Office Technology | What is

What Is Business Communication? A Small Business Guide
Published April 16, 2024
Published Apr 16, 2024
WRITTEN BY: Silvana Peters
This article is part of a larger series on Unified Communications .
- 1 Business Communications Explained
- 2 Types of Business Communication
- 3 Benefits of Effective Communication
- 4 Best Practices & Common Mistakes
- 5 Top VoIP Business Communication Systems
- 7 Bottom Line
Business communication involves sharing information between people within and outside an organization, including colleagues, partners, clients, and stakeholders. Effective business communication is the backbone of efficient operations and contributes to informed decision-making and reduced errors. In this article, we’ll cover what business communication is, its types and channels, and our recommended service providers.
Key Takeaways:
- Business communication is exchanging information, ideas, and messages between people within and outside an organization through any channel or medium. Many situations within the workplace involve business communications, such as meetings, file sharing, sharing updates via chat, and processing information in a business environment.
- The primary objective of business communication is to enhance organizational proceedings, improve collaboration, enhance updating and feedback mechanisms, and lower errors and mistakes.
- Effective business communication fosters mutual understanding, precise decision-making, and productive operations.
Business Communications Explained
A strong communication strategy is crucial to achieving business goals because it ensures teams receive and deliver clear messages to internal and external audiences. Business communication revolves around how people exchange information within a work or professional environment. Effective connection and collaboration allow companies to better align on fundamental values and objectives while enhancing organizational procedures.
Effective communication requires communication skills (e.g., active listening, providing feedback, and presenting) and the communication process (i.e., channels used). Communication’s importance and value can be seen in high sales, decision execution, and innovative ideas. Successful business interactions align goals, improve collaboration, boost productivity, and support a cohesive company and partnership culture.
5 Key Elements
Any interaction between different stakeholders, whether internal or external, can be categorized as business communication. To understand what business communication is, it is essential to grasp its five key elements and their significance.
- Sender: The source (person or group) initiates the communication and passes on the information.
- Message: This refers to the subject matter being transmitted or passed by the sender to another person or group. The message is the information a sender wants to communicate. It can be an opinion, order, suggestion, message, memo, email, or report.
- Channel: The sender selects the medium to transmit the information, such as phone, email, letter, or chat. Selecting the channel considers factors like time, accessibility, audience, and content.
- Receiver: These are the audience members or recipients of the business information.
- Feedback: When a receiver replies or acknowledges the sender’s message, feedback takes place. Communication is incomplete without feedback, making it an integral part of business communication. Feedback confirms whether the message is successfully sent and interpreted.
Types of Business Communication
The dynamic business landscape makes communication critical to achieving organizational objectives. Here is a breakdown of the four leading types of business communication: upward, downward, lateral, and external.
Benefits of Effective Communications
Clear communication ensures an uninterrupted and streamlined flow of information within and outside an organization. Here are some benefits small businesses can expect from effective communication:
Enhances Productivity & Efficiency
Business communication ensures team members are on the same page, reducing confusion and preventing duplication of effort. Since colleagues spend less time worrying about miscommunication and trying to understand their tasks and responsibilities, they can better focus on job performance and efficiency. This minimizes the need to repeat instructions or tasks, saving money, resources, and time.
Improves Teamwork & Collaboration
Communication is the pillar of business operations because it enables teams to function as a cohesive unit where everyone knows their responsibilities and tasks. Clarity fosters better relationships between colleagues and management, boosts teamwork and collaboration, and enhances team morale and job satisfaction.
For companies with remote workers or multiple locations, consider using video conferencing to host large meetings or facilitate online collaboration between geographically distributed teams. Providers like RingCentral, Nextiva, and Dialpad offer video conferencing solutions with their voice-over-internet-protocol (VoIP) phone systems for real-time collaboration.
For example, RingCentral, a cloud-based service provider, offers unlimited calling, team messaging, business texting, and robust call management tools. Its virtual meeting tool makes file sharing easy and comes with other features like in-meeting chat and editable backgrounds.
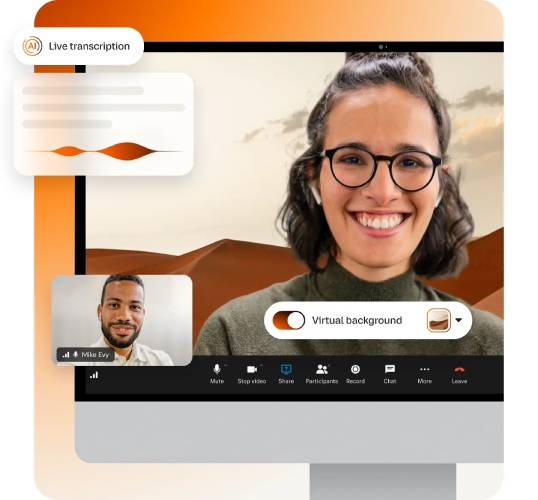
RingCentral integrates artificial intelligence (AI) tools to enhance in-meeting interactions. (Source: RingCentral )
Visit RingCentral
Builds & Maintains a Positive Reputation
Maintaining consistent and authentic messaging establishes trust and credibility, boosting your reputation as a reliable and efficient organization. Effective communication fosters trust, making product and service promotions and customer retention easier.
Ensures Compliance With Regulations
Clear communications ensure compliance with regulations, laws, and internal company policies, including health and safety regulations and labor laws. Compliance fast-tracks your company to success by reducing legal risk and financial penalties and streamlining processes.
Promotes Better Problem-solving & Decision-making
Ensure all pertinent information is accurately conveyed to leadership and decision-makers by providing clear context, implications, and potential outcomes of decisions. Effective business communication improves decision-making and information sharing, minimizing costly misunderstandings and oversight. Clear interaction among colleagues enables them to share different perspectives and consider multiple viewpoints more effectively.
Common Mistakes & Best Practices
Effective interactions establish trust, improve productivity, and resolve conflict. The easiest way to build a successful communication strategy is to understand and utilize best practices in the real world. Given the importance of business communications, knowing the common mistakes that hinder productivity allows businesses to address them proactively. Here’s a rundown of common communication pitfalls and suggestions for solving them:
Delivering Unclear Messages
When vague messages lack detail, they are open to interpretation, leading to confusion and misunderstanding. Unclear communication wastes time and resources as individuals spend more time seeking clarifications and rectifying errors rather than progressing toward the objectives. Concise communication can lead to frustration and dissatisfaction, erode trust, and poor outcomes due to incomplete or misunderstood details.
Best Practice: Convey Clear & Concise Messaging
Convey your message in a clear and easy-to-understand manner using simple language. Remember that the objective is to share information, so avoid jargon or technical terms that may confuse recipients. Structure your communication logically, eliminating unnecessary information with utmost clarity. Contextualize a task’s importance by explaining how it fits into the bigger picture so employees feel more motivated and valued.
Relatedly, workplace misunderstandings can occur because of differences in communication styles and the belief that your message is understood as intended. To avoid this issue, encourage team members to ask questions and seek clarification when necessary. Also, rather than waiting for them to reach out, periodically ask employees if something needs clarification.
Over-reliance on Email
Excessive use of email, or any communication tool, can contribute to information overload and cause response delays. While email offers instant and geographical reach, it has limitations when it comes to tone and nuance, which can lead to misinterpretation and feel impersonal. A high volume of emails with no alternative mode of communication can be overwhelming and cause difficulty in prioritizing communication.
Best Practice: Maximize Technology
Email is a great tool, but it might not be the most effective for real-time collaboration on complex projects. Explore alternative communication channels that support real-time collaboration and invest in practical internal communication tools like instant messaging to keep your team connected and organized.
Use available technology and communication tools to keep in touch with your colleagues, direct reports, partners, and supervisors. Use business communication tools like mobile apps and video conferencing to connect with others quickly and easily. Maintain a professional tone in all work-related communications, including text and instant messaging. Tailor your strategy and medium to each situation, considering the urgency, audience, and available resources.
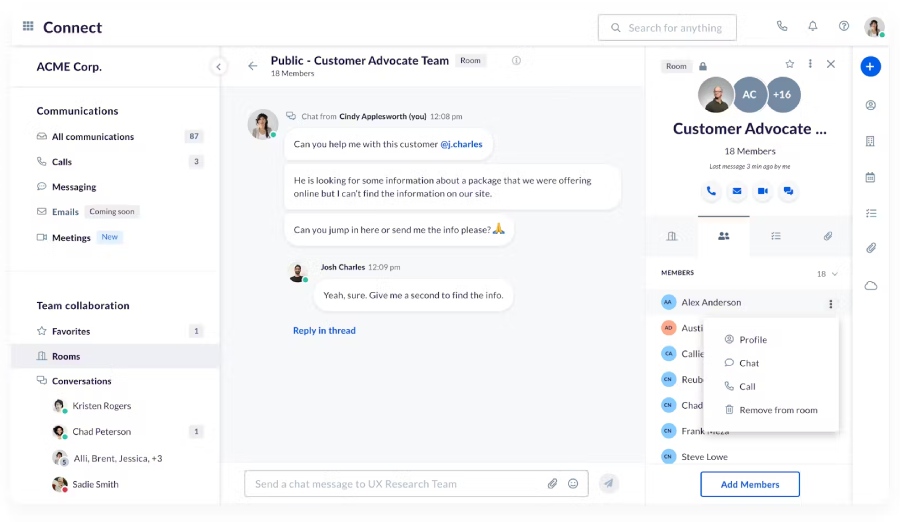
Use a centralized platform and collaborate across projects and teams using searchable files, links, and context. (Source: Nextiva )
Insufficient Feedback
With regular feedback or options for input and critique, team members will feel more connected, empowered, and relevant. Lack of performance feedback reduces motivation and irrelevance within an organization.
Best Practice: Encourage Feedback & Institute Recognition Programs
Feedback is essential to effective communication because it ensures messages and information are received as intended. Integrate routine feedback sessions across multiple channels, preferably weekly or monthly, so employees understand their performance and identify improvement areas. When providing feedback, focus on the behavior or outcome, not the individual, and highlight strengths and suggestions for continuous improvement.
To learn more about effective communication and how to create a culture of discourse, read our guide, which outlines seven expert tips for effective business communication to drive positive workplace interactions.
Information Hoarding & Silos
Working in isolation creates communication barriers, limits knowledge, and adversely affects response time and issue resolution. Departments or teams working in silos often lead to issues like duplication of efforts or misalignment in terms of priorities. This lack of cross-functional coordination leads to workflow inefficiency and decision-making, particularly when implementing change or adapting to new circumstances.
Best Practice: Build Cross-functional Teams
Establish a clear internal communication line with accountable persons so colleagues know who to turn to for guidance and action. Encourage teamwork and emphasize the importance of data and resource sharing across units and departments. By creating inter-departmental or interdisciplinary teams, you break down silos and facilitate information sharing. Lastly, as a manager or business owner, lead by example by demonstrating collaborative behavior,
As people interface, provide communication tools and skills through training and team-building programs that emphasize the importance of collaboration and provide employees with the skills they need to work effectively across departments. For example, include skills like active listening, which is intentional listening. Develop empathy and demonstrate concern during conversations to show understanding.
Top VoIP Business Communication Software
With more teams embracing remote and hybrid work models, the collaboration tools you use greatly impact team dynamics and business results. Unified communications (UC) tools integrate voice, video, messaging, fax, and email. Finding the right service to match your needs can be challenging, so we’ve curated a list of the top six providers for VoIP business communication solutions providers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How frequently do i need to communicate with colleagues & clients.
Communication frequency depends on different factors, including job responsibilities, season, and industry. In general, it’s best to communicate with colleagues regularly, often daily or weekly, depending on collaboration and workflow needs. For clients, the frequency varies widely based on project timelines, support requirements, and communication needs. Include this in your discussions at the start of the project and adjust check-ins as needs change.
Is there a way to measure successful communication?
Yes, you can measure communication success in several ways, including feedback surveys about communication frequency, quality, and experiences. Consider using network analysis, which identifies key communication leaders and studies communication patterns and interactions within an organization or network. Insights can enhance decision-making and strengthen relationships among team members.
What’s the best way to improve my communication skills?
To maximize your effectiveness in interpersonal interactions, you must be present and mindful when communicating. Focus on clear and concise messaging, building emotional intelligence, watching your tone, and being open to feedback. Remember, business communication aims to convey information effectively and efficiently to achieve specific goals, so focus on skills that support this, such as active listening and conflict resolution.
Bottom Line
Implementing the right communication strategies in business optimizes client engagement and fosters collaboration between colleagues. Effective communication in business is fundamental to company success and sustainability because it impacts all aspects of an organization. Organizations can better cultivate company culture by fully understanding business communication and its best practices.
About the Author

Find Silvana On LinkedIn
Silvana Peters
Silvana is an office technology writer at Fit Small Business, focusing on unified communications, virtual phone systems, and voice-over-internet protocol. She’s passionate about giving small business owners the information they need to succeed. Silvana’s been engaged by various businesses and organizations to produce technical reports and content ranging from current events, business, technology, lifestyle, and development.
Join Fit Small Business
Sign up to receive more well-researched small business articles and topics in your inbox, personalized for you. Select the newsletters you’re interested in below.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 1: Effective Business Communication
Venecia Williams
Learning Objectives
- Examine the importance of being a good communicator
- Define the communication process
- Explain 8 essential components of communication
- Discuss the role of ethics in communication
Communication is an activity, skill, and art that incorporates lessons learned across a wide spectrum of human knowledge. Perhaps the most time-honoured form of communication is storytelling. We’ve told each other stories for ages to help make sense of our world, anticipate the future, and certainly to entertain ourselves. The art of storytelling draws on your understanding of yourself, your message, and how you communicate it to an audience that is simultaneously communicating back to you. Your anticipation, reaction, and adaptation to the process will determine how successfully you are able to communicate. You were not born knowing how to write or even how to talk—but in the process of growing up, you have undoubtedly learned how to tell, and how not tell, a story out loud and in writing.
Effective communication takes preparation, practice, and persistence. There are many ways to learn communication skills; the school of experience, or “hard knocks,” is one of them. But in the business environment, a “knock” (or lesson learned) may come at the expense of your credibility through a blown presentation to a client. The classroom environment, with a compilation of information and resources such as a text, can offer you a trial run where you get to try out new ideas and skills before you have to use them to communicate effectively to make a sale or form a new partnership. Listening to yourself, or perhaps the comments of others may help you reflect on new ways to present or perceive, thoughts, ideas and concepts. The net result is your growth; ultimately your ability to communicate in business will improve, opening more doors than you might anticipate.
Importance of Good Communication Skills
Communication is key to your success—in relationships, in the workplace, as a citizen of your country, and across your lifetime. Your ability to communicate comes from experience, and experience can be an effective teacher, but this text and the related business communication course will offer you a wealth of experiences gathered from professional speakers across their lifetimes. You can learn from the lessons they’ve learned and be a more effective communicator right out of the gate.
Business communication can be thought of as a problem-solving activity in which individuals may address the following questions:
- What is the situation?
- What are some possible communication strategies?
- What is the best course of action?
- What is the best way to design the chosen message?
- What is the best way to deliver the message?
In this book, we will examine this problem-solving process and help you learn to apply it in the kinds of situations you are likely to encounter over the course of your career.
Communication Influences Your Thinking about Yourself and Others
We all share a fundamental drive to communicate. Communication can be defined as the process of understanding and sharing meaning (Pearson & Nelson, 2000). You share meaning in what you say and how you say it, both in oral and written forms. If you could not communicate, what would life be like? A series of never-ending frustrations? Not being able to ask for what you need or even to understand the needs of others?
Being unable to communicate might even mean losing a part of yourself, for you communicate your self-concept —your sense of self and awareness of who you are—in many ways. Do you like to write? Do you find it easy to make a phone call to a stranger or to speak to a room full of people? Perhaps someone told you that you don’t speak clearly or your grammar needs improvement. Does that make you more or less likely to want to communicate? For some, it may be a positive challenge, while for others it may be discouraging. But in all cases, your ability to communicate is central to your self-concept.
Take a look at your clothes. What are the brands you are wearing? What do you think they say about you? Do you feel that certain styles of shoes, jewelry, tattoos, music, or even automobiles express who you are? Part of your self-concept may be that you express yourself through texting, or through writing longer documents like essays and research papers, or through the way you speak.
On the other side of the coin, your communications skills help you to understand others—not just their words, but also their tone of voice, their nonverbal gestures, or the format of their written documents provide you with clues about who they are and what their values and priorities may be. Active listening and reading are also part of being a successful communicator.
Communication Influences How You Learn
When you were an infant, you learned to talk over a period of many months. When you got older, you didn’t learn to ride a bike, drive a car, or even text a message on your cell phone in one brief moment. You need to begin the process of improving your speaking and writing with the frame of mind that it will require effort, persistence, and self-correction.
You learn to speak in public by first having conversations, then by answering questions and expressing your opinions in class, and finally by preparing and delivering a “stand-up” speech. Similarly, you learn to write by first learning to read, then by writing and learning to think critically. Your speaking and writing are reflections of your thoughts, experience, and education. Part of that combination is your level of experience listening to other speakers, reading documents and styles of writing, and studying formats similar to what you aim to produce.
As you study business communication, you may receive suggestions for improvement and clarification from speakers and writers more experienced than yourself. Take their suggestions as challenges to improve; don’t give up when your first speech or first draft does not communicate the message you intend. Stick with it until you get it right. Your success in communicating is a skill that applies to almost every field of work, and it makes a difference in your relationships with others.
Remember, luck is simply a combination of preparation and timing. You want to be prepared to communicate well when given the opportunity. Each time you do a good job, your success will bring more success.
Communication Represents You and Your Employer
You want to make a good first impression on your friends and family, instructors, and employer. They all want you to convey a positive image, as it reflects on them. In your career, you will represent your business or company in spoken and written form. Your professionalism and attention to detail will reflect positively on you and set you up for success.
In both oral and written situations, you will benefit from having the ability to communicate clearly. These are skills you will use for the rest of your life. Positive improvements in these skills will have a positive impact on your relationships, your prospects for employment, and your ability to make a difference in the world.
Communication Skills Are Desired by Business and Industry
Oral and written communication proficiencies are consistently ranked in the top ten desirable skills by employer surveys year after year. In fact, high-powered business executives sometimes hire consultants to coach them in sharpening their communication skills. According to the National Association of Colleges and Employers (2018), the following are the top five personal qualities or skills potential employers seek:
- Communication skills (verbal and written)
- Strong work ethic
- Teamwork skills (works well with others, group communication)
- Analytical skills
Knowing this, you can see that one way for you to be successful and increase your promotion potential is to increase your abilities to speak and write effectively. An individual with excellent communication skills is an asset to every organization. No matter what career you plan to pursue, learning to express yourself professionally in speech and in writing will help you get there.
What is Communication?
Many theories have been proposed to describe, predict, and understand the behaviours and phenomena of which communication consists. When it comes to communicating in business, we are often less interested in theory than in making sure our communications generate the desired results. But in order to achieve results, it can be valuable to understand what communication is and how it works. All communication is composed of three parts that make a whole: sharing, understanding, and meaning.
Sharing means doing something together with one or more person(s). In communication, sharing occurs when you convey thoughts, feelings, ideas, or insights to others. You also share with yourself (a process called intrapersonal communication) when you bring ideas to consciousness, ponder how you feel about something, figure out the solution to a problem, or have a classic “Aha!” moment when something becomes clear.
The second keyword is understanding . “To understand is to perceive, to interpret, and to relate our perception and interpretation to what we already know.” (McLean, 2003) Understanding the words and the concepts or objects they refer to is an important part of the communication process.
Finally, meaning is what you share through communication. For example, by looking at the context of a word, and by asking questions, you can discover the shared meaning of the word and better understand the message.
Watch the following video reviewing Types of Communication
- Interpersonal communication is any message exchanged between two or more people.
- Written communication is any message using the written word.
- Verbal, or oral, communication is any message conveyed through speech.
- Nonverbal communication is any message inferred through observation of another person.
Communications Process: Encoding and Decoding
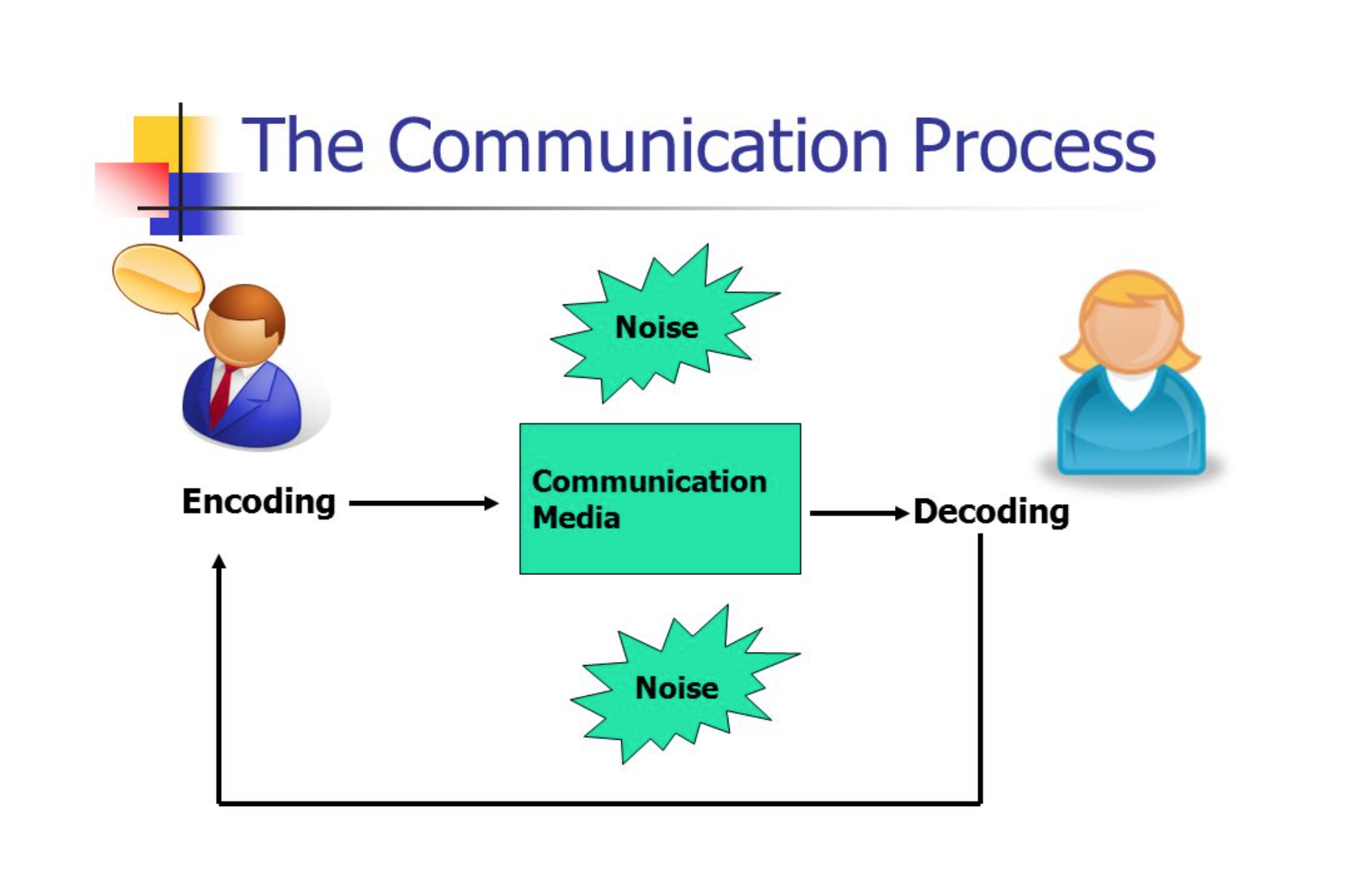
In basic terms, humans communicate through a process of encoding and decoding . The encoder is the person who develops and sends the message. As represented in Figure 1.1 below, the encoder must determine how the message will be received by the audience, and make adjustments so the message is received the way they want it to be received.
Encoding is the process of turning thoughts into communication. The encoder uses a ‘medium’ to send the message — a phone call, email, text message, face-to-face meeting, or other communication tools. The level of conscious thought that goes into encoding messages may vary. The encoder should also take into account any ‘noise’ that might interfere with their message, such as other messages, distractions, or influences.
The audience then ‘decodes’, or interprets, the message for themselves. Decoding is the process of turning communication into thoughts. For example, you may realize you’re hungry and encode the following message to send to your roommate: “I’m hungry. Do you want to get pizza tonight?” As your roommate receives the message, they decode your communication and turn it back into thoughts to make meaning.
Of course, you don’t just communicate verbally—you have various options, or channels, for communication. Encoded messages are sent through a channel, or a sensory route, on which a message travels to the receiver for decoding. While communication can be sent and received using any sensory route (sight, smell, touch, taste, or sound), most communication occurs through visual (sight) and/or auditory (sound) channels. If your roommate has headphones on and is engrossed in a video game, you may need to get their attention by waving your hands before you can ask them about dinner.
The transmission model of communication describes communication as a linear, one-way process in which a sender intentionally transmits a message to a receiver (Ellis & McClintock, 1990). This model focuses on the sender and message within a communication encounter. Although the receiver is included in the model, this role is viewed as more of a target or endpoint rather than part of an ongoing process. You are left to presume that the receiver either successfully receives and understands the message or does not. Think of how a radio message is sent from a person in the radio studio to you listening in your car. The sender is the radio announcer who encodes a verbal message that is transmitted by a radio tower through electromagnetic waves (the channel) and eventually reaches your (the receiver’s) ears via an antenna and speakers in order to be decoded. The radio announcer doesn’t really know if you receive their message or not, but if the equipment is working and the channel is free of static, then there is a good chance that the message was successfully received.
The interaction model of communication describes communication as a process in which participants alternate positions as sender and receiver and generate meaning by sending messages and receiving feedback within physical and psychological contexts (Schramm, 1997). Rather than illustrating communication as a linear, one-way process, the interaction model incorporates feedback, which makes communication a more interactive, two-way process. Feedback includes messages sent in response to other messages. For example, your instructor may respond to a point you raise during class discussion or you may point to the sofa when your roommate asks you where the remote control is. The inclusion of a feedback loop also leads to a more complex understanding of the roles of participants in a communication encounter. Rather than having one sender, one message, and one receiver, this model has two sender-receivers who exchange messages. Each participant alternates roles as sender and receiver in order to keep a communication encounter going. Although this seems like a perceptible and deliberate process, you alternate between the roles of sender and receiver very quickly and often without conscious thought.
The transaction model of communication describes communication as a process in which communicators generate social realities within social, relational, and cultural contexts. In this model, you don’t just communicate to exchange messages; you communicate to create relationships, form intercultural alliances, shape your self-concepts, and engage with others in dialogue to create communities. In short, you don’t communicate about your realities; communication helps to construct your realities (and the realities of others).
The roles of sender and receiver in the transaction model of communication differ significantly from the other models. Instead of labelling participants as senders and receivers, the people in a communication encounter are referred to as communicators. Unlike the interaction model, which suggests that participants alternate positions as sender and receiver, the transaction model suggests that you are simultaneously a sender and a receiver. For example, when meeting a new friend, you send verbal messages about your interests and background, your companion reacts nonverbally. You don’t wait until you are done sending your verbal message to start receiving and decoding the nonverbal messages of your new friend. Instead, you are simultaneously sending your verbal message and receiving your friend’s nonverbal messages. This is an important addition to the model because it allows you to understand how you are able to adapt your communication—for example, adapting a verbal message—in the middle of sending it based on the communication you are simultaneously receiving from your communication partner.
Eight Essential Components of Communication
The communication process can be broken down into a series of eight essential components, each of which serves an integral function in the overall process:
Environment
Interference.
The source imagines, creates, and sends the message. The source encodes the message by choosing just the right order or the best words to convey the intended meaning and presents or sends the information to the audience (receiver). By watching for the audience’s reaction, the source perceives how well they received the message and responds with clarification or supporting information.
“The message is the stimulus or meaning produced by the source for the receiver or audience” (McLean, 2005). The message brings together words to convey meaning but is also about how it’s conveyed — through nonverbal cues, organization, grammar, style, and other elements.
“The channel is the way in which a message or messages travel between source and receiver.” (McLean, 2005). Spoken channels include face-to-face conversations, speeches, phone conversations and voicemail messages, radio, public address systems, and Skype. Written channels include letters, memorandums, purchase orders, invoices, newspaper and magazine articles, blogs, email, text messages, tweets, and so forth.
“The receiver receives the message from the source, analyzing and interpreting the message in ways both intended and unintended by the source” (McLean, 2005).
When you respond to the source, intentionally or unintentionally, you are giving feedback. Feedback is composed of messages the receiver sends back to the source. Verbal or nonverbal, all these feedback signals allow the source to see how well, how accurately (or how poorly and inaccurately) the message was received (Leavitt & Mueller, 1951).
“The environment is the atmosphere, physical and psychological, where you send and receive messages” (McLean, 2005). Surroundings, people, animals, technology, can all influence your communication.
“The context of the communication interaction involves the setting, scene, and expectations of the individuals involved” (McLean, 2005). A professional communication context may involve business suits (environmental cues) that directly or indirectly influence expectations of language and behaviour among the participants.
Interference, also called noise, can come from any source. “Interference is anything that blocks or changes the source’s intended meaning of the message” (McLean, 2005). This can be external or internal/psychological. Noise interferes with normal encoding and decoding of the message carried by the channel between source and receiver.
Your Responsibilities as a Communicator – 4 tips
Whenever you speak or write in a business environment, you have certain responsibilities to your audience, your employer, and your profession. Your audience comes to you with an inherent set of expectations that is your responsibility to fulfill. The specific expectations may change given the context or environment, but two central ideas will remain: be prepared, and be ethical.
Preparation
Being prepared means that you have selected a topic appropriate to your audience, gathered enough information to cover the topic well, put your information into a logical sequence, and considered how best to present it.
Organization
Being organized involves the steps or points that lead your communication to a conclusion. Once you’ve invested time in researching your topic, you will want to narrow your focus to a few key points and consider how you’ll present them. You also need to consider how to link your main points together for your audience so they can follow your message from point to point.
You need to have a clear idea in your mind of what you want to say before you can say it clearly to someone else. It involves considering your audience, as you will want to choose words and phrases they understand and avoid jargon or slang that may be unfamiliar to them. Clarity also involves presentation and appropriate use of technology.
Conciseness
Concise means to be brief and to the point. In most business communications you are expected to ‘get down to business’ right away. Being prepared includes being able to state your points clearly and support them with trustworthy evidence in a relatively straightforward, linear way. Be concise in your choice of words, organization, and even visual aids. Being concise also involves being sensitive to time constraints. Be prepared to be punctual and adhere to deadlines or time limits. Some cultures also have a less strict interpretation of time schedules and punctuality. While it is important to recognize that different cultures have different expectations, the general rule holds true that good business communication does not waste words or time.
Ethics in Communication
Communicating ethically involves being egalitarian, respectful, and trustworthy—overall, practising the “golden rule” of treating your audience the way you would want to be treated. Communication can move communities, influence cultures, and change history. It can motivate people to take a stand, consider an argument, or purchase a product. The degree to which you consider both the common good and fundamental principles you hold to be true when crafting your message directly relates to how your message will affect others.
The Ethical Communicator Is Egalitarian
The word “egalitarian” comes from the root “equal.” To be egalitarian is to believe in basic equality: that all people should share equally in the benefits and burdens of a society. It means that everyone is entitled to the same respect, expectations, access to information, and rewards of participation in a group. To communicate in an egalitarian manner, speak and write in a way that is comprehensible and relevant to all your listeners or readers, not just those who are ‘like you’ in terms of age, gender, race or ethnicity, or other characteristics. In business, an effective communicator seeks to unify the audience by using ideas and language that are appropriate for all the message’s readers or listeners.
The Ethical Communicator Is Respectful
People are influenced by emotions as well as logic. The ethical communicator will be passionate and enthusiastic without being disrespectful. Losing one’s temper and being abusive are generally regarded as showing a lack of professionalism (and could even involve legal consequences for you or your employer). When you disagree strongly with a coworker, feel deeply annoyed with a difficult customer, or find serious fault with a competitor’s product, it is important to express such sentiments respectfully.
The Ethical Communicator Is Trustworthy
Trust is a key component in communication, and this is especially true in business. Your goal as a communicator is to build a healthy relationship with your audience and to do that you must show them how they can trust you and why the information you are about to share with them is believable. Your audience will expect that what you say is the truth as you understand it. This means that you have not intentionally omitted, deleted, or taken information out of context simply to prove your points. They will listen to what you say and how you say it, but also to what you don’t say or do. Being worthy of trust is something you earn with an audience. Many wise people have observed that trust is hard to build but easy to lose.
The “Golden Rule”
When in doubt, remember the “golden rule,” which is to treat others the way you would like to be treated. In all its many forms, the golden rule incorporates human kindness, cooperation, and reciprocity across cultures, languages, backgrounds, ad interests. Regardless of where you travel, with whom you communicate or what your audience is like, remember how you would feel if you were on the receiving end of your communication and act accordingly.
Being a good communicator is essential to becoming a successful business person. Therefore, it is important to learn how to communicate well. The first step in that process is understanding what effective communication means. This will help you to evaluate and improve your communication skills.
End of Chapter Activities
1a. thinking about the content.
What are your key takeaways from this chapter? What is something you have learned or something you would like to add from your experience?
1b. Review Questions
Discussion Questions
- Recall one time you felt offended or insulted in a conversation. What contributed to your perception?
- When someone lost your trust, were they able to earn it back?
- Does the communicator have a responsibility to the audience? Does the audience have a responsibility to the speaker? Why or why not?
1c. Applying chapter concepts to a situation
Communicating with a supervisor
Mako is an international student enrolled in a post-degree program in Vancouver. She has been working at a grocery store for the past three months on Tuesdays, Thursdays and Fridays when she doesn’t have class. Mako enjoys working at the grocery store and gets along well with her colleagues and supervisor. Customers often comment on her professionalism and friendliness and she has noticed that her communication skills have improved.
When she applied for the job and filled out her available hours, she made sure to state that she could only work a maximum of 20 hours per week as an international student. She mentioned it once more during the interview and was told it would not be a problem.
Since then her supervisor has asked her to work overtime in a few instances to accommodate a colleague who was running late. That was not a problem. However, recently her supervisor asked if she could pick up an extra shift for two weeks because one colleague was out sick. Mako is not comfortable working so many hours over her maximum, but she is worried her supervisor might be upset and think she is not a team player.
What should Mako do? How should she communicate her decision to her supervisor?
1d. Summary Writing
Read this article from Salesforce.com on the 10 Must-Have Communication Skills for Business Success . Summarize the article and identify which of these skills you would like to improve.
Content Attribution
This chapter contains content from Communication for Business Professionals – Canadian Edition which was adapted from Business Communication for Success in 2013 by University of Minnesota Libraries Publishing through the eLearning Support Initiative . The 2018 revision continues to be licensed with a Creative Commons license (CC BY-NC-SA) following the precedent of a publisher who has requested that they and the original author not receive attribution.
Ellis, R. and Ann McClintock, You Take My Meaning: Theory into Practice in Human Communication (London: Edward Arnold, 1990), 71.
Leavitt, H., & Mueller, R. (1951). Some effects of feedback on communication. Human Relations, 4 , 401–410.
McLean, S. (2003). The basics of speech communication . Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
McLean, S. (2005). The basics of interpersonal communication (p. 10). Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
NACE. (2018). Employers Want to See These Attributes on Students’ Resumes. Retrieved August 26, 2020, from https://www.naceweb.org/talent-acquisition/candidate-selection/employers-want-to-see-these-attributes-on-students-resumes/
Pearson, J. C., & Nelson, P. E. (2000). An introduction to human communication: understanding and sharing . Boston: McGraw Hill.
Schramm, W., The Beginnings of Communication Study in America (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 1997).
Video Attribution
This chapter contains the video Types of Communication Interpersonal, Non Verbal, Written Oral Video Lesson Transcript Stud by Zaharul Hafiq from YouTube.com.
Chapter 1: Effective Business Communication Copyright © 2020 by Venecia Williams is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Business Communication: (Definition, Types & Objectives)
- Post published: January 16, 2024
- Post author: Fonada
Be social with us Share this content
- Opens in a new window
In any organization, various management levels exist, particularly in larger and more complex setups. Managing such structures can be challenging, especially with a sizable customer database. That’s why businesses are increasingly adopting cloud telephony solutions to facilitate effective communication within the workforce. However, relying solely on advanced CPaaS solutions is not sufficient for maintaining an effective communication trail among all employees and customers.
To make a business successful, it’s vital for all employees to communicate well and collaborate efficiently on a regular basis. This means ensuring a continuous and smooth flow of information. In business, communication is not limited to talking to customers only. It heavily relies on getting feedback and prompting smoother communication among customers as well as employees. It’s like the heartbeat of a business, essential for its growth and progress.
This blog post aims to give you a clear picture of “what is business communication” and how it helps enterprises. It will cover everything from understanding how communication works to providing practical tips for overcoming common challenges. Whether it’s about getting feedback or breaking down communication barriers, this guide will help your business create a communication process that fosters growth and long-term success.
What Is Business Communication? (Definition)
In layman’s terms, business communication definition revolves around how individuals exchange information within a work or business environment. It includes talking, writing, sharing ideas, and leveraging advanced communication solutions to ensure everyone understands what needs to be done. It helps teams work together, make decisions, and keep the business running smoothly. Whether it’s emails, meetings, or even just chatting with colleagues, it’s all about getting the right messages across to achieve common goals in a company.
Read More: What Is Internet Communication & How Can We Communicate Over The Internet?
Importance and Objectives of Business Communication
Business communication meaning refers to the process of exchanging information within a company or with external parties to achieve business objectives effectively. It is like the glue that holds different aspects of a business together.
It helps in expressing ideas, making plans, carrying out decisions, reaching agreements, handling orders, making sales , conducting successful meetings, and maintaining a healthy feedback loop with both employees and customers. Without good communication, these processes could become confusing, inefficient, or prone to errors.
The objective of business communication lies in:
- Presenting options/new business ideas: Sharing and discussing new ideas or choices for the business.
- Making plans and proposals (business writing): Writing down and explaining plans and suggestions for the business.
- Executing decisions: Carrying out and putting into action the choices and plans made for the business.
- Reaching agreements: Coming to mutual understandings or decisions with others involved in the business.
- Sending and fulfilling orders: Communicating and making sure that orders placed by customers are delivered as expected.
- Successful selling: Effectively communicating to convince customers to buy products or services using IoT ( Internet of Things )
- Effective meetings: Making sure that meetings are productive and achieve their goals.
- Providing feedback to employees and customers: Sharing thoughts and comments with employees and customers helps them understand areas of excellence and improvement. This practice fosters healthy customer relationships and motivates employees.
Types of Business Communication
We can categorize business communication in three types:
Under the Organizational Structure:
- Formal Communication: This is a structured way for employees to talk about work-related matters in a business. Example: Imagine a scheduled meeting where employees discuss work projects using a planned agenda.
- Informal Communication: This is more casual communication that may or may not be about work. Example: Think of chatting with a colleague at the coffee machine about weekend plans or hobbies.
Taking Into Consideration The Direction:
- Downward Communication: Information flows from top management to lower-level employees. Managers use this to convey goals, procedures, rules, decisions, and instructions to subordinates. Example: Picture a manager informing their team about new company policies during a team meeting.
- Upward Communication: This is the opposite, where information moves from lower-level employees to higher management. The purpose is to provide feedback, suggestions, requests, and other details to higher-ups. Example: Consider an employee sharing feedback or ideas with their supervisor about improving office processes.
- Horizontal Communication: This involves communication among coworkers at the same hierarchical level. It is crucial for different parts of the organization to collaborate and work well together. Example: Think of colleagues from different departments coordinating on a joint project through regular discussions.
- External Communication: This refers to interactions with individuals outside the company, such as customers, stockholders, suppliers, partners, and regulatory organizations. External communication supports increased sales, efficient operations, and overall company sales performance. Example: Imagine a company reaching out to customers through emails or holding meetings with suppliers to discuss product orders.
According To The Mode Of Expression:
- Oral Communication: This involves spoken words and discussion on customer engagement strategies such as face-to-face meetings, seminars, video conferences, and lectures. It relies on body language and verbal intonation to convey meaning. Example: Picture a team gathering for a face-to-face brainstorming session where everyone shares their ideas.
- Written Communication: This includes emails, texts, notes, papers, and other written forms. These methods simplify communication by providing clear information and allowing recipients to clarify any misunderstandings. Example: Think of sending an email to a colleague with project updates or using a written report to communicate key findings in a business meeting.
Read More: How To Get A Temporary Phone Number?
Roles and Objectives Of Business Communication
The success of a company depends on how well its corporate communications work. Here is how it can help the business:
Top To Bottom
Peer to peer.
A huge proportion of our everyday activities depends on our relationship with coworkers. Yes, a solid relationship with your supervisor is vital, yet some go days without communicating.
Bottom To Top
Why effective business communication matters.
Effective business communication is crucial for several reasons:
Democratization:
- In organizations using democratic decision-making, hearing from underrepresented groups is more likely.
- A strategic approach to business choices, coupled with a culture of sharing information across the entire organization, enhances planning.
Boost Morale and Motivation:
- Vital for increasing employee productivity.
- Helps employees grasp plans, procedures, challenges, and corporate goals, leading to improved productivity.
Improve Relationships:
- Facilitates the exchange of ideas and needs between employees and management.
- Healthy labor relations contribute to stability and overall success.
Job Fulfillment:
- Effective, fair, and straightforward communication fosters understanding between employees and management.
- Results in greater job satisfaction, aligning individuals with business communication objectives.
Higher Efficiency:
- Fosters collaboration among employees, promoting mutual trust and understanding.
- Enables effective duty performance and reduces the likelihood of errors in assigned tasks.
Smooth Operation of Business:
- Helps managers run businesses more efficiently by facilitating tasks like planning, directing, organizing, and controlling.
- Quality leadership relies on a successful and efficient business communication system.
Facilitates Decision Making:
- Current knowledge is essential for effective decisions.
- Managers use effective communication to gather information from various sources, integrating it for informed decision-making.
Proper Planning:
- Enables organizations to develop excellent plans and policies.
- Precise data, communicated effectively, is essential for the timely development and execution of policies and plans.
Minimize Conflicts:
- Clear and effective communication allows business partners to share information easily.
- Results in fewer conflicts, arguments, and disagreements among various stakeholders.
How to Smoothen Your Business Communication Process?
Many employees feel that the way their companies communicate internally could be improved, with 29% expressing this sentiment. To enhance your process of business communication, follow these straightforward steps:
Business Communication Audit and Goals
- Every organization, regardless of size, should have a communication strategy.
- Identify areas that need improvement and prioritize them.
- The sender initiates the communication process by planning and writing the message.
Message Coding Format
- Allocate sufficient time for this task, especially for larger businesses.
- The sender formats the data for transmission, turning it into a visual representation like text or video.
Selecting a Channel
- Choose communication modes that align with your business goals and interactions among primary groups.
- No manual dictates the best tools, so the sender selects the most appropriate channel for the audience.
- Examples include YouTube videos, social media posts, and blog articles.
Process Documentation
- Document your actions during setup and make them accessible to the entire business.
- This serves as a guide for employees to follow the communication strategy in various scenarios.
- It simplifies the understanding of communication methods, especially for new employees.
- Feedback is must for understanding the effectiveness of the message.
- Encourage two-way communication to receive feedback from recipients.
- Both PR and marketing benefit from this interactive communication approach.
Read More: What Is Call Detail Record (CDR) ? (12 Key Benefits)
Methods Of Business Communication
It depends entirely on the circumstances to determine which option is superior or inferior for your business.
The following corporate communication approaches are relevant to any or all situations:
Digital Communication
This includes communications networks such as email and instant messaging . The advantages of emails and text messages include having efficient personal discussions in a busy workplace setting and simultaneously sharing a message with many individuals — ranging from several to hundreds.
Telephone Meetings
Phones have made efficient and fast-paced meetings possible anywhere. It allows for a better exchange of ideas than written communication because of the tone of voice and other non-verbal signals. Cloud phone systems accelerate onboarding and teamwork.
Video Conferencing
Video conferencing technology has enabled distant workers to meet regularly in in-person meetings. It has elevated the concept of phone meetings to the next level as one can see face expressions and reactions as well.
In-Person Meetings
In-person meetings can expedite the implementation of business ideas. According to research, in-person encounters generate better ideas than virtual ones. However, meetings must have a solid agenda.
Official Reports And Documentation
Documenting activities that influence other individuals and departments is essential for a successful business communication system. Referring to a formal document at any time reduces confusion and improves communication.
Presentations
Meetings with group members often include PowerPoint presentations and reports. These are excellent for sharing innovative thoughts in a structured manner that allows for questions and explanations.
Discussion Boards And Faqs
An internal space for employees to review FAQs on departmental issues and ask new ones to improve productivity and knowledge.
Surveys—internal and external—are useful for gathering input and ratings on crucial topics. Surveys allow a continuous cycle of improvements based on customer feedback and provide a communication line across all organizational levels.
Customer Relationship Management
This may involve any consumer relations-related endeavor. Live chat, CRM, onboarding, reviews, and more are a few examples.
Read More: Understanding Inbound And Outbound Meaning For Smooth Business Communication
Functions of Business Communication
One important part of talking within a company is ensuring people understand what they should do. When team members know their roles and how they contribute to the company’s goals, they work together better. Employees figure out their tasks by working together and understanding their duties.
Giving Useful Feedback
Another important part of business talk is giving employees and customers timely and clear feedback. Employees do better when they regularly hear about their work and what skills they can improve. This helps them see what they’re good at and where they can get better. Getting feedback from customers and stakeholders also helps a company improve its products and services. Communication within a company involves things like job descriptions, goals, and how well people are doing in their roles.
Talking to Clients
To persuade potential customers, clients, or business partners, businesses often use communication to make a convincing argument. This kind of talk can happen in person or in writing. For instance, a salesperson might convince a customer over the phone or through ads in a newspaper for a product launch. This type of communication needs to be trustworthy and appeal to emotions. It can also help with public relations and building a brand.
Encouraging Employees to Decide Better
Companies use communication as a tool to help employees make good decisions about their daily tasks and long-term goals. Bonuses or rewards motivate people to contribute to the company’s growth and meet goals faster.
Building Social Connections
Communication is crucial in helping employees build social networks. Some companies encourage all employees to interact with their bosses, while others follow a more structured chain of command.
Business Issues Resolved Through Effective Business Communication
Effective business communication is crucial for resolving various issues within an organization. Here are some common business issues that can be addressed through effective communication:
Unclear Roles and Responsibilities
When employees are unsure about their tasks and roles, it can lead to significant problems in a business. Even in companies that strive for a collaborative environment, failure to clearly explain responsibilities can result in employees assuming others will handle issues. This lack of clarity risks having an ineffective and dishonest workforce. Defining roles, authority, and success criteria is crucial for improving business operations, staff productivity, and retention rates.
Communication Gaps Between Departments
In organizations, different departments often work independently on assigned tasks. While this can be efficient, it becomes a problem when departments don’t communicate or understand each other’s roles. Communication across departments is vital for achieving overall organizational objectives, especially in larger companies. For instance, if the finance department is unaware of the activities of the market research department, it can lead to operational failures. Providing a comprehensive overview ensures streamlined operations.
Poorly Crafted Written Communications
Essential information, such as new projects, organizational updates, and workflows, is often communicated in writing. However, poorly written messages can confuse and frustrate employees. Investing time and resources in creating clear, well-written communications ensures that recipients can absorb the information and respond appropriately.
Negative Impact on Customer Service
Inadequate internal communication negatively affect s customer service in two ways. First, employees dealing with customers need access to relevant information. Second, low employee morale can harm the overall customer experience . Effective business communication is crucial to providing excellent customer service.
Clear communication is essential for employees to establish connections and foster a positive work environment. Some organizations encourage open communication among employees and superiors, while others follow a hierarchical chain of command. Regardless of the approach, the purpose of business communication is to create a competitive edge in the business world. Fonada offers various services to help businesses explore profitable alternatives.
Frequently Asked Questions of Business Communication
What is the importance of effective business communication.
Effective business communication fosters collaboration, ensures clarity, builds trust, enhances productivity, and facilitates informed decision-making. It is crucial for building strong relationships, boosting efficiency, and achieving organizational success.
How to Improve Internal Communication?
Enhance internal communication by implementing clear channels, using collaboration tools, fostering an open culture, providing regular updates, encouraging feedback, and utilizing platforms for seamless information sharing, ensuring transparency and unity.
What is the Role of non-verbal communication?
Non-verbal communication, encompassing gestures, body language, and facial expressions, complements verbal messages, conveying emotions, intentions, and context. It enhances understanding, strengthens relationships, and influences perceptions in interpersonal interactions.
What are the c hallenges in cr oss-cultural business communication?
Cross-cultural business communication faces challenges such as language barriers, differing communication styles, cultural nuances, misinterpretations, and varying expectations. Overcoming these challenges requires cultural awareness, adaptability, and effective intercultural communication skills.
What is a business communications plan?
A business communications plan is a strategic outline detailing how a company communicates internally and externally. It specifies goals, target audiences, channels, and messaging strategies to ensure effective and consistent communication.
How does business communication differ across cultures?
Business communication varies across cultures due to differences in communication styles, etiquette, and language nuances. Understanding cultural norms and adapting communication strategies helps navigate diverse business environments and fosters successful interactions.
What are the key components of business communication?
Key components of business communication include clear messaging, effective channels (e.g., emails, meetings), proper tone and etiquette, active listening, feedback mechanisms, and adaptability to diverse audiences and cultures for successful information exchange.
What is the role of technology in business communication?
Technology plays a vital role in business communication by facilitating efficient information exchange through channels like emails, video conferencing, and collaborative platforms. It enhances connectivity, speed, and accessibility, fostering effective, streamlined communication processes.
What do you understand by the term business communication Definition?
Business communication definition refers to the process of exchanging information within an organization or between organizations to achieve business objectives. It encompasses various methods like verbal, written, and visual communication for effective interaction and collaboration.
Request a Demo
Are you ready to save more time register now for demo, are you ready to save more time register now for demo.
Invalid value

Awarded Comprehensive Implementation of Customer Experience Designs in FinTech
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
© Copyright 2024 Shivtel Communications Pvt. Ltd. (AKA Rhythmus Technologies Pvt. Ltd.) All Rights Reserved
Effective Business Communication
What is communication, learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Define communication and describe communication as a process.
- Identify and describe the eight essential components of communication.
- Identify and describe two models of communication.
Many theories have been proposed to describe, predict, and understand the behaviors and phenomena of which communication consists. When it comes to communicating in business, we are often less interested in theory than in making sure our communications generate the desired results. But in order to achieve results, it can be valuable to understand what communication is and how it works.
Defining Communication
The root of the word “communication” in Latin is communicare , which means to share, or to make common ( Weekley, 1967). Communication is defined as the process of understanding and sharing meaning ( Pearson & Nelson, 2000, p. 6).
At the center of our study of communication is the relationship that involves interaction between participants. This definition serves us well with its emphasis on the process, which we’ll examine in depth across this text, of coming to understand and share another’s point of view effectively.
The first key word in this definition is process . A process is a dynamic activity that is hard to describe because it changes ( Pearson & Nelson, 2000). Imagine you are alone in your kitchen thinking. Someone you know (say, your mother) enters the kitchen and you talk briefly. What has changed? Now, imagine that your mother is joined by someone else, someone you haven’t met before—and this stranger listens intently as you speak, almost as if you were giving a speech. What has changed? Your perspective might change, and you might watch your words more closely. The feedback or response from your mother and the stranger (who are, in essence, your audience) may cause you to reevaluate what you are saying. When we interact, all these factors—and many more—influence the process of communication.
The second key word is understanding : “To understand is to perceive, to interpret, and to relate our perception and interpretation to what we already know” ( McLean, 2003). If a friend tells you a story about falling off a bike, what image comes to mind? Now your friend points out the window and you see a motorcycle lying on the ground. Understanding the words and the concepts or objects they refer to is an important part of the communication process.
Next comes the word sharing . Sharing means doing something together with one or more people. You may share a joint activity, as when you share in compiling a report; or you may benefit jointly from a resource, as when you and several coworkers share a pizza. In communication, sharing occurs when you convey thoughts, feelings, ideas, or insights to others. You can also share with yourself (a process called intrapersonal communication) when you bring ideas to consciousness, ponder how you feel about something, or figure out the solution to a problem and have a classic “Aha!” moment when something becomes clear.
Finally, meaning is what we share through communication. The word “bike” represents both a bicycle and a short name for a motorcycle. By looking at the context the word is used in and by asking questions, we can discover the shared meaning of the word and understand the message.
Eight Essential Components of Communication
In order to better understand the communication process, we can break it down into a series of eight essential components:
Environment
Interference.
Each of these eight components serves an integral function in the overall process. Let’s explore them one by one.
The source imagines, creates, and sends the message. In a public speaking situation, the source is the person giving the speech. He or she conveys the message by sharing new information with the audience. The speaker also conveys a message through his or her tone of voice, body language, and choice of clothing. The speaker begins by first determining the message—what to say and how to say it. The second step involves encoding the message by choosing just the right order or the perfect words to convey the intended meaning. The third step is to present or send the information to the receiver or audience. Finally, by watching for the audience’s reaction, the source perceives how well they received the message and responds with clarification or supporting information.
“The message is the stimulus or meaning produced by the source for the receiver or audience” ( McLean, 2005, p. 10) . When you plan to give a speech or write a report, your message may seem to be only the words you choose that will convey your meaning. But that is just the beginning. The words are brought together with grammar and organization. You may choose to save your most important point for last. The message also consists of the way you say it—in a speech, with your tone of voice, your body language, and your appearance—and in a report, with your writing style, punctuation, and the headings and formatting you choose. In addition, part of the message may be the environment or context you present it in and the noise that might make your message hard to hear or see.
Imagine, for example, that you are addressing a large audience of sales reps and are aware there is a World Series game tonight. Your audience might have a hard time settling down, but you may choose to open with, “I understand there is an important game tonight.” In this way, by expressing verbally something that most people in your audience are aware of and interested in, you might grasp and focus their attention.
“The channel is the way in which a message or messages travel between source and receiver” ( McLean, 2005, p. 10) . For example, think of your television. How many channels do you have on your television? Each channel takes up some space, even in a digital world, in the cable or in the signal that brings the message of each channel to your home. Television combines an audio signal you hear with a visual signal you see. Together they convey the message to the receiver or audience. Turn off the volume on your television. Can you still understand what is happening? Many times you can, because the body language conveys part of the message of the show. Now turn up the volume but turn around so that you cannot see the television. You can still hear the dialogue and follow the story line.
Similarly, when you speak or write, you are using a channel to convey your message. Spoken channels include face-to-face conversations, speeches, telephone conversations and voice mail messages, radio, public address systems, and voice over Internet protocol (VoIP). Written channels include letters, memorandums, purchase orders, invoices, newspaper and magazine articles, blogs, e-mail, text messages, tweets, and so forth.
“The receiver receives the message from the source, analyzing and interpreting the message in ways both intended and unintended by the source”( McLean, 2005, p. 10) . To better understand this component, think of a receiver on a football team. The quarterback throws the football (message) to a receiver, who must see and interpret where to catch the ball. The quarterback may intend for the receiver to “catch” his message in one way, but the receiver may see things differently and miss the football (the intended meaning) altogether.
As a receiver you listen, see, touch, smell, and/or taste to receive a message. Your audience “sizes you up,” much as you might check them out long before you take the stage or open your mouth. The nonverbal responses of your listeners can serve as clues on how to adjust your opening. By imagining yourself in their place, you anticipate what you would look for if you were them. Just as a quarterback plans where the receiver will be in order to place the ball correctly, you too can recognize the interaction between source and receiver in a business communication context. All of this happens at the same time, illustrating why and how communication is always changing.
When you respond to the source, intentionally or unintentionally, you are giving feedback. Feedback is composed of messages the receiver sends back to the source. Verbal or nonverbal, all these feedback signals allow the source to see how well, how accurately (or how poorly and inaccurately) the message was received. Feedback also provides an opportunity for the receiver or audience to ask for clarification, to agree or disagree, or to indicate that the source could make the message more interesting. As the amount of feedback increases, the accuracy of communication also increases (Leavitt & Mueller, 1951).
For example, suppose you are a sales manager participating in a conference call with four sales reps. As the source, you want to tell the reps to take advantage of the fact that it is World Series season to close sales on baseball-related sports gear. You state your message, but you hear no replies from your listeners. You might assume that this means they understood and agreed with you, but later in the month you might be disappointed to find that very few sales were made. If you followed up your message with a request for feedback (“Does this make sense? Do any of you have any questions?”) you might have an opportunity to clarify your message, and to find out whether any of the sales reps believed your suggestion would not work with their customers.
“The environment is the atmosphere, physical and psychological, where you send and receive messages” ( McLean, 2005, p. 11). The environment can include the tables, chairs, lighting, and sound equipment that are in the room. The room itself is an example of the environment. The environment can also include factors like formal dress, that may indicate whether a discussion is open and caring or more professional and formal. People may be more likely to have an intimate conversation when they are physically close to each other, and less likely when they can only see each other from across the room. In that case, they may text each other, itself an intimate form of communication. The choice to text is influenced by the environment. As a speaker, your environment will impact and play a role in your speech. It’s always a good idea to go check out where you’ll be speaking before the day of the actual presentation.
“The context of the communication interaction involves the setting, scene, and expectations of the individuals involved” ( McLean, 2005, p. 11). A professional communication context may involve business suits (environmental cues) that directly or indirectly influence expectations of language and behavior among the participants.
A presentation or discussion does not take place as an isolated event. When you came to class, you came from somewhere. So did the person seated next to you, as did the instructor. The degree to which the environment is formal or informal depends on the contextual expectations for communication held by the participants. The person sitting next to you may be used to informal communication with instructors, but this particular instructor may be used to verbal and nonverbal displays of respect in the academic environment. You may be used to formal interactions with instructors as well, and find your classmate’s question of “Hey Teacher, do we have homework today?” as rude and inconsiderate when they see it as normal. The nonverbal response from the instructor will certainly give you a clue about how they perceive the interaction, both the word choices and how they were said.
Context is all about what people expect from each other, and we often create those expectations out of environmental cues. Traditional gatherings like weddings or quinceañeras are often formal events. There is a time for quiet social greetings, a time for silence as the bride walks down the aisle, or the father may have the first dance with his daughter as she is transformed from a girl to womanhood in the eyes of her community. In either celebration there may come a time for rambunctious celebration and dancing. You may be called upon to give a toast, and the wedding or quinceañera context will influence your presentation, timing, and effectiveness.
In a business meeting, who speaks first? That probably has some relation to the position and role each person has outside the meeting. Context plays a very important role in communication, particularly across cultures.
Interference, also called noise, can come from any source. “ Interference is anything that blocks or changes the source’s intended meaning of the message” ( McLean, 2005, p. 11). For example, if you drove a car to work or school, chances are you were surrounded by noise. Car horns, billboards, or perhaps the radio in your car interrupted your thoughts, or your conversation with a passenger.
Psychological noise is what happens when your thoughts occupy your attention while you are hearing, or reading, a message. Imagine that it is 4:45 p.m. and your boss, who is at a meeting in another city, e-mails you asking for last month’s sales figures, an analysis of current sales projections, and the sales figures from the same month for the past five years. You may open the e-mail, start to read, and think, “Great—no problem—I have those figures and that analysis right here in my computer.” You fire off a reply with last month’s sales figures and the current projections attached. Then, at five o’clock, you turn off your computer and go home. The next morning, your boss calls on the phone to tell you he was inconvenienced because you neglected to include the sales figures from the previous years. What was the problem? Interference: by thinking about how you wanted to respond to your boss’s message, you prevented yourself from reading attentively enough to understand the whole message.
Interference can come from other sources, too. Perhaps you are hungry, and your attention to your current situation interferes with your ability to listen. Maybe the office is hot and stuffy. If you were a member of an audience listening to an executive speech, how could this impact your ability to listen and participate?
Noise interferes with normal encoding and decoding of the message carried by the channel between source and receiver. Not all noise is bad, but noise interferes with the communication process. For example, your cell phone ringtone may be a welcome noise to you, but it may interrupt the communication process in class and bother your classmates.
Two Models of Communication
Researchers have observed that when communication takes place, the source and the receiver may send messages at the same time, often overlapping. You, as the speaker, will often play both roles, as source and receiver. You’ll focus on the communication and the reception of your messages to the audience. The audience will respond in the form of feedback that will give you important clues. While there are many models of communication, here we will focus on two that offer perspectives and lessons for business communicators.
Rather than looking at the source sending a message and someone receiving it as two distinct acts, researchers often view communication as a transactional process ( Figure 1.3 “Transactional Model of Communication” ), with actions often happening at the same time. The distinction between source and receiver is blurred in conversational turn-taking, for example, where both participants play both roles simultaneously.
Figure 1.3 Transactional Model of Communication

Researchers have also examined the idea that we all construct our own interpretations of the message. As the State Department quote at the beginning of this chapter indicates, what I said and what you heard may be different. In the constructivist model ( Figure 1.4 “Constructivist Model of Communication” ), we focus on the negotiated meaning, or common ground, when trying to describe communication. (Pearce & Cronen, 1980; Cronen & Pearce, 1982).
Imagine that you are visiting Atlanta, Georgia, and go to a restaurant for dinner. When asked if you want a “Coke,” you may reply, “sure.” The waiter may then ask you again, “what kind?” and you may reply, “Coke is fine.” The waiter then may ask a third time, “what kind of soft drink would you like?” The misunderstanding in this example is that in Atlanta, the home of the Coca-Cola Company, most soft drinks are generically referred to as “Coke.” When you order a soft drink, you need to specify what type, even if you wish to order a beverage that is not a cola or not even made by the Coca-Cola Company. To someone from other regions of the United States, the words “pop,” “soda pop,” or “soda” may be the familiar way to refer to a soft drink; not necessarily the brand “Coke.” In this example, both you and the waiter understand the word “Coke,” but you each understand it to mean something different. In order to communicate, you must each realize what the term means to the other person, and establish common ground, in order to fully understand the request and provide an answer.
Figure 1.4 Constructivist Model of Communication

Because we carry the multiple meanings of words, gestures, and ideas within us, we can use a dictionary to guide us, but we will still need to negotiate meaning.
Key Takeaway
The communication process involves understanding, sharing, and meaning, and it consists of eight essential elements: source, message, channel, receiver, feedback, environment, context, and interference. Among the models of communication are the transactional process, in which actions happen simultaneously, and the constructivist model, which focuses on shared meaning.
1. Draw what you think communication looks like. Share your drawing with your classmates.
2. List three environmental cues and indicate how they influence your expectations for communication. Please share your results with your classmates.
3. How does context influence your communication? Consider the language and culture people grew up with, and the role these play in communication styles.
4. If you could design the perfect date, what activities, places, and/or environmental cues would you include to set the mood? Please share your results with your classmates.
5. Observe two people talking. Describe their communication. See if you can find all eight components and provide an example for each one.
6. What assumptions are present in transactional model of communication? Find an example of a model of communication in your workplace or classroom, and provide an example for all eight components.
- Communication for Business Success. Authored by : Anonymous. Provided by : Anonymous. Located at : http://2012books.lardbucket.org/books/communication-for-business-success/ . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike

Privacy Policy
Achieving Successful Business Communication
Introduction.
Communication is a very essential tool for the success of all business types. Success in this perspective can be identified by the achievements of the business which depend on the relationship between the management and the employees. It is also important to maintain high-quality relations with customers for the business to prosper. In addition, communication enables a company to address its market availability in identifying and analyzing its competitive position in the market. It is only through communication that a business can establish its performance from which it can realize and determine new and effective marketing strategies. The business is able to know whether it is a market leader, market challenger or a small market holder.
The most common communication methods on marketing are promotions and advertisement. Business communication can be very difficult at times but with the proper cooperation of models, the process gets simpler. Marketing communication models should consist of the sender, the message to be delivered, the medium through which the message will be delivered, the recipients as well as feedback.
In this essay, I will present the basis of communication, the steps involved in achieving efficient business communication skills as well as some examples. I will also look at some of the factors that are to be put into consideration when choosing a communication method. Finally, I will look at direct marketing as the most effective form of business communication, sales promotion and the use of the media in advertising.
Rationale for communication
With good marketing communication, a company or business is in a position to determine and improve its market share in the business world. Communication helps in evaluating a company’s operations from which it gets views from the public and knows how its products are ranked. The company will be able to employ better tactics in order to increase the market share as well as ensure customer satisfaction. Negative feedback concerning a certain product helps the company in identifying its weak areas in order to improve the quality of its product. All this is aimed at ensuring that the business gets returns as profits.
By working with other businesses, I have learned that the main purpose of communication in business is to inform customers of the existence of certain products or services so that they can buy them. Through marketing, the business is able to persuade its consumers to buy its product, and as a result, it benefits by registering sales increases which ensure maximum profits. Good communication attracts many people to a company’s products who in turn market the product by informing their friends and relatives. A business communication strategy that works best at earning customers’ confidence in the media. From my experience, I have learned that it is always good to appreciate companies and businesses that extra hard to maintain the customers’ satisfaction.
With the highly increasing competition in the business world, it takes communication to provide the necessary information to the consumers to help them compare different products. There is, therefore, the need for companies to do enough research when deciding on strategies to be used in marketing that would create the biggest impact on its clients.
Steps in achieving successful business communication
The first step in achieving successful communication is to identify any barrier in the business. This can be through sharing of ideas to classify challenges that are facing. Such challenges can be obtained by reviewing the daily activities that are carried out. A list of questionnaires may be necessary to give guidance to the review process. Some questions that may be included are: Have the employees been provided with good working conditions? Are they happy with what they are doing? Has the business been able to satisfy all its clients? Is proper information provided to all stakeholders? Is there a good flow of conversations?
While I was working in You – the Spa , one of my areas of concern was employee motivation. I made sure that employees were given incentives not only by paying them fairly but also by allowing them to air their views and trying to help them when faced with difficult situations. In addition, I went to the extent of organizing employees’ come-together parties where we celebrated any specific achievement made; we also had birthday parties for each and every employee. I tried to help them set goals, not only for the Spa but also for their own benefit. My main aim was to make sure that all employees were happy working for my organization because I knew this would be reflected in our customer service.
After reviewing the above issues, then the business has to address these challenges and prioritize those with the most adverse effects to the business. For instance, I once had a case of unsatisfied customers and after handling it, they got contented and left happy. By addressing the challenges faced, not only in businesses but also in other social organizations, the relationship is generally strengthened. It is, therefore, necessary to develop proactive and constructive communication skills in order to tackle these challenges early enough before they turn to the crisis. Once a challenge has been identified, its possible causes should be addressed systematically.
During my work experience, I have learned that communication is more than just giving out messages; it involves speaking, listening, sending and receiving messages. In communication, listening is the key element to make it a success although, without action, the information sent across will be less useful. For business communication to be effective, therefore, listening has to be proficient. When a company is faced with challenges, for instance, it is important to allow those who are aware of the problem to give their ideas concerning the subject. Though it may not always be easy to hold back and let others give their opinion, the practice is necessary for efficient communication in businesses.
After listening to different views on solutions to the problem at hand, a business then moves forward and defines what it intends to accomplish. This is a very critical stage and one has to be proactive in order to achieve success. For instance, one of the suggested solutions may be to improve the business’s relationship with its clients. Strategies to achieve this includes but are not limited to: answering calls in a polite manner, addressing all customers’ concerns, listening and responding to complaints, providing information and thanking customers for their loyalty. This helps in earning consumers’ confidence.
In 2006, I Completed the Incubator Seminar in Front Desk, System Development, and Compensation Plan for Employees, administered by Strategies Advanced Business Education Company from where I learned about the preparation of a communication plan. This is a plan that is prepared after a business defines what it wants to achieve. Things to be included in the plan include: taking employees to seminars that cover topics such as customer care, organizing get-together parties between employers and employees, rewarding employees, holding regular meetings, including major stakeholders in business decision making, and assurance to personal service among others. This plan does not concentrate on solving past problems but on laying down a good foundation that guarantees the future success of the business. A communication plan should take into consideration the availability of resources as well as the objective of the business; whether it is a long time or short time.
Once a communication plan has been prepared, the business now focuses on implementing it effectively. The expected outcome should be kept in mind and the main constituent of the plan reviewed to make sure they are in line with the expected result. The implementation process should involve all business stakeholders but with one member in charge of the process. Once the implementation process is comprehensively in place, the business should reflect on the process to check if it has met the objective of the plan.
The final step towards successful business communication is the evaluation of the results. The business should look back on the initial objectives and compare them with the results achieved to see if the expectations have been met. Once the business is satisfied with the results, it should thank all the parties involved in the process.
Factors to consider when choosing a form of communication
Customers’ needs and demands have changed with time especially with the various products to choose from. The big question today is, with the many competitive products in the market, what will the consumers choose? And how will marketers reach these clients? The media has expanded and new technologies have emerged. For a business to prosper, businessmen should take time to identify and familiarize themselves with customers’ needs. In order to serve clients better; whether old or new ones, businessmen have to first understand them well because different customers have different needs and preferences and they respond differently to different circumstances. Customer service management should be provided in every business organization. Through work and experience, I have realized that all staff members should be provided with sufficient education on customer care provision. Identifying consumers and forming a good relationships with them is the first and key step towards success in any business establishment. This can be achieved through the creation of an atmosphere where the client will feel free to ask for anything. Welcoming and greeting them, calling by their names, showing interest in some events in their lives among others constitute them from moving to other competitors for similar services. For instance, in you-The Spa, I made use of this idea to ensure clients were not kept in the waiting room for more than fifteen minutes, but rather provided with other services such as manicures or quick massages as they waited to be served. This ensures that they don’t feel like their time is being wasted which would otherwise annoy them and may push them away.
Often customers are concerned about the cost as well as the time they spend in obtaining a certain product. Businessmen should therefore adjust these two elements to suit the consumers’ needs as well as their own benefits. For instance, if the goods are made available within the customers’ reach, they will not need to drive far in order to acquire those goods but will buy those within their reach. Today, many products and services have become very competitive which has made some businessmen provide quick delivery methods in order to attract more customers. After identifying and obtaining potential clients, the supplier needs to improve service delivery methods that will ensure that ordered goods are delivered within the shortest time possible. Regular operations should be maintained including opening and closing periods of the business premises, methods of payment and provision of other services such as credit facilities.
External business communication
External business communication involves the use of brochures as well as different forms of advertisement, telephone calls and the use of the internet. The internet has become a very popular mode of communication not only in our social lives but also in business operations. Many businesses are using the internet to carry out their normal operations. This is because the internet is cheap and fast in the delivery of messages. With the changing times, many people are getting access to the internet and becoming more and more dependent on it for their daily activities. In external business communication, the most important thing is the image of the organization that is portrayed to the public. The logo should give a clear representation, the business letterhead should be intended to market self-explanatory and the telephone messages should give a reflection of the professional ability of the business.
Direct marketing
Direct marketing involves one on one approach between the buyer and the seller where marketers meet their targeted customers directly with the products to be sold. It’s a form of direct communication between the producers and the consumers. Direct marketing can be through telephone calls, emails, or the use of catalogs where producers send information on certain products or services directly to potential customers. For this method to be effective, the producer needs to have the contact information of the potential clients such as email addresses, telephone numbers, and mailing addresses. This method is the most cost-effective marketing strategy compared to the other methods but it requires cautious execution.
Direct marketing has been widely used over the years. With the improved technology, businessmen can keep customers’ mailing lists into punched cards and store information on magnetic tapes that are more secure. Computers are also advantageous to businessmen since they reduce the number of documents that have to be stored thus creating more space in the workplace. This way, marketing became easier and potential customers can access any information within seconds.
Businessmen are now keeping stock records and making accounts on computers making direct marketing even easier especially in supplies management. Today, almost every business organization relies partly or wholly on direct marketers to advertise its products and services. However, direct marketing requires more than just advertising. Clear objectives have to be laid down with more emphasis on a good relationship between the business and the customer. With the increased global competition, creativity has to be applied in order to make direct marketing successful.
Other forms of businesses may choose to market their products directly to the final consumer. This is done by the use of sales representatives who personally deliver goods to the doorsteps of customers. This method is best applicable in small companies which are introducing their new products and searching for clients. Through experience, I have realized that this marketing strategy is not only cheap but also efficient. While working in the spa, I designed a plan for launching a personal cosmetic line, Lava Rache and I used direct marketing which turned out to be cost-effective in creating public awareness for these products. It proved to be much cheaper compared to advertising mediums and promotion methods since the sales representatives’ payments depend on the sales made. The company is guaranteed increased sales and the final consumers can as well give their feedback which enables the business to improve the quality of its products where necessary. Direct contact with customers eliminates the costs that would have otherwise been used on discounts or middlemen as payments.
Almost all business organizations use promotion as a way of making their products or services known to the public. Promotion can be done through the media, such as the use of TV, radio, magazines, newspaper, or the internet. A promotion plan should be purposed on increasing sales and creation of the good corporate image. It can also be used to introduce new products.
Most promotion services involve discount offers which will affect the whole chain of transactions from the wholesalers down to final consumers. Since the discounts are offered for only a short period of time, all parties involved in the sales will purchase products in large quantities in order to enjoy the discount. In the end, consumers will get used to those products to the point of buying them even without the discount offer.
As the company becomes exposed, it realizes that it has a social responsibility to the community and all its stakeholders (the shareholders, customers, staff, society, government, etc). Through communication, companies are able to increase their sales which calls for increased profits and consequently, increased shareholders returns. It is the duty of the company to ensure that consumers get high-quality products as well as the provision of good working conditions. All these are best achieved through effective communication.
The most commonly used mode of advertisement by businesses is the media. This is due to its easy accessibility unlike other modes of communication such as newspapers. Effective media communication requires the use of simple language that is easy for the targeted audience to understand. However, the message should be informative enough and it should reflect the business’s mission statement as well. A business’ participation in social activities can be an added advantage in attracting the intended customers. Lastly, sound bites should be obtained from people with authority or holding high positions in the business in order to demonstrate how the business is committed to success.
Sound Bites
Sound bites are brief statements that are obtained from interviews of highly respected people such as politicians and business managers. They clearly state the aim of a business and the nature of certain products. It is therefore the duty of those who are responsible for editing to ensure that they get only the most important points. The points taken are then included in the news broadcast. For sound bites to be effective, the language used should have a clear but brief description that can be easily repeated.
These are impressive propositions that are widely accepted by their own merits. They are usually employed in business advertising to draw people’s attention towards particular features of a certain item. Like sound bites, slogans should give an impression of the benefits of a specific product. They too should be straight and concise, giving an incredible perception about the merchandise and making the consumer feel the need to have that particular product. The first step in designing a persuasive message is to identify the problem then find a fundamental assumption between the interests of both the business and the audience. The last step is to devise a message with a question statement at the end.
A slogan portrays the finest reflection of the product. It is always aimed at making the item appear as the best there is in the market. Examples of such slogans include: ‘Guinness is good for you’, Persil –‘washes whiter’. Some slogans used in water conservation include: ‘conserve water and conserve life’, ‘cut one tree plant two’, ‘rainwater tank, won’t break the bank’. The message in slogans is meant for a specific intention and for a particular audience. A good example of a slogan that has been productive is ‘keep that school girl completion’, Palmolive soap, ‘for survival obey your thirst spirit’. An example of a slogan meant for a specific audience is ‘choosy mother choose Jif peanuts butter’.
The success of any marketing activity in a business depends largely on the way in which the marketing message is sent and received by the targeted customers. Attention and respect are good values for marketers to show their customers in order to succeed in persuading them to buy their products. It is in the best interest of customers that they get all products under one roof to avoid moving from one store to another. Marketers should, therefore, ensure that all their products are easily accessible to customers at all times. The use of proper and polite language is an essential tool for marketers in persuading customers, especially for direct marketers since they interact with the customers instantly.
Success does not come easily especially in business where one needs to compete with the growing competitive world. In order to make business communication a success, companies should clearly identify the needs of their customers and develop good relationships between the customers and the employees as well. In the recent future, the direct marketing may replace most of the other conventional ways of advertisement because it is proving to be the most effective and most businessmen and marketers have been using it of late. The success of direct marketing has been greatly contributed by the use of the internet. Direct marketing is way better compared to a conventional advertisement which is very costly considering that the outcome cannot be predicted. The high competition in the markets requires skillful marketers in order to persuade customers to choose their products. It is therefore the duty of business managers to ensure that all their marketers receive the required training on proper marketing strategies in order to ensure maximum sales. It is very clear that marketing is the backbone of a successful business and it should therefore be taken seriously and handled professionally.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2022, April 28). Achieving Successful Business Communication. https://studycorgi.com/an-effective-business-communication/
"Achieving Successful Business Communication." StudyCorgi , 28 Apr. 2022, studycorgi.com/an-effective-business-communication/.
StudyCorgi . (2022) 'Achieving Successful Business Communication'. 28 April.
1. StudyCorgi . "Achieving Successful Business Communication." April 28, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/an-effective-business-communication/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "Achieving Successful Business Communication." April 28, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/an-effective-business-communication/.
StudyCorgi . 2022. "Achieving Successful Business Communication." April 28, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/an-effective-business-communication/.
This paper, “Achieving Successful Business Communication”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: April 28, 2022 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.
Business Communication: Definition, Functions, Types & Process
Business Communication is the act or process of transferring information from one person to another person, and every communication involves at least one sender, a message, or a receiver. Here in this article, we have shared complete details about business communication and its definition, function, types, process, and advantages.
►What is Business Communication?
Business communication is the act of sharing information between people within and outside the organization.
Effective communication is how employees and management interact to achieve organizational goals. It is an essential element in the success of any business.
✔ Definition of Business Communication
According to William G. Scott,
Business communication can be defined as “Administrative communication is a process which involves the transmission and accurate replication of ideas ensure by feedback to elicit actions which will accomplish an organizational goal”.
✔ Characteristics of Business Communication
- Business communication must be realistic.
- It should avoid imaginary or useless information for saving time.
- Any business communication must have a clear purpose or target.
- The concerned audience must be targeted.
✔ Need of Communication in business
- Communication is an important part of any Business organization.
- No business can grow in lack of Effective Communication.
- It is essential not only in business but in all types of organizations.
- Every activity in Business is impacted by communication.
- Effective communication is necessary for developing a trustworthy reputation.
Must Read : Types of Business Speech
✔ Importance of Business Communication
- Basis for decision-making
- Facilitates Smooth operations
- Facilitates Coordination
- Increases Managerial Efficiency
- Facilitates Control
- Promotes Industrial Peace
- Basis of Leadership
- Provides Motivation
✔ Advantages of Business Communication
- If there will be good communication among two people then it leads or promotes understanding.
- It will also increase employee productivity.
- If there will be proper communication then it will enhance loyalty to the company.
- There will be clarity of directions and goals for organizations and employees.
Must Read : Skills of HR Manager
✔ Scope of Business Communication
- Communication in decision making.
- Communication in management.
- Communication in publicity
- Communication in Industrial Relation
- Communication in International Relations
- Communication in Social life
1. Communication in decision making- Person or organization, each is to decide on various issues daily. In each case, proper information is vital to make perfect decisions and communication play a vital role here by supplying relevant information.
2. Communication in management- Proper business communication is very important in all steps of management in an organization.
3. Communication in publicity- In this world of information, every organization is keen to advertise itself in some distinctive ways. By communicating with concerned parties an organization does publicity also.
► Functions of Business Communication
There are four functions of communication.
- Information
- Emotional/Expression
✔ Information
The principal function of communication is used to provide information to others. Before providing or passing information one has to receive, collect information from various sources, both external and internal. It can be done verbally and Non verbally.
✔ Controlling
The next very important function of communication is to control ‘member behavior’ in several ways. As we all know that in every organization has formal guidelines that the employees are supposed to follow.
✔ Motivation
All business is goal-oriented. All possible efforts have to be made to achieve a target within a well thought- out framework of time. For this purpose, the team of workers must put in their very best efforts.
✔ Emotional/ Expression
The workgroup is a primary source of social interaction. The communication that takes place within the group is of vital importance in the sense that it gives them the best opportunity to share their frustrations as well as feelings of satisfaction.
Must Read : 5 Barriers in Communication

► Process Of Business Communication
Communication is a continuous process that mainly involves (at least) one sender, a message, and a recipient.
(Sender ➜ Message ➜ Encoding ➜ Channel/Medium ➜ Decoding ➜ Receiver)
(Receiver ➜ Feedback ➜ Sender)
The basic function of Management such as Planning, Organising, Staffing, Directing, and Controlling cannot be performed well without effective communication.
There are many ways of the Communication Process. But the famous communication process is the linear communication process which is applicable to almost all areas of communications.
✔ Linear Communication Process
The elements involved in the linear communication process are explained below in detail:
1. Sender: The sender is the source and the one who starts the communication process.
2. Message: Message refers to the idea, information, view, fact, feeling, etc. that is created by the sender and then communicated further.
3. Encoding: The message generated by the sender is encoded symbolically such as in the form of words, images, gestures, etc. before it is being conveyed.
4. Channel/Media: It is the medium in which the encoded message is transmitted. The message may be transmitted orally or in written form. The medium of communication includes telephone, social media, post, fax, e-mail, etc. The choice of medium or channel is decided by the sender.
5. Decoding: Decoding is the process of converting the message in encoded form by the sender. Then receiver decodes the message.
6. Receiver: The receiver is the person for whom the message was sent by the sender. Once the receiver gets the message and understands it in proper perspective and acts according to the message, only then the purpose of communication is successful.
7. Feedback: Feedback is the process when the receiver confirms to the sender that he has received the message and understood it. On this point, the process of communication is complete.
When the receiver will give feedback to the sender, if there are some doubts he will ask about that and the quality of response should be a good indicator of whether the message was properly received.
8. Noise: Noise refers to any obstruction that is caused by the sender, message, or receiver during the process of communication.
For example , Noise in communication consists of Poor telephone connection, faulty encoding, faulty decoding, inattentive receiver, poor understanding of message due to prejudice or inappropriate gestures, etc.
► Types of Flow of Communication
There are four types of communication flow.
- Upward communication
- Downward communication
- Horizontal communication
- Spiral or Diagonal communication
◉ Upward communication
It refers to that form of communication that flows from bottom to top management like the flow of communication between subordinate to a superior.
◉ Downward communication
It refers to that form of communication that flows from top to bottom management like the flow of communication between superior to subordinate.
◉ Horizontal communication
This communication includes communication between persons having the same level of designation like communication between a sales manager and purchase manager.
◉ Spiral/ Diagonal communication
This type of communication includes communication between any level of management at any time. It happens in case of emergency.
Must Read : All Types of Communication (in detail)
► What is Miscommunication?
Mis-communication can be defined as the ” Flow of wrong communication by the mediator in the organization”.
◉ Main causes of Miscommunication
- We have to use uncommon words of vocabulary while communicating.
- By physical barriers, arising at the end of the receiver’s or sender’s end.
- By poor listening of the receiver.
- By the poor speaking skill of sender.
- By using poor grammar.
- When the receivers make too many assumptions about what he/ she receives.
Q. What are the Repercussion of it?
Ans. A lack of communication can ultimately lead to low morale. Because effective communication can create misunderstandings, missed opportunities, conflict with the dissemination of misinformation, and mistrust, employees might just feel overall defeated.
► Tips for Effective Business Communication
Here are the factors that improve communication skills in any person whether they are students or employees of any organization.
- Participate in group discussion
- Create a Safe Ambiance or Working Environment
- Active Listening
- Create Teamwork
- Allow Students to share Opinions
- Positive Feedback
✔ Strategies for improving Business Communication
1. Whenever we talk with any new person we should have to use simple language.
2. If someone has done good work then he should get appreciation or good feedback in front of all which will encourage them and they will do better work next time.
3. An organization should have to avoid overload or burden in the head of employees which will make feel good to employees in the organization.
4. Be a good listener.
5. If there is any kind of problem then they have to talk directly with whom they have a problem (Walk the talk).
► What is Non-Verbal Communication?
Non-Verbal Communication is the transmission of messages or signals through a nonverbal platform such as eye contact facial expressions, gestures, posture, and the distance between two individuals.
✔ Benefits of Non-Verbal Communication
- Those people who don’t understand our language also help to communicate with those people.
- It helps in emergencies when there is no time for verbal communication.
- It is very helpful for communicating in silent zones.
✔ Tips for Effective Non-Verbal Communication
- There is a specific situation that is observed and understood.
- There should be proper eye contact while nonverbal communication.
- All should have to listen properly.
- The tone should be smooth, not harsh.
- There should be a good posture.
- Always show Gratitude/ Thanks.
- The power of touch.
- There could be cultural differences.
◉ Types of Non-Verbal Communication
1. Kinesics: Kinesics include facial expressions, gestures, postures.
2. Oculesics: Oculesics include eye contact.
3. Haptics: Haptics include the power of touch.
4. Proxemics: Proxemics include communication of space and proximity. 4.5 to 5 feet is neutral and 20 feet and more is for distance.
5. Appearance and Artifacts: Appearance and Artifacts include physical characteristics, hair, attire, accessories.
6. Vocalics/Paralanguage or Para Linguistics: Vocalists include pitch, speed, volume, causes, intensity, tone, inflection, articulation (voice modulation) system.
7. Chronemics: Chronemics include the effects of time on communication.
Related Posts

FA Syllabus in MBA – UTU Dehradun

PPM Syllabus in MBA

What is Business Communication, and why is it important?
Effective business communication involves exchanging information both within an organization and with individuals outside of it. This type of communication fosters interaction between employees and management to achieve common goals while streamlining organizational procedures and minimizing mistakes. To improve your business communication abilities, it’s essential to enhance your communication processes within and outside of your organization.
This blog aims to raise awareness about the importance of effective business communication and provide tips for improving communication skills and processes in the workplace.
Read more: Why choose MBA in marketing?
Definition of Business Communication
Business Communication book published in 2004 as part of Harvard Business Essentials defined business communication as follows:
“No matter whether it is written or verbal, it is the instrument through which business speaks to its consumers. It is the mechanism by which management influences its employees and guides their activities. It is also the means by which the employees provide information and feedback, which are necessary to the management to take smart decisions. Organizations which carry out clear, meaningful and effective communication with clients, employees, share-holders, creditors and the public have better chances of building reliable relationships and can count on good cooperation” Business Communication (2004)
Some other definitions of business communications are –
- Prof. J. Haste stated that when communication occurs between two or more business people for effective organization and administration of business, it is considered business communication.
- Raymond Lesikar views business communication as a process or activity that enables individuals to collaborate and work together.
- According to W.H., business communication is exchanging business-related views, ideas, and news among the related parties.
- Ricks and Gow defined business communication as a system that affects change throughout the whole organization.
Read more on essential skills to succeed in a management profession .
Types of business communication
An organization uses various communication techniques, including face-to-face meetings, phone calls, text messages, and other conventional forms of writing. There are several forms of corporate communication to take into account, which might change your tone or substance.
- Internal business communication
Internal business communication refers to communication between members of an organization. Both formal and informal communication are included in this conversation. Internal communication also includes many departments that communicate with employees through various channels. Internal communication should be effective since it is an important means of viewing and representing organizational concerns.
Effective internal business communication can boost employee job satisfaction, productivity, and efficiency while minimizing grievances and boosting revenues.
- Lateral business communication
The importance of business communication between co-workers, whether verbal or written, is referred to as lateral or horizontal communication. This can involve inter-departmental communication or communication across departments, as well as communication between persons of the same or similar status within a corporation. This communication is essential to accomplish intended objectives.
As a result, this communication occurs among personnel with equivalent hierarchy levels. Horizontal or lateral communication is essential for seeking cooperation and mutual support to achieve the functional effectiveness of distinct organizational units.
- External business communication
External business communication refers to interactions with people outside of the organization. These people can be clients, stockholders, suppliers, partners, regulatory organizations, etc. Email, ads, brochures, newsletters, content marketing, and other forms of external communication are common. External communication aims to facilitate communication among various organizations or entities.
Know more about the career options in marketing communication .
Roles of business communication
The effectiveness of corporate communications affects a company’s ability to succeed. Communication is considered the lifeblood of business because of this. Here’s how important effective communication is:
- Top to bottom
Top-to-bottom communication is an organizational communication approach in which information flows from senior management.
When major business choices are taken at the highest levels, businesses require an efficient method of communicating the decision throughout the organization. As a result, many firms adopt top-to-bottom communication to guarantee that information flows freely from senior management to IC-level personnel.
When done correctly, top-to-bottom communication can be incredibly effective. At its best, it may break down silos and give team members the confidence they need to succeed in the organization. At worst, it can hinder production and push staff to conform to an excessively hierarchical organization.
- Peer to peer
A lot of our daily work depends on having a good connection with our co-workers. Yes, having a good relationship with your boss is crucial, but some of us may go days without speaking to them.
Being able to successfully interact with our colleagues assists us in getting our duties done by answering questions, exchanging information, and providing feedback. Not to mention that excellent communication can increase workplace fun and vitality.
- Bottom to top
It is an organizational communication strategy in which information is disseminated throughout the corporation from lower-level managers and team members. While bottom-up communication is not as prevalent as top-down communication, it can be incredibly effective.
It not only allows employees to contribute to higher-level decision-making, but also allows them to give feedback and have confidence that it will be forwarded to senior management.
You may be interested to know about key soft skills to excel in your professional life .
Why is business communication important?
The following points demonstrate the importance of business communication in an organization –
- Democratization
Voices of otherwise minority populations are more equitably represented in organizations that contain democratic decision-making aspects. The strategy firms use in decision making is just as essential as the decision itself. Look for ways to enhance and foster a planning culture based on enterprise-wide information sharing and data-driven communication from top to bottom.
- Boost motivation and morale
Business communication is critical in enhancing employee efficiency. Different plans and policies, essential issues, organizational goals, and so on are described to employees through communication, which improves their knowledge and makes them more efficient in performing their responsibilities.
- To build a better relationship
Communication enables workers and management to express their thoughts and requirements. Healthy labor relations are critical to the success of any firm, and it helps sustain peace in this situation.
- Job satisfaction
Effective, fair and easy communication improves mutual connection and understanding between employees and management. This contributes to higher satisfaction levels among employees who work hard to attain their objectives.
- Higher productivity
Effective business communication boosts employee productivity by encouraging teamwork. It fosters an environment of trust and understanding among employers and employees. Cooperation with employees and understanding their wants and desires are required for effective communication.
Employees can complete their responsibilities more successfully and efficiently this way. Furthermore, excellent communication reduces the possibility of making mistakes during their task.
- For efficient functioning of the business
Managers’ operational efficiency improves as a result of effective communication. With fair communication, managers can accomplish many managerial activities, such as planning, directing, organizing, controlling, and so on. Furthermore, effective leadership can take place if communication is effective. A proper and smooth company communication system is required for qualitative leadership actions.
- Helps in decision making
Effective decisions necessitate current knowledge. Using good communication, managers can get information from various sources and use it to make sound decisions.
- Proper planning
Organizations may develop excellent plans and policies through effective business communication. These strategies and policies must be based on accurate information. Managers must communicate policies and plans within the organization to implement or execute them on time. They can convey strategies and policies to internal and external stakeholders through effective communication.
- Minimize conflicts
Different business parties can exchange information more smoothly with excellent communication. As a result, there are fewer conflicts, debates, and disagreements between them.
You would like to read top 10 blogs on management .
Methods or channels of business communication
Business communication involves various methods and channels through which information is exchanged within an organization and with external stakeholders. Here are some common methods of business communication:
- Email: Electronic messaging for formal written communication and document exchange within and outside the organization.
- Face-to-face meetings: In-person gatherings facilitating direct communication, ideal for discussions, decision-making, and collaboration.
- Video conferencing: Virtual face-to-face communication using technology, enabling real-time interaction for remote teams or clients.
- Telephone/Conference calls: Voice-based communication over the phone, including conference calls for multi-participant discussions.
- Instant messaging (IM): Real-time text-based communication for quick and informal exchanges within a team or organization.
- Memoranda (Memos): Written documents conveying official announcements or updates for internal communication.
- Reports and documentation: Formal creation of detailed documents for conveying information, analysis, or research findings.
- Presentations: Communicating information using visual aids, such as slides, in person or virtually.
- Social media: Utilizing online platforms for business communication, including customer engagement and brand promotion.
- Intranet: Private network within an organization facilitating internal communication, document sharing, and collaboration.
- Newsletters: Periodic publications offering updates and information to employees or external stakeholders.
- Blogs: Corporate blogs for sharing insights, industry updates, and company news with a wider audience.
Choosing the appropriate method depends on factors such as the nature of the information, the audience, and the desired level of formality. Often, a combination of these methods is used to ensure effective and comprehensive business communication.
7 C’s of an effective communication
Whatever field you operate in, you will need to interact professionally with others to close deals or work on projects. The seven C’s of effective communication assist you in increasing productivity and engagement by communicating messages that your audience can simply understand.
- Completeness
It is necessary to communicate completely. The audience should receive all the information they require from it. The sender must take the receiver’s viewpoint into account and correctly relay the message. The following components are included in a thorough communication-
- An organization’s reputation is built and enhanced by complete communication.
- Additionally, they save money because no important data is lost, and if the transmission is successful, no additional expenses are needed.
- Complete communication always offers extra details as required. It removes all uncertainty from the receiver’s mind.
- The audience, readers, or message recipients can make better decisions because they have access to all necessary and pertinent information when there is complete communication.
- It persuades the audience.
- Conciseness
Conciseness implies wordiness, i.e. communicating what you want to say in the fewest words possible while maintaining the other C’s of communication. Effective communication necessitates conciseness. Here’s how concise communication helps-
- It saves time while also saving money.
- It emphasizes the core message while avoiding the use of unnecessary words.
- Concise communication conveys a brief and important message to the audience in a minimum number of words.
- A brief message is more enticing and understandable to the listener.
- A brief message is not repeated.
- Consideration
Consideration entails “putting oneself in the shoes of others.” Effective communication must include the audience’s opinions, background, mindset, education level, and so on. Make an effort to imagine your audience, their needs, emotions, and difficulties.
Make sure that the audience’s self-esteem and emotions are not jeopardized. Modify your message’s terms to meet the needs of the audience while keeping your it complete.
When you are able to transmit your thoughts and opinions into the recipient’s mind, you know communication is effective. You don’t want the recipient to make assumptions or have a hazy understanding of what you’re expressing.
Only when they completely grasp your message will they be able to make the appropriate decision. It might occur when you employ plain and straightforward language to express your point to the recipient.
- Concreteness
Concrete communication entails being specific and explicit rather than vague and generic. Concreteness boosts confidence. Simply delivering your message through statements and questions will not captivate your audience. It is important to back up your claims with appropriate facts, numbers, and statistics. Otherwise, your audience will not know whether your message is genuine or not.
Courtesy in a message indicates that the message should reflect the sender’s expression while also respecting the receiver. The sender should be honest, polite, prudent, contemplative, empathetic, and enthusiastic.
- Correctness
Communication correctness implies that there are no grammatical errors in communication. Information correctness or factual accuracy is important in both verbal and nonverbal communication. You must choose the appropriate words at the right time while also ensuring that the information is reliable.
Etiquette of business communication
Business communication etiquette refers to the set of norms, conventions, and practices that govern how individuals interact and communicate in a professional setting. Following proper etiquette in business communication is essential for maintaining professionalism, fostering positive relationships, and ensuring effective communication. Here are some key aspects of business communication etiquette:
- Clarity and conciseness: Be clear and concise in your communication. Avoid unnecessary jargon or overly complex language. Clearly express your ideas to ensure that your message is easily understood.
- Professional tone: Maintain a professional and respectful tone in all written and verbal communication. Use formal language, and avoid slang or overly casual expressions, especially in written correspondence.
- Grammar and spelling: Pay attention to grammar, punctuation, and spelling. Mistakes can undermine the credibility of your communication. Review and proofread your messages before sending them.
- Timeliness: Respond to messages in a timely manner. Acknowledge receipt of emails promptly, and if a more detailed response is needed, communicate a realistic timeline for providing it.
- Appropriate language: Use language that is appropriate for the context and audience. Avoid offensive or discriminatory language, and be mindful of cultural differences that may influence communication norms.
- Professional greetings and sign-offs: Use appropriate greetings and sign-offs in emails and other written communication. “Dear,” “Sincerely,” and “Best regards” are common examples. Tailor your choice based on the formality of the communication.
- Subject lines: Craft clear and relevant subject lines for emails. This helps recipients quickly understand the purpose of the message and prioritize their responses.
- Respect for privacy: Respect the privacy of others. Avoid sharing sensitive or confidential information without proper authorization, and be mindful of data protection regulations.
- Active listening: Practice active listening in verbal communication. Give your full attention, avoid interrupting, and ask clarifying questions to demonstrate understanding.
- Professional formatting: Format written communication in a professional manner. Use standard fonts and formatting conventions, and ensure that the layout is visually appealing and easy to read.
- Meeting etiquette: Be punctual for meetings, contribute meaningfully to discussions, and avoid dominating the conversation. Follow any established meeting protocols, such as raising your hand to speak.
- Acknowledgment of receipt: Acknowledge receipt of important emails or messages, especially if they require further action. This helps reassure the sender that their communication was received.
- Adaptability: Be adaptable to the communication preferences of others. Some individuals may prefer email, while others may prefer phone calls or in-person meetings. Respect these preferences when possible.
Business communication vs. Organizational communication
Business communication and organizational communication are related concepts, but they have distinct scopes and focuses within the broader field of communication studies. Here are the key differences between business communication and organizational communication:
Business communication vs. Marketing communication
Business communication and marketing communication are two distinct but interconnected aspects of organizational communication. Here’s a comparison between the two:
You may like to know more about marketing communication and career options.
Communication barriers
We jeopardize ourselves and others when we fail to communicate properly, regardless of the mode of communication: spoken, nonverbal, written, listening, or visual. Apart from physical and technological hurdles, there are a few communication barriers that every employee and management should seek to eliminate.
- Cultural differences
Understanding cultural differences in communication is critical. You must think globally; remember that in Japan, one’s surname comes before their given name. There may also be regional differences within the organization’s limits, and failing to appreciate cultural differences could insult someone.
- Inability to listen to others
Active listening is a significant component of effective communication. You can’t engage with someone if you’re not listening to them because you’ll make assumptions about their needs based on your preconceptions rather than facts.
- L ack of transparency and trust
When there is a lack of transparency and trust, it is difficult to express anything. For example, if your employees believe you are withholding something, they will be worried, and some will speculate, making it more difficult for them to absorb any attempt you make to communicate with them.
- Communication style
Everyone has a unique style of communicating. Some people are quite straightforward, while others choose to be more oblique. Some employ specific facts, while others rely on broad strokes, and so on. Sometimes one individual is so entrenched in their communication style that they find it difficult to communicate with others who use a different style.
- Conflicts in the workplace
Conflict can arise for a variety of causes, and when it happens, it impedes efficient communication. What is crucial is that you strive to resolve the issue, not the nature of the conflict. When disagreement is not resolved, it escalates, and individuals begin to take sides, making effective communication even more difficult.
Learn more about skills & tools to become recession-proof professional .
Examples of effective business communication
People communicate with one another to share ideas, express feelings and opinions and solve issues. Errors arise when communication is not delivered or received as planned. You may improve your communication abilities by practicing both verbal and nonverbal communication.
- Nonverbal communication
Body language is another term for nonverbal communication. Nonverbal communication demonstrates to people that you are prepared to communicate effectively by maintaining eye contact, sitting attentively, and positioning your body to face the person speaking. Folding your arms across your chest, clenching your fists, and gazing downward indicate that you are distracted or uninterested, which might impede the conversation.
- Be open-minded
Maintain an open mind to facilitate efficient conversation. Avoid placing judgment on or criticizing communicated messages. You do not have to agree with the other person’s beliefs and opinions, but you must respect them.
- Active listening
Active listening allows you to gain a better grasp of the thoughts and feelings of another individual. To display this communication ability, concentrate your attention on the person speaking. Interrupting someone else’s speech might disrupt the flow of the conversation.
It is important to compromise while you’re communicating with someone. When an issue arises, both persons must work cooperatively to develop a list of prospective solutions as well as agreed-upon trade-offs.
Effective communication is crucial in assisting employees in forming a social circle or bond. Some firms have an open culture or work environment in which employees at all levels are free to speak with one another and with their supervisors. Other organizations prefer to communicate using a hierarchy or chain of command.
Effective business communication plays a significant role in providing a platform for the business to outperform its competition by building a healthy working environment. If you are looking to upskill yourself in any aspect in order to attract lucrative job opportunities, consider checking out the wide range of MBA courses offered by Manipal Academy of Higher Education (MAHE) on the Online Manipal platform and pave the way for a bright career.
Key takeaways:
- Sending and receiving effective communications within a corporation, organization, or business is referred to as business communication.
- The goals of corporate communication are to build relationships, encourage learning, foster trust, and promote a favorable public image.
- Business communication takes place internally, laterally or externally.
- There are three possible directions for business communication: upstream, downward, or peer-to-peer.
- Common communication hurdles might hinder or restrict business communication. Barriers to effective communication can skew a message or prevent someone from grasping its meaning.
- A process that is constantly evolving through assessment, observation, and implementation change is business communication.
Information related to companies and external organizations is based on secondary research or the opinion of individual authors and must not be interpreted as the official information shared by the concerned organization.
Additionally, information like fee, eligibility, scholarships, finance options etc. on offerings and programs listed on Online Manipal may change as per the discretion of respective universities so please refer to the respective program page for latest information. Any information provided in blogs is not binding and cannot be taken as final.
- Master of Business Administration
- online degree
- online education in India
- Online MBA for working professionals
Become future-ready with our online MBA program for working professionals

Transform your career with online degree courses - Apply today!
Course Master of Business Administration Bachelor of Business Administration Bachelor of Computer Applications Bachelor of Commerce Master of Computer Applications Master of Commerce Master of Arts in Journalism & Mass Communication MSc Data Science MSc Business Analytics PGCP Business Analytics PGCP Logistics and Supply Chain Bachelor of Arts MA in English MA in Sociology MA in Political Science
Institution Manipal University Jaipur Manipal Academy of Higher Education Manipal Institute of Technology Sikkim Manipal University
I authorize Online Manipal and its associates to contact me with updates & notifications via email, SMS, WhatsApp, and voice call. This consent will override any registration for DNC / NDNC.
Enter the code sent to your phone number to proceed with the application form
+91-9876543210 Edit
COURSE SELECTED Edit
Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA) Manipal University Jaipur
Please leave this field empty. Submit
Related Articles
Interested in our courses? Share your details and we'll get back to you.
Business Communication: Definition, Types, Examples, Importance, Methods, Functions
Introduction, definitions.
Different scholars have given different definitions of Business Communication. Few of them are mentioned below:
According to Ricks and Gow defined Business Communication as a system that is responsible to affect change throughout the whole organization.
According to W.H. Business Communication is exchanging business-related different views, ideas, and news within the related parties.
Prof. J. Haste stated that when the communication occurs between either two or more than two business people for the purpose of effective organization and administration of business then it is considered as Business Communication.
Effective business communication is the way employees and management communicate to achieve organizational goals. The objective is to improve organizational efficiency by reducing mistakes. Business Communication includes different aspects like marketing, public relations, customer relations, corporate and interpersonal communication, etc. Basic elements of Business communication:
- Business information
The above elements indicate business communication as a process in which information or news related to business is exchanged between different business parties like customers, suppliers, business clients, employees, etc. for the purpose of effective administration of the business.
Moreover, it involves a regular flow of information and feedback is considered as a crucial and important aspect of business communication. Due to different levels of hierarchy and involvement of a huge number of people, business communication plays an important role in different management functions i.e. planning, coordinating, organizing, directing, and controlling.
Types of Business Communication along with Examples
There are 4 main types of business communication in any organization or business i.e.
1. Internal Business Communication
Internal Business Communication means communication that occurs within the members of the organization. This communication includes both formal and informal communication. Also, different departments that transmit communication by different means to employees come under internal communication. Internal communication should be effective as it is a vital source of viewing and representing organizational issues. Effective internal business communication may increase job satisfaction level, productivity, the efficiency of employees by decreasing their turnover and grievances and helps in increasing profits.
We’ve thoroughly explained the Internal Business Communication in a separate article here ➡️ https://studiousguy.com/internal-communication/
It is further categorized as internal (upward) communication and internal (downward) communication.
a. Internal (Upward) Communication: This type of internal communication involves the bottom to the top management approach. Here, the information flows from subordinates to managers or any person that is on the upper in the hierarchy level.
For example, employees of the HR department of an organization prepare an attrition report and communicate the same to the HR Manager. The attrition report consists of information on the monthly or annual employee turnover of an organization and reasons for the same. This helps the HR Manager to understand the cause of attrition and to take corrective measures on time to reduce employee turnover.
The characteristics of upward internal business communication include:
- It includes bottom to top approach i.e. subordinates to superiors.
- Its nature is participative.
- The main purpose is to provide timely feedback, suggestions, making requests, escalating any issues or concerns, etc. to superiors.
- The flow of the information is from the lower level to the upper level.
b. Internal (Downward) Communication: In downward communication, the information flows from the top-level management to the employees in an organization. This information is related to passing on instructions to subordinates or employees to do their respective tasks. Downward communication is being used by managers to communicate different goals, procedures and policies, guidelines, decisions, instructions, etc. to their subordinates.
The process of downward communication in business includes passing on messages from the top level to the lower level through the chain of hierarchy. This type of communication can be in oral or written form. The written form includes different notices, manuals, news display in electronic form, etc. whereas, the oral form of downward communication includes different face-to-face conversations, telephonic communication, meetings, etc .
For example, the top-level management may instruct managers of different departments on certain new rules and regulations in the work area that need to be carried out in routine activities of different departments. Like there may be a change in the office working hours or office timings by the management and the same is communicated to employees by circular or notice or through the e-mail system.
The characteristics of downward internal business communication include:
- It includes top to bottom approach i.e. superiors to subordinates.
- Its nature is directive.
- Main purpose is to communicate organizational objective, plans and procedures, instructions, etc. to subordinates.
- The flow of the information is from the upper level to the lower level.
2. Horizontal/Lateral Business Communication
Lateral or horizontal communication is related to communication among co-workers i.e. either verbal communication or written communication. This may include inter-departmental communication or communication between cross-departments and can be between people of the same or similar rank in a company. This is a crucial communication to achieve the desired results. So, this communication happens among employees having an equal hierarchy level. To achieve the functional effectiveness of different organizational units, horizontal or lateral communication is required for seeking mutual cooperation and mutual help.
For example, the Marketing head of an organization is supposed to communicate about market trends, customer needs and expectations, product demand scenario, etc. to a production head for production of products accordingly.
Similarly, the HR manager of an organization works with different department heads for different functioning like hiring, training needs of employees, performance appraisals, welfare activities, etc.
3. External Business Communication
Communication with people who are external to the organization is known as external business communication. These people can be customers or shareholders or suppliers or partners or regulatory bodies, etc.
We’ve thoroughly explained the External Business Communication in a separate article here ➡️ https://studiousguy.com/external-communication/
For example , the purchase department supervisor may communicate with vendors for purchase quotations of raw-material and similarly, the sales department communicates with customers for sales of goods or services.
External communication facilitates increasing sales volume, effective operations, an increase in profits of organization, etc. This ultimately results in increasing corporate image, goodwill and overall performance of the organization by achieving its goals and customer satisfaction.
Importance of Business Communication
Importance of business communication in an organization can be seen in the below points:
1. Helps in increasing productivity: Effective business communication increases the productivity of staff by boosting up teamwork. It creates a trustworthy and understanding environment among employers and employees. Effective communication is related to cooperating with employees and understanding their needs and desires. By doing so, employees are able to accomplish their tasks more effectively and efficiently. Also, the scope of doing mistakes or errors during their work minimizes due to effective communication.
2. Helps in increasing customers: Customers are an important part of any business and effective business communication can facilitate in attracting new customers and retain the current customers. A well-defined marketing strategy and public relations campaign run by an organization generates the interest of customers in its goods or services and helps in building the corporate image in customers.
3. Enhances business partnerships: Business Communication also improves partnerships in business. It plays a significant role in dealing with external business clients or vendors. Vendors may be required to communicate on products regularly for improvements. Also, an effective and harmonious relationship with other businesses determines the further success of an organization. A business unit that has developed its image as an entity for easy partnership through its effective communication can attract other business units for forming business relationships with them.
4. Facilitates innovations in business: Effective business communication helps in business innovations as well as it facilitates employees to convey their ideas and suggestions openly. Similarly, at the time of launching any new product in the market, effective communication ensures the performance of the sales team, market acceptance of the product, fast delivery of products in the market, etc.
5. Information exchange: Business communication is required by an organization for exchanging information with internal and external stakeholders. This helps in achieving its goals effectively.
6. Preparation of plans and policies: Through effective business communication, organizations can make their plans and policies properly. Relevant information is required for preparing these plans and policies. Through communication, different managers source information through reliable channels.
7. Execution or implementation of plans and policies: To implement or execute the prepared policies and plans in a timely manner, managers are supposed to communicate these throughout the organization. Through effective communication, they are able to disseminate plans and policies to the internal and external stakeholders.
8. Boost the efficiency of employees: Effective business communication plays a key role in increasing the efficiency of staff. Through communication, different plans and policies, critical issues, goals of an organization, etc. are described to employees that enhance their knowledge and make them efficient to do their tasks effectively.
9. Goals achievement: Through effective business communication employees become attentive and productive in doing their jobs that result in the timely accomplishment of their tasks and easy goals attainment.
10. Helps in solving problems or issues: Through different communication channels, managers get information about different routine and non-routine issues and based upon that they can take required actions to sort out those issues.
11. Facilitates decision-making: Effective decisions require up-to-date information. Using effective communication, managers can acquire information from different sources and can utilize it for making correct decisions.
12. Improves worker-management industrial relations: In the workplace, workers and management have an industrial relation. The success of any business depends upon the healthy industrial relation. Business communication plays a significant role in maintaining harmony in this.
13. Helps in brand and product/service promotions: In today’s competitive business environment, lots of companies offer similar kinds of products or services. To sell their products in a good manner, businesses need better communication to promote products and services in an effective way.
14. Reduces chances of conflicts: Through effective communication different business parties can exchange information in a smooth way. This results in fewer conflicts, controversies, arguments between them.
15. Increases employee satisfaction level:
Effective communication which is fair and smooth creates better mutual bonding and the understanding between employees and management. This helps in increasing the satisfaction level among employees who put their maximum efforts to achieve the goals.
16. Increases employee loyalty: Through effective business communication, employees are well informed about their performance from time to time. Also, employees get appreciation, rewards in both monetary and non-monetary terms for their better performance. This enhances their loyalty towards the organization.
17. Enhances efficiency of managers and leads to effective leadership: Effective business communication leads to an increase in the operational efficiency of managers. With the help of fair communication, managers can perform different managerial functions like planning, directing, organizing, controlling, etc. smoothly. Moreover, if communication is effective then only effective leadership can be taken place. For qualitative leadership activities, a proper and smooth system of communication in business is essential.
18. Proper functioning of different departments: If information is shared smoothly and effectively in inter-departments and intra-departments then different departments of any business like accounts, finance, purchase, operations, HR, IT, and production, etc. can do their tasks more accurately and timely.
Business Communication Methods
Different methods of communicating in a business are as below:
1. In-person (Face-to-Face) Business Communication: In-person communication is the most common and preferred method of business communication. As it is generally in the form of meetings or conferences which is face to face communication format. This requires refined in-person skills. This method also includes non-verbal communication i.e. body language. While having a conversation between two or more people in business, body language like gestures, facial expression, etc. also play a vital role in communicating a person’s attitude towards others.
Good listening skills are also an element in better in-person communication. Most of the business communication includes listening skills to understand fast discussions.
3. Web conferencing: In the web conferencing method of business communication, the internet is being used for communication in meetings, conferences, presentations, seminars, and imparting training. It includes features like sharing of files, screens, real-time chatting, recording, etc. This can be considered as the most effective way of interacting with people sitting at different locations. Web conferencing is done by using the phone (teleconferencing) or video equipment (videoconferencing).
Workplaces also opt for the teleconferencing method of business communication. If it’s not feasible for people of an organization or business to attend a physical meeting or conference then communicating through telephone conferencing is an effective method. This also saves travel expenses as people who often require extensive traveling for business purposes so they can communicate through teleconference by sitting in their office.
Videoconferencing is also similar to teleconferencing except in videoconferencing one can see the people whom to communicate with. This requires video conferencing equipment that is arranged by the IT department of a business.
5. Other methods: There are other business communication methods like an instant messaging system. This technology is easy to use as one can easily connect with people while working offsite and have conversations without waiting so long.
Business Communication Functions
1. Communicating job functions to employees: Informing about assigned job roles is a crucial key function of business communication. Team members having clarity on expected job tasks and how they can contribute to achieving objectives of the organization by fulfilling their job functions, they can contribute more to the completion of their assigned tasks. In the absence of clarity of their roles, employees might not be able to complete their work as expected.
2. Providing adequate feedback: Providing timely and accurate feedback to employees and customers is also an important function of business communication. The performance of employees can be enhanced by providing regular feedback to them regarding their work performance and competencies. This helps them to understand their current skill set, strengths and also they can fill any gap in case of any shortage of required skills. Regular feedback from customers and other stakeholders on products and services of business facilitates the improvement in the production process and quality.
Different informative communication lies in an organization like job descriptions, assigned targets to achieve, performance management, etc.
3. Convincing clients: Business communication is also often used to convince prospective customers, clients and business partners in order to finish a business deal or transaction. This type of communication can be in both oral and written form like a Sales Officer may convince a client on phone call or in written form i.e. providing a mass advertisement in magazine or newspaper for a new product launch or exciting offers on existing products. Both credibility and emotions are an important element of this function of communication. Moreover, this type of communication can be utilized in PR (public relations) activities and to build the organization’s brand image.
4. Employee motivation for better decision-making: Communication in businesses is used in a strategic form to enhance the decision-making capability of employees related to their daily activities and for their long-term objectives related to the business. Like if performance-based bonuses or incentives are communicated among employees effectively then it motivates employees to contribute to the organization’s growth more efficiently and they can achieve their work expectations in a timely manner.
5. Building social bonds: Communication has a critical role in supporting employees to build a social circle or bond. Some organizations have an open culture or work environment in which employees from all levels can communicate with each other and their superiors freely. Other organizations prefer to follow a hierarchy or chain of command in communication.
When employees have a social bond with people whom they work with like their colleagues, supervisors, clients, etc., then their job efficiency improves as the team spirit increases.
Related Posts
Management consulting
Trait Theory of Leadership
5 Examples of Self-actualization Needs (Maslow’s Hierarchy)
Great Man Leadership Theory
Line Management
Staff Management
12 comments.
This information was definitely very helpful. Many thanks
This piece of information was very helpful. Thank you.
Add Comment Cancel Reply
- Explore our business calling software
- Book a demo today
- Turn CloudTalk into a much more powerful tool.
- View all integrations
- Integrations list
- Onboarding Portal
- Help Center
- Country Coverage
- Customer Stories
- Product Updates
- Discover & access advanced features
- Schedule a demo
World-class content, delivered to your inbox.
High-impact articles. No spam.
The Importance Of Business Communication – Definition, Types and Tips

People communicate with each other all the time. Without communication, we would not be able to do anything. It’s hard to think of a situation when you do not need any type of communication at all. Without this useful skill, many of the things we have accomplished so far as humans would just be dreams.
There is one specific type of communication that should be of particular interest to company owners, employees and employers, entrepreneurs, and pretty much anyone who deals with businesses on a daily basis – business communication.
What can you expect to learn from this piece? We will define business communication and the different types of it with examples, touch upon the 3 means of business communication , and provide you with a list of useful tips and tricks on how to master your business communication skills like a pro. Without further ado, let’s jump right in!
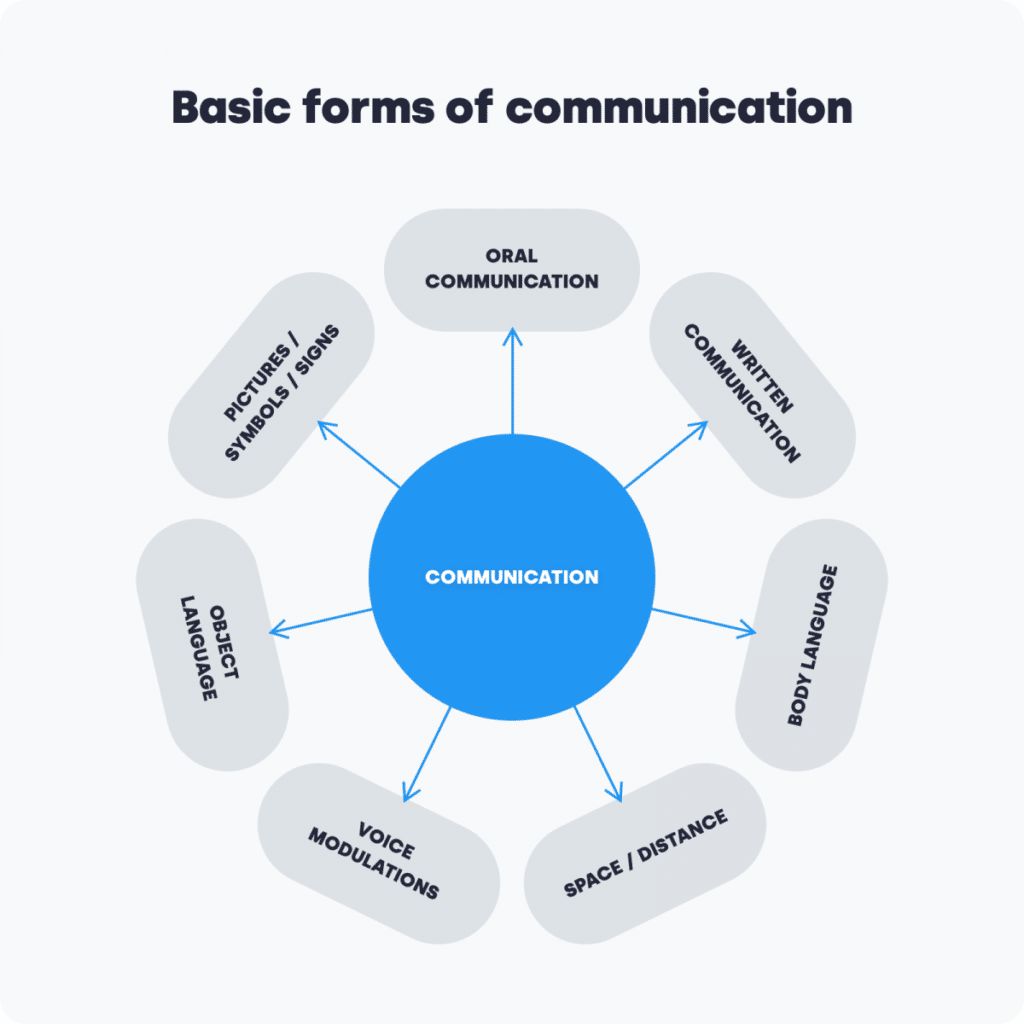
What exactly is business communication
To understand what business communication is, let’s focus on the term ‘communication’ first.
What does ‘communication’ mean?
The word communication usually refers to talking, speaking, writing, or sending information to another person. The whole idea of communication is very complex and focuses on various aspects, many of which include:
- ensuring the message has reached the target audience
- ensuring the receiver of the message understands and responds to it, if necessary
- ensuring, as the message sender, that you communicate with manners and with appropriate precision and clarity
15+ psychological principles to improve sales.

The role of communication in business
Business communication entails every sort of communication that occurs within a particular business environment. Business communication contributes to the development of an ability to influence others, bringing about changes in the attitudes and views of people, driving motivation, as well as creating and maintaining professional relationships.
Many scholars and business owners agree that it is the most important foundation skill for anyone in the world of work. Just think about your very first encounter with a company you are currently working at. Would you have gotten this job without professional communication?
In these times of fast-progressing globalisation and growing demand for teamwork, communication skills are absolutely crucial to the success of any business, regardless of its size. This helps streamline workflows and avoids overworking employees, which could lead to bad sleeping routines and poor decision-making. A rested employee is a productive worker!
Now that we know what business communication is, as well as how important it is, let’s explore the different types of it and look at some examples of them:
Types of business communication with examples
We have divided communication into two main categories: internal and external. Both can be further divided into two different forms: upward and downward. Let’s explore each of them:
#1 Internal upward
This means any information transfer from an individual working in a company up the organizational hierarchy, for example from a subordinate to a manager. Managers often need various types of messages from the people working in the teams they manage. When team members provide their managers with any type of information, we consider this internal upward communication.
- Sales reports
- Templates
- Summaries
- Systematic forms
- Feedback forms, grievances, and disputes
#2 Internal downward
Internal downward communication is the opposite of internal upward communication and occurs when a superior communicates with one or more subordinates. For example, managers reaching out to the employees they manage.
It is most commonly used for things like transferring crucial information, providing instructions, encouraging discussions between people, motivating staff, and increasing productivity.
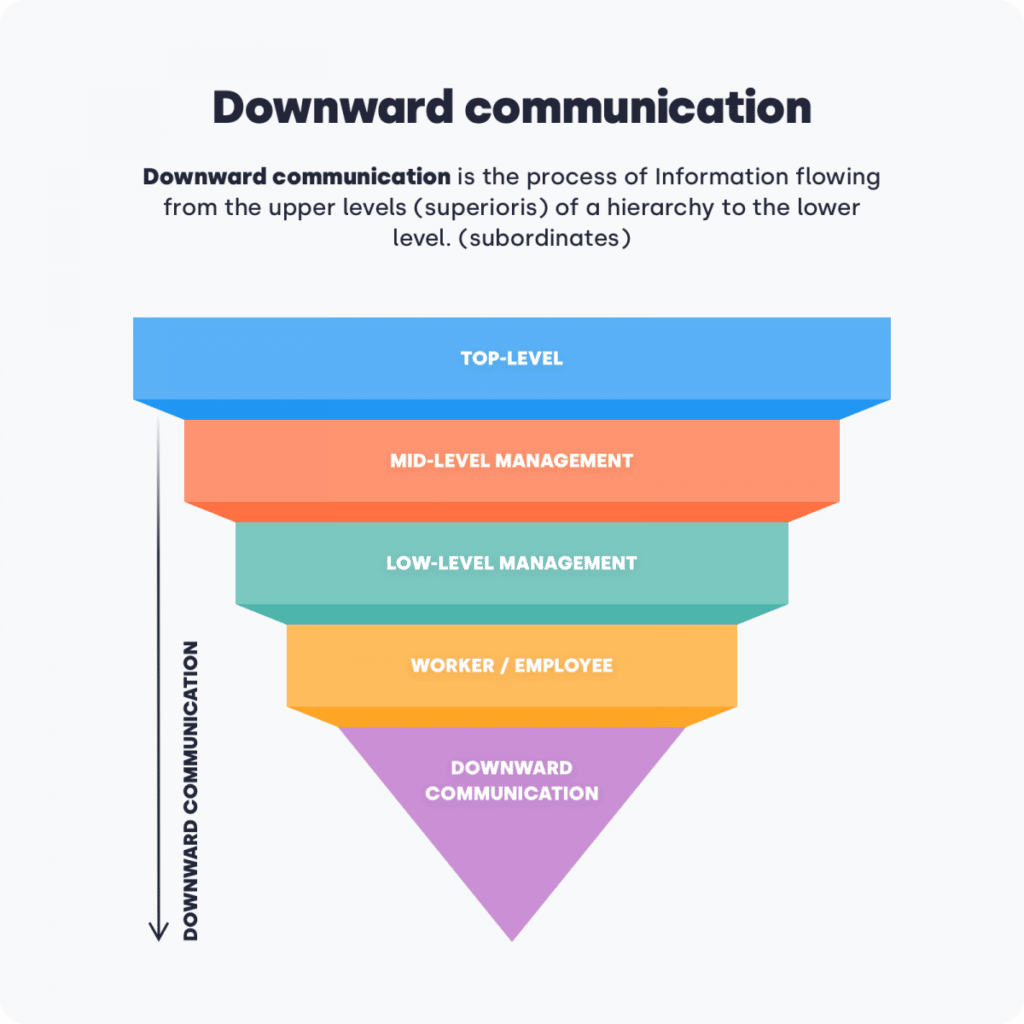
- Job instructions and rationale sent from directors to managers
- Forms sent from mid-level to low-level management employees
- Procedures and practices
- Performance feedback forms
- Presentations about a company’s strategy and core values presented to new employees during orientations
#3 External upward
External upward communication takes place between employees inside an organisation and stakeholders outside of it who are located higher in the hierarchy. External stakeholders include business partners, government officials, community residents, and external administrators, etc.
- Annual reports
- Purchase orders
- Newsletters
- Magazines
#4 External downward
In a similar fashion, external downward communication occurs between a company and its external stakeholders, but this time the party higher in the company is the one starting the communication. External communication typically includes brochure templates , email, newsletters , and posters that are all intended to attract potential customers, partners, and suppliers.
- Product training and support communication
- Promotional and marketing literature
- Communication with sales and delivery channels
Means of business communication
Business communication can be done in many ways, and we’ll explore 3 of them in this article:
Verbal
Verbal communication is basically any type of oral communication in the form of spoken language to send information to other people. In verbal communication, not only do people communicate with words, but they also often attach emotions, feelings, thoughts and ideas to them, whether intentionally or not.
Have you ever heard of the 7-38-55 rule? It is Albert Mehabrian’s theory concerning the communication of emotions. According to this concept, 7% of meaning is communicated through spoken words, 38% by tone of voice, and 55% via body language. You may want to remember about it next time you’re faced with an important conversation with your boss about a raise!
Written
Written communication, as the name suggests, consists of all types of information sharing that is in the form of written messages like emails, letters, reports, telegrams, bulletins, manuals, paper announcements, and more. Unlike verbal communication, it takes a bit more effort to communicate emotions and feelings with written communication.
Things to look out for when using written communication include choosing the correct level of formality, being aware of spelling and grammar mistakes, as well as the appropriate clarity for the receiver.
You may be familiar with ‘remote work’ that many employees are currently experiencing due to the COVID-19 pandemic, but are you familiar with remote communication? It occurs at a distance, mostly via electronic tools. Thanks to remote communication, you can work remotely without face-to-face interactions.
There are many tools out there allowing for remote communication. Some of them are:
- Telephone calls, like call center solutions
- Email ticketing system
- Online chats and conferences
- Work operating systems
- Video meetings, such as webinars
How to master your business communication skills – our 7 lucky tips and tricks!
Now that you know what business communication is, as well as the different types and methods, it’s about time we shared with you some of our secrets.
In the final section, we will give you our 7 top tips and tricks to mastering your business communication skills. Let’s get to know them:
Work on your body language
Your body language, as well as your appearance, plays a significant role in the way you are perceived during business communications. Pay attention to the language you use when you interact with people in a business environment, take care of your looks, and make sure you stick to the appropriate dress code. Finally, remember the aforementioned 7-38-55 theory.
Listen carefully
To communicate effectively, you need to keep your ears open. Communication works both ways, and you should always make a note of what the other person wants to communicate to you. This also shows respect and engagement.
“If you think communication is all talking, you haven’t been listening.” – Ashleigh Brilliant
Practice your general communication skills
Practice makes perfect. If you feel as though you lack some fundamental communication skills in a business environment, focus on practising them outside of your workspace. Make speeches, chat with friends about various topics, engage in discussions, and listen to podcasts. You will see great results quickly!
Use the right channels for different types of communication
It’s hugely important to use the right channels for various types of discussions and conversations that occur within a business environment. Set clear guidelines, make sure everyone knows them, and stick to them. This will contribute to maintaining a well-organized workplace with dedicated spaces to professionalism as well as out-of-work topics.
Setting up such channels might apply to your customer service as well. You could, for example, run a customer support line through a call center tool . Today, call centers are still highly regarded by customers, so this may be a good option for your business. There are many reliable tools to choose from, but CloudTalk is the only choice if you are looking for the best solution out there. Offer your customers a personalized experience and solve any issues quickly thanks to human-to-human interactions.
Expand your business vocabulary
If you work in a niche business, you may need or get acquainted with vocabulary and jargon that is specific to your niche. Read about your industry, watch movies, listen to podcasts, and chat with your coworkers. Everything takes time, but you will get there eventually.
Prepare for meetings to avoid stress
Stress can be a huge brain freezer, so make sure you always prepare for your business meetings in advance. There is nothing worse than having to think on the spot, especially if you are already struggling with communicating effectively. Avoid having to do so by preparing well and being relaxed when it is time to ‘do the talking’.
Engage in discussions
Engaging in vivid and lively discussions will be a great stimulation for your brain and communication skills. The more you interact with other people, the better you will become at it. Business communication is not as scary as it seems!
All-Things Business Communication Discovered!
Here we are! Richer in knowledge and insightful pieces of advice.
Business communication plays a significant role in any company, and it should always be one of the key fundamental elements of success. Excellent communication skills within a business environment vastly contribute to personal growth, increased quality of performance at work, and overall job satisfaction.
In this article we have:
- explained the term ‘business communication’
- given examples of the various type and methods of communication
- provided you with insightful tips on how to improve your business communication skills
Keep in mind that communication is very important everywhere, but especially in professional spaces. Follow this guide and our blog for more content on communication, specifically that regarding call centers and telephone support services.
What to read next
Recommended for you

World-class articles, delivered into the your box.
Zero spams. True articles.
CloudTalk is a 140+ person global tech company transforming customer experience by enabling businesses to build lasting relationships with their customers.
+44 20 3868 0167
+34 911 98 79 28
+32 2 808 12 83
+55 11 4680-2723
+1 888-487-1675
+49 32 221099159
+40 31 630 0197
+60 3-4065 2168
+61 2 8311 6777
+48 22 292 25 18
+41 43 508 21 35
+52 55 4170 3698
Bratislava Office The Spot Bottova 7939/2A 811 09 Bratislava Slovakia
Prague Office Václavské nám. 47 110 00 Prague Czech Republic

© 2024 CloudTalk. All rights reserved. Various trademarks held by their respective owners.
Service status
GDPR & Privacy Policy
Terms and Conditions
INTEGRATIONS
- Inbound Call Center
- Outbound Call Center
- Business Phone System
ABOUT CLOUDTALK
- Request a free trial
- Brand Assets & Newsroom
- Comparison overview
- Aircall Alternative
- JustCall Alternative
- RingCentral Alternative
- Five9 Alternative
- International numbers
- SMS / Text messages
- Improve Call Flows with IVR Technology
- Call Center Analytics
- Call Center Recording
- Interactive Voice Response
- Call Monitoring
- Click to Call
- Smart Dialer
- Power Dialer
A Beginner’s Guide to Business Communication
Business communication is the basis for the success of any organization regardless of its size, industry, or business model it operates in. In other words, communication is the key factor driving virtually any business activity. From internal collaboration and planning to customer relationship building, every process starts and ends with effective business communication.
In this guide, we will cover every aspect of business communication including:
- The definition and examples of effective business communication,
- The importance of effective business communication and the problems it solves,
- The types and methods of business communication,
- The tips and techniques on how to improve communication in business.
Table of Contents
What is business communication?
Before we get into a more detailed analysis of the factors that make up effective business communication, let’s first define the term and its key elements.
Business communication is the exchange of information between two or more people inside and outside an organization.
Ricks and Gow — authors of Business Communication: Systems and Applications — define business communication as “ a system that affects the change within the total organization .”
Essentially, any time we witness any type of interaction between different business subjects — internally or externally — we can categorize it as business communication.
The key five elements of business communication include:
- Sender(s) — or the source, is the person or a group initiating the communication (employee, manager, customers, agencies, suppliers, contractors, etc.).
- Business information — the piece of information the sender wants to communicate to others (message, memo, email, document, report, etc.).
- Channel(s) — the medium the sender uses to transmit the information (phone, email, letter, chat message, etc.).
- Receiver(s) — or the audience, are the recipients of the business information.
- Feedback — or the response, refers to the reply conveyed by the receiver of the message. Feedback is an integral part of the business communication process as it determines whether the business information (the message) is successfully sent and interpreted.
What is effective business communication?
Effective business communication refers to any type of exchange of information inside and outside an organization oriented towards achieving business goals. Essentially, the goal of effective business communication is to improve internal processes, minimize mistakes and meet organizational goals.
Effective business communication examples
To get a better understanding of effective business communication, let’s go over a couple of best practice examples using the business messaging app Pumble to illustrate the examples.
🔸 An example of effective business communication meant to improve processes
Neil is a team leader in a development department. He uses the dedicated channel in Pumble to discuss the tech the team will use for the upcoming project. Neil starts the conversation by introducing the topic to make sure everyone on the team is on the same page. He proceeds to outline previous discussions and conclusions regarding the tech they should use.
James is a team member. He joins the conversation and provides the pros and cons of the two types of tech suggested. James concludes his message by suggesting a final choice based on factual evidence and research.
Neil responds by agreeing with James’ choice.
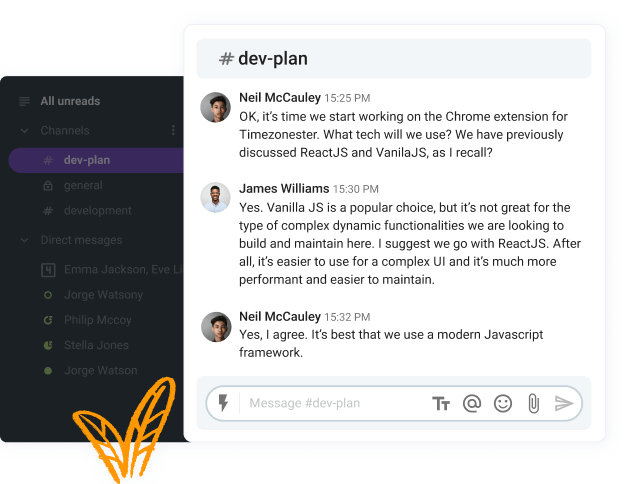
🔸 An example of effective business communication meant to minimize mistakes
Jack is a sales specialist. He received a technical question from a customer and he needs more information from the development team to be able to give an accurate answer. Jack explains the issue in the dedicated channel in Pumble asking someone from the development team to join the call with the customer.
James, a developer, volunteers to jump on a call.
Jack thanks his colleague and then continues with another technical question, to make sure no mistakes and no false promises to the customers are made. He mentions Neil, a team leader in the development department, to request an official response from him.
Neil responds by confirming Jack’s assumption.
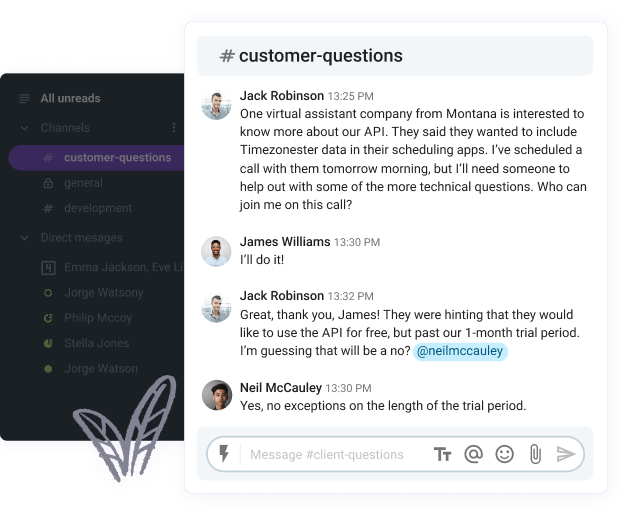
Why is effective business communication important?
Business communication is the tie that binds all processes, workflows, and people within an organization into a coherent and productive unit. In addition to affecting larger organizational processes, effective business communication is also integral to crafting proposals and plans, reaching agreements, conducting constructive meetings, and improving sales. Let’s get a more in-depth analysis of how business communication impacts different internal and external processes.
Effective business communication facilitates the preparation of plans and proposals
Effective business communication is critical to crafting plans and proposals.
Managers possessing strong communication skills are more likely to engage a large team around a project and successfully implement vital tasks without any delays or losses. At the same time, poor communication fails to communicate tasks clearly and, almost by default, reduces the chances of project success.
In fact, a study by PMI reveals that ineffective communication can cause a loss of $75 million out of every $1 billion spent on a project.
Every step in the process requires constructive communication to be properly implemented. From research and information sourcing to the actual writing, communication is the key component of any proposal preparation.
Although most of us would automatically associate proposal preparation with written communication exclusively, there’s also plenty of information sourcing, discussions, and brainstorming sessions that are conducted verbally.
Strong business communication skills secure the success of project or business proposals and plans.
Free business communication tool
Secure, real-time communication for professionals.
FREE FOREVER • UNLIMITED COMMUNICATION
Effective business communication helps present and discuss ideas
Similarly to the previous point, effective business communication determines how new business ideas are communicated, perceived, and accepted. Effective business communication enhances brainstorming, facilitates constructive dialogue, and supports transparency and understanding. Specific communication techniques and skills largely determine how successfully people will get their ideas across.
Effective business communication eradicates team silos
According to a 2016 survey by McKinsey , executives consider silo mentality as the number one issue hindering a functional digital culture.
With limited communication as one of the main causes for the origin of team silos , understandably, effective company-wide communication can prevent the issue from developing in the first place.
Transparent, assertive, and collaboration-based communication reduces the chances of developing the silo mentality and generates more opportunities for company-wide trust-building.
Effective business communication facilitates better decision making and execution
Business communication is instrumental to decision making and it also largely determines how the decisions will be applied. Effective communication facilities a constructive decision-making process by reducing the risk of information overload and excessive data.
Clear, concise, and structured information shared via effective business communication leaves more cognitive capacity for decision making rather than processing excessive information.
Moreover, effective business communication plays an important role in how the decisions will be perceived, and ultimately, realized. According to organizational communication literature , effective strategic communication is considered vital in communicating “t he contents of company strategy and important corporate decisions to key stakeholders, both internal and external .”
Effective business communication improves talent retention
Effective communication systems improve talent retention by 450% according to a Work Institute retention report . Unsurprisingly, employees are more likely to stay longer at organizations that cultivate effective internal and external communication practices. This is especially true for teams nurturing effective internal team communication built on trust and joint collaborative effort.
Effective business communication increases productivity
Clearly communicating to employees how their work impacts the larger goal can lead to 10% higher performance, Gartner reports . Moreover, Gartner also shares that more informed employees are more likely to outperform their less-informed peers by a staggering 77%. By installing effective business communication plans — that prioritize streamlined communication and collaboration — organizations are more likely to experience immense productivity returns.
Effective business communication facilitates more constructive meetings
According to an HBR study , 71% of senior managers believe meetings are unproductive and inefficient. These numbers are potentially even larger nowadays due to the prevalence of remote communication which often lacks verbal and non-verbal cues. Remote communication, especially when it relies on written and audio methods, can lead to potential misunderstandings and miscommunication which largely affect the meeting’s effectiveness. As one of the key factors affecting the atmosphere and the outcomes of meetings, a change in communication practices can create more productive meeting scenarios .
Effective business communication improves sales
Effective communication is the key driver of sales success. As revealed by a study on the role of communication skills for salesforce , clear task communication in teams and optimally developed presentation skills largely impact the success in reaching sales targets.
Communication still plays a major role in sales, even in a digital environment that dictates different interactions, another study on Salesperson communication effectiveness in a digital sales interaction reveals.
Effective business communication builds trust
According to Lexicon , over 80% of Americans cite effective communication as the key factor in building trust with their employers. At the same time, organizations lacking transparent and honest communication strategies are more likely to experience misunderstanding and mistrust and overall low employee morale that harms company culture. According to one Accountemps survey , 33% of HR managers link ineffective business communication to low employee morale, while 38% believe proper communication strategies are the most powerful means to tackle this problem.
🎓 Pumble Pro Tip
For more on how to promote transparent communication in your organization, visit our blog post:
- Transparent communication: why and how to embrace it at work
What are the types of business communication?
There are four main types of business communication in a typical organization:
- Internal upward communication
- Internal downward communication
- Internal lateral communication
- External communication
⬆️ Internal upward communication
Internal upward communication follows a bottom-up direction of communication. In other words, internal upward communication takes place each time a lower-level employee initiates a conversation with their superior.
🔸 Example of internal upward communication
Christopher has recently started a new job as a remote video designer. He is experiencing some challenges in his work and decides to DM his team leader, Stella, and ask for more frequent check-ins. Stella responds by agreeing to Christopher’s request and suggests a video meeting to discuss the matter in more detail. Christopher agrees and thanks Stella.
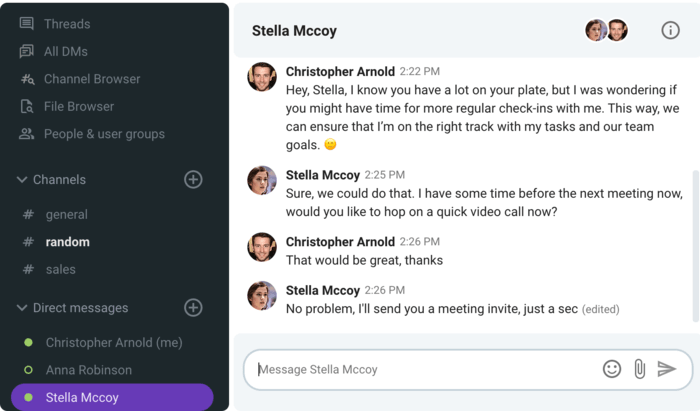
⬇️ Internal downward communication
Internal downward communication is a top-down communication flow that starts with the person at the highest hierarchical level and ends when the message reaches the lowest level employees. Downward communication is directive, instructional, and usually more immediate than internal upward communication.
🔸 Example of internal downward communication
Lena is a product manager at a software development company. After receiving a complaint from a client about a system malfunction, she notifies the team in a dedicated channel in Pumble. Neil, a development team leader, assigns Mari and Amelia (developers) to investigate and fix the problem. He mentions the two team members to make sure they get notified immediately. Mari replies to let everyone know they have received the message and are working on fixing the issue.
↔️ Internal lateral communication
Internal lateral communication refers to any type of interaction between individuals or groups belonging to the same hierarchical level in an organization. As opposed to the other two internal communication types, lateral communication is usually more immediate and less formal.
🔸 Example of internal lateral communication
Steve, Fiona, and Harry are part of the design team working on a new product series. They are using Pumble group chat to make quick plans.
➡️ External communication
External communication refers to communication with third parties , outside of the organization. Third parties, in this case, can include the general public, clients, suppliers, partners, vendors, and consultants.
🔸 Example of external communication
Neil is a marketing manager in a team that uses Pumble as a default communication channel. Helen is a marketing analyst working as an outside consultant on the current marketing project. She communicates and collaborates with the in-house team using the guest role access in Pumble .
What are the methods of business communication?
In a larger sense, business communication can be categorized into two main methods. In other words, every business communication takes place either in verbal or written form.
In addition, depending on the business model an organization is currently operating in, we can make further categorization of both main methods into in-person and remote verbal or written communication.
When it comes to the effectiveness of each method of business communication, there are no universally applicable rules. It is largely determined by the specifics of each organization and the model in which it operates. However, there are several more commonly used methods of business communication. Let’s get a more in-depth analysis of each to help you determine the specific communication method your team needs.
👩💼 👨💼 In-person meetings
Historically, in-person meetings have been the most common form of business communication. According to a Forbes survey , they are still considered the most favorable option. Namely, 84% of executives prefer in-person meetings, citing stronger relationship building and the ability to read non-verbal cues as the main reasons for their choice.
Moreover, a more recent study by the Journal of Experimental Social Psychology reveals in-person communication is perceived as more reliable and trustworthy than communication over email.
Although effective, face-to-face communication in meetings is not exactly feasible, especially in the largely remote-oriented business environment. Remote and hybrid organizations need to rely on other methods of business communication to keep their team connected and their operations flowing smoothly.
👩💻 Video conferencing
As the closest equivalent to in-person meetings, video conferencing is another commonly used method of business communication. From remote-first to fully in-office organizations, every business carries out the majority of their business meetings over video conferencing systems. While on-site teams would resort to video for client and other third-party meetings, remote teams use video by default to facilitate more transparent and efficient communication and to strengthen team connection .
☎️ Phone and audio conferencing
Telephone and audio facilitate more productive meetings in remote and fast-paced business environments. Despite the lessened non-verbal content when compared to video, audio meetings still provide more accuracy than written business communication. During a phone conversation, for example, participants are given more opportunities to decipher the tone of voice of other participants and thus reach a better understanding and faster agreement than over traditional, written communication.
📲 Web-based communication
Online channels such as email and business messaging apps like Pumble have enabled more immediate and faster business communication and collaboration. This is especially beneficial for remote and teams operating across time zones that rely on asynchronous communication and collaboration to meet their business objectives. Email and instant messaging enable distributed teams to more effectively share information and files over private, one-on-one conversations, or with entire organizations or groups simultaneously.
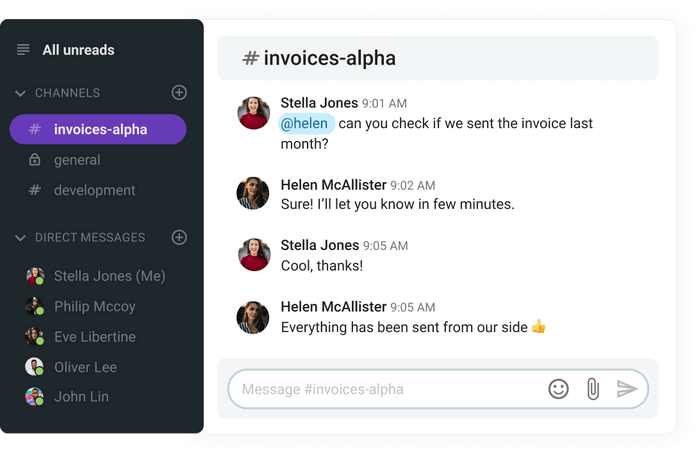
📂 Written communication over shared files
Presentations, official documents, and reports present an important method of (written) business communication applicable to virtually any business. Teams collaborate over shared files, comment on official documents, and use them as a reference for specific processes and activities. In addition, employees share reports and presentations during meetings or specific discussions.
Written business communication methods allow organizations to document processes, collaborate more tightly, share ideas, and have more transparent and clear communication. As mentioned above, remote and teams working across time zones in particular benefit from keeping vital business information in writing.
📝 Internal and external surveys
Although commonly associated with external, customer feedback, surveys are also an important asset in internal communication . Employee surveys are generally carried out in the form of anonymous online questionnaires. Internal surveys are most commonly used to gather employee feedback on company policies and processes, but they also provide beneficial methods of assessing employee engagement, morale, and achievements. Conversely, external surveys serve to evaluate customer needs, satisfaction, engagement, or to perform market research. As SurveyMonkey finds, analyzing customer feedback improves a company’s chance of regarding themselves as successful by 33%.
💬 Customer management
Communication related to customer management activities is another important method of business communication largely applicable in a modern business environment. From live chat support and customer reviews to customer relationship management systems (CRMs), there are plenty of ways businesses are communicating with customers in an effort to enhance their experience. It’s safe to say that customer satisfaction is directly related to the effectiveness and the quality of your customer management communication.
What methods of business communication does your team need?
When tasked with choosing the right communication methods for their team, organizations need to consider their unique needs and circumstances. There’s no single, universal solution that works for all business models and sizes.
Depending on the industry and the business model you’re operating in, you can find some less popular methods perfectly suited for your team, while others, generally more common may not be very effective.
For example, video conferencing and email, although generally applicable, may not necessarily be the best fit for your remote team that relies on quick exchange and fast collaboration. Or, you may invest in a high-end CRM system, only to realize the majority of your customer management activities are carried out via phone or live chats.
That being said, there’s still at least one universally applicable communication method the vast majority of organizations will find great use in. Web-based communication can be used across various business models and sizes both for internal and external communication, while other methods largely depend on the unique needs and models specific businesses operate in.
Consider outlining your specific communication needs, preferences, as well as priorities and objectives, and measure them against the list of communication methods listed above to make sure you are making a well-informed decision.
How to improve communication in business?
Improving your business communication brings immense rewards to your internal and external operations.
So, how do you create a successful business communication strategy in your organization?
Let’s break down some most effective tips on how to improve communication in business.
🔍 Assess the current state of your business communication and set goals
To successfully implement new communication plans and strategies, consider starting from the analysis of the current state of your business communication. This will help you identify any weak links and blocks to improve upon. It will also serve as a great basis for setting the right goals for your future business communication.
The assessment may be time-consuming, but it will most certainly pay off in the long run, as it will help to guide your plan of action.
For example, you may notice that your internal communication took a hit due to a transition to remote work. As a result, it may lack direction and transparency which are crucial for productive teamwork and overall team connectedness.
Once you are able to identify the issues, you can start crafting a plan that addresses those exact pain points. In this case, the goal may include setting clear guidelines on the volume and quality of internal communication in addition to actionable points on how to put these into practice.
🗣️ Identify key groups and analyze how they communicate with each other
Once you’ve analyzed the potential issues hindering your business communication as a whole, it’s time to take a more in-depth assessment of how core groups in your organization communicate.
This step can help you identify more specific issues and thus, set more relevant goals and action plans.
To get started, try to first define the key groups whose operations rely on efficient communication and information sharing. You can categorize these into different levels, including:
- Horizontal groups — teams, units, or departments, e.g. marketing, design, sales, finance, human resources , etc.
- Vertical groups — executives, managers, team leaders, team members.
- External groups — clients, partners, vendors, consultants, etc.
Once you identify key groups, analyze their interaction using relevant parameters such as feedback, reporting, frequency of communication, crisis communication , irrelevant conversations, and meetings, etc.
For horizontal groups, you can assess which people, teams, and groups rely on regular communication to support daily, weekly, or monthly operations.
When it comes to vertical level communication, consider analyzing the quality and frequency of feedback, reporting, progress tracking, and approval.
Similarly, external level communication can be analyzed by frequency and quality of customer and partner communication.
The insight gained through this analysis can help you determine the optimum volume of communication needed to better support different processes and teams. Moreover, it can help you make more informed decisions when it comes to choosing the right communication channels and tools.
📞 Define relevant methods of communication
As we mentioned earlier, there are several commonly used communication methods. However, not all of them are necessarily relevant to every business. The choice largely depends on the type and the size of the business, along with the specific business communication goals you’re aiming to achieve.
For example, if your goal is to improve your cross-department communication and collaboration , you could set a web-based method as a default one for quick exchange of information, files, and feedback between teams.
At the same time, the communication methods also largely depend on the size and the business model organizations are operating in. In line with this, a small in-office team would opt for in-person internal meetings, and they would use web-based messaging for collaboration and external communication. However, a large, fully remote organization would have to rely on video conferencing as an alternative to face-to-face meetings, in addition to the web-based asynchronous collaboration.
🔧 Apply the right tools
There’s no one-size-fits-all solution when it comes to choosing the right tools to facilitate business communication. It takes defining your unique needs and measuring them against the available tools to find the solution that perfectly aligns with your business communication strategy and objectives.
That being said, there are still several generally applicable functionalities to look for in a communication tool regardless of your business size, work model, or unique preferences. User-friendly interface, maximum security, and features enabling productive collaboration are some of the features universally relevant to every organization looking to optimize and streamline their business communication. Here are some rules to follow when choosing and adopting the right business communication tools :
- Use a centralized platform for emails and calendars to automatically sync availability and better manage communication and collaboration across your organization. Whichever your preference is in the battle of Google vs Outlook is completely fine as long as you make it universal for both calendar and emails.
- Store vital information and documents in the cloud with automatic backup to prevent losing critical data.
- Define some ground rules to have a consistent brand voice, tone, and chat etiquette across all communication channels. This will prevent potential misunderstandings and conflict from taking place, and ensure all teams are applying the principles of respectful communication in the workplace .
- Use a single business messaging tool company-wide. It’s very easy to fall into the miscommunication trap when one department uses Gmail Hangouts, while others are communicating over Pumble, for example.
- Look for multi-functional tools that facilitate streamlined collaboration . Features like file sharing, versatile messaging options, member availability, smart notifications, and seamless navigation provide more efficient communication and collaboration experience.
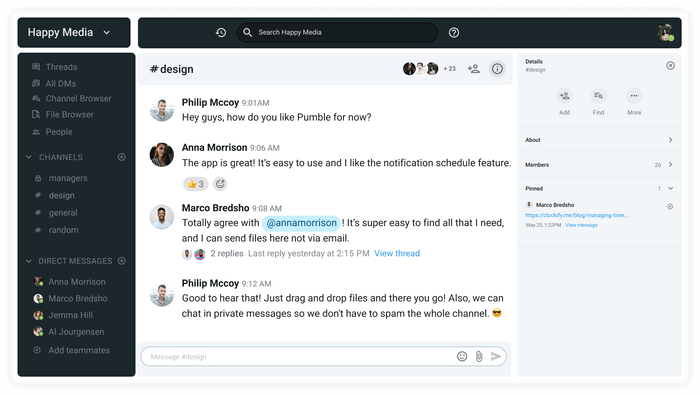
👩🏫 Identify and cultivate relevant business communication skills
In addition to fostering individual professional achievements and career advancement, business communication skills are equally beneficial in a larger, organizational sense. Companies that invest time and resources in improving communication skills in their workforce are more likely to experience higher employee performance, according to one TalentLMS survey . Understandably, higher employee performance and productivity lead to better overall business success.
To help you better identify and perfect relevant business communication skills in your organization, let’s get a closer look at all the vital skills for effective business communication.
Collaboration skills
Effective teamwork relies on effective communication between team members. To effectively collaborate, team members need to master the art of asking better questions at work , as well as learn how to solicit and give constructive feedback. Moreover, strong collaboration skills include being open to and considering different perspectives, along with providing support and encouragement to teammates. Creating space for the development of collaboration skills allows teams to work together more effectively and discover more efficient ways to reach organizational goals.
Diplomacy skills
Diplomacy skills are a vital component that makes up effective business communication regardless of the industry your business operates in. From conflict resolution and problem-solving to communicating empathy and compassion, diplomacy skills are integral in managing professional interactions both internally and externally. Strong diplomatic skills facilitate better relationship-building in the workplace, improve job performance, and conflict resolution.
At the same time, professionals with highly developed diplomacy skills are more successful in customer management and other public-facing roles.
Well-developed diplomatic skills allow sales representatives and customer support professionals to better understand customer perspectives and needs and thus provide better solutions and support.
Individually, professionals can seek more feedback and look for opportunities to practice their soft skills during regular workplace communication and collaboration.
On a larger, organizational level, teams can organize workshops and enroll in courses that focus on developing emotional intelligence, analytical thinking, and conflict resolution to build a better diplomacy skill set.
Negotiation skills
Although generally associated with winning new clients or business partners, negotiation skills are integral to several other business activities. Employees and managers are applying negotiation skills when discussing salaries or promotions, for example, while business owners rely on negotiation skills when communicating with investors.
Subskills you can practice when building your negotiation communication skills include:
- active listening
- expectation management
- adaptability
Unsurprisingly, the majority of the business communication skills are directly correlated which allows professionals and organizations to maximize their learning efforts.
Presentation skills
The ability to capture the audience’s attention and convince them to consider your ideas or viewpoint is another important business skill that largely relies on effective communication. Strong presentation skills are instrumental in crafting and delivering captivating presentations to different business audiences. In addition to managers and executives that usually have more opportunities to practice their presentation skills, team members also require solid presentation skills to communicate their ideas to their team effectively.
Mastering the presentation skills includes learning how to harness the power of verbal and nonverbal communication and present ideas using various visual and audio methods to make a strong impression on the audience.
Presenting the information in a clear and engaging way is a skill worth developing as it affects plenty of business activities and processes starting from effective collaboration to acquiring clients and making sales.
Public speaking skills
Similarly to the previous business communication skill, public speaking requires professionals to have a strong command of their verbal and non-verbal communication. A professional business environment demands a certain level of public speaking proficiency almost by default. From the moment we step into the professional environment and do our first job interview to delivering presentations and speaking at industry conferences, addressing investors or communities, most professionals are required to engage in some form of public speaking throughout their career. Strong public skills reflect in the ability to captivate the audience’s attention and create a connection through storytelling.
Active listening skills
Another very important business communication skill that ties in with several others is the active listening skill. Active listeners are characterized by the ability to be patient and present in communication while paying close attention to details and nuances to avoid misunderstandings and reach a better understanding. This business communication skill supports better work relationships and fosters more productive collaboration, in addition to being one of the key components of negotiation.
Business writing skills
The largest portion of modern business communication is carried out in writing. Even before the global transition to the remote work model, the effectiveness of business communication has been largely dependent on the business writing skills of the participants to get the right message across via emails, company memos, business messaging platforms, website copy, or social media posts.
Organizations and individuals alike need to commit to improving their business writing skills to reduce misunderstandings, improve collaboration, ensure clear task communication, and facilitate better work relationships.
🎓 Pumble Pro Tip
To learn more about enhancing your business writing skills, be sure to read our blog post:
- How to improve your work message skills
Conflict resolution skills
The ability to communicate your way out of a crisis, conflicts, and stressful situations in general, showcases strong conflict resolution skills. Naturally, managers and team leaders are more interested in developing these particular skills. However, other team members can also largely benefit from learning how to manage stressful situations and communicate to find creative solutions for the issues at hand.
Decision-making skills
As one of the business communication skills commonly related to leadership roles, good decision-making skills are key to successful goal-reaching both in terms of individual and organizational objectives. The ability to take an objective stand in critical conversations and quickly weigh out all the pros and cons and measure them against the main organizational goals and priorities is a skill that characterizes successful managers and leaders. The key to acquiring strong decision-making skills lies in applying a process that includes the following steps:
- Defining the situation or the issue.
- Identifying potential solutions or plans of action.
- Outlining all the pros and cons of each plan.
- Making the decision that best aligns with the previous steps and the overall goal.
To get a better insight on how to make better decisions remotely, be sure to check out our blog post:
- The 4 models that solve the challenges of remote decision-making
Nonverbal communication skills
Although the popular myth on the immense importance of nonverbal communication has been debunked by the more recent research on the basis of misinterpretation of the original research, nonverbal communication is still an important part of everyday and business communication. Nonverbal communication skills include specific body language cues we are using (intentionally or not) to convey our message. This includes everything from eye contact and facial expressions to our posture.
Professionals who mastered the skill of nonverbal communication have more success in getting the right message across in conversations with clients, team meetings, or industry conferences. Understanding nonverbal communication principles allows communicators to better read and understand the feelings and opinions of other participants in the conversation by observing their body language and facial expressions.
Feedback and input communication skills
Teams that foster constructive feedback in workplace communication are more likely to experience substantial benefits in organizational performance and commitment, a study finds.
Moreover, constructive feedback is equally valuable to employees on a more individual level as it supports faster career advancement. In fact, according to a Harvard Business Report Study, 57% of employees prefer receiving constructive feedback over praise.
To build strong feedback and input skills that drive collaboration and performance, organizations and individuals can consider working on trust-building, along with practicing honest, and respectful action-oriented feedback communication.
🎓 Pumble Pro Tip
You can read more on how to improve your constructive feedback communication, on our blog:
- How to give constructive feedback when working remotely
Delegation skills
Organizational management and leadership depend on strong delegation skills to effectively organize workload and strategically assign tasks for maximum productivity. However, delegation does not necessarily end with proper task assignments. Skillful delegators understand the importance of effectively communicating support and delivering relevant resources throughout the process.
📄 Document and share your business communication processes
While working to institute more effective business communication practices, organizations need to ensure everyone is getting access to strategies, procedures, resources, tools, and learning materials. Consider documenting your business communication processes and materials into one shared knowledge hub to serve as a checklist for new and existing employees to reference. Finally, share the document in a company-wide email, or pin it in a #general channel in your company team messaging app to make sure it stays accessible and top of mind with the entire organization.
Elevate your organization’s success with Pumble’s effective business communication
Effective business communication is the backbone of organizational success, driving collaboration, productivity, and employee engagement.
Recognizing its pivotal role, organizations are turning to dynamic solutions like Pumble to revolutionize their communication.
Pumble is a team communication app that streamlines clear communication and fosters collaboration among team members. With a focus on enhancing exchanges, Pumble offers a suite of robust features designed to boost productivity and harmony in the workplace.
Empower your workforce with Pumble’s versatile toolkit, which includes
- Customizable channels ,
- Threaded conversations ,
- Direct messages ,
- File sharing ,
- Screen sharing ,
- Video calls , and more.
These features enable teams to work more efficiently towards shared goals.
With Pumble as your ally, your team can communicate more effectively, collaborate seamlessly, and elevate your business communication strategies to new heights.
Make Pumble your team communication app and enhance business communication for company-wide success. Sign up today!
References :
- Bergman, C., Dellve, L., & Skagert, K. (2016, July 26). Exploring communication processes in workplace meetings: A mixed methods study in a Swedish Healthcare Organization . Work (Reading, Mass.). Retrieved December 23, 2021, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5147501/
- Bharadwaj, N., & Shipley, G. M. (2020, October). Salesperson Communication Effectiveness in a digital sales interaction . Industrial Marketing Management. Retrieved December 23, 2021, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7366081/
- Business meetings the case for face-to-face. Forbes. (n.d.). Retrieved January 4, 2022, from https://images.forbes.com/forbesinsights/StudyPDFs/Business_Meetings_FaceToFace.pdf
- Customer satisfaction: Surveys, questions & feedback templates . SurveyMonkey. (n.d.). Retrieved December 23, 2021, from https://www.surveymonkey.com/mp/customer-satisfaction-surveys/
- Employee engagement and performance communication . Gartner. (n.d.). Retrieved December 23, 2021, from https://www.gartner.com/en/corporate-communications/insights/employee-engagement-performance-communication
- Goran, J., LaBerge, L., & Srinivasan, R. (2020, February 13). Culture for a digital age . McKinsey Digital. Retrieved December 23, 2021, from https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/culture-for-a-digital-age
- Invernizzi, E., & Romenti, S. (2011). Strategic communication and decision-making processes: Toward the Communication Oriented Organisation. Academicus International Scientific Journal , 3 , 12–27. https://doi.org/10.7336/academicus.2011.03.0
- Lapakko, D. (2007). Communication is 93% nonverbal: An urban legend proliferates . Cornerstone Minnesota State University. Retrieved January 4, 2022, from https://cornerstone.lib.mnsu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1000&context=ctamj
- New study: How communication drives performance . Harvard Business Review. (2021, August 30). Retrieved December 23, 2021, from https://hbr.org/2009/11/new-study-how-communication-dr
- Project Management Institute. (2013, May). T he high cost of low performance: the essential role of communications . Retrieved January 4, 2022, from https://www.pmi.org/-/media/pmi/documents/public/pdf/learning/thought-leadership/pulse/the-essential-role-of-communications.pdf?v=e1f0e914-4b3a-456f-b75e-40101632258b
- Raghuram, J.N.V. R., & S. Yohitha (2020). A study on the role of communication skills for sales force — concerning online learning organizations. International Journal of Management, 11, 1965-1973 . Retrieved December 23, 2021, from https://iaeme.com/MasterAdmin/Journal_uploads/IJM/VOLUME_11_ISSUE_11/IJM_11_11_186.pdf
- Remote work statistics – work from Home Employee Training Trends . TalentLMS Blog. (2021, May 12). Retrieved January 4, 2022, from https://www.talentlms.com/blog/remote-work-statistics-survey/
- Ricks, B. R., & Gow, K. F. (1987). Business Communication: Systems and Applications . Prentice Hall Professional Technical Reference.
- Roebuck, C. (1996). Constructive feedback: Key to higher performance and commitment. Long Range Planning , 29 (3), 328–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/0024-6301(96)00028-3
- Roghanizad, M. M., & Bohns, V. K. (2017). Ask in person: You’re less persuasive than you think over email. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology , 69 , 223–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jesp.2016.10.002
- Your employees want the negative feedback you hate to give . Harvard Business Review. (2018, August 3). Retrieved January 4, 2022, from https://hbr.org/2014/01/your-employees-want-the-negative-feedback-you-hate-to-give
Explore further
Team Communication Fundamentals
Improving Team Communication

Improving Communication Effectiveness

Additional Materials

Free team chat app
Improve collaboration and cut down on emails by moving your team communication to Pumble.
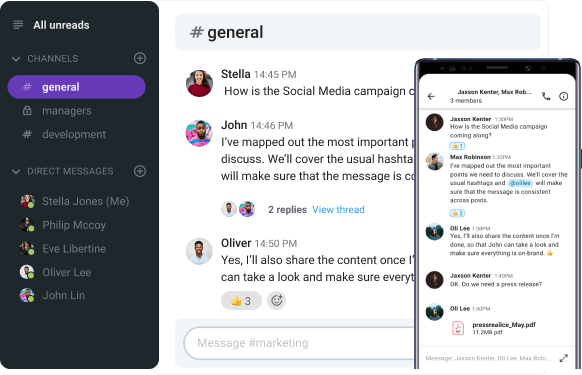

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.2: What Is Communication?
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 15075
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Learning Objectives
- Define communication and describe communication as a process.
- Identify and describe the eight essential components of communication.
- Identify and describe two models of communication.
Many theories have been proposed to describe, predict, and understand the behaviors and phenomena of which communication consists. When it comes to communicating in business, we are often less interested in theory than in making sure our communications generate the desired results. But in order to achieve results, it can be valuable to understand what communication is and how it works.
Defining Communication
The root of the word “communication” in Latin is communicare , which means to share, or to make common (Weekley, 1967). Communication is defined as the process of understanding and sharing meaning (Pearson & Nelson, 2000).
At the center of our study of communication is the relationship that involves interaction between participants. This definition serves us well with its emphasis on the process, which we’ll examine in depth across this text, of coming to understand and share another’s point of view effectively.
The first key word in this definition is process. A process is a dynamic activity that is hard to describe because it changes (Pearson & Nelson, 2000). Imagine you are alone in your kitchen thinking. Someone you know (say, your mother) enters the kitchen and you talk briefly. What has changed? Now, imagine that your mother is joined by someone else, someone you haven’t met before—and this stranger listens intently as you speak, almost as if you were giving a speech. What has changed? Your perspective might change, and you might watch your words more closely. The feedback or response from your mother and the stranger (who are, in essence, your audience) may cause you to reevaluate what you are saying. When we interact, all these factors—and many more—influence the process of communication.
The second key word is understanding: “To understand is to perceive, to interpret, and to relate our perception and interpretation to what we already know.” (McLean, 2003) If a friend tells you a story about falling off a bike, what image comes to mind? Now your friend points out the window and you see a motorcycle lying on the ground. Understanding the words and the concepts or objects they refer to is an important part of the communication process.
Next comes the word sharing. Sharing means doing something together with one or more people. You may share a joint activity, as when you share in compiling a report; or you may benefit jointly from a resource, as when you and several coworkers share a pizza. In communication, sharing occurs when you convey thoughts, feelings, ideas, or insights to others. You can also share with yourself (a process called intrapersonal communication) when you bring ideas to consciousness, ponder how you feel about something, or figure out the solution to a problem and have a classic “Aha!” moment when something becomes clear.
Finally, meaning is what we share through communication. The word “bike” represents both a bicycle and a short name for a motorcycle. By looking at the context the word is used in and by asking questions, we can discover the shared meaning of the word and understand the message.
Eight Essential Components of Communication
In order to better understand the communication process, we can break it down into a series of eight essential components:
Environment
Interference.
Each of these eight components serves an integral function in the overall process. Let’s explore them one by one.
The source imagines, creates, and sends the message. In a public speaking situation, the source is the person giving the speech. He or she conveys the message by sharing new information with the audience. The speaker also conveys a message through his or her tone of voice, body language, and choice of clothing. The speaker begins by first determining the message—what to say and how to say it. The second step involves encoding the message by choosing just the right order or the perfect words to convey the intended meaning. The third step is to present or send the information to the receiver or audience. Finally, by watching for the audience’s reaction, the source perceives how well they received the message and responds with clarification or supporting information.
“The message is the stimulus or meaning produced by the source for the receiver or audience.” (McLean, 2005) When you plan to give a speech or write a report, your message may seem to be only the words you choose that will convey your meaning. But that is just the beginning. The words are brought together with grammar and organization. You may choose to save your most important point for last. The message also consists of the way you say it—in a speech, with your tone of voice, your body language, and your appearance—and in a report, with your writing style, punctuation, and the headings and formatting you choose. In addition, part of the message may be the environment or context you present it in and the noise that might make your message hard to hear or see.
Imagine, for example, that you are addressing a large audience of sales reps and are aware there is a World Series game tonight. Your audience might have a hard time settling down, but you may choose to open with, “I understand there is an important game tonight.” In this way, by expressing verbally something that most people in your audience are aware of and interested in, you might grasp and focus their attention.
“The channel is the way in which a message or messages travel between source and receiver.” (McLean, 2005) For example, think of your television. How many channels do you have on your television? Each channel takes up some space, even in a digital world, in the cable or in the signal that brings the message of each channel to your home. Television combines an audio signal you hear with a visual signal you see. Together they convey the message to the receiver or audience. Turn off the volume on your television. Can you still understand what is happening? Many times you can, because the body language conveys part of the message of the show. Now turn up the volume but turn around so that you cannot see the television. You can still hear the dialogue and follow the story line.
Similarly, when you speak or write, you are using a channel to convey your message. Spoken channels include face-to-face conversations, speeches, telephone conversations and voice mail messages, radio, public address systems, and voice over Internet protocol (VoIP). Written channels include letters, memorandums, purchase orders, invoices, newspaper and magazine articles, blogs, e-mail, text messages, tweets, and so forth.
“The receiver receives the message from the source, analyzing and interpreting the message in ways both intended and unintended by the source.” (McLean, 2005) To better understand this component, think of a receiver on a football team. The quarterback throws the football (message) to a receiver, who must see and interpret where to catch the ball. The quarterback may intend for the receiver to “catch” his message in one way, but the receiver may see things differently and miss the football (the intended meaning) altogether.
As a receiver you listen, see, touch, smell, and/or taste to receive a message. Your audience “sizes you up,” much as you might check them out long before you take the stage or open your mouth. The nonverbal responses of your listeners can serve as clues on how to adjust your opening. By imagining yourself in their place, you anticipate what you would look for if you were them. Just as a quarterback plans where the receiver will be in order to place the ball correctly, you too can recognize the interaction between source and receiver in a business communication context. All of this happens at the same time, illustrating why and how communication is always changing.
When you respond to the source, intentionally or unintentionally, you are giving feedback. Feedback is composed of messages the receiver sends back to the source. Verbal or nonverbal, all these feedback signals allow the source to see how well, how accurately (or how poorly and inaccurately) the message was received. Feedback also provides an opportunity for the receiver or audience to ask for clarification, to agree or disagree, or to indicate that the source could make the message more interesting. As the amount of feedback increases, the accuracy of communication also increases (Leavitt & Mueller, 1951).
For example, suppose you are a sales manager participating in a conference call with four sales reps. As the source, you want to tell the reps to take advantage of the fact that it is World Series season to close sales on baseball-related sports gear. You state your message, but you hear no replies from your listeners. You might assume that this means they understood and agreed with you, but later in the month you might be disappointed to find that very few sales were made. If you followed up your message with a request for feedback (“Does this make sense? Do any of you have any questions?”) you might have an opportunity to clarify your message, and to find out whether any of the sales reps believed your suggestion would not work with their customers.
“The environment is the atmosphere, physical and psychological, where you send and receive messages.” (McLean, 2005) The environment can include the tables, chairs, lighting, and sound equipment that are in the room. The room itself is an example of the environment. The environment can also include factors like formal dress, that may indicate whether a discussion is open and caring or more professional and formal. People may be more likely to have an intimate conversation when they are physically close to each other, and less likely when they can only see each other from across the room. In that case, they may text each other, itself an intimate form of communication. The choice to text is influenced by the environment. As a speaker, your environment will impact and play a role in your speech. It’s always a good idea to go check out where you’ll be speaking before the day of the actual presentation.
“The context of the communication interaction involves the setting, scene, and expectations of the individuals involved.” (McLean, 2005) A professional communication context may involve business suits (environmental cues) that directly or indirectly influence expectations of language and behavior among the participants.
A presentation or discussion does not take place as an isolated event. When you came to class, you came from somewhere. So did the person seated next to you, as did the instructor. The degree to which the environment is formal or informal depends on the contextual expectations for communication held by the participants. The person sitting next to you may be used to informal communication with instructors, but this particular instructor may be used to verbal and nonverbal displays of respect in the academic environment. You may be used to formal interactions with instructors as well, and find your classmate’s question of “Hey Teacher, do we have homework today?” as rude and inconsiderate when they see it as normal. The nonverbal response from the instructor will certainly give you a clue about how they perceive the interaction, both the word choices and how they were said.
Context is all about what people expect from each other, and we often create those expectations out of environmental cues. Traditional gatherings like weddings or quinceañeras are often formal events. There is a time for quiet social greetings, a time for silence as the bride walks down the aisle, or the father may have the first dance with his daughter as she is transformed from a girl to womanhood in the eyes of her community. In either celebration there may come a time for rambunctious celebration and dancing. You may be called upon to give a toast, and the wedding or quinceañera context will influence your presentation, timing, and effectiveness.

In a business meeting, who speaks first? That probably has some relation to the position and role each person has outside the meeting. Context plays a very important role in communication, particularly across cultures.
Interference, also called noise, can come from any source. “Interference is anything that blocks or changes the source’s intended meaning of the message.”(McLean, 2005) For example, if you drove a car to work or school, chances are you were surrounded by noise. Car horns, billboards, or perhaps the radio in your car interrupted your thoughts, or your conversation with a passenger.
Psychological noise is what happens when your thoughts occupy your attention while you are hearing, or reading, a message. Imagine that it is 4:45 p.m. and your boss, who is at a meeting in another city, e-mails you asking for last month’s sales figures, an analysis of current sales projections, and the sales figures from the same month for the past five years. You may open the e-mail, start to read, and think, “Great—no problem—I have those figures and that analysis right here in my computer.” You fire off a reply with last month’s sales figures and the current projections attached. Then, at five o’clock, you turn off your computer and go home. The next morning, your boss calls on the phone to tell you he was inconvenienced because you neglected to include the sales figures from the previous years. What was the problem? Interference: by thinking about how you wanted to respond to your boss’s message, you prevented yourself from reading attentively enough to understand the whole message.
Interference can come from other sources, too. Perhaps you are hungry, and your attention to your current situation interferes with your ability to listen. Maybe the office is hot and stuffy. If you were a member of an audience listening to an executive speech, how could this impact your ability to listen and participate?
Noise interferes with normal encoding and decoding of the message carried by the channel between source and receiver. Not all noise is bad, but noise interferes with the communication process. For example, your cell phone ringtone may be a welcome noise to you, but it may interrupt the communication process in class and bother your classmates.
Two Models of Communication
Researchers have observed that when communication takes place, the source and the receiver may send messages at the same time, often overlapping. You, as the speaker, will often play both roles, as source and receiver. You’ll focus on the communication and the reception of your messages to the audience. The audience will respond in the form of feedback that will give you important clues. While there are many models of communication, here we will focus on two that offer perspectives and lessons for business communicators.
Rather than looking at the source sending a message and someone receiving it as two distinct acts, researchers often view communication as a transactional process (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)), with actions often happening at the same time. The distinction between source and receiver is blurred in conversational turn-taking, for example, where both participants play both roles simultaneously.

Researchers have also examined the idea that we all construct our own interpretations of the message. As the State Department quote at the beginning of this chapter indicates, what I said and what you heard may be different. In the constructivist model (Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\)), we focus on the negotiated meaning, or common ground, when trying to describe communication (Pearce & Cronen, 1980),
Imagine that you are visiting Atlanta, Georgia, and go to a restaurant for dinner. When asked if you want a “Coke,” you may reply, “sure.” The waiter may then ask you again, “what kind?” and you may reply, “Coke is fine.” The waiter then may ask a third time, “what kind of soft drink would you like?” The misunderstanding in this example is that in Atlanta, the home of the Coca-Cola Company, most soft drinks are generically referred to as “Coke.” When you order a soft drink, you need to specify what type, even if you wish to order a beverage that is not a cola or not even made by the Coca-Cola Company. To someone from other regions of the United States, the words “pop,” “soda pop,” or “soda” may be the familiar way to refer to a soft drink; not necessarily the brand “Coke.” In this example, both you and the waiter understand the word “Coke,” but you each understand it to mean something different. In order to communicate, you must each realize what the term means to the other person, and establish common ground, in order to fully understand the request and provide an answer.

Because we carry the multiple meanings of words, gestures, and ideas within us, we can use a dictionary to guide us, but we will still need to negotiate meaning.
Key Takeaway
The communication process involves understanding, sharing, and meaning, and it consists of eight essential elements: source, message, channel, receiver, feedback, environment, context, and interference. Among the models of communication are the transactional process, in which actions happen simultaneously, and the constructivist model, which focuses on shared meaning.
- Draw what you think communication looks like. Share your drawing with your classmates.
- List three environmental cues and indicate how they influence your expectations for communication. Please share your results with your classmates.
- How does context influence your communication? Consider the language and culture people grew up with, and the role these play in communication styles.
- If you could design the perfect date, what activities, places, and/or environmental cues would you include to set the mood? Please share your results with your classmates.
- Observe two people talking. Describe their communication. See if you can find all eight components and provide an example for each one.
- What assumptions are present in transactional model of communication? Find an example of a model of communication in your workplace or classroom, and provide an example for all eight components.
- Cronen, V., & Pearce, W. B. (1982). The coordinated management of meaning: A theory of communication. In F. E. Dance (Ed.), Human communication theory (pp. 61–89). New York, NY: Harper & Row.
- Leavitt, H., & Mueller, R. (1951). Some effects of feedback on communication. Human Relations, 4 , 401–410.
- McLean, S. (2003). The basics of speech communication . Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
- McLean, S. (2005). The basics of interpersonal communication (p. 10). Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
- Pearce, W. B., & Cronen, V. (1980). Communication, action, and meaning: The creating of social realities . New York, NY: Praeger.
- Pearson, J., & Nelson, P. (2000). An introduction to human communication: Understanding and sharing (p. 6). Boston, MA: McGraw-Hill.
- Weekley, E. (1967). An etymological dictionary of modern English (Vol. 1, p. 338). New York, NY: Dover Publications.

ESSAY SAUCE
FOR STUDENTS : ALL THE INGREDIENTS OF A GOOD ESSAY
Essay: Communication in business
Essay details and download:.
- Subject area(s): Business essays
- Reading time: 2 minutes
- Price: Free download
- Published: 22 October 2015*
- File format: Text
- Words: 477 (approx)
- Number of pages: 2 (approx)
Text preview of this essay:
This page of the essay has 477 words. Download the full version above.
Communication is the key to success in any business. Whether you are trying to sell a product , answer a query or complaint or convince your colleagues to adopt a certain course of action , good communication often means the difference between success and failure. Moreover, because of the globalisation of trade and the use of the Internet, the position of English as the international language of business is stronger than ever. ‘A man is as alive as he can communicate.’ (L. Ron Hubbard). This quotation emphasizes the importance of communication and its corresponding need. Communication plays a significant role in our lives at all levels. It is, in fact, an integral part or facet of our life. Communication is the only activity which is performed or indulged in all the time, and not occasionally or sporadically. The list of its benefits is endless. A glance at just a few of them will, however, suffice to underscore the importance and need for effective communication. Effective communication and success go together, for an individual as well as for an organization. It facilitates human endeavor and enhances all aspects of human life. Healthy working human relationships are the result of effective communication, as it influences and moulds human thinking, beliefs, frame of mind and value systems. It decides good human behaviour as well as social behaviour. In a way it helps to develop an effective democratic and multicultural society. It will not be an exaggeration to say that our personal, professional and civic lives revolve around communication. Communication has a definite role to play in business, as a business person spends 75-90% of his work-time in communication, whether it be speaking, reading, writing, or listening. Today, technological development, globalization and team-based organizational structures have given rise to a culturally diverse workforce in an organization. This, again, intensifies the need to communicate effectively. Higher administrative jobs require effective communication to a greater extent. It resolves conflicts between organizational complexity and individual needs. It encourages people to think in new ways. It boosts morale; motivates people; produces greater efficiency, leading to higher productivity; creates a healthy atmosphere, bringing about unity; maintains smooth functioning; promotes the control of factors necessary for successfully achieving the final goal of the organization; and so on. It helps quick decision-making. Reaching the final goal ensuring profitability is possible only with effective communication. Conversely, inability to communicate effectively will weaken the administration. It will result in problems like miscommunication, low morale, lack of motivation, inefficiency, chaos, lack of control, reduced productivity, lack of unity, and non-achievement of the final goal, and perhaps total failure. That is why effective communication is a must. Neglecting communication or underestimating its value and importance will take us back to the dark ages and will deprive us of all the latest developments. Good communication is today’s need. Its absence would make success unattainable
...(download the rest of the essay above)
About this essay:
If you use part of this page in your own work, you need to provide a citation, as follows:
Essay Sauce, Communication in business . Available from:<https://www.essaysauce.com/business-essays/essay-communication-in-business/> [Accessed 13-05-24].
These Business essays have been submitted to us by students in order to help you with your studies.
* This essay may have been previously published on Essay.uk.com at an earlier date.
Essay Categories:
- Accounting essays
- Architecture essays
- Business essays
- Computer science essays
- Criminology essays
- Economics essays
- Education essays
- Engineering essays
- English language essays
- Environmental studies essays
- Essay examples
- Finance essays
- Geography essays
- Health essays
- History essays
- Hospitality and tourism essays
- Human rights essays
- Information technology essays
- International relations
- Leadership essays
- Linguistics essays
- Literature essays
- Management essays
- Marketing essays
- Mathematics essays
- Media essays
- Medicine essays
- Military essays
- Miscellaneous essays
- Music Essays
- Nursing essays
- Philosophy essays
- Photography and arts essays
- Politics essays
- Project management essays
- Psychology essays
- Religious studies and theology essays
- Sample essays
- Science essays
- Social work essays
- Sociology essays
- Sports essays
- Types of essay
- Zoology essays
Importance of Communication in Business Essay
Communication in business is a highly important aspect (if not the most important one). I agree that different concerns can arise with regard to business communication, for example, language issues or misunderstandings based on culture. I would like to add technology as a possible mediator of communication. As Ivanovski and Gruevski (2014) point out, mediators that allow synchronous communication (chatting, video or audio communication) are more likely to enrich and facilitate the process of negotiations than tools that support asynchronous communication (e-mails, for example). As business communication can be dependent on language barriers, it is preferable to choose such tools that will help both sides overcome these barriers.
Another important aspect of communication is the ability to understand others and to present oneself accordingly. Addams and Allred (2015) point out that business students need to know not only how to present themselves to senior managers or other executives but also how to use one’s language to do it successfully. Thus, I agree that it is essential to research background information about the company or executives, both when communicating with domestic and international stakeholders or colleagues.
As businesses grow, so does the network that includes various business clusters around the world. The influence of culture is unavoidable in this case. Communication with representatives of different cultures can help us understand others and move beyond our perspective on a particular culture. It is suggested to involve students in international communication more often to help them understand how “to cope within the intricate context of international communication” (Goby, 2007, p. 435). Corporations also need to ensure that multicultural components are used in their training to make such communication more effective in real-life situations and challenges.
Addams, L. H., & Allred, A. T. (2015). Business communication course redesigned: All written and oral communication assignments based on building career skills. Academy of Educational Leadership Journal , 19 (1), 250-265.
Goby, V. P. (2007). Business communication needs: A multicultural perspective. Journal of Business and Technical Communication , 21 (4), 425-437.
Ivanovski, I., & Gruevski, D. (2014). Usage of virtual communication tools in business communication and negotiation – a factor of increased efficiency. TEM Journal , 3 (2), 167-174.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2020, October 11). Importance of Communication in Business. https://ivypanda.com/essays/importance-of-communication-in-business/
"Importance of Communication in Business." IvyPanda , 11 Oct. 2020, ivypanda.com/essays/importance-of-communication-in-business/.
IvyPanda . (2020) 'Importance of Communication in Business'. 11 October.
IvyPanda . 2020. "Importance of Communication in Business." October 11, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/importance-of-communication-in-business/.
1. IvyPanda . "Importance of Communication in Business." October 11, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/importance-of-communication-in-business/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Importance of Communication in Business." October 11, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/importance-of-communication-in-business/.
- HF Limited Company's Organizational Culture and Image
- Women’s Family and Social Responsibilities and Rights
- Virtual Schooling Programs
- Factors of Communication in International Business
- Marbles Construction Company's Conflict Management
- Impact of Text Message Use in Business Communication
- Chinese and Spanish Cultures in Business Communication
- Culture Shock and Intercultural Communication

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A Small Business Guide. Business communication involves sharing information between people within and outside an organization, including colleagues, partners, clients, and stakeholders. Effective business communication is the backbone of efficient operations and contributes to informed decision-making and reduced errors.
Communication is important in people's lives, as it is a mean of exchanging information from one person to another (Kushal, n.d, pp 1). In business, communication is necessary, as it plays a role in negotiation between an entrepreneur and the customer, and between the distributor and the entrepreneurs, among others. We will write a custom ...
Effective communication takes preparation, practice, and persistence. There are many ways to learn communication skills; the school of experience, or "hard knocks," is one of them. But in the business environment, a "knock" (or lesson learned) may come at the expense of your credibility through a blown presentation to a client.
Before writing a business communication essay, you need to understand perfectly what this term stands for. Business communication is an exchange of information, opinions, and ideas. This process can occur between people within one company or outside it. It can be intentional or unintentional, verbal or nonverbal, internal and external.
The objective of business communication lies in: Presenting options/new business ideas: Sharing and discussing new ideas or choices for the business. Making plans and proposals (business writing): Writing down and explaining plans and suggestions for the business. Executing decisions: Carrying out and putting into action the choices and plans ...
The root of the word "communication" in Latin is communicare, which means to share, or to make common ( Weekley, 1967). Communication is defined as the process of understanding and sharing meaning ( Pearson & Nelson, 2000, p. 6). At the center of our study of communication is the relationship that involves interaction between participants.
Business communication is the mechanism for instructing employees, and is also the way management receives feedback from them. It is also the means by which a company speaks to its customers.
No headers. Communication is key to your success—in relationships, in the workplace, as a citizen of your country, and across your lifetime. Your ability to communicate comes from experience, and experience can be an effective teacher, but this text and the related business communication course will offer you a wealth of experiences gathered from professional speakers across their lifetimes.
Business communication can be very difficult at times but with the proper cooperation of models, the process gets simpler. Marketing communication models should consist of the sender, the message to be delivered, the medium through which the message will be delivered, the recipients as well as feedback. In this essay, I will present the basis ...
What's going on in business and management communication courses. In M. Kogen (Ed.), Writing in the business professions (pp. 267-278). National Council of Teachers of English and the Association for Business Communication. Google Scholar. Reinsch, Lamar. (1991). Editorial: Boundaries and banners. The Journal of Business Communication, 28, 97-99.
Business Communication is the act or process of transferring information from one person to another person, and every communication involves at least one sender, a message, or a receiver. Here in this article, we have shared complete details about business communication and its definition, function, types, process, and advantages.
The communicator has to be careful and judicious when choosing a media and factors like reliability, formality, receiver, confidentiality, urgency, cost, speed, safety, and security should be the guiding principles when choosing a certain medium of communication. Today, a communicator can choose from the various ways of passing information in a ...
Definition of Business Communication. Business Communication book published in 2004 as part of Harvard Business Essentials defined business communication as follows: "No matter whether it is written or verbal, it is the instrument through which business speaks to its consumers. It is the mechanism by which management influences its employees ...
USC Marshall School of Business Abstract We asked editorial board members of major business communication journals to rate seventy-eight theories widely used in business communication research on four aspects: how knowledgeable they were about the theory, the theory's application to business activities, the theory's scientific support, and
Importance of business communication in an organization can be seen in the below points: 1. Helps in increasing productivity: Effective business communication increases the productivity of staff by boosting up teamwork. It creates a trustworthy and understanding environment among employers and employees.
Written communication, as the name suggests, consists of all types of information sharing that is in the form of written messages like emails, letters, reports, telegrams, bulletins, manuals, paper announcements, and more. Unlike verbal communication, it takes a bit more effort to communicate emotions and feelings with written communication.
In this guide, we will cover every aspect of business communication including: The definition and examples of effective business communication, The importance of effective business communication and the problems it solves, The types and methods of business communication, The tips and techniques on how to improve communication in business.
Effective business communication is how employees and management interact to reach organizational goals. Its purpose is to improve organizational practices and reduce errors. It's important to work on both your communication skills and communication processes to achieve effective business communication. The importance of business ...
The first key word in this definition is process. A process is a dynamic activity that is hard to describe because it changes (Pearson & Nelson, 2000). ... (McLean, 2005) A professional communication context may involve business suits (environmental cues) that directly or indirectly influence expectations of language and behavior among the ...
This page of the essay has 477 words. Download the full version above. Communication is the key to success in any business. Whether you are trying to sell a product , answer a query or complaint or convince your colleagues to adopt a certain course of action , good communication often means the difference between success and failure. Moreover ...
Importance of Communication in Business Essay. Communication in business is a highly important aspect (if not the most important one). I agree that different concerns can arise with regard to business communication, for example, language issues or misunderstandings based on culture. I would like to add technology as a possible mediator of ...
5 Multiple choice questions. Definition. Title Page - Should reflect the reports contents and clearly show its professional quality. Table of Contents - Optional in reports six pages or less. Lists topic headings and page number, helps readers understand a report that is longer. Letter of Transmittal - Optional.