Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.

4 Writing the Materials and Methods (Methodology) Section
The Materials and Methods section briefly describes how you did your research. In other words, what did you do to answer your research question? If there were materials used for the research or materials experimented on you list them in this section. You also describe how you did the research or experiment. The key to a methodology is that another person must be able to replicate your research—follow the steps you take. For example if you used the internet to do a search it is not enough to say you “searched the internet.” A reader would need to know which search engine and what key words you used.
Open this section by describing the overall approach you took or the materials used. Then describe to the readers step-by-step the methods you used including any data analysis performed. See Fig. 2.5 below for an example of materials and methods section.
Writing tips:
- Explain procedures, materials, and equipment used
- Example: “We used an x-ray fluorescence spectrometer to analyze major and trace elements in the mystery mineral samples.”
- Order events chronologically, perhaps with subheadings (Field work, Lab Analysis, Statistical Models)
- Use past tense (you did X, Y, Z)
- Quantify measurements
- Include results in the methods! It’s easy to make this mistake!
- Example: “W e turned on the machine and loaded in our samples, then calibrated the instrument and pushed the start button and waited one hour. . . .”

Technical Writing @ SLCC Copyright © 2020 by Department of English, Linguistics, and Writing Studies at SLCC is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write Your Methods

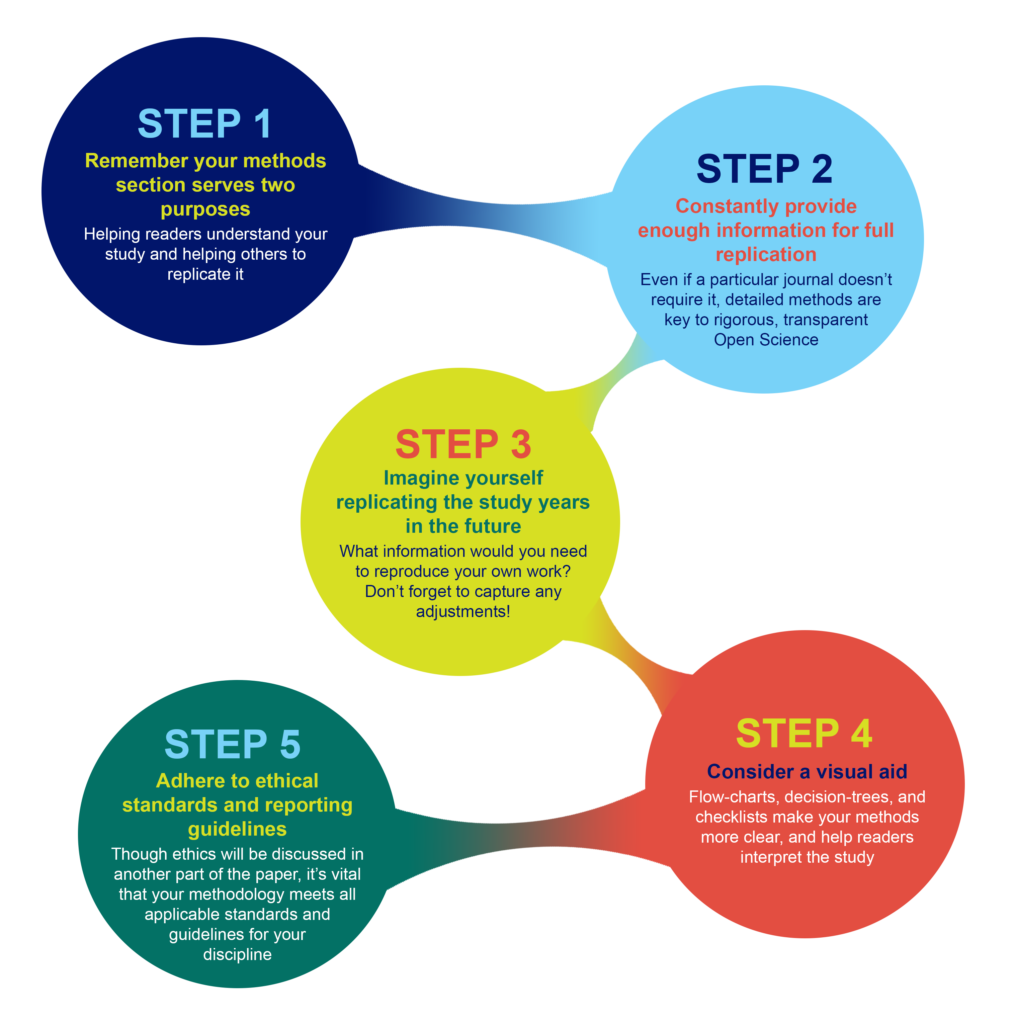
Ensure understanding, reproducibility and replicability
What should you include in your methods section, and how much detail is appropriate?
Why Methods Matter
The methods section was once the most likely part of a paper to be unfairly abbreviated, overly summarized, or even relegated to hard-to-find sections of a publisher’s website. While some journals may responsibly include more detailed elements of methods in supplementary sections, the movement for increased reproducibility and rigor in science has reinstated the importance of the methods section. Methods are now viewed as a key element in establishing the credibility of the research being reported, alongside the open availability of data and results.
A clear methods section impacts editorial evaluation and readers’ understanding, and is also the backbone of transparency and replicability.
For example, the Reproducibility Project: Cancer Biology project set out in 2013 to replicate experiments from 50 high profile cancer papers, but revised their target to 18 papers once they understood how much methodological detail was not contained in the original papers.
What to include in your methods section
What you include in your methods sections depends on what field you are in and what experiments you are performing. However, the general principle in place at the majority of journals is summarized well by the guidelines at PLOS ONE : “The Materials and Methods section should provide enough detail to allow suitably skilled investigators to fully replicate your study. ” The emphases here are deliberate: the methods should enable readers to understand your paper, and replicate your study. However, there is no need to go into the level of detail that a lay-person would require—the focus is on the reader who is also trained in your field, with the suitable skills and knowledge to attempt a replication.
A constant principle of rigorous science
A methods section that enables other researchers to understand and replicate your results is a constant principle of rigorous, transparent, and Open Science. Aim to be thorough, even if a particular journal doesn’t require the same level of detail . Reproducibility is all of our responsibility. You cannot create any problems by exceeding a minimum standard of information. If a journal still has word-limits—either for the overall article or specific sections—and requires some methodological details to be in a supplemental section, that is OK as long as the extra details are searchable and findable .
Imagine replicating your own work, years in the future
As part of PLOS’ presentation on Reproducibility and Open Publishing (part of UCSF’s Reproducibility Series ) we recommend planning the level of detail in your methods section by imagining you are writing for your future self, replicating your own work. When you consider that you might be at a different institution, with different account logins, applications, resources, and access levels—you can help yourself imagine the level of specificity that you yourself would require to redo the exact experiment. Consider:
- Which details would you need to be reminded of?
- Which cell line, or antibody, or software, or reagent did you use, and does it have a Research Resource ID (RRID) that you can cite?
- Which version of a questionnaire did you use in your survey?
- Exactly which visual stimulus did you show participants, and is it publicly available?
- What participants did you decide to exclude?
- What process did you adjust, during your work?
Tip: Be sure to capture any changes to your protocols
You yourself would want to know about any adjustments, if you ever replicate the work, so you can surmise that anyone else would want to as well. Even if a necessary adjustment you made was not ideal, transparency is the key to ensuring this is not regarded as an issue in the future. It is far better to transparently convey any non-optimal methods, or methodological constraints, than to conceal them, which could result in reproducibility or ethical issues downstream.
Visual aids for methods help when reading the whole paper
Consider whether a visual representation of your methods could be appropriate or aid understanding your process. A visual reference readers can easily return to, like a flow-diagram, decision-tree, or checklist, can help readers to better understand the complete article, not just the methods section.
Ethical Considerations
In addition to describing what you did, it is just as important to assure readers that you also followed all relevant ethical guidelines when conducting your research. While ethical standards and reporting guidelines are often presented in a separate section of a paper, ensure that your methods and protocols actually follow these guidelines. Read more about ethics .
Existing standards, checklists, guidelines, partners
While the level of detail contained in a methods section should be guided by the universal principles of rigorous science outlined above, various disciplines, fields, and projects have worked hard to design and develop consistent standards, guidelines, and tools to help with reporting all types of experiment. Below, you’ll find some of the key initiatives. Ensure you read the submission guidelines for the specific journal you are submitting to, in order to discover any further journal- or field-specific policies to follow, or initiatives/tools to utilize.
Tip: Keep your paper moving forward by providing the proper paperwork up front
Be sure to check the journal guidelines and provide the necessary documents with your manuscript submission. Collecting the necessary documentation can greatly slow the first round of peer review, or cause delays when you submit your revision.
Randomized Controlled Trials – CONSORT The Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) project covers various initiatives intended to prevent the problems of inadequate reporting of randomized controlled trials. The primary initiative is an evidence-based minimum set of recommendations for reporting randomized trials known as the CONSORT Statement .
Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses – PRISMA The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses ( PRISMA ) is an evidence-based minimum set of items focusing on the reporting of reviews evaluating randomized trials and other types of research.
Research using Animals – ARRIVE The Animal Research: Reporting of In Vivo Experiments ( ARRIVE ) guidelines encourage maximizing the information reported in research using animals thereby minimizing unnecessary studies. (Original study and proposal , and updated guidelines , in PLOS Biology .)
Laboratory Protocols Protocols.io has developed a platform specifically for the sharing and updating of laboratory protocols , which are assigned their own DOI and can be linked from methods sections of papers to enhance reproducibility. Contextualize your protocol and improve discovery with an accompanying Lab Protocol article in PLOS ONE .
Consistent reporting of Materials, Design, and Analysis – the MDAR checklist A cross-publisher group of editors and experts have developed, tested, and rolled out a checklist to help establish and harmonize reporting standards in the Life Sciences . The checklist , which is available for use by authors to compile their methods, and editors/reviewers to check methods, establishes a minimum set of requirements in transparent reporting and is adaptable to any discipline within the Life Sciences, by covering a breadth of potentially relevant methodological items and considerations. If you are in the Life Sciences and writing up your methods section, try working through the MDAR checklist and see whether it helps you include all relevant details into your methods, and whether it reminded you of anything you might have missed otherwise.
Summary Writing tips
The main challenge you may find when writing your methods is keeping it readable AND covering all the details needed for reproducibility and replicability. While this is difficult, do not compromise on rigorous standards for credibility!

- Keep in mind future replicability, alongside understanding and readability.
- Follow checklists, and field- and journal-specific guidelines.
- Consider a commitment to rigorous and transparent science a personal responsibility, and not just adhering to journal guidelines.
- Establish whether there are persistent identifiers for any research resources you use that can be specifically cited in your methods section.
- Deposit your laboratory protocols in Protocols.io, establishing a permanent link to them. You can update your protocols later if you improve on them, as can future scientists who follow your protocols.
- Consider visual aids like flow-diagrams, lists, to help with reading other sections of the paper.
- Be specific about all decisions made during the experiments that someone reproducing your work would need to know.

Don’t
- Summarize or abbreviate methods without giving full details in a discoverable supplemental section.
- Presume you will always be able to remember how you performed the experiments, or have access to private or institutional notebooks and resources.
- Attempt to hide constraints or non-optimal decisions you had to make–transparency is the key to ensuring the credibility of your research.
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
We have a new app!
Take the Access library with you wherever you go—easy access to books, videos, images, podcasts, personalized features, and more.
Download the Access App here: iOS and Android . Learn more here!
- Remote Access
- Save figures into PowerPoint
- Download tables as PDFs

Chapter 5: Materials and Methods
- Download Chapter PDF
Disclaimer: These citations have been automatically generated based on the information we have and it may not be 100% accurate. Please consult the latest official manual style if you have any questions regarding the format accuracy.
Download citation file:
- Search Book
Jump to a Section
- ORGANIZATION
- SUMMARY OF GUIDELINES FOR THE MATERIALS AND METHODS SECTION
- EXERCISE 5.1: A CLEARLY WRITTEN METHODS SECTION
- EXERCISE 5.2: CONTENT AND ORGANIZATION IN THE METHODS SECTION
- Full Chapter
- Supplementary Content
For hypothesis-testing papers, the function of the Materials and Methods section (often referred to as the Methods section) is to tell the reader what experiments you did to answer the question posed in the Introduction. Similarly, for descriptive studies, the Methods section tells what experiments you did to obtain the message stated in the Introduction. For methods papers, the Methods section has two functions: it describes the new method in complete detail and also tells what experiments you did to test the new method. For all types of paper, the Methods section should include sufficient detail and references to permit a trained scientist to evaluate your work fully or to repeat the experiments exactly as you did them.
Hypothesis-Testing and Descriptive Papers
We saw that the first step in the story line of a hypothesis-testing or a descriptive paper is presented in the Introduction. This first step is either the question being asked or the structure being described. In either case, the second step in the story line is an overview of the experiments you did. This overview of the experiments gives the strategy of the experiments, the plan that connects the methods to each other and to the question or the message.
Where the overview of the experiments is presented depends on the type of research:
Methods Papers
For a Methods paper, the first step in the story line is a statement that you are presenting a new or improved material, method, or apparatus. The second step in the story line has two parts: a complete description of the new method, material, or apparatus; and a description of how this new method, material, or apparatus was tested. These two steps are described in the Methods section.
In this chapter, we will consider only Methods sections for hypothesis-testing papers.
Sign in or create a free Access profile below to access even more exclusive content.
With an Access profile, you can save and manage favorites from your personal dashboard, complete case quizzes, review Q&A, and take these feature on the go with our Access app.
Pop-up div Successfully Displayed
This div only appears when the trigger link is hovered over. Otherwise it is hidden from view.
Please Wait
Setting the Scene: Best Practices for Writing Materials and Methods
- Peer Review
- Research Process
This free white paper tackles the best ways to write the Materials and Methods section of a scientific manuscript.
Updated on March 3, 2014

The Materials and Methods (or “Methods section”) is the section of a research paper that provides the reader
with all the information needed to understand your work and how the reported results were produced. Having read
the Introduction, the reader already knows why your work is important, so the next step is to connect that section to
the experimental design used to address your research questions.
Below is a preview of our free white paper tackling the best way to write the Materials and Methods section of a scientific manuscript. It covers the following topics:
Purpose and Structure
- Key Information
- Notation and Terminology
- Equipment and Materials Citations
- Acquisition and Definition of the Results
- Statistical Methods
- Concluding Statements
Depending on the type of paper, the Methods section can encompass anything from the parameters of a literature search to the methods employed in a field study to the details of bench work in the lab. The common feature is that the information needs to be presented in a way that is clear and familiar to the reader. It is important to note that the purpose of the Methods section is not just to convey what you did; a thorough and well-organized Methods section reflects your knowledge and understanding of appropriate research techniques and increases the reader's confidence in your work.
The Methods section is easiest to follow when it begins by providing a clear context for the detailed descriptions of the methods and materials used in the study. This context is best achieved by beginning with general characteristics and parameters (e.g., identification of sample sources or populations, descriptions of geographic areas, or characterizations of study participants). A reader who understands the foundation of your experiments will more easily understand the procedures that follow.
The underlying principle for what information to provide in the Methods section is that the reader should be able to replicate your study. This section must explain the methods used with enough detail to answer any of the reader's questions about how the study was performed. Because the Methods section is meant to convey how the research was conducted, conforming to the accepted conventions of the field is extremely important.
Generally, the Methods section should assemble familiar concepts and research activities into a logical series of events. Terminology and sentence structure should be consistent within the paper and conform to the conventions of the field, and repetition is accepted or even expected. Because Methods sections often rely on lists of information, consistency - i.e., the presentation of like elements using the same terminology, notation, and sentence structure - is especially important.
The information in the Methods section should follow the order of execution as closely as possible, although similar procedures should be presented together. For example, descriptions of sample or data collection should be described together, even if these are performed at different times or with intervening analysis, because a purely chronological account would mean switching back and forth between procedures.
Continue reading "Setting the Scene: Best Practices for Writing Materials and Methods" by downloading the full white paper here .
Check out our other "Best Practices for Writing" white papers to get tips for other sections of your research manuscript:
Getting a Strong Start: Best Practices for Writing an Introduction
Reaping the Rewards: Best Practices for Writing a Results Section

Michael Bendiksby, PhD
See our "Privacy Policy"
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write a Methods Section for a Psychology Paper
Tips and Examples of an APA Methods Section
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
Verywell / Brianna Gilmartin
The methods section of an APA format psychology paper provides the methods and procedures used in a research study or experiment . This part of an APA paper is critical because it allows other researchers to see exactly how you conducted your research.
Method refers to the procedure that was used in a research study. It included a precise description of how the experiments were performed and why particular procedures were selected. While the APA technically refers to this section as the 'method section,' it is also often known as a 'methods section.'
The methods section ensures the experiment's reproducibility and the assessment of alternative methods that might produce different results. It also allows researchers to replicate the experiment and judge the study's validity.
This article discusses how to write a methods section for a psychology paper, including important elements to include and tips that can help.
What to Include in a Method Section
So what exactly do you need to include when writing your method section? You should provide detailed information on the following:
- Research design
- Participants
- Participant behavior
The method section should provide enough information to allow other researchers to replicate your experiment or study.
Components of a Method Section
The method section should utilize subheadings to divide up different subsections. These subsections typically include participants, materials, design, and procedure.
Participants
In this part of the method section, you should describe the participants in your experiment, including who they were (and any unique features that set them apart from the general population), how many there were, and how they were selected. If you utilized random selection to choose your participants, it should be noted here.
For example: "We randomly selected 100 children from elementary schools near the University of Arizona."
At the very minimum, this part of your method section must convey:
- Basic demographic characteristics of your participants (such as sex, age, ethnicity, or religion)
- The population from which your participants were drawn
- Any restrictions on your pool of participants
- How many participants were assigned to each condition and how they were assigned to each group (i.e., randomly assignment , another selection method, etc.)
- Why participants took part in your research (i.e., the study was advertised at a college or hospital, they received some type of incentive, etc.)
Information about participants helps other researchers understand how your study was performed, how generalizable the result might be, and allows other researchers to replicate the experiment with other populations to see if they might obtain the same results.
In this part of the method section, you should describe the materials, measures, equipment, or stimuli used in the experiment. This may include:
- Testing instruments
- Technical equipment
- Any psychological assessments that were used
- Any special equipment that was used
For example: "Two stories from Sullivan et al.'s (1994) second-order false belief attribution tasks were used to assess children's understanding of second-order beliefs."
For standard equipment such as computers, televisions, and videos, you can simply name the device and not provide further explanation.
Specialized equipment should be given greater detail, especially if it is complex or created for a niche purpose. In some instances, such as if you created a special material or apparatus for your study, you might need to include an illustration of the item in the appendix of your paper.
In this part of your method section, describe the type of design used in the experiment. Specify the variables as well as the levels of these variables. Identify:
- The independent variables
- Dependent variables
- Control variables
- Any extraneous variables that might influence your results.
Also, explain whether your experiment uses a within-groups or between-groups design.
For example: "The experiment used a 3x2 between-subjects design. The independent variables were age and understanding of second-order beliefs."
The next part of your method section should detail the procedures used in your experiment. Your procedures should explain:
- What the participants did
- How data was collected
- The order in which steps occurred
For example: "An examiner interviewed children individually at their school in one session that lasted 20 minutes on average. The examiner explained to each child that he or she would be told two short stories and that some questions would be asked after each story. All sessions were videotaped so the data could later be coded."
Keep this subsection concise yet detailed. Explain what you did and how you did it, but do not overwhelm your readers with too much information.
Tips for How to Write a Methods Section
In addition to following the basic structure of an APA method section, there are also certain things you should remember when writing this section of your paper. Consider the following tips when writing this section:
- Use the past tense : Always write the method section in the past tense.
- Be descriptive : Provide enough detail that another researcher could replicate your experiment, but focus on brevity. Avoid unnecessary detail that is not relevant to the outcome of the experiment.
- Use an academic tone : Use formal language and avoid slang or colloquial expressions. Word choice is also important. Refer to the people in your experiment or study as "participants" rather than "subjects."
- Use APA format : Keep a style guide on hand as you write your method section. The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association is the official source for APA style.
- Make connections : Read through each section of your paper for agreement with other sections. If you mention procedures in the method section, these elements should be discussed in the results and discussion sections.
- Proofread : Check your paper for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors.. typos, grammar problems, and spelling errors. Although a spell checker is a handy tool, there are some errors only you can catch.
After writing a draft of your method section, be sure to get a second opinion. You can often become too close to your work to see errors or lack of clarity. Take a rough draft of your method section to your university's writing lab for additional assistance.
A Word From Verywell
The method section is one of the most important components of your APA format paper. The goal of your paper should be to clearly detail what you did in your experiment. Provide enough detail that another researcher could replicate your study if they wanted.
Finally, if you are writing your paper for a class or for a specific publication, be sure to keep in mind any specific instructions provided by your instructor or by the journal editor. Your instructor may have certain requirements that you need to follow while writing your method section.
Frequently Asked Questions
While the subsections can vary, the three components that should be included are sections on the participants, the materials, and the procedures.
- Describe who the participants were in the study and how they were selected.
- Define and describe the materials that were used including any equipment, tests, or assessments
- Describe how the data was collected
To write your methods section in APA format, describe your participants, materials, study design, and procedures. Keep this section succinct, and always write in the past tense. The main heading of this section should be labeled "Method" and it should be centered, bolded, and capitalized. Each subheading within this section should be bolded, left-aligned and in title case.
The purpose of the methods section is to describe what you did in your experiment. It should be brief, but include enough detail that someone could replicate your experiment based on this information. Your methods section should detail what you did to answer your research question. Describe how the study was conducted, the study design that was used and why it was chosen, and how you collected the data and analyzed the results.
Erdemir F. How to write a materials and methods section of a scientific article ? Turk J Urol . 2013;39(Suppl 1):10-5. doi:10.5152/tud.2013.047
Kallet RH. How to write the methods section of a research paper . Respir Care . 2004;49(10):1229-32. PMID: 15447808.
American Psychological Association. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). Washington DC: The American Psychological Association; 2019.
American Psychological Association. APA Style Journal Article Reporting Standards . Published 2020.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write the Methods Section of an APA Paper

3-minute read
- 23rd December 2021
If you’re a researcher writing an APA paper , you’ll need to include a Methods section. This part explains the methods you used to conduct your experiment or research study and is always written in the past tense.
It’s crucial that you include all the relevant information here because other researchers will use this section to recreate your study, as well as judge how valid and accurate your results are.
In this guide, we’ll show you how to write a clear and comprehensive Methods section for your research paper.
Structuring the Methods Section
This section of an APA paper is typically split into three subsections under the following subheadings:
- Participants —who took part in the experiment and why?
- Materials —what tools did you use to conduct the experiment?
- Procedure —what steps were involved in the experiment?
If necessary, you may add further subsections. Different institutions have specific rules on what subsections should be included (for example, some universities require a “Design” subsection), so make sure to check your institution’s requirements before you start writing your Methods section.
Writing the Participants Subsection
In this first subsection, you will need to identify the participants of your experiment or study. You should include:
● How many people took part, and how many were assigned to the experimental condition
● How they were selected for participation
● Any relevant demographic information (e.g., age, sex, ethnicity)
You’ll also need to address whether any restrictions were placed on who was selected and if any incentives were offered to encourage participants to take part.
Writing the Materials Subsection
In this subsection, you should address the materials, equipment, measures, and stimuli used in the study. These might include technology and computer software, tools such as questionnaires and psychological assessments, and, if relevant, the physical setting where the study took place.
You’ll need to describe specialist equipment in detail, especially if it has a niche purpose. However, you don’t need to provide specific information about common or standard equipment (e.g., the type of computer on which participants completed a survey) unless it’s relevant to the experiment.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
In addition, you don’t need to explain a material in depth if it’s well known within your field, such as a famous psychological assessment. Instead, you can provide a citation referring to that material.
If any materials were designed specifically for the experiment, such as a questionnaire, you’ll need to provide such materials in the appendix .
Writing the Procedure Subsection
The procedure subsection should describe what you had participants do in a step-by-step format. It should be detailed but concise and will typically include:
● A summary of the instructions given to participants (as well as any information that was intentionally withheld)
● A description of how participants in different conditions were treated
● How long each step of the process took
● How participants were debriefed or dismissed at the end of the experiment
After detailing the steps of the experiment, you should then address the methods you used to collect and analyze data.
Proofreading Your Methods Section
Because the Methods section of your paper will help other researchers understand and recreate your experiment, you’ll want your writing to be at its best.
Our expert research paper proofreaders can help your research get the recognition it deserves by making sure your work is clear, concise, and error-free. Why not try our services for free by submitting a trial document ?
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
How to insert a text box in a google doc.
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...
2-minute read
How to Cite the CDC in APA
If you’re writing about health issues, you might need to reference the Centers for Disease...
5-minute read
Six Product Description Generator Tools for Your Product Copy
Introduction If you’re involved with ecommerce, you’re likely familiar with the often painstaking process of...
What Is a Content Editor?
Are you interested in learning more about the role of a content editor and the...
4-minute read
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

Research Paper Writing: 5. Methods / Materials
- 1. Getting Started
- 2. Abstract
- 3. Introduction
- 4. Literature Review
- 5. Methods / Materials
- 6. Results / Analysis
- 7. Discussion
- 8. Conclusion
- 9. Reference
Methods / Materials Overview
These sections of the research paper should be concise. The audience reading the paper will always want to know what materials or methods that were used. The methods and materials may be under subheadings in the section or incorporated together. The main objective for these sections is to provide specialized materials, general procedures, and methods to judge the scientific value of the paper.
What to include in the sections
- Described separately
- Include the chemicals, biological, and any equipment
- Do not include common supplies, such as test tubes, pipette tips, beakers, etc. or standard lab equipment
- Single out sources like a specific type of equipment, enzyme, or a culture
- These should be mentioned in a separate paragraph with its own heading or highlighted in the procedure section if there is one
- Refer to solutions by name and describe
- Describes in detail how the analysis was conducted
- Be brief when presenting methods under the title devoted to a specific technique or groups of procedures
- Simplify and report what the procedure was
- Report the method by name
- Use third person passive voice, and avoid using first person
- Use normal text in these sections
- Avoid informal lists
- Use complete sentences
Example of a Methods Section
Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association Sixth Ed. 2010
- << Previous: 4. Literature Review
- Next: 6. Results / Analysis >>
- Last Updated: Nov 7, 2023 7:37 AM
- URL: https://wiu.libguides.com/researchpaperwriting
Training videos | Faqs

Materials and Methods Examples and Writing Tips
Abstract | Introduction | Literature Review | Research question | Materials & Methods | Results | Discussion | Conclusion
In this blog, we look at how to write the materials and methods section of a research paper. In most research papers, the materials and methods section follows the literature review section. This is generally the easiest section to write because you are simply reproducing what you did in your experiments. It is always a good idea to start writing your research paper with the materials and methods section.
1. What is the purpose of the materials and methods section?
Materials and methods should describe how you did your research and detail the experimental procedure. One of the most important things to bear in mind while writing the materials and methods section is that it should have enough detail so that other researchers in your field can replicate your experiments and reproduce your results. You should provide all the steps in a logical order so that your readers can follow your description easily.
2. Materials and Methods Examples
The structure of the methods section will very much depend on your discipline. If you are not sure about the structure, then the best place to start will be to go through the methods section of some previously published papers from your chosen journal. We will look at some examples of materials and methods structure in different disciplines.
2.1. Materials & methods example #1 (Engineering paper)
If you are writing an engineering sciences research paper in which you are introducing a new method, your materials and methods section would typically include the following information.
You can start with the top-level summary of the method. You can try to answer these questions. Are you proposing a new method? Or, Are you using a standard method from the literature? Or, Are you extending a previously published method? If so, is it your previous work? or work published by a different author?
Then you can talk about the reasons for choosing this method. You can quote previous papers that have used this method successfully to support your arguments. Then, you can talk about the actual implementation details of the methods.
Then you can talk about how the methods were validated to confirm that they are suitable for your research. You can also include information about any pilot or preliminary studies you conducted before the full study. Then you can explain how you propose to test and evaluate the methods to prove that they are better than the existing methods. Here, you can talk about metrics and statistical tests you will be using to evaluate your method.
2.2. Materials & methods example #2 (Measurement paper)
If you are writing a paper that deals with measurements, you would typically include the following information in your materials and methods section.

You can start by talking about the experimental setup. You can try to answer these questions. What equipment was used to perform the measurements? What was the make and the model of the equipment? How many technicians took the measurements? How experienced were the technicians?
Then you can talk about the parameters that were measured during the experiment. Then you can talk about the actual measurement procedure. How were the samples prepared for the measurements? How many measurements were taken? Were the measurements repeated for consistency? Was there a time interval between successive measurements?
Then you can talk about measurement conditions and constraints. Were the measurements performed at room temperature or under special conditions? Were there any practical difficulties while performing the measurements, if so, how did you overcome them?
Most importantly, you must list all the calculations in the form of detailed equations and formulas so that readers know exactly how the data was produced.
2.3. Materials & methods example #3 (Survey questionnaire paper)
If you are writing a survey questionnaire paper , you would typically include the following information in your materials and methods section.

You can start by talking about your participants. Who is your target population? What are their demographics? How did you recruit them? How did participants provide consent for your study? What sampling method did you use to select the participants?
Then you can talk about the survey type. Was it a phone interview? Was it a personal interview? Was it an online survey? Or, Was it a written survey?
Then you can talk about the questionnaire design. How did you choose the questions? How many questions were there? What type of questions were they? Were they open ended questions, or close ended questions, or rating scale questions, or a mixture of different types of questions?
Then you can talk about how the questionnaire was administered. If it is an online survey, how did you get the questionnaire to the participants? Did you email them? Or did you post the survey forms?
If you are doing a personal interview. How did you conduct the interviews? Was it one to one interview, or was it done in batches, or did you use focus groups? How did the participants behave during the interview?
Then you can talk about questionnaire testing. Did you test your questionnaire before the main study? Did you have to make any changes after initial testing? Did you have to translate the questionnaire into multiple languages? Then finally you can talk about different types of statistical tests you used to analyze the survey responses.
2.4. Materials & methods example #4 (Medical clinical trial paper)
If you are writing a medical research paper , your materials and methods section would typically include the following information.

You can start by providing information about the study design. Was it a randomized trial, or an observational trial? Was it a prospective study, or a retrospective study? Was the study double-blinded, or single-blinded?
Then, you can talk about how the ethical approval was obtained for the study and clarify if the clinical trial was registered. if so, then provide the registration number.
Then, you can talk about how the participants were recruited for the study, and explain the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Then, you can talk about how the participants were grouped into control and placebo groups, and explain how the medication was administered.
Then, you can talk about what outcomes were measured. What was the primary outcome? What was the secondary outcome? What was the follow up period? You can try to answer these questions. Then you can finish off with some information about the statistical tests you used to analyze the data.
3. Frequently Asked Questions
One of the common mistakes people make is using vague language in materials and methods. Reviewers won’t like it, and they will reject the paper on the basis that the section is not elaborate enough for other researchers to reproduce your experiments.
Make sure you write the materials and methods section in past tense, since you are reporting something that has already happened.
Acronyms & Abbrevations: Try to use acronyms and abbreviations for long method names. Abbreviations and acronyms are a great way to make your writing concise and save time. Define the acronyms and abbreviations during their first occurrence then use the short form in the rest of the text. The common practice is to put the acronym and abbreviations in parentheses after the full term.
Use different layouts: Another problem you are likely to face is that your methods section can sound like manual if you have too much text in it. In particular, if you are dealing with a very complex procedure, the readers might find it dry and tedious. So try to provide some variety to the layout. Try to use bullet points and numberings instead of long paragraphs to make it easy for the readers to understand the procedure. You can use flow diagrams to illustrate the process rather than describing it.
When you are using a standard method that is well described in literature, the standard practice is to reference the paper rather than repeating the entire procedure. You can also provide a brief summary of the procedure in your own words.
For example, you can say something like this, “The details of the procedure have been reported previously in…”, and reference the previous paper. And then, you can follow it up with a brief summary of the method from the previous paper.
If you are extending a previous method, then you can do something like this. You can say that, “Some minor modifications were made to the method described in…” and reference the previous paper. And then, you can follow it up with the list of refinements you made to the previous method in order to adapt it to your work.
Similar Posts

Writing a Questionnaire Survey Research Paper – Example & Format
In this blog, we will explain how to write a survey questionnaire paper and discuss all the important points to consider while writing the research paper.

3 Costly Mistakes to Avoid in the Research Introduction
In this blog, we will discuss three common mistakes that beginner writers make while writing the research paper introduction.

Useful Phrases and Sentences for Academic & Research Paper Writing
In this blog, we explain various sections of a research paper and give you an overview of what these sections should contain.

Figures and Tables in Research Papers – Tips and Examples
In this blog, we will look at best practices for presenting tables and figures in your research paper.

Literature Review Examples and Writing Tips
In this blog, we will go through many literature review examples and understand different ways to present past literature in your paper.

Research Methodology – 5 Beginner Writing Mistakes to Avoid
In this blog, we will look at five common mistakes to avoid while writing the methodology section of your research paper.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- 3 Share Facebook
- 1 Share Twitter
- 6 Share LinkedIn
- 3 Share Email
Vous l’avez sans doute déjà repéré : sur la plateforme OpenEdition Books, une nouvelle interface vient d’être mise en ligne. En cas d’anomalies au cours de votre navigation, vous pouvez nous les signaler par mail à l’adresse feedback[at]openedition[point]org.

Français FR
Ressources numériques en sciences humaines et sociales
Nos plateformes
Bibliothèques
Suivez-nous
Redirection vers OpenEdition Search.
- Open Book Publishers ›
- OBP collection ›
- Writing and Publishing Scientific Paper... ›
- Part II. Writing the paper ›
- 10. How to Write the Material and Metho...
- Open Book Publishers
Writing and Publishing Scientific Papers
Ce livre est recensé par
10. How to Write the Material and Methods Section
Plan détaillé, texte intégral.
1 Although traditionally, this section is only called “Material and Methods” (rarely: Study Site, Material and Methods), it can be composed of the following parts: study site, study organism, material, methods, statistical evaluation.
2 The aim of this section in scientific papers is to enable readers to assess the reliability of your work, and to be able to repeat it for verification if they want to do so. Science is about unearthing nature’s laws, and the cornerstone of the scientific method requires that experiments are repeatable: if the experiment is repeated under the same conditions, the same result should be obtained. A material and methods section should give enough detail to evaluate and, if needed, to repeat the experiments reported in the article.
3 You should carefully consider your potential readership. This allows you to provide enough, but not superfluous, information. Once you have reflected on what can be assumed as known by this readership about your setting, organisms, methods, etc., you can give detail accordingly: not too little, and not too much.
4 During peer review, this section is closely scrutinised. If the reviewer is in any doubt that the experiments are repeatable, or that the methods are appropriate, the manuscript will be rejected as unreliable, no matter how wonderful the findings are.
5 When describing your study site, consider your potential readership and give details accordingly (geographical particulars, history of the site, location, co-ordinates, maps). The aim is not to enable the reader to find your sampling plot, but to give a general understanding, a “feel” for the environment you worked in. Information on habitat, with photos, maps, drawings, is often useful, or wholly necessary.
Study Organism
6 Here, you should name all the species, strains, cultivars or races that were used in the experiments. You should also give precise information on their origin, storage or husbandry, including temperatures, photoperiod, feeding regimes, control, etc. Depending on the readership, you should consider giving other background information on life history, and the organism’s distribution in nature. If there is a long list of organisms or strains, consider preparing a table with this information.
7 Here, you should list all the materials necessary for your experiments. Give exact names, not generic or trade names, of chemicals used. Give a source (manufacturer with location) if the chemical in question is delicate (e.g. an enzyme), or rare, or its quality is critical. This would give additional information to the reader. This is, however, neither advertisement nor endorsement (for legal reasons, this should often be made explicit in the paper — see, e.g. the US public organisation policy: disclaimer: “The mention of any trade name does not constitute endorsement by XXX organisation”). For equipment used, give the name, specification/type, manufacturer, and conditions of use.
Sampling Methods and Measurements
8 Here, you should detail the procedures: how did you perform the observations, measurements, experiments? How many times, under what conditions? If you use a new method, give all the details necessary so that the reader can repeat your experiment from reading this section. If you used a published method, a reference to the original publication, preferably the one that first published the method, is usually sufficient with minimum description. If you modified a published method, detail the modification only. If the method is published, you should cite it — but consider where it was published? Is it a frequently used method? When was it published? A rarely-used method, published long ago in an obscure journal, needs a more detailed description than a much-used, current one. If the original publication is not widely available, you will have to provide detailed description. Editors often welcome more detail, especially if the published method is not in very wide use (with the appropriate reference, naturally). If you modified a published method that is widely available, detail the modification only.
9 When describing the procedure, be aware that only SI (Système International) units of measurement are allowed. A few units in common use are not official SI measurements and they cannot be used. Also, be aware of the precise use of measurement units — for example, in common use, weight is often given as grams, kilograms, etc., but these are units of mass, not of weight.
10 Any larger set of samples, measurements, or experiments will have the occasional error, a missing sample, a lost or mislaid tube. Do not keep silent about them. Indicate, clearly, how you dealt with errors, missing data, missing traps. This will not decrease your credibility — on the contrary.
Evaluation Methods/Statistics
11 Data will mostly be evaluated by using a statistical program. In most cases, a reference to the program (indicate the version used) is sufficient; give detail only if the method used is new. However, avoid the neophyte description: what’s new for you may not be new for readers. An experienced colleague can give advice on this matter. In general, it is always a good idea to discuss your chosen statistical method with others. Here, you should give a reason for the choice of statistical test, as well as stating how you tested the eventual conditions for using the chosen test (testing for assumptions for a given statistical test). The mention of the use of a commercial statistical program naturally assumes that you have valid access to the program in question. It is not unheard of program developers to search for the mention of their product in the literature to find out about illegal use.
12 Be careful with details when writing a material and methods section — your reputation is on the line! The reader was not by your side when the studies were done, so she will use the detail and clarity of this section as an indirect indication of your reliability and thoroughness.
13 A common error in this section is not offering enough detail. This does not happen because of the authors’ desire to hide anything — it is simply a mark of routine: many parts of the experimental protocol may become almost routine, and the small details are forgotten as they never change and are taken for granted. When the description is prepared, these details, vital for others, are often not included. A good test is whether a colleague, on reading the section, thinks she can repeat the experiment based on the given description of methods. Such a check is useful, because the writer often is too close to the methods, having done them countless times during the experimental process and, thus, omits some obvious but important, detail.
14 Specifically, take care with numbers, spelling, and punctuation. In this section, many “strange” names will occur: of chemicals, organisms, strains; concentrations, times and units of measurement are important. Meticulousness is the key word here: if you cannot be trusted to do simple things well, such as describing a method that you used hundreds of times, can you expect the readers to trust you when it comes to more significant and complicated aspects of reporting your research?
15 The order of description should be chronological; the description of what was done first should precede the later actions. However, you have to first mention all study sites, then all organisms, followed by a full list of all materials used, experiment-by-experiment and so on. Thus, if someone is only interested in all the details of, for example, your second experiment, she will have to jump from one part of this section to another. This seems a small price to pay for a consistent structure, which is followed by most journals.
16 This section describes your own work and, thus, the past tense is used, mostly, in this section. When describing the details, beware of the syntax. The following description is taken from Day and Gastel’s book (Day and Gastel, 2006), who, tongue-in-cheek, called it “the painful method”: “After standing in hot water for an hour, the flasks were examined”. I hope this was not performed as the sentence implies — probably the flasks, and not the researchers, were standing in hot water that long.
When to Write this Section?
17 It is best to start writing this section first, possibly even while working on the experiments. Otherwise, many details will be lost. Details and precision are vital here, and they are much easier to document during the work, or soon after, than weeks or months later. Additionally, there is often a practical reason, too. Most scientific work is done in teams; it is much easier to convince the team members to write their respective methods section while they are doing the work, or soon afterwards. Once the experiments are completed, and the team moves on to further projects, writing a complete methods section will take longer, and be done less satisfactorily.
18 Meticulousness pays, because, as stated above, reviewers are often of the opinion that if you cannot be trusted in doing simple things, you cannot expect trust in significant and complicated aspects of research. Science, in the view of many of its eminent practitioners is, after all, “99 % perspiration and 1 % inspiration”, so precise work, and the ability to describe things accurately, is a necessary condition of credibility. Science may well comprise a lot of precise work and fewer grand ideas; you prove your mastery of the methods applied by being able to describe them with clarity, in sufficient detail.

Le texte seul est utilisable sous licence Creative Commons - Attribution 4.0 International - CC BY 4.0 . Les autres éléments (illustrations, fichiers annexes importés) sont « Tous droits réservés », sauf mention contraire.

Altering Eye
Contemporary International Cinema
Robert Phillip Kolker

Les Bienveillantes de Jonathan Littell
Murielle Lucie Clément (dir.)

The End of the World
Apocalypse and its Aftermath in Western Culture
Maria Manuel Lisboa

Economic Fables
Ariel Rubinstein

Coleridge’s Laws
A Study of Coleridge in Malta
Barry Hough et Howard Davis

Brownshirt Princess
A Study of the “Nazy Conscience”
Lionel Gossman

The End and the Beginning
The Book of My Life
Hermynia Zur Mühlen

Bourdieu and Literature
John R. W. Speller

Telling Tales
The Impact of Germany on English Children’s Books 1780-1918
David Blamires

That Greece Might Still Be Free
The Philhellenes in the War of Independence
William St Clair

The Theatre of Shelley
Jacqueline Mulhallen

Henry James's Europe
Heritage and Transfer
Dennis Tredy, Annick Duperray et Adrian Harding

Accès ouvert freemium
PDF du chapitre
Édition imprimée
Merci, nous transmettrons rapidement votre demande à votre bibliothèque.
Vérifiez si votre bibliothèque a déjà acquis ce livre : authentifiez-vous à OpenEdition Freemium for Books . Vous pouvez suggérer à votre bibliothèque d’acquérir un ou plusieurs livres publiés sur OpenEdition Books. N’hésitez pas à lui indiquer nos coordonnées : access[at]openedition.org Vous pouvez également nous indiquer, à l’aide du formulaire suivant, les coordonnées de votre bibliothèque afin que nous la contactions pour lui suggérer l’achat de ce livre. Les champs suivis de (*) sont obligatoires.
Veuillez, s’il vous plaît, remplir tous les champs.
La syntaxe de l’email est incorrecte.
Le captcha ne correspond pas au texte.
Ce livre est diffusé en accès ouvert freemium. L’accès à la lecture en ligne est disponible. L’accès aux versions PDF et ePub est réservé aux bibliothèques l’ayant acquis. Vous pouvez vous connecter à votre bibliothèque à l’adresse suivante : https://freemium.openedition.org/oebooks
Si vous avez des questions, vous pouvez nous écrire à access[at]openedition.org
Référence numérique du chapitre
Référence numérique du livre
- SpringerLink shop
Materials and methods
The study’s methods are one of the most important parts used to judge the overall quality of the paper. In addition the Methods section should give readers enough information so that they can repeat the experiments. Reviewers should look for potential sources of bias in the way the study was designed and carried out, and for places where more explanation is needed.
The specific types of information in a Methods section will vary from field to field and from study to study. However, some general rules for Methods sections are:
- It should be clear from the Methods section how all of the data in the Results section were obtained.
- The study system should be clearly described. In medicine, for example, researchers need to specify the number of study subjects; how, when, and where the subjects were recruited, and that the study obtained appropriate ‘informed consent’ documents; and what criteria subjects had to meet to be included in the study.
- In most cases, the experiments should include appropriate controls or comparators. The conditions of the controls should be specified.
- The outcomes of the study should be defined, and the outcome measures should be objectively validated.
- The methods used to analyze the data must be statistically sound.
- For qualitative studies, an established qualitative research method (e.g. grounded theory is often used in sociology) must be used as appropriate for the study question.
- If the authors used a technique from a published study, they should include a citation and a summary of the procedure in the text. The method also needs to be appropriate to the present experiment.
- All materials and instruments should be identified, including the supplier’s name and location. For example, “Tests were conducted with a Vulcanizer 2.0 (XYZ Instruments, Mumbai, India).”
- The Methods section should not have information that belongs in another section (such as the Introduction or Results).
You may suggest if additional experiments would greatly improve the quality of the manuscript. Your suggestions should be in line with the study’s aims. Remember that almost any study could be strengthened by further experiments, so only suggest further work if you believe that the manuscript is not publishable without it.
Back │ Next
How to Write the Material (Patients) and Methods Section
- Open Access
- First Online: 24 October 2021
Cite this chapter
You have full access to this open access chapter

- Samiran Nundy 4 ,
- Atul Kakar 5 &
- Zulfiqar A. Bhutta 6
29k Accesses
1 Citations
In this segment, you should describe exactly and in detail how you did the study so that the readers will be able to (Fig. 19.1):
The method of science is logical and rational; the method of the humanities is one of imagination and sympathetic understanding. Andrew Louth British Theologian (1944–…).
You have full access to this open access chapter, Download chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others


Formulating the Research Question

The Beginning – Historical Aspects of Clinical Research, Clinical Research: Definitions, “Anatomy and Physiology,” and the Quest for “Universal Truth”

What Is a DMC?
1 what should be included in the material and methods section.
In this segment, you should describe exactly and in detail how you did the study so that the readers will be able to (Fig. 19.1 ):
Assess how the research was done.
How they might repeat the study, if they wish to do so [ 1 ].
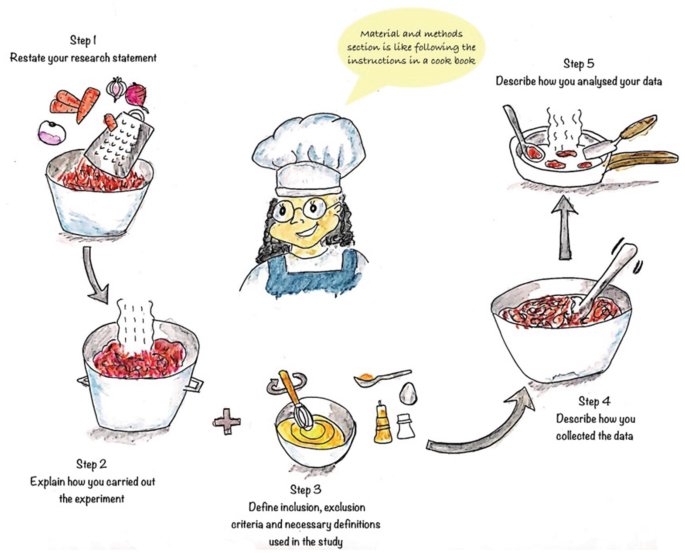
The section should be like following the instructions in a cookbook
You must mention ‘what’, ‘how much’, ‘how often’, ‘where’, ‘when’ and ‘why’ clearly to provide a step-by-step tutorial for your reader. It may not be possible to provide all the technical details while writing this section for a print journal, but these may perhaps be included in an online version of the article.
James Provenzale, in an editorial for American Journal of Roentgenology, stated, ‘One of the more common reasons for rejection of a manuscript is that the reviewers cannot fully understand how the study was conducted’ [ 2 ]. Many journals have page limits for the Materials and Methods section so we would suggest that only important steps should be included. Journals nowadays do provide an electronic access for their articles and all the extra information describing the methodology and results in detail can go into the supplementary online file. Most journals will also ask for clearance from an ethical committee or an Institutional Review Board (IRB) for studies involving human subjects and this should be recorded here.

2 What Are the Important Steps that Should be Followed?
The Material (or preferably Patients if it is a clinical study) is defined as any subjects, matter, investigations, chemicals, drugs or devices which have been included.
The Methods has been defined as the ‘particular procedures for accomplishing or approaching something’.
Describe which experimental animals, patients, volunteers or control subjects will be included. For a drug mention how the drug was taken and through which route it was administered stating the name of the source and the supplier in brackets. For immunological tests the technique used and the name of the manufacturer should be mentioned. The reagents used should also be mentioned in this section. For a surgical technique describe how it was different from a standard one in some detail [ 3 ].
We would recommend a five-step approach for writing this section for a journal. Open this section by stating the research question you wish to answer. Then mention how many patients were screened for the study, the number of patients who fulfilled the criteria for inclusion and how many were excluded. A CONSORT (Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials) flow chart may be a useful guide at this stage (Fig. 19.2 ).
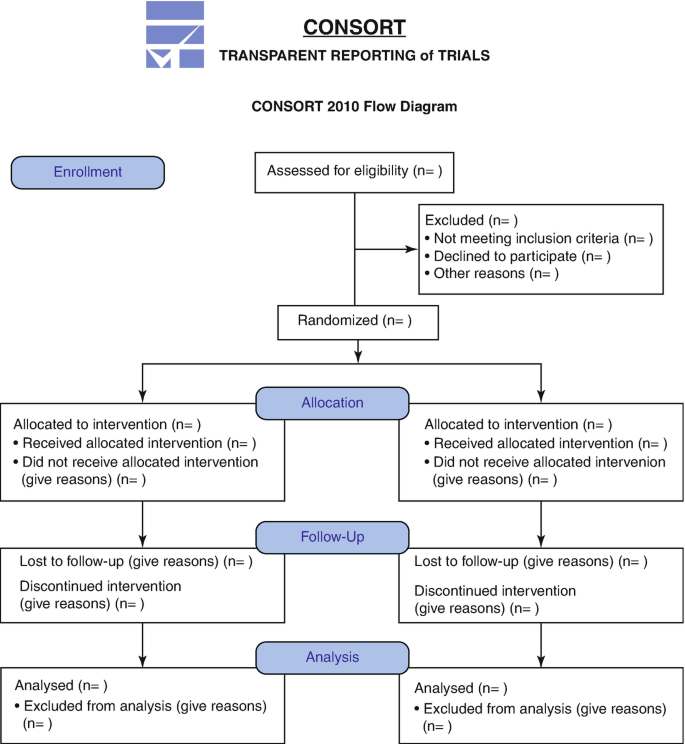
CONSORT Flow chart
3 In Which Tense Should the Methodology Be Written?
All the methodology should be written in the past tense preferably in an active voice [ 4 ]. According, to this you should use verbs like ‘investigated’, ‘evaluated’ or ‘performed’. Recently, terms showing the ownership of the investigation as ‘we performed’, ‘we evaluated’, ‘we implemented’ have taken priority. The communication to the reader should be clear and there should not be any cluttered thought. This section should be written in simple English and should be comprehensive.
4 What Are the Points Which Should Not be Missed in Methodology Section in a Biomedical Research Paper?
These include:
Date of initiation and termination.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Outcome measure with the definitions.
Statistics used.
Type of study design.
5 What Are the Common Errors Seen in this Section?
Many authors write this section as a set of instructions but what is required is a description of the experiments.
Mingling the results with the methods. Results should be discussed and analyzed in a subsequent section.
Including explanatory information and background—save these for the discussion section.
In this section include information relevant to the reader and minute details such as who helped to set up the experiment or who helped to input the data are not relevant. Many journals provide links for supplemental information which is available online but not in the print version.
Writing the pros and cons of the technology used to study the experiment in this section. This should be done in the discussion section.
6 Conclusions
Include in this section ‘What was done, how it was done, how the data was collected, and how the data was analyzed’.
Organize your methodology as what was the first step and then what were the subsequent steps.
Avoid writing stories in the methodology when the same can be conveyed in a flow chart.
Describe in detail the statistics used in the study.
Arceci RJ. The art and science of writing manuscripts. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2004;43:207–10.
Article Google Scholar
Tips for writing material and method section: introduction. Last accessed on 13th August 2020. Available on https://blog.scipress.com/posts/tips-for-writing-material-and-method-section-introduction .
Ng KH, Peh WC. Writing the materials and methods. Singap Med J. 2008;49:856–9.
CAS Google Scholar
Erdemir F. How to write a materials and methods section of a scientific article? Turk J Urol. 2013;39(Suppl 1):10–5.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Surgical Gastroenterology and Liver Transplantation, Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi, India
Samiran Nundy
Department of Internal Medicine, Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi, India
Institute for Global Health and Development, The Aga Khan University, South Central Asia, East Africa and United Kingdom, Karachi, Pakistan
Zulfiqar A. Bhutta
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Open Access This chapter is licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license and indicate if changes were made.
The images or other third party material in this chapter are included in the chapter's Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the chapter's Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Nundy, S., Kakar, A., Bhutta, Z.A. (2022). How to Write the Material (Patients) and Methods Section. In: How to Practice Academic Medicine and Publish from Developing Countries?. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5248-6_19
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5248-6_19
Published : 24 October 2021
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-16-5247-9
Online ISBN : 978-981-16-5248-6
eBook Packages : Medicine Medicine (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Journal of Materials Chemistry C
Research method and mechanism analysis of a novel high-performance quaternary zn–sr–co–sb varistor ceramic.

* Corresponding authors
a School of Environmental and Materials Engineering, Yantai University, 30 Qingquan Road, Yantai, China
b The State Key Lab of High Performance Ceramics and Superfine Microstructure, Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Chinese Academy of Science, Shanghai, China
In this paper, a novel high-performance bismuth-free ZnO varistor ceramic was developed involving only three doping elements: Sr, Co and Sb. To specifically study the role of each element in improving electrical properties, a stepwise research method was used for this novel ceramic employing the binary system of Zn–Sr, ternary system of Zn–Sr–Co and quaternary system of Zn–Sr–Co–Sb. Consequently, a possible mechanism corresponding to each doping element is proposed in this work. Moreover, excellent comprehensive properties consisting of a high nonlinear coefficient α of 74.30, ultra-low leakage current I L of 0.29 μA cm −2 and low breakdown voltage gradient E 1mA of 361.02 V mm −1 are exhibited in the quaternary Zn–Sr–Co–Sb varistor ceramic, which are superior to most advanced ZnO varistors with fewer dopants. This novel quaternary ZnO varistor ceramic without expensive, volatile, deliquescent and toxic dopants exhibits sustainability, environmental friendliness, low cost and high volume development, providing a new perspective for the design of novel high-performance bismuth-free ZnO varistor ceramics.
Article information
Download citation, permissions.
K. Wang, Z. Xu, R. Chu and G. Li, J. Mater. Chem. C , 2024, Advance Article , DOI: 10.1039/D4TC00876F
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content .
Social activity
Search articles by author.
This article has not yet been cited.
Advertisements
- Open access
- Published: 25 April 2024
A scoping review of academic and grey literature on migrant health research conducted in Scotland
- G. Petrie 1 ,
- K. Angus 2 &
- R. O’Donnell 2
BMC Public Health volume 24 , Article number: 1156 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
248 Accesses
8 Altmetric
Metrics details
Migration to Scotland has increased since 2002 with an increase in European residents and participation in the Asylum dispersal scheme. Scotland has become more ethnically diverse, and 10% of the current population were born abroad. Migration and ethnicity are determinants of health, and information on the health status of migrants to Scotland and their access to and barriers to care facilitates the planning and delivery of equitable health services. This study aimed to scope existing peer-reviewed research and grey literature to identify gaps in evidence regarding the health of migrants in Scotland.
A scoping review on the health of migrants in Scotland was carried out for dates January 2002 to March 2023, inclusive of peer-reviewed journals and grey literature. CINAHL/ Web of Science/SocIndex and Medline databases were systematically searched along with government and third-sector websites. The searches identified 2166 journal articles and 170 grey literature documents for screening. Included articles were categorised according to the World Health Organisation’s 2016 Strategy and Action Plan for Refugee and Migrant Health in the European region. This approach builds on a previously published literature review on Migrant Health in the Republic of Ireland.
Seventy-one peer reviewed journal articles and 29 grey literature documents were included in the review. 66% were carried out from 2013 onwards and the majority focused on asylum seekers or unspecified migrant groups. Most research identified was on the World Health Organisation’s strategic areas of right to health of refugees, social determinants of health and public health planning and strengthening health systems. There were fewer studies on the strategic areas of frameworks for collaborative action, preventing communicable disease, preventing non-communicable disease, health screening and assessment and improving health information and communication.
While research on migrant health in Scotland has increased in recent years significant gaps remain. Future priorities should include studies of undocumented migrants, migrant workers, and additional research is required on the issue of improving health information and communication.
Peer Review reports
The term migrant is defined by the International Organisation for Migration as “ a person who moves away from his or her place of usual residence, whether within a country or across an international border, temporarily or permanently, and for a variety of reasons. The term includes several well-defined legal categories of people, including migrant workers; persons whose particular types of movements are legally-defined, such as smuggled migrants; as well as those whose status are not specifically defined under international law, such as international students.” [ 1 ] Internationally there are an estimated 281 million migrants – 3.6% of the world population, including 26.4 million refugees and 4.1 million asylum seekers – the highest number ever recorded [ 2 ]. The UN Refugee Society defines the term refugee as “ someone who has been forced to flee his or her country because of persecution, war or violence…most likely, they cannot return home or are afraid to do so .” The term asylum-seeker is defined as “someone whose request for sanctuary has yet to be processed.” [ 3 ].
Net-migration to Europe was negative in the 19th century due to higher levels of emigration, however in the mid-20th century immigration began to rise, because of an increase in migrant workers and following conflicts in the Middle East and North Africa [ 4 ]. Current migration drivers include conflicts alongside world-wide economic instability, exacerbated by the Covid-19 pandemic [ 5 ]. Environmental damage due to climate change is expected to inflate the number of asylum seekers entering Europe in future [ 6 ]. The increase in migration to Europe is not a short-term influx but a long-term phenomenon, and European nations must adapt and find solutions to resulting financial, safeguarding and health challenges [ 7 ].
Data on healthcare use by migrants in Europe is variable, which means cross-country comparisons are inadequate [ 8 ]. Many countries do not record migration information within health records and all use disparate criteria to classify migrant status. The lack of comparative data hinders public health surveillance and effective interventions [ 9 ]. Even where information is available, results can be contradictory due to the multifarious migrant population. Migrants have a wide range of origin countries, socio-economic position, age and journeys undertaken which can affect health status [ 10 ].
Migrants initially may have better health than the general population, known as the ‘Healthy Migrant effect’ [ 11 ]. However, health declines with increasing length of residence [ 12 ] and over time to levels comparable with the general population [ 13 ]. Second generation immigrants may have higher mortality than average [ 14 ]. The process of acculturation to the host country, with adoption of unhealthy lifestyle and behaviours, increases the risk for chronic disease [ 15 ]. In addition, inequalities in health of migrants compared to host populations has been confirmed by wide-ranging research [ 16 ].
Host countries may limit healthcare access, with undocumented migrants sometimes only entitled to emergency care [ 17 ]. Even when access is granted, inequitable services can affect quality of care due to language barriers and cultural factors [ 18 ]. Poor working/living conditions and discrimination can exacerbate health inequalities [ 12 ]. Processing facilities for asylum seekers are frequently overpopulated, stressful environments [ 19 ] and threat of deportation, lack of citizenship rights and integration can negatively affect health and access to care [ 20 ]. Undocumented workers are unprotected by health and safety legislation leading to dangerous working conditions and injuries [ 15 ].
A systematic review of migrant health in the European Union (EU) found migrants have worse self-perceived health than the general population [ 21 ]. Research evidence indicates increased prevalence of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, mental health disorders and adverse pregnancy outcomes. Exposure to conflict, harsh travel conditions and suboptimal vaccine programmes can mean higher risk of communicable disease [ 22 ]. Scoping reviews have also been conducted to describe trends within migration health research in the United Kingdom (UK) [ 23 ] and identify gaps for future research agendas in the UK [ 23 ] and in the Republic of Ireland [ 24 ].
Almost three-quarters (73%) of published migration health research in the UK has been conducted in England, focusing primarily on infectious diseases and mental health. There is limited evidence on the social determinants of health, access to and use of healthcare and structural and behavioural factors behaviours that influence migrant health in the UK [ 23 ]. By contrast, a large amount of the migration research conducted in the Republic of Ireland has focused on the social determinants of health, and on health system adaptations, with a paucity of research focusing on improving health information systems [ 24 ].
Migration and Health in Scotland
Immigration to Scotland began to rise in 2003 with the expansion of the EU [ 25 ]. The population in Scotland increased from 5.11 million to 5.47 million between 2005 and 2020 and is predicted to continue rising until 2028 [ 26 ] despite low birth rates, with the increased population resulting from inward migration [ 27 ]. Scotland’s population is becoming more ethnically diverse [ 28 ] and susceptibility to different health conditions varies by ethnic group, which has implications for the planning and provision of health services [ 29 ]. 7% of the current Scottish population are non-UK nationals and 10% were born outside Britain. The commonest countries of origin were Poland, Ireland, Italy, Nigeria and India [ 30 ].
Within Scotland, linking health data to ethnicity is standard in order to monitor and improve health of minority groups [ 31 ]. Ethnic background can differ from country of birth which means migration status cannot be assumed [ 32 ], although health inequalities experienced by migrants often extend to affect all ethnic minority groups [ 33 ]. The Scottish Health and Ethnicity Linkage Study (SHELS) linked census data to health records of 91% of the population which has provided information on mortality and morbidity by ethnic group and country of birth [ 34 ]. SHELS research indicates that the white-Scottish population have a higher mortality rate than other ethnic groups. This may be consequent to the comparatively poor health of the Scottish population relative to other European nations: high mortality rates in the general population may cause a perception that the health of minorities is more advantageous than in reality [ 35 ].
Cezard et al’s [ 13 ] analysis of self-perceived health among people in Scotland found that being born abroad had a positive impact on health status. Health declined with increased length of residence, which may be explained by cultural convergence with the majority population. Allik et al. [ 36 ] compared health inequalities by ethnic background and found that with increasing age, health differences reduced thus people aged over 75 of all ethnicities had similar or worse health status than White-Scottish people. While working-age migrants appear to be healthier than the White Scottish population, it cannot be assumed that in future this would extend to older age groups.
Research has shown deprivation as a cause of heath inequalities among ethnic minority and migrant groups [ 37 ]. The socio-economic status of minority ethnic groups in Scotland is unusual, as most are of similar or higher status than the white-Scottish population [ 38 ]. Therefore, public health interventions targeting deprivation may not address risk-factors for ethnic minorities and migrants [ 36 ]. Further research on determinants of health in migrants can help with planning and design of inclusive policies.
The 2011 census indicated that 50% of immigrants lived in the cities of Edinburgh, Glasgow, and Aberdeen. Glasgow had a greater percentage of non-European immigrants due to participation in the Asylum dispersal programme [ 39 ]. 10% of UK asylum seekers are placed in Glasgow, but records are not kept following approval of asylum claims, therefore the size of the refugee population is unknown [ 40 ]. While immigration is controlled by the British government, in policy areas devolved to the Scottish government, refugees and asylum seekers have more rights than elsewhere in UK, including access to primary healthcare for undocumented migrants [ 40 ]. Despite the mitigating effect of Scottish policies, asylum seekers’ health is worsened by the asylum process and associated poverty, marginalisation, and discrimination [ 40 ]. Health deteriorates with increasing length of time in the asylum system [ 40 ] and asylum seekers and refugees have additional health needs and require enhanced support [ 41 ]. Research on the health needs of asylum seekers in Scotland is required to ensure adequate healthcare.
Aim and objectives
While scoping reviews on migrant health have been carried out in Europe [ 12 ], Ireland [ 24 ] and the UK [ 23 ] none are currently specific to the Scottish context. Given the devolved government of Scotland and demographics described above, a targeted review would help to clarify research priorities, with the aim of improving health and health care within the migrant community in Scotland. This work therefore builds on the published scoping review of migrant health in the Republic of Ireland [ 24 ]. The authors recommend replication of the study in other countries to facilitate cross-country comparison. Our aim was to scope peer-reviewed research and grey literature on migrant health conducted in Scotland and identify any gaps in the evidence. Our objectives were to: [1] understand the extent of the available research by topic area [2] summarise the types of research already conducted, populations studied, topics covered and approaches taken [3], map the existing research conducted in Scotland and [4] identify areas for future research based on any gaps in the evidence identified.
A scoping review was conducted as they can aid detection of evidence gaps [ 42 ] and allow incorporation of grey literature in topics with insufficient published research [ 43 ]. Arksey and O’Malley’s [ 44 ] five stage scoping review framework was used.
Stage 1: identifying the research question
Arskey and O’Malley [ 44 ] suggest maintaining a broad approach to identifying the research question, in order to generate breadth of coverage. On this basis, and in line with the research question identified in the Villarroel et al. [ 24 ] scoping review, our research question was framed as follows: What is the scope, main topics and gaps in evidence in the existing literature on health of international migrants living in Scotland? Arksey and O’Malley [ 44 ] highlight the importance of defining terminology at the outset of scoping reviews. For consistency, we used the broad definition of ‘migrant’ as per Villaroel et al. [ 24 ], from the International Organisation for Migration (IOM) [ 1 ]. References to refugees or asylum seekers followed the United Nations Refugee Agency definitions [ 3 ].
Stage 2: identifying relevant studies
Electronic database searches identified reports alongside a grey literature search, in line with Arskey and O’Malley’s [ 44 ] guidance to search for evidence via different sources. CINAHL, Web of Science, SocIndex and Medline academic databases were selected with input from co-authors. Search terms for the review were based upon those used by Villaroel et al. [ 24 ] with additional relevant terms from Hannigan et al. [ 9 ] The strategy combined three sets of terms for: Migrants (e.g., refugee, migrant, immigrant or newcomer), Scotland and Health. Both free text terms and index terms were used and adapted to the 4 academic databases and searches were run on 10th March 2023 (see Additional File 1 for database search strategies). Thirteen Government, University, and third-sector websites in Scotland were scoped for selection then hand-searched for grey literature (listed in Additional File 1 ).
Stage 3: study selection
Net-migration to Scotland increased in the 2000s [ 27 ] hence a date range of January 2002-March 2023 was used to identify evidence. The search was limited to English only. Inclusion/exclusion criteria for the studies were based on those used by Villaroel et al. [ 24 ] and expanded upon following discussion with co-authors (see Table 1 ). Reports were included if based on primary or secondary research on the health of international migrants in Scotland and used qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods research design. International or UK based reports were only included if Scottish results were documented separately. Reports on the health of ethnic minority groups in Scotland was included if place of birth was recorded. Research on internal (non-international) migrants within Scotland, either moving from one Scottish area to another or from another part of the United Kingdom to Scotland, were excluded.
Stage 4: data charting
All records were saved to RefWorks for screening. Records were first screened at title/abstract stage with 10% independently checked by the co-authors. The remaining reports were single screened using full text by the first author. Data from the included records was extracted and organised in tabular form under the following headings, which were agreed by team members: article type (peer-reviewed article or grey literature), publication date, geographical setting, study/intervention’s target population, funding, primary research focus on migrant health (y/n), study objective, data collection method, study design (qualitative/quantitative/mixed) and main finding. Reports were not critically appraised in this scoping review.
Stage 5: collating, summarising and reporting results
A report (either a peer-reviewed journal article or grey literature report) is used as our unit of analysis. In order to present the range of research identified, reports were grouped by the different headings in our data charting table and the outcomes considered for relevance to our scoping review’s aim. Our Results summarise the recency, focus, study designs and funding sources of the identified research, followed by the geographical settings and whether Scotland was included in international research reports. Reports were grouped by their study population and further sub-divided by publication type and geographical area for summarising. Finally, the WHO’s European strategy and action plan (SAAP) for refugee and migrant health [ 7 ] is a policy framework designed to help governments and other stakeholders monitor and improve migrant health in Europe. There are nine strategic areas in the WHO’s SAAP, which prioritise the most salient issues. In line with Villaroel et al’s [ 24 ] approach and in order to compare scoping review outcomes, these areas were used to categorise the findings of this review. Each report was matched to the most appropriate SAAP:
Establishing a Framework for Collaborative Action.
Advocating for the right to health of refugees.
Addressing the social determinants of health.
Achieving public health preparedness and ensuring an effective response.
Strengthening health systems and their resilience.
Preventing communicable disease.
Preventing and reducing the risks caused by non-communicable disease.
Ensuring ethical and effective health screening and assessment.
Improving health information and communication.
The primary focus (aims and objectives) of each report was used to identify the relevant SAAP area/areas. To improve reliability, results were compared using coding criteria used in Villaroel et al’s study (MacFarlane 2023, personal communication, 31st May). 10% of the reports were checked by one co-author to ensure consistent coding to SAAP categories. Any instances of uncertainty in mapping reports to the relevant SAAP area/areas were discussed and resolved by team members.
This scoping review of the literature on migrant health in Scotland identified 2166 records from academic literature databases, following duplicate removal, and 170 records from website searches (see Fig. 1 ). Following screening, a total of 71 peer-reviewed journal articles and 29 grey literature studies (totalling 100 reports) were included for analysis (Results table and reference list are presented in Additional File 2 ).
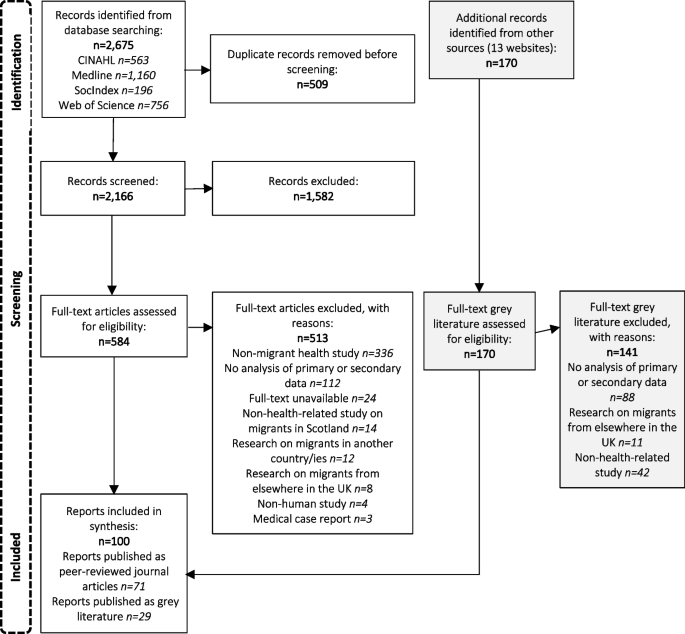
Flow chart illustrating the identification of sources of evidence included in the scoping review
Overall findings
The majority of reports were published between 2013 and 2022. Fifty-eight reports (58%) focused exclusively on migrant health [ 18 , 39 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 64 , 65 , 66 , 67 , 68 , 69 , 70 , 71 , 72 , 73 , 74 , 75 , 76 , 77 , 78 , 79 , 80 , 81 , 82 , 83 , 84 , 85 , 86 , 87 , 88 , 89 , 90 , 91 , 92 , 93 , 94 , 95 , 96 , 97 , 98 , 99 , 100 , 101 , 102 ]. 23 centred on health but included other populations in addition to migrants – for example research on ethnic minorities or other vulnerable groups [ 13 , 31 , 35 , 103 , 104 , 105 , 106 , 107 , 108 , 109 , 110 , 111 , 112 , 113 , 114 , 115 , 116 , 117 , 118 , 119 , 120 , 121 , 122 ]. Seventeen reports were included where the sample population were migrants, but the primary topic was not health – for example destitution, integration, and service needs [ 27 , 73 , 74 , 123 , 124 , 125 , 126 , 127 , 128 , 129 , 130 , 131 , 132 , 133 , 134 , 135 ]. Health data was reported as part of the wider subject matter. One report [ 136 ] looked at the social determinants of breastfeeding including migrant status and one [ 137 ] compared attitudes to aging and family support between countries.
Funding sources were not declared for 35 (35%) of reports. The Scottish Government funded 20 reports (20%) [ 13 , 27 , 32 , 39 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 66 , 77 , 88 , 99 , 100 , 101 , 102 , 113 , 116 , 119 , 121 , 129 , 134 ]. Other common sources of funding included Government funded public bodies ( n = 13) [ 45 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 104 , 107 , 113 , 116 , 131 , 136 ], the Scottish Health Service ( n = 18) (either the National Health Service (NHS) [ 13 , 54 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 102 , 113 , 116 ], local NHS trusts [ 45 , 60 , 61 , 77 , 102 , 103 , 112 ] or by Public Health Scotland [ 13 , 113 ]) Eleven reports (11%) were funded by Universities. The charity sector financed 15 (15%) reports [ 53 , 63 , 66 , 69 , 70 , 71 , 72 , 73 , 74 , 103 , 111 , 123 , 125 , 132 , 138 ] and the EU and Scottish local authorities funded four reports each [ 45 , 62 , 75 , 76 , 77 , 102 , 125 , 135 ]. Professional bodies financed one report [ 126 ] as did the Japanese government [ 64 ]. No reports received funding from the business sector. The biggest sources of funding for grey literature were Refugee charities (40%) and the Scottish government (30%) (see Fig. 2 ).
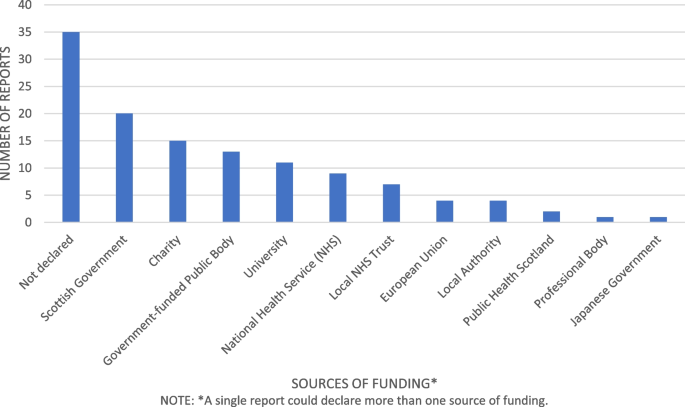
Sources of funding for migrant health research in Scotland
Research methods and data collection
52% of reports used qualitative research methods. Forty-five reports (86%) collected data using 1–1 interviews and 24 (46%) used focus groups. Other methods of data collection included questionnaires (six studies (11%)), workshops (two studies (3.85%)) and observation (two studies (3.85%)). Oral/written evidence, guided play sessions, family case studies and participatory activity sessions were used in one report each.
28% of reports used quantitative research methods, most commonly cross section design (ten studies (36%)) and cohort design (18 studies (64%)). Information was obtained from databases including medical records, Census data and national records in 21 reports (75%). Questionnaires were used in six reports (21%). Other methods including body measurements, food diaries, blood samples, interviews and case reviews were used in 1 report each.
20% of reports used mixed methods. The most common method of data collection was questionnaires in 14 reports (70%), interviews in ten reports (50%), focus groups in seven reports (35%), workshops in three reports (13.6%), and databases in three reports (13.6%). Other methods included literature review in two reports (10%), case note reviews in two reports (10%) and one reports each used mapping and school records.
Geographical areas of study
Ninety-one reports were situated in Scotland, of which 35 (38.5%) covered the whole country and 56 (61.5%) specified a city or area where research was undertaken. Some UK and international reports also specified the area of Scotland. The largest share of research within Scotland overall was in Glasgow with 36 reports, followed by Edinburgh with 16 reports, Lothian with six reports, Aberdeen with five reports and Grampian with three reports. The Northeast, Stirling, Highlands, Inverness, Lanarkshire, Motherwell and Selkirk had one report in each area.
There were seven international reports, three on mortality by country of birth [ 75 , 76 , 78 ], one on cross cultural communication [ 79 ], one on maternity care in Poland and Scotland [ 99 ], one comparing attitudes to aging in China and Scotland [ 137 ] and one on the link between birthweights and integration of migrants [ 64 ]. The remaining two reports were UK based, one on immunisation of Roma and traveller communities [ 117 ] and one on the link between ethnic diversity and mortality [ 104 ]. All the included international and UK reports documented the Scottish data separately within results.
Migrant population
Thirty-one reports included all migrants in the study population. The remaining reports included 30 studies on asylum seekers/refugees, 11 on Polish migrants, ten on Africans, six each on South Asians/Chinese/European, three on Arabs, and two on Roma populations (see Fig. 3 ). Most reports did not specify the country of origin for Asylum seekers and refugees - where country of birth was specified, reports were also included in the appropriate category.
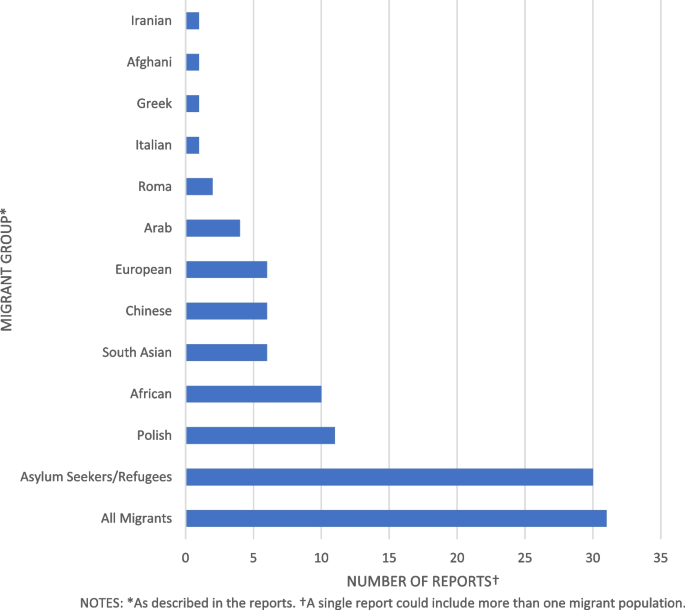
Migrant populations studied in health research in Scotland
Grey literature and peer-reviewed reports differed in population focus. The most common populations of interest in grey literature were asylum seekers/refugees consisting of 18 reports (62%) [ 27 , 47 , 54 , 55 , 59 , 63 , 70 , 71 , 72 , 73 , 74 , 123 , 125 , 127 , 128 , 132 , 134 , 138 ] while for peer-reviewed journals 24 reports (34%) focused on all migrants [ 13 , 35 , 45 , 48 , 64 , 76 , 78 , 79 , 80 , 81 , 104 , 105 , 108 , 109 , 113 , 114 , 115 , 116 , 118 , 120 , 121 , 122 , 136 ].
Migrant study population also differed by local area; Glasgow city, where the majority of research occurred, had 18 reports of 36 (50%) on Asylum seekers/refugees [ 47 , 48 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 58 , 63 , 70 , 71 , 72 , 82 , 83 , 127 , 128 , 130 , 138 , 139 ] eight reports (22%) on Africans [ 52 , 53 , 84 , 85 , 86 , 87 , 106 , 107 ], seven reports (19%) on all migrants [ 45 , 48 , 80 , 102 , 104 , 105 , 121 ] and two reports (5.5%) on Roma migrants [ 103 , 117 ]. Other populations had one reports each. In Edinburgh five reports of 16 (31%) were on the Polish population [ 56 , 67 , 68 , 89 , 90 ], and two reports (12.5%) on Asylum seekers/refugees [ 60 , 133 ], Chinese [ 62 , 137 ], South Asian [ 46 , 119 ], all migrants [ 105 , 121 ] and Africans [ 87 , 107 ]. The remaining migrant groups had one report each. Other areas of Scotland show no clear pattern with studies in disparate migrant population groups.
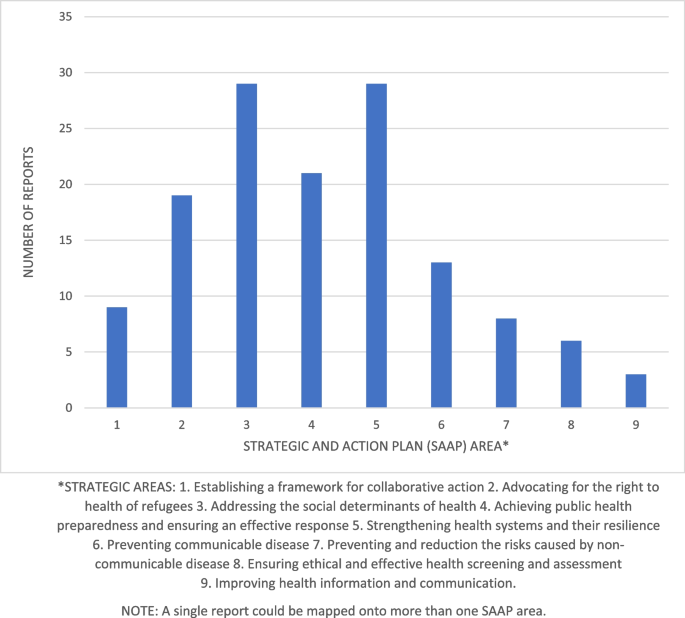
Number of reports per Strategic and Action Plan (SAAP) Area
SAAP Area mapping
1. establishing a framework for collaborative action.
Nine reports had a primary focus on collaborative action and were categorised under SAAP area 1 (see Fig. 4 ) [ 66 , 70 , 72 , 73 , 103 , 125 , 129 , 132 , 134 ]. Four reports (33%) used a mixed methods study design, the remaining five reports (67%) used a qualitative design. One report [ 66 ] focused on the epidemiology of female genital mutilation and a proposed intervention strategy. One report [ 66 ] focused on the epidemiology of female genital mutilation and a proposed intervention strategy. One report [ 103 ] evaluated service provision to the Roma community in Glasgow. The remaining reports focused on refugees and asylum seekers: four [ 73 , 125 , 132 , 134 ] evaluations of refugee integration projects, one [ 70 ] on services available to pregnant women, and one [ 72 ] an assessment of a peer-education service. One report [ 129 ] was a review of service provisions for migrants during the Covid-19 pandemic. All reports in SAAP area 1 were grey literature and three (37.5%) had a primary focus on migrant health while four (50%) focused on integration, one (11%) included data on ethnic minorities and one (11%) on services during the covid-19 pandemic. The majority (seven reports (78%)) were also categorised to another SAAP area most commonly area 2 (five studies (55%)) or area 5 (four studies (44%)).
2. Advocating for the right to health of refugees
Nineteen reports focused on SAAP area 2, advocating for the right to health of refugees (see Fig. 4 ) [ 47 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 63 , 70 , 71 , 83 , 103 , 123 , 124 , 125 , 127 , 128 , 129 , 134 , 138 , 140 ]. Sixteen reports (84%) had a qualitative study design and the remaining three (16%) reports used mixed methods. Nine reports (47%) focused on the health impact of the asylum system [ 52 , 55 , 71 , 74 , 123 , 127 , 128 , 129 , 138 ], five (26%) on health and access to care [ 47 , 54 , 83 , 103 , 124 ], two (10.5%) on maternity care [ 63 , 70 ], two (10.5%) on integration services [ 125 , 134 ] and one report on mental health in HIV positive migrants [ 53 ]. Nine reports (47%) had a primary focus on migrant health while the remaining 10 (53%) also involved wider social issues. The majority (15 (79%)) of reports were grey literature. All the articles in this group overlapped with another SAAP area. Area 3 is the most common joint category with ten reports (53%) followed by area 5 with seven reports (37%), area 1 shares five reports (26%), while areas 4 and 8 share one report each (5%).
3. Addressing the social determinants of health
Twenty-nine reports were categorised to SAAP area 3 – addressing the social determinants of health (see Fig. 4 ) [ 13 , 27 , 45 , 50 , 52 , 55 , 60 , 62 , 63 , 65 , 68 , 71 , 74 , 80 , 81 , 82 , 91 , 92 , 93 , 102 , 112 , 123 , 124 , 127 , 128 , 136 , 137 , 138 ]. The majority (14 (48%)) used a qualitative study method, eight (28%) used quantitative methodology and the remaining seven reports (24%) used mixed methods. Nineteen reports (65.5%) were peer-reviewed journals [ 13 , 45 , 50 , 52 , 60 , 62 , 63 , 65 , 68 , 80 , 81 , 82 , 91 , 92 , 93 , 104 , 112 , 124 , 136 , 137 ] and ten (34.5%) were grey literature [ 27 , 55 , 63 , 71 , 74 , 102 , 123 , 127 , 128 , 138 ]. Ten reports (34.5%) discussed the effects of the asylum system on health [ 27 , 52 , 63 , 71 , 74 , 123 , 124 , 127 , 128 , 137 ] and one (3.5%) migration and health [ 50 ]. Six reports (21%) focused on culture and ethnicity [ 82 , 92 , 102 , 104 , 112 , 137 ], five reports (17%) discussed economic and environmental determinants of health [ 13 , 45 , 67 , 81 , 93 ] and five reports (17%) the health impact of social activities [ 55 , 60 , 62 , 80 , 91 ]. Of the remaining reports, one [ 65 ] discussed Brexit and mental health of European migrants and one discussed the effect of coping strategies on wellbeing in Polish migrants [ 68 ]. Most reports, 18 (62%) had a primary focus on migrant health [ 45 , 50 , 52 , 55 , 60 , 62 , 63 , 65 , 67 , 68 , 71 , 80 , 81 , 82 , 91 , 92 , 93 , 102 ], six reports (21%) discussed wider social factors in addition to health [ 74 , 123 , 124 , 127 , 128 , 138 ]. Of the remaining reports three (10%) looked at ethnic background and country of birth [ 13 , 112 , 136 ], one [ 27 ] included other vulnerable groups and one [ 137 ] included people living in China and Chinese migrants to Scotland. Thirteen reports were also categorised to one or more additional SAAP area - ten (34%) were also applicable to area 2 [ 52 , 55 , 63 , 71 , 74 , 123 , 124 , 127 , 128 , 138 ], three (10%) to area 5 [ 63 , 82 , 92 ] and one (7%) to area 4 [ 27 ].
4. Achieving public health preparedness and ensuring an effective response
Twenty-one reports were assigned to SAAP area 4 (see Fig. 4 ) [ 27 , 31 , 35 , 39 , 47 , 57 , 64 , 75 , 76 , 77 , 78 , 94 , 104 , 108 , 109 , 111 , 113 , 114 , 116 , 120 , 135 ] of which fourteen (67%) used quantitative research methods, four (19%) mixed methods and three (14%) qualitative methods. Thirteen (62%) reports were peer-reviewed journals [ 35 , 59 , 64 , 75 , 78 , 104 , 108 , 109 , 111 , 113 , 114 , 116 , 120 ] and eight (38%) grey literature [ 27 , 31 , 39 , 47 , 57 , 77 , 94 , 135 ]. Most reports (12 (57%)) focused on morbidity and mortality in migrant populations [ 31 , 35 , 64 , 75 , 76 , 78 , 104 , 108 , 109 , 113 , 114 , 116 ]. Six (29%) investigated health status and healthcare needs in migrant groups in Scotland [ 39 , 47 , 57 , 77 , 94 , 135 ]. Two reports (9.5%) analysed the epidemiology of HIV infections [ 111 , 120 ] and the remaining report focused on the health needs of young people during the covid-19 pandemic [ 27 ]. Nine reports (43%) had a primary focus on migrant health [ 39 , 47 , 55 , 64 , 75 , 76 , 77 , 78 , 94 ] while eight (38%) also analysed data by ethnicity [ 31 , 35 , 104 , 108 , 109 , 113 , 114 , 116 ]. Of the remaining reports, three (14%) included other populations within Scotland [ 27 , 111 , 120 ] and one (5%) included other characteristics in addition to health information [ 135 ]. Ten reports (48%) were also categorised to another SAAP area; one to area 2 [ 47 ], one to area 3 [ 27 ], four to area 5 [ 47 , 57 , 77 , 135 ], two to area 6 [ 111 , 120 ] and two to area 9 [ 31 , 108 ].
5. Strengthening health systems and their resilience
Twenty-nine reports were assigned to SAAP area 5 (see Fig. 4 ) [ 18 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 54 , 57 , 63 , 69 , 70 , 72 , 77 , 79 , 82 , 83 , 92 , 95 , 96 , 97 , 99 , 101 , 103 , 118 , 119 , 126 , 129 , 131 , 133 , 135 , 141 ] of which 23 (79%) used qualitative research methods. Three reports used quantitative methods (10.3%) and the remaining three used mixed methods (10.3%). Twelve reports (41%) examined migrants needs and experiences of health care [ 47 , 49 , 54 , 57 , 58 , 77 , 83 , 95 , 103 , 119 , 129 , 135 ], eight (24%) focused on pregnancy and childcare [ 63 , 70 , 92 , 96 , 97 , 99 , 101 , 118 ] and two (7%) on barriers to healthcare access [ 48 , 131 ]. Two reports (7%) evaluated healthcare programmes [ 72 , 133 ] and two focused on communication in primary care [ 79 ] and maternity services [ 69 ]. The remaining three reports (10%) covered sexual health [ 82 ], health information needs of Syrian refugees [ 126 ] and general practitioner training [ 18 ]. Nineteen (65.5%) were peer reviewed journals [ 18 , 48 , 49 , 58 , 69 , 79 , 82 , 83 , 92 , 95 , 96 , 97 , 99 , 101 , 118 , 119 , 125 , 131 , 133 ] and ten (34.5%) were grey literature [ 47 , 54 , 57 , 63 , 70 , 72 , 77 , 103 , 129 , 135 ]. Twenty-one (72%) had a primary focus on migrant health [ 18 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 54 , 57 , 58 , 63 , 69 , 70 , 72 , 77 , 79 , 82 , 83 , 92 , 95 , 96 , 97 , 99 , 101 ]. Six reports (21%) included research on other characteristics or services [ 103 , 126 , 129 , 131 , 133 , 135 ]. The remaining two reports (7%) included ethnic groups as well as migrants in the data [ 118 , 119 ]. Nineteen reports (65.5%) were also assigned to one or more other category areas: five reports (17%) to area 1 [ 47 , 70 , 72 , 103 , 129 ], five reports (17%) to area 2 [ 54 , 63 , 83 , 103 , 129 ], three reports (10%) to area 3 [ 63 , 82 , 92 ], four reports (14%) to area 4 [ 47 , 57 , 77 , 135 ], one (3.5%) to area 7 [ 119 ] and one (3.5%) to area 9 [ 48 ].
6. Preventing communicable diseases
Fourteen reports were assigned to SAAP area 6 (see Fig. 4 ) [ 56 , 61 , 87 , 88 , 89 , 90 , 105 , 106 , 107 , 111 , 115 , 117 , 120 , 122 ] of which four (31%) used quantitative methods, five (38%) used qualitative methods and five (38%) used mixed methods. Five reports (38.5%) examined immunisation behaviour [ 56 , 61 , 89 , 90 , 117 ], five (38%) on epidemiology and treatment of HIV [ 106 , 107 , 111 , 120 , 122 ]. The remaining four reports (31%) focused on tuberculosis in healthcare workers [ 115 ], malaria [ 105 ] and sexual health services [ 87 , 88 ]. Only one reports was grey literature [ 88 ], the remainder were peer-reviewed journals. Six reports (46%) had a primary focus on migrant health [ 56 , 61 , 87 , 88 , 89 , 90 ] while seven reports (54%) also included other at-risk groups in the analysis. Four reports (31%) were also assigned to another SAAP category, two (15%) to area 4 [ 111 , 120 ] and two (15%) to area 8 [ 88 , 115 ].
7. Preventing and reducing the risks posed by non-communicable diseases
Eight reports were categorised to SAAP area 7 (see Fig. 4 ) [ 46 , 51 , 59 , 84 , 85 , 86 , 98 , 119 ] of which six (75%) used qualitative research methods, one (12.5%) used quantitative methods and one (12.5%) used mixed methods. Only one report (12.5%) was grey literature [ 59 ] the remaining seven reports (87.5%) were peer-reviewed journals [ 48 , 87 , 92 , 126 , 127 , 128 , 140 ]. Three reports (37.5%) focused on health behaviours [ 51 , 85 , 98 ], two (25%) on mental health, two (25%) on diabetes and one (12.5%) on chronic disease. Seven reports(87.5%) had a primary focus on migrant health [ 46 , 51 , 59 , 84 , 85 , 86 , 98 ], with the remaining report (12.5%) including ethnic minority groups [ 119 ]. One report (12.5%) was also assigned to SAAP area number 5 [ 119 ].
8. Ensuring ethical and effective health screening and assessment
There were six reports assigned to category 8 (see Fig. 4 ) [ 53 , 88 , 100 , 110 , 115 , 121 ] of which two (33%) used a quantitative research method, three (50%) used a qualitative method and one used mixed methods. One report (14%) was grey literature [ 88 ] the remaining five reports (83%) were peer reviewed journals [ 53 , 100 , 110 , 115 , 121 ]. Three reports (50%) focused on cancer screening in migrant women [ 21 , 100 , 110 ], one (17%) analysed access to HIV testing among African migrants [ 53 ], one (17%) on T.B in healthcare workers [ 72 ] and one (17%) on sexual health [ 36 ]. Three reports (50%) had a primary focus on migrant health [ 53 , 88 , 100 ] while the remaining three reports (50%) included other at-risk groups in the analysis [ 110 , 115 , 121 ]. There were three reports which overlapped with other SAAP areas: one [ 53 ] (17%) was categorised to area 2 while two [ 88 , 115 ] (33%) were categorised to area 6.
9. Improving health information and communication
Three reports were assigned to SAAP area 9 (see Fig. 4 ) [ 31 , 108 , 130 ]. One of these (33%) used a qualitative approach, one (33%) used a quantitative approach and one (33%) used mixed methods. Two [ 108 , 130 ] (66%) were peer-reviewed journal articles and one [ 31 ] (33%) was grey literature. Two reports (66%) focused on improving migrant demographics and health information using databases [ 31 , 108 ] while one (33%) described an information-needs matrix for refugees and asylum seekers [ 130 ]. Two [ 31 , 108 ] included ethnicities in the data while one [ 130 ] had a primary focus on migrant health. Two reports [ 31 , 108 ] (66%) also applied to SAAP area 4 while one report [ 130 ] (33%) was in SAAP area 9 only.
To our knowledge this is the first scoping review conducted on migrant health in Scotland. A previous rapid literature review [ 94 ] found most research focused on health behaviours, mental health, communicable disease and use of and access to healthcare; however, the review limited migrant definition to those who had immigrated within five years and asylum seekers were not included.
In our review, the majority of reports were published from 2013 onwards, aligning with the expansion in migrant research internationally [ 142 ]. 52% used qualitative research methods, 28% used quantitative methods and 20% used mixed methods. 58% focused on migrant health: the remaining papers included other populations or health as part of a wider remit. Research funding was mostly provided by the Scottish Government, NHS, refugee charities and Universities. No studies received funding from the private sector, although this sector has the potential resource and capacity to play a key role in funding future research to improve migrant health in Scotland. Geographically, most studies took place in Glasgow (36%), nationwide (38.5%) or Edinburgh (16%) – other areas were under-represented including Aberdeen (5%), despite being the city with the largest migrant population [ 30 ]. There was a lack of studies in rural localities. These findings concur with a UK migrant health review by Burns et al. [ 23 ] where research was concentrated in larger cities and data was sparse in rural areas relative to the migrant population.
Half of the research identified that was conducted in Glasgow focused on asylum seekers/refugees. Glasgow was previously the only Scottish city to host asylum seekers [ 143 ] and currently supports the most asylum seekers of any local authority in the UK [ 29 ]. In April 2022, the UK government widened the Asylum dispersal scheme to all local authorities [ 144 ]. Around 70% of Scotland’s refugee support services are based in Glasgow and the South-west [ 145 ]. As reduced access to services may impact the health of asylum seekers, research in Glasgow may not be generalizable to other regions of Scotland.
Almost one-third (30%) of all reports focused on asylum seekers and refugees – an overrepresentation given that only 18% of migrants to the UK are asylum seekers [ 146 ] and as low as 2% of all migrants in Scotland [ 147 ]. Asylum seekers and refugees are at risk of poor health due to trauma, difficult journeys, overcrowded camps, poor nutrition and lack of access to healthcare [ 148 ]. They have worse maternity outcomes and increased rates of mental illness [ 149 ]. Increased research on health of asylum seekers and refugees is necessary due to their additional vulnerabilities [ 142 ]. However, asylum seeker’s country of origin was generally not specified. Asylum seekers have heterogenic backgrounds [ 150 ] and nationality and trauma experience affect health status [ 151 ]. Further research focused on specific nationalities of asylum seekers would enhance understanding of the health needs in this population.
Almost one-third (31%) of studies did not specify a migrant group. This concurs with a Norwegian migrant health study by Laue et al. [ 152 ] where 36% of research did not identify country of birth. Where nationality was identified, Polish, African and South Asian were most prevalent. Poles are the largest migrant group in Scotland, however for the other most common immigrant groups of Irish, Italian and Nigerian [ 30 ] there was an absence of research. No studies took place on Nigerian migrants – nine studies indicated African populations, but country of birth was not specified. Since March 2022, 23,000 Ukrainians have migrated to Scotland [ 153 ], however no studies on Ukrainians were identified currently. Research may be underway which is yet to be published.
Only one study explored the impact of Brexit on European migrants’ health despite 56% of migrants to Scotland being EU nationals [ 30 ]. Again, research may be taking place currently, which is yet to be published. No studies involved undocumented migrants despite this populations’ high rates of poor physical/mental health exacerbated by poor housing and working conditions [ 154 ]. An estimated 7.2–9.5% of the workforce in the UK are migrant workers who have higher risks of poor working conditions and injury [ 155 ]. Scotland depends on a migrant workforce for some industries such as agriculture [ 156 ] but only two research papers specified migrant workers.
Most research papers related to the right to health of refugees (SAAP 2), social determinants of health (SAAP 3), public health planning (SAAP 4) and strengthening health systems (SAAP 5). Areas with less research were frameworks for collaborative action (SAAP 1), preventing communicable disease (SAAP 6), preventing non-communicable disease (SAAP 7) and health screening and assessment (SAAP 8). Only three studies related to improving health information and communication (SAAP 9). Lebano et al. [ 12 ] conducted a literature review of migrant health in Europe and found data collection unreliable and disorganised. There is a lack of data on the numbers and types of migrants entering Scotland and research tends not to differentiate between ethnic minorities and migrants [ 94 ]. As poor-quality information hinders surveillance and planning of services SAAP area 9 is an important consideration for increased research.
Villarroel et al. [ 24 ] also found more research in SAAP areas 3 to 5 and less in areas 6 to 9. However, their study returned no results in category 1, collaborative action, or 2, the right to health of refugees, while this study assigned 9% of articles to category 1 and 19% to category 2. Most articles in our study relating to categories 1 and 2 were grey literature, which was excluded from the original Irish scoping review. This highlights a potential difference in the focus of peer-reviewed articles compared to government/refugee charity commissioned reports. Collaborative action and the right to health of refugees and asylum seekers are entwined in Scotland due to the complex policy environment; the social determinants of health such as housing, education, welfare rights and social integration are influenced by a variety of UK and Scottish statutory bodies as well as third sector organisations [ 157 ]. Despite this complexity, organisations work well together [ 158 ]. Further academic research in this area would enhance joint working practices and networks.
A scoping review in the UK [ 23 ] found similar quantities of research corresponding to SAAP areas 3, 2 and 9. However in Scotland areas 1, 5 and 8 were a combined 44% of included papers compared with 27.8% of results on health systems and structures in Burns et al’s [ 23 ] study. Almost half of the articles in SAAP areas 1,5 and 8 were grey literature, which was not included in Burns et al’s [ 23 ] review. Conversely, Burns et al. [ 23 ] found 81.9% of research in the UK related to epidemiology, equivalent to SAAP categories 4,6 and 7. In a Norwegian scoping review of migrant health [ 152 ] 65% of research was related to epidemiological data on health and disease. Only 42% of the research in this current study related to epidemiological data; the quantity of evidence was reduced by excluding combined research from the UK. As Scotland has higher mortality and morbidity than elsewhere in the UK [ 29 ] it is important to undertake further epidemiological research limited to Scotland.
Strengths and weaknesses
Strengths of this review include the use of the WHO’s SAAP categories [ 7 ] to classify data, in accordance with the Villarroel et al’s [ 24 ] study: this means results are linked to policy on migrant health and facilitates comparability to the Irish study results. Additionally results include data on migrant groups, locality, and funding of included papers; these highlight potential omissions for future research consideration. Results include diverse research methods and published and grey literature giving a wide overview of available evidence, reported using the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) checklist (see Additional File 3 ) [ 159 ].
Limitations included the lack of an open-access protocol and search limitations of English language and selected databases. This means some relevant reports may be omitted. Due to time and resource limitations no quality appraisal was planned for included reports. Whilst we did not synthesise the findings for each topic area and migrant group, future systematic reviews could be undertaken to address this limitation and build on this work.
Conclusions
Immigration and ethnic diversity in Scotland have increased since 2002 which is reflected in the expansion of migrant health research. This review highlights evidence gaps including a lack of research in rural areas, undocumented migrants and migrant workers. There is a tendency to cluster asylum seekers together rather than differentiate between national groups. Within the SAAP areas there is less evidence relating to collaborative action, preventing communicable disease, preventing non-communicable disease and health screening and assessment. Further research is required on improving health information and communication for migrant populations in Scotland – a significant omission given the importance of accurate information for health service planning.
Availability of data and materials
All data analysed during this review comes from the papers listed in Additional file 2 .
Abbreviations
European Union
Human Immunodeficiency Virus
National Health Service
Strategy and Action Plan
The Scottish Health and Ethnicity Linkage Study
United Kingdom
World Health Organisation
International Organisation for Migration (IOM). IOM Definition of Migrant. 2024. Available from: https://www.iom.int/about-migration .Cited 2024 Feb 8.
International Organisation for Migration United Nations. World Migration Report. 2022. Available from: available: https://worldmigrationreport.iom.int/wmr-2022-interactive/ .
The United Nations Refugee Angency. Refugee facts: What is a refugee? 2024. Available from: https://www.unrefugees.org/refugee-facts/what-is-a-refugee/ . Cited 2024 Feb 8.
Migration Data Portal. Migration data in Europe. 2023. Available from: https://www.migrationdataportal.org/regional-data-overview/europe#past-and-present-trends . Cited 2023 Aug 22.
International Centre for Migration Policy Development. Migration Outlook 2022 Twelve migration issues to look out for in 2022 Origins, key events and priorities for Europe. 2022. Available from: https://www.icmpd.org/file/download/56783/file/ICMPD%2520Migration%2520Outlook%25202022.pdf .
European Parliament. Exploring migration causes: why people migrate. 2023. Available from: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/news/en/headlines/world/20200624STO81906/exploring-migration-causes-why-people-migrate .
World Health Organisation. Strategic plan: Strategy and Action Plan for Refugee and Migrant Health in the WHO European Region 2016–2022. 2016. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/strategic-plan-strategy-and-action-plan-for-refugee-and-migrant-health-in-the-who-european-region-2016-2022 .
Graetz V, Rechel B, Groot W, Norredam M, Pavlova M. Utilization of health care services by migrants in Europe—a systematic literature review. Br Med Bull. 2017;121(1):5–18. Available from: https://www.academic.oup.com/bmb/article-lookup/doi/10.1093/bmb/ldw057 .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Hannigan A, O'Donnell P, O'Keeffe M, MacFarlane A. How do Variations in Definitions of “Migrant” and their Application Influence the Access of Migrants to Health Care Services? Copenhagen: WHO Regional Office for Europe; 2016. (Health Evidence Network Synthesis Report, No. 46.) Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK391032/ .
Rechel B, Mladovsky P, Ingleby D, Mackenbach JP, McKee M. Migration and health in an increasingly diverse Europe. Lancet. 2013;381(9873):1235–45. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0140673612620868 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Giannoni M, Franzini L, Masiero G. Migrant integration policies and health inequalities in Europe. BMC Public Health. 2016;16(1):463. Available from: http://www.bmcpublichealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12889-016-3095-9 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Lebano A, Hamed S, Bradby H, Gil-Salmerón A, Durá-Ferrandis E, Garcés-Ferrer J, et al. Migrants’ and refugees’ health status and healthcare in Europe: a scoping literature review. BMC Public Health. 2020;20(1):1039. Available from: https://www.bmcpublichealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12889-020-08749-8 .
Cézard G, Finney N, Kulu H, Marshall A. Ethnic differences in self-assessed health in Scotland: The role of socio-economic status and migrant generation. Popul Space Place. 2022;28(3):e2403. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/psp.2403 .
Article Google Scholar
Anson J. The migrant mortality advantage: a 70 month follow-up of the brussels population. Eur J Popul. 2004;20(3):191–218.
World Health Organisation. Health of refugees and migrants. WHO European Region. 2018. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/health-of-refugees-and-migrants---who-european-region-(2018) .
Mladovsky P. A framework for analysing migrant health policies in Europe. Health Policy (New York). 2009;93(1):55–63. Available from: https://www.linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0168851009001444 .
De Vito E, de Waure C, Specchia ML, Parente P, Azzolini E, Frisicale EM, et al. Are undocumented migrants’ entitlements and barriers to healthcare a public health challenge for the European Union? Public Health Rev. 2016;37(1):13. Available from: http://publichealthreviews.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40985-016-0026-3 .
Katikireddi SV, Bhopal R, Quickfall JA. GPs need training and funding in caring for refugees and asylum seekers. BMJ. 2004;328(7442):770.1. Available from: https://www.bmj.com/lookup/doi/10.1136/bmj.328.7442.770 .
Carballo M, Hargreaves S, Gudumac I, Maclean EC. Evolving migrant crisis in Europe: implications for health systems. Lancet Glob Heal. 2017;5(3):e252-253. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2214109X17300402 .
Juárez SP, Honkaniemi H, Dunlavy AC, Aldridge RW, Barreto ML, Katikireddi SV et al. Effects of non-health-targeted policies on migrant health: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob Heal. 2019;7(4):e420–35. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2214109X18305606 .
Nielsen SS, Krasnik A. Poorer self-perceived health among migrants and ethnic minorities versus the majority population in Europe: a systematic review. Int J Public Health. 2010;55(5):357–71. Available from: ( http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00038-010-0145-4 ).
World Health Organsation. World report on the health of refugees and migrants. 2022. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240054462 .
Burns R, Zhang CX, Patel P, Eley I, Campos-Matos I, Aldridge RW. Migration health research in the United Kingdom: a scoping review. J Migr Heal. 2021;4:100061. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2666623521000283 .
Villarroel N, Hannigan A, Severoni S, Puthoopparambil S, MacFarlane A. Migrant health research in the Republic of Ireland: a scoping review. BMC Public Health. 2019;19(1):324. Available from: ( https://bmcpublichealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12889-019-6651-2 ).
Scottish Government. Demographic Change in Scotland. 2010. Available from: https://www.gov.scot/binaries/content/documents/govscot/publications/research-and-analysis/2010/11/demographic-change-scotland/documents/0108163-pdf/0108163-pdf/govscot%3Adocument/0108163.pdf .
National Records of Scotland. Projected Population of Scotland (Interim) 2020-based. 2022. Available from: https://www.nrscotland.gov.uk/files/statistics/population-projections/2020-based/pop-proj-2020-scot-nat-pub.pdf .
Scottish Government. Coronavirus (COVID-19) - experiences of vulnerable children, young people, and parents: research. 2021. Available from: https://www.gov.scot/publications/experiences-vulnerable-children-young-people-parents-during-covid-19-pandemic/ .
Scotland’s Census. Scotland’s Census: Ethnicity. 2011. Available from: https://www.scotlandscensus.gov.uk/census-results/at-a-glance/ethnicity/#:~:text=Scotland’spopulationwas96.0%25 .
Walsh D. The changing ethnic profiles of Glasgow and Scotland, and the implications for population health. 2017. Available from: https://www.gcph.co.uk/assets/0000/6255/The_changing_ethnic_profiles_of_Glasgow_and_Scotland.pdf .
National Records of Scotland. Migration Statistics Quarterly Summary for Scotland. 2021. Available from: https://www.nrscotland.gov.uk/files/statistics/migration/quarterly-summary/miration-statistics-quarterly-summary-february-2021.pdf .
The Scottish Ethnicity and Health Research Strategy Working Group. Health in our Multi-ethnic Scotland Future Research Priorities. 2009. Available from: https://www.healthscotland.scot/media/1842/health-in-our-multi-ethnic-scotland-full-report.pdf .
The Scottish Public Health Observatory. Ethnic minorities: defining ethnicity and race. 2023. Available from: https://www.scotpho.org.uk/population-groups/ethnic-minorities/defining-ethnicity-and-race/ . Cited 2023 Aug 22.
Krasnik A, Bhopal RS, Gruer L, Kumanyika SK. Advancing a unified, global effort to address health disadvantages associated with migration, ethnicity and race. Eur J Public Health. 2018;28(suppl_1). Available from: https://academic.oup.com/eurpub/article/doi/10.1093/eurpub/cky046/4956664 .
Bhopal R, Fischbacher C, Povey C, Chalmers J, Mueller G, Steiner M, et al. Cohort profile: scottish health and ethnicity linkage study of 4.65 million people exploring ethnic variations in disease in Scotland. Int J Epidemiol. 2011;40(5):1168–75. Available from: https://academic.oup.com/ije/article-lookup/doi/10.1093/ije/dyq118 .
Bhopal RS, Gruer L, Cezard G, Douglas A, Steiner MFC, Millard A, et al. Mortality, ethnicity, and country of birth on a national scale, 2001–2013: a retrospective cohort (Scottish Health and Ethnicity Linkage Study). Basu S, editor. Plos Med. 2018;15(3):e1002515. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002515 . Basu S, editor.
Allik M, Brown D, Dundas R, Leyland AH. Differences in ill health and in socioeconomic inequalities in health by ethnic groups: a cross-sectional study using 2011 Scottish census. Ethn Health. 2022;27(1):190–208. https://doi.org/10.1080/13557858.2019.1643009 ( https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/ ).
Watkinson RE, Sutton M, Turner AJ. Ethnic inequalities in health-related quality of life among older adults in England: secondary analysis of a national cross-sectional survey. Lancet Public Hea. 2021;6(3):e145-154.
Fischbacher CM, Cezard G, Bhopal RS, Pearce J, Bansal N. Measures of socioeconomic position are not consistently associated with ethnic differences in cardiovascular disease in Scotland: methods from the Scottish Health and Ethnicity Linkage Study (SHELS). Int J Epidemiol. 2014;43(1):129–39. Available from: https://academic.oup.com/ije/article-lookup/doi/10.1093/ije/dyt237 .
Scottish Government. Characteristics of Recent and Established EEA and non-EEA migrants in Scotland: Analysis of the 2011 Census. 2015. Available from: https://www.gov.scot/publications/characteristics-recent-established-eea-non-eea-migrants-scotland-analysis-2011-census/ .
House of Lords Library. Refugees and asylum-seekers: UK policy. 2022. https://lordslibrary.parliament.uk/refugees-and-asylum-seekers-uk-policy/ .
British Medical Association. Refugee and asylum seeker patient health toolkit. Unique health challenges for refugees and asylum seekers. 2022. Available from: https://www.bma.org.uk/advice-and-support/ethics/refugees-overseas-visitors-and-vulnerable-migrants/refugee-and-asylum-seeker-patient-health-toolkit/unique-health-challenges-for-refugees-and-asylum-seekers .
Khalil H, Peters M, Godfrey CM, McInerney P, Soares CB, Parker D. An evidence-based approach to scoping reviews. Worldviews Evidence-Based Nurs. 2016;13(2):118–23. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1111/wvn.12144 .
Levac D, Colquhoun H, O’Brien KK. Scoping studies: advancing the methodology. Implement Sci. 2010;5(1):69. Available from: ( http://implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1748-5908-5-69 ).
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8(1):19–32.Available from: http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/1364557032000119616 ).
Kearns A, Whitley E, Egan M, Tabbner C, Tannahill C. Healthy migrants in an unhealthy city? The Effects of time on the health of migrants living in deprived areas of glasgow. J Int Migr Integr. 2017;18(3):675–98. Available from: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s12134-016-0497-6 .
PubMed Google Scholar
Porqueddu T. Herbal medicines for diabetes control among Indian and Pakistani migrants with diabetes. Anthropol Med. 2017;24(1):17–31. Available from: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/13648470.2016.1249338 .
Roshan N. Supporting new communities: a qualitative study of health needs among asylum seekers and refugee communities in North Glasgow final report. 2005. Available from: https://www.stor.scot.nhs.uk/handle/11289/579930 .
Piacentini T, O’Donnell C, Phipps A, Jackson I, Stack N. Moving beyond the ‘language problem’: developing an understanding of the intersections of health, language and immigration status in interpreter-mediated health encounters. Lang Intercult Commun. 2019;19(3):256–71. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1353829214001233 .
Sime D. ‘I think that Polish doctors are better’: Newly arrived migrant children and their parents׳ experiences and views of health services in Scotland. Health Place. 2014;30:86–93. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1353829214001233 .
Steven K, Munoz S, Migrants, Matter. Report of a Peer Researched Project on EU Migrant Health in the Highlands of Scotland. University of the Highlands and Islands. 2016. Available from: https://www.spiritadvocacy.org.uk/assets/Birchwood-Highland-HUG-Migrants-Matter-study-2015-2016.pdf .
Anderson AS, Bush H, Lean M, Bradby H, Williams R, Lea E. Evolution of atherogenic diets in South Asian and Italian women after migration to a higher risk region. J Hum Nutr Diet. 2005;18(1):33–43. Available from: ( https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1365-277X.2004.00584.x ).
Isaacs A, Burns N, Macdonald S, O’Donnell CA. ‘I don’t think there’s anything I can do which can keep me healthy’: how the UK immigration and asylum system shapes the health and wellbeing of refugees and asylum seekers in Scotland. Crit Public Health. 2022;32(3):422–32. Available from: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/09581596.2020.1853058 .
Palattiyil G, Sidhva D. Caught in a web of multiple jeopardy: post-traumatic stress disorder and HIV-positive asylum seekers in Scotland. Clin Soc Work J. 2015;43(4):362–74. Available from: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10615-015-0542-5 ).
Abdulkadir J, Azzudin A, Buick A, Curtice L, Dzingisai M, Easton D, et al. What do you mean, I have a right to health? Participatory action research on health and human rights. 2016. Available from: https://strathprints.strath.ac.uk/58209/1/Abdulkadir_etal_IPPI_2016_What_do_you_mean_I_have_a_right_to_health.pdf .
Strang A, Quinn N. Integration or isolation? Mapping social connections and well-being amongst refugees in Glasgow. 2014. Available from: https://eresearch.qmu.ac.uk/bitstream/handle/20.500.12289/4139/eResearch%25204139.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y .
Gorman DR, Bielecki K, Larson HJ, Willocks LJ, Craig J, Pollock KG. Comparing vaccination hesitancy in polish migrant parents who accept or refuse nasal flu vaccination for their children. Vaccine. 2020;38(13):2795–9. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0264410X20302255 .
Love J, Vertigans S, Domaszk E, Zdeb K, Love A, Sutton P. Health & ethnicity in Aberdeenshire: a study of Polish in-migrants; a report for the Scottish Health Council. 2007. Available from: https://rgu-repository.worktribe.com/output/247667 .
O’Donnell CA, Higgins M, Chauhan R, Mullen K. Asylum seekers’ expectations of and trust in general practice: a qualitative study. Br J Gen Pract. 2008;58(557):e1-11. Available from: https://bjgp.org/lookup/doi/10.3399/bjgp08X376104 .
Quinn N, Shirjeel S, Siebelt L, Donnelly R, Pietka E. An evaluation of the sanctuary community conversation programme to address mental health stigma with asylum seekers and refugees in Glasgow. 2011. Available from: https://www.healthscotland.com/uploads/documents/5584-SanctuaryCommunityConversationEvaluation.pdf .
Ager A. Community contact and mental health amongst socially isolated refugees in Edinburgh. J Refug Stud. 2002;15(1):71–80. Available from: https://academic.oup.com/jrs/article-lookup/doi/10.1093/jrs/15.1.71 .
Sim JA, Ulanika AA, Katikireddi SV, Gorman D. Out of two bad choices, I took the slightly better one’: Vaccination dilemmas for Scottish and Polish migrant women during the H1N1 influenza pandemic. Public Health. 2011;125(8):505–11. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0033350611001697 .
Zhao S, Patuano A. International Chinese Students in the UK: association between use of green spaces and lower stress levels. Sustainability. 2021;4(1):89. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/14/1/89 .
Da Lomba S, Murray N. Women and Children First? Refused asylum seekers’ access to and experiences of maternity care in Glasgow. 2014. Available from: https://strathprints.strath.ac.uk/58655/1/Lomba_Murray_SRC_2014_Women_and_Children_First_Refused_Asylum_Seekers_Access_to_and_Experiences.pdf .
Sørbye IK, Vangen S, Juarez SP, Bolumar F, Morisaki N, Gissler M, et al. Birthweight of babies born to migrant mothers - What role do integration policies play? SSM - Popul Heal. 2019;9:100503. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2352827319301971 .
Teodorowski P, Woods R, Czarnecka M, Kennedy C. Brexit, acculturative stress and mental health among EU citizens in Scotland. Popul Space Place. 2021;27(6). Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/psp.2436 .
Baillot H, Murray N, Connelly E, Howard N. Tackling Female Genital Mutilation in Scotland: A Scottish model of intervention. 2014. Available from: https://www.celcis.org/application/files/8116/2185/5421/Tackling_Female_Genital_Mutilation_-_A_Scottish_Model_of_Intervention.pdf .
Weishaar HB. Consequences of international migration: a qualitative study on stress among Polish migrant workers in Scotland. Public Health. 2008;122(11):1250–6. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0033350608000942 .
Weishaar HB. You have to be flexible—coping among polish migrant workers in Scotland. Health Place. 2010;16(5):820–7. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1353829210000432 .
Crowther S, Lau A. Migrant polish women overcoming communication challenges in scottish maternity services: a qualitative descriptive study. Midwifery. 2019;72:30–8. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0266613819300361 .
Fassetta G, Da Lomba S, Quinn N. A healthy start? Experiences of pregnant refugee and asylum seeking women in Scotland. 2016. Available from: https://www.redcross.org.uk/-/media/documents/about-us/research-publications/refugee-support/a-healthy-start-report.pdf .
Positive Action in Housing. 12 months since the Park Inn Tragedy in Glasgow, one in three hotel asylum seekers say their mental health has deteriorated. 2021. Available from: https://www.paih.org/one-in-three-glasgow-asylum-seekers-suffering-depression-and-anxiety .
Strang A. Refugee Peer Education for Health and Well-being. Evaluation Report. 2015. Available from: https://www.scottishrefugeecouncil.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/Peer-Education-Evaluation-Report.pdf .
Strang A, Marsden R, Mignard E. The Holistic Integration Service: Learning and Evaluation Year 1. 2014. Available from: https://www.scottishrefugeecouncil.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/Holistic-Integration-Service-year-1-evaluation-report.pdf .
British Red Cross. How will we survive? Steps to preventing destitution in the asylum system. 2021. Available from: https://www.redcross.org.uk/-/media/documents/about-us/how-will-we-survive-preventing-destitution-in-the-asylum-system.pdf .
Bhopal RS, Rafnsson SB, Agyemang C, Fagot-Campagna A, Giampaoli S, Hammar N, et al. Mortality from circulatory diseases by specific country of birth across six European countries: test of concept. Eur J Public Health. 2012;22(3):353–9. Available from: https://academic.oup.com/eurpub/article-lookup/doi/10.1093/eurpub/ckr062 .
Rafnsson SB, Bhopal RS, Agyemang C, Fagot-Campagna A, Harding S, Hammar N, et al. Sizable variations in circulatory disease mortality by region and country of birth in six European countries. Eur J Public Health. 2013;23(4):594–605. Available from: https://academic.oup.com/eurpub/article-lookup/doi/10.1093/eurpub/ckt023 ).
de Lima P, Masud Chaudhry M, Whelton R, Arshad R. A study of migrant workers in Grampian. 2007. Available from: . http://www.communitiesscotland.gov.uk/stellent/groups/public/%0Adocuments/webpages/pubcs_019731.pdff .
Ikram UZ, Mackenbach JP, Harding S, Rey G, Bhopal RS, Regidor E, et al. All-cause and cause-specific mortality of different migrant populations in Europe. Eur J Epidemiol. 2016;31(7):655–65. Available from: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10654-015-0083-9 .
de Brún T, De-Brún MO, van Weel-Baumgarten E, van Weel C, Dowrick C, Lionis C, et al. Guidelines and training initiatives that support communication in cross-cultural primary-care settings: appraising their implementability using Normalization Process Theory. Fam Pract. 2015;cmv022. Available from: https://academic.oup.com/fampra/article-lookup/doi/10.1093/fampra/cmv022 .
García-Medrano S, Panhofer H. Improving migrant well-being: spontaneous movement as a way to increase the creativity, spontaneity and welfare of migrants in Glasgow. Body Mov Danc Psychother. 2020;15(3):189–203. Available from: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/17432979.2020.1767208 .
Jamil NA, Gray SR, Fraser WD, Fielding S, Macdonald HM. The relationship between vitamin D status and muscle strength in young healthy adults from sunny climate countries currently living in the northeast of Scotland. Osteoporos Int. 2017;28(4):1433–43. Available from: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00198-016-3901-3 .
Kaneoka M, Spence W. The cultural context of sexual and reproductive health support: an exploration of sexual and reproductive health literacy among female Asylum Seekers and Refugees in Glasgow. Int J Migr Heal Soc Care. 2019;16(1):46–64. Available from: https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/IJMHSC-01-2019-0002/full/html .
O’Donnell CA, Higgins M, Chauhan R, Mullen K. They think we’re OK and we know we’re not. A qualitative study of asylum seekers’ access, knowledge and views to health care in the UK. BMC Health Serv Res. 2007;7(1):75. Available from: https://bmchealthservres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1472-6963-7-75 .
Cooper M, Harding S, Mullen K, O’Donnell C. ‘A chronic disease is a disease which keeps coming back … it is like the flu’: chronic disease risk perception and explanatory models among French- and Swahili-speaking African migrants. Ethn Health. 2012;17(6):597–613. Available from: http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/13557858.2012.740003 .
Ezika EA. An exploration of smoking behavior of african male immigrants living in glasgow. Tob Use Insights. 2014;7:TUI .S13262. Available from: http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.4137/TUI.S13262 .
Karadzhov D, White R. Between the whispers of the devil and the revelation of the word : christian clergy’s mental health literacy and pastoral support for BME congregants. J Spiritual Ment Heal. 2020;22(2):147–72. Available from: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/19349637.2018.1537755 ).
Yakubu BD, Simkhada P, van Teijlingen E, Eboh W. Sexual health information and uptake of sexual health services by African women in Scotland: a pilot study. Int J Heal Promot Educ. 2010;48(3):79–84. Available from: http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/14635240.2010.10708186 .
Goff J, Kay K, Lima M, Shallangwa S, We All Have A. Different Consciousness About It: Exploring the Sexual Health Needs of People From African Communities in Scotland. 2021. Available from: https://www.waverleycare.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/We_All_Have_Different_Consciousness_About_It_Report.pdf .
Bielecki K, Craig J, Willocks LJ, Pollock KG, Gorman DR. Impact of an influenza information pamphlet on vaccination uptake among Polish pupils in Edinburgh, Scotland and the role of social media in parental decision making. BMC Public Health. 2020;20(1):1381. Available from: https://bmcpublichealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12889-020-09481-z .
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Gorman DR, Bielecki K, Willocks LJ, Pollock KG. A qualitative study of vaccination behaviour amongst female Polish migrants in Edinburgh, Scotland. Vaccine. 2019;37(20):2741–7. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0264410X19304220 .
Bak-Klimek A, Karatzias T, Elliott L, MacLean R. The determinants of well-being among polish economic immigrants. Testing the sustainable happiness model in migrant population. J Happiness Stud. 2018;19(6):1565–88. Available from: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10902-017-9877-7 .
Cheung NF. The cultural and social meanings of childbearing for Chinese and Scottish women in Scotland. Midwifery. 2002;18(4):279–95. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0266613802903281 .
Papadaki A, Scott J. The impact on eating habits of temporary translocation from a Mediterranean to a Northern European environment. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2002;56(5):455–61. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/1601337 .
McCann A, Mackie P. Improving the Health of Migrants to Scotland: An update for Scottish Directors of Public Health. 2016. Available from: https://www.scotphn.net/wp-content/uploads/2016/04/2016_03_23-Migrant-Health-Report-FINAL-1.pdf .
Ahmed A, Cameron S, Dickson C, Mountain K. Arabic-speaking students’ primary care experiences in Scotland. Community Pract J Community Pract Heal Visit Assoc. 2010;83(2):23–6.
Google Scholar
Bray J, Gorman D, Dundas K, Sim J. Obstetric care of New European migrants in Scotland: an audit of antenatal care, obstetric outcomes and communication. Scott Med J. 2010;55(3):26–31. Available from: ( http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1258/rsmsmj.55.3.26 .
Cheung NF. Choice and control as experienced by Chinese and Scottish childbearing women in Scotland. Midwifery. 2002;18(3):200–13. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0266613802903153 .
Spence W, Zhu L. Perceptions of smoking cessation among Glasgow’s Chinese community. Tob Prev Cessat. 2017;3(October). Available from: http://www.journalssystem.com/tpc/Perceptions-of-smoking-cessation-among-Glasgow-s-Chinese-community,77942,0,2.html .
Gorman DR, Katikireddi SV, Morris C, Chalmers JWT, Sim J, Szamotulska K, et al. Ethnic variation in maternity care: a comparison of Polish and Scottish women delivering in Scotland 2004–2009. Public Health. 2014;128(3):262–7. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0033350613003910 .
Gorman DR, Porteous LA. Influences on Polish migrants’ breast screening uptake in Lothian, Scotland. Public Health. 2018;158:86–92. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0033350617304018 .
Hogg R, de Kok B, Netto G, Hanley J, Haycock-Stuart E. Supporting Pakistani and Chinese families with young children: perspectives of mothers and health visitors. Child Care Health Dev. 2015;41(3):416–23. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/cch.12154 .
Kearns A, Whitley E. Health, Wellbeing and Social Inclusion of Migrants in North Glasgow. 2010. Available from: https://www.gowellonline.com/assets/0000/0521/Health_Wellbeing_and_Social_Inclusion_of_Migrants_in_North_Glasgow.pdf .
Poole L, Adamson K. Report on the Situation of the Roma Community in Govanhill, Glasgow. 2008. Available from: https://www.bemis.org.uk/resources/gt/scotland/reportonthesituationoftheromacommunityingovanhill,Glasgow.pdf .
Schofield L, Walsh D, Feng Z, Buchanan D, Dibben C, Fischbacher C, et al. Does ethnic diversity explain intra-UK variation in mortality? A longitudinal cohort study. BMJ Open. 2019;9(3):e024563. Available from: https://bmjopen.bmj.com/lookup/doi/10.1136/bmjopen-2018-024563 .
Unger HW, McCallum AD, Ukachukwu V, McGoldrick C, Perrow K, Latin G, et al. Imported malaria in Scotland – an overview of surveillance, reporting and trends. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2011;9(6):289–97. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1477893911001074 .
Young I, Flowers P, McDaid LM. Barriers to uptake and use of pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) among communities most affected by HIV in the UK: findings from a qualitative study in Scotland. BMJ Open. 2014;4(11):e005717. Available from: https://bmjopen.bmj.com/lookup/doi/10.1136/bmjopen-2014-005717 .
Young I, Flowers P, McDaid LM. Key factors in the acceptability of treatment as prevention (TasP) in Scotland: a qualitative study with communities affected by HIV. Sex Transm Infect. 2015;91(4):269–74. Available from: https://sti.bmj.com/lookup/doi/10.1136/sextrans-2014-051711 .
Bhopal R, Cm FI, Teiner SM, Halmers CJ, Ovey PC, Amieson J. Ethnicity and health in Scotland: Can we fill the information gap ? A demonstration project focusing on coronary heart disease and linkage of census and health records. Ethics. 2005. Available from: http://www.cphs.mvm.ed.ac.uk/docs/Retrocodingfinalreport.pdf .
Cezard GI, Bhopal RS, Ward HJT, Bansal N, Bhala N. Ethnic variations in upper gastrointestinal hospitalizations and deaths: the Scottish Health and Ethnicity Linkage Study. Eur J Public Health. 2016;26(2):254–60. Available from: https://academic.oup.com/eurpub/article-lookup/doi/10.1093/eurpub/ckv182 .
Christie-de Jong F, Kotzur M, Amiri R, Ling J, Mooney JD, Robb KA. Qualitative evaluation of a codesigned faith-based intervention for muslim women in Scotland to encourage uptake of breast, colorectal and cervical cancer screening. BMJ Open. 2022;12(5):e058739. Available from: https://bmjopen.bmj.com/lookup/doi/10.1136/bmjopen-2021-058739 .
Cree VE, Sidhva D. Children and HIV in Scotland: findings from a cross-sector needs assessment of children and young people infected and affected by HIV in Scotland. Br J Soc Work. 2011;41(8):1586–603. Available from: https://academic.oup.com/bjsw/article-lookup/doi/10.1093/bjsw/bcr036 .
Gallimore A, Irshad T, Cooper M, Cameron S. Influence of culture, religion and experience on the decision of Pakistani women in Lothian, Scotland to use postnatal contraception: a qualitative study. BMJ Sex Reprod Heal. 2021;47(1):43–8. Available from: https://jfprhc.bmj.com/lookup/doi/10.1136/bmjsrh-2019-200497 .
Gruer LD, Cézard GI, Wallace LA, Hutchinson SJ, Douglas AF, Buchanan D, et al. Complex differences in infection rates between ethnic groups in Scotland: a retrospective, national census-linked cohort study of 1.65 million cases. J Public Health (Bangkok). 2022;44(1):60–9. Available from: https://academic.oup.com/jpubhealth/article/44/1/60/6106111 .
Article CAS Google Scholar
Bhala N, Cézard G, Ward HJT, Bansal N, Bhopal R. Ethnic variations in liver- and alcohol-related disease hospitalisations and mortality: the Scottish health and ethnicity linkage study. Alcohol Alcohol. 2016;51(5):593–601. Available from: https://academic.oup.com/alcalc/article-lookup/doi/10.1093/alcalc/agw018 .
Pollock KG, McDonald E, Smith-Palmer A, Johnston F, Ahmed S. Tuberculosis in healthcare workers, Scotland. Scott Med J. 2017;62(3):101–3. Available from: http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/0036933017727963 .
Gruer LD, Millard AD, Williams LJ, Bhopal RS, Katikireddi SV, Cézard GI, et al. Differences in all-cause hospitalisation by ethnic group: a data linkage cohort study of 4.62 million people in Scotland, 2001–2013. Public Health. 2018;161:5–11. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0033350618301501 .
Jackson C, Bedford H, Cheater FM, Condon L, Emslie C, Ireland L, et al. Needles, Jabs and Jags: a qualitative exploration of barriers and facilitators to child and adult immunisation uptake among Gypsies, Travellers and Roma. BMC Public Health. 2017;17(1):254. Available from: http://bmcpublichealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12889-017-4178-y .
John JR, Curry G, Cunningham-Burley S. Exploring ethnic minority women’s experiences of maternity care during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic: a qualitative study. BMJ Open. 2021;11(9):e050666. Available from: https://bmjopen.bmj.com/lookup/doi/10.1136/bmjopen-2021-050666 .
Lawton J, Ahmad N, Hanna L, Douglas M, Hallowell N. Diabetes service provision: a qualitative study of the experiences and views of Pakistani and Indian patients with Type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2006;23(9):1003–7. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1464-5491.2006.01922.x .
Livingston MR, Shaw LE, Codere G, Goldberg DJ. Human immunodeficiency virus acquired heterosexually abroad: expert panel assessment of the indigenous/nonindigenous to the united kingdom status of cases. J Travel Med. 2006;12(1):19–25. Available from: https://academic.oup.com/jtm/article-lookup/doi/10.2310/7060.2005.00005 .
Nelson M, Patton A, Robb K, Weller D, Sheikh A, Ragupathy K, et al. Experiences of cervical screening participation and non-participation in women from minority ethnic populations in Scotland. Heal Expect. 2021;24(4):1459–72. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/hex.13287 .
Noble G, Okpo E, Tonna I, Fielding S. Factors associated with late HIV diagnosis in North-East Scotland: a six-year retrospective study. Public Health. 2016;139:36–43. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0033350616301020 .
Gillespie M. Trapped: Destitution and Asylum in Scotland. 2012. Available from: http://www.rst.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2012/11/Trapped-destitution-and-asylum-summary-final-compressed-pictures.pdf .
Hopkins P, Hill M. The needs and strengths of unaccompanied asylum-seeking children and young people in Scotland. Child Fam Soc Work. 2010;15(4):399–408. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1365-2206.2010.00687.x .
Marsden R, Harris C. “We started life again”: Integration experiences of refugee families reuniting in Glasgow. 2015. Available from: https://www.refworld.org/docid/560cde294.html .
Martzoukou K, Burnett S. Exploring the everyday life information needs and the socio-cultural adaptation barriers of Syrian refugees in Scotland. J Doc. 2018;74(5):1104–32. Available from: https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/JD-10-2017-0142/full/html .
McKenna R. From pillar to post: Destitution among people refused asylum in Scotland. 2019; Available from: https://www.rst.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/From-Pillar-to-Post-Feb-2019.pdf .
Independent Commission of Inquiry. Failings in the provision of care to New Scots during the Covid pandemic: Part 2. 2022. Available from: https://static1.squarespace.com/static/62af1289a666c80e00b17253/t/636b9190408f81778746eaa7/1667994032702/AIS+Phase+2+Report+Full.pdf .
Trevena P, Gawlewicz A, Wright S. Addressing the needs of Scotland’s migrant and minority ethnic populations under Covid-19: lessons for the future. 2022. Available from: https://migrantessentialworkers.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/SC-Migrant-C19-Innovations.pdf .
Oduntan O, Ruthven I. The information needs matrix: a navigational guide for refugee integration. Inf Process Manag. 2019;56(3):791–808. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0306457318306939 .
Sime D, Fox R, Migrant C. Social capital and access to services post-migration: transitions, negotiations and complex agencies. Child Soc. 2015;29(6):524–34. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/chso.12092 .
Strang A, Baillot H, Mignard E. Insights into integration pathways. New Scots and the Holistic Integration Service. A report drawing on year two of the Holistic Integration Service. 2015. Available from: https://scottishrefugeecouncil.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/Holistic-Integration-Service-Year-2-report.pdf .
Weir KEA, Wilson SJ, Gorman DR. The Syrian vulnerable person resettlement programme: evaluation of Edinburgh’s reception arrangements. J Public Health (Bangkok). 2018;40(3):451–60. Available from: https://academic.oup.com/jpubhealth/article/40/3/451/4600209 .
Hammond CN. Scots 2- Engagement analysis of the New Scot Refugee Integration Strategy 2018–2022. 2018. Available from: https://www.gov.scot/binaries/content/documents/govscot/publications/research-and-analysis/2018/06/news-scots-2-engagement-analysis-new-scots-refugee-integration-strategy/documents/00537019-pdf/00537019-pdf/govscot%3Adocument/00537019.pdf .
Blake Stevenson. A8 Nationals in Glasgow. 2007. Available from: http://crosshillandgovanhill.org.uk/grindocs/A8NationalsinGlasgow.pdf .
Ajetunmobi O, Whyte B, Chalmers J, Fleming M, Stockton D, Wood R. Informing the ‘early years’ agenda in Scotland: understanding infant feeding patterns using linked datasets. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2014;68(1):83–92. Available from: https://jech.bmj.com/lookup/doi/10.1136/jech-2013-202718 .
Laidlaw K, Wang D, Coelho C, Power M. Attitudes to ageing and expectations for filial piety across Chinese and British cultures: a pilot exploratory evaluation. Aging Ment Health. 2010;14(3):283–92. Available from: http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/13607860903483060 .
Marsden R, Aldegheri E, Khan A, Lowe M, Strang A, Salinas E, et al. “What’s going on?” A study into destitution and poverty faced by asylum seekers and refugees in Scotland. 2005. Available from: http://www.rst.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2012/11/Whats_going_on_A_study.pdf .
Quinn N. Participatory action research with asylum seekers and refugees experiencing stigma and discrimination: the experience from Scotland. Disabil Soc. 2014;29(1):58–70. Available from: http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/09687599.2013.769863 .
British Red Cross, Refugee Survival Trust. How will we survive? Steps to preventing destitution in the asylum system. 2021. Available from: https://mcusercontent.com/c17c136fc126588cb51e5471d/files/a35dd0e1-d785-f962-6a41-01e928493775/DASS_Research_Report_2021.pdf .
O’Donnell R, Angus K, McCulloch P, Amos A, Greaves L, Semple S. Fathers’ views and experiences of creating a smoke-free home: a scoping review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16(24):5164. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/16/24/5164 .
Sweileh WM, Wickramage K, Pottie K, Hui C, Roberts B, Sawalha AF, et al. Bibliometric analysis of global migration health research in peer-reviewed literature (2000–2016). BMC Public Health. 2018;18(1):777. Available from: https://bmcpublichealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12889-018-5689-x .
Wren K. Supporting asylum seekers and refugees in glasgow: the role of multi-agency networks. J Refug Stud. 2007;20(3):391–413. Available from: https://academic.oup.com/jrs/article-lookup/doi/10.1093/jrs/fem006 .
UK Government Home Office. A Fairer Asylum Accommodation System. 2022. Available from: https://www.emcouncils.gov.uk/write/Migration/Asylum_Dispersal_Factsheet_PDF.pdf .
Scottish Refugee Council. Scotland’s Welcome: an analysis of community support for refugee integration. 2020. Available from https://scottishrefugeecouncil.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/Community-support-analysis-2020.pdf .
Sturge G, UK Parliament House of Commons Library Asylum statistics Research Briefing. 2023. Available from: https://commonslibrary.parliament.uk/research-briefings/sn01403/#:~:text=IntheyearendingJune,ofimmigrantstotheUK .
The Migration Observatory. Where do migrants live in the UK? The Migration Observatory at the University of Oxford. 2022. Available from: https://migrationobservatory.ox.ac.uk/resources/briefings/where-do-migrants-live-in-the-uk .
Pavli A, Maltezou H. Health problems of newly arrived migrants and refugees in Europe. J Travel Med. 2017;24(4). Available from: http://academic.oup.com/jtm/article/doi/10.1093/jtm/tax016/3095987/Health-problems-of-newly-arrived-migrants-and .
Humphris R, Bradby H. Health Status of Refugees and Asylum Seekers in Europe. In: Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Global Public Health. Oxford University Press; 2017. Available from: https://oxfordre.com/publichealth/view/10.1093/acrefore/9780190632366.001.0001/acrefore-9780190632366-e-8 .
Bradby H, Humphris R, Newall D, Phillimore J. Public Health Aspects of Migrant Health: A Review of the Evidence on Health Status for Refugees and Asylum Seekers in the European Region. (Health Evidence Network Synthesis Report, No. 44.) ANNEX 2, DEFINITIONS OF REFUGEES, ASYLUM SEEKERS AND MIGRANTS IN THE LITERATURE. Copenhagen: Eerat; 2015. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK379415/ .
Gerritsen AAM, Bramsen I, Devillé W, van Willigen LHM, Hovens JE, van der Ploeg HM. Physical and mental health of Afghan, Iranian and Somali asylum seekers and refugees living in the Netherlands. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2006;41(1):18–26. Available from: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00127-005-0003-5 .
Laue J, Diaz E, Eriksen L, Risør T. Migration health research in Norway: a scoping review. Scand J Public Health. 2023;51(3):381–90. Available from: http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/14034948211032494 .
Scottish Refugee Council. Ukraine response one year on. 2023. Available from: https://scottishrefugeecouncil.org.uk/ukraine-response-one-year-on/ . Cited 2023 Aug 26.
Woodward A, Howard N, Wolffers I. Health and access to care for undocumented migrants living in the European Union: a scoping review. Health Policy Plan. 2014;29(7):818–30. Available from: https://academic.oup.com/heapol/article-lookup/doi/10.1093/heapol/czt061 .
Simon J, Kiss N, Laszewska A, Mayer S. Public health aspects of migrant health: a review of the evidence on health status for labour migrants in the European Region. Health Evidence Network Synthesis Report 43. 2015. Available from: http://www.epgencms.europarl.europa.eu/cmsdata/upload/114f16b6-1667-44ab-802b-a5a83dd50af0/WHO-HEN-Report-A5-1-Labour-FINAL_EN.pdf .
Scottish Government. Seasonal migrant workers in Scottish agriculture: research report. 2023. Available from: https://www.gov.scot/publications/seasonal-migrant-workers-scottish-agriculture/pages/10/ .
Scottish Government. New Scots: refugee integration strategy 2018–2022. 2018. Available from: https://www.gov.scot/publications/new-scots-refugee-integration-strategy-2018-2022/pages/11/ .
Oliva A, Palavra V, Caloun J. Refugees in Scotland: understanding the policy domain. 2016. Available from: https://www.academia.edu/34097718/REFUGEES_IN_SCOTLAND_UNDERSTANDING_THE_POLICY_DOMAIN .
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467–73. Available from: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M18-0850 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
Thank-you to Professor Anne MacFarlane and PHD student Anne Cronin, of the University of Limerick, Ireland for sharing the coding guidelines currently used in an update to Villarroel et. al’s 2019 study on Migrant Health in the Republic of Ireland.
No funding was received for this work, which was undertaken as G. Petrie’s Master of Public Health dissertation module at the University of Stirling.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Caledonia House, NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde, Glasgow, Scotland, UK
Institute for Social Marketing and Health, Faculty of Health Sciences and Sport, University of Stirling, Stirling, FK9 4LA, Scotland, UK
K. Angus & R. O’Donnell
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
KA, RO and GP finalised the study design collectively. GP conducted the searches, analysis and write up, with support from KA and RO. All three authors read and approved the manuscript prior to submission.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to R. O’Donnell .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1., supplementary material 2., supplementary material 3., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Petrie, G., Angus, K. & O’Donnell, R. A scoping review of academic and grey literature on migrant health research conducted in Scotland. BMC Public Health 24 , 1156 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-18628-1
Download citation
Received : 04 September 2023
Accepted : 16 April 2024
Published : 25 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-18628-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Asylum seekers
- Scoping review
- Research funding
- Immigration
BMC Public Health
ISSN: 1471-2458
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Disclaimer: Early release articles are not considered as final versions. Any changes will be reflected in the online version in the month the article is officially released.
Volume 30, Number 7—July 2024
Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Clade 2.3.4.4b Virus Infection in Domestic Dairy Cattle and Cats, United States, 2024
Suggested citation for this article
We report highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) virus in dairy cattle and cats in Kansas and Texas, United States, which reflects the continued spread of clade 2.3.4.4b viruses that entered the country in late 2021. Infected cattle experienced nonspecific illness, reduced feed intake and rumination, and an abrupt drop in milk production, but fatal systemic influenza infection developed in domestic cats fed raw (unpasteurized) colostrum and milk from affected cows. Cow-to-cow transmission appears to have occurred because infections were observed in cattle on Michigan, Idaho, and Ohio farms where avian influenza virus–infected cows were transported. Although the US Food and Drug Administration has indicated the commercial milk supply remains safe, the detection of influenza virus in unpasteurized bovine milk is a concern because of potential cross-species transmission. Continued surveillance of highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses in domestic production animals is needed to prevent cross-species and mammal-to-mammal transmission.
Highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) viruses pose a threat to wild birds and poultry globally, and HPAI H5N1 viruses are of even greater concern because of their frequent spillover into mammals. In late 2021, the Eurasian strain of H5N1 (clade 2.3.4.4b) was detected in North America ( 1 , 2 ) and initiated an outbreak that continued into 2024. Spillover detections and deaths from this clade have been reported in both terrestrial and marine mammals in the United States ( 3 , 4 ). The detection of HPAI H5N1 clade 2.3.4.4b virus in severe cases of human disease in Ecuador ( 5 ) and Chile ( 6 ) raises further concerns regarding the pandemic potential of specific HPAI viruses.
In February 2024, veterinarians were alerted to a syndrome occurring in lactating dairy cattle in the panhandle region of northern Texas. Nonspecific illness accompanied by reduced feed intake and rumination and an abrupt drop in milk production developed in affected animals. The milk from most affected cows had a thickened, creamy yellow appearance similar to colostrum. On affected farms, incidence appeared to peak 4–6 days after the first animals were affected and then tapered off within 10–14 days; afterward, most animals were slowly returned to regular milking. Clinical signs were commonly reported in multiparous cows during middle to late lactation; ≈10%–15% illness and minimal death of cattle were observed on affected farms. Initial submissions of blood, urine, feces, milk, and nasal swab samples and postmortem tissues to regional diagnostic laboratories did not reveal a consistent, specific cause for reduced milk production. Milk cultures were often negative, and serum chemistry testing showed mildly increased aspartate aminotransferase, gamma-glutamyl transferase, creatinine kinase, and bilirubin values, whereas complete blood counts showed variable anemia and leukocytopenia.
In early March 2024, similar clinical cases were reported in dairy cattle in southwestern Kansas and northeastern New Mexico; deaths of wild birds and domestic cats were also observed within affected sites in the Texas panhandle. In > 1 dairy farms in Texas, deaths occurred in domestic cats fed raw colostrum and milk from sick cows that were in the hospital parlor. Antemortem clinical signs in affected cats were depressed mental state, stiff body movements, ataxia, blindness, circling, and copious oculonasal discharge. Neurologic exams of affected cats revealed the absence of menace reflexes and pupillary light responses with a weak blink response.
On March 21, 2024, milk, serum, and fresh and fixed tissue samples from cattle located in affected dairies in Texas and 2 deceased cats from an affected Texas dairy farm were received at the Iowa State University Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory (ISUVDL; Ames, IA, USA). The next day, similar sets of samples were received from cattle located in affected dairies in Kansas. Milk and tissue samples from cattle and tissue samples from the cats tested positive for influenza A virus (IAV) by screening PCR, which was confirmed and characterized as HPAI H5N1 virus by the US Department of Agriculture National Veterinary Services Laboratory. Detection led to an initial press release by the US Department of Agriculture Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service on March 25, 2024, confirming HPAI virus in dairy cattle ( 7 ). We report the characterizations performed at the ISUVDL for HPAI H5N1 viruses infecting cattle and cats in Kansas and Texas.
Materials and Methods
Milk samples (cases 2–5) and fresh and formalin-fixed tissues (cases 1, 3–5) from dairy cattle were received at the ISUVDL from Texas on March 21 and from Kansas on March 22, 2024. The cattle exhibited nonspecific illness and reduced lactation, as described previously. The tissue samples for diagnostic testing came from 3 cows that were euthanized and 3 that died naturally; all postmortem examinations were performed on the premises of affected farms.
The bodies of 2 adult domestic shorthaired cats from a north Texas dairy farm were received at the ISUVDL for a complete postmortem examination on March 21, 2024. The cats were found dead with no apparent signs of injury and were from a resident population of ≈24 domestic cats that had been fed milk from sick cows. Clinical disease in cows on that farm was first noted on March 16; the cats became sick on March 17, and several cats died in a cluster during March 19–20. In total, >50% of the cats at that dairy became ill and died. We collected cerebrum, cerebellum, eye, lung, heart, spleen, liver, lymph node, and kidney tissue samples from the cats and placed them in 10% neutral-buffered formalin for histopathology.
At ISUVDL, we trimmed, embedded in paraffin, and processed formalin-fixed tissues from affected cattle and cats for hematoxylin/eosin staining and histologic evaluation. For immunohistochemistry (IHC), we prepared 4-µm–thick sections from paraffin-embedded tissues, placed them on Superfrost Plus slides (VWR, https://www.vwr.com ), and dried them for 20 minutes at 60°C. We used a Ventana Discovery Ultra IHC/ISH research platform (Roche, https://www.roche.com ) for deparaffinization until and including counterstaining. We obtained all products except the primary antibody from Roche. Automated deparaffination was followed by enzymatic digestion with protease 1 for 8 minutes at 37°C and endogenous peroxidase blocking. We obtained the primary influenza A virus antibody from the hybridoma cell line H16-L10–4R5 (ATCC, https://www.atcc.org ) and diluted at 1:100 in Discovery PSS diluent; we incubated sections with antibody for 32 minutes at room temperature. Next, we incubated the sections with a hapten-labeled conjugate, Discovery anti-mouse HQ, for 16 minutes at 37°C followed by a 16-minute incubation with the horse radish peroxidase conjugate, Discovery anti-HQ HRP. We used a ChromoMap DAB kit for antigen visualization, followed by counterstaining with hematoxylin and then bluing. Positive controls were sections of IAV-positive swine lung. Negative controls were sections of brain, lung, and eyes from cats not infected with IAV.
We diluted milk samples 1:3 vol/vol in phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4 (Gibco/Thermo Fisher Scientific, https://www.thermofisher.com ) by mixing 1 unit volume of milk and 3 unit volumes of phosphate buffered saline. We prepared 10% homogenates of mammary glands, brains, lungs, spleens, and lymph nodes in Earle’s balanced salt solution (Sigma-Aldrich, https://www.sigmaaldrich.com ). Processing was not necessary for ocular fluid, rumen content, or serum samples. After processing, we extracted samples according to a National Animal Health Laboratory Network (NAHLN) protocol that had 2 NAHLN-approved deviations for ISUVDL consisting of the MagMax Viral RNA Isolation Kit for 100 µL sample volumes and a Kingfisher Flex instrument (both Thermo Fisher Scientific).
We performed real-time reverse transcription PCR (rRT-PCR) by using an NAHLN-approved assay with 1 deviation, which was the VetMAX-Gold SIV Detection kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific), to screen for the presence of IAV RNA. We tested samples along with the VetMAX XENO Internal Positive Control to monitor the possible presence of PCR inhibitors. Each rRT-PCR 96-well plate had 2 positive amplification controls, 2 negative amplification controls, 1 positive extraction control, and 1 negative extraction control. We ran the rRT-PCR on an ABI 7500 Fast thermocycler and analyzed data with Design and Analysis Software 2.7.0 (both Thermo Fisher Scientific). We considered samples with cycle threshold (Ct) values <40.0 to be positive for virus.
After the screening rRT-PCR, we analyzed IAV RNA–positive samples for the H5 subtype and H5 clade 2.3.4.4b by using the same RNA extraction and NAHLN-approved rRT-PCR protocols as described previously, according to standard operating procedures. We performed PCR on the ABI 7500 Fast thermocycler by using appropriate controls to detect H5-specific IAV. We considered samples with Ct values <40.0 to be positive for the IAV H5 subtype.
We conducted genomic sequencing of 2 milk samples from infected dairy cattle from Texas and 2 tissue samples (lung and brain) from cats that died at a different Texas dairy. We subjected the whole-genome sequencing data to bioinformatics analysis to assemble the 8 different IAV segment sequences according to previously described methods ( 8 ). We used the hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA) sequences for phylogenetic analysis. We obtained reference sequences for the HA and NA segments of IAV H5 clade 2.3.4.4 from publicly available databases, including GISAID ( https://www.gisaid.org ) and GenBank. We aligned the sequences by using MAFFT version 7.520 software ( https://mafft.cbrc.jp/alignment/server/index.html ) to create multiple sequence alignments for subsequent phylogenetic analysis. We used IQTree2 ( https://github.com/iqtree/iqtree2 ) to construct the phylogenetic tree from the aligned sequences. The software was configured to automatically identify the optimal substitution model by using the ModelFinder Plus option, ensuring the selection of the most suitable model for the dataset and, thereby, improving the accuracy of the reconstructed tree. We visualized the resulting phylogenetic tree by using iTOL ( https://itol.embl.de ), a web-based platform for interactive tree exploration and annotation.
Gross Lesions in Cows and Cats
All cows were in good body condition with adequate rumen fill and no external indications of disease. Postmortem examinations of the affected dairy cows revealed firm mammary glands typical of mastitis; however, mammary gland lesions were not consistent. Two cows that were acutely ill before postmortem examination had grossly normal milk and no abnormal mammary gland lesions. The gastrointestinal tract of some cows had small abomasal ulcers and shallow linear erosions of the intestines, but those observations were also not consistent in all animals. The colon contents were brown and sticky, suggesting moderate dehydration. The feces contained feed particles that appeared to have undergone minimal ruminal fermentation. The rumen contents had normal color and appearance but appeared to have undergone minimal fermentation.
The 2 adult cats (1 intact male, 1 intact female) received at the ISUVDL were in adequate body and postmortem condition. External examination was unremarkable. Mild hemorrhages were observed in the subcutaneous tissues over the dorsal skull, and multifocal meningeal hemorrhages were observed in the cerebrums of both cats. The gastrointestinal tracts were empty, and no other gross lesions were observed.
Microscopic Lesions in Cows and Cats
Figure 1 . Mammary gland lesions in cattle in study of highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b virus infection in domestic dairy cattle and cats, United States, 2024. A, B) Mammary gland...
The chief microscopic lesion observed in affected cows was moderate acute multifocal neutrophilic mastitis ( Figure 1 ); however, mammary glands were not received from every cow. Three cows had mild neutrophilic or lymphocytic hepatitis. Because they were adult cattle, other observed microscopic lesions (e.g., mild lymphoplasmacytic interstitial nephritis and mild to moderate lymphocytic abomasitis) were presumed to be nonspecific, age-related changes. We did not observe major lesions in the other evaluated tissues. We performed IHC for IAV antigen on all evaluated tissues; the only tissues with positive immunoreactivity were mastitic mammary glands from 2 cows that showed nuclear and cytoplasmic labeling of alveolar epithelial cells and cells within lumina ( Figure 1 ) and multifocal germinal centers within a lymph node from 1 cow ( Table 1 ).
Figure 2 . Lesions in cat tissues in study of highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b virus infection in domestic dairy cattle and cats, United States, 2024. Tissue sections were stained with...
Both cats had microscopic lesions consistent with severe systemic virus infection, including severe subacute multifocal necrotizing and lymphocytic meningoencephalitis with vasculitis and neuronal necrosis, moderate subacute multifocal necrotizing and lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia, moderate to severe subacute multifocal necrotizing and lymphohistiocytic myocarditis, and moderate subacute multifocal lymphoplasmacytic chorioretinitis with ganglion cell necrosis and attenuation of the internal plexiform and nuclear layers ( Table 2 ; Figure 2 ). We performed IHC for IAV antigen on multiple tissues (brain, eye, lung, heart, spleen, liver, and kidney). We detected positive IAV immunoreactivity in brain (intracytoplasmic, intranuclear, and axonal immunolabeling of neurons), lung, and heart, and multifocal and segmental immunoreactivity within all layers of the retina ( Figure 2 ).
PCR Data from Cows and Cats
We tested various samples from 8 clinically affected mature dairy cows by IAV screening and H5 subtype-specific PCR ( Table 3 ). Milk and mammary gland homogenates consistently showed low Ct values: 12.3–16.9 by IAV screening PCR, 17.6–23.1 by H5 subtype PCR, and 14.7–20.0 by H5 2.3.4.4 clade PCR (case 1, cow 1; case 2, cows 1 and 2; case 3, cow 1; and case 4, cow 1). We forwarded the samples to the National Veterinary Services Laboratory, which confirmed the virus was an HPAI H5N1 virus strain.
When available, we also tested tissue homogenates (e.g., lung, spleen, and lymph nodes), ocular fluid, and rumen contents from 6 cows by IAV and H5 subtype-specific PCR ( Table 3 ). However, the PCR findings were not consistent. For example, the tissue homogenates and ocular fluid tested positive in some but not all cows. In case 5, cow 1, the milk sample tested negative by IAV screening PCR, but the spleen homogenate tested positive by IAV screening, H5 subtype, and H5 2.3.4.4 PCR. For 2 cows (case 3, cow 1; and case 4, cow 1) that had both milk and rumen contents available, both samples tested positive for IAV. Nevertheless, all IAV-positive nonmammary gland tissue homogenates, ocular fluid, and rumen contents had markedly elevated Ct values in contrast to the low Ct values for milk and mammary gland homogenate samples.
We tested brain and lung samples from the 2 cats (case 6, cats 1 and 2) by IAV screening and H5 subtype-specific PCR ( Table 3 ). Both sample types were positive by IAV screening PCR; Ct values were 9.9–13.5 for brain and 17.4–24.4 for lung samples, indicating high amounts of virus nucleic acid in those samples. The H5 subtype and H5 2.3.4.4 PCR results were also positive for the brain and lung samples; Ct values were consistent with the IAV screening PCR ( Table 3 ).
Phylogenetic Analyses
We assembled the sequences of all 8 segments of the HPAI viruses from both cow milk and cat tissue samples. We used the hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA) sequences specifically for phylogenetic analysis to delineate the clade of the HA gene and subtype of the NA gene.

Figure 3 . Phylogenetic analysis of hemagglutinin gene sequences in study of highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b virus infection in domestic dairy cattle and cats, United States, 2024. Colors indicate different...
For HA gene analysis, both HA sequences derived from cow milk samples exhibited a high degree of similarity, sharing 99.88% nucleotide identity, whereas the 2 HA sequences from cat tissue samples showed complete identity at 100%. The HA sequences from the milk samples had 99.94% nucleotide identities with HA sequences from the cat tissues, resulting in a distinct subcluster comprising all 4 HA sequences, which clustered together with other H5N1 viruses belonging to clade 2.3.4.4b ( Figure 3 ). The HA sequences were deposited in GenBank (accession nos. PP599465 [case 2, cow 1], PP599473 [case 2, cow 2], PP692142 [case 6, cat 1], and PP692195 [case 6, cat 2]).

Figure 4 . Phylogenetic analysis of neuraminidase gene sequences in study of highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b virus infection in domestic dairy cattle and cats, United States, 2024. Colors indicate different...
For NA gene analysis, the 2 NA sequences obtained from cow milk samples showed 99.93% nucleotide identity. Moreover, the NA sequences derived from the milk samples exhibited complete nucleotide identities (100%) with those from the cat tissues. The 4 NA sequences were grouped within the N1 subtype of HPAI viruses ( Figure 4 ). The NA sequences were deposited in GenBank (accession nos. PP599467 [case 2, cow 1], PP599475 [case 2, cow 2], PP692144 [case 6, cat 1], and PP692197 [case 6, cat 2]).
This case series differs from most previous reports of IAV infection in bovids, which indicated cattle were inapparently infected or resistant to infection ( 9 ). We describe an H5N1 strain of IAV in dairy cattle that resulted in apparent systemic illness, reduced milk production, and abundant virus shedding in milk. The magnitude of this finding is further emphasized by the high death rate (≈50%) of cats on farm premises that were fed raw colostrum and milk from affected cows; clinical disease and lesions developed that were consistent with previous reports of H5N1 infection in cats presumably derived from consuming infected wild birds ( 10 – 12 ). Although exposure to and consumption of dead wild birds cannot be completely ruled out for the cats described in this report, the known consumption of unpasteurized milk and colostrum from infected cows and the high amount of virus nucleic acid within the milk make milk and colostrum consumption a likely route of exposure. Therefore, our findings suggest cross-species mammal-to-mammal transmission of HPAI H5N1 virus and raise new concerns regarding the potential for virus spread within mammal populations. Horizontal transmission of HPAI H5N1 virus has been previously demonstrated in experimentally infected cats ( 13 ) and ferrets ( 14 ) and is suspected to account for large dieoffs observed during natural outbreaks in mink ( 15 ) and sea lions ( 16 ). Future experimental studies of HPAI H5N1 virus in dairy cattle should seek to confirm cross-species transmission to cats and potentially other mammals.
Clinical IAV infection in cattle has been infrequently reported in the published literature. The first report occurred in Japan in 1949, where a short course of disease with pyrexia, anorexia, nasal discharge, pneumonia, and decreased lactation developed in cattle ( 17 ). In 1997, a similar condition occurred in dairy cows in southwest England leading to a sporadic drop in milk production ( 18 ), and IAV seroconversion was later associated with reduced milk yield and respiratory disease ( 19 – 21 ). Rising antibody titers against human-origin influenza A viruses (H1N1 and H3N2) were later again reported in dairy cattle in England, which led to an acute fall in milk production during October 2005–March 2006 ( 22 ). Limited reports of IAV isolation from cattle exist; most reports occurred during the 1960s and 1970s in Hungary and in the former Soviet Union, where H3N2 was recovered from cattle experiencing respiratory disease ( 9 , 23 ). Direct detection of IAV in milk and the potential transmission from cattle to cats through feeding of unpasteurized milk has not been previously reported.
An IAV-associated drop in milk production in dairy cattle appears to have occurred during > 4 distinct periods and within 3 widely separated geographic areas: 1949 in Japan ( 17 ), 1997–1998 and 2005–2006 in Europe ( 19 , 21 ), and 2024 in the United States (this report). The sporadic occurrence of clinical disease in dairy cattle worldwide might be the result of changes in subclinical infection rates and the presence or absence of sufficient baseline IAV antibodies in cattle to prevent infection. Milk IgG, lactoferrin, and conglutinin have also been suggested as host factors that might reduce susceptibility of bovids to IAV infection ( 9 ). Contemporary estimates of the seroprevalence of IAV antibodies in US cattle are not well described in the published literature. One retrospective serologic survey in the United States in the late 1990s showed 27% of serum samples had positive antibody titers and 31% had low-positive titers for IAV H1 subtype-specific antigen in cattle with no evidence of clinical infections ( 24 ). Antibody titers for H5 subtype-specific antigen have not been reported in US cattle.
The susceptibility of domestic cats to HPAI H5N1 is well-documented globally ( 10 – 12 , 25 – 28 ), and infection often results in neurologic signs in affected felids and other terrestrial mammals ( 4 ). Most cases in cats result from consuming infected wild birds or contaminated poultry products ( 12 , 27 ). The incubation period in cats is short; clinical disease is often observed 2–3 days after infection ( 28 ). Brain tissue has been suggested as the best diagnostic sample to confirm HPAI virus infection in cats ( 10 ), and our results support that finding. One unique finding in the cats from this report is the presence of blindness and microscopic lesions of chorioretinitis. Those results suggest that further investigation into potential ocular manifestations of HPAI H5N1 virus infection in cats might be warranted.
The genomic sequencing and subsequent analysis of clinical samples from both bovine and feline sources provided considerable insights. The HA and NA sequences derived from both bovine milk and cat tissue samples from different Texas farms had a notable degree of similarity. Those findings strongly suggest a shared origin for the viruses detected in the dairy cattle and cat tissues. Further research, case series investigations, and surveillance data are needed to better understand and inform measures to curtail the clinical effects, shedding, and spread of HPAI viruses among mammals. Although pasteurization of commercial milk mitigates risks for transmission to humans, a 2019 US consumer study showed that 4.4% of adults consumed raw milk > 1 time during the previous year ( 29 ), indicating a need for public awareness of the potential presence of HPAI H5N1 viruses in raw milk.
Ingestion of feed contaminated with feces from wild birds infected with HPAI virus is presumed to be the most likely initial source of infection in the dairy farms. Although the exact source of the virus is unknown, migratory birds (Anseriformes and Charadriiformes) are likely sources because the Texas panhandle region lies in the Central Flyway, and those birds are the main natural reservoir for avian influenza viruses ( 30 ). HPAI H5N1 viruses are well adapted to domestic ducks and geese, and ducks appear to be a major reservoir ( 31 ); however, terns have also emerged as an important source of virus spread ( 32 ). The mode of transmission among infected cattle is also unknown; however, horizontal transmission has been suggested because disease developed in resident cattle herds in Michigan, Idaho, and Ohio farms that received infected cattle from the affected regions, and those cattle tested positive for HPAI H5N1 ( 33 ). Experimental studies are needed to decipher the transmission routes and pathogenesis (e.g., replication sites and movement) of the virus within infected cattle.
In conclusion, we showed that dairy cattle are susceptible to infection with HPAI H5N1 virus and can shed virus in milk and, therefore, might potentially transmit infection to other mammals via unpasteurized milk. A reduction in milk production and vague systemic illness were the most commonly reported clinical signs in affected cows, but neurologic signs and death rapidly developed in affected domestic cats. HPAI virus infection should be considered in dairy cattle when an unexpected and unexplained abrupt drop in feed intake and milk production occurs and for cats when rapid onset of neurologic signs and blindness develop. The recurring nature of global HPAI H5N1 virus outbreaks and detection of spillover events in a broad host range is concerning and suggests increasing virus adaptation in mammals. Surveillance of HPAI viruses in domestic production animals, including cattle, is needed to elucidate influenza virus evolution and ecology and prevent cross-species transmission.
Dr. Burrough is a professor and diagnostic pathologist at the Iowa State University College of Veterinary Medicine and Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory. His research focuses on infectious diseases of livestock with an emphasis on swine.
Acknowledgment
We thank the faculty and staff at the ISUVDL who contributed to the processing and analysis of clinical samples in this investigation, the veterinarians involved with clinical assessments at affected dairies and various conference calls in the days before diagnostic submissions that ultimately led to the detection of HPAI virus in the cattle, and the US Department of Agriculture National Veterinary Services Laboratory and NAHLN for their roles and assistance in providing their expertise, confirmatory diagnostic support, and communications surrounding the HPAI virus cases impacting lactating dairy cattle.
- Caliendo V , Lewis NS , Pohlmann A , Baillie SR , Banyard AC , Beer M , et al. Transatlantic spread of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 by wild birds from Europe to North America in 2021. Sci Rep . 2022 ; 12 : 11729 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Bevins SN , Shriner SA , Cumbee JC Jr , Dilione KE , Douglass KE , Ellis JW , et al. Intercontinental movement of highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4 virus to the United States, 2021. Emerg Infect Dis . 2022 ; 28 : 1006 – 11 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Puryear W , Sawatzki K , Hill N , Foss A , Stone JJ , Doughty L , et al. Highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) virus outbreak in New England seals, United States. Emerg Infect Dis . 2023 ; 29 : 786 – 91 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Elsmo EJ , Wünschmann A , Beckmen KB , Broughton-Neiswanger LE , Buckles EL , Ellis J , et al. Highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) virus clade 2.3.4.4b infections in wild terrestrial mammals, United States, 2022. Emerg Infect Dis . 2023 ; 29 : 2451 – 60 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Bruno A , Alfaro-Núñez A , de Mora D , Armas R , Olmedo M , Garcés J , et al. First case of human infection with highly pathogenic H5 avian influenza A virus in South America: a new zoonotic pandemic threat for 2023? J Travel Med. 2023 ;30:taad032.
- Pulit-Penaloza JA , Brock N , Belser JA , Sun X , Pappas C , Kieran TJ , et al. Highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) virus of clade 2.3.4.4b isolated from a human case in Chile causes fatal disease and transmits between co-housed ferrets. Emerg Microbes Infect . 2024 ; 2332667 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- United States Department of Agriculture Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service . Federal and state veterinary, public health agencies share update on HPAI detection in Kansas, Texas dairy herds. 2024 [ cited 2024 Mar 29 ]. https://www.aphis.usda.gov/news/agency-announcements/federal-state-veterinary-public-health-agencies-share-update-hpai
- Sharma A , Zeller MA , Souza CK , Anderson TK , Vincent AL , Harmon K , et al. Characterization of a 2016–2017 human seasonal H3 influenza A virus spillover now endemic to U.S. swine. MSphere . 2022 ; 7 : e0080921 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Sreenivasan CC , Thomas M , Kaushik RS , Wang D , Li F . Influenza A in bovine species: a narrative literature review. Viruses . 2019 ; 11 : 561 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Sillman SJ , Drozd M , Loy D , Harris SP . Naturally occurring highly pathogenic avian influenza virus H5N1 clade 2.3.4.4b infection in three domestic cats in North America during 2023. J Comp Pathol . 2023 ; 205 : 17 – 23 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Klopfleisch R , Wolf PU , Uhl W , Gerst S , Harder T , Starick E , et al. Distribution of lesions and antigen of highly pathogenic avian influenza virus A/Swan/Germany/R65/06 (H5N1) in domestic cats after presumptive infection by wild birds. Vet Pathol . 2007 ; 44 : 261 – 8 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Keawcharoen J , Oraveerakul K , Kuiken T , Fouchier RAM , Amonsin A , Payungporn S , et al. Avian influenza H5N1 in tigers and leopards. Emerg Infect Dis . 2004 ; 10 : 2189 – 91 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Kuiken T , Rimmelzwaan G , van Riel D , van Amerongen G , Baars M , Fouchier R , et al. Avian H5N1 influenza in cats. Science . 2004 ; 306 : 241 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Herfst S , Schrauwen EJA , Linster M , Chutinimitkul S , de Wit E , Munster VJ , et al. Airborne transmission of influenza A/H5N1 virus between ferrets. Science . 2012 ; 336 : 1534 – 41 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Agüero M , Monne I , Sánchez A , Zecchin B , Fusaro A , Ruano MJ , et al. Highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) virus infection in farmed minks, Spain, October 2022. Euro Surveill . 2023 ; 28 : 2300001 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Leguia M , Garcia-Glaessner A , Muñoz-Saavedra B , Juarez D , Barrera P , Calvo-Mac C , et al. Highly pathogenic avian influenza A (H5N1) in marine mammals and seabirds in Peru. Nat Commun . 2023 ; 14 : 5489 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Saito K . An outbreak of cattle influenza in Japan in the fall of 1949. J Am Vet Med Assoc . 1951 ; 118 : 316 – 9 . PubMed Google Scholar
- Gunning RF , Pritchard GC . Unexplained sporadic milk drop in dairy cows. Vet Rec . 1997 ; 140 : 488 . PubMed Google Scholar
- Brown IH , Crawshaw TR , Harris PA , Alexander DJ . Detection of antibodies to influenza A virus in cattle in association with respiratory disease and reduced milk yield. Vet Rec . 1998 ; 143 : 637 – 8 . PubMed Google Scholar
- Crawshaw TR , Brown I . Bovine influenza. Vet Rec . 1998 ; 143 : 372 . PubMed Google Scholar
- Gunning RF , Brown IH , Crawshaw TR . Evidence of influenza A virus infection in dairy cows with sporadic milk drop syndrome. Vet Rec . 1999 ; 145 : 556 – 7 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Crawshaw TR , Brown IH , Essen SC , Young SCL . Significant rising antibody titres to influenza A are associated with an acute reduction in milk yield in cattle. Vet J . 2008 ; 178 : 98 – 102 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Lopez JW , Woods GT . Influenza virus in ruminants: a review. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol . 1984 ; 45 : 445 – 62 . PubMed Google Scholar
- Jones-Lang K , Ernst-Larson M , Lee B , Goyal SM , Bey R . Prevalence of influenza A virus (H1N1) antibodies in bovine sera. New Microbiol . 1998 ; 21 : 153 – 60 . PubMed Google Scholar
- Briand FX , Souchaud F , Pierre I , Beven V , Hirchaud E , Hérault F , et al. Highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b virus in domestic cat, France, 2022. Emerg Infect Dis . 2023 ; 29 : 1696 – 8 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Frymus T , Belák S , Egberink H , Hofmann-Lehmann R , Marsilio F , Addie DD , et al. Influenza virus infections in cats. Viruses . 2021 ; 13 : 1435 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Songserm T , Amonsin A , Jam-on R , Sae-Heng N , Meemak N , Pariyothorn N , et al. Avian influenza H5N1 in naturally infected domestic cat. Emerg Infect Dis . 2006 ; 12 : 681 – 3 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Thiry E , Zicola A , Addie D , Egberink H , Hartmann K , Lutz H , et al. Highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 virus in cats and other carnivores. Vet Microbiol . 2007 ; 122 : 25 – 31 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Lando AM , Bazaco MC , Parker CC , Ferguson M . Characteristics of U.S. consumers reporting past year intake of raw (unpasteurized) milk: results from the 2016 Food Safety Survey and 2019 Food Safety and Nutrition Survey. J Food Prot . 2022 ; 85 : 1036 – 43 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Fourment M , Darling AE , Holmes EC . The impact of migratory flyways on the spread of avian influenza virus in North America. BMC Evol Biol . 2017 ; 17 : 118 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- Guan Y , Smith GJD . The emergence and diversification of panzootic H5N1 influenza viruses. Virus Res . 2013 ; 178 : 35 – 43 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- de Araújo AC , Silva LMN , Cho AY , Repenning M , Amgarten D , de Moraes AP , et al. Incursion of highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b virus, Brazil, 2023. Emerg Infect Dis . 2024 ; 30 : 619 – 21 . DOI PubMed Google Scholar
- American Veterinary Medical Association . States with HPAI-infected dairy cows grows to six. USDA provides guidance for veterinarians, producers on protecting cattle from the virus. 2024 [ cited 2024 Apr 10 ]. https://www.avma.org/news/states-hpai-infected-dairy-cows-grows-six
- Figure 1 . Mammary gland lesions in cattle in study of highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b virus infection in domestic dairy cattle and cats, United States, 2024. A, B) Mammary...
- Figure 2 . Lesions in cat tissues in study of highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b virus infection in domestic dairy cattle and cats, United States, 2024. Tissue sections were stained...
- Figure 3 . Phylogenetic analysis of hemagglutinin gene sequences in study of highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b virus infection in domestic dairy cattle and cats, United States, 2024. Colors indicate...
- Figure 4 . Phylogenetic analysis of neuraminidase gene sequences in study of highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b virus infection in domestic dairy cattle and cats, United States, 2024. Colors indicate...
- Table 1 . Microscopic lesions observed in cattle in study of highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b virus infection in domestic dairy cattle and cats, United States, 2024
- Table 2 . Microscopic lesions observed in cats in study of highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b virus infection in domestic dairy cattle and cats, United States, 2024
- Table 3 . PCR results from various specimens in study of highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b virus infection in domestic dairy cattle and cats, United States, 2024
Suggested citation for this article : Burrough ER, Magstadt DR, Petersen B, Timmermans SJ, Gauger PC, Zhang J, et al. Highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b virus infection in domestic dairy cattle and cats, United States, 2024. Emerg Infect Dis. 2024 Jul [ date cited ]. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid3007.240508
DOI: 10.3201/eid3007.240508
Original Publication Date: April 29, 2024
Table of Contents – Volume 30, Number 7—July 2024
Please use the form below to submit correspondence to the authors or contact them at the following address:
Eric R. Burrough, Iowa State University Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory, 1937 Christensen Dr, Ames, IA 50011, USA
Comment submitted successfully, thank you for your feedback.
There was an unexpected error. Message not sent.
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
Metric Details
What is the altmetric attention score.
The Altmetric Attention Score for a research output provides an indicator of the amount of attention that it has received. The score is derived from an automated algorithm, and represents a weighted count of the amount of attention Altmetric picked up for a research output.
- Open access
- Published: 17 April 2024
A data-driven combined prediction method for the demand for intensive care unit healthcare resources in public health emergencies
- Weiwei Zhang 1 &
- Xinchun Li 1
BMC Health Services Research volume 24 , Article number: 477 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
251 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Public health emergencies are characterized by uncertainty, rapid transmission, a large number of cases, a high rate of critical illness, and a high case fatality rate. The intensive care unit (ICU) is the “last line of defense” for saving lives. And ICU resources play a critical role in the treatment of critical illness and combating public health emergencies.
This study estimates the demand for ICU healthcare resources based on an accurate prediction of the surge in the number of critically ill patients in the short term. The aim is to provide hospitals with a basis for scientific decision-making, to improve rescue efficiency, and to avoid excessive costs due to overly large resource reserves.
A demand forecasting method for ICU healthcare resources is proposed based on the number of current confirmed cases. The number of current confirmed cases is estimated using a bilateral long-short-term memory and genetic algorithm support vector regression (BILSTM-GASVR) combined prediction model. Based on this, this paper constructs demand forecasting models for ICU healthcare workers and healthcare material resources to more accurately understand the patterns of changes in the demand for ICU healthcare resources and more precisely meet the treatment needs of critically ill patients.
Data on the number of COVID-19-infected cases in Shanghai between January 20, 2020, and September 24, 2022, is used to perform a numerical example analysis. Compared to individual prediction models (GASVR, LSTM, BILSTM and Informer), the combined prediction model BILSTM-GASVR produced results that are closer to the real values. The demand forecasting results for ICU healthcare resources showed that the first (ICU human resources) and third (medical equipment resources) categories did not require replenishment during the early stages but experienced a lag in replenishment when shortages occurred during the peak period. The second category (drug resources) is consumed rapidly in the early stages and required earlier replenishment, but replenishment is timelier compared to the first and third categories. However, replenishment is needed throughout the course of the epidemic.
The first category of resources (human resources) requires long-term planning and the deployment of emergency expansion measures. The second category of resources (drugs) is suitable for the combination of dynamic physical reserves in healthcare institutions with the production capacity reserves of corporations. The third category of resources (medical equipment) is more dependent on the physical reserves in healthcare institutions, but care must be taken to strike a balance between normalcy and emergencies.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
The outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in 2003 was the first global public health emergency of the 21st century. From SARS to the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic at the end of 2019, followed shortly by the monkeypox epidemic of 2022, the global community has witnessed eight major public health events within the span of only 20 years [ 1 ]. These events are all characterized by high infection and fatality rates. For example, the number of confirmed COVID-19 cases worldwide is over 700 million, and the number of deaths has exceeded 7 million [ 2 ]. Every major public health emergency typically consists of four stages: incubation, outbreak, peak, and decline. During the outbreak and transmission, surges in the number of infected individuals and the number of critically ill patients led to a corresponding increase in the urgent demand for intensive care unit (ICU) medical resources. ICU healthcare resources provide material security for rescue work during major public health events as they allow critically ill patients to be treated, which decreases the case fatality rate and facilitates the prevention and control of epidemics. Nevertheless, in actual cases of prevention and control, the surge in patients has often led to shortages of ICU healthcare resources and a short-term mismatch of supply and demand, which are problems that have occurred several times in different regions. These issues can drastically impact anti-epidemic frontline healthcare workers and the treatment outcomes of infected patients. According to COVID-19 data from recent years, many infected individuals take about two weeks to progress from mild to severe disease. As the peak of severe cases tends to lag behind that of infected cases, predicting the changes in the number of new infections can serve as a valuable reference for healthcare institutions in forecasting the demand for ICU healthcare resources. The accurate forecasting of the demand for ICU healthcare resources can facilitate the rational resource allocation of hospitals under changes in demand patterns, which is crucial for improving the provision of critical care and rescue efficiency. Therefore, in this study, we combined a support vector regression (SVR) prediction model optimized by a genetic algorithm (GA) with bidirectional long-short-term memory (BILSTM), with the aim of enhancing the dynamic and accurate prediction of the number of current confirmed cases. Based on this, we forecasted the demand for ICU healthcare resources, which in turn may enable more efficient resource deployment during severe epidemic outbreaks and improve the precise supply of ICU healthcare resources.
Research on the demand forecasting of emergency materials generally employs quantitative methods, and traditional approaches mainly include linear regression and GM (1,1). Linear regression involves the use of regression equations to make predictions based on data. Sui et al. proposed a method based on multiple regression that aimed to predict the demand for emergency supplies in the power grid system following natural disasters [ 3 ]. Historical data was used to obtain the impact coefficient of each factor on emergency resource forecasting, enabling the quick calculation of the demand for each emergency resource during a given type of disaster. However, to ensure prediction accuracy, regression analysis needs to be supported by data from a large sample size. Other researchers have carried out demand forecasting for emergency supplies from the perspective of grey prediction models. Li et al. calculated the development coefficient and grey action of the grey GM (1,1) model using the particle swarm optimization algorithm to minimize the relative errors between the real and predicted values [ 4 ]. Although these studies have improved the prediction accuracy of grey models, they mainly involve pre-processing the initial data series without considering the issue of the excessively fast increase in predicted values by traditional grey GM (1,1) models. In emergency situations, the excessively fast increase in predicted values compared to real values will result in the consumption of a large number of unnecessary resources, thereby decreasing efficiency and increasing costs. As traditional demand forecasting models for emergency supplies have relatively poor perfect order rates in demand analysis, which result in low prediction accuracy, they are not mainstream.
At present, dynamic models of infectious diseases and demand forecasting models based on machine learning are at the cutting edge of research. With regard to the dynamic models of infectious diseases, susceptible infected recovered model (SIR) is a classic mathematical model employed by researchers [ 5 , 6 , 7 ]. After many years of development, the SIR model has been expanded into various forms within the field of disease transmission, including susceptible exposed infected recovered model (SEIR) and susceptible exposed infected recovered dead model (SEIRD) [ 8 , 9 ]. Nevertheless, with the outbreak of COVID-19, dynamic models of infectious diseases have once again come under the spotlight, with researchers combining individual and group variables and accounting for different factors to improve the initial models and reflect the state of COVID-19 [ 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 ]. Based on the first round of epidemic data from Wuhan, Li et al. predicted the time-delay distributions, epidemic doubling time, and basic reproductive number [ 14 ]. Upon discovering the presence of asymptomatic COVID-19 infections, researchers began constructing different SEIR models that considered the infectivity of various viral incubation periods, yielding their respective predictions of the inflection point. Based on this, Anggriani et al. further considered the impact of the status of infected individuals and established a transmission model with seven compartments [ 15 ]. Efimov et al. set the model parameters for separating the recovered and the dead as uncertain and applied the improved SEIR model to analyze the transmission trend of the pandemic [ 16 ]. In addition to analyzing the transmission characteristics of normal COVID-19 infection to predict the status of the epidemic, many researchers have also used infectious disease models to evaluate the effects of various epidemic preventive measures. Lin et al. applied an SEIR model that considered individual behavioral responses, government restrictions on public gatherings, pet-related transmission, and short-term population movements [ 17 ]. Cao et al. considered the containment effect of isolation measures on the pandemic and solved the model using Euler’s numerical method [ 18 ]. Reiner et al. employed an improved SEIR model to study the impact of non-pharmaceutical interventions implemented by the government (e.g., restricting population movement, enhancing disease testing, and increasing mask use) on disease transmission and evaluated the effectiveness of social distancing and the closure of public spaces [ 19 ]. These studies have mainly focused on modeling the COVID-19 pandemic to perform dynamic forecasting and analyze the effectiveness of control measures during the epidemic. Infectious disease dynamics offer good predictions for the early transmission trends of epidemics. However, this approach is unable to accurately estimate the spread of the virus in open-flow environments. Furthermore, it is also impossible to set hypothetical parameters, such as disease transmissibility and the recovery probability constant, that are consistent with the conditions in reality. Hence, with the increase in COVID-19 data, this approach has become inadequate for the accurate long-term analysis of epidemic trends.
Machine learning has shown significant advantages in this regard [ 20 , 21 ]. Some researchers have adopted the classic case-based reasoning approach in machine learning to make predictions. However, it is not feasible to find historical cases that fully match the current emergency event, so this approach has limited operability. Other researchers have also employed neural network training in machine learning to make predictions. For example, Hamou et al. predicted the number of injuries and deaths, which in turn were used to forecast the demand for emergency supplies [ 22 ]. However, this approach requires a large initial dataset and a high number of training epochs, while uncertainty due to large changes in intelligence information can lead to significant errors in data prediction [ 23 , 24 , 25 ]. To address these problems, researchers have conducted investigations that account (to varying degrees) for data characterized by time-series and non-linearity and have employed time-series models with good non-linear fitting [ 26 , 27 , 28 ]. The use of LSTM to explore relationships within the data can improve the accuracy of predicting COVID-19 to some extent. However, there are two problems with this approach. First, LSTM neural networks require extremely large datasets, and each wave of the epidemic development cycle would be insufficient to support a dataset suitable for LSTM. Second, neural networks involve a large number of parameters and highly complex models and, hence, are susceptible to overfitting, which can prevent them from achieving their true and expected advantages in prediction.
Overall, Our study differs from other papers in the following three ways. First, the research object of this paper focuses on the specific point of ICU healthcare resource demand prediction, aiming to improve the rate of critical care patient treatment. However, past research on public health emergencies has focused more on resource prediction , such as N95 masks, vaccines, and generalized medical supplies during the epidemic , to mitigate the impact of rapid transmission and high morbidity rates. This has led to less attention being paid to the reality of the surge in critically ill patients due to their high rates of severe illness and mortality.
Second, the idea of this paper is to further forecast resource needs based on the projected number of people with confirmed diagnoses, which is more applicable to healthcare organizations than most other papers that only predict the number of people involved. However, in terms of the methodology for projecting the number of people, this paper adopts a combined prediction method that combines regression algorithms and recurrent neural networks to propose a BILSTM-GASVR prediction model for the number of confirmed diagnoses. It capitalizes on both the suitability of SVR for small samples and non-linear prediction as well as the learning and memory abilities of BILSTM in processing time-series data. On the basis of the prediction model for the number of infected cases, by considering the characteristics of ICU healthcare resources, we constructed a demand forecasting model of emergency healthcare supplies. Past public health emergencies are more likely to use infectious disease models or a single prediction model in deep learning. some of the articles, although using a combination of prediction, but also more for the same method domain combination, such as CNN-LSTM, GRU-LSTM, etc., which are all recurrent neural networks.
Third, in terms of specific categorization of resources to be forecasted, considering the specificity of ICU medical resources, we introduce human resource prediction on the basis of previous studies focusing on material security, and classified ICU medical resources into three categories: ICU human resources, drugs and medical equipment. The purpose of this classification is to match the real-life prediction scenarios of public health emergencies and improve the demand forecasting performance for local ICU healthcare resources. Thus, it is easy for healthcare institutions to grasp the overall development of events, optimizing decision-making, and reducing the risk of healthcare systems collapsing during the outbreak stage.
In this section, we accomplish the following two tasks. Firstly, we introduce the idea of predicting the number of infected cases and show the principle of the relevant models. Secondly, based on the number of infected cases, ICU healthcare resources are divided into two categories (healthcare workers and healthcare supplies), and their respective demand forecasting models are constructed.
Prediction model for the number of infected cases
Gasvr model.
Support vector machine (SVM) is a machine-learning language for classification developed by Vapnik [ 29 ]. Suppose there are two categories of samples: H1 and H2. If hyperplane H is able to correctly classify the samples into these two categories and maximize the margin between the two categories, it is known as the optimal separating hyperplane (OSH). The sample vectors closest to the OSH in H1 and H2 are known as the support vectors. To apply SVM to prediction, it is essential to perform regression fitting. By introducing the \(\varepsilon\) -insensitive loss function, SVM can be converted to a support vector regression machine, where the role of the OSH is to minimize the error of all samples from this plane. SVR has a theoretical basis in statistical learning and relatively high learning performance, making it suitable for performing predictions in small-sample, non-linear, and multi-dimensional fields [ 30 , 31 ].
Assume the training sample set containing \(l\) training samples is given by \(\{({x}_{i},{y}_{i}),i=\mathrm{1,2},...,l\}\) , where \({x}_{i}=[{x}_{i}^{1},{x}_{i}^{2},...,{x}_{i}^{d}{]}^{\rm T}\) and \({y}_{i}\in R\) are the corresponding output values.
Let the regression function be \(f(x)=w\Phi (x)+b\) , where \(\phi (x)\) is the non-linear mapping function. The linear \(\varepsilon\) -insensitive loss function is defined as shown in formula ( 1 ).
Among the rest, \(f(x)\) is the predicted value returned by the regression function, and \(y\) is the corresponding real value. If the error between \(f(x)\) and \(y\) is ≤ \(\varepsilon\) , the loss is 0; otherwise, the loss is \(\left|y-f(x)\right|-\varepsilon\) .
The slack variables \({\xi }_{i}\) and \({\xi }_{i}^{*}\) are introduced, and \(w\) , \(b\) are solved using the following equation as shown in formula ( 2 ).
Among the rest, \(C\) is the penalty factor, with larger values indicating a greater penalty for errors > \(\varepsilon\) ; \(\varepsilon\) is defined as the error requirement, with smaller values indicating a smaller error of the regression function.
The Lagrange function is introduced to solve the above function and transformed into the dual form to give the formula ( 3 ).
Among the rest, \(K({x}_{i},{x}_{j})=\Phi ({x}_{i})\Phi ({x}_{j})\) is the kernel function. The kernel function determines the structure of high-dimensional feature space and the complexity of the final solution. The Gaussian kernel is selected for this study with the function \(K({x}_{i},{x}_{j})=\mathit{exp}(-\frac{\Vert {x}_{i}-{x}_{j}\Vert }{2{\sigma }^{2}})\) .
Let the optimal solution be \(a=[{a}_{1},{a}_{2},...,{a}_{l}]\) and \({a}^{*}=[{a}_{1}^{*},{a}_{2}^{*},...,{a}_{l}]\) to give the formula ( 4 ) and formula ( 5 ).
Among the rest, \({N}_{nsv}\) is the number of support vectors.
In sum, the regression function is as shown in formula ( 6 ).
when some of the parameters are not 0, the corresponding samples are the support vectors in the problem. This is the principle of SVR. The values of the three unknown parameters (penalty factor C, ε -insensitive loss function, and kernel function coefficient \(\sigma )\) , can directly impact the model effect. The penalty factor C affects the degree of function fitting through the selection of outliers in the sample by the function. Thus, excessively large values lead to better fit but poorer generalization, and vice versa. The ε value in the ε-insensitive loss function determines the accuracy of the model by affecting the width of support vector selection. Thus, excessively large values lead to lower accuracy that does not meet the requirements and excessively small values are overly complex and increase the difficulty. The kernel function coefficient \(\sigma\) determines the distribution and range of the training sample by controlling the size of inner product scaling in high-dimensional space, which can affect overfitting.
Therefore, we introduce other algorithms for optimization of the three parameters in SVR. Currently the commonly used algorithms are 32and some heuristic algorithms. Although the grid search method is able to find the highest classification accuracy, which is the global optimal solution. However, sometimes it can be time-consuming to find the optimal parameters for larger scales. If a heuristic algorithm is used, we could find the global optimal solution without having to trace over all the parameter points in the grid. And GA is one of the most commonly used heuristic algorithms, compared to other heuristic algorithms, it has the advantages of strong global search, generalizability, and broader blending with other algorithms.
Given these factors, we employ a GA to encode and optimize the relevant parameters of the model. The inputs are the experimental training dataset, the Gaussian kernel function expression, the maximum number of generations taken by the GA, the accuracy range of the optimized parameters, the GA population size, the fitness function, the probability of crossover, and the probability of mutation. The outputs are the optimal penalty factor C, ε-insensitive loss function parameter \(\varepsilon ,\) and optimal Gaussian kernel parameter \(\sigma\) of SVR, thus achieving the optimization of SVR. The basic steps involved in GA optimization are described in detail below, and the model prediction process is shown in Fig. 1 .
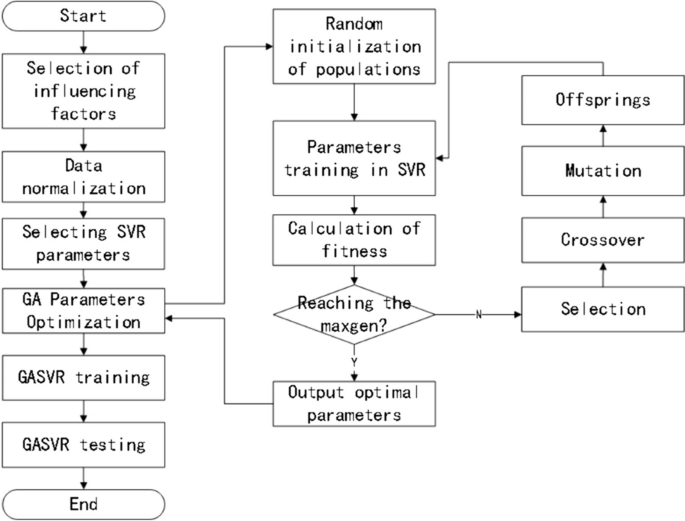
Prediction process of the GASVR model
Population initialization
The three parameters are encoded using binary arrays composed of 0–1 bit-strings. Each parameter consisted of six bits, and the initial population is randomly generated. The population size is set at 60, and the number of iterations is 200.
Fitness calculation
In the same dataset, the K-fold cross-validation technique is used to test each individual in the population, with K = 5. K-fold cross validation effectively avoids the occurrence of model over-learning and under-learning. For the judgment of the individual, this paper evaluates it in terms of fitness calculations. Therefore, combining the two enables the effective optimization of the model’s selected parameters and improves the accuracy of regression prediction.
Fitness is calculated using the mean error method, with smaller mean errors indicating better fitness. The fitness function is shown in formula ( 7 ) [ 32 ].
The individual’s genotype is decoded and mapped to the corresponding parameter value, which is substituted into the SVR model for training. The parameter optimization range is 0.01 ≤ C ≤ 100, 0.1 ≤ \(\sigma\) ≤ 20, and 0.001 ≤ ε ≤ 1.
Selection: The selection operator is performed using the roulette wheel method.
Crossover: The multi-point crossover operator, in which two chromosomes are selected and multiple crossover points are randomly chosen for swapping, is employed. The crossover probability is set at 0.9.
Mutation: The inversion mutation operator, in which two points are randomly selected and the gene values between them are reinserted to the original position in reverse order, is employed. The mutation probability is set at 0.09.
Decoding: The bit strings are converted to parameter sets.
The parameter settings of the GASVR model built in this paper are shown in Table 1 .
BILSTM model
The LSTM model is a special recurrent neural network algorithm that can remember the long-term dependencies of data series and has an excellent capacity for self-learning and non-linear fitting. LSTM automatically connects hidden layers across time points, such that the output of one time point can arbitrarily enter the output terminal or the hidden layer of the next time point. Therefore, it is suitable for the sample prediction of time-series data and can predict future data based on stored data. Details of the model are shown in Fig. 2 .
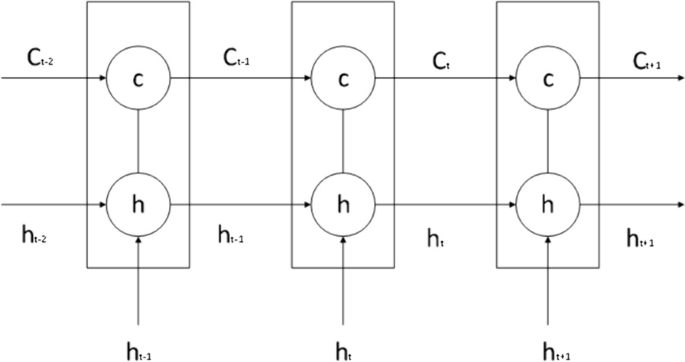
Schematic diagram of the LSTM model
LSTM consists of a forget gate, an input gate, and an output gate.
The forget gate combines the previous and current time steps to give the output of the sigmoid activation function. Its role is to screen the information from the previous state and identify useful information that truly impacts the subsequent time step. The equation for the forget gate is shown in formula ( 8 ).
Among the number, \(W_{f}\) is the weight of the forget gate, \({b}_{f}\) is the bias, \(\sigma\) is the sigmoid activation function, \({f}_{t}\) is the output of the sigmoid activation function, \(t-1\) is the previous time step, \(t\) is the current time step, and \({x}_{t}\) is the input time-series data at time step \(t\) .
The input gate is composed of the output of the sigmoid and tanh activation functions, and its role is to control the ratio of input information entering the information of a given time step. The equation for the input gate is shown in formula ( 9 ).
Among the number, \({W}_{i}\) is the output weight of the input gate, \({i}_{t}\) is the output of the sigmoid activation function, \({b}_{i}\) and \({b}_{C}\) are the biases of the input gate, and \({W}_{C}\) is the output of the tanh activation function.
The role of the output gate is to control the amount of information output at the current state, and its equation is shown in formula ( 10 ).
Among the number, \({W}_{o}\) is the weight of \({o}_{t}\) , and \({b}_{o}\) is the bias of the output gate.
The values of the above activation functions \(\sigma\) and tanh are generally shown in formulas ( 11 ) and ( 12 ).
\({C}_{t}\) is the data state of the current time step, and its value is determined by the input information of the current state and the information of the previous state. It is shown in formula ( 13 ).
Among the number, \(\widetilde{{C}_{t}}=\mathit{tan}h({W}_{c}[{h}_{t-1},{x}_{t}]+{b}_{c})\) .
\({h}_{t}\) is the state information of the hidden layer at the current time step, \({h}_{t}={o}_{t}\times \mathit{tan}h({c}_{t})\) .Each time step \({T}_{n}\) has a corresponding state \({C}_{t}\) . By undergoing the training process, the model can learn how to modify state \({C}_{t}\) through the forget, output, and input gates. Therefore, this state is consistently passed on, implying that important distant information will neither be forgotten nor significantly affected by unimportant information.
The above describes the principle of LSTM, which involves forward processing when applied. BILSTM consists of two LSTM networks, one of which processes the input sequence in the forward direction (i.e., the original order), while the other inputs the time series in the backward direction into the LSTM model. After processing both LSTM networks, the outputs are combined, which eventually gives the output results of the BILSTM model. Details of the model are presented in Fig. 3 .
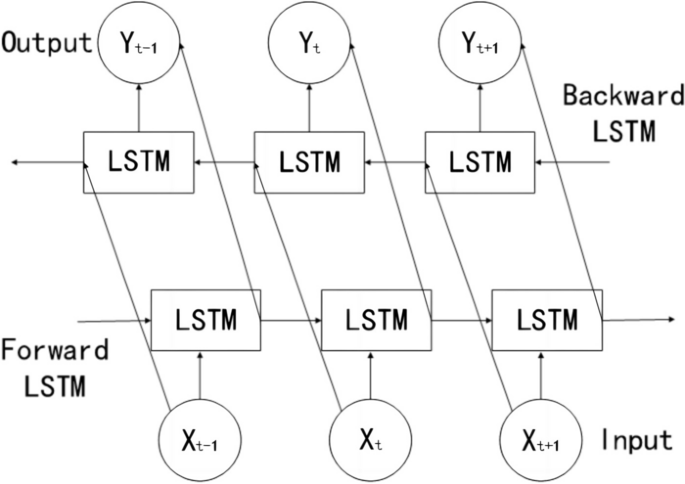
Schematic diagram of the BILSTM model
Compared to LSTM, BILSTM can achieve bidirectional information extraction of the time-series and connect the two LSTM layers onto the same output layer. Therefore, in theory, its predictive performance should be superior to that of LSTM. In BILSTM, the equations of the forward hidden layer( \(\overrightarrow{{h}_{t}}\) ) , backward hidden layer( \(\overleftarrow{{h}_{t}}\) ) , and output layer( \({o}_{t}\) ) are shown in formulas ( 14 ) , ( 15 ) and ( 16 ).
The parameter settings of the BILSTM model built in this paper are shown in Table 2 .
Informer model
The Informer model follows the compiler-interpreter architecture in the Transformer model, and based on this, structural optimizations have been made to reduce the computational time complexity of the algorithm and to optimize the output form of the interpreter. The two optimization methods are described in detail next.
With large amounts of input data, neural network models can have difficulty capturing long-term interdependencies in sequences, which can produce gradient explosions or gradient vanishing and affect the model's prediction accuracy. Informer model solves the existential gradient problem by using a ProbSparse Self-attention mechanism to make more efficient than conventional self-attention.
The value of Transformer self-attention is shown in formula ( 17 ).
Among them, \(Q\in {R}^{{L}_{Q}\times d}\) is the query matrix, \(K\in {R}^{{L}_{K}\times d}\) is the key matrix, and \(V\in {R}^{{L}_{V}\times d}\) is the value matrix, which are obtained by multiplying the input matrix X with the corresponding weight matrices \({W}^{Q}\) , \({W}^{K}\) , \({W}^{V}\) respectively, and d is the dimensionality of Q, K, and V. Let \({q}_{i}\) , \({k}_{i}\) , \(v_{i}\) represent the ith row in the Q, K, V matrices respectively, then the ith attention coefficient is shown in formula ( 18 ) as follows.
Therein, \(p({k}_{j}|{q}_{i})\) denotes the traditional Transformer's probability distribution formula, and \(k({q}_{i},{K}_{l})\) denotes the asymmetric exponential sum function. Firstly, q=1 is assumed, which implies that the value of each moment is equally important; secondly, the difference between the observed distribution and the assumed one is evaluated by the KL scatter, if the value of KL is bigger, the bigger the difference with the assumed distribution, which represents the more important this moment is. Then through inequality \(ln{L}_{k}\le M({q}_{i},K)\le {\mathit{max}}_{j}\left\{\frac{{q}_{i}{k}_{j}^{\rm T}}{\sqrt{d}}\right\}-\frac{1}{{L}_{k}}{\sum }_{j=1}^{{L}_{k}}\left\{\frac{{q}_{i}{k}_{j}^{\rm T}}{\sqrt{d}}\right\}+ln{L}_{k}\) , \(M({q}_{i},K)\) is transformed into \(\overline{M}({q}_{i},K)\) . According to the above steps, the ith sparsity evaluation formula is obtained as shown in formula ( 19 ) [ 33 ].
One of them, \(M({q}_{i},K)\) denotes the ith sparsity measure; \(\overline{M}({q}_{i},K)\) denotes the ith approximate sparsity measure; \({L}_{k}\) is the length of query vector. \(TOP-u\) quantities of \(\overline{M}\) are selected to form \(\overline{Q}\) , \(\overline{Q}\) is the first u sparse matrices, and the final sparse self-attention is shown in Formula ( 20 ). At this point, the time complexity is still \(O({n}^{2})\) , and to solve this problem, only l moments of M2 are computed to reduce the time complexity to \(O(L\cdot \mathit{ln}(L))\) .
Informer uses a generative decoder to obtain long sequence outputs.Informer uses the standard decoder architecture shown in Fig. 4 , in long time prediction, the input given to the decoder is shown in formula ( 21 ).
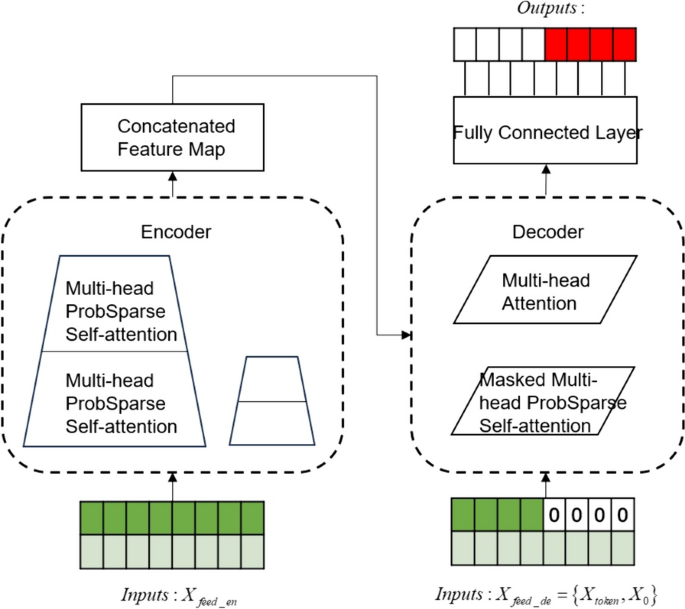
Informer uses a generative decoder to obtain long sequence outputs
Therein, \({X}_{de}^{t}\) denotes the input to the decoder; \({X}_{token}^{t}\in {R}^{({L}_{token}+{L}_{y})\times {d}_{\mathit{mod}el}}\) is the dimension of the encoder output, which is the starting token without using all the output dimensions; \({X}_{0}^{t}\in {R}^{({L}_{token}+{L}_{y})\times {d}_{\mathit{mod}el}}\) is the dimension of the target sequence, which is uniformly set to 0; and finally the splicing input is performed to the encoder for prediction.
The parameter settings of Informer model created in this paper are shown in Table 3 .
BILSTM-GASVR combined prediction model
SVR has demonstrated good performance in solving problems like finite samples and non-linearity. Compared to deep learning methods, it offers faster predictions and smaller empirical risks. BILSTM has the capacity for long-term memory, can effectively identify data periodicity and trends, and is suitable for the processing of time-series data. Hence, it can be used to identify the effect of time-series on the number of confirmed cases. Given the advantages of these two methods in different scenarios, we combined them to perform predictions using GASVR, followed by error repair using BILSTM. The basic steps for prediction based on the BILSTM-GASVR model are as follows:
Normalization is performed on the initial data.
The GASVR model is applied to perform training and parameter optimization of the data to obtain the predicted value \(\widehat{{y}_{i}}\) .
After outputting the predicted value of GASVR, the residual sequence between the predicted value and real data is extracted to obtain the error \({\gamma }_{i}\) (i.e., \({\gamma }_{i}={y}_{i}-\widehat{{y}_{i}}\) ).
The BILSTM model is applied to perform training of the error to improve prediction accuracy. The BILSTM model in this paper is a multiple input single output model. Its inputs are the true and predicted error values \({\gamma }_{i}\) and its output is the new error value \(\widehat{{\gamma }_{i}}\) predicted by BILSTM.
The final predicted value is the sum of the GASVR predicted value and the BILSTM residual predicted value (i.e., \({Y}_{i}=\widehat{{y}_{i}}+\widehat{{\gamma }_{i}}\) ).
The parameter settings of the BILSTM-GASVR model built in this paper are shown in Table 4 .
Model testing criteria
To test the effect of the model, the prediction results of the BILSTM-GASVR model are compared to those of GASVR, LSTM, BILSTM and Informer. The prediction error is mainly quantified using three indicators: mean squared error (MSE), root mean squared error (RMSE), and correlation coefficient ( \(R^{2}\) ). Their respective equations are shown in formulas ( 22 ), ( 23 ) and ( 24 ).
Demand forecasting model of ICU healthcare resources
ICU healthcare resources can be divided into human and material resources. Human resources refer specifically to the professional healthcare workers in the ICU. Material resources, which are combined with the actual consumption of medical supplies, can be divided into consumables and non-consumables. Consumables refer to the commonly used drugs in the ICU, which include drugs for treating cardiac insufficiency, vasodilators, anti-shock vasoactive drugs, analgesics, sedatives, muscle relaxants, anti-asthmatic drugs, and anticholinergics. Given that public health emergencies have a relatively high probability of affecting the respiratory system, we compiled a list of commonly used drugs for respiratory diseases in the ICU (Table 5 ).
Non-consumables refer to therapeutic medical equipment, including electrocardiogram machines, blood gas analyzers, electrolyte analyzers, bedside diagnostic ultrasound machines, central infusion workstations, non-invasive ventilators, invasive ventilators, airway clearance devices, defibrillators, monitoring devices, cardiopulmonary resuscitation devices, and bedside hemofiltration devices.
The demand forecasting model of ICU healthcare resources constructed in this study, as well as its relevant parameters and definitions, are described below. \({R}_{ij}^{n}\) is the forecasted demand for the \(i\) th category of resources on the \(n\) th day in region \(j\) . \({Y}_{j}^{n}\) is the predicted number of current confirmed cases on the \(n\) th day in region \(j\) . \({M}_{j}^{n}\) is the number of ICU healthcare workers on the \(n\) th day in region \(j\) , which is given by the following formula: number of healthcare workers the previous day + number of new recruits − reduction in number the previous day, where the reduction in number refers to the number of healthcare workers who are unable to work due to infection or overwork. In general, the number of ICU healthcare workers should not exceed 5% of the number of current confirmed cases (i.e., it takes the value range [0, \(Y_{j}^{n}\) ×5%]). \(U_{i}\) is the maximum working hours or duration of action of the \(i\) th resource category within one day. \({A}_{j}\) is the number of resources in the \(i\) th category allocated to patients (i.e., how many units of resources in the \(i\) th category is needed for a patient who need the \(i\) th unit of the given resource). \({\varphi }_{i}\) is the demand conversion coefficient (i.e., the proportion of the current number of confirmed cases who need to use the \(i\) th resource category). \({C}_{ij}^{n}\) is the available quantity of material resources of the \(i\) th category on the \(n\) th day in region \(j\) . At the start, this quantity is the initial reserve, and once the initial reserve is exhausted, it is the surplus from the previous day. The formula for this parameter is given as follows: available quantity from the previous day + replenishment on the previous day − quantity consumed on the previous day, where if \({C}_{ij}^{n}\) is a negative number, it indicates the amount of shortage for the given category of resources on the previous day.
In summary, the demand forecast for emergency medical supplies constructed in this study is shown in formula ( 25 ).
The number of confirmed cases based on data-driven prediction is introduced into the demand forecasting model for ICU resources to forecast the demand for the various categories of resources. In addition to the number of current confirmed cases, the main variables of the first demand forecasting model for human resources are the available quantity and maximum working hours. The main variable of the second demand forecasting model for consumable resources is the number of units consumed by the available quantity. The main variable of the third model for non-consumable resources is the allocated quantity. These three resource types can be predicted using the demand forecasting model constructed in this study.
Prediction of the number of current infected cases
The COVID-19 situation in Shanghai is selected for our experiment. A total of 978 entries of epidemic-related data in Shanghai between January 20, 2020, and September 24, 2022, are collected from the epidemic reporting platform. This dataset is distributed over a large range and belongs to a right-skewed leptokurtic distribution. The specific statistical description of data is shown in Table 6 . Part of the data is shown in Table 7 .
And we divided the data training set and test set in an approximate 8:2 ratio, namely, 798 days for training (January 20, 2020 to March 27, 2022) and 180 days for prediction (March 28, 2022 to September 24, 2022).
Due to the large difference in order of magnitude between the various input features, directly implementing training and model construction would lead to suboptimal model performance. Such effects are usually eliminated through normalization. In terms of interval selection, [0, 1] reflects the probability distribution of the sample, whereas [-1, 1] mostly reflects the state distribution or coordinate distribution of the sample. Therefore, [-1, 1] is selected for the normalization interval in this study, and the processing method is shown in formula ( 26 ).
Among the rest, \(X\) is the input sample, \({X}_{min}\) and \({X}_{max}\) are the minimum and maximum values of the input sample, and \({X}_{new}\) is the input feature after normalization.
In addition, we divide the data normalization into two parts, considering that the amount of data in the training set is much more than the test set in the real operating environment. In the first step, we normalize the training set data directly according to the above formula; in the second step, we normalize the test data set using the maximum and minimum values of the training data set.
The values of the preprocessed data are inserted into the GASVR, LSTM, Informer, BILSTM models and the BILSTM-GASVR model is constructed. Figures 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 and 9 show the prediction results. From Figs. 5 , 6 , and 7 , it can be seen that in terms of data accuracy, GASVR more closely matches the real number of infected people relative to BILSTM and LSTM. Especially in the most serious period of the epidemic in Shanghai (April 17, 2022 to April 30, 2022), the advantage of the accuracy of the predicted data of GASVR is even more obvious, which is due to the characteristics of GASVR for small samples and nonlinear prediction. However, in the overall trend of the epidemic, BILSTM and LSTM, which have the ability to learn and memorize to process time series data, are superior. It is clearly seen that in April 1, 2022-April 7, 2022 and May 10, 2022-May 15, 2022, there is a sudden and substantial increase in GASVR in these two time phases, and a sudden and substantial decrease in April 10, 2022-April 14, 2022. These errors also emphasize the stability of BILSTM and LSTM, which are more closely matched to the real epidemic development situation in the whole process of prediction, and the difference between BILSTM and LSTM prediction is that the former predicts data more accurately than the latter, which is focused on the early stage of prediction as well as the peak period of the epidemic. Informer is currently an advanced time series forecasting method. From Fig. 8 , it can be seen that the prediction data accuracy and the overall trend of the epidemic are better than the single prediction models of GASVR, LSTM and BILSTM. However, Informer is more suitable for long time series and more complex and large prediction problems, so the total sample size of less than one thousand cases is not in the comfort zone of Informer model. Figure 9 shows that the BILSTM-GASVR model constructed in this paper is more suitable for this smaller scale prediction problem, with the best prediction results, closest to the actual parameter (number of current confirmed cases), demonstrating small sample and time series advantages. In Short, the prediction effect of models is ranked as follows: BILSTM-GASVR> Informer> GASVR> BILSTM> LSTM.
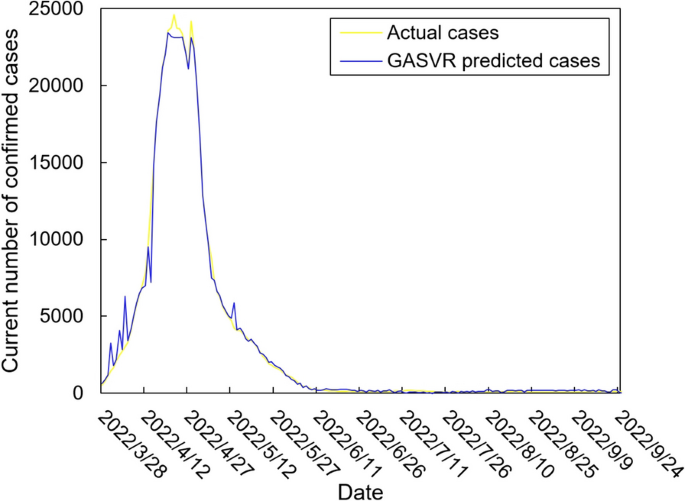
The prediction result of the GASVR model
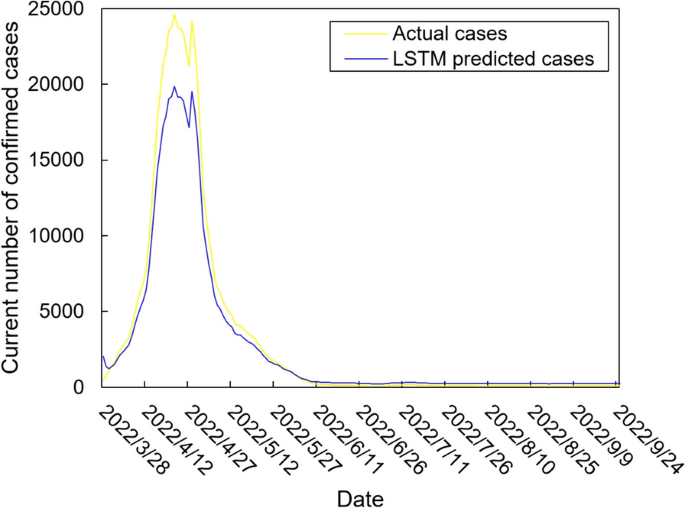
The prediction result of the LSTM model
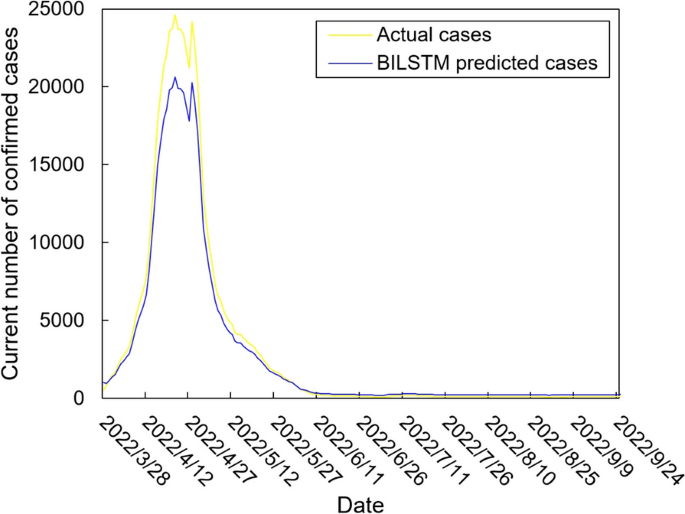
The prediction result of the BILSTM model
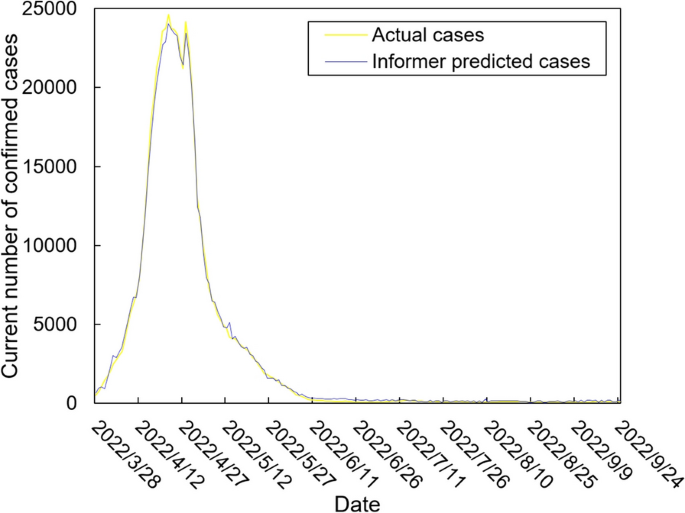
The prediction result of the Informer model
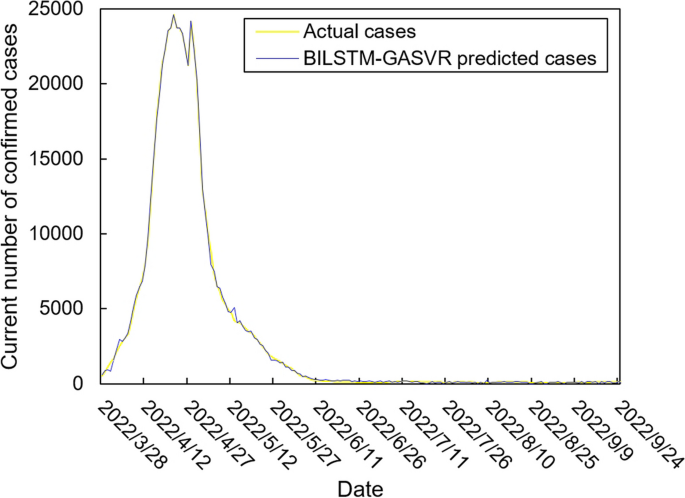
The prediction result of the BILSTM-GASVR model
The values of the three indicators (MSE, RMSE, and correlation coefficient \({R}^{2}\) ) for the five models are shown in Table 8 . MSE squares the error so that the larger the model error, the larger the value, which help capture the model's prediction error more sensitively. RMSE is MSE with a root sign added to it, which allows for a more intuitive representation of the order of magnitude difference from the true value. \({R}^{2}\) is a statistical indicator used to assess the overall goodness of fit of the model, which reflects the overall consistency of the predicted trend and does not specifically reflect the degree of data. The results in the Table 8 are consistent with the prediction results in the figure above, while the ranking of MSE, RMSE, and \({R}^{2}\) are also the same (i.e., BILSTM-GASVR> Informer> GASVR> BILSTM> LSTM).
In addition, we analyze the five model prediction data using significance tests as a way of demonstrating whether the model used is truly superior to the other baseline models. The test dataset with kurtosis higher than 4 does not belong to the approximate normal distribution, so parametric tests are not used in this paper. Given that the datasets predicted by each of the five models are continuous and independent datasets, this paper uses the Kruskal-Wallis test, which is a nonparametric test. The test steps are as follows.
Determine hypotheses (H0, H1) and significance level ( \(\alpha\) ).
For each data set, all its sample data are combined and ranked from smallest to largest. Then find the number of data items ( \({n}_{i}\) ), rank sum ( \({R}_{i}\) ) and mean rank of each group of data respectively.
Based on the rank sum, the test statistic (H) is calculated for each data set in the Kruskal-Wallis test. The specific calculation is shown in formula ( 27 ).
According to the test statistic and degrees of freedom, find the corresponding p-value in the Kruskal-Wallis distribution table. Based on the P-value, determine whether the original hypothesis is valid.
In the significance test, we set the significance setting original hypothesis (H0) as there is no significant difference between the five data sets obtained from the five predictive models. We set the alternative hypothesis (H1) as there is a significant difference between the five data sets obtained from the five predictive models. At the same time, we choose the most commonly used significance level taken in the significance test, namely 0.05. In this paper, multiple comparisons and two-by-two comparisons of the five data sets obtained from the five predictive models are performed through the SPSS software. The results of the test show that in the multiple comparison session, P=0.001<0.05, so H0 is rejected, which means that the difference between the five groups of data is significant. In the two-by-two comparison session, BILSTM-GASVR is less than 0.05 from the other four prediction models. The specific order of differences is Informer < GASVR < BILSTM < LSTM, which means that the BILSTM-GASVR prediction model does get a statistically significant difference between the dataset and the other models.
In summary, combined prediction using the BILSTM-GASVR model is superior to the other four single models in various aspects in the case study analysis of Shanghai epidemic with a sample size of 978.
Demand forecasting of ICU healthcare resources
Combined with the predicted number of current infected cases, representatives are selected from the three categories of resources for forecasting. The demand for nurses is selected as the representative for the first category of resources.
In view of the fact that there are currently no specific medications that are especially effective for this public health emergency, many ICU treatment measures involved helping patients survive as their own immune systems eliminated the virus. This involved, for example, administering antibiotics when patients developed a secondary bacterial infection. glucocorticoids are used to temporarily suppress the immune system when their immune system attacked and damaged lung tissues causing patients to have difficulty breathing. extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) is used for performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation when patients are suffering from cardiac arrest. In this study, we take dexamethasone injection (5 mg), a typical glucocorticoid drug, as the second category of ICU resources (i.e., drugs); and invasive ventilators as the third category of ICU resources (i.e., medical equipment).
During the actual epidemic in Shanghai, the municipal government organized nine critical care teams, which are stationed in eight municipally designated hospitals and are dedicated to the treatment of critically ill patients. In this study, the ICU nurses, dexamethasone injections, and invasive ventilators in Shanghai are selected as the prediction targets and introduced into their respective demand forecasting models. Forecasting of ICU healthcare resources is then performed for the period from March 28, 2022, to April 28, 2022, as an example. Part of the parameter settings for the three types of resources are shown in Tables 9 , 10 , and 11 , respectively.
Table 12 shows the forecasting results of the demand for ICU nurses, dexamethasone injections, and invasive ventilators during the epidemic wave in Shanghai between March 28, 2022, and April 28, 2022.
For the first category (i.e., ICU nurses), human resource support is only needed near the peak period, but the supply could not be replenished immediately. In the early stages, Shanghai could only rely on the nurses’ perseverance, alleviating the shortage of human resources by reducing the number of shifts and increasing working hours. This situation persisted until about April 10 and is only resolved when nurses from other provinces and regions successively arrived in Shanghai.
The second category of ICU resources is drugs, which are rapidly consumed. The pre-event reserve of 30,000 dexamethasone injections could only be maintained for a short period and is fully consumed during the outbreak. Furthermore, daily replenishment is still needed, even when the epidemic has passed its peak and begun its decline.
The third category is invasive ventilators, which are non-consumables. Thus, the reserve lasted for a relatively long period of time in the early stages and did not require replenishment after its maximum usage during the peak period.
Demand forecasting models are constructed based on the classification of healthcare resources according to their respective features. We choose ICU nurses, dexamethasone injections, and invasive ventilators as examples, and then forecast demand for the epidemic wave in Shanghai between March 28, 2022, and April 28, 2022. The main conclusions are as follows:
A long period of time is needed to train ICU healthcare workers who can independently be on duty, taking at least one year from graduation to entering the hospital, in addition to their requiring continuous learning, regular theoretical training, and the accumulation of clinical experience during this process. Therefore, for the first category of ICU healthcare resources, in the long term, healthcare institutions should place a greater emphasis on their talent reserves. Using China as an example, according to the third ICU census, the ratio of the number of ICU physicians to the number of beds is 0.62:1 and the ratio of the number of nurses to the number of beds is 1.96:1, which are far lower than those stipulated by China itself and those of developed countries. Therefore, a fundamental solution is to undertake proactive and systematic planning and construction to ensure the more effective deployment of human resources in the event of a severe outbreak. In the short term, healthcare institutions should focus on the emergency expansion capacity of their human resources. In case there are healthcare worker shortages during emergencies, the situation can be alleviated by summoning retired workers back to work and asking senior medical students from various universities to help in the hospitals to prevent the passive scenario of severely compressing the rest time of existing staff or waiting for external aid. However, it is worth noting that to ensure the effectiveness of such a strategy of using retired healthcare workers or senior students of university medical faculties, it is necessary for healthcare organizations to provide them with regular training in the norm, such as organizing 2-3 drills a year, to ensure the professionalism and proficiency of healthcare workers who are temporarily and suddenly put on the job. At the same time, it is also necessary to fully mobilize the will of individuals. Medical institutions can provide certain subsidies to retired health-care workers and award them with honorable titles. For senior university medical students, volunteer certificates are issued and priority is given to their internships, so that health-care workers can be motivated to self-realization through spiritual and material rewards.
Regarding the second category of ICU resources (i.e., drugs), healthcare institutions perform the subdivision of drug types and carry out dynamic physical preparations based on 15–20% of the service recipient population for clinically essential drugs. This will enable a combination of good preparedness during normal times and emergency situations. In addition, in-depth collaboration with corporations is needed to fully capitalize on their production capacity reserves. This helps medical institutions to be able to scientifically and rationally optimize the structure and quantity of their drug stockpiles to prevent themselves from being over-stressed. Yet the lower demand for medicines at the end of the epidemic led to the problem of excess inventory of enterprises at a certain point in time must be taken into account. So, the medical institutions should sign a strategic agreement on stockpiling with enterprises, take the initiative to bear the guaranteed acquisition measures, and consider the production costs of the cooperative enterprises. These measures are used to truly safeguard the enthusiasm of the cooperative enterprises to invest in the production capacity.
Regarding the third category of ICU resources (i.e., medical equipment), large-scale medical equipment cannot be rapidly mass-produced due to limitations in the capacity for emergency production and conversion of materials. In addition, the bulk procurement of high-end medical equipment is also relatively difficult in the short term. Therefore, it is more feasible for healthcare institutions to have physical reserves of medical equipment, such as invasive ventilators. However, the investment costs of medical equipment are relatively high. Ventilators, for example, cost up to USD $50,000, and subsequent maintenance costs are also relatively high. After all, according to the depreciable life of specialized hospital equipment, the ventilator, as a surgical emergency equipment, is depreciated over five years. And its depreciation rate is calculated at 20% annually for the first five years, which means a monthly depreciation of $835. Thus, the excessively low utilization rate of such equipment will also impact the hospital. Healthcare institutions should, therefore, conduct further investigations on the number of beds and the reserves of ancillary large-scale medical equipment to find a balance between capital investment and patient needs.
The limitations of this paper are reflected in the following three points. Firstly, in the prediction of the number of infections, the specific research object in this paper is COVID-19, and other public health events such as SARS, H1N1, and Ebola are not comparatively analyzed. The main reason for this is the issue of data accessibility, and it is easier for us to analyze events that have occurred in recent years. In addition, using the Shanghai epidemic as a specific case may be more representative of the epidemic situation in an international metropolis with high population density and mobility. Hence, it has certain regional limitations, and subsequent studies should expand the scope of the case study to reflect the characteristics of epidemic transmission in different types of urban areas and enhance the generalizability.
Secondly, the main emphasis of this study is on forecasting the demand for ICU healthcare resources across the entire region of the epidemic, with a greater focus on patient demand during public emergencies. Our aims are to help all local healthcare institutions more accurately identify changes in ICU healthcare resource demand during this local epidemic wave, gain a more accurate understanding of the treatment demands of critically ill patients, and carry out comprehensive, scientifically based decision-making. Therefore, future studies can examine individual healthcare institutions instead and incorporate the actual conditions of individual units to construct multi-objective models. In this way, medical institutions can further grasp the relationship between different resource inputs and the recovery rate of critically ill patients, and achieve the balance between economic and social benefits.
Finally, for the BILSTM-GASVR prediction method, in addition to the number of confirmed diagnoses predicted for an outbreak in a given region, other potential applications beyond this type of medium-sized dataset still require further experimentation. For example, whether the method is suitable for procurement planning of a certain supply in production management, forecasting of goods sales volume in marketing management, and other long-period, large-scale and other situations.
Within the context of major public health events, the fluctuations and uncertainties in the demand for ICU resources can lead to large errors between the healthcare supply and actual demand. Therefore, this study focuses on the question of forecasting the demand for ICU healthcare resources. Based on the number of current confirmed cases, we construct the BILSTM-GASVR model for predicting the number of patients. By comparing the three indicators (MSE, MAPE, and correlation coefficient \(R^{2}\) ) and the results of the BILSTM, LSTM, and GASVR models, we demonstrate that our model have a higher accuracy. Our findings can improve the timeliness and accuracy of predicting ICU healthcare resources and enhance the dynamics of demand forecasting. Hence, this study may serve as a reference for the scientific deployment of ICU resources in healthcare institutions during major public events.
Given the difficulty in data acquisition, only the Shanghai epidemic dataset is selected in this paper, which is one of the limitations mentioned in Part 4. Although the current experimental cases of papers in the same field do not fully conform to this paper, the results of the study cannot be directly compared. However, after studying the relevant reviews and the results of the latest papers, we realize that there is consistency in the prediction ideas and prediction methods [ 34 , 35 ]. Therefore, we summarize the similarities and differences between the results of the study and other research papers in epidemic forecasting as shown below.
Similarities: on the one hand, we all characterize trends in the spread of the epidemic and predict the number of infections over 14 days. On the other hand, we all select the current mainstream predictive models as the basis and combine or improve them. Moreover, we all use the same evaluation method (comparison of metrics such as MSE and realistic values) to evaluate the improvements against other popular predictive models.
Differences: on the one hand, other papers focus more on predictions at the point of the number of patients, such as hospitalization rate, number of infections, etc. This paper extends the prediction from the number of patients to the specific healthcare resources. This paper extends the prediction from the number of patients to specific healthcare resources. We have divided the medical resources and summarized the demand regularities of the three types of information in the epidemic, which provides the basis for decision-making on epidemic prevention to the government or medical institutions. On the other hand, in addition to the two assessment methods mentioned in the same point, this paper assesses the performance of the prediction methods with the help of significance tests, which is a statistical approach to data. This can make the practicality of the forecasting methodology more convincing.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Yuan, R., Yang, Y., Wang, X., Duo, J. & Li, J. Study on the forecasting and allocation of emergency medical material needs in the event of a major infectious disease outbreak. J Saf Environ. https://doi.org/10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2023.2448 .
Total epidemic data (global). 2024. Retrieved March 30, 2024, from: https://www.sy72.com/world/ .
Sui, K., Wang, Y., Wang, S., Chen, C., & Sun, X. A multiple regression analysis-based method for forecasting the demand of emergency materials for power grids. Electron Technol Softw Eng. 2016; (23), 195-197.
Li K, Liu L, Zhai J, Khoshgoftaar TM, Li T. The improved grey model based on particle swarm optimization algorithm for time series prediction. Eng Appl Artif Intell. 2016;55:285–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2016.07.005 .
Article Google Scholar
Fan R, Wang Y, Luo M. SEIR-based COVID-19 transmission model and inflection point prediction analysis. J Univ Electron Sci Technol China. 2020;49(3):369–74.
Google Scholar
Neves AGM, Guerrero G. Predicting the evolution of the COVID-19 epidemic with the A-SIR model: Lombardy, Italy and São Paulo state Brazil. Physica D. 2020;413:132693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physd.2020.132693 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Li R, Pei S, Chen B, Song Y, Zhang T, Wan Y, Shaman J. Substantial undocumented infection facilitates the rapid dissemination of novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2). Science. 2020;368(6490):489–93. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abb3221 .
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Kermack WO, McKendrick AG. A contribution to the mathematical theory of epidemics. Proc R Soc Lond. 1927;115(772):700–21. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1927.0118 .
Hethcote HW. The mathematics of infectious diseases. Siam Rev. 2000;42(4):599–653. https://doi.org/10.1137/SIREAD000042000004000655000001 .
Estrada E. COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2. Modeling the present, looking at the future. Phys Rep. 2020;869:1–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physrep.2020.07.005 .
Mizumoto K, Chowell G. Transmission potential of the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) onboard the diamond Princess Cruises Ship, 2020. Infect Dis Model. 2020;5:264–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idm.2020.02.003 .
Delamater PL, Street EJ, Leslie TF, Yang YT, Jacobsen KH. Complexity of the Basic Reproduction Number. Emerg Infect Dis. 2019;25(1):1–4. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2501.171901 .
Annas S, Isbar Pratama M, Rifandi M, Sanusi W, Side S. Stability analysis and numerical simulation of SEIR model for pandemic COVID-19 spread in Indonesia. Chaos Solit Fract. 2020;139:110072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2020.110072 .
Li Q, Guan X, Wu P, Wang X, Zhou L, Tong Y, Ren R, Leung KSM. Early Transmission Dynamics in Wuhan, China, of Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(13):1199–209. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2001316 .
Anggriani N, Ndii MZ, Amelia R, Suryaningrat W, Pratama MAA. A mathematical COVID-19 model considering asymptomatic and symptomatic classes with waning immunity. Alexandria Eng J. 2022;61(1):113–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2021.04.104 .
Efimov D, Ushirobira R. On an interval prediction of COVID-19 development based on a SEIR epidemic model. Ann Rev Control. 2021;51:477–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcontrol.2021.01.006 .
Lin Q, Zhao S, Gao D, Lou Y, Yang S, Musa SS, Wang MH. A conceptual model for the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in Wuhan, China with individual reaction and governmental action. Int J Infect Dis. 2020;93:211–16.
Chao L, Feng P, Shi P. Study on the epidemic development of COVID-19 in Hubei. J Zhejiang Univ (Med Sci). 2020;49(2):178–84.
Reiner RC, Barber RM, Collins JK, et al. Modeling COVID-19 scenarios for the United States. Nat Med. 2021;27(1):94–105. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-020-1132-9 .
Article CAS Google Scholar
Shahid F, Zameer A, Muneeb M. Predictions for COVID-19 with deep learning models of LSTM GRU and Bi-LSTM. Chaos Solit Fract. 2020;140:110212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2020.110212 .
Chimmula VKR, Zhang L. Time series forecasting of COVID-19 transmission in Canada using LSTM networks. Chaos Solit Fract. 2020;135:109864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2020.109864 .
Hamou AA, Azroul E, Hammouch Z, Alaoui AAL. A fractional multi-order model to predict the COVID-19 outbreak in Morocco. Appl Comput Math. 2021;20(1):177–203.
Zhou, L., Zhao, C., Liu, N., Yao, X., & Cheng, Z. Improved LSTM-based deep learning model for COVID-19 prediction using optimized approach. Eng Appl Artif Intell. 2023; 122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2023.106157 .
Huang C, Chen Y, Ma Y, Kuo P. Multiple-Input Deep Convolutional Neural Network Model for COVID-19 Forecasting in China. medRxiv. 2020;74822–34.
Gautam Y. Transfer Learning for COVID-19 cases and deaths forecast using LSTM network. Isa Trans. 2022;124:41–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isatra.2020.12.057 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Ghany KKA, Zawbaa HM, Sabri HM. COVID-19 prediction using LSTM algorithm: GCC case study. Inform Med Unlock. 2021;23:100566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imu.2021.100566 .
Devaraj J, Madurai Elavarasan R, Pugazhendhi R, Shafiullah GM, Ganesan S, Jeysree AK, Khan IA, Hossain E. Forecasting of COVID-19 cases using deep learning models: Is it reliable and practically significant? Results Phys. 2021;21:103817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2021.103817 .
Arora P, Kumar H, Panigrahi BK. Prediction and analysis of COVID-19 positive cases using deep learning models: a descriptive case study of India. Chaos Solit Fract. 2020;139:110017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2020.110017 .
Liu Q, Fung DLX, Lac L, Hu P. A Novel Matrix Profile-Guided Attention LSTM Model for Forecasting COVID-19 Cases in USA. Front Public Health. 2021;9:741030. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2021.741030 .
Ribeiro MHDM, Da Silva RG, Mariani VC, Coelho LDS. Short-term forecasting COVID-19 cumulative confirmed cases: perspectives for Brazil. Chaos Solit Fract. 2020;135:109853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2020.109853 .
Shoko C, Sigauke C. Short-term forecasting of COVID-19 using support vector regression: an application using Zimbabwean data. Am J Infect Control. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajic.2023.03.010 .
Feng T, Peng Y, Wang J. ISGS: A Combinatorial Model for Hysteresis Effects. Acta Electronica Sinica. 2023;09:2504–9.
Zhou H, Zhang S, Peng J, Zhang S, Li J, Xiong H, Zhang W. Informer: Beyond Efficient Transformer for Long Sequence Time-Series Forecasting. AAAI Conference Artif Intell. 2020;35(12):11106–15.
Rahimi I, Chen F, Gandomi AH. A review on COVID-19 forecasting models. Neural Comput Applic. 2023;35:23671–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-05626-8 .
Chen J, Creamer GG, Ning Y, Ben-Zvi T. Healthcare Sustainability: Hospitalization Rate Forecasting with Transfer Learning and Location-Aware News Analysis. Sustainability. 2023;15(22):15840. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152215840 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the hard and dedicated work of all the staff that implemented the intervention and evaluation components of the study.
No external funding received to conduct this study.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Logistics, Beijing Wuzi University, No.321, Fuhe Street, Tongzhou District, Beijing, 101149, China
Weiwei Zhang & Xinchun Li
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
WWZ and XCL conceived the idea and conceptualised the study. XCL collected the data. WWZ analysed the data. WWZ and XCL drafted the manuscript, then WWZ and XCLreviewed the manuscript. WWZ and XCL read and approved the final draft.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Xinchun Li .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Zhang, W., Li, X. A data-driven combined prediction method for the demand for intensive care unit healthcare resources in public health emergencies. BMC Health Serv Res 24 , 477 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-10955-8
Download citation
Received : 21 September 2023
Accepted : 05 April 2024
Published : 17 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-10955-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Public health emergency
- ICU healthcare resource demand
- Machine learning
- Combined prediction
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]

COMMENTS
The figures should be indicated within parentheses in their first mention in the "Materials and Methods" section. Headings and as a prevalent convention legends of the figures should be indicated at the end of the manuscript. If a different method is used in the study, this should be explained in detail.
The methods section of a research paper typically constitutes materials and methods; while writing this section, authors usually arrange the information under each category. The materials category describes the samples, materials, treatments, and instruments, while experimental design, sample preparation, data collection, and data analysis are ...
A reader would need to know which search engine and what key words you used. Open this section by describing the overall approach you took or the materials used. Then describe to the readers step-by-step the methods you used including any data analysis performed. See Fig. 2.5 below for an example of materials and methods section. Writing tips: Do:
To structure your methods section, you can use the subheadings of "Participants," "Materials," and "Procedures.". These headings are not mandatory—aim to organize your methods section using subheadings that make sense for your specific study. Note that not all of these topics will necessarily be relevant for your study.
The complexity of scientific inquiry necessitates that the writing of the methods be clear and orderly to avoid confusion and ambiguity. First, it is usually helpful to structure the methods section by: 1. Describing the materials used in the study 2. Explaining how the materials were prepared 3.
Your Methods Section contextualizes the results of your study, giving editors, reviewers and readers alike the information they need to understand and interpret your work. Your methods are key to establishing the credibility of your study, along with your data and the results themselves. A complete methods section should provide enough detail ...
7 Tips for Writing an Effective Materials and Methods Section in Your Research Manuscript: 1. Begin writing the Materials and Methods while you are performing your experiments. 2. Start with general information that applies to the entire manuscript and then move on to specific experimental details. 3.
For a Methods paper, the first step in the story line is a statement that you are presenting a new or improved material, method, or apparatus. The second step in the story line has two parts: a complete description of the new method, material, or apparatus; and a description of how this new method, material, or apparatus was tested.
This free white paper tackles the best ways to write the Materials and Methods section of a scientific manuscript. The Materials and Methods (or "Methods section") is the section of a research paper that provides the reader. with all the information needed to understand your work and how the reported results were produced.
To write your methods section in APA format, describe your participants, materials, study design, and procedures. Keep this section succinct, and always write in the past tense. The main heading of this section should be labeled "Method" and it should be centered, bolded, and capitalized. Each subheading within this section should be bolded ...
4. Use subheadings: Dividing the Methods section in terms of the experiments helps the reader to follow the section better. You may write the specific objective of each experiment as a subheading. Alternatively, if applicable, the name of each experiment can also be used as subheading. 5.
In this guide, we'll show you how to write a clear and comprehensive Methods section for your research paper. Structuring the Methods Section. ... Writing the Materials Subsection. In this subsection, you should address the materials, equipment, measures, and stimuli used in the study. These might include technology and computer software ...
Methods / Materials Overview. These sections of the research paper should be concise. The audience reading the paper will always want to know what materials or methods that were used. The methods and materials may be under subheadings in the section or incorporated together. The main objective for these sections is to provide specialized ...
In this blog, we look at how to write the materials and methods section of a research paper. In most research papers, the materials and methods section follows the literature review section. This is generally the easiest section to write because you are simply reproducing what you did in your experiments. It is always a good idea to start ...
1 Although traditionally, this section is only called "Material and Methods" (rarely: Study Site, Material and Methods), it can be composed of the following parts: study site, study organism, material, methods, statistical evaluation.. 2 The aim of this section in scientific papers is to enable readers to assess the reliability of your work, and to be able to repeat it for verification if ...
Materials and methods. The study's methods are one of the most important parts used to judge the overall quality of the paper. In addition the Methods section should give readers enough information so that they can repeat the experiments. Reviewers should look for potential sources of bias in the way the study was designed and carried out ...
The section should be like following the instructions in a cookbook. Full size image. You must mention 'what', 'how much', 'how often', 'where', 'when' and 'why' clearly to provide a step-by-step tutorial for your reader. It may not be possible to provide all the technical details while writing this section for a print ...
0:00 Introduction0:57 Components1:33 Instrument2:53 Supplies (Chemicals)3:32 Protocol4:14 Summary5:10 ConclusionIn how to How to write materials and methods ...
Introduction. Your lab report introduction should set the scene for your experiment. One way to write your introduction is with a funnel (an inverted triangle) structure: Start with the broad, general research topic. Narrow your topic down your specific study focus. End with a clear research question.
In this paper, a novel high-performance bismuth-free ZnO varistor ceramic was developed involving only three doping elements: Sr, Co and Sb. To specifically study the role of each element in improving electrical properties, a stepwise research method was used for this novel ceramic employing the binary system of Zn-Sr, ternary system of Zn-Sr-Co and quaternary system of Zn-Sr-Co-Sb.
In our review, the majority of reports were published from 2013 onwards, aligning with the expansion in migrant research internationally . 52% used qualitative research methods, 28% used quantitative methods and 20% used mixed methods. 58% focused on migrant health: the remaining papers included other populations or health as part of a wider ...
Materials and Methods. Milk samples (cases 2-5) and fresh and formalin-fixed tissues (cases 1, 3-5) from dairy cattle were received at the ISUVDL from Texas on March 21 and from Kansas on March 22, 2024. ... Further research, case series investigations, and surveillance data are needed to better understand and inform measures to curtail the ...
Journal of Geophysical Research: ... Contribution: Investigation, Writing - original draft, Writing - review & editing, Funding acquisition. Search for more papers by this author. E. Bruce Watson, ... 2 Materials and Methods 2.1 Paleomagnetic Sampling and Field Tests.
Lakes in the Alpine region are recognized as critical methane (CH 4) emitters, but a robust characterization of the magnitude and variability of CH 4 fluxes is missing. We developed a mobile platform for CH 4 eddy covariance (EC) flux measurements to tackle this gap. The mobile system was deployed at nine lakes across a latitudinal transect in the Alps and validated by comparing the measured ...
Background Public health emergencies are characterized by uncertainty, rapid transmission, a large number of cases, a high rate of critical illness, and a high case fatality rate. The intensive care unit (ICU) is the "last line of defense" for saving lives. And ICU resources play a critical role in the treatment of critical illness and combating public health emergencies. Objective This ...