Market Research

9 Key stages in your marketing research process
You can conduct your own marketing research. Follow these steps, add your own flair, knowledge and creativity, and you’ll have bespoke research to be proud of.
Marketing research is the term used to cover the concept, development, placement and evolution of your product or service, its growing customer base and its branding – starting with brand awareness , and progressing to (everyone hopes) brand equity . Like any research, it needs a robust process to be credible and useful.
Marketing research uses four essential key factors known as the ‘marketing mix’ , or the Four Ps of Marketing :
- Product (goods or service)
- Price ( how much the customer pays )
- Place (where the product is marketed)
- Promotion (such as advertising and PR)
These four factors need to work in harmony for a product or service to be successful in its marketplace.
The marketing research process – an overview
A typical marketing research process is as follows:
- Identify an issue, discuss alternatives and set out research objectives
- Develop a research program
- Choose a sample
- Gather information
- Gather data
- Organize and analyze information and data
- Present findings
- Make research-based decisions
- Take action based on insights
Step 1: Defining the marketing research problem
Defining a problem is the first step in the research process. In many ways, research starts with a problem facing management. This problem needs to be understood, the cause diagnosed, and solutions developed.
However, most management problems are not always easy to research, so they must first be translated into research problems. Once you approach the problem from a research angle, you can find a solution. For example, “sales are not growing” is a management problem, but translated into a research problem, it becomes “ why are sales not growing?” We can look at the expectations and experiences of several groups : potential customers, first-time buyers, and repeat purchasers. We can question whether the lack of sales is due to:
- Poor expectations that lead to a general lack of desire to buy, or
- Poor performance experience and a lack of desire to repurchase.
This, then, is the difference between a management problem and a research problem. Solving management problems focuses on actions: Do we advertise more? Do we change our advertising message? Do we change an under-performing product configuration? And if so, how?
Defining research problems, on the other hand, focus on the whys and hows, providing the insights you need to solve your management problem.
Step 2: Developing a research program: method of inquiry
The scientific method is the standard for investigation. It provides an opportunity for you to use existing knowledge as a starting point, and proceed impartially.
The scientific method includes the following steps:
- Define a problem
- Develop a hypothesis
- Make predictions based on the hypothesis
- Devise a test of the hypothesis
- Conduct the test
- Analyze the results
This terminology is similar to the stages in the research process. However, there are subtle differences in the way the steps are performed:
- the scientific research method is objective and fact-based, using quantitative research and impartial analysis
- the marketing research process can be subjective, using opinion and qualitative research, as well as personal judgment as you collect and analyze data
Step 3: Developing a research program: research method
As well as selecting a method of inquiry (objective or subjective), you must select a research method . There are two primary methodologies that can be used to answer any research question:
- Experimental research : gives you the advantage of controlling extraneous variables and manipulating one or more variables that influence the process being implemented.
- Non-experimental research : allows observation but not intervention – all you do is observe and report on your findings.
Step 4: Developing a research program: research design
Research design is a plan or framework for conducting marketing research and collecting data. It is defined as the specific methods and procedures you use to get the information you need.
There are three core types of marketing research designs: exploratory, descriptive, and causal . A thorough marketing research process incorporates elements of all of them.
Exploratory marketing research
This is a starting point for research. It’s used to reveal facts and opinions about a particular topic, and gain insight into the main points of an issue. Exploratory research is too much of a blunt instrument to base conclusive business decisions on, but it gives the foundation for more targeted study. You can use secondary research materials such as trade publications, books, journals and magazines and primary research using qualitative metrics, that can include open text surveys, interviews and focus groups.
Descriptive marketing research
This helps define the business problem or issue so that companies can make decisions, take action and monitor progress. Descriptive research is naturally quantitative – it needs to be measured and analyzed statistically , using more targeted surveys and questionnaires. You can use it to capture demographic information , evaluate a product or service for market, and monitor a target audience’s opinion and behaviors. Insights from descriptive research can inform conclusions about the market landscape and the product’s place in it.
Causal marketing research
This is useful to explore the cause and effect relationship between two or more variables. Like descriptive research , it uses quantitative methods, but it doesn’t merely report findings; it uses experiments to predict and test theories about a product or market. For example, researchers may change product packaging design or material, and measure what happens to sales as a result.
Step 5: Choose your sample
Your marketing research project will rarely examine an entire population. It’s more practical to use a sample - a smaller but accurate representation of the greater population. To design your sample, you’ll need to answer these questions:
- Which base population is the sample to be selected from? Once you’ve established who your relevant population is (your research design process will have revealed this), you have a base for your sample. This will allow you to make inferences about a larger population.
- What is the method (process) for sample selection? There are two methods of selecting a sample from a population:
1. Probability sampling : This relies on a random sampling of everyone within the larger population.
2. Non-probability sampling : This is based in part on the investigator’s judgment, and often uses convenience samples, or by other sampling methods that do not rely on probability.
- What is your sample size? This important step involves cost and accuracy decisions. Larger samples generally reduce sampling error and increase accuracy, but also increase costs. Find out your perfect sample size with our calculator .
Step 6: Gather data
Your research design will develop as you select techniques to use. There are many channels for collecting data, and it’s helpful to differentiate it into O-data (Operational) and X-data (Experience):
- O-data is your business’s hard numbers like costs, accounting, and sales. It tells you what has happened, but not why.
- X-data gives you insights into the thoughts and emotions of the people involved: employees, customers, brand advocates.
When you combine O-data with X-data, you’ll be able to build a more complete picture about success and failure - you’ll know why. Maybe you’ve seen a drop in sales (O-data) for a particular product. Maybe customer service was lacking, the product was out of stock, or advertisements weren’t impactful or different enough: X-data will reveal the reason why those sales dropped. So, while differentiating these two data sets is important, when they are combined, and work with each other, the insights become powerful.
With mobile technology, it has become easier than ever to collect data. Survey research has come a long way since market researchers conducted face-to-face, postal, or telephone surveys. You can run research through:
- Social media ( polls and listening )
Another way to collect data is by observation. Observing a customer’s or company’s past or present behavior can predict future purchasing decisions. Data collection techniques for predicting past behavior can include market segmentation , customer journey mapping and brand tracking .
Regardless of how you collect data, the process introduces another essential element to your research project: the importance of clear and constant communication .
And of course, to analyze information from survey or observation techniques, you must record your results . Gone are the days of spreadsheets. Feedback from surveys and listening channels can automatically feed into AI-powered analytics engines and produce results, in real-time, on dashboards.
Step 7: Analysis and interpretation
The words ‘ statistical analysis methods ’ aren’t usually guaranteed to set a room alight with excitement, but when you understand what they can do, the problems they can solve and the insights they can uncover, they seem a whole lot more compelling.
Statistical tests and data processing tools can reveal:
- Whether data trends you see are meaningful or are just chance results
- Your results in the context of other information you have
- Whether one thing affecting your business is more significant than others
- What your next research area should be
- Insights that lead to meaningful changes
There are several types of statistical analysis tools used for surveys. You should make sure that the ones you choose:
- Work on any platform - mobile, desktop, tablet etc.
- Integrate with your existing systems
- Are easy to use with user-friendly interfaces, straightforward menus, and automated data analysis
- Incorporate statistical analysis so you don’t just process and present your data, but refine it, and generate insights and predictions.
Here are some of the most common tools:
- Benchmarking : a way of taking outside factors into account so that you can adjust the parameters of your research. It ‘levels the playing field’ – so that your data and results are more meaningful in context. And gives you a more precise understanding of what’s happening.
- Regression analysis : this is used for working out the relationship between two (or more) variables. It is useful for identifying the precise impact of a change in an independent variable.
- T-test is used for comparing two data groups which have different mean values. For example, do women and men have different mean heights?
- Analysis of variance (ANOVA) Similar to the T-test, ANOVA is a way of testing the differences between three or more independent groups to see if they’re statistically significant.
- Cluster analysis : This organizes items into groups, or clusters, based on how closely associated they are.
- Factor analysis: This is a way of condensing many variables into just a few, so that your research data is less unwieldy to work with.
- Conjoint analysis : this will help you understand and predict why people make the choices they do. It asks people to make trade-offs when making decisions, just as they do in the real world, then analyzes the results to give the most popular outcome.
- Crosstab analysis : this is a quantitative market research tool used to analyze ‘categorical data’ - variables that are different and mutually exclusive, such as: ‘men’ and ‘women’, or ‘under 30’ and ‘over 30’.
- Text analysis and sentiment analysis : Analyzing human language and emotions is a rapidly-developing form of data processing, assigning positive, negative or neutral sentiment to customer messages and feedback.
Stats IQ can perform the most complicated statistical tests at the touch of a button using our online survey software , or data from other sources. Learn more about Stats iQ now .
Step 8: The marketing research results
Your marketing research process culminates in the research results. These should provide all the information the stakeholders and decision-makers need to understand the project.
The results will include:
- all your information
- a description of your research process
- the results
- conclusions
- recommended courses of action
They should also be presented in a form, language and graphics that are easy to understand, with a balance between completeness and conciseness, neither leaving important information out or allowing it to get so technical that it overwhelms the readers.
Traditionally, you would prepare two written reports:
- a technical report , discussing the methods, underlying assumptions and the detailed findings of the research project
- a summary report , that summarizes the research process and presents the findings and conclusions simply.
There are now more engaging ways to present your findings than the traditional PowerPoint presentations, graphs, and face-to-face reports:
- Live, interactive dashboards for sharing the most important information, as well as tracking a project in real time.
- Results-reports visualizations – tables or graphs with data visuals on a shareable slide deck
- Online presentation technology, such as Prezi
- Visual storytelling with infographics
- A single-page executive summary with key insights
- A single-page stat sheet with the top-line stats
You can also make these results shareable so that decision-makers have all the information at their fingertips.
Step 9 Turn your insights into action
Insights are one thing, but they’re worth very little unless they inform immediate, positive action. Here are a few examples of how you can do this:
- Stop customers leaving – negative sentiment among VIP customers gets picked up; the customer service team contacts the customers, resolves their issues, and avoids churn .
- Act on important employee concerns – you can set certain topics, such as safety, or diversity and inclusion to trigger an automated notification or Slack message to HR. They can rapidly act to rectify the issue.
- Address product issues – maybe deliveries are late, maybe too many products are faulty. When product feedback gets picked up through Smart Conversations, messages can be triggered to the delivery or product teams to jump on the problems immediately.
- Improve your marketing effectiveness - Understand how your marketing is being received by potential customers, so you can find ways to better meet their needs
- Grow your brand - Understand exactly what consumers are looking for, so you can make sure that you’re meeting their expectations
Download now: 8 Innovations to Modernize Market Research
Scott Smith
Scott Smith, Ph.D. is a contributor to the Qualtrics blog.
Related Articles
June 27, 2023
The fresh insights people: Scaling research at Woolworths Group
June 20, 2023
Bank less, delight more: How Bankwest built an engine room for customer obsession
June 16, 2023
How Qualtrics Helps Three Local Governments Drive Better Outcomes Through Data Insights
April 1, 2023
Academic Experience
Great survey questions: How to write them & avoid common mistakes
March 21, 2023
Sample size calculator
March 9, 2023
Experience Management
X4 2023: See the XM innovations unveiled for customer research, marketing, and insights teams
February 22, 2023
Achieving better insights and better product delivery through in-house research
December 6, 2022
Improved Topic Sentiment Analysis using Discourse Segmentation
Stay up to date with the latest xm thought leadership, tips and news., request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
How to Do Market Research: The Complete Guide
Learn how to do market research with this step-by-step guide, complete with templates, tools and real-world examples.
Access best-in-class company data
Get trusted first-party funding data, revenue data and firmographics
What are your customers’ needs? How does your product compare to the competition? What are the emerging trends and opportunities in your industry? If these questions keep you up at night, it’s time to conduct market research.
Market research plays a pivotal role in your ability to stay competitive and relevant, helping you anticipate shifts in consumer behavior and industry dynamics. It involves gathering these insights using a wide range of techniques, from surveys and interviews to data analysis and observational studies.
In this guide, we’ll explore why market research is crucial, the various types of market research, the methods used in data collection, and how to effectively conduct market research to drive informed decision-making and success.
What is market research?
Market research is the systematic process of gathering, analyzing and interpreting information about a specific market or industry. The purpose of market research is to offer valuable insight into the preferences and behaviors of your target audience, and anticipate shifts in market trends and the competitive landscape. This information helps you make data-driven decisions, develop effective strategies for your business, and maximize your chances of long-term growth.

Why is market research important?
By understanding the significance of market research, you can make sure you’re asking the right questions and using the process to your advantage. Some of the benefits of market research include:
- Informed decision-making: Market research provides you with the data and insights you need to make smart decisions for your business. It helps you identify opportunities, assess risks and tailor your strategies to meet the demands of the market. Without market research, decisions are often based on assumptions or guesswork, leading to costly mistakes.
- Customer-centric approach: A cornerstone of market research involves developing a deep understanding of customer needs and preferences. This gives you valuable insights into your target audience, helping you develop products, services and marketing campaigns that resonate with your customers.
- Competitive advantage: By conducting market research, you’ll gain a competitive edge. You’ll be able to identify gaps in the market, analyze competitor strengths and weaknesses, and position your business strategically. This enables you to create unique value propositions, differentiate yourself from competitors, and seize opportunities that others may overlook.
- Risk mitigation: Market research helps you anticipate market shifts and potential challenges. By identifying threats early, you can proactively adjust their strategies to mitigate risks and respond effectively to changing circumstances. This proactive approach is particularly valuable in volatile industries.
- Resource optimization: Conducting market research allows organizations to allocate their time, money and resources more efficiently. It ensures that investments are made in areas with the highest potential return on investment, reducing wasted resources and improving overall business performance.
- Adaptation to market trends: Markets evolve rapidly, driven by technological advancements, cultural shifts and changing consumer attitudes. Market research ensures that you stay ahead of these trends and adapt your offerings accordingly so you can avoid becoming obsolete.
As you can see, market research empowers businesses to make data-driven decisions, cater to customer needs, outperform competitors, mitigate risks, optimize resources and stay agile in a dynamic marketplace. These benefits make it a huge industry; the global market research services market is expected to grow from $76.37 billion in 2021 to $108.57 billion in 2026 . Now, let’s dig into the different types of market research that can help you achieve these benefits.
Types of market research
- Qualitative research
- Quantitative research
- Exploratory research
- Descriptive research
- Causal research
- Cross-sectional research
- Longitudinal research
Despite its advantages, 23% of organizations don’t have a clear market research strategy. Part of developing a strategy involves choosing the right type of market research for your business goals. The most commonly used approaches include:
1. Qualitative research
Qualitative research focuses on understanding the underlying motivations, attitudes and perceptions of individuals or groups. It is typically conducted through techniques like in-depth interviews, focus groups and content analysis — methods we’ll discuss further in the sections below. Qualitative research provides rich, nuanced insights that can inform product development, marketing strategies and brand positioning.
2. Quantitative research
Quantitative research, in contrast to qualitative research, involves the collection and analysis of numerical data, often through surveys, experiments and structured questionnaires. This approach allows for statistical analysis and the measurement of trends, making it suitable for large-scale market studies and hypothesis testing. While it’s worthwhile using a mix of qualitative and quantitative research, most businesses prioritize the latter because it is scientific, measurable and easily replicated across different experiments.
3. Exploratory research
Whether you’re conducting qualitative or quantitative research or a mix of both, exploratory research is often the first step. Its primary goal is to help you understand a market or problem so you can gain insights and identify potential issues or opportunities. This type of market research is less structured and is typically conducted through open-ended interviews, focus groups or secondary data analysis. Exploratory research is valuable when entering new markets or exploring new product ideas.
4. Descriptive research
As its name implies, descriptive research seeks to describe a market, population or phenomenon in detail. It involves collecting and summarizing data to answer questions about audience demographics and behaviors, market size, and current trends. Surveys, observational studies and content analysis are common methods used in descriptive research.
5. Causal research
Causal research aims to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables. It investigates whether changes in one variable result in changes in another. Experimental designs, A/B testing and regression analysis are common causal research methods. This sheds light on how specific marketing strategies or product changes impact consumer behavior.
6. Cross-sectional research
Cross-sectional market research involves collecting data from a sample of the population at a single point in time. It is used to analyze differences, relationships or trends among various groups within a population. Cross-sectional studies are helpful for market segmentation, identifying target audiences and assessing market trends at a specific moment.
7. Longitudinal research
Longitudinal research, in contrast to cross-sectional research, collects data from the same subjects over an extended period. This allows for the analysis of trends, changes and developments over time. Longitudinal studies are useful for tracking long-term developments in consumer preferences, brand loyalty and market dynamics.
Each type of market research has its strengths and weaknesses, and the method you choose depends on your specific research goals and the depth of understanding you’re aiming to achieve. In the following sections, we’ll delve into primary and secondary research approaches and specific research methods.
Primary vs. secondary market research
Market research of all types can be broadly categorized into two main approaches: primary research and secondary research. By understanding the differences between these approaches, you can better determine the most appropriate research method for your specific goals.
Primary market research
Primary research involves the collection of original data straight from the source. Typically, this involves communicating directly with your target audience — through surveys, interviews, focus groups and more — to gather information. Here are some key attributes of primary market research:
- Customized data: Primary research provides data that is tailored to your research needs. You design a custom research study and gather information specific to your goals.
- Up-to-date insights: Because primary research involves communicating with customers, the data you collect reflects the most current market conditions and consumer behaviors.
- Time-consuming and resource-intensive: Despite its advantages, primary research can be labor-intensive and costly, especially when dealing with large sample sizes or complex study designs. Whether you hire a market research consultant, agency or use an in-house team, primary research studies consume a large amount of resources and time.
Secondary market research
Secondary research, on the other hand, involves analyzing data that has already been compiled by third-party sources, such as online research tools, databases, news sites, industry reports and academic studies.

Here are the main characteristics of secondary market research:
- Cost-effective: Secondary research is generally more cost-effective than primary research since it doesn’t require building a research plan from scratch. You and your team can look at databases, websites and publications on an ongoing basis, without needing to design a custom experiment or hire a consultant.
- Leverages multiple sources: Data tools and software extract data from multiple places across the web, and then consolidate that information within a single platform. This means you’ll get a greater amount of data and a wider scope from secondary research.
- Quick to access: You can access a wide range of information rapidly — often in seconds — if you’re using online research tools and databases. Because of this, you can act on insights sooner, rather than taking the time to develop an experiment.
So, when should you use primary vs. secondary research? In practice, many market research projects incorporate both primary and secondary research to take advantage of the strengths of each approach.
One rule of thumb is to focus on secondary research to obtain background information, market trends or industry benchmarks. It is especially valuable for conducting preliminary research, competitor analysis, or when time and budget constraints are tight. Then, if you still have knowledge gaps or need to answer specific questions unique to your business model, use primary research to create a custom experiment.
Market research methods
- Surveys and questionnaires
- Focus groups
- Observational research
- Online research tools
- Experiments
- Content analysis
- Ethnographic research
How do primary and secondary research approaches translate into specific research methods? Let’s take a look at the different ways you can gather data:
1. Surveys and questionnaires
Surveys and questionnaires are popular methods for collecting structured data from a large number of respondents. They involve a set of predetermined questions that participants answer. Surveys can be conducted through various channels, including online tools, telephone interviews and in-person or online questionnaires. They are useful for gathering quantitative data and assessing customer demographics, opinions, preferences and needs. On average, customer surveys have a 33% response rate , so keep that in mind as you consider your sample size.
2. Interviews
Interviews are in-depth conversations with individuals or groups to gather qualitative insights. They can be structured (with predefined questions) or unstructured (with open-ended discussions). Interviews are valuable for exploring complex topics, uncovering motivations and obtaining detailed feedback.
3. Focus groups
The most common primary research methods are in-depth webcam interviews and focus groups. Focus groups are a small gathering of participants who discuss a specific topic or product under the guidance of a moderator. These discussions are valuable for primary market research because they reveal insights into consumer attitudes, perceptions and emotions. Focus groups are especially useful for idea generation, concept testing and understanding group dynamics within your target audience.
4. Observational research
Observational research involves observing and recording participant behavior in a natural setting. This method is particularly valuable when studying consumer behavior in physical spaces, such as retail stores or public places. In some types of observational research, participants are aware you’re watching them; in other cases, you discreetly watch consumers without their knowledge, as they use your product. Either way, observational research provides firsthand insights into how people interact with products or environments.
5. Online research tools
You and your team can do your own secondary market research using online tools. These tools include data prospecting platforms and databases, as well as online surveys, social media listening, web analytics and sentiment analysis platforms. They help you gather data from online sources, monitor industry trends, track competitors, understand consumer preferences and keep tabs on online behavior. We’ll talk more about choosing the right market research tools in the sections that follow.
6. Experiments
Market research experiments are controlled tests of variables to determine causal relationships. While experiments are often associated with scientific research, they are also used in market research to assess the impact of specific marketing strategies, product features, or pricing and packaging changes.
7. Content analysis
Content analysis involves the systematic examination of textual, visual or audio content to identify patterns, themes and trends. It’s commonly applied to customer reviews, social media posts and other forms of online content to analyze consumer opinions and sentiments.
8. Ethnographic research
Ethnographic research immerses researchers into the daily lives of consumers to understand their behavior and culture. This method is particularly valuable when studying niche markets or exploring the cultural context of consumer choices.
How to do market research
- Set clear objectives
- Identify your target audience
- Choose your research methods
- Use the right market research tools
- Collect data
- Analyze data
- Interpret your findings
- Identify opportunities and challenges
- Make informed business decisions
- Monitor and adapt
Now that you have gained insights into the various market research methods at your disposal, let’s delve into the practical aspects of how to conduct market research effectively. Here’s a quick step-by-step overview, from defining objectives to monitoring market shifts.
1. Set clear objectives
When you set clear and specific goals, you’re essentially creating a compass to guide your research questions and methodology. Start by precisely defining what you want to achieve. Are you launching a new product and want to understand its viability in the market? Are you evaluating customer satisfaction with a product redesign?
Start by creating SMART goals — objectives that are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound. Not only will this clarify your research focus from the outset, but it will also help you track progress and benchmark your success throughout the process.
You should also consult with key stakeholders and team members to ensure alignment on your research objectives before diving into data collecting. This will help you gain diverse perspectives and insights that will shape your research approach.
2. Identify your target audience
Next, you’ll need to pinpoint your target audience to determine who should be included in your research. Begin by creating detailed buyer personas or stakeholder profiles. Consider demographic factors like age, gender, income and location, but also delve into psychographics, such as interests, values and pain points.
The more specific your target audience, the more accurate and actionable your research will be. Additionally, segment your audience if your research objectives involve studying different groups, such as current customers and potential leads.
If you already have existing customers, you can also hold conversations with them to better understand your target market. From there, you can refine your buyer personas and tailor your research methods accordingly.
3. Choose your research methods
Selecting the right research methods is crucial for gathering high-quality data. Start by considering the nature of your research objectives. If you’re exploring consumer preferences, surveys and interviews can provide valuable insights. For in-depth understanding, focus groups or observational research might be suitable. Consider using a mix of quantitative and qualitative methods to gain a well-rounded perspective.
You’ll also need to consider your budget. Think about what you can realistically achieve using the time and resources available to you. If you have a fairly generous budget, you may want to try a mix of primary and secondary research approaches. If you’re doing market research for a startup , on the other hand, chances are your budget is somewhat limited. If that’s the case, try addressing your goals with secondary research tools before investing time and effort in a primary research study.
4. Use the right market research tools
Whether you’re conducting primary or secondary research, you’ll need to choose the right tools. These can help you do anything from sending surveys to customers to monitoring trends and analyzing data. Here are some examples of popular market research tools:
- Market research software: Crunchbase is a platform that provides best-in-class company data, making it valuable for market research on growing companies and industries. You can use Crunchbase to access trusted, first-party funding data, revenue data, news and firmographics, enabling you to monitor industry trends and understand customer needs.
- Survey and questionnaire tools: SurveyMonkey is a widely used online survey platform that allows you to create, distribute and analyze surveys. Google Forms is a free tool that lets you create surveys and collect responses through Google Drive.
- Data analysis software: Microsoft Excel and Google Sheets are useful for conducting statistical analyses. SPSS is a powerful statistical analysis software used for data processing, analysis and reporting.
- Social listening tools: Brandwatch is a social listening and analytics platform that helps you monitor social media conversations, track sentiment and analyze trends. Mention is a media monitoring tool that allows you to track mentions of your brand, competitors and keywords across various online sources.
- Data visualization platforms: Tableau is a data visualization tool that helps you create interactive and shareable dashboards and reports. Power BI by Microsoft is a business analytics tool for creating interactive visualizations and reports.
5. Collect data
There’s an infinite amount of data you could be collecting using these tools, so you’ll need to be intentional about going after the data that aligns with your research goals. Implement your chosen research methods, whether it’s distributing surveys, conducting interviews or pulling from secondary research platforms. Pay close attention to data quality and accuracy, and stick to a standardized process to streamline data capture and reduce errors.
6. Analyze data
Once data is collected, you’ll need to analyze it systematically. Use statistical software or analysis tools to identify patterns, trends and correlations. For qualitative data, employ thematic analysis to extract common themes and insights. Visualize your findings with charts, graphs and tables to make complex data more understandable.
If you’re not proficient in data analysis, consider outsourcing or collaborating with a data analyst who can assist in processing and interpreting your data accurately.

7. Interpret your findings
Interpreting your market research findings involves understanding what the data means in the context of your objectives. Are there significant trends that uncover the answers to your initial research questions? Consider the implications of your findings on your business strategy. It’s essential to move beyond raw data and extract actionable insights that inform decision-making.
Hold a cross-functional meeting or workshop with relevant team members to collectively interpret the findings. Different perspectives can lead to more comprehensive insights and innovative solutions.
8. Identify opportunities and challenges
Use your research findings to identify potential growth opportunities and challenges within your market. What segments of your audience are underserved or overlooked? Are there emerging trends you can capitalize on? Conversely, what obstacles or competitors could hinder your progress?
Lay out this information in a clear and organized way by conducting a SWOT analysis, which stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. Jot down notes for each of these areas to provide a structured overview of gaps and hurdles in the market.
9. Make informed business decisions
Market research is only valuable if it leads to informed decisions for your company. Based on your insights, devise actionable strategies and initiatives that align with your research objectives. Whether it’s refining your product, targeting new customer segments or adjusting pricing, ensure your decisions are rooted in the data.
At this point, it’s also crucial to keep your team aligned and accountable. Create an action plan that outlines specific steps, responsibilities and timelines for implementing the recommendations derived from your research.
10. Monitor and adapt
Market research isn’t a one-time activity; it’s an ongoing process. Continuously monitor market conditions, customer behaviors and industry trends. Set up mechanisms to collect real-time data and feedback. As you gather new information, be prepared to adapt your strategies and tactics accordingly. Regularly revisiting your research ensures your business remains agile and reflects changing market dynamics and consumer preferences.
Online market research sources
As you go through the steps above, you’ll want to turn to trusted, reputable sources to gather your data. Here’s a list to get you started:
- Crunchbase: As mentioned above, Crunchbase is an online platform with an extensive dataset, allowing you to access in-depth insights on market trends, consumer behavior and competitive analysis. You can also customize your search options to tailor your research to specific industries, geographic regions or customer personas.
- Academic databases: Academic databases, such as ProQuest and JSTOR , are treasure troves of scholarly research papers, studies and academic journals. They offer in-depth analyses of various subjects, including market trends, consumer preferences and industry-specific insights. Researchers can access a wealth of peer-reviewed publications to gain a deeper understanding of their research topics.
- Government and NGO databases: Government agencies, nongovernmental organizations and other institutions frequently maintain databases containing valuable economic, demographic and industry-related data. These sources offer credible statistics and reports on a wide range of topics, making them essential for market researchers. Examples include the U.S. Census Bureau , the Bureau of Labor Statistics and the Pew Research Center .
- Industry reports: Industry reports and market studies are comprehensive documents prepared by research firms, industry associations and consulting companies. They provide in-depth insights into specific markets, including market size, trends, competitive analysis and consumer behavior. You can find this information by looking at relevant industry association databases; examples include the American Marketing Association and the National Retail Federation .
- Social media and online communities: Social media platforms like LinkedIn or Twitter (X) , forums such as Reddit and Quora , and review platforms such as G2 can provide real-time insights into consumer sentiment, opinions and trends.
Market research examples
At this point, you have market research tools and data sources — but how do you act on the data you gather? Let’s go over some real-world examples that illustrate the practical application of market research across various industries. These examples showcase how market research can lead to smart decision-making and successful business decisions.
Example 1: Apple’s iPhone launch
Apple ’s iconic iPhone launch in 2007 serves as a prime example of market research driving product innovation in tech. Before the iPhone’s release, Apple conducted extensive market research to understand consumer preferences, pain points and unmet needs in the mobile phone industry. This research led to the development of a touchscreen smartphone with a user-friendly interface, addressing consumer demands for a more intuitive and versatile device. The result was a revolutionary product that disrupted the market and redefined the smartphone industry.
Example 2: McDonald’s global expansion
McDonald’s successful global expansion strategy demonstrates the importance of market research when expanding into new territories. Before entering a new market, McDonald’s conducts thorough research to understand local tastes, preferences and cultural nuances. This research informs menu customization, marketing strategies and store design. For instance, in India, McDonald’s offers a menu tailored to local preferences, including vegetarian options. This market-specific approach has enabled McDonald’s to adapt and thrive in diverse global markets.
Example 3: Organic and sustainable farming
The shift toward organic and sustainable farming practices in the food industry is driven by market research that indicates increased consumer demand for healthier and environmentally friendly food options. As a result, food producers and retailers invest in sustainable sourcing and organic product lines — such as with these sustainable seafood startups — to align with this shift in consumer values.
The bottom line? Market research has multiple use cases and is a critical practice for any industry. Whether it’s launching groundbreaking products, entering new markets or responding to changing consumer preferences, you can use market research to shape successful strategies and outcomes.
Market research templates
You finally have a strong understanding of how to do market research and apply it in the real world. Before we wrap up, here are some market research templates that you can use as a starting point for your projects:
- Smartsheet competitive analysis templates : These spreadsheets can serve as a framework for gathering information about the competitive landscape and obtaining valuable lessons to apply to your business strategy.
- SurveyMonkey product survey template : Customize the questions on this survey based on what you want to learn from your target customers.
- HubSpot templates : HubSpot offers a wide range of free templates you can use for market research, business planning and more.
- SCORE templates : SCORE is a nonprofit organization that provides templates for business plans, market analysis and financial projections.
- SBA.gov : The U.S. Small Business Administration offers templates for every aspect of your business, including market research, and is particularly valuable for new startups.
Strengthen your business with market research
When conducted effectively, market research is like a guiding star. Equipped with the right tools and techniques, you can uncover valuable insights, stay competitive, foster innovation and navigate the complexities of your industry.
Throughout this guide, we’ve discussed the definition of market research, different research methods, and how to conduct it effectively. We’ve also explored various types of market research and shared practical insights and templates for getting started.
Now, it’s time to start the research process. Trust in data, listen to the market and make informed decisions that guide your company toward lasting success.
Related Articles

- Entrepreneurs
- 15 min read
What Is Competitive Analysis and How to Do It Effectively
Rebecca Strehlow, Copywriter at Crunchbase
17 Best Sales Intelligence Tools for 2024

- Market research
- 10 min read
How to Do Market Research for a Startup: Tips for Success
Jaclyn Robinson, Senior Manager of Content Marketing at Crunchbase
Search less. Close more.
Grow your revenue with Crunchbase, the all-in-one prospecting solution. Start your free trial.
Market Research: A How-To Guide and Template
Discover the different types of market research, how to conduct your own market research, and use a free template to help you along the way.

MARKET RESEARCH KIT
5 Research and Planning Templates + a Free Guide on How to Use Them in Your Market Research

Updated: 02/21/24
Published: 02/21/24
Today's consumers have a lot of power. As a business, you must have a deep understanding of who your buyers are and what influences their purchase decisions.
Enter: Market Research.
![market research steps example → Download Now: Market Research Templates [Free Kit]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/6ba52ce7-bb69-4b63-965b-4ea21ba905da.png)
Whether you're new to market research or not, I created this guide to help you conduct a thorough study of your market, target audience, competition, and more. Let’s dive in.
Table of Contents
What is market research?
Primary vs. secondary research, types of market research, how to do market research, market research report template, market research examples.
Market research is the process of gathering information about your target market and customers to verify the success of a new product, help your team iterate on an existing product, or understand brand perception to ensure your team is effectively communicating your company's value effectively.
Market research can answer various questions about the state of an industry. But if you ask me, it's hardly a crystal ball that marketers can rely on for insights on their customers.
Market researchers investigate several areas of the market, and it can take weeks or even months to paint an accurate picture of the business landscape.
However, researching just one of those areas can make you more intuitive to who your buyers are and how to deliver value that no other business is offering them right now.
How? Consider these two things:
- Your competitors also have experienced individuals in the industry and a customer base. It‘s very possible that your immediate resources are, in many ways, equal to those of your competition’s immediate resources. Seeking a larger sample size for answers can provide a better edge.
- Your customers don't represent the attitudes of an entire market. They represent the attitudes of the part of the market that is already drawn to your brand.
The market research services market is growing rapidly, which signifies a strong interest in market research as we enter 2024. The market is expected to grow from roughly $75 billion in 2021 to $90.79 billion in 2025 .
.png)
Free Market Research Kit
- SWOT Analysis Template
- Survey Template
- Focus Group Template
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Why do market research?
Market research allows you to meet your buyer where they are.
As our world becomes louder and demands more of our attention, this proves invaluable.
By understanding your buyer's problems, pain points, and desired solutions, you can aptly craft your product or service to naturally appeal to them.
Market research also provides insight into the following:
- Where your target audience and current customers conduct their product or service research
- Which of your competitors your target audience looks to for information, options, or purchases
- What's trending in your industry and in the eyes of your buyer
- Who makes up your market and what their challenges are
- What influences purchases and conversions among your target audience
- Consumer attitudes about a particular topic, pain, product, or brand
- Whether there‘s demand for the business initiatives you’re investing in
- Unaddressed or underserved customer needs that can be flipped into selling opportunity
- Attitudes about pricing for a particular product or service
Ultimately, market research allows you to get information from a larger sample size of your target audience, eliminating bias and assumptions so that you can get to the heart of consumer attitudes.
As a result, you can make better business decisions.
To give you an idea of how extensive market research can get , consider that it can either be qualitative or quantitative in nature — depending on the studies you conduct and what you're trying to learn about your industry.
Qualitative research is concerned with public opinion, and explores how the market feels about the products currently available in that market.
Quantitative research is concerned with data, and looks for relevant trends in the information that's gathered from public records.
That said, there are two main types of market research that your business can conduct to collect actionable information on your products: primary research and secondary research.
Primary Research
Primary research is the pursuit of first-hand information about your market and the customers within your market.
It's useful when segmenting your market and establishing your buyer personas.
Primary market research tends to fall into one of two buckets:
- Exploratory Primary Research: This kind of primary market research normally takes place as a first step — before any specific research has been performed — and may involve open-ended interviews or surveys with small numbers of people.
- Specific Primary Research: This type of research often follows exploratory research. In specific research, you take a smaller or more precise segment of your audience and ask questions aimed at solving a suspected problem.
Secondary Research
Secondary research is all the data and public records you have at your disposal to draw conclusions from (e.g. trend reports, market statistics, industry content, and sales data you already have on your business).
Secondary research is particularly useful for analyzing your competitors . The main buckets your secondary market research will fall into include:
- Public Sources: These sources are your first and most-accessible layer of material when conducting secondary market research. They're often free to find and review — like government statistics (e.g., from the U.S. Census Bureau ).
- Commercial Sources: These sources often come in the form of pay-to-access market reports, consisting of industry insight compiled by a research agency like Pew , Gartner , or Forrester .
- Internal Sources: This is the market data your organization already has like average revenue per sale, customer retention rates, and other historical data that can help you draw conclusions on buyer needs.
- Focus Groups
- Product/ Service Use Research
- Observation-Based Research
- Buyer Persona Research
- Market Segmentation Research
- Pricing Research
- Competitive Analysis Research
- Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty Research
- Brand Awareness Research
- Campaign Research
1. Interviews
Interviews allow for face-to-face discussions so you can allow for a natural flow of conversation. Your interviewees can answer questions about themselves to help you design your buyer personas and shape your entire marketing strategy.
2. Focus Groups
Focus groups provide you with a handful of carefully-selected people that can test out your product and provide feedback. This type of market research can give you ideas for product differentiation.
3. Product/Service Use Research
Product or service use research offers insight into how and why your audience uses your product or service. This type of market research also gives you an idea of the product or service's usability for your target audience.
4. Observation-Based Research
Observation-based research allows you to sit back and watch the ways in which your target audience members go about using your product or service, what works well in terms of UX , and which aspects of it could be improved.
5. Buyer Persona Research
Buyer persona research gives you a realistic look at who makes up your target audience, what their challenges are, why they want your product or service, and what they need from your business or brand.
6. Market Segmentation Research
Market segmentation research allows you to categorize your target audience into different groups (or segments) based on specific and defining characteristics. This way, you can determine effective ways to meet their needs.
7. Pricing Research
Pricing research helps you define your pricing strategy . It gives you an idea of what similar products or services in your market sell for and what your target audience is willing to pay.
8. Competitive Analysis
Competitive analyses give you a deep understanding of the competition in your market and industry. You can learn about what's doing well in your industry and how you can separate yourself from the competition .
9. Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty Research
Customer satisfaction and loyalty research gives you a look into how you can get current customers to return for more business and what will motivate them to do so (e.g., loyalty programs , rewards, remarkable customer service).
10. Brand Awareness Research
Brand awareness research tells you what your target audience knows about and recognizes from your brand. It tells you about the associations people make when they think about your business.
11. Campaign Research
Campaign research entails looking into your past campaigns and analyzing their success among your target audience and current customers. The goal is to use these learnings to inform future campaigns.
- Define your buyer persona.
- Identify a persona group to engage.
- Prepare research questions for your market research participants.
- List your primary competitors.
- Summarize your findings.
1. Define your buyer persona.
You have to understand who your customers are and how customers in your industry make buying decisions.
This is where your buyer personas come in handy. Buyer personas — sometimes referred to as marketing personas — are fictional, generalized representations of your ideal customers.
Use a free tool to create a buyer persona that your entire company can use to market, sell, and serve better.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

25 Tools & Resources for Conducting Market Research

What is a Competitive Analysis — and How Do You Conduct One?
![market research steps example SWOT Analysis: How To Do One [With Template & Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/marketingplan_20.webp)
SWOT Analysis: How To Do One [With Template & Examples]

TAM SAM SOM: What Do They Mean & How Do You Calculate Them?
![market research steps example How to Run a Competitor Analysis [Free Guide]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/Google%20Drive%20Integration/how%20to%20do%20a%20competitor%20analysis_122022.jpeg)
How to Run a Competitor Analysis [Free Guide]
![market research steps example 5 Challenges Marketers Face in Understanding Audiences [New Data + Market Researcher Tips]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/challenges%20marketers%20face%20in%20understanding%20the%20customer%20.png)
5 Challenges Marketers Face in Understanding Audiences [New Data + Market Researcher Tips]

Causal Research: The Complete Guide

Total Addressable Market (TAM): What It Is & How You Can Calculate It

What Is Market Share & How Do You Calculate It?
![market research steps example 3 Ways Data Privacy Changes Benefit Marketers [New Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how-data-privacy-benefits-marketers_1.webp)
3 Ways Data Privacy Changes Benefit Marketers [New Data]
Free Guide & Templates to Help Your Market Research
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
10.2 Steps in the Marketing Research Process
Learning objective.
- Describe the basic steps in the marketing research process and the purpose of each step.
The basic steps used to conduct marketing research are shown in Figure 10.6 “Steps in the Marketing Research Process” . Next, we discuss each step.
Figure 10.6 Steps in the Marketing Research Process
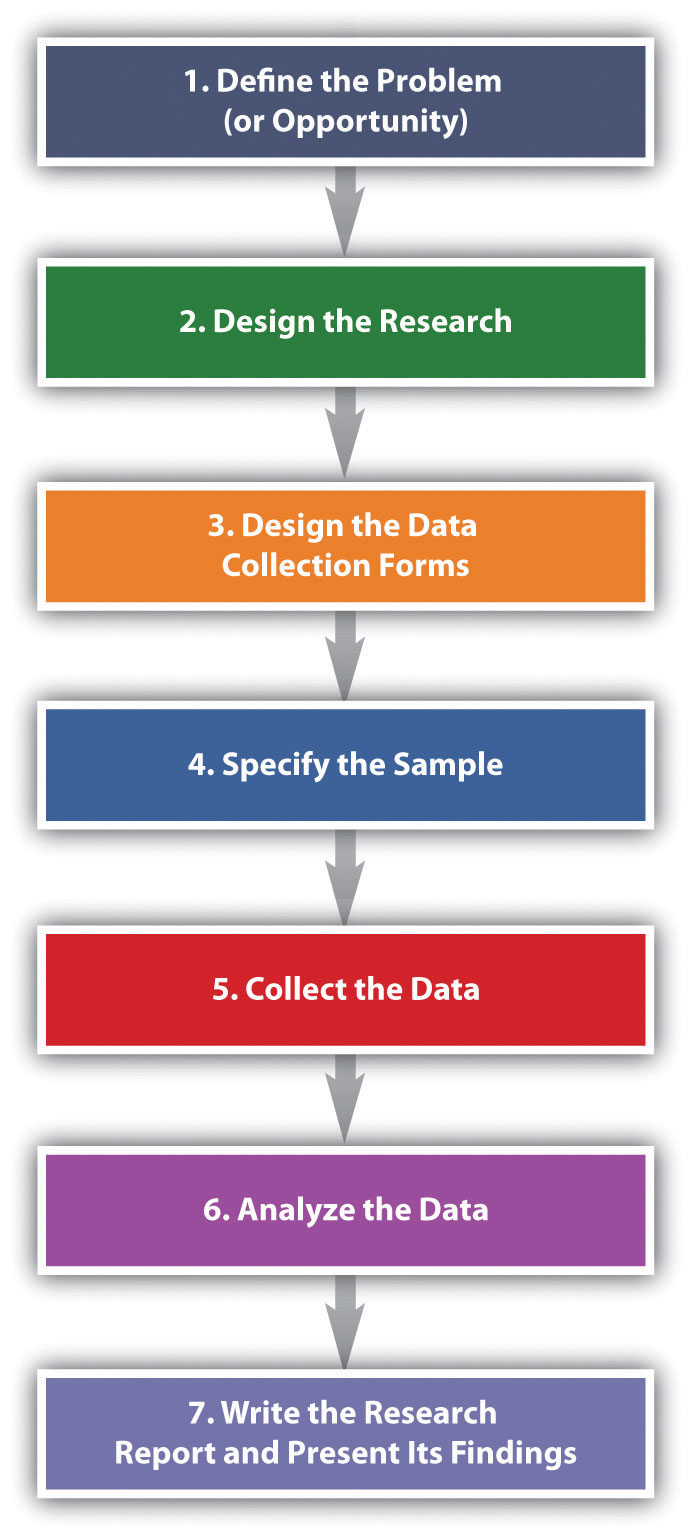
Step 1: Define the Problem (or Opportunity)
There’s a saying in marketing research that a problem half defined is a problem half solved. Defining the “problem” of the research sounds simple, doesn’t it? Suppose your product is tutoring other students in a subject you’re a whiz at. You have been tutoring for a while, and people have begun to realize you’re darned good at it. Then, suddenly, your business drops off. Or it explodes, and you can’t cope with the number of students you’re being asked help. If the business has exploded, should you try to expand your services? Perhaps you should subcontract with some other “whiz” students. You would send them students to be tutored, and they would give you a cut of their pay for each student you referred to them.
Both of these scenarios would be a problem for you, wouldn’t they? They are problems insofar as they cause you headaches. But are they really the problem? Or are they the symptoms of something bigger? For example, maybe your business has dropped off because your school is experiencing financial trouble and has lowered the number of scholarships given to incoming freshmen. Consequently, there are fewer total students on campus who need your services. Conversely, if you’re swamped with people who want you to tutor them, perhaps your school awarded more scholarships than usual, so there are a greater number of students who need your services. Alternately, perhaps you ran an ad in your school’s college newspaper, and that led to the influx of students wanting you to tutor them.
Businesses are in the same boat you are as a tutor. They take a look at symptoms and try to drill down to the potential causes. If you approach a marketing research company with either scenario—either too much or too little business—the firm will seek more information from you such as the following:
- In what semester(s) did your tutoring revenues fall (or rise)?
- In what subject areas did your tutoring revenues fall (or rise)?
- In what sales channels did revenues fall (or rise): Were there fewer (or more) referrals from professors or other students? Did the ad you ran result in fewer (or more) referrals this month than in the past months?
- Among what demographic groups did your revenues fall (or rise)—women or men, people with certain majors, or first-year, second-, third-, or fourth-year students?
The key is to look at all potential causes so as to narrow the parameters of the study to the information you actually need to make a good decision about how to fix your business if revenues have dropped or whether or not to expand it if your revenues have exploded.
The next task for the researcher is to put into writing the research objective. The research objective is the goal(s) the research is supposed to accomplish. The marketing research objective for your tutoring business might read as follows:
To survey college professors who teach 100- and 200-level math courses to determine why the number of students referred for tutoring dropped in the second semester.
This is admittedly a simple example designed to help you understand the basic concept. If you take a marketing research course, you will learn that research objectives get a lot more complicated than this. The following is an example:
“To gather information from a sample representative of the U.S. population among those who are ‘very likely’ to purchase an automobile within the next 6 months, which assesses preferences (measured on a 1–5 scale ranging from ‘very likely to buy’ to ‘not likely at all to buy’) for the model diesel at three different price levels. Such data would serve as input into a forecasting model that would forecast unit sales, by geographic regions of the country, for each combination of the model’s different prices and fuel configurations (Burns & Bush, 2010).”
Now do you understand why defining the problem is complicated and half the battle? Many a marketing research effort is doomed from the start because the problem was improperly defined. Coke’s ill-fated decision to change the formula of Coca-Cola in 1985 is a case in point: Pepsi had been creeping up on Coke in terms of market share over the years as well as running a successful promotional campaign called the “Pepsi Challenge,” in which consumers were encouraged to do a blind taste test to see if they agreed that Pepsi was better. Coke spent four years researching “the problem.” Indeed, people seemed to like the taste of Pepsi better in blind taste tests. Thus, the formula for Coke was changed. But the outcry among the public was so great that the new formula didn’t last long—a matter of months—before the old formula was reinstated. Some marketing experts believe Coke incorrectly defined the problem as “How can we beat Pepsi in taste tests?” instead of “How can we gain market share against Pepsi?” (Burns & Bush, 2010)
New Coke Is It! 1985
(click to see video)
This video documents the Coca-Cola Company’s ill-fated launch of New Coke in 1985.
1985 Pepsi Commercial—“They Changed My Coke”
This video shows how Pepsi tried to capitalize on the blunder.
Step 2: Design the Research
The next step in the marketing research process is to do a research design. The research design is your “plan of attack.” It outlines what data you are going to gather and from whom, how and when you will collect the data, and how you will analyze it once it’s been obtained. Let’s look at the data you’re going to gather first.
There are two basic types of data you can gather. The first is primary data. Primary data is information you collect yourself, using hands-on tools such as interviews or surveys, specifically for the research project you’re conducting. Secondary data is data that has already been collected by someone else, or data you have already collected for another purpose. Collecting primary data is more time consuming, work intensive, and expensive than collecting secondary data. Consequently, you should always try to collect secondary data first to solve your research problem, if you can. A great deal of research on a wide variety of topics already exists. If this research contains the answer to your question, there is no need for you to replicate it. Why reinvent the wheel?
Sources of Secondary Data
Your company’s internal records are a source of secondary data. So are any data you collect as part of your marketing intelligence gathering efforts. You can also purchase syndicated research. Syndicated research is primary data that marketing research firms collect on a regular basis and sell to other companies. J.D. Power & Associates is a provider of syndicated research. The company conducts independent, unbiased surveys of customer satisfaction, product quality, and buyer behavior for various industries. The company is best known for its research in the automobile sector. One of the best-known sellers of syndicated research is the Nielsen Company, which produces the Nielsen ratings. The Nielsen ratings measure the size of television, radio, and newspaper audiences in various markets. You have probably read or heard about TV shows that get the highest (Nielsen) ratings. (Arbitron does the same thing for radio ratings.) Nielsen, along with its main competitor, Information Resources, Inc. (IRI), also sells businesses scanner-based research . Scanner-based research is information collected by scanners at checkout stands in stores. Each week Nielsen and IRI collect information on the millions of purchases made at stores. The companies then compile the information and sell it to firms in various industries that subscribe to their services. The Nielsen Company has also recently teamed up with Facebook to collect marketing research information. Via Facebook, users will see surveys in some of the spaces in which they used to see online ads (Rappeport, Gelles, 2009).
By contrast, MarketResearch.com is an example of a marketing research aggregator. A marketing research aggregator is a marketing research company that doesn’t conduct its own research and sell it. Instead, it buys research reports from other marketing research companies and then sells the reports in their entirety or in pieces to other firms. Check out MarketResearch.com’s Web site. As you will see there are a huge number of studies in every category imaginable that you can buy for relatively small amounts of money.
Figure 10.7
Market research aggregators buy research reports from other marketing research companies and then resell them in part or in whole to other companies so they don’t have to gather primary data.
Source: http://www.marketresearch.com .
Your local library is a good place to gather free secondary data. It has searchable databases as well as handbooks, dictionaries, and books, some of which you can access online. Government agencies also collect and report information on demographics, economic and employment data, health information, and balance-of-trade statistics, among a lot of other information. The U.S. Census Bureau collects census data every ten years to gather information about who lives where. Basic demographic information about sex, age, race, and types of housing in which people live in each U.S. state, metropolitan area, and rural area is gathered so that population shifts can be tracked for various purposes, including determining the number of legislators each state should have in the U.S. House of Representatives. For the U.S. government, this is primary data. For marketing managers it is an important source of secondary data.
The Survey Research Center at the University of Michigan also conducts periodic surveys and publishes information about trends in the United States. One research study the center continually conducts is called the “Changing Lives of American Families” ( http://www.isr.umich.edu/home/news/research-update/2007-01.pdf ). This is important research data for marketing managers monitoring consumer trends in the marketplace. The World Bank and the United Nations are two international organizations that collect a great deal of information. Their Web sites contain many free research studies and data related to global markets. Table 10.1 “Examples of Primary Data Sources versus Secondary Data Sources” shows some examples of primary versus secondary data sources.
Table 10.1 Examples of Primary Data Sources versus Secondary Data Sources
Gauging the Quality of Secondary Data
When you are gathering secondary information, it’s always good to be a little skeptical of it. Sometimes studies are commissioned to produce the result a client wants to hear—or wants the public to hear. For example, throughout the twentieth century, numerous studies found that smoking was good for people’s health. The problem was the studies were commissioned by the tobacco industry. Web research can also pose certain hazards. There are many biased sites that try to fool people that they are providing good data. Often the data is favorable to the products they are trying to sell. Beware of product reviews as well. Unscrupulous sellers sometimes get online and create bogus ratings for products. See below for questions you can ask to help gauge the credibility of secondary information.
Gauging the Credibility of Secondary Data: Questions to Ask
- Who gathered this information?
- For what purpose?
- What does the person or organization that gathered the information have to gain by doing so?
- Was the information gathered and reported in a systematic manner?
- Is the source of the information accepted as an authority by other experts in the field?
- Does the article provide objective evidence to support the position presented?
Types of Research Design
Now let’s look specifically at the types of research designs that are utilized. By understanding different types of research designs, a researcher can solve a client’s problems more quickly and efficiently without jumping through more hoops than necessary. Research designs fall into one of the following three categories:
- Exploratory research design
- Descriptive research design
- Causal research design (experiments)
An exploratory research design is useful when you are initially investigating a problem but you haven’t defined it well enough to do an in-depth study of it. Perhaps via your regular market intelligence, you have spotted what appears to be a new opportunity in the marketplace. You would then do exploratory research to investigate it further and “get your feet wet,” as the saying goes. Exploratory research is less structured than other types of research, and secondary data is often utilized.
One form of exploratory research is qualitative research. Qualitative research is any form of research that includes gathering data that is not quantitative, and often involves exploring questions such as why as much as what or how much . Different forms, such as depth interviews and focus group interviews, are common in marketing research.
The depth interview —engaging in detailed, one-on-one, question-and-answer sessions with potential buyers—is an exploratory research technique. However, unlike surveys, the people being interviewed aren’t asked a series of standard questions. Instead the interviewer is armed with some general topics and asks questions that are open ended, meaning that they allow the interviewee to elaborate. “How did you feel about the product after you purchased it?” is an example of a question that might be asked. A depth interview also allows a researcher to ask logical follow-up questions such as “Can you tell me what you mean when you say you felt uncomfortable using the service?” or “Can you give me some examples?” to help dig further and shed additional light on the research problem. Depth interviews can be conducted in person or over the phone. The interviewer either takes notes or records the interview.
Focus groups and case studies are often utilized for exploratory research as well. A focus group is a group of potential buyers who are brought together to discuss a marketing research topic with one another. A moderator is used to focus the discussion, the sessions are recorded, and the main points of consensus are later summarized by the market researcher. Textbook publishers often gather groups of professors at educational conferences to participate in focus groups. However, focus groups can also be conducted on the telephone, in online chat rooms, or both, using meeting software like WebEx. The basic steps of conducting a focus group are outlined below.
The Basic Steps of Conducting a Focus Group
- Establish the objectives of the focus group. What is its purpose?
- Identify the people who will participate in the focus group. What makes them qualified to participate? How many of them will you need and what they will be paid?
- Obtain contact information for the participants and send out invitations (usually e-mails are most efficient).
- Develop a list of questions.
- Choose a facilitator.
- Choose a location in which to hold the focus group and the method by which it will be recorded.
- Conduct the focus group. If the focus group is not conducted electronically, include name tags for the participants, pens and notepads, any materials the participants need to see, and refreshments. Record participants’ responses.
- Summarize the notes from the focus group and write a report for management.
A case study looks at how another company solved the problem that’s being researched. Sometimes multiple cases, or companies, are used in a study. Case studies nonetheless have a mixed reputation. Some researchers believe it’s hard to generalize, or apply, the results of a case study to other companies. Nonetheless, collecting information about companies that encountered the same problems your firm is facing can give you a certain amount of insight about what direction you should take. In fact, one way to begin a research project is to carefully study a successful product or service.
Two other types of qualitative data used for exploratory research are ethnographies and projective techniques. In an ethnography , researchers interview, observe, and often videotape people while they work, live, shop, and play. The Walt Disney Company has recently begun using ethnographers to uncover the likes and dislikes of boys aged six to fourteen, a financially attractive market segment for Disney, but one in which the company has been losing market share. The ethnographers visit the homes of boys, observe the things they have in their rooms to get a sense of their hobbies, and accompany them and their mothers when they shop to see where they go, what the boys are interested in, and what they ultimately buy. (The children get seventy-five dollars out of the deal, incidentally.) (Barnes, 2009)
Projective techniques are used to reveal information research respondents might not reveal by being asked directly. Asking a person to complete sentences such as the following is one technique:
People who buy Coach handbags __________.
(Will he or she reply with “are cool,” “are affluent,” or “are pretentious,” for example?)
KFC’s grilled chicken is ______.
Or the person might be asked to finish a story that presents a certain scenario. Word associations are also used to discern people’s underlying attitudes toward goods and services. Using a word-association technique, a market researcher asks a person to say or write the first word that comes to his or her mind in response to another word. If the initial word is “fast food,” what word does the person associate it with or respond with? Is it “McDonald’s”? If many people reply that way, and you’re conducting research for Burger King, that could indicate Burger King has a problem. However, if the research is being conducted for Wendy’s, which recently began running an advertising campaign to the effect that Wendy’s offerings are “better than fast food,” it could indicate that the campaign is working.
Completing cartoons is yet another type of projective technique. It’s similar to finishing a sentence or story, only with the pictures. People are asked to look at a cartoon such as the one shown in Figure 10.8 “Example of a Cartoon-Completion Projective Technique” . One of the characters in the picture will have made a statement, and the person is asked to fill in the empty cartoon “bubble” with how they think the second character will respond.
Figure 10.8 Example of a Cartoon-Completion Projective Technique

In some cases, your research might end with exploratory research. Perhaps you have discovered your organization lacks the resources needed to produce the product. In other cases, you might decide you need more in-depth, quantitative research such as descriptive research or causal research, which are discussed next. Most marketing research professionals advise using both types of research, if it’s feasible. On the one hand, the qualitative-type research used in exploratory research is often considered too “lightweight.” Remember earlier in the chapter when we discussed telephone answering machines and the hit TV sitcom Seinfeld ? Both product ideas were initially rejected by focus groups. On the other hand, relying solely on quantitative information often results in market research that lacks ideas.
The Stone Wheel—What One Focus Group Said
Watch the video to see a funny spoof on the usefulness—or lack of usefulness—of focus groups.
Descriptive Research
Anything that can be observed and counted falls into the category of descriptive research design. A study using a descriptive research design involves gathering hard numbers, often via surveys, to describe or measure a phenomenon so as to answer the questions of who , what , where , when , and how . “On a scale of 1–5, how satisfied were you with your service?” is a question that illustrates the information a descriptive research design is supposed to capture.
Physiological measurements also fall into the category of descriptive design. Physiological measurements measure people’s involuntary physical responses to marketing stimuli, such as an advertisement. Elsewhere, we explained that researchers have gone so far as to scan the brains of consumers to see what they really think about products versus what they say about them. Eye tracking is another cutting-edge type of physiological measurement. It involves recording the movements of a person’s eyes when they look at some sort of stimulus, such as a banner ad or a Web page. The Walt Disney Company has a research facility in Austin, Texas, that it uses to take physical measurements of viewers when they see Disney programs and advertisements. The facility measures three types of responses: people’s heart rates, skin changes, and eye movements (eye tracking) (Spangler, 2009).
Figure 10.9

A woman shows off her headgear for an eye-tracking study. The gear’s not exactly a fashion statement but . . .
lawrencegs – Google Glass – CC BY 2.0.
A strictly descriptive research design instrument—a survey, for example—can tell you how satisfied your customers are. It can’t, however, tell you why. Nor can an eye-tracking study tell you why people’s eyes tend to dwell on certain types of banner ads—only that they do. To answer “why” questions an exploratory research design or causal research design is needed (Wagner, 2007).
Causal Research
Causal research design examines cause-and-effect relationships. Using a causal research design allows researchers to answer “what if” types of questions. In other words, if a firm changes X (say, a product’s price, design, placement, or advertising), what will happen to Y (say, sales or customer loyalty)? To conduct causal research, the researcher designs an experiment that “controls,” or holds constant, all of a product’s marketing elements except one (or using advanced techniques of research, a few elements can be studied at the same time). The one variable is changed, and the effect is then measured. Sometimes the experiments are conducted in a laboratory using a simulated setting designed to replicate the conditions buyers would experience. Or the experiments may be conducted in a virtual computer setting.
You might think setting up an experiment in a virtual world such as the online game Second Life would be a viable way to conduct controlled marketing research. Some companies have tried to use Second Life for this purpose, but the results have been somewhat mixed as to whether or not it is a good medium for marketing research. The German marketing research firm Komjuniti was one of the first “real-world” companies to set up an “island” in Second Life upon which it could conduct marketing research. However, with so many other attractive fantasy islands in which to play, the company found it difficult to get Second Life residents, or players, to voluntarily visit the island and stay long enough so meaningful research could be conducted. (Plus, the “residents,” or players, in Second Life have been known to protest corporations invading their world. When the German firm Komjuniti created an island in Second Life to conduct marketing research, the residents showed up waving signs and threatening to boycott the island.) (Wagner, 2007)
Why is being able to control the setting so important? Let’s say you are an American flag manufacturer and you are working with Walmart to conduct an experiment to see where in its stores American flags should be placed so as to increase their sales. Then the terrorist attacks of 9/11 occur. In the days afterward, sales skyrocketed—people bought flags no matter where they were displayed. Obviously, the terrorist attacks in the United States would have skewed the experiment’s data.
An experiment conducted in a natural setting such as a store is referred to as a field experiment . Companies sometimes do field experiments either because it is more convenient or because they want to see if buyers will behave the same way in the “real world” as in a laboratory or on a computer. The place the experiment is conducted or the demographic group of people the experiment is administered to is considered the test market . Before a large company rolls out a product to the entire marketplace, it will often place the offering in a test market to see how well it will be received. For example, to compete with MillerCoors’ sixty-four-calorie beer MGD 64, Anheuser-Busch recently began testing its Select 55 beer in certain cities around the country (McWilliams, 2009).
Figure 10.10
Select 55 beer: Coming soon to a test market near you? (If you’re on a diet, you have to hope so!)
Martine – Le champagne – CC BY-NC 2.0.
Many companies use experiments to test all of their marketing communications. For example, the online discount retailer O.co (formerly called Overstock.com) carefully tests all of its marketing offers and tracks the results of each one. One study the company conducted combined twenty-six different variables related to offers e-mailed to several thousand customers. The study resulted in a decision to send a group of e-mails to different segments. The company then tracked the results of the sales generated to see if they were in line with the earlier experiment it had conducted that led it to make the offer.
Step 3: Design the Data-Collection Forms
If the behavior of buyers is being formally observed, and a number of different researchers are conducting observations, the data obviously need to be recorded on a standardized data-collection form that’s either paper or electronic. Otherwise, the data collected will not be comparable. The items on the form could include a shopper’s sex; his or her approximate age; whether the person seemed hurried, moderately hurried, or unhurried; and whether or not he or she read the label on products, used coupons, and so forth.
The same is true when it comes to surveying people with questionnaires. Surveying people is one of the most commonly used techniques to collect quantitative data. Surveys are popular because they can be easily administered to large numbers of people fairly quickly. However, to produce the best results, the questionnaire for the survey needs to be carefully designed.
Questionnaire Design
Most questionnaires follow a similar format: They begin with an introduction describing what the study is for, followed by instructions for completing the questionnaire and, if necessary, returning it to the market researcher. The first few questions that appear on the questionnaire are usually basic, warm-up type of questions the respondent can readily answer, such as the respondent’s age, level of education, place of residence, and so forth. The warm-up questions are then followed by a logical progression of more detailed, in-depth questions that get to the heart of the question being researched. Lastly, the questionnaire wraps up with a statement that thanks the respondent for participating in the survey and information and explains when and how they will be paid for participating. To see some examples of questionnaires and how they are laid out, click on the following link: http://cas.uah.edu/wrenb/mkt343/Project/Sample%20Questionnaires.htm .
How the questions themselves are worded is extremely important. It’s human nature for respondents to want to provide the “correct” answers to the person administering the survey, so as to seem agreeable. Therefore, there is always a hazard that people will try to tell you what you want to hear on a survey. Consequently, care needs to be taken that the survey questions are written in an unbiased, neutral way. In other words, they shouldn’t lead a person taking the questionnaire to answer a question one way or another by virtue of the way you have worded it. The following is an example of a leading question.
Don’t you agree that teachers should be paid more ?
The questions also need to be clear and unambiguous. Consider the following question:
Which brand of toothpaste do you use ?
The question sounds clear enough, but is it really? What if the respondent recently switched brands? What if she uses Crest at home, but while away from home or traveling, she uses Colgate’s Wisp portable toothpaste-and-brush product? How will the respondent answer the question? Rewording the question as follows so it’s more specific will help make the question clearer:
Which brand of toothpaste have you used at home in the past six months? If you have used more than one brand, please list each of them 1 .
Sensitive questions have to be asked carefully. For example, asking a respondent, “Do you consider yourself a light, moderate, or heavy drinker?” can be tricky. Few people want to admit to being heavy drinkers. You can “soften” the question by including a range of answers, as the following example shows:
How many alcoholic beverages do you consume in a week ?
- __0–5 alcoholic beverages
- __5–10 alcoholic beverages
- __10–15 alcoholic beverages
Many people don’t like to answer questions about their income levels. Asking them to specify income ranges rather than divulge their actual incomes can help.
Other research question “don’ts” include using jargon and acronyms that could confuse people. “How often do you IM?” is an example. Also, don’t muddy the waters by asking two questions in the same question, something researchers refer to as a double-barreled question . “Do you think parents should spend more time with their children and/or their teachers?” is an example of a double-barreled question.
Open-ended questions , or questions that ask respondents to elaborate, can be included. However, they are harder to tabulate than closed-ended questions , or questions that limit a respondent’s answers. Multiple-choice and yes-and-no questions are examples of closed-ended questions.
Testing the Questionnaire
You have probably heard the phrase “garbage in, garbage out.” If the questions are bad, the information gathered will be bad, too. One way to make sure you don’t end up with garbage is to test the questionnaire before sending it out to find out if there are any problems with it. Is there enough space for people to elaborate on open-ended questions? Is the font readable? To test the questionnaire, marketing research professionals first administer it to a number of respondents face to face. This gives the respondents the chance to ask the researcher about questions or instructions that are unclear or don’t make sense to them. The researcher then administers the questionnaire to a small subset of respondents in the actual way the survey is going to be disseminated, whether it’s delivered via phone, in person, by mail, or online.
Getting people to participate and complete questionnaires can be difficult. If the questionnaire is too long or hard to read, many people won’t complete it. So, by all means, eliminate any questions that aren’t necessary. Of course, including some sort of monetary incentive for completing the survey can increase the number of completed questionnaires a market researcher will receive.
Step 4: Specify the Sample
Once you have created your questionnaire or other marketing study, how do you figure out who should participate in it? Obviously, you can’t survey or observe all potential buyers in the marketplace. Instead, you must choose a sample. A sample is a subset of potential buyers that are representative of your entire target market, or population being studied. Sometimes market researchers refer to the population as the universe to reflect the fact that it includes the entire target market, whether it consists of a million people, a hundred thousand, a few hundred, or a dozen. “All unmarried people over the age of eighteen who purchased Dirt Devil steam cleaners in the United States during 2011” is an example of a population that has been defined.
Obviously, the population has to be defined correctly. Otherwise, you will be studying the wrong group of people. Not defining the population correctly can result in flawed research, or sampling error. A sampling error is any type of marketing research mistake that results because a sample was utilized. One criticism of Internet surveys is that the people who take these surveys don’t really represent the overall population. On average, Internet survey takers tend to be more educated and tech savvy. Consequently, if they solely constitute your population, even if you screen them for certain criteria, the data you collect could end up being skewed.
The next step is to put together the sampling frame , which is the list from which the sample is drawn. The sampling frame can be put together using a directory, customer list, or membership roster (Wrenn et. al., 2007). Keep in mind that the sampling frame won’t perfectly match the population. Some people will be included on the list who shouldn’t be. Other people who should be included will be inadvertently omitted. It’s no different than if you were to conduct a survey of, say, 25 percent of your friends, using friends’ names you have in your cell phone. Most of your friends’ names are likely to be programmed into your phone, but not all of them. As a result, a certain degree of sampling error always occurs.
There are two main categories of samples in terms of how they are drawn: probability samples and nonprobability samples. A probability sample is one in which each would-be participant has a known and equal chance of being selected. The chance is known because the total number of people in the sampling frame is known. For example, if every other person from the sampling frame were chosen, each person would have a 50 percent chance of being selected.
A nonprobability sample is any type of sample that’s not drawn in a systematic way. So the chances of each would-be participant being selected can’t be known. A convenience sample is one type of nonprobability sample. It is a sample a researcher draws because it’s readily available and convenient to do so. Surveying people on the street as they pass by is an example of a convenience sample. The question is, are these people representative of the target market?
For example, suppose a grocery store needed to quickly conduct some research on shoppers to get ready for an upcoming promotion. Now suppose that the researcher assigned to the project showed up between the hours of 10 a.m. and 12 p.m. on a weekday and surveyed as many shoppers as possible. The problem is that the shoppers wouldn’t be representative of the store’s entire target market. What about commuters who stop at the store before and after work? Their views wouldn’t be represented. Neither would people who work the night shift or shop at odd hours. As a result, there would be a lot of room for sampling error in this study. For this reason, studies that use nonprobability samples aren’t considered as accurate as studies that use probability samples. Nonprobability samples are more often used in exploratory research.
Lastly, the size of the sample has an effect on the amount of sampling error. Larger samples generally produce more accurate results. The larger your sample is, the more data you will have, which will give you a more complete picture of what you’re studying. However, the more people surveyed or studied, the more costly the research becomes.
Statistics can be used to determine a sample’s optimal size. If you take a marketing research or statistics class, you will learn more about how to determine the optimal size.
Of course, if you hire a marketing research company, much of this work will be taken care of for you. Many marketing research companies, like ResearchNow, maintain panels of prescreened people they draw upon for samples. In addition, the marketing research firm will be responsible for collecting the data or contracting with a company that specializes in data collection. Data collection is discussed next.
Step 5: Collect the Data
As we have explained, primary marketing research data can be gathered in a number of ways. Surveys, taking physical measurements, and observing people are just three of the ways we discussed. If you’re observing customers as part of gathering the data, keep in mind that if shoppers are aware of the fact, it can have an effect on their behavior. For example, if a customer shopping for feminine hygiene products in a supermarket aisle realizes she is being watched, she could become embarrassed and leave the aisle, which would adversely affect your data. To get around problems such as these, some companies set up cameras or two-way mirrors to observe customers. Organizations also hire mystery shoppers to work around the problem. A mystery shopper is someone who is paid to shop at a firm’s establishment or one of its competitors to observe the level of service, cleanliness of the facility, and so forth, and report his or her findings to the firm.
Make Extra Money as a Mystery Shopper
Watch the YouTube video to get an idea of how mystery shopping works.
Survey data can be collected in many different ways and combinations of ways. The following are the basic methods used:
- Face-to-face (can be computer aided)
- Telephone (can be computer aided or completely automated)
- Mail and hand delivery
- E-mail and the Web
A face-to-face survey is, of course, administered by a person. The surveys are conducted in public places such as in shopping malls, on the street, or in people’s homes if they have agreed to it. In years past, it was common for researchers in the United States to knock on people’s doors to gather survey data. However, randomly collected door-to-door interviews are less common today, partly because people are afraid of crime and are reluctant to give information to strangers (McDaniel & Gates, 1998).
Nonetheless, “beating the streets” is still a legitimate way questionnaire data is collected. When the U.S. Census Bureau collects data on the nation’s population, it hand delivers questionnaires to rural households that do not have street-name and house-number addresses. And Census Bureau workers personally survey the homeless to collect information about their numbers. Face-to-face surveys are also commonly used in third world countries to collect information from people who cannot read or lack phones and computers.
A plus of face-to-face surveys is that they allow researchers to ask lengthier, more complex questions because the people being surveyed can see and read the questionnaires. The same is true when a computer is utilized. For example, the researcher might ask the respondent to look at a list of ten retail stores and rank the stores from best to worst. The same question wouldn’t work so well over the telephone because the person couldn’t see the list. The question would have to be rewritten. Another drawback with telephone surveys is that even though federal and state “do not call” laws generally don’t prohibit companies from gathering survey information over the phone, people often screen such calls using answering machines and caller ID.
Probably the biggest drawback of both surveys conducted face-to-face and administered over the phone by a person is that they are labor intensive and therefore costly. Mailing out questionnaires is costly, too, and the response rates can be rather low. Think about why that might be so: if you receive a questionnaire in the mail, it is easy to throw it in the trash; it’s harder to tell a market researcher who approaches you on the street that you don’t want to be interviewed.
By contrast, gathering survey data collected by a computer, either over the telephone or on the Internet, can be very cost-effective and in some cases free. SurveyMonkey and Zoomerang are two Web sites that will allow you to create online questionnaires, e-mail them to up to one hundred people for free, and view the responses in real time as they come in. For larger surveys, you have to pay a subscription price of a few hundred dollars. But that still can be extremely cost-effective. The two Web sites also have a host of other features such as online-survey templates you can use to create your questionnaire, a way to set up automatic reminders sent to people who haven’t yet completed their surveys, and tools you can use to create graphics to put in your final research report. To see how easy it is to put together a survey in SurveyMonkey, click on the following link: http://help.surveymonkey.com/app/tutorials/detail/a_id/423 .
Like a face-to-face survey, an Internet survey can enable you to show buyers different visuals such as ads, pictures, and videos of products and their packaging. Web surveys are also fast, which is a major plus. Whereas face-to-face and mailed surveys often take weeks to collect, you can conduct a Web survey in a matter of days or even hours. And, of course, because the information is electronically gathered it can be automatically tabulated. You can also potentially reach a broader geographic group than you could if you had to personally interview people. The Zoomerang Web site allows you to create surveys in forty different languages.
Another plus for Web and computer surveys (and electronic phone surveys) is that there is less room for human error because the surveys are administered electronically. For instance, there’s no risk that the interviewer will ask a question wrong or use a tone of voice that could mislead the respondents. Respondents are also likely to feel more comfortable inputting the information into a computer if a question is sensitive than they would divulging the information to another person face-to-face or over the phone. Given all of these advantages, it’s not surprising that the Internet is quickly becoming the top way to collect primary data. However, like mail surveys, surveys sent to people over the Internet are easy to ignore.
Lastly, before the data collection process begins, the surveyors and observers need to be trained to look for the same things, ask questions the same way, and so forth. If they are using rankings or rating scales, they need to be “on the same page,” so to speak, as to what constitutes a high ranking or a low ranking. As an analogy, you have probably had some teachers grade your college papers harder than others. The goal of training is to avoid a wide disparity between how different observers and interviewers record the data.
Figure 10.11

Training people so they know what constitutes different ratings when they are collecting data will improve the quality of the information gathered in a marketing research study.
Ricardo Rodriquez – Satisfaction survey – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
For example, if an observation form asks the observers to describe whether a shopper’s behavior is hurried, moderately hurried, or unhurried, they should be given an idea of what defines each rating. Does it depend on how much time the person spends in the store or in the individual aisles? How fast they walk? In other words, the criteria and ratings need to be spelled out.
Collecting International Marketing Research Data
Gathering marketing research data in foreign countries poses special challenges. However, that doesn’t stop firms from doing so. Marketing research companies are located all across the globe, in fact. Eight of the ten largest marketing research companies in the world are headquartered in the United States. However, five of these eight firms earn more of their revenues abroad than they do in the United States. There’s a reason for this: many U.S. markets were saturated, or tapped out, long ago in terms of the amount that they can grow. Coke is an example. As you learned earlier in the book, most of the Coca-Cola Company’s revenues are earned in markets abroad. To be sure, the United States is still a huge market when it comes to the revenues marketing research firms generate by conducting research in the country: in terms of their spending, American consumers fuel the world’s economic engine. Still, emerging countries with growing middle classes, such as China, India, and Brazil, are hot new markets companies want to tap.
What kind of challenges do firms face when trying to conduct marketing research abroad? As we explained, face-to-face surveys are commonly used in third world countries to collect information from people who cannot read or lack phones and computers. However, face-to-face surveys are also common in Europe, despite the fact that phones and computers are readily available. In-home surveys are also common in parts of Europe. By contrast, in some countries, including many Asian countries, it’s considered taboo or rude to try to gather information from strangers either face-to-face or over the phone. In many Muslim countries, women are forbidden to talk to strangers.
And how do you figure out whom to research in foreign countries? That in itself is a problem. In the United States, researchers often ask if they can talk to the heads of households to conduct marketing research. But in countries in which domestic servants or employees are common, the heads of households aren’t necessarily the principal shoppers; their domestic employees are (Malhotra).
Translating surveys is also an issue. Have you ever watched the TV comedians Jay Leno and David Letterman make fun of the English translations found on ethnic menus and products? Research tools such as surveys can suffer from the same problem. Hiring someone who is bilingual to translate a survey into another language can be a disaster if the person isn’t a native speaker of the language to which the survey is being translated.
One way companies try to deal with translation problems is by using back translation. When back translation is used, a native speaker translates the survey into the foreign language and then translates it back again to the original language to determine if there were gaps in meaning—that is, if anything was lost in translation. And it’s not just the language that’s an issue. If the research involves any visual images, they, too, could be a point of confusion. Certain colors, shapes, and symbols can have negative connotations in other countries. For example, the color white represents purity in many Western cultures, but in China, it is the color of death and mourning (Zouhali-Worrall, 2008). Also, look back at the cartoon-completion exercise in Figure 10.8 “Example of a Cartoon-Completion Projective Technique” . What would women in Muslim countries who aren’t allowed to converse with male sellers think of it? Chances are, the cartoon wouldn’t provide you with the information you’re seeking if Muslim women in some countries were asked to complete it.
One way marketing research companies are dealing with the complexities of global research is by merging with or acquiring marketing research companies abroad. The Nielsen Company is the largest marketing research company in the world. The firm operates in more than a hundred countries and employs more than forty thousand people. Many of its expansions have been the result of acquisitions and mergers.
Step 6: Analyze the Data
Step 6 involves analyzing the data to ensure it’s as accurate as possible. If the research is collected by hand using a pen and pencil, it’s entered into a computer. Or respondents might have already entered the information directly into a computer. For example, when Toyota goes to an event such as a car show, the automaker’s marketing personnel ask would-be buyers to complete questionnaires directly on computers. Companies are also beginning to experiment with software that can be used to collect data using mobile phones.
Once all the data is collected, the researchers begin the data cleaning , which is the process of removing data that have accidentally been duplicated (entered twice into the computer) or correcting data that have obviously been recorded wrong. A program such as Microsoft Excel or a statistical program such as Predictive Analytics Software (PASW, which was formerly known as SPSS) is then used to tabulate, or calculate, the basic results of the research, such as the total number of participants and how collectively they answered various questions. The programs can also be used to calculate averages, such as the average age of respondents, their average satisfaction, and so forth. The same can done for percentages, and other values you learned about, or will learn about, in a statistics course, such as the standard deviation, mean, and median for each question.
The information generated by the programs can be used to draw conclusions, such as what all customers might like or not like about an offering based on what the sample group liked or did not like. The information can also be used to spot differences among groups of people. For example, the research might show that people in one area of the country like the product better than people in another area. Trends to predict what might happen in the future can also be spotted.
If there are any open-ended questions respondents have elaborated upon—for example, “Explain why you like the current brand you use better than any other brand”—the answers to each are pasted together, one on top of another, so researchers can compare and summarize the information. As we have explained, qualitative information such as this can give you a fuller picture of the results of the research.
Part of analyzing the data is to see if it seems sound. Does the way in which the research was conducted seem sound? Was the sample size large enough? Are the conclusions that become apparent from it reasonable?
The two most commonly used criteria used to test the soundness of a study are (1) validity and (2) reliability. A study is valid if it actually tested what it was designed to test. For example, did the experiment you ran in Second Life test what it was designed to test? Did it reflect what could really happen in the real world? If not, the research isn’t valid. If you were to repeat the study, and get the same results (or nearly the same results), the research is said to be reliable . If you get a drastically different result if you repeat the study, it’s not reliable. The data collected, or at least some it, can also be compared to, or reconciled with, similar data from other sources either gathered by your firm or by another organization to see if the information seems on target.
Stage 7: Write the Research Report and Present Its Findings
If you end up becoming a marketing professional and conducting a research study after you graduate, hopefully you will do a great job putting the study together. You will have defined the problem correctly, chosen the right sample, collected the data accurately, analyzed it, and your findings will be sound. At that point, you will be required to write the research report and perhaps present it to an audience of decision makers. You will do so via a written report and, in some cases, a slide or PowerPoint presentation based on your written report.
The six basic elements of a research report are as follows.
- Title Page . The title page explains what the report is about, when it was conducted and by whom, and who requested it.
- Table of Contents . The table of contents outlines the major parts of the report, as well as any graphs and charts, and the page numbers on which they can be found.
- Executive Summary . The executive summary summarizes all the details in the report in a very quick way. Many people who receive the report—both executives and nonexecutives—won’t have time to read the entire report. Instead, they will rely on the executive summary to quickly get an idea of the study’s results and what to do about those results.
Methodology and Limitations . The methodology section of the report explains the technical details of how the research was designed and conducted. The section explains, for example, how the data was collected and by whom, the size of the sample, how it was chosen, and whom or what it consisted of (e.g., the number of women versus men or children versus adults). It also includes information about the statistical techniques used to analyze the data.
Every study has errors—sampling errors, interviewer errors, and so forth. The methodology section should explain these details, so decision makers can consider their overall impact. The margin of error is the overall tendency of the study to be off kilter—that is, how far it could have gone wrong in either direction. Remember how newscasters present the presidential polls before an election? They always say, “This candidate is ahead 48 to 44 percent, plus or minus 2 percent.” That “plus or minus” is the margin of error. The larger the margin of error is, the less likely the results of the study are accurate. The margin of error needs to be included in the methodology section.
- Findings . The findings section is a longer, fleshed-out version of the executive summary that goes into more detail about the statistics uncovered by the research that bolster the study’s findings. If you have related research or secondary data on hand that back up the findings, it can be included to help show the study did what it was designed to do.
- Recommendations . The recommendations section should outline the course of action you think should be taken based on the findings of the research and the purpose of the project. For example, if you conducted a global market research study to identify new locations for stores, make a recommendation for the locations (Mersdorf, 2009).
As we have said, these are the basic sections of a marketing research report. However, additional sections can be added as needed. For example, you might need to add a section on the competition and each firm’s market share. If you’re trying to decide on different supply chain options, you will need to include a section on that topic.
As you write the research report, keep your audience in mind. Don’t use technical jargon decision makers and other people reading the report won’t understand. If technical terms must be used, explain them. Also, proofread the document to ferret out any grammatical errors and typos, and ask a couple of other people to proofread behind you to catch any mistakes you might have missed. If your research report is riddled with errors, its credibility will be undermined, even if the findings and recommendations you make are extremely accurate.
Many research reports are presented via PowerPoint. If you’re asked to create a slideshow presentation from the report, don’t try to include every detail in the report on the slides. The information will be too long and tedious for people attending the presentation to read through. And if they do go to the trouble of reading all the information, they probably won’t be listening to the speaker who is making the presentation.
Instead of including all the information from the study in the slides, boil each section of the report down to key points and add some “talking points” only the presenter will see. After or during the presentation, you can give the attendees the longer, paper version of the report so they can read the details at a convenient time, if they choose to.
Key Takeaway
Step 1 in the marketing research process is to define the problem. Businesses take a look at what they believe are symptoms and try to drill down to the potential causes so as to precisely define the problem. The next task for the researcher is to put into writing the research objective, or goal, the research is supposed to accomplish. Step 2 in the process is to design the research. The research design is the “plan of attack.” It outlines what data you are going to gather, from whom, how, and when, and how you’re going to analyze it once it has been obtained. Step 3 is to design the data-collection forms, which need to be standardized so the information gathered on each is comparable. Surveys are a popular way to gather data because they can be easily administered to large numbers of people fairly quickly. However, to produce the best results, survey questionnaires need to be carefully designed and pretested before they are used. Step 4 is drawing the sample, or a subset of potential buyers who are representative of your entire target market. If the sample is not correctly selected, the research will be flawed. Step 5 is to actually collect the data, whether it’s collected by a person face-to-face, over the phone, or with the help of computers or the Internet. The data-collection process is often different in foreign countries. Step 6 is to analyze the data collected for any obvious errors, tabulate the data, and then draw conclusions from it based on the results. The last step in the process, Step 7, is writing the research report and presenting the findings to decision makers.
Review Questions
- Explain why it’s important to carefully define the problem or opportunity a marketing research study is designed to investigate.
- Describe the different types of problems that can occur when marketing research professionals develop questions for surveys.
- How does a probability sample differ from a nonprobability sample?
- What makes a marketing research study valid? What makes a marketing research study reliable?
- What sections should be included in a marketing research report? What is each section designed to do?
1 “Questionnaire Design,” QuickMBA , http://www.quickmba.com/marketing/research/qdesign (accessed December 14, 2009).
Barnes, B., “Disney Expert Uses Science to Draw Boy Viewers,” New York Times , April 15, 2009, http://www.nytimes.com/2009/04/14/arts/television/14boys.html?pagewanted=1&_r=1 (accessed December 14, 2009).
Burns A. and Ronald Bush, Marketing Research , 6th ed. (Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 2010), 85.
Malhotra, N., Marketing Research: An Applied Approach , 6th ed. (Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall), 764.
McDaniel, C. D. and Roger H. Gates, Marketing Research Essentials , 2nd ed. (Cincinnati: South-Western College Publishing, 1998), 61.
McWilliams, J., “A-B Puts Super-Low-Calorie Beer in Ring with Miller,” St. Louis Post-Dispatch , August 16, 2009, http://www.stltoday.com/business/next-matchup-light-weights-a-b-puts-super-low-calorie/article_47511bfe-18ca-5979-bdb9-0526c97d4edf.html (accessed April 13, 2012).
Mersdorf, S., “How to Organize Your Next Survey Report,” Cvent , August 24, 2009, http://survey.cvent.com/blog/cvent-survey/0/0/how-to-organize-your-next-survey-report (accessed December 14, 2009).
Rappeport A. and David Gelles, “Facebook to Form Alliance with Nielsen,” Financial Times , September 23, 2009, 16.
Spangler, T., “Disney Lab Tracks Feelings,” Multichannel News 30, no. 30 (August 3, 2009): 26.
Wagner, J., “Marketing in Second Life Doesn’t Work…Here Is Why!” GigaOM , April 4, 2007, http://gigaom.com/2007/04/04/3-reasons-why-marketing-in-second-life-doesnt-work (accessed December 14, 2009).
Wrenn, B., Robert E. Stevens, and David L. Loudon, Marketing Research: Text and Cases , 2nd ed. (Binghamton, NY: Haworth Press, 2007), 180.
Zouhali-Worrall, M., “Found in Translation: Avoiding Multilingual Gaffes,” CNNMoney.com , July 14, 2008, http://money.cnn.com/2008/07/07/smallbusiness/language_translation.fsb/index.htm (accessed December 14, 2009).
Principles of Marketing Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 6: Marketing Research
6.1 Steps in the Marketing Research Process
Learning Objectives
- Describe the basic steps in the marketing research process and the purpose of each step.
The basic steps used to conduct marketing research are shown in figure 6.1 . Next, we discuss each step.
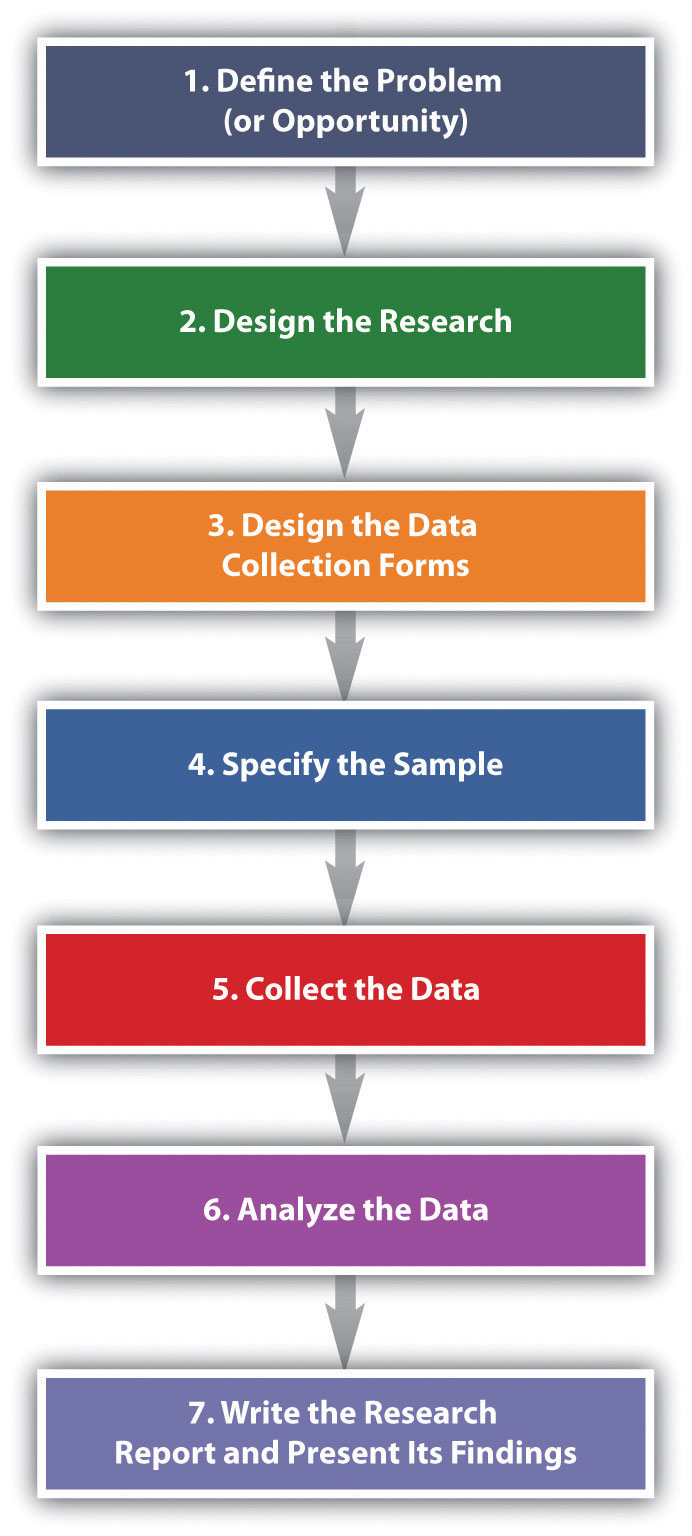
Step 1: Define the Problem (or Opportunity)
There’s a saying in marketing research that a problem half defined is a problem half solved. Defining the “problem” of the research sounds simple, doesn’t it? Suppose your “product” is tutoring other students in a subject you enjoy. You have been tutoring for a while, and people have begun to realize you’re very good at it. Then, suddenly, your business declines. Or it explodes, and you can’t cope with the number of students you’re being asked to help. If the business has exploded, should you try to expand your services? Perhaps you should subcontract with some other smart students. You would send them students to be tutored, and they would give you a cut of their pay for each student you referred to them.
Both of these scenarios would be a problem for you, wouldn’t they? They are problems insofar as they cause you headaches. But are they really the problem? Or are they the symptoms of something bigger? For example, maybe your business has dropped off because your school is experiencing decreased enrollment so there are fewer total students on campus who need your services. Conversely, if you’re swamped with people who want you to tutor them, perhaps your school has increased enrollment so there are a greater number of students who need your services. Alternately, perhaps you posted your services on social media and that led to the influx of students wanting you to tutor them.
Businesses are in the same boat. They take a look at symptoms and try to narrow down the potential causes. If you approach a marketing research company with either scenario—either too much or too little business—the firm will seek more information from you such as the following:
- In what semester(s) did your tutoring revenues fall (or rise)?
- In what subject areas did your tutoring revenues fall (or rise)?
- In what sales channels did revenues fall (or rise): Were there fewer (or more) referrals from professors or other students? Did the social media post result in fewer (or more) referrals this month than in the past months?
- Among what demographic groups did your revenues fall (or rise)— people with certain majors, or first-year, second-, third-, or fourth-year students, local or international students?
The key is to look at all potential causes so as to narrow the parameters of the study to the information you actually need to make a good decision about how to fix your business if revenues have dropped or whether or not to expand it if your revenues have exploded.
The next task for the researcher is to put the research objective into writing. The research objective is the goal(s) the research is supposed to accomplish. The marketing research objective for your tutoring business might read as follows:
To survey university professors who teach 100- and 200-level math courses to determine why the number of students referred for tutoring dropped in the second semester.
This is admittedly a simple example designed to help you understand the basic concept. If you take a marketing research course, you will learn that research objectives get a lot more complicated than this. The following is an example:
“To gather information from a sample representative of the U.S. population among those who are ‘very likely’ to purchase an automobile within the next 6 months, which assesses preferences (measured on a 1–5 scale ranging from ‘very likely to buy’ to ‘not likely at all to buy’) for the model diesel at three different price levels. Such data would serve as input into a forecasting model that would forecast unit sales, by geographic regions of the country, for each combination of the model’s different prices and fuel configurations.” (Burns & Bush, 2010) [1]
Now do you understand why defining the problem is complicated and half the battle? Many a marketing research effort has been doomed from the start because the problem was improperly defined. Coke’s ill-fated decision to change the formula of Coca-Cola in 1985 is a case in point: Pepsi had been creeping up on Coke in terms of market share over the years as well as running a successful promotional campaign called the “Pepsi Challenge,” in which consumers were encouraged to do a blind taste test to see if they agreed that Pepsi was better. Coke spent four years researching “the problem.” Indeed, people seemed to like the taste of Pepsi better in blind taste tests. Thus, the formula for Coke was changed. But the outcry among the public was so great that the new formula didn’t last long—a matter of months—before the old formula was reinstated. Some marketing experts believe Coke incorrectly defined the problem as “How can we beat Pepsi in taste tests?” instead of “How can we gain market share against Pepsi?” (Burns & Bush, 2010) [2]
Video 6.1 documents the Coca-Cola Company’s ill-fated launch of New Coke in 1985.
Video 6.1. New Coke Is It! 1985. Source: The 1985 launch of New Coke on Christian Budtz .
Video 6.2 shows how Pepsi tried to capitalize on the mistake.
Video 6.2. 1985 Pepsi Commercial “They Changed My Coke”. Source: 1985 Pepsi commercial: They changed my Coke on eyeh8cbs .
Step 2: Design the Research
The next step in the marketing research process is to do a research design. The research design outlines what data you are going to gather and from whom, how and when you will collect the data, and how you will analyze them once they’ve been obtained. Let’s look at the data you’re going to gather first.
There are two basic types of data you can gather. The first is primary data. Primary data is information you collect yourself, using hands-on tools such as interviews or surveys, specifically for the research project you’re conducting. Secondary data are data that have already been collected by someone else, or data you have already collected for another purpose. Collecting primary data is more time-consuming, work-intensive, and expensive than collecting secondary data. Consequently, you should always try to collect secondary data first to solve your research problem, if you can. A great deal of research on a wide variety of topics already exists. If this research contains the answer to your question, there is no need for you to replicate it. Why reinvent the wheel?
Sources of Secondary Data
Your company’s internal records are a source of secondary data. So are any data you collect as part of your regular marketing intelligence-gathering efforts. You can also purchase syndicated research. Syndicated research is primary data that marketing research firms collect on a regular basis and sell to other companies. J.D. Power & Associates is a provider of syndicated research. The company conducts independent, unbiased surveys of customer satisfaction, product quality, and buyer behaviour for various industries. The company is best known for its research in the automobile sector. One of the best-known sellers of syndicated research is the Nielsen Company, which produces the Nielsen ratings. The Nielsen ratings measure the size of television, radio, and newspaper audiences in various markets. You have probably read or heard about TV shows that get the highest (Nielsen) ratings (Arbitron does the same thing for radio ratings). Nielsen, along with its main competitor, Information Resources, Inc. (IRI), also sells businesses scanner-based research . Scanner-based research is information collected by scanners at checkout stands in stores. Each week, Nielsen and IRI collect information on the millions of purchases made at stores. The companies then compile the information and sell it to firms in various industries that subscribe to their services. The Nielsen Company has also recently teamed up with Facebook to collect marketing research information. Via Facebook, users will see surveys in some of the spaces in which they used to see online ads (Rappeport & Gelles, 2009). [3]
By contrast, MarketResearch.com is an example of a marketing research aggregator. A marketing research aggregator is a marketing research company that doesn’t conduct its own research and sell it; instead, it buys research reports from other marketing research companies and then sells the reports in their entirety or in pieces to other firms. Check out MarketResearch.com’s website ( figure 6.2 ). As you will see, there are a huge number of studies in every category imaginable that you can buy for relatively small amounts of money.
Your school library is a good place to gather free secondary data. It has searchable databases as well as handbooks, dictionaries, and books, some of which you can access online. Government agencies also collect and report information on demographics, economic and employment data, health information, and balance-of-trade statistics, among a lot of other information. Statistics Canada collects census data every ten years to gather information about who lives where. Basic demographic information about sex, age, race, and types of housing in which people live in each province, metropolitan area, and rural area is gathered so that population shifts can be tracked for various purposes.
The World Bank and the United Nations are two international organizations that collect a great deal of information. Their websites contain many free research studies and data related to global markets. Table 6.1 shows some examples of primary versus secondary data sources.
Gauging the Quality of Secondary Data
When you are gathering secondary information, it’s always good to be a little skeptical. Sometimes, studies are commissioned to produce the result a client wants to hear—or wants the public to hear. For example, throughout the twentieth century, numerous studies found that smoking was good for people’s health. The problem was the studies were commissioned by the tobacco industry. Web research can also pose certain hazards. There are many biased sites that try to fool people into thinking they are providing good data. Often, the data are favourable to the products they are trying to sell. Beware of product reviews as well. Unscrupulous sellers sometimes get online and create bogus ratings for products. See below for questions you can ask to help gauge the credibility of secondary information.
Gauging the Credibility of Secondary Data: Questions to Ask
- Who gathered this information?
- For what purpose?
- What does the person or organization that gathered the information have to gain by doing so?
- Was the information gathered and reported in a systematic manner?
- Is the source of the information accepted as an authority by other experts in the field?
- Does the article provide objective evidence to support the position presented?
Types of Research Designs
Now let’s look at the most common type of research design: exploratory.
An exploratory research design is useful when you are initially investigating a problem but you haven’t defined it well enough to do an in-depth study of it. Perhaps via your regular market intelligence, you have spotted what appears to be a new opportunity in the marketplace. You would then do exploratory research to investigate it further. Exploratory research is less structured than other types of research, and secondary data are often utilized.
One form of exploratory research is qualitative research. Qualitative research is any form of research that includes gathering data that are not quantitative, and it often involves exploring questions such as why as much as what or how much . Different forms, such as in-depth interviews and focus group interviews, are common in marketing research.
Interviews —engaging in detailed, one-on-one, question-and-answer sessions with potential buyers—is an exploratory research technique. However, unlike surveys, the people being interviewed aren’t asked a series of standard questions. Instead, the interviewer is armed with some general topics and asks questions that are open ended, meaning that they allow the interviewee to elaborate. “How did you feel about the product after you purchased it?” is an example of a question that might be asked. An interview also allows a researcher to ask logical follow-up questions such as “Can you tell me what you mean when you say you felt uncomfortable using the service?” or “Can you give me some examples?” to help dig further and shed additional light on the research problem. Interviews can be conducted in person or over the phone. The interviewer either takes notes or records the interview.
Focus groups and case studies are often utilized for exploratory research as well. A focus group is a group of potential buyers who are brought together to discuss a marketing research topic with one another. A moderator is used to focus the discussion, the sessions are recorded, and the main points of consensus are later summarized by the market researcher. Textbook publishers often gather groups of professors at educational conferences to participate in focus groups. However, focus groups can also be conducted on the telephone or online using meeting software like Zoom. The basic steps of conducting a focus group are outlined below.
The Basic Steps of Conducting a Focus Group
- Establish the objectives of the focus group. What is its purpose?
- Identify the people who will participate in the focus group. What makes them qualified to participate? How many of them will you need and what they will be paid?
- Obtain contact information for the participants and send out invitations (e-mails are usually most efficient).
- Develop a list of questions.
- Choose a facilitator.
- Choose a location in which to hold the focus group and the method by which it will be recorded.
- Conduct the focus group. If the focus group is not conducted electronically, include name tags for the participants, pens and notepads, any materials the participants need to see, and refreshments. Record participants’ responses.
- Summarize the notes from the focus group and write a report for management.
A case study looks at how another company solved the problem that’s being researched. Sometimes, multiple cases, or companies, are used in a study. Case studies nonetheless have a mixed reputation. Some researchers believe it’s hard to generalize, or apply, the results of a case study to other companies. Nonetheless, collecting information about companies that encountered the same problems your firm is facing can give you a certain amount of insight about what direction you should take. In fact, one way to begin a research project is to carefully study a successful product or service.
Two other types of qualitative data used for exploratory research are ethnographies and projective techniques. In ethnography , researchers interview, observe, and often videotape people while they work, live, shop, and play. The Walt Disney Company has recently begun using ethnographers to uncover the likes and dislikes of boys aged six to fourteen, a financially attractive market segment for Disney, but one in which the company has been losing market share. The ethnographers visit the homes of boys, observe the things they have in their rooms to get a sense of their hobbies, and accompany them and their mothers when they shop to see where they go, what the boys are interested in, and what they ultimately buy (Barnes, 2009). [4]
Projective techniques are used to reveal information research respondents might not reveal by being asked directly. Asking a person to complete sentences such as the following is one technique:
People who buy Gucci handbags __________. (Will he or she reply with “are cool,” “are affluent,” or “are pretentious,” for example?)
KFC’s grilled chicken is ______.
Or the person might be asked to finish a story that presents a certain scenario. Word associations are also used to discern people’s underlying attitudes toward goods and services. When using a word-association technique, a market researcher asks a person to say or write the first word that comes to his or her mind in response to another word. If the initial word is “fast food,” what word does the person associate it with or respond with? Is it “McDonald’s”? If many people reply that way, and you’re conducting research for Burger King, that could indicate Burger King has a problem. However, if the research is being conducted for Wendy’s, which recently began running an advertising campaign with the message that Wendy’s offerings are “better than fast food,” it could indicate that the campaign is working.
In some cases, your research might end with exploratory research. Perhaps you have discovered your organization lacks the resources needed to produce the product. In other cases, you might decide you need more in-depth, quantitative research such as descriptive research or causal research, which are discussed next. Most marketing research professionals suggest using both types of research, if it’s feasible. On the one hand, the qualitative type of research used in exploratory research is often considered too “lightweight.” On the other hand, relying solely on quantitative information often results in market research that lacks ideas.
Watch video 6.3 to see a funny spoof on the usefulness—or lack of usefulness—of focus groups.
Video 6.3. The Stone Wheel: What One Focus Group Said. Source: stone and stone wheel on smack1313 .
Step 3: Design the Data-Collection Forms
If the behaviour of buyers is being formally observed and a number of different researchers are conducting observations, the data obviously need to be recorded on a standardized data-collection form that’s either paper or electronic; otherwise, the data collected will not be comparable. The items on the form could include a shopper’s sex; his or her approximate age; whether the person seemed hurried, moderately hurried, or unhurried; and whether or not he or she read the label on products, used coupons, and so forth.
The same is true when it comes to surveying people with questionnaires. Surveying people is one of the most commonly used techniques to collect quantitative data. Surveys are popular because they can be easily administered to large numbers of people fairly quickly. However, to produce the best results, the questionnaire for the survey needs to be carefully designed.
Questionnaire Design
Most questionnaires follow a similar format: They begin with an introduction describing what the study is for, followed by instructions for completing the questionnaire and, if necessary, returning it to the market researcher. The first few questions that appear on the questionnaire are usually basic, warm-up questions their respondent can readily answer, such as the respondent’s age, level of education, place of residence, and so forth. The warm-up questions are then followed by a logical progression of more detailed, in-depth questions that get to the heart of the question being researched. Lastly, the questionnaire wraps up with a statement that thanks the respondent for participating in the survey and providing information and explains when and how they will be paid for participating.
How the questions themselves are worded is extremely important. It’s human nature for respondents to want to provide the “correct” answers to the person administering the survey so as to seem agreeable. Therefore, there is always a hazard that people will try to tell you what you want to hear on a survey. Consequently, care needs to be taken that the survey questions are written in an unbiased, neutral way. In other words, they shouldn’t lead a person taking the questionnaire to answer a question one way or another by virtue of the way you have worded it. The following is an example of a leading question.
Do you agree that teachers should be paid more ?
The questions also need to be clear and unambiguous. Consider the following question:
Which brand of toothpaste do you use ?
The question sounds clear enough, but is it really? What if the respondent recently switched brands? What if she uses Crest at home, but while away from home or travelling she uses Colgate’s Wisp portable toothpaste-and-brush product? How will the respondent answer the question? Rewording the question as follows so it’s more specific will help make the question clearer:
Which brand of toothpaste have you used at home in the past six months? If you have used more than one brand, please list each of them (“Questionnaire Design,” n.d.). [5]
Sensitive questions have to be asked carefully. For example, asking a respondent, “Do you consider yourself a light, moderate, or heavy drinker?” can be tricky. Few people want to admit to being heavy drinkers. You can “soften” the question by including a range of answers, as the following example shows:
How many alcoholic beverages do you consume in a week ?
- __0–5 alcoholic beverages
- __5–10 alcoholic beverages
- __10–15 alcoholic beverages
Many people don’t like to answer questions about their income levels. Asking them to specify income ranges rather than divulge their actual incomes can help.
Other research question “don’ts” include using jargon and acronyms that could confuse people. “How often do you Snap?” is an example. Also, don’t confuse people by asking two questions in the same question, something researchers refer to as a double-barrelled question . “Do you think parents should spend more time with their children and/or their teachers?” is an example of a double-barrelled question.
Open-ended questions , or questions that ask respondents to elaborate, can be included. However, they are harder to tabulate than closed-ended questions , or questions that limit a respondent’s answers. Multiple-choice, true/false and yes/no questions are examples of closed-ended questions.
Testing the Questionnaire
If the questions are bad, the information gathered will also be bad. One way to avoid this is to test the questionnaire before sending it out to find out if there are any problems with it. Is there enough space for people to elaborate on open-ended questions? Is the font readable? To test the questionnaire, marketing research professionals first administer it to a number of respondents face to face. This gives the respondents the chance to ask the researcher about questions or instructions that are unclear or don’t make sense to them. The researcher then administers the questionnaire to a small subset of respondents in the actual way the survey is going to be disseminated, whether it’s delivered via phone, in person, by mail, or online.
Getting people to participate and complete questionnaires can be difficult. If the questionnaire is too long or hard to read, many people won’t complete it. So, by all means, eliminate any questions that aren’t necessary. Of course, including some sort of monetary incentive for completing the survey can increase the number of completed questionnaires a market researcher will receive.
Step 4: Specify the Sample
Once you have created your questionnaire or other marketing study, how do you figure out who should participate in it? Obviously, you can’t survey or observe all potential buyers in the marketplace; instead, you must choose a sample. A sample is a subset of potential buyers that are representative of your entire target market or population being studied. Sometimes market researchers refer to the population as the universe to reflect the fact that it includes the entire target market, whether it consists of a million people, a hundred thousand, a few hundred, or a dozen. “All single people over the age of eighteen who purchased an air fryer in Canada during 2020” is an example of a population that has been defined.
Obviously, the population has to be defined correctly. Otherwise, you will be studying the wrong group of people. Not defining the population correctly can result in flawed research or a sampling error. A sampling error is any type of marketing research mistake that occurs because a sample was utilized. One criticism of Internet surveys is that the people who take these surveys don’t really represent the overall population. On average, Internet survey takers tend to be more educated and tech savvy. Consequently, if they solely constitute your population, even if you screen them for certain criteria, the data you collect could end up being skewed.
There are two main categories of samples in terms of how they are drawn: probability samples and nonprobability samples. A probability sample is one in which each would-be participant has a known and equal chance of being selected. The chance is known because the total number of people in the sampling frame is known. For example, if every other person from the sampling frame were chosen, each person would have a 50 percent chance of being selected.
A nonprobability sample is any type of sample that’s not drawn in a systematic way, so the chances of each would-be participant being selected can’t be known. A convenience sample is one type of nonprobability sample. It is a sample a researcher draws because it’s readily available and convenient to do so. Surveying people on the street as they pass by is an example of a convenience sample. The question is, are these people representative of the target market?
Lastly, the size of the sample has an effect on sampling error. Larger samples generally produce more accurate results. The larger your sample is, the more data you will have, which will give you a more complete picture of what you’re studying. However, the more people surveyed or studied, the more costly the research becomes.
Statistics can be used to determine a sample’s optimal size. If you take a marketing research or statistics class, you will learn more about how to determine the optimal size.
Of course, if you hire a marketing research company, much of this work will be taken care of for you. Many marketing research companies maintain panels of prescreened people they draw upon for samples. In addition, the marketing research firm will be responsible for collecting the data or contracting with a company that specializes in data collection. Data collection is discussed next.
Step 5: Collect the Data
As we have explained, primary marketing research data can be gathered in a number of ways. Surveys, taking physical measurements, and observing people are just three of the ways we discussed. If you’re observing customers as part of gathering the data, keep in mind that if shoppers are aware of the fact, it can have an effect on their behaviour. For example, if a customer shopping for feminine hygiene products in a supermarket aisle realizes she is being watched, she could become embarrassed and leave the aisle, which would adversely affect your data. To get around problems such as these, some companies set up cameras or two-way mirrors to observe customers. Organizations also hire mystery shoppers to work around the problem. A mystery shopper is someone who is paid to shop at a firm’s establishment or one of its competitors to observe the level of service, cleanliness of the facility, and so forth and report his or her findings to the firm.
Watch the YouTube video 6.4 to get an idea of how mystery shopping works.
Video 6.4. Make Extra Money as a Mystery Shopper by KSSAyisha .
Survey data can be collected in many different ways and combinations of ways. The following are the basic methods used:
- Face-to-face (can be computer aided)
- Telephone (can be computer aided or completely automated)
- Mail and hand delivery
- E-mail and the Web
A face-to-face survey is, of course, administered by a person. The surveys are conducted in public places such as in shopping malls, on the street, or in people’s homes if they have agreed to it. In years past, it was common for researchers to knock on people’s doors to gather survey data. However, randomly collected door-to-door interviews are less common today, partly because people are afraid of crime and are reluctant to give information to strangers (McDaniel & Gates, 1998). [6]
Nonetheless, knocking on doors is still a legitimate way questionnaire data are collected. When Statistics Canada collects data on the nation’s population, it hand delivers questionnaires to rural households that do not have street-name and house-number addresses. And workers personally survey the homeless to collect information about their numbers. Face-to-face surveys are also commonly used in some countries to collect information from people who cannot read or lack phones and computers.
An advantage of face-to-face surveys is that they allow researchers to ask lengthier, more complex questions because the people being surveyed can see and read the questionnaires. The same is true when a computer is utilized. For example, the researcher might ask the respondent to look at a list of ten retail stores and rank the stores from best to worst. The same question wouldn’t work so well over the telephone because the person couldn’t see the list. The question would have to be rewritten. Another drawback with telephone surveys is that even though federal and state “do not call” laws generally don’t prohibit companies from gathering survey information over the phone, people often screen such calls using answering machines and caller ID.
Probably the biggest drawback of both surveys conducted face-to-face and administered over the phone by a person is that they are labour intensive and therefore costly. Mailing out questionnaires is costly, too, and the response rates can be rather low. Think about why that might be so: if you receive a questionnaire in the mail, it is easy to throw it in the trash; it’s harder to tell a market researcher who approaches you on the street that you don’t want to be interviewed.
By contrast, gathering survey data collected by a computer, either over the telephone or on the Internet, can be cost-effective and in some cases free. SurveyMonkey and Qualtrics are two websites that will allow you to create online questionnaires, e-mail them to up to one hundred people for free, and view the responses in real time as they come in. For larger surveys, you have to pay a subscription price of a few hundred dollars. But that still can be extremely cost-effective. See how easy it is to put together a survey in SurveyMonkey .
Like a face-to-face survey, an Internet survey can enable you to show buyers different visuals such as ads, pictures, and videos of products and their packaging. Web surveys are also fast, which is a major plus. While face-to-face and mailed surveys often take weeks to collect, you can conduct a web survey in a matter of days or even hours. And, of course, because the information is electronically gathered it can be automatically tabulated. You can also potentially reach a broader geographic group than you could if you had to personally interview people.
Another plus for web and computer surveys (and electronic phone surveys) is that there is less room for human error because the surveys are administered electronically. For instance, there’s no risk that the interviewer will ask a question wrong or use a tone of voice that could mislead the respondents. Respondents are also likely to feel more comfortable inputting the information into a computer if a question is sensitive than they would divulging the information to another person face to face or over the phone. Given all of these advantages, it’s not surprising that the Internet is quickly becoming the top way to collect primary data. However, like mail surveys, surveys sent to people over the Internet are easy to ignore.
Lastly, before the data collection process begins, the surveyors and observers need to be trained to look for the same things, ask questions the same way, and so forth. If they are using rankings or rating scales, they need to agree as to what constitutes a high ranking or a low ranking. The goal of training is to avoid a wide disparity between how different observers and interviewers record the data.
For example, if an observation form asks the observers to describe whether a shopper’s behaviour is hurried, moderately hurried, or unhurried, they should be given an idea of what defines each rating. Does it depend on how much time the person spends in the store or in the individual aisles? Is how fast they walk taken into account? In other words, the criteria and ratings need to be spelled out.
Step 6: Analyze the Data
Step 6 involves analyzing the data to ensure they’re as accurate as possible. If the research is collected by hand using a pen and pencil, it’s entered into a computer. Or respondents might have already entered the information directly into a computer. For example, when Toyota goes to an event such as a car show, the automaker’s marketing personnel ask would-be buyers to complete questionnaires directly on computers. Companies are also beginning to experiment with software that can be used to collect data using mobile phones.
The information generated by the programs can be used to draw conclusions, such as what all customers might like or not like about an offering based on what the sample group liked or did not like. The information can also be used to spot differences among groups of people. For example, the research might show that people in one area of the country like the product better than people in another area. Trends to predict what might happen in the future can also be spotted.
If there are any open-ended questions respondents have elaborated upon—for example, “Explain why you like the current brand you use better than any other brand”—the answers to each are pasted together, one on top of another, so researchers can compare and summarize the information. As we have explained, qualitative information such as this can give you a fuller picture of the results of the research.
Part of analyzing the data is to see if they seem sound. Does the way in which the research was conducted seem sound? Was the sample size large enough? Are the conclusions reached from it reasonable?
Step 7: Write the Research Report and Present Its Findings
If you end up becoming a marketing professional and conducting a research study after you graduate, hopefully you will do a great job putting the study together. You will have defined the problem correctly, chosen the right sample, collected the data accurately, analyzed them, and your findings will be sound. At that point, you will be required to write the research report and perhaps present it to an audience of decision makers. You will do so via a written report and, in some cases, a slide or PowerPoint presentation based on your written report.
The six basic elements of a research report are as follows.
- Title Page . The title page explains what the report is about, when it was conducted and by whom, and who requested it.
- Table of Contents . The table of contents outlines the major parts of the report as well as any graphs and charts and their page numbers.
- Executive Summary . The executive summary summarizes all the details in the report in a quick way. Many people who receive the report—both executives and nonexecutives—won’t have time to read the entire report. Instead, they will rely on the executive summary to quickly get an idea of the study’s results and what to do about those results.
- Methodology and Limitations . The methodology section of the report explains the technical details of how the research was designed and conducted. The section explains, for example, how the data were collected and by whom, the size of the sample, how it was chosen, and whom or what it consisted of (e.g., the number of women versus men or children versus adults). It also includes information about the statistical techniques used to analyze the data. Every study has errors—sampling errors, interviewer errors, and so forth. The methodology section should explain these details so decision makers can consider their overall impact. The margin of error is the overall tendency of the study to be off kilter—that is, how far it could have gone wrong in either direction. Remember how newscasters present the presidential polls before an election? They always say, “This candidate is ahead 48 to 44 percent, plus or minus 2 percent.” That “plus or minus” is the margin of error. The larger the margin of error is, the less likely the results of the study are accurate. The margin of error needs to be included in the methodology section.
- Findings . The findings section is a longer, fleshed-out version of the executive summary that goes into more detail about the statistics uncovered by the research that bolster the study’s findings. If you have related research or secondary data on hand that back up the findings, they can be included to help show the study did what it was designed to do.
- Recommendations . The recommendations section should outline the course of action you think should be taken based on the findings of the research and the purpose of the project. For example, if you conducted a global market research study to identify new locations for stores, make a recommendation for the locations (Mersdorf, 2009). [7]
As we have said, these are the basic sections of a marketing research report. However, additional sections can be added as needed. For example, you might need to add a section on the competition and each firm’s market share. If you’re trying to decide on different supply chain options, you will need to include a section on that topic.
As you write the research report, keep your audience in mind. Don’t use technical jargon decision makers and other people reading the report won’t understand. If technical terms must be used, explain them. Also, proofread the document to identify any grammatical errors and typos and ask a couple of other people to proofread it to catch any mistakes you might have missed. If your research report is riddled with errors, its credibility will be undermined, even if the findings and recommendations you make are extremely accurate.
Many research reports are presented via PowerPoint. If you’re asked to create a slideshow presentation from the report, don’t try to include every detail in the report on the slides. The information will be too long and tedious for people attending the presentation to read through. And if they do go to the trouble of reading all the information, they probably won’t be listening to the speaker who is making the presentation.
Instead of including all the information from the study in the slides, boil each section of the report down to key points and add some “talking points” only the presenter will see. After or during the presentation, you can give the attendees the longer, paper version of the report so they can read the details at a convenient time.
Key Takeaways
- Step 1 in the marketing research process is to define the problem. Businesses look at what they believe are symptoms and drill down to the potential causes so as to precisely define the problem. The next task for the researcher is to put into writing the research objective, or goal, the research is supposed to accomplish.
- Step 2 in the process is to design the research. The research design is the “plan of attack.” It outlines what data you are going to gather, from whom, how, and when, and how you’re going to analyze it once it has been obtained.
- Step 3 is to design the data-collection forms, which need to be standardized so the information gathered on each is comparable. Surveys are a popular way to gather data because they can be quickly and easily administered to large numbers of people. However, to produce the best results, survey questionnaires need to be carefully designed and pretested before they are used.
- Step 4 is drawing the sample, or a subset of potential buyers who are representative of your entire target market. If the sample is not correctly selected, the research will be flawed.
- Step 5 is to actually collect the data, whether they’re collected by a person face to face, over the phone, or with the help of computers or the Internet. The data-collection process is often different in foreign countries.
- Step 6 is to analyze the data collected for any obvious errors, tabulate the data, and then draw conclusions from them based on the results. The last step in the process,
- Step 7 is writing the research report and presenting the findings to decision makers.
Review and Reflect
- Explain why it’s important to carefully define the problem or opportunity a marketing research study is designed to investigate.
- Describe the different types of problems that can occur when marketing research professionals develop questions for surveys.
- What sections should be included in a marketing research report? What is each section designed to do?
Media Attributions
- Steps in the Marketing Research Process © University of Minnesota Libraries Publishing is licensed under a CC BY-NC-SA (Attribution NonCommercial ShareAlike) license
- Burns, A., & Bush, R. (2010). Marketing research (6th ed.). Prentice Hall. ↵
- Rappeport, A., & Gelles, D. (2009, September 23). Facebook to form alliance with Nielsen. Financial Times, 16 . ↵
- Barnes, B. (2009, April 15). Disney expert uses science to draw boy viewers . New York Times . Accessed December 14, 2009. ↵
- Questionnaire design . (n.d.). QuickMBA. Accessed December 14, 2009. ↵
- McDaniel, C. D., & Gates, R. H. (1998). Marketing research essentials (2nd ed.). South-Western College Publishing. ↵
- Mersdorf, S. (2009, August 24). How to organize your next survey report . Cvent. Accessed July 31, 2023). ↵
the goal(s) the research is supposed to accomplish
what data you are going to gather and from whom, how and when you will collect the data, and how you will analyze them once they’ve been obtained
information you collect yourself, using hands-on tools such as interviews or surveys, specifically for the research project you’re conducting
data that have already been collected by someone else, or data you have already collected for another purpose
primary data that marketing research firms collect on a regular basis and sell to other companies
information collected by scanners at checkout stands in stores
a marketing research company that buys research reports from other marketing research companies and then sells the reports in their entirety or in pieces to other firms
when you are initially investigating a problem but you haven’t defined it well enough to do an in-depth study of it
any form of research that includes gathering data that are not quantitative, and it often involves exploring questions such as why as much as what or how much
engaging in detailed, one-on-one, question-and-answer sessions with potential buyers
a group of potential buyers who are brought together to discuss a marketing research topic with one another
analyzes how another company solved the problem that’s being researched
researchers interview, observe, and often videotape people while they work, live, shop, and play
used to reveal information research respondents might not reveal by being asked directly
asking two questions in the same question
questions that ask respondents to elaborate
questions that limit a respondent’s answers
a subset of potential buyers that are representative of your entire target market
from which you derive your target market
any type of marketing research mistake that occurs because a sample was utilized
each would-be participant has a known and equal chance of being selected
any type of sample that’s not drawn in a systematic way
a sample a researcher draws because it’s readily available and convenient to do so
someone who is paid to shop at a firm’s establishment or one of its competitors to observe the level of service, cleanliness of the facility, and so forth and report his or her findings to the firm
the overall tendency of the study to be off kilter
Introduction to Marketing Copyright © 2024 by Pamela Ip is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
The Ultimate Guide to Market Research: Types, Benefits, and Real-World Examples
Team Fratzke

Today's consumers hold a lot of power when making purchase decisions. With a quick inquiry in a search engine or search bar within a social media platform, they can access genuine reviews from their peers without relying on sales reps.
Considering this shift in consumer behavior, adjusting your marketing strategy so it caters to the modern-day buying process is essential . To achieve this, you must thoroughly understand your target audience, the market you operate in, and the factors influencing their decision-making.
This is where market research can be leveraged so you stay current with your audience and industry.
Article Overview
In this article, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about how to conduct market research, including:
- Why market research is essential for understanding your target audience, the market you operate in, and factors influencing decision-making
- What are the different types of market research, such as primary and secondary market research
- How to collect information about your customers and target market to determine the success of a new or existing product, improve your brand, and communicate your company's value
- Real-world examples of companies leveraging market research

What is market research?
Market research is a necessary process that involves collecting and documenting information about your target market and customers. This helps you determine the success of a new product, improve an existing one, or understand how your brand is perceived. You can then turn this research into profits by developing marketing strategies and campaigns to effectively communicate your company's value .
While market research can provide insights into various aspects of an industry, it is not a crystal ball that can predict everything about your customers. Market researchers typically explore multiple areas of the market, which can take several weeks or even months to get a complete picture of the business landscape.
Even by researching just one of those areas, you can gain better insights into who your buyers are and what unique value proposition you can offer them that no other business currently provides.
Of course, you can simply use your industry experience and existing customer insights to make sound judgment calls. However, it's important to note that market research provides additional benefits beyond these strategies. There are two things to consider:
- Your competitors also have experienced individuals in the industry and a customer base. Your immediate resources may equal those of your competition's immediate resources. Seeking a larger sample size for answers can provide a better edge.
- Your brand's customers do not represent the entire market's attitudes, only those who are attracted to your brand.
The market research services industry is experiencing rapid growth , indicating a strong interest in market research as we enter 2024. The market is expected to grow from approximately $75 billion in 2021 to $90.79 billion in 2025, with a compound annual growth rate of 5%.
Your competitors have highly skilled individuals within the industry, meaning your available personnel resources are likely similar to those of your competitors. So what are you going to do to get ahead?
You’re going to do thorough market research, which is why seeking answers from a larger sample size is essential. Remember that your customers represent only a portion of the market already attracted to your brand, and their attitudes may not necessarily reflect those of the entire market. You could be leaving money on the table by leaving out untapped customers .
Why do market research?
Market research helps you meet your buyers where they are. Understanding your buyer's problems, pain points, and desired outcomes is invaluable as our world becomes increasingly noisy and demanding. This knowledge will help you tailor your product or service to appeal to them naturally.
What’s even better is when you're ready to grow your business, market research can also guide you in developing an effective market expansion strategy.
Market research provides valuable insights into factors that impact your profits and can help you to :

- Identify where your target audience and current customers are conducting their product or service research
- Determine which competitors your target audience looks to for information, options, or purchases
- Keep up with the latest trends in your industry and understand what your buyers are interested in
- Understand who makes up your market and what challenges they are facing
- Determine what influences purchases and conversions among your target audience
- Analyze consumer attitudes about a particular topic, pain, product, or brand
- Assess the demand for the business initiatives you're investing in
- Identify unaddressed or underserved customer needs that can be turned into selling opportunities
- Understand consumer attitudes about pricing for your product or service.
Market research provides valuable information from a larger sample size of your target audience, enabling you to obtain accurate consumer attitudes. By eliminating any bias or assumptions you have about your target audience, you can make better business decisions based on the bigger picture.
As you delve deeper into your market research, you will come across two types of research: primary and secondary market research . Simply put, think of two umbrellas beneath market research - one for primary and one for secondary research. In the next section, we will discuss the difference between these two types of research. That way, if you work with a market who wants to use them, you’ll be ready with an understanding of how they can each benefit your business.
Primary vs. Secondary Research
Both primary and secondary research are conducted to collect actionable information on your product. That information can then be divided into two types: qualitative and quantitative research. Qualitative research focuses on public opinion and aims to determine how the market feels about the products currently available. On the other hand, quantitative research seeks to identify relevant trends in the data gathered from public records.
Let's take a closer look at these two types.

Primary Research
Primary research involves gathering first-hand information about your market and its customers. It can be leveraged to segment your market and create focused buyer personas . Generally, primary market research can be categorized into exploratory and specific studies.
Exploratory Primary Research
This type of primary market research is not focused on measuring customer trends; instead, it is focused on identifying potential problems worth addressing as a team. It is usually conducted as an initial step before any specific research is done and may involve conducting open-ended interviews or surveys with a small group of people.
Specific Primary Research
After conducting exploratory research, businesses may conduct specific primary research to explore issues or opportunities they have identified as necessary. Specific research involves targeting a smaller or more precise audience segment and asking questions aimed at solving a suspected problem. Specific primary research reveals problems that are unique to your audience so you can then offer a unique (and valuable) solution.
Secondary Research
Secondary research refers to collecting and analyzing data that has already been published or made available in public records. This may include market statistics, trend reports, sales data, and industry content you already can access. Secondary research really shines when you go to your competitors . The most commonly used sources of secondary market research include:
- Public sources
- Commercial sources
- Internal sources
Public Sources
When conducting secondary market research, the first and most accessible sources of information are usually free . That’s right–these public sources are free and at your fingertips so there’s no reason for you to not be checking them out and leveraging them for your own gain.
One of the most common types of public sources is government statistics. According to Entrepreneur, two examples of public market data in the United States are the U.S. Census Bureau and the Bureau of Labor & Statistics. These sources offer helpful information about the state of various industries nationwide including:
Commercial Sources
Research agencies such as Pew, Fratzke, Gartner, or Forrester often provide market reports containing industry insights from their own in-depth studies . These reports usually come at a cost if you want to download and obtain the information, but these agencies are experts at what they do, so the research is most likely valuable.
Internal Sources
Internal sources of market data can include average revenue per sale, customer retention rates, and other data on the health of old and new accounts. They are often overlooked when it comes to conducting market research because of how specific the data is; however, these sources can be valuable as they provide information on the organization's historical data.
By analyzing this information, you can gain insights into what your customers want now . In addition to these broad categories, there are various ways to conduct market research. Let’s talk about them.
Types of Market Research
- Interviews (in-person or remote)
Focus Groups
- Product/ Service Use Research
Observation-Based Research
Buyer persona research, market segmentation research, pricing research.
- Competitive Analysis Research
Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty Research
Brand awareness research, campaign research.

Interviews can be conducted face-to-face or virtually, allowing for a natural conversation flow while observing the interviewee's body language. By asking questions about themselves, the interviewee can help you create buyer personas , which are made by using information about the ideal customer, such as:
- Family size
- Challenges faced at work or in life
And other aspects of their lifestyle. This buyer profile can shape your entire marketing strategy , from the features you add to your product to the content you publish on your website. Your target audience will feel that the marketing was made just for them and will be drawn to your product or service.
Focus groups are market research involving a few carefully selected individuals who can test your product, watch a demonstration, offer feedback, and answer specific questions. This research can inspire ideas for product differentiation or highlight the unique features of your product or brand that set it apart from others in the market. This is a great market research option to gain specific feedback, which you can use to improve your services .
Product/Service Use Research
Product or service usage research provides valuable insights into how and why your target audience uses your product or service. This research can help in various ways including:
- Identifying specific features of your offering that appeal to your audience.
- Allowing you to assess the usability of your product or service for your target audience.
According to a report published in 2020, usability testing was rated the most effective method for discovering user insights, with a score of 8.7 out of 10. In comparison, digital analytics scored 7.7, and user surveys scored 6.4.
Observation-based research is a process that involves observing how your target audience members use your product or service. The way that you intended your product or service to be used may not be the actual way that it is used. Observation-based research helps you understand what works well in terms of customer experience (CX) and user experience (UX), what problems they face, and which aspects of your product or service can be improved to make it easier for them to use.
To better understand how your potential customers make purchasing decisions in your industry, it is essential to know who they are. This is where buyer persona research comes in handy. Buyer or marketing personas are fictional yet generalized representations of your ideal customers. They give you someone to whom you want your marketing efforts to empathize and move, even though they don’t really exist.
Gathering survey data and additional research to correctly identify your buyer personas will help you to visualize your audience so you can streamline your communications and inform marketing strategy . Key characteristics to include in a buyer persona are:
- Job title(s)
- Family size
- Major challenges

Market segmentation research enables you to classify your target audience into various groups or segments based on specific and defining characteristics. This method allows you to understand their needs, pain points, expectations, and goals more effectively.
Pricing research can provide valuable insights about the prices of similar products or services in your market. It can help you understand what your target audience expects to pay for your offerings and what would be a reasonable price for you to set. Correct pricing is important because if you set it too high, consumers will go to your cheaper competitor; but if you set it too low, your consumers may become suspicious of your product or service and still end up with your competitor. This information allows you to develop a solid pricing strategy aligning with your business goals and objectives.
Competitive Analysis
Competitive analyses are incredibly valuable as they provide a deep understanding of your market and industry competition. Through these analyses, you can gain insights like:
- What works well in your industry
- What your target audience is already interested in regarding products like yours
- Which competitors you should work to keep up with and surpass
- How you can differentiate yourself from the competition
Understanding customer satisfaction and loyalty is crucial to encouraging repeat business and identifying what drives customers to return (such as loyalty programs, rewards, and exceptional customer service). Researching this area will help you determine the most effective methods to keep your customers coming back again and again. If you have a CRM system, consider further utilizing automated customer feedback surveys to improve your understanding of their needs and preferences.
Brand awareness research helps you understand the level of familiarity your target audience has with your brand. It provides insights into your audience members' perceptions and associations when they think about your business.This type of research reveals what they believe your brand represents. This information is valuable for developing effective marketing strategies, improving your brand's reputation, and increasing customer loyalty .
To improve your marketing campaigns, you need to research by analyzing the success of your past campaigns among your target audience and current customers. This requires experimentation and thoroughly examining the elements that resonate with your audience. By doing so, you can identify the aspects of your campaigns that matter most to your audience and use them as a guide for future campaigns.
Now that you understand the different market research categories and types let's look at how to conduct your market research. Using our expertise and experience, we’ve created a step-by-step guide to conducting market research.
How to Do Market Research (Detailed Roadmap)
- Define the problem or objective of the research.
- Determine the type of data needed.
- Identify the sources of data.
- Collect the data.
- Analyze the data.
- Interpret the results.
- Report the findings.
- Take action based on the findings.

1. Define the problem or objective of the research
Defining the problem or objective of the research is the first step in conducting market research. This involves identifying the specific issue that the research is trying to address. It is essential to be clear and specific about the research problem or objective, as it will guide the entire research process.
2. Determine the type of data needed
After defining the research problem or objective, the next step is determining the data type needed to address the issue. This involves deciding whether to collect primary or secondary data. Primary data is collected directly from the source, while secondary data is collected from existing sources such as government reports or market research studies.
3. Identify the sources of data
Once the data type has been determined, the next step is identifying the data sources. This involves identifying potential sources of primary and secondary data that can be used to address the research problem or objective. Primary data sources can include surveys, focus groups, and interviews, while secondary data sources can include government reports, industry publications, and academic journals.
4. Collect the data
After identifying the data sources, the next step is to collect the data. This involves designing and implementing a data collection plan consistent with the research problem or objective. The data collection plan should specify the methods and procedures for collecting data, sample size, and sampling method.
5. Analyze the data
Once the data has been collected, the next step is to analyze the data. This involves organizing, summarizing, and interpreting the data to identify patterns, relationships, and trends. The research problem or objective should guide the data analysis process and be conducted using appropriate statistical methods and software.
6. Interpret the results
After analyzing the data, the next step is to interpret the results. This involves drawing conclusions from the data analysis and using the results to address the research problem or objective. It is essential to analyze the results objectively and to avoid making assumptions or drawing conclusions that are not supported by the data.
7. Report the findings
Try identifying common themes to create a story and action items.To make the process easier, use your favorite presentation software to create a report, as it will make it easy to add quotes, diagrams, or call clips.
Feel free to add your flair, but the following outline should help you craft a clear summary:
- Background: What are your goals, and why did you conduct this study?
- Participants: Who you talked to? A table works well to break groups down by persona and customer/prospect.
- Executive Summary: What were the most exciting things you learned? What do you plan to do about it?
- Key Findings: Identify the key findings using data visualizations and emphasize key points.
- Recommendations + Action Plan: Your analysis will uncover actionable insights to fuel strategies and campaigns you can run to get your brand in front of buyers earlier and more effectively. Provide your list of priorities, action items , a timeline, and its impact on your business.
8. Take action based on the findings
The final step in conducting market research is to take action based on the findings. This involves using the results to make informed decisions about the marketing strategy, product development, or other business decisions. It is important to use the findings to drive action and to monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of the action taken continuously.
How to Prepare for Market Research Projects
Identify a persona group to engage, prepare research questions for your market research participants, list your primary competitors.
The idea is to use your persona as a reference point for understanding and reaching out to your industry's audience members. Your business might cater to more than one persona, and that's completely acceptable! However, you must be mindful of each persona while strategizing and planning your content and campaigns.
How to Identify the Right People to Engage for Market Research
When selecting a group on which to conduct market research , it is essential to consider individuals with the same characteristics as your target audience.
If you need to research multiple target audiences, recruit separate groups for each one. Select people who have recently interacted with you by looking through social media for post interactions or seeing if they’ve made recent purchases from you.
If you are planning to conduct an evaluation, it is recommended that you focus on people who have completed it within the last six months. However, if you have a longer sales cycle or a specific market, you can extend the period up to a year. It is crucial to ask detailed questions during the evaluation, so the participants' experience must be fresh.
Gather a mix of participants
If you want to expand your customer base, you’re going to want to get viewpoints of your product or service from every angle. Consider getting this mix by recruiting individuals who have already purchased your product, those who have bought a competitor's product, and those who haven't purchased anything. While targeting your existing customers may be the easiest option, gathering information from non-customers can help you gain a more balanced market perspective .
We recommend taking the following steps to select a mix of participants:
- Create a list of customers who made a recent purchase . This is usually the most accessible group to recruit. If you have a CRM system with list segmentation capabilities, run a report of deals that closed within the past six months and filter it for the characteristics you're looking for. Otherwise, work with your sales team to get them a list of appropriate accounts.
- Create a list of customers who were in an active evaluation but didn't make a purchase. You should get a mix of buyers who either purchased from a competitor or decided not to purchase. Again, you can obtain this list from your CRM or your Sales team's system to track deals.
- Use social media to call for participants. Try reaching out to people who follow you on social media but decided not to buy from you. Some may be willing to talk to you and explain why they did not purchase your product.
- Leverage your network . Spread the word that you're conducting a study to your coworkers, former colleagues, and LinkedIn connections. Even if your direct connections don't qualify, some will likely have a coworker, friend, or family member who does.
- Choose an incentive to motivate participants to spend time on your study. If you're on a tight budget , you can reward participants for free by giving them exclusive access to content.
Related Resources:
- Digital Marketing Strategy: Keep It Simple
- 5 Marketing Predictions for the Looming Recession
- Recession Proof Marketing Strategies for Your Business
- Marketing Operations Framework - The Five Ps
- Biggest Marketing Challenges Leaders Face
- Digital Marketing Benchmarks & KPIs - How To Compare Your Performance
Preparation is key when conducting research in hopes of gaining productive and informative conversations. This involves creating a discussion guide, whether it is for a focus group, an online survey, or a phone interview. The guide should help you cover all the relevant topics and manage your time efficiently.
The discussion guide should be in an outline format, with an allocated time and open-ended questions for each section. All the questions must be open-ended, as asking closed questions may lead the interviewee to respond with a simple "yes" or "no" answer. You may need more detailed answers to make informed decisions, so be sure to ask follow-up questions as necessary. Also leave out any leading questions as they may unintentionally influence the interviewee's response, skewing your research results.
It's essential to identify your competitors accurately and you may even have some hidden in plain sight. There are some instances where your company's business division might compete with your main product or service, even though that company's brand might have a different focus. Take a look at Apple: the company is known primarily for its laptops and mobile devices, but Apple Music competes with Spotify over its music streaming service.
From a content perspective, you might compete with a blog, YouTube channel, or similar publication for inbound website visitors — even though their products don't overlap with yours. An example of this is when a toothpaste company might compete with publications like Health.com or Prevention on specific blog topics related to health and hygiene, even though the magazines don't sell oral care products.
Here are a few ways to build your competitor list:
- Check your industry quadrant on G2 Crowd: This is a significant first step for secondary market research in some industries. G2 Crowd aggregates user ratings and social data to create "quadrants" that show companies as contenders, leaders, niche players, or high performers in their respective industries. G2 Crowd specializes in digital content, IT services, HR, e-commerce, and related business services.
- Download a market report: Companies like Forrester and Gartner offer free and gated market forecasts yearly on the vendors leading their industry. On Forrester's website, for example, you can select "Latest Research" from the navigation bar and browse Forrester's latest material using a variety of criteria to narrow your search. These reports are good assets to save on your computer.
- Use social media : Social networks can be excellent company directories if you use the search bar correctly. On LinkedIn, for example, select the search bar and enter the name of the industry you're pursuing. Then, under "More," select "Companies" to narrow your results to the businesses that include this or a similar industry term on their LinkedIn profile.
Identifying Content Competitors
Search engines can be beneficial when it comes to secondary market research . To identify the online publications competing with your business, start with the overarching industry term you identified earlier, and then come up with more specific industry terms that are related to your company . For example, if you run a catering business, you might consider yourself a "food service" company, as well as a vendor in "event catering," "cake catering," "baked goods," and so on.
Once you have this list, follow these steps:
- Google it: Running a search on Google for the industry terms that describe your company can be very beneficial. You may come across a mix of product developers, blogs, magazines, and other websites.
- Compare your search results against your buyer persona: Remember the persona you created during the primary research stage? You can use it to evaluate whether a publication you found through Google could steal website traffic from you. If the website's content aligns with what your buyer persona would want to see, it is a potential competitor and should be added to your list of competitors.
After a series of similar Google searches for the industry terms you identify with, look for repetition in the website domains that have come up.
When searching, examine the first two or three pages of results. These websites are considered reputable sources of content in your industry and should be monitored closely as you create your collection of videos, reports, web pages, and blog posts.

Market Research Examples
Mcdonald's focus on customer feedback and profiling.
McDonald's invests in developing a detailed consumer profile to attract and retain customers, including parents of young children who appreciate the family-friendly atmosphere and menus. The brand seeks feedback from customers through surveys and questionnaires in stores, social media, and its mobile app. It also monitors customer feedback on digital channels.
Nike's Extensive Research and Collaboration for Running Shoes Development
Nike invests heavily in creating running shoes that cater to the needs of its customers, which it determines through extensive market research and customer surveys. The brand goes to great lengths to understand its customers' preferences, such as the type of running surface, the distance they run, and their running style, to develop shoes that meet their specific needs.
In addition to customer surveys, Nike also collaborates with athletes to develop shoes that cater to their specific requirements. This research helps Nike improve its existing running shoe models and innovate new ones, ensuring that the brand stays ahead of the competition.
Disney employs focus groups that specifically cater to children to test out their new characters and ideas.
The Walt Disney Company invests millions of dollars in creating captivating stories tested for their effectiveness with children, the intended audience. Disney executives hold focus groups with preschoolers and kindergartners several times a year to gather their opinions and feedback on TV episodes, Disney characters, and more.
This market research strategy is effective because children are the ultimate audience that Disney aims to please. The collected feedback helps the company improve existing content to meet the preferences of its audience and ensure continued success as a multi-billion dollar enterprise.
KFC tested its meatless product in specific markets before launching it nationwide.
In 2019, KFC began developing and testing a meatless version of its famous chicken. However, instead of immediately launching the product nationwide, they decided to test it in select stores in the Atlanta, Georgia area.
This is an innovative and practical approach to market research, as it allows the company to determine the product's sales performance on a smaller scale before committing too many resources to it. If the meatless chicken fails to gain popularity in Georgia, KFC can make the necessary changes to the product before introducing it to the broader market.
Yamaha conducted a survey to determine whether to use knobs or sliding faders on the Montage keyboard.
Yamaha is a Japanese corporation that produces various products, from motorcycles to golf cars to musical instruments. When it began developing its new Montage keyboard, the team was unsure whether to use knobs or sliding faders on the product.
To address this dilemma, Yamaha used Qualtrics to send a survey to their customers. Within just a few hours , they received 400 responses. By using survey feedback, Yamaha ensured that it was designing a product that would perfectly meet the preferences of its audiences.
The Body Shop used social listening to determine how to reposition brand campaigns based on customer feedback.
The Body Shop is a well-known brand that offers ethically sourced and natural products. They take pride in their core value of sustainability. The Body Shop team tracked conversations to understand the sustainability subtopics that were most important to their audiences.
They found that their customers cared a lot about refills. Based on this information, the Body Shop team confidently relaunched their Refill Program across 400 stores globally in 2021, with plans to add another 400 in 2022. Market research confirmed that their refill concept was on the right track and also highlighted the need for increased efforts to demonstrate how much the Body Shop cares about its customers' values .
VideoTranscript
The takeaway.
Fratzke Consulting offers a comprehensive suite of market research services to help brands gain valuable insights into their target market, competitors, and industry trends. Our expert team utilizes various primary and secondary research methods to gather accurate and unbiased data, including surveys, competitive research, and industry reports. With Fratzke Consulting, you'll have the tools to succeed in today's rapidly evolving business landscape.
Interested in learning more? Book a free audit consultation today.
Stay in the know
Get the latest insights sent directly to your inbox.
Related Posts
Fractional CMO: What is it and Why Your Brand May Need One
Learn about fractional CMOs, their responsibilities, and why your business might benefit from hiring one. With a fractional CMO, you can get expert marketing strategy and leadership without the cost of a full-time CMO.
100 of the Best Website Designs to Inspire You in 2024 (A-Z)
100 inspiring website designs that can fuel your next web project in 2024. From visually stunning e-commerce sites to user-friendly SaaS platforms, Fratzke Consulting showcases our favorite designs.
What Is an SEO Consultant, and Do You Need One?
Discover the importance of hiring an SEO consultant for your business and the different types of SEO consultants. Learn More.
201 Harbor Blvd. Suite 203 Fullerton, CA, 92832 Phone: (714) 614-2881 Hours: Monday - Friday 8AM-6PM
Stay in the loop
© 2024 by Fratzke
Learn / Blog / Article
Back to blog
How to do market research in 4 steps: a lean approach to marketing research
From pinpointing your target audience and assessing your competitive advantage, to ongoing product development and customer satisfaction efforts, market research is a practice your business can only benefit from.
Learn how to conduct quick and effective market research using a lean approach in this article full of strategies and practical examples.

Last updated
Reading time.
A comprehensive (and successful) business strategy is not complete without some form of market research—you can’t make informed and profitable business decisions without truly understanding your customer base and the current market trends that drive your business.
In this article, you’ll learn how to conduct quick, effective market research using an approach called 'lean market research'. It’s easier than you might think, and it can be done at any stage in a product’s lifecycle.
How to conduct lean market research in 4 steps
What is market research, why is market research so valuable, advantages of lean market research, 4 common market research methods, 5 common market research questions, market research faqs.
We’ll jump right into our 4-step approach to lean market research. To show you how it’s done in the real world, each step includes a practical example from Smallpdf , a Swiss company that used lean market research to reduce their tool’s error rate by 75% and boost their Net Promoter Score® (NPS) by 1%.
Research your market the lean way...
From on-page surveys to user interviews, Hotjar has the tools to help you scope out your market and get to know your customers—without breaking the bank.
The following four steps and practical examples will give you a solid market research plan for understanding who your users are and what they want from a company like yours.
1. Create simple user personas
A user persona is a semi-fictional character based on psychographic and demographic data from people who use websites and products similar to your own. Start by defining broad user categories, then elaborate on them later to further segment your customer base and determine your ideal customer profile .
How to get the data: use on-page or emailed surveys and interviews to understand your users and what drives them to your business.
How to do it right: whatever survey or interview questions you ask, they should answer the following questions about the customer:
Who are they?
What is their main goal?
What is their main barrier to achieving this goal?
Pitfalls to avoid:
Don’t ask too many questions! Keep it to five or less, otherwise you’ll inundate them and they’ll stop answering thoughtfully.
Don’t worry too much about typical demographic questions like age or background. Instead, focus on the role these people play (as it relates to your product) and their goals.
How Smallpdf did it: Smallpdf ran an on-page survey for a couple of weeks and received 1,000 replies. They learned that many of their users were administrative assistants, students, and teachers.
Next, they used the survey results to create simple user personas like this one for admins:
Who are they? Administrative Assistants.
What is their main goal? Creating Word documents from a scanned, hard-copy document or a PDF where the source file was lost.
What is their main barrier to achieving it? Converting a scanned PDF doc to a Word file.
💡Pro tip: Smallpdf used Hotjar Surveys to run their user persona survey. Our survey tool helped them avoid the pitfalls of guesswork and find out who their users really are, in their own words.
You can design a survey and start running it in minutes with our easy-to-use drag and drop builder. Customize your survey to fit your needs, from a sleek one-question pop-up survey to a fully branded questionnaire sent via email.
We've also created 40+ free survey templates that you can start collecting data with, including a user persona survey like the one Smallpdf used.
2. Conduct observational research
Observational research involves taking notes while watching someone use your product (or a similar product).
Overt vs. covert observation
Overt observation involves asking customers if they’ll let you watch them use your product. This method is often used for user testing and it provides a great opportunity for collecting live product or customer feedback .
Covert observation means studying users ‘in the wild’ without them knowing. This method works well if you sell a type of product that people use regularly, and it offers the purest observational data because people often behave differently when they know they’re being watched.
Tips to do it right:
Record an entry in your field notes, along with a timestamp, each time an action or event occurs.
Make note of the users' workflow, capturing the ‘what,’ ‘why,’ and ‘for whom’ of each action.

Don’t record identifiable video or audio data without consent. If recording people using your product is helpful for achieving your research goal, make sure all participants are informed and agree to the terms.
Don’t forget to explain why you’d like to observe them (for overt observation). People are more likely to cooperate if you tell them you want to improve the product.
💡Pro tip: while conducting field research out in the wild can wield rewarding results, you can also conduct observational research remotely. Hotjar Recordings is a tool that lets you capture anonymized user sessions of real people interacting with your website.
Observe how customers navigate your pages and products to gain an inside look into their user behavior . This method is great for conducting exploratory research with the purpose of identifying more specific issues to investigate further, like pain points along the customer journey and opportunities for optimizing conversion .
With Hotjar Recordings you can observe real people using your site without capturing their sensitive information
How Smallpdf did it: here’s how Smallpdf observed two different user personas both covertly and overtly.
Observing students (covert): Kristina Wagner, Principle Product Manager at Smallpdf, went to cafes and libraries at two local universities and waited until she saw students doing PDF-related activities. Then she watched and took notes from a distance. One thing that struck her was the difference between how students self-reported their activities vs. how they behaved (i.e, the self-reporting bias). Students, she found, spent hours talking, listening to music, or simply staring at a blank screen rather than working. When she did find students who were working, she recorded the task they were performing and the software they were using (if she recognized it).
Observing administrative assistants (overt): Kristina sent emails to admins explaining that she’d like to observe them at work, and she asked those who agreed to try to batch their PDF work for her observation day. While watching admins work, she learned that they frequently needed to scan documents into PDF-format and then convert those PDFs into Word docs. By observing the challenges admins faced, Smallpdf knew which products to target for improvement.
“Data is really good for discovery and validation, but there is a bit in the middle where you have to go and find the human.”
3. Conduct individual interviews
Interviews are one-on-one conversations with members of your target market. They allow you to dig deep and explore their concerns, which can lead to all sorts of revelations.
Listen more, talk less. Be curious.
Act like a journalist, not a salesperson. Rather than trying to talk your company up, ask people about their lives, their needs, their frustrations, and how a product like yours could help.
Ask "why?" so you can dig deeper. Get into the specifics and learn about their past behavior.
Record the conversation. Focus on the conversation and avoid relying solely on notes by recording the interview. There are plenty of services that will transcribe recorded conversations for a good price (including Hotjar!).
Avoid asking leading questions , which reveal bias on your part and pushes respondents to answer in a certain direction (e.g. “Have you taken advantage of the amazing new features we just released?).
Don't ask loaded questions , which sneak in an assumption which, if untrue, would make it impossible to answer honestly. For example, we can’t ask you, “What did you find most useful about this article?” without asking whether you found the article useful in the first place.
Be cautious when asking opinions about the future (or predictions of future behavior). Studies suggest that people aren’t very good at predicting their future behavior. This is due to several cognitive biases, from the misguided exceptionalism bias (we’re good at guessing what others will do, but we somehow think we’re different), to the optimism bias (which makes us see things with rose-colored glasses), to the ‘illusion of control’ (which makes us forget the role of randomness in future events).
How Smallpdf did it: Kristina explored her teacher user persona by speaking with university professors at a local graduate school. She learned that the school was mostly paperless and rarely used PDFs, so for the sake of time, she moved on to the admins.
A bit of a letdown? Sure. But this story highlights an important lesson: sometimes you follow a lead and come up short, so you have to make adjustments on the fly. Lean market research is about getting solid, actionable insights quickly so you can tweak things and see what works.
💡Pro tip: to save even more time, conduct remote interviews using an online user research service like Hotjar Engage , which automates the entire interview process, from recruitment and scheduling to hosting and recording.
You can interview your own customers or connect with people from our diverse pool of 200,000+ participants from 130+ countries and 25 industries. And no need to fret about taking meticulous notes—Engage will automatically transcribe the interview for you.
4. Analyze the data (without drowning in it)
The following techniques will help you wrap your head around the market data you collect without losing yourself in it. Remember, the point of lean market research is to find quick, actionable insights.
A flow model is a diagram that tracks the flow of information within a system. By creating a simple visual representation of how users interact with your product and each other, you can better assess their needs.
You’ll notice that admins are at the center of Smallpdf’s flow model, which represents the flow of PDF-related documents throughout a school. This flow model shows the challenges that admins face as they work to satisfy their own internal and external customers.
Affinity diagram
An affinity diagram is a way of sorting large amounts of data into groups to better understand the big picture. For example, if you ask your users about their profession, you’ll notice some general themes start to form, even though the individual responses differ. Depending on your needs, you could group them by profession, or more generally by industry.
We wrote a guide about how to analyze open-ended questions to help you sort through and categorize large volumes of response data. You can also do this by hand by clipping up survey responses or interview notes and grouping them (which is what Kristina does).
“For an interview, you will have somewhere between 30 and 60 notes, and those notes are usually direct phrases. And when you literally cut them up into separate pieces of paper and group them, they should make sense by themselves.”
Pro tip: if you’re conducting an online survey with Hotjar, keep your team in the loop by sharing survey responses automatically via our Slack and Microsoft Team integrations. Reading answers as they come in lets you digest the data in pieces and can help prepare you for identifying common themes when it comes time for analysis.
Hotjar lets you easily share survey responses with your team
Customer journey map
A customer journey map is a diagram that shows the way a typical prospect becomes a paying customer. It outlines their first interaction with your brand and every step in the sales cycle, from awareness to repurchase (and hopefully advocacy).
The above customer journey map , created by our team at Hotjar, shows many ways a customer might engage with our tool. Your map will be based on your own data and business model.
📚 Read more: if you’re new to customer journey maps, we wrote this step-by-step guide to creating your first customer journey map in 2 and 1/2 days with free templates you can download and start using immediately.
Next steps: from research to results
So, how do you turn market research insights into tangible business results? Let’s look at the actions Smallpdf took after conducting their lean market research: first they implemented changes, then measured the impact.

Implement changes
Based on what Smallpdf learned about the challenges that one key user segment (admins) face when trying to convert PDFs into Word files, they improved their ‘PDF to Word’ conversion tool.
We won’t go into the details here because it involves a lot of technical jargon, but they made the entire process simpler and more straightforward for users. Plus, they made it so that their system recognized when you drop a PDF file into their ‘Word to PDF’ converter instead of the ‘PDF to Word’ converter, so users wouldn’t have to redo the task when they made that mistake.
In other words: simple market segmentation for admins showed a business need that had to be accounted for, and customers are happier overall after Smallpdf implemented an informed change to their product.
Measure results
According to the Lean UX model, product and UX changes aren’t retained unless they achieve results.
Smallpdf’s changes produced:
A 75% reduction in error rate for the ‘PDF to Word’ converter
A 1% increase in NPS
Greater confidence in the team’s marketing efforts
"With all the changes said and done, we've cut our original error rate in four, which is huge. We increased our NPS by +1%, which isn't huge, but it means that of the users who received a file, they were still slightly happier than before, even if they didn't notice that anything special happened at all.”
Subscribe to fresh and free monthly insights.
Over 50,000 people interested in UX, product, digital empathy, and beyond, receive our newsletter every month. No spam, just thoughtful perspectives from a range of experts, new approaches to remote work, and loads more valuable insights. If that floats your boat, why not become a subscriber?
I have read and accepted the message outlined here: Hotjar uses the information you provide to us to send you relevant content, updates and offers from time to time. You can unsubscribe at any time by clicking the link at the bottom of any email.
Market research (or marketing research) is any set of techniques used to gather information and better understand a company’s target market. This might include primary research on brand awareness and customer satisfaction or secondary market research on market size and competitive analysis. Businesses use this information to design better products, improve user experience, and craft a marketing strategy that attracts quality leads and improves conversion rates.
David Darmanin, one of Hotjar’s founders, launched two startups before Hotjar took off—but both companies crashed and burned. Each time, he and his team spent months trying to design an amazing new product and user experience, but they failed because they didn’t have a clear understanding of what the market demanded.
With Hotjar, they did things differently . Long story short, they conducted market research in the early stages to figure out what consumers really wanted, and the team made (and continues to make) constant improvements based on market and user research.
Without market research, it’s impossible to understand your users. Sure, you might have a general idea of who they are and what they need, but you have to dig deep if you want to win their loyalty.
Here’s why research matters:
Obsessing over your users is the only way to win. If you don’t care deeply about them, you’ll lose potential customers to someone who does.
Analytics gives you the ‘what’, while research gives you the ‘why’. Big data, user analytics , and dashboards can tell you what people do at scale, but only research can tell you what they’re thinking and why they do what they do. For example, analytics can tell you that customers leave when they reach your pricing page, but only research can explain why.
Research beats assumptions, trends, and so-called best practices. Have you ever watched your colleagues rally behind a terrible decision? Bad ideas are often the result of guesswork, emotional reasoning, death by best practices , and defaulting to the Highest Paid Person’s Opinion (HiPPO). By listening to your users and focusing on their customer experience , you’re less likely to get pulled in the wrong direction.
Research keeps you from planning in a vacuum. Your team might be amazing, but you and your colleagues simply can’t experience your product the way your customers do. Customers might use your product in a way that surprises you, and product features that seem obvious to you might confuse them. Over-planning and refusing to test your assumptions is a waste of time, money, and effort because you’ll likely need to make changes once your untested business plan gets put into practice.
Lean User Experience (UX) design is a model for continuous improvement that relies on quick, efficient research to understand customer needs and test new product features.
Lean market research can help you become more...
Efficient: it gets you closer to your customers, faster.
Cost-effective: no need to hire an expensive marketing firm to get things started.
Competitive: quick, powerful insights can place your products on the cutting edge.
As a small business or sole proprietor, conducting lean market research is an attractive option when investing in a full-blown research project might seem out of scope or budget.
There are lots of different ways you could conduct market research and collect customer data, but you don’t have to limit yourself to just one research method. Four common types of market research techniques include surveys, interviews, focus groups, and customer observation.
Which method you use may vary based on your business type: ecommerce business owners have different goals from SaaS businesses, so it’s typically prudent to mix and match these methods based on your particular goals and what you need to know.
1. Surveys: the most commonly used
Surveys are a form of qualitative research that ask respondents a short series of open- or closed-ended questions, which can be delivered as an on-screen questionnaire or via email. When we asked 2,000 Customer Experience (CX) professionals about their company’s approach to research , surveys proved to be the most commonly used market research technique.
What makes online surveys so popular?
They’re easy and inexpensive to conduct, and you can do a lot of data collection quickly. Plus, the data is pretty straightforward to analyze, even when you have to analyze open-ended questions whose answers might initially appear difficult to categorize.
We've built a number of survey templates ready and waiting for you. Grab a template and share with your customers in just a few clicks.
💡 Pro tip: you can also get started with Hotjar AI for Surveys to create a survey in mere seconds . Just enter your market research goal and watch as the AI generates a survey and populates it with relevant questions.
Once you’re ready for data analysis, the AI will prepare an automated research report that succinctly summarizes key findings, quotes, and suggested next steps.
An example research report generated by Hotjar AI for Surveys
2. Interviews: the most insightful
Interviews are one-on-one conversations with members of your target market. Nothing beats a face-to-face interview for diving deep (and reading non-verbal cues), but if an in-person meeting isn’t possible, video conferencing is a solid second choice.
Regardless of how you conduct it, any type of in-depth interview will produce big benefits in understanding your target customers.
What makes interviews so insightful?
By speaking directly with an ideal customer, you’ll gain greater empathy for their experience , and you can follow insightful threads that can produce plenty of 'Aha!' moments.
3. Focus groups: the most unreliable
Focus groups bring together a carefully selected group of people who fit a company’s target market. A trained moderator leads a conversation surrounding the product, user experience, or marketing message to gain deeper insights.
What makes focus groups so unreliable?
If you’re new to market research, we wouldn’t recommend starting with focus groups. Doing it right is expensive , and if you cut corners, your research could fall victim to all kinds of errors. Dominance bias (when a forceful participant influences the group) and moderator style bias (when different moderator personalities bring about different results in the same study) are two of the many ways your focus group data could get skewed.
4. Observation: the most powerful
During a customer observation session, someone from the company takes notes while they watch an ideal user engage with their product (or a similar product from a competitor).
What makes observation so clever and powerful?
‘Fly-on-the-wall’ observation is a great alternative to focus groups. It’s not only less expensive, but you’ll see people interact with your product in a natural setting without influencing each other. The only downside is that you can’t get inside their heads, so observation still isn't a recommended replacement for customer surveys and interviews.
The following questions will help you get to know your users on a deeper level when you interview them. They’re general questions, of course, so don’t be afraid to make them your own.
1. Who are you and what do you do?
How you ask this question, and what you want to know, will vary depending on your business model (e.g. business-to-business marketing is usually more focused on someone’s profession than business-to-consumer marketing).
It’s a great question to start with, and it’ll help you understand what’s relevant about your user demographics (age, race, gender, profession, education, etc.), but it’s not the be-all-end-all of market research. The more specific questions come later.
2. What does your day look like?
This question helps you understand your users’ day-to-day life and the challenges they face. It will help you gain empathy for them, and you may stumble across something relevant to their buying habits.
3. Do you ever purchase [product/service type]?
This is a ‘yes or no’ question. A ‘yes’ will lead you to the next question.
4. What problem were you trying to solve or what goal were you trying to achieve?
This question strikes to the core of what someone’s trying to accomplish and why they might be willing to pay for your solution.
5. Take me back to the day when you first decided you needed to solve this kind of problem or achieve this goal.
This is the golden question, and it comes from Adele Revella, Founder and CEO of Buyer Persona Institute . It helps you get in the heads of your users and figure out what they were thinking the day they decided to spend money to solve a problem.
If you take your time with this question, digging deeper where it makes sense, you should be able to answer all the relevant information you need to understand their perspective.
“The only scripted question I want you to ask them is this one: take me back to the day when you first decided that you needed to solve this kind of problem or achieve this kind of a goal. Not to buy my product, that’s not the day. We want to go back to the day that when you thought it was urgent and compelling to go spend money to solve a particular problem or achieve a goal. Just tell me what happened.”
— Adele Revella , Founder/CEO at Buyer Persona Institute

Bonus question: is there anything else you’d like to tell me?
This question isn’t just a nice way to wrap it up—it might just give participants the opportunity they need to tell you something you really need to know.
That’s why Sarah Doody, author of UX Notebook , adds it to the end of her written surveys.
“I always have a last question, which is just open-ended: “Is there anything else you would like to tell me?” And sometimes, that’s where you get four paragraphs of amazing content that you would never have gotten if it was just a Net Promoter Score [survey] or something like that.”
What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative research?
Qualitative research asks questions that can’t be reduced to a number, such as, “What is your job title?” or “What did you like most about your customer service experience?”
Quantitative research asks questions that can be answered with a numeric value, such as, “What is your annual salary?” or “How was your customer service experience on a scale of 1-5?”
→ Read more about the differences between qualitative and quantitative user research .
How do I do my own market research?
You can do your own quick and effective market research by
Surveying your customers
Building user personas
Studying your users through interviews and observation
Wrapping your head around your data with tools like flow models, affinity diagrams, and customer journey maps
What is the difference between market research and user research?
Market research takes a broad look at potential customers—what problems they’re trying to solve, their buying experience, and overall demand. User research, on the other hand, is more narrowly focused on the use (and usability ) of specific products.
What are the main criticisms of market research?
Many marketing professionals are critical of market research because it can be expensive and time-consuming. It’s often easier to convince your CEO or CMO to let you do lean market research rather than something more extensive because you can do it yourself. It also gives you quick answers so you can stay ahead of the competition.
Do I need a market research firm to get reliable data?
Absolutely not! In fact, we recommend that you start small and do it yourself in the beginning. By following a lean market research strategy, you can uncover some solid insights about your clients. Then you can make changes, test them out, and see whether the results are positive. This is an excellent strategy for making quick changes and remaining competitive.
Net Promoter, Net Promoter System, Net Promoter Score, NPS, and the NPS-related emoticons are registered trademarks of Bain & Company, Inc., Fred Reichheld, and Satmetrix Systems, Inc.
Related articles

6 traits of top marketing leaders (and how to cultivate them in yourself)
Stepping into a marketing leadership role can stir up a mix of emotions: excitement, optimism, and, often, a gnawing doubt. "Do I have the right skills to truly lead and inspire?" If you've ever wrestled with these uncertainties, you're not alone.
Hotjar team

The 7 best BI tools for marketers in 2024 (and how to use them)
Whether you're sifting through campaign attribution data or reviewing performance reports from different sources, extracting meaningful business insights from vast amounts of data is an often daunting—yet critical—task many marketers face. So how do you efficiently evaluate your results and communicate key learnings?
This is where business intelligence (BI) tools come in, transforming raw data into actionable insights that drive informed, customer-centric decisions.

6 marketing trends that will shape the future of ecommerce in 2023
Today, marketing trends evolve at the speed of technology. Ecommerce businesses that fail to update their marketing strategies to meet consumers where they are in 2023 will be left out of the conversations that drive brand success.

Geoff Whiting
Send us an email
How to do market research: The complete guide for your brand
Written by by Jacqueline Zote
Published on April 13, 2023
Reading time 10 minutes
Blindly putting out content or products and hoping for the best is a thing of the past. Not only is it a waste of time and energy, but you’re wasting valuable marketing dollars in the process. Now you have a wealth of tools and data at your disposal, allowing you to develop data-driven marketing strategies . That’s where market research comes in, allowing you to uncover valuable insights to inform your business decisions.
Conducting market research not only helps you better understand how to sell to customers but also stand out from your competition. In this guide, we break down everything you need to know about market research and how doing your homework can help you grow your business.
Table of contents:
What is market research?
Why is market research important, types of market research, where to conduct market research.
- Steps for conducting market research
- Tools to use for market research
Market research is the process of gathering information surrounding your business opportunities. It identifies key information to better understand your audience. This includes insights related to customer personas and even trends shaping your industry.
Taking time out of your schedule to conduct research is crucial for your brand health. Here are some of the key benefits of market research:
Understand your customers’ motivations and pain points
Most marketers are out of touch with what their customers want. Moreover, these marketers are missing key information on what products their audience wants to buy.
Simply put, you can’t run a business if you don’t know what motivates your customers.
And spoiler alert: Your customers’ wants and needs change. Your customers’ behaviors today might be night and day from what they were a few years ago.
Market research holds the key to understanding your customers better. It helps you uncover their key pain points and motivations and understand how they shape their interests and behavior.
Figure out how to position your brand
Positioning is becoming increasingly important as more and more brands enter the marketplace. Market research enables you to spot opportunities to define yourself against your competitors.
Maybe you’re able to emphasize a lower price point. Perhaps your product has a feature that’s one of a kind. Finding those opportunities goes hand in hand with researching your market.
Maintain a strong pulse on your industry at large
Today’s marketing world evolves at a rate that’s difficult to keep up with.
Fresh products. Up-and-coming brands. New marketing tools. Consumers get bombarded with sales messages from all angles. This can be confusing and overwhelming.
By monitoring market trends, you can figure out the best tactics for reaching your target audience.
Not everyone conducts market research for the same reason. While some may want to understand their audience better, others may want to see how their competitors are doing. As such, there are different types of market research you can conduct depending on your goal.
Interview-based market research allows for one-on-one interactions. This helps the conversation to flow naturally, making it easier to add context. Whether this takes place in person or virtually, it enables you to gather more in-depth qualitative data.
Buyer persona research
Buyer persona research lets you take a closer look at the people who make up your target audience. You can discover the needs, challenges and pain points of each buyer persona to understand what they need from your business. This will then allow you to craft products or campaigns to resonate better with each persona.
Pricing research
In this type of research, brands compare similar products or services with a particular focus on pricing. They look at how much those products or services typically sell for so they can get more competitive with their pricing strategy.
Competitive analysis research
Competitor analysis gives you a realistic understanding of where you stand in the market and how your competitors are doing. You can use this analysis to find out what’s working in your industry and which competitors to watch out for. It even gives you an idea of how well those competitors are meeting consumer needs.
Depending on the competitor analysis tool you use, you can get as granular as you need with your research. For instance, Sprout Social lets you analyze your competitors’ social strategies. You can see what types of content they’re posting and even benchmark your growth against theirs.
Brand awareness research
Conducting brand awareness research allows you to assess your brand’s standing in the market. It tells you how well-known your brand is among your target audience and what they associate with it. This can help you gauge people’s sentiments toward your brand and whether you need to rebrand or reposition.
If you don’t know where to start with your research, you’re in the right place.
There’s no shortage of market research methods out there. In this section, we’ve highlighted research channels for small and big businesses alike.
Considering that Google sees a staggering 8.5 billion searches each day, there’s perhaps no better place to start.
A quick Google search is a potential goldmine for all sorts of questions to kick off your market research. Who’s ranking for keywords related to your industry? Which products and pieces of content are the hottest right now? Who’s running ads related to your business?
For example, Google Product Listing Ads can help highlight all of the above for B2C brands.

The same applies to B2B brands looking to keep tabs on who’s running industry-related ads and ranking for keyword terms too.

There’s no denying that email represents both an aggressive and effective marketing channel for marketers today. Case in point, 44% of online shoppers consider email as the most influential channel in their buying decisions.
Looking through industry and competitor emails is a brilliant way to learn more about your market. For example, what types of offers and deals are your competitors running? How often are they sending emails?

Email is also invaluable for gathering information directly from your customers. This survey message from Asana is a great example of how to pick your customers’ brains to figure out how you can improve your quality of service.

Industry journals, reports and blogs
Don’t neglect the importance of big-picture market research when it comes to tactics and marketing channels to explore. Look to marketing resources such as reports and blogs as well as industry journals
Keeping your ear to the ground on new trends and technologies is a smart move for any business. Sites such as Statista, Marketing Charts, AdWeek and Emarketer are treasure troves of up-to-date data and news for marketers.
And of course, there’s the Sprout Insights blog . And invaluable resources like The Sprout Social Index™ can keep you updated on the latest social trends.
Social media
If you want to learn more about your target market, look no further than social media. Social offers a place to discover what your customers want to see in future products or which brands are killin’ it. In fact, social media is become more important for businesses than ever with the level of data available.
It represents a massive repository of real-time data and insights that are instantly accessible. Brand monitoring and social listening are effective ways to conduct social media research . You can even be more direct with your approach. Ask questions directly or even poll your audience to understand their needs and preferences.

The 5 steps for how to do market research
Now that we’ve covered the why and where, it’s time to get into the practical aspects of market research. Here are five essential steps on how to do market research effectively.
Step 1: Identify your research topic
First off, what are you researching about? What do you want to find out? Narrow down on a specific research topic so you can start with a clear idea of what to look for.
For example, you may want to learn more about how well your product features are satisfying the needs of existing users. This might potentially lead to feature updates and improvements. Or it might even result in new feature introductions.
Similarly, your research topic may be related to your product or service launch or customer experience. Or you may want to conduct research for an upcoming marketing campaign.
Step 2: Choose a buyer persona to engage
If you’re planning to focus your research on a specific type of audience, decide which buyer persona you want to engage. This persona group will serve as a representative sample of your target audience.
Engaging a specific group of audience lets you streamline your research efforts. As such, it can be a much more effective and organized approach than researching thousands (if not millions) of individuals.
You may be directing your research toward existing users of your product. To get even more granular, you may want to focus on users who have been familiar with the product for at least a year, for example.
Step 3: Start collecting data
The next step is one of the most critical as it involves collecting the data you need for your research. Before you begin, make sure you’ve chosen the right research methods that will uncover the type of data you need. This largely depends on your research topic and goals.
Remember that you don’t necessarily have to stick to one research method. You may use a combination of qualitative and quantitative approaches. So for example, you could use interviews to supplement the data from your surveys. Or you may stick to insights from your social listening efforts.
To keep things consistent, let’s look at this in the context of the example from earlier. Perhaps you can send out a survey to your existing users asking them a bunch of questions. This might include questions like which features they use the most and how often they use them. You can get them to choose an answer from one to five and collect quantitative data.
Plus, for qualitative insights, you could even include a few open-ended questions with the option to write their answers. For instance, you might ask them if there’s any improvement they wish to see in your product.
Step 4: Analyze results
Once you have all the data you need, it’s time to analyze it keeping your research topic in mind. This involves trying to interpret the data to look for a wider meaning, particularly in relation to your research goal.
So let’s say a large percentage of responses were four or five in the satisfaction rating. This means your existing users are mostly satisfied with your current product features. On the other hand, if the responses were mostly ones and twos, you may look for opportunities to improve. The responses to your open-ended questions can give you further context as to why people are disappointed.
Step 5: Make decisions for your business
Now it’s time to take your findings and turn them into actionable insights for your business. In this final step, you need to decide how you want to move forward with your new market insight.
What did you find in your research that would require action? How can you put those findings to good use?
The market research tools you should be using
To wrap things up, let’s talk about the various tools available to conduct speedy, in-depth market research. These tools are essential for conducting market research faster and more efficiently.
Social listening and analytics
Social analytics tools like Sprout can help you keep track of engagement across social media. This goes beyond your own engagement data but also includes that of your competitors. Considering how quickly social media moves, using a third-party analytics tool is ideal. It allows you to make sense of your social data at a glance and ensure that you’re never missing out on important trends.

Email marketing research tools
Keeping track of brand emails is a good idea for any brand looking to stand out in its audience’s inbox.
Tools such as MailCharts , Really Good Emails and Milled can show you how different brands run their email campaigns.
Meanwhile, tools like Owletter allow you to monitor metrics such as frequency and send-timing. These metrics can help you understand email marketing strategies among competing brands.
Content marketing research
If you’re looking to conduct research on content marketing, tools such as BuzzSumo can be of great help. This tool shows you the top-performing industry content based on keywords. Here you can see relevant industry sites and influencers as well as which brands in your industry are scoring the most buzz. It shows you exactly which pieces of content are ranking well in terms of engagements and shares and on which social networks.

SEO and keyword tracking
Monitoring industry keywords is a great way to uncover competitors. It can also help you discover opportunities to advertise your products via organic search. Tools such as Ahrefs provide a comprehensive keyword report to help you see how your search efforts stack up against the competition.

Competitor comparison template
For the sake of organizing your market research, consider creating a competitive matrix. The idea is to highlight how you stack up side-by-side against others in your market. Use a social media competitive analysis template to track your competitors’ social presence. That way, you can easily compare tactics, messaging and performance. Once you understand your strengths and weaknesses next to your competitors, you’ll find opportunities as well.
Customer persona creator
Finally, customer personas represent a place where all of your market research comes together. You’d need to create a profile of your ideal customer that you can easily refer to. Tools like Xtensio can help in outlining your customer motivations and demographics as you zero in on your target market.

Build a solid market research strategy
Having a deeper understanding of the market gives you leverage in a sea of competitors. Use the steps and market research tools we shared above to build an effective market research strategy.
But keep in mind that the accuracy of your research findings depends on the quality of data collected. Turn to Sprout’s social media analytics tools to uncover heaps of high-quality data across social networks.
- Marketing Disciplines
- Team Collaboration
How to build a marketing tech stack that scales your business
- Customer Experience
Brand trust: What it is and why it matters
- Leveling Up
The 43 best marketing resources we recommend in 2024
Executing a successful demand generation strategy [with examples]
- Now on slide
Build and grow stronger relationships on social
Sprout Social helps you understand and reach your audience, engage your community and measure performance with the only all-in-one social media management platform built for connection.
START YOUR ECOMMERCE BUSINESS FOR JUST $1
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
A magazine for young entrepreneurs
The best advice in entrepreneurship
Subscribe for exclusive access, the complete guide to market research: what it is, why you need it, and how to do it.

Written by Mary Kate Miller | June 1, 2021
Comments -->

Get real-time frameworks, tools, and inspiration to start and build your business. Subscribe here
Market research is a cornerstone of all successful, strategic businesses. It can also be daunting for entrepreneurs looking to launch a startup or start a side hustle . What is market research, anyway? And how do you…do it?
We’ll walk you through absolutely everything you need to know about the market research process so that by the end of this guide, you’ll be an expert in market research too. And what’s more important: you’ll have actionable steps you can take to start collecting your own market research.
What Is Market Research?
Market research is the organized process of gathering information about your target customers and market. Market research can help you better understand customer behavior and competitor strengths and weaknesses, as well as provide insight for the best strategies in launching new businesses and products. There are different ways to approach market research, including primary and secondary research and qualitative and quantitative research. The strongest approaches will include a combination of all four.
“Virtually every business can benefit from conducting some market research,” says Niles Koenigsberg of Real FiG Advertising + Marketing . “Market research can help you piece together your [business’s] strengths and weaknesses, along with your prospective opportunities, so that you can understand where your unique differentiators may lie.” Well-honed market research will help your brand stand out from the competition and help you see what you need to do to lead the market. It can also do so much more.
The Purposes of Market Research
Why do market research? It can help you…
- Pinpoint your target market, create buyer personas, and develop a more holistic understanding of your customer base and market.
- Understand current market conditions to evaluate risks and anticipate how your product or service will perform.
- Validate a concept prior to launch.
- Identify gaps in the market that your competitors have created or overlooked.
- Solve problems that have been left unresolved by the existing product/brand offerings.
- Identify opportunities and solutions for new products or services.
- Develop killer marketing strategies .
What Are the Benefits of Market Research?
Strong market research can help your business in many ways. It can…
- Strengthen your market position.
- Help you identify your strengths and weaknesses.
- Help you identify your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses.
- Minimize risk.
- Center your customers’ experience from the get-go.
- Help you create a dynamic strategy based on market conditions and customer needs/demands.
What Are the Basic Methods of Market Research?
The basic methods of market research include surveys, personal interviews, customer observation, and the review of secondary research. In addition to these basic methods, a forward-thinking market research approach incorporates data from the digital landscape like social media analysis, SEO research, gathering feedback via forums, and more. Throughout this guide, we will cover each of the methods commonly used in market research to give you a comprehensive overview.
Primary vs. Secondary Market Research
Primary and secondary are the two main types of market research you can do. The latter relies on research conducted by others. Primary research, on the other hand, refers to the fact-finding efforts you conduct on your own.
This approach is limited, however. It’s likely that the research objectives of these secondary data points differ from your own, and it can be difficult to confirm the veracity of their findings.
Primary Market Research
Primary research is more labor intensive, but it generally yields data that is exponentially more actionable. It can be conducted through interviews, surveys, online research, and your own data collection. Every new business should engage in primary market research prior to launch. It will help you validate that your idea has traction, and it will give you the information you need to help minimize financial risk.
You can hire an agency to conduct this research on your behalf. This brings the benefit of expertise, as you’ll likely work with a market research analyst. The downside is that hiring an agency can be expensive—too expensive for many burgeoning entrepreneurs. That brings us to the second approach. You can also do the market research yourself, which substantially reduces the financial burden of starting a new business .
Secondary Market Research
Secondary research includes resources like government databases and industry-specific data and publications. It can be beneficial to start your market research with secondary sources because it’s widely available and often free-to-access. This information will help you gain a broad overview of the market conditions for your new business.
Identify Your Goals and Your Audience
Before you begin conducting interviews or sending out surveys, you need to set your market research goals. At the end of your market research process, you want to have a clear idea of who your target market is—including demographic information like age, gender, and where they live—but you also want to start with a rough idea of who your audience might be and what you’re trying to achieve with market research.
You can pinpoint your objectives by asking yourself a series of guiding questions:
- What are you hoping to discover through your research?
- Who are you hoping to serve better because of your findings?
- What do you think your market is?
- Who are your competitors?
- Are you testing the reception of a new product category or do you want to see if your product or service solves the problem left by a current gap in the market?
- Are you just…testing the waters to get a sense of how people would react to a new brand?
Once you’ve narrowed down the “what” of your market research goals, you’re ready to move onto how you can best achieve them. Think of it like algebra. Many math problems start with “solve for x.” Once you know what you’re looking for, you can get to work trying to find it. It’s a heck of a lot easier to solve a problem when you know you’re looking for “x” than if you were to say “I’m gonna throw some numbers out there and see if I find a variable.”

How to Do Market Research
This guide outlines every component of a comprehensive market research effort. Take into consideration the goals you have established for your market research, as they will influence which of these elements you’ll want to include in your market research strategy.
Secondary Data
Secondary data allows you to utilize pre-existing data to garner a sense of market conditions and opportunities. You can rely on published market studies, white papers, and public competitive information to start your market research journey.
Secondary data, while useful, is limited and cannot substitute your own primary data. It’s best used for quantitative data that can provide background to your more specific inquiries.
Find Your Customers Online
Once you’ve identified your target market, you can use online gathering spaces and forums to gain insights and give yourself a competitive advantage. Rebecca McCusker of The Creative Content Shop recommends internet recon as a vital tool for gaining a sense of customer needs and sentiment. “Read their posts and comments on forums, YouTube video comments, Facebook group [comments], and even Amazon/Goodreads book comments to get in their heads and see what people are saying.”
If you’re interested in engaging with your target demographic online, there are some general rules you should follow. First, secure the consent of any group moderators to ensure that you are acting within the group guidelines. Failure to do so could result in your eviction from the group.
Not all comments have the same research value. “Focus on the comments and posts with the most comments and highest engagement,” says McCusker. These high-engagement posts can give you a sense of what is already connecting and gaining traction within the group.
Social media can also be a great avenue for finding interview subjects. “LinkedIn is very useful if your [target customer] has a very specific job or works in a very specific industry or sector. It’s amazing the amount of people that will be willing to help,” explains Miguel González, a marketing executive at Dealers League . “My advice here is BE BRAVE, go to LinkedIn, or even to people you know and ask them, do quick interviews and ask real people that belong to that market and segment and get your buyer persona information first hand.”
Market research interviews can provide direct feedback on your brand, product, or service and give you a better understanding of consumer pain points and interests.
When organizing your market research interviews, you want to pay special attention to the sample group you’re selecting, as it will directly impact the information you receive. According to Tanya Zhang, the co-founder of Nimble Made , you want to first determine whether you want to choose a representative sample—for example, interviewing people who match each of the buyer persona/customer profiles you’ve developed—or a random sample.
“A sampling of your usual persona styles, for example, can validate details that you’ve already established about your product, while a random sampling may [help you] discover a new way people may use your product,” Zhang says.
Market Surveys
Market surveys solicit customer inclinations regarding your potential product or service through a series of open-ended questions. This direct outreach to your target audience can provide information on your customers’ preferences, attitudes, buying potential, and more.
Every expert we asked voiced unanimous support for market surveys as a powerful tool for market research. With the advent of various survey tools with accessible pricing—or free use—it’s never been easier to assemble, disseminate, and gather market surveys. While it should also be noted that surveys shouldn’t replace customer interviews , they can be used to supplement customer interviews to give you feedback from a broader audience.
Who to Include in Market Surveys
- Current customers
- Past customers
- Your existing audience (such as social media/newsletter audiences)
Example Questions to Include in Market Surveys
While the exact questions will vary for each business, here are some common, helpful questions that you may want to consider for your market survey. Demographic Questions: the questions that help you understand, demographically, who your target customers are:
- “What is your age?”
- “Where do you live?”
- “What is your gender identity?”
- “What is your household income?”
- “What is your household size?”
- “What do you do for a living?”
- “What is your highest level of education?”
Product-Based Questions: Whether you’re seeking feedback for an existing brand or an entirely new one, these questions will help you get a sense of how people feel about your business, product, or service:
- “How well does/would our product/service meet your needs?”
- “How does our product/service compare to similar products/services that you use?”
- “How long have you been a customer?” or “What is the likelihood that you would be a customer of our brand?
Personal/Informative Questions: the deeper questions that help you understand how your audience thinks and what they care about.
- “What are your biggest challenges?”
- “What’s most important to you?”
- “What do you do for fun (hobbies, interests, activities)?”
- “Where do you seek new information when researching a new product?”
- “How do you like to make purchases?”
- “What is your preferred method for interacting with a brand?”
Survey Tools
Online survey tools make it easy to distribute surveys and collect responses. The best part is that there are many free tools available. If you’re making your own online survey, you may want to consider SurveyMonkey, Typeform, Google Forms, or Zoho Survey.
Competitive Analysis
A competitive analysis is a breakdown of how your business stacks up against the competition. There are many different ways to conduct this analysis. One of the most popular methods is a SWOT analysis, which stands for “strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.” This type of analysis is helpful because it gives you a more robust understanding of why a customer might choose a competitor over your business. Seeing how you stack up against the competition can give you the direction you need to carve out your place as a market leader.
Social Media Analysis
Social media has fundamentally changed the market research landscape, making it easier than ever to engage with a wide swath of consumers. Follow your current or potential competitors on social media to see what they’re posting and how their audience is engaging with it. Social media can also give you a lower cost opportunity for testing different messaging and brand positioning.
SEO Analysis and Opportunities
SEO analysis can help you identify the digital competition for getting the word out about your brand, product, or service. You won’t want to overlook this valuable information. Search listening tools offer a novel approach to understanding the market and generating the content strategy that will drive business. Tools like Google Trends and Awario can streamline this process.
Ready to Kick Your Business Into High Gear?
Now that you’ve completed the guide to market research you know you’re ready to put on your researcher hat to give your business the best start. Still not sure how actually… launch the thing? Our free mini-course can run you through the essentials for starting your side hustle .

About Mary Kate Miller
Mary Kate Miller writes about small business, real estate, and finance. In addition to writing for Foundr, her work has been published by The Washington Post, Teen Vogue, Bustle, and more. She lives in Chicago.
Related Posts

How to Create a Marketing Plan In 2024 (Template + Examples)
What Is UGC and Why It’s a Must-Have for Your Brand

Ad Expert Phoenix Ha on How to Make Creative Ads without Breaking Your Budget
14 Punchy TikTok Marketing Strategies to Amplify Your Growth

How to Grow Your YouTube Channel and Gain Subscribers Quickly

How to Get More Views on Snapchat with These 12 Tactics

12 Instagram Growth Hacks For More Engaged Followers (Without Running Ads)

Create Viral Infographics That Boost Your Organic Traffic
How to Create a Video Sales Letter (Tips and Tricks from a 7-Figure Copywriter)

How to Write a Sales Email That Converts in 2024

What Is a Media Kit: How to Make One in 2024 (With Examples)

Namestorming: How to Choose a Brand Name in 20 Minutes or Less

10 Ways to Increase Brand Awareness without Increasing Your Budget

What Is a Content Creator? A Deep Dive Into This Evolving Industry

Content Creator vs Influencer: What’s the Difference?
FREE TRAINING FROM LEGIT FOUNDERS
Actionable Strategies for Starting & Growing Any Business.
Don't Miss Out! Get Instant Access to foundr+ for Just $1!
1000+ lessons. customized learning. 30,000+ strong community..

Module 6: Marketing Information and Research
The marketing research process, learning objectives.
- Identify the steps of conducting a marketing research project
A Standard Approach to Research Inquiries
Marketing research is a useful and necessary tool for helping marketers and an organization’s executive leadership make wise decisions. Carrying out marketing research can involve highly specialized skills that go deeper than the information outlined in this module. However, it is important for any marketer to be familiar with the basic procedures and techniques of marketing research.
It is very likely that at some point a marketing professional will need to supervise an internal marketing research activity or to work with an outside marketing research firm to conduct a research project. Managers who understand the research function can do a better job of framing the problem and critically appraising the proposals made by research specialists. They are also in a better position to evaluate their findings and recommendations.
Periodically marketers themselves need to find solutions to marketing problems without the assistance of marketing research specialists inside or outside the company. If you are familiar with the basic procedures of marketing research, you can supervise and even conduct a reasonably satisfactory search for the information needed.

Step 1: Identify the Problem
The first step for any marketing research activity is to clearly identify and define the problem you are trying to solve. You start by stating the marketing or business problem you need to address and for which you need additional information to figure out a solution. Next, articulate the objectives for the research: What do you want to understand by the time the research project is completed? What specific information, guidance, or recommendations need to come out of the research in order to make it a worthwhile investment of the organization’s time and money?
It’s important to share the problem definition and research objectives with other team members to get their input and further refine your understanding of the problem and what is needed to solve it. At times, the problem you really need to solve is not the same problem that appears on the surface. Collaborating with other stakeholders helps refine your understanding of the problem, focus your thinking, and prioritize what you hope to learn from the research. Prioritizing your objectives is particularly helpful if you don’t have the time or resources to investigate everything you want.
To flesh out your understanding of the problem, it’s useful to begin brainstorming actual research questions you want to explore. What are the questions you need to answer in order to get to the research outcomes? What is the missing information that marketing research will help you find? The goal at this stage is to generate a set of preliminary, big-picture questions that will frame your research inquiry. You will revisit these research questions later in the process, but when you’re getting started, this exercise helps clarify the scope of the project, whom you need to talk to, what information may already be available, and where to look for the information you don’t yet have.
Applied Example: Marketing Research for Bookends
To illustrate the marketing research process, let’s return to Uncle Dan and his ailing bookstore, Bookends. You need a lot of information if you’re going to help Dan turn things around, so marketing research is a good idea. You begin by identifying the problem and then work to set down your research objectives and initial research questions:
Step 2: Develop a Research Plan
Once you have a problem definition, research objectives, and a preliminary set of research questions, the next step is to develop a research plan. Essential to this plan is identifying precisely what information you need to answer your questions and achieve your objectives. Do you need to understand customer opinions about something? Are you looking for a clearer picture of customer needs and related behaviors? Do you need sales, spending, or revenue data? Do you need information about competitors’ products, or insight about what will make prospective customers notice you? When do need the information, and what’s the time frame for getting it? What budget and resources are available?
Once you have clarified what kind of information you need and the timing and budget for your project, you can develop the research design. This details how you plan to collect and analyze the information you’re after. Some types of information are readily available through secondary research and secondary data sources. Secondary research analyzes information that has already been collected for another purpose by a third party, such as a government agency, an industry association, or another company. Other types of information need to from talking directly to customers about your research questions. This is known as primary research , which collects primary data captured expressly for your research inquiry. Marketing research projects may include secondary research, primary research, or both.
Depending on your objectives and budget, sometimes a small-scale project will be enough to get the insight and direction you need. At other times, in order to reach the level of certainty or detail required, you may need larger-scale research involving participation from hundreds or even thousands of individual consumers. The research plan lays out the information your project will capture—both primary and secondary data—and describes what you will do with it to get the answers you need. (Note: You’ll learn more about data collection methods and when to use them later in this module.)
Your data collection plan goes hand in hand with your analysis plan. Different types of analysis yield different types of results. The analysis plan should match the type of data you are collecting, as well as the outcomes your project is seeking and the resources at your disposal. Simpler research designs tend to require simpler analysis techniques. More complex research designs can yield powerful results, such as understanding causality and trade-offs in customer perceptions. However, these more sophisticated designs can require more time and money to execute effectively, both in terms of data collection and analytical expertise.
The research plan also specifies who will conduct the research activities, including data collection, analysis, interpretation, and reporting on results. At times a singlehanded marketing manager or research specialist runs the entire research project. At other times, a company may contract with a marketing research analyst or consulting firm to conduct the research. In this situation, the marketing manager provides supervisory oversight to ensure the research delivers on expectations.
Finally, the research plan indicates who will interpret the research findings and how the findings will be reported. This part of the research plan should consider the internal audience(s) for the research and what reporting format will be most helpful. Often, senior executives are primary stakeholders, and they’re anxious for marketing research to inform and validate their choices. When this is the case, getting their buy-in on the research plan is recommended to make sure that they are comfortable with the approach and receptive to the potential findings.
Applied Example: A Bookends Research Plan
You talk over the results of your problem identification work with Dan. He thinks you’re on the right track and wants to know what’s next. You explain that the next step is to put together a detailed plan for getting answers to the research questions.
Dan is enthusiastic, but he’s also short on money. You realize that such a financial constraint will limit what’s possible, but with Dan’s help you can do something worthwhile. Below is the research plan you sketch out:
Step 3: Conduct the Research
Conducting research can be a fun and exciting part of the marketing research process. After struggling with the gaps in your knowledge of market dynamics—which led you to embark on a marketing research project in the first place—now things are about to change. Conducting research begins to generate information that helps answer your urgent marketing questions.
Typically data collection begins by reviewing any existing research and data that provide some information or insight about the problem. As a rule, this is secondary research. Prior research projects, internal data analyses, industry reports, customer-satisfaction survey results, and other information sources may be worthwhile to review. Even though these resources may not answer your research questions fully, they may further illuminate the problem you are trying to solve. Secondary research and data sources are nearly always cheaper than capturing new information on your own. Your marketing research project should benefit from prior work wherever possible.
After getting everything you can from secondary research, it’s time to shift attention to primary research, if this is part of your research plan. Primary research involves asking questions and then listening to and/or observing the behavior of the target audience you are studying. In order to generate reliable, accurate results, it is important to use proper scientific methods for primary research data collection and analysis. This includes identifying the right individuals and number of people to talk to, using carefully worded surveys or interview scripts, and capturing data accurately.
Without proper techniques, you may inadvertently get bad data or discover bias in the responses that distorts the results and points you in the wrong direction. The module on Marketing Research Techniques discusses these issues in further detail, since the procedures for getting reliable data vary by research method.
Applied Example: Getting the Data on Bookends
Dan is on board with the research plan, and he’s excited to dig into the project. You start with secondary data, getting a dump of Dan’s sales data from the past two years, along with related information: customer name, zip code, frequency of purchase, gender, date of purchase, and discounts/promotions (if any).
You visit the U.S. Census Bureau Web site to download demographic data about your metro area. The data show all zip codes in the area, along with population size, gender breakdown, age ranges, income, and education levels.
The next part of the project is customer-survey data. You work with Dan to put together a short survey about customer attitudes toward Bookends, how often and why they come, where else they spend money on books and entertainment, and why they go other places besides Bookends. Dan comes up with the great idea of offering a 5 percent discount coupon to anyone who completes the survey. Although it eats into his profits, this scheme gets more people to complete the survey and buy books, so it’s worth it.

For a couple of days, you and Dan take turns doing “man on the street” interviews (you interview the guy in the red hat, for instance). You find people who say they’ve never been to Bookends and ask them a few questions about why they haven’t visited the store, where else they buy books and other entertainment, and what might get them interested in visiting Bookends sometime. This is all a lot of work, but for a zero-budget project, it’s coming together pretty well.
Step 4: Analyze and Report Findings
Analyzing the data obtained in a market survey involves transforming the primary and/or secondary data into useful information and insights that answer the research questions. This information is condensed into a format to be used by managers—usually a presentation or detailed report.
Analysis starts with formatting, cleaning, and editing the data to make sure that it’s suitable for whatever analytical techniques are being used. Next, data are tabulated to show what’s happening: What do customers actually think? What’s happening with purchasing or other behaviors? How do revenue figures actually add up? Whatever the research questions, the analysis takes source data and applies analytical techniques to provide a clearer picture of what’s going on. This process may involve simple or sophisticated techniques, depending on the research outcomes required. Common analytical techniques include regression analysis to determine correlations between factors; conjoint analysis to determine trade-offs and priorities; predictive modeling to anticipate patterns and causality; and analysis of unstructured data such as Internet search terms or social media posts to provide context and meaning around what people say and do.
Good analysis is important because the interpretation of research data—the “so what?” factor—depends on it. The analysis combs through data to paint a picture of what’s going on. The interpretation goes further to explain what the research data mean and make recommendations about what managers need to know and do based on the research results. For example, what is the short list of key findings and takeaways that managers should remember from the research? What are the market segments you’ve identified, and which ones should you target? What are the primary reasons your customers choose your competitor’s product over yours, and what does this mean for future improvements to your product?
Individuals with a good working knowledge of the business should be involved in interpreting the data because they are in the best position to identify significant insights and make recommendations from the research findings. Marketing research reports incorporate both analysis and interpretation of data to address the project objectives.
The final report for a marketing research project may be in written form or slide-presentation format, depending on organizational culture and management preferences. Often a slide presentation is the preferred format for initially sharing research results with internal stakeholders. Particularly for large, complex projects, a written report may be a better format for discussing detailed findings and nuances in the data, which managers can study and reference in the future.
Applied Example: Analysis and Insights for Bookends
Getting the data was a bit of a hassle, but now you’ve got it, and you’re excited to see what it reveals. Your statistician cousin, Marina, turns out to be a whiz with both the sales data and the census data. She identified several demographic profiles in the metro area that looked a lot like lifestyle segments. Then she mapped Bookends’ sales data into those segments to show who is and isn’t visiting Bookends. After matching customer-survey data to the sales data, she broke down the segments further based on their spending levels and reasons they visit Bookends.
Gradually a clearer picture of Bookends’ customers is beginning to emerge: who they are, why they come, why they don’t come, and what role Bookends plays in their lives. Right away, a couple of higher-priority segments—based on their spending levels, proximity, and loyalty to Bookends—stand out. You and your uncle are definitely seeing some possibilities for making the bookstore a more prominent part of their lives. You capture these insights as “recommendations to be considered” while you evaluate the right marketing mix for each of the new segments you’d like to focus on.
Step 5: Take Action
Once the report is complete, the presentation is delivered, and the recommendations are made, the marketing research project is over, right? Wrong.
What comes next is arguably the most important step of all: taking action based on your research results.
If your project has done a good job interpreting the findings and translating them into recommendations for the marketing team and other areas of the business, this step may seem relatively straightforward. When the research results validate a path the organization is already on, the “take action” step can galvanize the team to move further and faster in that same direction.
Things are not so simple when the research results indicate a new direction or a significant shift is advisable. In these cases, it’s worthwhile to spend time helping managers understand the research, explain why it is wise to shift course, and explain how the business will benefit from the new path. As with any important business decision, managers must think deeply about the new approach and carefully map strategies, tactics, and available resources to plan effectively. By making the results available and accessible to managers and their execution teams, the marketing research project can serve as an ongoing guide and touchstone to help the organization plan, execute, and adjust course as it works toward desired goals and outcomes.
It is worth mentioning that many marketing research projects are never translated into management action. Sometimes this is because the report is too technical and difficult to understand. In other cases, the research conclusions fail to provide useful insights or solutions to the problem, or the report writer fails to offer specific suggestions for translating the research findings into management strategy. These pitfalls can be avoided by paying due attention to the research objectives throughout the project and allocating sufficient time and resources to do a good job interpreting research results for those who will need to act on them.
Applied Example: Bookends’ New Customer Campaign
Your research findings and recommendations identified three segments for Bookends to focus on. Based on the demographics, lifestyle, and spending patterns found during your marketing research, you’re able to name them: 1) Bored Empty-Nesters, 2) Busy Families, and 3) Hipster Wannabes. Dan has a decent-sized clientele across all three groups, and they are pretty good spenders when they come in. But until now he hasn’t done much to purposely attract any of them.
With newly identified segments in focus, you and Dan begin brainstorming about a marketing mix to target each group. What types of books and other products would appeal to each one? What activities or events would bring them into the store? Are there promotions or particular messages that would induce them to buy at Bookends instead of Amazon or another bookseller? How will Dan reach and communicate with each group? And what can you do to bring more new customers into the store within these target groups?
Even though Bookends is a real-life project with serious consequences for your uncle Dan, it’s also a fun laboratory where you can test out some of the principles you’re learning in your marketing class. You’re figuring out quickly what it’s like to be a marketer.
Well done, rookie!
Check Your Understanding
Answer the question(s) below to see how well you understand the topics covered in this outcome. This short quiz does not count toward your grade in the class, and you can retake it an unlimited number of times.
Use this quiz to check your understanding and decide whether to (1) study the previous section further or (2) move on to the next section.
- Revision and Adaptation. Authored by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Chapter 3: Marketing Research: An Aid to Decision Making, from Introducing Marketing. Authored by : John Burnett. Provided by : Global Text. Located at : http://solr.bccampus.ca:8001/bcc/file/ddbe3343-9796-4801-a0cb-7af7b02e3191/1/Core%20Concepts%20of%20Marketing.pdf . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Urban life (Version 2.0). Authored by : Ian D. Keating. Located at : https://www.flickr.com/photos/ian-arlett/19313315520/ . License : CC BY: Attribution
How To Do Market Research: Definition, Types, Methods
Jan 2, 2024
11 min. read
Market research isn’t just collecting data. It’s a strategic tool that allows businesses to gain a competitive advantage while making the best use of their resources. Research reveals valuable insights into your target audience about their preferences, buying habits, and emerging demands — all of which help you unlock new opportunities to grow your business.
When done correctly, market research can minimize risks and losses, spur growth, and position you as a leader in your industry.
Let’s explore the basic building blocks of market research and how to collect and use data to move your company forward:
Table of Contents
What Is Market Research?
Why is market research important, market analysis example, 5 types of market research, what are common market research questions, what are the limitations of market research, how to do market research, improving your market research with radarly.
Market Research Definition: The process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting information about a market or audience.

Market research studies consumer behavior to better understand how they perceive products or services. These insights help businesses identify ways to grow their current offering, create new products or services, and improve brand trust and brand recognition .
You might also hear market research referred to as market analysis or consumer research .
Traditionally, market research has taken the form of focus groups, surveys, interviews, and even competitor analysis . But with modern analytics and research tools, businesses can now capture deeper insights from a wider variety of sources, including social media, online reviews, and customer interactions. These extra layers of intel can help companies gain a more comprehensive understanding of their audience.
With consumer preferences and markets evolving at breakneck speeds, businesses need a way to stay in touch with what people need and want. That’s why the importance of market research cannot be overstated.
Market research offers a proactive way to identify these trends and make adjustments to product development, marketing strategies , and overall operations. This proactive approach can help businesses stay ahead of the curve and remain agile as markets shift.
Market research examples abound — given the number of ways companies can get inside the minds of their customers, simply skimming through your business’s social media comments can be a form of market research.
A restaurant chain might use market research methods to learn more about consumers’ evolving dining habits. These insights might be used to offer new menu items, re-examine their pricing strategies, or even open new locations in different markets, for example.
A consumer electronics company might use market research for similar purposes. For instance, market research may reveal how consumers are using their smart devices so they can develop innovative features.
Market research can be applied to a wide range of use cases, including:
- Testing new product ideas
- Improve existing products
- Entering new markets
- Right-sizing their physical footprints
- Improving brand image and awareness
- Gaining insights into competitors via competitive intelligence
Ultimately, companies can lean on market research techniques to stay ahead of trends and competitors while improving the lives of their customers.
Market research methods take different forms, and you don’t have to limit yourself to just one. Let’s review the most common market research techniques and the insights they deliver.
1. Interviews
3. Focus Groups
4. Observations
5. AI-Driven Market Research
One-on-one interviews are one of the most common market research techniques. Beyond asking direct questions, skilled interviewers can uncover deeper motivations and emotions that drive purchasing decisions. Researchers can elicit more detailed and nuanced responses they might not receive via other methods, such as self-guided surveys.

Interviews also create the opportunity to build rapport with customers and prospects. Establishing a connection with interviewees can encourage them to open up and share their candid thoughts, which can enrich your findings. Researchers also have the opportunity to ask clarifying questions and dig deeper based on individual responses.
Market research surveys provide an easy entry into the consumer psyche. They’re cost-effective to produce and allow researchers to reach lots of people in a short time. They’re also user-friendly for consumers, which allows companies to capture more responses from more people.
Big data and data analytics are making traditional surveys more valuable. Researchers can apply these tools to elicit a deeper understanding from responses and uncover hidden patterns and correlations within survey data that were previously undetectable.
The ways in which surveys are conducted are also changing. With the rise of social media and other online channels, brands and consumers alike have more ways to engage with each other, lending to a continuous approach to market research surveys.
3. Focus groups
Focus groups are “group interviews” designed to gain collective insights. This interactive setting allows participants to express their thoughts and feelings openly, giving researchers richer insights beyond yes-or-no responses.

One of the key benefits of using focus groups is the opportunity for participants to interact with one another. They spark discussions while sharing diverse viewpoints. These sessions can uncover underlying motivations and attitudes that may not be easily expressed through other research methods.
Observing your customers “in the wild” might feel informal, but it can be one of the most revealing market research techniques of all. That’s because you might not always know the right questions to ask. By simply observing, you can surface insights you might not have known to look for otherwise.
This method also delivers raw, authentic, unfiltered data. There’s no room for bias and no potential for participants to accidentally skew the data. Researchers can also pick up on non-verbal cues and gestures that other research methods may fail to capture.
5. AI-driven market research
One of the newer methods of market research is the use of AI-driven market research tools to collect and analyze insights on your behalf. AI customer intelligence tools and consumer insights software like Meltwater Radarly take an always-on approach by going wherever your audience is and continuously predicting behaviors based on current behaviors.
By leveraging advanced algorithms, machine learning, and big data analysis , AI enables companies to uncover deep-seated patterns and correlations within large datasets that would be near impossible for human researchers to identify. This not only leads to more accurate and reliable findings but also allows businesses to make informed decisions with greater confidence.
Tip: Learn how to use Meltwater as a research tool , how Meltwater uses AI , and learn more about consumer insights and about consumer insights in the fashion industry .
No matter the market research methods you use, market research’s effectiveness lies in the questions you ask. These questions should be designed to elicit honest responses that will help you reach your goals.
Examples of common market research questions include:
Demographic market research questions
- What is your age range?
- What is your occupation?
- What is your household income level?
- What is your educational background?
- What is your gender?
Product or service usage market research questions
- How long have you been using [product/service]?
- How frequently do you use [product/service]?
- What do you like most about [product/service]?
- Have you experienced any problems using [product/service]?
- How could we improve [product/service]?
- Why did you choose [product/service] over a competitor’s [product/service]?
Brand perception market research questions
- How familiar are you with our brand?
- What words do you associate with our brand?
- How do you feel about our brand?
- What makes you trust our brand?
- What sets our brand apart from competitors?
- What would make you recommend our brand to others?
Buying behavior market research questions
- What do you look for in a [product/service]?
- What features in a [product/service] are important to you?
- How much time do you need to choose a [product/service]?
- How do you discover new products like [product/service]?
- Do you prefer to purchase [product/service] online or in-store?
- How do you research [product/service] before making a purchase?
- How often do you buy [product/service]?
- How important is pricing when buying [product/service]?
- What would make you switch to another brand of [product/service]?
Customer satisfaction market research questions
- How happy have you been with [product/service]?
- What would make you more satisfied with [product/service]?
- How likely are you to continue using [product/service]?
Bonus Tip: Compiling these questions into a market research template can streamline your efforts.
Market research can offer powerful insights, but it also has some limitations. One key limitation is the potential for bias. Researchers may unconsciously skew results based on their own preconceptions or desires, which can make your findings inaccurate.
- Depending on your market research methods, your findings may be outdated by the time you sit down to analyze and act on them. Some methods struggle to account for rapidly changing consumer preferences and behaviors.
- There’s also the risk of self-reported data (common in online surveys). Consumers might not always accurately convey their true feelings or intentions. They might provide answers they think researchers are looking for or misunderstand the question altogether.
- There’s also the potential to miss emerging or untapped markets . Researchers are digging deeper into what (or who) they already know. This means you might be leaving out a key part of the story without realizing it.
Still, the benefits of market research cannot be understated, especially when you supplement traditional market research methods with modern tools and technology.
Let’s put it all together and explore how to do market research step-by-step to help you leverage all its benefits.
Step 1: Define your objectives
You’ll get more from your market research when you hone in on a specific goal : What do you want to know, and how will this knowledge help your business?
This step will also help you define your target audience. You’ll need to ask the right people the right questions to collect the information you want. Understand the characteristics of the audience and what gives them authority to answer your questions.
Step 2: Select your market research methods
Choose one or more of the market research methods (interviews, surveys, focus groups, observations, and/or AI-driven tools) to fuel your research strategy.
Certain methods might work better than others for specific goals . For example, if you want basic feedback from customers about a product, a simple survey might suffice. If you want to hone in on serious pain points to develop a new product, a focus group or interview might work best.
You can also source secondary research ( complementary research ) via secondary research companies , such as industry reports or analyses from large market research firms. These can help you gather preliminary information and inform your approach.

Step 3: Develop your research tools
Prior to working with participants, you’ll need to craft your survey or interview questions, interview guides, and other tools. These tools will help you capture the right information , weed out non-qualifying participants, and keep your information organized.
You should also have a system for recording responses to ensure data accuracy and privacy. Test your processes before speaking with participants so you can spot and fix inefficiencies or errors.
Step 4: Conduct the market research
With a system in place, you can start looking for candidates to contribute to your market research. This might include distributing surveys to current customers or recruiting participants who fit a specific profile, for example.
Set a time frame for conducting your research. You might collect responses over the course of a few days, weeks, or even months. If you’re using AI tools to gather data, choose a data range for your data to focus on the most relevant information.
Step 5: Analyze and apply your findings
Review your findings while looking for trends and patterns. AI tools can come in handy in this phase by analyzing large amounts of data on your behalf.
Compile your findings into an easy-to-read report and highlight key takeaways and next steps. Reports aren’t useful unless the reader can understand and act on them.
Tip: Learn more about trend forecasting , trend detection , and trendspotting .
Meltwater’s Radarly consumer intelligence suite helps you reap the benefits of market research on an ongoing basis. Using a combination of AI, data science, and market research expertise, Radarly scans multiple global data sources to learn what people are talking about, the actions they’re taking, and how they’re feeling about specific brands.

Our tools are created by market research experts and designed to help researchers uncover what they want to know (and what they don’t know they want to know). Get data-driven insights at scale with information that’s always relevant, always accurate, and always tailored to your organization’s needs.
Learn more when you request a demo by filling out the form below:
Continue Reading

What Are Consumer Insights? Meaning, Examples, Strategy

How Coca-Cola Collects Consumer Insights

Market Intelligence 101: What It Is & How To Use It
9 Top Consumer Insights Tools & Companies
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is Market Research?
- How It Works
- Primary vs. Secondary
- How to Conduct Research
The Bottom Line
- Marketing Essentials
How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/dd453b82d4ef4ce8aac2e858ed00a114__alexandra_twin-5bfc262b46e0fb0026006b77.jpeg)
Joules Garcia / Investopedia
Market research examines consumer behavior and trends in the economy to help a business develop and fine-tune its business idea and strategy. It helps a business understand its target market by gathering and analyzing data.
Market research is the process of evaluating the viability of a new service or product through research conducted directly with potential customers. It allows a company to define its target market and get opinions and other feedback from consumers about their interest in a product or service.
Research may be conducted in-house or by a third party that specializes in market research. It can be done through surveys and focus groups, among other ways. Test subjects are usually compensated with product samples or a small stipend for their time.
Key Takeaways
- Companies conduct market research before introducing new products to determine their appeal to potential customers.
- Tools include focus groups, telephone interviews, and questionnaires.
- The results of market research inform the final design of the product and determine how it will be positioned in the marketplace.
- Market research usually combines primary information, gathered directly from consumers, and secondary information, which is data available from external sources.
Market Research
How market research works.
Market research is used to determine the viability of a new product or service. The results may be used to revise the product design and fine-tune the strategy for introducing it to the public. This can include information gathered for the purpose of determining market segmentation . It also informs product differentiation , which is used to tailor advertising.
A business engages in various tasks to complete the market research process. It gathers information based on the market sector being targeted by the product. This information is then analyzed and relevant data points are interpreted to draw conclusions about how the product may be optimally designed and marketed to the market segment for which it is intended.
It is a critical component in the research and development (R&D) phase of a new product or service introduction. Market research can be conducted in many different ways, including surveys, product testing, interviews, and focus groups.
Market research is a critical tool that companies use to understand what consumers want, develop products that those consumers will use, and maintain a competitive advantage over other companies in their industry.
Primary Market Research vs. Secondary Market Research
Market research usually consists of a combination of:
- Primary research, gathered by the company or by an outside company that it hires
- Secondary research, which draws on external sources of data
Primary Market Research
Primary research generally falls into two categories: exploratory and specific research.
- Exploratory research is less structured and functions via open-ended questions. The questions may be posed in a focus group setting, telephone interviews, or questionnaires. It results in questions or issues that the company needs to address about a product that it has under development.
- Specific research delves more deeply into the problems or issues identified in exploratory research.
Secondary Market Research
All market research is informed by the findings of other researchers about the needs and wants of consumers. Today, much of this research can be found online.
Secondary research can include population information from government census data , trade association research reports , polling results, and research from other businesses operating in the same market sector.
History of Market Research
Formal market research began in Germany during the 1920s. In the United States, it soon took off with the advent of the Golden Age of Radio.
Companies that created advertisements for this new entertainment medium began to look at the demographics of the audiences who listened to each of the radio plays, music programs, and comedy skits that were presented.
They had once tried to reach the widest possible audience by placing their messages on billboards or in the most popular magazines. With radio programming, they had the chance to target rural or urban consumers, teenagers or families, and judge the results by the sales numbers that followed.
Types of Market Research
Face-to-face interviews.
From their earliest days, market research companies would interview people on the street about the newspapers and magazines that they read regularly and ask whether they recalled any of the ads or brands that were published in them. Data collected from these interviews were compared to the circulation of the publication to determine the effectiveness of those ads.
Market research and surveys were adapted from these early techniques.
To get a strong understanding of your market, it’s essential to understand demand, market size, economic indicators, location, market saturation, and pricing.
Focus Groups
A focus group is a small number of representative consumers chosen to try a product or watch an advertisement.
Afterward, the group is asked for feedback on their perceptions of the product, the company’s brand, or competing products. The company then takes that information and makes decisions about what to do with the product or service, whether that's releasing it, making changes, or abandoning it altogether.
Phone Research
The man-on-the-street interview technique soon gave way to the telephone interview. A telephone interviewer could collect information in a more efficient and cost-effective fashion.
Telephone research was a preferred tactic of market researchers for many years. It has become much more difficult in recent years as landline phone service dwindles and is replaced by less accessible mobile phones.
Survey Research
As an alternative to focus groups, surveys represent a cost-effective way to determine consumer attitudes without having to interview anyone in person. Consumers are sent surveys in the mail, usually with a coupon or voucher to incentivize participation. These surveys help determine how consumers feel about the product, brand, and price point.
Online Market Research
With people spending more time online, market research activities have shifted online as well. Data collection still uses a survey-style form. But instead of companies actively seeking participants by finding them on the street or cold calling them on the phone, people can choose to sign up, take surveys, and offer opinions when they have time.
This makes the process far less intrusive and less rushed, since people can participate on their own time and of their own volition.
How to Conduct Market Research
The first step to effective market research is to determine the goals of the study. Each study should seek to answer a clear, well-defined problem. For example, a company might seek to identify consumer preferences, brand recognition, or the comparative effectiveness of different types of ad campaigns.
After that, the next step is to determine who will be included in the research. Market research is an expensive process, and a company cannot waste resources collecting unnecessary data. The firm should decide in advance which types of consumers will be included in the research, and how the data will be collected. They should also account for the probability of statistical errors or sampling bias .
The next step is to collect the data and analyze the results. If the two previous steps have been completed accurately, this should be straightforward. The researchers will collect the results of their study, keeping track of the ages, gender, and other relevant data of each respondent. This is then analyzed in a marketing report that explains the results of their research.
The last step is for company executives to use their market research to make business decisions. Depending on the results of their research, they may choose to target a different group of consumers, or they may change their price point or some product features.
The results of these changes may eventually be measured in further market research, and the process will begin all over again.
Benefits of Market Research
Market research is essential for developing brand loyalty and customer satisfaction. Since it is unlikely for a product to appeal equally to every consumer, a strong market research program can help identify the key demographics and market segments that are most likely to use a given product.
Market research is also important for developing a company’s advertising efforts. For example, if a company’s market research determines that its consumers are more likely to use Facebook than X (formerly Twitter), it can then target its advertisements to one platform instead of another. Or, if they determine that their target market is value-sensitive rather than price-sensitive, they can work on improving the product rather than reducing their prices.
Market research only works when subjects are honest and open to participating.
Example of Market Research
Many companies use market research to test new products or get information from consumers about what kinds of products or services they need and don’t currently have.
For example, a company that’s considering starting a business might conduct market research to test the viability of its product or service. If the market research confirms consumer interest, the business can proceed confidently with its business plan . If not, the company can use the results of the market research to make adjustments to the product to bring it in line with customer desires.
What Are the Main Types of Market Research?
The main types of market research are primary research and secondary research. Primary research includes focus groups, polls, and surveys. Secondary research includes academic articles, infographics, and white papers.
Qualitative research gives insights into how customers feel and think. Quantitative research uses data and statistics such as website views, social media engagement, and subscriber numbers.
What Is Online Market Research?
Online market research uses the same strategies and techniques as traditional primary and secondary market research, but it is conducted on the Internet. Potential customers may be asked to participate in a survey or give feedback on a product. The responses may help the researchers create a profile of the likely customer for a new product.
What Are Paid Market Research Surveys?
Paid market research involves rewarding individuals who agree to participate in a study. They may be offered a small payment for their time or a discount coupon in return for filling out a questionnaire or participating in a focus group.
What Is a Market Study?
A market study is an analysis of consumer demand for a product or service. It looks at all of the factors that influence demand for a product or service. These include the product’s price, location, competition, and substitutes as well as general economic factors that could influence the new product’s adoption, for better or worse.
Market research is a key component of a company’s research and development (R&D) stage. It helps companies understand in advance the viability of a new product that they have in development and to see how it might perform in the real world.
Britannica Money. “ Market Research .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Market Research and Competitive Analysis .”
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans for May 2024 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How To Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Term-Definitions_Target-market-49a03b58f6d54ddd88d46521f248fc8a.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- Login to Survey Tool Review Center
- Step by Step Guide to the Market Research Process
Summary: The market research process requires decisions related to budget, target sample, development of data collection tools, fielding, analysis, and reporting. Here is a check list to make the process easier.
5 minutes to read. By author Michaela Mora on March 15, 2022 Topics: Business Strategy , Market Research

The market research process requires making decisions at many steps that can be overwhelming for non-researchers put in charge of research projects.
Consider these practical tips to conduct the following 6 steps during the implementation of a market research project.
Step 1. Define the Problem and Translate It into Research Objectives
- This is the most important step. It sets the direction of the whole market research process. Ask clients how they will use the research results, and what business decisions they will make based on the data. They should be specific. Get a consensus among key stakeholders on the main research objectives. Get them involved from the start.
- Avoid objective creep. Don’t try to research everything under the sky in a project. Focus on what’s needed for decision-making. Trying to cram many things into a project because of budget constraints is often a waste of money as data quality suffers.
- Discuss limitations early in the process. Set clear expectations of what the research will cover and what data it will provide.
- Do secondary research , and check if previous research has been conducted on the same issue to avoid effort duplication and waste of money. Interview key stakeholders to put the research objectives into a greater context.
- Exploratory primary research may be needed with your target market (customers /users, non-customers) to better define the information needs.
- DO NOT select a data collection method before establishing clear objectives and identifying the target population. Think objectives firsts, methods second. Not the other way around.
- How much are the key stakeholders willing to invest in the requested research? Get a number! If there is no commitment to a budget, you will be wasting your time (RFP) and your research vendor’s time (proposal). There is always a trade-off between research quality, deadline, and cost. Make your internal clients aware of that. There is a limit to “ better, faster, and cheaper ” in market research. Push it too hard and you will get fast cheap, crappy research.
Step 2. Formulate the Approach
- Based on the research objective think, which research methodology would be the best fit. Start with the broader categories: Secondary? Primary? Qualitative? Quantitative?
- Based on the decisions that will be made, determine what type of data is needed and expected.
- Example: Need to know how to price a new product before it goes to market? Conjoint Analysis may be a good fit. Check: Conjoint Analysis And Realism In Price Research
- Example: Need to pick the product name that elicits the highest purchase intent from a list of 30? Consider MaxDiff. Check: Making the Case for MaxDiff
- Example: Need to find new growth opportunities? Segmentation research can help to find segments with the highest potential. Check: Segmentation is Key to Success
- The analysis techniques selected will also influence the decision on sample size.
- Ideally, if budget permits do qualitative research before or after quantitative research
- Consider qualitative research for exploration before quantitative and deep-diving after quantitative research.
- Consider quantitative research if a go/no go decision will be made. DO NOT make these types of decisions based only on qualitative research
Step 3. Define The Research Design
Define the target population for the research.
- Who do you want to gather data from? Customers? Non-Customers? Category users? Be realistic. Given your budget, you may or may not be able to reach your target population.
- Sample definition helps decide on what data collection method we use. More than one method may be needed. To read more about mixed-mode data collection check: Mixed Data Collection Modes – Round-Up
- Create clear screening criteria. Discuss them with key stakeholders. Make sure they align with the research objectives.
- Discuss the caveats and limitations of the sample definition and how they will affect the results and decision-making.
- Determine the sample size based on your tolerance for risk. Check Sample Size Matter
- A large sample doesn’t guarantee representativeness. Check: Does A Large Sample Size Guarantee A Representative Sample?
- If you have access to a customer database with emails, use it for studies related to customer retention goals and new product development.
- For customer acquisition, efforts use samples of non-customers in the category.
- If the study is online get bids from multiple online panels.
- Don’t buy third-party email lists and blast them with survey invites. It is illegal (SPAM-CAN Act).
- If you are conducting qualitative research , small samples are expected given the exploration nature of this methodology category. Consider issues of sample size saturation . Depending on the overall research objectives, results from qualitative research may need validation via quantitative research.
Select Data Collection Method (s)
- Objectives, sample plan, analytical plan, and cost have the highest influence on which methods we use. Be open to using hybrid approaches combining qualitative and quantitative data collection methods
- Discuss which methods are the best fit to research the target pop. Some target groups may be difficult to reach with the same method
- If you decide on mixed-mode surveys, be aware of potential measurement errors each mode introduces. Check: Understanding the Pros and Cons of Mixed-Mode Research
- Once the data collection methods are selected, determine if you can do it with internal resources or need a research vendor.
- If time, staff, or lack of tools are limitations, consider outsourcing the project to an external research vendor. For more on this check: When Do You Need A Market Research Vendor ?
- If you are doing surveys, put time into its design. To create surveys that gather quality data check: 10 Things to Consider in Survey Design
- Considering focus groups? Check if it makes sense here: When Using Focus Groups Makes Sense
- If you are doing focus groups, avoid common mistakes. To know which they are, check: Common Mistakes When Doing Focus Groups
- Consider online qualitative research techniques. Check: Online Qualitative Research Techniques Review
Step 4. Collect Data
- Do a soft launch if you are doing online surveys to catch any potential problems.
- Get involved, monitor. early to catch any potential issues that can affect data quality (e.g., bad respondents, programming errors, etc.).
Step 5. Data Processing
- Clean your data. It doesn’t matter if it is quantitative or qualitative data, quality controls are needed.
- Fraudulent research participants are always trying to game the system to get their incentives. Try to catch them on the fly with the help of fraud prevention software and smart programming in recruitment screeners and question design and programming.
- Code open-ended questions to find patterns in the data.
- Create cross-tabulated tables to help organize the data if you do surveys.
- Transcribe interviews and focus group discussions to use tools to organize qualitative data to facilitate thematic analysis.
Step 6. Analyze & Report
- Keep the key objectives in mind to connect market research to business impact. Check: How To Connect Market Research To Business Impact
- Share preliminary results with key stakeholders, discuss, and check if they make sense from a practical standpoint.
- Focus on the story behind the numbers and how it supports your recommendations. Don’t do a data dump. Focus on insights.
Related Articles
- 10 Key Pieces of Advice On How to Do And Use Market Research
- Your Market Research Plan to Succeed As a Startup
- When to Use Different Types of Market Research
- Insightful Planning On A Tight Market Research Budget
- Top Reason Why Businesses Fail & What To Do About It
- Why Faster, Cheaper, and Better Market Research Is a Dangerous Illusion
- How to Align Business Goals With Market Research
- Myths & Misunderstandings About UX – MR Realities Podcast
- Savvy Businesses Realize the Value of Market Research
- Use Research Insights to Connect with Your Customers
- How To Connect Market Research To Business Impact
- Getting The Price Right Takes More Than Guesswork
- What To Value In A Market Research Vendor
- Don’t Let The Budget Dictate Your Market Research Approach
- Don’t Just Trust Your Gut — Do Research
- Market Segmentation Is Key To Success
- How To Use Social Media In Market Research
- 9 Product Development Strategies to Consider
- UX Research Methods For User-Centric Design
- Awareness, Attitude & Usage Metrics That Will Guide Your Success
- When Do You Need A Market Research Vendor?
Subscribe to our newsletter to get notified about future articles
Subscribe and don’t miss anything!
Recent Articles
- How AI Can Further Remove Researchers in Search of Productivity and Lower Costs
- Re: Design/Growth Podcast – Researching User Experiences for Business Growth
- Why You Need Positioning Concept Testing in New Product Development
- Why Conjoint Analysis Is Best for Price Research
- The Rise of UX
- Making the Case Against the Van Westendorp Price Sensitivity Meter
- How to Future-Proof Experience Management and Your Business
- When Using Focus Groups Makes Sense
- How to Make Segmentation Research Actionable
- How To Integrate Market Research and UX Research for Desired Business Outcomes
Popular Articles
- Which Rating Scales Should I Use?
- What To Consider in Survey Design
- 6 Decisions To Make When Designing Product Concept Tests
- Write Winning Product Concepts To Get Accurate Results In Concept Tests
- What Is Market Research?
- How to Use Qualitative and Quantitative Research in Product Development
- The Opportunity of UX Research Webinar
- 12 Research Techniques to Solve Choice Overload
- Concept Testing for UX Researchers
- UX Research Geeks Podcast – Using Market Research for Better Context in UX
- A Researcher’s Path – Data Stories Leaders At Work Podcast
- How to Leverage UX and Market Research To Understand Your Customers
- How To Improve Racial and Gender Inclusion in Survey Design

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
What is Marketing Research? Examples and Best Practices
12 min read

Marketing research is essentially a method utilized by companies to collect valuable information regarding their target market. Through the common practice of conducting market research, companies gather essential information that enables them to make informed decisions and develop products that resonate with consumers. It encompasses the gathering, analysis, and interpretation of data, which aids in identifying consumer demands, anticipating market trends, and staying ahead of the competition.
Exploratory research is one of the initial steps in the marketing research process. It helps businesses gain broad insights when specific information is unknown. If you are seeking insight into how marketing research can influence the trajectory of your SaaS, then you have come to the right place!
- Market research is a systematic and objective process crucial for understanding target markets, refining business strategies, and informing decisions, which includes collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data on customers, competitors, and the industry.
- Primary market research gathers specific data directly from the target audience using tools like surveys and focus groups, while secondary market research utilizes existing data from various sources to provide broader market insights.
- Effective market research combines both qualitative methods, which explore consumer motivations, and quantitative methods, which provide measurable statistics, to create comprehensive insights that guide business strategy and decision-making.
Try Userpilot and Take Your Product Marketing to the Next Level
- 14 Day Trial
- No Credit Card Required

Defining marketing research

Launching a product without knowing what your target audience wants is like walking in the dark. Market research lights the way, helping you collect, analyze, and understand information about your target market. This allows you to refine your business strategies and make decisions based on solid evidence.
Gone are the days when just intuition or subjective judgment was enough. Objective insights from market research help avoid costly mistakes and meet consumer needs by identifying trends and changes in the market. This is crucial for assessing a product’s potential success, optimizing marketing strategies, and preparing for market shifts.
Market research is a systematic approach that provides essential information, helping businesses navigate the complexities of the commercial world. Partnering with market research companies can offer additional benefits, leveraging their expertise in understanding market demands, trends, market size, economic indicators, location, market saturation, and pricing. Whether starting a new business, developing products, or updating marketing plans, understanding how to conduct effective market research is key to success.
To conduct market research effectively, businesses must determine study goals, identify target consumers, collect and analyze data, and use the findings to make informed decisions. This process is vital for evaluating past performance, measuring changes over time, and addressing specific business needs. It guides businesses in product development, marketing strategies, and overall decision-making, ensuring a better ROI and providing an eye-opening view of the market through various research methods, whether conducted in-house or outsourced.
The purpose of marketing research
Conducting marketing research is more than just gathering data; it’s about turning that data into actionable insights to refine your business strategies. This process helps you understand what motivates your customers, enabling you to tailor your products and services to minimize risks from the start. Importantly, market research plays a pivotal role in measuring and enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty, which are critical for understanding key demographics, improving user experience, designing better products, and driving customer retention. Customer satisfaction is measured as a key outcome, directly linked to the success of marketing strategies and business activities.
For SaaS product managers, market research, including competitive analysis, is crucial. It evaluates past strategies and gauges the potential success of new offerings. This research provides essential insights into brand strength, consumer behavior, and market position, which are vital for teams focused on sales, marketing, and product development.
A key aspect of market research is analyzing customer attitudes and usage. This analysis offers detailed insights into what customers want, the choices they make, and the challenges they face. It helps identify opportunities in the market and aids in formulating effective strategies for market entry.
Overall, market research equips SaaS entrepreneurs with the knowledge to meet their target audience’s needs effectively, guiding product adjustments and innovations based on informed decisions.
Key components of market research
Conducting market research is analogous to preparing a cake, requiring precise ingredients in specific quantities to achieve the intended outcome. Within this realm, necessary components consist of primary and secondary data gathering, thorough analysis, and insightful interpretation.
Primary research techniques such as exploratory studies, product evolution inquiries, estimations of market dimensions and shares, and consumer behavior examinations play a crucial role in collecting targeted information that can be directly applied. These methods afford a deeper understanding of your target demographic, allowing for customized strategy development.
In contrast, secondary research enriches the specificity of primary findings by adding wider context. It taps into external resources encompassing works from other investigators, sector-specific reports, and demographics data, which provide an expansive yet less particularized landscape view of the marketplace.
The subsequent phase involves meticulous analysis of collated data offering unbiased perspectives critical for identifying deficiencies while recognizing emerging patterns. Technological progress now facilitates examination efforts on both structured and unstructured datasets effectively addressing large-scale analytical complexities.
Ultimately, it’s through expert-led interpretation that value transcends raw figures, yielding strategies grounded in deep comprehension. Akin to decoding recipes using selected ingredients—this interpretative step enables crafting optimal business maneuvers just as one would bake their ideal confectionery creation utilizing proper culinary guidance.
Types of market research: primary and secondary
Now that you know the importance of clear research objectives, let’s explore the different types of market research and the techniques available to achieve these goals. Market research methods can be divided into two main categories: primary research and secondary research . The choice between these depends on factors like your budget, time constraints, and whether you need exploratory data or definitive answers.
Primary research involves collecting new data directly from sources. This process is like mining for precious metals, as it requires using various methods to gather fresh insights.
- Surveys (here – in-app survey templates from Userpilot ).
- Interviews.
- Focus groups.
- Product trials.
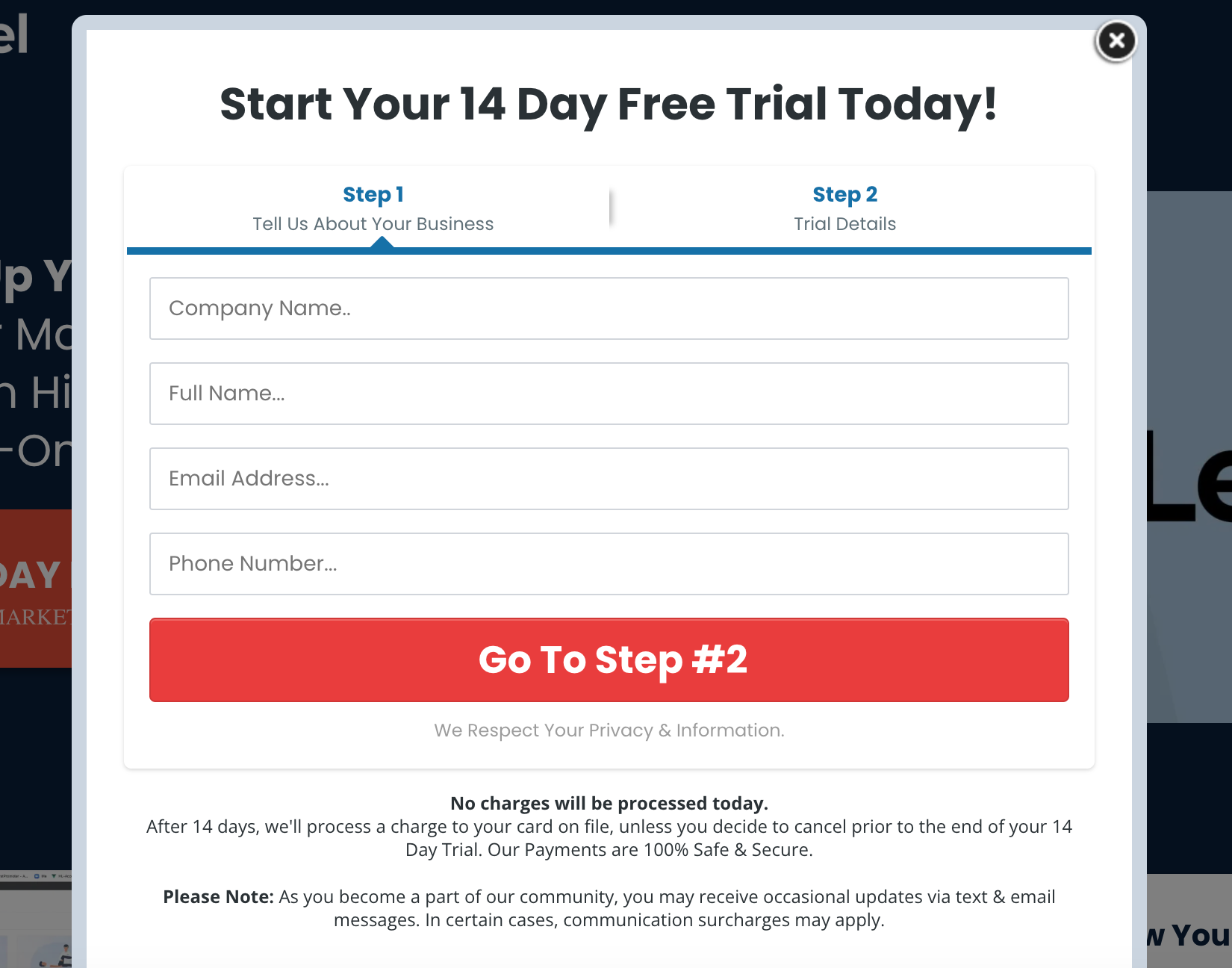
This approach gives you first-hand insight into your target audience.
Conversely, secondary research uses already established datasets of primary data – which can add depth and reinforcement to your firsthand findings.
Conducting your own market research using primary research tools can be a cost-effective strategy, allowing businesses to gather valuable insights directly and tailor their research to specific needs.
Let’s look a bit deeper into them now.
What is primary market research?
Market research uses primary market research as an essential tool. This involves collecting new data directly from your target audience using various methods, such as surveys , focus groups, and interviews.
Each method has its benefits. For example, observational studies allow you to see how consumers interact with your product.
There are many ways to conduct primary research.
Focus Groups : Hold discussions with small groups of 5 to 10 people from your target audience. These discussions can provide valuable feedback on products, perceptions of your company’s brand name, or opinions on competitors. Additionally, these discussions can help understand the characteristics, challenges, and buying habits of target customers, optimizing brand strategy.
Interviews : Have one-on-one conversations to gather detailed information from individuals in your target audience.
Surveys : These are a common tool in primary market research and can be used instead of focus groups to understand consumer attitudes. Surveys use structured questions and can reach a broad audience efficiently.
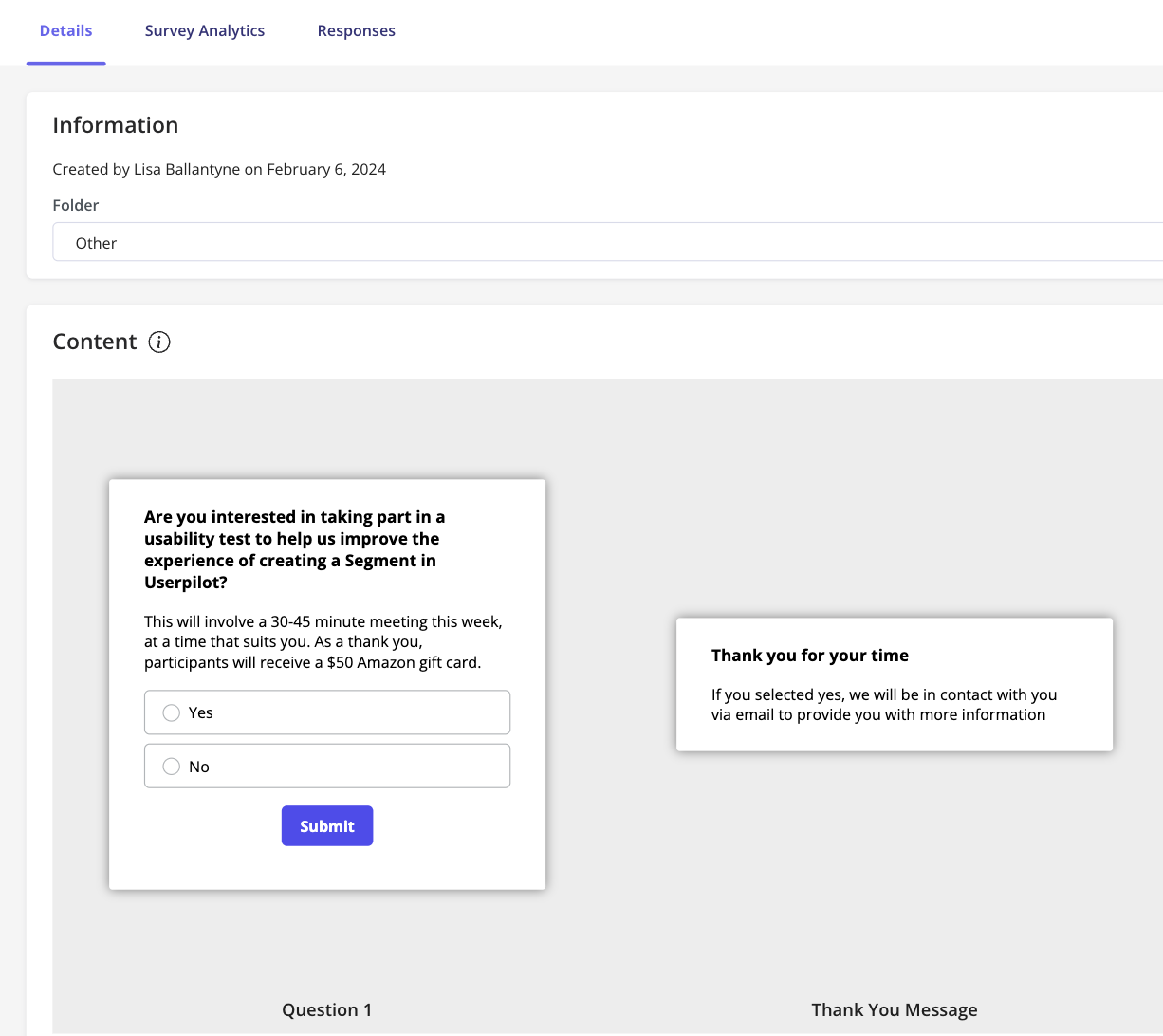
Navigating secondary market research
While marketing research using primary methods is like discovering precious metals, secondary market research technique is like using a treasure map. This approach uses data collected by others from various sources, providing a broad industry view. These sources include market analyses from agencies like Statista, historical data such as census records, and academic studies.
Secondary research provides the basic knowledge necessary for conducting primary market research goals but may lack detail on specific business questions and could also be accessible to competitors.
To make the most of secondary market research, it’s important to analyze summarized data to identify trends, rely on reputable sources for accurate data, and remain unbiased in data collection methods.
The effectiveness of secondary research depends significantly on how well the data is interpreted, ensuring that this information complements the insights from primary research.
Qualitative vs quantitative research
Market research employs both qualitative and quantitative methods, offering distinct insights that complement each other. Qualitative research aims to understand consumer behaviors and motivations through detailed analysis, while quantitative research collects measurable data for statistical analysis.
The selection of qualitative or quantitative methods should align with your research goals. If you need to uncover initial insights or explore deep consumer motivations, qualitative techniques like surveys or interviews are ideal.
On the other hand, if you need data that can be measured and analyzed for reliability, quantitative methods are more suitable.
However, these approaches don’t have to be used separately. Combining qualitative and quantitative methods in mixed-method studies allows you to capture both detailed exploratory responses and concrete numerical data. This integration offers a comprehensive view of the market, leveraging the strengths of both approaches to provide a fuller understanding of market conditions.
Implementing market research tools: Userpilot’s role
Similar to how a compass is essential for navigation at sea, businesses need appropriate instruments to carry out effective market research. Userpilot’s suite of product analytics and in-app engagement tools are critical components for this purpose.
Acting as a Buyer Persona Research instrument, Userpilot’s product analytics provide key quantitative research capabilities. This helps clearly define and comprehend the attributes and behaviors of potential customers, providing you with insights into your ICP (Ideal Customer Persona), user preferences, and product-market fit.
Beyond product analytics, Userpilot offers robust in-app engagement features such as modals and surveys that support real time collection of market research information. These interactive features work synergistically with the analytical tools to enable companies to gather detailed data and feedback crucial for informed business decision-making.
Marketing research process: Step-by-step guide
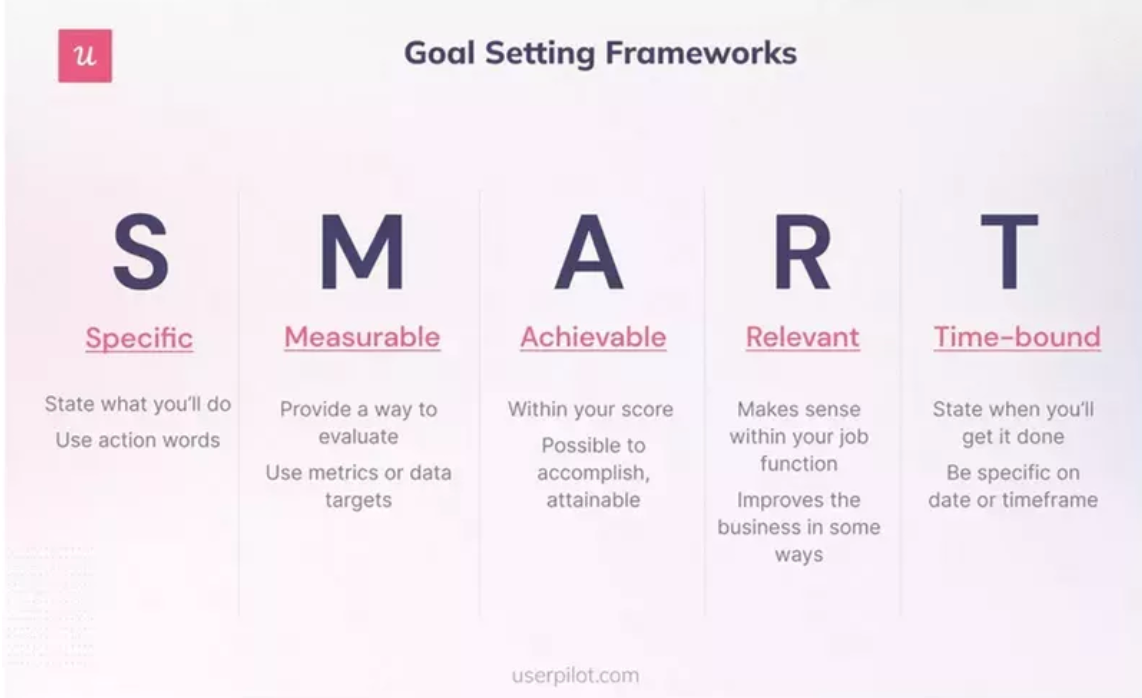
Marketing research conists of several critical stages:
- Defining precise goals.
- Delving into the knowledge of your target demographic.
- Collecting and scrutinizing data.
- Revealing insights that can be translated into tangible actions.
Following these steps allows you to gather critical information that guides business decisions.
An effective research strategy is crucial and involves:
- Properly allocating funds.
- Formulating testable hypotheses.
- Choosing appropriate methods for the study.
- Determining the number of study participants.
- Considering external variables.
A well-planned strategy ensures that your market research is focused, efficient, and produces useful outcomes.
After collecting data, the next step is to analyze it. This involves comparing the data to your initial questions to draw conclusions relevant to your business strategies.
Userpilot makes your data analysis easier by providing handy analytics dashboards for key user metrics such as activation, engagement, core feature adoption, and retention out of the box:
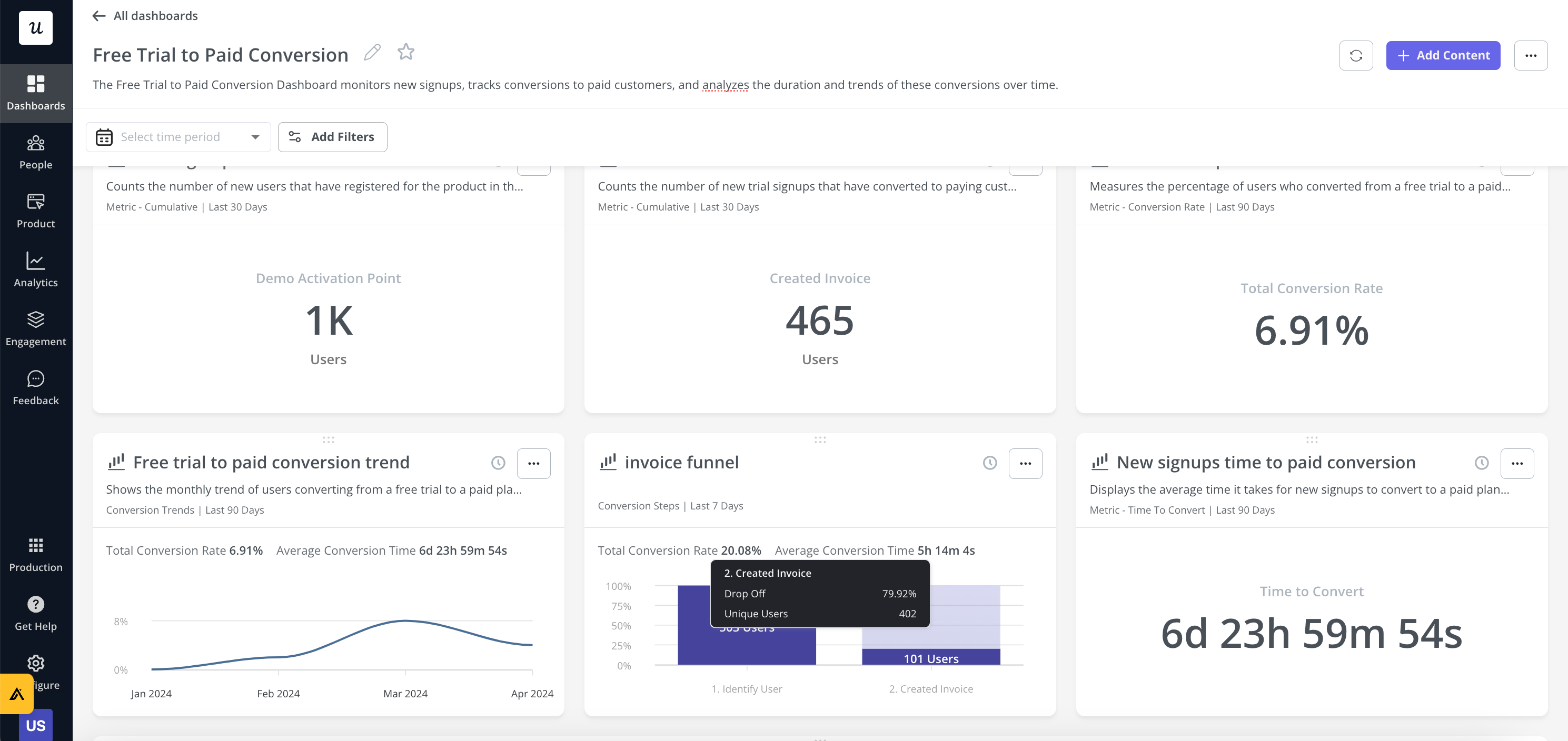
Finally, you report the findings and the process, providing recommendations based on the evidence. This is like solving a puzzle: each piece helps to complete the overall picture.
Challenges and best practices in market research
Delving into market research comes with its own set of hurdles. Those conducting the research must deliver more profound insights within increasingly shorter timespans, and they need to cultivate strategic, continuous research methods to stay abreast of an ever-changing business landscape.
Ensuring high-quality data can be demanding due to issues such as disjointed tools or insufficient analytical expertise. New solutions like Userpilot are surfacing that make these obstacles less daunting by offering accessible and user-friendly options. Maintaining clear lines of communication with your market research team is crucial for achieving both punctuality and quality in outcomes.
The advantages of engaging in marketing research cannot be overstated.
Real-life examples of successful market research
Real-life examples of market research in the SaaS industry often showcase innovative approaches to understanding customer needs and product-market fit.
For instance, Slack, the communication platform, utilized extensive market research to identify gaps in communication tools and understand the workflows of teams. This led to the development of features that seamlessly integrated with other tools and catered to the needs of various team sizes and structures.
Another example is HubSpot, which conducted market research to understand the pain points of small to medium-sized businesses in managing customer relationships. The insights gained helped shape their all-in-one inbound marketing, sales, and service platform, which has become integral to their users’ daily operations. These examples demonstrate how SaaS companies can employ market research to inform product development, improve user experience, and strategically position themselves in a competitive market.
Choosing the right market research tools
For B2B SaaS product managers aiming to do market research, having the right set of tools can make a significant difference. Here’s a list of valuable SaaS tools that can be leveraged for effective market research:
- Userpilot : A comprehensive Product Growth Platform offering in-depth product analytics, a code-free in-app experience builder, bespoke in-app survey capabilities, and robust integration options with platforms like Salesforce and Hubspot. This tool is particularly useful for understanding user behavior, enhancing user engagement, and gathering targeted feedback.
- Qualtrics : Known for its powerful survey tools, Qualtrics helps businesses gather and analyze customer feedback effectively. Its advanced analytics features are ideal for testing market hypotheses and understanding customer sentiments.
- SurveyMonkey : A versatile tool that enables product managers to create, send, and analyze surveys quickly and easily. SurveyMonkey is suitable for gauging customer satisfaction and collecting feedback on potential new features.
- Mixpanel : Specializes in user behavior analytics, offering detailed insights into how users interact with your product. This is essential for identifying patterns and optimizing product features.
- Hotjar : Combines analytics and feedback tools to give teams insights into user behavior and preferences. Hotjar’s heatmaps and session recordings are invaluable for understanding the user experience on a deeper level.
- Tableau : A leading platform for business intelligence and data visualization, Tableau allows product managers to create comprehensive visual reports that can inform strategic decisions based on user data analysis.
Each of these tools provides unique functionalities that can assist SaaS product managers in conducting thorough market research, thereby ensuring that their products are perfectly aligned with user needs and market demands.
Measuring the impact of market research
The pivotal challenge for market research lies in demonstrating its return on investment (ROI) and overall influence on corporate success sufficiently enough to justify regular financial commitment from company leaders. The worth attributed to a market research firm hinges not only on their ability to deliver relevant and high-caliber information, but also on their pricing structures and their contribution towards propelling organizational growth.
To gauge how effectively business choices made based on market research findings succeed, various metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) are utilized. These numerical tools act as navigational aids directing enterprises toward achieving objectives while simultaneously verifying that efforts invested in conducting market analysis are yielding fruitful guidance.
Throughout our look at market research, we’ve seen its importance and impact. Our discussion covered the basics of market research, its key components, and different types, including both qualitative and quantitative methods, and the role of Userpilot’s tools. We’ve examined the details of the market research process, tackled challenges, identified best practices, and shared success stories. We also provided advice on choosing the right market research partner and how to measure the effectiveness of your market research.
In today’s data-driven world, comprehensive market research is crucial for companies that want to succeed. It acts like a guide, helping businesses navigate the complex market landscape. Start your own detailed research today, supported by insightful analytics to help you succeed.
Frequently asked questions
What is market research and why is it important.
Understanding your target market, honing business strategies, and making informed decisions are all essential components that depend heavily on effective market research. It offers objective insights to help avoid expensive errors and foresees the needs of customers .
What is the difference between primary and secondary market research?
Primary market research is characterized by the direct gathering of data, in contrast to secondary market research which leverages existing information from alternative sources for addressing research inquiries.
Such a distinction can guide you in selecting an approach that aligns with your precise needs for conducting specific research.
What are some examples of successful market research?
Examples of successful market research are evident in the operations of well-known companies such as Starbucks, Apple, and McDonald’s. They have harnessed this tool to fine-tune their business strategies and make decisions based on solid information.
By employing market research, these businesses have managed to gain insight into their customers’ desires and needs, which has contributed significantly to their success.
How can I choose the right market research partner?
Selecting an ideal market research ally involves identifying a firm that resonates with your project requirements, financial plan, and corporate goals while also verifying their track record of dependability and consistency via reviews from previous clients.
Best wishes on your endeavor!
How is the impact of market research measured?
The effectiveness of market research hinges on the precision, representativeness, and pertinence of its data, along with how successful business decisions are when they’re based on the findings from this research. These elements define the impact of the research conducted.
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Get The Insights!
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth,Management & Trends.
The coolest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends. Delivered fresh to your inbox, weekly.
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends.
You might also be interested in ...
What are marketing funnels a comprehensive guide to streamlining your user journey, best marketing analytics software for saas, 24 customer retention marketing tactics to grow your customer base.
Aazar Ali Shad
Types of market research: Methods and examples

- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on LinkedIn

Here at GWI we publish a steady stream of blogs, reports, and other resources that dig deep into specific market research topics.
But what about the folks who’d appreciate a more general overview of market research that explains the big picture? Don’t they deserve some love too?
Of course they do. That’s why we’ve created this overview guide focusing on types of market research and examples. With so many market research companies to choose from, having a solid general understanding of how this sector works is essential for any brand or business that wants to pick the right market research partner.
So with that in mind, let’s start at the very beginning and get clear on…
Market research definition
At the risk of stating the slightly obvious, market research is the gathering and analyzing of data on consumers, competitors, distributors, and markets. As such it’s not quite the same as consumer research , but there’s significant overlap.
Market research matters because it can help you take the guesswork out of getting through to audiences. By studying consumers and gathering information on their likes, dislikes, and so on, brands can make evidence-based decisions instead of relying on instinct or experience.
What is market research?
Market research is the organized gathering of information about target markets and consumers’ needs and preferences. It’s an important component of business strategy and a major factor in maintaining competitiveness.
If a business wants to know – really know – what sort of products or services consumers want to buy, along with where, when, and how those products and services should be marketed, it just makes sense to ask the prospective audience.
Without the certainty that market research brings, a business is basically hoping for the best. And while we salute their optimism, that’s not exactly a reliable strategy for success.
What are the types of market research?
Primary research .
Primary research is a type of market research you either conduct yourself or hire someone to do on your behalf.
A classic example of primary research involves going directly to a source – typically customers or prospective customers in your target market – to ask questions and gather information about a product or service. Interviewing methods include in-person, online surveys, phone calls, and focus groups.
The big advantage of primary research is that it’s directly focused on your objectives, so the outcome will be conclusive, detailed insights – particularly into customer views – making it the gold standard.
The disadvantages are it can be time-consuming and potentially costly, plus there’s a risk of survey bias creeping in, in the sense that research samples may not be representative of the wider group.
Secondary research
Primary market research means you collect the data your business needs, whereas the types of market research known as secondary market research use information that’s already been gathered for other purposes but can still be valuable. Examples include published market studies, white papers, analyst reports, customer emails, and customer surveys/feedback.
For many small businesses with limited budgets, secondary market research is their first choice because it’s easier to acquire and far more affordable than primary research.
Secondary research can still answer specific business questions, but with limitations. The data collected from that audience may not match your targeted audience exactly, resulting in skewed outcomes.
A big benefit of secondary market research is helping lay the groundwork and get you ready to carry out primary market research by making sure you’re focused on what matters most.

Qualitative research
Qualitative research is one of the two fundamental types of market research. Qualitative research is about people and their opinions. Typically conducted by asking questions either one-on-one or in groups, qualitative research can help you define problems and learn about customers’ opinions, values, and beliefs.
Classic examples of qualitative research are long-answer questions like “Why do you think this product is better than competitive products? Why do you think it’s not?”, or “How would you improve this new service to make it more appealing?”
Because qualitative research generally involves smaller sample sizes than its close cousin quantitative research, it gives you an anecdotal overview of your subject, rather than highly detailed information that can help predict future performance.
Qualitative research is particularly useful if you’re developing a new product, service, website or ad campaign and want to get some feedback before you commit a large budget to it.
Quantitative research
If qualitative research is all about opinions, quantitative research is all about numbers, using math to uncover insights about your audience.
Typical quantitative research questions are things like, “What’s the market size for this product?” or “How long are visitors staying on this website?”. Clearly the answers to both will be numerical.
Quantitative research usually involves questionnaires. Respondents are asked to complete the survey, which marketers use to understand consumer needs, and create strategies and marketing plans.
Importantly, because quantitative research is math-based, it’s statistically valid, which means you’re in a good position to use it to predict the future direction of your business.
Consumer research
As its name implies, consumer research gathers information about consumers’ lifestyles, behaviors, needs and preferences, usually in relation to a particular product or service. It can include both quantitative and qualitative studies.
Examples of consumer research in action include finding ways to improve consumer perception of a product, or creating buyer personas and market segments, which help you successfully market your product to different types of customers.
Understanding consumer trends , driven by consumer research, helps businesses understand customer psychology and create detailed purchasing behavior profiles. The result helps brands improve their products and services by making them more customer-centric, increasing customer satisfaction, and boosting bottom line in the process.
Product research
Product research gives a new product (or indeed service, we don’t judge) its best chance of success, or helps an existing product improve or increase market share.
It’s common sense: by finding out what consumers want and adjusting your offering accordingly, you gain a competitive edge. It can be the difference between a product being a roaring success or an abject failure.
Examples of product research include finding ways to develop goods with a higher value, or identifying exactly where innovation effort should be focused.
Product research goes hand-in-hand with other strands of market research, helping you make informed decisions about what consumers want, and what you can offer them.
Brand research
Brand research is the process of gathering feedback from your current, prospective, and even past customers to understand how your brand is perceived by the market.
It covers things like brand awareness, brand perceptions, customer advocacy, advertising effectiveness, purchase channels, audience profiling, and whether or not the brand is a top consideration for consumers.
The result helps take the guesswork out of your messaging and brand strategy. Like all types of market research, it gives marketing leaders the data they need to make better choices based on fact rather than opinion or intuition.
Market research methods
So far we’ve reviewed various different types of market research, now let’s look at market research methods, in other words the practical ways you can uncover those all-important insights.
Consumer research platform
A consumer research platform like GWI is a smart way to find on-demand market research insights in seconds.
In a world of fluid markets and changing attitudes, a detailed understanding of your consumers, developed using the right research platform, enables you to stop guessing and start knowing.
As well as providing certainty, consumer research platforms massively accelerate speed to insight. Got a question? Just jump on your consumer research platform and find the answer – job done.
The ability to mine data for answers like this is empowering – suddenly you’re in the driving seat with a world of possibilities ahead of you. Compared to the most obvious alternative – commissioning third party research that could take weeks to arrive – the right consumer research platform is basically a magic wand.
Admittedly we’re biased, but GWI delivers all this and more. Take our platform for a quick spin and see for yourself.
And the downside of using a consumer research platform? Well, no data set, however fresh or thorough, can answer every question. If you need really niche insights then your best bet is custom market research , where you can ask any question you like, tailored to your exact needs.
Face-to-face interviews
Despite the rise in popularity of online surveys , face-to-face survey interviewing – using mobile devices or even the classic paper survey – is still a popular data collection method.
In terms of advantages, face-to-face interviews help with accurate screening, in the sense the interviewee can’t easily give misleading answers about, say, their age. The interviewer can also make a note of emotions and non-verbal cues.
On the other hand, face-to-face interviews can be costly, while the quality of data you get back often depends on the ability of the interviewer. Also, the size of the sample is limited to the size of your interviewing staff, the area in which the interviews are conducted, and the number of qualified respondents within that area.
Social listening
Social listening is a powerful solution for brands who want to keep an ear to the ground, gathering unfiltered thoughts and opinions from consumers who are posting on social media.
Many social listening tools store data for up to a couple of years, great for trend analysis that needs to compare current and past conversations.
Social listening isn’t limited to text. Images, videos, and emojis often help us better understand what consumers are thinking, saying, and doing better than more traditional research methods.
Perhaps the biggest downside is there are no guarantees with social listening, and you never know what you will (or won’t) find. It can also be tricky to gauge sentiment accurately if the language used is open to misinterpretation, for example if a social media user describes something as “sick”.
There’s also a potential problem around what people say vs. what they actually do. Tweeting about the gym is a good deal easier than actually going. The wider problem – and this may shock you – is that not every single thing people write on social media is necessarily true, which means social listening can easily deliver unreliable results.
Public domain data
Public domain data comes from think tanks and government statistics or research centers like the UK’s National Office for Statistics or the United States Census Bureau and the National Institute of Statistical Sciences. Other sources are things like research journals, news media, and academic material.
Its advantages for market research are it’s cheap (or even free), quick to access, and easily available. Public domain datasets can be huge, so potentially very rich.
On the flip side, the data can be out of date, it certainly isn’t exclusive to you, and the collection methodology can leave much to be desired. But used carefully, public domain data can be a useful source of secondary market research.
Telephone interviews
You know the drill – you get a call from a researcher who asks you questions about a particular topic and wants to hear your opinions. Some even pay or offer other rewards for your time.
Telephone surveys are great for reaching niche groups of consumers within a specific geographic area or connected to a particular brand, or who aren’t very active in online channels. They’re not well-suited for gathering data from broad population groups, simply because of the time and labor involved.
How to use market research
Data isn’t an end in itself; instead it’s a springboard to make other stuff happen. So once you’ve drawn conclusions from your research, it’s time to think of what you’ll actually do based on your findings.
While it’s impossible for us to give a definitive list (every use case is different), here are some suggestions to get you started.
Leverage it . Think about ways to expand the use – and value – of research data and insights, for example by using research to support business goals and functions, like sales, market share or product design.
Integrate it . Expand the value of your research data by integrating it with other data sources, internal and external. Integrating data like this can broaden your perspective and help you draw deeper insights for more confident decision-making.
Justify it . Enlist colleagues from areas that’ll benefit from the insights that research provides – that could be product management, product development, customer service, marketing, sales or many others – and build a business case for using research.
How to choose the right type of market research
Broadly speaking, choosing the right research method depends on knowing the type of data you need to collect. To dig into ideas and opinions, choose qualitative; to do some testing, it’s quantitative you want.
There are also a bunch of practical considerations, not least cost. If a particular approach sounds great but costs the earth then clearly it’s not ideal for any brand on a budget.
Then there’s how you intend to use the actual research, your level of expertise with research data, whether you need access to historical data or just a snapshot of today, and so on.
The point is, different methods suit different situations. When choosing, you’ll want to consider what you want to achieve, what data you’ll need, the pros and cons of each method, the costs of conducting the research, and the cost of analyzing the results.
Market research examples
Independent agency Bright/Shift used GWI consumer insights to shape a high-impact go-to-market strategy for their sustainable furniture client, generating £41K in revenue in the first month. Here’s how they made the magic happen .
Never miss a post
By subscribing you confirm you’re happy for us to send you our latest articles.
You’ve read our blog, now see our platform
Every business has questions about its audiences, GWI has answers. Powered by consistent, global research, our platform is an on-demand window into their world.
What Is Market Research?
Market research is a process where businesses collect and analyze data on specific markets, customers and consumers.
With the goal of becoming a customer-focused company , organizations will follow research methods to gain a better understanding of their desired audiences and how to interact with them. Any information gathered provides insights into how companies can make their products more appealing to potential customers.
What are the main purposes of market research?
- Knowing what people want ahead of time enables companies to make more informed business decisions.
Releasing a product or service without knowing how it will perform presents a huge risk. Market research exists to gain more insight before going all-in on a new product. Companies conduct research to determine what problems their audiences face and how their products can resolve these issues.
Understanding customer preferences has become crucial to saving companies time and money, making market research a key component of the product development process. Rather than just releasing products into the market, businesses take the time to determine how these products will perform. This approach enables companies to spend resources more efficiently while earning the trust of consumers with more relevant products.
What are the types of market research?
- Different circumstances call for unique types of market research, which range from one-on-one interviews to focus group conversations.
Market research takes on many forms, so teams must determine the types of market research that best serve their needs. If a company wants to elicit feedback from larger samples, surveys and focus groups are ideal options. However, businesses should keep in mind that these practices deliver breadth at the expense of depth.
Interviews cater more to companies that want to dive into specific details with customers. Unique value propositions may require these more intimate interactions as businesses pursue ways to improve customers’ experiences with their products. Observations and field tests also provide genuine customer reactions, but with a subtler approach. Companies can decide on the best method by defining the initial problem and goals for their research.
What are the steps in the marketing research process?
- Before marketing teams undertake product launches , they need to gather extensive insights into audience preferences and general market trends.
To enhance a product or service, a company must gather plenty of information on its ideal customers and competitors. Defining a target audience allows teams to get a sense of what issues customers may face and how their products can address those concerns. In addition, conducting a competitor analysis lets teams know what companies in their market are doing and how they can help their product stand out from similar ones.
Once marketing teams sort out these details, they can focus their attention on executing a research plan. Determining the sample size and desired outcome helps members decide what type of research methods they want to employ. By following these practices, companies can craft more minimum viable products , which customers will find better suited to their needs.
Recent Expert Contributors Articles


Research Questionnaire
Questionnaire generator.

When a researcher creates a research paper using the scientific method they will need to use a gathering method that is adjacent to the research topic. This means that the researcher will use a quantitative research method for a quantitive topic and a qualitative method for a qualitative one. The research questionnaire is one of the quantitative data-gathering methods a researcher can use in their research paper.
1. Market Research Questionnaire Template Example
- Google Docs
- Apple Pages
Size: 38 KB
2. Market Research Questionnaire Example

Size: 94 KB
3. Research Questionnaire Example

4. Sample Market Research Questionnaire
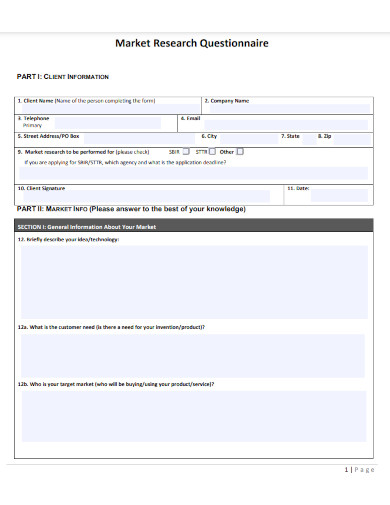
Size: 35 KB
5. Research Survey Questionnaire

Size: 42 KB
6. Research Survey Questionnaire Construction

Size: 80 KB
7. Research Questionnaire Survey of Consumers

Size: 39 KB
8. Guide to the Design of Research Questionnaires

Size: 77 KB
9. Planning Survey Research Questionnaires

Size: 85 KB
10. Climate Change Survey Questionnaires
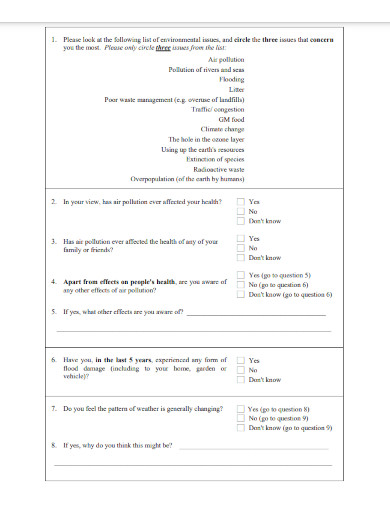
Size: 41 KB
11. Survey Questionnaire Design

Size: 96 KB
12. Developing Questionnaires for Educational Research

Size: 81 KB
13. Graudate Research Student Questionnaires

14. Sample Research Survey Questionnaires

Size: 46 KB
15. Market Research Questionnaire Example

16. Research Survey Questionnaire Example
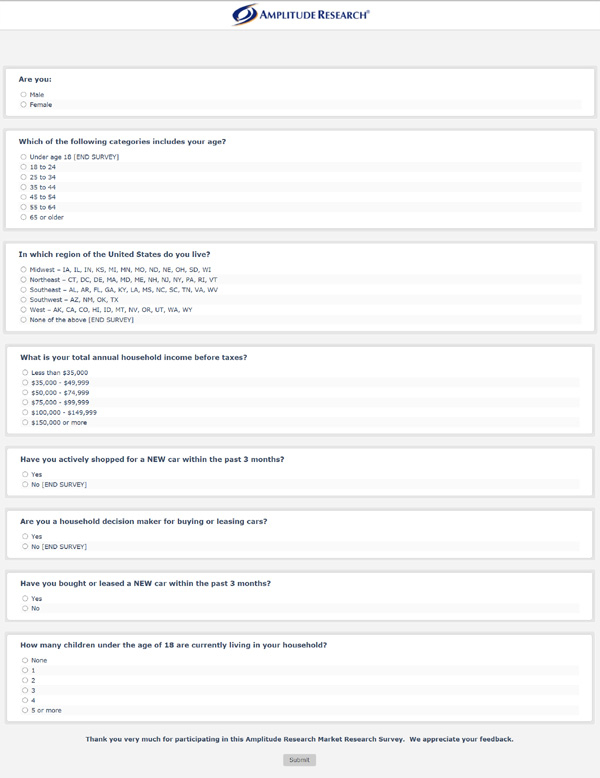
17. Product X Research Study Questionnaire Example

What Is a Research Questionnaire?
A research questionnaire is a physical or digital questionnaire that researchers use to obtain quantitative data. The research questionnaire is a more in-depth version of a survey as its questions often delve deeper than survey questions .
How to Write a Research Questionnaire
A well-made research questionnaire can effectively and efficiently gather data from the population. Creating a good research questionnaire does not require that many writing skills , soft skills , or hard skills , it just requires the person to properly understand the data set they are looking for.
Step 1: Select a Topic or Theme for the Research Questionnaire
Begin by choosing a topic or theme for the research questionnaire as this will provide much-needed context for the research questionnaire. Not only that but the topic will also dictate the tone of the questions in the questionnaire.
Step 2: Obtain or Use a Research Questionnaire Outline
You may opt to use a research questionnaire outline or outline format for your research questionnaire. This outline will provide you with a structure you can use to easily make your research questionnaire.
Step 3: Create your Research Questionnaire
Start by creating questions that will help provide you with the necessary data to prove or disprove your research question. You may conduct brainstorming sessions to formulate the questions for your research questionnaire.
Step 4: Edit and Have Someone Proofread the Questionnaire
After you have created and completed the research questionnaire, you must edit the contents of the questionnaire. Not only that but it is wise to have someone proofread the contents of your questionnaire before deploying the questionnaire.
How does a research questionnaire help businesses?
A successful business or company utilizes research questionnaires to not only obtain data from their customers but also to gather data about the performance and quality of the employees in the business. The research questionnaire provides the business or company with actionable data, which they can use to improve the product, service, or commodity to obtain more customers.
Do I need to provide a consent form when I ask someone to answer the research questionnaire?
Yes, consent is very important as without this the data you have gathered from your questionnaires or surveys are useless. Therefore it is important to provide a consent form with your research questionnaire when you are asking a participant to answer the document.
What type of answers are allowed in the research questionnaire?
Research questionnaires can host a multitude of types of questions each with its specific way of answering. A questionnaire can use multiple-choice questions, open-ended questions, and closed questions. Just be sure to properly pace the questions as having too many different types of answering styles can demotivate or distract the target audience, which might lead to errors.
A research questionnaire is a data-gathering document people can use to obtain information and data from a specific group of people. Well-made and crafted research questionnaires will provide much-needed information one can use to answer a specific research question.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a fun quiz to find out which historical figure you're most like in your study habits
Design a survey to discover students' favorite school subjects and why they love them.
Mobile Menu Overlay
The White House 1600 Pennsylvania Ave NW Washington, DC 20500
FACT SHEET: Biden- Harris Administration Announces Temporary Pause on Pending Approvals of Liquefied Natural Gas Exports
President Biden has been clear that climate change is the existential threat of our time – and we must act with the urgency it demands to protect the future for generations to come. That’s why, since Day One, President Biden has led and delivered on the most ambitious climate agenda in history, which is lowering energy costs for hardworking Americans, creating millions of good-paying jobs, safeguarding the health of our communities, and ensuring America leads the clean energy future. Today, the Biden-Harris Administration is announcing a temporary pause on pending decisions on exports of Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) to non-FTA countries until the Department of Energy can update the underlying analyses for authorizations. The current economic and environmental analyses DOE uses to underpin its LNG export authorizations are roughly five years old and no longer adequately account for considerations like potential energy cost increases for American consumers and manufacturers beyond current authorizations or the latest assessment of the impact of greenhouse gas emissions. Today, we have an evolving understanding of the market need for LNG, the long-term supply of LNG, and the perilous impacts of methane on our planet. We also must adequately guard against risks to the health of our communities, especially frontline communities in the United States who disproportionately shoulder the burden of pollution from new export facilities. The pause, which is subject to exception for unanticipated and immediate national security emergencies, will provide the time to integrate these critical considerations. The U.S. is already the number one exporter of LNG worldwide – with U.S. LNG exports expected to double by the end of this decade. At the same time, the U.S. remains unwavering in our commitment to supporting our allies around the world. Today’s announcement will not impact our ability to continue supplying LNG to our allies in the near-term. Last year, roughly half of U.S. LNG exports went to Europe, and the U.S. has worked with the E.U. to successfully economize consumption and manage its storage to ensure that unprovoked acts of aggression cannot threaten its supply. Furthermore, in 2022, the E.U and U.S. pledged to work toward the goal of ensuring additional LNG volumes for the E.U. market – with the U.S. exceeding our annual delivery targets to the E.U. in each of the past two years. Through existing LNG production and export infrastructure, the U.S. has – and will continue – to deliver for our allies. As Republicans in Congress continue to deny the very existence of climate change while attempting to strip their constituents of the economic, environmental and health benefits of the President’s historic climate investments, the Biden-Harris Administration will continue to lead the way in ambitious climate action while ensuring the American economy remains the envy of the world. Biden-Harris Administration’s Top Climate Accomplishments:
- Signed into law the largest climate investment in history, the Inflation Reduction Act , which has already created 210,000 new jobs across nearly every state and attracted more than $200 billion in private clean energy investments ($365 billion since President Biden took office), while putting the U.S. on a path to meet our climate goals and reach 80% clean energy by 2030 – in addition to securing the American Rescue Plan, Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, and CHIPS and Science Act
- Established a whole-of-government strategy to tackle methane emissions – from plugging wells and leaks in the oil and gas sector, to reclaiming abandoned coal mines, to reducing food waste and agricultural emissions, and finalized a historic rule to reduce methane emissions from oil and gas operations by nearly 80%, delivering billions of dollars in health and economic benefits
- Launched the American Climate Corps to mobilize a new, diverse generation of Americans – putting them to work conserving and restoring our lands and waters, bolstering community resilience, deploying clean energy, implementing energy efficient technologies, and advancing environmental justice, all while creating pathways to high-quality, good-paying jobs
- Advancing the most ambitious environmental justice agenda in history , including by signing a historic Executive Order that calls on the federal government to bring clean energy and healthy environments to all and mitigate harm to those who have suffered from toxic pollution and other environmental burdens like climate change; delivering on the Justice40 initiative, which is ensuring that the benefits of President Biden’s historic investments in America – from clean energy projects to floodwater protections – reach communities that need them most; replacing lead pipes and taking action to protect communities from PFAS pollution; accelerating Superfund cleanups; tightening air quality enforcement near pollution facilities; and more
- Protected 26 million acres of lands and waters – on track to conserve more lands and waters than any President in history – including five new national monuments that include protections for lands in Colorado, Nevada, Texas, and most recently, the Baaj Nwaavjo I’tah Kukveni – Ancestral Footprints of the Grand Canyon National Monument in Arizona; initiating new national marine sanctuaries as part of the President’s goal of conserving 30% of lands and waters by 2030, delivering billions of dollars to accelerate land, water, and wildlife conservation efforts in all 50 states, territories, the District of Columbia, and Tribal nations; and more
- Canceled remaining oil and gas leases issued by the previous administration in the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge, proposed protections for more than 13 million acres in the National Petroleum Reserve in Alaska, and withdrew approximately 2.8 million acres of the Beaufort Sea, ensuring the entire United States Arctic Ocean is off limits to new oil and gas leasing
- Signed an Executive Order that sets an ambitious target to make half of all new vehicles sold in 2030 zero-emissions , while proposing strongest-ever limits on tail pipe emissions and issuing fuel economy standards , giving Americans more choices about the cars they drive, and saving Americans hundreds of dollars at the pump
- Proposed carbon pollution standards for coal and gas-fired power plant emissions that would avoid hundreds of millions of tons of carbon dioxide emissions and protect people’s health
- Accelerated permitting of clean energy projects , including 47 projects on public lands that total 11.2 megawatts of wind, solar and geothermal energy on public lands – enough to power more than 3.5 million homes, and broke ground on 10 major transmission projects , which are slated to connect 19.5 gigawatts of new generation to the grid
- Rallied world leaders to raise global climate ambition , including by securing commitments from more than 155 countries to reduce methane emissions by at least 30 percent by 2030, joining leaders at COP28 to commit, for the first time, to transition away from fossil fuels, end new unabated coal capacity globally, and agree to triple renewable energy globally by 2030
- Invoked the Defense Production Act using emergency authority on the basis of climate change to increase domestic production of key clean energy technologies , such as solar, transformers and electric grid components, and heat pumps
Stay Connected
We'll be in touch with the latest information on how President Biden and his administration are working for the American people, as well as ways you can get involved and help our country build back better.
Opt in to send and receive text messages from President Biden.
4.3 Steps in the Marketing Research Process
Learning objectives.
After reading this section, students should be able to …
- Describe the basic steps in the marketing research process and the purpose of each step.
The basic steps used to conduct marketing research are shown in Figure 4.6 “Steps in the Marketing Research Process”. Next, we discuss each step.
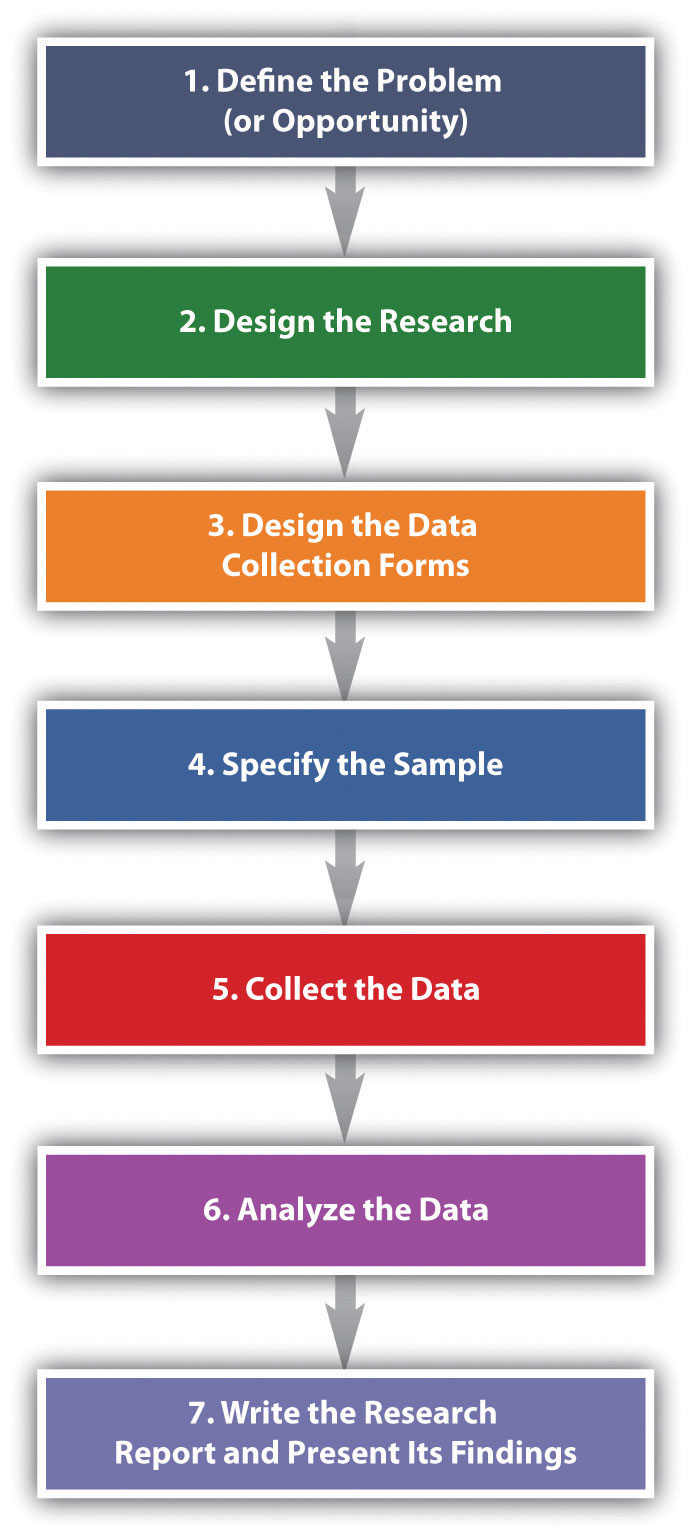
Figure 4.6: Steps in the Marketing Research Process
Step 1: Define the Problem (or Opportunity)
There’s a saying in marketing research that a problem half defined is a problem half solved. Defining the “problem” of the research sounds simple, doesn’t it? Suppose your product is tutoring other students in a subject you’re a whiz at. You have been tutoring for a while, and people have begun to realize you’re darned good at it. Then, suddenly, your business drops off. Or it explodes, and you can’t cope with the number of students you’re being asked help. If the business has exploded, should you try to expand your services? Perhaps you should subcontract with some other “whiz” students. You would send them students to be tutored, and they would give you a cut of their pay for each student you referred to them.
Both of these scenarios would be a problem for you, wouldn’t they? They are problems insofar as they cause you headaches. But are they really the problem? Or are they the symptoms of something bigger? For example, maybe your business has dropped off because your school is experiencing financial trouble and has lowered the number of scholarships given to incoming freshmen. Consequently, there are fewer total students on campus who need your services. Conversely, if you’re swamped with people who want you to tutor them, perhaps your school awarded more scholarships than usual, so there are a greater number of students who need your services. Alternately, perhaps you ran an ad in your school’s college newspaper, and that led to the influx of students wanting you to tutor them. Businesses are in the same boat you are as a tutor. They take a look at symptoms and try to drill down to the potential causes. If you approach a marketing research company with either scenario—either too much or too little business—the firm will seek more information from you such as the following:
• In what semester(s) did your tutoring revenues fall (or rise)?
• In what subject areas did your tutoring revenues fall (or rise)?
• In what sales channels did revenues fall (or rise): Were there fewer (or more) referrals from professors or other students? Did the ad you ran result in fewer (or more) referrals this month than in the past months?
• Among what demographic groups did your revenues fall (or rise)—women or men, people with certain majors, or first-year, second-, third-, or fourth-year students?
The key is to look at all potential causes so as to narrow the parameters of the study to the information you actually need to make a good decision about how to fix your business if revenues have dropped or whether or not to expand it if your revenues have exploded. The next task for the researcher is to put into writing the research objective. The research objective is the goal(s) the research is supposed to accomplish. The marketing research objective for your tutoring business might read as follows:
To survey college professors who teach 100- and 200-level math courses to determine why the number of students referred for tutoring dropped in the second semester. This is admittedly a simple example designed to help you understand the basic concept. If you take a marketing research course, you will learn that research objectives get a lot more complicated than this. The following is an example:
“To gather information from a sample representative of the U.S. population among those who are ‘very likely’ to purchase an automobile within the next 6 months, which assesses preferences (measured on a 1–5 scale ranging from ‘very likely to buy’ to ‘not likely at all to buy’) for the model diesel at three different price levels. Such data would serve as input into a forecasting model that would forecast unit sales, by geographic regions of the country, for each combination of the model’s different prices and fuel configurations (Burns & Bush, 2010).”
Now do you understand why defining the problem is complicated and half the battle? Many a marketing research effort is doomed from the start because the problem was improperly defined. Coke’s ill-fated decision to change the formula of Coca-Cola in 1985 is a case in point: Pepsi had been creeping up on Coke in terms of market share over the years as well as running a successful promotional campaign called the “Pepsi Challenge,” in which consumers were encouraged to do a blind taste test to see if they agreed that Pepsi was better. Coke spent four years researching “the problem.” Indeed, people seemed to like the taste of Pepsi better in blind taste tests. Thus, the formula for Coke was changed. But the outcry among the public was so great that the new formula didn’t last long—a matter of months—before the old formula was reinstated. Some marketing experts believe Coke incorrectly defined the problem as “How can we beat Pepsi in taste tests?” instead of “How can we gain market share against Pepsi?” (Burns & Bush, 2010)
Watch Video Clip: New Coke Is It! 1985
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W6t7deaplgY
This video documents the Coca-Cola Company’s ill-fated launch of New Coke in 1985.
Watch Video Clip: 1985 Pepsi Commercial—“They Changed My Coke”
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8_hvOBnsirI
This video shows how Pepsi tried to capitalize on the blunder.
Step 2: Design the Research
The next step in the marketing research process is to do a research design. The research design is your “plan of attack.” It outlines what data you are going to gather and from whom, how and when you will collect the data, and how you will analyze it once it’s been obtained. Let’s look at the data you’re going to gather first.
There are two basic types of data you can gather. The first is primary data. Primary data is information you collect yourself, using hands-on tools such as interviews or surveys, specifically for the research project you’re conducting. Secondary data is data that has already been collected by someone else, or data you have already collected for another purpose. Collecting primary data is more time consuming, work intensive, and expensive than collecting secondary data. Consequently, you should always try to collect secondary data first to solve your research problem, if you can. A great deal of research on a wide variety of topics already exists. If this research contains the answer to your question, there is no need for you to replicate it. Why reinvent the wheel?
Sources of Secondary Data
Your company’s internal records are a source of secondary data. So are any data you collect as part of your marketing intelligence gathering efforts. You can also purchase syndicated research. Syndicated research is primary data that marketing research firms collect on a regular basis and sell to other companies. J.D. Power & Associates is a provider of syndicated research. The company conducts independent, unbiased surveys of customer satisfaction, product quality, and buyer behavior for various industries. The company is best known for its research in the automobile sector. One of the best-known sellers of syndicated research is the Nielsen Company, which produces the Nielsen ratings. The Nielsen ratings measure the size of television, radio, and newspaper audiences in various markets. You have probably read or heard about TV shows that get the highest (Nielsen) ratings. (Arbitron does the same thing for radio ratings.) Nielsen, along with its main competitor, Information Resources, Inc. (IRI), also sells businesses scanner-based research. Scanner-based research is information collected by scanners at checkout stands in stores. Each week Nielsen and IRI collect information on the millions of purchases made at stores. The companies then compile the information and sell it to firms in various industries that subscribe to their services. The Nielsen Company has also recently teamed up with Facebook to collect marketing research information. Via Facebook, users will see surveys in some of the spaces in which they used to see online ads (Rappeport, Gelles, 2009)
By contrast, MarketResearch.com is an example of a marketing research aggregator. A marketing research aggregator is a marketing research company that doesn’t conduct its own research and sell it. Instead, it buys research reports from other marketing research companies and then sells the reports in their entirety or in pieces to other firms. Check out MarketResearch.com’s Web site. As you will see there are a huge number of studies in every category imaginable that you can buy for relatively small amounts of money
Figure 4.7: Secondary data
Market research aggregators buy research reports from other marketing research companies and then resell them in part or in whole to other companies so they don’t have to gather primary data.
Your local library is a good place to gather free secondary data. It has searchable databases as well as handbooks, dictionaries, and books, some of which you can access online. Government agencies also collect and report information on demographics, economic and employment data, health information, and balance-of-trade statistics, among a lot of other information. The U.S. Census Bureau collects census data every ten years to gather information about who lives where. Basic demographic information about sex, age, race, and types of housing in which people live in each U.S. state, metropolitan area, and rural area is gathered so that population shifts can be tracked for various purposes, including determining the number of legislators each state should have in the U.S. House of Representatives. For the U.S. government, this is primary data. For marketing managers it is an important source of secondary data.
The Survey Research Center at the University of Michigan also conducts periodic surveys and publishes information about trends in the United States. One research study the center continually conducts is called the “Changing Lives of American Families” (http://www.isr.umich.edu/home/news/research-update/2007-01.pdf). This is important research data for marketing managers monitoring consumer trends in the marketplace. The World Bank and the United Nations are two international organizations that collect a great deal of information. Their Web sites contain many free research studies and data related to global markets. Table 10.1 “Examples of Primary Data Sources versus Secondary Data Sources” shows some examples of primary versus secondary data sources.
Table 4.2 Examples of Primary Data Sources versus Secondary Data Sources
Gauging the Quality of Secondary Data
When you are gathering secondary information, it’s always good to be a little skeptical of it. Sometimes studies are commissioned to produce the result a client wants to hear—or wants the public to hear. For example, throughout the twentieth century, numerous studies found that smoking was good for people’s health. The problem was the studies were commissioned by the tobacco industry. Web research can also pose certain hazards. There are many biased sites that try to fool people that they are providing good data. Often the data is favorable to the products they are trying to sell. Beware of product reviews as well. Unscrupulous sellers sometimes get online and create bogus ratings for products. See below for questions you can ask to help gauge the credibility of secondary information.
Gauging the Credibility of Secondary Data: Questions to Ask
- Who gathered this information?
- For what purpose?
- What does the person or organization that gathered the information have to gain by doing so?
- Was the information gathered and reported in a systematic manner?
- Is the source of the information accepted as an authority by other experts in the field?
- Does the article provide objective evidence to support the position presented?
Types of Research Design
Now let’s look specifically at the types of research designs that are utilized. By understanding different types of research designs, a researcher can solve a client’s problems more quickly and efficiently without jumping through more hoops than necessary. Research designs fall into one of the following three categories:
- Exploratory research design
- Descriptive research design
- Causal research design (experiments)
An exploratory research design is useful when you are initially investigating a problem but you haven’t defined it well enough to do an in-depth study of it. Perhaps via your regular market intelligence, you have spotted what appears to be a new opportunity in the marketplace. You would then do exploratory research to investigate it further and “get your feet wet,” as the saying goes. Exploratory research is less structured than other types of research, and secondary data is often utilized.
One form of exploratory research is qualitative research. Qualitative research is any form of research that includes gathering data that is not quantitative, and often involves exploring questions such as why as much as what or how much. Different forms, such as depth interviews and focus group interviews, are common in marketing research.
The depth interview—engaging in detailed, one-on-one, question-and-answer sessions with potential buyers—is an exploratory research technique. However, unlike surveys, the people being interviewed aren’t asked a series of standard questions. Instead the interviewer is armed with some general topics and asks questions that are open ended, meaning that they allow the interviewee to elaborate. “How did you feel about the product after you purchased it?” is an example of a question that might be asked. A depth interview also allows a researcher to ask logical follow-up questions such as “Can you tell me what you mean when you say you felt uncomfortable using the service?” or “Can you give me some examples?” to help dig further and shed additional light on the research problem. Depth interviews can be conducted in person or over the phone. The interviewer either takes notes or records the interview
Focus groups and case studies are often utilized for exploratory research as well. A focus group is a group of potential buyers who are brought together to discuss a marketing research topic with one another. A moderator is used to focus the discussion, the sessions are recorded, and the main points of consensus are later summarized by the market researcher. Textbook publishers often gather groups of professors at educational conferences to participate in focus groups. However, focus groups can also be conducted on the telephone, in online chat rooms, or both, using meeting software like WebEx. The basic steps of conducting a focus group are outlined below.
The Basic Steps of Conducting a Focus Group
- Establish the objectives of the focus group. What is its purpose?
- Identify the people who will participate in the focus group. What makes them qualified to participate? How many of them will you need and what they will be paid?
- Obtain contact information for the participants and send out invitations (usually e-mails are most efficient).
- Develop a list of questions.
- Choose a facilitator.
- Choose a location in which to hold the focus group and the method by which it will be recorded.
- Conduct the focus group. If the focus group is not conducted electronically, include name tags for the participants, pens and notepads, any materials the participants need to see, and refreshments. Record participants’ responses.
- Summarize the notes from the focus group and write a report for management.
A case study looks at how another company solved the problem that’s being researched. Sometimes multiple cases, or companies, are used in a study. Case studies nonetheless have a mixed reputation. Some researchers believe it’s hard to generalize, or apply, the results of a case study to other companies. Nonetheless, collecting information about companies that encountered the same problems your firm is facing can give you a certain amount of insight about what direction you should take. In fact, one way to begin a research project is to carefully study a successful product or service.
Two other types of qualitative data used for exploratory research are ethnographies and projective techniques. In an ethnography, researchers interview, observe, and often videotape people while they work, live, shop, and play. The Walt Disney Company has recently begun using ethnographers to uncover the likes and dislikes of boys aged six to fourteen, a financially attractive market segment for Disney, but one in which the company has been losing market share. The ethnographers visit the homes of boys, observe the things they have in their rooms to get a sense of their hobbies, and accompany them and their mothers when they shop to see where they go, what the boys are interested in, and what they ultimately buy. (The children get seventy-five dollars out of the deal, incidentally.) (Barnes, 2009)
Projective techniques are used to reveal information research respondents might not reveal by being asked directly. Asking a person to complete sentences such as the following is one technique:
People who buy Coach handbags __________. (Will he or she reply with “are cool,” “are affluent,” or “are pretentious,” for example?)
KFC’s grilled chicken is ______.
Or the person might be asked to finish a story that presents a certain scenario. Word associations are also used to discern people’s underlying attitudes toward goods and services. Using a word-association technique, a market researcher asks a person to say or write the first word that comes to his or her mind in response to another word. If the initial word is “fast food,” what word does the person associate it with or respond with? Is it “McDonald’s”? If many people reply that way, and you’re conducting research for Burger King, that could indicate Burger King has a problem. However, if the research is being conducted for Wendy’s, which recently began running an advertising campaign to the effect that Wendy’s offerings are “better than fast food,” it could indicate that the campaign is working.
Completing cartoons is yet another type of projective technique. It’s similar to finishing a sentence or story, only with the pictures. People are asked to look at a cartoon such as the one shown in Figure 10.8 “Example of a Cartoon-Completion Projective Technique”. One of the characters in the picture will have made a statement, and the person is asked to fill in the empty cartoon “bubble” with how they think the second character will respond.
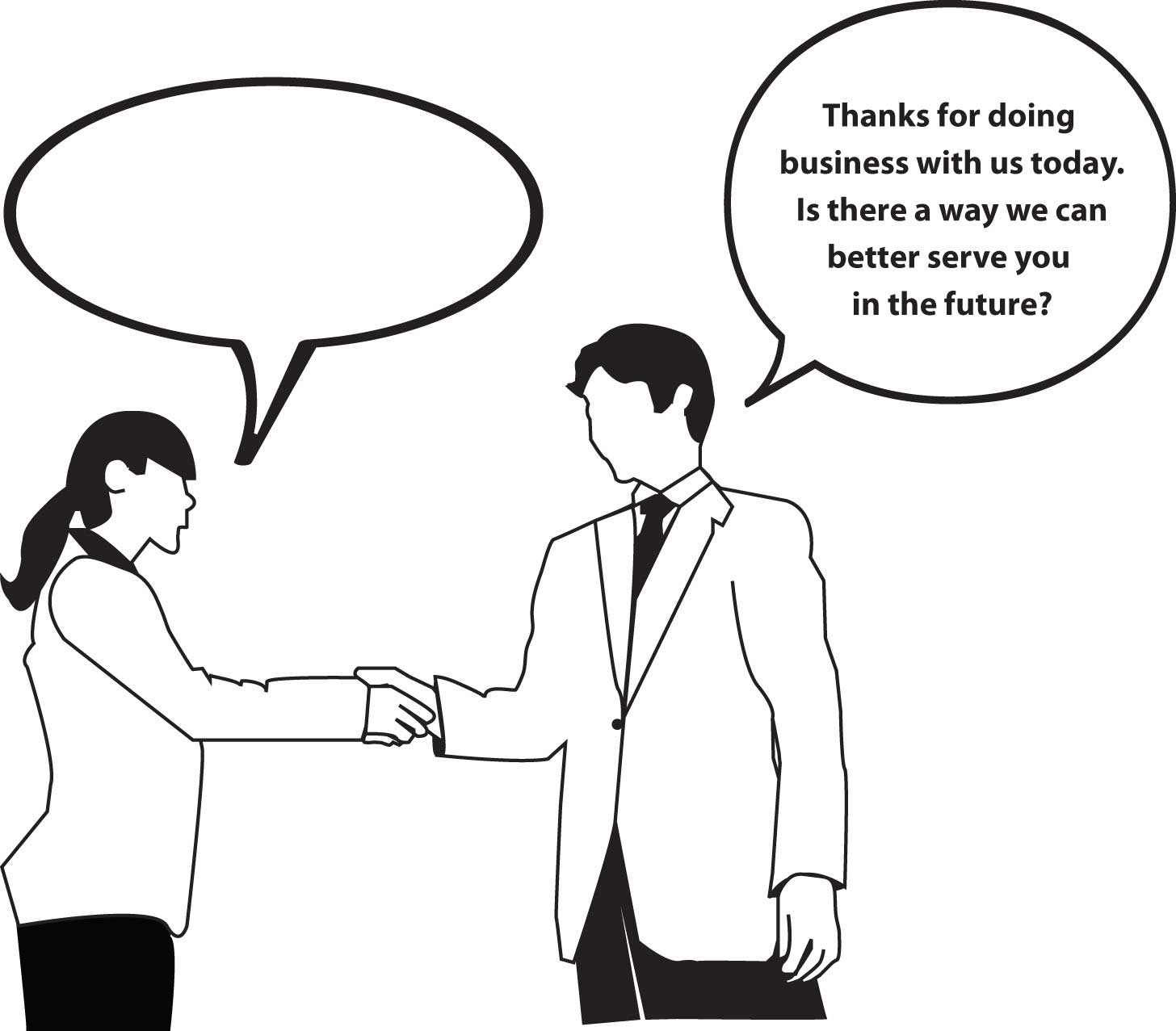

Figure 4.8: Example of a Cartoon-Completion Projective Technique
In some cases, your research might end with exploratory research. Perhaps you have discovered your organization lacks the resources needed to produce the product. In other cases, you might decide you need more in-depth, quantitative research such as descriptive research or causal research, which are discussed next. Most marketing research professionals advise using both types of research, if it’s feasible. On the one hand, the qualitative-type research used in exploratory research is often considered too “lightweight.” Remember earlier in the chapter when we discussed telephone answering machines and the hit TV sitcom Seinfeld? Both product ideas were initially rejected by focus groups. On the other hand, relying solely on quantitative information often results in market research that lacks ideas.
Watch Video Clip: The Stone Wheel—What One Focus Group Said
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OORnMYoWX9c
Watch the video to see a funny spoof on the usefulness—or lack of usefulness—of focus groups.
Descriptive Research
Anything that can be observed and counted falls into the category of descriptive research design. A study using a descriptive research design involves gathering hard numbers, often via surveys, to describe or measure a phenomenon so as to answer the questions of who, what, where, when, and how. “On a scale of 1–5, how satisfied were you with your service?” is a question that illustrates the information a descriptive research design is supposed to capture.
Physiological measurements also fall into the category of descriptive design. Physiological measurements measure people’s involuntary physical responses to marketing stimuli, such as an advertisement. Elsewhere, we explained that researchers have gone so far as to scan the brains of consumers to see what they really think about products versus what they say about them. Eye tracking is another cutting-edge type of physiological measurement.
It involves recording the movements of a person’s eyes when they look at some sort of stimulus, such as a banner ad or a Web page. The Walt Disney Company has a research facility in Austin, Texas, that it uses to take physical measurements of viewers when they see Disney programs and advertisements. The facility measures three types of responses: people’s heart rates, skin changes, and eye movements (eye tracking) (Spangler, 2009).

Figure 4.9: Descriptive research
A woman shows off her headgear for an eye-tracking study. The gear’s not exactly a fashion statement but . . .
(lawrencegs – Google Glass – CC BY 2.0)
A strictly descriptive research design instrument—a survey, for example—can tell you how satisfied your customers are. It can’t, however, tell you why. Nor can an eye-tracking study tell you why people’s eyes tend to dwell on certain types of banner ads—only that they do. To answer “why” questions an exploratory research design or causal research design is needed (Wagner, 2007).
Causal Research
Causal research design examines cause-and-effect relationships. Using a causal research design allows researchers to answer “what if” types of questions. In other words, if a firm changes X (say, a product’s price, design, placement, or advertising), what will happen to Y (say, sales or customer loyalty)? To conduct causal research, the researcher designs an experiment that “controls,” or holds constant, all of a product’s marketing elements except one (or using advanced techniques of research, a few elements can be studied at the same time). The one variable is changed, and the effect is then measured. Sometimes the experiments are conducted in a laboratory using a simulated setting designed to replicate the conditions buyers would experience. Or the experiments may be conducted in a virtual computer setting.
You might think setting up an experiment in a virtual world such as the online game Second Life would be a viable way to conduct controlled marketing research. Some companies have tried to use Second Life for this purpose, but the results have been somewhat mixed as to whether or not it is a good medium for marketing research. The German marketing research firm Komjuniti was one of the first “real-world” companies to set up an “island” in Second Life upon which it could conduct marketing research. However, with so many other attractive fantasy islands in which to play, the company found it difficult to get Second Life residents, or players, to voluntarily visit the island and stay long enough so meaningful research could be conducted. (Plus, the “residents,” or players, in Second Life have been known to protest corporations invading their world. When the German firm Komjuniti created an island in Second Life to conduct marketing research, the residents showed up waving signs and threatening to boycott the island.) (Wagner, 2007)
Why is being able to control the setting so important? Let’s say you are an American flag manufacturer and you are working with Walmart to conduct an experiment to see where in its stores American flags should be placed so as to increase their sales. Then the terrorist attacks of 9/11 occur. In the days afterward, sales skyrocketed—people bought flags no matter where they were displayed. Obviously, the terrorist attacks in the United States would have skewed the experiment’s data.
An experiment conducted in a natural setting such as a store is referred to as a field experiment. Companies sometimes do field experiments either because it is more convenient or because they want to see if buyers will behave the same way in the “real world” as in a laboratory or on a computer. The place the experiment is conducted or the demographic group of people the experiment is administered to is considered the test market. Before a large company rolls out a product to the entire marketplace, it will often place the offering in a test market to see how well it will be received. For example, to compete with MillerCoors’ sixty-four-calorie beer MGD 64, Anheuser-Busch recently began testing its Select 55 beer in certain cities around the country (McWilliams, 2009).
Figure 4.10: Test Market

Select 55 beer: Coming soon to a test market near you? (If you’re on a diet, you have to hope so!)
(Martine – Le champagne – CC BY-NC 2.0)
Many companies use experiments to test all of their marketing communications. For example, the online discount retailer O.co (formerly called Overstock.com) carefully tests all of its marketing offers and tracks the results of each one. One study the company conducted combined twenty-six different variables related to offers e-mailed to several thousand customers. The study resulted in a decision to send a group of e-mails to different segments. The company then tracked the results of the sales generated to see if they were in line with the earlier experiment it had conducted that led it to make the offer.
Step 3: Design the Data-Collection Forms
If the behavior of buyers is being formally observed, and a number of different researchers are conducting observations, the data obviously need to be recorded on a standardized data-collection form that’s either paper or electronic. Otherwise, the data collected will not be comparable. The items on the form could include a shopper’s sex; his or her approximate age; whether the person seemed hurried, moderately hurried, or unhurried; and whether or not he or she read the label on products, used coupons, and so forth.
The same is true when it comes to surveying people with questionnaires. Surveying people is one of the most commonly used techniques to collect quantitative data. Surveys are popular because they can be easily administered to large numbers of people fairly quickly. However, to produce the best results, the questionnaire for the survey needs to be carefully designed.
Questionnaire Design
Most questionnaires follow a similar format: They begin with an introduction describing what the study is for, followed by instructions for completing the questionnaire and, if necessary, returning it to the market researcher. The first few questions that appear on the questionnaire are usually basic, warm-up type of questions the respondent can readily answer, such as the respondent’s age, level of education, place of residence, and so forth. The warm-up questions are then followed by a logical progression of more detailed, in-depth questions that get to the heart of the question being researched. Lastly, the questionnaire wraps up with a statement that thanks the respondent for participating in the survey and information and explains when and how they will be paid for participating.
To see some examples of questionnaires and how they are laid out, click on the following link: http://cas.uah.edu/wrenb/ mkt343/Project/Sample%20Questionnaires.htm.
How the questions themselves are worded is extremely important. It’s human nature for respondents to want to provide the “correct” answers to the person administering the survey, so as to seem agreeable. Therefore, there is always a hazard that people will try to tell you what you want to hear on a survey. Consequently, care needs to be taken that the survey questions are written in an unbiased, neutral way. In other words, they shouldn’t lead a person taking the questionnaire to answer a question one way or another by virtue of the way you have worded it. The following is an example of a leading question.
Don’t you agree that teachers should be paid more?
The questions also need to be clear and unambiguous.
Consider the following question: Which brand of toothpaste do you use?
The question sounds clear enough, but is it really? What if the respondent recently switched brands? What if she uses Crest at home, but while away from home or traveling, she uses Colgate’s Wisp portable toothpasteand-brush product? How will the respondent answer the question? Rewording the question as follows so it’s more specific will help make the question clearer:
Which brand of toothpaste have you used at home in the past six months? If you have used more than one brand, please list each of them (1).
Sensitive questions have to be asked carefully. For example, asking a respondent, “Do you consider yourself a light, moderate, or heavy drinker?” can be tricky. Few people want to admit to being heavy drinkers. You can “soften” the question by including a range of answers, as the following example shows:
- __0–5 alcoholic beverages
- __5–10 alcoholic beverages
- __10–15 alcoholic beverages
Many people don’t like to answer questions about their income levels. Asking them to specify income ranges rather than divulge their actual incomes can help.
Other research question “don’ts” include using jargon and acronyms that could confuse people. “How often do you IM?” is an example. Also, don’t muddy the waters by asking two questions in the same question, something researchers refer to as a double-barreled question. “Do you think parents should spend more time with their children and/or their teachers?” is an example of a double-barreled question.
Open-ended questions, or questions that ask respondents to elaborate, can be included. However, they are harder to tabulate than closed-ended questions, or questions that limit a respondent’s answers. Multiple-choice and yes-and-no questions are examples of closed-ended questions.
Testing the Questionnaire
You have probably heard the phrase “garbage in, garbage out.” If the questions are bad, the information gathered will be bad, too. One way to make sure you don’t end up with garbage is to test the questionnaire before sending it out to find out if there are any problems with it. Is there enough space for people to elaborate on open-ended questions? Is the font readable? To test the questionnaire, marketing research professionals first administer it to a number of respondents face to face. This gives the respondents the chance to ask the researcher about questions or instructions that are unclear or don’t make sense to them. The researcher then administers the questionnaire to a small subset of respondents in the actual way the survey is going to be disseminated, whether it’s delivered via phone, in person, by mail, or online.
Getting people to participate and complete questionnaires can be difficult. If the questionnaire is too long or hard to read, many people won’t complete it. So, by all means, eliminate any questions that aren’t necessary. Of course, including some sort of monetary incentive for completing the survey can increase the number of completed questionnaires a market researcher will receive.
Step 4: Specify the Sample
Once you have created your questionnaire or other marketing study, how do you figure out who should participate in it? Obviously, you can’t survey or observe all potential buyers in the marketplace. Instead, you must choose a sample. A sample is a subset of potential buyers that are representative of your entire target market, or population being studied. Sometimes market researchers refer to the population as the universe to reflect the fact that it includes the entire target market, whether it consists of a million people, a hundred thousand, a few hundred, or a dozen. “All unmarried people over the age of eighteen who purchased Dirt Devil steam cleaners in the United States during 2011” is an example of a population that has been defined.
Obviously, the population has to be defined correctly. Otherwise, you will be studying the wrong group of people. Not defining the population correctly can result in flawed research, or sampling error. A sampling error is any type of marketing research mistake that results because a sample was utilized. One criticism of Internet surveys is that the people who take these surveys don’t really represent the overall population. On average, Internet survey takers tend to be more educated and tech savvy. Consequently, if they solely constitute your population, even if you screen them for certain criteria, the data you collect could end up being skewed.
The next step is to put together the sampling frame, which is the list from which the sample is drawn. The sampling frame can be put together using a directory, customer list, or membership roster (Wrenn et. al., 2007). Keep in mind that the sampling frame won’t perfectly match the population. Some people will be included on the list who shouldn’t be. Other people who should be included will be inadvertently omitted. It’s no different than if you were to conduct a survey of, say, 25 percent of your friends, using friends’ names you have in your cell phone. Most of your friends’ names are likely to be programmed into your phone, but not all of them. As a result, a certain degree of sampling error always occurs.
There are two main categories of samples in terms of how they are drawn: probability samples and nonprobability samples. A probability sample is one in which each would-be participant has a known and equal chance of being selected. The chance is known because the total number of people in the sampling frame is known. For example, if every other person from the sampling frame were chosen, each person would have a 50 percent chance of being selected
A nonprobability sample is any type of sample that’s not drawn in a systematic way. So the chances of each would-be participant being selected can’t be known. A convenience sample is one type of nonprobability sample. It is a sample a researcher draws because it’s readily available and convenient to do so. Surveying people on the street as they pass by is an example of a convenience sample. The question is, are these people representative of the target market?
For example, suppose a grocery store needed to quickly conduct some research on shoppers to get ready for an upcoming promotion. Now suppose that the researcher assigned to the project showed up between the hours of 10 a.m. and 12 p.m. on a weekday and surveyed as many shoppers as possible. The problem is that the shoppers wouldn’t be representative of the store’s entire target market. What about commuters who stop at the store before and after work? Their views wouldn’t be represented. Neither would people who work the night shift or shop at odd hours. As a result, there would be a lot of room for sampling error in this study. For this reason, studies that use nonprobability samples aren’t considered as accurate as studies that use probability samples. Nonprobability samples are more often used in exploratory research.
Lastly, the size of the sample has an effect on the amount of sampling error. Larger samples generally produce more accurate results. The larger your sample is, the more data you will have, which will give you a more complete picture of what you’re studying. However, the more people surveyed or studied, the more costly the research becomes.
Statistics can be used to determine a sample’s optimal size. If you take a marketing research or statistics class, you will learn more about how to determine the optimal size.
Of course, if you hire a marketing research company, much of this work will be taken care of for you. Many marketing research companies, like ResearchNow, maintain panels of prescreened people they draw upon for samples. In addition, the marketing research firm will be responsible for collecting the data or contracting with a company that specializes in data collection. Data collection is discussed next
Step 5: Collect the Data
As we have explained, primary marketing research data can be gathered in a number of ways. Surveys, taking physical measurements, and observing people are just three of the ways we discussed. If you’re observing customers as part of gathering the data, keep in mind that if shoppers are aware of the fact, it can have an effect on their behavior. For example, if a customer shopping for feminine hygiene products in a supermarket aisle realizes she is being watched, she could become embarrassed and leave the aisle, which would adversely affect your data. To get around problems such as these, some companies set up cameras or two-way mirrors to observe customers. Organizations also hire mystery shoppers to work around the problem. A mystery shopper is someone who is paid to shop at a firm’s establishment or one of its competitors to observe the level of service, cleanliness of the facility, and so forth, and report his or her findings to the firm.
Watch Video Clip
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Rsth2qvWFfw
Make Extra Money as a Mystery Shopper
Watch the YouTube video to get an idea of how mystery shopping works.
Survey data can be collected in many different ways and combinations of ways. The following are the basic methods used:
- Face-to-face (can be computer aided)
- Telephone (can be computer aided or completely automated)
- Mail and hand delivery
- E-mail and the Web
A face-to-face survey is, of course, administered by a person. The surveys are conducted in public places such as in shopping malls, on the street, or in people’s homes if they have agreed to it. In years past, it was common for researchers in the United States to knock on people’s doors to gather survey data. However, randomly collected door-to-door interviews are less common today, partly because people are afraid of crime and are reluctant to give information to strangers (McDaniel & Gates, 1998).
Nonetheless, “beating the streets” is still a legitimate way questionnaire data is collected. When the U.S. Census Bureau collects data on the nation’s population, it hand delivers questionnaires to rural households that do not have street-name and house-number addresses. And Census Bureau workers personally survey the homeless to collect information about their numbers. Face-to-face surveys are also commonly used in third world countries to collect information from people who cannot read or lack phones and computers.
A plus of face-to-face surveys is that they allow researchers to ask lengthier, more complex questions because the people being surveyed can see and read the questionnaires. The same is true when a computer is utilized. For example, the researcher might ask the respondent to look at a list of ten retail stores and rank the stores from best to worst. The same question wouldn’t work so well over the telephone because the person couldn’t see the list. The question would have to be rewritten. Another drawback with telephone surveys is that even though federal and state “do not call” laws generally don’t prohibit companies from gathering survey information over the phone, people often screen such calls using answering machines and caller ID.
Probably the biggest drawback of both surveys conducted face-to-face and administered over the phone by a person is that they are labor-intensive and therefore costly. Mailing out questionnaires is costly, too, and the response rates can be rather low. Think about why that might be so: if you receive a questionnaire in the mail, it is easy to throw it in the trash; it’s harder to tell a market researcher who approaches you on the street that you don’t want to be interviewed.
By contrast, gathering survey data collected by a computer, either over the telephone or on the Internet, can be very cost-effective and in some cases free. SurveyMonkey and Zoomerang are two Web sites that will allow you to create online questionnaires, e-mail them to up to one hundred people for free, and view the responses in real-time as they come in. For larger surveys, you have to pay a subscription price of a few hundred dollars. But that still can be extremely cost-effective. The two Web sites also have a host of other features such as online-survey templates you can use to create your questionnaire, a way to set up automatic reminders sent to people who haven’t yet completed their surveys, and tools you can use to create graphics to put in your final research report. To see how easy it is to put together a survey in SurveyMonkey, click on the following link: http://help.surveymonkey.com/app/tutorials/ detail/a_id/423.
Like a face-to-face survey, an Internet survey can enable you to show buyers different visuals such as ads, pictures, and videos of products and their packaging. Web surveys are also fast, which is a major plus. Whereas face-to-face and mailed surveys often take weeks to collect, you can conduct a Web survey in a matter of days or even hours. And, of course, because the information is electronically gathered it can be automatically tabulated. You can also potentially reach a broader geographic group than you could if you had to personally interview people. The Zoomerang Web site allows you to create surveys in forty different languages.
Another plus for Web and computer surveys (and electronic phone surveys) is that there is less room for human error because the surveys are administered electronically. For instance, there’s no risk that the interviewer will ask a question wrong or use a tone of voice that could mislead the respondents. Respondents are also likely to feel more comfortable inputting the information into a computer if a question is sensitive than they would divulging the information to another person face-to-face or over the phone. Given all of these advantages, it’s not surprising that the Internet is quickly becoming the top way to collect primary data. However, like mail surveys, surveys sent to people over the Internet are easy to ignore.
Lastly, before the data collection process begins, the surveyors and observers need to be trained to look for the same things, ask questions the same way, and so forth. If they are using rankings or rating scales, they need to be “on the same page,” so to speak, as to what constitutes a high ranking or a low ranking. As an analogy, you have probably had some teachers grade your college papers harder than others. The goal of training is to avoid a wide disparity between how different observers and interviewers record the data.
Figure 4.11: Data collection

Training people so they know what constitutes different ratings when they are collecting data will improve the quality of the information gathered in a marketing research study.
(Ricardo Rodriquez – Satisfaction survey – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0)
For example, if an observation form asks the observers to describe whether a shopper’s behavior is hurried, moderately hurried, or unhurried, they should be given an idea of what defines each rating. Does it depend on how much time the person spends in the store or in the individual aisles? How fast they walk? In other words, the criteria and ratings need to be spelled out.
Student Example
Over the 4th of July week, I went to Home Depot to get some fertilizer. In the aisle, a person came up to me and asked if I wanted to take a survey. He said it wouldn’t take long so I agreed. He asked some questions about tap water, e.g., if I use a filter or not. Then he concluded by asking for my phone number in which I declined. It made me wonder what the goal of this survey was, whether the specific details gathered from my answers would be used to sell something to me, or if they truly wanted to know what customers wanted, data which would be input into their marketing research system.
Class of 2020
In my most recent trip to Disneyland, I encountered Cast Members stationed down Main Street, with tablet computers in hand, ready to approach guests as they leave the park for the day. The Cast Members were actively collecting data from park guests through either a brief interview in which the information was input into their tablet, or offered to send an email data collection form to willing respondents. I appreciate how the researchers utilized both in-person interviews and online surveys to gather pertinent information from a varied group of guests.
Lacey Lober
Collecting International Marketing Research Data
Gathering marketing research data in foreign countries poses special challenges. However, that doesn’t stop firms from doing so. Marketing research companies are located all across the globe, in fact. Eight of the ten largest marketing research companies in the world are headquartered in the United States. However, five of these eight firms earn more of their revenues abroad than they do in the United States. There’s a reason for this: many U.S. markets were saturated, or tapped out, long ago in terms of the amount that they can grow. Coke is an example. As you learned earlier in the book, most of the Coca-Cola Company’s revenues are earned in markets abroad. To be sure, the United States is still a huge market when it comes to the revenues marketing research firms generate by conducting research in the country: in terms of their spending, American consumers fuel the world’s economic engine. Still, emerging countries with growing middle classes, such as China, India, and Brazil, are hot new markets companies want to tap.
What kind of challenges do firms face when trying to conduct marketing research abroad? As we explained, face-to-face surveys are commonly used in third world countries to collect information from people who cannot read or lack phones and computers. However, face-to-face surveys are also common in Europe, despite the fact that phones and computers are readily available. In-home surveys are also common in parts of Europe. By contrast, in some countries, including many Asian countries, it’s considered taboo or rude to try to gather information from strangers either face-to-face or over the phone. In many Muslim countries, women are forbidden to talk to strangers. And how do you figure out whom to research in foreign countries? That in itself is a problem. In the United States, researchers often ask if they can talk to the heads of households to conduct marketing research. But in countries in which domestic servants or employees are common, the heads of households aren’t necessarily the principal shoppers; their domestic employees are (Malhotra).
Translating surveys is also an issue. Have you ever watched the TV comedians Jay Leno and David Letterman make fun of the English translations found on ethnic menus and products? Research tools such as surveys can suffer from the same problem. Hiring someone who is bilingual to translate a survey into another language can be a disaster if the person isn’t a native speaker of the language to which the survey is being translated.
One way companies try to deal with translation problems is by using back translation. When back translation is used, a native speaker translates the survey into the foreign language and then translates it back again to the original language to determine if there were gaps in meaning—that is, if anything was lost in translation. And it’s not just the language that’s an issue. If the research involves any visual images, they, too, could be a point of confusion. Certain colors, shapes, and symbols can have negative connotations in other countries. For example, the color white represents purity in many Western cultures, but in China, it is the color of death and mourning (Zouhali-Worrall, 2008). Also, look back at the cartoon-completion exercise in Figure 10.8 “Example of a CartoonCompletion Projective Technique”. What would women in Muslim countries who aren’t allowed to converse with male sellers think of it? Chances are, the cartoon wouldn’t provide you with the information you’re seeking if Muslim women in some countries were asked to complete it.
One way marketing research companies are dealing with the complexities of global research is by merging with or acquiring marketing research companies abroad. The Nielsen Company is the largest marketing research company in the world. The firm operates in more than a hundred countries and employs more than forty thousand people. Many of its expansions have been the result of acquisitions and mergers.
Step 6: Analyze the Data
Step 6 involves analyzing the data to ensure it’s as accurate as possible. If the research is collected by hand using a pen and pencil, it’s entered into a computer. Or respondents might have already entered the information directly into a computer. For example, when Toyota goes to an event such as a car show, the automaker’s marketing personnel ask would-be buyers to complete questionnaires directly on computers. Companies are also beginning to experiment with software that can be used to collect data using mobile phones.
Once all the data is collected, the researchers begin the data cleaning, which is the process of removing data that have accidentally been duplicated (entered twice into the computer) or correcting data that have obviously been recorded wrong. A program such as Microsoft Excel or a statistical program such as Predictive Analytics Software (PASW, which was formerly known as SPSS) is then used to tabulate, or calculate, the basic results of the research, such as the total number of participants and how collectively they answered various questions. The programs can also be used to calculate averages, such as the average age of respondents, their average satisfaction, and so forth. The same can done for percentages, and other values you learned about, or will learn about, in a statistics course, such as the standard deviation, mean, and median for each question.
The information generated by the programs can be used to draw conclusions, such as what all customers might like or not like about an offering based on what the sample group liked or did not like. The information can also be used to spot differences among groups of people. For example, the research might show that people in one area of the country like the product better than people in another area. Trends to predict what might happen in the future can also be spotted.
If there are any open-ended questions respondents have elaborated upon—for example, “Explain why you like the current brand you use better than any other brand”—the answers to each are pasted together, one on top of another, so researchers can compare and summarize the information. As we have explained, qualitative information such as this can give you a fuller picture of the results of the research.
Part of analyzing the data is to see if it seems sound. Does the way in which the research was conducted seem sound? Was the sample size large enough? Are the conclusions that become apparent from it reasonable?
The two most commonly used criteria used to test the soundness of a study are (1) validity and (2) reliability. A study is valid if it actually tested what it was designed to test. For example, did the experiment you ran in Second Life test what it was designed to test? Did it reflect what could really happen in the real world? If not, the research isn’t valid. If you were to repeat the study, and get the same results (or nearly the same results), the research is said to be reliable. If you get a drastically different result if you repeat the study, it’s not reliable. The data collected, or at least some it, can also be compared to, or reconciled with, similar data from other sources either gathered by your firm or by another organization to see if the information seems on target.
Stage 7: Write the Research Report and Present Its Findings
If you end up becoming a marketing professional and conducting a research study after you graduate, hopefully you will do a great job putting the study together. You will have defined the problem correctly, chosen the right sample, collected the data accurately, analyzed it, and your findings will be sound. At that point, you will be required to write the research report and perhaps present it to an audience of decision makers. You will do so via a written report and, in some cases, a slide or PowerPoint presentation based on your written report.
The six basic elements of a research report are as follows.
1. Title Page . The title page explains what the report is about, when it was conducted and by whom, and who requested it.
2. Table of Contents. The table of contents outlines the major parts of the report, as well as any graphs and charts, and the page numbers on which they can be found.
3. Executive Summary. The executive summary summarizes all the details in the report in a very quick way. Many people who receive the report—both executives and nonexecutives—won’t have time to read the entire report. Instead, they will rely on the executive summary to quickly get an idea of the study’s results and what to do about those results.
4. Methodology and Limitations. The methodology section of the report explains the technical details of how the research was designed and conducted. The section explains, for example, how the data was collected and by whom, the size of the sample, how it was chosen, and whom or what it consisted of (e.g., the number of women versus men or children versus adults). It also includes information about the statistical techniques used to analyze the data. Every study has errors—sampling errors, interviewer errors, and so forth. The methodology section should explain these details, so decision makers can consider their overall impact. The margin of error is the overall tendency of the study to be off kilter—that is, how far it could have gone wrong in either direction. Remember how newscasters present the presidential polls before an election? They always say, “This candidate is ahead 48 to 44 percent, plus or minus 2 percent.” That “plus or minus” is the margin of error. The larger the margin of error is, the less likely the results of the study are accurate. The margin of error needs to be included in the methodology section.
5. Findings. The findings section is a longer, fleshed-out version of the executive summary that goes into more detail about the statistics uncovered by the research that bolster the study’s findings. If you have related research or secondary data on hand that back up the findings, it can be included to help show the study did what it was designed to do.
6. Recommendations. The recommendations section should outline the course of action you think should be taken based on the findings of the research and the purpose of the project. For example, if you conducted a global market research study to identify new locations for stores, make a recommendation for the locations (Mersdorf, 2009).
As we have said, these are the basic sections of a marketing research report. However, additional sections can be added as needed. For example, you might need to add a section on the competition and each firm’s market share. If you’re trying to decide on different supply chain options, you will need to include a section on that topic.
As you write the research report, keep your audience in mind. Don’t use technical jargon decision makers and other people reading the report won’t understand. If technical terms must be used, explain them. Also, proofread the document to ferret out any grammatical errors and typos, and ask a couple of other people to proofread behind you to catch any mistakes you might have missed. If your research report is riddled with errors, its credibility will be undermined, even if the findings and recommendations you make are extremely accurate.
Many research reports are presented via PowerPoint. If you’re asked to create a slideshow presentation from the report, don’t try to include every detail in the report on the slides. The information will be too long and tedious for people attending the presentation to read through. And if they do go to the trouble of reading all the information, they probably won’t be listening to the speaker who is making the presentation.
Instead of including all the information from the study in the slides, boil each section of the report down to key points and add some “talking points” only the presenter will see. After or during the presentation, you can give the attendees the longer, paper version of the report so they can read the details at a convenient time, if they choose to.
- Step 1 in the marketing research process is to define the problem. Businesses take a look at what they believe are symptoms and try to drill down to the potential causes so as to precisely define the problem. The next task for the researcher is to put into writing the research objective, or goal, the research is supposed to accomplish.
- Step 2 in the process is to design the research. The research design is the “plan of attack.” It outlines what data you are going to gather, from whom, how, and when, and how you’re going to analyze it once it has been obtained.
- Step 3 is to design the data-collection forms, which need to be standardized so the information gathered on each is comparable. Surveys are a popular way to gather data because they can be easily administered to large numbers of people fairly quickly. However, to produce the best results, survey questionnaires need to be carefully designed and pretested before they are used.
- Step 4 is drawing the sample, or a subset of potential buyers who are representative of your entire target market. If the sample is not correctly selected, the research will be flawed.
- Step 5 is to actually collect the data, whether it’s collected by a person face-to-face, over the phone, or with the help of computers or the Internet. The data-collection process is often different in foreign countries.
- Step 6 is to analyze the data collected for any obvious errors, tabulate the data, and then draw conclusions from it based on the results.
- The last step in the process, Step 7, is writing the research report and presenting the findings to decision makers.
(1) “Questionnaire Design,” QuickMBA, http://www.quickmba.com/marketing/research/qdesign (accessed December 14, 2009).
Barnes, B., “Disney Expert Uses Science to Draw Boy Viewers,” New York Times, April 15, 2009, http://www.nytimes.com/2009/04/14/arts/television/14boys.html?pagewanted=1&_r=1 (accessed December 14, 2009).
Burns A. and Ronald Bush, Marketing Research, 6th ed. (Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 2010), 85.
Malhotra, N., Marketing Research: An Applied Approach, 6th ed. (Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall), 764.
McDaniel, C. D. and Roger H. Gates, Marketing Research Essentials, 2nd ed. (Cincinnati: South-Western College Publishing, 1998), 61.
McWilliams, J., “A-B Puts Super-Low-Calorie Beer in Ring with Miller,” St. Louis Post-Dispatch, August 16, 2009, http://www.stltoday.com/business/next-matchup-light-weights-a-b-puts-super-low-calorie/article_47511bfe-18ca-5979-bdb9-0526c97d4edf.html (accessed April 13, 2012).
Mersdorf, S., “How to Organize Your Next Survey Report,” Cvent, August 24, 2009, http://survey.cvent.com/blog/cvent-survey/0/0/how-to-organize-your-next-survey-report (accessed December 14, 2009).
Rappeport A. and David Gelles, “Facebook to Form Alliance with Nielsen,” Financial Times, September 23, 2009, 16.
Spangler, T., “Disney Lab Tracks Feelings,” Multichannel News 30, no. 30 (August 3, 2009): 26.
Wagner, J., “Marketing in Second Life Doesn’t Work…Here Is Why!” GigaOM, April 4, 2007,http://gigaom.com/2007/04/04/3-reasons-why-marketing-in-second-life-doesnt-work (accessed December 14,2009).
Wrenn, B., Robert E. Stevens, and David L. Loudon, Marketing Research: Text and Cases, 2nd ed. (Binghamton, NY: Haworth Press, 2007), 180.
Zouhali-Worrall, M., “Found in Translation: Avoiding Multilingual Gaffes,” CNNMoney.com, July 14, 2008, http://money.cnn.com/2008/07/07/smallbusiness/language_translation.fsb/index.htm (accessed December 14, 2009).
Share This Book
- Increase Font Size

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The marketing research process - an overview. A typical marketing research process is as follows: Identify an issue, discuss alternatives and set out research objectives. Develop a research program. Choose a sample. Gather information. Gather data. Organize and analyze information and data. Present findings.
These examples showcase how market research can lead to smart decision-making and successful business decisions. Example 1: Apple's iPhone launch. Apple's iconic iPhone launch in 2007 serves as a prime example of market research driving product innovation in tech. Before the iPhone's release, Apple conducted extensive market research to ...
Integrate with 100+ apps and plug-ins to get more done. SurveyMonkey Forms. Build and customize online forms to collect info and payments. SurveyMonkey Genius. Create better surveys and spot insights quickly with built-in AI. Market Research Solutions. Purpose-built solutions for all of your market research needs. INDUSTRIES.
Exploratory Primary Research: This kind of primary market research normally takes place as a first step — before any specific research has been performed — and may involve open-ended interviews or surveys with small numbers of people. ... Market Research Examples 1. TikTok uses in-app research surveys to better understand consumer viewing ...
Step 2: Design the Research. The next step in the marketing research process is to do a research design. The research design is your "plan of attack.". It outlines what data you are going to gather and from whom, how and when you will collect the data, and how you will analyze it once it's been obtained.
The basic steps used to conduct marketing research are shown in figure 6.1. Next, we discuss each step. Figure 6.1. Steps in the Marketing Research Process. [Read full image description.] Step 1: Define the Problem (or Opportunity) There's a saying in marketing research that a problem half defined is a problem half solved.
Conducting effective market research can help you understand your target audience, improve your products or services, and stay ahead of the competition. Read our ultimate guide to learn about the different types of market research, its benefits, and real-world examples. Fratzke Consulting offers expert market research services to help you stay ahead of the game.
How to conduct lean market research in 4 steps. The following four steps and practical examples will give you a solid market research plan for understanding who your users are and what they want from a company like yours. 1. Create simple user personas. A user persona is a semi-fictional character based on psychographic and demographic data ...
The future of market research isn't expensive full-service projects that take months—it's agile, DIY market research. In this guide, we'll teach you how to conduct your own market research project from start to finish, including how to design your survey, who to target, and analysis best practices from our survey experts.
June 3, 2021 28 min read. Market research is a process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting information about a given market. It takes into account geographic, demographic, and psychographic data about past, current, and potential customers, as well as competitive analysis to evaluate the viability of a product offer.
The 6 steps in the marketing process. The market research process is designed to paint a thorough picture of a company's marketing plan, helping to identify where the weaknesses and strengths exist. The first step in the marketing research process is defining the problem or the question your research is trying to answer, followed by ...
Here are five essential steps on how to do market research effectively. Step 1: Identify your research topic. ... for example. Step 3: Start collecting data. The next step is one of the most critical as it involves collecting the data you need for your research. Before you begin, make sure you've chosen the right research methods that will ...
There are different ways to approach market research, including primary and secondary research and qualitative and quantitative research. The strongest approaches will include a combination of all four. "Virtually every business can benefit from conducting some market research," says Niles Koenigsberg of Real FiG Advertising + Marketing.
From identifying customer needs to evaluating the competition and assessing market potential, market research empowers companies to navigate the dynamic marketplace with confidence. For instance, here are 4 different examples of how market research can be used in the real world: 1. Measuring customer satisfaction.
Step 1: Identify the Problem. The first step for any marketing research activity is to clearly identify and define the problem you are trying to solve. You start by stating the marketing or business problem you need to address and for which you need additional information to figure out a solution.
Step 4: Conduct the market research. With a system in place, you can start looking for candidates to contribute to your market research. This might include distributing surveys to current customers or recruiting participants who fit a specific profile, for example. Set a time frame for conducting your research.
The market research process is a systematic methodology for informing business decisions. The figure below breaks the process down into six steps: Step 1. Define the Objective & Your "Problem". Perhaps the most important step in the market research process is defining the goals of the project. At the core of this is understanding the root ...
Market research is the process of assessing the viability of a new good or service through research conducted directly with the consumer which allows a company to ...
The first step in market research is to clearly define the research objectives. This involves identifying the specific information needed, the target audience, and the desired outcomes of the research. Step 2. Design Research Plan. ... Here are some examples of market research. These examples illustrate the diverse applications of market ...
Consider these practical tips to conduct the following 6 steps during the implementation of a market research project. Step 1. Define the Problem and Translate It into Research Objectives. This is the most important step. It sets the direction of the whole market research process. Ask clients how they will use the research results, and what ...
Exploratory research is one of the initial steps in the marketing research process. It helps businesses gain broad insights when specific information is unknown. ... Real-life examples of market research in the SaaS industry often showcase innovative approaches to understanding customer needs and product-market fit. For instance, Slack, the ...
Examples include published market studies, white papers, analyst reports, customer emails, and customer surveys/feedback. For many small businesses with limited budgets, secondary market research is their first choice because it's easier to acquire and far more affordable than primary research. Secondary research can still answer specific ...
Step 6: Document Your Research. In this last step, compile all your research in written format. Create an action plan that includes a tactical list of steps to take. This way, you can discuss and prioritize steps to take with your team. Aim to be concise as you create this competitor analysis document.
Market research is a process where businesses collect and analyze data on specific markets, customers and consumers. With the goal of becoming a customer-focused company, organizations will follow research methods to gain a better understanding of their desired audiences and how to interact with them.Any information gathered provides insights into how companies can make their products more ...
Download. State the objectives, scope of work, research methodology, target market, and other such important information of your market research by downloading and using this above-shown research proposal example template. This ready-made template's content can be edited and customized in various file formats such as MS Word, Pages, Gooogle ...
The research questionnaire is one of the quantitative data-gathering methods a researcher can use in their research paper. 1. Market Research Questionnaire Template Example. Details. File Format. MS Word. Google Docs. Apple Pages. PDF.
A vital step in developing a brand strategy is to create and or review your brand style guide. A brand style guide will give you, and everyone on your team, instructions on creating a consistent visual identity. Step #6: Review Crucial Customer Touchpoints. The sixth step in creating a brand strategy is to review crucial customer touchpoints.
In a duopoly, the two businesses will typically compete with one another to keep the market from becoming a monopoly, in which a single business controls the whole market. This research paper analyzes the strategies that McDonalds and Kentucky Fried Chicken (KFC) use in the duopoly market to understand the real world better using economic models by introducing the history of the development of ...
Furthermore, in 2022, the E.U and U.S. pledged to work toward the goal of ensuring additional LNG volumes for the E.U. market - with the U.S. exceeding our annual delivery targets to the E.U. in ...
Step 2: Design the Research. The next step in the marketing research process is to do a research design. The research design is your "plan of attack.". It outlines what data you are going to gather and from whom, how and when you will collect the data, and how you will analyze it once it's been obtained.