically linked to the roles and contributions of key stakeholders, such as internal teams, customers, and technology partners. Strategic considerations and tools must be selected in light of potential challenges, like cultural resistance and skill gaps, ensuring alignment with stakeholder capabilities and expectations for a seamless integration of digital technologies with traditional offerings. This strategic alignment is pivotal in overcoming obstacles and realizing anticipated benefits, such as enhanced customer value and competitive positioning. These benefits, in turn, lead to tangible outcomes, like improved customer satisfaction and operational efficiency, which feedback into the market, influencing ongoing strategic imperatives and shaping the evolution of digital servitization strategies. This dynamic interplay highlights a continuous feedback loop where outcomes inform underlying reasons, reinforcing the need for adaptability and strategic foresight in the digital servitization journey.
The contribution of the DASOBI framework to the existing literature is manifold. By synthesizing empirical findings with theoretical insights from servitization and digital transformation research, this framework addresses identified gaps, such as the integration of digital technologies in traditional servitization models and the management of organizational changes associated with such transitions (Baines and Lightfoot 2013 ; Vargo and Lusch 2008 ). Specifically, the DASOBI framework aids in conceptualizing how companies can strategically navigate the complexities of digital servitization, providing a structured approach that is missing in previous studies. This not only extends the theoretical discourse around servitization but also sets a foundation for future research to explore the dynamic interactions between digital technologies and service strategies in manufacturing sectors.
In conclusion, this conceptual framework serves as a comprehensive guide for firms embarking on the digital servitization journey. It provides a structured approach to understanding and implementing the necessary changes, ensuring a smooth transition and realization of the potential benefits of digital servitization. Figure 6 summarizes this meticulously formulated model (DASOBI), referred to as the Drivers (underlying reasons for the shift), Actors (key actors involved), Strategies (strategic considerations and tools), Obstacles (potential challenges and obstacles), Benefits (anticipated benefits of the transition), and Impact (expected outcomes and impact) of Digital Servitization Strategy, offers a robust framework for scholarly exploration, grounded in an exhaustive review of extant literature.
Source: Authors’ own work
Conceptual theoretical model for the analysis of Digital Servitization.
The DASOBI framework orchestrates the shift from traditional service strategies to digitally-enhanced service offerings, underpinned by the alignment of core elements: Drivers, Actors, Strategy, Obstacles, Benefits, and Impact. The model emphasizes a strategic approach, incorporating digital catalytic factors to augment adaptability, customer-centric analytics, and the pursuit of novel revenue streams through digital innovations.
Within this framework, the digital knowledge and capability development are crucial. Firms must harness Big Data to distill customer insights, leverage Artificial Intelligence for identifying opportunities, and increase the flexibility of their service offerings via digital platforms. The role of digital service providers is pivotal, offering expertise to mitigate transition risks, assure service quality, and bolster productivity with cutting-edge technological solutions.
However, the shift is not without its challenges. The resistance to digital transformation and the complexity of measuring profitability in the digital service landscape can impede progress. Moreover, the implications of Industry 4.0 are profound, necessitating organizational restructuring, workforce upskilling, and technological investments to realize the potential of digital servitization.
The anticipated benefits of this digital shift are manifold. Enhanced customer understanding through sophisticated data analytics, improved market positioning through digital innovation, and elevated creative capability with advanced technology are but a few of the advantages. Furthermore, embracing Industry 4.0 technologies within digital servitization amplifies these benefits, leading to superior product quality via smart manufacturing, greater adaptability in production, and increased operational efficiency ensuring timely delivery.
In summary, the DASOBI model meticulously integrates the transition to digital servitization with the digital economy’s imperatives, presenting a coherent roadmap for firms aspiring to harness the full spectrum of benefits offered by Industry 4.0 innovations.
6 Conclusions, limitations, and further research
This study embarked on an exhaustive journey through three decades of literature on servitization and its evolution toward digital servitization within the manufacturing sector. Through a systematic literature review, we explored the strategic transformation that involves integrating advanced services and digital technologies into product offerings, a change driven by the need to enhance competitiveness, customer engagement, and value creation in a rapidly evolving digital economy.
Our research findings have identified key drivers, actors, strategies, challenges, and benefits associated with the transition toward digital servitization. The DASOBI conceptual framework tries to provide a structured guide for understanding and managing this complex transition. This framework emphasizes the importance of recognizing the underlying reasons for adopting digital servitization models, the necessity of aligning and collaborating with diverse stakeholders, and the use of specific strategies to overcome the inherent challenges of this process.
Despite this study’s contribution to the body of knowledge on digital servitization, we acknowledge several limitations. The geographical concentration of the research activity analyzed might limit the generalizability of our findings across diverse cultural and economic contexts. The rapid evolution of digital technologies and business models also suggests that the relevance of our discoveries could be challenged by future developments. Additionally, our research focused primarily on manufacturing firms, which limits the applicability of the findings to other sectors.
These limitations open several avenues for future research. It is imperative to validate and test the generalizability of the DASOBI framework across various organizational and industry contexts. Further research is also needed to develop specific metrics that can measure the impacts of digital servitization. Longitudinal studies could provide a deeper understanding of how servitization strategies influence business outcomes over time.
This study contributes to the academic discussion by clarifying and deepening the concept of servitization and its intersection with digitalization, offering an integrative view that can assist manufacturing firms in navigating the complex landscape of servitization and digital servitization. Although we have tried to establish a solid foundation for future research, it is evident that the field of digital servitization remains dynamic and evolving, requiring ongoing examination to fully comprehend its impact on business strategy and practice.
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Alghisi A, Saccani N (2015) Internal and external alignment in the servitization journey—overcoming the challenges. Prod Plann Control 26:1219–1232. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537287.2015.1033496
Article Google Scholar
Ayala NF, Paslauski CA, Ghezzi A, Frank AG (2017) Knowledge sharing dynamics in service suppliers’ involvement for servitization of manufacturing companies. Int J Prod Econ 193:538–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2017.08.019
Ayala NF, Gerstlberger W, Frank AG (2019) Managing servitization in product companies: the moderating role of service suppliers. Int J Oper Prod Manag 39(1):43–74. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOPM-08-2017-0484
Baines T, Lightfoot H (2013) Servitization of the manufacturing firm: exploring the operations practices and technologies that deliver advanced services. Int J Oper Prod Manag 34(1):2–35. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOPM-02-2012-0086
Baines T, Shi VG (2015) A Delphi study to explore the adoption of servitization in UK companies. Prod Plann Control 26:1171–1187. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537287.2015.1033490
Baines T, Lightfoot HW, Evans S, Neely A et al (2007) State-of-the-art in product-service systems. J Eng Manuf 221(10):1543–1552. https://doi.org/10.1243/09544054JEM858
Baines T, Lightfoot H, Benedettini O, Kay JM (2009a) The servitization of manufacturing: a review of literature and reflection on future challenges. J Manuf Technol Manag 20(5):547–567. https://doi.org/10.1108/17410380910960984
Baines T, Lightfoot H, Peppard J, Johnson M et al (2009b) Towards an operations strategy for product-centric servitization. Int J Oper Prod Manag 29(5):494–519. https://doi.org/10.1108/01443570910953603
Baines T, Lightfoot H, Smart P (2011) Servitization within manufacturing: exploring the provision of advanced services and their impact on vertical integration. J Manuf Technol Manag 22(7):947–954. https://doi.org/10.1108/17410381111160988
Baines T, Ziaee Bigdeli A, Bustinza OF, Shi VG et al (2017) Servitization: revisiting the state-of-the-art and research priorities. Int J Oper Prod Manag 37(2):256–278. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOPM-06-2015-0312
Baines T, Ziaee Bigdeli A, Sousa R, Schroeder A (2020) Framing the servitization transformation process: a model to understand and facilitate the servitization journey. Int J Prod Econ 221:1–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2019.07.036
Barney J (1991) Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. J Manag 17(1):99–120
Google Scholar
Barquet APB, De Oliveira MG, Amigo CR, Cunha VP, Rozenfeld H (2013) Employing the business model concept to support the adoption of product-service systems (PSS). Ind Mark Manag 42(5):693–704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2013.05.003
Bastl M, Johnson M, Lightfoot H, Evans S (2012) Buyer-supplier relationships in a servitized environment. Int J Oper Prod Manag 32(6):650–675. https://doi.org/10.1108/01443571211230916
Benedettini O, Neely A, Swink M (2015) Why do servitized firms fail? A risk-based explanation. Int J Oper Prod Manag 35(6):946–979. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOPM-02-2014-0052
Bettiol M, Capestro M, Di Maria E, Micelli S (2022) Overcoming pandemic challenges through product innovation: the role of digital technologies and servitization. Eur Manag J 40(5):707–717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emj.2022.05.003
Bortoluzzi G, Chiarvesio M, Romanello R, Tabacco R, Veglio V (2022) Servitisation and performance in the business-to-business context: the moderating role of Industry 4.0 technologies. J Manuf Technol Manag 33(9):108–128. https://doi.org/10.1108/JMTM-08-2021-0317
Brady T, Davies A, Gann D (2005) Creating value by delivering integrated solutions. Int J Proj Manag 23(5):360–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijproman.2005.01.001
Brax SA (2005) A manufacturer becoming service provider—challenges and a paradox. Manag Serv Qual 15(2):142–155. https://doi.org/10.1108/09604520510585334
Brax SA, Jonsson K (2009) Developing integrated solution offerings for remote diagnostics: a comparative case study of two manufacturers. Int J Oper Prod Manag 29(5):539–560. https://doi.org/10.1108/01443570910953621
Brax SA, Calabrese A, Levialdi Ghiron N, Tiburzi L, Gronroos C (2021) Explaining the servitization paradox: a configurational theory and a performance measurement framework. Int J Oper Prod Manag 41(5):517–546. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOPM-08-2020-0535
Brekke T, Lenka S, Kohtamaki M, Parida V, Solem BAA (2023) Overcoming barriers to transformation in manufacturing firms. A path-dependence perspective of digital servitization. Rev Manag Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11846-023-00641-0
Bustinza OF, Bigdeli AZ, Baines T, Elliot C (2015) Servitization and competitive advantage: the importance of organizational structure and value chain position. Res Technol Manag 58:53–60. https://doi.org/10.5437/08956308X5805354
Bustinza OF, Gomes E, Vendrell-Herrero F, Tarba SY (2018) An organizational change framework for digital servitization: evidence from the Veneto region. Strateg Change 27:111–119. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsc.2186
Calabrese A, Levialdi Ghiron N, Tiburzi L, Baines T, Ziaee Bigdeli A (2019) The measurement of degree of servitization: literature review and recommendations. Prod Plann Control 30:1118–1135. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537287.2019.1592260
Ceci F, Masini A (2011) Balancing specialized and generic capabilities in the provision of integrated solutions. Ind Corp Change 20(1):91–131. https://doi.org/10.1093/icc/dtq069
Chen Y, Visnjic I, Parida V, Zhang Z (2021) On the road to digital servitization—the (dis)continuous interplay between business model and digital technology. Int J Oper Prod Manag 41(5):694–722. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOPM-08-2020-0544
Chen M, Pu X, Zhang M, Cai Z et al (2022a) Data analytics capability and servitization: the moderated mediation role of bricolage and innovation orientation. Int J Oper Prod Manag 42(4):440–470. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOPM-10-2021-0663
Chen Y, Wu Z, Yi W, Wang B et al (2022b) Bibliometric method for manufacturing servitization: a review and future research directions. Sustainability 14:1–26. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148743
Chen L, Dai Y, Ren F, Dong X (2023) Data-driven digital capabilities enable servitization strategy—from service supporting the product to service supporting the client. Technol Forecast Soc Change 197:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2023.122901
Chirumalla K, Leoni L, Oghazi P (2023) Moving from servitization to digital servitization: identifying the required dynamic capabilities and related microfoundations to facilitate the transition. J Bus Res 158:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2023.113668
Chowdhury S, Haftor D, Pashkevich N (2018) Smart product-service systems (Smart PSS) in industrial firms: a literature review. Procedia CIRP 73:26–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2018.03.333
Ciasullo MV, Polese F, Montera R, Carrubbo L (2021) A digital servitization framework for viable manufacturing companies. J Bus Ind Mark 36(13):142–160. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-07-2020-0349
Coreynen W, Matthyssens P, Van Bockhaven W (2017) Boosting servitization through digitization: pathways and dynamic resource configurations for manufacturers. Ind Mark Manag 60:42–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2016.04.012
Cusumano MA (2008) The changing software business: moving from products to services. Computer 41:20–27. https://doi.org/10.1109/MC.2008.29
Cusumano MA, Kahl SJ, Suárez FF (2014) Services, industry evolution, and the competitive strategies of product firms. Strateg Manag J 36:559–575. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2378868
Dalenogare LS, Benitez GB, Ayala NF, Frank AG (2018) The expected contribution of Industry 4.0 technologies for industrial performance. Int J Prod Econ 204:383–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2018.08.019
Davies A, Brady T, Hobday M (2007) Organizing for solutions: systems seller vs. systems integrator. Ind Mark Manag 36(2):183–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2006.04.009
Davies P, Bustinza OF, Parry G, Jovanovic M (2023) Unpacking the relationship between digital capabilities, services capabilities, and firm financial performance: a moderated mediation model. Ind Mark Manag 115:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2023.09.005
Díaz-Garrido E, Pinillos MJ, Soriano-Pinar I, García-Magro C (2018) Changes in the intellectual basis of servitization research: a dynamic analysis. J Eng Technol Manag JET M 48:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jengtecman.2018.01.005
Durugbo C (2014) Strategic framework for industrial product-service co-design: findings from the microsystems industry. Int J Prod Res 52:2881–2900. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2013.857054
Eggert A, Hogreve J, Ulaga W, Muenkhoff E (2014) Revenue and profit implications of industrial service strategies. J Serv Res 17:23–39. https://doi.org/10.1177/1094670513485823
Favoretto C, Mendes G, Oliveira M, Cauchick-Miguel P, Coreynen W (2022) From servitization to digital servitization: how digitalization transforms companies’ transition towards services. Ind Mark Manag 102:104–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2022.01.003
Frank AG, Mendes GHS, Ayala NF, Ghezzi A (2019) Servitization and Industry 4.0 convergence in the digital transformation of product firms: a business model innovation perspective. Technol Forecast Soc Change 141:341–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2019.01.014
Gaiardelli P, Songini L, Saccani N (2014) The automotive industry: heading towards servitization in turbulent times. Servitization in Industry. Springer, Cham
Gaiardelli P, Pezzotta G, Rondini A, Romero D et al (2021) Product-service systems evolution in the era of Industry 4.0. Serv Bus 15:177–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11628-021-00438-9
Galbraith JR (2002) Organizing to deliver solutions. Organ Dyn 31(2):194–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0090-2616(02)00101-8
García Martin PC, Schroeder A, Bigdeli AZ (2019) The value architecture of servitization: expanding the research scope. J Bus Res 104:438–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.04.010
Gebauer H (2008) Identifying service strategies in product manufacturing companies by exploring environment—strategy configurations. Ind Mark Manage 37(3):278–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2007.05.018
Gebauer H, Fleisch E (2007) An investigation of the relationship between behavioral processes, motivation, investments in the service business and service revenue. Ind Mark Manag 36(3):337–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2005.09.005
Gebauer H, Kowalkowski C (2012) Customer-focused and service-focused orientation in organizational structures. J Bus Ind Mark 27(7):527–537. https://doi.org/10.1108/08858621211257293
Gebauer H, Elgar F, Thomas F (2005) Overcoming the service paradox in manufacturing companies. Eur Manag J 23:14–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emj.2004.12.006
Gebauer H, Gustafsson A, Witell L (2011) Competitive advantage through service differentiation by manufacturing companies. J Bus Res 64(12):1270–1280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2011.01.015
Gebauer H, Paiola M, Saccani N (2013) Characterizing service networks for moving from products to solutions. Ind Mark Manag 42:31–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2012.11.002
Grandinetti R, Ciasullo MV, Paiola M, Schiavone F (2020) Fourth industrial revolution, digital servitization and relationship quality in Italian B2B manufacturing firms. Explor Study TQM J 32(4):647–671. https://doi.org/10.1108/TQM-01-2020-0006
Haase RP, Pigosso DCA, McAloone TC (2017) Product/service-system origins and trajectories: a systematic literature review of PSS definitions and their characteristics. Procedia CIRP 64:157–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2017.03.053
Harrmann LK, Eggert A, Böhm E (2023) Digital technology usage as a driver of servitization paths in manufacturing industries. Eur J Mark 57(3):834–857. https://doi.org/10.1108/EJM-11-2021-0914
Hertzberg S, Rudner L (1999) Quality of researchers’ searches of the ERIC database. Educ Policy Anal Arch. https://doi.org/10.14507/epaa.v7n25.1999
Hyun M, Kim J (2021) Challenge or opportunity? A case of tire rental servitization from financial and channel perspectives. Serv Bus 15:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11628-020-00433-6
Ibarra D, Ganzarain J, Igartua JI (2018) Business model innovation through Industry 4.0: a review. Procedia Manuf 22:4–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PROMFG.2018.03.002
Johnson M, Mena C (2008) Supply chain management for servitised products: a multi-industry case study. Int J Prod Econ 114:27–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2007.09.011
Johnstone S, Dainty A, Wilkinson A (2009) Integrating products and services through life: an aerospace experience. Int J Oper Prod Manag 29(5):520–538. https://doi.org/10.1108/01443570910953612
Kamp B, Alcalde H (2014) Servitization in the basque economy. Strateg Change 23:359–374. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsc.1982
Kamp B, Parry G (2017) Servitization and advanced business services as levers for competitiveness. Ind Mark Manag 60:11–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2016.12.008
Kanninen T, Penttinen E, Tinnilä M, Kaario K (2017) Exploring the dynamic capabilities required for servitization: the case process industry. Bus Process Manag J 23(2):226–247. https://doi.org/10.1108/BPMJ-03-2015-0036
Kans M, Ingwald A (2016) Business model development towards service management 4.0. Procedia CIRP 47:489–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PROCIR.2016.03.228
Khanra S, Dhir A, Parida V, Kohtamäki M (2021) Servitization research: a review and bibliometric analysis of past achievements and future promises. J Bus Res 131:151–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.03.056
Kharlamov AA, Parry G (2021) The impact of servitization and digitization on productivity and profitability of the firm: a systematic approach. Prod Plann Control 32:185–197. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537287.2020.1718793
Kimita K, McAloone T, Ogata K, Pigosso D (2022) Servitization maturity model: developing distinctive capabilities for successful servitization in manufacturing companies. J Manuf Technol Manag 33(9):61–87. https://doi.org/10.1108/JMTM-07-2021-0248
Kindström D, Kowalkowski C (2014) Service innovation in product-centric firms: a multidimensional business model perspective. J Bus Ind Mark 29(2):96–111. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-08-2013-0165
Kohtamaki M, Henneberg SC, Martinez V, Kimita K, Gebauer H (2019a) A configurational approach to servitization: review and research directions. Serv Sci 11(3):1–29. https://doi.org/10.1287/serv.2019.0245
Kohtamaki M, Rabetino R, Einola S, Parida V, Patel P (2021) Unfolding the digital servitization path from products to product-service-software systems: practicing change through intentional narratives. J Bus Res 137:379–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.08.027
Kohtamäki M, Partanen J (2016) Co-creating value from knowledge-intensive business services in manufacturing firms: the moderating role of relationship learning in supplier-customer interactions. J Bus Res 69(7):2498–2506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2016.02.019
Kohtamäki M, Parida V, Oghazi P, Gebauer H, Baines T (2019b) Digital servitization business models in ecosystems: a theory of the firm. J Bus Res 104:380–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.06.027
Kohtamäki M, Einola S, Rabetino R (2020a) Exploring servitization through the paradox lens: coping practices in servitization. Int J Prod Econ 226:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2020.107619
Kohtamäki M, Parida V, Patel P, Gebauer H (2020b) The relationship between digitalization and servitization: the role of servitization in capturing the financial potential of digitalization. Technol Forecast Soc Change 151:1–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2019.119804
Kolagar M, Parida V, Sjödin D (2022) Ecosystem transformation for digital servitization: a systematic review, integrative framework, and future research agenda. J Bus Res 146:176–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2022.03.067
Kowalkowski C, Gebauer H, Kamp B, Parry G (2017) Servitization and deservitization: overview, concepts, and definitions. Ind Mark Manag 60:4–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2016.12.007
Kreye ME, Roehrich JK, Lewis MA (2015) Servitizing manufacturers: the impact of service complexity and contractual and relational capabilities. Prod Plann Control 26:1233–1246. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537287.2015.1033489
Le-Dain MA, Benhayoun L, Matthews J, Liard M (2023) Barriers and opportunities of digital servitization for SMEs: the effect of smart product-service system business models. Serv Bus 17:359–393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11628-023-00520-4
Lee J, Kao HA, Yang S (2014) Service innovation and smart analytics for Industry 4.0 and big data environment. Procedia CIRP 16:3–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2014.02.001
Leoni L, Aria M (2021) A thirty-year bibliometric analysis on servitization. Int J Serv Sci Manag Eng Technol 12(3):73–95. https://doi.org/10.4018/IJSSMET.2021050105
Levitt T (1972) Production-line approach to service. Harv Bus Rev 50:41–52
Lightfoot H, Baines T, Smart P (2013) The servitization of manufacturing: a systematic literature review of interdependent trends. Int J Oper Prod Manag 33(11/12):1408–1434. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOPM-07-2010-0196
Lindman M, Pennanen K, Rothenstei J, Scozzi B, Vincze Z (2016) The value space: how firms facilitate value creation. Bus Process Manag J 22(4):736–762. https://doi.org/10.1108/BPMJ-09-2015-0126
Luoto S, Brax SA, Kohtamäki M (2017) Critical meta-analysis of servitization research: constructing a model-narrative to reveal paradigmatic assumptions. Ind Mark Manag 60:89–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2016.04.008
Manzini E, Vezzoli C (2003) A strategic design approach to develop sustainable product service systems: examples taken from the ‘environmentally friendly innovation’ Italian prize. J Clean Prod 11(8):851–857. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0959-6526(02)00153-1
Marcon É, Marcon A, Ayala NF, Frank AG et al (2022) Capabilities supporting digital servitization: a multi-actor perspective. Ind Mark Manag 103:97–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2022.03.003
Martínez V, Bastl M, Kingston J, Evans S (2010) Challenges in transforming manufacturing organizations into product-service providers. J Manuf Technol Manag 21(4):449–469. https://doi.org/10.1108/17410381011046571
Martín-Peña ML, Ziaee Bigdeli A (2016) Servitization: academic research and business practice. Univ Bus Rev 49:18–31
Martín-Peña ML, Pinillos MJ, Reyes LE (2017) The intellectual basis of servitization: a bibliometric analysis. J Eng Technol Manag JET M 43:83–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jengtecman.2017.01.005
Martín-Peña ML, Díaz-Garrido E, Sánchez-López JM (2018) The digitalization and servitization of manufacturing: a review on digital business models. Strateg Change 27:91–99. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsc.2184
Martín-Peña ML, Sánchez-López JM, Díaz-Garrido E (2020) Servitization and digitalization in manufacturing: the influence on firm performance. J Bus Ind Mark 35(3):564–574. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-12-2018-0400
Martín-Peña ML, Sanchez-Lopez JM, Kamp B, Gimenez-Fernandez EM (2023) The innovation antecedents behind the servitization-performance relationship. R D Manag 53:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1111/radm.12586
Mathieu V (2001) Service strategies within the manufacturing sector: benefits, costs and partnership. Int J Serv Ind Manag 12(5):451–475. https://doi.org/10.1108/EUM0000000006093
Matthyssens P, Vandenbempt K (2010) Service addition as business market strategy: identification of transition trajectories. J Serv Manag 21(5):693–714. https://doi.org/10.1108/09564231011079101
Minaya PE, Avella L, Trespalacios JA (2023) The effects of digital servitization on business competitiveness: A case study of Spanish manufacturers. J Int Entrep 21:180–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10843-023-00333-6
Momeni K, Raddats C, Martinsuo M (2023) Mechanisms for developing operational capabilities in digital servitization. Int J Oper Prod Manag 43(13):101–127. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOPM-04-2022-0259
Mont O (2002) Clarifying the concept of product-service system. J Clean Prod 10(3):237–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0959-6526(01)00039-7
Mosch P, Schweikl S, Obermaier R (2021) Trapped in the supply chain? Digital servitization strategies and power relations in the case of an industrial technology supplier. Int J Prod Econ 236:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2021.108141
Müller JM, Buliga O, Voigt KI (2021) The role of absorptive capacity and innovation strategy in the design of Industry 4.0 business models—a comparison between SMEs and large enterprises. Eur Manag J 39(3):333–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emj.2020.01.002
Münch C, Marx E, Benz L, Hartmann E, Matzner M (2022) Capabilities of digital servitization: evidence from the socio-technical systems theory. Technol Forecast Soc Change 176:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.121361
Naik P, Schroeder A, Kapoor K, Ziaee Bigdeli A (2020) Behind the scenes of digital servitization: actualising IoT-enabled affordances. Ind Mark Manag 89:232–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2020.03.010
Neely A, Benedettini O, Visnjic I (2011) The servitization of manufacturing: further evidence. University of Cambridge, Cambridge, pp 1–11
Nordin F, Kowalkowski C (2010) Solutions offerings: a critical review and reconceptualization. J Serv Manag 21(4):441–459. https://doi.org/10.1108/09564231011066105
Oliva R, Kallenberg R (2003) Managing the transition from products to services. Int J Serv Ind Manag 14(2):160–172. https://doi.org/10.1108/09564230310474138
Oliveira MG, Mendes GH, Rozenfeld H (2015) Bibliometric analysis of the product-service system research field. Procedia CIRP 30:114–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2015.02.139
Opazo-Basáez M, Vendrell-Herrero F, Bustinza OF (2021) Digital service innovation: a paradigm shift in technological innovation. J Serv Manag 33:97–120. https://doi.org/10.1108/JOSM-11-2020-0427
Ostrom AL, Bitner MJ, Brown SW, Burkhard KA et al (2010) Moving forward and making a difference: research priorities for the science of service. J Serv Res 13:4–36. https://doi.org/10.1177/1094670509357611
Paiola M, Gebauer H (2020) Internet of things technologies, digital servitization and business model innovation in BtoB manufacturing firms. Ind Mark Manag 89:245–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2020.03.009
Paiola M, Saccani N, Perona M, Gebauer H (2013) Moving from products to solutions: strategic approaches for developing capabilities. Eur Manag J 31(4):390–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emj.2012.10.002
Parida V, Sjödin DR, Wincent J, Kohtamäki M (2014) Mastering the transition to product-service provision: insights into business models, learning activities, and capabilities. Res Technol Manag 57:44–52. https://doi.org/10.5437/08956308X5703227
Paschou T, Rapaccini M, Adrodegari F, Saccani N (2020) Digital servitization in manufacturing: a systematic literature review and research agenda. Ind Mark Manag 89:278–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2020.02.012
Pessôa MVP, Becker JMJ (2017) Overcoming the product-service model adoption obstacles. Procedia CIRP 64:163–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2017.03.062
Pettigrew AM (1988) The management of strategic change. B. Blackwell, Oxford
Pinillos MJ, Díaz-Garrido E, Martín-Peña ML (2022) The origin and evolution of the concept of servitization: a co-word and network analysis. J Bus Ind Mark 37(7):1497–1514. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-02-2021-0120
Pombo D, Franco M (2023) A qualitative investigation of infusing products with service via strategic alliances among SMEs: a case of servitization. Serv Bus 17:529–555. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11628-023-00530-2
Pye A, Pettigrew A (2005) Studying board context, process and dynamics: some challenges for the future. Brit J Manag 16:27–38. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8551.2005.00445.x
Qi Y, Mao Z, Zhang M, Guo H (2020) Manufacturing practices and servitization: the role of mass customization and product innovation capabilities. Int J Prod Econ 228:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2020.107747
Rabetino R, Kohtamäki M, Gebauer H (2017) Strategy map of servitization. Int J Prod Econ 192:144–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2016.11.004
Rabetino R, Kohtamäki M, Brax SA, Sihvonen J (2021) The tribes in the field of servitization: discovering latent streams across 30 years of research. Ind Mark Manag 95:70–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2021.04.005
Rabetino R, Kohtamäki M, Huikkola T (2023) Digital service innovation (DSI): a multidisciplinary (re)view of its origins and progress using bibliometric and text mining methods. J Serv Manag. https://doi.org/10.1108/JOSM-12-2022-0375
Raddats C (2011) Aligning industrial services with strategies and sources of market differentiation. J Bus Ind Mark 26(5):332–343. https://doi.org/10.1108/08858621111144398
Raddats C, Baines T, Burton J, Story VM, Zolkiewski J (2016) Motivations for servitization: the impact of product complexity. Int J Oper Prod Manag 36(5):572–591. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOPM-09-2014-0447
Raddats C, Zolkiewski J, Story VM, Burton J et al (2017) Interactively developed capabilities: evidence from dyadic servitization relationships. Int J Oper Prod Manag 37(3):382–400. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOPM-08-2015-0512
Raddats C, Kowalkowski C, Benedettini O, Burton J, Gebauer H (2019) Servitization: a contemporary thematic review of four major research streams. Ind Mark Manag 83:207–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2019.03.015
Raddats C, Naik P, Ziaee Bigdeli A (2022) Creating value in servitization through digital service innovations. Ind Mark Manag 104:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2022.04.002
Rakic S, Pero M, Sianesi A, Marjanovic U (2022) Digital servitization and firm performance: technology intensity approach. Eng Econ 33(4):398–413. https://doi.org/10.5755/j01.ee.33.4.29649
Reim W, Parida V, Örtqvist D (2015) Product-Service Systems (PSS) business models and tactics—a systematic literature review. J Clean Prod 97:61–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2014.07.003
Reim W, Sjödin DR, Parida V (2019) Servitization of global service network actors—a contingency framework for matching challenges and strategies in service transition. J Bus Res 104:461–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.01.032
Rogers EM (2003) Diffusion of innovations. Free Press, New York
Ruiz-Martín A, Díaz-Garrido E (2021) A review of servitization theoretical foundations. J Ind Eng Manag 14(3):496–519. https://doi.org/10.3926/jiem.3466
Sandström S, Edvardsson B, Kristensson P, Magnusson P (2008) Value in use through service experience. Manag Serv Qual 18(2):112–126. https://doi.org/10.1108/09604520810859184
Santamaría L, Jesús Nieto M, Miles I (2012) Service innovation in manufacturing firms: evidence from Spain. Technovation 32(2):144–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.technovation.2011.08.006
Schroeder A, Baines T, Sakao T (2022) Increasing value capture by enhancing manufacturer commitment-managing the servitization process. IEEE Eng Manag Rev 50(3):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1109/EMR.2022.3197075
Shen L, Sun W, Parida V (2023) Consolidating digital servitization research: a systematic review, integrative framework, and future research directions. Technol Forecast Soc Change 191:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2023.122478
Sjödin D, Parida V, Kohtamaki M, Wincent J (2020) An agile co-creation process for digital servitization: a micro-service innovation approach. J Bus Res 112:478–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.01.009
Sousa R, Da Silveira G (2017) Capability antecedents and performance outcomes of servitization: differences between basic and advanced services. Int J Oper Prod Manag 37(4):444–467. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOPM-11-2015-0696
Spring M, Araujo L (2013) Beyond the service factory: service innovation in manufacturing supply networks. Ind Mark Manag 42:59–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2012.11.006
Tao F, Qi Q (2017) New IT driven service-oriented smart manufacturing: framework and characteristics. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern -Syst 49:81–91. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2017.2723764
Thomé AMT, Scavarda LF, Scavarda AJ (2016) Conducting systematic literature review in operations management. Prod Plann Control 27(5):408–420. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537287.2015.1129464
Tian J, Coreynen W, Matthyssens P, Shen L (2022) Platform-based servitization and business model adaptation by established manufacturers. Technovation 118:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.technovation.2021.102222
Tranfield D, Denyer D, Smart P (2003) Towards a methodology for developing evidence-informed management knowledge by means of systematic review. Brit J Manag 14:207–222. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8551.00375
Tronvoll B, Sklyar A, Sorhammar D, Kowalkowski C (2020) Transformational shifts through digital servitization. Ind Mark Manag 89:293–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2020.02.005
Tukker A (2004) Eight types of product-service system: eight ways to sustainability? Experience from SusProNet. Bus Strategy Environ 13:246–260. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.414
Tukker A (2015) Product services for a resource-efficient and circular economy—a review. J Clean Prod 97:76–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2013.11.049
Tukker A, Tischner U (2006) Product-services as a research field: past, present and future. Reflections from a decade of research. J Clean Prod 14(17):1552–1556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2006.01.022
Tuli KR, Kohli AK, Bharadwaj SG (2007) Rethinking customer solutions: from product bundles to relational processes. J Mark 71(3):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1509/jmkg.71.3.1
Vandermerwe S, Rada J (1988) Servitization of business: adding value by adding services. Eur Manag J 6(4):314–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/0263-2373(88)90033-3
Vargo SL, Lusch RF (2008) Service-dominant logic: continuing the evolution. J Acad Mark Sci 36(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-007-0069-6
Vendrell-Herrero F, Bustinza OF, Parry G, Georgantzis N (2017) Servitization, digitization and supply chain interdependency. Ind Mark Manag 60:69–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2016.06.013
Visnjic I, Van Looy B (2013) Servitization: disentangling the impact of service business model innovation on manufacturing firm performance. J Oper Manag 31(4):169–180. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2407380
Wang W, Lai K, Shou Y (2018) The impact of servitization on firm performance: a meta-analysis. Int J Oper Prod Manag 38(7):1562–1588. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOPM-04-2017-0204
Wang Z, Chen CH, Zheng P, Li X, Khoo LP (2021) A graph-based context-aware requirement elicitation approach in smart product-service systems. Int J Prod Res 59(2):635–651. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2019.1702227
Windahl C, Lakemond N (2006) Developing integrated solutions: the importance of relationships within the network. Ind Mark Manag 35(7):806–818. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.INDMARMAN.2006.05.010
Xing Y, Liu Y, Davies P (2023) Servitization innovation: a systematic review, integrative framework, and future research directions. Technovation 122:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.technovation.2022.102641
Yan K, Li G, Cheng TCE (2020) The impact of service-oriented organizational design factors on firm performance: the moderating role of service-oriented corporate culture. Int J Prod Econ 228:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2020.107745
Yu Y, Sung TJ (2023) A value-based view of the smart PSS adoption: a study of smart kitchen appliances. Serv Bus 17:499–527. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11628-023-00529-9
Zhang W, Banerji S (2017) Challenges of servitization: a systematic literature review. Ind Mark Manag 65:217–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2017.06.003
Zhang K, Feng L, Wang J, Lin KY, Li Q (2023) Servitization in business ecosystem: a systematic review and implications for business-to-business servitization research. Technol Anal Strateg Manag 35(11):1480–1496. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537325.2021.2010698
Zheng P, Lin T, Chen C, Xu X (2018) A systematic design approach for service innovation of smart product-service systems. J Clean Prod 201:657–667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.101
Zheng P, Liu Y, Tao F, Wang Z, Chen C (2019) Smart product-service systems solution design via hybrid crowd sensing approach. IEEE Access 7:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2939828
Zhou C, Song W (2021) Digitalization as a way forward: a bibliometric analysis of 20 years of servitization research. J Clean Prod 300:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126943
Zhou D, Yan T, Dai W, Feng J (2021) Disentangling the interactions within and between servitization and digitalization strategies: a service-dominant logic. Int J Prod Econ 238:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2021.108175
Ziaee Bigdeli A, Baines T, Bustinza OF, Guang Shi V (2017) Organisational change towards servitization: a theoretical framework. Compet Rev 27(1):12–39. https://doi.org/10.1108/CR-03-2015-0015
Ziaee Bigdeli A, Baines T, Schroeder A, Brown S (2018) Measuring servitization progress and outcome: the case of ‘advanced services.’ Prod Plann Control 29(4):315–332. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537287.2018.1429029
Zighan S, Abualqumboz M (2022) Dual focus: service-product orientation to manage the change paradox following servitization strategy. Serv Bus 16:29–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11628-022-00483-y
Download references
Open Access funding provided thanks to the CRUE-CSIC agreement with Springer Nature.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Management and Business Economics Department, University of Leon, Leon, Spain
Pedro E. Minaya
Business Administration Department, University of Oviedo, Oviedo, Spain
Lucía Avella & Juan A. Trespalacios
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Pedro E. Minaya .
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Minaya, P.E., Avella, L. & Trespalacios, J.A. Synthesizing three decades of digital servitization: a systematic literature review and conceptual framework proposal. Serv Bus (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11628-024-00559-x
Download citation
Received : 28 September 2023
Accepted : 16 April 2024
Published : 08 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11628-024-00559-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Digital servitization
- Industry 4.0
- Product-service system
- Systematic literature review
- Business competitiveness
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

Mumbai: Proposal seeks to make English optional for Std XI, XII students
I f the new draft proposal of the State Curriculum Framework (SCF) gets a thumbs up from stakeholders and no one objects to it, English will no longer be mandatory for Std XI and XII students in government schools and junior colleges across the state. The Maharashtra State Council for Educational Research and Training (SCERT) has invited objections and suggestions from stakeholders until June 3.
English has been a mandatory subject from Std I to XII. However, according to the draft proposal released by the SCF of SCERT on Wednesday, starting from the new academic year, students will no longer have English as a compulsory subject for Std XI and XII. Instead, they can choose two languages: one Indian and one international/foreign language, including English, the proposal suggests.
Kamaladevi Awate, in charge of SCF-SCERT , told mid-day, “This is just a draft proposal. The final draft will be prepared incorporating the feedback from the stakeholders. If the majority of stakeholders give their feedback in favour of making English an elective, we will go ahead with that. If we receive objections against the proposed change, we will not make the changes. So, it now depends on the feedback we receive.”
Multidisciplinary education
As per the draft proposal, Std XI and XII students will be able to select eight subjects in total: two languages (one has to be an Indian language and the second an international/foreign language), environmental education, physical education, and four other subjects of their choice. The SCF aims to eventually remove stream-specific (Arts, Commerce, Science) learning and promote multidisciplinary education.
“One of the languages must be of Indian origin, according to the SCF’s language chart, which lists 17 native Indian languages and nine foreign languages, with English being one of them. It will be the child`s choice, and depending on the availability at their respective school or junior college, the student can elect to study Russian, French, Spanish, German, or any other language too. The idea is to promote multilingualism in line with the NCF,” added Awate.
The list of native languages includes Marathi, Sanskrit, Hindi, Gujarati, Urdu, Kannada, Tamil, Telugu, Malayalam, Sindhi, Bengali, Punjabi, Pali, Ardhamagadhi, Maharashtri Prakrit and Avesta-Pahlavi. Tongues classified as non-native or foreign are English, German, French, Russian, Japanese, Spanish, Chinese, Persian and Arabic.
The first draft of the curriculum framework, which was largely a replica of the National Curriculum Framework for Foundation Stage (NCF-FS), was released in October last year for public feedback. The state received over 2,000 responses, following which some tweaks were made to the document. The latest draft was released on Wednesday.
Ancient wisdom
Apart from this, the new curriculum framework, prepared by a committee of education experts, also mentions the inclusion of the Indian Knowledge System—yoga, astronomy, dancing, Kathak, Odissi, etc, as part of the formal education system. The draft proposal also mentions that henceforth, experiential learning and teaching methods should be used to develop effective communication, discussion, and writing skills in languages. It states that this should include all literary genres in prose and poetry (both ancient and modern). Lifelong enrichment should be provided through reading, speaking, conversation and writing, the framework further states.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management" Example research proposal #2: "Medical Students as Mediators of ...
The purpose of the research proposal (its job, so to speak) is to convince your research supervisor, committee or university that your research is suitable (for the requirements of the degree program) and manageable (given the time and resource constraints you will face). The most important word here is "convince" - in other words, your ...
Here is an explanation of each step: 1. Title and Abstract. Choose a concise and descriptive title that reflects the essence of your research. Write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. It should provide a brief overview of your proposal. 2.
Conduct a literature review for your research proposal. 4. Define a research gap and research question. 5. Establish a theoretical framework for your research proposal. 6. Specify an empirical focus for your research proposal. 7. Emphasise the scientific and societal relevance of your research proposal.
Research proposals contain extensive literature reviews. They must provide persuasive evidence that a need exists for the proposed study. In addition to providing a rationale, a proposal describes detailed methodology for conducting the research consistent with requirements of the professional or academic field and a statement on anticipated ...
Writing a research proposal template in structured steps ensures a comprehensive and coherent presentation of your research project. Let's look at the explanation for each of the steps here: Step 1: Title and Abstract. Step 2: Introduction. Step 3: Research objectives. Step 4: Literature review.
A research proposal is a roadmap that brings the researcher closer to the objectives, takes the research topic from a purely subjective mind, and manifests an objective plan. It shows us what steps we need to take to reach the objective, what questions we should answer, and how much time we need. It is a framework based on which you can perform ...
A quality example of a research proposal shows one's above-average analytical skills, including the ability to coherently synthesize ideas and integrate lateral and vertical thinking. Communication skills. The proposal also demonstrates your proficiency to communicate your thoughts in concise and precise language.
A theoretical framework guides the research process like a roadmap for the study, so you need to get this right. Theoretical framework 1,2 is the structure that supports and describes a theory. A theory is a set of interrelated concepts and definitions that present a systematic view of phenomena by describing the relationship among the variables for explaining these phenomena.
A proposal needs to show how your work fits into what is already known about the topic and what new paradigm will it add to the literature, while specifying the question that the research will answer, establishing its significance, and the implications of the answer. [ 2] The proposal must be capable of convincing the evaluation committee about ...
The theoretical framework is the structure that can hold or support a theory of a research study. The theoretical framework encompasses not just the theory, but the narrative explanation about how the researcher engages in using the theory and its underlying assumptions to investigate the research problem. It is the structure of your paper that ...
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: 'A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management'.
The task of developing a theoretical framework starts with asking a research question, proceeds through the task of identifying key variables and the relationships among them, and results in a plan for empirically observing those variables and relationships. Theory construction is always an iterative process.
Research proposal framework The following is a suggested framework for a research proposal. Your supervisor can give more detail on the exact order and elements of your framework. 1. Cover Page . The cover page should show: the title; the candidate's name and student number;
It puts the proposal in context. 3. The introduction typically begins with a statement of the research problem in precise and clear terms. 1. The importance of the statement of the research problem 5: The statement of the problem is the essential basis for the construction of a research proposal (research objectives, hypotheses, methodology ...
The conceptual framework helps you cultivate research questions and then match . the methodological aspects of the study with these questions. In this sense, the con-ceptual framework helps align the analytic tools and methods of a study with the focal topics and . core constructs. as they are embedded within the research questions. This
A conceptual framework is a structured approach to organizing and understanding complex ideas, theories, or concepts. It provides a systematic and coherent way of thinking about a problem or topic, and helps to guide research or analysis in a particular field. A conceptual framework typically includes a set of assumptions, concepts, and ...
A theoretical framework is a foundational review of existing theories that serves as a roadmap for developing the arguments you will use in your own work. Theories are developed by researchers to explain phenomena, draw connections, and make predictions. In a theoretical framework, you explain the existing theories that support your research ...
E-book on How to Write the Conceptual Framework in a Research Proposal. To be more effective in addressing the readers' queries, I wrote the e-book titled "Conceptual Framework Development Handbook: A Step-by-Step Guide with Five Practical Examples."The e-book is a compilation of all conceptual framework related articles that I previously wrote in this site and other blogging websites.
Proposal templates ensure your document follows a standardized format, structure and content; By having a pre-designed proposal framework, you can save time and resources, stay organized and minimize the risk of leaving out important details. A well-designed proposal template enhances your brand image and gives your document a professional touch.
Theoretical Framework Example for a Thesis or Dissertation. Published on October 14, 2015 by Sarah Vinz . Revised on July 18, 2023 by Tegan George. Your theoretical framework defines the key concepts in your research, suggests relationships between them, and discusses relevant theories based on your literature review.
The draft International Education and Skills Strategic Framework (the Framework) has been released. Download Draft International Education and Skills Strategic Framework as a DOCX (298.31kb)
This study, through a systematic literature review spanning 1990 to 2023, interrogates how servitization, and nowadays digital servitization, enhances manufacturing competitiveness. It introduces the DASOBI (Drivers, Actors, Strategies, Obstacles, Benefits, and Impact) framework for navigating the digital servitization transition, emphasizing strategic adaptability and technological alignment ...
Urban mobility is a critical aspect of sustainable urban development, with significant environmental, social, and economic implications. Assessing the sustainability of urban mobility systems in order to create more carbon neutral, liveable, healthier, and sustainable cities and neighborhoods for the future requires a multidimensional approach that integrates diverse factors. However, the lack ...
If the new draft proposal of the State Curriculum Framework (SCF) gets a thumbs up from stakeholders and no one objects to it, English will no longer be mandatory for Std XI and XII students in ...