

Editing and Proofreading
What this handout is about.
This handout provides some tips and strategies for revising your writing. To give you a chance to practice proofreading, we have left seven errors (three spelling errors, two punctuation errors, and two grammatical errors) in the text of this handout. See if you can spot them!
Is editing the same thing as proofreading?
Not exactly. Although many people use the terms interchangeably, editing and proofreading are two different stages of the revision process. Both demand close and careful reading, but they focus on different aspects of the writing and employ different techniques.
Some tips that apply to both editing and proofreading
- Get some distance from the text! It’s hard to edit or proofread a paper that you’ve just finished writing—it’s still to familiar, and you tend to skip over a lot of errors. Put the paper aside for a few hours, days, or weeks. Go for a run. Take a trip to the beach. Clear your head of what you’ve written so you can take a fresh look at the paper and see what is really on the page. Better yet, give the paper to a friend—you can’t get much more distance than that. Someone who is reading the paper for the first time, comes to it with completely fresh eyes.
- Decide which medium lets you proofread most carefully. Some people like to work right at the computer, while others like to sit back with a printed copy that they can mark up as they read.
- Try changing the look of your document. Altering the size, spacing, color, or style of the text may trick your brain into thinking it’s seeing an unfamiliar document, and that can help you get a different perspective on what you’ve written.
- Find a quiet place to work. Don’t try to do your proofreading in front of the TV or while you’re chugging away on the treadmill. Find a place where you can concentrate and avoid distractions.
- If possible, do your editing and proofreading in several short blocks of time. Your concentration may start to wane if you try to proofread the entire text at one time.
- If you’re short on time, you may wish to prioritize. Make sure that you complete the most important editing and proofreading tasks.
Editing is what you begin doing as soon as you finish your first draft. You reread your draft to see, for example, whether the paper is well-organized, the transitions between paragraphs are smooth, and your evidence really backs up your argument. You can edit on several levels:
Have you done everything the assignment requires? Are the claims you make accurate? If it is required to do so, does your paper make an argument? Is the argument complete? Are all of your claims consistent? Have you supported each point with adequate evidence? Is all of the information in your paper relevant to the assignment and/or your overall writing goal? (For additional tips, see our handouts on understanding assignments and developing an argument .)
Overall structure
Does your paper have an appropriate introduction and conclusion? Is your thesis clearly stated in your introduction? Is it clear how each paragraph in the body of your paper is related to your thesis? Are the paragraphs arranged in a logical sequence? Have you made clear transitions between paragraphs? One way to check the structure of your paper is to make a reverse outline of the paper after you have written the first draft. (See our handouts on introductions , conclusions , thesis statements , and transitions .)
Structure within paragraphs
Does each paragraph have a clear topic sentence? Does each paragraph stick to one main idea? Are there any extraneous or missing sentences in any of your paragraphs? (See our handout on paragraph development .)
Have you defined any important terms that might be unclear to your reader? Is the meaning of each sentence clear? (One way to answer this question is to read your paper one sentence at a time, starting at the end and working backwards so that you will not unconsciously fill in content from previous sentences.) Is it clear what each pronoun (he, she, it, they, which, who, this, etc.) refers to? Have you chosen the proper words to express your ideas? Avoid using words you find in the thesaurus that aren’t part of your normal vocabulary; you may misuse them.
Have you used an appropriate tone (formal, informal, persuasive, etc.)? Is your use of gendered language (masculine and feminine pronouns like “he” or “she,” words like “fireman” that contain “man,” and words that some people incorrectly assume apply to only one gender—for example, some people assume “nurse” must refer to a woman) appropriate? Have you varied the length and structure of your sentences? Do you tends to use the passive voice too often? Does your writing contain a lot of unnecessary phrases like “there is,” “there are,” “due to the fact that,” etc.? Do you repeat a strong word (for example, a vivid main verb) unnecessarily? (For tips, see our handouts on style and gender-inclusive language .)
Have you appropriately cited quotes, paraphrases, and ideas you got from sources? Are your citations in the correct format? (See the UNC Libraries citation tutorial for more information.)
As you edit at all of these levels, you will usually make significant revisions to the content and wording of your paper. Keep an eye out for patterns of error; knowing what kinds of problems you tend to have will be helpful, especially if you are editing a large document like a thesis or dissertation. Once you have identified a pattern, you can develop techniques for spotting and correcting future instances of that pattern. For example, if you notice that you often discuss several distinct topics in each paragraph, you can go through your paper and underline the key words in each paragraph, then break the paragraphs up so that each one focuses on just one main idea.
Proofreading
Proofreading is the final stage of the editing process, focusing on surface errors such as misspellings and mistakes in grammar and punctuation. You should proofread only after you have finished all of your other editing revisions.
Why proofread? It’s the content that really matters, right?
Content is important. But like it or not, the way a paper looks affects the way others judge it. When you’ve worked hard to develop and present your ideas, you don’t want careless errors distracting your reader from what you have to say. It’s worth paying attention to the details that help you to make a good impression.
Most people devote only a few minutes to proofreading, hoping to catch any glaring errors that jump out from the page. But a quick and cursory reading, especially after you’ve been working long and hard on a paper, usually misses a lot. It’s better to work with a definite plan that helps you to search systematically for specific kinds of errors.
Sure, this takes a little extra time, but it pays off in the end. If you know that you have an effective way to catch errors when the paper is almost finished, you can worry less about editing while you are writing your first drafts. This makes the entire writing proccess more efficient.
Try to keep the editing and proofreading processes separate. When you are editing an early draft, you don’t want to be bothered with thinking about punctuation, grammar, and spelling. If your worrying about the spelling of a word or the placement of a comma, you’re not focusing on the more important task of developing and connecting ideas.
The proofreading process
You probably already use some of the strategies discussed below. Experiment with different tactics until you find a system that works well for you. The important thing is to make the process systematic and focused so that you catch as many errors as possible in the least amount of time.
- Don’t rely entirely on spelling checkers. These can be useful tools but they are far from foolproof. Spell checkers have a limited dictionary, so some words that show up as misspelled may really just not be in their memory. In addition, spell checkers will not catch misspellings that form another valid word. For example, if you type “your” instead of “you’re,” “to” instead of “too,” or “there” instead of “their,” the spell checker won’t catch the error.
- Grammar checkers can be even more problematic. These programs work with a limited number of rules, so they can’t identify every error and often make mistakes. They also fail to give thorough explanations to help you understand why a sentence should be revised. You may want to use a grammar checker to help you identify potential run-on sentences or too-frequent use of the passive voice, but you need to be able to evaluate the feedback it provides.
- Proofread for only one kind of error at a time. If you try to identify and revise too many things at once, you risk losing focus, and your proofreading will be less effective. It’s easier to catch grammar errors if you aren’t checking punctuation and spelling at the same time. In addition, some of the techniques that work well for spotting one kind of mistake won’t catch others.
- Read slow, and read every word. Try reading out loud , which forces you to say each word and also lets you hear how the words sound together. When you read silently or too quickly, you may skip over errors or make unconscious corrections.
- Separate the text into individual sentences. This is another technique to help you to read every sentence carefully. Simply press the return key after every period so that every line begins a new sentence. Then read each sentence separately, looking for grammar, punctuation, or spelling errors. If you’re working with a printed copy, try using an opaque object like a ruler or a piece of paper to isolate the line you’re working on.
- Circle every punctuation mark. This forces you to look at each one. As you circle, ask yourself if the punctuation is correct.
- Read the paper backwards. This technique is helpful for checking spelling. Start with the last word on the last page and work your way back to the beginning, reading each word separately. Because content, punctuation, and grammar won’t make any sense, your focus will be entirely on the spelling of each word. You can also read backwards sentence by sentence to check grammar; this will help you avoid becoming distracted by content issues.
- Proofreading is a learning process. You’re not just looking for errors that you recognize; you’re also learning to recognize and correct new errors. This is where handbooks and dictionaries come in. Keep the ones you find helpful close at hand as you proofread.
- Ignorance may be bliss, but it won’t make you a better proofreader. You’ll often find things that don’t seem quite right to you, but you may not be quite sure what’s wrong either. A word looks like it might be misspelled, but the spell checker didn’t catch it. You think you need a comma between two words, but you’re not sure why. Should you use “that” instead of “which”? If you’re not sure about something, look it up.
- The proofreading process becomes more efficient as you develop and practice a systematic strategy. You’ll learn to identify the specific areas of your own writing that need careful attention, and knowing that you have a sound method for finding errors will help you to focus more on developing your ideas while you are drafting the paper.
Think you’ve got it?
Then give it a try, if you haven’t already! This handout contains seven errors our proofreader should have caught: three spelling errors, two punctuation errors, and two grammatical errors. Try to find them, and then check a version of this page with the errors marked in red to see if you’re a proofreading star.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Especially for non-native speakers of English:
Ascher, Allen. 2006. Think About Editing: An ESL Guide for the Harbrace Handbooks . Boston: Wadsworth Cengage Learning.
Lane, Janet, and Ellen Lange. 2012. Writing Clearly: Grammar for Editing , 3rd ed. Boston: Heinle.
For everyone:
Einsohn, Amy. 2011. The Copyeditor’s Handbook: A Guide for Book Publishing and Corporate Communications , 3rd ed. Berkeley: University of California Press.
Lanham, Richard A. 2006. Revising Prose , 5th ed. New York: Pearson Longman.
Tarshis, Barry. 1998. How to Be Your Own Best Editor: The Toolkit for Everyone Who Writes . New York: Three Rivers Press.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Places on our 2024 summer school are filling fast. Don’t miss out. Enrol now to avoid disappointment
- 13 Essential Editing Tips to Use in Your Essay Writing

The good student strives constantly to achieve a better essay each time they write one.
It can be a challenge to find ways to keep improving, but one way of making your essays instantly better is effective editing. Editing your essay before you submit it could mean the difference between a good grade and a brilliant one, so it’s worth taking fifteen minutes or so before you send it off just checking through it to make sure that the structure and wording is as good as it can be. In this article, we give you some tips to think about when you’re editing your own writing. Keep these tips alongside you to use as a checklist and you can’t go far wrong!
1. Start by getting the structure right
If you have time, try to leave a bit of time between finishing your essay and starting the editing process. This gives you time to approach it feeling reasonably fresh; if you edit immediately after spending a long time on something, you might find that you’re so close to it that you’re unable to spot errors. When you do sit down to look through it, start by looking at its structure. Think about the overarching shape of the argument you’re developing and check that the points you’ve made help build your essay towards a logical conclusion. You may have written an essay with the points in order of when they occurred to you, but is this really the most sensible order? Does one point follow logically on from the other? Would it make the essay more interesting to include a certain point near the beginning to tease the reader, or are you revealing too much in the opening, meaning it would be better to move some points nearer the end? These are just a few of the ways in which it might be possible to improve the structure, so it helps to keep in mind your overall argument and ensure your structure puts it across as effectively as possible. With word processors now the primary means of writing essays, it couldn’t be easier to rearrange paragraphs into a more logical structure by dragging and dropping or cutting and pasting paragraphs. If you do this, don’t forget to reread the essay to ensure that the wording works with this new order, otherwise you may end up with a sentence leading into the wrong paragraph.
2. Prune long sentences and paragraphs
Whether you’ve exceeded your word count or not, long sentences and paragraphs should be edited because they can be trickier to read, and risk being boring or hard to follow. Try, therefore, to keep sentences to a maximum of two or three clauses (or segments). Avoid long paragraphs by starting a new one if you find one getting longer than three or four sentences: a wall of text can be off-putting to the reader. Leave a space between paragraphs if you’re typing your essay, as we’re doing in this article. Another way of keeping sentences to a reasonable length is to go through what you’ve written and tighten up the wording. If you find yourself writing long sentences, try to look for ways in which you can reword them to express what you’re trying to say more concisely. You’ll probably find numerous instances of phrases that take many words to say what could be said in two or three.
3. Keep overly complicated language in check
It’s going to look obvious if you’ve had a thesaurus next to you while writing, just so that you can replace all the simple words with more complicated ones. The thing is, it doesn’t always make you look intelligent; you may, for instance, inadvertently choose the wrong synonym , not realising that even close synonyms can have subtly different meanings or connotations. Sometimes using big words where simple ones would suffice can seem contrived and pompous; aim for clear, concise language to avoid being verbose or pretentious. That’s not to say you shouldn’t use more complex words at all – just choose the situation carefully and don’t overdo it.
4. Watch for repetition of ideas and words
It’s easy to repeat yourself without realising it when you’re writing, but the editing process is there to enable you to spot this before your teacher or lecturer sees it. As you read through your essay, keep a look out for ideas you’ve repeated and delete whichever repetitions add nothing to your essay (don’t forget that the first instance of the idea may not be the most appropriate place for it, so consider which is the best moment to introduce it and delete the other mentions). On a related note, look out for instances in which you’ve laboured the point. Going on about a particular point for too long can actually undermine the strength of your argument, because it makes you look as though you’re desperately grappling to find supporting facts; sometimes a simple, clear statement with a brief piece of evidence to back it up is all that’s needed. You should be equally wary of repetition of words within the same sentence or paragraph. It’s fine to repeat common words such as “the”, obviously, but it’s best to avoid using the same connecting words, such as “also”, more than once in the same paragraph. Rephrase using alternative expressions, such as “what’s more”. More unusual words should be used just once per paragraph – words such as “unavoidable”, for example – unless it’s for emphasis.
5. Don’t rely on the spellcheck
It’s a tip we’ve told you before, but it’s worth repeating because it’s very important! The spellcheck will not pick up every single error in your essay. It may highlight some typos and misspellings, but it won’t tell you if you’ve inadvertently used the wrong word altogether. For example, you may have meant to write the word “from”, but accidentally mistyped it as “form” – which is still a word, so the spellchecker won’t register it. But it’s not the word you meant to write.
6. Spotting typos
It’s said that if you read through your work backwards, you’re more likely to spot typos. This is probably because it’s giving you a new perspective on what you’ve written, making it easier to spot glaring errors than if you read through it in the order in which you wrote it and in which you know what to expect. So, start with the last sentence and keep going in reverse order until you get to the beginning of your essay. Another tip is to print out your essay and take a red pen to it, circling or underlining all the errors and then correcting them on the computer later. It’s often easier to read a document from a printed version, and it also means that you can follow what you’re doing by touching each word with the end of your pencil to make sure you’re not skimming over any errors.
7. Omit unnecessary words and eradicate weasel words
Without even realising it, you’ve probably used plenty of unnecessary words in your writing – words that add to the word count without adding to the meaning – and you’ll find that your writing works just as well without them. An example is the word “very”, which almost always adds nothing to what you’re trying to say. As Mark Twain said , “Substitute ‘damn’ every time you’re inclined to write ‘very’; your editor will delete it and the writing will be just as it should be”. Weasel words are worse, as they are used to hide weak or objectionable arguments. A study of Wikipedia found that these tend to fall into three different categories: numerical vagueness (such as “many people say” without specifying who these people are), the use of the passive voice to distance the writer from what they’re saying (“it is often said”, for example, without saying by whom it is often said), and the use of adverbs designed to soften a point (such as “probably”). Look out for these in your own writing and rephrase to remove them; they are disingenuous and your essay will be stronger without them.
8. Remove tautologies
A tautology is a stylistic error involving redundant words, in this case the use of two consecutive words that mean the same thing, such as “the big giant” (referring simply to a “giant” would have been sufficient to convey the meaning). Students often use them when they’re trying to make their writing wordier, not realising that they simply make their writing worse.
9. Watch the commas
People tend either to put too many commas into a sentence, or too few. Too many, and the sentence sounds broken and odd; too few, and the reader has to read the sentence several times to figure out what you’re trying to say, because it comes out in a long, jumbled mess. The secret is to put commas in where you would naturally pause when speaking aloud. If it helps, try reading your writing aloud to see if it flows. Where you would pause for slightly longer, a semi-colon might be more appropriate than a comma. Use a semi-colon to connect two independent clauses that would work as two separate sentences.
10. Consistent spelling
Some words have more than one correct spelling, and the important thing is to be consistent with which one you use. You could, if you wanted to make your life a little easier, delve into the settings on your word processor and manipulate the spellcheck so that it highlights the version you decided against – or even autocorrects to the right version. If you’re writing in the UK, ensure that your word processor’s default language is set to UK English so that you don’t end up inadvertently correcting English spellings to US ones (“colour” to “color”, for example).
11. Get rid of exclamation marks and ellipses
In virtually every case, you don’t need to use an exclamation mark, and – at least in academic writing – your use of one may result in your writing not being taken quite so seriously. Only use them in exceptional circumstances when you really want to convey a feeling of surprise or outrage. Ellipses (“…”) should also be avoided except when you’re indicating the truncation of a quote from another writer (that is, where you left a bit out).
12. Attribute quotations
Quotations from authors or academic writers should be attributed to them. As you read through your essay, keep a look out for any quotations you’ve mentioned and make sure that you say where they’re from. If you’re writing an essay for university, a footnote would be an appropriate way of citing another writer. If you are using footnotes, this gives an extra area on which to focus your editing skills; ensure that all footnotes are consistently formatted, and don’t forget to put a bibliography containing all the books you’ve used at the end.
13. Consistent formatting
The appearance of your essay matters, too – and the formatting should not be neglected when you’re in editing mode. This means being consistent with your use of fonts, using italics or underline for emphasis rather than using them interchangeably, ensuring that the spacing between lines is consistent throughout, and other such minor aesthetic points. This may not sound very important, but consistent formatting helps your essay look professional; if you’ve used different fonts or line spacing or anything like that, your essay will look a mess even if what you’ve said in it is good. You could make use of the pre-populated formatting options in your word processor to ensure consistency throughout, with header 1 for the title, header 2 for subheadings and ‘normal text’ for the body of the document. If you find that there are too many things on this list to think about in one go when you’re reading through your essay, you could read through it several times looking out for different things each time. All this may seem a lot to think about when you’ve already put in so much effort to write the essay in the first place, but trust us: it will pay off with a sleek and polished piece.
How to Edit an Essay: Tips and Tricks for a Flawless Paper

How to Edit a Paper: 9 Tips You Need to Know
Often overlooked as an easy task, essay editing is way more important step of the writing process than you can imagine. Writing a compelling introduction, crafting comprehensive body paragraphs, knowing what words to use in college essays, and finishing it off with a memorable conclusion are essential, but revising what you wrote can take your essay to a whole new level.
Professional writers know that revising a text is an art of its own, and if you want to play in the top league, you should master it too. Our research paper writing service sets a goal to share the intricate details of how to edit a paper and help you become a skillful storyteller.
Besides the obvious, like correcting grammar, spelling, syntax, and so on, editing allows you to see the full picture and make sure that your paper meets the initial goals. The true essence of editing lies in scrutinizing whether your paper is well-crafted and logically coherent while meeting the academic guidelines and thesis statement. Additionally, it demands you assess if you have adequately addressed all specific requirements and whether you have used proper essay language.
Revisiting your written piece can enable you to refine areas that may lack consistency or clarity, thereby enabling you to tell an engaging story in a more professional manner. By adopting this approach, any informational gaps or inconsistencies could be swiftly addressed, giving readers a comprehensive account for them to enjoy reading.

Essay Editing Tip #1: Take a Break!
No matter how many essays you have written and where you stand on a scale of professional writers, you must still be wondering how to make an essay better.
Believe it or not, taking a break and stepping back might be the best thing to do. Once you are done telling the story and have all the necessary aspects of a great essay, it's time to relax. Don't start paper editing, and by no means submit an essay straight away.
Sometimes when our brains get stuck on one thing, we lose the ability to see things clearly. We get emotionally attached and can't see the obvious mistakes. Clear your head, watch a movie, take a walk, or do whatever makes you happy and feel at peace. Don't start writing the night before; give yourself a few hours or even days to distance yourself from the writing process.
Once you feel all fresh, come back and start revising. You will notice mistakes that were there all this time, but you were unable to notice them. You will see logical inconsistencies and grammatical errors. Trust us, once you realize those grammatical errors could ruin your fascinating story, you'll be happy you did not submit the essay straight away.
Essay Editing Tip #2: Change the Font and Size
Do you want to know what the next hack for editing an essay is? You should do everything to make it visually look like a different essay. Professional writers recommend changing the font and size.
Remember when we talked about being unable to see the mistakes in front of our eyes? When you stare at an object for a while, it starts to lose its shape and other characteristics and kinda blends into a homogenous thing. You need to step away or look at it from a different angle to start seeing them again.
Yes, a paper is not a painting or an object, and you use words for essays, but you are still visually perceiving it. On average, writing a paper takes at least a day. Imagine starting at something and thinking about it for a day. It would turn into a borderless mixture in your head.
Changing the font and size is like changing the angle. You will get a fresh perspective and start to notice grammar mistakes, misused topic sentences, and so on. Don't be afraid to look at your essay from an outside point of view; it will only make your writing better.
Essay Editing Tip #3: Print Out Your Paper
Another great way to change your perspective is to print out your own paper. The constant strain of staring at a computer screen for prolonged periods can cause distractions and leave you feeling mentally drained. A tired brain can no longer detect grammar errors, and all your proofreading digitally can go in vain.
By physically holding your research paper in hand, you afford yourself the opportunity to take a step back from the screen and approach the task with renewed spirit. You might have already corrected grammar, but what about formatting mistakes? Maybe some overlooked margins or improperly sized font types made their way into your work. You might have used a lot of long sentences and big words that need to go. Chances are you may have missed some good words to use in essays, and now you get a fresh opportunity to turn your paper into something else.
Check what other good essay words would complement specific passages and improve expression quality overall!
Essay Editing Tip #4: Use a Highlighter
Your writing skills can catapult if you start using some old-fashioned methods of self-editing. Old school writers always walk around with a highlighter in their hands. Highlighting is a great way to focus on individual sentences and vigorously proof check them.
When editing an essay, finding a mistake and immediately correcting them can lead you to lose focus. It's better to first find all the mistakes and areas of improvement and take action later.
One of the greatest editing tips from our expert writing services is to use different color highlighters for different kinds of issues. There are four different issue types you may want to look out for. Highlight grammar mistakes, formatting issues, problematic areas, and important information. Use different highlighters for categorizing them so when you come back for refinement; you know what you are dealing with.
Highlighting can help you quickly and easily find very intricate mistakes that otherwise would be missed, such as identifying misplaced great essay phrases and changing their location to where they make more sense.
Need a Hand in Polishing Your Paper?
Choose our professional essay editing service and relax knowing your paper has exceptional grammar, spelling, style, and clarity!
Essay Editing Tip #5: Read Your Paper Backwards
What about analyzing your final draft upside down? You can challenge your paper and make the editing process fun. Follow our guide on how to edit your essay, and you will never make rookie mistakes.
The essay should make sense from top to bottom and vice versa. Every paragraph you write should be linked with one another and make sense on its own.
Start at the end and question the last sentence. Does it make sense? Is it compelling? Does it relate to the thesis statement? Could a random person figure out what the rest of the essay was about? Step by step, move upwards and question each paragraph carefully.
Focus on sentence fragments and individual words. Question if they are proper words to use in an essay. This will not only help you notice spelling mistakes and typos but also improve the overall quality of your academic writing.
Listen to the flow. When reading backward, it is easier to notice whether the text is well-constructed and easy to follow. You will be able to notice where the paper needs refinement with better transitional sentences. You may have used faulty parallelism or unnecessary information that needs to be removed.
Don't forget to look for consistency. Check the formatting and citation style and make sure they comply with the requirements. Students often forget to proofread the reference list.
Essay Editing Tip #6: Use a Checklist
To ensure that your essay is error-free and effectively transmits your intended message, you can use an editing checklist. It is always a good idea to check your writing against pre-set criteria. Here are some of the items from our ' do my essay ' experts you can put on your checklist and use while editing an essay.
Introduction - Does it introduce readers to the background story and context? Is it engaging?
Thesis statement - Does it effectively convey what the essay is about? Is it clear and concise?
Central paragraphs - Are main arguments well supported? Are they well-organized and logically coherent?
Transitions - Do the paragraphs link with one another with proper transitional sentences?
Conclusion - Does it provide an effective summary of the essay? Is it memorable?
Grammar - Are there any spelling errors? Did you use the correct syntax? Have you used proper words for essays?
Formatting - Does the citation style follow the proposed guide of essay writing format ? Have you referenced every source?
Essay Editing Tip #7: Read Your Paper Out Loud
Another step in our guide on how to edit an essay is reading the document out loud. Once you finish writing and there is little time remaining to catch a breath, you need to get creative and quickly look at your essay with fresh eyes.
By audibly hearing the sound of each sentence and phrase, you'll gain fresh insight into how well your ideas flow together cohesively. Research has confirmed that reading the document out loud can help enhance students' writing proficiency as it enables them to easily identify structural issues in their work.
This increased level of focus will help bring attention to any areas that feel particularly clunky or repetitive – issues that may not have been immediately apparent otherwise. It will help you see all the awkward essay language, long sentences, and repeated words.
Beyond basic grammar checks or typos correction, when reading aloud, students also have the opportunity to hone in on things like tone and audience engagement; So next time you finish writing something - don't forget about giving those vocal cords a little exercise!
Essay Editing Tip #8: Change the Environment
The authors of our guide on how to edit a paper say that changing the environment is all it takes to reset. Essay writing takes a lot of focus and determination and therefore is very exhausting. Taking a break is just as important; stretching and moving from room to room is just as important as finding the right words for essays.
Before revising the paper, go to a park, library, or to your favorite cafe and get a fresh start. Find a comfortable, quiet spot and take over the job. To detect and correct grammar mistakes, you will need a well-rested mind and no distractions.
Sometimes changing the scenery can boost your creativity and give you fresh insights. By doing so, you will likely discover areas within the text that require more attention and refinement, and the solutions will come quicker.
It's important to remember that crafting well-written papers takes time and effort - rushing through them typically results in poor quality.
Essay Editing Tip #9: Use a Dictionary
To enhance the appeal of your writing style, you can find fancy words to use in essays. In the preliminary drafts, allow yourself to express yourself freely through simple sentences and phrases while leaving room for improvements during editing.
Dictionaries can turn into a long-term solution. Use them to improve your spelling. Even some commonly made errors could easily be eliminated with this practice.
Using a dictionary can also introduce good essay words in your vocabulary. Incorporating advanced terms into limited word count assignments can significantly elevate its quality from average to exceptional whilst enhancing clarity in expression as well.

Use Our Expert Editing Help
This article is proof that editing takes much more time and attention than it seems at first glance, but it also is an essential part of producing quality work. It guarantees clarity, accuracy, and professionalism in any piece of writing.
Don't skip one of the most important steps in crafting a top-notch essay because you are falling short on time. Get help from our essay editing service . Or, you can even buy research paper from our team of professional writers who will help you craft and polish your work.
Are You Ready to Level Up Your Writing?
Let our expert writers improve your grades by always delivering top-quality, plagiarism-free papers in no time!
FAQs: What Else You Need to Know on Editing an Essay
Our team of experienced writers diligently researched the internet's most frequently asked questions on how to make an essay better and answered them all for you to equip you with all the necessary tools for enhancing your writing skills.
So take some time out, read through our comprehensive responses, and unlock your full potential as a writer!
What are the 5 C's of Editing?
How can i edit for free, what are the common mistakes while editing.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
Related Articles
.webp)
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
How to Edit Your Own Writing
Writing is hard, but don’t overlook the difficulty — and the importance — of editing your own work before letting others see it. Here’s how.

By Harry Guinness
The secret to good writing is good editing. It’s what separates hastily written, randomly punctuated, incoherent rants from learned polemics and op-eds, and cringe-worthy fan fiction from a critically acclaimed novel. By the time this article is done, I’ll have edited and rewritten each line at least a few times. Here’s how to start editing your own work.
Understand that what you write first is a draft
It doesn’t matter how good you think you are as a writer — the first words you put on the page are a first draft. Writing is thinking: It’s rare that you’ll know exactly what you’re going to say before you say it. At the end, you need, at the very least, to go back through the draft, tidy everything up and make sure the introduction you wrote at the start matches what you eventually said.
My former writing teacher, the essayist and cartoonist Timothy Kreider, explained revision to me: “One of my favorite phrases is l’esprit d’escalier, ‘the spirit of the staircase’ — meaning that experience of realizing, too late, what the perfect thing to have said at the party, in a conversation or argument or flirtation would have been. Writing offers us one of the rare chances in life at a do-over: to get it right and say what we meant this time. To the extent writers are able to appear any smarter or wittier than readers, it’s only because they’ve cheated by taking so much time to think up what they meant to say and refining it over days or weeks or, yes, even years, until they’ve said it as clearly and elegantly as they can.”
The time you put into editing, reworking and refining turns your first draft into a second — and then into a third and, if you keep at it, eventually something great. The biggest mistake you can make as a writer is to assume that what you wrote the first time through was good enough.
Now, let’s look at how to do the actual editing.
Watch for common errors
Most writing mistakes are depressingly common; good writers just get better at catching them before they hit the page. If you’re serious about improving your writing, I recommend you read “The Elements of Style” by William Strunk Jr. and E.B. White, a how-to guide on writing good, clear English and avoiding the most common mistakes. “ Politics and the English Language ” by George Orwell is also worth studying if you want to avoid “ugly and inaccurate” writing.
Some of the things you’ll learn to watch for (and that I have to fix all the time in my own writing) are:
Overuse of jargon and business speak . Horrible jargon like “utilize,” “endeavor” or “communicate” — instead of “use,” “try” or “chat” — creep in when people (myself included) are trying to sound smart. It’s the kind of writing that Orwell railed against in his essay. All this sort of writing does is obscure the point you want to make behind false intellectualism. As Orwell said, “Never use a long word when a short one will do.”
Clichés. Clichés are as common as mud but at least getting rid of them is low-hanging fruit. If you’re not sure whether something is a cliché, it’s better to just avoid it. Awful, right? Clichés are stale phrases that have lost their impact and novelty through overuse. At some point, “The grass is always greener on the other side” was a witty observation, but it’s a cliché now. Again, Orwell said it well: “Never use a metaphor, simile, or other figure of speech which you are used to seeing in print.” Oh, and memes very quickly become clichés — be warned.
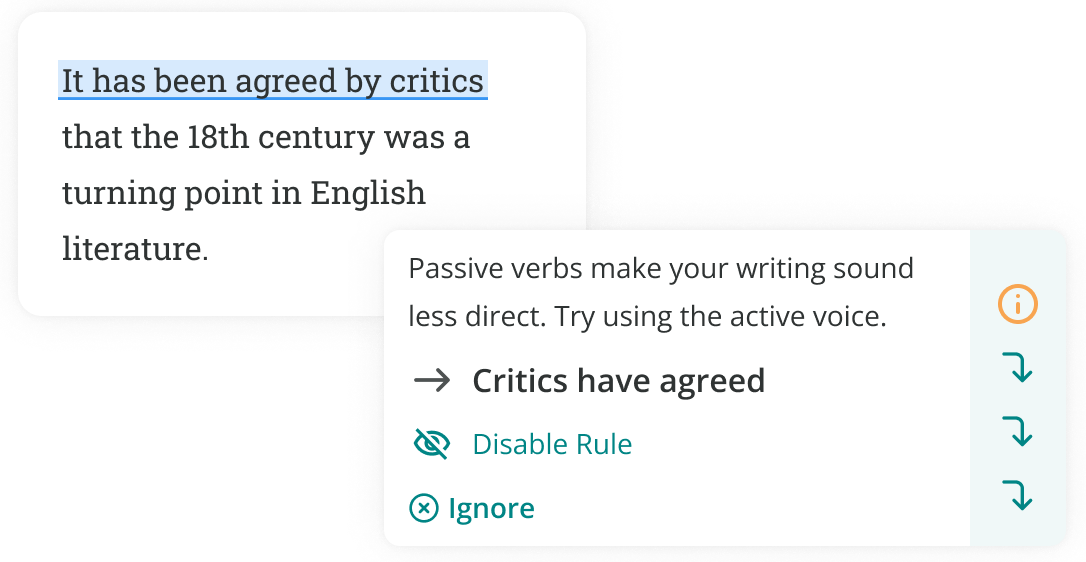
The passive voice. In most cases, the subject of the sentence should be the person or thing taking action, not the thing being acted on. For example, “This article was written by Harry” is written in the passive voice because the subject (“this article”) is the thing being acted on. The equivalent active construction would be: “Harry wrote this article.” Prose written in the passive voice tends to have an aloofness and passivity to it, which is why it’s generally better to write an active sentence.
Rambling . When you’re not quite sure what you want to say, it’s easy to ramble around a point, phrasing it in three or four different ways and then, instead of cutting them down to a single concise sentence, slapping all four together into a clunky, unclear paragraph. A single direct sentence is almost always better than four that tease around a point.
Give your work some space
When you write something, you get very close to it. It’s almost impossible to have the distance to edit properly straight away. Instead, you need to step away and come back later with fresh eyes. The longer you can leave a draft before editing it, the better. I have some essays I go back to every few months for another pass — they’re still not done yet. For most things, though, somewhere from half an hour to two days is enough of a break that you can then edit well. Even 10 minutes will do in a pinch for things like emails.
And when you sit down to edit, read your work out loud.
By forcing yourself to speak the words, rather than just scanning them on a computer screen, you’ll catch more problems and get a better feel for how everything flows. If you stumble over something, your reader will probably stumble over it, too. Some writers even print out their drafts and make edits with a red pen while they read them aloud.
Cut, cut, cut
Overwriting is a bigger problem than underwriting. It’s much more likely you’ve written too much than too little. It’s a lot easier to throw words at a problem than to take the time to find the right ones. As Blaise Pascal, a 17th-century writer and scientist (no, not Mark Twain) wrote in a letter, “I have made this longer than usual because I have not had time to make it shorter.”
The rule for most writers is, “If in doubt, cut it.” The Pulitzer Prize-winning writer John McPhee has called the process “writing by omission.” Novelist Sir Arthur Quiller-Couch (and not William Faulkner, although he may have popularized this version of it) exhorted a version of the oft-repeated phrase, “In writing you must kill all your darlings.” This is true at every level: If a word isn’t necessary in a sentence, cut it; if a sentence isn’t necessary in a paragraph, cut it; and if a paragraph isn’t necessary, cut it, too.
Go through what you’ve written and look for the bits you can cut without affecting the whole — and cut them. It will tighten the work and make everything you’re trying to say clearer.
Spend the most time on the beginning
The beginning of anything you write is the most important part. If you can’t catch someone’s attention at the start, you won’t have a chance to hold it later. Whether you’re writing a novel or an email, you should spend a disproportionate amount of time working on the first few sentences, paragraphs or pages. A lot of problems that can be glossed over in the middle are your undoing at the start.
Pay attention to structure
The structure is what your writing hangs on. It doesn’t matter how perfectly the individual sentences are phrased if the whole thing is a nonsensical mess. For emails and other short things, the old college favorite of a topic sentence followed by supporting paragraphs and a conclusion is hard to get wrong. Just make sure you consider your intended audience. A series of long, unrelenting paragraphs will discourage people from reading. Break things up into concise points and, where necessary, insert subheads — as there are in this article. If I’d written this without them, you would just be looking at a stark wall of text.
For longer pieces, structure is something you’ll need to put a lot of work into. Stream of consciousness writing rarely reads well and you generally don’t have the option to break up everything into short segments with subheads. Narratives need to flow and arguments need to build. You have to think about what you’re trying to say in each chapter, section or paragraph, and consider whether it’s working — or if that part would be better placed elsewhere. It’s normal (and even desirable) that the structure of your work will change drastically between drafts; it’s a sign that you’re developing the piece as a whole, rather than just fixing the small problems.
A lot of the time when something you’ve written “just doesn’t work” for people, the structure is to blame. They might not be able to put the problems into words, but they can feel something’s off.
Use all the resources you can
While you might not be lucky enough to have access to an editor (Hey, Alan!), there are services that can help.
Grammarly is a writing assistant that flags common writing, spelling and grammatical errors; it’s great for catching simple mistakes and cleaning up drafts of your work. A good thesaurus (or even Thesaurus.com ) is also essential for finding just the right word. And don’t neglect a second pair of eyes: Ask relatives and friends to read over your work. They might catch some things you missed and can tell you when something is amiss.
Editing your work is at least as important as writing it in the first place. The tweaking, revisiting and revising is what takes something that could be good — and makes it good. Don’t neglect it.
Correction: This article has been updated to reflect that the phrase “kill your darlings,” originated with novelist Sir Arthur Quiller-Couch , who actually said “murder your darlings,” and not William Faulkner, to whom the phrase is often attributed.
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
15 Tips for Writing, Proofreading, and Editing Your College Essay
What’s covered:, our checklist for writing, proofreading, and editing your essay, where to get your college essays edited.
Your college essay is more than just a writing assignment—it’s your biggest opportunity to showcase the person behind your GPA, test scores, and extracurricular activities. In many ways, it’s the best chance you have to present yourself as a living, breathing, and thoughtful individual to the admissions committee.
Unlike test scores, which can feel impersonal, a well-crafted essay brings color to your application, offering a glimpse into your passions, personality, and potential. Whether you’re an aspiring engineer or an artist, your college essay can set you apart, making it essential that you give it your best.
1. Does the essay address the selected topic or prompt?
Focus on responding directly and thoughtfully to the prompt. If the question asks about your reasons for choosing a specific program or your future aspirations, ensure that your essay revolves around these themes. Tailor your narrative to the prompt, using personal experiences and reflections that reinforce your points.
- Respond directly to the prompt: It’s imperative that you thoughtfully craft your responses so that the exact themes in the prompt are directly addressed. Each essay has a specific prompt that serves a specific purpose, and your response should be tailored in a way that meets that objective.
- Focus: Regardless of what the prompt is about—be it personal experiences, academic achievements, or an opinion on an issue—you must keep the focus of the response on the topic of the prompt .
2. Is the college essay well organized?
An essay with a clear structure is easier to follow and is more impactful. Consider organizing your story chronologically, or use a thematic approach to convey your message. Each paragraph should transition smoothly to the next, maintaining a natural flow of ideas. A well-organized essay is not only easier for the reader to follow, but it can also aid your narrative flow. Logically structured essays can guide the reader through complex and hectic sequences of events in your essay. There are some key factors involved in good structuring:
- A strong hook: Start with a sentence or a paragraph that can grab the attention of the reader. For example, consider using a vivid description of an event to do this.
- Maintain a thematic structure: Maintaining a thematic structure involves organizing your response around a central theme, allowing you to connect diverse points of your essay into a cohesive centralized response.
- Transitioning: Each paragraph should clearly flow into the next, maintaining continuity and coherence in narrative.
3. Include supporting details, examples, and anecdotes.
Enhance your narrative with specific details, vivid examples, and engaging anecdotes. This approach brings your story to life, making it more compelling and relatable. It helps the reader visualize your experiences and understand your perspectives.
4. Show your voice and personality.
Does your personality come through? Does your essay sound like you? Since this is a reflection of you, your essay needs to show who you are.
For example, avoid using vocabulary you wouldn’t normally use—such as “utilize” in place of “use”—because you may come off as phony or disingenuous, and that won’t impress colleges.
5. Does your essay show that you’re a good candidate for admission?
Your essay should demonstrate not only your academic strengths. but also the ways in which your personal qualities align with the specific character and values of the school you’re applying to . While attributes like intelligence and collaboration are universally valued, tailor your essay to reflect aspects that are uniquely esteemed at each particular institution.
For instance, if you’re applying to Dartmouth, you might emphasize your appreciation for, and alignment with, the school’s strong sense of tradition and community. This approach shows a deeper understanding of and a genuine connection to the school, beyond its surface-level attributes.
6. Do you stick to the topic?
Your essay should focus on the topic at hand, weaving your insights, experiences, and perspectives into a cohesive narrative, rather than a disjointed list of thoughts or accomplishments. It’s important to avoid straying into irrelevant details that don’t support your main theme. Instead of simply listing achievements or experiences, integrate them into a narrative that highlights your development, insights, or learning journey.
Example with tangent:
“My interest in performing arts began when I was five. That was also the year I lost my first tooth, which set off a whole year of ‘firsts.’ My first play was The Sound of Music.”
Revised example:
“My interest in performing arts began when I was five, marked by my debut performance in ‘The Sound of Music.’ This experience was the first step in my journey of exploring and loving the stage.”
7. Align your response with the prompt.
Before finalizing your essay, revisit the prompt. Have you addressed all aspects of the question? Make sure your essay aligns with the prompt’s requirements, both in content and spirit. Familiarize yourself with common college essay archetypes, such as the Extracurricular Essay, Diversity Essay, Community Essay, “Why This Major” Essay (and a variant for those who are undecided), and “Why This College” Essay. We have specific guides for each, offering tailored advice and examples:
- Extracurricular Essay Guide
- Diversity Essay Guide
- Community Essay Guide
- “Why This Major” Essay Guide
- “Why This College” Essay Guide
- Overcoming Challenges Essay Guide
- Political/Global Issues Essay Guide
While these guides provide a framework for each archetype, respectively, remember to infuse your voice and unique experiences into your essay to stand out!
8. Do you vary your sentence structure?
Varying sentence structure, including the length of sentences, is crucial to keep your writing dynamic and engaging. A mix of short, punchy sentences and longer, more descriptive ones can create a rhythm that makes your essay more enjoyable to read. This variation helps maintain the reader’s interest and allows for more nuanced expression.
Original example with monotonous structure:
“I had been waiting for the right time to broach the topic of her health problem, which had been weighing on my mind heavily ever since I first heard about it. I had gone through something similar, and I thought sharing my experience might help.”
Revised example illustrating varied structure:
“I waited for the right moment to discuss her health. The issue had occupied my thoughts for weeks. Having faced similar challenges, I felt that sharing my experience might offer her some comfort.”
In this revised example, the sentences vary in length and structure, moving from shorter, more impactful statements to longer, more descriptive ones. This variation helps to keep the reader’s attention and allows for a more engaging narrative flow.
9. Revisit your essay after a break.
- Give yourself time: After completing a draft of your essay, step away from it for a day or two. This break can clear your mind and reduce your attachment to specific phrases or ideas.
- Fresh perspective: When you come back to your essay, you’ll likely find that you can view your work with fresh eyes. This distance can help you spot inconsistencies, unclear passages, or stylistic issues that you might have missed earlier.
- Enhanced objectivity: Distance not only aids in identifying grammatical errors or typos, but it also allows you to assess the effectiveness of your argument or narrative more objectively. Does the essay really convey what you intended? Are there better examples or stronger pieces of evidence you could use?
- Refine and polish: Use this opportunity to fine-tune your language, adjust the flow, and ensure that your essay truly reflects your voice and message.
Incorporating this tip into your writing process can significantly improve the quality and effectiveness of your college essay.
10. Choose an ideal writing environment.
By identifying and consistently utilizing an ideal writing environment, you can enhance both the enjoyment and effectiveness of your essay-writing process.
- Discover your productive spaces: Different environments can dramatically affect your ability to think and write effectively. Some people find inspiration in the quiet of a library or their room, while others thrive in the lively atmosphere of a coffee shop or park.
- Experiment with settings: If you’re unsure what works best for you, try writing in various places. Notice how each setting affects your concentration, creativity, and mood.
- Consider comfort and distractions: Make sure your chosen spot is comfortable enough for long writing sessions, but also free from distracting elements that could hinder your focus.
- Time of day matters: Pay attention to the time of day when you’re most productive. Some write best in the early morning’s tranquility, while others find their creative peak during nighttime hours.
11. Are all words spelled correctly?
While spell checkers are a helpful tool, they aren’t infallible. It’s crucial to read over your essay meticulously, possibly even aloud, to catch any spelling errors. Reading aloud can help you notice mistakes that your eyes might skip over when reading silently. Be particularly attentive to words that spellcheck might not catch, such as proper nouns, technical jargon, or homophones (e.g., “there” vs. “their”). Attention to detail in spelling reflects your care and precision, both of which are qualities that admissions committees value.
12. Do you use proper punctuation and capitalization?
Correct punctuation and capitalization are key to conveying your message clearly and professionally . A common mistake in writing is the misuse of commas, particularly in complex sentences.
Example of a misused comma:
Incorrect: “I had an epiphany, I was using commas incorrectly.”
In this example, the comma is used incorrectly to join two independent clauses. This is known as a comma splice. It creates a run-on sentence, which can confuse the reader and disrupt the flow of your writing.
Corrected versions:
Correct: “I had an epiphany: I was using commas incorrectly.”
Correct: “I had an epiphany; I was using commas incorrectly.”
Correct: “I had an epiphany—I was using commas incorrectly.”
Correct: “I had an epiphany. I was using commas incorrectly.”
The corrections separate the two clauses with more appropriate punctuation. Colons, semicolons, em dashes, and periods can all be used in this context, though periods may create awkwardly short sentences.
These punctuation choices are appropriate because the second clause explains or provides an example of the first, creating a clear and effective sentence structure. The correct use of punctuation helps maintain the clarity and coherence of your writing, ensuring that your ideas are communicated effectively.
13. Do you abide by the word count?
Staying within the word count is crucial in demonstrating your ability to communicate ideas concisely and effectively. Here are some strategies to help reduce your word count if you find yourself going over the prescribed limits:
- Eliminate repetitive statements: Avoid saying the same thing in different ways. Focus on presenting each idea clearly and concisely.
- Use adjectives judiciously: While descriptive words can add detail, using too many can make your writing feel cluttered and overwrought. Choose adjectives that add real value.
- Remove unnecessary details: If a detail doesn’t support or enhance your main point, consider cutting it. Focus on what’s essential to your narrative or argument.
- Shorten long sentences: Long, run-on sentences can be hard to follow and often contain unnecessary words. Reading your essay aloud can help you identify sentences that are too lengthy or cumbersome. If you’re out of breath before finishing a sentence, it’s likely too long.
- Ensure each sentence adds something new: Every sentence should provide new information or insight. Avoid filler or redundant sentences that don’t contribute to your overall message.
14. Proofread meticulously.
Implementing a thorough and methodical proofreading process can significantly elevate the quality of your essay, ensuring that it’s free of errors and flows smoothly.
- Detailed review: After addressing bigger structural and content issues, focus on proofreading for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors. This step is crucial for polishing your essay and making sure it’s presented professionally.
- Different techniques: Employ various techniques to catch mistakes. For example, read your essay backward, starting from the last sentence and working your way to the beginning. This method can help you focus on individual sentences and words, rather than getting caught up in the content.
- Read aloud: As mentioned before, reading your essay aloud is another effective technique. Hearing the words can help identify awkward phrasing, run-on sentences, and other issues that might not be as obvious when reading silently.
15. Utilize external feedback.
While self-editing is crucial, external feedback can provide new perspectives and ideas that enhance your writing in unexpected ways. This collaborative process can help you keep your essay error-free and can also help make it resonate with a broader audience.
- Fresh perspectives: Have a trusted teacher, mentor, peer, or family member review your drafts. Each person can offer unique insights and perspectives on your essay’s content, structure, and style.
- Identify blind spots: We often become too close to our writing to see its flaws or areas that might be unclear to others. External reviewers can help identify these blind spots.
- Constructive criticism: Encourage your reviewers to provide honest, constructive feedback. While it’s important to stay true to your voice and story, be open to suggestions that could strengthen your essay.
- Diverse viewpoints: Different people will focus on different aspects of your writing. For example, a teacher might concentrate on your essay’s structure and academic tone, while a peer might provide insights into how engaging and relatable your narrative is.
- Incorporate feedback judiciously: Use the feedback to refine your essay, but remember that the final decision on any changes rests with you. It’s your story and your voice that ultimately need to come through clearly.
When it comes to refining your college essays, getting external feedback is crucial. Our free Peer Essay Review tool allows you to receive constructive criticism from other students, providing fresh perspectives that can help you see your work in a new light. This peer review process is invaluable and can help you both identify areas for improvement and gain different viewpoints on your writing.
For more tailored expert advice, consider the guidance of a CollegeVine advisor . Our advisors, experienced in the college admissions process, offer specialized reviews to enhance your essays. Their insights into what top schools are looking for can elevate your narrative, ensuring that your application stands out. Whether it’s through fine-tuning your grammar or enriching your story’s appeal, our experts’ experience and expertise can significantly increase your likelihood of admission to your dream school!
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
How to Edit an Essay

Krystal N. Craiker

The work isn't done when you finish writing your essay. To get the best grade possible, you'll need to edit your paper.
Editing academic writing can be tricky, and good editing involves more than just running your work through an essay checker .
Here are our six top tips on how to edit an essay, so you can get a top grade every time.
How to Edit Your Essay
Where to find essay editing help.
Writing an essay is hard work! Once you put in time researching, outlining, and writing, you want to be sure to turn in a near-perfect essay.
Editing your essay to perfection can be done in just a few simple steps.

Strengthen Your Thesis Statement
The thesis statement is the backbone of your essay . You can think of your thesis statement as the answer to the question or prompt.
If someone asks, "What is your essay about?" the thesis statement would be the one or two sentence response to that question.
The thesis guides the rest of your paper. It's the main idea of your essay. Generally, a thesis statement is just one sentence. That's a lot of work for one little sentence to do in your essay.
When you edit, be sure your thesis statement is strong. A strong thesis will answer the prompt or guiding research question, but it will also be succinct. It should be clear, so eliminate any wordiness.

You should also ensure it aligns with the rest of the essay.
If you wrote your thesis at the beginning of your writing process, your essay might have taken a slightly different track from what you intended. If this is the case, adjust your thesis statement accordingly.
Note that a thesis can be longer than just one sentence, but this isn't typical for a regular term paper–style essay.
If your essay is much longer than average, or it's a write-up of an original experiment or study, you might need more than one sentence.
Your thesis also doesn't have to be a long sentence, although it can be. Rather than worrying about the length of your thesis, focus on whether it is clear and answers the question.
Make Sure Every Argument Supports the Thesis
Every argument or point in your essay should support the thesis statement. In essays, the main arguments make up the body paragraphs.
Sometimes, an essay draft might feature weak arguments or points that oppose the thesis. Perhaps you've included a paragraph that doesn’t fit the topic at all.
Edit without mercy. Look for weak or unnecessary arguments. As you analyze every point, ask yourself if it supports the thesis. If it doesn't, remove it entirely.
But what if cutting out a paragraph affects your word count? You should not have anything in your essay just to add words.
A well-developed and cohesive essay with a strong argument is always more important than hitting the requisite word count or page number.
In fact, if your essay is strong enough, your professors probably won't even notice if you're a hundred words shy. You will, however, lose marks for unnecessary information.

Double-Check Your Citations
Use citations to avoid plagiarism. When you write an essay, it's important that you attribute every fact or idea that you didn't come up with yourself. You must cite it whether it's a direct quote or a paraphrase.
Your professor probably gave you a specific style guide to follow, such as MLA or Chicago.
Not only do you need to be sure you've cited everything, you must cite properly according to the style guide.
Be sure you've added the appropriate spaces and correct punctuation to your in-text citations. Check requirements from your style guide.
Clean Up Your Sentences and Paragraphs
It's easy to add unnecessary words when you're writing. But when you're editing, you want to clean up anything that makes your writing feel wordy.
Being verbose isn't the best approach to writing an essay.
Students often fall into the trap of wordiness in order to sound "smart" or to reach the required number of words. But you'll sound smarter if you can explain your position with tighter sentences.
One area to look at is your connecting words . These are words that help you connect ideas and transition from one point to another.
Keeping transitions to one or two words is a good idea. Instead of saying, "as a further example," you can just say, "furthermore." Say "next" instead of saying, "The next argument is."
Unnecessary words also show up when you over-explain or repeat an idea. Are you saying the same thing with different wording?
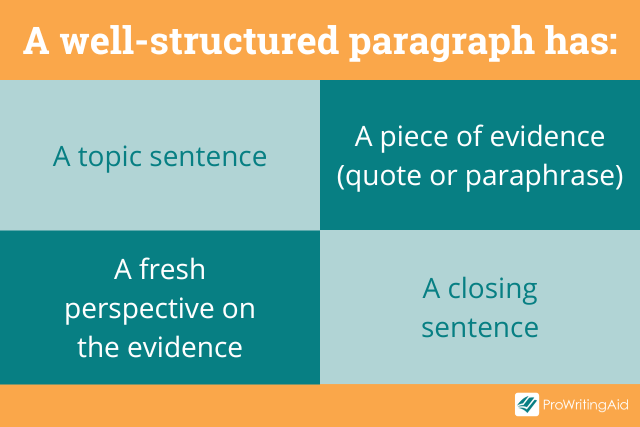
Pay attention to your paragraph structure. A good paragraph structure for an essay is:
- A topic sentence
- A piece of evidence (quote or paraphrase)
- A fresh perspective on the evidence
- Closing sentence
You can also have more than one piece of evidence and commentary per paragraph. This general structure will help cut down on wordiness.
You don't need to quote something, paraphrase it , add commentary, and then reword that commentary. Say each thing once.
Check Your Spelling and Grammar
Spelling and grammar errors can make an otherwise great essay get a failing grade. Grammar mistakes affect how clear your writing is.
Don't feel bad if spelling and grammar aren't your strong suit. Many professional writers struggle with the mechanics of a language.
Read through your essay to look for obvious errors, then use an editing software to find more mistakes.
If your university has a writing center, you can also have someone look over your essay to find additional mistakes. This is usually a free service.
A final step you can use for editing your essay is reading it aloud. This technique is a great way to catch errors that slipped past you and an editing program.
You'll be surprised how many errors you can find when you read aloud a final draft. Often, these mistakes are typos, strange syntax, and missing words.
Reading aloud helps you find sentences that are unclear, even if they're grammatically correct.
ProWritingAid is here to help with all your essay editing needs. We're more than a grammar checker.
Our app will help you find unnecessary words, poor syntax, and transition issues. It will point out vague word choices, passive voice, and readability issues.
Unlike other editing programs, you get access to all of our editing reports for free. If you're worried about plagiarism, you can also run a plagiarism check on your essay for a nominal cost.
Want to improve your essay writing skills?
Use prowritingaid.
Are your teachers always pulling you up on the same errors? Maybe you're losing clarity by writing overly long sentences or using the passive voice too much.
ProWritingAid helps you catch these issues in your essay before you submit it.

Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Krystal N. Craiker is the Writing Pirate, an indie romance author and blog manager at ProWritingAid. She sails the seven internet seas, breaking tropes and bending genres. She has a background in anthropology and education, which brings fresh perspectives to her romance novels. When she’s not daydreaming about her next book or article, you can find her cooking gourmet gluten-free cuisine, laughing at memes, and playing board games. Krystal lives in Dallas, Texas with her husband, child, and basset hound.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
We use cookies to personalize and improve your browsing experience.
To learn more about how we store and use this data, visit our privacy policy here .
Home / Blog / Colleges / How to Edit an Essay: A Step-By-Step Guide to Perfecting Your Paper
How to Edit an Essay: A Step-By-Step Guide to Perfecting Your Paper
If writing is an art, editing is a science..

The moment you finish composing your essay comes the time to begin the process of perfecting it. Carrying out proper edits and revisions is the final step to creating a great paper. Good editing, like writing, is a skill, which must be perfected over time. Even the works of the most prominent writers require skillful editing.
So, how do you actually go about editing your paper to avoid essay pitfalls ? How do you determine what changes you should make? This step-by-step guide will show you how to eliminate errors and perfect your writing.
It can be tempting to complete your work within minutes. Avoid your urge to get everything done in one go. Instead, take a break when you complete your writing. Spend time doing something unrelated so that you can return to your paper with a fresh eye.
Do the easy part first
Check the formatting guidelines and use an editing software to ensure that you followed general guidelines and formatting requirements. Simple punctuation mistakes and fixable formatting errors will seem careless and unprofessional to your reader.
Keep things clear
A good piece of writing has a clear structure, coherent and obvious transitions between sentences and paragraphs. For example, a standard format would be:
- A gripping, exciting first paragraph . This is your chance to gain the attention and goodwill of your readers. This is a time to bring up interesting details and tell your readers what point you’re going to make.
- Your thesis statement declares the purpose of your writing and must appear early in your essay. It is commonly written as the first sentence of the second paragraph.
- A well-structured body . The body of your writing should cover all of the relevant points that you wish to discuss. Be sure that your piece is written with the clear goal of proving your thesis correct.
- A strong conclusion . Your conclusion should restate the strongest points that you covered in the body of the document. If the reader is expected to take further action, this is the place to advise them of that.
Say what you mean
Review the writing to ensure that your language is both clear and precise. Your goal is to concisely convey the relevant information. Use words that create clear, short sentences. Avoid loose language and meaningless fragments. Eliminate all jargon and colloquialisms. Little known terms and clichés must also be removed. It can be tempting to include industry specific phrases and notions in order to make a piece of writing sound more thoroughly researched an authoritative. Be careful with it! The machinations required to fit these things into your writing will stand out to your readers as forced and unnatural.
One of the biggest mistakes young writers make is falling in love with their phrasing and word choices. Don’t structure whole paragraphs in the interest of one sentence. Don’t rewrite pages because you’re attached to a turn of a phrase. Be ruthless in your editing and eliminate anything that does not make your paper more readable.
Timothy Davis, an essay expert and tutor at Best Essays shared his thoughts, “Students tend to write long-winded paragraphs that tell rather than show. This can result in essays that are long, but seemingly pointless. I like to encourage students to eliminate every word that does not make their argument.”

Get your facts straight
Double check any facts or figures that your present in your paper. Don’t just make sure the numbers are accurate. Ensure that the numbers you’ve referenced are sourced from the document you mentioned. Ensure quotes are correct, sources are cited, and relevant images are properly noted.
Once is enough
You wrote a stellar introduction that has your readers excited and engaged. They have a solid understanding of your thesis and a vested interest in how you will prove it. Your reader is paying attention, so you only need to say things once. Repetition is a complex literary device. The shorter your piece, the harder it is to use this tactic correctly. Better to play it safe and avoid irritating your reader with repeated call backs and overused phrases.
Be an authority
Professional writers maintain active voice in order to write clear projects that are pleasant to read. Use these two simple tips to write in active voice:
- Structure your sentences so that the subjects of your sentences take action. For example, write “I put the notebook on the table.” instead of “The notebook was put on the table.”
- Avoid too many chances of the verb “to be.” Variations can include has been, will be, had been Find ways to paraphrase your sentences. The statement “What he said today is an obvious contradiction to what he said yesterday.” you can exchange with “What he said today contradicts to what he said yesterday.”
Keep it simple
This is not the time to experiment with sentence structure or grammar theory. When producing a piece for an academic audience, it’s best to use the simplest punctuation possible . Rather than proving intelligence, or composing a sentence with an attractive flow, students should aim for standardization and simplicity in both form and structure.
Check it again
When the content is perfect, proofread your document a few times and check for spelling and grammar errors. Try reading your piece backwards for a fresh perspective.
Share for feedback
Share your writing with a friend or your knowledgeable family member to find areas in need of improvement. They can provide valuable insight about the clarity of your writing and spot some issues you may have overlooked.
Review this list every time you finish writing a paper, and you will quickly find that editing according to these rules becomes second nature. After a while, you’ll find that you write your pieces with a much clearer concept of what your final product should sound like. Learning to edit your pieces well will make you a much better writer.
Sophia Anderson is an associate educator and a freelance writer. She is passionate about covering topics on learning, writing, careers, self-improvement, motivation and others. She believes in the driving force of positive attitude and constant development. Talk to her on Facebook or LinkedIn .
All views and opinions of guest authors are theirs alone and are not representative of the views of Petersons.com.
Related Posts

How to Study for the ACT

Peterson’s LLC Successfully Completes Acquisition of RMC Learning Solutions

How 529 College Savings Plans Have Changed

How to Edit an Essay

How to Edit an Essay– An Overview
When editing an essay, it's crucial to first ensure that the overall structure is coherent and logical. Begin by shortening lengthy sentences and paragraphs to improve readability. Avoid using overly complex language, which can obscure your message. Be vigilant for any repetitive ideas or words, as they can detract from the clarity of your argument. While spellcheck can be helpful, don't rely solely on it for accuracy. Actively search for and correct typos. Lastly, remove any superfluous words and be cautious of using vague or non-committal language that can weaken your statements.
Editing an essay effectively involves several key steps to enhance clarity, coherence, and overall impact. Here's a step-by-step guide:
- Review the Structure : Ensure your essay has a clear introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction should present your thesis statement or main argument, the body should contain your supporting points, and the conclusion should summarize and restate your main points.
- Check for Clarity and Coherence : Ensure each paragraph has a clear main idea and that ideas flow logically from one paragraph to the next. Use transitional phrases to help guide the reader.
- Focus on Sentence Structure : Vary your sentence lengths and structures to maintain reader interest. Avoid overly long sentences, as they can be confusing.
- Simplify Language : Remove jargon and unnecessarily complex vocabulary. The goal is to be clear and concise, making your essay accessible to a broader audience.
- Eliminate Repetition : Check for repeated words, phrases, or ideas and eliminate them. Repetition can be redundant and detract from the effectiveness of your argument.
- Correct Grammar and Spelling : While software can help, manually check for grammar and spelling errors to ensure accuracy.
- Watch for Punctuation and Formatting : Proper punctuation and consistent formatting contribute to the professionalism of your essay.
- Trim Unnecessary Words : Remove filler words and phrases that don't add value to your argument.
- Fact-Check : Verify the accuracy of any data, quotes, or references you use.
- Seek Feedback : If possible, have someone else read your essay. Fresh eyes can spot errors and inconsistencies you might have missed.
- Read Aloud : Reading your essay aloud can help you catch awkward phrasing and errors that you might not see when reading silently.
- Final Review : Go through your essay one last time to ensure all your edits have improved clarity, logic, and flow.
Remember, effective editing often requires multiple read-throughs and revisions. Take your time to refine your essay until it clearly and effectively communicates your ideas.
How to Edit a Essay By Following These Editing Principles?
When we are writing an essay– or any other writeup there is, we are often guided by different principles. These principles are like a clear pathway toward creating a compelling and well-thought-out work of art. They separate the best from the rest, aesthetic and unpleasing, masterpiece and trash.
The same goes for the process of editing. This process likewise follows some key principles that regulate editors on their work as revisioners. While they help editors foster a set of ethical standards for editing, they also ensure that the content of the writeup itself is beneficial: it can serve its purpose. The following are the principles of editing and the key questions that you might want to ask yourself in consideration:
From the word itself, the writeup must be clear. In what sense? In the skill of writing, clarity may be straightforward, but it takes a lot of work for us to make a writeup that is easy to understand.
We are confounded with various writing guidelines and things to integrate into our writing. This condition takes us away from the principle of clarity.
The rule of thumb here, though, is this: clear your desk (translate: mind), set your mind on your ultimate writing goal (translate: main idea), and keep it as apparent as possible in your writing. In a broader explanation, you have to set aside other writing endeavors – choosing complex words, forming lots of paragraphs, introducing tropes and figurative language, and focusing on the important thing: constructing your thesis statement and using writing techniques that can make your idea more comprehensible.
2. Coherence
We have a lot to say, and the best thing to relay these ideas and thoughts is through writing.
When we have numerous things to rely upon, emotions may run high and take over our writing, causing us to make some “mess” and deviate from sharing our ideas neatly. Yes, you heard it right: writing does not just communicate our minds in whatever manner we want. This macro skill also demands us to write neatly – logically and lucidly.
In doing so, we have to maintain a logical and consistent flow of thoughts. It is like being one with nature: although we cannot understand it in its simplest form, we feel like everything goes fine because of its order and flow.
Coherence, the principle that talks about flow, also means the ideas are connected logically, and transitions from one idea to another are built well. Coherence can go a long way in a writeup, as it guides your readers from the start to the end of your writing, all while making sure that they have grasped the important points of your writing.
3. Grammar and Style
Grammar and style are probably the most sought-after principles, along with being the most tedious ones to handle in writing. These principles can be too technical and book-ish, and it takes years to be accurate grammatically and stylistically. You must learn various grammatical concepts and create your own writing style that follows certain conventions and tropes that you only apply to your writing endeavors.
However, we do not follow these principles for nothing. Aside from effective communication and clarity of expression, which have their own principles by the way, grammar reflects the uprightness and credibility of a writer. Since a written piece upholds quality and refinement, we do not want to risk the possibility of committing mistakes that will leave a disappointing impression on our readers.
In fact, it is generally believed that readers prefer written pieces that are well-written– those that are free from any grammatical lapses. Imagine if you committed those mistakes (especially if they are too common): you will definitely walk in shame and contact an essay editing service in no time!
How to Go Around Essay Editing In 3 Stages?
Just like writing, the process of editing is scientific and objective. Contrary to popular belief, essay editing starts with a specific process and ends similarly. One process must be done before the other. Missing one process does not satisfy the rigor of editing.
In the simplest sense, all the editing processes we will discuss in this section are important and should not be overlooked. There are three editing stages: content editing, copy editing, and proofreading. Each stage plays a crucial role in the whole process, refining the document, spotting crucial errors, and maximizing readability and comprehension.
1. Content Editing
Content editing, with its other name substantive editing , is the initial stage of the editing process. At this stage, the editor concentrates on the writeup’s substance, structure, and overall quality. As we all know, nothing beats the comprehensiveness of a writeup’s content, and it gets even more comprehensive in the process of editing! You can edit my essay and do this editing stage if you want to experience the rigor.
The main aims of content editing are to ensure that the content is clear, coherent, and effectively conveys the intended message to the target audience. In short, it edits the content to maximize its capability to relay its intended purpose.
Key Sub-processes of Content Editing:
* Assess Overall Structure and Organization. Logical sequence and coherence are put in check on this sub-process.
* Evaluate Content and Clarity . The editor assures that the message or argument is well-defined and substantiated with appropriate evidence.
* Enhance Transitions and Signposting . The editor looks for means to enhance transitions between paragraphs and sections, making the text smoother and more reader-friendly. Aside from transition devices used in the first parts of each of the paragraphs, one may use signposts like topic sentences and headings to steer the reader through the content.
* Revise and Rewrite on Critical Content Issues . When deemed necessary, the editor may recommend or make significant revisions or rewrites to strengthen the content, eliminate redundancy, and enhance clarity.
2. Copy editing
This is the stage where it gets a bit technical for editors. Copy editing is the second stage of the entire editing process and focuses on the technical elements of the text. It concerns checking for grammatical and punctuation errors and ensuring consistent language usage, style, and compliance with a specific style guide. Copy editing’s main goal is to enhance the readability and correctness of the text, as well as establish the text’s credibility and trustworthiness.
Key Sub-processes of Copy Editing:
* Grammar and Punctuation . The editor implements grammar checks for spelling errors or other grammatical errors, including but not limited to subject-verb agreement, verb tense, and sentence structure. The text’s mechanics, or checking punctuation marks, may also be a focus for editing.
* Spelling and Usage . Spelling mistakes and inconsistencies in word usage (per the type of English one is using) are identified and corrected. Editors catch errors with redundant words, word count, body paragraphs, and passive voice.
* Capitalization and Formatting . The editor verifies that capitalization, headings, and formatting are uniform and appropriate to the type of writing.
* Fact-Checking . This sub-section ensures the accuracy of data, facts, figures, and references. The editor cross-references information with trustworthy sources and flags any instances of plagiarism and incorrect referencing.
* Style and Clarity . Editors persevere to improve sentence structure, eliminate vagueness, and enhance text readability.
3. Proofreading
This is the final stage of the editing process and is focused on scanning the document for “crumbs” left during the previous two stages– minor errors and inconsistencies. It is the last opportunity for the editor to catch any remaining typos, formatting issues, or other small mistakes before the document is brought to finality.
Key Sub-processes of Proofreading:
*Final Grammar and Spelling Check . The editor conducts a final review to identify and correct any grammatical or spelling errors that may have been overlooked. The final draft has an immaculate paragraph structure that's free of unnecessary words, grammar mistakes, or sentence fragments.
*Formatting and Layout . This step guarantees that the document adheres to consistent formatting, including margins, fonts, and spacing.
*Page Numbers and Table of Contents. The editor confirms that page numbers, footnotes, and the table of contents are correct and properly formatted.
* Hyperlinks and References . For digital documents, the editor checks that hyperlinks are functional and correctly correspond to the anchor text. They also ensure that references and citations are correct.
*Overall Readability . Finally, the editor scans the entire document one last time to identify any minimal errors, inconsistencies, or issues that might have been missed in previous stages.
How to Edit Essays: A Step-by-Step Guide
Now that you are familiar with the three main stages of editing essays– content editing, copy editing, and proofreading, we are confident that you may now have an understanding of how an entire editing process may come into play. The best thing is that you may take off your editing journey without being too pressured to follow a certain blueprint.
Yes, you read it correctly: you can craft your own editing process. Just ensure that you capture every essence of the three main stages. To provide you with a guide, the following is a 7-point checklist that you may use to edit your essay.
This table is a synthesis of everything we discussed in the three stages of editing.
Leverage the Studyfy Way
One may definitely follow a guideline like the one above, but an essay revision service can do so much more. At Studyfy, you can avail of its high-quality writing services, where a roster of competent writers and editors completely transform a writing prompt into a creative masterpiece– one that adheres to the perfect style, formatting, and instructions.
Enjoy Studyfy’s no-mark-up scheme and affordable price range without worrying about the finished product’s reliability and readability– quality is a top priority, indeed. How to edit an essay well: sorted!
How to Edit Your Essay in Various Forms?
Essays are pieces of writing that discuss various topics and hold different functions depending on the writing prompt, purpose, and audience, among others. Given its eclectic nature, essays can be tricky to edit. Some principles on how to edit an essay may not be as important in some types, and some steps are as important as others.
We know the difficulty that you might contend with in editing different forms of essays, so we are here to help you by providing a cheat sheet on the common essay types and some techniques on how to edit them.
How to Edit an Essay Using Various Editing Techniques
Reflective essay.
How to Write a Reflective Essay ? This essay involves self-introspection and analysis.Similar to a narrative essay, the goal of this essay type is to internalize and explore their thoughts and narrate a personal experience to readers who are likewise experiencing it.
Self-Reflection Enhancemen
- Ensure that the essay effectively relays personal experiences, thoughts, and insights.
- Evaluate the thesis statement in consideration of its essence and clarity.
- Evaluate the depth of self-analysis and introspection.
- Assess the essay’s emotional resonance and the perceived emotional impact on the reader.
- Analyze the organization of content, ensuring a structured format and exploration of themes.
Argumentative Essay
- This essay type presents a debatable proposition, a stand, and pieces of evidence that substantiate the writer’s stand.
- It is used to persuade the reader to take a particular viewpoint.
Argument Strengthening
- When editing an essay, ensure that the proposition is clear and debatable.
- Check for the logical flow of arguments and counterarguments.
- Evaluate the evidence and examples that support the claims.
- Verify that the conclusion aligns with the main argument and discourses opposing views.
Expository Essay
- It is embedded with facts, figures, findings, and other related factual information.
- Its aim is to provide and explain concepts, ideas, theories, or topics.
Clarity and Information Flow Enhancement
- Check if the essay has a clear and informative introduction.
- Check for the organization of content to ensure a logical sequence of ideas.
- When editing an essay, elucidate complex concepts with definitions and examples.
- Cross-reference facts and figures for exactness.
Narrative Essay
- A winning narrative piece is one that vividly tells a story– ensuring that the readers are inside the world that you want to immortalize.
- It is supplied with descriptive words, figurative language, a clear plot structure, and a consistent point of view.
Storytelling Focusing while Editing Essays
- Ensure the essay has a clear plot structure– beginning, middle, and end.
- Check for reasonable character development.
- Pay attention to imagery and descriptive language to enhance the reader's experience.
- Check for the pacing of the narrative to maintain engagement.
Persuasive Essay
- It uses persuasive diction and techniques, pieces of evidence, and logical reasoning to take persuasion to effect.
- Its aim is to make the reader adopt a certain and fresh perspective and subsequently take a course of action.
Persuasion Intensification and How to Edit Essay
- Evaluate the thesis statement in terms of influence and clarity.
- Integrate persuasive techniques like ethos, pathos, and logos .
- Assess the soundness and relevance of supporting evidence and examples.
- Ensure that counterarguments are accepted and refuted effectively.
- Ensure a conclusion that leaves a lasting impression.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How can editing help me ace my writing assignments if it’s another burden to do.
Editing may be a tough act to do after writing, but it can be a walk in the park if you master the skill. Practice it continuously and be devoted (translate: consistent) to doing it until you no longer find it difficult and laborious.
How can editing an essay be simplified if I no longer have sufficient time to do it?
You can always simplify your editing routine when time is running out. Editing essays can be as simple as having three pointers: (a) Checking for major grammar lapses; (b) Evaluating content based on its clarity and coherence; and (c) Checking for formatting guidelines.
How to edit an essay well if the guidelines are only specific to one element of text?
In connection with the previous question, you may opt to use a personalized editing routine and that includes considering one element over the others. You may allot a big remainder of your time editing that element, but always ensure that you edit the important things on a text, no matter how focused you are on a particular element.
To edit an essay is really hard for me. Do I have the option to just skip it?
I probably can think of a scenario where you are asking a question like this: “Can somebody write my paper and edit it? This is way too much for me!” While writing and editing are intertwined, and we have no means of skipping them, writing and editing services like Studyfy can finish the work for you.
Created personally for you and your writing needs, these services are strong with competent and reliable writers who can go the extra mile in finishing your writeups while adhering to the intended style, format, and content.
Sharper Pens, Clearer Minds: Editing Revising Tips for Perfecting Your Paper
Table of contents
- 1 The Initial Review
- 2.1 Take a Break
- 2.2 Read Aloud
- 2.3 Use Editing Tools
- 2.4 Focus on One Aspect at a Time
- 2.5 Check Grammar and Punctuation
- 2.6 Improve Clarity and Conciseness
- 2.7 Eliminate Redundancy and Cliches
- 2.8 Verify Sources and Citations
- 2.9 Address Transitions
- 2.10 Consult a Style Guide
- 2.11 Read Backwards
- 2.12 Consider Professional Editing
- 3 Ready to Start Editing?
Essay writing is among the most common assignments students of different majors receive. Embarking on the journey of writing a research paper or essay is the first step in crafting a compelling work. The true magic lies in editing, where your initial draft transforms into a polished masterpiece. Editing essays is not merely a task to correct grammatical errors. It is a nuanced process that involves refining ideas, improving clarity, and enhancing the quality of your writing.
From this article, you will learn:
- what to pay attention to while writing and editing an essay;
- essential rules for editing academic writing;
- how to bring your text to perfection.
So keep reading!
The Initial Review
The initial review of your essay’s plan is a foundational process akin to taking a step back to appreciate your work. It helps to focus on big-picture elements that lay the groundwork for a well-crafted piece. The emphasis is not on the meticulous correction of commas or typos. The main task of editing in the writing process is to check the structural integrity, organizational coherence, and logical flow of your writing.
Consider the initial review as the unveiling of the blueprint of your work. It’s time to examine the architecture, ensuring that each section aligns with the next and that ideas unfold logically. Ask yourself: Does the introduction effectively set the stage for what follows? Is the body of your work structured logically, guiding the reader through a clear and understandable narrative? Are transitions smooth, facilitating a seamless flow of ideas?
During the initial review, these questions helped to create a more efficient and targeted editing articles process. It allows you to identify and rectify any structural weaknesses or organizational lapses. Besides, it helps to prevent the need for extensive revisions in later stages. The initial review in the essay outline serves as a strategic investment of your time, ensuring that your writing meets the expectations of grammatical correctness and captivates your audience with a well-crafted and organized narrative.
12 Tips on Editing Your Paper
Start editing once you have assessed your work and found no critical or logical errors. This process may be lengthy, but it will only improve your text. So, how to edit a paper? Are there any editing techniques in writing? Below are some tips that will help you revise and edit efficiently.
Take a Break
The first thing you need to do before editing is to pause and take a break. You can go for a walk, cook a meal, or chat with friends. You can do anything that distracts you from your paper’s text. After you have rested, you will be able to notice all the shortcomings and errors with a fresh look and edit an essay efficiently. If necessary, take breaks several times, and take a break every time you see that you have stopped noticing errors in the text.
The next important thing to do while working on your paper is to read aloud. You can’t always notice minor flaws when you silently read your paper. When you speak the essay’s text, you can immediately see logical errors and how you can improve the written sentences. If the text looks complicated and confusing, simplify what you have written and replace it with synonyms. After you edit your own writing, read the text aloud again. Also, use overwriting.
Use Editing Tools
Editing tools serve as invaluable companions. They offer insights and corrections beyond manual review capabilities.
Consider these grammar and spell-check software:
- Grammarly ;
- ProWritingAid .
It can catch overlooked errors, ensuring a polished and error-free manuscript. Style guides provide writers with rules for style consistency and coherence. Additionally, tools like Hemingway Editor analyze writing for readability and suggest improvements.
Professional essay editing tools don’t mean relinquishing creative control. It empowers writers to refine their work more comprehensively.
Focus on One Aspect at a Time
This tip will help you cut down on all your shortcomings quickly. It focuses on individual tasks and assists you to complete the task more efficiently. Self-editing is a process that takes place in several stages. Imagine you decided to eliminate punctuation errors first, so read the text, focusing only on this. The second time you decide that it’s time to remove the passive voice, focus only on this and make edits. You need to be careful if you fall into the use of passive voice . This way, step by step, you will improve your paper and make it more simple and interesting. Moreover, you will not miss anything important with this method.
Check Grammar and Punctuation
Now, let’s review the points you should check in your text. Of course, the most important thing is grammar and punctuation. They show not just your mastery of the subject but your education in general. Thus, you need to do a spelling check. No one will want to read a text full of errors and typos. Do not be lazy to spend more time editing your writing and eliminate all the errors.
Improve Clarity and Conciseness
A well-constructed essay not only conveys ideas but does so with meticulous precision and transparency.
The process involves:
- eliminating ambiguity;
- eradicating redundancies;
- embracing a language.
Each word must contribute purposefully, facilitating effortless comprehension and engendering reader engagement. Through assiduous proofreading, one must meticulously pare down superfluous elements, sculpting sentences to embody clarity. Simplicity should be embraced without compromising substance, ensuring a seamless narrative flow. In this pursuit, each word becomes a brushstroke on the canvas of your essay ─ contributing to a lucid, compelling picture. Mastery of the delicate equilibrium between clarity and conciseness empowers your writing, transforming it into a potent medium that resonates with impact and captures your audience with precision and insight. It is one of the most important self-editing tips.
Eliminate Redundancy and Cliches
In pursuing articulate and impactful writing, eliminating redundancy and cliches is paramount. Redundant expressions, often unintentional echoes of the same idea, can dilute the clarity and precision of your message. Common cliches , once vivid, lose their potency through overuse and can detract from the originality of your work. Consider this an opportunity to infuse freshness into your writing, making every word count.
For instance, phrases like “future plans” or “free gift” carry inherent duplicity; the terms imply the concept. Instead, precision can be achieved by employing concise alternatives such as “plans” or “gift.”
By conscientiously identifying and excising these linguistic redundancies and cliches, your essay not only attains a heightened level of sophistication but also ensures that each expression contributes uniquely to the richness of your narrative. Embrace the challenge of crafting economical and distinctive language, and watch your ideas shine through with newfound clarity and impact.
Verify Sources and Citations
In the meticulous process of essay refinement, verifying sources and citations is a crucial step toward academic integrity. Accurate and adequately attributed sources lend credibility to your work, substantiating claims and bolstering arguments. Rigorously cross-checking citations ensures the reliability of your information, guarding against unintentional errors and upholding the standards of scholarly writing. A vigilant approach to source verification fortifies your essay’s credibility and reinforces your commitment to intellectual honesty and the pursuit of accurate knowledge.
Address Transitions
Navigating the terrain of effectively writing your essay involves more than just conveying ideas ─ it demands fluidity in transitioning between them. Addressing transitions ensures a seamless flow, guiding readers through the narrative effortlessly. Transitional word phrases, or employing thematic connections, are thoughtfully crafted transitions bridges the gaps between ideas, enhancing coherence. Elevate your essay by considering transitions not as mere connectors but as architectural threads binding your thoughts into a cohesive, compelling whole.
Consult a Style Guide
A style guide is an indispensable companion in the pursuit of impeccable writing. Consulting a guide ensures formatting, citations, and language conventions uniformity. This meticulous approach adds professional polish to your essay. Also, it conveys a commitment to standards. A style guide is your compass, from punctuation nuances to citation intricacies, for navigating the terrain of writing academic papers .
Read Backwards
Professional editors use this unique technique, and it indeed improves your writing. For a concentrated spelling and grammar review, flip the script. Read your essay backward, starting from the last sentence and progressing upward. It helps a concentrated spelling and grammar review flip the script. This technique unveils overlooked errors by disrupting the conventional flow. Elevate your editing prowess by adopting this reverse perspective.
Consider Professional Editing
The last in our list of tips for editing writing is professional help from a writing service . Use the editing help to make your work easier if you doubt your editing progress or the document’s significance. A skilled editor polishes grammar and style. By outsourcing improvement, you ensure your document reaches its goal. Embrace the assurance of professional scrutiny, allowing your work to be experienced.
Don’t be afraid to ask for help. A professional editor will know what to look for and how to get your essay into shape.
Ready to Start Editing?
As you can see, the editing process is not as scary as it seems to be at first glance. Follow the editing tips from this article, and you will get an essay of high quality without errors, typos, and cliches.
Remember that an influential paper contains:
- verified data;
- a balance of active and passive voices;
- examples, etc.
Your task is to ensure that the essay reveals the topic and that everything is clear and easy to read. Remember to show sources and proper citations to ensure the paper is original and omits plagiarism.
These simple editing tips for writers will simplify the work on any paper and take your writing to the next level!
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Edit Quotes in an Essay
4-minute read
- 29th April 2019
Quoting sources is vital when writing an essay . But what if the quote doesn’t fit the surrounding text? Or what if it’s too long?
The good news is you can change a quote if you need to. But you also need to highlight your edits clearly in the text. Check out our guide below, then, to find out how to edit quotes in academic writing.
Omitting Text from Quotations with Ellipses
If a quote is too long, it may interrupt the flow of your writing. For instance:
Smith (2007, p. 24) describes blancmange as “a sweet dessert that is generally made with milk or cream and sugar, although I also once had one that contained none of these ingredients, that has been thickened with gelatin, corn starch or Irish moss.”
The middle part of this quote isn’t necessary for describing blancmange, so we might want to leave it out. To do this, we would use an ellipsis to show where we had cut something from the original source:
Smith (2007, p. 24) describes blancmange as “a sweet dessert that is generally made with milk or cream and sugar…that has been thickened with gelatin, corn starch or Irish moss.”
We now have the text we wanted to quote, but we haven’t had to include the middle bit. This makes it clearer and more succinct.
Keep in mind, too, that you can write an ellipsis in several ways, including:
- In square brackets […]
- Spaced (. . .) or unspaced (…)
- With a space before and after the ellipsis or without spaces
As such, always check your style guide for advice on how to write ellipses. If you do not have a style guide, simply apply one type of ellipsis consistently.
Changing or Adding Words in Quotations
You can edit quotes by changing or adding words in order to:
- Integrate quoted text into your own writing
- Clarify the meaning of something
- Correct an error in the original text
If you do any of these, use square brackets to show where you have changed the original text. For example, imagine we found the following in a book:
Blancmange is delicious. The first time I ate it, I was in love.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
We might then want to quote the second sentence. But without the first sentence, it wouldn’t be clear what the “it” refers to. As such, we could edit the second sentence so that it works by itself:
Smith (2007, p. 31) says, “The first time I ate [blancmange], I was in love.”
It is now clear what Smith is saying without having to include the first sentence, but the reader can also see where we have changed the quote.
Marking Errors in Quotations
Finally, what if you don’t want to change an error in a quote? Or what if it contains something that looks like an error, such as an old-fashioned spelling?
In cases like these, you can use the Latin term “sic” to show that you’ve kept something non-standard from the original text. This is short for sic erat scriptum , which translates to “thus was it written.”
Usually, to use “sic” like this, you would place it in square brackets:
His writings were riddled with errors due to his addiction, which he described as “a terrible but delishus [sic] shame” (Smith 2017, p. 2).
The reader will then know that the spelling “delishus” comes from the quoted text, so it is not a transcription error.
Unless you have a good reason for preserving an error, though, it is usually better to fix it and put the correction in square brackets instead.
Summary: How to Edit Quotes in an Essay
If you need to edit quotes in your writing, keep the following in mind:
- Use an ellipsis to indicate omissions in the text. Check your style guide for how to format ellipses (e.g., in brackets or not, spaced or unspaced).
- Mark additions or changes by placing the edited text in square brackets .
- Use the term “[Sic]” to show that you’ve duplicated an error from a source. This will ensure the reader doesn’t think you’ve made a mistake yourself.
Different style guides may vary on these rules, so make sure to check yours if you have one. And don’t forget to have your work proofread .
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
How to Edit Quotes
| Candace Osmond
| Punctuation
Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond studied Advanced Writing & Editing Essentials at MHC. She’s been an International and USA TODAY Bestselling Author for over a decade. And she’s worked as an Editor for several mid-sized publications. Candace has a keen eye for content editing and a high degree of expertise in Fiction.
Quoting sources gives your essay or research paper credibility. But what if the quote requires context or doesn’t fit your sentences? How do you modify a quote?
As a content creator, I’m always quoting people and sources. But sometimes, I have to tweak things or chop them up to fit with my writing format.
Keep reading to learn the rules for editing quotes. Find out how to omit irrelevant text, correct a writer’s errors, or clarify meaning within direct quotations.
Is it Okay to Edit Quotes?
Yes, editing quotes is acceptable if you don’t take them out of context. I do it all the time! You must also ensure that the readers still know the original quote by using brackets for your inserted ideas.
This method is common, especially among run-in quotations. A run-in quote is a quote inserted within your sentence using quotation marks.
You’ll find periods and commas within run-in quotes. There may also be question marks and exclamation points outside them if they are not original to the quoted statement.
Remember that you can only edit quotes to:
- Integrate quoted text in your writing.
- Omit irrelevant text from the quotation.
- Correct a spelling or grammar error.
- Clarify the meaning of the quote.
I edit and use quotes all the time in my content writing and my works of fiction. For example, the fourth book in my Dark Tides series features a quote from my favorite poet because the statement goes so well with the story.

Because this was a public quote from him that can be found anywhere on the internet, I was able to use it as long as I sourced and credited it properly. However, the original quote is long, and I only need a snippet of it.
So, I picked one paragraph, inserted it with quotation marks, and credited the poet. In most cases, this is all you need to do. But, if I were only to use pieces of this paragraph or even omit parts, I’d need to do a little more. Let’s dive in deeper.
Editing Quotes Rules
Learn how to modify a quote in an essay with these guidelines for editing quotations.

Clarifying Quotations
Learning how to change a quote to fit your sentences or add more information is essential to make your message clear to the readers. There are instances when you want to put personal ideas with quotations without confusing your audience about the original statement.
“It [formal education] teaches us the usage of this art and science in everyday life, and that is how a child becomes a learned person” (Foxes Media, 2022).
Never put the in-text citation in brackets. Instead, use parentheses.
You can also use those square brackets to show changes in letter cases.
Foxes Media (2022) explains that “[i]t teaches us the usage of this art and science in everyday life, and that is how a child becomes a learned person.”
Quotations Within Quotations
To quote a quoted statement from another book, you should mention the primary and secondary sources. You don’t have to change anything within the entire quotation.
Bretts (2015) states that “It’s good to be afraid. You need to be afraid even when there’s no need, it keeps you alert” (as cited in Ferrante, 2019).
You can also directly quote the secondary source by citing the primary source using single quotation marks. However, this method is complicated and not recommended.

“Ferrante (2019) states that ‘it’s good to be afraid. You need to be afraid even when there’s no need, it keeps you alert” (Bretts, 2015).
Make sure the period comes after the in-text citation mark and not before the closing quotation mark.
How Do You Correct a Mistake in a Quote?
Some sentences contain spelling and grammar errors when they were written or mentioned by the original person. Personally, I leave it. I feel that the reader will see that it’s a quote and will understand that the mistake isn’t mine.
But major style guides recommend paraphrasing the statement instead of using a quotation. Just make sure that the paraphrased sentence still conveys the same message.
For the APA style, if you want to use direct quotations, you might consider using brackets with the word “sic.” Place “[ sic ]” after the quotation in italics.
- According to Nowak (2019), “people have an obligation to care for there [ sic ] pets.”
- Gilmore (2020) wrote, “if you’re going to throw your life away, he better have a motorcycle [ sic ].”
The word “sic” is Latin that means “as such,” which is the problem in the original text. I had no idea, actually had to look that up!
How Do You Take Out Parts of a Quote?
It’s common for academic writing to include only the relevant information, hence the need to cut out parts of a quote. You might want to leave out a superfluous sentence through ellipses to maintain the flow of your writing.
Here’s an example of the original statement:
Unfortunately, in the United States, many educators who claim to be Freirean in their pedagogical orientation mistakenly transform Freire’s notion of dialogue into a method, thus losing sight of the fact that the fundamental goal of dialogical teaching is to create a process of learning and knowing that invariably involves theorizing about the experiences shared in the dialogue process. Some strands of critical pedagogy engage in an overdose of experiential celebration that offers a reductionistic view of identity.
The statement to quote:
To quote this statement, we don’t use double quotation marks anymore. Block quotations are used to cite long passages. Use a colon at the end of the introduction, then indent the passage by five spaces on the left.
The Pedagogy of the Oppressed stated explained it best:
Unfortunately, in the United States, many educators who claim to be Freirean in their pedagogical orientation mistakenly transform Freire’s notion of dialogue into a method… Some strands of critical pedagogy engage in an overdose of experiential celebration that offers a reductionistic view of identity. (Freire, 2005).
Final Word on How to Edit Quotes
My post has detailed how to modify a quote, so I hope you feel confident doing it now. Remember that you can only change a quote to fit your sentence, clarify meanings, and correct errors. You can also remove parts of a quote that are irrelevant to your writing. Here are the basic editing quotes rules:
- Use square brackets for additions to the quoted material.
- Use an ellipsis to cut out text from the quoted statement.
- Use “[ sic ]” to show you’ve copied an error from the original author.
- Use blocked quotations for long passages.
Grammarist is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. When you buy via the links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no cost to you.
2024 © Grammarist, a Found First Marketing company. All rights reserved.
Free All-in-One Office Suite with PDF Editor
Edit Word, Excel, and PPT for FREE.
Read, edit, and convert PDFs with the powerful PDF toolkit.
Microsoft-like interface, easy to use.
Windows • MacOS • Linux • iOS • Android
Select areas that need to improve
- Didn't match my interface
- Too technical or incomprehensible
- Incorrect operation instructions
- Incomplete instructions on this function
Fields marked * are required please
Please leave your suggestions below
- Quick Tutorials
- Practical Skills
How to Add Footnotes in Word? [For Students]
Being a student can be tough. They say it’s one of the best days of your life, but with all the assignments and thesis work, it can definitely take the fun out of it. To excel as a student, you need to ensure you submit your best work. That means your essays need to be convincing, with all the right citations placed correctly. In this article, I’ll show you how to add footnotes in Word for students so you can properly cite your sources.
Footnotes in APA, MLA and Chicago Format
You haven't truly completed the format if you haven't added the citations and footnotes in the right way. Citations are a crucial component of academic writing, ensuring you give proper credit to sources and maintain scholarly integrity. Each citation style—APA, MLA, and Chicago—has its own specific rules for citing sources and adding footnotes. This can get complicated, especially when you're trying to meet tight deadlines or juggle multiple assignments. Here's what proper citation and footnote placement looks like when you are aiming to meet your academic standards:
APA format:
In APA format, footnotes are used by inserting superscript numbers in the text that correspond to the footnote numbers. Here's how to format footnotes:
Double-space footnotes.
Indent the first line.
Add a space between the superscript number and the note text.
For example, in a research paper, you might cite a book like this:
Antony Grafton, The Footnote: A Curious History (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1999), 221.
And a chapter from a book might be cited like this:
W. Jones and R. Smith, 2010, Photojournalism, 21, p. 122. (Copyright 2007 by Copyright Holder. Reprinted with permission.)
These footnotes include detailed citations, including author names, book titles, publication years, and page numbers.
MLA format:
In MLA format, footnotes are used for citing sources within the text. Here's how to format footnotes:
Place superscript numbers within the text to correspond with the footnote numbers.
Include detailed citation information in the footnote.
Single-space entries, with double-spacing between footnotes.
Chicago Format:
In Chicago style, footnotes are used for citing sources within the text. Here's how to format footnotes:
Separate multiple citations with semicolons.
Ensure consistency in citation style throughout the document.
How to Add Footnotes in Your Essay?
Adding footnotes correctly is incredibly important for academic writing, allowing you to reference sources and add explanations or additional information. To ensure you do this right, follow the steps below, designed to be compatible with various devices. To make sure you can follow along on your mobile, Windows, or Mac, I'll use WPS Office for the demo. It's a free office software that's compatible with all Word document versions and can even convert your papers to PDF without losing format.
1.On the References tab
As we move forward in this tutorial, let's address a common query students encounter when working on projects under strict professorial guidelines: how to add footnotes and endnotes in a Word document. Word simplifies this process. By navigating to the "Reference" tab, you can effortlessly insert footnotes and endnotes in your document.
Step 1: Let's launch WPS Writer, a simplified yet advanced writing software, and open our project where we need to insert footnotes.
Step 2: Now, within our document, place the cursor where you want to add the footnote.
Step 3: Next, the option to insert a footnote is located in the "Reference" tab. So, navigate to the Reference tab and click on "Insert Footnote" in the reference ribbon.
Step 4: A subscript will be added next to the text where you placed the cursor, and you will be directed to the bottom of the page where the footnote will appear.
That's how easily footnotes can be added in WPS Writer for your school projects. Another significant reason for using WPS Writer was its user-friendly interface, making it easy for me as a student. Additionally, it is budget-friendly while providing all the necessary tools.
2.Footnotes formatting
Probably the most important thing to keep in mind is the style requested by the instructor to follow: APA, MLA, or any other. Different styles entail different formatting. In this part, I'll show you how to add footnotes in APA style formatting. So, let's open WPS Writer and delve into formatting our footnotes.
Step 1: The first thing to remember is proper footnote referencing; ensure to follow the citation format when adding it to the footnote.
Step 2: To change the numbering format or starting position of your footnotes, right-click on your footnotes and select "Footnote/Endnote" from the context menu.
Step 3: In the Footnote and Endnote dialog box, select the numbering format according to the style in the "Number Format" field.
Step 4: Using the "Start at" field, you can start numbering your footnotes as desired.
Step 5: In APA style, our footnotes should be double-spaced. So, let's select our footnotes and navigate to the Home tab.
Step 6: In the Home ribbon, click on the "Line Spacing" icon and select "2.0" to change the line spacing to double.
With these easy steps, you'll be creating well-structured and formatted footnotes in no time. WPS Writer lets you concentrate on your writing and leaves the technicalities to the software. With a simple and clean interface and powerful tools that support all student needs, WPS Writer is my preferred choice for my writing needs. Plus, there's no bill at the end of each month just for using a writing software!
Use Word, Excel, and PPT for FREE, No Ads.
Edit PDF files with the powerful PDF toolkit.
Microsoft-like interface. Easy to learn. 100% Compatibility.
Boost your productivity with WPS's abundant free Word, Excel, PPT, and CV templates.
1.How to Revise Your Essay Easily?
When you're tackling a long essay, going through every sentence to ensure correct grammar, spelling, and formatting can be quite the challenge. This task can be especially daunting when you're juggling multiple assignments or working under tight deadlines. Thankfully, you don’t have to worry about any of that because with its WPS AI spell check and AI writer functions, you can automatically scan your essay for spelling errors, grammatical mistakes, and formatting inconsistencies.
The AI spell check feature helps you correct typos and other errors in real time, allowing you to focus on refining your ideas rather than hunting for misplaced commas or incorrect word choices. The AI writer function can also help you refine your writing style, offering suggestions for rewording sentences to make them clearer or more impactful. This combination of automated proofreading and writing assistance saves you time and ensures that your essay maintains a high standard of quality, allowing you to submit your work with confidence.
To ensure your thesis/assignment is error-free, let's utilize the WPS AI Spell Check to proofread your document.
Step 1: Open your document in WPS Writer and ensure the "AI Spell Check" toggle is activated in the status bar.
Step 2: Click on any incorrect word or phrase highlighted with a colored dotted underline in your document.
Step 3: This action will open the WPS AI Check pane on the right side of the screen.
Step 4: You will see all suggestions in the "All Suggestions" tab. To view different suggestions, click on each tab and make the correction.
2.How to Convert Word to PDF without Losing Format
Dealing with your thesis or professional essay requires very careful attention to detail, especially when it comes to proper formatting and final submissions. However, converting your essay to PDFwhich is a crucial step for academic or professional submissions—can be a source of frustration, particularly when using Microsoft Word 365, where the process might disrupt your APA or MLA formatting.
Unexpected changes in margins, font sizes, or spacing can turn a polished document into a chaotic one. WPS Office is really helpful in regard to allowing you to convert your essay to PDF while preserving your original formatting. Unlike Word, WPS Office ensures that your APA or MLA style remains intact, with no unexpected shifts in headers, footnotes, or page layout. With just a few clicks, you can convert your document to PDF and be confident that it looks exactly as intended, avoiding last-minute adjustments.
Here is how WPS Writer can help you convert your work with footnotes into PDF in a few easy steps:
Step 1: Open your Word document in WPS Office. Look for the Menu button at the top left corner of the screen.
Step 2: Click on "Save as" in the menu. Then choose "Other formats" .
Step 3: In the options, pick "PDF" from the list. Click "Save" to change your document to a PDF file.
FAQs about adding Footnotes in Word
1. how do you insert multiple footnotes in word.
Here's a straightforward guide on how to insert multiple footnotes in Word:
Step 1: Position your cursor in the main text where you want the footnote number to be displayed.
Step 2: Navigate to the References tab located in the ribbon toolbar.
Step 3: Click on the "Insert Footnote" option. This action will direct you to the bottom of the page, where you can input your footnote text.
Step 4: Enter the content of your footnote according to the required style.
Step 5: Repeat the process for each additional footnote needed. Word will automatically adjust the numbering for you.
2. How do you put two footnotes in one sentence?
According to the Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS), if you have more than one citation relating to the same concept or idea, all relevant citations can be included in a single footnote, each separated by a semi-colon. This method ensures clarity and organization in your references
3. How do you footnote something already footnoted?
Place the Cursor: Click where you want to insert the new footnote.
Insert a Footnote: Use the "Insert Footnote" option, typically in the "References" or "Insert" tab.
Add Reference: In the new footnote, refer to the existing footnote. You can quote, summarize, or mention the original footnote number (e.g., "See footnote 1" ).
Check Footnote Numbering: Ensure that the numbering is correct. Adjust if needed.
Proofread: Confirm that the new footnote is clear and that the document's structure remains intact.
Stop Struggling with Footnotes: Here's the Word Hack You Need
Your essay isn't complete without proper citations, which usually come in the form of footnotes. Once you learn how to add footnotes in Word for students, it's crucial to double-check them to ensure they're correctly formatted and contain all the necessary information. This step is especially important to maintain academic integrity and avoid plagiarism. WPS AI can be a tremendous help in this regard. It can scan your document for errors, suggesting corrections if you've missed a citation or formatted something incorrectly. With WPS AI's assistance, you can confidently complete your footnotes, knowing that you've referenced your sources accurately and consistently. So do yourself a favor and download WPS Writer to make your academic life easier.
- 1. How to Add Page Numbers in Word for Your Papers? [For Students]
- 2. How to Check Word Count for Your Essays in Word [For Students]
- 3. How to insert footnotes in word
- 4. How to Remove Section Breaks in Word? [For Students]
- 5. How to Add a Line in Word [For Students]
- 6. How to Convert PDF to Word for Students
15 years of office industry experience, tech lover and copywriter. Follow me for product reviews, comparisons, and recommendations for new apps and software.

COMMENTS
Make sure that you complete the most important editing and proofreading tasks. Editing. Editing is what you begin doing as soon as you finish your first draft. You reread your draft to see, for example, whether the paper is well-organized, the transitions between paragraphs are smooth, and your evidence really backs up your argument.
2. Prune long sentences and paragraphs. Whether you've exceeded your word count or not, long sentences and paragraphs should be edited because they can be trickier to read, and risk being boring or hard to follow. Try, therefore, to keep sentences to a maximum of two or three clauses (or segments). Avoid long paragraphs by starting a new one ...
Essay Editing Tip #4: Use a Highlighter. Your writing skills can catapult if you start using some old-fashioned methods of self-editing. Old school writers always walk around with a highlighter in their hands. Highlighting is a great way to focus on individual sentences and vigorously proof check them.
This is true at every level: If a word isn't necessary in a sentence, cut it; if a sentence isn't necessary in a paragraph, cut it; and if a paragraph isn't necessary, cut it, too. Go ...
Step 1: Look at the essay as a whole. There's no sense in perfecting a sentence if the whole paragraph will later be cut, and there's no sense in focusing on a paragraph if the whole section needs to be reworked.. For these reasons, work from general to specific: start by looking at the overall purpose and organization of your text, and don't worry about the details for now.
This variation helps to keep the reader's attention and allows for a more engaging narrative flow. 9. Revisit your essay after a break. Give yourself time: After completing a draft of your essay, step away from it for a day or two. This break can clear your mind and reduce your attachment to specific phrases or ideas.
When you edit, be sure your thesis statement is strong. A strong thesis will answer the prompt or guiding research question, but it will also be succinct. It should be clear, so eliminate any wordiness. You should also ensure it aligns with the rest of the essay.
I usually begin by looking at content. Build a content list, similar to the assembly list for your bookshelf, to evaluate the arguments and ideas you've generated thus far. Make sure you have: ☐ Answered the prompt. ☐ A clear introduction with the appropriate contextual information to set up your argument.
The moment you finish composing your essay comes the time to begin the process of perfecting it. Carrying out proper edits and revisions is the final step to creating a great paper. Good editing, like writing, is a skill, which must be perfected over time. Even the works of the most prominent writers require skillful editing.
Why Revise. To make the draft more accessible to the reader. To sharpen and clarify the focus and argument. To improve and further develop ideas. Revision VS. Editing. Revising a piece of your own writing is more than just fixing errors—that's editing. Revision happens before editing. Revising involves re-seeing your essay from the eyes of a ...
8. Embrace re-reading. Editing isn't a one-off process, and chances are you'll need multiple read-throughs in order to find all of your weak sentences, grammar mistakes, punctuation errors, and spelling errors. 9. Mind your syntax. Be on the lookout for issues with grammar and word choice.
1. Helps correct structural inconsistencies. Effective editing helps detect structural and tonal inconsistencies that don't fit in with a particular paragraph or the essay as a whole. These inconsistencies can then be rephrased, restructured, or completely eliminated from your essay. 2.
Editing an essay effectively involves several key steps to enhance clarity, coherence, and overall impact. Here's a step-by-step guide: Review the Structure: Ensure your essay has a clear introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction should present your thesis statement or main argument, the body should contain your supporting points ...
1 The Initial Review. 2 12 Tips on Editing Your Paper. 2.1 Take a Break. 2.2 Read Aloud. 2.3 Use Editing Tools. 2.4 Focus on One Aspect at a Time. 2.5 Check Grammar and Punctuation. 2.6 Improve Clarity and Conciseness. 2.7 Eliminate Redundancy and Cliches.
Learn how to write effectively for academic, professional, and personal purposes at the Purdue Online Writing Lab, a free resource for writers of all levels.
The online proofreader. It's really straightforward. Just paste the text into the tool. All your errors will now be underlined in red. You can hover over these mistakes to see how they can be addressed. If you agree, just click on the button "Fix all errors," and your mistakes will be fixed instantly!
5. Take a break. Walking away from the writing and coming back to it later with fresh eyes can greatly improve your ability to spot spelling mistakes and various other errors. Take a stroll outside, get a drink of water, or try meditating for a few minutes to reset your mind and come back to it anew.
The full Essay Writing Jumpstarter Course has re-opened! Take the full course here: https://helpfulprofessor.com/courseEditing your essay is so important for...
Once you've made sure the writing is clear, you can move forward to the next step. 2. Use a grammar and spell checker program. Sometimes it's easy to miss spelling and grammar errors when you're focused on writing. But as you go edit an article, use a spell checker or a grammar program to help you catch everything.
If you need to edit quotes in your writing, keep the following in mind: Use an ellipsis to indicate omissions in the text. Check your style guide for how to format ellipses (e.g., in brackets or not, spaced or unspaced). Mark additions or changes by placing the edited text in square brackets. Use the term " [Sic]" to show that you've ...
Candace Osmond studied Advanced Writing & Editing Essentials at MHC. She's been an International and USA TODAY Bestselling Author for over a decade. And she's worked as an Editor for several mid-sized publications. Candace has a keen eye for content editing and a high degree of expertise in Fiction.
Being a student can be tough. They say it's one of the best days of your life, but with all the assignments and thesis work, it can definitely take the fun out of it. To excel as a student, you need to ensure you submit your best work. That means your essays need to be convincing, with all the right citations placed correctly. In this article, I'll show you how to add footnotes in Word for ...