Have a language expert improve your writing
Check your paper for plagiarism in 10 minutes, generate your apa citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Using AI tools
- What Is an Algorithm? | Definition & Examples

What Is an Algorithm? | Definition & Examples
Published on August 9, 2023 by Kassiani Nikolopoulou . Revised on August 29, 2023.
An algorithm is a set of steps for accomplishing a task or solving a problem. Typically, algorithms are executed by computers, but we also rely on algorithms in our daily lives. Each time we follow a particular step-by-step process, like making coffee in the morning or tying our shoelaces, we are in fact following an algorithm.
In the context of computer science , an algorithm is a mathematical process for solving a problem using a finite number of steps. Algorithms are a key component of any computer program and are the driving force behind various systems and applications, such as navigation systems, search engines, and music streaming services.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is an algorithm, how do algorithms work, examples of algorithms, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about algorithms.
An algorithm is a sequence of instructions that a computer must perform to solve a well-defined problem. It essentially defines what the computer needs to do and how to do it. Algorithms can instruct a computer how to perform a calculation, process data, or make a decision.
The best way to understand an algorithm is to think of it as a recipe that guides you through a series of well-defined actions to achieve a specific goal. Just like a recipe produces a replicable result, algorithms ensure consistent and reliable outcomes for a wide range of tasks in the digital realm.
And just like there are numerous ways to make, for example, chocolate chip cookies by following different steps or using slightly different ingredients, different algorithms can be designed to solve the same problem, with each taking a distinct approach but achieving the same result.
Algorithms are virtually everywhere around us. Examples include the following:
- Search engines rely on algorithms to find and present relevant results as quickly as possible
- Social media platforms use algorithms to prioritize the content that we see in our feeds, taking into account factors like our past behavior, the popularity of posts, and relevance.
- With the help of algorithms, navigation apps determine the most efficient route for us to reach our destination.
- It must be correct . In other words, it should take a given problem and provide the right answer or result, even if it stops working due to an error.
- It must consist of clear, practical steps that can be completed in a limited time, whether by a person or the machine that must execute the algorithm. For example, the instructions in a cookie recipe might be considered sufficiently concrete for a human cook, but they would not be specific enough for programming an automated cookie-making machine.
- There should be no confusion about which step comes next , even if choices must be made (e.g., when using “if” statements).
- It must have a set number of steps (not an infinite number) that can be managed using loops (statements describing repeated actions or iterations).
- It must eventually reach an endpoint and not get stuck in a never-ending loop.
Check for common mistakes
Use the best grammar checker available to check for common mistakes in your text.
Fix mistakes for free
Algorithms use a set of initial data or input , process it through a series of logical steps or rules, and produce the output (i.e., the outcome, decision, or result).
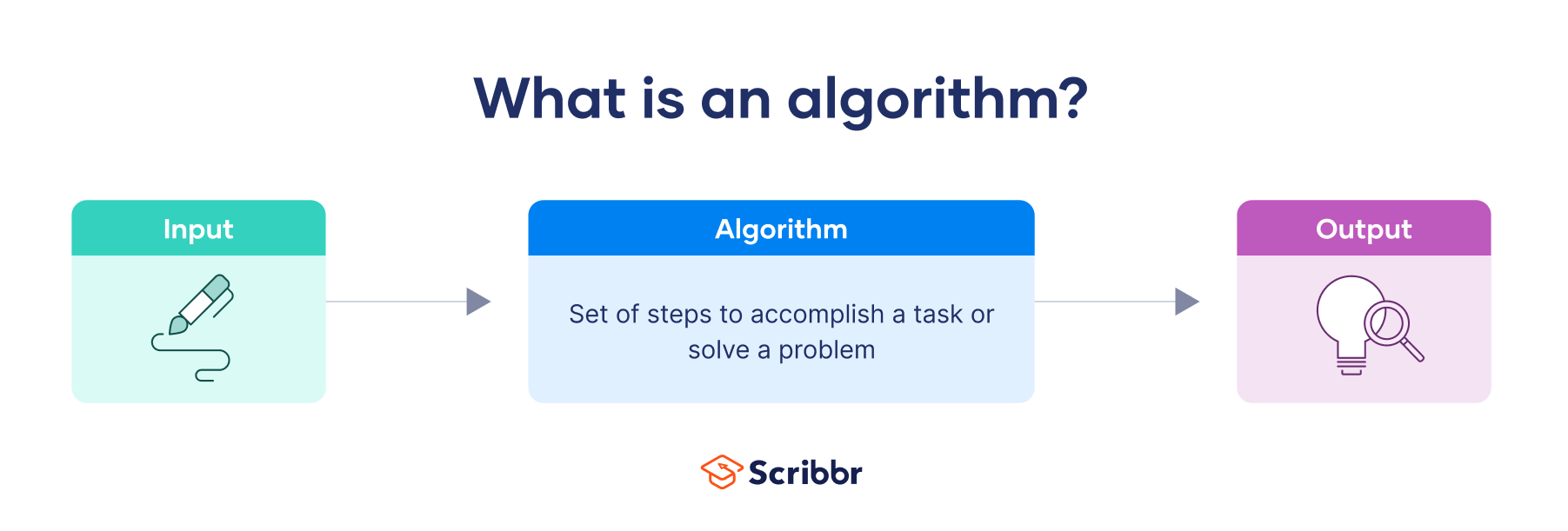
If you want to make chocolate chip cookies, for instance, the input would be the ingredients and quantities, the process would be the recipe you choose to follow, and the output would be the cookies.
Algorithms are eventually expressed in a programming language that a computer can process. However, when an algorithm is being created, it will be people, not a computer, who will need to understand it. For this reason, as a first step, algorithms are written as plain instructions.
- Input: the input data is a single-digit number (e.g., 5).
- Transformation/processing: the algorithm takes the input (number 5) and performs the specific operation (i.e., multiplies the number by itself).
- Output: the result of the calculation is the square of the input number, which, in this case, would be 25 (since 5 * 5 = 25).
We could express this as an algorithm in the following way:
Algorithm: Calculate the square of a number
- Input the number (N) whose square you want to find.
- Multiply the number (N) by itself.
- Store the result of the multiplication in a variable (result).
- Output the value of the variable (result), which represents the square of the input number.
It is important to keep in mind that an algorithm is not the same as a program or code. It is the logic or plan for solving a problem represented as a simple step-by-step description. Code is the implementation of the algorithm in a specific programming language (like C++ or Python), while a program is an implementation of code that instructs a computer on how to execute an algorithm and perform a task.
Instead of telling a computer exactly what to do, some algorithms allow computers to learn on their own and improve their performance on a specific task. These machine learning algorithms use data to identify patterns and make predictions or conduct data mining to uncover hidden insights in data that can inform business decisions.
Broadly speaking, there are three different types of algorithms:
- Linear sequence algorithms follow a specific set or steps, one after the other. Just like following a recipe, each step depends on the success of the previous one.
- For example, in the context of a cookie recipe, you would include the step “if the dough is too sticky, you might need to refrigerate it.”
- For example, a looping algorithm could be used to handle the process of making multiple cookies from a single batch of dough. The algorithm would repeat a specific set of instructions to form and bake cookies until all the dough has been used.
Algorithms are fundamental tools for problem-solving in both the digital world and many real-life scenarios. Each time we try to solve a problem by breaking it down into smaller, manageable steps, we are in fact using algorithmic thinking.
- Identify which clothes are clean.
- Consider the weather forecast for the day.
- Consider the occasion for which you are getting dressed (e.g., work or school etc.).
- Consider personal preferences (e.g., style or which items match).
In mathematics, algorithms are standard methods for performing calculations or solving equations because they are efficient, reliable, and applicable to various situations.
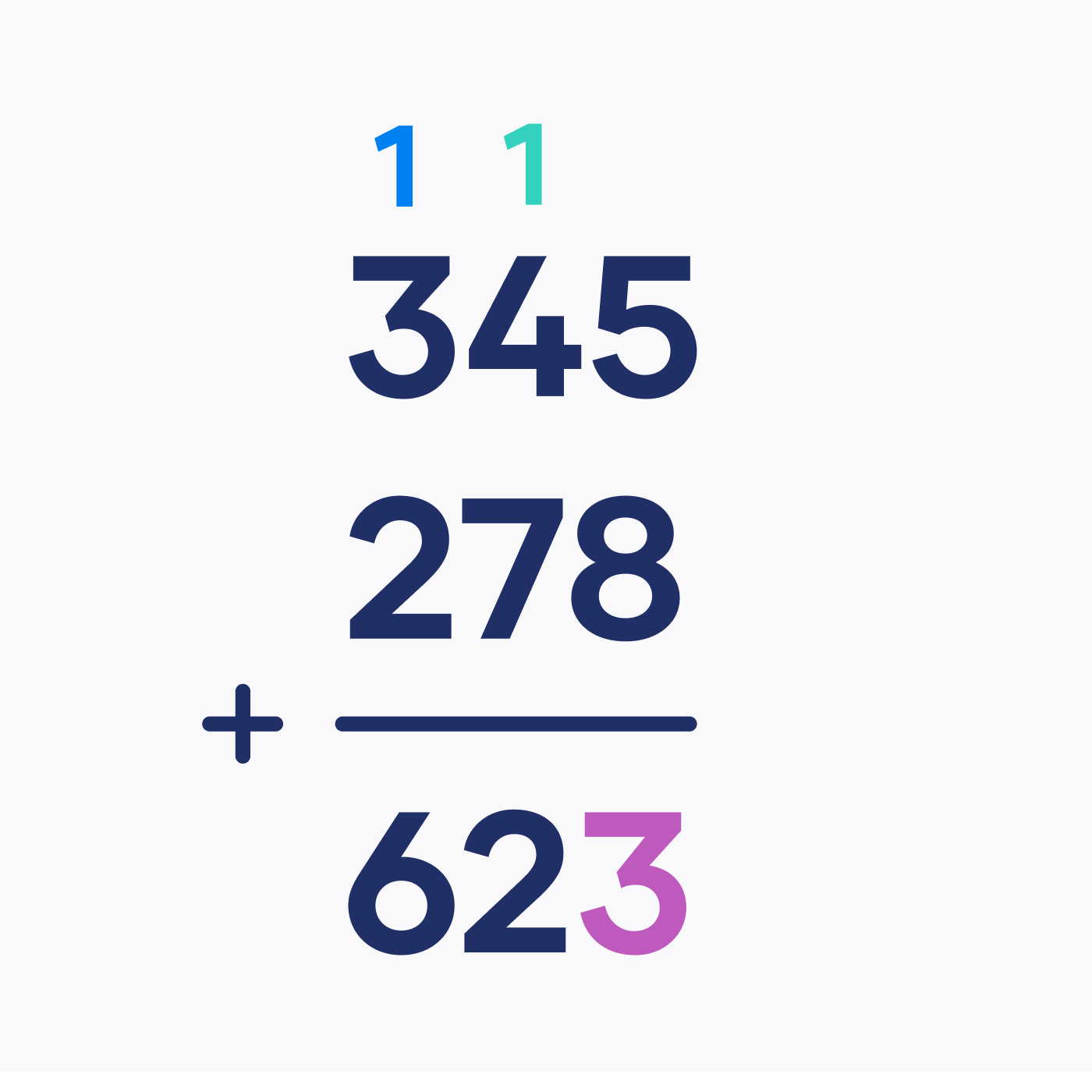
Suppose you want to add the numbers 345 and 278. You would follow a set of steps (i.e., the standard algorithm for addition):
- Write down the numbers so the digits align.
- Start from the rightmost digits (the ones place) and add them together: 5 + 8 = 13. Write down the 3 and carry over the 1 to the next column.
- Move to the next column (the tens place) and add the digits along with the carried-over value: 4 + 7 + 1 = 12. Write down the 2 and carry over the 1 to the next column.
- Move to the leftmost column (the hundreds place) and add the digits along with the carried-over value: 3 + 2 + 1 = 6. Write down the 6.
The final result is 623
Navigation systems are another example of the use of algorithms. Such systems use algorithms to help you find the easiest and fastest route to your destination while avoiding traffic jams and roadblocks.
If you want to know more about ChatGPT, AI tools , fallacies , and research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- ChatGPT vs human editor
- ChatGPT citations
- Is ChatGPT trustworthy?
- Using ChatGPT for your studies
- Sunk cost fallacy
- Straw man fallacy
- Slippery slope fallacy
- Red herring fallacy
- Ecological fallacy
- Logical fallacy
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Framing bias
- Cognitive bias
- Optimism bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Unconscious bias
In computer science, an algorithm is a list of unambiguous instructions that specify successive steps to solve a problem or perform a task. Algorithms help computers execute tasks like playing games or sorting a list of numbers. In other words, computers use algorithms to understand what to do and give you the result you need.
Algorithms and artificial intelligence (AI) are not the same, however they are closely related.
- Artificial intelligence is a broad term describing computer systems performing tasks usually associated with human intelligence like decision-making, pattern recognition, or learning from experience.
- Algorithms are the instructions that AI uses to carry out these tasks, therefore we could say that algorithms are the building blocks of AI—even though AI involves more advanced capabilities beyond just following instructions.
Algorithms and computer programs are sometimes used interchangeably, but they refer to two distinct but interrelated concepts.
- An algorithm is a step-by-step instruction for solving a problem that is precise yet general.
- Computer programs are specific implementations of an algorithm in a specific programming language. In other words, the algorithm is the high-level description of an idea, while the program is the actual implementation of that idea.
Algorithms are valuable to us because they:
- Form the basis of much of the technology we use in our daily lives, from mobile apps to search engines.
- Power innovations in various industries that augment our abilities (e.g., AI assistants or medical diagnosis).
- Help analyze large volumes of data, discover patterns and make informed decisions in a fast and efficient way, at a scale humans are simply not able to do.
- Automate processes. By streamlining tasks, algorithms increase efficiency, reduce errors, and save valuable time.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Nikolopoulou, K. (2023, August 29). What Is an Algorithm? | Definition & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 15, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/ai-tools/what-is-an-algorithm/
Is this article helpful?

Kassiani Nikolopoulou
Other students also liked, what is deep learning | a beginner's guide, what is data mining | definition & techniques, what is machine learning | a beginner's guide.

Kassiani Nikolopoulou (Scribbr Team)
Thanks for reading! Hope you found this article helpful. If anything is still unclear, or if you didn’t find what you were looking for here, leave a comment and we’ll see if we can help.
Still have questions?
"i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Browse Course Material
Course info, instructors.
- Prof. Erik Demaine
- Prof. Srini Devadas
- Prof. Nancy Lynch
Departments
- Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
- Mathematics
As Taught In
- Algorithms and Data Structures
- Computer Networks
- Cryptography
- Applied Mathematics
Learning Resource Types
Design and analysis of algorithms, class on design and analysis of algorithms, solutions to quiz 1.
This resource contains information regarding class on design and analysis of algorithms, solutions quiz 1.

You are leaving MIT OpenCourseWare

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Choose all that apply. A-It saves time. B-It reduces errors. C-It makes a company look modern. D-It frees up employee time for manual tasks. A-It saves time. B-It reduces errors. D-It frees up employee time for manual tasks. unit 4 Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free.
algorithm. The fundamental concept in computer science. pseudocode. An informal notation for representing algorithms. assignment statement. A means of saving the result of a computation for future use. if-else statement. A means of producing different actions depending on a condition. stepwise refinement.
a. The expression on the right is processed and the result is stored in the variable on the left. b. The variable's current value is overwritten by the newly assigned value. c. The assignment operator is a plus sign '+'. d. The assigned value must match the variable's data type. c. Correct.
Bake Set Pour Grease Spread. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like 1).List the four steps in Polya's How-To-Solve-It list., 2).Describe the four steps listed in Exercise 1 in your own words., 3).List the problem-solving strategies discussed in this chapter. and more.
There are three building blocks of algorithms: sequencing, selection, and iteration. Sequencing is the sequential execution of operations, selection is the decision to execute one operation versus another operation (like a fork in the road), and iteration is repeating the same operations a certain number of times or until something is true.
Level up on all the skills in this unit and collect up to 800 Mastery points! Learn to define algorithms, express them in flow chart and pseudocode, and assess their correctness and efficiency. See how algorithms can be used as shortcuts to solve problems that cannot be solved in a reasonable amount of time, and how this applies to undecidable ...
Quiz 1. Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. Khan Academy is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere.
Design and Analysis of Algorithms. Menu. More Info Syllabus Calendar Instructor Insights Meet the Educator Video Playlist Lecture Notes Lecture Videos ... assignment_turned_in Problem Sets with Solutions. grading Exams with Solutions. notes Lecture Notes. co_present Instructor Insights.
Hint: Recall the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra: A degree-d polynomial has (at most) d roots. [5 points] Design a randomized algorithm to check whether p(x) · q(x) = r(x) that is correct with probability at least 1 − ε. Analyze your algorithm in terms of n and 1/ε. Problem 6.
Quizzes with solutions for 6.006 Introduction to Algorithms. Browse Course Material Syllabus Calendar Lecture Videos Lecture Notes Quizzes ... assignment_turned_in Problem Sets with Solutions. grading Exams with Solutions. notes Lecture Notes. Download Course.
This resource contains information regarding class on design and analysis of algorithms, quiz 1. Resource Type: Exams. pdf. 214 kB Class on Design and Analysis of Algorithms, Quiz 1 Download File ... assignment_turned_in Problem Sets with Solutions. grading Exams with Solutions. notes Lecture Notes. co_present Instructor Insights.
Algorithm. [webster.com] A procedure for solving a mathematical problem (as of finding the greatest common divisor) in a finite number of steps that frequently involves repetition of an operation. [Knuth, TAOCP] An algorithm is a finite, definite, effective procedure, with some input and some output.
An algorithm is a sequence of instructions that a computer must perform to solve a well-defined problem. It essentially defines what the computer needs to do and how to do it. Algorithms can instruct a computer how to perform a calculation, process data, or make a decision. The best way to understand an algorithm is to think of it as a recipe ...
Answers. In your own words describe the 'knapsack problem'. Further, compare and contrast the use of a brute force. and a dynamic programming algorithm to solve this problem in terms of the advantage and disadvantages. of each. An analysis of the asymptotic complexity of each is required as part of this assignment.
In the balanced assignment problem, both parts of the bipartite graph have the same number of vertices, denoted by n. One of the first polynomial-time algorithms for balanced assignment was the Hungarian algorithm. It is a global algorithm - it is based on improving a matching along augmenting paths (alternating paths between unmatched vertices).
course link: https://www.coursera.org/learn/algorithms-on-strings?Full Specialization : https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLp6Cogm9IdcqhYnySZ6Lgnrgmm_UM9...
This video is for providing Quiz on Design and analysis of algorithmsThis video is for Education PurposeThis Course is provided by NPTEL - Online courses ...
This resource contains information regarding class on design and analysis of algorithms, solutions quiz 1. Browse Course Material Syllabus Calendar ... assignment_turned_in Problem Sets with Solutions. grading Exams with Solutions. notes Lecture Notes. co_present Instructor Insights.
Design a divide and conquer algorithm to find the k-th quantiles of a given set S of n numbers. You may assume that k is a. Here is a detailed explanation of a divide and conquer algorithm to find the k-th quantiles of a set of distinct real numbers: Explanation: Sort the set S in increasing order: To find the k-th
Question: Rearrange the following algorithm that uses only assignment statements to replace the triplet (x, y, z) with ly, Z, X). (You must provide an answer before moving to the next part.) Rank the options below. x=y No answer temp := x 1 y = 2 2 3 z:= temp 4 procedure interchange (x, y, z: real numbers) 5. Here's the best way to solve it.