

30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
Essay on Importance of Mathematics in our Daily Life in 100, 200, and 350 words.

- Updated on
- Dec 22, 2023

Mathematics is one of the core aspects of education. Without mathematics, several subjects would cease to exist. It’s applied in the science fields of physics, chemistry, and even biology as well. In commerce accountancy, business statistics and analytics all revolve around mathematics. But what we fail to see is that not only in the field of education but our lives also revolve around it. There is a major role that mathematics plays in our lives. Regardless of where we are, or what we are doing, mathematics is forever persistent. Let’s see how maths is there in our lives via our blog essay on importance of mathematics in our daily life.
Table of Contents
- 1 Essay on Importance of Mathematics in our Daily life in 100 words
- 2 Essay on Importance of Mathematics in our Daily life in 200 words
- 3 Essay on Importance of Mathematics in our Daily Life in 350 words
Essay on Importance of Mathematics in our Daily life in 100 words
Mathematics is a powerful aspect even in our day-to-day life. If you are a cook, the measurements of spices have mathematics in them. If you are a doctor, the composition of medicines that make you provide prescription is made by mathematics. Even if you are going out for just some groceries, the scale that is used for weighing them has maths, and the quantity like ‘dozen apples’ has maths in it. No matter the task, one way or another it revolves around mathematics. Everywhere we go, whatever we do, has maths in it. We just don’t realize that. Maybe from now on, we will, as mathematics is an important aspect of our daily life.
Also Read:- Importance of Internet
Essay on Importance of Mathematics in our Daily life in 200 words
Mathematics, as a subject, is one of the most important subjects in our lives. Irrespective of the field, mathematics is essential in it. Be it physics, chemistry, accounts, etc. mathematics is there. The use of mathematics proceeds in our daily life to a major extent. It will be correct to say that it has become a vital part of us. Imagining our lives without it would be like a boat without a sail. It will be a shock to know that we constantly use mathematics even without realising the same.
From making instalments to dialling basic phone numbers it all revolves around mathematics.
Let’s take an example from our daily life. In the scenario of going out shopping, we take an estimate of hours. Even while buying just simple groceries, we take into account the weight of vegetables for scaling, weighing them on the scale and then counting the cash to give to the cashier. We don’t even realise it and we are already counting numbers and doing calculations.
Without mathematics and numbers, none of this would be possible.
Hence we can say that mathematics helps us make better choices, more calculated ones throughout our day and hence make our lives simpler.
Also Read:- My Aim in Life
Essay on Importance of Mathematics in our Daily Life in 350 words
Mathematics is what we call a backbone, a backbone of science. Without it, human life would be extremely difficult to imagine. We cannot live even a single day without making use of mathematics in our daily lives. Without mathematics, human progress would come to a halt.
Maths helps us with our finances. It helps us calculate our daily, monthly as well as yearly expenses. It teaches us how to divide and prioritise our expenses. Its knowledge is essential for investing money too. We can only invest money in property, bank schemes, the stock market, mutual funds, etc. only when we calculate the figures. Let’s take an example from the basic routine of a day. Let’s assume we have to make tea for ourselves. Without mathematics, we wouldn’t be able to calculate how many teaspoons of sugar we need, how many cups of milk and water we have to put in, etc. and if these mentioned calculations aren’t made, how would one be able to prepare tea?
In such a way, mathematics is used to decide the portions of food, ingredients, etc. Mathematics teaches us logical reasoning and helps us develop problem-solving skills. It also improves our analytical thinking and reasoning ability. To stay in shape, mathematics helps by calculating the number of calories and keeping the account of the same. It helps us in deciding the portion of our meals. It will be impossible to think of sports without mathematics. For instance, in cricket, run economy, run rate, strike rate, overs bowled, overs left, number of wickets, bowling average, etc. are calculated. It also helps in predicting the result of the match. When we are on the road and driving, mathetics help us keep account of our speeds, the distance we have travelled, the amount of fuel left, when should we refuel our vehicles, etc.
We can go on and on about how mathematics is involved in our daily lives. In conclusion, we can say that the universe revolves around mathematics. It encompasses everything and without it, we cannot imagine our lives.
Also Read:- Essay on Pollution
Ans: Mathematics is a powerful aspect even in our day-to-day life. If you are a cook, the measurements of spices have mathematics in them. If you are a doctor, the composition of medicines that make you provide prescription is made by mathematics. Even if you are going out for just some groceries, the scale that is used for weighing them has maths, and the quantity like ‘dozen apples’ has maths in it. No matter the task, one way or another it revolves around mathematics. Everywhere we go, whatever we do, has maths in it. We just don’t realize that. Maybe from now on, we will, as mathematics is an important aspect of our daily life.
Ans: Mathematics, as a subject, is one of the most important subjects in our lives. Irrespective of the field, mathematics is essential in it. Be it physics, chemistry, accounts, etc. mathematics is there. The use of mathematics proceeds in our daily life to a major extent. It will be correct to say that it has become a vital part of us. Imagining our lives without it would be like a boat without a sail. It will be a shock to know that we constantly use mathematics even without realising the same. From making instalments to dialling basic phone numbers it all revolves around mathematics. Let’s take an example from our daily life. In the scenario of going out shopping, we take an estimate of hours. Even while buying just simple groceries, we take into account the weight of vegetables for scaling, weighing them on the scale and then counting the cash to give to the cashier. We don’t even realise it and we are already counting numbers and doing calculations. Without mathematics and numbers, none of this would be possible. Hence we can say that mathematics helps us make better choices, more calculated ones throughout our day and hence make our lives simpler.
Ans: Archimedes is considered the father of mathematics.
Related Reads:
Hope you find this information useful. For more information on such informative topics for your school, visit our essay writing and follow Leverage Edu.
Deepansh Gautam
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us

30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today.

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
current events conversation
What Students Are Saying About the Value of Math
We asked teenagers: Do you see the point in learning math? The answer from many was “yes.”

By The Learning Network
“Mathematics, I now see, is important because it expands the world,” Alec Wilkinson writes in a recent guest essay . “It is a point of entry into larger concerns. It teaches reverence. It insists one be receptive to wonder. It requires that a person pay close attention.”
In our writing prompt “ Do You See the Point in Learning Math? ” we wanted to know if students agreed. Basic arithmetic, sure, but is there value in learning higher-level math, such as algebra, geometry and calculus? Do we appreciate math enough?
The answer from many students — those who love and those who “detest” the subject alike — was yes. Of course math helps us balance checkbooks and work up budgets, they said, but it also helps us learn how to follow a formula, appreciate music, draw, shoot three-pointers and even skateboard. It gives us different perspectives, helps us organize our chaotic thoughts, makes us more creative, and shows us how to think rationally.
Not all were convinced that young people should have to take higher-level math classes all through high school, but, as one student said, “I can see myself understanding even more how important it is and appreciating it more as I get older.”
Thank you to all the teenagers who joined the conversation on our writing prompts this week, including students from Bentonville West High School in Centerton, Ark, ; Harvard-Westlake School in Los Angeles ; and North High School in North St. Paul, Minn.
Please note: Student comments have been lightly edited for length, but otherwise appear as they were originally submitted.
“Math is a valuable tool and function of the world.”
As a musician, math is intrinsically related to my passion. As a sailor, math is intertwined with the workings of my boat. As a human, math is the building block for all that functions. When I was a child, I could very much relate to wanting a reason behind math. I soon learned that math IS the reason behind all of the world’s workings. Besides the benefits that math provides to one’s intellect, it becomes obvious later in life that math is a valuable tool and function of the world. In music for example, “adolescent mathematics” are used to portray functions of audio engineering. For example, phase shifting a sine wave to better project sound or understanding waves emitted by electricity and how they affect audio signals. To better understand music, math is a recurring pattern of intervals between generating pitches that are all mathematically related. The frets on a guitar are measured precisely to provide intervals based on a tuning system surrounding 440Hz, which is the mathematically calculated middle of the pitches humans can perceive and a string can effectively generate. The difference between intervals in making a chord are not all uniform, so guitar frets are placed in a way where all chords can sound equally consonant and not favor any chord. The power of mathematics! I am fascinated by the way that math creeps its way into all that I do, despite my plentiful efforts to keep it at a safe distance …
— Renan, Miami Country Day School
“Math isn’t about taking derivatives or solving for x, it’s about having the skills to do so and putting them to use elsewhere in life.”
I believe learning mathematics is both crucial to the learning and development of 21st century students and yet also not to be imposed upon learners too heavily. Aside from the rise in career opportunity in fields centered around mathematics, the skills gained while learning math are able to be translated to many facets of life after a student’s education. Learning mathematics develops problem solving skills which combine logic and reasoning in students as they grow. The average calculus student may complain of learning how to take derivatives, arguing that they will never have to use this after high school, and in that, they may be right. Many students in these math classes will become writers, musicians, or historians and may never take a derivative in their life after high school, and thus deem the skill to do so useless. However, learning mathematics isn’t about taking derivatives or solving for x, it’s about having the skills to do so and putting them to use elsewhere in life. A student who excels at calculus may never use it again, but with the skills of creativity and rational thinking presented by this course, learning mathematics will have had a profound effect on their life.
— Cam, Glenbard West
“Just stop and consider your hobbies and pastimes … all of it needs math.”
Math is timing, it’s logic, it’s precision, it’s structure, and it’s the way most of the physical world works. I love math — especially algebra and geometry — as it all follows a formula, and if you set it up just right, you can create almost anything you want in at least two different ways. Just stop and consider your hobbies and pastimes. You could be into skateboarding, basketball, or skiing. You could be like me, and sit at home for hours on end grinding out solves on a Rubik’s cube. Or you could be into sketching. Did you know that a proper drawing of the human face places the eyes exactly halfway down from the top of the head? All of it needs math. Author Alec Wilkinson, when sharing his high school doubting view on mathematics, laments “If I had understood how deeply mathematics is embedded in the world …” You can’t draw a face without proportions. You can’t stop with your skis at just any angle. You can’t get three points without shooting at least 22 feet away from the basket, and get this: you can’t even ride a skateboard if you can’t create four congruent wheels to put on it.
— Marshall, Union High School, Vancouver, WA
“Math gives us a different perspective on everyday activities.”
Even though the question “why do we even do math?” is asked all the time, there is a deeper meaning to the values it shares. Math gives us a different perspective on everyday activities, even if those activities in our routine have absolutely nothing to do with mathematical concepts itself. Geometry, for instance, allows us to think on a different level than simply achieving accuracy maintains. It trains our mind to look at something from various viewpoints as well as teaching us to think before acting and organizing chaotic thoughts. The build up of learning math can allow someone to mature beyond the point where if they didn’t learn math and thought through everything. It paves a way where we develop certain characteristics and traits that are favorable when assisting someone with difficult tasks in the future.
— Linden, Harvard-Westlake High School, CA
“Math teaches us how to think.”
As explained in the article, math is all around us. Shapes, numbers, statistics, you can find math in almost anything and everything. But is it important for all students to learn? I would say so. Math in elementary school years is very important because it teaches how to do simple calculations that can be used in your everyday life; however middle and high school math isn’t used as directly. Math teaches us how to think. It’s far different from any other subject in school, and truly understanding it can be very rewarding. There are also many career paths that are based around math, such as engineering, statistics, or computer programming, for example. These careers are all crucial for society to function, and many pay well. Without a solid background in math, these careers wouldn’t be possible. While math is a very important subject, I also feel it should become optional at some point, perhaps part way through high school. Upper level math classes often lose their educational value if the student isn’t genuinely interested in learning it. I would encourage all students to learn math, but not require it.
— Grey, Cary High School
“Math is a valuable tool for everyone to learn, but students need better influences to show them why it’s useful.”
Although I loved math as a kid, as I got older it felt more like a chore; all the kids would say “when am I ever going to use this in real life?” and even I, who had loved math, couldn’t figure out how it benefits me either. This was until I started asking my dad for help with my homework. He would go on and on about how he used the math I was learning everyday at work and even started giving me examples of when and where I could use it, which changed my perspective completely. Ultimately, I believe that math is a valuable tool for everyone to learn, but students need better influences to show them why it’s useful and where they can use it outside of class.
— Lilly, Union High School
“At the roots of math, it teaches people how to follow a process.”
I do believe that the math outside of arithmetic, percentages, and fractions are the only math skills truly needed for everyone, with all other concepts being only used for certain careers. However, at the same time, I can’t help but want to still learn it. I believe that at the roots of math, it teaches people how to follow a process. All mathematics is about following a formula and then getting the result of it as accurately as possible. It teaches us that in order to get the results needed, all the work must be put and no shortcuts or guesses can be made. Every equation, number, and symbol in math all interconnect with each other, to create formulas that if followed correctly gives us the answer needed. Everything is essential to getting the results needed, and skipping a step will lead to a wrong answer. Although I do understand why many would see no reason to learn math outside of arithmetic, I also see lessons of work ethics and understanding the process that can be applied to many real world scenarios.
— Takuma, Irvine High School
“I see now that math not only works through logic but also creativity.”
A story that will never finish resembling the universe constantly expanding, this is what math is. I detest math, but I love a never-ending tale of mystery and suspense. If we were to see math as an adventure it would make it more enjoyable. I have often had a closed mindset on math, however, viewing it from this perspective, I find it much more appealing. Teachers urge students to try on math and though it seems daunting and useless, once you get to higher math it is still important. I see now that math not only works through logic but also creativity and as the author emphasizes, it is “a fundamental part of the world’s design.” This view on math will help students succeed and have a more open mindset toward math. How is this never-ending story of suspense going to affect YOU?
— Audrey, Vancouver, WA union high school
“In some word problems, I encounter problems that thoroughly interest me.”
I believe math is a crucial thing to learn as you grow up. Math is easily my favorite subject and I wish more people would share my enthusiasm. As Alec Wilkinson writes, “Mathematics, I now see, is important because it expands the world.” I have always enjoyed math, but until the past year, I have not seen a point in higher-level math. In some of the word problems I deal with in these classes, I encounter problems that thoroughly interest me. The problems that I am working on in math involve the speed of a plane being affected by wind. I know this is not riveting to everyone, but I thoroughly wonder about things like this on a daily basis. The type of math used in the plane problems is similar to what Alec is learning — trigonometry. It may not serve the most use to me now, but I believe a thorough understanding of the world is a big part of living a meaningful life.
— Rehan, Cary High School
“Without high school classes, fewer people get that spark of wonder about math.”
I think that math should be required through high school because math is a use-it-or-lose-it subject. If we stop teaching math in high school and just teach it up to middle school, not only will many people lose their ability to do basic math, but we will have fewer and fewer people get that spark of wonder about math that the author had when taking math for a second time; after having that spark myself, I realized that people start getting the spark once they are in harder math classes. At first, I thought that if math stopped being required in high school, and was offered as an elective, then only people with the spark would continue with it, and everything would be okay. After thinking about the consequences of the idea, I realized that technology requires knowing the seemingly unneeded math. There is already a shortage of IT professionals, and stopping math earlier will only worsen that shortage. Math is tricky. If you try your best to understand it, it isn’t too hard. However, the problem is people had bad math teachers when they were younger, which made them hate math. I have learned that the key to learning math is to have an open mind.
— Andrew, Cary High School
“I think math is a waste of my time because I don’t think I will ever get it.”
In the article Mr. Wilkinson writes, “When I thought about mathematics at all as a boy it was to speculate about why I was being made to learn it, since it seemed plainly obvious that there was no need for it in adult life.” His experience as a boy resonates with my experience now. I feel like math is extremely difficult at some points and it is not my strongest subject. Whenever I am having a hard time with something I get a little upset with myself because I feel like I need to get everything perfect. So therefore, I think it is a waste of my time because I don’t think I will ever get it. At the age of 65 Mr. Wilkinson decided to see if he could learn more/relearn algebra, geometry and calculus and I can’t imagine myself doing this but I can see myself understanding even more how important it is and appreciating it more as I get older. When my dad was young he hated history but, as he got older he learned to appreciate it and see how we can learn from our past mistakes and he now loves learning new things about history.
— Kate, Cary High School
“Not all children need to learn higher level math.”
The higher levels of math like calculus, algebra, and geometry have shaped the world we live in today. Just designing a house relates to math. To be in many professions you have to know algebra, geometry, and calculus such as being an economist, engineer, and architect. Although higher-level math isn’t useful to some people. If you want to do something that pertains to math, you should be able to do so and learn those high levels of math. Many things children learn in math they will never use again, so learning those skills isn’t very helpful … Children went through so much stress and anxiety to learn these skills that they will never see again in their lives. In school, children are using their time learning calculus when they could be learning something more meaningful that can prepare them for life.
— Julyssa, Hanover Horton High School
“Once you understand the basics, more math classes should be a choice.”
I believe that once you get to the point where you have a great understanding of the basics of math, you should be able to take more useful classes that will prepare you for the future better, rather than memorizing equations after equations about weird shapes that will be irrelevant to anything in my future. Yes, all math levels can be useful to others’ futures depending on what career path they choose, but for the ones like me who know they are not planning on encountering extremely high level math equations on the daily, we should not have to take math after a certain point.
— Tessa, Glenbard West High School
“Math could shape the world if it were taught differently.”
If we learned how to balance checkbooks and learn about actual life situations, math could be more helpful. Instead of learning about rare situations that probably won’t come up in our lives, we should be learning how to live on a budget and succeed money-wise. Since it is a required class, learning this would save more people from going into debt and overspending. In schools today, we have to take a specific class that doesn’t sound appealing to the average teenager to learn how to save and spend money responsibly. If it was required in math to learn about that instead of how far Sally has to walk then we would be a more successful nation as a whole. Math could shape the world differently but the way it is taught in schools does not have much impact on everyday life.
— Becca, Bentonville West High School
“To be honest, I don’t see the point in learning all of the complicated math.”
In a realistic point of view, I need to know how to cut a cake or a piece of pie or know how to divide 25,000 dollars into 10 paychecks. On the other hand, I don’t need to know the arc and angle. I need to throw a piece of paper into a trash can. I say this because, in all reality and I know a lot of people say this but it’s true, when are we actually going to need this in our real world lives? Learning complicated math is a waste of precious learning time unless you desire to have a career that requires these studies like becoming an engineer, or a math professor. I think that the fact that schools are still requiring us to learn these types of mathematics is just ignorance from the past generations. I believe that if we have the technology to complete these problems in a few seconds then we should use this technology, but the past generations are salty because they didn’t have these resources so they want to do the same thing they did when they were learning math. So to be honest, I don’t see the point in learning all of the complicated math but I do think it’s necessary to know the basic math.
— Shai, Julia R Masterman, Philadelphia, PA
Learn more about Current Events Conversation here and find all of our posts in this column .
Home — Essay Samples — Science — Mathematics in Everyday Life — Mathematics In Everyday Life: Most Vital Discipline
Mathematics in Everyday Life: Most Vital Discipline
- Categories: Mathematics in Everyday Life
About this sample

Words: 795 |
Published: Mar 14, 2019
Words: 795 | Pages: 2 | 4 min read
Works Cited
- Benacerraf, P. (1991). Mathematics as an object of knowledge. In P. Benacerraf & H. Putnam (Eds.), Philosophy of mathematics: Selected readings (pp. 1-13). Cambridge University Press.
- EdReady. (n.d.). Home. Retrieved from https://www.edready.org/
- Puttaswamy, T. K. (2012). Engineering mathematics. Dorling Kindersley (India) Pvt. Ltd.
- Steen, L. A. (Ed.). (2001). Mathematics today: Twelve informal essays. Springer Science & Business Media.
- Suter, B. W. (2012). Mathematics education: A critical introduction. Bloomsbury Academic.
- Tucker, A. W. (2006). Applied combinatorics. John Wiley & Sons.
- Vakil, R. (2017). A mathematical mosaic: Patterns & problem solving. Princeton University Press.
- Wolfram MathWorld. (n.d.). MathWorld--The web's most extensive mathematics resource. Retrieved from http://mathworld.wolfram.com/
- Wu, H. H. (2011). The mis-education of mathematics teachers. Educational Studies in Mathematics, 77(1), 1-20.
- Ziegler, G. M., & Aigner, M. (2012). Proofs from THE BOOK. Springer Science & Business Media.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Science

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 589 words
1 pages / 649 words
1 pages / 424 words
2 pages / 1068 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Mathematics in Everyday Life
Background information on field experience school: Miami Coral Park Senior High School has 2,891 students of which 92% are Hispanic, 2% are Black, 4% White, and 2% Asian. 13% of the school’s students are ELL/LEP. The grades [...]
In this 'Mathematics in Architecture' essay, the researcher delves into the question if it is possible for architecture to stand alone without the help of mathematics? This research paper will also determine how Mathematics is [...]
Algebra, a branch of mathematics that involves symbols, equations, and variables, is often met with mixed feelings among students. Some see it as a challenging and abstract subject, while others recognize its practicality and [...]
Mathematics has thousands of branches, and each branch means something different to every person. Some may know it as a useful tool that is a key to getting civilizations rolling. Others may just see it as bothersome and a tough [...]
For this project, Grade 10 Math Project, we have to pick something from real life that I can explain how math affects it. I chose to do my project about the Pharmaceutical industry. The pharmaceutical mathematics curriculum [...]
The spiral model combines the idea of iterative development with the systematic, controlled aspects of the waterfall model. The spiral model has four phases. A software project repeatedly passes through these phases in [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Essays About Math: Top 10 Examples and Writing Prompts
Love it or hate it, an understanding of math is said to be crucial to success. So, if you are writing essays about math, read our top essay examples.
Mathematics is the study of numbers, shapes, and space using reason and usually a special system of symbols and rules for organizing them . It can be used for a variety of purposes, from calculating a business’s profit to estimating the mass of a black hole. However, it can be considered “controversial” to an extent.
Most students adore math or regard it as their least favorite. No other core subject has the same infamy as math for generating passionate reactions both for and against it. It has applications in every field, whether basic operations or complex calculus problems. Knowing the basics of math is necessary to do any work properly.
If you are writing essays about Math, we have compiled some essay examples for you to get started.
1. Mathematics: Problem Solving and Ideal Math Classroom by Darlene Gregory
2. math essay by prasanna, 3. short essay on the importance of mathematics by jay prakash.
- 4. Math Anxiety by Elias Wong
5. Why Math Isn’t as Useless as We Think by Murtaza Ali
1. mathematics – do you love or hate it, 2. why do many people despise math, 3. how does math prepare you for the future, 4. is mathematics an essential skill, 5. mathematics in the modern world.
“The trait of the teacher that is being strict is we know that will really help the students to change. But it will give a stress and pressure to students and that is one of the causes why students begin to dislike math. As a student I want a teacher that is not so much strict and giving considerations to his students. A teacher that is not giving loads of things to do and must know how to understand the reasons of his students.”
Gregory discusses the reasons for most students’ hatred of math and how teachers handle the subject in class. She says that math teachers do not explain the topics well, give too much work, and demand nothing less than perfection. To her, the ideal math class would involve teachers being more considerate and giving less work.
You might also be interested in our ordinal number explainer.
“Math is complicated to learn, and one needs to focus and concentrate more. Math is logical sometimes, and the logic needs to be derived out. Maths make our life easier and more straightforward. Math is considered to be challenging because it consists of many formulas that have to be learned, and many symbols and each symbol generally has its significance.”
In her essay, Prasanna gives readers a basic idea of what math is and its importance. She additionally lists down some of the many uses of mathematics in different career paths, namely managing finances, cooking, home modeling and construction, and traveling. Math may seem “useless” and “annoying” to many, but the essay gives readers a clear message: we need math to succeed.
“In this modern age of Science and Technology, emphasis is given on Science such as Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Medicine and Engineering. Mathematics, which is a Science by any criterion, also is an efficient and necessary tool being employed by all these Sciences. As a matter of fact, all these Sciences progress only with the aid of Mathematics. So it is aptly remarked, ‘Mathematics is a Science of all Sciences and art of all arts.’”
As its title suggests, Prakash’s essay briefly explains why math is vital to human nature. As the world continues to advance and modernize, society emphasizes sciences such as medicine, chemistry, and physics. All sciences employ math; it cannot be studied without math. It also helps us better our reasoning skills and maximizes the human mind. It is not only necessary but beneficial to our everyday lives.
4. Math Anxiety by Elias Wong
“Math anxiety affects different not only students but also people in different ways. It’s important to be familiar with the thoughts you have about yourself and the situation when you encounter math. If you are aware of unrealistic or irrational thoughts you can work to replace those thoughts with more positive and realistic ones.”
Wong writes about the phenomenon known as “math anxiety.” This term is used to describe many people’s hatred or fear of math- they feel that they are incapable of doing it. This anxiety is caused mainly by students’ negative experiences in math class, which makes them believe they cannot do well. Wong explains that some people have brains geared towards math and others do not, but this should not stop people from trying to overcome their math anxiety. Through review and practice of basic mathematical skills, students can overcome them and even excel at math.
“We see that math is not an obscure subject reserved for some pretentious intellectual nobility. Though we may not be aware of it, mathematics is embedded into many different aspects of our lives and our world — and by understanding it deeply, we may just gain a greater understanding of ourselves.”
Similar to some of the previous essays, Ali’s essay explains the importance of math. Interestingly, he tells a story of the life of a person name Kyle. He goes through the typical stages of life and enjoys typical human hobbies, including Rubik’s cube solving. Throughout this “Kyle’s” entire life, he performed the role of a mathematician in various ways. Ali explains that math is much more prevalent in our lives than we think, and by understanding it, we can better understand ourselves.
Writing Prompts on Essays about Math
Math is a controversial subject that many people either passionately adore or despise. In this essay, reflect on your feelings towards math, and state your position on the topic. Then, give insights and reasons as to why you feel this way. Perhaps this subject comes easily to you, or perhaps it’s a subject that you find pretty challenging. For an insightful and compelling essay, you can include personal anecdotes to relate to your argument.

It is well-known that many people despise math. In this essay, discuss why so many people do not enjoy maths and struggle with this subject in school. For a compelling essay, gather interview data and statistics to support your arguments. You could include different sections correlating to why people do not enjoy this subject.
In this essay, begin by reading articles and essays about the importance of studying math. Then, write about the different ways that having proficient math skills can help you later in life. Next, use real-life examples of where maths is necessary, such as banking, shopping, planning holidays, and more! For an engaging essay, use some anecdotes from your experiences of using math in your daily life.
Many people have said that math is essential for the future and that you shouldn’t take a math class for granted. However, many also say that only a basic understanding of math is essential; the rest depends on one’s career. Is it essential to learn calculus and trigonometry? Choose your position and back up your claim with evidence.
Prasanna’s essay lists down just a few applications math has in our daily lives. For this essay, you can choose any activity, whether running, painting, or playing video games, and explain how math is used there. Then, write about mathematical concepts related to your chosen activity and explain how they are used. Finally, be sure to link it back to the importance of math, as this is essentially the topic around which your essay is based.
If you are interested in learning more, check out our essay writing tips !
For help with your essays, check out our round-up of the best essay checkers

Martin is an avid writer specializing in editing and proofreading. He also enjoys literary analysis and writing about food and travel.
View all posts

Essay on Importance of Mathematics in Our Daily Life
Students are often asked to write an essay on Importance of Mathematics in Our Daily Life in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Importance of Mathematics in Our Daily Life
Introduction.
Mathematics is a crucial part of everyday life. It helps us make sense of the world around us and solve practical problems.
Mathematics in Daily Tasks
From shopping to cooking, we use math. It helps us calculate costs, quantities, and time.
Mathematics in Professions
In professions like engineering, computer science, and finance, math is indispensable.
Mathematics in Decision Making
Math helps us make informed decisions by analyzing data and predicting outcomes.
Thus, math plays a vital role in our daily lives, making it an essential subject to learn.
250 Words Essay on Importance of Mathematics in Our Daily Life
The pervasive presence of mathematics.
Mathematics, often perceived as a complex and abstract discipline, is in fact an integral part of our everyday lives. It forms the foundation for many of the decisions we make and the actions we perform daily, from managing finances to navigating directions.
A Tool for Logical Reasoning
Mathematics fosters logical reasoning and problem-solving skills. It cultivates an analytical mindset, enabling us to break down complex problems into simpler, manageable parts. This approach is not just confined to mathematical problems but extends to various real-life situations, thereby honing our decision-making abilities.
Mathematics in Technological Advancements
The rapid progress in technology, which has become an inseparable part of our lives, is deeply rooted in mathematical principles. Algorithms, which form the basis of computing, are mathematical models. The internet, smartphones, GPS, and even AI owe their existence to mathematical concepts.
Financial Management and Mathematics
Managing personal finances, a critical life skill, is essentially a mathematical exercise. Budgeting, calculating interest, understanding the implications of loans and mortgages, or even evaluating investment options, all require a good grasp of mathematics.
Mathematics and Scientific Understanding
Mathematics is the language of science. It helps us quantitatively understand and describe the physical world around us, from the trajectory of planets to the behavior of subatomic particles.
In conclusion, mathematics is a vital part of our daily lives. It is not just a subject to be studied in school, but a tool for understanding, navigating, and shaping the world around us. Its importance cannot be overstated, as it is the foundation of critical thinking, technological progress, financial management, and scientific understanding.
500 Words Essay on Importance of Mathematics in Our Daily Life
Mathematics, often perceived as a complex and abstract subject, is in fact deeply intertwined with our daily lives. It is the foundation of numerous activities we engage in, from basic tasks such as shopping and cooking to more complex ones like planning finances or solving problems.
The Ubiquity of Mathematics
Mathematics is everywhere. It is used in our everyday activities, often without our conscious realization. When we shop, we use mathematics to calculate prices, discounts, and taxes. When we cook, we use it to measure ingredients. When we travel, we use it to calculate distances, time, and fuel consumption. Even in our leisure activities such as playing games or music, mathematics plays a crucial role in understanding patterns, probabilities, and rhythms.
Mathematics in the Professional Sphere
In the professional world, the significance of mathematics is even more pronounced. Engineers use mathematical principles to design and build infrastructure. Economists use it to predict market trends. Computer scientists use algorithms and data structures, which are fundamentally mathematical in nature, to design efficient software. Even in fields that are traditionally considered non-mathematical, such as literature and arts, mathematical concepts such as symmetry, geometry, and proportion play a key role in creating aesthetic appeal.
Mathematics and Problem-Solving
Mathematics also enhances our problem-solving skills. It teaches us to approach problems logically and systematically. It encourages us to break down complex problems into simpler parts, solve them individually, and combine the solutions to solve the original problem. This skill is not just applicable to mathematical problems but to any problem we encounter in life.
Mathematics and Critical Thinking
Furthermore, mathematics fosters critical thinking. It trains us to question assumptions, identify patterns, and draw conclusions based on evidence. It also teaches us to understand the limitations of our solutions and consider alternative approaches. These are valuable skills that can be applied in various aspects of life, from making informed decisions to evaluating the credibility of information.
Mathematics and the Digital Age
In the digital age, the importance of mathematics has grown exponentially. It is the backbone of modern technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, data analysis, cryptography, and quantum computing. Understanding mathematics is essential to navigate and thrive in this digital world.
In conclusion, mathematics is not just a subject we learn in school. It is a powerful tool that helps us understand and navigate the world around us. It enhances our problem-solving and critical thinking skills, and it opens up a world of opportunities in the professional sphere. Therefore, it is essential that we appreciate the importance of mathematics in our daily lives, and strive to improve our mathematical literacy.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Importance of Electricity in Our Life
- Essay on My Favourite Season Spring
- Essay on The Power of Social Media
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Math Essay Ideas for Students: Exploring Mathematical Concepts
Are you a student who's been tasked with writing a math essay? Don't fret! While math may seem like an abstract and daunting subject, it's actually full of fascinating concepts waiting to be explored. In this article, we'll delve into some exciting math essay ideas that will not only pique your interest but also impress your teachers. So grab your pens and calculators, and let's dive into the world of mathematics!
- The Beauty of Fibonacci Sequence
Have you ever wondered why sunflowers, pinecones, and even galaxies exhibit a mesmerizing spiral pattern? It's all thanks to the Fibonacci sequence! Explore the origin, properties, and real-world applications of this remarkable mathematical sequence. Discuss how it manifests in nature, art, and even financial markets. Unveil the hidden beauty behind these numbers and show how they shape the world around us.
- The Mathematics of Music
Did you know that music and mathematics go hand in hand? Dive into the relationship between these two seemingly unrelated fields and develop your writing skills . Explore the connection between harmonics, frequencies, and mathematical ratios. Analyze how musical scales are constructed and why certain combinations of notes create pleasant melodies while others may sound dissonant. Explore the fascinating world where numbers and melodies intertwine.
- The Geometry of Architecture
Architects have been using mathematical principles for centuries to create awe-inspiring structures. Explore the geometric concepts that underpin iconic architectural designs. From the symmetry of the Parthenon to the intricate tessellations in Islamic art, mathematics plays a crucial role in creating visually stunning buildings. Discuss the mathematical principles architects employ and how they enhance the functionality and aesthetics of their designs.
- Fractals: Nature's Infinite Complexity
Step into the mesmerizing world of fractals, where infinite complexity arises from simple patterns. Did you know that the famous Mandelbrot set , a classic example of a fractal, has been studied extensively and generated using computers? In fact, it is estimated that the Mandelbrot set requires billions of calculations to generate just a single image! This showcases the computational power and mathematical precision involved in exploring the beauty of fractal geometry.
Explore the beauty and intricacy of fractal geometry, from the famous Mandelbrot set to the Sierpinski triangle. Discuss the self-similarity and infinite iteration that define fractals and how they can be found in natural phenomena such as coastlines, clouds, and even in the structure of our lungs. Examine how fractal mathematics is applied in computer graphics, art, and the study of chaotic systems. Let the captivating world of fractals unfold before your eyes.
- The Game Theory Revolution
Game theory isn't just about playing games; it's a powerful tool used in various fields, from economics to biology. Dive into the world of strategic decision-making and explore how game theory helps us understand human behavior and predict outcomes. Discuss in your essay classic games like The Prisoner's Dilemma and examine how mathematical models can shed light on complex social interactions. Explore the cutting-edge applications of game theory in diverse fields, such as cybersecurity and evolutionary biology. If you still have difficulties choosing an idea for a math essay, find a reliable expert online. Ask them to write me an essay or provide any other academic assistance with your math assignments.
- Chaos Theory and the Butterfly Effect
While writing an essay, explore the fascinating world of chaos theory and how small changes can lead to big consequences. Discuss the famous Butterfly Effect and how it exemplifies the sensitive dependence on initial conditions. Delve into the mathematical principles behind chaotic systems and their applications in weather forecasting, population dynamics, and cryptography. Unravel the hidden order within apparent randomness and showcase the far-reaching implications of chaos theory.
- The Mathematics Behind Cryptography
In an increasingly digital world, cryptography plays a vital role in ensuring secure communication and data protection. Did you know that the global cybersecurity market is projected to reach a staggering $248.26 billion by 2023? This statistic emphasizes the growing importance of cryptography in safeguarding sensitive information.
Explore the mathematical foundations of cryptography and how it allows for the creation of unbreakable codes and encryption algorithms. Discuss the concepts of prime numbers, modular arithmetic, and public-key cryptography. Delve into the fascinating history of cryptography, from ancient times to modern-day encryption methods. In your essay, highlight the importance of mathematics in safeguarding sensitive information and the ongoing challenges faced by cryptographers.

Writing a math essay doesn't have to be a daunting task. By choosing a captivating topic and exploring the various mathematical concepts, you can turn your essay into a fascinating journey of discovery. Whether you're uncovering the beauty of the Fibonacci sequence, exploring the mathematical underpinnings of music, or delving into the game theory revolution, there's a world of possibilities waiting to be explored. So embrace the power of mathematics and let your creativity shine through your words!
Remember, these are just a few math essay ideas to get you started. Feel free to explore other mathematical concepts that ignite your curiosity. The world of mathematics is vast, and each concept has its own unique story to tell. So go ahead, unleash your inner mathematician, and embark on an exciting journey through the captivating realm of mathematical ideas!
Tobi Columb, a math expert, is a dedicated educator and explorer. He is deeply fascinated by the infinite possibilities of mathematics. Tobi's mission is to equip his students with the tools needed to excel in the realm of numbers. He also advocates for the benefits of a gluten-free lifestyle for students and people of all ages. Join Tobi on his transformative journey of mathematical mastery and holistic well-being.
Related Calculators
In case you have any suggestion, or if you would like to report a broken solver/calculator, please do not hesitate to contact us .
log in to your account
Reset password.

High School Mathematics at Work: Essays and Examples for the Education of All Students (1998)
Chapter: part one: connecting mathematics with work and life, part one— connecting mathematics with work and life.
Mathematics is the key to opportunity. No longer just the language of science, mathematics now contributes in direct and fundamental ways to business, finance, health, and defense. For students, it opens doors to careers. For citizens, it enables informed decisions. For nations, it provides knowledge to compete in a technological community. To participate fully in the world of the future, America must tap the power of mathematics. (NRC, 1989, p. 1)
The above statement remains true today, although it was written almost ten years ago in the Mathematical Sciences Education Board's (MSEB) report Everybody Counts (NRC, 1989). In envisioning a future in which all students will be afforded such opportunities, the MSEB acknowledges the crucial role played by formulae and algorithms, and suggests that algorithmic skills are more flexible, powerful, and enduring when they come from a place of meaning and understanding. This volume takes as a premise that all students can develop mathematical understanding by working with mathematical tasks from workplace and everyday contexts . The essays in this report provide some rationale for this premise and discuss some of the issues and questions that follow. The tasks in this report illuminate some of the possibilities provided by the workplace and everyday life.
Contexts from within mathematics also can be powerful sites for the development of mathematical understanding, as professional and amateur mathematicians will attest. There are many good sources of compelling problems from within mathematics, and a broad mathematics education will include experience with problems from contexts both within and outside mathematics. The inclusion of tasks in this volume is intended to highlight particularly compelling problems whose context lies outside of mathematics, not to suggest a curriculum.
The operative word in the above premise is "can." The understandings that students develop from any encounter with mathematics depend not only on the context, but also on the students' prior experience and skills, their ways of thinking, their engagement with the task, the environment in which they explore the task—including the teacher, the students, and the tools—the kinds of interactions that occur in that environment, and the system of internal and external incentives that might be associated with the activity. Teaching and learning are complex activities that depend upon evolving and rarely articulated interrelationships among teachers, students, materials, and ideas. No prescription for their improvement can be simple.
This volume may be beneficially seen as a rearticulation and elaboration of a principle put forward in Reshaping School Mathematics :
Principle 3: Relevant Applications Should be an Integral Part of the Curriculum.
Students need to experience mathematical ideas in the context in which they naturally arise—from simple counting and measurement to applications in business and science. Calculators and computers make it possible now to introduce realistic applications throughout the curriculum.
The significant criterion for the suitability of an application is whether it has the potential to engage students' interests and stimulate their mathematical thinking. (NRC, 1990, p. 38)
Mathematical problems can serve as a source of motivation for students if the problems engage students' interests and aspirations. Mathematical problems also can serve as sources of meaning and understanding if the problems stimulate students' thinking. Of course, a mathematical task that is meaningful to a student will provide more motivation than a task that does not make sense. The rationale behind the criterion above is that both meaning and motivation are required. The motivational benefits that can be provided by workplace and everyday problems are worth mentioning, for although some students are aware that certain mathematics courses are necessary in order to gain entry into particular career paths, many students are unaware of how particular topics or problem-solving approaches will have relevance in any workplace. The power of using workplace and everyday problems to teach mathematics lies not so much in motivation, however, for no con-
text by itself will motivate all students. The real power is in connecting to students' thinking.
There is growing evidence in the literature that problem-centered approaches—including mathematical contexts, "real world" contexts, or both—can promote learning of both skills and concepts. In one comparative study, for example, with a high school curriculum that included rich applied problem situations, students scored somewhat better than comparison students on algebraic procedures and significantly better on conceptual and problem-solving tasks (Schoen & Ziebarth, 1998). This finding was further verified through task-based interviews. Studies that show superior performance of students in problem-centered classrooms are not limited to high schools. Wood and Sellers (1996), for example, found similar results with second and third graders.
Research with adult learners seems to indicate that "variation of contexts (as well as the whole task approach) tends to encourage the development of general understanding in a way which concentrating on repeated routine applications of algorithms does not and cannot" (Strässer, Barr, Evans, & Wolf, 1991, p. 163). This conclusion is consistent with the notion that using a variety of contexts can increase the chance that students can show what they know. By increasing the number of potential links to the diverse knowledge and experience of the students, more students have opportunities to excel, which is to say that the above premise can promote equity in mathematics education.
There is also evidence that learning mathematics through applications can lead to exceptional achievement. For example, with a curriculum that emphasizes modeling and applications, high school students at the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics have repeatedly submitted winning papers in the annual college competition, Mathematical Contest in Modeling (Cronin, 1988; Miller, 1995).
The relationships among teachers, students, curricular materials, and pedagogical approaches are complex. Nonetheless, the literature does supports the premise that workplace and everyday problems can enhance mathematical learning, and suggests that if students engage in mathematical thinking, they will be afforded opportunities for building connections, and therefore meaning and understanding.
In the opening essay, Dale Parnell argues that traditional teaching has been missing opportunities for connections: between subject-matter and context, between academic and vocational education, between school and life, between knowledge and application, and between subject-matter disciplines. He suggests that teaching must change if more students are to learn mathematics. The question, then, is how to exploit opportunities for connections between high school mathematics and the workplace and everyday life.
Rol Fessenden shows by example the importance of mathematics in business, specifically in making marketing decisions. His essay opens with a dialogue among employees of a company that intends to expand its business into
Japan, and then goes on to point out many of the uses of mathematics, data collection, analysis, and non-mathematical judgment that are required in making such business decisions.
In his essay, Thomas Bailey suggests that vocational and academic education both might benefit from integration, and cites several trends to support this suggestion: change and uncertainty in the workplace, an increased need for workers to understand the conceptual foundations of key academic subjects, and a trend in pedagogy toward collaborative, open-ended projects. Further-more, he observes that School-to-Work experiences, first intended for students who were not planning to attend a four-year college, are increasingly being seen as useful in preparing students for such colleges. He discusses several such programs that use work-related applications to teach academic skills and to prepare students for college. Integration of academic and vocational education, he argues, can serve the dual goals of "grounding academic standards in the realistic context of workplace requirements and introducing a broader view of the potential usefulness of academic skills even for entry level workers."
Noting the importance and utility of mathematics for jobs in science, health, and business, Jean Taylor argues for continued emphasis in high school of topics such as algebra, estimation, and trigonometry. She suggests that workplace and everyday problems can be useful ways of teaching these ideas for all students.
There are too many different kinds of workplaces to represent even most of them in the classrooms. Furthermore, solving mathematics problems from some workplace contexts requires more contextual knowledge than is reasonable when the goal is to learn mathematics. (Solving some other workplace problems requires more mathematical knowledge than is reasonable in high school.) Thus, contexts must be chosen carefully for their opportunities for sense making. But for students who have knowledge of a workplace, there are opportunities for mathematical connections as well. In their essay, Daniel Chazan and Sandra Callis Bethell describe an approach that creates such opportunities for students in an algebra course for 10th through 12th graders, many of whom carried with them a "heavy burden of negative experiences" about mathematics. Because the traditional Algebra I curriculum had been extremely unsuccessful with these students, Chazan and Bethell chose to do something different. One goal was to help students see mathematics in the world around them. With the help of community sponsors, Chazen and Bethell asked students to look for mathematics in the workplace and then describe that mathematics and its applications to their classmates.
The tasks in Part One complement the points made in the essays by making direct connections to the workplace and everyday life. Emergency Calls (p. 42) illustrates some possibilities for data analysis and representation by discussing the response times of two ambulance companies. Back-of-the-Envelope Estimates (p. 45) shows how quick, rough estimates and calculations
are useful for making business decisions. Scheduling Elevators (p. 49) shows how a few simplifying assumptions and some careful reasoning can be brought together to understand the difficult problem of optimally scheduling elevators in a large office building. Finally, in the context of a discussion with a client of an energy consulting firm, Heating-Degree-Days (p. 54) illuminates the mathematics behind a common model of energy consumption in home heating.
Cronin, T. P. (1988). High school students win "college" competition. Consortium: The Newsletter of the Consortium for Mathematics and Its Applications , 26 , 3, 12.
Miller, D. E. (1995). North Carolina sweeps MCM '94. SIAM News , 28 (2).
National Research Council. (1989). Everybody counts: A report to the nation on the future of mathematics education . Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
National Research Council. (1990). Reshaping school mathematics: A philosophy and framework for curriculum . Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
Schoen, H. L. & Ziebarth, S. W. (1998). Assessment of students' mathematical performance (A Core-Plus Mathematics Project Field Test Progress Report). Iowa City: Core Plus Mathematics Project Evaluation Site, University of Iowa.
Strässer, R., Barr, G. Evans, J. & Wolf, A. (1991). Skills versus understanding. In M. Harris (Ed.), Schools, mathematics, and work (pp. 158-168). London: The Falmer Press.
Wood, T. & Sellers, P. (1996). Assessment of a problem-centered mathematics program: Third grade. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education , 27 (3), 337-353.
1— Mathematics as a Gateway to Student Success
DALE PARNELL
Oregon State University
The study of mathematics stands, in many ways, as a gateway to student success in education. This is becoming particularly true as our society moves inexorably into the technological age. Therefore, it is vital that more students develop higher levels of competency in mathematics. 1
The standards and expectations for students must be high, but that is only half of the equation. The more important half is the development of teaching techniques and methods that will help all students (rather than just some students) reach those higher expectations and standards. This will require some changes in how mathematics is taught.
Effective education must give clear focus to connecting real life context with subject-matter content for the student, and this requires a more ''connected" mathematics program. In many of today's classrooms, especially in secondary school and college, teaching is a matter of putting students in classrooms marked "English," "history," or "mathematics," and then attempting to fill their heads with facts through lectures, textbooks, and the like. Aside from an occasional lab, workbook, or "story problem," the element of contextual teaching and learning is absent, and little attempt is made to connect what students are learning with the world in which they will be expected to work and spend their lives. Often the frag-
mented information offered to students is of little use or application except to pass a test.
What we do in most traditional classrooms is require students to commit bits of knowledge to memory in isolation from any practical application—to simply take our word that they "might need it later." For many students, "later" never arrives. This might well be called the freezer approach to teaching and learning. In effect, we are handing out information to our students and saying, "Just put this in your mental freezer; you can thaw it out later should you need it." With the exception of a minority of students who do well in mastering abstractions with little contextual experience, students aren't buying that offer. The neglected majority of students see little personal meaning in what they are asked to learn, and they just don't learn it.
I recently had occasion to interview 75 students representing seven different high schools in the Northwest. In nearly all cases, the students were juniors identified as vocational or general education students. The comment of one student stands out as representative of what most of these students told me in one way or another: "I know it's up to me to get an education, but a lot of times school is just so dull and boring. … You go to this class, go to that class, study a little of this and a little of that, and nothing connects. … I would like to really understand and know the application for what I am learning." Time and again, students were asking, "Why do I have to learn this?" with few sensible answers coming from the teachers.
My own long experience as a community college president confirms the thoughts of these students. In most community colleges today, one-third to one-half of the entering students are enrolled in developmental (remedial) education, trying to make up for what they did not learn in earlier education experiences. A large majority of these students come to the community college with limited mathematical skills and abilities that hardly go beyond adding, subtracting, and multiplying with whole numbers. In addition, the need for remediation is also experienced, in varying degrees, at four-year colleges and universities.
What is the greatest sin committed in the teaching of mathematics today? It is the failure to help students use the magnificent power of the brain to make connections between the following:
- subject-matter content and the context of use;
- academic and vocational education;
- school and other life experiences;
- knowledge and application of knowledge; and
- one subject-matter discipline and another.
Why is such failure so critical? Because understanding the idea of making the connection between subject-matter content and the context of application
is what students, at all levels of education, desperately require to survive and succeed in our high-speed, high-challenge, rapidly changing world.
Educational policy makers and leaders can issue reams of position papers on longer school days and years, site-based management, more achievement tests and better assessment practices, and other "hot" topics of the moment, but such papers alone will not make the crucial difference in what students know and can do. The difference will be made when classroom teachers begin to connect learning with real-life experiences in new, applied ways, and when education reformers begin to focus upon learning for meaning.
A student may memorize formulas for determining surface area and measuring angles and use those formulas correctly on a test, thereby achieving the behavioral objectives set by the teacher. But when confronted with the need to construct a building or repair a car, the same student may well be left at sea because he or she hasn't made the connection between the formulas and their real-life application. When students are asked to consider the Pythagorean Theorem, why not make the lesson active, where students actually lay out the foundation for a small building like a storage shed?
What a difference mathematics instruction could make for students if it were to stress the context of application—as well as the content of knowledge—using the problem-solving model over the freezer model. Teaching conducted upon the connected model would help more students learn with their thinking brain, as well as with their memory brain, developing the competencies and tools they need to survive and succeed in our complex, interconnected society.
One step toward this goal is to develop mathematical tasks that integrate subject-matter content with the context of application and that are aimed at preparing individuals for the world of work as well as for post-secondary education. Since many mathematics teachers have had limited workplace experience, they need many good examples of how knowledge of mathematics can be applied to real life situations. The trick in developing mathematical tasks for use in classrooms will be to keep the tasks connected to real life situations that the student will recognize. The tasks should not be just a contrived exercise but should stay as close to solving common problems as possible.
As an example, why not ask students to compute the cost of 12 years of schooling in a public school? It is a sad irony that after 12 years of schooling most students who attend the public schools have no idea of the cost of their schooling or how their education was financed. No wonder that some public schools have difficulty gaining financial support! The individuals being served by the schools have never been exposed to the real life context of who pays for the schools and why. Somewhere along the line in the teaching of mathematics, this real life learning opportunity has been missed, along with many other similar contextual examples.
The mathematical tasks in High School Mathematics at Work provide students (and teachers) with a plethora of real life mathematics problems and
challenges to be faced in everyday life and work. The challenge for teachers will be to develop these tasks so they relate as close as possible to where students live and work every day.
Parnell, D. (1985). The neglected majority . Washington, DC: Community College Press.
Parnell, D. (1995). Why do I have to learn this ? Waco, TX: CORD Communications.
D ALE P ARNELL is Professor Emeritus of the School of Education at Oregon State University. He has served as a University Professor, College President, and for ten years as the President and Chief Executive Officer of the American Association of Community Colleges. He has served as a consultant to the National Science Foundation and has served on many national commissions, such as the Secretary of Labor's Commission on Achieving Necessary Skills (SCANS). He is the author of the book The Neglected Majority which provided the foundation for the federally-funded Tech Prep Associate Degree Program.
2— Market Launch
ROL FESSENDEN
L. L. Bean, Inc.
"OK, the agenda of the meeting is to review the status of our launch into Japan. You can see the topics and presenters on the list in front of you. Gregg, can you kick it off with a strategy review?"
"Happy to, Bob. We have assessed the possibilities, costs, and return on investment of opening up both store and catalog businesses in other countries. Early research has shown that both Japan and Germany are good candidates. Specifically, data show high preference for good quality merchandise, and a higher-than-average propensity for an active outdoor lifestyle in both countries. Education, age, and income data are quite different from our target market in the U.S., but we do not believe that will be relevant because the cultures are so different. In addition, the Japanese data show that they have a high preference for things American, and, as you know, we are a classic American company. Name recognition for our company is 14%, far higher than any of our American competition in Japan. European competitors are virtually unrecognized, and other Far Eastern competitors are perceived to be of lower quality than us. The data on these issues are quite clear.
"Nevertheless, you must understand that there is a lot of judgment involved in the decision to focus on Japan. The analyses are limited because the cultures are different and we expect different behavioral drivers. Also,
much of the data we need in Japan are simply not available because the Japanese marketplace is less well developed than in the U.S. Drivers' license data, income data, lifestyle data, are all commonplace here and unavailable there. There is little prior penetration in either country by American retailers, so there is no experience we can draw upon. We have all heard how difficult it will be to open up sales operations in Japan, but recent sales trends among computer sellers and auto parts sales hint at an easing of the difficulties.
"The plan is to open three stores a year, 5,000 square feet each. We expect to do $700/square foot, which is more than double the experience of American retailers in the U.S. but 45% less than our stores. In addition, pricing will be 20% higher to offset the cost of land and buildings. Asset costs are approximately twice their rate in the U.S., but labor is slightly less. Benefits are more thoroughly covered by the government. Of course, there is a lot of uncertainty in the sales volumes we are planning. The pricing will cover some of the uncertainty but is still less than comparable quality goods already being offered in Japan.
"Let me shift over to the competition and tell you what we have learned. We have established long-term relationships with 500 to 1000 families in each country. This is comparable to our practice in the U.S. These families do not know they are working specifically with our company, as this would skew their reporting. They keep us appraised of their catalog and shopping experiences, regardless of the company they purchase from. The sample size is large enough to be significant, but, of course, you have to be careful about small differences.
"All the families receive our catalog and catalogs from several of our competitors. They match the lifestyle, income, and education demographic profiles of the people we want to have as customers. They are experienced catalog shoppers, and this will skew their feedback as compared to new catalog shoppers.
"One competitor is sending one 100-page catalog per quarter. The product line is quite narrow—200 products out of a domestic line of 3,000. They have selected items that are not likely to pose fit problems: primarily outerwear and knit shirts, not many pants, mostly men's goods, not women's. Their catalog copy is in Kanji, but the style is a bit stilted we are told, probably because it was written in English and translated, but we need to test this hypothesis. By contrast, we have simply mailed them the same catalog we use in the U.S., even written in English.
"Customer feedback has been quite clear. They prefer our broader assortment by a ratio of 3:1, even though they don't buy most of the products. As the competitors figured, sales are focused on outerwear and knits, but we are getting more sales, apparently because they like looking at the catalog and spend more time with it. Again, we need further testing. Another hypothesis is that our brand name is simply better known.
"Interestingly, they prefer our English-language version because they find it more of an adventure to read the catalog in another language. This is probably
a built-in bias of our sampling technique because we specifically selected people who speak English. We do not expect this trend to hold in a general mailing.
"The English language causes an 8% error rate in orders, but orders are 25% larger, and 4% more frequent. If we can get them to order by phone, we can correct the errors immediately during the call.
"The broader assortment, as I mentioned, is resulting in a significantly higher propensity to order, more units per order, and the same average unit cost. Of course, paper and postage costs increase as a consequence of the larger format catalog. On the other hand, there are production efficiencies from using the same version as the domestic catalog. Net impact, even factoring in the error rate, is a significant sales increase. On the other hand, most of the time, the errors cause us to ship the wrong item which then needs to be mailed back at our expense, creating an impression in the customers that we are not well organized even though the original error was theirs.
"Final point: The larger catalog is being kept by the customer an average of 70 days, while the smaller format is only kept on average for 40 days. Assuming—we need to test this—that the length of time they keep the catalog is proportional to sales volumes, this is good news. We need to assess the overall impact carefully, but it appears that there is a significant population for which an English-language version would be very profitable."
"Thanks, Gregg, good update. Jennifer, what do you have on customer research?"
"Bob, there's far more that we need to know than we have been able to find out. We have learned that Japan is very fad-driven in apparel tastes and fascinated by American goods. We expect sales initially to sky-rocket, then drop like a stone. Later on, demand will level out at a profitable level. The graphs on page 3 [ Figure 2-1 ] show demand by week for 104 weeks, and we have assessed several scenarios. They all show a good underlying business, but the uncertainty is in the initial take-off. The best data are based on the Italian fashion boom which Japan experienced in the late 80s. It is not strictly analogous because it revolved around dress apparel instead of our casual and weekend wear. It is, however, the best information available.

FIGURE 2-1: Sales projections by week, Scenario A

FIGURE 2-2: Size distributions, U.S. vs. Japan
"Our effectiveness in positioning inventory for that initial surge will be critical to our long-term success. There are excellent data—supplied by MITI, I might add—that show that Japanese customers can be intensely loyal to companies that meet their high service expectations. That is why we prepared several scenarios. Of course, if we position inventory for the high scenario, and we experience the low one, we will experience a significant loss due to liquidations. We are still analyzing the long-term impact, however. It may still be worthwhile to take the risk if the 2-year ROI 1 is sufficient.
"We have solid information on their size scales [ Figure 2-2 ]. Seventy percent are small and medium. By comparison, 70% of Americans are large and extra large. This will be a challenge to manage but will save a few bucks on fabric.
"We also know their color preferences, and they are very different than Americans. Our domestic customers are very diverse in their tastes, but 80% of Japanese customers will buy one or two colors out of an offering of 15. We are still researching color choices, but it varies greatly for pants versus shirts, and for men versus women. We are confident we can find patterns, but we also know that it is easy to guess wrong in that market. If we guess wrong, the liquidation costs will be very high.
"Bad news on the order-taking front, however. They don't like to order by phone. …"
In this very brief exchange among decision-makers we observe the use of many critically important skills that were originally learned in public schools. Perhaps the most important is one not often mentioned, and that is the ability to convert an important business question into an appropriate mathematical one, to solve the mathematical problem, and then to explain the implications of the solution for the original business problem. This ability to inhabit simultaneously the business world and the mathematical world, to translate between the two, and, as a consequence, to bring clarity to complex, real-world issues is of extraordinary importance.
In addition, the participants in this conversation understood and interpreted graphs and tables, computed, approximated, estimated, interpolated, extrapolated, used probabilistic concepts to draw conclusions, generalized from
small samples to large populations, identified the limits of their analyses, discovered relationships, recognized and used variables and functions, analyzed and compared data sets, and created and interpreted models. Another very important aspect of their work was that they identified additional questions, and they suggested ways to shed light on those questions through additional analysis.
There were two broad issues in this conversation that required mathematical perspectives. The first was to develop as rigorous and cost effective a data collection and analysis process as was practical. It involved perhaps 10 different analysts who attacked the problem from different viewpoints. The process also required integration of the mathematical learnings of all 10 analysts and translation of the results into business language that could be understood by non-mathematicians.
The second broad issue was to understand from the perspective of the decision-makers who were listening to the presentation which results were most reliable, which were subject to reinterpretation, which were actually judgments not supported by appropriate analysis, and which were hypotheses that truly required more research. In addition, these business people would likely identify synergies in the research that were not contemplated by the analysts. These synergies need to be analyzed to determine if—mathematically—they were real. The most obvious one was where the inventory analysts said that the customers don't like to use the phone to place orders. This is bad news for the sales analysts who are counting on phone data collection to correct errors caused by language problems. Of course, we need more information to know the magnitude—or even the existance—of the problem.
In brief, the analyses that preceded the dialogue might each be considered a mathematical task in the business world:
- A cost analysis of store operations and catalogs was conducted using data from existing American and possibly other operations.
- Customer preferences research was analyzed to determine preferences in quality and life-style. The data collection itself could not be carried out by a high school graduate without guidance, but 80% of the analysis could.
- Cultural differences were recognized as a causes of analytical error. Careful analysis required judgment. In addition, sources of data were identified in the U.S., and comparable sources were found lacking in Japan. A search was conducted for other comparable retail experience, but none was found. On the other hand, sales data from car parts and computers were assessed for relevance.
- Rates of change are important in understanding how Japanese and American stores differ. Sales per square foot, price increases,
- asset costs, labor costs and so forth were compared to American standards to determine whether a store based in Japan would be a viable business.
- "Nielsen" style ratings of 1000 families were used to collect data. Sample size and error estimates were mentioned. Key drivers of behavior (lifestyle, income, education) were mentioned, but this list may not be complete. What needs to be known about these families to predict their buying behavior? What does "lifestyle" include? How would we quantify some of these variables?
- A hypothesis was presented that catalog size and product diversity drive higher sales. What do we need to know to assess the validity of this hypothesis? Another hypothesis was presented about the quality of the translation. What was the evidence for this hypothesis? Is this a mathematical question? Sales may also be proportional to the amount of time a potential customer retains the catalog. How could one ascertain this?
- Despite the abundance of data, much uncertainty remains about what to expect from sales over the first two years. Analysis could be conducted with the data about the possible inventory consequences of choosing the wrong scenario.
- One might wonder about the uncertainty in size scales. What is so difficult about identifying the colors that Japanese people prefer? Can these preferences be predicted? Will this increase the complexity of the inventory management task?
- Can we predict how many people will not use phones? What do they use instead?
As seen through a mathematical lens, the business world can be a rich, complex, and essentially limitless source of fascinating questions.
R OL F ESSENDEN is Vice-President of Inventory Planning and Control at L. L. Bean, Inc. He is also Co-Principal Investigator and Vice-Chair of Maine's State Systemic Initiative and Chair of the Strategic Planning Committee. He has previously served on the Mathematical Science Education Board, and on the National Alliance for State Science and Mathematics Coalitions (NASSMC).
3— Integrating Vocational and Academic Education
THOMAS BAILEY
Columbia University
In high school education, preparation for work immediately after high school and preparation for post-secondary education have traditionally been viewed as incompatible. Work-bound high-school students end up in vocational education tracks, where courses usually emphasize specific skills with little attention to underlying theoretical and conceptual foundations. 1 College-bound students proceed through traditional academic discipline-based courses, where they learn English, history, science, mathematics, and foreign languages, with only weak and often contrived references to applications of these skills in the workplace or in the community outside the school. To be sure, many vocational teachers do teach underlying concepts, and many academic teachers motivate their lessons with examples and references to the world outside the classroom. But these enrichments are mostly frills, not central to either the content or pedagogy of secondary school education.
Rethinking Vocational and Academic Education
Educational thinking in the United States has traditionally placed priority on college preparation. Thus the distinct track of vocational education has been seen as an option for those students who are deemed not capable of success in the more desirable academic track. As vocational programs acquired a reputation
as a ''dumping ground," a strong background in vocational courses (especially if they reduced credits in the core academic courses) has been viewed as a threat to the college aspirations of secondary school students.
This notion was further reinforced by the very influential 1983 report entitled A Nation at Risk (National Commission on Excellence in Education, 1983), which excoriated the U.S. educational system for moving away from an emphasis on core academic subjects that, according to the report, had been the basis of a previously successful American education system. Vocational courses were seen as diverting high school students from core academic activities. Despite the dubious empirical foundation of the report's conclusions, subsequent reforms in most states increased the number of academic courses required for graduation and reduced opportunities for students to take vocational courses.
The distinction between vocational students and college-bound students has always had a conceptual flaw. The large majority of students who go to four-year colleges are motivated, at least to a significant extent, by vocational objectives. In 1994, almost 247,000 bachelors degrees were conferred in business administration. That was only 30,000 less than the total number (277,500) of 1994 bachelor degree conferred in English, mathematics, philosophy, religion, physical sciences and science technologies, biological and life sciences, social sciences, and history combined . Furthermore, these "academic" fields are also vocational since many students who graduate with these degrees intend to make their living working in those fields.
Several recent economic, technological, and educational trends challenge this sharp distinction between preparation for college and for immediate post-high-school work, or, more specifically, challenge the notion that students planning to work after high school have little need for academic skills while college-bound students are best served by an abstract education with only tenuous contact with the world of work:
- First, many employers and analysts are arguing that, due to changes in the nature of work, traditional approaches to teaching vocational skills may not be effective in the future. Given the increasing pace of change and uncertainty in the workplace, young people will be better prepared, even for entry level positions and certainly for subsequent positions, if they have an underlying understanding of the scientific, mathematical, social, and even cultural aspects of the work that they will do. This has led to a growing emphasis on integrating academic and vocational education. 2
- Views about teaching and pedagogy have increasingly moved toward a more open and collaborative "student-centered" or "constructivist" teaching style that puts a great deal of emphasis on having students work together on complex, open-ended projects. This reform strategy is now widely implemented through the efforts of organizations such as the Coalition of Essential Schools, the National Center for Restructuring Education, Schools, and Teaching at
- Teachers College, and the Center for Education Research at the University of Wisconsin at Madison. Advocates of this approach have not had much interaction with vocational educators and have certainly not advocated any emphasis on directly preparing high school students for work. Nevertheless, the approach fits well with a reformed education that integrates vocational and academic skills through authentic applications. Such applications offer opportunities to explore and combine mathematical, scientific, historical, literary, sociological, economic, and cultural issues.
- In a related trend, the federal School-to-Work Opportunities Act of 1994 defines an educational strategy that combines constructivist pedagogical reforms with guided experiences in the workplace or other non-work settings. At its best, school-to-work could further integrate academic and vocational learning through appropriately designed experiences at work.
- The integration of vocational and academic education and the initiatives funded by the School-to-Work Opportunities Act were originally seen as strategies for preparing students for work after high school or community college. Some educators and policy makers are becoming convinced that these approaches can also be effective for teaching academic skills and preparing students for four-year college. Teaching academic skills in the context of realistic and complex applications from the workplace and community can provide motivational benefits and may impart a deeper understanding of the material by showing students how the academic skills are actually used. Retention may also be enhanced by giving students a chance to apply the knowledge that they often learn only in the abstract. 3
- During the last twenty years, the real wages of high school graduates have fallen and the gap between the wages earned by high school and college graduates has grown significantly. Adults with no education beyond high school have very little chance of earning enough money to support a family with a moderate lifestyle. 4 Given these wage trends, it seems appropriate and just that every high school student at least be prepared for college, even if some choose to work immediately after high school.
Innovative Examples
There are many examples of programs that use work-related applications both to teach academic skills and to prepare students for college. One approach is to organize high school programs around broad industrial or occupational areas, such as health, agriculture, hospitality, manufacturing, transportation, or the arts. These broad areas offer many opportunities for wide-ranging curricula in all academic disciplines. They also offer opportunities for collaborative work among teachers from different disciplines. Specific skills can still be taught in this format but in such a way as to motivate broader academic and theoretical themes. Innovative programs can now be found in many vocational
high schools in large cities, such as Aviation High School in New York City and the High School of Agricultural Science and Technology in Chicago. Other schools have organized schools-within-schools based on broad industry areas.
Agriculturally based activities, such as 4H and Future Farmers of America, have for many years used the farm setting and students' interest in farming to teach a variety of skills. It takes only a little imagination to think of how to use the social, economic, and scientific bases of agriculture to motivate and illustrate skills and knowledge from all of the academic disciplines. Many schools are now using internships and projects based on local business activities as teaching tools. One example among many is the integrated program offered by the Thomas Jefferson High School for Science and Technology in Virginia, linking biology, English, and technology through an environmental issues forum. Students work as partners with resource managers at the Mason Neck National Wildlife Refuge and the Mason Neck State Park to collect data and monitor the daily activities of various species that inhabit the region. They search current literature to establish a hypothesis related to a real world problem, design an experiment to test their hypothesis, run the experiment, collect and analyze data, draw conclusions, and produce a written document that communicates the results of the experiment. The students are even responsible for determining what information and resources are needed and how to access them. Student projects have included making plans for public education programs dealing with environmental matters, finding solutions to problems caused by encroaching land development, and making suggestions for how to handle the overabundance of deer in the region.
These examples suggest the potential that a more integrated education could have for all students. Thus continuing to maintain a sharp distinction between vocational and academic instruction in high school does not serve the interests of many of those students headed for four-year or two-year college or of those who expect to work after high school. Work-bound students will be better prepared for work if they have stronger academic skills, and a high-quality curriculum that integrates school-based learning into work and community applications is an effective way to teach academic skills for many students.
Despite the many examples of innovative initiatives that suggest the potential for an integrated view, the legacy of the duality between vocational and academic education and the low status of work-related studies in high school continue to influence education and education reform. In general, programs that deviate from traditional college-prep organization and format are still viewed with suspicion by parents and teachers focused on four-year college. Indeed, college admissions practices still very much favor the traditional approaches. Interdisciplinary courses, "applied" courses, internships, and other types of work experience that characterize the school-to-work strategy or programs that integrate academic and vocational education often do not fit well into college admissions requirements.
Joining Work and Learning
What implications does this have for the mathematics standards developed by the National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM)? The general principle should be to try to design standards that challenge rather than reinforce the distinction between vocational and academic instruction. Academic teachers of mathematics and those working to set academic standards need to continue to try to understand the use of mathematics in the workplace and in everyday life. Such understandings would offer insights that could suggest reform of the traditional curriculum, but they would also provide a better foundation for teaching mathematics using realistic applications. The examples in this volume are particularly instructive because they suggest the importance of problem solving, logic, and imagination and show that these are all important parts of mathematical applications in realistic work settings. But these are only a beginning.
In order to develop this approach, it would be helpful if the NCTM standards writers worked closely with groups that are setting industry standards. 5 This would allow both groups to develop a deeper understanding of the mathematics content of work.
The NCTM's Curriculum Standards for Grades 9-12 include both core standards for all students and additional standards for "college-intending" students. The argument presented in this essay suggests that the NCTM should dispense with the distinction between college intending and non-college intending students. Most of the additional standards, those intended only for the "college intending" students, provide background that is necessary or beneficial for the calculus sequence. A re-evaluation of the role of calculus in the high school curriculum may be appropriate, but calculus should not serve as a wedge to separate college-bound from non-college-bound students. Clearly, some high school students will take calculus, although many college-bound students will not take calculus either in high school or in college. Thus in practice, calculus is not a characteristic that distinguishes between those who are or are not headed for college. Perhaps standards for a variety of options beyond the core might be offered. Mathematics standards should be set to encourage stronger skills for all students and to illustrate the power and usefulness of mathematics in many settings. They should not be used to institutionalize dubious distinctions between groups of students.
Bailey, T. & Merritt, D. (1997). School-to-work for the collegebound . Berkeley, CA: National Center for Research in Vocational Education.
Hoachlander, G . (1997) . Organizing mathematics education around work . In L.A. Steen (Ed.), Why numbers count: Quantitative literacy for tomorrow's America , (pp. 122-136). New York: College Entrance Examination Board.
Levy, F. & Murnane, R. (1992). U.S. earnings levels and earnings inequality: A review of recent trends and proposed explanations. Journal of Economic Literature , 30 , 1333-1381.
National Commission on Excellence in Education. (1983). A nation at risk: The imperative for educational reform . Washington, DC: Author.
T HOMAS B AILEY is an Associate Professor of Economics Education at Teachers College, Columbia University. He is also Director of the Institute on Education and the Economy and Director of the Community College Research Center, both at Teachers College. He is also on the board of the National Center for Research in Vocational Education.
4— The Importance of Workplace and Everyday Mathematics
JEAN E. TAYLOR
Rutgers University
For decades our industrial society has been based on fossil fuels. In today's knowledge-based society, mathematics is the energy that drives the system. In the words of the new WQED television series, Life by the Numbers , to create knowledge we "burn mathematics." Mathematics is more than a fixed tool applied in known ways. New mathematical techniques and analyses and even conceptual frameworks are continually required in economics, in finance, in materials science, in physics, in biology, in medicine.
Just as all scientific and health-service careers are mathematically based, so are many others. Interaction with computers has become a part of more and more jobs, and good analytical skills enhance computer use and troubleshooting. In addition, virtually all levels of management and many support positions in business and industry require some mathematical understanding, including an ability to read graphs and interpret other information presented visually, to use estimation effectively, and to apply mathematical reasoning.
What Should Students Learn for Today's World?
Education in mathematics and the ability to communicate its predictions is more important than ever for moving from low-paying jobs into better-paying ones. For example, my local paper, The Times of Trenton , had a section "Focus
on Careers" on October 5, 1997 in which the majority of the ads were for high technology careers (many more than for sales and marketing, for example).
But precisely what mathematics should students learn in school? Mathematicians and mathematics educators have been discussing this question for decades. This essay presents some thoughts about three areas of mathematics—estimation, trigonometry, and algebra—and then some thoughts about teaching and learning.
Estimation is one of the harder skills for students to learn, even if they experience relatively little difficulty with other aspects of mathematics. Many students think of mathematics as a set of precise rules yielding exact answers and are uncomfortable with the idea of imprecise answers, especially when the degree of precision in the estimate depends on the context and is not itself given by a rule. Yet it is very important to be able to get an approximate sense of the size an answer should be, as a way to get a rough check on the accuracy of a calculation (I've personally used it in stores to detect that I've been charged twice for the same item, as well as often in my own mathematical work), a feasibility estimate, or as an estimation for tips.
Trigonometry plays a significant role in the sciences and can help us understand phenomena in everyday life. Often introduced as a study of triangle measurement, trigonometry may be used for surveying and for determining heights of trees, but its utility extends vastly beyond these triangular applications. Students can experience the power of mathematics by using sine and cosine to model periodic phenomena such as going around and around a circle, going in and out with tides, monitoring temperature or smog components changing on a 24-hour cycle, or the cycling of predator-prey populations.
No educator argues the importance of algebra for students aiming for mathematically-based careers because of the foundation it provides for the more specialized education they will need later. Yet, algebra is also important for those students who do not currently aspire to mathematics-based careers, in part because a lack of algebraic skills puts an upper bound on the types of careers to which a student can aspire. Former civil rights leader Robert Moses makes a good case for every student learning algebra, as a means of empowering students and providing goals, skills, and opportunities. The same idea was applied to learning calculus in the movie Stand and Deliver . How, then, can we help all students learn algebra?
For me personally, the impetus to learn algebra was at least in part to learn methods of solution for puzzles. Suppose you have 39 jars on three shelves. There are twice as many jars on the second shelf as the first, and four more jars on the third shelf than on the second shelf. How many jars are there on each shelf? Such problems are not important by themselves, but if they show the students the power of an idea by enabling them to solve puzzles that they'd like to solve, then they have value. We can't expect such problems to interest all students. How then can we reach more students?
Workplace and Everyday Settings as a Way of Making Sense
One of the common tools in business and industry for investigating mathematical issues is the spreadsheet, which is closely related to algebra. Writing a rule to combine the elements of certain cells to produce the quantity that goes into another cell is doing algebra, although the variables names are cell names rather than x or y . Therefore, setting up spreadsheet analyses requires some of the thinking that algebra requires.
By exploring mathematics via tasks which come from workplace and everyday settings, and with the aid of common tools like spreadsheets, students are more likely to see the relevance of the mathematics and are more likely to learn it in ways that are personally meaningful than when it is presented abstractly and applied later only if time permits. Thus, this essay argues that workplace and everyday tasks should be used for teaching mathematics and, in particular, for teaching algebra. It would be a mistake, however, to rely exclusively on such tasks, just as it would be a mistake to teach only spreadsheets in place of algebra.
Communicating the results of an analysis is a fundamental part of any use of mathematics on a job. There is a growing emphasis in the workplace on group work and on the skills of communicating ideas to colleagues and clients. But communicating mathematical ideas is also a powerful tool for learning, for it requires the student to sharpen often fuzzy ideas.
Some of the tasks in this volume can provide the kinds of opportunities I am talking about. Another problem, with clear connections to the real world, is the following, taken from the book entitled Consider a Spherical Cow: A Course in Environmental Problem Solving , by John Harte (1988). The question posed is: How does biomagnification of a trace substance occur? For example, how do pesticides accumulate in the food chain, becoming concentrated in predators such as condors? Specifically, identify the critical ecological and chemical parameters determining bioconcentrations in a food chain, and in terms of these parameters, derive a formula for the concentration of a trace substance in each link of a food chain. This task can be undertaken at several different levels. The analysis in Harte's book is at a fairly high level, although it still involves only algebra as a mathematical tool. The task could be undertaken at a more simple level or, on the other hand, it could be elaborated upon as suggested by further exercises given in that book. And the students could then present the results of their analyses to each other as well as the teacher, in oral or written form.
Concepts or Procedures?
When teaching mathematics, it is easy to spend so much time and energy focusing on the procedures that the concepts receive little if any attention. When teaching algebra, students often learn the procedures for using the quadratic formula or for solving simultaneous equations without thinking of intersections of curves and lines and without being able to apply the procedures in unfamiliar settings. Even
when concentrating on word problems, students often learn the procedures for solving "coin problems" and "train problems" but don't see the larger algebraic context. The formulas and procedures are important, but are not enough.
When using workplace and everyday tasks for teaching mathematics, we must avoid falling into the same trap of focusing on the procedures at the expense of the concepts. Avoiding the trap is not easy, however, because just like many tasks in school algebra, mathematically based workplace tasks often have standard procedures that can be used without an understanding of the underlying mathematics. To change a procedure to accommodate a changing business climate, to respond to changes in the tax laws, or to apply or modify a procedure to accommodate a similar situation, however, requires an understanding of the mathematical ideas behind the procedures. In particular, a student should be able to modify the procedures for assessing energy usage for heating (as in Heating-Degree-Days, p. 54) in order to assess energy usage for cooling in the summer.
To prepare our students to make such modifications on their own, it is important to focus on the concepts as well as the procedures. Workplace and everyday tasks can provide opportunities for students to attach meaning to the mathematical calculations and procedures. If a student initially solves a problem without algebra, then the thinking that went into his or her solution can help him or her make sense out of algebraic approaches that are later presented by the teacher or by other students. Such an approach is especially appropriate for teaching algebra, because our teaching of algebra needs to reach more students (too often it is seen by students as meaningless symbol manipulation) and because algebraic thinking is increasingly important in the workplace.
An Example: The Student/Professor Problem
To illustrate the complexity of learning algebra meaningfully, consider the following problem from a study by Clement, Lockhead, & Monk (1981):
Write an equation for the following statement: "There are six times as many students as professors at this university." Use S for the number of students and P for the number of professors. (p. 288)
The authors found that of 47 nonscience majors taking college algebra, 57% got it wrong. What is more surprising, however, is that of 150 calculus-level students, 37% missed the problem.
A first reaction to the most common wrong answer, 6 S = P , is that the students simply translated the words of the problems into mathematical symbols without thinking more deeply about the situation or the variables. (The authors note that some textbooks instruct students to use such translation.)
By analyzing transcripts of interviews with students, the authors found this approach and another (faulty) approach, as well. These students often drew a diagram showing six students and one professor. (Note that we often instruct students to draw diagrams when solving word problems.) Reasoning
from the diagram, and regarding S and P as units, the student may write 6 S = P , just as we would correctly write 12 in. = 1 ft. Such reasoning is quite sensible, though it misses the fundamental intent in the problem statement that S is to represent the number of students, not a student.
Thus, two common suggestions for students—word-for-word translation and drawing a diagram—can lead to an incorrect answer to this apparently simple problem, if the students do not more deeply contemplate what the variables are intended to represent. The authors found that students who wrote and could explain the correct answer, S = 6 P , drew upon a richer understanding of what the equation and the variables represent.
Clearly, then, we must encourage students to contemplate the meanings of variables. Yet, part of the power and efficiency of algebra is precisely that one can manipulate symbols independently of what they mean and then draw meaning out of the conclusions to which the symbolic manipulations lead. Thus, stable, long-term learning of algebraic thinking requires both mastery of procedures and also deeper analytical thinking.
Paradoxically, the need for sharper analytical thinking occurs alongside a decreased need for routine arithmetic calculation. Calculators and computers make routine calculation easier to do quickly and accurately; cash registers used in fast food restaurants sometimes return change; checkout counters have bar code readers and payment takes place by credit cards or money-access cards.
So it is education in mathematical thinking, in applying mathematical computation, in assessing whether an answer is reasonable, and in communicating the results that is essential. Teaching mathematics via workplace and everyday problems is an approach that can make mathematics more meaningful for all students. It is important, however, to go beyond the specific details of a task in order to teach mathematical ideas. While this approach is particularly crucial for those students intending to pursue careers in the mathematical sciences, it will also lead to deeper mathematical understanding for all students.
Clement, J., Lockhead, J., & Monk, G. (1981). Translation difficulties in learning mathematics. American Mathematical Monthly , 88 , 286-290.
Harte, J. (1988). Consider a spherical cow: A course in environmental problem solving . York, PA: University Science Books.
J EAN E. T AYLOR is Professor of Mathematics at Rutgers, the State University of New Jersey. She is currently a member of the Board of Directors of the American Association for the Advancement of Science and formerly chaired its Section A Nominating Committee. She has served as Vice President and as a Member-at-Large of the Council of the American Mathematical Society, and served on its Executive Committee and its Nominating Committee. She has also been a member of the Joint Policy Board for Mathematics, and a member of the Board of Advisors to The Geometry Forum (now The Mathematics Forum) and to the WQED television series, Life by the Numbers .
5— Working with Algebra
DANIEL CHAZAN
Michigan State University
SANDRA CALLIS BETHELL
Holt High School
Teaching a mathematics class in which few of the students have demonstrated success is a difficult assignment. Many teachers avoid such assignments, when possible. On the one hand, high school mathematics teachers, like Bertrand Russell, might love mathematics and believe something like the following:
Mathematics, rightly viewed, possesses not only truth, but supreme beauty—a beauty cold and austere, like that of sculpture, without appeal to any part of our weaker nature, without the gorgeous trappings of painting or music, yet sublimely pure, and capable of a stern perfection such as only the greatest art can show. … Remote from human passions, remote even from the pitiful facts of nature, the generations have gradually created an ordered cosmos, where pure thought can dwell as in its nature home, and where one, at least, of our nobler impulses can escape from the dreary exile of the natural world. (Russell, 1910, p. 73)
But, on the other hand, students may not have the luxury, in their circumstances, of appreciating this beauty. Many of them may not see themselves as thinkers because contemplation would take them away from their primary
focus: how to get by in a world that was not created for them. Instead, like Jamaica Kincaid, they may be asking:
What makes the world turn against me and all who look like me? I won nothing, I survey nothing, when I ask this question, the luxury of an answer that will fill volumes does not stretch out before me. When I ask this question, my voice is filled with despair. (Kincaid, 1996, pp. 131-132)
Our Teaching and Issues it Raised
During the 1991-92 and 1992-93 school years, we (a high school teacher and a university teacher educator) team taught a lower track Algebra I class for 10th through 12th grade students. 1 Most of our students had failed mathematics before, and many needed to pass Algebra I in order to complete their high school mathematics requirement for graduation. For our students, mathematics had become a charged subject; it carried a heavy burden of negative experiences. Many of our students were convinced that neither they nor their peers could be successful in mathematics.
Few of our students did well in other academic subjects, and few were headed on to two- or four-year colleges. But the students differed in their affiliation with the high school. Some, called ''preppies" or "jocks" by others, were active participants in the school's activities. Others, "smokers" or "stoners," were rebelling to differing degrees against school and more broadly against society. There were strong tensions between members of these groups. 2
Teaching in this setting gives added importance and urgency to the typical questions of curriculum and motivation common to most algebra classes. In our teaching, we explored questions such as the following:
- What is it that we really want high school students, especially those who are not college-intending, to study in algebra and why?
- What is the role of algebra's manipulative skills in a world with graphing calculators and computers? How do the manipulative skills taught in the traditional curriculum give students a new perspective on, and insight into, our world?
- If our teaching efforts depend on students' investment in learning, on what grounds can we appeal to them, implicitly or explicitly, for energy and effort? In a tracked, compulsory setting, how can we help students, with broad interests and talents and many of whom are not college-intending, see value in a shared exploration of algebra?
An Approach to School Algebra
As a result of thinking about these questions, in our teaching we wanted to avoid being in the position of exhorting students to appreciate the beauty or utility of algebra. Our students were frankly skeptical of arguments based on
utility. They saw few people in their community using algebra. We had also lost faith in the power of extrinsic rewards and punishments, like failing grades. Many of our students were skeptical of the power of the high school diploma to alter fundamentally their life circumstances. We wanted students to find the mathematical objects we were discussing in the world around them and thus learn to value the perspective that this mathematics might give them on their world.
To help us in this task, we found it useful to take what we call a "relationships between quantities" approach to school algebra. In this approach, the fundamental mathematical objects of study in school algebra are functions that can be represented by inputs and outputs listed in tables or sketched or plotted on graphs, as well as calculation procedures that can be written with algebraic symbols. 3 Stimulated, in part, by the following quote from August Comte, we viewed these functions as mathematical representations of theories people have developed for explaining relationships between quantities.
In the light of previous experience, we must acknowledge the impossibility of determining, by direct measurement, most of the heights and distances we should like to know. It is this general fact which makes the science of mathematics necessary. For in renouncing the hope, in almost every case, of measuring great heights or distances directly, the human mind has had to attempt to determine them indirectly, and it is thus that philosophers were led to invent mathematics. (Quoted in Serres, 1982, p. 85)
The "Sponsor" Project
Using this approach to the concept of function, during the 1992-93 school year, we designed a year-long project for our students. The project asked pairs of students to find the mathematical objects we were studying in the workplace of a community sponsor. Students visited the sponsor's workplace four times during the year—three after-school visits and one day-long excused absence from school. In these visits, the students came to know the workplace and learned about the sponsor's work. We then asked students to write a report describing the sponsor's workplace and answering questions about the nature of the mathematical activity embedded in the workplace. The questions are organized in Table 5-1 .
Using These Questions
In order to determine how the interviews could be structured and to provide students with a model, we chose to interview Sandra's husband, John Bethell, who is a coatings inspector for an engineering firm. When asked about his job, John responded, "I argue for a living." He went on to describe his daily work inspecting contractors painting water towers. Since most municipalities contract with the lowest bidder when a water tower needs to be painted, they will often hire an engineering firm to make sure that the contractor works according to specification. Since the contractor has made a low bid, there are strong
TABLE 5-1: Questions to ask in the workplace
financial incentives for the contractor to compromise on quality in order to make a profit.
In his work John does different kinds of inspections. For example, he has a magnetic instrument to check the thickness of the paint once it has been applied to the tower. When it gives a "thin" reading, contractors often question the technology. To argue for the reading, John uses the surface area of the tank, the number of paint cans used, the volume of paint in the can, and an understanding of the percentage of this volume that evaporates to calculate the average thickness of the dry coating. Other examples from his workplace involve the use of tables and measuring instruments of different kinds.
Some Examples of Students' Work
When school started, students began working on their projects. Although many of the sponsors initially indicated that there were no mathematical dimensions to their work, students often were able to show sponsors places where the mathematics we were studying was to be found. For example, Jackie worked with a crop and soil scientist. She was intrigued by the way in which measurement of weight is used to count seeds. First, her sponsor would weigh a test batch of 100 seeds to generate a benchmark weight. Then, instead of counting a large number of seeds, the scientist would weigh an amount of seeds and compute the number of seeds such a weight would contain.
Rebecca worked with a carpeting contractor who, in estimating costs, read the dimensions of rectangular rooms off an architect's blueprint, multiplied to find the area of the room in square feet (doing conversions where necessary), then multiplied by a cost per square foot (which depended on the type of carpet) to compute the cost of the carpet. The purpose of these estimates was to prepare a bid for the architect where the bid had to be as low as possible without making the job unprofitable. Rebecca used a chart ( Table 5-2 ) to explain this procedure to the class.
Joe and Mick, also working in construction, found out that in laying pipes, there is a "one by one" rule of thumb. When digging a trench for the placement of the pipe, the non-parallel sides of the trapezoidal cross section must have a slope of 1 foot down for every one foot across. This ratio guarantees that the dirt in the hole will not slide down on itself. Thus, if at the bottom of the hole, the trapezoid must have a certain width in order to fit the pipe, then on ground level the hole must be this width plus twice the depth of the hole. Knowing in advance how wide the hole must be avoids lengthy and costly trial and error.
Other students found that functions were often embedded in cultural artifacts found in the workplace. For example, a student who visited a doctor's office brought in an instrument for predicting the due dates of pregnant women, as well as providing information about average fetal weight and length ( Figure 5-1 ).
TABLE 5-2: Cost of carpet worksheet

FIGURE 5-1: Pregnancy wheel
While the complexities of organizing this sort of project should not be minimized—arranging sponsors, securing parental permission, and meeting administrators and parent concerns about the requirement of off-campus, after-school work—we remain intrigued by the potential of such projects for helping students see mathematics in the world around them. The notions of identifying central mathematical objects for a course and then developing ways of identifying those objects in students' experience seems like an important alternative to the use of application-based materials written by developers whose lives and social worlds may be quite different from those of students.
Chazen, D. (1996). Algebra for all students? Journal of Mathematical Behavior , 15 (4), 455-477.
Eckert, P. (1989). Jocks and burnouts: Social categories and identity in the high school . New York: Teachers College Press.
Fey, J. T., Heid, M. K., et al. (1995). Concepts in algebra: A technological approach . Dedham, MA: Janson Publications.
Kieran, C., Boileau, A., & Garancon, M. (1996). Introducing algebra by mean of a technology-supported, functional approach. In N. Bednarz et al. (Eds.), Approaches to algebra , (pp. 257-293). Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands.
Kincaid, J. (1996). The autobiography of my mother . New York: Farrar, Straus, Giroux.
Nemirovsky, R. (1996). Mathematical narratives, modeling and algebra. In N. Bednarz et al. (Eds.) Approaches to algebra , (pp. 197-220). Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands.
Russell, B. (1910). Philosophical Essays . London: Longmans, Green.
Schwartz, J. & Yerushalmy, M. (1992). Getting students to function in and with algebra. In G. Harel & E. Dubinsky (Eds.), The concept of function: Aspects of epistemology and pedagogy , (MAA Notes, Vol. 25, pp. 261-289). Washington, DC: Mathematical Association of America.
Serres, M. (1982). Mathematics and philosophy: What Thales saw … In J. Harari & D. Bell (Eds.), Hermes: Literature, science, philosophy , (pp. 84-97). Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins.
Thompson, P. (1993). Quantitative reasoning, complexity, and additive structures. Educational Studies in Mathematics , 25 , 165-208.
Yerushalmy, M. & Schwartz, J. L. (1993). Seizing the opportunity to make algebra mathematically and pedagogically interesting. In T. A. Romberg, E. Fennema, & T. P. Carpenter (Eds.), Integrating research on the graphical representation of functions , (pp. 41-68). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
D ANIEL C HAZAN is an Associate Professor of Teacher Education at Michigan State University. To assist his research in mathematics teaching and learning, he has taught algebra at the high school level. His interests include teaching mathematics by examining student ideas, using computers to support student exploration, and the potential for the history and philosophy of mathematics to inform teaching.
S ANDRA C ALLIS B ETHELL has taught mathematics and Spanish at Holt High School for 10 years. She has also completed graduate work at Michigan State University and Western Michigan University. She has interest in mathematics reform, particularly in meeting the needs of diverse learners in algebra courses.
Emergency Calls
A city is served by two different ambulance companies. City logs record the date, the time of the call, the ambulance company, and the response time for each 911 call ( Table 1 ). Analyze these data and write a report to the City Council (with supporting charts and graphs) advising it on which ambulance company the 911 operators should choose to dispatch for calls from this region.
TABLE 1: Ambulance dispatch log sheet, May 1–30
This problem confronts the student with a realistic situation and a body of data regarding two ambulance companies' response times to emergency calls. The data the student is provided are typically "messy"—just a log of calls and response times, ordered chronologically. The question is how to make sense of them. Finding patterns in data such as these requires a productive mixture of mathematics common sense, and intellectual detective work. It's the kind of reasoning that students should be able to do—the kind of reasoning that will pay off in the real world.
Mathematical Analysis
In this case, a numerical analysis is not especially informative. On average, the companies are about the same: Arrow has a mean response time of 11.4 minutes compared to 11.6 minutes for Metro. The spread of the data is also not very helpful. The ranges of their distributions are exactly the same: from 6 minutes to 19 minutes. The standard deviation of Arrow's response time is a little longer—4.3 minutes versus 3.4 minutes for Metro—indicating that Arrow's response times fluctuate a bit more.
Graphs of the response times (Figures 1 and 2 ) reveal interesting features. Both companies, especially Arrow, seem to have bimodal distributions, which is to say that there are two clusters of data without much data in between.

FIGURE 1: Distribution of Arrow's response times

FIGURE 2: Distribution of Metro's response times
The distributions for both companies suggest that there are some other factors at work. Might a particular driver be the problem? Might the slow response times for either company be on particular days of the week or at particular times of day? Graphs of the response time versus the time of day (Figures 3 and 4 ) shed some light on these questions.

FIGURE 3: Arrow response times by time of day

FIGURE 4: Metro response times by time of day
These graphs show that Arrow's response times were fast except between 5:30 AM and 9:00 AM, when they were about 9 minutes slower on average. Similarly, Metro's response times were fast except between about 3:30 PM and 6:30 PM, when they were about 5 minutes slower. Perhaps the locations of the companies make Arrow more susceptible to the morning rush hour and Metro more susceptible to the afternoon rush hour. On the other hand, the employees on Arrow's morning shift or Metro's afternoon shift may not be efficient. To avoid slow responses, one could recommend to the City Council that Metro be called during the morning and that Arrow be called during the afternoon. A little detective work into the sources of the differences between the companies may yield a better recommendation.
Comparisons may be drawn between two samples in various contexts—response times for various services (taxis, computer-help desks, 24-hour hot lines at automobile manufacturers) being one class among many. Depending upon the circumstances, the data may tell very different stories. Even in the situation above, if the second pair of graphs hadn't offered such clear explanations, one might have argued that although the response times for Arrow were better on average the spread was larger, thus making their "extremes" more risky. The fundamental idea is using various analysis and representation techniques to make sense of data when the important factors are not necessarily known ahead of time.
Back-of-the-Envelope Estimates
Practice "back-of-the-envelope" estimates based on rough approximations that can be derived from common sense or everyday observations. Examples:
- Consider a public high school mathematics teacher who feels that students should work five nights a week, averaging about 35 minutes a night, doing focused on-task work and who intends to grade all homework with comments and corrections. What is a reasonable number of hours per week that such a teacher should allocate for grading homework?
- How much paper does The New York Times use in a week? A paper company that wishes to make a bid to become their sole supplier needs to know whether they have enough current capacity. If the company were to store a two-week supply of newspaper, will their empty 14,000 square foot warehouse be big enough?
Some 50 years ago, physicist Enrico Fermi asked his students at the University of Chicago, "How many piano tuners are there in Chicago?" By asking such questions, Fermi wanted his students to make estimates that involved rough approximations so that their goal would be not precision but the order of magnitude of their result. Thus, many people today call these kinds of questions "Fermi questions." These generally rough calculations often require little more than common sense, everyday observations, and a scrap of paper, such as the back of a used envelope.
Scientists and mathematicians use the idea of order of magnitude , usually expressed as the closest power of ten, to give a rough sense of the size of a quantity. In everyday conversation, people use a similar idea when they talk about "being in the right ballpark." For example, a full-time job at minimum wage yields an annual income on the order of magnitude of $10,000 or 10 4 dollars. Some corporate executives and professional athletes make annual salaries on the order of magnitude of $10,000,000 or 10 7 dollars. To say that these salaries differ by a factor of 1000 or 10 3 , one can say that they differ by three orders of magnitude. Such a lack of precision might seem unscientific or unmathematical, but such approximations are quite useful in determining whether a more precise measurement is feasible or necessary, what sort of action might be required, or whether the result of a calculation is "in the right ballpark." In choosing a strategy to protect an endangered species, for example, scientists plan differently if there are 500 animals remaining than if there are 5,000. On the other hand, determining whether 5,200 or 6,300 is a better estimate is not necessary, as the strategies will probably be the same.
Careful reasoning with everyday observations can usually produce Fermi estimates that are within an order of magnitude of the exact answer (if there is one). Fermi estimates encourage students to reason creatively with approximate quantities and uncertain information. Experiences with such a process can help an individual function in daily life to determine the reasonableness of numerical calculations, of situations or ideas in the workplace, or of a proposed tax cut. A quick estimate of some revenue- or profit-enhancing scheme may show that the idea is comparable to suggesting that General Motors enter the summer sidewalk lemonade market in your neighborhood. A quick estimate could encourage further investigation or provide the rationale to dismiss the idea.
Almost any numerical claim may be treated as a Fermi question when the problem solver does not have access to all necessary background information. In such a situation, one may make rough guesses about relevant numbers, do a few calculations, and then produce estimates.
The examples are solved separately below.
Grading Homework
Although many component factors vary greatly from teacher to teacher or even from week to week, rough calculations are not hard to make. Some important factors to consider for the teacher are: how many classes he or she teaches, how many students are in each of the classes, how much experience has the teacher had in general and has the teacher previously taught the classes, and certainly, as part of teaching style, the kind of homework the teacher assigns, not to mention the teacher's efficiency in grading.
Suppose the teacher has 5 classes averaging 25 students per class. Because the teacher plans to write corrections and comments, assume that the students' papers contain more than a list of answers—they show some student work and, perhaps, explain some of the solutions. Grading such papers might take as long as 10 minutes each, or perhaps even longer. Assuming that the teacher can grade them as quickly as 3 minutes each, on average, the teacher's grading time is:

This is an impressively large number, especially for a teacher who already spends almost 25 hours/week in class, some additional time in preparation, and some time meeting with individual students. Is it reasonable to expect teachers to put in that kind of time? What compromises or other changes might the teacher make to reduce the amount of time? The calculation above offers four possibilities: Reduce the time spent on each homework paper, reduce the number of students per class, reduce the number of classes taught each day, or reduce the number of days per week that homework will be collected. If the teacher decides to spend at most 2 hours grading each night, what is the total number of students for which the teacher should have responsibility? This calculation is a partial reverse of the one above:

If the teacher still has 5 classes, that would mean 8 students per class!
The New York Times
Answering this question requires two preliminary estimates: the circulation of The New York Times and the size of the newspaper. The answers will probably be different on Sundays. Though The New York Times is a national newspaper, the number of subscribers outside the New York metropolitan area is probably small compared to the number inside. The population of the New York metropolitan area is roughly ten million people. Since most families buy at most one copy, and not all families buy The New York Times , the circulation might be about 1 million newspapers each day. (A circulation of 500,000 seems too small and 2 million seems too big.) The Sunday and weekday editions probably have different
circulations, but assume that they are the same since they probably differ by less than a factor of two—much less than an order of magnitude. When folded, a weekday edition of the paper measures about 1/2 inch thick, a little more than 1 foot long, and about 1 foot wide. A Sunday edition of the paper is the same width and length, but perhaps 2 inches thick. For a week, then, the papers would stack 6 × 1/2 + 2 = 5 inches thick, for a total volume of about 1 ft × 1 ft × 5/12 ft = 0.5 ft 3 .
The whole circulation, then, would require about 1/2 million cubic feet of paper per week, or about 1 million cubic feet for a two-week supply.
Is the company's warehouse big enough? The paper will come on rolls, but to make the estimates easy, assume it is stacked. If it were stacked 10 feet high, the supply would require 100,000 square feet of floor space. The company's 14,000 square foot storage facility will probably not be big enough as its size differs by almost an order of magnitude from the estimate. The circulation estimate and the size of the newspaper estimate should each be within a factor of 2, implying that the 100,000 square foot estimate is off by at most a factor of 4—less than an order of magnitude.
How big a warehouse is needed? An acre is 43,560 square feet so about two acres of land is needed. Alternatively, a warehouse measuring 300 ft × 300 ft (the length of a football field in both directions) would contain 90,000 square feet of floor space, giving a rough idea of the size.
After gaining some experience with these types of problems, students can be encouraged to pay close attention to the units and to be ready to make and support claims about the accuracy of their estimates. Paying attention to units and including units as algebraic quantities in calculations is a common technique in engineering and the sciences. Reasoning about a formula by paying attention only to the units is called dimensional analysis.
Sometimes, rather than a single estimate, it is helpful to make estimates of upper and lower bounds. Such an approach reinforces the idea that an exact answer is not the goal. In many situations, students could first estimate upper and lower bounds, and then collect some real data to determine whether the answer lies between those bounds. In the traditional game of guessing the number of jelly beans in a jar, for example, all students should be able to estimate within an order of magnitude, or perhaps within a factor of two. Making the closest guess, however, involves some chance.
Fermi questions are useful outside the workplace. Some Fermi questions have political ramifications:
- How many miles of streets are in your city or town? The police chief is considering increasing police presence so that every street is patrolled by car at least once every 4 hours.
- When will your town fill up its landfill? Is this a very urgent matter for the town's waste management personnel to assess in depth?
- In his 1997 State of the Union address, President Clinton renewed his call for a tax deduction of up to $10,000 for the cost of college tuition. He estimates that 16.5 million students stand to benefit. Is this a reasonable estimate of the number who might take advantage of the tax deduction? How much will the deduction cost in lost federal revenue?
Creating Fermi problems is easy. Simply ask quantitative questions for which there is no practical way to determine exact values. Students could be encouraged to make up their own. Examples are: ''How many oak trees are there in Illinois?" or "How many people in the U.S. ate chicken for dinner last night?" "If all the people in the world were to jump in the ocean, how much would it raise the water level?" Give students the opportunity to develop their own Fermi problems and to share them with each other. It can stimulate some real mathematical thinking.
Scheduling Elevators
In some buildings, all of the elevators can travel to all of the floors, while in others the elevators are restricted to stopping only on certain floors. What is the advantage of having elevators that travel only to certain floors? When is this worth instituting?
Scheduling elevators is a common example of an optimization problem that has applications in all aspects of business and industry. Optimal scheduling in general not only can save time and money, but it can contribute to safety (e.g., in the airline industry). The elevator problem further illustrates an important feature of many economic and political arguments—the dilemma of trying simultaneously to optimize several different needs.
Politicians often promise policies that will be the least expensive, save the most lives, and be best for the environment. Think of flood control or occupational safety rules, for example. When we are lucky, we can perhaps find a strategy of least cost, a strategy that saves the most lives, or a strategy that damages the environment least. But these might not be the same strategies: generally one cannot simultaneously satisfy two or more independent optimization conditions. This is an important message for students to learn, in order to become better educated and more critical consumers and citizens.
In the elevator problem, customer satisfaction can be emphasized by minimizing the average elevator time (waiting plus riding) for employees in an office building. Minimizing wait-time during rush hours means delivering many people quickly, which might be accomplished by filling the elevators and making few stops. During off-peak hours, however, minimizing wait-time means maximizing the availability of the elevators. There is no reason to believe that these two goals will yield the same strategy. Finding the best strategy for each is a mathematical problem; choosing one of the two strategies or a compromise strategy is a management decision, not a mathematical deduction.
This example serves to introduce a complex topic whose analysis is well within the range of high school students. Though the calculations require little more than arithmetic, the task puts a premium on the creation of reasonable alternative strategies. Students should recognize that some configurations (e.g., all but one elevator going to the top floor and the one going to all the others) do not merit consideration, while others are plausible. A systematic evaluation of all possible configurations is usually required to find the optimal solution. Such a systematic search of the possible solution space is important in many modeling situations where a formal optimal strategy is not known. Creating and evaluating reasonable strategies for the elevators is quite appropriate for high school student mathematics and lends itself well to thoughtful group effort. How do you invent new strategies? How do you know that you have considered all plausible strategies? These are mathematical questions, and they are especially amenable to group discussion.
Students should be able to use the techniques first developed in solving a simple case with only a few stories and a few elevators to address more realistic situations (e.g., 50 stories, five elevators). Using the results of a similar but simpler problem to model a more complicated problem is an important way to reason in mathematics. Students
need to determine what data and variables are relevant. Start by establishing the kind of building—a hotel, an office building, an apartment building? How many people are on the different floors? What are their normal destinations (e.g., primarily the ground floor or, perhaps, a roof-top restaurant). What happens during rush hours?
To be successful at the elevator task, students must first develop a mathematical model of the problem. The model might be a graphical representation for each elevator, with time on the horizontal axis and the floors represented on the vertical axis, or a tabular representation indicating the time spent on each floor. Students must identify the pertinent variables and make simplifying assumptions about which of the possible floors an elevator will visit.
This section works through some of the details in a particularly simple case. Consider an office building with six occupied floors, employing 240 people, and a ground floor that is not used for business. Suppose there are three elevators, each of which can hold 10 people. Further suppose that each elevator takes approximately 25 seconds to fill on the ground floor, then takes 5 seconds to move between floors and 15 seconds to open and close at each floor on which it stops.
Scenario One
What happens in the morning when everyone arrives for work? Assume that everyone arrives at approximately the same time and enters the elevators on the ground floor. If all elevators go to all floors and if the 240 people are evenly divided among all three elevators, each elevator will have to make 8 trips of 10 people each.
When considering a single trip of one elevator, assume for simplicity that 10 people get on the elevator at the ground floor and that it stops at each floor on the way up, because there may be an occupant heading to each floor. Adding 5 seconds to move to each floor and 15 seconds to stop yields 20 seconds for each of the six floors. On the way down, since no one is being picked up or let off, the elevator does not stop, taking 5 seconds for each of six floors for a total of 30 seconds. This round-trip is represented in Table 1 .
TABLE 1: Elevator round-trip time, Scenario one
Since each elevator makes 8 trips, the total time will be 1,400 seconds or 23 minutes, 20 seconds.
Scenario Two
Now suppose that one elevator serves floors 1–3 and, because of the longer trip, two elevators are assigned to floors 4–6. The elevators serving the top
TABLE 2: Elevator round-trip times, Scenario two
floors will save 15 seconds for each of floors 1–3 by not stopping. The elevator serving the bottom floors will save 20 seconds for each of the top floors and will save time on the return trip as well. The times for these trips are shown in Table 2 .
Assuming the employees are evenly distributed among the floors (40 people per floor), elevator A will transport 120 people, requiring 12 trips, and elevators B and C will transport 120 people, requiring 6 trips each. These trips will take 1200 seconds (20 minutes) for elevator A and 780 seconds (13 minutes) for elevators B and C, resulting in a small time savings (about 3 minutes) over the first scenario. Because elevators B and C are finished so much sooner than elevator A, there is likely a more efficient solution.
Scenario Three
The two round-trip times in Table 2 do not differ by much because the elevators move quickly between floors but stop at floors relatively slowly. This observation suggests that a more efficient arrangement might be to assign each elevator to a pair of floors. The times for such a scenario are listed in Table 3 .
Again assuming 40 employees per floor, each elevator will deliver 80 people, requiring 8 trips, taking at most a total of 920 seconds. Thus this assignment of elevators results in a time savings of almost 35% when compared with the 1400 seconds it would take to deliver all employees via unassigned elevators.
TABLE 3: Elevator round-trip times, Scenario three
Perhaps this is the optimal solution. If so, then the above analysis of this simple case suggests two hypotheses:
- The optimal solution assigns each floor to a single elevator.
- If the time for stopping is sufficiently larger than the time for moving between floors, each elevator should serve the same number of floors.
Mathematically, one could try to show that this solution is optimal by trying all possible elevator assignments or by carefully reasoning, perhaps by showing that the above hypotheses are correct. Practically, however, it doesn't matter because this solution considers only the morning rush hour and ignores periods of low use.
The assignment is clearly not optimal during periods of low use, and much of the inefficiency is related to the first hypothesis for rush hour optimization: that each floor is served by a single elevator. With this condition, if an employee on floor 6 arrives at the ground floor just after elevator C has departed, for example, she or he will have to wait nearly two minutes for elevator C to return, even if elevators A and B are idle. There are other inefficiencies that are not considered by focusing on the rush hour. Because each floor is served by a single elevator, an employee who wishes to travel from floor 3 to floor 6, for example, must go via the ground floor and switch elevators. Most employees would prefer more flexibility than a single elevator serving each floor.
At times when the elevators are not all busy, unassigned elevators will provide the quickest response and the greatest flexibility.
Because this optimal solution conflicts with the optimal rush hour solution, some compromise is necessary. In this simple case, perhaps elevator A could serve all floors, elevator B could serve floors 1-3, and elevator C could serve floors 4-6.
The second hypothesis, above, deserves some further thought. The efficiency of the rush hour solution Table 3 is due in part to the even division of employees among the floors. If employees were unevenly distributed with, say, 120 of the 240 people working on the top two floors, then elevator C would need to make 12 trips, taking a total of 1380 seconds, resulting in almost no benefit over unassigned elevators. Thus, an efficient solution in an actual building must take into account the distribution of the employees among the floors.
Because the stopping time on each floor is three times as large as the traveling time between floors (15 seconds versus 5 seconds), this solution effectively ignores the traveling time by assigning the same number of employees to each elevator. For taller buildings, the traveling time will become more significant. In those cases fewer employees should be assigned to the elevators that serve the upper floors than are assigned to the elevators that serve the lower floors.
The problem can be made more challenging by altering the number of elevators, the number of floors, and the number of individuals working on each floor. The rate of movement of elevators can be determined by observing buildings in the local area. Some elevators move more quickly than others. Entrance and exit times could also be measured by students collecting
data on local elevators. In a similar manner, the number of workers, elevators, and floors could be taken from local contexts.
A related question is, where should the elevators go when not in use? Is it best for them to return to the ground floor? Should they remain where they were last sent? Should they distribute themselves evenly among the floors? Or should they go to floors of anticipated heavy traffic? The answers will depend on the nature of the building and the time of day. Without analysis, it will not be at all clear which strategy is best under specific conditions. In some buildings, the elevators are controlled by computer programs that "learn" and then anticipate the traffic patterns in the building.
A different example that students can easily explore in detail is the problem of situating a fire station or an emergency room in a city. Here the key issue concerns travel times to the region being served, with conflicting optimization goals: average time vs. maximum time. A location that minimizes the maximum time of response may not produce the least average time of response. Commuters often face similar choices in selecting routes to work. They may want to minimize the average time, the maximum time, or perhaps the variance, so that their departure and arrival times are more predictable.
Most of the optimization conditions discussed so far have been expressed in units of time. Sometimes, however, two optimization conditions yield strategies whose outcomes are expressed in different (and sometimes incompatible) units of measurement. In many public policy issues (e.g., health insurance) the units are lives and money. For environmental issues, sometimes the units themselves are difficult to identify (e.g., quality of life).
When one of the units is money, it is easy to find expensive strategies but impossible to find ones that have virtually no cost. In some situations, such as airline safety, which balances lives versus dollars, there is no strategy that minimize lives lost (since additional dollars always produce slight increases in safety), and the strategy that minimizes dollars will be at $0. Clearly some compromise is necessary. Working with models of different solutions can help students understand the consequences of some of the compromises.
Heating-Degree-Days
An energy consulting firm that recommends and installs insulation and similar energy saving devices has received a complaint from a customer. Last summer she paid $540 to insulate her attic on the prediction that it would save 10% on her natural gas bills. Her gas bills have been higher than the previous winter, however, and now she wants a refund on the cost of the insulation. She admits that this winter has been colder than the last, but she had expected still to see some savings.
The facts: This winter the customer has used 1,102 therms, whereas last winter she used only 1,054 therms. This winter has been colder: 5,101 heating-degree-days this winter compared to 4,201 heating-degree-days last winter. (See explanation below.) How does a representative of the energy consulting firm explain to this customer that the accumulated heating-degree-days measure how much colder this winter has been, and then explain how to calculate her anticipated versus her actual savings.
Explaining the mathematics behind a situation can be challenging and requires a real knowledge of the context, the procedures, and the underlying mathematical concepts. Such communication of mathematical ideas is a powerful learning device for students of mathematics as well as an important skill for the workplace. Though the procedure for this problem involves only proportions, a thorough explanation of the mathematics behind the procedure requires understanding of linear modeling and related algebraic reasoning, accumulation and other precursors of calculus, as well as an understanding of energy usage in home heating.
The customer seems to understand that a straight comparison of gas usage does not take into account the added costs of colder weather, which can be significant. But before calculating any anticipated or actual savings, the customer needs some understanding of heating-degree-days. For many years, weather services and oil and gas companies have been using heating-degree-days to explain and predict energy usage and to measure energy savings of insulation and other devices. Similar degree-day units are also used in studying insect populations and crop growth. The concept provides a simple measure of the accumulated amount of cold or warm weather over time. In the discussion that follows, all temperatures are given in degrees Fahrenheit, although the process is equally workable using degrees Celsius.
Suppose, for example, that the minimum temperature in a city on a given day is 52 degrees and the maximum temperature is 64 degrees. The average temperature for the day is then taken to be 58 degrees. Subtracting that result from 65 degrees (the cutoff point for heating), yields 7 heating-degree-days for the day. By recording high and low temperatures and computing their average each day, heating-degree-days can be accumulated over the course of a month, a winter, or any period of time as a measure of the coldness of that period.
Over five consecutive days, for example, if the average temperatures were 58, 50, 60, 67, and 56 degrees Fahrenheit, the calculation yields 7, 15, 5, 0, and 9 heating-degree-days respectively, for a total accumulation of 36 heating-degree-days for the five days. Note that the fourth day contributes 0 heating-degree-days to the total because the temperature was above 65 degrees.
The relationship between average temperatures and heating-degree-days is represented graphically in Figure 1 . The average temperatures are shown along the solid line graph. The area of each shaded rectangle represents the number of heating-degree-days for that day, because the width of each rectangle is one day and the height of each rectangle is the number of degrees below 65 degrees. Over time, the sum of the areas of the rectangles represents the number of heating-degree-days accumulated during the period. (Teachers of calculus will recognize connections between these ideas and integral calculus.)
The statement that accumulated heating-degree-days should be proportional to gas or heating oil usage is based primarily on two assumptions: first, on a day for which the average temperature is above 65 degrees, no heating should be required, and therefore there should be no gas or heating oil usage; second, a day for which the average temperature is 25 degrees (40 heating-degree-days) should require twice as much heating as a day for which the average temperature is 45

FIGURE 1: Daily heating-degree-days
degrees (20 heating-degree-days) because there is twice the temperature difference from the 65 degree cutoff.
The first assumption is reasonable because most people would not turn on their heat if the temperature outside is above 65 degrees. The second assumption is consistent with Newton's law of cooling, which states that the rate at which an object cools is proportional to the difference in temperature between the object and its environment. That is, a house which is 40 degrees warmer than its environment will cool at twice the rate (and therefore consume energy at twice the rate to keep warm) of a house which is 20 degrees warmer than its environment.
The customer who accepts the heating-degree-day model as a measure of energy usage can compare this winter's usage with that of last winter. Because 5,101/4,201 = 1.21, this winter has been 21% colder than last winter, and therefore each house should require 21% more heat than last winter. If this customer hadn't installed the insulation, she would have required 21% more heat than last year, or about 1,275 therms. Instead, she has required only 5% more heat (1,102/1,054 = 1.05), yielding a savings of 14% off what would have been required (1,102/1,275 = .86).
Another approach to this would be to note that last year the customer used 1,054 therms/4,201 heating-degree-days = .251 therms/heating-degree-day, whereas this year she has used 1,102 therms/5,101 heating-degree-days = .216 therms/heating-degree-day, a savings of 14%, as before.
How good is the heating-degree-day model in predicting energy usage? In a home that has a thermometer and a gas meter or a gauge on a tank, students could record daily data for gas usage and high and low temperature to test the accuracy of the model. Data collection would require only a few minutes per day for students using an electronic indoor/outdoor thermometer that tracks high and low temperatures. Of course, gas used for cooking and heating water needs to be taken into account. For homes in which the gas tank has no gauge or doesn't provide accurate enough data, a similar experiment could be performed relating accumulated heating-degree-days to gas or oil usage between fill-ups.
It turns out that in well-sealed modern houses, the cutoff temperature for heating can be lower than 65 degrees (sometimes as low as 55 degrees) because of heat generated by light bulbs, appliances, cooking, people, and pets. At temperatures sufficiently below the cutoff, linearity turns out to be a good assumption. Linear regression on the daily usage data (collected as suggested above) ought to find an equation something like U = -.251( T - 65), where T is the average temperature and U is the gas usage. Note that the slope, -.251, is the gas usage per heating-degree-day, and 65 is the cutoff. Note also that the accumulation of heating-degree-days takes a linear equation and turns it into a proportion. There are some important data analysis issues that could be addressed by such an investigation. It is sometimes dangerous, for example, to assume linearity with only a few data points, yet this widely used model essentially assumes linearity from only one data point, the other point having coordinates of 65 degrees, 0 gas usage.
Over what range of temperatures, if any, is this a reasonable assumption? Is the standard method of computing average temperature a good method? If, for example, a day is mostly near 20 degrees but warms up to 50 degrees for a short time in the afternoon, is 35 heating-degree-days a good measure of the heating required that day? Computing averages of functions over time is a standard problem that can be solved with integral calculus. With knowledge of typical and extreme rates of temperature change, this could become a calculus problem or a problem for approximate solution by graphical methods without calculus, providing background experience for some of the important ideas in calculus.
Students could also investigate actual savings after insulating a home in their school district. A customer might typically see 8-10% savings for insulating roofs, although if the house is framed so that the walls act like chimneys, ducting air from the house and the basement into the attic, there might be very little savings. Eliminating significant leaks, on the other hand, can yield savings of as much as 25%.
Some U.S. Department of Energy studies discuss the relationship between heating-degree-days and performance and find the cutoff temperature to be lower in some modern houses. State energy offices also have useful documents.
What is the relationship between heating-degree-days computed using degrees Fahrenheit, as above, and heating-degree-days computed using degrees Celsius? Showing that the proper conversion is a direct proportion and not the standard Fahrenheit-Celsius conversion formula requires some careful and sophisticated mathematical thinking.
Traditionally, vocational mathematics and precollege mathematics have been separate in schools. But the technological world in which today's students will work and live calls for increasing connection between mathematics and its applications. Workplace-based mathematics may be good mathematics for everyone.
High School Mathematics at Work illuminates the interplay between technical and academic mathematics. This collection of thought-provoking essays—by mathematicians, educators, and other experts—is enhanced with illustrative tasks from workplace and everyday contexts that suggest ways to strengthen high school mathematical education.
This important book addresses how to make mathematical education of all students meaningful—how to meet the practical needs of students entering the work force after high school as well as the needs of students going on to postsecondary education.
The short readable essays frame basic issues, provide background, and suggest alternatives to the traditional separation between technical and academic mathematics. They are accompanied by intriguing multipart problems that illustrate how deep mathematics functions in everyday settings—from analysis of ambulance response times to energy utilization, from buying a used car to "rounding off" to simplify problems.
The book addresses the role of standards in mathematics education, discussing issues such as finding common ground between science and mathematics education standards, improving the articulation from school to work, and comparing SAT results across settings.
Experts discuss how to develop curricula so that students learn to solve problems they are likely to encounter in life—while also providing them with approaches to unfamiliar problems. The book also addresses how teachers can help prepare students for postsecondary education.
For teacher education the book explores the changing nature of pedagogy and new approaches to teacher development. What kind of teaching will allow mathematics to be a guide rather than a gatekeeper to many career paths? Essays discuss pedagogical implication in problem-centered teaching, the role of complex mathematical tasks in teacher education, and the idea of making open-ended tasks—and the student work they elicit—central to professional discourse.
High School Mathematics at Work presents thoughtful views from experts. It identifies rich possibilities for teaching mathematics and preparing students for the technological challenges of the future. This book will inform and inspire teachers, teacher educators, curriculum developers, and others involved in improving mathematics education and the capabilities of tomorrow's work force.
READ FREE ONLINE
Welcome to OpenBook!
You're looking at OpenBook, NAP.edu's online reading room since 1999. Based on feedback from you, our users, we've made some improvements that make it easier than ever to read thousands of publications on our website.
Do you want to take a quick tour of the OpenBook's features?
Show this book's table of contents , where you can jump to any chapter by name.
...or use these buttons to go back to the previous chapter or skip to the next one.
Jump up to the previous page or down to the next one. Also, you can type in a page number and press Enter to go directly to that page in the book.
Switch between the Original Pages , where you can read the report as it appeared in print, and Text Pages for the web version, where you can highlight and search the text.
To search the entire text of this book, type in your search term here and press Enter .
Share a link to this book page on your preferred social network or via email.
View our suggested citation for this chapter.
Ready to take your reading offline? Click here to buy this book in print or download it as a free PDF, if available.
Get Email Updates
Do you enjoy reading reports from the Academies online for free ? Sign up for email notifications and we'll let you know about new publications in your areas of interest when they're released.
Extended Essay Essentials
- Individuals and Societies
- Interdisciplinary
- Mathematics
Contact Your Librarian

Trish Pearson
she/her/hers
What's in this guide?
What's in this guide.

In this guide, you will find essential documents for writing the EE in
Essential documents include Subject Specific Guidelines and Sample Essays.
Introduction to the EE in Mathematics
From Mathematics: An Introduction:
An extended essay (EE) in mathematics is intended for students who are writing on any topic that has a mathematical focus and it need not be confined to the theory of mathematics itself.
Essays in this group are divided into six categories:
- the applicability of mathematics to solve both real and abstract problems
- the beauty of mathematics in the proving of theorems - e.g., number theory
- the history of mathematics; the origin and subsequent development of a branch of mathematics over a period of time, measured in tens, hundreds, or thousands of years
- in forging links between different branches of mathematics,
- or in bringing about a new branch of mathematics, or causing a particular branch to flourish.
For a longer general overview of an arts-related EE, see Mathematics: An Introduction . This document contains information on:
- Topic Selection
- Examples of Topics
- Treatment of the Topic
- Research Methods
- A Framework for the EE in the Mathematics.
Mathematics EE
- Mathematics Subject Specific Guidelines - A short guide on how to write the Mathematics EE
- Score Reports - See what students did (and did not do) well in these short reports from the chief examiner.
- Sample Papers - Read sample EE papers provided by IB and see how they scored
- Mathematics Subject Specific Guidelines
- 2021 Mathematics Score Report
- 2018 Mathematics Score Report
- << Previous: Languages
- Next: Sciences >>
- Last Updated: Mar 26, 2024 1:52 PM
- URL: https://uwcchina.libguides.com/extendedessayessentials
- Have your assignments done by seasoned writers. 24/7
- Contact us:
- +1 (213) 221-0069
- [email protected]

25 Interesting Math Topics: How to Write a Good Math Essay

writing good math essay
Mathematics is a fascinating world of numbers, shapes, and patterns.
Whether you are a student looking to grasp math concepts or someone who finds math intriguing, these topics will spark your curiosity and help you discover the beauty of mathematics straightforwardly and engagingly.
In this article, I will explore interesting math topics that make this subject not only understandable but also enjoyable.

Why Write About Mathematics
First, it helps demystify a subject that many find intimidating. By breaking down complex mathematical concepts into simple, understandable language, we can make math accessible to a wider audience, fostering greater understanding and appreciation.

Second, writing about mathematics allows us to showcase the practical applications of math in everyday life, from managing personal finances to solving real-world problems.
This helps readers recognize the relevance of math and its role in various fields and industries.
Additionally, writing about mathematics can inspire curiosity and a love for learning.
It encourages critical thinking and problem-solving skills, promoting intellectual growth and academic success.
Finally, mathematics is a universal language that transcends cultural and linguistic barriers.
After discussing math topics, we can connect with a global audience, fostering a sense of unity and collaboration in the pursuit of knowledge
25 Interesting Math Topics to Write On
Mathematics is a vast and intriguing field, offering a multitude of interesting topics to explore and write about.
Here are 25 such topics that promise to engage both math enthusiasts and those seeking a deeper understanding of this fascinating subject.
1. Fibonacci Sequence: Delve into the mesmerizing world of numbers with this sequence, where each number is the sum of the two preceding ones.
2. Golden Ratio: Explore the ubiquity of the golden ratio in art, architecture, and nature.
3. Prime Numbers: Investigate the mysterious properties of prime numbers and their role in cryptography.
4. Chaos Theory: Understand the unpredictability of chaotic systems and how small changes can lead to drastically different outcomes.
5. Game Theory: Examine the strategies and decision-making processes behind games and real-world situations.
6. Cryptography: Uncover the mathematical principles behind secure communication and encryption.
7. Fractals: Discover the self-replicating geometric patterns that occur in nature and mathematics.
8. Probability Theory: Dive into the world of uncertainty and randomness, where math helps us make informed predictions.

9. Number Theory: Explore the properties and relationships of integers, including divisibility and congruence.
10. Geometry of Art: Analyze how geometry and math principles influence art and design.
11. Topology: Study the properties of space that remain unchanged under continuous transformations, leading to the concept of “rubber-sheet geometry.”
12. Knot Theory: Investigate the mathematical study of knots and their applications in various fields.
13. Number Systems: Learn about different number bases, such as binary and hexadecimal, and their significance in computer science.
14. Graph Theory: Explore networks, relationships, and the mathematics of connections.
15. The Monty Hall Problem: Delight in this famous probability puzzle based on a game show scenario.
16. Calculus: Examine the principles of differentiation and integration that underlie a wide range of scientific and engineering applications.
17. The Riemann Hypothesis: Consider one of the most famous unsolved problems in mathematics involving the distribution of prime numbers.
18. Euler’s Identity: Marvel at the beauty of Euler’s equation, often described as the most elegant mathematical formula.
19. The Four-Color Theorem: Uncover the fascinating problem of coloring maps with only four colors without adjacent regions sharing the same color.
20. P vs. NP Problem: Delve into one of the most critical unsolved problems in computer science, addressing the efficiency of algorithms.
21. The Bridges of Konigsberg: Explore a classic problem in graph theory that inspired the development of topology.
22. The Birthday Paradox: Understand the surprising likelihood of shared birthdays in a group.
23. Non-Euclidean Geometry: Step into the world of geometries where Euclid’s parallel postulate doesn’t hold, leading to intriguing alternatives like hyperbolic and elliptic geometry.
24. Perfect Numbers: Learn about the properties of numbers that are the sum of their proper divisors.
25. Zero: The History of Nothing: Trace the historical and mathematical significance of the number zero and its role in the development of mathematics.
How to Write a Good Math Essay
Mathematics essays , though often perceived as daunting, can be a rewarding way to delve into the world of mathematical concepts, problem-solving, and critical thinking.
Whether you are a student assigned to write a math essay or someone who wants to explore math topics in-depth, this guide will provide you with the key steps to write a good math essay that is clear, concise, and engaging.
1. Understanding the Essay Prompt

Before you begin writing, it’s crucial to understand the essay prompt or question.
Analyze the specific topic, the scope of the essay, and any guidelines or requirements provided by your instructor.
Mostly, this initial step sets the direction for your essay and ensures you stay on topic.
2. Research and Gather Information
You need to gather relevant information and resources to write a strong math essay. This includes textbooks, academic papers, and reputable websites.
Make sure to cite your sources properly using a recognized citation style such as APA, MLA, or Chicago.
3. Structuring Your Math Essay
Start with a clear introduction that provides an overview of the topic and the main thesis or argument of your essay. This section should capture the reader’s attention and present a roadmap for what to expect.
The body of your essay is where you present your arguments, explanations, and evidence. Use clear subheadings to organize your ideas. Ensure that your arguments are logical and well-structured.
Begin by defining any important mathematical concepts or terms necessary to understand your topic.
Clearly state your main arguments or theorems. Please support them with evidence, equations, diagrams, or examples.
Explain the logical steps or mathematical reasoning behind your arguments. This can include proofs, derivations, or calculations.
Ensure your writing is clear and free from jargon that might confuse the reader. Explain complex ideas in a way that’s accessible to a broader audience.
Whenever applicable, include diagrams, graphs, or visual aids to illustrate your points. Visual representations can enhance the clarity of your essay.
Summarize your main arguments, restate your thesis, and offer a concise conclusion. Address the significance of your findings and the implications of your research or discussion.
4. Proofreading and Editing

Once you’ve written your math essay, take the time to proofread and edit it. Pay attention to grammar, spelling, punctuation, and the overall flow of your writing.
Ensure that your essay is well-organized and free from errors.
Consider seeking feedback from peers or an instructor to gain a fresh perspective.
5. Presentation and Formatting
A well-presented essay is more likely to engage the reader. Follow these formatting guidelines:
- Use a legible font (e.g., Times New Roman or Arial) in a standard size (12-point).
- Double-space your essay and include page numbers if required.
- Create a title page with your name, essay title, course information, and date.
- Use section headings and subheadings for clarity.
- Include a reference page to cite your sources appropriately.
6. Mathematical Notation and Symbols
Mathematics relies heavily on notation and symbols. Ensure that you use mathematical notation correctly and consistently.
If you introduce new symbols or terminology, define them clearly for the reader’s understanding.
7. Seek Clarification
If you encounter difficulties or ambiguities in your math essay, don’t hesitate to seek clarification from your instructor or peers.
Discussing complex mathematical concepts with others can help you refine your understanding and improve your essay.

8. Practice and Feedback
Writing math essays, like any skill, improves with practice. The more you write and receive feedback, the better you’ll become.
Take your time with initial challenges. Instead, view them as opportunities for growth and learning.
With dedication and attention to detail, you can craft a math essay that not only conveys your mathematical knowledge but also engages and informs your readers.

Josh Jasen or JJ as we fondly call him, is a senior academic editor at Grade Bees in charge of the writing department. When not managing complex essays and academic writing tasks, Josh is busy advising students on how to pass assignments. In his spare time, he loves playing football or walking with his dog around the park.
Related posts

essay writing problems
10 Essay Writing Problems and their Easy Solutions

writing essay on your phone
How to Write an Essay or paper on your Phone: 3 Easy Ways

essay writing is important
7 reasons why Writing is Important in College & in Life

ESSAY SAUCE
FOR STUDENTS : ALL THE INGREDIENTS OF A GOOD ESSAY
- Mathematics essays
Our free mathematics essay examples include popular topics such as algorithms, applied mathematics, calculus, knot theory, linear algebra, and more.
Euler’s identity
Euler’s identity is an equality found in mathematics that has been compared to a Shakespearean sonnet and described as “the most beautiful equation.” It is a special case of a foundational equation in complex arithmetic called Euler’s Formula, which the late great physicist Richard Feynman called in his lectures “our jewel” and “the most remarkable formula in … Read more
The Banach-Tarski paradox
Mathematics is seen by many as a mysterious and often unsettling subject. Answers often hide behind layers and layers of complicated equations, formulas and ciphers, the application of advanced concepts to real life is limited and I often find myself more confused after class than when I first entered. However, the real beauty of Mathematics … Read more
Pascal’s triangle, binomial theorem
What is Pascal’s Triangle? Pascal’s Triangle was named after Blaise Pascal. Pascal’s triangle starts with the number 1 and goes down the scale. When you start with one, add more numbers in a triangular shape, like a pyramid of some sort. All the numbers on the surrounding right and left sides of the triangle are … Read more
My journey of teaching and learning mathematics since embarking on a PGCE Mathematics course
Before I came to study a Post Graduate Certificate (PGCE) Mathematics course at University College London Institute of Education (UCL IOE), I had been working as an Academic Tutor at a behavioural centre, linked to a mainstream secondary school for the past 7 months. Students placed here had either learning difficulties or behaviour issues experienced … Read more
Aircraft – mathematics
Math SL Internal Assessment Lift and Drag Introduction When you look at aircrafts, they look like they shouldn’t be able to leave the ground because of how big they are. I always watched aircrafts, take off and land, over and over. According to Newton’s Third Law, every action has an equal and opposite reaction, lift … Read more
The World of Mathematics
Mathematics is often considered a useless discipline because people think they do not use advanced math in their life. It is a misunderstanding. Not using advanced math does not mean it is not vital. If you trade stocks, you will read many stock analysis reports. These reports use mathematical knowledge. Many students in the United … Read more
The history of algebra
We all use algebra. Even if it’s for the simple stuff, we use some form of algebra in our everyday lives. While reading chapters 1-10, I came across the word algebra and became quite curious about the subject for I have never really understood nor cared for it honestly, I just figured it’s the usual … Read more
Mathematics introduction
Mathematics belongs to the science discourse community. The word science means knowledge and comes from the Latin “Scientia”. In university, science is made up of a lot of discourse communities, such as Mathematics, Physics, and Chemistry. By searching the definition of science in Webster’s New Collegiate Dictionary, science is “knowledge covering general truths of the … Read more
Niels Henrik Abel
For over two centuries, mathematicians had trouble in finding a solution to the quintic equation, that is until Niels Henrik Abel formulated a theory. Abel was a Norwegian mathematician born on August 5, 1802, and his talent and potential in the field of mathematics was already present at a young age, leading him to become … Read more
The narrative of zero
Numbers surround us. They stamp our days, light our evenings, foresee our climate, and keep us on course. They drive business and support human progress. The beginning of the numerals makes disarray between the historical backdrop of mathematics and the historical backdrop of our modern numerals. The narrative of zero alludes to something can be … Read more
Emmy Noether
She was more than a mathematician to the people she met and to the people she inspired. She even has managed to inspire people long after she has passed. Emmy Noether was born on March 23, 1882 in Bavaria Germany. Growing up she wanted to go to college but back then women weren’t allowed to … Read more
Bitopological Approximation Space with Application to Data Reduction in Multivalued Information Systems
Abstract: In this work we generalize Pawlak approximation space to bitopological approximation space. One binary relation can define two subbases of two topological spaces. Membership, equillity and inclusion relations using rough approximations are defined and studied in bitopological aapproximation space. Some new measures that measure the accuracy and the quality of approximations are defined and … Read more
Statistics overview
Statistics is a form of mathematical analysis that uses quantified models, representations and synopses for a given set of experimental data or real life studies. Statistical analysis involves the process of gathering and evaluating data and then summarizing the data into a mathematical form. Statistics is a term used to summarize a process that a … Read more
Numerical Weather Prediction
You turn on the television, and often the first channel that pops up is the weather. It’s going 24/7 with predictions that go from weekly all the way down to hourly, with conditions that go from humidity to temperature. But what goes on behind the scenes is heavily entrenched in mathematics– meteorology’s backbone is a … Read more
The Mathematics of Our Universe
Abstract In this report, we start by defining key aspects of classical Lagrangian mechanics including the principle of least action and how one can use this to derive the Euler-Lagrange equations. Momentum and Conservation laws shall also be introduced, deriving relations between position, momenta and the Lagrangian of a given system. Following this, we develop … Read more
Ideas for your next mathematics essay
Stuck for a title for your next essay? Here are some ideas to inspire you:
- The Mathematics of Music: Exploring the Relationship between Mathematics and Music – This essay would examine the connections between music and mathematics, including the use of mathematical concepts in musical composition and the study of the mathematics of sound.
- The Golden Ratio: A Mathematical and Aesthetic Marvel – This essay would discuss the concept of the golden ratio and its applications in art, architecture, and design. It would explore the beauty and symmetry of this mathematical principle.
- Mathematics in Sports: Analyzing the Numbers Behind Athletic Performance – This essay would explore the use of mathematics in sports, including the use of statistics and analytics to analyze athletic performance and predict outcomes.
- Chaos Theory: The Science of Nonlinear Systems – This essay would discuss the concept of chaos theory and its applications in various fields, such as meteorology, physics, and economics. It would explore the idea that small changes in initial conditions can have a significant impact on the final outcome of a system.
- The Mathematics of Cryptography: Securing Information in the Digital Age – This essay would examine the use of mathematics in cryptography, including the principles of encryption and decryption, and how these concepts are applied to secure information in the digital age.
- Fractals: The Beauty of Infinite Complexity – This essay would explore the concept of fractals and their applications in art, nature, and science. It would discuss the beauty and complexity of these repeating patterns found in nature and how they are used in various fields of study.
- Mathematical Models in Biology: Understanding the Complexities of Life – This essay would discuss the use of mathematical models in biology, including the modeling of population growth, the spread of disease, and the behavior of organisms. It would explore how these models help scientists understand the complex systems that make up living organisms.
- The Mathematics of Finance: Analyzing Investments and Markets – This essay would examine the use of mathematics in finance, including the principles of financial analysis, investments, and risk management. It would explore how mathematics is used to understand and predict market trends.
- Geometry in Art: The Intersection of Math and Creativity – This essay would discuss the use of geometry in art, including the use of shapes, patterns, and symmetry. It would explore how artists use mathematical concepts to create beautiful and compelling works of art.
- The History of Mathematics: From Ancient Times to Modern-Day Advances – This essay would trace the history of mathematics, from its origins in ancient civilizations to modern-day advancements in the field. It would explore the contributions of key mathematicians throughout history and the evolution of mathematical concepts and principles over time.
Essay Categories:
- Accounting essays
- Architecture essays
- Business essays
- Computer science essays
- Criminology essays
- Economics essays
- Education essays
- Engineering essays
- English language essays
- Environmental studies essays
- Essay examples
- Finance essays
- Geography essays
- Health essays
- History essays
- Hospitality and tourism essays
- Human rights essays
- Information technology essays
- International relations
- Leadership essays
- Linguistics essays
- Literature essays
- Management essays
- Marketing essays
- Media essays
- Medicine essays
- Military essays
- Miscellaneous essays
- Music Essays
- Nursing essays
- Philosophy essays
- Photography and arts essays
- Politics essays
- Project management essays
- Psychology essays
- Religious studies and theology essays
- Sample essays
- Science essays
- Social work essays
- Sociology essays
- Sports essays
- Types of essay
- Zoology essays
260 Interesting Math Topics for Essays & Research Papers
Mathematics is the science of numbers and shapes. Writing about it can give you a fresh perspective and help to clarify difficult concepts. You can even use mathematical writing as a tool in problem-solving.
In this article, you will find plenty of interesting math topics. Besides, you will learn about branches of mathematics that you can choose from. And if the thought of letters and numbers makes your head swim, try our custom writing service . Our professionals will craft a paper for you in no time!
And now, let’s proceed to math essay topics and tips.
🔝 Top 10 Interesting Math Topics
✅ branches of mathematics, ✨ fun math topics.
- 🏫 Math Topics for High School
- 🎓 College Math Topics
- 🤔 Advanced Math
- 📚 Math Research
- ✏️ Math Education
- 💵 Business Math
🔍 References
- Number theory in everyday life.
- Logicist definitions of mathematics.
- Multivariable vs. vector calculus.
- 4 conditions of functional analysis.
- Random variable in probability theory.
- How is math used in cryptography?
- The purpose of homological algebra.
- Concave vs. convex in geometry.
- The philosophical problem of foundations.
- Is numerical analysis useful for machine learning?
What exactly is mathematics ? First and foremost, it is very old. Ancient Greeks and Persians were already utilizing mathematical tools. Nowadays, we consider it an interdisciplinary language.
Biologists, linguists, and sociologists alike use math in their work. And not only that, we all deal with it in our daily lives. For instance, it manifests in the measurement of time. We often need it to calculate how much our groceries cost and how much paint we need to buy to cover a wall.

Simply put, mathematics is a universal instrument for problem-solving. We can divide pure math into three branches: geometry, arithmetic, and algebra. Let’s take a closer look:
- Geometry By studying geometry, we try to comprehend our physical surroundings. Geometric shapes can be simple, like a triangle. Or, they can form complicated figures, like a rhombicosidodecahedron.
- Arithmetic Arithmetic deals with numbers and simple operations: subtraction, addition, division, and multiplication.
- Algebra Algebra is used when the exact numbers are unclear. Instead, they are replaced with letters. Businesses often need algebra to predict their sales.
It’s true that most high school students don’t like math. However, that doesn’t mean it can’t be a fun and compelling subject. In the following section, you will find plenty of enthralling mathematical topics for your paper.
If you’re struggling to start working on your essay, we have some fun and cool math topics to offer. They will definitely engage you and make the writing process enjoyable. Besides, fun math topics can show everyone that even math can be entertaining or even a bit silly.
- The link between mathematics and art – analyzing the Golden Ratio in Renaissance-era paintings.
- An evaluation of Georg Cantor’s set theory.
- The best approaches to learning math facts and developing number sense.
- Different approaches to probability as explored through analyzing card tricks.
- Chess and checkers – the use of mathematics in recreational activities.
- The five types of math used in computer science.
- Real-life applications of the Pythagorean Theorem .
- A study of the different theories of mathematical logic.
- The use of game theory in social science.
- Mathematical definitions of infinity and how to measure it.
- What is the logic behind unsolvable math problems?
- An explanation of mean, mode, and median using classroom math grades.
- The properties and geometry of a Möbius strip.
- Using truth tables to present the logical validity of a propositional expression.
- The relationship between Pascal’s Triangle and The Binomial Theorem.
- The use of different number types: the history.
- The application of differential geometry in modern architecture.
- A mathematical approach to the solution of a Rubik’s Cube.
- Comparison of predictive and prescriptive statistical analyses.
- Explaining the iterations of the Koch snowflake.
- The importance of limits in calculus.
- Hexagons as the most balanced shape in the universe.
- The emergence of patterns in chaos theory.
- What were Euclid’s contributions to the field of mathematics?
- The difference between universal algebra and abstract algebra.
🏫 Math Essay Topics for High School
When writing a math paper, you want to demonstrate that you understand a concept. It can be helpful if you need to prepare for an exam. Choose a topic from this section and decide what you want to discuss.
- Explain what we need Pythagoras’ theorem for.
- What is a hyperbola?
- Describe the difference between algebra and arithmetic.
- When is it unnecessary to use a calculator ?
- Find a connection between math and the arts.
- How do you solve a linear equation?
- Discuss how to determine the probability of rolling two dice.
- Is there a link between philosophy and math?
- What types of math do you use in your everyday life?
- What is the numerical data?
- Explain how to use the binomial theorem.
- What is the distributive property of multiplication?
- Discuss the major concepts in ancient Egyptian mathematics .
- Why do so many students dislike math?
- Should math be required in school?
- How do you do an equivalent transformation?
- Why do we need imaginary numbers?
- How can you calculate the slope of a curve?
- What is the difference between sine, cosine, and tangent?
- How do you define the cross product of two vectors?
- What do we use differential equations for?
- Investigate how to calculate the mean value.
- Define linear growth.
- Give examples of different number types.
- How can you solve a matrix?
🎓 College Math Topics for a Paper
Sometimes you need more than just formulas to explain a complex idea. That’s why knowing how to express yourself is crucial. It is especially true for college-level mathematics. Consider the following ideas for your next research project:
- What do we need n-dimensional spaces for?
- Explain how card counting works.
- Discuss the difference between a discrete and a continuous probability distribution .
- How does encryption work?
- Describe extremal problems in discrete geometry.
- What can make a math problem unsolvable?
- Examine the topology of a Möbius strip.
- What is K-theory?
- Discuss the core problems of computational geometry.
- Explain the use of set theory .
- What do we need Boolean functions for?
- Describe the main topological concepts in modern mathematics.
- Investigate the properties of a rotation matrix.
- Analyze the practical applications of game theory.
- How can you solve a Rubik’s cube mathematically?
- Explain the math behind the Koch snowflake.
- Describe the paradox of Gabriel’s Horn.
- How do fractals form?
- Find a way to solve Sudoku using math.
- Why is the Riemann hypothesis still unsolved?
- Discuss the Millennium Prize Problems.
- How can you divide complex numbers?
- Analyze the degrees in polynomial functions.
- What are the most important concepts in number theory?
- Compare the different types of statistical methods.
🤔 Advanced Topics in Math to Write a Paper on
Once you have passed the trials of basic math, you can move on to the advanced section. This area includes topology, combinatorics, logic, and computational mathematics. Check out the list below for enticing topics to write about:
- What is an abelian group?
- Explain the orbit-stabilizer theorem.
- Discuss what makes the Burnside problem influential.
- What fundamental properties do holomorphic functions have?
- How does Cauchy’s integral theorem lead to Cauchy’s integral formula?
- How do the two Picard theorems relate to each other?
- When is a trigonometric series called a Fourier series?
- Give an example of an algorithm used for machine learning.
- Compare the different types of knapsack problems.
- What is the minimum overlap problem?
- Describe the Bernoulli scheme.
- Give a formal definition of the Chinese restaurant process.
- Discuss the logistic map in relation to chaos.
- What do we need the Feigenbaum constants for?
- Define a difference equation.
- Explain the uses of the Fibonacci sequence.
- What is an oblivious transfer?
- Compare the Riemann and the Ruelle zeta functions.
- How can you use elementary embeddings in model theory?
- Analyze the problem with the wholeness axiom and Kunen’s inconsistency theorem.
- How is Lie algebra used in physics ?
- Define various cases of algebraic cycles.
- Why do we need étale cohomology groups to calculate algebraic curves?
- What does non-Euclidean geometry consist of?
- How can two lines be ultraparallel?
📚 Math Research Topics for a Paper
Choosing the right topic is crucial for a successful research paper in math. It should be hard enough to be compelling, but not exceeding your level of competence. If possible, stick to your area of knowledge. This way your task will become more manageable. Here are some ideas:
- Write about the history of calculus.
- Why are unsolved math problems significant?
- Find reasons for the gender gap in math students.
- What are the toughest mathematical questions asked today?
- Examine the notion of operator spaces.
- How can we design a train schedule for a whole country?
- What makes a number big?
- How can infinities have various sizes?
- What is the best mathematical strategy to win a game of Go?
- Analyze natural occurrences of random walks in biology.
- Explain what kind of mathematics was used in ancient Persia.
- Discuss how the Iwasawa theory relates to modular forms.
- What role do prime numbers play in encryption?
- How did the study of mathematics evolve?
- Investigate the different Tower of Hanoi solutions.
- Research Napier’s bones. How can you use them?
- What is the best mathematical way to find someone who is lost in a maze?
- Examine the Traveling Salesman Problem. Can you find a new strategy?
- Describe how barcodes function.
- Study some real-life examples of chaos theory. How do you define them mathematically?
- Compare the impact of various ground-breaking mathematical equations .
- Research the Seven Bridges of Königsberg. Relate the problem to the city of your choice.
- Discuss Fisher’s fundamental theorem of natural selection.
- How does quantum computing work?
- Pick an unsolved math problem and say what makes it so difficult.
✏️ Math Education Research Topics
For many teachers, the hardest part is to keep the students interested. When it comes to math, it can be especially challenging. It’s crucial to make complicated concepts easy to understand. That’s why we need research on math education.
- Compare traditional methods of teaching math with unconventional ones.
- How can you improve mathematical education in the U.S.?
- Describe ways of encouraging girls to pursue careers in STEM fields.
- Should computer programming be taught in high school?
- Define the goals of mathematics education .
- Research how to make math more accessible to students with learning disabilities .
- At what age should children begin to practice simple equations?
- Investigate the effectiveness of gamification in algebra classes.
- What do students gain from taking part in mathematics competitions?
- What are the benefits of moving away from standardized testing ?
- Describe the causes of “ math anxiety .” How can you overcome it?
- Explain the social and political relevance of mathematics education.
- Define the most significant issues in public school math teaching.
- What is the best way to get children interested in geometry?
- How can students hone their mathematical thinking outside the classroom?
- Discuss the benefits of using technology in math class.
- In what way does culture influence your mathematical education?
- Explore the history of teaching algebra.
- Compare math education in various countries.
- How does dyscalculia affect a student’s daily life?
- Into which school subjects can math be integrated?
- Has a mathematics degree increased in value over the last few years?
- What are the disadvantages of the Common Core Standards?
- What are the advantages of following an integrated curriculum in math?
- Discuss the benefits of Mathcamp.
🧮 Algebra Topics for a Paper
The elegance of algebra stems from its simplicity. It gives us the ability to express complex problems in short equations. The world was changed forever when Einstein wrote down the simple formula E=mc². Now, if your algebra seminar requires you to write a paper, look no further! Here are some brilliant prompts:
- Give an example of an induction proof.
- What are F-algebras used for?
- What are number problems?
- Show the importance of abstract algebraic thinking .
- Investigate the peculiarities of Fermat’s last theorem.
- What are the essentials of Boolean algebra?
- Explore the relationship between algebra and geometry.
- Compare the differences between commutative and noncommutative algebra.
- Why is Brun’s constant relevant?
- How do you factor quadratics?
- Explain Descartes’ Rule of Signs.
- What is the quadratic formula?
- Compare the four types of sequences and define them.
- Explain how partial fractions work.
- What are logarithms used for?
- Describe the Gaussian elimination.
- What does Cramer’s rule state?
- Explore the difference between eigenvectors and eigenvalues.
- Analyze the Gram-Schmidt process in two dimensions.
- Explain what is meant by “range” and “domain” in algebra.
- What can you do with determinants?
- Learn about the origin of the distance formula.
- Find the best way to solve math word problems.
- Compare the relationships between different systems of equations.
- Explore how the Rubik’s cube relates to group theory.
📏 Geometry Topics for a Research Paper
Shapes and space are the two staples of geometry. Since its appearance in ancient times, it has evolved into a major field of study. Geometry’s most recent addition, topology, explores what happens to an object if you stretch, shrink, and fold it. Things can get pretty crazy from here! The following list contains 25 interesting geometry topics:
- What are the Archimedean solids?
- Find real-life uses for a rhombicosidodecahedron.
- What is studied in projective geometry?
- Compare the most common types of transformations.
- Explain how acute square triangulation works.
- Discuss the Borromean ring configuration.
- Investigate the solutions to Buffon’s needle problem.
- What is unique about right triangles?
- Describe the notion of Dirac manifolds.
- Compare the various relationships between lines.
- What is the Klein bottle?
- How does geometry translate into other disciplines, such as chemistry and physics?
- Explore Riemannian manifolds in Euclidean space.
- How can you prove the angle bisector theorem?
- Do a research on M.C. Escher’s use of geometry.
- Find applications for the golden ratio .
- Describe the importance of circles.
- Investigate what the ancient Greeks knew about geometry.
- What does congruency mean?
- Study the uses of Euler’s formula.
- How do CT scans relate to geometry?
- Why do we need n-dimensional vectors?
- How can you solve Heesch’s problem?
- What are hypercubes?
- Analyze the use of geometry in Picasso’s paintings.
➗ Calculus Topics to Write a Paper on
You can describe calculus as a more complicated algebra. It’s a study of change over time that provides useful insights into everyday problems. Applied calculus is required in a variety of fields such as sociology, engineering, or business. Consult this list of compelling topics on a calculus paper:
- What are the differences between trigonometry, algebra, and calculus?
- Explain the concept of limits.
- Describe the standard formulas needed for derivatives.
- How can you find critical points in a graph?
- Evaluate the application of L’Hôpital’s rule.
- How do you define the area between curves?
- What is the foundation of calculus?

- How does multivariate calculus work?
- Discuss the use of Stokes’ theorem.
- What does Leibniz’s integral rule state?
- What is the Itô stochastic integral?
- Explore the influence of nonstandard analysis on probability theory.
- Research the origins of calculus.
- Who was Maria Gaetana Agnesi?
- Define a continuous function.
- What is the fundamental theorem of calculus?
- How do you calculate the Taylor series of a function?
- Discuss the ways to resolve Runge’s phenomenon.
- Explain the extreme value theorem.
- What do we need predicate calculus for?
- What are linear approximations?
- When does an integral become improper?
- Describe the Ratio and Root Tests.
- How does the method of rings work?
- Where do we apply calculus in real-life situations?
💵 Business Math Topics to Write About
You don’t have to own a company to appreciate business math. Its topics range from credits and loans to insurance, taxes, and investment. Even if you’re not a mathematician, you can use it to handle your finances. Sounds interesting? Then have a look at the following list:
- What are the essential skills needed for business math?
- How do you calculate interest rates?
- Compare business and consumer math.
- What is a discount factor?
- How do you know that an investment is reasonable?
- When does it make sense to pay a loan with another loan?
- Find useful financing techniques that everyone can use.
- How does critical path analysis work?
- Explain how loans work.
- Which areas of work utilize operations research?
- How do businesses use statistics?
- What is the economic lot scheduling problem?
- Compare the uses of different chart types.
- What causes a stock market crash?
- How can you calculate the net present value?
- Explore the history of revenue management.
- When do you use multi-period models?
- Explain the consequences of depreciation.
- Are annuities a good investment?
- Would the U.S. financially benefit from discontinuing the penny?
- What caused the United States housing crash in 2008?
- How do you calculate sales tax?
- Describe the notions of markups and markdowns.
- Investigate the math behind debt amortization.
- What is the difference between a loan and a mortgage?
With all these ideas, you are perfectly equipped for your next math paper. Good luck!
- What Is Calculus?: Southern State Community College
- What Is Mathematics?: Tennessee Tech University
- What Is Geometry?: University of Waterloo
- What Is Algebra?: BBC
- Ten Simple Rules for Mathematical Writing: Ohio State University
- Practical Algebra Lessons: Purplemath
- Topics in Geometry: Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- The Geometry Junkyard: All Topics: Donald Bren School of Information and Computer Sciences
- Calculus I: Lamar University
- Business Math for Financial Management: The Balance Small Business
- What Is Mathematics: Life Science
- What Is Mathematics Education?: University of California, Berkeley
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

Cause and effect essays examine how an event happened and what consequences it had. Gaining weight after eating lots of fast food is an example of a cause-and-effect relationship. Possible topics cover a variety of subjects ranging from mental health to history and politics. This article gives you an outline...

An analysis essay aims to break down the subject in order to understand it. You can choose to analyze a text, a process, or an idea. This article will help you write a great essay! Selecting an interesting topic makes writing a lot easier. We’ve prepared a list of excellent...

Everybody knows that being healthy requires effort. We should exercise regularly and maintain a balanced diet. However, the reward is worth it. A healthy lifestyle prevents chronic illnesses and leads to better body performance. Besides, if you improve your physical well-being, your mental health will strengthen as well! In this...

Environment affects us all, whether we want it or not. Political leaders and students alike discuss ways to tackle environmental topics & issues. Some might argue about the role humans play in all this. The fact remains that our environment is a delicate matter. That’s why we must educate ourselves...

Our code of ethics is derived from what we think is right or wrong. On top of that, we have to agree to the moral standards established by the society we live in. Conventional norms generally label theft, murder, or harassment as bad. However, there are many influences that impact...

A definition explains the meaning of a term or a concept. In a dictionary, you’ll find a definition in a single sentence. A definition paper, however, encompasses several paragraphs. Such an essay, amongst other things, can include personal experience and examples. To write a successful definition paper, you need to...

As simple as it is, the purpose of the descriptive essay is to explain or portray its subject. It can focus on any topic or issue you want to write about. Be sure that any middle school, high school, or college student can manage this type of creative writing assignment!...

Rhetorical analysis essay focuses on assessing the method used for delivering a message. This assignment isn’t about giving an opinion on the topic. The purpose is to analyze how the author presents the argument and whether or not they succeeded. Keep reading to find out more strategies and prompts for...

A narrative essay tells a story about a series of events. At the core of this kind of essay can be a personal experience or a fictional plot. Any story can be a basis for a narrative essay! Narratives can look similar to descriptions. Still, they are different. A descriptive...

Similar to the instructions in a recipe book, process essays convey information in a step-by-step format. In this type of paper, you follow a structured chronological process. You can also call it a how-to essay. A closely related type is a process analysis essay. Here you have to carefully consider...

In a classification essay, you divide the subject into categories. To create these categories, you single out certain attributes of things. You can classify them according to their characteristics, themes, or traits. Sounds complicated? Be sure that any high school or college student can manage this type of essay!

Throughout your high school years, you are likely to write many evaluative papers. In an evaluation essay you aim is to justify your point of view through evidence.
I need a writer on algebra. I am a PhD student.Can i be helped by anybody/expert?
Please I want to do my MPhil research on algebra if you can help me
shall your university help me on research in mathematics ?
how I get the full pdf of those tittles
Print as pdf.

Extended Essay: Group 5: Mathematics
- General Timeline
- Group 1: English Language and Literature
- Group 2: Language Acquisition
- Group 3: Individuals and Societies
- Group 4: Sciences
- Group 5: Mathematics
- Group 6: The Arts
- Interdisciplinary essays
- Six sub-categories for WSEE
- IB Interdisciplinary EE Assessment Guide
- Brainstorming
- Pre-Writing
- Research Techniques
- The Research Question
- Paraphrasing, Summarising and Quotations
- Writing an EE Introduction
- Writing the main body of your EE
- Writing your EE Conclusion
- Sources: Finding, Organising and Evaluating Them
- Conducting Interviews and Surveys
- Citing and Referencing
- Check-in Sessions
- First Formal Reflection
- Second Formal Reflection
- Final Reflection (Viva Voce)
- Researcher's Reflection Space (RRS) Examples
- Information for Supervisors
- How is the EE Graded?
- EE Online Resources
- Stavanger Public Library
- Exemplar Essays
- Extended Essay Presentations
- ISS High School Academic Honesty Policy
Mathematics

An extended essay (EE) in mathematics is intended for students who are writing on any topic that has a mathematical focus and it need not be confined to the theory of mathematics itself.
Essays in this group are divided into six categories:
- the applicability of mathematics to solve both real and abstract problems
- the beauty of mathematics—eg geometry or fractal theory
- the elegance of mathematics in the proving of theorems—eg number theory
- the history of mathematics: the origin and subsequent development of a branch of mathematics over a period of time, measured in tens, hundreds or thousands of years
- the effect of technology on mathematics:
- in forging links between different branches of mathematics,
- or in bringing about a new branch of mathematics, or causing a particular branch to flourish.
These are just some of the many different ways that mathematics can be enjoyable or useful, or, as in many cases, both.
For an Introduction in a Mathematics EE look HERE .
Choice of topic
The EE may be written on any topic that has a mathematical focus and it need not be confined to the theory of mathematics itself.
Students may choose mathematical topics from fields such as engineering, the sciences or the social sciences, as well as from mathematics itself.
Statistical analyses of experimental results taken from other subject areas are also acceptable, provided that they focus on the modeling process and discuss the limitations of the results; such essays should not include extensive non-mathematical detail.
A topic selected from the history of mathematics may also be appropriate, provided that a clear line of mathematical development is demonstrated. Concentration on the lives of, or personal rivalries between, mathematicians would be irrelevant and would not score highly on the assessment criteria.
It should be noted that the assessment criteria give credit for the nature of the investigation and for the extent that reasoned arguments are applied to an appropriate research question.
Students should avoid choosing a topic that gives rise to a trivial research question or one that is not sufficiently focused to allow appropriate treatment within the requirements of the EE.
Students will normally be expected either to extend their knowledge beyond that encountered in the Diploma Programme mathematics course they are studying or to apply techniques used in their mathematics course to modeling in an appropriately chosen topic.
However, it is very important to remember that it is an essay that is being written, not a research paper for a journal of advanced mathematics, and no result, however impressive, should be quoted without evidence of the student’s real understanding of it.
Example and Treatment of Topic
Examples of topics
These examples are just for guidance. Students must ensure their choice of topic is focused (left-hand column) rather than broad (right-hand column

Treatment of the topic
Whatever the title of the EE, students must apply good mathematical practice that is relevant to the
chosen topic, including:
• data analysed using appropriate techniques
• arguments correctly reasoned
• situations modeled using correct methodology
• problems clearly stated and techniques at the correct level of sophistication applied to their solution.
Research methods
Students must be advised that mathematical research is a long-term and open-ended exploration of a set of related mathematical problems that are based on personal observations.
The answers to these problems connect to and build upon each other over time.
Students’ research should be guided by analysis of primary and secondary sources.
A primary source for research in mathematics involves:
• data-gathering
• visualization
• abstraction
• conjecturing
• proof.
A secondary source of research refers to a comprehensive review of scholarly work, including books, journal articles or essays in an edited collection.
A literature review for mathematics might not be as extensive as in other subjects, but students are expected to demonstrate their knowledge and understanding of the mathematics they are using in the context of the broader discipline, for example how the mathematics they are using has been applied before, or in a different area to the one they are investigating.
Writing the essay
Throughout the EE students should communicate mathematically:
• describing their way of thinking
• writing definitions and conjectures
• using symbols, theorems, graphs and diagrams
• justifying their conclusions.
There must be sufficient explanation and commentary throughout the essay to ensure that the reader does not lose sight of its purpose in a mass of mathematical symbols, formulae and analysis.
The unique disciplines of mathematics must be respected throughout. Relevant graphs and diagrams are often important and should be incorporated in the body of the essay, not relegated to an appendix.
However, lengthy printouts, tables of results and computer programs should not be allowed to interrupt the development of the essay, and should appear separately as footnotes or in an appendix. Proofs of key results may be included, but proofs of standard results should be either omitted or, if they illustrate an important point, included in an appendix.
Examples of topics, research questions and suggested approaches
Once students have identified their topic and written their research question, they can decide how to
research their answer. They may find it helpful to write a statement outlining their broad approach. These
examples are for guidance only.

An important note on “double-dipping”
Students must ensure that their EE does not duplicate other work they are submitting for the Diploma Programme. For example, students are not permitted to repeat any of the mathematics in their IA in their EE, or vice versa.
The mathematics EE and internal assessment
An EE in mathematics is not an extension of the internal assessment (IA) task. Students must ensure that they understand the differences between the two.
- The EE is a more substantial piece of work that requires formal research
- The IA is an exploration of an idea in mathematics.
It is not appropriate for a student to choose the same topic for an EE as the IA. There would be too much danger of duplication and it must therefore be discouraged.
- << Previous: Group 4: Sciences
- Next: Group 6: The Arts >>
- Last Updated: May 17, 2024 8:11 AM
- URL: https://isstavanger.libguides.com/c.php?g=695888
Mathematics: Discovered or Created? Essay (Critical Writing)
Mathematics is a branch of science that has had far-reaching impacts on many spheres of life. Through mathematics, man has made remarkable advances in technology and other fields of life. Mathematics also provides us with a logical order for describing the various prototypes and structures that comprise nature. Mathematics is also responsible for some of the greatest breakthroughs that have been made by humanity so far.
For instance, mathematics has played a hand in humanity’s foray into the cosmos and it has been responsible for the modern internet advancements. Albert Einstein once asked, “How can it be that mathematics, being after all a product of human thought which is independent of experience, is so admirably appropriate to the objects of reality?” (Ernest 9). This question is part of a big debate on whether math is a product of human creation or human discovery. Consequently, if math is part of human discovery what are some of the laws and notions that are subject to this discovery? This paper explores the issues surrounding the debate on whether math is a product of human creation or human discovery.
First, it is important to note that math acts like the outline to our universe. Many mathematicians agree that the universe is governed by a singular order that is defined using mathematical principles. Consequently, even if the universe ceased to exist, all mathematical principles would still be true. Therefore, like other aspects of human nature, mathematics is part of human discovery. Furthermore, there are several mathematical principles that are yet to be discovered. When these principles are discovered, they “will then assist us in building models that will give us predictive power and understanding of the physical phenomena we seek to control” (Ernest 10). Therefore, math is a natural concept that is to be discovered and used by humanity. This argument is common among lovers of mathematics.
Another viable explanation of the existence of mathematics is that it is merely part of the human creation. The argument about math being part of the intricate web of nature could be easily refuted by the view that human beings invented mathematics as a tool that could aid in the description of the physical world. Therefore, mathematics is only popular among human beings because it suits their needs when they are exploring the world.
It is also true that some mathematical concepts have been changed and altered for them to be palatable to human beings. Furthermore, if the universe ceased to exist, there would be no need for mathematics and it would not exist. Mathematics has been made possible by geography, astronomy, and physics among other areas of universal studies. Mathematics exists solely to satisfy the needs of studying and understanding the universe but it is not part of these studies. Therefore, mathematics is not something that is discovered but it is a human creation.
These two arguments form the basis of our understanding of the institution of mathematics. However, in my understanding, mathematics is a human creation. The argument for mathematics being part of human discovery is far-fetched and fanatical. For instance, mathematics only describes certain variables of the physical universe. There are several other factors of the universe that cannot be defined or explained by mathematical concepts. Therefore, the argument about mathematics being part of human discovery can be nullified by the idea that there are discoveries that are outside of the mathematical realm. In my view, when discoveries about the physical world are made, man proceeds to create mathematical concepts that can help him analyze and explain these new discoveries.
Works Cited
Ernest, Paul. “Is mathematics discovered or invented.” Philosophy of Mathematics Education Journal 12.1 (2009): 9-13. Print.
- Albert Einstein’s Contributions to Science
- Albert Einstein, His Life and Career
- Women Mathematicians: Maria Agnesi, Sophie Germain
- Statistical Thinking and Collection of Information
- Quantitative Approach to Research
- Statistics: Chi-Square Test and Regression Analysis
- P-Value Definition and Role
- Statistical Process in Data Analysis
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2020, June 7). Mathematics: Discovered or Created? https://ivypanda.com/essays/mathematics-discovered-or-created/
"Mathematics: Discovered or Created?" IvyPanda , 7 June 2020, ivypanda.com/essays/mathematics-discovered-or-created/.
IvyPanda . (2020) 'Mathematics: Discovered or Created'. 7 June.
IvyPanda . 2020. "Mathematics: Discovered or Created?" June 7, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/mathematics-discovered-or-created/.
1. IvyPanda . "Mathematics: Discovered or Created?" June 7, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/mathematics-discovered-or-created/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Mathematics: Discovered or Created?" June 7, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/mathematics-discovered-or-created/.
“What is Mathematics?” and why we should ask, where one should experience and learn that, and how to teach it
- Conference paper
- Open Access
- First Online: 02 November 2017
- Cite this conference paper
You have full access to this open access conference paper

- Günter M. Ziegler 3 &
- Andreas Loos 4
Part of the book series: ICME-13 Monographs ((ICME13Mo))
110k Accesses
9 Citations
3 Altmetric
“What is Mathematics?” [with a question mark!] is the title of a famous book by Courant and Robbins, first published in 1941, which does not answer the question. The question is, however, essential: The public image of the subject (of the science, and of the profession) is not only relevant for the support and funding it can get, but it is also crucial for the talent it manages to attract—and thus ultimately determines what mathematics can achieve, as a science, as a part of human culture, but also as a substantial component of economy and technology. In this lecture we thus
discuss the image of mathematics (where “image” might be taken literally!),
sketch a multi-facetted answer to the question “What is Mathematics?,”
stress the importance of learning “What is Mathematics” in view of Klein’s “double discontinuity” in mathematics teacher education,
present the “Panorama project” as our response to this challenge,
stress the importance of telling stories in addition to teaching mathematics, and finally,
suggest that the mathematics curricula at schools and at universities should correspondingly have space and time for at least three different subjects called Mathematics.
This paper is a slightly updated reprint of: Günter M. Ziegler and Andreas Loos, Learning and Teaching “ What is Mathematics ”, Proc. International Congress of Mathematicians, Seoul 2014, pp. 1201–1215; reprinted with kind permission by Prof. Hyungju Park, the chairman of ICM 2014 Organizing Committee.
You have full access to this open access chapter, Download conference paper PDF
Similar content being viewed by others

The Missing Element for Teachers: Learning What Mathematics Is

Educational Paths to Mathematics: Which Paths Forward to What Mathematics?

Mathematics at the Center of Distinct Fields: A Response to Michael and Ted
What is mathematics.
Defining mathematics. According to Wikipedia in English, in the March 2014 version, the answer to “What is Mathematics?” is
Mathematics is the abstract study of topics such as quantity (numbers), [2] structure, [3] space, [2] and change. [4][5][6] There is a range of views among mathematicians and philosophers as to the exact scope and definition of mathematics. [7][8] Mathematicians seek out patterns (Highland & Highland, 1961 , 1963 ) and use them to formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proof. When mathematical structures are good models of real phenomena, then mathematical reasoning can provide insight or predictions about nature. Through the use of abstraction and logic, mathematics developed from counting, calculation, measurement, and the systematic study of the shapes and motions of physical objects. Practical mathematics has been a human activity for as far back as written records exist. The research required to solve mathematical problems can take years or even centuries of sustained inquiry.
None of this is entirely wrong, but it is also not satisfactory. Let us just point out that the fact that there is no agreement about the definition of mathematics, given as part of a definition of mathematics, puts us into logical difficulties that might have made Gödel smile. Footnote 1
The answer given by Wikipedia in the current German version, reads (in our translation):
Mathematics […] is a science that developed from the investigation of geometric figures and the computing with numbers. For mathematics , there is no commonly accepted definition; today it is usually described as a science that investigates abstract structures that it created itself by logical definitions using logic for their properties and patterns.
This is much worse, as it portrays mathematics as a subject without any contact to, or interest from, a real world.
The borders of mathematics. Is mathematics “stand-alone”? Could it be defined without reference to “neighboring” subjects, such as physics (which does appear in the English Wikipedia description)? Indeed, one possibility to characterize mathematics describes the borders/boundaries that separate it from its neighbors. Even humorous versions of such “distinguishing statements” such as
“Mathematics is the part of physics where the experiments are cheap.”
“Mathematics is the part of philosophy where (some) statements are true—without debate or discussion.”
“Mathematics is computer science without electricity.” (So “Computer science is mathematics with electricity.”)
contain a lot of truth and possibly tell us a lot of “characteristics” of our subject. None of these is, of course, completely true or completely false, but they present opportunities for discussion.
What we do in mathematics . We could also try to define mathematics by “what we do in mathematics”: This is much more diverse and much more interesting than the Wikipedia descriptions! Could/should we describe mathematics not only as a research discipline and as a subject taught and learned at school, but also as a playground for pupils, amateurs, and professionals, as a subject that presents challenges (not only for pupils, but also for professionals as well as for amateurs), as an arena for competitions, as a source of problems, small and large, including some of the hardest problems that science has to offer, at all levels from elementary school to the millennium problems (Csicsery, 2008 ; Ziegler, 2011 )?
What we teach in mathematics classes . Education bureaucrats might (and probably should) believe that the question “What is Mathematics?” is answered by high school curricula. But what answers do these give?
This takes us back to the nineteenth century controversies about what mathematics should be taught at school and at the Universities. In the German version this was a fierce debate. On the one side it saw the classical educational ideal as formulated by Wilhelm von Humboldt (who was involved in the concept for and the foundation 1806 of the Berlin University, now named Humboldt Universität, and to a certain amount shaped the modern concept of a university); here mathematics had a central role, but this was the classical “Greek” mathematics, starting from Euclid’s axiomatic development of geometry, the theory of conics, and the algebra of solving polynomial equations, not only as cultural heritage, but also as a training arena for logical thinking and problem solving. On the other side of the fight were the proponents of “Realbildung”: Realgymnasien and the technical universities that were started at that time tried to teach what was needed in commerce and industry: calculation and accounting, as well as the mathematics that could be useful for mechanical and electrical engineering—second rate education in the view of the classical German Gymnasium.
This nineteenth century debate rests on an unnatural separation into the classical, pure mathematics, and the useful, applied mathematics; a division that should have been overcome a long time ago (perhaps since the times of Archimedes), as it is unnatural as a classification tool and it is also a major obstacle to progress both in theory and in practice. Nevertheless the division into “classical” and “current” material might be useful in discussing curriculum contents—and the question for what purpose it should be taught; see our discussion in the Section “ Three Times Mathematics at School? ”.
The Courant–Robbins answer . The title of the present paper is, of course, borrowed from the famous and very successful book by Richard Courant and Herbert Robbins. However, this title is a question—what is Courant and Robbins’ answer? Indeed, the book does not give an explicit definition of “What is Mathematics,” but the reader is supposed to get an idea from the presentation of a diverse collection of mathematical investigations. Mathematics is much bigger and much more diverse than the picture given by the Courant–Robbins exposition. The presentation in this section was also meant to demonstrate that we need a multi-facetted picture of mathematics: One answer is not enough, we need many.
Why Should We Care?
The question “What is Mathematics?” probably does not need to be answered to motivate why mathematics should be taught, as long as we agree that mathematics is important.
However, a one-sided answer to the question leads to one-sided concepts of what mathematics should be taught.
At the same time a one-dimensional picture of “What is Mathematics” will fail to motivate kids at school to do mathematics, it will fail to motivate enough pupils to study mathematics, or even to think about mathematics studies as a possible career choice, and it will fail to motivate the right students to go into mathematics studies, or into mathematics teaching. If the answer to the question “What is Mathematics”, or the implicit answer given by the public/prevailing image of the subject, is not attractive, then it will be very difficult to motivate why mathematics should be learned—and it will lead to the wrong offers and the wrong choices as to what mathematics should be learned.
Indeed, would anyone consider a science that studies “abstract” structures that it created itself (see the German Wikipedia definition quoted above) interesting? Could it be relevant? If this is what mathematics is, why would or should anyone want to study this, get into this for a career? Could it be interesting and meaningful and satisfying to teach this?
Also in view of the diversity of the students’ expectations and talents, we believe that one answer is plainly not enough. Some students might be motivated to learn mathematics because it is beautiful, because it is so logical, because it is sometimes surprising. Or because it is part of our cultural heritage. Others might be motivated, and not deterred, by the fact that mathematics is difficult. Others might be motivated by the fact that mathematics is useful, it is needed—in everyday life, for technology and commerce, etc. But indeed, it is not true that “the same” mathematics is needed in everyday life, for university studies, or in commerce and industry. To other students, the motivation that “it is useful” or “it is needed” will not be sufficient. All these motivations are valid, and good—and it is also totally valid and acceptable that no single one of these possible types of arguments will reach and motivate all these students.
Why do so many pupils and students fail in mathematics, both at school and at universities? There are certainly many reasons, but we believe that motivation is a key factor. Mathematics is hard. It is abstract (that is, most of it is not directly connected to everyday-life experiences). It is not considered worth-while. But a lot of the insufficient motivation comes from the fact that students and their teachers do not know “What is Mathematics.”
Thus a multi-facetted image of mathematics as a coherent subject, all of whose many aspects are well connected, is important for a successful teaching of mathematics to students with diverse (possible) motivations.
This leads, in turn, to two crucial aspects, to be discussed here next: What image do students have of mathematics? And then, what should teachers answer when asked “What is Mathematics”? And where and how and when could they learn that?
The Image of Mathematics
A 2008 study by Mendick, Epstein, and Moreau ( 2008 ), which was based on an extensive survey among British students, was summarized as follows:
Many students and undergraduates seem to think of mathematicians as old, white, middle-class men who are obsessed with their subject, lack social skills and have no personal life outside maths. The student’s views of maths itself included narrow and inaccurate images that are often limited to numbers and basic arithmetic.
The students’ image of what mathematicians are like is very relevant and turns out to be a massive problem, as it defines possible (anti-)role models, which are crucial for any decision in the direction of “I want to be a mathematician.” If the typical mathematician is viewed as an “old, white, male, middle-class nerd,” then why should a gifted 16-year old girl come to think “that’s what I want to be when I grow up”? Mathematics as a science, and as a profession, looses (or fails to attract) a lot of talent this way! However, this is not the topic of this presentation.
On the other hand the first and the second diagnosis of the quote from Mendick et al. ( 2008 ) belong together: The mathematicians are part of “What is Mathematics”!
And indeed, looking at the second diagnosis, if for the key word “mathematics” the images that spring to mind don’t go beyond a per se meaningless “ \( a^{2} + b^{2} = c^{2} \) ” scribbled in chalk on a blackboard—then again, why should mathematics be attractive, as a subject, as a science, or as a profession?
We think that we have to look for, and work on, multi-facetted and attractive representations of mathematics by images. This could be many different, separate images, but this could also be images for “mathematics as a whole.”
Four Images for “What Is Mathematics?”
Striking pictorial representations of mathematics as a whole (as well as of other sciences!) and of their change over time can be seen on the covers of the German “Was ist was” books. The history of these books starts with the series of “How and why” Wonder books published by Grosset and Dunlop, New York, since 1961, which was to present interesting subjects (starting with “Dinosaurs,” “Weather,” and “Electricity”) to children and younger teenagers. The series was published in the US and in Great Britain in the 1960s and 1970s, but it was and is much more successful in Germany, where it was published (first in translation, then in volumes written in German) by Ragnar Tessloff since 1961. Volume 18 in the US/UK version and Volume 12 in the German version treats “Mathematics”, first published in 1963 (Highland & Highland, 1963 ), but then republished with the same title but a new author and contents in 2001 (Blum, 2001 ). While it is worthwhile to study the contents and presentation of mathematics in these volumes, we here focus on the cover illustrations (see Fig. 1 ), which for the German edition exist in four entirely different versions, the first one being an adaption of the original US cover of (Highland & Highland, 1961 ).
The four covers of “Was ist was. Band 12: Mathematik” (Highland & Highland, 1963 ; Blum, 2001 )
All four covers represent a view of “What is Mathematics” in a collage mode, where the first one represents mathematics as a mostly historical discipline (starting with the ancient Egyptians), while the others all contain a historical allusion (such as pyramids, Gauß, etc.) alongside with objects of mathematics (such as prime numbers or \( \pi \) , dices to illustrate probability, geometric shapes). One notable object is the oddly “two-colored” Möbius band on the 1983 cover, which was changed to an entirely green version in a later reprint.
One can discuss these covers with respect to their contents and their styles, and in particular in terms of attractiveness to the intended buyers/readers. What is over-emphasized? What is missing? It seems more important to us to
think of our own images/representations for “What is Mathematics”,
think about how to present a multi-facetted image of “What is Mathematics” when we teach.
Indeed, the topics on the covers of the “Was ist was” volumes of course represent interesting (?) topics and items discussed in the books. But what do they add up to? We should compare this to the image of mathematics as represented by school curricula, or by the university curricula for teacher students.
In the context of mathematics images, let us mention two substantial initiatives to collect and provide images from current mathematics research, and make them available on internet platforms, thus providing fascinating, multi-facetted images of mathematics as a whole discipline:
Guy Métivier et al.: “Image des Maths. La recherche mathématique en mots et en images” [“Images of Maths. Mathematical research in words and images”], CNRS, France, at images.math.cnrs.fr (texts in French)
Andreas D. Matt, Gert-Martin Greuel et al.: “IMAGINARY. open mathematics,” Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach, at imaginary.org (texts in German, English, and Spanish).
The latter has developed from a very successful travelling exhibition of mathematics images, “IMAGINARY—through the eyes of mathematics,” originally created on occasion of and for the German national science year 2008 “Jahr der Mathematik. Alles was zählt” [“Year of Mathematics 2008. Everything that counts”], see www.jahr-der-mathematik.de , which was highly successful in communicating a current, attractive image of mathematics to the German public—where initiatives such as the IMAGINARY exhibition had a great part in the success.
Teaching “What Is Mathematics” to Teachers
More than 100 years ago, in 1908, Felix Klein analyzed the education of teachers. In the introduction to the first volume of his “Elementary Mathematics from a Higher Standpoint” he wrote (our translation):
At the beginning of his university studies, the young student is confronted with problems that do not remind him at all of what he has dealt with up to then, and of course, he forgets all these things immediately and thoroughly. When after graduation he becomes a teacher, he has to teach exactly this traditional elementary mathematics, and since he can hardly link it with his university mathematics, he soon readopts the former teaching tradition and his studies at the university become a more or less pleasant reminiscence which has no influence on his teaching (Klein, 1908 ).
This phenomenon—which Klein calls the double discontinuity —can still be observed. In effect, the teacher students “tunnel” through university: They study at university in order to get a degree, but nevertheless they afterwards teach the mathematics that they had learned in school, and possibly with the didactics they remember from their own school education. This problem observed and characterized by Klein gets even worse in a situation (which we currently observe in Germany) where there is a grave shortage of Mathematics teachers, so university students are invited to teach at high school long before graduating from university, so they have much less university education to tunnel at the time when they start to teach in school. It may also strengthen their conviction that University Mathematics is not needed in order to teach.
How to avoid the double discontinuity is, of course, a major challenge for the design of university curricula for mathematics teachers. One important aspect however, is tied to the question of “What is Mathematics?”: A very common highschool image/concept of mathematics, as represented by curricula, is that mathematics consists of the subjects presented by highschool curricula, that is, (elementary) geometry, algebra (in the form of arithmetic, and perhaps polynomials), plus perhaps elementary probability, calculus (differentiation and integration) in one variable—that’s the mathematics highschool students get to see, so they might think that this is all of it! Could their teachers present them a broader picture? The teachers after their highschool experience studied at university, where they probably took courses in calculus/analysis, linear algebra, classical algebra, plus some discrete mathematics, stochastics/probability, and/or numerical analysis/differential equations, perhaps a programming or “computer-oriented mathematics” course. Altogether they have seen a scope of university mathematics where no current research becomes visible, and where most of the contents is from the nineteenth century, at best. The ideal is, of course, that every teacher student at university has at least once experienced how “doing research on your own” feels like, but realistically this rarely happens. Indeed, teacher students would have to work and study and struggle a lot to see the fascination of mathematics on their own by doing mathematics; in reality they often do not even seriously start the tour and certainly most of them never see the “glimpse of heaven.” So even if the teacher student seriously immerges into all the mathematics on the university curriculum, he/she will not get any broader image of “What is Mathematics?”. Thus, even if he/she does not tunnel his university studies due to the double discontinuity, he/she will not come back to school with a concept that is much broader than that he/she originally gained from his/her highschool times.
Our experience is that many students (teacher students as well as classical mathematics majors) cannot name a single open problem in mathematics when graduating the university. They have no idea of what “doing mathematics” means—for example, that part of this is a struggle to find and shape the “right” concepts/definitions and in posing/developing the “right” questions and problems.
And, moreover, also the impressions and experiences from university times will get old and outdated some day: a teacher might be active at a school for several decades—while mathematics changes! Whatever is proved in mathematics does stay true, of course, and indeed standards of rigor don’t change any more as much as they did in the nineteenth century, say. However, styles of proof do change (see: computer-assisted proofs, computer-checkable proofs, etc.). Also, it would be good if a teacher could name “current research focus topics”: These do change over ten or twenty years. Moreover, the relevance of mathematics in “real life” has changed dramatically over the last thirty years.
The Panorama Project
For several years, the present authors have been working on developing a course [and eventually a book (Loos & Ziegler, 2017 )] called “Panorama der Mathematik” [“Panorama of Mathematics”]. It primarily addresses mathematics teacher students, and is trying to give them a panoramic view on mathematics: We try to teach an overview of the subject, how mathematics is done, who has been and is doing it, including a sketch of main developments over the last few centuries up to the present—altogether this is supposed to amount to a comprehensive (but not very detailed) outline of “What is Mathematics.” This, of course, turns out to be not an easy task, since it often tends to feel like reading/teaching poetry without mastering the language. However, the approach of Panorama is complementing mathematics education in an orthogonal direction to the classic university courses, as we do not teach mathematics but present (and encourage to explore ); according to the response we get from students they seem to feel themselves that this is valuable.
Our course has many different components and facets, which we here cast into questions about mathematics. All these questions (even the ones that “sound funny”) should and can be taken seriously, and answered as well as possible. For each of them, let us here just provide at most one line with key words for answers:
When did mathematics start?
Numbers and geometric figures start in stone age; the science starts with Euclid?
How large is mathematics? How many Mathematicians are there?
The Mathematics Genealogy Project had 178854 records as of 12 April 2014.
How is mathematics done, what is doing research like?
Collect (auto)biographical evidence! Recent examples: Frenkel ( 2013 ) , Villani ( 2012 ).
What does mathematics research do today? What are the Grand Challenges?
The Clay Millennium problems might serve as a starting point.
What and how many subjects and subdisciplines are there in mathematics?
See the Mathematics Subject Classification for an overview!
Why is there no “Mathematical Industry”, as there is e.g. Chemical Industry?
There is! See e.g. Telecommunications, Financial Industry, etc.
What are the “key concepts” in mathematics? Do they still “drive research”?
Numbers, shapes, dimensions, infinity, change, abstraction, …; they do.
What is mathematics “good for”?
It is a basis for understanding the world, but also for technological progress.
Where do we do mathematics in everyday life?
Not only where we compute, but also where we read maps, plan trips, etc.
Where do we see mathematics in everyday life?
There is more maths in every smart phone than anyone learns in school.
What are the greatest achievements of mathematics through history?
Make your own list!
An additional question is how to make university mathematics more “sticky” for the tunneling teacher students, how to encourage or how to force them to really connect to the subject as a science. Certainly there is no single, simple, answer for this!
Telling Stories About Mathematics
How can mathematics be made more concrete? How can we help students to connect to the subject? How can mathematics be connected to the so-called real world?
Showing applications of mathematics is a good way (and a quite beaten path). Real applications can be very difficult to teach since in most advanced, realistic situation a lot of different mathematical disciplines, theories and types of expertise have to come together. Nevertheless, applications give the opportunity to demonstrate the relevance and importance of mathematics. Here we want to emphasize the difference between teaching a topic and telling about it. To name a few concrete topics, the mathematics behind weather reports and climate modelling is extremely difficult and complex and advanced, but the “basic ideas” and simplified models can profitably be demonstrated in highschool, and made plausible in highschool level mathematical terms. Also success stories like the formula for the Google patent for PageRank (Page, 2001 ), see Langville and Meyer ( 2006 ), the race for the solution of larger and larger instances of the Travelling Salesman Problem (Cook, 2011 ), or the mathematics of chip design lend themselves to “telling the story” and “showing some of the maths” at a highschool level; these are among the topics presented in the first author’s recent book (Ziegler, 2013b ), where he takes 24 images as the starting points for telling stories—and thus developing a broader multi-facetted picture of mathematics.
Another way to bring maths in contact with non-mathematicians is the human level. Telling stories about how maths is done and by whom is a tricky way, as can be seen from the sometimes harsh reactions on www.mathoverflow.net to postings that try to excavate the truth behind anecdotes and legends. Most mathematicians see mathematics as completely independent from the persons who explored it. History of mathematics has the tendency to become gossip , as Gian-Carlo Rota once put it (Rota, 1996 ). The idea seems to be: As mathematics stands for itself, it has also to be taught that way.
This may be true for higher mathematics. However, for pupils (and therefore, also for teachers), transforming mathematicians into humans can make science more tangible, it can make research interesting as a process (and a job?), and it can be a starting/entry point for real mathematics. Therefore, stories can make mathematics more sticky. Stories cannot replace the classical approaches to teaching mathematics. But they can enhance it.
Stories are the way by which knowledge has been transferred between humans for thousands of years. (Even mathematical work can be seen as a very abstract form of storytelling from a structuralist point of view.) Why don’t we try to tell more stories about mathematics, both at university and in school—not legends, not fairy tales, but meta-information on mathematics—in order to transport mathematics itself? See (Ziegler, 2013a ) for an attempt by the first author in this direction.
By stories, we do not only mean something like biographies, but also the way of how mathematics is created or discovered: Jack Edmonds’ account (Edmonds, 1991 ) of how he found the blossom shrink algorithm is a great story about how mathematics is actually done . Think of Thomas Harriot’s problem about stacking cannon balls into a storage space and what Kepler made out of it: the genesis of a mathematical problem. Sometimes scientists even wrap their work into stories by their own: see e.g. Leslie Lamport’s Byzantine Generals (Lamport, Shostak, & Pease, 1982 ).
Telling how research is done opens another issue. At school, mathematics is traditionally taught as a closed science. Even touching open questions from research is out of question, for many good and mainly pedagogical reasons. However, this fosters the image of a perfect science where all results are available and all problems are solved—which is of course completely wrong (and moreover also a source for a faulty image of mathematics among undergraduates).
Of course, working with open questions in school is a difficult task. None of the big open questions can be solved with an elementary mathematical toolbox; many of them are not even accessible as questions. So the big fear of discouraging pupils is well justified. On the other hand, why not explore mathematics by showing how questions often pop up on the way? Posing questions in and about mathematics could lead to interesting answers—in particular to the question of “What is Mathematics, Really?”
Three Times Mathematics at School?
So, what is mathematics? With school education in mind, the first author has argued in Ziegler ( 2012 ) that we are trying cover three aspects the same time, which one should consider separately and to a certain extent also teach separately:
A collection of basic tools, part of everyone’s survival kit for modern-day life—this includes everything, but actually not much more than, what was covered by Adam Ries’ “Rechenbüchlein” [“Little Book on Computing”] first published in 1522, nearly 500 years ago;
A field of knowledge with a long history, which is a part of our culture and an art, but also a very productive basis (indeed a production factor) for all modern key technologies. This is a “story-telling” subject.
An introduction to mathematics as a science—an important, highly developed, active, huge research field.
Looking at current highschool instruction, there is still a huge emphasis on Mathematics I, with a rather mechanical instruction on arithmetic, “how to compute correctly,” and basic problem solving, plus a rather formal way of teaching Mathematics III as a preparation for possible university studies in mathematics, sciences or engineering. Mathematics II, which should provide a major component of teaching “What is Mathematics,” is largely missing. However, this part also could and must provide motivation for studying Mathematics I or III!
What Is Mathematics, Really?
There are many, and many different, valid answers to the Courant-Robbins question “What is Mathematics?”
A more philosophical one is given by Reuben Hersh’s book “What is Mathematics, Really?” Hersh ( 1997 ), and there are more psychological ones, on the working level. Classics include Jacques Hadamard’s “Essay on the Psychology of Invention in the Mathematical Field” and Henri Poincaré’s essays on methodology; a more recent approach is Devlin’s “Introduction to Mathematical Thinking” Devlin ( 2012 ), or Villani’s book ( 2012 ).
And there have been many attempts to describe mathematics in encyclopedic form over the last few centuries. Probably the most recent one is the gargantuan “Princeton Companion to Mathematics”, edited by Gowers et al. ( 2008 ), which indeed is a “Princeton Companion to Pure Mathematics.”
However, at a time where ZBMath counts more than 100,000 papers and books per year, and 29,953 submissions to the math and math-ph sections of arXiv.org in 2016, it is hopeless to give a compact and simple description of what mathematics really is, even if we had only the “current research discipline” in mind. The discussions about the classification of mathematics show how difficult it is to cut the science into slices, and it is even debatable whether there is any meaningful way to separate applied research from pure mathematics.
Probably the most diplomatic way is to acknowledge that there are “many mathematics.” Some years ago Tao ( 2007 ) gave an open list of mathematics that is/are good for different purposes—from “problem-solving mathematics” and “useful mathematics” to “definitive mathematics”, and wrote:
As the above list demonstrates, the concept of mathematical quality is a high-dimensional one, and lacks an obvious canonical total ordering. I believe this is because mathematics is itself complex and high-dimensional, and evolves in unexpected and adaptive ways; each of the above qualities represents a different way in which we as a community improve our understanding and usage of the subject.
In this sense, many answers to “What is Mathematics?” probably show as much about the persons who give the answers as they manage to characterize the subject.
According to Wikipedia , the same version, the answer to “Who is Mathematics” should be:
Mathematics , also known as Allah Mathematics , (born: Ronald Maurice Bean [1] ) is a hip hop producer and DJ for the Wu-Tang Clan and its solo and affiliate projects. This is not the mathematics we deal with here.
Blum, W. (2001). Was ist was. Band 12: Mathematik , Tessloff Verlag, Nürnberg. Revised version, with new cover, 2010.
Google Scholar
Cook, W. (2011). In pursuit of the traveling salesman: Mathematics at the limits of computation . Princeton NJ: Princeton University Press.
Courant, R., & Robbins, H. (1941). What is mathematics? an elementary approach to ideas and methods (2nd ed.), Oxford: Oxford University Press. Stewart, I (ed), 1996.
Csicsery, G. (2008). Hard problems. the road to the world’s toughest math contest , Documentary film, 82 minutes (feature)/45 minutes (classroom version), Washington, DC: Mathematical Association of America.
Devlin, K. J. (2012). Introduction to mathematical thinking , published by Keith Devlin, Palo Alto CA.
Edmonds, J. (1991). A glimpse of heaven, In: J. K. Lenstra, A. Schrijver, & A. Rinnooy Kan (eds.) History of mathematical programming—A collection of personal reminiscences (pp. 32–54). Amsterdam: CWI and North-Holland.
Frenkel, E. (2013). Love & math. The heart of hidden reality . Philadelphia PA: Basic Books/Perseus Books.
Gowers, Timothy, Leader, Imre, & Barrow-Green, June (Eds.). (2008). The princeton companion to mathematics . Princeton NJ: Princeton University Press.
Highland, E. H., & Highland, H. J. (1961). The how and why wonder book of mathematics . New York: Grosset & Dunlop.
Highland, E. H., & Highland, H. J. (1963). Was ist was. Band 12: Mathematik , Neuer Tessloff Verlag, Hamburg, 1963. Revised edition 1969. New cover 1983.
Hersh, R. (1997). What is mathematics, really? . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Klein, F.(1933). Elementarmathematik vom höheren Standpunkte aus. Teil I: Arithmetik, Algebra, Analysis , B. G. Teubner, Leipzig, 1908. Vierte Auflage. Heidelberg: Springer.
Lamport, L., Shostak, R., & Pease, M. (1982). The byzantine generals problem. ACM Transactions on Programming Languages and Systems, 4, 382–401.
Article Google Scholar
Langville, A. N., & Meyer, C. D. (2006). Google’s pagerank and beyond. The science of search engine rankings . Princeton and Oxford: Princeton University Press.
Loos, A., & Ziegler, G. M. (2017). Panorama der Mathematik . Heidelberg: Springer Spectrum, to appear.
Mendick, H., Epstein, D., & Moreau, M.-P. (2008). Mathematical images and identities: Education, entertainment, social justice . London: Institute for Policy Studies in Education, London Metropolitan University.
Page, L. (2001) Method for node ranking in a linked database , United States Patent No. US 6,285,999 B1, (submitted: January 9, 1998), http://www.google.com/patents/US6285999
Rota, G.-C. (1996). Indiscrete thoughts . Basel: Birkhäuser.
Tao, T. (2007). What is good mathematics? Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society, 44 (4), 623–634.
Villani, C. (2012). Théorème vivant . Paris: Bernard Grasset. (in French).
Ziegler, G. M. (2011). Three competitions. In D. Schleicher & M. Lackmann (Eds.), Invitation to mathematics. From competition to research (pp. 195–205). Berlin: Springer.
Chapter Google Scholar
Ziegler, G. M. (2012). Mathematics school education provides answers—To which questions? EMS Newsletter (84), 8–11.
Ziegler, G. M.(2013a). Do I count? stories from mathematics , Boca Raton FL: CRC Press/Taylor & Francis. English translation of “Darf ich Zahlen? Geschichten aus der Mathematik”, Piper, München, 2010.
Ziegler, G. M. (2013b). Mathematik—Das ist doch keine Kunst! . München: Knaus.
Download references
Acknowledgment
The authors’ work has received funding from the European Research Council under the European Union’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013)/ERC grant agreement no. 247029, the DFG Research Center Matheon, and the the DFG Collaborative Research Center TRR 109 “Discretization in Geometry and Dynamics”.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Institut Für Mathematik, FU Berlin, Arnimallee 2, 14195, Berlin, Germany
Günter M. Ziegler
Zeit Online, Askanischer Platz 1, 10963, Berlin, Germany
Andreas Loos
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Günter M. Ziegler .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Faculty of Education, Universität Hamburg, Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany
Gabriele Kaiser
Rights and permissions
Open Access Except where otherwise noted, this chapter is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 The Author(s)
About this paper
Cite this paper.
Ziegler, G.M., Loos, A. (2017). “What is Mathematics?” and why we should ask, where one should experience and learn that, and how to teach it. In: Kaiser, G. (eds) Proceedings of the 13th International Congress on Mathematical Education. ICME-13 Monographs. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-62597-3_5
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-62597-3_5
Published : 02 November 2017
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-62596-6
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-62597-3
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
The Best Writing on Mathematics 12
Mircea pitici, series editor.
This annual anthology brings together the year’s finest mathematics writing from around the world. Featuring promising new voices alongside some of the foremost names in the field, The Best Writing on Mathematics makes mathematical writing available to a wide audience.

The year’s finest mathematical writing from around the world

The year's finest mathematical writing from around the world

The year's finest mathematics writing from around the world

The year's finest writing on mathematics from around the world

The year's finest writing on mathematics from around the world, with a foreword by Nobel Prize – winning physicist Roger Penrose

The year’s most memorable writing on mathematics
Stay connected for new books and special offers. Subscribe to receive a welcome discount for your next order.
50% off sitewide with code FIFTY | May 7 – 31 | Some exclusions apply. See our FAQ .
- ebook & Audiobook Cart

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
IB Math Extended Essay Topics: 20+ Ideas for Inspiration
by Antony W
September 3, 2022
Do you feel stuck on searching for and choosing the best IB Math Extended Essay topics? Or maybe you already have a topic for consideration but it isn’t viable enough to fit the scope of the assignment?
You’ve come to the right place.
In this guide, we’ll give you 15+ IB Math ideas that you can use as inspiration to come up with your own topic or modify and investigate further in your extended essay.
What’s the Purpose of IB Math Extended Essay?
An extended essay in mathematics gives you the chance to demonstrate an understanding of any part of the subject.
You can give an expression on the beauty of mathematics in geometry or fractal theory, the elegance of mathematics in the proving of theorems, and the origin and subsequent development of a branch of mathematics over a period.
The extended essay also allows you to demonstrate the link between the different branches of mathematics and the powerful structures that enable many different problems to be solved by a single theory and the way in which mathematics is applied to real-world situations.
Your essay requires a well-defined and focused research question. An abstract is no longer necessary in an extended essay , but you’re welcome to include it if you believe it will summarizes your strategy to solving the research question and your findings
Math Extended Essay Writing Assistance
While Math opens up an opportunity to explore complex issues beyond the IB Diploma course , the subject can be extremely challenging for some IB students.
If you’re one of the students who chose Math for the Extended Essay project but you find the subject challenging, you can get help online from experts in the subject.
Help for Assessment offers the most comprehensive Extended Essay help in Mathematics, even on a topic that you would consider too complex to handle. With our help, you’ll find complex concepts easy to understand, not to mention you’ll get your Math assignment completed on time.
We understand that Math tasks can be costly and involving. However, we’ve made our writing service as affordable as possible, so you can get professional writing help.
We can write you first draft before the first reflection session with your supervisor and equally help you fine-tune the last draft for the final submission.
IB Math Extended Essay Topics
The following are examples of IB Math Extended Essay topics that you might find worth investigating further:
- What is the return percentage of a certain three-reel slot machine?
- What are the alternatives to Euclidean geometry and what are their practical applications?
- Comparison of population growth models for Country X for the past n years, with projections for the future.
- The exploration of geometric series in musical instruments, such as the fret position on a guitar
- How many convex polygons can you construct from seven tangram pieces?
- An examination of the alteration of a message's truthful substance during transmission between persons
- Is there a connection between the golden ratio and human’s perception on natural beauty, with a focus on the human face and form?
- Is there a relationship between SAT scores and school test results/GPA?
- Leibniz and Newton independently developed calculus at around the same time. Compare their techniques and analyze which notation is currently more prevalent.
- What is the Binomial Theorem, and how has it contributed to human history?
- Complex number problem-solving techniques: What types of real-world issues do complex numbers assist solve?
- Applying Newton's Forward Difference Formula to predict the number of triangles created by subdividing the sides of an equilateral triangle n times.
- RSA Public Key Cryptography's use of modular arithmetic and huge prime integers to achieve anonymity
- Investigating the link between Pascal's Triangle and the Fibonacci sequence
- How can mathematical modeling that employs differential equations determine population growth patterns for a predator and its prey?
- How can the population of cells be determined throughout time? Which mathematical model approximates an actual experiment more precisely?
- A study of Riemann Sums (conventional integration to get areas) and Numerical Integration
- Vedic Mathematics: an investigation of its effectiveness and exploration of its applications
- How are Laplace transforms utilized in the solution of second-order differential equations?
- A statistical examination of the impact of background music on pupils' short-term memory ability
- Analytical and geometric formulations of parabolic and cubic Bezier curves as used in computer graphics software
- A quantitative analysis of the efficacy of two herbs for treating impetigo skin condition
- A study of the nature of beats and the relative consonance of pure-tone dyads
- The link between logical-mathematical intelligence and academic achievement at the undergraduate level
- A study of the link between a bond's coupon rate, yield to maturity, and its clean price
- Using the addition of sine curves to analyze the harmony of Chinese and Western musical scales
- The correlation between students' attitudes toward mathematics and their mathematical performance
- How near is the approximation of the Taylor Series to the original function
- What criteria determine whether the movement of employees on a building site achieves "equilibrium"?
- The efficacy of an English Tuition Program in enhancing the English skills of participants
- A statistical examination of the causes of fatal traffic accidents throughout the holiday season
- Does studying a third language have any influence on the short-term memory retention of lower secondary students?
Keep in mind that this list is not exhaustive by any means. So if none of these topic ideas appeals to you, doing additional research can make a difference.
Related Reading
- The Complete Guide for IB Math Extended Essay
- Get a List of Psychology Extended Essay Topics Here
- Learn More About Physics Extended Essay Assignment
Some Tips to Help You Choose a Relevant Math EE Topic
You can write an extended essay in math on any subject with a mathematical focus. Because IB doesn’t limit the assignment to mathematical theories, you may select mathematical themes from engineering, sciences, and the social sciences.
Statistical analyses of experimental results from other disciplines are also appropriate, as long as they focus on the modeling method and address the limits of the results.
A topic chosen from the history of mathematics may also be acceptable, provided you bring out a clear progression of mathematical growth.
Focusing on the lives of mathematicians or their personal rivalry would be irrelevant and would not score highly on the grading criteria.
Notably, the evaluation criteria provide points for the nature of the inquiry and the extent to which reasoned arguments are suitable for a research issue.
You need to avoid selecting a topic that generates a trivial research question or is insufficiently concentrated to permit suitable presentation in an essay of the right length.
Typically, you will have to challenge yourself to either extend their knowledge beyond the Diploma Program course or apply techniques learned in their mathematics course to the modeling of an adequately chosen topic.
Final Thoughts
One of the most important thing to keep in mind once you find a suitable Math EE topic is that you will be working on an essay, not a research article for a journal of advanced mathematics.
Also, no finding, no matter how remarkable, should appear in your work without proof of your actual understanding of it.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.
- Kids Learning
- English Essays for Kids
My Favourite Subject Essay For Kids
Kids usually enjoy writing my favourite subject essay when given an opportunity to write about their views. Mathematics is one such subject which captivates the interest of many students. It is a boon for kids who love playing with numbers and enjoy solving different types of mathematical problems like addition, subtraction, division or multiplication. Although it may be fun and fascinating for a few, it may be a nightmare for others who have trouble working with numbers.
In this article, we bring you my favourite subject Mathematics essay for kids so that they can understand what fascinates them about the subject. Let’s begin!
Download PDF of “Essay On My Favourite Subject Mathematics” for Free
My favourite subject maths essay for kids.
By practising various arithmetical sums and questions, it sharpens my knowledge and boosts my energy to explore further. Whenever I face some difficulty in solving any problem, I check either with my Maths teacher at school or with my parents while I’m at home.
The main reason why I love Maths is that it does not require me to memorise or retain complex and lengthy concepts in mind. It is an easy-to-score subject if you’re aware of the various mathematical formulas. The more I practice, the better I become in solving difficult sums and problems. My Maths teacher at school also taught us some useful tips and tricks to solve complex mathematical questions with speed and accuracy.
Mathematics is, therefore, an intriguing subject and it plays a vital role in our daily lives. The most amazing part of the subject is that it is the only subject where a student can score full marks and thereby raise his/her overall percentage.”
We hope the above essay on my favourite subject Mathematics would help young learners to get a clear idea about how to write an essay about their favourite subject and the points that they can include in the essay. To explore a set of captivating English essays for kids , you may check the linked article.
For a huge variety of absorbing content and attention-gripping study materials and resources, you can explore our Kids Learning section and gift your child the best learning experience.
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Along with Stanford news and stories, show me:
- Student information
- Faculty/Staff information
We want to provide announcements, events, leadership messages and resources that are relevant to you. Your selection is stored in a browser cookie which you can remove at any time using “Clear all personalization” below.
For everyone whose relationship with mathematics is distant or broken, Jo Boaler , a professor at Stanford Graduate School of Education (GSE), has ideas for repairing it. She particularly wants young people to feel comfortable with numbers from the start – to approach the subject with playfulness and curiosity, not anxiety or dread.
“Most people have only ever experienced what I call narrow mathematics – a set of procedures they need to follow, at speed,” Boaler says. “Mathematics should be flexible, conceptual, a place where we play with ideas and make connections. If we open it up and invite more creativity, more diverse thinking, we can completely transform the experience.”
Boaler, the Nomellini and Olivier Professor of Education at the GSE, is the co-founder and faculty director of Youcubed , a Stanford research center that provides resources for math learning that has reached more than 230 million students in over 140 countries. In 2013 Boaler, a former high school math teacher, produced How to Learn Math , the first massive open online course (MOOC) on mathematics education. She leads workshops and leadership summits for teachers and administrators, and her online courses have been taken by over a million users.
In her new book, Math-ish: Finding Creativity, Diversity, and Meaning in Mathematics , Boaler argues for a broad, inclusive approach to math education, offering strategies and activities for learners at any age. We spoke with her about why creativity is an important part of mathematics, the impact of representing numbers visually and physically, and how what she calls “ishing” a math problem can help students make better sense of the answer.
What do you mean by “math-ish” thinking?
It’s a way of thinking about numbers in the real world, which are usually imprecise estimates. If someone asks how old you are, how warm it is outside, how long it takes to drive to the airport – these are generally answered with what I call “ish” numbers, and that’s very different from the way we use and learn numbers in school.
In the book I share an example of a multiple-choice question from a nationwide exam where students are asked to estimate the sum of two fractions: 12/13 + 7/8. They’re given four choices for the closest answer: 1, 2, 19, or 21. Each of the fractions in the question is very close to 1, so the answer would be 2 – but the most common answer 13-year-olds gave was 19. The second most common was 21.
I’m not surprised, because when students learn fractions, they often don’t learn to think conceptually or to consider the relationship between the numerator or denominator. They learn rules about creating common denominators and adding or subtracting the numerators, without making sense of the fraction as a whole. But stepping back and judging whether a calculation is reasonable might be the most valuable mathematical skill a person can develop.
But don’t you also risk sending the message that mathematical precision isn’t important?
I’m not saying precision isn’t important. What I’m suggesting is that we ask students to estimate before they calculate, so when they come up with a precise answer, they’ll have a real sense for whether it makes sense. This also helps students learn how to move between big-picture and focused thinking, which are two different but equally important modes of reasoning.
Some people ask me, “Isn’t ‘ishing’ just estimating?” It is, but when we ask students to estimate, they often groan, thinking it’s yet another mathematical method. But when we ask them to “ish” a number, they're more willing to offer their thinking.
Ishing helps students develop a sense for numbers and shapes. It can help soften the sharp edges in mathematics, making it easier for kids to jump in and engage. It can buffer students against the dangers of perfectionism, which we know can be a damaging mindset. I think we all need a little more ish in our lives.
You also argue that mathematics should be taught in more visual ways. What do you mean by that?
For most people, mathematics is an almost entirely symbolic, numerical experience. Any visuals are usually sterile images in a textbook, showing bisecting angles, or circles divided into slices. But the way we function in life is by developing models of things in our minds. Take a stapler: Knowing what it looks like, what it feels and sounds like, how to interact with it, how it changes things – all of that contributes to our understanding of how it works.
There’s an activity we do with middle-school students where we show them an image of a 4 x 4 x 4 cm cube made up of smaller 1 cm cubes, like a Rubik’s Cube. The larger cube is dipped into a can of blue paint, and we ask the students, if they could take apart the little cubes, how many sides would be painted blue? Sometimes we give the students sugar cubes and have them physically build a larger 4 x 4 x 4 cube. This is an activity that leads into algebraic thinking.
Some years back we were interviewing students a year after they’d done that activity in our summer camp and asked what had stayed with them. One student said, “I’m in geometry class now, and I still remember that sugar cube, what it looked like and felt like.” His class had been asked to estimate the volume of their shoes, and he said he’d imagined his shoes filled with 1 cm sugar cubes in order to solve that question. He had built a mental model of a cube.
When we learn about cubes, most of us don’t get to see and manipulate them. When we learn about square roots, we don’t take squares and look at their diagonals. We just manipulate numbers.
I wonder if people consider the physical representations more appropriate for younger kids.
That’s the thing – elementary school teachers are amazing at giving kids those experiences, but it dies out in middle school, and by high school it’s all symbolic. There’s a myth that there’s a hierarchy of sophistication where you start out with visual and physical representations and then build up to the symbolic. But so much of high-level mathematical work now is visual. Here in Silicon Valley, if you look at Tesla engineers, they're drawing, they're sketching, they're building models, and nobody says that's elementary mathematics.
There’s an example in the book where you’ve asked students how they would calculate 38 x 5 in their heads, and they come up with several different ways of arriving at the same answer. The creativity is fascinating, but wouldn’t it be easier to teach students one standard method?
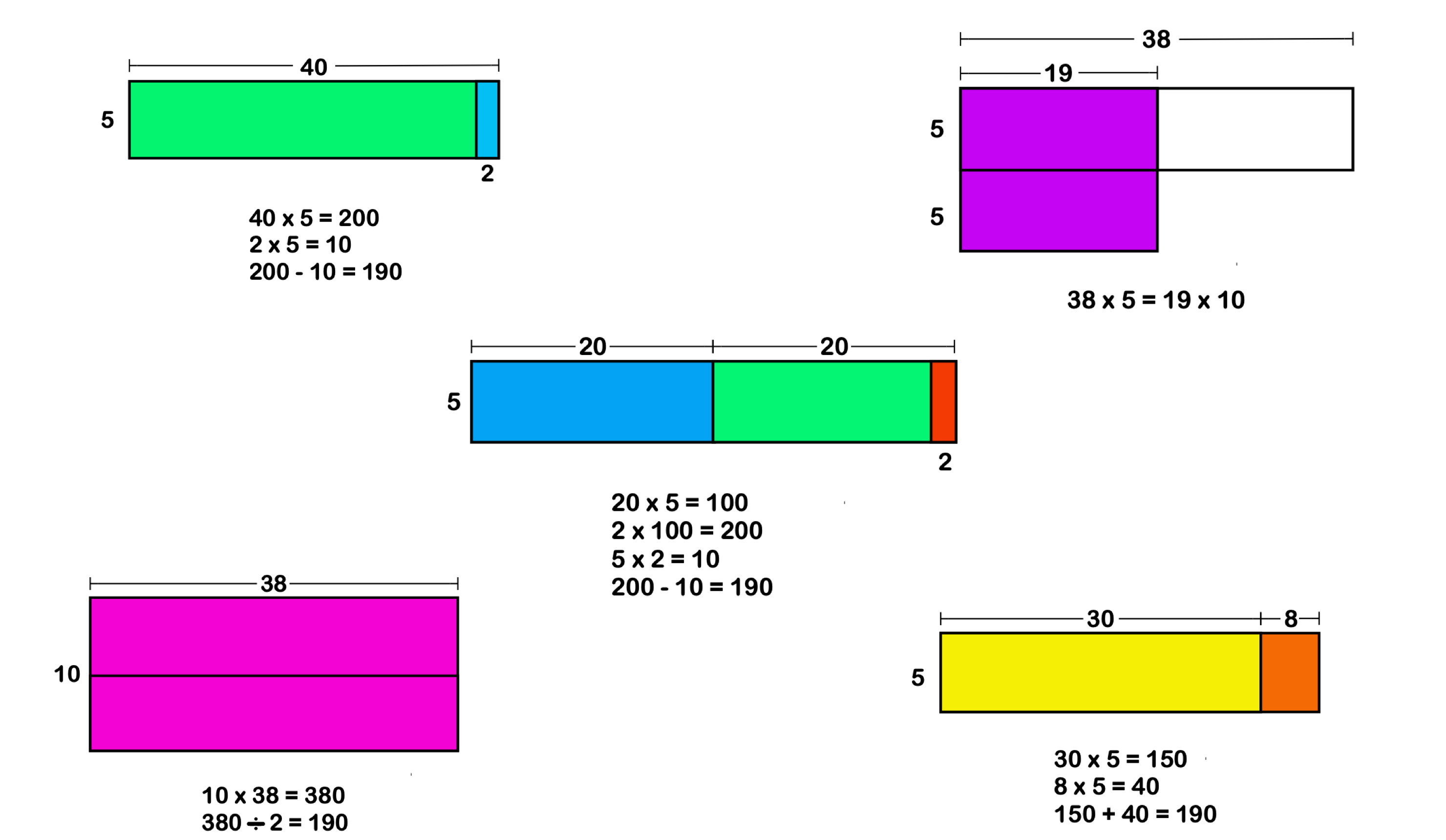
A depiction of various ways to calculate 38 x 5, numerically and visually. | Courtesy Jo Boaler
That narrow, rigid version of mathematics where there’s only one right approach is what most students experience, and it’s a big part of why people have such math trauma. It keeps them from realizing the full range and power of mathematics. When you only have students blindly memorizing math facts, they’re not developing number sense. They don’t learn how to use numbers flexibly in different situations. It also makes students who think differently believe there’s something wrong with them.
When we open mathematics to acknowledge the different ways a concept or problem can be viewed, we also open the subject to many more students. Mathematical diversity, to me, is a concept that includes both the value of diversity in people and the diverse ways we can see and learn mathematics. When we bring those forms of diversity together, it’s powerful. If we want to value different ways of thinking and problem-solving in the world, we need to embrace mathematical diversity.
share this!
May 21, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
The case for 'math-ish' thinking
by Stanford University

For everyone whose relationship with mathematics is distant or broken, Jo Boaler, a professor at Stanford Graduate School of Education (GSE), has ideas for repairing it. She particularly wants young people to feel comfortable with numbers from the start—to approach the subject with playfulness and curiosity, not anxiety or dread.
"Most people have only ever experienced what I call narrow mathematics—a set of procedures they need to follow, at speed," Boaler says. "Mathematics should be flexible, conceptual, a place where we play with ideas and make connections. If we open it up and invite more creativity, more diverse thinking, we can completely transform the experience."
Boaler, the Nomellini and Olivier Professor of Education at the GSE, is the co-founder and faculty director of Youcubed, a Stanford research center that provides resources for math learning that has reached more than 230 million students in over 140 countries. In 2013 Boaler, a former high school math teacher, produced How to Learn Math, the first massive open online course (MOOC) on mathematics education . She leads workshops and leadership summits for teachers and administrators, and her online courses have been taken by over a million users.
In her new book, " Math-ish: Finding Creativity, Diversity, and Meaning in Mathematics ," Boaler argues for a broad, inclusive approach to math education, offering strategies and activities for learners at any age. We spoke with her about why creativity is an important part of mathematics, the impact of representing numbers visually and physically, and how what she calls "ishing" a math problem can help students make better sense of the answer.
What do you mean by 'math-ish' thinking?
It's a way of thinking about numbers in the real world, which are usually imprecise estimates. If someone asks how old you are, how warm it is outside, how long it takes to drive to the airport—these are generally answered with what I call "ish" numbers, and that's very different from the way we use and learn numbers in school.
In the book I share an example of a multiple-choice question from a nationwide exam where students are asked to estimate the sum of two fractions: 12/13 + 7/8. They're given four choices for the closest answer: 1, 2, 19, or 21. Each of the fractions in the question is very close to 1, so the answer would be 2—but the most common answer 13-year-olds gave was 19. The second most common was 21.
I'm not surprised, because when students learn fractions, they often don't learn to think conceptually or to consider the relationship between the numerator or denominator. They learn rules about creating common denominators and adding or subtracting the numerators, without making sense of the fraction as a whole. But stepping back and judging whether a calculation is reasonable might be the most valuable mathematical skill a person can develop.
But don't you also risk sending the message that mathematical precision isn't important?
I'm not saying precision isn't important. What I'm suggesting is that we ask students to estimate before they calculate, so when they come up with a precise answer, they'll have a real sense for whether it makes sense. This also helps students learn how to move between big-picture and focused thinking, which are two different but equally important modes of reasoning.
Some people ask me, "Isn't 'ishing' just estimating?" It is, but when we ask students to estimate, they often groan, thinking it's yet another mathematical method. But when we ask them to "ish" a number, they're more willing to offer their thinking.
Ishing helps students develop a sense for numbers and shapes. It can help soften the sharp edges in mathematics, making it easier for kids to jump in and engage. It can buffer students against the dangers of perfectionism, which we know can be a damaging mindset. I think we all need a little more ish in our lives.
You also argue that mathematics should be taught in more visual ways. What do you mean by that?
For most people, mathematics is an almost entirely symbolic, numerical experience. Any visuals are usually sterile images in a textbook, showing bisecting angles, or circles divided into slices. But the way we function in life is by developing models of things in our minds. Take a stapler: Knowing what it looks like, what it feels and sounds like, how to interact with it, how it changes things—all of that contributes to our understanding of how it works.
There's an activity we do with middle-school students where we show them an image of a 4 x 4 x 4 cm cube made up of smaller 1 cm cubes, like a Rubik's Cube. The larger cube is dipped into a can of blue paint, and we ask the students, if they could take apart the little cubes, how many sides would be painted blue? Sometimes we give the students sugar cubes and have them physically build a larger 4 x 4 x 4 cube. This is an activity that leads into algebraic thinking.
Some years back we were interviewing students a year after they'd done that activity in our summer camp and asked what had stayed with them. One student said, "I'm in geometry class now, and I still remember that sugar cube, what it looked like and felt like." His class had been asked to estimate the volume of their shoes, and he said he'd imagined his shoes filled with 1 cm sugar cubes in order to solve that question. He had built a mental model of a cube.
When we learn about cubes, most of us don't get to see and manipulate them. When we learn about square roots, we don't take squares and look at their diagonals. We just manipulate numbers.
I wonder if people consider the physical representations more appropriate for younger kids.
That's the thing—elementary school teachers are amazing at giving kids those experiences, but it dies out in middle school, and by high school it's all symbolic. There's a myth that there's a hierarchy of sophistication where you start out with visual and physical representations and then build up to the symbolic. But so much of high-level mathematical work now is visual. Here in Silicon Valley, if you look at Tesla engineers, they're drawing, they're sketching, they're building models, and nobody says that's elementary mathematics.
There's an example in the book where you've asked students how they would calculate 38 x 5 in their heads, and they come up with several different ways of arriving at the same answer. The creativity is fascinating, but wouldn't it be easier to teach students one standard method?
That narrow, rigid version of mathematics where there's only one right approach is what most students experience, and it's a big part of why people have such math trauma. It keeps them from realizing the full range and power of mathematics. When you only have students blindly memorizing math facts, they're not developing number sense.
They don't learn how to use numbers flexibly in different situations. It also makes students who think differently believe there's something wrong with them.
When we open mathematics to acknowledge the different ways a concept or problem can be viewed, we also open the subject to many more students. Mathematical diversity, to me, is a concept that includes both the value of diversity in people and the diverse ways we can see and learn mathematics.
When we bring those forms of diversity together, it's powerful. If we want to value different ways of thinking and problem-solving in the world, we need to embrace mathematical diversity.
Provided by Stanford University
Explore further
Feedback to editors
Researchers develop organic photoredox catalysts with enhanced stability and recyclability
9 hours ago

Theory and experiment combine to shine a new light on proton spin

On repeat: Biologists observe recurring evolutionary changes, over time, in stick insects
New findings on fertility: Sperm can adapt to sexually transmitted microbes
10 hours ago
Observing mammalian cells with superfast soft X-rays

New study challenges conventional wisdom that Americans are 'pocketbook voters'
Carbon dioxide, the main culprit of global warming, reborn as an antioxidant substance
11 hours ago
New study offers a cleaner path for controlling water, transforming greenhouse gases

Heavy water: How melting ice sheets and pumped groundwater can lower local sea levels—and boost them elsewhere
12 hours ago

Unveiling a novel AAK1 inhibitor: How chemical proteomics unlock therapeutic potential
13 hours ago
Relevant PhysicsForums posts
Memorizing trigonometric identities, conformal flatness of ellipsoid, graphing trip efficiency - distance over time.
May 20, 2024
Help with Recurrence Equation
May 18, 2024
Numerically how to approximate exponential decay in a discrete signal
May 16, 2024
Flat surface to curved surface
May 13, 2024
More from General Math
Related Stories

Changing students' attitudes to mathematics improves test scores
May 10, 2018

Math degrees are becoming less accessible—and this is a problem for business, government and innovation
May 5, 2024
Former math teacher explains why some students are 'good' at math and others lag behind
Nov 3, 2022

Studies recommend increased research into achievement, engagement to raise student math scores
Feb 15, 2024

5 tips to get your children excited about math
Jan 17, 2020

Future teachers often think memorization is the best way to teach math and science – until they learn a different way
Sep 17, 2020
Recommended for you

Math discovery provides new method to study cell activity, aging

First-generation medical students face unique challenges and need more targeted support, say researchers

Mechanistic model shows how much gossip is needed to foster social cooperation
May 15, 2024
Random processes shape science and math: Researchers propose a unified, probabilistic framework
May 9, 2024

Study of new method used to preserve privacy with US census data suggests accuracy has suffered
May 6, 2024

New study is first to use statistical physics to corroborate 1940s social balance theory
May 3, 2024
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Long Essay on Math 500 Words in English. Long Essay on Math is usually given to classes 7, 8, 9, and 10. Mathematics is one of the common subjects that we study since our childhood. It is generally used in our daily life. Every person needs to learn some basics of it. Even counting money also includes math.
Q.2. How mathematics is useful in our daily life essay? Ans: Mathematics, as a subject, is one of the most important subjects in our lives. Irrespective of the field, mathematics is essential in it. Be it physics, chemistry, accounts, etc. mathematics is there. The use of mathematics proceeds in our daily life to a major extent.
mathematics, the science of structure, order, and relation that has evolved from elemental practices of counting, measuring, and describing the shapes of objects. It deals with logical reasoning and quantitative calculation, and its development has involved an increasing degree of idealization and abstraction of its subject matter.
Nov. 10, 2022. "Mathematics, I now see, is important because it expands the world," Alec Wilkinson writes in a recent guest essay. "It is a point of entry into larger concerns. It teaches ...
In conclusion, I would confidently like to mention that Mathematics is a vital discipline in every person's life. It enables one to have an open mind on how to solve problems because one can approach a problem in math using very many different ways. It also enables one to be alert so as not to commit unnecessary errors and to only aim for ...
Math may seem "useless" and "annoying" to many, but the essay gives readers a clear message: we need math to succeed. 3. Short essay on the importance of Mathematics by Jay Prakash. "In this modern age of Science and Technology, emphasis is given on Science such as Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Medicine and Engineering.
Mathematics is the language of science. It helps us quantitatively understand and describe the physical world around us, from the trajectory of planets to the behavior of subatomic particles. In conclusion, mathematics is a vital part of our daily lives. It is not just a subject to be studied in school, but a tool for understanding, navigating ...
Discuss in your essay classic games like The Prisoner's Dilemma and examine how mathematical models can shed light on complex social interactions. Explore the cutting-edge applications of game theory in diverse fields, such as cybersecurity and evolutionary biology. If you still have difficulties choosing an idea for a math essay, find a ...
Check our 100% free math essay, research paper examples. Find inspiration and ideas Best topics Daily updates.
For our students, mathematics had become a charged subject; it carried a heavy burden of negative experiences. Many of our students were convinced that neither they nor their peers could be successful in mathematics. ... High School Mathematics at Work: Essays and Examples for the Education of All Students. Washington, DC: The National ...
An extended essay (EE) in mathematics is intended for students who are writing on any topic that has a mathematical focus and it need not be confined to the theory of mathematics itself. Essays in this group are divided into six categories: or in bringing about a new branch of mathematics, or causing a particular branch to flourish.
Here are 25 such topics that promise to engage both math enthusiasts and those seeking a deeper understanding of this fascinating subject. 1. Fibonacci Sequence: Delve into the mesmerizing world of numbers with this sequence, where each number is the sum of the two preceding ones. 2.
Mathematics is a versatile and always changing subject as people research and theorize new ideas. Calvin Clawson proclaimed that "the single most compelling reason to explore the world of mathematics is that it is beautiful, and pondering its intriguing ideas is great fun" (2).
It would explore the contributions of key mathematicians throughout history and the evolution of mathematical concepts and principles over time. Our free mathematics essay examples include popular topics such as algorithms, applied mathematics, calculus, knot theory, linear algebra, and more.
Practical Algebra Lessons: Purplemath. Topics in Geometry: Massachusetts Institute of Technology. The Geometry Junkyard: All Topics: Donald Bren School of Information and Computer Sciences. Calculus I: Lamar University. Business Math for Financial Management: The Balance Small Business.
See Mathematics: Subject-specific guidance - Use tabs on the left under Mathematics: Subject Specific Guide for more information.. Overview. An extended essay (EE) in mathematics is intended for students who are writing on any topic that has a mathematical focus and it need not be confined to the theory of mathematics itself.
Essay (Critical Writing) Mathematics is a branch of science that has had far-reaching impacts on many spheres of life. Through mathematics, man has made remarkable advances in technology and other fields of life. Mathematics also provides us with a logical order for describing the various prototypes and structures that comprise nature.
Mathematics is the abstract study of topics such as quantity (numbers), [2] structure, [3] space, [2] and change. [4][5][6] There is a range of views among mathematicians and philosophers as to the exact scope and definition of mathematics. [7][8] Mathematicians seek out patterns (Highland & Highland, 1961, 1963) and use them to formulate new conjectures.. Mathematicians resolve the truth or ...
Featuring promising new voices alongside some of the foremost names in the field, The Best Writing on Mathematics makes mathematical writing available to a wide audience. The Best Writing on Mathematics 2021 Mircea Pitici. The year's finest mathematical writing from around the world. The Best Writing on Mathematics 2020 Edited by Mircea Pitici.
An extended essay (EE) in mathematics is intended for students who are writing on any topic that has a mathematical focus and it need not be confined to the theory of mathematics itself. Essays in this group are divided into six categories: • the applicability of mathematics to solve both real and abstract problems
An extended essay in mathematics gives you the chance to demonstrate an understanding of any part of the subject. You can give an expression on the beauty of mathematics in geometry or fractal theory, the elegance of mathematics in the proving of theorems, and the origin and subsequent development of a branch of mathematics over a period.
My Favourite Subject Maths Essay For Kids. "Mathematics is my favourite subject as I love to solve mathematical problems like addition, subtraction, division and multiplication. I enjoy playing with numbers and it gives me an immense level of satisfaction when I'm able to solve a mathematical problem without any hassle.
Many mathematics journals ask authors of research papers and expository articles to list subject codes from the Mathematics Subject Classification in their papers. The subject codes so listed are used by the two major reviewing databases, Mathematical Reviews and Zentralblatt MATH.
In this introduction, we set the stage for a collection of papers from the Co-constructing Mathematics Motivation in Primary Education-A Longitudinal Study in Six European Countries Project (MATHMot for short), an international study aiming to identify the factors that shape the development of motivation in mathematics from a comparative perspective in primary education. Students ...
In 2013 Boaler, a former high school math teacher, produced How to Learn Math, the first massive open online course (MOOC) on mathematics education. She leads workshops and leadership summits for ...
For everyone whose relationship with mathematics is distant or broken, Jo Boaler, a professor at Stanford Graduate School of Education (GSE), has ideas for repairing it. She particularly wants ...