- Dissertation
- PowerPoint Presentation
- Book Report/Review
- Research Proposal
- Math Problems
- Proofreading
- Movie Review
- Cover Letter Writing
- Personal Statement
- Nursing Paper
- Argumentative Essay
- Research Paper
- Discussion Board Post

90+ Strong Health Essay Topics And How To Handle Them

Table of Contents

You can write about healthy lifestyle, rehabilitation after traumas, childcare, common or rare diseases, global advances in health and medicine, environmental health issues, and more.
How to deal with essay on health?
Your essay will be the most impressive if you choose a topic that is familiar to you or you can write about something you have experience with. It will be easier for you to do a health essay paper and build a convincing argument. Another approach is choosing a topic which is not familiar to you but in which you are interested in. It would be a great opportunity for you to educate yourself.
If you pick an interesting essay topic idea which is too broad to cover in your essay, you should do additional keyword research and look for some specific aspects of this topic to narrow it.
Keep in mind that you should look for a narrow topic which has enough available resources that you can use for researching it.
Before you start writing, make sure you have found enough evidence and examples to support your argument. A good idea is to create a working outline or a mind map for your essay that will guide your writing and help you stay focused on your key points.
First, create a strong thesis statement and think about several main points to support it.
If you are looking for health topics to write about and are not sure what to write about, here we have gathered a lot of exciting ideas that you won’t find on any other essay writing services.
Feel free to use them as inspiration own topic ideas or for writing your essays.
Health topics to write about
- How Can We Help Children Maintain a Healthy Body Weight?
- Ethical and Legal Issues of Surrogate Pregnancy.
- How Dangerous are Long-term Consequences of Anorexia?
- Principles of Preventing Medical Errors in Hospitals.
- How Can Doctors Promote Healthy Lifestyle?
- Why is Homeopathy a Pseudo-Science?
- What Are Side Effects of Blood Transfusion?
- Types of Eating Disorders.
- Can a Vegan Diet Be Healthy?
- The Best Strategies to Maintain Healthy Body Weight.
- Psychological Issues of Breast Cancer.
- Importance of Organ Donation after Death.
- Can Cloning Help Save Lives?
- Ethics in Human Experimentation.
- Symptoms of Heart Attacks in Women.
- Is It Possible to Cure Diabetes in the Future?
Interesting health topics to write about
- What is the Difference Between Western Medicine and Alternative Medicine?
- Health Consequences of Eating Disorders.
- Bioprinting as the Future of Organ Transplants.
- Use of Stem Cell Technologies for Cancer Treatment.
- Ethical and Social Issues of Cosmetic Surgery.
- How Does Advertising Influence Healthy Food Choices?
- Role of Nutrition Education in Promoting Healthy Diets.
- Fast Food Consumption and Obesity.
- How Can Exercise Help Senior Improve Strength and Balance?
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Weight Loss Surgery.
- Obesity as a Medical and Social Problem.
- Strategies for Heart Disease Prevention.
- How Long Can Humans Actually Live?
- Pros and Cons of Clinical Trials.
- Alternative Ways to Treat Depression.
- Is There a Cure for HIV or AIDS?
Controversial health essay topics
- Is There a Link Between Sugary Drinks and Cancer?
- Health Consequences of Caffeine.
- Can Little Kid Food Habits Signal Autism?
- Should Euthanasia Be Legalized?
- Pros and Cons of Medical Marijuana.
- Is Alternative Medicine Dangerous?
- Is Doing Sports always Healthy?
- Which Diet Is Better: Low-Fat or Low-Carb?
- Discuss Measures for Prevention of Communicable Diseases.
- Social Determinants That Influence People’s Well-being.
- Are Doctors Responsible for the Opioid Epidemic?
- Is Religion a Mental Disorder?
- Is Nuclear Waste Really Dangerous for People?
- Is a No-Carb Diet Safe?
- Are We Too Dependent on Antibiotics?
- Are Natural Medicines a Good Alternative to Pharmaceutical?
- Can Blockchain Help Improve the Trust in the Accuracy of Clinical Trials Data?
Mental health argumentative essay topics
- Influence of Environmental Factors on Mental Health.
- Drug Misuse and Mental Disorders.
- Social Effects of Mental Disorders.
- Alcohol Addiction and Psychiatric Disorders.
- Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment of Teen Depression.
- How to Protect Your Mental Health from Social Media Dangers.
- Effects of Social Isolation and Loneliness on Severe Mental Disorders.
- Negative Effects of Total Isolation on Physical and Mental Health.
- Mental Health Benefits Associated with Physical Activity.
- Association between Exercise and Mood.
- Mental Health Problems of Homeless People.
- Stress as a Risk Factor for Mental Disorders.
- Effect of Disposer to Violence on Mental Disorders.
- Common Mental Disorders in the USA.
- Depression and Anxiety Disorders among Adults.
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy for Anxiety Disorders.
- Economic Burden of Depression and Anxiety Disorders.
- Influence of Anxiety Disorders on the Quality of Life.
Health care essay topics
- Advantages and Challenges of E-health Technology.
- Application of Big Data to the Medical Care System.
- Risk Connected with Untested Methods of Alternative Medicine.
- Controversial Issues in the US Medical Care System.
- Telemedicine and Other Disruptive Innovations in Health Care System.
- How Can We Achieve Health Equity?
- Impact of Racism on the Well-Being of the Nation.
- School-based Health Care and Educational Success of Children.
- Role of School-based Health Care in Preventing Dropout.
- What Can Be Done to Curb Rising Suicide Rates?
- Do Adults and Senior Still Need Vaccines?
- What Human Rights Issues Have an Impact on Public Health?
- What Measures Should Be Taken to Prevent Heat-related Deaths?
- Discuss Healthy Housing Standards.
- What Are Common Strategies for Prevention of Chronic Diseases?
Health essay topics for high school students
- Can Computers Displace Doctors?
- Can People Become Immortal?
- Can Happiness Cure Diseases?
- How to Prevent Teen Pregnancy?
- The Biggest Health Challenges Facing Youth.
- Importance of Balanced Diet for Teenagers.
- Does Being Healthy Make You Happy?
- Why Is Exercise Important to Teenagers?
- Why Is Obesity Becoming an Epidemic?
- How to Become a Healthy Person.
- Importance of Healthy Lifestyle for Teens.
- Negative Impact of Smoking Teenagers.
- How Does Stress Affect Teenagers?
- Why Do Teenagers Experiment with Drugs?
- How to Develop Healthy Eating Habits.
Need a health essay overnight? Here’s a deal! Buy argumentative essay help by choosing any topic from our list and handing it to our writers. Complete confidentiality and the brilliant result are guaranteed.

How to Write a Discussion Post That Fetches Excellent Marks?

One-And-Done Guide To A-Grade Worthy Essays On Nature

How to write a conflict essay
- Undergraduate
- High School
- Architecture
- American History
- Asian History
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- Linguistics
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- IT Management
- Mathematics
- Investments
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Aeronautics
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Public Relations
- Educational Theories
- Teacher's Career
- Chicago/Turabian
- Company Analysis
- Education Theories
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Movie Review
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Marketing Plan
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Personal Statement
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Reaction Paper
Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- SWOT analysis
- Thesis Paper
- Online Quiz
- Literature Review
- Movie Analysis
- Statistics problem
- Math Problem
- All papers examples
- How It Works
- Money Back Policy
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- We Are Hiring
Health Care in the United States, Essay Example
Pages: 4
Words: 1013
Hire a Writer for Custom Essay
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.
In the United States, there has long been discussion about the quality and nature of the delivery of healthcare. The debates have included who may receive such services, whether or not healthcare is a privilege or an entitlement, whether and how to make patient care affordable to all segments of the population, and the ways in which the government should, or should not, be involved in the provision of such services. Indeed, many people feel that the healthcare in this country is the best in the world; others believe tha (The Free Dictionary)t our health delivery system is broken. This paper shall examine different aspects of the healthcare system in our country, discussing whether it has been successful in providing essential services to American citizens.
The delivery of healthcare services is considered to be a system; according to the Free Diction- ary (Farlex, 2010), a system is defined as “a group of interacting, interrelated, or interdependent elements forming a complex whole.” This is an apt description of our healthcare structure, as it is compiled of patients, medical and mental health providers, hospitals, clinics, laboratories, insurance companies, and many other parties that are reliant on each other and that, when combined, make up the entity known as our healthcare system.
Those who believe that our healthcare system is the best in the world often point to the fact that leaders as well as private citizens from countries throughout the world frequently come to the United States to have surgeries and other treatments that they require for survival. A more cynical view of this phenomenon is that if people have the money, they are able to purchase quality care in the U.S., a “survival of the fittest” situation. Those who lack the resources to travel to the U.S. for medical treatment are simply out of luck, and often will die without the needed care.
In fact, reports by the World Health Organization and other groups consistently indicate that while the United States spends more than any other country on healthcare costs, Americans receive lower quality, less efficient and less fairness from the system. These conclusions come as a result of studying quality of care, access to care, equity and the ability to lead long, productive lives. (World Health Organization,2001.) What cannot be disputed is that the cost of healthcare is constantly rising, a fact which was the precipitant to the large movement to reform healthcare in our country in 2010. More than 10 years ago, the goal of managed care was to drive down the costs of healthcare, but those promises did not materialize (Garsten, 2010.) A large segment of the population is either uninsured or underinsured, and it is speculated that over the next decade, these problems will only increase while other difficulties will arise (Garson, 2010.)
When examining the healthcare system, there are three aspects of care that call for evaluation: the impact of delivering care on the patient, the benefits and harms of that treatment, and the functioning of the healthcare system, as described in an article by Adrian Levy. Levy argues that each of these outcomes should be assessed and should include both the successes and the limitations of each aspect. The idea is that there should be operational measurements of patients’ interactions with the healthcare system that would include patients’ experiences in hospitals, using measurements of their functional abilities and their qualities of life following discharge. The results of patients’ interactions with the healthcare system should be utilized to develop and improve the delivery of healthcare treatment, as well as to develop policy changes that would affect the entire field of healthcare in the United States.
One view of the state of American healthcare is that the system is fragmented; there have been many failed attempts by several presidents to introduce the idea of universal healthcare. Instead, American citizens are saddled with a system in which government pays either directly or indirectly for over 50% of the healthcare in our country, but the actual delivery of insurance and of care is undertaken by an assortment of private insurers, for-profit hospitals, and other parties who raise costs without increasing quality of service (Wells, Krugman, 2006.) If the United States were to switch to a single-payer system such as that provided in Canada, the government would directly provide insurance which would most likely be less expensive and provide better results than our current system.
It is clear that throwing money at a problem does not necessarily resolve it; the fact that the United States spends more than twice as much on healthcare provision as any other country in the world only makes it more ironic that when it comes to evaluating the service, Americans fall appallingly flat. In my opinion, if the new healthcare reform bill had included a public option which would have taken the profit margin out of the equation, the nation and its citizens would have been in a much better position to receive quality healthcare. The fact that people die every day from preventable illnesses and conditions simply because they do not have affordable insurance is a national disgrace. In addition, many of the people who have been the most adamantly against government “intrusion” into their healthcare are actually on Medicaid or Medicare, federally-funded programs. Their lack of understanding of what the debate actually involves is striking, and they are rallying against what is in their own best interests. These are people that equate Federal involvement in healthcare as socialism. Unless and until our healthcare system is able to provide what is needed to all of its citizens, all claims that we have the best healthcare system in the world are, sadly, utterly hollow.
Adrian R Levy (2005, December). Categorizing outcomes of Health Care delivery. Clinical and investigative medicine, pp. 347-351.
Arthur Garson (2000). The U.S. Healthcare System 2010: Problems Principles and Potential Solutions. Retrieved July 3, 2010, from Circulation: The Journal of the American Heart Association: http://circ.ahajournals.org/cgi/reprint/101/16/2015
The Free Dictionary. (n.d.). Farlex. Retrieved July 3, 2010. http://www.thefreedictionary.com/system
World Health Organization. (2003, July). WHO World Health Report 2000. Retrieved July 3, 2010, from State of World Health: http://faculty.washington.edu/ely/Report2000.htm
Stuck with your Essay?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!
Using Learning Journals in Continuing and Higher Education, Article Critique Example
Prolonged Exposure Therapy, Research Paper Example
Time is precious
don’t waste it!
Plagiarism-free guarantee
Privacy guarantee
Secure checkout
Money back guarantee

Related Essay Samples & Examples
Voting as a civic responsibility, essay example.
Pages: 1
Words: 287
Utilitarianism and Its Applications, Essay Example
Words: 356
The Age-Related Changes of the Older Person, Essay Example
Pages: 2
Words: 448
The Problems ESOL Teachers Face, Essay Example
Pages: 8
Words: 2293
Should English Be the Primary Language? Essay Example
Words: 999
The Term “Social Construction of Reality”, Essay Example
Words: 371
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
5 Critical Priorities for the U.S. Health Care System
- Marc Harrison

A guide to making health care more accessible, affordable, and effective.
The pandemic has starkly revealed the many shortcomings of the U.S. health care system — as well as the changes that must be implemented to make care more affordable, improve access, and do a better job of keeping people healthy. In this article, the CEO of Intermountain Healthcare describes five priorities to fix the system. They include: focus on prevention, not just treating sickness; tackle racial disparities; expand telehealth and in-home services; build integrated systems; and adopt value-based care.
Since early 2020, the dominating presence of the Covid-19 pandemic has redefined the future of health care in America. It has revealed five crucial priorities that together can make U.S. health care accessible, more affordable, and focused on keeping people healthy rather than simply treating them when they are sick.
- Marc Harrison , MD, is president and CEO of Salt Lake City-based Intermountain Healthcare.
Partner Center

Presentations made painless
- Get Premium
124 Healthcare Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
Inside This Article
Healthcare is a diverse and complex field that encompasses a wide range of topics, issues, and challenges. Whether you are studying healthcare as a student, working in the healthcare industry, or simply interested in learning more about this important area, there are countless essay topics that you can explore. To help you get started, here are 124 healthcare essay topic ideas and examples that you can use for inspiration:
- The impact of healthcare disparities on patient outcomes
- Strategies for improving access to healthcare in underserved communities
- The role of technology in transforming healthcare delivery
- The ethics of healthcare rationing
- The importance of diversity and inclusion in healthcare organizations
- The rise of telemedicine and its implications for patient care
- The impact of the opioid epidemic on healthcare systems
- The role of nurses in promoting patient safety
- The challenges of providing mental health care in a primary care setting
- The future of healthcare: personalized medicine and precision healthcare
- The role of healthcare providers in addressing social determinants of health
- The impact of climate change on public health
- The role of public health campaigns in promoting healthy behaviors
- The challenges of healthcare delivery in rural areas
- The impact of healthcare reform on the uninsured population
- The role of healthcare informatics in improving patient outcomes
- The importance of cultural competency in healthcare delivery
- The ethical implications of genetic testing and personalized medicine
- The impact of healthcare costs on patient access to care
- The role of healthcare administrators in shaping the future of healthcare delivery
- The challenges of implementing electronic health records in healthcare settings
- The impact of healthcare privatization on patient care
- The role of healthcare providers in promoting patient autonomy
- The challenges of providing end-of-life care in a healthcare setting
- The impact of healthcare disparities on maternal and child health outcomes
- The role of healthcare providers in addressing the opioid crisis
- The challenges of providing healthcare to undocumented immigrants
- The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on healthcare systems
- The role of healthcare providers in promoting vaccination uptake
- The challenges of healthcare delivery in conflict zones
- The impact of healthcare disparities on LGBTQ+ populations
- The role of healthcare providers in promoting healthy aging
- The challenges of providing healthcare to homeless populations
- The impact of healthcare disparities on rural communities
- The role of healthcare providers in addressing food insecurity
- The challenges of providing healthcare to refugees and asylum seekers
- The impact of healthcare disparities on people with disabilities
- The role of healthcare providers in promoting mental health awareness
- The challenges of providing healthcare to incarcerated populations
- The impact of healthcare disparities on immigrant populations
- The role of healthcare providers in promoting sexual health education
- The challenges of providing healthcare to indigenous populations
- The impact of healthcare disparities on veterans' health outcomes
- The role of healthcare providers in promoting healthy lifestyles
- The challenges of providing healthcare to low-income populations
- The impact of healthcare disparities on minority populations
- The role of healthcare providers in promoting preventive care
- The challenges of providing healthcare to elderly populations
- The impact of healthcare disparities on women's health outcomes
- The role of healthcare providers in promoting maternal health
- The challenges of providing healthcare to children and adolescents
- The impact of healthcare disparities on mental health outcomes
- The role of healthcare providers in promoting substance abuse treatment
- The challenges of providing healthcare to homeless youth
- The impact of healthcare disparities on LGBTQ+ youth
- The role of healthcare providers in promoting healthy relationships
- The challenges of providing healthcare to LGBTQ+ youth
- The impact of healthcare disparities on transgender populations
- The role of healthcare providers in promoting gender-affirming care
- The challenges of providing healthcare to LGBTQ+ elders
- The impact of healthcare disparities on people of color
- The role of healthcare providers in promoting racial equity
- The challenges of providing healthcare to immigrant populations
- The impact of healthcare disparities on refugee populations
- The role of healthcare providers in promoting cultural competency
- The challenges of providing healthcare to non-English speaking populations
- The role of healthcare providers in promoting disability rights
- The challenges of providing healthcare to people with mental illnesses
- The impact of healthcare disparities on people experiencing homelessness
- The role of healthcare providers in promoting housing stability
- The challenges of providing healthcare to people living in poverty
- The impact of healthcare disparities on incarcerated populations
- The role of healthcare providers in promoting criminal justice reform
- The challenges of providing healthcare to veterans
- The impact of healthcare
Want to create a presentation now?
Instantly Create A Deck
Let PitchGrade do this for me
Hassle Free
We will create your text and designs for you. Sit back and relax while we do the work.
Explore More Content
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
© 2023 Pitchgrade
The independent source for health policy research, polling, and news.
Americans’ Challenges with Health Care Costs
Lunna Lopes , Alex Montero , Marley Presiado , and Liz Hamel Published: Mar 01, 2024
This issue brief was updated on March 1, 2024 to include the latest KFF polling data.
For many years, KFF polling has found that the high cost of health care is a burden on U.S. families, and that health care costs factor into decisions about insurance coverage and care seeking. These costs and the prospect of unexpected medical bills also rank as the top financial worries for adults and their families, and recent polling shows that lowering out-of-pocket health care costs is by and large the public’s top health care priority. Health care affordability is also one of the top issues that voters want to hear presidential candidates talk about during the 2024 election. This data note summarizes recent KFF polling on the public’s experiences with health care costs. Main takeaways include:
- About half of U.S. adults say it is difficult to afford health care costs, and one in four say they or a family member in their household had problems paying for health care in the past 12 months. Younger adults, those with lower incomes, adults in fair or poor health, and the uninsured are particularly likely to report problems affording health care in the past year.
- The cost of health care can lead some to put off needed care. One in four adults say that in the past 12 months they have skipped or postponed getting health care they needed because of the cost. Notably six in ten uninsured adults (61%) say they went without needed care because of the cost.
- The cost of prescription drugs prevents some people from filling prescriptions. About one in five adults (21%) say they have not filled a prescription because of the cost while a similar share say they have instead opted for over-the-counter alternatives. About one in ten adults say they have cut pills in half or skipped doses of medicine in the last year because of the cost.
- Those who are covered by health insurance are not immune to the burden of health care costs. About half (48%) of insured adults worry about affording their monthly health insurance premium and large shares of adults with employer-sponsored insurance (ESI) and those with Marketplace coverage rate their insurance as “fair” or “poor” when it comes to their monthly premium and to out-of-pocket costs to see a doctor.
- Health care debt is a burden for a large share of Americans. About four in ten adults (41%) report having debt due to medical or dental bills including debts owed to credit cards, collections agencies, family and friends, banks, and other lenders to pay for their health care costs, with disproportionate shares of Black and Hispanic adults, women, parents, those with low incomes, and uninsured adults saying they have health care debt.
- Notable shares of adults still say they are worried about affording medical costs such as unexpected bills, the cost of health care services (including out-of-pocket costs not covered by insurance, such as co-pays and deductibles), prescription drug costs, and long-term care services for themselves or a family member. About three in four adults say they are either “very” or “somewhat worried” about being able to afford unexpected medical bills (74%) or the cost of health care services (73%) for themselves and their families. Additionally, about half of adults would be unable to pay an unexpected medical bill of $500 in full without going into debt.
Difficulty Affording Medical Costs
Many U.S. adults have trouble affording health care costs. While lower income and uninsured adults are the most likely to report this, those with health insurance and those with higher incomes are not immune to the high cost of medical care. About half of U.S. adults say that it is very or somewhat difficult for them to afford their health care costs (47%). Among those under age 65, uninsured adults are much more likely to say affording health care costs is difficult (85%) compared to those with health insurance coverage (47%). Additionally, at least six in ten Black adults (60%) and Hispanic adults (65%) report difficulty affording health care costs compared to about four in ten White adults (39%). Adults in households with annual incomes under $40,000 are more than three times as likely as adults in households with incomes over $90,000 to say it is difficult to afford their health care costs (69% v. 21%). (Source: KFF Health Care Debt Survey: Feb.-Mar. 2022 )
When asked specifically about problems paying for health care in the past year, one in four adults say they or a family member in their household had problems paying for care, including three in ten adults under age 50 and those with lower household incomes (under $40,000). Affording health care is particularly a problem for those who may need it the most as one-third of adults who describe their physical health as “fair” or “poor” say they or a family member had problems paying for health care in the past 12 months. Among uninsured adults, half (49%) say they or a family member in their household had problems paying for health care, including 51% of uninsured adults who say they are in fair or poor health.
The cost of care can also lead some adults to skip or delay seeking services. One-quarter of adults say that in the past 12 months, they have skipped or postponed getting health care they needed because of the cost. The cost of care can also have disproportionate impacts among different groups of people; for instance, women are more likely than men to say they have skipped or postponed getting health care they needed because of the cost (28% vs. 21%). Adults ages 65 and older, most of whom are eligible for health care coverage through Medicare, are much less likely than younger age groups to say they have not gotten health care they needed because of cost.
One in four immigrant adults (22%) say they have skipped or postponed care in the past year, rising to about a third (36%) among those who are uninsured. Seven in ten (69%) of immigrant adults who skipped or postponed care (15% of all immigrant adults) said they did so due to cost or lack of health coverage. (Source: The 2023 KFF/LA Times Survey of Immigrants: Apr.-June 2023 )
Six in ten uninsured adults (61%) say they have skipped or postponed getting health care they needed due to cost. Health insurance, however, does not offer ironclad protection as one in five adults with insurance (21%) still report not getting health care they needed due to cost.
KFF health polling from March 2022 also looked at the specific types of care adults are most likely to report putting off and found that dental services are the most common type of medical care that people report delaying or skipping, with 35% of adults saying they have put it off in the past year due to cost. This is followed by vision services (25%), visits to a doctor’s offices (24%), mental health care (18%), hospital services (14%), and hearing services, including hearing aids (10%). (Source: KFF Health Tracking Poll: March 2022 )
A 2022 KFF report found that people who already have debt due to medical or dental care are disproportionately likely to put off or skip medical care. Half (51%) of adults currently experiencing debt due to medical or dental bills say in the past year, cost has been a probititor to getting the medical test or treatment that was recommended by a doctor. (Source: KFF Health Care Debt Survey: Feb.-Mar. 2022 )
Prescription Drug Costs
For many U.S. adults, prescription drugs are a component of their routine care. More than one in four (28%) adults say it is either “somewhat” or “very difficult” for them to afford to pay for prescription drugs. Affording prescription drugs is particularly difficult for adults who take four or more prescription medications (37%) and those in households with annual incomes under $40,000 (40%). Black and Hispanic adults are also more likely than White adults to say it is difficult for them to afford to pay for prescription drugs. (Source: KFF Health Tracking Poll: July 2023 )
The high cost of prescription drugs also leads some people to cut back on their medications in various ways. About one in five adults (21%) say in the past 12 months they have not filled a prescription because of the cost. A similar share (21%) say they have taken an over-the-counter drug instead of getting a prescription filled – rising to about one third of Hispanic adults (32%) and more than one in four adults (27%) with annual household incomes under $40,000. About one in ten adults say that in the past 12 months they have cut pills in half or skipped doses of medicine due to cost. (Source: KFF Health Tracking Poll: July 2023 )
Health Insurance Cost Ratings
Overall, most insured adults rate their health insurance as “excellent” or “good” when it comes to the amount they have to pay out-of-pocket for their prescriptions (61%), the amount they have to pay out-of-pocket to see a doctor (53%), and the amount they pay monthly for insurance (54%). However, at least three in ten rate their insurance as “fair” or “poor” on each of these metrics, and affordability ratings vary depending on the type of coverage people have.
Adults who have private insurance through employer-sponsored insurance or Marketplace coverage are more likely than those with Medicare or Medicaid to rate their insurance negatively when it comes to their monthly premium, the amount they have to pay out of pocket to see a doctor, and their prescription co-pays. About one in four adults with Medicare give negative ratings to the amount they have to pay each month for insurance and to their out-of-pocket prescription costs, while about one in five give their insurance a negative rating when it comes to their out-of-pocket costs to see a doctor.
Medicaid enrollees are less likely than those with other coverage types to give their insurance negative ratings on these affordability measures (Medicaid does not charge monthly premiums in most states, and copays for covered services, where applied, are required to be nominal.) (Source: KFF Survey of Consumer Experiences with Health Insurance )
Health Care Debt
In June 2022, KFF released an analysis of the KFF Health Care Debt Survey , a companion report to the investigative journalism project on health care debt conducted by KFF Health News and NPR, Diagnosis Debt . This project found that health care debt is a wide-reaching problem in the United States and that 41% of U.S. adults currently have some type of debt due to medical or dental bills from their own or someone else’s care, including about a quarter of adults (24%) who say they have medical or dental bills that are past due or that they are unable to pay, and one in five (21%) who have bills they are paying off over time directly to a provider. One in six (17%) report debt owed to a bank, collection agency, or other lender from loans taken out to pay for medical or dental bills, while similar shares say they have health care debt from bills they put on a credit card and are paying off over time (17%). One in ten report debt owed to a family member or friend from money they borrowed to pay off medical or dental bills.
While four in ten U.S. adults have some type of health care debt, disproportionate shares of lower income adults, the uninsured, Black and Hispanic adults, women, and parents report current debt due to medical or dental bills.
Vulnerabilities and Worries About Health Care and Long-Term Care Costs
A February 2024 KFF Health Tracking Poll shows unexpected medical bills and the cost of health care services are at the top of the list of people’s financial worries, with about three-quarters of the public – and similar shares of insured adults younger than 65 – saying they are at least somewhat worried about affording unexpected medical bills (74%) or the cost of health care services (73%) for themselves and their families. Just over half (55%) of the public say they are “very” or “somewhat worried” about being able to afford their prescription drug costs, while about half (48%) of insured adults say they are worried about affording their monthly health insurance premium.
Worries about health care costs pervade among a majority of adults regardless of their financial situation . Among adults who report difficulty affording their monthly bills, more than eight in ten say they are worried about the cost of health care services (86%) or unexpected medical bills (83%). Among those who report being just able to afford their bills, about eight in ten say they are worried about being able to afford unexpected medical bills (84%) or health care services (83%). And even among adults who say they can afford their bills with money left over, six in ten nonetheless say they are “very” or “somewhat worried” about being able to afford unexpected medical bills (62%) or the cost of health care services (60%) for themselves and their family. (Source: KFF Health Tracking Poll: February 2024 )
Many U.S. adults may be one unexpected medical bill from falling into debt. About half of U.S. adults say they would not be able to pay an unexpected medical bill that came to $500 out of pocket. This includes one in five (19%) who would not be able to pay it at all, 5% who would borrow the money from a bank, payday lender, friends or family to cover the cost, and one in five (21%) who would incur credit card debt in order to pay the bill. Women, those with lower household incomes, Black and Hispanic adults are more likely than their counterparts to say they would be unable to afford this type of bill. (Source: KFF Health Care Debt Survey: Feb.-Mar. 2022 )
Among older adults, the costs of long-term care and support services are also a concern. Almost six in ten (57%) adults 65 and older say they are at least “somewhat anxious” about affording the cost of a nursing home or assisted living facility if they needed it, and half say they feel anxious about being able to afford support services such as paid nurses or aides. These concerns also loom large among those between the ages of 50 and 64, with more than seven in ten saying they feel anxious about affording residential care (73%) and care from paid nurses or aides (72%) if they were to need these services. See The Affordability of Long-Term Care and Support Services: Findings from a KFF Survey for a deeper dive into concerns about the affordability of nursing homes and support services.
- Health Costs
- Racial Equity and Health Policy
- Private Insurance
- Affordability
- High Deductible Plans
- Tracking Poll
- Survey on Racism, Discrimination and Health
Also of Interest
- Survey on Racism, Discrimination and Health Project
- Health Care Debt In The U.S.: The Broad Consequences Of Medical And Dental Bills
- KFF Health Tracking Poll – March 2022: Economic Concerns and Health Policy, The ACA, and Views of Long-term Care Facilities
- KFF’s Kaiser Health News and NPR Launch Diagnosis: Debt, a Yearlong Reporting Partnership Exploring the Scale, Impact, and Causes of the Health Care Debt Crisis in America
- How Financially Vulnerable are People with Medical Debt?
Select Your Interests
Customize your JAMA Network experience by selecting one or more topics from the list below.
- Academic Medicine
- Acid Base, Electrolytes, Fluids
- Allergy and Clinical Immunology
- American Indian or Alaska Natives
- Anesthesiology
- Anticoagulation
- Art and Images in Psychiatry
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assisted Reproduction
- Bleeding and Transfusion
- Caring for the Critically Ill Patient
- Challenges in Clinical Electrocardiography
- Climate and Health
- Climate Change
- Clinical Challenge
- Clinical Decision Support
- Clinical Implications of Basic Neuroscience
- Clinical Pharmacy and Pharmacology
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Consensus Statements
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Critical Care Medicine
- Cultural Competency
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Diagnostic Test Interpretation
- Drug Development
- Electronic Health Records
- Emergency Medicine
- End of Life, Hospice, Palliative Care
- Environmental Health
- Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion
- Facial Plastic Surgery
- Gastroenterology and Hepatology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Genomics and Precision Health
- Global Health
- Guide to Statistics and Methods
- Hair Disorders
- Health Care Delivery Models
- Health Care Economics, Insurance, Payment
- Health Care Quality
- Health Care Reform
- Health Care Safety
- Health Care Workforce
- Health Disparities
- Health Inequities
- Health Policy
- Health Systems Science
- History of Medicine
- Hypertension
- Images in Neurology
- Implementation Science
- Infectious Diseases
- Innovations in Health Care Delivery
- JAMA Infographic
- Law and Medicine
- Leading Change
- Less is More
- LGBTQIA Medicine
- Lifestyle Behaviors
- Medical Coding
- Medical Devices and Equipment
- Medical Education
- Medical Education and Training
- Medical Journals and Publishing
- Mobile Health and Telemedicine
- Narrative Medicine
- Neuroscience and Psychiatry
- Notable Notes
- Nutrition, Obesity, Exercise
- Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Occupational Health
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopedics
- Otolaryngology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Care
- Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
- Patient Care
- Patient Information
- Performance Improvement
- Performance Measures
- Perioperative Care and Consultation
- Pharmacoeconomics
- Pharmacoepidemiology
- Pharmacogenetics
- Pharmacy and Clinical Pharmacology
- Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
- Physical Therapy
- Physician Leadership
- Population Health
- Primary Care
- Professional Well-being
- Professionalism
- Psychiatry and Behavioral Health
- Public Health
- Pulmonary Medicine
- Regulatory Agencies
- Reproductive Health
- Research, Methods, Statistics
- Resuscitation
- Rheumatology
- Risk Management
- Scientific Discovery and the Future of Medicine
- Shared Decision Making and Communication
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports Medicine
- Stem Cell Transplantation
- Substance Use and Addiction Medicine
- Surgical Innovation
- Surgical Pearls
- Teachable Moment
- Technology and Finance
- The Art of JAMA
- The Arts and Medicine
- The Rational Clinical Examination
- Tobacco and e-Cigarettes
- Translational Medicine
- Trauma and Injury
- Treatment Adherence
- Ultrasonography
- Users' Guide to the Medical Literature
- Vaccination
- Venous Thromboembolism
- Veterans Health
- Women's Health
- Workflow and Process
- Wound Care, Infection, Healing
- Download PDF
- Share X Facebook Email LinkedIn
- Permissions
Confronting Challenges in the US Health Care System : Potential Opportunity in a Time of Crisis
- 1 Deputy Editor, JAMA Health Forum
- 2 Department of Health Policy, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, Tennessee
- Editorial The Near-Term Future of Health Care Reform Ezekiel J. Emanuel, MD, PhD JAMA
- Editorial Crucial Questions for US Health Policy in the Next Decade John Z. Ayanian, MD, MPP JAMA
The sheer number of challenges facing the Biden Administration and the 117th Congress in the health policy sphere is staggering, as is the range of potential solutions offered by the authors of the Viewpoints in the JAMA Health Policy series. 1 The most pressing challenges involve addressing the global COVID-19 pandemic. Yet policy makers would be remiss if they did not leverage this opportunity to also address the fundamental problems with the US health system laid bare by the nation’s response to the pandemic. These include major challenges related to health insurance coverage, the solvency of publicly funded programs, the stability of the health care safety net, market power and consolidation, inequities in health care access and outcomes, public health infrastructure, and the failure to effectively use technology to help counteract these problems.
Personal health crises, such as experiencing a myocardial infarction, can spur patients and their care teams to work to improve underlying health habits and conditions that contributed to the health event. Similarly, the havoc wrought by the COVID-19 pandemic is a clarion call to improve US health care coverage, financing, and organization. The status quo practices of the health system in the US—like poor health habits of a patient with heart disease—have left it susceptible to poor outcomes.
The high cost of the US health care system is its biggest weakness. In the US, national expenditures on health care goods and services were approximately $4 trillion in 2020, accounting for an estimated 18% of gross domestic product. 2 High prices for care explain a large part of the difference in spending between the US and other developed countries. Surprise billing is just one aspect of the pricing problem, but one that, as Colla 3 describes, illustrates many troubling trends in medicine. Consolidation of hospitals, insurers, and large and small practices has accelerated during the pandemic and as Dafny 4 explains, can be expected to lead to higher prices in the commercial market in the future. Chernew 5 elegantly discusses how market power and consolidation in the health care industry, exacerbated by the pandemic, could lead to still higher prices and a cycle of harms for individuals, governments, and society as a whole.
Those harms include incomplete insurance coverage, both in terms of numbers of people covered and the generosity of that coverage, due to high prices that lead to high insurance premiums. Higher premiums have meant that many people who are not eligible for subsidies on the health insurance exchanges find insurance unaffordable. The Biden campaign proposals to extend subsidies to higher income groups are designed to help solve this problem but will not address its root causes. High premiums have also contributed to wage stagnation for US workers with employment-based health insurance and to higher cost-sharing, which has been shown to reduce access to necessary care.
In addition, higher health care costs put pressure on state and federal budgets. As Gee et 6 al discuss, 12 states have not chosen to expand Medicaid to date, and a concern that even being responsible for 10% of the increased costs could be burdensome is one of the reasons cited for this choice. Frank and Neuman 7 emphasize that the looming deficits in the Medicare Part A Trust Fund will also put pressure on federal policy makers to find sources of new revenues or to cut benefits or payment rates. Perhaps even more important, as described by Venkataramani and colleagues, 8 high health care prices contribute to limited budgets for other social goods like education and housing that could improve health outcomes, possibly even more than direct spending on health care.
Similarly, it is now clear that the US has spent an increasing amount of resources on health care, but spending on public health has been inadequate. Investments in surveillance officers and systems and in stockpiles of equipment and medications are less appealing ways to spend public resources than covering new drugs or services. The pandemic has revealed the shortcomings of the US public health infrastructure and illustrates that neglecting to reinvest in public health after a pandemic will more severely compromise the ability to respond effectively to the next public health crisis. 9 Although none of the Viewpoints in this series focused on specific public health proposals, they should be part of every discussion of improving health and health care going forward. Public health policy must be central not only to health policy, but to economic policy and national security policy as well.
High health care prices might be less of a problem if the US health care system was uniformly delivering high-quality care and yielding high value. The US does prioritize health as a society and voters are reluctant to endorse solutions that limit access to the latest innovations in health care. However, a fundamental shortcoming in the US health care system is the tendency to create and perpetuate incentives to deliver higher-margin treatments and specialty care instead of primary care, preventive care, and public health. The central need to refine the focus on value was highlighted in many articles in the series.
Several Viewpoints in the Health Policy series provided worthy suggestions and policy recommendations the could help the US health care system recover from the current crises stronger. Berwick and Gilfillan 10 call for speeding the cycle time of demonstrations under the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Innovation, Dafny 4 suggests examining mergers and acquisitions more closely, and Chernew 5 proposes implementing “backstop” prices in commercial markets.
Another important step will be using data and technology strategically. During the pandemic, the health care system rapidly adopted telemedicine in clinical care. Millions of people accessed readily available data dashboards that illustrated the course of the pandemic and the extent of infections in specific areas, and many used the information to demand better and more equal care. As described by Adler-Milstein, 11 a digital transformation in the US health care system could make it possible to continuously monitor and use real-time data to inform preparedness and population-level care planning. Such data systems also could be used to help address and reduce disparities and inequities in care and to improve health system transparency, including around prices. Moreover, these systems could save money and reduce the reporting and patient tracking burdens on health care centers, physicians, and other clinicians participating in value-based care; administrative costs are estimated by Kocher et al 12 at $2500 per person per year.
Can commitments to improving health care coverage, financing, and organization be made in the midst of a pandemic and an affordability crisis? There are reasons to hope the answer is yes. The pandemic has substantially changed care patterns, shown the risks of fee-for-service payment and a reliance on highly reimbursed surgical procedures, and revealed the need for a stronger public health infrastructure and greater preparedness. Health systems will be increasingly held accountable for ensuring delivery of high-value care and for addressing health equity issues in ways that do not rely on outdated models of care. No one could have imagined or would wish the current economic, societal, or health care challenges of the COVID-19 pandemic on a new administration or Congress. But all have hope that leaders can confront these crises as potential opportunities for developing solutions to address the ongoing major challenges in the US health care system.
Correction: This article was updated on June 7, 2021, to correct the spelling of Dr Venkataramani’s name in the fifth paragraph.
Corresponding Author: Melinda B. Buntin, PhD, Department of Health Policy, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, 2525 West End Ave, Ste 1200, Nashville, TN 37203 ( [email protected] ).
Conflict of Interest Disclosures: Dr Buntin reported being an unpaid board member of the Harvard Medical Faculty Practice in Boston, Massachusetts.
See More About
Buntin MB. Confronting Challenges in the US Health Care System : Potential Opportunity in a Time of Crisis . JAMA. 2021;325(14):1399–1400. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.1471
Manage citations:
© 2024
Artificial Intelligence Resource Center
Cardiology in JAMA : Read the Latest
Browse and subscribe to JAMA Network podcasts!
Others Also Liked
- Register for email alerts with links to free full-text articles
- Access PDFs of free articles
- Manage your interests
- Save searches and receive search alerts
The Case for Universal Healthcare: Ensuring Health as a Human Right
This essay is about the importance of universal healthcare and argues that healthcare should be accessible to everyone, regardless of financial status. It emphasizes that health is a basic human right and that universal healthcare promotes equality, economic benefits, and social cohesion. The essay highlights how universal healthcare can reduce overall healthcare costs through preventative care, alleviate medical debt, and address health disparities among different socio-economic groups. It also counters criticisms about increased government spending by pointing out the long-term economic gains and successful examples from countries with universal healthcare systems. The essay concludes that universal healthcare is essential for a just and prosperous society.
How it works
The domain of healthcare constitutes a quintessential facet of human existence, engendering a discourse spanning the global spectrum regarding its universal accessibility. The contention surrounding this issue remains fervent and pervasive. There exist compelling rationales advocating for the universality of healthcare, positing it as an entitlement irrespective of one’s pecuniary status. At the crux of this discourse lies the axiom that healthcare embodies an elemental human entitlement, indispensable for the sustenance and flourishing of individuals and collectives alike. This exposition shall delve into the imperative for the universal accessibility of healthcare, scrutinizing diverse vantages and ramifications.
Primarily and paramountly, the accessibility of healthcare epitomizes an inalienable human entitlement. The capacity to procure medical attention in times of exigency stands as a linchpin for leading a fruitful and gratifying existence. The deprivation of healthcare owing to fiscal constraints constitutes a transgression against this foundational entitlement. Across myriad societies, the chasms in healthcare access are glaring, with indigent individuals and households often precluded from availing themselves of indispensable medical amenities. This schism not only adversely impacts the individuals directly implicated but also begets broader societal repercussions. Robust individuals serve as societal assets, fostering positive contributions both economically and socially. Ensuring equitable access to healthcare stands as a stride toward actualizing parity and socio-judicial rectitude.
Moreover, the universality of healthcare holds the potential for substantial economic dividends. Prophylactic measures, which are more apt to be embraced in an environment where healthcare is universally accessible, harbor the potential to curtail the incidence of grave maladies necessitating exorbitant remediation. Preventative interventions, encompassing immunizations, routine check-ups, and timely interventions, epitomize cost-efficient modalities for nurturing public health. By preemptively addressing health maladies, individuals can forestall the onset of more severe health adversities, which are prodigiously dearer to rectify and manage. This not only mitigates aggregate healthcare expenditures but also alleviates the financial encumbrance borne by individuals and households. Additionally, a robust populace fosters heightened productivity, engendering augmented economic outputs and diminished absenteeism within occupational spheres. Nations espousing universal healthcare paradigms, such as Canada and the United Kingdom, frequently manifest superior health outcomes and reduced healthcare expenditures vis-à-vis nations bereft of analogous frameworks.
Another salient contention for universal healthcare pertains to its ameliorative impact on the specter of medical indebtedness. In nations devoid of universal healthcare, healthcare expenses can burgeon precipitously, precipitating fiscal destitution for myriad families. In the United States, for instance, medical indebtedness ranks among the preeminent triggers for insolvency. Families grappling with towering medical bills are frequently confronted with onerous choices, compelled to arbitrate between defraying healthcare expenses and attending to other imperative requisites, such as habitation, education, and sustenance. This fiscal exigency can engender enduring repercussions, perpetuating cycles of indigence and circumscribing prospects for economic ascension. By extending healthcare to all denizens, the onus of medical indebtedness is alleviated, endowing individuals with the latitude to concentrate on their health and well-being sans the augmented stressors borne of fiscal adversity.
Universal healthcare further assumes a pivotal mantle in mitigating health disparateness. Across sundry nations, yawning lacunae in health outcomes between disparate socio-economic cohorts are palpable. These disparages frequently stem from disparate access to healthcare amenities. Low-income denizens and marginalized communities are predisposed to deleterious health outcomes due to their incapacity to defray requisite medical expenses. By effectuating the universality of healthcare, these disparages can be attenuated, fostering more equanimous health outcomes. This assumes particular salience for susceptible demographics, such as the aged, juveniles, and those afflicted by chronic infirmities, who may be disproportionately impacted by the paucity of healthcare access. Ensuring equitable access to commensurate calibers of care fosters societal cohesion and undergirds the fortification of healthier communities.
Furthermore, universal healthcare engenders social equilibrium and engenders confidence in governance. When denizens perceive their cardinal exigencies to be met, they are more predisposed to vest their trust in and buttress their governance and societal apparatuses. This can usher in a milieu typified by stability and serenity, wherein individuals are predisposed to contribute to the commonweal. Conversely, when sizable cohorts of the populace are precluded from pivotal services like healthcare, it can foment societal tumult and schism. Universal healthcare can help efface these schisms, fostering a sense of solidarity and shared accountability.
Detractors of universal healthcare often propound that its instantiation augurs augmented governmental expenditures and amplified levies. While it holds veracity that endowing universal healthcare necessitates substantial investment, the concomitant longue durée boons frequently eclipse the outlays. By fostering a milieu of hale and hearty populace, abating medical indebtedness, and augmenting productivity, the economic dividends can offset the initial disbursements. Furthermore, myriad nations boasting universal healthcare frameworks manage to furnish superlative care sans extravagant outlays, attesting to the feasibility of striking an equilibrium between affordability and accessibility. Adroit management and apportionment of resources constitute cardinal tenets for rendering universal healthcare sustainable and efficacious.
Another focal point of contention pivots upon the caliber of care attendant upon universal healthcare paradigms. Certain quarters posit that the instantiation of universal healthcare might engender a debasement in the caliber of care, owing to the concomitant surge in demand and strain upon extant systems. Notwithstanding, empirical evidence gleaned from nations espousing entrenched universal healthcare systems proffers a contrarian narrative. Such nations oftentimes boast robust healthcare infrastructures, comprehensive training regimens for healthcare practitioners, and meticulously regulated benchmarks of care. By prioritizing preventative care and premature interventions, universal healthcare systems can sustain superlative care standards while efficaciously managing demand.
Universal healthcare, in addition, propounds a more holistic paradigm vis-à-vis health and well-being. When healthcare is rendered universally accessible, greater accentuation is accorded to preventative care, mental health services, and communal health initiatives. This comprehensive framework addresses the root causatives of health maladies and champions holistic well-being. By synthesizing corporeal, cerebral, and communal health amenities, universal healthcare can precipitate ameliorated health outcomes and a loftier quality of life for individuals and collectives.
The ethical rationale for universal healthcare is also compelling. In an equitable and just society, every denizen ought to be endowed with the opportunity to attain optimal health. The preclusion of healthcare predicated upon one’s fiscal prowess is fundamentally unjust, perpetuating inequity and undercutting the underpinnings of parity and human dignity. Universal healthcare constitutes a moral mandate, consonant with the tenets of benevolence, empathy, and societal responsibility.
The COVID-19 pandemic has additionally underscored the exigency for universal healthcare. The pandemic laid bare the vulnerabilities and lacunae entrenched within healthcare systems across the globe, particularly in jurisdictions bereft of universal healthcare frameworks. The accessibility of healthcare metamorphosed into a veritable matter of life and death, underscoring the import of having a system undergirding the capacity of all to receive medical care in epochs of crisis. Universal healthcare not only bolsters the resilience of healthcare infrastructures but also amplifies their responsiveness to exigent health crises. By provisioning comprehensive coverage, universal healthcare can better safeguard individuals and collectives from the repercussions of pandemics and sundry health exigencies.
In summation, the assertion for universal healthcare stands as robust and manifold. It constitutes a crucible of human rights, economic efficacy, societal equity, and societal stability. Guaranteeing universal access to healthcare is a sine qua non for cultivating healthier, more fecund, and more equitable societies. The long-range benefits of universal healthcare eclipse the tribulations thereof, rendering it an indispensable constituent of a fair and flourishing society. As we continue to broach the discourse apropos the future of healthcare, it behooves us to retain the fundamental dictum that health is an entitlement, not a privilege. By committing to universal healthcare, we can espouse a society that prizes the health and well-being of all its constituents, auguring a future wherein all are endowed with the opportunity to lead robust and gratifying lives.
Cite this page
The Case for Universal Healthcare: Ensuring Health as a Human Right. (2024, May 21). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/the-case-for-universal-healthcare-ensuring-health-as-a-human-right/
"The Case for Universal Healthcare: Ensuring Health as a Human Right." PapersOwl.com , 21 May 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/the-case-for-universal-healthcare-ensuring-health-as-a-human-right/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Case for Universal Healthcare: Ensuring Health as a Human Right . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-case-for-universal-healthcare-ensuring-health-as-a-human-right/ [Accessed: 29 May. 2024]
"The Case for Universal Healthcare: Ensuring Health as a Human Right." PapersOwl.com, May 21, 2024. Accessed May 29, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/the-case-for-universal-healthcare-ensuring-health-as-a-human-right/
"The Case for Universal Healthcare: Ensuring Health as a Human Right," PapersOwl.com , 21-May-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-case-for-universal-healthcare-ensuring-health-as-a-human-right/. [Accessed: 29-May-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Case for Universal Healthcare: Ensuring Health as a Human Right . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-case-for-universal-healthcare-ensuring-health-as-a-human-right/ [Accessed: 29-May-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers

Top Nursing Argumentative Essay Topics: Engage in Thought-Provoking Debates

This article was written in collaboration with Christine T. and ChatGPT, our little helper developed by OpenAI.

Nursing is a diverse and evolving field, constantly presenting new challenges and debates. As a nursing student or professional, engaging in these discussions allows you to develop critical thinking and writing skills while expanding your field knowledge. This blog post will explore various nursing argumentative essay topics to help you find inspiration for your next paper.
Patient Care and Ethics
- The ethics of administering experimental treatments to terminally ill patients
- Balancing patient autonomy and nurse responsibility in care decisions
- Addressing cultural and religious beliefs in end-of-life care
- The role of informed consent in patient care and treatment decisions
- Ethical considerations in the allocation of scarce medical resources
- The ethics of withholding information from patients for their benefit
- Patient privacy and confidentiality in the age of electronic health records
- Comparing faith practices in healthcare: Sikhism, Judaism, Bahaism, and Christianity
- The ethics of using restraints in patient care
- The ethical implications of non-compliance with prescribed treatments
- The role of nursing in advocating for patients’ rights
- Ethical considerations in caring for patients with mental health disorders
- The ethics of mandatory vaccinations for healthcare workers
- Addressing moral distress among nurses in patient care situations
- The ethics of caring for patients who refuse life-saving treatments
- The role of advance directives in ethical decision-making for patient care
- Ethical considerations in the care of patients with substance use disorders
- The ethics of healthcare rationing in times of crisis
- The ethical implications of assisted reproductive technologies
- Addressing ethical dilemmas in neonatal and pediatric nursing
- The ethics of pain management in nursing practice
- Pediatric oncology: working towards better treatment through evidence-based research
- Ethical considerations in the care of patients with dementia and cognitive decline
- The ethics of genetic testing and personalized medicine in patient care
- The ethical implications of clinical trials and research involving human subjects
- The role of nursing in addressing ethical issues related to organ transplantation
- Ethical considerations in the care of prisoners and detainees
- The ethics of involuntary treatment and psychiatric care
- Euthanasia: an analysis of utilitarian approach
- Addressing ethical challenges in the care of patients with disabilities
- The ethical implications of medical tourism and cross-border healthcare
- The role of nursing in addressing ethical issues related to global health
- Ethical considerations in the care of military veterans and their families
- The ethics of surrogate decision-making in patient care
- Addressing ethical challenges in the care of patients with chronic and terminal illnesses
- The role of nursing in promoting patient advocacy and self-determination
- Ethical considerations in the care of patients with rare diseases and conditions
- The ethics of care rationing in the context of an aging population
- The role of nursing in addressing ethical issues related to access to healthcare
- Ethical considerations in the care of patients during public health emergencies
- The ethics of triage and prioritization of care in emergencies
- The role of nursing in promoting environmental sustainability and addressing ethical issues related to climate change
- Ethical challenges in the care of patients at the end of life
Medical Studies Overwhelming?
Delegate Your Nursing Papers to the Pros!
Get 15% Discount
+ Plagiarism Report for FREE
Technological Advancements in Nursing
- The impact of electronic health records on nursing practice and patient care
- The role of telemedicine in expanding access to healthcare services
- How wearables and remote monitoring devices are changing nursing care
- The integration of artificial intelligence in nursing practice and decision-making
- The use of virtual reality in nursing education and training
- Ethical considerations in the use of advanced technologies in nursing practice
- The role of robotics in patient care and nursing support
- The impact of mobile health apps on nursing practice and patient engagement
- The use of big data and analytics in improving patient outcomes and nursing practice
- The role of 3D printing in medical device innovation and patient care
- The integration of telehealth in the management of chronic conditions
- The use of social media and online platforms for professional development and networking in nursing
- Usability, integration, and interoperability of healthcare technology
- The impact of advanced diagnostics and imaging technologies on nursing practice
- The role of blockchain technology in improving healthcare data security and management
- The use of gamification in nursing education and patient engagement
- The impact of technology on nursing workflow and time management
- The role of virtual assistants and chatbots in patient care and nursing support
- Clinical laboratory IT security: challenges, implications, and solutions
- The use of augmented reality in nursing education and practice
- The integration of telepsychiatry and mental health services in nursing care
- The impact of technology on nurse-patient communication and relationship-building
- The role of electronic prescribing and medication management systems in reducing medication errors
- The use of telemonitoring and remote care in the management of high-risk pregnancies
- The impact of technology on infection control and prevention in healthcare settings
- The role of smart home technologies in supporting aging-in-place and home-based care
- The use of technology in promoting self-care and patient empowerment
- Safeguarding patient information: nursing informatics best practices for privacy and security in healthcare
- The integration of genomics and personalized medicine in nursing practice
- The role of technology in addressing healthcare disparities and promoting health equity
- The impact of technology on nursing workforce planning and resource allocation
- The use of predictive analytics in identifying high-risk patients and improving care coordination
- The role of technology in promoting interprofessional collaboration and communication in healthcare
- The impact of technology on nursing education and the development of future nursing competencies
- The role of technology in supporting disaster response and emergency preparedness in nursing
- The use of technology in promoting patient safety and reducing medical errors
- The impact of technology on nursing leadership and management
- The role of technology in addressing the social determinants of health and promoting community health
- The integration of technology in palliative and end-of-life care
- The use of technology in enhancing patient engagement and satisfaction in nursing care
- The role of technology in promoting evidence-based practice and research in nursing
- The impact of technology on nursing ethics and professional boundaries
- The role of technology in addressing the global nursing shortage and promoting workforce sustainability
Nursing Education and Professional Development
- The role of simulation-based learning in nursing education
- The impact of online learning on nursing education outcomes
- Integrating cultural competence in nursing curricula
- Strategies for promoting lifelong learning in nursing practice
- The role of mentorship in nursing professional development
- Addressing the transition from student nurse to professional nurse
- The impact of interprofessional education on nursing practice and patient outcomes
- The role of nursing preceptorship in clinical education
- Strategies for reducing nursing student attrition and promoting retention
- The integration of evidence-based practice in nursing education
- The role of reflective practice in nursing professional development
- Addressing the nursing faculty shortage: Challenges and solutions
- The impact of standardized testing on nursing education and practice
- The role of nursing leadership development in healthcare transformation
- Strategies for enhancing critical thinking skills in nursing education
- Global health learning in nursing and health care disparities
- The impact of clinical experience on nursing students’ confidence and competence
- The role of continuing education in maintaining nursing competency and licensure
- Addressing the needs of diverse learners in nursing education
- The impact of technology on nursing education and the development of digital literacy skills
- Digital healthcare and organizational learning: enhancing patient care through technology and knowledge management
- The role of nursing education in promoting health literacy and patient education
- Strategies for promoting resilience and self-care in nursing education
- The impact of global health experiences on nursing students’ cultural competence and professional development
- The role of nurse educators in shaping the future of nursing practice
- Addressing the challenges of teaching nursing ethics and professional values
- The impact of accreditation standards on nursing education and program quality
- The role of professional nursing organizations in supporting continuing education and development
- Strategies for fostering a culture of learning and professional growth in nursing practice
- The impact of nursing education on patient outcomes and quality of care
- The role of nursing education in addressing healthcare disparities and promoting health equity
- The integral role of nurses in healthcare systems: the importance of education and experience
- Addressing the challenges of teaching and assessing clinical judgment in nursing education
- The impact of nursing education on workforce development and nursing shortages
- The role of nursing education in promoting environmental sustainability and planetary health
- Strategies for promoting effective communication and teamwork in nursing education
- The impact of nursing education on patient safety and error prevention
- The role of nursing education in promoting innovation and entrepreneurship in healthcare
- Addressing the needs of adult learners and nontraditional students in nursing education
- The impact of nursing education on interprofessional collaboration and healthcare team dynamics
- The role of nursing education in promoting ethical decision-making and moral courage in practice
- Strategies for enhancing nursing students’ clinical reasoning and decision-making skills
- The impact of nursing education on the development of professional identity and role socialization
Healthcare Policies and Nursing Practice
- The role of nurses in shaping healthcare policy and advocating for reform
- The impact of the Affordable Care Act on nursing practice and patient care
- Addressing the nursing shortage: policy initiatives and workforce strategies
- Understanding the impact of the American Healthcare System Regulatory Acts
- The role of nursing scope of practice regulations on healthcare delivery and outcomes
- The impact of healthcare reimbursement policies on nursing practice and patient care
- The role of nursing in addressing the opioid crisis: policy and practice implications
- The impact of public health policies on nursing practice and community health
- The role of nursing in promoting healthcare access and reducing disparities
- The impact of healthcare quality and safety regulations on nursing practice
- The role of nursing in implementing evidence-based practice guidelines and policies
- The impact of health information technology policies on nursing practice and patient care
- The role of nursing in addressing social determinants of health through policy and practice interventions
- The impact of nurse staffing regulations on patient outcomes and workforce planning
- The role of nursing in promoting health literacy and patient-centered care through policy and practice initiatives
- Healthcare management: career paths and requirements
- The impact of healthcare privacy and confidentiality policies on nursing practice and patient trust
- The role of nursing in promoting environmental sustainability and climate change policies in healthcare
- The impact of healthcare workforce diversity policies on nursing practice and cultural competence
- The role of nursing in promoting global health and addressing international healthcare challenges
- The impact of mental health policies on nursing practice and the care of patients with mental health disorders
- The role of nursing in promoting value-based care and payment models in healthcare
- The impact of healthcare cost containment policies on nursing practice and resource allocation
- The role of nursing in promoting patient safety and quality improvement through policy and practice initiatives
- The impact of healthcare reform on nursing education and workforce development
- Understanding the US health care reform: necessity, challenges, and implementation
- The role of nursing in promoting health equity and addressing healthcare disparities through policy and practice interventions
- The impact of healthcare policies on nursing leadership and management roles
- The role of nursing in promoting interprofessional collaboration and teamwork through policy and practice initiatives
- The impact of healthcare policies on the integration of technology in nursing practice and patient care
- The role of nursing in promoting ethical decision-making and moral courage through policy and practice initiatives
- The impact of healthcare policies on nursing practice in rural and underserved communities
- The role of nursing in promoting innovation and entrepreneurship in healthcare through policy and practice initiatives
- Combating health care-associated infections: a community-based approach
- The impact of healthcare policies on advanced practice nursing roles and scope of practice
- The role of nursing in promoting palliative and end-of-life care through policy and practice initiatives
- The impact of healthcare policies on infection control and prevention in nursing practice and patient care
- The role of nursing in addressing the challenges of an aging population through policy and practice initiatives
- The impact of healthcare policies on nursing practice in the care of patients with chronic and complex conditions
- The role of nursing in promoting patient advocacy and self-determination through policy and practice initiatives
- The impact of healthcare policies on nursing practice in disaster response and emergency preparedness
- The role of nursing in promoting evidence-based practice and research through policy and practice initiatives
- The impact of healthcare policies on nursing practice in the care of vulnerable and high-risk populations
- The role of nursing in addressing the global nursing shortage and promoting workforce sustainability through policy and practice initiatives
Cultural Competence and Health Equity
- The role of cultural competence in reducing healthcare disparities
- Integrating cultural competence into nursing education and practice
- Addressing implicit bias in nursing practice and patient care
- The impact of cultural competence on patient satisfaction and outcomes
- The role of nursing in promoting health literacy among diverse populations
- Strategies for effective communication with patients from diverse backgrounds
- Mental health and gender inequality
- The impact of cultural competence on nurse-patient relationship-building and trust
- The role of nursing in addressing social determinants of health and promoting health equity
- Addressing the challenges of providing culturally competent care in rural and remote settings
- The impact of cultural competence on interprofessional collaboration and teamwork
- Bridging the gap: tackling maternal and child health disparities between developed and underdeveloped countries
- The role of nursing in promoting cultural competence in healthcare organizations
- Addressing health disparities among LGBTQ+ populations through culturally competent nursing care
- The impact of cultural competence on the prevention and management of chronic diseases
- The role of nursing in promoting culturally competent mental health care
- Addressing health disparities among immigrant and refugee populations through culturally competent nursing care
- The impact of cultural competence on patient safety and error prevention
- The role of nursing in promoting cultural competence in palliative and end-of-life care
- Addressing health disparities among indigenous populations through culturally competent nursing care
- The impact of cultural competence on the care of patients with disabilities
- The role of nursing in promoting culturally competent care for patients with substance use disorders
- Addressing health disparities among racial and ethnic minority populations through culturally competent nursing care
- The impact of cultural competence on the care of patients with rare diseases and conditions
- The role of nursing in promoting culturally competent care in global health settings
- Addressing the challenges of providing culturally competent care in disaster response and emergency preparedness
- The impact of cultural competence on nursing leadership and management
- The role of nursing in promoting culturally competent care in the context of an aging population
- Addressing health disparities among low-income populations through culturally competent nursing care
- The impact of cultural competence on nursing practice in the care of patients with complex and chronic conditions
- The role of nursing in promoting culturally competent care for military veterans and their families
- Addressing health disparities among women and girls through culturally competent nursing care
- The impact of cultural competence on nursing practice in the care of patients with infectious diseases
- The role of nursing in promoting culturally competent care for incarcerated individuals and detainees
- Addressing health disparities among individuals with limited English proficiency through culturally competent nursing care
- The impact of cultural competence on nursing practice in the care of patients at the end of life
- The role of nursing in promoting culturally competent care in the context of climate change and environmental health
- Addressing health disparities among individuals experiencing homelessness through culturally competent nursing care
- The impact of cultural competence on nursing practice in the care of patients with traumatic experiences
- The role of nursing in promoting culturally competent care in the context of medical tourism and cross-border healthcare
- Addressing health disparities among individuals with low health literacy through culturally competent nursing care
- The impact of cultural competence on nursing practice in the care of vulnerable and high-risk populations
Mental Health and Burnout in Nursing
- The prevalence of burnout among nursing professionals
- Strategies for preventing and addressing nurse burnout
- The impact of nurse burnout on patient care and outcomes
- The role of nursing leadership in addressing mental health and burnout
- Promoting self-care and resilience among nursing professionals
- The impact of nurse burnout on job satisfaction and retention
- The role of nursing education in addressing mental health and burnout
- Strategies for fostering a healthy work-life balance in nursing
- The impact of nurse burnout on interprofessional collaboration and teamwork
- The role of peer support and mentorship in addressing mental health and burnout
- The impact of nurse burnout on nursing errors and patient safety
- The role of workplace wellness programs in addressing mental health and burnout
- Strategies for managing stress and anxiety in nursing practice
- The impact of nurse burnout on professional development and career progression
- The role of professional nursing organizations in addressing mental health and burnout
- The impact of nurse burnout on healthcare costs and resource allocation
- The role of nursing research in understanding and addressing mental health and burnout
- Strategies for promoting emotional intelligence and self-awareness in nursing practice
- The impact of nurse burnout on the nursing workforce and workforce planning
- The role of nursing in promoting mental health and well-being among patients and families
- The impact of nurse burnout on ethical decision-making and moral distress
- The role of nursing in addressing mental health disparities and stigma
- Strategies for promoting a culture of empathy and compassion in nursing practice
- The impact of nurse burnout on nurse-patient communication and relationship-building
- The role of nursing in addressing mental health needs in rural and underserved communities
- The impact of nurse burnout on nursing advocacy and policy engagement
- The role of nursing in promoting mental health and well-being in global health settings
- Strategies for addressing mental health and burnout among nursing students and new graduates
- The impact of nurse burnout on nursing education and faculty well-being
- The role of nursing in addressing mental health needs in disaster response and emergency preparedness
- The impact of nurse burnout on nursing practice in the care of patients with mental health disorders
- The role of nursing in promoting mental health and well-being in the context of an aging population
- Strategies for addressing mental health and burnout among advanced practice nurses
- The impact of nurse burnout on nursing practice in the care of patients with chronic and complex conditions
- The role of nursing in promoting mental health and well-being among military veterans and their families
- The impact of nurse burnout on nursing practice in the care of patients with substance use disorders
- The role of nursing in addressing mental health needs in the context of climate change and environmental health
- Strategies for addressing mental health and burnout among nurses working with vulnerable and high-risk populations
- The impact of nurse burnout on nursing practice in the care of patients at the end of life
- The role of nursing in promoting mental health and well-being in the context of healthcare innovation and change
Now that you have a list of thought-provoking nursing argumentative essay topics, you can engage in meaningful debates and expand your knowledge in the field. Consider various perspectives, use credible sources to support your arguments, and practice clear, concise writing. Happy writing!
📎 Related Articles
1. Mental Health Nursing Research Topics: Inspiring Ideas for Students 2. Top Nursing Topics for Discussion: Engaging Conversations for Healthcare Professionals 3. Key EBP Nursing Topics: Enhancing Patient Results through Evidence-Based Practice 4. Top Nursing Research Topics for Students and Professionals 5. Nursing Debate Topics: The Importance of Discussing and Debating Nursing Issues 6. Exploring Controversial Issues in Nursing: Key Topics and Examples 7. Pediatric Nursing Research Topics for Students: A Comprehensive Guide
Table of content
Crafted with Care:
Nursing Essays!
Precision, Passion, & Professionalism in Every Page.
580 Health Essay Topics
🏆 best essay topics on health, ✍️ health essay topics for college, 👍 good health research topics & essay examples, 🌶️ hot health ideas to write about, 🎓 most interesting health research titles, 💡 simple health essay ideas, 📌 easy health essay topics.
- The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health
- Filipino Culture Values and Practices in Relation to Health Care
- Global Health Issues: Essay Example
- Free Healthcare: Advantages and Disadvantages
- Bullying at School and Impact on Mental Health
- Negative Effects of Social Media on Health
- Application of Statistics in Healthcare
- Types of Health Information Management Systems Health information management systems are divided into three types: clinical systems, financial systems, and operational systems.
- Children’s Functional Health Pattern Assessment This paper includes children’s functional health pattern assessment, similarities and differences between the analyzed age groups and nurses’ responsibilities in handling a child.
- Analysis of Health Promotion Theories A model of health promotion is a framework that helps healthcare practitioners to explain, plan and evaluate health enhancing activities.
- Environmental Health Theory and Climate Change In the environmental health theory, there is a view on how environmental health, human ecology, and health affect the public.
- Biomedical and Biopsychosocial Models of Health and Illness According to the biopsychosocial model, psychological factors that contribute to a person’s disease include behavior, beliefs, pain, illness perceptions, stress, and coping.
- Religion and Its Health Benefits Religion and spirituality offer potential health benefits in reducing mortality risks and improving coping techniques, which leads to enhanced recovery among patients.
- Effective Communication in Health Care Effective communication in healthcare is critical for numerous medical processes such as correct diagnosis, correct care and treatment, legal and ethical issues.
- The Importance of Health and Safety Training at the Workplace One of the benefits of health and safety training is the prevention of injury and illness at the workplace. Training programs help employees to gain awareness regarding the health.
- Motivational Theories in Healthcare This paper discusses why health service managers should understand what motivates health workers by looking at their needs with the help of various motivational theories.
- Annotated Bibliography: Social Media and Mental Health This article describes several sources about the connection and some other issues about social media and people’s mental health.
- Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare Artificial intelligence (AI) and similar technologies are becoming more common in business and society, and now even integrating into healthcare.
- Pareto Efficiency. Health Care System “Pareto or Social efficiency occurs when it is not possible to make someone better off without making someone else worse off”.
- Insomnia and Its Negative Health Effects Individuals who suffer from insomnia face a great number of unwanted health effects because sleep can heal the human body naturally.
- Healthcare Information Systems: Components, Benefits Health care information systems have numerous benefits for companies and care providers. They allow for cost savings and help improve care quality by reducing medical errors
- Tuberculosis, Health Determinants and Nurse’s Role Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease that affects the lungs and that is caused by a strain of bacterium knows as Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- Family Characteristics Contributing to Dysfunctional Health Patterns It is important for families to foster healthy habits. Otherwise, children risk developing dysfunctional health patterns, decreasing physical and mental well-being.
- The Role of Nurses in Environmental Health This paper explores the factors that affect health and the roles of nurses in improving or eliminating environmental barriers to health.
- Effects of Water Pollution on Human Health This study will evaluate the main causes of water pollution, the effects on human health, and how to mitigate them.
- Effect of Social Media on Adolescent Mental Health This study aims to assess the current relationship between social media use and its impact on adolescent mental health.
- The Impact of Technology on Mental Health The paper uncovers the consequences of technology use on mental health. It examines the relationship between technology use and mental illnesses.
- Stress Effect on Physical and Mental Health The paper analyzes the primary effects of stress on human health. The study outlines the concept of stress as well as estimates its ultimate causes.
- Addressing Mental Health in Schools Mental health promotion interventions should be conducted in schools because these institutions serve as a perfect basis for this purpose.
- Effects of Air Pollution on Health The main effects of air pollution on health, the main air pollutants, and the policies necessary to reduce the levels of air pollution.
- Poverty Effects on Mental Health This paper examines the link between poverty and mental health, the literature findings on the topic, and proposes a potential solution.
- Pantene Shampoo: Negative Impact on Health Pantene shampoo falls under the category of beauty products. The ingredients in Pantene shampoo can have numerous negative effects on the health of consumers.
- The Importance of Healthcare Management Healthcare organizations need healthcare management because healthcare nowadays requires high levels of coordination among multiple stakeholders.
- Paired and Independent T-Test in Healthcare Scenario The difference between matched (paired) and independent samples is that paired samples t-test can be used when testing the same person twice.
- The Effects of the Lack of Teamwork in Healthcare This paper discusses the importance of interprofessional collaboration in healthcare and how a lack of teamwork negatively impacts patient outcomes.
- Environmental Issues and Human Health The purpose of this paper is to discuss the impact of environmental threats on human health and the strategies developed to address them.
- Importance of Partnership While Working in a Health and Social Care Partnership working indicates a shift from an organisational competition culture of public organisation to a service user need-guided approach to service delivery.
- Nursing Profession: Health and Economic Issues The research served for the exploration of several issues related to health and economics that are advantageous or harmful for nursing.
- Transtheoretical Model vs. Health Belief Model The paper argues that the transtheoretical model, in contrast to the health belief model, outlines a systematic process that would explain people’s path towards wellbeing.
- Health-Illness Continuum Relevance on the Patient Care This paper aims to discuss the relevance of the health-illness continuum to patient care and present a perspective on the author’s current state of health.
- South Africa Health Care System This paper determines the role the health care systems of South Africa play in delivering the population access to appropriate health care services.
- Hospital Revenue Sources and Models in Healthcare Industry Like any other business, healthcare organizations have to perform effective revenue management in order to maintain stable financial status and avoid critical losses.
- Health Care: Fundamentals and Importance Care is a crucial part of healthcare services provided as a method promoting patients’ physical and mental wellbeing and as an essential factor in a competitive aspect.
- Nurses’ Role in Environmental Health Nurses should support policies of eliminating barriers to environmental health, and assist, educate, monitor the environmental health of individuals and communities.
- Mental Health Theories: Behaviorism Versus Cognitivism Theories that focus on the aspect of mental health are intended to help clients understand their issues and deal with them. Mental health specialists can use one and more theories.
- Physical Activity’s Lack Effects on Health Problems A sedentary lifestyle is a common phenomenon in today’s world and is characterized by minimal and irregular physical activity.
- Application of Statistical Methods in Healthcare Statistical evaluation of clinical research results determines doctors’ decisions in favor of the method of treatment being studied.
- Health Information Systems: Types and Use Phases The research explores health information systems, their types, four phases of their use, elements of the needs assessment, selection process and training needs for end users.
- The Negative Influence of Social Media on Teenagers’ Mental Health This essay is purposed to explain the aspects in which excessive use of social media affects teenagers’ mental health.
- Importance of Health Equity It is efficient if everyone who needs assistance receives adequate care, which is possible because of Health Equity.
- The US and New Zealand: Healthcare Profiles Comparison This essay compares the healthcare profiles of the United States and New Zealand and discusses how the latter may have paved the way for the former’s much-needed improvement.
- Statistics Application in Healthcare and Nursing Statistical analyses are efficient mechanisms for obtaining accurate data based on calculations and affecting not only the quality of care.
- Effects of Poor Communication in Healthcare Reviewing various categories of interactions within the healthcare system will enable an in-depth understanding of the effects of poor communication.
- Physical Health Indicator: Pulse Rate Experiment An examination of a person’s pulse can provide insight into their health, especially when measuring the before and after the pulse of an individual engaged in exercise.
- Mental Health from Religious & Spiritual Perspectives The thread that is to be discussed is the relationship between spirituality and mental health with the aim to give an individual the tools to achieve the desired outcomes.
- The Effect of Mental Health Programs on Students Academic Performance Mental health is an essential aspect of every individual as it affects how they behave, control their emotions, and think.
- Organization Theory Improving Healthcare Operations Organizational theories explain the relationships between the business and its environment and how it affects its operation mode.
- Environmental Health and Health Effects of Environment Environmental change has both beneficial and severe effects on human well-being. Some effects of environmental change are easy to detect, while others are hard to identify.
- Electronic Health Record System’s Life Cycle The essay focuses on the electronic health record system and its lifecycle: needs assessment and analysis, system selection and design, implementation, evaluation and maintenance.
- How to Improve Mental Health in the Community Mental health is defined as human psychological, emotional, and social prosperity. It influences how people think, feel, and act as they contend with life.
- Health and Safety Regulations in the Engineering Environment In this essay, the health and safety regulations in mechanical and electrical engineering environments are discussed by looking at their unique features.
- Nola Pender’s Health Promotion Model Nola Pender is one of the greatest nursing theorists of the 20th century. Pender’s Health Promotion Model (HPM) theory supports the best health practices towards a quality life.
- History of Public Health The targeted course will explore the major issues associated with public health towards professional nursing practice.
- Goals and Objectives of the Community Health Needs It is important to learn how to inform the community about the ideas and ways of public health improvement. This week will be dedicated to the planning of health interventions.
- Supply and Demand of Healthcare and Automobiles This paper’s purpose is to examine the differences and peculiarities of the health care market, as well as analyze current trends in this field.
- Quality Management in Healthcare Quality management in healthcare is essential to ensure patient safety. It is helpful by providing the opportunity to evaluate quality in healthcare organizations.
- Impact of Outdoor Activities on Mental Health This paper explores the therapeutic value of outdoor activities for human mental health and well-being and discusses the positive effects of spending time in nature.
- Social Determinants of Health in Wolverhampton Town This paper examines an overview of Wolverhampton town located in the West Midlands area of England. It examines the demographic profile.
- The SWOT Analysis in Health Care The assessment will define the importance and usability of the SWOT analysis in strategic planning in health care.
- The Value of PowerPoint Presentations for Healthcare Management In the fast-evolving spheres like healthcare, technologies play a crucial role in the achievement of health-promotional, educational, strategic, and developmental goals.
- The Healthcare Manager’s Role in Information Technology Management This article focuses on the role that a healthcare manager plays in ensuring the efficient execution of medical operations through the use of new technologies.
- Food Additives: Dangers and Health Impact Research shows that synthetic food additives have a negative human health and consumer dissatisfaction effect which calls for stricter regulation of their use in products.
- Leadership in Health Care: Situational Leadership Theory The paper discusses the leadership issues in health care. It demonstrates that the particularities of emergency care units necessitate a flexible approach to leadership.
- Helvie Energy Theory of Nursing and Health The objective of this paper is to pay specific attention to the concept of the environment, as viewed in the energy theory of health and nursing developed by Carl Helvie.
- The U.S Healthcare System and the Roemer Model Roemer’s model of a healthcare system demonstrates how a socialist healthcare system operates. This paper explores the entire U.S healthcare system in relation to Roemer’s model.
- The Purpose of Health Promotion This paper discusses the purpose of health promotion and how the nursing role and responsibilities are evolving health promotion.
- Health-Illness Continuum and Its Role This paper aims to discuss the relation of this model to health care practices and define the ways to move towards wellness.
- Pros and Cons of the Gatekeeper Healthcare System The article describes the levels of the healthcare system, its advantages and disadvantages, while the author believes that the advantages outweigh.
- Primary Health Care: Issues and Challenges Primary health care as a concept gained popularity following the 1978 International Conference on Primary Health Care jointly held by WHO and UNICEF at Alma-Ata.
- Mental Health Advocacy for Children Mental disorders are increasingly becoming rampant due to an array of issues affecting all individuals across the lifespan.
- The Connection of Spirituality and Mental Health Nowadays, spirituality plays a huge role for many people around the world, and the connection between the inner feelings of every person with the outside world is a crucial part.
- Health Teaching Plan Elements for Adolescents Given the significance of adolescence to overall well-being, healthcare professionals should seize the opportunity to promote health and offer preventive services.
- Cash Flow Statement as a Reflection of Financial Health Lack of working capital, a constant search for money to repay debts to suppliers, employees, budget all lead to the fact that a company cannot manage its obligations.
- Social Determinants of Health: Case Study The impact of SDOH is one of the priorities within the framework of improving the population’s health and eliminating inequalities in the well-being of all citizens.
- Concepts of Women’s Health Education Women’s health education is crucial for safe childbirth, healthy living, and successful parenthood. The proposal will investigate the feasibility of using women’s health campaign.
- Pets Effects on Their Owners’ Health Pets affect their owners’ health positively. They enhance mood, give positive emotions, maintain stable blood pressure rates and help to avoid CVD, etc.
- Social Work in Mental Health Settings Social workers are regarded as highly trained individuals working closely to foster the standard of life and the well-being of other people through crisis intervention.
- Preventive Health Care Issues Preventive healthcare does not primarily refer to medicine; it may refer to measures taken to prevent occurrences of given diseases.
- Health and Social Care Services: Barriers to Working Partnerships This paper gives a comprehensive discussion on the major barriers that affect the sustainability of working partnerships between two healthcare services and social providers.
- Overcrowding in Prisons and Its Impact on Health Overcrowding in prison is a significant issue that affects a lot of countries and it is challenging to detect as there is no uniform internationally accepted standard.
- Regression Analysis for Healthcare Organization The paper studies the regression analysis that enables managers to evaluate the patterns within the health care organization and make predictions for decision-making.
- Asthma Patients’ Health Education and Promotion The purpose of this paper is to discuss the health education, health promotion information, and strategies that should be used when working with asthma patients.
- Healthcare in Canada: Problems and Solutions The issue of the challenges that face Medicare in Canada is increasingly turning out to be a controversial subject; even as far as the politics of Canada are concerned.
- Gordon’s Functional Health Patterns in a Community In the community under consideration, there are certain resources that could help assess its needs, strengths, weaknesses, and other necessary details.
- Patient Assessment, Health Patterns and Family Characteristics Family characteristics may significantly promote either potential or actual dysfunctional health patterns. One of the characteristics refers to family relationships.
- Risk Management in Healthcare Construction Projects A risk is any occurrence that has the potential to alter the progress of a project significantly. A risk may be positive or negative.
- Calgary Family Assessment Model in Healthcare Calgary Family Assessment Model is a tool utilized by health care specialists to evaluate the overall wellbeing of a family.
- Nursing Informatics: Electronic Health Records Nursing informatics entail the use of health care technology such as the EHR. Electronic health records provide integrated data that nurses can use to support safe and patient-centered care.
- Advantages of Computer Technology in Healthcare The emergence of computer technology within healthcare is the catalyst of changes that began to display the improvement of medical procedures and care quality.
- Role of Family in Healthcare and How Culture Affects Health Beliefs The paper will discuss how family shapes the role of care and attitudes towards health and how culture affects health beliefs and community health.
- The Role of Microbes and Microbiology in Health The purpose of this paper is to consider both the positive and negative effects of microorganisms on people and the role of microbiology in the health industry.
- Public Health. Precaution Adoption Process Model The paper argues the Precaution Adoption Process model strives to explain what happens before people take action and explains how people translate these decisions into action.
- Personal Health Initiative Report: Achieving a Normal Body Mass Index This paper reports on the initiatives taken to achieve change in eating behavior and achieve a normal body mass index.
- The Family Health Assessment This essay seeks to provide a family health assessment of an Amish family using the Friedman Family Assessment Model, analyze family data and develop a plan of care for the family.
- Public Health in 21st Century Public Health Professionals, ranging from doctors to nurses, even the chemist shop owners, are now well trained to deal with different diseases.
- Community Health Nursing: Concept and Scope Community Health Nursing is a specific field of nursing characterized by the combination of public health, nursing skills, and some elements of social assistance.
- Summary of Family Health Assessment and Nursing Wellness Diagnoses The primary goal of the paper is to present the summary of family assessment while covering different topics such as sexuality, nutrition, and coping strategies.
- Sexual Health Nurses: Functions and Responsibilities Sexual health nurses focus on family planning, but their functions do not end there. Their responsibilities also include advising patients about sexually transmitted infections.
- Applying Ethical Principles in Healthcare Modern medical field requires new, high-quality ways of treating patients, considering the objective moral code.practice and help them in ethical decision-making process.
- Qualitative and Quantitative Methods in Public Health Qualitative and quantitative methods alike can be helpful in public health and work in accord to offer a clearer picture and a more thorough understanding of a given matter.
- Electronic Health Records: A Review of the Literature The articles included in the annotated bibliography research the use of electronic health record data and its importance.
- Why Health Insurance Should Cover Art and Music Therapy? In the article, the author talks about the benefits of art therapy and music therapy for the mental health of patients.
- Importance of Theory in Health Promotion Effectual health promotion initiatives assist persons to uphold and advancing health, lessening disease risks, and controlling persistent illness.
- Science of Human Flourishing and Health The state of human flourishing determines the happiness, longevity, and prosperity of both the individual and the entire nation.
- Socioeconomic Health Determinants in a Concept Map This paper presents a map that demonstrates the fact that there are complex interrelations between various social and economic factors and highlights the key elements of SEDH.
- Chickenpox Epidemiology and Community Health Nurse Chickenpox, which is also referred to as Varicella, is a viral disease with considerably high rates of transmissibility and is caused by varicella zoster virus.
- Ethical Issues in Healthcare Essay: Ethical Dilemma This paper describes an ethical dilemma in healthcare, its specific characteristics, violated ethical principles, and existent barriers to ethical practice.
- Benefits of the Beach: Effects on the Mental and Physical Aspects of Health in People This paper aims at discussing the benefits of the beach: advantages of seawater, sunshine, walking on the sand, its positive impact on health and bodyweight.
- Common Mental Health Problems Mental health forms a significant aspect of human health because it determines the general health of a person.
- Role of Mandatory Health Insurance The health care system is one of the U.S. government priorities but has been in a crisis, and even for an elementary procedure, a patient can be billed thousand dollars.
- Intercultural Communication in Business, Education, and Healthcare The rules of communication vary depending on different contexts; that’s why this paper aims to discuss intercultural communication in business, education, and healthcare.
- Expectancy Theory in the Healthcare Sector This paper explores the fundamentals of Expectancy Theory and applies it to the healthcare sector. Expectancy theory has found use in healthcare education contexts.
- Influence of Cultural Beliefs on Health Behaviors and Use of Health Services This paper presents cultural beliefs and health care. Culture can be comprehended as the identity of a person.
- Access to Healthcare Services This paper will focus on identifying the most appropriate legislation to address the problem of access to care, describing the impact of the issue on nursing practice.
- Nursing Informatics Policy and Its Influence on Healthcare Delivery The development of nursing information structures is an essential factor in improving the delivery of health services. It includes the development of regulations.
- The Food Quality Impact on Economy and Health The problem of food quality and its impact on the economy and health of not only one country but the whole world cannot be overemphasized.
- Healthcare Manager’s Conceptual, Technical, and Interpersonal Skills A healthcare manager is a person who facilitates, administrates, and influences the healthcare system as a manager is an indispensable part of the medical system.
- Health Promotion for Obesity in Adults This is a health promotion proposal for preventing obesity among adults in the US. People get obesity when they acquire a given body mass index.
- Mental Health in the Community Health institutions set goals to improve the mental health of the population. Two of those goals are to reduce the instance of suicide and disordered eating among adolescents.
- Health: The Benefits of Running The purpose of this article is to consider such an exercise as running, as well as the positive impact it has on health.
- Egyptian and Filipino Heritage and Health Beliefs While Egyptian and Filipino cultural heritages have different backgrounds, there are also some similarities including the aspects related to healthcare.
- Bullying Effects on Health and Life Quality When children are subject to bullying by their peers, it affects their feelings and evokes negative emotions in the first place.
- Employee Mental Health and Workplace Wellbeing Managers adjust the overall workplace atmosphere, including decision-making procedures, to enhance the recuperation and engagement of the affected workers.
- Digital Health Information Technologies The essay will explore the two common digital health technologies, Electronic Health Records and Health Information Exchange, to identify how they help healthcare institutions.
- Creating App in Healthcare: Business Plan In order to create the most effective app in healthcare, it is necessary to monitor trends in this area and implement them.
- Typhoid Fever: Health Promotion Pamphlet Parents /guardian should pay close attention on their children especially in monitoring the kind of food and water that they take.
- Healthcare Problems of Modern Society The public health system, as an organizational construct of a social institution, affects the formation and effective use of human capital.
- Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: Pros & Cons Rapidly advancing artificial intelligence technologies are gradually changing health care practices and bring a paradigm shift to the medical system.
- Demand and Supply of Healthcare Workforce in Oman There has been continued indication of the shortages of physicians and nurses in hospitals across Oman and this is often seen in the media on regular basis.
- Levels of Health Prevention The types of care that are maintained in healthcare institutions largely determine the nature of a particular treatment plan, the features of recovery, and patient outcomes.
- Healthcare Technological Trends and HRM Strategies Today our world is developing extremely quickly mainly due to the enormous technological development. This paper analyzes technological trends in the sphere of healthcare.
- Influenza and Community Health Nurse’s Role Influenza is a viral infection that is caused by the influenza virus. It affects the respiratory system and causes complications such as bacterial pneumonia and dehydration.
- Environmental Changes: Negative and Positive Impact on Human Health Environmental changes have both negative and positive impacts on human health. While some effects are direct, others are hard to decipher.
- Health Effects of Environmental Change The paper will describe how both food scarcity and obesity increase due the modern environment.It describes the roles of a nurse in ensuring a healthy environment.
- Health Promotion Proposal Obesity Prevention The purpose of this proposal is to inform and educate parents, children and adolescents of the importance of having a well balance diet and exercise in their daily lives to avoid obesity.
- Issues and Possible Solutions in the Healthcare Sector It is hard to disagree that healthcare is one of the most fundamental and intricate sectors playing a crucial role in people’s lives.
- How Social Media Contribute to Mental Health While social media enhances individuals’ communication and interaction with other people, spending a lot of time on social networks can make people lonely.
- Positive and Negative Impacts of Social Media on Mental Health Social media became popular only several decades ago, but at present, they constitute an important part of everyone’s daily routine.
- The Connection Between Education and Better Health The objective of this assignment is to discern the relationship between education and good health and how the two phenomena interrelate with each other.
- Promoting Health and Wellbeing of Older People and Raising Community Awareness The care of older people has become an important issue due to increased life expectancy and improved healthcare and health education.
- Risk Management in Health Care This essay seeks to define risk management in health care delivery, discuss the basics of sentinel reporting, the legal implications of sentinel events.
- Stages of Life and Influence of Age in Healthcare Age is a factor in the way patients interact with the healthcare system. This paper discusses the stages of life and the influence of age in healthcare from the patient’s perspective.
- Social Change: The Nurse’s Role in Global Healthcare To advocate for the global perspective on the issue of the opioid crisis and the need to change the current standards for opioid prescription.
- Electronic Health Records Implementation Examples Electronic Health Records (EHRs) are becoming increasingly popular with the growing demand for convenient and high-quality healthcare services.
- Single-Parent Family Health Assessment The current family development stage is ‘a family with school-aged children’, and the family managed to accomplish the tasks of previous stages rather well.
- Healthcare Information System and Its Application In modern society, the healthcare information system plays a critical role in defining the quality of healthcare offered in healthcare centers.
- Health Education Plan The present description is based on the Health education plan on obesity keeping in view of Windshield Survey and Friedman Family Assessment.
- Why Is Public Health Important Health promotion, disease prevention, and life extension are public health goals. Public health aims to maintain and promote people’s health in their communities.
- Computer Technology’s Impact on Personal Health The computer has a detrimental effect on health in many aspects. The influence of the Internet on modern society cannot be assessed unambiguously.
- Healthcare Organizations’ Mission, Vision and Values This project identifies four health organizations coupled with reviewing their vision, mission, and values and proposes changes to the organizations’ missions, visions, and values.
- The Role of Cultural Relativism in Healthcare The Nacirema is a group of North Americans living in the territory between the “Canadian Cree, the Yaqui and Tarahumara of Mexico, and the Carib and Arawak of the Antilles”
- Family Health Assessment Using Gordon’s Patterns The family health assessment was conducted on the family of the Browns based upon Gordon’s functional health patterns.
- Health and Safety Assessment Health and safety laws are designed to ensure that working environments are safe for all workers. The law requires that both employers and employees take caution.
- Health Promotion in School Health Center The purpose of education activities is to inform the audience about healthy lifestyles and address the social issues affecting their well-being and health.
- Sexual and Reproductive Health Education The participation of women in sexual and reproductive health education can increase their level of adaptation in society and improve health and behavioral outcomes.
- The Role of a Nurse in Mental Health Nurse might want to consider the option of specialization. It means the process of becoming an expert in a chosen subject by expanding the scope of knowledge and practice.
- Virtual Reality in Healthcare and Education The beginnings of virtual reality can found throughout human history. This paper explores its emergence and development, and its influence in healthcare and education.
- Healthcare Problems in South Africa
- Patient-Centered Healthcare Coordination Plan
- Capstone Project Change Proposal in Healthcare Sector
- Cause and Effect: Living with Pets Improves Their Owners’ Health
- Private Hospitals’ Health Facility Capacity
- Noise Pollution and Its Effect on Health
- US and Canada Healthcare Systems Comparison
- Social Determinants of Health
- Perceived Health. A Healthy Body
- Online Learning and Students’ Mental Health
- Health Care, Economy, and Their Effect of People
- Prominent Health Concerns in Developed Countries
- Critique of Population Health Intervention
- Principles of Primary Health Care
- High Taxes’ Benefits for Education and Healthcare
- Earthquakes: Effects on People’s Health
- The Health Benefits of the Green Tea
- Healthcare in the Russian Federation
- Healthcare in the United Kingdom
- Change Management in Healthcare
- HCA Healthcare Corporation’s Strategic Analysis
- Evaluation in Nursing Education and Healthcare Organization
- Ethics, Morals, and Values in Healthcare
- The Novant Health Organization’s Structure & Management
- Mission and Vision Statements in a Health Organization
- Behavioral and Cognitive Mental Health Theories
- Russian and American Healthcare Systems Comparison
- Health Care Strategical Marketing Proposal
- Information Technology Applications in Healthcare
- Legal Aspect of Health Care Administrator
- Irish Healthcare System: HR Management and Financing
- Cultural Barriers in Healthcare Management
- Sentinel Town Community Health Assessment
- Training and Education in Health Care Organization
- Quality Documentation and Reporting in Primary Health Care
- Globalization and Health
- Shift Work: Negative Effects on the Health and Performance of Nurses
- Community Health Promotion as a Nurse’s Role
- Leadership Theories in the Healthcare Industry
- Barriers to Collecting a Health History
- Occupational Health and Safety Communication
- Community Health Assessment
- The Effectiveness of the Internet in Healthcare
- Diffusion of Innovations Theory in Public Health
- Biomedical View of Health
- Financial Analysis in Healthcare Organizations
- Evolution of Healthcare Information Systems
- Public Health in the UK
- Healthcare Management and Leadership
- Ethical and Legal Issues in Healthcare Services
- Littering on Campus: The Issue of Maintaining Cleanliness and Averting Health Hazards
- Malawi Health and Education System Analysis
- Nurse Manager’s Interview on Health Policies
- Climate Change and Impact on Human Health
- Refugee Mental Health Issue
- Healthcare Employee Recruitment and Selection
- Patient with Sore Throat: Nursing Health Assessment
- American and Spanish Healthcare Systems
- Healthcare Disparities in the LGBT Community
- Nola J. Pender’s Health Promotion Model in Nursing
- Quality Improvement Team in Healthcare Institution
- Social Psychology and Health Issues
- Public Health Career Opportunities
- Ethical Issues in Health and Wellness Coaching
- The Challenges Faced by Healthcare Workers
- Modern Healthcare Management: The Role of Information Technologies
- Nurse’s Role in Health Promotion
- Mental Health Issues in College Students
- Categorical Variables in a Healthcare Research
- Canada’s Public Health System
- A Mental Health Nursing Social Interventions for Patients With Schizophrenia
- The Role of Religious Beliefs and Spirituality in Health Care
- Health-Illness Continuum Review
- Occupational Health Nursing Theory and Model
- Microplastics and Environmental Health
- Community Health: Assessment of New York’s Chinatown
- The Impact of Ageism on Mental Health and Addiction
- US and Singapore Healthcare Systems Comparison
- Cultural Beliefs in Health Education
- Colonization and Indigenous Australian-Aboriginal Health Issues
- Occupational Safety and Health Threat Scenarios
- Environmental Factors and Barriers to Health
- Health and Lifestyle in Russian Culture
- Motivational Axiom, Health Behavior and Promotion
- Healthcare Regulatory Agencies in the US
- Childhood Obesity and Health Promotion
- Healthcare in South Africa
- Health Information in Print and Digital Media
- Conflict Resolution in a Healthcare Setting
- Customer Focus in Healthcare Project Management
- The Family Health Assessment in the Nursing Practice
- Communicating in Health and Social Care Organisation
- Public Health Promotion in Everyday Life
- Evaluation of Mental Health Project Presentation
- Project Management in Healthcare
- Importance of Education for Healthcare Professionals
- Effects of Poor Workplace Culture on Healthcare Organizations
- Health Education and Health Promotion
- Management and Leadership in Healthcare
- The Future of Health Care: Observing New Trends
- How Digital Literacy Skills Will Help Me in the Healthcare Setting
- Spain’s Current Healthcare System
- Environment and Health Relationship
- Infectious Disease and Public Health Focus
- Healthcare Services: Right or Privilege?
- The US and Singapore Health Systems Comparison
- Health and Safety Effects of Computer Use
- Quality Improvement in Healthcare
- Cost Allocation in Healthcare Analysis
- The Issue of Ethics in Healthcare
- Major Health Concerns in Sentinel City
- Implementation of Healthcare Organizational Design
- Health Information Systems Project
- Family Health and Nursing Process
- Community Health: Disaster Recovery Plan
- Administrative and Financial System in Healthcare
- Disaster Planning and Health Information Management
- Universal Health Care: Arguments For and Against
- The Health Care System in the United States
- What Is E-Health: Discussion
- Gender Roles and Psychological Health
- Governmental and Quasi-Governmental Agencies that Affect Public Health Systems
- Healthcare Robotics Impact
- Steps in the Process of Risk Management in Healthcare
- Childhood Obesity Study and Health Belief Model
- Person, Health, Environment in Nursing Philosophy
- Health Promotion Strategies for Obesity
- Time Management in the Healthcare Sector
- Trust and Transparency in Management and Leadership of Health Care Organizations
- Basketball: History and Health Benefits
- Evidence-Based Population Health Improvement Plan
- CVS Health Corporation’s SWOT Analysis
- NYU Langone Health Center’s Strategic (SWOT) Analysis
- Agile-Scrum in Healthcare Project Management
- Teacup Dogs: Appearance, History, Health Complications, Art
- Discussion: Smoking and Health Risks
- Analysis of Limited Access to Healthcare
- Healthcare Environment: Challenges to Teamwork and Collaboration
- Healthcare Professions: EMT and Occupational Therapist
- The Importance of Community Health Education
- Leadership and Change in Healthcare Management
- Continuous Probability Distributions in Biostatistics and Public Health
- Practice in the Field of Healthcare: Literature Review
- The Influence of Social Media on Mental Health
- Health Care Delivery Models and Nursing Practice
- Impact of COVID-19 on People’s Livelihoods, Their Health and Our Food Systems
- Key Elements in Motivating Clients to Improve Health Behaviors
- Health Psychology and Stress: Correlations
- COVID-19: The Impact on Mental Health
- Family Health Assessment: Weaknesses and Strengths
- Health Promotion Among Hispanic-Latino Population
- Cash Versus Accrual Accounting Methods in Healthcare Organizations
- Maternal Health Nursing Theories and Practice
- GE Energy and GE Healthcare: Strategic Customer Relationships
- Conflict Stages and Its Resolution in Healthcare
- Professional Nurses’ Involvement in Health Policy
- Comparison of Healthcare Systems: The United States and Switzerland
- Margaret Newman’s Theory of Health as Expanding Consciousness
- Healthcare Human Resources Management and Changes
- Examples of Environment in Nursing Metaparadigm
- Health Promotion Role in Public Health
- Community Health Nursing: Family Health Assessment
- Mental Health: General Hospital Psychiatry
- Research Designs in Healthcare Research
- Obesity as a Global Health Issue
- The Right to Healthcare as a Basic Human Right
- Hospital Ownership Types and Impacts on Healthcare Finance
- Mental Health in Children and Adolescents
- Benefits of Health Information Technology
- The Importance of Mental Health Care
- Healthcare: The Importance of Accessibility
- Performance Appraisal Process in a Healthcare Organization
- The History of Mental Health Legislation in England and Wales
- Diversity Project Kickoff: Diversity in Health Care
- Enhancing Patient Safety Through Interprofessional Teams
- Health Information Exchange (HIE) Models
- Sociological Analysis of Health and Illness
- Sudden Infant Death Syndrome: Health Promotion Plan
- The Crisis of Lethality: Suicide as Health Phenomenon
- Sanitation, Inspection and Public Health Administration
- Health Belief Model of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- Alberta Health Services: Organizational Structure
- Public Dental Health Policies: Allocative and Regulatory
- US and French Health Care Systems Comparison
- The Importance of Health Literacy
- Dental Public Health Project
- Health Problems in Children Analysis
- The Healthcare Information: Security and Privacy
- IT in Healthcare: Barcode Medication Administration System
- Maintenance of Health and Nursing Intervention
- Impact of Social Media on Mental Health
- Ethical Professional Codes of Healthcare
- Health Information Technology Service Management
- Pathogenic and Salutogenic Concepts of Health
- Rising Health Care Costs: Analyzing Issues
- Improving Mental Health by Preventing Mental Illness
- Healthcare System in Republic of Panama
- The Importance of Good Health
- The Negative Impact of Long Working Shifts on Nurses’ Efficient Practice and Health
- Personal Health Records in Examples
- Financial Management Role in Healthcare
- Pender’s Health Promotion Model and Parse’s Theory
- Medical Technologies Developing Healthcare
- Holistic Health Principles in Nursing
- The Caffeine Impact on Health and Behavior
- Health and Health Promotion
- The Consent Role and Aspects in Healthcare
- The Flo Health App and Technological Utopia
- Equality, Diversity, and Rights in Health and Social Care
- Health Informatics and Its Definition
- Social Media Impact on Mental Health
- Mental Health Nursing, Interventions and Strategies
- Patient Identity Management Policy in Healthcare
- Cybersecurity and Protection in Healthcare
- Effects of Social Media on Mental Health
- Healthcare Social Issue for Indigenous People in Canada
- Healthcare Reimbursement Models
- Summary of the Health History Interview
- Mental Health & Burnout Prevention in Nursing Training
- Mental Health Challenges and Their Stigmatization
- The Ontological Basis for Participant Action Research in Healthcare
- Fast Food and Health Relations
- Research Proposal on Justice in Health Care
- Partnering to Heal: Healthcare-Associated Infections Prevention
- Case-Control Study in the Field of Health
- The Health Promotion Model by Nola Pender
- Leadership in Motivating Healthcare Staff to Increase Performance
- Healthcare Accreditation and Licensing
- Application of Pender’s Health Promotion Model
- CDC’s Top Ten Public Health Achievements of Workplace Safety
- Mental Health in “The Tell-Tale Heart” by Edgar Allan Poe and “The Yellow Wallpaper” by Charlotte Perkins Gilman
- Health and Physical Education Curriculum
- Pornography as a Health Issue
- Quality Healthcare and Its Aims
- Absenteeism and Lateness in the Healthcare Field
- Creating a Safe and High-Quality Health Care Environment
- The Roles of a Community Health Nurse
- Policies and Protocols in Healthcare
- Healthcare Database Design and Development
- Health and Safety Training for Early Childhood Educators
- Health Assessment of a Nuclear Family
- The Internet of Things (IoT) and Healthcare
- Malnutrition and Patient Safety Healthcare Policy
- Efficacy of Telemedicine and Its Application in Healthcare
- Graphs, Statistical and Clinical Significance in Healthcare
- Role of Ethics in Healthcare Leadership
- Restraint and Seclusion in Healthcare
- Non-traditional Healthcare Practices: Can It Replace the Actual Medicine?
- Faith Factor and Mental Health in Young People
- Abortion: Women’s Health as Their Integral Right
- Non-Verbal Communication in Mental Health Nursing
- Ethics and Social Justice in Mental Health System
- Factors of Decision-Making by Healthcare Managers
- Police Officers’ Wellness and Mental Health
- Factors Influencing Food Choices and Their Impact on Health
- Social Problems and Policy: Youth Unemployment and Mental Health
- Women’s Mental Health Program Proposal
- Atrium Health Hospital’s Organizational Change
- Effects of Climate Variability on Water Resources, Food Security, and Human Health
- Professional Relationships in Healthcare
- Food Safety Sanitation Requirements for a Child’s Health
- The Action Research in Healthcare
- Advocacy in Mental Health Counseling
- Shared Decision Making in Health Care
- Mental Health and COVID-19 Pandemic
- Importance of Mental Health Policy
- The Healthcare System: Effects of Social Media
- Mental Health Issues in Uganda
- Impact of Grassroots Policy Initiatives on Nurse Leaders in Improving Health
- Leadership in Healthcare Management & Administration
- Patient Education: Improving Health Status
- Managed Care in Behavioral Health
- Health Service in New Zealand
- Quality Improvement and Transformation of Healthcare
- The German Healthcare System: Key Aspects
- Research Questions and Testable Hypothesis on Public Health
- Applying Theory to Public Health Practice
- Teamwork and Collaboration in Healthcare
- Community Health and Nursing
- The Banner Health Care System Strategic Plan
- Major Third-party Payers to Healthcare Providers
- Day Care Centers: Health Risks
- Research Approaches in Health and Social Care
- Ethical and Religious Directives for Catholic Healthcare Services
- Health Maintenance, Protection, and Restoration
- Healthcare Professional Training and Development
- Sexual Health: Teaching Plan for Students
- Adolescent Mental Health: Depression
- Issues in Health Psychology
- Interpersonal Communication Skills in Healthcare
- Healthcare Disparities and Potential Solutions
- Community Health Nursing and Occupational Safety
- Determinants of Health: Factors Influencing Health Status
- Community Needs and Health Screening Initiative
- NMC Healthcare Organization and Its Culture
- Blockchain Revolution in the Healthcare Industry
- Relevance to Transcultural Health Care
- Logic Models in Developing Public Health Programs
- Fulmer SPICES Tool in Patient Health Assessment
- Occupational Health and Safety: Workers Neglect of Precautionary Measures
- Health Education Effects on Patients With Hypertension
- The Implication of Information Technology on Marketing Strategy of Healthcare Industry
- Verbal De-Escalation in Mental Health Units
- Mental Healthcare Provision & Barriers to Innovation
- Organizational Change in Healthcare
- Culture of the Nacirema in Modern Healthcare
- Marijuana and Its Use in Healthcare
- Strategic and Program Evaluation in Healthcare
- Governmental Role in Health and Education Fields
- Healthcare Facility Expansion Funding
- Aspects of Palliative Care in Healthcare
- The Gauteng Department of Health: Financial Strategy
- The Basic Level of Healthcare: H. Engelhardt’s and N. Daniels’ Perspectives
- Legal and Ethical Issues in Health Care
- Strategic Planning in Healthcare
- Mental Health Institutions in Prisons
- Economic Evaluation Of The Health Care System
- Using of Virtual Reality in Healthcare
- Pollution and Children’s Health
- Traditional Public-Health Prevention Model
- Healthcare Professional Burnout and Its Effects
- Lifestyle Challenges: Convenience Over Health
- Artificial Intelligence: Integrated in Healthcare
- Perfect Competition and the Cost of Healthcare
- Social Media and Mental Health in Adolescents
- Cuban Cultural Communication in Relation to Healthcare
- Roles of a Financial Manager in Healthcare
- Building Rapport on Public Health Issue
- Community Health and Its Impact on Maternal Child Health
- Health Campaign Audience and Implementation
- Pressure Ulcers in Elderly in Health Settings
- The Impact of Socioeconomic Status on Health
- Impact of Leisure and Recreation on Mental Health
- Theory, Risk, and Quality Management in Healthcare Facilities
- Health Promotions in Preschools
- Social Media and Its Effect on Mental Health
- Indian Healthcare Information System
- Legal Aspects of Health Care Management
- Nursing: Community Health Project by Nola Pender
- Health and Medicine: Facility Planning
- The Public Health Campaign on STDs Among the Youth
- Implementing Effective Management in Healthcare
- Health Promotion to Reduce Lung Cancer: Grant Proposal Template
- Using of Statistics in Healthcare
- Vulnerable Populations: Homeless People and Health Inequalities
- Is Bottled Water Safe for Public Health?
- Elements of Strategic Planning in Health Organizations
- Contrast of Health Care Systems: Italy v. the United States
- The Definition of Public Health Leadership
- Workplace Bullying and Its Impact on People’s Mental Health
- Australian Social Determinants of Health
- Behavioral Cues in Healthcare Behaviors
- Spirituality in Health Care Analysis
- Choice of Career: Health Information Management
- School Nurse Role in Providing School Health Services
- Health Maintenance Plan for Diverse Developmental Stages
- Health Information Technology and Nursing Practice
- The Importance of Value-Based Care in Health Promotion
- French Huna for Health
- The Interdisciplinary Health Care Delivery Model
- Healthcare Management: Past, Present, and Future
- Building Trust Within the Healthcare Setting
- Implementation Strategy in the Healthcare Sector: Implementation Stages Analysis
- Lifestyle Influences on Physical Health
- Improve the Quality of Health Care Using TQM Methods
- Afro-Latin Culture and Approach to Healthcare
- The Capella University Mental Health Counseling Program
- How to Reduce Obesity and Maintain Health?
- Health Clubs and Fitness Centers Popularity
- Vila Health Independence Medical Center: Stakeholder Communication
- Women’s Health: Nursing Care for Lesbians
- Using the PRECEDE-PROCEED Model in Designing a Community-Based Health Program
- Patient Safety in the Healthcare Workplace Culture
- Global Health Crisis and Initiatives to Tackle It
- Unionization and Magnet Accreditation in Healthcare
- Healthcare for Hindus: Purnell Model for Cultural Competence
- Effective Professional Teamwork in Healthcare
- People With Disabilities: Health-Care Disparities
- Diabetes Type 2 Treatment and Health Promotion
- Importance of Nursing in Women’s Health
- South African and Namibian Healthcare
- United Healthcare Group and Its Strategic Plan
- Water Quality Improvement for Global Health
- Little Havana Health Programs: Caring for Populations
- Team-Based Healthcare in Nursing Practice
- Mental Health: Strategic Action Plan
- Teenage Pregnancy, Its Health and Social Outcomes
- Occupation and Health in Saudi Arabia
- Health Promotion and Ethical Considerations
- Technology in Health Care: Current Trends
- The Health Issues of South Africa
- Fashion Affecting People’s Health
- Using of the Electronic Health Record
- Meditech Electronic Health Records
- Hazardous Materials, Environment and Health
- Diagnosis-Related Groups in Healthcare Research
- Future Trends in Healthcare
- Social Media’s Multifaceted Impact on Mental Health
- Online Training on Health: A Proposal Memorandum
- Application of Blockchain in Healthcare
- Ramsay Health Care: Financial Management
- Interprofessional Collaboration Examples in Nursing Case Study
- Risk and Quality Management in Healthcare
- Epic Systems: Electronic Health Records
- Biological, Social, and Psychological Variables of Mental Health
- The Gibbs Reflection Cycle Method in Healthcare
- Corruption in South Africa’s Healthcare Sector
- Health Aspects of Young Adulthood
- The Inmate Mental Health Issue Analysis
- Organizational Theory in Healthcare
- Ethical Dilemmas in Healthcare
- Scheduling Management in Healthcare
- Social Media and Mental Health Relationship
Cite this post
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2022, June 5). 580 Health Essay Topics. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/health-essay-topics/
"580 Health Essay Topics." StudyCorgi , 5 June 2022, studycorgi.com/ideas/health-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . (2022) '580 Health Essay Topics'. 5 June.
1. StudyCorgi . "580 Health Essay Topics." June 5, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/health-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "580 Health Essay Topics." June 5, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/health-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . 2022. "580 Health Essay Topics." June 5, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/health-essay-topics/.
These essay examples and topics on Health were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy. Please ensure you properly reference the materials if you’re using them to write your assignment.
This essay topic collection was updated on January 8, 2024 .

- Issue Brief
Health Care Costs: What’s the Problem?
The cost of health care in the United States far exceeds that in other wealthy nations across the globe. In 2020, U.S. health care costs grew 9.7%, to $4.1 trillion, reaching about $12,530 per person. 1 At the same time, the United States lags far behind other high-income countries when it comes to both access to care and some health care outcomes. 2 As a result, policymakers and health care systems are facing increasing demands for more care at lower costs for more people. And, of course, everyone wants to know why their health care costs are so high.
The answer depends, in part, on who’s asking this question: Why does U.S. health care cost so much? Public policy often highlights and targets the total cost of the health care system or spending as a percentage of the gross domestic product (GDP), while most patients (the public) are more concerned with their own out-of-pocket costs and whether they have access to affordable, meaningful insurance. Providers feel public pressure to contain costs while trying to provide the highest-quality care to patients.
This brief is the first in a series of papers intended to better define some of the key questions policymakers should be asking about health care spending: What costs are too high? And can they be controlled through policy while improving access to care and the health of the population?
What (or Who) Is to Blame for the High Costs of Care?
Total U.S. health care spending has increased steadily for decades, as have costs and spending in other segments of the U.S. economy. In 2020, health care spending was $1.5 trillion more than in 2010 and $2.8 trillion more than in 2000. While total spending on clinical care has increased in the past two decades, health care spending as a percentage of GDP has remained steady and has hovered around 20% of GDP in recent years (with the largest single increase being in 2020 during the COVID-19 pandemic). 1 Health care spending in 2020 (particularly public outlays) increased more than in previous years because of increased federal government support of critical COVID-19-related services and expanded access to care during the pandemic. Yet, no single sector’s health care cost — doctors, hospitals, equipment, or any other sector — has increased disproportionately enough over time to be the single cause of high costs.
One of the areas in health care with the highest levels of spending in the United States is hospital care, which has accounted for about 30% of national health care spending 3 for the past 60 years (and has remained very close to 31% for the past 20 years) (Figure 1). Although hospital spending is the focus of many cost-control policies and public attention, the increases are consistent with the increases seen across other areas of health care, such as for physicians and other professional services. Total spending for some smaller parts of nonhospital care has more than doubled over the past few decades and makes up an increasing proportion of total spending. For instance, home health care as a percentage of total spending tripled between 1980 and 2020, from 0.9% to 3.0%, and drug spending nearly doubled as a proportion of health care spending between 1980 and 2006, from 4.8% to 10.5%, and currently represent 8.4% of health care spending. 1
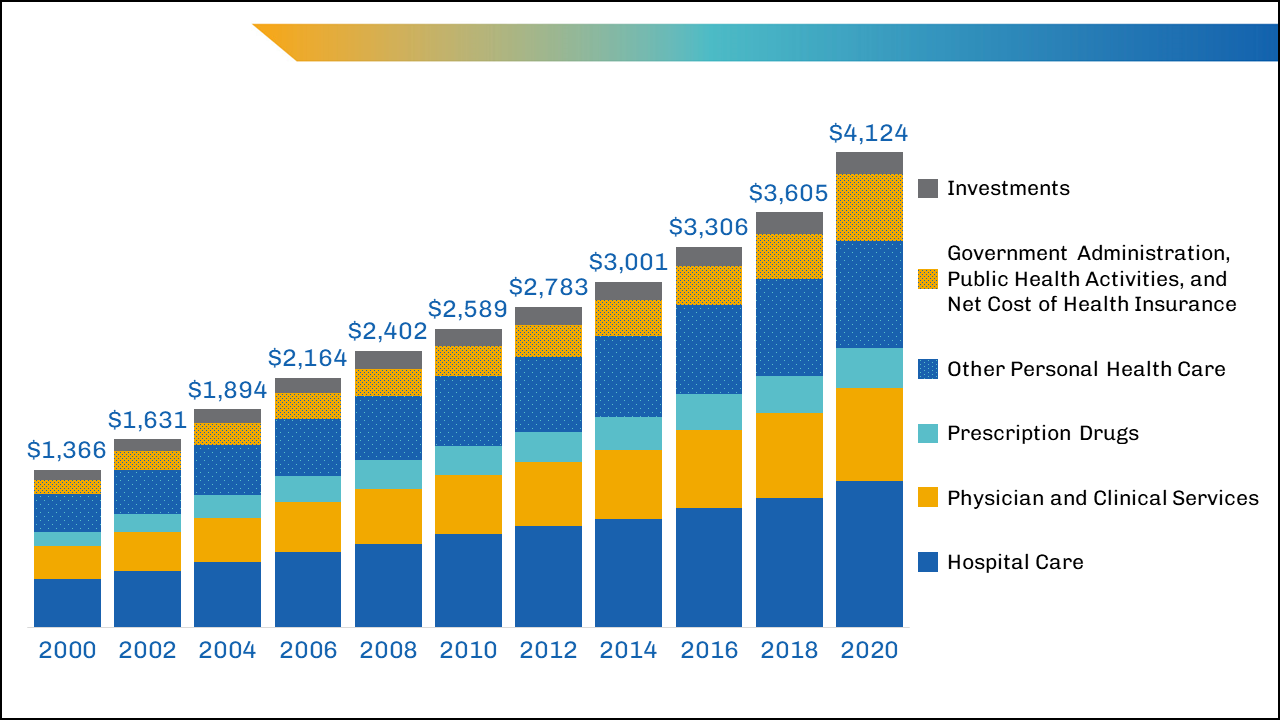
image description
The largest areas of spending that might yield the greatest potential for savings — such as inpatient care and physician-provided care — are unlikely to be reduced by lowering the total number of insured patients or visits per person, given the growing, aging U.S. population and the desire to cover more, not fewer, individuals with adequate health insurance.
In the past decade, policymaker and insurer interventions intended to change the mix of services by keeping patients out of high-cost settings (such as the hospital) have not always succeeded at reducing costs, although they have had other benefits for patients. 4
Breaking Down the Costs of Care
Thinking about total health care spending as an equation, one might define it as the number of services delivered per person multiplied by the number of people to whom services are delivered, multiplied again by the average cost of each service:
Health Care Spending=(number of services delivered per person)×(number of people to whom services are delivered)×(average cost of each service)
Could health care spending be lowered by making major changes to the numbers or types of services delivered or by lowering the average cost per service?
Although recent data on the overall utilization of health care are limited, in 2011, the number of doctor consultations per capita in the United States was below that in many comparable countries, but the number of diagnostic procedures (such as imaging) per capita remained higher. 5 Furthermore, no identifiable groups of individuals (by race/ethnicity, geographic location, etc.) appear to be outliers that consume extraordinary numbers of services. 6 The exception is that the sickest people do cost more to take care of, but even the most cost-conscious policymakers appear to be reluctant to abandon these patients.
In addition to the fact that the average number of health care services delivered per person in the United States was below international benchmarks in 2020,7 the percentage of people in the United States covered by health insurance was also lower than that in many other wealthy nations. Although millions of people gained insurance8 through the Affordable Care Act and provisions enacted during the COVID-19 pandemic, 10% of the nonelderly population remained uninsured in 2020. 9 When policymakers focus on reducing health care spending, considering the equation above, and see that the United States already has a lower proportion of its population insured and fewer services delivered to patients than other wealthy nations, their focus often shifts to the average cost of services.
It's Still the Prices … and the Wages
A report comparing the international prices of health care in 2017 found that the median list prices (charges) for medical procedures in the United States heavily outweighed the list prices in other countries, such as the United Kingdom, New Zealand, Australia, Switzerland, and South Africa. 10
For example, the 2017 U.S. median health care list price for a hospital admission with a hip replacement was $32,500, compared with $20,900 in Australia and $12,200 in the United Kingdom. In comparisons of the list prices of other procedures, such as deliveries by cesarean section, appendectomies, and knee replacements, the U.S. median list prices of elective and needed services were thousands of dollars — if not tens of thousands of dollars — more. 10 Yet, the list price for these services in the United States is often much higher than the actual payments made to providers by public or private insurance companies. 11
Public-payer programs (particularly Medicare and Medicaid) tend to pay hospitals rates that are lower than the cost of delivering care12 (though many economists argue these payments are slightly above actual costs, and providers argue they are at least slightly below actual costs), while private payers historically have paid about twice as much as public payers. 13 (See another brief in this series, “ Surprise! Why Medical Bills Are Still a Problem for U.S. Health Care ,” for more information about public and private payers’ role in health care costs.) However, the average cost per service is still high by international standards, even if it’s not as high as list prices may suggest. The high average costs are partially driven by the highly labor-intensive nature of health care, with labor consuming almost 55% of the share of total U.S. hospital costs in 2018. 14 These costs are growing due to the labor shortages exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Reducing U.S. health care spending by reducing labor costs could, theoretically, be achieved by reducing wages or eliminating positions; however, both of those policies would be problematic, with potential unintended consequences, such as driving clinicians away from the workforce at a time of growing need.
Wage reductions, particularly for clinicians, would require a vastly expanded labor pool that would take years to achieve (and even then, lower per person wages for nonphysicians may not decrease total spending related to health care labor). 15 Reducing or replacing clinical workers over time would require major changes to policy (both public and private) and major shifts in how health care is provided — neither of which has occurred rapidly, even since the implementation of the Affordable Care Act.
What’s a Policymaker to Do?
Nearly one in five Americans has medical debt, 16 and affordability is still an issue for a large proportion of the population, whether uninsured or insured, which suggests that policymakers should focus on patients’ costs. This may prove more impactful to the individual than reducing total health care spending.
A majority of the country agrees that the federal government should ensure some basic health insurance for all citizens. 17,18 Although most Americans consider reducing costs to individuals and expanding insurance coverage to be important, no clear consensus about who should bear any associated increased costs exists among patients or policymakers. Half of insured adults currently report difficulty affording medical or dental care, even when they are insured, because of the rising total costs of care and the increasing absolute amount of out-of-pocket spending. 19 Out-of-pocket spending for health care has doubled in the past 20 years, from $193.5 billion in 2000 to $388.6 billion in 2020. 1 These rising health care costs have disproportionately fallen on those with the fewest resources, including people who are uninsured, Black people, Hispanic people, and families with low incomes. 19 Increased cost sharing through copays and coinsurance may force difficult spending choices for even solidly middle-class families.
The severity and burden of out-of-pocket spending are hidden by the use of data averages; on average, U.S. residents have twice the average household net adjusted disposable income 20 of many other comparable nations and spend more than twice 21 as much per capita on health care. Yet, for those who fall outside these averages — average income, average costs, or both — the financial pain felt at the hospital, clinic, and pharmacy is very real.
In any given year, a small number of patients account for a disproportionate amount of health care spending because of the complexity and severity of their illnesses. Even careful international comparisons of end-of-life care for cancer patients demonstrate costs in the United States are similar to those in many comparable nations (although U.S. patients are more likely to receive chemotherapy, they spend fewer days in the hospital during the last 6 months of life than patients in other countries). 22 Similarly, although prevention efforts may delay or avoid the onset of illness in targeted populations, such efforts would not significantly reduce the number of services delivered for many years and may lead to an increase in care delivered over the course of an extended life span.
To the average person in the United States, immediate cost-control efforts might best be focused on reducing the cost burden for families and patients. Policymakers should continue to seek ways to promote better health care quality at lower costs rather than try to achieve unrealistic, drastic reductions in national health care spending. Investing in prevention, seeking to avoid preventable admissions or readmissions, and otherwise improving the quality of care are desirable, but these improvements are not quick solutions to lowering the national health care costs in the near term. Long-term policy actions could incrementally address health care spending but should clearly articulate the problem to be solved, the desired outcomes, and the trade-offs the nation is willing to make (as discussed in two companion pieces).
The U.S. health care system continues to place a disproportionate cost burden on the patients who can least afford it. In the short term, policymakers could focus on targeted subsidies to specific populations — the families and individuals whose household incomes fall outside the average or who have health care expenses that fall outside the average — whose health care costs are unmanageable. Such subsidies could expand existing premium subsidies or triggers that increase support for costs that exceed target amounts. Targeted subsidies are likely to increase total health care spending (especially public spending) but would address the problem of cost from the average consumer, or patient, perspective. Broader policies to ease costs for patients could also be considered by category of service; for instance, consumers have been largely shielded from the increased costs of care related to COVID-19 by the waiving of copays for patients and families. These policies would likely increase national spending as well, but they would make medical care more affordable to some families.
Download Brief
Cite this source: Grover A, Orgera K, Pincus L. Health Care Costs: What's The Problem? Washington, DC: AAMC; 2022. https://doi.org/10.15766/rai_dozyvvh2
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. National Health Expenditure Data. https://www.cms.gov/Research-Statistics-Data-and-Systems/Statistics-Trends-and-Reports/NationalHealthExpendData/NHE-Fact-Sheet . Published Dec. 1, 2021. Accessed Feb. 24, 2022.
- Schneider EC, Shah A, Doty MM, Tikkanen R, Fields K, Williams RD II. Mirror, Mirror 2021 — Reflecting Poorly: Health Care in the U.S. Compared to Other High-Income Countries. Washington, DC: The Commonwealth Fund. https://doi.org/10.26099/01DV-H208 . Published August 2021. Accessed April 21, 2022.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. National Health Expenditure Data: Historical. https://www.cms.gov/Research-Statistics-Data-and-Systems/Statistics-Trends-and-Reports/NationalHealthExpendData/NationalHealthAccountsHistorical . Published Dec. 15, 2021. Accessed April 22, 2022.
- Berkowitz S, Ricks KB, Wang J, Parker M, Rimal R, DeWalt D. Evaluating a nonemergency medical transportation benefit for accountable care organization members. Health Affairs. 2022;41(3):406-413. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2021.00449.
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. Health Care Utilisation. Paris, France: Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. https://stats.oecd.org/index.aspx?queryid=30166# . Published Nov. 9, 2021. Accessed Feb. 24, 2022.
- Abelson R. Harris G. Critics question study cited in health debate. New York Times. June 2, 2010. https://www.nytimes.com/2010/06/03/business/03dartmouth.html?ref=business&pagewanted=all . Accessed Feb. 24, 2022.
- The Commonwealth Fund. Selected Health & System Statistics: Average Annual Number of Physician Visits per Capita. https://www.commonwealthfund.org/international-health-policy-center/system-stats/annual-physician-visits-per-capita . Published June 5, 2020. Accessed April 21, 2022.
- Tolbert J, Orgera K. Key Facts About the Uninsured Population. San Francisco, CA: KFF. https://www.kff.org/uninsured/issue-brief/key-facts-about-the-uninsured-population/ . Published Nov. 6, 2020. Accessed April 21, 2022.
- Tolbert J, Orgera K, Damico A. What Does the CPS Tell Us About Health Insurance Coverage in 2020? San Francisco, CA: KFF. https://www.kff.org/uninsured/issue-brief/what-does-the-cps-tell-us-about-health-insurance-coverage… . Published Sept. 23, 2021. Accessed April 21, 2022.
- Hargraves J, Bloschichak A. International Comparisons of Health Care Prices From the 2017 iFHP Survey. Washington DC: Health Care Cost Institute. https://healthcostinstitute.org/hcci-research/international-comparisons-of-health-care-prices-2017-ifhp-survey . Published Dec. 2019. Accessed April 21, 2022.
- Bai G. Anderson G. Extreme markup: The fifty US hospitals with the highest charge-to-cost ratios. Health Affairs. 2015;34(6):922-928. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2014.1414.
- Congressional Budget Office. The Prices That Commercial Health Insurers and Medicare Pay for Hospitals’ and Physicians’ Services. Washington, DC: Congressional Budget Office. https://www.cbo.gov/system/files/2022-01/57422-medical-prices.pdf . Published January 2022. Accessed April 21, 2022.
- Lopez E, Neuman T, Jacobson G, Levitt L. How Much More Than Medicare Do Private Insurers Pay? A Review of the Literature. San Francisco, CA: The Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation. https://www.kff.org/medicare/issue-brief/how-much-more-than-medicare-do-private-insurers-pay-a-review-of-the-literature/ . Published April 15, 2020. Accessed March 22, 2022.
- Daly R. Hospitals Innovate to Control Labor Costs. Westchester, IL: Healthcare Financial Management Association. https://www.hfma.org/topics/hfm/2019/october/hospitals-innovate-to-control-labor-costs.html . Published Oct. 1, 2019. Accessed Feb. 24, 2022.
- Batson BN, Crosby SN, Fitzpatrick, JM. Mississippi frontline: Targeting value-based care with physician-led care teams. J Miss State Med Assoc. 2022;63(1):19-21. https://ejournal.msmaonline.com/publication/?m=63060&i=735364&p=20&ver=html5 .
- Kluender R, Mahoney N, Wong F, et al. Medical debt in the US, 2009-2020. JAMA. 2021;326(3):250-256. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.8694.
- Jones B. Increasing Share of Americans Favor a Single Government Program to Provide Health Care Coverage. Washington, DC: Pew Research Center. https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2020/09/29/increasing-share-of-americans-favor-a-single-government-program-to-provide-health-care-coverage/ . Published Sept. 29, 2020. Accessed April 21, 2022.
- Bialik K. More Americans Say Government Should Ensure Health Care Coverage. Washington, DC: Pew Research Center. https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2017/01/13/more-americans-say-government-should-ensure-health-care-coverage/ . Published Jan. 13, 2017. Accessed March 22, 2022.
- Kearney A, Hamel L, Stokes M, Brodie M. Americans’ Challenges With Health Care Costs. San Francisco, CA: The Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation. https://www.kff.org/health-costs/issue-brief/americans-challenges-with-health-care-costs/ . Published Dec. 14, 2021. Accessed Feb. 24, 2022.
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. Income. Better Life Index. Paris, France: Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. https://www.oecdbetterlifeindex.org/topics/income/ . Accessed April 21, 2022.
- Wager E, Ortaliza J, Cox C; The Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation. Health System Tracker. How Does Health Spending in the U.S. Compare to Other Countries? San Francisco, CA: The Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation. https://www.healthsystemtracker.org/chart-collection/health-spending-u-s-compare-countries-2/ . Published Jan. 21, 2022. Accessed April 21, 2022.
- Bekelman JE, Halpern SD, Blankart CR, et al. Comparison of site of death, health care utilization, and hospital expenditures for patients dying with cancer in 7 developed countries. JAMA. 2016;315(3):272-283. doi:10.1001/jama.2015.18603.

IvyPanda . (2020) 'Healthcare Issues of Elderly Population'. 17 May.
IvyPanda . 2020. "Healthcare Issues of Elderly Population." May 17, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/healthcare-issues-of-elderly-population/.
1. IvyPanda . "Healthcare Issues of Elderly Population." May 17, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/healthcare-issues-of-elderly-population/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Healthcare Issues of Elderly Population." May 17, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/healthcare-issues-of-elderly-population/.
Essay on Health for Students and Children
500+ words essay on health.
Essay on Health: Health was earlier said to be the ability of the body functioning well. However, as time evolved, the definition of health also evolved. It cannot be stressed enough that health is the primary thing after which everything else follows. When you maintain good health , everything else falls into place.

Similarly, maintaining good health is dependent on a lot of factors. It ranges from the air you breathe to the type of people you choose to spend your time with. Health has a lot of components that carry equal importance. If even one of them is missing, a person cannot be completely healthy.
Constituents of Good Health
First, we have our physical health. This means being fit physically and in the absence of any kind of disease or illness . When you have good physical health, you will have a longer life span. One may maintain their physical health by having a balanced diet . Do not miss out on the essential nutrients; take each of them in appropriate quantities.
Secondly, you must exercise daily. It may be for ten minutes only but never miss it. It will help your body maintain physical fitness. Moreover, do not consume junk food all the time. Do not smoke or drink as it has serious harmful consequences. Lastly, try to take adequate sleep regularly instead of using your phone.
Next, we talk about our mental health . Mental health refers to the psychological and emotional well-being of a person. The mental health of a person impacts their feelings and way of handling situations. We must maintain our mental health by being positive and meditating.
Subsequently, social health and cognitive health are equally important for the overall well-being of a person. A person can maintain their social health when they effectively communicate well with others. Moreover, when a person us friendly and attends social gatherings, he will definitely have good social health. Similarly, our cognitive health refers to performing mental processes effectively. To do that well, one must always eat healthily and play brain games like Chess, puzzles and more to sharpen the brain.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Physical Health Alone is Not Everything
There is this stigma that surrounds mental health. People do not take mental illnesses seriously. To be completely fit, one must also be mentally fit. When people completely discredit mental illnesses, it creates a negative impact.
For instance, you never tell a person with cancer to get over it and that it’s all in their head in comparison to someone dealing with depression . Similarly, we should treat mental health the same as physical health.
Parents always take care of their children’s physical needs. They feed them with nutritious foods and always dress up their wounds immediately. However, they fail to notice the deteriorating mental health of their child. Mostly so, because they do not give it that much importance. It is due to a lack of awareness amongst people. Even amongst adults, you never know what a person is going through mentally.
Thus, we need to be able to recognize the signs of mental illnesses . A laughing person does not equal a happy person. We must not consider mental illnesses as a taboo and give it the attention it deserves to save people’s lives.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- About Health Effects of Cigarette Smoking
- Secondhand Smoke
- E-cigarettes (Vapes)
- Menthol Tobacco Products
- Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Reports (MMWR)
- About Surveys
- Other Tobacco Products
- Smoking and Tobacco Use Features
- Patient Care Settings and Smoking Cessation
- Patient Care
- Funding Opportunity Announcements
- State and Community Work
- National and State Tobacco Control Program
- Multimedia and Tools
- Tobacco - Health Equity
- Tobacco - Surgeon General's Reports
- State Tobacco Activities Tracking and Evaluation (STATE) System
- Global Tobacco Control
Health Effects of Vaping
At a glance.
Learn more about the health effects of vaping.
- No tobacco products, including e-cigarettes, are safe.
- Most e-cigarettes contain nicotine, which is highly addictive and is a health danger for pregnant people, developing fetuses, and youth. 1
- Aerosol from e-cigarettes can also contain harmful and potentially harmful substances. These include cancer-causing chemicals and tiny particles that can be inhaled deep into lungs. 1
- E-cigarettes should not be used by youth, young adults, or people who are pregnant. E-cigarettes may have the potential to benefit adults who smoke and are not pregnant if used as a complete substitute for all smoked tobacco products. 2 3 4
- Scientists still have a lot to learn about the short- and long-term health effects of using e-cigarettes.
Most e-cigarettes, or vapes, contain nicotine, which has known adverse health effects. 1
- Nicotine is highly addictive. 1
- Nicotine is toxic to developing fetuses and is a health danger for pregnant people. 1
- Acute nicotine exposure can be toxic. Children and adults have been poisoned by swallowing, breathing, or absorbing vaping liquid through their skin or eyes. More than 80% of calls to U.S. poison control centers for e-cigarettes are for children less than 5 years old. 5
Nicotine poses unique dangers to youth because their brains are still developing.
- Nicotine can harm brain development which continues until about age 25. 1
- Youth can start showing signs of nicotine addiction quickly, sometimes before the start of regular or daily use. 1
- Using nicotine during adolescence can harm the parts of the brain that control attention, learning, mood, and impulse control. 1
- Adolescents who use nicotine may be at increased risk for future addiction to other drugs. 1 6
- Youth who vape may also be more likely to smoke cigarettes in the future. 7 8 9 10 11 12
Other potential harms of e-cigarettes
E-cigarette aerosol can contain substances that can be harmful or potentially harmful to the body. These include: 1
- Nicotine, a highly addictive chemical that can harm adolescent brain development
- Cancer-causing chemicals
- Heavy metals such as nickel, tin, and lead
- Tiny particles that can be inhaled deep into the lungs
- Volatile organic compounds
- Flavorings such as diacetyl, a chemical linked to a serious lung disease. Some flavorings used in e-cigarettes may be safe to eat but not to inhale because the lungs process substances differently than the gut.
E-cigarette aerosol generally contains fewer harmful chemicals than the deadly mix of 7,000 chemicals in smoke from cigarettes. 7 13 14 However, this does not make e-cigarettes safe. Scientists are still learning about the immediate and long-term health effects of using e-cigarettes.
Dual use refers to the use of both e-cigarettes and regular cigarettes. Dual use is not an effective way to safeguard health. It may result in greater exposure to toxins and worse respiratory health outcomes than using either product alone. 2 3 4 15
Some people who use e-cigarettes have experienced seizures. Most reports to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA ) have involved youth or young adults. 16 17
E-cigarettes can cause unintended injuries. Defective e-cigarette batteries have caused fires and explosions, some of which have resulted in serious injuries. Most explosions happened when the batteries were being charged.
Anyone can report health or safety issues with tobacco products, including e-cigarettes, through the FDA Safety Reporting Portal .
Health effects of vaping for pregnant people
The use of any tobacco product, including e-cigarettes, is not safe during pregnancy. 1 14 Scientists are still learning about the health effects of vaping on pregnancy and pregnancy outcomes. Here's what we know now:
- Most e-cigarettes, or vapes, contain nicotine—the addictive substance in cigarettes, cigars, and other tobacco products. 18
- Nicotine is a health danger for pregnant people and is toxic to developing fetuses. 1 14
- Nicotine can damage a fetus's developing brain and lungs. 13
- E-cigarette use during pregnancy has been associated with low birth weight and pre-term birth. 19 20
Nicotine addiction and withdrawal
Nicotine is the main addictive substance in tobacco products, including e-cigarettes. With repeated use, a person's brain gets used to having nicotine. This can make them think they need nicotine just to feel okay. This is part of nicotine addiction.
Signs of nicotine addiction include craving nicotine, being unable to stop using it, and developing a tolerance (needing to use more to feel the same). Nicotine addiction can also affect relationships with family and friends and performance in school, at work, or other activities.
When someone addicted to nicotine stops using it, their body and brain have to adjust. This can result in temporary symptoms of nicotine withdrawal which may include:
- Feeling irritable, jumpy, restless, or anxious
- Feeling sad or down
- Having trouble sleeping
- Having a hard time concentrating
- Feeling hungry
- Craving nicotine
Withdrawal symptoms fade over time as the brain gets used to not having nicotine.
Nicotine addiction and mental health
Nicotine addiction can harm mental health and be a source of stress. 21 22 23 24 More research is needed to understand the connection between vaping and mental health, but studies show people who quit smoking cigarettes experience: 25
- Lower levels of anxiety, depression, and stress
- Improved positive mood and quality of life
Mental health is a growing concern among youth. 26 27 Youth vaping and cigarette use are associated with mental health symptoms such as depression. 22 28
The most common reason middle and high school students give for currently using e-cigarettes is, "I am feeling anxious, stressed, or depressed." 29 Nicotine addiction or withdrawal can contribute to these feelings or make them worse. Youth may use tobacco products to relieve their symptoms, which can lead to a cycle of nicotine addiction.

- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. E-Cigarette Use Among Youth and Young Adults: A Report of the Surgeon General . Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2016. Accessed Feb 14, 2024.
- Goniewicz ML, Smith DM, Edwards KC, et al. Comparison of nicotine and toxicant exposure in users of electronic cigarettes and combustible cigarettes . JAMA Netw Open. 2018;1(8):e185937.
- Reddy KP, Schwamm E, Kalkhoran S, et al. Respiratory symptom incidence among people using electronic cigarettes, combustible tobacco, or both . Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021;204(2):231–234.
- Smith DM, Christensen C, van Bemmel D, et al. Exposure to nicotine and toxicants among dual users of tobacco cigarettes and e-cigarettes: Population Assessment of Tobacco and Health (PATH) Study, 2013-2014 . Nicotine Tob Res. 2021;23(5):790–797.
- Tashakkori NA, Rostron BL, Christensen CH, Cullen KA. Notes from the field: e-cigarette–associated cases reported to poison centers — United States, April 1, 2022–March 31, 2023 . MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:694–695.
- Yuan M, Cross SJ, Loughlin SE, Leslie FM. Nicotine and the adolescent brain . J Physiol. 2015;593(16):3397–3412.
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Public Health Consequences of E-Cigarettes . The National Academies Press; 2018.
- Barrington-Trimis JL, Kong G, Leventhal AM, et al. E-cigarette use and subsequent smoking frequency among adolescents . Pediatrics. 2018;142(6):e20180486.
- Barrington-Trimis JL, Urman R, Berhane K, et al. E-cigarettes and future cigarette use . Pediatrics. 2016;138(1):e20160379.
- Bunnell RE, Agaku IT, Arrazola RA, et al. Intentions to smoke cigarettes among never-smoking US middle and high school electronic cigarette users: National Youth Tobacco Survey, 2011-2013 . Nicotine Tob Res. 2015;17(2):228–235.
- Soneji S, Barrington-Trimis JL, Wills TA, et al. Association between initial use of e-cigarettes and subsequent cigarette smoking among adolescents and young adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis . JAMA Pediatr. 2017;171(8):788–797.
- Sun R, Méndez D, Warner KE. Association of electronic cigarette use by U.S. adolescents with subsequent persistent cigarette smoking . JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(3):e234885.
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. How Tobacco Smoke Causes Disease: The Biology and Behavioral Basis for Smoking-Attributable Disease . Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2010. Accessed Feb 13, 2024.
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. The Health Consequences of Smoking: 50 Years of Progress. A Report of the Surgeon General . Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2014. Accessed Feb 12, 2024.
- Mukerjee R, Hirschtick JL, LZ Arciniega, et al. ENDS, cigarettes, and respiratory illness: longitudinal associations among U.S. youth . AJPM. Published online Dec 2023.
- Faulcon LM, Rudy S, Limpert J, Wang B, Murphy I. Adverse experience reports of seizures in youth and young adult electronic nicotine delivery systems users . J Adolesc Health . 2020;66(1):15–17.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. E-cigarette: Safety Communication - Related to Seizures Reported Following E-cigarette Use, Particularly in Youth and Young Adults . U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; 2019. Accessed Feb 14, 2024.
- Marynak KL, Gammon DG, Rogers T, et al. Sales of nicotine-containing electronic cigarette products: United States, 2015 . Am J Public Health . 2017;107(5):702-705.
- Regan AK, Bombard JM, O'Hegarty MM, Smith RA, Tong VT. Adverse birth outcomes associated with prepregnancy and prenatal electronic cigarette use . Obstet Gynecol. 2021;138(1):85–94.
- Regan AK, Pereira G. Patterns of combustible and electronic cigarette use during pregnancy and associated pregnancy outcomes . Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):13508.
- Kutlu MG, Parikh V, Gould TJ. Nicotine addiction and psychiatric disorders . Int Rev Neurobiol. 2015;124:171–208.
- Obisesan OH, Mirbolouk M, Osei AD, et al. Association between e-cigarette use and depression in the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, 2016-2017 . JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(12):e1916800.
- Prochaska JJ, Das S, Young-Wolff KC. Smoking, mental illness, and public health . Annu Rev Public Health. 2017;38:165–185.
- Wootton RE, Richmond RC, Stuijfzand BG, et al. Evidence for causal effects of lifetime smoking on risk for depression and schizophrenia: a Mendelian randomisation study . Psychol Med. 2020;50(14):2435–2443.
- Taylor G, McNeill A, Girling A, Farley A, Lindson-Hawley N, Aveyard P. Change in mental health after smoking cessation: systematic review and meta-analysis . BMJ. 2014;348:g1151.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Youth Risk Behavior Survey Data Summary & Trends Report: 2011–2021 . U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; 2023. Accessed Dec 15, 2023.
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Protecting Youth Mental Health: The U.S. Surgeon General's Advisory . Office of the Surgeon General; 2021. Accessed Jan 5, 2024.
- Lechner WV, Janssen T, Kahler CW, Audrain-McGovern J, Leventhal AM. Bi-directional associations of electronic and combustible cigarette use onset patterns with depressive symptoms in adolescents . Prev Med. 2017;96:73–78.
- Gentzke AS, Wang TW, Cornelius M, et al. Tobacco product use and associated factors among middle and high school students—National Youth Tobacco Survey, United States, 2021 . MMWR Surveill Summ. 2022;71(No. SS-5):1–29.
Smoking and Tobacco Use
Commercial tobacco use is the leading cause of preventable disease, disability, and death in the United States.
For Everyone
Health care providers, public health.
- Share full article

When Prison and Mental Illness Amount to a Death Sentence
The downward spiral of one inmate, Markus Johnson, shows the larger failures of the nation’s prisons to care for the mentally ill.
Supported by
By Glenn Thrush
Photographs by Carlos Javier Ortiz
Glenn Thrush spent more than a year reporting this article, interviewing close to 50 people and reviewing court-obtained body-camera footage and more than 1,500 pages of documents.
- Published May 5, 2024 Updated May 7, 2024
Markus Johnson slumped naked against the wall of his cell, skin flecked with pepper spray, his face a mask of puzzlement, exhaustion and resignation. Four men in black tactical gear pinned him, his face to the concrete, to cuff his hands behind his back.
He did not resist. He couldn’t. He was so gravely dehydrated he would be dead by their next shift change.
Listen to this article with reporter commentary
“I didn’t do anything,” Mr. Johnson moaned as they pressed a shield between his shoulders.
It was 1:19 p.m. on Sept. 6, 2019, in the Danville Correctional Center, a medium-security prison a few hours south of Chicago. Mr. Johnson, 21 and serving a short sentence for gun possession, was in the throes of a mental collapse that had gone largely untreated, but hardly unwatched.
He had entered in good health, with hopes of using the time to gain work skills. But for the previous three weeks, Mr. Johnson, who suffered from bipolar disorder and schizophrenia, had refused to eat or take his medication. Most dangerous of all, he had stealthily stopped drinking water, hastening the physical collapse that often accompanies full-scale mental crises.
Mr. Johnson’s horrific downward spiral, which has not been previously reported, represents the larger failures of the nation’s prisons to care for the mentally ill. Many seriously ill people receive no treatment . For those who do, the outcome is often determined by the vigilance and commitment of individual supervisors and frontline staff, which vary greatly from system to system, prison to prison, and even shift to shift.
The country’s jails and prisons have become its largest provider of inpatient mental health treatment, with 10 times as many seriously mentally ill people now held behind bars as in hospitals. Estimating the population of incarcerated people with major psychological problems is difficult, but the number is likely 200,000 to 300,000, experts say.
Many of these institutions remain ill-equipped to handle such a task, and the burden often falls on prison staff and health care personnel who struggle with the dual roles of jailer and caregiver in a high-stress, dangerous, often dehumanizing environment.
In 2021, Joshua McLemore , a 29-year-old with schizophrenia held for weeks in an isolation cell in Jackson County, Ind., died of organ failure resulting from a “refusal to eat or drink,” according to an autopsy. In April, New York City agreed to pay $28 million to settle a lawsuit filed by the family of Nicholas Feliciano, a young man with a history of mental illness who suffered severe brain damage after attempting to hang himself on Rikers Island — as correctional officers stood by.
Mr. Johnson’s mother has filed a wrongful-death suit against the state and Wexford Health Sources, a for-profit health care contractor in Illinois prisons. The New York Times reviewed more than 1,500 pages of reports, along with depositions taken from those involved. Together, they reveal a cascade of missteps, missed opportunities, potential breaches of protocol and, at times, lapses in common sense.

Prison officials and Wexford staff took few steps to intervene even after it became clear that Mr. Johnson, who had been hospitalized repeatedly for similar episodes and recovered, had refused to take medication. Most notably, they did not transfer him to a state prison facility that provides more intensive mental health treatment than is available at regular prisons, records show.
The quality of medical care was also questionable, said Mr. Johnson’s lawyers, Sarah Grady and Howard Kaplan, a married legal team in Chicago. Mr. Johnson lost 50 to 60 pounds during three weeks in solitary confinement, but officials did not initiate interventions like intravenous feedings or transfer him to a non-prison hospital.
And they did not take the most basic step — dialing 911 — until it was too late.
There have been many attempts to improve the quality of mental health treatment in jails and prisons by putting care on par with punishment — including a major effort in Chicago . But improvements have proved difficult to enact and harder to sustain, hampered by funding and staffing shortages.
Lawyers representing the state corrections department, Wexford and staff members who worked at Danville declined to comment on Mr. Johnson’s death, citing the unresolved litigation. In their interviews with state police investigators, and in depositions, employees defended their professionalism and adherence to procedure, while citing problems with high staff turnover, difficult work conditions, limited resources and shortcomings of co-workers.
But some expressed a sense of resignation about the fate of Mr. Johnson and others like him.
Prisoners have “much better chances in a hospital, but that’s not their situation,” said a senior member of Wexford’s health care team in a deposition.
“I didn’t put them in prison,” he added. “They are in there for a reason.”
Markus Mison Johnson was born on March 1, 1998, to a mother who believed she was not capable of caring for him.
Days after his birth, he was taken in by Lisa Barker Johnson, a foster mother in her 30s who lived in Zion, Ill., a working-class city halfway between Chicago and Milwaukee. Markus eventually became one of four children she adopted from different families.
The Johnson house is a lively split level, with nieces, nephews, grandchildren and neighbors’ children, family keepsakes, video screens and juice boxes. Ms. Johnson sits at its center on a kitchen chair, chin resting on her hand as children wander over to share their thoughts, or to tug on her T-shirt to ask her to be their bathroom buddy.
From the start, her bond with Markus was particularly powerful, in part because the two looked so much alike, with distinctive dimpled smiles. Many neighbors assumed he was her biological son. The middle name she chose for him was intended to convey that message.
“Mison is short for ‘my son,’” she said standing over his modest footstone grave last summer.
He was happy at home. School was different. His grades were good, but he was intensely shy and was diagnosed with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in elementary school.
That was around the time the bullying began. His sisters were fierce defenders, but they could only do so much. He did the best he could, developing a quick, taunting tongue.
These experiences filled him with a powerful yearning to fit in.
It was not to be.
When he was around 15, he called 911 in a panic, telling the dispatcher he saw two men standing near the small park next to his house threatening to abduct children playing there. The officers who responded found nothing out of the ordinary, and rang the Johnsons’ doorbell.
He later told his mother he had heard a voice telling him to “protect the kids.”
He was hospitalized for the first time at 16, and given medications that stabilized him for stretches of time. But the crises would strike every six months or so, often triggered by his decision to stop taking his medication.
His family became adept at reading signs he was “getting sick.” He would put on his tan Timberlands and a heavy winter coat, no matter the season, and perch on the edge of his bed as if bracing for battle. Sometimes, he would cook his own food, paranoid that someone might poison him.
He graduated six months early, on the dean’s list, but was rudderless, and hanging out with younger boys, often paying their way.
His mother pointed out the perils of buying friendship.
“I don’t care,” he said. “At least I’ll be popular for a minute.”
Zion’s inviting green grid of Bible-named streets belies the reality that it is a rough, unforgiving place to grow up. Family members say Markus wanted desperately to prove he was tough, and emulated his younger, reckless group of friends.
Like many of them, he obtained a pistol. He used it to hold up a convenience store clerk for $425 in January 2017, according to police records. He cut a plea deal for two years of probation, and never explained to his family what had made him do it.
But he kept getting into violent confrontations. In late July 2018, he was arrested in a neighbor’s garage with a handgun he later admitted was his. He was still on probation for the robbery, and his public defender negotiated a plea deal that would send him to state prison until January 2020.
An inpatient mental health system
Around 40 percent of the about 1.8 million people in local, state and federal jails and prison suffer from at least one mental illness, and many of these people have concurrent issues with substance abuse, according to recent Justice Department estimates.
Psychological problems, often exacerbated by drug use, often lead to significant medical problems resulting from a lack of hygiene or access to good health care.
“When you suffer depression in the outside world, it’s hard to concentrate, you have reduced energy, your sleep is disrupted, you have a very gloomy outlook, so you stop taking care of yourself,” said Robert L. Trestman , a Virginia Tech medical school professor who has worked on state prison mental health reforms.
The paradox is that prison is often the only place where sick people have access to even minimal care.
But the harsh work environment, remote location of many prisons, and low pay have led to severe shortages of corrections staff and the unwillingness of doctors, nurses and counselors to work with the incarcerated mentally ill.
In the early 2000s, prisoners’ rights lawyers filed a class-action lawsuit against Illinois claiming “deliberate indifference” to the plight of about 5,000 mentally ill prisoners locked in segregated units and denied treatment and medication.
In 2014, the parties reached a settlement that included minimum staffing mandates, revamped screening protocols, restrictions on the use of solitary confinement and the allocation of about $100 million to double capacity in the system’s specialized mental health units.
Yet within six months of the deal, Pablo Stewart, an independent monitor chosen to oversee its enforcement, declared the system to be in a state of emergency.
Over the years, some significant improvements have been made. But Dr. Stewart’s final report , drafted in 2022, gave the system failing marks for its medication and staffing policies and reliance on solitary confinement “crisis watch” cells.
Ms. Grady, one of Mr. Johnson’s lawyers, cited an additional problem: a lack of coordination between corrections staff and Wexford’s professionals, beyond dutifully filling out dozens of mandated status reports.
“Markus Johnson was basically documented to death,” she said.
‘I’m just trying to keep my head up’
Mr. Johnson was not exactly looking forward to prison. But he saw it as an opportunity to learn a trade so he could start a family when he got out.
On Dec. 18, 2018, he arrived at a processing center in Joliet, where he sat for an intake interview. He was coherent and cooperative, well-groomed and maintained eye contact. He was taking his medication, not suicidal and had a hearty appetite. He was listed as 5 feet 6 inches tall and 256 pounds.
Mr. Johnson described his mood as “go with the flow.”
A few days later, after arriving in Danville, he offered a less settled assessment during a telehealth visit with a Wexford psychiatrist, Dr. Nitin Thapar. Mr. Johnson admitted to being plagued by feelings of worthlessness, hopelessness and “constant uncontrollable worrying” that affected his sleep.
He told Dr. Thapar he had heard voices in the past — but not now — telling him he was a failure, and warning that people were out to get him.
At the time he was incarcerated, the basic options for mentally ill people in Illinois prisons included placement in the general population or transfer to a special residential treatment program at the Dixon Correctional Center, west of Chicago. Mr. Johnson seemed out of immediate danger, so he was assigned to a standard two-man cell in the prison’s general population, with regular mental health counseling and medication.
Things started off well enough. “I’m just trying to keep my head up,” he wrote to his mother. “Every day I learn to be stronger & stronger.”
But his daily phone calls back home hinted at friction with other inmates. And there was not much for him to do after being turned down for a janitorial training program.
Then, in the spring of 2019, his grandmother died, sending him into a deep hole.
Dr. Thapar prescribed a new drug used to treat major depressive disorders. Its most common side effect is weight gain. Mr. Johnson stopped taking it.
On July 4, he told Dr. Thapar matter-of-factly during a telehealth check-in that he was no longer taking any of his medications. “I’ve been feeling normal, I guess,” he said. “I feel like I don’t need the medication anymore.”
Dr. Thapar said he thought that was a mistake, but accepted the decision and removed Mr. Johnson from his regular mental health caseload — instructing him to “reach out” if he needed help, records show.
The pace of calls back home slackened. Mr. Johnson spent more time in bed, and became more surly. At a group-therapy session, he sat stone silent, after showing up late.
By early August, he was telling guards he had stopped eating.
At some point, no one knows when, he had intermittently stopped drinking fluids.
‘I’m having a breakdown’
Then came the crash.
On Aug. 12, Mr. Johnson got into a fight with his older cellmate.
He was taken to a one-man disciplinary cell. A few hours later, Wexford’s on-site mental health counselor, Melanie Easton, was shocked by his disoriented condition. Mr. Johnson stared blankly, then burst into tears when asked if he had “suffered a loss in the previous six months.”
He was so unresponsive to her questions she could not finish the evaluation.
Ms. Easton ordered that he be moved to a 9-foot by 8-foot crisis cell — solitary confinement with enhanced monitoring. At this moment, a supervisor could have ticked the box for “residential treatment” on a form to transfer him to Dixon. That did not happen, according to records and depositions.
Around this time, he asked to be placed back on his medication but nothing seems to have come of it, records show.
By mid-August, he said he was visualizing “people that were not there,” according to case notes. At first, he was acting more aggressively, once flicking water at a guard through a hole in his cell door. But his energy ebbed, and he gradually migrated downward — from standing to bunk to floor.
“I’m having a breakdown,” he confided to a Wexford employee.
At the time, inmates in Illinois were required to declare an official hunger strike before prison officials would initiate protocols, including blood testing or forced feedings. But when a guard asked Mr. Johnson why he would not eat, he said he was “fasting,” as opposed to starving himself, and no action seems to have been taken.
‘Tell me this is OK!’
Lt. Matthew Morrison, one of the few people at Danville to take a personal interest in Mr. Johnson, reported seeing a white rind around his mouth in early September. He told other staff members the cell gave off “a death smell,” according to a deposition.
On Sept. 5, they moved Mr. Johnson to one of six cells adjacent to the prison’s small, bare-bones infirmary. Prison officials finally placed him on the official hunger strike protocol without his consent.
Mr. Morrison, in his deposition, said he was troubled by the inaction of the Wexford staff, and the lack of urgency exhibited by the medical director, Dr. Justin Young.
On Sept. 5, Mr. Morrison approached Dr. Young to express his concerns, and the doctor agreed to order blood and urine tests. But Dr. Young lived in Chicago, and was on site at the prison about four times a week, according to Mr. Kaplan. Friday, Sept. 6, 2019, was not one of those days.
Mr. Morrison arrived at work that morning, expecting to find Mr. Johnson’s testing underway. A Wexford nurse told him Dr. Young believed the tests could wait.
Mr. Morrison, stunned, asked her to call Dr. Young.
“He’s good till Monday,” Dr. Young responded, according to Mr. Morrison.
“Come on, come on, look at this guy! You tell me this is OK!” the officer responded.
Eventually, Justin Duprey, a licensed nurse practitioner and the most senior Wexford employee on duty that day, authorized the test himself.
Mr. Morrison, thinking he had averted a disaster, entered the cell and implored Mr. Johnson into taking the tests. He refused.
So prison officials obtained approval to remove him forcibly from his cell.
‘Oh, my God’
What happened next is documented in video taken from cameras held by officers on the extraction team and obtained by The Times through a court order.
Mr. Johnson is scarcely recognizable as the neatly groomed 21-year-old captured in a cellphone picture a few months earlier. His skin is ashen, eyes fixed on the middle distance. He might be 40. Or 60.
At first, he places his hands forward through the hole in his cell door to be cuffed. This is against procedure, the officers shout. His hands must be in back.
He will not, or cannot, comply. He wanders to the rear of his cell and falls hard. Two blasts of pepper spray barely elicit a reaction. The leader of the tactical team later said he found it unusual and unnerving.
The next video is in the medical unit. A shield is pressed to his chest. He is in agony, begging for them to stop, as two nurses attempt to insert a catheter.
Then they move him, half-conscious and limp, onto a wheelchair for the blood draw.
For the next 20 minutes, the Wexford nurse performing the procedure, Angelica Wachtor, jabs hands and arms to find a vessel that will hold shape. She winces with each puncture, tries to comfort him, and grows increasingly rattled.
“Oh, my God,” she mutters, and asks why help is not on the way.
She did not request assistance or discuss calling 911, records indicate.
“Can you please stop — it’s burning real bad,” Mr. Johnson said.
Soon after, a member of the tactical team reminds Ms. Wachtor to take Mr. Johnson’s vitals before taking him back to his cell. She would later tell Dr. Young she had been unable to able to obtain his blood pressure.
“You good?” one of the team members asks as they are preparing to leave.
“Yeah, I’ll have to be,” she replies in the recording.
Officers lifted him back onto his bunk, leaving him unconscious and naked except for a covering draped over his groin. His expressionless face is visible through the window on the cell door as it closes.
‘Cardiac arrest.’
Mr. Duprey, the nurse practitioner, had been sitting inside his office after corrections staff ordered him to shelter for his own protection, he said. When he emerged, he found Ms. Wachtor sobbing, and after a delay, he was let into the cell. Finding no pulse, Mr. Duprey asked a prison employee to call 911 so Mr. Johnson could be taken to a local emergency room.
The Wexford staff initiated CPR. It did not work.
At 3:38 p.m., the paramedics declared Markus Mison Johnson dead.
Afterward, a senior official at Danville called the Johnson family to say he had died of “cardiac arrest.”
Lisa Johnson pressed for more information, but none was initially forthcoming. She would soon receive a box hastily crammed with his possessions: uneaten snacks, notebooks, an inspirational memoir by a man who had served 20 years at Leavenworth.
Later, Shiping Bao, the coroner who examined his body, determined Mr. Johnson had died of severe dehydration. He told the state police it “was one of the driest bodies he had ever seen.”
For a long time, Ms. Johnson blamed herself. She says that her biggest mistake was assuming that the state, with all its resources, would provide a level of care comparable to what she had been able to provide her son.
She had stopped accepting foster care children while she was raising Markus and his siblings. But as the months dragged on, she decided her once-boisterous house had become oppressively still, and let local agencies know she was available again.
“It is good to have children around,” she said. “It was too quiet around here.”
Read by Glenn Thrush
Audio produced by Jack D’Isidoro .
Glenn Thrush covers the Department of Justice. He joined The Times in 2017 after working for Politico, Newsday, Bloomberg News, The New York Daily News, The Birmingham Post-Herald and City Limits. More about Glenn Thrush
Advertisement

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Healthcare Issues, Systems, And Policies America, once the global leader in the health of its population and among the nations with the highest quality and most readily available healthcare services, has now fallen behind almost twenty other countries, including some that only became industrialized in the last third of the 20th century, and with substantial assistance from the United States.
This essay discusses health policies, the determinants of health, and the connections between the two. The determinants of health are individual and environmental factors that affect people's physical and mental well-being and the ability to […] Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare and Medicine.
Health essay topics for high school students. It's not easy to decide what you want to write about when it comes to choosing a single topic out of the wide variety of health essay topics. You can write about healthy lifestyle, rehabilitation after traumas, childcare, common or rare diseases, global advances in health and medicine ...
StudyCorgi has prepared an extensive list of health care topics to write about! Here, you'll find title ideas for various healthcare fields, including healthcare management, ethics, administration, leadership, policy, finance, care quality, and issues faced by healthcare workers. Our topics are suitable for both high school students and ...
A Crisis in Public Health. The United States has 4% of the world's population but, as of July 16, approximately 26% of its Covid-19 cases and 24% of its Covid-19 deaths. 17 These startling ...
The delivery of healthcare services is considered to be a system; according to the Free Diction- ary (Farlex, 2010), a system is defined as "a group of interacting, interrelated, or interdependent elements forming a complex whole.". This is an apt description of our healthcare structure, as it is compiled of patients, medical and mental ...
Regulatory and Allocative Healthcare Policymaking. This essay discusses health policies, the determinants of health, and the connections between the two. The determinants of health are individual and environmental factors that affect people's physical and mental well-being and the ability to […] The Health Care Policy in the United Kingdom.
They include: focus on prevention, not just treating sickness; tackle racial disparities; expand telehealth and in-home services; build integrated systems; and adopt value-based care. Since early ...
339 essay samples found. Health care encompasses a range of services provided by medical professionals to maintain or improve people's health. Essays on health care could explore the different health care systems across countries, challenges in healthcare delivery, ethical concerns, or the impact of technology and policy on healthcare services.
124 Healthcare Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. Healthcare is a diverse and complex field that encompasses a wide range of topics, issues, and challenges. Whether you are studying healthcare as a student, working in the healthcare industry, or simply interested in learning more about this important area, there are countless essay topics that you ...
1 page / 508 words. "A Walk to Beautiful" is a documentary film that provides a poignant look into the lives of women in Ethiopia affected by obstetric fistula. The film, directed by Mary Olive Smith, follows the journey of five women who suffer from this devastating childbirth injury as... Health Care Policy. 9.
Adults in households with annual incomes under $40,000 are more than three times as likely as adults in households with incomes over $90,000 to say it is difficult to afford their health care ...
Several solutions can address the problems in the health care system. Universal health care coverage, for example, can ensure that everyone has access to essential health care services. Health care cost regulation can help control the high cost of healthcare, making it more affordable for everyone. Reforming insurance and payment systems can ...
Some Relevant Public Health Essay Topics. Writing about public health has always been of interest to many students and medical professionals alike. The current events and the COVID-19 pandemic have only made public health essay topics more popular. Analyzing the Effectiveness of Public Health Campaigns on Smoking Cessation.
Health systems will be increasingly held accountable for ensuring delivery of high-value care and for addressing health equity issues in ways that do not rely on outdated models of care. No one could have imagined or would wish the current economic, societal, or health care challenges of the COVID-19 pandemic on a new administration or Congress.
Introduction. This is an essay on health care issues in the United States, which highlights the challenges faced by Americans due to the high cost of medical care. Currently, around 44 million people in the US do not have any health insurance, and an additional 38 million have inadequate coverage. This issue is exacerbated by the exorbitant ...
It emphasizes that health is a basic human right and that universal healthcare promotes equality, economic benefits, and social cohesion. The essay highlights how universal healthcare can reduce overall healthcare costs through preventative care, alleviate medical debt, and address health disparities among different socio-economic groups.
Exploring Controversial Issues in Nursing: Key Topics and Examples. 7. Pediatric Nursing Research Topics for Students: A Comprehensive Guide. Explore various nursing argumentative essay topics to inspire thought-provoking discussions and help you develop strong critical thinking and writing skills.
Realigning our health system around the need to prevent and treat chronic disease, which affects some 100 million people in the U.S. and represents more than 80 cents out of every dollar spent on health care. Solving the dilemma of data liquidity so that information can more seamlessly be shared across systems.
Health care information systems have numerous benefits for companies and care providers. They allow for cost savings and help improve care quality by reducing medical errors ... The essay will discuss different health issues in advanced and emerging countries and factors that contribute to global health disparities. Steps in the Process of Risk ...
The cost of health care in the United States far exceeds that in other wealthy nations across the globe. In 2020, U.S. health care costs grew 9.7%, to $4.1 trillion, reaching about $12,530 per person. 1 At the same time, the United States lags far behind other high-income countries when it comes to both access to care and some health care ...
Healthcare Issues of Elderly Population Essay. The elderly population is faced with a myriad of problems, not least because their bodies are frail, and as such, they are more susceptible to getting sick. In addition, because their income is reduced, they are likely to get access to proper nutrition and the right healthcare services (Tobin, 2009).
500+ Words Essay on Health. Essay on Health: Health was earlier said to be the ability of the body functioning well. However, as time evolved, the definition of health also evolved. It cannot be stressed enough that health is the primary thing after which everything else follows. When you maintain good health, everything else falls into place.
Nicotine. Most e-cigarettes, or vapes, contain nicotine, which has known adverse health effects. 1. Nicotine is highly addictive. 1. Nicotine is toxic to developing fetuses and is a health danger for pregnant people. 1. Acute nicotine exposure can be toxic. Children and adults have been poisoned by swallowing, breathing, or absorbing vaping ...
It was 1:19 p.m. on Sept. 6, 2019, in the Danville Correctional Center, a medium-security prison a few hours south of Chicago. Mr. Johnson, 21 and serving a short sentence for gun possession, was ...
How many refugees are there around the world? At least 108.4 million people around the world have been forced to flee their homes. Among them are nearly 35.3 million refugees, around 41 per cent of whom are under the age of 18.. There are also millions of stateless people, who have been denied a nationality and lack access to basic rights such as education, health care, employment and freedom ...