
Criss Cross Classes || Notes
Our Content is Our Power
- Globalisation (CH-9) Notes in English || Class 12 Political Science Book 1 Chapter 9 in English ||
- Class 12 Notes
- Class 12 Political Science Notes in English


Chapter – 9
Globalization .
In this post, we have given the detailed notes of class 12 Political Science Chapter 9 (Globalisation) in English. These notes are useful for the students who are going to appear in class 12 board exams.
- 1. Chapter – 9
- 2.1.1. Reasons of globalization
- 2.2.1. Political consequences
- 2.2.2. Financial consequences
- 2.2.3. Cultural consequences
- 2.3.1. India’s New Economic Policy (1991)
- 2.4.1. Left-wing
- 2.4.2. Right-wing
- 3. More Important Links
What is Globalization?
Globalization is the flow of people, goods, ideas, and capital from one country to another..
- Transfer of ideas from one part to another
- Movement of goods from one country to another
- Transfer of capital from one country to another
- Movement of people from one country to another
Reasons of globalization
- Rapid growth of technology
- Variation in Level of Development
- Unequal availability of resources
- Cultural diversity
Consequences of globalization
Political consequences, positive impact.
- Governance reform
- Integration of Technology in Governance
- Qualitative increase in the functioning of the government
- Transparency
- Simplification of governance
Negative impact
- A welfare state is a state that works for the welfare of the people.
- The least interfering state is said to be that state which is limited only to the governance system and does not pay much attention to the welfare of the people.
- Less government intervention in industries
Financial consequences
Positive impact.
- Increase in the pace of development
- Fast reach to new technology
- High utilization of resources
- Growth in employment
- Growth in quality due to market competition
- Multinational companies are companies that operate business in many countries at the same time.
- The collapse of small industries
- Uneven development
- Difficult to do business due to increased competition
- Strict visa policy of developed countries
Cultural consequences
- Openness of thought
- Development of mixed culture
- Improvement in the status of women
- Change in eating and living habits
- A great influence of American culture
- Loss of the culture of small countries
- Development of one-sided culture
India and Globalization
- India was a British colony before independence.
- In that era, raw materials were taken from India and manufactured into products in Britain and sold back in India.
- After independence, India tried to end this dependence and decided that India would produce all those things in the country that it was importing from outside.
- This arrangement lasted till about 1991 and after that India adopted a new economic policy.
India’s New Economic Policy (1991)
Liberalization.
- Liberalization means simplifying the policies of doing business i.e. Eliminating licenses and other barriers.
Privatization
- Privatization means by promoting the private sector, that is, giving the private sector an opportunity to develop and remove the compulsion imposed on it.
Globalization
- The uninterrupted flow of people, goods, capital, and ideas from one country to another is called globalization.
After adopting this policy, there was an increase in the pace of development inside India and due to the simplification of rules, businesses became bigger.
Critique of Globalization
- Globalization has been criticized all over the world
- It has two sides
- Leftists are people who support the poor
- Leftists say that the condition of the poor has worsened due to globalization
- The government is running away from its responsibilities
- Simultaneously poor is getting poorer and poorer and rich is getting richer and richer
- Right-wing people who speak in favor of the rich.
- Right-wingers say that globalization is very necessary for rapid development and to bring the condition of equal development all over the world.
We hope that Class 12 Political Science Chapter 9 (Globalisation) notes in English helped you. If you have any queries about class 12 Political Science Chapter 9 (Globalisation) notes in English or about any other notes of class 12 political science in English, so you can comment below. We will reach you as soon as possible…
More Important Links
- Class 12 All Video Courses
- Class 12 All Important Notes
- Class 12 All Important Questions
- Class 12 All Important Quizzes
- Class 12 All Important Objective Questions
- Class 12 All Sample Papers
- Class 12 All Last Year Questions Papers
- Class 12 All PDF E-books
- Class 11 All Video Courses
- Class 11 All Important Notes
- Class 11 All Important Questions
- Class 11 All Important Quizzes
- Class 11 All Important Objective Questions
- Class 11 All Sample Papers
- Class 11 All Last Year Questions Papers
- Class 11 All PDF E-books
- Class 10 All Video Courses
- Class 10 All Important Notes
- Class 10 All Important Questions
- Class 10 All Important Quizzes
- Class 10 All Important Objective Questions
- Class 10 All Sample Papers
- Class 10 All Last Year Questions Papers
- Class 10 All PDF E-books
One thought on “ Globalisation (CH-9) Notes in English || Class 12 Political Science Book 1 Chapter 9 in English || ”
The notes are very helpful , but cultural heterogenisation and homogenization terms can be included
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
JOIN US on Telegram for Latest Updates

Recent Notes
- Change and Development in Industrial Society (Ch-5) Notes in English || Class 12 Sociology Book 2 Chapter 5 in English ||
- Change and Development in Rural Society (Ch-4) Notes in English || Class 12 Sociology Book 2 Chapter 4 in English ||
- The Story of Indian Democracy (Ch-3) Notes in English || Class 12 Sociology Book 2 Chapter 3 in English ||
- Cultural Change (Ch-2) Notes in English || Class 12 Sociology Book 2 Chapter 2 in English ||
- Structural Change (Ch-1) Notes in English || Class 12 Sociology Book 2 Chapter 1 in English ||
Important Notes
Other notes.
- Class 10 English Notes (32)
- Class 11 English Notes (21)
- Class 12 Economics Notes in English (1)
- Class 12 English Notes (29)
- Class 12 Geography Notes in English (15)
- Class 12 History Notes in English (15)
- Class 12 Political Science Notes in English (18)
- Class 12 Sociology Notes in English (14)
- Class 9 English Notes (31)
- Uncategorized (3)

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- ML Aggarwal Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- Important Info
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Sample Papers
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
Globalisation Class 12 Notes PDF (Handwritten & Short Notes)
If you have missed anything important during your regular lectures, you can benefit from Globalisation class 12 notes as it helps you to cover all the important topics in detail. It is advisable for all the students to go through these Political Science notes before exams. These notes have detailed explanations of all the topics and concepts which can help a student to score well in exams.
Subject matter experts of Selfstudys have created the Political Science Globalisation class 12 notes to help students understand the concepts and score well in exams. These notes can be downloaded easily from the Selfstudys website for free.
About Globalisation Class 12 Notes PDF
Students can have access to Globalisation class 12 notes PDF notes 24*7. These notes are available free of cost for all the students and are easy to download.
Globalisation class 12 notes can be a game changer for all the students who want to test their knowledge after completing their exam preparation and want to identify their strengths and weaknesses.
Topic Wise Globalisation Class 12 Notes PDF
The Political Science Globalisation class 12 notes PDF are created for each topic to give a clear understanding of the topic to the student and make it easier for them to find.
The notes of Globalisation class 12 can help a student increase their confidence, improve memory, boost their skills, and study for the examinations effectively.
Globalisation class 12 notes PDF also increase the adaptability and help them to adapt to new concepts more easily.
Learning from Globalisation Class 12 Political Science Notes PDF can help the student to develop the ability to analyze and evaluate information.
How to Download Globalisation Class 12 Notes PDF?
Below are the steps to download the notes of Globalisation class 12 in PDF Format:
Let’s discuss the steps to download Climate Class 11 Notes PDF Format:
- Go to the website selfstudys.com
- After going to the website, you need to click on NCERT Books and Solutions
- After clicking on the NCERT Books and Solutions, a sub category will open.
- Choose the NCERT Notes Menu, after clicking on that, a new page will appear and you can choose the subject and class to download Globalisation class 12 notes PDF Format.
What Are The Benefits of The Political Science Globalisation Class 12 Notes?
Below are the benefits of the notes of Globalisation class 12 Political Science:
- You will never miss any topic: The subject matter experts of Selfstudys have developed Globalisation class 12 notes PDF in a detailed manner to ensure that a student never misses any important topic while studying them.
- Increases attention: Globalisation class 12 notes are written in an easy to understand language which increases the attention of the student while studying. The students can study notes of Globalisation thoroughly to score well in the exam.
- Learning beyond the classroom: Another reason why a student should study Globalisation class 12 notes PDF is that a student can learn beyond the classroom which can promote healthy learning. Also, studying a concept repeatedly sticks it in a student’s memory.
- Condensed Information: Globalisation class 12 notes are written in condensed information to make it easier for the student to grasp all the concepts fast and easily.
- Improves Learning Capacity: Our highly qualified subject matter experts have created these notes to improve the learning capacity of the student and to help them score well in their exams.
- Organized Study Material: Globalisation class 12 notes PDF are systematically designed to make it easier for the student to study and score well in their exams.
- Easy to understand language: It can be very hard for the student to memorize a tricky or lengthy definition so in order to help them, selfstudys can help with Globalisation class 12 notes PDF which are written in easy language.
How to Do Exam Preparation From The Notes of Globalisation Class 12 Political Science?
Political science subject require an in-depth understanding of various topics. Below are the points to discuss how you can do exam preparation from the notes of Globalisation:
- Go through the syllabus thoroughly so you are aware of what you are studying
- Study from Globalisation class 12 notes. Highlight the important points and make your own notes.
- To understand the information in Globalisation class 12 notes, use the first reading and then to remember the information, use the subsequent readings to remember the information.
- Make mind maps and flashcards to easily remember and recall all the information for a longer period of time. It can make complicated topics easy to understand for the student. It also helps you make links between the ideas which can help you in creative thinking. Apart from this, using mind maps can be a great way to revise all the concepts.
- One of the most important points which every student should follow is that they should start studying Globalisation class 12 notes PDF at the last moment as it can make them stressed and anxious. They should always start exam preparation early to prepare well and score good marks in the examination.
- It is advisable for all the students to create a learning environment that helps them to study Globalisation class 12 notes well and also increase their efficiency. Political science is a subject which requires an in-depth understanding and effective learning. However, the learning technique is different for each student. Some students can do effective learning in a closed room without any disturbance. On the other hand, others find it helpful when they learn while listening to soft music.
Features of the Notes Of Globalisation Class 12?
Let’s have a look at the important features of the notes of Globalisation class 12:
- Detailed Explanations: The subject matter experts of Selfstudys have developed Globalisation class 12 notes in a detailed manner to ensure that a student never misses any important topic while studying them.
- Available in the PDF Format: Globalisation class 12 notes are also available in the PDF Format which can be easily downloaded in Mobile, Laptop, Tablet etc. and can be carried anywhere.
- Each and Every Topic is covered: It can also be ensured that a student will not miss any topic while doing exam preparation from these Notes as each and every course topic of political science is covered in Globalisation class 12 notes.
- Simpler Language: Our subject matter experts have created Globalisation class 12 notes in a simple language to make it easy to understand for students and to help them score well for their final exams.
- According to the latest syllabus: These notes of Globalisation class 12 are created as per the latest curriculum of CBSE to create a strong base for the students and also help them to score well in their examination.
- Explained through diagrams: Globalisation class 12 notes have topics that are explained through diagrams to help the student understand the concepts thoroughly which can help them to score well in exams.
Tips to Cover The Chapter Globalisation With The Help of Notes
Below are the tips to cover the chapter Globalisation with the help of notes which can help students to score well in their exams:
- Go through the topics and notes: To complete Globalisation class 12 notes, all the students are advised to go through the various topics and chapters. It can give an idea to all the students about the topics and concepts which they will read.
- Start studying: After going through the syllabus, a student should start studying from the notes of Globalisation class 12.
- Solving Doubts: By studying from Globalisation class 12 notes, a student can clear all their doubts. This helps to remove confusion in all the chapters.
- Diagrams are given : Diagrams are given in the notes of Globalisation class 12 to help you understand the topic thoroughly and helps you to remember it for a longer period of time.
- Best Revision Tool: Globalisation class 12 notes can be treated as the best revision tool for all the students as it helps them to identify their strengths and weaknesses and also makes them aware about the topic in which they are lacking.
- Practicing questions: After completing Globalisation class 12 notes, all the students need to practice various types of questions which can help them in improving their exam scores.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

One Last Step...

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

- Bihar Board
SRM University
Hpbose 12th result.
- HP Board Result 2024
- Punjab Board Result 2024
- JAC Board Result 2024
- WB Board Result 2024
- UK Board Result 2024
- Karnataka Board Result 2024
- Shiv Khera Special
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- नए भारत का नया उत्तर प्रदेश
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
- CBSE Class 12 Chapter Notes
Globalisation Class 12 Notes: CBSE 12th Political Science Chapter 7 Globalisation, Download PDF
Cbse class 12 globalisation notes: this article provides detailed notes for chapter 7: globalisation of the class 12 political science book ‘contemporary world politics’. the downloadable pdf of these notes is also available at the end of this article..

Latest Education News
Optical Illusion Eye Test: Find the hidden letter in 6 seconds!
UPSC CAPF Salary 2024: Check In-Hand Pay, Structure, Perks and Allowances
UBSE Result 2024 Live: Uttarakhand Board 10th, 12th Results Tomorrow at 11:30 AM, Check Online by Roll Number
HP Board 12th Result 2024: Check Improvement of Performance HPBOSE Class 12 Re-Evaluation/Re-Checking Details Here
TS SSC Results 2024 LIVE Updates: Manabadi BSE Telangana 10th Result Tomorrow at 11 AM, Check Website Link
RPF Constable Cut Off 2024: RPF Previous Year State-wise Cutoff Marks
GSSSB Clerk Cut Off 2024: Category-wise Expected Cut Off & Minimum Qualifying Marks
TS Board Results 2024: Check TS Intermediate Result Manabadi Link at tsbie.cgg.gov.in and Jagran Josh
Madras High Court Recruitment 2024: Apply Online for 2329 Vacancies at mhc.tn.gov.in
FMGE June 2024 Registration Begins Today: April 29, Check Steps To Apply, Exam Dates, Eligibility Criteria Here
TS SSC Result 2024: Telangana 10th SSC Result Date And Time at bse.telangana.gov.in
Jharkhand Board 12th Result 2024 Date and Time: जारी हुई जैक 12वीं रिजल्ट की तारीखें, यहाँ देखें परिणाम से जुड़ी सभी जरुरी बातें
Today’s School Assembly Headlines (30 April): ESCMID global congress 2024, VVPAT supreme court order, G7 Italy Presidency and Other News in English
UPSC CMS Previous Year Paper: PDF Download
Bihar D.El.Ed Expected Cut Off 2024: Category-wise Minimum Qualifying Marks
Satavahana University Result 2024 OUT at satavahana.ac.in: Download UG, PG Marksheet
HPBOSE 12th Result 2024 OUT: एसएमएस और डिजिलॉकर पर आज जारी होगी एचपी बोर्ड इंटर की मार्कशीट
UPSC Recruitment 2024: Apply Online for 69 Assistant Professor Vacancies
NEHU Result OUT on exams.nehu.ac.in, Download UG and PG Semester Result PDF
Illusion Personality Test: What You See First Reveals If You Are Strong or Weak
Globalization | Chapter 6 Notes
Globalization.
globlisation is the process of interaction and international integration among people, companies, and governments worldwide.
It is the interchange of world views, products, capital, ideas, commodities and people across different parts of the world.
Globalisation basically deals with flows of ideas moving from one part of the world to another and commodities being traded across borders and so on.
The key factor is the worldwide inter connectedness which is created and sustained as a result of these constant flows.
It is a multidimensional concept, which has political, economic and cultural aspects.
It is primarily an economic process of interaction and integration associated with social and cultural aspects.

Causes Of Globalisation
Globalization has accelerated since the 18th century due to advancement of transportation and communication technology, worldwide interconnectedness that is created and sustained.
This increase in global interactions causes growth in international trade and the exchange of ideas, beliefs, and culture.
Along with other causes technology affects more than anything else. The ability of ideas, capital, commodities and people to move from one part of the world to another is majorly due to technological advances.
Invention of printing, Integrated Chips (IC) , telephone, internet has revolutionised communication between people in different parts of the world.
Due to faster communication & transportation ideas, commodities and capital move more easily to any part of the globe than ever.
People recognise these mediums is the best to connect to rest of the world
Interconnections are also an important factor of globalisation. Any event that takes place in one part of the world could affect another part of the world.
However, disputes and diplomacy are also reasons for modern globalization.
Consequences of Globalisation
Globalisation has both positive & negative consequences for the people. It affects some societies and some part more than others
It has brought benefits in developed countries as well as negative effects.
The positive effects include a number of factors which are education, trade, technology, competition, investments and capital flows, employment, culture, and organization structure.
Positive consequences
Gives Access to a Larger Market
- Countries and companies have access to a bigger consumer base worldwide.
Promotes World Peace and Unity :
- It brings governments together so that they can tackle common goals together.
Better Quality and Variety :
- Due to competition from different countries companies make better quality and variety products.
Job opportunities :
- Multinational companies provide new jobs and skills worldwide
More foreign currency :
- MNC’s bring foreign currency to local economies when they buy local products and services. It leads to better economy of the country.
Vibrant culture :
- The mixing of people and cultures enables the sharing of ideas and lifestyles, creating vibrant cultural diversity.
Holiday destinations :
- People can go for holidays in any part of the world
Best choices for consumers
- Consumers enjoy a big choice of goods and services at cheaper prices.
Labour availability :
- Migration of people reduced skilled labour shortages.
Awareness :
- It helps make people more aware of global issues, such as covid pandemic and global warming, and able to work together to tackle these issues.
Helps government :
- It help governments to work together to tackle global issues such as a natural disaster.
Negative consequences
Limited approach :
- It operates mostly with the rich countries, who continue to dominate world trade.
Suppress local business :
- Multinational companies may drive local companies out of business
Hamper culture :
- It threatens the local traditions and languages and makes the whole world more fit the western model.
Uneven control :
- Some nations feel losing control over key decisions and sacrificing their sovereignty.
Negative impact of Migration
- Migration of people across the world may cause social tensions and conflict of ideologies.
India and Globalisation
Since colonial period (British rule), India was exporting primary goods and raw materials and importing finished goods.
After independence, India decided to be a self dependent country rather than being dependent on others. India started making things on their own on a large scale.
India reduces importing things from outside to enhance the domestic products and Indian industries.
This step generated some major problems. So, in spite of some advancements made in certain areas, sectors such as health, housing and primary education suffer a lot. They did not receive the proper attention they deserved.
As a result…
India had a slow rate of economic growth.
In 1991, responding to a financial crisis and to the desire for higher rates of economic growth, India began a much needed programme of economic reforms that opened doors for trade and FDI (Foreign Direct Investment).
Resistance to Globalisation
Globalisation has also invited strong criticism from all over the world. In 1999, at the World Trade Organisation (WTO) ministerial meeting, there were big protests at Seattle.
Some were alleging unfair trading practices by the economically powerful states. That makes the rich countries richer and the poor countries more poorer.
Culturally, they are also worried that their traditional culture will be harmed. People will lose their age-old values and ways.
Many anti-globalisation movements are not against the idea of globalisation, but they are opposed to a specific programme of globalisation, which they see as a form of imperialism.
It was state that the interests of the developing world were not given sufficient and required importance in the evolving global economic system.
The World Social Forum (WSF) is another global platform, which brings together human rights activists, environmentalists, labour, youth and women activists opposed to neo-liberal globalisation.
India and Resistance to Globalisation
Resistance to globalisation in India has come from political parties as well as through Indian Social Forum.
Trade unions of industrial workers as well as those representing farmer interests have started protesting against the entry of multinationals.
The patenting of certain plants like Neem by American and European firms has also generated considerable opposition
Resistance to globalisation has also come from the political right. This has taken the forum to object particularly to various cultural influences.
Keywords To Remember
- Globalisation : It is the integration of an economy with the economies of other countries under the process of free flow of trade and capital.
- World Social Forum : A global platform which brings together a wide coalition of human rights activists, environmentalists and women activists.
- Privatisation : It allows many private sector companies to produce goods and services in a country.
- Liberalisation : It signifies relaxation of government rules and regulations relating to activities in the industrial sector.
- Cultural heterogenization : It signifies cultural differences generated by globalisation.
You have covered a detailed explanation of Globalization. We hope that above mentioned notes of globalisation of world will definitely help you to get pretty good marks in your exam.
Other Chapter Notes
- Class 12 Political Science Syllabus
- Chapter 1: Cold War Era and Non aligned Movement
- C hapter 2: The End of Bipolarity
- C hapter 3: New Centre Of Power
- C hapter 4: South Asia and The Contemporary World
- C hapter 5: United Nation And Its Organisations
- Capter 6: present
- C hapter 7: Challenge Of Nation Building
- C hapter 8: Planned Development
- Chapter 9: India’s Foreign Policy
- C hapter 10: Parties And The Party Systems In India
- C hapter 11: Democratic Resurgence
- C hapter 12: Indian Politics: Trends And Developments
MCQ & Syllabus Notes

Political Science
- Solved Papers
Frequently Asked Questions
What is globalization.
Answer: Globlisation is the process of interaction and international integration among people, companies, and governments worldwide.
What are the causes of ?
Answer: Globalization has accelerated since the 18th century due to advancement of transportation and communication technology, worldwide interconnectedness that is created and sustained
What are the effects of globalisation?
Answer: The positive effects include a number of factors which are education, trade, technology, competition, investments and capital flows, employment, culture, and organization structure.
Globalization Unit 6 CBSE, class 12 Political science notes. This cbse Political Science class 12 notes has a brief explanation of every topic that NCERT syllabus has. You will also get ncert solutions, cbse class 12 Political Science sample paper, cbse Political Science class 12 previous year paper.
Final Words
From the above article you must have learnt about ncert cbse class 12 Political Science notes of unit 6 Globalization. We hope that this crisp and latest Political Science class 12 notes will definitely help you in your exam.
CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free
Case Study Chapter 9 Globalisation
Students can read the Case Study questions given below for Globalisation Class 12 Political Science. All Globalisation Class 12 Notes and questions with solutions have been prepared based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. You should read all Case Study Questions provided by us and the Class 12 Political Science Case Study Questions provided for all chapters to get better marks in examinations.
Case Study Questions of Globalisation Class 12
There are certain organisations which are set up for providing services to its members and the public in general. Such organisations are called Not for Profit Organisation. Eg: Clubs, charitable institutions, schools, welfare societies etc.
Question. Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows: While everything may not be known about the economic facets of globalisation, this particular dimension shapes a large part of the content and direction of contemporary debates surrounding globalisation. A part of the problem has to do with defining economic globalisation itself. The mention of economic globalisation draws our attention immediately to the role of international institutions like the IMF and the WTO and the role they play in determining economic policies across the world. Yet, globalisation must not be viewed in such narrow terms. Economic globalisation involves many actors other than these international institutions. A much broader way of understanding of economic globalisation requires us to look at the distribution of economic gains, i.e. who gets the most from globalisation and who gets less, indeed who loses from it. What is often called economic globalisation usually involves greater economic flows among different countries of the world. Some of this is voluntary and some forced by international institutions and powerful countries. As we saw in the examples at the beginning of this chapter, this flow or exchange can take various forms: commodities, capital, people and ideas. Globalisation has involved greater trade in commodities across the globe; the restrictions imposed by different countries on allowing the imports of other countries have been reduced. Similarly, the restrictions on movement of capital across countries have also been reduced. In operational terms, it means that investors in the rich countries can invest their money in countries other than their own, including developing countries, where they might get better returns.
Question. Where does economic globalisation draw our attention to? (A) Declining economy (B) Poverty in the third world countries (C) To the role of international institutions like the IMF and the WTO (D) All of the above
Question. According to broader way of looking at globalisation, what should we focus on? (A) The distribution of economic gains (B) Increasing poverty in third world countries (C) Unemployment in economic sectors (D) Increasing population of the world
Question. In terms of trade, what is the impact of globalisation? (A) Countries are divided in groups and trading with their groups only. (B) Developing countries are not given importance in trade. (C) Any country can receive the opportunity of trading with the other countries. (D) None of the above
Question. How globalisation should not be viewed? (A) in broader terms (B) in narrow terms (C) positively (D) None of the above
Question. Study the cartoon carefully and give the answers to the question that follows:
Question. How did globalization help in the medical field? (A) Exports of medicines increased. (B) Helped in finding effective and speedy cure for the diseases with the collaboration of the medical facilities and knowledge of many countries. (C) Inviting foreign doctors and creating employment opportunities in the various countries. (D) All of the above
Question. Why is Africa featured in the above picture? (A) Because it is the centre of globalization. (B) The diseases mentioned in the picture have their epicentre in Africa. (C) Because Africa is a poor country. (D) Because world aims at developing Africa.
Question. Who identified the four basic aspects of globalization? (A) IMF (B) UN (C) EU (D) World Bank
Question. What is depicted in the picture? (A) Spread of nuclear weapons (B) Spread of various diseases (C) Attacks by using biological weapons (D) None of the above
Question Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows: The most visible impacts of globalization are definitely the ones affecting the economic world. Globalization has led to a sharp increase in trade and economic exchanges, but also to a multiplication of financial exchanges. In the 1970s world economies opened up and the development of free trade policies accelerated the globalization phenomenon. Between 1950 and 2010, world exports increased 33-fold. This significantly contributed to increasing the interactions between different regions of the world. This acceleration of economic exchanges has led to strong global economic growth. It fostered as well a rapid global industrial development that allowed the rapid development of many of the technologies and commodities we have available nowadays. Knowledge became easily shared and international cooperation among the brightest minds speeded things up. According to some analysts, globalization has also contributed to improving global economic conditions, creating much economic wealth. At the same time, finance also became globalized. From the 1980s, driven by neo- liberal policies, the world of finance gradually opened. Many states, particularly the US under Ronald Reagan and the UK under Margaret Thatcher introduced the famous “3D Policy”: Disintermediation, Decommissioning, and Deregulation.
Question. What is the impact of increase in the economic exchanges between the countries of the world? (A) Strong global economic growth (B) Sharp decline in the trade (C) Decline in the unemployment numbers (D) Increase in the index of poverty and hunger index
Question. We can see “a sharp increase” due to globalisation in ………………………….. ? (A) employment and capital (B) trade and economic exchanges (C) poverty and hunger (D) All of the above
Question. In between which years the world’s export has increased 33-fold? (A) 1970-1980 (B) 1950-1990 (C) 1950-2000 (D) 1950-2010
Question. After the 1980s, which policy was introduced by US and UK? (A) 4D Policy (B) 3D Policy (C) Fair Trade Policy (D) None of the above
Question. Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows: At the most simple level, globalisation results in an erosion of state capacity, that is, the ability of government to do what they do. All over the world, the old ‘welfare state’ is now giving way to a more minimalist state that performs certain core functions such as the maintenance of law and order and the security of its citizens. However, it ithdraws from many of its earlier welfare functions directed at economic and social wellbeing. In place of the welfare state, it is the market that becomes the prime determinant of economic and social priorities. The entry and the increased role of multinational companies all over the world leads to a reduction in the capacity of governments to take decisions on their own. What is important is for people in different parts of the world to recognise these interconnections with the rest of the world. Currently, we are aware of the fact that events taking place in one part of the world could have an impact on another part of the world. The Bird flu or tsunami is not confined to any particular nation. It does not respect national boundaries. Similarly, when major economic events take place, their impact is felt outside their immediate local, national or regional environment at the global level.
Question. The increase in the MNCs all over the world has resulted in ………………….. . (A) the governments’ inability to cater to their needs. (B) the capacity of the nations to incorporate these MNCs. (C) poverty to the population where these companies are set up. (D) reduction in the capacity of governments to take decisions on their own.
Question. At the most simple level, globalisation results in an erosion of ……………………. . (A) political capacity (B) state capacity (C) capital capacity (D) global capacity
Question. What do the new states withdraw as a result of globalisation? (A) Many of its ethics for the welfare of human race (B) The ideal world order (C) Many of its earlier welfare functions directed at economic and social well-being. (D) All of the above
Question. What is given way recently by the old “Welfare state”? (A) More minimalist state (B) More capitalist state (C) More socialist state (D) More democratic state

Related Posts
Data handling using pandas – i class 12 informatics practices important questions.

Understanding Partition Class 12 History Important Questions

Principles of Inheritance and Variation Class 12 Biology Important Questions

NCERT Solutions for Class 12: Ch 9 Globalisation Political Science
Contact form.
NCERT Notes for Class 12 Political Science Chapter 9 Globalisation
Class 12 political science chapter 9 globalisation.
NCERT Notes for Class 12 Political Science Chapter 9 Globalisation , (Political Science) exam are Students are taught thru NCERT books in some of the state board and CBSE Schools. As the chapter involves an end, there is an exercise provided to assist students to prepare for evaluation. Students need to clear up those exercises very well because the questions inside the very last asked from those.
Sometimes, students get stuck inside the exercises and are not able to clear up all of the questions. To assist students, solve all of the questions, and maintain their studies without a doubt, we have provided step-by-step NCERT Notes for the students for all classes. These answers will similarly help students in scoring better marks with the assist of properly illustrated Notes as a way to similarly assist the students and answer the questions right
The Concept of Globalisation
- Globalisation is the flows of ideas, capital, commodities and people from one part of the world to another part.
- Technological advancement in transport and communication is one of the major factories behind the globalisation.
- Globalisation is a multi-dimensional concept. It has Political, economic and cultural dimensions.
Causes of Globalisation
- Developments in technology.
- Neo Colonialism.
- New Liberal Capitalism.
- Quick and Wide movement of capital and commodities.
- The growth of electronic media.
- Liberalisation
- Privatization
- Commercialization
- Free Markets
Consequences of Globalization
- It has brought about radical changes in all walks of life.
- It produced both positive and negative consequences.
Political consequences
- Increased role of multinational companies reduced the capacity of govts.
- Role of the govts is limited to the maintenance of Law and Order and the security of the people.
- Role of the state is important.
- Essential functions are done by the state.
- Rivalry between the states still exist.
- Modern technology is helpful for the states to collect more information about their citizens.
Economic consequences
- The economic flows between different Countries of the world, in the various forms such as commodities, capital, People and ideas.
- Globalisation involves greater trade across the world.
- Restrictions or imports or trade barriers among the countries have been reduced.
- Spread of internet also fasterned globalisation process.
- The rich countries have gained and the poor countries have lost from globalization.
- Globalization has ruined the agricultural sector.
- It advocated anti-labour agendas like destruction of the organised power of the workers, ending of permanent appointments, the denial of the right to strike.
- It led to the ruin of the native industries and retail outlets.
- It destroyed the economy of the third World countries.
3. Cultural Consequences
- Globalisation leads to Uniform Culture or cultural Homogenisation.
- Uniform culture is not a global culture but it is the imposition of Western culture.
- It poses a threat to the cultures of the world.
- It shapes our thoughts and desires.
- It decides what we eat, drink, wear and think.
Resistance/ Criticisms against Globalisation
- It makes the rich richer and the poor poorer.
- Western domination.
- Weakening of the state.
- Crisis in small scale industries.
- Poor farmers are the true victims of Globalisation.
- Traditional culture is harmed.
- The World Social Forum (WSF) is giving leadership to the anti-globalisation, The European Forum stands against globalisation.
- The anti-globalisation forces in Asia formed Asian Social Forum.
India and Globalisation
- During colonial period, India was compelled to be an exporter of primary goods and a consumer of finished goods. It shattered Indian economy.
- After Independence, India decided to adopt Protectionism.
- Import of goods was restricted to protect Indian economy.
- Protectionism caused sluggish economic growth in India.
- India adopted new economic Policy to respond the financial crisis.
- New eonomic Policy includes Liberalisation, Privatisation and Globalisation.
India and Resistance to Globalization
- The strong protest against the economic globalisation in India came from the Leftist Parties.
- Industrial Workers’ and farmers’ unions organized protests against the entry of multinational companies into India.
- The Rightists thinkers raised their voice against the cultural Globalisation. They were against various cultural influences like the availability of foreign T.V channels, Celebration of Valentine’s day, Westernization of dress etc.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Privacy Policy

Globalisation Class 12 Notes, Class 12 political science chapter 9 notes
Class 12 political science chapter 9 notes: globalisation class 12 notes.
Globalisation Class 12 Notes, Class 12 political science chapter 9 notes here we will be learn about Globalisation: Meaning, Manifestation and Debates etc.
What is Globalisation ?
🔹 Globalisation as a concept fundamentally deals with flows. These flows could be of various kinds , ideas , capital commodities and people. The crucial element is the worldwide interconnectedness that is created and sustained as a consequence of these constant flows.
🔹 Globalisation is a multidimentional concept ; it has political , economic and cultural manifestations and these must be adequately distingu sghed ; it is wrong to assume that globalisation has purely economic dimensions just as it would also be mistaken to assume that it is a purely cultural phenome non.
Examples of Globalisation : –
🔹 If we look for examples of the use of the term ‘globalisation’ in real life, we will realise that it is used in various contexts. Let us look at some examples : –
- Availability of various foreign goods in India.
- Provide various new career opportunities for youth.
- To provide services by an Indian according to the American calendar and time.
- Some farmers committed suicide because their crops failed. They had bought very expensive seeds supplied by a multinational company (MNC).
- An Indian company bought a major rival company based in Europe, despite protests by some of the current owners.
- Many retail shopkeepers fear that they would lose their livelihoods if some major international companies open retail chains in the country.
- A film producer in Mumbai was accused of lifting the story of his film from another film made in Hollywood.
- A militant group issued a statement threatening college girls who wear western clothes.
🔹 These examples show us that globalisation need not always be positive; it can have negative consequences for the people.
Cause of Globalisation : –
🔹 Technology and economic interdependence are important causes of globalisation due to which world has become a Global Village today.
🔹 Telegraph , telephone , microchip , internet has revolutionised communication between different parts of the world in more recent times.
🔹 The events that are taking place in one part of the world could have an impact on another part of the world. The bird flu or Tusanami or covid – 19 is not confined to any particular nation. It does not respect National boundaries.
🔹 Similarly when major economic events take place , their impact is felt outside their immediate local , national or regional environment at the global level.
Main components of worldwide mutual engagement : –
🔹 All the Countries of the world are closely involved by development of information and communication system , mutual dependence and mutual support.
🔹 Components : – Internet , Telephone Telegraph , Microchip etc.
Charactistic of Globalisation : –
- Free flow of ideas capital commodities and people.
- Capitalism , openness and increase in world trade.
- Worldwide interconnectedness and inter dependence.
- Global cooperation and influence in various economic events like recession and boom epidemics like ebola , swine flu and HIV AIDS.
Effects of Globalisation : –
🔸 ECONOMIC Effects : –
- Increased economic impact
- Increase in business activities
- Increased in Economic growth
- Prevents mutual dependency
- Blocks the flow of history.
- Gap between rich and poor increases .
- More benefits to developed countries.
- Economic colonialism.
🔸 POLITICAL Effects : –
- Increase in efficiency of states due to the rise of technology and information.
- Alternative means of protection.
- The role of available states has diminished but not eliminated.
- Minimum intervention of State
- Determinates Market Economy
- Increase in MNCS
- After State Sovereignty
- Less Role of Public Welfare State
🔸 CULTURAL Effects : –
- Cultural Homogeneity
- Increases the area of choice due to external cultural influence.
- Ending of originality of culture of each county.
- Disappearance of culture of less powerful society.
- The culture of least developed and Developing Countries is being westernized.
Expressions of Globalisation : –
🔹 Globalisation is a multi – dimensional concept having political , economic and cultural manifestations.
- POLITICAL CONSEQUENCES
- ECONOMIC CONSEQUENCES
- CULTURAL CONSEQUENCES
POLITICAL CONSEQUENCES : –
🔹 Globalisation results in decline of state capacity that is the ability of the government to perform tasks gets reduced. Globalisation has impacted the way the state functions.
🔹 Market becomes a prime determinant to settle down social and economic priorities in place of welfare.
🔹 The increased role of MNC all over the world leads to a reduction in the capacity of governments to take decisions on their own .
🔹 In some respects state capacity has received a boost as a consequence of globalisation, with enhanced technologies available at the disposal of the state to collect information about its citizens. With this information, the state is better able to rule, not less able. Thus, states become more powerful than they were earlier as an outcome of the new technology.
ECONOMIC CONSEQUENCES : –
🔹 The role of international institutions like the IMF and the WTO in making economic policies.
🔹 Domination of rich , infuential and development countries in these institutions.
🔹 Movement of commodities , capital , people and ideas Globalisation has involved greater trade in commodities across the globe.
🔹 The spread of internet and computer related services is increasing.
🔹 Developed countries have carefully guarded their borders with visa policies to ensure that citizens of other countries cannot take away the jobs of their own citizens.
🔹 Advocates of economic globalisation argue that it generates great economic growth and well – being for larger sections of the population when there is deregulation.
🔹 Economic globalisation is inevitable and it is not wise to resist the March of history.
🔹 As a result of globalisation there is increased momentum towards interdependence and integration between governments , businesses and ordinary people in different parts of the world.
CULTURAL CONSEQUENCES : –
🔹 Cultural homogenisation leads to imposition of western culture on the rest of the world.
🔹 Globalisation poses threat to cultures in the world.
🔹 It leads to the shrinking of the rich cultural heritage of the entire globe Sometimes external influences in food and clothings simply enlarge our choices.
🔹 It leads to each culture becoming more different and distinctive.
Cultural Homogenisation : –
🔹 It is an important aspect of cultural globalisation. It refers to the rise of uniform culture or different cultural practices into one common culture. Although , rise of a uniform culture is not the emergence of a global culture. It somehow leads to the shrinking of the rich cultural heritage of the entire globe.
Cultural Heterogenisation : –
🔹 Cultural homogenisation is an aspect of globalisation which also generates an opposite effect. The process leads to each culture becoming more different and distinctive in nature. This phenomenon is defined as cultural heterogenisation.
McDonaldisation : –
🔹 Domination of western cultureover the culture of other Nations is called McDonaldisation.
Economic impact of globalisation : –
- Economic growth balanced by equal trade and labour laws.
- Determination of the rules of international trade by western countries.
- Demage to small scale industries because of MNC’s
INDIA AND GLOBALISATION : –
🔹 During the colonial period as a consequence of Britain’s imperial ambitions , India became an exporter of primary goods and raw materials and a consumer of finished goods.
🔹 After independence we decided to make things ourselves rather than relying on other. This protectionism generated its own problems while some advances were made in certain areas critical sectors such as health housing and primary education did not receive the attention they deserts.
🔹 India had a fairly sluggish rate of economic growth in 1991 responding to a financial crisis and to the , desire for higfer rates of economic growth India embarked on a programme of economic reforms that has sought increasingly to deregulate various sectors including trade and foreign investment.
Impact of globalisation on India : –
- Rapid economic growth
- Availability of new opportunites
- Emergence of new challenges in domestic industries.
- Important place of India in world politics.
- Non Residents of India ( NRI ) are promoting Indian culture abroad.
- People of India have managed to establish their dominance in computer software.
- Today Indians have succeeded in occupying high positions globally.
Influence of Globalisation on India : –
- Rapid economic development ,
- Important place of India in world politics
- Availability of new opportunities
- Negative Impact on the status of workers and peasants.
- Cultural Differentiation
- Rise in New Challenges in Domestic Industries
RESISTANCE TO GLOBALISATION : –
🔹 GLOBALISATION is a very contentious subject and has invited strong criticisms all over the globe.
🔹 Those on the left argue that contemporary globalisution represents a particular phase of global capitalism that makes the rich richer and ( fewer ) and the poor poorer.
🔹 Critics of globalisation from the political right express anxiety over the political economic and cultural effects.
🔹 They fear the weakening of the state and want to return to self – reliance and protectionism.
🔹 They are worried that traditional culture will be harmed and people will lose their age old values and ways.
🔹 The world social forum ( WSF ) is another Global platform which bring together a wide coalition composed of human rights activists , environmentalists , labour , youth and women activists opposed to Neo liberal globalisation.
🔹 The first WSF meeting was organised in Porto alegre ( Brazil ) in 2001.

Related Chapters
The Cold War Era ( Deleted ) The End of Bipolarity US Hegemony in World Politics ( Deleted ) Contemporary Centres of Power Contemporary South Asia International Organisations Security in the Contemporary World Environment and Natural Resources Globalisation
Legal Notice
This is copyrighted content of GRADUATE PANDA and meant for Students use only. Mass distribution in any format is strictly prohibited. We are serving Legal Notices and asking for compensation to App, Website, Video, Google Drive, YouTube, Facebook, Telegram Channels etc distributing this content without our permission. If you find similar content anywhere else, mail us at [email protected] . We will take strict legal action against them.
- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
Chapter 3 IED Liberalisation, Privatisation And Globalisation
- Chapter 1 IED Indian Economy On The Eve Of Independence
- Chapter 2 IED Indian Economy 1950-1990
- Chapter 4 IED Poverty
- Chapter 5 IED Human Capital Formation In India
- Chapter 6 IED Rural Development
- Chapter 7 IED Employment: Growth Informalisation Other Issues
- Chapter 8 IED Infrastructure
- Chapter 9 IED Environment And Sustainable Development
- Chapter 10 IED Comparative Development Experiences of India
- Globalisation
Last updated at April 16, 2024 by Teachoo
What is Globalisation?
It means Integration of Country's economy with World's economy.

Important Points of Globalisation
Globalisation means following set of policies which lead to:
1 Greater interdependence and integration of world
2 Happenings In India are Influenced by happening far away
3 Various Economic ,Social Geoghraphical boundaries are broken
4 World becomes borderless (Different countries of world become one whole)

Outcomes of Globalisation - Examples
Earlier, we used to purchase goods and services within India
But now due to globalisation, we are free to buy goods and services from outside India also
Due to Globalisation, Foreign MNC are free to set up business in India and earn profit
This has led to job opportunities for millions of people
Due to Globalisation, Foreign Companies outsource their work to India
This has led to new outsourcing business set up in India as well as jobs to India'a people

MCQ Other Books
In the following questions, select the correct answers:
_____ means integrating the domestic economy with the world economy.
- Liberalisation
- Disinvestment
- Privatisation
A. Globalisation
Globalisation means Integration of Country's economy with World's economy.
- Greater interdependence and integration of world
- Happenings In India are Influenced by happening far away
- Various Economic ,Social Geoghraphical boundaries are broken
- World becomes borderless (Different countries of world become one whole)
Globalization-Meaning and Example North Korea No interaction with Other Countries Very Little Import, Export, Foreign Trade Very less Tourist visit North Korea Not much Affected by World Events (COVID, Stock market Crash etc.) India Properly Integrated with Outside World Large Imports, Exports, Foreign Trade Large number of Tourist visit India, go abroad Much Affected by World Events (If US Stock Market Crashed, India's Stock Market also crashes) This is due to Globalization What is Globalization? It is integration of Domestic Economy with Global Economy. What is Globalisation? It means integration Of Country’s Domestic economy with World’s Economy Important Points of Globalisation It means following set of policies which lead to Greater interdependence and integration of world Happenings In India are Influenced by happening far away. Example-COVID Various Economic ,Social Geographical boundaries are broken (We can travel and work anywhere) World becomes borderless (Different countries of world become one whole) Effect of Globalisation in India Before 1991 Indian Customers purchased mostly Indian Goods Maruti 800 (INDIA) Not many Foreign Companies (MNC) in India Netherland MNC in India American MNC in India After 1991 Reforms Indian Customers have a choice They can Purchase Either Indian or Foreign Goods Maruti 800 (INDIA) Hyundai Santro (South Korea) Lot of MNC (Multi-National Companies) Both Foreign and Indian Providing Jobs to lakhs of People Foreign MNC in India Indian MNC Operating worldwide Effect of Globalisation in India BEFORE 1991 No Outsourcing to India USA Company USA Call Center AFTER 1991 REFORMS Large Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) to India USA Company Indian Call Center Indian Call Center working for US Client Benefits Providing Business to Outsourcing Companies Jobs to Employees

Maninder Singh
CA Maninder Singh is a Chartered Accountant for the past 14 years and a teacher from the past 18 years. He teaches Science, Economics, Accounting and English at Teachoo
Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.

Economics Project on Globalisation – CBSE Class 12
Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION :
The term globalization is derived from the word globalize, which refers to the emergence of an international network of the economic systems. Since its inception, the concept of globalization has inspired competing for definition and interpretations, with antecedents dating back to the great movements of trade and empire across Asia and the Indian ocean from the 15 th century onwards. Due to the complexity of the concept, research projects, articles, and discussions often remain focused on a single aspect of globalization. Globalization can be located on a continuum with the local, national, and regional. At one end of the continuum lie social and economic relations and networks which are organized on a local on a national basis at the other end lie social and economic relations which crystallize the wider scale of global interactions.
- To know more about the Globalisation and also about its Merits and Demerits.
- To understand about the behand the globalization.
- To analysis the value measures of globalization.
- To know about the positives and negatives of the globalization in the Economy.
NEEDS AND SIGNIFICANCE:
- It helps to know about the interconnection between two or more countries.
- It helps to know more about the transfer of goods and services.
- Globalization makes the whole market into one as it reduces the barriers across the world.
- Globalization helps to access technology as it helps in more production propose in the international market.
There are both distal and proximate causes, which can be traced to the historical factors affecting globalization. Large-scale globalization began in the 19 th century. Globalization is not a new phenomenon. For centuries individuals have been buying and selling goods to individuals in other lands. Through the years, globalization has continued to spread through the passing of information and communication. International commodity markets, labor markets, and capital markets make up the economy and define economic globalization. Beginning as early as 4000 BCE, people were trading livestock, tools, and other items. In early civilization, in Mesopotamia, a token system was the first form of commodity money.
GLOBALISATION:
Globalization refers to the integration of markets in the global economy, leading to the increased interconnectedness of national economies, or it is the process of rapid integration or interconnection between countries. Markets, where globalization is particularly common, to include financial markets, such as capital market, money and credit market and insurance market, commodity markets, including markets for oil, coffee, tin and gold, and product market, etc. MNC’s that are Multi-National Countries are playing a major role in the process of globalization. More and more goods and services, investments, and technology are moving between countries. This is the integration of economies, industries , markets, culture, and policymaking around the world. Globalization describes a process by which national and regional economies, societies, and cultures have been integrated through the global network of trade, communication, immigration, and transportation. In the more recent past, globalization was often primarily focused on the economic side of the world, such as trade, foreign direct investment, and international capital flow, more recently the team has been expanded to include a broader range of areas and activities such as culture, media, technology, socio-cultural, political and even biological factors, e.g., climate change. Globalization is defined as a system related to increasing interaction, growing economic independence, and widening economic integration is the world economy. It encourages the integration of the economy of the country with the world economy. It is an outcome of a set of various policies that are aimed at transforming the world towards greater interdependence and integration. It involves the creation of networks and activities transcending economic, social, and geographical boundaries. It encourages foreign trade, private and institutional foreign investment. It practically removes all hindrance and restriction of foreign trade.
CHARACTERISTICS OF GLOBALISATION:
Globalization is a process of deeper integration between countries and regions of the world involving:
- Greater trade across the border in goods and services.
- An increase in transfers of capital, including the expansion of foreign direct investment (FDI) by transnational companies (TNCs) and the rising influence of Sovereign Wealth Funds. Fifty-one of the largest economies in the world are corporations.
- The development of global brands that serve markets in lower, middle, and higher-income countries.
- Greater use of outsourcing and offshoring of production. The classic example is the iPhone, which is part of a complex global supply chain . The product was conceived and designed in Silicon Valley in the USA, and the software enhanced by engineers working in India. Most iPhones are assembled in China and Taiwan.
- High levels of labor migration both within and between countries.
- New nations joining the trading system, for example, Russia joined the World Trade Organization (WTO) in 2012. The latest countries to join the WTO are Yemen (2014), Seychelles (2015), Kazakhstan (2015), and Afghanistan (2016).
- A shift in the balance of economic and financial powers from developed to emerging economies and markets – i.e., a change in the center of gravity in the world economy.
- Increasing spending on capital investment, innovation, and infrastructure across a large part of the world.
- Globalization is a process of making the world economy more connected and inter-dependent.
- Many industrializing (emerging) countries are winning a rising share of world trade, and their economies are growing faster than developed nations. Emerging and developing countries now account for more than 57% of global GDP adjusted for purchasing power according to 2015 data published by the IMF. The 28 – nation European Union has a share of global GDP that is the Gross Domestic Products of less than 17%.
- Globalization reform allows free interaction of an economy with the rest of the world
Shares of World Economic Output in 2015
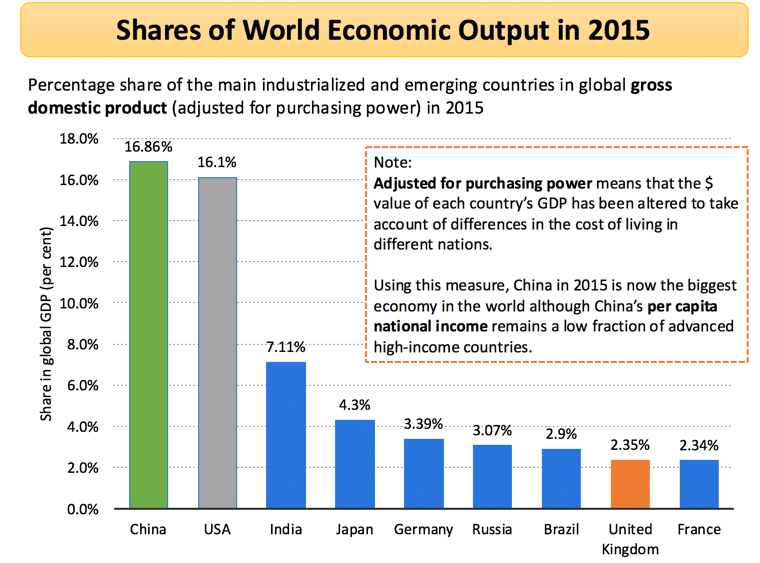
The percentage share of the main industrialized and emerging countries in the global gross domestic product (adjusted for purchasing power) in 2015
Adjusted for purchasing power means that the $ value of each country’s GDP has been altered to take account of differences in the cost of living in different nations
Using this measure, China in 2015 is now the biggest economy in the world, although China’s per capita national income remains a low fraction of advanced high-income countries.
Our new economic policy contributed to globalization in the following ways:
- Raising foreign equity participation.
- Devaluation of Rupee.
- Convertibility of Rupee.
- Long Period trade policy.
- Encouragement to open competition.
- Modification of custom and Tariffs.
ADVANTAGES OF GLOBALISATION:

- Globalization brings several potential benefits to international producers and national economies, including:
- Providing an incentive for countries to specialize and benefit from the application of the principle of comparative advantage.
- Globalization enables World Wide access to sources of cheap raw materials, and this enables from to have cost comparative in their market and overseas markets.
- In the long term, increased trade is likely to lead to the creation of more employment in all countries that are involved.
- Globalization has been able to establish links is such a way that the happening (advancement) in India can be influenced by events happening miles away from the rest of the world.
- Globalization has been able to turn the world into one whole on creating a boundary-less world as it provides easy asses to the global market.
- We are now exposed to advance technology and can develop indigence production in the international markets.
- Globalization should be seen as an opportunity in the teams of greater asses to global markets and increase the possibility of large industries of developing countries to become an important player in the international arena.
DISADVANTAGES OF GLOBALISATION:

There are also several disadvantages of globalization as the coin had two sides with it:
- Jobs may be lost because of the structural changes arising from globalization. Structural changes may lead to structural unemployment and may also widen the gap between rich and poor within a country.
- Increased trade associated with globalization has increased pollution and helped contributed to Co 2 emission and global warming. Trade growth has also accelerated the depletion of non-renewable resources such as oil.
- Globalization has compromised the welfare and identity of people belonging to poor counties.
NEGATIVE EFFECT
- Developed nations have outsourced
- Exploitation of labor
- Job insecurity
- Sophisticated weapons enhancing their ability
- Bad aspects of foreign cultures
- Reduced the government’s ability
IMPACT OF GLOBALISATION IN INDIAN ECONOMY:

- The impact of globalization has been highly positive in almost all spheres of economic and social life and virtually no negative effects.
- India’s economic growth has been high, exports have boomed, incidence of poverty has been reduced, employment has surged, begging by India for economic and has stopped, long term inflation rate has gone down, scarcely of goods have disappeared, the quality of products available have improved substantially and overall India has become progressively vibrant and internationally competitive.
- The service sector is the lifeline for the social, economic growth of a country.
- The real reason for the growth of the service sector is due to the increase in urbanization, privatization, and more demand for intermediate and final consumer services.
- In advanced economies, the growth in the primary and secondary sectors is directly dependent on the growth of services like banking, insurance, trade, commerce, entertainment, etc.
Economic Impacts:
- Greater Numbers of Jobs:
The advent of foreign companies and growth in the economy has led to job creation. However, these jobs are concentrated more on the services sector, and this has led to the rapid growth of the service sector creating problems for individuals with low levels of education. The last decade came to be known for its jobless growth as job creation was not satisfied with the level of economic growth.
- More choice to consumers:
Globalization has led to a boom in the consumer product market. We have a range of choices in selecting goods, unlike the times where there were just a couple of manufacturers.
- Higher Disposable Incomes!
People in cities working in high paying jobs have a higher income to spend on lifestyle goods. There has been an increase in the demand for products like meals, eggs, pulses, organic food as a result. It has also led to protein inflation.
IMPACT OF GLOBALISATION ON INDUSTRIAL SECTOR:

- The effect of globalization on Indian industry started when the government opened the country’s markets to foreign investment in the early 1990s.
- The globalisation of the Indian industry took place in its various sectors, such as steel, cement, retail, pharmaceutical, petroleum, chemical, textile, and BPO, which helps in providing employment.
- Globalisation has increased across the world in recent years due to the fast progress that has been made in the field of technology, especially in transport and communication. The government of India made changes in its economic policy in 1991 by which it allowed direct foreign investment in the country.
- Globalisation helps in reducing the level of unemployment and the poverty level in the country.
- The benefit of the effect of globalisation on the Indian industry is that the foreign companies brought in highly advanced technology with them, and this helped to make the Indian Industry more technologically advanced.
- The negative effects of globalisation on the Indian industry are that with the coming of technology, the numbers of labor required decreased, and this resulted in many people being removed from their jobs. This happened mainly in the pharmaceutical, chemical manufacturing, and cement industries.
OUTSOURCING:
This is one of the most important outcomes of the globalisation process. In outsourcing, a company hires a regular service from external sources, mostly from other countries, which was previously provided internally or from within the country like [legal advice, computer service, advertisement, securities each provided by the respective department of the country) a form of economic activity. Outsourcing has been intensified in the recent times because of fast modes of communication, particularly the growth of information technology with the help of modern telecommunication links including internet, the text, voice, and visual data in respect of these are digitized and transmitted in real-time over the continents and national companies. Most Multi-National Corporations and even small companies are outsourcing their services to India, where they can be availed at a cheaper cost with a reasonable degree of shell and accuracy.
LPG MODEL IN INDIA:
After Independence in 1947, the Indian government faced a major problem in developing the economy and to solve issues. Considering the issues pertaining at that time, the government decided to follow LPG Model [Liberalization, Privatization, and Globalisation model]. The economic growth conditions of India at that time were not very good. This was because it did not have proper resources for the development, not in terms of natural resources but terms of financial and industrial development. At that time, India needed the path of economics, and for that use, the Five Years Plan concept of which was taken from Russia and feet that it will provide a fast development like that of Russia, under the view of the socialistic pattern society. India had practiced several restrictions ever since the introduction of the first industrial policy resolution in 1948.
- More and more Multi-National Companies (MNCs) are looking for locations around the world that are cheap for their production because MNCs are playing a major role in the globalisation process.
- Globalisation has benefited well- off consumers and also producers with skill, education, and wealth. Many small producers and workers have suffered as a result of rising competition.
- Fair globalization would create opportunities for all and also ensure that the benefits of globalization are shared better.
CONCLUSION :
Globalisation is the process of rapid integration of countries. This is happening through greater foreign trade and foreign investment. Technology, particularly IT, has played a big role in organizing production across countries. Also, the liberalization of trade and investment has facilitated globalisation by removing barriers to trade and investment. Globalisation is now a reality, and the question is how to make globalisation fairer? Fair globalisation would create opportunities for all, and also ensures that the benefits of globalisation are shared better.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
- www.ecoglob.com
- Science technology and globalisation.
- www.globalWorld.com.
- NCERT textbook of class 11 th , economics,
- NCERT textbook of class 12 th business studies.
- NCERT textbook of class 8th economics,
DOWNLOAD PDF OF THE PROJECT

Password: hscprojects.com
In order to download the PDF, You must follow on Youtube. Once done, Click on Submit
Subscribed? Click on Confirm
Download Economics Project on Globalisation – CBSE Class 12 PDF
Related articles.

Social Science Project Topics For Class 10 CBSE

Solar Vacuum Cleaner & Floor Cleaner Robot Project

Cam Shaft Mechanism DIY Ventilator Project

Android Hostel Management System
It’s best for making project file. Thanks alotttttttttt!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Thanku………….. Amazing project….. Loved it
It helps me a lot in doing my project .
Thanks to your team
It helped a lot !!!!…
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.

Please Enable JavaScript in your Browser to Visit this Site.
- School Guide
- Class 12 Syllabus
- Class 12 Revision Notes
- Maths Notes Class 12
- Physics Notes Class 12
- Chemistry Notes Class 12
- Biology Notes Class 12
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths
- RD Sharma Solutions Class 12
- Class 11 Political Science Notes: Political Theory - An Introduction
- CBSE Class 9 Political Science Revision Notes
- Class 10 Political Science Notes
- Citizen and Nation Class 11 Political Science Notes
- Right to Self-Determination Class 11 Polity Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Political Science Previous Year Question Paper
- NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Political Science Chapter-1 The Constitution
- Harm Principle| Class 11 Polity Notes
- Political Theory - Major Aspects, Scope, Relevance, and Parameter
- CBSE Class 9 Social Science Revision Notes
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Political Science (Civics)
- CBSE Class 8 Social Science Revision Notes
- Mongol Society & Politics Nomadic Empire Class 11 History Notes
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Political Science (Civics) Chapter 4: Gender, Religion and Caste
- Class 11 Notes History-Paths to Modernisation: China
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Political Science (Civics) Social Science Chapter 1 : Power-sharing
- Nationalism and Pluralism Class 11 Polity Notes
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Political Science Chapter 8 : Challenges to Democracy
- The Story of Taiwan Theme 7 Class 11 History Notes
- Causes of Resistance to Change
- Chapter 5: Understanding Marginalisation NCERT Solutions of Class 8
- Paths to Modernisation Chapter 7 | Class 11 History Notes
- CBSE Class 9 History Notes Chapter 2: Socialism in Euope and the Russian Revolution
- Impact of Liberalisation, Privatisation, and Globalisation
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 History Social Science Chapter 3 : The Making of a Global World
- CBSE Class 10 Social Science Notes
- CBSE Class 9 History Revision Notes
- Effects of Globalisation on Indian Society
- The Making of Global World Class 10 History Notes Chapter 3
Resistance to Globalisation| Class 12 Political Science Notes
Resistance to globalization has emerged as a significant phenomenon driven by concerns about its socio-economic and cultural impacts. Critics from diverse backgrounds, including activists, scholars, and policymakers, express apprehensions about inequality, loss of sovereignty, and cultural homogenization. Anti-globalization movements, such as protests at international summits and the World Social Forum, serve as platforms for voicing dissent and advocating for alternative visions of global governance.
In this article, we will look into the Resistance to Globalization, Concerns about Globalization and Resistance and Anti-Globalization Movements with examples. It is an important concept of Class 12 Political Science. Students can go through this article to get comprehensive notes on “ Resistance to Globalisation”.
Resistance to Globalization
Resistance to globalization is a broad term that refers to the actions and struggles of individuals and social groups in response to the effects of neoliberal reforms. These effects can be seen in the economy, politics, and culture/identity. It arises due to concerns about widening economic inequality, weakening state intervention, and cultural homogenization. Critics fear that globalization primarily benefits the wealthy elite while leaving the poor marginalized, and it undermines traditional values and cultural diversity.
Anti-globalization movements, such as protests at international summits and the World Social Forum, advocate for alternative visions of globalization and challenge dominant narratives .
Concerns about Globalization
Concerns related to globalisation includes:
- Economic Inequality : Globalization widens the gap between the rich and the poor, benefiting the wealthy elite while leaving marginalized communities behind.
- Weakened State Intervention : It reduces the ability of governments to protect the interests of their citizens, particularly the poor and vulnerable.
- Cultural Erosion : Globalization threatens to homogenize cultures, leading to the loss of traditional values, languages, and customs in the face of dominant global influences.
- Labor Exploitation : Globalization can lead to exploitation of labor, particularly in developing countries, where workers are often subjected to low wages, poor working conditions, and lack of job security.
- Loss of Sovereignty : Increased economic integration under globalization may compromise the sovereignty of nations, limiting their ability to regulate trade, investment, and environmental policies in the interest of their citizens.
- Dependency on Global Markets : Developing countries may become overly reliant on global markets for trade and investment, leaving them vulnerable to economic shocks and fluctuations in the global economy.
Resistance and Anti-Globalization Movements
Anti-globalization movements have emerged as a response to the perceived negative impacts of globalization. These movements participate in global networks, forming alliances with like-minded individuals and groups in other countries. Many anti-globalization movements are not opposed to globalization per se, but rather to specific programs of globalization that they see as promoting inequality and exploitation. They view globalization as a form of imperialism, where powerful nations impose their economic and cultural agendas on weaker states. These movements are explained below:
Global Participation in Movements
- Anti-globalization movements participate in global networks, forming alliances with like-minded individuals and groups across borders.
- The protests at the 1999 World Trade Organization (WTO) Ministerial Meeting in Seattle, where demonstrators from various countries rallied against unfair trading practices.
- Many anti-globalization movements oppose specific programs of globalization, viewing them as forms of imperialism.
- The World Social Forum (WSF), which brings together activists from diverse backgrounds to challenge neoliberal globalization, as seen in its meetings in Porto Alegre, Brazil, and Mumbai.
Alternate Methods
- Anti-globalization movements advocate for alternative visions of globalization that prioritize social justice, environmental sustainability, and cultural diversity.
- Environmentalists, human rights activists, and labor groups coming together at the WSF to promote fair trade practices and advocate for policies that protect the interests of marginalized communities.
Resistance to Corporate Power
- Anti-globalization movements resist the increasing influence of multinational corporations, which they view as prioritizing profits over people.
- Protests against corporate-led globalization, such as those targeting the practices of large corporations accused of exploiting workers and damaging the environment.
Demand for Equitable Development
- Anti-globalization movements demand equitable development that prioritizes the needs and interests of local communities over the interests of global elites.
- Grassroots movements in developing countries advocating for land rights, fair wages, and access to essential services, in contrast to the neoliberal policies promoted by international financial institutions.
Challenges to Neoliberal Policies
- Anti-globalization movements challenge neoliberal policies that prioritize deregulation, privatization, and austerity measures, which they argue increase inequality and undermine social welfare.
- Protests against austerity measures imposed by governments as part of structural adjustment programs by international financial institutions like the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund.
Promotion of Social Justice
- Anti-globalization movements promote social justice by advocating for policies that address the root causes of poverty, inequality, and environmental degradation.
- Campaigns for debt relief, fair trade, and climate justice, which aim to hold governments and corporations accountable for their actions and promote a more equitable distribution of resources and opportunities.
Examples of Resistance to Globalisation
Resistance to globalization can take various forms, from protests and demonstrations to advocacy campaigns and alternative economic models. Some examples are:
Protests at International Summits
One of the most visible forms of resistance is protests and demonstrations at international summits and meetings, where activists gather to voice their opposition to globalization policies. For instance, the protests at the 1999 World Trade Organization (WTO) Ministerial Meeting in Seattle, known as the “Battle of Seattle,” saw thousands of activists protesting against unfair trade practices and corporate-led globalization.
Anti-Free Trade Agreements
Resistance movements often target free trade agreements, viewing them as promoting the interests of multinational corporations at the expense of workers and the environment. Examples include protests against the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) and the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP), which critics argue prioritize corporate profits over social and environmental concerns.
Indigenous Rights Movements
Indigenous communities around the world have been at the forefront of resistance to globalization, particularly in defense of their land, resources, and cultural heritage. Examples include the protests against the construction of the Dakota Access Pipeline in the United States and the resistance of Indigenous peoples in the Amazon rainforest against deforestation and resource extraction.
Labor Movements
Workers’ rights movements resist globalization policies that prioritize deregulation and labor flexibility, leading to exploitation and precarious working conditions. Examples include strikes and protests by workers in the garment industry in countries like Bangladesh and Cambodia, demanding better wages, working conditions, and labor rights.
Conclusion: Resistance to Globalisation
In conclusion, resistance to globalization manifests through diverse movements worldwide, from protests against unfair trade practices to advocacy for indigenous rights and environmental conservation. These movements challenge the dominance of multinational corporations and advocate for alternative economic models that prioritize social justice and sustainability. By voicing opposition to globalization’s negative impacts on labor, culture, and the environment, these movements strive to create a more equitable and inclusive global order.
- Impact of Globalization on India
- Globalization and the Indian Economy
- What are the advantages of globalisation in India?
Resistance to Globalisation- FAQs
What are examples of resistance to globalization.
Example of resistance to globalization is the protests against unfair trade practices at international summits like the WTO Ministerial Meeting in Seattle.
What is the meaning of global resistance?
Global resistance movements are collective efforts by individuals or groups to seek political, social, or economic change on an international scale. These movements often challenge power structures and advocate for justice or equality.
Why did people resist globalization?
People resist globalization due to concerns about its negative impacts on economic inequality, cultural homogenization, and environmental degradation.
Has there been resistance to globalisation in India?
Yes, there has been resistance to globalization in India, particularly concerning issues such as land acquisition for industrial projects, agricultural policies, and the impact on traditional livelihoods.
Is globalization good or bad?
The impact of globalization can be both positive and negative, depending on various factors such as economic development, cultural exchange, and environmental sustainability.
What are effects of globalisation?
The effects of globalization include increased interconnectedness, economic integration, and cultural exchange across borders.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Chapterwise-Notes-Class-12
- School Polity
- Social Science

Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
NCERT Books and Solutions for all classes
Globalisation Class 12 Political Science Exam Questions
Please refer to the Globalisation Class 12 Political Science Exam Questions provided below. These questions and answers for Class 12 Political Science have been designed based on the past trend of questions and important topics in your class 12 Political Science books. You should go through all Class 12 Political Science Important Questions provided by our teachers which will help you to get more marks in upcoming exams.
Class 12 Political Science Exam Questions Globalisation
Class 12 Political Science students should read and understand the important questions and answers provided below for Globalisation which will help them to understand all important and difficult topics.
Question. Globalisation began in – (a) 1990 (b) 1991 (c) 1992 (d) 1993
Question. The fourth WSF meeting was held in – (a) Brazil (b) India (c) China (d) Bangladesh
Question. Globalisation is (a) An uni dimensional (b) Multi-dimensional phenomenon (c) A Political Phenomenon (d) A Cultural Phenomenon
Question. Globalisation heads to each culture becoming – (a) More different (b) More distinctive (c) More different and distinctive (d) More transparent
Question. The first WSF meeting was organized in the earth summit was held in – (a) Mumbai in 2004 (b) Delhi in 2004 (c) Porto Alerge in 2001 (d) Paris in 2001
Fill in the Blanks:
Question. The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate change was held in ______ .
Question. World Environment day is celebrated each year on _____________ .
Short answer type question:
Question. What is the problem of increasing interdependent of countries? Ans. The increasing interdependence of countries in a globalised world makes them more vulnerable to economic problems.
Question. What are the prime determinants of economic and social priorities? Ans. In place of the welfare state, it is the market that becomes the prime determinants of economic and social priorities.
Question. What is cultural heterogenisation? Ans. The phenomenon in which globalization leads to each culture becoming more different and distinctive is known as cultural heterogenisation.
Question. Give one benefit of international migration? Ans. International migration has let to greater recognition of diversity and respect for cultural identities. Which is improving democracy and access to human rights?
Question. What is globalization? Ans . Globalization means linking the economy of the country with the economies of other countries by means of free trade and free mobility of capital, labor etc.
Question. What is WTO? Ans. The world trade organization (WTO) is a global international organization dealing with rules of trade between nations.
Question. When was new economic policy adopted? Ans. The new economic policy was adopted in 1991.
Question. What may be the effect of modern globalised culture? Ans. Indigenous and national culture and languages can be eroded by the modern globalised culture.
Question. Do you think that the impact of globalization is vastly uneven? Ans. Yes, the impact of globalization is vastly uneven. It affects some societies more them others and some parts of some societies more than other.
Question. When was the first WSF meeting held? Ans. The first WSF meeting was organized in porto Alegre, Brazil in 2001.
Question. Give one examples of negative impact of globalization? Ans. Some farmers committed suicide because their crops failed. They had bought very expensive seeds supplied by a multinational company (MNC)
Very short answer type question:
Question. Do you agree with the argument that globalization leads to cultural. Ans. Yes, I agree with argument that globalization leads to cultural heterogeneity. In fact globalization leads to each culture becoming more different and distinctive this phenomenon is cultural hetrogenisation.
Question. Write a not on world social forum? Ans. The World Social Forum :- (WSF) The world social forum (WSF) in an amalgamation of many political social movements from around the world. It was created to openly discuss alternatives to the model for globalization formulated by the world economic forum, large multinational corporations national governments, IMF, the world bank and the WTO. It is working to demonstrate that the path to sustainable development social and economic justice lies in alternative models for people cantered and self reliant progress rather than in neo liberal globalization.
Question. „Cultures are not static things‟. Explain the statement? Ans. Cultures are not static things. All cultures accept outside influence all the time. Some external influences are negative because they reduce our choices. But sometimes they modify our culture without overwhelming the traditional for example; the burger is no substitute for a masala dosa and therefore does not pose any real challenges. It is simply added on to our food choices blue jeans, on the other hand, can go well with a homespun khadi kurta. Here the outcome of outside influence is a new combination that is unique a khadi kurta worn over jeans. This clothing combination has been exported back to the country that gave us blue jeans so that it is possible to see young Americans wearing a kurta and jeans.
Long answer type question:
Question. Describe arguments in favor and against the economic globalization? Ans. Economic globalization has created an intense division of opinion all over the world. Those who are concerned about social justice are worried about the justice are worried about the extent of state withdrawal caused by processes of economic globalization. They point out that it is likely to benefit only a small section of the population while impoverishing those who were dependent on the government for jobs and welfare (education, health, sanitation etc.) they have emphasized the need to ensure institutional safeguards or creating „Social Safety Nets‟ to minimize the negative effects of globalization on those who are economically weak. Many movements all over the world feel that safety nets are insufficient or unworkable. They have called for a half to forced economic globalization, for its results would lead to economic globalization, for its results would lead to economic ruin for the weaker countries, especially for the poor with in these countries. Some economists have described economic globalization as recolonisation of the world. Advocates of economic globalization argue that it generates greater economic growth and well being for larger section of the population when there is de-regulation. Greater trade among countries allows each economy to do what it does best. This would benefit the whole world. They also argue that economic, globalization is inevitable and it is not wise to resist the march of history more moderate supporters of globalization say that globalization provides a challenge that can be responded to intelligently without accepting it uncritically, what however, cannot be denied is the increased momentum towards interdependence and integration between government businesses and ordinary people in different parts or the world as a result of globalization.

Related Posts:

Related Posts
Amines class 12 chemistry exam questions.

Enterprise marketing Class 12 Entrepreneurship Exam Questions

Transport and Communication Class 12 Geography Exam Questions

- Data Structure
- Coding Problems
- C Interview Programs
- C++ Aptitude
- Java Aptitude
- C# Aptitude
- PHP Aptitude
- Linux Aptitude
- DBMS Aptitude
- Networking Aptitude
- AI Aptitude
- MIS Executive
- Web Technologie MCQs
- CS Subjects MCQs
- Databases MCQs
- Programming MCQs
- Testing Software MCQs
- Digital Mktg Subjects MCQs
- Cloud Computing S/W MCQs
- Engineering Subjects MCQs
- Commerce MCQs
- More MCQs...
- Machine Learning/AI
- Operating System
- Computer Network
- Software Engineering
- Discrete Mathematics
- Digital Electronics
- Data Mining
- Embedded Systems
- Cryptography
- CS Fundamental
- More Tutorials...
- Tech Articles
- Code Examples
- Programmer's Calculator
- XML Sitemap Generator
- Tools & Generators

Home » MCQs » Class 12 Political Science MCQs
Globalisation – Class 12 Political Science MCQs
Globalisation is the process of interaction and integration among people, companies, and governments worldwide.
This section contains the multiple-choice questions and answers on Class 12 Political Science - Globalisation . Practice these MCQs to learn and test the skills of Globalisation.
MCQs on Globalisation
1. What is globalisation?
- Flows of Ideas
- Exchange of goods
- Flows of capital
- All of the above
Answer: D) All of the above
Explanation:
Globalisation means the flows of ideas, capital, commodities, and people across different parts of the world. It is a multidimensional concept.
2. What is the IMF?
- Indian monetary fund
- International monetary fund
- Investment monetary fund
- Indian military fund
Answer: B) International monetary fund
IMF stands for The International Monetary Fund.
3. Which of the following is an example of globalization?
- None of the following
Answer: A) McDonald's
McDonald's is the most prominent representation and symbol of globalization.
4. What are trade barriers?
- restraint on the flow of international goods or services
- restraint on the flow of Indian goods or services
- Ban on the making of goods
- Tags on the packed goods
Answer: A) restraint on the flow of international goods or services
A barrier to trade is a government-imposed restraint on the flow of international goods or services.
5. Who came first to India for trading?
- Vasco de Gama
- William Hawkins
Answer: C) Vasco de Gama
Portuguese explorer Vasco de Gama becomes the first European to reach India via the Atlantic Ocean when he arrives at Calicut on the Malabar Coast.
6. Where did the 1857 revolt start?
Answer: C) Meerut
1857 revolt was started in Meerut.
7. Who started east India?
- Thomas Smythe
- Both B and C
Answer: D) Both B and C
Thomas Smythe and JohnWatts started the East India Company.
8. Which of the following are the basic aspects of globalization?
- Transactions
In 2000, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) identified four basic aspects of globalization: trade and transactions, capital and investment movements, migration and movement of people, and the dissemination of knowledge.
9. In which year did India remove trade barriers?
Answer: D) 1991
In New Economic Policy in 1991, the government wished to remove these barriers because it felt that domestic producers were ready to compete with foreign industries.
10. The first WSF meeting was held in?
Answer: A) Brazil
The World Social Forum is an annual meeting of civil society organizations that was first held in Brazil.
Related MCQs
- The Cold War Era – Class 12 Political Science MCQs
- The End of Bipolarity – Class 12 Political Science MCQs
- US Hegemony in World Politics – Class 12 Political Science MCQs
- Alternative Centres of Power – Class 12 Political Science MCQs
- Contemporary South Asia – Class 12 Political Science MCQs
- International Organisations – Class 12 Political Science MCQs
- Security in the Contemporary World – Class 12 Political Science MCQs
- Environment and Natural Resources – Class 12 Political Science MCQs
- Challenges of Nation Building – Class 12 Political Science MCQs
- Era of One Party Dominance – Class 12 Political Science MCQs
- Politics of Planned Development – Class 12 Political Science MCQs
- India's External Relations – Class 12 Political Science MCQs
- Challenges to and Restoration of Congress System – Class 12 Political Science MCQs
- Crisis of Democratic Order – Class 12 Political Science MCQs
- Rise of Popular Movements – Class 12 Political Science MCQs
- Regional Aspirations – Class 12 Political Science MCQs
- Recent Developments in Indian Politics – Class 12 Political Science MCQs
Comments and Discussions!
Load comments ↻
- Marketing MCQs
- Blockchain MCQs
- Artificial Intelligence MCQs
- Data Analytics & Visualization MCQs
- Python MCQs
- C++ Programs
- Python Programs
- Java Programs
- D.S. Programs
- Golang Programs
- C# Programs
- JavaScript Examples
- jQuery Examples
- CSS Examples
- C++ Tutorial
- Python Tutorial
- ML/AI Tutorial
- MIS Tutorial
- Software Engineering Tutorial
- Scala Tutorial
- Privacy policy
- Certificates
- Content Writers of the Month
Copyright © 2024 www.includehelp.com. All rights reserved.
- List of Commerce Articles
Globalisation
Table of Content
- Globalisation Effect
Globalisation in the Indian economy
What is globalisation.
The term globalisation refers to the integration of the economy of the nation with the world economy. It is a multifaceted aspect. It is a result of the collection of multiple strategies that are directed at transforming the world towards a greater interdependence and integration.
It includes the creation of networks and pursuits transforming social, economical, and geographical barriers. Globalisation tries to build links in such a way that the events in India can be determined by the events happening distances away.
To put it in other words, globalisation is the method of interaction and union among people, corporations, and governments universally.
Also Check: Important Questions for Liberalisation, Privatisation and Globalisation
Effect of Globalisation in India
India is one of the countries that succeeded significantly after the initiation and implementation of globalisation. The growth of foreign investment in the field of corporate, retail, and the scientific sector is enormous in the country.
It also had a tremendous impact on the social, monetary, cultural, and political areas. In recent years, globalisation has increased due to improvements in transportation and information technology. With the improved global synergies, comes the growth of global trade, doctrines, and culture.

Indian society is changing drastically after urbanisation and globalisation. The economic policies have had a direct influence in forming the basic framework of the economy.
Economic policies established and administered by the government also performed an essential role in planning levels of savings, employment, income, and investments in the society.
Cross country culture is one of the critical impacts of globalisation on Indian society. It has significantly changed several aspects of the country, including cultural, social, political, and economical.
However, economic unification is the main factor that contributes maximum to a country’s economy into an international economy.
Also Read: What are Economic Reforms?
Advantages of Globalisation in India
Increase in employment: With the opportunity of special economic zones (SEZ), there is an increase in the number of new jobs available. Including the export processing zones (EPZ) centre in India is very useful in employing thousands of people.
Another additional factor in India is cheap labour. This feature motivates the big companies in the west to outsource employees from other regions and cause more employment.
Increase in compensation: After globalisation, the level of compensation has increased as compared to the domestic companies due to the skill and knowledge a foreign company offers. This opportunity also emerged as an alteration of the management structure.
High standard of living: With the outbreak of globalisation, the Indian economy and the standard of living of an individual has increased. This change is notified with the purchasing behaviour of a person, especially with those who are associated with foreign companies. Hence, many cities are undergoing a better standard of living along with business development.
Impact of Globalisation
Outsourcing : This is one of the principal results of the globalisation method. In outsourcing, a company recruits regular service from the outside sources, often from other nations, that was earlier implemented internally or from within the nation (like computer service, legal advice, security, each presented by individual departments of the corporation, and advertisement).
As a kind of economic venture, outsourcing has increased, in recent times, because of the increase in quick methods of communication, especially the growth of information technology (IT).
Many of the services such as voice-based business processes (commonly known as BPS, BPO, or call centres), accountancy, record keeping, music recording, banking services, book transcription, film editing, clinical advice, or teachers are being outsourced by the companies from the advanced countries to India.
Debate on Globalisation
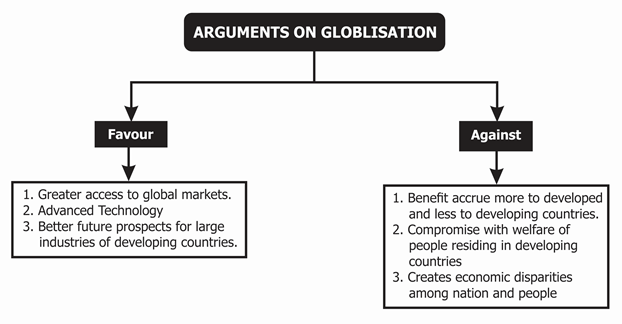
Solved Questions.
For more data on Economics Class 11 Syllabus, commerce notifications and sample papers for Class 11 commerce, stay tuned to BYJU’S.
Frequently Asked Questions on Globalisation
What are the different kinds of globalisation.
The top five types of globalisation are:
1. Financial globalisation. 2. Economic globalisation. 3. Technological globalisation. 4. Political globalisation. 5. Cultural globalisation.
What are examples of Globalisation?
The two examples of globalisation are as follows:
1. Travel: The capacity to travel to other places and experience their cultures. 2. Transportation: The international transportation systems, such as air travel and shipping.
What is the importance of Globalisation?
Globalisation is important to expand the markets and enable a business to make a sensible utilisation of the available resources. It also solves various issues of an individual and the nation, giving them many options to choose from and satisfy their needs. Globalisation boosts exports, discourages import, and uplifts foreign exchange.
What are the main reasons that caused Globalisation?
The main reason that caused globalisation are as follows:
1. Making global travel easier by improving transportation. 2. Advanced technology made communication and sharing of information easier. 3. Minimised tariff barriers and encouraged global trade. 4. Broadening of global media.
What are the positive impacts of Globalisation?
The four positive impacts of globalisation are as follows:
1. Creates efficient markets 2. Increases competition 3. Stabilises security 4. Increases wealth equality across the world
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Very helpful and nice way of explanation
I am so happy with your way of explaination of every topic.
This is very helpful for us. It explains everything so well.
It is very helpful for us and very easy to understand all the things
It is very helpful for us.
amazing notes
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
We hope that Class 12 Political Science Chapter 9 (Globalisation) notes in English helped you. If you have any queries about class 12 Political Science Chapter 9 (Globalisation) notes in English or about any other notes of class 12 political science in English, so you can comment below. We will reach you as soon as possible…
Globalisation means the flows of ideas, capital, commodities and people across different parts of the world. It is a multidimensional concept. It has political, economic and cultural manifestations and these must be adequately distinguished. Globalisation need not always be positive. It can have negative consequences for the people.
Students who are preparing for their Class 12 exams must go through NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Contemporary World Politics Chapter 9 Globalisation. Going through the solutions provided on this page will help you to know how to approach and solve the problems. Students can also find NCERT intext, exercises and back of chapter questions.
Answer: Globalisation has two thrust areas: 1. Liberalisation provides freedom of trade and investment, eliminate restrictions imposed on external trade and payments and expand technological progress to globalise faster. 2. Privatisation permits MNCs to produce goods and services inside the country to attract FDI. 4.
The Political Science Globalisation class 12 notes PDF are created for each topic to give a clear understanding of the topic to the student and make it easier for them to find. The notes of Globalisation class 12 can help a student increase their confidence, improve memory, boost their skills, and study for the examinations effectively.
Globalisation Class 12 Notes: Get here CBSE Class 12 Political Science Full and Short Notes for Political Science (Contemporary World Politics) of Chapter 7 for upcoming Board exam revision.
Globalisation basically deals with flows of ideas moving from one part of the world to another and commodities being traded across borders and so on. The key factor is the worldwide inter connectedness which is created and sustained as a result of these constant flows. It is a multidimensional concept, which has political, economic and cultural ...
All Globalisation Class 12 Notes and questions with solutions have been prepared based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. You should read all Case Study Questions provided by us and the Class 12 Political Science Case Study Questions provided for all chapters to get better marks in examinations.
1. Which of the statements are 'True' about globalisation? (a) Globalisation is purely an economic phenomenon. (b) Globalisation began in 1991. (c) Globalisation is the same thing as westernisation. (d) Globalisation is a multi-dimensional phenomenon. Answer. (d) Globalisation is a multi-dimensional phenomenon. 2.
OVERVIEW. In this final chapter of the book we look at globalisation, something that has been referred to in many chapters of this book and textbooks of many other subjects. We begin by analysing the concept of globalisation and then examine its causes. We then discuss at length the political, economic and cultural consequences of globalisation.
Globalisation is a multi-dimensional concept. It has political, economic, cultural aspects, etc. (a) Political Aspect: Globalisation has shifted the power to regulate certain activities from the government to international institutions. (b) Economic Aspect: Globalisation has reduced the economic power of the state and privatisation is gaining ...
Class 12 Political Science Chapter 9 Globalisation. NCERT Notes for Class 12 Political Science Chapter 9 Globalisation, (Political Science) exam are Students are taught thru NCERT books in some of the state board and CBSE Schools. As the chapter involves an end, there is an exercise provided to assist students to prepare for evaluation.
POLITICAL CONSEQUENCES : -. 🔹 Globalisation results in decline of state capacity that is the ability of the government to perform tasks gets reduced. Globalisation has impacted the way the state functions. 🔹 Market becomes a prime determinant to settle down social and economic priorities in place of welfare.
Globalisation means following set of policies which lead to: 1 Greater interdependence and integration of world. 2 Happenings In India are Influenced by happening far away. 3 Various Economic ,Social Geoghraphical boundaries are broken. 4 World becomes borderless (Different countries of world become one whole) Outcomes of Globalisation - Examples.
Answer. Question 12. Mention one feature of globalisation. Answer: Global economy is an important feature of globalisation. Answer. Question 13. Write one advantage of globalisation. Answer: Globalisation has promoted universal brotherhood and sharing of joys and pains. Question 14.
Globalization is defined as a system related to increasing interaction, growing economic independence, and widening economic integration is the world economy. It encourages the integration of the economy of the country with the world economy. It is an outcome of a set of various policies that are aimed at transforming the world towards greater ...
In this article, we will look into India and Globalisation, the liberalization reforms of 1991 and the challenges of Globalization in India. It is an important concept of Class 12 Political Science. Students can go through this article to get comprehensive notes on " India and Globalisation".
Resistance to globalization has emerged as a significant phenomenon driven by concerns about its socio-economic and cultural impacts. Critics from diverse backgrounds, including activists, scholars, and policymakers, express apprehensions about inequality, loss of sovereignty, and cultural homogenization.
Class 12 Political Science Exam Questions Globalisation. Class 12 Political Science students should read and understand the important questions and answers provided below for Globalisation which will help them to understand all important and difficult topics. Question. Globalisation began in -. Question. The fourth WSF meeting was held in -.
Globalisation - Class 12 Political Science MCQs. Globalisation is the process of interaction and integration among people, companies, and governments worldwide. This section contains the multiple-choice questions and answers on Class 12 Political Science - Globalisation. Practice these MCQs to learn and test the skills of Globalisation.
1. Creates efficient markets. 2. Increases competition. 3. Stabilises security. 4. Increases wealth equality across the world. Globalisation can, therefore, be perceived as a phenomenon of the change of economic, technological, socio-cultural and political organisations at local or regional levels to an international system.