Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts

Peer Review Presentation

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This presentation is designed to acquaint your students with the concept of peer review. This presentation will include the who, what, where, when, and why of peer review. The slides presented here are designed to aid the facilitator in an interactive presentation of the elements of peer review. This presentation is ideal for any level of writing, including freshman composition.

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 10 Peer Feedback Templates with Samples and Examples

Naveen Kumar
"Make feedback normal. Not a performance review," said Ed Catmull, co-founder of Pixar Animation Studios. One meaning of these words is that feedback should be an everyday part of the business culture rather than an occasional event. By making feedback part of day-to-day business, organizations can create a learning environment of continuous, reciprocal exchange of insights and constructive criticism. This environment helps employees in their personal and professional growth.
One way to create this learning environment is to have employees help each other learn by sharing peer feedback.
What is Peer Feedback
Peer feedback refers to the process through which employees provide constructive criticism, support, and suggestions to their colleagues. Unlike traditional feedback mechanisms that flow vertically from managers to employees, peer feedback operates on a horizontal exchange of insights among individuals at the same organizational level.
This feedback process allows employees to give and receive insights into their work, behaviors, and skills from immediate team members. Peer feedback is predicated on mutual respect and shared goals to foster a collaborative culture that values personal and professional development.
Peer Feedback into Business Learnings
Peer feedback democratizes the process, allowing employees to share their views or voices regardless of their hierarchical position. It promotes diversity of perspectives and ideas, leading to innovation and more effective problem-solving. Also, peers can share a more accurate and holistic view of an employee's performance and behaviors than management.
Integrating peer feedback mechanisms helps build trust and strengthen team members' relationships. This sense of belonging and mutual respect improves employee engagement and retention and contributes to long-term business success.
Challenges in Implementing Peer Feedback and Easy Solution
Effective implementation of the peer feedback process has challenges, like maintaining consistency, objectivity, and openness to constructive criticism. A lack of structure and clear guidelines can lead to vague and unhelpful feedback.
The fear of negative repercussions can deter employees from sharing honest feedback, while some may struggle with speaking their thoughts in a constructive manner. Our Pre-designed peer feedback templates can help businesses overcome these challenges.
These content-ready peer feedback templates provide a structured framework to organizations that help share specific, relevant, and aligned feedback with predefined criteria. With these PPT Designs, the usefulness and actionability of feedback can be improved. The 100% customizable nature of these PowerPoint slides provides flexibility for easy editing.
Pre-designed Peer Feedback Templates
This peer feedback templates bundle will help teams understand the integral role of peer feedback in employee development. It describes key performance indicators (KPIs) essential for measuring and enhancing individual progress through mutual assessment. The deck provides a robust framework for tracking engagement and cultivating a culture of active participation within peer review processes. It outlines structured criteria for objective feedback and discusses best practices to avoid common pitfalls, ensuring the effectiveness of the feedback mechanism.
Including a qualitative peer feedback questionnaire in this bundle further improves the evaluation process and allows comprehensive and thoughtful discussions.
With visually engaging graphics, this interactive slide set will help organizations leverage peer insights for developmental success.

Download this complete deck
Template 1: Peer Feedback Template with Employee Development KPIs
This slide is designed to facilitate peer feedback within employee development programs. It measures progress by highlighting KPIs like skill improvement, development plan completion, and learning program effectiveness. The slide outlines clear descriptions, action steps, targets, and examples for each KPI, providing a structured approach to peer feedback. It will assist organizations in measuring and improving the growth of employees through peer-to-peer review. With this PPT Layout, companies can track development plans, align career aspirations with company goals, and refine learning initiatives by designing informed by peer assessments.
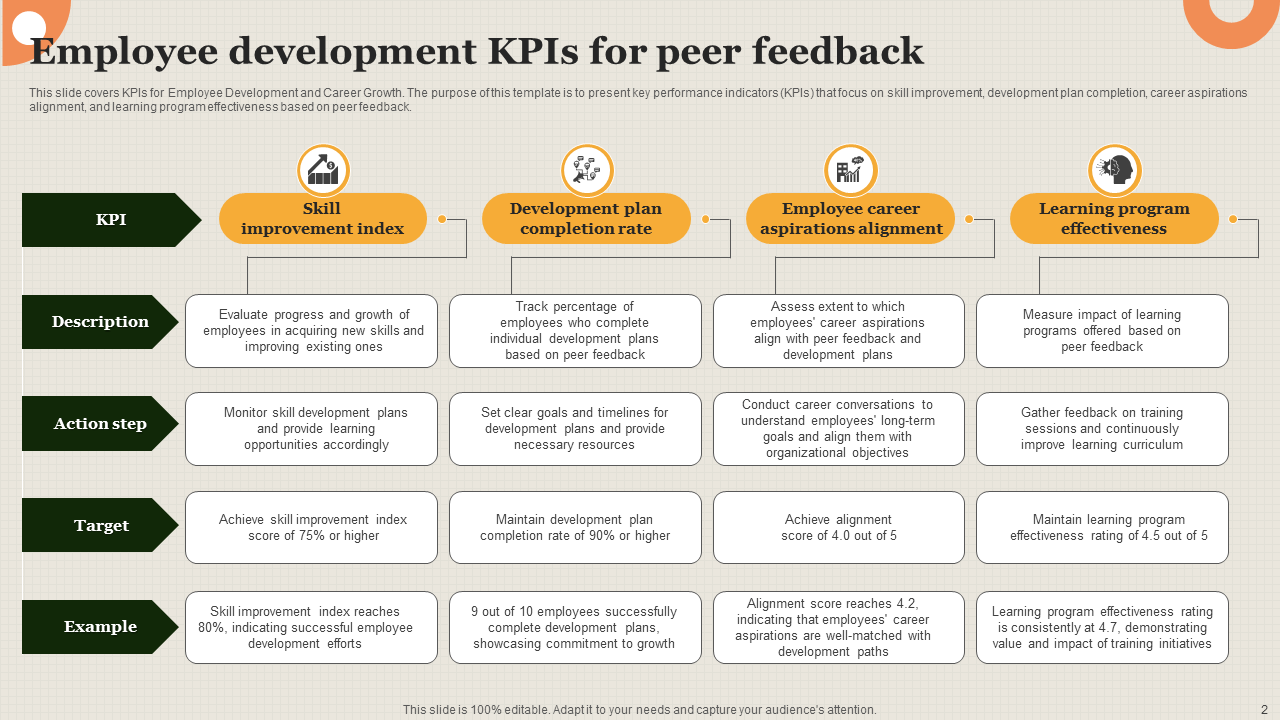
Download this template
Template 2: Peer Feedback Template to Track Employee Engagement
This PPT Template helps organizations enhance workplace dynamics through peer feedback. It provides a structured approach to tracking and analyzing employee engagement with KPIs such as peer recognition rate, feedback frequency, and collaboration index. Descriptive measures, actionable steps, and example targets, outlined in this PPT Template for each KPI, serve as a practical guide for managers to foster a supportive and interactive environment. With this slide, businesses can encourage a culture of appreciation, consistent feedback exchanges, and collaboration for enhanced employee productivity and job satisfaction.

Template 3: Peer Feedback KPIs Template for Team Collaboration
This PowerPoint Design offers a suite of KPIs designed to showcase team collaboration through peer feedback. It measures and enhances cross-functional teamwork, communication effectiveness, conflict resolution, diversity & inclusion, and engagement index. The template provides a clear description, action steps, benchmark targets, and achieved score for each KPI. This PPT Slide is ideal for managers to cultivate a cooperative, inclusive environment with constructive communication.

Template 4: Peer Performance Feedback Rating Criteria Template
This presentation slide is a structured framework for evaluating peer performance with a detailed rating system for key competencies. It includes ratings for communication, teamwork, time management, problem-solving, knowledge-sharing, adaptability, and more in a tabular format. Spaces to add specific comments and notes related to rating or skill allow sharing brief and modest feedback to make the peer review process more effective. It helps in a holistic assessment by allowing reviewers to rate each skill and boost the professional development and growth of peers.

Template 5: Peer Feedback Template Showing Mistakes to Avoid
This presentation slide is a crucial tool for enhancing the quality of peer feedback within teams. It outlines pitfalls to avoid, such as focusing on a single type of feedback, being vague or judgmental and insulting, ignoring context and personal challenges, and providing feedback without listening. These mistakes can undermine the effectiveness of the feedback process. The PPT Layout encourages a balanced and constructive approach that promotes growth, learning, and mutual respect among peers.

Template 6: Effective Peer Feedback Elements Presentation Template
Use this Presentation Template as a guide for effective peer feedback implementation. It explains core components necessary for constructive peer feedback along with their uses or working in an easy-to-understand manner. The Likert Scale used for ratings, strengths, improvement areas, and the strategic use of open-ended questions for comprehensive feedback are explained. It helps design a well-rounded feedback process to ensure that responses aid in professional growth and team cohesion. Grab it today!

Template 7: Peer Feedback Template to Improve Evaluation Process
This PowerPoint Set is an actionable roadmap for enhancing the peer feedback process in professional settings. It outlines steps such as scheduling feedback conversations, creating strategies to address areas for improvement, setting measurable goals, and establishing learning programs and teams. The design includes space to describe each step and real-life examples. Organizations can create a culture of continuous improvement and collaborative success using this design

Template 8: Peer Feedback Template with Constructive and Actionable Insights
This PPT Design will guide businesses in delivering peer feedback with a focus on constructive critique and actionable recommendations. It shares a format for communicating feedback backed by statistical evidence to reinforce the points made. The slide contains sections for direct commentary, complemented with corresponding data that underscore the feedback's relevance. This approach ensures that feedback is heard and anchored in tangible metrics for continuous improvement and clear team communication.

Template 9: Peer Feedback Implementation Process Presentation Template
This presentation slide will help organizations understand the benefits and impacts of peer feedback and enhance its implementation mechanisms. It outlines employee and business benefits from peer feedback, like gaining new insights, increased employee retention, new training insights, better remote culture, and clear career paths. With examples and actionable steps, it is a blueprint for creating a dynamic, supportive work environment.

Template 10: Peer Feedback Questionnaire Template for Qualitative Approach
This PPT Template provides a comprehensive Peer Feedback Questionnaire focused on bringing out qualitative feedback within teams. It includes well-thought-out and strategic questions addressing skills development, collaboration, project management, and feedback reception. The template helps gather in-depth insights into team members' perspectives with questions on sharing problem-solving instances and suggestions for improvement. Organizations can use this questionnaire to pinpoint improvement area and celebrate strengths.

Bonus Template 1: Peer Feedback and Employee Review Questionnaire Template
This PowerPoint Design provides a structured Peer Feedback and Employee Review Questionnaire Template to facilitate exhaustive peer evaluations. It includes attributes to be rated on a numerical rating scale of 1-5, allowing for an assessment of an individual's performance aligned with the organization's standards. This template aids in identifying areas of strength and opportunities like synergy with organization goals, integrity, helpfulness, professionalism, accountability, etc. Instructions are provided in a side segment.
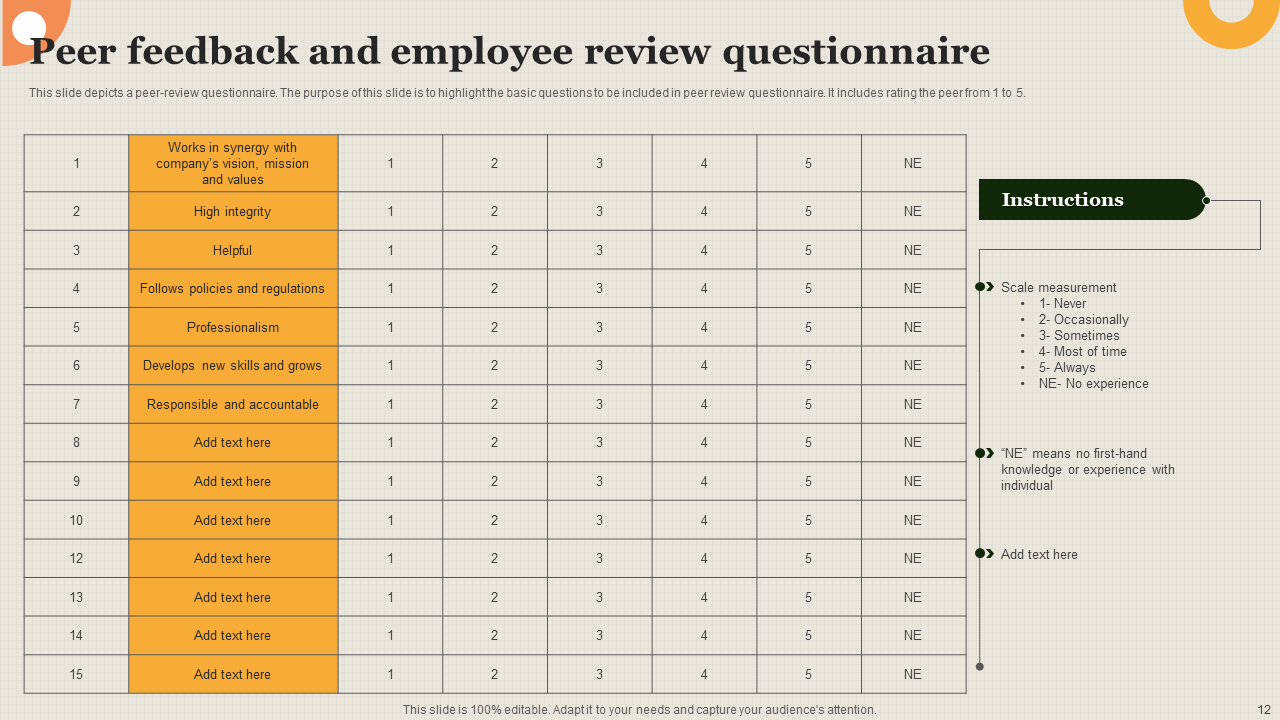
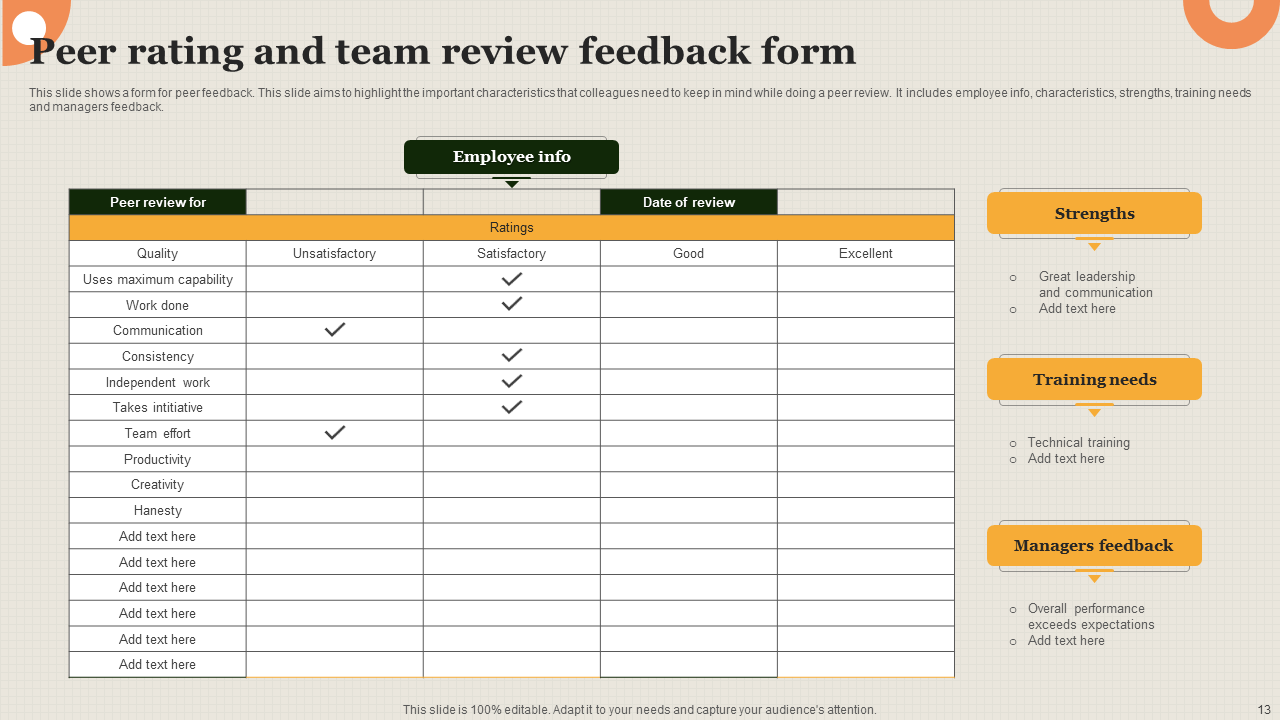
Bonus Template 2: Peer Rating and Team Review Feedback Form Template
This well-organized and expert-designed presentation template will help streamline the peer evaluation process. It enables a detailed review by providing a form for rating employee KPIs like performance, work quality, communication, honesty, consistency, leadership, and more. With designated sections for strengths, training needs, and managerial feedback, this PPT Design helps record and monitor individual contributions.
ACTIONABLE, RELEVANT FEEDBACK MATTERS
Peer feedback offers a platform to employees for receiving and sharing timely, specific, and relevant feedback. Since peers understand the challenges and nuances of the work, their feedback is applicable and actionable. This immediacy and relevance make it easier for employees to implement changes and see improvements in their performance. Giving and receiving feedback requires employees to practice active listening, communicate their thoughts with clarity, and respond to criticism in a constructive way.
SlideTeam's peer feedback templates include prompts and examples of constructive feedback that help employees express thoughts, and create a more supportive and productive feedback culture. These PPT Layouts streamline the feedback process and enhance its quality and impact, facilitating a more open, engaged, and improvement-focused workplace environment.
Related posts:
- How to Design the Perfect Service Launch Presentation [Custom Launch Deck Included]
- Quarterly Business Review Presentation: All the Essential Slides You Need in Your Deck
- [Updated 2023] How to Design The Perfect Product Launch Presentation [Best Templates Included]
- 99% of the Pitches Fail! Find Out What Makes Any Startup a Success
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 7 Event Feedback Templates with Samples and Examples

Must-have Interview Feedback Templates with Examples and Samples
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

Sales funnel results presentation layouts
3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Future plan powerpoint template slide

Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

Agenda powerpoint slide show

Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

Meet our team representing in circular format

Loading metrics
Open Access
Ten simple rules for effective presentation slides
* E-mail: [email protected]
Affiliation Biomedical Engineering and the Center for Public Health Genomics, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, Virginia, United States of America
- Kristen M. Naegle

Published: December 2, 2021
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009554
- Reader Comments
Citation: Naegle KM (2021) Ten simple rules for effective presentation slides. PLoS Comput Biol 17(12): e1009554. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009554
Copyright: © 2021 Kristen M. Naegle. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Funding: The author received no specific funding for this work.
Competing interests: The author has declared no competing interests exist.
Introduction
The “presentation slide” is the building block of all academic presentations, whether they are journal clubs, thesis committee meetings, short conference talks, or hour-long seminars. A slide is a single page projected on a screen, usually built on the premise of a title, body, and figures or tables and includes both what is shown and what is spoken about that slide. Multiple slides are strung together to tell the larger story of the presentation. While there have been excellent 10 simple rules on giving entire presentations [ 1 , 2 ], there was an absence in the fine details of how to design a slide for optimal effect—such as the design elements that allow slides to convey meaningful information, to keep the audience engaged and informed, and to deliver the information intended and in the time frame allowed. As all research presentations seek to teach, effective slide design borrows from the same principles as effective teaching, including the consideration of cognitive processing your audience is relying on to organize, process, and retain information. This is written for anyone who needs to prepare slides from any length scale and for most purposes of conveying research to broad audiences. The rules are broken into 3 primary areas. Rules 1 to 5 are about optimizing the scope of each slide. Rules 6 to 8 are about principles around designing elements of the slide. Rules 9 to 10 are about preparing for your presentation, with the slides as the central focus of that preparation.
Rule 1: Include only one idea per slide
Each slide should have one central objective to deliver—the main idea or question [ 3 – 5 ]. Often, this means breaking complex ideas down into manageable pieces (see Fig 1 , where “background” information has been split into 2 key concepts). In another example, if you are presenting a complex computational approach in a large flow diagram, introduce it in smaller units, building it up until you finish with the entire diagram. The progressive buildup of complex information means that audiences are prepared to understand the whole picture, once you have dedicated time to each of the parts. You can accomplish the buildup of components in several ways—for example, using presentation software to cover/uncover information. Personally, I choose to create separate slides for each piece of information content I introduce—where the final slide has the entire diagram, and I use cropping or a cover on duplicated slides that come before to hide what I’m not yet ready to include. I use this method in order to ensure that each slide in my deck truly presents one specific idea (the new content) and the amount of the new information on that slide can be described in 1 minute (Rule 2), but it comes with the trade-off—a change to the format of one of the slides in the series often means changes to all slides.
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
Top left: A background slide that describes the background material on a project from my lab. The slide was created using a PowerPoint Design Template, which had to be modified to increase default text sizes for this figure (i.e., the default text sizes are even worse than shown here). Bottom row: The 2 new slides that break up the content into 2 explicit ideas about the background, using a central graphic. In the first slide, the graphic is an explicit example of the SH2 domain of PI3-kinase interacting with a phosphorylation site (Y754) on the PDGFR to describe the important details of what an SH2 domain and phosphotyrosine ligand are and how they interact. I use that same graphic in the second slide to generalize all binding events and include redundant text to drive home the central message (a lot of possible interactions might occur in the human proteome, more than we can currently measure). Top right highlights which rules were used to move from the original slide to the new slide. Specific changes as highlighted by Rule 7 include increasing contrast by changing the background color, increasing font size, changing to sans serif fonts, and removing all capital text and underlining (using bold to draw attention). PDGFR, platelet-derived growth factor receptor.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009554.g001
Rule 2: Spend only 1 minute per slide
When you present your slide in the talk, it should take 1 minute or less to discuss. This rule is really helpful for planning purposes—a 20-minute presentation should have somewhere around 20 slides. Also, frequently giving your audience new information to feast on helps keep them engaged. During practice, if you find yourself spending more than a minute on a slide, there’s too much for that one slide—it’s time to break up the content into multiple slides or even remove information that is not wholly central to the story you are trying to tell. Reduce, reduce, reduce, until you get to a single message, clearly described, which takes less than 1 minute to present.
Rule 3: Make use of your heading
When each slide conveys only one message, use the heading of that slide to write exactly the message you are trying to deliver. Instead of titling the slide “Results,” try “CTNND1 is central to metastasis” or “False-positive rates are highly sample specific.” Use this landmark signpost to ensure that all the content on that slide is related exactly to the heading and only the heading. Think of the slide heading as the introductory or concluding sentence of a paragraph and the slide content the rest of the paragraph that supports the main point of the paragraph. An audience member should be able to follow along with you in the “paragraph” and come to the same conclusion sentence as your header at the end of the slide.
Rule 4: Include only essential points
While you are speaking, audience members’ eyes and minds will be wandering over your slide. If you have a comment, detail, or figure on a slide, have a plan to explicitly identify and talk about it. If you don’t think it’s important enough to spend time on, then don’t have it on your slide. This is especially important when faculty are present. I often tell students that thesis committee members are like cats: If you put a shiny bauble in front of them, they’ll go after it. Be sure to only put the shiny baubles on slides that you want them to focus on. Putting together a thesis meeting for only faculty is really an exercise in herding cats (if you have cats, you know this is no easy feat). Clear and concise slide design will go a long way in helping you corral those easily distracted faculty members.
Rule 5: Give credit, where credit is due
An exception to Rule 4 is to include proper citations or references to work on your slide. When adding citations, names of other researchers, or other types of credit, use a consistent style and method for adding this information to your slides. Your audience will then be able to easily partition this information from the other content. A common mistake people make is to think “I’ll add that reference later,” but I highly recommend you put the proper reference on the slide at the time you make it, before you forget where it came from. Finally, in certain kinds of presentations, credits can make it clear who did the work. For the faculty members heading labs, it is an effective way to connect your audience with the personnel in the lab who did the work, which is a great career booster for that person. For graduate students, it is an effective way to delineate your contribution to the work, especially in meetings where the goal is to establish your credentials for meeting the rigors of a PhD checkpoint.
Rule 6: Use graphics effectively
As a rule, you should almost never have slides that only contain text. Build your slides around good visualizations. It is a visual presentation after all, and as they say, a picture is worth a thousand words. However, on the flip side, don’t muddy the point of the slide by putting too many complex graphics on a single slide. A multipanel figure that you might include in a manuscript should often be broken into 1 panel per slide (see Rule 1 ). One way to ensure that you use the graphics effectively is to make a point to introduce the figure and its elements to the audience verbally, especially for data figures. For example, you might say the following: “This graph here shows the measured false-positive rate for an experiment and each point is a replicate of the experiment, the graph demonstrates …” If you have put too much on one slide to present in 1 minute (see Rule 2 ), then the complexity or number of the visualizations is too much for just one slide.
Rule 7: Design to avoid cognitive overload
The type of slide elements, the number of them, and how you present them all impact the ability for the audience to intake, organize, and remember the content. For example, a frequent mistake in slide design is to include full sentences, but reading and verbal processing use the same cognitive channels—therefore, an audience member can either read the slide, listen to you, or do some part of both (each poorly), as a result of cognitive overload [ 4 ]. The visual channel is separate, allowing images/videos to be processed with auditory information without cognitive overload [ 6 ] (Rule 6). As presentations are an exercise in listening, and not reading, do what you can to optimize the ability of the audience to listen. Use words sparingly as “guide posts” to you and the audience about major points of the slide. In fact, you can add short text fragments, redundant with the verbal component of the presentation, which has been shown to improve retention [ 7 ] (see Fig 1 for an example of redundant text that avoids cognitive overload). Be careful in the selection of a slide template to minimize accidentally adding elements that the audience must process, but are unimportant. David JP Phillips argues (and effectively demonstrates in his TEDx talk [ 5 ]) that the human brain can easily interpret 6 elements and more than that requires a 500% increase in human cognition load—so keep the total number of elements on the slide to 6 or less. Finally, in addition to the use of short text, white space, and the effective use of graphics/images, you can improve ease of cognitive processing further by considering color choices and font type and size. Here are a few suggestions for improving the experience for your audience, highlighting the importance of these elements for some specific groups:
- Use high contrast colors and simple backgrounds with low to no color—for persons with dyslexia or visual impairment.
- Use sans serif fonts and large font sizes (including figure legends), avoid italics, underlining (use bold font instead for emphasis), and all capital letters—for persons with dyslexia or visual impairment [ 8 ].
- Use color combinations and palettes that can be understood by those with different forms of color blindness [ 9 ]. There are excellent tools available to identify colors to use and ways to simulate your presentation or figures as they might be seen by a person with color blindness (easily found by a web search).
- In this increasing world of virtual presentation tools, consider practicing your talk with a closed captioning system capture your words. Use this to identify how to improve your speaking pace, volume, and annunciation to improve understanding by all members of your audience, but especially those with a hearing impairment.
Rule 8: Design the slide so that a distracted person gets the main takeaway
It is very difficult to stay focused on a presentation, especially if it is long or if it is part of a longer series of talks at a conference. Audience members may get distracted by an important email, or they may start dreaming of lunch. So, it’s important to look at your slide and ask “If they heard nothing I said, will they understand the key concept of this slide?” The other rules are set up to help with this, including clarity of the single point of the slide (Rule 1), titling it with a major conclusion (Rule 3), and the use of figures (Rule 6) and short text redundant to your verbal description (Rule 7). However, with each slide, step back and ask whether its main conclusion is conveyed, even if someone didn’t hear your accompanying dialog. Importantly, ask if the information on the slide is at the right level of abstraction. For example, do you have too many details about the experiment, which hides the conclusion of the experiment (i.e., breaking Rule 1)? If you are worried about not having enough details, keep a slide at the end of your slide deck (after your conclusions and acknowledgments) with the more detailed information that you can refer to during a question and answer period.
Rule 9: Iteratively improve slide design through practice
Well-designed slides that follow the first 8 rules are intended to help you deliver the message you intend and in the amount of time you intend to deliver it in. The best way to ensure that you nailed slide design for your presentation is to practice, typically a lot. The most important aspects of practicing a new presentation, with an eye toward slide design, are the following 2 key points: (1) practice to ensure that you hit, each time through, the most important points (for example, the text guide posts you left yourself and the title of the slide); and (2) practice to ensure that as you conclude the end of one slide, it leads directly to the next slide. Slide transitions, what you say as you end one slide and begin the next, are important to keeping the flow of the “story.” Practice is when I discover that the order of my presentation is poor or that I left myself too few guideposts to remember what was coming next. Additionally, during practice, the most frequent things I have to improve relate to Rule 2 (the slide takes too long to present, usually because I broke Rule 1, and I’m delivering too much information for one slide), Rule 4 (I have a nonessential detail on the slide), and Rule 5 (I forgot to give a key reference). The very best type of practice is in front of an audience (for example, your lab or peers), where, with fresh perspectives, they can help you identify places for improving slide content, design, and connections across the entirety of your talk.
Rule 10: Design to mitigate the impact of technical disasters
The real presentation almost never goes as we planned in our heads or during our practice. Maybe the speaker before you went over time and now you need to adjust. Maybe the computer the organizer is having you use won’t show your video. Maybe your internet is poor on the day you are giving a virtual presentation at a conference. Technical problems are routinely part of the practice of sharing your work through presentations. Hence, you can design your slides to limit the impact certain kinds of technical disasters create and also prepare alternate approaches. Here are just a few examples of the preparation you can do that will take you a long way toward avoiding a complete fiasco:
- Save your presentation as a PDF—if the version of Keynote or PowerPoint on a host computer cause issues, you still have a functional copy that has a higher guarantee of compatibility.
- In using videos, create a backup slide with screen shots of key results. For example, if I have a video of cell migration, I’ll be sure to have a copy of the start and end of the video, in case the video doesn’t play. Even if the video worked, you can pause on this backup slide and take the time to highlight the key results in words if someone could not see or understand the video.
- Avoid animations, such as figures or text that flash/fly-in/etc. Surveys suggest that no one likes movement in presentations [ 3 , 4 ]. There is likely a cognitive underpinning to the almost universal distaste of pointless animations that relates to the idea proposed by Kosslyn and colleagues that animations are salient perceptual units that captures direct attention [ 4 ]. Although perceptual salience can be used to draw attention to and improve retention of specific points, if you use this approach for unnecessary/unimportant things (like animation of your bullet point text, fly-ins of figures, etc.), then you will distract your audience from the important content. Finally, animations cause additional processing burdens for people with visual impairments [ 10 ] and create opportunities for technical disasters if the software on the host system is not compatible with your planned animation.
Conclusions
These rules are just a start in creating more engaging presentations that increase audience retention of your material. However, there are wonderful resources on continuing on the journey of becoming an amazing public speaker, which includes understanding the psychology and neuroscience behind human perception and learning. For example, as highlighted in Rule 7, David JP Phillips has a wonderful TEDx talk on the subject [ 5 ], and “PowerPoint presentation flaws and failures: A psychological analysis,” by Kosslyn and colleagues is deeply detailed about a number of aspects of human cognition and presentation style [ 4 ]. There are many books on the topic, including the popular “Presentation Zen” by Garr Reynolds [ 11 ]. Finally, although briefly touched on here, the visualization of data is an entire topic of its own that is worth perfecting for both written and oral presentations of work, with fantastic resources like Edward Tufte’s “The Visual Display of Quantitative Information” [ 12 ] or the article “Visualization of Biomedical Data” by O’Donoghue and colleagues [ 13 ].
Acknowledgments
I would like to thank the countless presenters, colleagues, students, and mentors from which I have learned a great deal from on effective presentations. Also, a thank you to the wonderful resources published by organizations on how to increase inclusivity. A special thanks to Dr. Jason Papin and Dr. Michael Guertin on early feedback of this editorial.
- View Article
- PubMed/NCBI
- Google Scholar
- 3. Teaching VUC for Making Better PowerPoint Presentations. n.d. Available from: https://cft.vanderbilt.edu/guides-sub-pages/making-better-powerpoint-presentations/#baddeley .
- 8. Creating a dyslexia friendly workplace. Dyslexia friendly style guide. nd. Available from: https://www.bdadyslexia.org.uk/advice/employers/creating-a-dyslexia-friendly-workplace/dyslexia-friendly-style-guide .
- 9. Cravit R. How to Use Color Blind Friendly Palettes to Make Your Charts Accessible. 2019. Available from: https://venngage.com/blog/color-blind-friendly-palette/ .
- 10. Making your conference presentation more accessible to blind and partially sighted people. n.d. Available from: https://vocaleyes.co.uk/services/resources/guidelines-for-making-your-conference-presentation-more-accessible-to-blind-and-partially-sighted-people/ .
- 11. Reynolds G. Presentation Zen: Simple Ideas on Presentation Design and Delivery. 2nd ed. New Riders Pub; 2011.
- 12. Tufte ER. The Visual Display of Quantitative Information. 2nd ed. Graphics Press; 2001.

- LibGuides Home (current)
- Collections & Services
- General Research
- Resource Specific
- Scholarly & Research
- Subject & Topic
- Course & Assignment
Peer Review and Research
- Annual Library Symposium This link opens in a new window
- Committee Info This link opens in a new window
- Clear Goals
- Adequate Preparation
- Appropriate Methods
- Significant Results
Effective Presentation
Recommended reading.
- Reflective Critique
- Submitting Papers to Peer Reviewed Publications
- Toolbox for Library Researchers
Schedule a Pre or Post Conference Presentation
- Lunchtime brown bag: Noon - 1:00 p.m.
- Late afternoon coffee/tea brown bag: after 3:00 p.m.
- Types of Presentation
- Additional Suggestions for Success
Communication
- The work should clearly communicate the content without calls for clarification.
- If written for the general public, simplification of terms and provision of background information would allow attendees to easily grasp the concepts and research results being reported.
- If written for fellow scholars and researchers, the content would presume no need for topic education is necessary, that terminology is consistent with the subject area, and research reporting would be at the level of scholarly writing.
- The work should be free of grammatical and punctuation errors.
- Numbers and data, if used, should be presented in a manner which makes understanding easy to achieve.
Ask yourself:
- Does the content wording and use of terms match the intended audience?
- Is evidence presented logically and use appropriately?
- Is the work clearly and succinctly organized?
- Are discussions and research results of subjects, either individual or groups, presented in an objective and respectful manner?
- Are sensitive topics and issues presented with thoughtfulness and courtesy?
- Works submitted for publication in traditional print resources should follow the publisher’s guide to submissions, especially criteria involving relevant value to the readers.
- Works submitted for publication in an electronic format – web site, digital, PDF, etc. – should be cognizant of the type of format and the format’s strengths in appealing to the reader by use of technology, programming, and audio or video motion.
- Is the work suitable to the audience targeted?
- Does the work present an appropriate and suitable style?
- The work should clearly state the purpose of the work, the goals that were designed, the results that occurred, any differences between the goals and the results, and the importance of the research results to the audience or area of interest.
- The author should demonstrate scholarship in the field by the quality of supporting evidence, research method, research results, and interpretation of those results.
- Is the work objective in its content and presentation?
- Are conclusions reached without predeterminations and outside influence?
- Is there sufficient evidence, both in terms of amount and substance, to effectively support the outcome?
- Does the work provide new evidence or research results that would be of interest to the field, practitioners, and scholars?
Blogs, Listservs, and Social Media
Electronic presentations are a great way to gage collegial ideas and opinions about the topic you have selected to pursue. These formats can be done at varying and convenient times.
- Online brevity is the best – adopt Twitter’s 140 character limit, and select words carefully.
- Use simple statements.
- DON’T SHOUT.
- Seek feedback and comments.
Exhibits consist of a visual display of a collection, program, initiative, or body of work (i.e. paintings, drawings, prints, posters, photography, sculpture, ceramics, video, installation, multi-media).
- Include a general statement of purpose and statements to provide an intellectual context both for the collection as a whole and for its individual pieces.
- Be prepared to respond to comments and questions.
Facilitated Discussions
Facilitated discussions involve the arranging of attendees into groups, such as tables or round chair setup, and provide topics for discussion. Topics can be the same for all attendees and groups, or vary by group.
- Provide a brief introduction – remember that you are not the presenter, and the discussions are the purpose of this event.
- Develop discussion points, topics, and questions well in advance by polling registered attendees.
- Be willing to accept ad-hoc discussion topics relevant to the content.
- Provide for adequate Q&A and open comment time at the end.
- Ensure that the majority of time allotted for the event is reserved for discussion and report-back.
- Record group report-back’s on flip charts or other method, so that attendees may view the report-back comments as they are read out, and receive a written copy after the event.
- Foster collegial conversational exchange.
- Mingle among the groups or tables to see if attendees are participating, but avoid becoming involved in their discussions.
Keynote Address
The keynote address is perhaps the most challenging presentation. What you say and how well you communicate your ideas, research, findings, and experience sets the tone for the event. High level competency and established experience are the minimum content goals. See Oral Presentations for additional guidance.
- Presentation much be absolutely relevant to the event.
- This is a stand-alone presentation.
- Be prepared to “wow” the audience with a dynamic content, excellent slides, well developed public speaking skills, and inspiration.
- Professional credibility is presumed.
Oral Presentations
Oral presentations involve the presentation of a paper or research project with or without visual aids. This is an excellent opportunity to share research findings with colleagues, seek comments, listen to advice, and facilitate discussion and comment.
- Focus on the purpose, methodology, challenges, and findings of the research.
- Report laboratory and data results, if applicable.
- Clearly provide the reason that motivated research interest and commencement.
- Disclose the strengths and weakness of the research process, and what was learned from failures.
- PowerPoint presentations should be well done. See PowerPoint Use in Presentation for more details.
- Subject mastery is presumed.
- Expect questions and comments that indicate doubt or disagreement, and respond collegially.
- Include a Q&A section at the end of the presentation.
- Provide contact information.
Panel Discussions
Panel discussions involve a limited number of panelists, usually 3-5, presenting and discussing their views on a scholarly topic and responding to audience questions.
- Select speakers from different perspectives to give balanced presentations.
- Before finalizing speaker selection, discuss panel content and purpose to ensure that potential speakers understand the purpose of the panel discussion.
- Ask panelists to state their points concisely and clearly, mindful of the limited time for each panelist.
- Anticipate questions from both the audience and panelists.
- Defer comment and questions from the audience to panelists.
- Provide ample time for individual presentations, statements, general discussion, and Q&A.
Peer Review Publications
Poster sessions.
Posters present a visual display of work on poster boards. Presenters should be able to provide a scholarly introduction to their work and be prepared to entertain the viewers’ questions.
- Include both charts and pictures.
- Develop an eye catching format and design.
- Brevity works best, both for what is on the poster and for answering visitors.
- Have a one-sheet handout for the main take-away points, including your contact information.
- Have business cards available.
- Be prepared for many repeats of your 60-second verbal summary.
- Expect fast and furious turnovers.
- Balance the content – not too sparse but not too detailed and complex.
PowerPoint Use in Presentations
Using PowerPoint or any slide programmed should be viewed as a supplemental visual tool for many types of presentations. They should not be treated as “the” presentation.
- Don’t read from the slides.
- Look at the screen as little as possible.
- Present from knowledge and experience, not from the slides.
- Slides should be limited in numbers and complexity.
- Charts, graphics, pictures, and other inserts should be simple and visually clear.
- Sound, video, and images add value, if content relevant.
- Use bullet points. PowerPoint slides do not need full sentences, and should never have a paragraph full of information.
- Use images effectively. You should have as little text as possible on the slide. One way to accomplish this is to have images on each slide, accompanied by a small amount of text.
- Slides provide focus and guidance, not full details.
- Never put your presentation on the slides and read from the slides.
Workshops consist of a brief presentation followed by interaction with the audience. The purpose of a workshop is to introduce the audience to your subject and involve them in using a skill or technique. Learning objectives and anticipated outcomes should be clearly stated.
- Content should be timely and relevant.
- Content should be take-away – attendees should be able to leave the workshop, go back to their jobs, and begin brainstorming ideas, developing strategies, and implementing projects soon.
- Go short on theories and long on how-to methods.
- Develop learning objectives and anticipated outcomes, and build content around these goals.
- Develop an agenda that more resembles a syllabus.
- Select preparation materials, such as articles and documents to read before the workshop.
- Include data but do not overwhelm attendees with too much or complex data.
- Provide a bibliography or list of suggested readings.
Academic Presentation Formula
Newbies are strongly encouraged to follow this formula. Later and with experience, deviation from the formula is more feasible.
- Introduction/Overview/Hook
- Theoretical Framework/Research Question
- Methodology/Case Selection
- Background/Literature Review
- Discussion of Data/Results
- Q&A, if permitted
The Audience Is Ready to Listen
Avoid presenting too much information about what is already known, and provide this information, if needed, in the introduction. Only discuss literature and background information that relates directly to the topic and research results being presented. Keep this portion of the presentation to five minutes or less. More time will be needed for the presentation of the research results and audience questions and comments.
Practice Practice Practice
Practice the presentation from start to finish before delivering the presentation – several times. Repeated practicing provides delivery confidence, efficient time management, and better speaking skills. Make sure the presentation fits within the time parameters. Practicing also makes it flow better.
Keep To the Time Limit
If the time allotted for the presentation is ten minutes, prepare ten minutes of material. Regardless of the amount of time provided, a little or a lot, finish within or at the end of the allotted time. Practice the presentation with a stopwatch to ensure complicity.
- << Previous: Significant Results
- Next: Reflective Critique >>
- Last Updated: Sep 26, 2023 12:52 PM
- URL: https://library.fiu.edu/PeerReview
Information
Fiu libraries floorplans, green library, modesto a. maidique campus, hubert library, biscayne bay campus.

Directions: Green Library, MMC
Directions: Hubert Library, BBC

Peer review templates, expert examples and free training courses

Joanna Wilkinson
Learning how to write a constructive peer review is an essential step in helping to safeguard the quality and integrity of published literature. Read on for resources that will get you on the right track, including peer review templates, example reports and the Web of Science™ Academy: our free, online course that teaches you the core competencies of peer review through practical experience ( try it today ).
How to write a peer review
Understanding the principles, forms and functions of peer review will enable you to write solid, actionable review reports. It will form the basis for a comprehensive and well-structured review, and help you comment on the quality, rigor and significance of the research paper. It will also help you identify potential breaches of normal ethical practice.
This may sound daunting but it doesn’t need to be. There are plenty of peer review templates, resources and experts out there to help you, including:
Peer review training courses and in-person workshops
- Peer review templates ( found in our Web of Science Academy )
- Expert examples of peer review reports
- Co-reviewing (sharing the task of peer reviewing with a senior researcher)
Other peer review resources, blogs, and guidelines
We’ll go through each one of these in turn below, but first: a quick word on why learning peer review is so important.
Why learn to peer review?
Peer reviewers and editors are gatekeepers of the research literature used to document and communicate human discovery. Reviewers, therefore, need a sound understanding of their role and obligations to ensure the integrity of this process. This also helps them maintain quality research, and to help protect the public from flawed and misleading research findings.
Learning to peer review is also an important step in improving your own professional development.
You’ll become a better writer and a more successful published author in learning to review. It gives you a critical vantage point and you’ll begin to understand what editors are looking for. It will also help you keep abreast of new research and best-practice methods in your field.
We strongly encourage you to learn the core concepts of peer review by joining a course or workshop. You can attend in-person workshops to learn from and network with experienced reviewers and editors. As an example, Sense about Science offers peer review workshops every year. To learn more about what might be in store at one of these, researcher Laura Chatland shares her experience at one of the workshops in London.
There are also plenty of free, online courses available, including courses in the Web of Science Academy such as ‘Reviewing in the Sciences’, ‘Reviewing in the Humanities’ and ‘An introduction to peer review’
The Web of Science Academy also supports co-reviewing with a mentor to teach peer review through practical experience. You learn by writing reviews of preprints, published papers, or even ‘real’ unpublished manuscripts with guidance from your mentor. You can work with one of our community mentors or your own PhD supervisor or postdoc advisor, or even a senior colleague in your department.
Go to the Web of Science Academy
Peer review templates
Peer review templates are helpful to use as you work your way through a manuscript. As part of our free Web of Science Academy courses, you’ll gain exclusive access to comprehensive guidelines and a peer review report. It offers points to consider for all aspects of the manuscript, including the abstract, methods and results sections. It also teaches you how to structure your review and will get you thinking about the overall strengths and impact of the paper at hand.
- Web of Science Academy template (requires joining one of the free courses)
- PLoS’s review template
- Wiley’s peer review guide (not a template as such, but a thorough guide with questions to consider in the first and second reading of the manuscript)
Beyond following a template, it’s worth asking your editor or checking the journal’s peer review management system. That way, you’ll learn whether you need to follow a formal or specific peer review structure for that particular journal. If no such formal approach exists, try asking the editor for examples of other reviews performed for the journal. This will give you a solid understanding of what they expect from you.
Peer review examples
Understand what a constructive peer review looks like by learning from the experts.
Here’s a sample of pre and post-publication peer reviews displayed on Web of Science publication records to help guide you through your first few reviews. Some of these are transparent peer reviews , which means the entire process is open and visible — from initial review and response through to revision and final publication decision. You may wish to scroll to the bottom of these pages so you can first read the initial reviews, and make your way up the page to read the editor and author’s responses.
- Pre-publication peer review: Patterns and mechanisms in instances of endosymbiont-induced parthenogenesis
- Pre-publication peer review: Can Ciprofloxacin be Used for Precision Treatment of Gonorrhea in Public STD Clinics? Assessment of Ciprofloxacin Susceptibility and an Opportunity for Point-of-Care Testing
- Transparent peer review: Towards a standard model of musical improvisation
- Transparent peer review: Complex mosaic of sexual dichromatism and monochromatism in Pacific robins results from both gains and losses of elaborate coloration
- Post-publication peer review: Brain state monitoring for the future prediction of migraine attacks
- Web of Science Academy peer review: Students’ Perception on Training in Writing Research Article for Publication
F1000 has also put together a nice list of expert reviewer comments pertaining to the various aspects of a review report.
Co-reviewing
Co-reviewing (sharing peer review assignments with senior researchers) is one of the best ways to learn peer review. It gives researchers a hands-on, practical understanding of the process.
In an article in The Scientist , the team at Future of Research argues that co-reviewing can be a valuable learning experience for peer review, as long as it’s done properly and with transparency. The reason there’s a need to call out how co-reviewing works is because it does have its downsides. The practice can leave early-career researchers unaware of the core concepts of peer review. This can make it hard to later join an editor’s reviewer pool if they haven’t received adequate recognition for their share of the review work. (If you are asked to write a peer review on behalf of a senior colleague or researcher, get recognition for your efforts by asking your senior colleague to verify the collaborative co-review on your Web of Science researcher profiles).
The Web of Science Academy course ‘Co-reviewing with a mentor’ is uniquely practical in this sense. You will gain experience in peer review by practicing on real papers and working with a mentor to get feedback on how their peer review can be improved. Students submit their peer review report as their course assignment and after internal evaluation receive a course certificate, an Academy graduate badge on their Web of Science researcher profile and is put in front of top editors in their field through the Reviewer Locator at Clarivate.
Here are some external peer review resources found around the web:
- Peer Review Resources from Sense about Science
- Peer Review: The Nuts and Bolts by Sense about Science
- How to review journal manuscripts by R. M. Rosenfeld for Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery
- Ethical guidelines for peer review from COPE
- An Instructional Guide for Peer Reviewers of Biomedical Manuscripts by Callaham, Schriger & Cooper for Annals of Emergency Medicine (requires Flash or Adobe)
- EQUATOR Network’s reporting guidelines for health researchers
And finally, we’ve written a number of blogs about handy peer review tips. Check out some of our top picks:
- How to Write a Peer Review: 12 things you need to know
- Want To Peer Review? Top 10 Tips To Get Noticed By Editors
- Review a manuscript like a pro: 6 tips from a Web of Science Academy supervisor
- How to write a structured reviewer report: 5 tips from an early-career researcher
Want to learn more? Become a master of peer review and connect with top journal editors. The Web of Science Academy – your free online hub of courses designed by expert reviewers, editors and Nobel Prize winners. Find out more today.
Related posts
Journal citation reports 2024 preview: unified rankings for more inclusive journal assessment.

Introducing the Clarivate Academic AI Platform

Reimagining research impact: Introducing Web of Science Research Intelligence

Facilitating Effective Peer Review Sessions
Main navigation.
PWR is committed to the use of small-group writing workshops. While some students doubt the value of peer group work, when well executed these groups can be both effective and enjoyable. While some instructors keep students in the same small groups all quarter, other instructors create new student groups for every assignment. Both strategies have merit.
Peer Review Group Suggestions
- Pay attention to the way you present the concept of peer review to your students. Explain clearly the rationale for doing this activity and demonstrate your commitment to it.
- Make the work count. You may assign points for it as a part of your class activities and informal writing component of your grade; remember that you need to be transparent in your evaluation criteria for anything that you are “grading,” including group work.
- Prepare clear and specific Peer Response Guideline Sheets for each peer response session.
- In a remote learning context, consider creating peer review groups by student time zone, especially if the peer review groups are meeting outside of class time.
- Spend some time with each group. Take notes on the activity, on how well the group is working; who is contributing strong, focused responses; who needs to improve, etc.
- At the end of the session, remind the students to turn in all their peer responses with their revised essays.
- Take time to respond briefly but cogently to each peer response, noting areas of strength and weakness and ways in which the responder can offer more explicit and helpful advice.
- Take time in the next class to refer to some of the most useful comments made in peer response and specify why they are more helpful than others.
- Be patient. Experienced instructors say that getting the groups working well together takes several weeks; with persistence and encouragement from you, they will get there.
- Consider changing the peer response structure. For instance, have the peer groups act as the editorial board of a journal.
See also some examples of peer review sheets from our PWR Canvas Archive

Track changes in PowerPoint for the web during a peer review
PowerPoint for the web doesn’t have a Track Changes feature. However, you can use the Comments feature to keep track of peer feedback in your presentation.
When you send your presentation out for review, give your reviewers these instructions to provide feedback to you:
Select the item on the slide that you want to add a comment about.
On the Insert tab, click Comment .
Enter your comments, and press Enter.
To reply to a comment, click in the Reply box, and enter your message.

After your peers have reviewed your presentation, you’ll want to read their comments in the Comments pane.

Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders
Microsoft 365 Insiders
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.

Example of PowerPoint Presentation used at a Peer Review Session
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- Access provided by Google Indexer
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
About The BMJ
- Resources for reviewers
- Reviewer training materials
What do we know about peer review?
In 2011 the House of Commons Science and Technology Committee held an inquiry into peer review and sought written and oral evidence from a wide range of experts and organisations. BMJ's written evidence reviewed the latest research evidence on the strengths and weaknesses of peer review as a quality control mechanism for scientists, publishers, and the public including:
• Measures to strengthen peer review; • The processes by which reviewers with the requisite skills and knowledge are identified, in particular as the volume of multidisciplinary research increases; • The impact of IT and greater use of online resources on the peer review process; • Possible alternatives to peer review.
Training package for The BMJ's peer reviewers
Do you review work for The BMJ , or are you thinking about becoming a reviewer for The BMJ ? If so, we hope you will use this training pack. It will help you to learn more about peer review, and to understand what makes a review really useful to editors and authors.
The pack includes PowerPoint presentations and written exercises. Much of the material here relates to the general art of peer review, but we have also included specific guidance on what The BMJ needs from you.
We developed this pack for use in a randomised controlled trial of peer reviewer training. Now you can use it as you wish; for your own learning or to teach others. There are four objectives:
• To inform participants on the state of peer review research; • To make clear what constitutes a good review; • To help participants understand what matters to editors about reviews; and • To give participants help in producing a good review.
Objective One: To inform participants on the state of peer review research
Download What we know about peer review (Microsoft PowerPoint presentation, 261 KB)
Further reading:
Objective Two: To make clear what constitutes a good review
What editors want (Microsoft PowerPoint presentation - 244 KB)
Objective Three: To help participants understand what matters to editors about reviews
Below are three reviews of manuscripts recently published in The BMJ . Having read the presentation on what editors want from reviewers, we would like you to read these three reviews and note their strengths and weaknesses. This exercise should take approximately 15 minutes. Having noted the strengths and weaknesses of each review, read our critique of each review from the editorial perspective.
Objective Four: To give participants help in producing a good review
We would like you to do a practice rapid review of the paper titled: Magnetic bracelets for relieving pain in lower-limb osteoarthritis: a randomised controlled trial. To help guide your review, we have also provided a question sheet, and links to our standard Guidance for Reviewers and the CONSORT statement. You should spend approximately 30 minutes on this exercise. It is not a "formal" review, and we do not want you to send us your review.
• Manuscript to review (PDF - 114 KB) • Question sheet to help guide your review (Microsoft Word - 22KB) • General guidance for The BMJ's peer reviewers • CONSORT statement
This paper was published in The BMJ in 2004. Below are links to the reviews of the submitted version (and an extra review commissioned for this training package) and also the published version of this paper. Please do not read these reviews until after you have completed the exercise above.
- Publishing model
- Editorial staff
- Advisory panels
- Explore The BMJ
- BMJ Student
- How green is The BMJ?
- Sources of revenue
- Resources for authors
- Resources for advertisers and sponsors
- Resources for BMA members
- Resources for media
- Resources for subscribers
- Resources for readers
- Guidance for BMJ Patient and Public Reviewers
- The BMJ's reviewers 2013-2023
- About The BMJ app
- Poll archive
- International jobs
This week's poll
Read related article
See previous polls
Center for Excellence in Teaching
Home > Resources > Peer feedback form for group presentations
Peer feedback form for group presentations
A sample form for use by students when they are observing other students’ class presentations, focusing on constructive suggestions for improvement.
Download this file
Download this file [61.44 KB]
Back to Resources Page

How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
A demo is the first step to transforming your business. Meet with us to develop a plan for attaining your goals.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.
For Business
For Individuals
30 presentation feedback examples

Jump to section
You're doing great
You should think of improving
Tips to improve
3 things to look for when providing presentation feedback
3 tips for giving effective feedback.
We’re all learning as we go.
And that’s perfectly OK — that’s part of being human. On my own personal growth journey, I know I need to get better at public speaking and presenting. It’s one of those things that doesn’t necessarily come naturally to me.
And I know there are plenty of people in my shoes. So when it comes to presenting in the workplace, it can be intimidating. But there’s one thing that can help people continue to get better at presentations: feedback .
The following examples not only relate to presentations. They can also be helpful for public speaking and captivating your audience.
You’re doing great
- You really have the natural ability to hand out presentation material in a very organized way! Good job!
- Your presentations are often compelling and visually stunning. You really know how to effectively captivate the audience. Well done!
- You often allow your colleagues to make presentations on your behalf. This is a great learning opportunity for them and they often thrive at the challenge.
- Keeping presentations focused on key agenda items can be tough, but you’re really good at it. You effectively outline exactly what it is that you will be discussing and you make sure you keep to it. Well done!!
- You created downloadable visual presentations and bound them for the client. Excellent way to portray the company! Well done!
- Your content was relevant and your format was visually appealing and easy to follow and understand. Great job! You’re a real designer at heart!
- You always remain consistent with the way you present and often your presentations have the same style and layout. This is great for continuity. Well done!
- You always remain consistent with every presentation, whether it be one on ones, small group chats, with peers, direct reports, and the company bosses. You have no problem presenting in any one of these situations. Well done!
- You are an effective presenter both to employees and to potential clients. When controversial topics come up, you deal with them in a timely manner and you make sure these topics are fully dealt with before moving on. Well done!
- You effectively command attention and you have no problem managing groups during the presentation.

You should think of improving
- You’re a great presenter in certain situations, but you struggle to present in others. Try to be more consistent when presenting so that you get one single-minded message across. This will also help you broaden your presentation skills by being able to portray one single idea or message.
- You tend to be a little shy when making presentations. You have the self-confidence in one-on-one conversations , so you definitely have the ability to make compelling presentations. Come on! You can do it!
- During presentations, there seems to be quite a lack of focus . I know it can be difficult to stick to the subject matter, however you need to in order for people to understand what the presentation is about and what is trying to be achieved.
- To engage with your audience and make them attentively listen to what you have to say, you need to be able to use your voice in an effective manner to achieve this. Try to focus on certain words that require extra attention and emphasis these words during your presentation.
- Knowing your audience is critical to the success of any presentation. Learn to pick up on their body language and social cues to gauge your style and tone. Listen to what your audience has to say and adjust your presentation accordingly.

- During presentations, it’s expected that there will be tough questions . Try to prepare at least a couple of days before the time so that you can handle these questions in an effective manner.
- To be an effective presenter you need to be able to adjust to varying audiences and circumstances. Try learning about who will be in the room at the time of the presentation and adjust accordingly.
- Remember not to take debate as a personal attack. You tend to lose your cool a little too often, which hinders the discussion and people feel alienated. You can disagree without conflict .
- The only way you are going to get better at public speaking is by practicing, practicing, practicing. Learn your speech by heart, practice in the mirror, practice in front of the mirror. Eventually, you’ll become a natural and you won't be afraid of public speaking any longer.
- Your presentations are beautiful and I have no doubt you have strong presentation software skills. However, your content tends to be a bit weak and often you lack the substance. Without important content, the presentation is empty.
Tips to improve
- Remember it’s always good to present about the things you are passionate about . When you speak to people about your passions they can sense it. The same goes for presentations. Identify what it is that excites you and somehow bring it into every presentation. it’ll make it easier to present and your audience will feel the energy you portray.
- Sometimes it can be easier to plan with the end result in mind. Try visualizing what it is you are exactly expecting your audience to come away with and develop your presentation around that.
- Simplicity is a beautiful thing. Try to keep your presentations as simple as possible. Make it visually appealing with the least amount of words possible. Try interactive pictures and videos to fully immerse your audience in the presentation.
- It’s a fine balance between winging the presentation and memorizing the presentation. If you wing it too much it may come across as if you didn't prepare. If you memorize it, the presentation may come off a bit robotic. Try to find the sweet spot, if you can.
- When presenting, try to present in a way that is cause for curiosity . Make people interested in what you have to say to really captivate them. Have a look at some TED talks to get some tips on how you can go about doing this.
- Remember presentations should be about quality, not quantity. Presentations that are text-heavy and go on for longer than they should bore your audience and people are less likely to remember them.
- Try to arrive at every staff meeting on time and always be well prepared. This will ensure that meetings will go smoothly in the future.
- Remember to respect other people's time by always arriving on time or five minutes before the presentation.
- Remember to ask the others in the meeting for their point of view if there are individuals during presentations.
- If you notice presentations are deviating off-topic, try to steer it back to the important topic being discussed.
Presentation feedback can be intimidating. It’s likely the presenter has spent a good deal of time and energy on creating the presentation.
As an audience member, you can hone in on a few aspects of the presentation to help frame your feedback. If it's an oral presentation, you should consider also audience attention and visual aids.
It’s important to keep in mind three key aspects of the presentation when giving feedback.

Communication
- Were the key messages clear?
- Was the speaker clear and concise in their language?
- Did the presenter clearly communicate the key objectives?
- Did the presenter give the audience clear takeaways?
- How well did the presenter’s voice carry in the presentation space?
Delivery
- Was the presentation engaging?
- How well did the presenter capture their audience?
- Did the presenter engage employees in fun or innovative ways?
- How interactive was the presentation?
- How approachable did the presenter appear?
- Was the presentation accessible to all?
Body language and presence
- How did the presenter carry themselves?
- Did the presenter make eye contact with the audience?
- How confident did the presenter appear based on nonverbal communication?
- Were there any nonverbal distractions to the presentation? (i.e. too many hand gestures, facial expressions, etc.)
There are plenty of benefits of feedback . But giving effective feedback isn’t an easy task. Here are some tips for giving effective feedback.
1. Prepare what you’d like to say
I’m willing to bet we’ve all felt like we’ve put our foot in our mouth at one point or another. Knee-jerk, emotional reactions are rarely helpful. In fact, they can do quite the opposite of help.
Make sure you prepare thoughtfully. Think through what feedback would be most impactful and helpful for the recipient. How will you word certain phrases? What’s most important to communicate? What feedback isn’t helpful to the recipient?
You can always do practice runs with your coach. Your coach will serve as a guide and consultant. You can practice how you’ll give feedback and get feedback … on your feedback. Sounds like a big loop, but it can be immensely helpful.
2. Be direct and clear (but lead with empathy)
Have you ever received feedback from someone where you’re not quite sure what they’re trying to say? Me, too.
I’ve been in roundabout conversations where I walk away even more confused than I was before. This is where clear, direct, and concise communication comes into play.
Be clear and direct in your message. But still, lead with empathy and kindness . Feedback doesn’t need to be harsh or cruel. If it’s coming from a place of care, the recipient should feel that care from you.
3. Create dialogue (and listen carefully)
Feedback is never a one-way street. Without the opportunity for dialogue, you’re already shutting down and not listening to the other person. Make sure you’re creating space for dialogue and active listening . Invite questions — or, even better, feedback. You should make the person feel safe, secure, and trusted . You should also make sure the person feels heard and valued.
Your point of view is just that: it's one perspective. Invite team members to share their perspectives, including positive feedback .
You might also offer the recipient the opportunity for self-evaluation . By doing a self-evaluation, you can reflect on things like communication skills and confidence. They might come to some of the same important points you did — all on their own.
Now, let’s go practice that feedback
We're all learners in life.
It's OK to not be perfect . In fact, we shouldn't be. We're perfectly imperfect human beings, constantly learning , evolving, and bettering ourselves.
The same goes for tough things like presentations. You might be working on perfecting your students' presentation. Or you might want to get better at capturing your audience's attention. No matter what, feedback is critical to that learning journey .
Even a good presentation has the opportunity for improvement . Don't forget the role a coach can play in your feedback journey.
Your coach will be able to provide a unique point of view to help you better communicate key points. Your coach can also help with things like performance reviews , presentation evaluations, and even how to communicate with others.
Enhance your presentation skills
Unlock new heights in your career with personalized coaching tailored to boost your presentation prowess.
Madeline Miles
Madeline is a writer, communicator, and storyteller who is passionate about using words to help drive positive change. She holds a bachelor's in English Creative Writing and Communication Studies and lives in Denver, Colorado. In her spare time, she's usually somewhere outside (preferably in the mountains) — and enjoys poetry and fiction.
How to not be nervous for a presentation — 13 tips that work (really!)
6 presentation skills and how to improve them, josh bersin on the importance of talent management in the modern workplace, how to give a good presentation that captivates any audience, 8 clever hooks for presentations (with tips), how to make a presentation interactive and exciting, reading the room gives you an edge — no matter who you're talking to, the self presentation theory and how to present your best self, coaching insider: trusting your team as a new manager, similar articles, 30 communication feedback examples, impression management: developing your self-presentation skills, 30 leadership feedback examples for managers, 30 customer service review examples to develop your team, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead™
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care®
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Life Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences
- Preferences

Peer Review: Ensuring Quality, Rigor, and Transparency in Scientific Publishing - PowerPoint PPT Presentation

Peer Review: Ensuring Quality, Rigor, and Transparency in Scientific Publishing
Peer review is a process where experts in the field review a researcher's work before it is published. the goal of peer review is to ensure that the research is well done and logical. reviewers who are knowledgeable about the subject matter provide advice and feedback to help improve the research quality and determine if it is ready to share with the world. – powerpoint ppt presentation.
- Introduction
- Peer Review An Overview
- Pubrica's Peer Review Services
- Pubrica's Editorial Team
- The Importance of Peer Review
- The Peer Review Process A Step-by-step Guide
- The Role of Expert Teams in Peer Review
- Challenges in Peer Review and the Role of Expert Teams
- About Pubrica
- Peer review is a process where experts in the field review a researcher's work before it is published.
- The goal of peer review is to ensure that the research is well done and logical.
- Reviewers who are knowledgeable about the subject matter provide advice and feedback to help improve the research quality and determine if it is ready to share with the world.
- This process helps prevent errors and enhances the accuracy and usefulness of the research.
- However, peer review can sometimes be lengthy or biased, which is why journals have smart teams to make the process better, faster, and more reliable.
- In the end, the goal of peer review is to ensure that what we learn from research is truly factual and beneficial.
- Peer review is the rigorous evaluation of scholarly work, research, or ideas by independent experts who are well-versed in the same field.
- These experts, known as peer reviewers, carefully assess the submitted work to ensure its quality, accuracy, and adherence to accepted journal standards.
- We are verifying the validity of the research findings.
- We are assessing the originality and novelty of the work.
- They are ensuring that unwarranted claims or personal biases are not published without expert scrutiny.
- Pre-Submission Peer Review Before submitting their work to journals, authors can seek feedback from Pubrica's panel of experts.
- The reviewers evaluate When submitting literary work, authors should consider if it aligns with the journal's scope, the clarity of the research topic, the appropriateness of the approach, methodology, reproducibility, ethical considerations, readability, and logical construction. Constructive feedback may also be provided.
- Post-Submission Peer Review After submission, Pubrica's experts continue to assess manuscripts, ensuring they meet high standards.
- Partnerships with Elite Publishers Pubrica collaborates with prestigious publishers and journals, including Elsevier, COPE, Wolters Kluwer, Nature, The Lancet, and more.
- The peer review process aids in maintaining the quality of scientific literature. It acts as a filter, ensuring that only high-quality research is published.
- The process also provides authors with feedback on their work, helping them to improve the quality of their research and writing.
- This feedback can lead to significant improvements in the final version of the research paper, enhancing its clarity, depth, and impact.
- Submission of Manuscript The researcher submits their manuscript to a journal for consideration.
- Initial Screening The journal's editorial staff conducts an initial screening to check if the manuscript meets the journal's guidelines and scope.
- Review by Experts If the manuscript passes the initial screening, it is sent to a panel of experts for review.
- Feedback and Revision The reviewers provide feedback on the manuscript, and the author may be asked to revise their work based on this feedback.
- Final Decision Based on the reviewers' feedback and the author's revisions, the editorial staff makes a final decision on whether to accept or reject the manuscript for publication.
- Expert teams play a decisive role in the peer review process. These teams, often composed of experienced researchers and academics, bring a wealth of knowledge and expertise to the review process.
- The primary role of these teams is to evaluate the submitted manuscripts, checking for accuracy, validity, and originality.
- They also provide constructive feedback to the authors, helping them to improve their work.
- Expert teams can help to ensure that the peer review process is fair, transparent, and efficient.
- They can guide the process, ensuring that all reviewers adhere to the same standards and that all feedback is constructive and helpful.
- Despite its importance, the peer review process is not without challenges. These can include bias, inconsistency, and a lack of transparency.
- Expert teams address these challenges. By bringing a diverse range of perspectives and expertise, they can help to reduce bias and increase consistency in the review process.
- Besides, expert teams can help to increase transparency in peer review. This can be achieved by clearly documenting the review process and providing feedback to authors.
- Peer review is a fundamental process in scientific research publication, ensuring the validity and quality of research. Expert teams play a crucial role in this process, helping to ensure its fairness, transparency, and efficiency. Despite the challenges, the peer review process remains a cornerstone of scientific integrity and quality.
- Through continuous innovation and the dedication of expert teams, we can work towards a more efficient, transparent, and effective peer review process, further enhancing the quality and impact of scientific research.
- At Pubrica, their Peer Reviewing Expertise Team is committed to upholding the highest standards of scientific publication, providing comprehensive and insightful reviews that contribute to the improvement and advancement of research. Trust them to deliver rigorous and constructive feedback that will enhance your research and ensure its success in the scientific community.
- Donahue, C., Foster-Johnson, L. (2019). Peer review in biology Of novices, experts, and disciplines. The Journal of Writing Analytics, 3(1), 96-124.
- Phillips, J. S. (2011). Expert bias in peer review. Current medical research and opinion, 27(12), 2229-2233.
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics , the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.

- Open access
- Published: 21 May 2024
Effectively teaching cultural competence in a pre-professional healthcare curriculum
- Karen R. Bottenfield 1 ,
- Maura A. Kelley 2 ,
- Shelby Ferebee 3 ,
- Andrew N. Best 1 ,
- David Flynn 2 &
- Theresa A. Davies 1 , 2
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 553 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
54 Accesses
Metrics details
There has been research documenting the rising numbers of racial and ethnic minority groups in the United States. With this rise, there is increasing concern over the health disparities that often affect these populations. Attention has turned to how clinicians can improve health outcomes and how the need exists to educate healthcare professionals on the practice of cultural competence. Here we present one successful approach for teaching cultural competence in the healthcare curriculum with the development of an educational session on cultural competence consisting of case-based, role-play exercises, class group discussions, online discussion boards, and a lecture PowerPoint presentation.
Cultural competence sessions were delivered in a pre-dental master’s program to 178 students between 2017 and 2020. From 2017 to 2019, the sessions were implemented as in-person, case-based, role-play exercises. In 2020, due to in-person limitations caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, students were asked to read the role-play cases and provide a reflection response using the online Blackboard Learn discussion board platform. Evaluation of each session was performed using post-session survey data.
Self-reported results from 2017 to 2020 revealed that the role-play exercises improved participant’s understanding of components of cultural competence such as communication in patient encounters (95%), building rapport with patients (94%), improving patient interview skills (95%), and recognition of students own cultural biases when working with patients (93%).
Conclusions
Students were able to expand their cultural awareness and humility after completion of both iterations of the course session from 2017 to 2019 and 2020. This session can be an effective method for training healthcare professionals on cultural competence.
Peer Review reports
It is projected that by the year 2050, racial and ethnic minority groups will make up over 50% of the United States population [ 1 ]. With a more multicultural society, growing concern has emerged over how to address the health disparities that effect these populations and the ways in which healthcare professionals can increase positive health outcomes. Continuing evidence suggests that many patients from racial and ethnic minority groups are not satisfied with the current state of healthcare which has been attributed to implicit bias on the part of physicians and current challenges faced by practitioners who feel underprepared to address these issues due to differences in language, financial status, and healthcare practice [ 2 , 3 , 4 ].
To contend with health disparities and the challenges faced by practitioners working with a more diverse population, healthcare educators have begun to emphasize the importance of educating healthcare workforce on the practice of cultural competence and developing a skilled-based set of behaviors, attitudes and policies that effectively provides care in the wake of cross-cultural situations and differences [ 4 , 5 , 6 ]. There are several curricular mandates from both medical and dental accreditation bodies to address this issue [ 7 , 8 , 9 ], and large amounts of resources, ideas, and frameworks that exist for implementing and training future and current healthcare providers on the inadequacies of the healthcare system and cultural competence [ 10 , 11 , 12 ]. These current institutional guidelines for accreditation and the numerous amounts of resources for training cultural competence, continue to evolve with work documenting the need for blended curriculum that is continuous throughout student education, starting early as we have done here with pre-dental students, including in-person didactic or online sessions, a service learning component, community engagement and a reflective component [ 4 , 5 , 13 , 14 ].
This study investigates teaching cultural competence in a healthcare curriculum. We hypothesized that early educational exposure to cultural competence through role playing case studies, can serve as an effective mechanism for training early pre-doctoral students the practice of cultural competence. Utilizing student self-reported survey data conducted in a predental master’s curriculum, in which two iterations of role-playing case studies were used to teach components of cultural competence, this study aims to evaluate and support research that suggests role-playing case studies as effective means for educating future clinical professionals on the practice of cultural competence.
This study was determined to be exempt by the Institutional Review Board of Boston University Medical Campus, Protocol # H-37,232. Informed consent was received from all subjects.
Data collection
The role-playing, case-based simulated patient encounter exercises were developed and administered at Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine to predental students in the Master of Science in Oral Health Sciences Program (see Table 1 ). From 2017 to 2020, we administered patient encounter cases [see Additional File 1 ] to students ( n = 178) in the program as a portion of a case-based, role-playing exercise to teach the importance of cultural competence and cultural awareness during patient encounters. During years 2017–2019, real actors portrayed the patient and physician. In 2020, the session was conducted online via a discussion board through a Blackboard Course Site. The original case was published as part of a master’s students thesis work in 2021 [ 15 ].
Description of patient encounter cases 1 and 2
Patient Encounter Case 1 [see Additional file 1 ] is composed of two subsections, scenario 1 A and scenario 1B, and is centered around a patient/physician interaction in which a patient who is pregnant presents with pain upon urination. The physician in 1 A is short and terse with the patient, immediately looking at a urine sample, prescribing medication for a urinary tract infection, and telling the patient to return for a follow-up in 2 weeks. In scenario 1B, a similar situation ensues; however, in this scenario the physician takes more time with the patient providing similar care as the physician in 1 A, but asking for more information about the patients personal and medical history. At the conclusion of the scenario, the patient is offered resources for an obstetrician and a dentist based on the information that is provided about the patient’s background. The patient is then sent on their way and asked to follow-up in 2 weeks. The patient does not return.
Patient Encounter Case 2 [see Additional file 1 ] follows a similar format to the Patient Encounter Case 1. In scenario 2 A, the same patient from Case 1 returns with tooth pain after giving birth. The physician in 2 A, like 1 A, is short with the patient and quickly refers the patient to a dentist. In 2B, the physician again takes more time with the patient to receive background information on the patient, make a connection, and provides an antibiotic and dental referral.
Each Patient Encounter Case explored topics such as the importance of building a trusting physician/patient relationship, the importance of asking a patient for patient history, making a connection, and the importance of a physician taking all facets of a patient’s circumstances into consideration [ 15 ].
Session outline
The sessions conducted between 2017 and 2019 were composed of three parts: (1) enactment of an abridged patient encounter facilitated by session administrators, (2) group discussion and reflection during which time students were asked to critically reflect and discuss the theme and key take-aways from the role play exercise, and (3) a PowerPoint presentation emphasizing take-away points from the role-play exercise. At the conclusion of the cultural competence training sessions, students participated in a post-session Qualtrics generated survey administered electronically to assess each student’s feelings about the session [see Additional file 3 ].
Role-play enactment
Facilitators dressed-up in clothing to mimic both the physician and patient for all case scenarios in Patient Encounter Case 1 and Case 2. At the conclusion of the role play portion of each of the cases, the facilitators paused to lead students in a real-time class group discussion. After Case 1, students were asked questions such as: What did you think ? Were the patient’s needs met? Did you expect the patient to return? Following Case 2, similar questions were asked by the facilitators, including: What did you think ? Were the patient’s needs met? Did you expect the patient to accept help?
At the conclusion of this portion of the session, the facilitators led a larger general discussion about both cases and how they related to one another. Finally, the course session concluded with a PowerPoint presentation that reinforced the take-home points from the session [see Additional file 2 ] [ 15 ].
Change in session modality due to COVID-19 pandemic
In Fall 2020, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the course modality moved to an online platform and consisted of three parts on a Blackboard Discussion Board (Blackboard, Inc.). Students were required to: (1) read each of the Patient Encounter Cases and add a brief reflection comparing the scenarios, (2) then comment on at least two peer’s posts in the discussion forum and (3) attend class to hear a PowerPoint presentation by a course session facilitator on the key take-aways from each scenario [ 15 ].
Student surveys
At the conclusion of the cultural competence training sessions, students participated in a post-session Qualtrics ( https://www.qualtrics.com ) generated survey administered electronically to assess each student’s feelings about the sessions [see Additional file 3 ]. The format of the survey included 5 questions with the following Likert scale response options: strongly agree, agree, disagree, strongly disagree. These post-session surveys were not required but rather optional [ 15 ].
A total of 178 students completed the cultural competence sessions between 2017 and 2020. Of these participants, 112 voluntarily completed a post-session survey on the effectiveness of the course in teaching cultural competence and cultural awareness during patient encounters. Between 2017 and 2019, 99 students completed post-session surveys following sessions with role play exercises. In 2020, 13 students completed post-session surveys following discussion board sessions.
Role-play exercises enhanced cultural competence
In responding to post-session survey questions following cultural competence sessions that included role-play exercises (2017–2019), 71% of students surveyed strongly agreed and 24% agreed that the role-play exercises helped them to identify the importance of communication in patient encounters. In asking participants if the role-play exercises made them more aware of different strategies to improve their patient interview skills, 72% strongly agreed and 23% agreed. Also, 68% of the students strongly agreed and 26% agreed that the exercises helped them to better identify the importance of building rapport and trust during patient encounters. When asked if the exercises helped the students to better understand their own bias and/or cultural awareness when working with patients, the results of the survey showed that 62% of students strongly agreed and 31% agreed with this statement. In addition, most students found the role-play exercises to be enjoyable (72% strongly agreed and 22% agreed). See results shown in Fig. 1 .
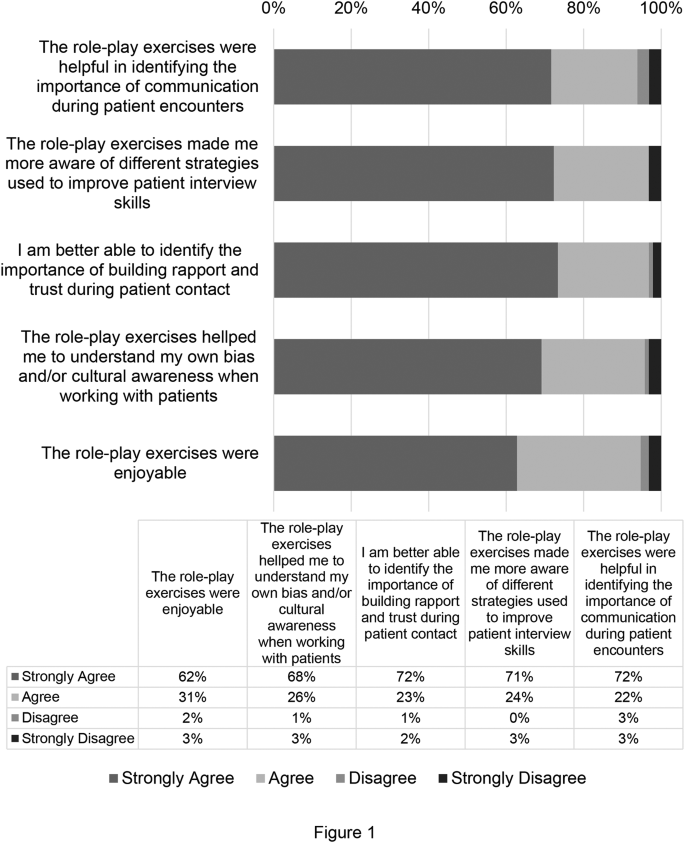
Cultural Competence Session Survey Data from the Year 2017–2019. Survey data from students at Boston University’s Oral Health Sciences Program for the years 2017–2019. Data is presented as percent of respondents ( n = 99)
Discussion boards and reflections enhanced cultural competence
Cultural competence sessions held during 2020 did not include role-play exercises due to the Covid-19 pandemic. Instead, students participated in discussion boards and reflections on Blackboard. In response to the post-session survey question asking if the discussion board exercises were helpful in identifying the importance of communication during patient encounters, 67% of students strongly agreed and 25% agreed with this statement. Also, 75% of students strongly agreed and 17% agreed that the discussion board exercises helped them identify the importance of building rapport and trust during patient contact. When asked if the exercises helped the students to better understand their own bias and/or cultural awareness when working with patients, the results of the survey showed that 67% of students strongly agreed and 25% agreed with this statement. In addition, most students found the discussion board exercises to be enjoyable (67% strongly agreed and 22% agreed). See results shown in Fig. 2 .
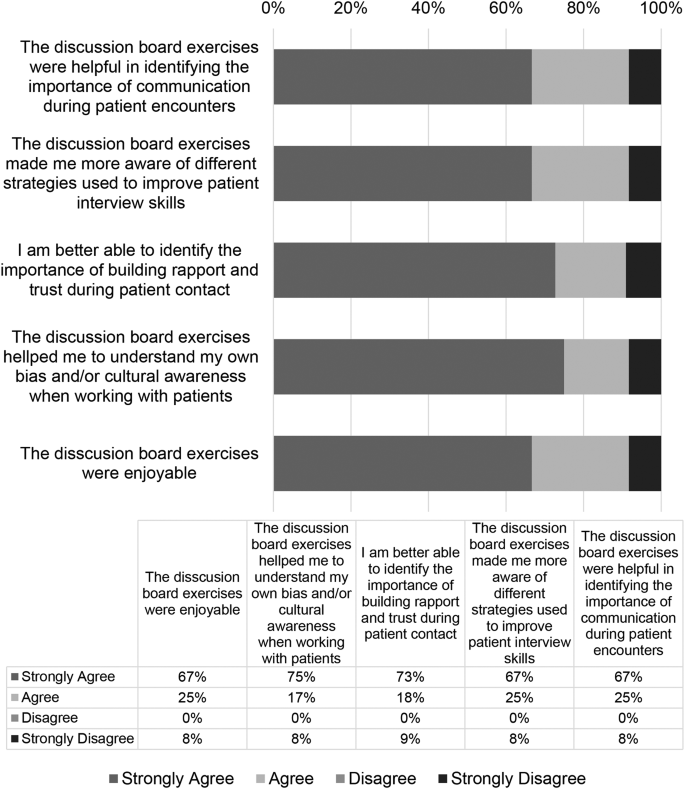
Cultural competence session survey data from the Year 2020. Survey data from students at Boston University’s Oral Health Sciences Program for the year 2020. Data is presented as percent of respondents ( n = 13)
Student responses to the reflection portion of the online cultural competency sessions were recorded and categorized. Five themes were selected and 441 reflection responses were coded using NVivo (Version 12). The results showed that 29% of reflections demonstrated student’s ability to understand a holistic approach to clinical care, 24.3% understood the importance of collecting a patient history, 6.8% recognized the socioeconomic factors during a patient encounter, 27.9% reflected on the importance of the patient clinical relationship, and 12% on the effects on improving health outcomes (Table 1 ). Representative student responses to these themes are shown in Table 1 .
There exists a need to develop novel and effective means for teaching and training the next generation of healthcare professionals the practice of cultural competence. Thus, two iterations of a course session using case-based patient centered encounters were developed to teach these skills to pre-professional dentals students. Overall, the results of this study demonstrated that participation in the course, subsequent group discussion sessions, and take-away PowerPoint sessions significantly improved the participant’s understanding of the importance of communication skills and understanding of socioeconomic, environmental, and cultural disparities that can affect a patient’s health outcome.
According to results from the course session implemented in-person from 2017 to 2019, the role-playing exercise significantly improved participants understanding of important components that can be used to improve health outcomes that may be affected due to health disparities. Students were strongly able to identify the importance of communication in patient encounters, to understand strategies such as communication and compassionate care in patient encounters, identify the importance of building a patient-physician relationship with patients, and were able to recognize their own cultural biases. Similarly, in 2020, even with a change in course modality to on-line learning due to COVID-19, students were able to understand the same key take-aways from the course session as demonstrated by reflections using the discussion board regarding the need for a holistic approach to care, importance of the patient clinician relationship, and importance of taking a patient history. Despite promising implications of both iterations of the session, students completing the session online did not find the same success in “understanding my own bias/and or cultural awareness when working with patients.” This decrease may be attributed to change in course modality and the strengths of the role-play enactment of the patient encounter. It is important to recognize that additional learning components, including video recordings of the role-play enactment, may be necessary if the discussion board is used as the primary learning method in the future.
In contrast to previous studies that attempted to determine the effectiveness of cultural competence training methods, this session had many unique characteristics. The simulated role-playing exercise enabled student participants to see first-hand an interactive patient scenario that could be used as an example for when students begin working with patients or communicating with patients who are culturally diverse. Additionally, the nature of the cases created for the course session which were divided into a part A in which the patient physician was more straightforward when diagnosing and treating the patient and a part B with a more comprehensive and nurturing approach to care, allowed the students to compare the scenarios and make their own assumptions and comments on the effectiveness of each portion of the case. Another strength of this training, was the faculty with cultural competence training were uniquely involved in case creation and facilitation of the course session. According to previous studies with similar aims, it was noted that direct observation and feedback from a faculty member who had cultural competence training and direct contact with patients can provide students with a more memorable and useful experience when educating students [ 12 ]. The facilitators of this session were able to emphasize from their own personal experiences how to work with culturally diverse populations.
An important aspect of the 2020 iteration of the course session in which a discussion board format was used, was that it allowed students who may feel uncomfortable with sharing their thoughts on a case and their own biases, the opportunity to share in a space that may feel safer than in person [ 4 ]. Previous studies have mentioned challenges with online discussion boards [ 4 ] but here we had robust participation, albeit required. Students often contributed more than the required number of comments and they were often lengthy and engaging when responding to peers. Finally, in contrast to previous studies, this course session took place in a pre-professional master’s program, the M.S. in Oral Health Sciences Program at Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine. This program, in which students are given the opportunity to enhance their credentials for professional school, provided students with early exposure to cultural competence training. Students that completed this session in their early pre-professional curriculum should be better prepared than peers who did not receive any cultural competence training until they entered their designated professional school. This session is part of an Evidence Based Dentistry course, which incorporates a larger component of personal reflection that serves to engage students in critical thinking as they begin to develop the skills to be future clinicians. Students that understand different cultures, society and themselves through self-assessments will grow and be best suited in time to treat future patients [ 4 , 16 , 17 ].
One limitation of the present study was the number of survey participants that competed the post-session surveys, as survey completion was not required. Thus, the number of student participants declined over the years, reaching its lowest number of participants in 2020 when the discussion board course session was implemented, and students may have been over surveyed due to the pandemic. Another limitation to this study, was the lack of both a pre and post survey that could be used to determine how student’s understanding of cultural competence had evolved from their entry into the course to the conclusion of the course as well as individual bias and self-reporting measures.
In the future, the course should implement both a role-playing format and subsequent discussion board reflections within the same course session. Studies have shown that alternatives ways of drawing students to reflect whether role play, personal narratives, etc. can be extremely advantageous in developing personal reflection and awareness building competency [ 4 , 16 , 17 , 18 ]. It is noted that role-playing exercises that allow students to provide feedback with student colleagues can provide students with more insight into their own behaviors. It has also been shown in previous studies that student writing and reflection activities can also facilitate student’s reflections on their own beliefs and biases [ 4 , 11 ]. Reflective writing skills are an important and effective means for students to continue to gauge their cultural competence throughout the remainder of their academic training and as future clinicians [ 4 , 17 , 19 ]. Further, students may experience emotional responses through the process of reflective writing as they recognize personal bias or stereotypes, creating a profound and impactful response resulting in enhanced understanding of cultural differences and beliefs [ 4 ]. By combining both learning techniques, students would be able to understand their own bias and their classmates and create a dialogue that could be more beneficial than just one learning method alone. Furthermore, by implementing the discussion board into the role-playing session, as stated previously, students that are more cautious about sharing their point of view or about their own implicit bias in a traditional classroom setting would be able to express their opinions and facilitate a more comprehensive discussion more thoroughly.
Here we show an effective means to utilize role-play of a multi-scenario case-based patient encounter to teach pre-professional healthcare student’s components of cultural competence, emphasizing the importance of provider-patient interactions, holistic patient care, and patient history and socioeconomic factors in provider care. This study contributes to the larger body of work that seeks to address this important aspect of education as it relates to enhancing patient health care outcomes.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Albino JEN, Inglehart MR, Tedesco LA. Dental education and changing oral health care needs: disparities and demands. J Dent Educ. 2012;76(1):75–88.
Article Google Scholar
Constantinou CS, Papageorgiou A, Samoutis G, McCrorie P. Acquire, apply, and activate knowledge: a pyramid model for teaching and integrating cultural competence in medical curricula. Patient Educ Couns. 2018;101(6):1147–51.
DallaPiazza M, Padilla-Register M, Dwarakanath M, Obamedo E, Hill J, Soto-Greene ML. Exploring racism and health: an intensive interactive session for medical students. MedEdPORTAL. 2018;14:10783.
Forsyth CJ, Irving MJ, Tennant M, Short SD, Gilroy JA. Teaching Cultural competence in Dental Education: a systematic review and exploration of implications for indigenous populations in Australia. J Dent Educ. 2017;81(8):956–68.
Betancourt JR. Cultural competence and medical education: many names, many perspectives, one goal. Acad Med. 2006;81(6):499–501.
Jernigan VBB, Hearod JB, Tran K, Norris KC, Buchwald D. An examination of cultural competence training in US medical education guided by the tool for assessing cultural competence training. J Health Disparities Res Pract. 2016;9(3):150–67.
Google Scholar
Behar-Horenstein LS, Warren RC, Dodd VJ, Catalanotto FA. Addressing oral Health disparities Via Educational Foci on Cultural competence. Am J Public Health. 2017;107(S1):S18–23.
Lie D, Boker J, Cleveland E. Using the tool for assessing cultural competence training (TACCT) to measure faculty and medical student perceptions of cultural competence instruction in the first three years of the curriculum. Acad Med. 2006;81(6):557–64.
Holyfield LJ, Miller BH. A tool for assessing cultural competence training in dental education. J Dent Educ. 2013;77(8):990–7.
Vasquez Guzman CE, Sussman AL, Kano M, Getrich CM, Williams RL. A comparative case study analysis of cultural competence training at 15 U.S. medical schools. Acad Med. 2021;96(6):894–9.
Jernigan VB, Hearod JB, Tran K, Norris KC, Buchwald D. An examination of cultural competence training in US medical education guided by the tool for assessing cultural competence training. J Health Dispar Res Pract. 2016;9(3):150–67.
Kripalani S, Bussey-Jones J, Katz MG, Genao I. A prescription for cultural competence in medical education. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21(10):1116–20.
Mariño R, Satur J, Tuncer E, Tran M, Milford E, Tran VMTH, Tran PQ, Tsai RP. Cultural competence of Australian dental students. BMC Med Educ. 2021;21(1):155.
Beagan BL. Teaching social and cultural awareness to medical students: it’s all very nice to talk about it in theory, but ultimately it makes no difference. Acad Med. 2003;78(6):605–14.
Ferrebee S, Boston University School of Medicine Master’s Thesis. (2021). Effectively Teaching Cultural Competence in Healthcare Education. Available at Boston University Libraries: Open BU: https://open.bu.edu/handle/2144/43838 .
Crosson JC, Deng W, Brazeau C, Boyd L, Soto-Greene M. Evaluating the effect of cultural competency training on medical student attitudes. Fam Med. 2004;36(3):199–203.
Cathryn F, Michelle I, Short S, Tennant M, Gilroy J. Strengthening indigenous cultural competence in dentistry and oral health education: academic perspectives. Eur J Dent Educ. 2019;23(1). https://doi.org/10.1111/eje.12398
DasGupta S, Meyer D, Calero-Breckheimer A, Costley AW, Guillen S. Teaching cultural competency through narrative medicine: intersections of classroom and community. Teach Learn Med. 2006;18(1):14–7.
Woldt JL, Nenad MW. Reflective writing in dental education to improve critical thinking and learning: A systematic review. J Dent Educ. 2021;85(6):778–785. https://doi.org/10.1002/jdd.12561 . Epub 2021 Feb 11. PMID: 33576055.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge Boston University’s Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine’s Graduate Medical Science students and study participants.
No funding was used for the completion of this study.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Graduate Medical Sciences, Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine, 72 East Concord Street, L317, R-1017, Boston, MA, 02118, USA
Karen R. Bottenfield, Andrew N. Best & Theresa A. Davies
Department of Medical Sciences & Education, Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine, 72 East Concord Street, Boston, MA, 02118, USA
Maura A. Kelley, David Flynn & Theresa A. Davies
University of Maryland School of Dentistry, 650 W Baltimore Street, Baltimore, MD, 21201, USA
Shelby Ferebee
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
TAD designed the original study concept, taught the classes (roleplay), conducted the surveys, and collected data; MAK designed the original case and PowerPoint, and performed roleplay; DBF and SF evaluated data and drafted original figures; ANB assisted in drafting the manuscript; KRB finalized figures and the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Theresa A. Davies .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This study was determined to be EXEMPT by the Institutional Review Board of Boston University Medical Campus, Protocol # H-37232.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Informed consent was received from all subjects.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Supplementary material 2, supplementary material 3, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Bottenfield, K.R., Kelley, M.A., Ferebee, S. et al. Effectively teaching cultural competence in a pre-professional healthcare curriculum. BMC Med Educ 24 , 553 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05507-x
Download citation
Received : 27 October 2023
Accepted : 02 May 2024
Published : 21 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05507-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Communication
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

COMMENTS
This presentation will include the who, what, where, when, and why of peer review. The slides presented here are designed to aid the facilitator in an interactive presentation of the elements of peer review. This presentation is ideal for any level of writing, including freshman composition. This resource is enhanced by a PowerPoint file.
Bonus Template 1: Peer Feedback and Employee Review Questionnaire Template. This PowerPoint Design provides a structured Peer Feedback and Employee Review Questionnaire Template to facilitate exhaustive peer evaluations. It includes attributes to be rated on a numerical rating scale of 1-5, allowing for an assessment of an individual's ...
Rule 2: Spend only 1 minute per slide. When you present your slide in the talk, it should take 1 minute or less to discuss. This rule is really helpful for planning purposes—a 20-minute presentation should have somewhere around 20 slides. Also, frequently giving your audience new information to feast on helps keep them engaged.
The goal of this rubric is to identify and assess elements of research presentations, including delivery strategies and slide design. • Self-assessment: Record yourself presenting your talk using your computer's pre-downloaded recording software or by using the coach in Microsoft PowerPoint. Then review your recording, fill in the rubric ...
Think about structuring your review like an inverted pyramid. Put the most important information at the top, followed by details and examples in the center, and any additional points at the very bottom. Here's how your outline might look: 1. Summary of the research and your overall impression. In your own words, summarize what the manuscript ...
1. Define your goals and criteria. 2. Choose your peers and methods. 3. Incorporate feedback into your revisions. 4. Thank your peers and share your results. 5.
The following templates propose criteria your students can use to assess their peers' work and to provide constructive open-ended feedback. Ideally, these criteria will reflect how you intend to grade. We have focused on two types of assignments: a writing-intensive assignment and a class presentation. Framing negatives as actionable ways the st...
Schedule a Pre or Post Conference Presentation Do a first run to receive feedback, or share a recent presentation with us. The Peer Review and Research Committee can schedule a session for you to speak with small or large groups. Lunchtime brown bag: Noon - 1:00 p.m. Late afternoon coffee/tea brown bag: after 3:00 p.m.
Peer review training courses and in-person workshops. We strongly encourage you to learn the core concepts of peer review by joining a course or workshop. You can attend in-person workshops to learn from and network with experienced reviewers and editors. As an example, Sense about Science offers peer review
Instructions to Peer Reviewers. Each student, apart from the presenter, should fill in a copy of this form during each student presentation. Note that these comments will be returned to the presenter anonymously. For each section above the reviewer should tick the most appropriate score box, circle each positive and/or negative comment that ...
Be actionable. Giving students your opinions on their presentation is important, but make sure that you give them a specific action they can do to implement your feedback. Examples of how feedback can be improved with actions is below: Weak pieces of feedback. Stronger pieces of feedback.
Peer Review Group Suggestions. Pay attention to the way you present the concept of peer review to your students. Explain clearly the rationale for doing this activity and demonstrate your commitment to it. Make the work count. You may assign points for it as a part of your class activities and informal writing component of your grade; remember ...
The BMJ: Leading Medical Research, News, Education, Opinion ... 1
However, you can use the Comments feature to keep track of peer feedback in your presentation. When you send your presentation out for review, give your reviewers these instructions to provide feedback to you: Select the item on the slide that you want to add a comment about. On the Insert tab, click Comment. Enter your comments, and press Enter.
What Is Peer Review? • Download as PPTX, PDF •. 12 likes • 12,513 views. J. Jerry Stovall. Peer Review is the Process used to judge the quality of articles submitted for publication in a scholarly journal. Peer Reviewed articles are considered the best source to use when writing a research paper. Read more. Education.
Example of PowerPoint Presentation used at a Peer Review Session. Screening for Lung Cancer; Papers shared at Peer Review Sessions. Triage for out of hours paper; Instructions for how to navigate RL6 system. How to Assign a Case; Submitting A Case 11/23/2021; How to review a case Updated 2021; How To Submit A Case 11/23/2021. Submitting a Case ...
The pack includes PowerPoint presentations and written exercises. Much of the material here relates to the general art of peer review, but we have also included specific guidance on what The BMJ needs from you. We developed this pack for use in a randomised controlled trial of peer reviewer training. Now you can use it as you wish; for your own ...
This presentation will include the who, what, where, when, and why of peer review. The slides presented here are designed to aid the facilitator in an interactive presentation of the elements of peer review. This presentation is ideal for any level of writing, including freshman composition. This presentation may be supplemented with OWL ...
Peer feedback form for group presentations. A sample form for use by students when they are observing other students' class presentations, focusing on constructive suggestions for improvement. Download this file. Download this file [61.44 KB] Back to Resources Page.
She holds a bachelor's in English Creative Writing and Communication Studies and lives in Denver, Colorado. In her spare time, she's usually somewhere outside (preferably in the mountains) — and enjoys poetry and fiction. Use these 30 presentation feedback examples to help you (and your team) get better at giving presentations.
Strengthening NIH Peer Review - ... OIT PowerPoint Widescreen Presentation Author: U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Information and Technology Keywords: PPT, OIT, presentation, Office of Information and Technology Created Date: 5/8/2024 11:05:52 AM ...
A peer review is a formal review of a document. produced by a colleague, fellow scholar, or. expert. Peer reviews describe the strengths and. weaknesses of a document. Peer reviews evaluate a document and argue. whether it should be published or presented. Peer reviewers advise writers how to improve. their document.
Slide Formats. 16:9. 4:3. Showcase the entire functionality of the peer review process in a compelling manner using our uniquely-crafted Peer Review PPT template. The deck is a perfect blend of creativity and professionalism; thus, it will give your existing and future business and marketing presentations a creative makeover.
Peer review is a process where experts in the field review a researcher's work before it is published. The goal of peer review is to ensure that the research is well done and logical. Reviewers who are knowledgeable about the subject matter provide advice and feedback to help improve the research quality and determine if it is ready to share with the world. - A free PowerPoint PPT ...
Students were required to: (1) read each of the Patient Encounter Cases and add a brief reflection comparing the scenarios, (2) then comment on at least two peer's posts in the discussion forum and (3) attend class to hear a PowerPoint presentation by a course session facilitator on the key take-aways from each scenario . Student surveys