
Future Perfect Tense With Examples, Rules, Usage
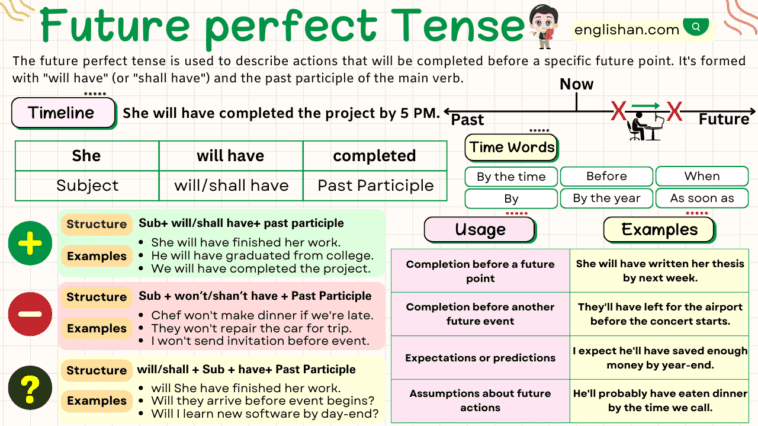
The Future Perfect Tense is a verb tense used to describe an action that will be completed at some point in the future before another action or time. In this tense, we combine “will have” with the past participle of the main verb. It emphasizes the completion of an action before a specific point or event in the future.
- She will have finished her homework by 8 PM.
- They will have left for the airport by the time you arrive.
- I won’t have completed the puzzle by lunchtime.
- They won’t have fixed the car before the mechanic arrives.
- Will you have submitted your report by tomorrow?
- By Friday, will they have chosen a new team captain?
Table of Contents
Usages of the Future Perfect Tense
Completed Action Before a Point in the Future
The future perfect tense describes an action that will be finished before a specific time or event.
- She will have completed her chores before dinner.
- By the time you arrive, I will have finished writing the report.
- They will have built the new playground before the school year starts.
- I won’t have finished my homework before the movie begins.
- They won’t have completed the project by the deadline.
- She won’t have cooked dinner before the guests arrive.
- Will you have completed the assignment by tomorrow?
- By the time they get here, will you have finished cleaning?
- Will they have renovated the kitchen by the end of the month?
Emphasizing Duration
The future perfect tense can be used to emphasize the duration of an action that will be completed before a specific point in the future.
- She will have lived in the city for a decade by next year.
- By the time I graduate, I will have studied engineering for five years.
- They will have known each other for twenty years by their anniversary.
- I won’t have worked at this job for more than a year by the time I leave.
- By next month, she won’t have lived in the neighborhood for even a year.
- They won’t have known each other for a decade by their reunion.
- Will you have worked here for five years by the end of the contract?
- By next summer, will she have lived in the city for ten years?
- Will they have been married for twenty years by their anniversary?
Hypothetical Situations
The future perfect tense can be used to discuss hypothetical situations or possibilities that may be completed by a certain time in the future.
- If she practices every day, she will have become a skilled pianist by the end of the year.
- If you save money regularly, you will have enough for a vacation by next summer.
- If they start now, they will have planted a beautiful garden by the time of the party.
- If she doesn’t water the flowers, they won’t have bloomed by the wedding.
- If you miss the bus, you won’t have arrived at the event on time.
- If they don’t practice, they won’t have memorized the lines for the play.
- If you study hard, will you have completed the assignment by tomorrow?
- If we start early, will we have reached the summit by noon?
- If they work together, will they have finished the project by the deadline?
Future Perfect Tense Chart
Signal Words
Signal words are words or phrases that indicate the use of the future perfect tense. They often help identify when an action will be completed or its relationship to other events.
- By (specific time): By tomorrow, By the end of the week, By next year.
- Before (specific time): Before the party starts, Before the deadline, Before the meeting .
- By the time (specific time): By the time you arrive, By the time the movie starts.
- At (specific time): At 6 PM, At the concert.
- In (period of time): In a month, In a year.
- She will have completed her project by tomorrow.
- They will have fixed the car before the weekend.
- We will have arrived at the destination by noon.
- He will have finished his homework by the time you call.
- I will have graduated from school by next year.
- I won’t have received the package by the end of the day.
- They won’t have cleaned the house before the guests arrive.
- She won’t have cooked dinner by the time you get home.
- He won’t have fixed the computer by tomorrow morning.
- We won’t have completed the puzzle before bedtime.
- By next month, will you have finished the book?
- Before the meeting, will they have prepared the presentation?
- By the end of the week, will she have visited all the museums?
- By the time of the event, will he have learned the dance?
- Before the deadline, will we have completed the project?
Time Expressions
Time expressions in the future perfect tense are phrases or words that indicate when an action is expected to be completed. These expressions help provide context and specify the point in the future when the action will be finished.
Here are some common time expressions:
By + specific time, Before + specific time, By the time + specific time, At + specific time, In + period of time.
- By next Sunday, she will have finished reading the book.
- They will have completed the renovation before the end of the month.
- By the time the movie starts, we will have bought our tickets.
- He will have graduated from college by the year 2025.
- By the end of the day, she will have written five articles.
- Before the exam, I won’t have studied the entire syllabus.
- They won’t have painted the house by next weekend.
- Before the presentation, he won’t have prepared the slides.
- By the time the party begins, she won’t have baked the cake.
- Before the trip, they won’t have packed their bags.
- By next month, will you have completed the project?
- Before the concert, will they have rehearsed all the songs?
- By the time we arrive, will she have set up the decorations?
- By the end of the week, will he have submitted the report?
- Before the deadline, will they have finalized the proposal?
Forming the Future Perfect Tense
Affirmative Sentences
Affirmative sentences in the future perfect tense are statements that express actions or events that will be completed or finished before a specific point in the future. These sentences typically use the auxiliary verb “will” or shall followed by have and the past participle of the main verb, forming the structure:
Subject + will /shall + have + verb(3rd form) + object.
- She will have finished her book by next Sunday.
- By the end of the day, they will have completed the puzzle.
- He will have fixed the computer before dinner.
- By next month, I will have learned to swim.
- They will have visited all the museums by the time they leave the city.
- She will have written five letters by tomorrow.
- By the time you wake up, the sun will have risen.
- We will have planted flowers in the garden by the weekend.
- By next year, he will have saved enough money for a car.
- They will have finished the construction before the rainy season.
- She will have graduated from college by the year 2024.
The sentences given above are broken down according to their grammatical structure.
Negative Sentences
Negative sentences in the future perfect tense are statements that express actions or events that will not be completed or finished before a specific point in the future. These sentences typically use the negative form of the auxiliary verb will (will not) or the contraction won’t, followed by have and the past participle of the main verb. The structure for negative sentences in the future perfect tense is:
Subject + will /shall +not + have + verb(3rd form) + object.
- I won’t have completed the assignment by tomorrow.
- By the end of the week, they won’t have fixed the broken window.
- He won’t have learned to ride a bike by next month.
- By next year, she won’t have finished writing her novel.
- They won’t have visited the new museum before it closes.
- I won’t have cooked dinner by the time you come home.
- By the weekend, we won’t have planted flowers in the garden.
- He won’t have saved enough money for the vacation by the end of the year.
- They won’t have completed the renovation before the holiday season.
- She won’t have graduated from college by the year 2025.
Interrogative Sentences
Interrogative sentences in the future perfect tense are questions that inquire about actions or events expected to be completed before a specific point in the future. These questions typically use the auxiliary verb will or shall, followed by the subject, have, the past participle of the main verb, and additional elements. The structure for interrogative sentences in the future perfect tense is:
Will /Shall + subject + have + verb(3rd form) + object.
- By tomorrow, will you have finished the assignment?
- Will they have repaired the broken window by the end of the week?
- By next month, will he have mastered riding a bike?
- Will she have completed her novel by next year?
- Will they have visited the new museum before it closes?
- Will you have cooked dinner by the time you come home?
- By the weekend, will we have planted flowers in the garden?
- Will he have saved enough money for the vacation by the end of the year?
- Will they have finished the renovation before the holiday season?
- By the year 2025, will she have graduated from college?
Spelling Rules
Spelling rules in the future perfect tense are generally consistent with the regular rules for forming past participles .
Here are some key spelling rules to keep in mind:
Regular Verbs
Verbs Ending in -e
One-Syllable Verbs with a Single Vowel Followed by a Single Consonant:
Irregular Verbs
Verbs Ending in -y
Future Perfect vs. Simple Future Tense
The future perfect tense and the simple future tense are two distinct verb tenses in English, each used to convey different aspects of time and completion.
Let’s compare these two tenses:
Avoiding Common Mistakes
To avoid common mistakes in the future perfect tense, consider the following tips:
- Use of “Will Have” or “Shall Have”:
Ensure that the auxiliary verb “will” or “shall” is used correctly with “have” to form the future perfect tense.
- Incorrect: “I have finished my work by tomorrow.”
- Correct: “I will have finished my work by tomorrow.”
- Correct Placement of “Not” in Negative Sentences:
Place “not” after “will” or use the contraction “won’t” for negative sentences.
- Incorrect: “I will not have completed the assignment.”
- Correct: “I will not have completed the assignment.” or “I won’t have completed the assignment.”
- Accurate Use of Past Participles :
Ensure that the past participles are used correctly, especially for irregular verbs.
- Incorrect: “She will have went to the store.”
- Correct: “She will have gone to the store.”
- Proper Use of Time Expressions:
Use appropriate time expressions to indicate when the action will be completed.
- Incorrect: “I will have finished the project tomorrow.”
- Correct: “I will have finished the project by tomorrow.”
- Consistent Use of Time Frames:
Ensure consistency in expressing different actions in relation to each other within a sentence.
- Incorrect: “He will have finished his work before he will go to the meeting.”
- Correct: “He will have finished his work before he goes to the meeting.”
- Avoiding Redundancy:
Be cautious not to use unnecessary words that may make the sentence redundant.
- Incorrect : “By next month, I will have completed the task and finished it.”
- Correct : “By next month, I will have completed the task.”
- Understanding the Concept of Completion:
Remember that the future perfect tense emphasizes completion before a specific point in the future.
- Incorrect: “By the end of the day, I will have started my assignment.”
- Correct: “By the end of the day, I will have completed my assignment.”
Future Perfect Tense Example Sentences
- Our teacher will have taught us lesson.
- I shall have finished my homework.
- You will have received the money order.
- Good players will have got prizes.
- The cook will have cooked food before the sun rises.
- They will have read the newspaper.
- We shall have taken rest.
- By next week, I will have memorized all the lines.
- He will have completed the marathon by the time you finish breakfast.
- By the time you return, I will have cleaned the entire house.
- They will have cooked dinner before the guests arrive.
- By the end of the concert, she will have sung all her favorite songs.
- We will have learned a new language by the end of the course.
- By next spring, he will have grown a beautiful garden.
- She will have bought a birthday present by the weekend.
- By the time the meeting starts, I will have prepared the presentation.
- They will have finished the project before the deadline.
- By the end of the day, he will have read three books.
- By next month, they will have adopted a new pet.
- The postman will not have brought my letter.
- He will not have made this mistake.
- The hunter will not have caught any bird.
- They will not have waited for us.
- We shall not have taken tea before you come.
- I shall not have opened your letter.
- The sun will not have risen when the train comes.
- He won’t have completed the marathon by the time you finish breakfast.
- By the time you return, I won’t have cleaned the entire house.
- They won’t have cooked any dinner before the guests arrive.
- By the end of the concert, she won’t have sung any songs.
- We won’t have learned a new language by the end of the course.
- By next spring, he won’t have grown any plants in the garden.
- She won’t have bought a birthday present by the weekend.
- By the time the meeting starts, I won’t have prepared any presentation.
- They won’t have finished any project before the deadline.
- By the end of the day, he won’t have read any books.
- She won’t have fixed any leaky faucets before they cause damage.
- By next month, they won’t have adopted any new pets.
- I won’t have painted any pictures by the end of the week.
- Why will he have forgiven you?
- Who will have locked the door?
- Will the passengers have bought tickets?
- Will she have boiled eggs?
- Will the guests have come?
- Will the peon have rung the bell when reach school?
- By the time you finish breakfast, will he have completed the marathon?
- Will I have tidied up the entire house by the time you return?
- Will they have prepared any dinner before the guests arrive?
- By the end of the concert, will she have sung any songs?
- Will we have acquired a new language by the end of the course?
- By next spring, will he have cultivated any plants in the garden?
- Will she have purchased a birthday present by the weekend?
- By the time the meeting starts, will I have formulated any presentation?
- Will they have completed any project before the deadline?
- By the end of the day, will he have perused any books?
- Will she have repaired any leaky faucets before they cause damage?
- By next month, will they have adopted any new pets?
- Will you have crafted any pictures by the end of the week?
- Will they have organized the house before the guests arrive?
- a) will have completed
- b) completed
- a) will have finished
- b) finished
- a) will have read
- a) will have submitted
- b) submitted
- a) will have built
- a) will have earned
- a) will have sold
1. What is the future perfect tense?
The future perfect tense is a verb tense that expresses an action that will be completed before a specific point in the future.
2. How is the future perfect tense formed?
It is formed using the auxiliary verb “will” or “shall” + “have” + the past participle of the main verb.
3. When do we use the future perfect tense?
We use the future perfect tense to indicate that an action will be completed before another action or a specific point in the future.
5. What are the signal words for the future perfect tense?
Signal words often associated with the future perfect tense include “by,” “before,” “by the time,” and specific time expressions.
7. Can you use “shall” instead of “will” in the future perfect tense?
Yes, “shall” can be used instead of “will” in the future perfect tense, although “will” is more commonly used in modern English.
8. What is the difference between the future perfect and future perfect continuous tense?
The future perfect tense focuses on the completion of an action by a specific point in the future, while the future perfect continuous tense emphasizes the duration of an action leading up to that point.
9. Are there irregular verbs in the future perfect tense?
Yes, irregular verbs have irregular past participles . For example, “eat” becomes “eaten,” and “go” becomes “gone.” Regular verbs form the past participle by adding “-ed.”
Free Grammar and Vocabulary Worksheets Resources
- Worksheet Tenses
- English Worksheets
- Action Verbs Worksheets
- Future Perfect Tense Worksheets
- Future Perfect Continuous Worksheets
You May Also Like
- Present Tenses With Examples
- Present Perfect Tense With Examples
- Time Expressions in English
- Future Perfect Tense With Examples
Future Perfect Future Perfect Tense Future Perfect Tense Definition Future Perfect Tense Example Sentences Future Perfect Tense Exercise future perfect tense formula Future Perfect Tense In English Future Perfect Tense In Grammar Future Perfect Tense Rules Future Perfect Tense Structure Future Perfect Tense Usages
Present Perfect Continuous Tense With Examples, Rules, Usage
Coordinating Conjunctions | Definition, Rules, Usage and Examples
Copyright © 2024 by englishan
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
Forgot password?
Enter your account data and we will send you a link to reset your password.
Your password reset link appears to be invalid or expired.
Privacy policy.
To use social login you have to agree with the storage and handling of your data by this website. %privacy_policy%
Add to Collection
Public collection title
Private collection title
No Collections
Here you'll find all collections you've created before.
How to Use the Future Perfect Tense
Perfect english grammar.

Download this explanation in PDF here. Read about how to make the future perfect here.
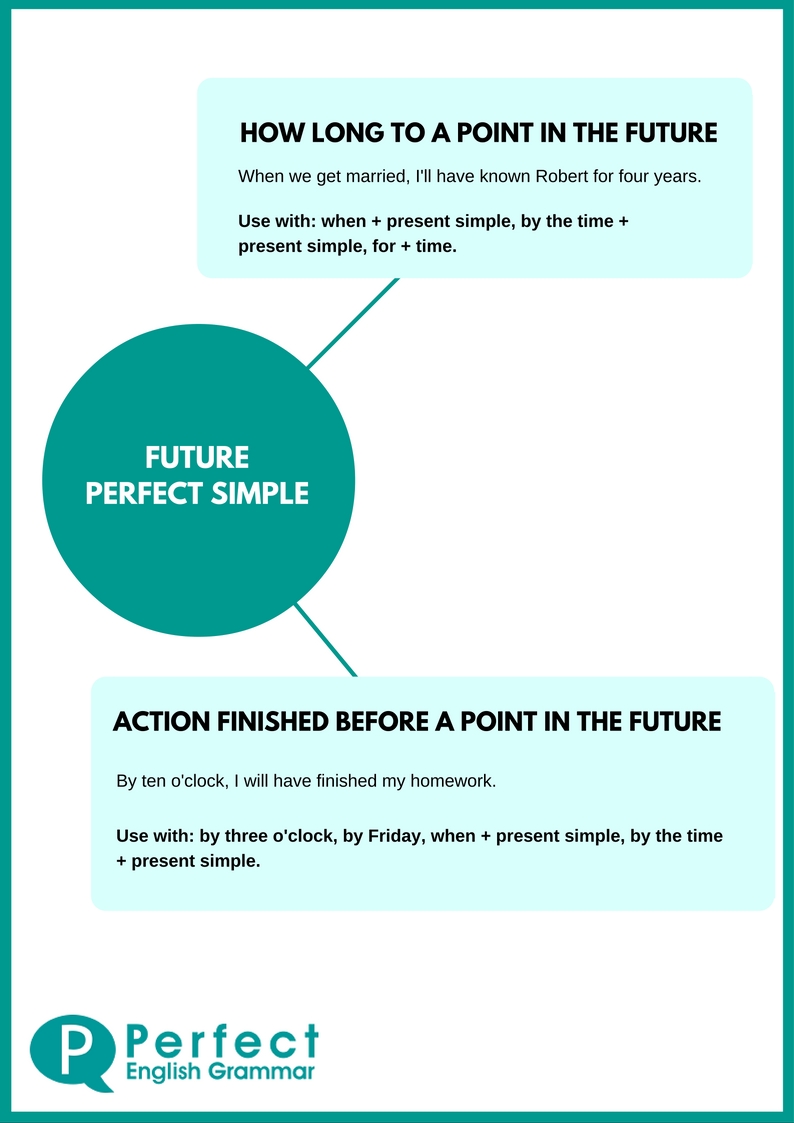
- When we get married, I'll have known Robert for four years.
- At 4 o'clock, I'll have been in this office for 24 hours.
- I've lived here for 11 months and three weeks. (This is correct, but the time is not an easy number.)
- On Tuesday, I will have lived here for one year. (A much easier number.)
- By 10 o'clock, I will have finished my homework. (= I will finish my homework some time before 10, but we don't know exactly when.)
- By the time I'm sixty, I will have retired. (= I will retire sometime before I'm sixty. Maybe when I'm fifty-nine, maybe when I'm fifty-two.)

Hello! I'm Seonaid! I'm here to help you understand grammar and speak correct, fluent English.

Read more about our learning method
- Verb Tense Intro.
- Types of Verbs
- Active/Passive
- Simple Present
- Present Continuous
- Simple Past
- Past Continuous
- Present Perfect
- Present Perf. Cont.
- Past Perfect
- Past Perfect Cont.
- Simple Future
- Future Continuous
Future Perfect
- Future Perfect Cont.
- Would Always
- Future in the Past
Future perfect has two different forms: "will have done" and "be going to have done." Unlike simple future forms, future perfect forms are usually interchangeable.
FORM Future Perfect with "Will"
[will have + past participle]
- You will have perfected your English by the time you come back from the U.S.
- Will you have perfected your English by the time you come back from the U.S.?
- You will not have perfected your English by the time you come back from the U.S.
FORM Future Perfect with "Be Going To"
[am/is/are + going to have + past participle]
- You are going to have perfected your English by the time you come back from the U.S.
- Are you going to have perfected your English by the time you come back from the U.S.?
- You are not going to have perfected your English by the time you come back from the U.S.
NOTE: It is possible to use either "will" or "be going to" to create the future perfect with little or no difference in meaning.
USE 1 Completed Action Before Something in the Future
The future perfect expresses the idea that something will occur before another action in the future. It can also show that something will happen before a specific time in the future.
- By next November, I will have received my promotion.
- By the time he gets home, she is going to have cleaned the entire house.
- I am not going to have finished this test by 3 o'clock.
- Will she have learned enough Chinese to communicate before she moves to Beijing?
- Sam is probably going to have completed the proposal by the time he leaves this afternoon.
- By the time I finish this course, I will have taken ten tests.
- How many countries are you going to have visited by the time you turn 50?
Notice in the examples above that the reference points ( marked in italics ) are in simple present rather than simple future . This is because the interruptions are in time clauses , and you cannot use future tenses in time clauses.
USE 2 Duration Before Something in the Future (Non-Continuous Verbs)
With non-continuous verbs and some non-continuous uses of mixed verbs , we use the future perfect to show that something will continue up until another action in the future.
- I will have been in London for six months by the time I leave.
- By Monday, Susan is going to have had my book for a week.
Although the above use of future perfect is normally limited to non-continuous verbs and non-continuous uses of mixed verbs, the words "live," "work," "teach," and "study" are sometimes used in this way even though they are NOT non-continuous verbs.
REMEMBER No Future in Time Clauses
Like all future forms, the future perfect cannot be used in clauses beginning with time expressions such as: when, while, before, after, by the time, as soon as, if, unless, etc. Instead of future perfect, present perfect is used.
- I am going to see a movie when I will have finished my homework. Not Correct
- I am going to see a movie when I have finished my homework. Correct
ADVERB PLACEMENT
The examples below show the placement for grammar adverbs such as: always, only, never, ever, still, just, etc.
- You will only have learned a few words.
- Will you only have learned a few words?
- You are only going to have learned a few words.
- Are you only going to have learned a few words?
ACTIVE / PASSIVE
- They will have completed the project before the deadline. Active
- The project will have been completed before the deadline. Passive
- They are going to have completed the project before the deadline. Active
- The project is going to have been completed before the deadline. Passive
More About Active / Passive Forms
Future Perfect Exercises
- Verb Tense Exercise 25 Future Perfect and Future Perfect Continuous
- Verb Tense Exercise 26 Future Perfect and Future Perfect Continuous
- Verb Tense Exercise 27 Future Perfect and Future Perfect Continuous
- Verb Tense Exercise 28 Future Perfect and Future Perfect Continuous
- Verb Tense Practice Test Cumulative Verb Tense Review
- Verb Tense Final Test Cumulative Verb Tense Review
- Weekly Lesson
- Grammar Book
- Verb Tenses
- Conditionals
- Prepositions
- Mini-tutorials
- Irregular Verbs
- Reading Room
- Listening Lounge
- Phrasal Verb Dictionary
- Verb + Preposition Dictionary
- Grammar Lessons
- Grammar Exercises
- Grammar Quizzes
- Mixed Tests
- PDF Worksheets
- Beginners Lessons
- Easy Worksheets
- Beginners Tests
- Reading Exercises
- Drag & Drop Grammar
- English For Kids
- Kids Word Games
- Picture Vocabulary
- Reading Tests
- Short Dialogues
- Short Sentences
- Closest in Meaning
- Irrelevant Sentence
- ESL Paragraphs
- GRE Reading
- Text Completion
- GRE Equivalence
- SAT Sentence
- Essay Writing
- Vocabulary Exercises
- Study Skills Tips
- Drag & Drop Vocab
Future Perfect Tense
Forming future perfect tense, quick exercise.
Future Tense: A Guide to Understanding and Using Future Tense in English Grammar
By: Author English Study Online
Posted on Last updated: November 13, 2023
Sharing is caring!
Future tense is an essential aspect of the English language. It is used to describe actions or events that will happen in the future. As such, it is a crucial aspect of English grammar that learners must master. In this article, we will explore the future tense in detail, including its definition, usage, and examples.
Table of Contents
Understanding Future Tense
The future tense is used to describe actions that will occur in the future. It is one of the three main verb tenses in English, along with the past tense and the present tense.
To form the future tense, we typically use the auxiliary verb “ will ” followed by the base form of the main verb. For example, “ I will go to the store .” In some cases, we can also use “ going to ” to indicate future events. For example, “ I am going to study for my exam tomorrow .”
There are four main future tenses in English: simple future, future continuous, future perfect, and future perfect continuous. Each tense has a specific use and is formed differently.
The simple future tense is used to describe actions that will happen in the future.
- For example, “I will go to the gym tomorrow.”
The future continuous tense is used to describe actions that will be ongoing in the future.
- For example, “I will be studying for my exam all night.”
The future perfect tense is used to describe actions that will be completed by a certain point in the future.
- For example, “I will have finished my project by Friday.”
The future perfect continuous tense is used to describe actions that will have been ongoing for a certain amount of time before a specific point in the future.
- For example, “I will have been working on this project for three weeks by the time it is due.”
Types of Future Tense
In English grammar, there are four types of future tense. These are Simple Future Tense, Future Continuous Tense, Future Perfect Tense, and Future Perfect Continuous Tense.
Simple Future Tense
Simple Future Tense is used to describe actions that will happen in the future. It is formed by adding the auxiliary verbs “will” or “shall” to the base form of the verb.
- For example, “ I will eat breakfast tomorrow” or “She shall graduate next year.”
Future Continuous Tense
Future Continuous Tense is used to describe actions that will be in progress at a specific time in the future. It is formed by using the auxiliary verb “will” with the present participle (-ing) form of the verb.
- For example, “ I will be studying at 9 PM tomorrow ” or “ They will be playing soccer at noon .”
Future Perfect Tense
Future Perfect Tense is used to describe actions that will be completed at a specific time in the future. It is formed by using the auxiliary verb “will” with the past participle form of the verb.
- For example, “ I will have finished my homework by 10 PM ” or “ She will have graduated by next summer .”
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
Future Perfect Continuous Tense is used to describe actions that will have been in progress for a certain amount of time before a specific time in the future. It is formed by using the auxiliary verb “will” with “have been” and the present participle (-ing) form of the verb.
- For example, “ I will have been studying for three hours by 9 PM tomorrow ” or “ They will have been playing soccer for two hours by noon .”
Formation of Future Tense Sentences
In English grammar, the future tense is used to describe actions or events that will happen in the future. To form a sentence in the future tense, we need to use auxiliary verbs such as “will” or “shall” followed by the base form of the verb. Here’s how to form sentences in the future tense:
The simple future tense is used to describe actions or events that will happen in the future. To form a sentence in the simple future tense, use the auxiliary verb “ will ” or “ shall ” followed by the base form of the verb. For example:
- I will go to the gym tomorrow.
- She will finish her homework before dinner.
- They will travel to Europe next summer.
The future continuous tense is used to describe actions or events that will be in progress at a certain time in the future. To form a sentence in the future continuous tense, use the auxiliary verb “ will ” or “ shall ” followed by “ be ” and the present participle (-ing form) of the verb. For example:
- I will be studying for my exam at this time tomorrow.
- She will be cooking dinner when we arrive.
- They will be playing soccer at 4 pm tomorrow.
The future perfect tense is used to describe actions or events that will be completed by a certain time in the future. To form a sentence in the future perfect tense, use the auxiliary verb “ will ” or “ shall ” followed by “ have ” and the past participle of the verb. For example:
- I will have finished my work by 5 pm.
- She will have graduated from college in two years.
- They will have traveled to six different countries by the end of next year.
The future perfect continuous tense is used to describe actions or events that will have been in progress for a certain amount of time by a certain time in the future. To form a sentence in the future perfect continuous tense, use the auxiliary verb “ will ” or “ shall ” followed by “ have been ” and the present participle (-ing form) of the verb. For example:
- I will have been working on this project for three hours by the time you arrive.
- She will have been living in New York for five years next month.
- They will have been studying English for six months by the end of this year.
Usage of Future Tense
In English, the future tense is used to talk about events or actions that will happen in the future. It is one of the twelve verb tenses in English and is used to convey information about events that have not yet occurred. In this section, we will cover the different ways the future tense is used.
Predictions
The future tense is often used to make predictions about the future. We can use the word “will” followed by the base form of the verb to make these predictions.
- For example, “ It will rain tomorrow ,” or “ The stock market will go up next week. “
The future tense is also used to make promises or commitments about the future. We can use the word “will” followed by the base form of the verb to make these promises.
- For example, “ I will meet you at the restaurant at 7 pm ,” or “ We will finish the project by Friday .”
The future tense is used to make offers or suggestions about the future. We can use the word “will” followed by the base form of the verb to make these offers.
- For example, “ I will help you with your homework, ” or “ We will go to the beach next weekend .”
The future tense is used to talk about decisions that will be made in the future. We can use the word “will” followed by the base form of the verb to talk about these decisions.
- For example, “ I will apply for the job ,” or “ We will buy a new car next year. “
Practice Exercises with Answers
In order to master the future tense in English, it is important to practice using it in various contexts. Here are some exercises with answers to help you hone your skills:
Choose the correct verb form to complete the sentence.
- By this time next year, I ___________ (graduate/ will graduate) from college.
- She ___________ (will be/ is) very happy when she hears the news.
- They ___________ (will have/ have) been married for 10 years next month.
- We ___________ (will go/ are going) to the beach this weekend.
- I am sure he ___________ (will pass/ passes) the exam.
- will graduate
Choose the correct verb tense to complete the sentence.
- By the time we arrive, the movie ___________ (will start/ will have started).
- If it rains, we ___________ (will stay/ stay) at home.
- He ___________ (will be/ is) tired after working all day.
- I ___________ (will call/ call) you as soon as I get home.
- They ___________ (will have/ have) finished their project by tomorrow.
- will have started
- We ___________ (will visit/ are visiting) Paris next month.
- She ___________ (will have/ has) a baby in December.
- If I have time, I ___________ (will go/ go) to the gym.
- They ___________ (will be/ are) here in 10 minutes.
- I am sure he ___________ (will like/ likes) the gift.
- are visiting
Practice makes perfect, so keep practicing and using the future tense in different situations. With time and effort, you will become more comfortable and confident in your use of this important tense.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the four types of future tense in English grammar?
In English grammar, there are four types of future tense. The first one is the simple future tense, which is used to describe an action that will happen in the future. The second one is the future continuous tense, which is used to describe an action that will be ongoing in the future. The third one is the future perfect tense, which is used to describe an action that will have been completed in the future. The fourth one is the future perfect continuous tense, which is used to describe an action that will have been ongoing and completed in the future.
What are some examples of future perfect tense?
The future perfect tense is used to describe an action that will have been completed in the future. For example, “By the time we arrive, they will have finished their dinner.” or “I will have completed my work by Friday.”
What is the difference between future continuous and future perfect tense?
The future continuous tense is used to describe an action that will be ongoing in the future, while the future perfect tense is used to describe an action that will have been completed in the future. For example, “She will be sleeping at a hotel tonight” is an example of future continuous tense, while “They will have eaten dinner by 8:00 PM” is an example of future perfect tense.
- Recent Posts
- Juridical Process vs. Judicial Process: Understanding the Crucial Differences - December 14, 2023
- Compound Nouns: How to Use Them Effectively in English - November 9, 2023
- English Tenses: A Beginner’s Guide in English - November 6, 2023

Shopping Cart
No products in the cart.
Free English grammar course with certificate
English tenses.
- Sentence structure exercises with answers
- Types of tenses in English with examples
- Simple present tense exercise with answers
- Simple Past Tense exercise with answers
- Future simple tense: Rules And Examples
- Past continuous tense: Rules And Examples
- Present continuous tense: Rules And Examples
- Future continuous tense: Rules And Examples
- Past perfect tense: Rules And Examples
- Present perfect tense: Rules And Examples
Future perfect tense: Rules And Examples
- Frequently asked questions about English Grammar
Writing Correction

IELTS Vocabulary Builder Series
Download IELTS Vocabulary Builder book series for free!
In this lesson from the free English grammar course from Simply IELTS, you will learn the structure and formula of the future perfect tense and how to use it in the IELTS exam .

What is the formula of the Future perfect tense?
The future perfect tense is used to describe an action or event that will be completed at a specific time in the future, before another action or event takes place. It is formed with the auxiliary verb “will” or “shall” followed by the verb “have” and the past participle form of the main verb.
Here are a few rules for using the future perfect tense:
- Use the auxiliary verb “will” or “shall” followed by the verb “have” and the past participle form of the main verb. The past participle form of a verb is typically the base form of the verb plus -ed, but there are many irregular verbs with different past participle forms. For example: “I will have finished,” “she will have studied,” “they will have eaten.”
- Use the future perfect tense to describe an action or event that will be completed at a specific time in the future, before another action or event takes place. For example: “I will have finished my homework before 6:00,” “she will have studied for her exams before 7:00,” “they will have eaten lunch before 8:00.”
Examples of the future simple tense
Here are a few examples of the future perfect tense in action :
- I will have finished my homework before the phone rings.
- She will have studied for her exams before I see her.
- They will have eaten lunch before the storm starts.
In the negative form , the auxiliary verb “will” or “shall” is followed by “not” and the verb “have” and the past participle form of the main verb. For example:
- I will not have finished my homework before the phone rings.
- She will not have studied for her exams before I see her.
- They will not have eaten lunch before the storm starts.
In the question form , the auxiliary verb “will” or “shall” is placed before the subject and the verb “have” and the past participle form of the main verb is placed after the subject. For example:
- Will I have finished my homework before the phone rings?
- Will she have studied for her exams before I see her?
- Will they have eaten lunch before the storm starts?
How to use future perfect tense in IELTS exam?
To use the future perfect tense in the IELTS exam, it is important to use it correctly and consistently in your writing and speaking tasks. Make sure to use the correct form of the auxiliary verb “will” or “shall” and the verb “have” and the past participle form of the main verb.
Use the future perfect tense to describe an action or event that will be completed at a specific time in the future, before another action or event takes place. Make sure not to mix tenses within a sentence or paragraph.
Examples of using future perfect tense in IELTS exam
Here are a few examples of how you might use the present perfect tense in the IELTS exam:
Writing Task 1:
“By the time I start cooking dinner at 6:00 tomorrow evening, I will have finished all of my errands for the day. My husband will also have finished his work and will be ready to relax on the couch.”
Speaking part 2 ( cue cards ):
“By the time I go on my trip to the countryside next weekend, I will have visited my parents several times. They will have shown me around their new house and we will have spent some quality time together.”
Writing Task 2:
“Many people believe that technology will have taken over our lives in the future. While it is true that technology has become more prevalent in recent years, I do not think it will have completely taken over. There will still be many people who will have lived simple lives and will not have relied on technology as much as others.”
Recent IELTS exams:
- Successful sports professionals can earn a great deal IELTS 7 band essay
- Countries should try to produce all the food IELTS 7 band Essay
- Many countries spend a lot of money on major sports competitions IELTS 7 band essay
- Tourists visiting places where conditions are difficult IELTS Essay
- Everyone wore clothes according to their culture IELTS 7 band essay
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Privacy Overview
There was a problem reporting this post.
Block Member?
Please confirm you want to block this member.
You will no longer be able to:
- Mention this member in posts
Please allow a few minutes for this process to complete.
Download Book for free
Ielts vocabulary builder.
Understanding Future Perfect: Formation, usage and example sentences
Learn everything about the Future Perfect Tense ! How is it formed, what signal words are there and what events does it describe? We explain everything you need to know about the Future Perfect Tense with example sentences and exercises.
Deepen your English grammar knowledge and your understanding of the Future Perfect Tense together with us. Soon you will be using the Future Perfect Tense in your own texts and conversations.
» Formation of the Future Perfect tense » Use of the Future Perfect tense » Example sentences Future Perfect tense » Signal words for Future Perfect tense
The formation of the Future Perfect Tense
Basically, the Future Perfect Tense is formed by using the auxiliary verb will or, in some cases, shall in Future Simple tense and combining it with the Partzip Perfect of the main verb. For a better understanding, have a look at the following rule for forming the Future Perfect:
Subject + wil/shall + have + Participle Perfect of the main verb.
To form the Future Perfect tense negatively, you simply have to put the word "not" between the auxiliary verb and the participle perfect of the main clause. Here is an example of the negative use of the future perfect tense : "I will not have finished my homework by tomorrow. Have a look at the table below for more example sentences in the future perfect tense.
The use of the Future Perfect tense
The future perfect tense is used to talk about events that will already be completed at a certain time in the future. So with the future perfect tense, you emphasise the completeness of the action and put special focus on the fact that the action or state you are referring to is already completed before a later state in the future.
You also need to form the Future Perfect tense to express assumptions or predictions about the past that are made on the basis of events in the present. This special form of the future perfect tense is also called the Future perfect progressive tense.
At first glance, this sounds rather complicated. It will certainly become clearer if you take a closer look at the example sentences below and also form a sentence or two of your own in the future perfect tense.
Signal words for the Future Perfect tense
There are also a few signal words for the future perfect tense that indicate that you have to use the future perfect tense. Take a look at the following list of signal words for the future perfect tense to help you recognise when you need to use it.
EnglishGrammarSoft


Future Tenses in English (Structure & 10 Examples Each)
Future tenses indicate an action that will happen in the future. These are used to talk about the future; to describe what will happen (or will be happening) in future; and to make predictions about what might happen.
The future tenses of verb are used to describe events that have not yet happened. The future tense can be used to express:
- Actions that will take place in the future
- Probability or likelihood of an event occurring
- Intentions or plans for the future
There are a few different ways to form the future tense in English. The most common is to use the auxiliary verb “will” followed by the base form of the main verb. For example:
- I will go to the store later.
- She will read the book tonight.
- They will finish their homework before dinner.
Another way to form the future tense is by using “going to” followed by the base form of the main verb. This is used to express plans or intentions for the future. For example:
- I am going to go to the store later.
- She is going to read the book tonight.
- They are going to finish their homework before dinner.
Finally, the future tense can also be expressed using the present tense form (base form) of the main verb. This is typically used for scheduled events that will occur in the future. For example:
- The train leaves at 6:00 pm.
- His flight arrives at 9:30 am tomorrow.
- The meeting starts in five minutes.
The future tense is a verb tense used to indicate that an action or event is expected to take place in the future. The future tense can be used to express actions, events, or states of being that will occur at some point in the future.
Types of Future Tenses
There are four types of future tenses in English:
- The simple future tense is used to describe an action or event that will happen in the future. For example, “I will go to the store.”
- The future continuous tense is used to describe an action or event that will be happening at some point in the future. For example, “I will be going to the store.”
- The future perfect tense is used to describe an action or event that will have happened at some point in the future. For example, “I will have gone to the store.”
- The future perfect continuous tense is used to express an action that will continue up to a specific point in the future. For example, “The students will have been studying for two hours by the time we arrive.”
What is Simple Future Tense?
The simple future tense is used to describe an event that will take place in the future. It is typically expressed using the modal verb “will”. For example, the sentence “I will go to the store.” expresses the fact that going to the store is something that will happen in the future.
Other ways of expressing the simple future tense include using the verb “shall” or using the base form of the verb with no auxiliary verb. In some cases, a present tense form may be used to express futurity, such as with the phrase “I am leaving tomorrow.”
The simple future tense can also be used to express probability or likelihood, as in the sentence “This will be my last chance to see her.”
When Simple Future Tense is Used?
- The Simple Future tense is used to express an action that will happen in the near future, e.g., She will write a book.
- We use will + infinitive for actions that are certain and definite, e.g., I will go to the party this weekend; She will buy a new car next month; We’ll see each other soon!
- We use going to + infinitive for actions that are likely but not certain, e.g., It’s going to rain tomorrow; He is going to fail his exam tomorrow because he didn’t study enough; They’re going to win their next match because they’re so good at tennis!
Structure of Simple Future Tense
The structure of simple future tense is:
Subject + will + base form of verb
He/She/It/I/We/They/You + will + base form
10 Examples of Simple Future Tense
- He will drive the car.
- She will teach the class.
- It will rain tomorrow.
- He will be able to do it.
- We will go to the park tomorrow.
- He will play tennis with his friends.
- They will visit their grandparents next week.
- I will read a book tonight.
- She will help me with my homework.
- They will go to the movies tomorrow.
What is Future Continuous (Progressive) Tense?
The Future Progressive Tense is used to express actions that will be in progress at a specific time in the future. The time can be expressed explicitly, or it can be implied. For example:
- I will be studying for my test at 6pm tonight. (The time is expressed explicitly.)
- Next week, I ‘ll be getting my hair cut. (The time is implied.)
However, there are some subtle differences in meaning between the two forms. In general, will is used for actions that are sure to happen, while be going to is used for actions that are more likely or planned. For example:
- The sun will rise at 6am tomorrow. (This is a sure thing.)
- I am going to study for my test tonight. (This is something I have planned.)
There are also some differences in how we use these forms in spoken English. Will is more common in written English, while be going to is more common in spoken English. You can read here more detail regarding usage of will and going to.
When Future Continuous Tense is Used?
- The future continuous tense is used for actions that will occur in the near future – often within one or two days ( For example: I will be leaving tomorrow.)
- It is used with stative verbs to describe a change in state that will continue in the future ( For example : The sun will be rising soon.)
- Future Continuous Tense can also be used to talk about actions that are likely to happen in the near future but haven’t been scheduled yet (or set in stone). In this case, we use “will be going” instead of “will be.” For example: They will be going on vacation next month.
Structure of Future Continuous Tense
Subject + will be + present participle
He/She/It/I/You/We/They + will be + present participle
10 Examples of Future Continuous Tense
- She will be eating dinner at 6:00 p.m.
- They will be arriving at the airport at 3:00 p.m.
- He will be playing tennis with his friends later this afternoon.
- Next week we will be going on a field trip to the zoo.
- I will be taking my final exams next month.
- They will be playing soccer on Saturday morning.
- In a month, we will be moving to a new house.
- She will be walking the dog at six o’clock tomorrow morning.
- You will be finishing your report by 5:00 PM today.
- Later tonight, I will be doing some laundry and cleaning the kitchen.
What is Future Perfect Tense?
The Future Perfect Tense is used to express an action that will be completed before a certain time in the future. This tense is formed by using the auxiliary verb “will” along with the present participle of the main verb. For example, “I will have finished my essay by noon tomorrow.”
- By the time she arrives at 3 pm, I will have cleaned the entire house.
- They will have arrived in New York by noon tomorrow.
- You will have completed your homework before you go to bed.
As you can see, the future perfect tense is used to describe an event that will happen before another event in the future. In order to form this tense, you need to use the correct verb conjugation of “will” followed by the correct verb conjugation of “have” and the past participle of the main verb.
When Future Perfect Tense is Used?
Here are some examples of how to use the future perfect tense:
- “I will have finished by 10 pm.” This sentence shows that you have already planned to finish something by 10 pm, or it shows that you intend to finish something by 10 pm.
- “She will be ready when we get there.” This sentence shows that she has already planned or decided on a time when she will be ready for something, such as meeting with someone else at a certain time and place.
- “We won’t have eaten lunch by 3 o’clock.” This sentence shows that we haven’t yet planned on eating lunch at 3 o’clock (or any other time), but we know we will eat lunch sometime before that time arrives.
Structure of Future Perfect Tense
Structure of future perfect tense is:
Subject + will have + past participle
10 Examples of Future Perfect Tense
- By six PM tonight, the delivery will have arrived.
- I will have graduated by this time next year.
- They will have finished the project by Monday morning.
- We will have reached our destination before dark.
- She will have read the entire book by tomorrow afternoon.
- By the end of this month, we will have paid our rent.
- You will have received your promotion by next week.
- They will have built the new bridge by 2024.
- We will have published our book by then.
- She will have cleaned the house before her guests arrive.
What is Future Perfect Progressive Tense?
The future perfect progressive tense is used to describe an ongoing action that will be completed at some point in the future. This tense is formed by using the present tense of the verb “to be” followed by the present participle of the main verb. For example:
I will have been studying French for two years by the time I go to Paris.
In this sentence, the action of studying French is ongoing and will be completed in the future.
When Future Perfect Continuous Tense is Used?
The Future Perfect Continuous Tense is used to express an action that will be unfinished at a certain time in the future. It can also be used to talk about an action that will have been going on for some time when another event happens.
- I will have been working here for ten years when I retire. (When I retire, it will have been ten years since I started working here.)
- She will not have been waiting for more than 5 minutes when her sister arrives. (Her sister hasn’t arrived yet, but she has been waiting for more than 5 minutes.)
- He will not have been waiting long when he got his flight number called by the gate agent. (He was probably waiting only a short time before getting his flight number called.)
Structure of Future Perfect Continuous Tense
Structure of present perfect tense is:
Subject + will have been + present participle
He/She/It/I/You/We/They + will have been + present participle
10 Examples of Future Perfect Continuous Tense
- Next month, Sarah will have been working at her new job for six months.
- Within the next few weeks, the construction workers will have been working on the new bridge.
- I will have been flying to Australia for the first time in two days.
- I will have been playing the piano for six months by the time my recital comes around.
- He will have been writing his book for two years by the time it is finally published.
- She will have been taking dance classes for eight years by the time she graduates from college.
- She will have been jogging for an hour by the time she gets home.
- I will have been cooking dinner for half an hour by the time you get home.
- By the time we finish this race, we will have been running for over an hour.
- I will have been writing articles for the website for three years by the time I graduate.

Further Reading
- Simple Future Tense Sentences
- Simple Future Tense Worksheet
- Future Continuous Tense Sentences
- Future Continuous Tense Worksheet
- Future Perfect Tense Sentences
- Future Perfect Tense Worksheet
- Future Perfect Continuous Tense Sentences
- Future Perfect Continuous Tense Worksheet
Similar Posts

Adverb of Quantity (Examples, List & Worksheet)
What is Adverb of Quantity? An adverb of quantity modifies the adverb, adjective or a verb. It describes how much of something is present or…

Essay on Library & Its Importance
Libraries are a place where knowledge and literature is preserved and shared. They play an integral role in the cultural and social development of communities…
Define Listening Skills and its Types | What are the 8 barriers to listening?
Listening skills is one of the key attributes for every professional. In personal and professional life, we are always listening to something. We may be…

Starting Sentences for Essays & Tips for Opening Sentences
Starting sentences for essays A good opening sentence can make or break your essay. It’s what catches the reader’s attention and makes them want to…

Future Perfect Continuous Tense Worksheets with Answers
Future Perfect Continuous Tense Worksheets with Answers Worksheet No.1 Recall the formula of future perfect continuous tense and fill in the blanks. I ____________ (watch)…

12 Types of Metaphor with Examples | Metaphor Vs Simile
Metaphor Definition Metaphor is a figure of speech where we compare two unrelated or different things. These two things must have one thing in common….
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.


Mastering the Future Perfect Tense: Predict Your Future!
By: Author ESLBUZZ
Posted on Last updated: December 12, 2023
Sharing is caring!
If you’re an English learner, you’ve probably come across Future Perfect Tense before, but may not have a full understanding of how to use it. Fear not! This article will provide you with a clear explanation of the Future Perfect Tense, along with plenty of examples to help you master it.
In this article, we’ll cover everything you need to know about the Future Perfect Tense, including its formation, usage, and common mistakes to avoid. We’ll also provide you with plenty of examples and exercises to help you practice using this tense correctly. By the end of this article, you’ll have a solid understanding of the Future Perfect Tense and be able to use it confidently in your own writing and speaking. So, let’s get started!
Future Perfect Tense – Image

Understanding Future Perfect Tense
The Future Perfect Tense is used to describe an action that will be completed at some point in the future before another action takes place. It is formed by using the auxiliary verb “will” followed by “have” and the past participle of the main verb. For example, “By the time I arrive at the party, the cake will have been cut.”
Here are some important things to keep in mind when using the Future Perfect Tense:
- The Future Perfect Tense is used to describe an action that will be completed before a specific point in the future.
- The auxiliary verb “will” is always used in the Future Perfect Tense.
- The auxiliary verb “have” is followed by the past participle of the main verb.
- The Future Perfect Tense can be used with both regular and irregular verbs.
It is important to note that the Future Perfect Tense is not used very often in everyday conversation. However, it is commonly used in written English, especially in academic and technical writing.
Here are some examples of sentences using the Future Perfect Tense:
- By the time I finish my homework, my sister will have already gone to bed.
- They will have been married for 25 years next month.
- By the end of the week, I will have completed all of my assignments.
Formation of Future Perfect Tense
Affirmative Sentences
To form an affirmative sentence in Future Perfect tense, use the subject followed by “will have” and the past participle of the main verb. Here are some examples:
- By next year, I will have graduated from college.
- They will have completed the project by the end of the week.
- She will have visited all the continents by the time she turns 30.
Negative Sentences
To form a negative sentence in Future Perfect tense, use the subject followed by “will not have” and the past participle of the main verb. Here are some examples:
- I will not have finished my work by the time you arrive.
- They will not have found a new apartment by the end of the month.
- She will not have learned how to play the guitar by next year.
Interrogative Sentences
To form an interrogative sentence in Future Perfect tense, invert the subject and “will” and add the past participle of the main verb. Here are some examples:
- Will you have completed the report by tomorrow?
- Will they have finished the construction by the end of the year?
- Will she have found a new job by next month?
It’s important to note that Future Perfect tense is often used with time expressions such as “by,” “by the time,” “by the end of,” and “by next year/month/week,” which indicate the time when the action will be completed.
Usage of Future Perfect Tense
Completed Action Before Something in the Future
We use the future perfect tense to talk about actions that will be completed before a specific point in the future. This could be a certain time, an event, or even another action that will take place later.
For example:
- By the time we arrive at the party, the cake will have been cut.
- She will have finished her homework before she goes to bed.
Duration Before Something in the Future
We also use the future perfect tense to talk about the duration of an action that will continue up until a certain point in the future. This is often used with the preposition “for” to indicate the length of time.
- By next year, I will have been working at this company for 10 years.
- They will have been living in this house for 5 years next month.
- By the end of the month, he will have been studying for his exams for 3 weeks.
It’s important to note that the future perfect tense is often used in conjunction with other tenses to provide a more complete picture of the action. Additionally, stative verbs are usually used in the simple future perfect tense, while dynamic verbs are used in the future perfect continuous tense.
Keywords That Signal Future Perfect Tense
In English grammar, the Future Perfect Tense is used to describe an action that will be completed at some point in the future. It is formed by using the auxiliary verb “will” followed by “have” and the past participle of the main verb. Here are some keywords that signal the presence of the Future Perfect Tense:
- By the time
- By the end of
- By next week
- By tomorrow
- By the time I get there
- By the time he arrives
- By the time she finishes
- By the time they leave
- By the time we arrive
- By the time you arrive
- By the end of the year
- By the end of the month
- By the end of the week
- By the end of the day
These keywords indicate that the action will be completed by a specific point in the future. For example:
- By the time I finish my work, I will have been working for eight hours.
- Before you arrive, I will have finished cooking dinner.
- By the end of the month, we will have saved enough money to go on vacation.
Here are some exercises to help you practice using the Future Perfect Tense with these keywords:
- By the time we get home, __________ all the laundry. (do)
- Before the concert starts, __________ our seats. (find)
- By the time I graduate, __________ a job. (find)
- By the end of the day, __________ all the paperwork. (complete)
- By the time the party starts, __________ the decorations. (put up)
Answer: 1. will have done 2. will have found 3. will have found 4. will have completed 5. will have put up
Common Mistakes in Future Perfect Tense
Mistake 1: Using the Wrong Auxiliary Verb
The Future Perfect Tense is formed by using the auxiliary verb “will have” followed by the past participle of the main verb. One common mistake is using the wrong auxiliary verb, such as “would have” or “should have.” Remember that “will have” is the only correct auxiliary verb to use in the Future Perfect Tense.
Incorrect: By the time I get there, I would have finished my work. Correct: By the time I get there, I will have finished my work.
Mistake 2: Incorrectly Forming the Past Participle
Another common mistake is incorrectly forming the past participle of the main verb. Remember that regular verbs form the past participle by adding “-ed” to the base form of the verb. However, irregular verbs have their own unique past participle forms that must be memorized.
Incorrect: By the time we arrive, he will have went home. Correct: By the time we arrive, he will have gone home.
Mistake 3: Using the Future Perfect Tense When Not Appropriate
Using the Future Perfect Tense when it is not appropriate can also lead to confusion. The Future Perfect Tense is used to describe an action that will be completed by a specific time in the future. If the time frame is not clear or specific, it is better to use the Simple Future Tense.
Incorrect: I will have a meeting tomorrow. Correct: I have a meeting tomorrow.
Mistake 4: Forgetting to Include the Time Frame
Finally, forgetting to include the time frame can also be a common mistake when using the Future Perfect Tense. Remember that the Future Perfect Tense always includes a specific time frame, such as “by tomorrow” or “by the end of the week.”
Incorrect: I will have finished my project. Correct: I will have finished my project by the end of the week.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you form the Future Perfect tense in English grammar?
To form the Future Perfect tense, use the auxiliary verb “will” followed by “have” and the past participle of the main verb. For example, “By next month, I will have finished my project.”
What is the difference between Future Perfect and Future Perfect Continuous?
The Future Perfect tense is used to describe an action that will be completed at a specific time in the future. The Future Perfect Continuous tense is used to describe an action that will be ongoing until a specific time in the future. For example, “By next year, I will have written my book” vs. “By next year, I will have been writing my book for three years.”
What are some examples of sentences in the Future Perfect tense?
- By the time we arrive, the movie will have started.
- She will have finished her homework by the time her friends come over.
- They will have been married for 20 years next month.
What is the helping verb used in the Future Perfect tense?
The helping verb used in the Future Perfect tense is “will have.”
What is the structure of the Future Perfect tense in English grammar?
The Future Perfect tense is formed with the auxiliary verb “will” followed by “have” and the past participle of the main verb. For example, “I will have eaten breakfast by 8 am.”
To form the Future Perfect tense, use the auxiliary verb \"will\" followed by \"have\" and the past participle of the main verb. For example, \"By next month, I will have finished my project.\"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What is the difference between Future Perfect and Future Perfect Continuous?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
The Future Perfect tense is used to describe an action that will be completed at a specific time in the future. The Future Perfect Continuous tense is used to describe an action that will be ongoing until a specific time in the future. For example, \"By next year, I will have written my book\" vs. \"By next year, I will have been writing my book for three years.\"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What are some examples of sentences in the Future Perfect tense?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What is the helping verb used in the Future Perfect tense?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
The helping verb used in the Future Perfect tense is \"will have.\"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"Can you provide some exercises to practice using the Future Perfect tense?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
- Complete the sentence: By the time I __________ (graduate), I will have been studying for four years.
- Write a sentence using the Future Perfect tense about something you will have accomplished by next year.
- Rewrite the sentence in the Future Perfect tense: \"I have been working here for five years.\"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What is the structure of the Future Perfect tense in English grammar?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
The Future Perfect tense is formed with the auxiliary verb \"will\" followed by \"have\" and the past participle of the main verb. For example, \"I will have eaten breakfast by 8 am.\"
- Recent Posts
- Ed Words: Expand Your Vocabulary and Improve Your Writing! - April 15, 2024
- List of Ethnicities and Their Cultures from Around the World - April 2, 2024
- Mastering English Writing: Essential Transitional Words for Body Paragraphs - March 25, 2024
Related posts:
- Verb Tenses in English
- Mastering Verb Tenses: Time Travel with the Tenses of the Verbs
- Mastering Present Perfect Tense: Your Ultimate Guide to Perfecting Your English Grammar
- Mastering Past Perfect Continuous Tense: Your Ultimate Guide to Fluent English Grammar
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Future perfect continuous ( I will have been working here ten years )
Future perfect continuous: form.
We use will/shall + have + been + the - ing form of the verb.
We use shall only for future time reference with I and we. Shall is more formal and less common than will .
Note: Shall I, shall we and shan’t I, shan’t we in future perfect continuous questions are rare.
Future perfect continuous: use
Emphasising the length of an event at a time in the future.
We use the future perfect continuous form when we are looking back to the past from a point in the future and we want to emphasise the length or duration of an activity or event:
In September the head teacher will have been teaching at the school for 20 years.
In September, she will have been living in France for a year.
I will have been studying English for three years by the end of this course.
We’re late. I think they ’ll have been waiting for us. We’d better go.
Future: will and shall

Word of the Day
have your head in the clouds
to not know the facts of a situation

Apples and oranges (Talking about differences, Part 2)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
To add ${headword} to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add ${headword} to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.

by Kitty Nash
Module 3, Verbs: Types, Tenses, and Moods, Lesson 8:
Tenses of verbs, module {moduleid}, {moduletitle}.
Definition: Earlier in this module you learned that verbs are action words. Verbs have multiple forms called tenses that tell us when an action occurs. In this lesson you'll learn about the simple, progressive, and perfect tenses.
Simple Tenses
The present, past, and future tenses are called simple tenses .
Simple Present Tense
The term present tense is a little deceiving. You're probably thinking to yourself, "It's a no-brainer, isn't it? The present tense is used for actions that are happening now, right?"—not exactly. Although it's true that the present tense does have to do with current events, there are several specific ways in which it's used, including:
Talking about actions that occur repeatedly These are actions that happen on a regular basis, such as habits or routines. They can have a specific or general time frame.
I brush my teeth every morning and every night . Bret runs five miles every day . We visit my grandparents twice a year . Sometimes Sean and Jaimie go to the pool. Mom never lets us eat chocolate cake for breakfast.
Discussing current facts, basic truths, or widely accepted beliefs
The sky is blue, and the grass is green. Cats catch mice. Stealing is unethical.
Describing people or things Use the present tense to describe physical characteristics, personality traits, feelings, abilities, and likes and dislikes that are true in the present.
Her brothers are both over six feet tall. He is the nicest person I know. I feel sick today. My best friend plays minor league baseball. Many people love dogs, but many also love cats. This milk smells funny. Your new rose bush looks beautiful!
You already learned how to form the present tense in Lesson 5 , but let's review. The base alone is used for most forms of the present tense, including the first person ( I and we ), second person ( you ), and third person plural ( they ). The only time the base changes is in the third person singular ( he , she , it ). To form the third person singular, just add the letter -s to the end of the base.
Simple Past Tense
The past tense is more straightforward than the present tense—you only use it to talk about actions, events, or feelings that happened at an earlier point in time.
Olivia closed the door behind her. We pushed through the crowd to get a better view of the stage.
Let's also review how to form the past tense. Simply take the base form and add -ed . If the base ends in a silent e , just add -d , not -ed . Unlike the present tense, the past tense always uses the same form regardless of person or number. If you would like to see more examples, you can go back to Lesson 5 .
Future Tense
The future tense is one of the easiest tenses to learn because it has no irregular forms. Just as its name suggests, it's used to describe actions that will happen in the future. It is formed by combining the helping verb will with the base form of the main verb.
Tomorrow I will walk home from school.
Progressive Tenses (A.K.A. the Continuous Tenses)
Progressive tenses are used to discuss ongoing or continuing actions. They can also be used to talk about an action that is, was, or will be occurring at the same time as another action. The progressive tenses use a form of the verb to be plus the present participle of the verb.
Present Progressive
The present progressive tense is typically used to talk about something that is happening right now. It can also be used to talk about a future action or an action that is occurring at the same time as another one. It is formed by using a present tense form of the verb to be plus the present participle of the main verb.
I am walking to school right now . (current action) He is walking to school tomorrow . (future action) Most days we are walking to school when you see us. (simultaneous actions: are walking and see )
Past Progressive
The past progressive is used to describe an action that was occurring at the same time as another past action.
Yesterday I was walking to school when you saw me. (simultaneous actions: was walking and saw )
Future Progressive
The future progressive is usually used to describe an action that will occur at the same time as another future action. To form the future progressive tense, use this formula: will be + present participle.
Tomorrow I will be walking to school when you see me. (simultaneous actions: will be walking and see )
Notice how the verb see is in the present tense, not the future tense. When people talk about future simultaneous actions, usually one verb is in the future progressive and the other is in the simple present .
Perfect Tenses
Perfect tenses show when an action happened in relation to another action. To form the perfect tenses, use a form of the helping verb have ( have , has , had , will have ) plus the past participle of the main verb. The verb have changes to show the tense.
Present Perfect
An action in the present perfect began in the past and continues in the present or has ended by the present. It can also be used to talk about past actions that happened multiple times. To form the present perfect, use the present tense of the verb to have plus the past participle of the main verb.
Most days I take the bus to school, but for the last two weeks I have walked to school. I have finished my homework already.
Past Perfect
An action in the past perfect began and ended before another past event. To form the past perfect, use the past tense of the verb to have plus the past participle of the main verb.
Yesterday I rode the bus to school, but the day before I had walked to school. I was watching TV because I had finished my homework already.
Future Perfect
An action in the future perfect tense will be finished by a particular time in the future. To form this tense, use this formula: will + have + past participle.
By the time I arrive at school tomorrow, I will have walked to school 100 days in a row. By 8 p.m. I will have finished my homework.
Perfect Progressive Tenses
Perfect progressive tenses are a combination of perfect (completed before) and progressive (ongoing) tenses, which show that something began, continued, and ended before another action. The perfect progressive tenses combine the perfect ( have , has , had , will have ), the progressive ( been ) and the present participle of the main verb.
Present Perfect Progressive
This tense is used for recent past actions that happened repeatedly.
I have been walking to school on sunny days. He has been finishing his homework by 7 p.m. every day this week.
It is also used for continuous past actions that are affecting the present in some way.
I have been walking to school a lot, so I'm in much better shape than I was before. He has been finishing all his homework, and his grades have improved a lot.
Past Perfect Progressive
Use the past perfect tense to express actions that happened in the more distant past that happened repeatedly. This tense is frequently used in relation to another past action that occurred at a later time.
I had been walking to school every day, but then the weather turned cold. Isabella had been finishing her homework on time all month, but then she caught a cold and missed school.
Future Perfect Progressive
This tense is used when you are anticipating a time in the future when a continuous action will be finished.
By tomorrow I will have been walking to school for six weeks straight.
Emphatic Forms
Not a tense, but logically included in this section is the emphatic form . The emphatic form emphasizes that an action happened. It is also used in questions and in negative statements. The emphatic form uses the verb do with the present form of the verb.
Practice What You've Learned

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The structure for negative sentences in the future perfect tense is: Subject + will /shall +not + have + verb (3rd form) + object. Examples: I won't have completed the assignment by tomorrow. By the end of the week, they won't have fixed the broken window. He won't have learned to ride a bike by next month.
I will have finished my homework by 10 PM tonight. She will have studied for her exam for two hours by 11 AM tomorrow. They will have visited their grandparents for three hours by 5 PM next week. Future Perfect Continuous Tense. The Future Perfect Continuous Tense is used to talk about actions that will have been in progress for a specific ...
2: We use the future perfect with a future time word, (and often with 'by') to talk about an action that will finish before a certain time in the future, but we don't know exactly when. By 10 o'clock, I will have finished my homework. (= I will finish my homework some time before 10, but we don't know exactly when.)
To form the future perfect simple, use will have + V3 (past participle) form of the verb. Subject. will /will not + have + (V3) form of the verb (Past Participle) Rest of Sentence. I / You / We / They He / She / It. will have worked. here for three years by the time the visa needs to be renewed.
USE 1 Completed Action Before Something in the Future. The future perfect expresses the idea that something will occur before another action in the future. It can also show that something will happen before a specific time in the future. Examples: By next November, I will have received my promotion. By the time he gets home, she is going to ...
My sister (graduate) from the university when you meet her again. 3. Henry and Tina (get married) by the time it's summer. 4. My son (be born) by the time you come back from your trip. 5. I guarantee you he (not find) a job this time next year either. 6. I (finish) my homework by the time you eat so we can go out.
For example, "I will have finished my homework by 10 PM" or ... I will go to the gym tomorrow. She will finish her homework before dinner. They will travel to Europe next summer. Future Continuous Tense. The future continuous tense is used to describe actions or events that will be in progress at a certain time in the future.
Here are a few examples of how you might use the present perfect tense in the IELTS exam: Writing Task 1: "By the time I start cooking dinner at 6:00 tomorrow evening, I will have finished all of my errands for the day. My husband will also have finished his work and will be ready to relax on the couch.". Speaking part 2 ( cue cards ):
1. In "I'll have finished ...", finished is a verb. In "I'll be finished ...", finished is an adjective, and it can be ambiguous because it can mean either "at the end of a task" or "doomed". However, when being used in "I'll be finished with my work by tomorrow," the meaning of finished is clear and the sentence means roughly the same as I'll ...
I have no homework for tomorrow. I will not be doing any homework tonight. I am going to do my homework tonight. I will have finished my homework by tomorrow. The show starts at 9 p. m. and it ends an hour later. We will be watching the show between 9 and 10 p.m. The show ends just a few minutes before ten o'clock. The show will have ended by ...
Here is an example of the negative use of the future perfect tense : "I will not have finished my homework by tomorrow. Have a look at the table below for more example sentences in the future perfect tense. They will have been married for 20 years next month.
80 Example Sentences with Future Perfect. She will have unlocked all the secrets by the time she finishes her research project. I will have finished my work when you arrive. We will have finished repairing the boat. I will have found a new house by the time my parents visit. She will have tried it in the afternoon. I will have done it by tomorrow.
For example, "I will have finished my essay by noon tomorrow." By the time she arrives at 3 pm, I will have cleaned the entire house. They will have arrived in New York by noon tomorrow. You will have completed your homework before you go to bed.
Future perfect simple ( I will have worked eight hours ) - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
By the time I finish my homework, my sister will have already gone to bed. They will have been married for 25 years next month. By the end of the week, I will have completed all of my assignments. ... Incorrect: I will have a meeting tomorrow. Correct: I have a meeting tomorrow. Mistake 4: Forgetting to Include the Time Frame.
Future perfect continuous ( I will have been working here ten years ) - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
Actions finished in the future. We use the future perfect for actions that will be finished before a certain time in the future. By 2050, researchers will have found a cure for cancer. By this time next year, I 'll have graduated. When you arrive tomorrow, we 'll have left. Duration until some time in the future
An action in the future perfect tense will be finished by a particular time in the future. To form this tense, use this formula: will + have + past participle. By the time I arrive at school tomorrow, I will have walked to school 100 days in a row. By 8 p.m. I will have finished my homework. Perfect Progressive Tenses
1. Both are fine grammatically but your alternative version changes the context. "We hope to have finished by X" refers to the situation after completion, implying that there will then be other issues to consider - issues affected by the completion. In contrast, "We hope to finish by X" only discusses the task itself, leaving open the ...
2. The question really comes down to the context in which we use these two constructions. Typically, we say things like: I will be finishing the lesson around six so I should be able to meet you shortly after that. The speaker looks ahead to a likely situation in order to make a subsequent arrangement. On the other hand, the future perfect ...
3. Most of the time a sentence that looks like this is used, it means the same thing as: I will finish it by tomorrow. For instance: imagine your teacher asks when you are going to turn in an essay. If you say "I will have it done by tomorrow.", he will not think you are hiring someone else to do your homework!
I'll go to bed as soon as I finish my homework. When I am 65, I will retire. I won't leave until you arrive. As happens with conditional sentences, we use a comma when we begin the sentence with a time clause. But we don't use a comma if we put the time clause at the end of the sentence. When I am 65, I will retire. I will retire when I ...