Cyber security is an essential tool for managing risks in today’s increasingly dynamic and capable cyber threat landscape. Yet the market for cyber security remains small, and organizations are making only tactical investments in cyber security measures—one of the reasons why there has been an increase in cyber attacks. Evidence suggests that this trend will last for some time to come. However, the anticipation of an increasingly open and mobile enterprise should help refocus the spotlight on strategic investments in areas like cyber security. Cyber security professionals who wish to see cyber security move up in IT’s priority queue should take immediate steps such as demanding secure software from suppliers and requiring rigorous acceptance tests for third-party code to help promote cyber security in the long run.
Because cyber security has a significant impact on vulnerability management, one could infer that the spotlight is only shifting to a different perspective and that commitment to cyber security may not have declined in the final analysis. Although viewed as a priority by many cyber security professionals, cyber security has not seen the appropriate commitment level reflected in IT’s budget allocation.
For example, data breaches resulting from web application hacking are almost always accomplished through the exploitation of application vulnerabilities like SQL injection or cross-site scripting. If cyber security is not improved at a larger scale, the industry will continue to be plagued with security incidents that result in data breaches or other consequences that are even more disastrous. Changing the attitude toward cyber security, however, would require a culture shift, a shift that places importance on proactive risk management rather than immediate ROI. This shift won�t happen overnight. In the meantime, cyber security professionals should follow these recommendations to implement a few immediate measures to effect positive changes:
- Demand software quality and security from suppliers.
- Perform stringent acceptance tests for third-party code.
- Disable default accounts from applications.
- Establish a secure operational environment for applications.
- Implement effective bug-reporting and handling.
As the buyer side starts to demand secure cyber software, the power balance will start to shift toward more strategic approaches to managing cyber-level risks. Cyber security professionals can encourage this change by engaging in these longer-term initiatives:
- Work toward an industry certification program for secure development practices.
- Implement a cyber security program.
- Continue to drive awareness of the changing cyber threat landscape.
So, in order to improve cyber security, companies and cyber security professionals should work in a concerted fashion to cultivate a culture that values and promotes cyber security. To help usher in such a culture, cyber security professionals should:
- Do their part to promote a cyber security ecosystem.
- Use mobile proliferation as a catalyst for cyber security.
Cybercriminals from China have spent more than six years cautiously working to obtain data from more than 70 government agencies, corporations and non-profit groups. The campaign, named Operation Shady RAT (remote access tool) was discovered by the security firm McAfee.
While most of the targets have removed the malware, the operation persists. The good news: McAfee gained access to a command-and-control server used by the cyber attackers and has been watching, silently. U.S. law enforcement officials are working to shut down the operation. The Chinese government is denying that it sanctioned the cyber attack operation; although, configuration plans for the new DoD F-35 stealth figher were comprised by the cyber attackers. So, with the preceding in mind, the following are five things that came to light:
- Seventy-two (72) organizations were compromised.
- It was just not North America and Europe.
- When the coast was determined to be clear, the cyber attackers struck.
- This was a single operation by a single group (probably the Chinese).
- The only organizations that are exempt from this cyber threat were those that didn’t have anything valuable or interesting worth stealing, from a national security point of view.
The loss of this data represents a massive economic cyber threat not just to individual companies and industries, but to entire countries that face the prospect of decreased economic growth in a suddenly more competitive landscape; the loss of jobs in industries that lose out to unscrupulous competitors in another part of the world; not to mention, the national security impact of the loss of sensitive intelligence or defense information.
Yet, the public (and often the industry) understanding of this significant national cyber security threat is largely minimal due to the very limited number of voluntary disclosures by victims of intrusion activity compared to the actual number of compromises that take place. With the goal of raising the level of public awareness today, this is not a new cyber attack, and the vast majority of the victims have long since remediated these specific infections. Although, whether most victims realized the seriousness of the intrusion or simply cleaned up the infected machine without further analysis into the data loss remains an open question.
The actual intrusion activity may have begun well before 2006, but that is the earliest evidence that was found for the start of the compromises. The compromises themselves were standard procedure for these types of targeted intrusions: a spear-phishing email containing an exploit is sent to an individual with the right level of access at the company, and the exploit when opened on an unpatched system will trigger a download of the implant malware. That malware will execute and initiate a backdoor communication channel to the web server and interpret the instructions encoded in the hidden comments embedded in the webpage code. This will be quickly followed by live intruders jumping on to the infected machine and proceeding to quickly escalate privileges and move laterally within the organization to establish new persistent footholds via additional compromised machines running implant malware; as well as, targeting for quick exfiltration the key data that the cyber attackers came for. In the end, one very critical question remains unanswered: Why wasn’t the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) all over this cyber breach during the last 6 years when “Operation Shady Rat” was alive and well?? After all, isn’t DHS supposed to be the security guardians of the cyber world?
If “Operation Shady Rat,” wasn’t bad enough, hackers are now using outfitted model planes/drones to hack into your wireless system. Built from an old Air Force target drone, the Wireless Aerial Surveillance Platform (WASP) packs a lot of technological power into a flying high-end cyber endurance package.
- In order to implement a few immediate measures to effect positive changes, what recommendations should cyber security professionals follow?
Cyber security professionals should follow these recommendations to implement a few immediate measures to effect positive changes:
- Cyber security professionals can encourage change by engaging in which longer-term initiatives?
As the buyer side starts to demand secure cyber software, the power balance will start to shift toward more strategic approaches to managing cyber-level risks. Cyber security professionals can encourage this change by engaging in the following longer-term initiatives:
- Which of the following five things came to light, after cybercriminals from China spent more than six years cautiously working to obtain data from more than 70 government agencies, corporations and non-profit groups?
The following five things came to light, after cybercriminals from China spent more than six years cautiously working to obtain data from more than 70 government agencies, corporations and non-profit groups:
- The only organizations that are exempt from this cyber threat were those that didn�t have anything valuable or interesting worth stealing, from a national security point of view.
Copyright © 2012, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
https://www.nist.gov/itl/smallbusinesscyber/cybersecurity-basics/case-study-series

Small Business Cybersecurity Corner
Small business cybersecurity case study series.
Ransomware, phishing, and ATM skimming are just a few very common and very damaging cybersecurity threats that Small Businesses need to watch out for. The following Case Studies were created by the National Cyber Security Alliance , with a grant from NIST, and should prove useful in stimulating ongoing learning for all business owners and their employees.
- Case 1: A Business Trip to South America Goes South Topic: ATM Skimming and Bank Fraud
- Case 2: A Construction Company Gets Hammered by a Keylogger Topic: Keylogging, Malware and Bank Fraud
- Case 3: Stolen Hospital Laptop Causes Heartburn Topic: Encryption and Business Security Standards
- Case 4: Hotel CEO Finds Unwanted Guests in Email Account Topic: Social Engineering and Phishing
- Case 5: A Dark Web of Issues for a Small Government Contractor Topic: Data Breach
- Trending Now
- Foundational Courses
- Data Science
- Practice Problem
- Machine Learning
- System Design
- DevOps Tutorial
- Cyber Security Salary in India
Cyber Security
- Cyber Security Tutorial
- Cyber Security, Types and Importance
- Difference between Network Security and Cyber Security
- Top 10 Cyber Security Specialist Skills in 2024
Cyber Security Interview Questions
- Software Developer Salary Per Month in India: Average Salary, Starting Salary
- Salary of a Data Scientist in India – For Freshers & Experienced
- Software Engineer Salary in India 2024: Freshers & Experienced
- Data Analyst Salary In India 2024
- Java Developer Salary In India - For Freshers & Experienced
- Average Web Developer Salary in India - For Freshers & Experienced
- Full Stack Developer Salary in India (2024)
- Project Manager Salary In India 2024
- UI/UX Designer Salary in India in 2023: Fresher to Experienced
- IPS Officer Salary 2024 - Basic Pay, Perks & Allowances
- IAS Officer Salary Structure, Per Month, Allowances & More (2024)
- Data Engineer Salary in India for Freshers & Experienced (2023)
- Product Manager Salary in India 2024
- Business Analyst Salary in India 2024: Fresher to Experienced
Cybersecurity is the act of protecting systems, networks, and programs from digital attacks that can compromise the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data. These cyber-attacks can take various forms, such as malware, phishing, ransomware, denial-of-service, or advanced persistent threats. They typically aim to access, alter or destroy sensitive information, extort money from users, or disrupt normal business processes.
In this article, We covered the top 60 most asked cyber security interview questions with answers that cover everything from basic of cybersecurity to advanced cybersecurity concepts such as Threat Intelligence, Incident Response, Malware analysis penetration testing, red teaming and more. Whether you are a fresher or an experienced cyber security architect, this article gives you all the confidence you need to ace your next cybersecurity interview.

Table of Content
Cyber security interview questions for freshers, cyber security interview questions for intermediate, cyber security interview questions for experienced, 1. what are the common cyberattacks.
Some basic Cyber attacks are as follows:
- Phishing: Phishing is the fraudulent practice of sending spam emails by impersonating legitimate sources.
- Social Engineering Attacks: Social engineering attacks can take many forms and can be carried out anywhere human collaboration is required.
- Ransomware: Ransomware is documented encryption programming that uses special cryptographic calculations to encrypt records in a targeted framework.
- Cryptocurrency Hijacking: As digital currencies and mining become more popular, so do cybercriminals. They have found an evil advantage in cryptocurrency mining, which involves complex calculations to mine virtual currencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, Monero, and Litecoin.
- Botnet Attacks: Botnet attacks often target large organizations and entities that obtain vast amounts of information. This attack allows programmers to control countless devices in exchange for cunning intent.
For more details please refer to the article: Types of Cyber Attacks
2. What are the elements of cyber security?
There are various elements of cyber security as given below:
- Application Security: Application security is the most important core component of cyber security , adding security highlights to applications during the improvement period to defend against cyber attacks.
- Information Security: Information security is a component of cyber security that describes how information is protected against unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, alteration, or deletion.
- Network Security: Network security is the security provided to a network from unauthorized access and threats. It is the network administrator’s responsibility to take precautions to protect the network from potential security threats. Network security is another element of IT security, the method of defending and preventing unauthorized access to computer networks.
- Disaster Recovery Planning: A plan that describes the continuity of work after a disaster quickly and efficiently is known as a disaster recovery plan or business continuity plan. A disaster recovery methodology should start at the business level and identify applications that are generally critical to carrying out the association’s activities.
- Operational Security: In order to protect sensitive data from a variety of threats, the process of allowing administrators to see activity from a hacker’s perspective is called operational security (OPSEC)n or procedural security.
- End User Education: End-user training is the most important component of computer security. End users are becoming the number one security threat to any organization because they can happen at any time. One of the major errors that lead to information corruption is human error. Associations must prepare their employees for cyber security.
For more details please refer to the article: Elements of Cybersecurity
3. Define DNS?
The Domain Name System (DNS) translates domain names into IP addresses that browsers use to load web pages. Every device connected to the Internet has its own IP address , which other devices use to identify it in simple language, we can say that DNS Defines the Service of the network.
To know more please refer to the article: Domain Name System (DNS) in Application Layer
4. What is a Firewall?
A firewall is a hardware or software-based network security device that monitors all incoming and outgoing traffic and accepts, denies, or drops that particular traffic based on a defined set of security rules.
Please refer to the article: Introduction of Firewall to know more about this topic.
5. What is a VPN?
VPN stands for Virtual Private Network. A virtual private network (VPN) is a technology that creates a secure, encrypted connection over an insecure network like the Internet. A virtual private network is a method of extending a private network using a public network such as the Internet. The name only indicates that it is a virtual “private network”. A user may be part of a local area network at a remote location. Create a secure connection using a tunnelling protocol.
Please refer to the article: Virtual Private Network (VPN) to learn more about this topic.
6. What are the different sources of malware?
The different sources of malware are given below:
- Worms: A worm is basically a type of malicious malware that spreads rapidly from one computer to another via email and file sharing. Worms do not require host software or code to execute.
- Spyware: Spyware is basically a type of malicious malware that runs in the background of your computer, steals all your sensitive data, and reports this data to remote attackers.
- Ransomware: Ransomware is used as malware to extort money from users for ransom by gaining unauthorized access to sensitive user information and demanding payment to delete or return that information from the user.
- Virus: A virus is a type of malicious malware that comes as an attachment with a file or program. Viruses usually spread from one program to another program, and they will run only when the host file gets executed. The virus can only cause damage to the computer until the host file runs.
- Trojan: Trojans are malicious, non-replicating malware that often degrades computer performance and efficiency. Trojans have the ability to leak sensitive user information and modify and delete this data.
- Adware: Adware is another type of malware that tracks the usage of various types of programs and files on your computer and displays personalized ad recommendations based on your usage history.
Please refer to the article: Different Sources of Malware to learn more about this topic.
7. How does email work?
When a sender uses an e-mail program to send an e-mail, it is redirected to a simple e-mail transfer protocol. In this protocol, the recipient’s email address belongs to a different domain name or the same domain name as the sender (Gmail, Outlook, etc.). After that, the e-mail will be stored on the server, and later he will send it using the POP or IMAP protocol. Then, if the recipient has a different domain name address, the SMTP protocol communicates with the DNS (Domain Name Server) for the different addresses that the recipient uses. Then the sender’s SMTP communicates with the receiver’s SMTP, and the receiver’s SMTP performs the communication. This way the email is delivered to the recipient’s SMTP. If certain network traffic issues prevent both the sender’s SMTP and the recipient’s SMTP from communicating with each other, outgoing emails will be queued at the recipient’s SMTP and finally to be received by the recipient. Also, if a message stays in the queue for too long due to terrible circumstances, the message will be returned to the sender as undelivered.
Please refer to the article: Working of Email to learn more about this topic.
8. What is the difference between active and passive cyber attacks?
- Active Cyber Attack: An active attack is a type of attack in which the attacker modifies or attempts to modify the content of the message. Active attacks are a threat to integrity and availability. Active attacks can constantly corrupt the system and modify system resources. Most importantly, if there is an active attack, the victim is notified of the attack.
- Passive Cyber Attack: A passive attack is a type of attack in which the attacker observes the message content or copies the message content. Passive attacks are a threat to confidentiality. Since it is a passive attack, there is no damage to the system. Most importantly, when attacking passively, the victim is not notified of the attack.
Please refer to the article: Difference between Active Attack and Passive Attack to know more about it.
9. What is a social engineering attack?
Social engineering is the act of manipulating individuals to take actions that may or may not be in the best interests of the “target”. This may include obtaining information, obtaining access, or obtaining a goal to perform a particular action. It has the ability to manipulate and deceive people. A phone call accompanied by a survey or a quick internet search can bring up dates of birthdays and anniversaries and arm you with that information. This information is enough to create a password attack list.
Please refer to the article: Social Engineering to know more.
10. Who are black hat hackers and white hat hackers?
- White Hat Hacker: A white hat hacker is a certified or certified hacker who works for governments and organizations by conducting penetration tests and identifying cybersecurity gaps. It also guarantees protection from malicious cybercrime.
- Black Hat Hackers: They are often called crackers. Black hat hackers can gain unauthorized access to your system and destroy your important data. The attack method uses common hacking techniques learned earlier. They are considered criminals and are easy to identify because of their malicious behavior.
Please refer to the article: Types of Hackers to know more.
11. Define encryption and decryption?
Encryption is the process of transforming an ordinary message (plaintext) into a meaningless message (ciphertext). Decryption is the process of transforming a meaningless message (ciphertext) into its original form (plaintext). The main difference between covert writing and covert writing is that it converts the message into a cryptic format that cannot be deciphered unless the message is decrypted. Covert writing, on the other hand, is reconstructing the original message from the encrypted information.
Please refer to the article: Difference between Encryption and Decryption to know more.
12. What is the difference between plaintext and cleartext?
The plaintext is not encrypted at all and cannot be considered encrypted and Clear text is a text sent or stored that has not been encrypted and was not intended to be encrypted. So you don’t need to decrypt to see the plaintext. In its simplest form.
Please refer to the article: Encryption and Decryption to know more.
13. What is a block cipher?
Block Cipher Converts plaintext to ciphertext using one block of plaintext at a time. Use 64-bit or 64-bit or greater. The complexity of block ciphers is simple. The algorithm modes used in block ciphers are ECB (Electronic Code Book) and CBC (Cipher Block Chaining).
Please refer to the article: Difference between Block Cipher and Stream Cipher to know more.
14. What is the CIA triangle?
When it comes to network security, the CIA Triad is one of the most important models developed to guide information security policy within an organization. CIA stands for:
- Confidentiality
- availability
Please refer to the article: CIA Triad in Cryptography to know more.
15. What is the Three-way handshake?
TCP uses a three-way handshake to establish reliable connections. The connection is full-duplex, with synchronization (SYN) and acknowledgment (ACK) on both sides. The exchange of these four flags is done in three steps: SYN, SYN to ACK, and ACK.
Please refer to the article: TCP 3-Way Handshake to know more about it.
16. How can identity theft be prevented?
Steps to prevent identity theft:
- Use a strong password and don’t share her PIN with anyone on or off the phone.
- Use two-factor notifications for email. Protect all your devices with one password.
- Do not install software from the Internet. Do not post confidential information on social media.
- When entering a password with a payment gateway, check its authenticity.
- Limit the personal data you run. Get in the habit of changing your PIN and password regularly.
- Do not give out your information over the phone.
Please refer to the article: Cyber Crime – Identity Theft to know more about it.
17. What are some common Hashing functions?
The hash function is a function that converts a specific numerical key or alphanumeric key into a small practical integer value. The mapped integer value is used as an index for hash tables. Simply put, a hash function maps any valid number or string to a small integer that can be used as an index into a hash table. The types of Hash functions are given below:
- Division Method.
- Mid Square Method.
- Folding Method.
- Multiplication Method.
Please refer to the article Hash Functions to know more about this topic.
18. What do you mean by two-factor authentication?
Two-factor authentication refers to using any two independent methods from a variety of authentication methods. Two-factor authentication is used to ensure users have access to secure systems and to enhance security. Two-factor authentication was first implemented for laptops due to the basic security needs of mobile computing. Two-factor authentication makes it more difficult for unauthorized users to use mobile devices to access secure data and systems.
Please refer to the article Two-factor Authentication to learn more about this topic.
19. What does XSS stand for? How can it be prevented?
Cross-site scripting (XSS) is a vulnerability in web applications that allows third parties to execute scripts on behalf of the web application in the user’s browser. Cross-site scripting is one of the most prevalent security vulnerabilities on the Internet today. Exploiting her XSS against users can have a variety of consequences, including Account compromise, account deletion, privilege escalation, malware infection, etc. Effective prevention of XSS vulnerabilities requires a combination of the following countermeasures:
- Filter entrance on arrival. As user input comes in, filter expected or valid input as closely as possible. Encode the data on output. When user-controllable data is emitted in an HTTP response, encode the output so that it is not interpreted as active content.
- Depending on the output context, it may be necessary to apply a combination of HTML, URL, JavaScript, and CSS encoding. Use proper response headers.
- To prevent XSS in HTTP responses that should not contain HTML or JavaScript, use the Content-Type and X-Content-Type-Options headers to force the browser to interpret the response as intended. Content Security Policy. As a last line of defence, a Content Security Policy (CSP) can be used to mitigate the severity of remaining XSS vulnerabilities.
Please refer to the article Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) to learn more about this topic.
20. What do you mean by Shoulder Surfing?
A shoulder surfing attack describes a situation in which an attacker can physically look at a device’s screen or keyboard and enter passwords to obtain personal information. Used to – access malware. Similar things can happen from nosy people, leading to an invasion of privacy.
Please refer to the article Shoulder Surfing to learn more about this topic.
21. What is the difference between hashing and encryption?
Please refer to the article Hashing and Encryption to learn more about this topic.
22. Differentiate between Information security and information assurance.
- Information Assurance: It can be described as the practice of protecting and managing risks associated with sensitive information throughout the process of data transmission, processing, and storage. Information assurance primarily focuses on protecting the integrity, availability, authenticity, non-repudiation, and confidentiality of data within a system. This includes physical technology as well as digital data protection.
- Information security: on the other hand, is the practice of protecting information by reducing information risk. The purpose is usually to reduce the possibility of unauthorized access or illegal use of the data. Also, destroy, detect, alter, examine, or record any Confidential Information. This includes taking steps to prevent such incidents. The main focus of information security is to provide balanced protection against cyber-attacks and hacking while maintaining data confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Please refer to the article Information Assurance vs. Information Security to learn more about this topic.
23. Write a difference between HTTPS and SSL.
Please refer to the article SSL vs. HTTPS to learn more about this topic.
24. What do you mean by System Hardening?
The attack surface includes all flaws and vulnerabilities that a hacker could use to gain access to your system, such as default passwords, improperly configured firewalls, etc. The idea of system hardening is to make a system more secure by reducing the attack surface present in the design of the system. System hardening is the process of reducing a system’s attack surface, thereby making it more robust and secure. This is an integral part of system security practices.
Please refer to the article System Hardening to learn more about this topic.
25. Differentiate between spear phishing and phishing.
- Phishing: This is a type of email attack in which an attacker fraudulently attempts to discover a user’s sensitive information through electronic communications, pretending to be from a relevant and trusted organization. The emails are carefully crafted by the attackers, targeted to specific groups, and clicking the links installs malicious code on your computer.
- Spear phishing: Spear phishing is a type of email attack that targets specific individuals or organizations. In Spear, a phishing attacker tricks a target into clicking a malicious link and installing malicious code, allowing the attacker to obtain sensitive information from the target’s system or network.
Please refer to the article Phishing and Spear Phishing to learn more about this topic.
26. What do you mean by Perfect Forward Secrecy?
Perfect Forward Secrecy is a style of encryption that creates a temporary exchange of secret keys between the server and client. It is primarily used to call apps, websites, and messaging apps where user privacy is paramount. A new session key is generated each time the user performs an action. This keeps your data uncompromised and safe from attackers. This is separate from special keys. The basic idea behind Perfect Forward Secrecy technology is to generate a new encryption key each time a user initiates a session. So, if only the encryption key is compromised, the conversation is leaked, and if the user’s unique key is compromised, the conversation will continue. Encryption keys generated by Perfect Forward Secrecy keep you safe from attackers. Essentially, it provides double protection from attackers.
Please refer to the article Perfect Forward Secrecy to learn more about this topic.
27. How to prevent MITM?
- Strong WEP/WAP Encryption on Access Points
- Strong Router Login Credentials Strong Router Login Credentials
- Use Virtual Private Network.
Please refer to the article How to Prevent Man In the Middle Attack? to learn more about this topic.
28. What is ransomware?
Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts data to make it inaccessible to computer users. Cybercriminals use it to extort money from the individuals and organizations that hacked the data and hold the data hostage until a ransom is paid.
Please refer to the article: Ransomware to know more about this.
29. What is Public Key Infrastructure?
A Public Key Infrastructure, or PKI, is the governing authority behind the issuance of digital certificates. Protect sensitive data and give users and systems unique identities. Therefore, communication security is ensured. The public key infrastructure uses keys in public-private key pairs to provide security. Public keys are vulnerable to attacks, so maintaining public keys requires a healthy infrastructure.
Please refer to the article: Public Key Infrastructure to know more.
30. What is Spoofing?
Spoofing is a type of attack on computing devices in which an attacker attempts to steal the identity of a legitimate user and pretend to be someone else. This type of attack is performed to compromise system security or steal user information.
Types of Spoofing:
- IP Spoofing: IP is a network protocol that allows messages to be sent and received over the Internet. Her IP address of the sender is included in the message header of all emails sent to her messages (sender address).
- ARP Spoofing: ARP spoofing is a hacking technique that redirects network traffic to hackers . Spying on LAN addresses in both wired and wireless LAN networks is called ARP spoofing.
- Email Spoofing : Email spoofing is the most common form of identity theft on the Internet. Phishers use official logos and headers to send emails to many addresses impersonating bank, corporate, and law enforcement officials.
Please refer to the article: What is Spoofing? to know more.
31. What are the steps involved in hacking a server or network?
The following steps must be ensured in order to hack any server or network:
- Access your web server.
- Use anonymous FTP to access this network to gather more information and scan ports.
- Pay attention to file sizes, open ports, and processes running on your system.
- Run a few simple commands on your web server like “clear cache” or “delete all files” to highlight the data stored by the server behind these programs. This helps in obtaining more sensitive information that can be used in application-specific exploits.
- Connect to other sites on the same network, such as Facebook and Twitter, so that you can check the deleted data. Access the server using the conversion channel.
- Access internal network resources and data to gather more information.
- Use Metasploit to gain remote access to these resources.
To know more about this topic please refer to the article: How to Hack a Web Server?
32. What are the various sniffing tools?
Lists of some main Networking Sniffing Tools:
- SolarWinds Network Packet Sniffer
- Paessler PRTG
- ManageEngine NetFlow Analyzer
- NetworkMiner
Please refer to the article: Sniffing Tools to learn more about sniffing tools in ethical hacking.
33. What is SQL injection?
SQL injection is a technique used to exploit user data through web page input by injecting SQL commands as statements. Essentially, these instructions can be used by a malicious user to manipulate her web server for your application. SQL injection is a code injection technique that can corrupt your database. Preventing SQL Injection is given below:
- Validation of user input by pre-defining user input length, type, input fields, and authentication.
- Restrict user access and determine how much data outsiders can access from your database. Basically, you shouldn’t give users permission to access everything in your database.
- Do not use system administrator accounts.
To know more about this topic, Please read the article: SQL Injection
34. What is a Distributed Denial of Service attack (DDoS)?
A denial of service (DoS) is a cyber attack against an individual computer or website aimed at denying service to intended users. Its purpose is to interfere with the organization’s network operations by denying her access. Denial of service is usually achieved by flooding the target machine or resource with excessive requests, overloading the system, and preventing some or all legitimate requests from being satisfied.
Please refer to the article: Denial of Service and Prevention to know more.
35. How to avoid ARP poisoning?
Following are the five ways of avoiding ARP Poisoning attacks:
- Static ARP Tables: If you can verify the correct mapping of MAC addresses to IP addresses, half the problem is solved. This is doable but very costly to administer. ARP tables to record all associations and each network change are manually updated in these tables. Currently, it is not practical for an organization to manually update its ARP table on every host.
- Switch Security: Most Ethernet switches have features that help mitigate ARP poisoning attacks. Also known as Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI), these features help validate ARP messages and drop packets that indicate any kind of malicious activity.
- Physical Security: A very simple way to mitigate ARP poisoning attacks is to control the physical space of your organization. ARP messages are only routed within the local network. Therefore, an attacker may have physical proximity to the victim’s network.
- Network Isolation: A well-segmented network is better than a regular network because ARP messages have a range no wider than the local subnet. That way, if an attack were to occur, only parts of the network would be affected and other parts would be safe. Attacks on one subnet do not affect devices on other subnets.
- Encryption: Encryption does not help prevent ARP poisoning, but it does help reduce the damage that could be done if an attack were to occur. Credentials are stolen from the network, similar to the MiTM attack.
Please refer to the article: How to Avoid ARP Poisoning? to know more.
36. What is a proxy firewall?
The proxy firewall monitors application-level information using a firewall proxy server. A proxy firewall server creates and runs a process on the firewall that mirrors the services as if they were running on the end host. The application layer has several protocols such as HTTP (a protocol for sending and receiving web pages) and SMTP (a protocol for e-mail messages on the Internet). A proxy server like Web Proxy Server is like a process that mirrors the behavior of the HTTP service. Similarly, the FTP proxy server reflects how his FTP service works.
Please refer to the article: What is a Proxy Firewall? to know more.
37. Explain SSL Encryption.
Secure Socket Layer (SSL) provides security for data transferred between web browsers and servers. SSL encrypts the connection between your web server and your browser, keeping all data sent between them private and immune to attack. Secure Socket Layer Protocols: SSL recording protocol.
Please refer to the article: Secure Socket Layer to know more about it.
38. What do you mean by penetration testing?
Penetration testing is done to find vulnerabilities, malicious content, flaws, and risks. It’s done to make the organization’s security system defend the IT infrastructure. It is an official procedure that can be deemed helpful and not a harmful attempt. It is part of an ethical hacking process that specifically focuses only on penetrating the information system.
Please refer to the article Penetration Testing to learn more about this topic.
39. What are the risks associated with public Wi-Fi?
- Malware, Viruses, and Worms.
- Rogue Networks.
- Unencrypted Connections
- Network Snooping.
- Log-in Credential Vulnerability.
- System Update Alerts.
- Session Hijacking.
Please refer to the article Risks Associated with Public Wi-Fi to learn more about this topic.
40. Explain the main difference between Diffie-Hellman and RSA.
- Diffie-Hellman (DH) algorithm: It is a key exchange protocol that allows two parties to communicate over a public channel and establish a shared secret without sending it over the Internet. DH allows two people to use their public key to encrypt and decrypt conversations or data using symmetric cryptography.
- RSA : It is a type of asymmetric encryption that uses two different linked keys. RSA encryption allows messages to be encrypted with both public and private keys. The opposite key used to encrypt the message is used to decrypt the message.
Please refer to the article to learn more about this topic.
41. Give some examples of asymmetric encryption algorithms.
Asymmetric key cryptography is based on public and private key cryptography. It uses two different keys to encrypt and decrypt messages. More secure than symmetric key cryptography, but much slower.
- You need two keys, a public key, and a private key. One for encryption and one for decryption.
- The ciphertext size is equal to or larger than the original plaintext.
- Slow encryption process.
- Used to transfer small amounts of data.
- Provides confidentiality, authenticity, and non-repudiation.
Please refer to the article Symmetric and Asymmetric Key Encryption to learn more about this topic.
42. Explain social engineering and its attacks.
Social engineering is a hacking technique based on forging someone’s identity and using socialization skills to obtain details. There are techniques that combine psychological and marketing skills to influence targeted victims and manipulate them into obtaining sensitive information. The types of social engineering attacks are given below:
- Impersonation: This is a smart choice for attackers. This method impersonates organizations, police, banks, and tax authorities. Then they steal money or anything they want from the victim. And the same goes for organizations that obtain information about victims legally through other means.
- Phishing: Phishing is like impersonating a well-known website such as Facebook and creating a fake girlfriend website to trick users into providing account credentials and personal information. Most phishing attacks are carried out through social media such as Instagram, Facebook, and Twitter.
- Vishing: Technically speaking, this is called “voice phishing”. In this phishing technique, attackers use their voice and speaking skills to trick users into providing personal information. In general, this is most often done by organizations to capture financial and customer data.
- Smithing: Smithing is a method of carrying out attacks, generally through messages. In this method, attackers use their fear and interest in a particular topic to reach out to victims through messages. These topics are linked to further the phishing process and obtaining sensitive information about the target.
Please refer to the article Social Engineering: The Attack on Human Brain and Trust to learn more about this topic.
43. State the difference between a virus and worm.
- Worms: Worms are similar to viruses, but do not modify the program. It replicates more and more to slow down your computer system. The worm can be controlled with a remote control. The main purpose of worms is to eat up system resources. The 2000 WannaCry ransomware worm exploits the resource-sharing protocol Windows Server Message Block (SMBv1).
- Virus: A virus is malicious executable code attached to another executable file that can be harmless or modify or delete data. When a computer program runs with a virus, it performs actions such as B. Delete the file from your computer system. Viruses cannot be controlled remotely. The ILOVEYOU virus spreads through email attachments.
Please refer to the article Difference between Worms and Virus to know more about this topic.
44. Explain the concept of session hijacking.
Session hijacking is a security attack on user sessions over a protected network. The most common method of session hijacking is called IP spoofing, where an attacker uses source-routed IP packets to inject commands into the active communication between two nodes on a network, allowing an authenticated impersonation of one of the users. This type of attack is possible because authentication usually only happens at the beginning of a TCP session. The types of session hijacking are given below:
- Packet Sniffing
- CSRF (Cross-site Request Forgery)
- Cross-site Scripting
- IP spoofing
Please refer to the article Session Hijacking to learn more about this topic.
45. Explain the honeypot and its types.
A honeypot is a networked system that acts as a trap for cyber attackers to detect and investigate hacker tactics and types of attacks. Acting as a potential target on the Internet, it notifies defenders of unauthorized access to information systems. Honeypots are classified based on their deployment and intruder involvement. Based on usage, honeypots are classified as follows:
- Research honeypots: Used by researchers to analyze hacking attacks and find different ways to prevent them.
- Production Honeypots: Production honeypots are deployed with servers on the production network. These honeypots act as a front-end trap for attackers composed of false information, giving administrators time to fix all vulnerabilities in real systems.
Please refer to the article What is Honeypot? to know more about this topic.
46. What do you mean by a Null Session?
Null session attacks have existed since Windows 2000 was widely used. However, system administrators do not consider this type of attack when implementing network security measures. This can have unimaginable consequences, as this type of attack allows hackers to obtain all the information they need to access your system remotely. This type of attack is more difficult to execute if the customer is using a newer version of the operating system, but Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 are still the most common.
Please refer to the article Null Session to learn more about this topic.
47. What is IP blocklisting?
IP blacklisting is a method used to block unauthorized or malicious IP addresses from accessing your network. A blacklist is a list of ranges or individual IP addresses to block.
Please refer to the article What is IP blocklisting? to know more about this topic.
48. What are Polymorphic viruses?
“Poly” refers to many and “morphic” refers to the shape. Thus, polymorphic viruses, as the name suggests, are complex computer viruses that change shape as they spread in order to avoid detection by antivirus programs. This is a self-encrypting virus that combines a mutation engine with a self-propagating code. A polymorphic virus consists of:
- Encrypted virus body mutation engine that generates random decryption routines.
- A polymorphic virus has its mutation engine and virus body encrypted. When an infected program is run, a virus decryption routine takes control of the computer and decrypts the virus body and mutation engine.
- Control is then passed to the virus to detect new programs to infect. Since the body of the virus is encrypted and the decryption routine varies from infection to infection, virus scanners cannot look for a fixed signature or fixed decryption routine, making detection more difficult.
Please refer to the article Polymorphic Viruses to learn more about this topic.
49. What is a Botnet?
A botnet (short for “robot network”) is a network of malware-infected computers under the control of a single attacker known as a “bot herder”. An individual machine under the control of a bot herder is called a bot.
Please refer to the article Botnet in Computer Networks to learn more about this topic.
50. What is an Eavesdropping Attack?
Eavesdropping occurs when a hacker intercepts, deletes or modifies data sent between two devices. Eavesdropping, also known as sniffing or snooping, relies on unsecured network communications to access data sent between devices.
Please refer to the article Eavesdropping Attack to learn more about this topic.
51. What is the man-in-the-middle attack?
This is a type of cyber attack in which the attacker stays between the two to carry out their mission. The type of function it can perform is to modify the communication between two parties so that both parties feel like they are communicating over a secure network.
Please refer to the article: Man In the Middle Attack to learn more about this topic.
52. What is a traceroute? Why is it used?
Traceroute is a widely used command line tool available on almost all operating systems. A complete route to the destination address is displayed. It also shows the time (or delay) between intermediate routers.
Uses of traceroute:
- It enables us to locate where the data was unable to be sent along
- Traceroute helps provide a map of data on the internet from source to destination
- It works by sending ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) packets.
- You can do a visual traceroute to get a visual representation of each hop.
Please refer to the article: Traceroute in Network Layer to know more about it.
53. What is the difference between HIDS and NIDS?
- HIDS: This intrusion detection system sees the host itself as a whole world. It can be a computer (PC) or a server that can act as a standalone system and analyze and monitor its own internals. It works by looking at the files/data coming in and out of the host you’re working on. It works by taking existing file system snapshots from a previously taken file system and comparing them to each other. If they are the same, it means the host is safe and not under attack, but a change could indicate a potential attack.
- NIDS: This system is responsible for installation points across the network and can operate in mixed and hybrid environments. Alerts are triggered when something malicious or anomalous is detected in your network, cloud, or other mixed environments.
Please refer to the article: Difference between HIDs and NIDs to know more about it.
54. What is the difference between VA (Vulnerability Assessment) and PT (Penetration Testing)?
- Penetration testing: This is performed to find vulnerabilities, malicious content, bugs, and risks. Used to set up an organization’s security system to protect its IT infrastructure. Penetration testing is also known as penetration testing. This is an official procedure that can be considered helpful, not a harmful attempt. This is part of an ethical hacking process that focuses solely on breaking into information systems.
- Vulnerability assessment: It is the technique of finding and measuring (scanning) security vulnerabilities in a particular environment. This is a location-comprehensive evaluation (result analysis) of information security. It is used to identify potential vulnerabilities and provide appropriate mitigations to eliminate them or reduce them below the risk level.
Please refer to the article: Differences between Penetration Testing and Vulnerability Assessments to know more.
55. What is RSA?
The RSA algorithm is an asymmetric encryption algorithm. Asymmetric means that it actually works with two different keys. H. Public and Private Keys. As the name suggests, the public key is shared with everyone and the private key remains secret.
Please refer to the article: RSA Algorithm in Cryptography to know more.
56. What is the Blowfish algorithm?
Blowfish is an encryption technique developed by Bruce Schneier in 1993 as an alternative to the DES encryption technique. It is considerably faster than DES and provides excellent encryption speed even though no effective cryptanalysis techniques have been discovered so far. It was one of the first secure block ciphers to be patent-free and therefore freely available to everyone.
- Block size: 64 bits
- keys: variable size from 32-bit to 448-bit
- Number of subkeys: 18 [P array]
- Number of rounds: 16
- Number of replacement boxes: 4 [each with 512 entries of 32 bits]
Please refer to the article: Blowfish Algorithm to know more.
57. What is the difference between a vulnerability and an exploit?
- Vulnerability: A vulnerability is an error in the design or implementation of a system that can be exploited to cause unexpected or undesirable behaviour. There are many ways a computer can become vulnerable to security threats. A common vulnerability is for attackers to exploit system security vulnerabilities to gain access to systems without proper authentication.
- Exploit: Exploits are tools that can be used to exploit vulnerabilities. They are created using vulnerabilities. Exploits are often patched by software vendors as soon as they are released. They take the form of software or code that helps control computers and steal network data.
Please refer to the article: Difference Between Vulnerability and Exploit to know more about it.
58. What do you understand by Risk, Vulnerability and threat in a network?
- Cyber threats are malicious acts aimed at stealing or corrupting data or destroying digital networks and systems. A threat can also be defined as the possibility of a successful cyberattack to gain unethical access to sensitive data on a system.
- Vulnerabilities in cybersecurity are deficiencies in system designs, security procedures, internal controls, etc. that can be exploited by cybercriminals. In very rare cases, cyber vulnerabilities are the result of cyberattacks rather than network misconfigurations.
- Cyber risk is the potential result of loss or damage to assets or data caused by cyber threats. You can’t eliminate risk completely, but you can manage it to a level that meets your organization’s risk tolerance. Therefore, our goal is not to build a system without risk but to keep the risk as low as possible.
Please refer to the article: Difference Between Threat, Vulnerability and Risk in Computer Networks to know more.
59. Explain Phishing and how to prevent it.
Phishing is a type of cyber attack. The name phishing comes from the word ‘phish’, which means fish. Placing bait to catch fish is a common phenomenon. Phishing works similarly. Tricking users or victims into clicking on malicious websites is an unethical practice.
Here’s how to protect your users from phishing attacks.
- Download software only from authorized sources
- Do not share personal information on unknown links.
- Always check website URLs to prevent such attacks.
- If you receive an email from a known source, but the email seems suspicious, contact the sender with a new email instead of using the reply option.
- Avoid posting personal information such as phone numbers, addresses, etc. on social media.
- Monitor compromised websites with malicious content using phishing detection tools. Try to avoid free Wi-Fi.
Please refer to the article Phishing to know more about this topic.
60. What do you mean by Forward Secrecy and how does it work?
Forward secrecy is a feature of some key agreement protocols that guarantees that the session keys will remain secure even if the server’s private key is compromised. Perfect forward secrecy, also known as PFS, is the term used to describe this. The “Diffie-Hellman key exchange” algorithm is employed to achieve this.
In summary, today, implementing effective cybersecurity measures is especially challenging due to the increasing number of devices relative to humans and the constant innovation by attackers. Therefore, cybersecurity professionals must employ various tools and techniques, including encryption, firewalls, antivirus software, anti-phishing measures, and vulnerability assessments, to proactively safeguard against and respond to cyber threats. As a result, the demand for cybersecurity professionals is expected to remain high in the future.
Wondering about the salary of a cyber security analyst? Take a look at our specialized article on Average Cyber Security Salary .
Frequently Asked Cyber Security Interview Questions
1. what is cryptography.
Cryptography is the practice of securing information and communications by transforming them into a form that cannot be easily understood by unauthorized parties. This can be done by using encryption algorithms to scramble the data, making it unreadable without the decryption key. Cryptography is used in a wide variety of applications, including secure communication, data storage, and digital signatures.
2. What is a traceroute? Mention its uses.
A traceroute is a diagnostic tool used to track the path that packets take from a source to a destination on the internet. It does this by sending packets with increasing time-to-live (TTL) values and recording the IP addresses of the routers that the packets pass through. Traceroute can be used to identify the location of network bottlenecks, troubleshoot connectivity problems, and map the topology of an internet network. Uses of traceroute: To identify the path that a packet takes from a source to a destination. To troubleshoot connectivity problems. To map the topology of an internet network. To identify the location of network bottlenecks. To test the performance of a network. To investigate denial-of-service attacks.
3. Define firewall, and why is it used?
A firewall is a network security device that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic. Firewalls can be used to block unauthorized access to a network, prevent malware from spreading, and protect sensitive data. There are two main types of firewalls: Packet-filtering firewalls: These firewalls examine the headers of network packets to determine whether they should be allowed to pass through. Application-level firewalls: These firewalls examine the content of network packets to determine whether they should be allowed to pass through.
4. Why is a firewall used?
Firewalls are used to protect networks from a variety of threats, including: Unauthorized access: Firewalls can block unauthorized users from accessing a network. Malware: Firewalls can prevent malware from spreading from one computer to another. Denial-of-service attacks: Firewalls can help to protect networks from denial-of-service attacks, which are attacks that attempt to overwhelm a network with traffic. Data leaks: Firewalls can help to protect sensitive data from being leaked from a network.
5. What is a three-way handshake?
A three-way handshake is a networking term for the process of establishing a connection between two hosts on a network. The three-way handshake is used in the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), which is a reliable connection-oriented protocol. The three-way handshake consists of the following steps: The client sends a SYN packet to the server. The server sends a SYN-ACK packet to the client. The client sends an ACK packet to the server. Once the three-way handshake is complete, the two hosts have established a connection and can begin exchanging data.
6. What is a response code?
A response code is a three-digit number that is used to indicate the status of an HTTP request. Response codes are sent by web servers in response to requests from web browsers. The first digit of the response code indicates the class of response. The second and third digits indicate the specific status code. Here are some of the most common response codes: 200 OK: The request was successful. 400 Bad Request: The request was malformed. 401 Unauthorized: The request requires authentication. 403 Forbidden: The request is not allowed. 404 Not Found: The requested resource could not be found. 500 Internal Server Error: An error occurred on the server. 503 Service Unavailable: The server is temporarily unavailable
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Cyber-security
- interview-questions
- Ethical Hacking
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
- Quick links
- 10 Trends Shaping 2024
- Global Private Equity Risk Index Highlights Risky Insight From Digital Chatter
- 2023 Fraud and Financial Crime Report
- Popular topics
- Valuation Advisory Services
- Compliance and Regulation
- Corporate Finance and Restructuring
- Investigations and Disputes
- Digital Technology Solutions
- Business Services
- Environmental, Social and Governance Advisory Services (ESG)
- Environmental, Social and Governance
- Consumer and Retail
- Financial Services
- Industrials
- Technology, Media and Telecom
- Energy and Mining
- Healthcare and Life Sciences
- Real Estate
- Our Experts
- Client Stories
- Transactions
- Restructuring Administration Cases
- Settlement Administration Cases
- Anti-Money Laundering
- Artificial Intelligence
- Cost of Capital
- Cryptocurrency
- Financial Crime
- M&A Updates
Valuation Outlook
- Blogs / Publications
- Webcasts and Videos
Cyber Security Case Studies
Managed detection and response case studies, managed detection and response, building cyber resilience amid azure migration.

Client Story
Seamless response to ransomware and a cyber resilience upgrade.

Reducing a Hospitality Company’s Cyber Risk Surface

Enhancing Security Visibility for a Leading Asset Management Firm

Elevating Cyber Security Maturity of a Housebuilding Company

Protecting the 2008 U.S. Presidential Election from Cyber Attacks
by Alan Brill

Endpoint Detection and Response to Increase Plastics Manufacturer’s Cyber Posture

Stronger Threat Detection and Response for UK Bank: Reduced False Positives, Swifter Response

Enhanced Ransomware Defences for Global Shipping Business with Robust MDR

Large Hospital Leverages Managed Detection and Response for Increased Resilience and Compliance Reporting

Defending Healthcare Organization Against Persistent Trickbot Attacks

Optimized Security Operations and Cyber Governance for Asset Management Firm

Digital Forensics and Incident Response Case Studies
Digital forensics and incident response, online skimming attack facilitated by work-from-home arrangements.
by Christopher Ballod

Electronic Gift Card Fraud Investigation Uncovers Contractual Risks

Spearphishing Compromises Fuel Chain Credit Card Transactions, Ends in Ransomware

Insider Threat Case Study: Digital Forensics Reveals Fraud, Potential Regulatory Concerns
by Kevin Wong, Ben Hawkins

Kroll Contains, Remediates SWIFT System Cyber Fraud for Middle Eastern Bank
by Kevin Wong, Imran Khan

Transatlantic Cyber Investigation Unmasks Insider Threat, Preempts Ransom Attempt
by Michael Quinn, Ben Hawkins, Justin Price

Office 365 Business Email Compromise Investigation Leads to Stronger Security
by Devon Ackerman

Business Email Compromise Attack Investigation and Remediation for Insurance Broker

Proactive Services Case Studies
Penetration testing, continuous penetration testing optimizes security in agile product development for software startup.

Scaling Up Application Security for a Global Telecommunications Company

Penetration Testing and Attack Simulation for VotingWorks’ Risk-Limiting Audit Software Arlo

AWS Penetration Testing Gives In-Depth Cyber Risk Insight to Specialist Bank

State of Arkansas Cyber Security Assessment
by Frank Marano, Jeff Macko

Red Team Exercise Helps International Trade Organization Comply with FCA Cyber Security Mandates

Other Cyber Security Case Studies
Cyber governance and risk, gdpr assessment and u.s. data privacy laws action plan for a global biopharmaceutical company.

Cyber Litigation Support
Uncovering critical historical data to progress a complex legal case.

Taking an Underwriter’s Security Posture From At-Risk to Resilient

Cloud Security
Cloud native security platform (cnsp) design and implementation for top five media firm.

Incident response, digital forensics, breach notification, managed detection services, penetration testing, cyber assessments and advisory.
Agile Penetration Testing Program
Integrated into your software development lifecycle (SDLC), Kroll’s agile penetration testing program is designed to help teams address security risks in real time and on budget.
Penetration Testing Services
Validate your cyber defenses against real-world threats. Kroll’s world-class penetration testing services bring together front-line threat intelligence, thousands of hours of cyber security assessments completed each year and a team of certified cyber experts — the foundation for our sophisticated and scalable approach.
Application Threat Modeling Services
Kroll helps development teams design and build internal application threat modeling programs to identify and manage their most pressing vulnerabilities.
Application Security Services
Kroll’s product security experts upscale your AppSec program with strategic application security services catered to your team’s culture and needs, merging engineering and security into a nimble unit.
Cloud Security Services
Kroll’s multi-layered approach to cloud security consulting services merges our industry-leading team of AWS and Azure-certified architects, cloud security experts and unrivalled incident expertise.
24x7 Incident Response
Kroll is the largest global IR provider with experienced responders who can handle the entire security incident lifecycle.
Connect With Us

Chief Financial Officers Ignoring Cyber Risk Worth Millions of Dollars According to Kroll Report

Kroll Acquires Crisp, Trusted Provider of Real-time Risk Intelligence
by Andrew Burke
Kroll Partners with Armis to Extend Preparedness and Response for OT and ICS Environments

Kroll Acquires Resolver, a Leader in Risk Intelligence Technology

Threat Intelligence
Q1 2024 cyber threat landscape virtual briefing.
Join the Q1 2024 Cyber Threat Landscape Virtual Briefing as Kroll’s cyber threat analysts outline notable trends and insights from our incident response intelligence.

Kroll at 2024 Gartner Security & Risk Management Summit
Join Kroll experts at Gartner SRM in National Harbor from June 3-5, 2024. Stop by booth 556 to meet our team.

Kroll at Infosecurity Europe 2024
Join our cyber risk experts at Infosecurity Europe in London, June 4–6, Stand C35. Get the latest threat intel, win prizes, and more.

IVSC Valuation Webinar Series 2024
Kroll and the International Valuations Standards Council (IVSC) are pleased to invite you to the 2024 Valuation Webinar Series.

Kroll is headquartered in New York with offices around the world.
More About Kroll
- Trending Topics
- Find an Expert
- Media Inquiry

- Accessibility
- Code of Conduct
- Data Privacy Framework
- Kroll Ethics Hotline
- Modern Slavery Statement
- Privacy Policy

Top 100+ Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers
Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers for Freshers
1) what is cybersecurity.
Cybersecurity refers to the protection of hardware, software, and data from attackers. The primary purpose of cyber security is to protect against cyberattacks like accessing, changing, or destroying sensitive information.
2) What are the elements of cybersecurity?
Major elements of cybersecurity are:
- Information security
- Network security
- Operational security
- Application security
- End-user education
- Business continuity planning
3) What are the advantages of cyber security?
Benefits of cyber security are as follows:
- It protects the business against ransomware, malware, social engineering, and phishing.
- It protects end-users.
- It gives good protection for both data as well as networks.
- Increase recovery time after a breach.
- Cybersecurity prevents unauthorized users.
4) Define Cryptography.
It is a technique used to protect information from third parties called adversaries. Cryptography allows the sender and recipient of a message to read its details.

5) Differentiate between IDS and IPS.
Intrusion Detection System (IDS) detects intrusions. The administrator has to be careful while preventing the intrusion. In the Intrusion Prevention System (IPS), the system finds the intrusion and prevent it.
6) What is CIA?
Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability (CIA) is a popular model which is designed to develop a security policy. CIA model consists of three concepts:
- Confidentiality: Ensure the sensitive data is accessed only by an authorized user.
- Integrity: Integrity means the information is in the right format.
- Availability: Ensure the data and resources are available for users who need them.
7) What is a Firewall?
It is a security system designed for the network. A firewall is set on the boundaries of any system or network which monitors and controls network traffic. Firewalls are mostly used to protect the system or network from malware, worms, and viruses. Firewalls can also prevent content filtering and remote access.
8) Explain Traceroute
It is a tool that shows the packet path. It lists all the points that the packet passes through. Traceroute is used mostly when the packet does not reach the destination. Traceroute is used to check where the connection breaks or stops or to identify the failure.

9) Differentiate between HIDS and NIDS.
10) explain ssl.
SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer. It is a technology creating encrypted connections between a web server and a web browser. It is used to protect the information in online transactions and digital payments to maintain data privacy.
11) What do you mean by data leakage?
Data leakage is an unauthorized transfer of data to the outside world. Data leakage occurs via email, optical media, laptops, and USB keys.
12) Explain the brute force attack. How to prevent it?
It is a trial-and-error method to find out the right password or PIN. Hackers repetitively try all the combinations of credentials. In many cases, brute force attacks are automated where the software automatically works to login with credentials. There are ways to prevent Brute Force attacks. They are:
- Setting password length.
- Increase password complexity.
- Set limit on login failures.
13) What is port scanning?
It is the technique for identifying open ports and service available on a specific host. Hackers use port scanning technique to find information for malicious purposes.
14) Name the different layers of the OSI model.
Seven different layers of OSI models are as follows:
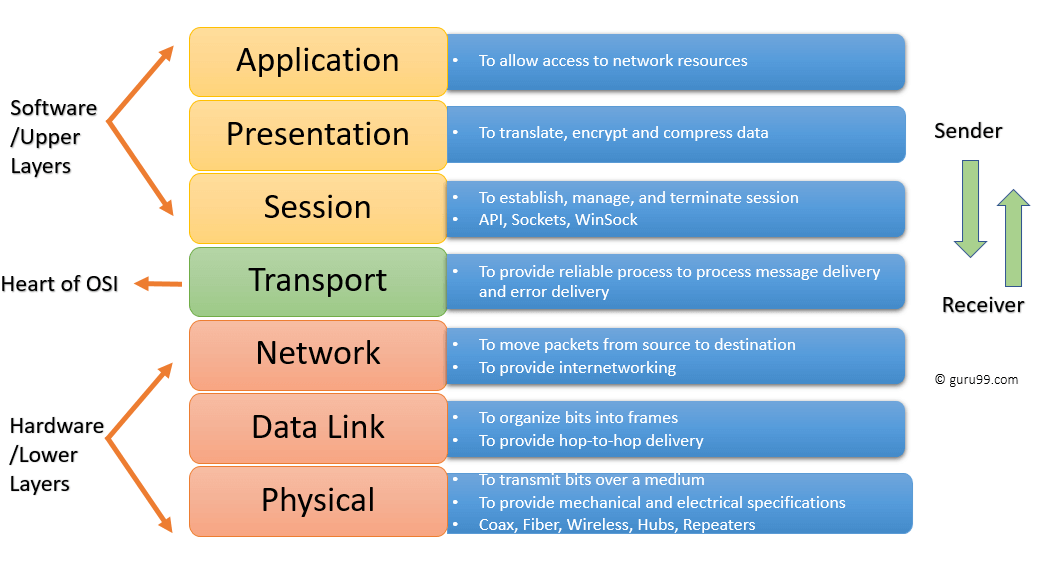
- Physical Layer
- Data Link Layer
- Network Layer
- Transport Layer
- Session Layer
- Presentation Layer
- Application Layer
15) What is a VPN?
VPN stands for Virtual Private Network. It is a network connection method for creating an encrypted and safe connection. This method protects data from interference, snooping, censorship.
16) What are black hat hackers?
Black hat hackers are people who have a good knowledge of breaching network security. These hackers can generate malware for personal financial gain or other malicious reasons. They break into a secure network to modify, steal, or destroy data so that the network can not be used by authorized network users.
17) What are white hat hackers?
White hat hackers or security specialist are specialized in Penetration testing . They protect the information system of an organization.
18) What are grey hat hackers?
Grey hat hackers are computer hacker who sometimes violate ethical standards, but they do not have malicious intent.
19) How to reset a password-protected BIOS configuration?
There are various ways to reset BIOS password. Some of them are as follows:
- Remove CMOS battery.
- By utilizing the software.
- By utilizing a motherboard jumper.
- By utilizing MS-DOS.
20) What is MITM attack?
A MITM or Man-in-the-Middle is a type of attack where an attacker intercepts communication between two persons. The main intention of MITM is to access confidential information.
21) Define ARP and its working process.
It is a protocol used for finding MAC address associated with IPv4 address. This protocol work as an interface between the OSI network and OSI link layer.
22) Explain botnet.
It’s a number of internet-connected devices like servers, mobile devices, IoT devices, and PCs that are infected and controlled by malware.
23) What is the main difference between SSL and TLS?
The main difference between these two is that SSL verifies the identity of the sender. SSL helps you to track the person you are communicating to. TLS offers a secure channel between two clients.
24) What is the abbreviation of CSRF?
CSRF stands for Cross-Site Request Forgery.

25) What is 2FA? How to implement it for a public website?
TFA stands for Two Factor Authentication. It is a security process to identify the person who is accessing an online account. The user is granted access only after presenting evidence to the authentication device.
Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers for Experienced
26) explain the difference between asymmetric and symmetric encryption..
Symmetric encryption requires the same key for encryption and decryption. On the other hand, asymmetric encryption needs different keys for encryption and decryption.
27) What is the full form of XSS?
XSS stands for cross-site scripting.
28) Explain WAF
29) what is hacking.
Hacking is a process of finding weakness in computer or private networks to exploit its weaknesses and gain access.
For example, using password cracking technique to gain access to a system.
30) Who are hackers?
A Hacker is a person who finds and exploits the weakness in computer systems, smartphones, tablets, or networks to gain access. Hackers are well experienced computer programmers with knowledge of computer security.
31) What is network sniffing?
Network sniffing is a tool used for analyzing data packets sent over a network. This can be done by the specialized software program or hardware equipment. Sniffing can be used to:
- Capture sensitive data such as password.
- Eavesdrop on chat messages
- Monitor data package over a network
32) What is the importance of DNS monitoring?
Yong domains are easily infected with malicious software. You need to use DNS monitoring tools to identify malware.
33) Define the process of salting. What is the use of salting?
Salting is that process to extend the length of passwords by using special characters. To use salting, it is very important to know the entire mechanism of salting. The use of salting is to safeguard passwords. It also prevents attackers testing known words across the system.
For example, Hash(“QxLUF1bgIAdeQX”) is added to each and every password to protect your password. It is called as salt.
34) What is SSH?
SSH stands for Secure Socket Shell or Secure Shell. It is a utility suite that provides system administrators secure way to access the data on a network.
35) Is SSL protocol enough for network security?
SSL verifies the sender’s identity, but it does not provide security once the data is transferred to the server. It is good to use server-side encryption and hashing to protect the server against a data breach.
36) What is black box testing and white box testing?
- Black box testing: It is a software testing method in which the internal structure or program code is hidden.
- White box testing: A software testing method in which internal structure or program is known by tester.
37) Explain vulnerabilities in network security.
Vulnerabilities refer to the weak point in software code which can be exploited by a threat actor. They are most commonly found in an application like SaaS (Software as a service) software.
38) Explain TCP Three-way handshake.
It is a process used in a network to make a connection between a local host and server. This method requires the client and server to negotiate synchronization and acknowledgment packets before starting communication.
39) Define the term residual risk. What are three ways to deal with risk?
It is a threat that balances risk exposure after finding and eliminating threats.
Three ways to deal with risk are:
40) Define Exfiltration.
41) what is exploit in network security.
An exploit is a method utilized by hackers to access data in an unauthorized way. It is incorporated into malware.
42) What do you mean by penetration testing?
It is the process of checking exploitable vulnerabilities on the target. In web security, it is used to augment the web application firewall.
43) List out some of the common cyber-attack.
Following are the common cyber-attacks which can be used by hackers to damage network:
- Password attacks
- Man in the middle
- Drive-by downloads
- Malvertising
- Rogue software
44) How to make the user authentication process more secure?
In order to authenticate users, they have to provide their identity. The ID and Key can be used to confirm the user’s identity. This is an ideal way how the system should authorize the user.
45) Explain the concept of cross-site scripting.
Cross-site scripting refers to a network security vulnerability in which malicious scripts are injected into websites. This attack occurs when attackers allow an untrusted source to inject code into a web application.
46) Name the protocol that broadcast the information across all the devices.
Internet Group Management Protocol or IGMP is a communication protocol that is used in game or video streaming. It facilitates routers and other communication devices to send packets.
47) How to protect email messages?
Use cipher algorithm to protect email, credit card information, and corporate data.
48) What are the risks associated with public Wi-Fi?
Public Wi-Fi has many security issues. Wi-Fi attacks include karma attack, sniffing, war-driving, brute force attack, etc.
Public Wi-Fi may identify data that is passed through a network device like emails, browsing history, passwords, and credit card data.
49) What is Data Encryption? Why it is important in network security?
Data encryption is a technique in which the sender converts the message into a code. It allows only authorized user to gain access.
50) Explain the main difference between Diffie-Hellman and RSA.
Diffie-Hellman is a protocol used while exchanging key between two parties while RSA is an algorithm that works on the basis two keys called private and public key.
51) What is a remote desktop protocol?
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is developed by Microsoft, which provides GUI to connect two devices over a network.
The user uses RDP client software to serve this purpose while other device must run RDP server software. This protocol is specifically designed for remote management and to access virtual PCs, applications, and terminal server.
52) Define Forward Secrecy.
Forward Secrecy is a security measure that ensures the integrity of unique session key in event that long term key is compromised.
53) Explain the concept of IV in encryption.
IV stands for the initial vector is an arbitrary number that is used to ensures that identical text encrypted to different ciphertexts. Encryption program uses this number only once per session.
54) Explain the difference between stream cipher and block cipher.
55) give some examples of a symmetric encryption algorithm..
Following are some examples of symmetric encryption algorithm.
- Rijndael (AES)
56) What is the abbreviation of ECB and CBC?
The full form of ECB is Electronic Codebook, and the full form of CBC is Cipher Block Chaining.
57) Explain a buffer overflow attack.
Buffer overflow attack is an attack that takes advantage of a process that attempts to write more data to a fixed-length memory block.
58) Define Spyware.
Spyware is a malware that aims to steal data about the organization or person. This malware can damage the organization’s computer system.
59) What is impersonation?
It is a mechanism of assigning the user account to an unknown user.
60) What do you mean by SRM?
SRM stands for Security Reference Monitor provides routines for computer drivers to grant access rights to object.
61) What is a computer virus?
A virus is a malicious software that is executed without the user’s consent. Viruses can consume computer resources, such as CPU time and memory. Sometimes, the virus makes changes in other computer programs and insert its own code to harm the computer system.
A computer virus may be used to:
- Access private data like user id and passwords
- Display annoying messages to the user
- Corrupt data in your computer
- Log the user’s keystrokes
62) What do you mean by Authenticode?
Authenticode is a technology that identifies the publisher of Authenticode sign software. It allows users to ensure that the software is genuine and not contain any malicious program.
63) Define CryptoAPI
CryptoAPI is a collection of encryption APIs which allows developers to create a project on a secure network.
64) Explain steps to secure web server.
Follow the following steps to secure your web server:
- Update ownership of file.
- Keep your webserver updated.
- Disable extra modules in the webserver.
- Delete default scripts.
65) What is Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer?
Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer or MBSA is a graphical and command-line interface that provides a method to find missing security updates and misconfigurations.
66) What is Ethical hacking?
Ethical hacking is a method to improve the security of a network. In this method, hackers fix vulnerabilities and weakness of computer or network. Ethical hackers use software tools to secure the system.
67) Explain social engineering and its attacks.
Social engineering is the term used to convince people to reveal confidential information.
There are mainly three types of social engineering attacks: 1) Human-based, 2) Mobile-based, and 3) Computer-based.
- Human-based attack: They may pretend like a genuine user who requests higher authority to reveal private and confidential information of the organization.
- Computer-based attack: In this attack, attackers send fake emails to harm the computer. They ask people to forward such email.
- Mobile-based attack: Attacker may send SMS to others and collect important information. If any user downloads a malicious app, then it can be misused to access authentication information.
68) What is IP and MAC Addresses?
IP Address is the acronym for Internet Protocol address. An internet protocol address is used to uniquely identify a computer or device such as printers, storage disks on a computer network.
MAC Address is the acronym for Media Access Control address. MAC addresses are used to uniquely identify network interfaces for communication at the physical layer of the network.
69) What do you mean by a worm?
A Worm is a type of malware which replicates from one computer to another.
70) State the difference between virus and worm
71) name some tools used for packet sniffing..
Following are some tools used for packet sniffing.
- NetworkMiner
72) Explain anti-virus sensor systems
Antivirus is software tool that is used to identify, prevent, or remove the viruses present in the computer. They perform system checks and increase the security of the computer regularly.
73) List out the types of sniffing attacks.
Various types of sniffing attacks are:
- Protocol Sniffing
- Web password sniffing
- Application-level sniffing
- TCP Session stealing
- LAN Sniffing
- ARP Sniffing
74) What is a distributed denial-of-service attack (DDoS)?
It is an attack in which multiple computers attack website, server, or any network resource.
75) Explain the concept of session hijacking.
TCP session hijacking is the misuse of a valid computer session. IP spoofing is the most common method of session hijacking. In this method, attackers use IP packets to insert a command between two nodes of the network.
76) List out various methods of session hijacking.
Various methods of session hijacking are:
- Using packet Sniffers
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS Attack)
- IP Spoofing
- Blind Attack
77) What are Hacking Tools?
Hacking Tools are computer programs and scripts that help you find and exploit weaknesses in computer systems, web applications, servers, and networks. There are varieties of such tools available on the market. Some of them are open source, while others are a commercial solution.
78) Explain honeypot and its Types.
Honeypot is a decoy computer system which records all the transactions, interactions, and actions with users.
Honeypot is classified into two categories: 1) Production honeypot and 2) Research honeypot.
- Production honeypot: It is designed to capture real information for the administrator to access vulnerabilities. They are generally placed inside production networks to increase their security.
- Research Honeypot: It is used by educational institutions and organizations for the sole purpose of researching the motives and tactics of the back-hat community for targeting different networks.
79) Name common encryption tools.
Tools available for encryptions are as follows:
80) What is Backdoor?
It is a malware type in which security mechanism is bypassed to access a system.
81) Is it right to send login credentials through email?
It is not right to send login credentials through email because if you send someone userid and password in the mail, chances of email attacks are high.
82) Explain the 80/20 rule of networking?
This rule is based on the percentage of network traffic, in which 80% of all network traffic should remain local while the rest of the traffic should be routed towards a permanent VPN.
83) Define WEP cracking.
It is a method used for a security breach in wireless networks. There are two types of WEP cracking: 1) Active cracking and 2) Passive cracking.
84) What are various WEP cracking tools?
Well known WEP cracking tools are:
85) What is a security auditing?
Security auditing is an internal inspection of applications and operating systems for security flaws. An audit can also be done via line by line inspection of code.
86) Explain phishing.
It is a technique used to obtain a username, password, and credit card details from other users.
87) What is Nano-scale encryption?
Nano encryption is a research area which provides robust security to computers and prevents them from hacking.
88) Define Security Testing?
Security Testing is defined as a type of Software Testing that ensures software systems and applications are free from any vulnerabilities, threats, risks that may cause a big loss.
89) Explain Security Scanning.
Security scanning involves identifying network and system weaknesses and later provides solutions for reducing these risks. This scanning can be performed for both Manual as well as Automated scanning.
90) Name the available hacking tools.
Following is a list of useful hacking tools.
- Angry IP scanner:
91) What is the importance of penetration testing in an enterprise?
Here are two common application of Penetration testing.
- Financial sectors like stock trading exchanges, investment banking, want their data to be secured, and penetration testing is essential to ensure security.
- In case if the software system is already hacked and the organization would like to determine whether any threats are still present in the system to avoid future hacks.
92) What are the disadvantages of penetration testing?
Disadvantages of penetration testing are:
- Penetration testing cannot find all vulnerabilities in the system.
- There are limitations of time, budget, scope, skills of penetration testers.
- Data loss and corruption
- Down Time is high which increase costs
93) Explain security threat
Security threat is defined as a risk which can steal confidential data and harm computer systems as well as organization.
94) What are physical threats?
A physical threat is a potential cause of an incident that may result in loss or physical damage to the computer systems.
95) Give examples of non-physical threats
Following are some examples of non-physical threat:
- Loss of sensitive information
- Loss or corruption of system data
- Cyber security Breaches
- Disrupt business operations that rely on computer systems
- Illegal monitoring of activities on computer systems
96) What is Trojan virus?
Trojan is a malware employed by hackers and cyber-thieves to gain access to any computer. Here attackers use social engineering techniques to execute the trojan on the system.
97) Define SQL Injection
It is an attack that poisons malicious SQL statements to database. It helps you to take benefit of the design flaws in poorly designed web applications to exploit SQL statements to execute malicious SQL code. In many situations, an attacker can escalate SQL injection attack in order to perform other attack, i.e. denial-of-service attack.
98) List security vulnerabilities as per Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP).
Security vulnerabilities as per open web application security project are as follows:
- SQL Injection
- Cross-site request forgery
- Insecure cryptographic storage
- Broken authentication and session management
- Insufficient transport layer protection
- Unvalidated redirects and forwards
- Failure to restrict URL access
99) Define an access token.
An access token is a credential which is used by the system to check whether the API should be granted to a particular object or not.
100) Explain ARP Poisoning
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) Poisoning is a type of cyber-attack which is used to convert IP address to physical addresses on a network device. The host sends an ARP broadcast on the network, and the recipient computer responds back with its physical address.
ARP poisoning is sending fake addresses to the switch so that it can associate the fake addresses with the IP address of a genuine computer on a network and hijack the traffic.
101) Name common types of non-physical threats.
Following are various types of non-physical threats:
- Denial of Service Attacks
- Distributed Denial of Service Attacks
- Key loggers
- Unauthorized access to computer systems resources
102) Explain the sequence of a TCP connection.
The sequence of a TCP connection is SYN-SYN ACK-ACK.
103) Define hybrid attacks.
Hybrid attack is a blend of dictionary method and brute force attack. This attack is used to crack passwords by making a change of a dictionary word with symbols and numbers.
104) What is Nmap?
Nmap is a tool which is used for finding networks and in security auditing.
105) What is the use of EtterPeak tool?
EtterPeak is a network analysis tool that is used for sniffing packets of network traffic.
106) What are the types of cyber-attacks?
There are two types of cyberattacks: 1) Web-based attacks, 2) System based attacks.
107) List out web-based attacks
Some web-based attacks are: 1) SQL Injection attacks, 2) Phishing, 3) Brute Force, 4) DNS Spoofing, 4) Denial of Service , and 5) Dictionary attacks.
108) Give examples of System-based attacks
Examples of system-based attacks are:
109) List out the types of cyber attackers
There are four types of cyber attackers. They are: 1) cybercriminals, 2) hacktivists, 3) insider threats, 4) state-sponsored attackers.
110) Define accidental threats
They are threats that are accidently done by organization employees. In these threats, an employee unintentionally deletes any file or share confidential data with outsiders or a business partner going beyond the policy of the company.
These interview questions will also help in your viva(orals)
- What is Digital Forensics? History, Process, Types, Challenges
- What is Cybercrime? Types, Tools, Examples
- CompTIA Certification Tutorial: Career Path & Study Material
- 10 Best FREE DDoS Attack Online Tool & Websites (2024)
- Top 25 Ethical Hacking Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
- 10 BEST Operating System (OS) for Hacking in 2024
- Deep Web vs Dark Web – Difference Between Them
- PoW vs PoS – Difference Between Proof of Work & Stake
- The Open University
- Guest user / Sign out
- Study with The Open University
My OpenLearn Profile
Personalise your OpenLearn profile, save your favourite content and get recognition for your learning
About this free course
Become an ou student, download this course, share this free course.

Start this free course now. Just create an account and sign in. Enrol and complete the course for a free statement of participation or digital badge if available.
2 Case study 1: WannaCry
On 12 May 2017, a piece of malware spread rapidly and infected many computers across the globe. Many data files in infected computers were not openable. What was happening?
The next sections will answer the following questions:
- What was the attack?
- How did it work?
- Who were the attackers?
- What lessons can be learnt?
100 Best Case Study Questions for Your Next Customer Spotlight
Published: November 29, 2022
Case studies and testimonials are helpful to have in your arsenal. But to build an effective library, you need to ask the right case study questions. You also need to know how to write a case study .

Case studies are customers' stories that your sales team can use to share relevant content with prospects . Not only that, but case studies help you earn a prospect's trust, show them what life would be like as your customer, and validate that your product or service works for your clients.
Before you start building your library of case studies, check out our list of 100 case study questions to ask your clients. With this helpful guide, you'll have the know-how to build your narrative using the " Problem-Agitate-Solve " Method.

What makes a good case study questionnaire?
The ultimate list of case study questions, how to ask your customer for a case study, creating an effective case study.
Certain key elements make up a good case study questionnaire.
A questionnaire should never feel like an interrogation. Instead, aim to structure your case study questions like a conversation. Some of the essential things that your questionnaire should cover include:
- The problem faced by the client before choosing your organization.
- Why they chose your company.
- How your product solved the problem clients faced.
- The measurable results of the service provided.
- Data and metrics that prove the success of your service or product, if possible.
You can adapt these considerations based on how your customers use your product and the specific answers or quotes that you want to receive.
What makes a good case study question?
A good case study question delivers a powerful message to leads in the decision stage of your prospective buyer's journey.
Since your client has agreed to participate in a case study, they're likely enthusiastic about the service you provide. Thus, a good case study question hands the reins over to the client and opens a conversation.
Try asking open-ended questions to encourage your client to talk about the excellent service or product you provide.
Free Case Study Templates
Tell us about yourself to access the templates..

Categories for the Best Case Study Questions
- Case study questions about the customer's business
- Case study questions about the environment before the purchase
- Case study questions about the decision process
- Case study questions about the customer's business case
- Case study questions about the buying team and internal advocates
- Case study questions about customer success
- Case study questions about product feedback
- Case study questions about willingness to make referrals
- Case study question to prompt quote-worthy feedback
- Case study questions about the customers' future goals

Showcase your company's success using these three free case study templates.
- Data-Driven Case Study Template
- Product-Specific Case Study Template
- General Case Study Template
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Case Study Interview Questions About the Customer's Business
Knowing the customer's business is an excellent way of setting the tone for a case study.
Use these questions to get some background information about the company and its business goals. This information can be used to introduce the business at the beginning of the case study — plus, future prospects might resonate with their stories and become leads for you.
- Would you give me a quick overview of [company]? This is an opportunity for the client to describe their business in their own words. You'll get useful background information and it's an easy prompt to get the client talking.
- Can you describe your role? This will give you a better idea of the responsibilities they are subject to.
- How do your role and team fit into the company and its goals? Knowing how the team functions to achieve company goals will help you formulate how your solution involves all stakeholders.
- How long has your company been in business? Getting this information will help the reader gauge if pain points are specific to a startup or new company vs. a veteran company.
- How many employees do you have? Another great descriptor for readers to have. They can compare the featured company size with their own.
- Is your company revenue available? If so, what is it? This will give your readers background information on the featured company's gross sales.
- Who is your target customer? Knowing who the target audience is will help you provide a better overview of their market for your case study readers.
- How does our product help your team or company achieve its objectives? This is one of the most important questions because it is the basis of the case study. Get specifics on how your product provided a solution for your client. You want to be able to say "X company implemented our solution and achieved Y. "
- How are our companies aligned (mission, strategy, culture, etc.)? If any attributes of your company's mission or culture appealed to the client, call it out.
How many people are on your team? What are their roles? This will help describe key players within the organization and their impact on the implementation of your solution.

Case Study Interview Questions About the Environment Before the Purchase
A good case study is designed to build trust. Ask clients to describe the tools and processes they used before your product or service. These kinds of case study questions will highlight the business' need they had to fulfill and appeal to future clients.
- What was your team's process prior to using our product? This will give the reader a baseline to compare the results for your company's product.
- Were there any costs associated with the process prior to using our product? Was it more expensive? Was it worth the cost? How did the product affect the client's bottom line? This will be a useful metric to disclose if your company saved the client money or was more cost-efficient.
- What were the major pain points of your process prior to using our product? Describe these obstacles in detail. You want the reader to get as much information on the problem as possible as it sets up the reasoning for why your company's solution was implemented.
- Did our product replace a similar tool or is this the first time your team is using a product like this? Were they using a similar product? If so, having this information may give readers a reason to choose your brand over the competition.
- What other challenges were you and your team experiencing prior to using our product? The more details you can give readers regarding the client's struggles, the better. You want to paint a full picture of the challenges the client faced and how your company resolved them.
- Were there any concerns about how your customers would be impacted by using our product? Getting answers to this question will illustrate to readers the client's concerns about switching to your service. Your readers may have similar concerns and reading how your client worked through this process will be helpful.
- Why didn't you buy our product or a similar product earlier? Have the client describe any hesitations they had using your product. Their concerns may be relatable to potential leads.
- Were there any "dealbreakers" involved in your decision to become a customer? Describing how your company was able to provide a solution that worked within those parameters demonstrates how accommodating your brand is and how you put the customer first. It's also great to illustrate any unique challenges the client had. This better explains their situation to the reader.
- Did you have to make any changes you weren't anticipating once you became a customer? Readers of your case study can learn how switching to your product came with some unexpected changes (good or bad) and how they navigated them. If you helped your client with troubleshooting, ask them to explain that here.
How has your perception of the product changed since you've become a customer? Get the interviewee to describe how your product changed how they do business. This includes how your product accomplished what they previously thought was impossible.

Case Study Interview Questions About the Decision Process
Readers of the case study will be interested in which factors influenced the decision-making process for the client. If they can relate to that process, there's a bigger chance they'll buy your product.
The answers to these questions will help potential customers through their decision-making process.
- How did you hear about our product? If the client chose to work with you based on a recommendation or another positive case study, include that. It will demonstrate that you are a trusted brand with an established reputation for delivering results.
- How long had you been looking for a solution to this problem? This will add to the reader's understanding of how these particular challenges impacted the company before choosing your product.
- Were you comparing alternative solutions? Which ones? This will demonstrate to readers that the client explored other options before choosing your company.
- Would you describe a few of the reasons you decided to buy our product? Ask the interviewee to describe why they chose your product over the competition and any benefits your company offered that made you stand out.
- What were the criteria you used when deciding to buy our product? This will give readers more background insight into the factors that impacted their decision-making process.
- Were there any high-level initiatives or goals that prompted the decision to buy? For example, was this decision motivated by a company-wide vision? Prompt your clients to discuss what lead to the decision to work with you and how you're the obvious choice.
- What was the buying process like? Did you notice anything exceptional or any points of friction? This is an opportunity for the client to comment on how seamless and easy you make the buying process. Get them to describe what went well from start to finish.
- How would you have changed the buying process, if at all? This is an opportunity for you to fine-tune your process to accommodate future buyers.
- Who on your team was involved in the buying process? This will give readers more background on the key players involved from executives to project managers. With this information, readers can see who they may potentially need to involve in the decision-making process on their teams.

Case Study Interview Questions About the Customer's Business Case
Your case study questions should ask about your product or solution's impact on the customer's employees, teams, metrics, and goals. These questions allow the client to praise the value of your service and tell others exactly what benefits they derived from it.
When readers review your product or service's impact on the client, it enforces the belief that the case study is credible.
- How long have you been using our product? This will help readers gauge how long it took to see results and your overall satisfaction with the product or service.
- How many different people at your company use our product? This will help readers gauge how they can adapt the product to their teams if similar in size.
- Are there multiple departments or teams using our product? This will demonstrate how great of an impact your product has made across departments.
- How do you and your team currently use the product? What types of goals or tasks are you using the product to accomplish? Get specifics on how the product actively helps the client achieve their goals.
- If other teams or departments are using our product, do you know how they're using it? With this information, leads can picture how they can use your product across their teams and how it may improve their workflow and metrics.
- What was the most obvious advantage you felt our product offered during the sales process? The interviewee should explain the benefits they've gained from using your product or service. This is important for convincing other leads you are better than the competition.
- Were there any other advantages you discovered after using the product more regularly? Your interviewee may have experienced some additional benefits from using your product. Have them describe in detail what these advantages are and how they've helped the company improve.
- Are there any metrics or KPIs you track with our product? What are they? The more numbers and data the client can provide, the better.
- Were you tracking any metrics prior to using our product? What were they? This will allow readers to get a clear, before-and-after comparison of using your product.
- How has our product impacted your core metrics? This is an opportunity for your clients to drive home how your product assisted them in hitting their metrics and goals.

Case Study Interview Questions About the Buying Team and Internal Advocates
See if there are any individuals at the customer's company who are advocates for your product.
- Are there any additional team members you consider to be advocates for our product? For example, does anyone stick out as a "power user" or product expert on your team? You may want to interview and include these power users in your case study as well. Consider asking them for tips on using your service or product.
- Is there anyone else on your team you think we should talk to? Again, the more people can share their experience using your product, the better.
- Are there any team members who you think might not be the biggest fans of our product or who might need more training? Providing extra support to those struggling with your product may improve their user experience and turn into an opportunity to not only learn about their obstacles but turn them into a product fan
- Would you share some details about how your team implemented our product? Get as much information as possible about the rollout. Hopefully, they'll gush about how seamless the process was.
- Who from your company was involved in implementing our product? This will give readers more insight into who needs to be involved for a successful rollout of their own.
- Were there any internal risks or additional costs involved with implementing our product? If so, how did you address them? This will give insight into the client's process and rollout and this case study question will likely provide tips on what potential leads should be on the lookout for.
- Is there a training process in place for your team's use of our product? If so, what does it look like? If your company provided support and training to the client, have them describe that experience.
- About how long does it take a new team member to get up to speed with our product? This will help leads determine how much time it will take to onboard an employee to your using your product. If a new user can quickly get started seamlessly, it bodes well for you.
- What was your main concern about rolling this product out to your company? Describing their challenges in detail will provide readers with useful insight.

Case Study Interview Questions About Customer Success
Has the customer found success with your product? Ask these questions to learn more.
- By using our product can you measure any reduced costs? If it has, you'll want to emphasize those savings in your case study.
- By using our product can you measure any improvements in productivity or time savings? Any metrics or specific stories your interviewee can provide will help demonstrate the value of your product.
- By using our product can you measure any increases in revenue or growth? Again, say it with numbers and data whenever possible.
- Are you likely to recommend our product to a friend or colleague? Recommendations from existing customers are some of the best marketing you can get.
- How has our product impacted your success? Your team's success? Getting the interviewee to describe how your product played an integral role in solving their challenges will show leads that they can also have success using your product.
- In the beginning, you had XYZ concerns; how do you feel about them now? Let them explain how working with your company eliminated those concerns.
- I noticed your team is currently doing XYZ with our product. Tell me more about how that helps your business. Illustrate to your readers how current customers are using your product to solve additional challenges. It will convey how versatile your product is.
- Have you thought about using our product for a new use case with your team or at your company? The more examples of use cases the client can provide, the better.
- How do you measure the value our product provides? Have the interviewee illustrate what metrics they use to gauge the product's success and how. Data is helpful, but you should go beyond the numbers. Maybe your product improved company morale and how teams work together.

Case Study Interview Questions About Product Feedback
Ask the customer if they'd recommend your product to others. A strong recommendation will help potential clients be more open to purchasing your product.
- How do other companies in this industry solve the problems you had before you purchased our product? This will give you insight into how other companies may be functioning without your product and how you can assist them.
- Have you ever talked about our product to any of your clients or peers? What did you say? This can provide you with more leads and a chance to get a referral.
- Why would you recommend our product to a friend or client? Be sure they pinpoint which features they would highlight in a recommendation.
- Can you think of any use cases your customers might have for our product? Similar industries may have similar issues that need solutions. Your interviewee may be able to provide a use case you haven't come up with.
- What is your advice for other teams or companies who are tackling problems similar to those you had before you purchased our product? This is another opportunity for your client to talk up your product or service.
- Do you know someone in X industry who has similar problems to the ones you had prior to using our product? The client can make an introduction so you can interview them about their experience as well.
- I noticed you work with Company Y. Do you know if they are having any pain points with these processes? This will help you learn how your product has impacted your client's customers and gain insight into what can be improved.
- Does your company participate in any partner or referral programs? Having a strong referral program will help you increase leads and improve customer retention.
- Can I send you a referral kit as a thank-you for making a referral and give you the tools to refer someone to us? This is a great strategy to request a referral while rewarding your existing customers.
- Are you interested in working with us to produce additional marketing content? The more opportunities you can showcase happy customers, the better.

Case Study Interview Questions About Willingness to Make Referrals
- How likely are you to recommend our product to a friend or client? Ideally, they would definitely refer your product to someone they know.
- Can you think of any use cases your customers might have for our product? Again, your interviewee is a great source for more leads. Similar industries may have similar issues that need solutions. They may be able to provide a use case you haven't come up with.
- I noticed you work with Company Y; do you know if they are having any pain points with these processes? This will help you learn how your product has impacted your client's customers and gain insight into what can be improved.

Case Study Interview Questions to Prompt Quote-Worthy Feedback
Enhance your case study with quotable soundbites from the customer. By asking these questions, prospects have more insight into other clients and their success with your product — which helps build trust.
- How would you describe your process in one sentence prior to using our product? Ideally, this sentence would quickly and descriptively sum up the most prominent pain point or challenge with the previous process.
- What is your advice to others who might be considering our product? Readers can learn from your customer's experience.
- What would your team's workflow or process be like without our product? This will drive home the value your product provides and how essential it is to their business.
- Do you think the investment in our product was worthwhile? Why? Have your customer make the case for the value you provide.
- What would you say if we told you our product would soon be unavailable? What would this mean to you? Again, this illustrates how integral your product is to their business.
- How would you describe our product if you were explaining it to a friend? Your customers can often distill the value of your product to their friends better than you can.
- What do you love about your job? Your company? This gives the reader more background on your customer and their industry.
- What was the worst part of your process before you started using our product? Ideally, they'd reiterate how your product helped solve this challenge.
- What do you love about our product? Another great way to get the customer's opinion about what makes your product worth it.
- Why do you do business with us? Hopefully, your interviewee will share how wonderful your business relationship is.

Case Study Interview Questions About the Customers' Future Goals
Ask the customer about their goals, challenges, and plans for the future. This will provide insight into how a business can grow with your product.
- What are the biggest challenges on the horizon for your industry? Chances are potential leads within the same industry will have similar challenges.
- What are your goals for the next three months? Knowing their short-term goals will enable your company to get some quick wins for the client.
- How would you like to use our product to meet those challenges and goals? This will help potential leads understand that your product can help their business as they scale and grow.
- Is there anything we can do to help you and your team meet your goals? If you haven't covered it already, this will allow your interviewee to express how you can better assist them.
- Do you think you will buy more, less, or about the same amount of our product next year? This can help you gauge how your product is used and why.
- What are the growth plans for your company this year? Your team? This will help you gain insight into how your product can help them achieve future goals.
- How can we help you meet your long-term goals? Getting specifics on the needs of your clients will help you create a unique solution designed for their needs.
- What is the long-term impact of using our product? Get their feedback on how your product has created a lasting impact.
- Are there any initiatives that you personally would like to achieve that our product or team can help with? Again, you want to continue to provide products that help your customers excel.
- What will you need from us in the future? This will help you anticipate the customer's business needs.
- Is there anything we can do to improve our product or process for working together in the future? The more feedback you can get about what is and isn't working, the better.

Before you can start putting together your case study, you need to ask your customer's permission.
If you have a customer who's seen success with your product, reach out to them. Use this template to get started:
Thank you & quick request
Hi [customer name],
Thanks again for your business — working with you to [solve X, launch Y, take advantage of Z opportunity] has been extremely rewarding, and I'm looking forward to more collaboration in the future.
[Name of your company] is building a library of case studies to include on our site. We're looking for successful companies using [product] to solve interesting challenges, and your team immediately came to mind. Are you open to [customer company name] being featured?
It should be a lightweight process — [I, a product marketer] will ask you roughly [10, 15, 20] questions via email or phone about your experience and results. This case study will include a blurb about your company and a link to your homepage (which hopefully will make your SEO team happy!)
In any case, thank you again for the chance to work with you, and I hope you have a great week.
[Your name]
If one of your customers has recently passed along some praise (to you, their account manager, your boss; on an online forum; to another potential customer; etc.), then send them a version of this email:
Hey [customer name],
Thanks for the great feedback — I'm really glad to hear [product] is working well for you and that [customer company name] is getting the results you're looking for.
My team is actually in the process of building out our library of case studies, and I'd love to include your story. Happy to provide more details if you're potentially interested.
Either way, thank you again, and I look forward to getting more updates on your progress.
You can also find potential case study customers by usage or product data. For instance, maybe you see a company you sold to 10 months ago just bought eight more seats or upgraded to a new tier. Clearly, they're happy with the solution. Try this template:
I saw you just [invested in our X product; added Y more users; achieved Z product milestone]. Congratulations! I'd love to share your story using [product] with the world -- I think it's a great example of how our product + a dedicated team and a good strategy can achieve awesome results.
Are you open to being featured? If so, I'll send along more details.
Case Study Benefits
- Case studies are a form of customer advocacy.
- Case studies provide a joint-promotion opportunity.
- Case studies are easily sharable.
- Case studies build rapport with your customers.
- Case studies are less opinionated than customer reviews.
1. Case studies are a form of customer advocacy.
If you haven't noticed, customers aren't always quick to trust a brand's advertisements and sales strategies.
With every other brand claiming to be the best in the business, it's hard to sort exaggeration from reality.
This is the most important reason why case studies are effective. They are testimonials from your customers of your service. If someone is considering your business, a case study is a much more convincing piece of marketing or sales material than traditional advertising.
2. Case studies provide a joint-promotion opportunity.
Your business isn't the only one that benefits from a case study. Customers participating in case studies benefit, too.
Think about it. Case studies are free advertisements for your customers, not to mention the SEO factor, too. While they're not promoting their products or services, they're still getting the word out about their business. And, the case study highlights how successful their business is — showing interested leads that they're on the up and up.
3. Case studies are easily sharable.
No matter your role on the sales team, case studies are great to have on hand. You can easily share them with leads, prospects, and clients.
Whether you embed them on your website or save them as a PDF, you can simply send a link to share your case study with others. They can share that link with their peers and colleagues, and so on.
Case studies can also be useful during a sales pitch. In sales, timing is everything. If a customer is explaining a problem that was solved and discussed in your case study, you can quickly find the document and share it with them.
4. Case studies build rapport with your customers.
While case studies are very useful, they do require some back and forth with your customers to obtain the exact feedback you're looking for.
Even though time is involved, the good news is this builds rapport with your most loyal customers. You get to know them on a personal level, and they'll become more than just your most valuable clients.
And, the better the rapport you have with them, the more likely they'll be to recommend your business, products, or services to others.
5. Case studies are less opinionated than customer reviews.
Data is the difference between a case study and a review. Customer reviews are typically based on the customer's opinion of your brand. While they might write a glowing review, it's completely subjective and there's rarely empirical evidence supporting their claim.
Case studies, on the other hand, are more data-driven. While they'll still talk about how great your brand is, they support this claim with quantitative data that's relevant to the reader. It's hard to argue with data.
An effective case study must be genuine and credible. Your case study should explain why certain customers are the right fit for your business and how your company can help meet their specific needs. That way, someone in a similar situation can use your case study as a testimonial for why they should choose your business.
Use the case study questions above to create an ideal customer case study questionnaire. By asking your customers the right questions, you can obtain valuable feedback that can be shared with potential leads and convert them into loyal customers.
Editor’s Note: This article was originally published in June 2021 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

ACV: What It Means & How to Calculate It

What Is An Account Development Manager? (And How to Become One)
Strategic Account Managers, Here's How to Amplify Your Efforts

3 Questions that Ensure Key Account Success
![information security case study questions and answers Account Management vs. Sales: What's the Difference? [FAQ]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/136_Account%20Management%20vs.jpg)
Account Management vs. Sales: What's the Difference? [FAQ]
Showcase your company's success using these free case study templates.
Powerful and easy-to-use sales software that drives productivity, enables customer connection, and supports growing sales orgs

- Undergraduate Students
- Doctoral Students
- Master’s Students
- Engineering Master’s Students
- Faculty & Staff
- Parents & Families
- Asian / Pacific Islander
- Black/African American
- First Generation/Low Income
- Hispanic/Latinx
- International
- Native American/Indigenous
- Neurodiverse
- Student Athletes
- Students with Disabilities
- Undocumented
- What is a Career Community?
- Business, Finance & Consulting
- Data, Technology & Engineering
- Discovery & Exploration
- Education, Government, Nonprofit & Policy
- Energy, Environment & Sustainability
- Entertainment, Media & Arts
- Healthcare & Biomedical Sciences
- Innovation, Entrepreneurship & Design
- Know Yourself
- Explore Options
- Focus & Prepare
- Take Action
- Evaluate & Refine
- Featured Opportunities
- Career Readiness Resources
- Personalize Your Hub
- For Employers
61 Cybersecurity Job Interview Questions and Answers
- Share This: Share 61 Cybersecurity Job Interview Questions and Answers on Facebook Share 61 Cybersecurity Job Interview Questions and Answers on LinkedIn Share 61 Cybersecurity Job Interview Questions and Answers on X
61 Cybersecurity Job Interview Questions and Answers was originally published on Springboard .
As with any job interview, an applicant for a cybersecurity position needs to speak knowledgeably about the specific job’s responsibilities and the field in general. Information security job interview questions might revolve around one specific task—say, designing firewalls or safeguarding information in certain applications.
However, depending on the role and how encompassing it is, cybersecurity analyst interview questions may require showing a breadth of knowledge regarding various technologies and programming languages . And given that cybersecurity positions involve protecting sensitive business data, you must prove that you are trustworthy, reliable, and possess problem-solving skills, ingenuity, and calm when facing a difficult situation.
These 61 sample cybersecurity interview questions should give you an idea of what to expect when interviewing with a well-respected organization like MITRE, Deloitte, Accenture, Cisco, Google, Lockheed, and others. Preparation is the key to making a good impression and landing a job in cybersecurity, so study these questions carefully.
Getting-to-Know-You Questions
Before delving into the more technical aspects of what the job will require, your interviewer may want to get a sense of who you are. They may be interested in where you are in your career and ask about your background and schooling.
For these types of security analyst interview questions, you should have a brief, concise elevator pitch. Tell them who you are, what you’ve done, and what you’re looking to do next. Highlight your achievements and skills, what you’ve learned, and how you want to apply your knowledge to your next position.
1. Why are you looking for a new position?
An interviewer asking this wants to understand what has prompted a change in your career. Are you looking for more responsibility? A chance to expand your skillset? Do you feel that you outgrew your old position? Are you looking for more pay and less travel? Well then, why do you deserve more money, and how are you more efficient working more from a central location? Explain your motivation for finding a new job in a way that shows that you view this new position as a positive change for both you and the organization.
2. What are your greatest strengths and accomplishments?
Take the opportunity to show how you helped your old company. Did you design its latest firewalls that prevented breaches? Did you reroute the routers? Help with information access security? Do you work well with people and show leadership skills? Talk about the types of technology you know well and how you made a positive impact in your last position. Explain how you built solid relationships with your coworkers and how you all worked together on successful projects—and how you intend to do the same at this new company.
3. What are your greatest weaknesses? (Related: How did you overcome a problem?)
Everyone makes mistakes, and no one is good at everything. You should honestly assess what you can improve and how you plan to show that improvement in your new role. Dig into your past: You might have overseen the response to a breach or some other serious problem. It might not have been your fault, but how you handled it shows your professionalism, problem-solving abilities. and perhaps even outside-of-the-box thinking. Show that you are willing to learn from mistakes, even if they’re not your own, and that you can handle a crisis. Explain how you took responsibility and stepped up to be a leader.
4. How do you envision your first 90 days on the job?
Your answer should encompass how you intend to meet with your team members to find out more about them and how you can work together. You should talk about how you will prioritize gaining an understanding of what your managers need from you and what all the stakeholders hope to achieve while also building strong rapport with your co-workers. You should ask what you can do to make an impact right away. Talk about how you intend to learn and get into the midst of business as soon as you can.
(Get some additional insight from a recruiter here .)
Technical Interview Questions
At some point, the interviewer will turn to more technical and cybersecurity-focused questions to determine how well you would do in the position. You need to display your cybersecurity knowledge and give examples from your work history of how you performed tasks and prevented or solved problems. Some of these are fundamental definitions, while others require more thoughtful responses, but all should be part of your interview arsenal, including network security interview questions, technical questions on tools, and questions you might see in a Security+ certification test or a CEH.
5. What is on your home network?
Your home network is typically a test environment. How you work with it gives an indication of what you would do with someone else’s network.
6. What is the difference between a threat, a vulnerability, and a risk?
Answering this question calls for a deep understanding of cybersecurity and anyone working in the field should be able to give a strong response. You should expect a follow-up question asking which of the three to focus more on. A simple way to put it: a threat is from someone targeting a vulnerability (or weakness) in the organization that was not mitigated or taken care of since it was not properly identified as a risk.
7. How do you go about securing a server?
You might want to break this answer down into steps, especially if it refers to a specific type of server. Your answer will give a glimpse into your decision-making abilities and thought process. There are multiple ways to answer this question, just as there are multiple ways to secure a server. You might reference the concept of trust no one or the principle of least privilege . Let your expertise guide your response to this question and the others following it.
8. Why is DNS monitoring important?
Some argue that this is not necessary and that saying otherwise indicates that there are weaknesses in the domain name services. Others say DNS monitoring is prudent because DNS queries are a data-exfiltration vector from networks that allow any host to communicate to the Internet on Port 53.
9. What port does ping work over?
Watch out for this. Ping is a layer-3 protocol like IP; ports are an element of the layer-4 protocols TCP and UDP.
10. What is the difference between encoding, encrypting, and hashing?
This question should inspire a short conversation about encryption, which gives you the chance to explain your knowledge of it. Though you’re often going to be implementing and choosing between encryption systems rather than building them, it should be something that you know about in theory.
(There’s more on encryption here .)
11. What is SSL?
SSL is a standard security technology for creating an encrypted link between a server and a client (usually a web server and a web browser).
12. What are the differences between HTTPS, SSL, and TLS?
HTTPS is hypertext transfer protocol and secures communications over a network. TLS is transport layer security and is a successor protocol to SSL. You have to demonstrate that you know the differences between the three and how network-related protocols are used to understand the inherent risks involved.
13. What sorts of anomalies would you look for to identify a compromised system?
There are multiple ways to answer this, but again, you need to show your expertise and ingenuity. One possible answer is drawing out a basic network architecture with its IPS/IDS, firewalls, and other security technologies to describe the type of traffic and other signs of compromise. This is the sort of answer you’ll need to tackle in order to resolve network security interview questions.
14. If you had to both compress and encrypt data during a transmission, which would you do first?
Compress and then encrypt, since encrypting first might make it hard to show compression having much of an effect.
15. Which of the following would be MOST appropriate if an organization’s requirements mandate complete control over the data and applications stored in the cloud?
- Hybrid cloud
- Community cloud
- Private cloud
- Public cloud
16. How would you defend against a cross-site scripting (XSS) attack?
Every cybersecurity professional should know this , even if it is difficult to answer. Come prepared with a thoughtful, concise plan for defending against this JavaScript vulnerability.
17. What are the differences between cybersecurity in the cloud and on-premises?
Show that you understand the security risks inherent to both and which might be more appropriate for the company. It’ll be good to trace out your thinking as it might form a critical component of network security interview questions.
18. What does RDP stand for?
Remote desktop protocol and its port number is 3389.
19. What is the difference between symmetric and asymmetric encryption?
Symmetric encryption uses the same key to encrypt and decrypt, while asymmetric encryption uses different keys for encryption and decryption. Asymmetric encryption is commonly used to secure an initial key-sharing conversation, but then the actual conversation is secured using symmetric crypto. Communication using symmetric crypto is usually faster due to the slightly simpler math involved in the encryption/decryption process and because the session setup doesn’t involve PKI certificate checking.”
(For more reading: What Is PKI and How Does It Bolster Your Cybersecurity Defenses? )
20. What is the difference between UDP and TCP?
Both are protocols for sending packets of information over the internet and are built on top of the internet protocol. TCP stands for transmission control protocol and is more commonly used. It numbers the packets it sends to guarantee that the recipient receives them. UDP stands for user datagram protocol. While it operates similarly to TCP, it does not use TCP’s error-checking abilities, which speeds up the process, but makes it less reliable.
21. What is a traceroute?
A traceroute, or tracert, can help you see where a breakdown of communications occurred. It shows what routers you touch as you move along to your final destination. If there is somewhere you cannot connect, you can see where it happened.
22. What is Snort?
Snort is a free open-source intrusion detection software . You should be familiar with different cybersecurity tools and their potential uses, a common topic that is tested in the Security+ certification from CompTIA.
23. What is vishing?
Vishing is when somebody impersonates somebody you trust through voice calls to get you to reveal to them sensitive and private information. It is a variant of phishing attacks, except the main difference is that it is mostly conducted via voice rather than written text.
24. What is a black box penetration test?
A black box penetration test is one where the tester is given no access to company systems or information and has only public information to go on. While many cybersecurity roles don’t require you to conduct penetration tests, you should at least know the basics involved with them.
25. What is the fastest way to crack a hashed password?
Rainbow tables provide pre-computed results for cracking hashed passwords and is one of, if not the fastest way to un-hash a password.
26. What are the default ports for HTTP and for HTTPS?
The default port for HTTP is 80, while the default port for HTTPS, the secure version of HTTP, is 443.
27. What is sideloading?
Sideloading is the act of downloading apps outside of official app stores, either on Apple or Android. This is something that puts people at increased risk of downloading malware, as the apps are not approved by the app store providers. As a matter of company policy, most companies will try to prevent sideloading on any company-issued mobile devices.
28. What is the protocol used for secure file transfers?
SFTP uses SSH and securely transmits files, as opposed to FTPS which uses the unsecured FTP protocol. Secure file transfers should use the SFTP protocol.
29. What are honeypots?
Honeypots are targets placed for an attack in order to study how different attackers are attempting exploits. While often used in an academic setting, private organizations and governments can use the same idea to study their vulnerabilities.
30. What is a clean desk policy?
A clean desk policy is something that ensures all data is secure even when employees are not at work. This is a critical part of cybersecurity as data security should not be dependent on employees showing up to work all the time.
31. What is a BYOD policy and what’s an easy security measure to help mitigate some of the risks?
BYOD policy stands for “bring your own device”, allowing employees to bring their own devices. Setting up a guest WiFi network allows for segmentation from these possibly untrusted devices and core networks.
32. Which of the following works by implanting software on systems but delays execution until a specific set of conditions are met?
33. What is a polymorphic virus?
A polymorphic virus is one that changes to avoid detection and then returns to its routine code when scans are done in order to neutralize anti-virus measures.
34. What port is typically used by Telnet?
Telnet typically uses port 23. There may be a few questions like this (that are certainly present on the Security+ exam itself) that test your general knowledge of networking and the overall layout of ports and the standards used for each one.
35. What is a null session?
A null session is one where the user is not authenticated by either username or password. It can be a bit of a security risk for applications since this means that the person behind the request is unknown.
36. What is the difference between spear phishing and phishing?
Spear phishing is a phishing attack targeted towards a limited number of high-priority targets — oftentimes just one. Phishing usually involves a mass targeted email or message that targets large groups of people. This means that practically speaking, spear-phishing will be much more individualized and probably more well-researched (for the individual) while phishing is more like an actual fishing expedition that catches whoever bites the hook.
37. What is it called when a user is attacked by directing them to what they think is a legitimate site, but which is actually a scam site?
This is called pharming. An attacker will often use another sort of attack to impersonate a real site and then get users to submit information to a scam one.
38. Why should 802.1X wireless connections always be encrypted?
802.1X wireless links will be passed in clear form without any encryption. Data emanation occurs because 802.1X wireless transmits radio-frequency signals that can be detectable. Attackers can amplify the signal and sniff the traffic and see what’s being transmitted with almost no effort if there is no encryption.
39. What’s the difference between auditing and logging?
Auditing involves going through logs and looking for events, while logging is simply compiling events into logs. You can think of it as usually being a two-part process: first, you log events, then you audit your logs to see if anything is abnormal.
40. Which of the following is the BEST reason for placing a password lock on a mobile device?
- Prevents an unauthorized user from accessing the owner’s data
- Enables remote wipe capabilities
- Stops an unauthorized user from using the device again
- Prevents an unauthorized user from making phone calls
41. Why might you do a vulnerability assessment instead of a penetration test?
Vulnerability assessments tend to be less expensive and take less time than a penetration test. They’re also lower-risk: a penetration test will involve actual exploits of production-level services, which might lead to disruption or downtime for critical services.
42. What kind of cookie would a spyware attack typically use?
A spyware attack would typically use a tracking cookie rather than a session cookie, which would persist across different sessions rather than stopping at one session.
43. What is shoulder surfing?
Shoulder surfing is a physical attack that involves actually physically sneaking looks at people’s screens as they’re typing in information in a semi-public space.
44. What is the difference between a worm and a virus?
The difference between the two is subtle, but it involves the self-replicating nature of worms, which can spread from system to system in a network, while a virus oftentimes tends to be self-contained in one system. This is a critical example of a set of network security interview questions you might encounter.
45. What should be the steps taken to prevent outdated software from being exploited?
There’s a fine balance of issues here. Obviously, the most protective step would be to unbranch certain systems from the Internet itself, or to prevent the installation of certain software. But that’s not a step that marries usability and security very well. Instead, the appropriate step is to keep posted on breaking security bulletins and updates, and to use the Internet and web tools to monitor for upcoming vulnerabilities, for example, with the CVE database.
46. Which of the following attacks involves the use of previously captured network traffic?
47. What is it called when somebody is forced to reveal cryptographic secrets through physical threats?
Attacks like this when you have somebody reveal their secrets due to physical threats are called a rubber hose attack.
48. What tool would you use to quickly search through logs with regular expression?
This is more of an advanced question, something you might see on a more advanced certification such as the CEH rather than an intro-level interview. Yet, it’s worth going through a few of those to describe the workflow involved with scripting and programming. You would probably use a tool such as grep. In an interview setting, you might be asked to describe what regular expressions and patterns you use to quickly locate key events.
49. How would you XOR the two following numbers?
The XOR is a critical function in cryptography where there’s additive encryption . There’s encryption and decryption that can rely on this. For more advanced cybersecurity roles, you might want to know how to go back and forth between two different numbers.
50. What is the best standard for a botnet to communicate?
Either HTTP or IRC, since those are the fastest for communication between multiple clients. This is something you would only really know if you were thinking through defensive and offensive operations with tons of different clients like botnets, and will be more of an advanced cybersecurity issue.
(Check out Glassdoor for more examples of technical questions for cybersecurity analysts and cybersecurity engineers .)
Wrapping Up
After going through his or her list of technical questions to gauge your knowledge and expertise, an interviewer will wrap up with a few final questions that give you a chance to make a lasting impression.
51. What tech blogs do you follow?
Show that you stay current by telling the interviewer how you get your cybersecurity news. These days, there are blogs for everything, but you might also have news sites, newsletters, and books that you can reference.
52. What do you do in your spare time outside of cybersecurity?
The interviewer is hoping to get a better sense of you as a person to determine whether you’re trustworthy, reliable, and of good character. He or she also wants to see if you would be a good culture fit and someone others would enjoy collaborating with. You don’t need to get too personal with the details, but you can talk about your hobbies, your family, the last vacation you took, or how often you like to work out, among other things. Show some personality here.
53. Where do you see yourself in five years?
Most people expect to advance in their cybersecurity careers in five years, which could mean a promotion or raise (or a few). Emphasize how you are looking to further your knowledge and skills—and how that will benefit the company. Tell the interviewer that you see yourself moving up to a more senior position and continuing to contribute to the organization in a significant way. Drive home the point that the investment made in you will be a good one.
54. Do you have any questions?
This is your chance to find out more about the company and position. Remember that an interview is a two-way street. You are interviewing them as much as they are interviewing you (even though it doesn’t always feel that way). Ask about the work environment and what the company expects of you. Find out more about the day-to-day responsibilities and whether there are any special projects on the horizon. And see if you and the company are a good fit culture-wise.
55. Where do you get your cybersecurity news?
This question is meant to test how on top you are of cybersecurity developments and how sophisticated your sources are. Strive to answer with more specific niche resources, such as well-known security researchers like Bruce Schneier rather than more mainstream sources for the average audience.
56. What do you think about the SolarWinds hack?
This kind of question tracks how you’re keeping up to date with recent cybersecurity breaches, an important quality in anybody looking to break into a fast-moving field such as cybersecurity. There’s a blog post about this particular topic from Brad Smith, the President of Microsoft. As of the time of publishing for this article, this was the most trending cybersecurity breach — but the general point is to stay on top of cybersecurity events and the approaches attackers use with high-quality, vetted sources.
57. What’s your personal threat model?
An interesting question that looks into how you think about cybersecurity on a personal basis. Have you been introspective enough to think about what data might be at risk in your current job? With your personal life? The way this mentality extends to proactive consideration of cybersecurity can make you look good in front of any potential employers.
58. How do you keep your data protected?
As you might become a custodian and guardian of company data, showing that you have personal discipline and a process for protecting your own data can be important. You’ll want to cite the use of strong passwords, two-factor authentication, and any steps you’ve taken to secure your home network or devices from attacks, including full-disk encryption and even perhaps physical security measures.
59. What’s something you’ve learned from failure?
As you might have to confront the risk of failure in any defensive cybersecurity role, understanding the amount of introspection and thought you put into learning from failure is a critical trait. Prepare some case studies and some deeper answers—spend the time really thinking through when something didn’t go right at work and what you did to bounce back.
60. How familiar are you with industry cybersecurity law?
This kind of question tests your knowledge of the legal frameworks and requirements in different industries. If you’re applying for a job with a sensitive regulated industry (such as financial services or healthcare), you’ll want to be proactive and do research around the guidelines and laws governing that industry.
61. Teach me something in five minutes.
This kind of question tests your communication skills—a critical trait to have as a cybersecurity professional. Make sure you’ve practiced and can demonstrate clear communication as well as some story-telling.
Be sure to have done your research on what a typical cybersecurity position like this pays and what you should expect in compensation at this stage of your career. Also, finish the interview with a brief summation of your strengths and how you are a good fit for the position.
Use the questions the interviewer asked and your answers to emphasize the skills you have that they are looking for. More than anything else, remain confident during the interview and be yourself. Companies invest in people, and you are not a robot giving out rote answers. You are a person with valuable experience that you can draw on to answer cybersecurity questions and make the case that you are the right person for the job.
Is cybersecurity the right career for you?
According to Cybersecurity Ventures, the cybersecurity industry is expected to have 3.5 million high-paying, unfilled jobs this year .
This post was co-written with Michael McNichols and was originally published in 2018. It has been updated to include more current information.
The post 61 Cybersecurity Job Interview Questions and Answers appeared first on Springboard Blog .

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Answers to Study Questions
1. What are the five components that make up an information system?
a. h ardware, software, data, people, process
2. What are three examples of information system hardware?
a. There are a number of possible answers: a PC, a printer, a mouse, tablets, mobile phones , etc .
3. Microsoft Windows is an example of which component of information systems?
a. It is an operating system, which is a part of the software component.
4. What is application software?
a. Software that does something useful.
5. What roles do people play in information systems?
a. The text includes examples such as helpdesk support, systems analyst, programmer, and CIO.
6. What is the definition of a process?
a. A process is a series of steps undertaken to achieve a desired outcome or goal.
7. What was invented first, the personal computer or the Internet (ARPANET)?
a. The Internet was activated in 1969; the personal computer was introduced in 1975.
8. In what year were restrictions on commercial use of the Internet first lifted? When were eBay and Amazon founded?
a. Restrictions were lifted in 1991, Amazon was founded in 1994, and eBay was founded in 1995 .
9. What does it mean to say we are in a “post-PC world”?
a. The personal computer will no longer be the primary way that people interact and do business.
10. What is Carr’s main argument about information technology?
a. That information technology is just a commodity and cannot be used to gain a competitive advantage.
1. Write your own description of what the term information systems hardware means.
a. Answers will vary , but should say something about information systems hardware consisting of the physical parts of computing devices that can actually be touched.
2. What is the impact of Moore’s Law on the various hardware components described in this chapter?
a. The student should pick one of the components and discuss the impact of the fact that computing doubles in speed every two years. Most devices are getting smaller, faster, cheaper, and this should be indicated in the answer.
3. Write a summary of one of the items linked to in the “Integrated Computing” section.
a. The student should write a summary of one of the linked articles.
4. Explain why the personal computer is now considered a commodity.
a. The PC has become a commodity in the sense that there is very little differentiation between computers, and the primary factor that controls their sale is their price.
5. The CPU can also be thought of as the _____________ of the computer.
6. List the following in increasing order (slowest to fastest): megahertz, kilohertz, gigahertz.
a. kilohertz, megahertz, gigahertz
7. What is the bus of a computer?
a. The bus is the electrical connection between different computer components.
8. Name two differences between RAM and a hard disk.
a. RAM is volatile; the hard disk is non-volatile. Data access in RAM is faster than on the hard disk.
9. What are the advantages of solid-state drives over hard disks?
a. The main advantage is spe ed: an SSD has much faster data- access speeds than a traditional hard disk.
10. How heavy was the first commercially successful portable computer?
a. The Compaq PC was 28 pounds.
1. Come up with your own definition of software. Explain the key terms in your definition.
a. A variety of answers are possible, but should be similar to the definition in the text: Software is the set of instructions that tell the hardware what to do. Software is created through the process of programming.
2. What are the functions of the operating system?
a. The operating system manages the hardware resources of the computer, provides the user-interface components, and provides a platform for software developers to write applications.
3. Which of the following are operating systems and which are applications: Microsoft Excel, Google Chrome, iTunes, Windows, Android, Angry Birds.
a. Microsoft Excel (application), Google Chrome (application), iTunes (application), WIndows (operating system), Android (operating sys tem), Angry Birds (application)
4. What is your favorite software application? What tasks does it help you accomplish?
a. Students will have various answers to this question. They should pick an application, not an operating system. They should be able to list at least one thing that it helps them accomplish.
5. What is a “killer” app? What was the killer app for the PC?
a. A killer app is application software that is so useful that people will purchase the hardware just so they can run it. The killer app for the PC was the spreadsheet ( Visicalc ).
6. How would you categorize the software that runs on mobile devices? Break down these apps into at least three basic categories and give an example of each.
a. There are various ways to answer this question. Students should identify that there are mobile operating systems and mobile apps. Most likely, students will break down mobile apps into multiple categories: games, GPS, reading, communication, etc.
7. Explain what an ERP system does.
a. An ERP (enterprise resource p lanning) system is a software application with a centralized database that is implemented across the entire organization.
8. What is open-source software? How does it differ from closed-source software? Give an example of each.
a. Open-source software is software that makes the source code available for anyone to copy and use. It is free to download, copy, and distribute. Closed-source software does not make the source code available and generally is not free to download, copy, and distribute. There are many examples of both, such as: Firefox (open source), Linux (open source), iTunes (closed source), Microsoft Office (closed source).
9. What does a software license grant?
a. Software licenses are not all the same, but generally the y grant the user the right to use the software on a limited basis. The terms of the license dictate users’ rights in detail .
10. How did the Y2K (year 2000) problem affect the sales of ERP systems?
a. Organizations purchased ERP software to replace their older systems in order to avoid any problems with the year 2000 in their software.
1. What is the difference between data, information, and knowledge?
a. Data are the raw bits and pieces of facts and statistics with no context. Data can be quantitative or qualitative. Information is data that has been given context. Knowledge is information that has been aggregated and analyzed and can be used for making decisions.
2. Explain in your own words how the data component relates to the hardware and software components of information systems.
a. There are numerous answers to this question, but all should be variations on the following : Data is processed by the hardware via software. A database is software that runs on the hardware. Hardware stores the data, software processes the data.
3. What is the difference between quantitative data and qualitative data? In what situations could the number 42 be considered qualitative data?
a. Quantitative data is numeric, the result of a measurement, count, or some other mathematical calculation. Qualitative data is descriptive. The number 42 could be qualitative if it is a designation instead of a measurement, count, or calculation. For example: that player ’ s jersey has number 42 on it.
4. What are the characteristics of a relational database?
a. A relational database is one in which data is organized into one or more tables. Each table has a set of fields, which define the nature of the data stored in the table. A record is one instance of a set of fields in a table. All the tables are related by one or more fields in common.
5. When would using a personal DBMS make sense?
a. When working on a smaller database for personal use, or when disconnected from the network.
6. What is the difference between a spreadsheet and a database? List three differences between them.
a. A database is generally more powerful and complex than a spreadsheet, with the ability to handle multiple types of data and link them together. Some differences: A database has defined field types, a spreadsheet does not. A database uses a standardized query language (such as SQL), a spreadsheet does not. A database can hold much larger amounts of data than a spreadsheet.
7. Describe what the term normalization means.
a. To normalize a database means to design it in a way that: 1) reduces duplication of data between tables and 2) gives the table as much flexibility as possible.
8. Why is it important to define the data type of a field when designing a relational database?
a. A data type tells the database what functions can be performed with the data. The second important reason to define the data type is so that the proper amount of storage space is allocated for the data.
9. Name a database you interact with frequently. What would some of the field names be?
a. The student can choose any sort of system that they interact with, such as Amazon or their school ’ s online systems. The fields would be the names of data being collected, such as “ first name ” , or “ address ” .
10. What is metadata?
a. Metadata is data about data . It refers to the data used to describe other data, such as the length of a song in iTunes, which describes the music file.
11. Name three advantages of using a data warehouse.
a. The text lists the following ( the student should pick at least three of these ) :
i. The process of developing a data warehouse forces an organization to better understand the data that it is currently collecting and, equally important, what data is not being collected.
ii. A data warehouse provides a centralized view of all data being collected across the enterprise and provides a means of determining data that is inconsistent.
iii. Once all data is identified as consistent, an organization can generate one version of the truth. This is important when the company wants to report consistent statistics about itself, such as revenue or number of employees.
iv. By having a data warehouse, snapshots of data can be taken over time. This creates a historical record of data, which allows for an analysis of trends.
v. A data warehouse provides tools to combine data, which can provide new information and analysis.
12. What is data mining?
a. Data mining is the process of analyzing data to find previously unknown trends, patterns, and associations in order to make decisions.
1. What were the first four locations hooked up to the Internet (ARPANET)?
a. UCLA, Stanford, MIT, and the University of Utah
2. What does the term packet mean?
a. The fundamental unit of data transmitted over the Internet. Each packet has the sender ’ s address, the destination address, a sequence number, and a piece of the overall message to be sent.
3. Which came first, the Internet or the World Wide Web?
a. t he Internet
4. What was revolutionary about Web 2.0?
a. Anyone could post content to the web, without the need for understanding HTML or web-server technology.
5. What was the so-called killer app for the Internet?
a. e lectronic mail (e- mail)
6. What makes a connection a broadband connection?
a. A broadband connection is defined as one that has speeds of at least 256,000 bps.
7. What does the term VoIP mean?
a. Voice over Internet protocol – a way to have voice conversations over the Internet.
8. What is an LAN?
a. A n LAN is a local network, usually operating in the same building or on the same campus.
9. What is the difference between an intranet and an extranet?
a. An intranet consists of t he set of web pages and resources availab le on a company’s internal network. These items are not available to those outside of the company. An extranet is a part of the company’s network that is made available securely to those outside of the company. Extranets can be used to allow customers to log in and check the status of their orders, or for suppliers to check their customers’ inventory levels.
10. What is Metcalfe’s Law?
a. Metcalfe’s Law states that the value of a telecommunications network is proportional to the square of the number of connected users of the system.
1. Briefly define each of the three members of the information security triad.
a. T he three members are as follows:
i. Confidentiality: we want to be able to restrict access to those who are allowed to see given information.
ii. Integrity: the assurance that the information being accessed has not been altered and tr uly represents what is intended.
iii. Availability: information can be accessed and modified by anyone authorized to do so in an appropriate timeframe.
2. What does the term authentication mean?
a. The process of ensuring that a person is who he or she claim s to be.
3. What is multi-factor authentication?
a. The use of more than one method of authentication. The methods are: something you know, something you have, and something you are.
4. What is role-based access control?
a. With role-based access control (RBAC), instead of giving specific users access rights to an information resource, users are assigned to roles and then those roles are assigned the access.
5. What is the purpose of encryption?
a. To keep transmitted data secret so that only those with the proper key can read it.
6. What are two good examples of a complex password?
a. There are many examples of this. Students need to provide examples of passwords that are a minimum of eight characters, with at least one upper-case letter, one special character, and one number.
7. What is pretexting?
a. Pretexting occurs when an attacker calls a helpdesk or security administrator and pretends to be a particular authorized user having trouble logging in . Then, by providing some personal information about the authorized user , the attacker convince s the security person to reset the password and tell him what it is .
8. What are the components of a good backup plan?
a. Knowing what needs to be backed up, regular backups of all data , offsite storage of all backed- up data, and a test of the restoration process.
9. What is a firewall?
a. A firewall can be either a hardware firewall or a software firewall. A hardware firewall is a device that is connected to the network and filters the packets based on a set of rules. A software firewall runs on the operating system and intercepts packets as they arrive to a computer.
10. What does the term physical security mean?
a. Physical security is the protection of the actual hardware and networking components that store and transmit information resources.
1. What is the productivity paradox?
a. The productivity paradox is based on Erik Brynjolfsson’s finding , based on research he conducted in the early 1990s, that the addition of information technology to business had not improved productivity at all.
2. Summarize Carr’s argument in “Does IT Matter.”
a. Information technology is now a commodity and cannot be used to provide an organization with competitive advantage.
3. How is the 2008 study by Brynjolfsson and McAfee different from previous studies? How is it the same?
a. It is different because it shows that IT can bring a competitive advantage, given the right conditions. It is the same in the sense that it shows that IT, by itself, does not bring competitive advantage.
4. What does it mean for a business to have a competitive advantage?
a. A company is said to have a competitive advantage over its rivals when it is able to sustain profits that exceed average for the industry.
5. What are the primary activities and support activities of the value chain?
a. The primary activities are those that directly impact the creation of a product or service. The support activities are those that support the primary activities. Primary: inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, sales/marketing, and service. Support: firm infrastructure, human resources, technology development, and procurement .
6. What has been the overall impact of the Internet on industry profitability? Who has been the true winner?
a. The overall impact has been a reduction in average industry profitability. The consumer has been the true winner.
7. How does EDI work?
a. EDI is the computer-to-computer exchange of business documents in a standard electronic format between business partners.
8. Give an example of a semi-structured decision and explain what inputs would be necessary to provide assistance in making the decision.
a. A semi-structured decision is one in which most of the factors needed for making the decision are known but human experience and other outside factors may still play a role. The student should provide an example of a decision that uses an information system to provide information but is not made by the system. Examples would include: budgeting decisions, diagnosing a medical condition, and investment decisions.
9. What does a collaborative information system do?
a. A collaborative system is software that allows multiple users to interact on a document or topic in order to complete a task or make a decision.
10. How can IT play a role in competitive advantage, according to the 2008 article by Brynjolfsson and McAfee?
a. The article suggests that IT can influence competitive advantage when good management develops and delivers IT-supported process innovation .
1. What does the term business process mean?
a. A process is a series of tasks that are completed in order to accomplish a goal. A business process, therefore, is a process that is focused on achieving a goal for a business.
2. What are three examples of business process from a job you have had or an organization you have observed?
a. Students can answer this in almost any way. The examples should consist of more than a single step.
3. What is the value in documenting a business process?
a. There are many answers to this. From the text: it allows for better control of the process , and for standardization.
4. What is an ERP system? How does an ERP system enforce best practices for an organization?
a. An ERP (enterprise resource p lanning) system is a software application with a centralized database that is implemented across the entire organization. It enforces best practices through the business processes embedded in the software.
5. What is one of the criticisms of ERP systems?
a. ERP system s can lead to the commoditization of business processes, meaning that every company that uses an ERP system will perform business processes the same way.
6. What is business process reengineering? How is it different from incrementally improving a process?
a. Business process r eengineering (BPR) occurs when a business process is redesigned from the ground up. It is different from incrementally improving a process in that it does not simply take the existing process and modify it.
7. Why did BPR get a bad name?
a. BPR became an excuse to lay off employees and try to complete the same amount of work using fewer employees.
8. List the guidelines for redesigning a business process.
a. The guidelin es are as follows:
i. Organize around outcomes, not tasks.
ii. Have those who use the outcomes of the process perform the process.
iii. Subsume information-processing work into the real work that produces the information. Treat geographically dispersed resources as though they were centralized.
iv. Link parallel activities instead of integrating their results.
v. Put the decision points where the work is performed, and build controls into the process.
vi. Capture information once, at the source.
9. What is business process management? What role does it play in allowing a company to differentiate itself?
a. Business process management (BPM) can be thought of as an intentional effort to plan, document, implement, and distribute an organization ’ s business processes with the support of information technology. It can play a role in differentiation through built-in reporting, and by empowering employees, enforcing best practices, and enforcing consistency.
10. What does ISO certification signify?
a. ISO certification shows that you know what you do, do what you say, and have documented your processes.
1. Describe the role of a systems analyst.
a. To understand business requirements and translate them into the requirements of an information system.
2. What are some of the different roles for a computer engineer?
a. hardware engineer, software engineer, net work engineer, systems engineer
3. What are the duties of a computer operator?
a. D uties include keeping the operating systems up to date, ensuring available memory and disk storage, and overseeing the physical environment of the computer.
4. What does the CIO do?
a. The CI O aligns the plans and operations of the information systems with the strategic goals of the organization. This includes tasks such as budgeting, strategic planning, and personnel decisions relevant to the information-systems function.
5. Describe the job of a project manager.
a. A project manager is responsible for keeping projects on time and on budget. This person works with the stakeholders of the project to keep the team organized and communicates the status of the project to management.
6. Explain the point of having two different career paths in information systems.
a. To allow for career growth for those who do not want to manage other employees but instead want to focus on technical skills.
7. What are the advantages and disadvantages of centralizing the IT function?
a. There are several possible answers here. Advantages of centralizing include more control over the company’s systems and data. Disadvantages include a more limited availability of IT resources.
8. What impact has information technology had on the way companies are organized?
a. The organizational structure has been flattened, with fewer layers of management.
9. What are the five types of information-systems users?
a. i nnovators, early adopters, early majo rity, late majority, laggards
10. Why would an organization outsource?
a. Because it needs a specific ski ll for a limited amount of time, and/ or because it can cut costs by outsourcing.
1. What are the steps in the SDLC methodology?
a. The steps are Preliminary Analysis, System Analysis, System Design, Programming, Testing, Implementation, and Maintenance.
2. What is RAD software development?
a. Rapid application development (RAD) is a software-development (or systems-development) methodology that focuses on quickly building a working model of the software, getting feedback from users, and then using that feedback to update the working model.
3. What makes the lean methodology unique?
a. The biggest difference between the lean methodology and the other methodologies is that the full set of requirements for the system is not known when the project is launched.
4. What are three differences between second-generation and third-generation languages?
a. Three k ey differences are as follows:
i. The words used in the language: third generation languages use more English -like words than second-generation languages.
ii. Hardware specificity: third generation languages are not specific to hardware, second-generation languages are.
iii. Learning curve: third generation languages are easier to learn and use.
5. Why would an organization consider building its own software application if it is cheaper to buy one?
a. They may wish to build their own in order t o have something that is unique ( d ifferent from their competitors), and/or something that more closely matches their business processes. They also may choose to do this if they have more time and/ or more money available to do it.
6. What is responsive design?
a. Responsive design is a method of developing websites that allows them to be viewed on many different types of devices without losing capability or effectiveness. With a responsive website, images resize themselves based on the size of the device ’ s screen, and text flows and sizes itself properly for optimal viewing.
7. What is the relationship between HTML and CSS in website design?
a. While HTML is used to define the components of a web page, cascading style sheets (CSS) are used to define the styles of the components on a page.
8. What is the difference between the pilot implementation methodology and the parallel implementation methodology?
a. The pilot methodology implement s new software for just one group of people while the rest of the users use the previous version of the software. The parallel implementation methodology use s both the old and the new applications at the same time.
9. What is change management?
a. The oversight of the changes brought about in an organization.
10. What are the four different implementation methodologies?
a. d irect c utover, pilot, parallel, phased
1. What does the term globalization mean?
a. Globalization refer s to the integration of goods, services, and culture s among the nations of the world.
2. How does Friedman define the three eras of globalization?
a. The three eras are as follows:
i. “ Globalization 1.0 ” occurred from 1492 until about 1800. In this era, globalization was centered around countries. It was about how much horsepower, wind power, and steam power a country had and how creatively it was deployed. The world shrank from size “ large ” to size “ medium. ”
ii. “ Globalization 2.0 ” occurred from about 1800 until 2000, interrupted only by the two World Wars. In this era, the dynamic force driving change was comprised of multinational companies. The world shrank from size “ medium ” to size “ small. ”
iii. “ Globalization 3.0 ” is our current era, beginning in the year 2000. The convergence of the personal computer, fiber-optic Internet connections, and software has created a “ flat-world platform ” that allows small groups and even individuals to go global. The world has shrunk from size “ small ” to size “ tiny. ”
3. Which technologies have had the biggest effect on globalization?
a. There are several answers to this. Probably the most obvious are the Internet, the graphical interface of Windows and the World Wide Web, and workflow software.
4. What are some of the advantages brought about by globalization?
a. Advantages include the ability to locate expertise and labor around the world, the ability to operate 24 hours a day, and a larger market for products.
5. What are the challenges of globalization?
a. Challenges include infrastructure differences, labor laws and regulations, legal restrictions, and differe nt languages, customs, and preferences.
6. What does the term digital divide mean?
a. The separation betwe en those who have access to the global network and those who do not. The digital divide can occur between countries, regions, or even neighborhoods.
7. What are Jakob Nielsen’s three stages of the digital divide?
a. e cono mic, usability, and empowerment
8. What was one of the key points of The Rise of the Network Society ?
a. There are two key points to choose from. One is that economic activity was, when the book was published in 1996, being organized around the networks that the new tel ecommunication technologies had provided. The other is that this new, global economic activity was different from the past, because “ it is an economy with the capacity to work as a unit in real time on a planetary scale. ”
9. Which country has the highest average Internet speed? How does your country compare?
a. According to the chart in the chapter, South Korea has the highest Internet speeds. S tudent s will need to look up their own to compare.
10. What is the OLPC project? Has it been successful?
a. One Laptop Per Child. By most measures, it has not been a successful program.
1. What does the term information systems ethics mean?
a. There are various ways of answering this question , but the answer should include s omething about the application of ethics to the new capabilities and cultural norms brought about by information technology.
2. What is a code of ethics? What is one advantage and one disadvantage of a code of ethics?
a. A code of ethics is a document that outlines a set of acceptable behaviors for a professional or social group. A nswers may differ for the second part, but from the text: o ne advantage of a code of ethics is that it clarifies the acceptable standards of behavior for a professional group. One disadvantage is that it does not necessarily have legal authority.
3. What does the term intellectual property mean? Give an example.
a. Intellectual property is defined as “ property (as an idea, invention, or process) that derives from the work of the mind or intellect. ”
4. What protections are provided by a copyright? How do you obtain one?
a. Copyright protections address the following : who can make copies of the work, who can make derivative works from the original work, who can perform the work publicly, who can display the work publicly, and who can distribute the work. You obtain a copyright as soon as the work is put into tangible form.
5. What is fair use?
a. Fair use is a limitation on copyright law that allows for the use of protected works without prior authorization in specific cases.
6. What protections are provided by a patent? How do you obtain one?
a. Once a patent is granted, it provides the inventor with protection from others infringing on the patent. In the US, a patent holder has the right to “ exclude others from making, using, offering for sale, or selling the invention throughout the United States or importing the invention into the United States for a limited time in exchange for public disclosure of the invention when the patent is granted. ” You obtain a patent by filing an application with the patent office. A patent will be granted if the work is deemed to be original, useful, and non-obvious.
7. What does a trademark protect? How do you obtain one?
a. A trademark protects a word, phrase, logo, shape , or sound that identifies a source of goods or services. You can obtain one by registering with the Patent and Trademark Office (US). There is also a common- law trademark.
8. What does the term per sonally identifiable information mean?
a. Information about a person that can be used to uniquely establish that person ’ s identit y is called personally identifiable information, or PII.
9. What protections are provided by HIPAA, COPPA, and FERPA?
a. The a nswers are as follows :
i. HIPAA: protects records related to health care as a special class of personally identifiable information.
ii. COPPA: protects information collected from children under the age of thirteen.
iii. FERPA: protects student educational records.
10. How would you explain the concept of NORA?
a. There are various ways to answer this. The basic answer is that NORA (non-obvious relationship a wareness) is the process of collecting large quantities of a variety of information and then combining it to create profiles of individuals.
1. Which countries are the biggest users of the Internet? Social media? Mobile?
a. S tudents will need to look outside the text for this, as it changes all the time. There are also different ways of measurement: number of users, % of population , most active users, etc. Some good sites to use are Internet World Stats , Kissmetrics , and the World Bank .
2. Which country had the largest Internet growth (in %) between 2008 and 2012?
a. Iran, at 205%
3. How will most people connect to the Internet in the future?
a. via mobile devices
4. What are two different applications of wearable technologies?
a. There are many answers to this question; two examples are Google Glass and Jawbone UP.
5. What are two different applications of collaborative technologies?
a. There are many answers to this; two examples are software that routes us to our destination in the shortest amount of time and websites that review different companies.
6. What capabilities do printable technologies have?
a. Using 3-D printers, designers can quickly test prototypes or build something as a proof of concept. Printable technologies also make it possible to bring manufacturing to the desktop computer.
7. How will advances in wireless technologies and sensors make objects “findable”?
a. Advances in wireless technologies and sensors will allow physical objects to send and receive data about themselves.
8. What is enhanced situational awareness?
a. Data from large numbers of sensors can give decision makers a heightened awareness of real-time events, particularly when the sensors are used with advanced display or visualization technologies.
9. What is a nanobot?
a. A nanobot is a robot whose components are on the scale of about a nanometer.
10. What is a UAV?
a. An unmanned aerial vehicle – a small airplane or helicopter that can fly without a pilot. UAVs are run by computer or remote control .
Information Systems for Business and Beyond Copyright © 2014 by CC BY: David T. Bourgeois, Ph.D. is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
TechRepublic

8 Best Data Science Tools and Software
Apache Spark and Hadoop, Microsoft Power BI, Jupyter Notebook and Alteryx are among the top data science tools for finding business insights. Compare their features, pros and cons.

EU’s AI Act: Europe’s New Rules for Artificial Intelligence
Europe's AI legislation, adopted March 13, attempts to strike a tricky balance between promoting innovation and protecting citizens' rights.

10 Best Predictive Analytics Tools and Software for 2024
Tableau, TIBCO Data Science, IBM and Sisense are among the best software for predictive analytics. Explore their features, pricing, pros and cons to find the best option for your organization.

Tableau Review: Features, Pricing, Pros and Cons
Tableau has three pricing tiers that cater to all kinds of data teams, with capabilities like accelerators and real-time analytics. And if Tableau doesn’t meet your needs, it has a few alternatives worth noting.

Top 6 Enterprise Data Storage Solutions for 2024
Amazon, IDrive, IBM, Google, NetApp and Wasabi offer some of the top enterprise data storage solutions. Explore their features and benefits, and find the right solution for your organization's needs.
Latest Articles

How Can Businesses Defend Themselves Against Common Cyberthreats?
TechRepublic consolidated expert advice on how businesses can defend themselves against the most common cyberthreats, including zero-days, ransomware and deepfakes.

Top 10 CRM Features and Functionalities
Discover the top CRM features for business success. Explore a curated list of key capabilities to consider when choosing the right CRM solution, including marketing tools, activity tracking and more.

Combatting Deepfakes in Australia: Content Credentials is the Start
The production of deepfakes is accelerating at more than 1,500% in Australia, forcing organisations to create and adopt standards like Content Credentials.

The Top 5 Pipedrive Alternatives for 2024
Discover the top alternatives to Pipedrive. Explore a curated list of CRM platforms with similar features, pricing and pros and cons to find the best fit for your business.

The Australian Government’s Manufacturing Objectives Rely on IT Capabilities
The intent of the Future Made in Australia Act is to build manufacturing capabilities across all sectors, which will likely lead to more demand for IT skills and services.

Udemy Report: Which IT Skills Are Most in Demand in Q1 2024?
Informatica PowerCenter, Microsoft Playwright and Oracle Database SQL top Udemy’s list of most popular tech courses.

Gartner: 4 Bleeding-Edge Technologies in Australia
Gartner recently identified emerging tech that will impact enterprise leaders in APAC. Here’s what IT leaders in Australia need to know about these innovative technologies.

Llama 3 Cheat Sheet: A Complete Guide for 2024
Learn how to access Meta’s new AI model Llama 3, which sets itself apart by being open to use under a license agreement.

Zoho vs Salesforce (2024): Which CRM Is Better?
Look at Zoho CRM and Salesforce side-by-side to compare the cost per functionality and top pros and of each provider to determine which is better for your business needs.

9 Innovative Use Cases of AI in Australian Businesses in 2024
Australian businesses are beginning to effectively grapple with AI and build solutions specific to their needs. Here are notable use cases of businesses using AI.

How Are APAC Tech Salaries Faring in 2024?
The year 2024 is bringing a return to stable tech salary growth in APAC, with AI and data jobs leading the way. This follows downward salary pressure in 2023, after steep increases in previous years.

Anthropic Releases Claude Team Enterprise AI Plan and iOS App
The enterprise plan seeks to fill a need for generative AI tools for small and medium businesses. Plus, a Claude app is now on iOS.

Top Tech Conferences & Events to Add to Your Calendar in 2024
A great way to stay current with the latest technology trends and innovations is by attending conferences. Read and bookmark our 2024 tech events guide.

TechRepublic Premium Editorial Calendar: Policies, Checklists, Hiring Kits and Glossaries for Download
TechRepublic Premium content helps you solve your toughest IT issues and jump-start your career or next project.

IBM Acquires HashiCorp for $6.4 Billion, Expanding Hybrid Cloud Offerings
The deal is intended to strengthen IBM’s hybrid and multicloud offerings and generative AI deployment.
Create a TechRepublic Account
Get the web's best business technology news, tutorials, reviews, trends, and analysis—in your inbox. Let's start with the basics.
* - indicates required fields
Sign in to TechRepublic
Lost your password? Request a new password
Reset Password
Please enter your email adress. You will receive an email message with instructions on how to reset your password.
Check your email for a password reset link. If you didn't receive an email don't forgot to check your spam folder, otherwise contact support .
Welcome. Tell us a little bit about you.
This will help us provide you with customized content.
Want to receive more TechRepublic news?
You're all set.
Thanks for signing up! Keep an eye out for a confirmation email from our team. To ensure any newsletters you subscribed to hit your inbox, make sure to add [email protected] to your contacts list.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Correct Answer. The following five things came to light, after cybercriminals from China spent more than six years cautiously working to obtain data from more than 70 government agencies, corporations and non-profit groups: Seventy-two (72) organizations were compromised. It was just not North America and Europe.
Case 1: A Business Trip to South America Goes South. Topic: ATM Skimming and Bank Fraud. Case 2: A Construction Company Gets Hammered by a Keylogger. Topic: Keylogging, Malware and Bank Fraud. Case 3: Stolen Hospital Laptop Causes Heartburn. Topic: Encryption and Business Security Standards.
Cybersecurity is the act of protecting systems, networks, and programs from digital attacks that can compromise the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data. In this article, We covered the top 60 most asked cyber security interview questions with answers that cover everything from basic of cybersecurity to advanced cybersecurity concepts
Lets get started! This free practice quiz includes questions from ISACA ® 's test prep solutions that are the same level of difficulty you can expect on ISACA's official CISA exam. Begin Quiz. Join the CISA community to gain insights and prepare for the Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) exam.
Questions to consider 11 Presentation structure 13 4. Glossary 14 2 Cyber Security Case Study. PwC Overview 3 Company Overview Fledgling social media platform, 'Chatter' launched in September 2017. Its main users are 13-21 year olds. Users can: ... Cyber Security Case Study. case.
Validate your cyber defenses against real-world threats. Kroll's world-class penetration testing services bring together front-line threat intelligence, thousands of hours of cyber security assessments completed each year and a team of certified cyber experts — the foundation for our sophisticated and scalable approach.
Let's face it, there's no shortage in potential questions at any given interview across a wide variety of topics in information security.On top of that, InfoSec means a lot of different things to a lot of different people. For example, information security covers everyone from the guy at Best Buy running a copy of Norton all the way up to the cryptomasters at the NSA.
38) Explain TCP Three-way handshake. It is a process used in a network to make a connection between a local host and server. This method requires the client and server to negotiate synchronization and acknowledgment packets before starting communication. 39) Define the term residual risk.
Take your learning further. Making the decision to study can be a big step, which is why you'll want a trusted University. We've pioneered distance learning for over 50 years, bringing university to you wherever you are so you can fit study around your life. Take a look at all Open University courses.
Implement zero trust security where authentication and authorization are conducted every time employees want to access the organization's systems. 7. Use blockchain technology to secure user data ...
Relevant answer. Mohit Tiwari. Dec 31, 2023. Answer. Information Security and Systems Security, while often used interchangeably, refer to distinct aspects of security in the digital world ...
Information security is the 'application of any technical methods and managerial processes on the information resources (hardware, software and data) in order to keep organizational assets and personal privacy protected' (Hong, Chi, Chao & Tang, 2006).Whereas, information security management (ISM) consists the set of activities involved in configuring resources in order to meet information ...
Analyze the situation: Gather all the relevant information and data provided in the case study. Identify the key issues, stakeholders, and any potential constraints or challenges that need to be considered. 3. Develop a hypothesis: Based on your analysis, formulate a hypothesis or a proposed solution to the problem.
Computer Science questions and answers; Question 3 Cyber Security Case Study THE CASE SCENARIO The victim: A bank with 400 networked windows 100 in a central office, with another 300 in a branch offices. Upon arrival of the incident response team, we identify that the client had no security security protection in place.
Case study questions about the buying team and internal advocates. Case study questions about customer success. Case study questions about product feedback. Case study questions about willingness to make referrals. Case study question to prompt quote-worthy feedback. Case study questions about the customers' future goals.
These 61 sample cybersecurity interview questions should give you an idea of what to expect when interviewing with a well-respected organization like MITRE, Deloitte, Accenture, Cisco, Google, Lockheed, and others. Preparation is the key to making a good impression and landing a job in cybersecurity, so study these questions carefully.
That information technology is just a commodity and cannot be used to gain a competitive advantage. Chapter 2. 1. Write your own description of what the term information systems hardware means. a. Answers will vary, but should say something about information systems hardware consisting of the physical parts of computing devices that can ...
Here the answer of Question 1: A) Risk Identification: View the full answer Step 2. Unlock. Answer. Unlock. Previous question Next question. Transcribed image text: Read the following case study and answer below questions: Case study 2: Information Security Risk Management at XYZ Company XYZ Company is a mid-sized organization that operates in ...
Join us at 6 PM (WAT) this Thursday May 9, 2024, as our distinguish guest will be discussing the topic: GEN-Z ACCOUNTANTS: Redefining Traditional...
Big Data Big Data 8 Best Data Science Tools and Software . Apache Spark and Hadoop, Microsoft Power BI, Jupyter Notebook and Alteryx are among the top data science tools for finding business insights.
As this is. Read the case study and answer the questions that follow. You are an Information Security Officer (ISO) in one of the reputed companies in Melbourne. Company has a huge IT infrastructure in its head office and more than 50 branches all across the Asia Pacific. More than 300 staffs work in the company including all the branches and ...
it is question of information security subject of computer science. here a case study is given.on lower part 1,2,3,4 questions are asked based on this case study.plz answer elaborately. with mentioning related question number.thanks. plz donot waste. my time asking again and again.thats all i have been given in my assignment.