Two ways to set trusted locations and UNC paths using Intune
- 14. July 2023
- - Lars Omlin
- - Modern Workplace
- - Last Updated on 26. September 2023

Introduction
In this scenario we have the problem that we want to access an SMB file share with an AAD device. This may be the case if you are still dependent on this server in a larger project. It becomes particularly problematic if an application needs to access this share. So we need to set trusted locations on the client device.
Table of Contents
Security Warning Message
The following security message may appear in the background without the user noticing. Two different ways of dealing with this problem are explained here.
Why manage with Microsoft Intune?
The answer is obvious: We can simply distribute the configuration globally or granularly by group assignment and monitor their configuration status. We simply reduce the administration effort many times over! Since we don’t have a local domain controller, we can do this with the Intune Portal . We do nothing but the following configurations in the Internet options:
Using PowerShell Script
There is the first possibility to set the configurations via scripts. I have made a combined version for you once. From this you can also tinker together the individual functions. To set your servers as trusted, you only change the IP addresses.
This script must be executed on the device with administrative privileges!
This script can now be released and rolled out in Intune to the device group you selected
Important: Make sure that the script is not executed with the logged in User. Use system context to run the script
Using the Intune configuration profile
So we go to the Intune configuration profile menu:
We select Windows 10 and later, and can enter the configuration with the Settings catalog. It is also possible with the Administrative Templates, this is optional.
We now start searching for our desired functions. These are: Site to Zone Assignment List and Intranet Sites: Include all network paths (UNCs)
It should look something like this:
Value – A number indicating the zone with which this site should be associated for security settings. The Internet Explorer zones described above are 1-4.
You should see the final result here:
Possible malfunction
It is possible that the set hook will fall out again without a specifically recognizable pattern. In this case, it is worthwhile to take a look at the security baselines. You can also find a configuration there, which might cause problems for us. You can find a detailed configuration catalog for the Internet Explorer there again!
This simple method allows administrators to store trusted servers in the Internet Options on the local intranet. This can be handy if you want to access an SMB or UNC share provided by linux from a Windows machine.
Recent Posts
- Network Security Hardening (ICMP) with Microsoft Intune
- Linux Bash Script Deployment with Intune
- Most used Microsoft 365 Certified Integrated Apps
- Auto Subscription RDP Client for AVD / W365 via Intune
- How to Clean-Up your Cloud managed Devices in Intune, Autopilot and AAD
Writer & Blogger
Be the first in line.
Sign up for a Newsletter.
- Allgemein (1)
- Microsoft 365 (9)
- Microsoft Azure (10)
- Modern Workplace (14)
- alwaysonvpn
- anti-malware
- anti-phishing
- application
- certificate
- configuration
- deep inspection
- exchange online
- Microsoft AI
- microsoft365
- microsoft365lighthouse
- microsoftintune
- Notification
- powerautomate
- powerautomate app
- remediation
- Retention Policies
- rss notifications
- safe attachments
- step-by-step
- troubleshooter
- Privacy Policy
© 2023 Copyright
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Assign DFS share to intranet zone via GPO?
This seems like it shouldn't be hard, but I haven't had any luck with either guessing or searching. I'll admit I'm no Windows guru, so forgive me if the answer should be obvious.
I'm trying to get Windows to stop giving me security warnings when I open files or links from a DFS share. I already have a GPO in place which does this for a couple of other network shares:
Here, I've added host1.mydomain.org and host2.mydomain.org to zone 1 (intranet), and the network shares from these hosts are correctly treated as trusted intranet sites.
However, I now want to add \\mydomain.org\shares to the intranet zone as well. Adding it just like that appears not to work (and on my client machine it appears in the list as file://*.mydomain.org ). Other things I've tried include *.mydomain.org and explicitly listing the hosts where the DFS shares originate.
"Turn on automatic detection of the intranet" is also enabled, although I've never been clear on how that actually works.
Servers and DCs are 2008 R2 and clients are (mostly) 7 Pro.
Edit: The next day, it appears that the listing of mydomain.org is in fact having the desired effect. I hadn't logged out and back in during testing; I just did a gpupdate /force and confirmed that the GPO settings appeared in the Internet Options dialog. Is this a bug or just another arcane Windows thing that I don't quite understand?
- group-policy
- For those finding this via a search: run gpedit.msc to edit the policy nicely enumerated above, then gpupdate /force – Stan May 12, 2016 at 22:48
2 Answers 2
When refreshing group policy it is usually necessary to log out and for some settings a restart (sometimes 2!) is necessary. I wouldn't call it arcane but it won't be obvious if you haven't documentation regarding group policy processing.
- 1 I understand that, but when I saw that the GPO settings appeared properly in the Internet Settings after the gpupdate, I naturally assumed they had been applied. – eaj Oct 6, 2011 at 14:30
- 1 Ok. I wonder if the network connection to the share was still alive, then had to be recreated to be recognized under the new security zone setting for the policy to take affect? – will Oct 6, 2011 at 15:20
- 1 That sounds like a pretty good theory to me. You win the green checkmark. :) – eaj Oct 6, 2011 at 15:27
The shell (explorer.exe) is caching the policy. Simply restart the shell and many settings will start to be applied. There is no need to log out/back in for many scenarios.
Exiting the shell:
- Windows 7: Ctrl+Shift+right click on blank area of Start Menu | Exit Explorer
- Windows 8: Ctrl+Shift+right click on Start Menu button | Exit Explorer
Restarting shell:
- Ctrl+Shift+Esc, File | New Task (Run...) | "explorer"
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged windows group-policy dfs ..
- The Overflow Blog
- How to prevent your new chatbot from giving away company secrets
- Introducing Staging Ground: The private space to get feedback on questions...
- Featured on Meta
- Testing a new version of Stack Overflow Jobs
Hot Network Questions
- Python matrix class
- Can you cook tomatoes in water without leaking/bursting them?
- Why don't professors seem to use learning strategies like spaced repetition and note-taking?
- Is it idiomatic to say "home to diverse population"?
- Why raise livestock only in newer planetary settlements?
- Is this "leak" expected from a brand new sump pump?
- Implicit function equation f(x) + log(f(x)) = x
- How is this function's assembly implementing the conditional?
- Confirming receipt of document in formal email
- Why are so many professors' websites out of date?
- I fear he wants you to finish
- How to justify formula for area of triangle (or parallelogram)
- Visual Studio Code crashes with [...ERROR:process_memory_range.cc(75)] read out of range
- Who are the mathematicians interested in the history of mathematics?
- Filter by partition number when the table is partitioned by computed column
- How much extra did a color RF modulator cost?
- Is it legal to deposit a check that says pay to the order of cash
- Leaders and Rulers
- What should I get paid for if I can't work due to circumstances outside of my control?
- Can campaign promises be enforced by a contract, or has it ever happened they were?
- unable to ping my router from outside
- How to use cp's --update=none-fail option
- How can I hang heavy bikes under a thick wooden shelf?
- Is bike tyre pressure info deliberately hard to read?
Looking Ahead into 2018 » « SRP Calendar Control
Resolving Open File Security Warning when Launching OpenInsight

In this article we’ll cover 3 methods to prevent the Open File – Security Warning by configuring Windows to trust the shared OpenInsight network location.
Determine The OpenInsight Server Name
The first step to setup a trusted network location is to locate the server name where OINSIGHT.exe is being launched from. This is important because the name could be a:
- Short network name – \\augusta
- Fully qualified domain name (FQDN) – \\augusta.lan
- IP address – \\192.168.0.2
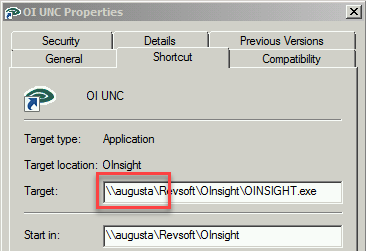
Option 1: Add the Path to OpenInsight as a Local Intranet Site
For networks with only a few users or workstations not part of the active directory network the easiest option is to add the OpenInsight server as a trusted intranet site on a per user basis. This is accomplished by following these steps on each user desktop running OpenInsight:
- Open the Internet Explorer browser and go to settings .
- Open the Security tab.
- Click Local intranet.
- Click the Sites button .
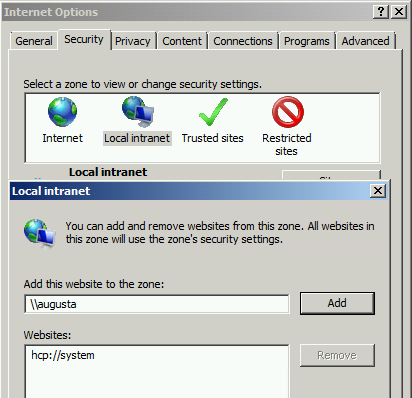
- Close the open settings window and try launching OpenInsight. The change should take effect immediately and OpenInsight should launch without displaying the file security warning. If not, log out and log back in or check the path.
Option 2: Using a Script to Add the OpenInsight Path as a Local Intranet Site
The OpenInsight server can also be added as a local intranet site by setting a registry entry. This is a more flexible version of the first option because it can be setup using:
- A network login script
- An OpenInsight Basic+ program
- A custom installer for your application
- A setting pushed over the network
Note: When used from an OpenInsight Basic+ program during your application launch the user will see at least one security warning message. After the warning message is acknowledged OpenInsight can launch, run your application’s start-up routine, and set the registry changes to prevent the user from seeing the security warning on subsequent launches.
To setup a new trusted site using the registry:
- Create a new registry path containing the name of the server. For example: HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\EscDomains\augusta Where augusta is the name of the server used in this example.
- In the path create a new registry key named file of type DWORD.
- Set the file registry key value of to be “1” to indicate the zone type is local intranet.
- Logout of your desktop and log back in to test the setting. Launching the OpenInsight shortcut should no longer display the file security warning.
The registry entry can be created from a batch or login script without any special tools using the command:
Substitute augusta with the name of your server.
Option 3: Using Group Policy to Configured the Local Intranet Site
Workstations managed through Active Directory can be configured by creating a group policy setting to trust network locations. This is especially important in Remote App or Citrix environments where users might never see their desktop. Setting up a group policy is beyond the scope of this article so please check with your network administrator on how to deploy these settings.
The Site to Zone Assignment List policy instructs Windows what zone a particular server should be placed in. Enable the group policy: “User Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Internet Explorer > Internet Control Panel > Security Page > Site to Zone Assignment List”
Add an entry into the policy zone list for the OpenInsight server by entering the server name as the Value name with a Value of 1 as shown below.
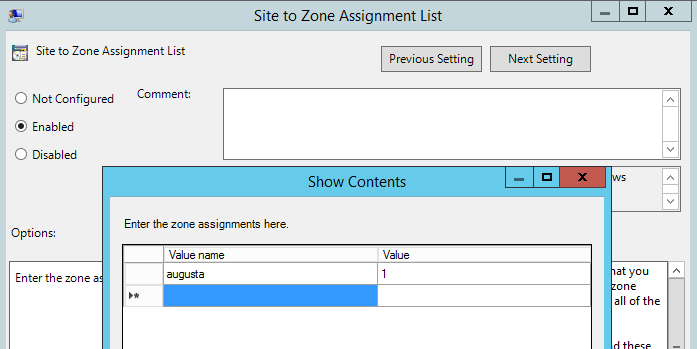
Then the policy is applied and propagated to users they should no longer see the security warning when launching OpenInsight.
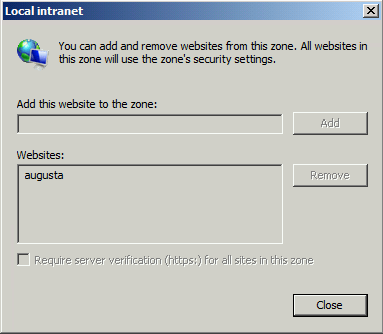
If your system administrator is unable to disable IE ESC for your users the policy Turn on automatic detection of intranet may help recognize some network locations as intranet sites. Lab testing revealed this setting usually detected short UNC paths like \\augusta as local intranet sites while paths using IP or FQDN addresses such as \\192.168.0.2 or \\augusta.lan continued to remain untrusted locations.
We hope this information helps you support your OpenInsight application and bring a greater level of trust to users by not showing unnecessary security warnings.
3 Responses to Resolving Open File Security Warning when Launching OpenInsight
What if you are using mapped drives? i.e. n:\oi Site I’m at doesn’t appear to allow UNC paths for target path.
Mapped drives are basically aliases to UNC paths and Windows will resolve the mapped drive to a UNC path when deciding if it should trust a network location. For example, if your mapped drive is N:\ and you enter that into Internet Explorer’s Local intranet zone list as shown in option 1 then IE will translate N: to the server it points to when you click the Add button. So if N: points to \\myserver\share then the entry would translate to file://myserver when added to the list.
The UNC was more complicated then we thought got that to take but a group policy prevents adding trusted sites through IE apparently
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
- Terminate that TERM Command
- New Release: SRP ActiveX Controls
- SRP Controls, Utilities, and Editor Get DPI Support
- Farewell to a Revelation Legend
- Matt Crozier on Configuring the OpenInsight Debugger
- Don Bakke on Picking the Correct XMLHTTP Object
- PJO on Picking the Correct XMLHTTP Object
- Problem with record locks
- Cant Open OI 10.2 IDE
- embedded image in Beta issues
Enter your email address to sign up for email notifications of new posts.
Email Address
- February 2024
- October 2023
- August 2021
- September 2020
- August 2020
- January 2020
- November 2019
- August 2019
- January 2019
- October 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- October 2017
- February 2017
- November 2016
- October 2016
- September 2016
- August 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- August 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2014
- October 2014
- August 2014
- January 2014
- December 2013
- November 2013
- October 2013
- September 2013
- August 2013
How to add a server to trusted sites
I’m not quite sure how to add a server as a trusted site with group policy. I know how to add URLs to trusted sites. I’m more confused on the syntax.
Do i just type in “serverA” or “\serverA” or do i just put the IP address? If it’s an IP address do i enter “file://10.0.0.1”?
Open the Group Policy Management Console.
Navigate to the Group Policy Object that you want to edit.
Expand the Computer Configuration or User Configuration folder, depending on whether you want to apply the policy to all users or just specific users.
Expand the Administrative Templates folder.
Expand the Windows Components folder.
Expand the Internet Explorer folder.
Click on the Security Zones and Content Ratings folder.
Double-click on the Site to Zone Assignment List policy.
Click the Enabled radio button.
Click the Show button.
In the Value name field, enter the server name in the following format: “file://servername” (replace “servername” with the actual name of the server).
In the Value field, enter the corresponding zone number for the zone that you want to add the server to:
1 for Intranet zone
2 for Trusted Sites zone
3 for Internet zone
4 for Restricted Sites zone
Click the OK button.
@spiceuser-9i0os
Thank you! I just didn’t know what to enter for the value.
Related Topics
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
GPO: Defining sites to local intranet zone - Does it overwrite existing sites defined?
If I want to add a domain to local intranet sites in my entire network of +2000 computers and clients, does using GPO to do it potentially overwrite any existing defined sites on the clients?
We have lots of users who we've defined these local intranet sites manually on each client. And each client is usually a little different from the other one. But now I need to add a site that will apply for the entire network. I really want to avoid doing this manually if possible.
The specific GPO-settings I am asking about is located here:
User Configuration/Policies/Administrative Templates/Windows Components/Internet Explorer/Internet Control Panel/Security Page
The object being Site to Zone Assignment List
- group-policy
- windows-domain
Creating that GPO will overwrite users settings and prevent them modifying settings
This may help you https://blog.thesysadmins.co.uk/group-policy-internet-explorer-security-zones.html
- Whilst this may theoretically answer the question, it would be preferable to include the essential parts of the answer here, and provide the link for reference. – MMM Jan 15, 2020 at 14:22
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged group-policy windows-domain ..
- The Overflow Blog
- How to prevent your new chatbot from giving away company secrets
- Introducing Staging Ground: The private space to get feedback on questions...
- Featured on Meta
- Testing a new version of Stack Overflow Jobs
Hot Network Questions
- Confirming receipt of document in formal email
- Accelerating Expansion of Universe - Why Not Caused by Radiation?
- How to justify formula for area of triangle (or parallelogram)
- A story about a boy with a fever who falls in the creek and is saved by an angel and grows up to be Hitler
- In Catholicism, is it OK to join a church in a different neighborhood if I don't like the local one?
- are "I will check your homework later" and "I will check on your homework later" similar?
- unable to ping my router from outside
- Who are the mathematicians interested in the history of mathematics?
- Why raise livestock only in newer planetary settlements?
- Memory ordering with multiple releases and a single acquire
- Is it legal to deposit a check that says pay to the order of cash
- What can I plant to retain a steep slope?
- Why do airplanes sometimes turn more than 180 degrees after takeoff?
- Connecting to very old Linux OS with ssh
- How to attract hummingbirds to my feeder when my neighbor also has an established feeder
- Almost everywhere-periodic functions with many periods
- Transform sequence into ragged list
- Tools like leanblueprint for other proof assistants, especially Coq?
- Which ability checks are rolled for a shove attack?
- Why didn't CPUs multiplex address pins like DRAM?
- Can LLMs have intention?
- Print all correct parenthesis sequences of () and [] of length n in lexicographical order
- In Acts 10 why does Peter not know the gospel is not only for the Jewish people?
- SF story where classical element theory is correct; space battle to reduce elemental earth fortress

The World According to Mitch
The day to day ramblings of an IT Professional (and so much more…)
Folder Redirection: Where’d these warnings come from?
Congratulations. You have decided to implement a Folder Redirection policy on your domain. There are real advantages to this, not the least of which is that all of your users’ profile folders will get backed up centrally… and that when they change computers their files and settings are just there.
You have created a Group Policy Object (GPO) in Active Directory that you have called Folder Redirection , and you have applied it to the Organizational Unit (OU) that your user account is in, and as is so often the case with Desktop Administrators, you have made yourself the guinea pig. From Windows you run the command gpupdate /force , and are informed that in order for the Folder Redirection policy to be applied, you will have to log off and then log on again. You do.
It must have worked! Why do you I say that? Because unlike most of the time, when logging on takes a few seconds, it took a full ten minutes this time. As a seasoned Desktop Admin you understand that this is because all of the folders that you set to redirect – Documents, Pictures, Videos, Favorites, Downloads – are being copied to the server before you are actually allowed onto your desktop. However a few minutes later, once you are logged on, you open Windows Explorer, and in the navigation pane you right-click on Documents , and see that the My Documents folder is no longer at c:\Users\Mitch , but at \\Sharename\Mitch .
Unfortunately there is one step that you are now saying to yourself ‘Mitch, you missed one thing!’ Because you know that when you clicked on Windows Explorer in the task bar, you got a warning message that looked like this:

As a seasoned IT Pro you know that security warnings are a way of life, and it wouldn’t bother you if you had to accept this every time… but you know your end users are going to go ape, so you need a solution. No problem.
I should mention that while these steps will work for all versions of Windows since Windows Vista, the way you access the screens may be a little different.
1) Open Control Panel . Don’t be alarmed, you are going to get the same security warning when opening the CP.
2) In the Search window type Internet Options . When it comes up, click on it.
3) In the Internet Properties window select the Security tab.
4) On the Security tab click on Local Intranet . Then click on Sites . Note that the Sites button will be greyed out until you select Local Intranet .
6) In the Local Intranet window click the Advanced button.
5) In the Local Intranet (Advanced) window type the location of your folder redirection share into the box marked Add this website to the zone: Uncheck the box marked Require server verification ( https:// ) for all sites in this zone . Click Add . Then click Close .
6) Close the Internet Properties window.
Now try opening Windows Explorer again. It should open without the security warning.
If You’re Gonna Do IT Then Do IT Right…
Okay, so you know how to configure this setting for your individual desktop… but you don’t really want to have to go to every desktop/laptop/tablet in the organization and do this, do you? Of course not, that is what Group Policy is for!
We are going to make one change to your Folder Redirection policy.
1) Open Group Policy Management Console.
2) Right-click on your Folder Redirection policy and click Edit…
3) Navigate to: User Configuration – Policies – Administrative Templates – Windows Components – Internet Explorer – Internet Control Panel – Security Page .
4) Right-click on Site to Zone Assignment List .
5) Enable the policy.
6) In the Options box click on Show…
7) In the Value name cell enter the UNC path of your file share.
8) In the Value cell next to the UNC path you just entered enter the value 1 . (Where 1=Intranet/Local Zone, 2=Trusted Sites, 3=Internet/Public Zone, and 4=Restricted Sites). Click OK then click OK in the Site to Zone Assignment List dialogue box.
9) Close Group Policy Management Editor .
That should be it… remember you will have to re-run your gpupdate /force on your machine, but even if you don’t it will apply in the next few logoffs, right?
**Thanks to Joseph Moody for the list of settings for the Zone Value list!
Share this:
Mitch Garvis
Leave a comment Cancel reply
- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar

Somewhere out there!
Adding a local file server to your trusted site gpo.
April 14, 2007 @ 1:33 pm · Filed under Terminal Server , Windows
By default Windows Terminal Server is quite annoying when dealing with shortcuts and applications mount from a local file server. A per usual with Windows there is quite a lot of documentation out there with information, although it not all clear.
- “Site to Zone Assignment List” GPO = trusted site?
- Site to Zone Assignment List – best method here
- Behavior of Site to Zone Assignment List
- The Site to Zone Assignment List policy prevents Internet Explorer from using other zone configuration settings when the Internet Explorer Enhanced Security Configuration feature is enabled on a Windows Server 2003 SP1-based computer
- How to lock down a Windows Server 2003 or Windows 2000 Terminal Server session
Regardless of the above I found the best way to deal in Windows 2003R2 with the GPO was:
Edit the GPO object you wish to apply these settings too. Select [User Configuration\Windows Settings\Internet Explorer Maintenance\Security]. Then double click [Security Zones and Content Ratings], click [Import the current security zones and privacy settings], and then click [Modify Settings]. It should be pretty straight-forward from there. I added my file server sites into Local Intranet , using the form file://uncserver . I found this easy than the “Site to Zone Assignment List” GPO method.
Share this:
Comments are closed.
- December 2011
- October 2009
- August 2009
- February 2009
- January 2009
- December 2008
- November 2008
- October 2008
- September 2008
- August 2008
- February 2008
- January 2008
- December 2007
- November 2007
- October 2007
- September 2007
- August 2007
- February 2007
- January 2007
- October 2006
- September 2006
- August 2006
- February 2006
- January 2006
- December 2005
- November 2005
- October 2005
- September 2005
- August 2005
- February 2005
- January 2005
- December 2004
- November 2004
- October 2004
- September 2004
- August 2004
- Terminal Server
- Uncategorized
- PhoenixBlue
- Phoenixtheme

Windows security encyclopedia
#microsoft #windows #security
Search form
Site to zone assignment list.
This policy setting allows you to manage a list of sites that you want to associate with a particular security zone. These zone numbers have associated security settings that apply to all of the sites in the zone.Internet Explorer has 4 security zones numbered 1-4 and these are used by this policy setting to associate sites to zones. They are: (1) Intranet zone (2) Trusted Sites zone (3) Internet zone and (4) Restricted Sites zone. Security settings can be set for each of these zones through other policy settings and their default settings are: Trusted Sites zone (Low template) Intranet zone (Medium-Low template) Internet zone (Medium template) and Restricted Sites zone (High template). (The Local Machine zone and its locked down equivalent have special security settings that protect your local computer.)If you enable this policy setting you can enter a list of sites and their related zone numbers. The association of a site with a zone will ensure that the security settings for the specified zone are applied to the site. For each entry that you add to the list enter the following information:Valuename – A host for an intranet site or a fully qualified domain name for other sites. The valuename may also include a specific protocol. For example if you enter http://www.contoso.com as the valuename other protocols are not affected. If you enter just www.contoso.com then all protocols are affected for that site including http https ftp and so on. The site may also be expressed as an IP address (e.g. 127.0.0.1) or range (e.g. 127.0.0.1-10). To avoid creating conflicting policies do not include additional characters after the domain such as trailing slashes or URL path. For example policy settings for www.contoso.com and www.contoso.com/mail would be treated as the same policy setting by Internet Explorer and would therefore be in conflict.Value - A number indicating the zone with which this site should be associated for security settings. The Internet Explorer zones described above are 1-4.If you disable or do not configure this policy users may choose their own site-to-zone assignments.
Policy path:
Scope: , supported on: , registry settings: , filename: , related content.

an endpoint admin's journal
- Recent Posts
- Popular Posts
- Recent Comments

Deploy Trusted sites zone assignment using Intune
November 6, 2023

Zoom Desktop Client – Download older build versions from Zoom
October 31, 2023

Uninstall Teams chat app using remediation script and a configuration profile in Intune
October 30, 2023

Intune Last Check-in date not updating for Windows device
October 25, 2023

How to use Event Viewer to check cause of Blue screen of Death (BSOD)
October 23, 2023
5 Quick Mac OS Terminal commands to make a Mac user life easier

Powershell : Find disabled users and computers in AD
- Active Directory (1)
- Windows (7)
- November 2023
- October 2023
Deploy a set of trusted sites overriding users’ ability to add trusted sites themselves. To acheive this, an Intune configuration profile Trusted site zone assignment can be deployed to devices/users group as required.
Login to Intune Portal and navigate to: Devices > Windows > Configuration Profiles .
Hit the Create button and Select New policy

From the Create a profile menu, select Windows 10 and later for Platform , Templates for Profile type. Select Administrative templates and click Create .

Give the profile desired name and click Next .

In Configurations settings, select Computer Configuration and search for keyword “ Site to Zone “, Site to Zone Assignment List setting will be listed under search results. Go ahead click on it to Select it.

Once selected, a Site to Zone Assignment List page will appear on right side explaining different zones and values required for these zone for setup. Since this profile is being used for trusted sites, we will use the Value “2” . Go ahead and select Enabled button and start entering the trusted sites as required. please ensure to set each value to “2” . See example below:
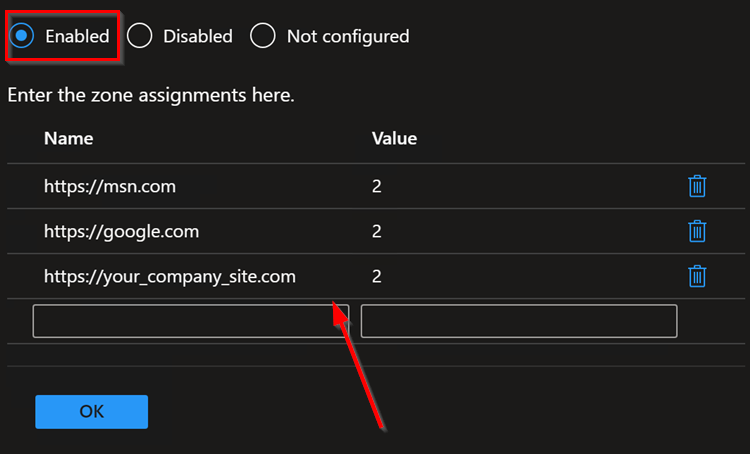
Once done adding the list of sites, click OK to close it and Hit Next on Configuration settings page.
Add Scope tags if needed.
Under Assignments , Click Add groups to target the policy deployment to specific group of devices/users. You can also select Add all users / All all devices .
Hit Next . Then Hit Review + Save button to save.
Tags: Intune Windows
You may also like...

[Windows 10] How to completely uninstall Flash player

- Previous Zoom Desktop Client – Download older build versions from Zoom
thanks! I was just looking for this exact solution!

Managing Internet Explorer Trusted Sites with Group Policy
Internet Explorer Maintenance is dead. We all have our regrets, missed chances, and memories. But we have to move on. Depending on your love for power, you have two options. You can take the totalitarian route (known as Administrative Templates) or the benevolent method (known as Group Policy Preferences). Here are the two ways that you can configure Internet Explorer Trusted Sites with Group Policy.
Configuring IE Trusted Sites with Administrative Templates
Site to Zone Mapping allows you to configure trusted sites with Group Policy Administrative Templates. This setting can be found at:
- Computer Configuration/Policies/Administrative Templates/Windows Components/Internet Explorer / Internet Control Panel/Security Page/Site to Zone Assignment List
- User Configuration/Policies/Administrative Templates/Windows Components/Internet Explorer / Internet Control Panel/Security Page/Site to Zone Assignment List
When possible, use the computer configuration option as it will not impact user logons. When you enable the setting, you will be prompted for a value name (the website) and a value (the zone list). Here are the possible values and the zone that they correspond to:
- 1 = Intranet/Local Zone
- 2 = Trusted Sites
- 3 = Internet/Public Zone
- 4 = Restricted Sites

The screenshot above shows one trusted site and one restricted site. There is a potential downside to managing trusted sites with Administrative Templates. You will not be able to edit the trusted sites list within Internet Explorer. If you have more than four items listed, you won’t be able to see the entire list in the IE Trusted Sites window. If you view the site properties (Alt – File – Properties), you can check a specific site’s zone though. Remember this trick as it will help you when troubleshooting! You can view the entire list in the Registry by navigating to HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\Domains. If you are an administrator, you can edit/add/remote items from this list for testing. Just be sure to run a GPUpdate /force to undo your changes.
Bonus Points : Leave a comment below explaining why a GPUpdate /force is required to undo your changes. Super Bonus Points if you answer in a haiku.
Configuring IE Trusted Sites with Group Policy Preferences Registry
You would think that Group Policy Preferences Internet Settings could set trusted sites. Unfortunately, that setting is greyed out.

You can still configure IE site mappings with Group Policy Registry Preferences though.* The benefit of this is that your users can edit the zone lists and view all of the added sites. To set this up, create a new user side registry preference. This trick will not work under computer configuration. Enter in the following details:
- Keypath: Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\Domains\WEBSITENAME
- Value Name: http
- Value Type: REG_DWORD
- Value Data: 2
Here is an example showing DeployHappiness being set as a trusted site with registry preferences:

If your site isn’t being placed in the Trusted Sites list, add it manually and then navigate to the registry location above. Ensure that the manual addition exactly matches your registry preference. You will also need to ensure that no Administrative Template Site to Zone settings are applied. If they are, they will wipe out your preference settings. Remember that Policies always win!
You can search your domain for site to zone settings by using this Group Policy Search script. Alan Burchill taught me this trick.
To see additional ways to configure site to zone mappings, read this very in depth example guide.
24 thoughts on “ Managing Internet Explorer Trusted Sites with Group Policy ”
I hope to replace our Site to Zone list to allow our users to enter their own in but I am not sure how to enter our entries that don’t specify a specific protocal such as http or https. So can someone tell me how I would create an entry for this:
*://*.sharepoint.com
and what about something like this – how would this be entered?
https://192.192.192.192 .:9443 (example only)
As for your first question, this info should help: https://community.spiceworks.com/topic/326140-add-trusted-sites-via-gpo-but-still-allow-users-to-add-trusted-sites?page=1#entry-2849140
As for the second question, I don’t know of a way to handle ports. In reference to your example, a link like that would be entered like this: *://192.192.192.192
This is excellent – I have used the GP preferences to add trused sites without locking users out of the setting if they need to add a site. But what about this – a program in the startup group – it is a shortcut to a file on a server – a member server of the local domain – domain.local. I want to prevent this program from prompting end-users to run it, and make sure it will run without prompting. Can this be accomplished with a GP preference as well? If so, do I need to add it to trusted sites, or to the local intranet zone or local machine zone? It would seem to be a local intranet or local machine zone I am working with here. I am not sure how to add it – whether I just need to add the local domain, or the computer name FQDN, or the path to the shared folder and the file. thanks!
This sounds like two different problems: 1. How do I get an app to run without prompting? 2. How do I make it run on startup with group policy?
The latter is easy, create it as a scheduled task that runs on startup. The former depends on what type of script it is. If it’s a vbscript then run it with cscript /b “name.vbs”.
With the old approach we had a file under trusted sites to allow the file to run. It has stopped working under 2012. Could I use this with a file? The old setting was:
file:\\Domain.com\netlogon\AsmallExe.exe
See this article on what you can configure with trusted sites: http://evilgpo.blogspot.com/2016/03/internet-explorer-site-to-zone.html
Just the ticket. Thanks a lot.
I have double-checked that the site to zone assignment policy is not configured, both under user and computer settings. We used group policy preferences because we do not want to lock down the trusted sites – only to push out the sites we want to be trusted. But for some absurd reason, the trusted sites are locked down and greyed out half the time – one day I will look and the sites are not dimmed out and will let me add or remove them. Then the next day they will be greyed out again. It is amazingly ridiculous. I am the only admin; no one else knows how to mess with the settings even if they had the admin credentials. So I have no clue why it keeps reverting back to the wrong settings. I thing our active directory needs to have dcdiag run on it a few times. Any ideas will be sincerely appreciated.
If it is locked down, it is a GP policy that is doing it (the site to zone assignment one) or a registry key that is enabling that site to zone assignment.
When you see one that does it, run a GPResult /h report.htm /f and look through that report.htm. You will see any GP settings that would block it then.
A reply to my own post – the problem was corrupted group policy on the Windows 7 computers – some of the computers were working fine. The ones that were not working, we had to delete the corrupt policy (it was preventing the updated policy settings from being applied). It was in the path C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Group Policy\History\{policy GUID}. After deleting the corrupt policy and rebooting, it fixed the problem!
Thanks for the update Sam!
You’re welcome! I am still having some issues with the trusted sites being greyed out in IE, even though I made certain not to use site to zone assignment in the policy, and only used GP preferences to add registry items for the sites in the trusted zone. Do you know what registry key I need to be looking for, that might be causing this issue?
Many thanks! Sam S.
Are you making sure that you’re applying it under HKCU, and not under HKLM? If you configure it under HKCU, users will still have the ability to add their own entries. But if you configure it under HKLM, the option to add entries will be greyed out.
Yes, I definitely deployed the preferences under the Users GP Preferences and not computer policy/preferences. However, there are some policy settings that I set in both computer and user settings in the GPO. None of these are site to zone assignments though. These settings are for all the security settings within the zones, like, download signed activeX controls – enable, download unsigned activeX controls, Prompt… etc.. – these settings are set in the computer policy and the user policy which is probably what is wrong. I should probably just disable the computer policies in the GPO. I will try that and see if it helps. Why are all these settings available in the computer side and the user side both? Is there a reason someone would set these settings in one policy over the other?
A computer side policy is available for every user that logs in already. These are generally faster to apply and are my preferred way to configure something. However, times like this are when a user side policy would be the best route for you. Remove the computer side settings and try John’s suggestions. Let us know what you find out.
Sam, another thing you can try is to access the GPO from a Windows 7 workstation running IE 9 (and make sure that there are no current Internet Explorer policies being applied to the workstation; put it in an OU that is blocking inheritance if you have to), then drill down to “User Config\Policies\Windows Settings\Internet Explorer Maintenance\Security\Security Zones and Content Ratings”. Double-click on “Security Zones and Content Ratings”, then choose “Import…” under “Security Zones and Privacy’, click “Continue” when prompted, then click “Modify Settings, then “Trusted Sites”, then the “Sites” button. You can then make whatever changes you want (add a site, remove a site, remove the check from the https box, etc). This should give you the freedom you’re looking for :).
i`ve add multiple Sites to the Site to Zone assigment list (Trusted Sites). After a new logon, i`ve check my settings, start IE11, visit the site i`ve add to the list, press Alt – File – Properties and check the Zone. Some of the sites are correct, shown in the trusted site zone, some of them not, they are in an unkown zone (mixed). I want to check the registry path Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\Domains but this key is empty, for HKLM and HKCU. What`s wrong?
Thanks and Regards Patrick
Are you deploying the trusted sites with Policies or registry preferences?
> comment below explaining why GPUpdate /force is required to undo your changes.
For Group Policy to apply efficiently changes trigger it.
Exceptions apply. GPUPDate force is one. Security too.
Less obtusely said: “Group Policy will normally only reprocess client side extensions that have at least one policy element that changed. The exceptions to this are Security Option settings which reapply every ~16 hours on most machines and every 5 minutes on Domain Controllers. The other exceptions are when you run a gpupdate /force, and any CSEs you configure to auto-reapply. You can view this decision tree by enabling UserEnv logging as described in http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc775423%28v=ws.10%29.aspx ” … But not as haiku.
Hi, Is it possible to select the users you want that this GPO applies? It is because I need to add a web to trusted sites, but only to two users. Any idea?
You would need to configure these settings under user configuration. Then change the scope of the GPO from authenticated users to a group containing those two users.
With regards to deploying trusted sites via GPO, while allowing users to add their own entries, see if this post helps: http://community.spiceworks.com/topic/post/2849140
I’m finding that when I deploy Trusted Sites using GPP and the registry, users aren’t able to add entries themselves (it allows them to add to the list, but the entries don’t stick and are gone as soon as you reopen the dialog). Any ideas?
You sir, have a good last name! 🙂
Do you have any delete preferences configured to that registry key? If you manually browse to that key, do you see what the user added?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
- Security Essentials
- Deploying Windows 10 (without touching a client)
- Group Policy – Preferences to Software and Everything In Between
- OneNote Can Centralize Your Documentation
- Lunch and Learn: PowerShell 3
- Lunch and Learn: Software Extraction
- Disclosure Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Rebuild the Administrative Start Menu
- Guest Posting
- What’s This? Q&A on Sponsored Posts
- Blogs that I Follow – 2018 Edition
- Books to Boost Your Career!
- Top Articles to Teach You Now!
- Top Gadgets to be more Productive!
- Software Tools
- Other – eBooks, Virtual labs, etc
- My Articles
- Clients and Desktops
- Group Policy
- Deployment/MDT
- About DeployHappiness
- February 2024
- October 2023
- January 2023
- October 2021
- November 2020
- October 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- November 2019
- October 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- October 2018
- August 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- October 2016
- September 2016
- August 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- August 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2014
- October 2014
- September 2014
- August 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- December 2013
- November 2013
- October 2013
- September 2013
- August 2013
- Group Policy (85)
- Best Practice (90)
- Hardware (9)
- Management (100)
- Networking (3)
- Office 365 (8)
- Performance (23)
- Quick Tip (26)
- PowerShell (87)
- Security (28)
- Server (16)
- Thinking about IT (14)
- Training (6)
- TroubleShooting (36)
- Uncategorized (29)
- Walkthrough (109)
- Entries (RSS)
- Comments (RSS)
techlauve.com – a knowledge base for IT professionals.
Inhale problems, exhale solutions..
- Nick’s Blog
- Active Directory
- Privacy Policy
« Outlook: “Sending and Receiving reported error (OX80040600)”
Terminal Server Does Not Accept Enough Client Connections »
Adding Sites to Internet Security Zones Using Group Policy
Sometimes it is useful to leverage the power of Group Policy in Active Directory to add sites to certain security zones in Internet Explorer. This can save the network admin the trouble of managing the security zone lists for each computer (or user) separately. In the following example, each user on the network needs to have a specific site added to the Trusted Sites list.
This tutorial assumes that group policy is in good working order on the domain and that all client users and computers can access the directory.
- Open the Group Policy Management MMC console.
- Right-click the organization unit (OU) that the policy should apply to, taking special care to consider whether the policy should apply to computers or users on this particular network.
- Select “Create and Link a GPO Here…” to create a new group policy object.
- In the “New GPO” window, enter a good, descriptive name for this new policy and click “OK”. (ex. “Trusted Sites Zone – Users” or something even more descriptive)
- Locate the newly created GPO in the left-side navigation pane, right-click it and select “Edit…”
- Expand “Administrative Templates” under either “Computer Configuration” or “User Configuration” depending on which type of OU the new policy was linked to in step 2.
- The path to the settings that this example will be using is: Administrative Templates -- Windows Components -- Internet Explorer -- Internet Control Panel -- Security Page
- In the right-hand pane, double-click “Site to Zone Assignment List”.
- Enable the policy and click the “Show…” button next to “Enter the zone assignments here.” This will pop up the “Show Contents” window.
- Click the “Add…” button. This will pop up the “Add Item” window.
- In the first box, labeled “Enter the name of the item to be added:”, enter the URL to the site. (ex. https://secure.ourimportantwebapp.com) . Keep in mind that wildcards can be used. (ex. https://*.ourimportantdomain.com) . Leave off any trailing slashes or sub-folders unless that type of specific control is called for.
- 1 – Intranet Zone
- 2 – Trusted Sites Zone
- 3 – Internet Zone
- 4 – Restricted Sites Zone
- Once the zone assignment has been entered, click “OK”. This will once again show the “Show Contents” window and the new entry should be present.
- Click “OK” and “OK” again to get back to the Group Policy Management Console.
The new policy will take effect at the next group policy refresh interval, which is usually 15 minutes. To test immediately, run a gpupdate /force on a user/computer that falls into the scope of the new policy and go to “Tools -> Internet Options -> Security -> Trusted Sites -> Sites”. The site(s) added should be in the list. If the sites do not show up, check the event logs for any group policy processing errors.
Related content:
- How To: Time Sync Across Windows Network
- Group Policy Not Applied To Remote VPN Users
- QuickBooks Payroll Opens/Saves the Wrong W2 Form
- Microsoft Virtual Server Web Console Constantly Asks For Password
- Group Policy: Applying Different User Policies to the Same User for Workstations and Terminal Server
No comment yet
Juicer breville says:.
November 26, 2012 at 12:11 am (UTC -5)
Hurrah, that’s what I was looking for, what a information! existing here at this web site, thanks admin of this web page.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
You may use these HTML tags and attributes: <a href="" title=""> <abbr title=""> <acronym title=""> <b> <blockquote cite=""> <cite> <code> <del datetime=""> <em> <i> <q cite=""> <s> <strike> <strong>
Submit Comment
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Remember Me
Connect With Us
Connect with us.
Social Connect by NewsPress
Not finding the answer that you're looking for? Need more help with a problem that is addressed in one of our articles?
techlauve.com is affiliated with Rent-A-Nerd, Inc. in New Orleans, LA.
- DFS Replication (1)
- Group Policy (1)
- Microsoft Exhange (3)
- Microsoft Outlook (11)
- Copiers (1)
- Multi Function Devices (1)
- Printers (2)
- Scanners (1)
- Blackberry (1)
- Firewalls (2)
- Wireless (2)
- Hard Drives (1)
- SAN Systems (1)
- Hyper-V (3)
- Virtual Server (1)
- WordPress (1)
- Security (7)
- QuickBooks (2)
- Quicken (1)
- Antivirus/Antimalware (4)
- Backup Exec (2)
- Internet Explorer (5)
- Microsoft SQL (1)
- Licensing (2)
- Steinberg Nuendo (1)
- Mac OS X (1)
- Server 2003 (12)
- Server 2008 (14)
- Small Business Server 2003 (7)
- Terminal Server (6)
- Updates (2)
- Windows 7 (9)
- Windows XP (11)
- Reviews (1)
- Rent-A-Nerd, Inc.
Except where otherwise noted, content on this site is licensed under a Creative Commons Licence .
Valid XHTML 1.0 Strict Valid CSS Level 2.1
techlauve.com - a knowledge base for IT professionals. uses Graphene theme by Syahir Hakim.

Disable Security Warning for Drives mapped to dfs servers
[email protected]
Bernd Köster
Anthony [MVP]
< [email protected] > wrote in message news:[email protected]...
> > Bernd K�ster
< [email protected] > wrote in message news:[email protected]...
[email protected] Svante Johnson
[email protected]
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Troubleshoot "Internet Explorer Zonemapping" failures when processing Group Policy
- 4 contributors
When you execute GPUpdate /force , you may see the following output:
When you run GPRESULT /H GPReport.html and examine the report, you see the following information under Component Status :
The System event log contains an event ID 1085 that indicates a Group Policy processing error related to "Internet Explorer ZoneMapping," like the following one:
This event can occur if you enter an invalid entry within the Site To Zone Assignment List policy in the following paths:
Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Internet Explorer\Internet Control Panel\Security Page
User Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Internet Explorer\Internet Control Panel\Security Page
The "Site To Zone Assignment List" policy
The format of the Site To Zone Assignment List policy is described within the policy. This policy setting allows you to manage a list of sites that you want to associate with a particular security zone. These zone numbers have associated security settings that apply to all sites in the zone.
Internet Explorer has four security zones, which are used by this policy setting to associate sites with zones. They're numbered 1 to 4 and defined in descending order of most to least trusted:
- Local Intranet zone
- Trusted Sites zone
- Internet zone
- Restricted Sites zone
The security settings can be set for each of these zones through other policy settings, and their default settings are:
- Trusted Sites zone (Low template)
- Intranet zone (Medium-Low template)
- Internet zone (Medium template)
- Restricted Sites zone (High template)
The Local Machine zone and its locked-down equivalent have special security settings that protect your local computer.
If you enable this policy setting, you can enter a list of sites and their related zone numbers. The association of a site with a zone ensures that the security settings for the specified zone are applied to that site. For each entry that you add to the list, enter the following information:
Valuename : It's used to specify a host for an intranet site, or a fully qualified domain name for other sites. The valuename may also include a specific protocol. For example, if you enter https://www.contoso.com as the valuename , other protocols aren't affected. If you just enter www.contoso.com , all protocols for that site are affected, including http, https, ftp, and so on. The site may also be expressed as an IP address (such as 127.0.0.1) or a range (such as 127.0.0.1-10). To avoid creating conflicting policies, don't include other characters after the domain, such as a trailing slash or URL path. For example, the policy settings for www.contoso.com and www.contoso.com/mail would be treated as the same policy setting by Internet Explorer, and therefore, conflict.
Value : It's the number of the zone you want to associate the site with security settings. The Value of the above Internet Explorer zones is 1 to 4 .
When you enter data in the Group Policy Editor, there's no syntax or logical error checking available. This error checking is performed on the client when the Internet Explorer Zonemapping Group Policy Extension converts the registry into the format used by Internet Explorer. During that conversion, the same methods are implemented when you manually add a site to a specific security zone. If an entry is rejected when you add it manually, the conversion also fails if the Group Policy is used and the event 1085 is issued. For example, when you try to add a wildcard entry to a top-level domain (TLD) (like *.com or *.co.uk ) while adding a site, the wildcard entry is rejected. Now, the question is, which entries are treated as TLDs; by default, the following schemes are treated as TLDs in Internet Explorer:
- Flat domains (such as .com ).
- Two-letter domains in a two-letter TLD (such as .co.uk ).
The following blog post includes a granular explanation of domains:
Understanding Domain Names in Internet Explorer
To identify incorrect entries in the policy, download and run the IEDigest tool. After creating a report and opening it in your web browser, you'll see a Warnings section where incorrect entries are named. These entries need to be removed (or corrected) in the Group Policy. Here's an example of how it looks like when trying to add *.com to a zone:
Warnings Description Key Name Value Invalid entry in Site to Zone Assignment List. Click here for more info HKCU\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMapKey *.com is invalid
More information
- Intranet site is identified as an Internet site when you use an FQDN or an IP address
- Security Zones in Microsoft Edge
Third-party contact disclaimer
Microsoft provides third-party contact information to help you find additional information about this topic. This contact information may change without notice. Microsoft does not guarantee the accuracy of third-party contact information.
Was this page helpful?
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback .
Submit and view feedback for
Additional resources

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Value = 1 (Intranet zone) Intranet Zone. Show security warning for potentially unsafe files > Enabled > Enable. If you enable this policy setting and set the drop-down box to Enable, these files open without a security warning. If you set the drop-down box to Prompt, a security warning appears before the files open. Share.
In Internet Explorer: Tools menu → Internet Options → Security tab. Click Local Intranet icon to select it. Click Sites. Check Automatically detect intranet network. Click Advanced. In the Add this website to the zone: text box type file://computername or IP (in your case file://path ). Click Add.
Site to Zone Assignment List and Intranet Sites: Include all network paths (UNCs) It should look something like this: Value - A number indicating the zone with which this site should be associated for security settings. The Internet Explorer zones described above are 1-4. You should see the final result here: Possible malfunction
Modify the Site to Zone Assignment List policy: Double-click on the "Site to Zone Assignment List" policy to edit it. Enable the policy and add the network drive as a trusted site: Select the "Enabled" option and click the "Show..." button. In the "Value name" field, enter the UNC path of the Azure file share (e.g., file://server/share).
Open Group Policy Management Console. Navigate to the desired GPO or create a new one. Expand User Configuration or Computer Configuration and go to Preferences -> Windows Settings -> Registry. Right-click and select New -> Registry Item. Configure the Registry Item to delete the specified entries under the ZoneMap registry key.
Policies Administrative Templates Windows Components Internet Explorer Internet Control Panel Security Page Site to Zone Assignment List Here, I've added host1.mydomain.org and host2.mydomain.org to zone 1 (intranet), and the network shares from these hosts are correctly treated as trusted intranet sites.
Open the Security tab. Click Local intranet. Click the Sites button. Type your server name in the field Add this website to the zone as shown below. Click Add when completed. The site will appear in the list formatted with the prefix 'file://'. Close the open settings window and try launching OpenInsight.
Click on the Security Zones and Content Ratings folder. Double-click on the Site to Zone Assignment List policy. Click the Enabled radio button. Click the Show button. In the Value name field, enter the server name in the following format: "file://servername" (replace "servername" with the actual name of the server).
To set trusted sites via GPO -Open the Group Policy Management Editor. -Go to User Configuration > Policies > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Internet Explorer > Internet Control Panel > Security Page. -Select the Site to Zone Assignment List. -Select Enabled and click Show to edit the list.
The object being Site to Zone Assignment List. group-policy; windows-domain; Share. Improve this question. Follow asked Aug 20, 2019 at 5:24. Alexander ... Microsoft Sync Center not working properly after UNC path referencing was changed via gpo. 4. Sharing a printer with GPO fails.
Partially valid entry - consist of protocol, host and path. The path will be transparently stripped, it will be applied for all paths on that host. *://www.microsoft.com. Valid entry - since the protocol is a wildcard, it is identical to specifyingwww.microsoft.com (without a protocol) *.mycorp.com
4) Right-click on Site to Zone Assignment List. 5) Enable the policy. 6) In the Options box click on Show… 7) In the Value name cell enter the UNC path of your file share. 8) In the Value cell next to the UNC path you just entered enter the value 1. (Where 1=Intranet/Local Zone, 2=Trusted Sites, 3=Internet/Public Zone, and 4=Restricted Sites).
To add your trusted sites to your local browser for less permanent access, follow this FAQ: EasySSO Browser Settings. To Create a new Group Policy Object. Click Start → Control Panel → Administrative Tools → Group Policy Management; Expand Forest: <domain> → Domains → <domain>
Then double click [Security Zones and Content Ratings], click [Import the current security zones and privacy settings], and then click [Modify Settings]. It should be pretty straight-forward from there. I added my file server sites into Local Intranet, using the form file://uncserver. I found this easy than the "Site to Zone Assignment List ...
Steps performed: 1- Configuration Profiles --> Site to Zone Assignment List completed (\Windows Components\Internet Explorer\Internet Control Panel\Security Page) --> no changes in sites under Internet options-> Trusted sites, still shows the old ones. 2- Security Baseline, IE (users adding sites / changing policies set to "NOT Configured" ).
Site to Zone Assignment List. This policy setting allows you to manage a list of sites that you want to associate with a particular security zone. These zone numbers have associated security settings that apply to all of the sites in the zone.Internet Explorer has 4 security zones numbered 1-4 and these are used by this policy setting to ...
Deploy a set of trusted sites overriding users' ability to add trusted sites themselves. To acheive this, an Intune configuration profile Trusted site zone assignment can be deployed to devices/users group as required. Login to Intune Portal and navigate to: Devices > Windows > Configuration Profiles. Hit the Create button and Select New ...
Users can use the Internet Control Panel to assign specific sites to Zones and to configure the permission results for each zone. In managed environments, administrators can use Group Policy to assign specific sites to Zones (via "Site to Zone Assignment List" policy) and specify the settings for URLActions on a per-zone basis.
When possible, use the computer configuration option as it will not impact user logons. When you enable the setting, you will be prompted for a value name (the website) and a value (the zone list). Here are the possible values and the zone that they correspond to: 1 = Intranet/Local Zone. 2 = Trusted Sites. 3 = Internet/Public Zone.
The path to the settings that this example will be using is: Administrative Templates -- Windows Components -- Internet Explorer -- Internet Control Panel -- Security Page; In the right-hand pane, double-click "Site to Zone Assignment List". Enable the policy and click the "Show…" button next to "Enter the zone assignments here."
The file://server is set. This is set to the dfs path. I have no problem starting an executable using the unc path \\domain\dfs\path\sub\executable.exe. Now I use: net use /persistent:yes Z: \\domain\dfs\path. Starting the Z:\sub.executable from the windows explorer throw the security warning. The automatic detection of the intranet is turned off.
The "Site To Zone Assignment List" policy. The format of the Site To Zone Assignment List policy is described within the policy. This policy setting allows you to manage a list of sites that you want to associate with a particular security zone. These zone numbers have associated security settings that apply to all sites in the zone.
the Internet Explorer Trusted Sites security zone. 1) A local file system, such as e:\ 2) A network share that is accessed by a drive letter, such as when mapped to z:\ through net use z: \\server\sharename I see that the Trusted Sites list can take a URL that includes the directive file:\\ directive. References such as this one work: